Patents
Literature
394 results about "User design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enabling communication between users surfing the same web page
InactiveUS20060026233A1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb browserChat room
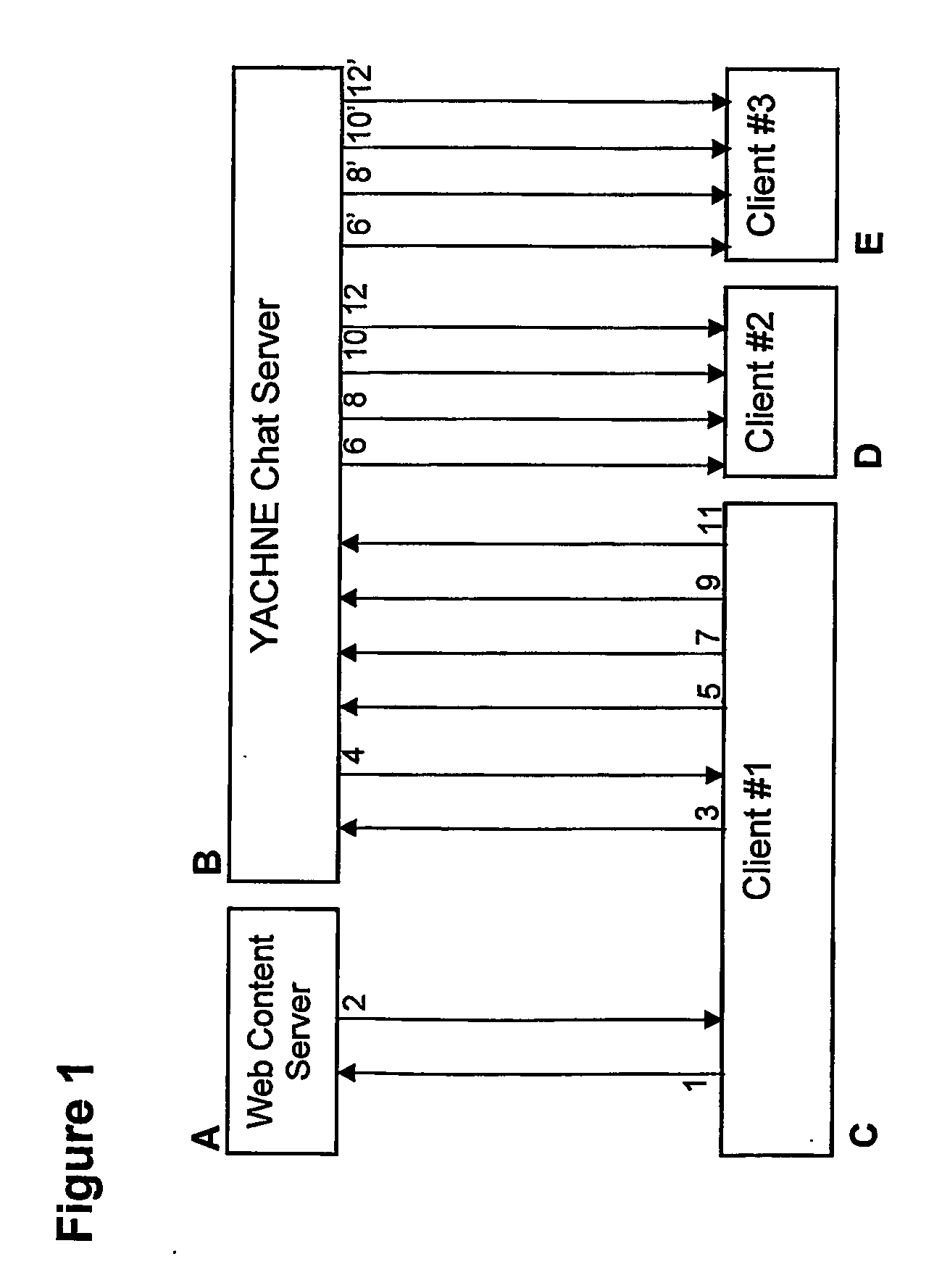
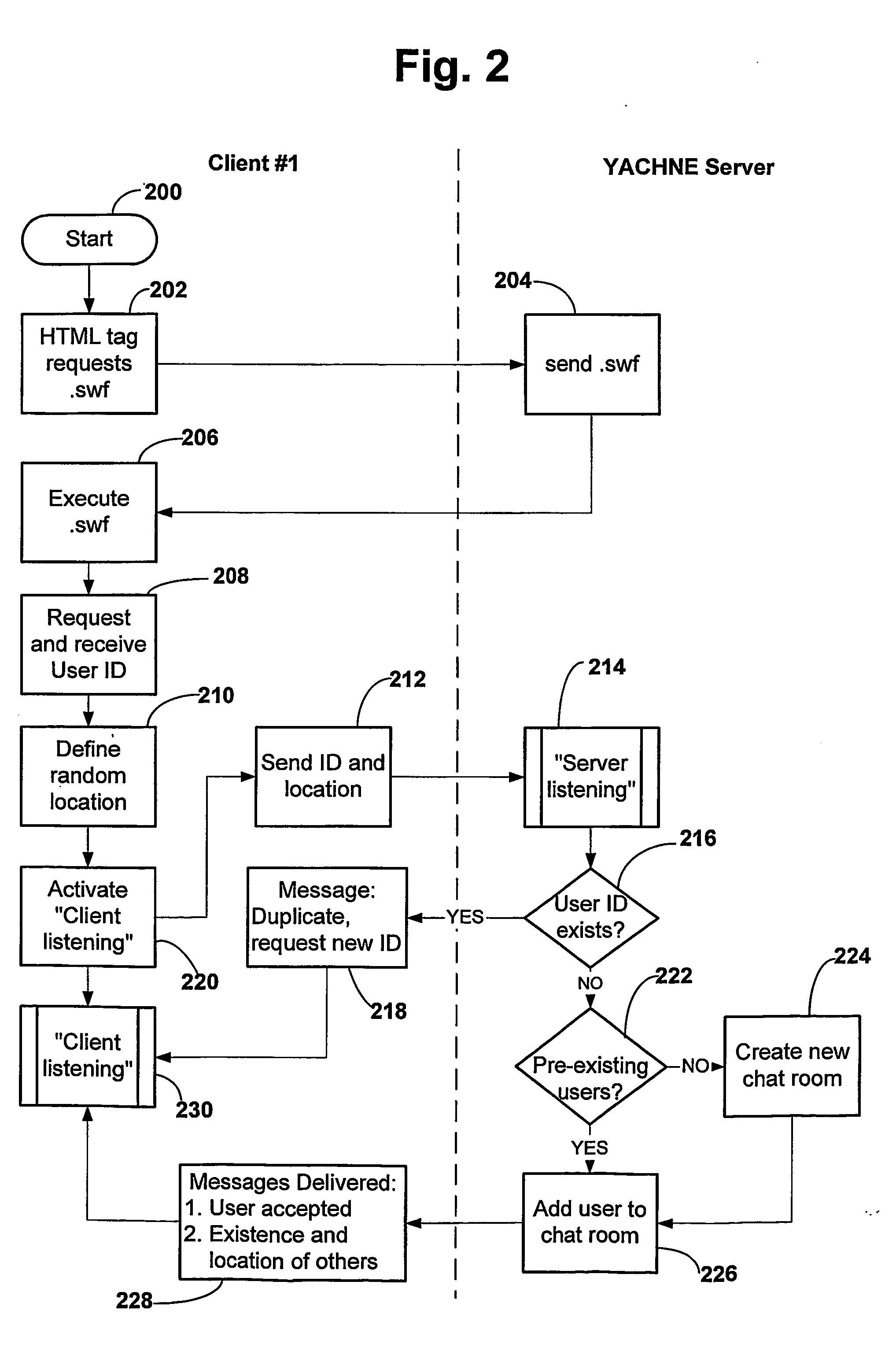
A web page is YACHNEE™ enabled by providing an icon on the page which allows actuation upon being clicked. The user is then able to design a character to represent him on the screen. He also sees characters on screen representing other users, which characters have been designed by the users. A user may move his character all over the screen by dragging it with his mouse and may rotate it towards or away from other characters. The characters may speak to each other, either through a voice communication or typing, in which case the text appears in a bubble (cartoon fashion). A user may change the appearance of a character to reflect an emotion (e.g. anger) and he may invite other characters to a private chat. When a user leaves the web page, the corresponding character disappears from all other users' screens. Communication among users viewing the same web page is facilitated without the need for any program or plug-in other than what is standard in a web browser. Additionally, such features as the automatic generation and de-activation of chat-rooms are possible, which in previous applications are pre-defined and independent of the presence of users.
Owner:PI TRUST
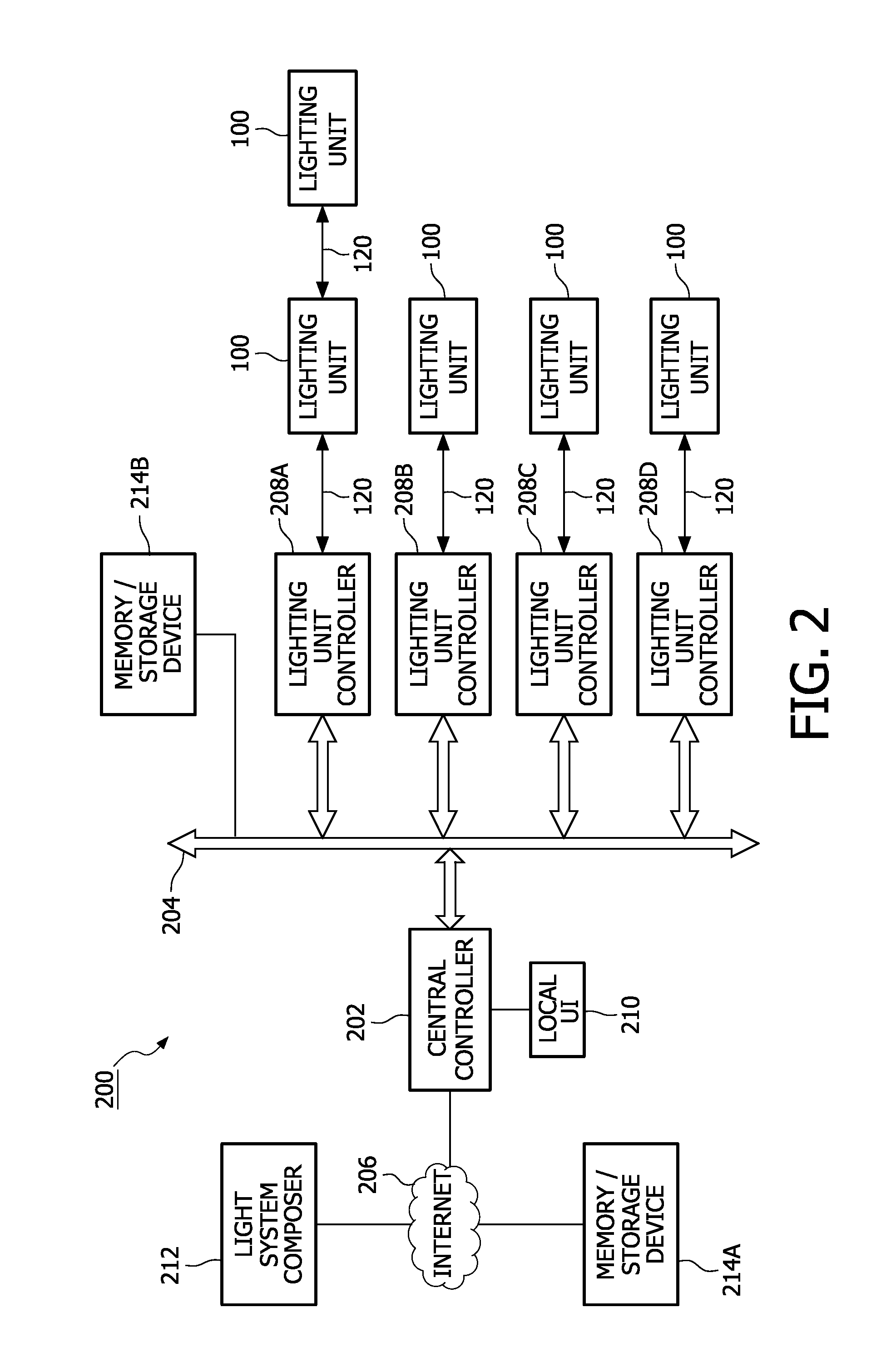
Methods and apparatus for facilitating design, selection and/or customization of lighting effects or lighting shows
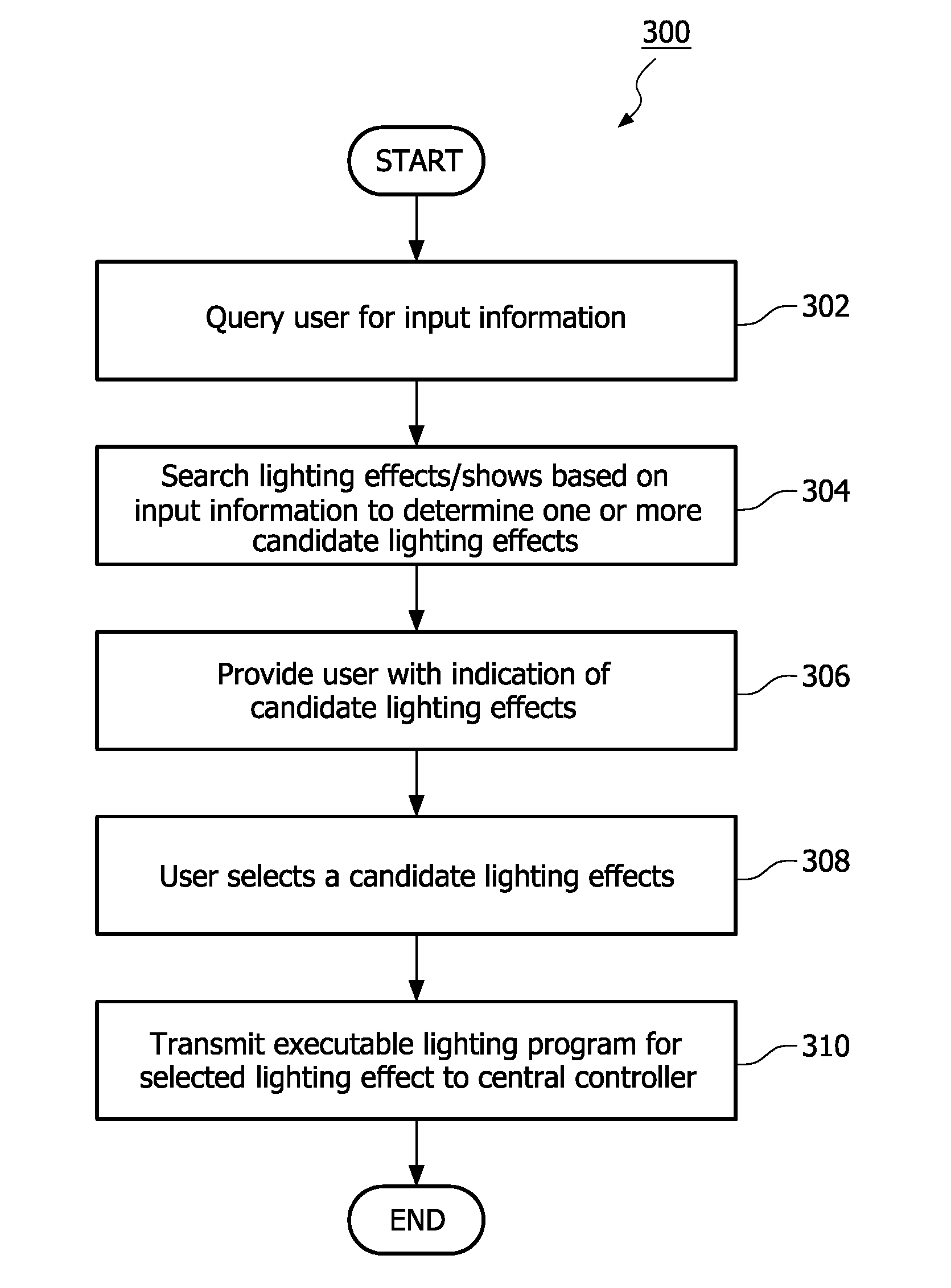
Methods and apparatus for facilitating a process of designing, selecting, and / or customizing lighting effects or lighting shows. A library of indexed (tagged) predefined lighting effects or shows is searched by a search engine, based upon information provided by a user / designer, to identify a set of effects or shows having attributes that are in some way related to the information provided by the user. The user is then presented with search results, i.e., a manageable subset of intelligently chosen lighting effects or shows, which may be ranked in terms of relevance, any one or more of which may be readily selected by the user. The user may select one or more effects or shows from the search results “as is” for execution by a lighting system, may combine one or more effects or shows from the search results, or may modify one or more effects or shows from the search results to refine some aspect of the effect(s) / show(s) in accordance with user preferences. In one exemplary implementation, the library of lighting effects / shows and / or the search engine may be hosted by a web site and accessible via the Internet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Formation of columnar application specific circuitry using a columnar programmable device
A columnar programmable device (PD) design converted to a columnar application specific integrated circuit-like (ASIC-like) design is described. A user design is instantiated in a PD having a columnar architecture associated with the columnar PD design. The columnar architecture has adjacent columns of circuitry, and one or more of the columns of circuitry as associated with instantiation of the user design in the PD are identified. At least a portion of one or more of the identified columns are swapped with application specific circuitry for implementing all or part of the user design for converting the columnar PD design to the columnar ASIC-like design.
Owner:XILINX INC
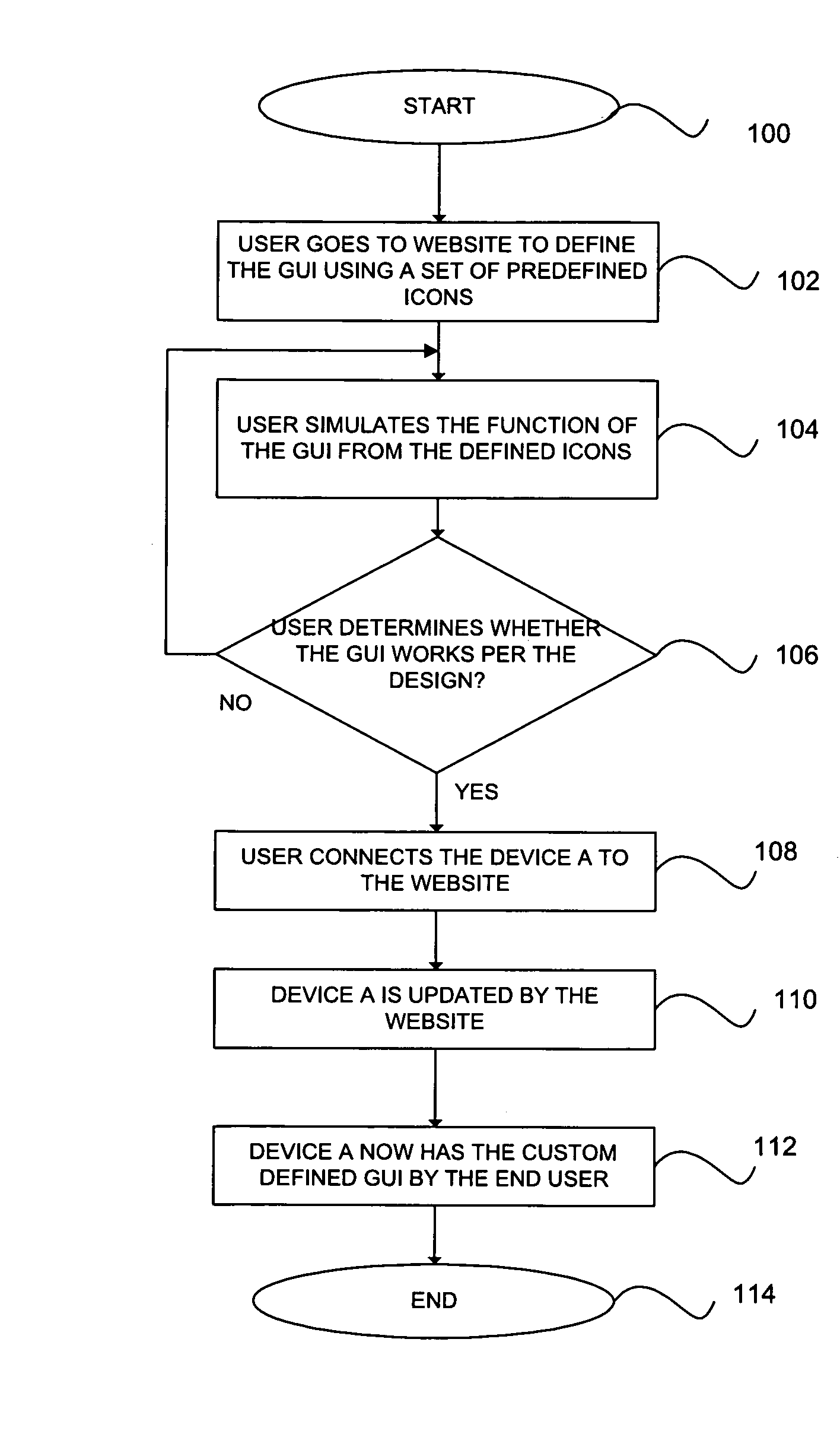
Method for remotely configuring user interfaces for portable devices
InactiveUS20080276182A1Service provisioningInformation formatHuman–computer interactionComputer science
A method of configuring the user interface of a portable electronic device is provided. A user designed user interface is created using authoring tools at a remote server and stored. A remote server file is accessed that stores a user designed user interface. The customized interface is selected and downloaded to the device.
