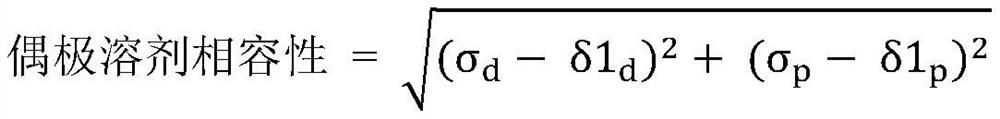Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Maintain optical performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
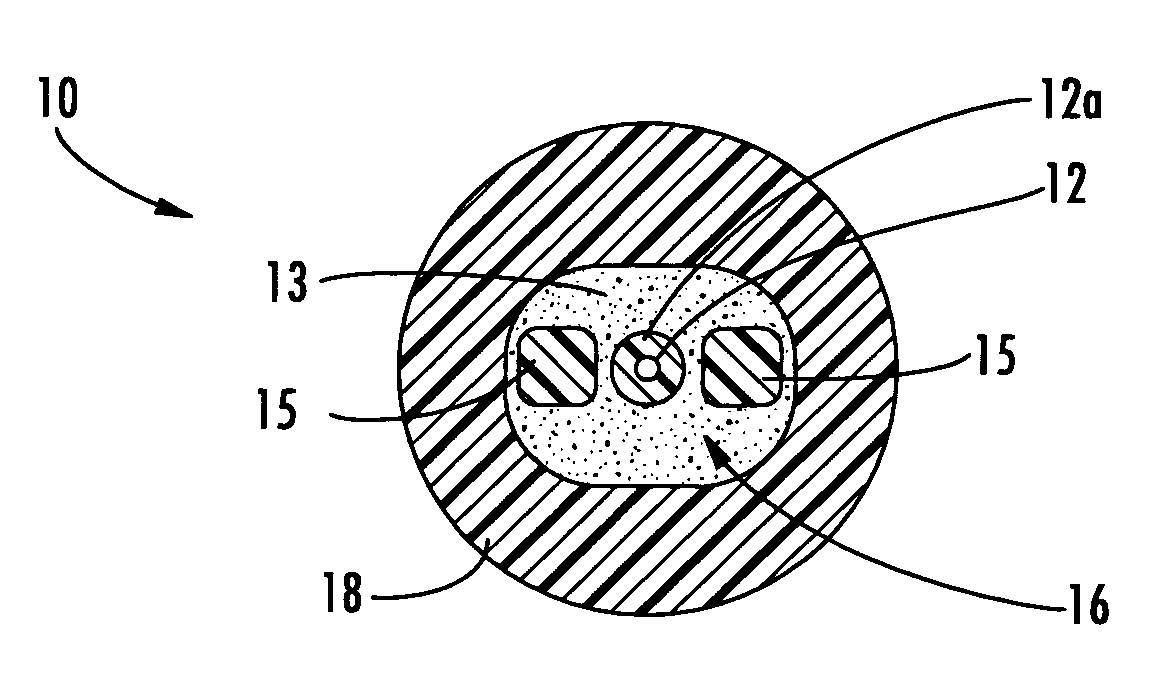
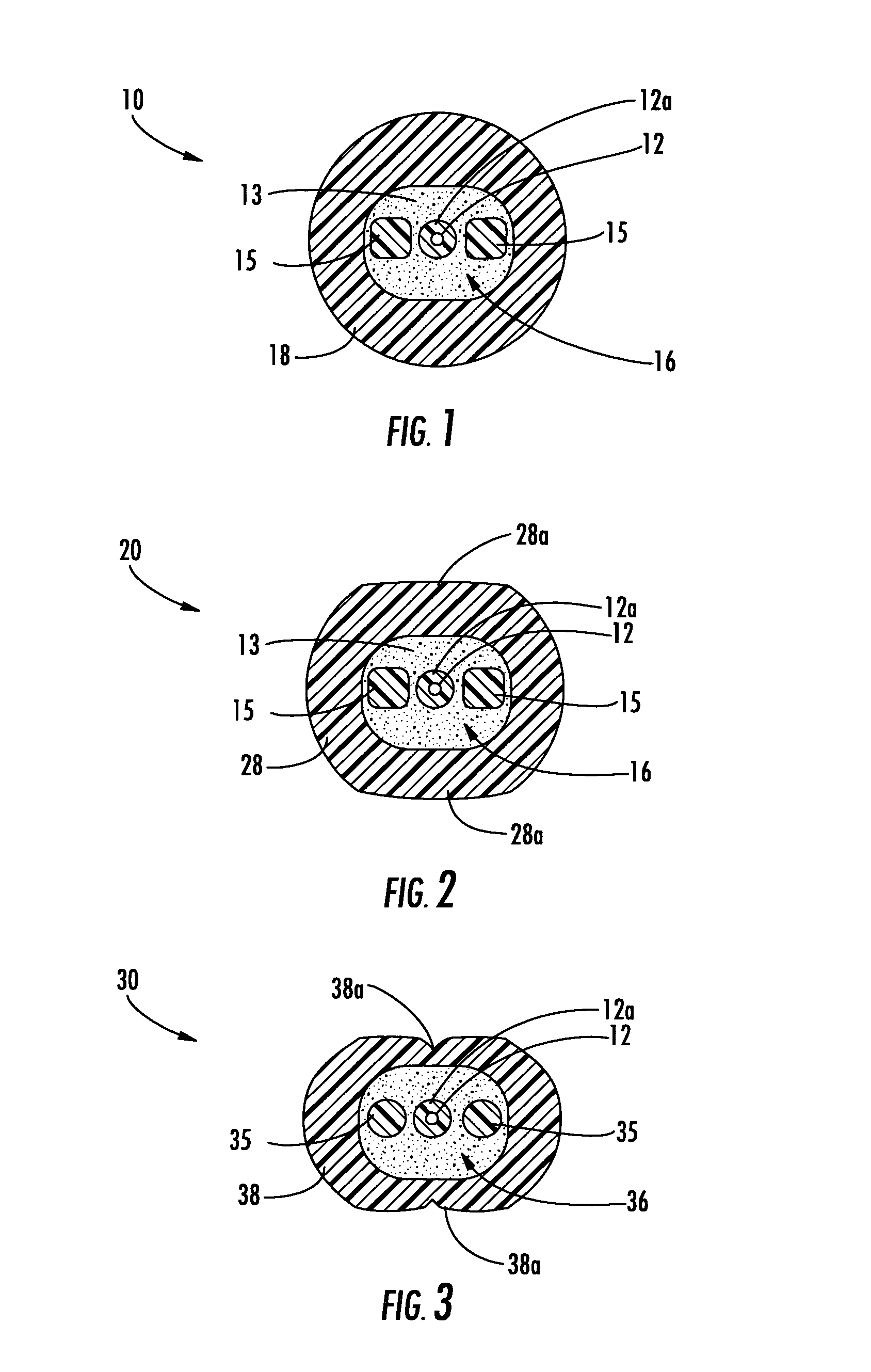
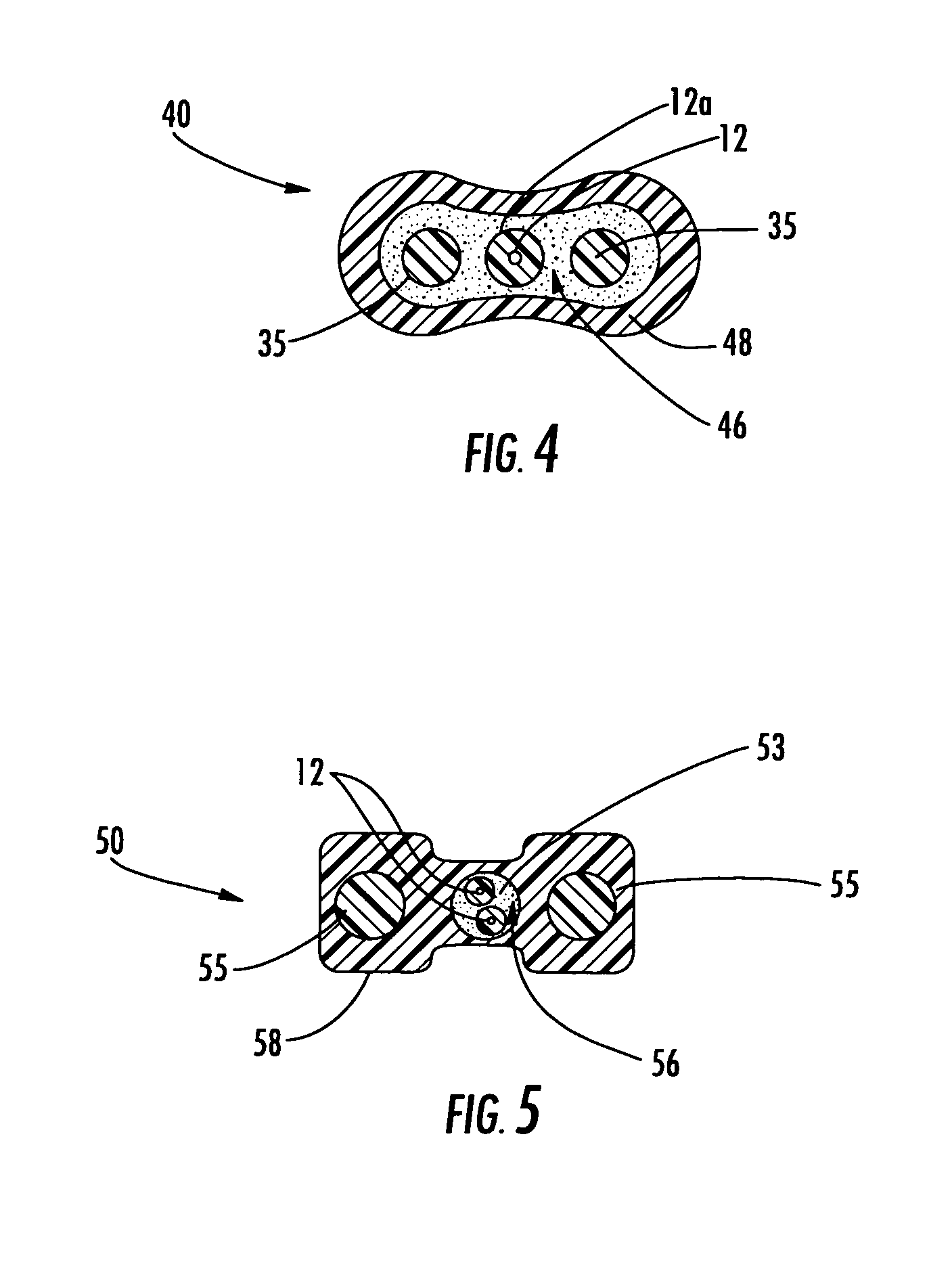
