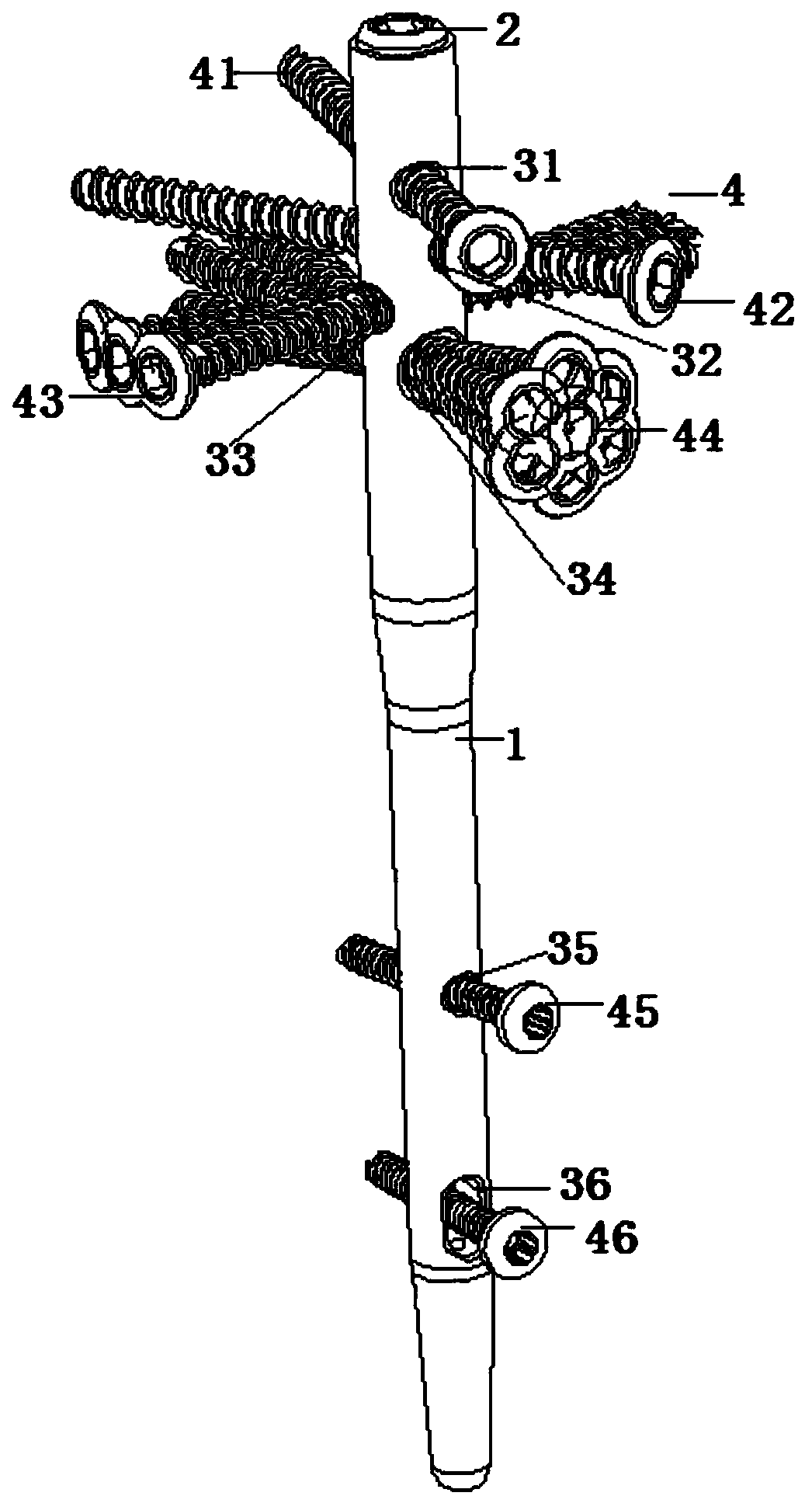
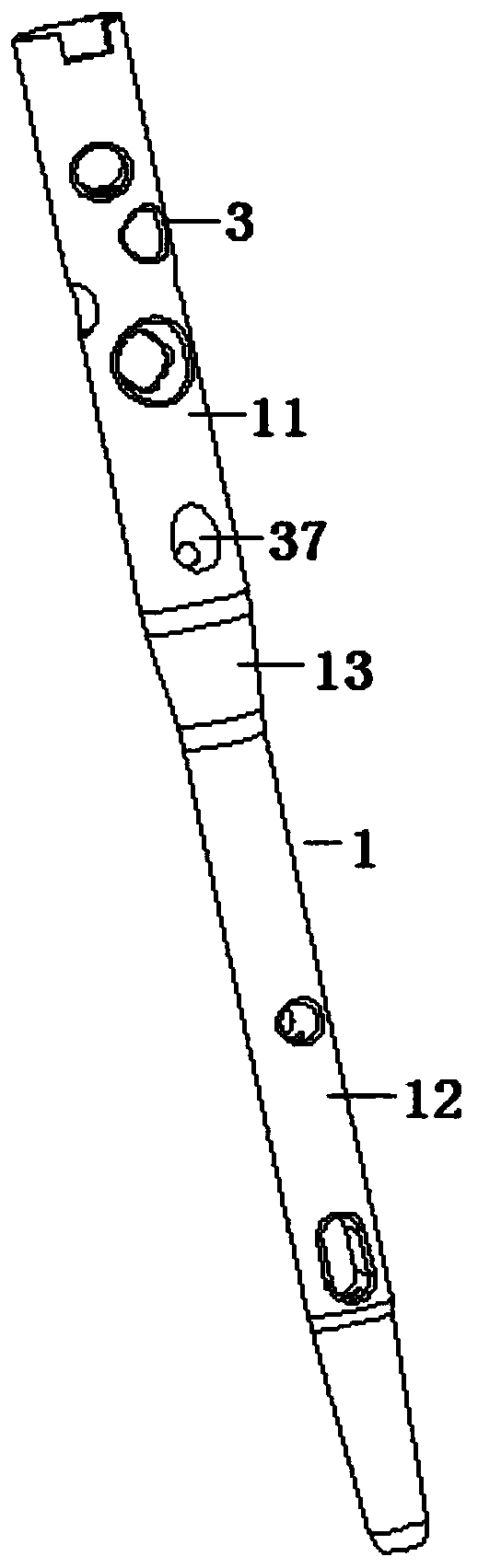
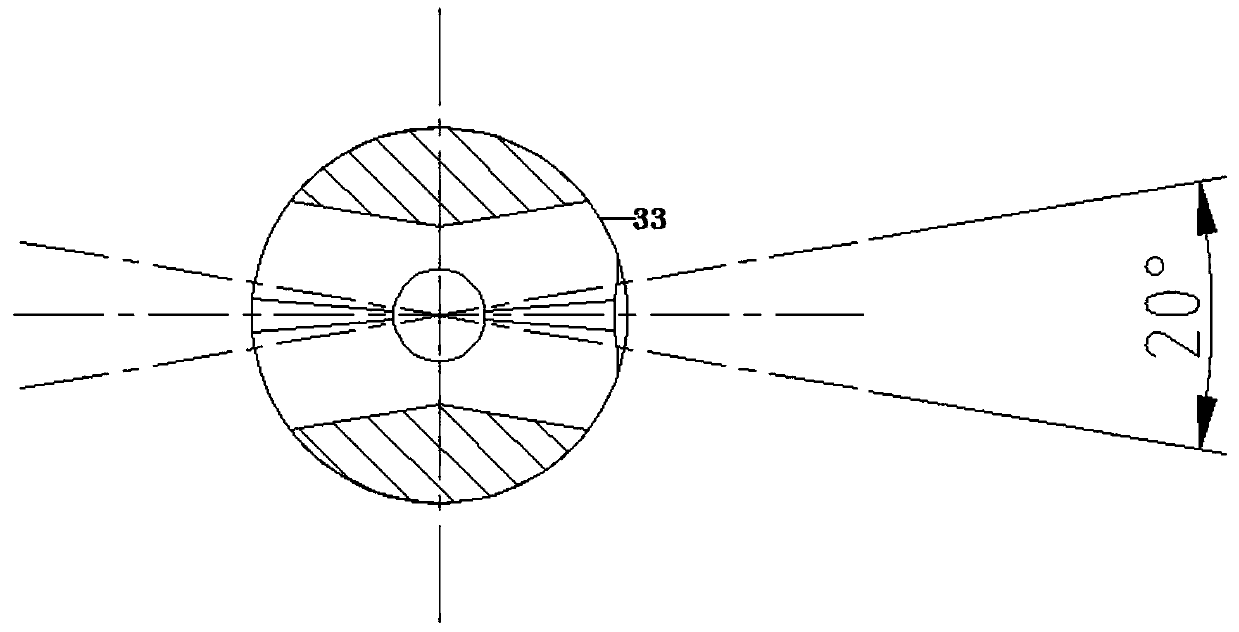
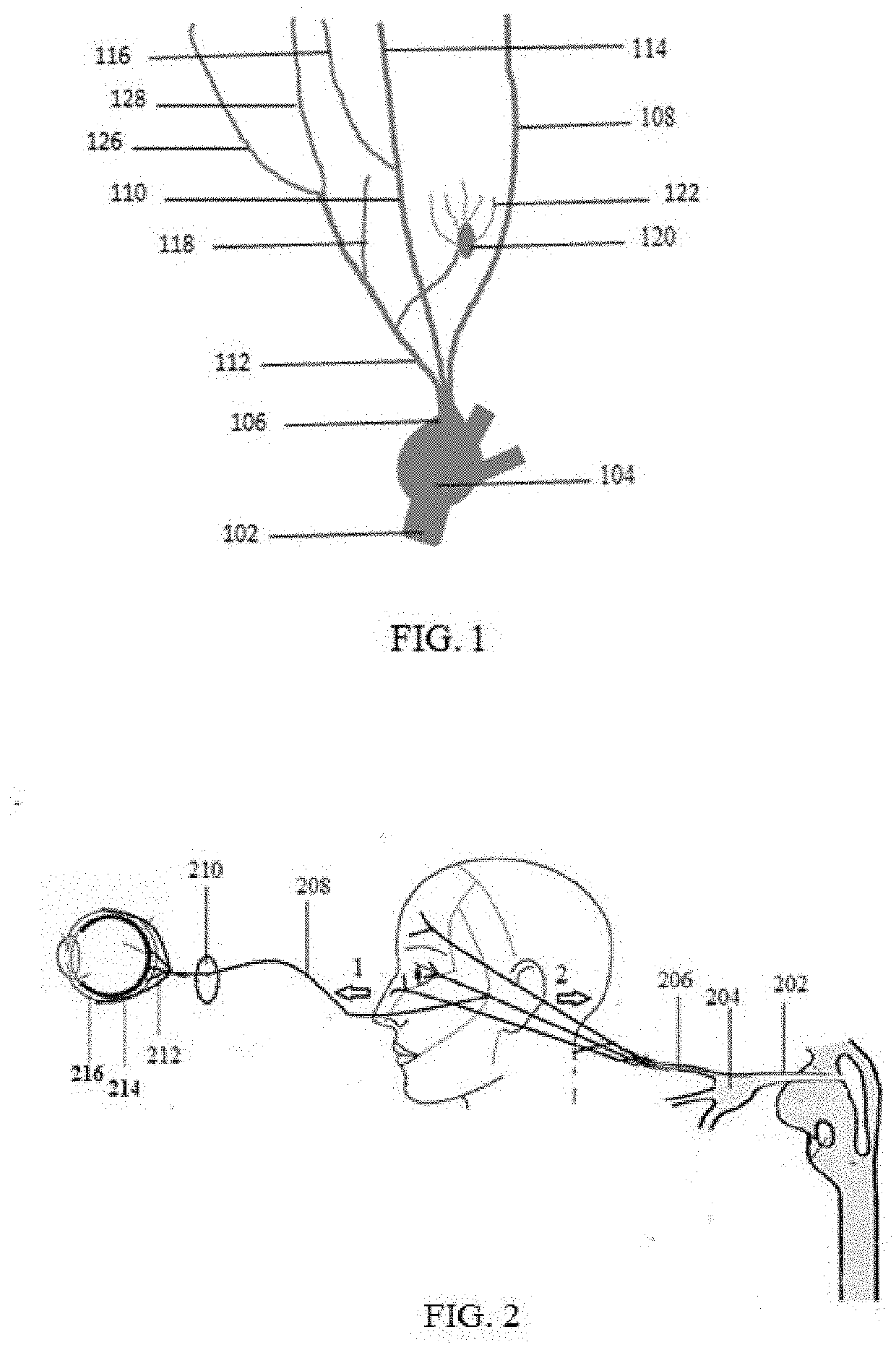
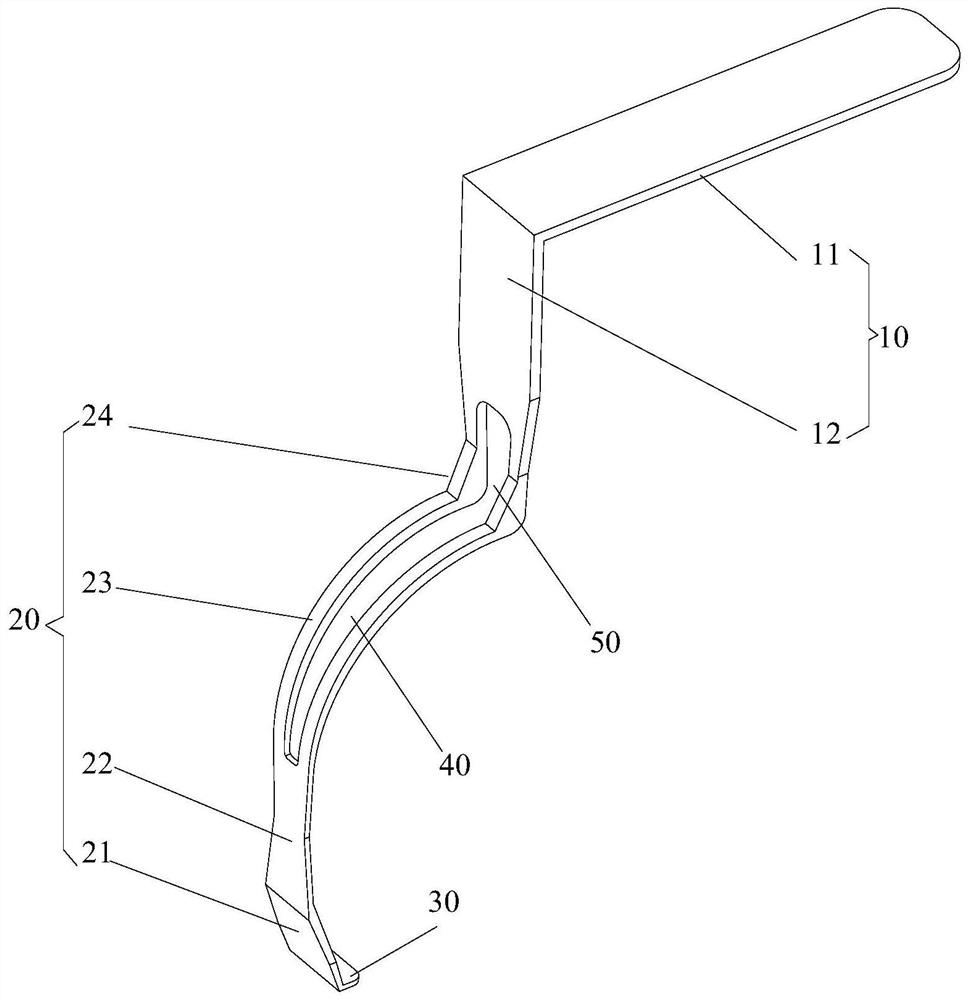
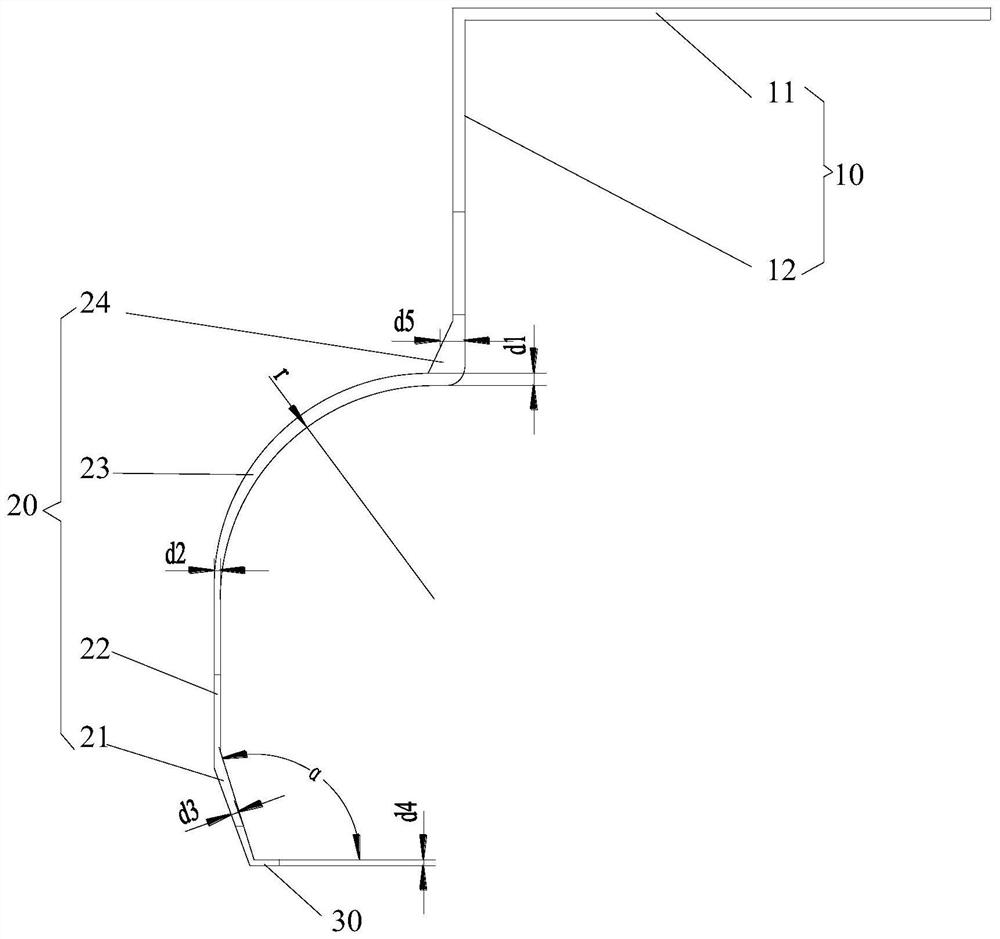
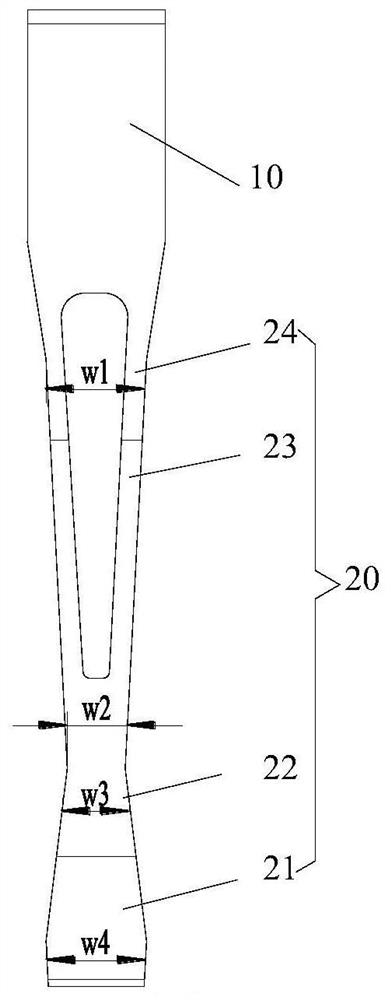
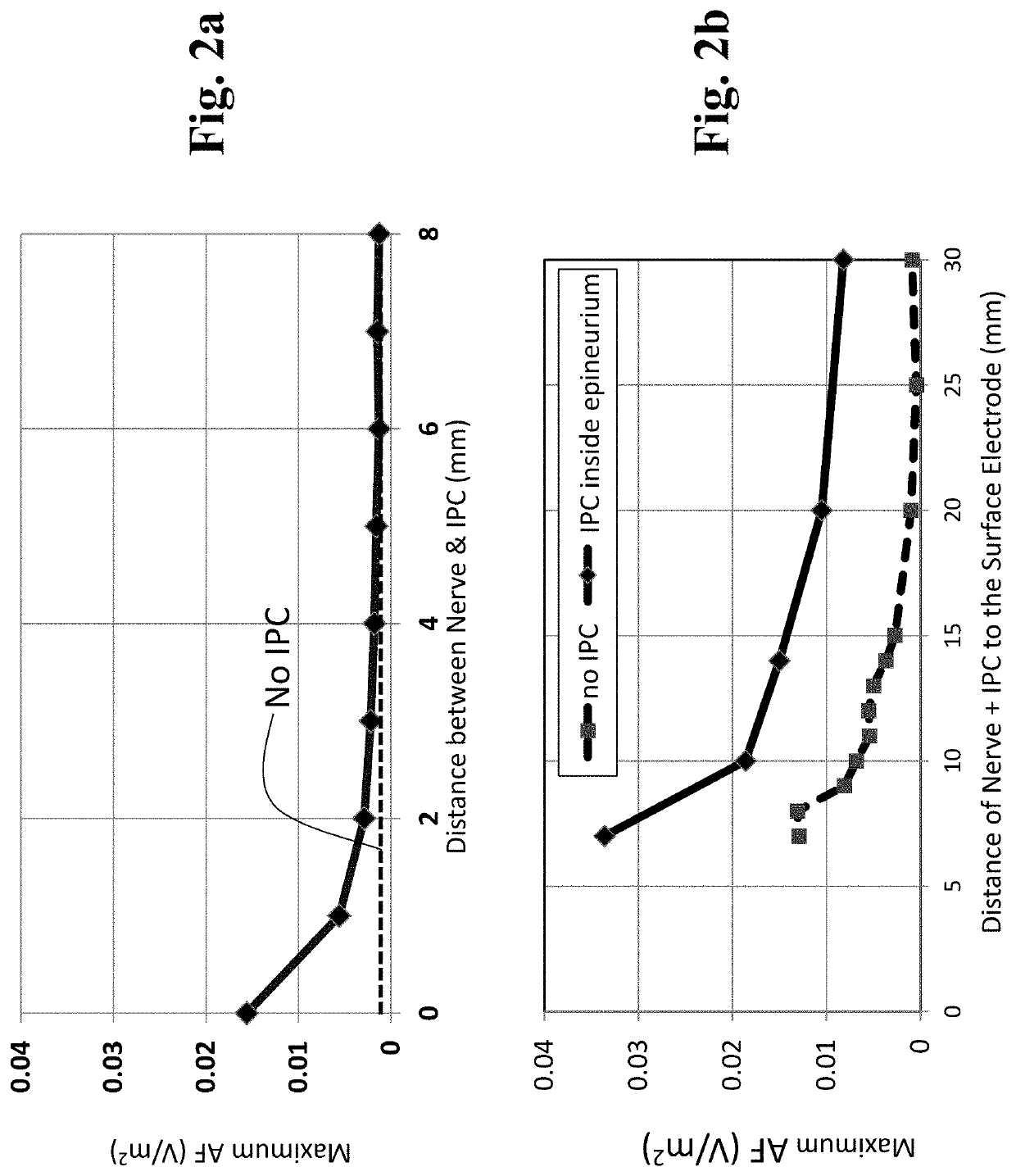
Patents
Literature
117 results about "Infra-orbital nerve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
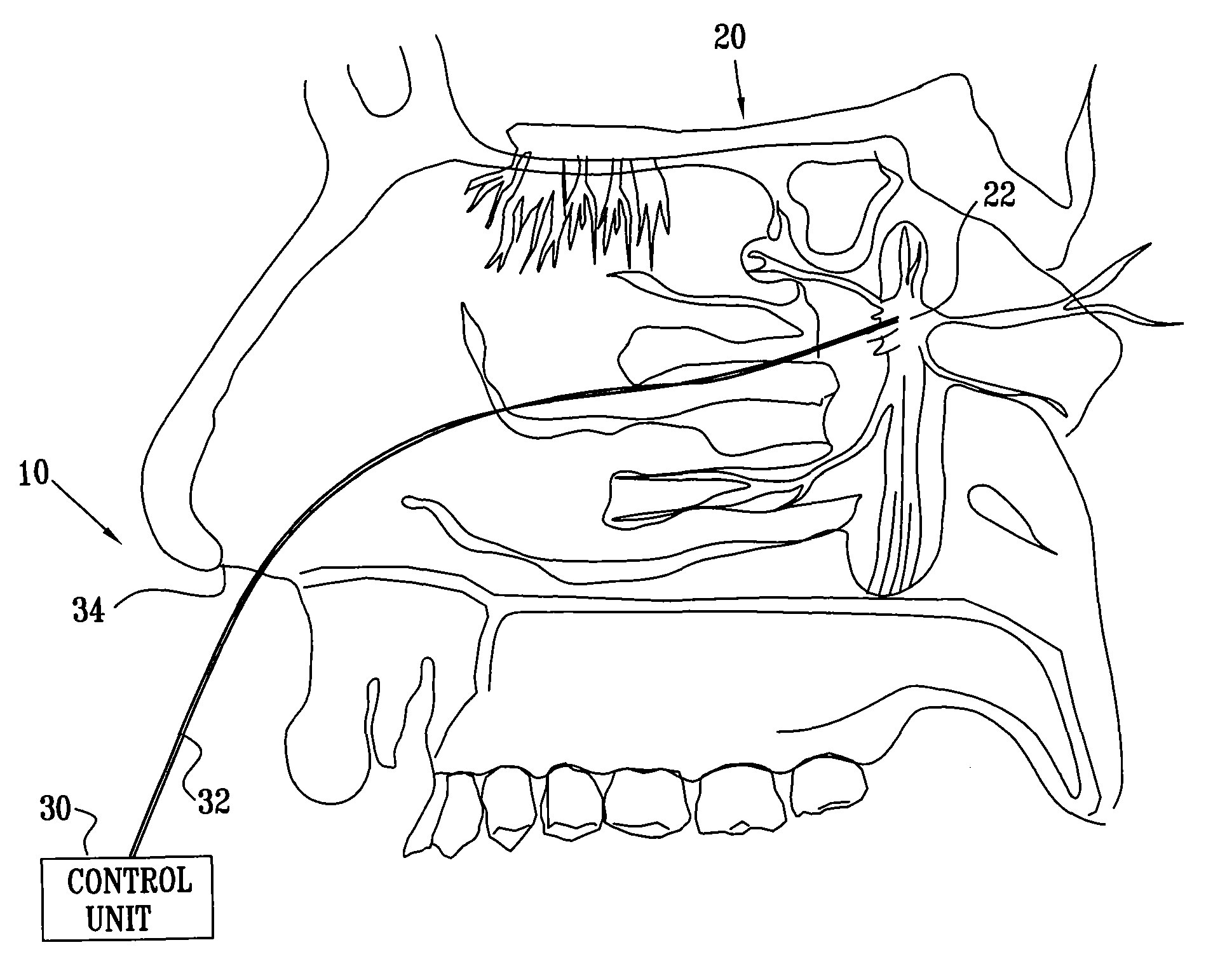
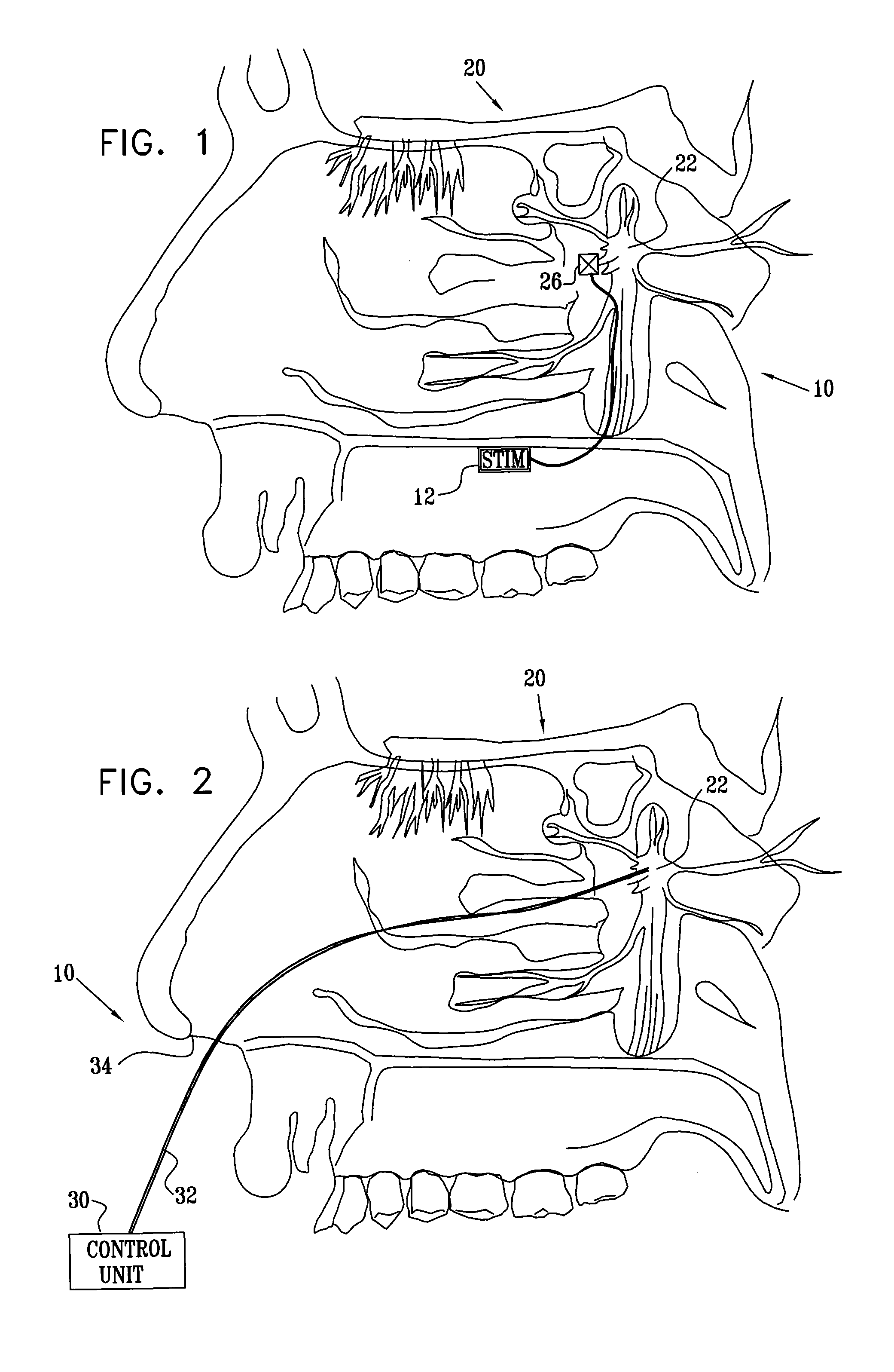
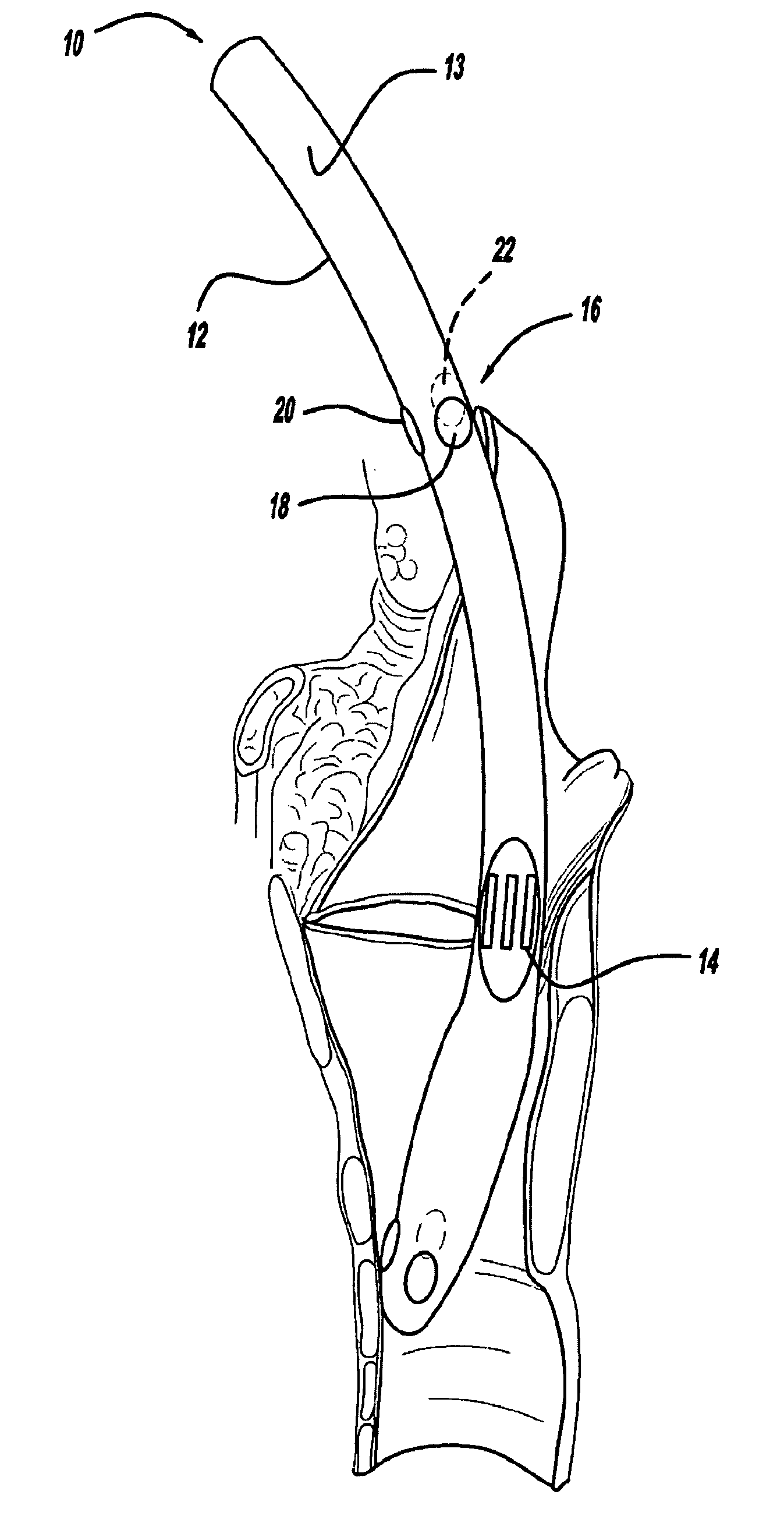
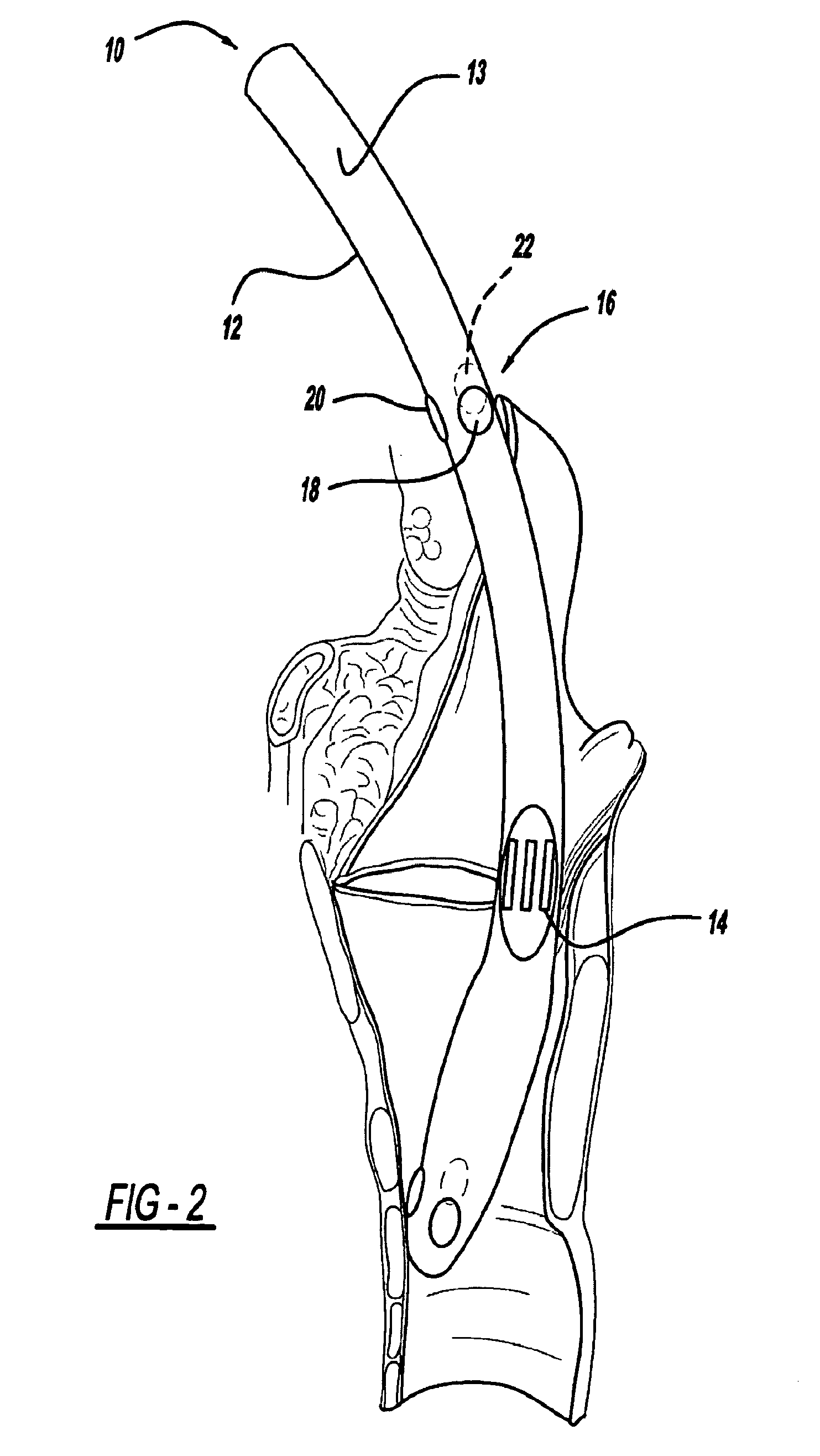
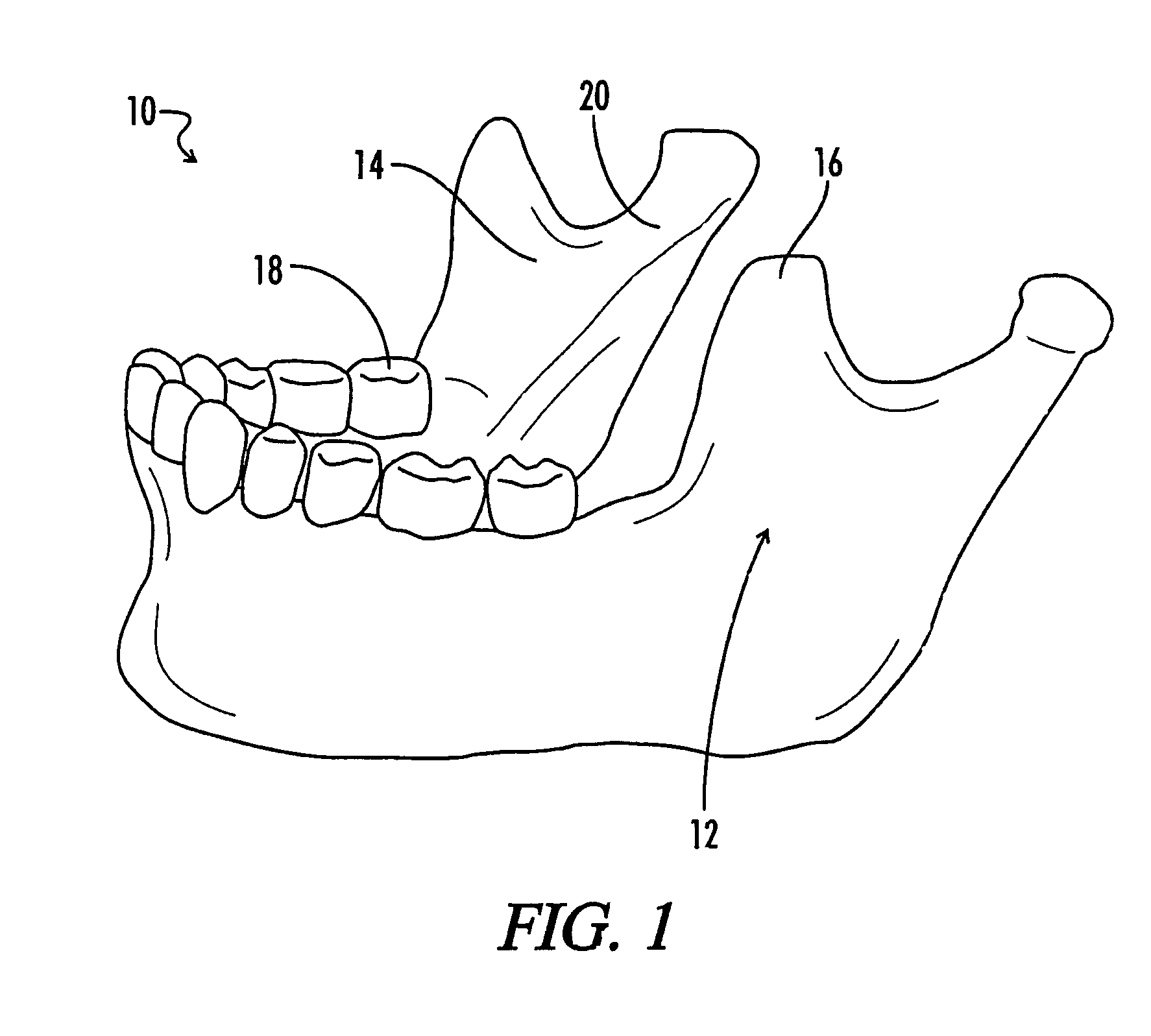
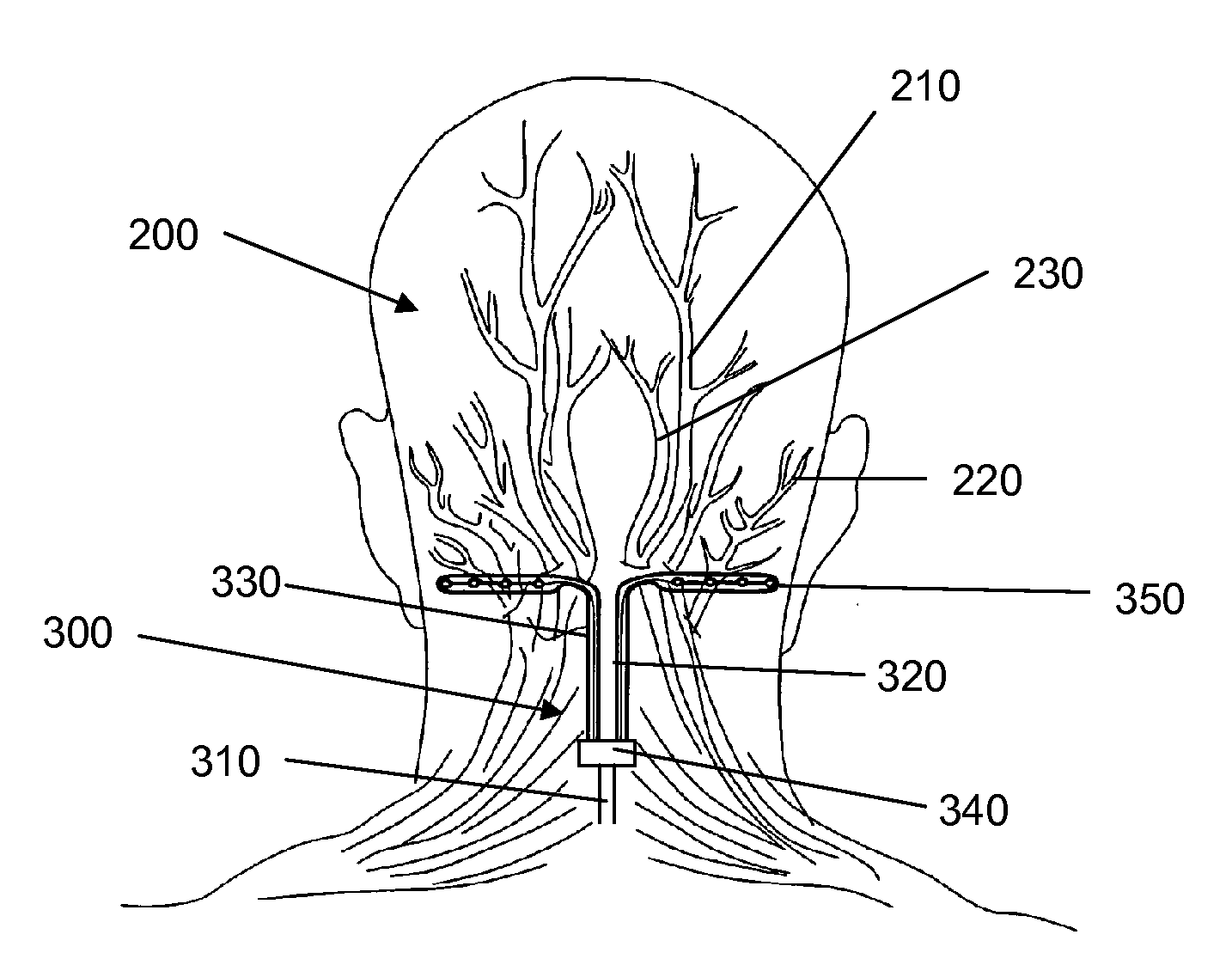
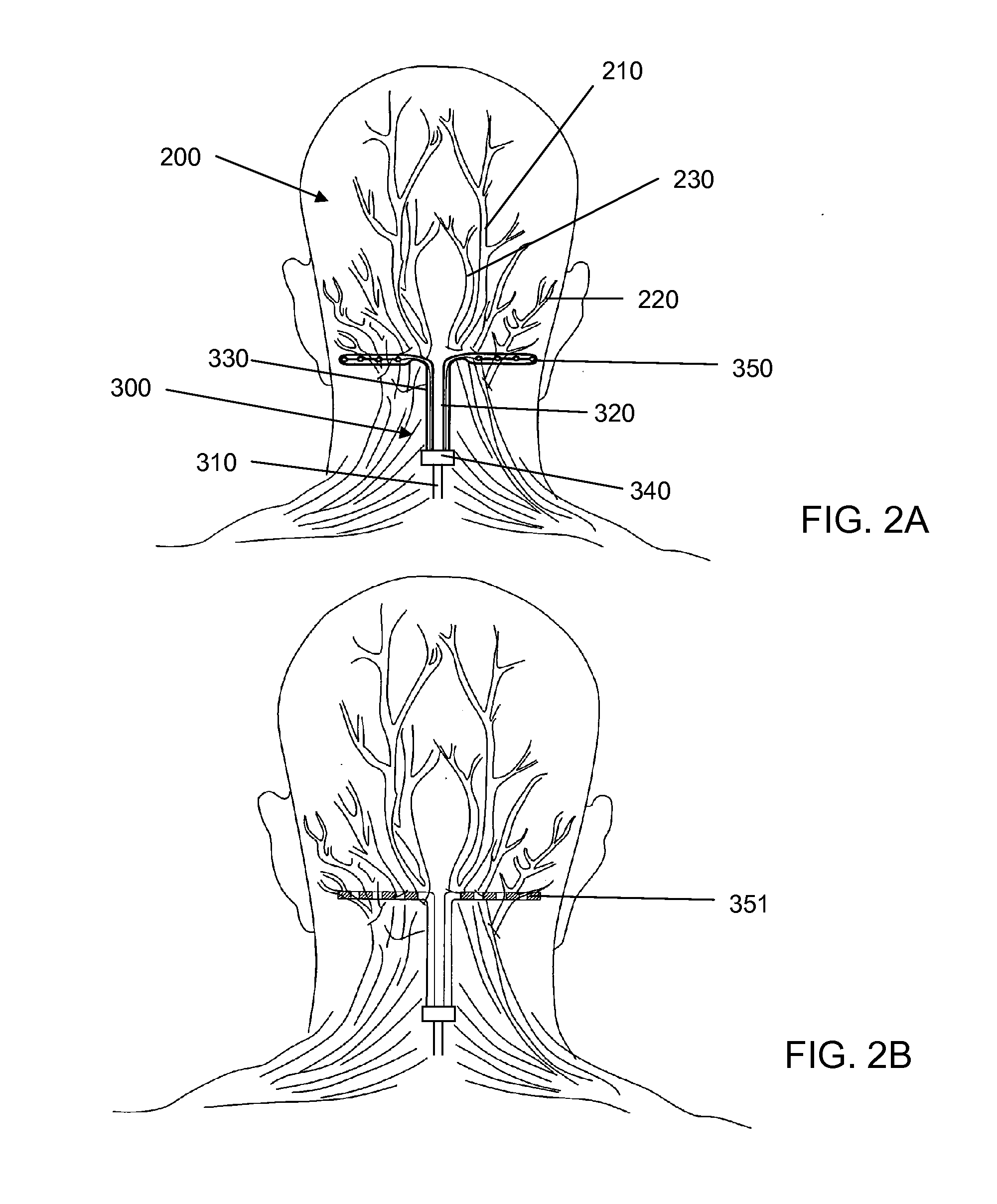
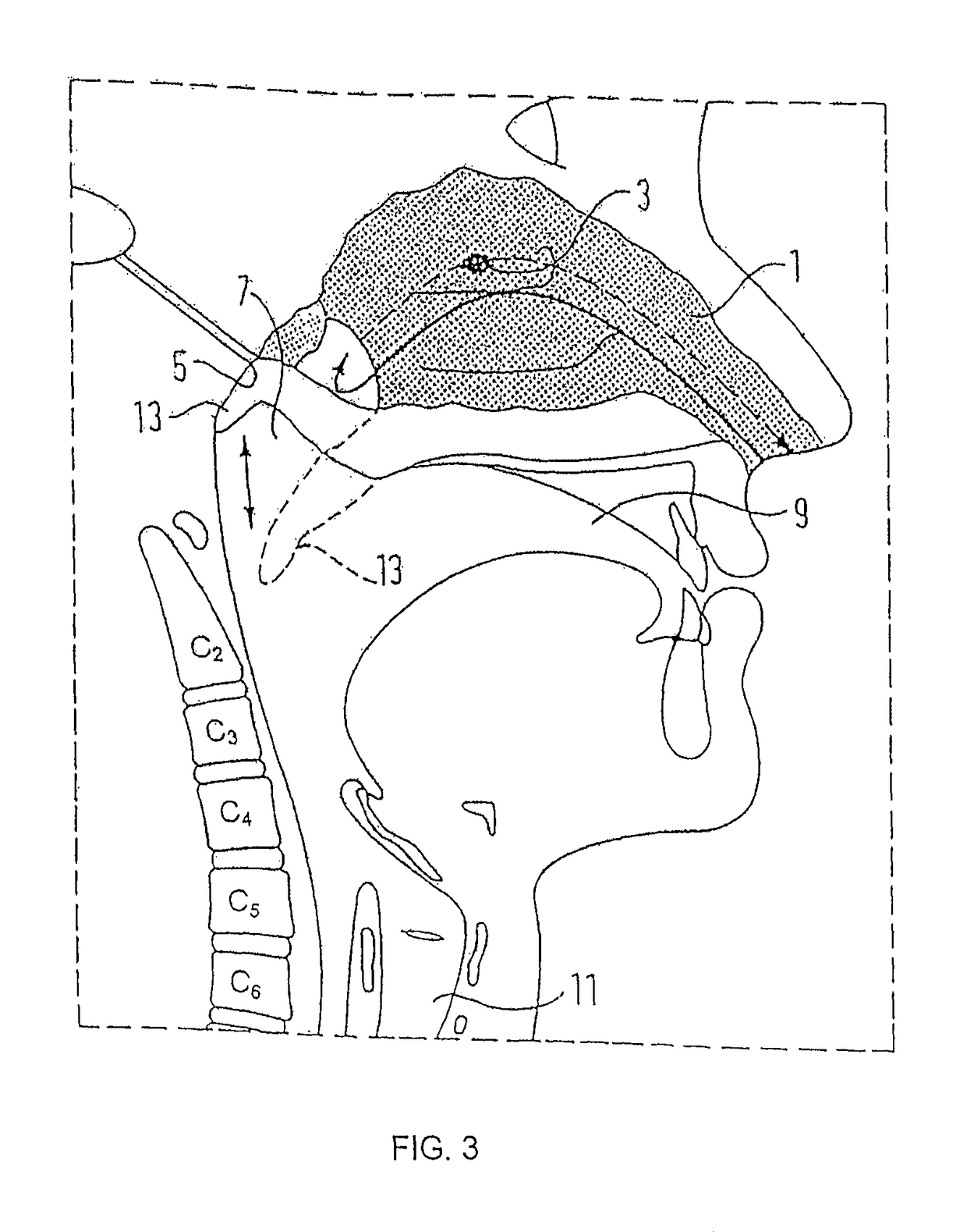
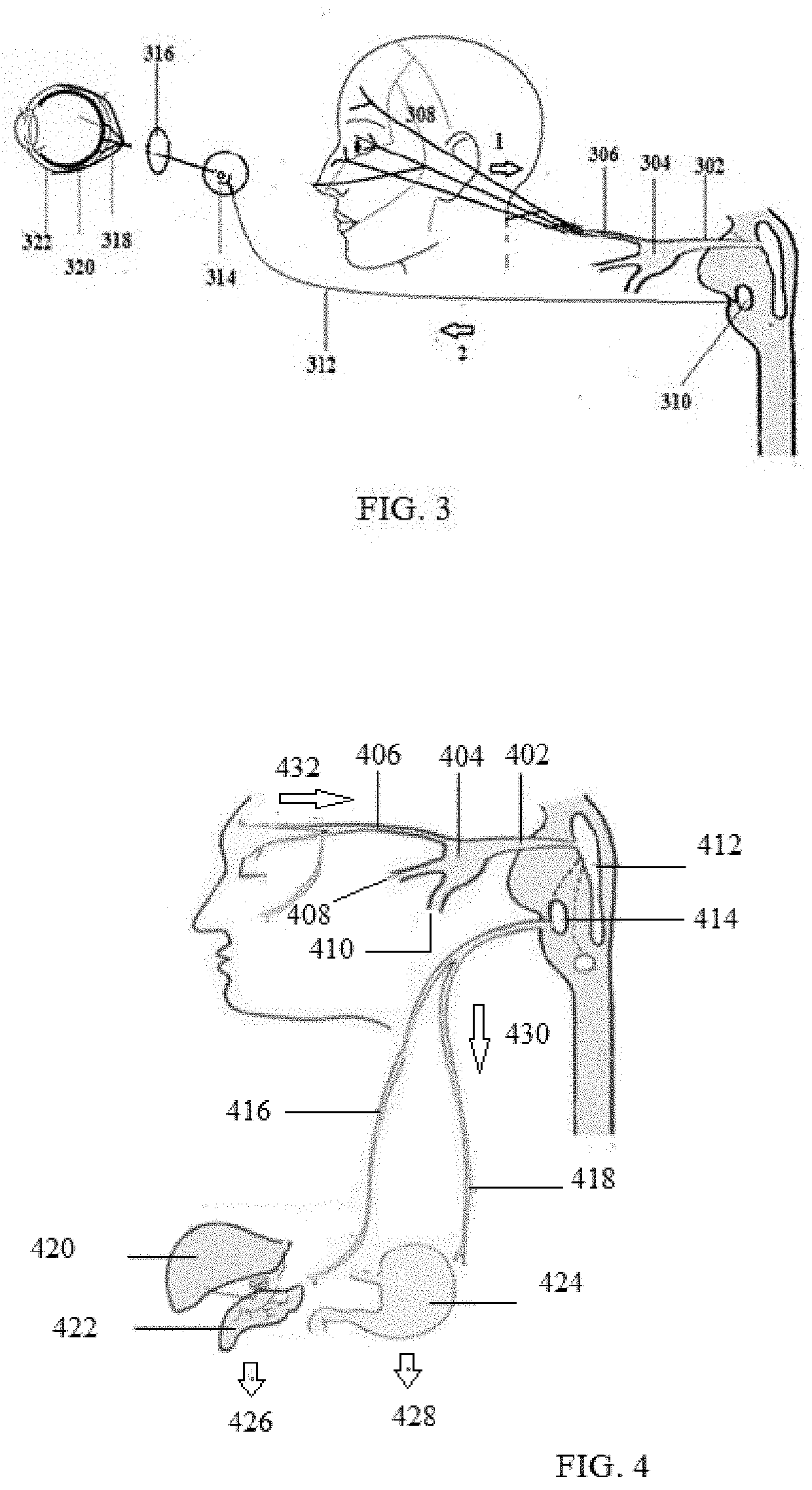
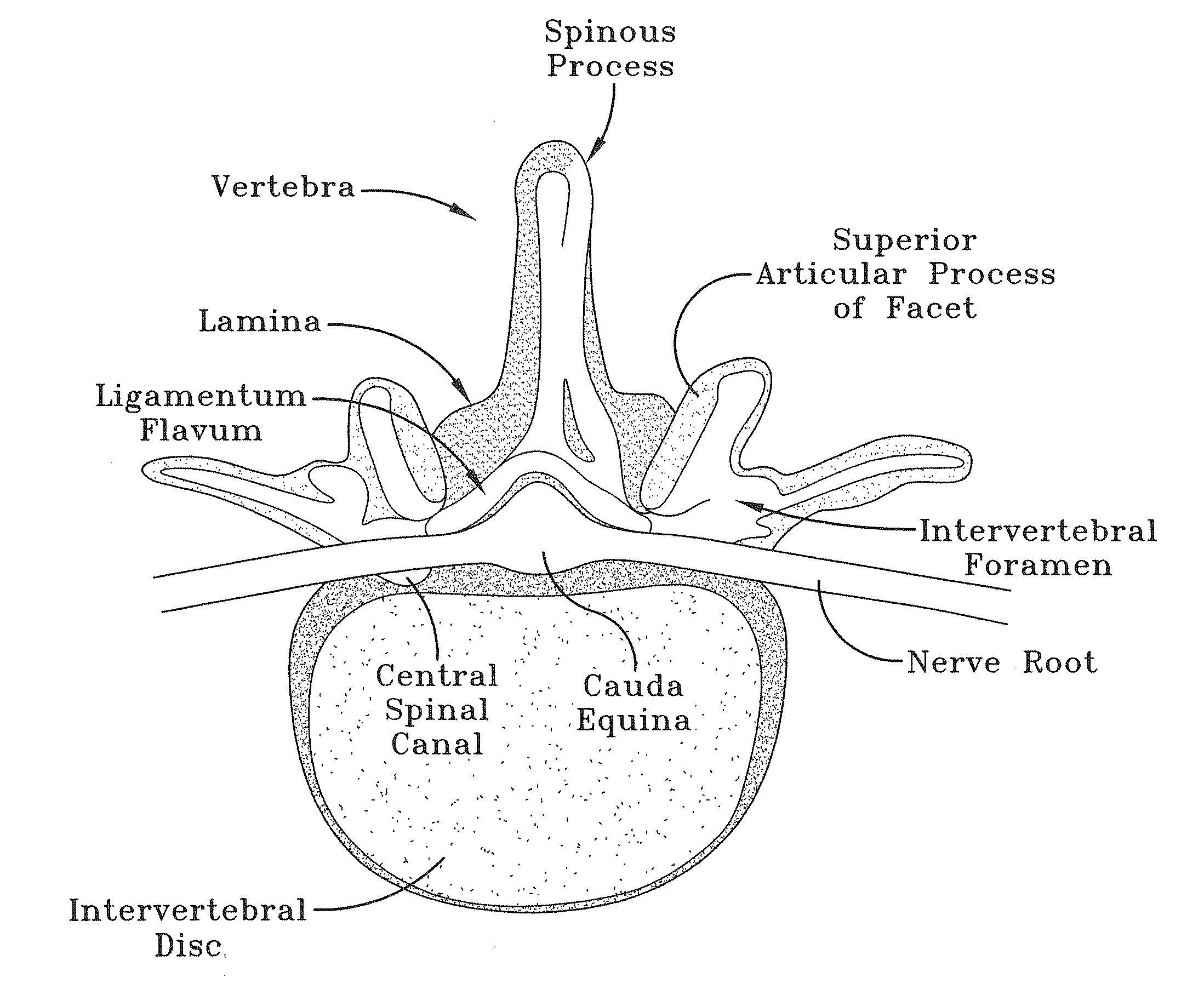
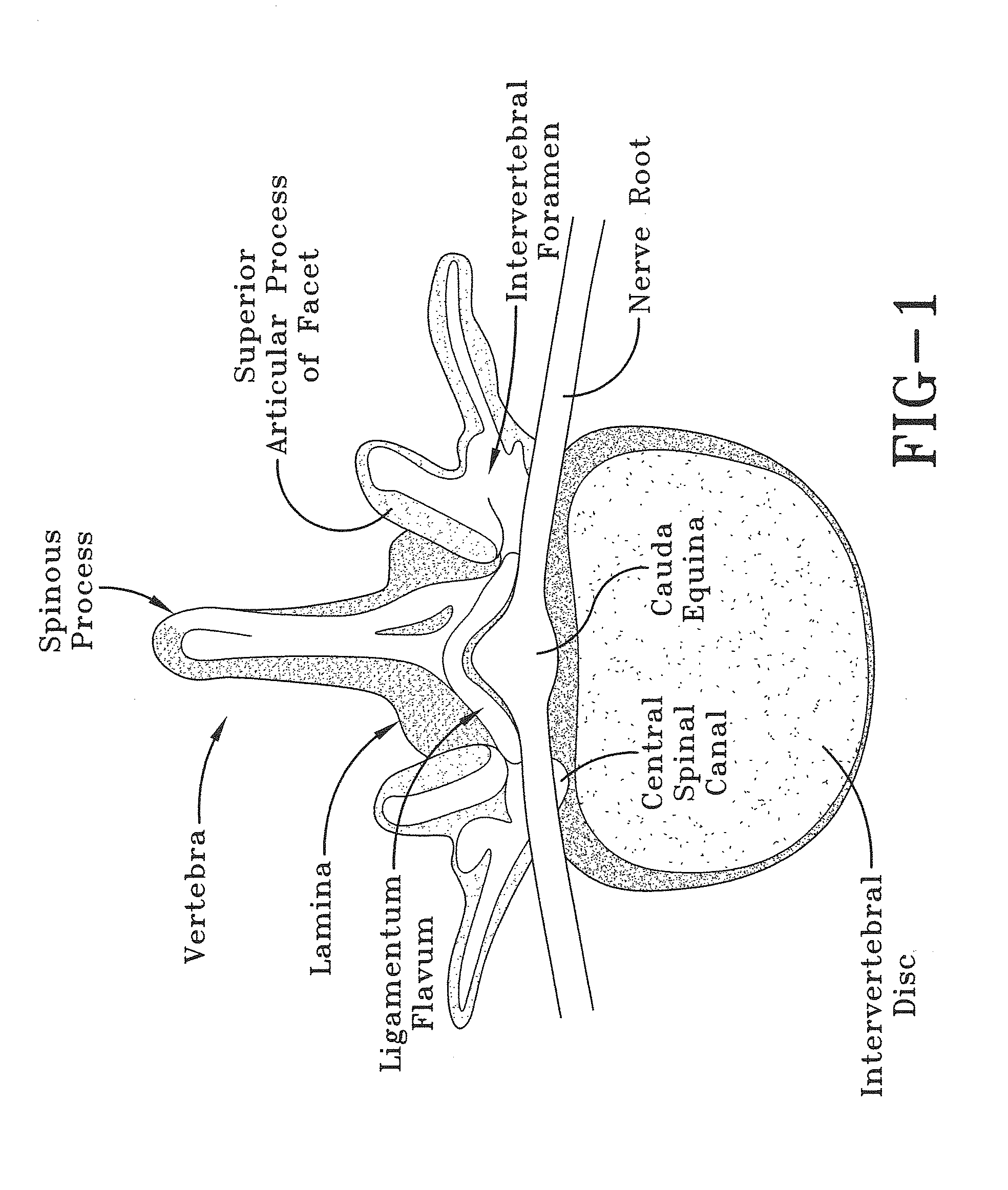
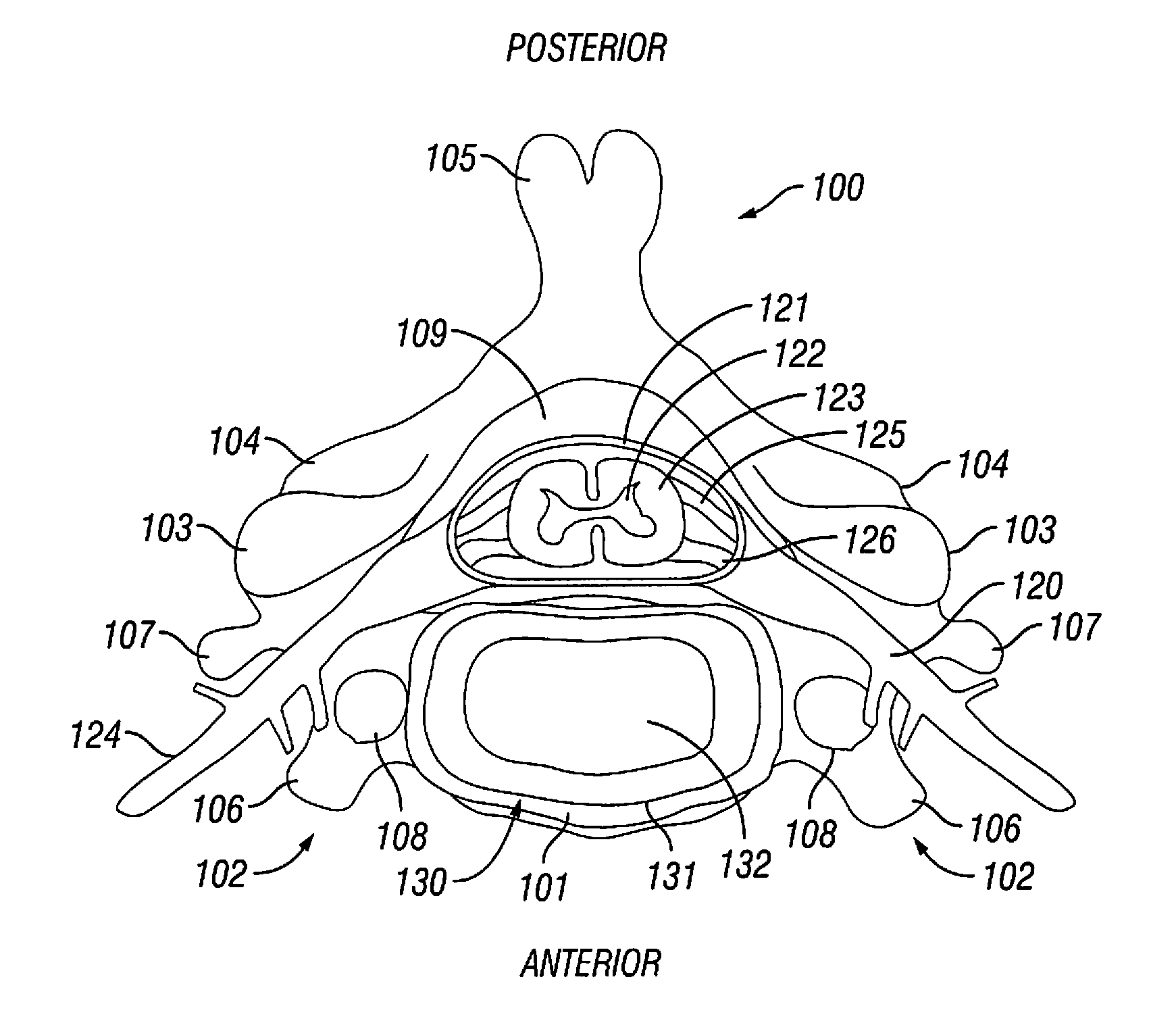
After the maxillary nerve enters the infraorbital canal, the nerve is frequently called the infraorbital nerve. This nerve innervates (sensory) the lower eyelid, upper lip, and part of the nasal vestibule and exits the infraorbital foramen of the maxilla.
Vestibular stimulation system and method
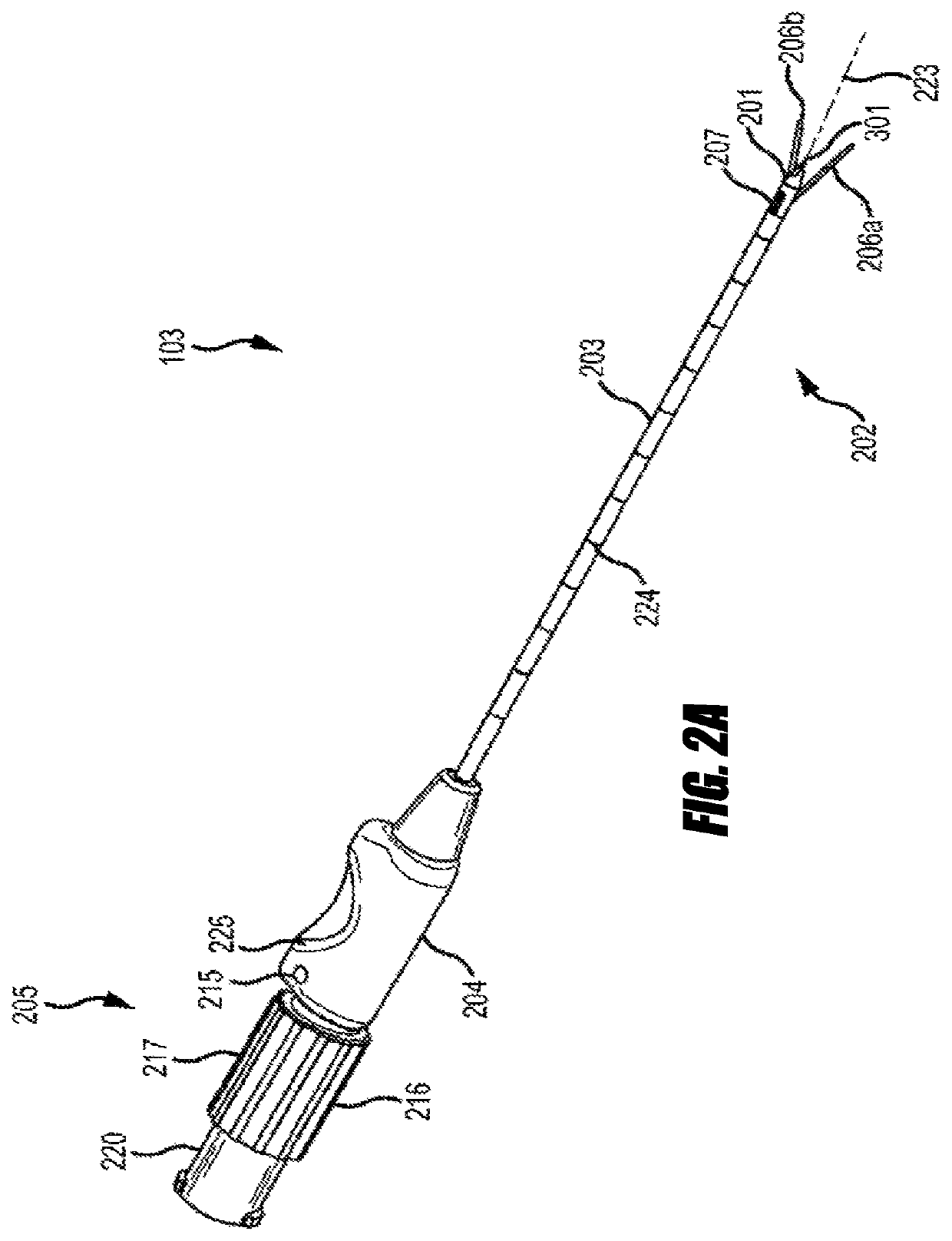
InactiveUS6314324B1Augmenting or controlling a patient's natural respiratory functionImprovement effortsInternal electrodesExternal electrodesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
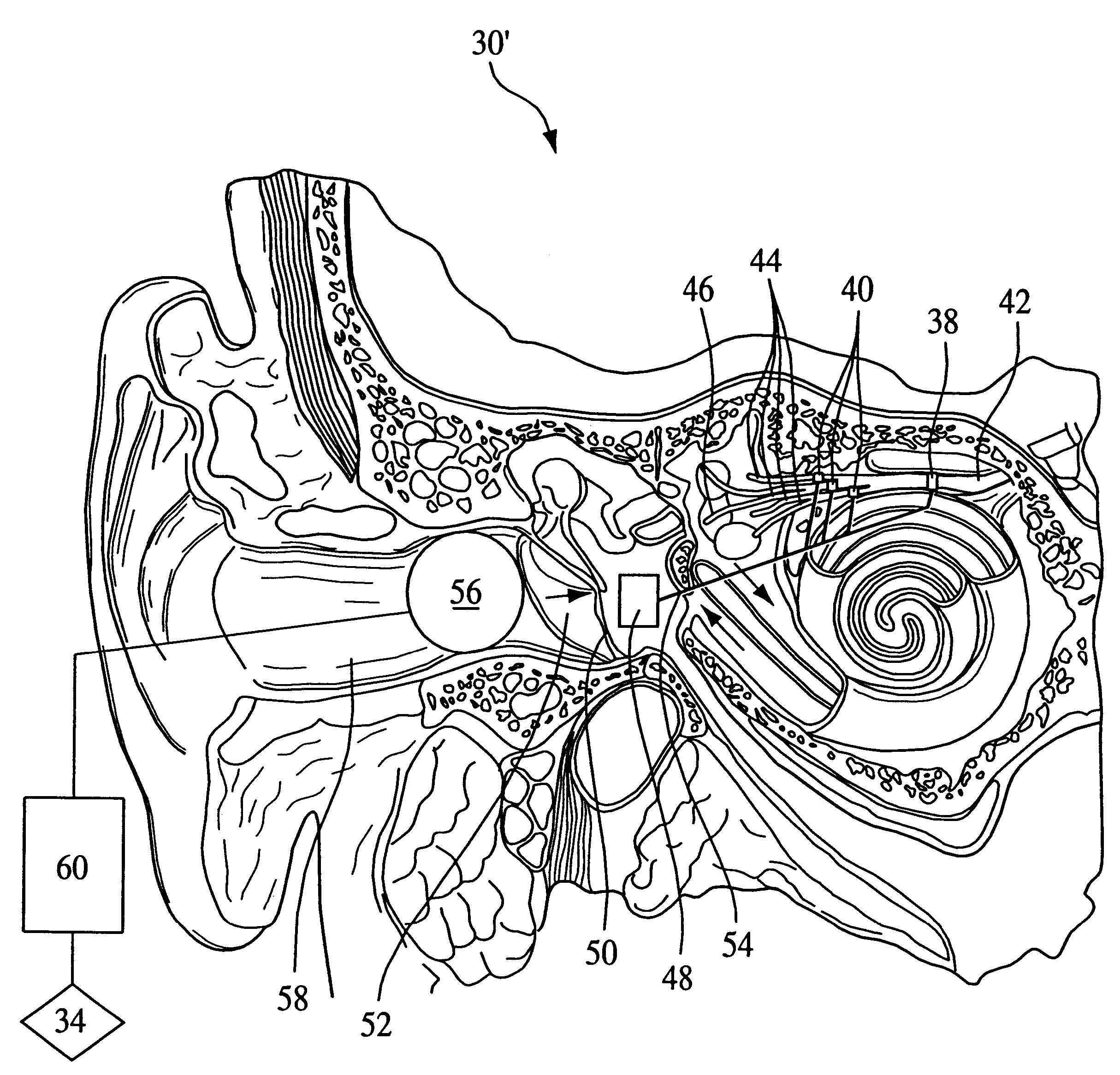
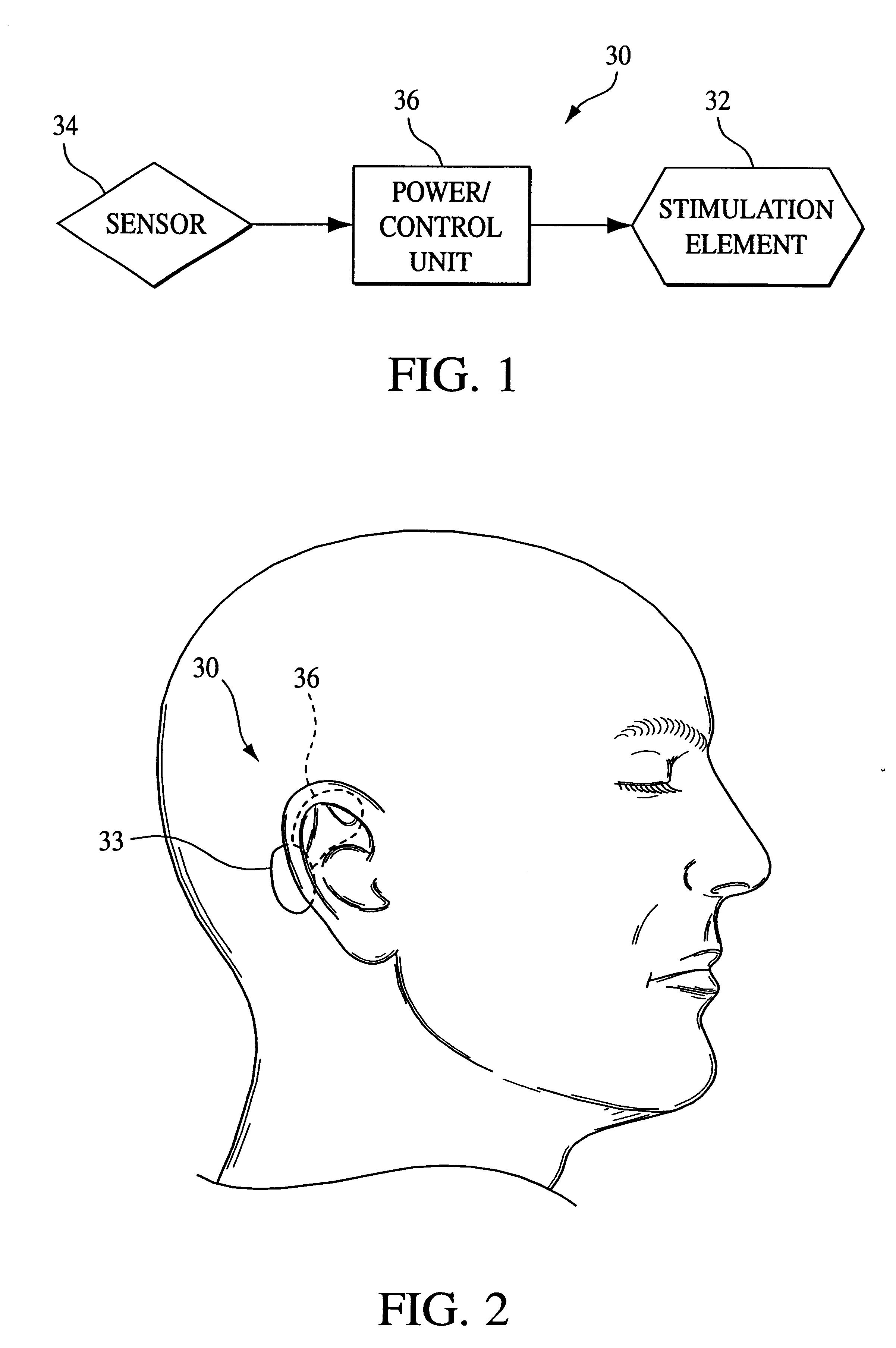
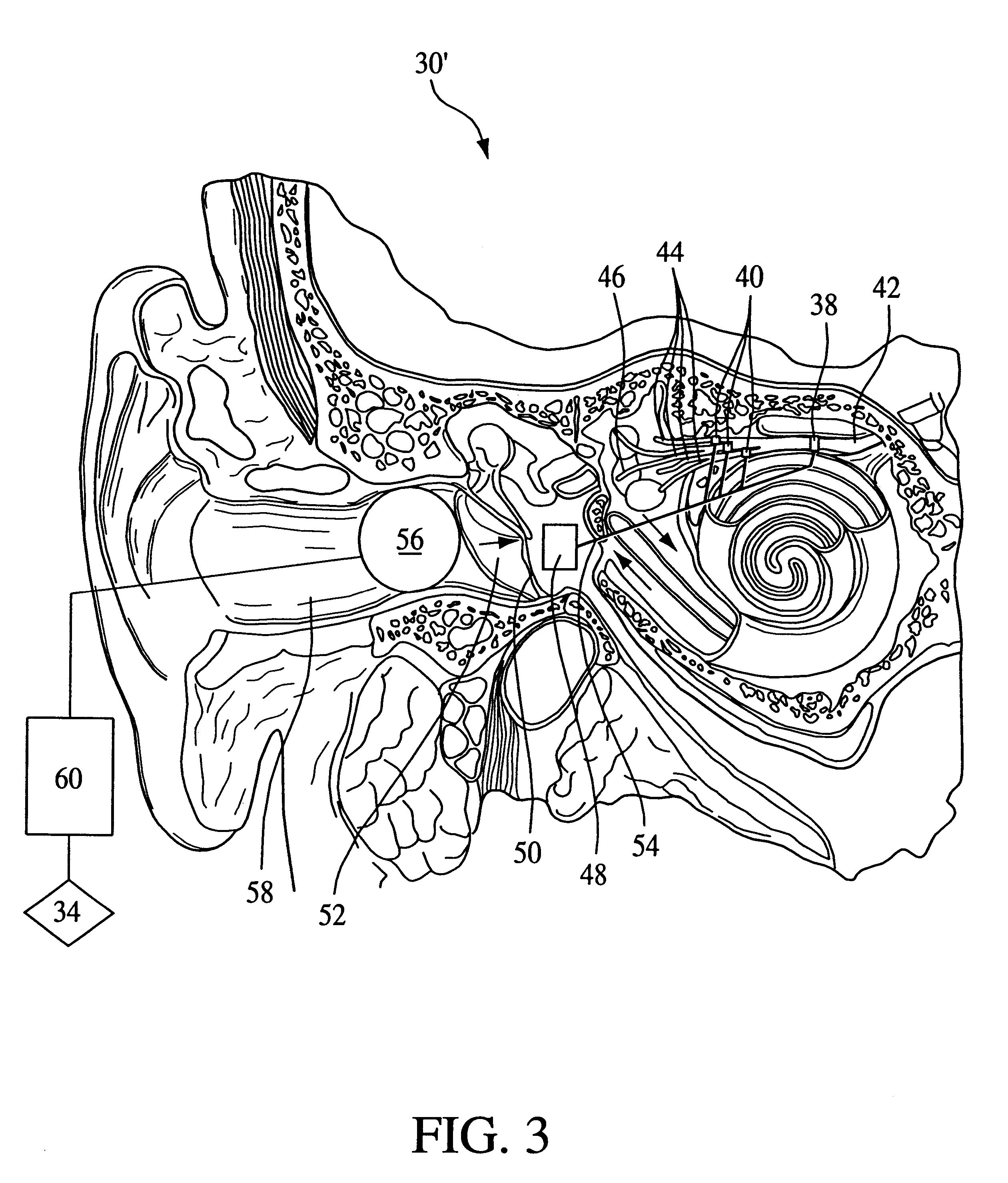
An apparatus and method in which the portions of the labyrinth associated with the labyrinthine sense and / or the nerves associated therewith are stimulated to perform at least one of the following functions: augment or control a patient's respiratory function, open the patient's airway, induce sleep, and / or counteract vertigo. In one embodiment, the vestibular stimulating system of the present invention includes 1) a stimulation element that performs the actual