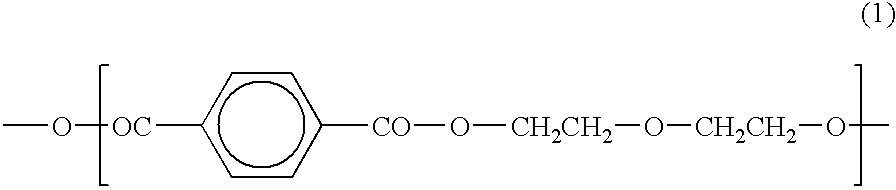Patents
Literature
132results about How to "Pressure resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
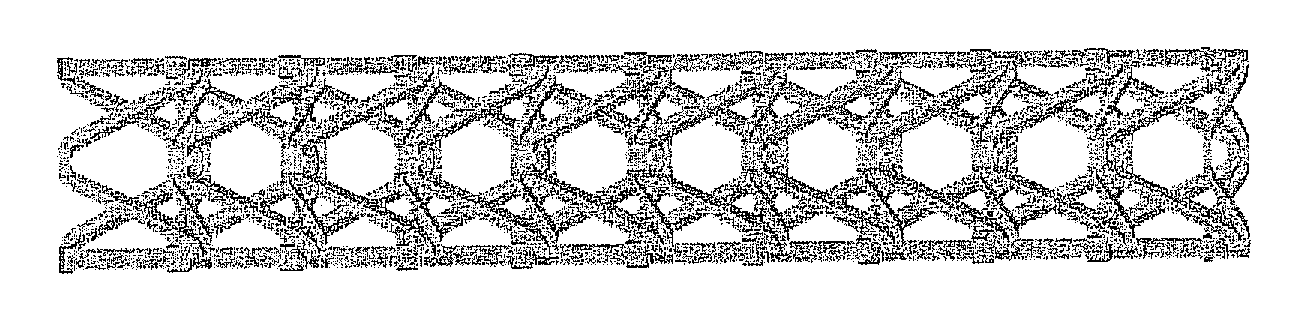
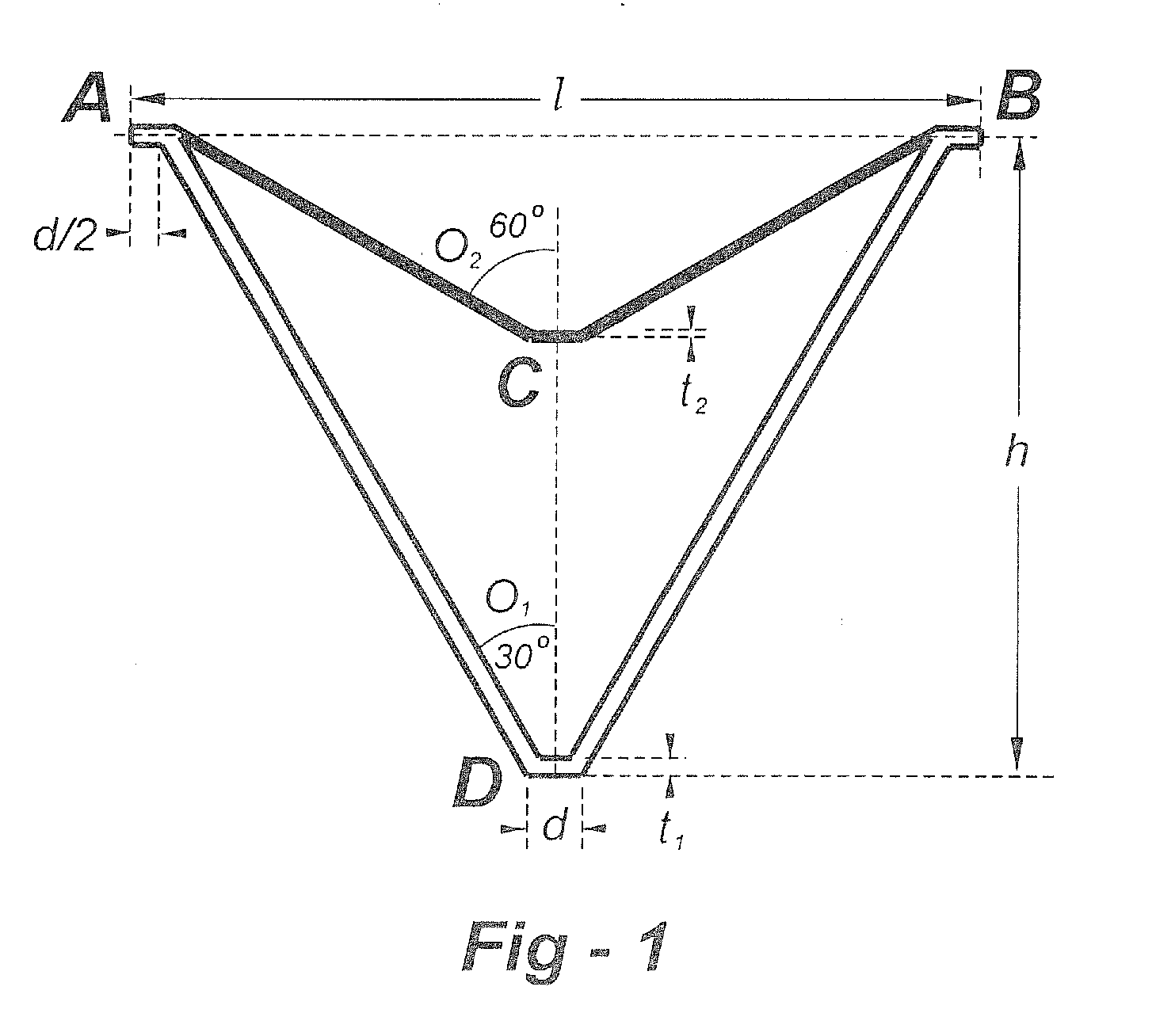
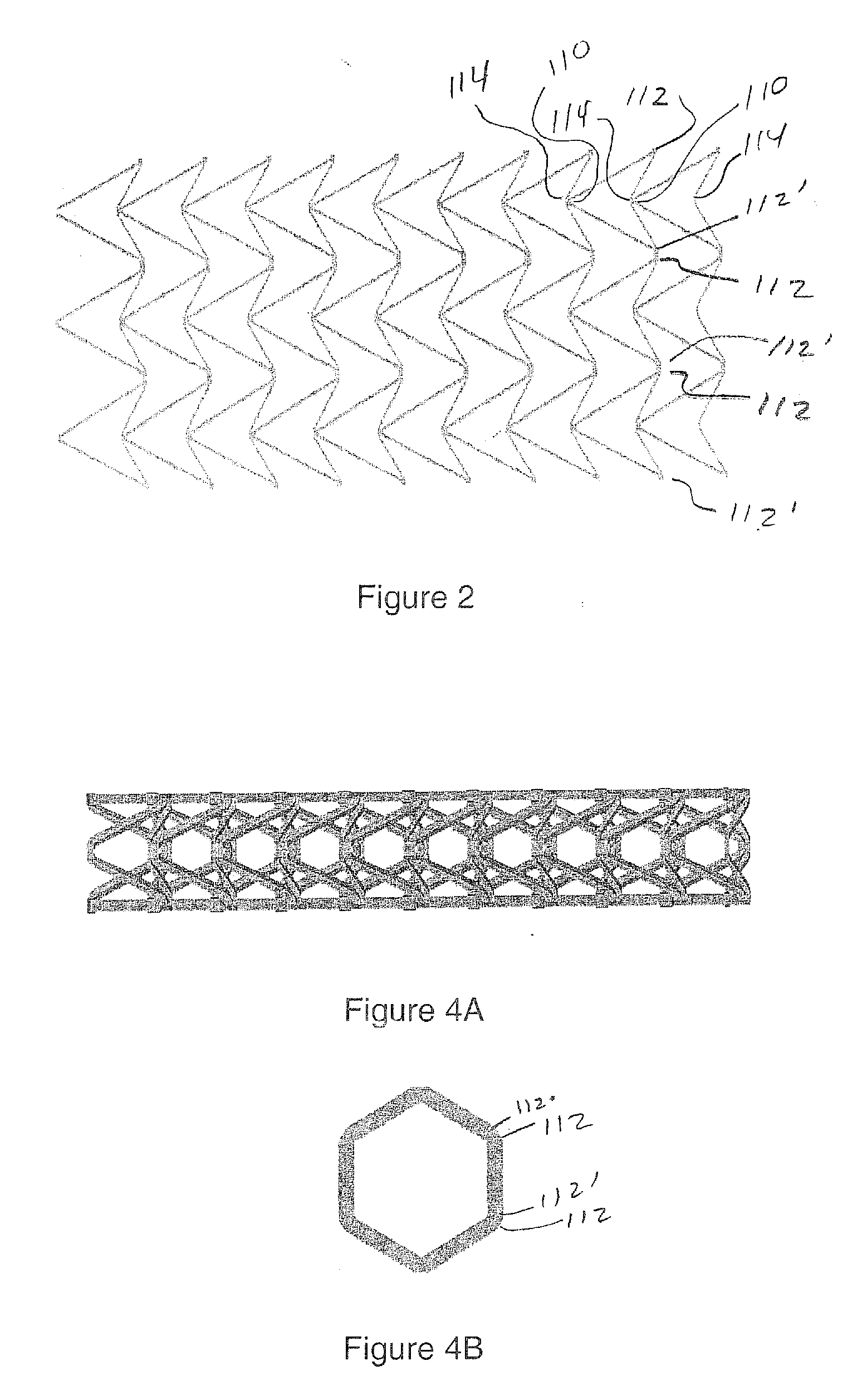
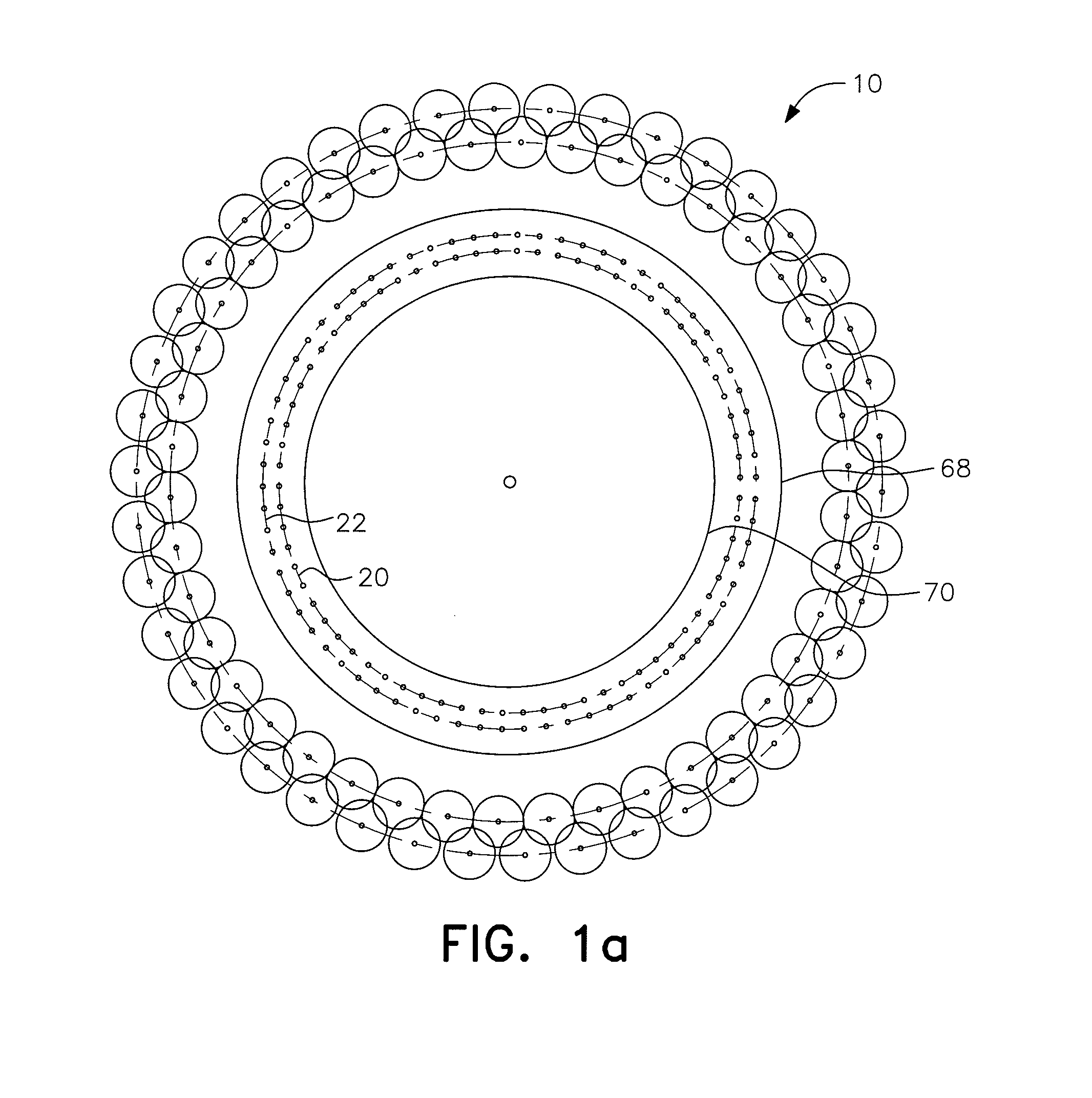
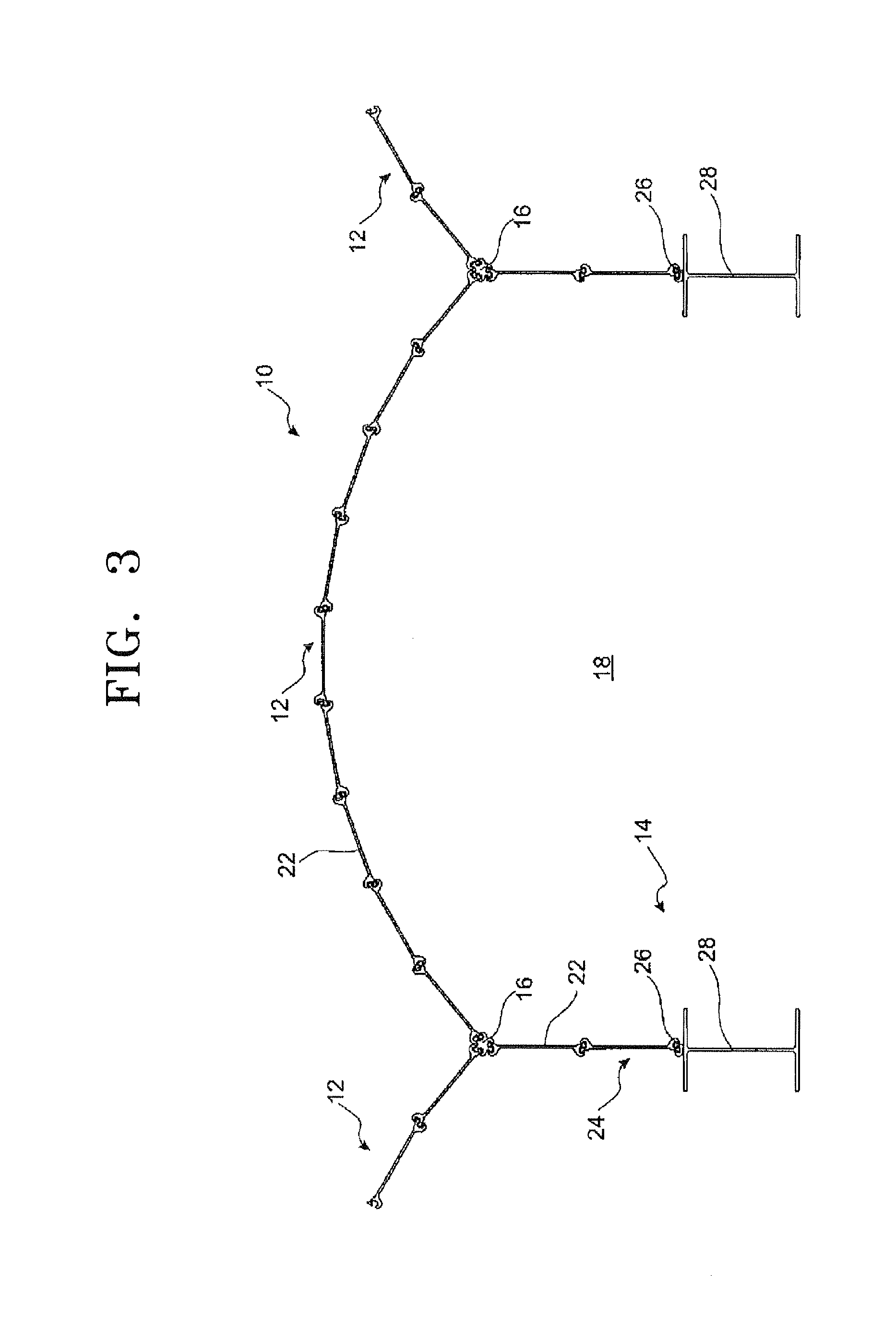
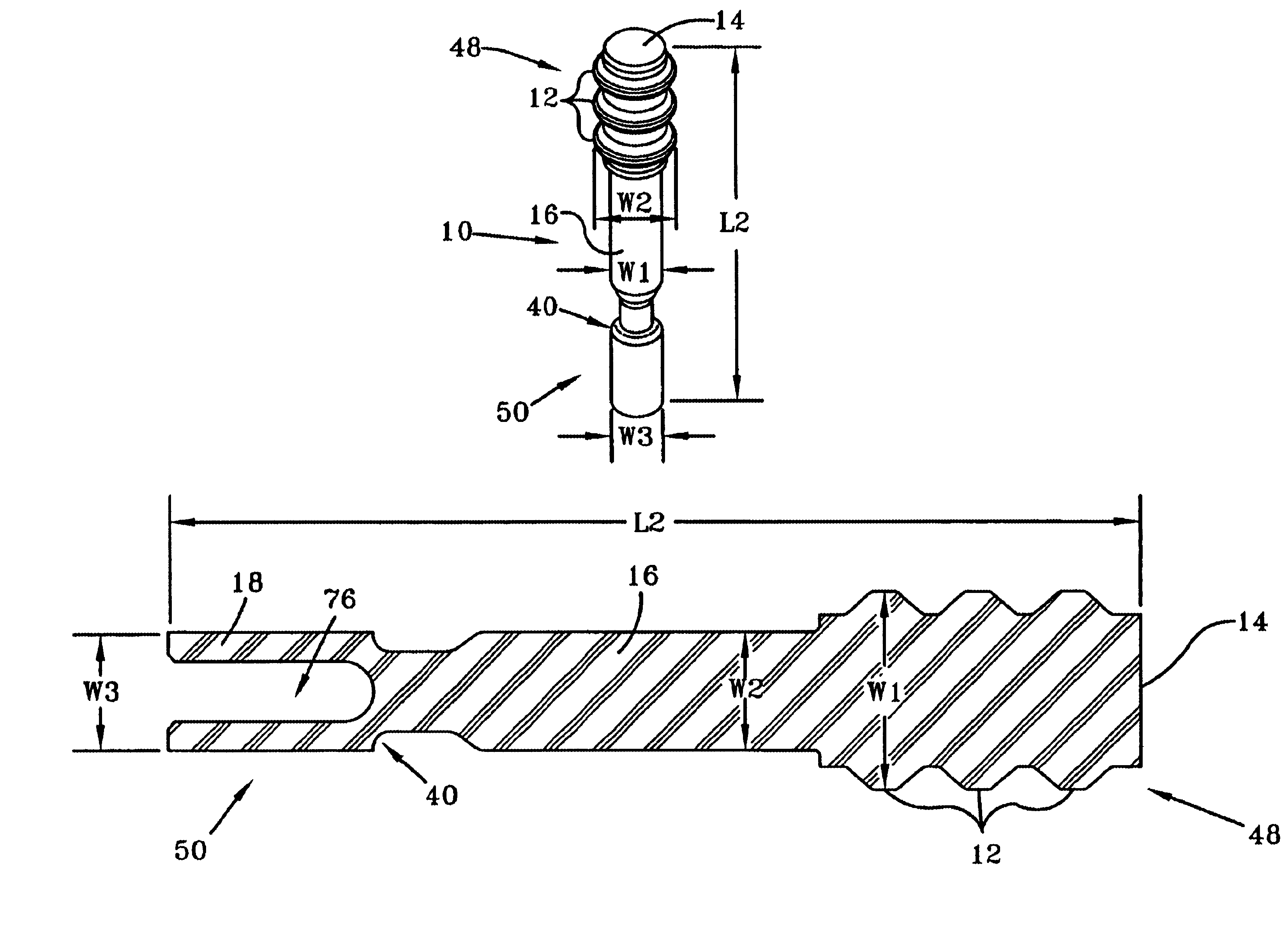
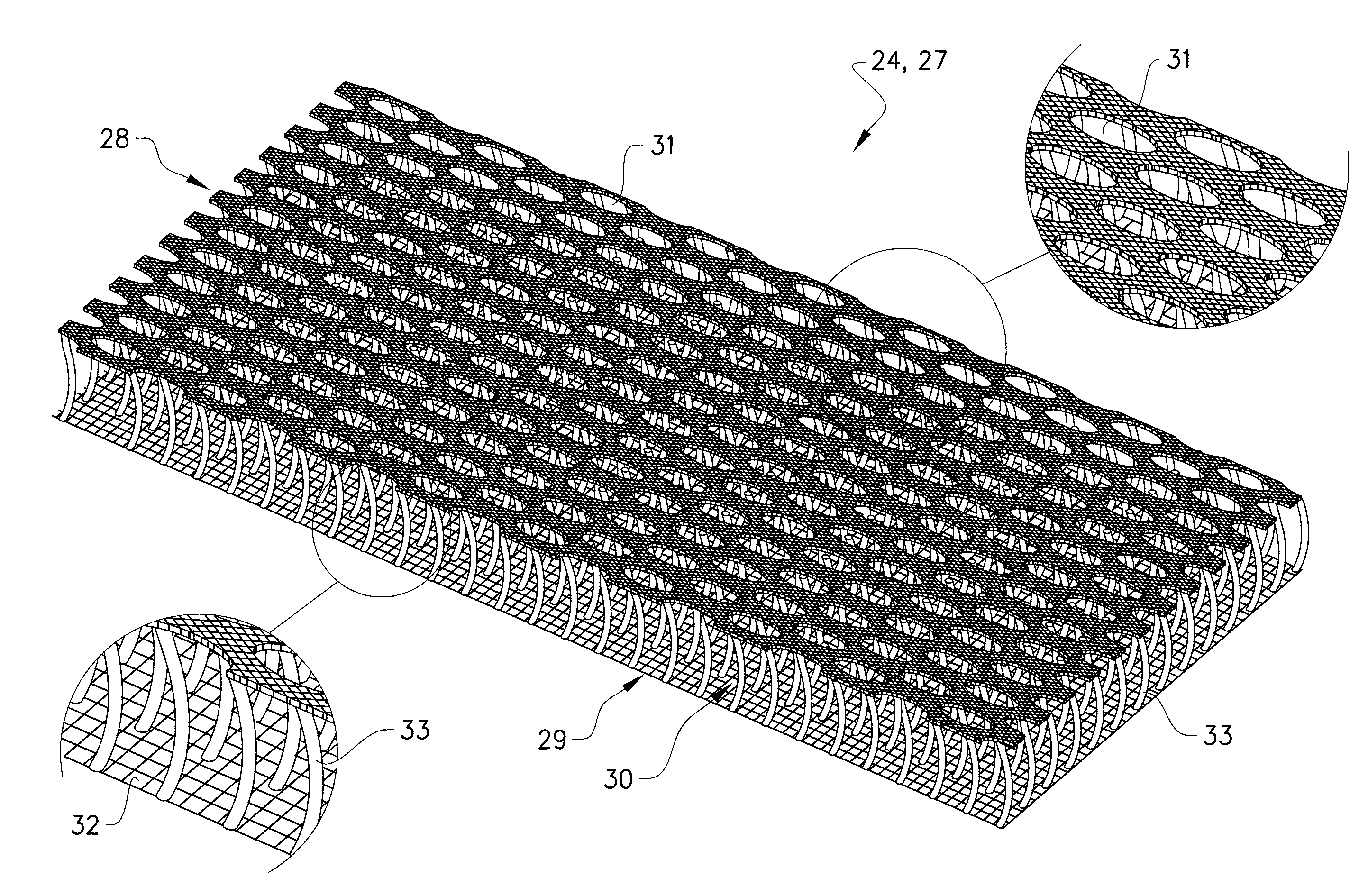
Auxetic stents
Stents of the type used to treat and prevent localized flow constriction in body vessels are based upon negative Poisson's ratio (NPR) structures. An auxetic stent constructed in accordance with this invention comprises a tubular structure having two ends defining a length with a central longitudinal axis and an axial view defining a cross section. The tubular structure is composed of a plurality of unit cells with two different configurations, called V-type and X-type. In V-type auxetic stents, each unit cell comprises a pair of side points A and B defining a width, a first pair of members interconnecting points A and B and intersecting at a point C forming a first V shape, and a second pair of members interconnecting points A and B and intersecting at a point D forming a second V shape. In X-type auxetic stents, each unit cell comprises eight points from A to H defining an outline of the unit cell. Eight straight or curved members interconnecting points A and B, B and C, C and D, C and E, E and F, F and G, G and H, G and A, respectively, forming the X-type unit cell. In both configurations, the unit cells are connected in rows and columns, such that compression of the structure between the two ends thereof causes the cross section of the structure to shrink in size. The auxetic structure configurations invented can also be used, with similar dimensions or significantly different dimensions, for other applications, such as in a nano-structural device, a tubal fastener design, or in an application associated with a large oil pipe or other pipelines.
