Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Shock and vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
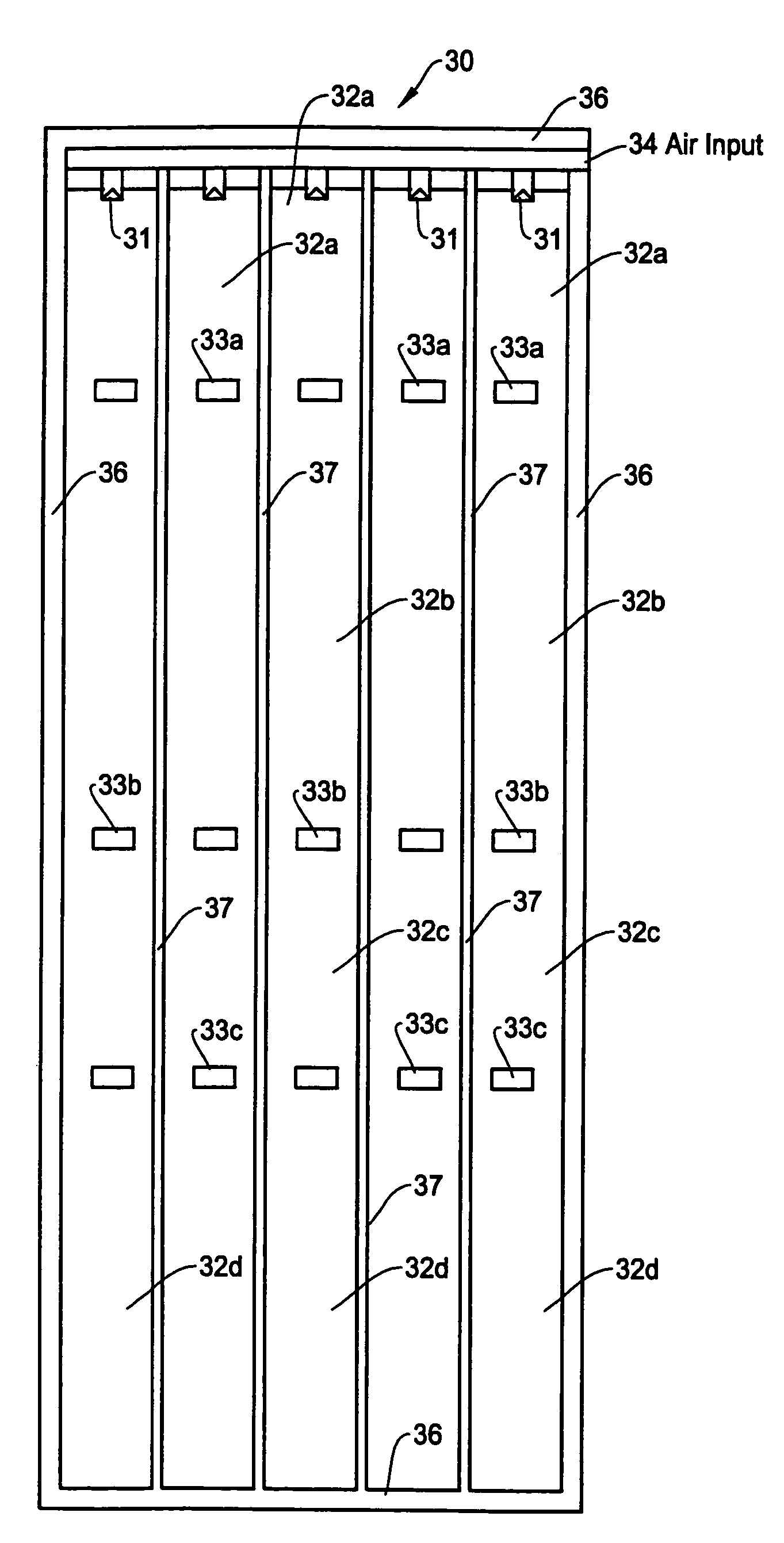
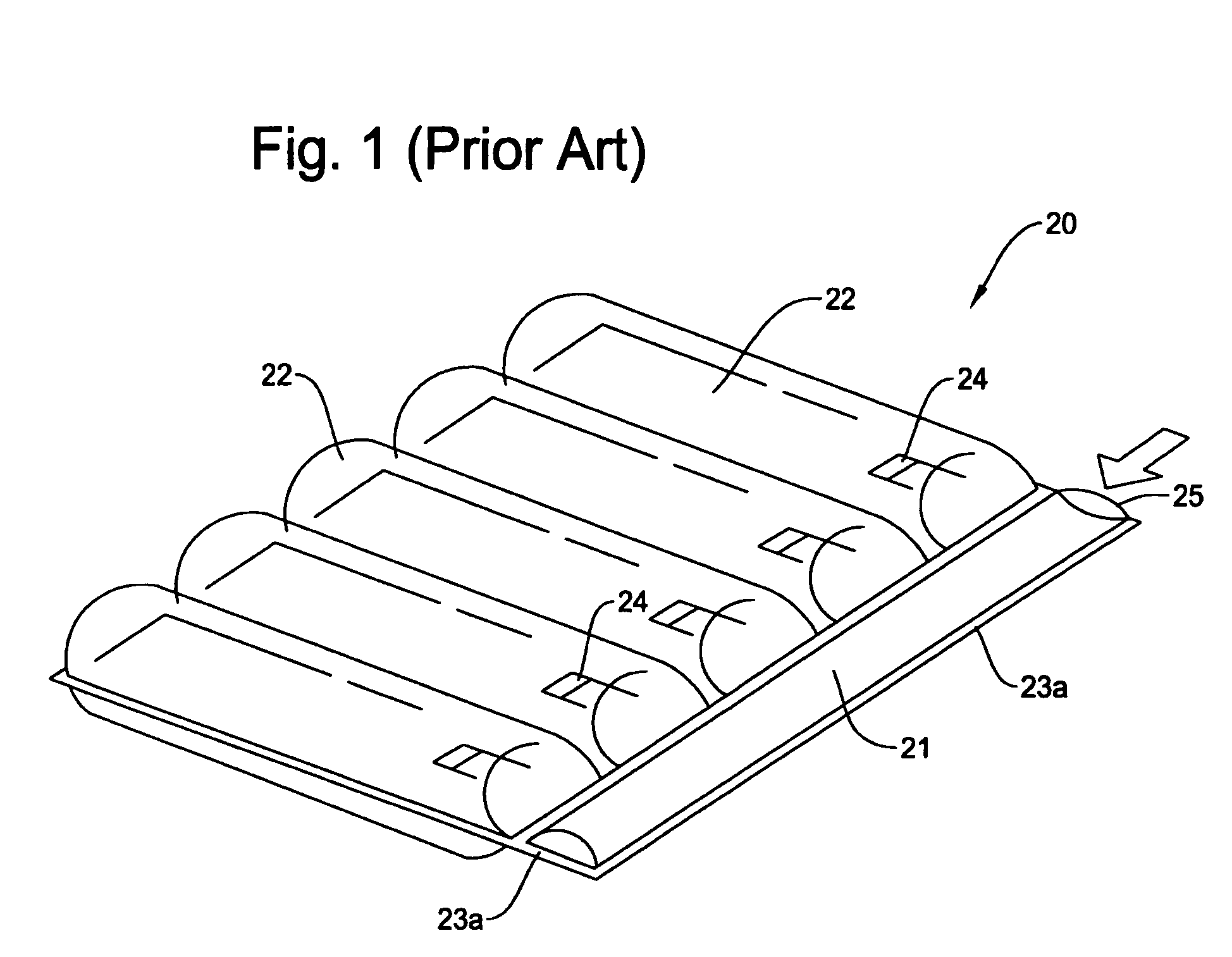
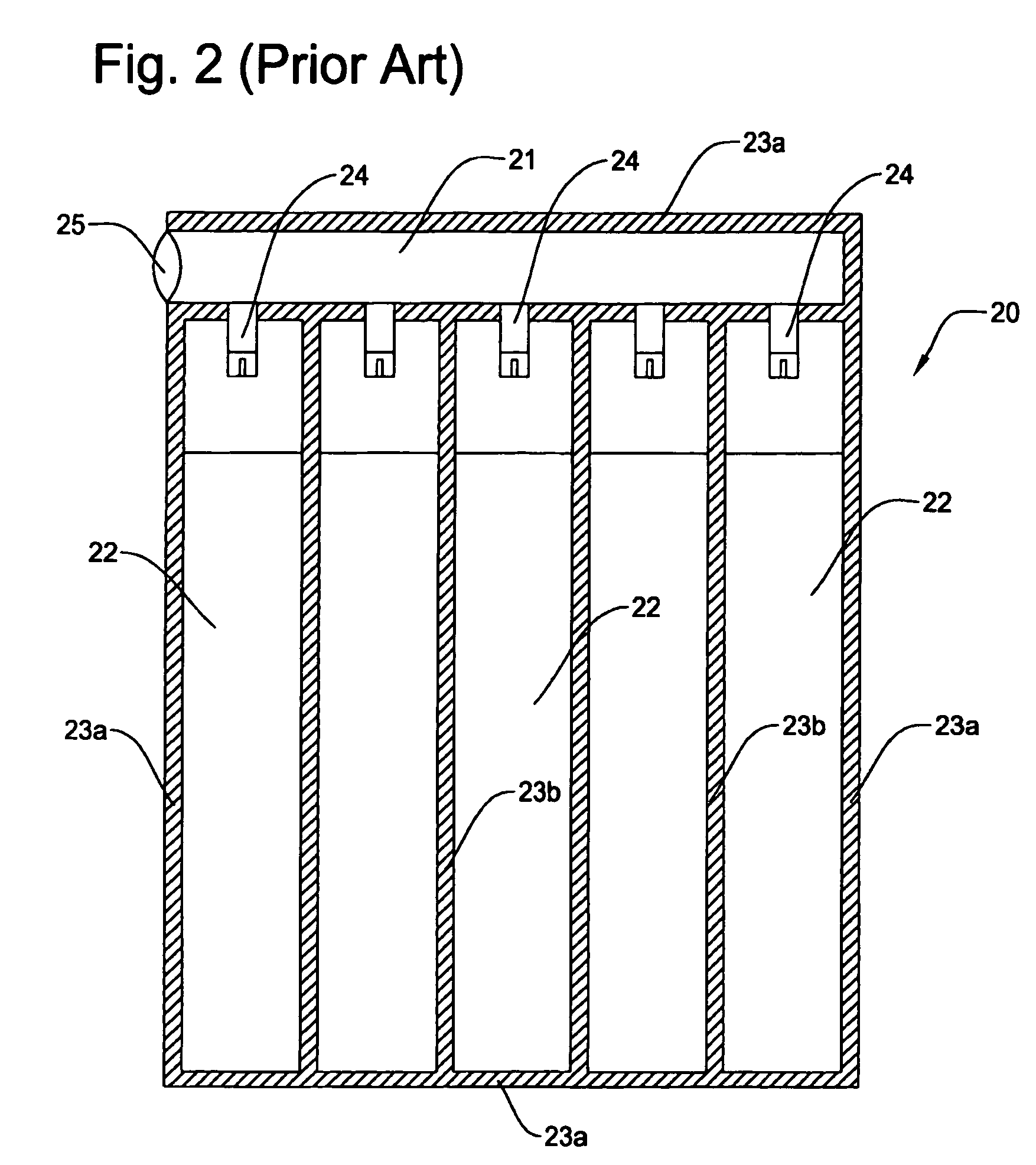
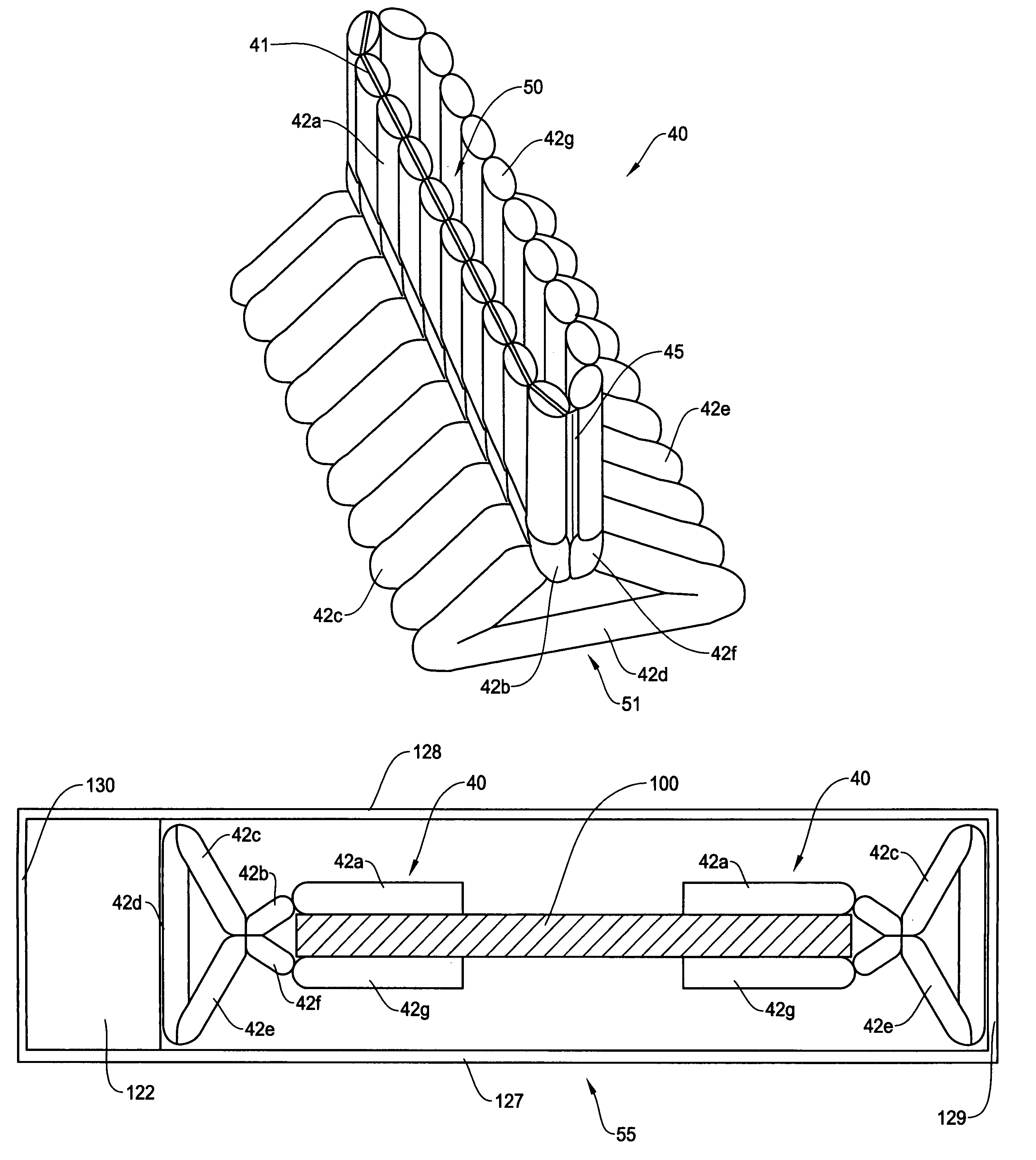
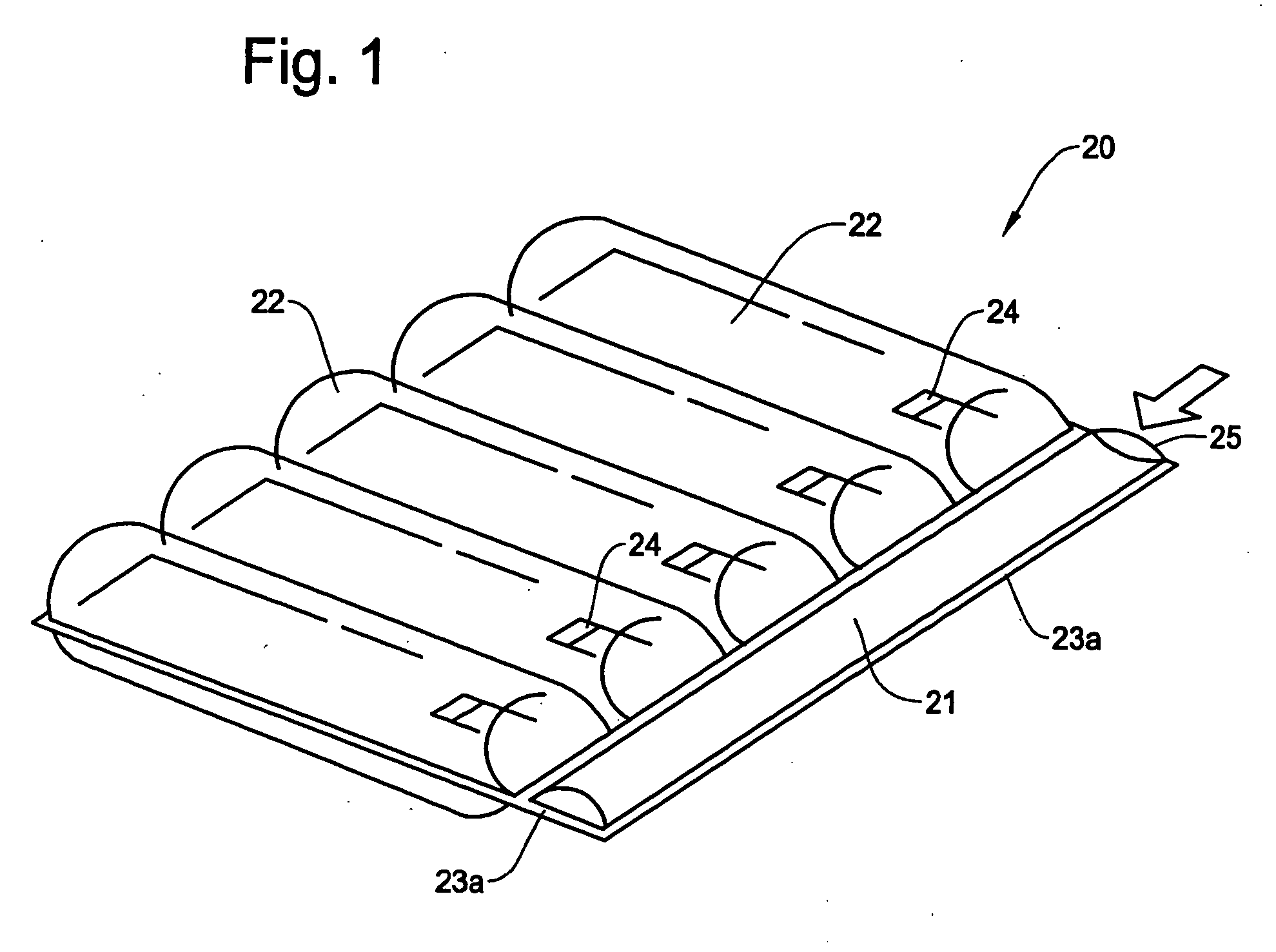
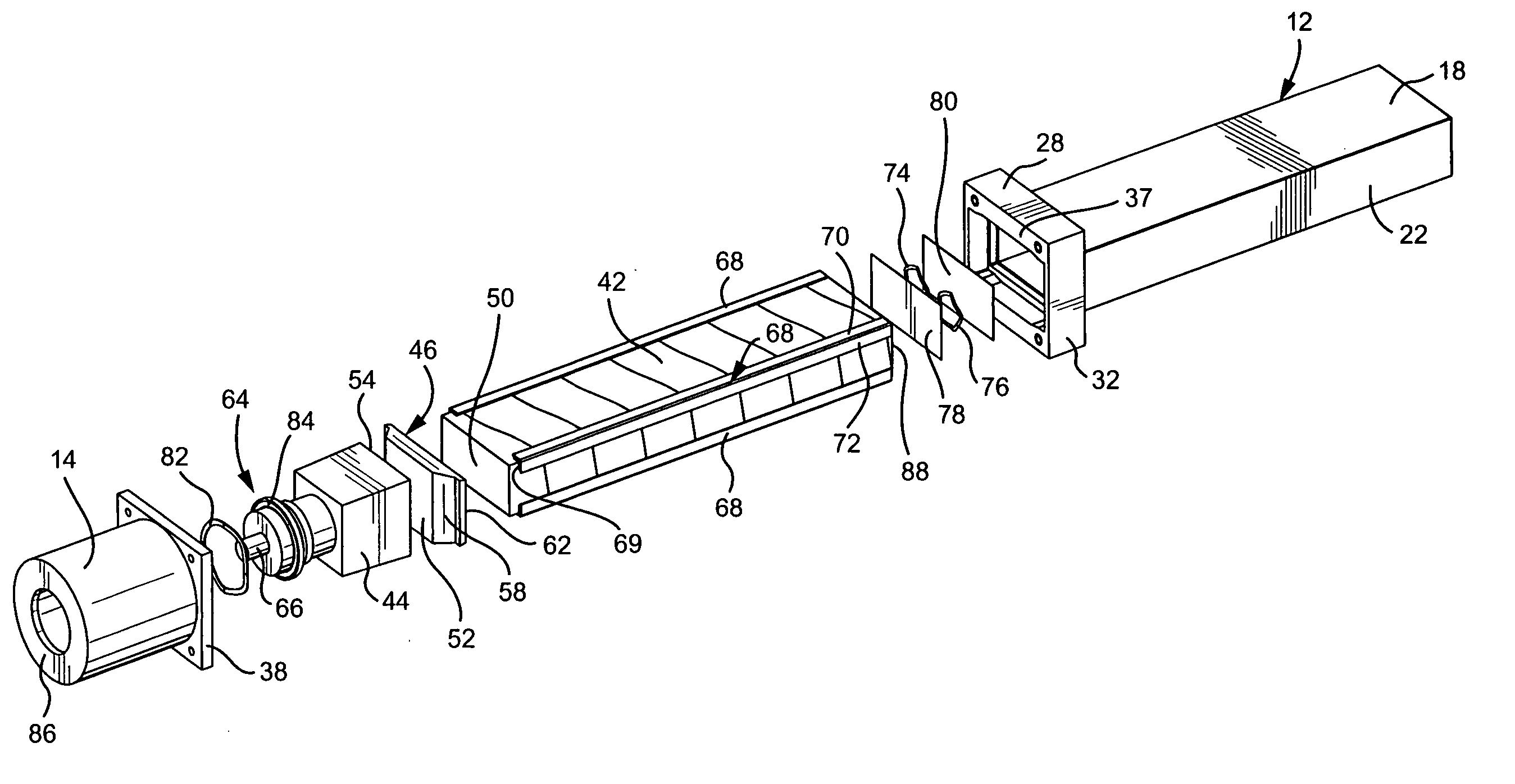
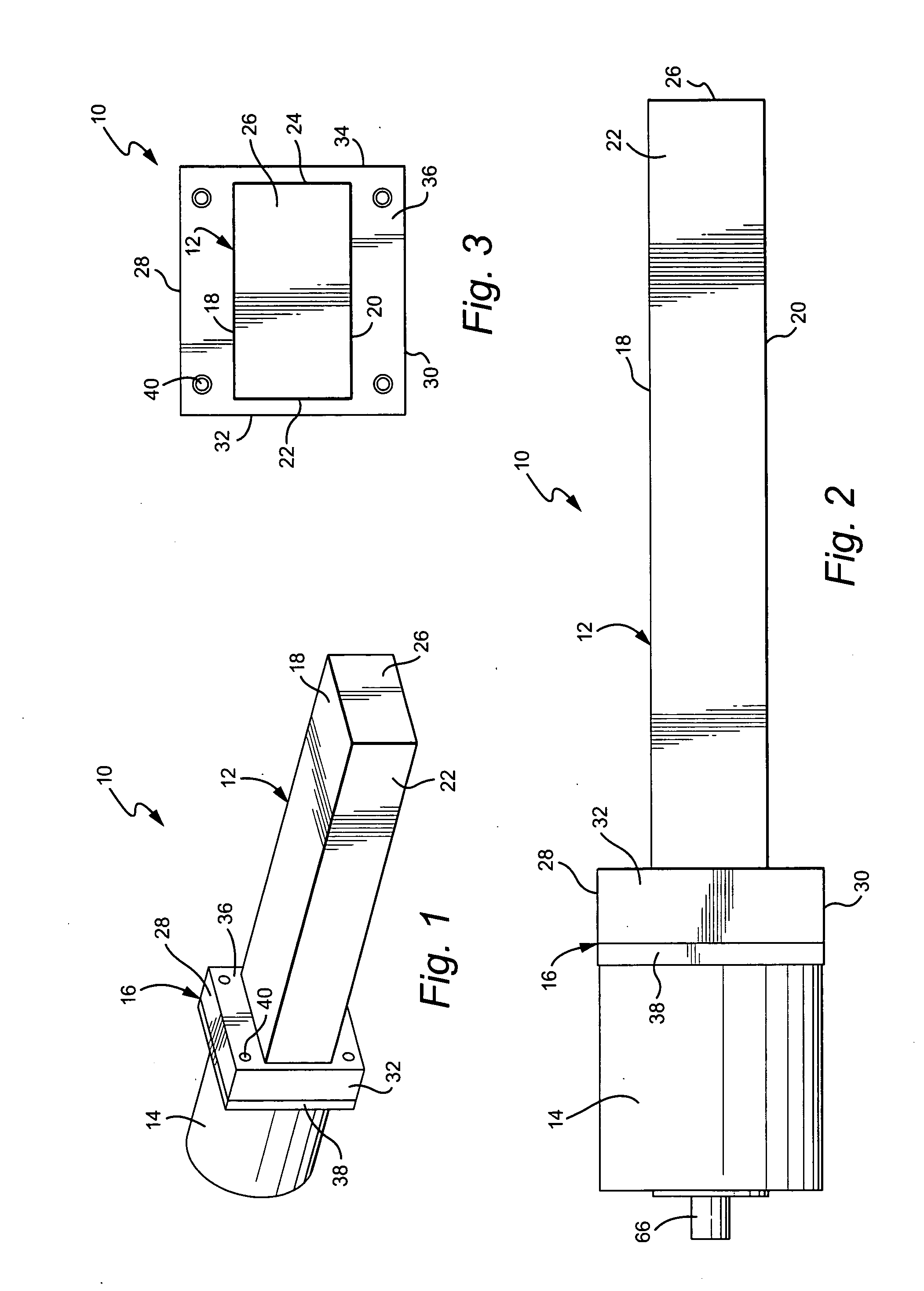
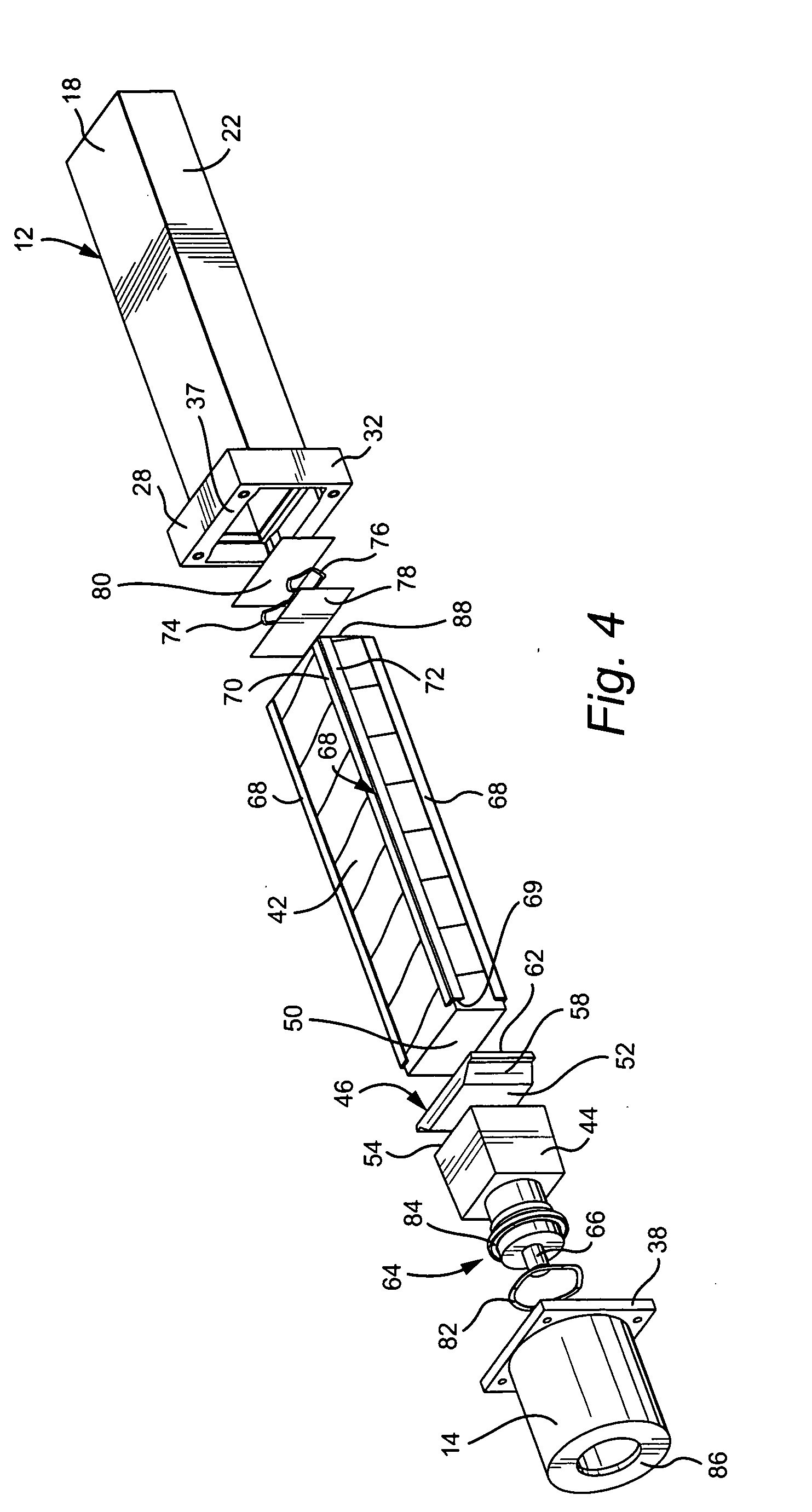
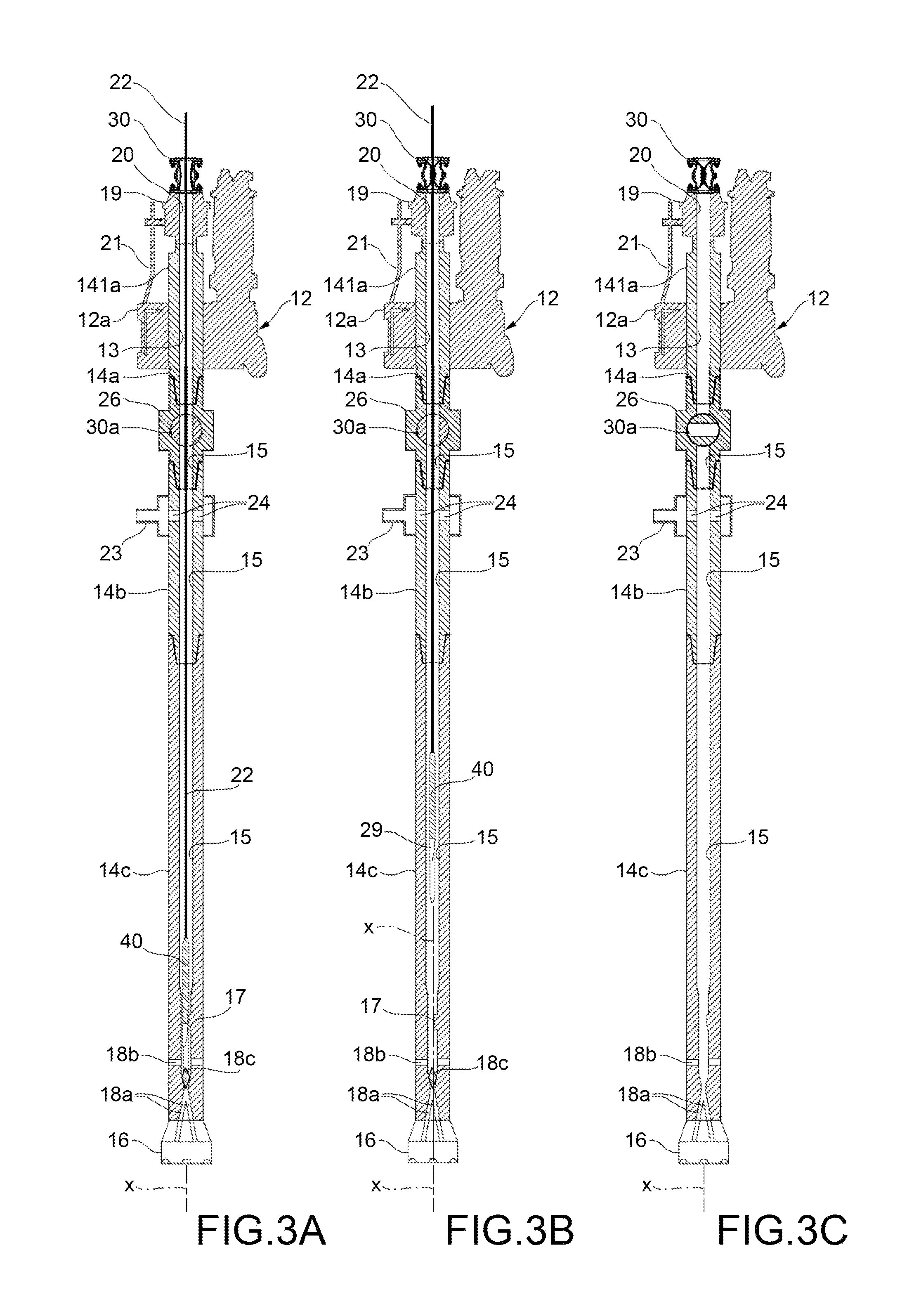
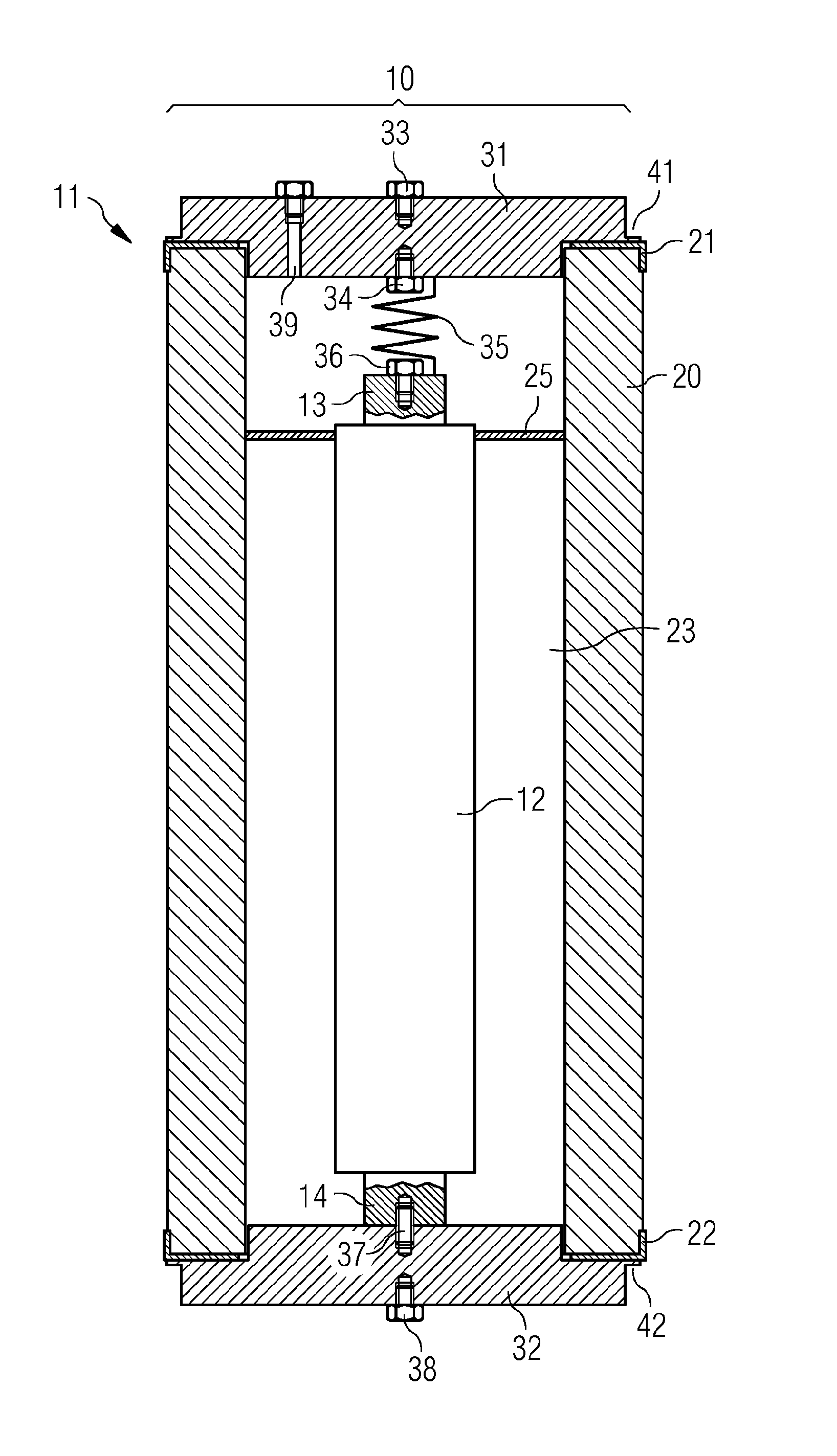
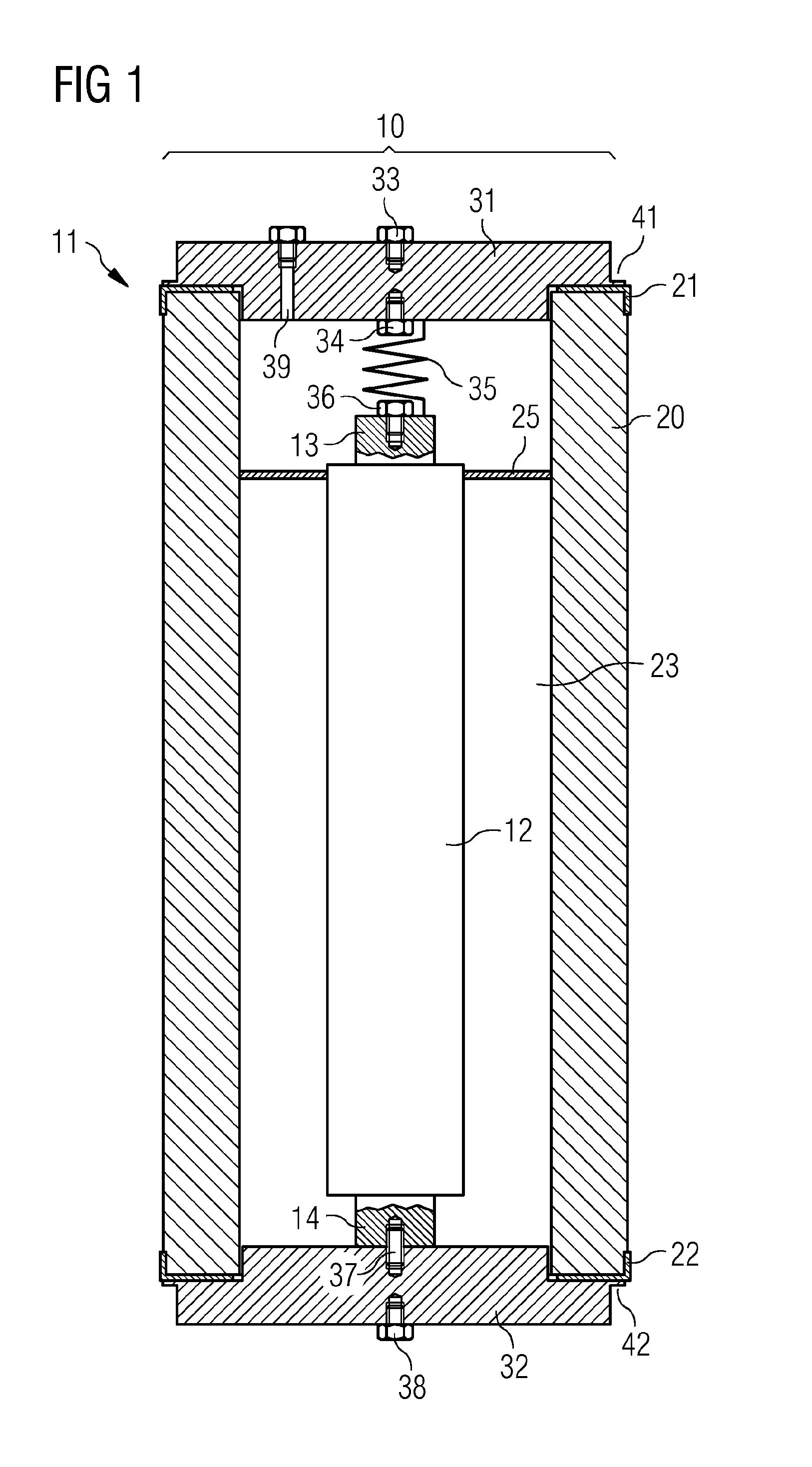
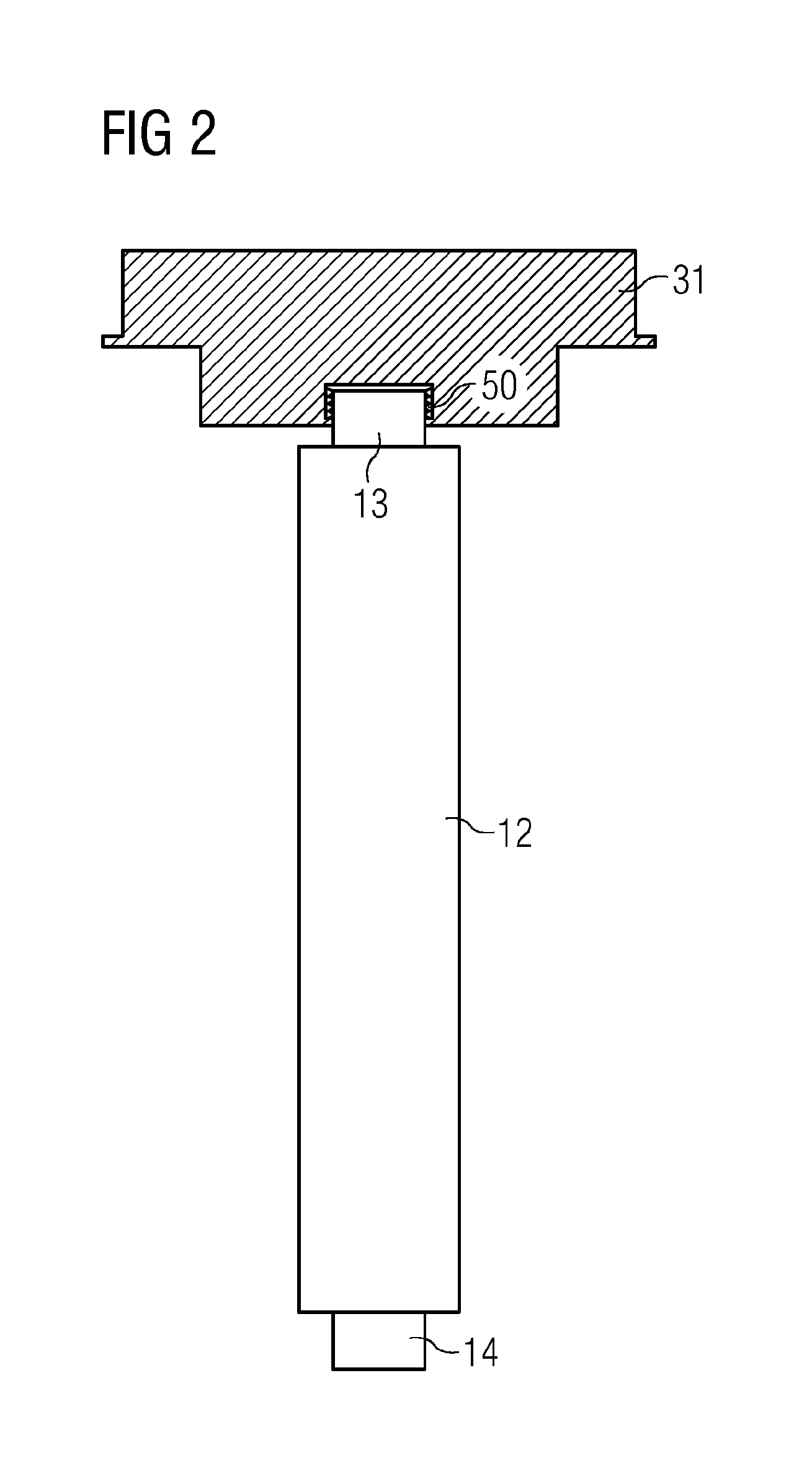
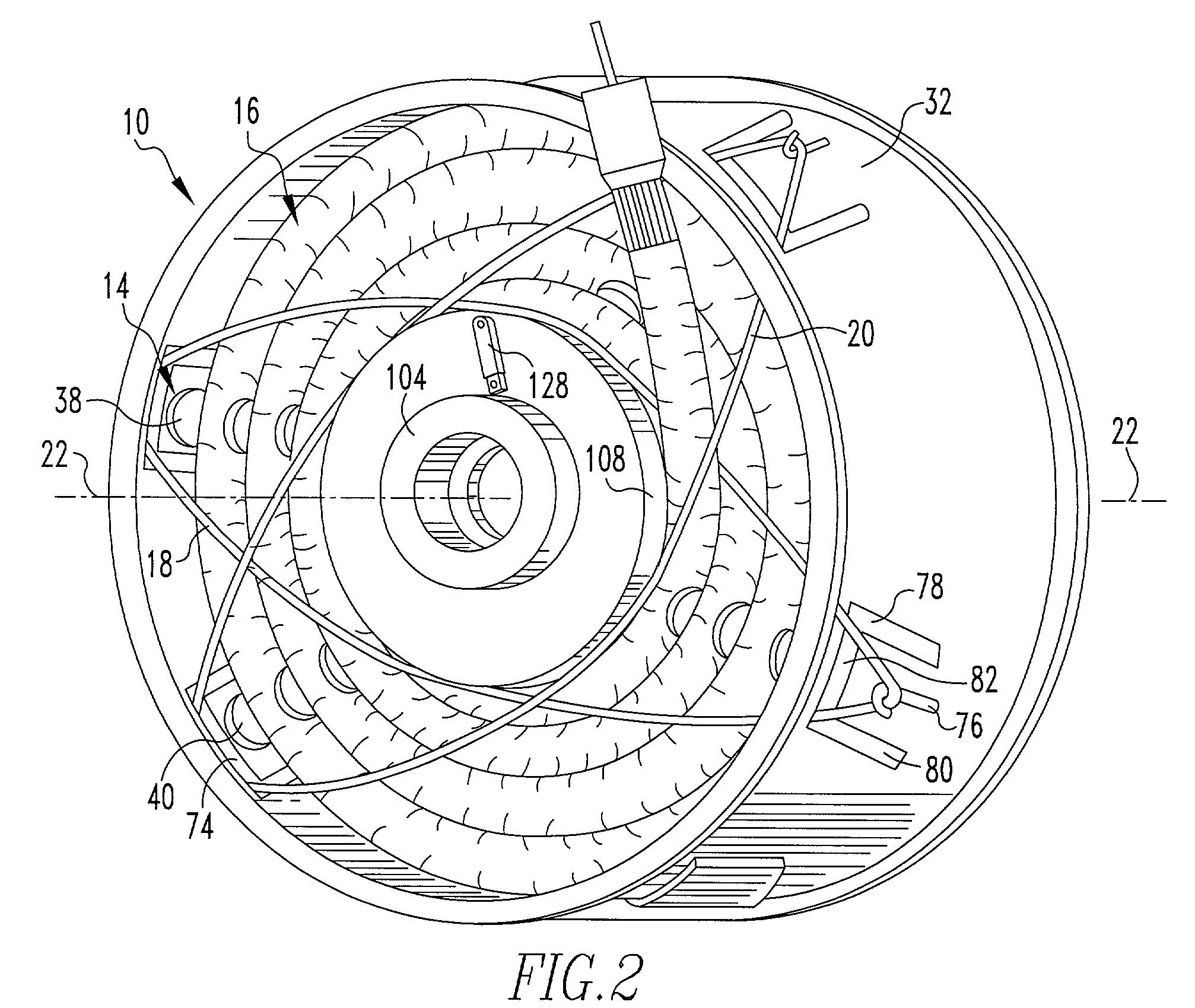
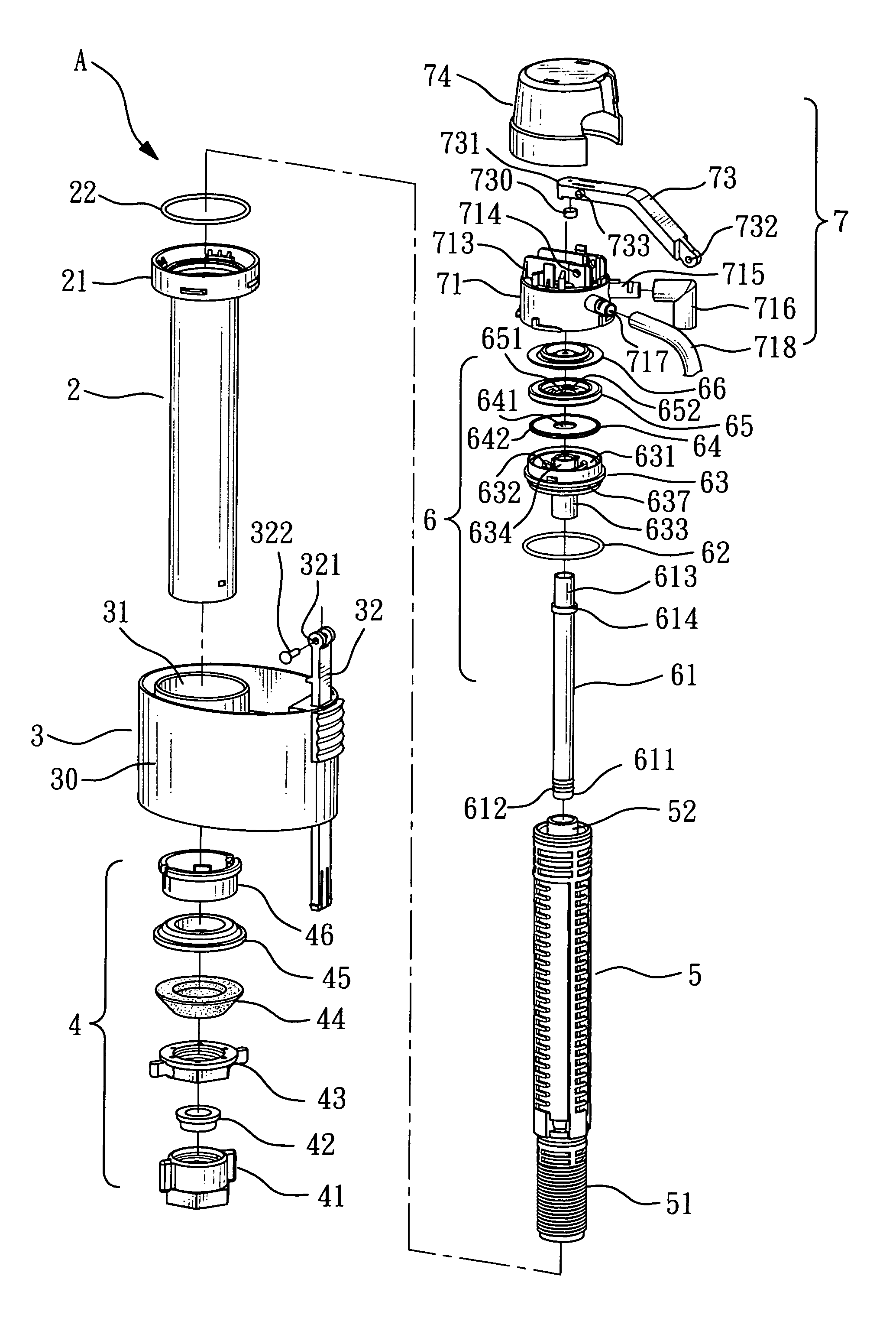
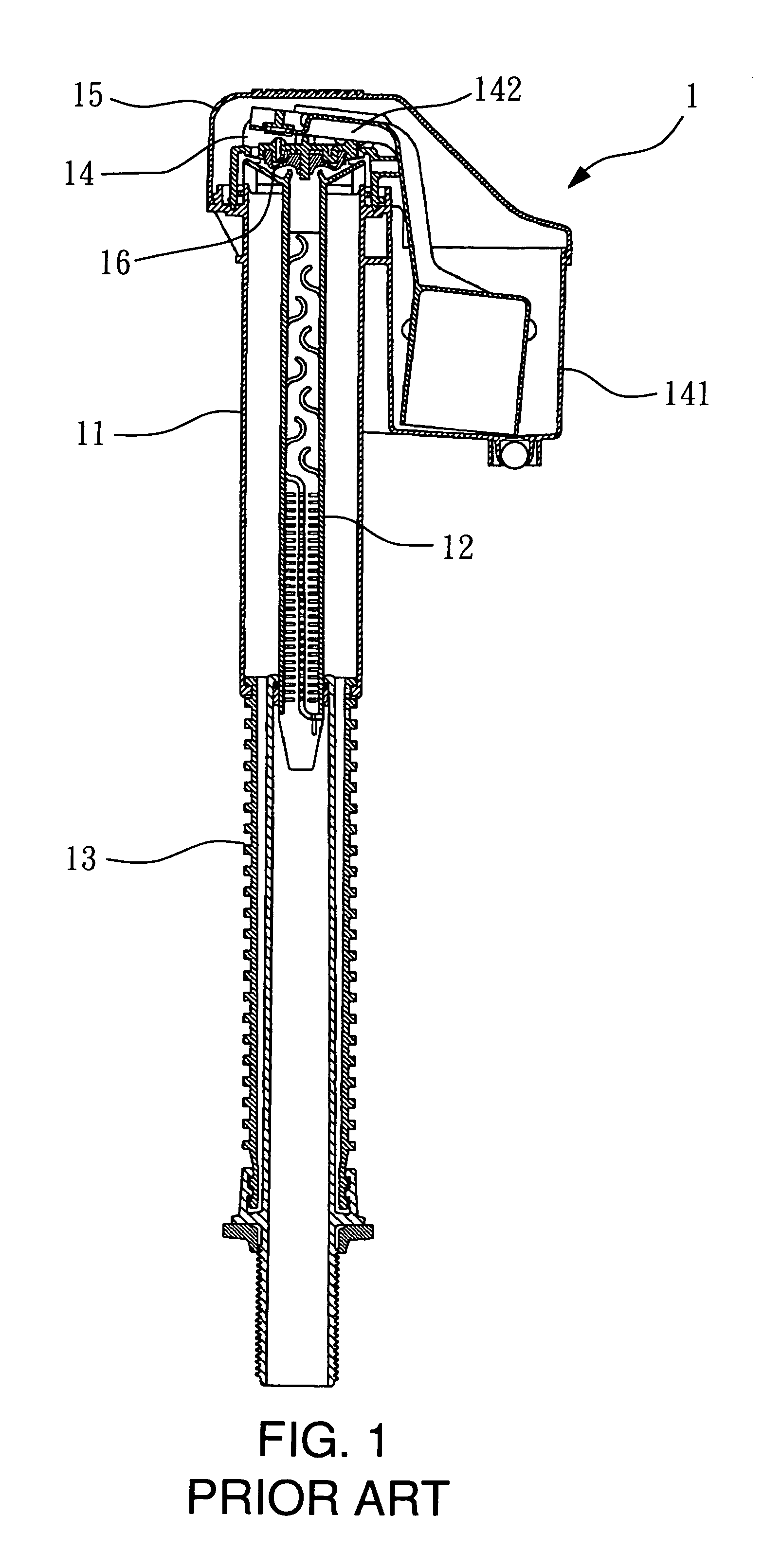
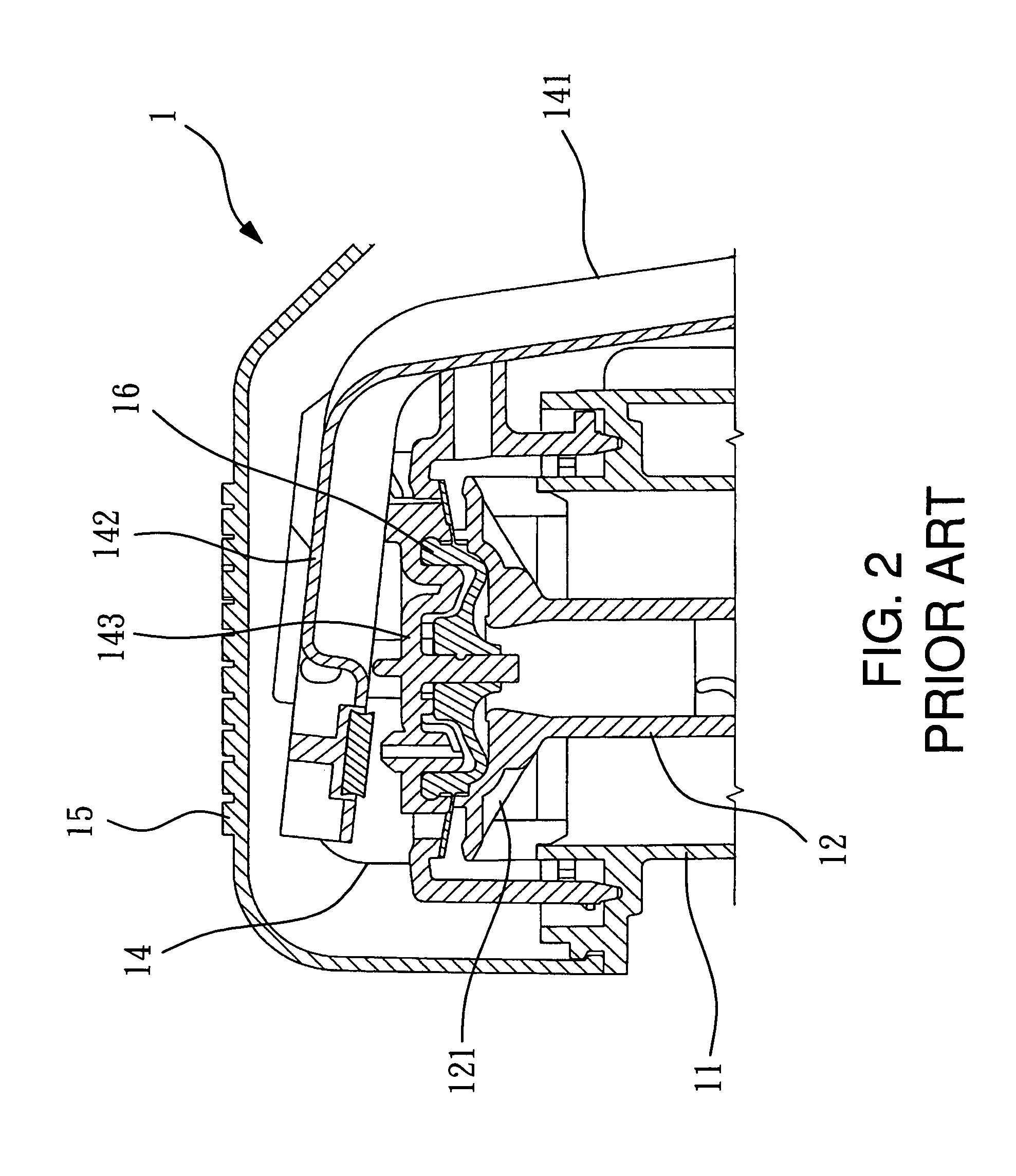
Structure of air-packing device
InactiveUS7165677B2Vibration minimizationPrevent reverse flow of airBagsSacksInterior spaceEngineering
An air-packing device has an improved shock absorbing capability to protect a product in a container box. The air-packing device is configured by first and second plastic films which are bonded at predetermined portions thereby creating a plurality of air containers, each of the air containers having a plurality of series connected air cells; a plurality of check valves established at inputs of the corresponding air containers for allowing compressed air to flow only in a forward direction; and an air input commonly connected to the plurality of check valves. Through a post heat-seal treatments, predetermined edge portions are bonded, thereby creating an inner space for packing a product therein and an opening for loading the product therethrough.