stimulation of the tissue, 2) a sensor to detect a physiological condition of the patient, and 3) a power / control unit that receives the signals provided by the sensor and causes stimulation energy to be provided to the stimulation element at an appropriate timing, level, pattern, and / or frequency to achieve the desired function. However, the present invention also contemplates eliminating the sensor in favor of applying a predetermined pattern of stimulation to the patient.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Systems and methods for bilateral stimulation of left and right branches of the dorsal genital nerves to treat urologic dysfunctions
Systems and methods treat urologic dysfunctions by implanting a lead and electrode in a tissue region affecting urologic function, and coupling the lead to an external pulse generator. If desired results are achieved, the external pulse generator is removed and an implantable pulse generator is implanted in an anterior pelvic region remote from the electrode. Bilateral stimulation of the left and / or right branches of the dorsal genital nerves using a single lead implanted in adipose or other tissue in the region at or near the pubic symphysis is able to treat urologic dysfunctions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
Stimulation for treating brain events and other conditions
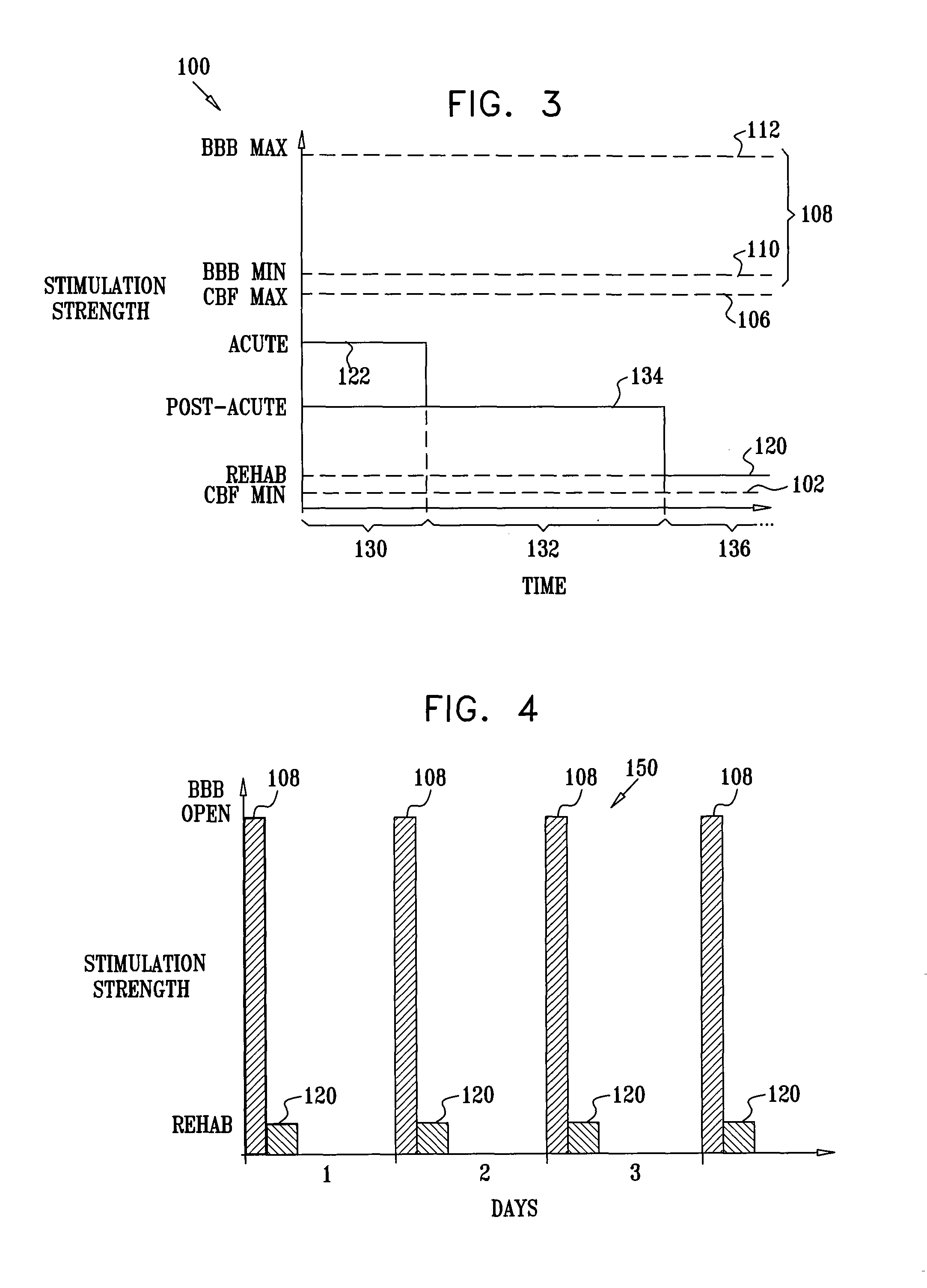
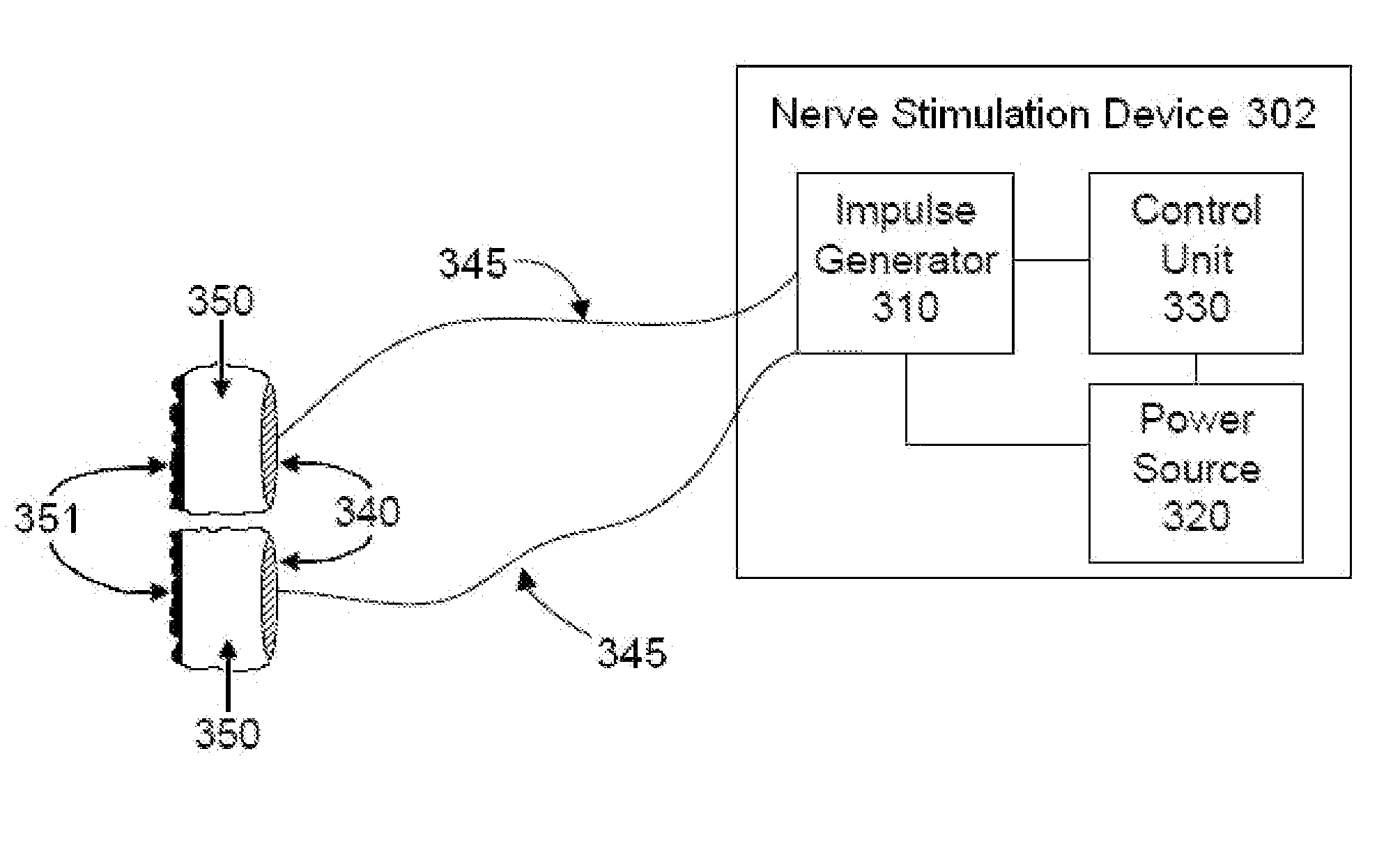
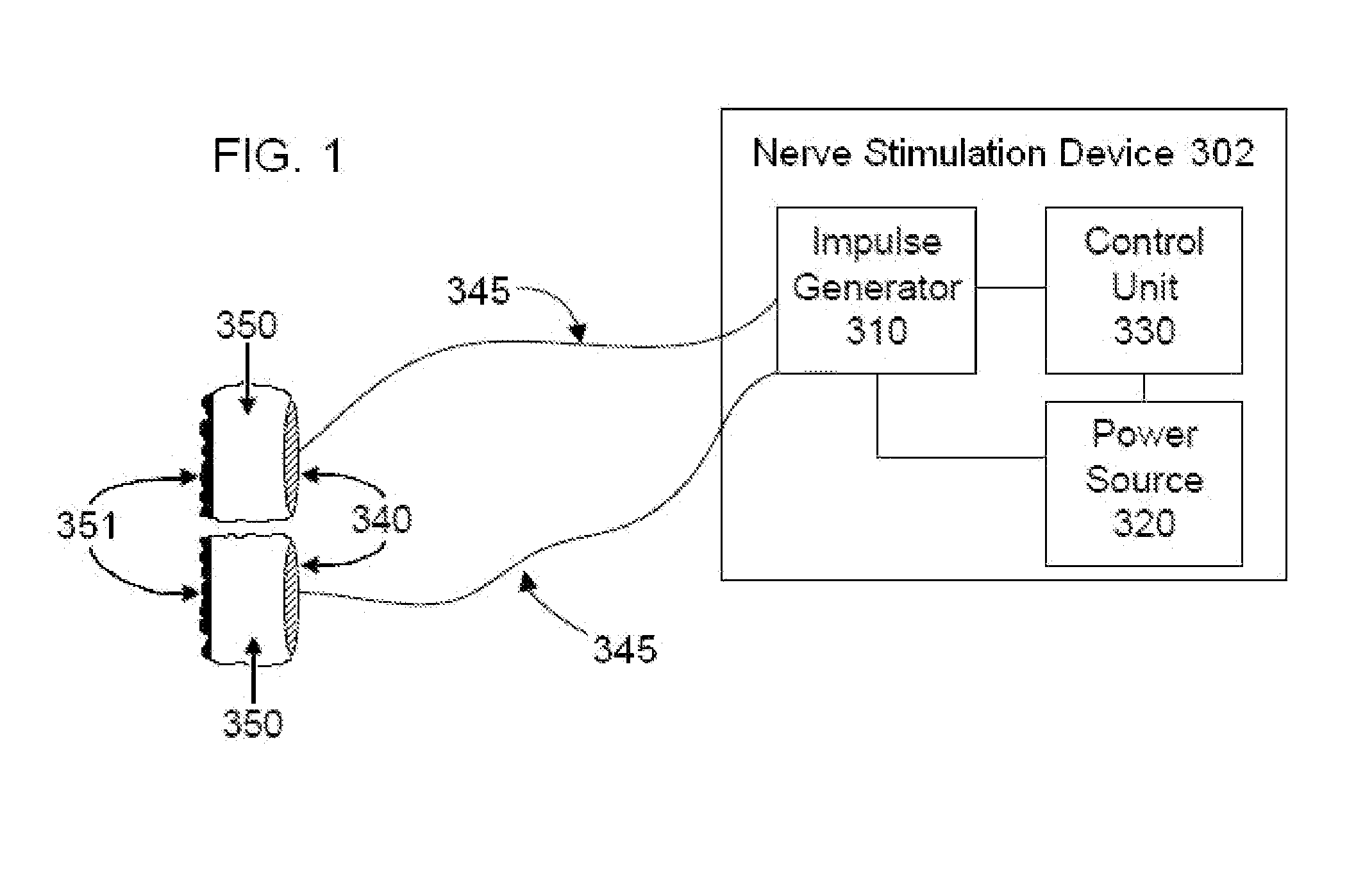
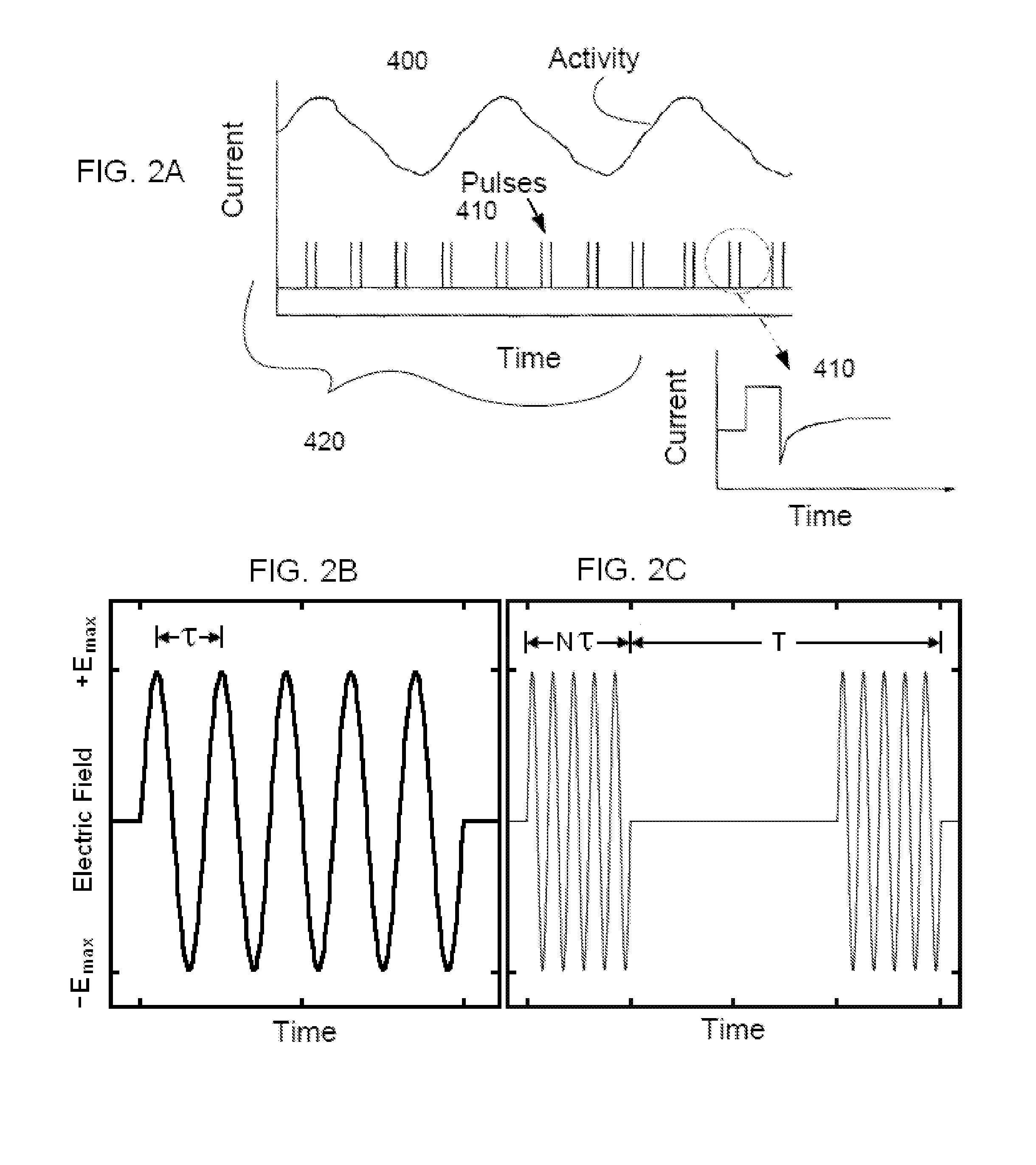
ActiveUS20070083245A1Increase cerebral blood flowReduce harmSpinal electrodesDeep petrosal nerveMedicine
Apparatus for treatment is provided, including one or more electrodes, configured to be applied to a site of a subject, and adverse cerebrovascular condition treatment functionality. The functionality comprises a control unit configured to drive the one or more electrodes to apply electrical stimulation to the site during a plurality of stimulation periods which includes at least first and last stimulation periods, set