Owner:MKP STRUCTURAL DESIGN ASSOCS
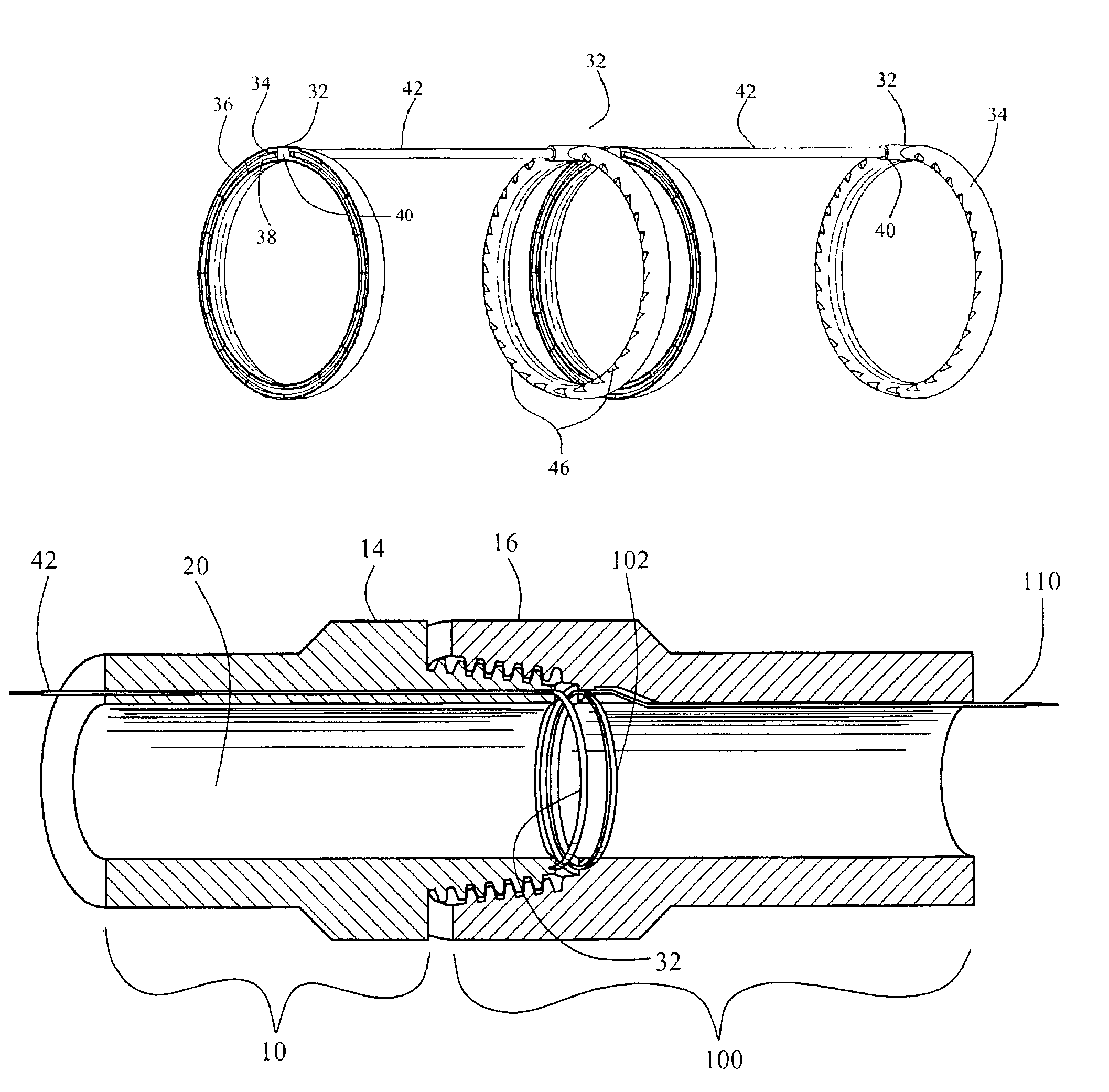
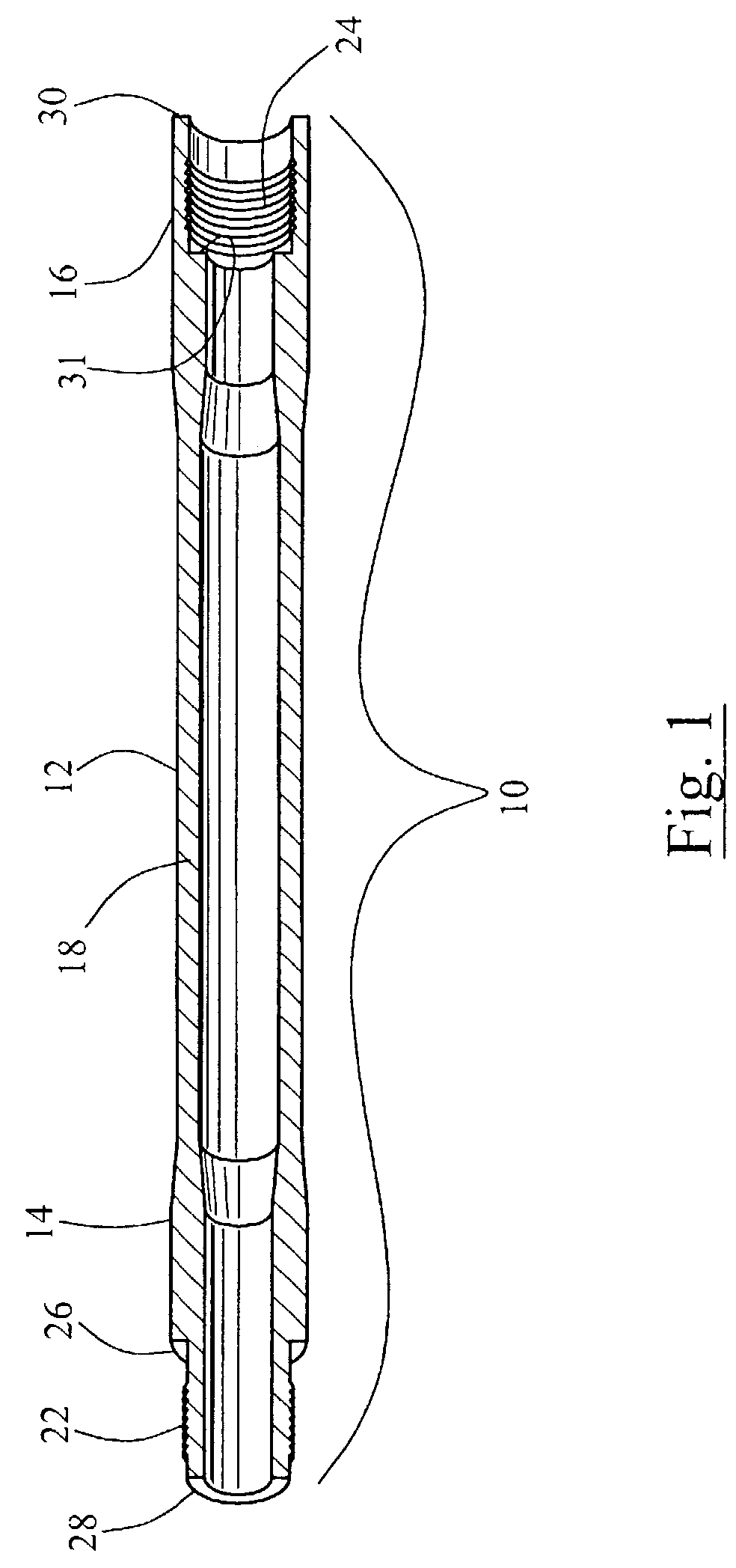
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving data to and from a downhole tool
ActiveUS7190280B2Accurately and reliably transmits and receivesHigh degree of accuracyTwo pole connectionsDrilling rodsTransmission lineCoaxial cable
A transmission line network system for transmitting and / or receiving data from a downhole tool. The invention is achieved by providing one or more transceiving elements, preferably rings, at either end of a downhole tool. A conduit containing a coaxial cable capable of communicating an electrical signal is attached to the transceiving element and extends through a central bore of the downhole tool and through the central bore of any tool intermediate the first transceiving element and a second transceiving element. Upon receiving an electrical signal from the cable, the second transceiving element may convert such signal to a magnetic field. The magnetic field may be detected by a third transceiving element in close proximity to the second transceiving element. In this manner, many different tools may be included in a downhole transmission network without requiring substantial modification, if any, of any particular tool.
Owner:INTELLISERV
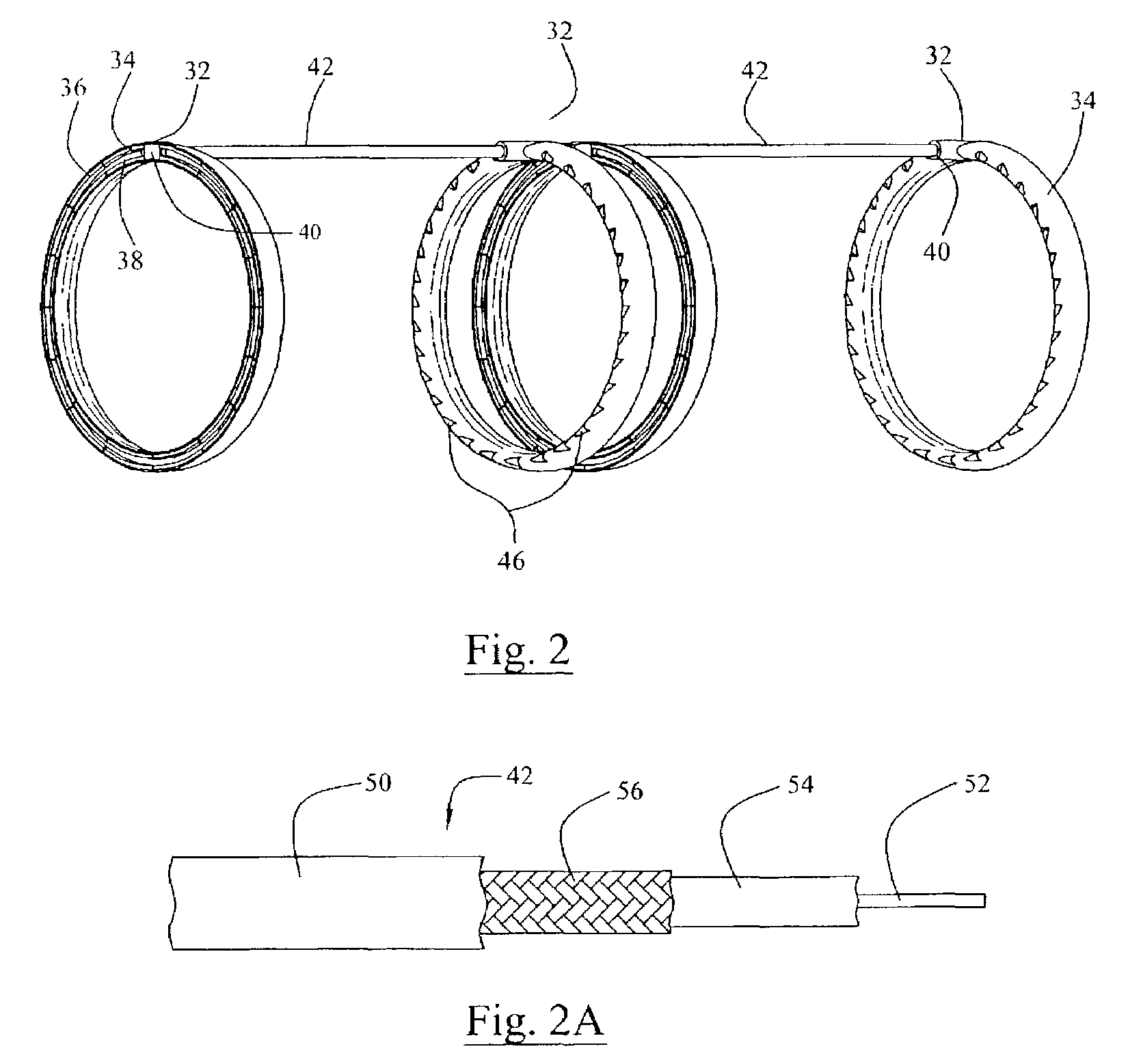
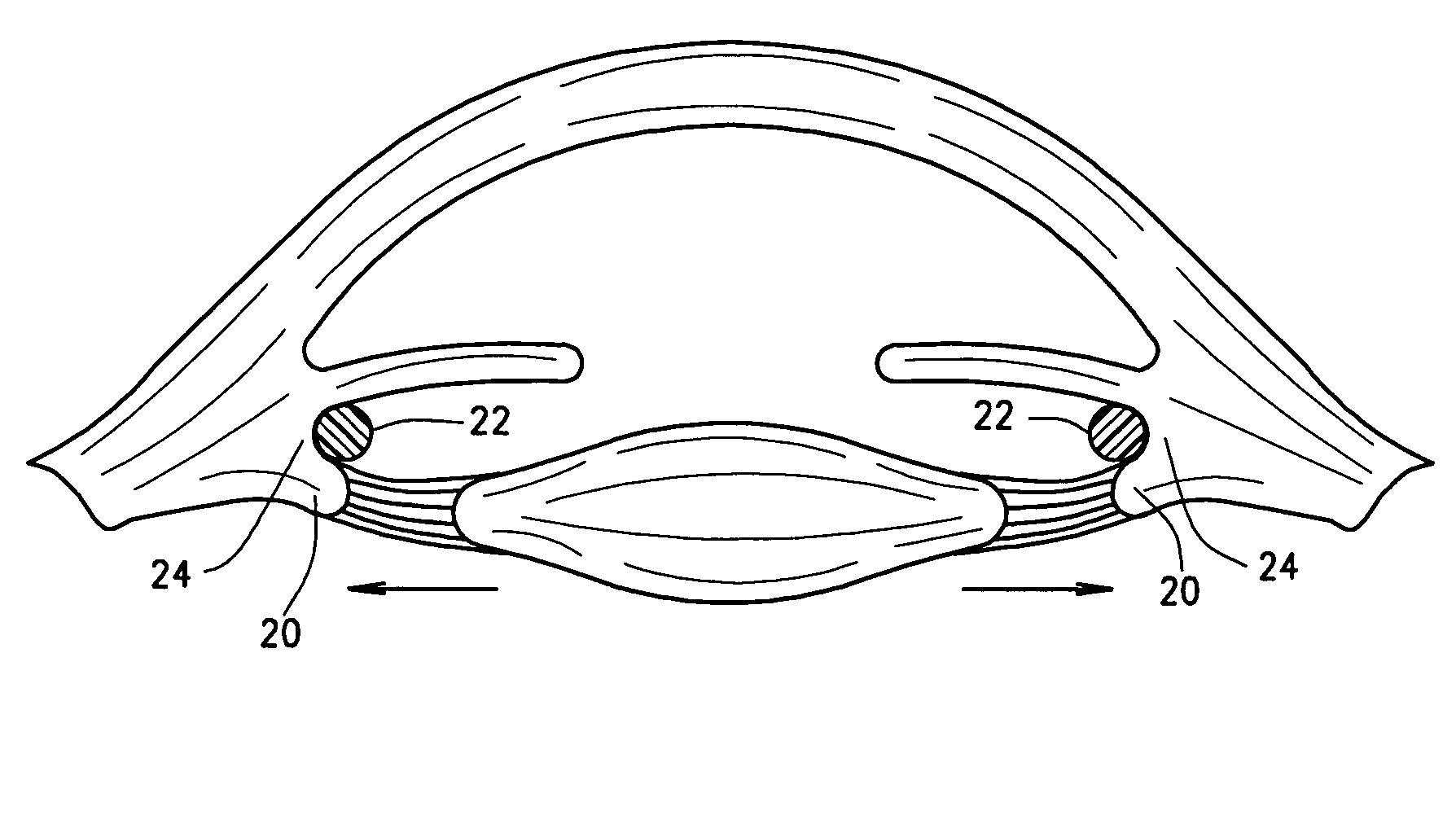
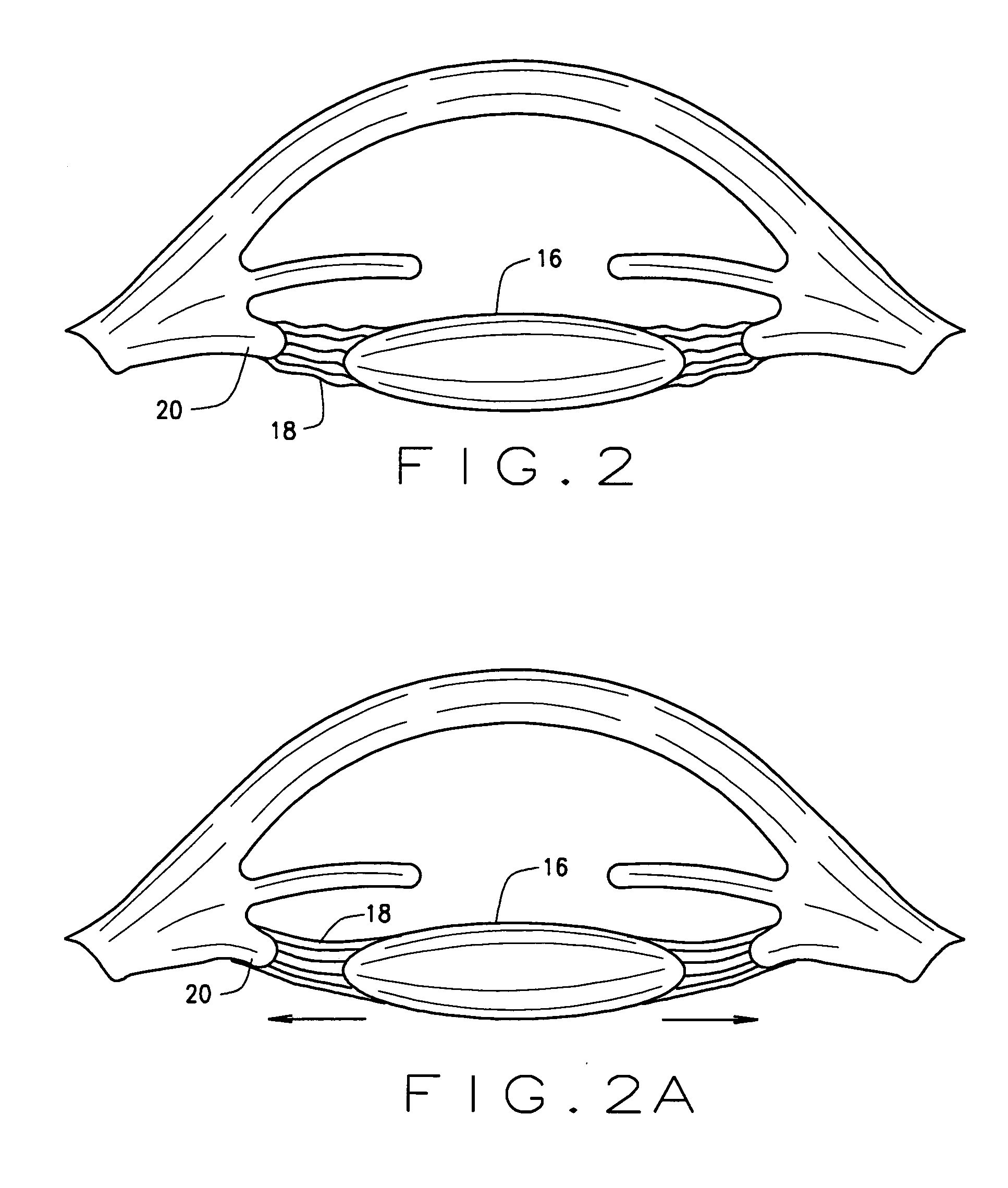
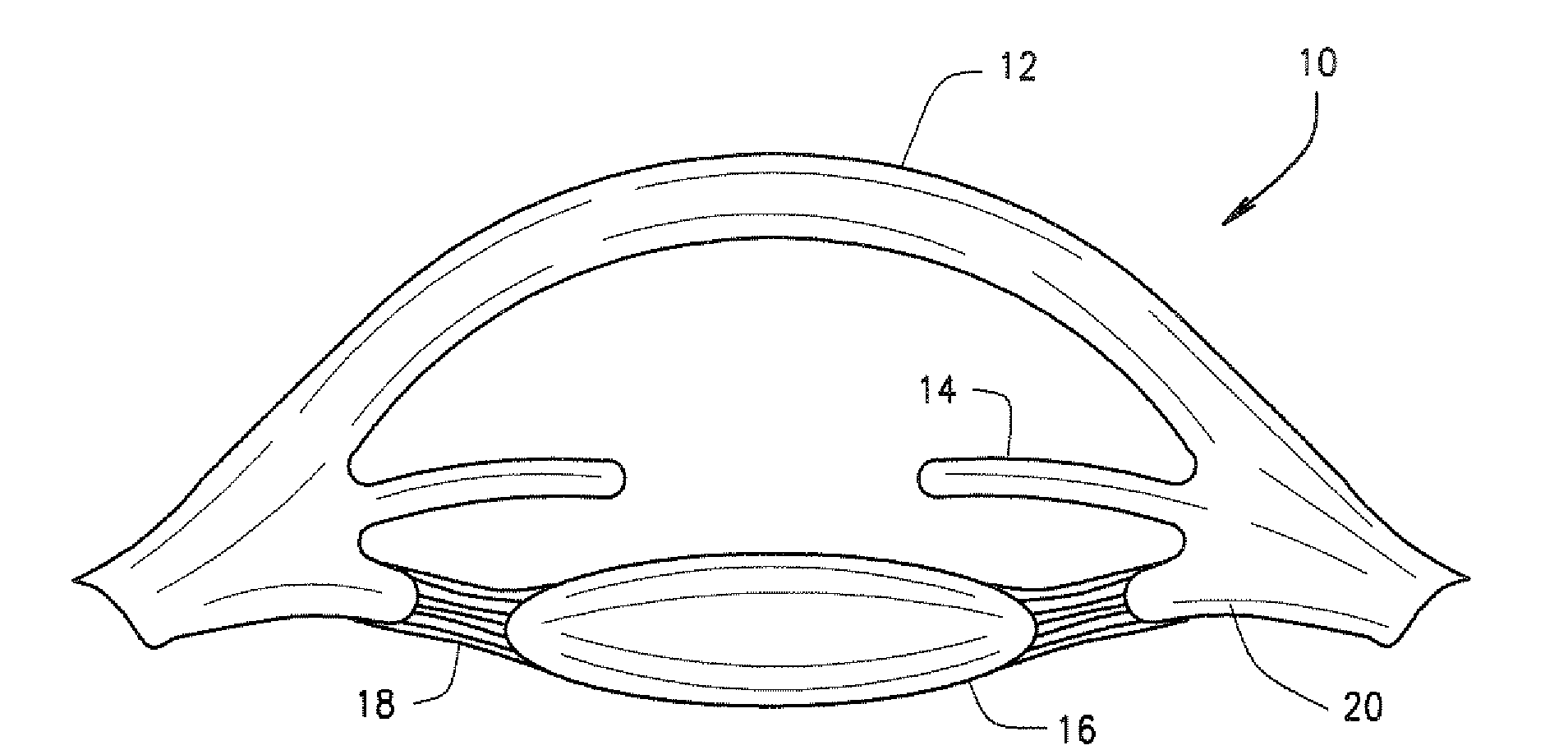
Ophthalmological zonular stretch segment for treating presbyopia
The invention comprises a device for treating presbyopia. A stretch segment is provided for intraocular implantation into the annular sulcus region defined by the intersection of the iris and ciliary body. The stretch segment engages and exerts an outward radial tension against the ciliary body. The segment is designed to take up slack in the equatorial zonules in the presbyopic eye, such that their effective working distance is enhanced. This aids in the accommodation process which affects the curvature of the lens for near viewing. The segment may a closed ring, or may be open ended.
Owner:BOXER WACHLER BRIAN S
Concrete water-permeable brick using steel slag as aggregate
The invention discloses a concrete permeable brick of steel slag as aggregate, which comprises the following steps: allocating raw material with 70-85% steel slag with grinding value less than 5% and free calcium oxide less than 3%, 10-25% C52.5 low-alkaline cement, 0.5-6% reinforcer, 0-3% coloring powder and 3.5-5% water; blending raw materials in the mixer; distributing; molding; obtaining the product.