Owner:ZIILABS INC LTD A ORGANIZED UNDER THE LAWS OF BERMUDA
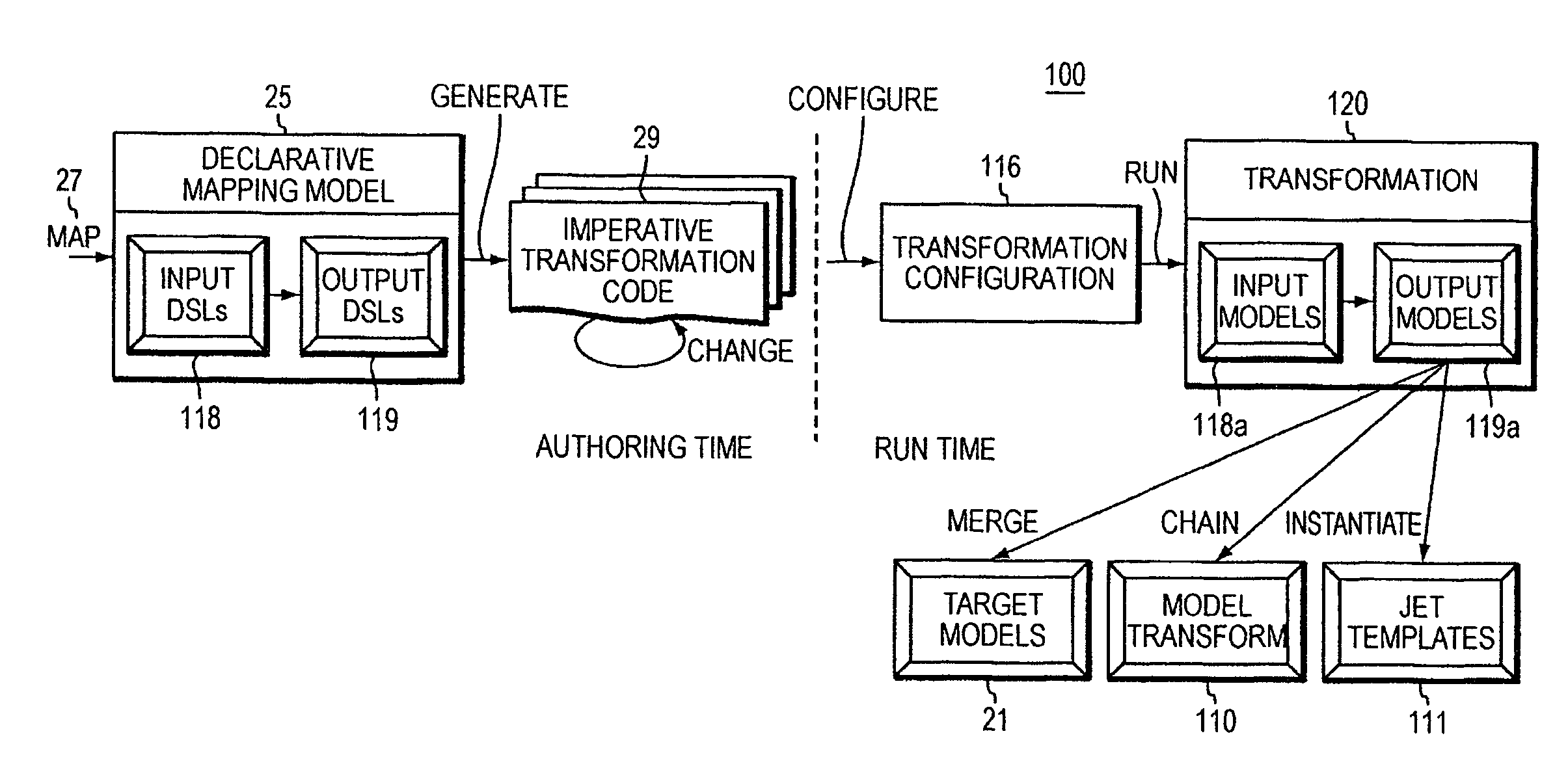
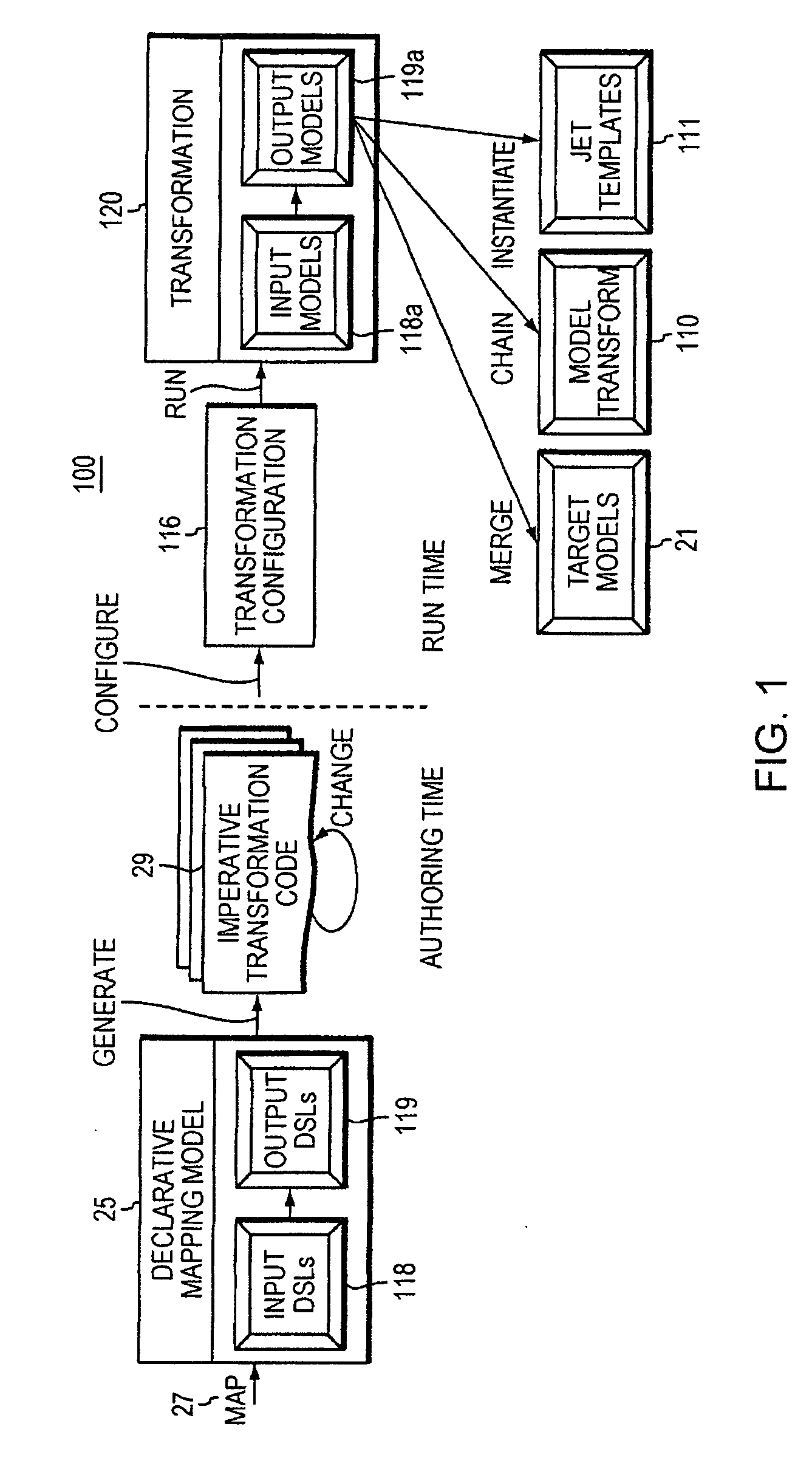
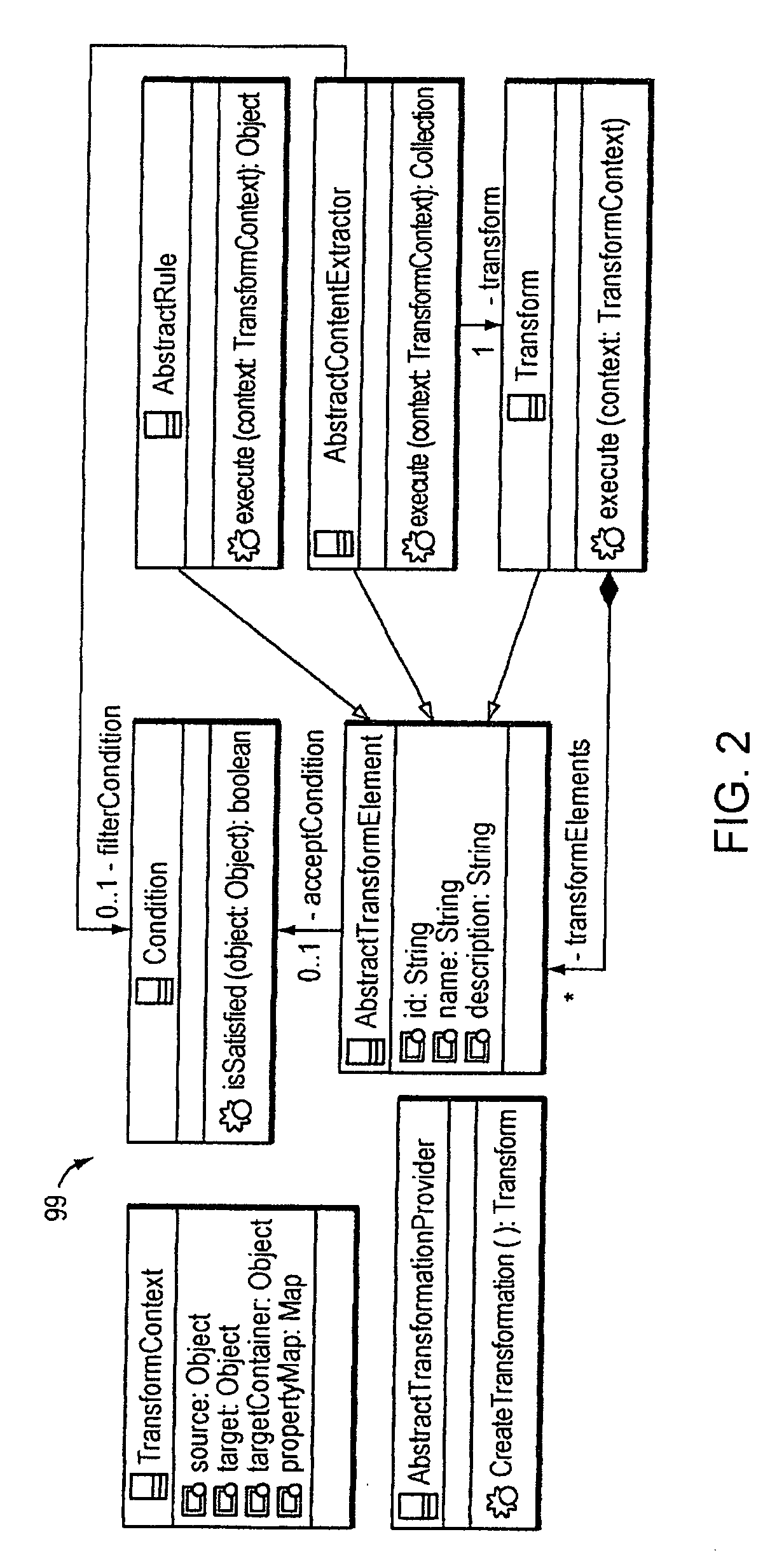
Computer Method and Apparatus for Providing Model to Model Transformation Using an MDA Approach
InactiveUS20090150854A1Specification is simpleEasy to integrateModel driven codeRequirement analysisTheoretical computer scienceA domain
A Model Transformation Authoring Framework (MTAF)method and apparatus for authoring and providing model-to-model transformations from one domain to another domain is disclosed. Given a domain and a target domain, at least the given domain having a respective structured hierarchy, the invention system enables a user to specify a declarative mapping (transformation declarative) between a domain specific language modeling the given domain and a modeling language modeling the target domain. The declarative mapping models how the domain specific language modeling the given domain relates to the modeling language of the target domain. The system generates a transformation code implementation of a transformation from the given domain to the target domain. The MTAF provides to the user design decisions with respect to Specification, Transformation Rules, Rule Organization, Rule Application Control, Source-Target Relationship, Incrementality, and Directionality and Tracing. The generated transformation code is executed at runtime to perform the transformation of the domain specific language of the given domain to the modeling language of the target domain. Instances of models of the target domain resulting from the performed transformation at runtime may be output to other model transformations, to JET templates, or may be persisted, merged or chained among other post processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
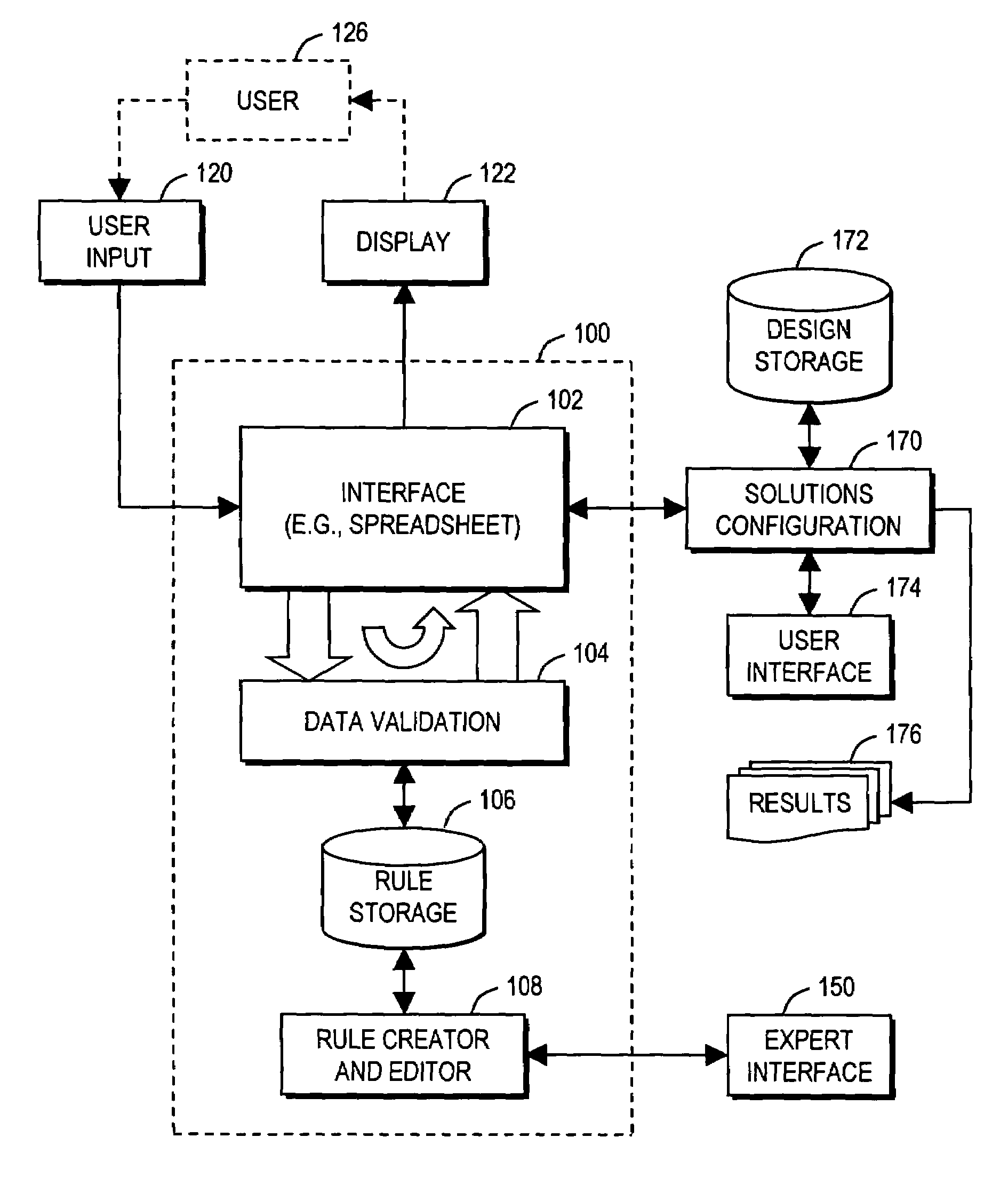
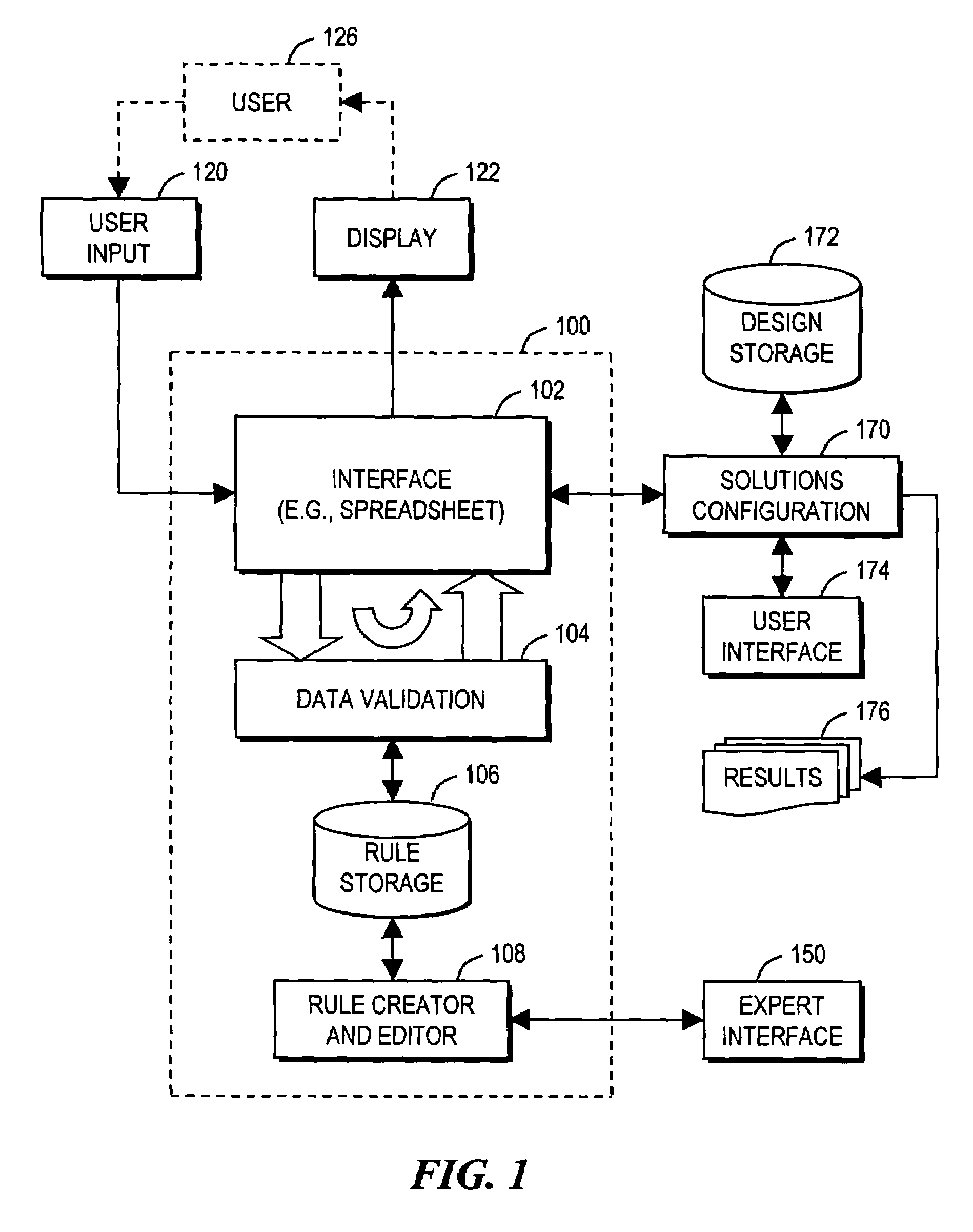
Arrangement for guiding user design of comprehensive product solution using on-the-fly data validation
A computer-implemented method guides a user in designing a product defined by data. The method involves examining (420) items of the data to detect whether each item conforms to rules (106) or violates the rules; performing (431 . . . ) at least one action in response to a detection of a rule violation; displaying (450) the data to the user in a manner emphasizing at least one particular data item that caused the rule violation; receiving (460) any new data input from the user; and repeating the examining, action performing, and displaying steps using the new data. The displaying step may involve displaying data defining a current state of the product in a tabular (spreadsheet) format, including displaying data detected to have caused the rule violation in a first manner that is visibly distinct from displaying other data that is not detected to have caused the rule violation.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Inter-chip communication system
InactiveUS20050102125A1Decrease in performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsCAD circuit designData packCommunications system
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Inter-chip communication system
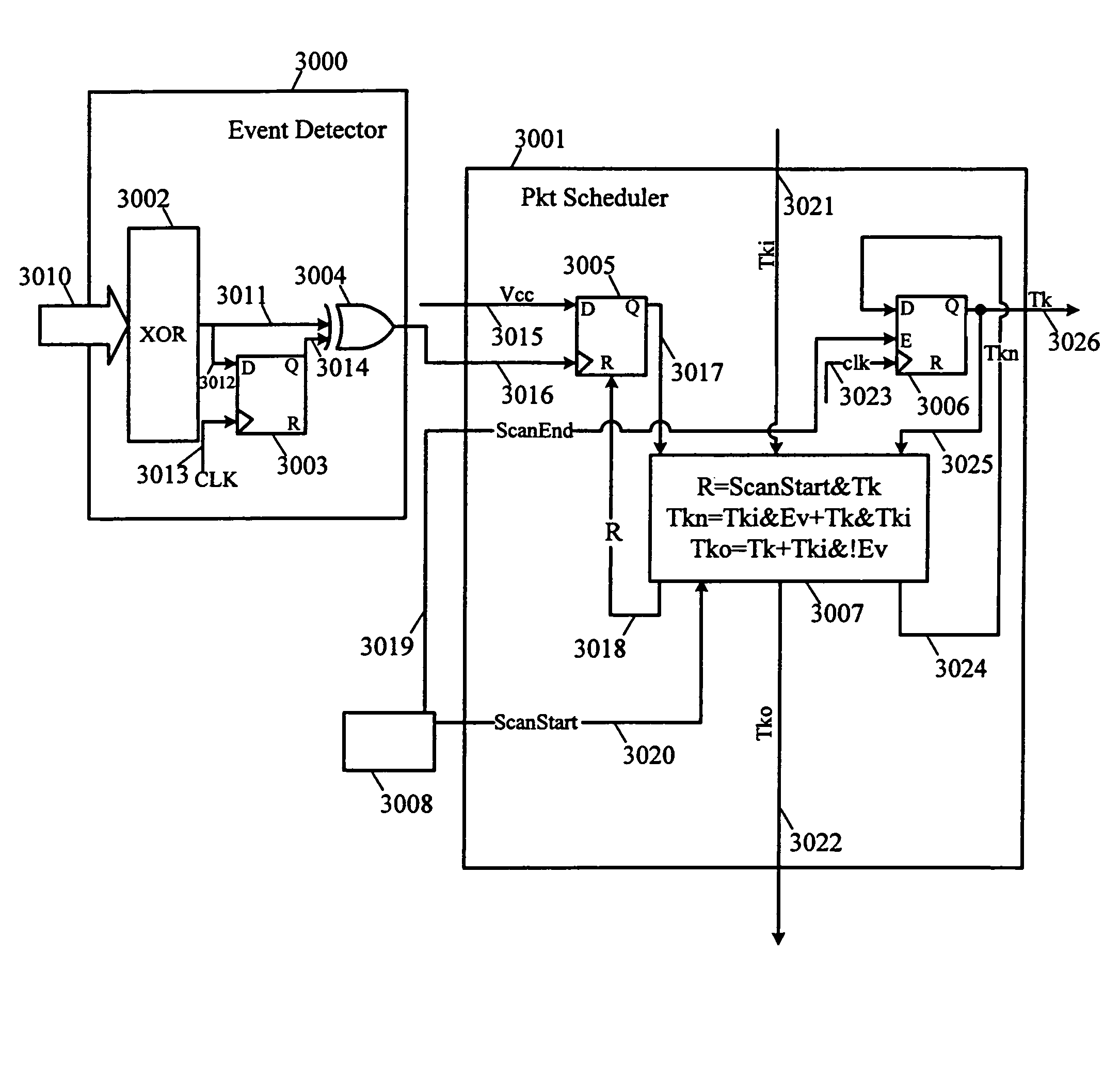
InactiveUS7512728B2Decrease in performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsCAD circuit designCommunications systemPacket scheduling
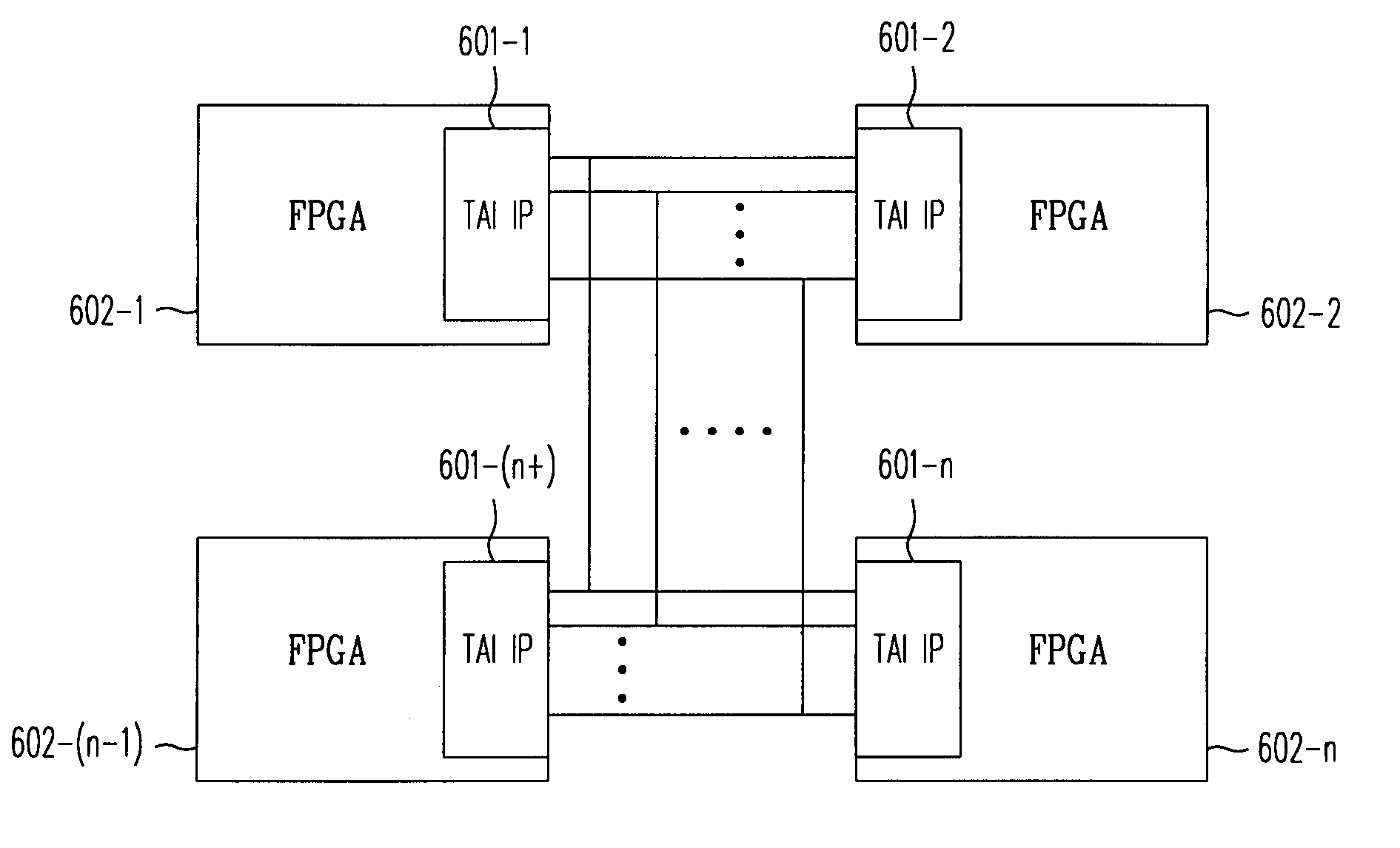
The complexity of user designs, the limited capacity of FPGA chips, and the limited number of chip pinouts have resulted in the development of inter-chip communication technology that necessitates the transfer of a large amount of data across a limited number of pins in the shortest amount of time. The inter-chip communication system transfers signals across FPGA chip boundaries only when these signals change values. Thus, no cycles are wasted and every event signal has a fair chance of achieving communication across chip boundaries. The inter-chip communication system includes a series of event detectors that detect changes in signal values and packet schedulers which can then schedule the transfer of these changed signal values to another designated chip. Working with a plurality of signal groups that represents signals at the separated connections, the event detector detects events (or changes in signal values). When an event has been detected, the event detector alerts the packet scheduler. The packet scheduler employs a token ring scheme as follows. When the packet scheduler receives a token and detects an event, the packet scheduler “grabs” the token and schedules the transmission of this packet in the next packet cycle. If, however, the packet scheduler receives the token but does not detect an event, it will pass the token to the next packet scheduler. At the end of each packet cycle, the packet scheduler that grabbed the token will pass the token to the next logic associated with another packet.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
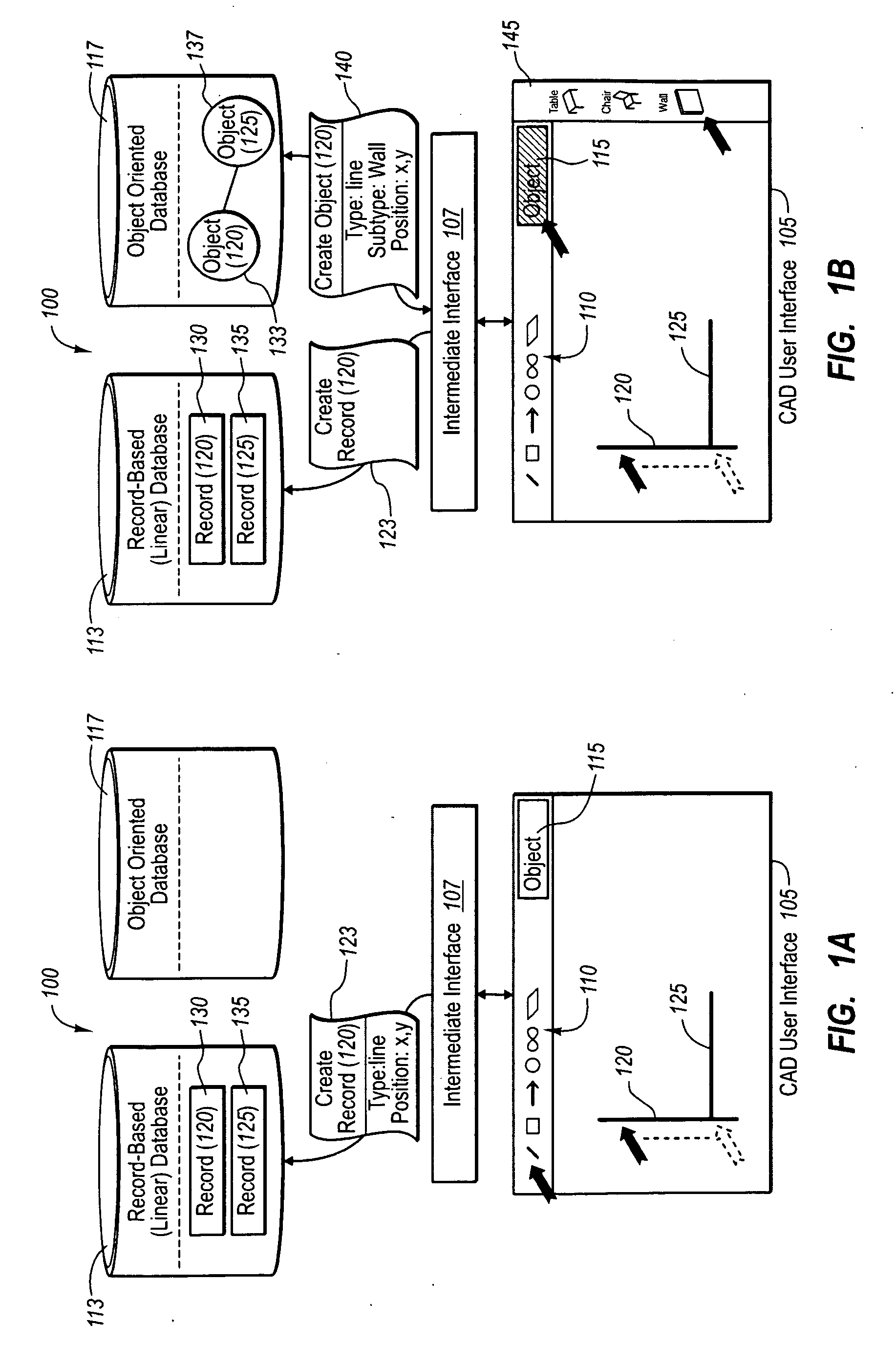
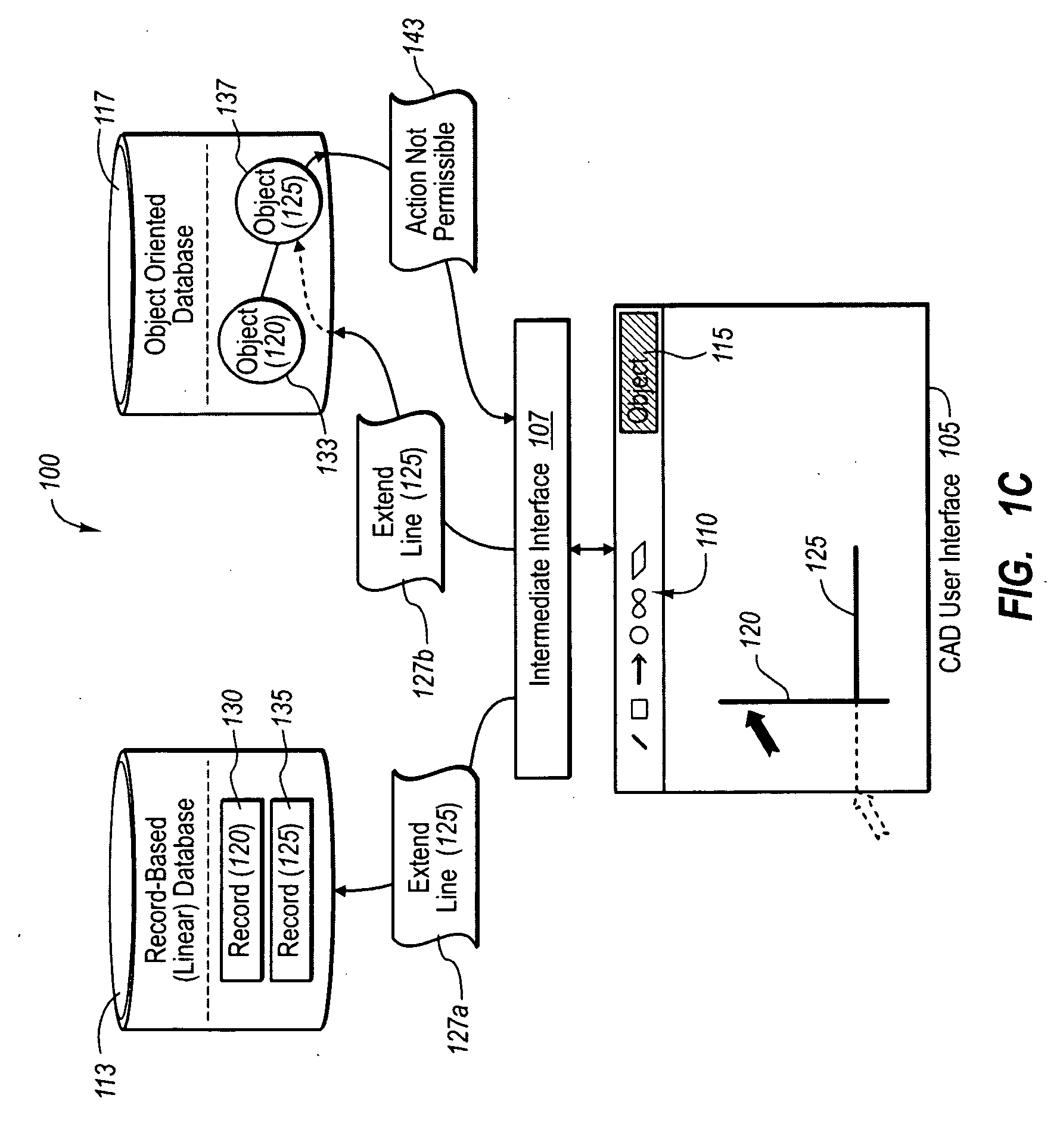
Rendering and modifying cad design entities in object-oriented applications
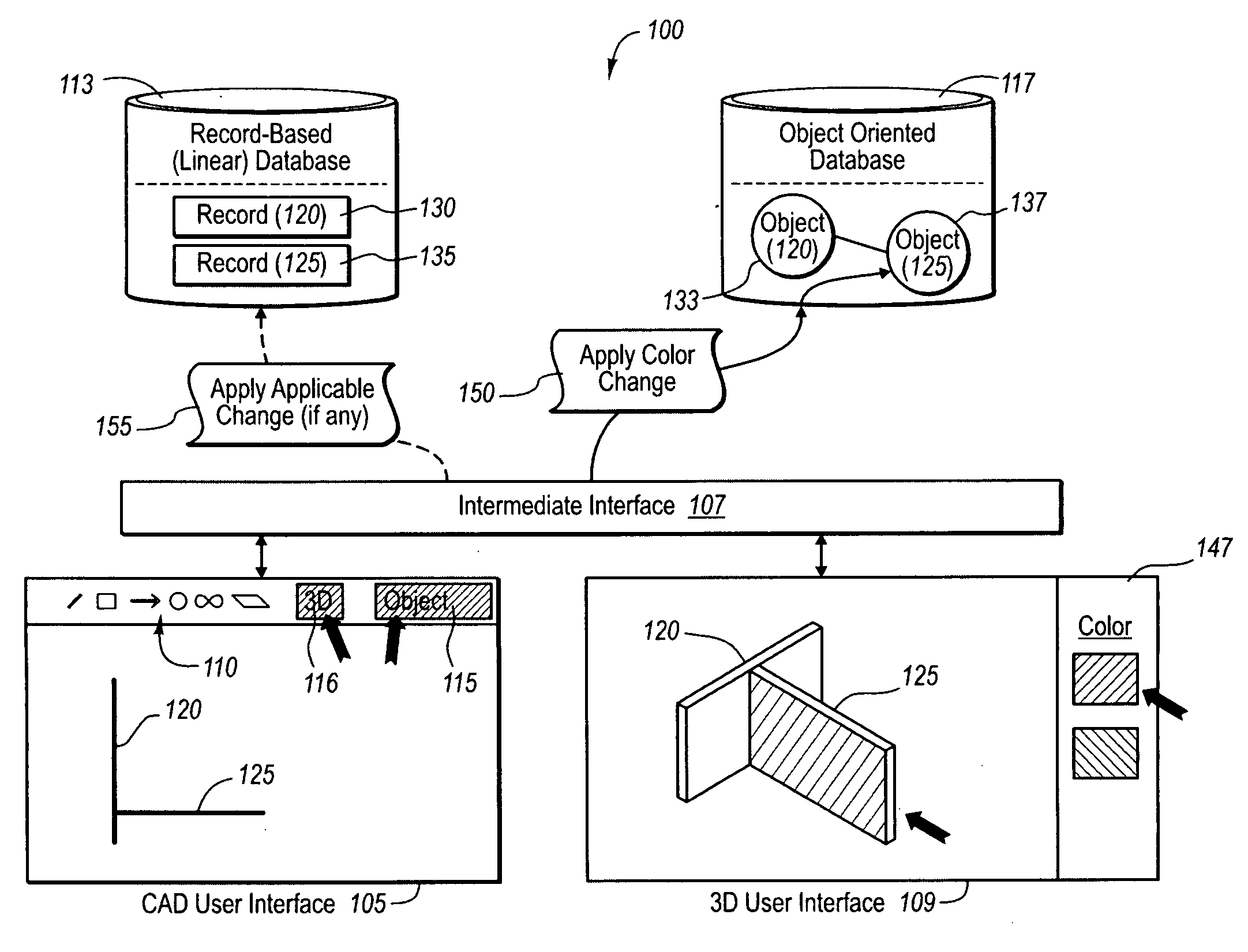
ActiveUS20100268513A1View effectivelyGuaranteed accuracyGeometric CADSpecific program execution arrangementsImage resolutionSoftware engineering
An object-oriented design program provides is configured to instantly render in a three-dimensional interface user CAD designs received as CAD-based design elements (e.g., CAD blocks or lines). The object-oriented program renders the user CAD designs regardless of whether the user designs are practical, or use finishes or colors that are in-stock for the selected design elements. In addition, the object-oriented program can also create intelligent software objects for the CAD-based elements at a later time, upon request by the user. The intelligent software objects can be configured to automatically resolve themselves in view of one or more system limitations and rules in related components, and to replicate any such resolution back to the CAD-based blocks if desired. Thus, a user can have the benefits of instant 3D rendering of CAD drawings with or without the automatic resolution provided by intelligent software objects, depending on the situation.