an inter-period interval between initiation of the first stimulation period and initiation of the last stimulation period to be at least 24 hours, and configure the stimulation during the first and last stimulation periods to induce at least one neuroprotective occurrence selected from the group consisting of: an increase in cerebral blood flow (CBF) of the subject, and a release of one or more neuroprotective substances. The site is selected from the group consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG), a greater palatine nerve, a lesser palatine nerve, a sphenopalatine nerve, a communicating branch between a maxillary nerve and an SPG, an otic ganglion, an afferent fiber going into the otic ganglion, an efferent fiber going out of the otic ganglion, an infraorbital nerve, a vidian nerve, a greater superficial petrosal nerve, and a lesser deep petrosal nerve. Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Delivery of polynucleotide agents to the central nervous system
InactiveUS20060216317A1Inhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOligonucleotideTrigeminal nerve
The present invention provides a method for delivering polynucleotide agents, particularly oligonucleotides, to the CNS of a mammal by way of a neural pathway originating in the nasal cavity or through a neural pathway originating in an extranasal tissue that is innervated by the trigeminal nerve.
Owner:REINHARD CHRISTOPH +1
Mobile phone for stimulating the trigeminal nerve to treat disorders
ActiveUS20140330336A1Avoid stimulationMaximum effectivenessElectrotherapyDevices with sensorDiseaseMental nerve
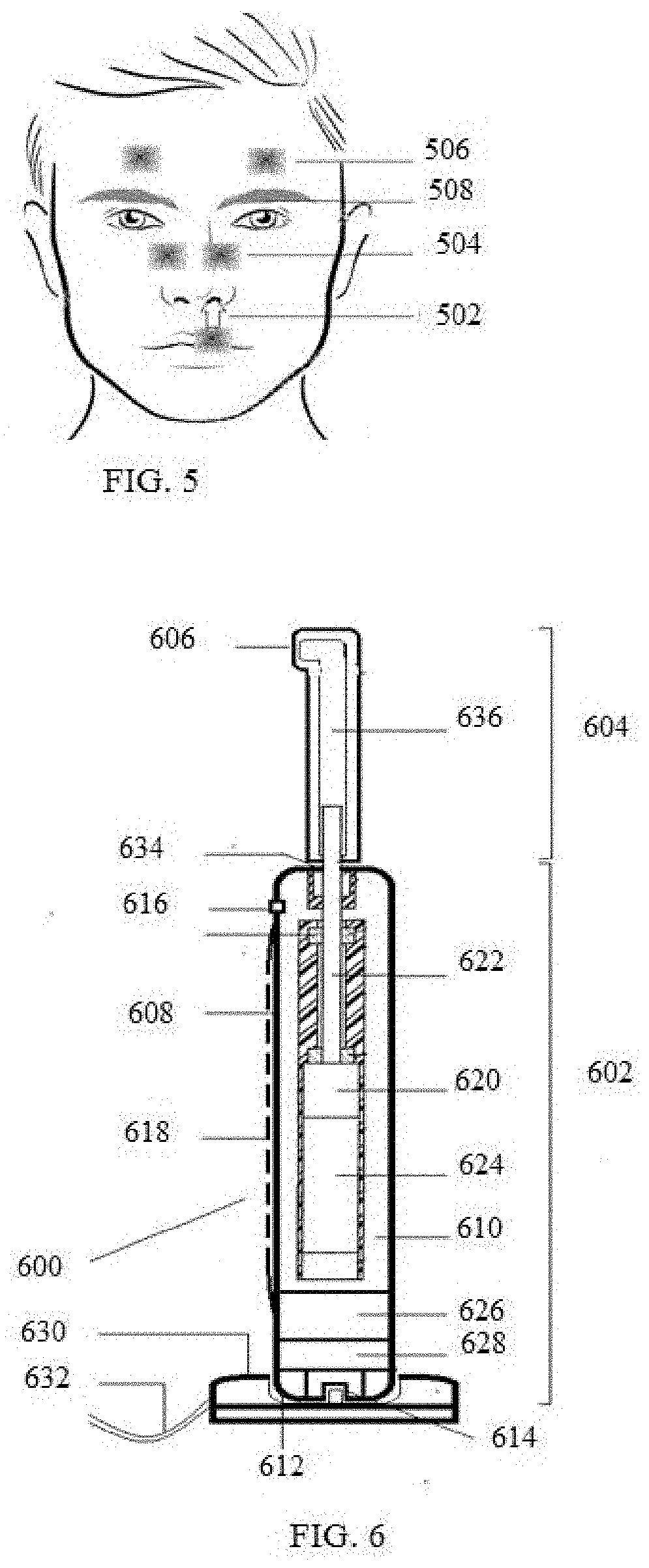
Devices and methods are disclosed that allow a patient to self-treat a medical condition, such as migraine headache and trigeminal neuralgia and the like, by noninvasive electrical stimulation of nerves of the head, particularly supraorbital, supratrochlear, infraorbital, and mental nerves in the vicinity of their foramen or notch. The system comprises a handheld mobile device, such as a smartphone, that