Owner:SUZHOU HUAJIA NEW BUILDING
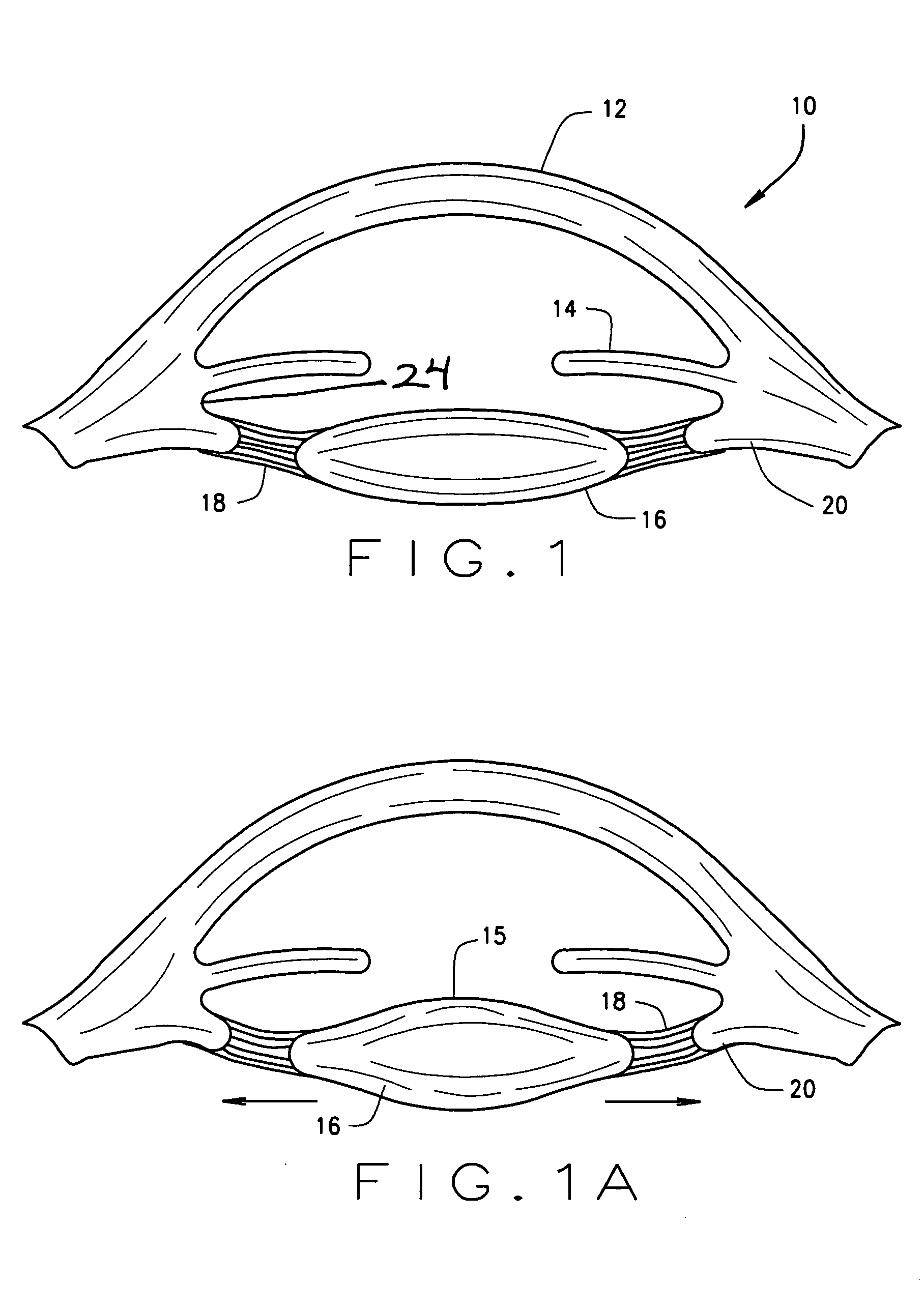
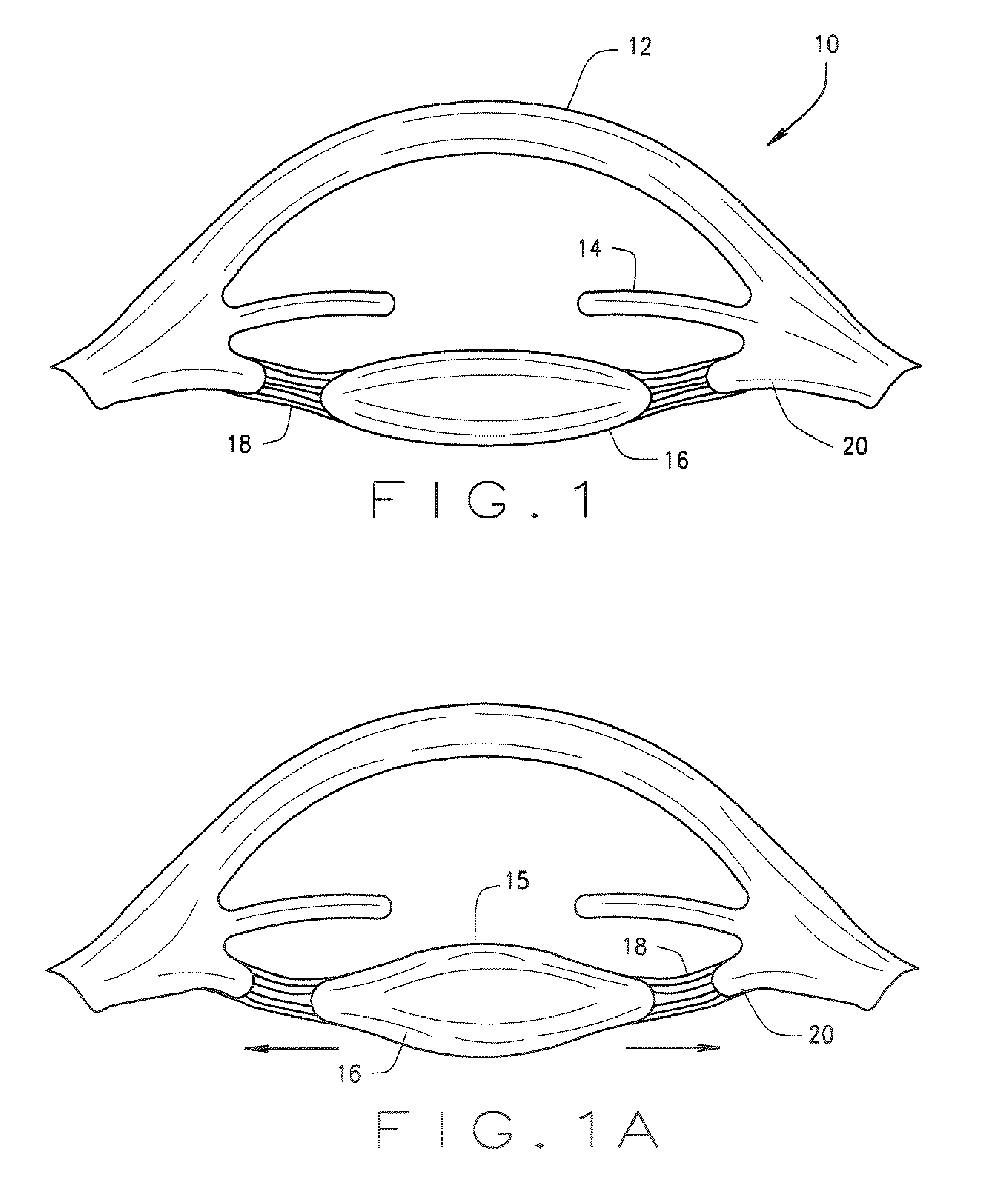
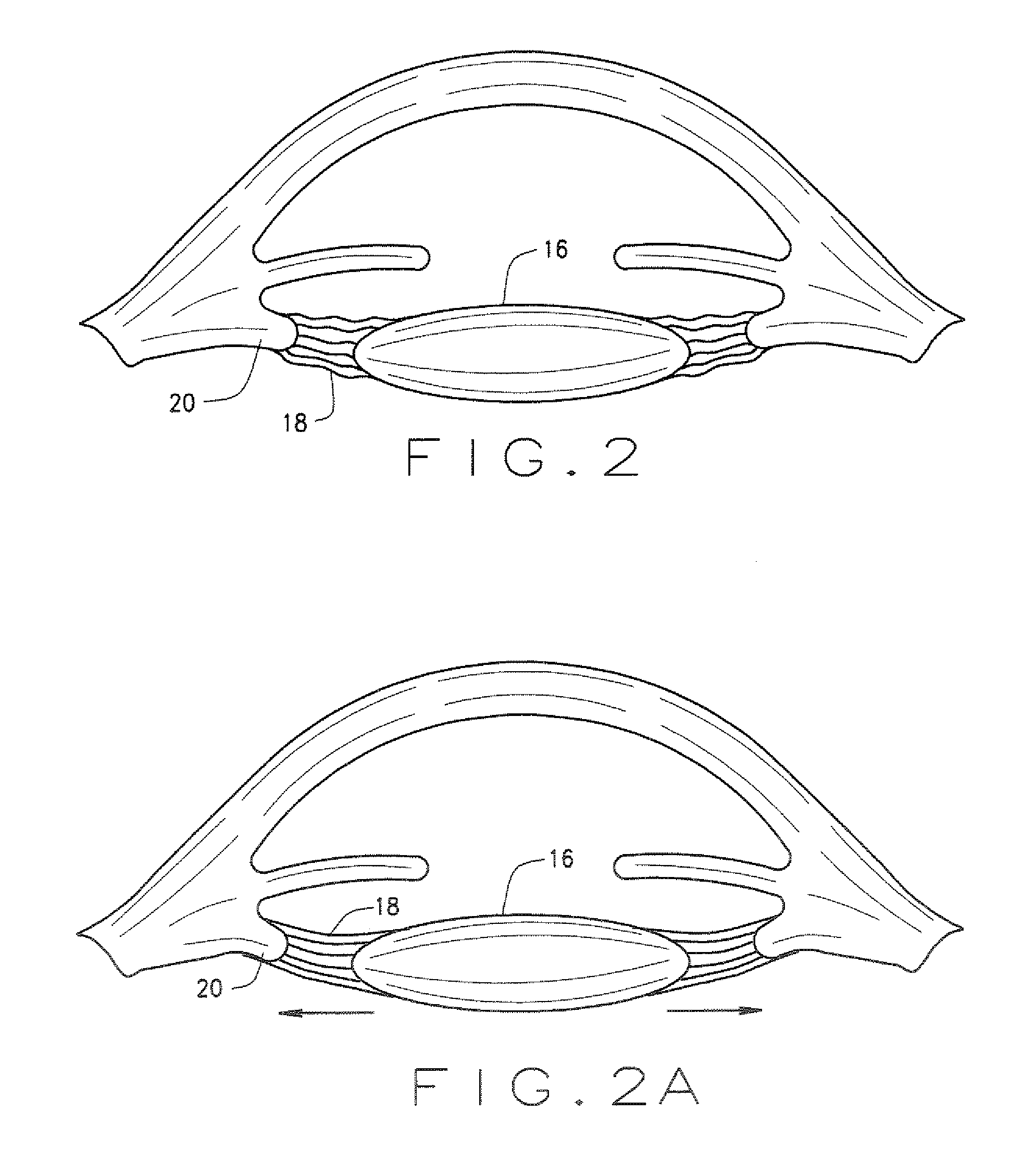
Ophthalmological zonular stretch segment for treating presbyopia
The invention comprises a device for treating presbyopia. A stretch segment is provided for intraocular implantation into the annular sulcus region defined by the intersection of the iris and ciliary body. The stretch segment engages and exerts an outward radial tension against the ciliary body. The segment is designed to take up slack in the equatorial zonules in the presbyopic eye, such that their effective working distance is enhanced. This aids in the accommodation process which affects the curvature of the lens for near viewing. The segment may a closed ring, or may be open ended.
Owner:BOXER WACHLER BRIAN S
Heat pipe with micro-pore tubes array and making method thereof and heat exchanging system
ActiveUS20110203777A1Reduce welding efficiencyReduce heat resistance requirementsSolar heating energySolar heat devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A heat pipe with micro tubes (2), comprised of a solid heat conductor (1) provided therein with two or more parallel micro tubes (2), the micro tubes being filled therein with working medium which exchanges heat through phrase change; and the two ends of the heat conductor (1) are sealed and at least one of them is provided with a sealing strip of gradually shrinking shape that is formed from cold welding. A manufacturing process for the heat pipe and a heat-exchange system comprised of the heat pipe.
Owner:GUANGWEI HETONG ENERGY TECH BEIJING CO LTD
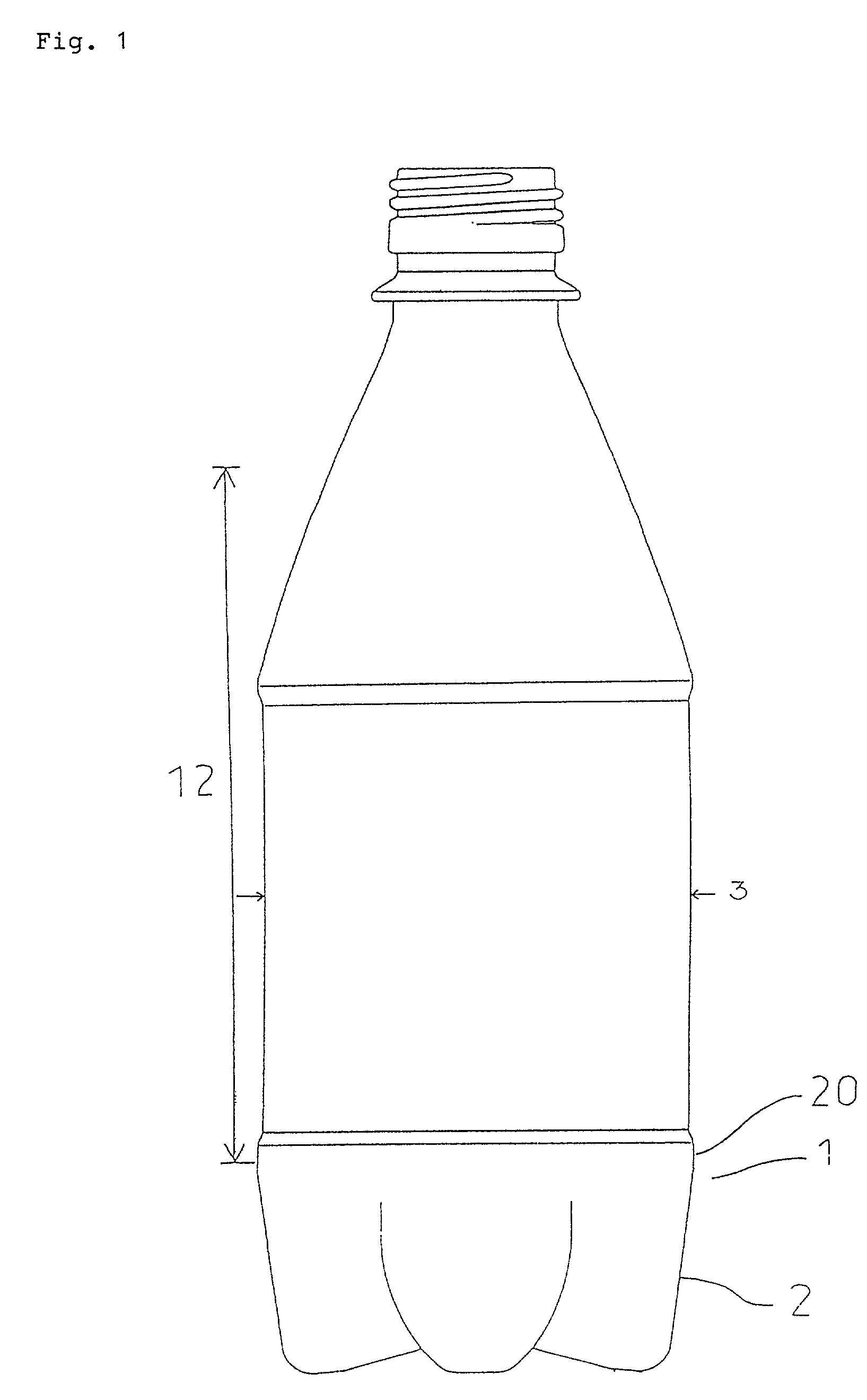
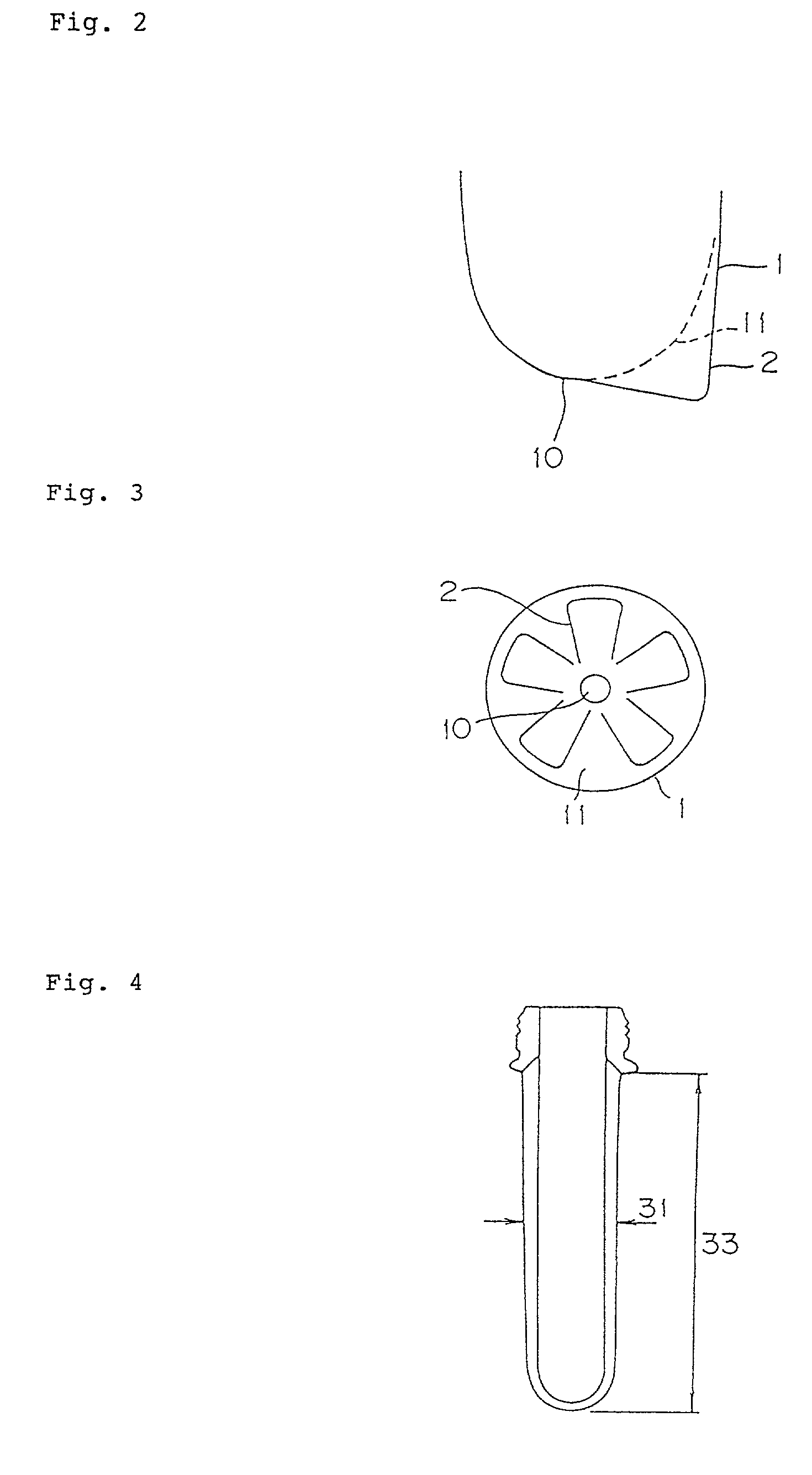
Polyester resin composition and a bottle therefrom
The present invention relates to a resin composition comprising polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene naphthalate and a process for preparing the composition. The present invention relates also to a bottle produced from the composition and a process for the preparation of the bottle. The resin composition according to the present invention is prepared by melt-kneading (A) polyethylene terephthalate with (B) polyethylene naphthalate in a proportion of the ethylene naphthalate unit to a total of (A) and (B) of from 5 to 15 mole %, with a kneading extruder in a ratio of an extruder output rate to a screw rotation speed of 0.1 to 1.4 kg / hr.rpm. The present composition gives a bottle superior in transparency and in resistance to heat and pressure despite that it has a transesterification of 20% or lower.
Owner:NISHIHARA SHUN ICHI +3
Perimeter pile anchor foundation
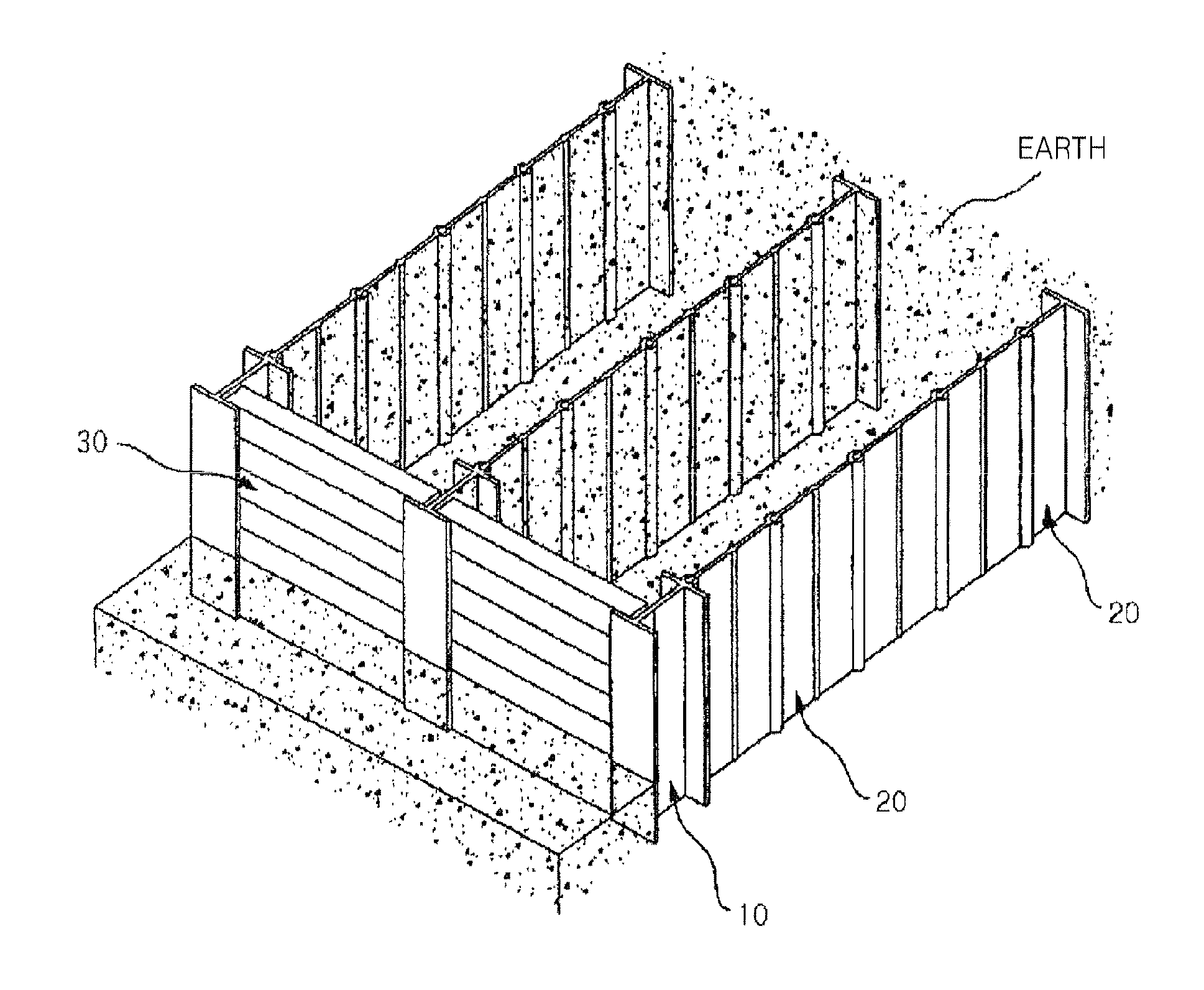
A perimeter pile anchor foundation is built by forming a plurality of individual perimeter pile anchors in a large generally circular pattern to form a perimeter wall. The individual pile anchors are contiguous, each pile overlapping the adjacent piles on either side. The overlapping pile anchors form an arch such that compression and friction between the pile anchors resist soil caving and sloughing pressure when soil inside the perimeter wall is excavated, enabling the perimeter pile foundation to be effectively constructed in weak saturated soils and / or cohesionless sands that will not allow conventional concrete foundation excavations. A concrete foundation ring is formed inside the pile perimeter wall to support a tall and / or heavy tower or other structure subject to high upset forces.
Owner:TERRACON CONSULTANTS INC
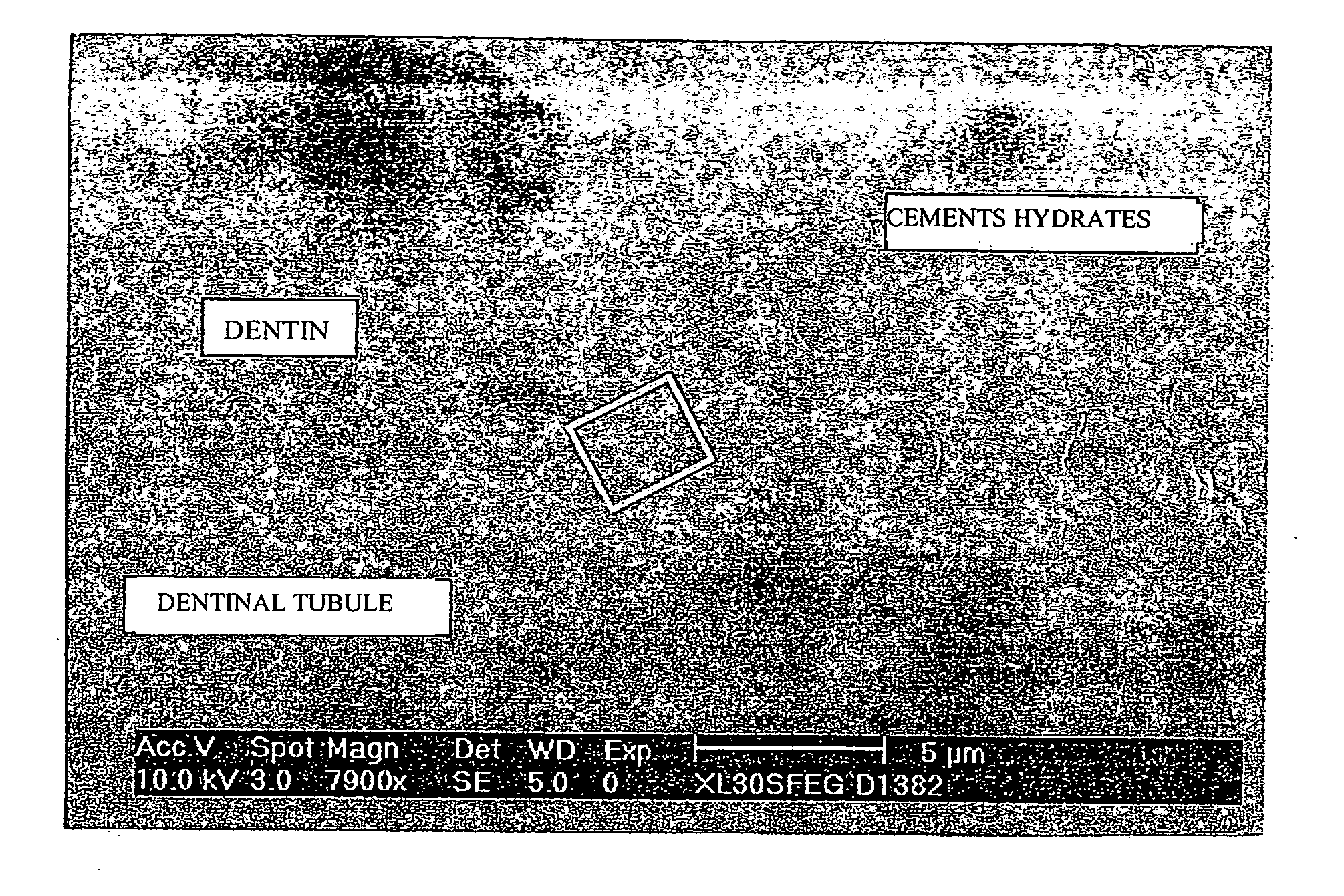
Preparation for producing a material used to restore a mineralised substance, particularly in the dental field
ActiveUS20060102049A1Increase rangeColor matchingImpression capsOther chemical processesChlorideReducing agent
A preparation contains an aqueous liquid part, a solid part comprising at least one silicate selected from tricalcium silicate Ca3SiO5 and dicalcium silicate Ca2SiO4; and calcium chloride CaCl2 and a water reducing agent which are both contained in at least one of the aforementioned parts. According to the invention, the solid part and the liquid part are intended to be mixed in order to obtain the material. The preparation can be used to restore a mineralized substance, particularly in the dental field.