Owner:AIR PAQ
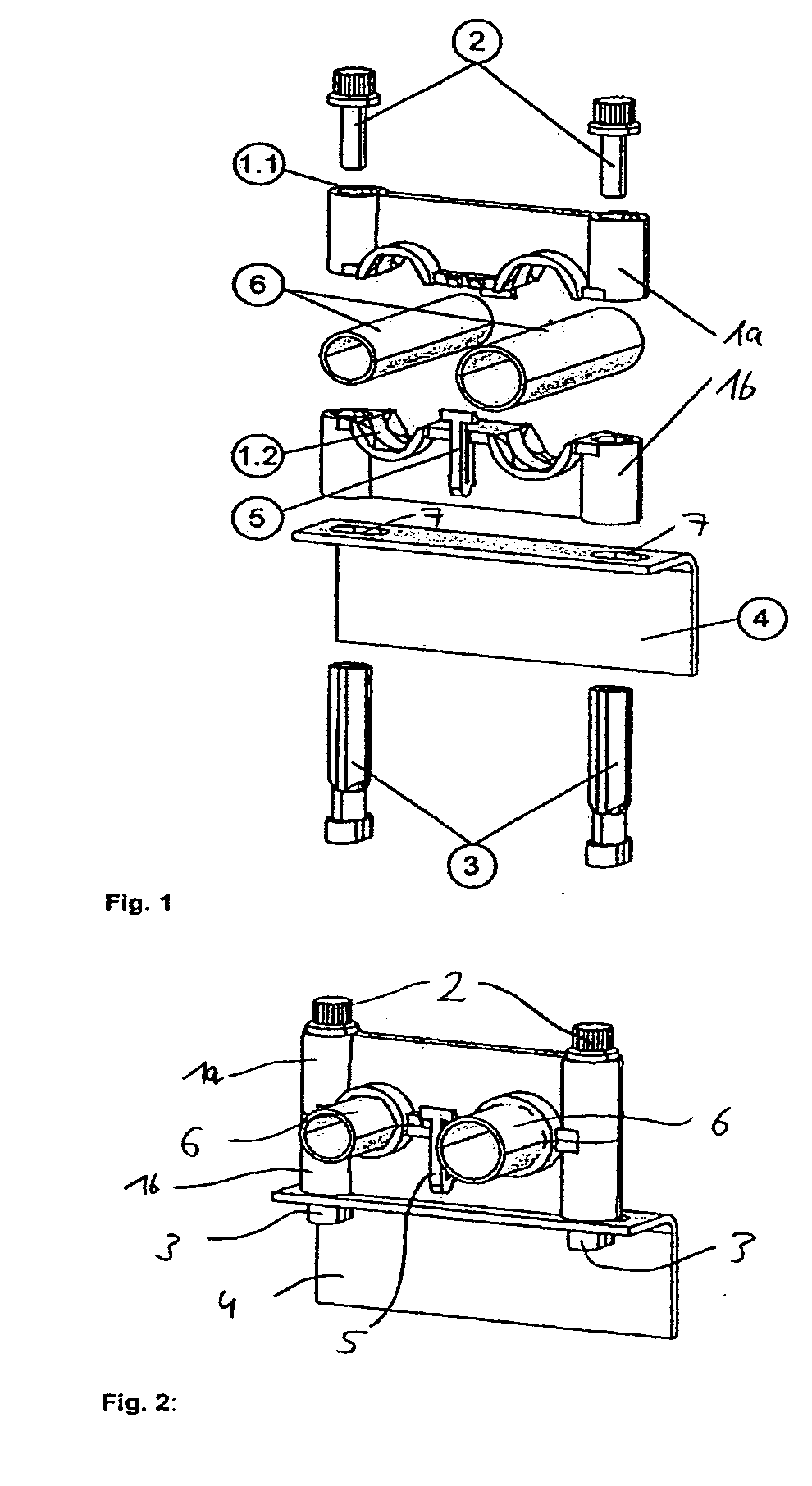
Mounting system for guiding and fastening one or several pipes or similarly formed objects
InactiveUS20060249636A1Prevent automatic releaseAvoid disconnectionPipe supportsPipe elementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Structure of air-packing device having improved shock absorbing capability
An air-packing device has an improved shock absorbing capability to protect a product in a container box. The air-packing device is configured by first and second plastic films which are bonded at predetermined portions thereby creating a plurality of air containers, each of the air containers having a plurality of series connected air cells; a plurality of check valves established at inputs of the corresponding air containers for allowing compressed air to flow in a forward direction; an air input commonly connected to the plurality of check valves; and heat-seal flanges formed on side edges of the air-packing device. Through a post heat-seal treatment, predetermined points on the air containers and the heat-seal flanges are bonded, thereby creating a container portion having an opening for packing a product therein and a cushion portion for supporting the container portion when the air-packing device is inflated by the compressed air.
Owner:AIR PAQ
Structure of air-packing device having improved shock absorbing capability
InactiveUS20050263425A1Vibration minimizationImprove shock absorptionBagsSacksEngineeringPlastic film
An air-packing device has an improved shock absorbing capability to protect a product in a container box. The air-packing device is configured by first and second plastic films which are bonded at predetermined portions thereby creating a plurality of air containers, each of the air containers having a plurality of series connected air cells; a plurality of check valves established at inputs of the corresponding air containers for allowing compressed air to flow in a forward direction; an air input commonly connected to the plurality of check valves; and heat-seal flanges formed on side edges of the air-packing device. Through a post heat-seal treatment, predetermined points on the air containers and the heat-seal flanges are bonded, thereby creating a container portion having an opening for packing a product therein and a cushion portion for supporting the container portion when the air-packing device is inflated by the compressed air.
Owner:AIR PAQ
Full function precision welding system
InactiveUS20070297556A1Increase corrosion and abrasion resistanceAmple powerNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringElectric machineryEngineering
A welding system for performing a welding process on a pipe in a confined space includes a motor housing, a weld head assembly and an insertion tube that extends between the motor housing and the weld head assembly with the weld head assembly remote from the motor housing. The motor housing is supported on a platform for rotational and translational movement of the weld head assembly and houses a motor for positioning the weld head assembly relative to the pipe. The weld head assembly includes a clamp assembly for attaching the weld head assembly to the pipe and a weld tool assembly mounted adjacent the clamp assembly for welding the pipe. An arc length gear and a travel gear adjust the distance between a torch assembly and the pipe and adjust the location of the torch assembly around the pipe when the weld head assembly is attached to the pipe.
Owner:SPENCER KEITH
Radar absorbing coatings
InactiveUS6909395B1Improve adhesionMinimizing detectionLayered productsMetallic material coating processesRadarInfrared signature
A method for preventing the discovery of military aircraft and missiles by enemy and infrared detectors. The method involves applying a coating of a ferrite containing glass composition to the surfaces of those metal or ceramic substrates that are susceptible to detection through their radar or infrared signature.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Structure of air-packing device
