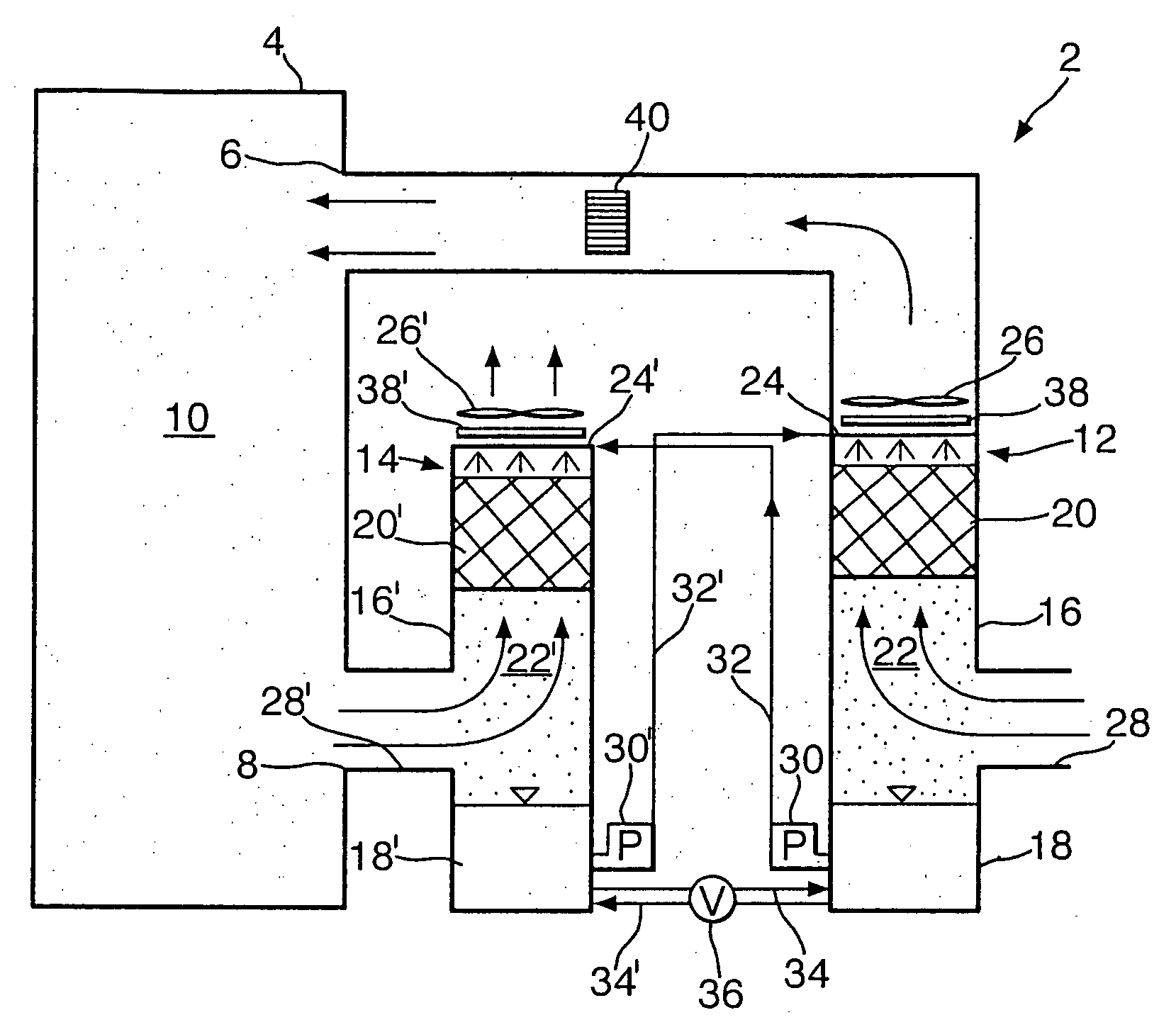
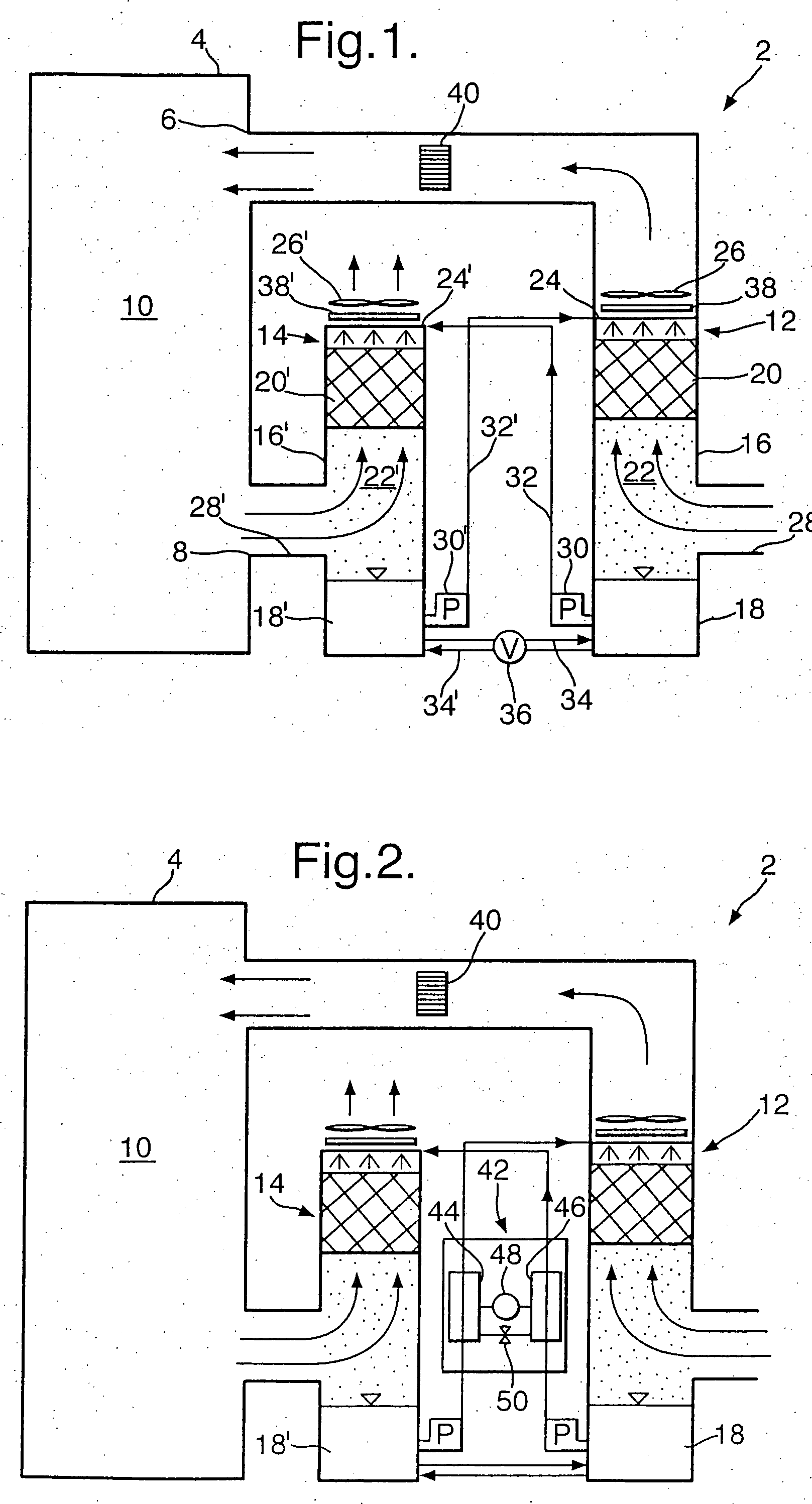
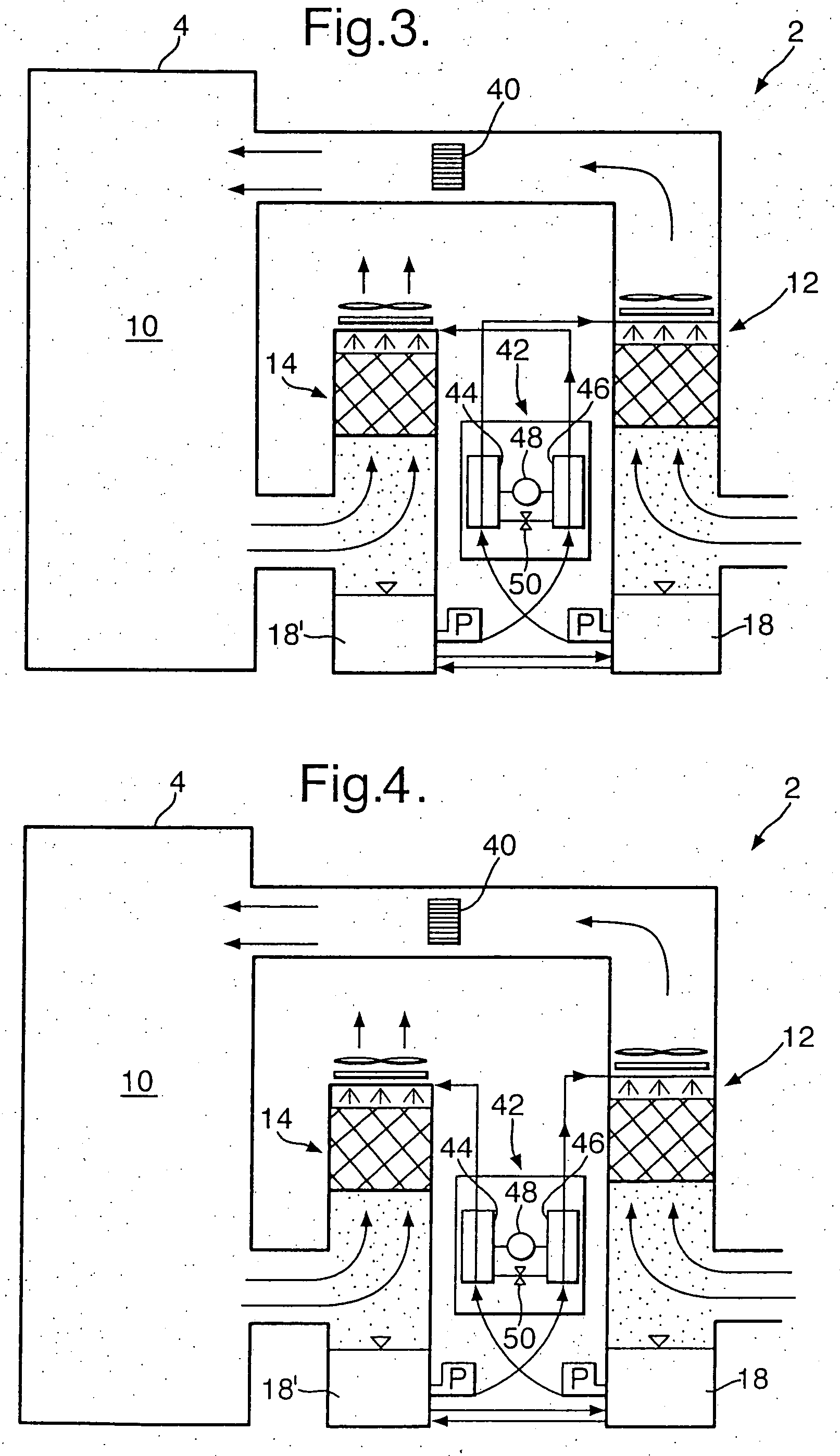
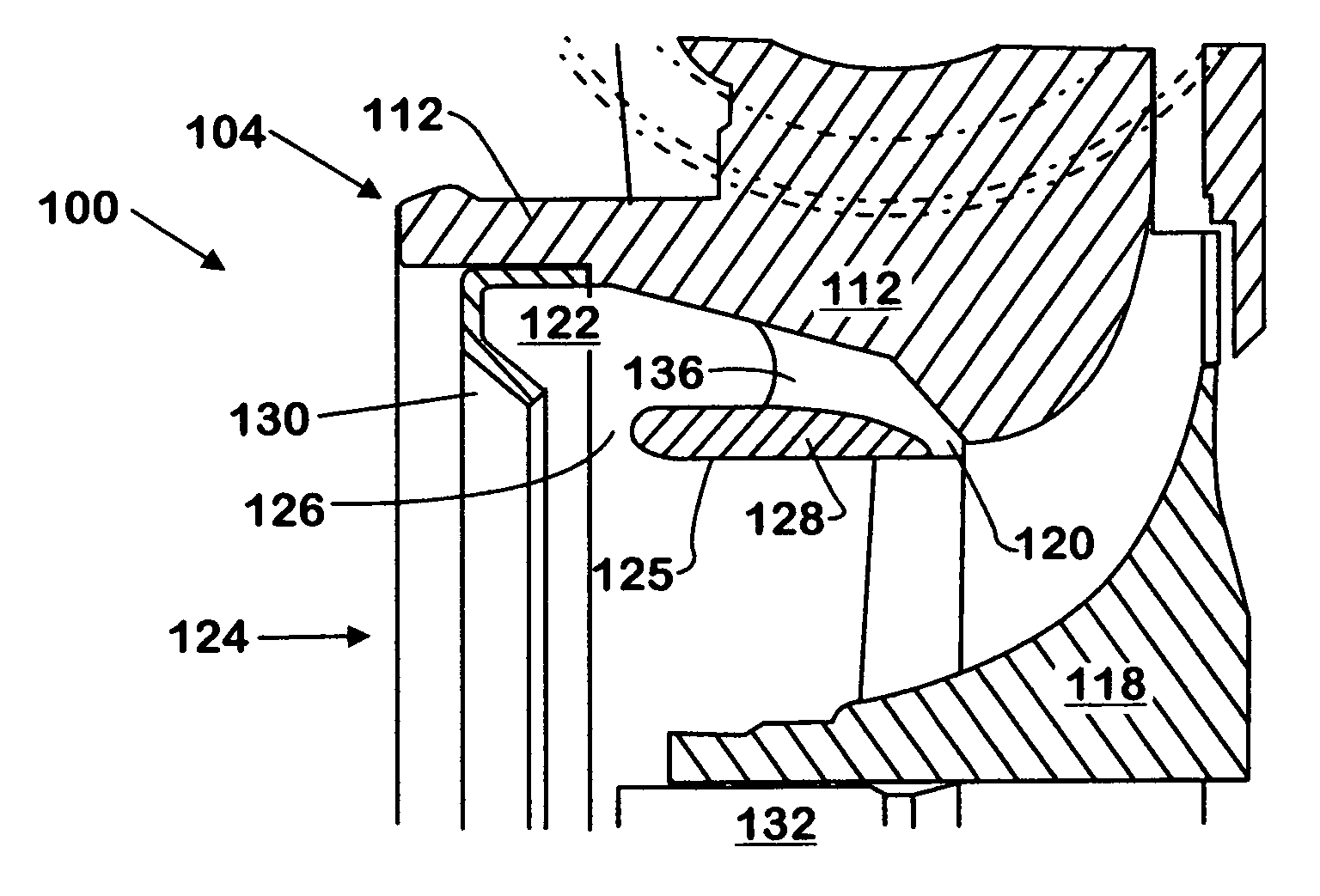
Patents
Literature
649results about "Secondary air addition to fuel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
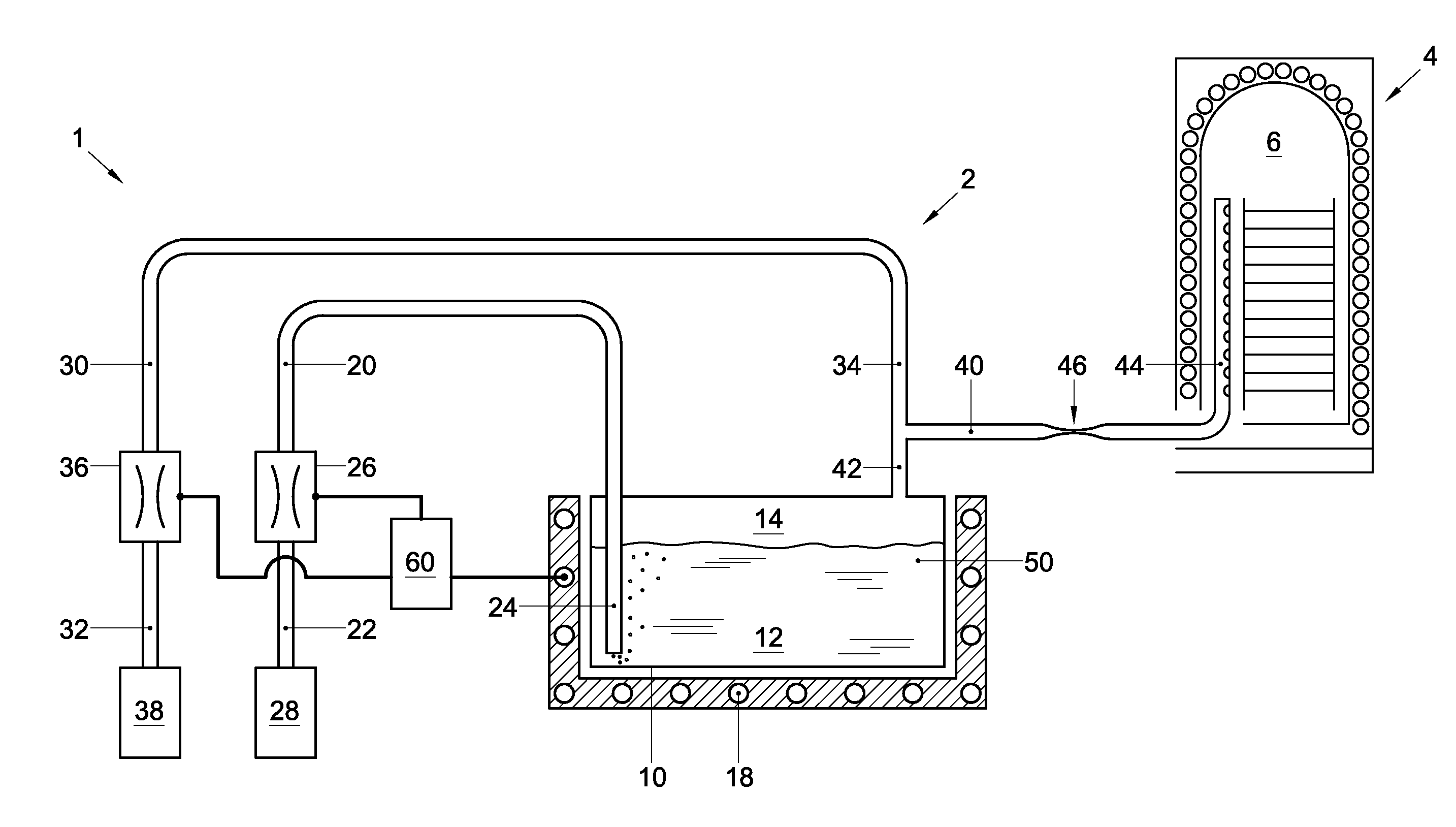
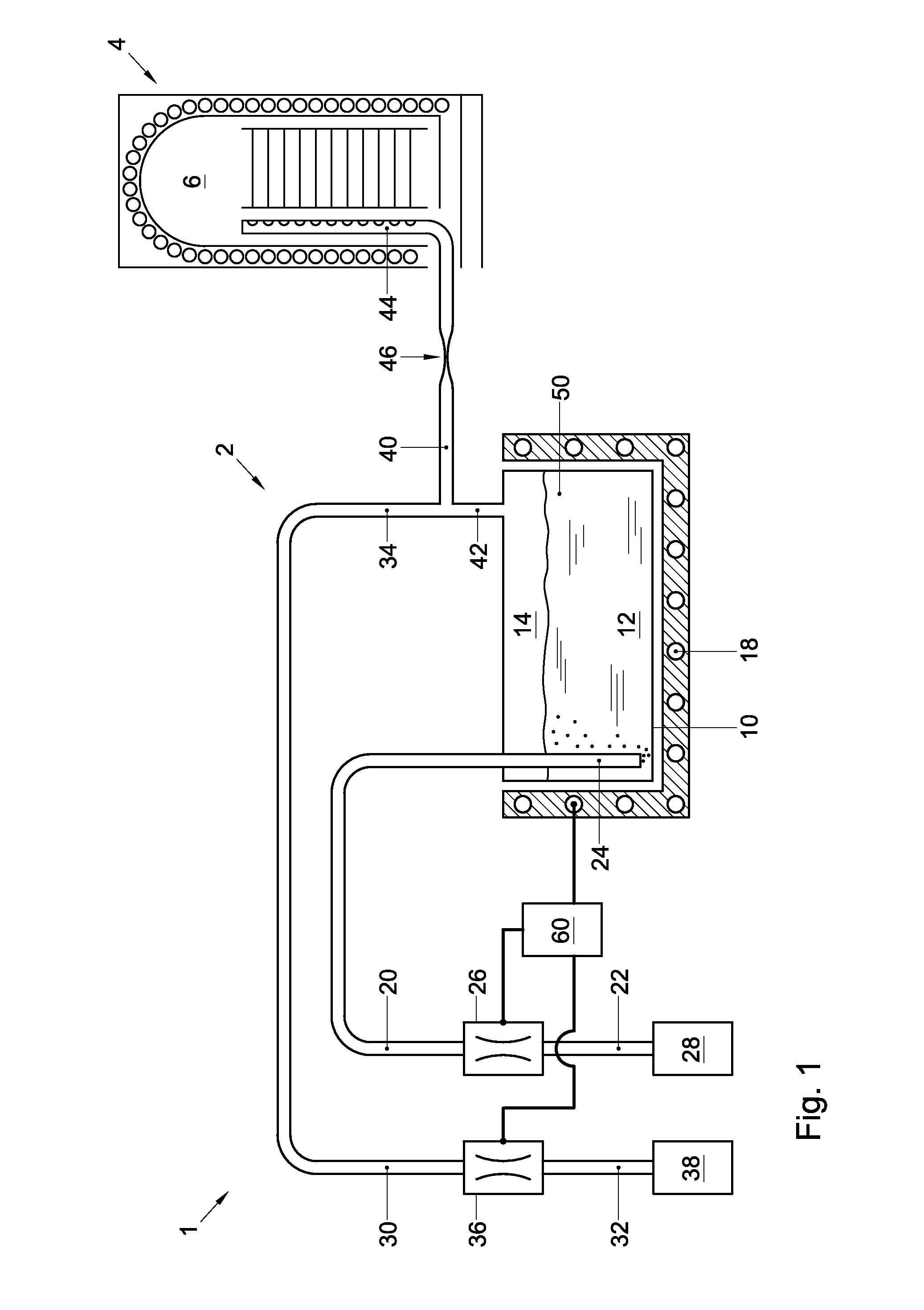
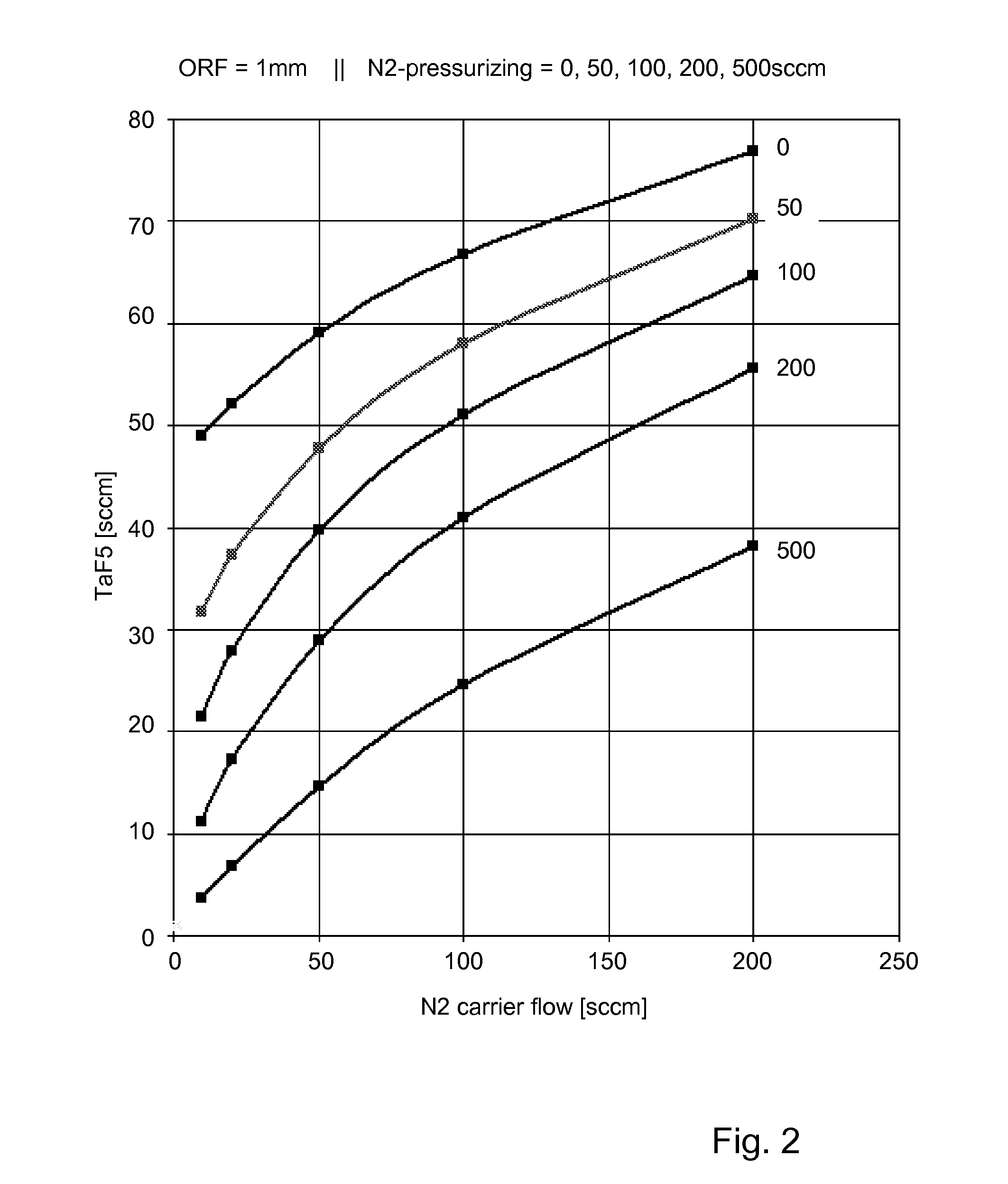
Bubbler assembly and method for vapor flow control
InactiveUS20120304935A1Mitigate and overcomeLess expensiveUsing liquid separation agentMixing methodsSource materialEngineering
Disclosed is a bubbler assembly. The bubbler assembly includes a vessel configured to contain a liquid source material and its vapor. It also includes a carrier gas supply line, a downstream end of which discharges in a lower portion of the vessel, and a gas outlet line, an upstream end of which is in fluid communication with an upper portion of the vessel. The gas outlet line includes a constriction. The bubbler assembly further includes a pressurizing gas supply line, a downstream end of which discharges in either the upper portion of the vessel or in the gas outlet line at a point upstream of the constriction.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
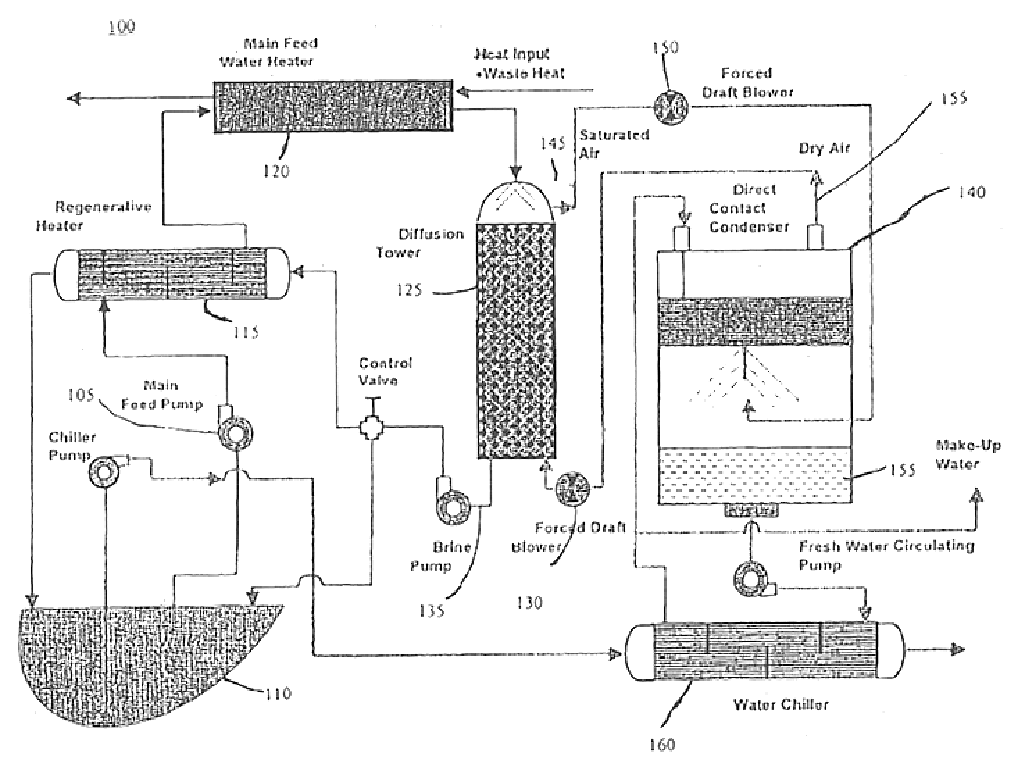
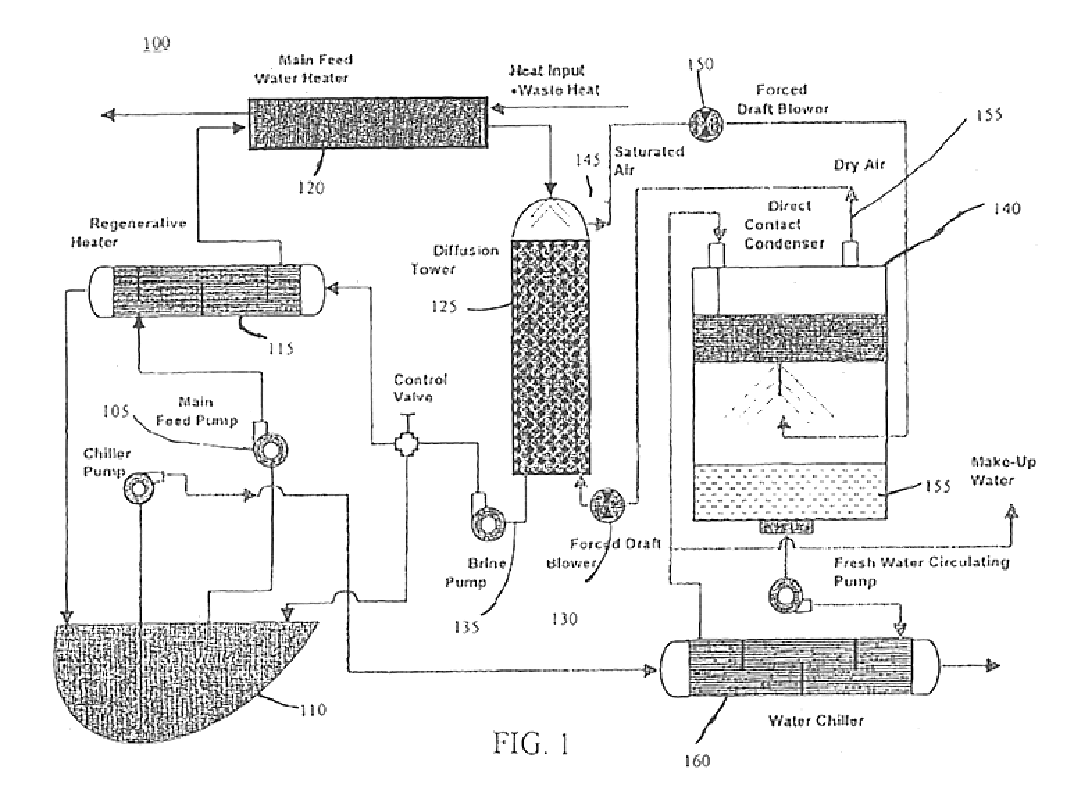
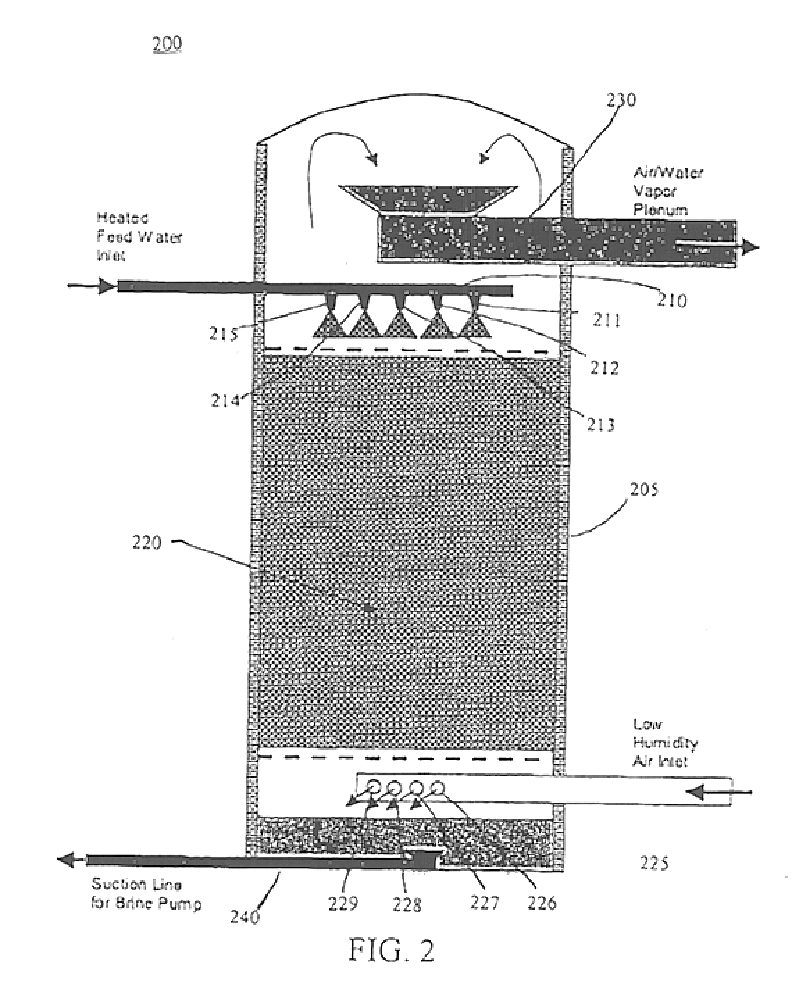
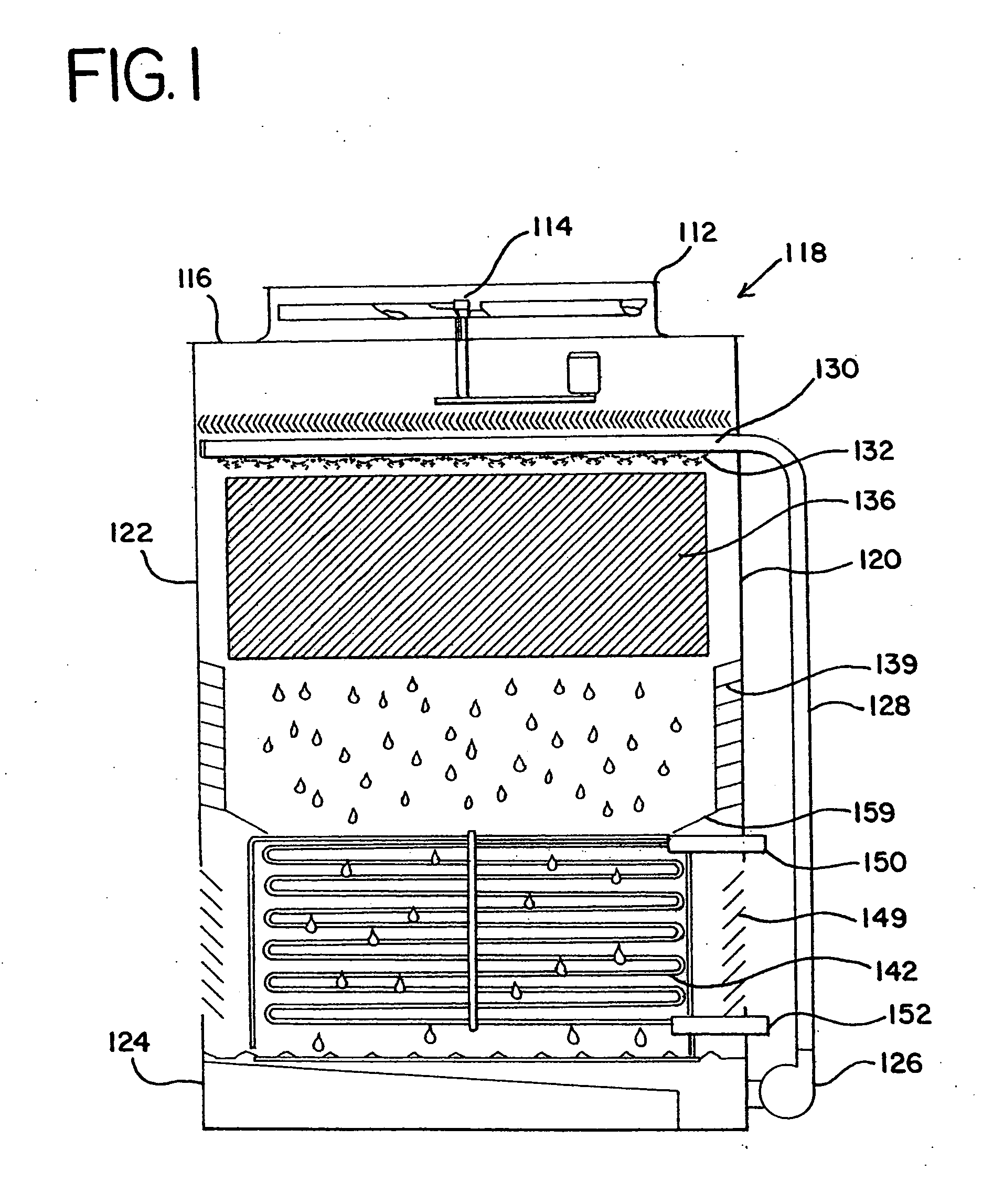
Diffusion driven desalination apparatus and process