Owner:SEPTODONT SPECIALITES SEPTODONT
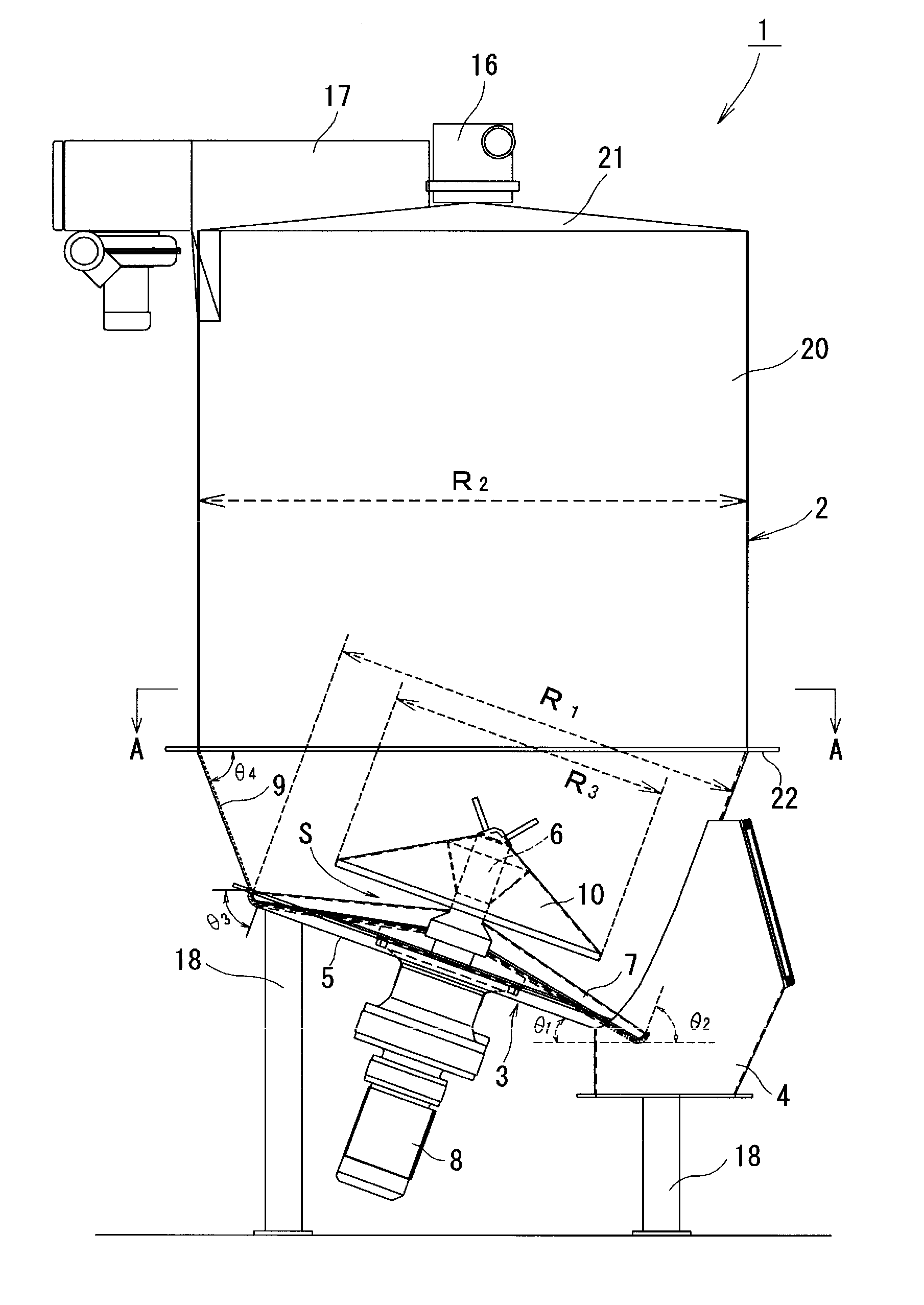
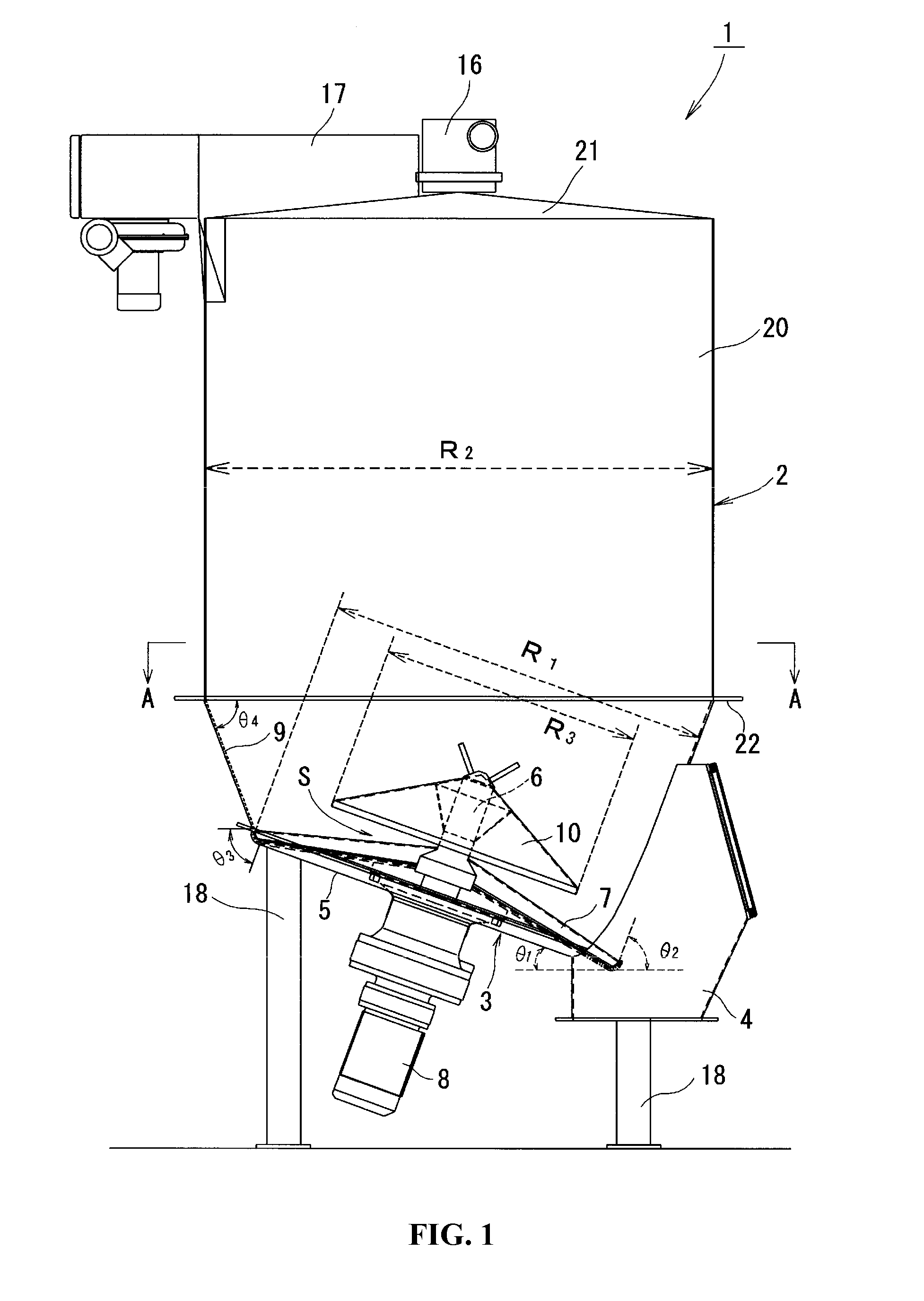
Table feeder
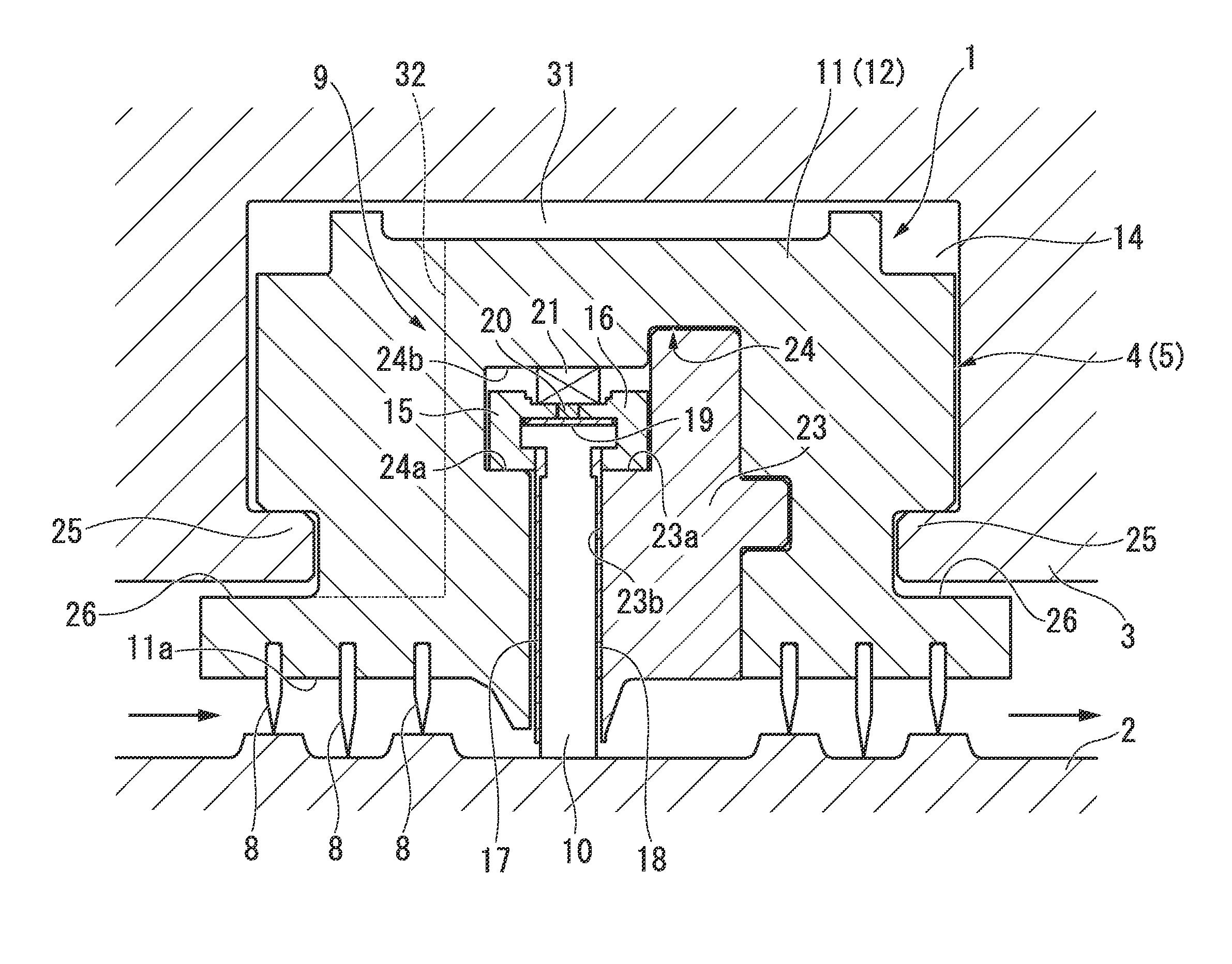
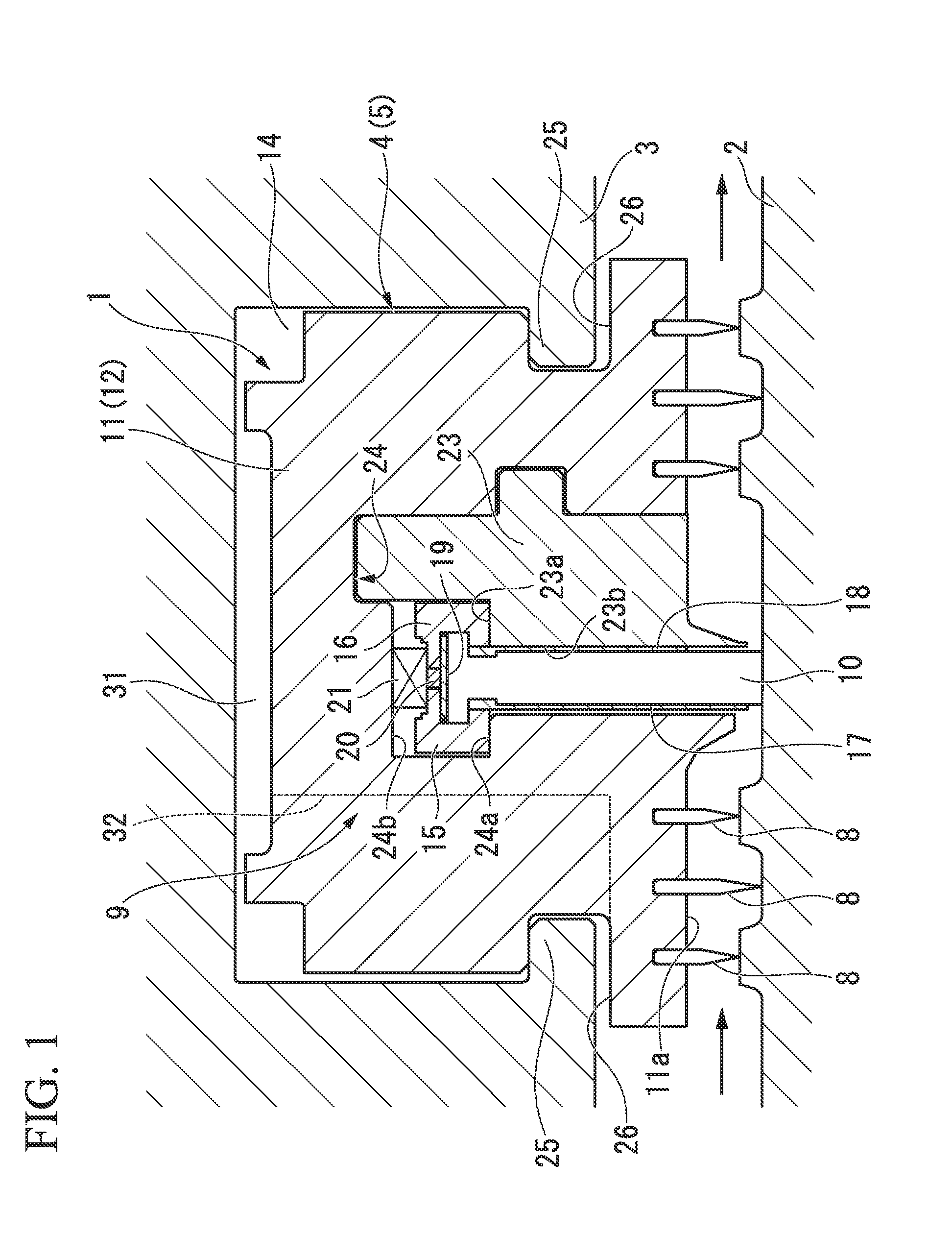
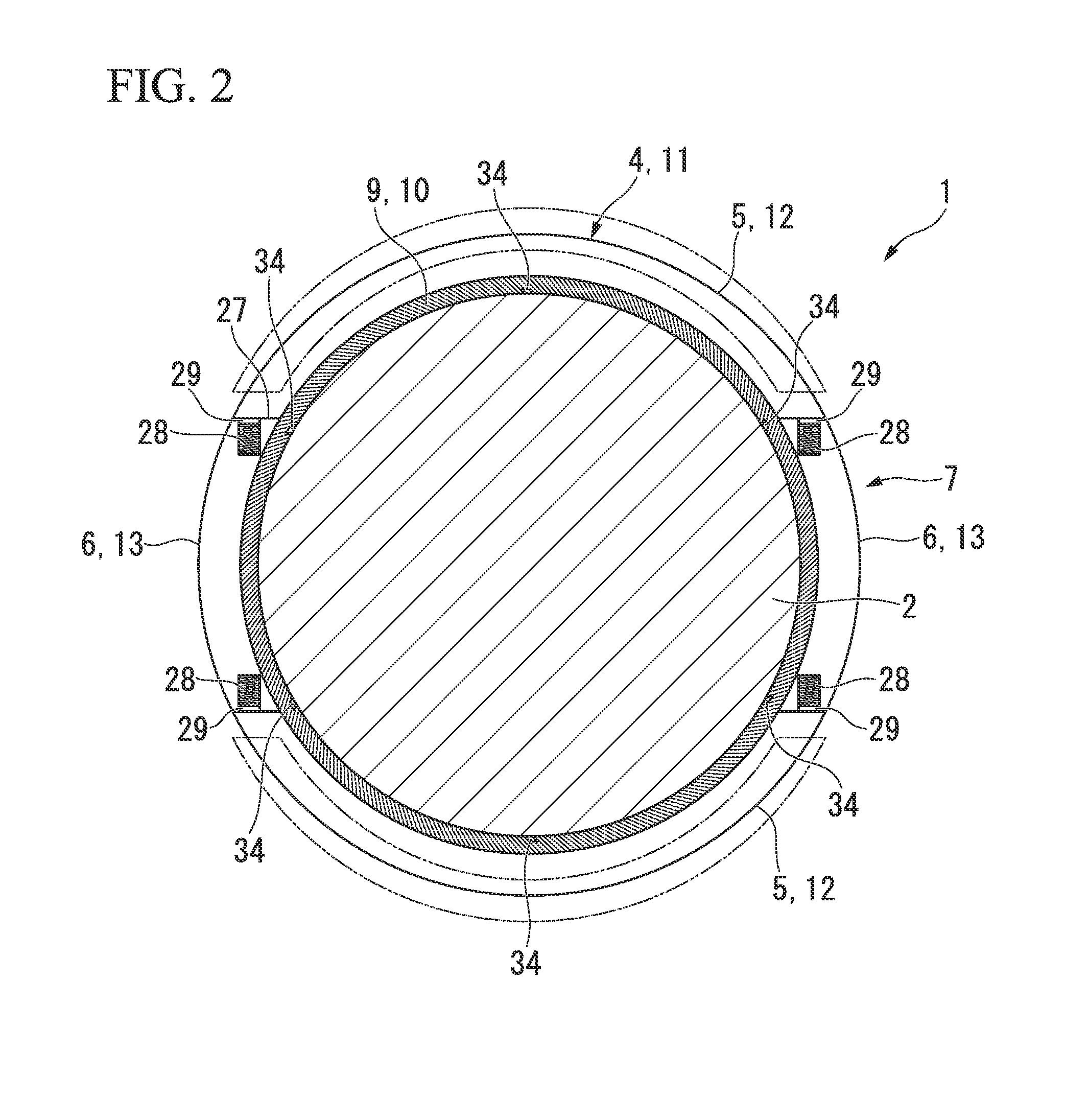
InactiveUS20110031280A1Good stress reliefLarge power capacityMovable measuring chambersLarge containersDischargerParticulate material
A table feeder 1 has a bottom assembly 3 of a particulate material processing vessel 2, a discharger 4 provided in the bottom assembly 3 to discharge a particulate material P kept in the vessel 2, a bottom plate 5 included in the bottom assembly 3, a rotating shaft 6 provided vertically to a main face 5a of the bottom plate 5 to rotate on the center of the bottom plate 5, rotary vanes 7 to discharge the particulate material P kept in the particulate material processing vessel 2 via the discharger 4 and a drive device 8 configured to drive and rotate the rotary vanes 7. A cone 10 having a smaller diameter than a diameter of the rotary vanes 7 is provided in the space above the rotary vanes 7 coaxially with the rotary vanes7 to extend over a central area of the rotary vane 7.
Owner:TSUKASA
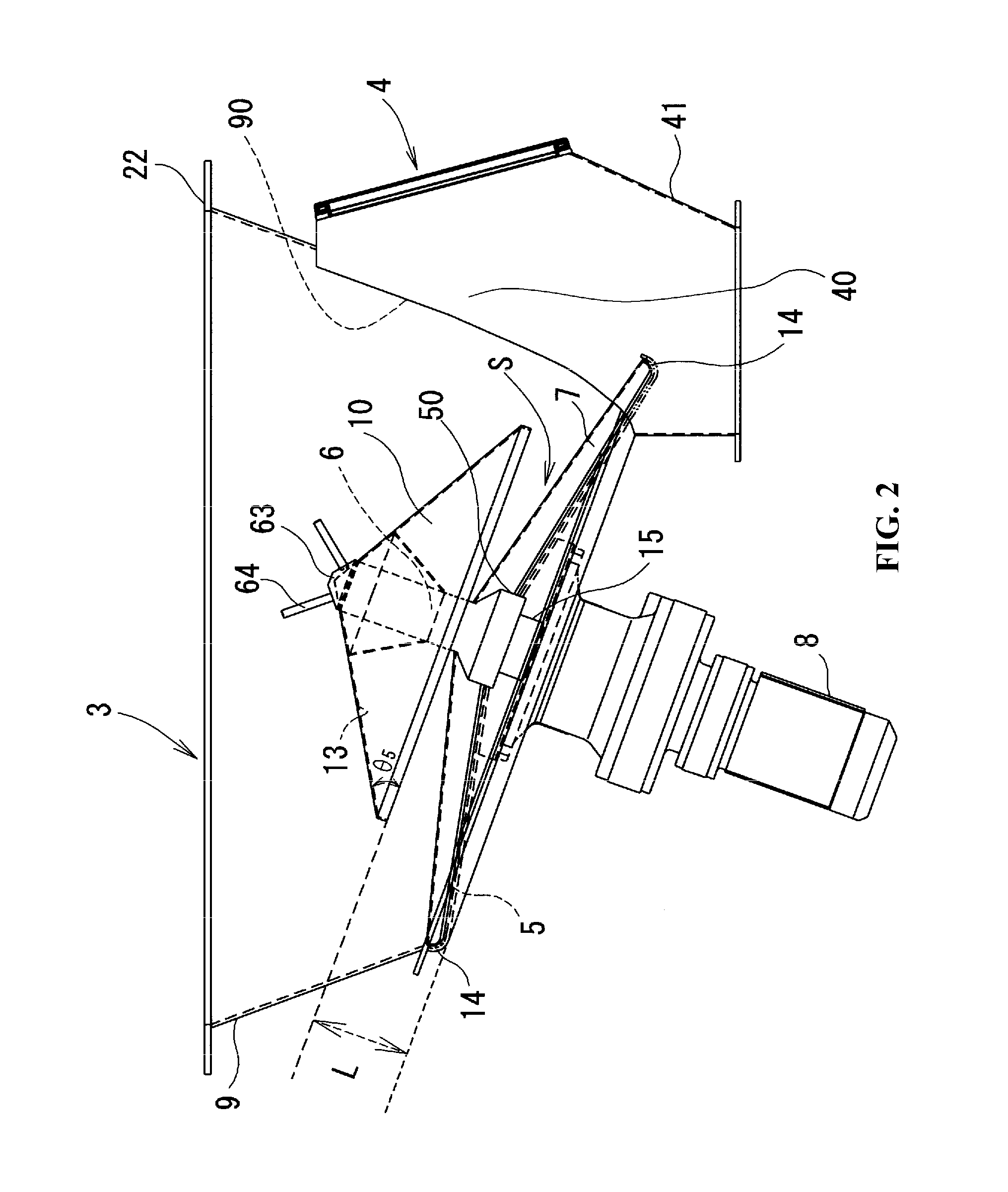
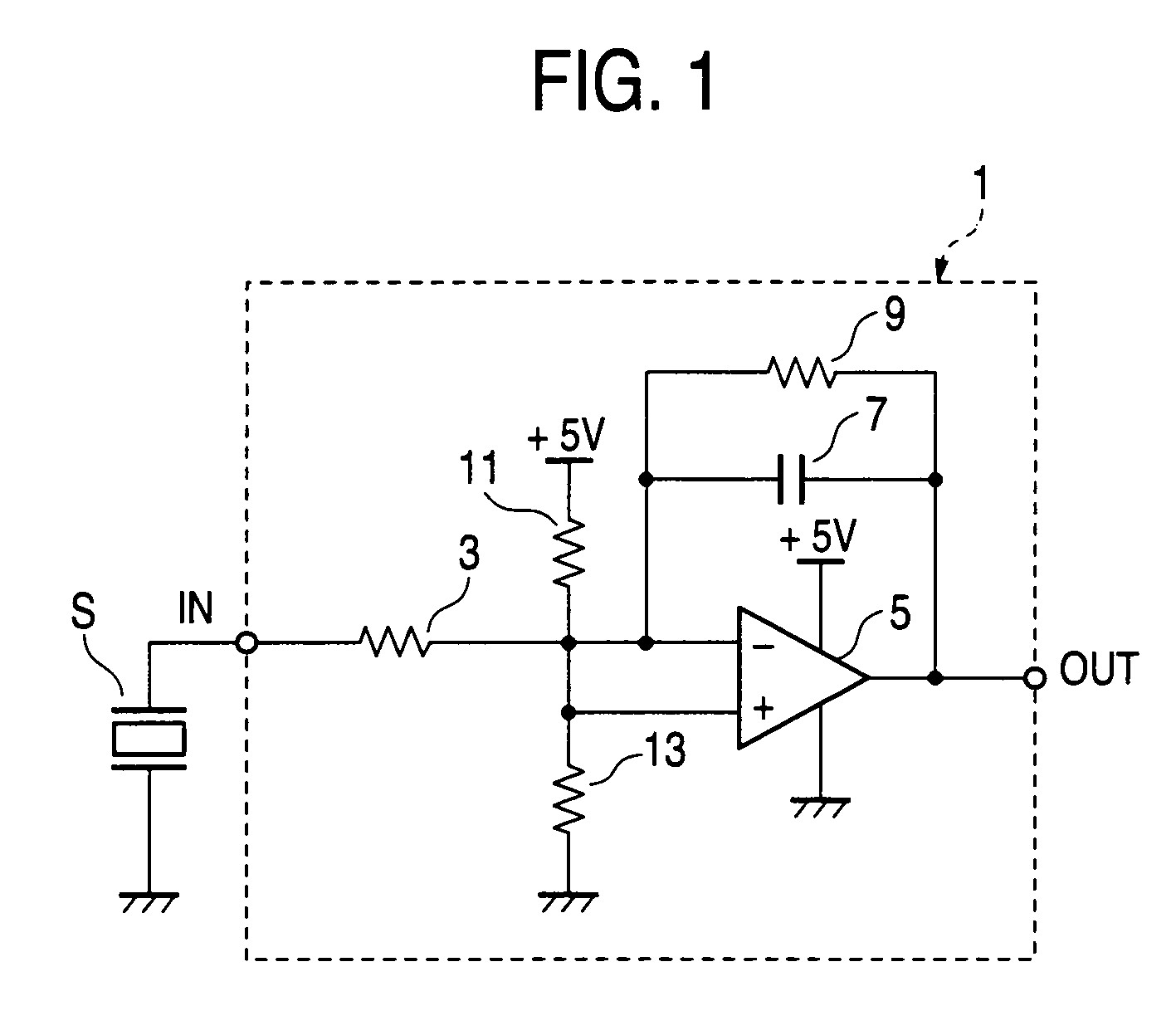
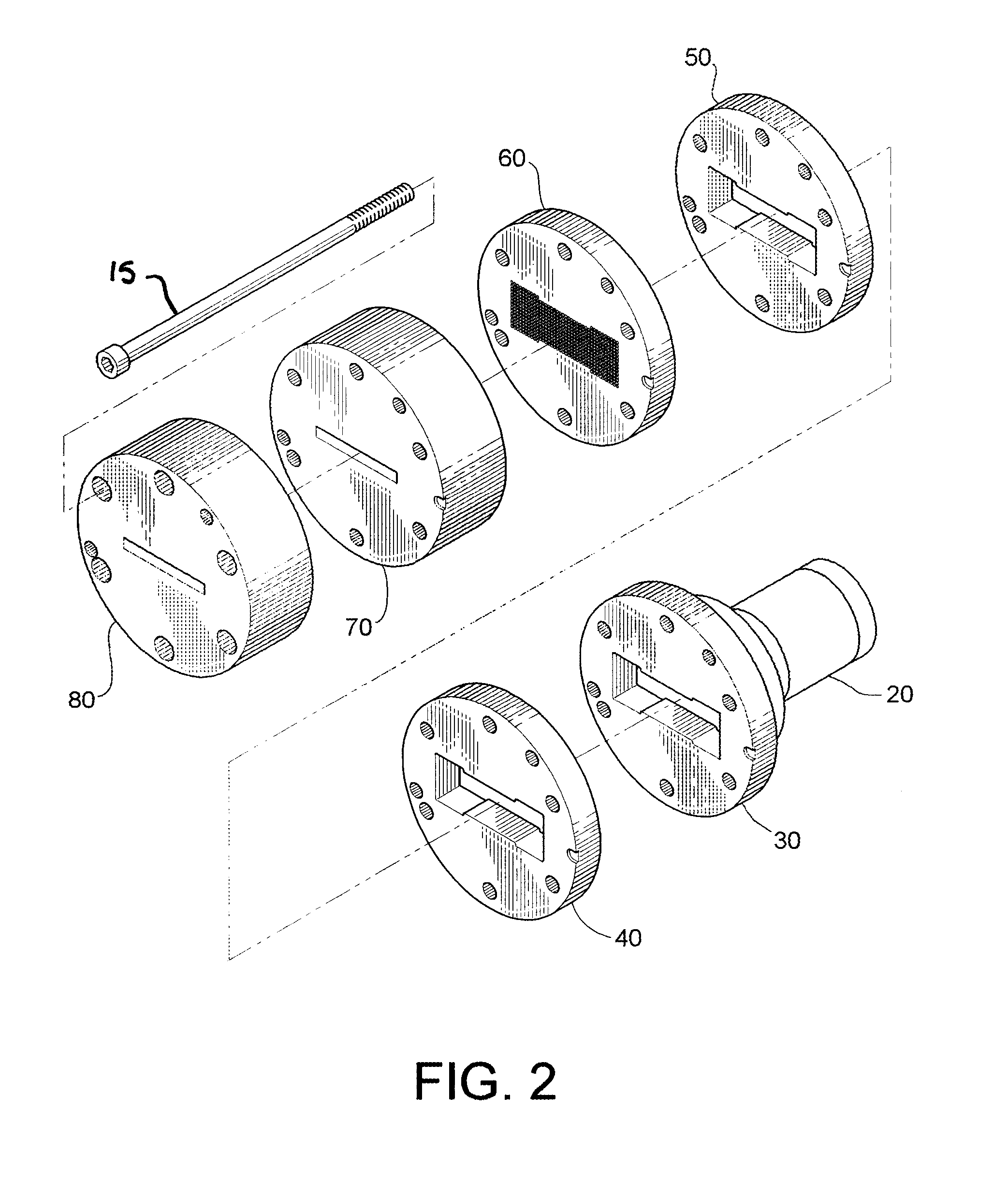
Charge amplifier for piezoelectric pressure sensor
InactiveUS7042288B2Efficient processPressure resistanceFluid pressure measurement using piezo-electric devicesMachines/enginesElectricityAudio power amplifier
An object of the present invention is to provide a charge amplifier which can be operated at low cost so that electric charge generated in a piezoelectric pressure sensor having one end grounded is converted into a voltage signal.In the charge amplifier (1) according to an embodiment of the present invention, a plus side power source input terminal of an operational amplifier (5) is connected to a plus power source (+5 V) while a minus side power source input terminal of the operational amplifier (5) is grounded, so that the operational amplifier (5) is supplied with a single power source. Further, an offset voltage lower than the plus power source voltage but higher than the ground potential is applied to a non-inverted input terminal of the operational amplifier (5). Accordingly, change of pressure in both positive and negative directions can be converted into a voltage signal with the offset voltage as its center though the operational amplifier (5) is driven by a single power source. That is, cost can be suppressed because a double power source is not required.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Ultrasonic transducer for use in a fluid medium
InactiveUS8596139B2Ensure relative distancePressure resistancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityUltrasonic sensor
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Circuit board and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7898820B2High strengthLow costPrinted circuit groundingCross-talk/noise/interference reductionProtection layerElectrical and Electronics engineering
A circuit board is provided, comprising a substrate, a first conductive layer, at least one through hole, a protection layer, a plurality of contacts and a fixing element. The first conductive layer is formed on the substrate. The through hole is formed on the substrate and the first conductive layer. The protection layer is formed on the first conductive layer, wherein the protection layer comprises a plurality of hollow portions, the hollow portions surround the through hole, and the first conductive layer is exposed in the hollow portions. The contacts are disposed in the hollow portions, wherein the contacts are protruding from a surface of the protection layer. The fixing element is fixed in the through hole, wherein the fixing element contacts the contacts.