An air-packing device has an improved shock absorbing capability to protect a product in a container box. The air-packing device is configured by first and second plastic films which are bonded at predetermined portions thereby creating a plurality of air containers, each of the air containers having a plurality of series connected air cells; a plurality of check valves established at inputs of the corresponding air containers for allowing compressed air to flow only in a forward direction; and an air input commonly connected to the plurality of check valves. Through a post heat-seal treatment predetermined edge portions are bonded, thereby creating an inner space for packing a product therein and an opening for loading the product therethrough.
Owner:AIR PAQ
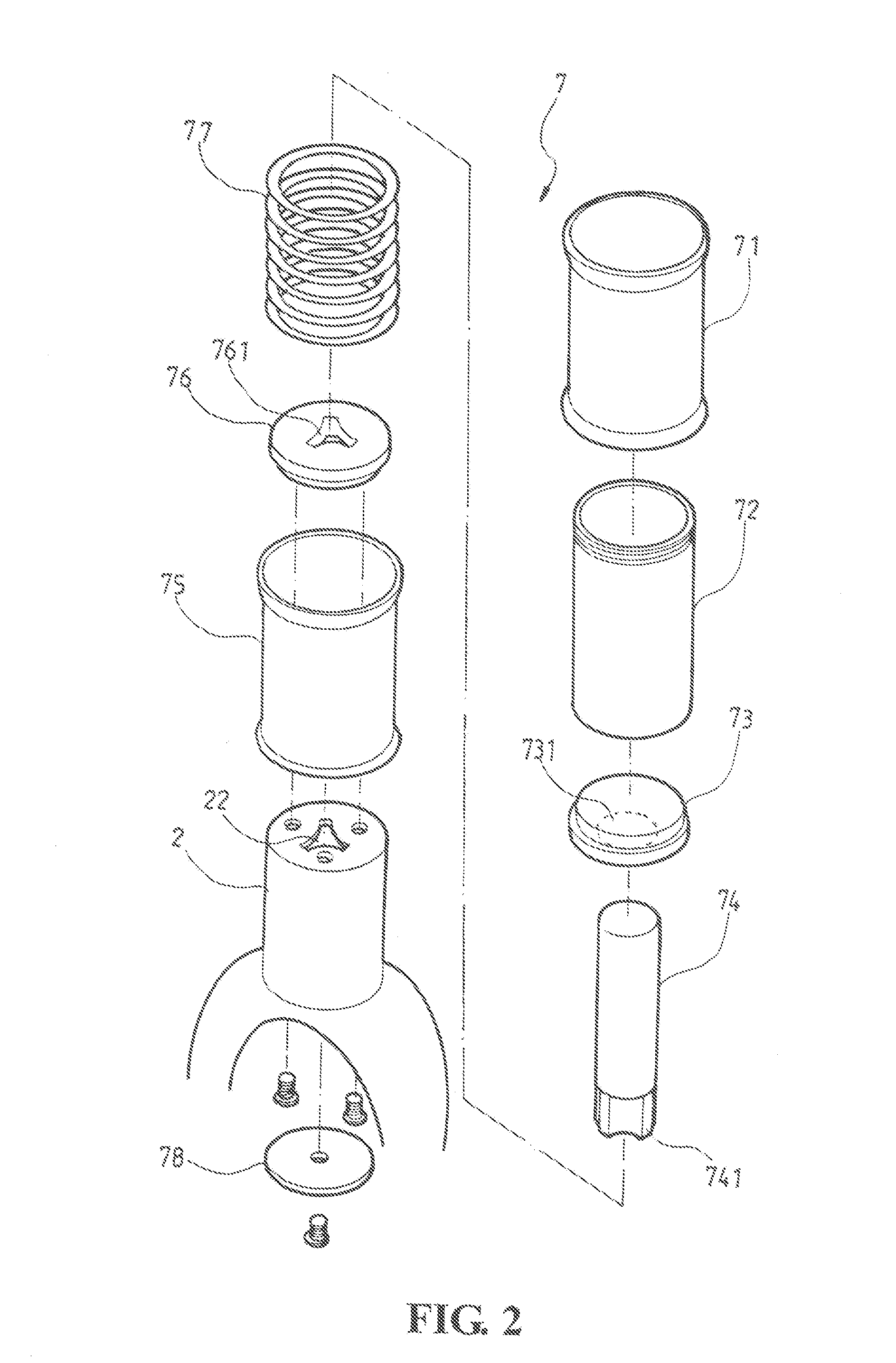
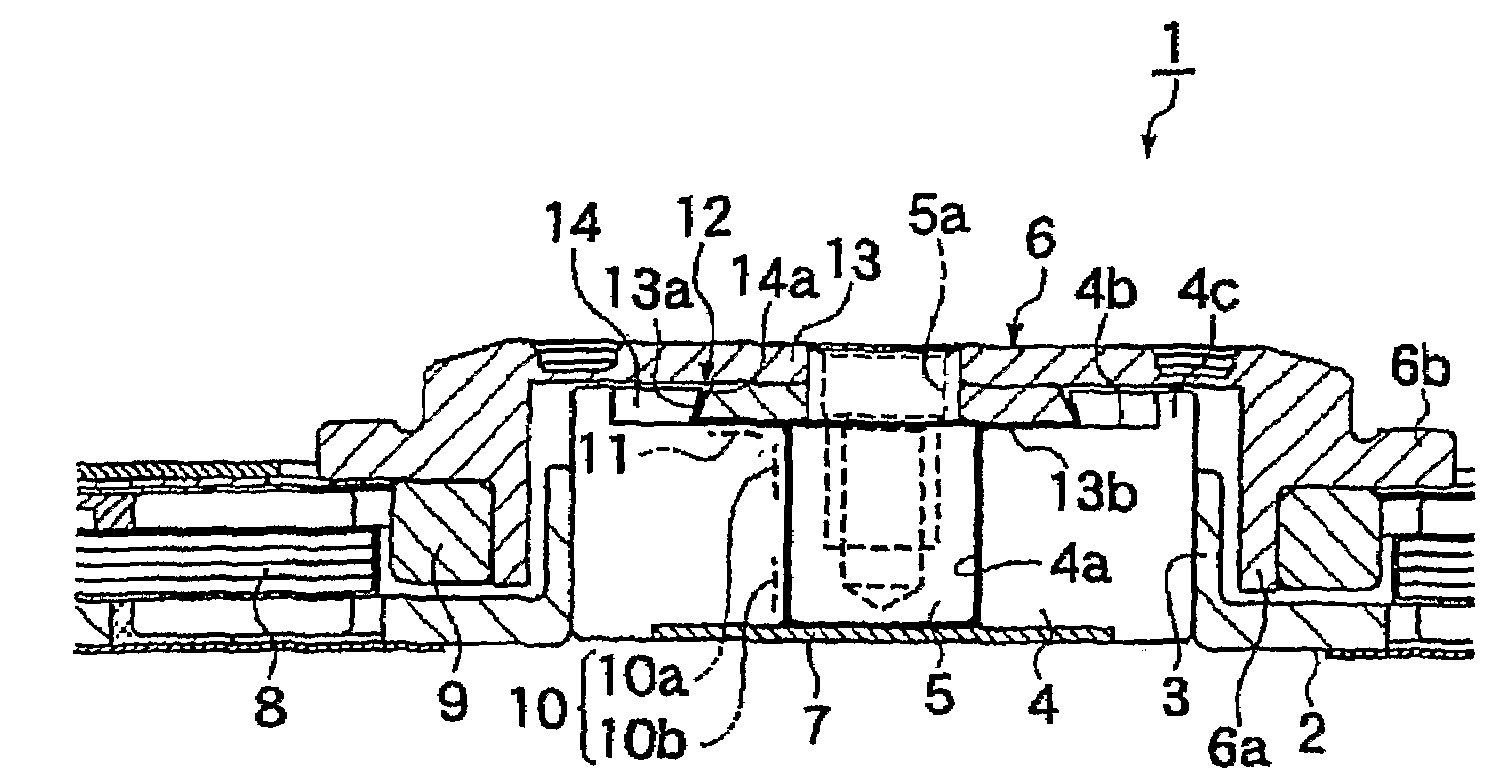
Fluid Dynamic Bearing Mechanism for a Motor
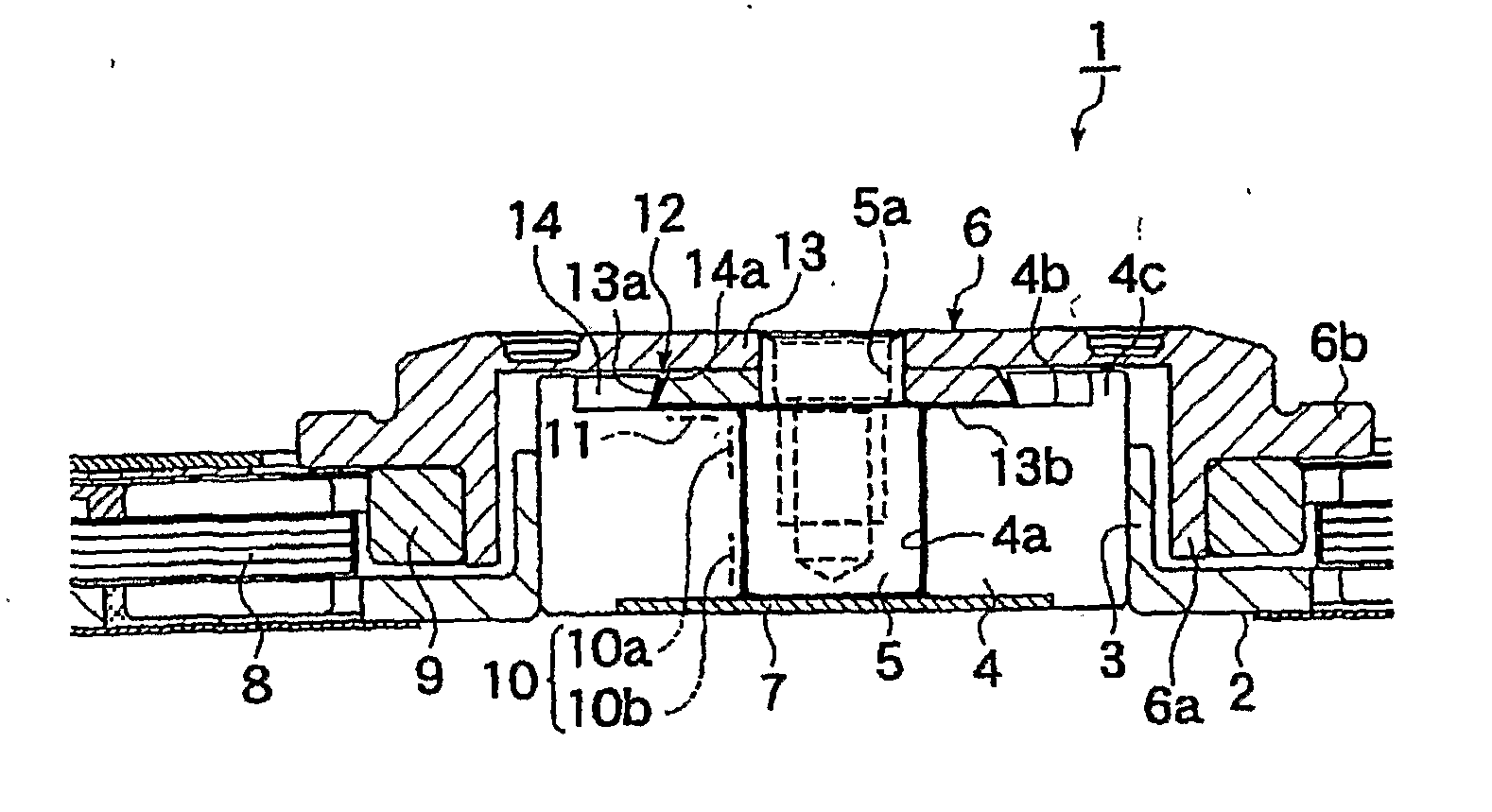
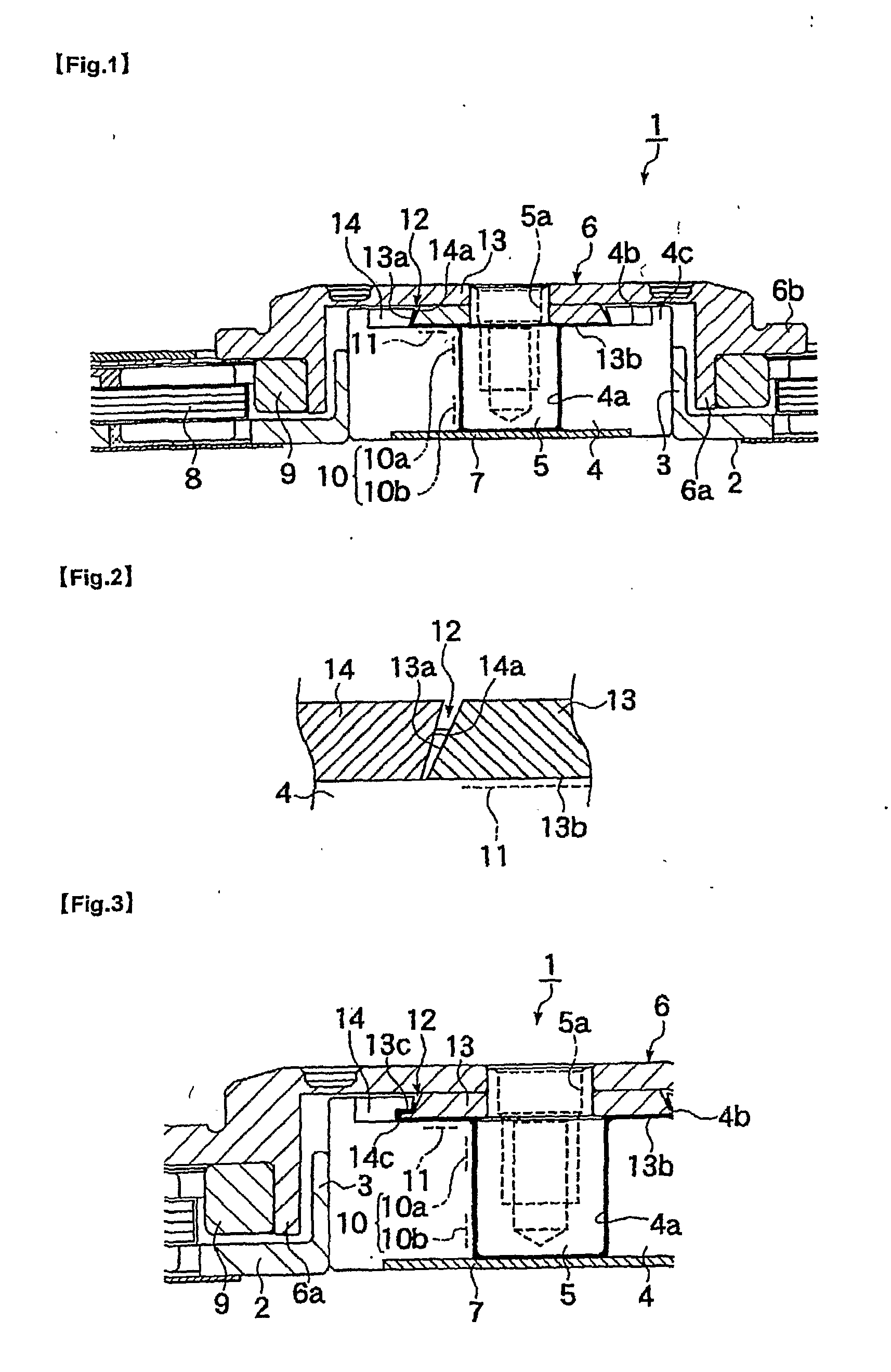
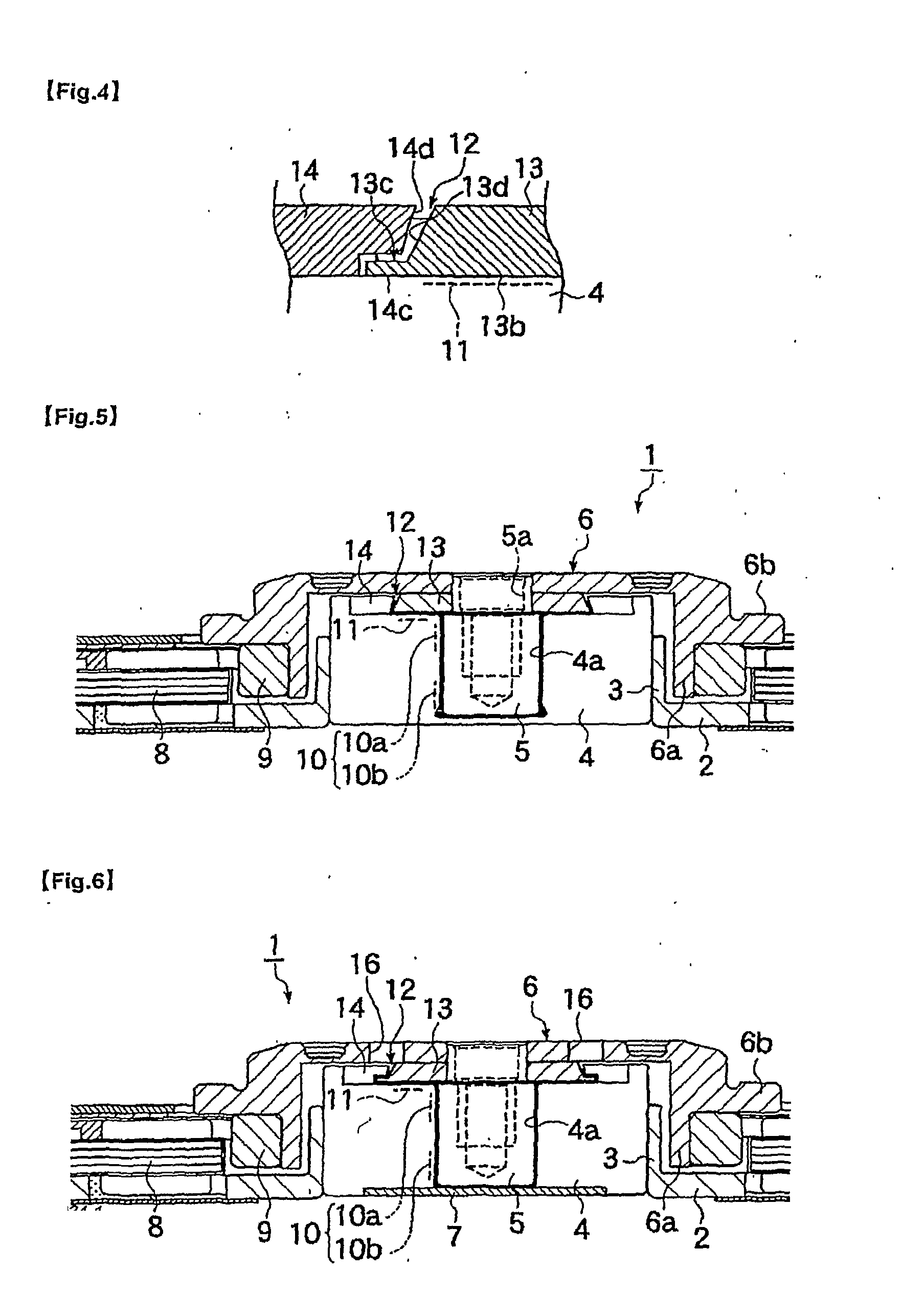
InactiveUS20070211971A1Improve bearing rigidityHigh rotation accuracyShaftsRecord information storageCapillaria obsignataDynamic pressure
A fluid dynamic bearing mechanism for a motor (1) suitable for use in a hard disk drive and having a compact and thin shape, high bearing rigidity, and high rotating accuracy, and which securely keeps the rotor member (6) in place against shocks, and allows the inspection of lubricant supply amount easily. A fluid dynamic bearing mechanism having a capillary seal part (12) on one end of lubricant supply part formed by a minute gap including dynamic pressure grooves (10) formed on a shaft member (5) or a bearing member (4) is provided. An annular member (13) is fitted on the shaft member at the location corresponding to the capillary seal part, another annular member (14) is fitted on the bearing member at the location corresponding to the capillary seal part, a taper or step (13a, 14a) is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the annular member on the shaft member side and the inner peripheral surface of the annular member on the bearing member side. These inner and outer peripheral surfaces are arranged to be close to and facing with each other so that the rotor member is prevented from disengaging from the bearing member, and the capillary seal part can be formed at the same time. An axial dynamic pressure bearing unit (1) is formed between the annular member on the shaft member side and one end of the bearing member.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
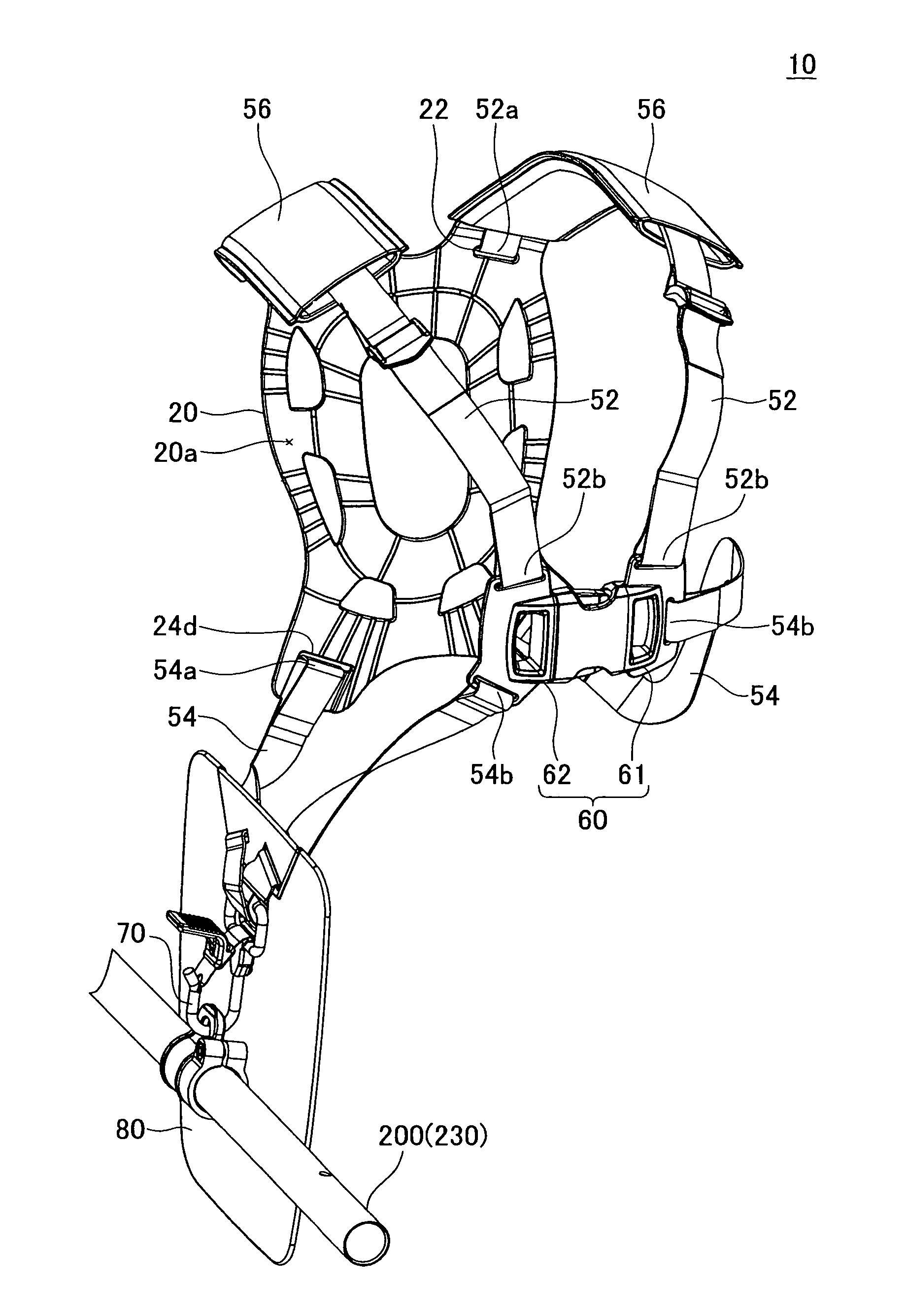
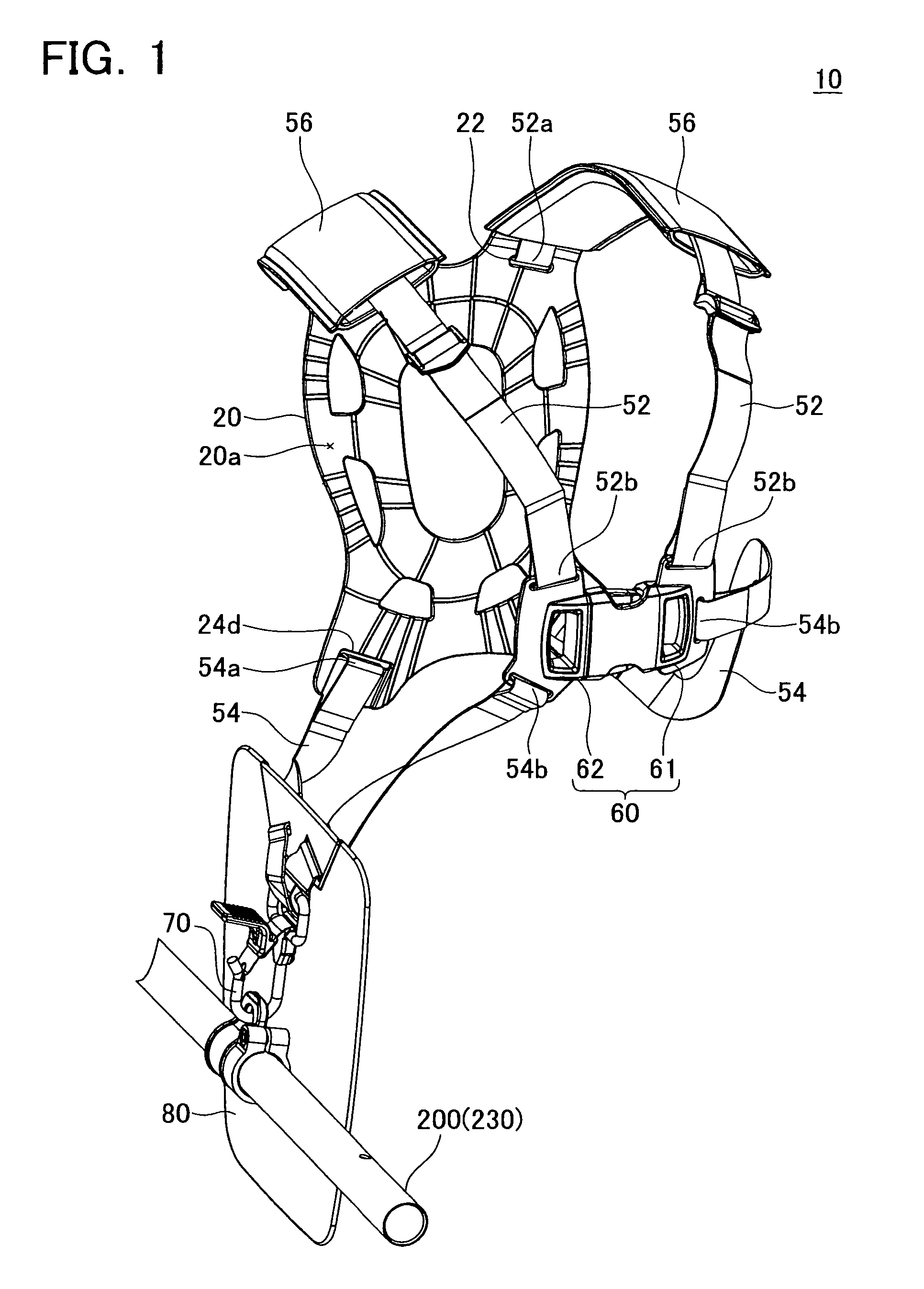
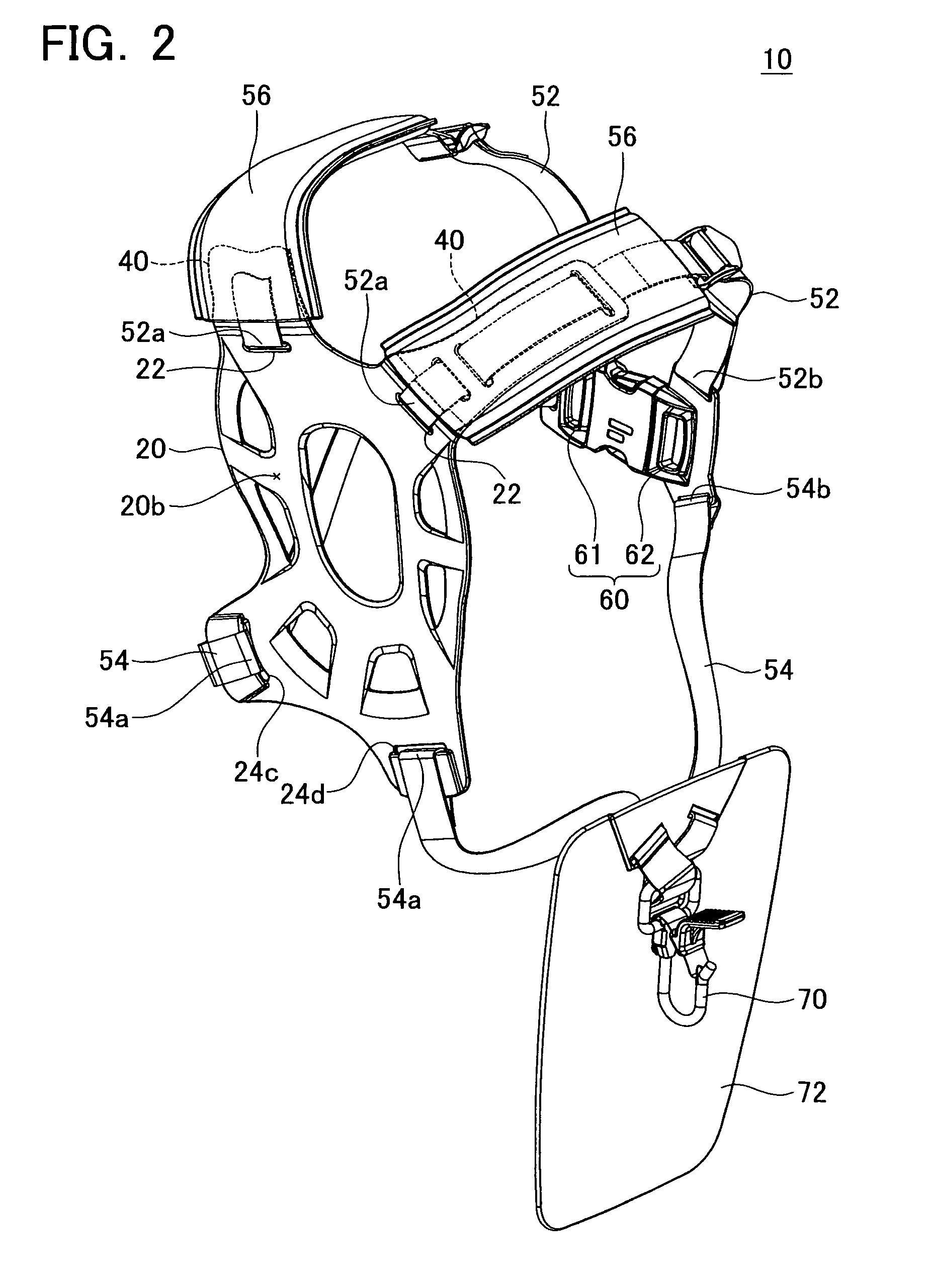
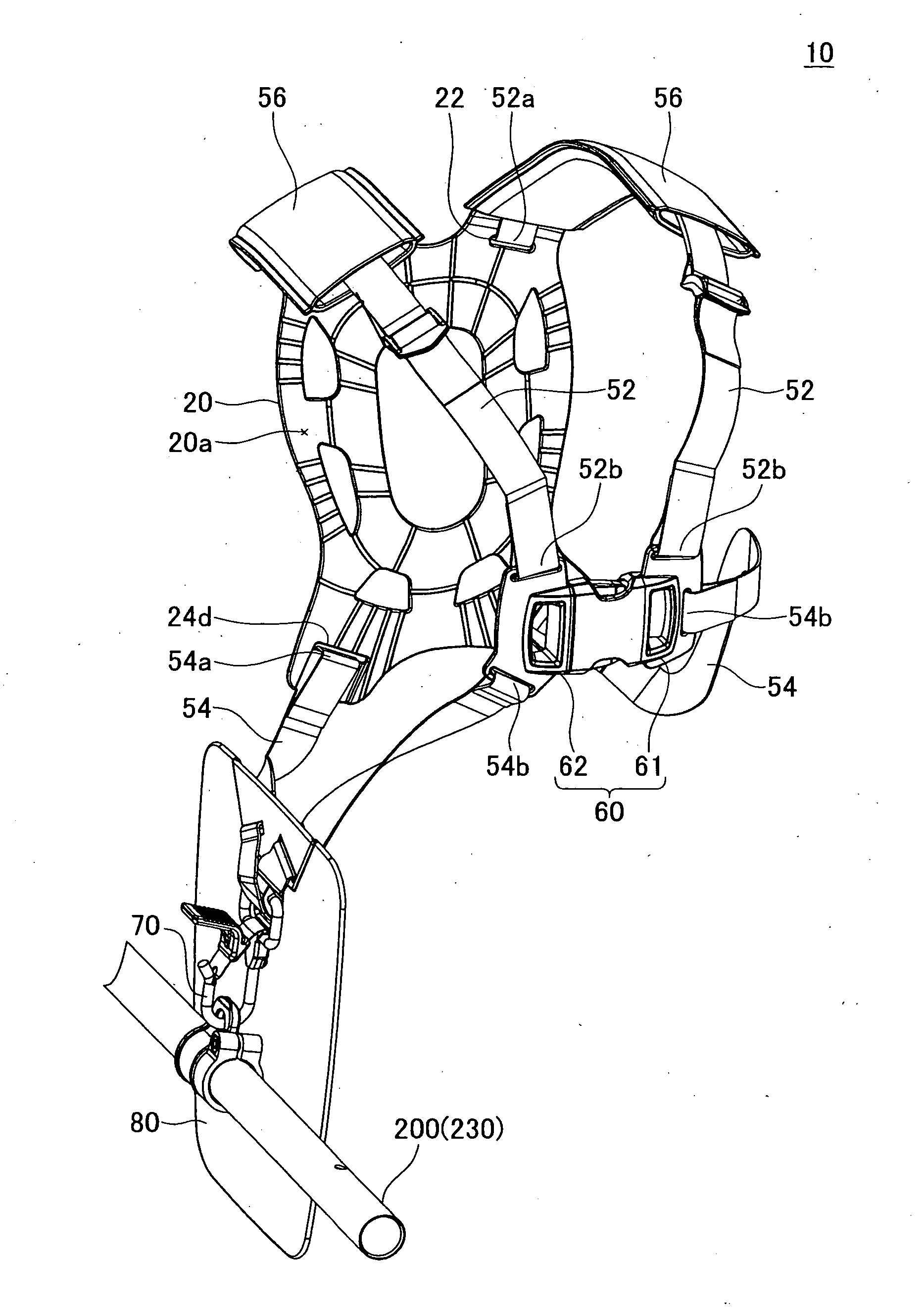
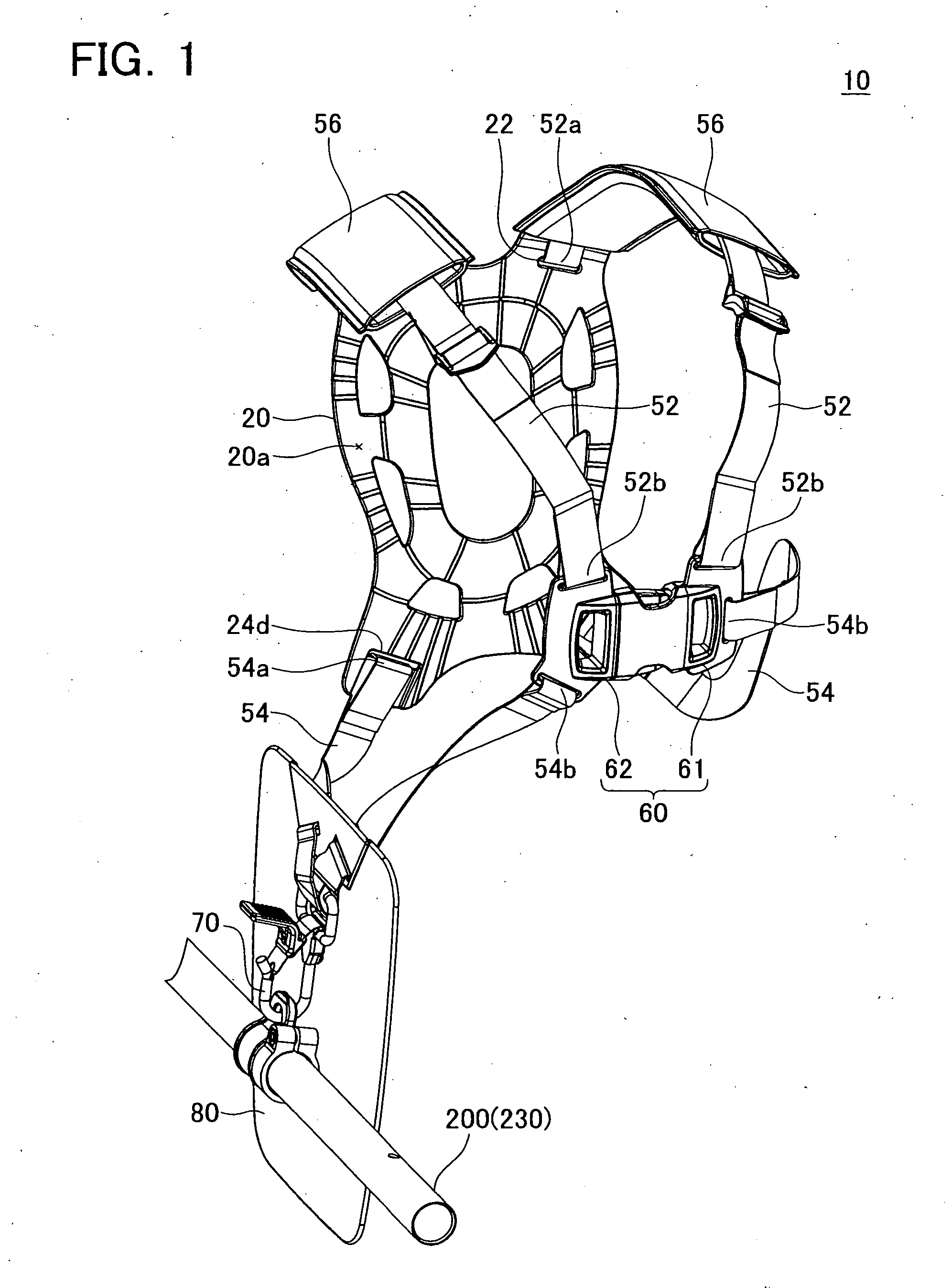
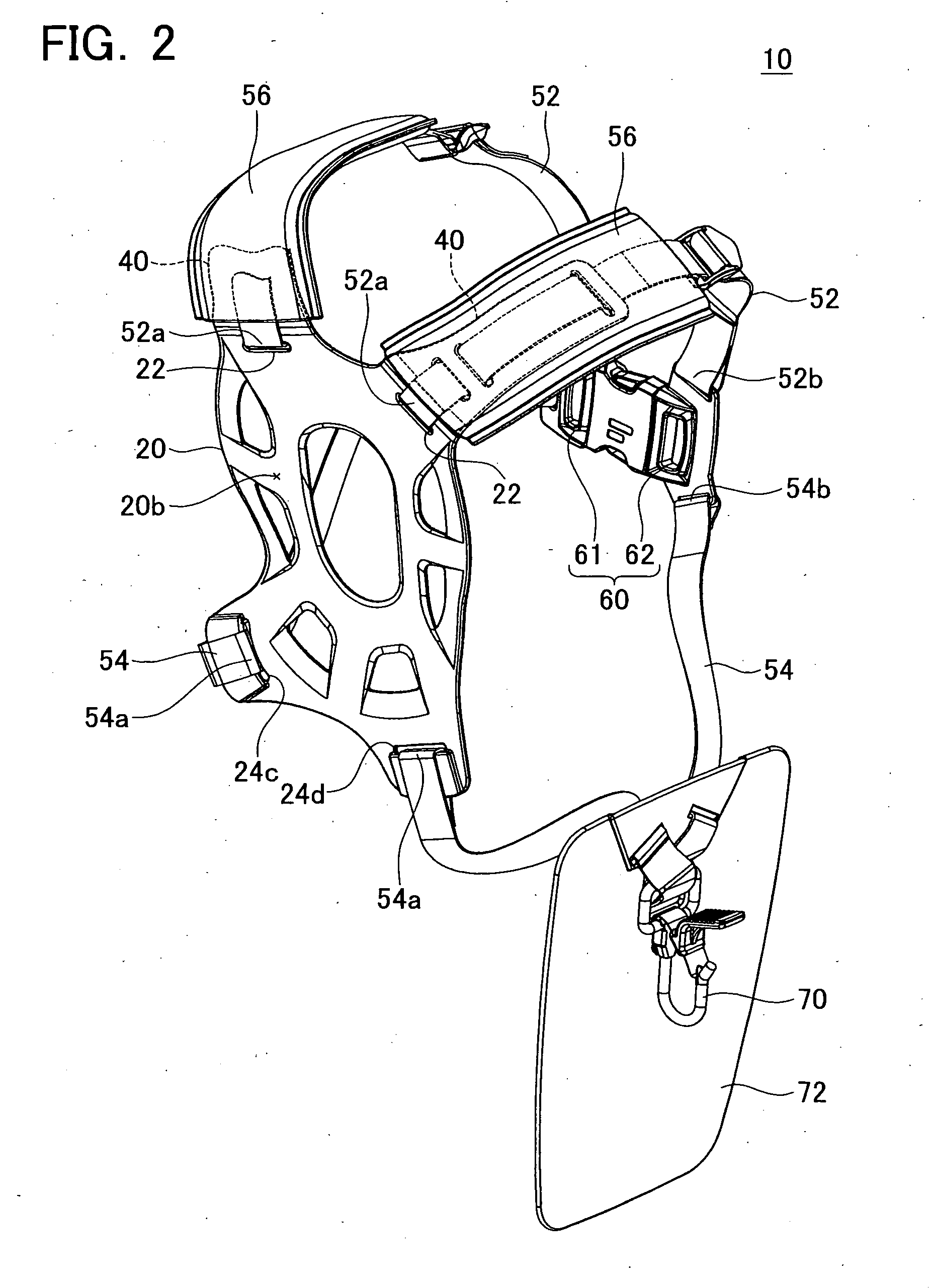
Harness for a handheld power equipment
InactiveUS8925774B2Reduces vibration and shockComplicated constructionTravelling sacksPursesEngineeringPower equipment
The harness comprises a backplate, a plurality of belts and an attachment. The backplate is arranged on the back of the user. The plurality of belts is configured so that one end of each belt is connected to the backplate and another end of each belt is connected to each other on the front of the user. The attachment is supported by at least one of the backplate and the plurality of belts, and is configured to be attached to the power equipment. The backplate preferably comprises at least one ventilation groove formed on its inner surface and extending to the edge of the backplate, which allows air to pass between the user and backplate easily.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
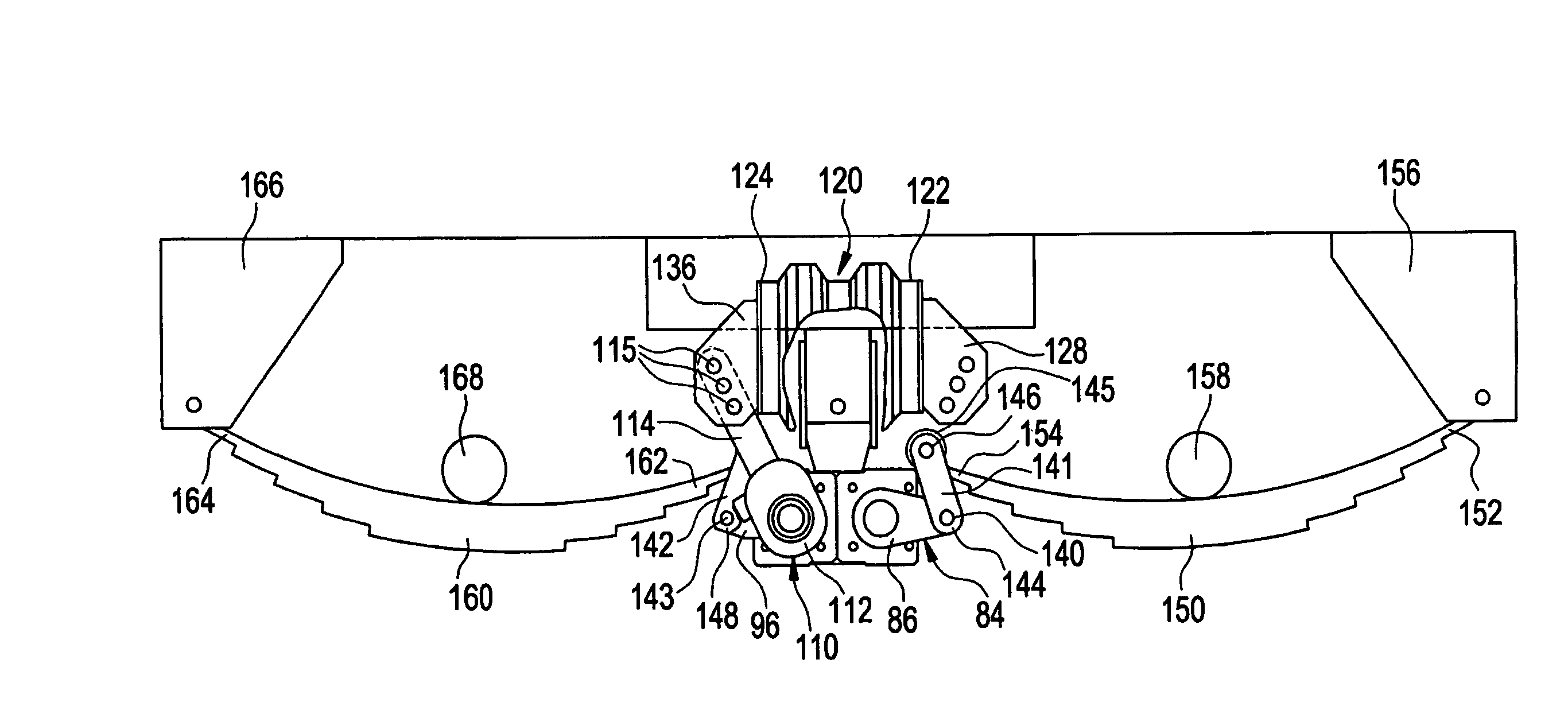
Suspension isolator equalizer
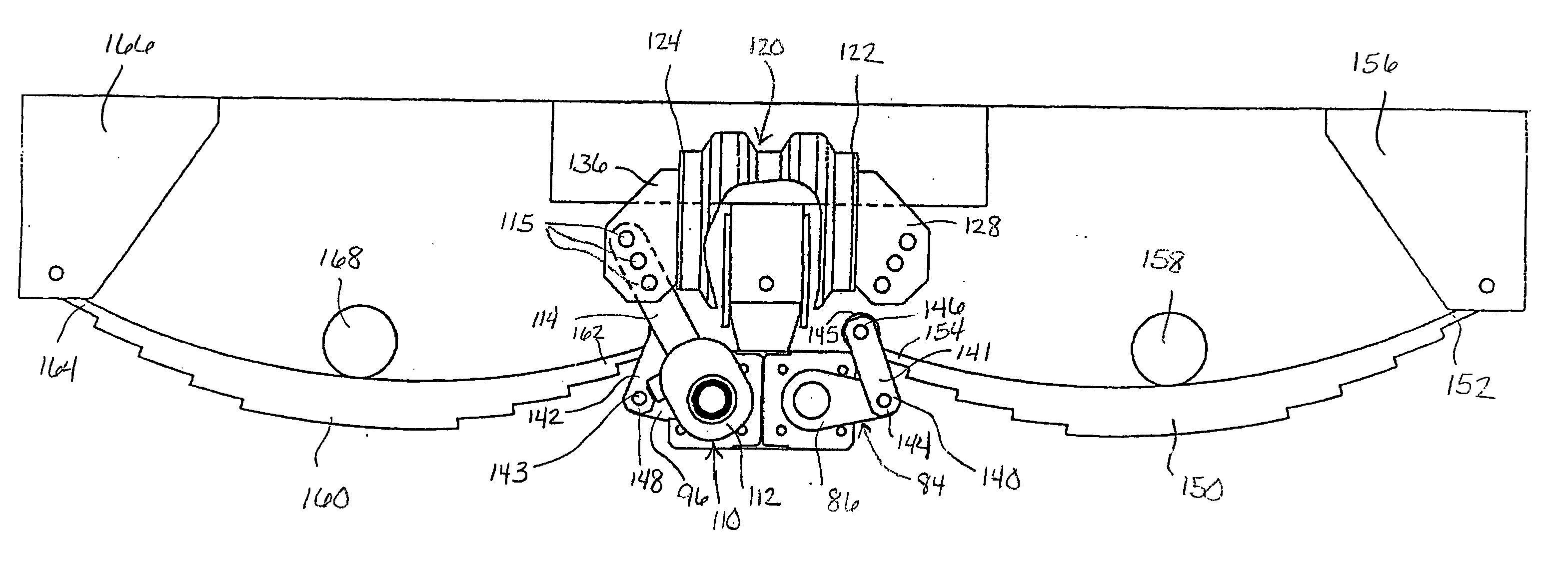
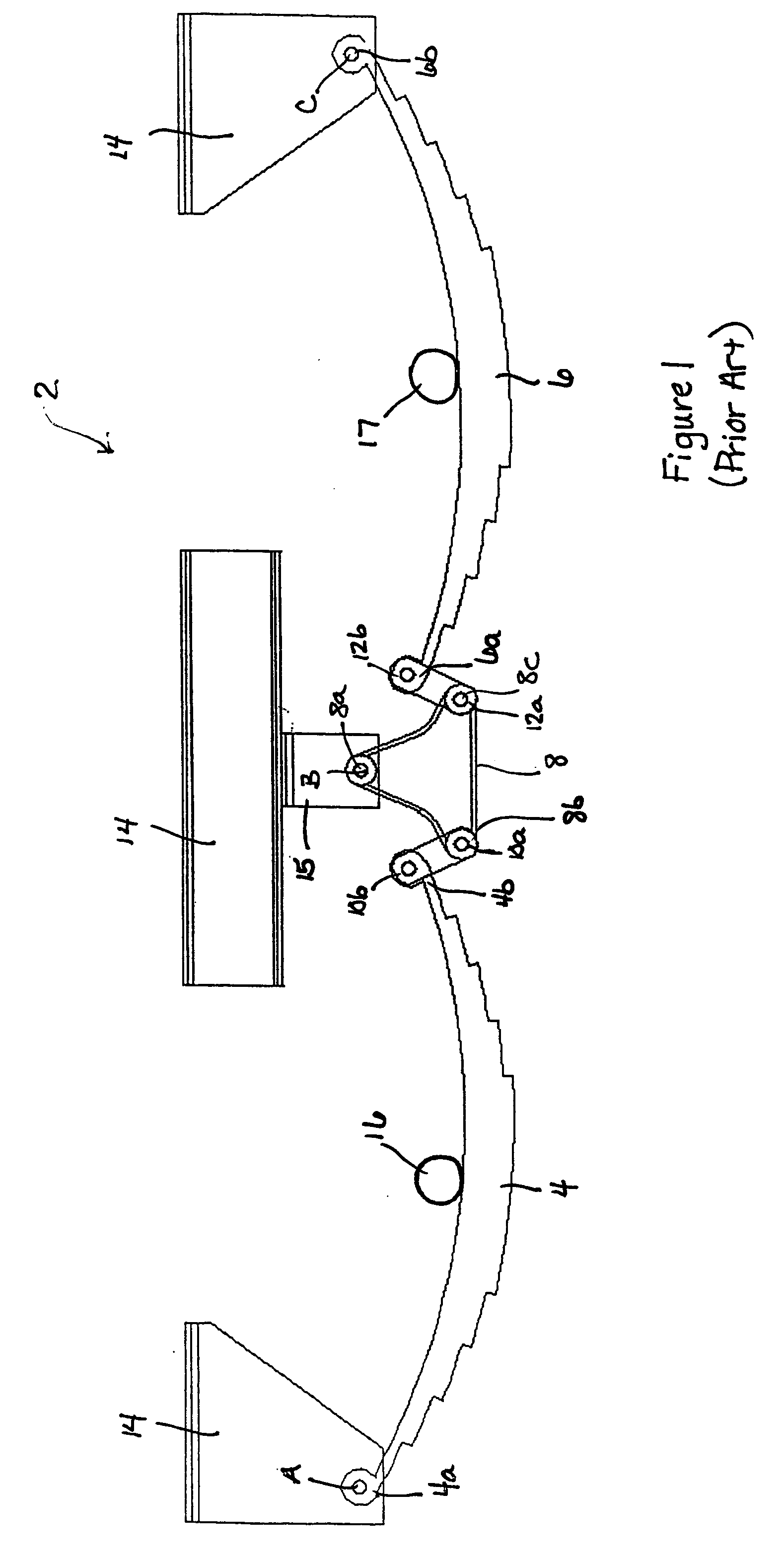
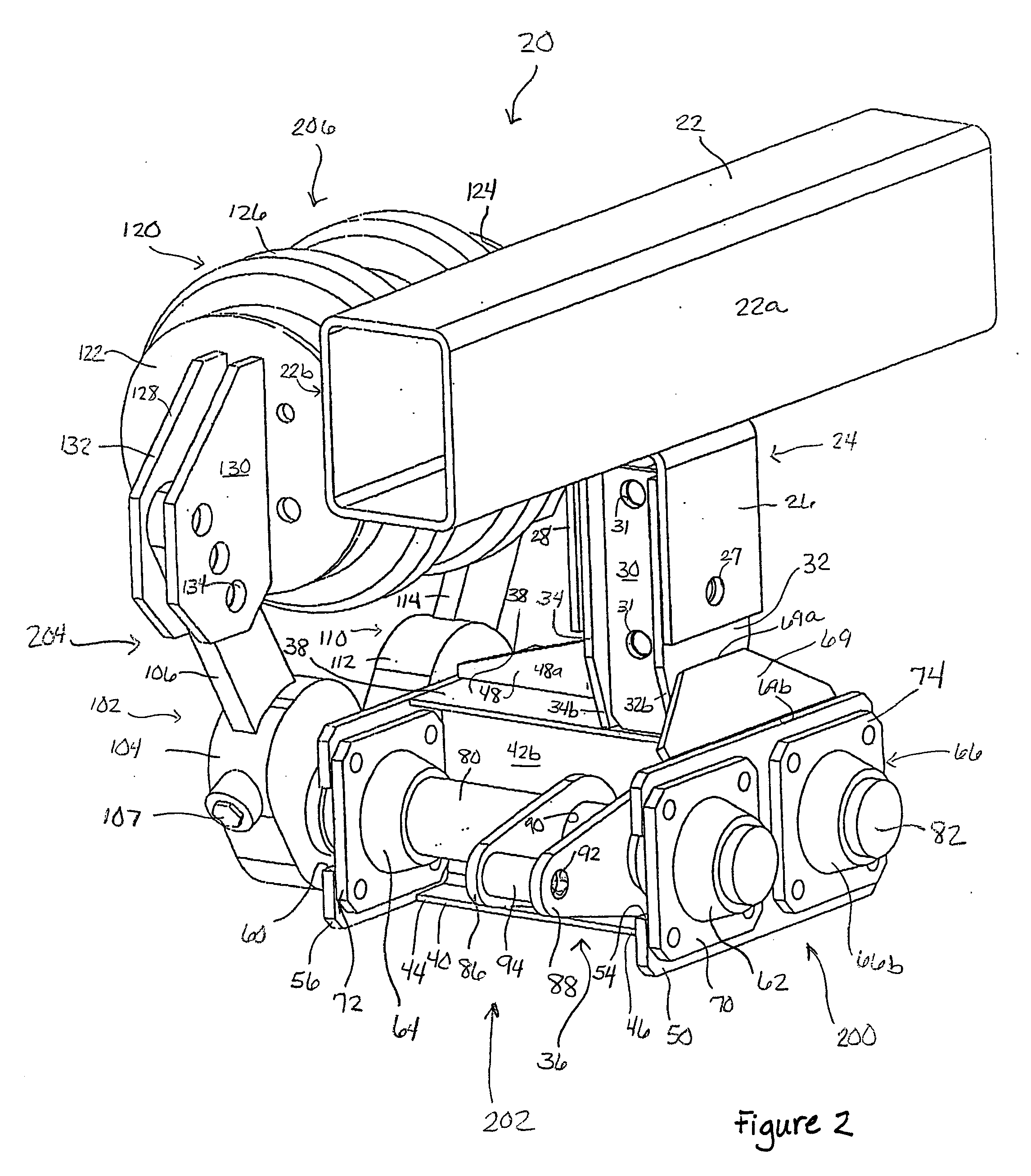
ActiveUS7144031B2Shock and vibrationEliminate interaction forceLeaf springsRigid suspensionsClassical mechanicsEngineering