Owner:ARMSTRONG WORLD INDUSTRIES +1
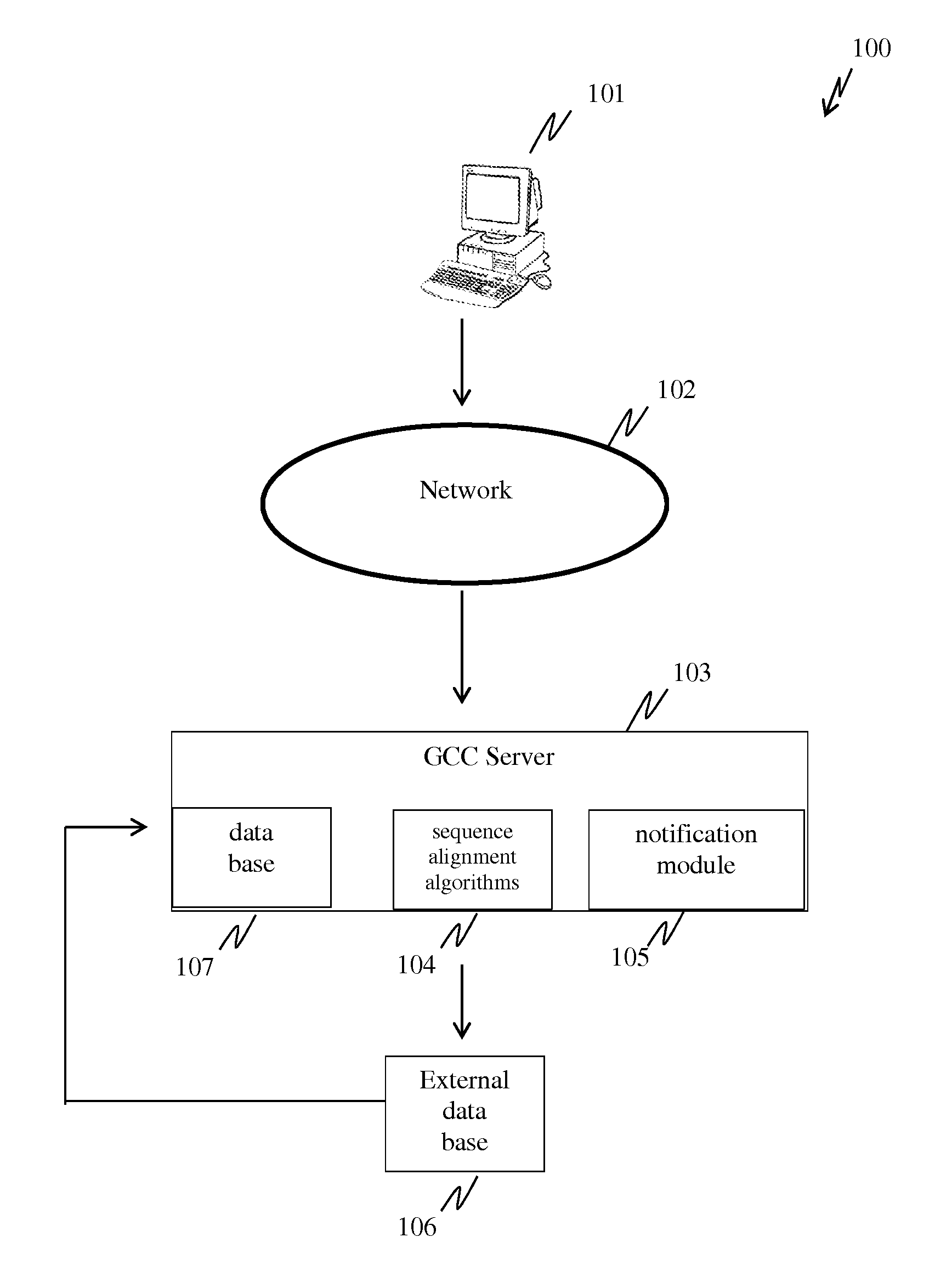
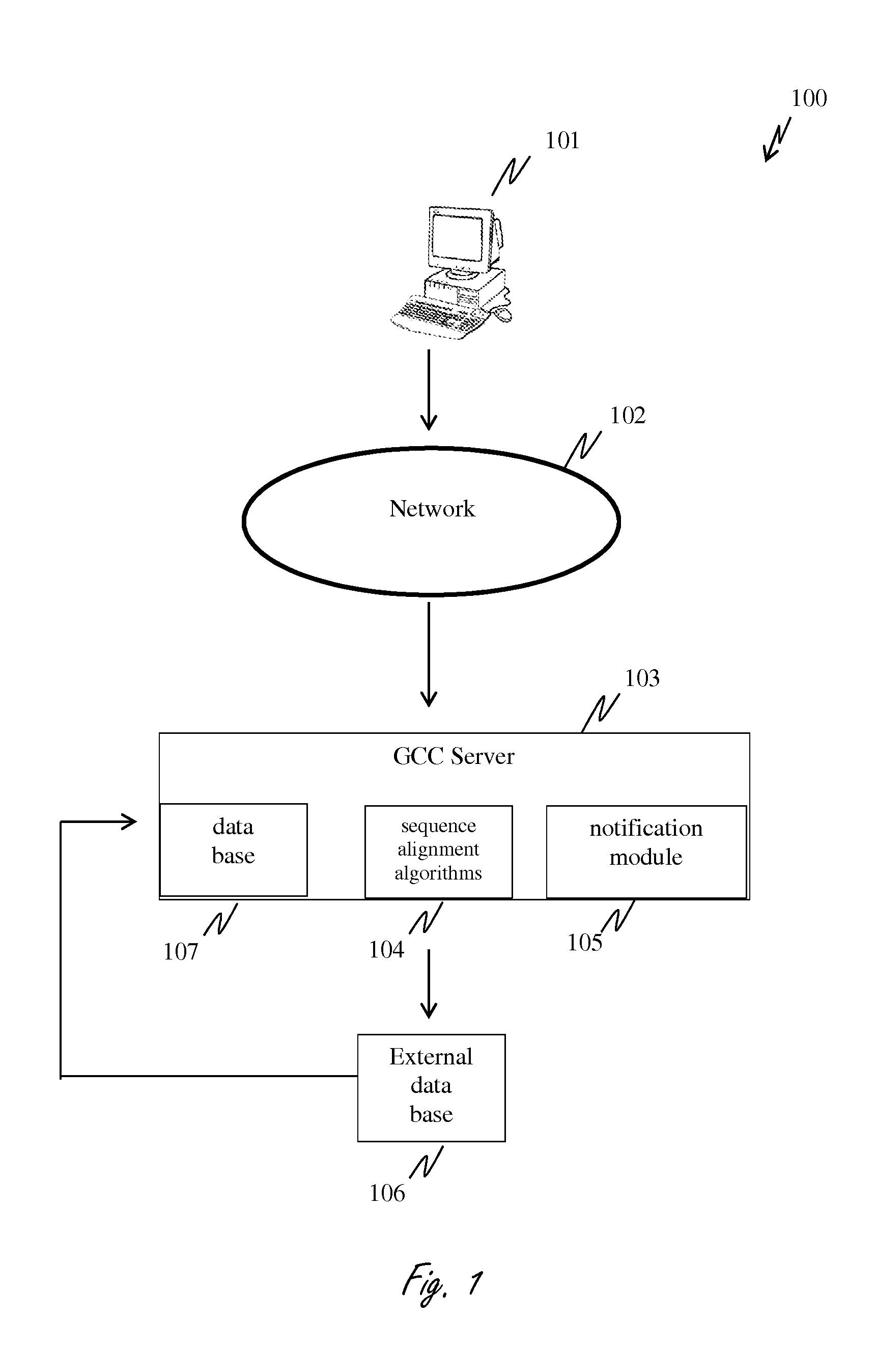
System for polynucleotide construct design, visualization and transactions to manufacture the same
InactiveUS20150120265A1Cost easeShorten speedData visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesNetwork connectionComputerized system
The present invention disclose a computerized system for designing nucleic acid sequences for gene expression comprising; (a) a server [103] for hosting a database [106] (b) a network connection [102] and (c) a computer readable medium [101] comprising functional modules including (i) a design module for enabling designing of nucleic acid constructs; (ii) interactive user interface module for visualizing biological information relating to design operations; (iii) transaction module for purchasing a user-designed or pre-stocked nucleic acid constructs (iv) a detecting module for detecting designed nucleic acid sequences comprises harmful sequences; the system is operating in a method of: (a) visualizing biological information; (b) designing nucleic acid sequences; (c) detecting and notifying when harmful sequences are designed; (d) providing means for transactions regarding ordering and purchasing said synthesized nucleic acids.
Owner:TWIST MERGER SUB INC
Geometric design and modeling system using control geometry
InactiveUS7196702B1Efficient regenerationComputationally efficientData processing applications3D-image renderingComputer Aided DesignAnimation
A method and system for computer aided design (CAD) is disclosed for designing geometric objects. The present invention interpolates and / or blends between such geometric objects sufficiently fast so that real time deformation of such objects occurs while deformation data is being input. Thus, a user designing with the present invention obtains immediate feedback to input modifications without separately entering a command for performing such deformations. The present invention utilizes novel computational techniques for blending between geometric objects, wherein weighted sums of points on the geometric objects are used in deriving a new blended geometric object. The present invention is particularly useful for designing the shape of surfaces. Thus, the present invention is applicable to various design domains such as the design of, e.g., bottles, vehicles, and watercraft. Additionally, the present invention provides for efficient animation via repeatedly modifying surfaces of an animated object such as a representation of a face.
Owner:CAD-SENSE LLC
Trigger circuits and event counters for an IC
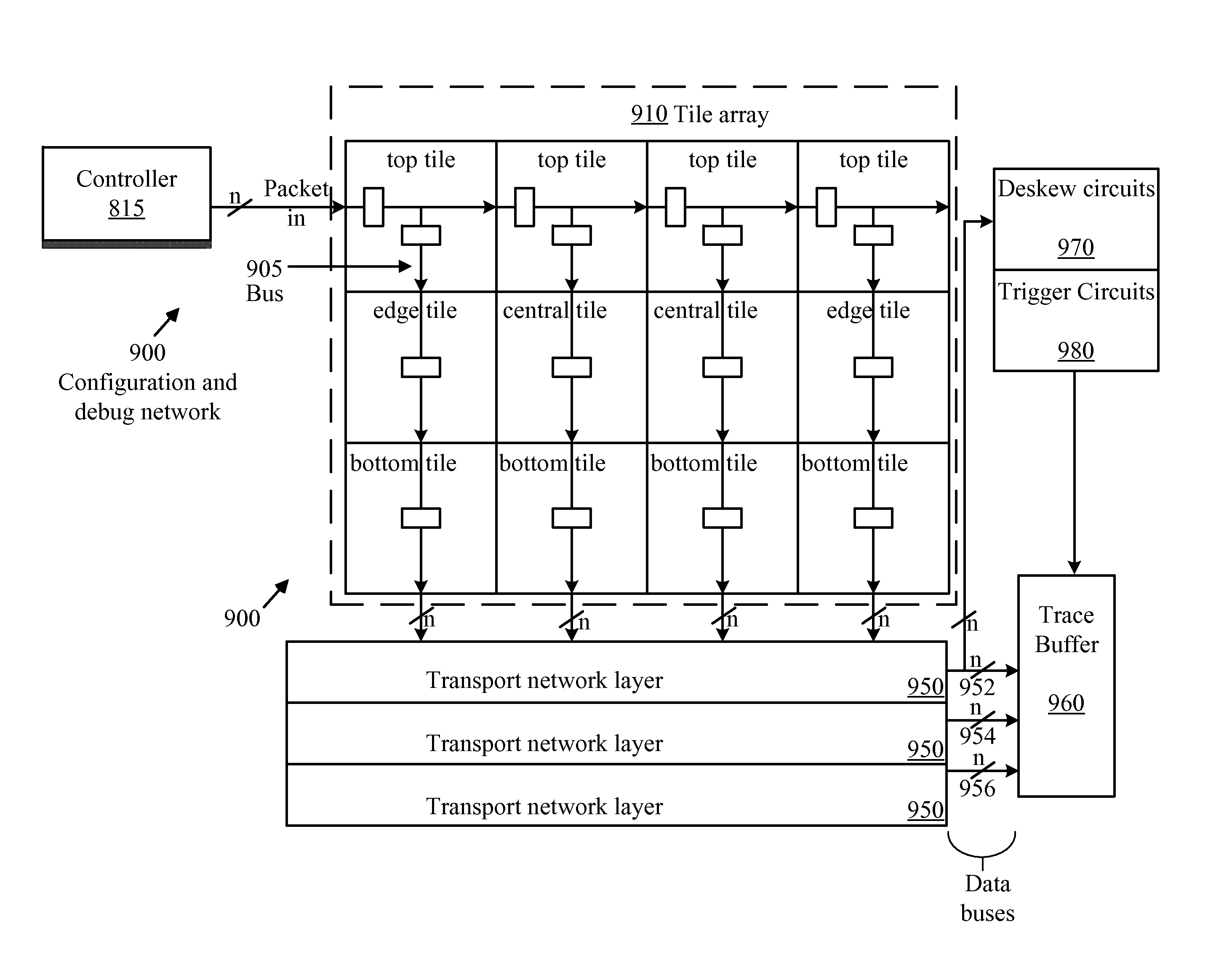
ActiveUS20110199117A1Easy to useProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer hardwareHemt circuits
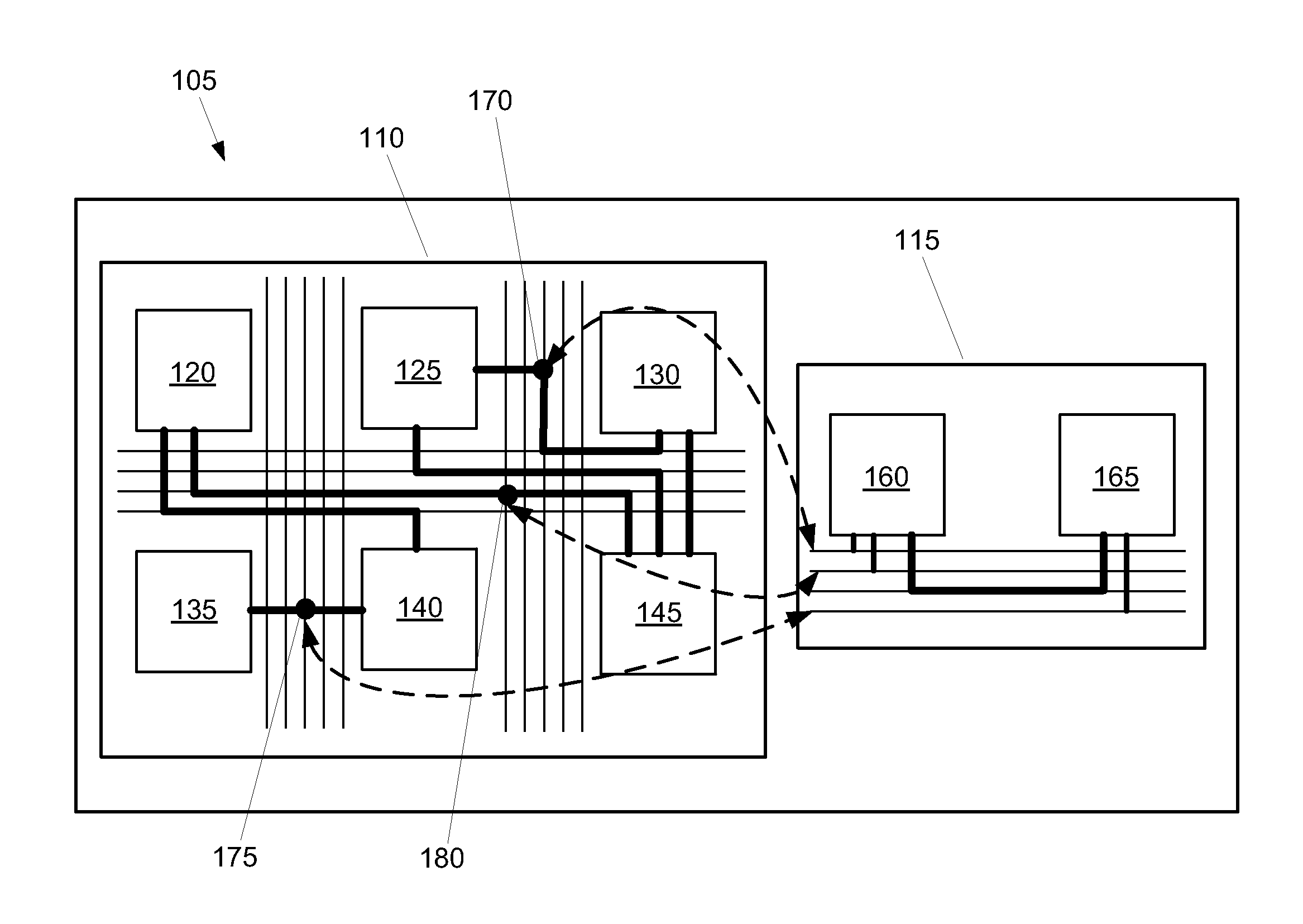
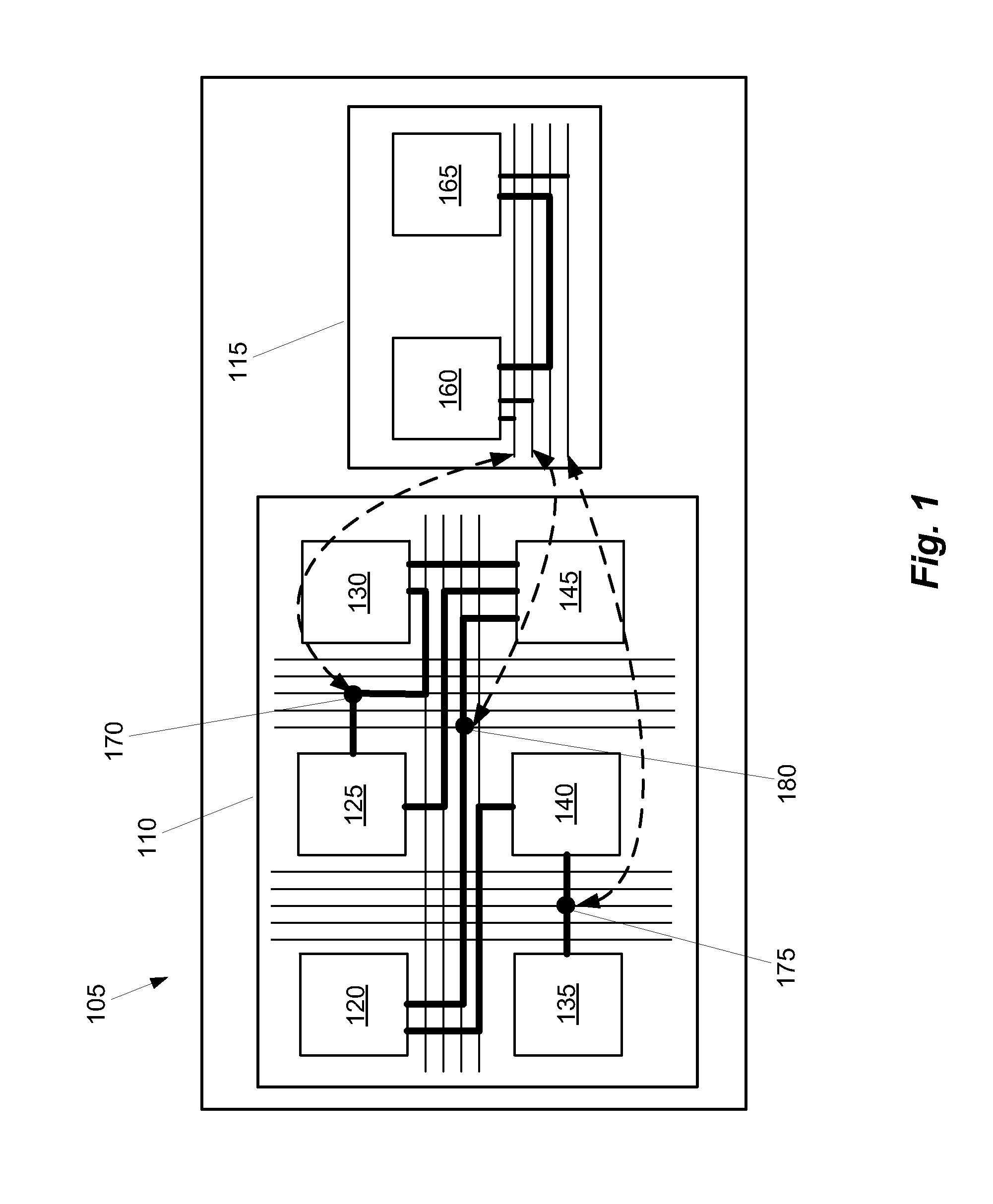
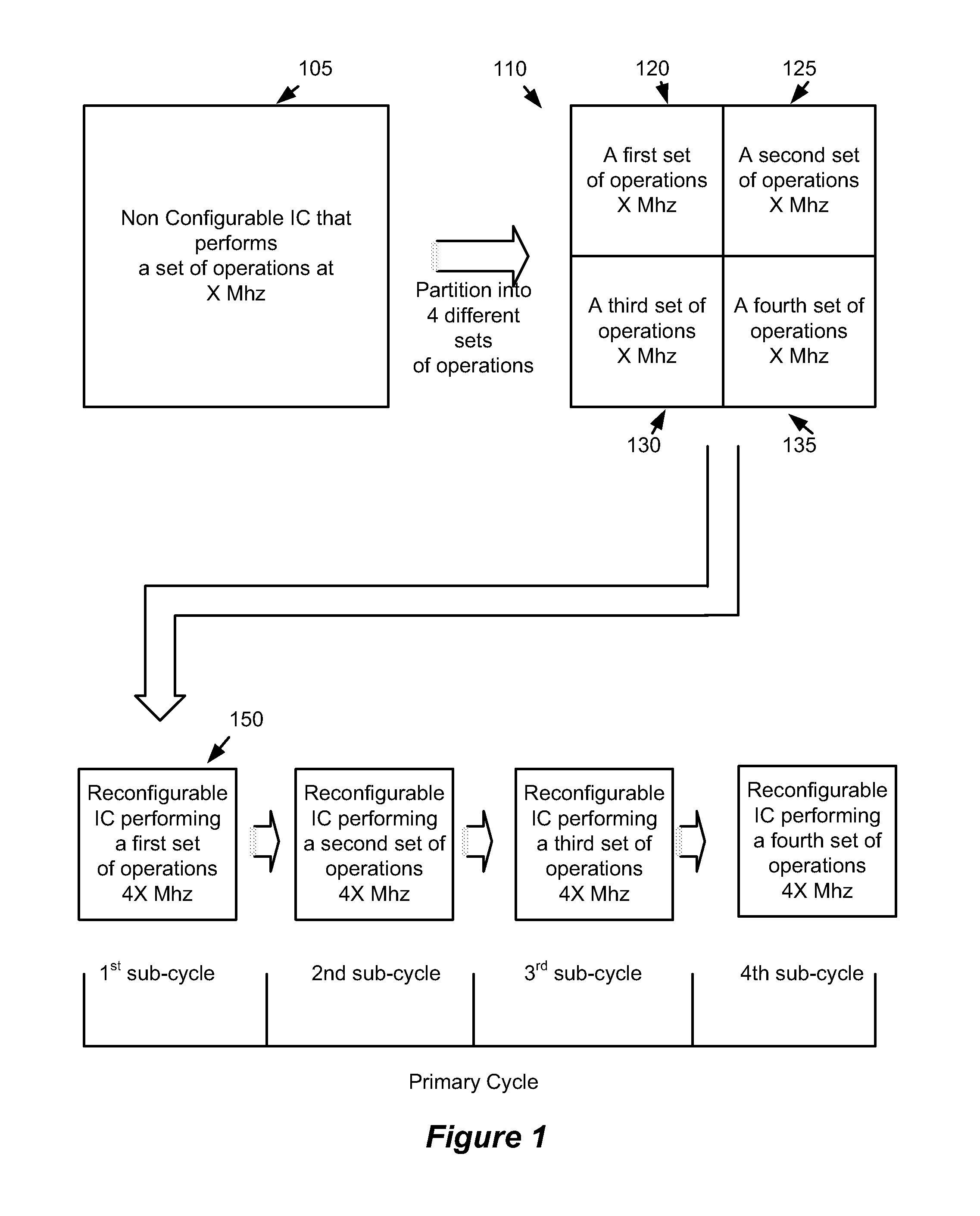