A diffusion driven desalination apparatus and related method includes structure for receiving a heated water stream and creating at least one region having a thin film of water and structure for forcing a low humidity air stream over the thin film of water, wherein water from the thin film of water evaporates and diffuses into the air stream to create a humidified air stream. A diffusion tower including at least one plenum can be used to create and transfer the humidified air stream. At least one condenser, such as a direct contact condenser, condenses the humidified air stream, wherein purified water is produced. Waste heat from a power plant can be used to provide the heated water stream and power plants can use the waste heat generated to inexpensively provide purified water.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
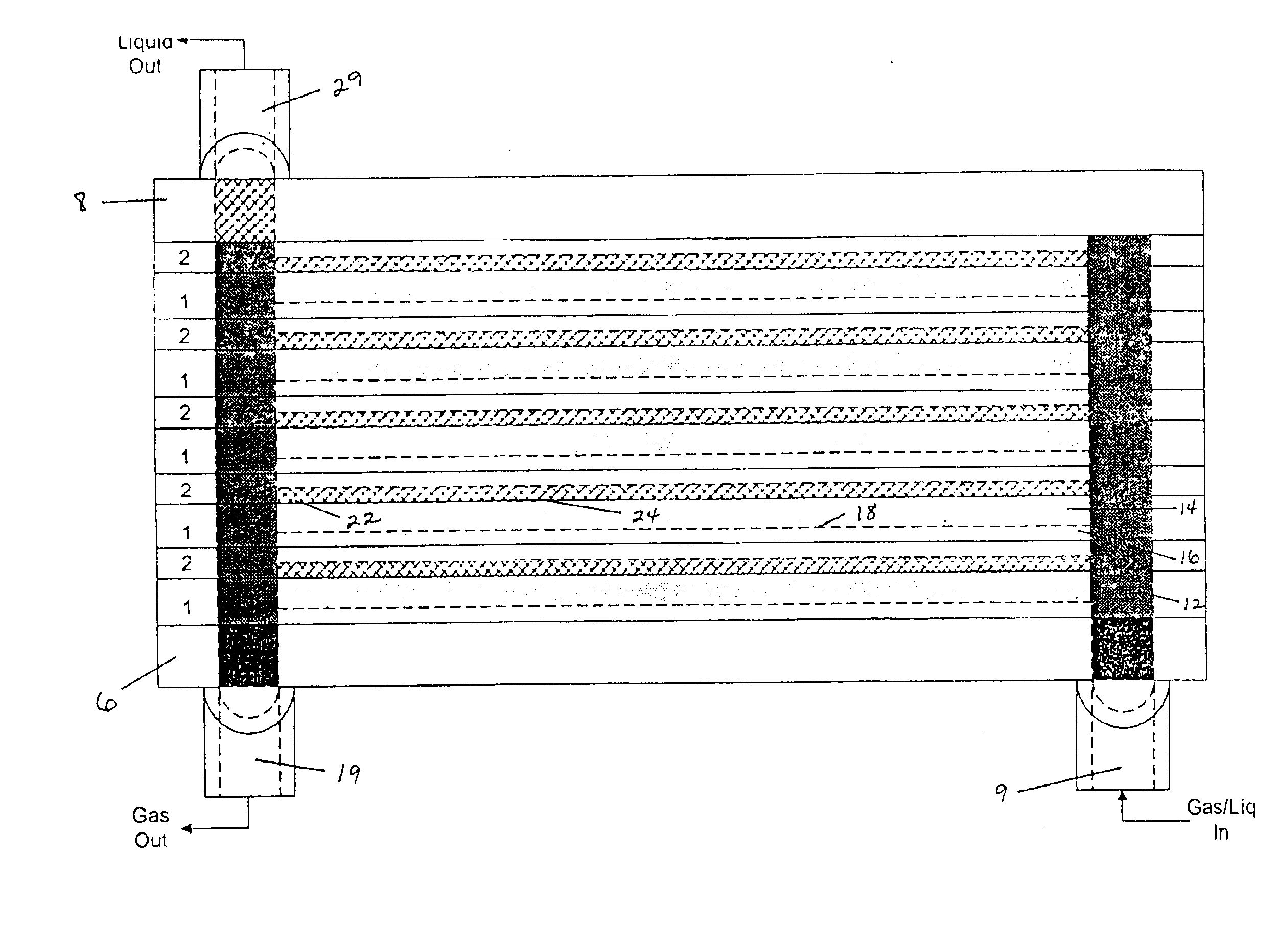
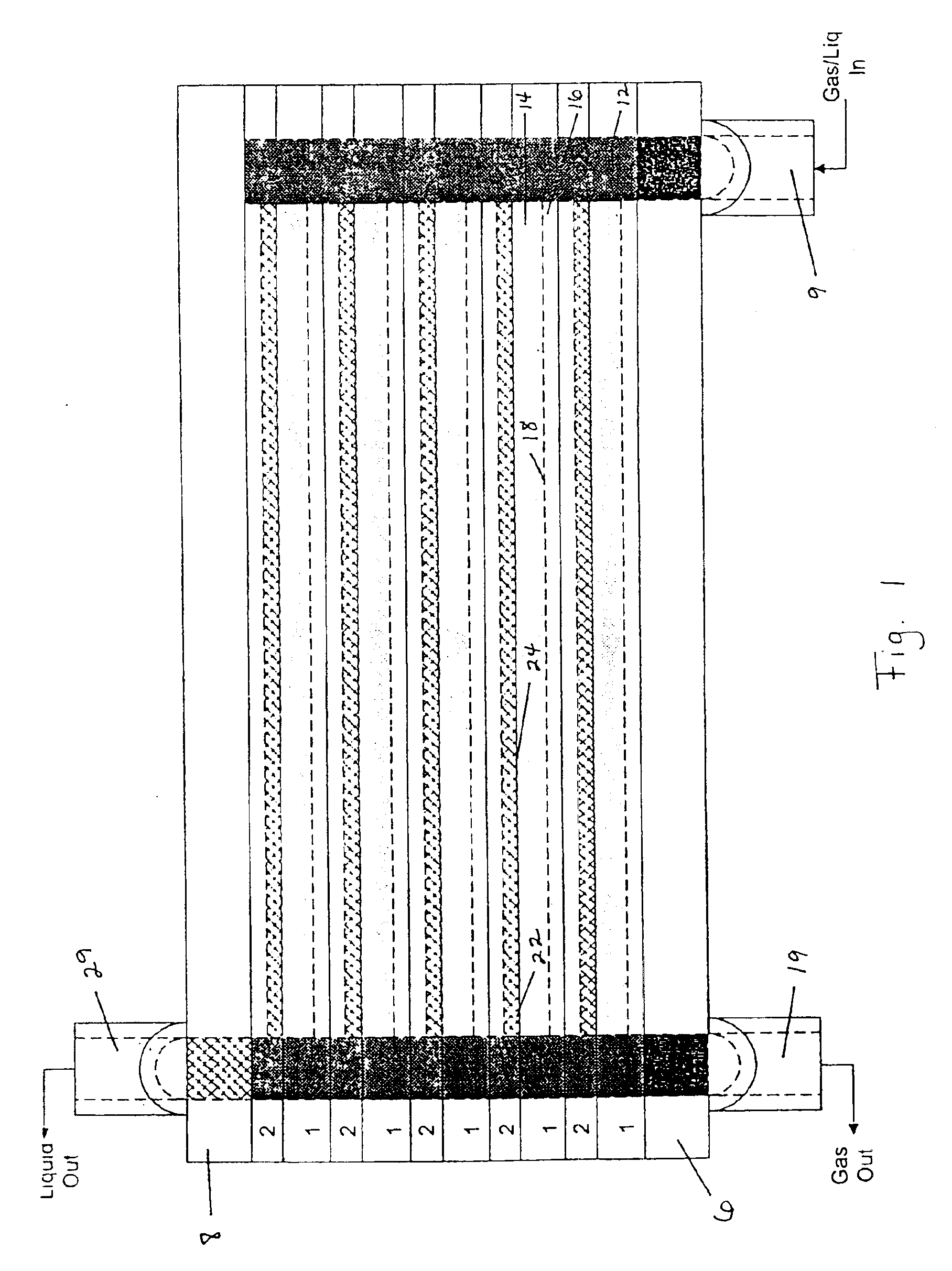
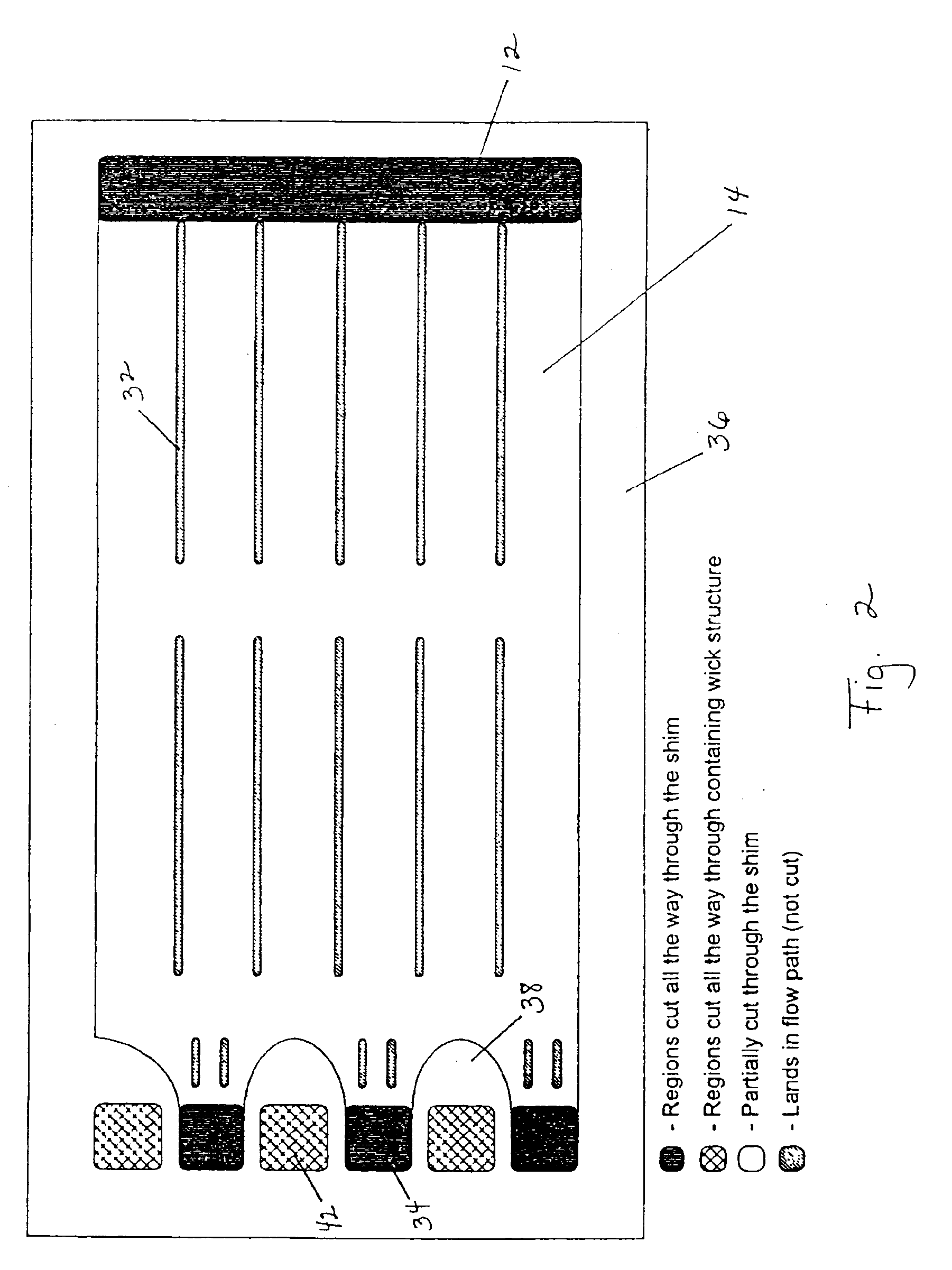
Heat and mass exchanger
ActiveUS7269966B2Additional exchangeEfficient exchangeSpacing meansDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringContinuous flow
Owner:AIL RES
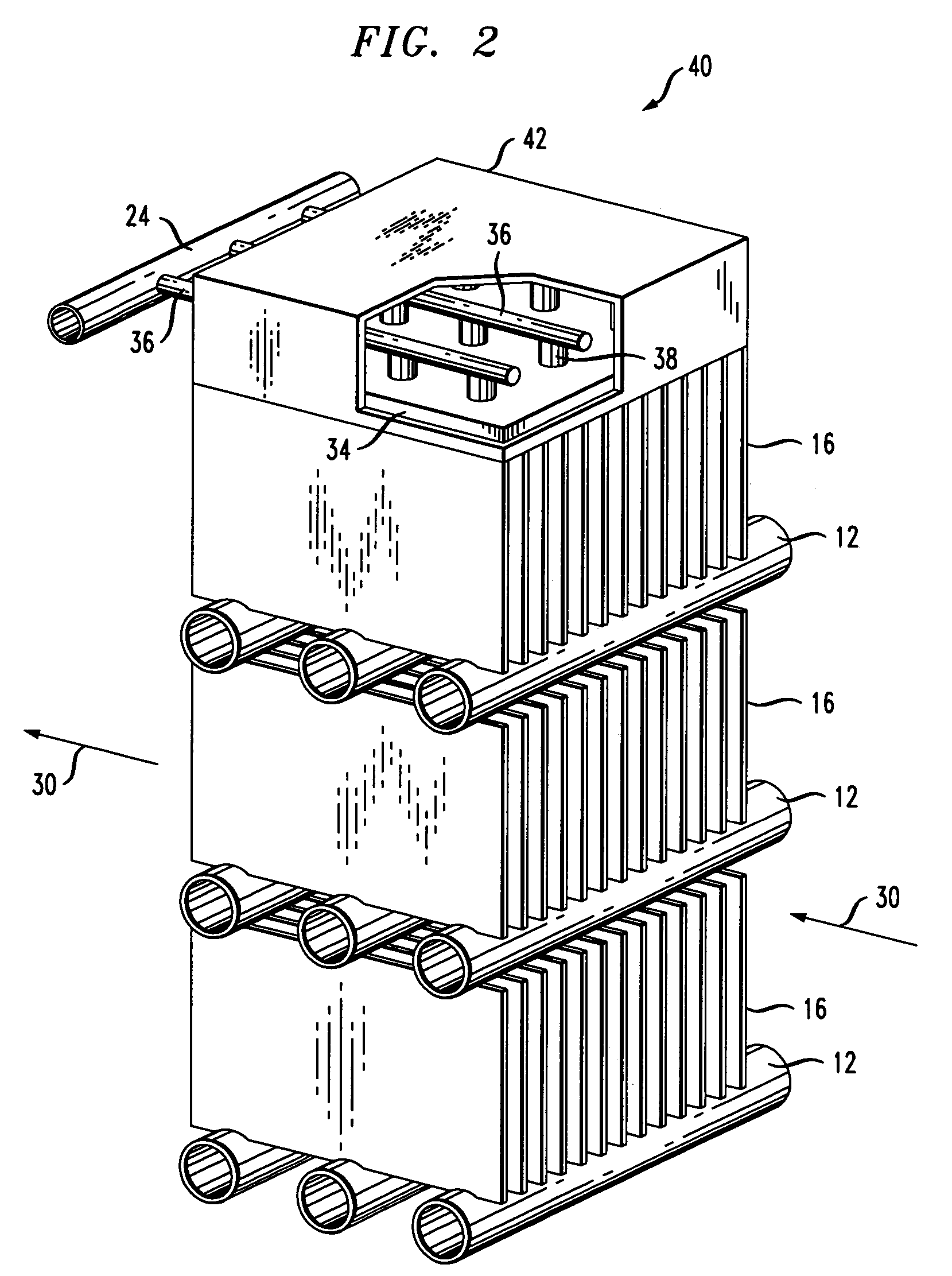
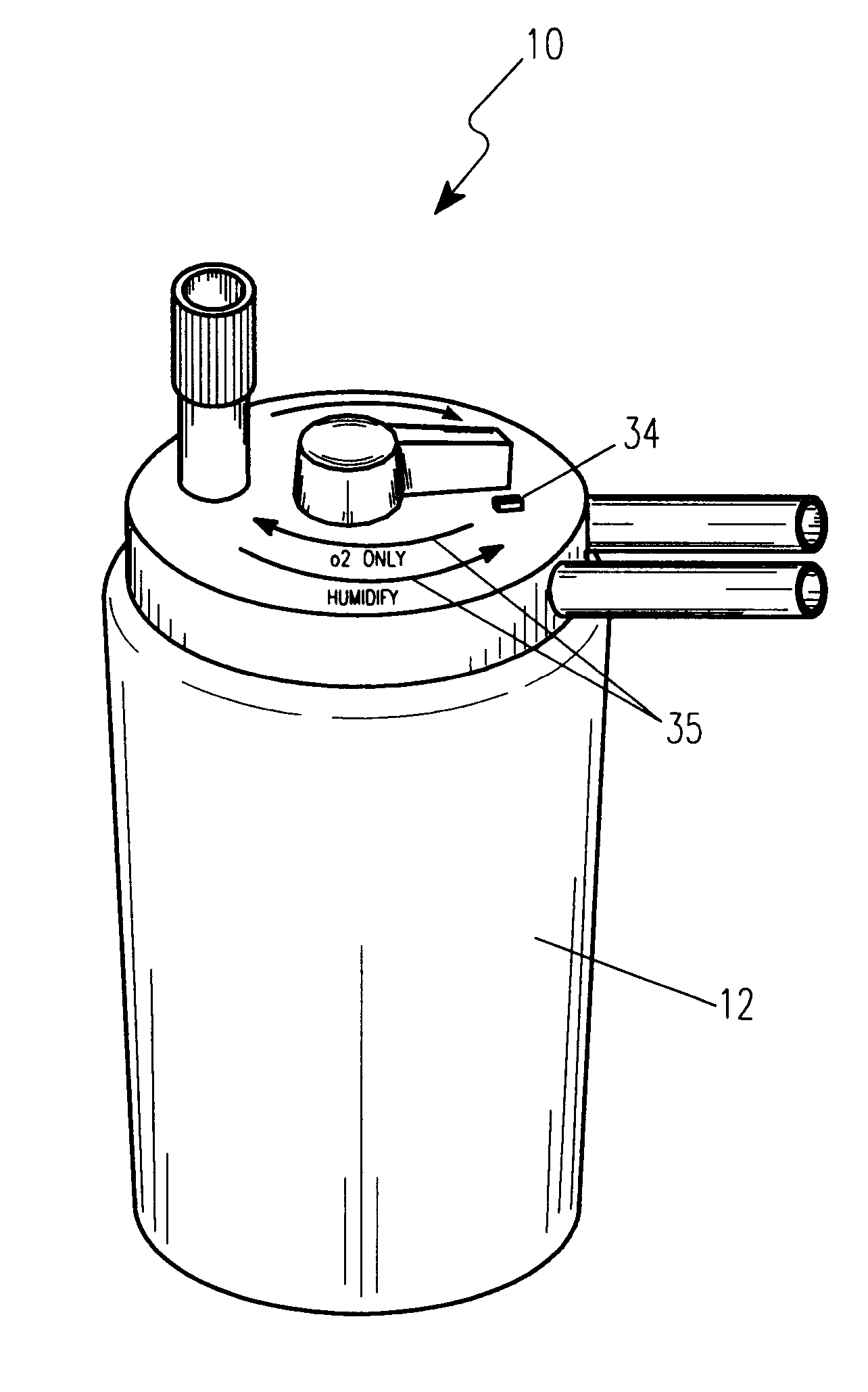
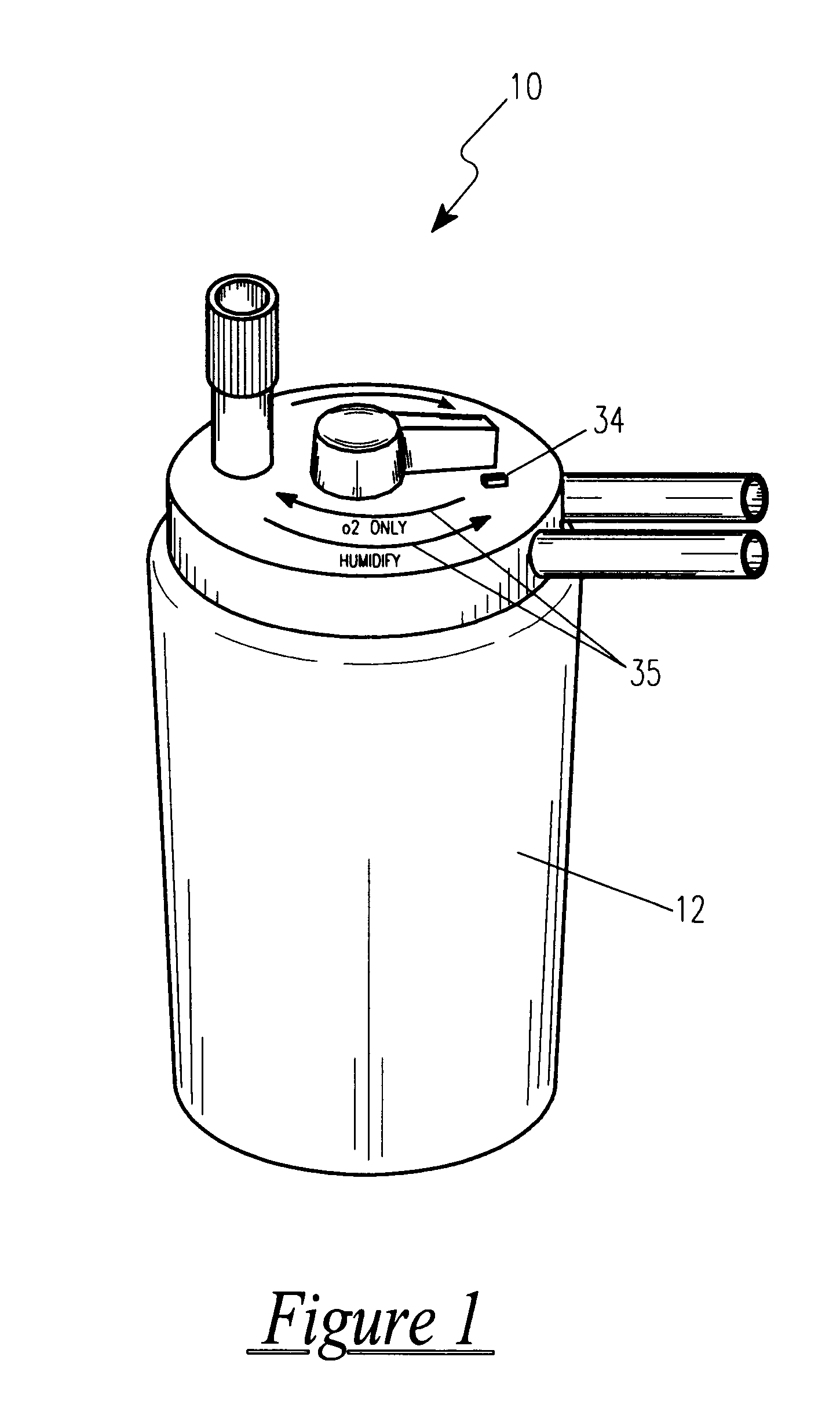
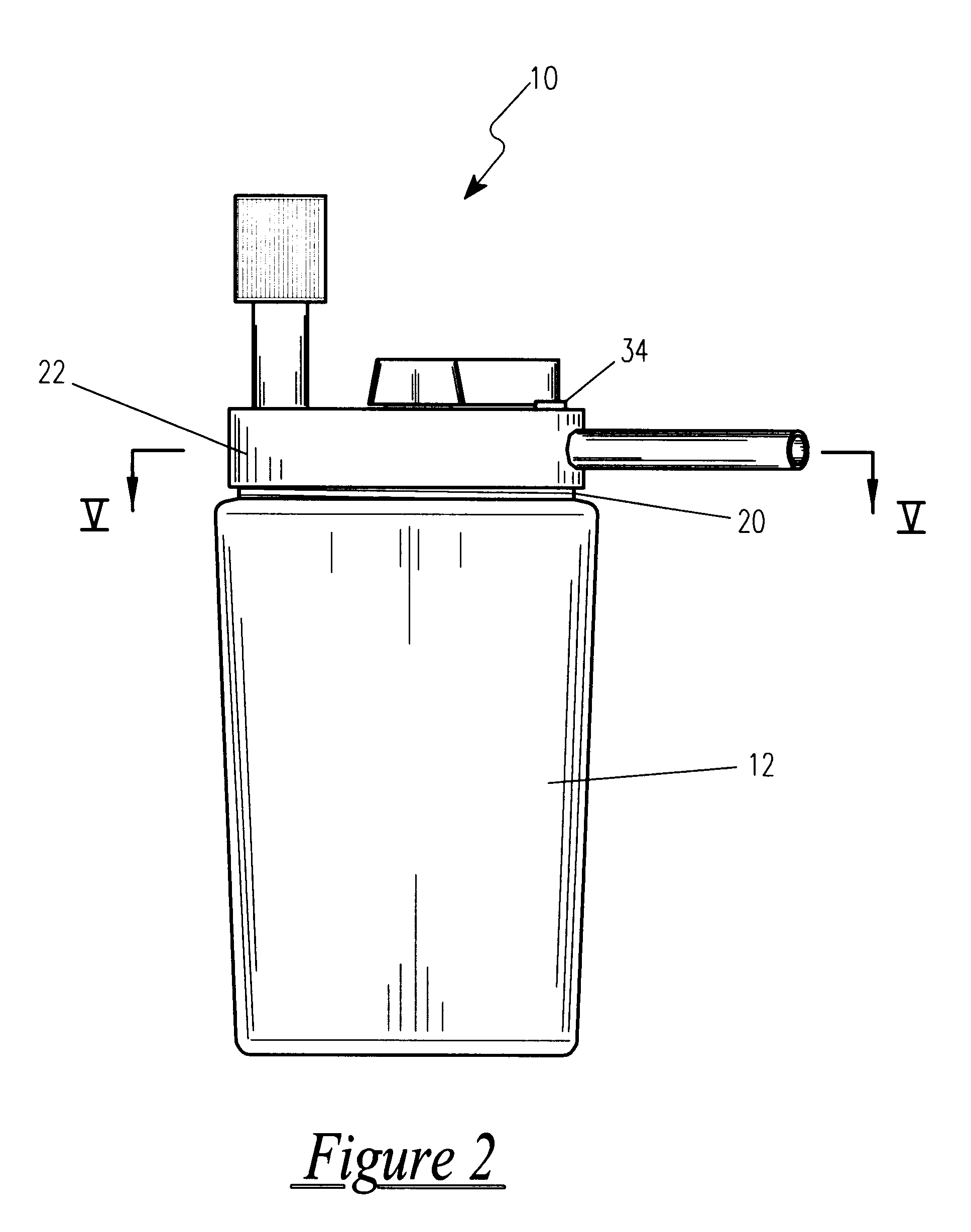
Dual port medical oxygen humidifier
InactiveUS6189870B1Easy to switchReduces and eliminates possibilityLighting and heating apparatusTransportation and packagingEngineeringMoisture
An improved disposable bubble oxygen humidifier is provided having a humidifying chamber included for the blending of oxygen and moisture. A slide switch on the top of the humidifier directs pure oxygen to the patient, or alternately, routes the oxygen through the humidifier and on to the patient. Hoses are attached at an inlet supply port and an outlet discharge port.
