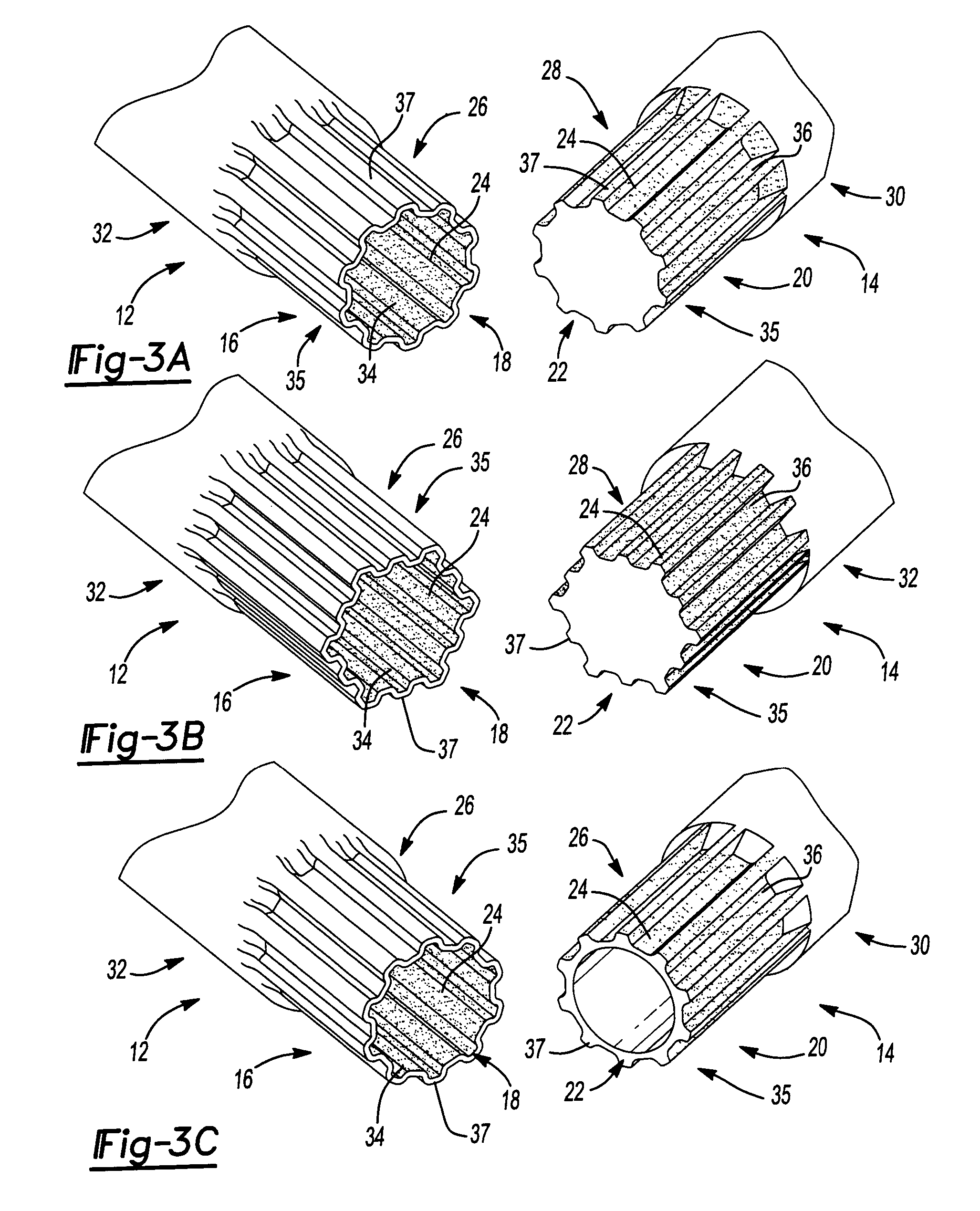
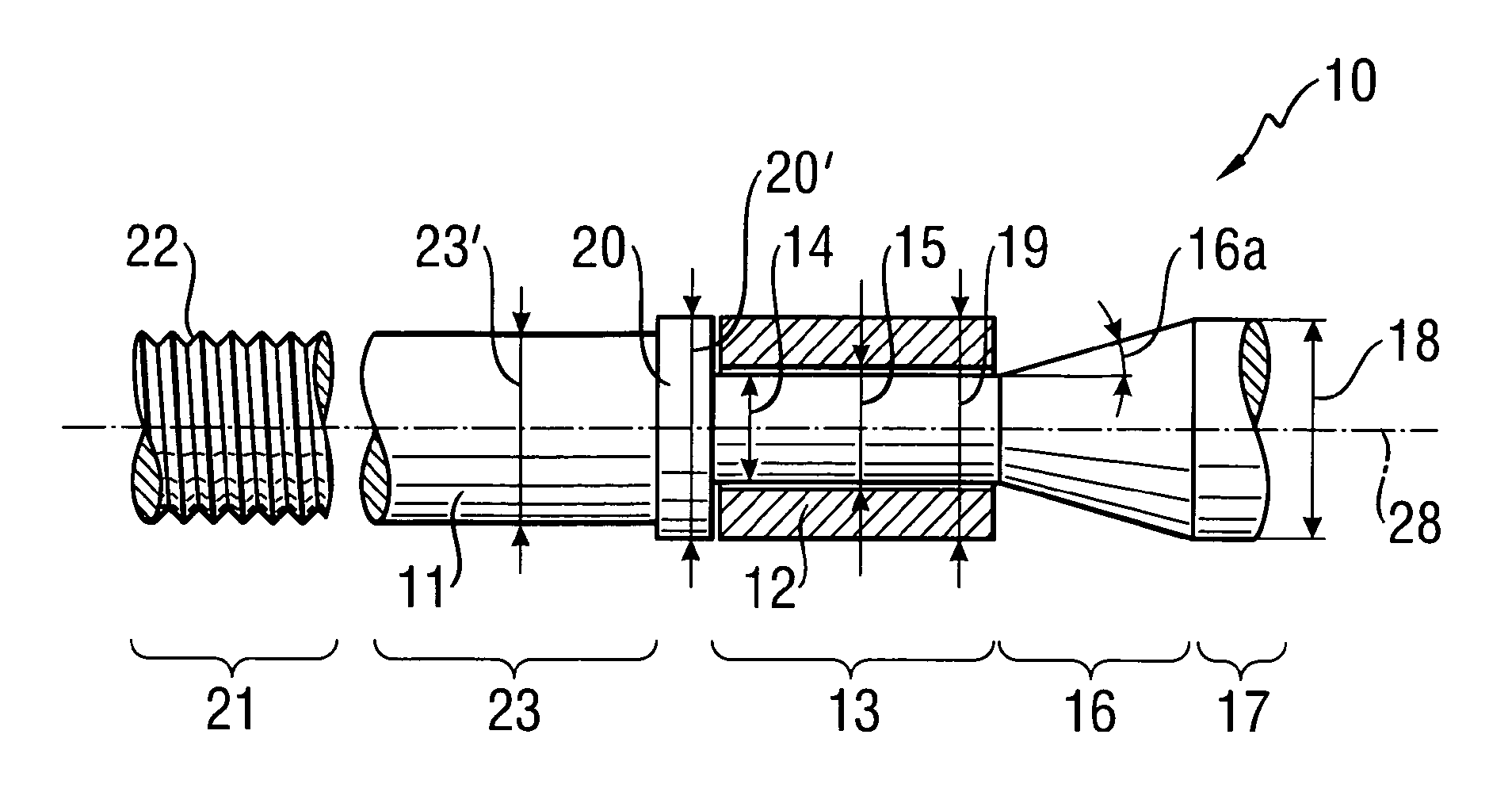
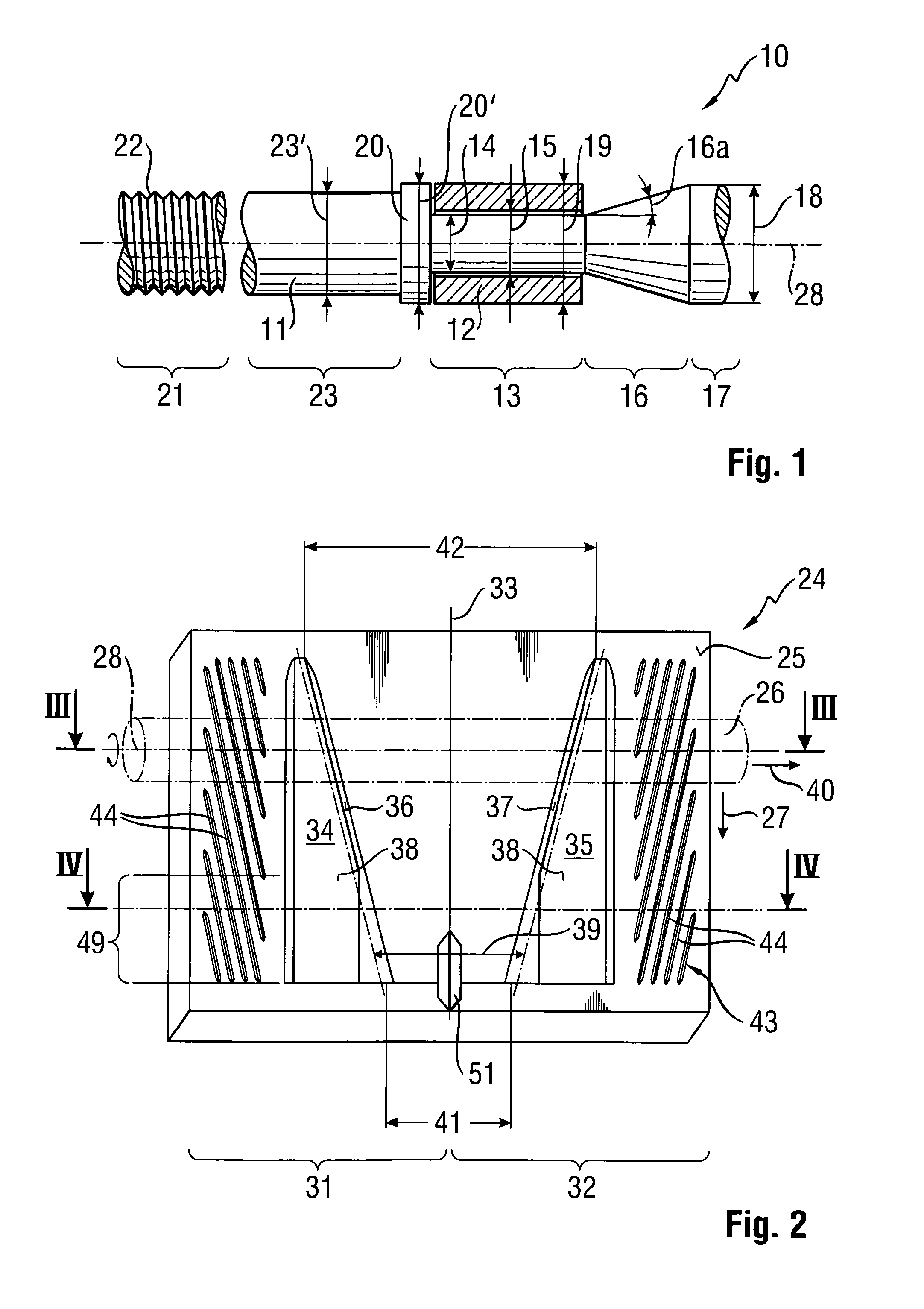
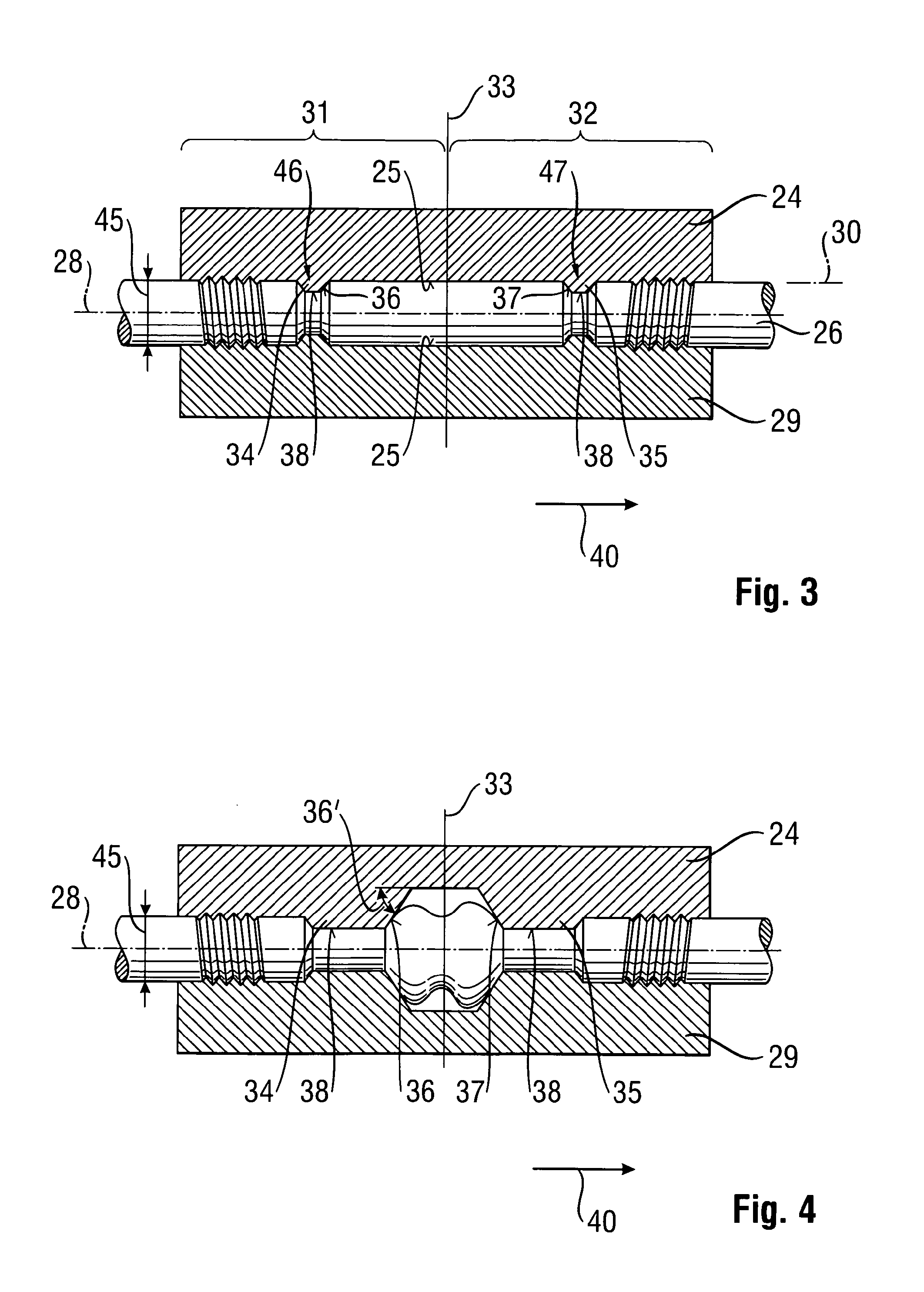
Patents
Literature
131results about "Grooves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
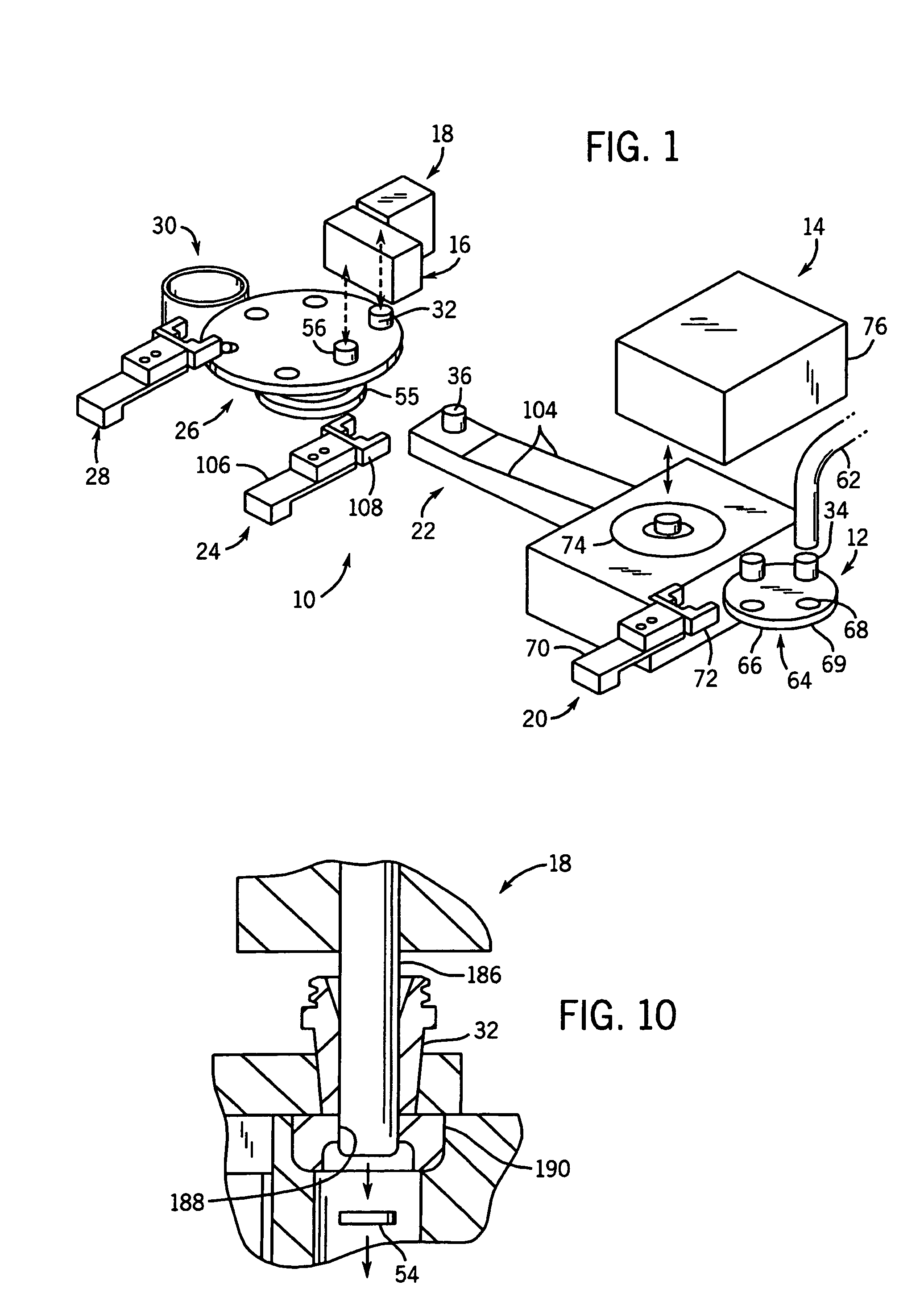
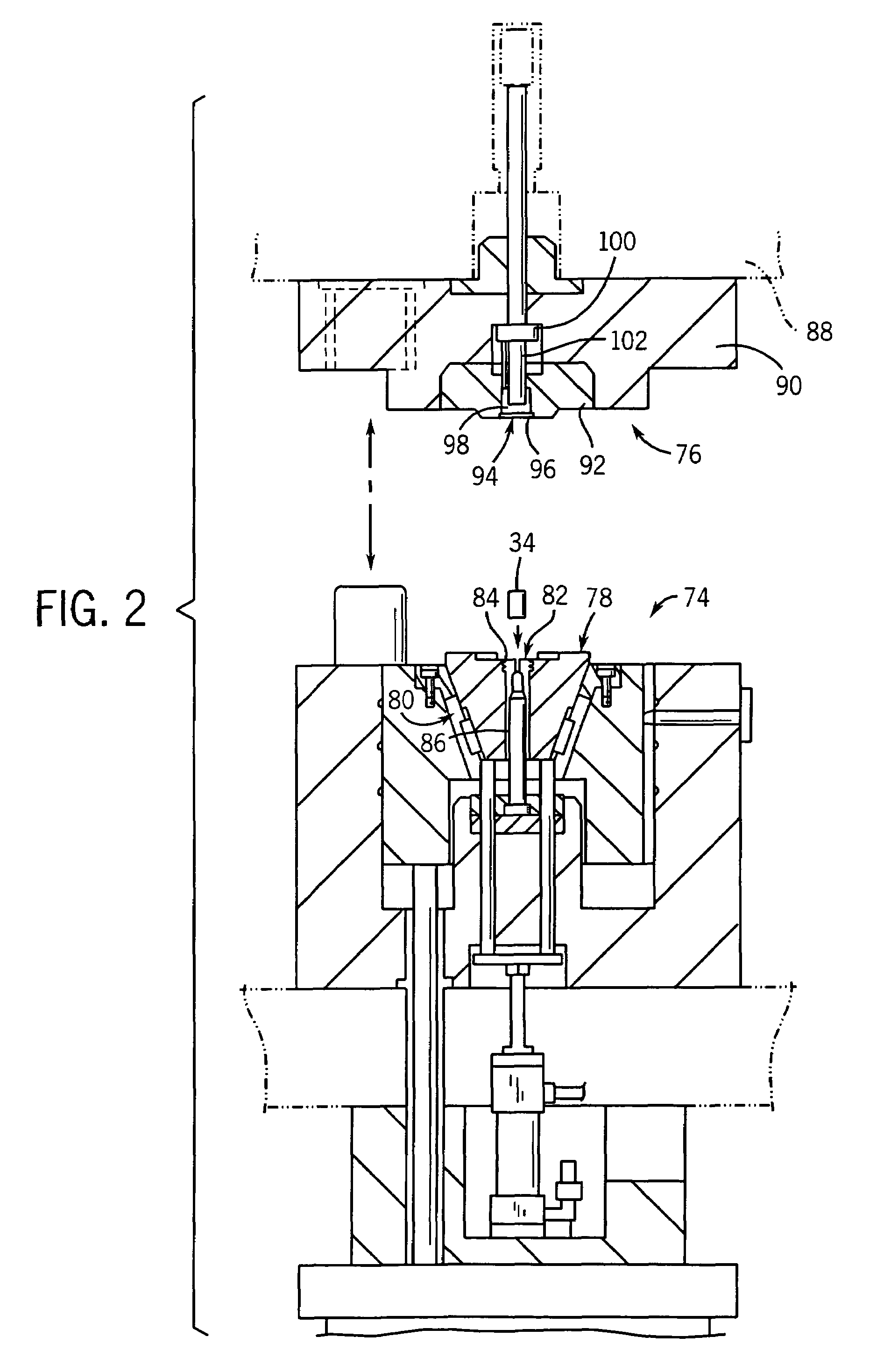
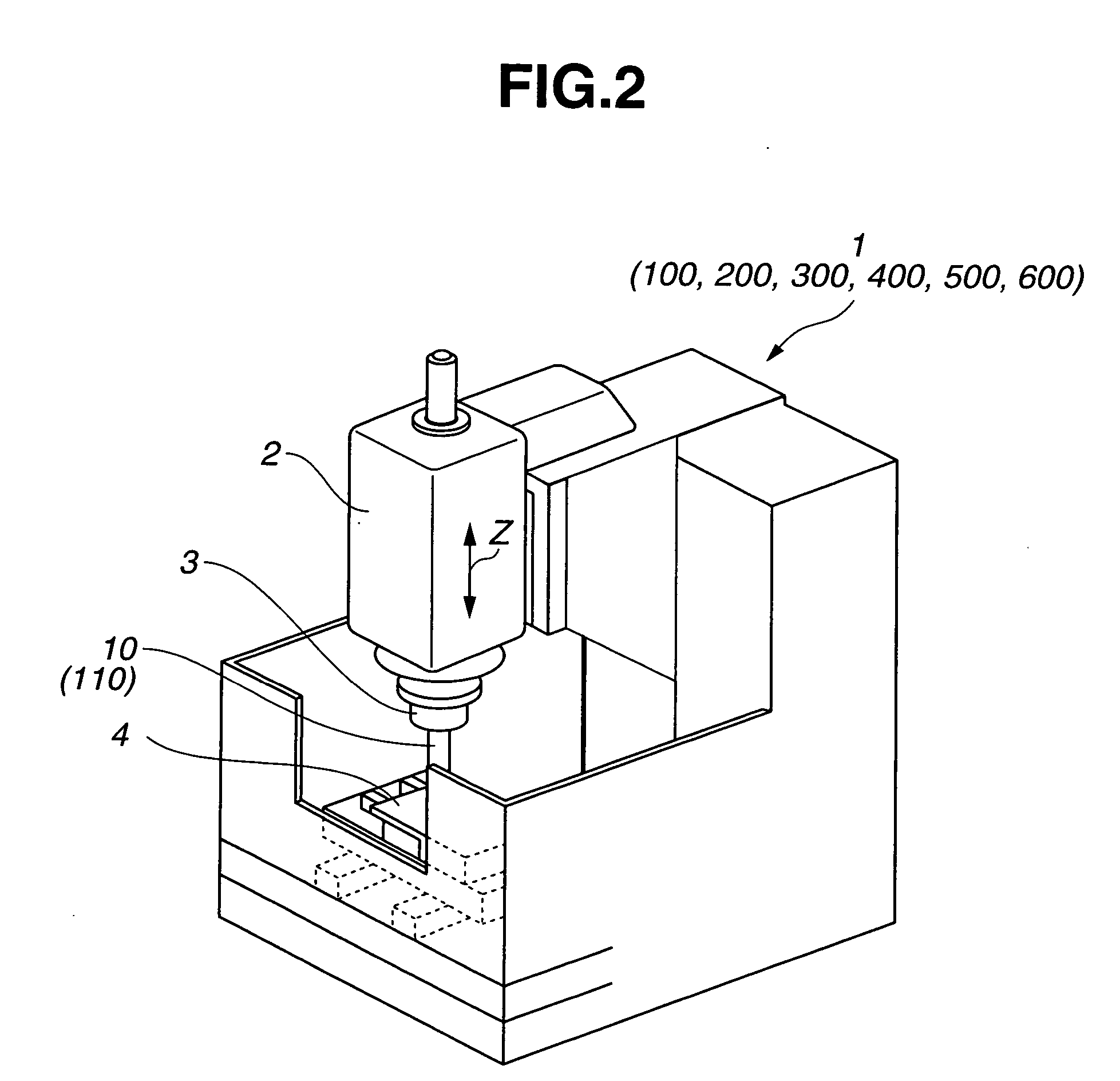
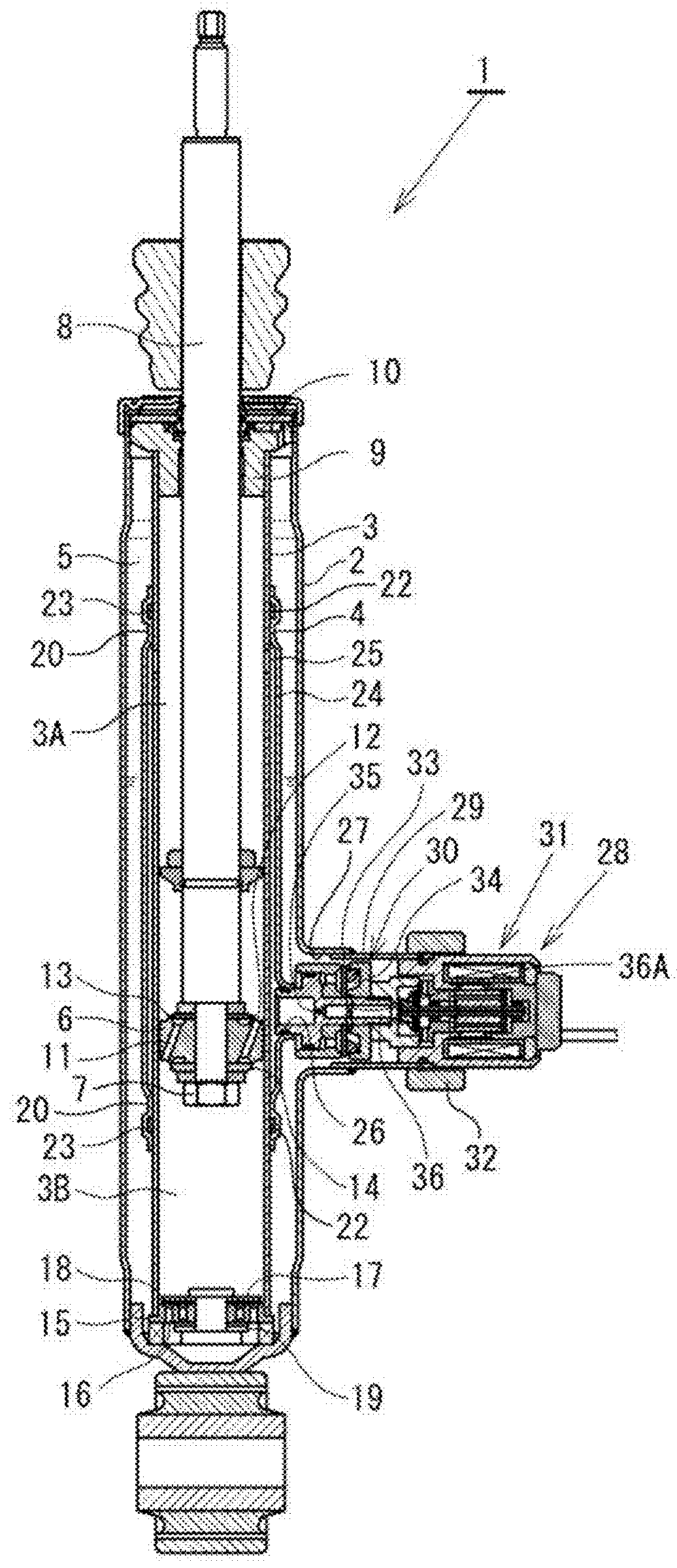
Rolling tool and roller for rolling, particularly deep rolling, a work piece
InactiveUS20050107230A1High quality and reproducibilityRolling force can be constantRolling equipment maintainenceBurnishing machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ECOROLL WERKZEUGTECHN
Method and apparatus for manufacturing a battery terminal with undercut rings
InactiveUS7021101B2Prevent electrolyte leakageEasy to manufactureLead-acid accumulatorsSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsCold formedMetal forming
A method and apparatus utilizing a radial rolling process to cold form rings on a lead battery terminal with undercuts or overhangs to improve the sealing properties of the rings. The apparatus includes a fixture configured to securely position the battery terminal beneath a rolling station. The rolling station includes a radial rolling spindle having a plurality of cam shaped rollers configured to transform at least one ring on the battery terminal from having an initial rectangular cross-sectional shape into a desired arrowhead cross-sectional shape when the terminal and cold metal forming member are rotated relative to each other. A drive assembly is configured to rotate the battery terminal and radial rolling head relative to each other.