Owner:GIGA BYTE TECH CO LTD
Dummy plug for wiring harness
InactiveUS20010007802A1Simple and efficientAdvantageous resultSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersLive contact access preventionCable harnessPogo pin
A dummy plug for wiring harnesses is disclosed. The dummy plug is used in an unused connector cavity of the wiring harness, thereby electrically isolating the connector cavity in the wiring harness to prevent short circuits. The dummy plug is substantially flush with the latch arm of the wiring harness, so that a pogo pin can determine whether or not the connector cavity is in use. The dummy plug has a design such that pressure blowout is prevented. A method for plugging an unused connector cavity is also disclosed, the method including the steps of providing a dummy plug having a head, a stem, and a female end, providing a wiring harness having at least one connector cavity and at least one latch arm and inserting the dummy plug into the unused connector cavity so that the female end is substantially flush with the latch arm.
Owner:QUALITY SYNTHETIC RUBBER INC
Processing apparatus and processing method
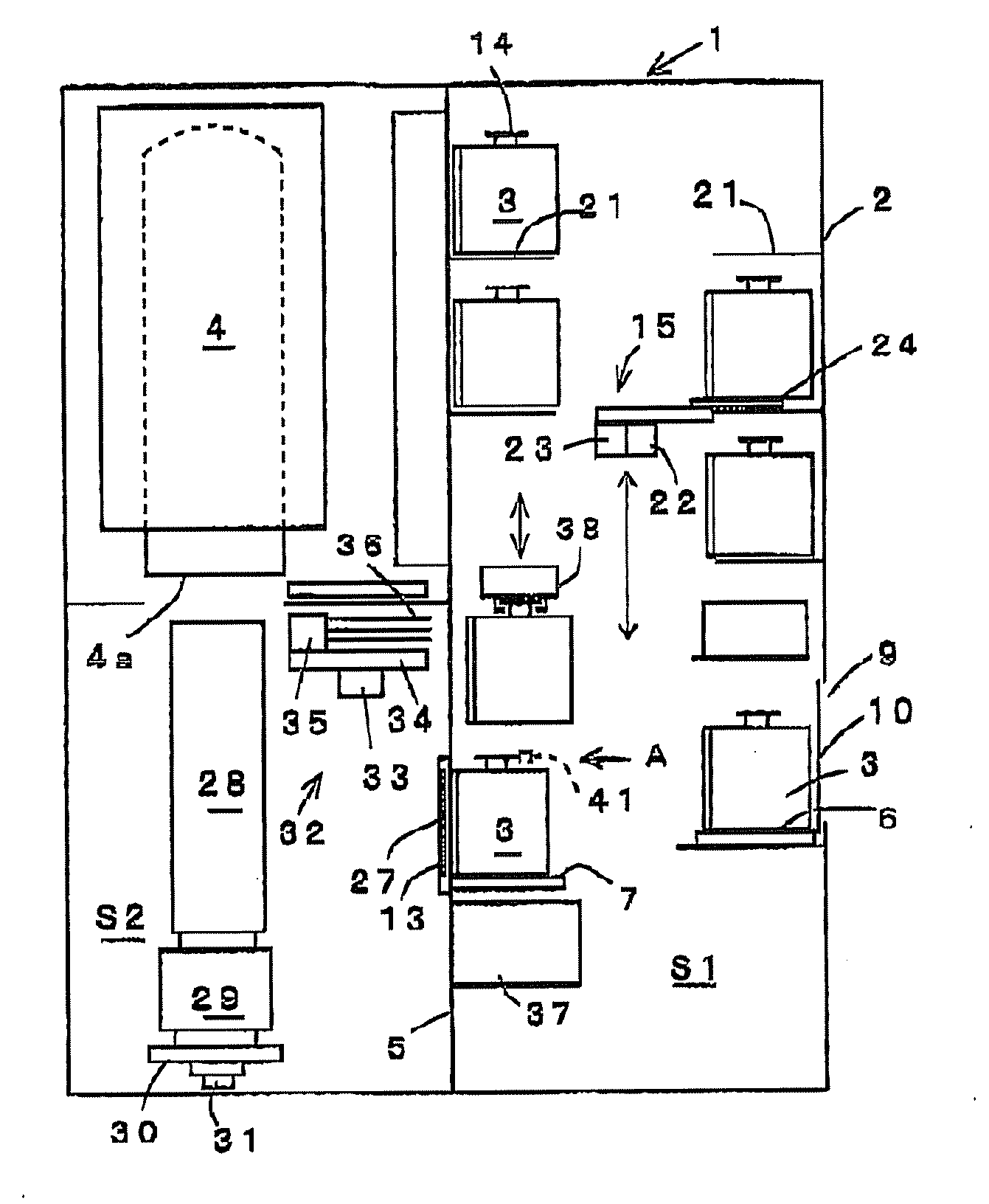
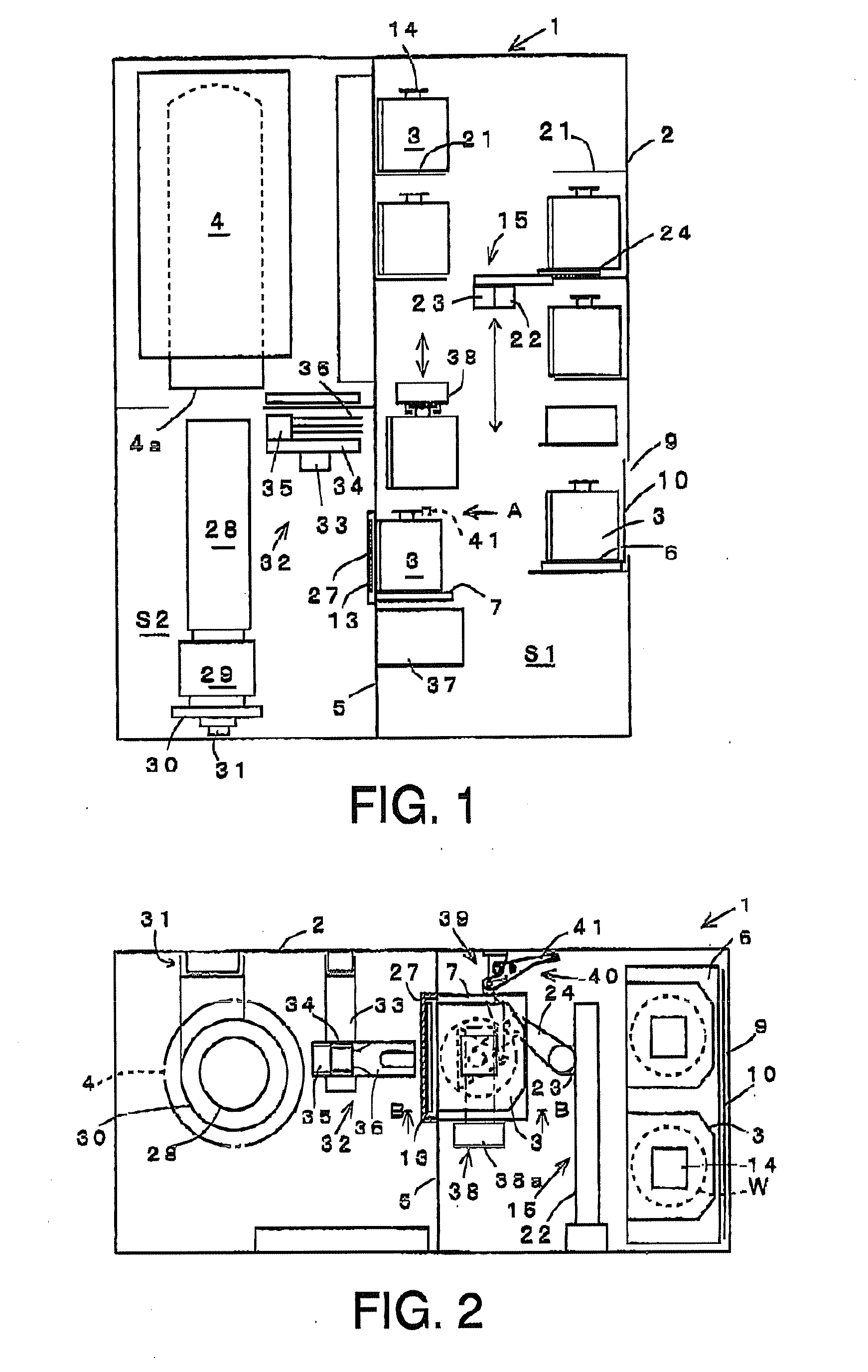
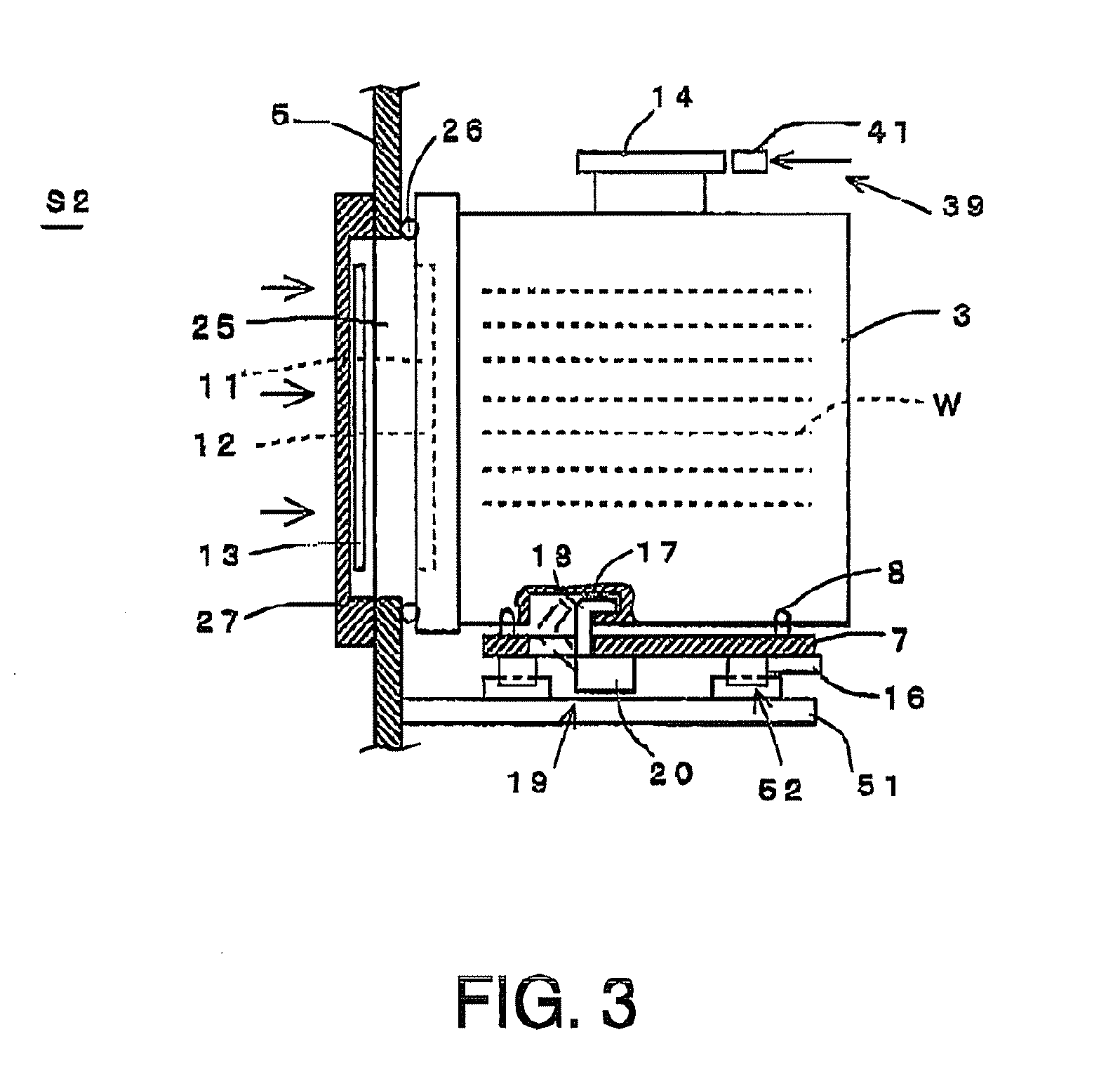
ActiveUS20100098517A1Pressure resistanceAvoid partialConveyorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A processing apparatus including: a carry-in area into which a container containing substrates to be processed is carried, the container having a flange part on an upper part thereof and an opening in a front surface thereof, with a lid being detachably fixed to the opening; a transfer area whose atmosphere is maintained differently from an atmosphere of the carry-in area; a partition wall separating the carry-in area and transfer area; a through-hole formed in the partition wall; a door configured to open and close the through-hole; and a table on which the container can be placed in the carry-in area. After the container has been placed and then held on the table, the container is brought into contact with the through-hole, the door and the lid are opened, and the substrates to be processed in the container are conveyed to the transfer area so as to process the substrates.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
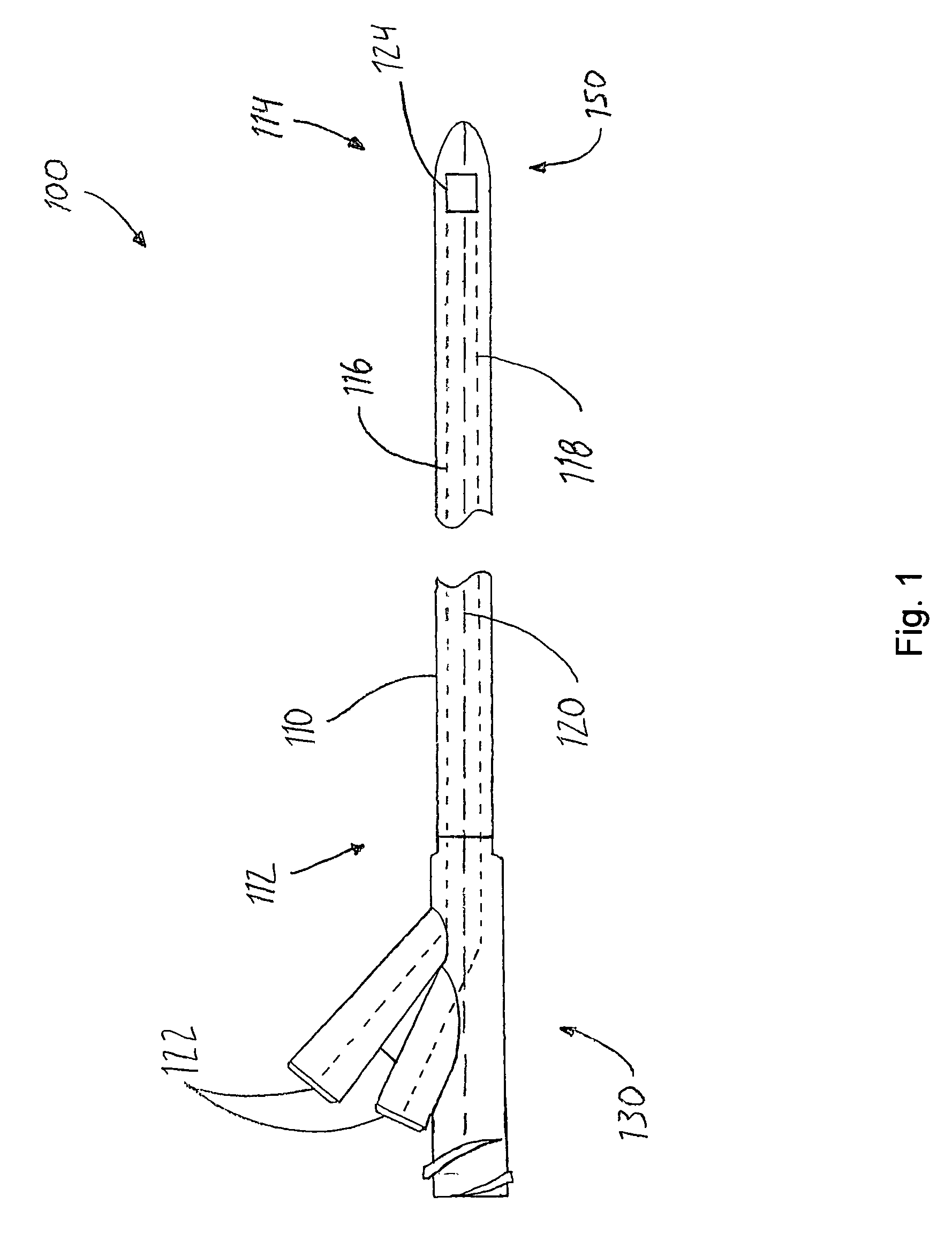
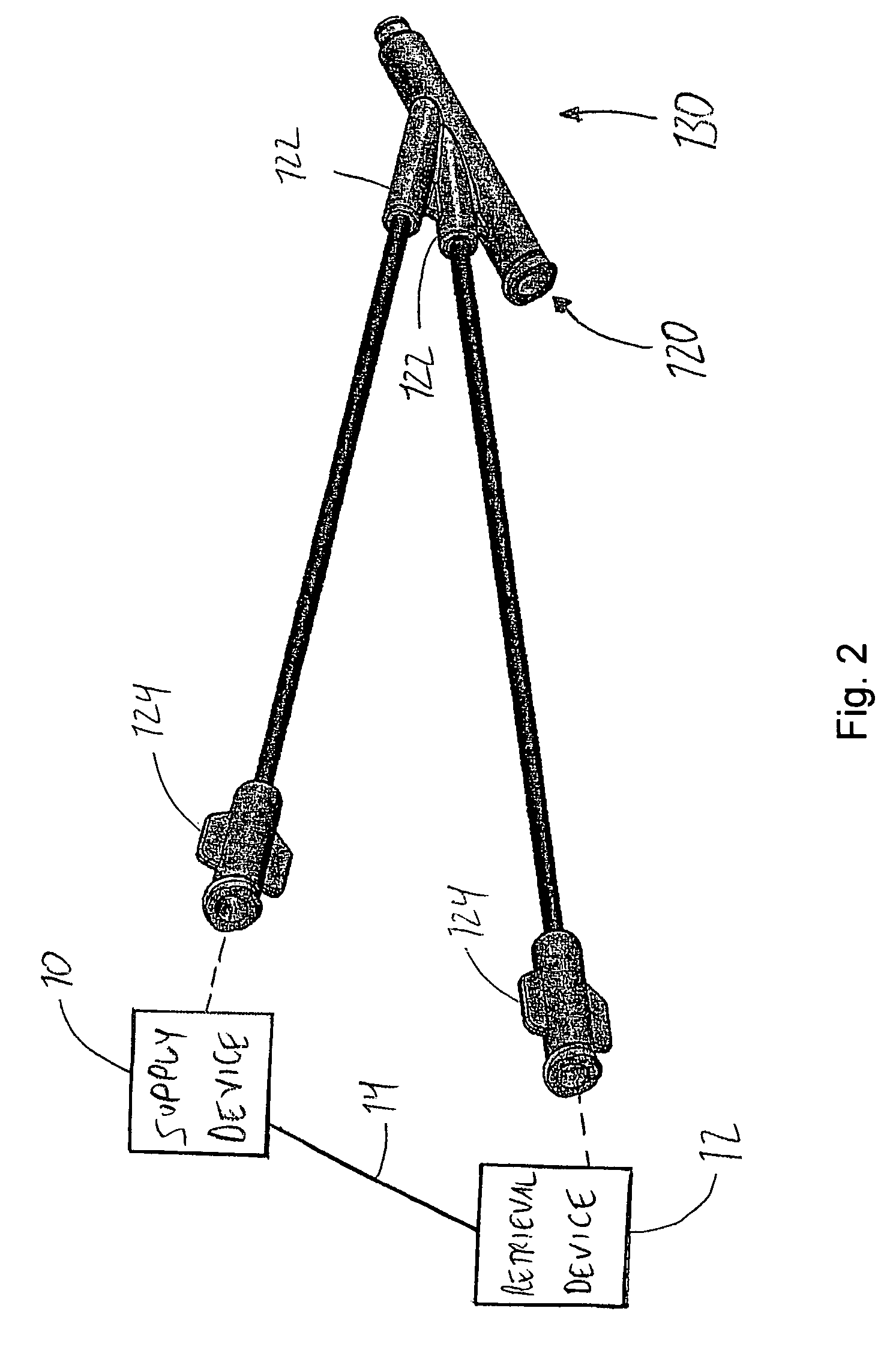
Catheter for treatment of total occlusions and methods for manufacture and use of the catheter
InactiveUS7399291B2Facilitates crossing CTOsIncreasing crossBalloon catheterSurgeryVitrificationTotal occlusion
A catheter for treatment of chronic total occlusions includes an occlusion breach device, a catheter body made of a temperature-dependent softening, shape-memory, thermoplastic polymer having a first flexible state and a second stiff state. The catheter body has a heat transfer conduit and a conduit for slidably receiving the breach device. A heat-transferring device selectively changes a temperature of the heat transfer conduit to, thereby, change stiffness of the catheter body between the two states. To treat a CTO with the catheter, it is warmed above the glass-transition temperature and below the melting-temperature to make the catheter flexible. The catheter has a shape when inserted at the occlusion site and is cooled to, thereby, stiffen. Breaching of the occlusion is assisted with the stiff catheter. The catheter is removed by warming the polymer. Also provided is a method for manufacturing such a selectively stiffening catheter.