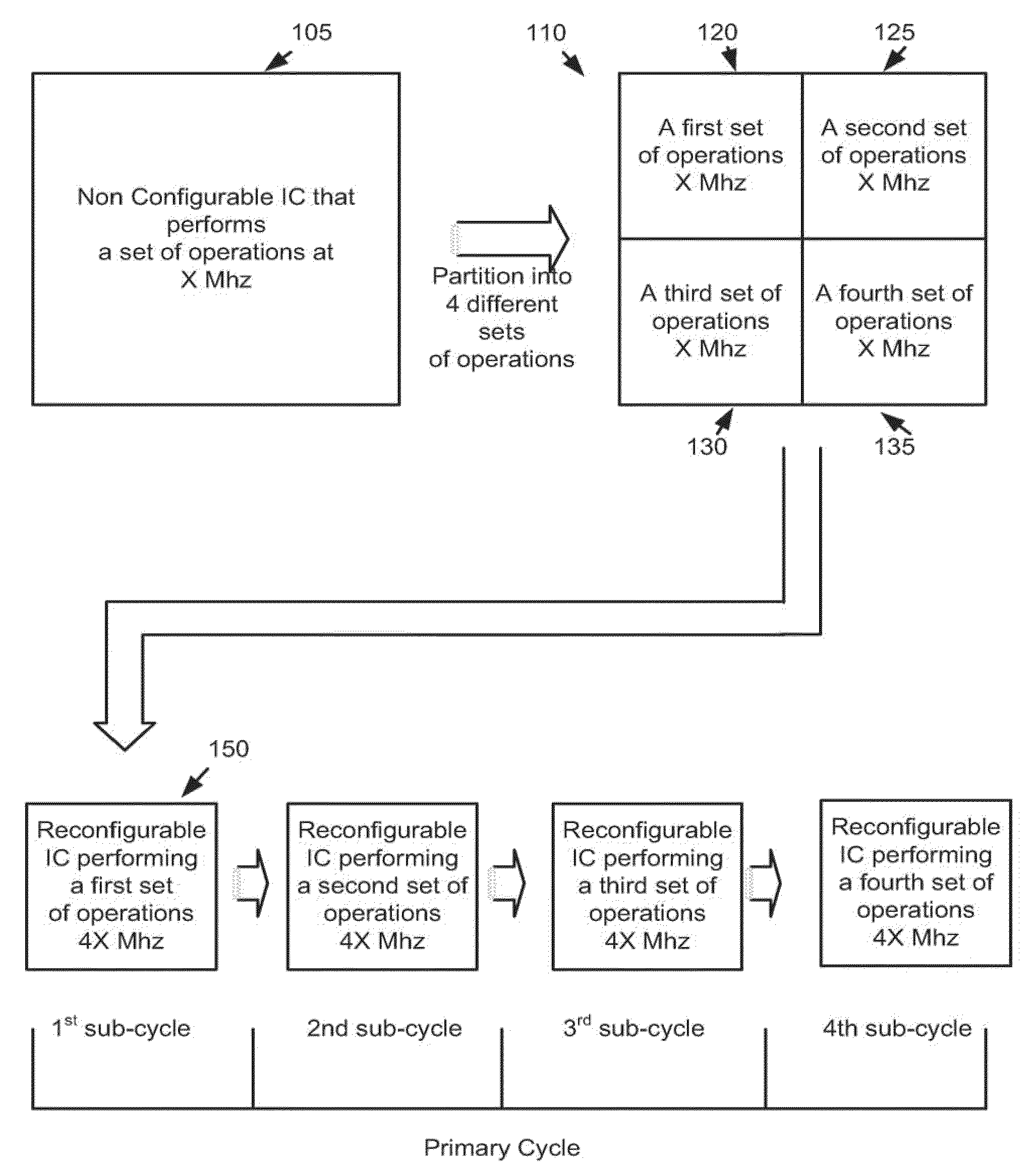
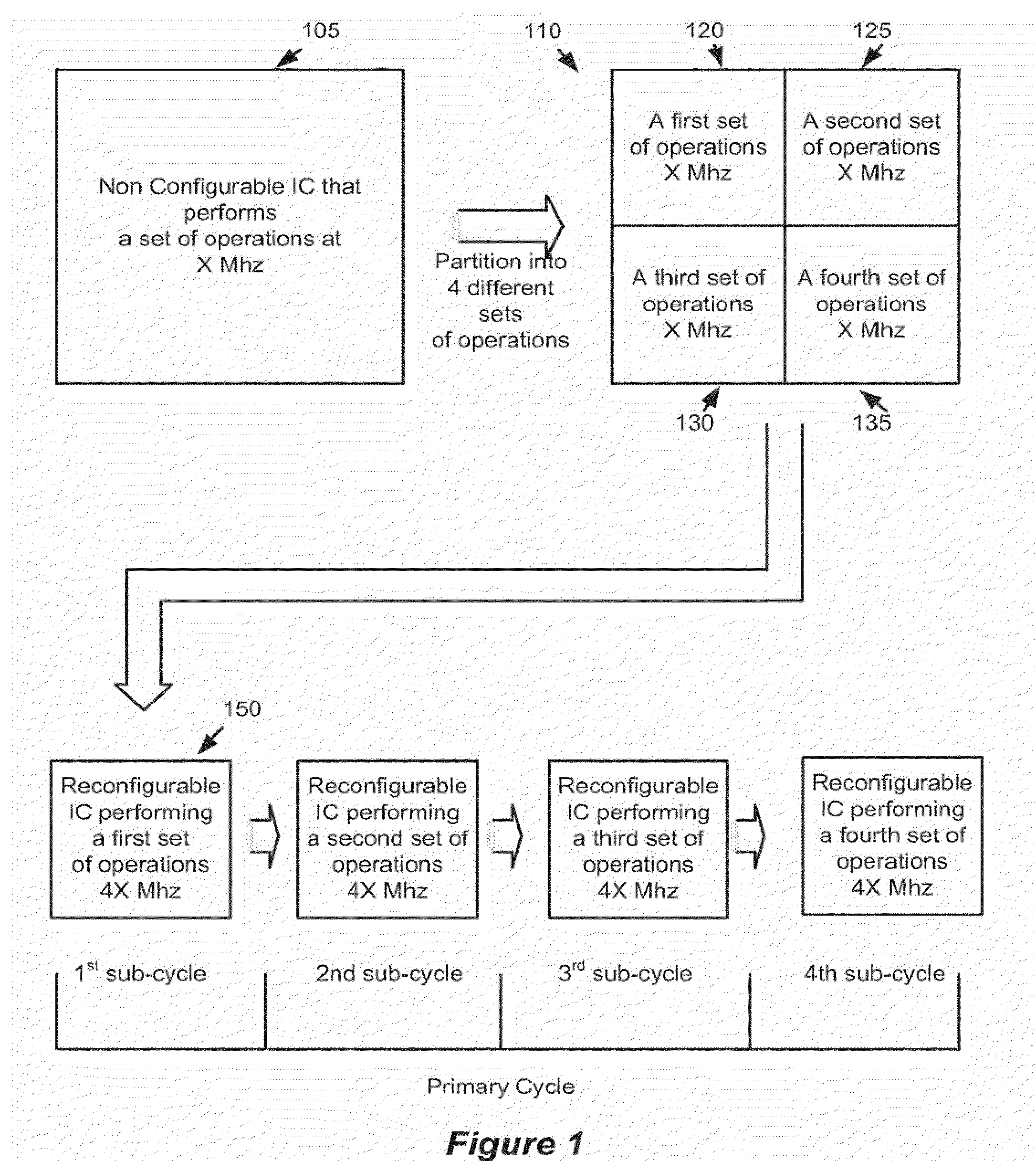
Some embodiments provide an integrated circuit (‘IC’). The IC includes multiple configurable circuits that configurably perform operations of a user design based on configuration data. The IC also includes a configurable trigger circuit that receives a set of configuration data that specifies an operational event. The configurable trigger circuit also determines whether the operational event has occurred during implementation of the user design of the IC. Additionally, the operational trigger event outputs a trigger signal upon determining that the operational trigger event has occurred.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Integrated circuit (IC) with primary and secondary networks and device containing such an IC
ActiveUS20110029830A1Halt operation of systemComplex functionFault responseElectronic circuit testingEngineeringIntegrated circuit
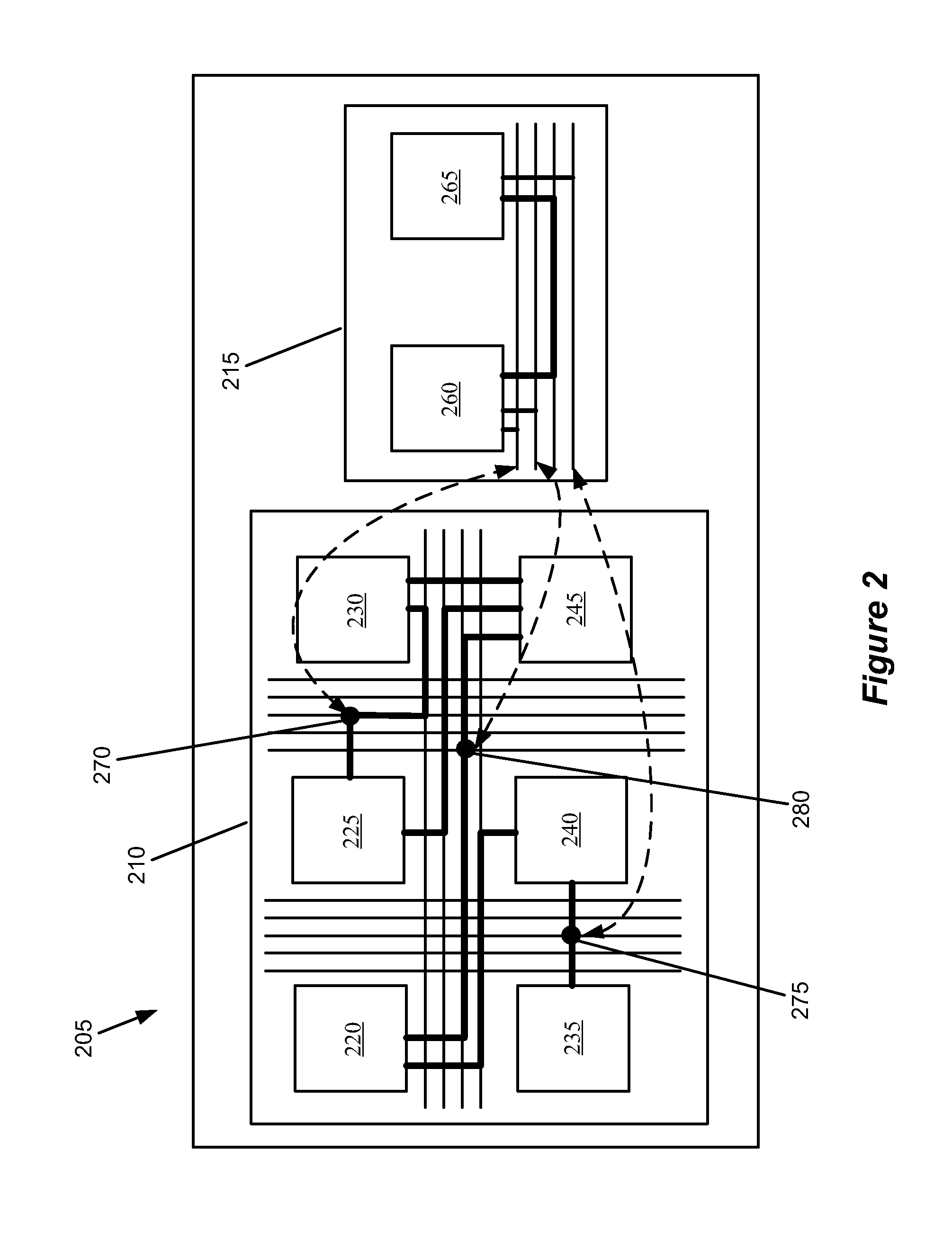
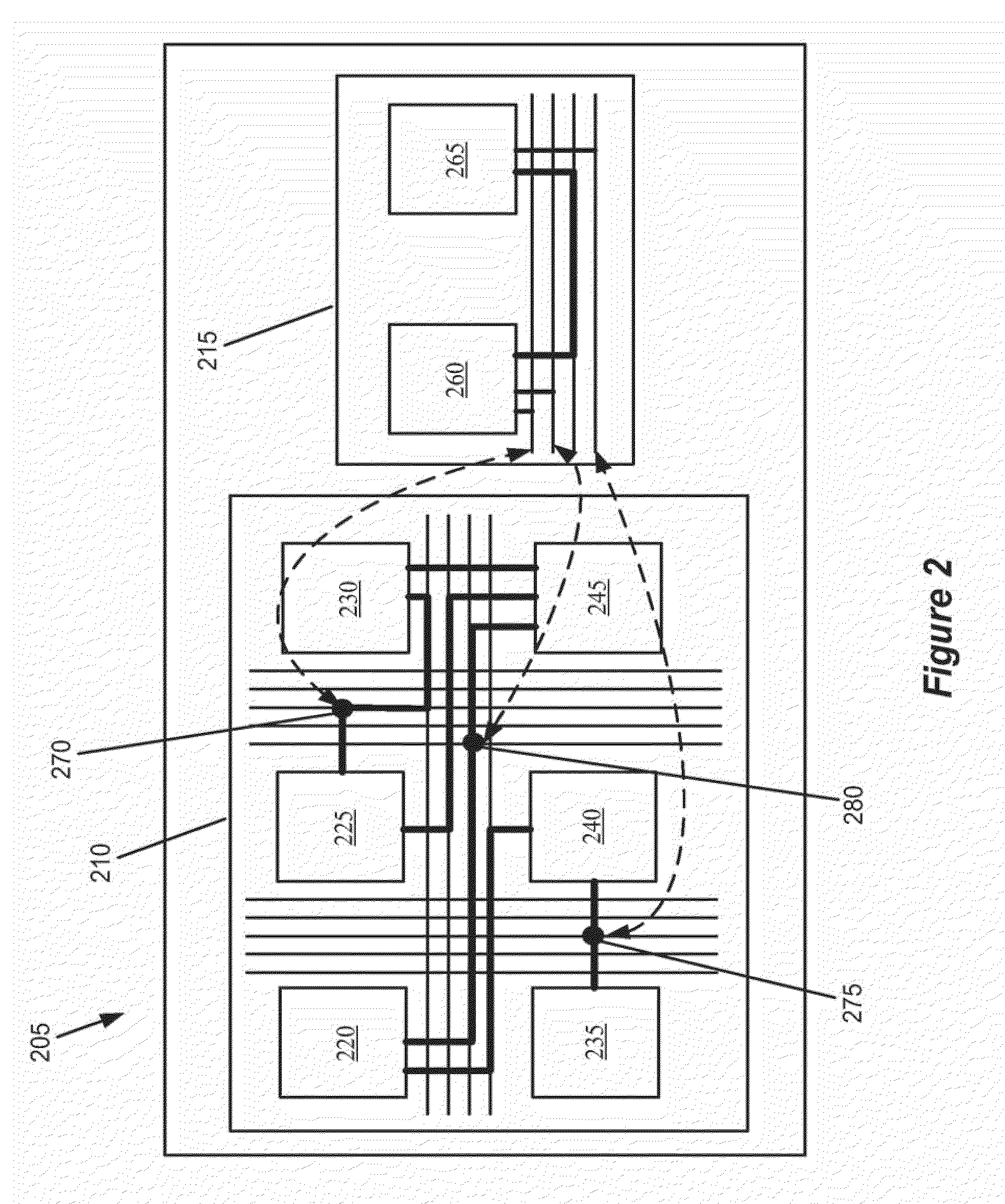
Some embodiments provide an integrated circuit (“IC”) with a primary circuit structure. The primary circuit structure is for performing multiple operations that implement a user design. The primary circuit structure includes multiple circuits. The IC also includes a secondary monitoring structure for monitoring multiple operations. The secondary monitoring structure includes a network communicatively coupled to multiple circuits of the primary circuit structure. The secondary monitoring circuit structure is for analyzing the monitored operations and reporting on the analysis to a circuit outside of the IC.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Design software incorporating efficient 3-D rendering
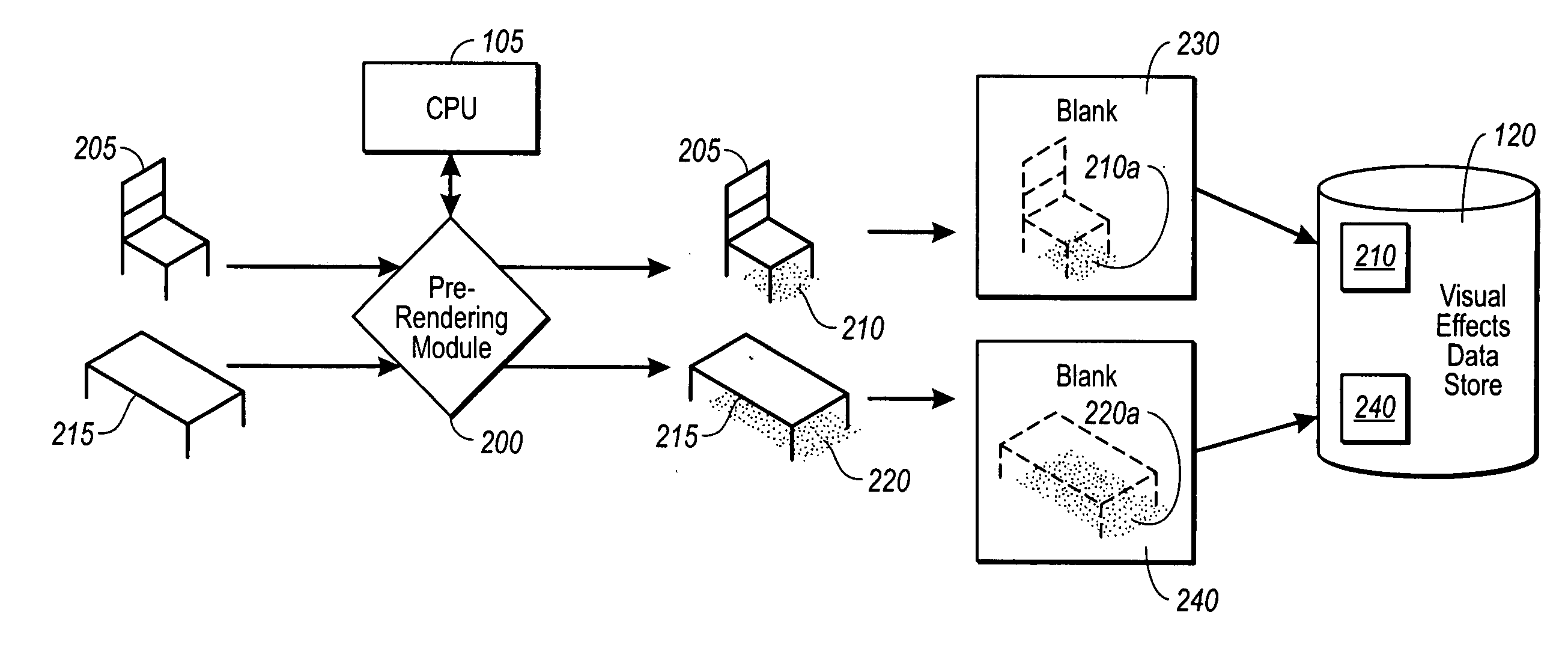
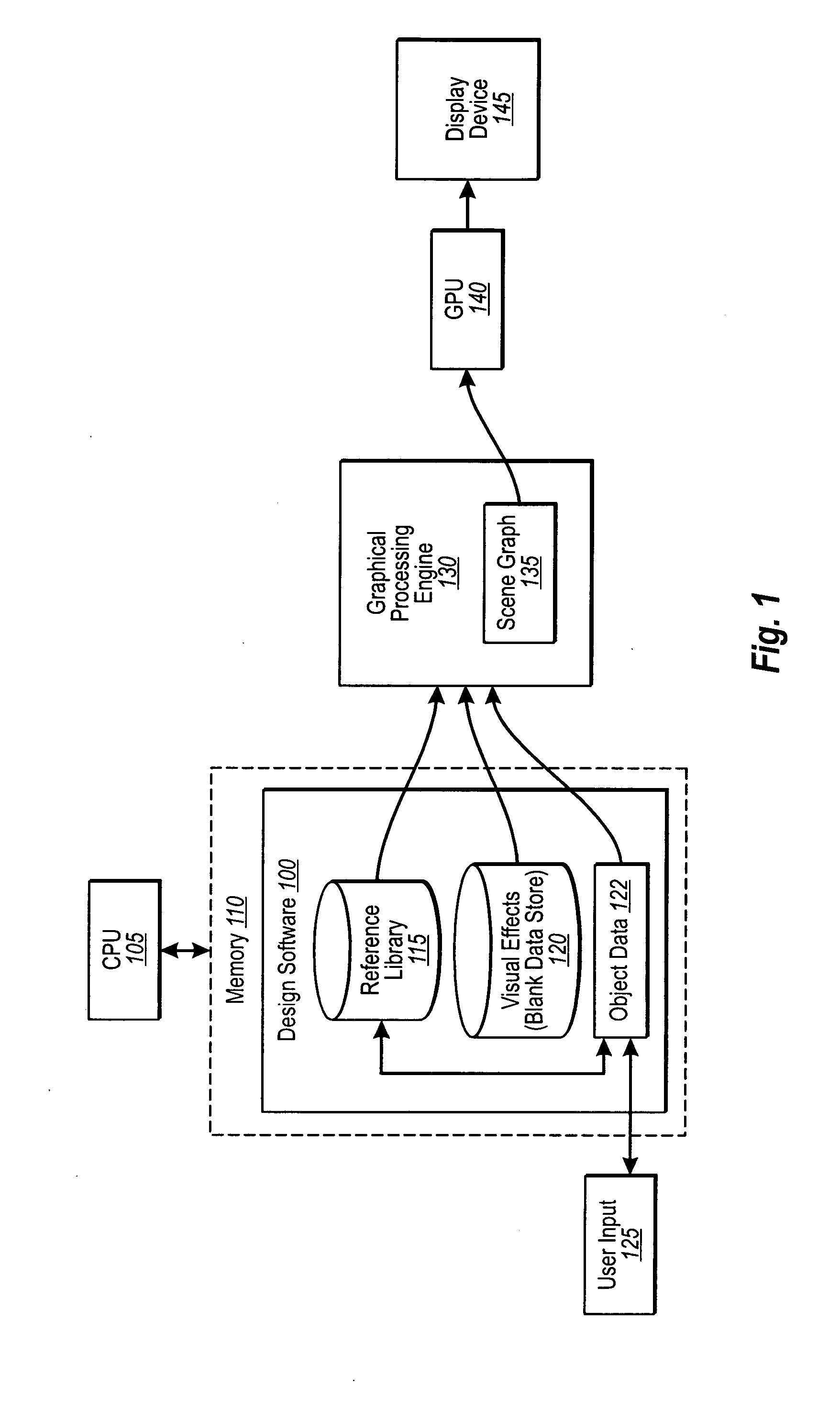
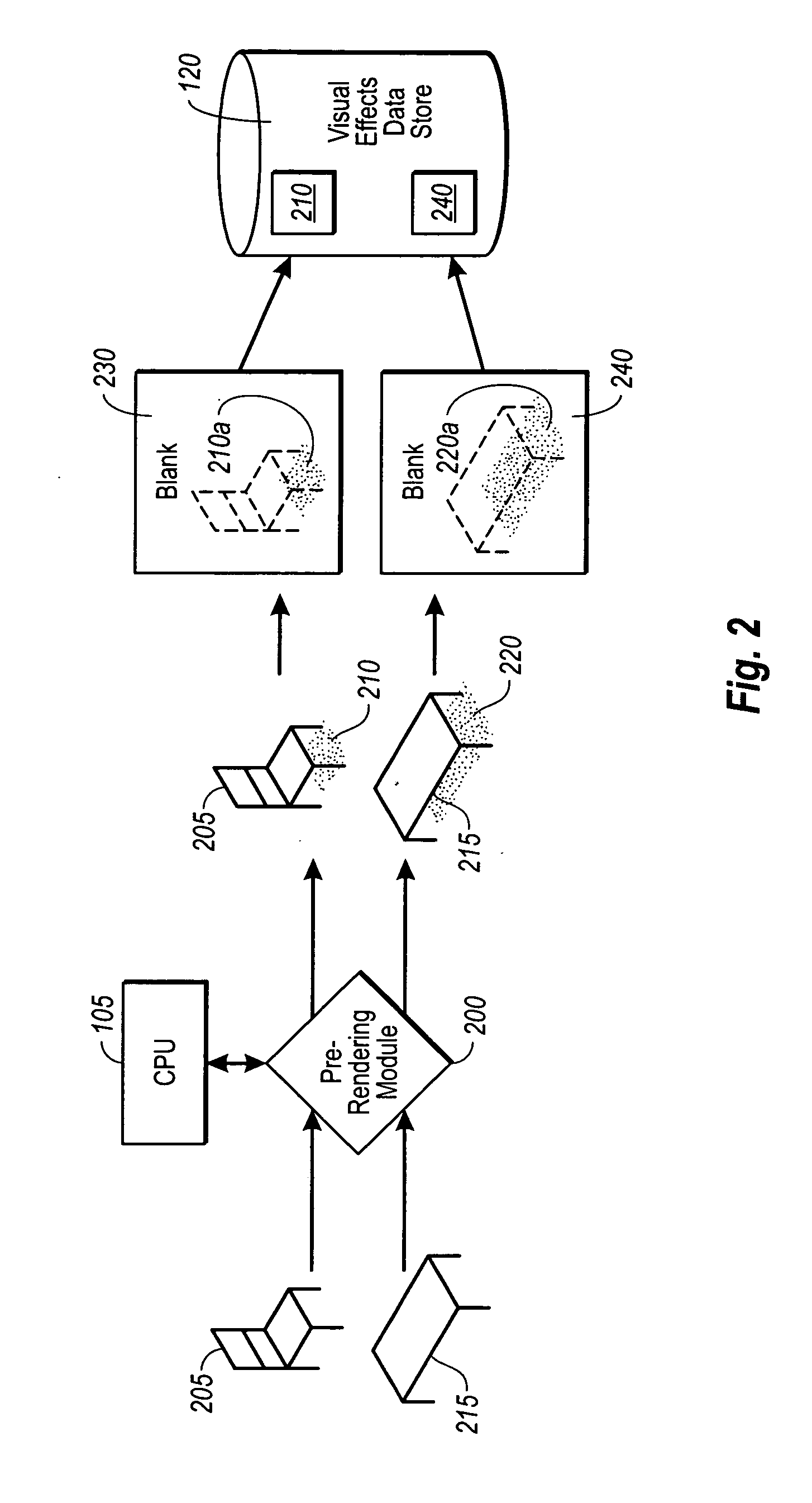
ActiveUS20060055696A1Efficient and accurateAccurate dataCathode-ray tube indicatorsEducational modelsComputer graphics (images)Design software
Design software in accordance with an implementation of the present invention is configured to provide believable three-dimensional representations of user selections in real-time. Design elements that would otherwise be difficult to efficiently render three-dimensionally in real-time are prerendered for realistic visual effects, such as realistic shading, which correspond to various positions of the elements in a design space. Blanks of the visual effects for each position are then stored in a data store for visual effects. At run time, data associated with user design choices, as well as the blanks for any corresponding design elements are fed in one implementation to peripheral processing hardware, such as a GPU, which sends the processed data to a display device. The user is therefore able to view complex visual data of certain design choices efficiently with added realism.