Owner:WITHALL GORDON
Air conditioning system and methods
An air conditioning system for conditioning the space within an enclosure having at least one inlet and one outlet, the system comprising first and second liquid / air heat exchangers; the first heat exchanger having an opening for receiving fresh air from the environment and for propelling the fresh air through the first heat exchanger to exchange heat with the liquid before it is entered into the enclosure, and the second heat exchanger having an opening for receiving air from the enclosure and for propelling it through the second heat exchanger to exchange heat with the liquid before it is expelled into the atmosphere. There are also provided methods for air-conditioning an enclosed space and for evaporation of industrial wastes.
Owner:AGAM ENERGY SYST
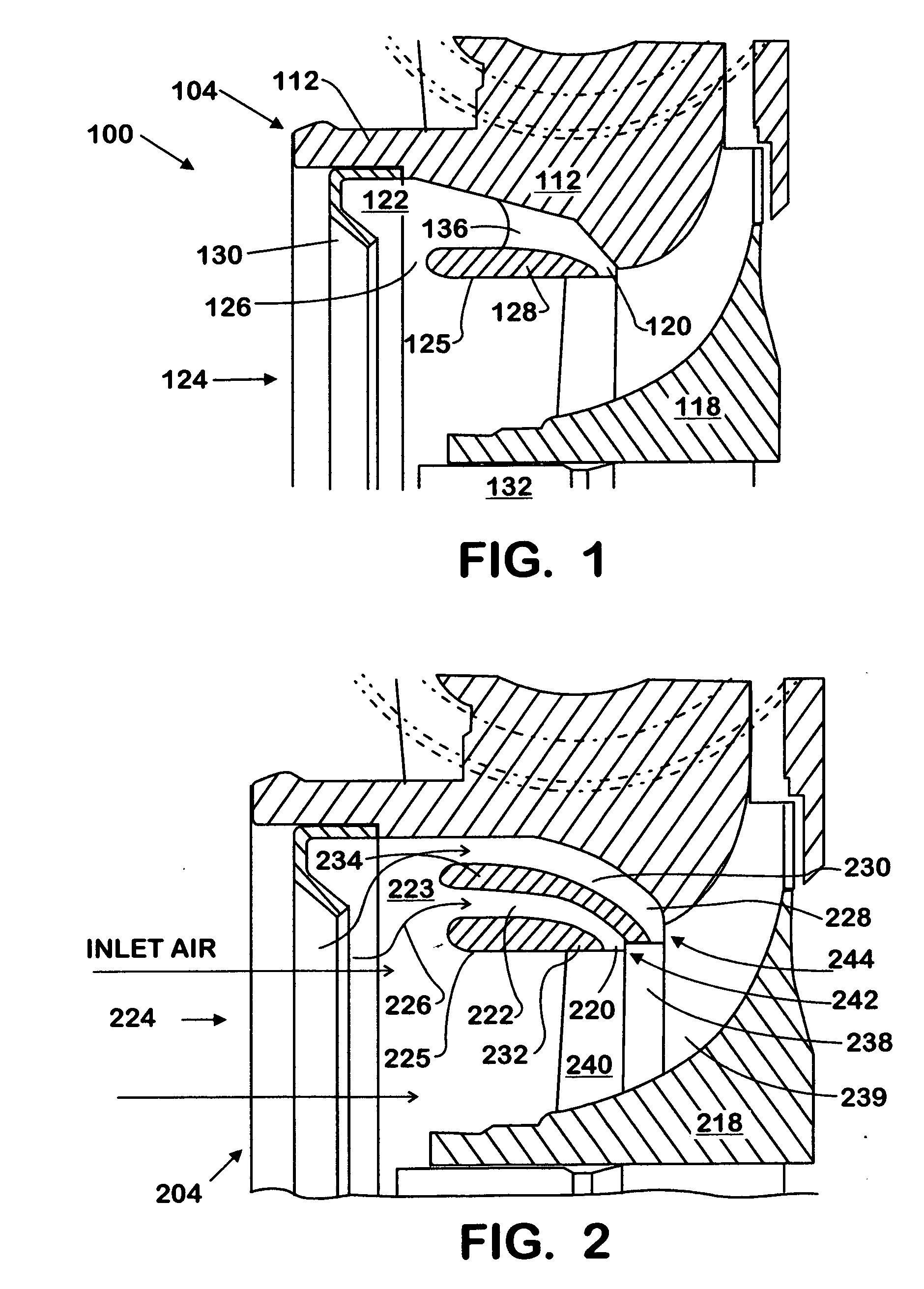
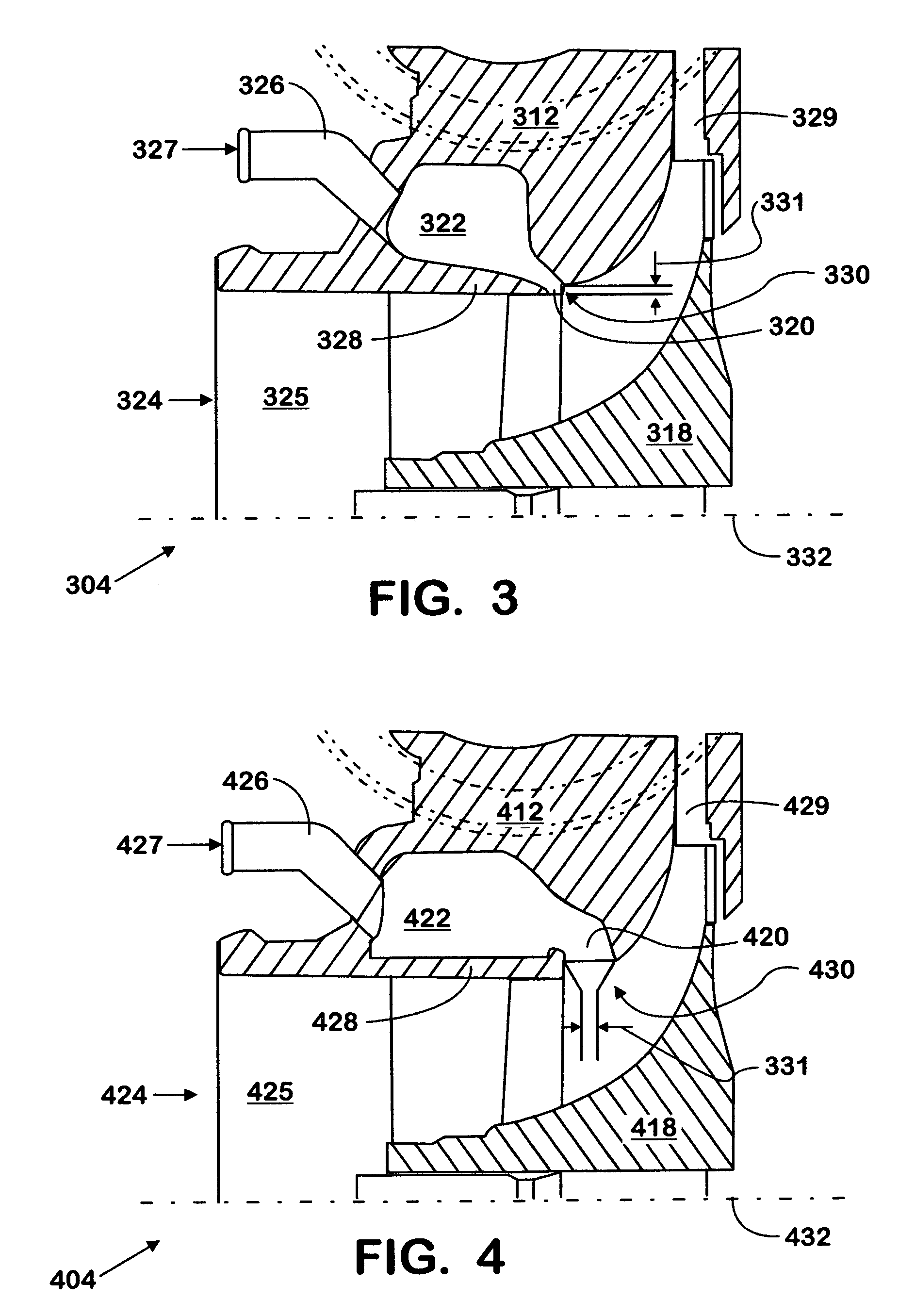
Engine intake air compressor and method
A compressor assembly (304) includes a compressor housing (312) having a main air inlet (324) and an annular wall (328) defining an inducer bore (325). A secondary inlet passage (322) is disposed around the inducer bore (325). The secondary inlet passage (322) has an inlet slot (320) operatively intersecting the inducer bore (325) to permit the entry of a fluid thereinto through an inlet port (327). The inlet slot (320) advantageously defines an augmented inducer diameter region (331). Preferably the secondary inlet passage (322) may be selectively partially or completely isolated from the main air inlet (324). A compressor wheel (318) is located in the compressor housing (312) and has a stepped portion (330) formed by at least one plurality of vanes (238) operatively associated with the augmented inducer diameter region (331) adjacent to the inlet slot (320) of the housing (312) to receive fluid therefrom.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Heat and mass exchanger
ActiveUS20060156750A1Additional exchangeEfficient exchangeSpacing meansDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringContinuous flow
A mass and heat exchanger includes at least one first substrate with a surface for supporting a continuous flow of a liquid thereon that either absorbs, desorbs, evaporates or condenses one or more gaseous species from or to a surrounding gas; and at least one second substrate operatively associated with the first substrate. The second substrate includes a surface for supporting the continuous flow of the liquid thereon and is adapted to carry a heat exchange fluid therethrough, wherein heat transfer occurs between the liquid and the heat exchange fluid.
Owner:AIL RES
Cooling tower and method for optimizing use of water and electricity
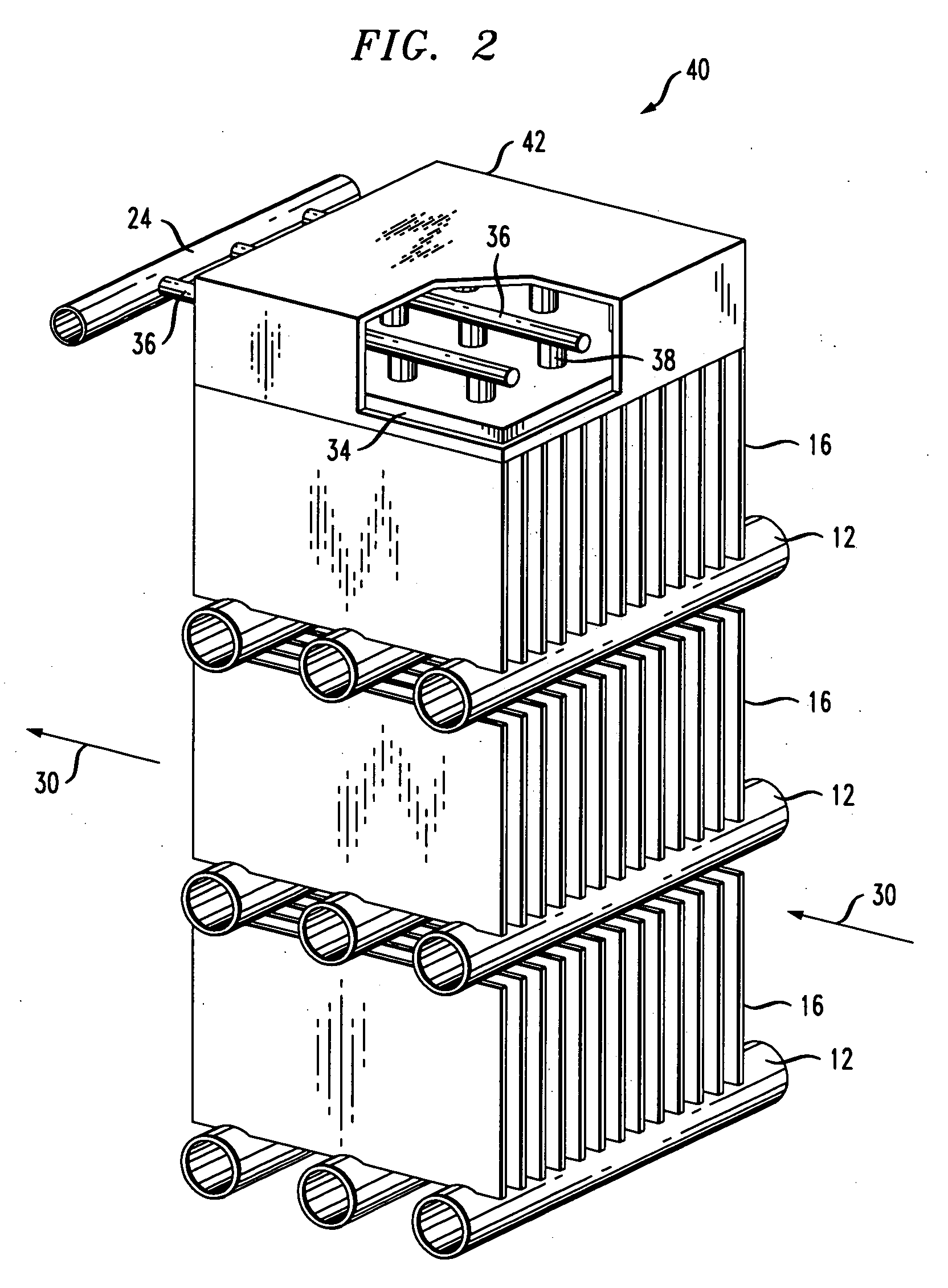
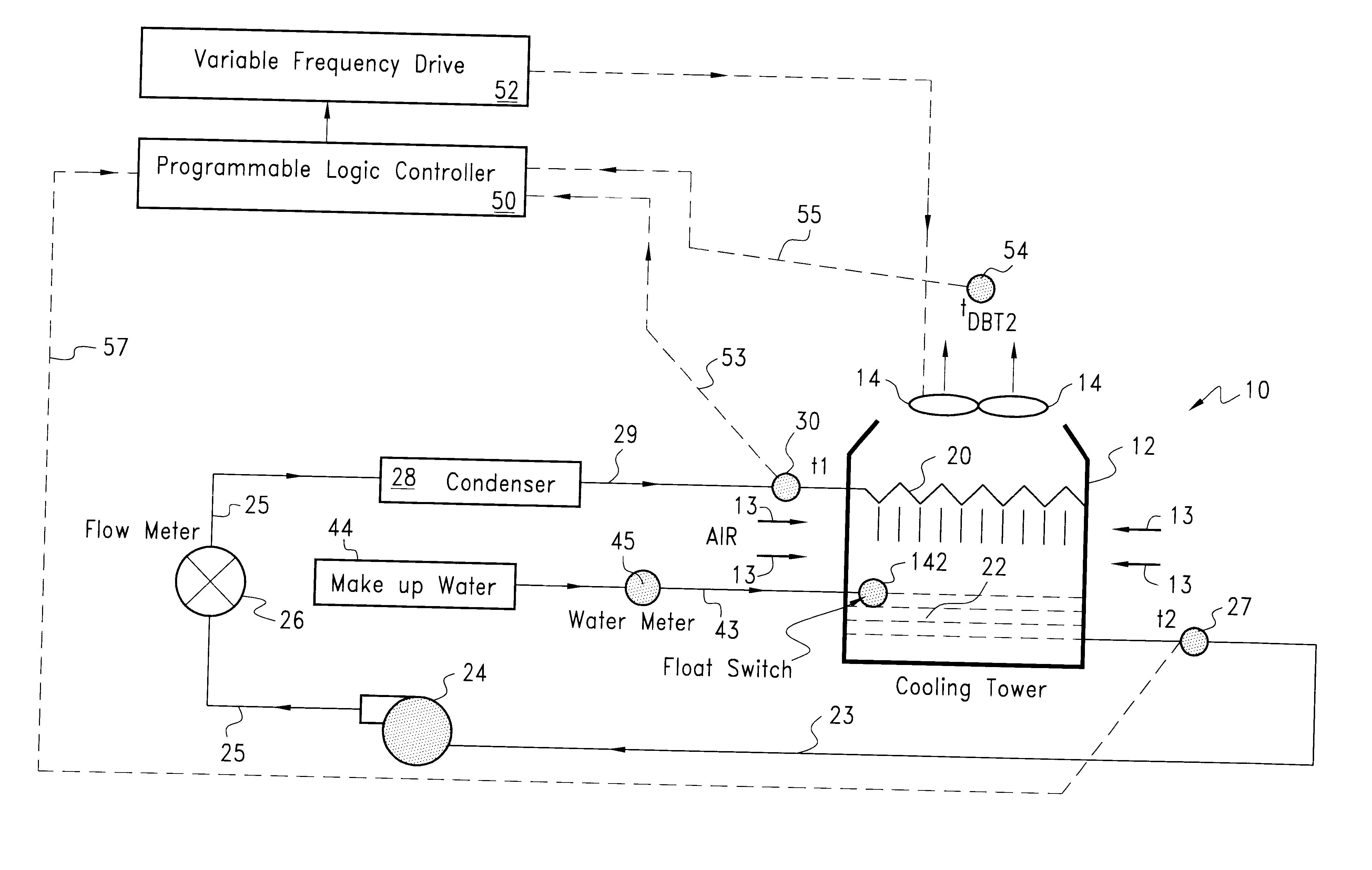
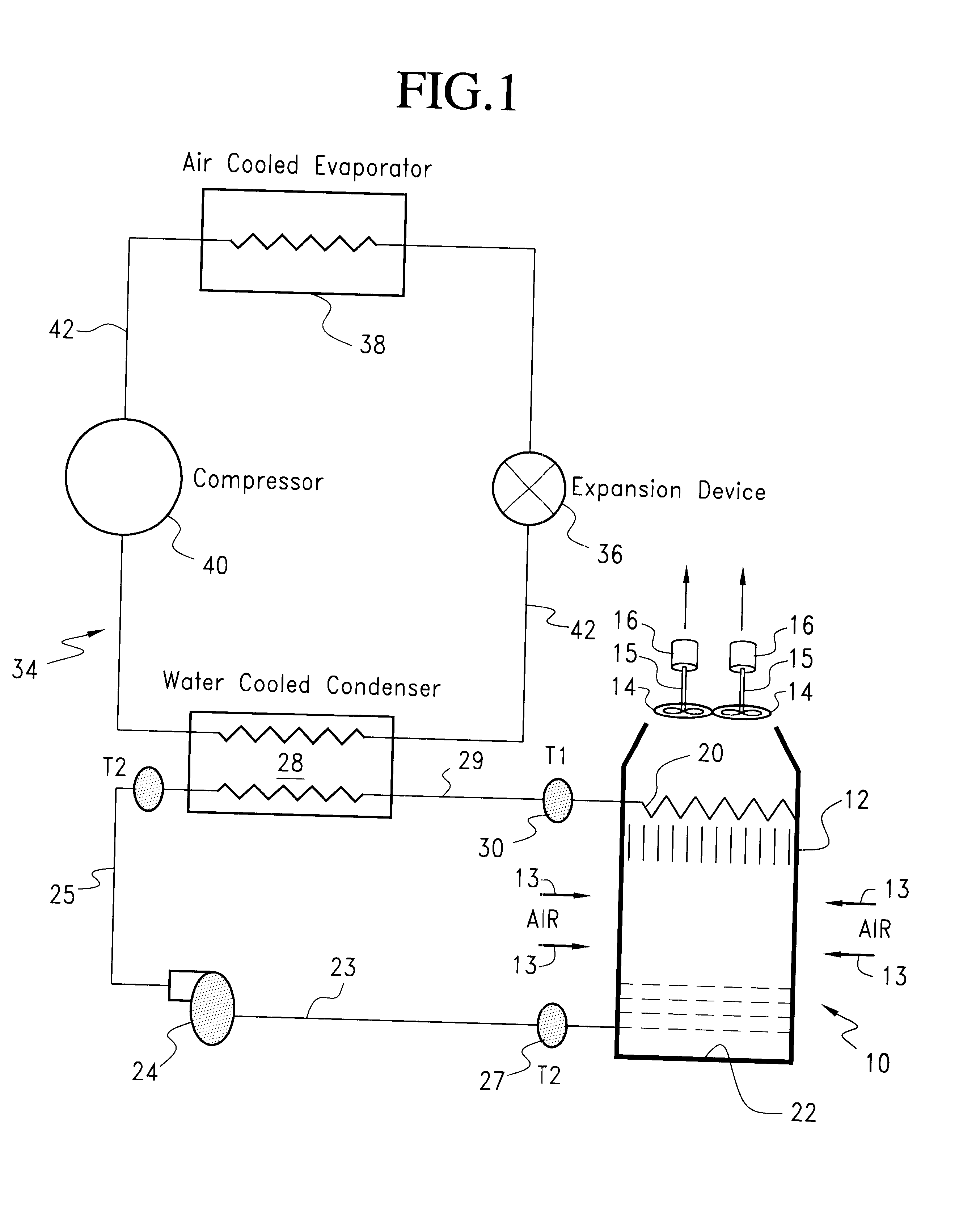
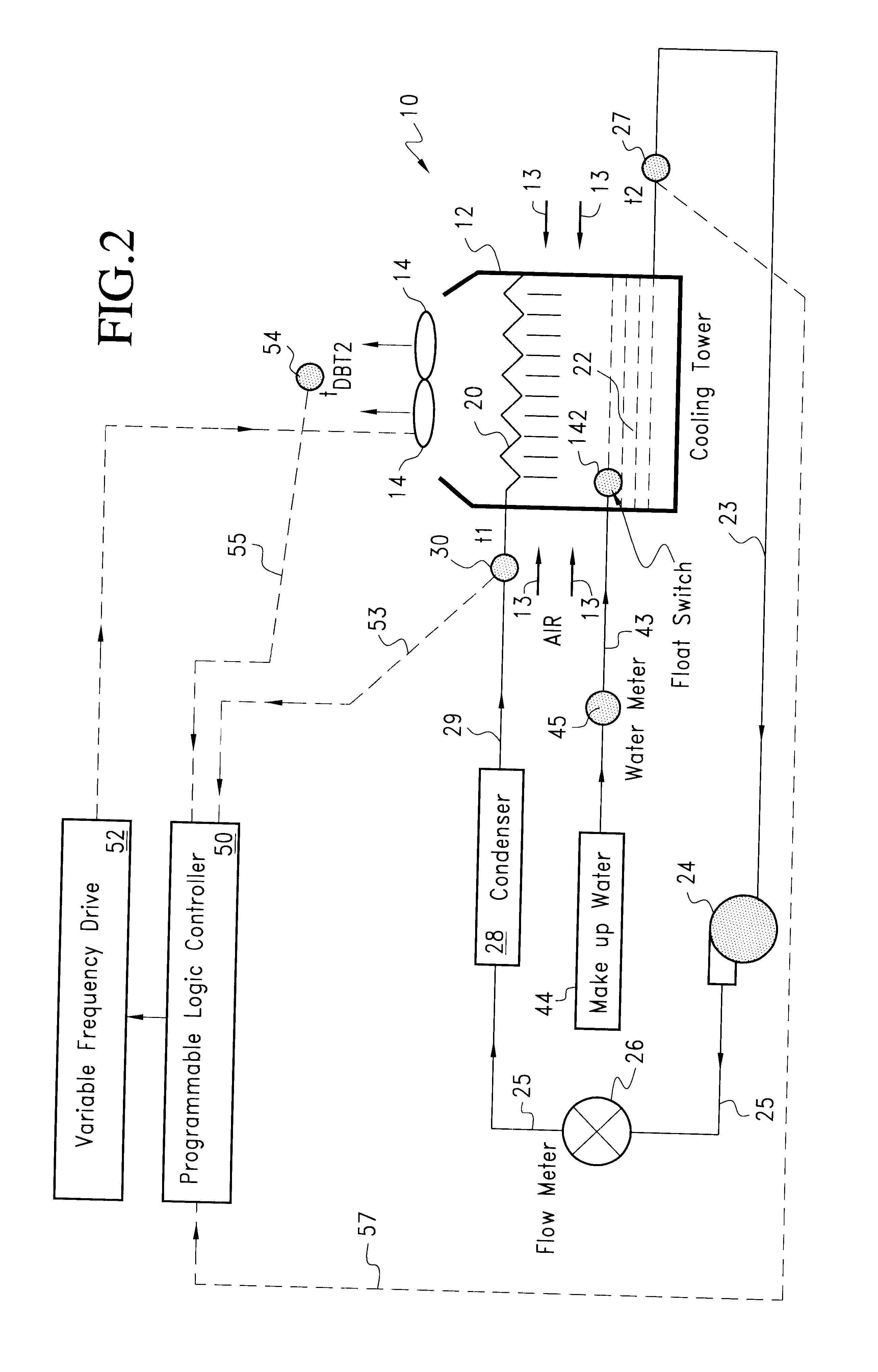
A forced air cooling tower includes an upright casing, and elevated water distribution system disposed in an upper portion of the casing and one or more fans for drawing air through the tower. The tower also includes a catch basin for collecting the cooled air and a pump for circulating the cooled water through a condenser and back to the top of the tower and to the water distribution system. The cooling tower also includes a controller and a variable frequency device for regulating the flow of air through the tower. A first temperature sensor senses the temperature T1 of the hot process water delivered to the water distribution system and a second sensor senses the dry bulb temperature of the air leaving the tower Tdbt2. A third sensor senses the temperature of the cooled water leaving the tower. The controller such as a computer and variable frequency drive controls the speed of the fan to minimize the difference in T1 and Tdbt2. A submaster control prevents the fan speed from being further reduced when a predetermined T2 (temperature of the cooled water) is reached.