Owner:TULIP MOLDED PLASTICS CORP
Point contact densification
InactiveUS6110419AUniform densificationLess `` damage ''Bearing componentsGear wheelsPoint contactMetal
Owner:STACKPOLE INT POWDER METAL LTD
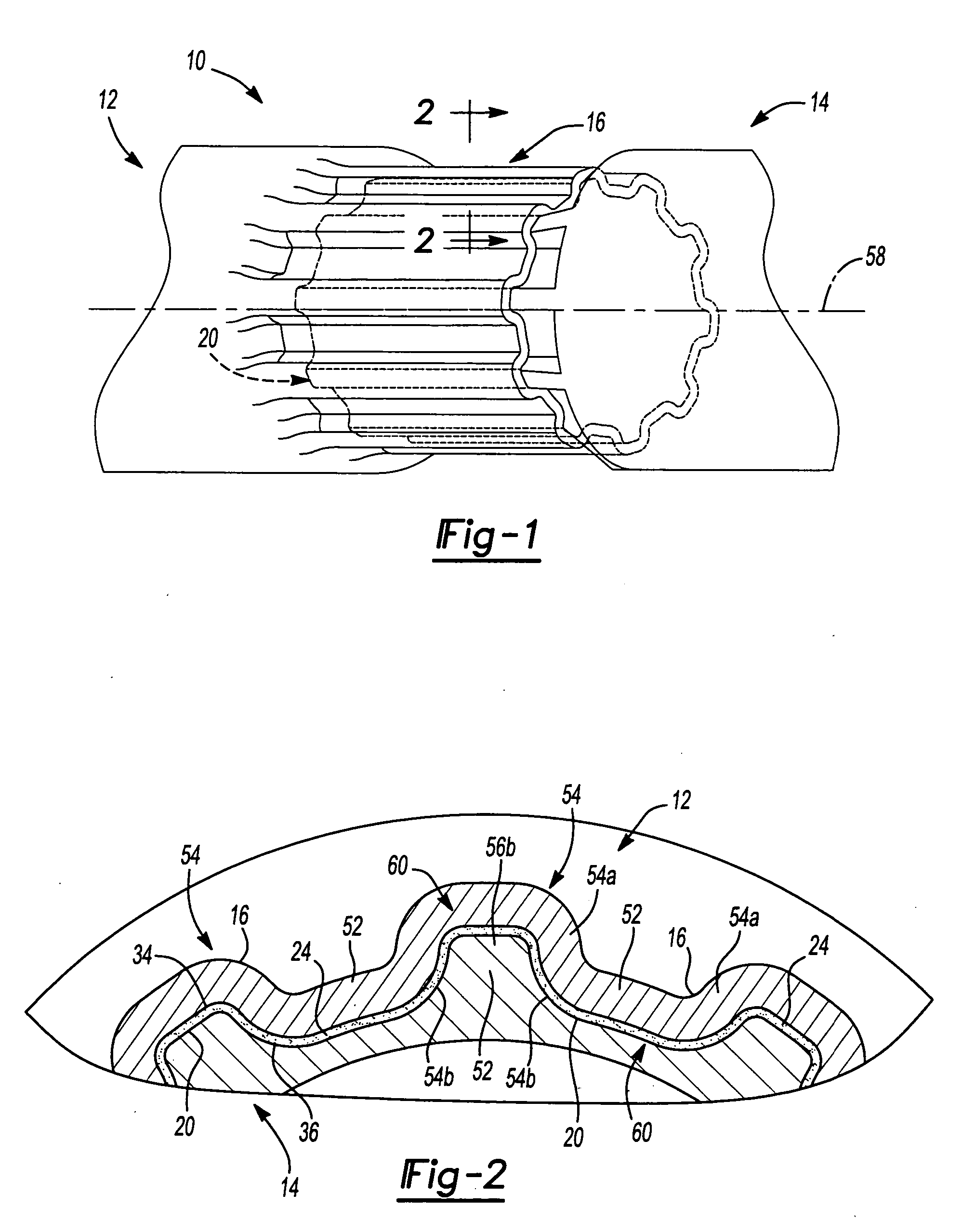
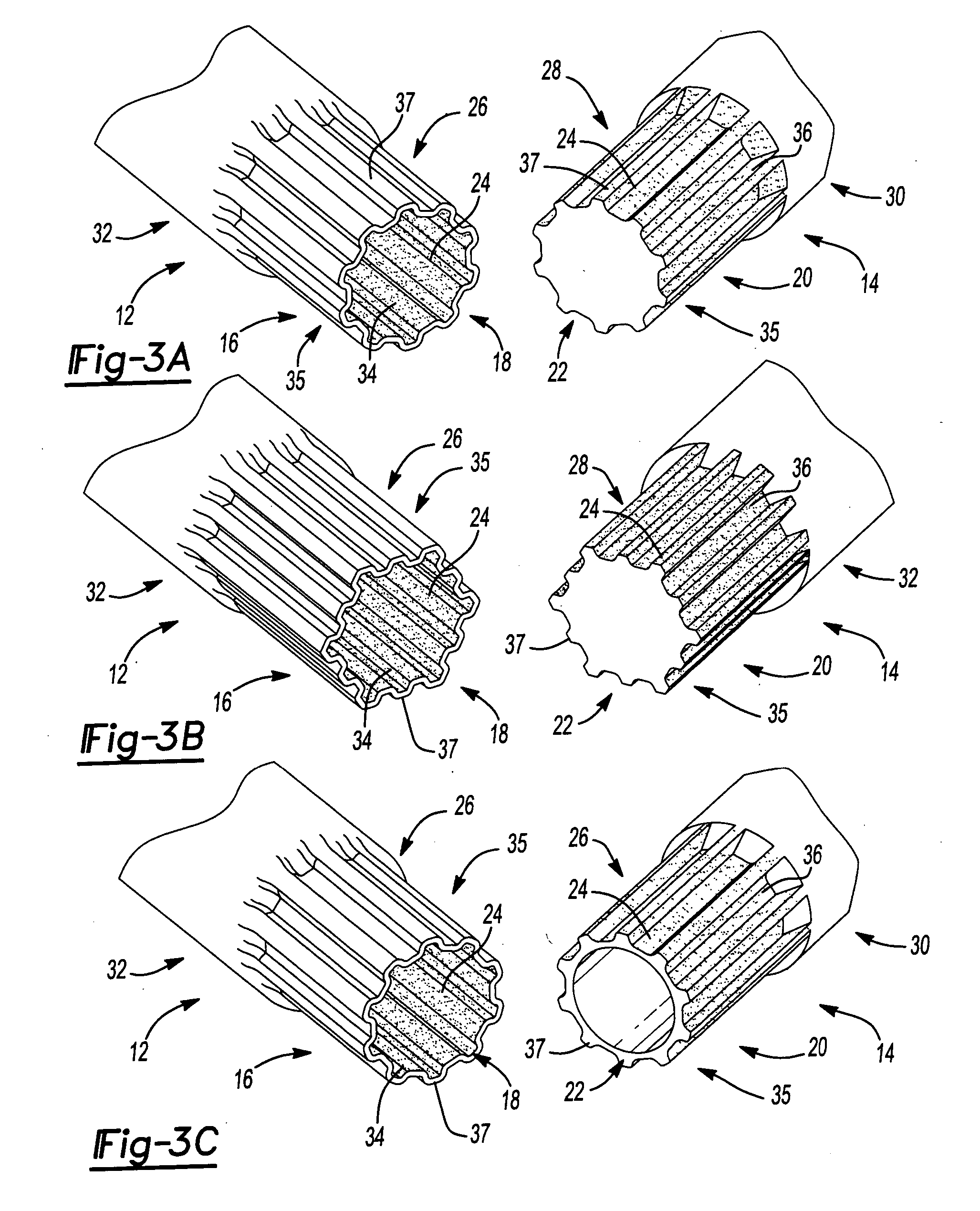
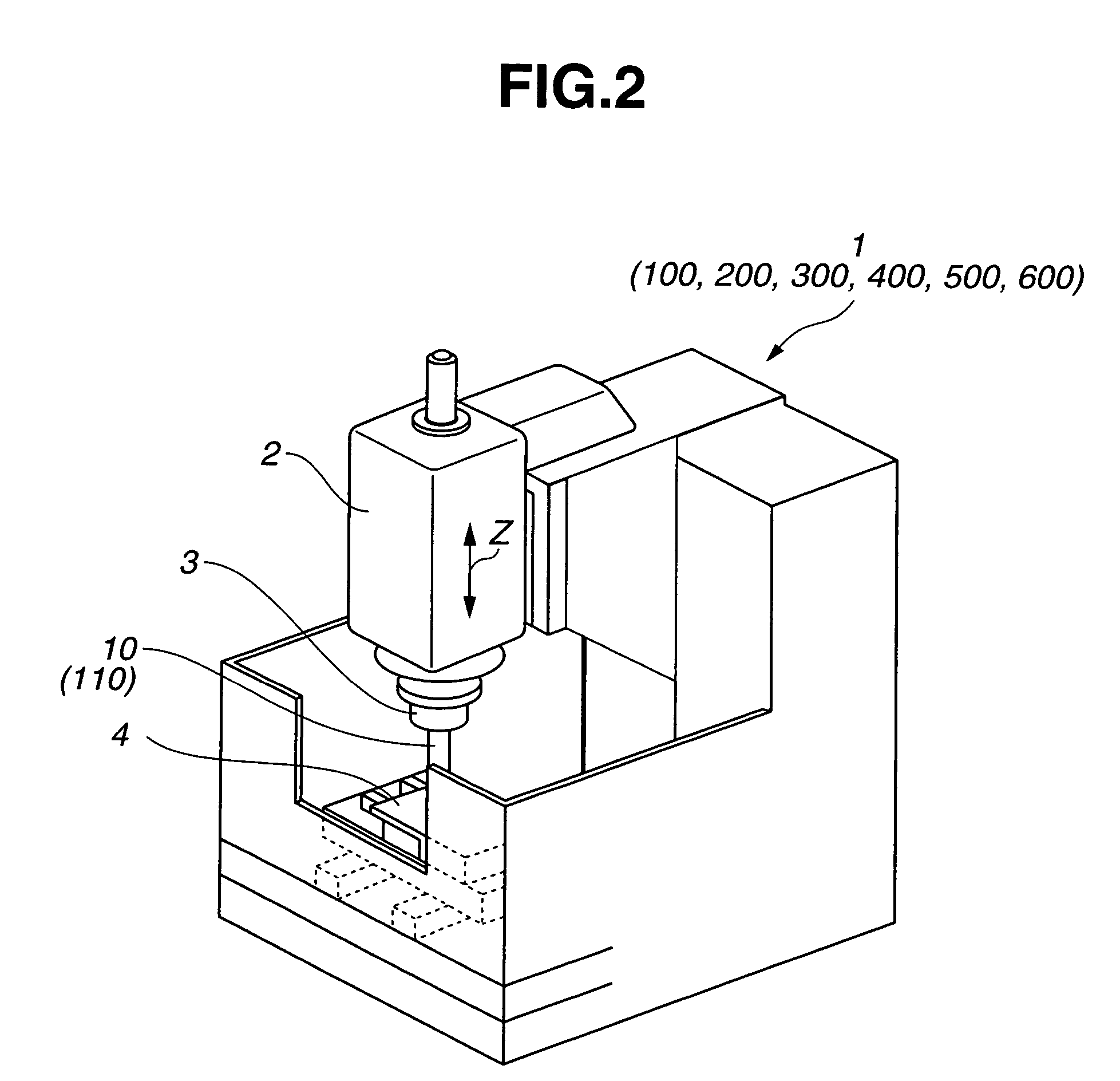
Slot shaping appts.
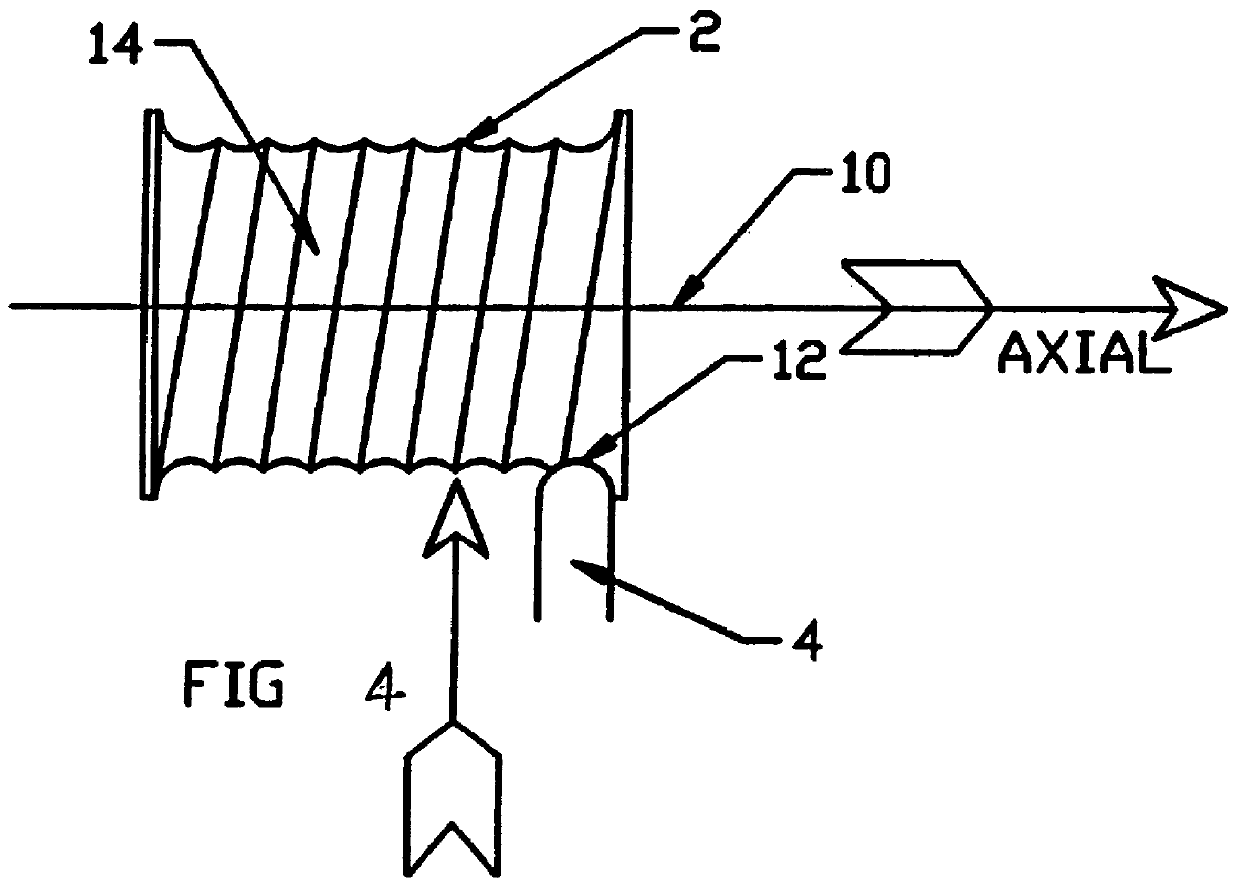
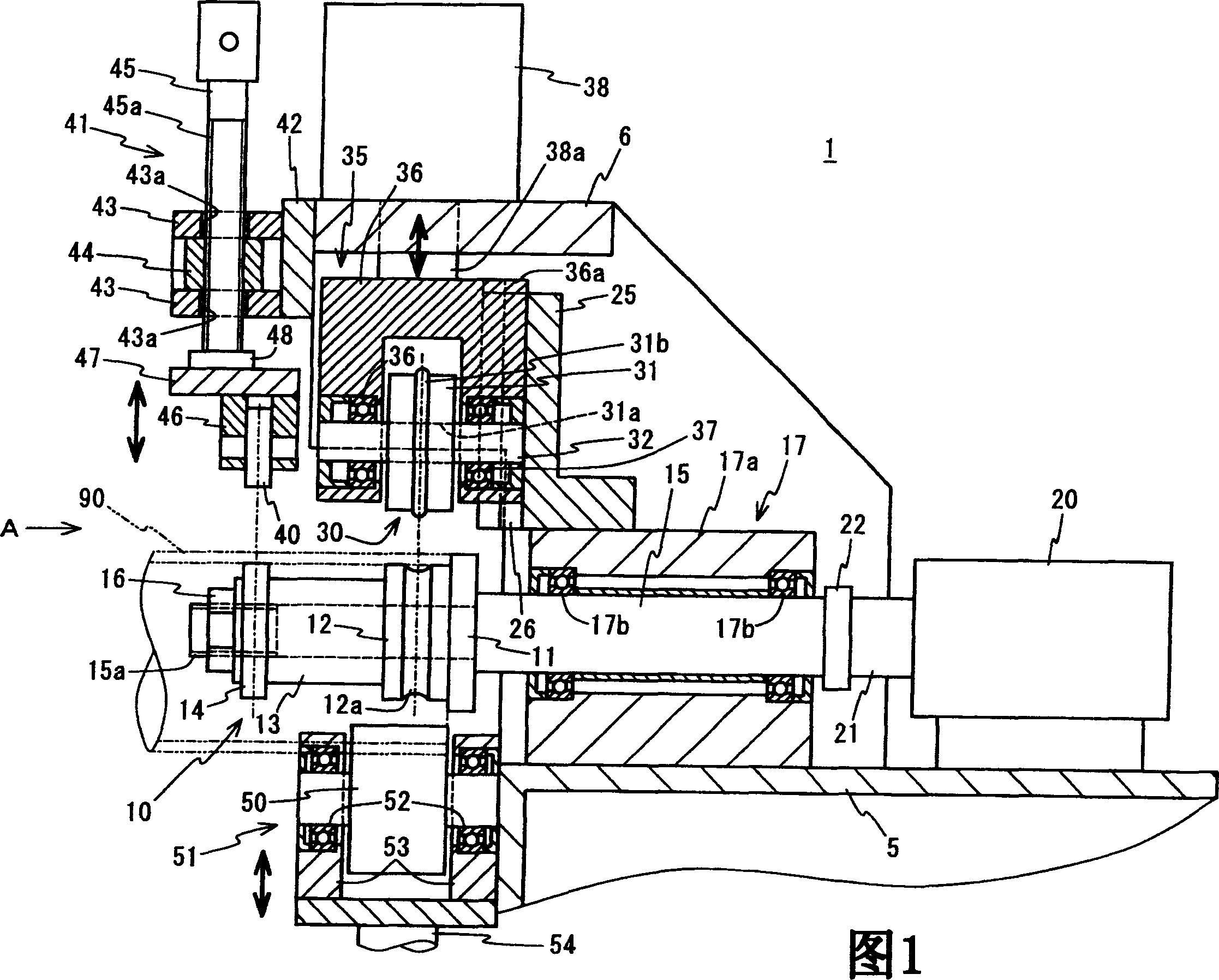
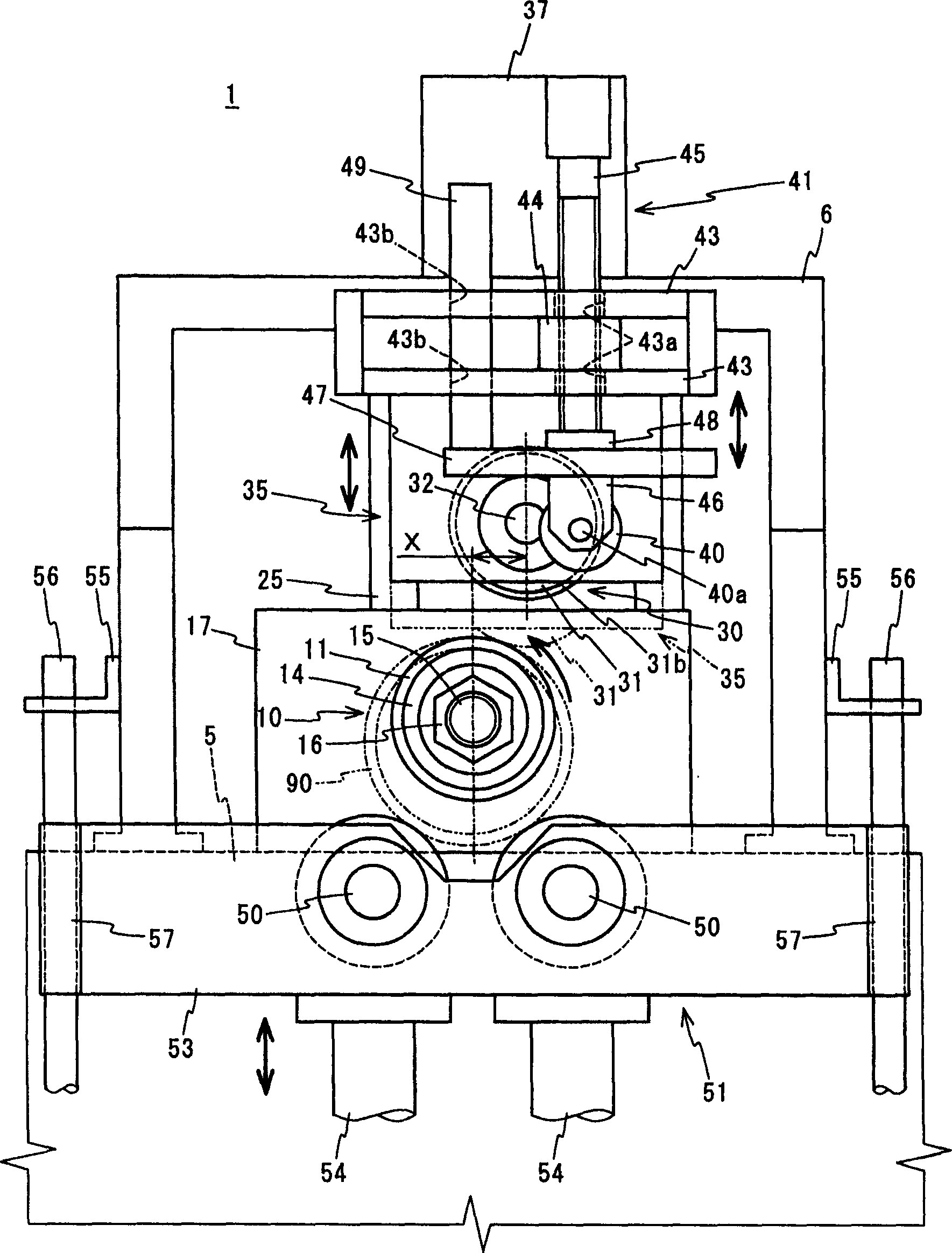
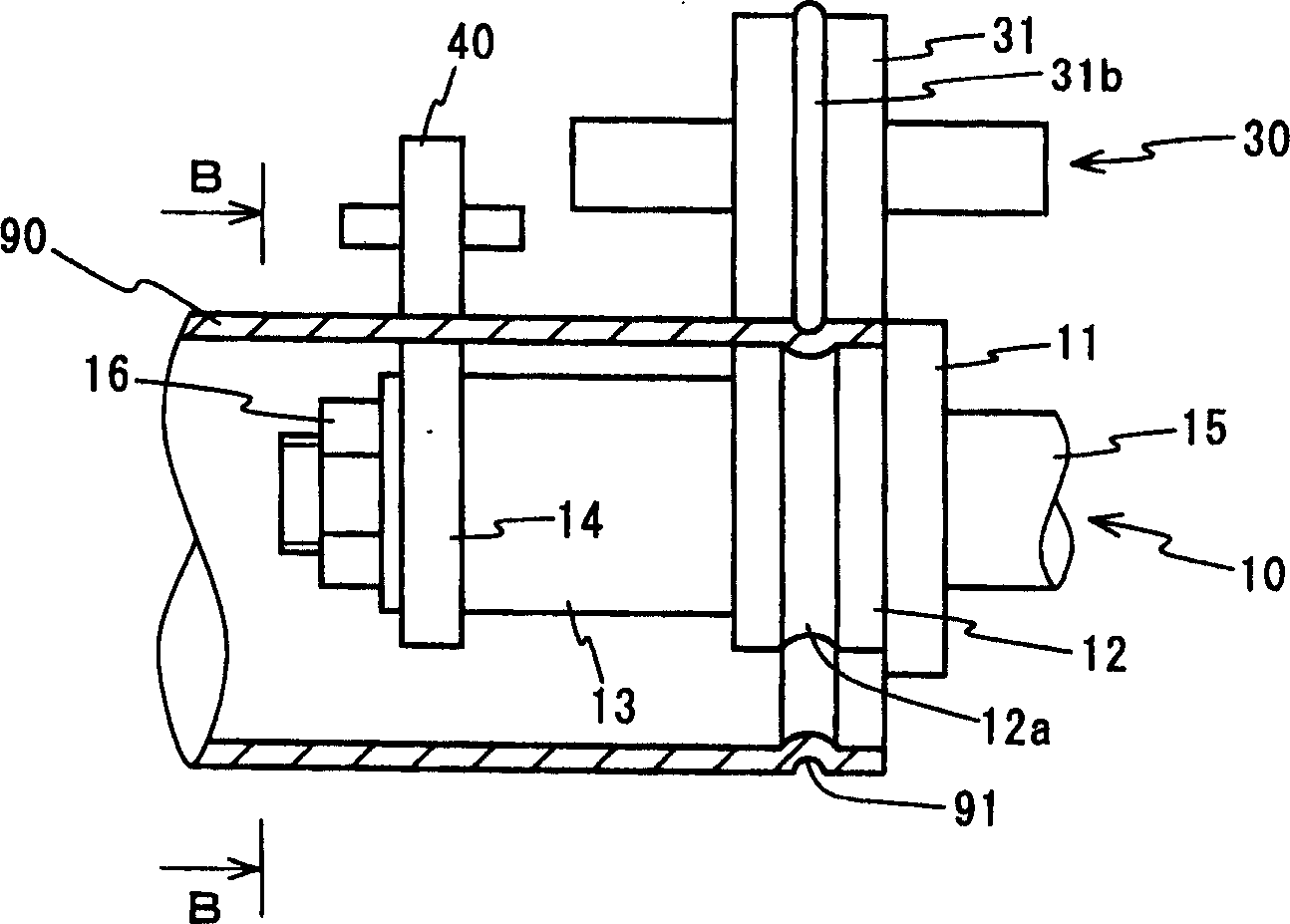
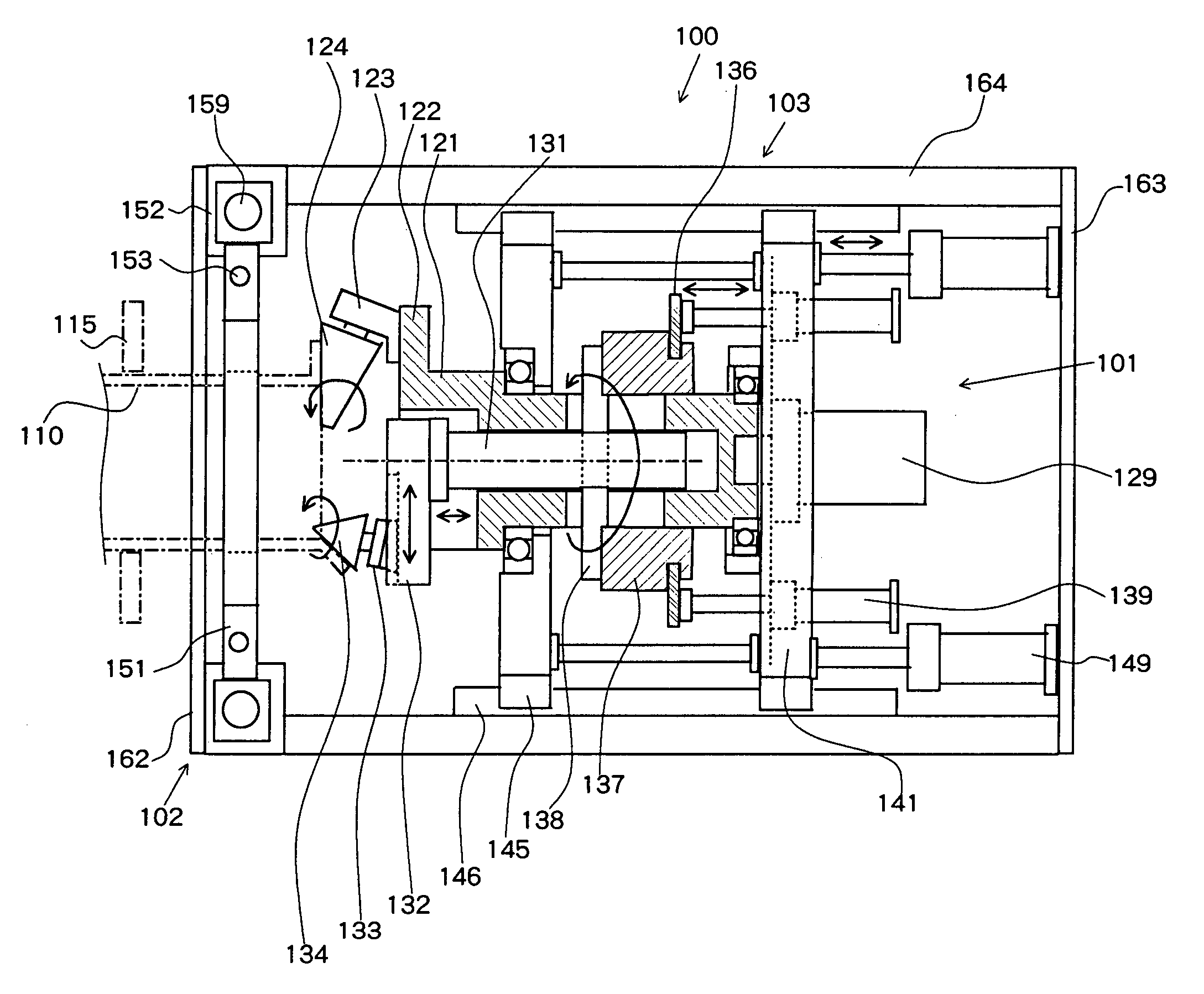
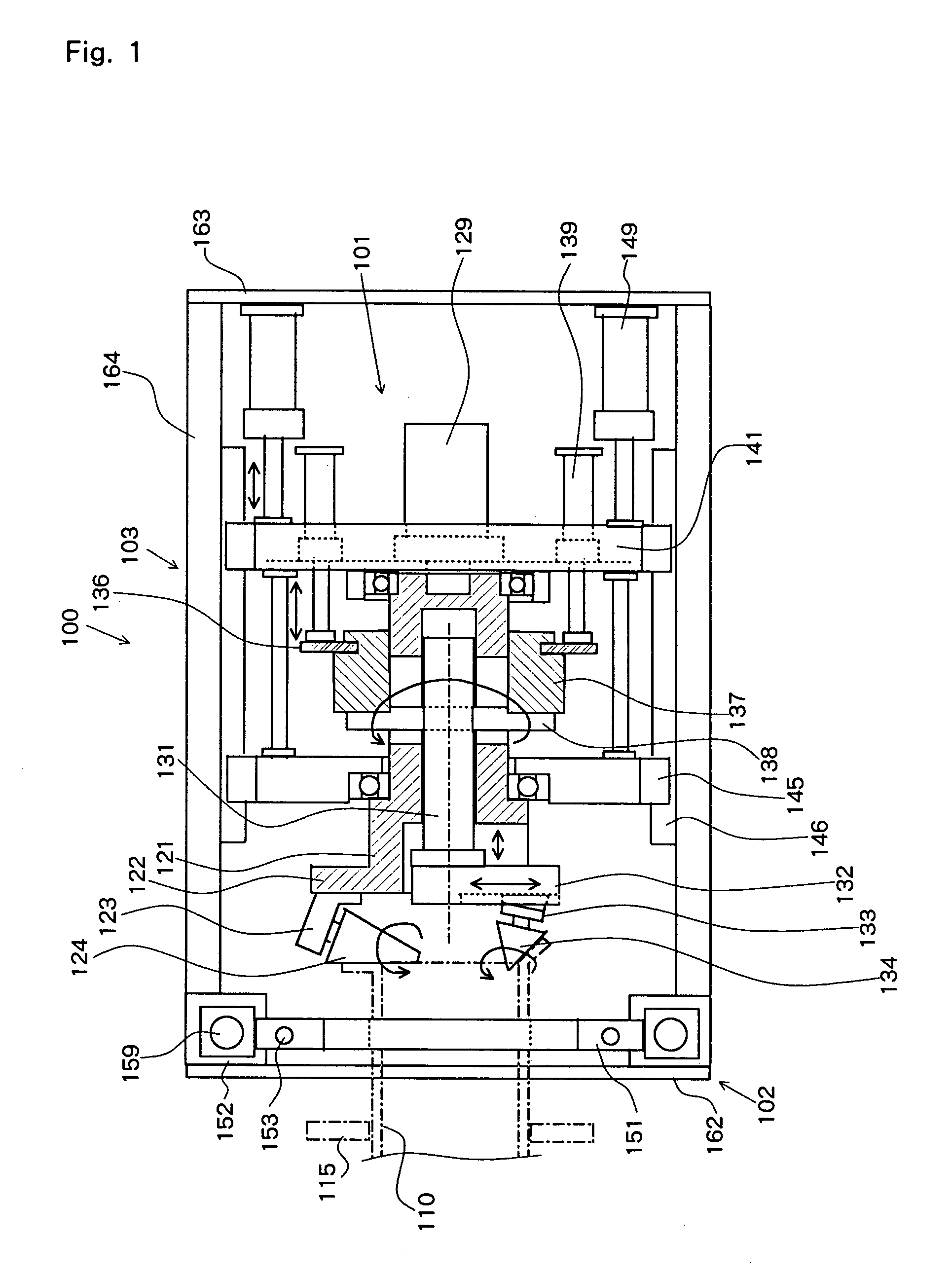
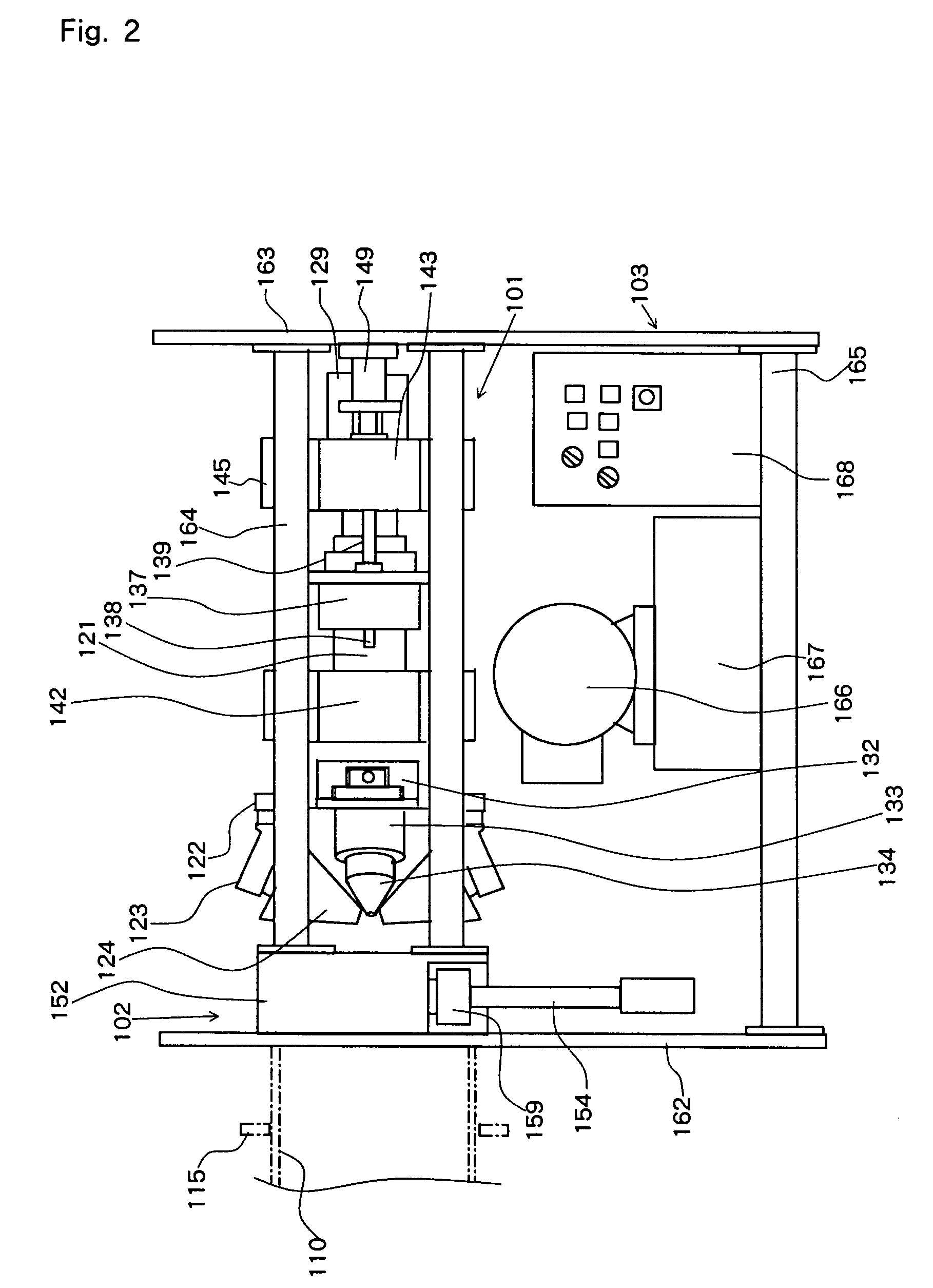
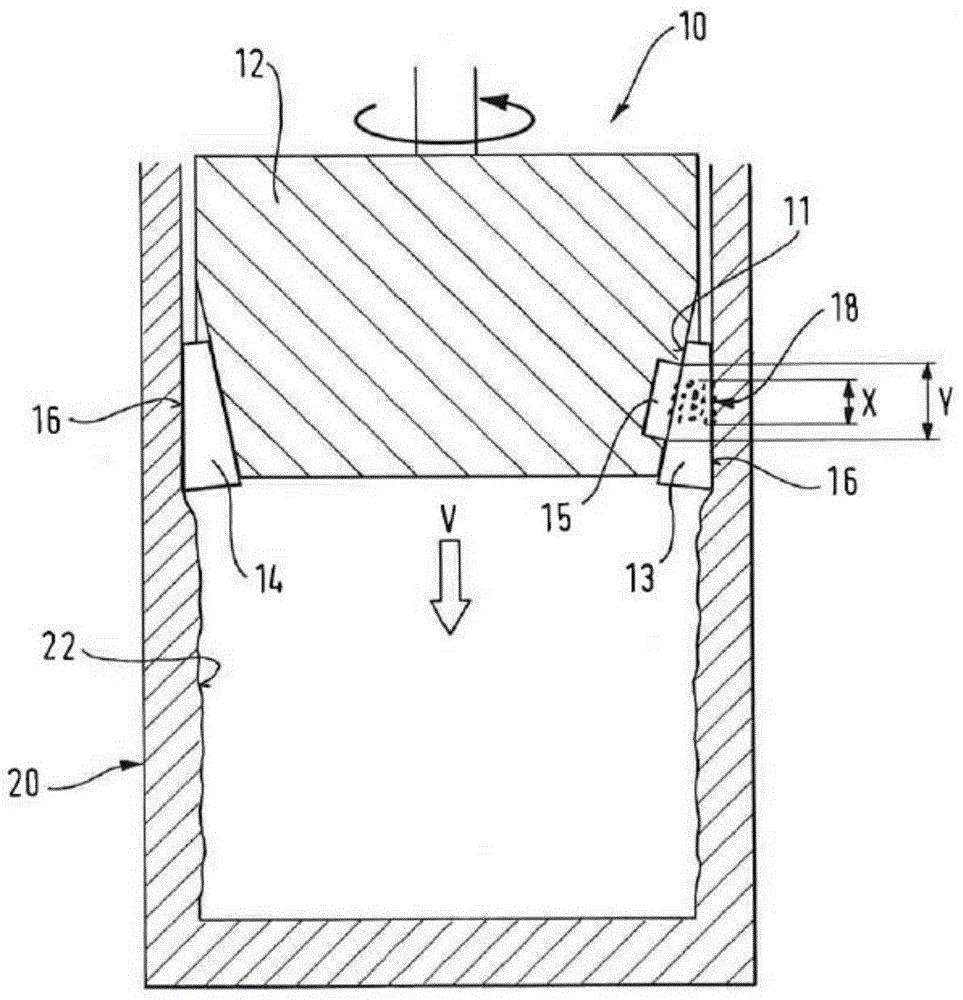
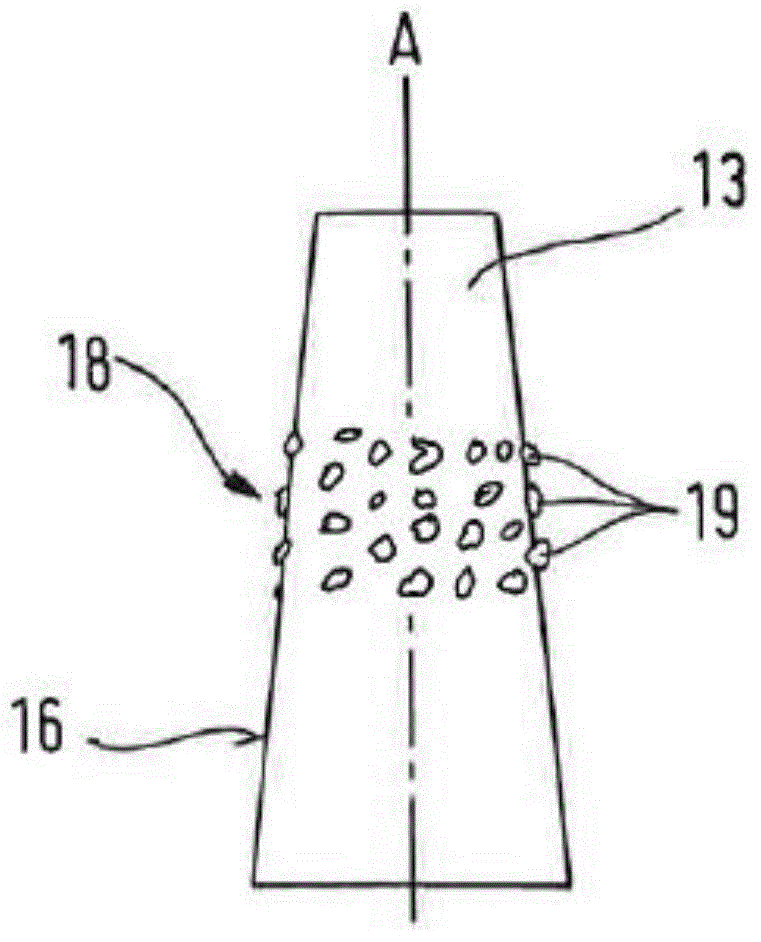
Provided is a groove forming apparatus with which an annular groove having high accuracy of shape is formed on a metallic pipe. This groove forming apparatus is provided with a supporting roller 10 having an annular concave groove 12a formed along the peripheral direction on the outer peripheral surface, a driving motor 20 for rotating the supporting roller 10 around the axial center, a press roller 30 which is provided with an annular projected line part 31b formed along the peripheral direction on the outer peripheral surface and elevating and lowering mechanisms 25, 35, 38 for vertically elevating and lowering the press roller 30 and constituted so that the annular groove 91 is formed on the outer peripheral surface in the end part by clamping and pressing the metallic pipe 90 with the press roller 30 and the supporting roller 10. The press roller 30 is arranged in a position where is offset on the opposite side to the rotating direction of the supporting roller 10 on the basis of a vertical plane including the axial line of the supporting roller 10.