An isolator for use in a suspension system includes a front shaft and a rear shaft. A front spring arm and a front transitional arm are mounted to the front shaft. A rear spring arm and a rear transitional arm are mounted to the rear shaft. A resilient member is mounted between the front and rear transitional arms. As forces are applied to the front and rear link arms, the front and rear shafts rotate causing the front and rear transitional arms to rotate. As the front and rear transitional arms rotate, the resilient member is compressed and expanded accordingly.
Owner:LIPPERT COMPONENTS MFG INC
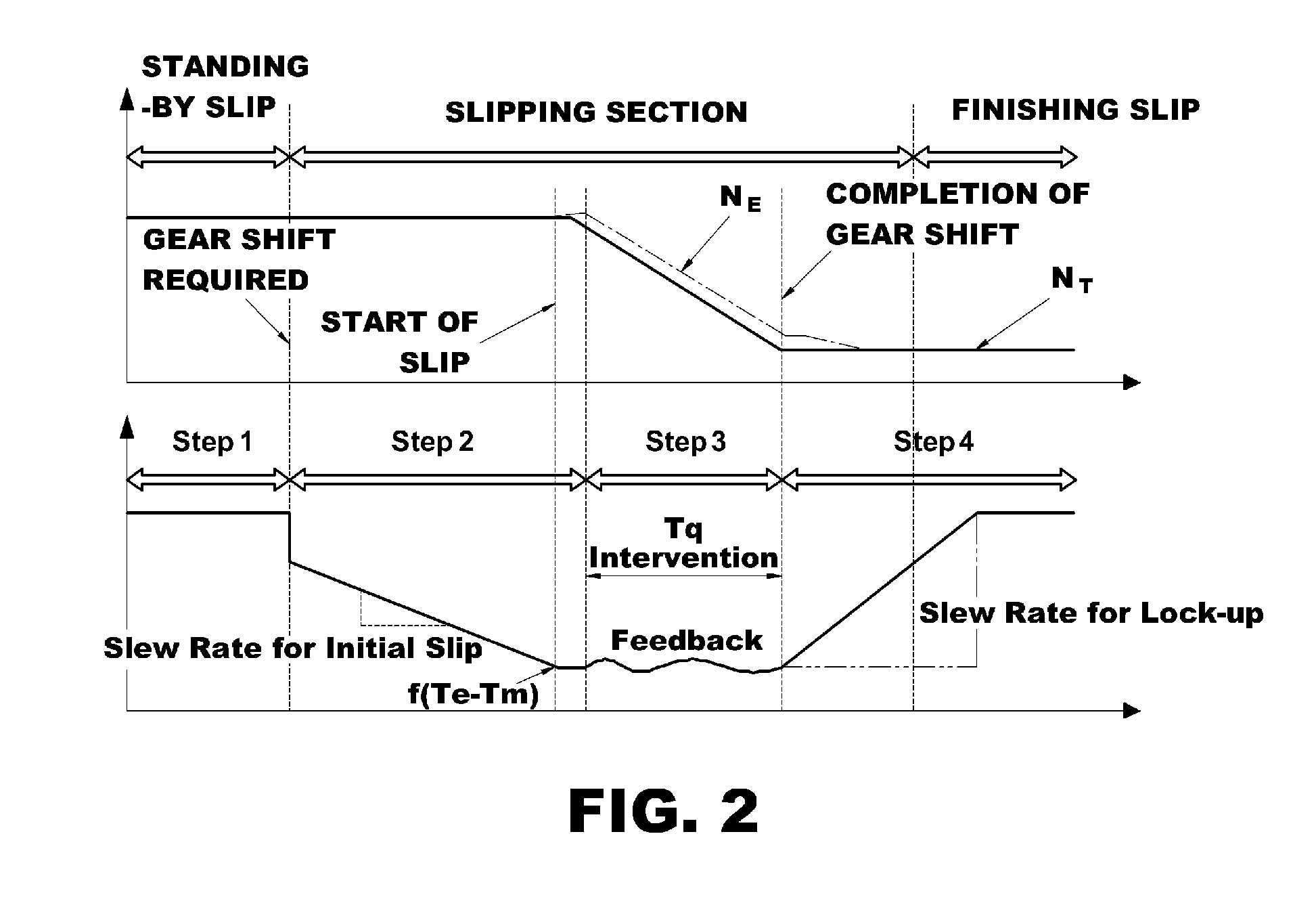
Method for reducing gear shifting shock of hybrid electric vehicle
The present invention provides a method which controls the hydraulic pressure of a clutch (an engine clutch) disposed between an engine and a drive motor, thus reducing gear shifting shock and vibration. The method comprises a slip preparation step of determining that gear shifting is required and reducing the hydraulic pressure of the clutch to a preset target hydraulic pressure from a point in time at which the gear shifting is required. The method further comprises a slip maintaining step of feedback-controlling the hydraulic pressure of the clutch such that a slip rate of the clutch is maintained constant after the hydraulic pressure of the clutch reaches the target hydraulic pressure; and a clutch lock-up completing step of increasing the hydraulic pressure of the clutch, from a point in time at which the gear shifting is completed, to a maximum hydraulic pressure for making a lock-up state of the clutch.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Ruggedized scintillation detector for portal monitors and light pipe incorporated therein
InactiveUS20050184241A1Reduce decreaseWeaken energyMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementLight pipePhotomultiplier
A radiation detector includes a housing, an elongated, rectangular crystal having four longitudinally extending corners, and a photomultiplier tube both supported in the housing, with a light pipe located axially between respective facing ends of the photomultiplier tube and the crystal; and a plurality of elongated rails extending along respective ones of the longitudinally extending corners of the rectangular crystal, establishing an air gap between the crystal and the housing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
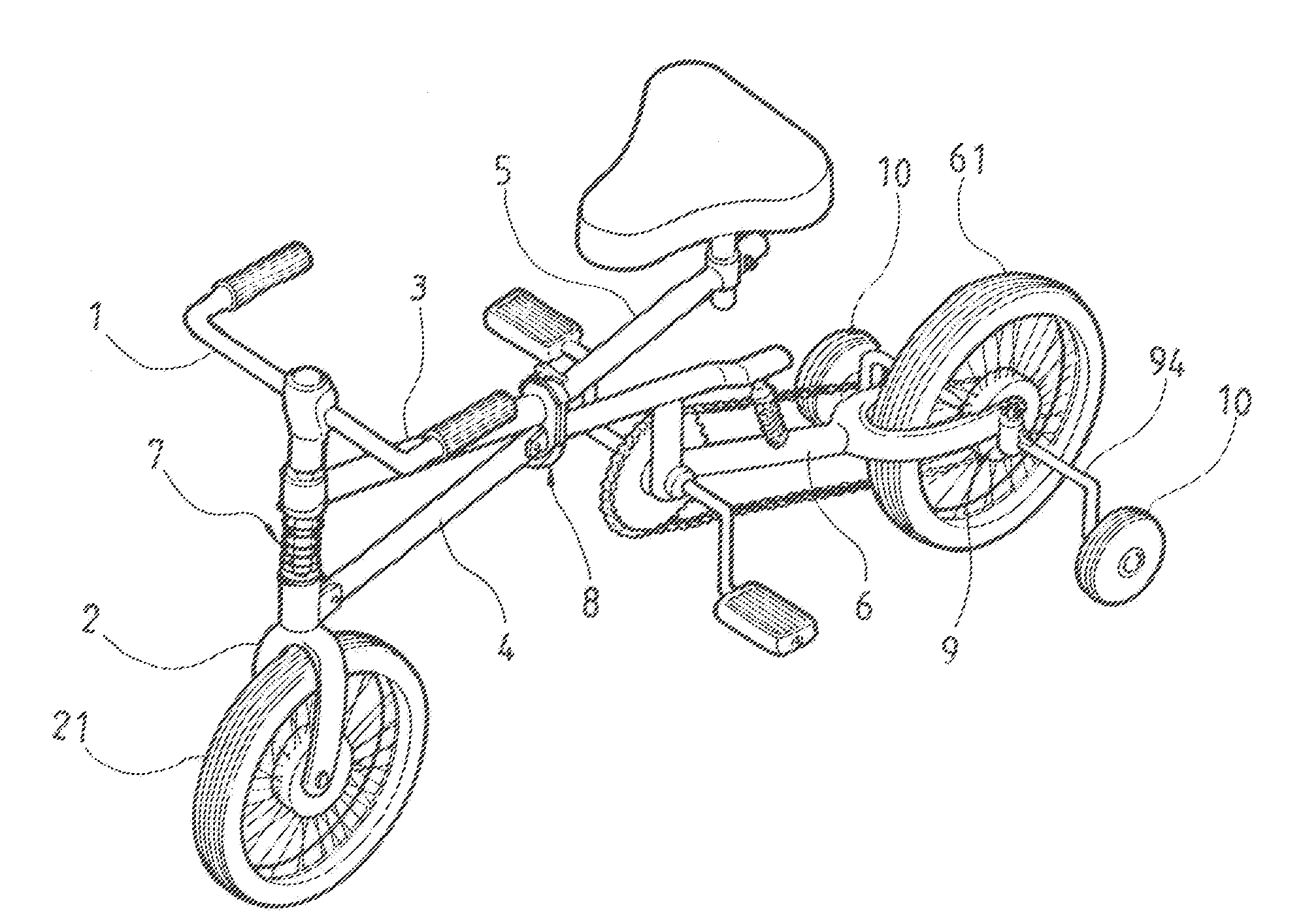
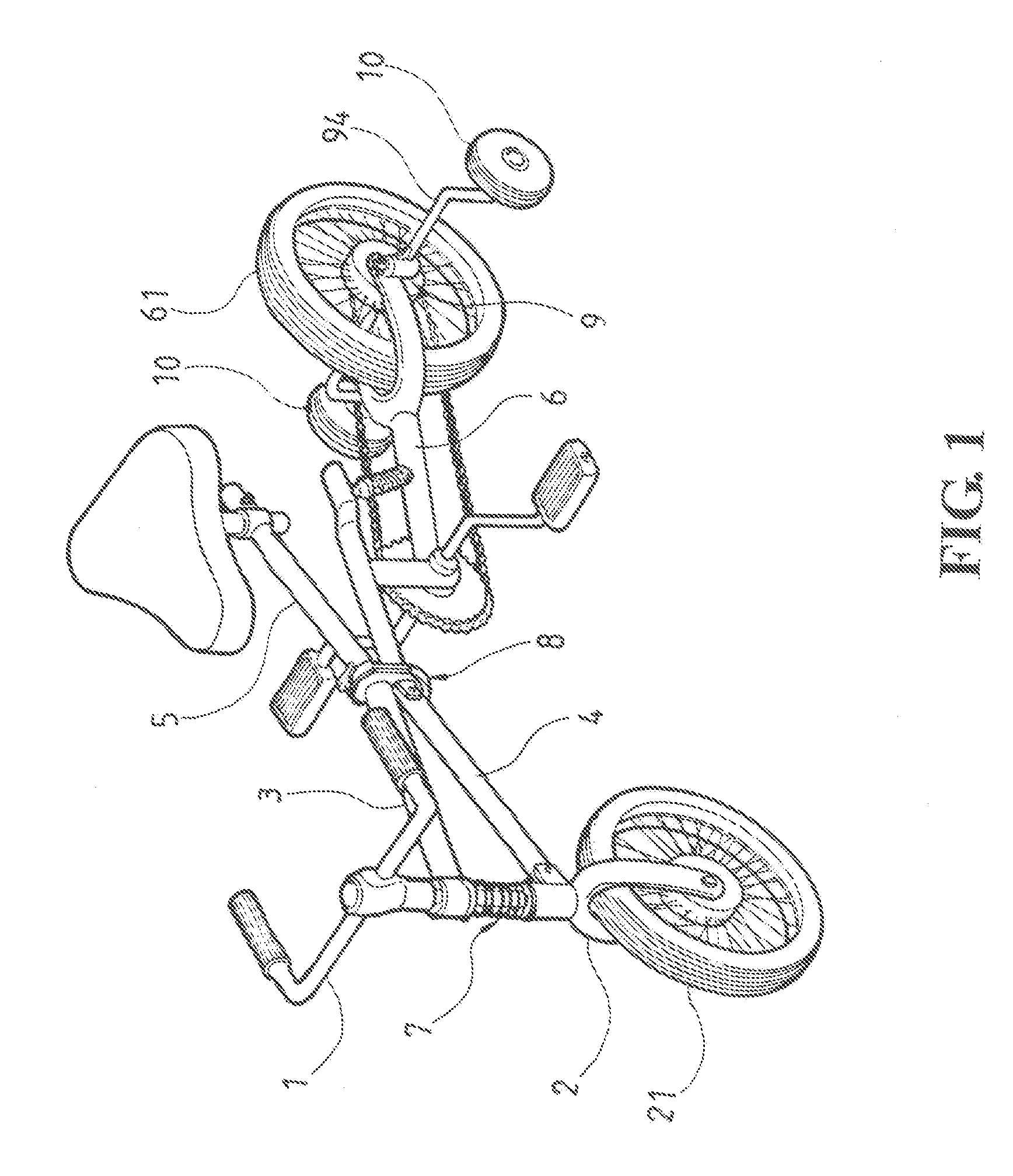
Foldable bicycle having x-shaped frame
InactiveUS20080157502A1Comfortable rideEasy and convenient stowageFoot-driven leversWheel based transmissionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FU KUANG HUAN
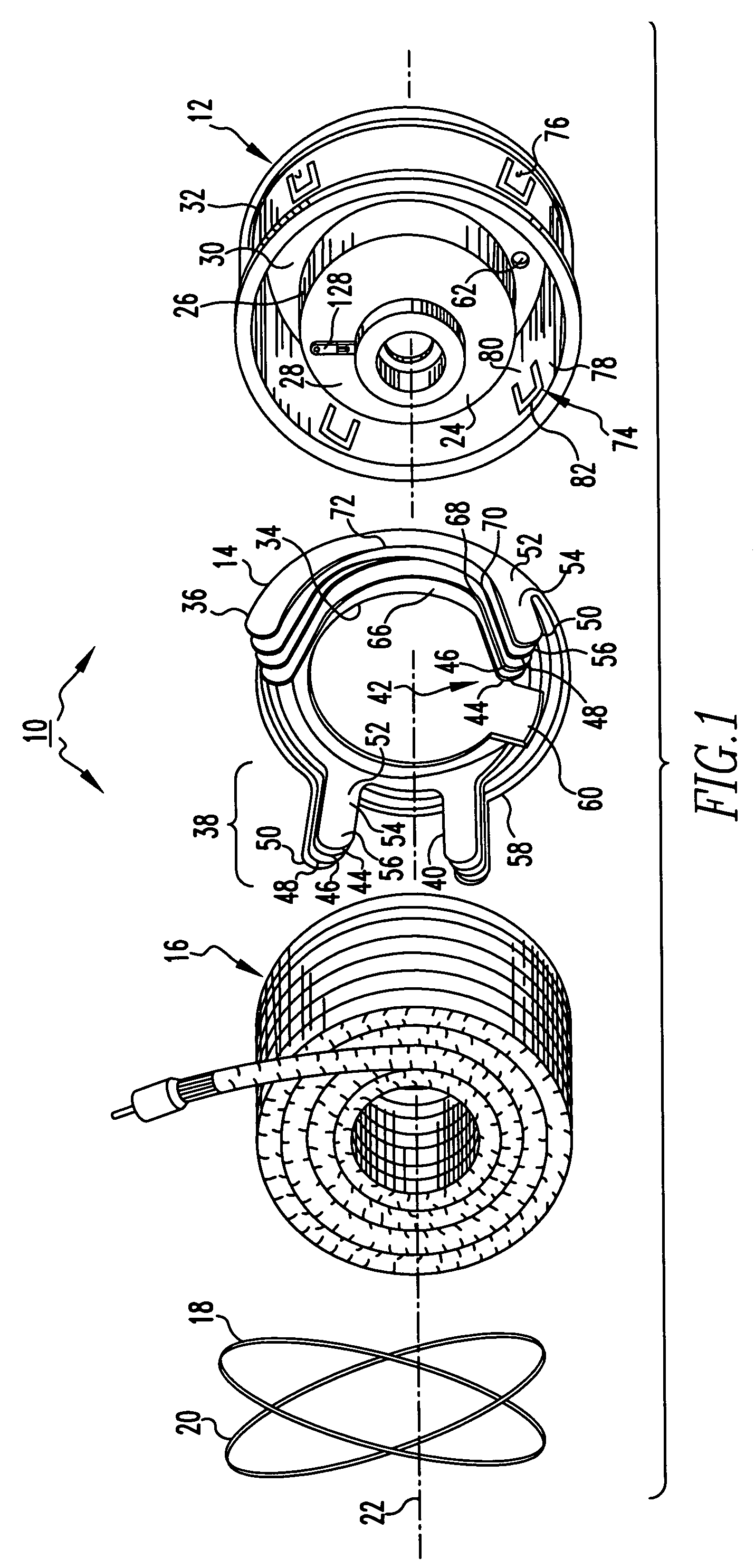
Rf Mems Switch With a Flexible and Free Switch Membrane
InactiveUS20080237024A1Shock and vibrationShort switching timeElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysElectronic switchingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:DELFMEMS SAS
Adhesive composition and article including the same
ActiveUS20160068726A1Increased formulation versatilityImprove stabilityNutsPretreated surfacesEpoxyAdhesive
An adhesive composition (“composition”) comprises an epoxy resin, a binder, and a curing agent. Typically, the composition further comprises an aqueous solvent (e.g. water) such that the composition can be referred to as an aqueous adhesive composition. The epoxy resin is typically encapsulated to prevent premature cure of the composition. After rupture of the encapsulated epoxy resin, the composition cures to form an adhesive. The composition is useful for articles such as fasteners (e.g. nuts and bolts) such that it can be referred to as a fastener adhesive. Typically, the composition is disposed on a threaded surface of the fastener. The fastener can be used for an assembly in which the composition generally cures after installation of the fastener. To make the fastener, the adhesive composition can be applied on the threaded surface. After application, the composition can be dried in instances where the composition still includes the aqueous solvent.