Owner:KUWAIT INST FOR SCI RES
Indirect evaporative cooling mechanism
InactiveUS20050218535A1Improve economyImprove efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesFree-cooling systemsDesiccantPlastic materials
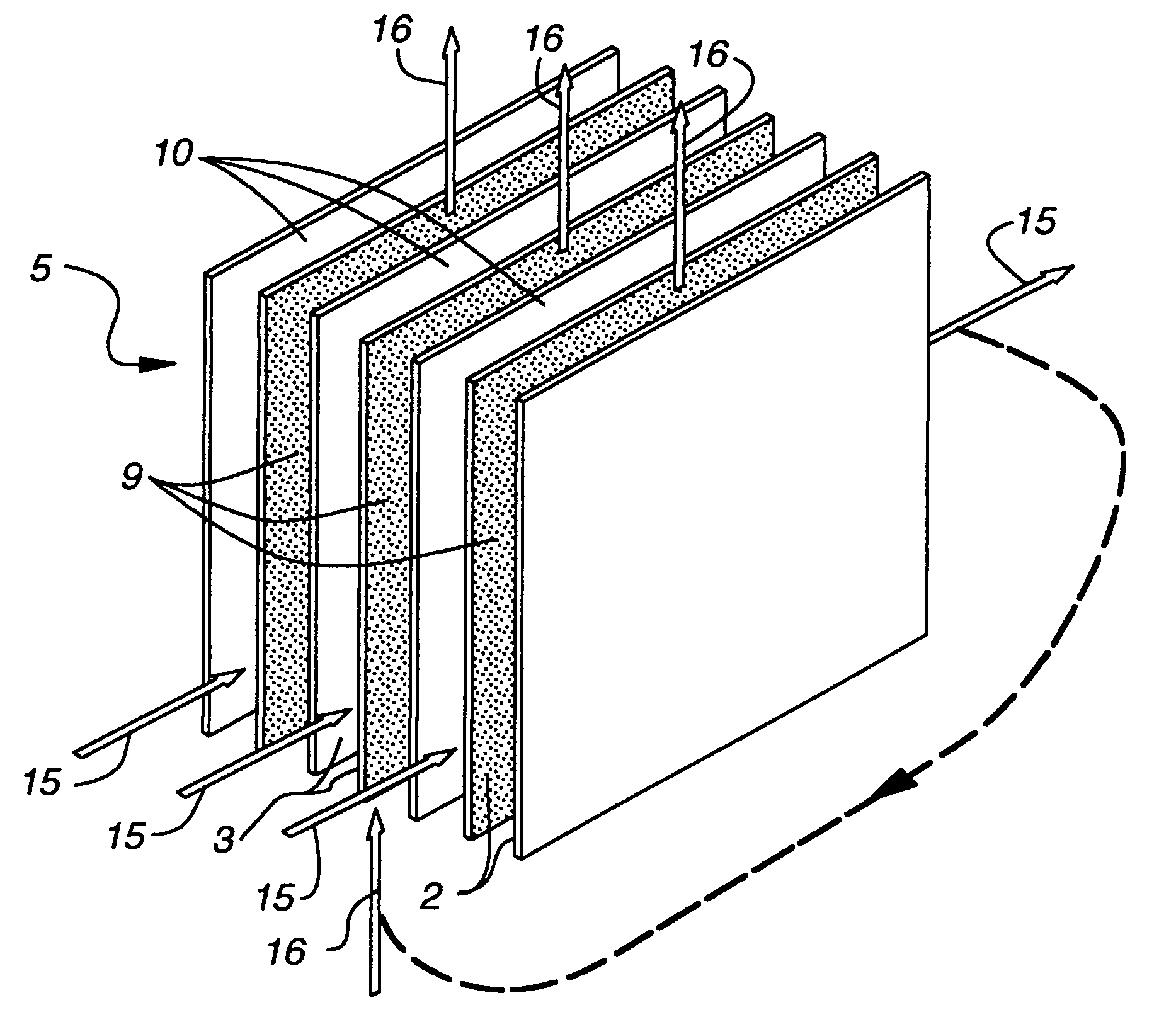
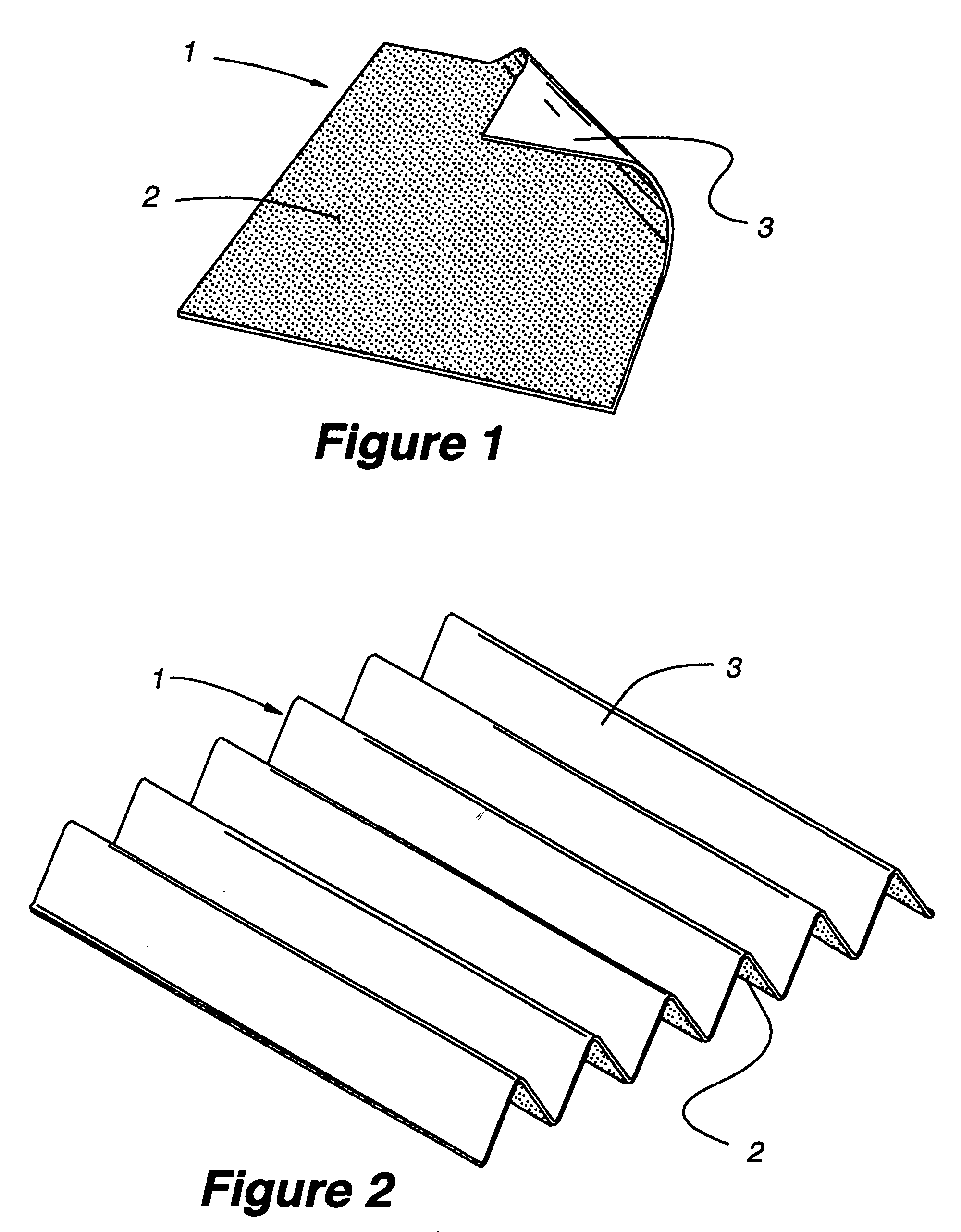
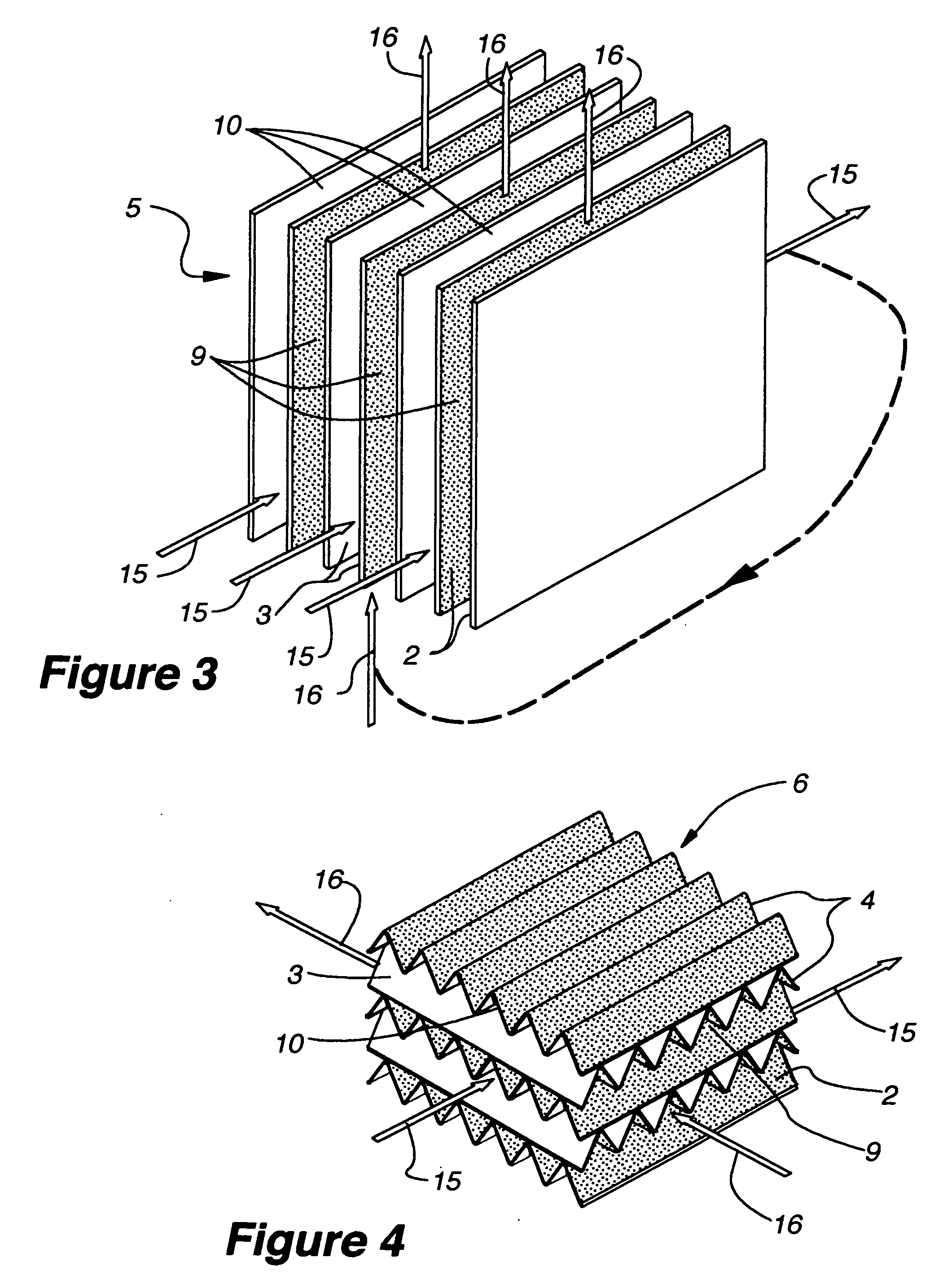
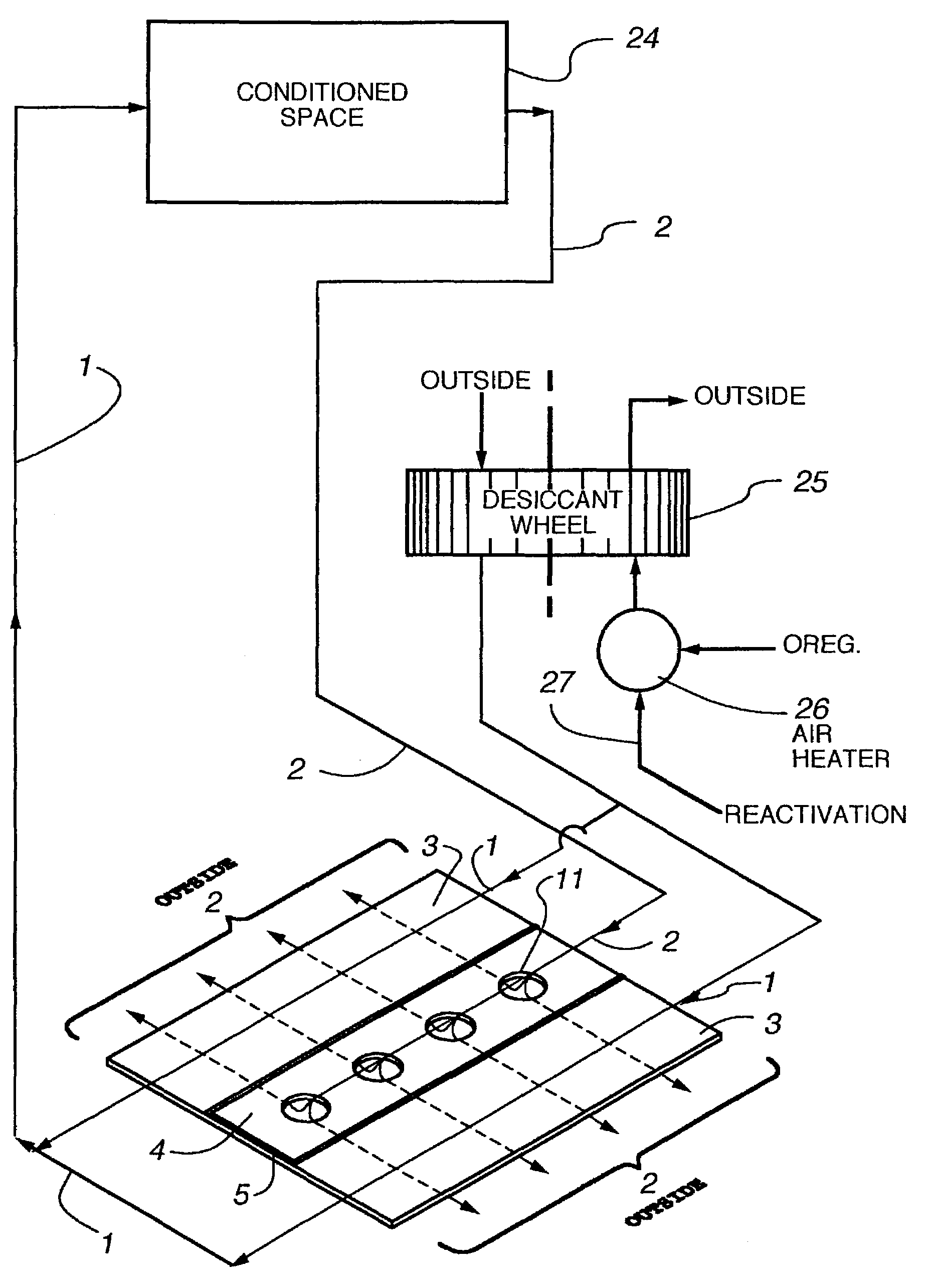
The present invention relates to methods for indirect evaporative air-cooling with the use of plates, heat exchangers and feeder wicks—of the indirect evaporative type. Several components for an indirect evaporative heat exchanger described as follows: A plate for an indirect evaporative heat exchanger where the plate is made of laminate material having one sheet of wicking material for wet zone(s) and the other of a water proof plastic material for the dry zone(s). An evaporative heat exchanger is created by assembling the plates forming spacing for wet channels, (they are created by the wet zone of the plates,) and dry channels, (they are created by the dry zone of the plates,) with channel guides or corrugated plates. The spacing between the plates is defined to reduce pressure drop for increased airflow. A feeder wick system creates the wetting of the wet channels without excess water. Sometimes the wet zone of the plate can be made of a membrane material where the opposite side of this membrane material is covered by a solid desiccant creating the wet zone of this desiccant plate. An indirect evaporative heat exchanger that is created by assembling both wick coated with plastic plates and desiccant plates, can realize not only the evaporative cooling but also the dehumidification of air.
Owner:MAISOTSENKO VALERIY +3
Method and plate apparatus for dew point evaporative cooler
InactiveUS7197887B2Small pressure dropReduce temperature differenceAir treatment detailsFree-cooling systemsEvaporative coolerFiber
An improved method and apparatus for indirect evaporative cooling of a fluid stream to substantially its dew point temperature. Plate heat exchanger has perforations 11 and channels 3, 4 and 5 for gas or a low temperature for liquids on a dry side and wet side. Fluid streams 1 flow across the dry side 9, transferring heat to the plate. Gas stream 2 flows across the dry side and through perforations to channels 5 on wet side 10, which it then cools by evaporative cooling as well as conductive and radiative transfer of heat from plate. A wicking material provides wetting of wet side. In other embodiments, a desiccant wheel may be used to dehumidify the gas, air streams may be recirculated, feeder wicks 13 and a pump may be used to bring water from a water reservoir, and fans may be used to either force or induce a draft. The wicking material may be cellulose, organic fibers, organic based fibers, polyester, polypropylene, carbon-based fibers, silicon based fibers, fiberglass, or combinations of them. The device may be operated in winter months to scavenge heat from exhaust gases of a space and thus pre-heat fresh air, while simultaneously humidifying the fresh air.
Owner:F F SEELEY NOMINEES
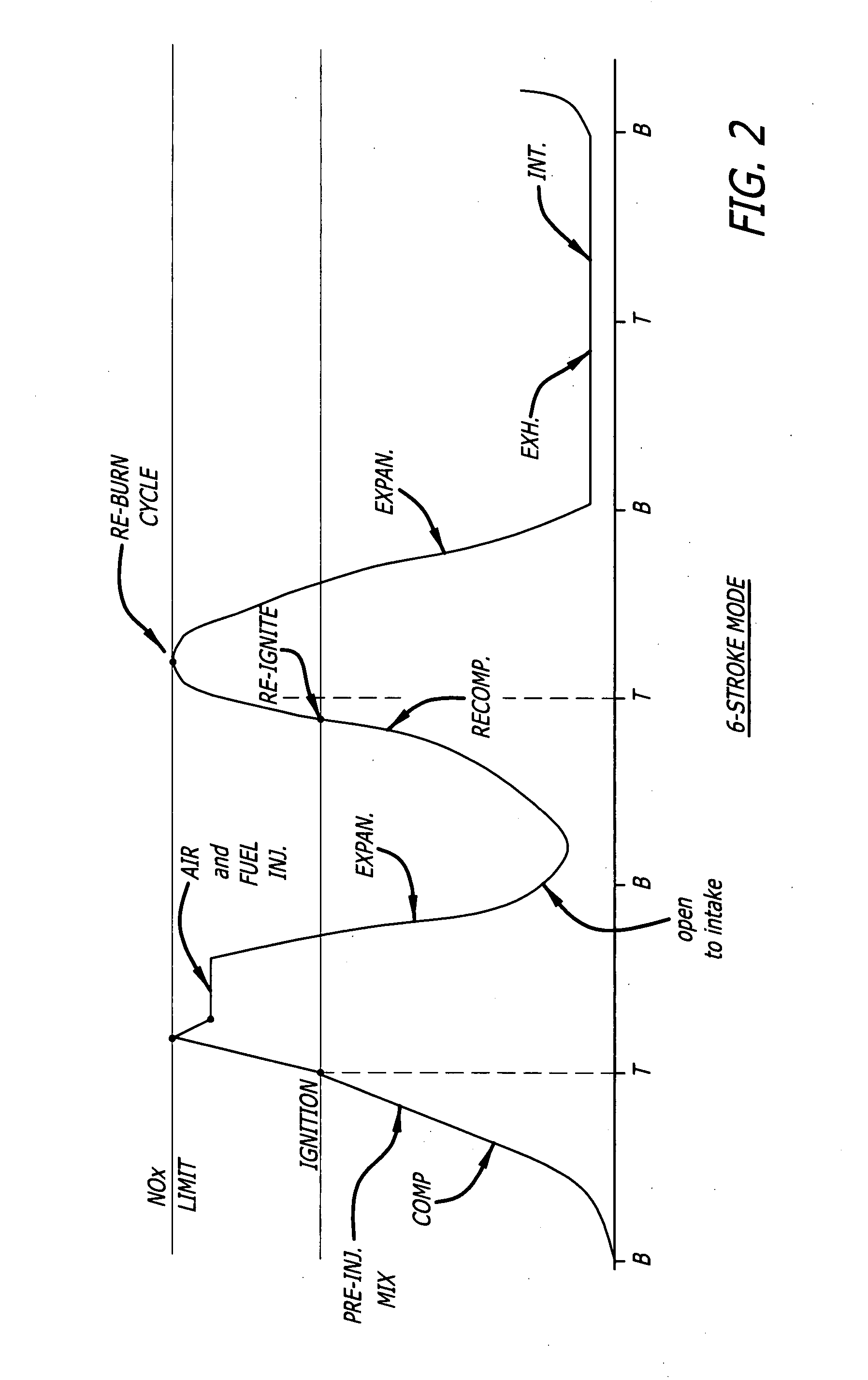
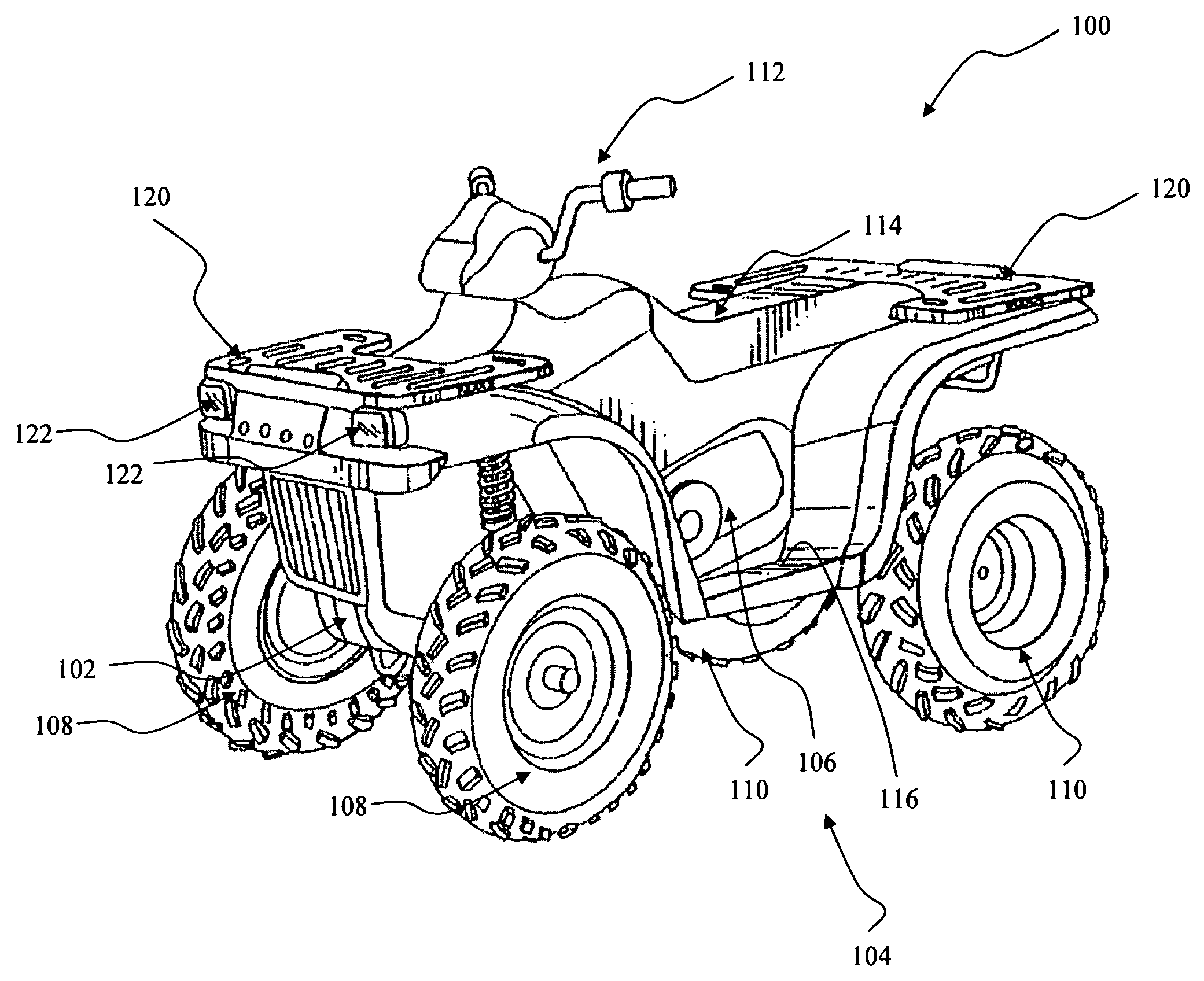
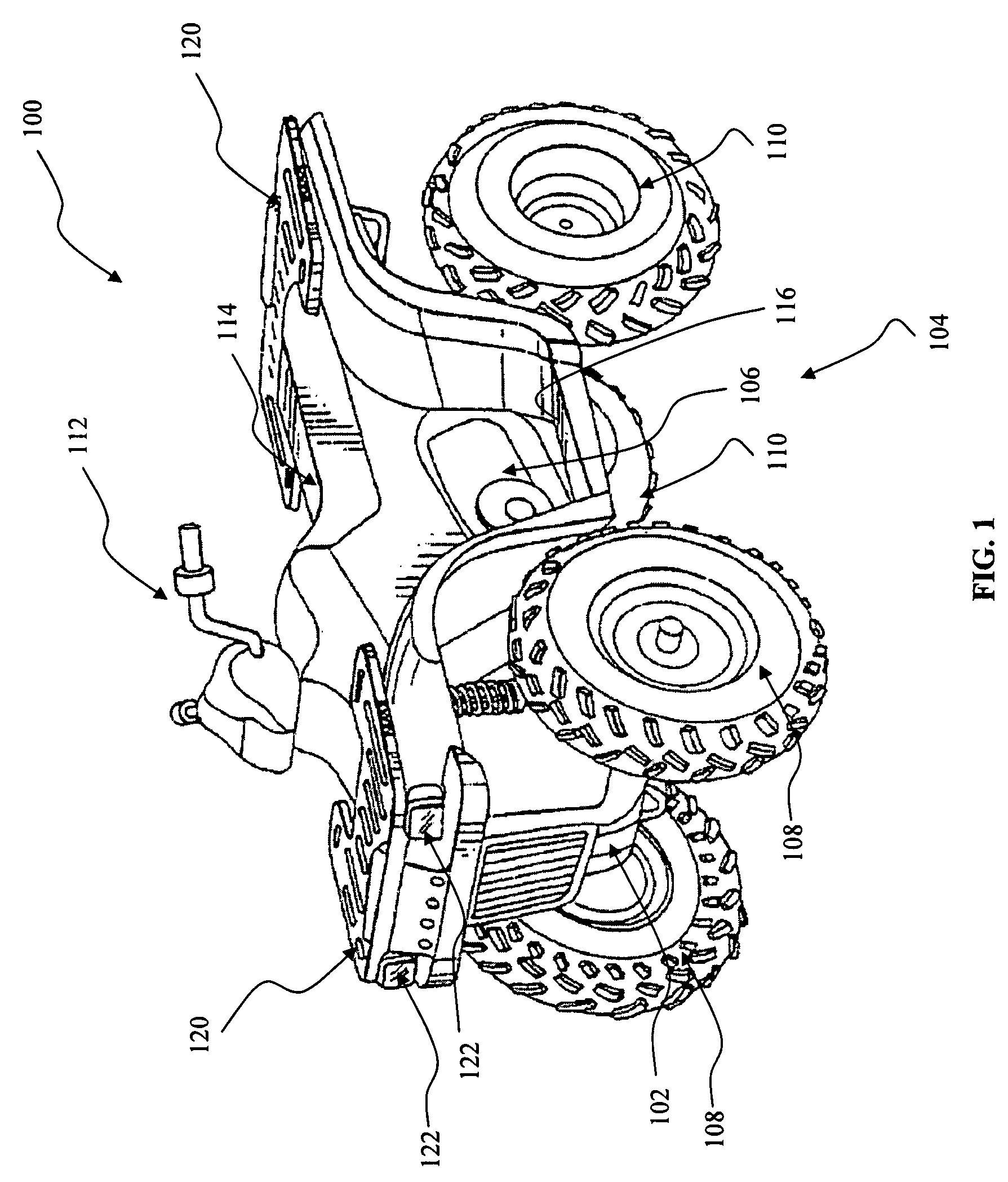
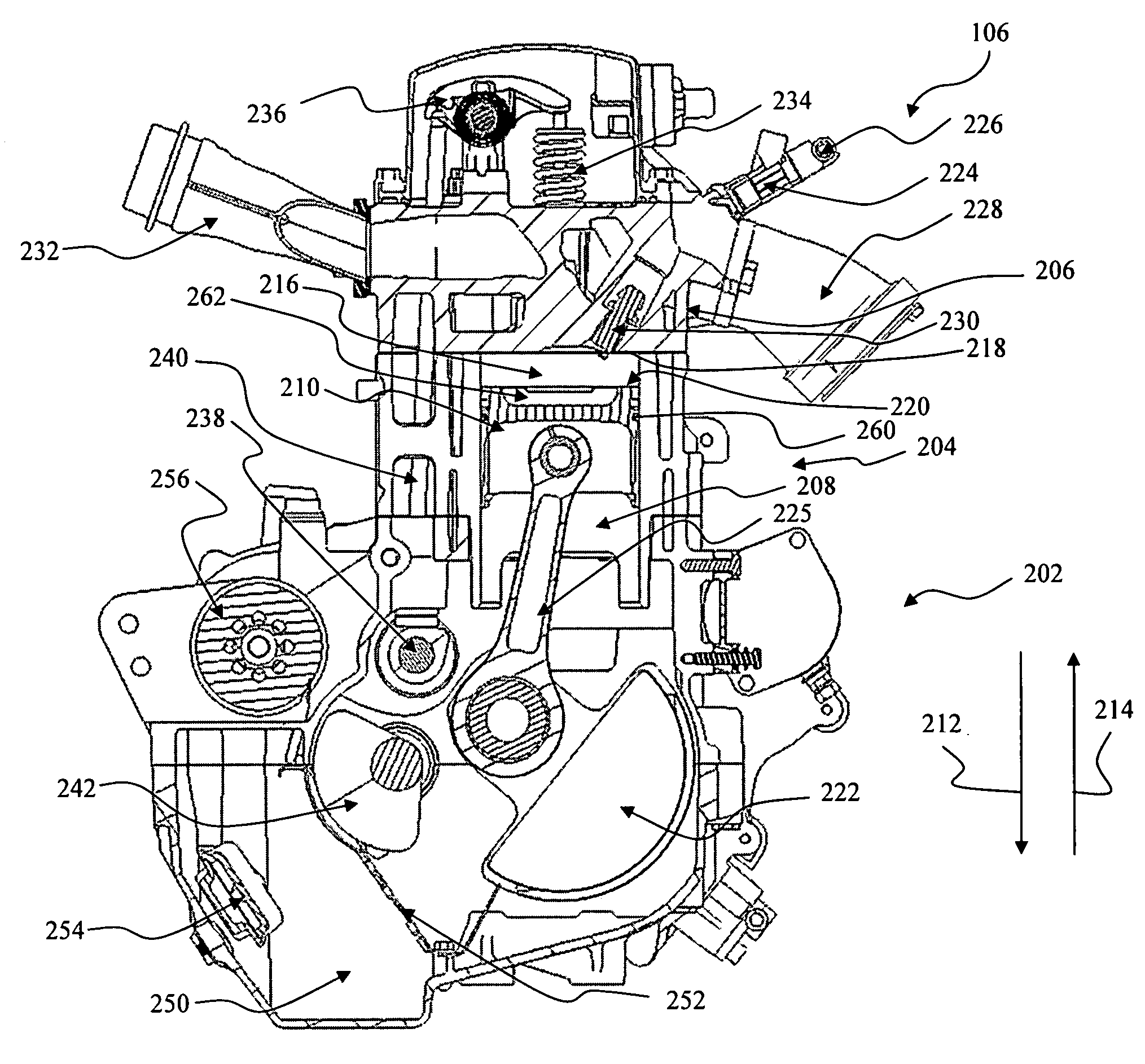
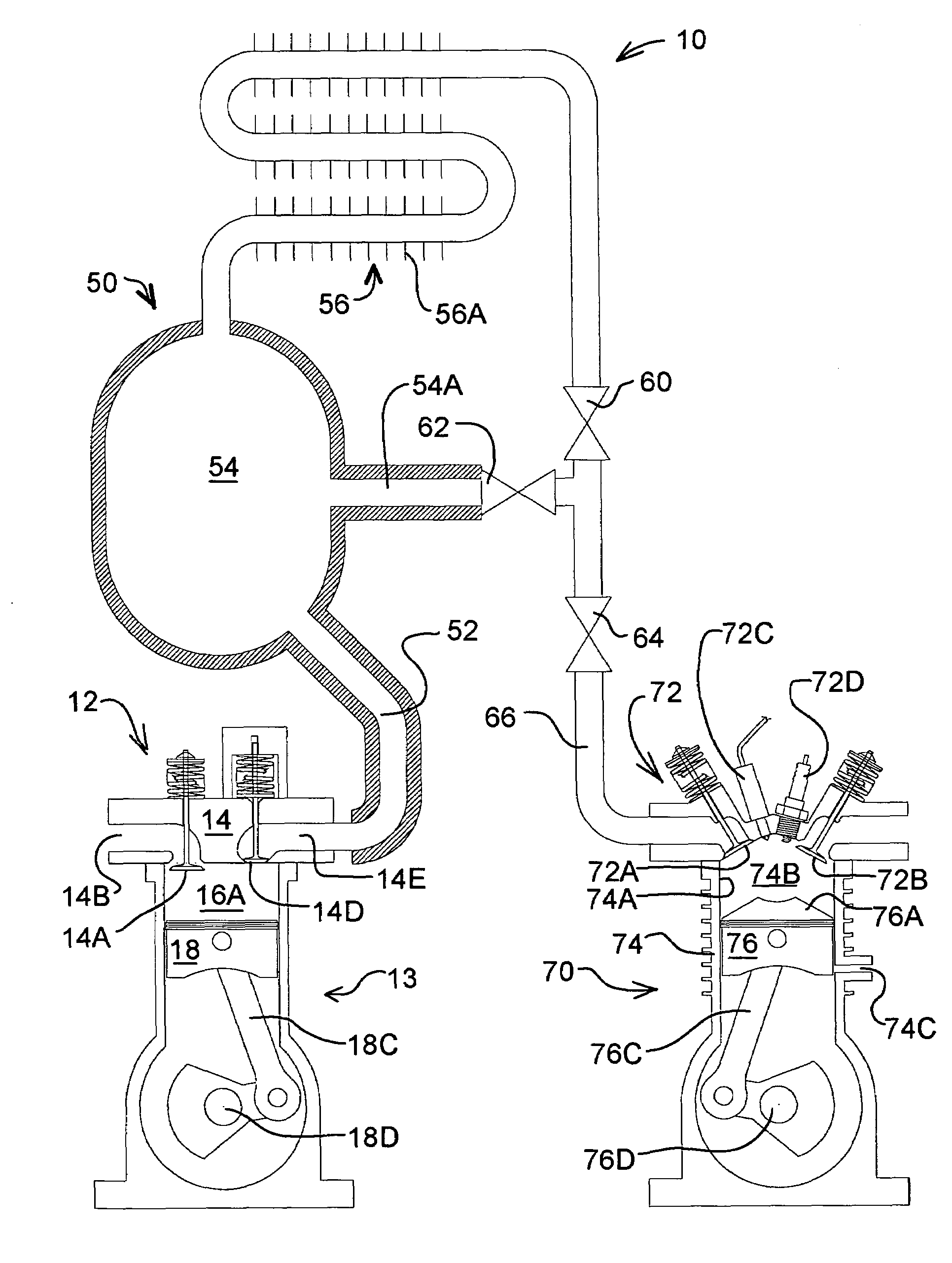
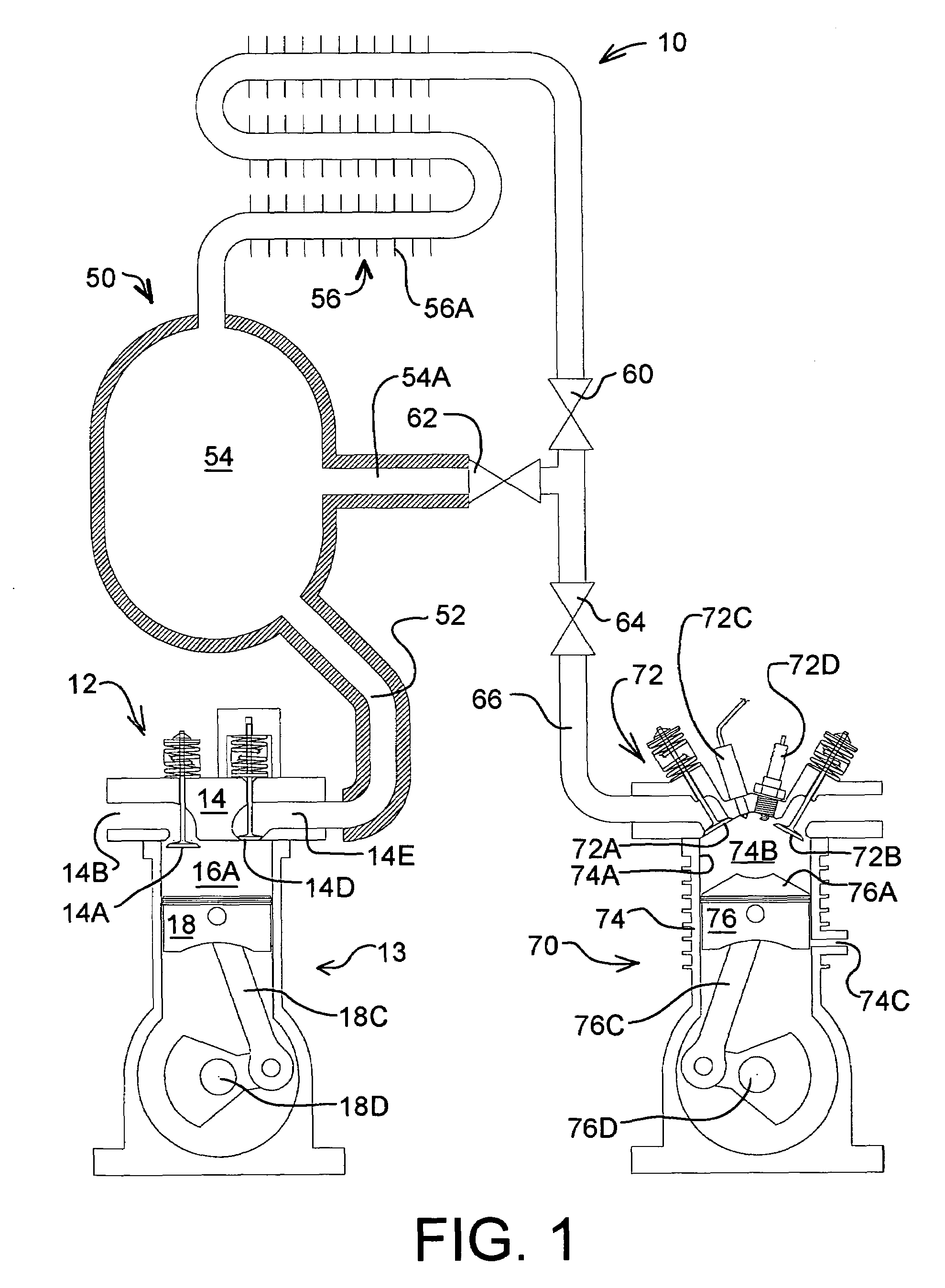
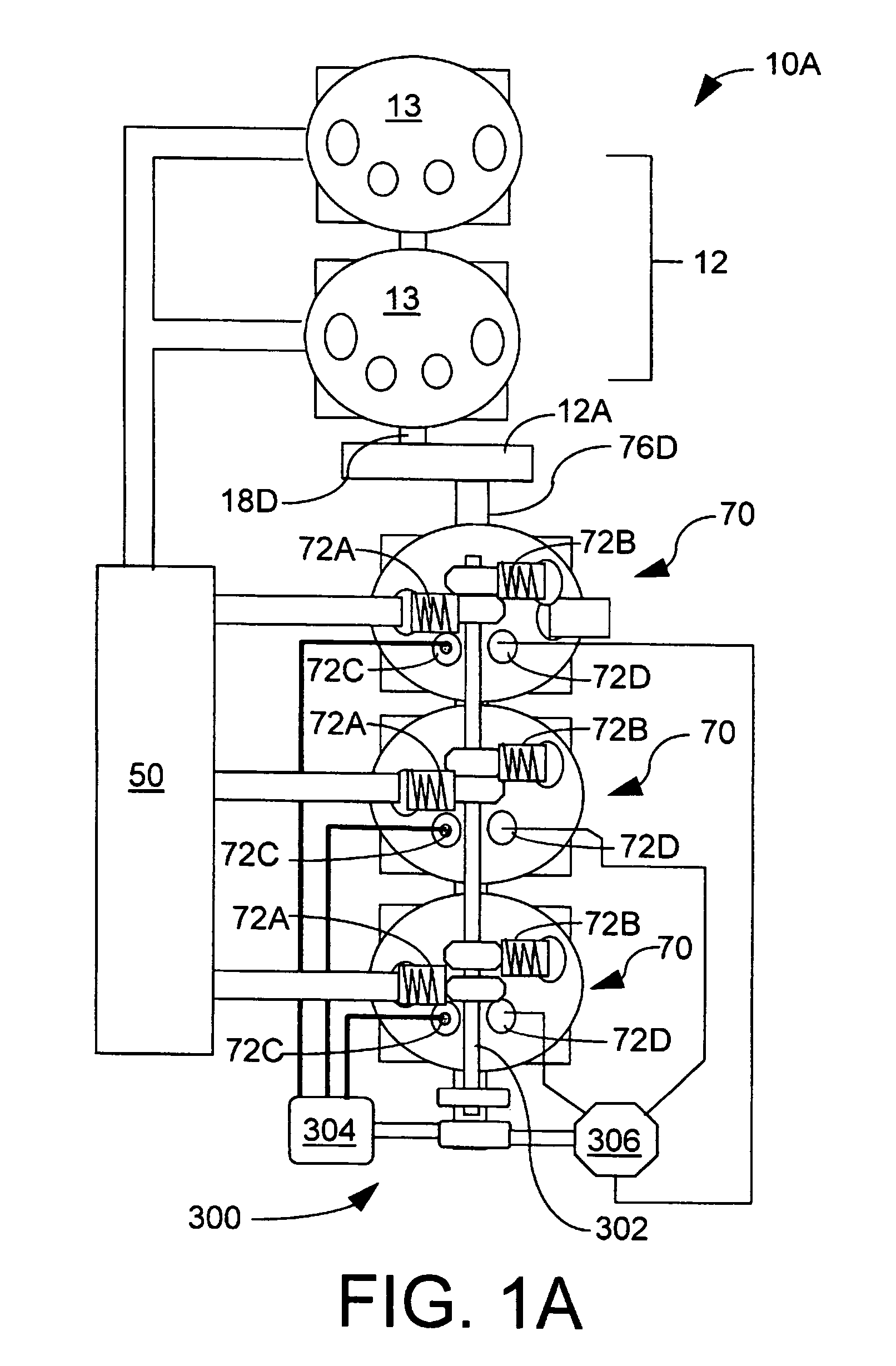
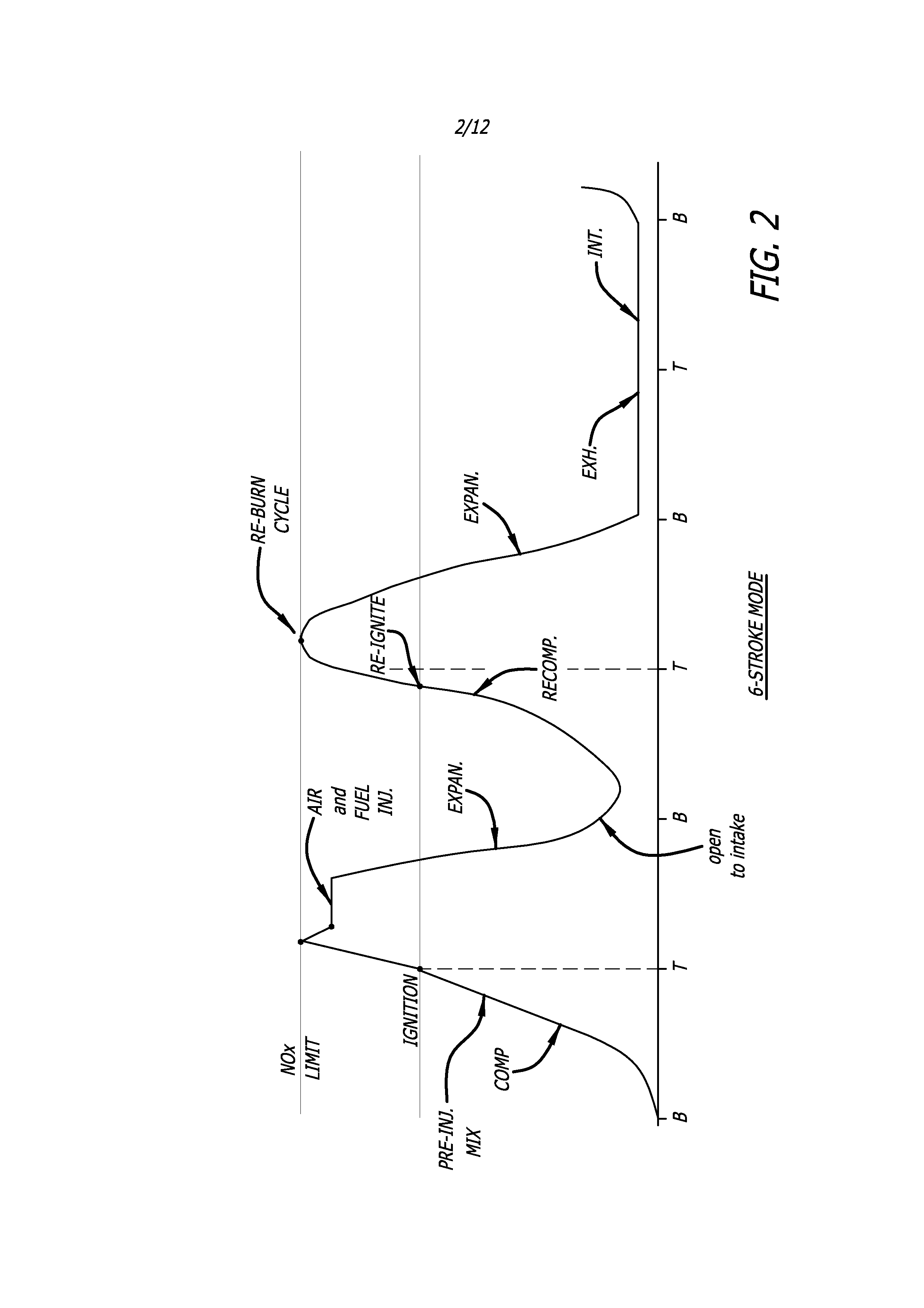
Low emission high performance engines, multiple cylinder engines and operating methods
InactiveUS20070245982A1Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberTop dead center