Owner:川口工业株式会社
Support tool for deep rolling crankshaft fillets
InactiveUS6094956AEasy to controlLimit lateral shiftingRevolution surface grinding machinesBurnishing machinesEngineeringCrankshaft
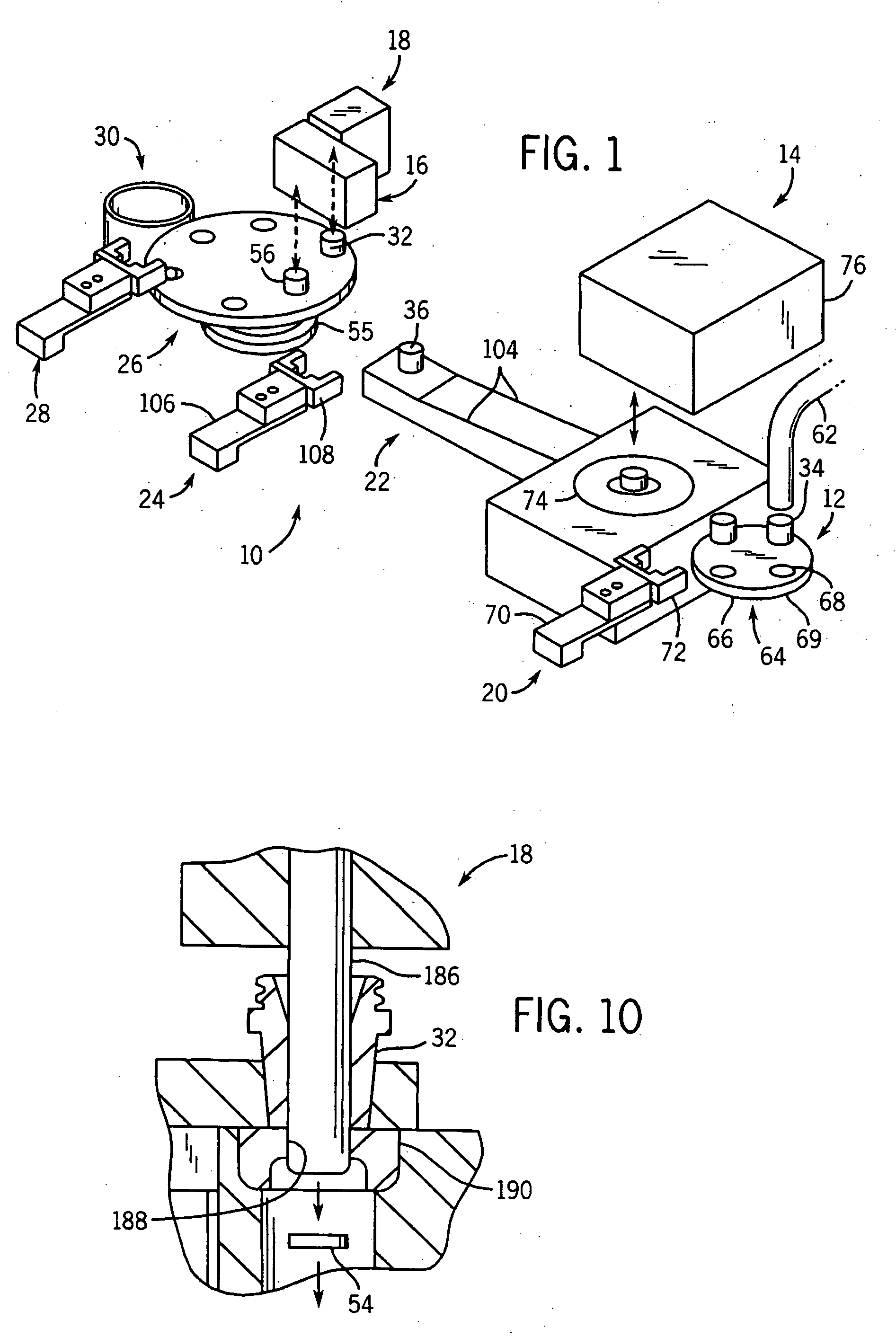
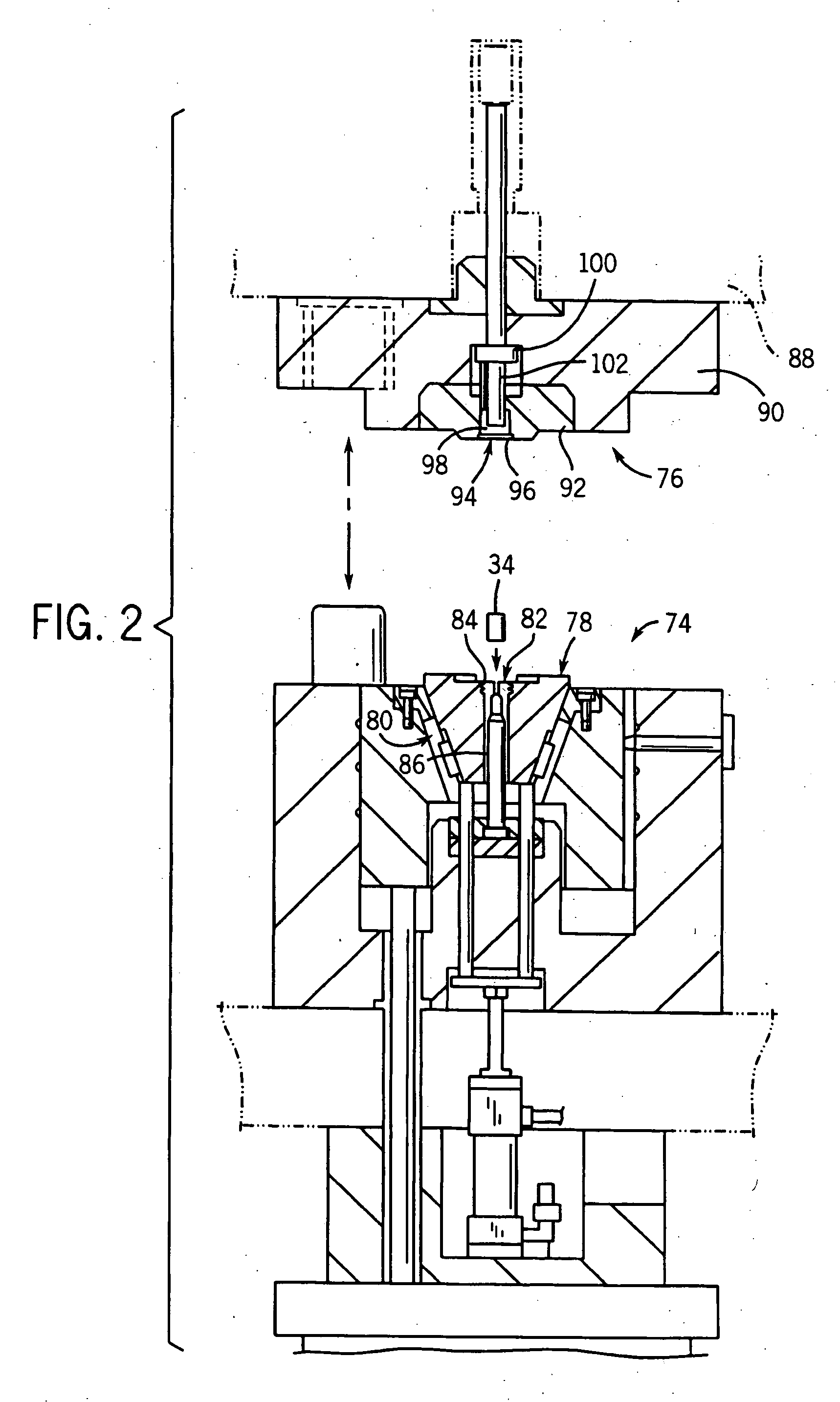
PCT No. PCT / US98 / 09524 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 15, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 15, 1999 PCT Filed May 13, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 51432 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 19, 1998Deep rolling equipment for cold working fillet radii of annular undercuts on opposite sides of main bearing and crank pin journals of an engine crankshaft while being rotatably driven. The equipment has pairs of jaws movable between an open position for receiving the crankshaft journal and a closed position for rolling the fillets thereof. The upper jaw mounts fillet rolling tools for high load rolling engagement in the annular undercuts and a lower tool on the opposing lower jaw for support of the journal. The lower tool has a pair of support rollers with annular journal support portions which contact and support the journal while the fillet radii of the undercuts on either side of the journal are being rolled. These support rollers importantly have work stabilizing annular flanges outboard of the support portion with larger diameters that ride in the undercuts and limit lateral movement of the crankshaft with respect to the rolling and support tools so that the crankshaft is not abraded or otherwise damaged by side contact of the jaws and tools with portions of the crankshaft.
Owner:HEGENSCHEIDT MFD
Apparatus and method for rolling workpieces
InactiveUS6895793B2Eliminate needImprove reliabilityCrankshaftsBurnishing machinesEngineeringStrain sensor
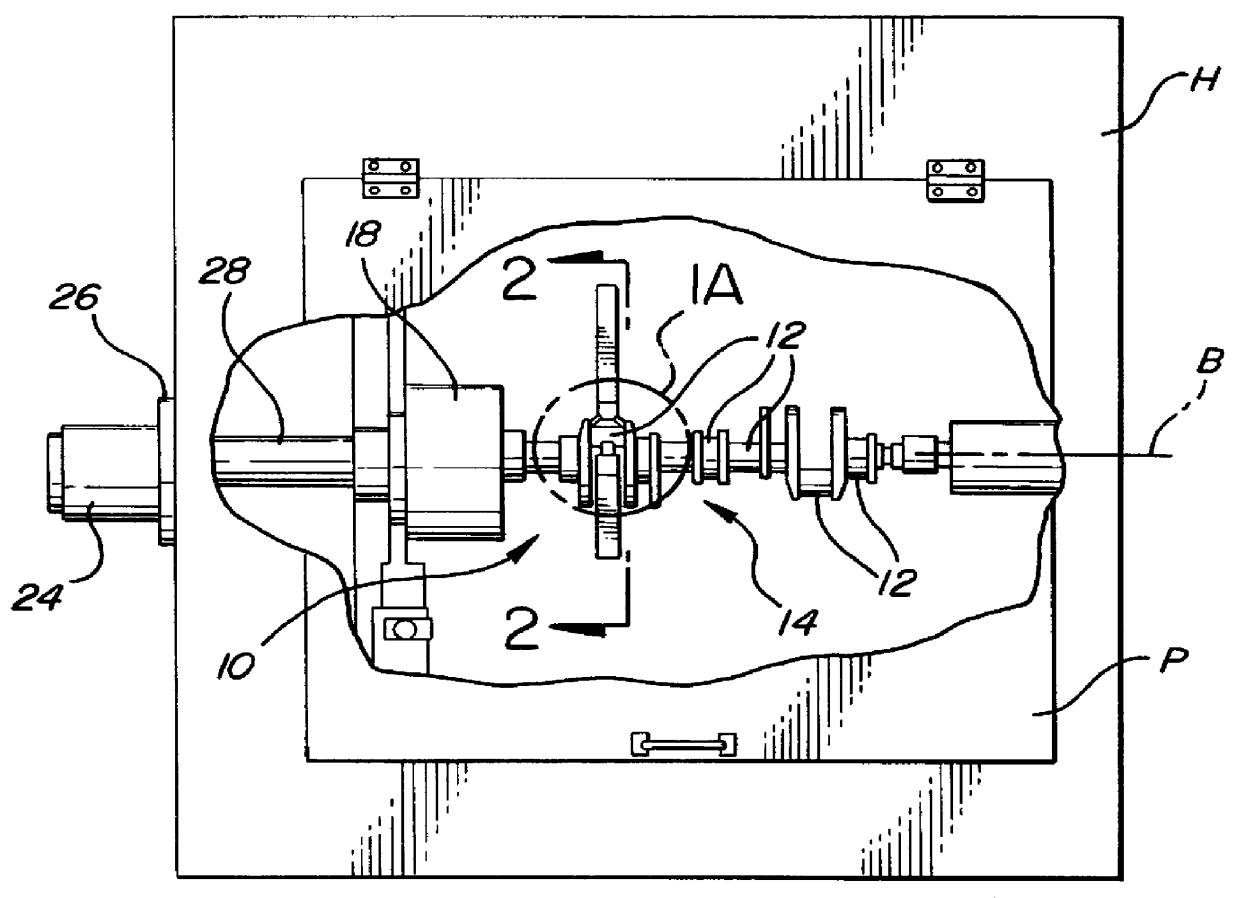
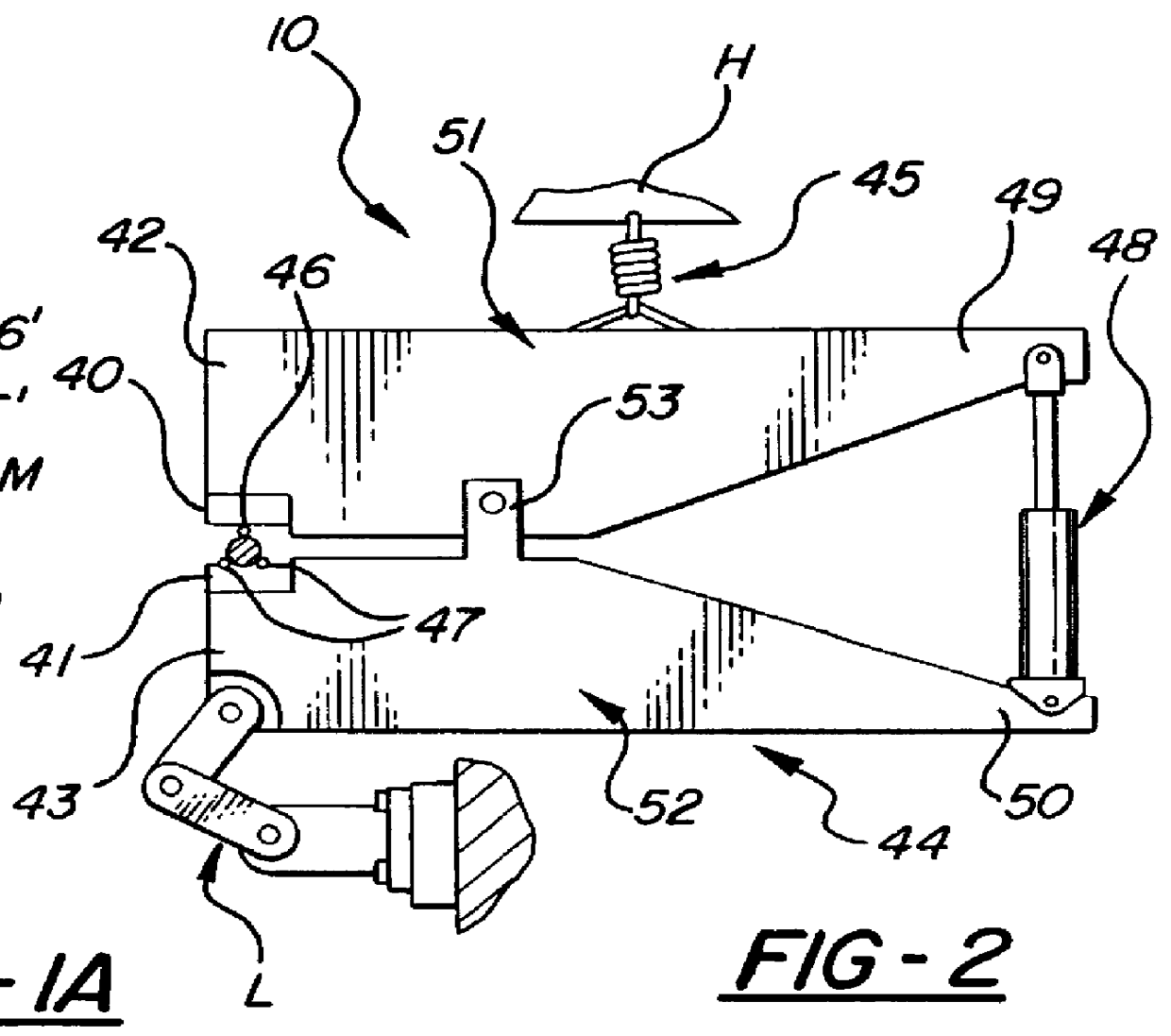
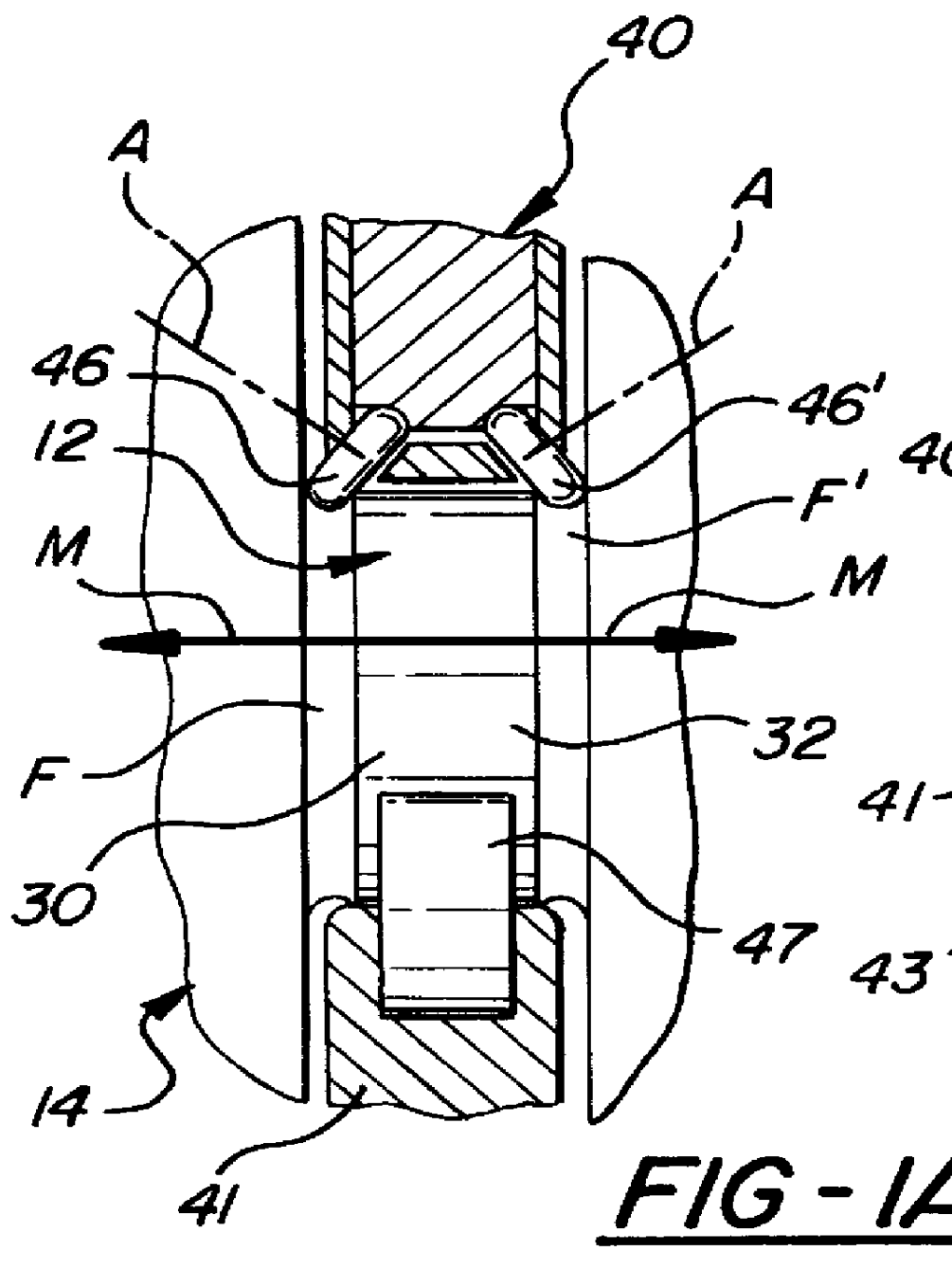
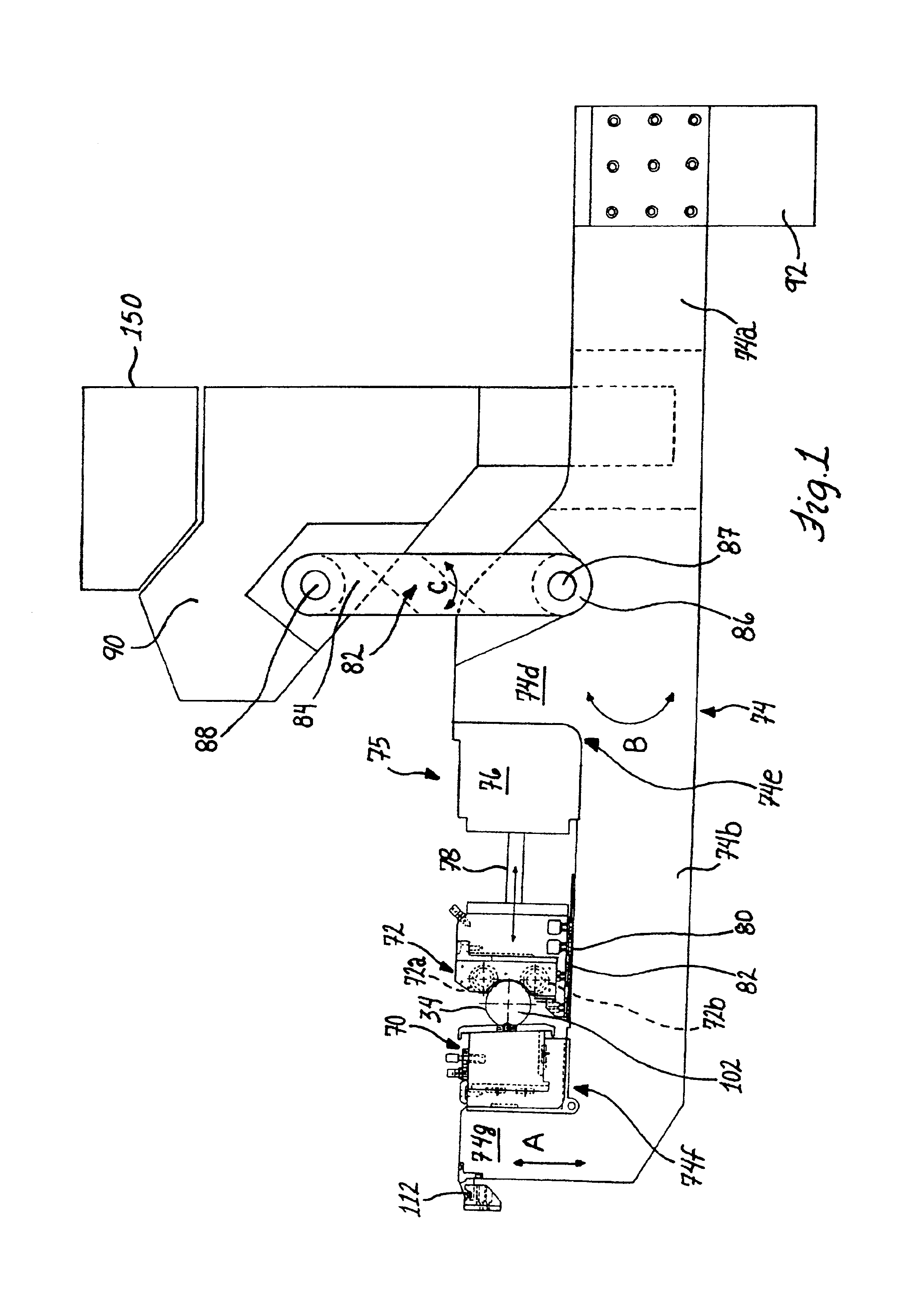
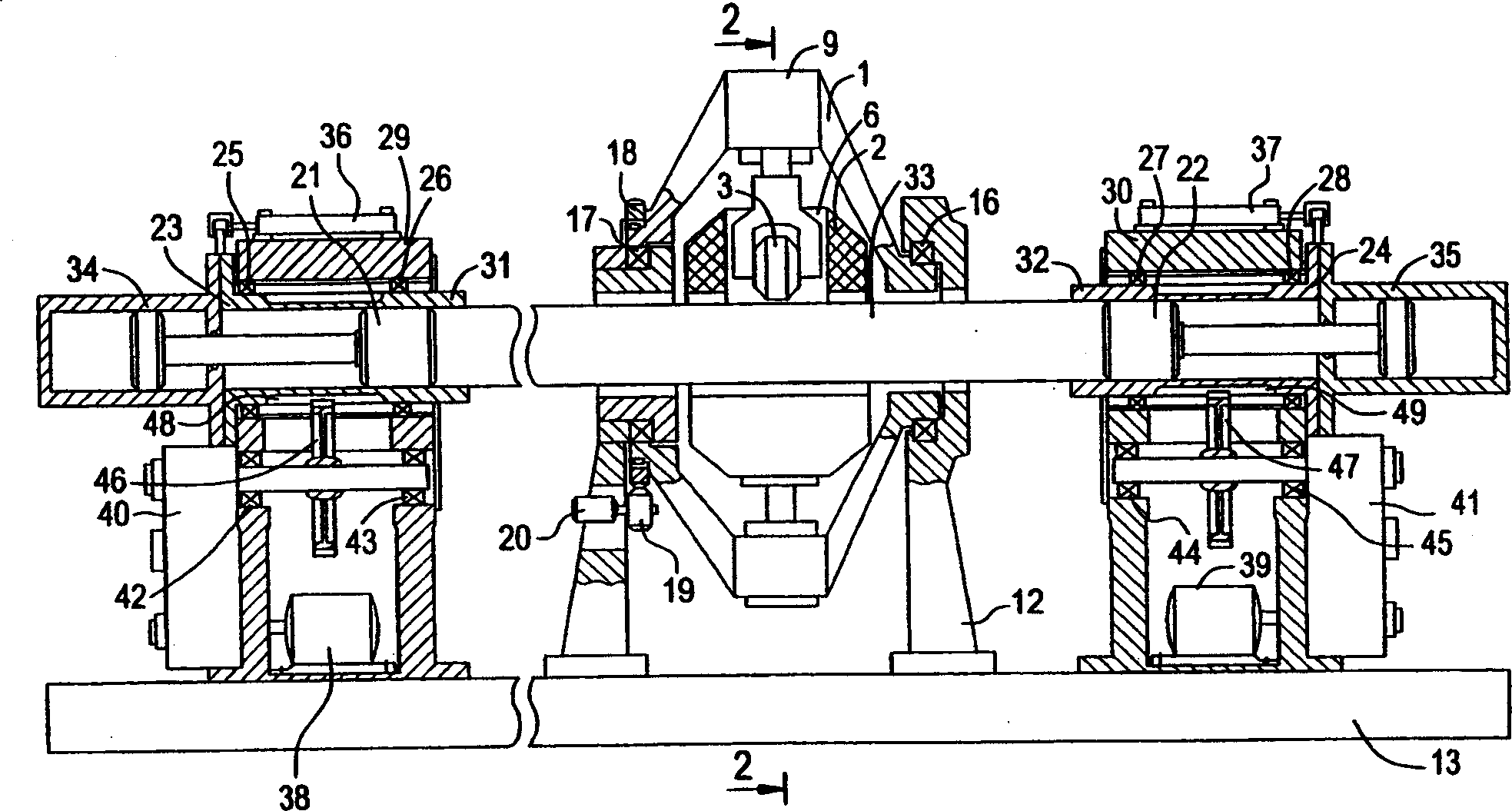
There is provided a new and improved apparatus and method for rolling workpieces such as crankshafts. The apparatus has first and second rolling heads mounted at spaced positions along a common rolling arm to receive a crankshaft bearing therebetween which can then be shifted relative to one another along the common rolling arm to close the heads or rolling tools for clamping onto the workpiece. The in-line clamping action and force provided by the tools on the rolling arm are created by actuation of a tall, thin cylinder assembly including a number of aligned individual cylinders sized to keep the width of the cylinder assembly to a minimum so that all of the rolling arms can likewise be of a thin construction pivotally mounted on one side of the crankshaft and axially spaced according to the crankshaft bearing spacing for rolling all of the bearings in a single rolling operation. A strain sensor can be utilized to generate clamping force readouts that are based on the amount of structural deflection of the arm detected by the sensor.