Owner:ARMSTRONG WORLD INDUSTRIES +1
Retrieving data from a configurable IC
InactiveUS7595655B2Solid-state devicesSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureLogical operations
Some embodiments provide a configurable integrated circuit (IC). The IC has configurable logic circuits for performing logical operations, configurable routing circuits for routing signals between the configurable logic circuits, and a network for monitoring data. In some embodiments a method uses at least a subset of the configurable logic circuits and a first subset of the configurable routing circuits to implement a user design circuit on the configurable IC. The method uses a second subset of the configurable routing circuits to pass signals to the network.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
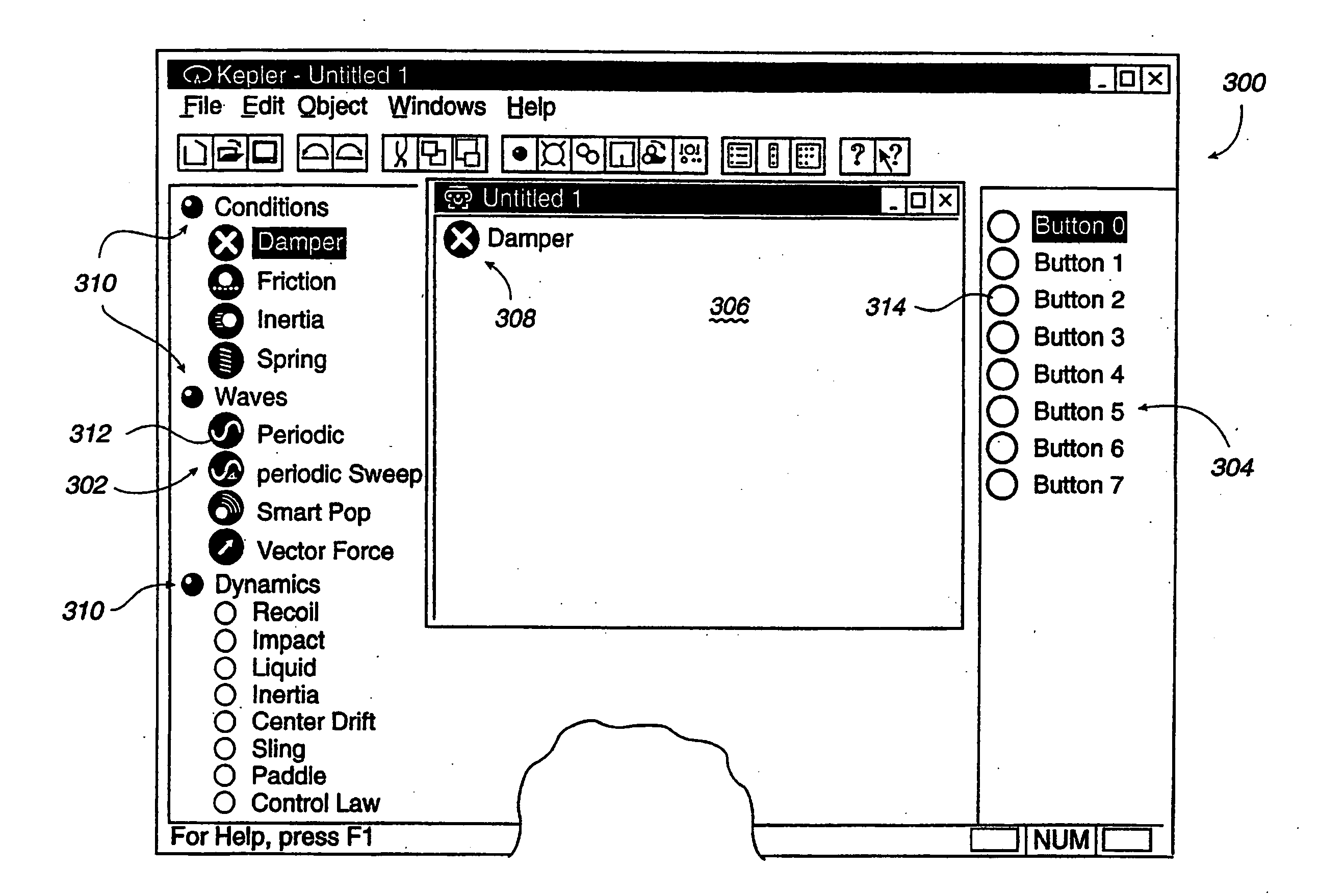
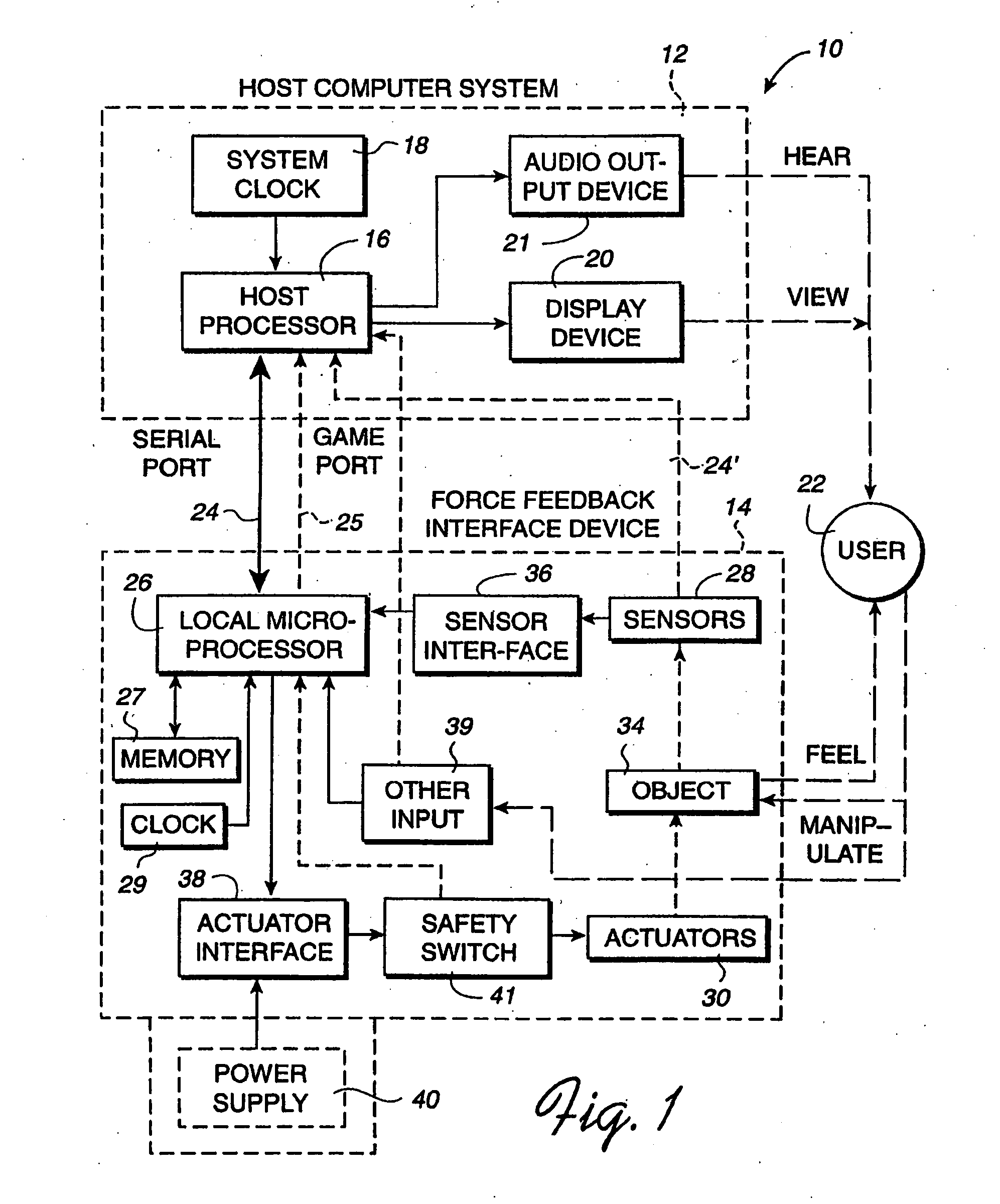
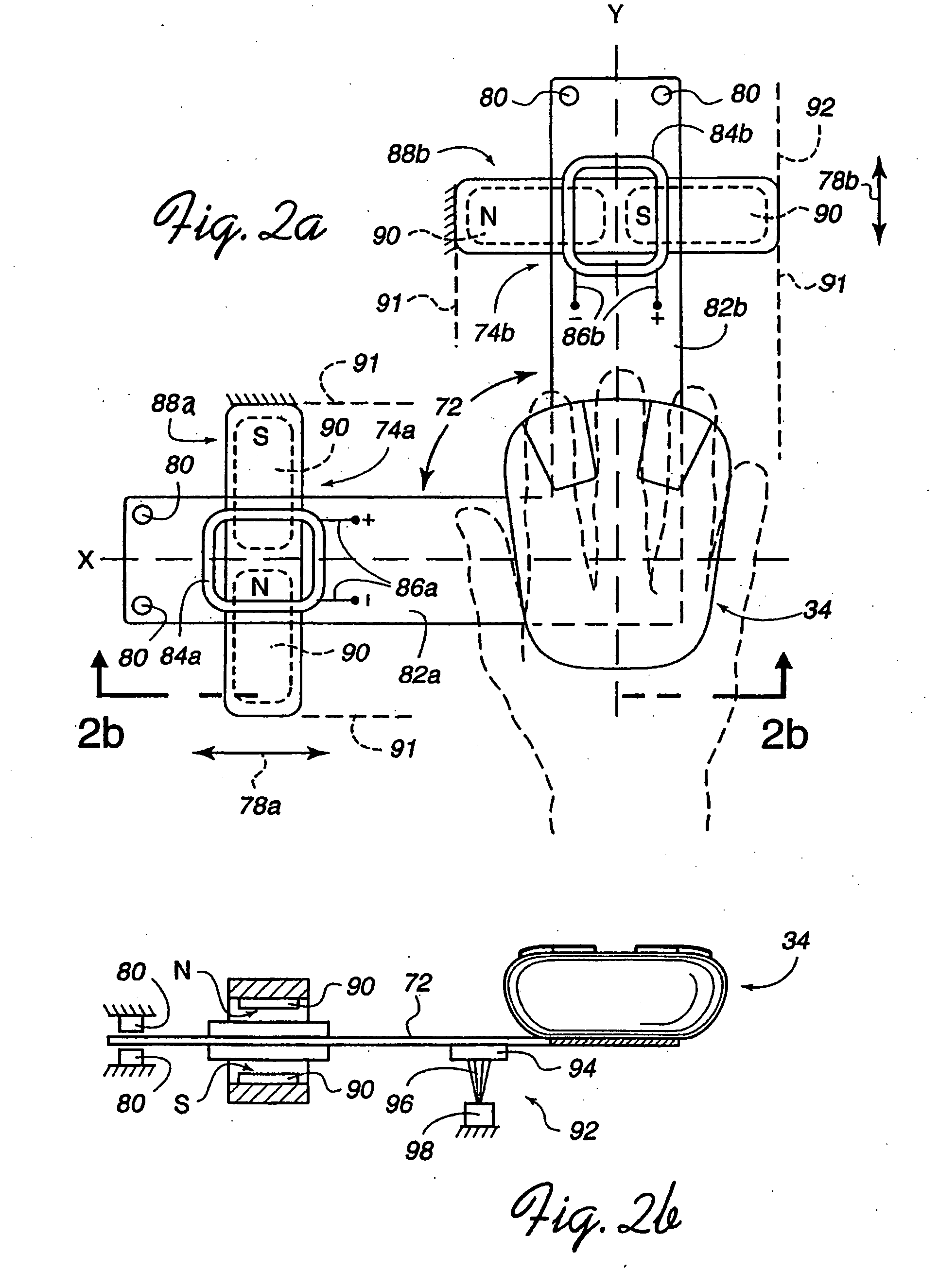
Method and apparatus for designing force sensations in force feedback computer applications
InactiveUS20060187201A1Simple and intuitive designEfficient use ofInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersGraphicsEngineering
A design interface tool for designing force sensations for use with a host computer and force feedback interface device. A force feedback device is connected to a host computer that displays the interface tool. Input from a user is received in the interface to select a type of force sensation to be commanded by a host computer and output by a force feedback interface device. Input, such as parameters, is then received from the user which designs and defines physical characteristics of the selected force sensation. A graphical representation of the characterized force sensation is displayed on the host computer which provides a visual demonstration of a feel of the characterized force sensation so that the user can view an effect of parameters on said force sensation. The characterized force sensation is output to a user manipulatable object of the force feedback device so that the user can feel the designed force sensation, where the graphical representation is updated in conjunction with the output of the force sensation. The user can iteratively modify force sensation characteristics and feel the results, and store the characterized force sensations.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
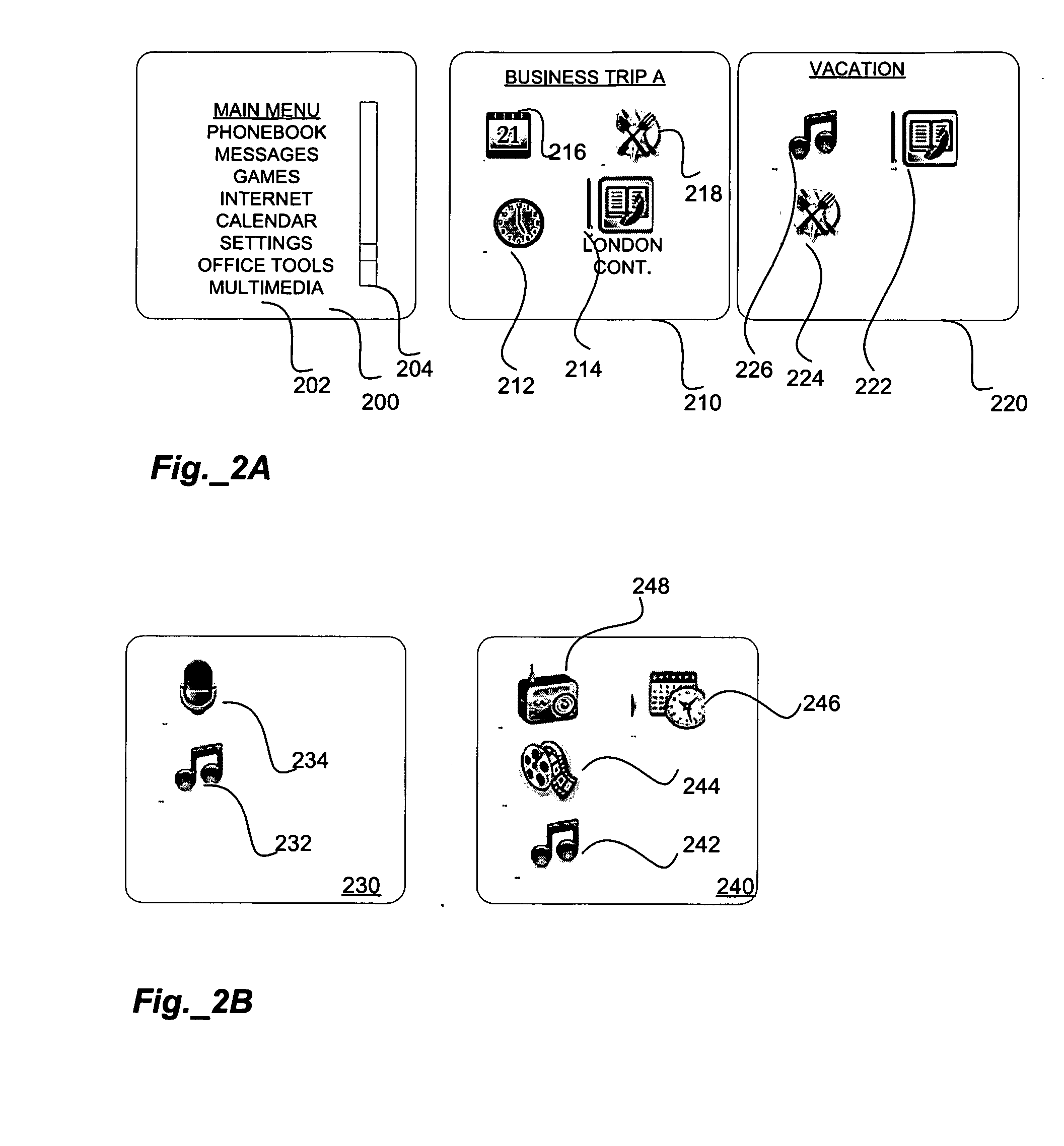
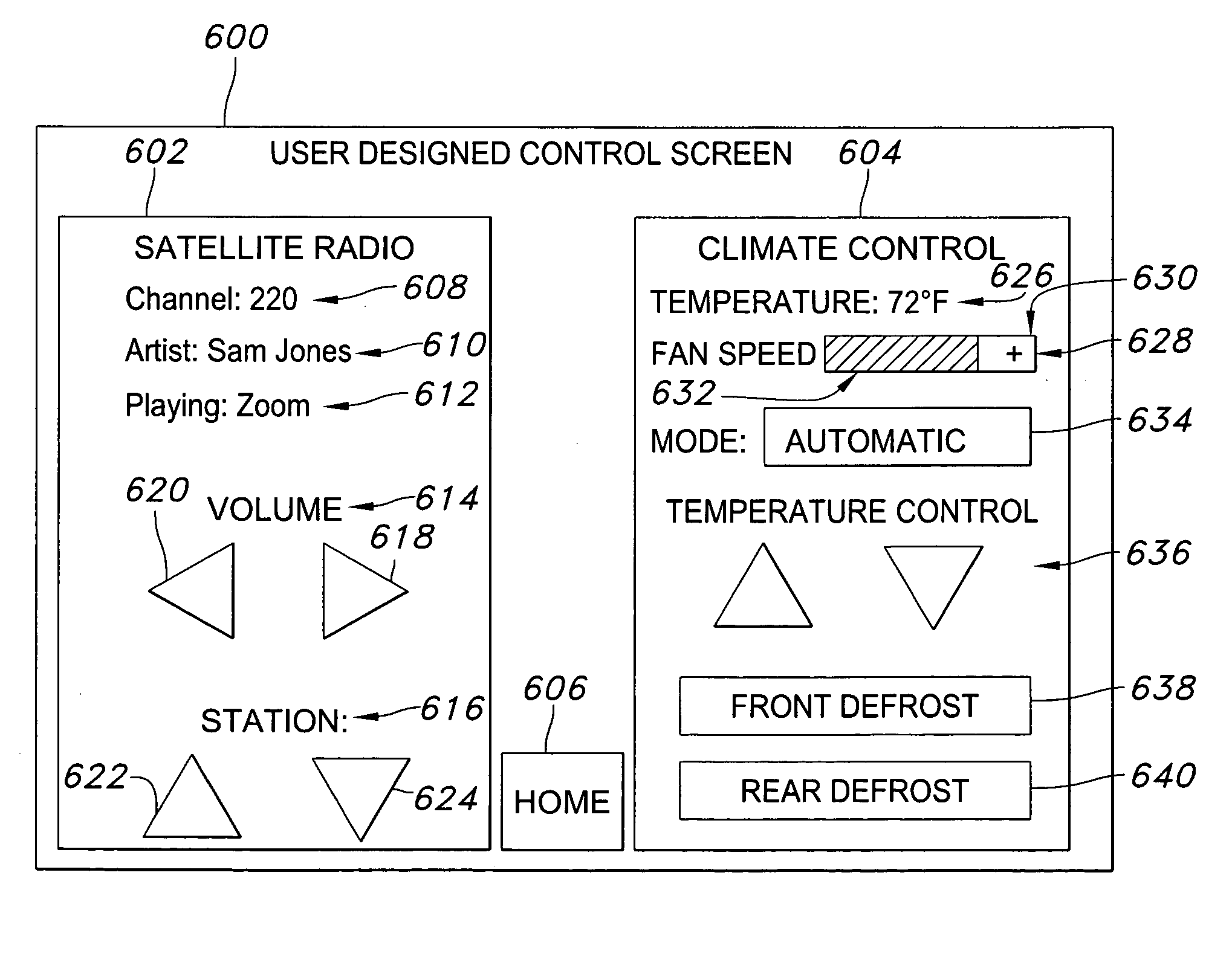
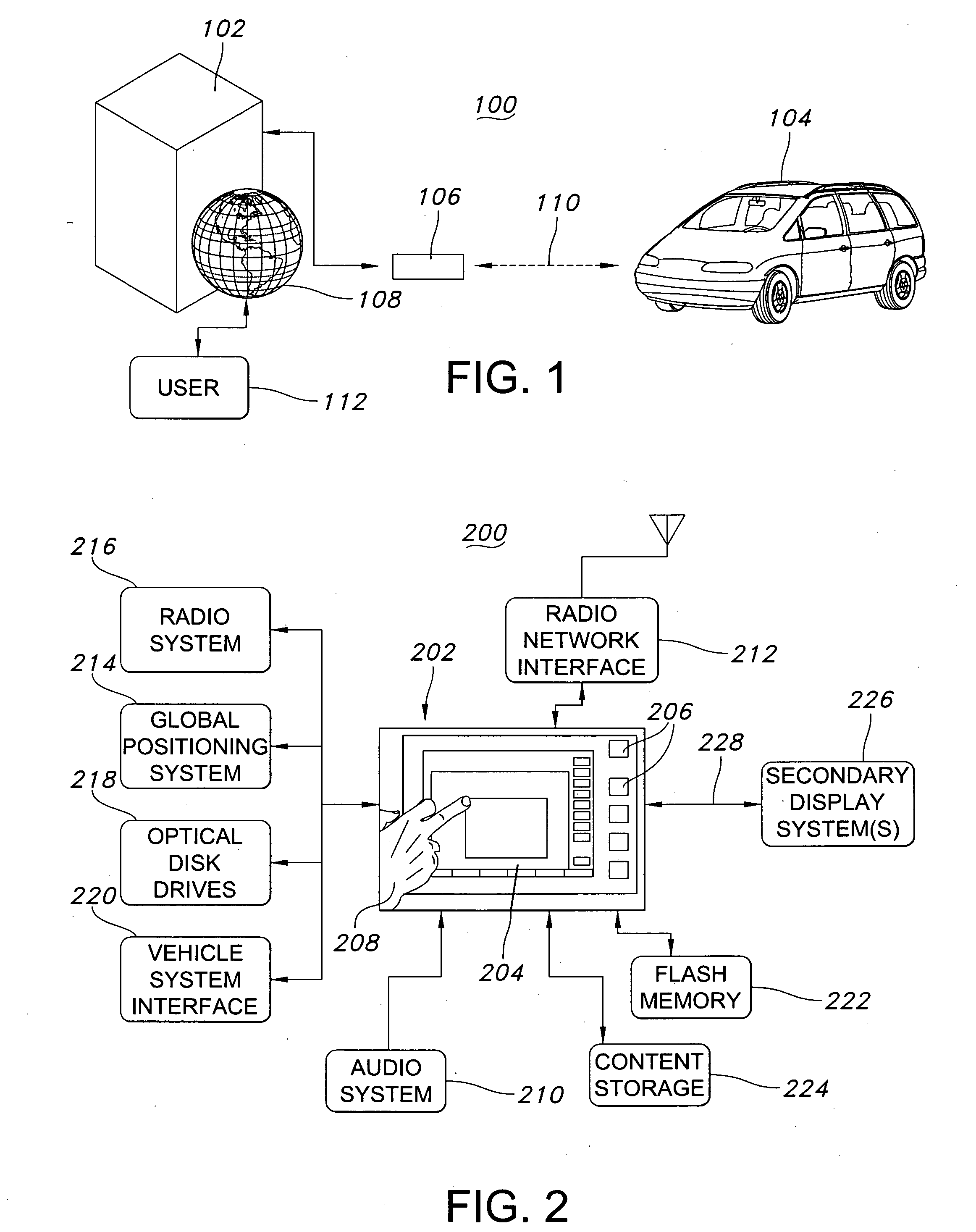
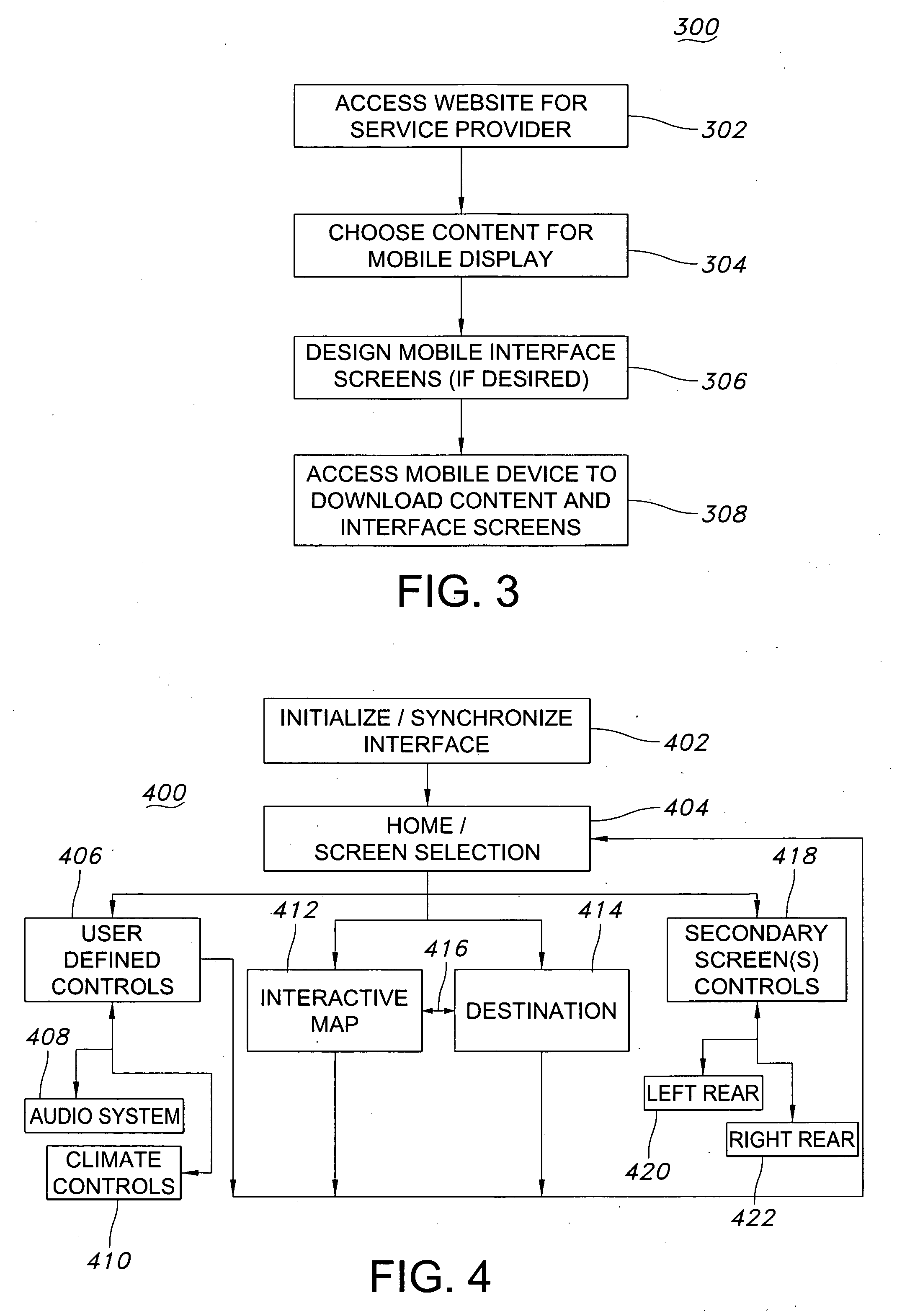
Virtual feature management for vehicle information and entertainment systems
InactiveUS20100235045A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPersonalizationCapability management
Exemplary embodiments of the present invention relate to a mobile information display system that may be configured by a user to have customized interface screens and to display individualized content. For example, upon starting of the ignition system, the mobile information display system may access a remote server using a radio network interface to download interface screens that have previously been designed by a user. Further, the mobile information display system may download information and content from the remote server, or from other websites, including, for example, navigational information, destination information, calendar and alarm entries, e-mail messages, voice mail messages, personal networking pages, internet phone service, internet audio programs, and internet video programs, among others.