Low emission high performance engines, multiple cylinder engines and operating methods based on compression ignition of a combustion chamber charge already containing at least some fuel and air. Air is injected into the combustion chamber after top dead center is reached to maintain combustion until all fuel is consumed. Various modes of operation are disclosed.
Owner:STURMAN DIGITAL SYST
Conditions for fluid separations in microchannels, capillary-driven fluid separations, and laminated devices capable of separating fluids
InactiveUS6875247B2Rapid mass transportImprove heat transfer performanceCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentImproved methodChemistry
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method and operation of an engine
An engine is disclosed which may operate in a first operating state wherein a spark ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter and a second operating state wherein a compression ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter. A compression ratio in the combustion chamber being up to about eight to one. The engine may be a four-stroke engine. The engine may include a piston having a top portion with a recessed central portion.
Owner:POLARIS IND INC
Unit for adjusting humidification
InactiveUS6557551B2Readily disposed into patient circuitAvoid passingRespiratorsOther heat production devicesFiberBreathing gas
A humidification unit adapted to be disposed in a patient circuit for humidifying the flow of breathing gas delivered to the patient via the patient circuit by an artificial ventilator system. The humidification unit includes an exothermic member having an outer surface and a plurality of hollow fibers disposed on the outer surface of the exothermic member. Each hollow fiber is defined by a peripheral wall having minute openings large enough to allow a gas to pass therethrough yet small enough to prevent a liquid from passing therethrough. Liquid delivered to the hollow fibers is heated by the exothermic member and the gas vapor resulting from the heating passes through the hollow fiber walls and humidifies the flow of breathing gas delivered to the patient.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Internal combustion engine and method of operating internal combustion engine
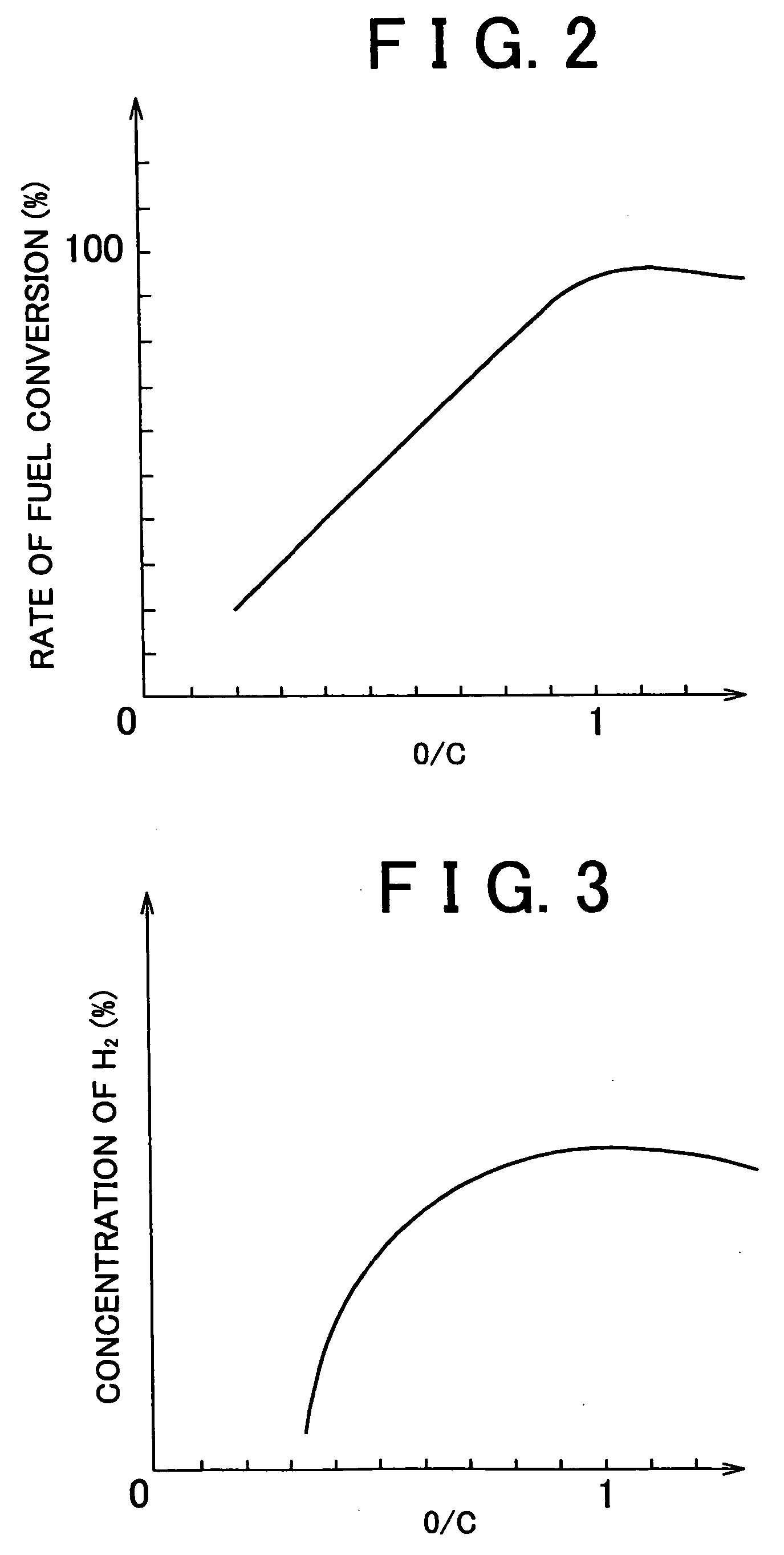
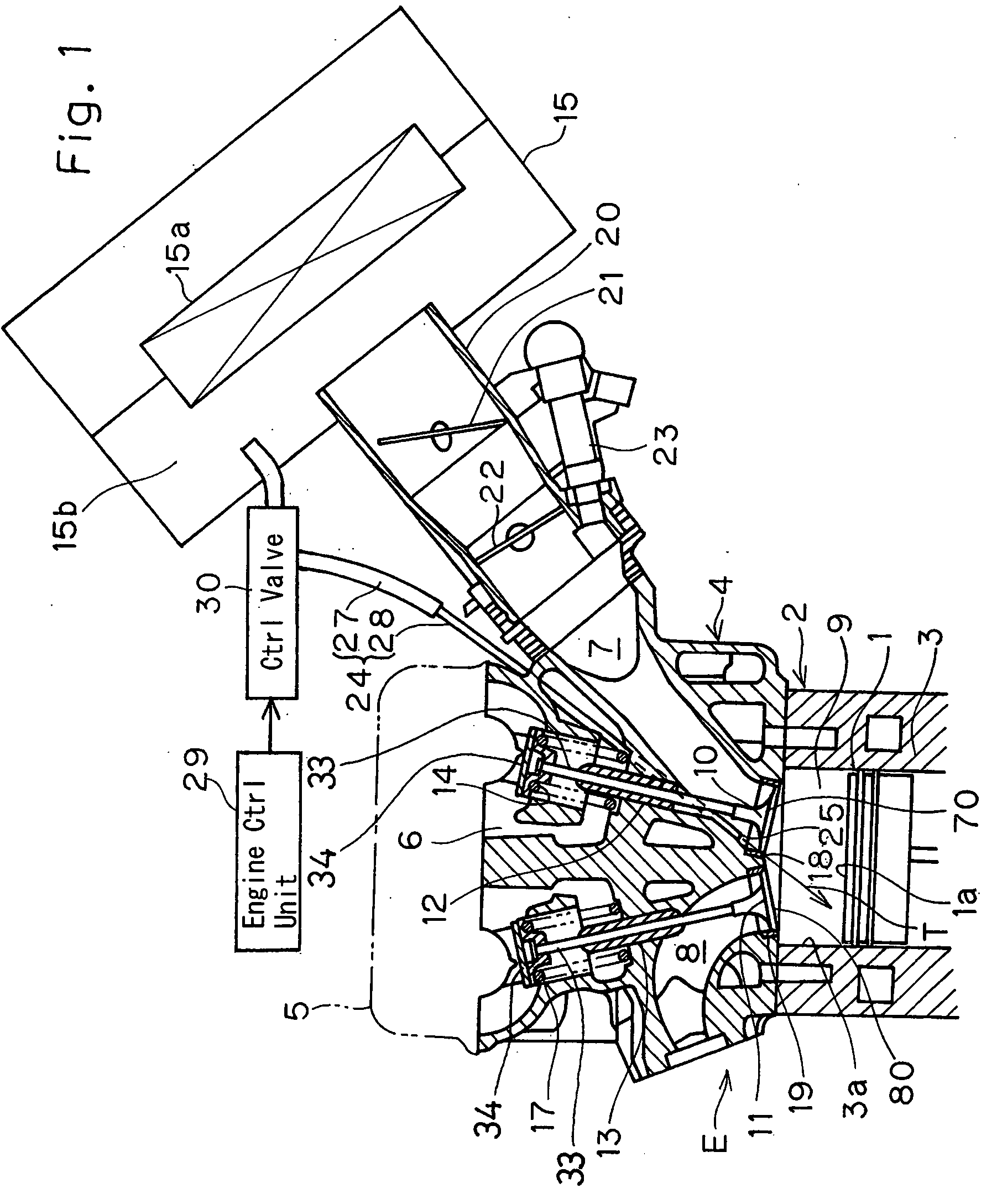
InactiveUS6997142B2Accurate graspPrecise proportionHydrogenElectrical controlCombustion chamberAir–fuel ratio
An internal combustion engine in accordance with one aspect of the invention is characterized by comprising a combustion chamber, a reformer, and a control portion. A predetermined fuel component is burnt in the combustion chamber. The reformer has a reforming catalyst, and that produces a reformed gas which contains the fuel component obtained by reforming a mixture of fuel and air and which supplied to the combustion chamber. The control portion sets an air-fuel ratio of the mixture in the reformer such that a reforming efficiency of the reformer is held within a predetermined range, and sets an amount of the mixture supplied to the reformer such that an actual output torque of the internal combustion engine coincides with a target torque.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
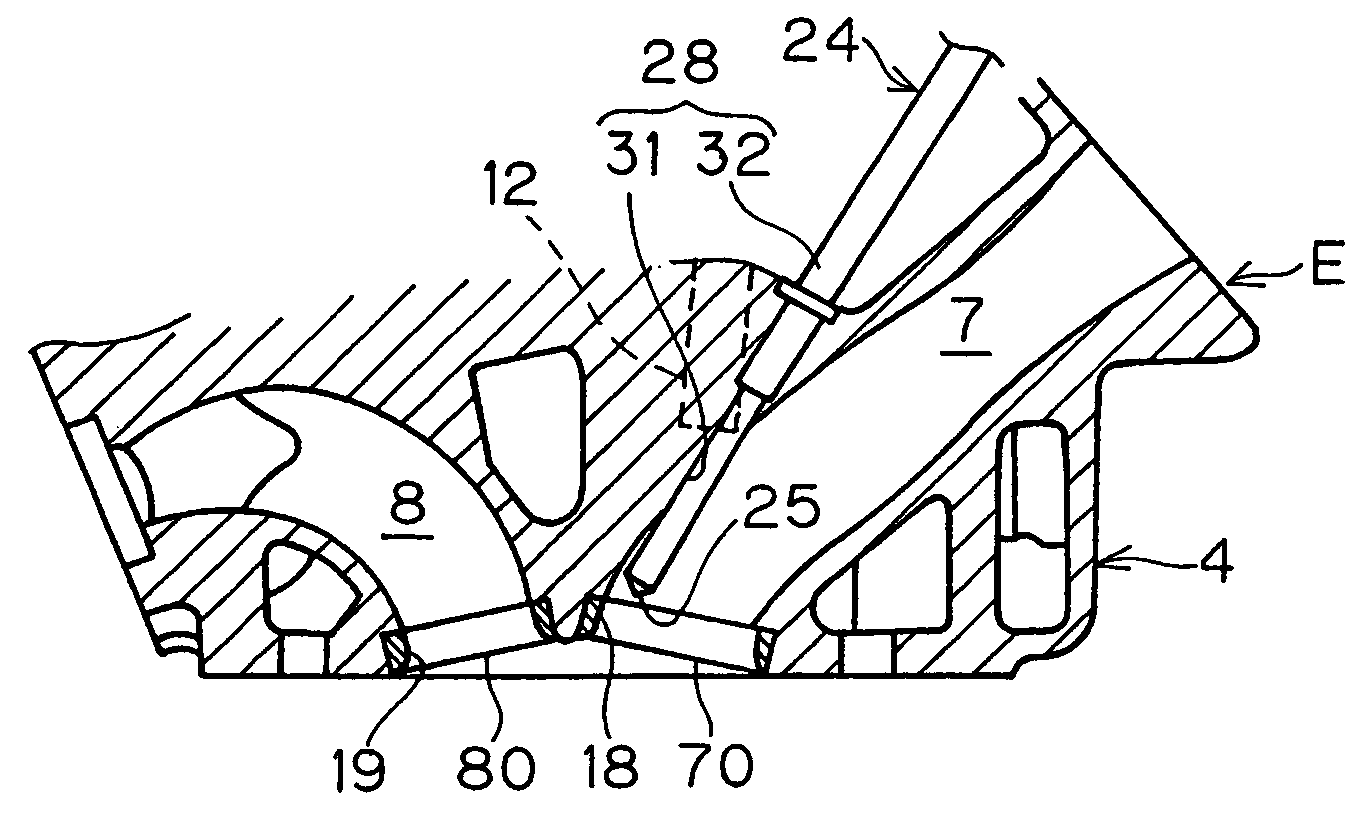
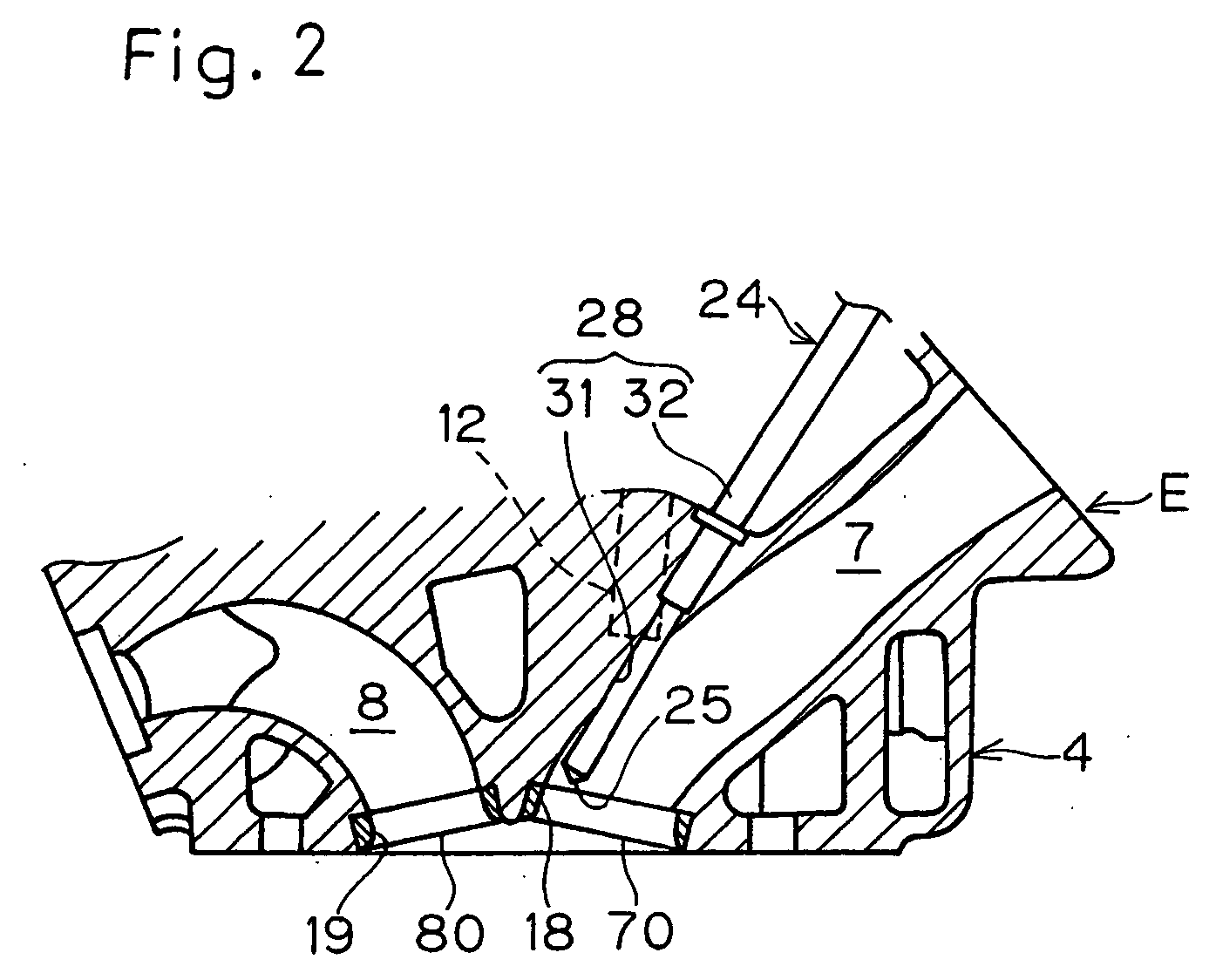
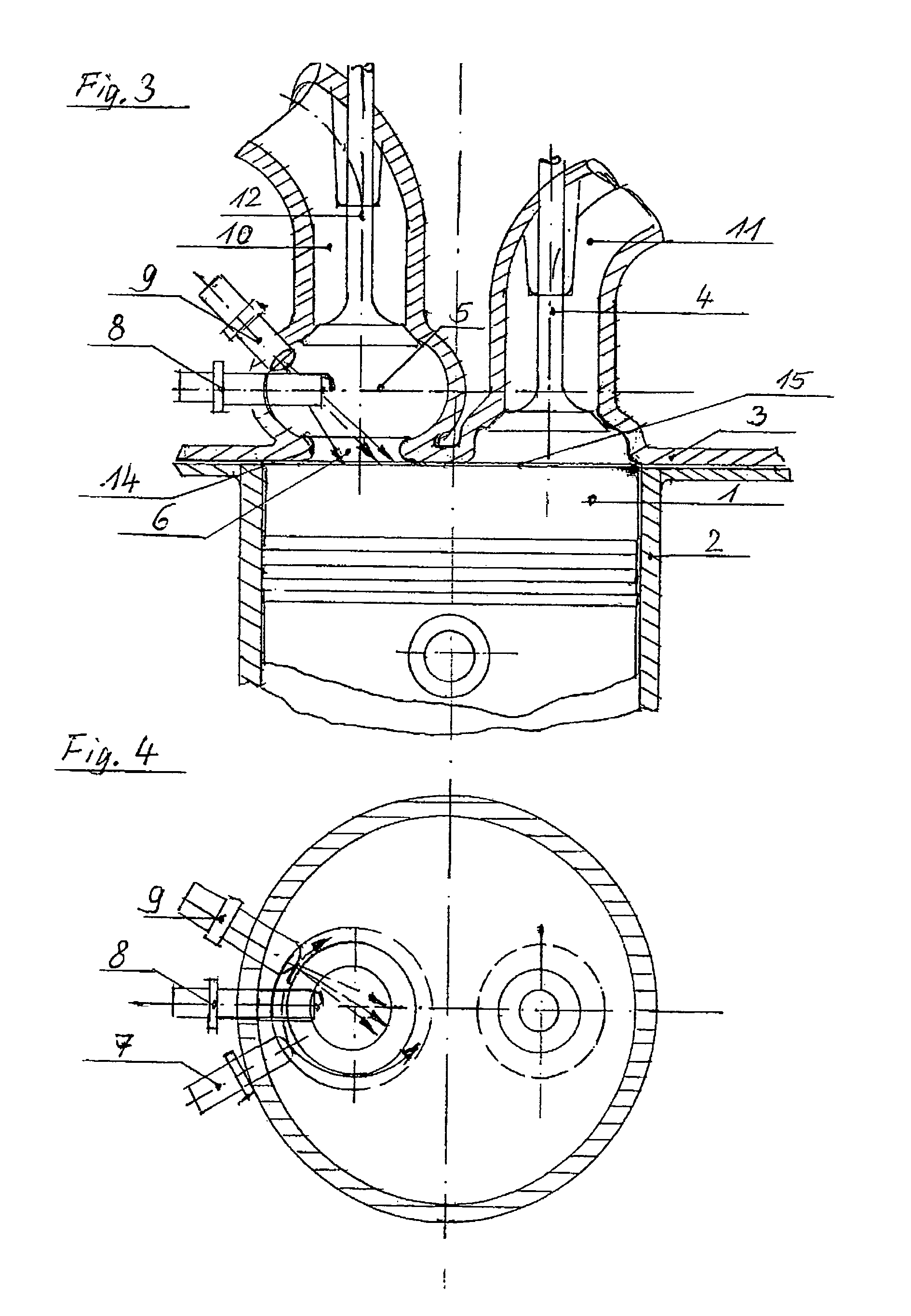
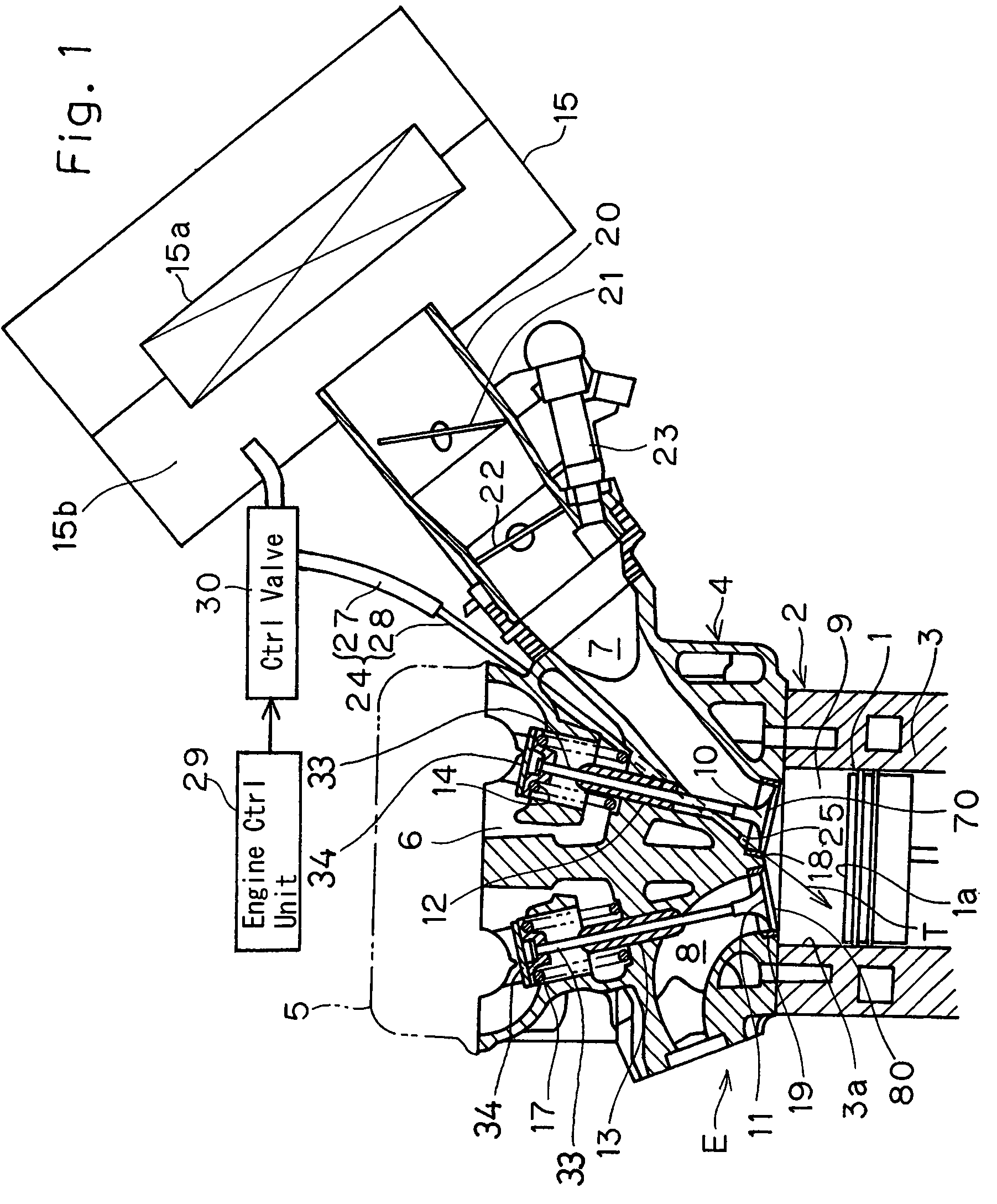
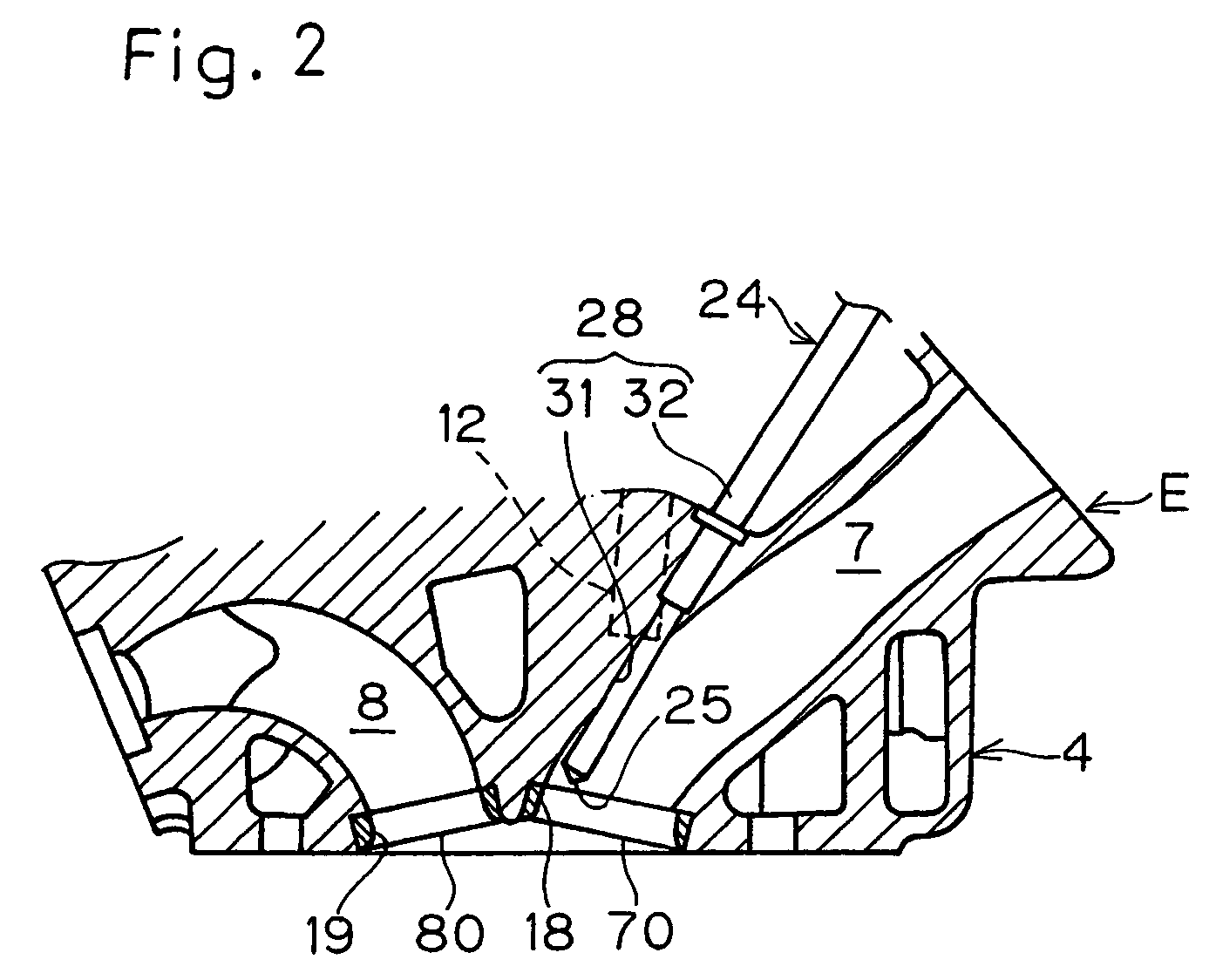
Swirl forming device in combustion engine
InactiveUS20050193976A1Promote effectiveInternal combustion piston enginesAir intakes for fuelCombustion chamberEngineering