Owner:SYN VARIFLEX LLC
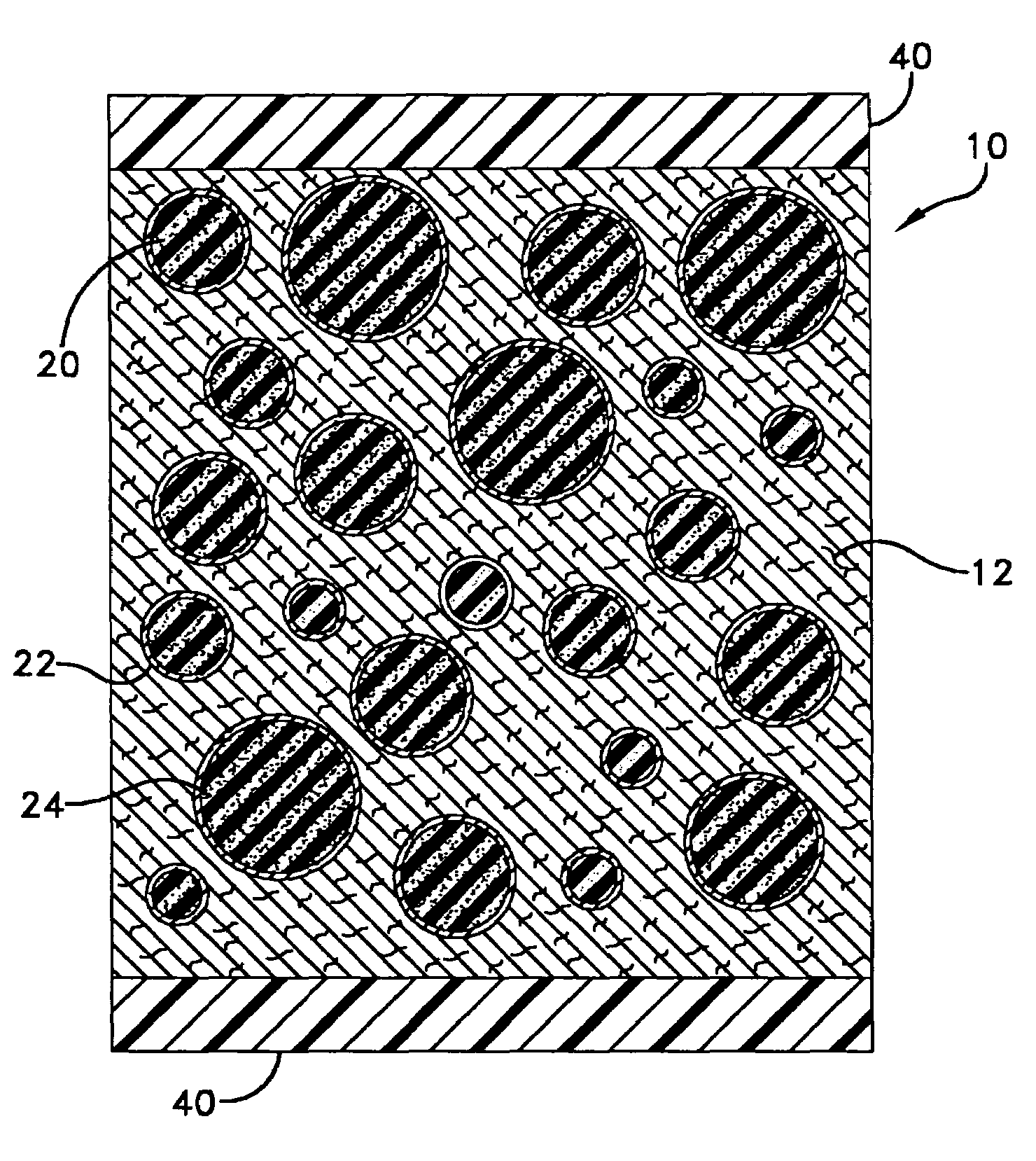
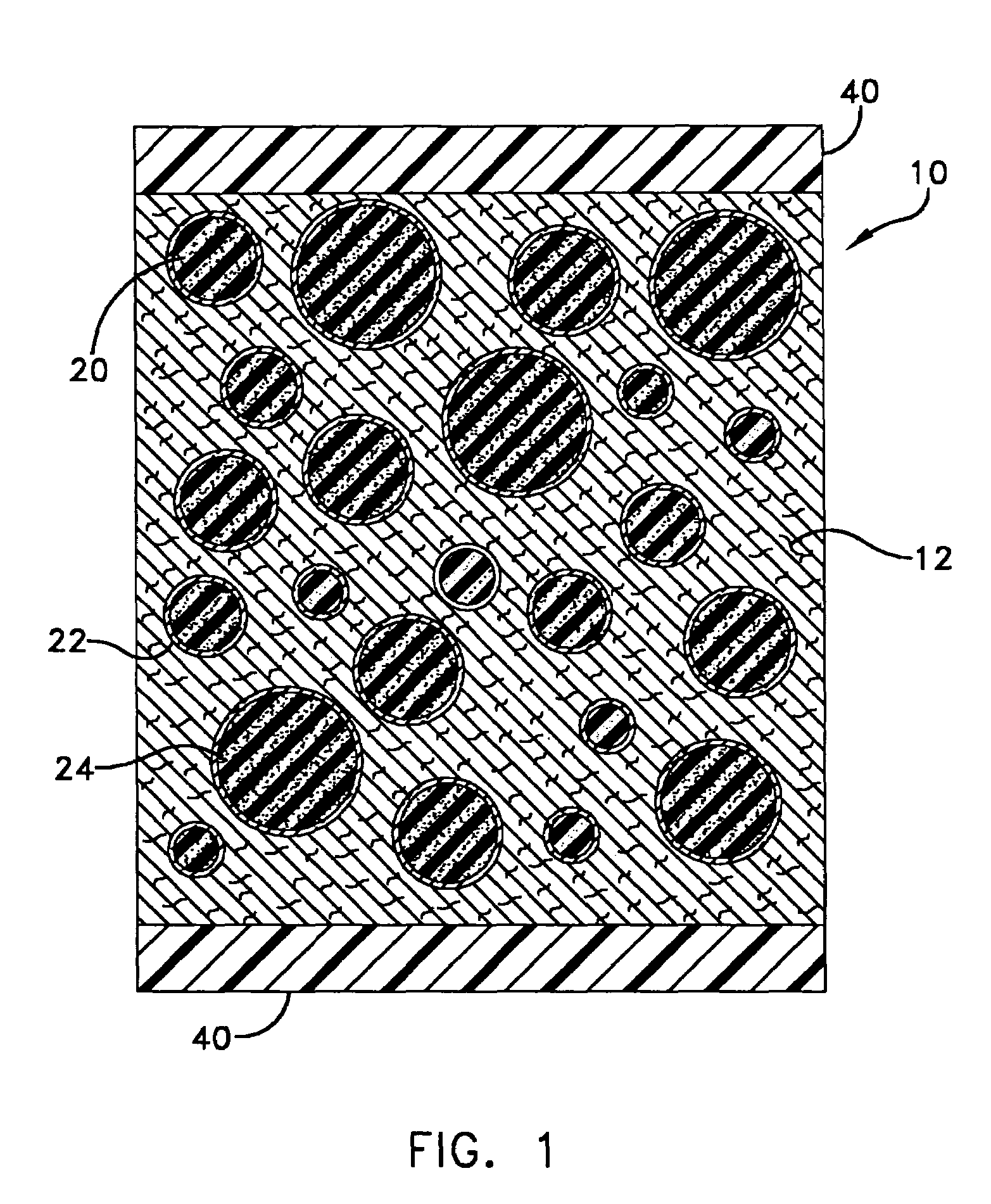
Pressure resistant anechoic coating for undersea platforms
InactiveUS7205043B1Resistant to deteriorationSmall wall thicknessCeilingsSynthetic resin layered productsOcean bottomCoating
A composite material containing inclusions of spherical shells in which each spherical shell encapsulates a rubber core with ferrite loading. The inclusions are embedded in a matrix material of syntactic foam. The spherical shells are made from glass and therefore acoustically transparent and in combination with the cores are statically stiffer than the surrounding matrix material. The composite material with the matrix material and inclusions allows the composite material to be acoustically dissipating with a stiffness in which the energy of forces associated with undersea platforms is resisted.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
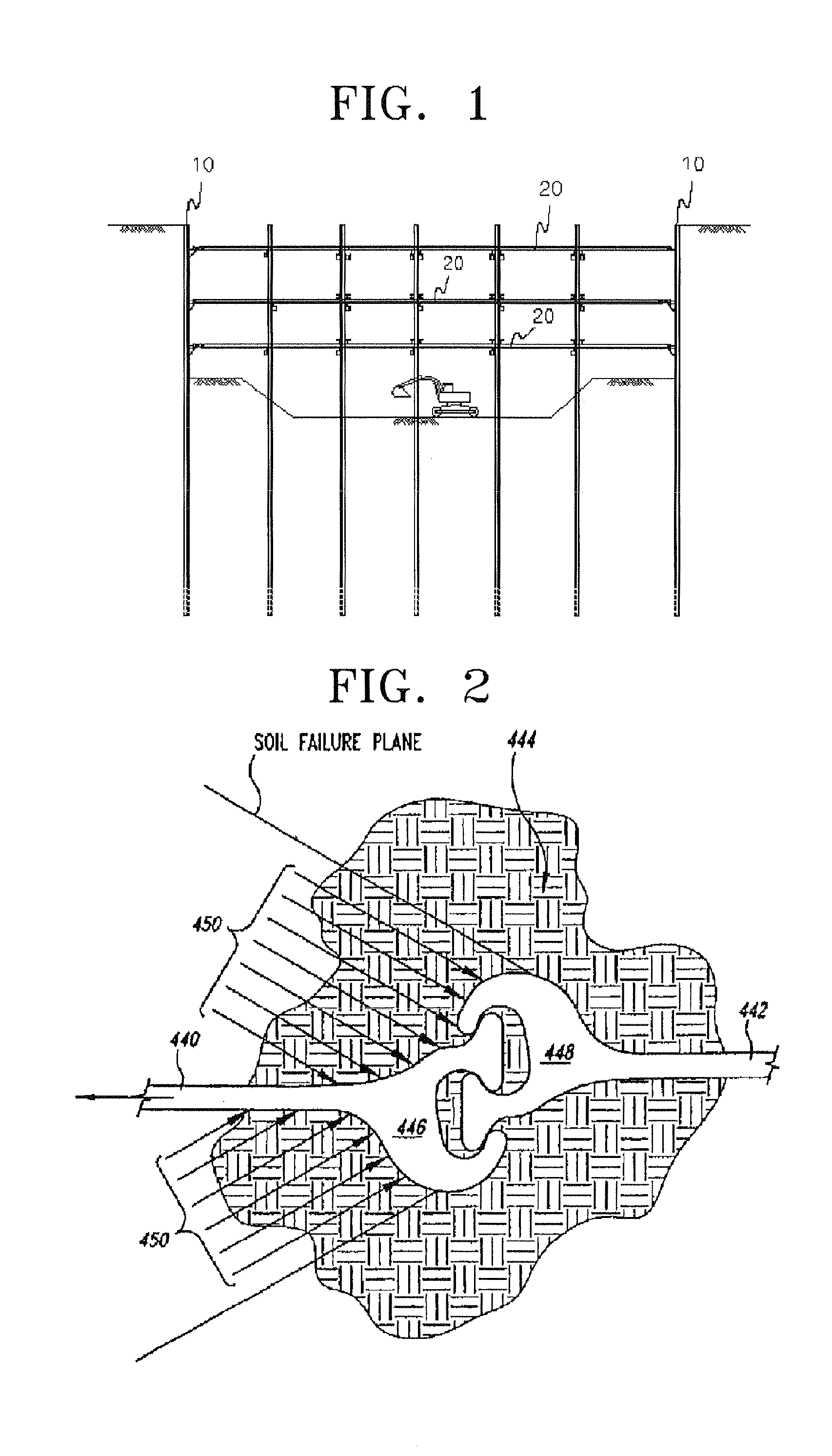
Reinforced self-standing earth retaining structure using an arching effect and an underground excavation construction method using the same
In a reinforced self-standing earth retaining structure using an arching effect, a soldier pile integrally formed with a soldier pile insertion portion in a vertical direction in a flange at one end of the soldier pile in which a lagging is inserted is installed at a width B to be perpendicular to the ground. A sheet panel protruding portion is inserted in and connected to the soldier pile insertion portion. A sheet panel protruding portion is serially inserted in a sheet panel insertion portion. A compression support plate protruding portion is inserted in and coupled to the sheet panel insertion portion. A relationship between a length L of a group of serial sheet panels and the width B between two groups of serial sheet panels is 0.5≦L / B≦3.0 in a range of an internal friction angle of earth φ=10˜34° and a range of an adhesive power C=0.0˜5.0 ton / m2 so that a back earth pressure is not applied to the front lagging due to the arching effect.
Owner:PARK GANG HO +1
Dummy plug for wiring harness
InactiveUS6808418B2Simple and efficientAdvantageous resultSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersCoupling contact membersCable harnessPogo pin
A dummy plug for wiring harnesses is disclosed. The dummy plug is used in an unused connector cavity of the wiring harness, thereby electrically isolating the connector cavity in the wiring harness to prevent short circuits. The dummy plug is substantially flush with the latch arm of the wiring harness, so that a pogo pin can determine whether or not the connector cavity is in use. The dummy plug has a design such that pressure blowout is prevented. A method for plugging an unused connector cavity is also disclosed, the method including the steps of providing a dummy plug having a head, a stem, and a female end, providing a wiring harness having at least one connector cavity and at least one latch arm and inserting the dummy plug into the unused connector cavity so that the female end is substantially flush with the latch arm.
Owner:QUALITY SYNTHETIC RUBBER INC
Pump
InactiveUS20080112824A1Increased durabilityIncreasing durability of casingPump componentsPiston pumpsPump chamberEngineering
In a pump having a rotor inside a pump chamber which is formed inside a case which is formed of a resin material, and a resin mold compound in which an armature is molded with resin, a metallic cover is provided on a portion of an outer surface of the case inside the pump, wherein the portion has inferior durability compared with the rest of the outer surface.
Owner:NIDEC SHIBAURA CORP
Fastening assembly and cushion having fastening assembly
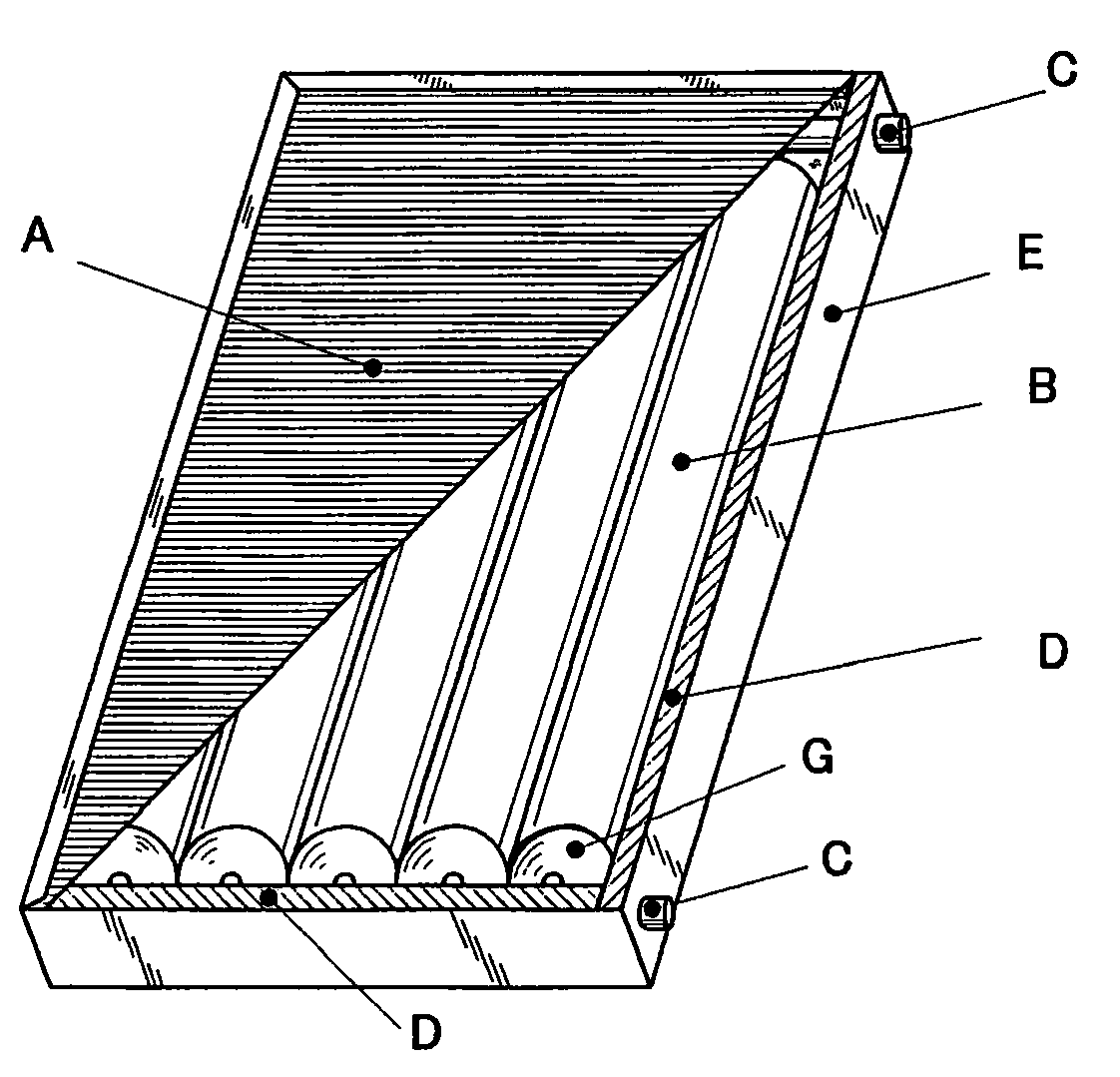
ActiveUS7927681B2Pressure resistanceEasy to fixStuffed mattressesDomestic upholsteryProtection layerCushion
A fastening assembly and a cushion having the same are provided. The fastening assembly includes a first strip and a second strip. The first strip has a first surface protrudingly provided with a plurality of hooks, and a second surface to which the second strip is bonded. The fastening assembly further includes a first protective layer and a second protective layer, both comprising a magnetic substance. The first protective layer is disposed lengthwise along both lateral sides of the first surface of the first strip so as to form sidewalls respectively and embed some of the hooks. The second protective layer is attached to the first protective layer so as to cover the hooks on the first surface of the first strip.
Owner:TAIWAN PAIHO LTD
Shaft sealing apparatus
Provided is a shaft sealing apparatus, which includes a seal ring that is installed in an annular space between a rotor and a stator surrounding an outer circumference side of the rotor, that is formed in a divided structure from a movable seal ring and a stationary seal ring whose circumferential ends are adjacent to each other, and that is configured so that the movable seal ring is biased toward a radial outer side thereof by an elastic body, a seal body that is formed by stacking a plurality of thin seal pieces, which extend from the seal ring toward a radial inner side of the rotor, in a circumferential direction of the rotor, and a communicating part that causes the low-pressure side region and the high-pressure side region to communicate with each other.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Solar energy absorber
InactiveUS20090288657A1Easy to shapeReduce weightSolar heating energySolar heat devicesWater flowSolar absorber
The solar energy absorber is capable of reducing weight, being directly connected to a water supply pipe, increasing pressure of heated water, omitting a pressurizing pump, etc. The solar energy absorber comprises: a water-flowing section including heat collection tubes, which are composed of stainless steel, and connecting pipes; a heat-retaining box accommodating the water-flowing section, including a heat insulating material and having an opening part which is located on the heat collection side; and a cover plate being composed of a transparent multilayer plastic and closing the opening part of the heat-retaining box. The heat collection tubes are arranged parallel. End plates closing ends of the heat collection tubes are connected to the connecting pipes. Each of the heat insulating tubes is coated with a heat-absorbing layer. Parts of the heat collection tubes which are located on the opposite side of the heat collection side contact the heat insulating material.