Owner:INGERSOLL CM SYST
Process for finish-machining crank shafts for motor car engines
InactiveUS7827684B2Improve fatigue strengthSmall penetration depthCrankshaftsRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringCrankshaft
The invention relates to a process for finish-machining of bearing positions on main bearing journals and connecting rod bearing journals of crankshafts for motor car engines, whereby the crankshafts have roundings between the bearing positions and transitions adjacent in each case to the bearing positions. The roundings are deep rolled with a deep rolling tool and then, while maintaining a distance interval to an individual transition in each case the bearing position concerned is machined with removal of material with a small cutting depth.
Owner:HEGENSCHEIDT MFD
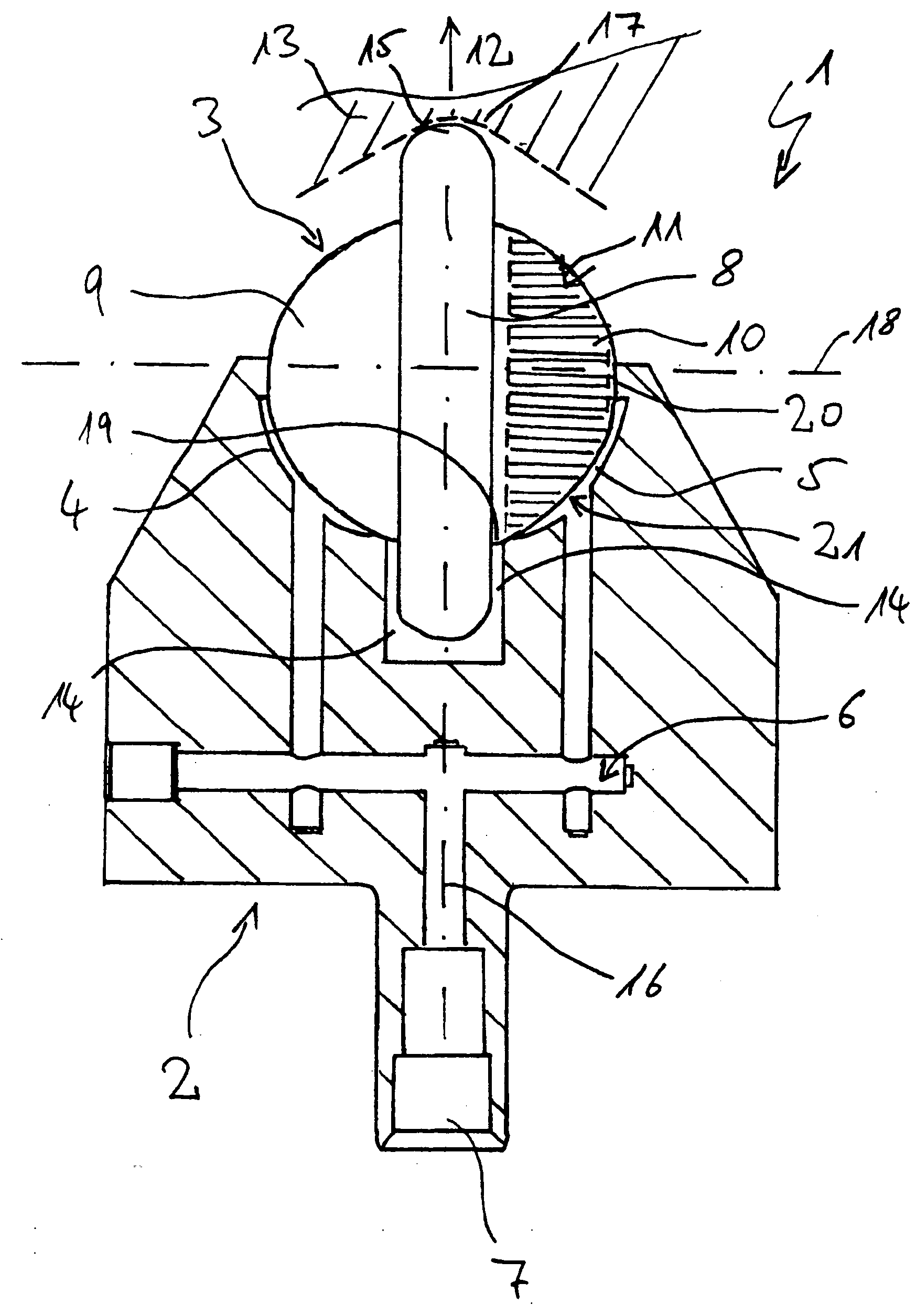
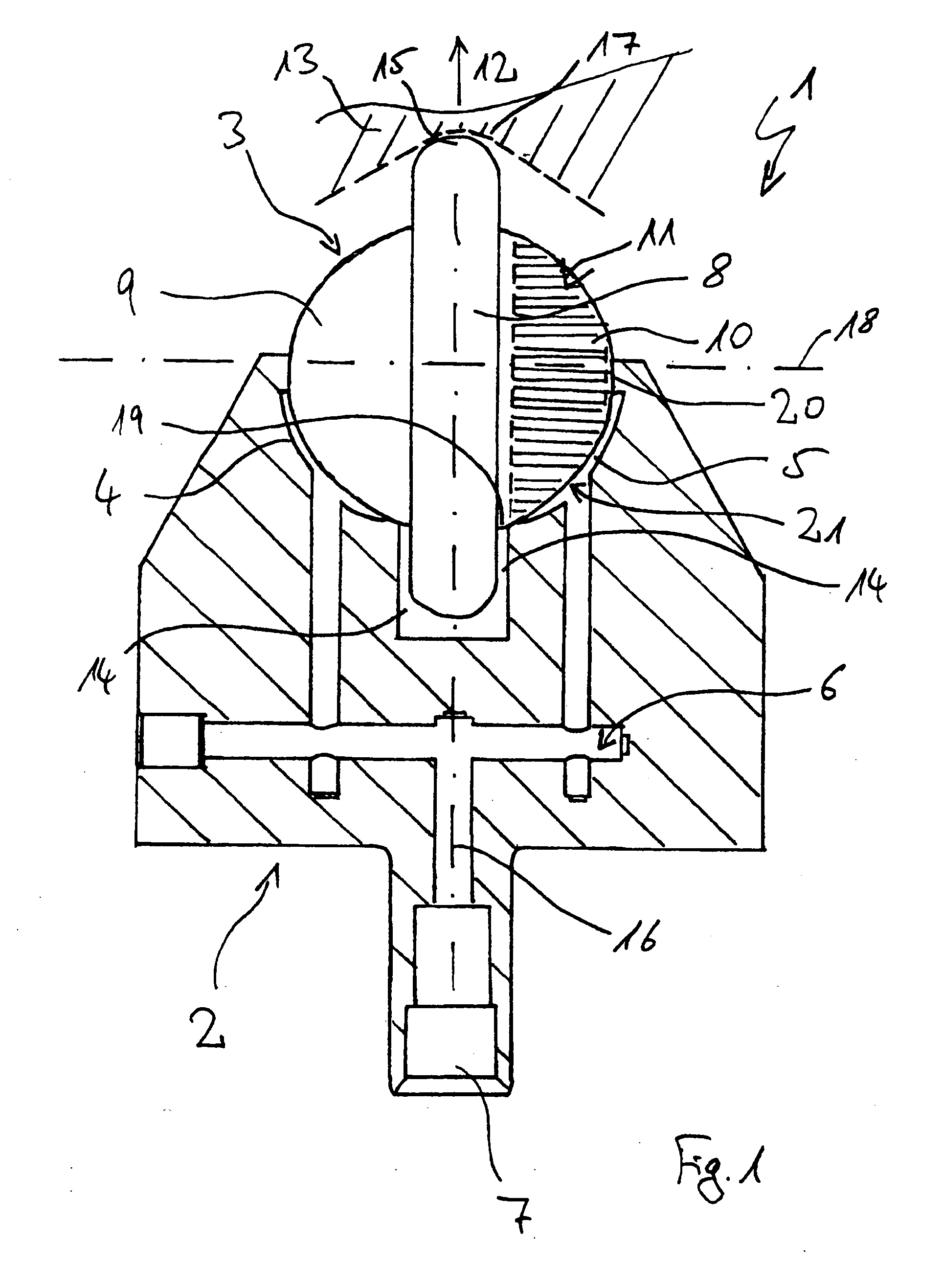
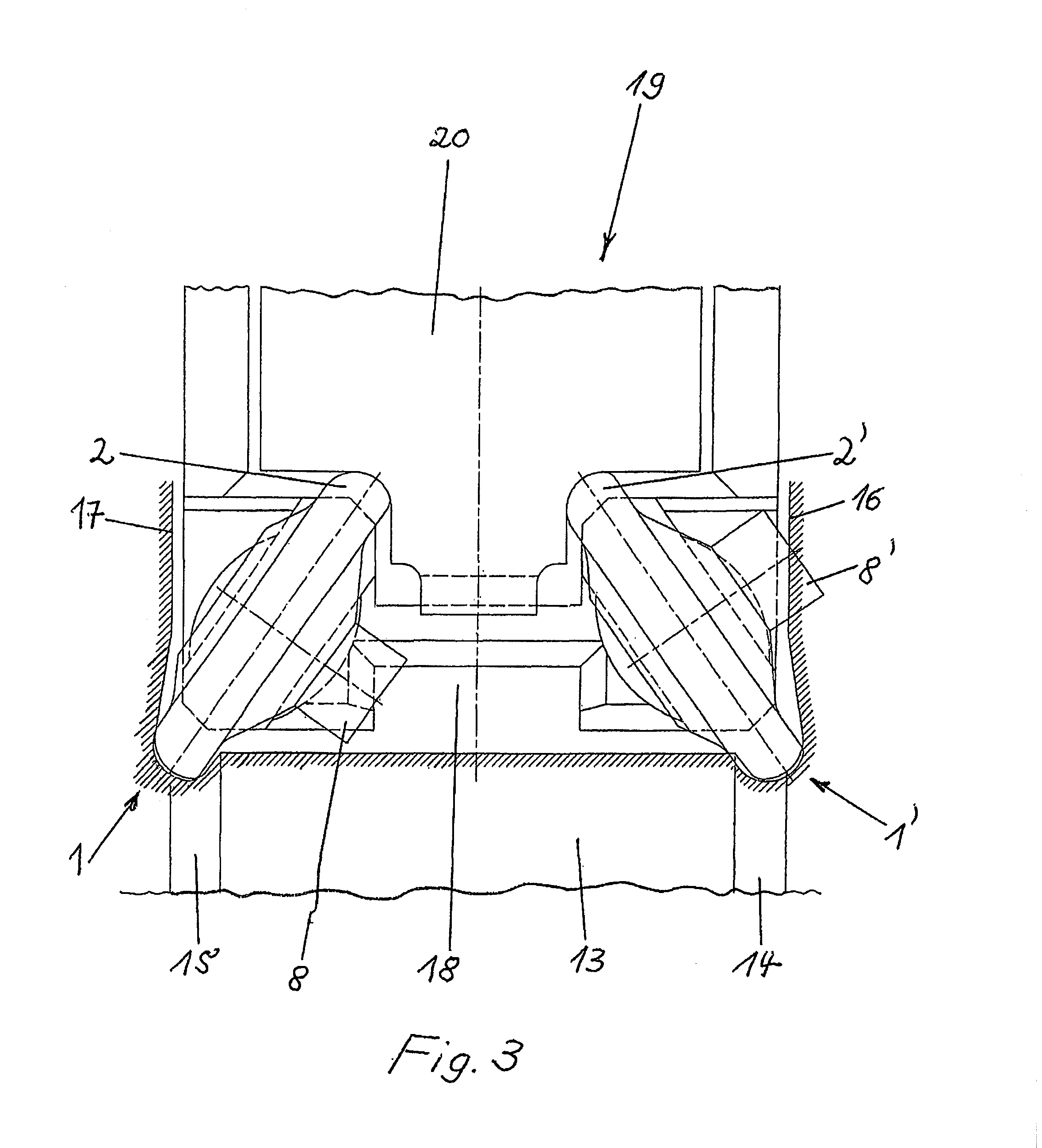
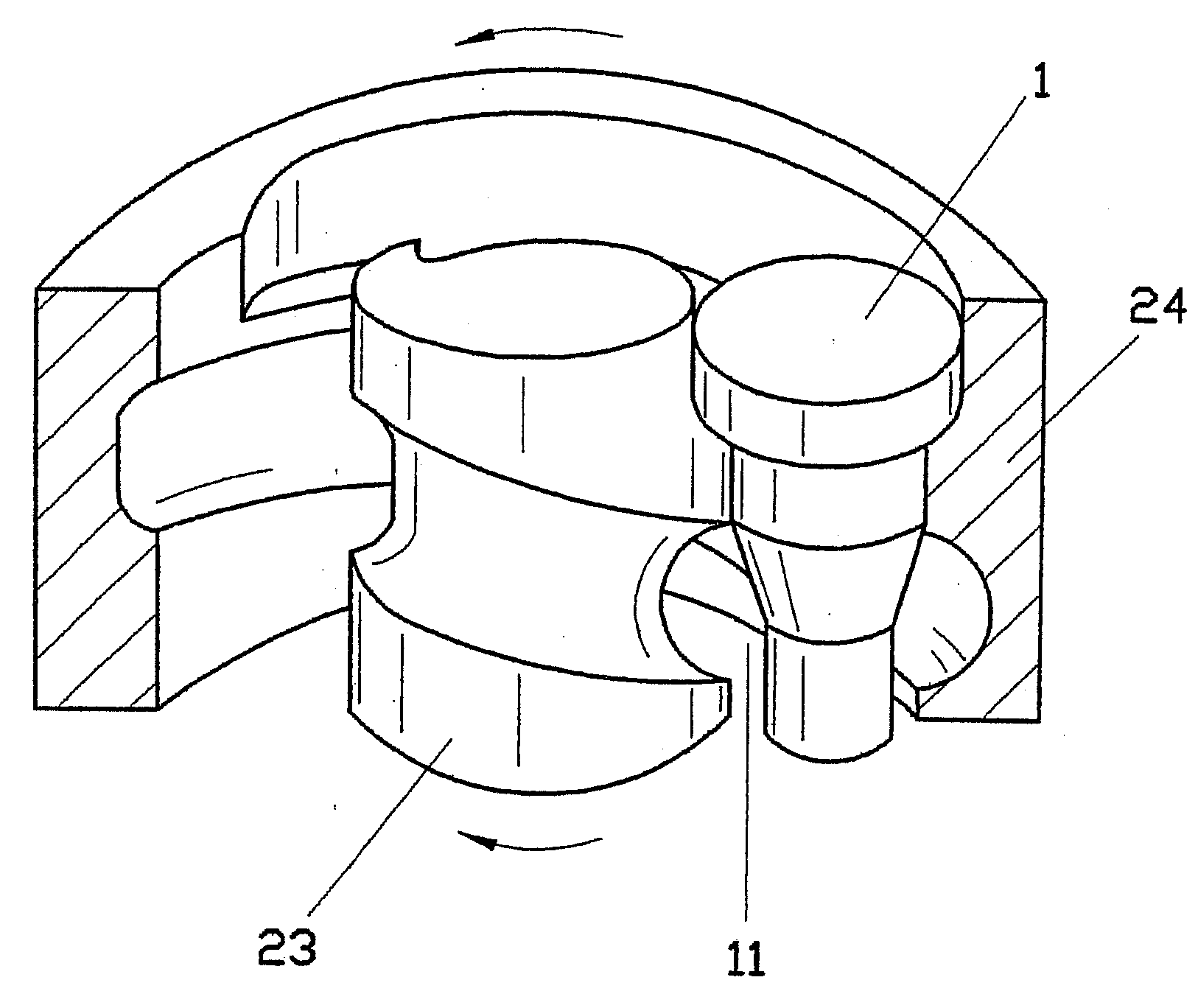
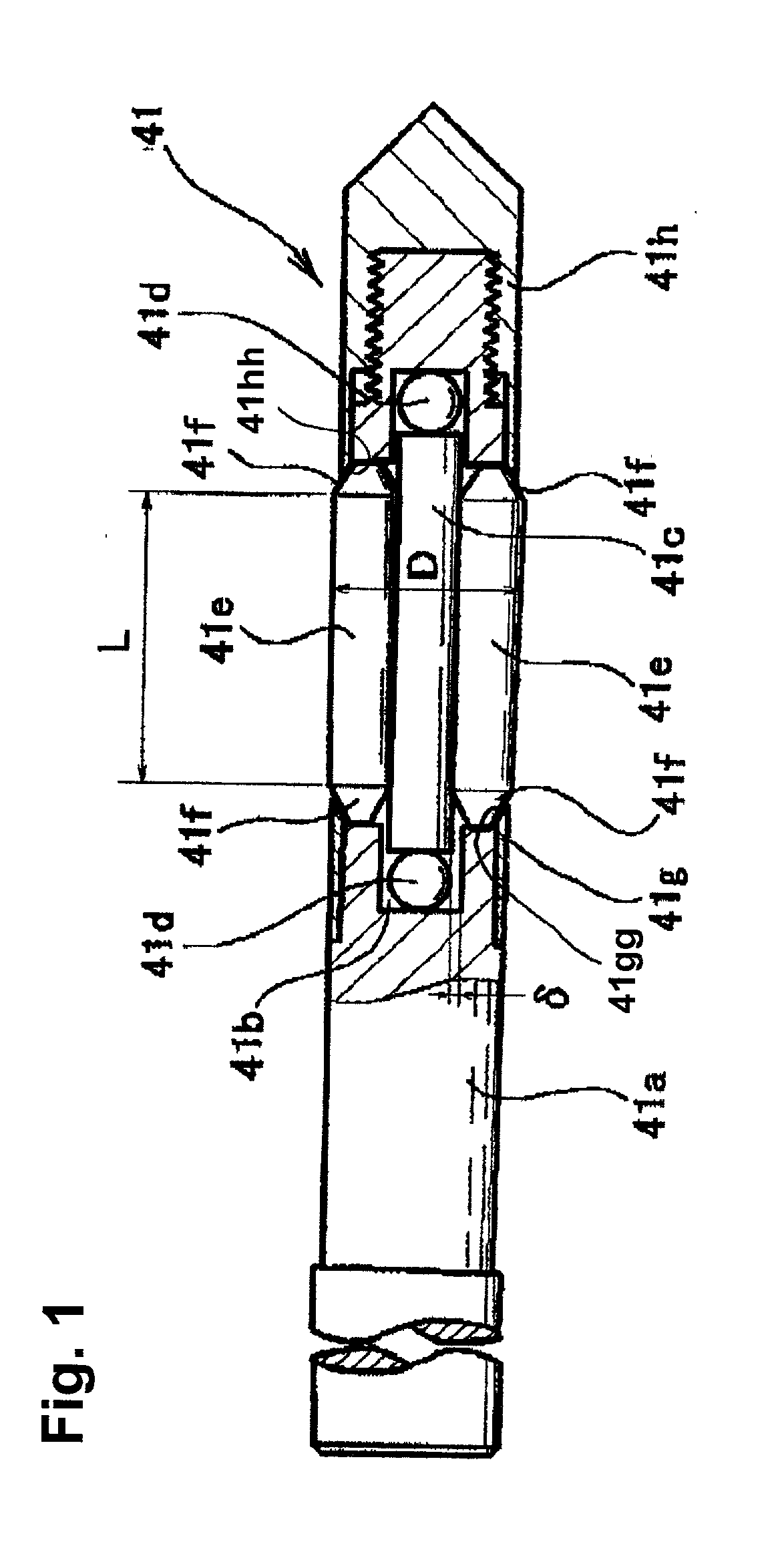
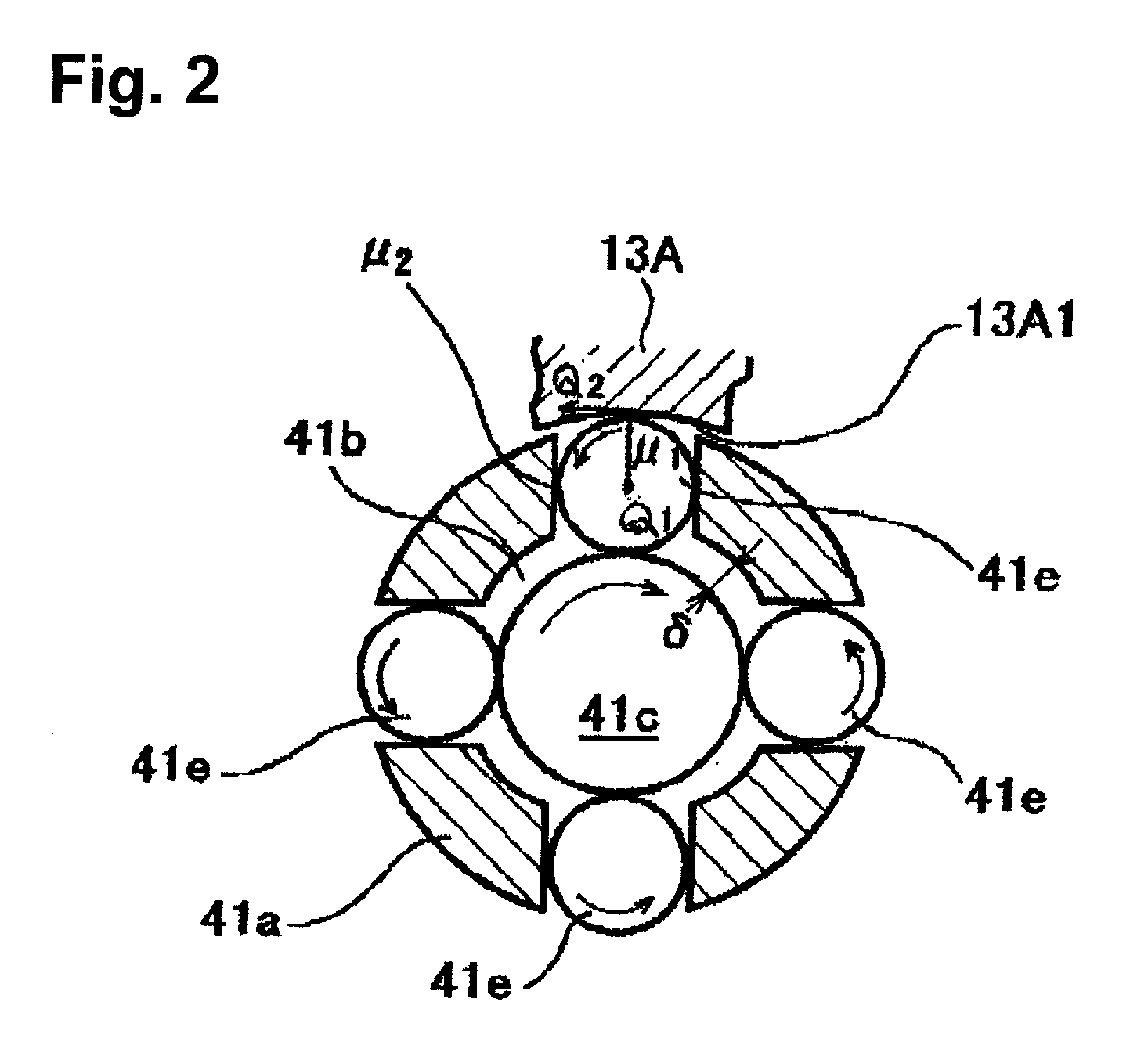
Tool for deep rolling of grooves on crankshaft journals or crank pins
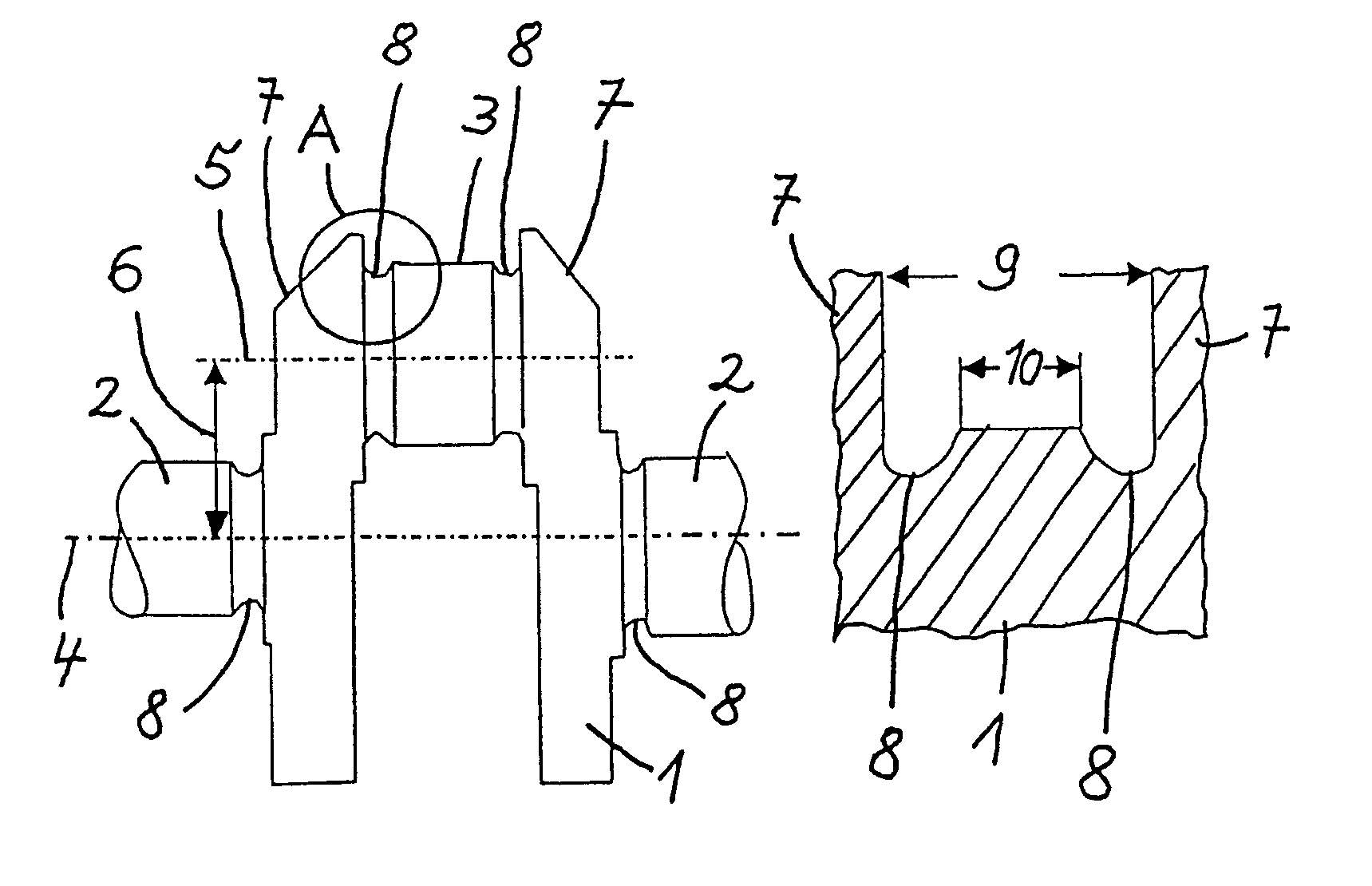
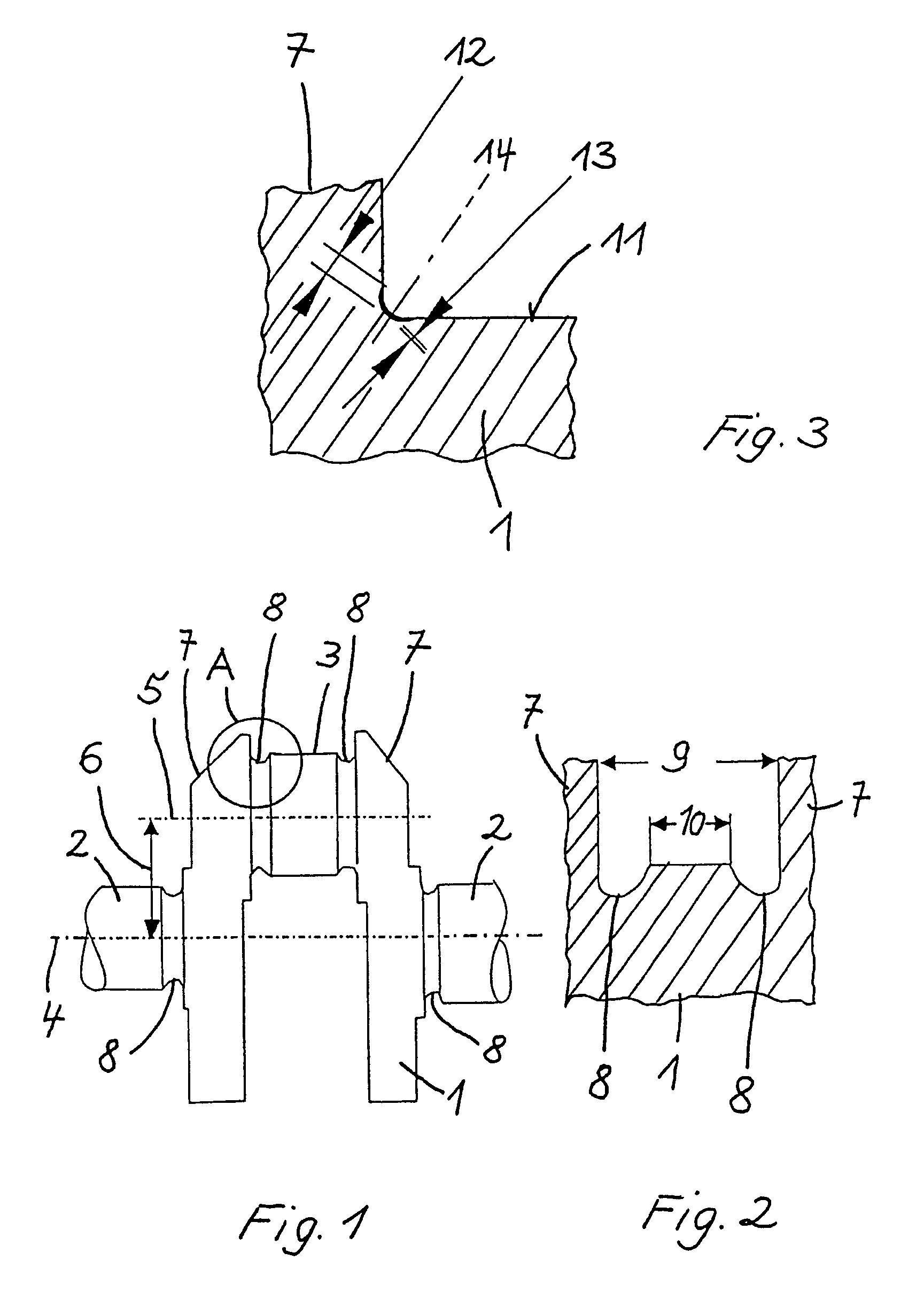
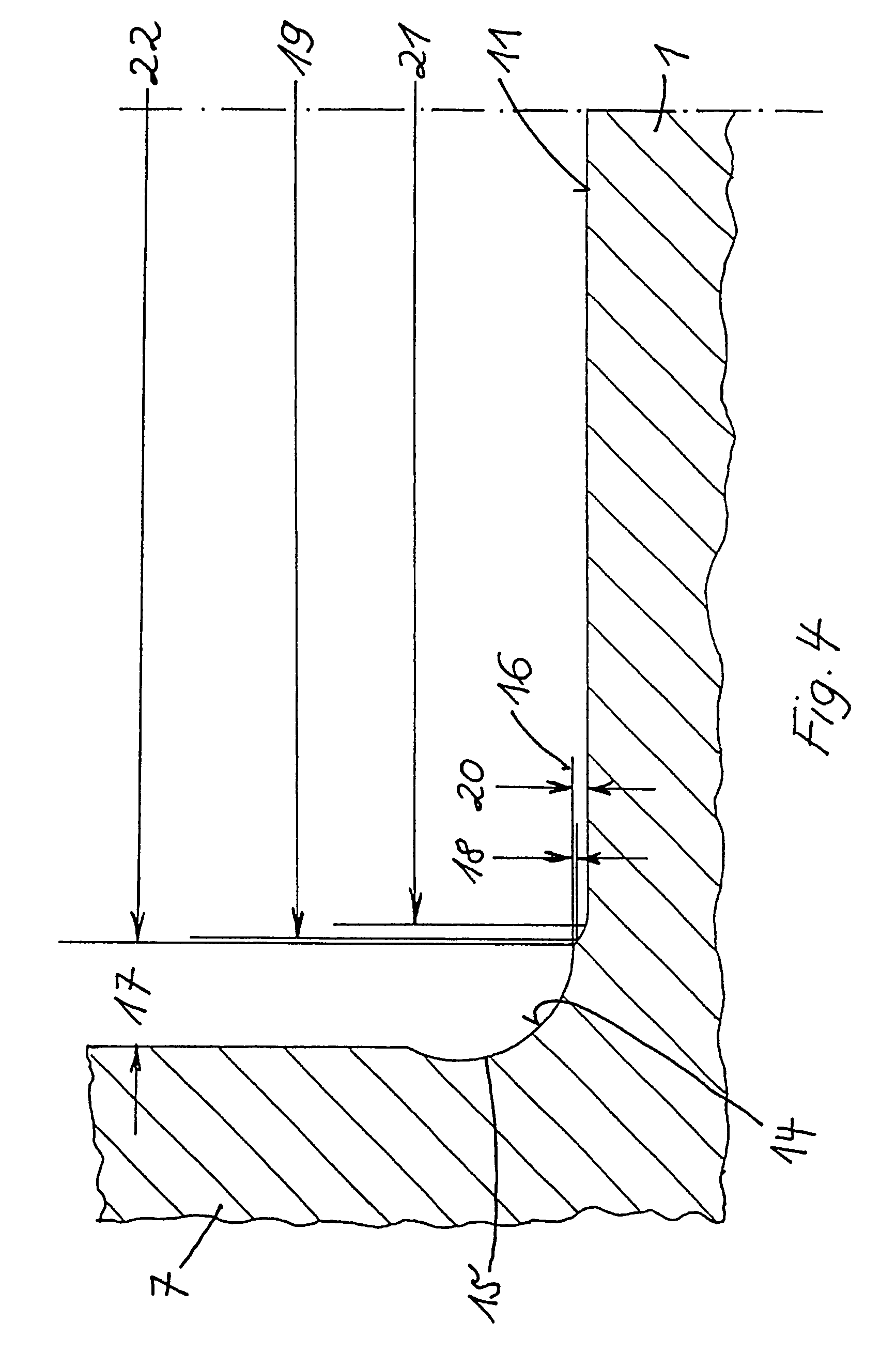
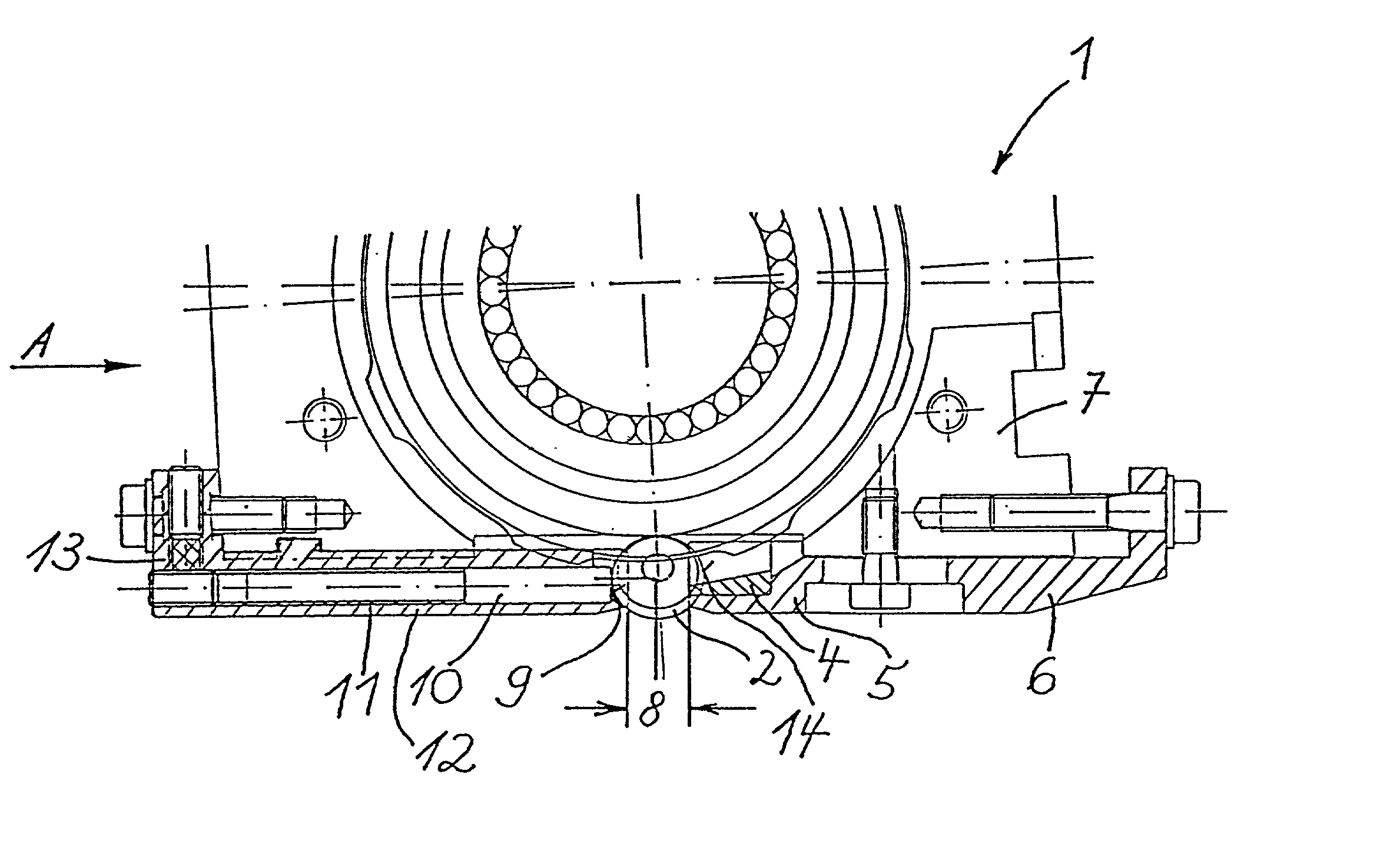
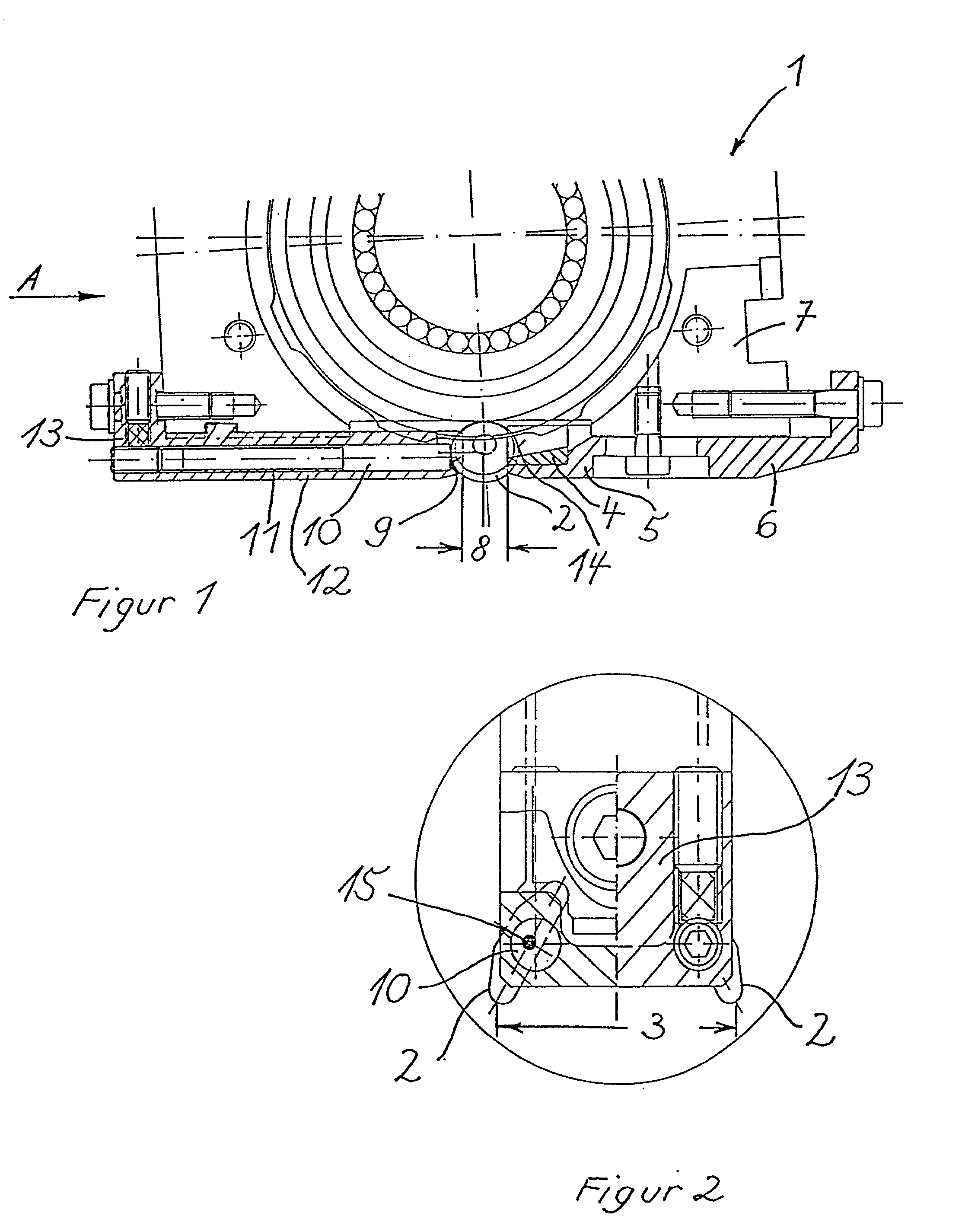
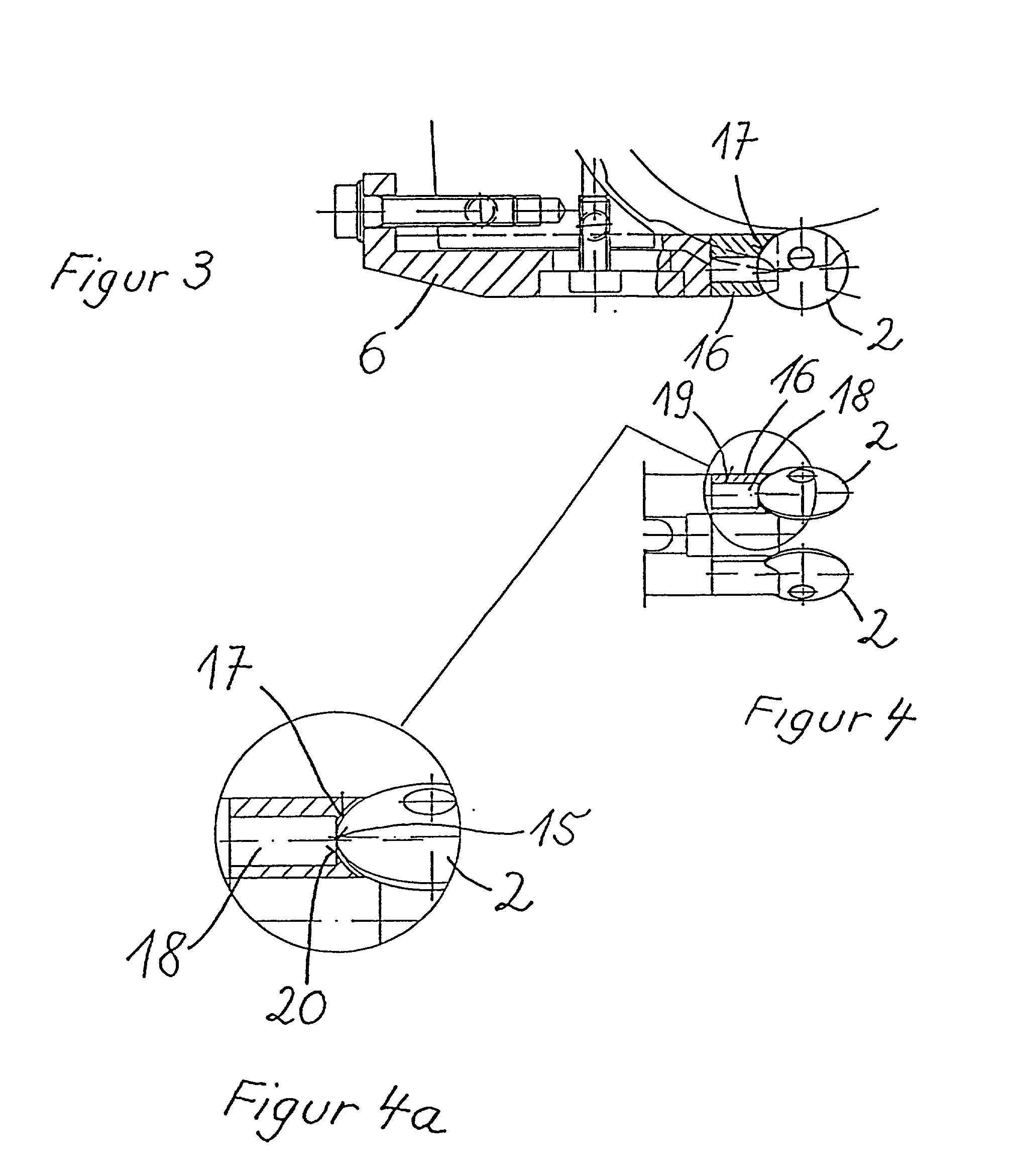
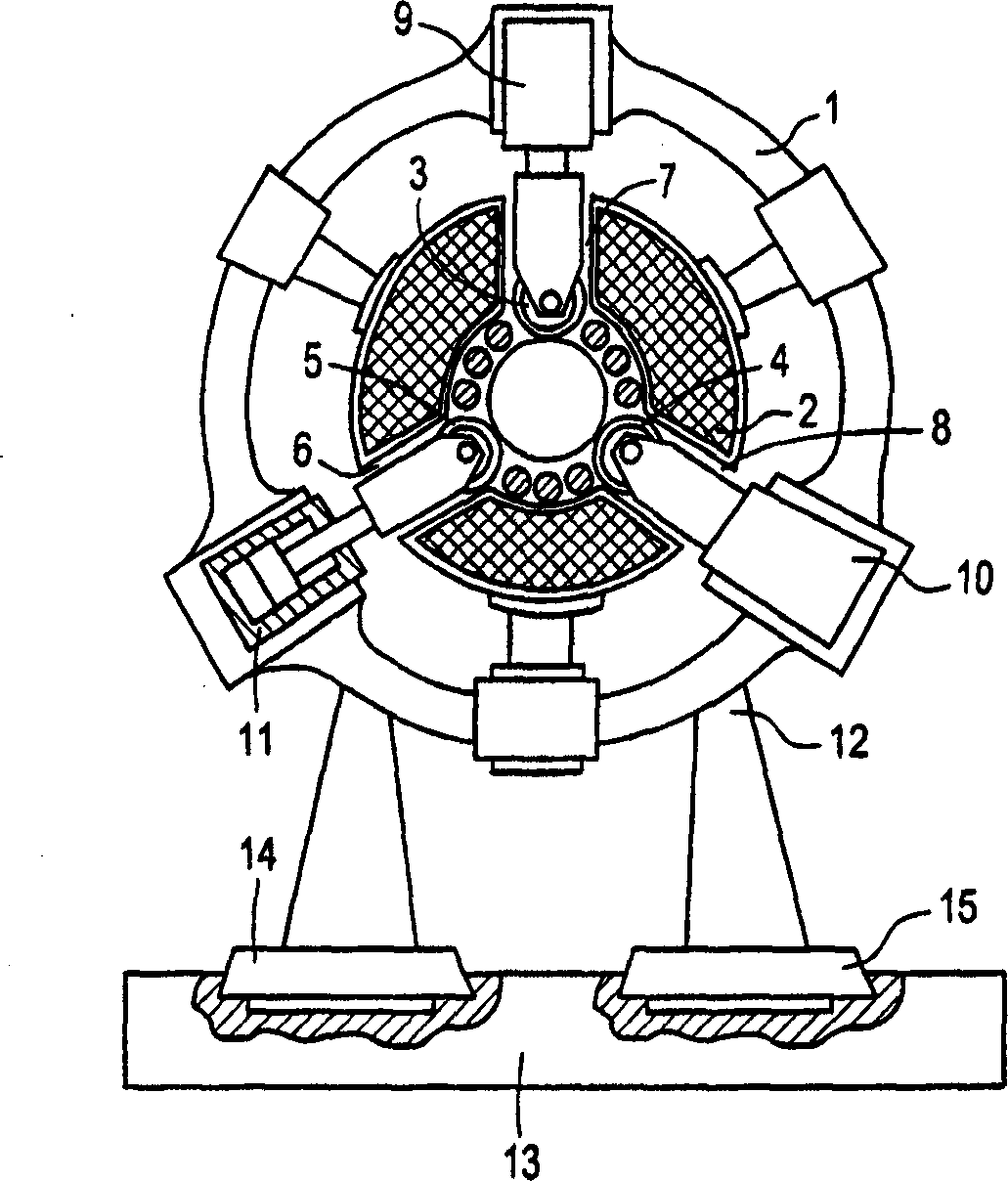
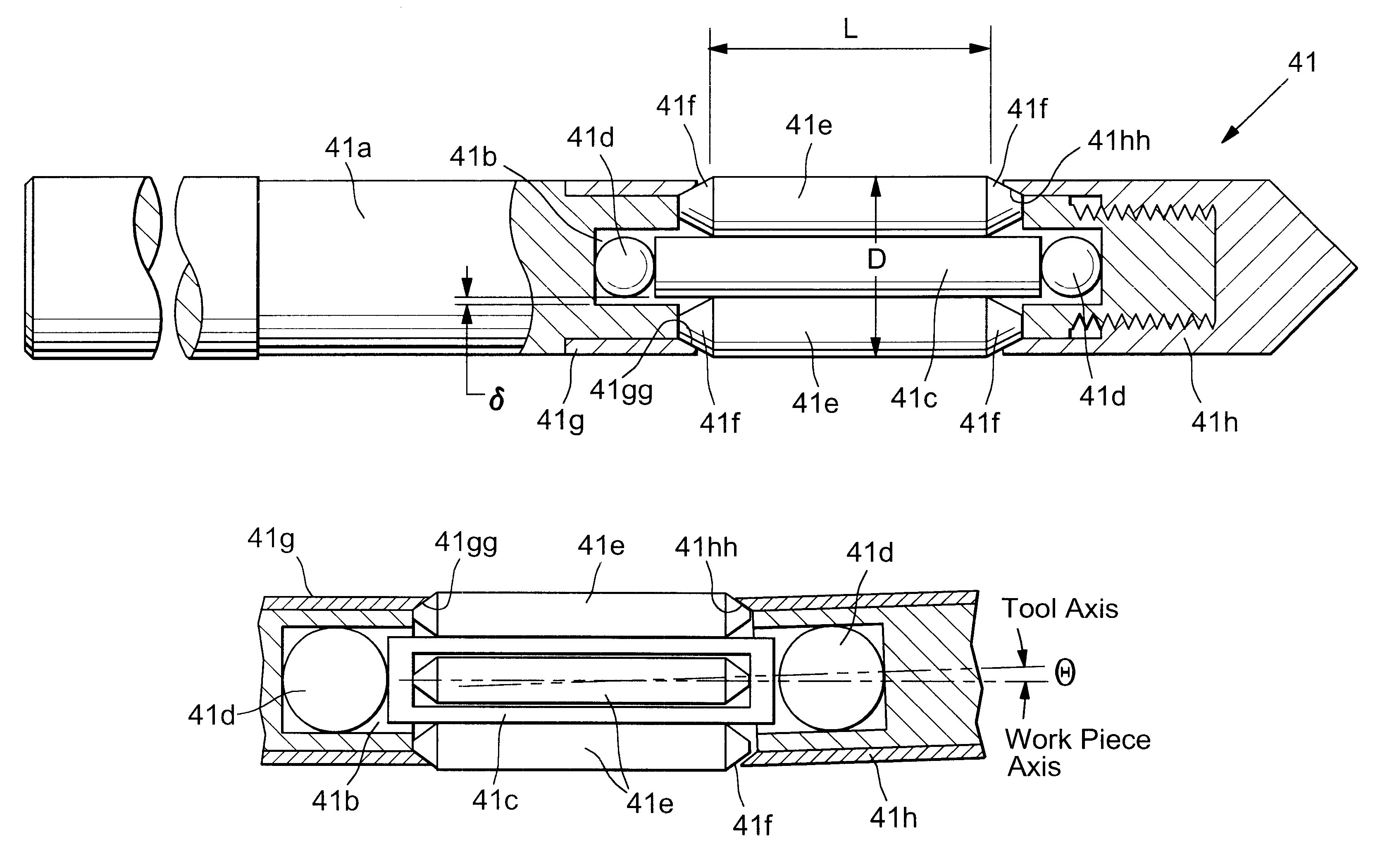
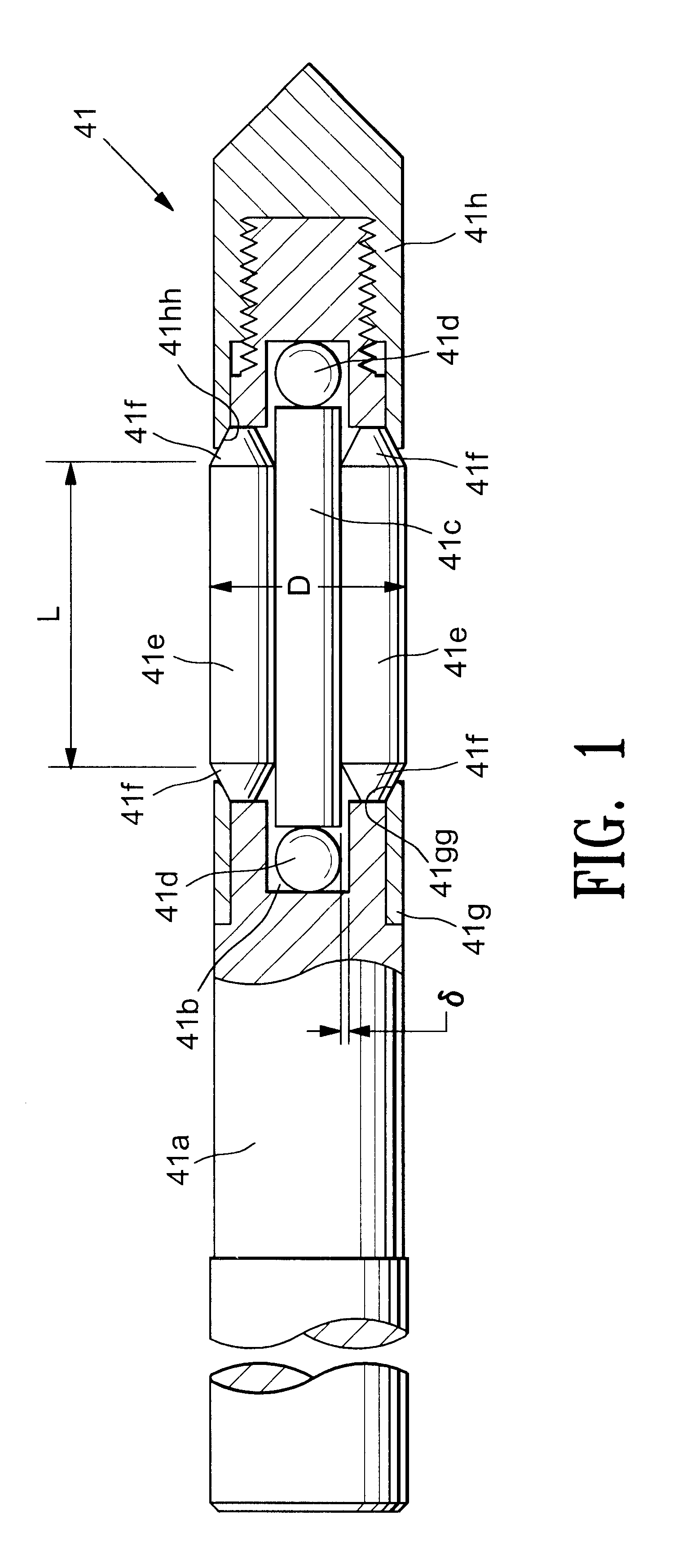
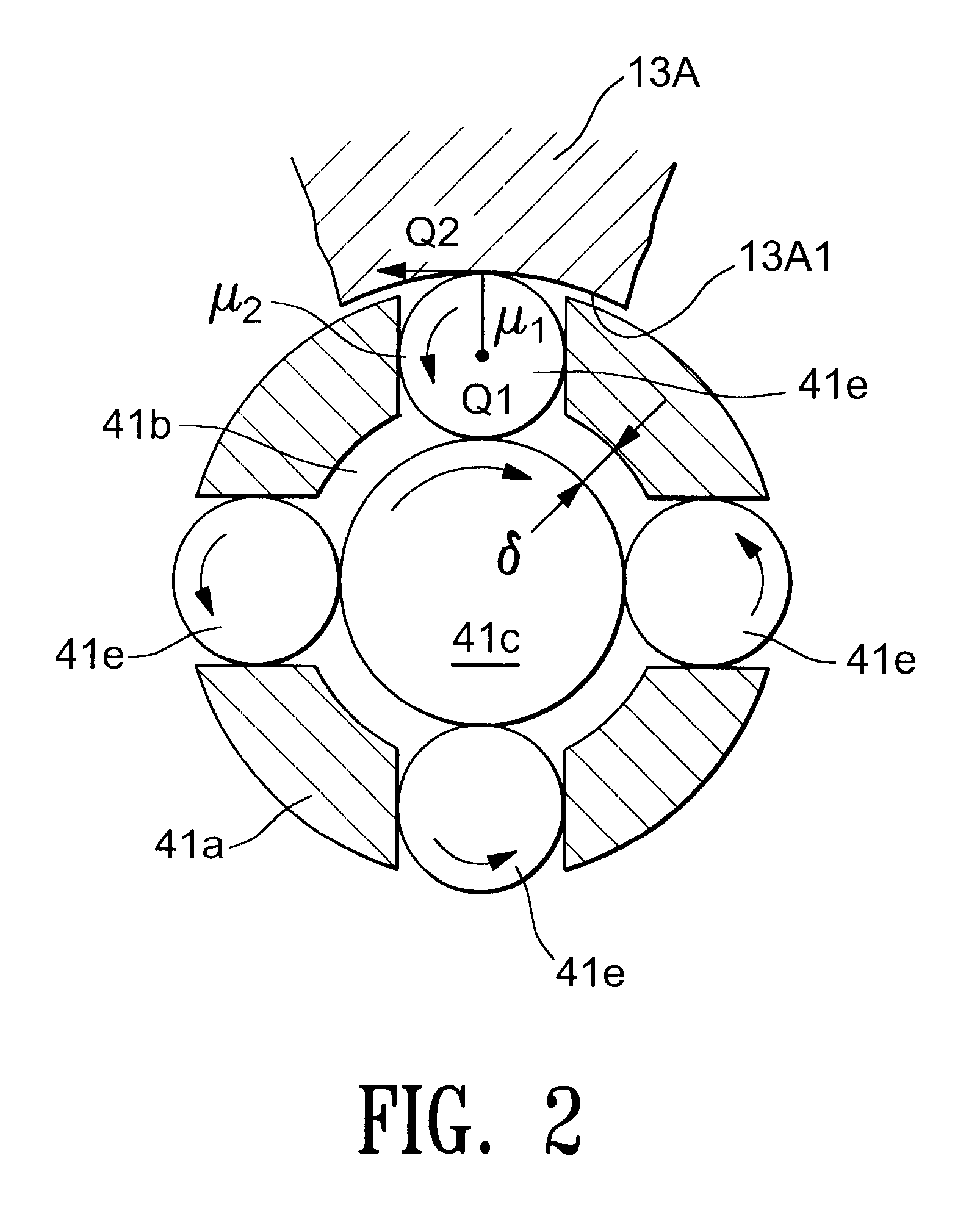
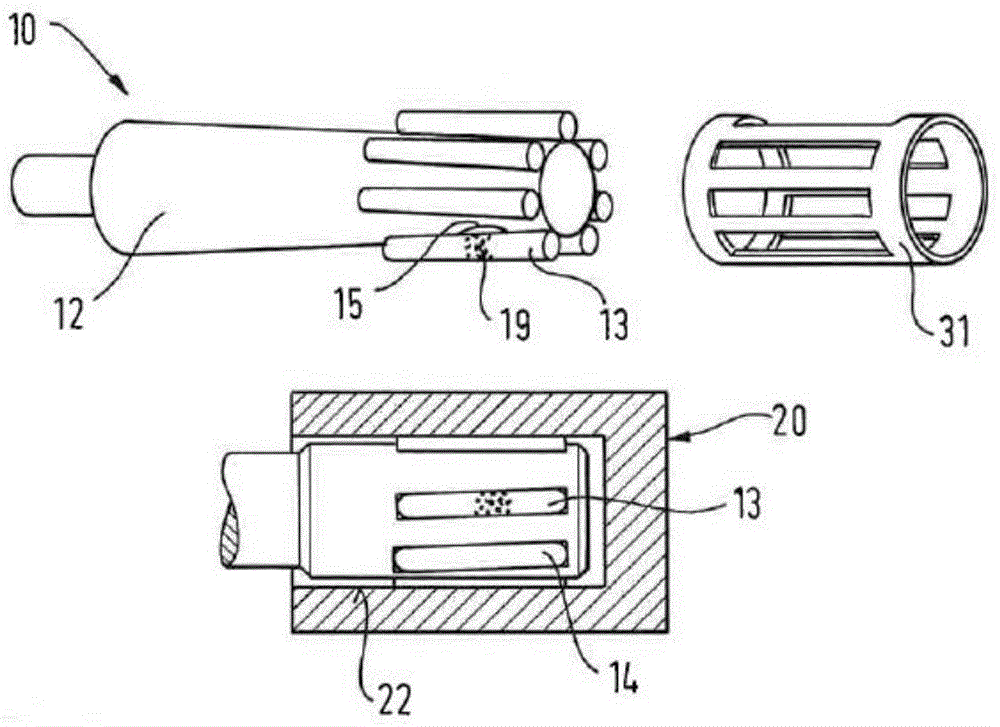
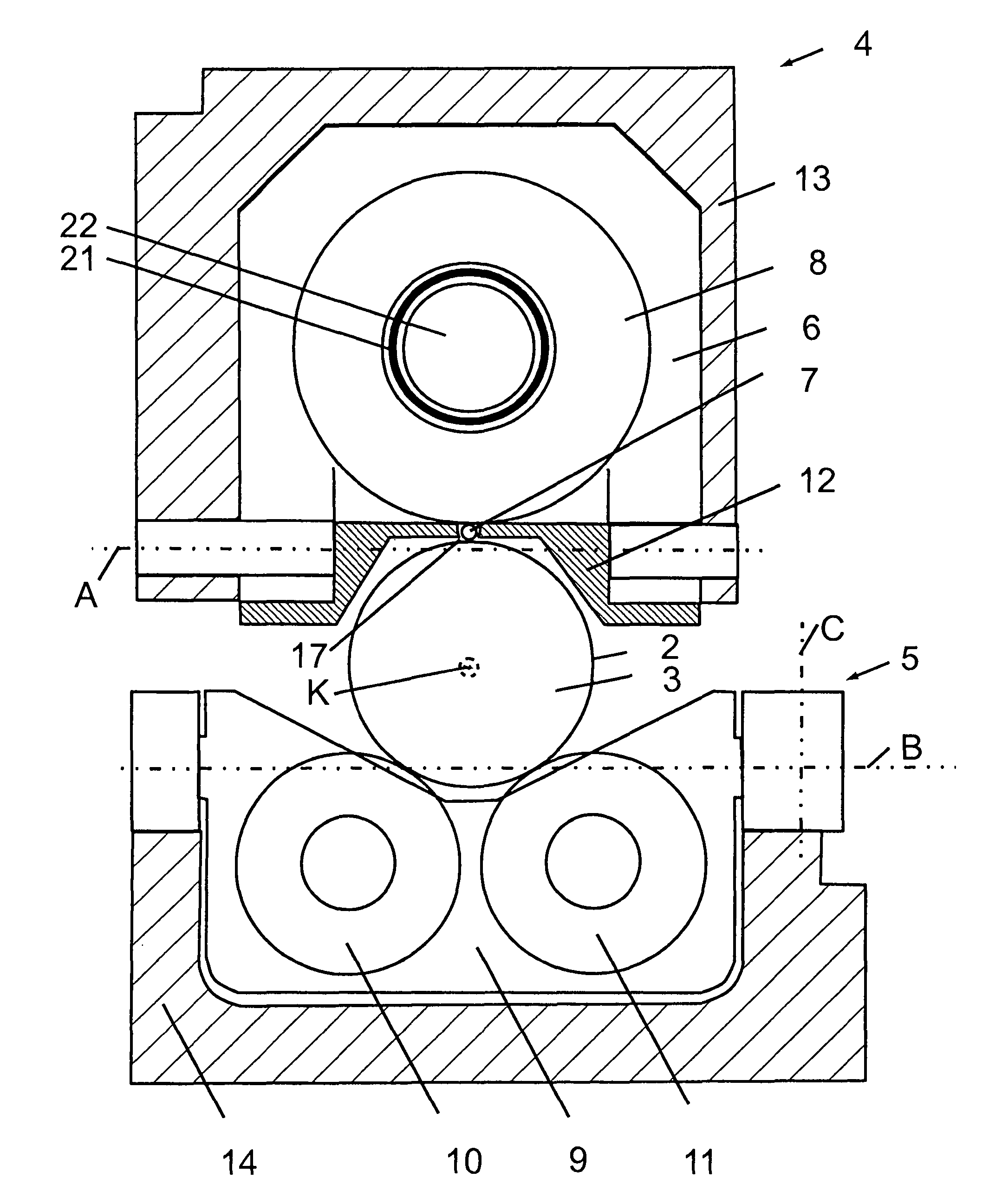
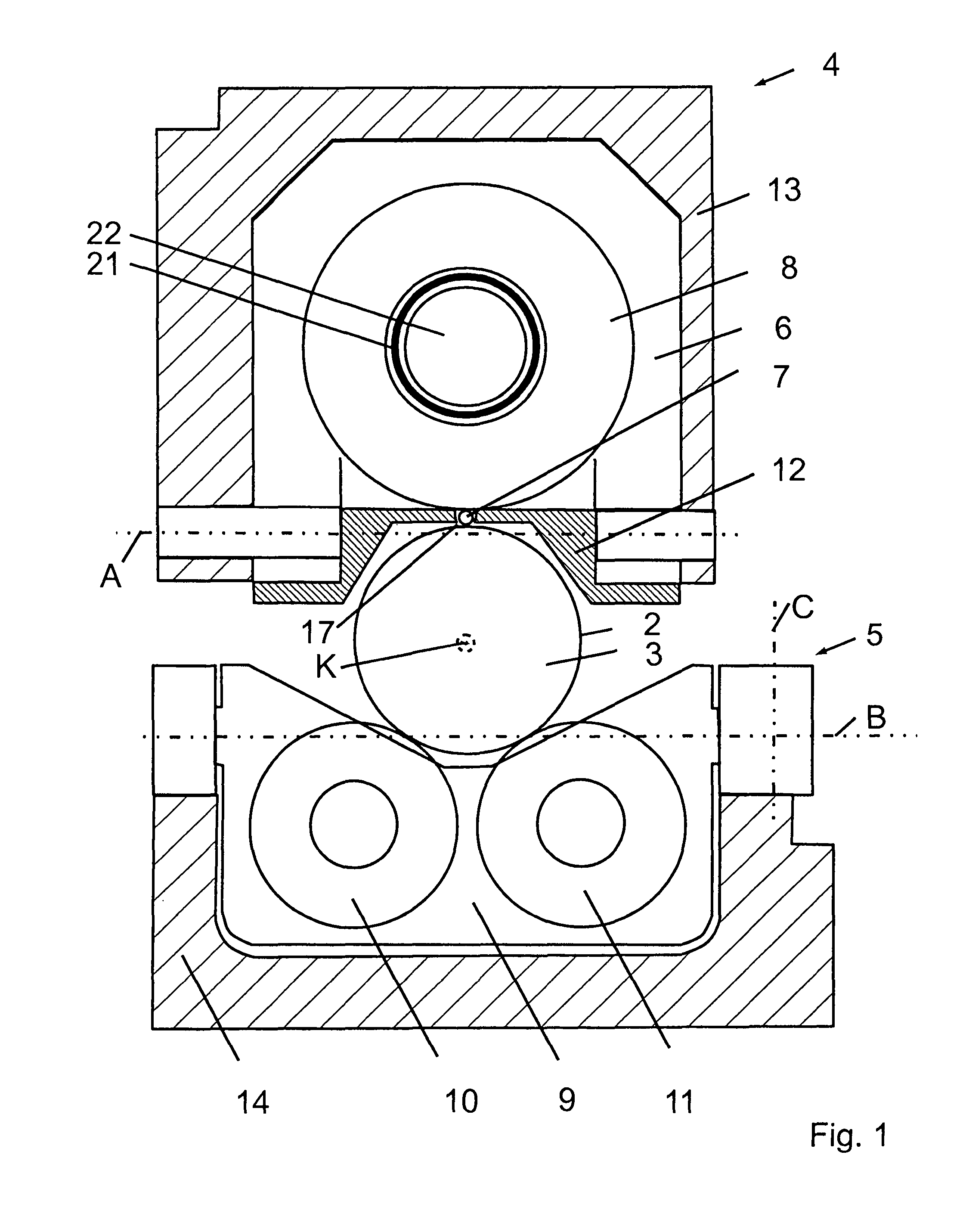
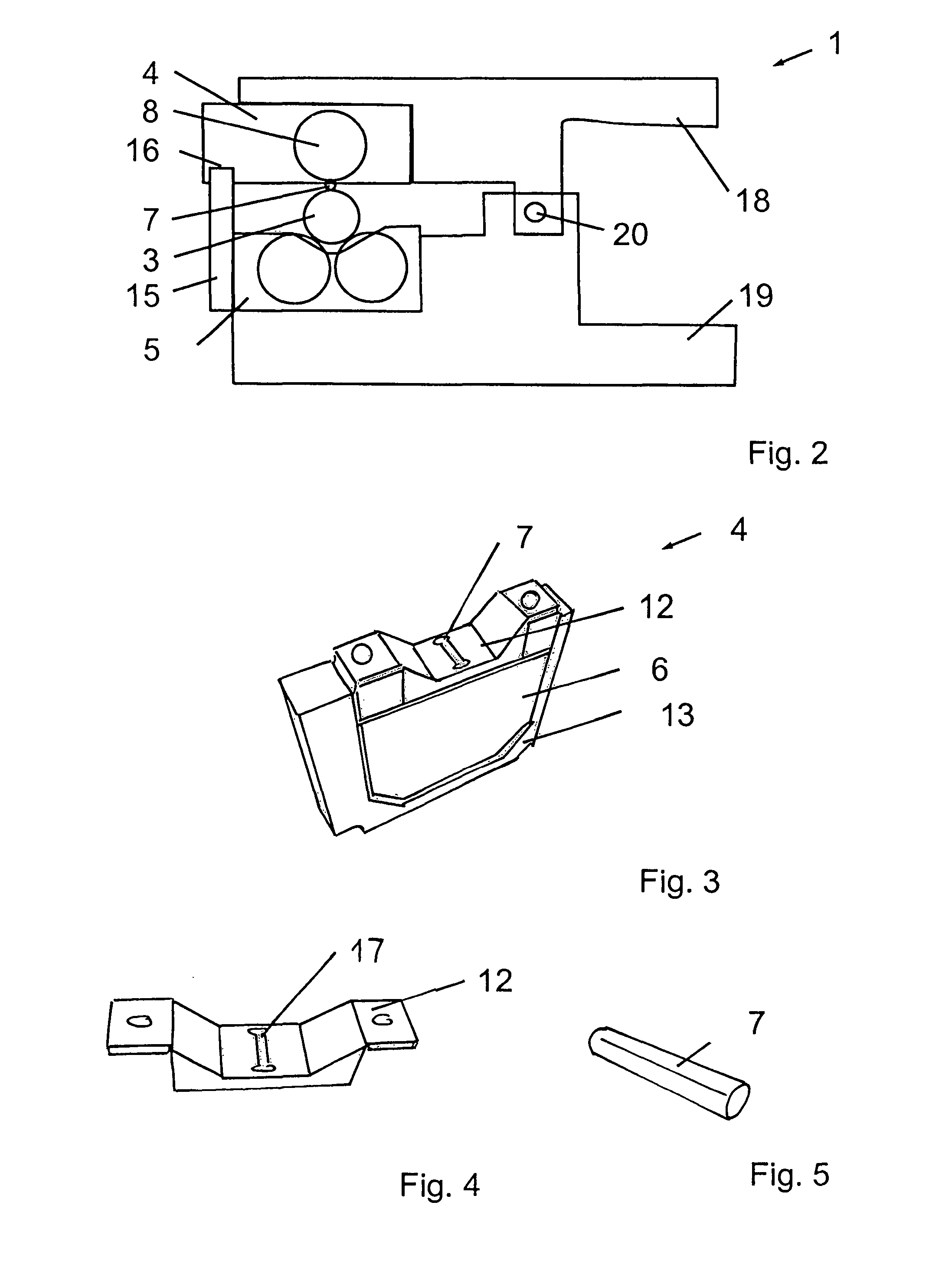
InactiveUS20020020202A1Extended service lifeImprove mobilityRevolution surface grinding machinesBurnishing machinesHardnessEngineering
A tool is provided having two deep rolling work rollers (2) made of a hard material which, for the deep rolling of grooves in crankshaft journals or crank pins, are arranged at a first mutual distance that corresponds to the specific width of the journals. Each of the work rollers (2) is supported to float in a pocket-shaped recess (14) provided in a cage (4), in accordance with the first