Owner:PANASONIC AUTOMOTIVE SYST OF AMERICA
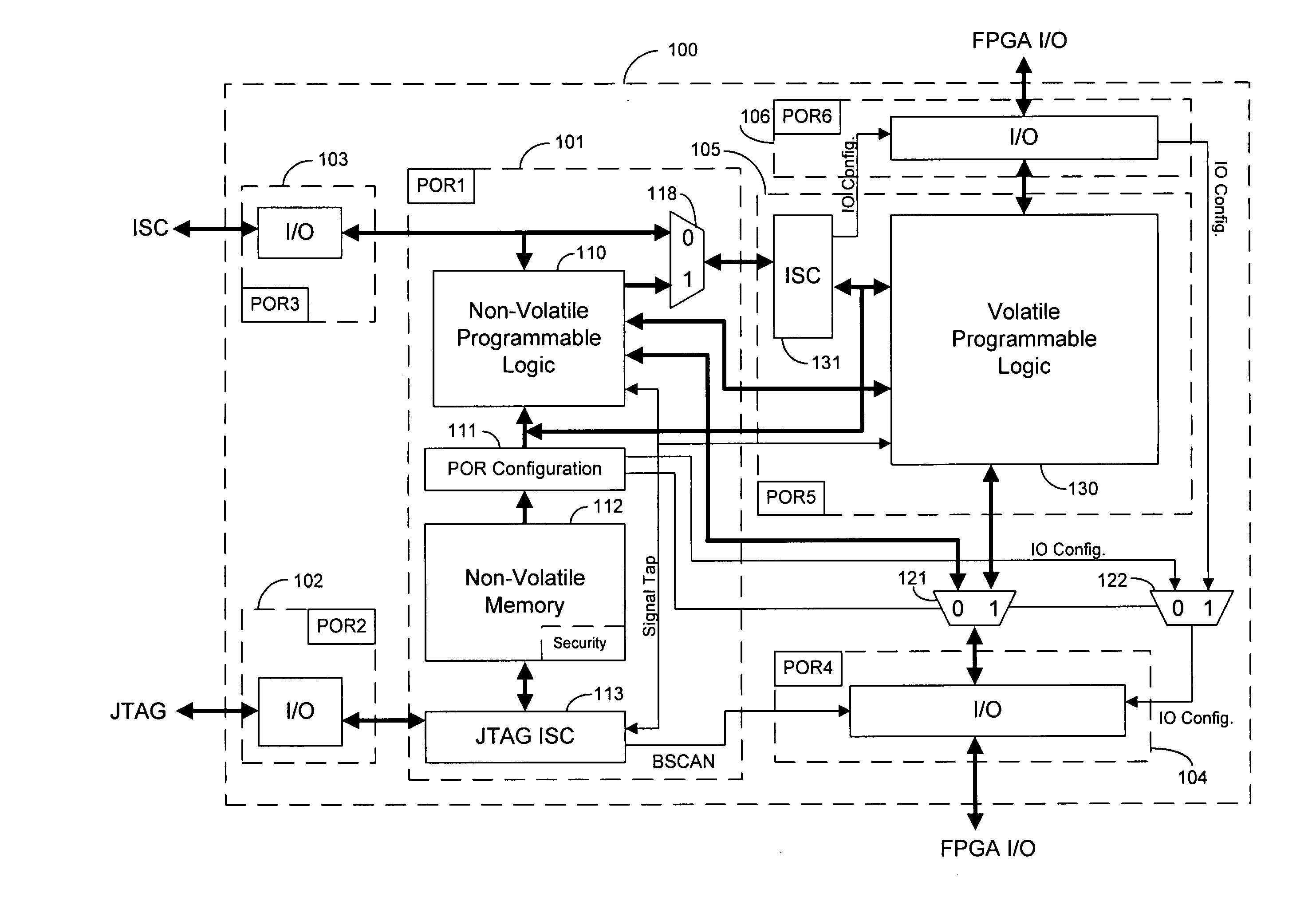
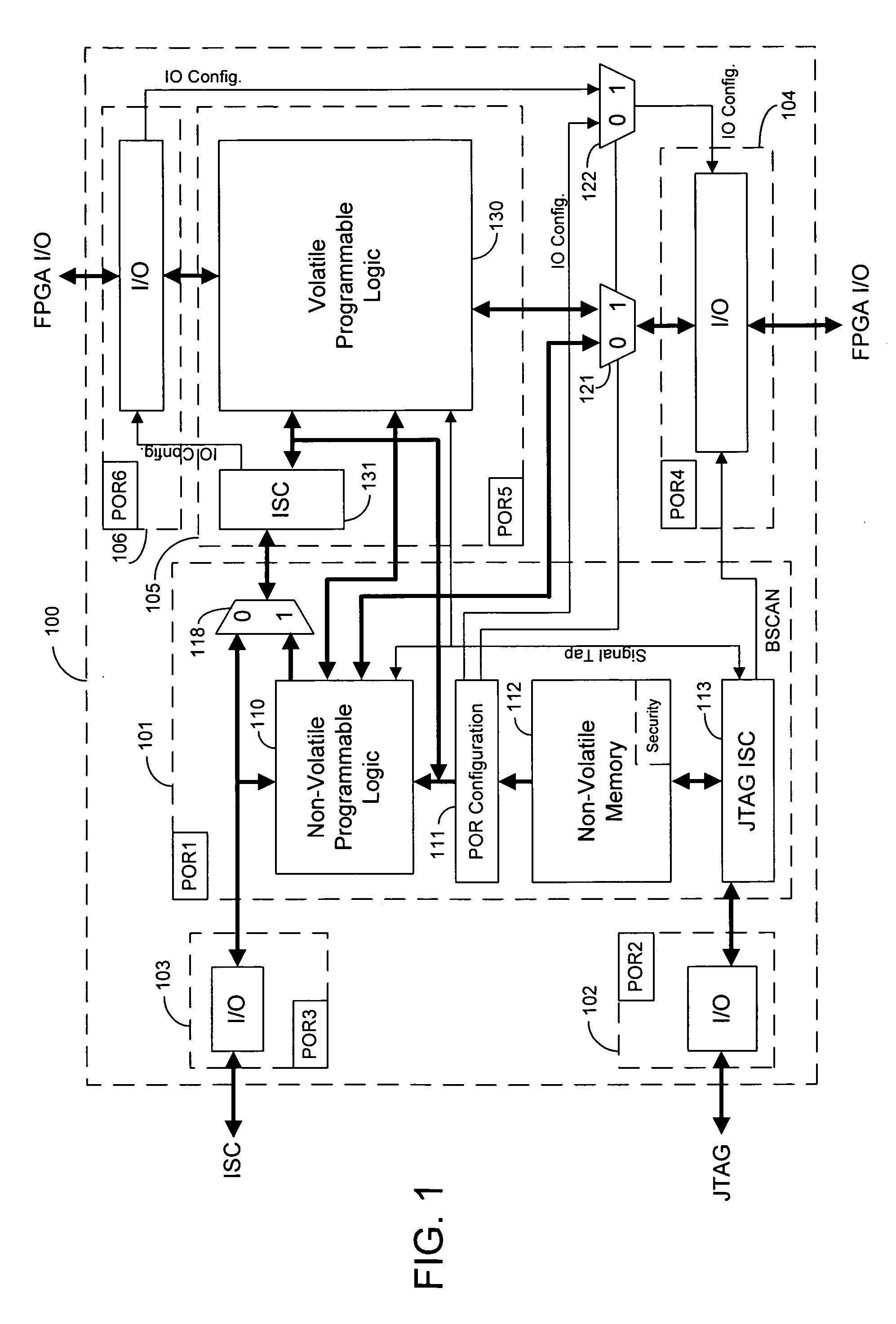
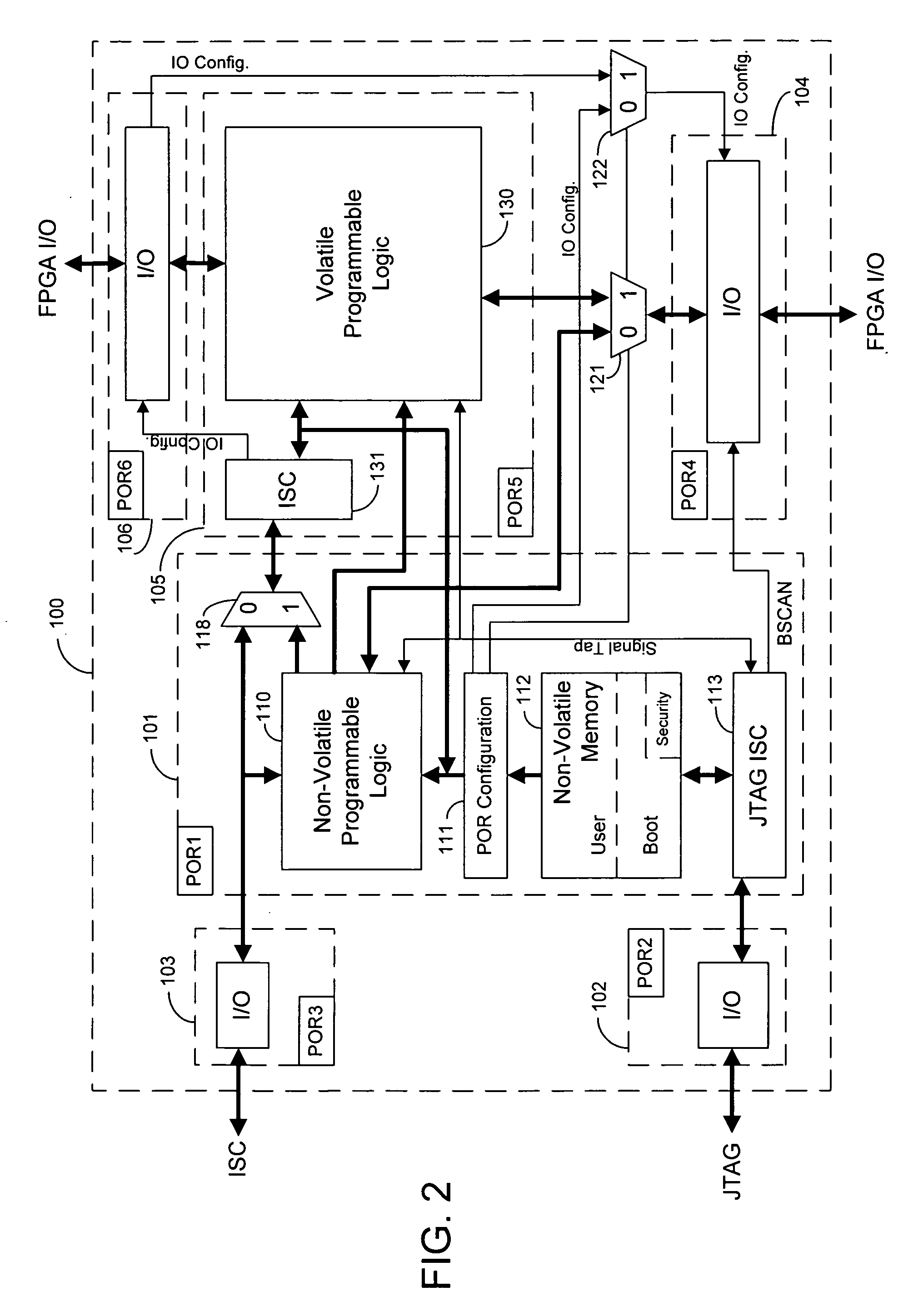
Techniques for combining volatile and non-volatile programmable logic on an integrated circuit
InactiveUS20060119384A1Fully functionalSufficient independenceSolid-state devicesDigital computer detailsEncryptionIntegrated circuit
Techniques for combining volatile and non-volatile programmable logic into one integrated circuit (IC) are provided. An IC is segregated into two portions. A first block of programmable logic is configured by bits stored in on-chip non-volatile memory. A second block of programmable logic is configured by bits stored in off-chip memory. The function of IO banks on the IC is multiplexed between the two logic blocks of the IC. The programmable logic in the first block can be configured and fully functional in a fraction of the time that the programmable logic in the second block can be configured. The programmable logic in the first block can configure fast enough and have enough independence to assist in the configuration of the second block. The non-volatile memory can also provide security features to a user design, such as encryption.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Non-intrusive monitoring and control of integrated circuits
ActiveUS20150008957A1Error detection/correctionCAD circuit designIntegrated circuit layoutMonitoring and control
A method of monitoring operations of a set of ICs. The method loads a first set of configuration data into a first IC for configuring a group of configurable circuits of the first IC to perform operations of a user design. The method receives a definition of an event based on values of a set of signals in the user design and a set of corresponding actions to take when the event occurs. The set of signals includes at least one signal received from a second IC. The method generates an incremental second set of configuration data based on the definition of the event and the set of corresponding actions. While the first IC is performing the operations of the user design, the method loads the incremental second set of configuration data into the first IC and monitors the signals received from the second IC at the first IC.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
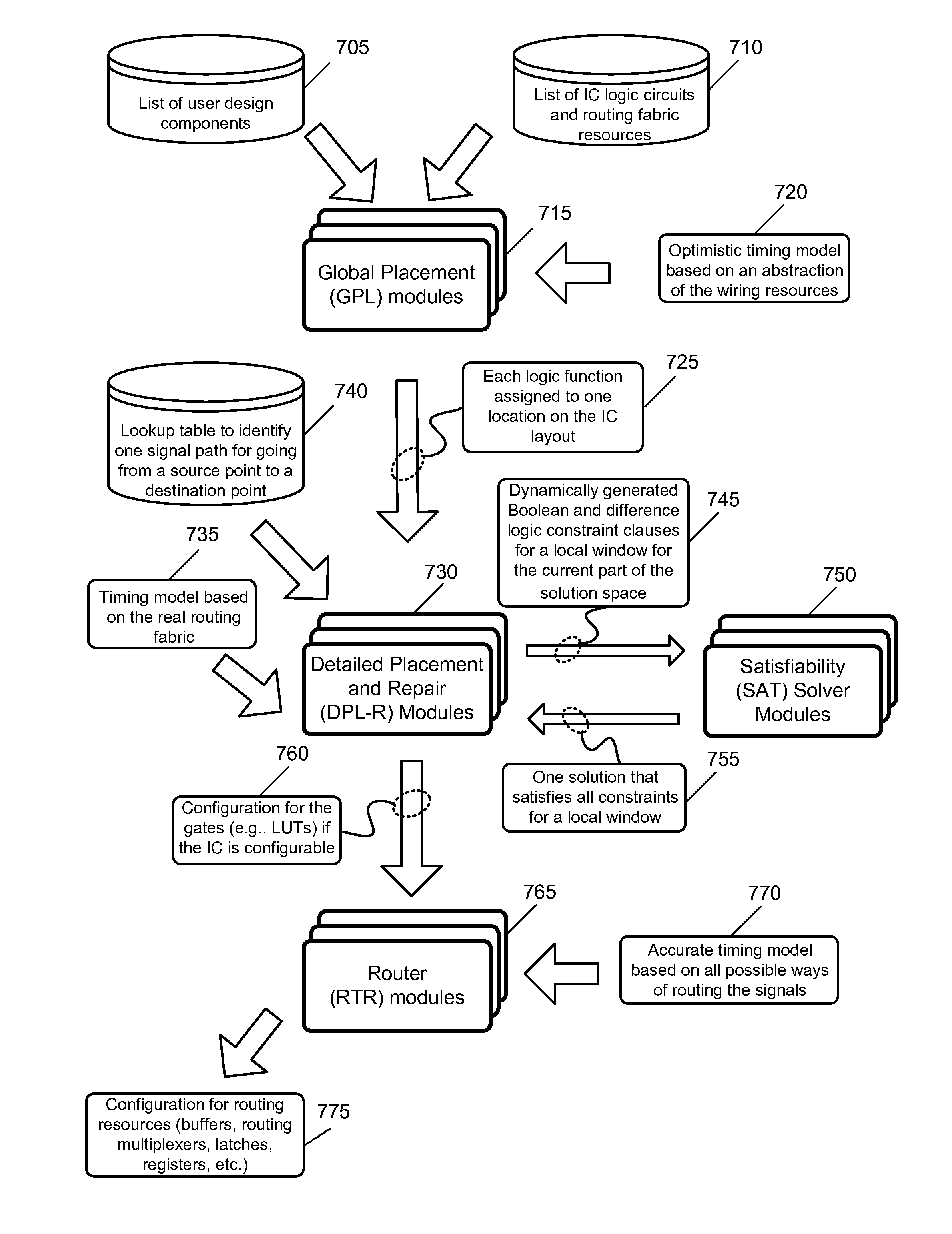
Detailed placement with search and repair
ActiveUS8984464B1Avoid checkingReduce in quantityDetecting faulty computer hardwareDesign optimisation/simulationSatisfiabilitySolver
A method of detailed placement for ICs is provided. The method receives an initial placement and iteratively builds sets of constraints for placement of different groups of cells in the IC design and uses a satisfiability solver to resolve placement violations. In some embodiments, the constraints include mathematical expressions that express timing requirements. The method in some embodiments converts the mathematical expressions into Boolean clauses and sends the clauses to a satisfiability solver that is only capable of solving Boolean clauses. In some embodiments, the method groups several cells in the user design and several sites on the IC fabric and uses the satisfiability solver to resolve all placement issues in the group. The satisfiability solver informs placer after each cell is moved to a different site. The method then dynamically builds more constraints based on the new cell placement and sends the constraints to the satisfiability solver.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
New Sci & Tech. cipher lock and design method of key thereof
The present invention belongs to the field of cipher lock technology, and is especially hi-tech cipher lock and key design method. The hi-tech cipher lock and key design method has user designed cipher stored in a mobile memory and thus expanded cipher source, high reliability and high security. At the same time, the method adopts hand writing input device as the cipher input device and the user can give full play to his imaginative power to create hard-to-unravel cipher.
Owner:姜仁忠
Error handling and representation in a computer-aided design environment
InactiveUS7168012B2Hardware monitoringNon-redundant fault processingComputer Aided DesignError processing
The invention includes computer instructions that operate to generate a failure indication upon encountering a failure during an operation performed for a user design. The instructions further operate to automatically facilitate a user in determining a solution for the failure. As a result, the invention provides improved error reporting and recovery.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Apparatus and method for changing web design
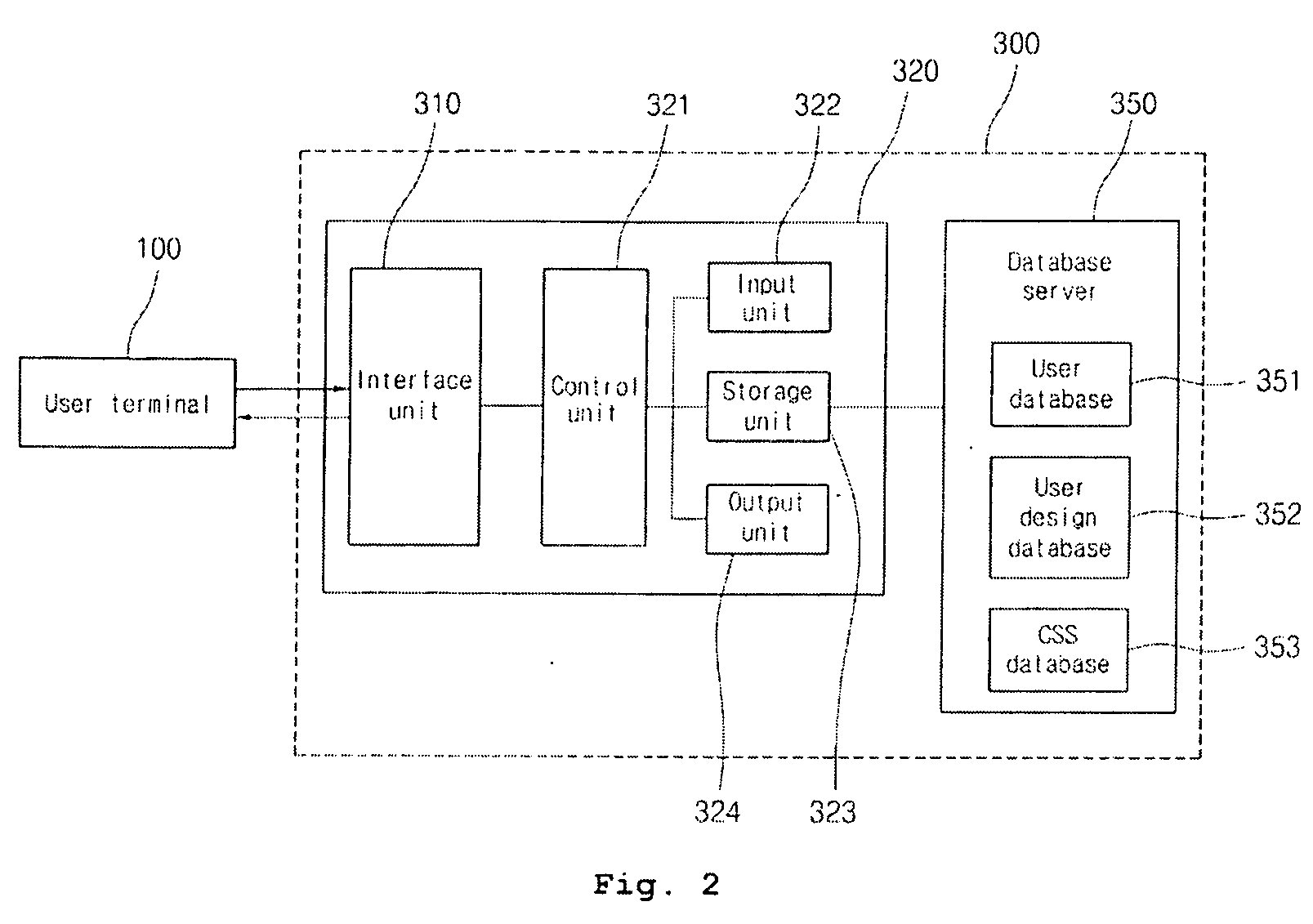
InactiveUS20090024930A1Good varietySmall sizeDigital data information retrievalSpannersDatabase serverWeb design
A web design changing apparatus includes a web server for displaying a web screen on a user terminal when a user logs in a web member page through the user terminal, the web server displaying the web screen by activating a web menu screen according to a controlled menu position, a controlled menu color and a controlled menu shape if the position, the color and the shape of the menu are controlled by the user; and a database server having a user database, a user design database and a CSS (cascade style sheet) database, the database server being connected to the web server. The web server combines CSS information with HTML codes to thereby output them on the user terminal, and stores CSS information modified by the user terminal in the database server.
Owner:KIM TAEK HUN
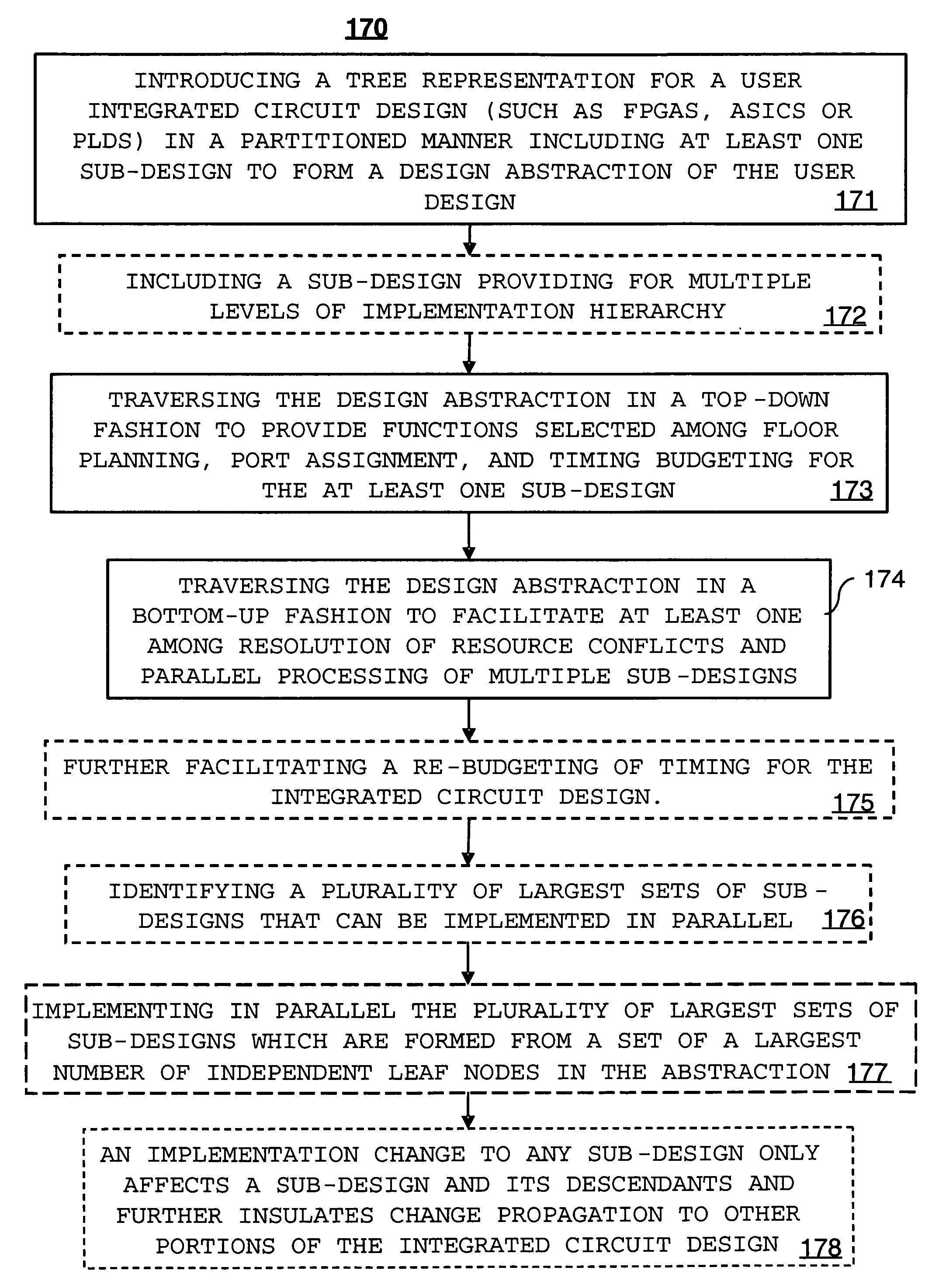
Method and system for implementing a circuit design in a tree representation
ActiveUS7146583B1Simple interfaceEliminate dependenciesCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel processingCircuit design
A method of implementing a user integrated circuit (IC) design in a tree representation includes the step of introducing the tree representation for the user IC design in a partitioned manner including at least one sub-design to form a design abstraction of the user design. At least one sub-design can include a sub-design providing for multiple levels of implementation hierarchy. The method can further include the step of traversing the design abstraction in a top-down fashion to provide functions selected among floor planning, port assignment, and timing budgeting for at least one sub-design, and the step of traversing the design abstraction in a bottom-up fashion to facilitate at least one among resolution of resource conflicts and parallel processing of multiple sub-designs. Traversing the design abstraction in the bottom-up fashion can facilitate a re-budgeting of timing for the integrated circuit design.