Owner:ND IND INC
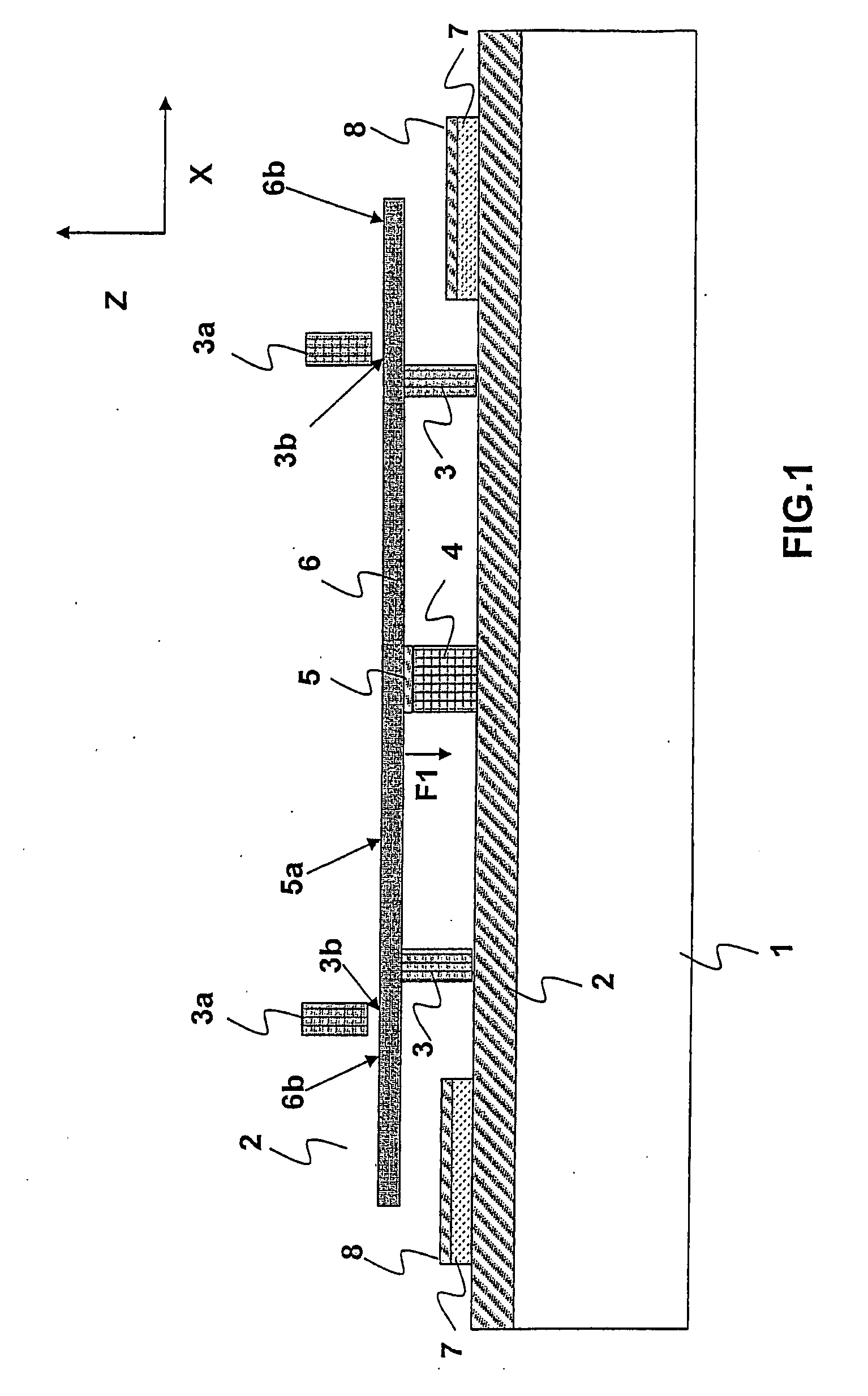
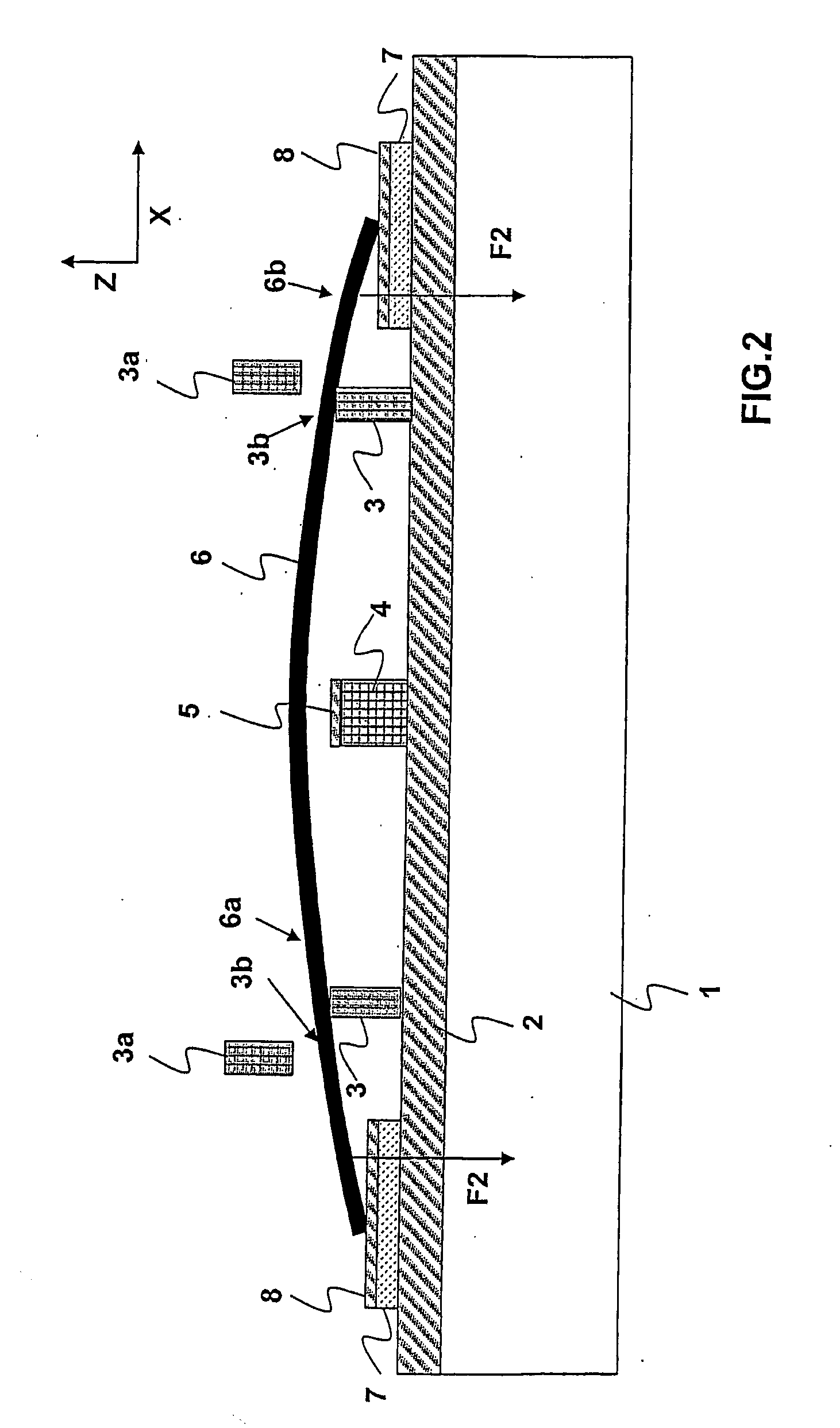
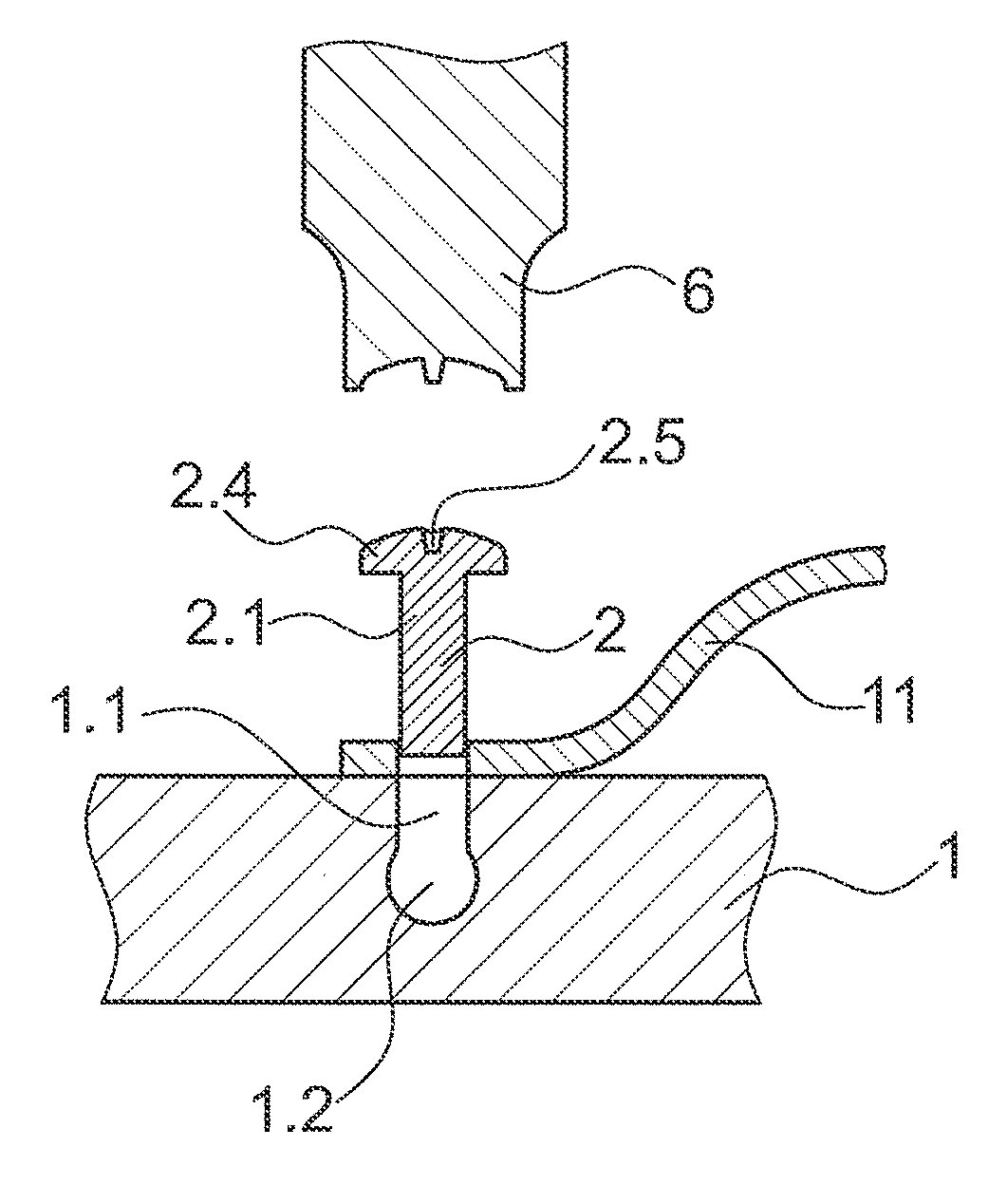
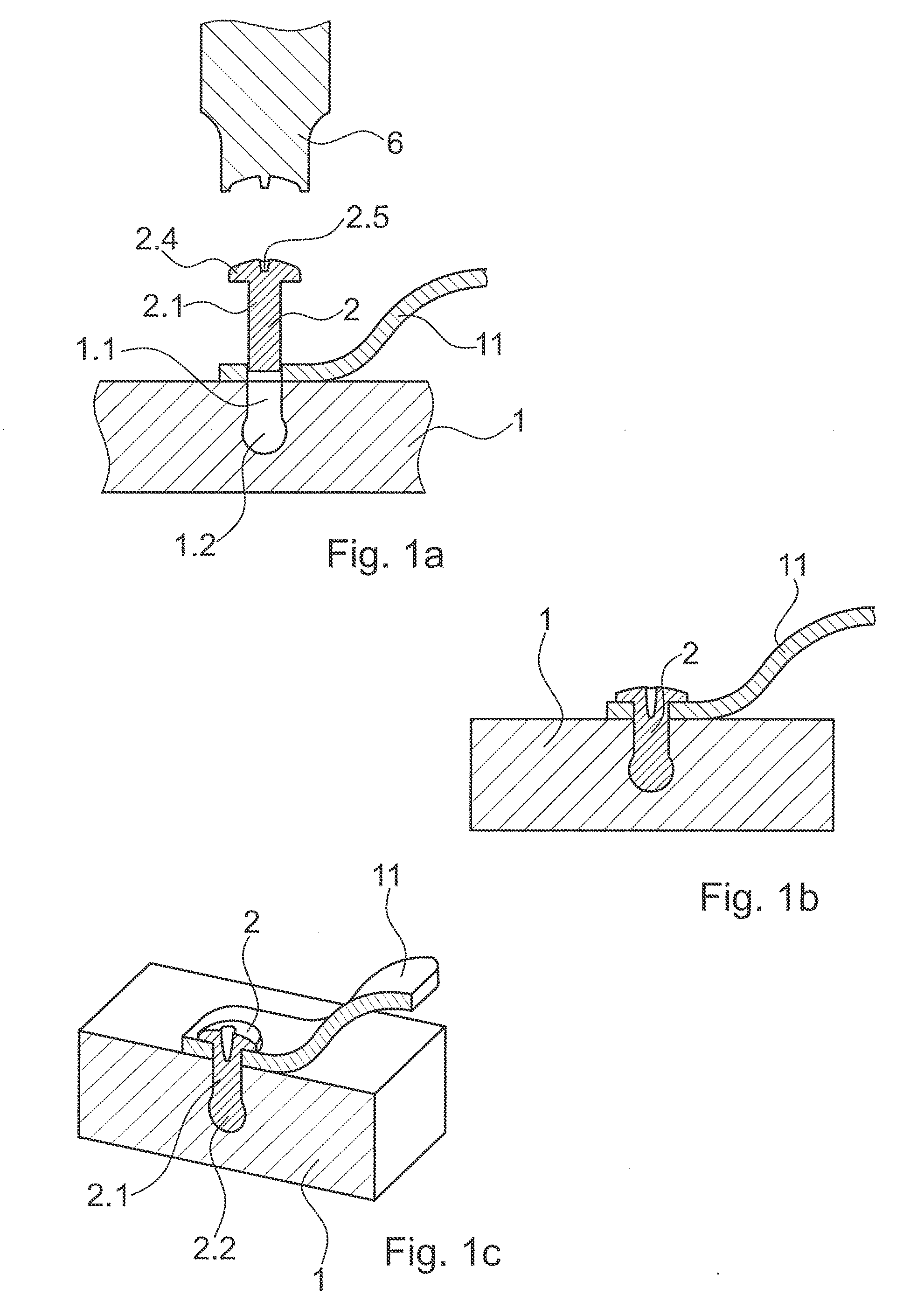
Method for connecting parts relative to one another
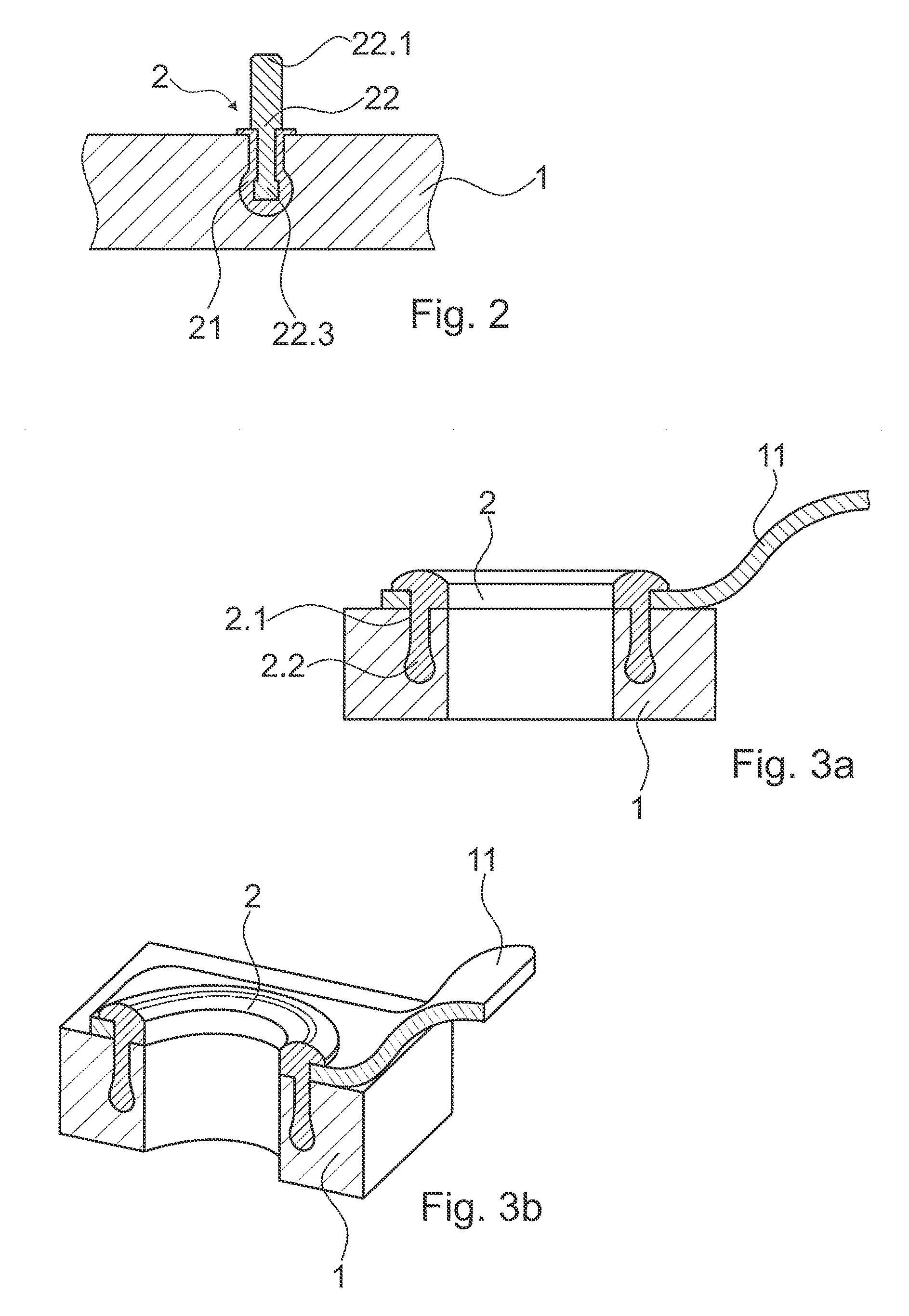
ActiveUS20150300389A1Shock and vibrationRelieve pressureLaminationKey type connectionsMechanical energyEngineering
A method of connecting parts relative to one another includes the steps of providing a first part, the first part having an opening; providing a second part, the second part having thermoplastic material in a solid state; arranging the first part and the second part relative to one another, so that the second part reaches into the opening, while a volume with an undercut is defined in the opening; causing a mechanical pressure and mechanical energy to act on the second part until at least a part of the thermoplastic material is caused to liquefy and to fill the volume; and causing the thermoplastic material to re-solidify, thereby anchoring the second part in the first part.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Ruggedized scintillation detector for portal monitors and light pipe incorporated therein
InactiveUS7154098B2Reduce decreaseWeaken energyMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementLight pipeEngineering
A radiation detector includes a housing, an elongated, rectangular crystal having four longitudinally extending corners, and a photomultiplier tube both supported in the housing, with a light pipe located axially between respective facing ends of the photomultiplier tube and the crystal; and a plurality of elongated rails extending along respective ones of the longitudinally extending corners of the rectangular crystal, establishing an air gap between the crystal and the housing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Suspension isolator equalizer
ActiveUS20040119260A1Shock and vibrationEasy to adjustLeaf springsRigid suspensionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An isolator for use in a suspension system includes a front shaft and a rear shaft. A front spring arm and a front transitional arm are mounted to the front shaft. A rear spring arm and a rear transitional arm are mounted to the rear shaft. A resilient member is mounted between the front and rear transitional arms. As forces are applied to the front and rear link arms, the front and rear shafts rotate causing the front and rear transitional arms to rotate. As the front and rear transitional arms rotate, the resilient member is compressed and expanded accordingly.
Owner:LIPPERT COMPONENTS MFG INC
Method And Apparatus For Controlling The Flow Of Fluids From A Well Below The Surface Of The Water
InactiveUS20120018174A1Convenient guidanceShock and vibrationDrilling rodsFluid removalWellheadPetroleum
An apparatus and method is provided for controlling and / or halting the uncontrolled flow of petroleum and / or natural gas from an open well head on the sea floor in which the well head is in communication with a subterranean formation. The method includes lowering a fluid control device from a drilling ship to an alignment means positioned above an open well casing through which the petroleum and / or natural gas is flowing in an uncontrolled manner, then lowering the fluid control device through and / or adjacent to the alignment means and into the open well casing until a lower section of a fluid control device enters the open well casing. The fluid control device includes an elongated member at its tip, having a diameter smaller than the inside diameter of the well head casing. A tapered section is in connection with the elongated section, the tapered section, or another section in connection with the tapered section, having a maximum diameter equal to or greater than the inside diameter of the well casing, and an end section in communication with the tapered section having a diameter greater than or equal to the outside diameter of the well head casing. The fluid control device can have a mass sufficiently great to overcome any upward forces created by flowing petroleum and / or natural gas, resulting in sufficient downward movement of the fluid control device and contact with the open well casing to seal same. Alternatively, a drilling rig in connection with the fluid control device can exert sufficient downward pressure thereon so as to overcome the pressure of the flowing petroleum, gas, etc., thereby creating a seal between the fluid control device and the well head.
Owner:KOTEFSKI STOJAN +2
Drill rig and methods for directional drilling
InactiveUS20150275583A1Good orientationShock and vibrationSurveyBuilding repairsClassical mechanicsElectric cables
A device for measuring inclination is suspended to a cable passing through a duct formed in the rods of the drill string. A mechanism for winding and unwinding the cable allows to raise and drop the measuring device within the lowermost rod, engaging it with or disengaging from a mule shoe. This is performed without the need to unscrew the rods and open the string. A valve element may close the duct through which the cable passes. In one embodiment, directional drilling is performed supplying low pressure fluid through tubular rods having a single duct. In another embodiment, high pressure fluids are supplied through rods having two or more coaxial ducts.