distance. The cage (4) consists of a material which, compared to the material of the work rollers (2), has a lower degree of hardness but superior sliding characteristics. The cage (4) is located at the extreme end of the long leg (5) of an L-shaped tool holder (6), and has a second distance (8) to a second cage for support of the same work rollers (2). A minimum of one of the recesses (14) of the second cage is configured in a way to provide the work roller (2), at least in the direction of the first distance, with increased mobility, and in addition, a support surface is provided which engages the outer circumference of the work roller (2)
Owner:HEGENSCHEIDT MFD
Composite fabrication facility of steel tube and fabrication method of steel tube
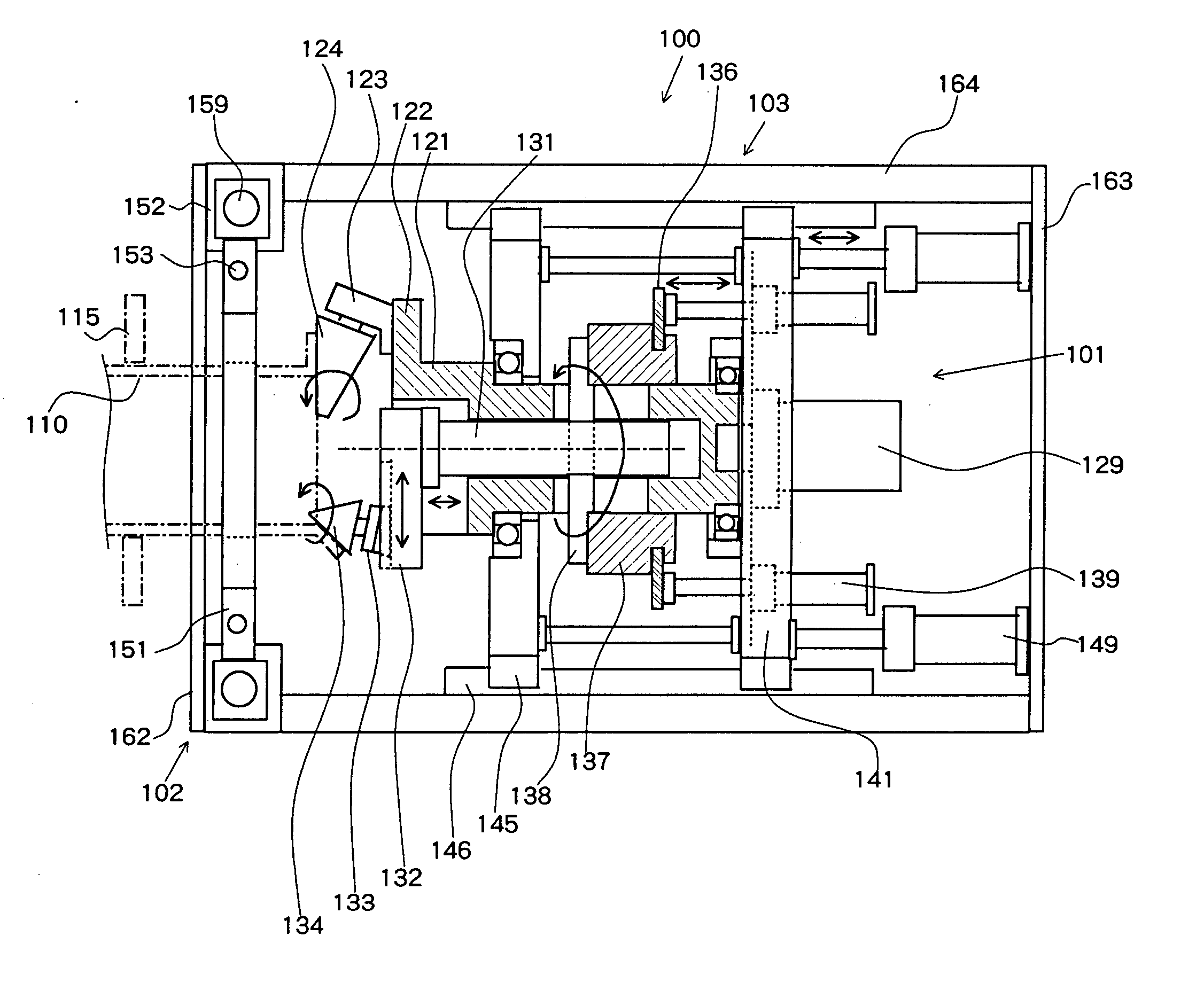
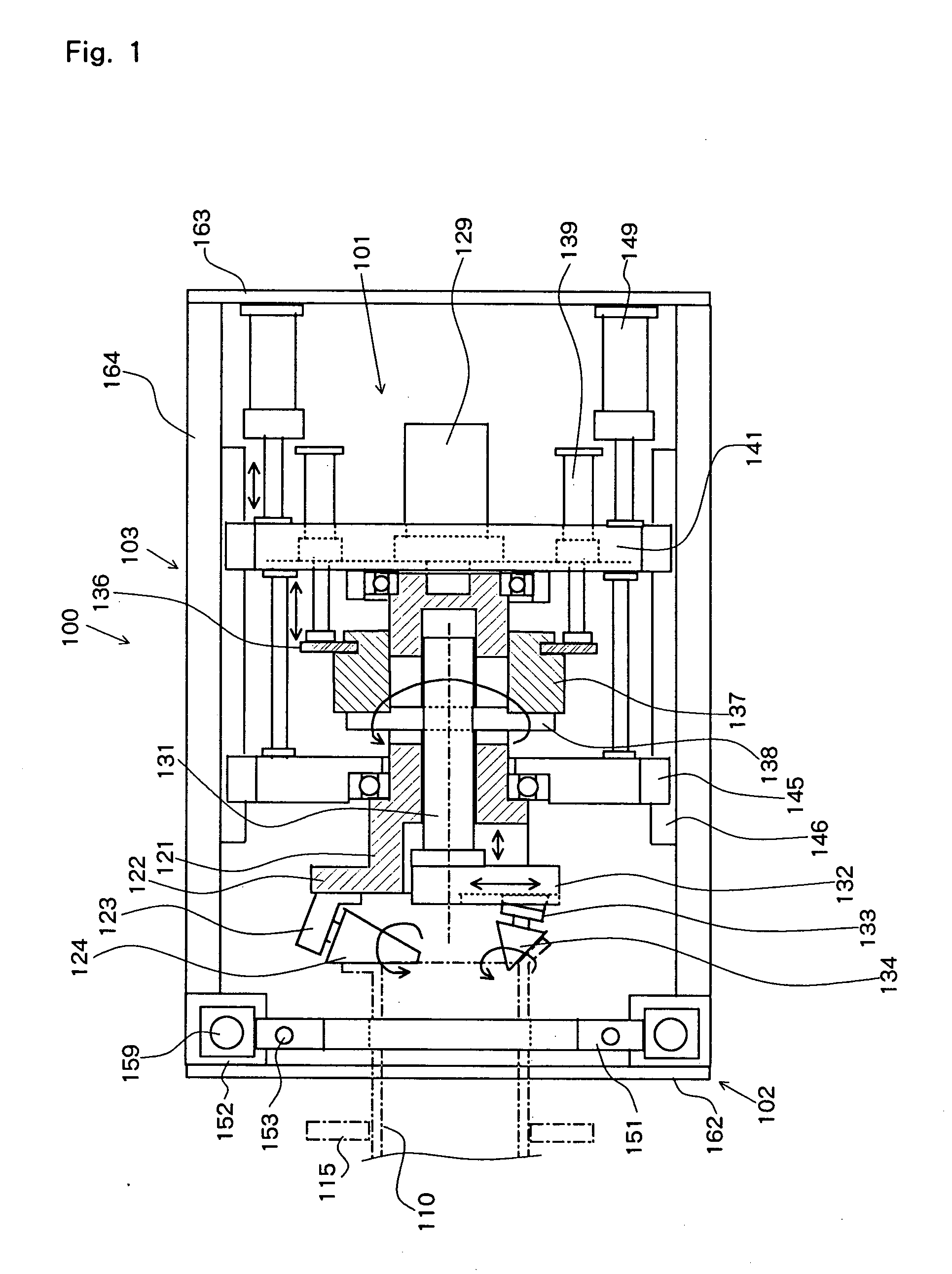
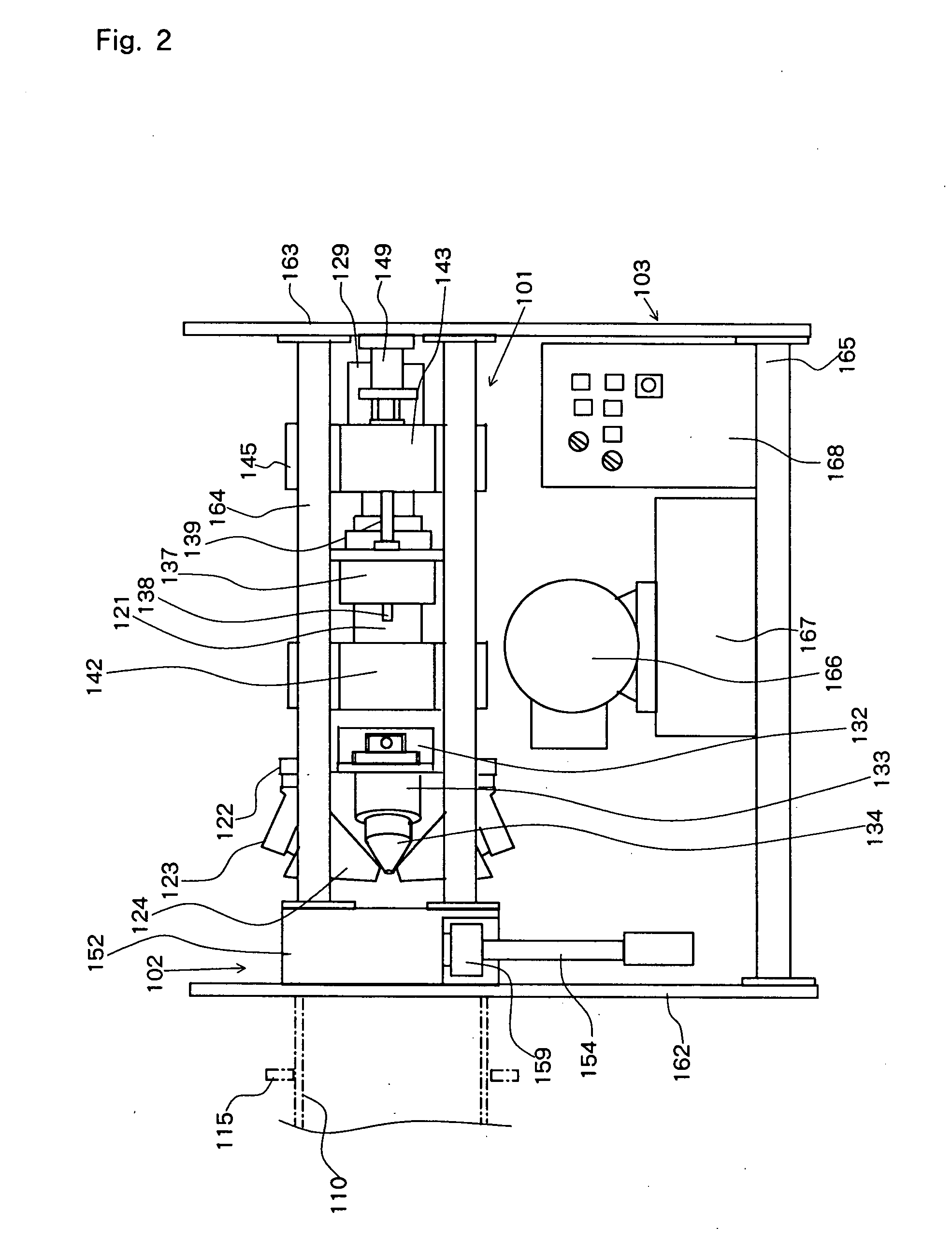
InactiveUS20060162410A1Small sizeEasy to moveEdge grinding machinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsMachiningSteel tube
The present invention pertains to a combined machining equipment for steel tubes, and a machining method is of a small size, can easily be moved, and is capable of not only flaring a steel tube, but also grinding a flared surface, forming a groove, and peeling off a lining. A main shaft (121) is rotatably mounted on a slide frame (141) slidable with respect to a common mount (103), and a second machining head (124) is mounted on a flange on the distal end of the main shaft (121). An auxiliary shaft (131) is slidably disposed in the main shaft (121) for rotation therewith. A first machining head (134) is mounted on a mount base (132) on the distal end of the auxiliary shaft (131). When the main shaft (121) is rotated and moved back and forth and the auxiliary shaft (131) is moved back and forth with respect to the main shaft (121), the first machining head (134) spreads the tip end of a steel tube (110) held by a steel tube holding apparatus (102) to a first position, and the second machining head (124) spreads the tip end of the steel tube (110) to a predetermined flanged position, thus flaring the tip end of the steel tube (110).
Owner:OGAWA KIYOSHI
Slip joint assembly with coated splines and method