To provide an improved swirl forming device in a combustion engine, which is effective to promote a vigorous and massive swirling motion of the charge mixture within the combustion chamber, the swirl forming device includes an auxiliary passage (24) for introducing an auxiliary gas, which may be either air or a charge mixture, into the combustion chamber (9) from a location immediately upstream of the intake port (70) that is selectively opened and closed by the intake valve (10). This auxiliary passage (24) has an open end (25) positioned adjacent the exhaust port (80), such that when viewed from top in a direction conforming to the longitudinal axis (CC) of the cylinder bore (3), the auxiliary gas is introduced in a direction different from the direction (N) normal to the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3) to thereby form a swirl (S) along the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3).
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Method and apparatus for simultaneous heat and mass transfer utilizing a carrier-gas
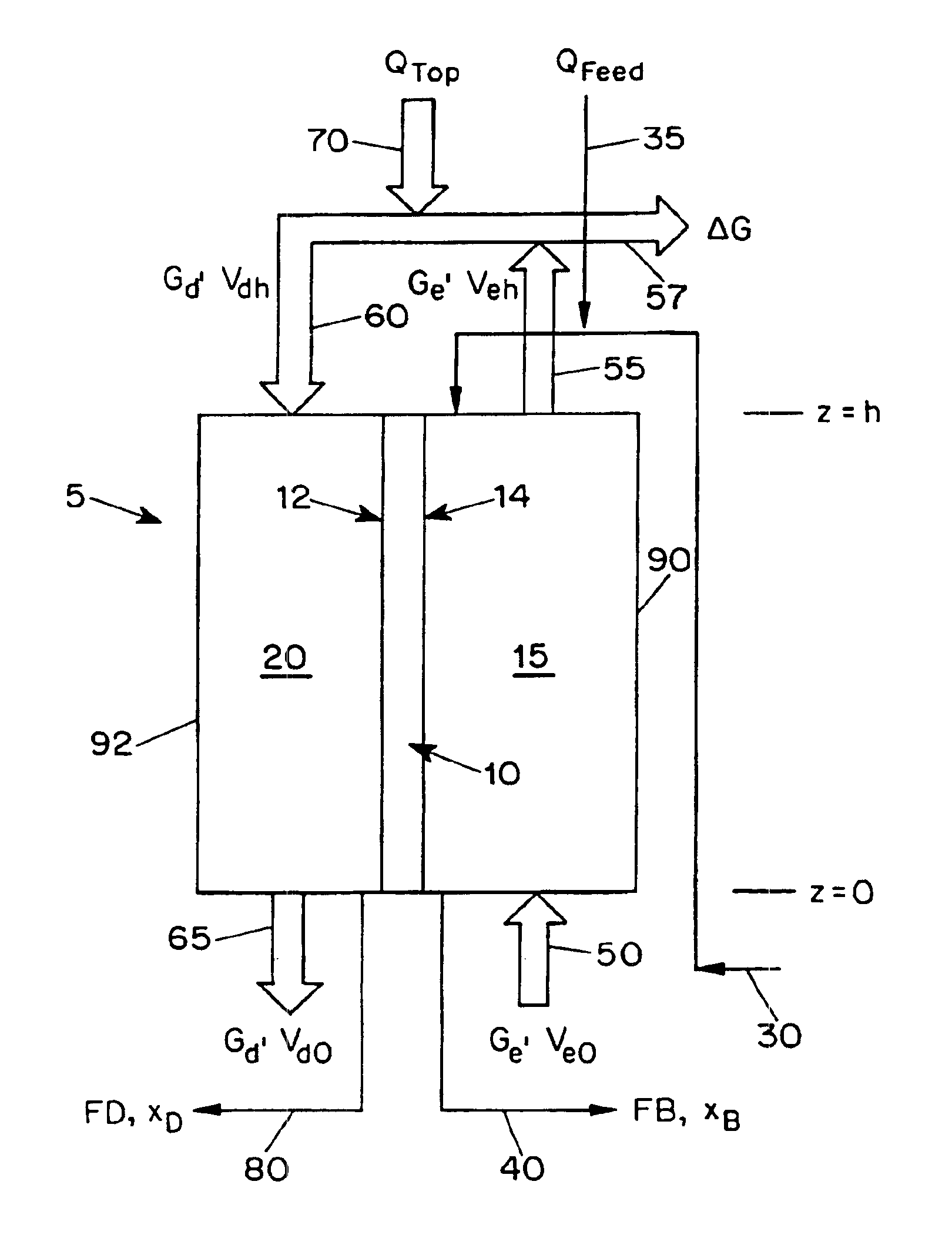
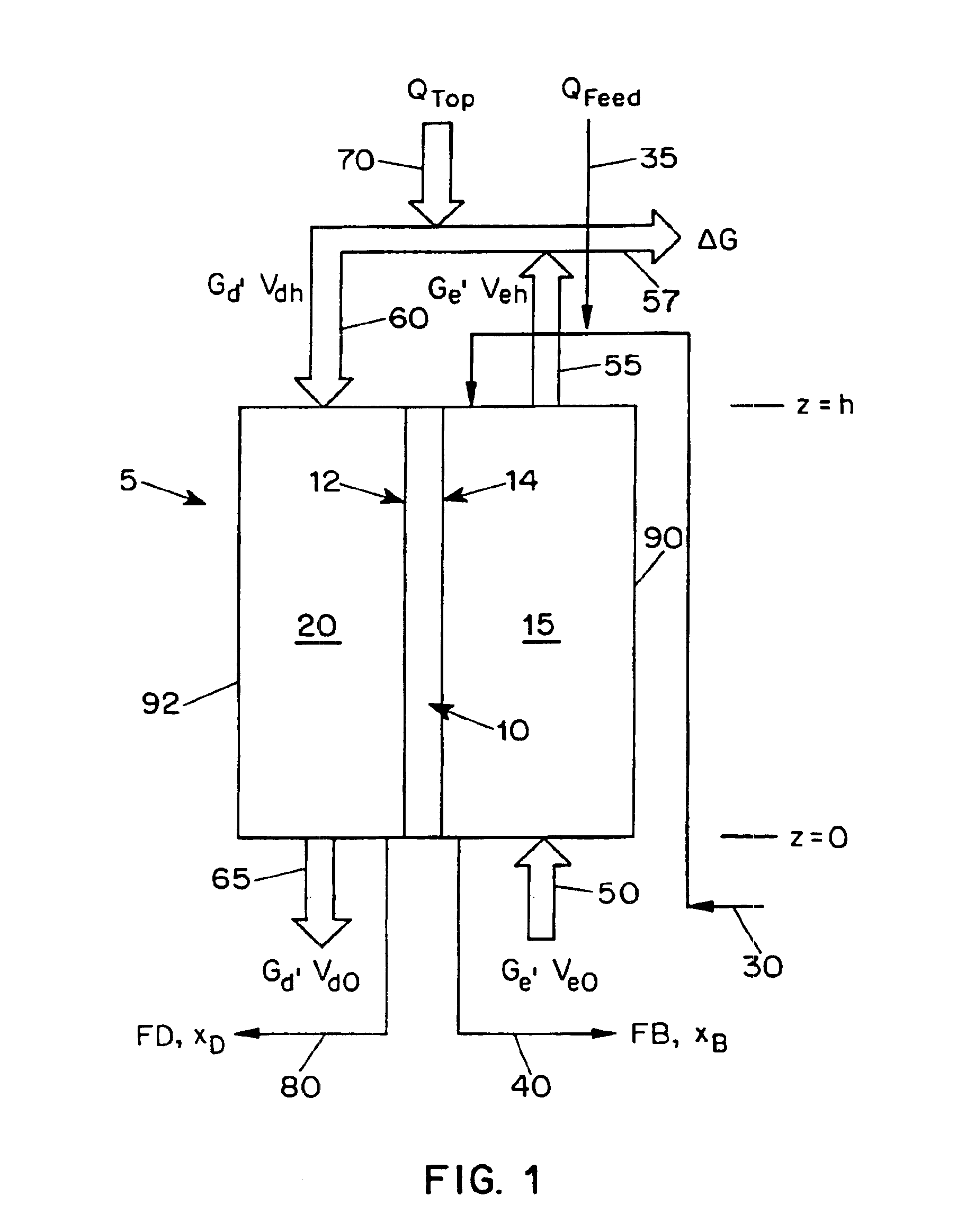
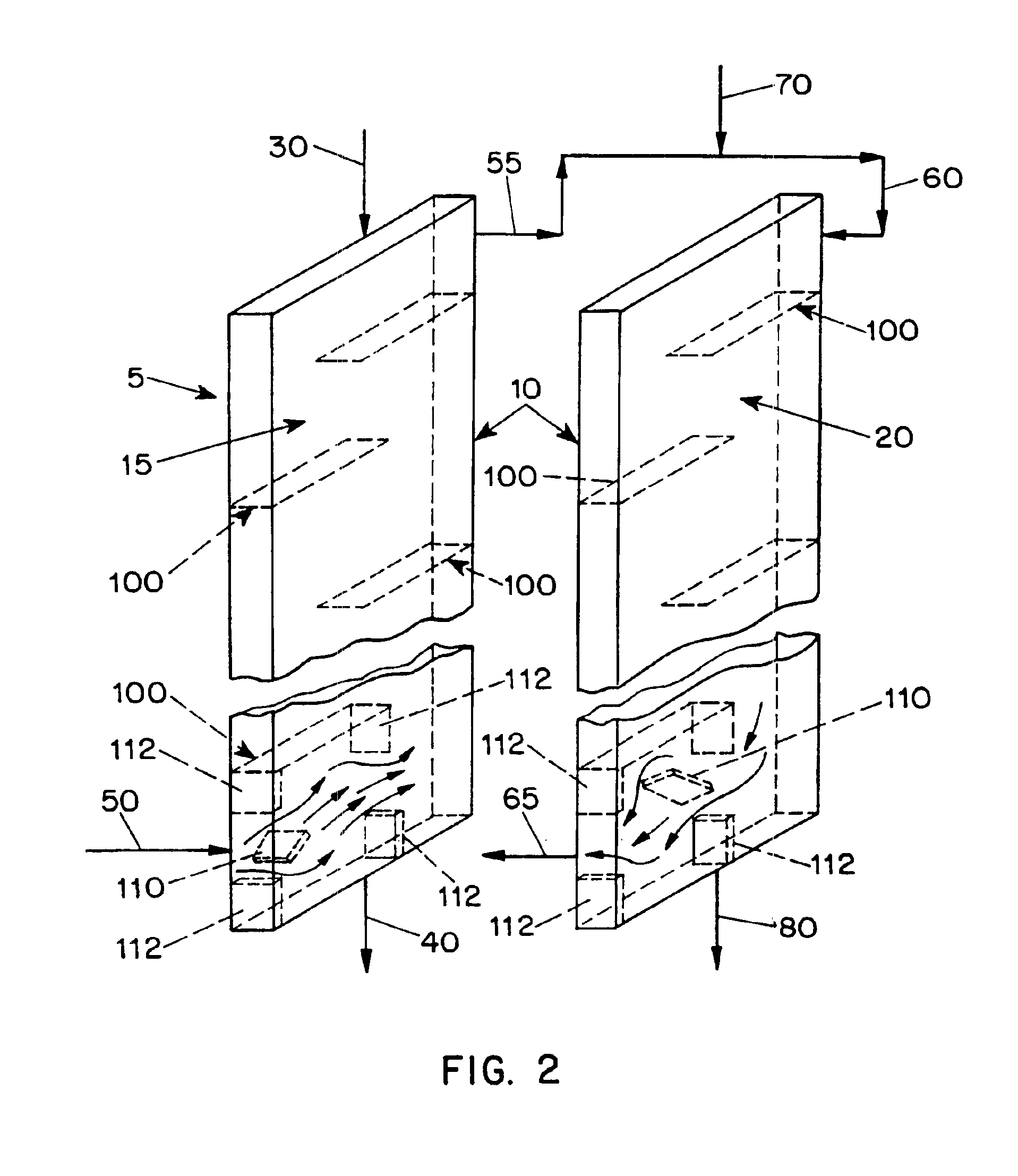
InactiveUS6911121B1Improve concentrationDistillation regulation/controlEnergy based wastewater treatmentDewEvaporation chamber
The present application is directed to a continuous contacting apparatus for separating a liquid component from a liquid mixture. The apparatus comprises: (i) an evaporation chamber (15) having first and second ends, an inlet (50) and an outlet (55) for a carrier gas, and an inlet (30) and an outlet (40) for a liquid mixture, wherein the inlet (30) for the liquid mixture and the outlet (55) of the carrier gas are located on the first end of the evaporation chamber (15); (ii) a dew-formation chamber (20) having an inlet (60) and an outlet (65) for a carrier gas and an outlet for the separable liquid component (80), wherein the inlet for the carrier gas (60) of the dew-formation chamber (20) is situated in a countercurrent manner to the inlet for the carrier gas of the evaporation chamber; (iii) a common heat transfer wall (10) providing thermal communication between the evaporation chamber (15) and the dew-formation chamber (20); (iv) a feeding device for providing the liquid mixture onto the evaporation side of the heat transfer wall; (v) an air mover for controlling a flow of a carrier gas through the chambers, wherein the gas flow in the evaporation chamber is countercurrent to the gas flow in the dew-formation chamber; and (vi) a heating apparatus for heating the carrier gas from the outlet of the evaporation chamber, wherein the heated carrier gas is directed to flow into the inlet of the dew-formation chamber. Also described is a process for separating a liquid component from a liquid mixture in a continuous contacting manner comprising employing such an apparatus for such separation.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Method and operation of an engine
ActiveUS20080041335A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFour-stroke engineCompression ratio
An engine is disclosed which may operate in a first operating state wherein a spark ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter and a second operating state wherein a compression ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter. A compression ratio in the combustion chamber being up to about eight to one. The engine may be a four-stroke engine. The engine may include a piston having a top portion with a recessed central portion.