Owner:TREVI
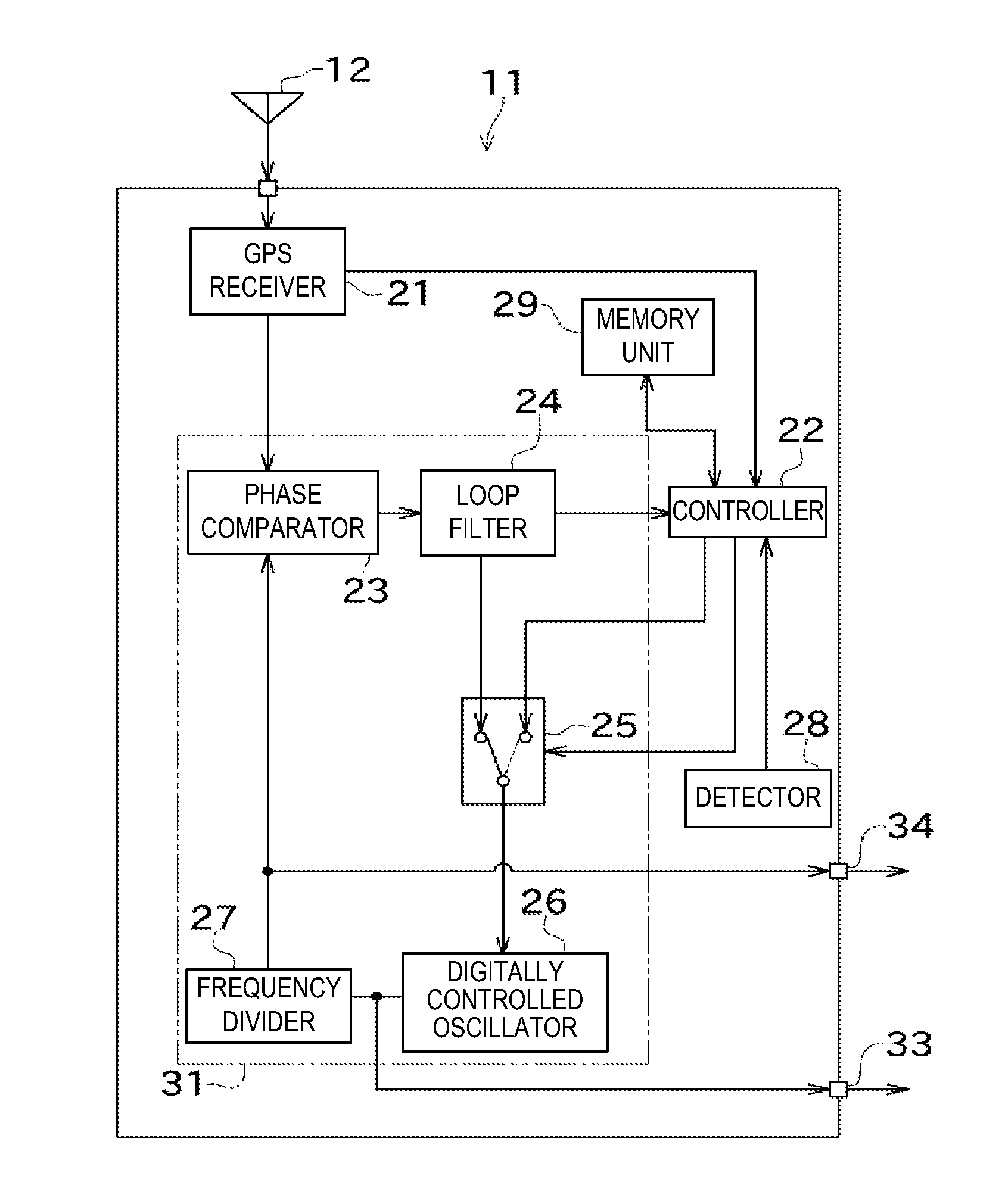
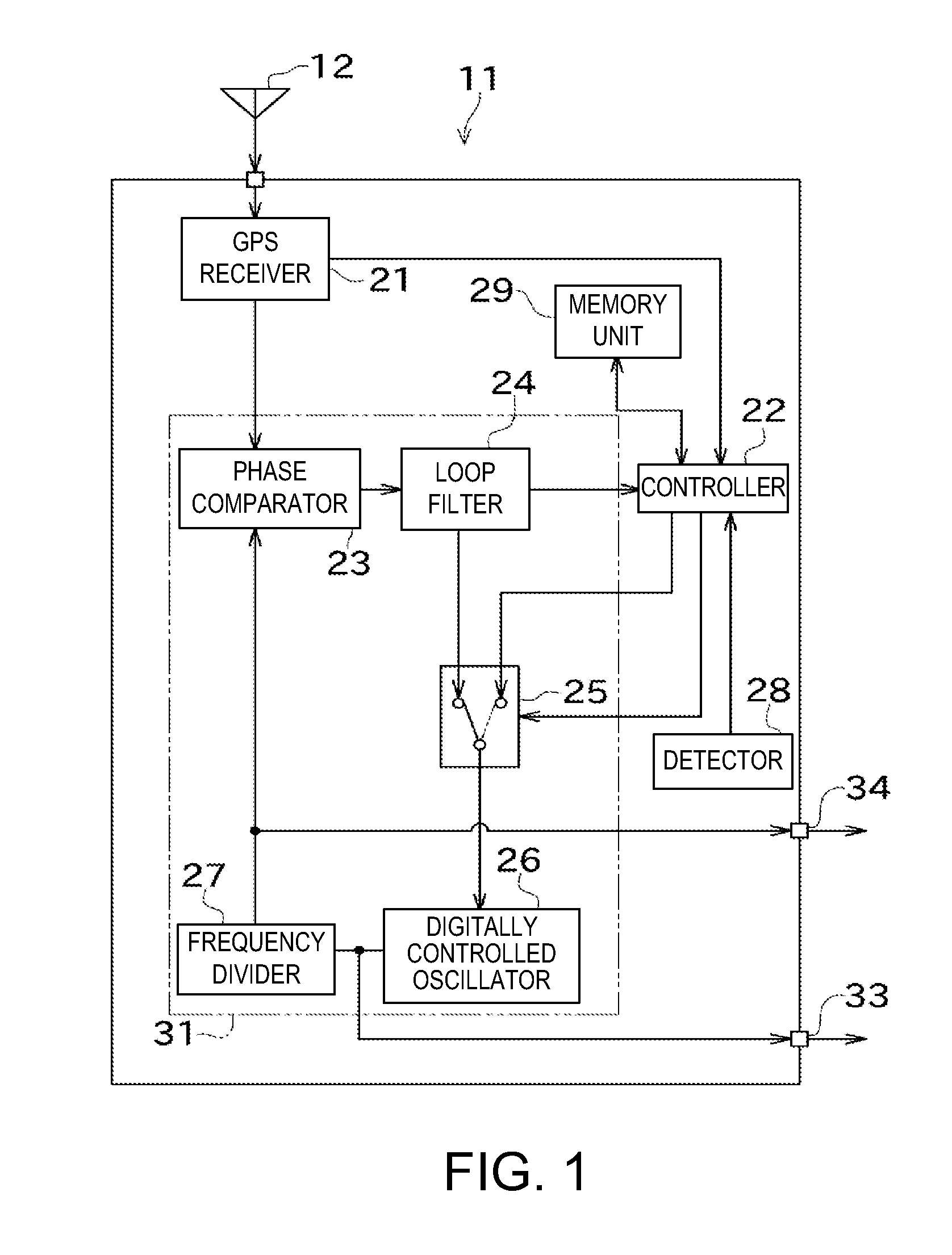
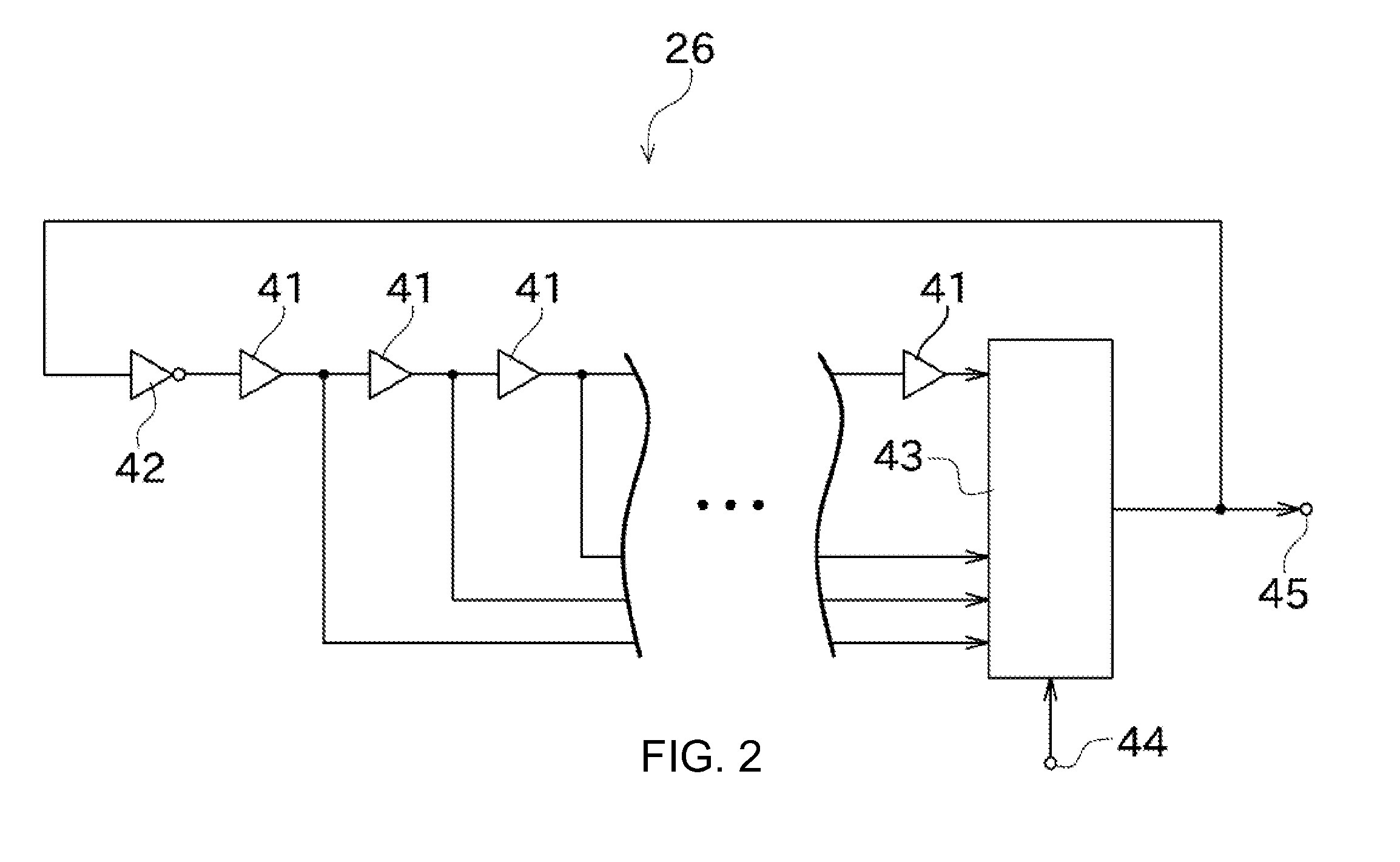
Reference frequency generating device
InactiveUS20120007642A1Improve accuracyImprove precision controlPulse automatic controlControl signalGps receiver
The disclosed is a reference frequency generating device (11), which includes a GPS receiver (21), a PLL circuit (31), a detector (28), a memory unit (29), and a controller (22). The PLL circuit (31) controls the digitally controlled oscillator (26) based on a synchronizing control signal acquired based on a reference signal from the GPS receiver (21). The memory unit (29) stores a correspondence relation between a control value of the synchronizing control signal, and a voltage value and a temperature at that time. When the reference signal is not acquired, the controller 22 determines a holdover control signal based on the correspondence relation, and the voltage and temperature detected by the detector 28, and controls the digitally controlled oscillator (26).
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Pressure Resistant Housing for an Electric Component
ActiveUS20140374132A1Improve usabilityPressure resistanceClosed casingsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsMetalMaterials science
A pressure resistant housing for an electric component is provided. The pressure resistant housing is adapted for the use in a subsea application. A ceramic housing body houses the electric component. The ceramic housing body has a first opening and a second opening that are closed by a first metal lid and a second metal lid, respectively.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY AS
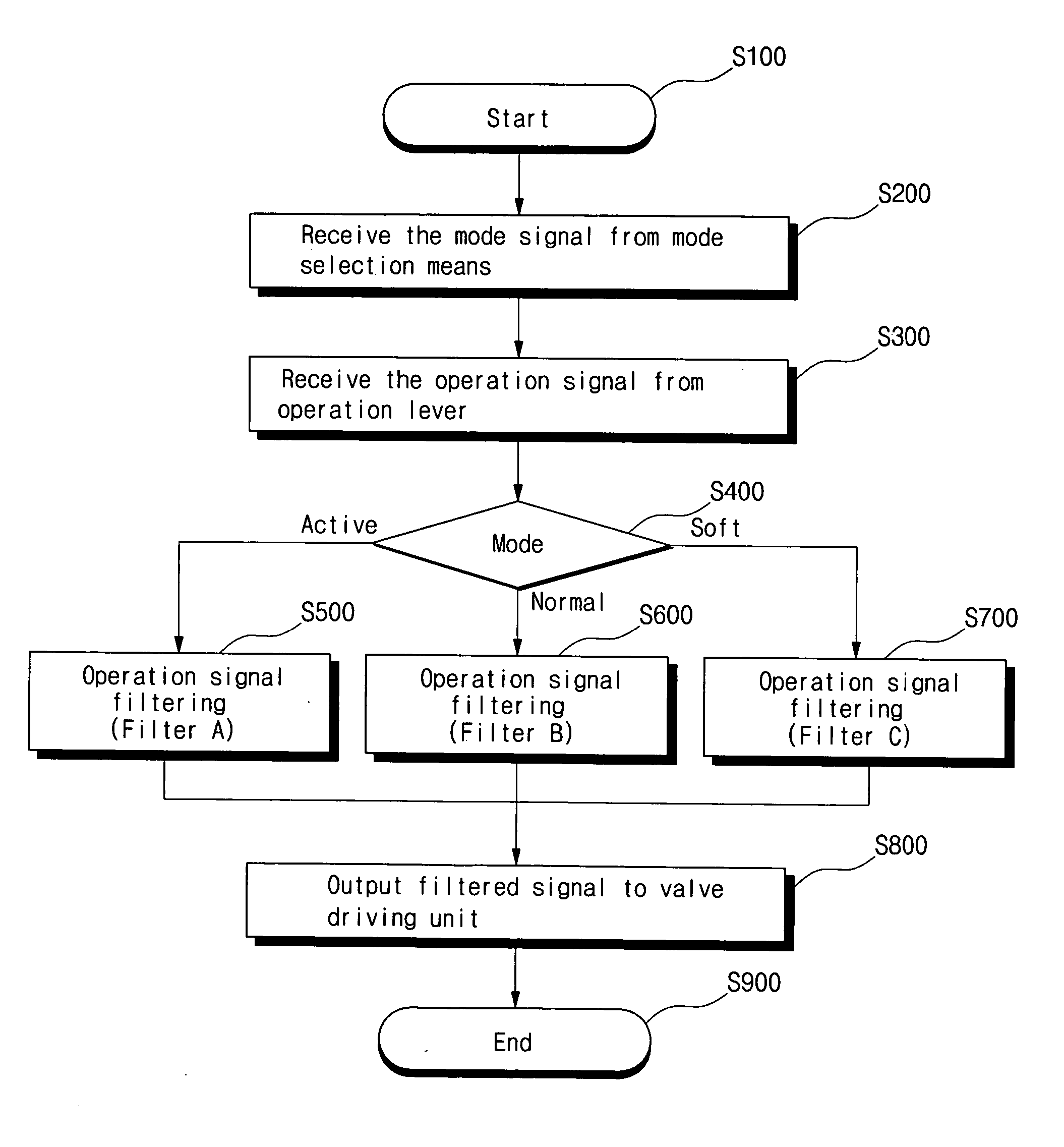
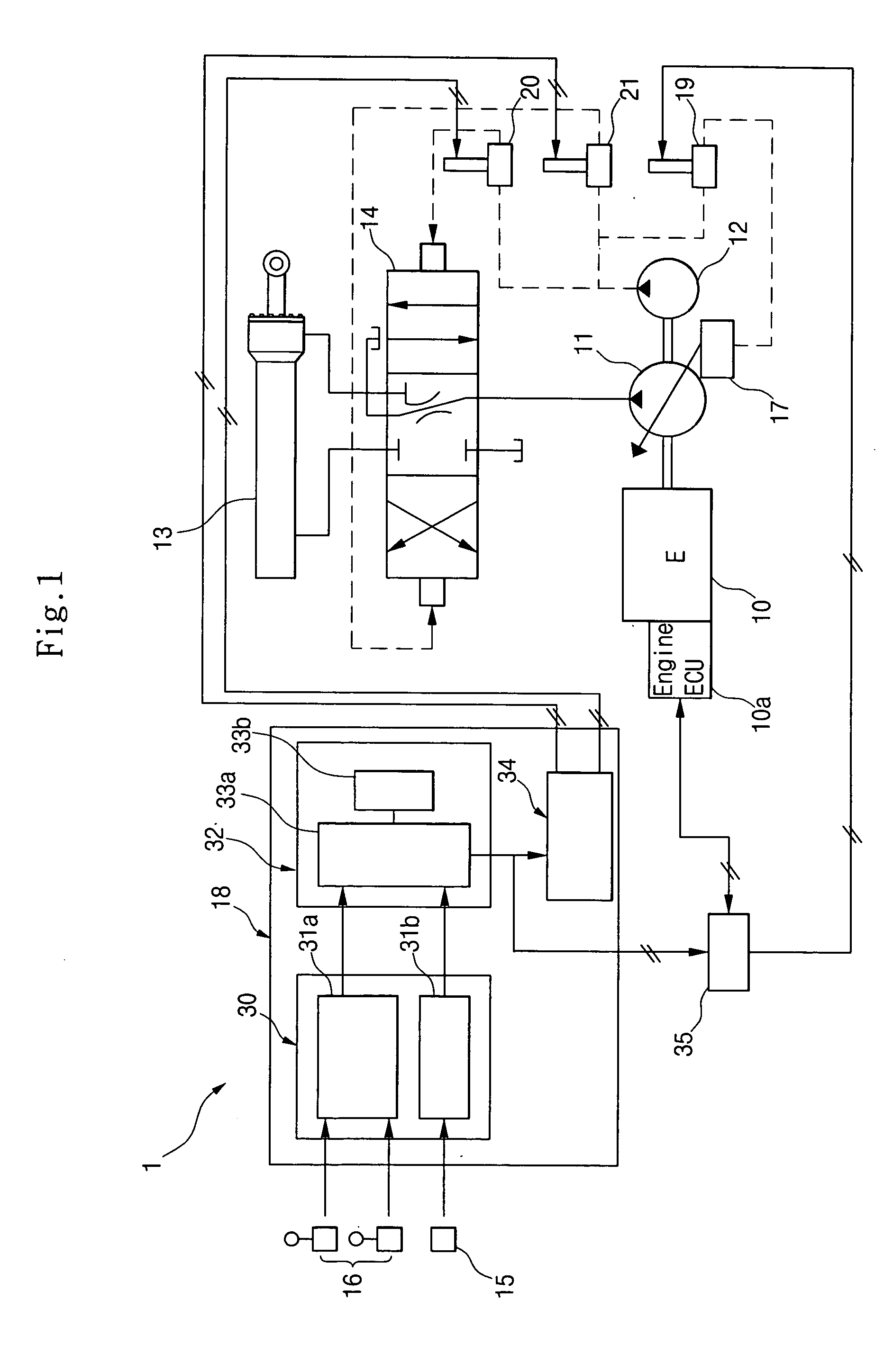
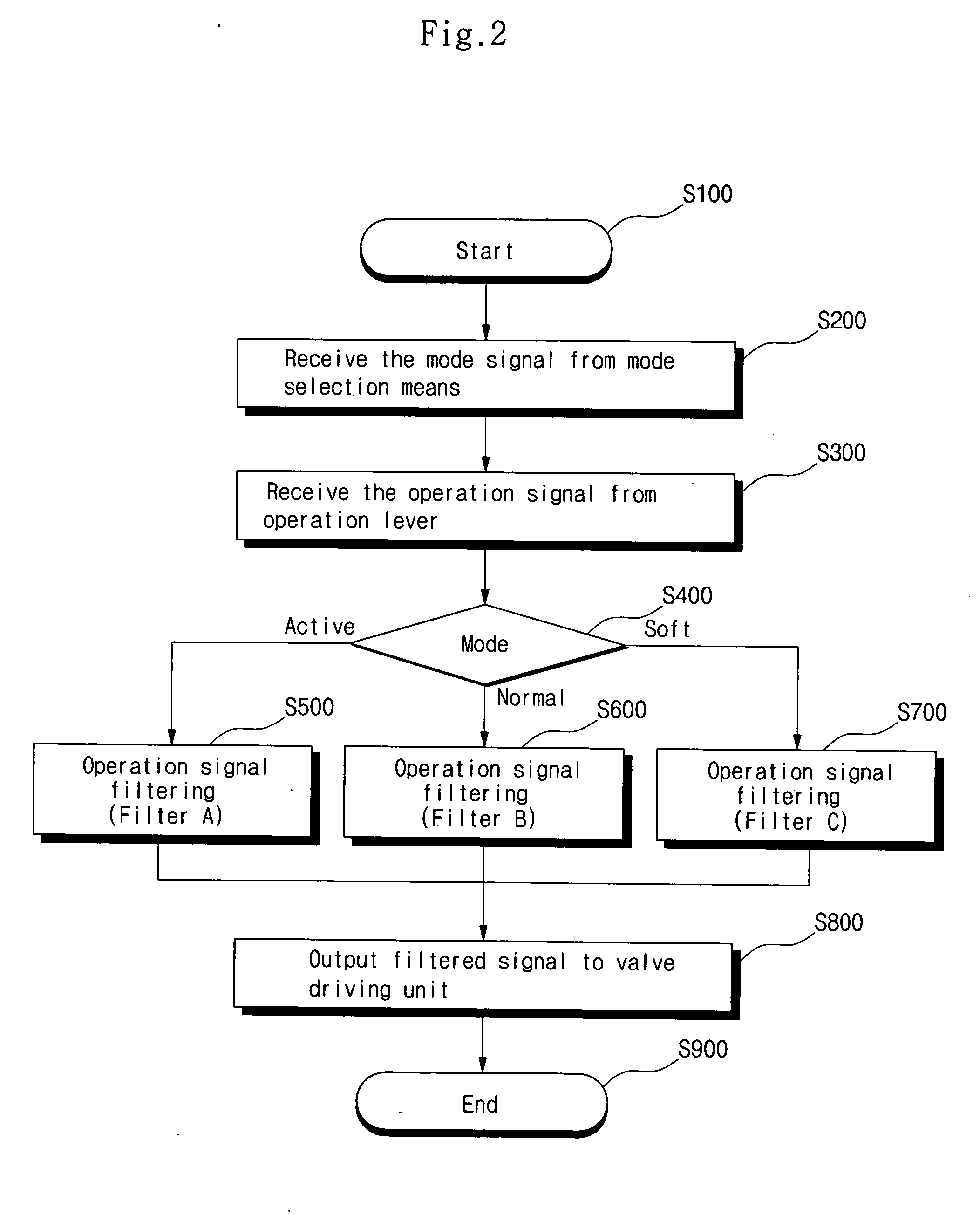
Method for setting response modes of construction vehicle operation lever
InactiveUS20050207897A1Reduce fatigueShock and vibrationFluid couplingsSoil-shifting machines/dredgersDriver/operatorControl signal
The present invention discloses a method for freely setting response modes of the operation lever of construction vehicle, according to driver's skills or proficiency and work characteristics, in which the method includes the steps of: receiving a mode signal from a mode selection means, and selecting one of a plurality of selection modes; receiving an operation signal from the operation lever; filtering the operation signal through a filter which is operating in response to the selected response mode; and outputting a filtered control signal.
Owner:VOLVO CONSTR EQUIP
Torpedo mounted dispenser incorporating a shock mount bumper
InactiveUS7574971B2Minimize impactConsiderable weightNon-magnetic metal hullsTorpedo launchersCushioningMultiple layer
A torpedo tail mounted dispenser (TMD) for deploying an elongated, flexible article generally along a deployment axis, which includes a receptacle for storing the article in a multiple-turn, multiple-layer configuration about the deployment axis in a storage volume. There is also a torpedo connector mechanism having a terminal forward face and a lateral peripheral surface extending away from the receptacle along the deployment axis. An elastomeric cushioning feature is mounted on the lateral peripheral surface of the connector mechanism. An annular elastomeric bumper is mounted on a forward peripheral face of the cushioning feature, the annular opening of the bumper surrounding the connector mechanism to allow connection of the TMD to a torpedo. The bumper provides protection to the TMD and torpedo under certain shock and vibration levels.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Harness for a handheld power equipment
InactiveUS20100270344A1Reduces vibration and shockComplicated constructionTravelling sacksMowersPower equipmentBackplane
The harness comprises a backplate, a plurality of belts and an attachment. The backplate is arranged on the back of the user. The plurality of belts is configured so that one end of each belt is connected to the backplate and another end of each belt is connected to each other on the front of the user. The attachment is supported by at least one of the backplate and the plurality of belts, and is configured to be attached to the power equipment. The backplate preferably comprises at least one ventilation groove formed on its inner surface and extending to the edge of the backplate, which allows air to pass between the user and backplate easily.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
Water inlet device for a water tank
InactiveUS20130074953A1Improve mute effectShock and vibrationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFlushing devicesWater pipeEngineering
The invention relates to the structure of a water inlet device of a water tank, wherein a float seat is slipped outside an external water-lifting pipe, an internal water-lifting pipe is installed inside the external water lifting pipe, a control valve is fixedly connected on the upper end of the external water-lifting pipe, a valve set is set inside the control valve, the valve set includes a membrane, a positioning plate, a silencing washer, a water feeding plate and a water supply pipe. The shock and vibration caused by inflowing water current may be buffered by using the construction of the valve set, to thereby enhance the silence effect and achieve the purpose of reducing noise.