A method includes providing a shaft having a coupling section. The coupling section has a generally cylindrical exterior surface. The method includes applying a coating to the coupling section to form an engaging surface. The method further includes cold-forming the shaft and the coating such that a plurality of protrusions is formed in the engaging surface. The cold-forming of the shaft and the coating is performed contemporaneously.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Apparatus for forming microscopic recesses on a cylindrical bore surface and method of forming the microscopic recesses on the cylindrical bore surface by using the apparatus
ActiveUS20070010173A1Increase production costSimple materialBurnishing machinesGroovesEngineeringCentrifugal force
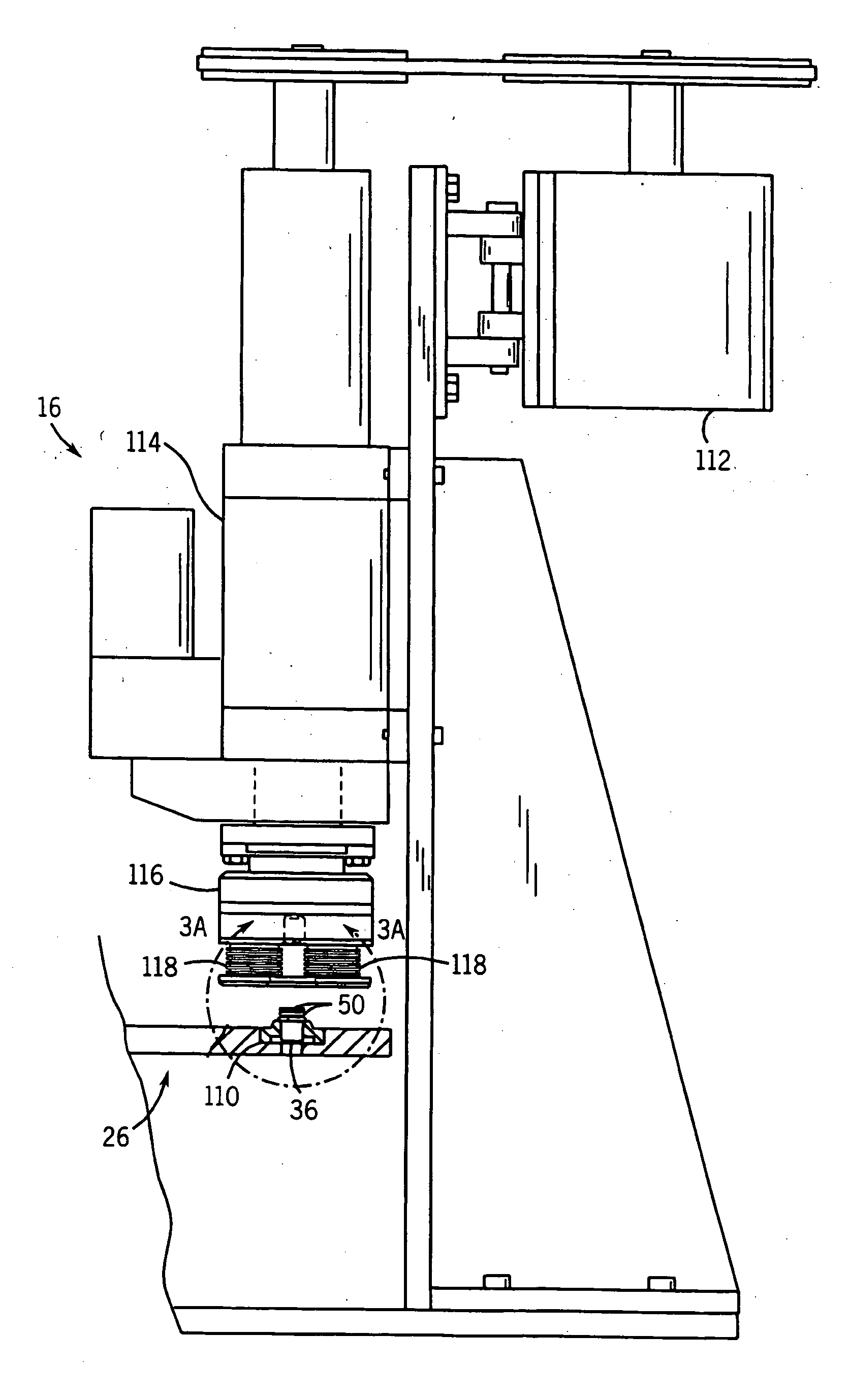
An apparatus for forming microscopic recesses on a circumferential surface that defines a cylindrical bore in a workpiece, including a tool holder rotatably about a rotation axis, a form roller support moveable in a direction perpendicular to the rotation axis of the tool holder, a form roller rotatable about a rotation axis parallel to the rotation axis of the tool holder, and control means for controlling the form roller support such that the form roller is allowed to be in press contact with the circumferential surface of the cylindrical bore at a press contact load of a predetermined value on the basis of a centrifugal force which is exerted on the form roller support and the form roller during rotation of the tool holder.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
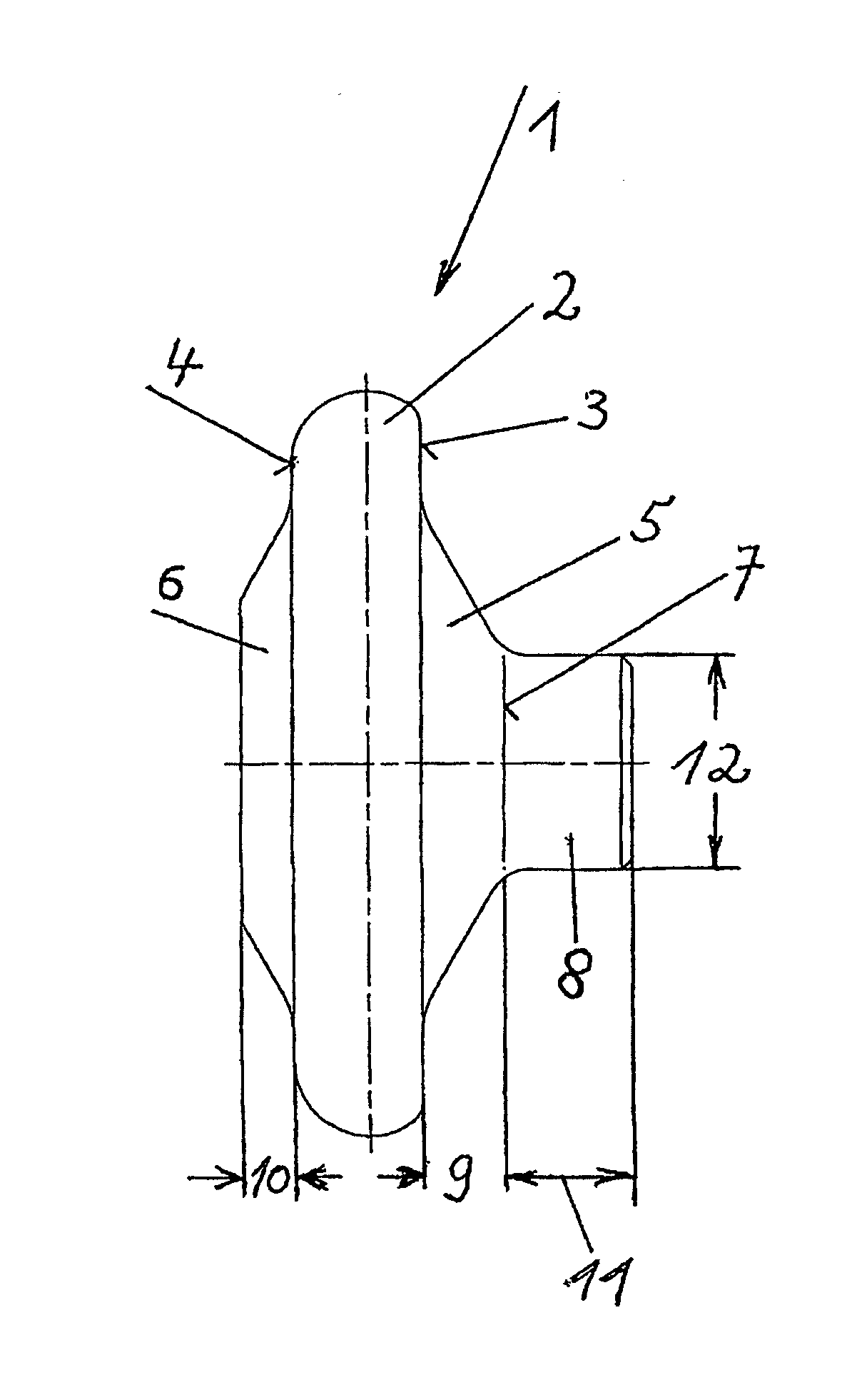
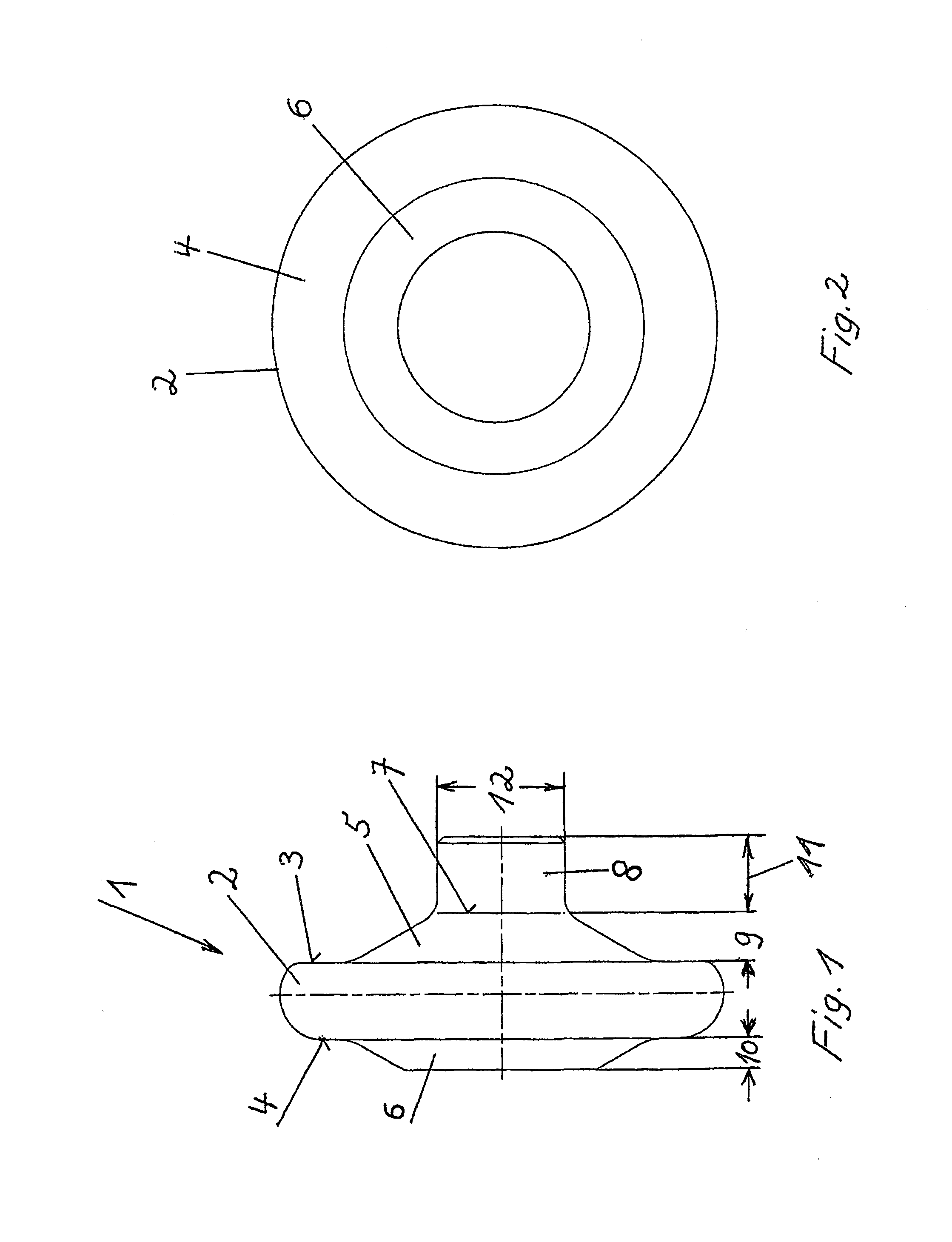
Hard-rolling roller
ActiveUS20140326032A1Premature wearMachining errorBurnishing machinesRollsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a hard-rolling roller for a deep rolling tool having a torus-shaped base body for deep rolling of radiuses or recesses which limit the bearing trunnion on crankshafts on both sides, and two at least approximately truncated cone-shaped central bodies, rising on both sides of the body. A cylindrical body rises on the upper end surface of one of the two central bodies.