Owner:POLARIS IND INC
High compression spark-ignition engine with throttle control, externally supplied ignition, and direct fuel injection into a precombustion chamber
InactiveUS7370626B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesThrottle controlCombustion chamber
The invention relates to a spark-ignition engine with a highly structural compression ratio greater than 15:1, throttle regulation, externally supplied ignition and with direct fuel injection into a precombustion chamber, which is connected to the main combustion chamber via an overflow channel. The fuel is injected into the precombustion chamber during the compression stroke and is ignited by a spark plug located in a manner that is as central as possible. The invention relates to a spark-ignition engine with a highly structural compression ratio greater than 15:1, throttle regulation, externally supplied ignition and with direct fuel injection into a precombustion chamber, which is connected to the main combustion chamber via an overflow channel. The fuel is injected into the precombustion chamber during the compression stroke and is ignited by a spark plug located in a manner that is as central as possible.
Owner:SCHUBERT GOTTFRIED
Air injection engine
InactiveUS7007639B1Improve power densityHigh expansion rateInternal combustion piston enginesOutput powerCombustionExternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine of the present invention features separate compression and expansion cycles. The engine includes a separate compressor device which pressurizes air by a ratio greater than 15 to 1, at least one two stroke combustion cylinder and a compressed air conduit for transferring compressed air from the compressor to the at least one combustion cylinder. An air injection valve injects the compressed air into the combustion cylinder during the second half portion of the return stroke of the combustion cylinder. The compressed air is mixed with fuel and combusted for expansion during a power stroke. In this engine compression occurs only to a minor degree in the combustion cylinder. Accordingly, the compression ratio of the present engine may be significantly higher or lower than the volumetric expansion ratio of the combustion cylinder thus resulting in corresponding increases in either power density or thermodynamic efficiency respectively.
Owner:D J ENG
Air conditioning system and methods
An air conditioning system for conditioning the space within an enclosure having at least one inlet and one outlet, the system comprising first and second liquid / air heat exchangers; the first heat exchanger having an opening for receiving fresh air from the environment and for propelling the fresh air through the first heat exchanger to exchange heat with the liquid before it is entered into the enclosure, and the second heat exchanger having an opening for receiving air from the enclosure and for propelling it through the second heat exchanger to exchange heat with the liquid before it is expelled into the atmosphere. There are also provided methods for air-conditioning an enclosed space and for evaporation of industrial wastes.
Owner:AGAM ENERGY SYST
Swirl forming device in combustion engine
InactiveUS7140347B2Promote effectiveInternal combustion piston enginesAir intakes for fuelCombustion chamberInlet valve
To provide an improved swirl forming device in a combustion engine, which is effective to promote a vigorous and massive swirling motion of the charge mixture within the combustion chamber, the swirl forming device includes an auxiliary passage (24) for introducing an auxiliary gas, which may be either air or a charge mixture, into the combustion chamber (9) from a location immediately upstream of the intake port (70) that is selectively opened and closed by the intake valve (10). This auxiliary passage (24) has an open end (25) positioned adjacent the exhaust port (80), such that when viewed from top in a direction conforming to the longitudinal axis (CC) of the cylinder bore (3), the auxiliary gas is introduced in a direction different from the direction (N) normal to the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3) to thereby form a swirl (S) along the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3).
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
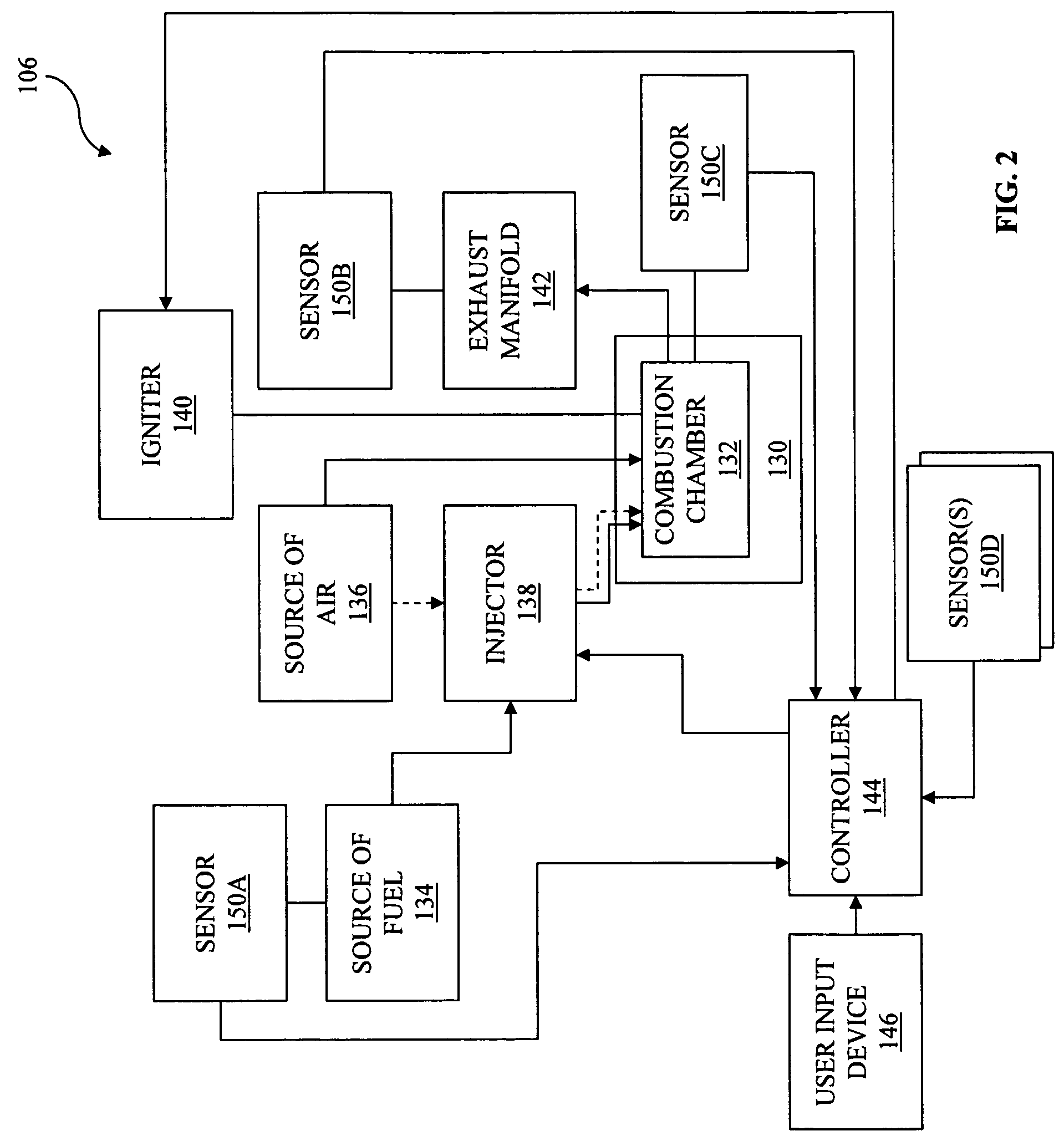
High performance, low emission engines, multiple cylinder engines and operating methods
ActiveUS7954472B1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
High performance, low emission engines, multiple cylinder engines and operating methods based on compression ignition of a combustion chamber charge. In accordance with the methods, fuel is injected into the combustion chamber after the exhaust valve closes, and air is injected into the combustion cylinder before the end of the compression stroke in an amount to limit the temperature after ignition to less than the temperature at which NOX forms. After ignition and during the power stroke, more air is injected into the combustion chamber to sustain combustion until all fuel is consumed, the air being injected so as to again limit the combustion temperatures to less than the temperature at which NOX forms. The air injected during the compression stroke is injected at substantially the same combustion chamber pressure as the air injected during the power stroke, so that air may efficiently be injected from the same pressurized source. The fuel injected into the combustion chamber may be all the fuel needed, or additional fuel may be injected during the power stoke.
Owner:STURMAN DIGITAL SYST
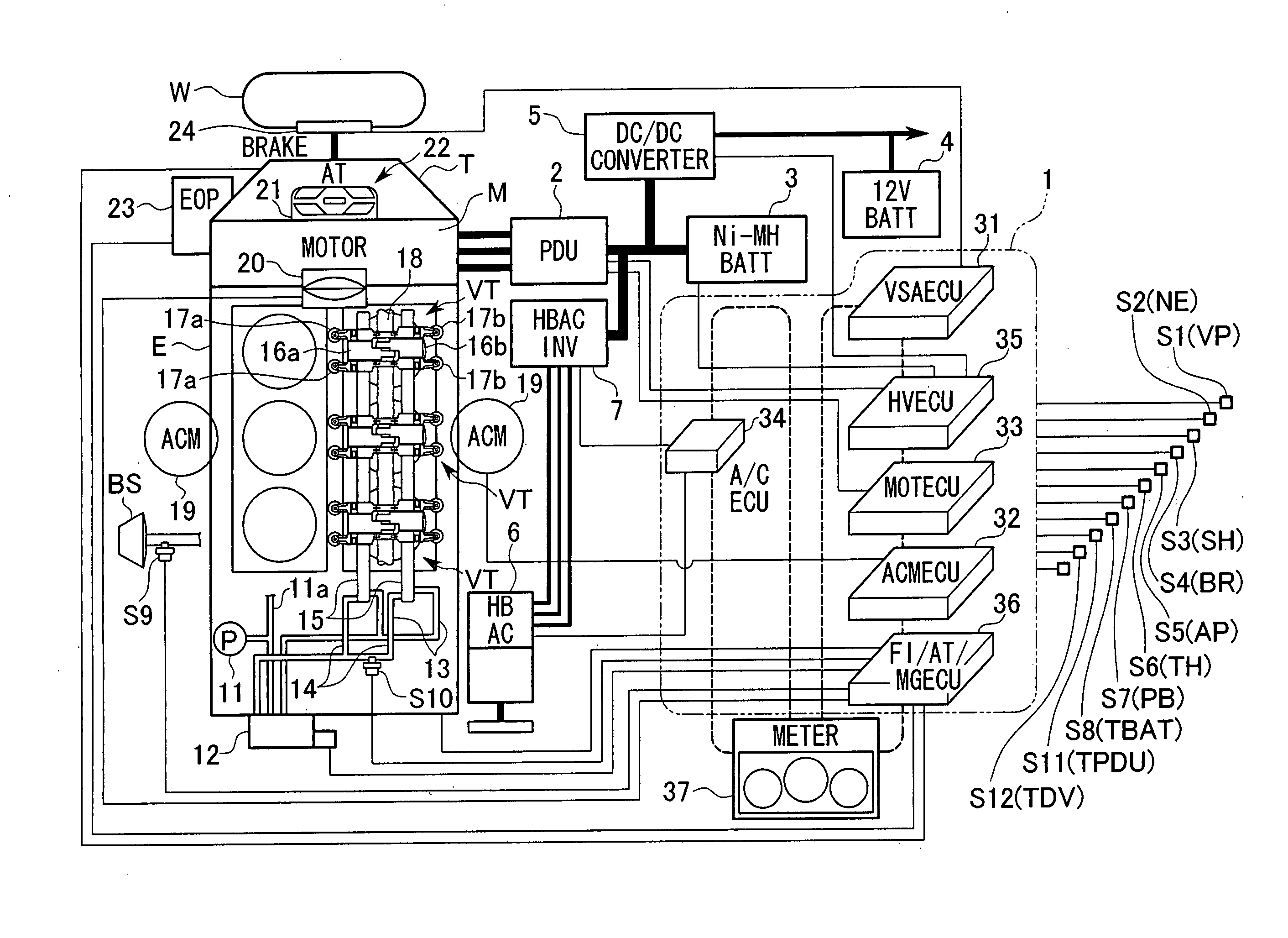
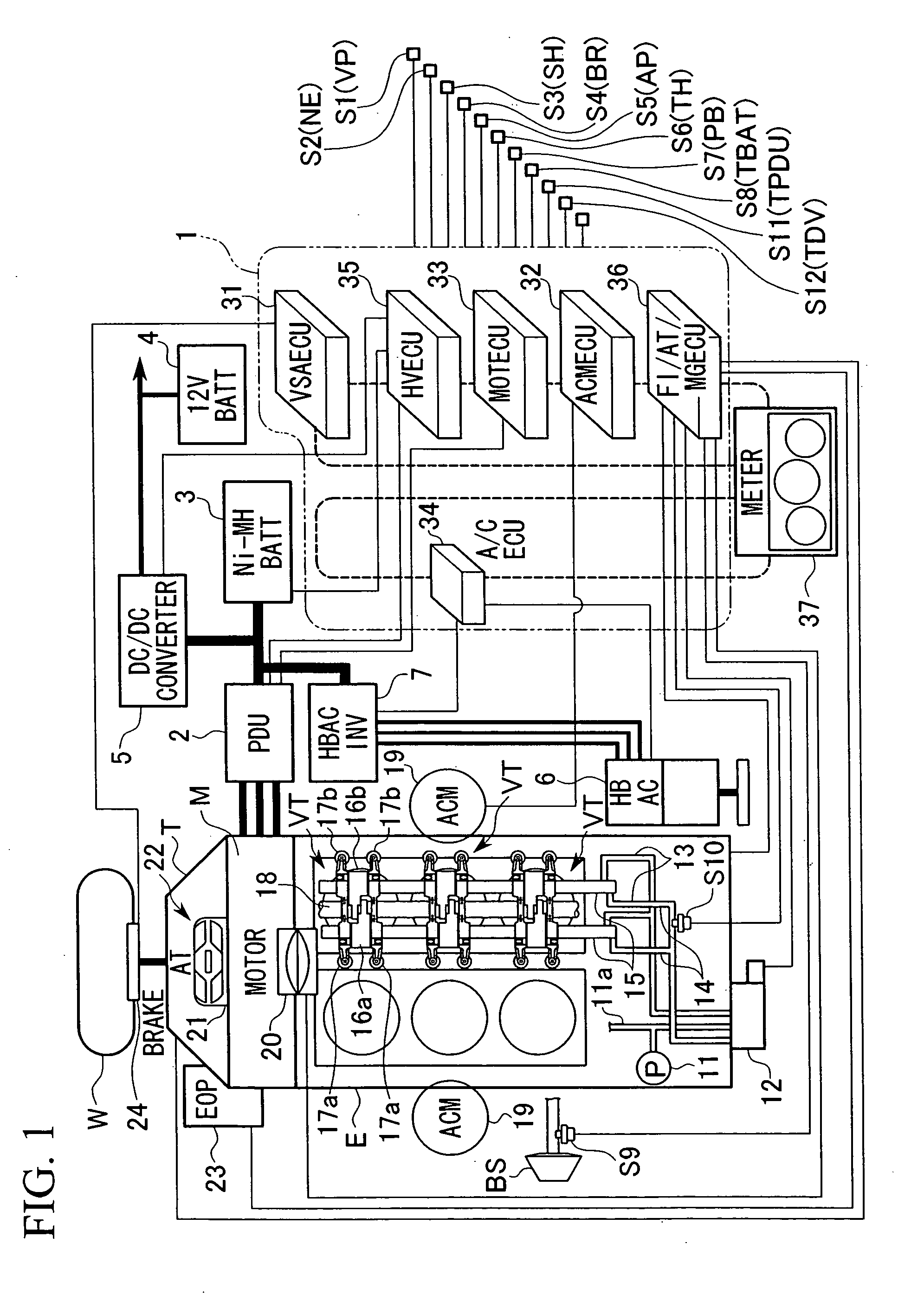
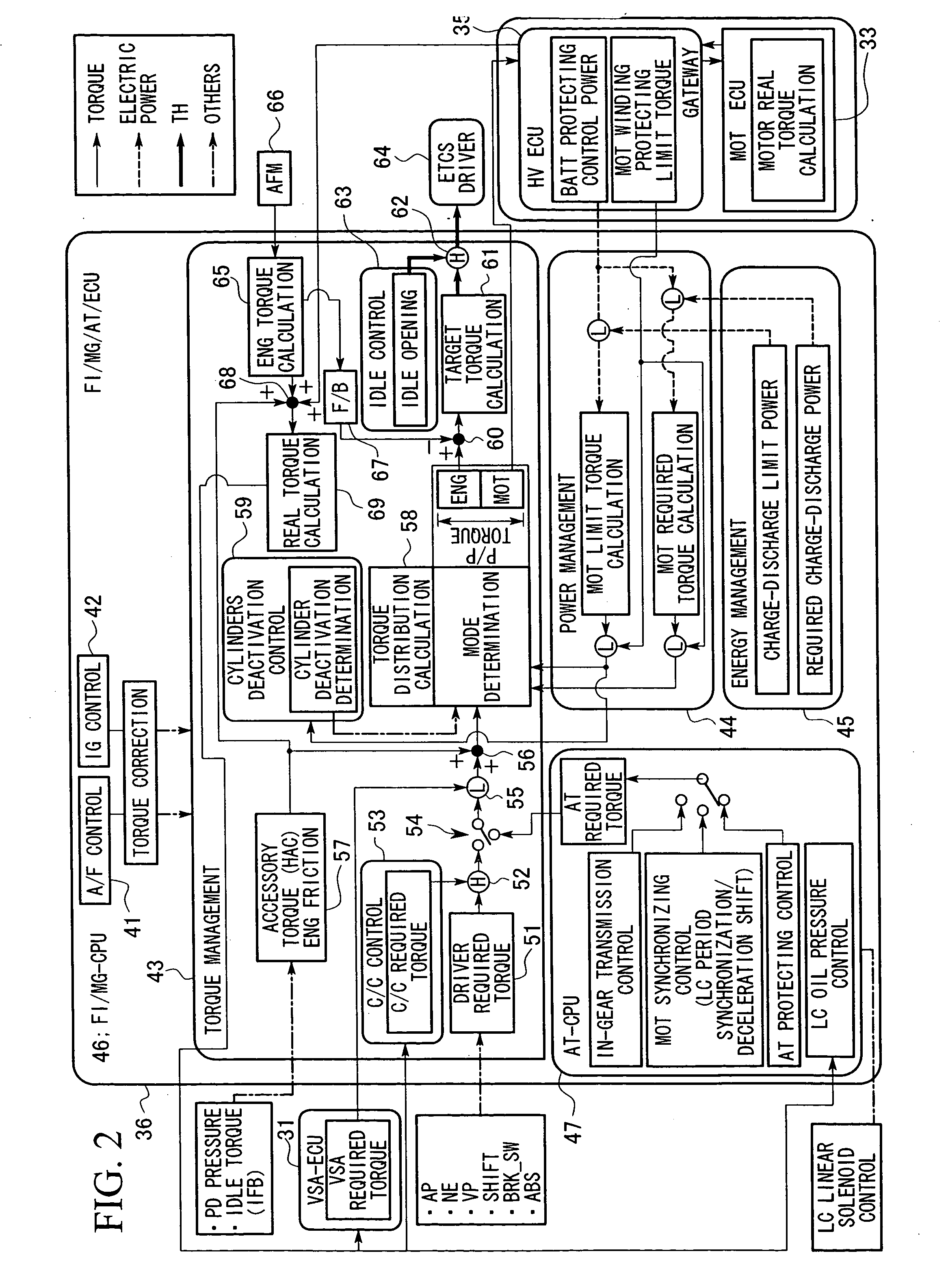
Control apparatus for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20050003926A1Suppress generationAccurate calculationElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingPower stationDrive wheel
A control apparatus for a hybrid vehicle which comprises an internal-combustion engine and a motor as a power source, and connects at least one of the internal-combustion engine and the motor to driving wheels of the vehicle through a transmission so as to transmit a driving force to the driving wheels, comprises: a target torque setting device which sets a target torque with respect to a crank end torque, which is a torque at the end of a crank shaft, of the power plant torque output from the power plant being the internal combustion engine and the motor, based on a change of accelerator pedal opening from fully opened to fully closed; and a torque allocation device which allocates the target torque corresponding to the accelerator pedal opening, to an engine torque instruction, being a required value with respect to the output torque from the internal combustion engine, and to a motor torque instruction, being a required value with respect to the output torque from the motor. The generation of torque fluctuations which are not expected by the occupants of the vehicle are suppressed, and a torque which unerringly reflects the driver's intention is output.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Oxygen content system and method for controlling memory resistance properties
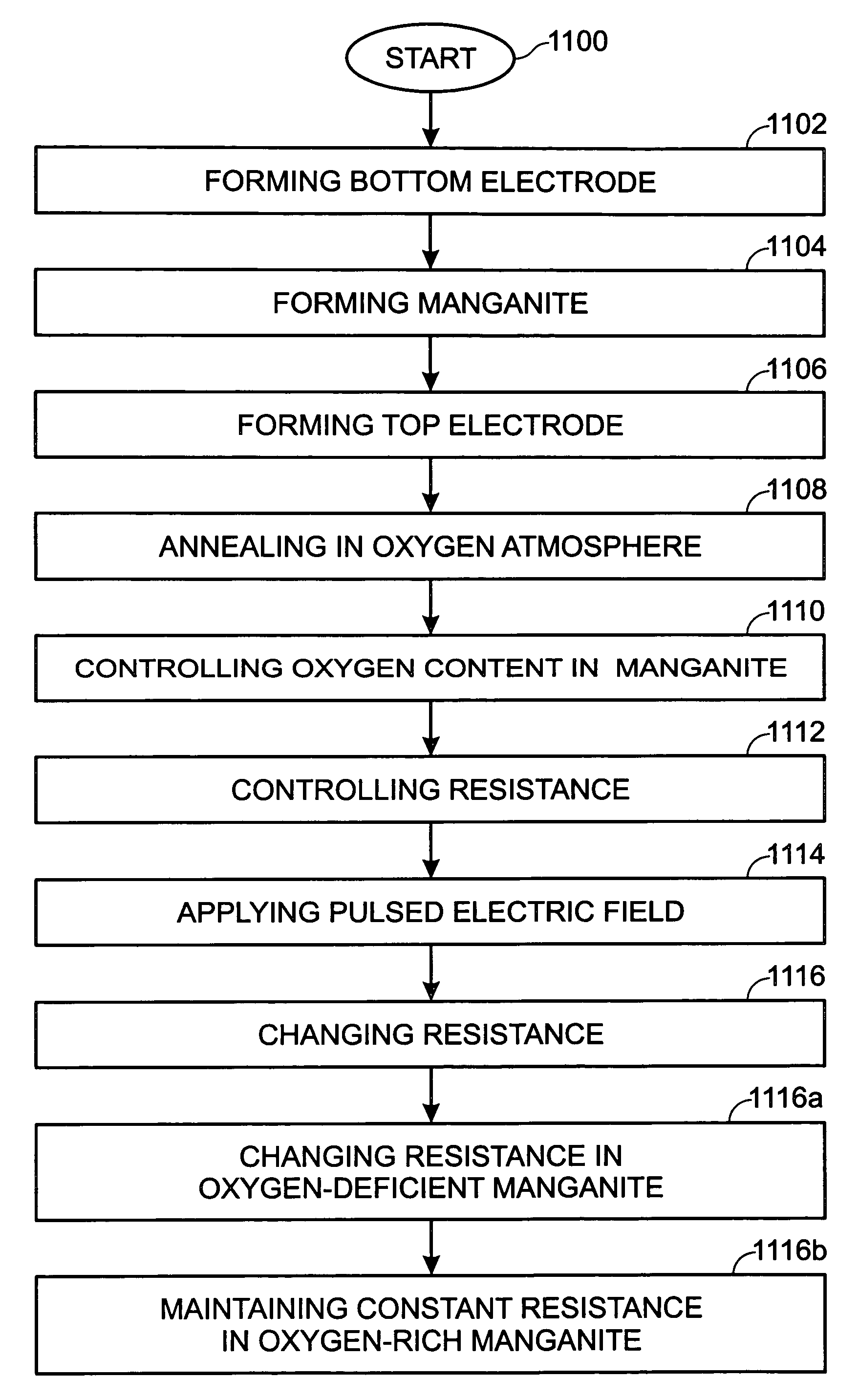
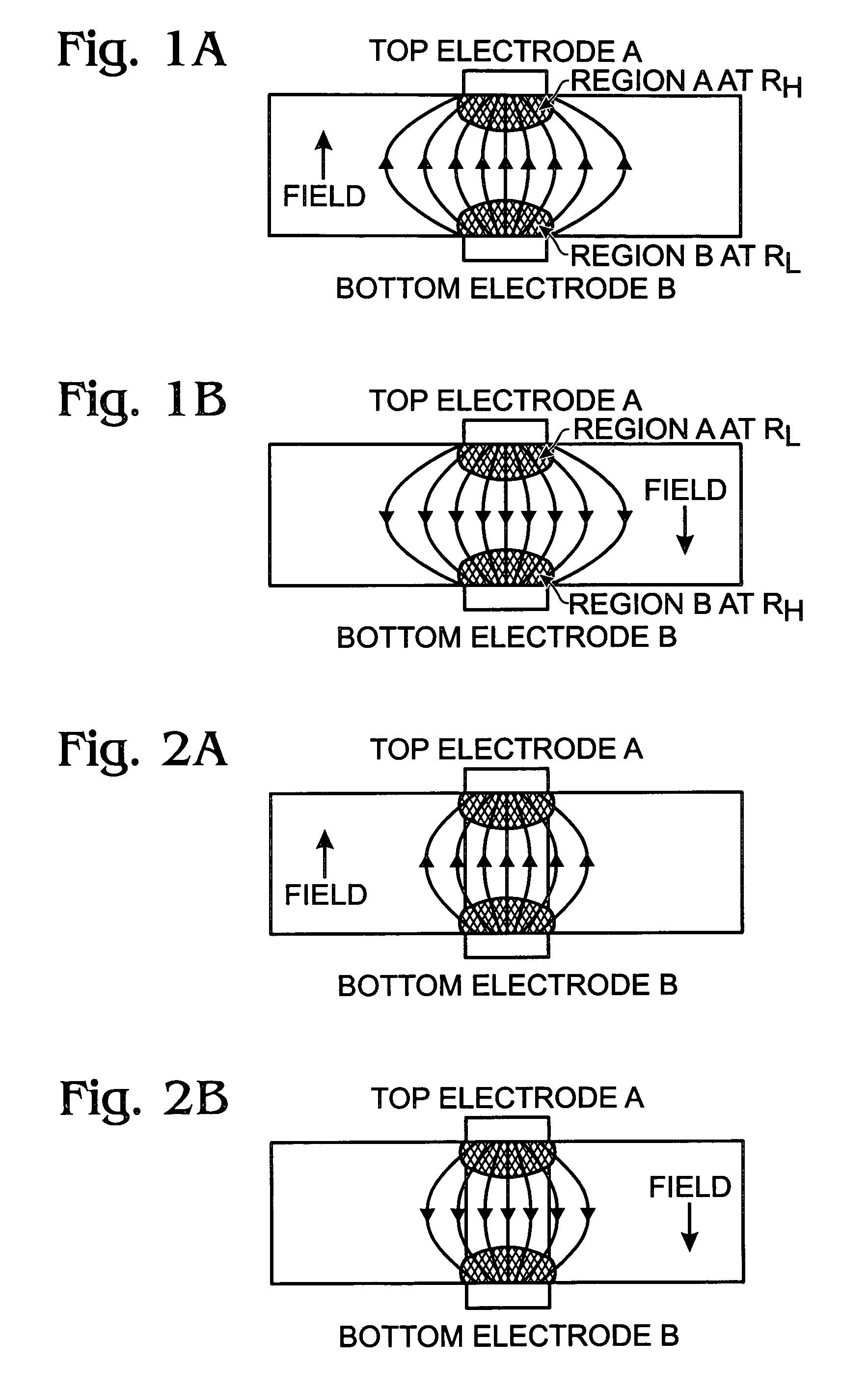
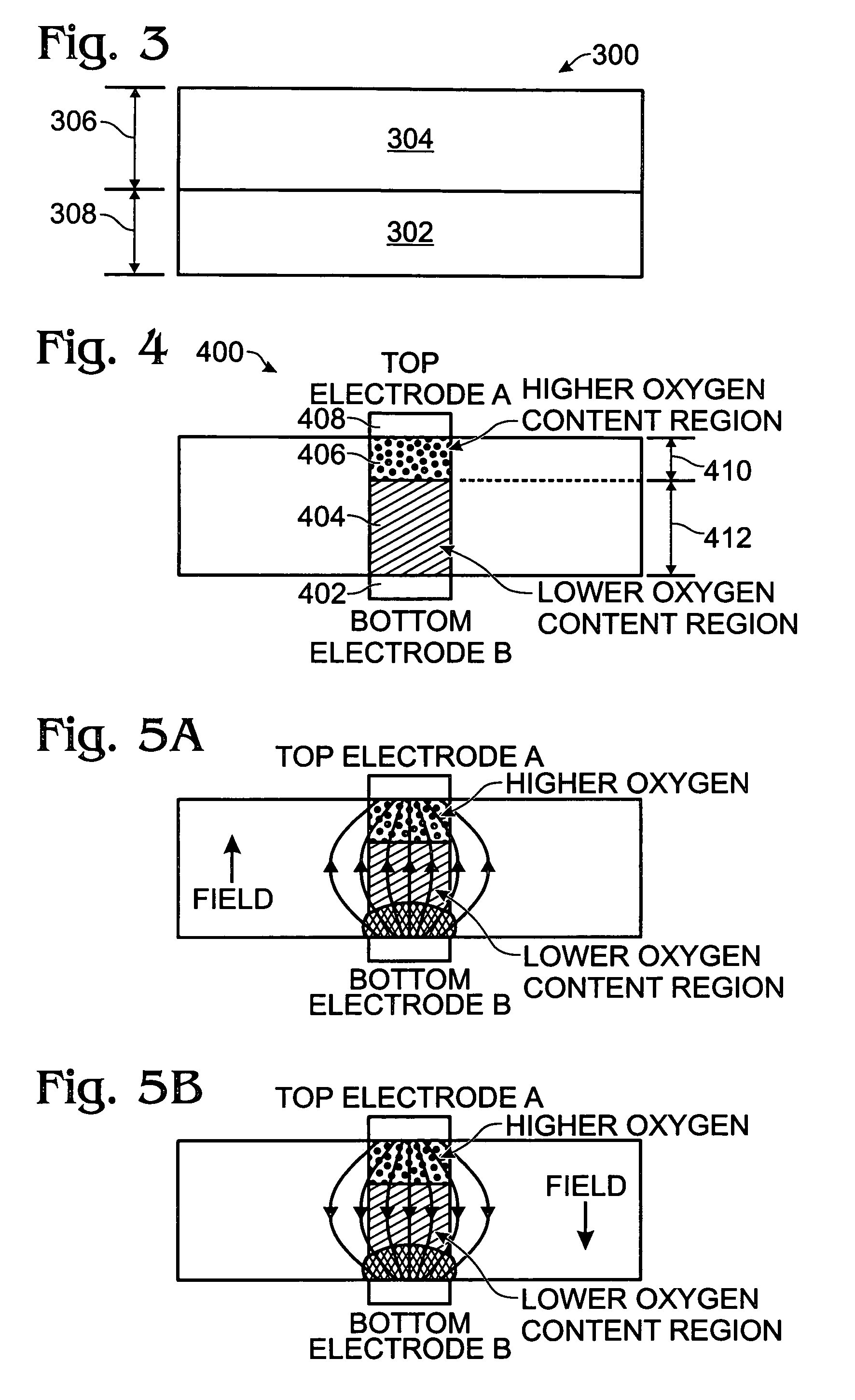
ActiveUS6972238B2Reliably programmedCombustion-air/fuel-air treatmentSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceManganese oxide
A memory cell and method for controlling the resistance properties in a memory material are provided. The method comprises: forming manganite; annealing the manganite in an oxygen atmosphere; controlling the oxygen content in the manganite in response to the annealing; and, controlling resistance through the manganite in response to the oxygen content. The manganite is perovskite-type manganese oxides with the general formula RE1-xAExMnOy, where RE is a rare earth ion and AE is an alkaline-earth ion, with x in the range between 0.1 and 0.5. Controlling the oxygen content in the manganite includes forming an oxygen-rich RE1-xAExMnOy region where y is greater than 3. A low resistance results in the oxygen-rich manganite region. When y is less than 3, a high resistance is formed. More specifically, the process forms a low resistance oxygen-rich manganite region adjacent an oxygen-deficient high resistance manganite region.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
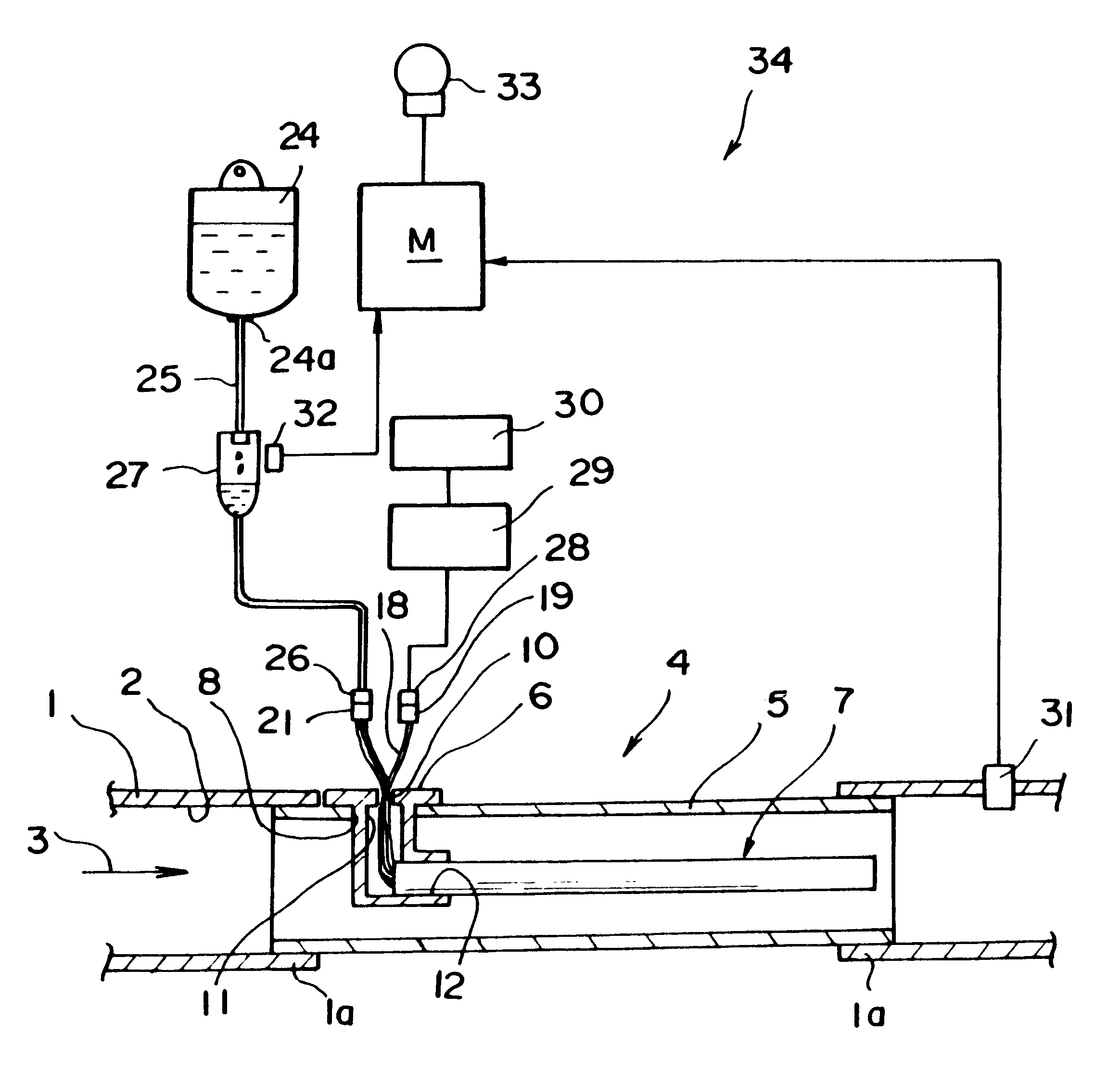
Humidifier for breathable gas apparatus
A humidifier for use with a breathable gas supply apparatus includes a hollow body adapted for partial filling with water to a predetermined maximum water level, a gas inlet to the body above the maximum water level and a gas outlet from the body above the maximum water level. The humidifier further includes a temperature heating element for heating the water and / or an adjustable flow divider adapted to divide the interior of the body above the maximum water level into a relatively dry gas region and a relatively wet gas region. The position of the divider is variable so as to vary the relative proportion of the gas flowing from the inlet to the outlet that passes through the relatively dry and relatively wet gas regions to thereby vary the amount of humidification thereof.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Air-to-air atmospheric heat exchanger for condensing cooling tower effluent
InactiveUS20050077637A1Reduce air contentThin materialCarburetting airUsing liquid separation agentCooling towerEngineering
A sheet for use in a heat exchange apparatus. The sheet includes a first vertical rib that extends in a first direction generally parallel to the vertical axis of the heat exchange apparatus, wherein said first vertical rib protrudes in a second direction out of the plane. The sheet also includes a second vertical rib that extends in the first direction along the sheet, substantially all the way between the first and second edges of the sheet generally parallel to the first vertical rib. The second vertical rib also protrudes in the second direction out of the plane. The sheet further includes a first horizontal rib that extends in a third direction along the sheet substantially all the way between the third and fourth edges of the sheet, wherein the first horizontal rib protrudes in a fourth direction opposite said second direction. The sheet additionally includes a second horizontal rib that extends in the third direction along the sheet substantially all the way between the third and fourth edges of the sheet generally parallel to the first horizontal rib. The second horizontal rib protrudes in a fourth direction opposite the second direction, into the plane and intersects said second vertical rib.