Owner:XILINX INC
Intergrated circuit (IC) with primary and secondary networks and device containing such IC
ActiveUS20110060546A1Complex functionData detection is convenientResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingTelecommunicationsHemt circuits
Some embodiments provide an integrated circuit (“IC”) with a primary circuit structure. The primary circuit structure is for performing multiple operations that implement a user design. The primary circuit structure includes multiple circuits. The IC also includes a secondary monitoring structure for monitoring multiple operations. The secondary monitoring structure includes a network communicatively coupled to multiple circuits of the primary circuit structure. The secondary monitoring circuit structure is for analyzing the monitored operations and reporting on the analysis to a circuit outside of the IC.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
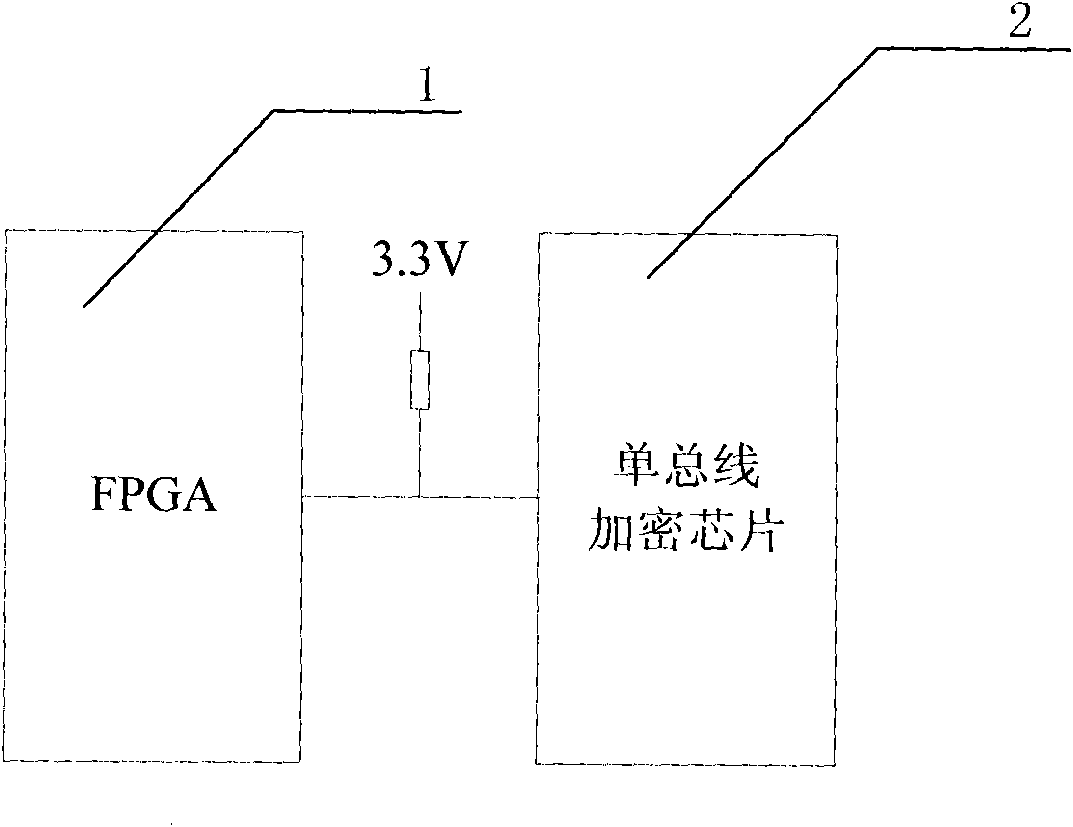
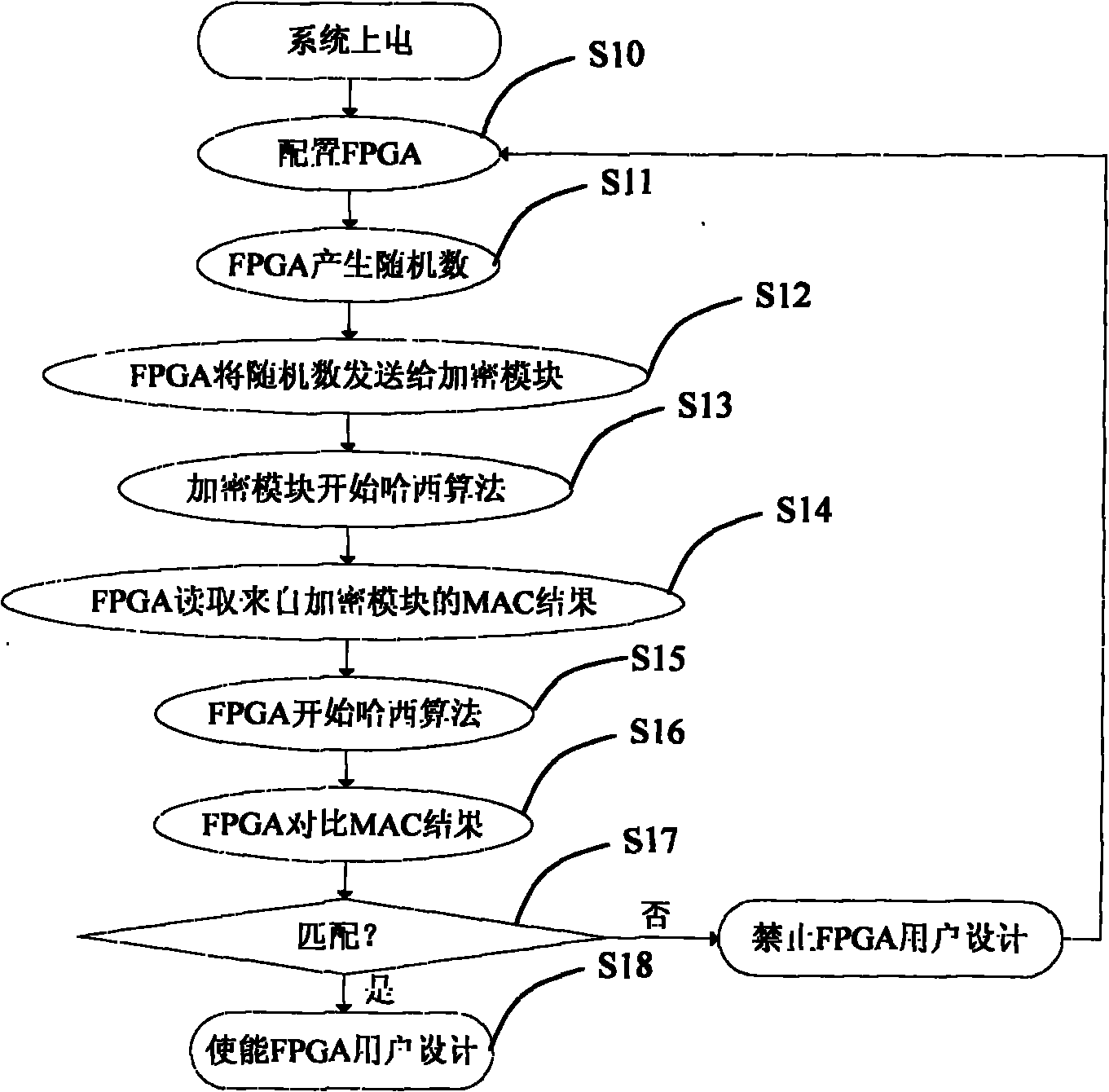
Circuit system design encryption circuit and encryption method thereof
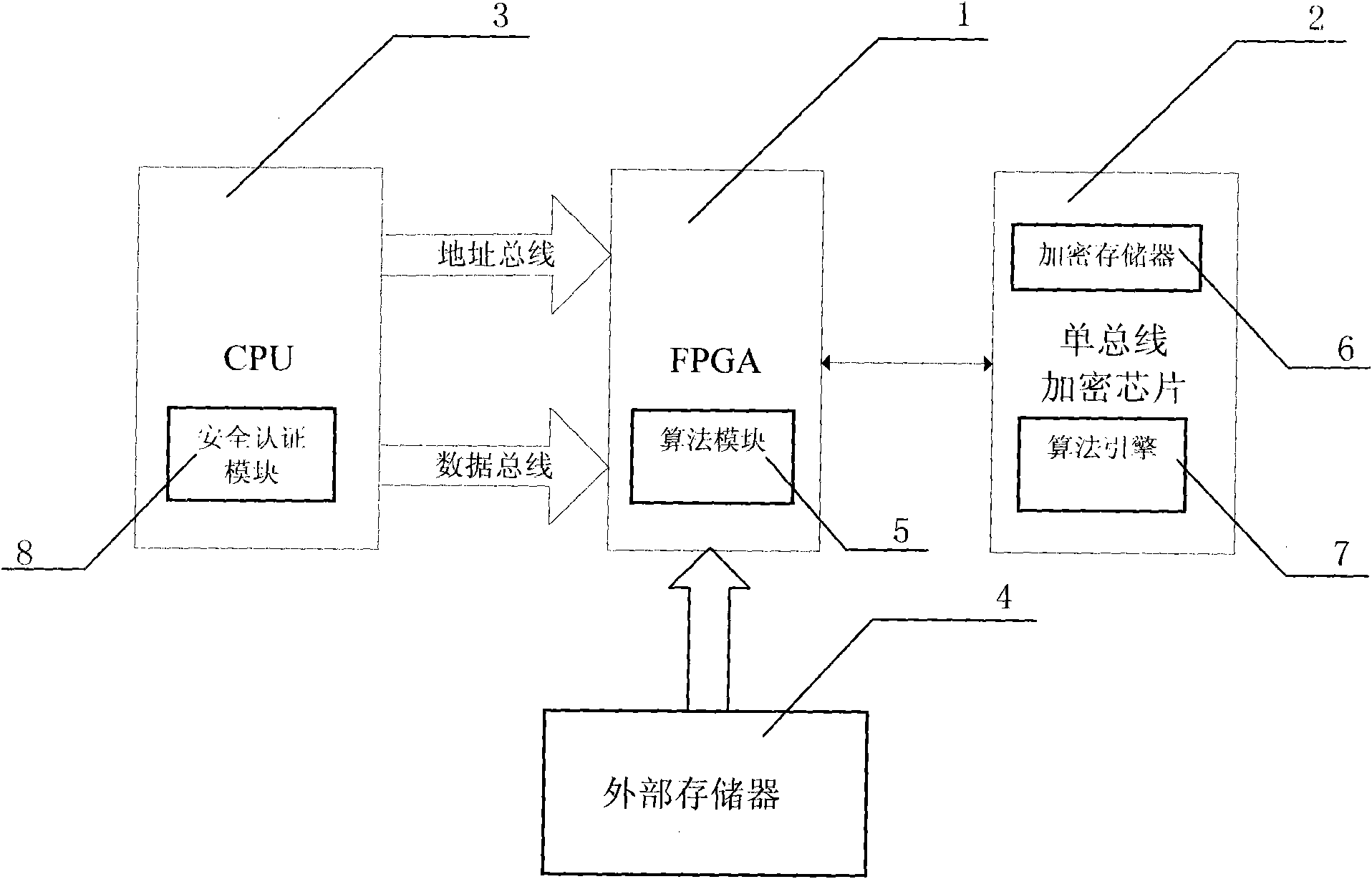
ActiveCN101854243APrevent imitationProtect interestsKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationElectricityExternal storage
The invention discloses a circuit system design encryption circuit and an encryption method thereof. The encryption circuit comprises an FPGA and a CPU, wherein the CPU is connected with the FPGA through an address bus and a data bus; when the system is electrified, the configuration data bit stream in the FPGA is transmitted between the FPGA and an external memory; the circuit system design encryption circuit also comprises an encryption module connected with the FPGA; the encryption module comprises an algorithm engine and a corresponding key is stored in the encryption module; an algorithmmodule is also embedded in the FPGA and a key matched with that in the encryption module is also included in the FPGA; when the system is electrified, the FPGA reads the calculation result from the encryption module, compares the calculation result with that of the algorithm module in the FPGA and the user design is used if the results are matched with each other, if not, the user design is not used. The encryption design of the circuit is realized through an economic and reliable method so as to effectively prevent imitation of competitors and protect the interests per se.
Owner:HUNAN CRRC TIMES SIGNAL & COMM CO LTD
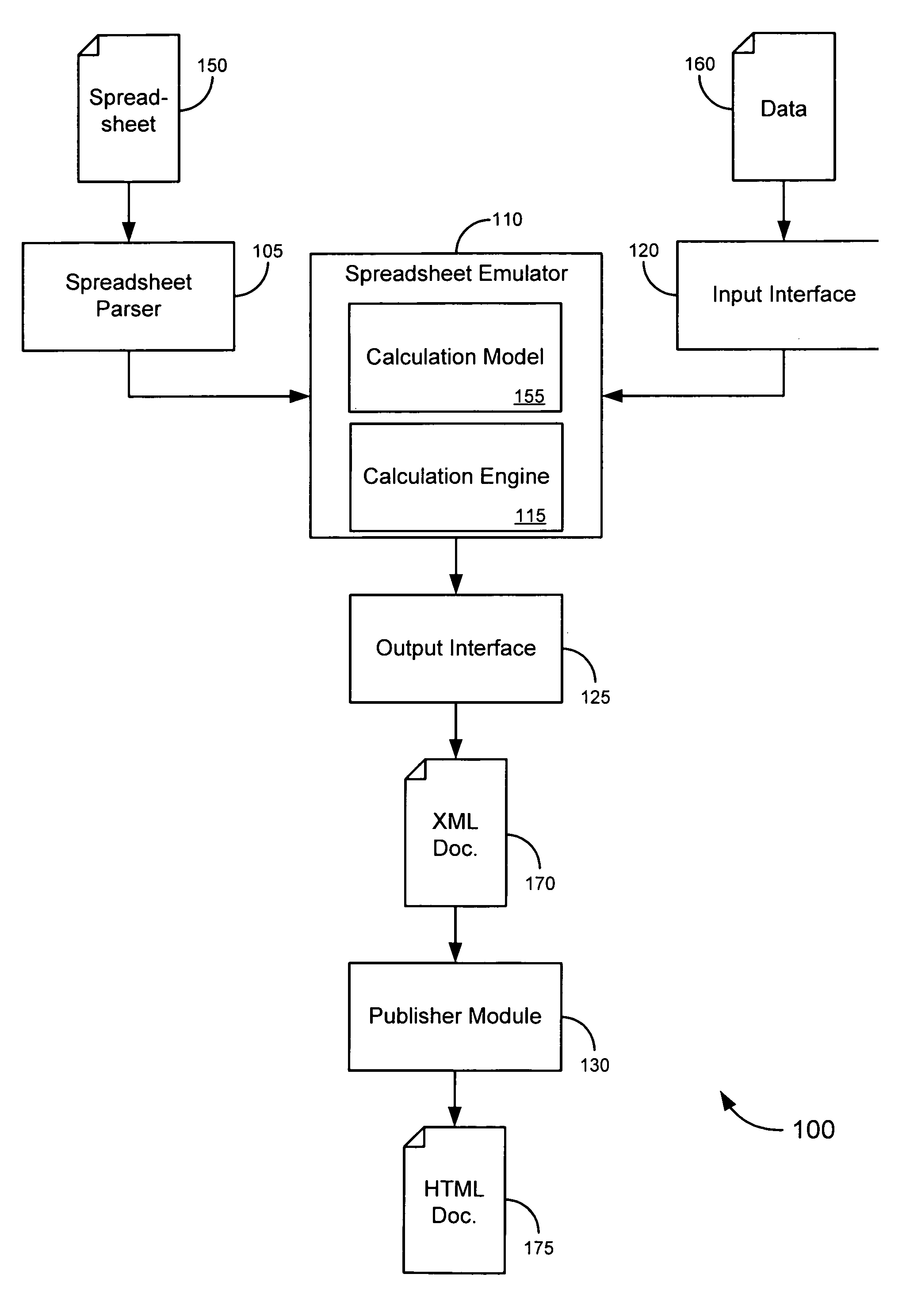
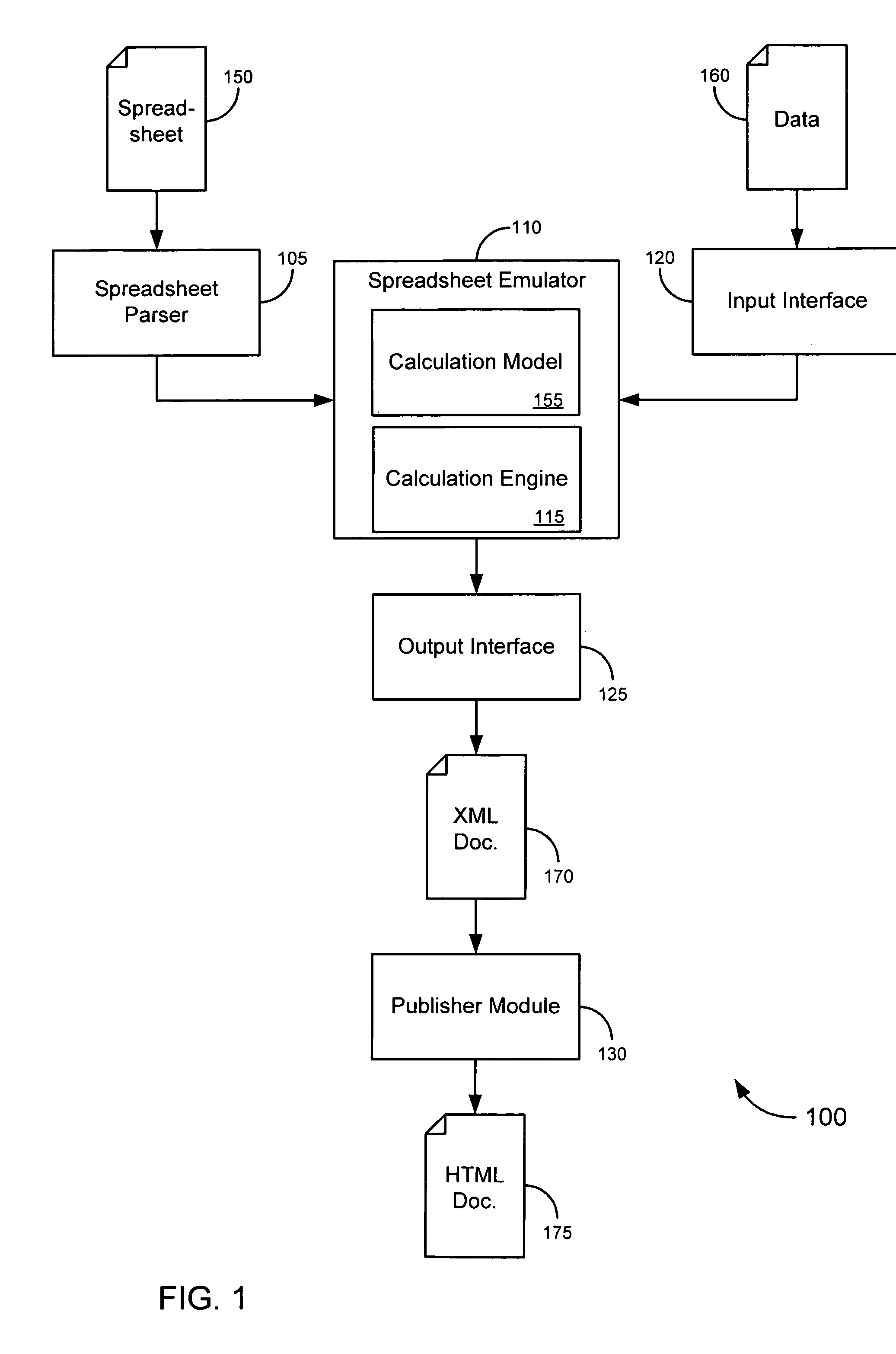
Using a spreadsheet engine as a server-side calculation model
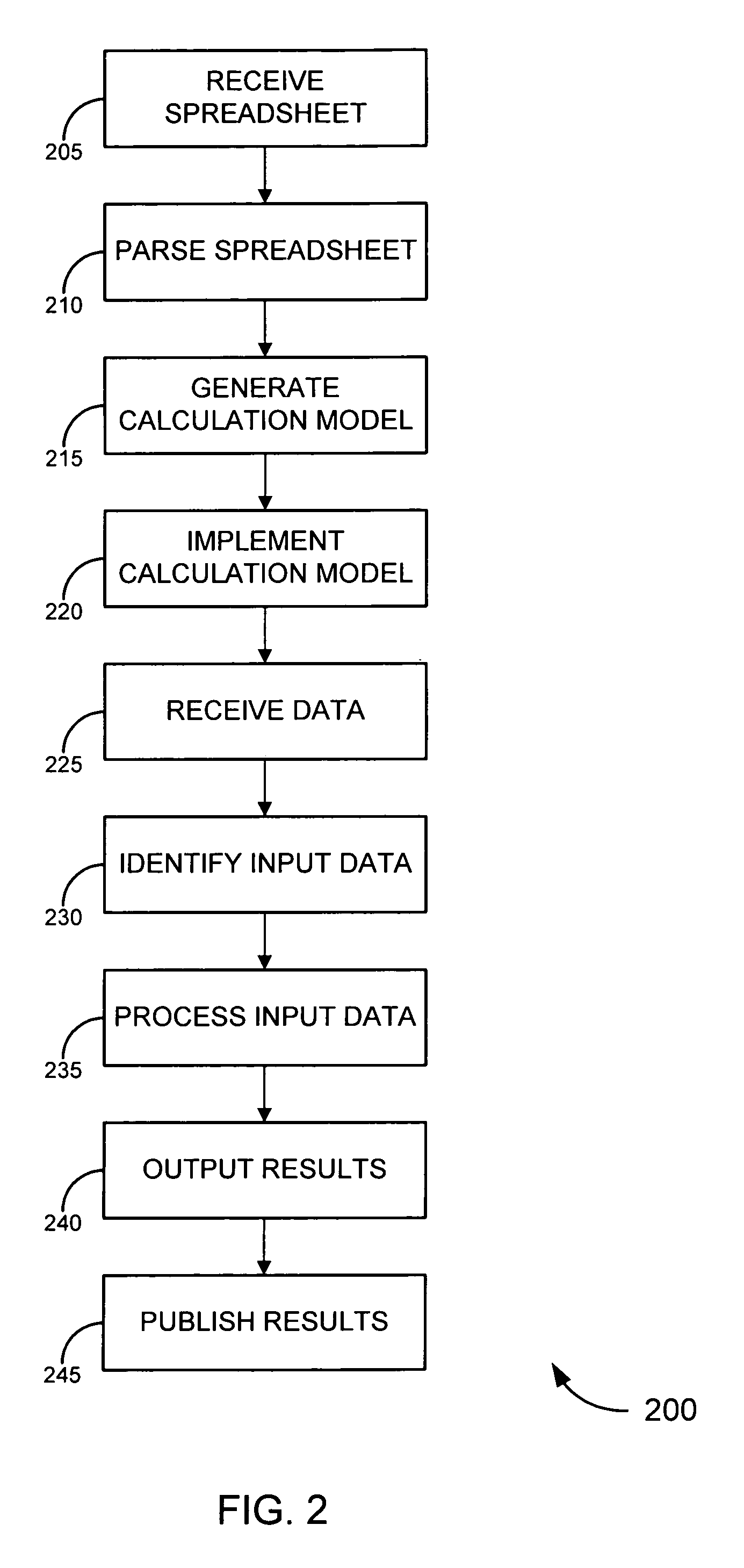
ActiveUS20070250764A1Enhanced data input/output flexibilityEasy maintenanceText processingDigital computer detailsApplication serverDatabase server
This disclosure is directed to novel solutions for processing data in a manner similar to that employed by traditional spreadsheet applications (including, merely by way of example, evaluating expressions, producing reports and the like) without the need for a spreadsheet application. In an aspect, a spreadsheet calculation engine might be emulated in a Java environment, allowing for enhanced data input / output flexibility while still maintaining the ease with which traditional spreadsheet applications allow users to design a calculation model. In another aspect, the spreadsheet engine might be provided on a web server, database server and / or application server, allowing for data (including, for instance, reports comprising data processed and / or produced by the spreadsheet calculation engine) to be published easily (and, in some cases dynamically) on the web.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Dynamically tracking data values in a configurable IC
Some embodiments provide a method of dynamically tracking data values in a configurable integrated circuit (IC). The method, during a run time of the configurable IC, receives a request for a data value and dynamically configures the configurable IC to monitor the data value.In some embodiments, the method, in dynamically configuring the configurable IC, dynamically configures a debug network of the configurable IC. In some such embodiments, the method, in dynamically configuring the configurable IC, further dynamically configures a set of configurable routing circuits of the configurable IC. In some embodiments the configuration is performed while the IC is implementing a user design circuit.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
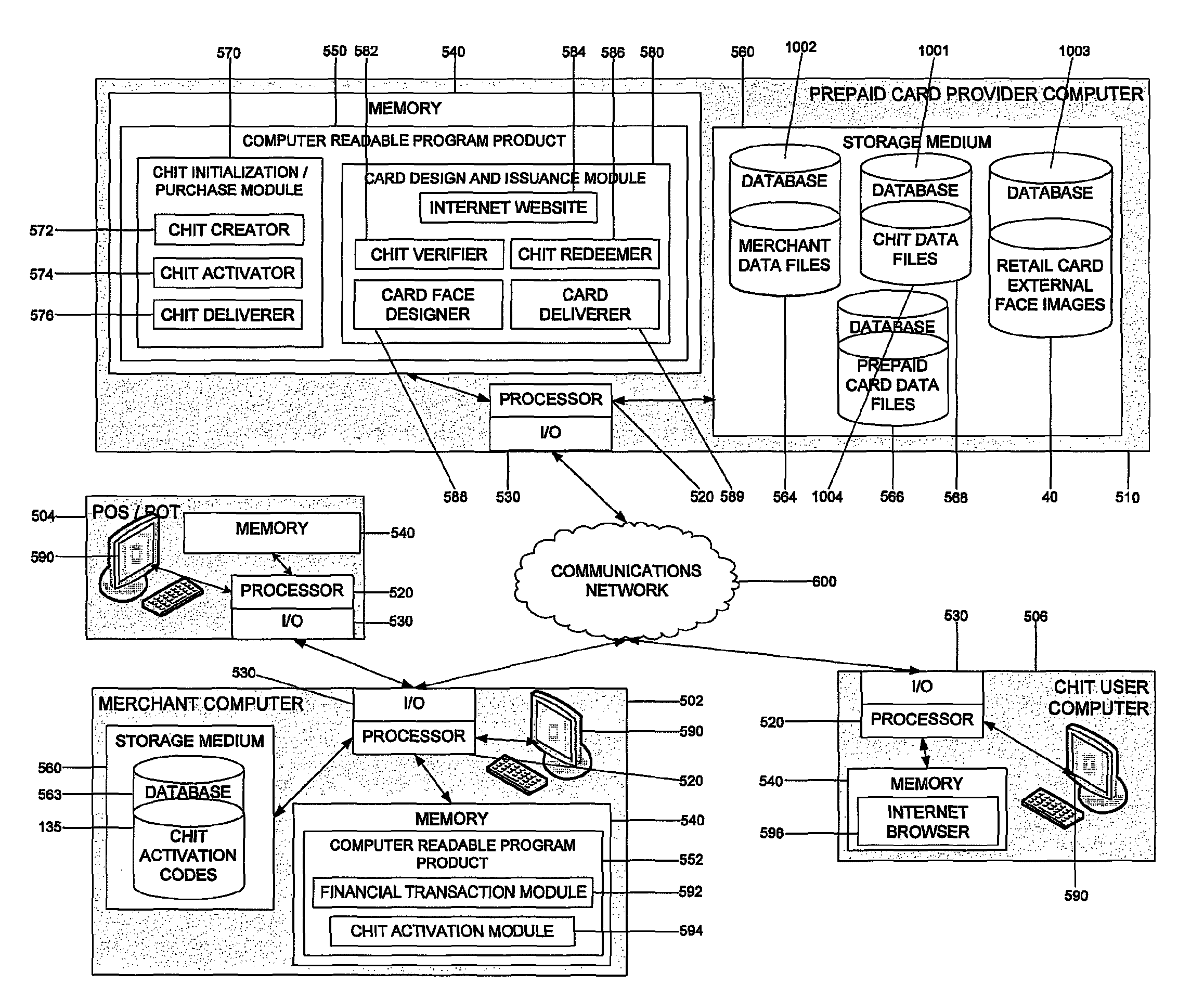
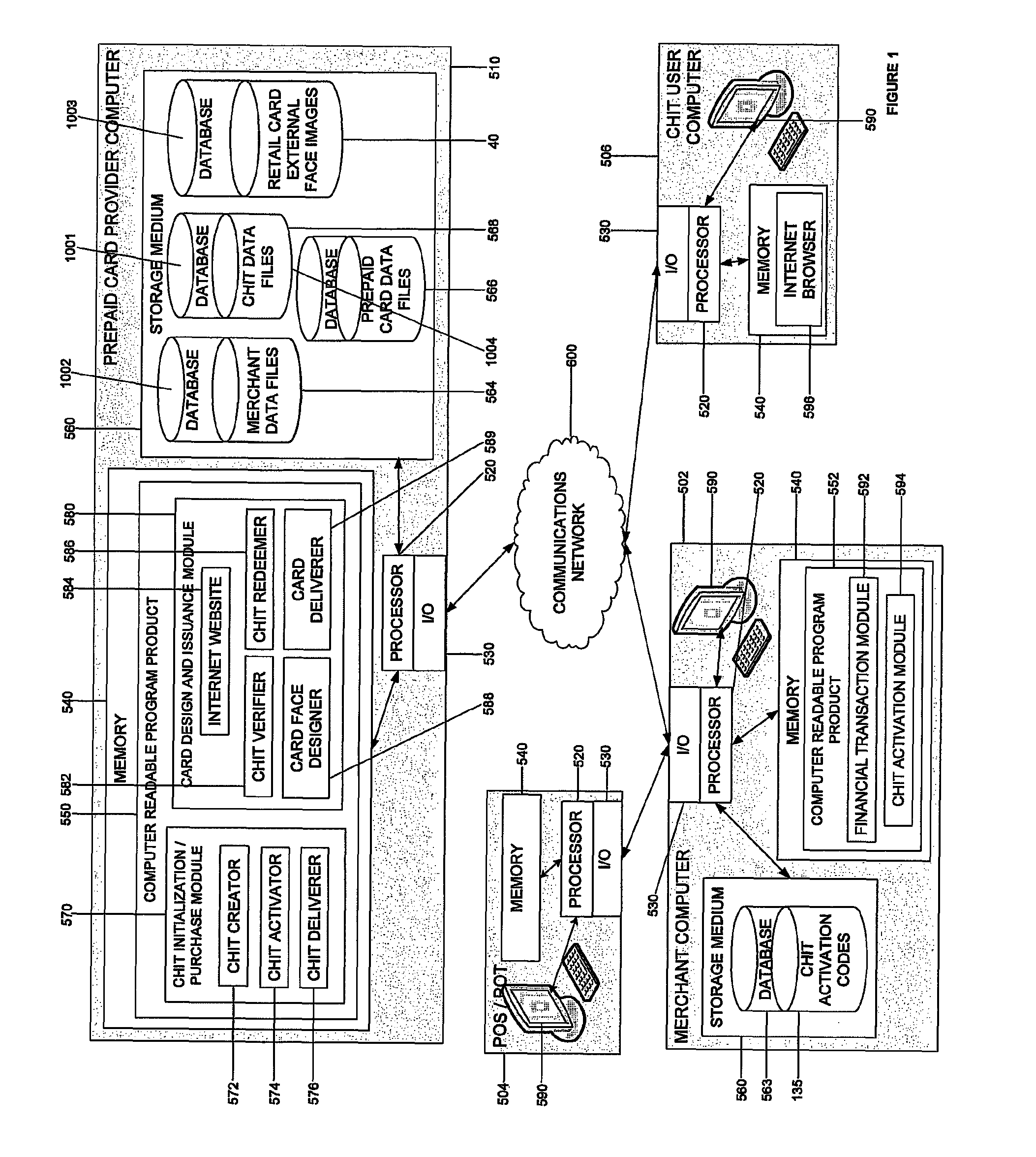
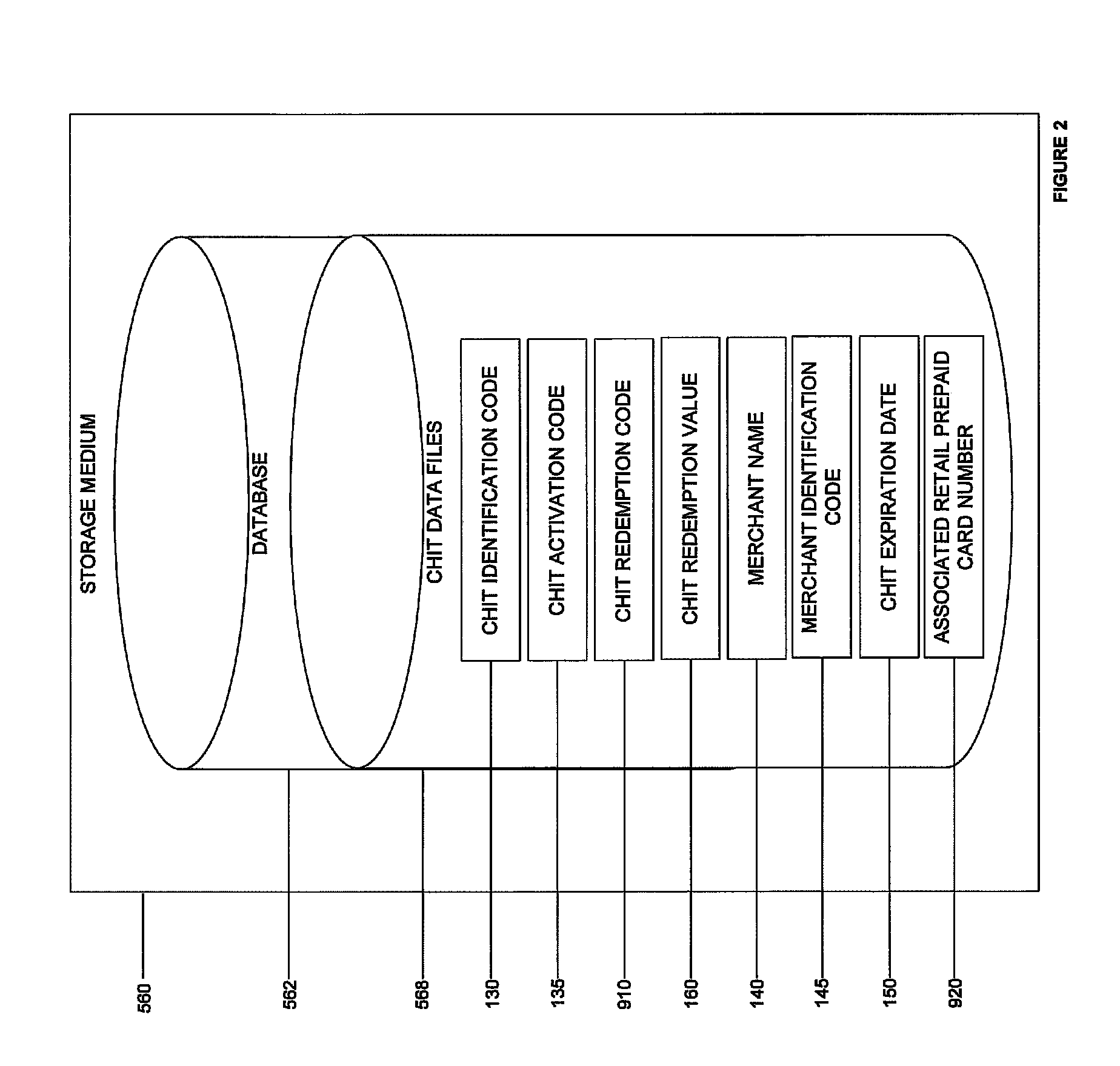
System and computer program product to issue a retail prepaid card including a user-designed external face using a chit and related computer implemented methods
ActiveUS8286863B1Improve visualizationComplete banking machinesAcutation objectsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Embodiments of systems, computer program product, and related computer implemented methods to issue a closed-loop retail prepaid card including a user-designed external face using a chit, the chit being defined by an identification mechanism representing a financial commitment to issue a closed-loop retail prepaid card in an amount associated with a value paid for the chit, are provided. Embodiments of the present invention advantageously provide a service that enables a consumer to purchase, at the storefront of a retail establishment, a chit card that the consumer can subsequently redeem through a graphical user interface of an Internet website for a closed-loop retail prepaid card with a user-designed external face. The user-designed closed-loop retail prepaid card, for example, can be subsequently printed and delivered to an intended recipient. Advantageously, such a service can be made available to any retail establishment that uses a point-of-sale system.