is applied to the surface of the patient's head. One or more electrodes on the mobile device apply electrical impulses transcutaneously through the patient's skin to the targeted nerve to treat the medical condition. The system is designed to address problems that arise particularly during self-treatment, when a medical professional is not present.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Nerve monitoring device
InactiveUS20100063376A1Rotational errorAccurate monitoringSensorsNeuroelectric signal measurementRotational errorMultielectrode array
The present invention provides a nerve monitoring device. The device includes a cannula, a sensor for monitoring the nerve and an alignment device. The cannula can be any surgical cannula, and is preferably an endotracheal tube. The sensor can be an electrode or other sensor that is capable of sensing nerve activity. The alignment device is a device that ensures that after insertion of the nerve sensor into a patient, the sensors are aligned to properly monitor the target nerve or muscle. The internal alignment device may communicate externally to surgeon by using electromagnetic energy as either a transmittor or a receiver. The mismatch of triangular laryngeal anatomy to circular cannula anatomy can be compensated for by a) altering the geometry (external shape) of the cannula and b) using soft, felt-like expandable electrodes. Rotational error can be compensated for by using a multi-electrode array wherein the optimized recording montage can be simply selected on the external recording device.
Owner:THE MAGSTIM
Inferior alveolar nerve block guide
InactiveUS8257341B1Accurate locationFine surfaceInternal osteosythesisFastening prosthesisInferior alveolar nerveBody contour
A guide for administering an injection including a guide body contoured for a human mandible; and at least one needle indexing guide on the guide body for the insertion of a needle there through, the guide use to provide a predictable and repeatable way of administering an injection to block a nerve.