Owner:NISHIHARA HIDETABUGU
Extruded cellulose-polymer composition and system for making same
ActiveUS20080113190A1Cell density can not be enhancedIncrease pressureFrozen sweetsConfectioneryElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The present invention is directed to a device for the production of a cellular wood plastic composite material comprised of an orifice that conducts the composite material from the adapter of the extruder to the transition die plate in such a manner that a uniform flow of material reaches the transition die plate; a transition die plate that further directs the flow of material to a flow restriction die plate in a manner ensuring that equal amounts of material are delivered to all areas of the flow restriction die plate; a flow restriction die plate that provides sufficient resistance to material flow to increase the melt pressure of the portion of the material that is upstream in relation to the flow restriction die plate and controls the temperature increase caused by this restriction by dividing the flow into numerous suitably sized and shaped streams; a compression die plate that fuses the separate streams issuing from the flow restriction die plate into a single stream of material and maintains the melt pressure at a level which will prevent premature development of cells in the material; a shaping die plate that is designed to shape the material in such a way that the fully expanded material will approximate the shape of the desired profile and to control the rate of cell development and expansion so that large numbers of uniform cells are produced.
Owner:CPG INT
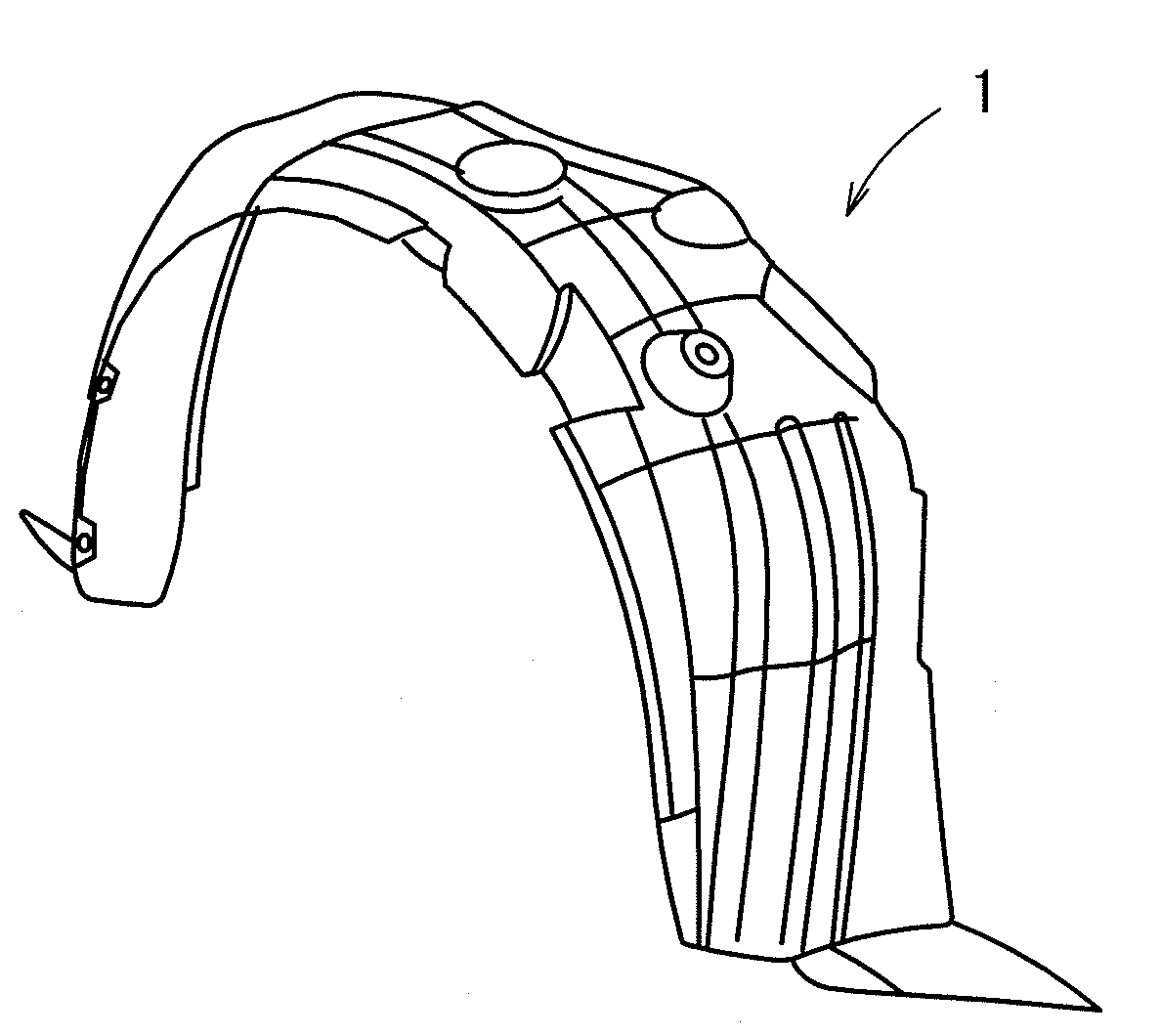
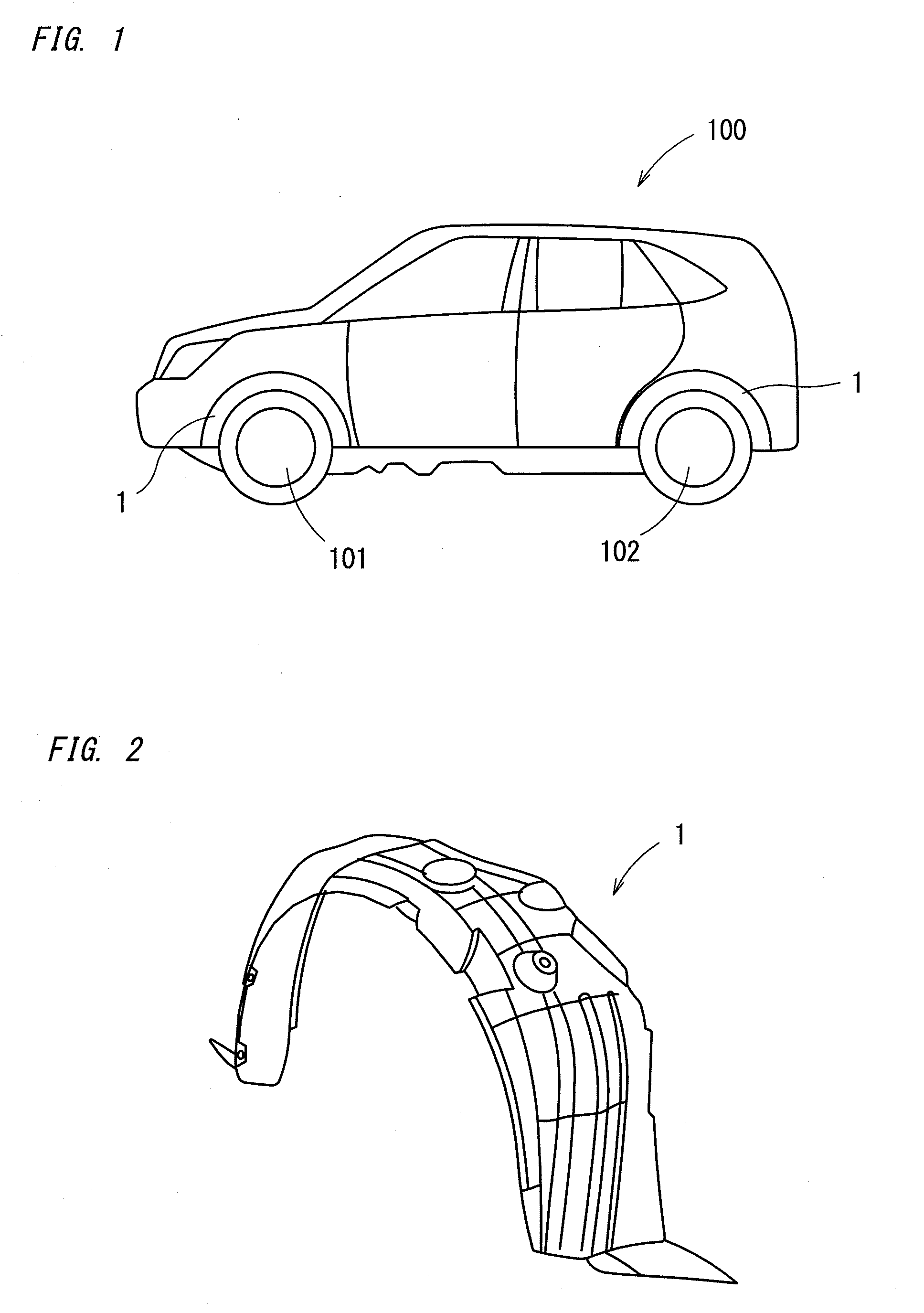
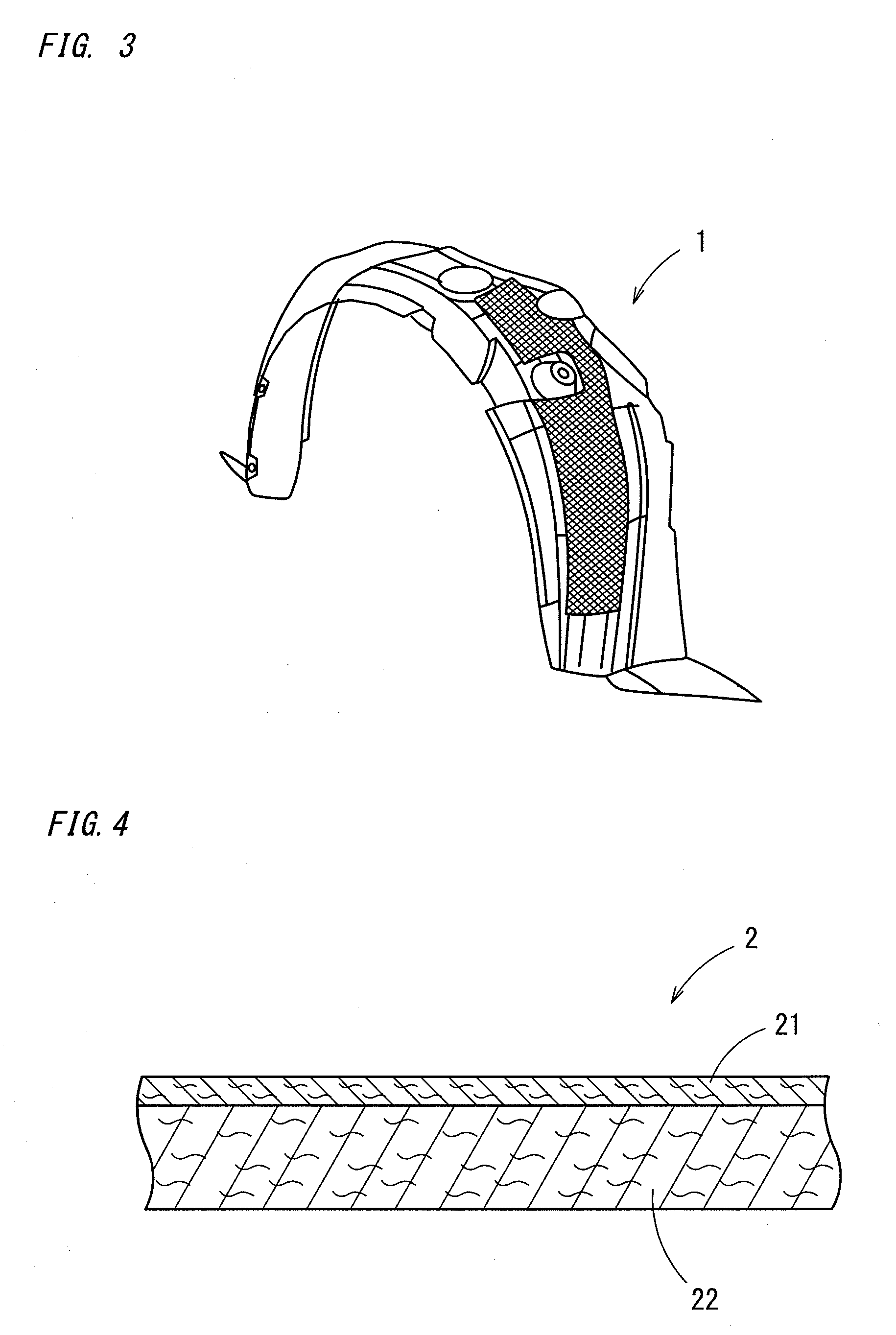
Fender liner and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20090256345A1Improve sound insulationEasy to separateSuperstructure subunitsHigh densityPunching
The present invention provides a fender liner and a method for producing the same that allows reduction of noise caused by collision with pebbles etc. kicked by tires, that has sufficient rigidity, and that allows easier separation of attached ice. The fender liner comprises a low density nonwoven fabric layer, disposed on a side of the outside surface when it is attached to the outside surface, and a high density nonwoven fabric layer, the density of which is 0.6 to 0.9 g / cm3, in a thickness direction. The method comprises: obtaining a compound nonwoven fabric by intertwining and integrating a first and a second nonwoven fabric having predetermined amounts of mass per unit area and thicknesses respectively by a needle punching method; obtaining a nonwoven fabric laminated product for liners by heating the fabric from a side of the first nonwoven fabric layer with simultaneous pressurization; and die forming the product.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
Blow out protector valve employing ball baffle assembly for use with high-pressure fluids
ActiveUS8042615B1Prevent any blow-outGuaranteed uptimeDrilling rodsFluid removalMechanical componentsEngineering
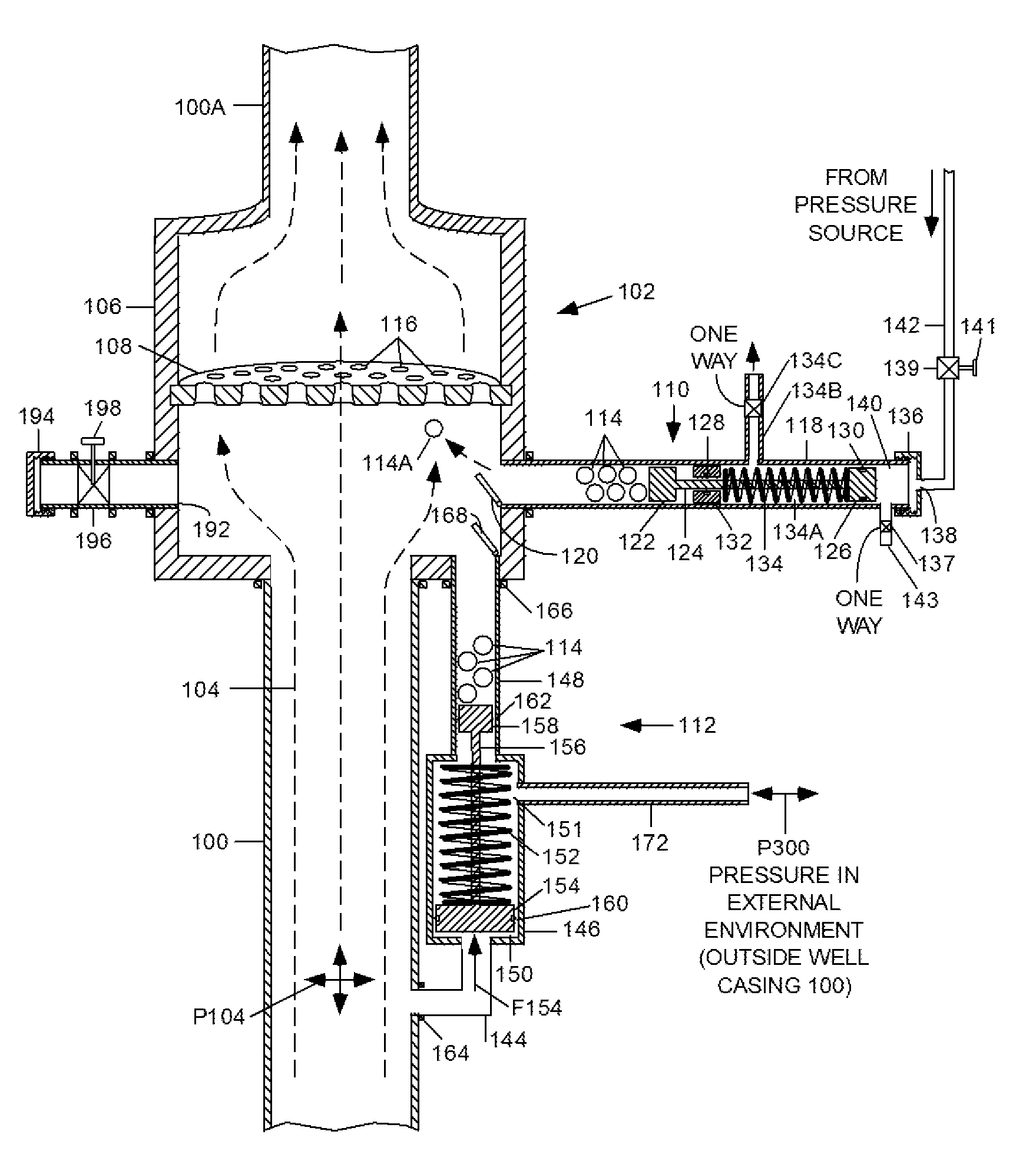
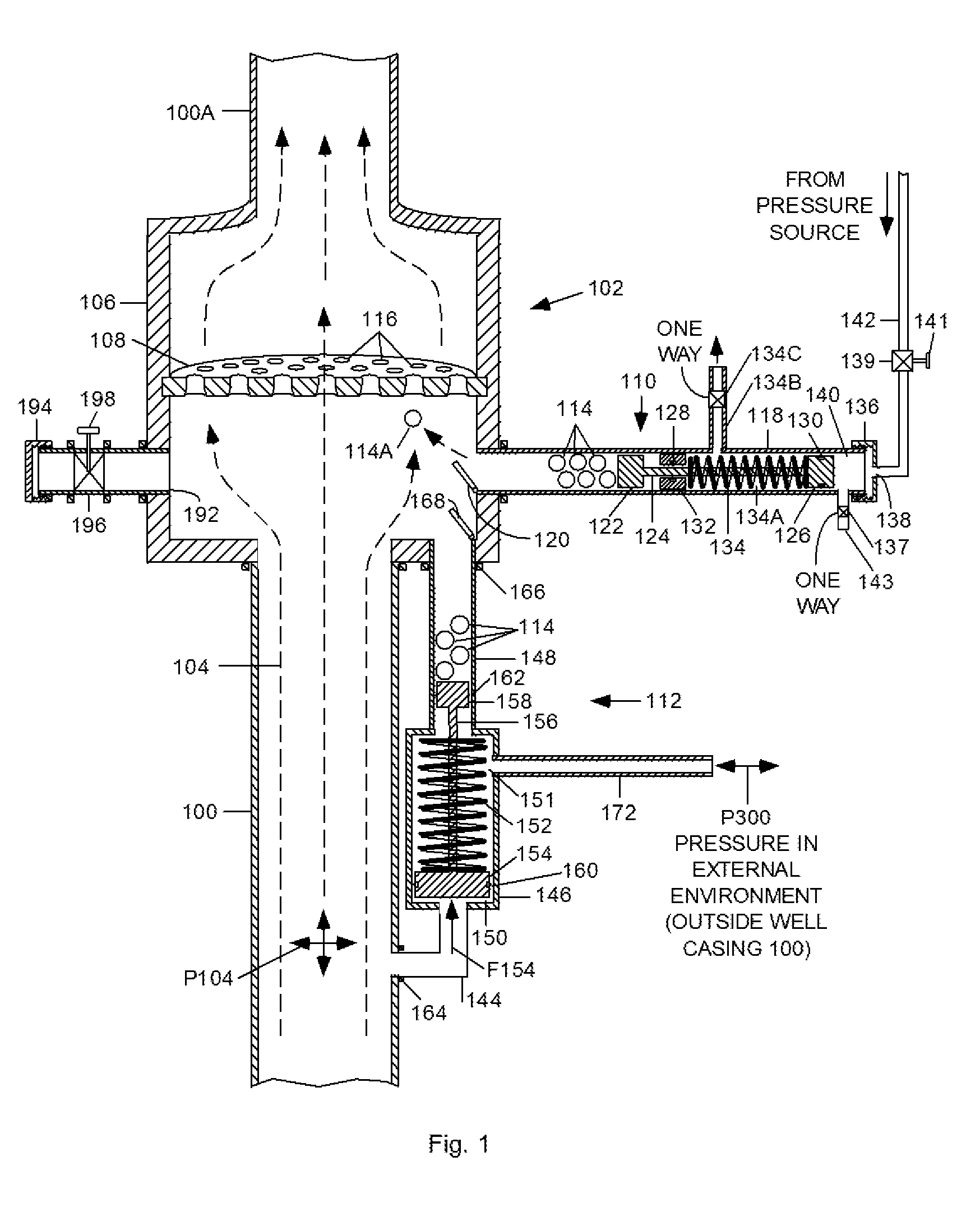
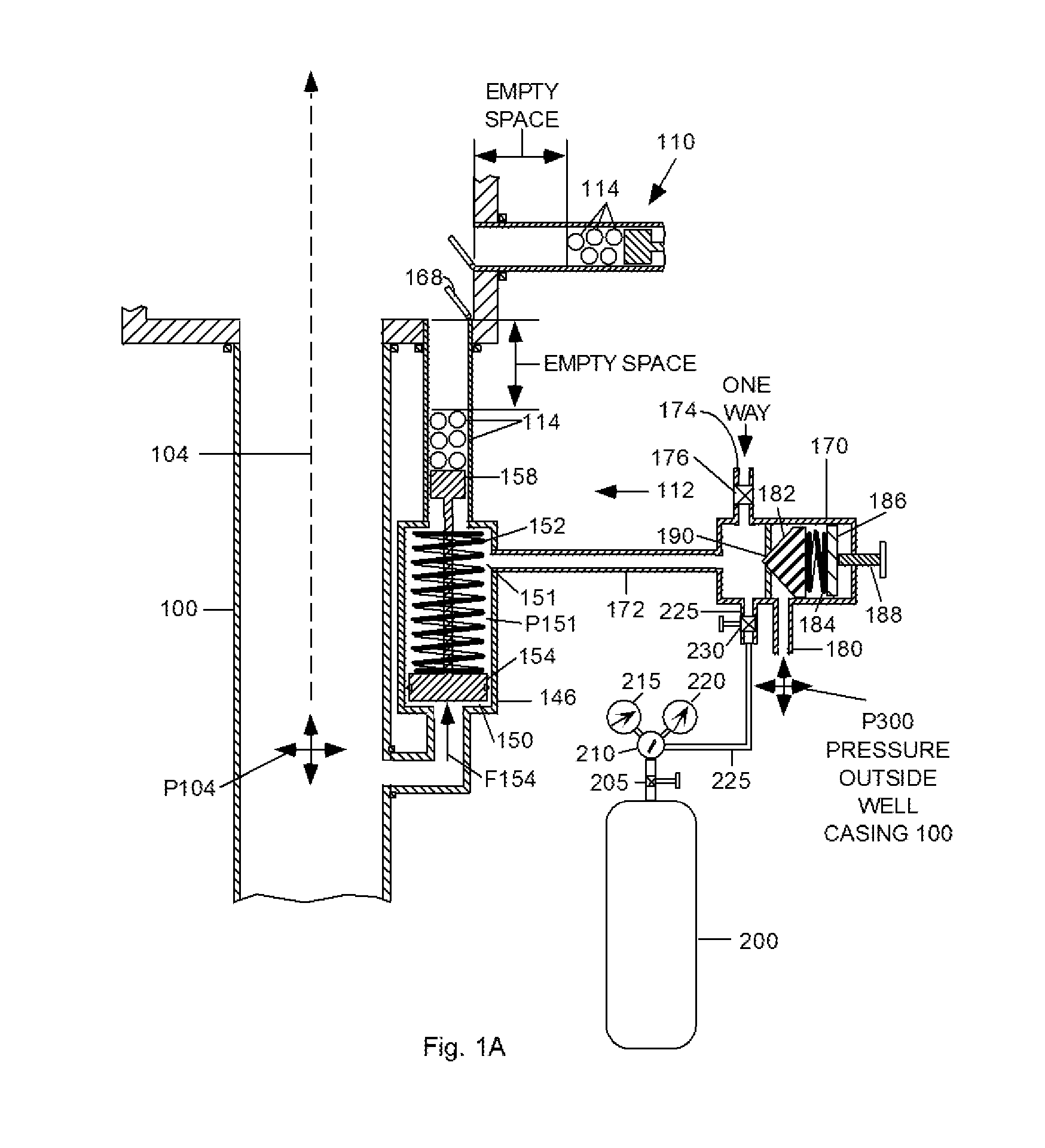
A Ball Baffle Blowout Preventer (BBBOP) (102) or shut-off valve generally comprises a housing (106) and a baffle (108) secured within the housing and containing a plurality of holes. The housing is mounted in the path of the well pipe but the holes in the baffle allow normal production fluid to pass. One or more ball dispensing mechanisms (BDM) (110, 112) are connected to the housing. Each BDM contains a plurality of balls (114) and one or more valves (196). When a blowout condition occurs, a plurality of balls (114) are released beneath baffle (108) and are carried upward by the upwardly gushing fluid to plug the holes. The balls (114) are held in place by the pressure differential below and above the baffle. The balls can be removed from the baffle by the forcing fluid down the well. All operations can be controlled undersea by remotely operated vehicles (ROVs). A plurality of BBBOPs can be stacked and each can be set to operate at a different pressure and flow rates. The BBBOP may also include a Threshold Pressure Detection Unit for actuating the BDM that requires no electro-mechanical components; it uses only the energy of pressurized fluids in a well bore. The manual and self-actuating BDMs are not disabled by slow leaks of ambient well pressures past the hydraulic seals used therein. In another embodiment an additional baffle (250) can be provided below the first baffle (108) to contain the balls after they are released from the first baffle.
Owner:WATTENBURG WILLARD HARVEY
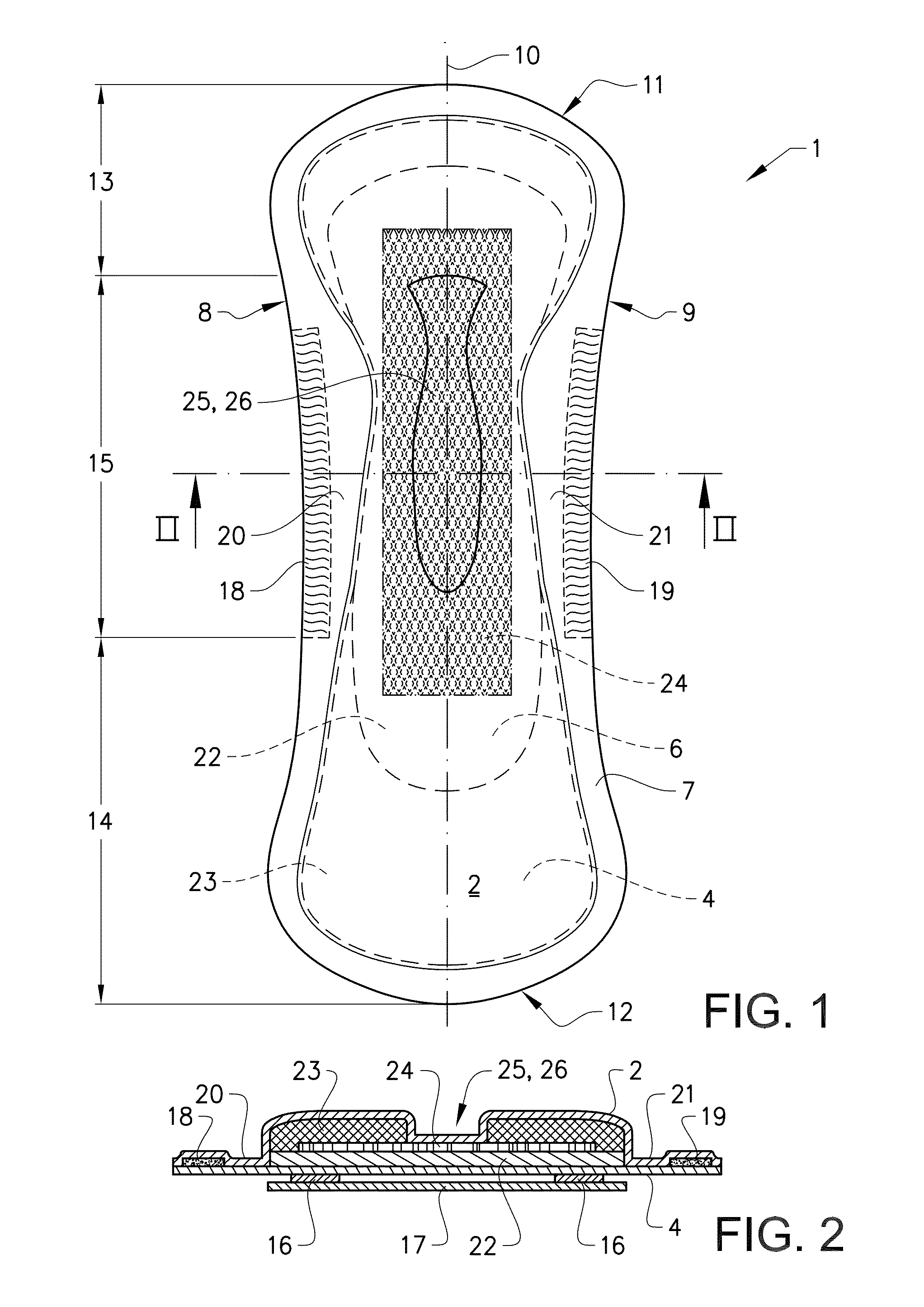
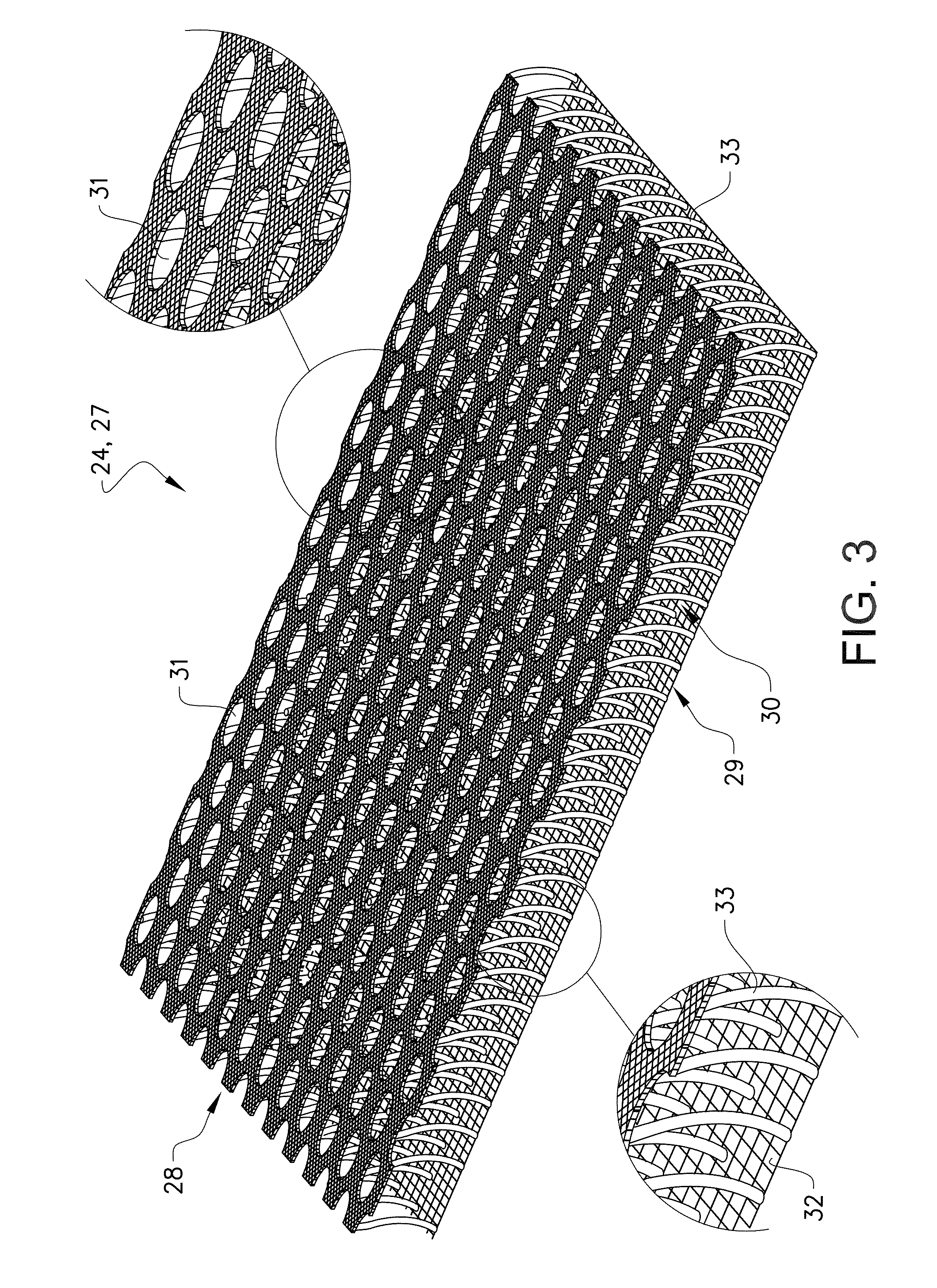
Absorbent article having fluid flow control member
An absorbent article, the absorbent article being a personal hygiene article, includes a liquid permeable top sheet, a liquid impermeable back sheet, an absorbent core enclosed between the top sheet and the back sheet, and a fluid flow control member arranged between the top sheet and the backsheet. The fluid flow control member is a spacer fabric having a basis weight of 150-300 gsm and including a top layer, a bottom layer and an interconnecting layer of pile filaments between the top layer and the bottom layer. The pile filaments have a fineness of 80-130 dtex and the density of pile filament connections is 50-150 / cm2.
Owner:ESSITY HYGIENE & HEALTH AB
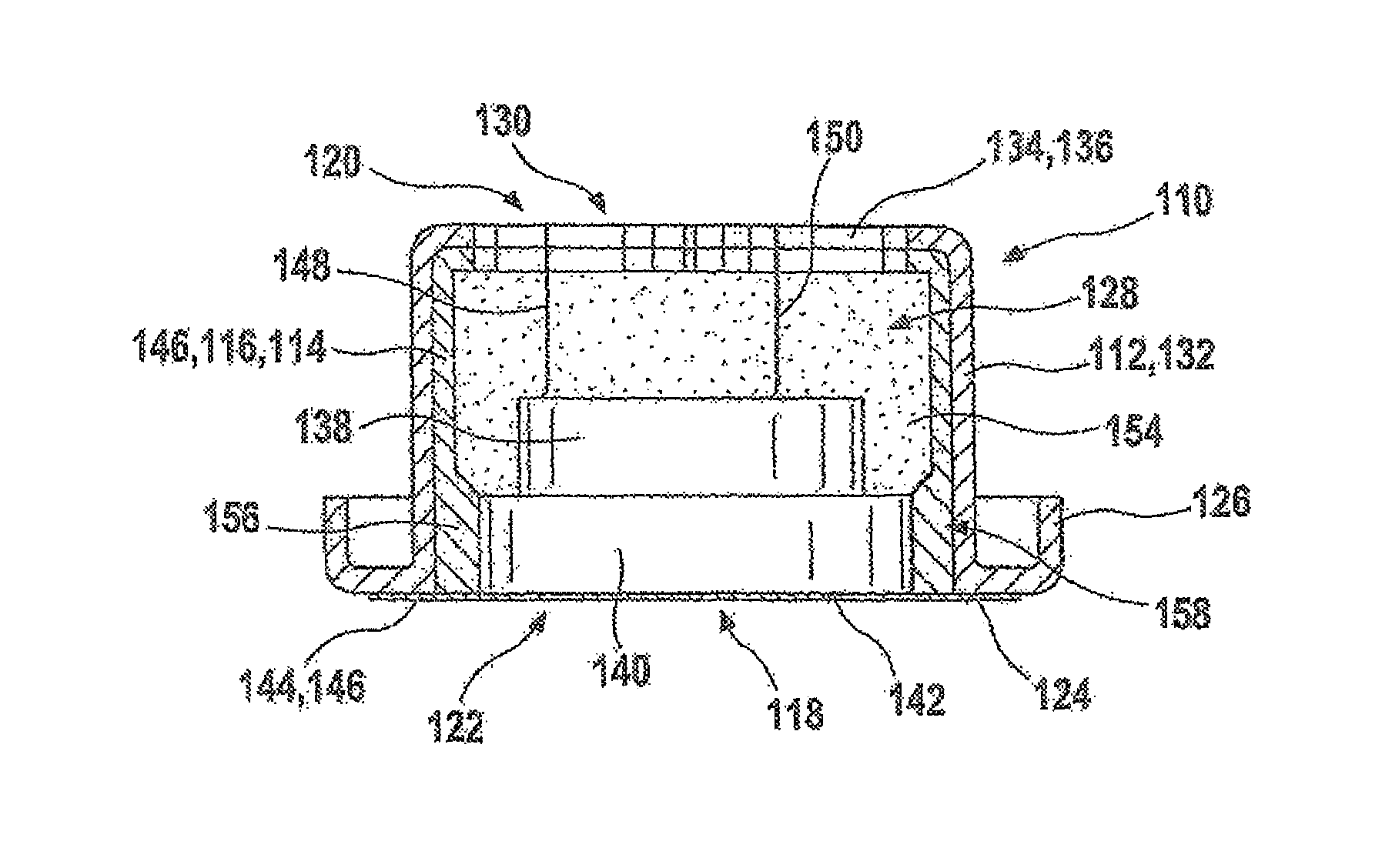
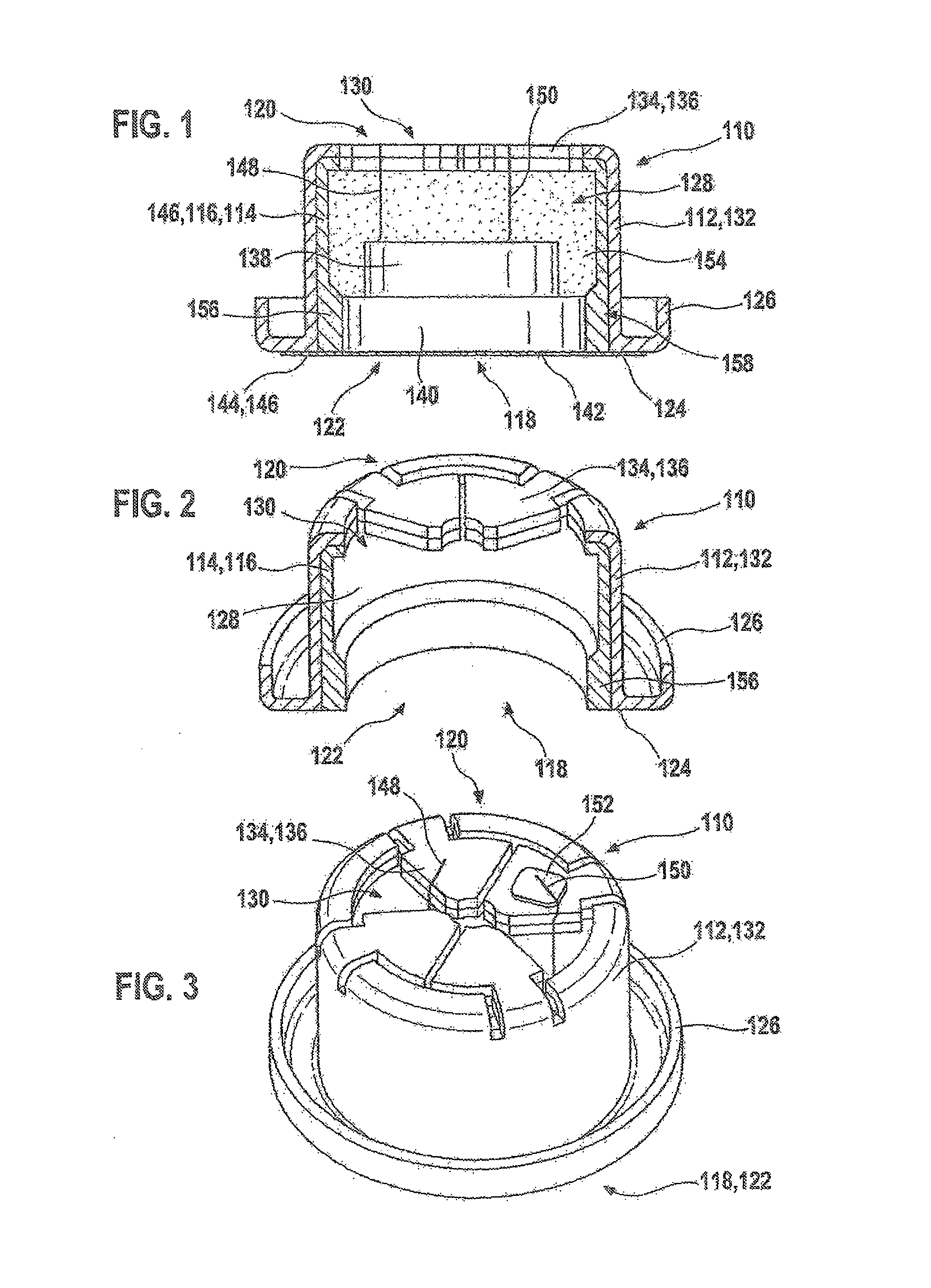
Fastening assembly and cushion having fastening assembly
ActiveUS20100139004A1Pressure resistanceReadily secured in positionStuffed mattressesDomestic upholsteryCushionProtection layer
A fastening assembly and a cushion having the same are provided. The fastening assembly includes a first strip and a second strip. The first strip has a first surface protrudingly provided with a plurality of hooks, and a second surface to which the second strip is bonded. The fastening assembly further includes a first protective layer and a second protective layer, both comprising a magnetic substance. The first protective layer is disposed lengthwise along both lateral sides of the first surface of the first strip so as to form sidewalls respectively and embed some of the hooks. The second protective layer is attached to the first protective layer so as to cover the hooks on the first surface of the first strip.