Owner:HUANG SO MEI
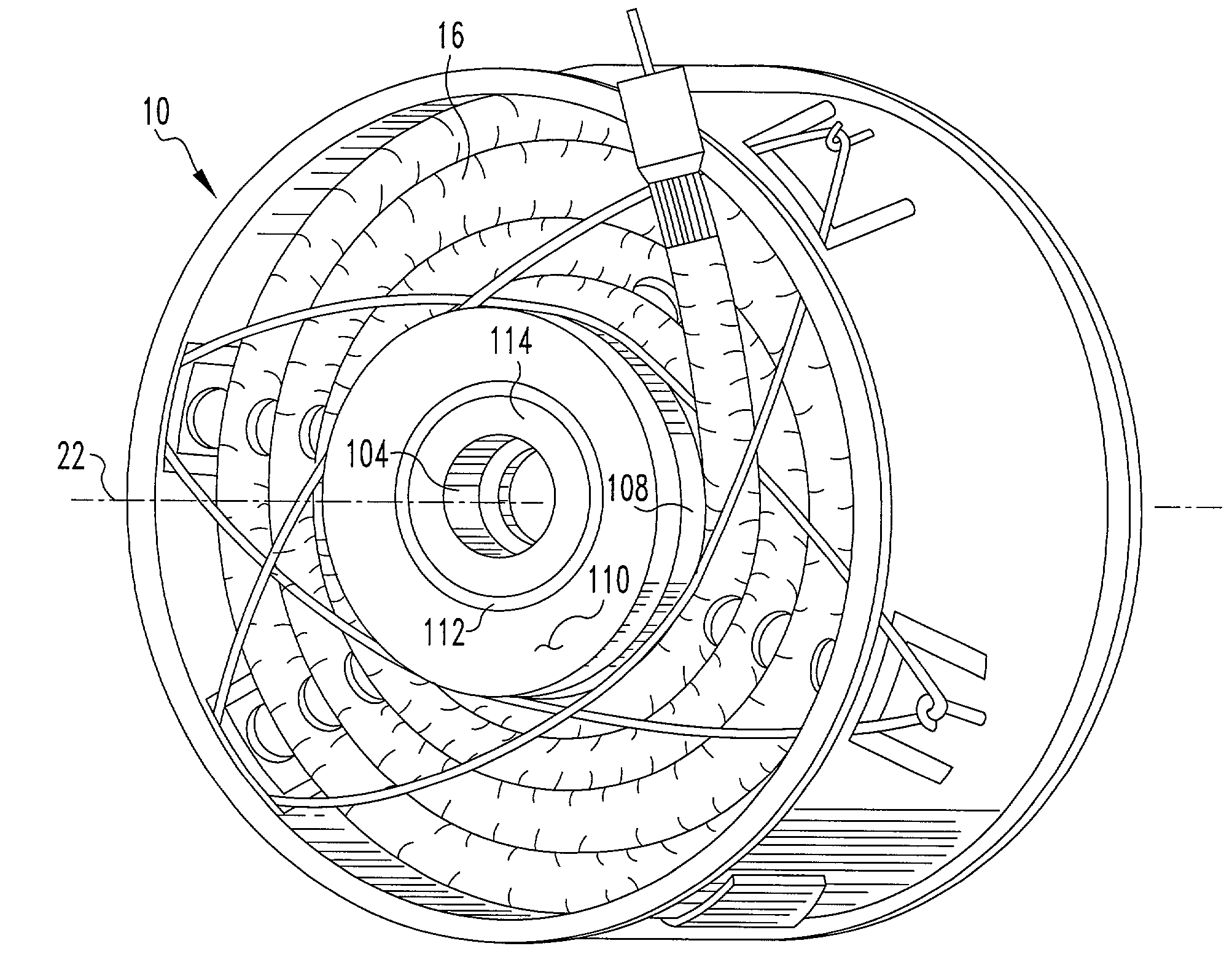
Fluid dynamic bearing mechanism for a motor
InactiveUS7654744B2Easily check amount of lubricantImprove accuracyShaftsRecord information storageHard disc driveCapillaria obsignata
A fluid dynamic bearing mechanism for a motor (1) suitable for use in a hard disk drive and having a compact and thin shape, high bearing rigidity, and high rotating accuracy, and which securely keeps the rotor member (6) in place against shocks, and allows the inspection of lubricant supply amount easily. A fluid dynamic bearing mechanism having a capillary seal part (12) on one end of lubricant supply part formed by a minute gap including dynamic pressure grooves (10) formed on a shaft member (5) or a bearing member (4) is provided. An annular member (13) is fitted on the shaft member at the location corresponding to the capillary seal part, another annular member (14) is fitted on the bearing member at the location corresponding to the capillary seal part, a taper or step (13a, 14a) is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the annular member on the shaft member side and the inner peripheral surface of the annular member on the bearing member side. These inner and outer peripheral surfaces are arranged to be close to and facing with each other so that the rotor member is prevented from disengaging from the bearing member, and the capillary seal part can be formed at the same time. An axial dynamic pressure bearing unit (1) is formed between the annular member on the shaft member side and one end of the bearing member.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
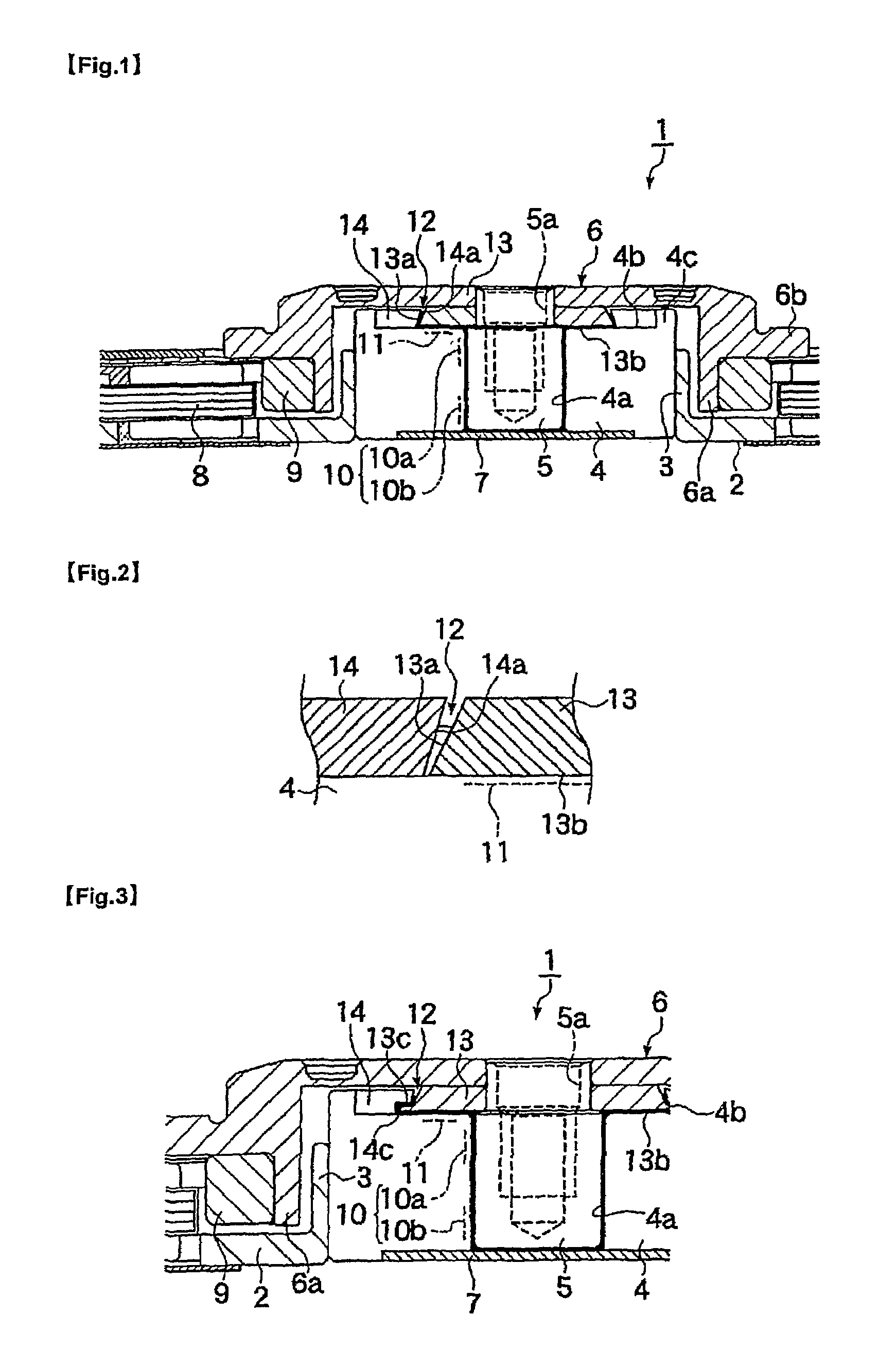
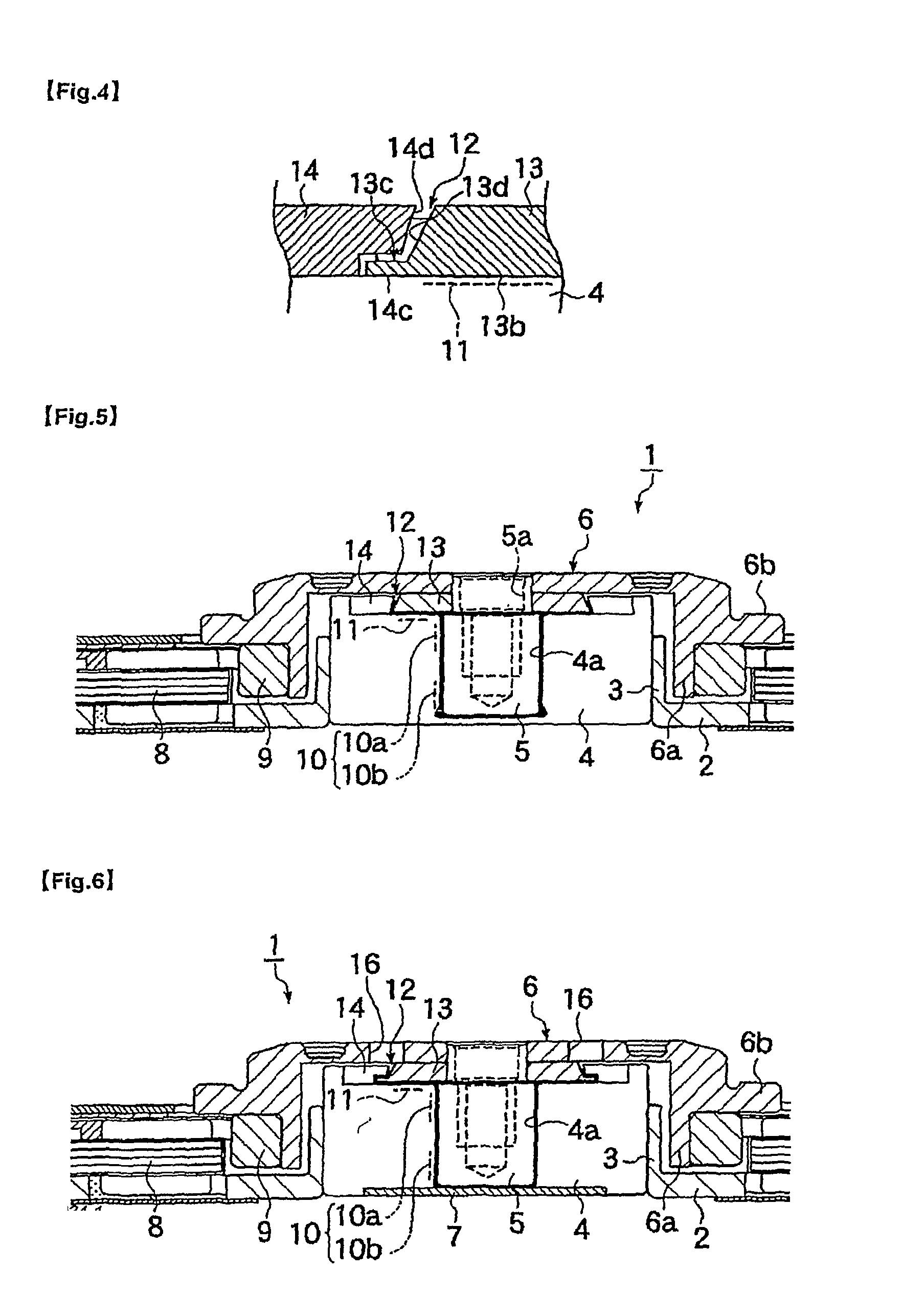
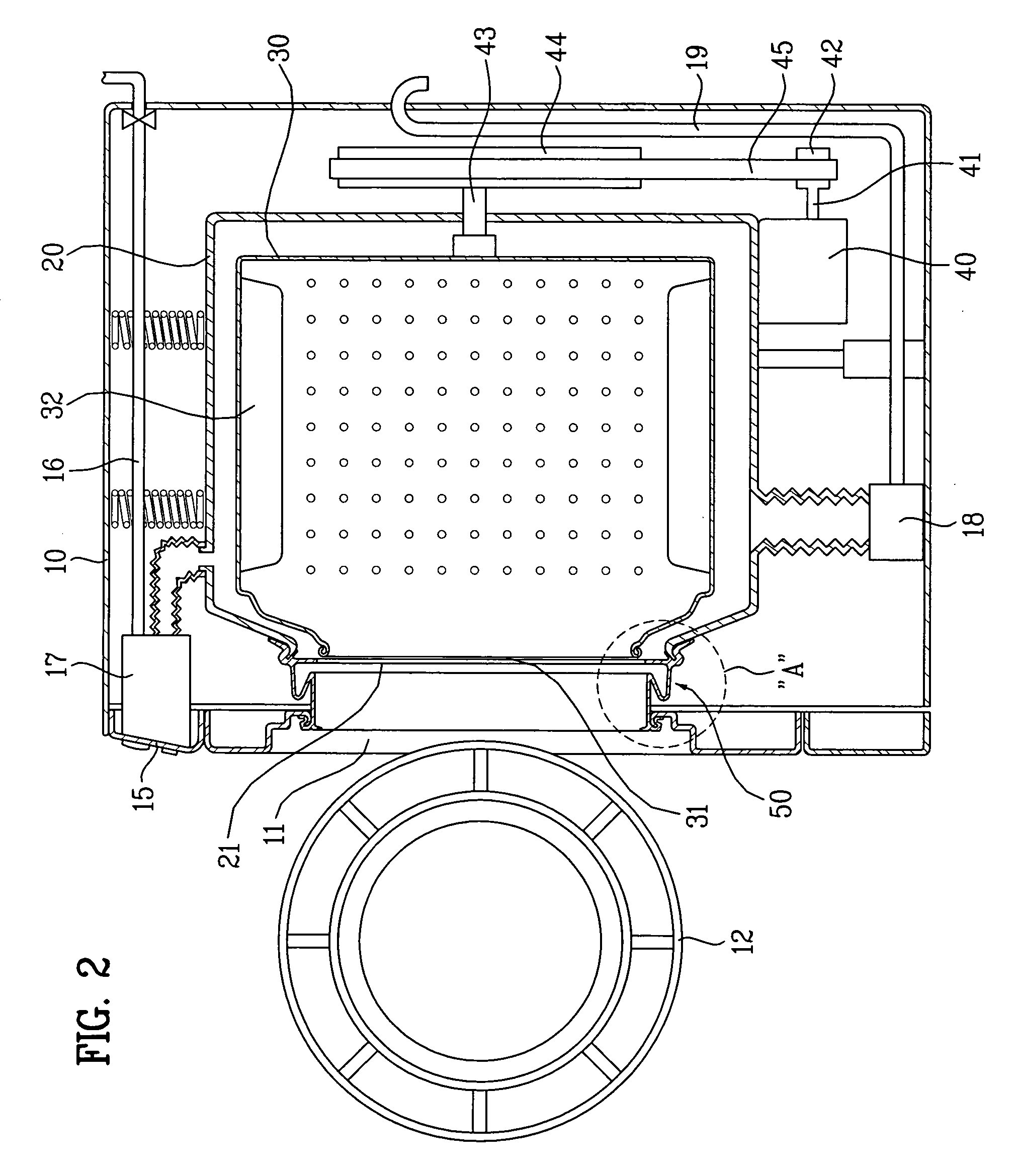
Gasket and washing machine using the same
InactiveUS7293437B2Prevent leakageShock and vibrationTextile treatment machine partsOther washing machinesWater leakageEngineering
A drum washing machine having a gasket to prevent leakage of water in the tub and the laundry from being stuck in a laundry opening part. The washing machine including a cabinet having a first opening through which a laundry is put in the cabinet, a tub installed in the cabinet to have a second opening corresponding to the first opening, a drum installed in the tub to have a third opening corresponding to the second opening, and a gasket including a leakage preventing part having one end connected to a rim of the first opening and the other end connected to a rim of the second opening to prevent water leakage and a laundry-stuck preventing part provided on an inner circumference of the leakage preventing part to prevent the laundry from being stuck in a space between the first and third openings.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Card edge connector
ActiveUS20190199023A1Shock and vibrationCompact dimensionsCoupling device detailsMounting boards securingElectrical connectorEdge connector
The present disclosure provides an electrical connector. The electrical connector comprises an insulative housing, a plurality of conductive terminals and a board fastener. The insulative housing has a mounting surface and a mating surface on opposite sides in a mating direction and a mounting chamber. The mounting chamber has a top accommodating portion and a bottom accommodating portion extending and penetrating the mounting surface from the top accommodating portion in the mating direction, two side walls defining the mounting chamber each are formed with a top limiting surface and a bottom limiting surface which define the top accommodating portion. The fastener has a mounting section accommodated in the top accommodating portion, an intermediate section extending from the mounting section and accommodated in the bottom accommodating portion and a tail section extending out of the mounting surface of the insulative housing from the intermediate section.
Owner:MOLEX INC
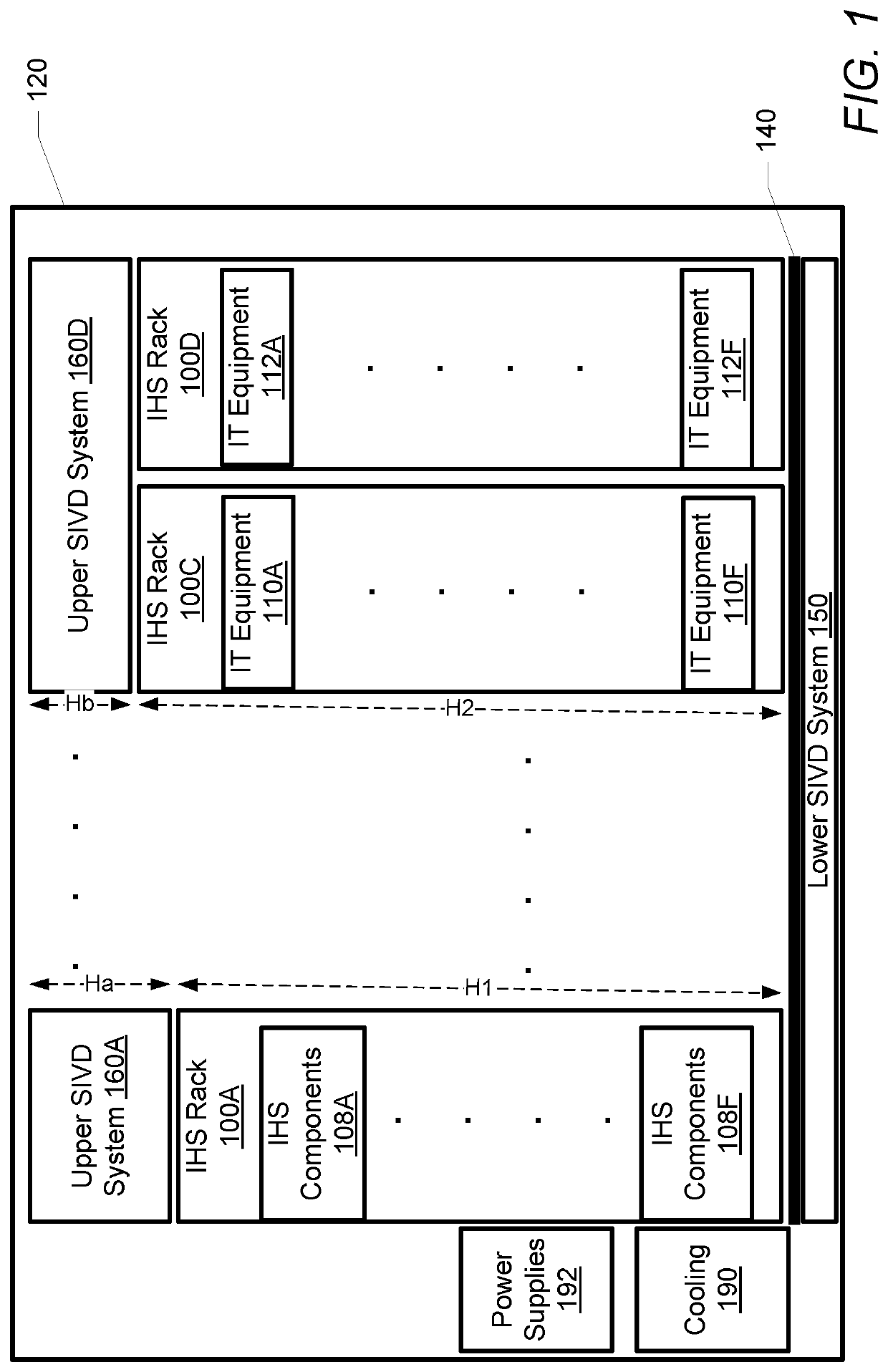
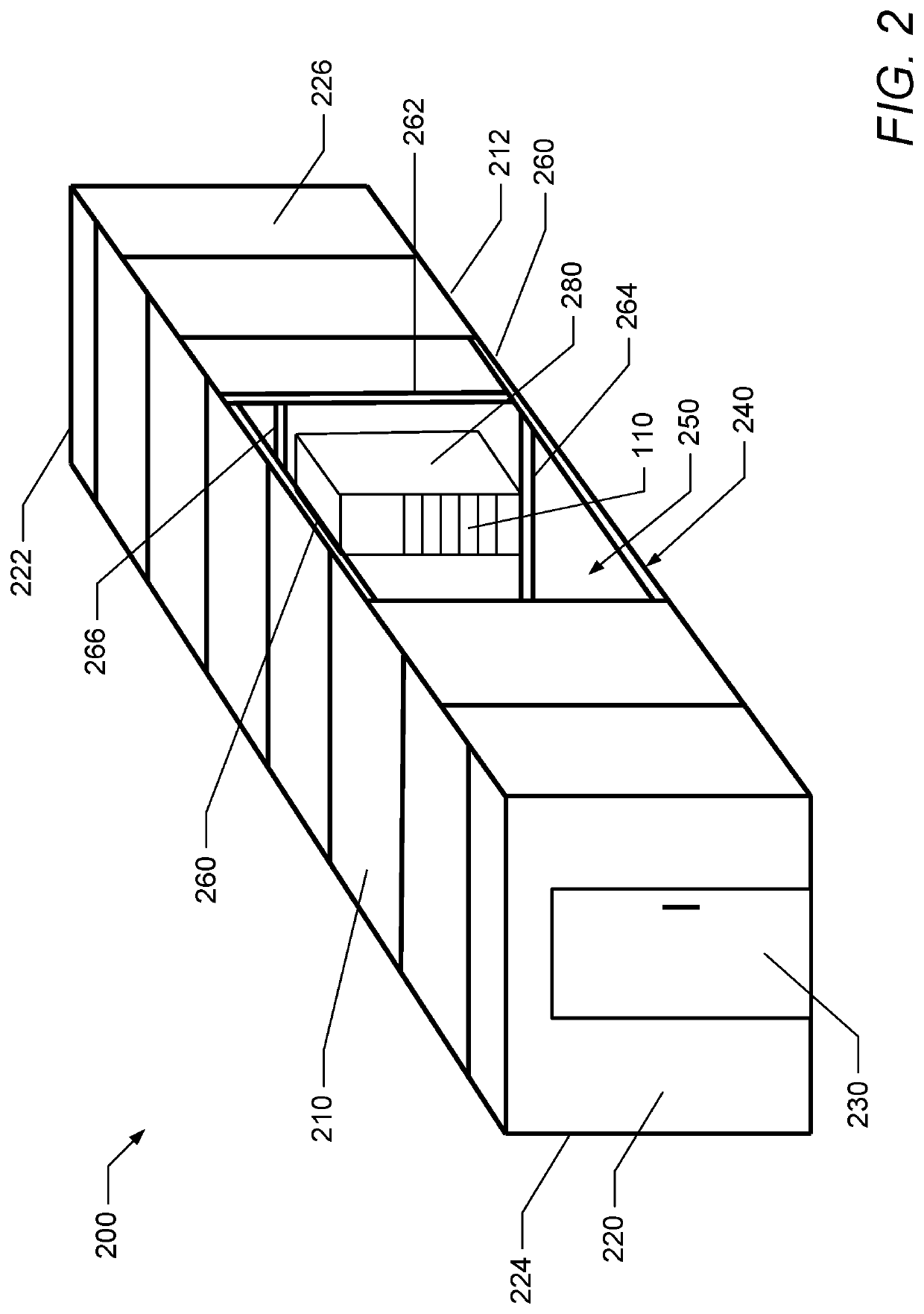
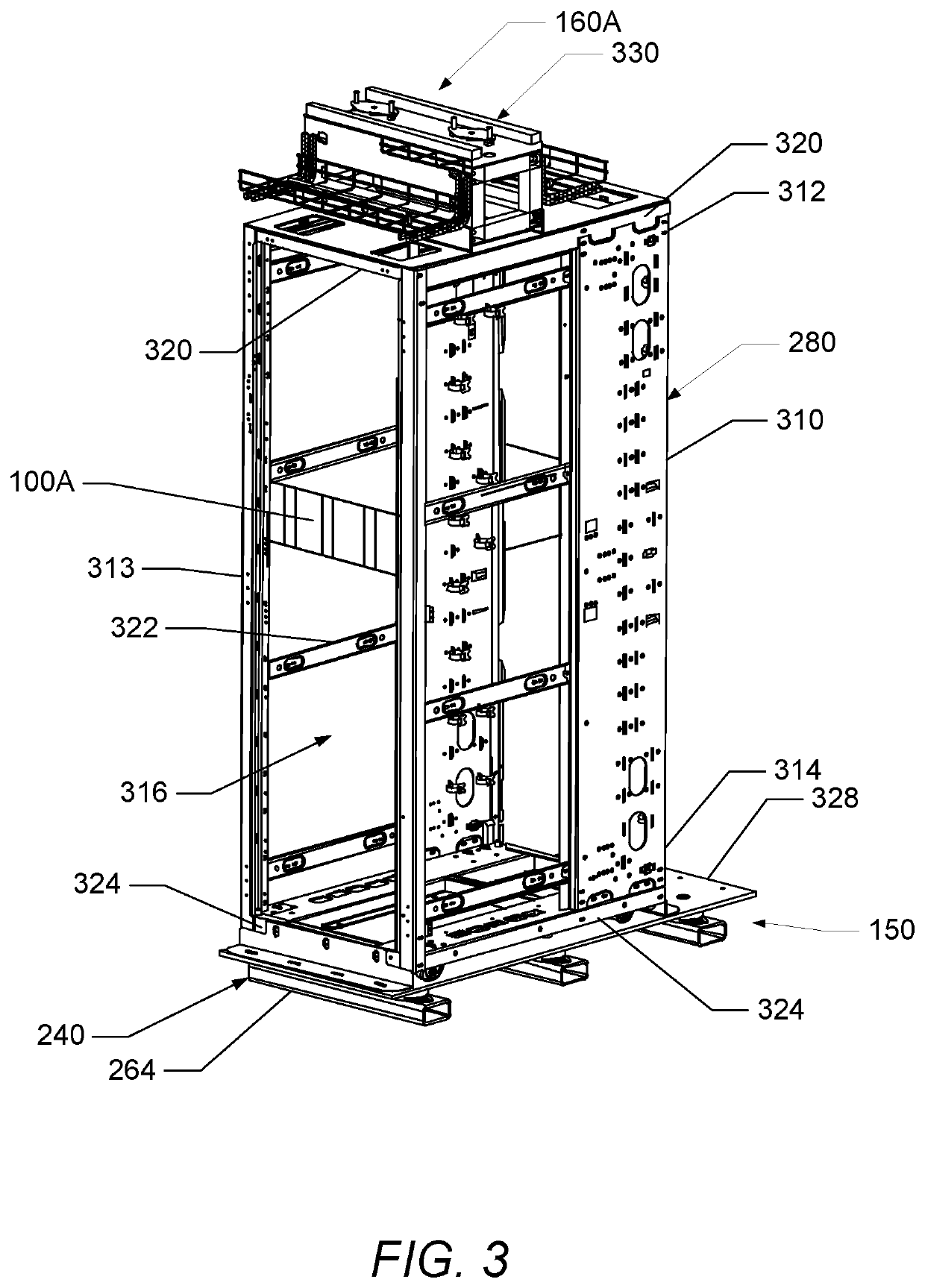
Isolating information handling system racks from shock and vibration in a modular data center
A modular data center includes a container for housing at least one rack containing an information handling system. A frame is disposed within the container. The frame has several upper cross-members and several lower cross-members. A floor is coupled to the lower cross-members and the at least one rack is disposed on an upper surface of the floor. At least one lower bracket extends between the floor and the first rack and is affixed to the floor and a first rack to couple / secure the first rack to the floor. Several first isolators are mounted between the floor and the lower cross-members. The first isolators protect the first rack from mechanical shock and vibration.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com