Owner:FLETCHER JACK MAURICE
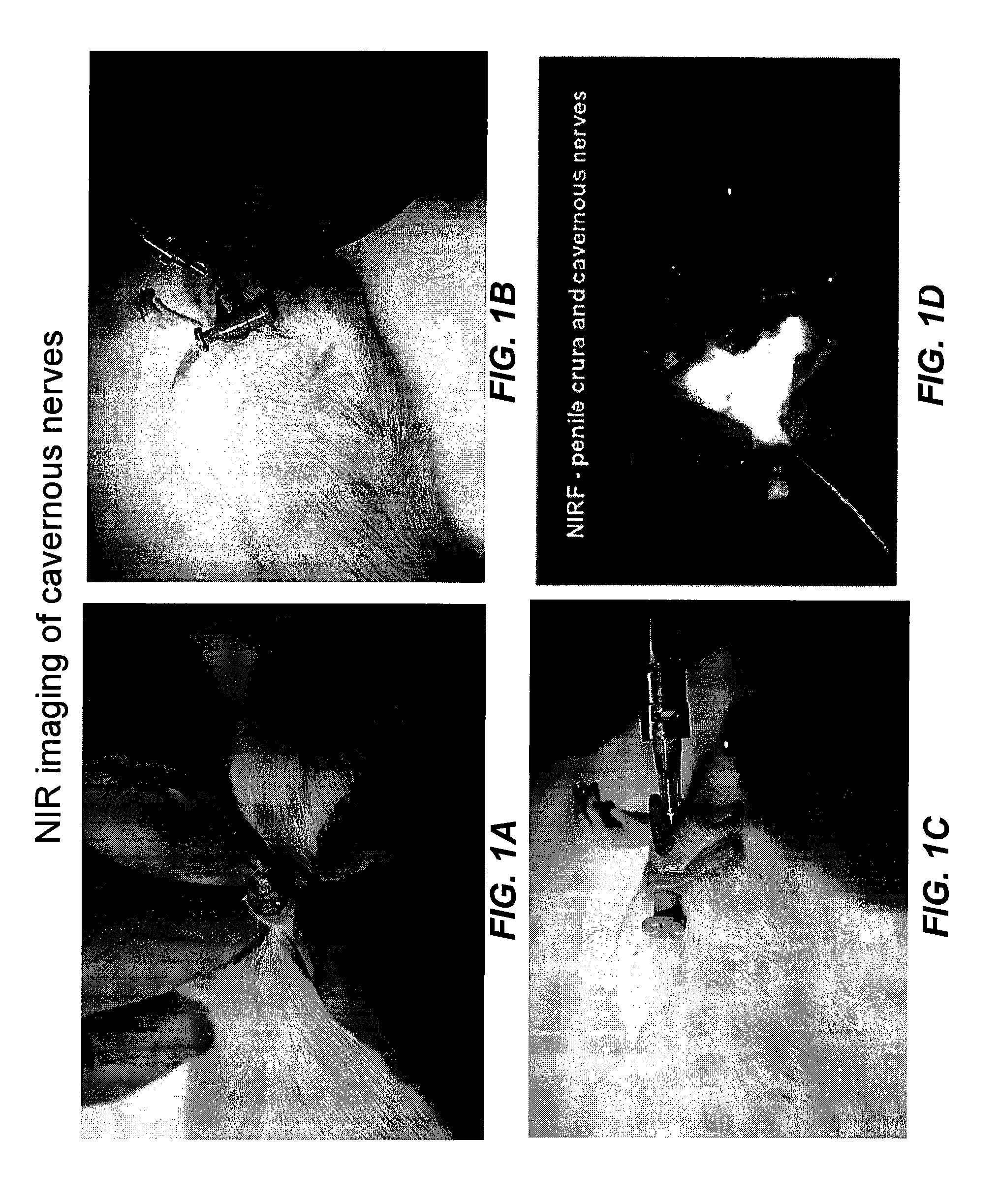
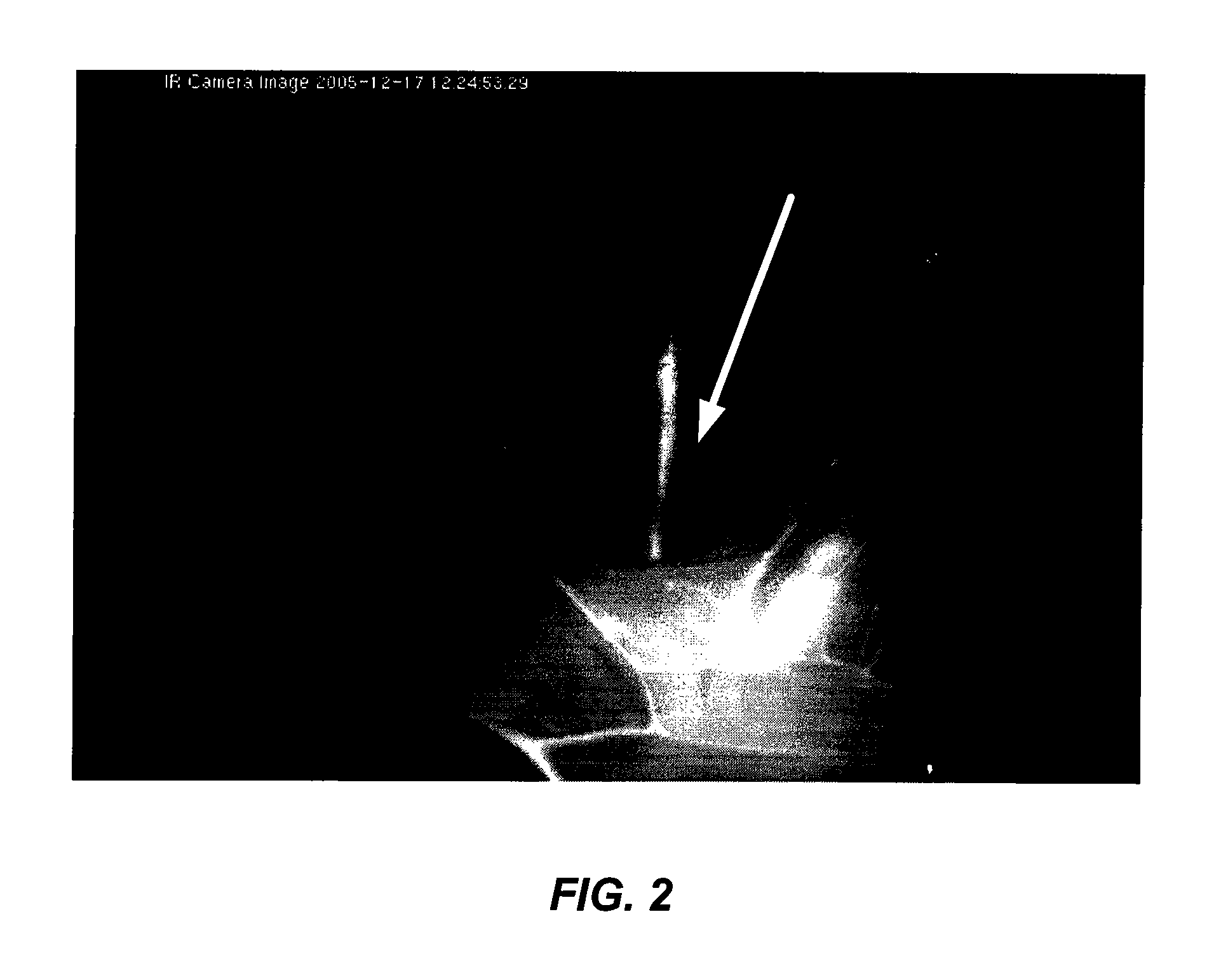
Intraoperative determination of nerve location
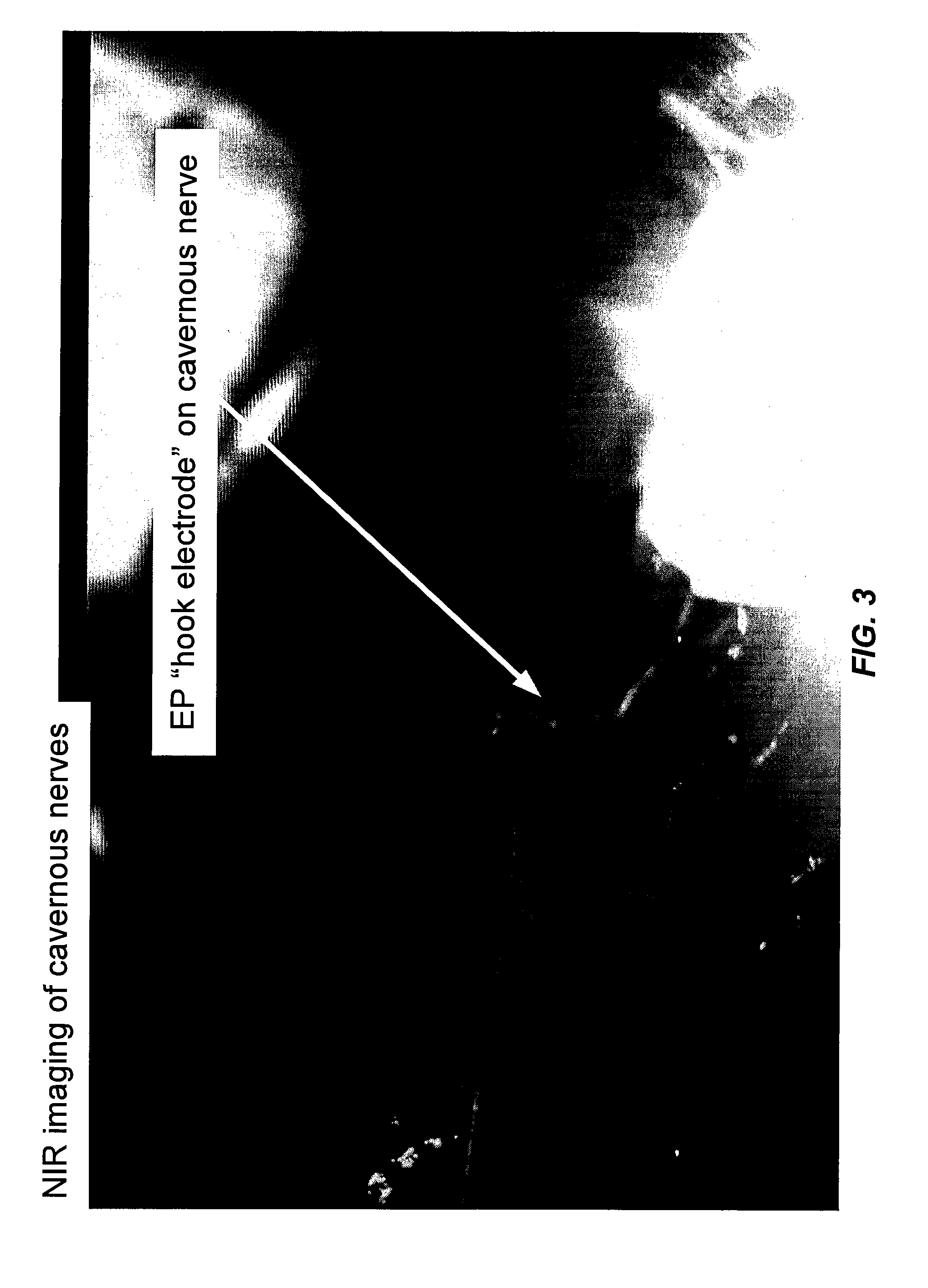
The invention provides methods for intraoperatively determining the location of nerves by use of fluorescent dyes. The methods are particularly useful for locating the cavernous nerves innervating the penis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Stimulation for treating brain events and other conditions
ActiveUS8055347B2Increase cerebral blood flowHarmful conditionSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationDiseaseDeep petrosal nerve
Apparatus for treatment is provided, including one or more electrodes, configured to be applied to a site of a subject, and adverse cerebrovascular condition treatment functionality. The functionality comprises a control unit configured to drive the one or more electrodes to apply electrical stimulation to the site during a plurality of stimulation periods which includes at least first and last stimulation periods, set an inter-period interval between initiation of the first stimulation period and initiation of the last stimulation period to be at least 24 hours, and configure the stimulation during the first and last stimulation periods to induce at least one neuroprotective occurrence selected from the group consisting of: an increase in cerebral blood flow (CBF) of the subject, and a release of one or more neuroprotective substances. The site is selected from the group consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG), a greater palatine nerve, a lesser palatine nerve, a sphenopalatine nerve, a communicating branch between a maxillary nerve and an SPG, an otic ganglion, an afferent fiber going into the otic ganglion, an efferent fiber going out of the otic ganglion, an infraorbital nerve, a vidian nerve, a greater superficial petrosal nerve, and a lesser deep petrosal nerve. Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Bifurcated lead system and apparatus
InactiveUS20110071606A1Reduce surgery time and invasivenessReduce invasivenessSpinal electrodesHead electrodesOccipital nerveAnatomical location
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
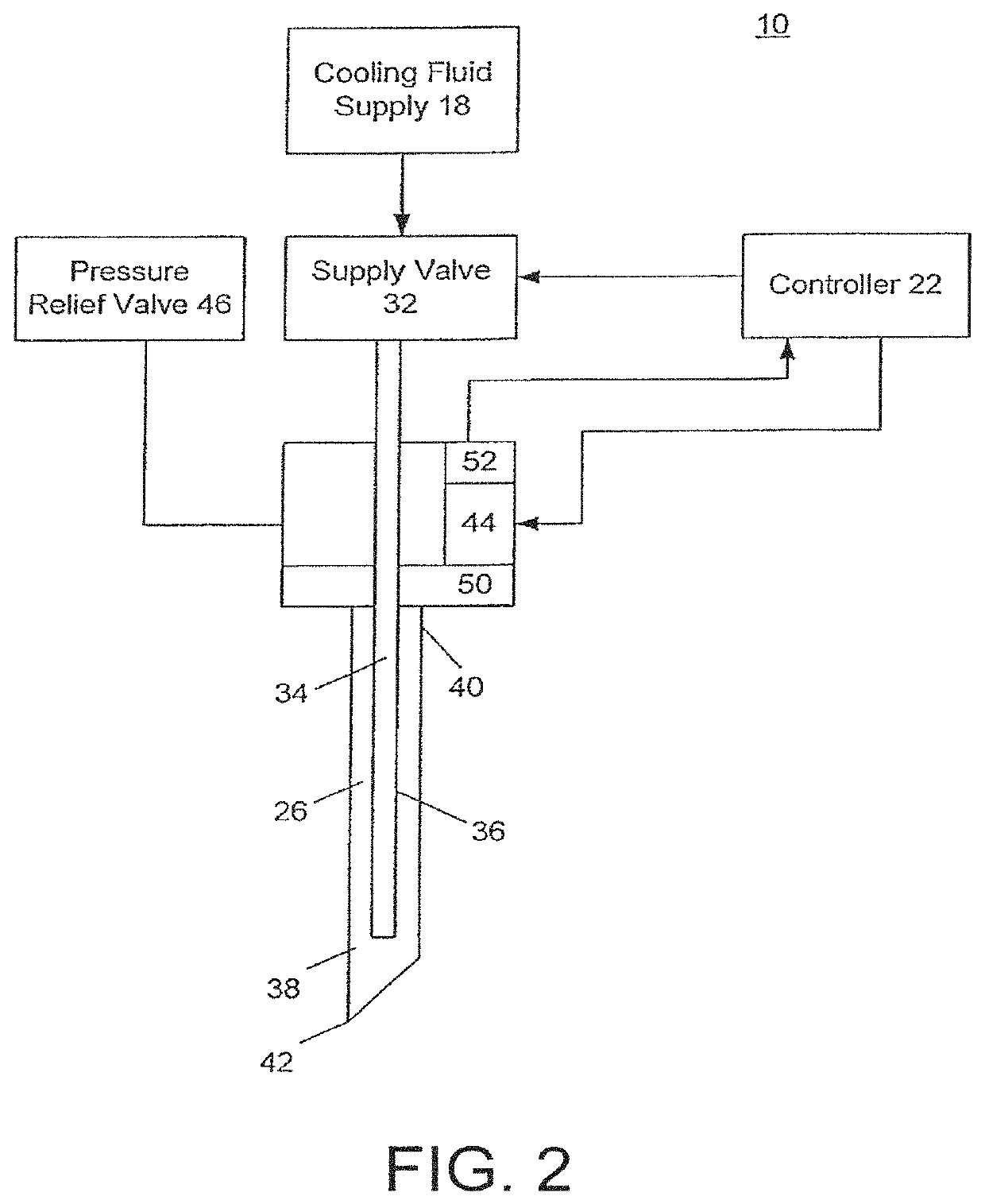
Cryogenic blunt dissection methods and devices
ActiveUS10888366B2Further the therapeutic effectLess-flexibleSurgical instruments for coolingTherapeutic coolingBlunt dissectionTherapeutic effect
A point of incision is created within tissue, the tissue having a temporoparietal fascia-deep temporoparietal fascia layer (TPF-sDTF) beneath skin and a temporal branch of a target nerve extending along a portion of the TPF-sDTF, the point of incision being laterally displaced from the target nerve. A cryogenic probe having a distal tip extending from an elongated body is inserted into the point of incision. The TPF-sDTF is bluntly dissected using the cryogenic probe such that a treating portion of the cryogenic probe is directly adjacent to a first treatment portion of the target nerve. The cryogenic probe is activated to create a first treatment zone at the first treatment portion of the target nerve to cause a therapeutic effect.
Owner:PACIRA CRYOTECH INC
Nasal delivery
ActiveUS9949923B2Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNasal cavityPosterior region
A nasal delivery device for and method of delivering a substance, preferably comprising oxytocin, non-peptide agonists thereof and antagonists thereof, preferably as one of a liquid, as a suspension or solution, or a powder to the nasal airway of a subject, preferably the posterior region of the nasal airway, and preferably the upper posterior region of the nasal airway which includes the olfactory bulb and the trigeminal nerve, and preferably in the treatment of neurological conditions and disorders.
Owner:OPTINOSE INC
Systems and methods to place one or more leads in tissue to electrically stimulate nerves to treat pain
ActiveUS10668285B2Reduce distanceInternal electrodesExternal electrodesSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
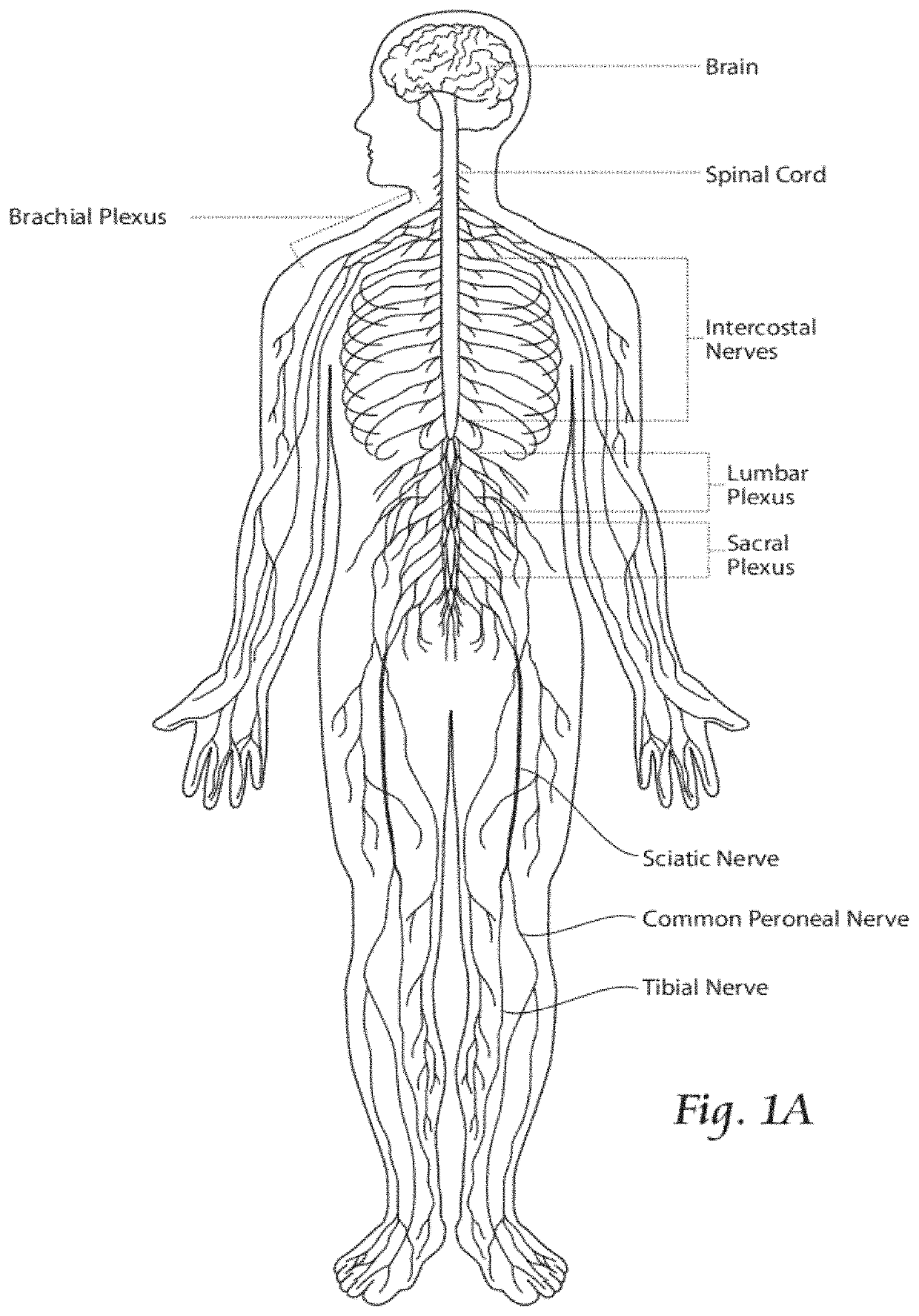
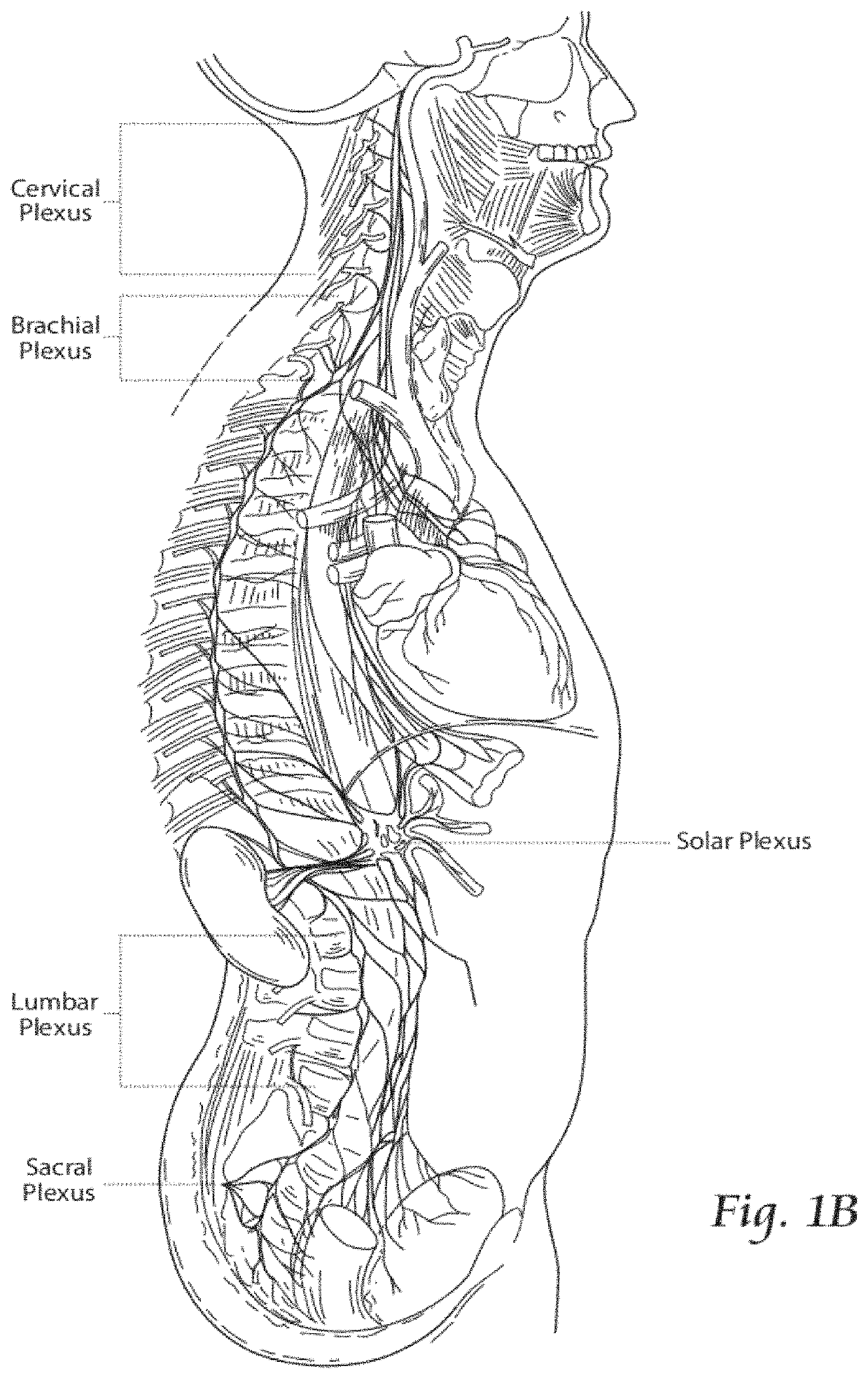
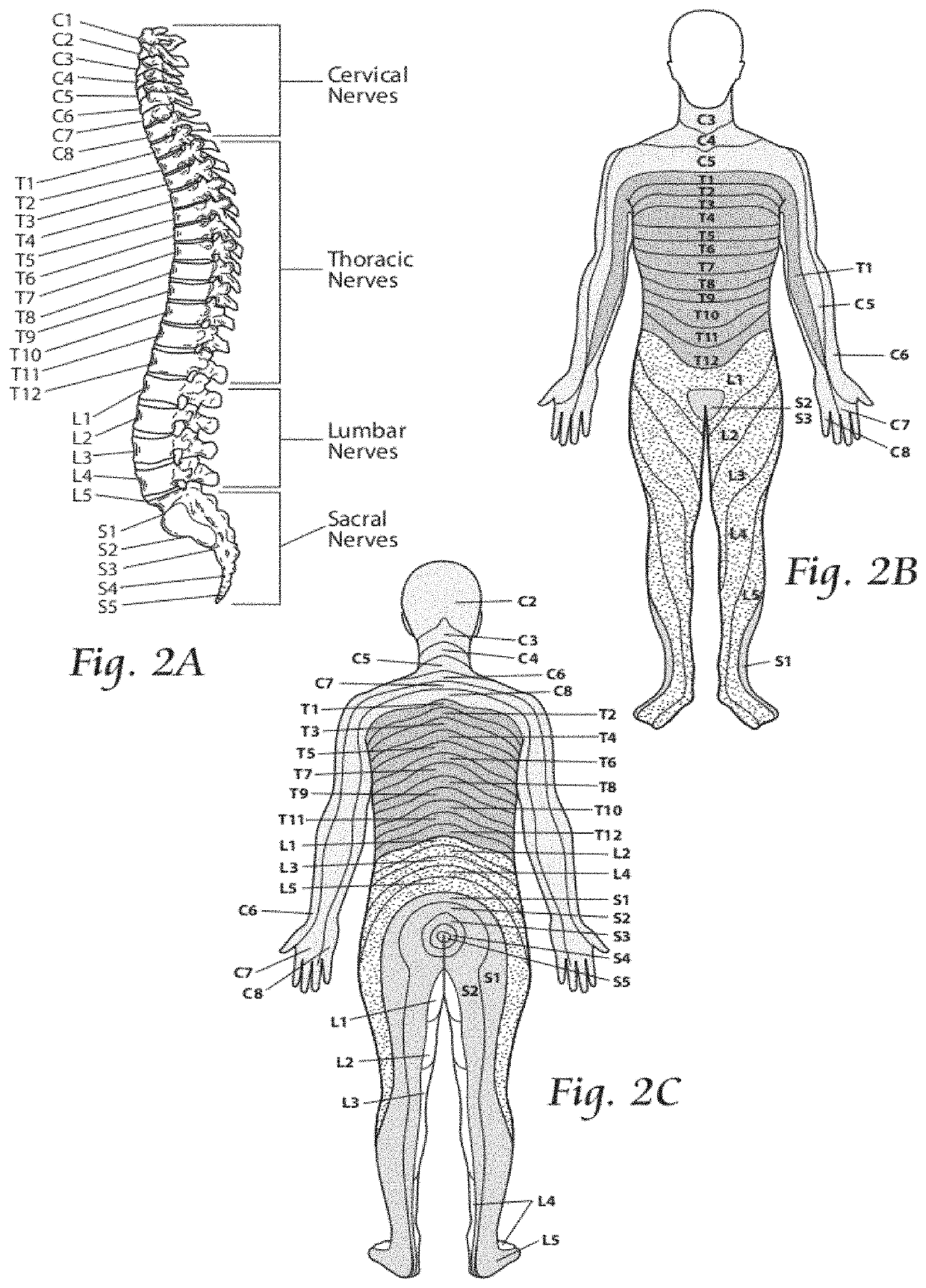
It has been discovered that pain felt in a given region of the body can be treated, not by motor point stimulation of muscle in the local region where pain is felt, but by stimulating muscle spaced from a “nerve of passage” in a region that is superior (i.e., cranial or upstream toward the spinal column) to the region where pain is felt. Spinal nerves such as the intercostal nerves or nerves passing through a nerve plexus, which comprise trunks that divide by divisions and / or cords into branches, comprise “nerves of passage.”