Owner:HEGENSCHEIDT MFD
Composite fabrication facility of steel tube and fabrication method of steel tube
InactiveUS7216521B2Small sizeEasy to moveEdge grinding machinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsMachiningSteel tube
The present invention pertains to a combined machining equipment for steel tubes, and a machining method is of a small size, can easily be moved, and is capable of not only flaring a steel tube, but also grinding a flared surface, forming a groove, and peeling off a lining. A main shaft (121) is rotatably mounted on a slide frame (141) slidable with respect to a common mount (103), and a second machining head (124) is mounted on a flange on the distal end of the main shaft (121). An auxiliary shaft (131) is slidably disposed in the main shaft (121) for rotation therewith. A first machining head (134) is mounted on a mount base (132) on the distal end of the auxiliary shaft (131). When the main shaft (121) is rotated and moved back and forth and the auxiliary shaft (131) is moved back and forth with respect to the main shaft (121), the first machining head (134) spreads the tip end of a steel tube (110) held by a steel tube holding apparatus (102) to a first position, and the second machining head (124) spreads the tip end of the steel tube (110) to a predetermined flanged position, thus flaring the tip end of the steel tube (110).
Owner:OGAWA KIYOSHI
Method and apparatus for manufacturing a battery terminal with undercut rings
InactiveUS20060162417A1Improve sealingPrevent electrolyte leakageLead-acid accumulatorsForging hammersCold formedElectrical battery
A method and apparatus to cold form rings or a lead battery terminal with undercuts or overhangs to improve the sealing properties of the rings. The apparatus can be one of a segmented die device and a die device wherein one die member moves relative to the other die member. In either apparatus at least one ring on the battery terminal is transferred from having a first shape into a second different shape with an overhang.
Owner:TULIP MOLDED PLASTICS CORP
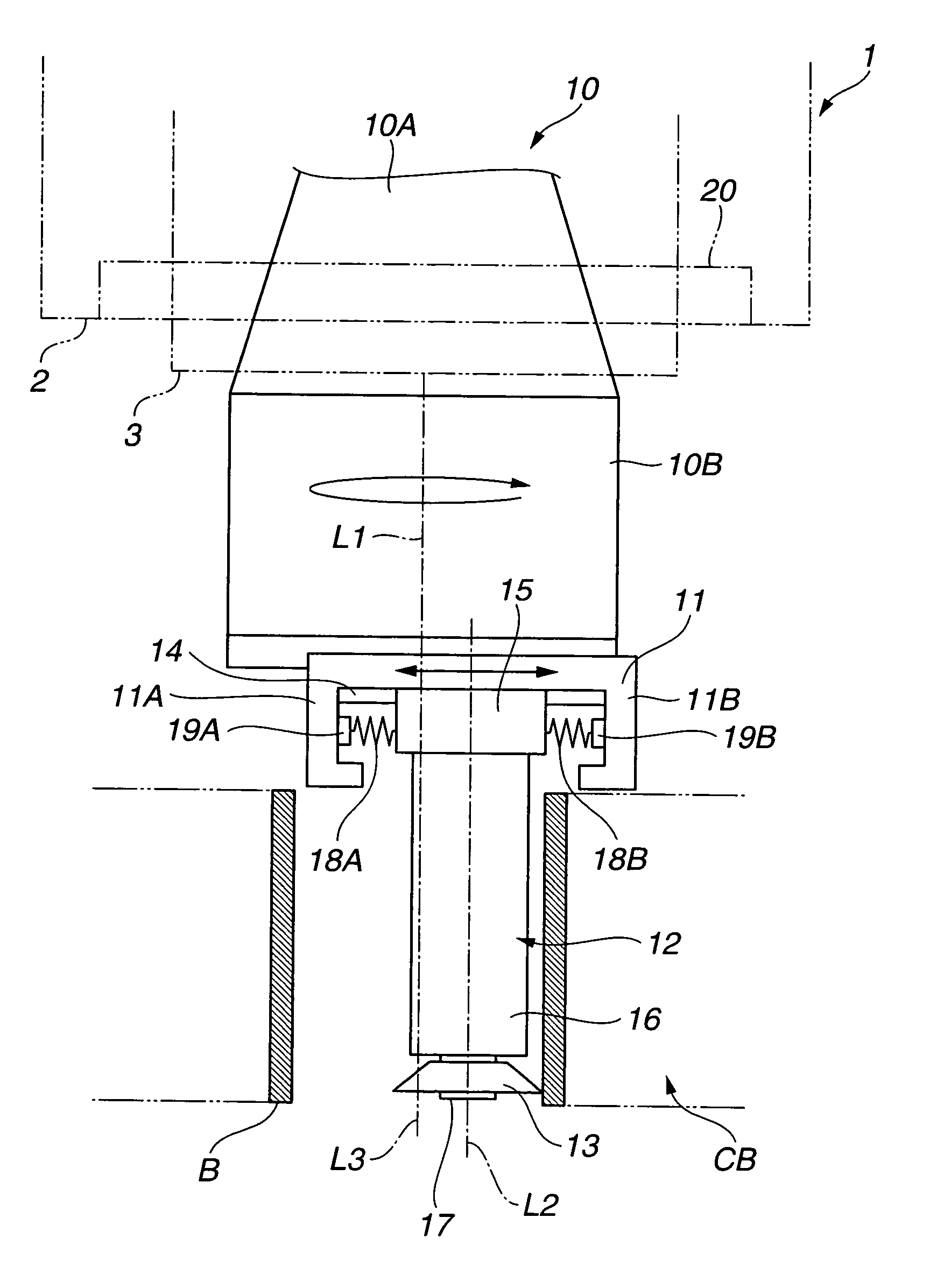
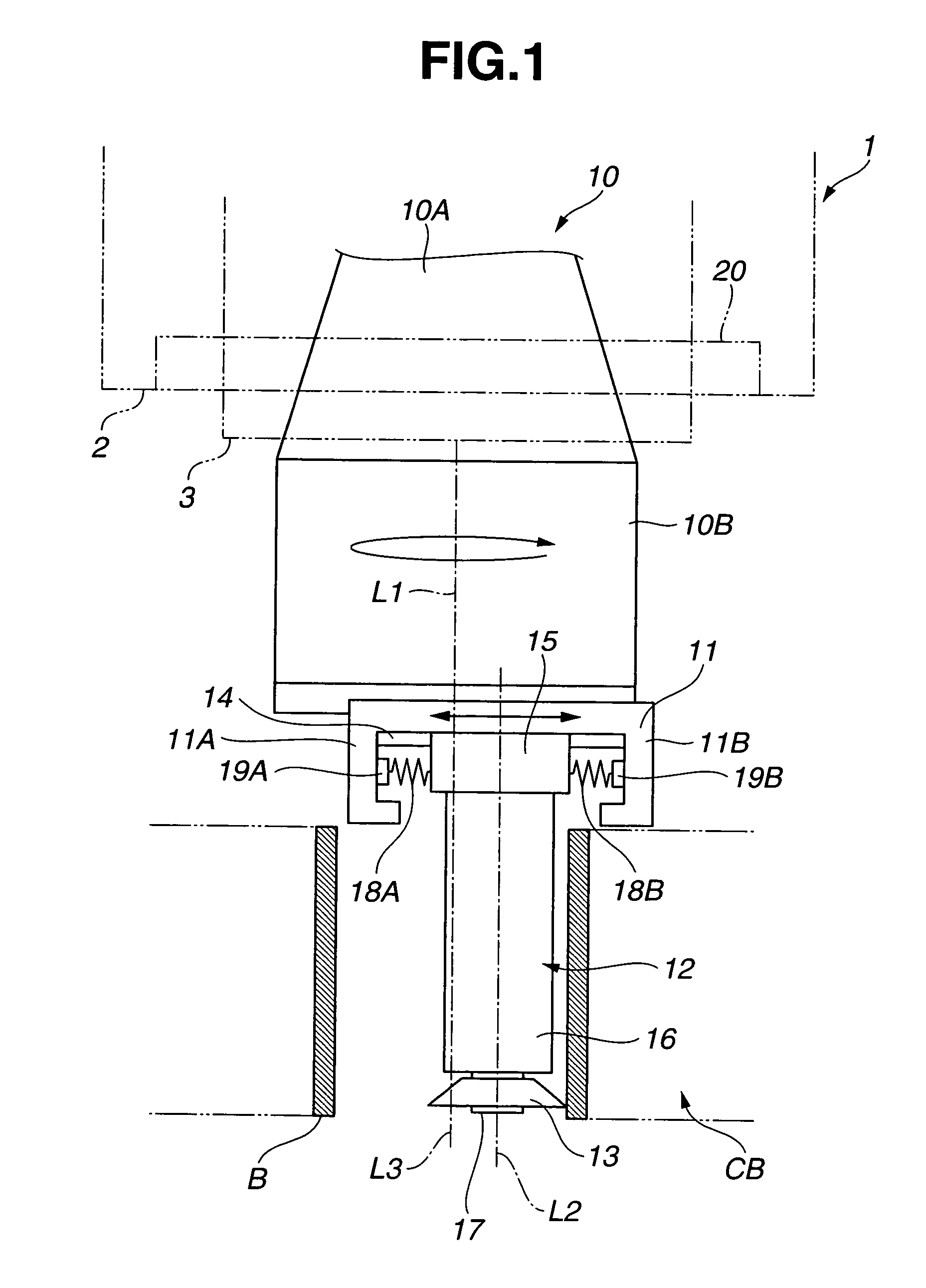
Deep-rolling apparatus of a deep rolling machine crankshafts
InactiveUS7021100B2Work lessRevolution surface grinding machinesBurnishing machinesEngineeringCrankshaft
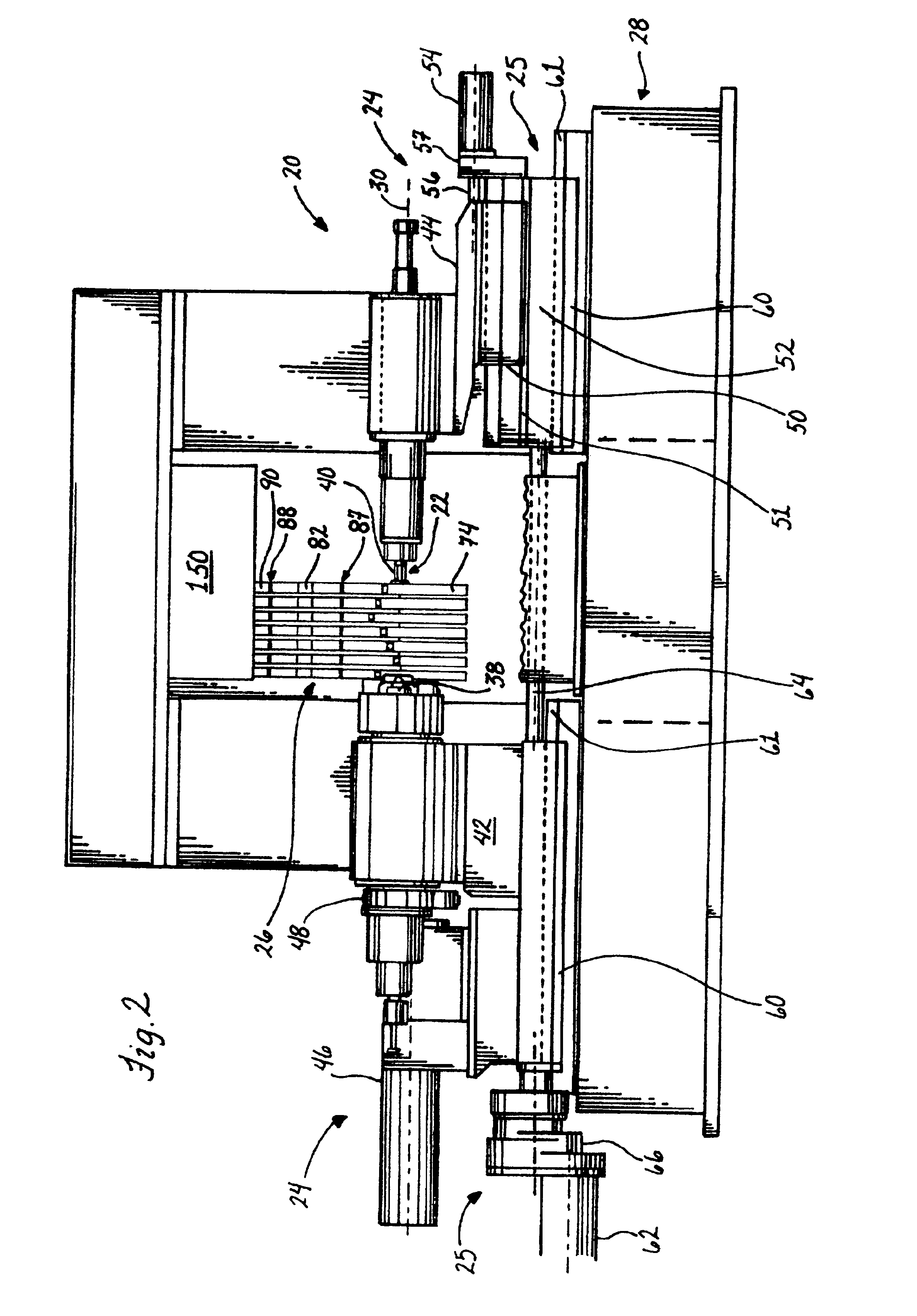
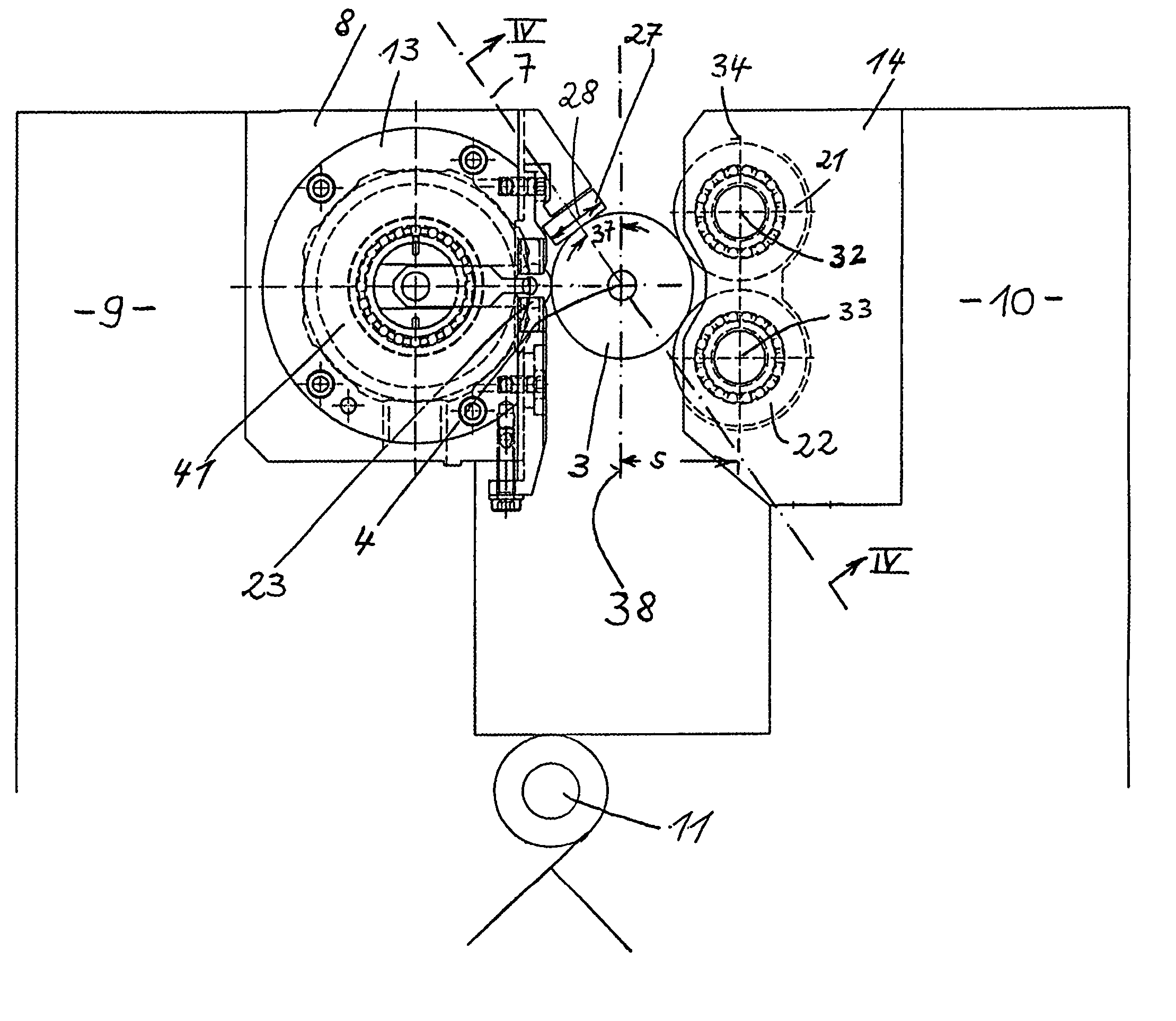
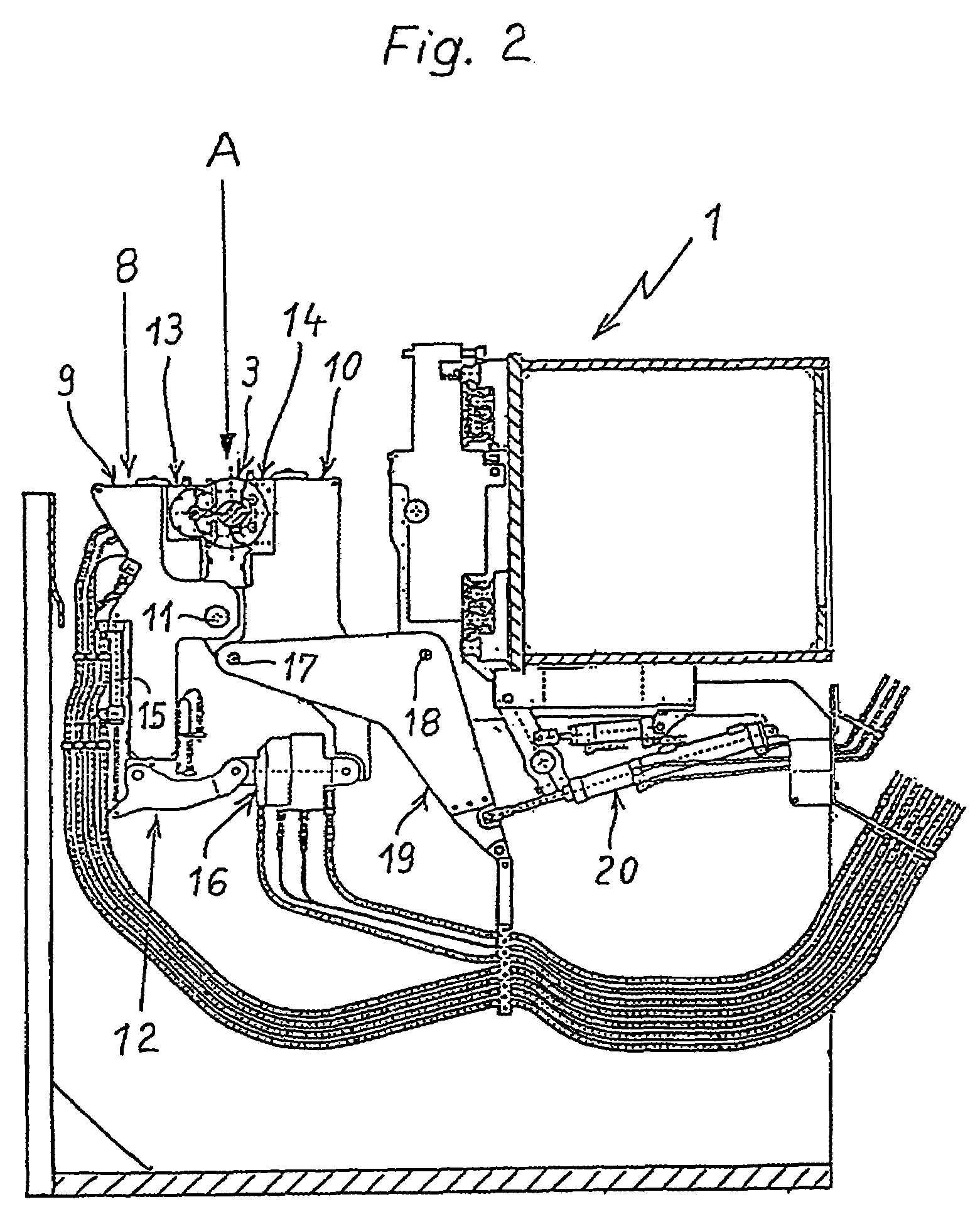
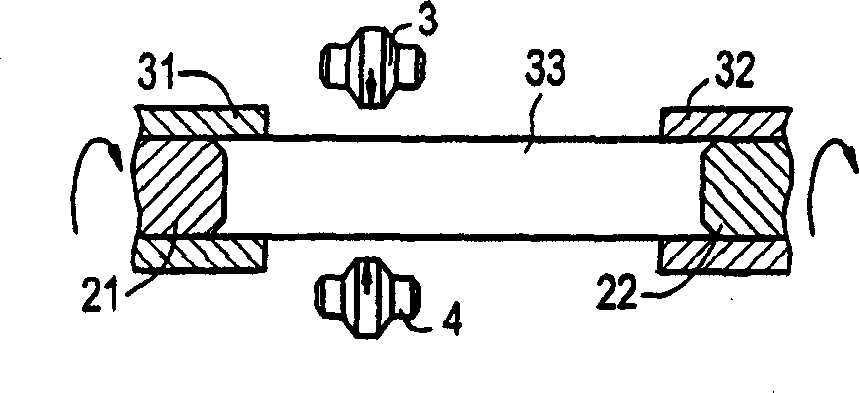
The present invention relates to the deep rolling apparatus (8) of a deep rolling machine 1 for crankshafts (3) in which two arms (9, 10) across from each other support a deep rolling head (13) or a support roller head (14). The support roller head (14) has two support rollers (21, 22) with parallel axes and the deep rolling head (13) has two work rollers (23, 24) entering the radii or fillets of the main bearing or crank pin journals or journals of the crankshafts (3). In one embodiment of the deep rolling apparatus (8) in scissor-like construction an axial guide roller (27) is provided on the deep rolling head (13) and is centered relative to the deep rolling head (13), its axis of rotation being perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the crankshaft (3). The axial guide roller (27) has a diameter that is slightly smaller than the distance between two oil collars (25, 26) of a main crank pin journal (5) of the crankshaft.
Owner:HEGENSCHEIDT MFD
Method for processing billets out of metals and alloys and article
This method refers to a method by which the physical and mechanical properties intrinsic to a fine-grain structure may be formed in metal billets using pressure treatment. The method is designed to treat rods, bars and other particularly long billets. This method is designed to lower the cost of deformational treatment for long rods and large diameter billets and creates a pre-specified microstructure, including micro-crystal structure, and specific physical and mechanical properties. This may be achieved using various treatment techniques, one of which includes the deformation of at least a part of the billet through reduction of the billets cross-section. In this method, a long rod shaped billet is used. Reduction of the cross-section is achieved using tools that permit movement along and across the billet's axis as well as being rolled about its surface, for example, a roller. In this case at least one support stand is employed for correct placement of the billet. Additionally, a pre-specified strain level is achieved using at least one of the techniques of deformation: torsion, settling and extension using tools, for example the above-mentioned stand. The stand is designed to apply a specified scheme of deformation to the billet at the deformed (strained) section and at a specified temperature. This obtains specified structure with intrinsic physical and mechanical properties.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Machining tool for manufacturing radial bearings, and manufacturing apparatus and manufacturing method using the same
InactiveUS6543139B2Improve accuracyHigh precision alignmentBearing componentsBurnishing machinesSurface finishMachine tool
A machining tool for manufacturing a radial bearing, and a manufacturing apparatus and a manufacturing method using the machining tool are provided. The machining tool includes an inner surface finishing tool to finish an inner circumference surface of a bearing hole provided on a radial bearing. The inner surface finishing tool includes a tool shaft main body member that defines a hollow storage section provided within the tool shaft main body member, a rotatable core piece member mounted inside the hollow storage section in a manner to be rotatable within the tool shaft main body member, and a plurality of roll machining members each with a circular cross-sectional roll machining surface. The plurality of roll machining members rollably abut against the outer circumference surface of the rotatable core piece member. The plurality of roll machining members are in contact under pressure with the inner circumference surface of the bearing hole. The rotatable core piece member is movable in the radial direction and can be tilted with respect to the central axis of the tool shaft main body member.
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Tube and shock absorber
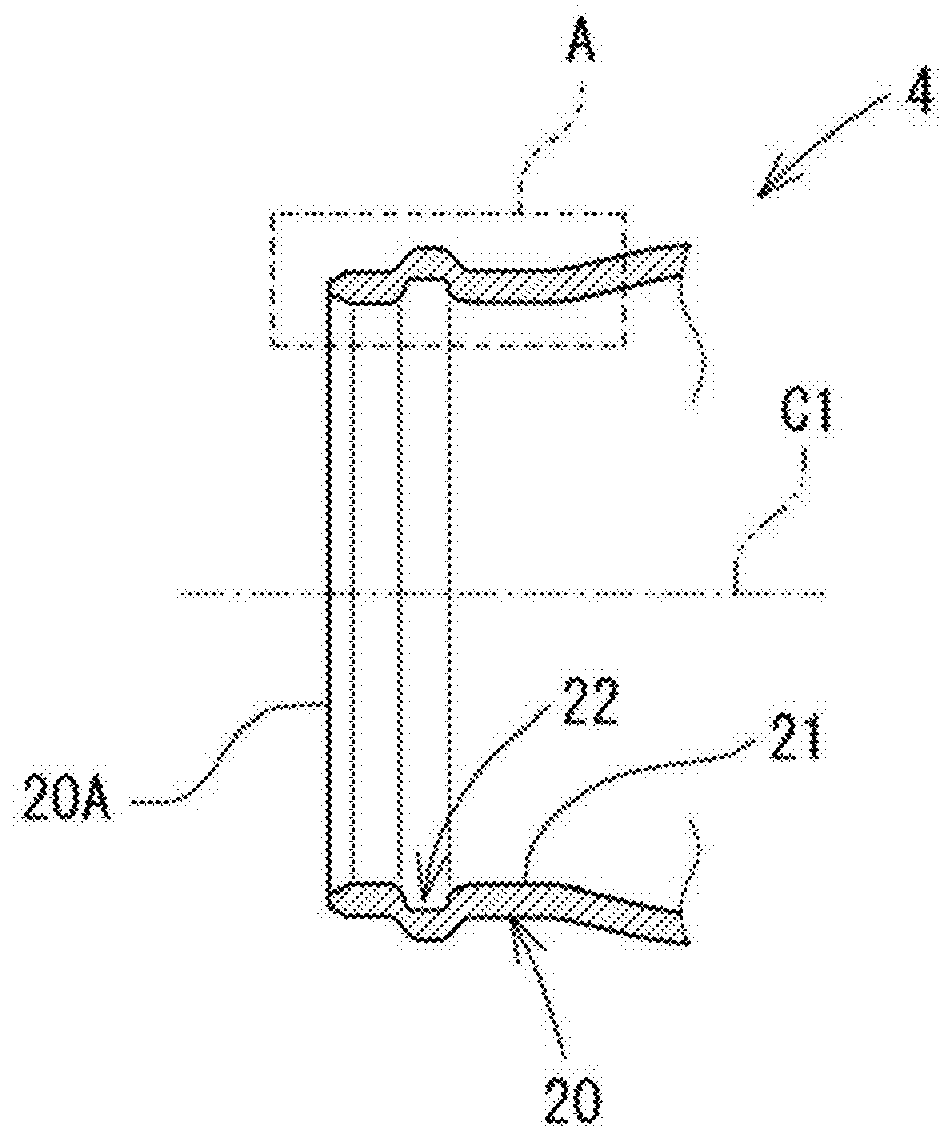
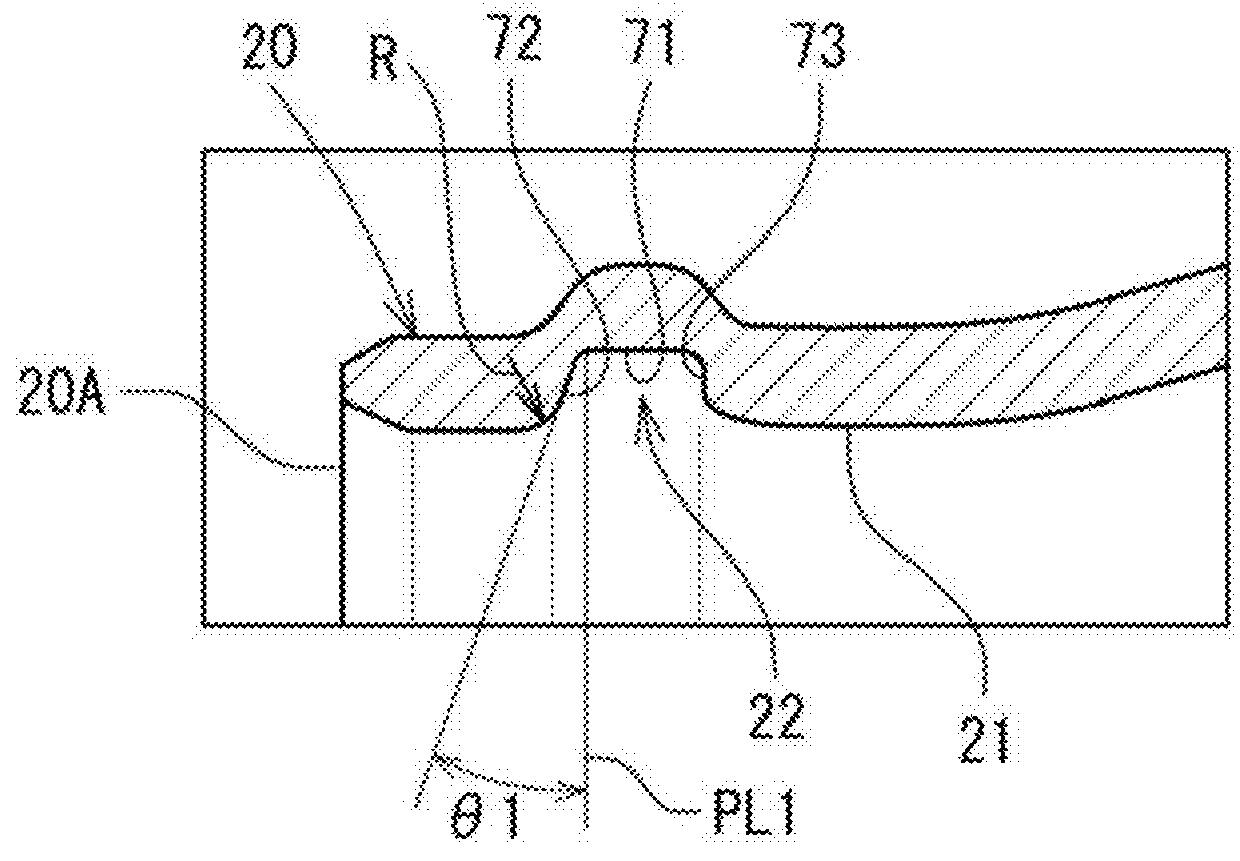
ActiveUS20160052361A1Improved seal durabilityIncreased durabilityEngine sealsSpringsTension stressShock absorber
A tube having sealing ring grooves formed by a sequential rotational process and a shock absorber including the tube, in which durability of a sealing ring fitted in each of the sealing ring grooves is enhanced. An inclination angle (θ1) formed with respect to a plane (PL1) perpendicular to an axis of a separator tube by a side surface of the sealing ring groove, which is located on an opening end side of the separator tube, is set to 8° or more. With this, a maximum tensile stress to be applied to an O-ring can be reduced to be smaller than a maximum tensile stress in a case of using a backup ring. As a result, the durability of the O-ring can be set equivalent to or enhanced to be higher than durability in the case of using the backup ring.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Hollow bolt comprising a longitudinal bore
ActiveUS8635894B2Without risk of deformationEasy to tapScrewsScrew-threads articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A process for producing hollow bolts including a longitudinal bore with the hollow bolts being provided with circumferential notches. The hollow bolts are provided with longitudinal grooves extending between elevations determining the bolt diameter, wherein circumferential notches are rolled onto the hollow bolts provided with the longitudinal grooves and the elevations, the longitudinal grooves being of such cross-section that some of the material displaced during rolling-on of the notches flows into the longitudinal grooves.