Owner:PATHWARD NAT ASSOC
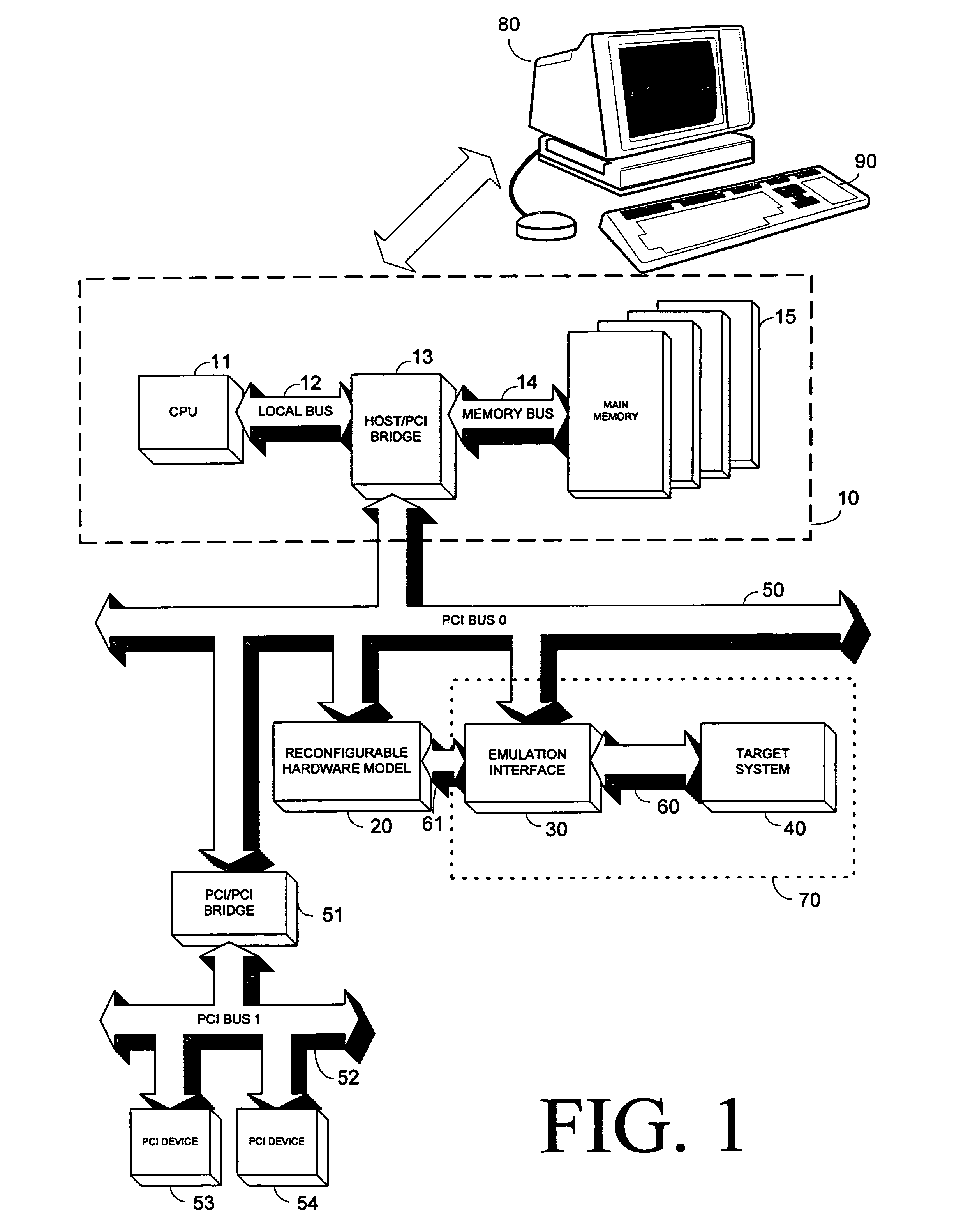
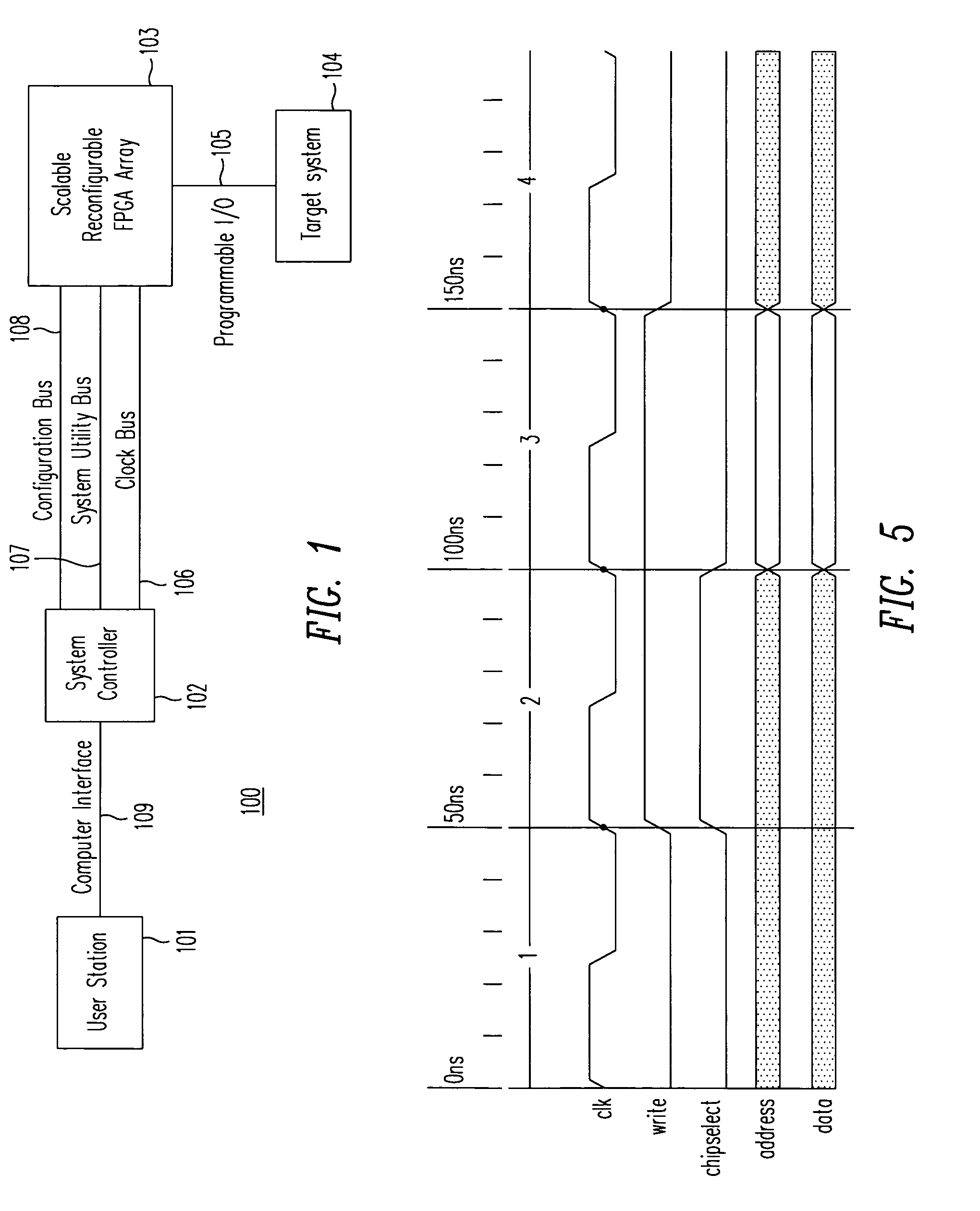
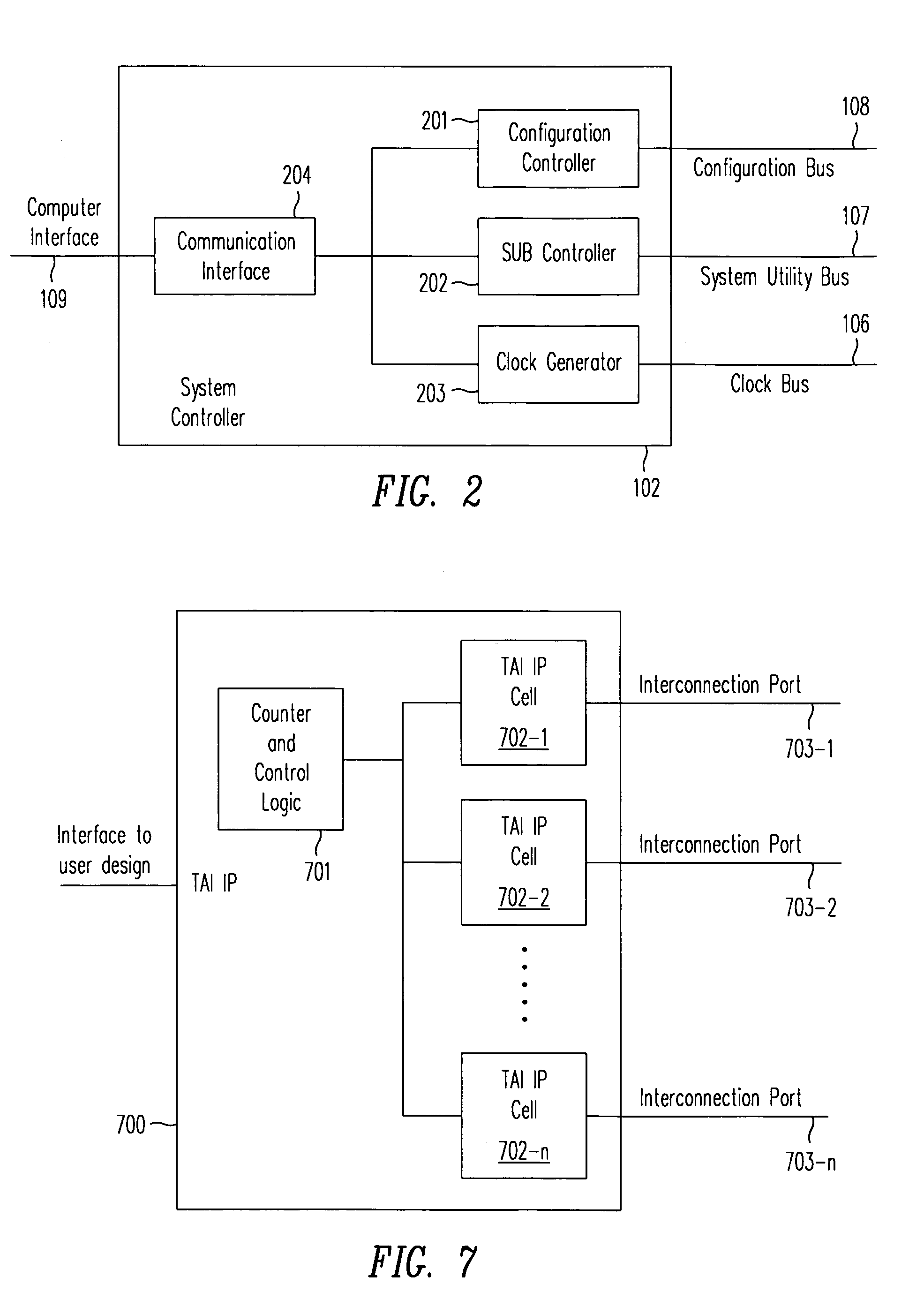
Scalable reconfigurable prototyping system and method
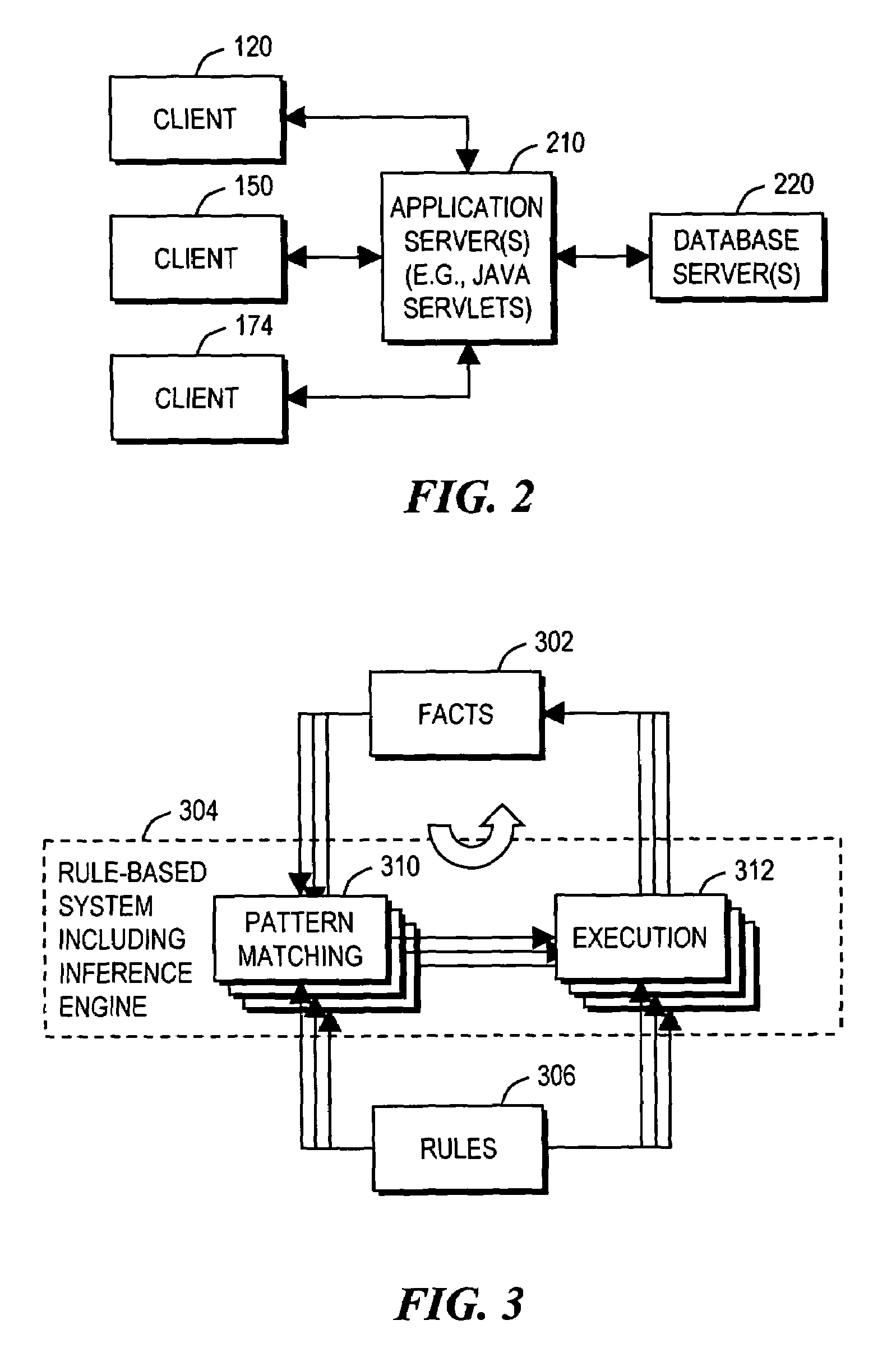
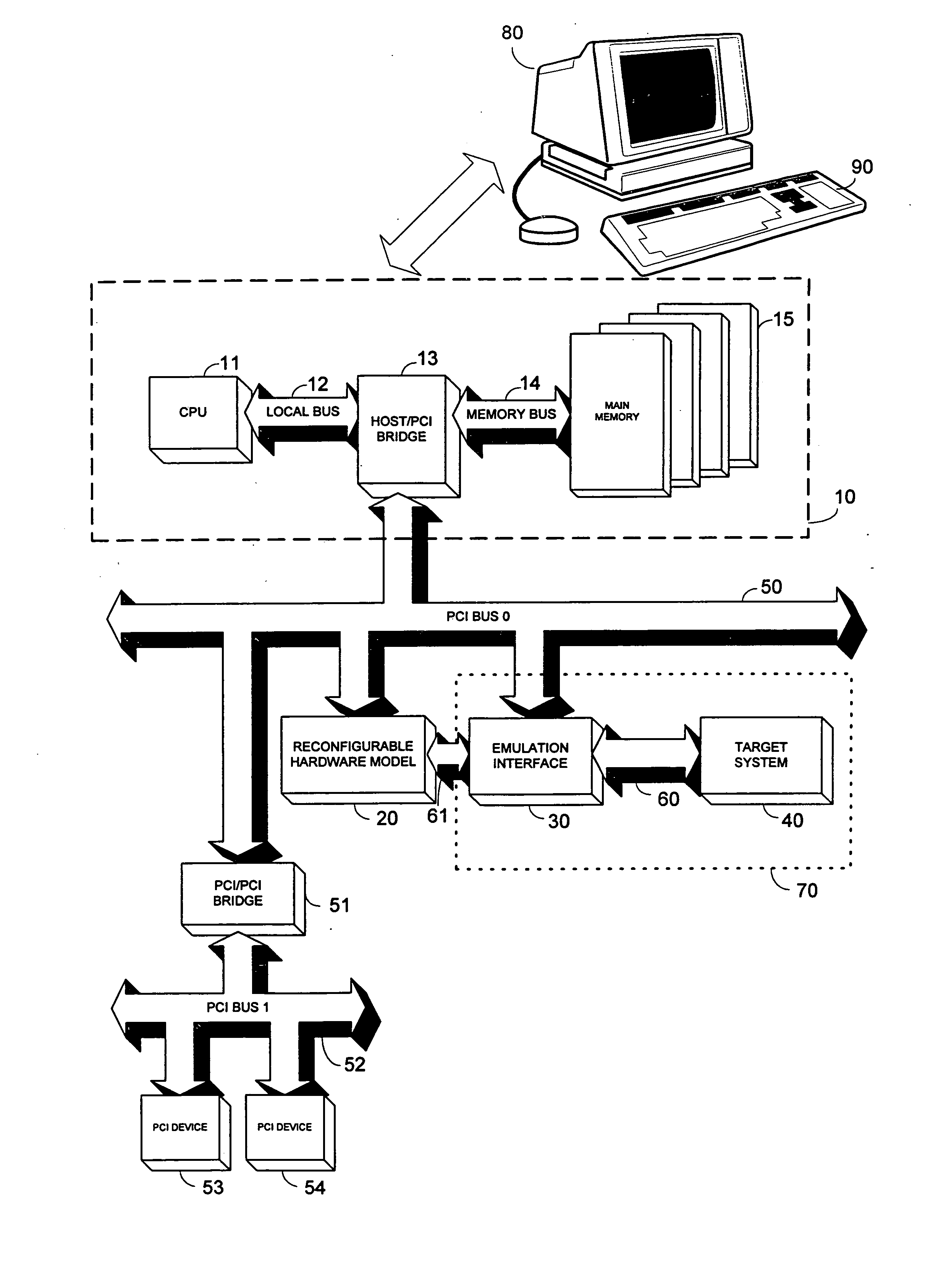
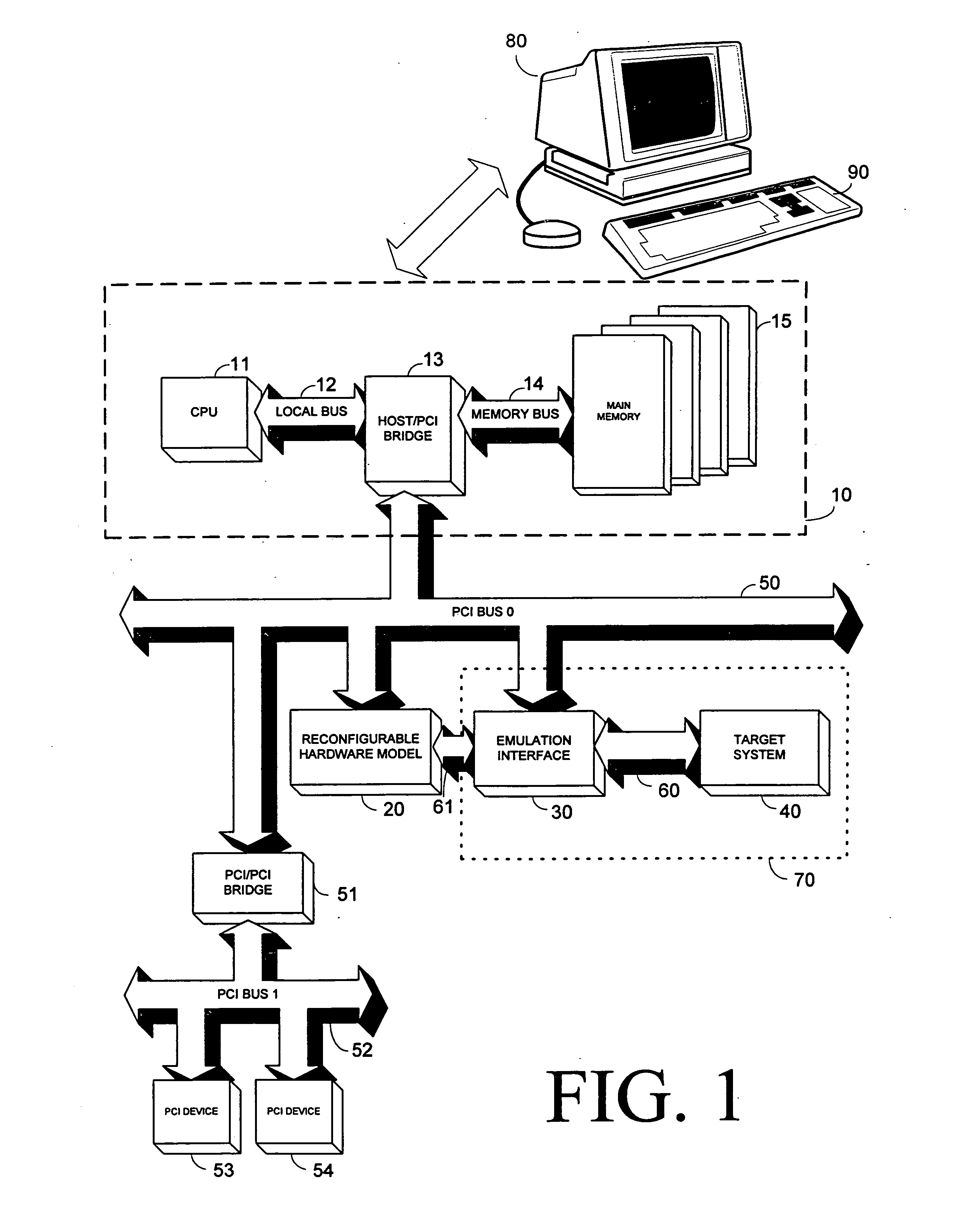
ActiveUS7353162B2Electronic circuit testingAnalogue computers for electric apparatusThird partyComputer architecture
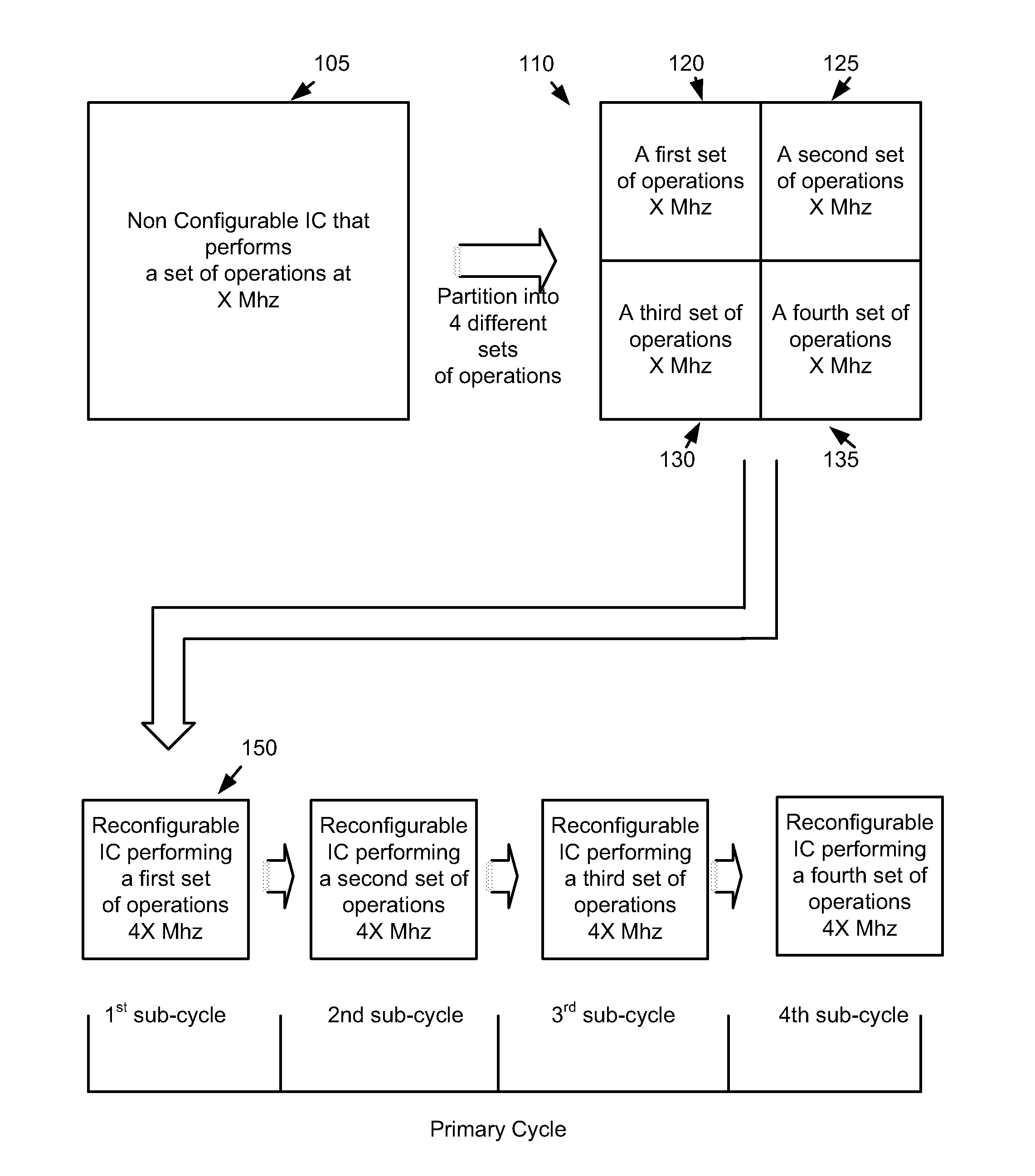
A method and a system provide a reconfigurable platform for designing and emulating a user design. The method and system facilitates design and emulation of a system-on-a-chip type user design. The netlist of a user design may be included with netlists from customized or optimized third party circuits in an emulation using a platform including a number of field programmable devices. Various customized circuits for specific development activities, such as debugging, performance analysis, and simulator linkage may be configured to interact with the user design.
Owner:S2C LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com