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
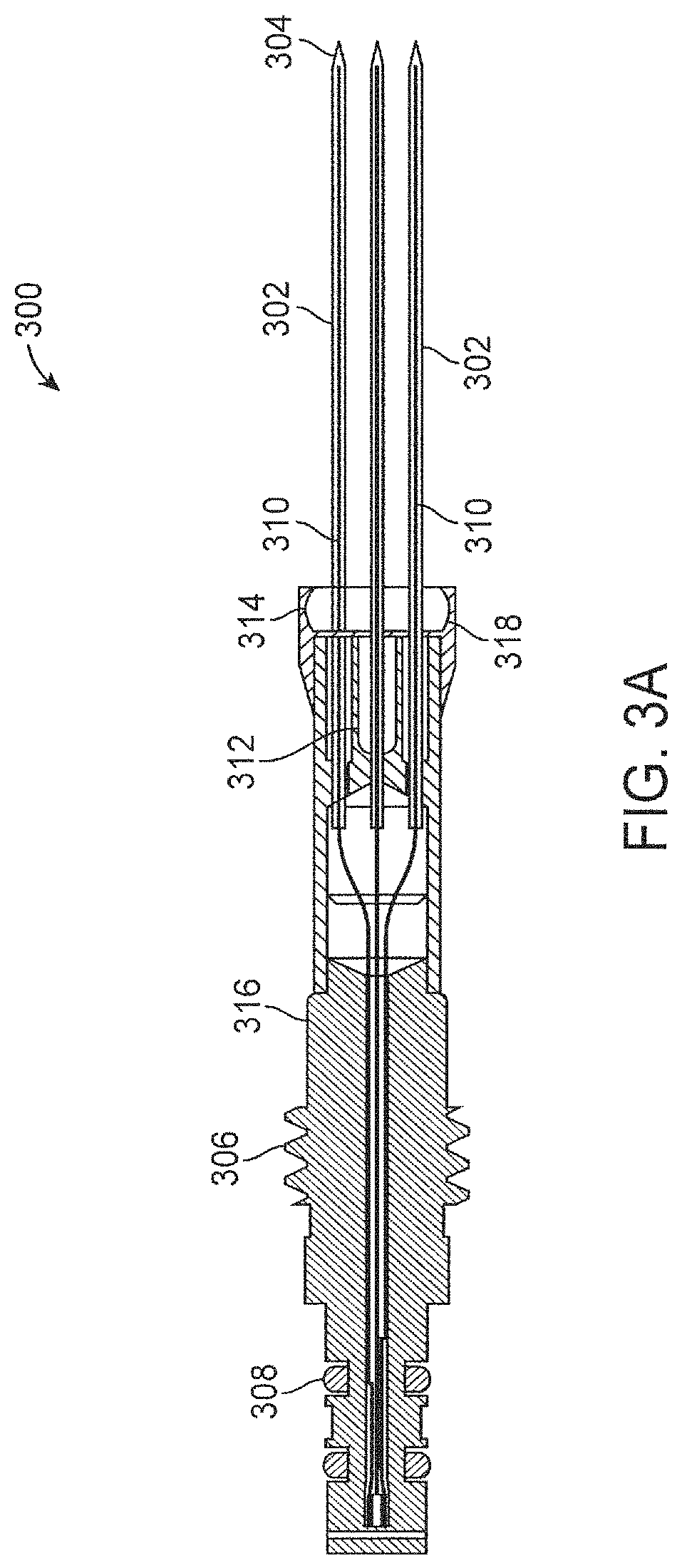
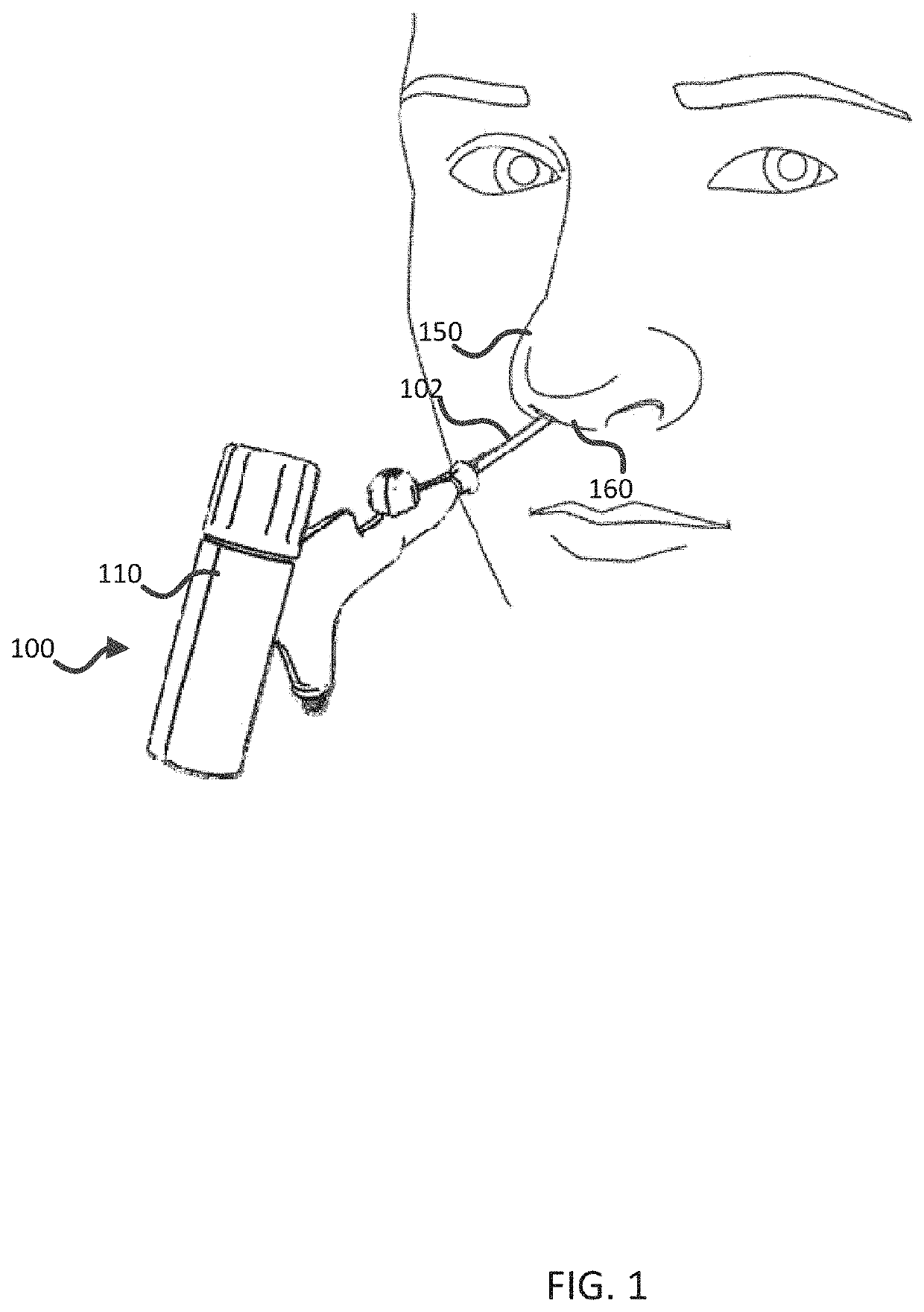
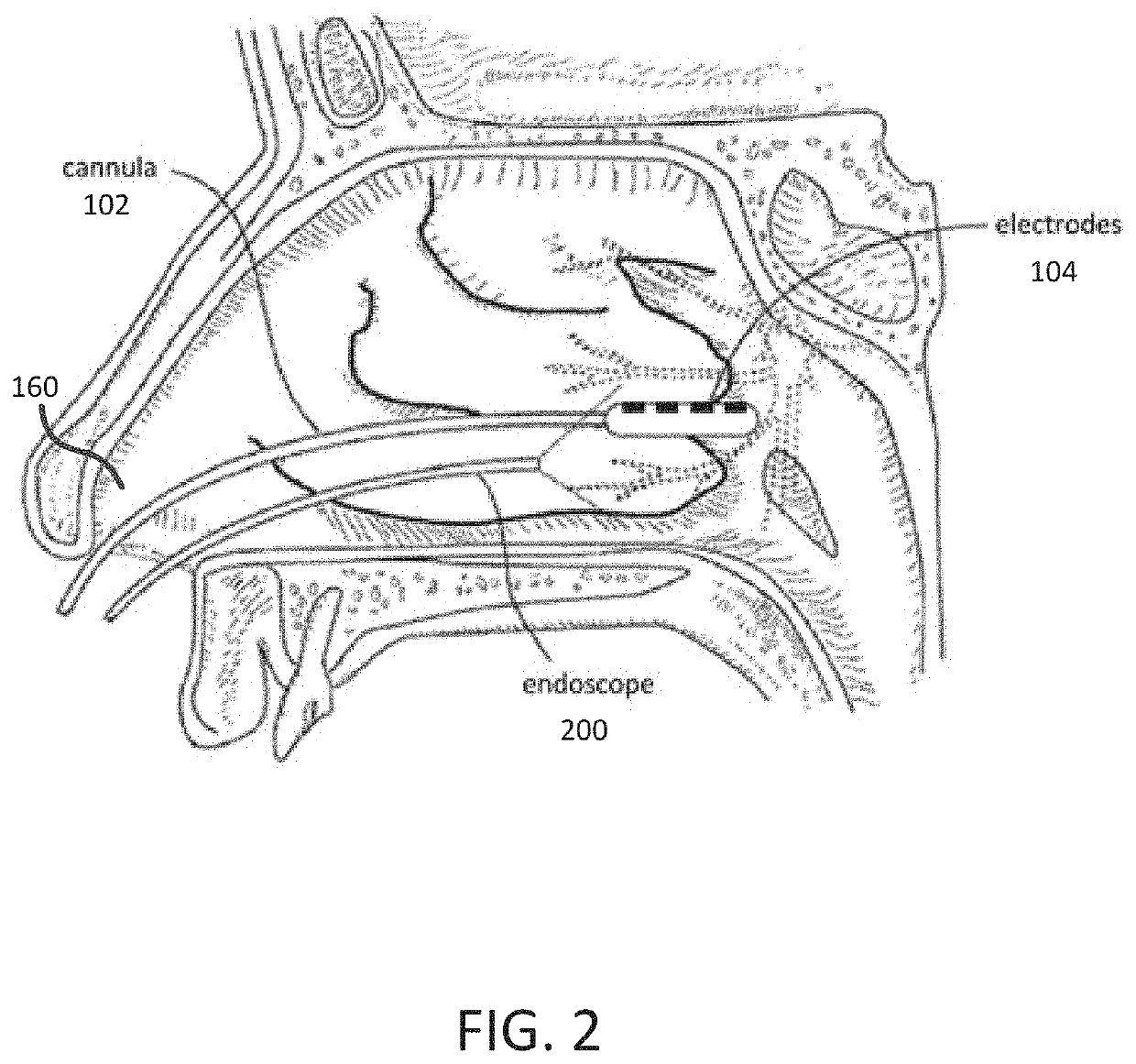
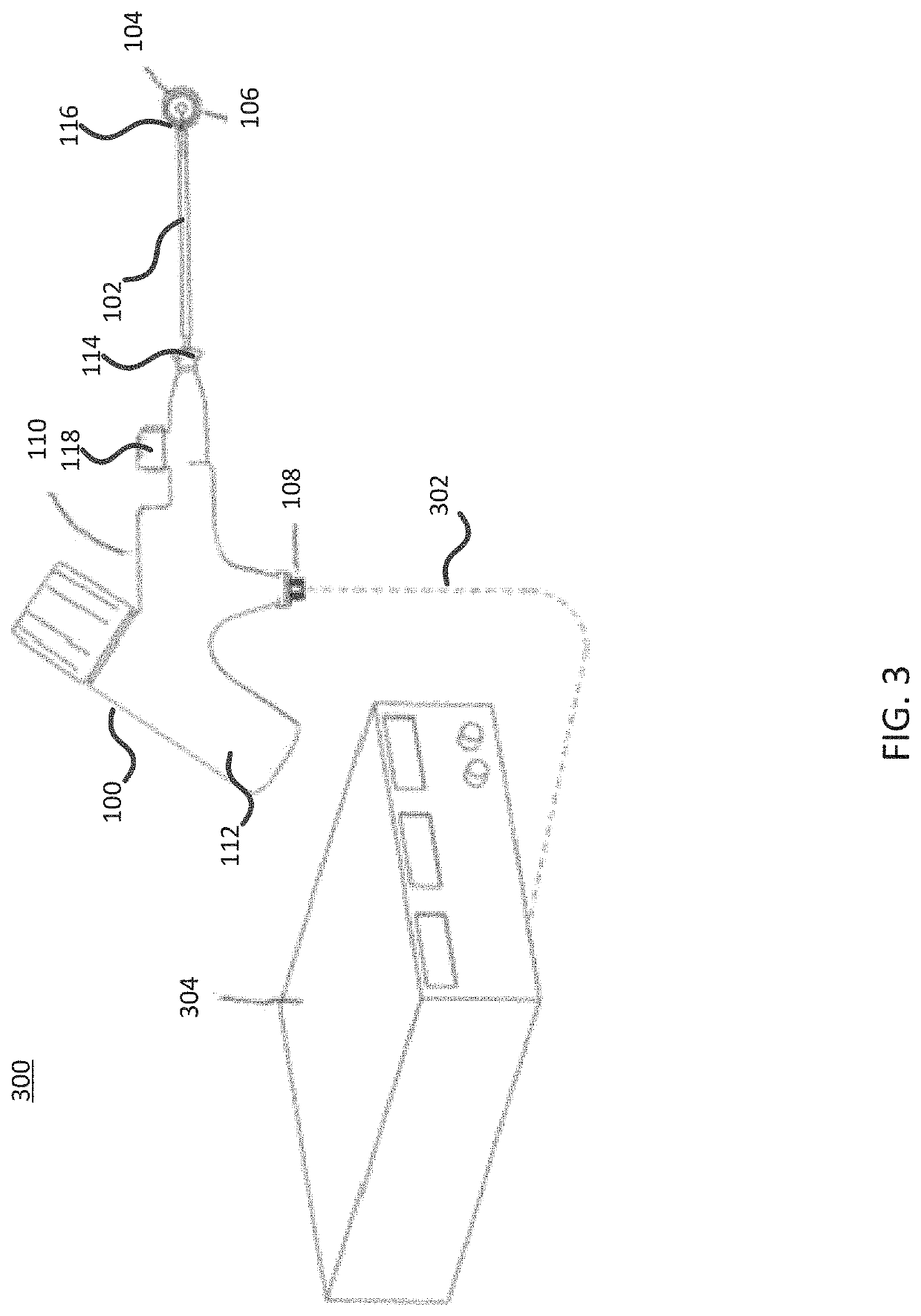
Integrated nasal nerve detector ablation-apparatus, nasal nerve locator, and methods of use
Systems and related methods for identifying and / or ablating targeted nerves are provided. A probe with stimulating electrodes and / or ablation members are provided. The probe may be inserted into a nasal cavity and current may be introduced through the electrodes to stimulate a targeted area. The response to stimulation may be used to identify the targeted nerve. Once identified, the ablation member may ablate the targeted nerve.
Owner:ARRINEX INC
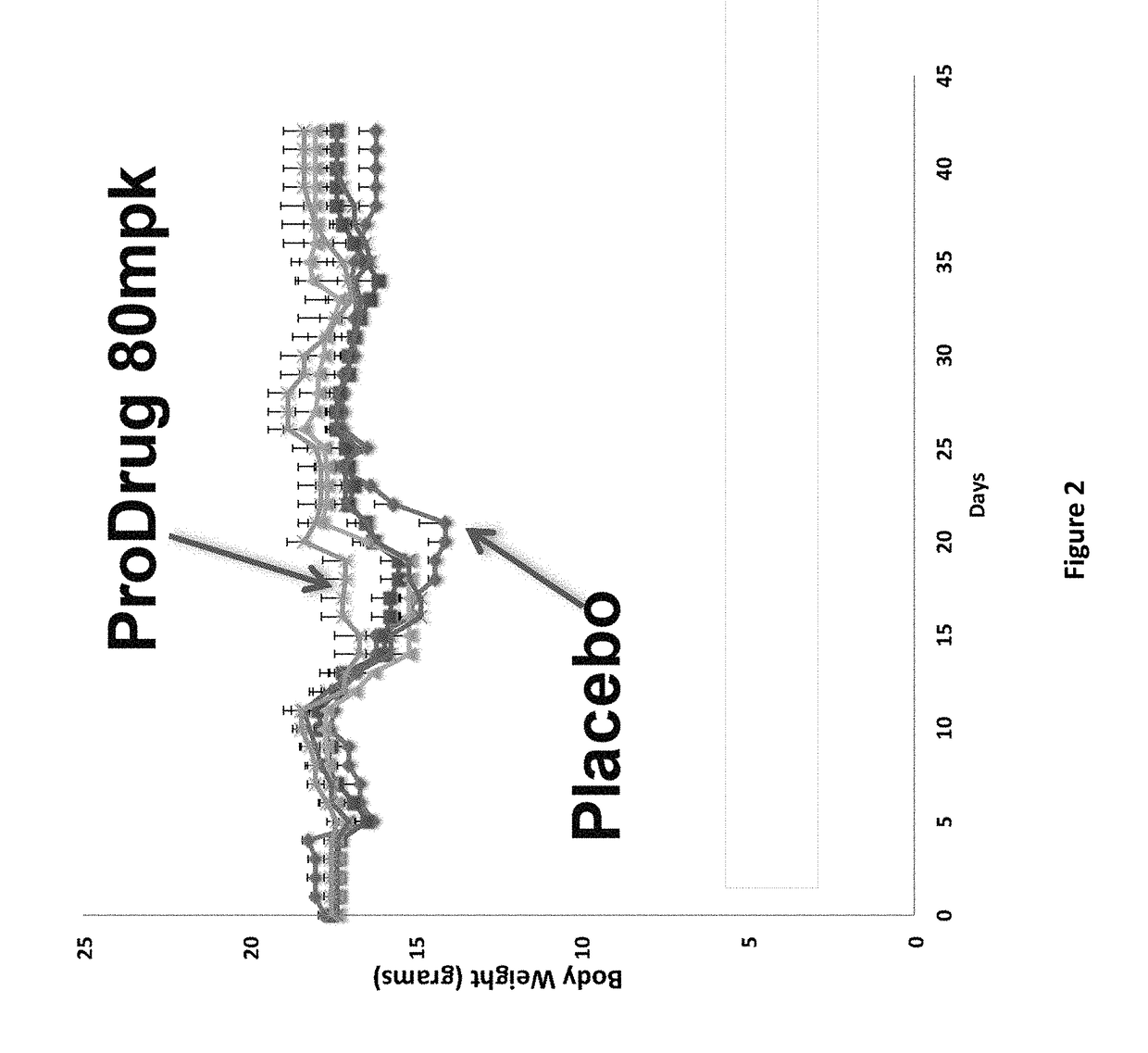
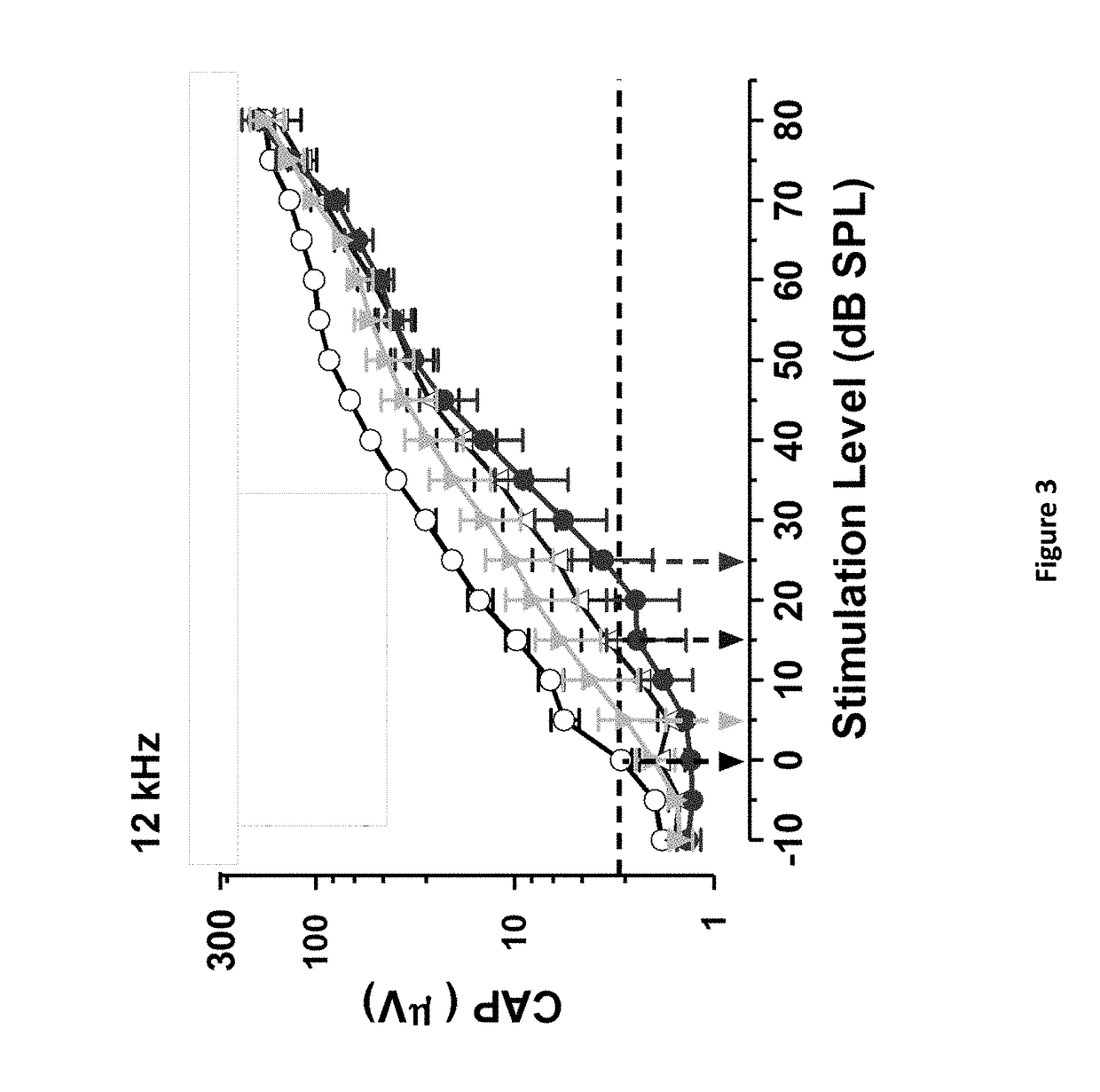
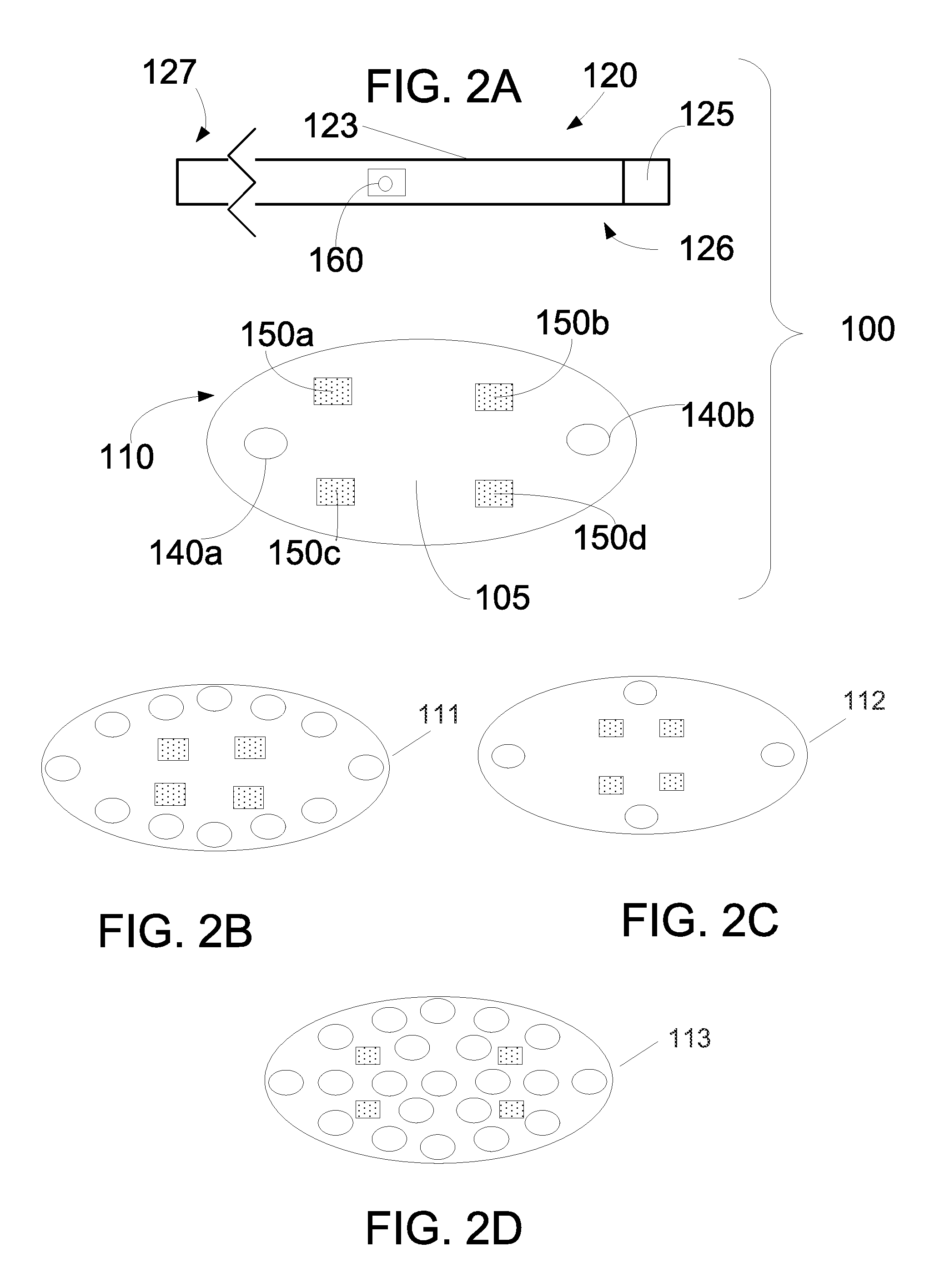
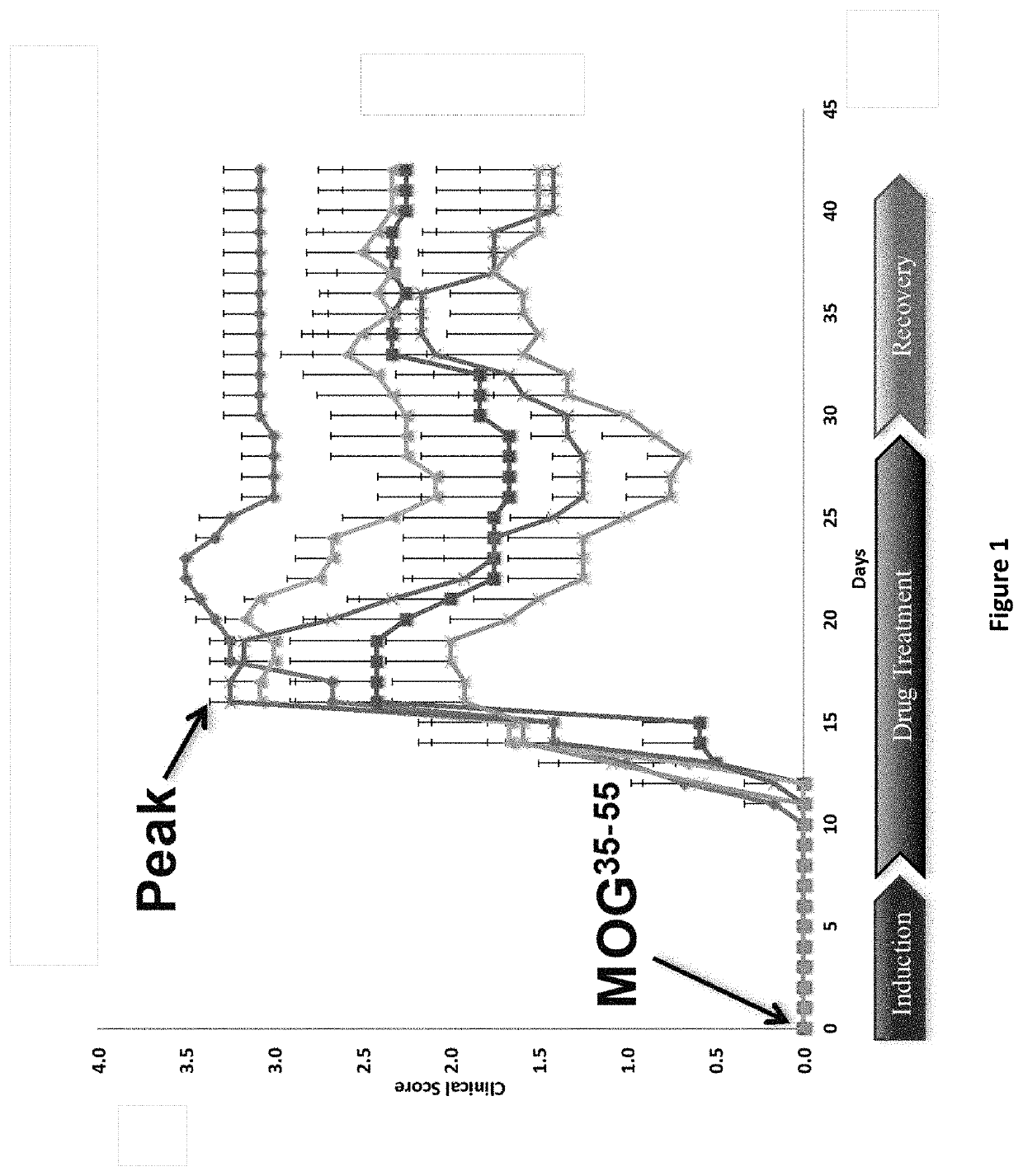
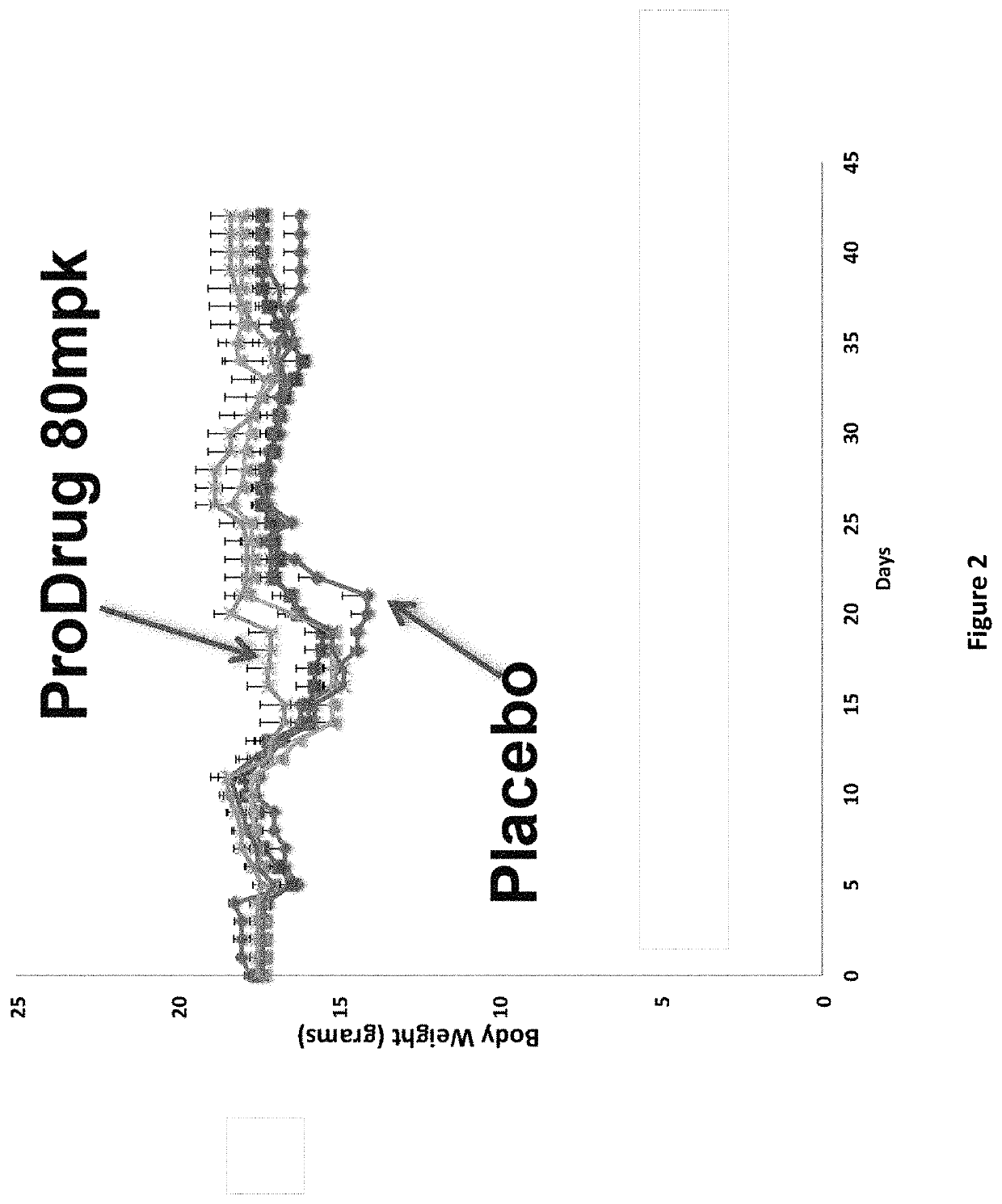
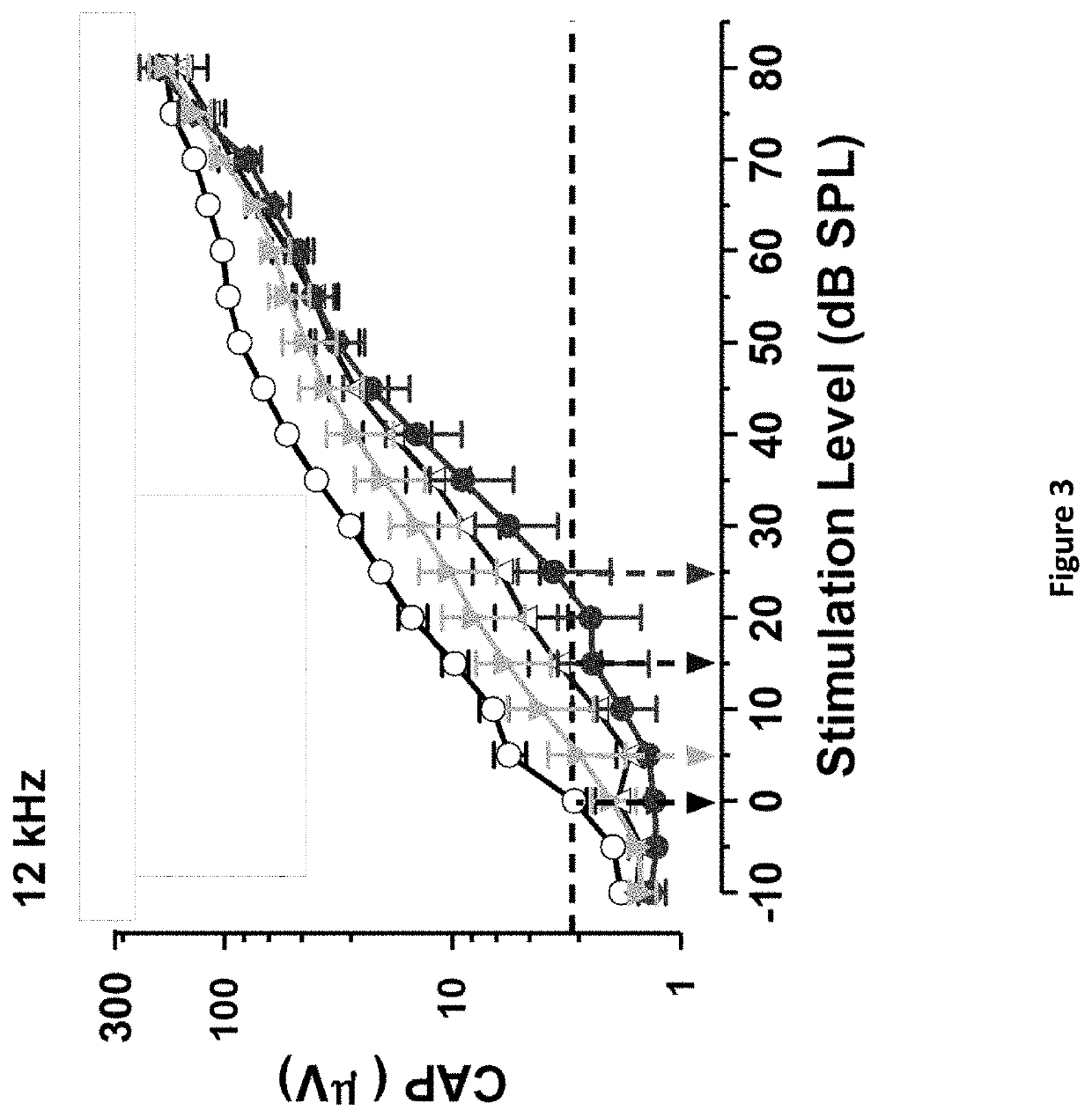
DNP and DNP Prodrug Treatment of Neuromuscular, Neurodegenerative, Autoimmune, Developmental, Traumatic Brain Injury, Concussion, Dry Eye Disease, Hearing Loss and/or Metabolic Diseases
ActiveUS20170252347A1Good blood pressureImprove blood sugar levelsSenses disorderNervous disorderHL - Hearing lossDepressant
A composition and method of treatment of neuromuscular, neuromuscular degenerative, neurodegenerative, autoimmune, developmental, traumatic, hearing loss related, and / or metabolic diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) syndrome (SMA1, SMA2, SMA3, and SMA4, also called Type I, II, III and IV), traumatic brain injury (TBI), concussion, keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Dry Eye Disease), glaucoma, Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, post-LASIK surgery, anti-depressants