Owner:EJOT GMBH & CO KB
Cold forming process for manufacturing ball pivots
InactiveUS20090038157A1Necessary manufacturing costs can be significantly reducedIncrease the number ofShaftsCylindersWork in processEngineering
A cold forming process for manufacturing ball pivots with a ball area, a cone area and a thread area for installation in ball and socket joints by cold forming is presented, in which a ball pivot blank (1) with a shaped cone area (3) and cylindrical areas for the thread (2) and the ball (5) is manufactured at first from a bar-shaped semifinished bar stock by extrusion. The extrusion operation is followed by the forming of the ball area as another manufacturing step by means of a rolling processes. At the same time, the thread area can be formed in its final shape. Thus, the ball pivot is manufactured as a whole by cold forming only and it makes it possible to significantly increase the production output per unit of time compared to the processes known from the state of the art. At the same time, it is possible to use less expensive grades of steel, because sufficient fatigue strength of the ball pivot can be guaranteed by the cold forming.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Machining tool for manufacturing radial bearings, and manufacturing apparatus and manufacturing method using the same
InactiveUS20020020062A1Simple and reliable to makeBearing componentsBurnishing machinesSurface finishEngineering
A machining tool for manufacturing a radial bearing, and a manufacturing apparatus and a manufacturing method using the machining tool are provided. The machining tool includes an inner surface finishing tool to finish an inner circumference surface of a bearing hole provided on a radial bearing. The inner surface finishing tool includes a tool shaft main body member that defines a hollow storage section provided within the tool shaft main body member, a rotatable core piece member mounted inside the hollow storage section in a manner to be rotatable within the tool shaft main body member, and a plurality of roll machining members each with a circular cross-sectional roll machining surface. The plurality of roll machining members rollably abut against the outer circumference surface of the rotatable core piece member. The plurality of roll machining members are in contact under pressure with the inner circumference surface of the bearing hole. The rotatable core piece member is movable in the radial direction and can be tilted with respect to the central axis of the tool shaft main body member.
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Method for forming a slip joint assembly with coated splines
A method includes providing a shaft having a coupling section. The coupling section has a generally cylindrical exterior surface. The method includes applying a coating to the coupling section to form an engaging surface. The method further includes cold-forming the shaft and the coating such that a plurality of protrusions is formed in the engaging surface. The cold-forming of the shaft and the coating is performed contemporaneously.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Method of Forming Anchors
ActiveUS20130040743A1Large caliberThread cutting toolsMetal rolling stand detailsWedge shapeAnchor bolt
Owner:HILTI AG
Machining process of NPR steel bar wire rod
ActiveCN110523801AAvoid surface scratchesAvoid bending etc.Wire articlesMetal rolling arrangementsWire rodButt welding
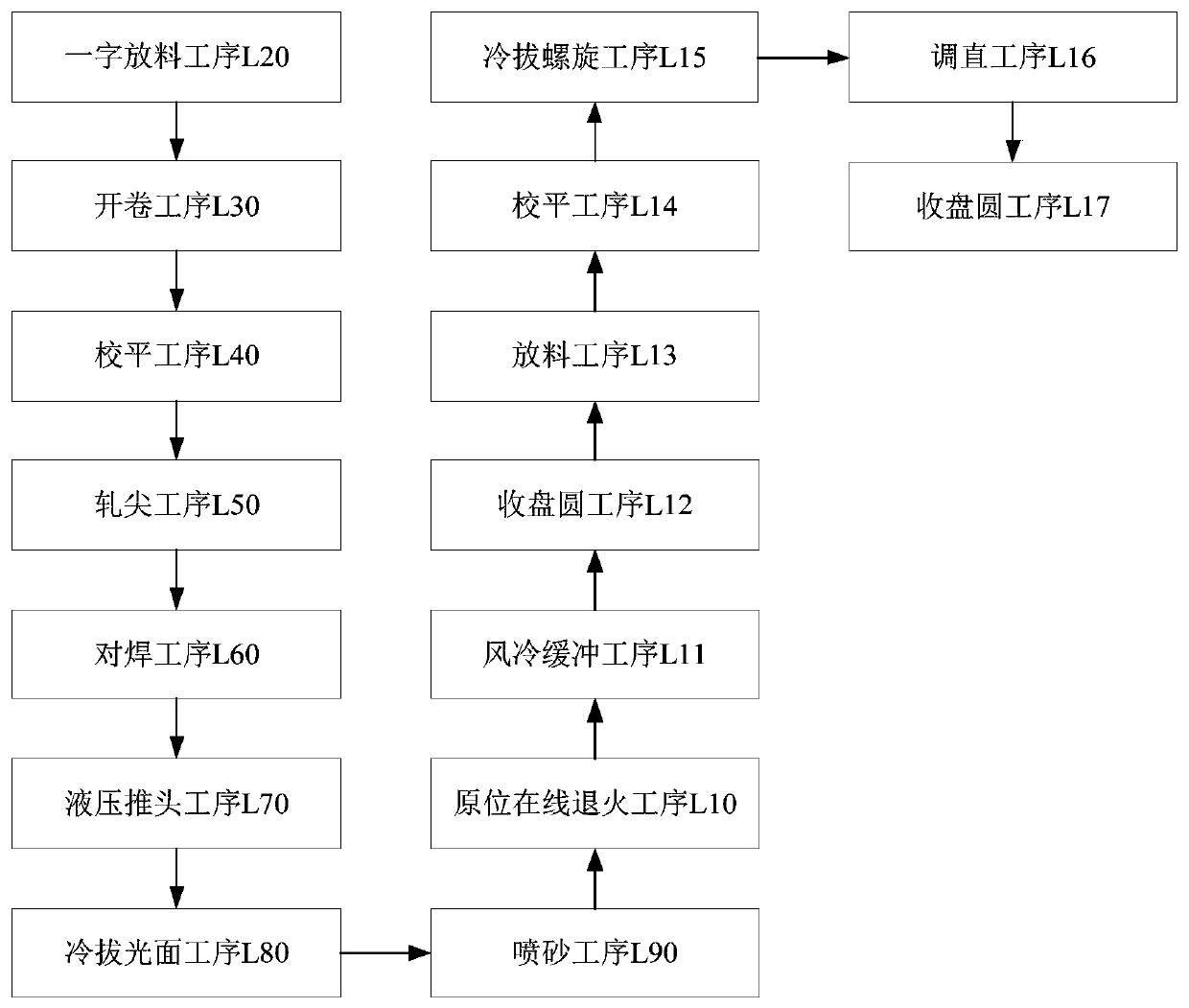
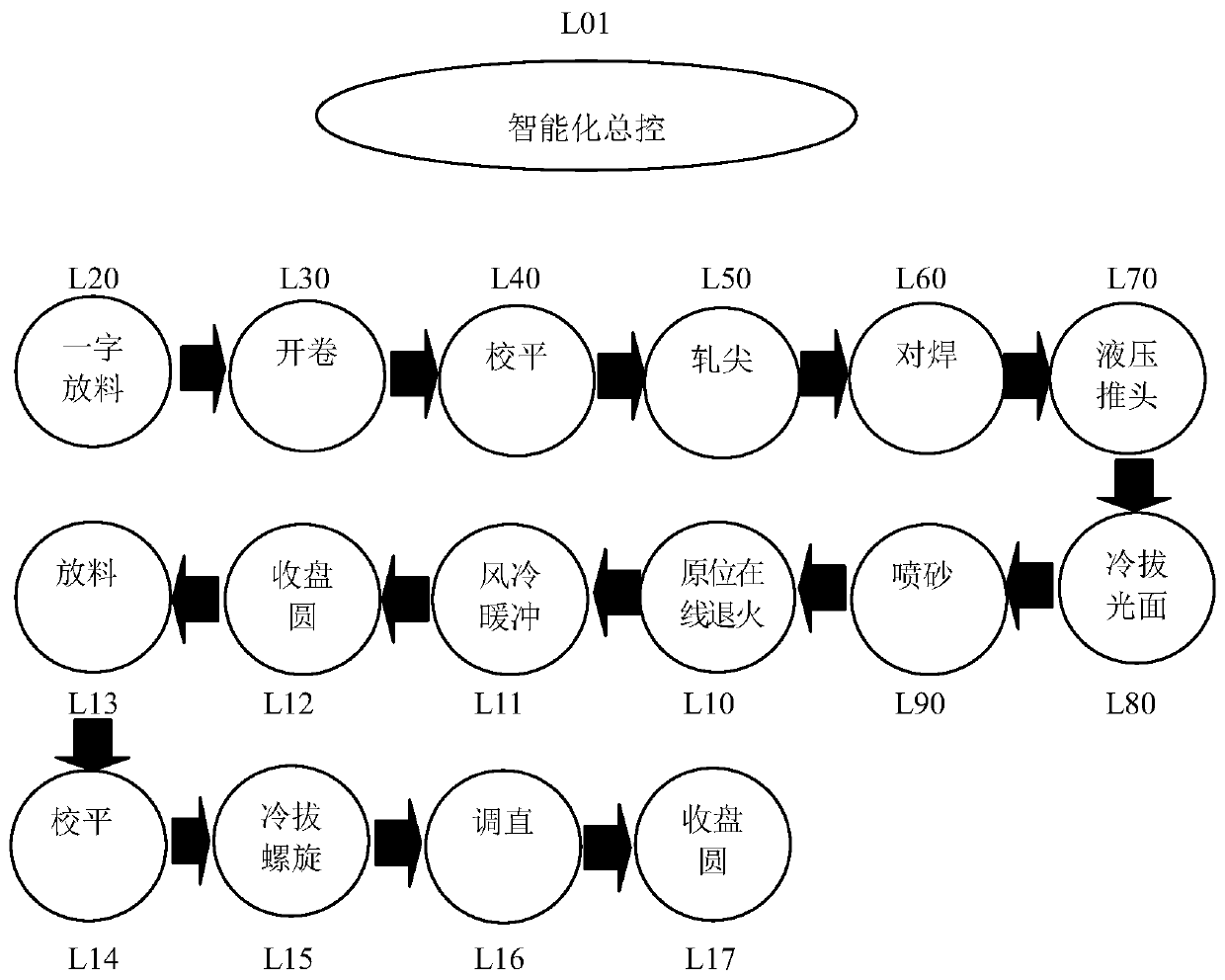
The invention discloses a machining process of an NPR steel bar wire rod. An NPR steel bar is in a cold machining state, the diameter of the NPR steel bar is smaller than 14 mm, the yield strength ofthe NPR steel bar is 800 MPa to 950 MPa, the tensile strength is 900 MPa to 1100 MPa, and the maximum force elongation rate is larger than or equal to 20%. The machining process comprises the following steps of a linear emptying process L20; an uncoiling process L30; a leveling process L40; a pointing process L50; a butt welding process L60; a hydraulic head pushing process L70; a cold drawing smooth surface process L80; a sand blasting process L90; an in-situ online annealing process L10; an air cooling buffer process L11; a coiling process L12; an emptying process L13; a leveling process L14; a cold drawing spiral process L15; a straightening process L16; and a coiling process L17. According to the machining process of the NPR steel bar wire rod, the whole-process intellectualization canbe achieved, the machining requirement of the NPR steel bar wire rod is met, and the full-automatic intellectualized production requirement of the NPR steel bars, the NPR cold-rolled spiral steel bars and the NPR prestressed steel bars is met.
Owner:何满潮 +1
Rolling tool
ActiveCN104625558AEffective roughRemove roughnessMolten spray coatingBurnishing machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a rolling tool with a roller support protruding in a feed direction. One or more rolling rollers are arranged on the periphery of the roller support and can rotate with the axis of the rollers. The rolling tool is used for processing a workpiece surface. One of the rolling rollers has a contact surface for contacting the workpiece. The contact surface has a rough segment with a projection protruding outwards in a radial direction about the axis of the rollers. The invention also relates to a method for processing a workpiece surface with the rolling tool in the invention.
Owner:HOFFMANN GMBH QUALITATSWERKZEUGE
Apparatus for forming microscopic recesses on a cylindrical bore surface and method of forming the microscopic recesses on the cylindrical bore surface by using the apparatus
ActiveUS8641335B2Increase production costSimple materialThread cutting toolsTransportation and packagingEngineeringCentrifugal force
An apparatus for forming recesses on a circumferential surface that defines a cylindrical bore in a workpiece includes a tool holder disposed coaxially with the cylindrical bore; a form roller support retained on the tool holder; a form roller rotatably supported on the form roller support, the form roller including projections on an outer circumferential surface thereof which are configured to form the recesses on the circumferential surface that defines the cylindrical bore in the workpiece. A control assembly is configured to control the form roller support such that the form roller is allowed to be in press contact with the circumferential surface that defines the cylindrical bore in the workpiece at a press contact load of a predetermined value on the basis of a centrifugal force which is exerted on the form roller support and the form roller during rotation of the tool holder.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Machining method and machining tool for machining curved workpiece surface, and workpiece
ActiveCN103442823AMolten spray coatingInternal combustion piston enginesRough surfaceContact pressure
The invention relates to a machining method for machining a curved workpiece surface (210) of a workpiece (200), in which a roll forming operation is carried out. At least one roller element (180A, 180B, 180C) of a machining tool (100) is rolled under a contact pressure against a segment (198) of the curved workpiece to be machined. An outer surface of the roller element comprises a rough surface structure in at least one working segment (190A, 190B, 190C) intended for rolling contact with the workpiece surface. The contact pressure is set so that a rough roll-formed structure is generated when rolling by locally deforming the workpiece material without removing material in the area of the workpiece surface being machined. The machining method can be used, for example, for machining the inner surface of a hole in a workpiece, in particular for roughening the workpiece surface for subsequent coating. The invention further relates to the machining tool and the workpiece thus produced.
Owner:ELGAN DIAMANTWERKZEUGE
Rolling tool
ActiveUS20160167107A1Reduce surface roughnessReduce fuel consumptionCrankshaftsGrinding carriagesEngineeringBearing surface
A rolling tool for the roller finishing of bearing surfaces of a crankshaft is pivotable around a crankshaft axis, with a finishing roller head and with a support roller head. In order to prevent damage to the guide mechanisms, the roller finishing roller is guided on all sides in a roller cage and the finishing roller head has a frame wherein it is mounted pivotably around a first pivot axis which is perpendicular to the crankshaft axis and parallel to a tangent on a working side of the roller finishing roller. Additionally or alternatively, the support roller head comprises a support roller frame in which the support roller housing is mounted pivotably around a second pivot axis perpendicular to the crankshaft axis and parallel to the first pivot axis, and around a third pivot axis perpendicular to the crankshaft axis and perpendicular to the first pivot axis.
Owner:HEGENSCHEIDT MFD
Rolling die of ballscrew
InactiveCN1480666APrevent hardeningIncreased durabilityGearingScrew-threads articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The roller for a ball spindle comprises a cylindrical section with a helical form protrusion formed in an outer circumferential face in order to form a helical ball track in the raw material of the spindle shaft, and a conical lead-in section formed in one end section of the cylindrical section and comprising a number of truncated cone shaped sections, the contact angle of which in relation to the raw material of the spindle shaft is established becomes continuously larger in the direction from the cylindrical section to the end of the lead-in section.
Owner:NSK LTD
Method and device for making at least partly profiled tubes
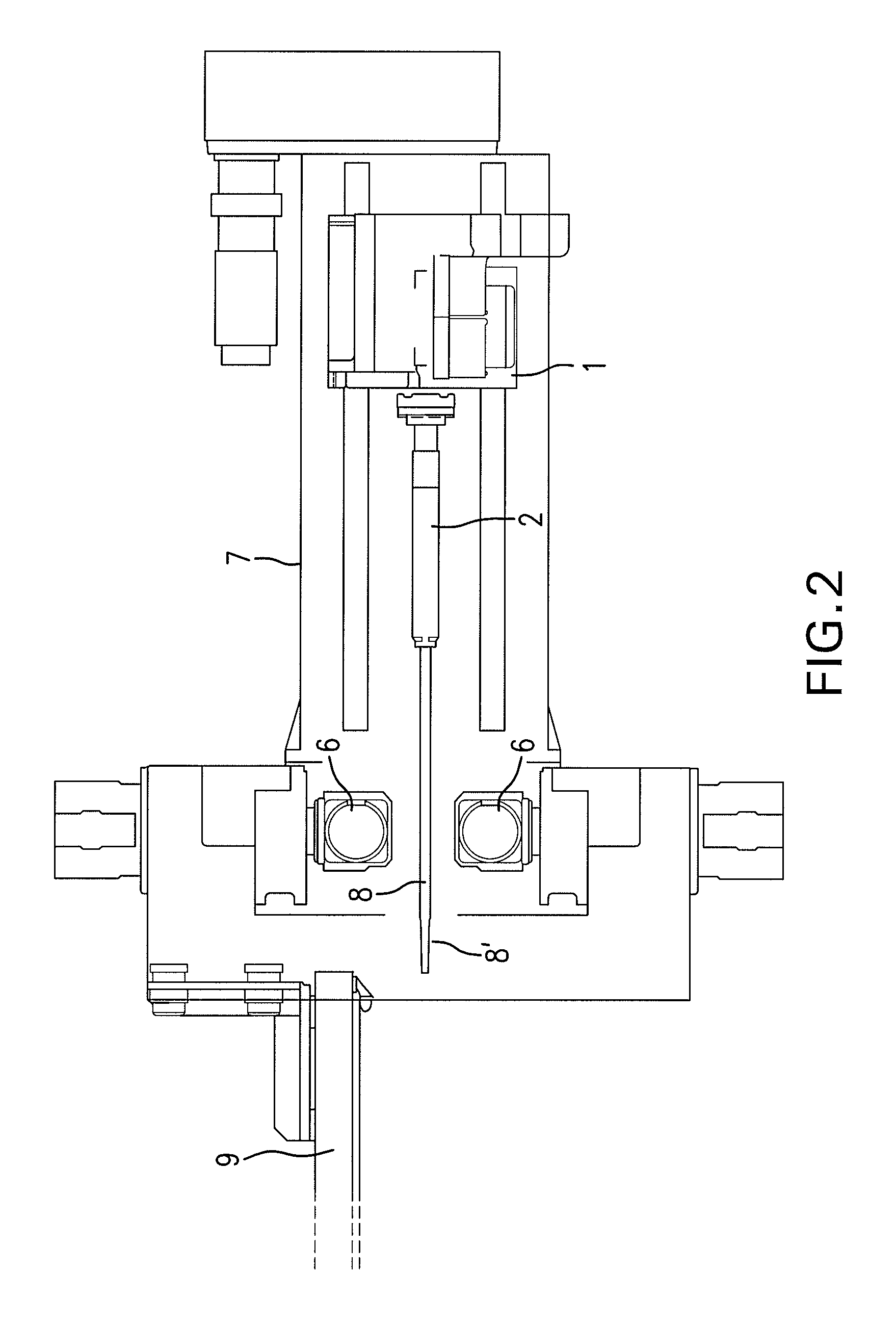
ActiveUS7861572B2Small dimensionPowerful and reliable clampingForging hammersExtrusion mandrelsEngineeringMachining
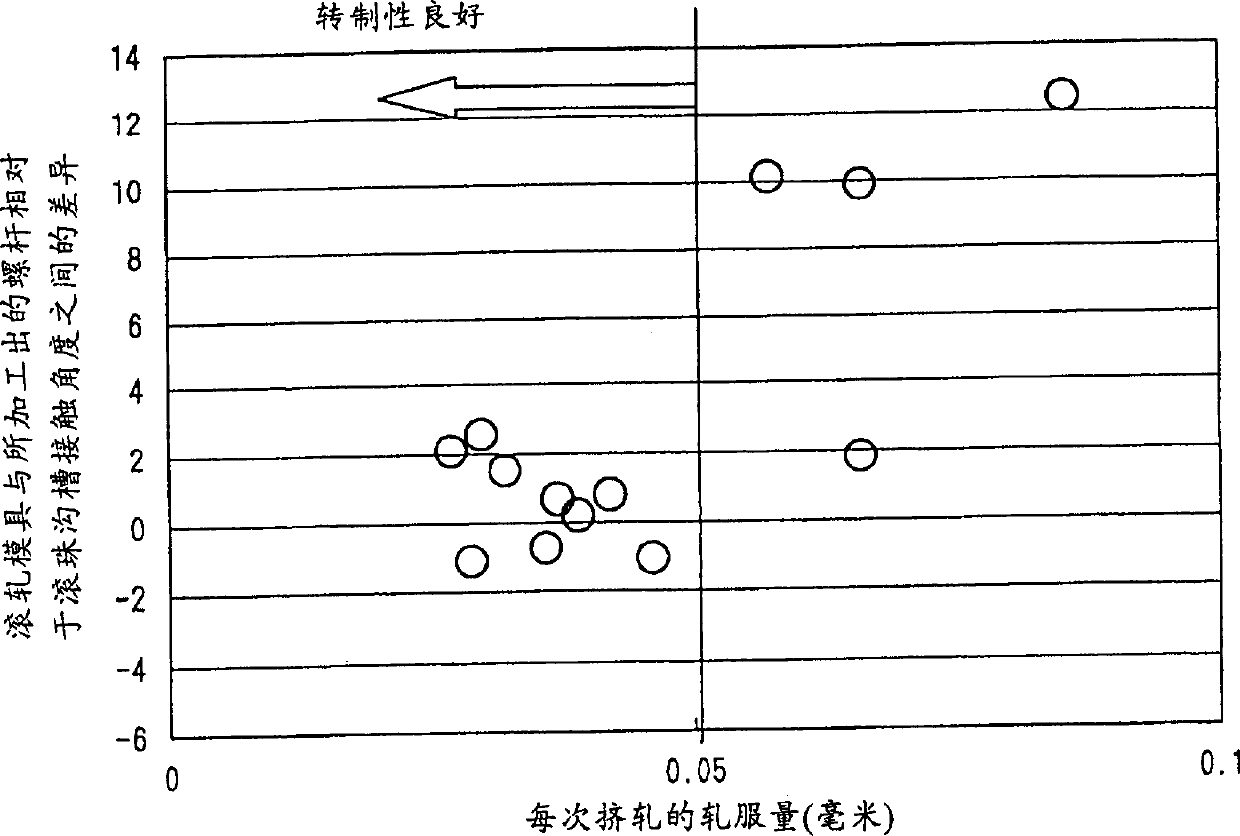
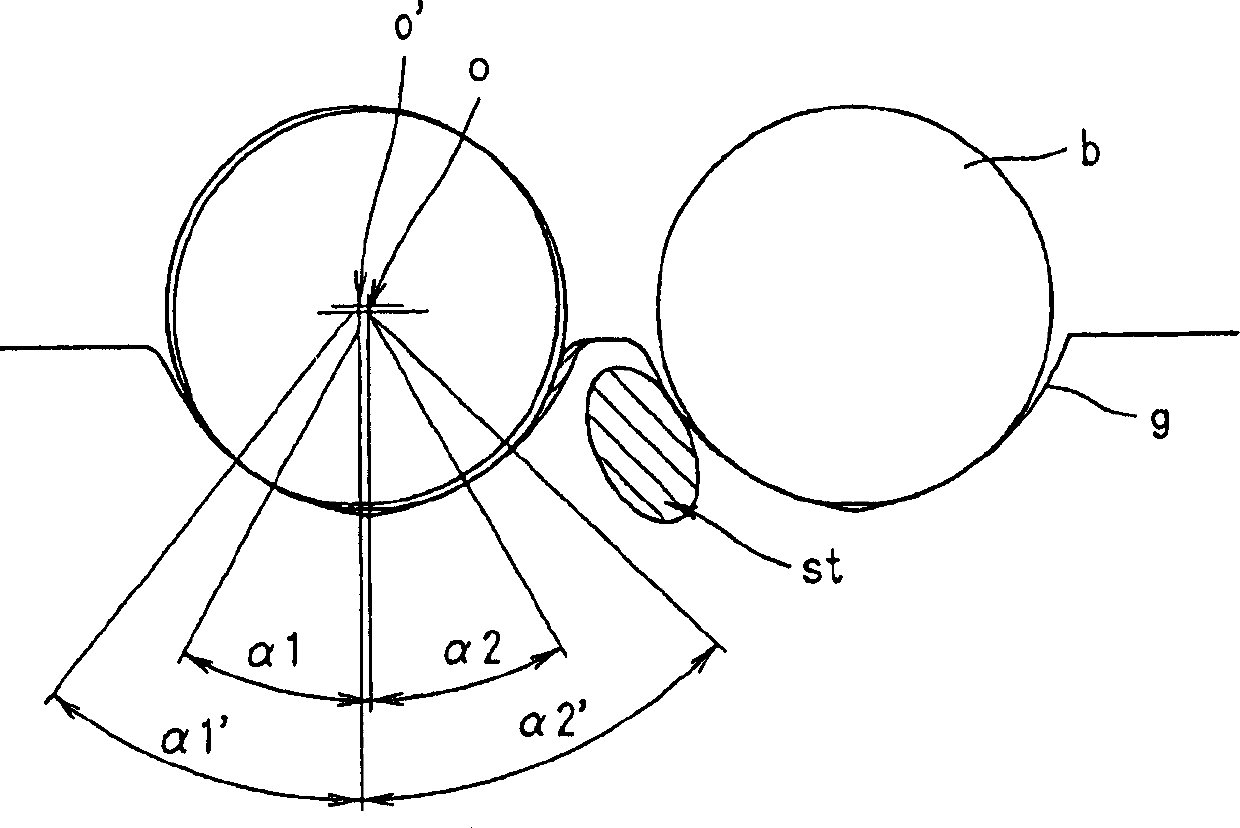
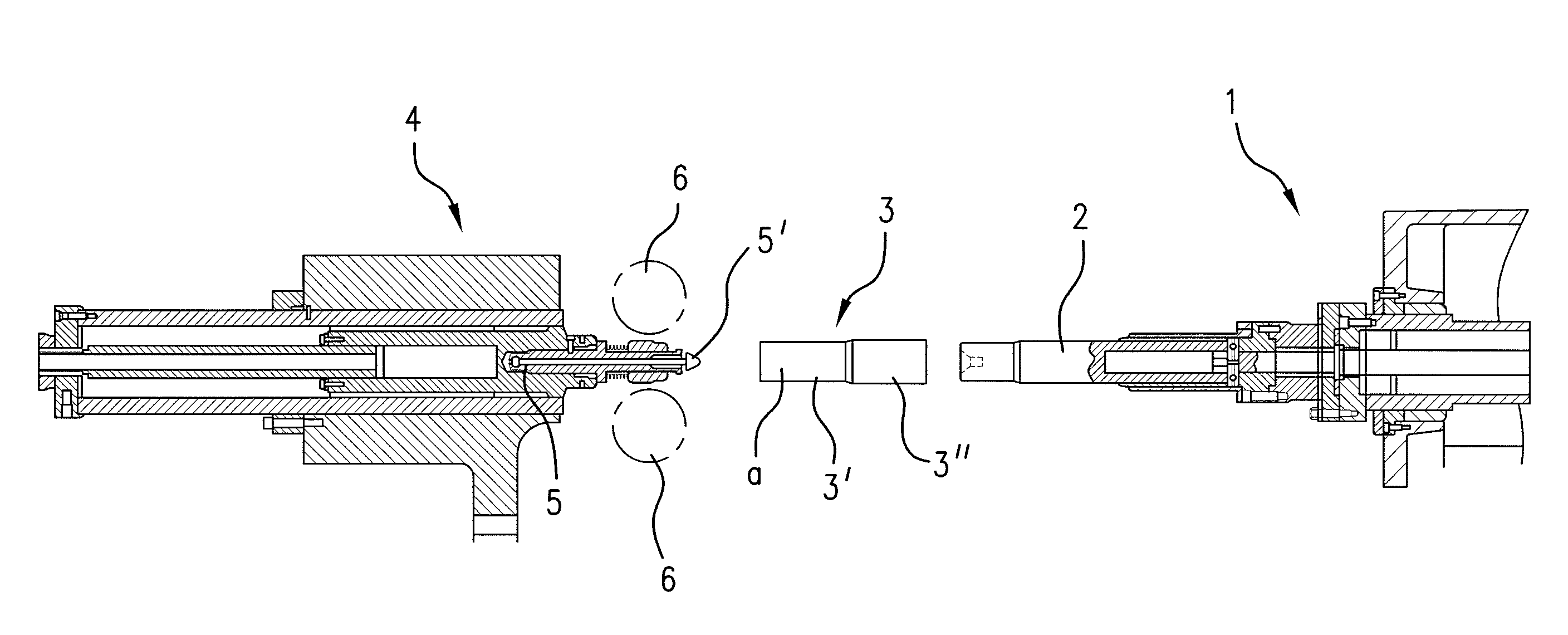
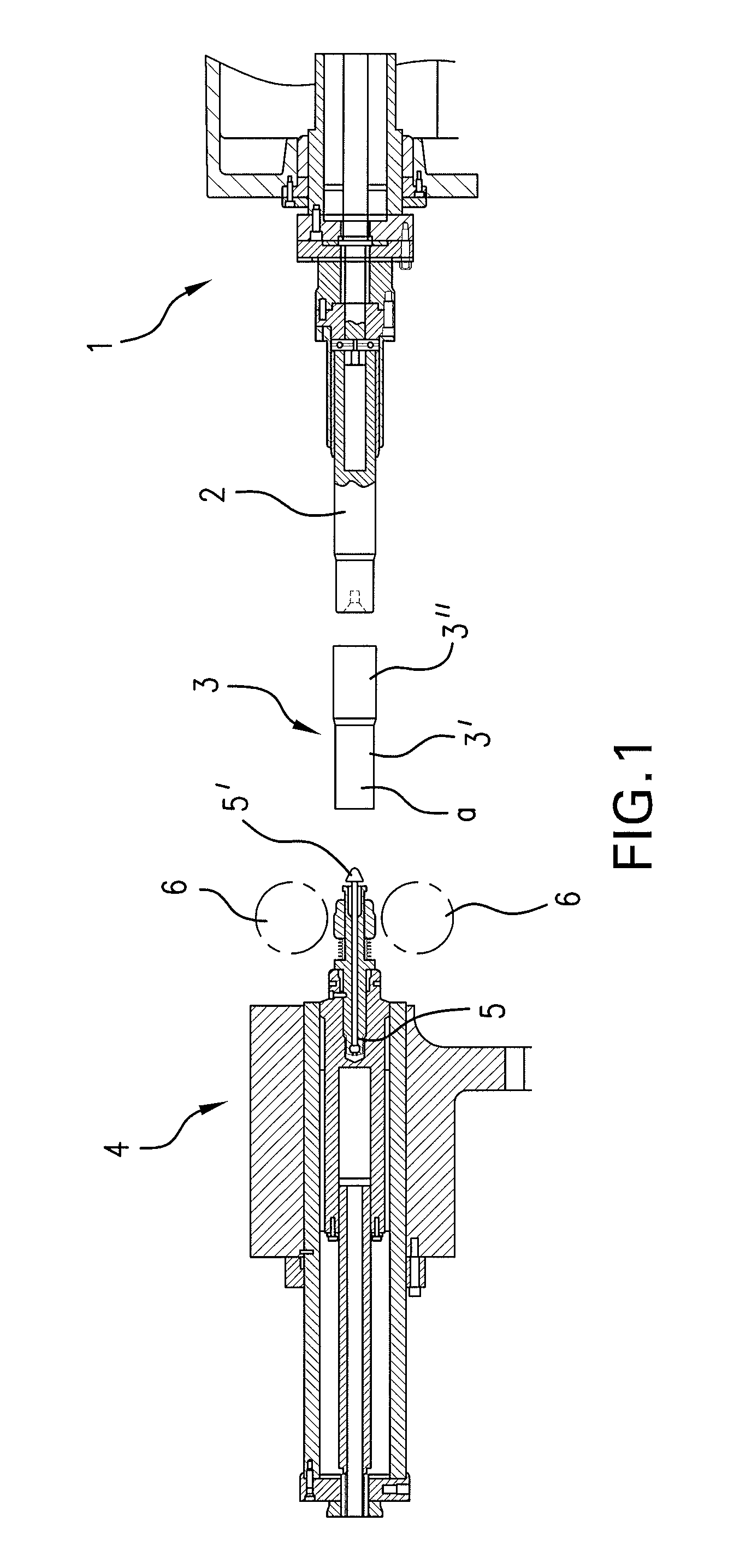
A method and device are disclosed for producing tubes that are at least partially profiled on their interior and preferably on their exterior from a hollow cylindrical blank (3), using a mechanical cold forming method, wherein the end of the blank (3) that is not to be machined (3′) is fed to a clamping device (10). The blank (3) is then secured in the clamping device (10) and a mandrel (2) is subsequently inserted into the end of region (3) of the blank (3) that is to be machined. A lance (8) is guided in the mandrel so that it can be coaxially displaced in a longitudinal direction and the free end of the lance (8′) can be introduced into the clamping device (10). The tip (8′) of the lance (8) is then brought into a positive fit with the clamping device (10) in the axial direction of the blank (3) and the mandrel (2), together with the clamping device (10) and the blank (3) is guided axially through a fixed machining point (6). Radial exterior machining of the surface of the blank (3) along the section that is to be machined (3′) takes place at the machining point (6), to create the interior and exterior profiling of the blank (3). During the process, the mandrel (2) is preferably rotated about its axis in an intermittent manner.
Owner:ERNST GROB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com