Owner:TAIWAN PAIHO LTD
Internally grooved heat transfer tube for high-pressure refrigerant
InactiveUS20070199684A1Improve heat transfer effectImprove stress resistanceEvaporators/condensersCorrosion preventionEngineeringHigh pressure
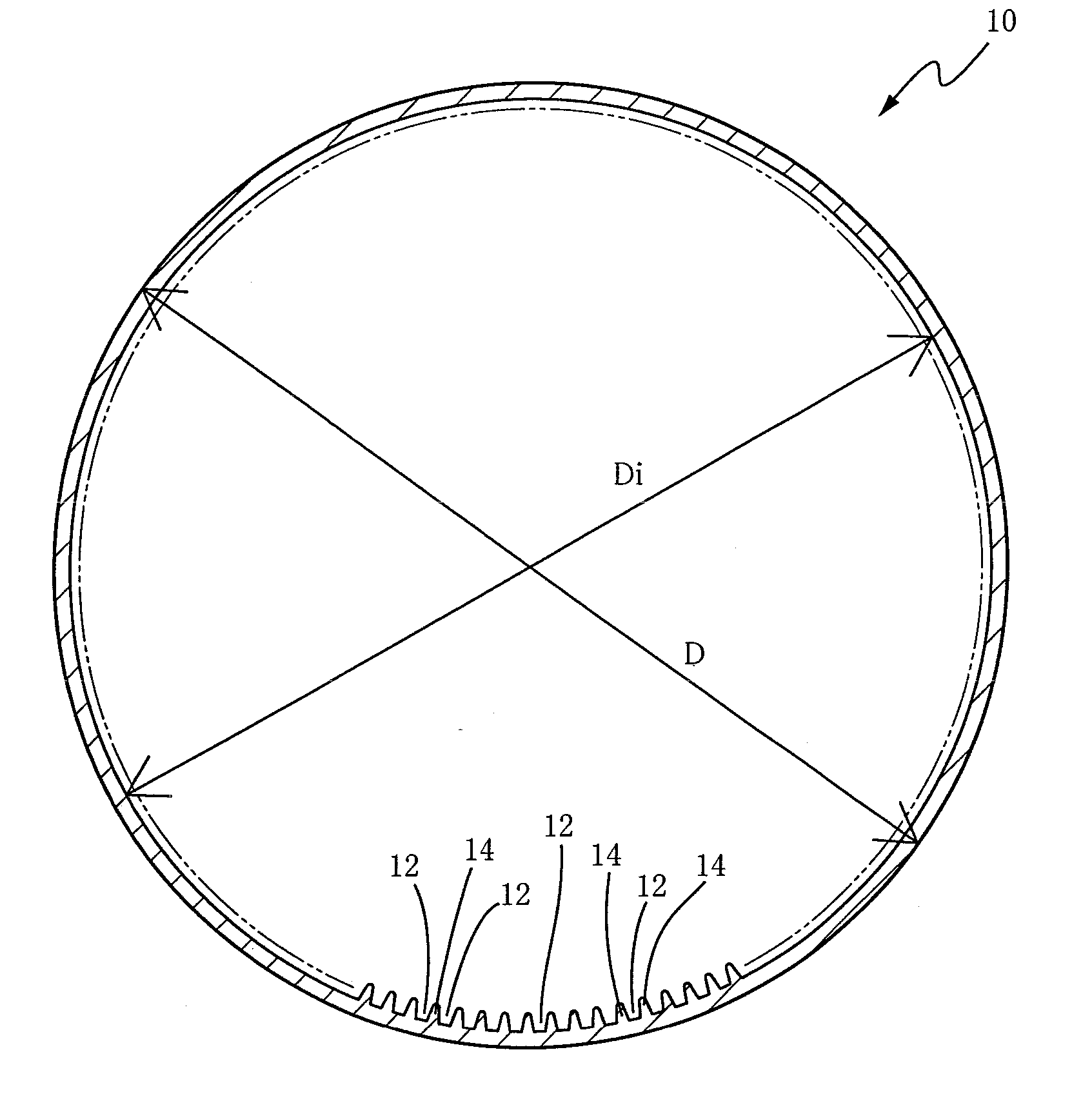
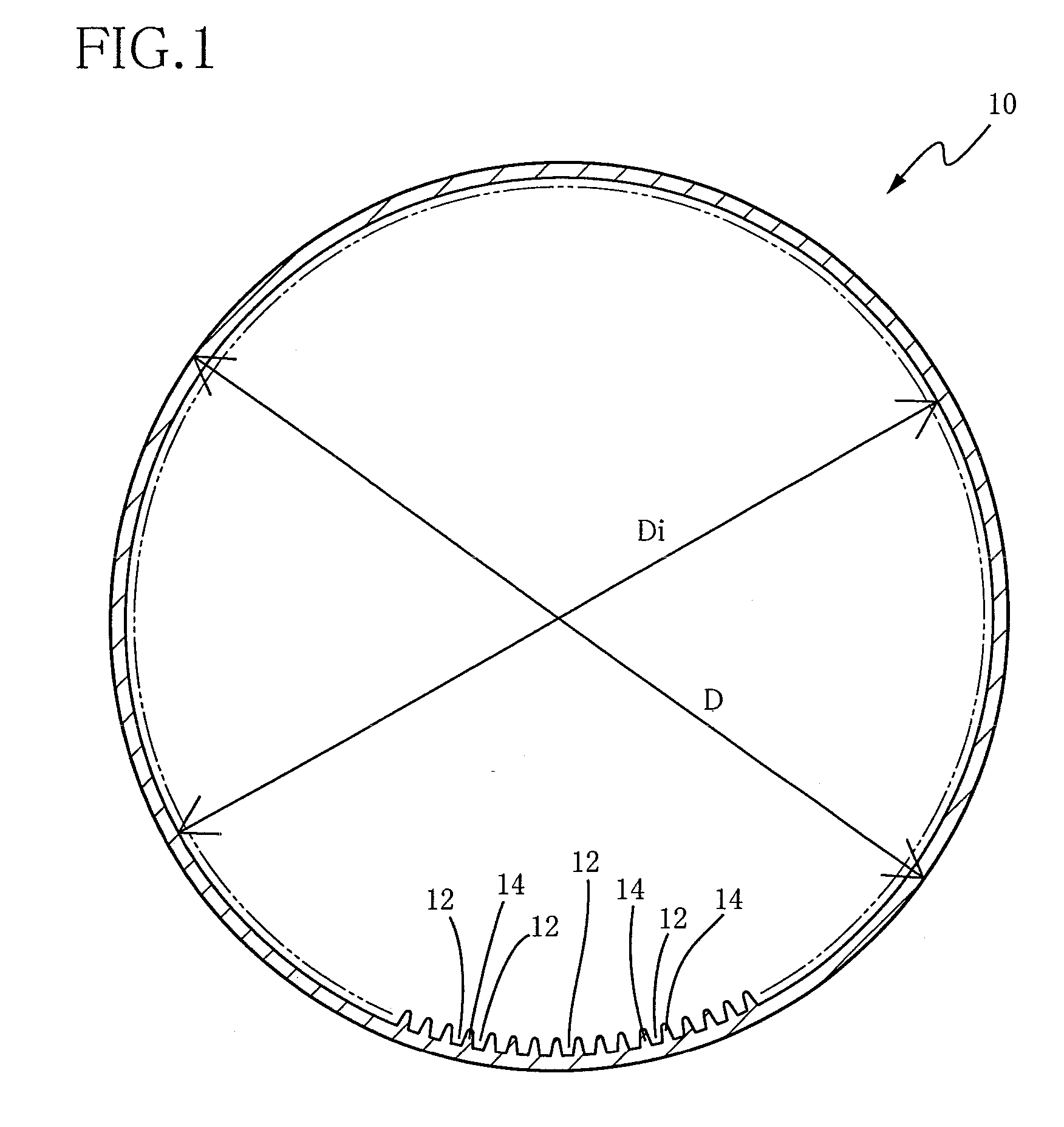
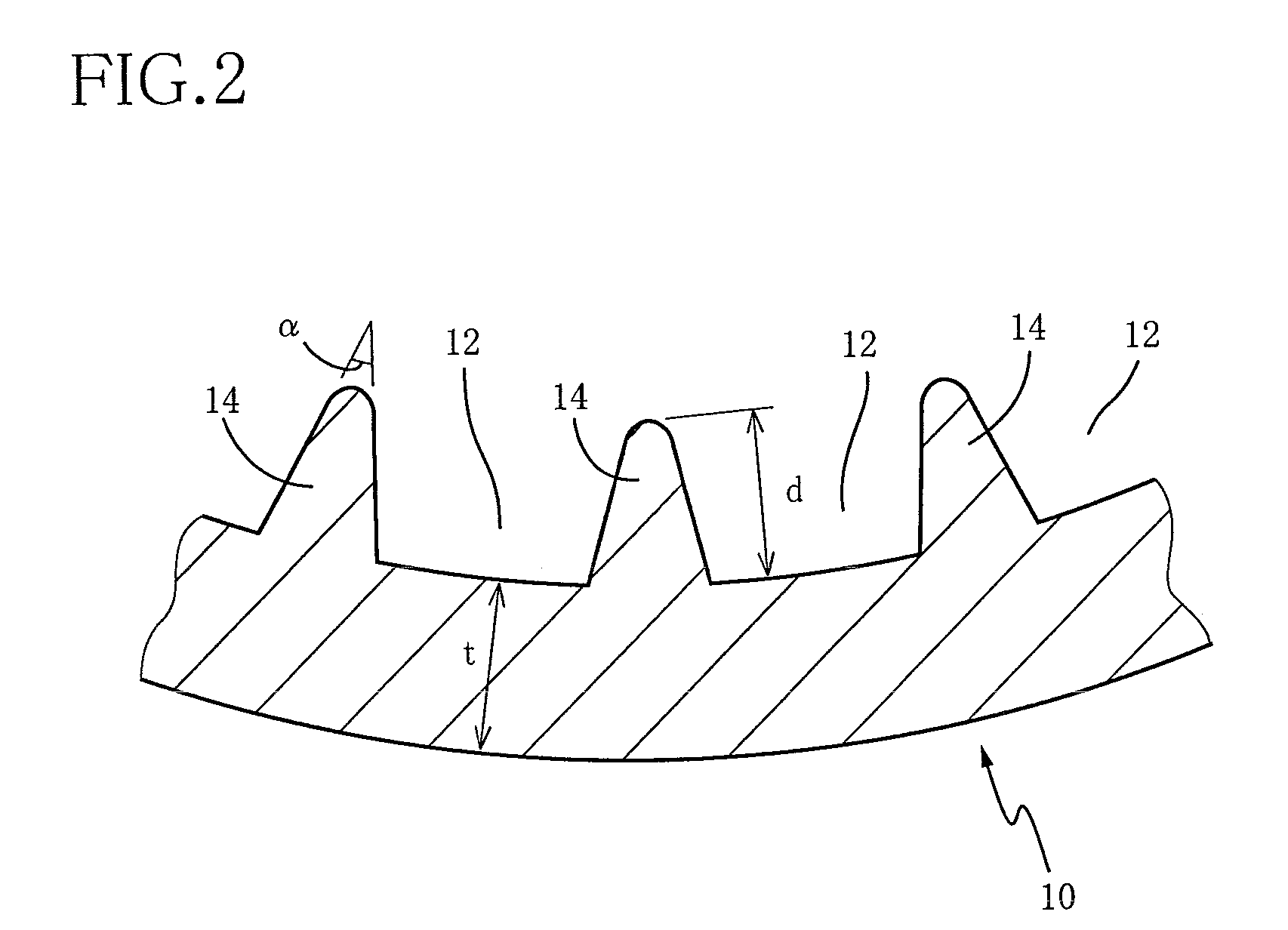
An internally grooved heat transfer tube for a cross fin tube type heat exchanger of a refrigerating air-conditioning water supply apparatus using a high-pressure refrigerant, wherein an intra-tubular heat transfer rate is improved while maintaining a sufficient strength for pressure resistance. A heat transfer tube formed of copper or copper alloy has internal fins between internal grooves. In the tube, t / D is not smaller than 0.041 and not greater than 0.146, d2 / A is not smaller than 0.75 and not greater than 1.5, where D [mm] is an outside diameter of the tube, t [mm] is a groove bottom thickness, d [mm] is a depth of each groove, and A [mm2] is a cross sectional area of each groove. N / Di is not smaller than 8 and not greater than 24 where N is a number of grooves, and Di is a maximum inside diameter corresponding to an inside diameter of the tube.
Owner:SUMITOMO LIGHT METAL INDS LTD
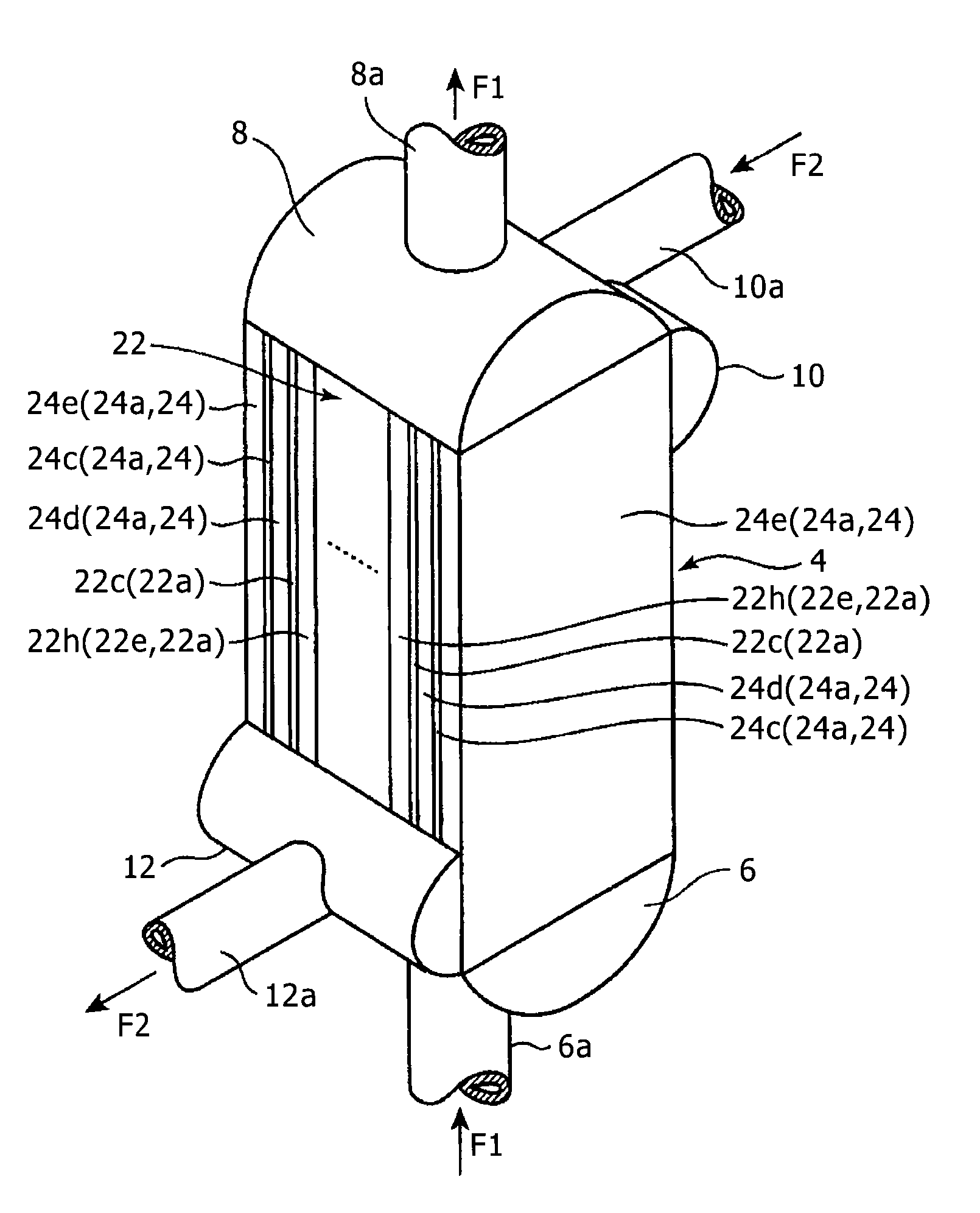
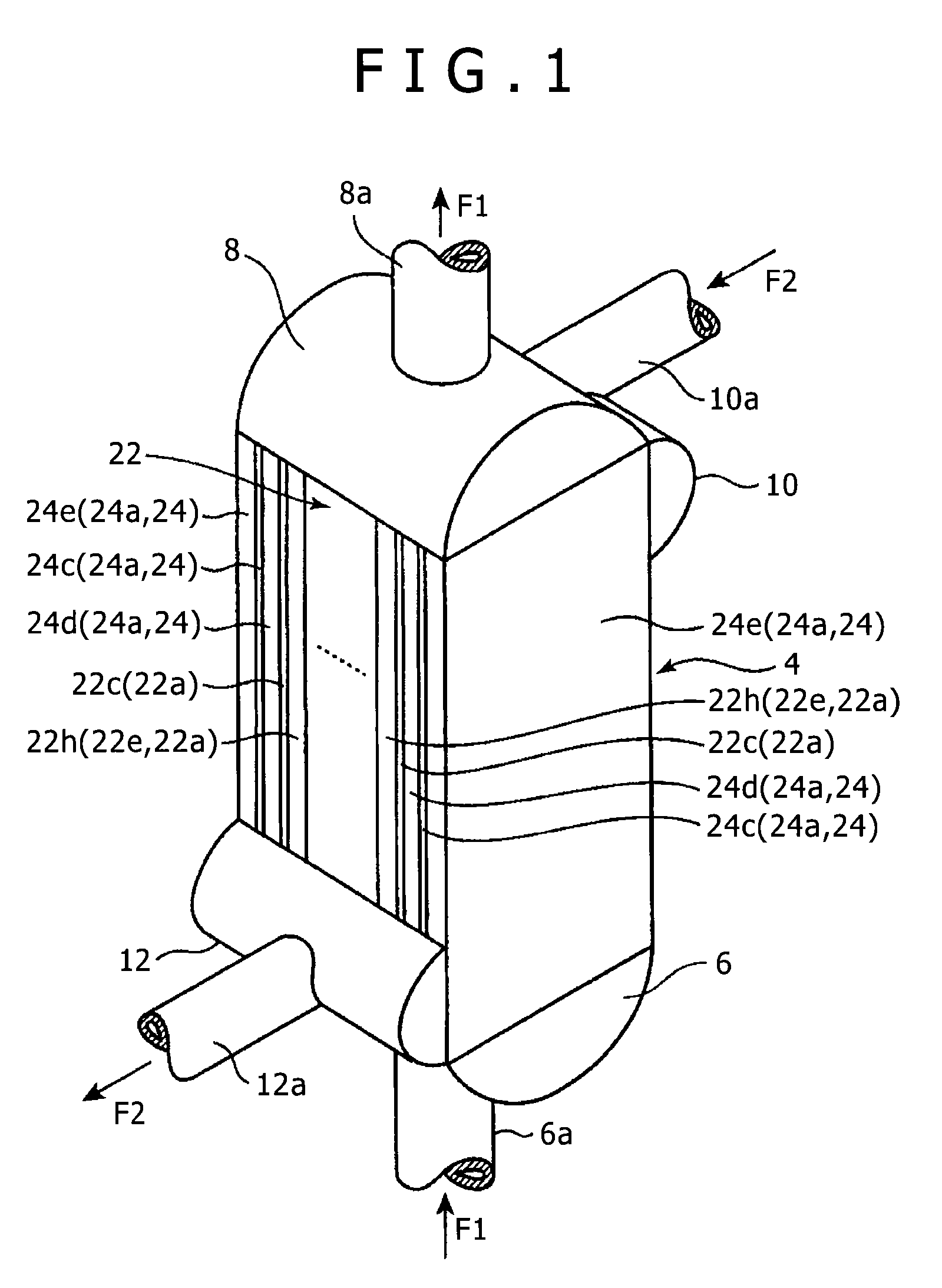
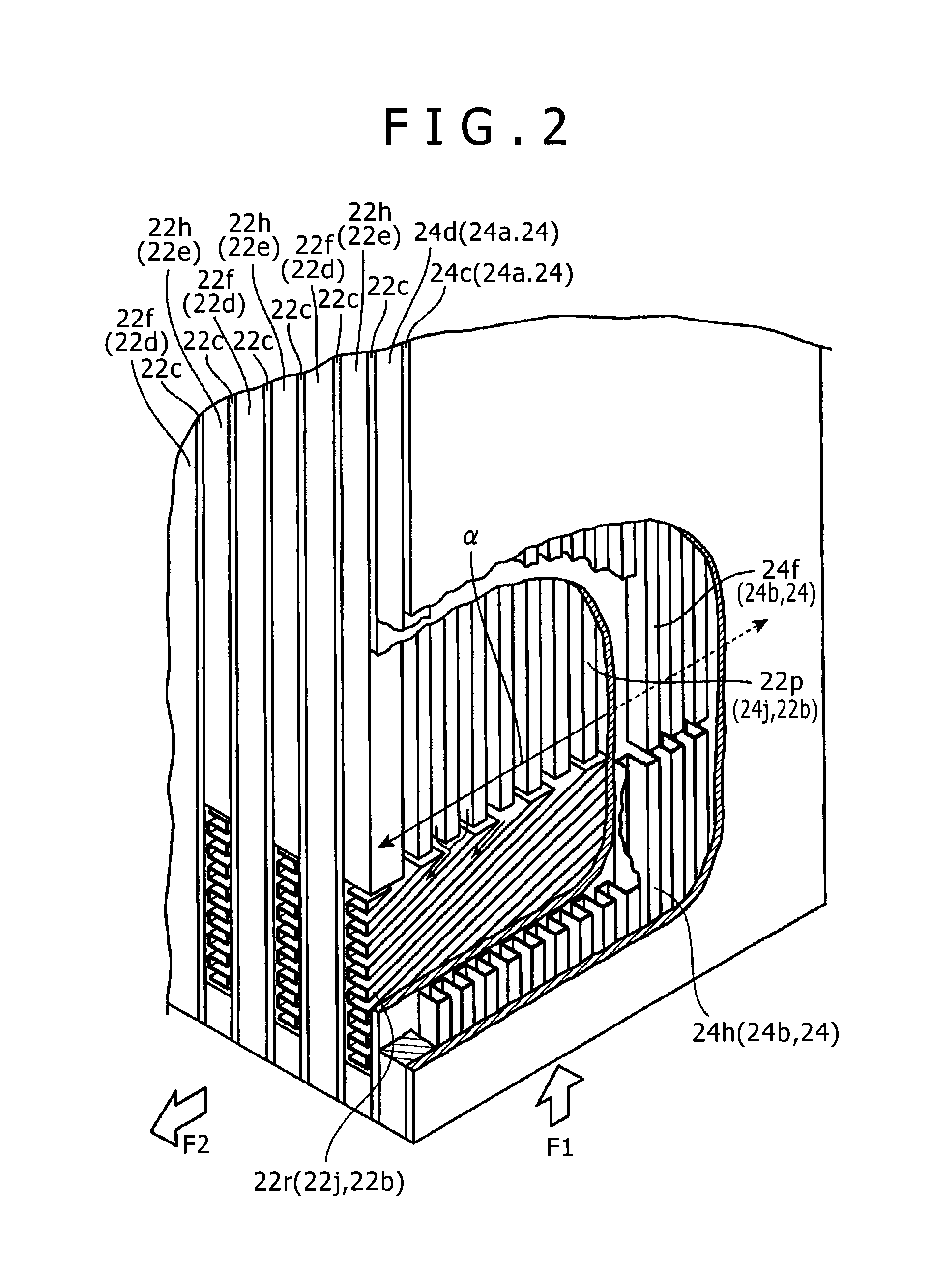
Plate fin heat exchanger and repair method for plate fin heat exchanger
InactiveUS20140054022A1Sufficient pressure resistance performanceShort processSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusHeat exhanger sealing arrangementInternal pressureEngineering
In a heat exchanger of the present invention, a release port for, in a case where a fluid flows into an internal space, releasing the fluid to an exterior is provided in a protection unit main body of each of protection units arranged on both outer sides of a heat exchange unit, and a protection unit fin plate of the protection unit has such strength that a coupling state between an outer surface of an outermost-layer partition plate and a bonding plate of the protection unit main body facing the outer surface is maintained even in a case where an inner pressure set as a design pressure for a part of the heat exchange unit constituting an outermost-layer flow passage adjacent to the protection unit is applied to the internal space of the protection unit main body of the protection unit.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com