use, Wolfram Syndrome, and Wolcott-Rallison syndrome. The composition is selected from the group consisting of 2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP, bipartite 2,3-dinitrophenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol, 2,5-dinitrophenol, 2,6-dinitrophenol, 3,4-dinitrophenol, or 3,5-dinitrophenol (2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP) prodrugs; Gemini prodrugs, bioprecursor molecules, and combinations thereof. A dose of the composition for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases may be from about 0.01 mg / kg of body weight to about 50 mg / kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment. A dose of the composition for treatment of metabolic diseases may be from about 1 mg / 70 kg of body weight to about 100 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment, and a maximum dose per day is about 200 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment.
Owner:MITOCHON PHARMA INC +1
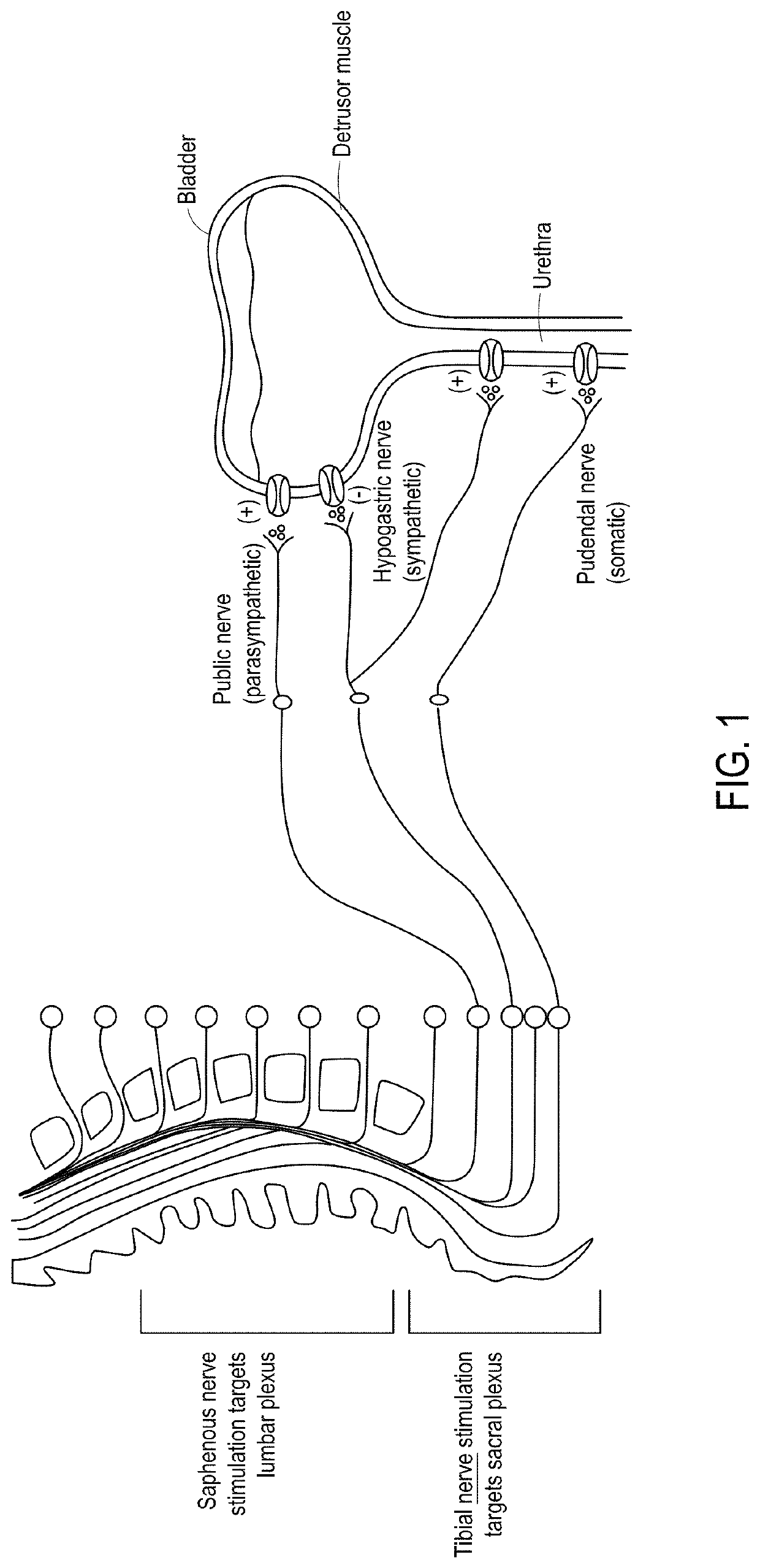
Systems, methods and devices for peripheral neuromodulation for treating diseases related to overactive bladder
ActiveUS11344722B2Relieve symptomsSymptoms improvedExternal electrodesArtificial respirationSaphenous nervePeripheral neuron
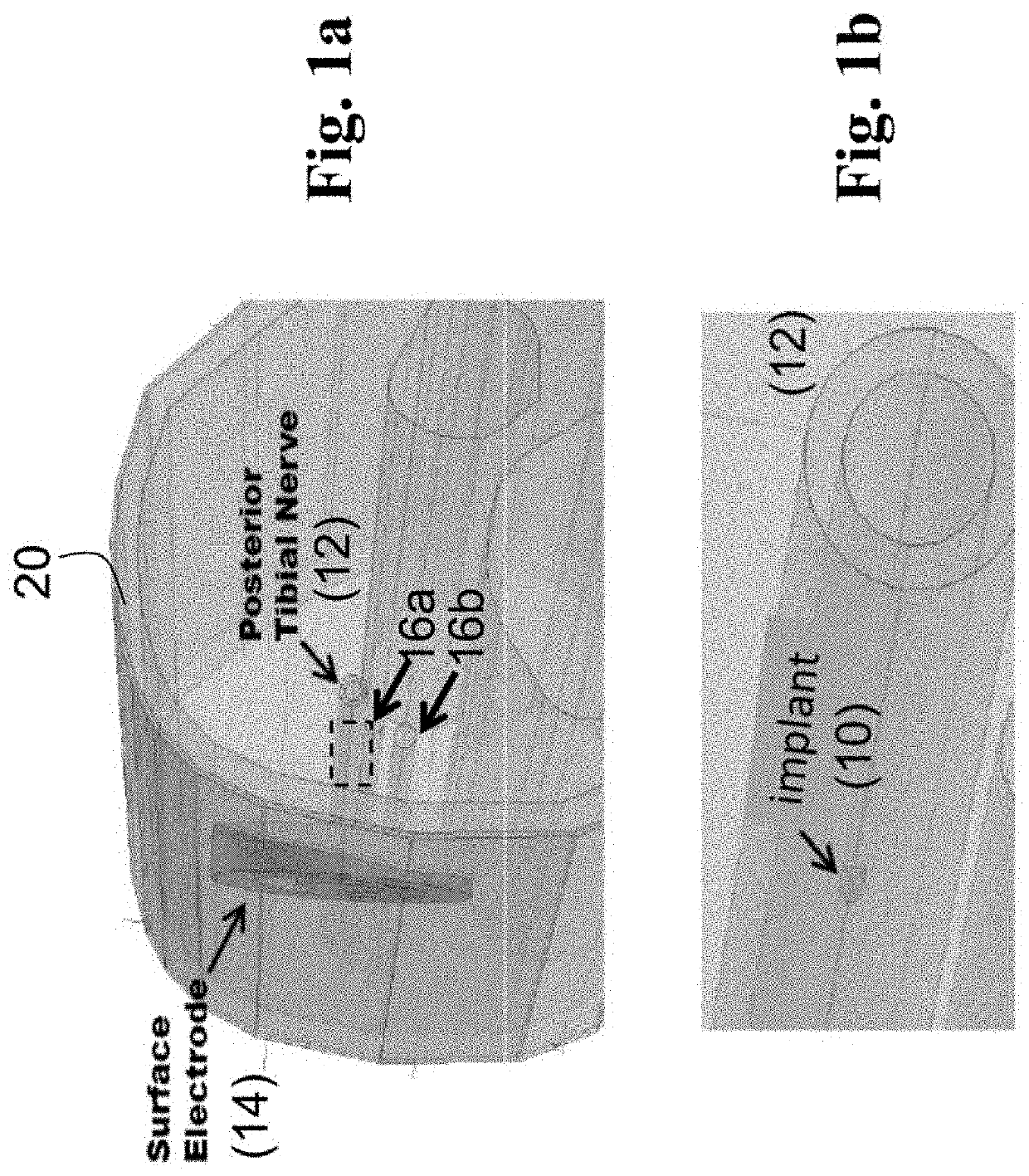
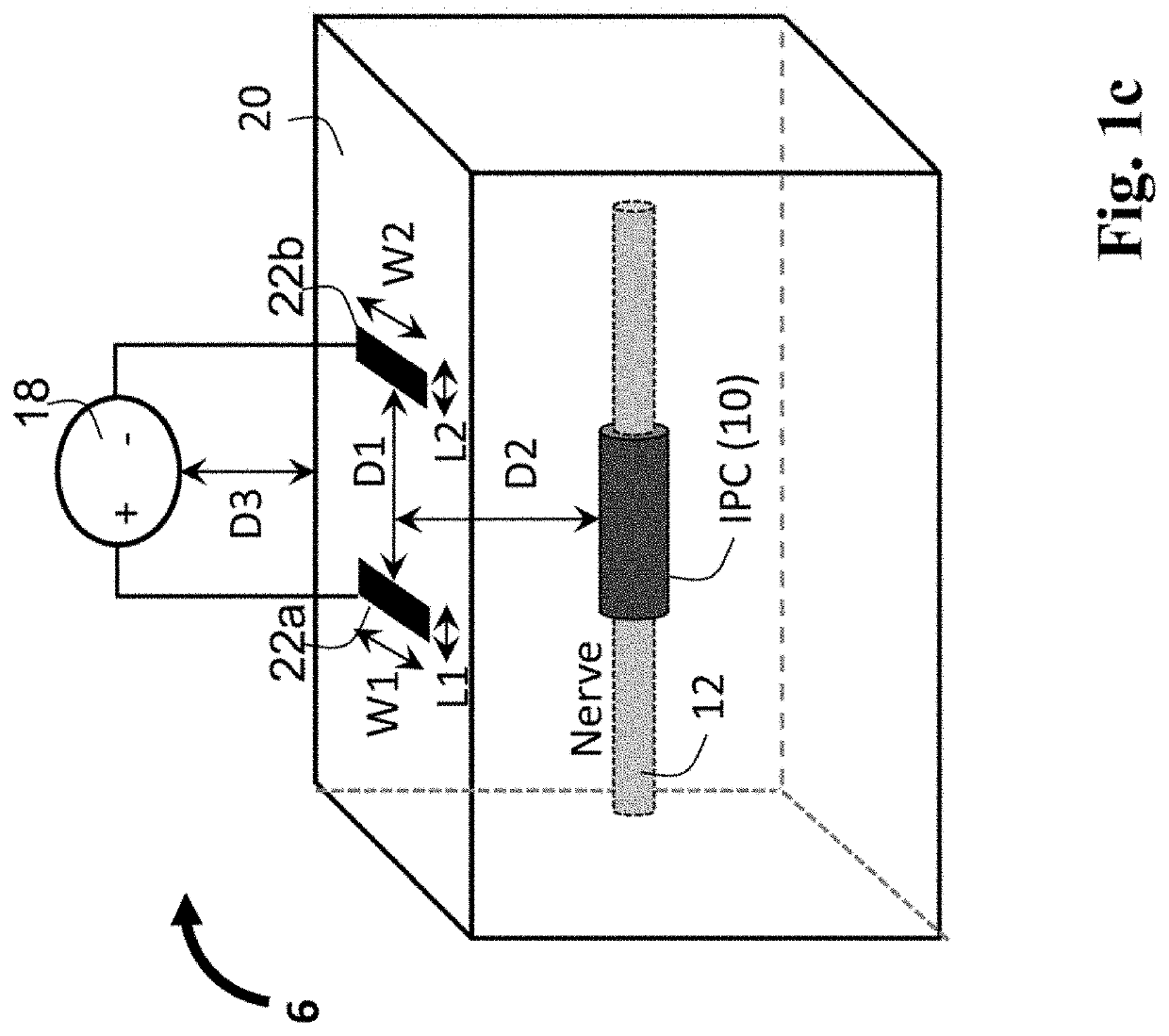
In some embodiments, systems and methods can include a wearable device with an electrically conductive skin interface that excites the underlying nerves from a transcutaneous surface stimulator. The device may be sized for a range of user sizes with stimulation electrodes positioned to target the appropriate nerves, such as the saphenous and / or posterior tibial nerves. Transcutaneous afferent stimulation of one, two, or more peripheral nerves can modulate a brain or spinal pathway associated with bladder function.