Owner:SPX COOLING TECH
Throttle body fuel injection system with improved idle air control
ActiveUS9303578B2Improve performanceOptimal fuel distribution and idle control circuitryElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFuel distributionClosed loop
A single point fuel injection throttle body assembly including an idle air control circuit having an port opening into main intake bores downstream of the point of fuel distribution into the air stream. When the idle air control circuit is open, an air / fuel mixture, rather than simply air, is drawn into the into the intake manifold, thereby reducing the tendency for a lean fuel mixture at idle. A unique engine control unit “feed forward” algorithm controls the fuel injection as a function of the position of the idle air control motor so that as the idle air control circuit is opened, the pulse widths of the fuel injector signals are increased. This feature allows the initial open-loop-based fuel mixture supplied by system to be more accurate and eliminates rough unstable idle associated with closed-loop control lag times.
Owner:MSD LLC
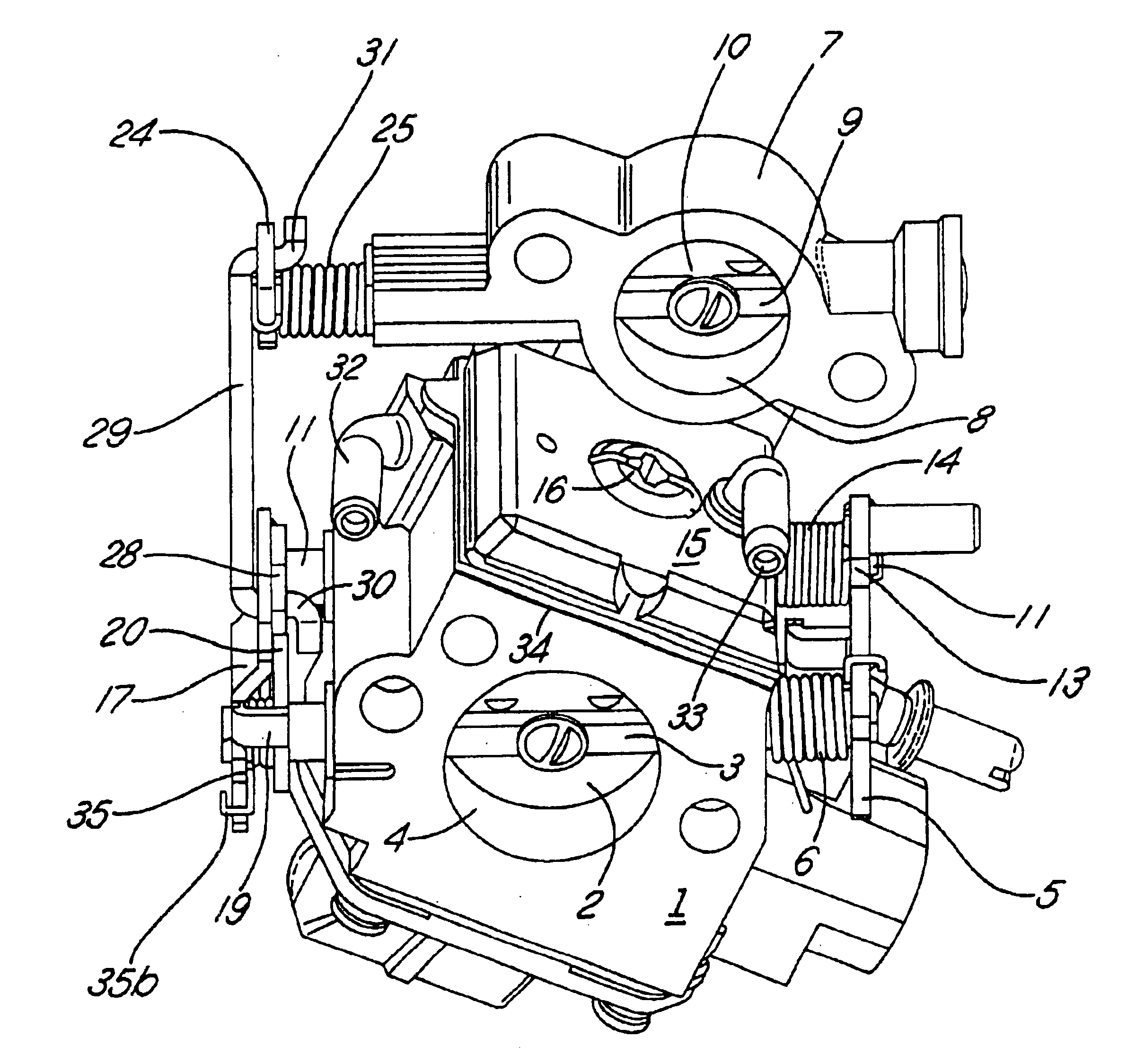
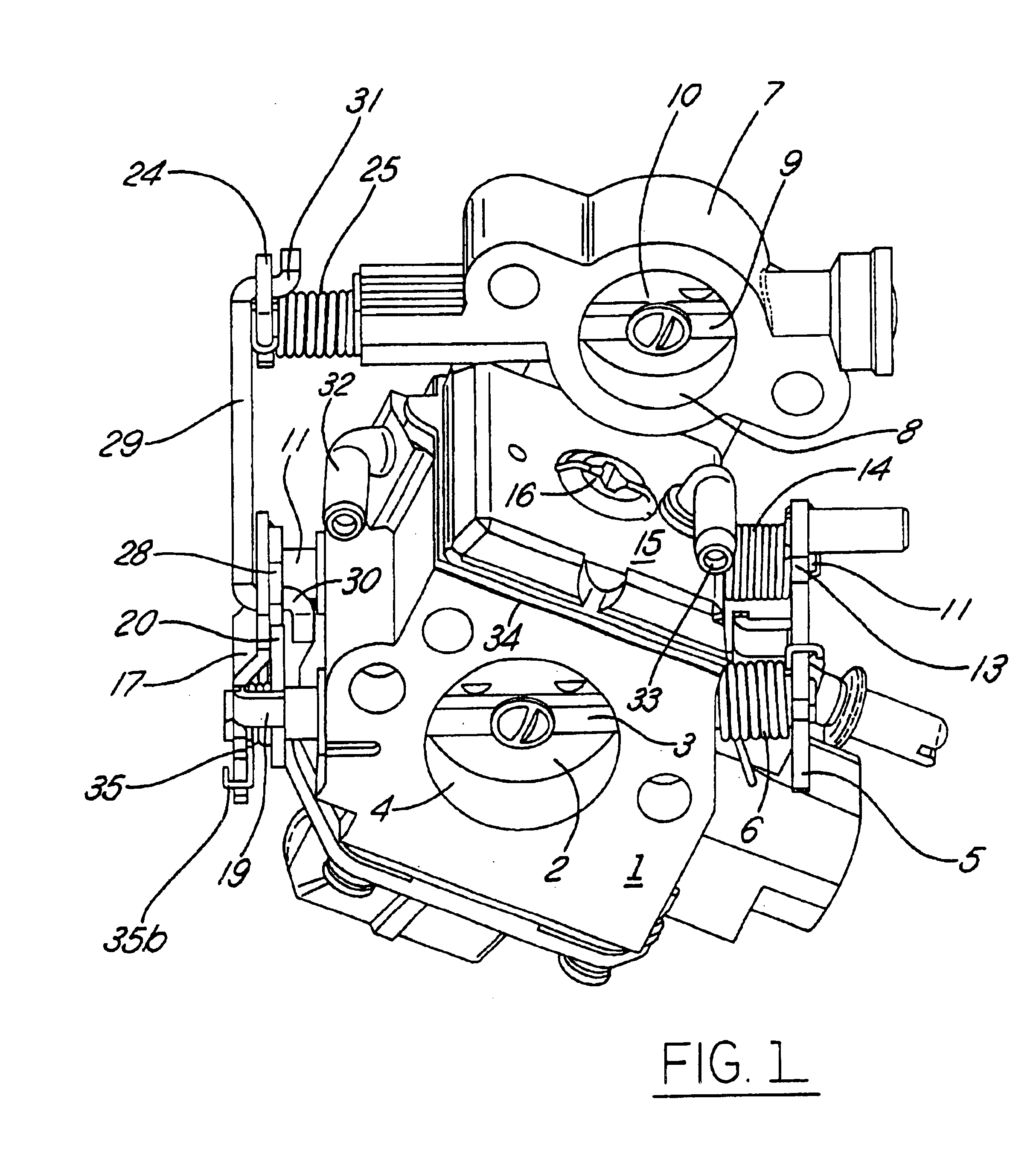
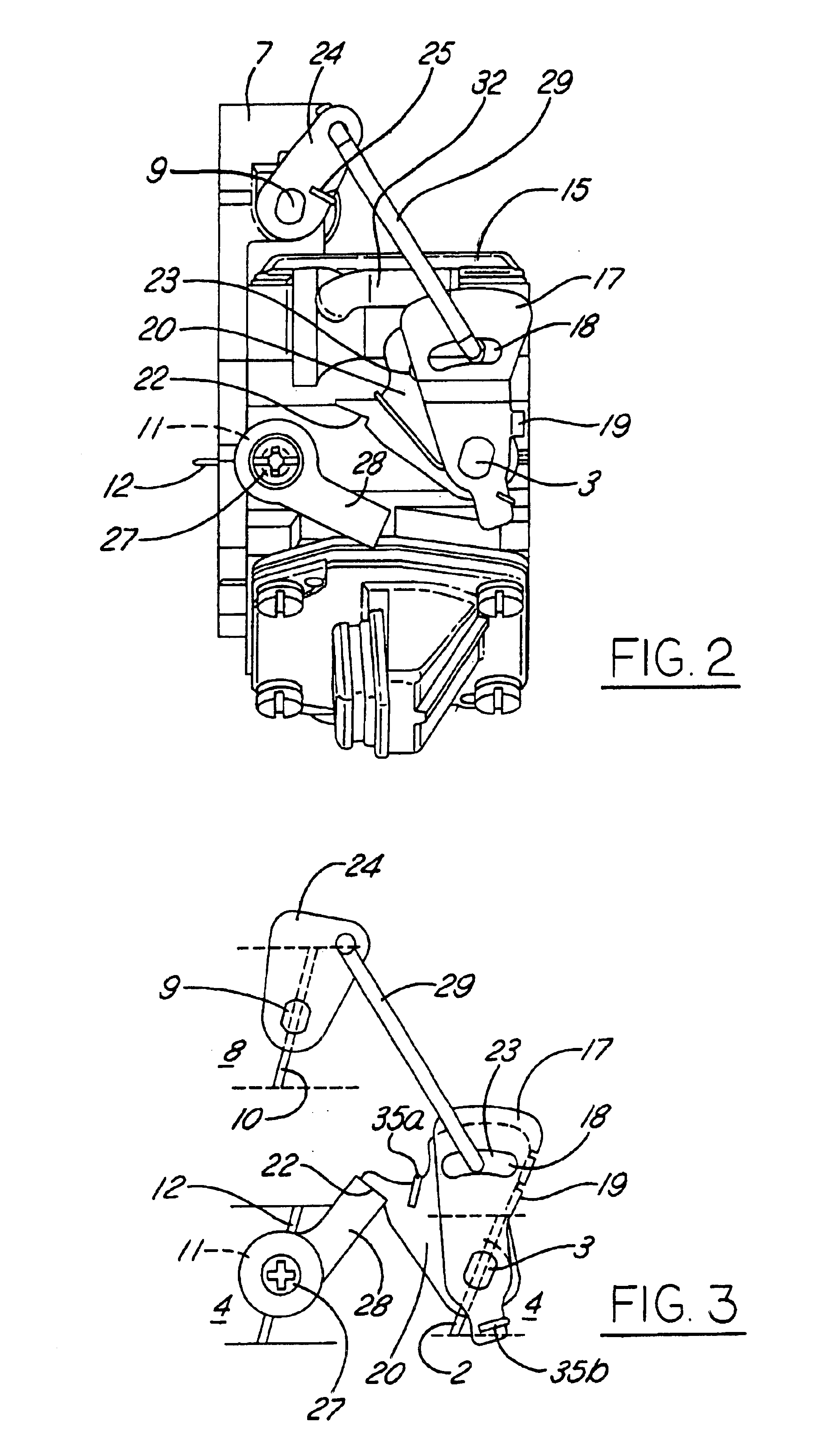
Stratified scavenging carburetor
A stratified scavenging carburetor with a lost motion coupling permits limited relative movement of a throttle valve relative to an air valve so that initial opening of the throttle valve off idle does not open the air valve to avoid diluting with scavenging air the fuel and air mixture delivered to an engine. Rotation of the throttle valve beyond a predetermined amount from idle causes a corresponding opening of the air valve to provide scavenging air to the engine. Closing a choke valve engages a lock lever with the throttle valve to move the throttle valve off idle to a start position without opening the air valve. In another embodiment, closing the choke valve prevents the air valve from opening even if the throttle valve is moved beyond where the throttle valve would cause the air valve to open if the choke valve were open. Thus, a richer than normal fuel and air mixture can be supplied to the engine during a choke-assisted start and warm-up of the engine.
Owner:NIPPON WALBRO KK
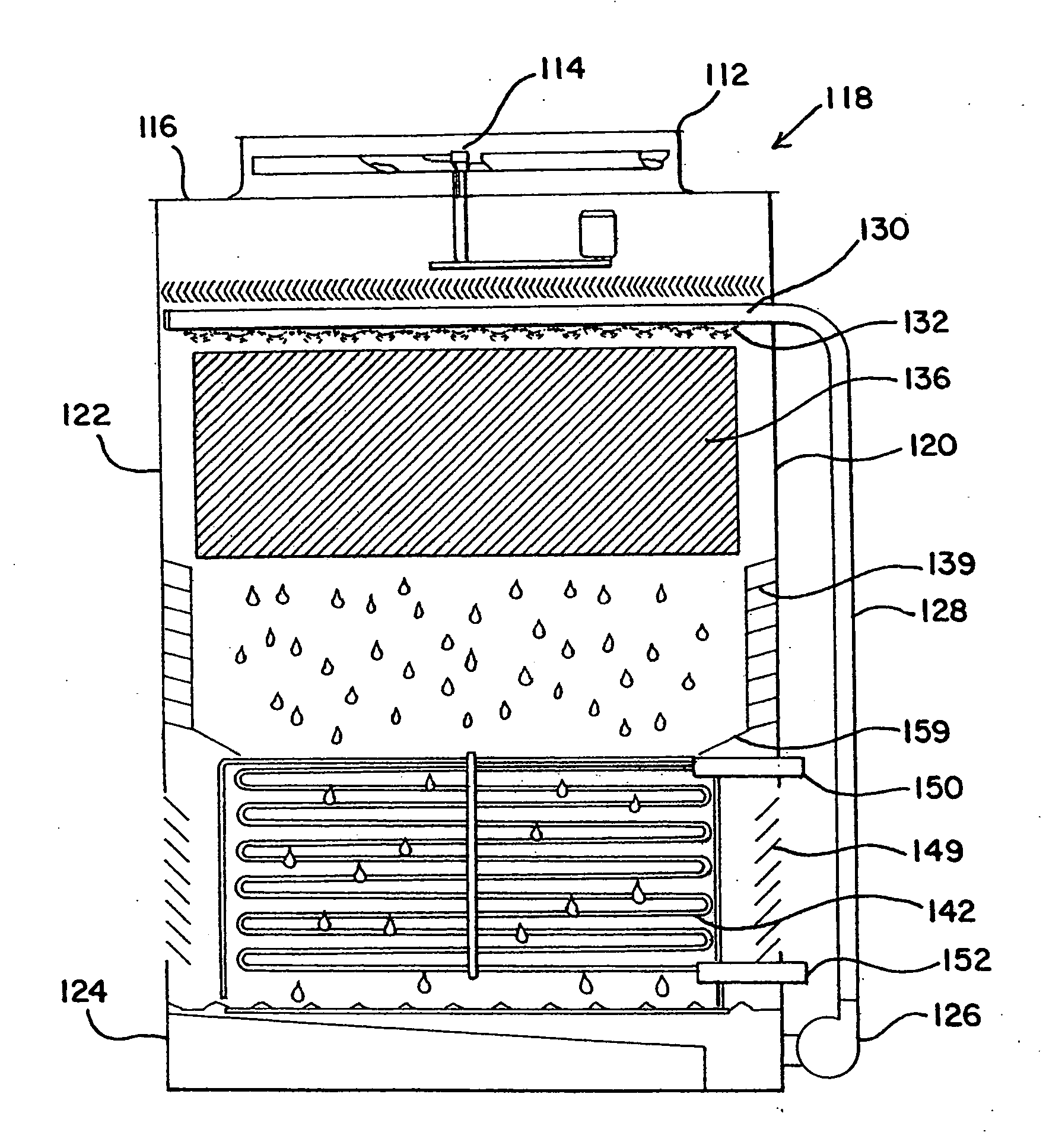
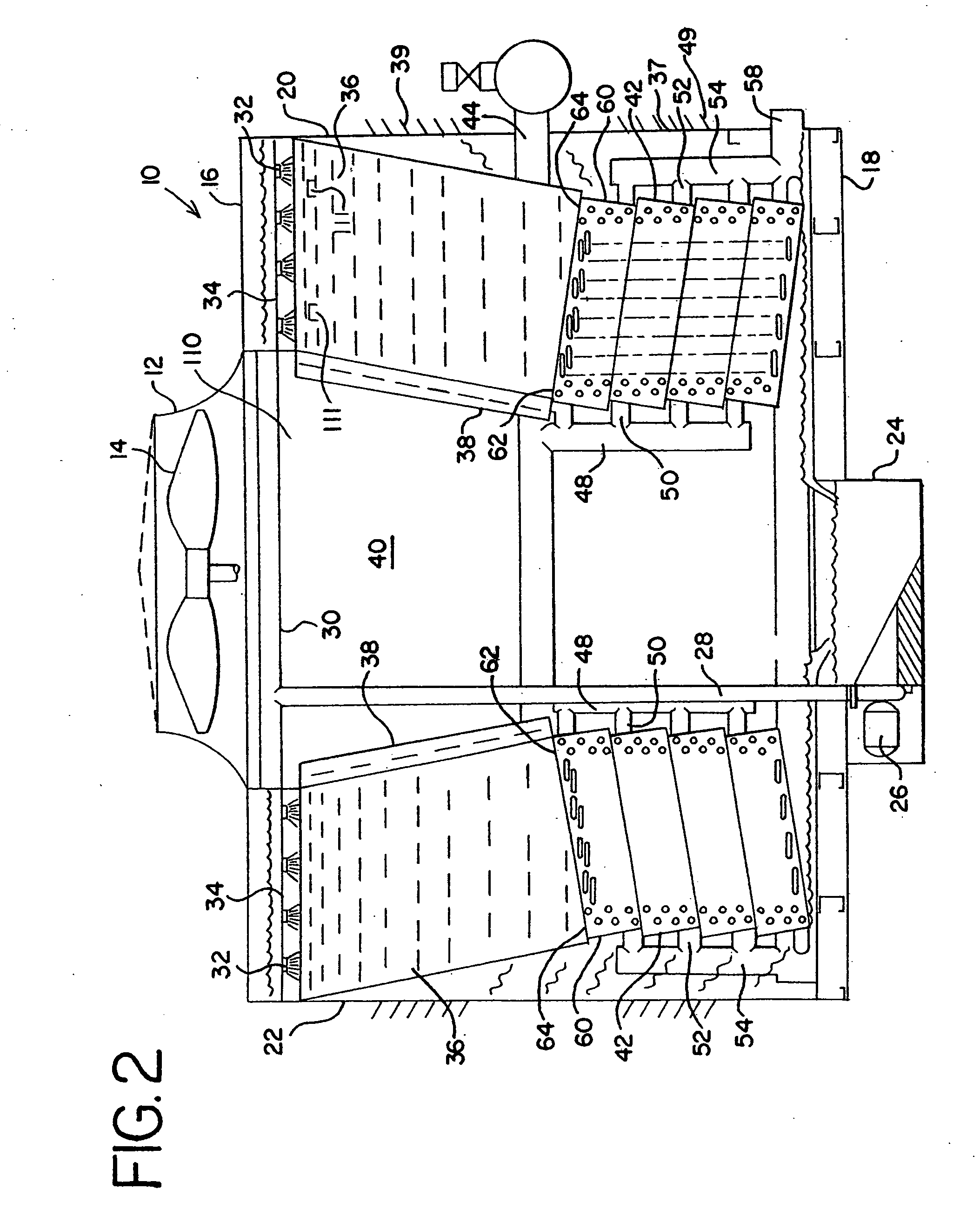
Cooling tower with direct and indirect cooling sections
ActiveUS20070187851A1Direct coolingLiquid degasificationMixing methodsCooling towerMechanical engineering
A mechanical draft cooling tower includes an air inlet and an air outlet. A liquid spray assembly is provided below the air outlet. A fill shell assembly is provided below the liquid spray assembly such that liquid can be sprayed onto the fill sheet assembly. An indirect heat exchange assembly is mounted beneath the fill sheet assembly. The indirect assembly usually comprises a series of coils through which a fluid to be cooled is circulated. A first air inlet is provided beneath the fill sheet assembly and includes a closing assembly. A second air inlet is provided beneath a top surface of the indirect assembly and includes a closing assembly.
Owner:BALTIMORE AIRCOIL CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com