Owner:CALA HEALTH
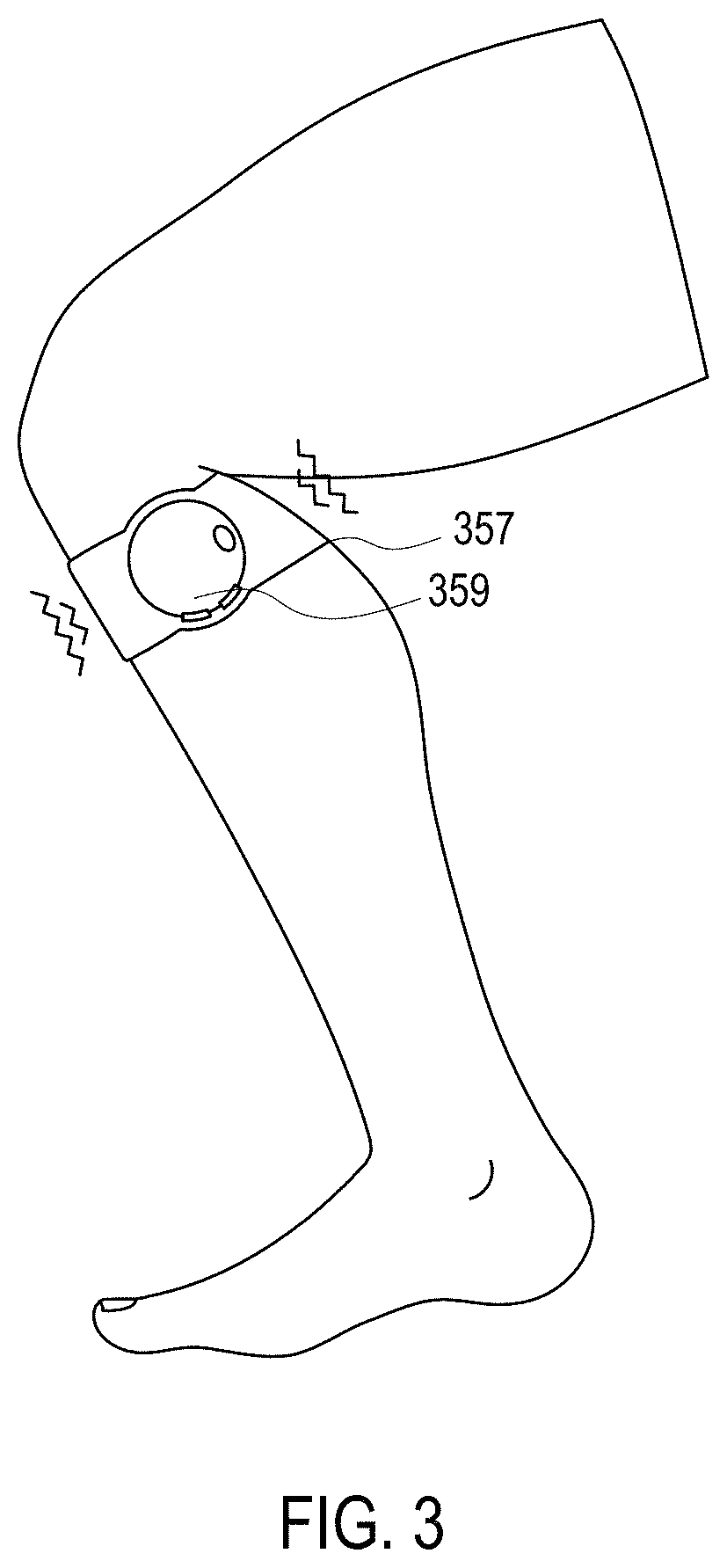
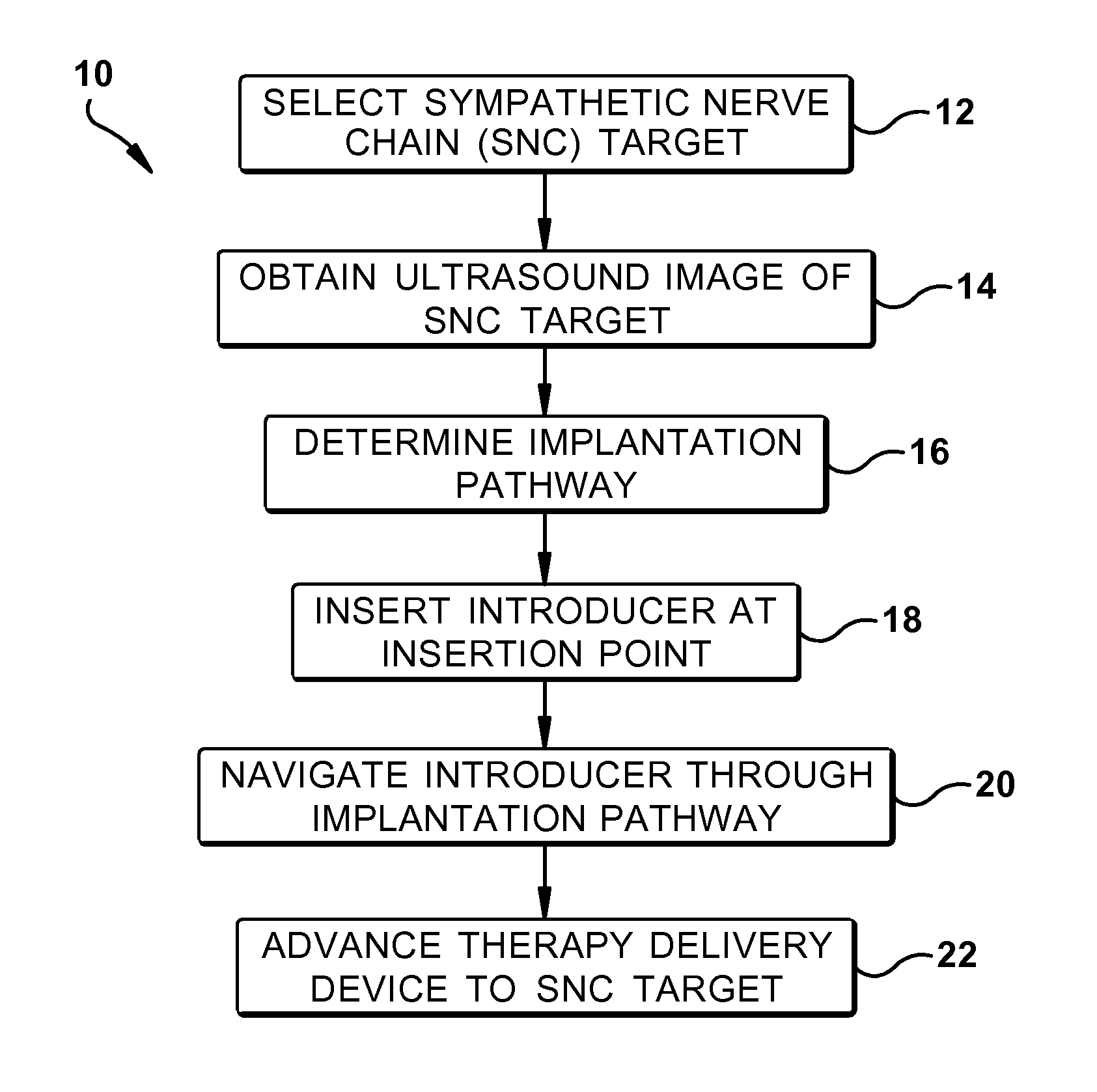
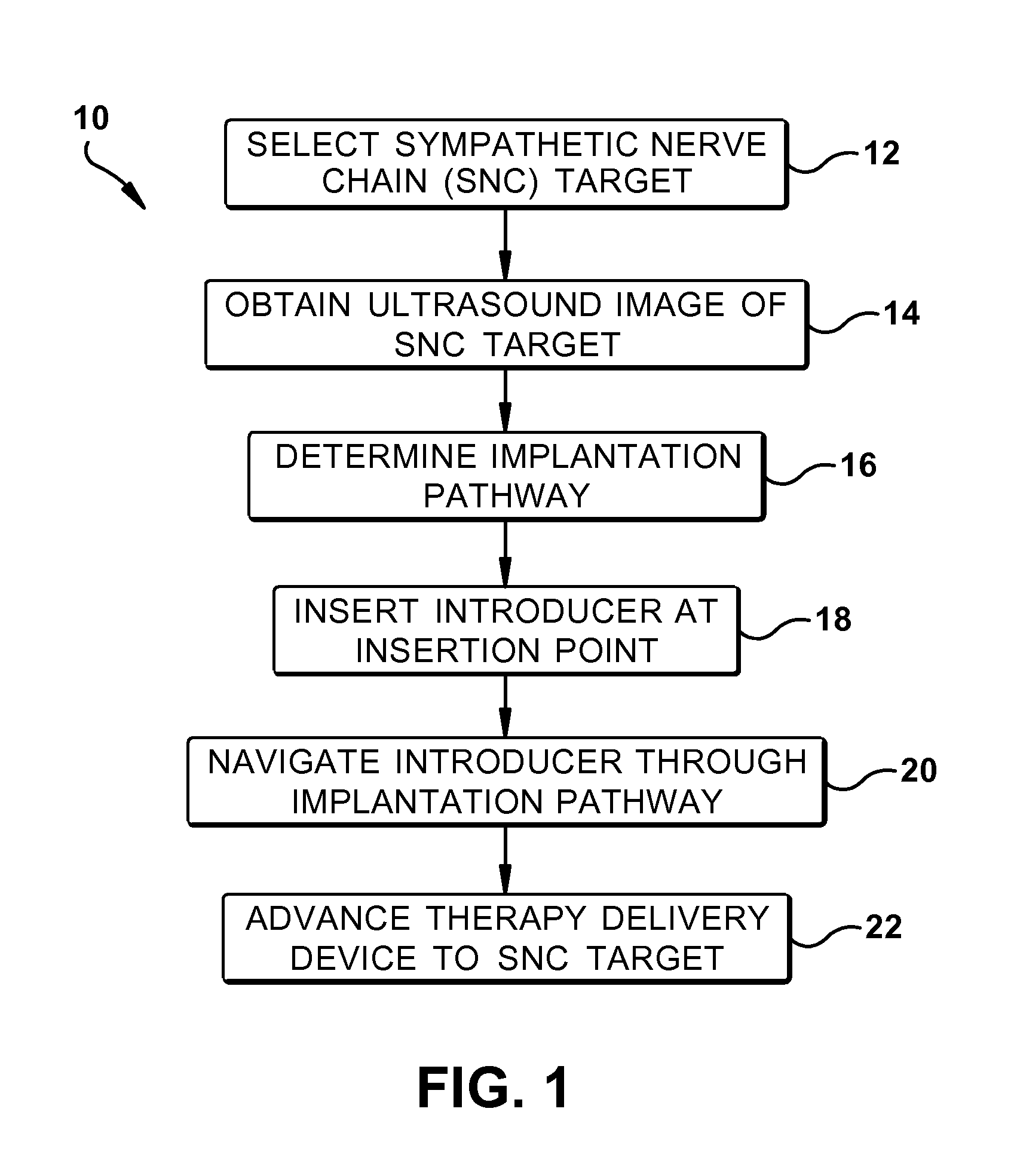
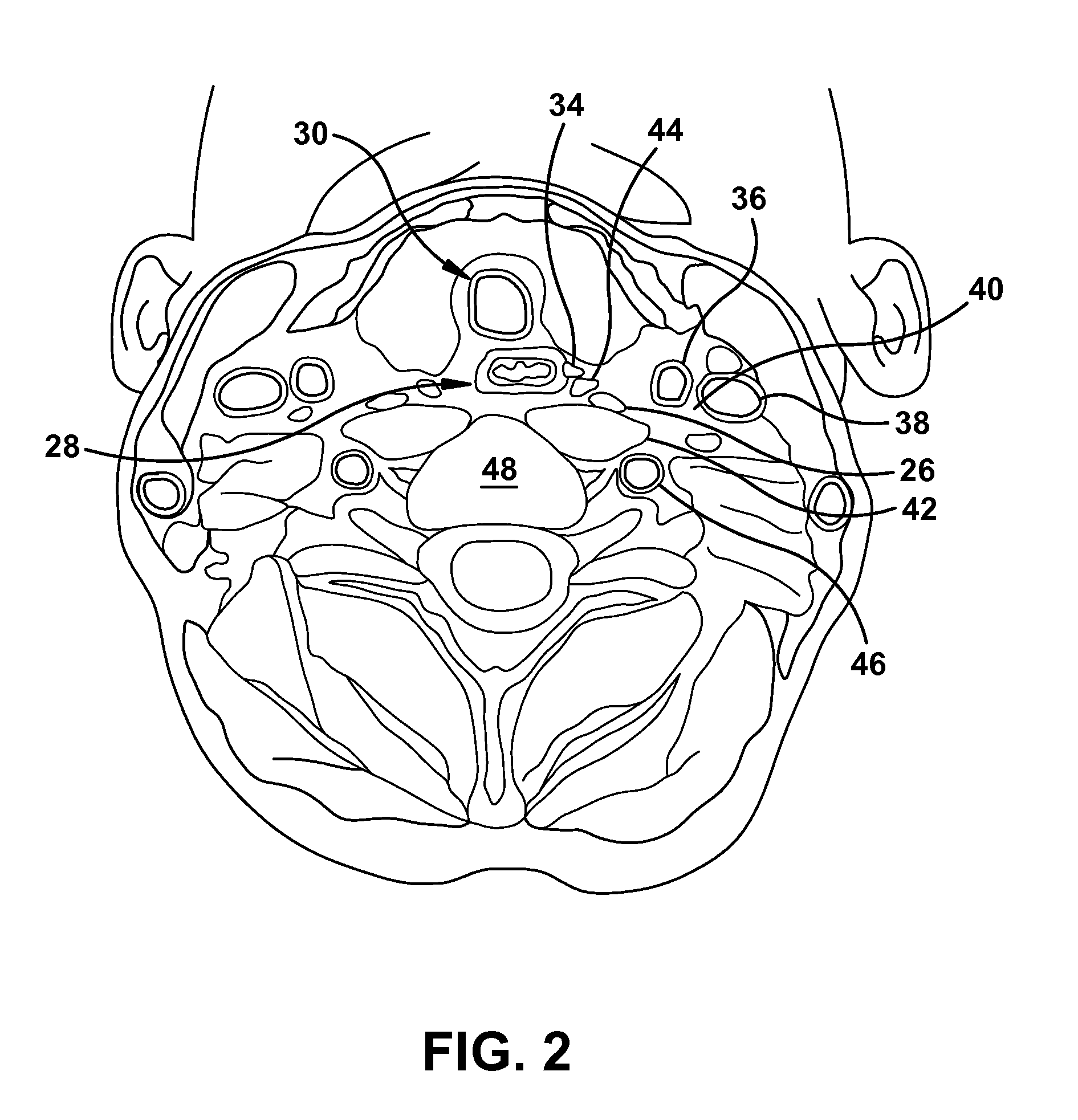
Ultrasound-guided delivery of a therapy delivery device to a nerve target
ActiveUS8870773B2Spinal electrodesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingAnatomical structures
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pin
PendingCN110934630AHigh strengthAvoid slight misalignmentInternal osteosythesisSurgical riskBone humerus
The invention discloses a multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pin. The multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pincomprises a humerus intramedullary pin main pin, wherein the humerus intramedullary pin main pin adopts a hollow structure, and comprises a near end intramedullary pin, a far end intramedullary pin and a connecting section; the diameter of the near end intramedullary pin is greater than that of the far end intramedullary pin; one end of the near end intramedullary pin is in transition connectionwith the far end intramedullary pin through the connecting section, and the inner part of the other end of the near end intramedullary pin is connected with a terminal cap; the near end intramedullarypin, the far end intramedullary pin and the connecting section adopt an integrated structure; the diameter of the near end intramedullary pin is 9mm, a plurality of pin holes are formed in the near end intramedullary pin and the far end intramedullary pin; bone screws are arranged in the pin holes; and the bone screws in the near end intramedullary pin are multi-angle screws. According to the multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pin disclosed by the invention, the opportunity of selecting appropriate humerus intramedullary pin main pin according tohumerus individual dissection differences is increased, and the operation risk of generating fracture of humeral head and injury of axillary nerve caused by that an opening in the humerus head part islarge is reduced.
Owner:上海伯塔医疗器械有限公司
Neuromodulation for treatment of retinal, choroidal and optic nerve disorders and/or dysregulated reduced ocular blood flow (OBF)
Disclosed are devices, systems and methods for non-invasive neuromodulation system for treating inherited or acquired retinal, choroidal and optic nerve disorders caused by acute or chronic dysregulated reduced ocular blood flow (OBF) and / or energy failure by up regulation of trigemino-vascular system (TVS), trigeminal autonomic brain reflexes (TABRs) and pancreatic trigemino-vagal reflex (TVR) through stimulation of ophthalmic nerve (V1), more specifically but not limited to SP, and CGRP containing unmyelinated C nerve fibers. The invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to the methods for enhancing SP and CGRP expression in neurovascular tissue of the retina and choroid. The invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to SP / CGRP mediated pathways, including those involved in vasodilatation, augmentation of OBF, RPE proliferation, prevention of apoptosis, suppressing neuroinflammation, promoting migration and differentiation of vascular endothelial cells as well as mobilization of endogenous mesenchymal stem cells (EMSCs) from the bone marrow to the circulation to accelerate tissue repair. The site of stimulation of V1 nerve includes but not limited to; nasal vestibule nasal bridge, forehead, and upper eyelids. Additionally or alternatively, the subject's sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is down regulated by sympatholytic agents specifically antioxidants. The subject's TVS and autonomic nervous system (ANS) are modulated in a manner that is effective to treat the subject for retinal, choroidal and / or optic nerve disorders. In some embodiments, the devices are handheld, portable with nose supported, having one or more intra-nasal or extra-nasal application heads. The signal can include vibration, chemical, ultrasonic, optical, electrical, hybrid electro-optical or combination of two or more of these types of stimuli. The invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to a method for decreasing vascular resistance, enhancing vasodilatation in ophthalmic artery and its branches by the release of Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP),substance P and CGRP thereof increasing OBF to the retina, choroid and optic nerve in subject's with acute or chronic dysregulated, reduced OBF. The invention, in some embodiments thereof, is also related to the methods for improving delivery of oxygen, glucose, vitamin A, humoral mediators, growth factors, stem cells and pharmacological agents to the targeted tissues of the retina, choroid and optic nerve. The invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to the methods for improving pancreatic insulin secretion, thereof to enhance glucose uptake by PRs and other retinal cells. Additionally or alternatively, the invention relates to restoration of transduction of signaling in cone PRs by ONS induced glutamate release. The methods of the invention, in some embodiments thereof, include priming of the retina choroid and optic nerve thereof to enhance the efficacy of cell transplantation therapy. The methods of the invention, in some embodiments thereof, also include identifying a subject prone to or suffering from a disease or condition associated with reduced OBF. Methods of the invention, in some embodiments thereof, may also include monitoring the subject for prophylactic treatment where the patients are at pre-clinical stage of the disease. The OBF of subjects who had received neuromodulation treatment may also be monitored for re-treatment.The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to a method and / or device for treatment of dysregulated reduced blood (e.g. reduced ocular blood flow) and, more particularly, but not exclusively, to methods and / or devices for treatment retinal, choroidal and optic nerve disorders. Optionally, treatment may include application of an effective amount of ONS ophthalmic nerve stimulation alone and / or in combination with pen-ocular administration of substance Neuropeptides / Platelet Rich Plasma (N / PRP) and / or ascorbic acid as a sympatholytic agent
Owner:MUSALLAM ISMAIL MOHAMMED YOUSIF
Systems and methods for tissue ablation
Owner:STRATUS MEDICAL LLC
Orifice probe apparatus and a method of use thereof
An orifice probe, particularly for detecting if a patient has or has a risk of having cauda equina syndrome and a method for using same, the probe having a body for insertion into the anus of a patient, a sensing device for measuring at least one of the rectal tone and perianal or rectal sensation, and an output device for yielding at least one of the measurement of the rectal tone of the patient and whether the patient has perianal or rectal sensation.
Owner:AHN NICHOLAS
Methods and compositions for treating carpal tunnel syndrome
Methods are provided for treating a host suffering from a condition resulting from pressure applied to the median nerve of the carpal tunnel, e.g. carpal tunnel syndrome. In the subject methods, an effective amount of a topical NSAID formulation is applied to the palmar dermal surface proximal to the target median nerve. Practice of the above methods results in an amelioration of at least one symptom associated with the condition being treated. Also provided are kits for practicing the subject methods.
Owner:TEIKOKU PHARMA USA INC
Sacral nerve puncture guide plate and construction method thereof
ActiveCN112244956AAvoid puncture errorsEnsuring Structural AccuracySpinal electrodesAdditive manufacturing apparatusGuide tubeBiomedical engineering
The invention provides a sacral nerve puncture guide plate and a construction method thereof. The guide plate comprises a base plate, an outer guide pipe and an inner guide pipe, wherein the outer guide pipe is arranged on the outer side face of the base plate; the inner guide pipe is coaxially arranged in the outer guide pipe; the inner guide pipe penetrates through the base plate; and the end face of the end, penetrating through the base plate, of the inner guide pipe is flush with the inner side face of the base plate. According to the sacral nerve puncture guide plate provided by the invention, the end face of the end, penetrating through the base plate, of the inner guide pipe is flush with the inner side face of the base plate, so that the tail end face of the inner guide pipe directly abuts against the skin in use and can be attached to the surface of the skin, whole-course guided puncture is achieved, and puncture errors are avoided.
Owner:西安点云生物科技有限公司
Restless leg syndrome or overactive nerve treatment
Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) or Periodic Limb Movement Disorder (PLMD) can be treated using high frequency (HF) electrostimulation. This can include selecting or receiving a subject presenting with RLSor PLMD. At least one electrostimulation electrode can be located at a location associated with at least one of, or at least one branch of, a sural nerve, a peroneal nerve, or a femoral nerve. HF electrostimulation can be delivered to the subject, which can include delivering subsensory, subthreshold, AC electrostimulation at a frequency that exceeds 500 Hz and is less than 15,000 Hz to the location to help reduce or alleviate the one or more symptoms associated with RLS or PLMD. A charge-balanced controlled-current HF electrostimulation waveform can be used.
Owner:NOCTRIX HEALTH INC
Anchor assembly for use in occipital nerve stimulation
A system that includes an anchor assembly, the anchor assembly including: at least one anchoring structure configured to be anchored in a head of a patient; and at least one lead anchoring structure; and b. at least one lead, the at least one lead including a lead body extending from a distal end to a proximal end; at least one electrode located on or in the distal end of the lead body; and at least one lead anchor located on or in the lead body proximal to the electrode, wherein the at least one lead anchor of the lead and the lead anchoring structure are configured to cooperate to secure the at least one lead to the anchor assembly.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
DNP and DNP Prodrug Treatment of Neuromuscular, Neurodegenerative, Autoimmune, Developmental, Traumatic Brain Injury, Concussion, Dry Eye Disease, Hearing Loss and/or Metabolic Diseases
A composition and method of treatment of neuromuscular, neuromuscular degenerative, neurodegenerative, autoimmune, developmental, traumatic, hearing loss related, and / or metabolic diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) syndrome (SMA1, SMA2, SMA3, and SMA4, also called Type I, II, III and IV), traumatic brain injury (TBI), concussion, keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Dry Eye Disease), glaucoma, Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, post-LASIK surgery, anti-depressants use, Wolfram Syndrome, and Wolcott-Rallison syndrome. The composition is selected from the group consisting of 2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP, bipartite 2,3-dinitrophenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol, 2,5-dinitrophenol, 2,6-dinitrophenol, 3,4-dinitrophenol, or 3,5-dinitrophenol (2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP) prodrugs; Gemini prodrugs, bioprecursor molecules, and combinations thereof. A dose of the composition for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases may be from about 0.01 mg / kg of body weight to about 50 mg / kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment. A dose of the composition for treatment of metabolic diseases may be from about 1 mg / 70 kg of body weight to about 100 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment, and a maximum dose per day is about 200 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC +1
Nerve retractor
The invention provides a nerve hook. The nerve hook comprises a handle, a middle connecting part and a hook body section; the handle comprises a first handle section and a second handle section, and the first end of the second handle section is vertically connected with the first handle section; the first end of the middle connecting part is connected with the second end of the second handle section; and the hook body section is connected with the second end of the middle connecting part, wherein the first handle section and the hook body section are arranged in parallel. By applying the technical scheme, the problems that in the prior art, a nerve hook is inconvenient to use in the traction process, the dural sac and the nerve root are prone to being damaged, and shaking is prone to occurring in the operation can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
Expandable Intervertebral Spacer and Method of Posterior Insertion Thereof
ActiveUS20140228956A1Increase heightIncrease widthSpinal implantsPosterior approachIntervertebral spaces
An expandable intervertebral spacer has a plurality of arms. The arms can be retracted or extended. The spacer has a width that is narrower than the width between the nerve roots near the posterior approach to an intervertebral space. Once inserted into the intervertebral space, the arms can be deployed. The deployed arms expand the height and width of the spacer. Once deployed, the spacer stabilizes two adjacent vertebrae. The arms are interconnected mechanically to deploy simultaneously.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Treatment of pelvic floor disorders using targeted lower limb nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20200139118A1Increase the number ofReduce frequencyUltrasound therapyExternal electrodesNervous systemTherapy related
Methods and systems for improving nerve stimulation are disclosed which relate to shaping characteristics of the stimulation field such as by using different geometries and locations of stimulation. In embodiments, systems and methods are provided to improve selective modulation of specific targeted neural substrate, while minimizing the activation of adjacent non-targeted nervous tissue. While aspects of the disclosed technologies can be applied to any part of the central and peripheral nervous systems for treatment various disorders and providing symptom relief to provide for therapy related to pelvic floor disorders such as overactive bladder
Owner:EBT MEDICAL INC
Sacrum nerve puncture path simulation planning system and device
PendingCN113940735ASimulation is accurateImprove fitSurgical needlesDiagnostic markersSacral BoneEngineering
The invention provides a sacrum nerve puncture path simulation planning system and device, and relates to puncture operation simulation. The sacrum nerve puncture path simulation planning system comprises an image obtaining module and a path simulation planning module, and the image obtaining module is configured to obtain scanning images of sacrum, sacral foramen and a positioning grid located at a lumbosacral part; and the path simulation planning module is configured to establish a three-dimensional model of the sacrum, the sacral foramen and the positioning grid according to the scanned image, and acquire a virtual puncture path penetrating through the positioning grid to reach a sacrum set position and an intersection point of the positioning grid and the virtual puncture path according to the three-dimensional model. The problems that at present, sacral nerve holes are directly punctured for many times, and pain of patients is large are solved. By acquiring the scanning images of the positioning grid, sacrum and sacral foramen, taking the positioning grid as a positioning reference, reconstructing the three-dimensional model of the sacrum, the sacral foramen and the positioning grid, taking a reference of penetrating through the positioning grid to reach a sacrum set position, and establishing a plurality of virtual puncture paths, a human organ state and an actual puncture process are simulated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com