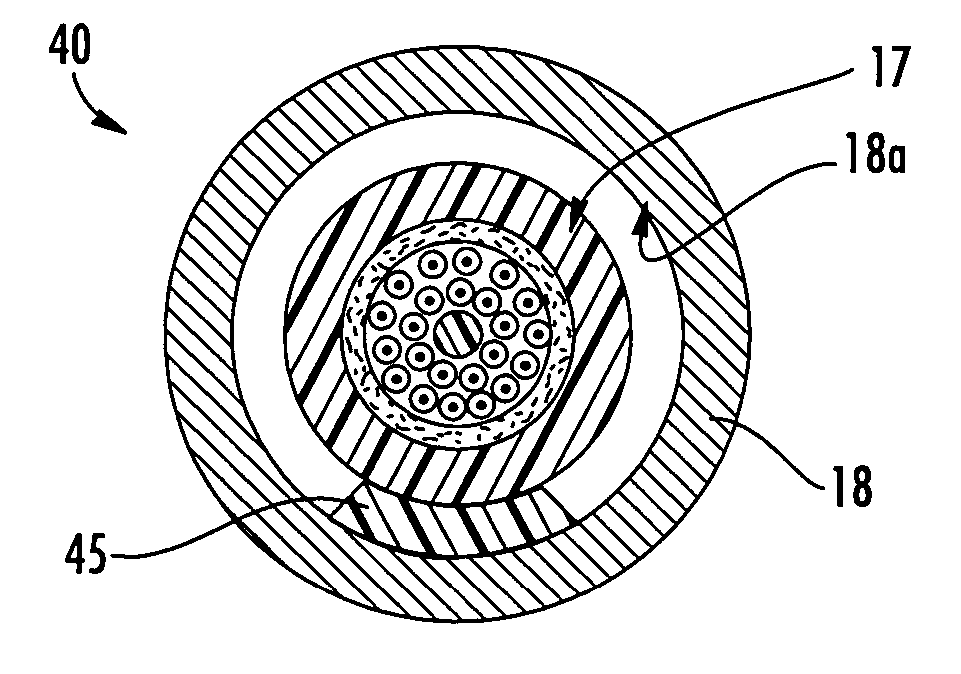
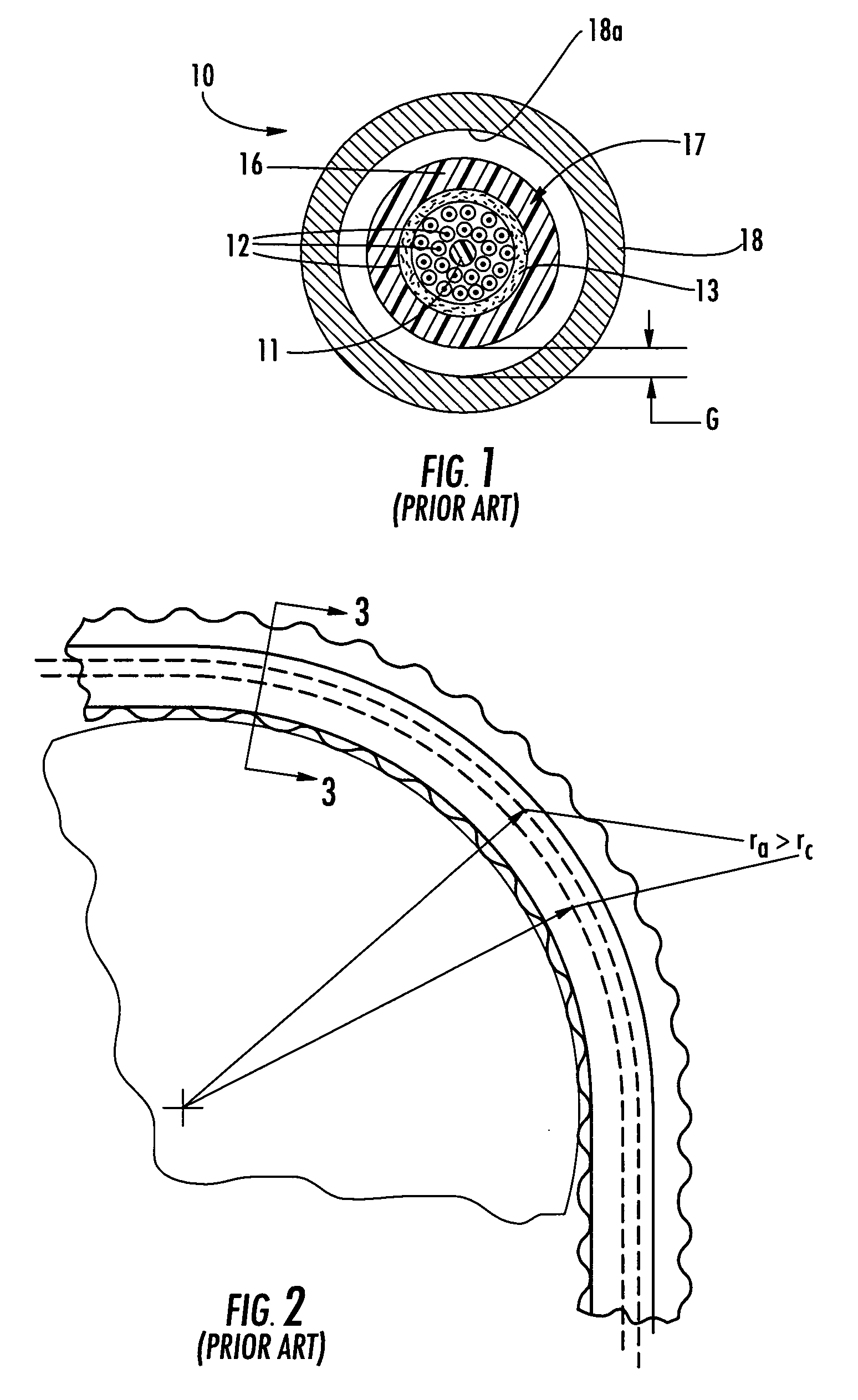
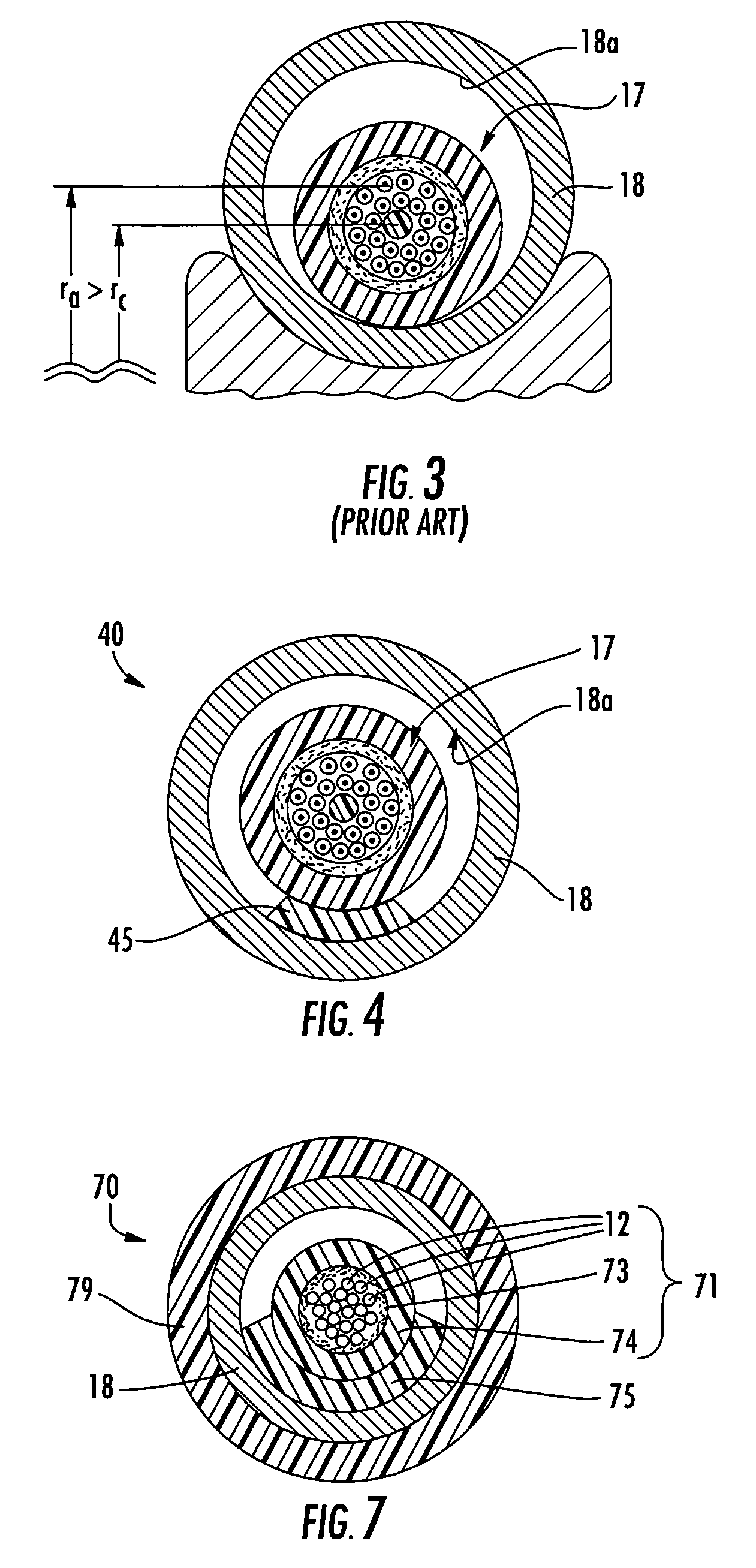
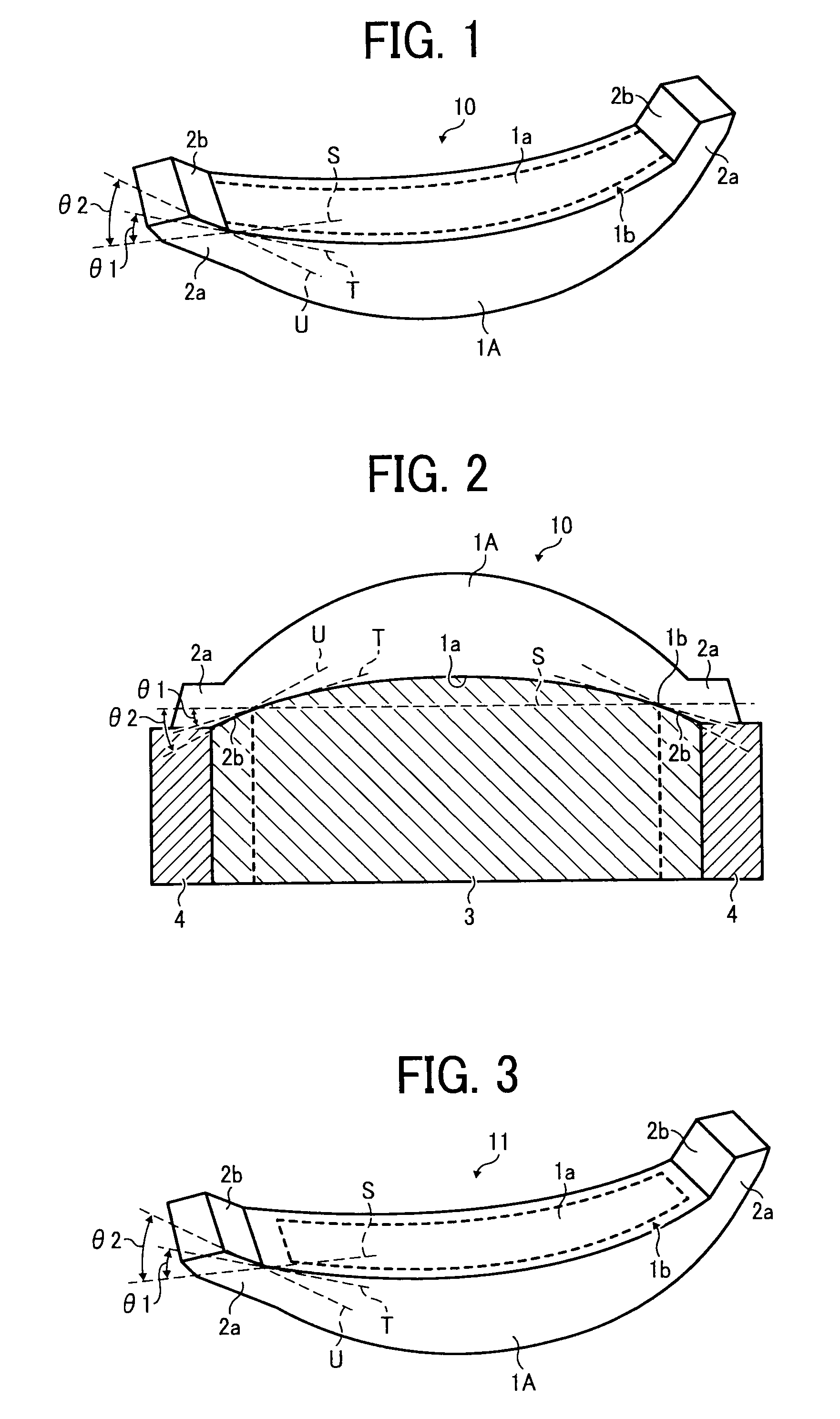
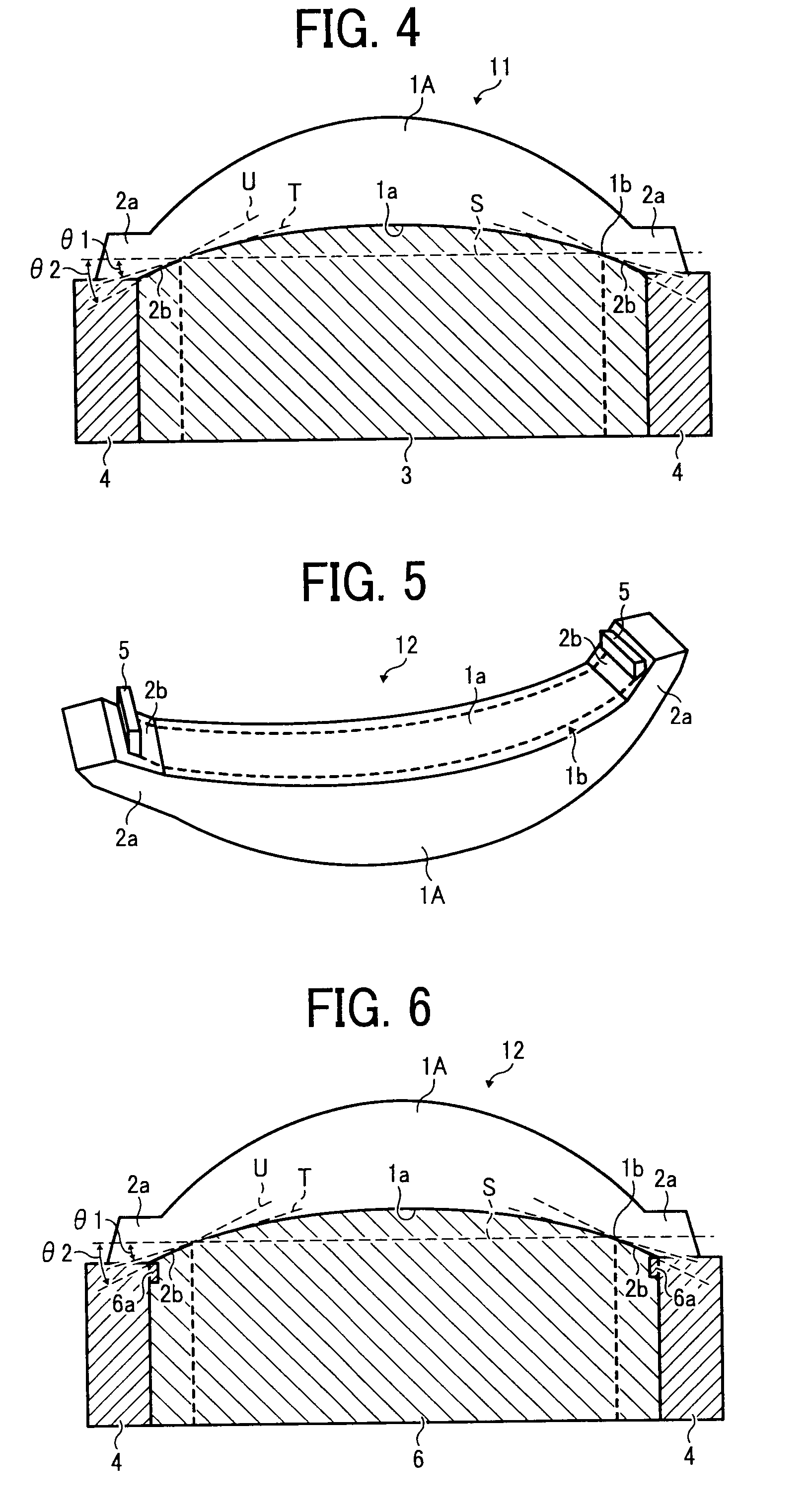
Fiber optic cables that kink with small bend radii
ActiveUS7289704B1Maintain optical performanceSuitable level of optical performanceFibre mechanical structuresFiberEngineering
Fiber optic cables are disclosed that allow a relatively small bend radius and / or may kink while still preserving optical performance. In one embodiment, the fiber optic cable includes at least one optical fiber, a first strength member, a second strength member, a core material, and a cable jacket. The core material generally surrounds the optical fiber, the first strength member, and the second strength member and the core material is deformable for cushioning the optical fiber. The cable jacket generally surrounds the core material and allows a bending radius of about 10 millimeters or less while maintaining a suitable level of optical performance.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Lightguide illuminator embedded display
InactiveUS20110149201A1Limit Fresnel reflectionMaintain performanceNon-linear opticsDynamic contrastRefractive index
A polymer-dispersed liquid crystal based display is embedded inside a lightguide illuminator sheet which provides illumination of the display without the need for a backlight or frontlight. Light from one or more light sources is coupled into the lightguide sheet and is guided within a range of high angles of incidence within the sheet by total internal reflection. The guided light illuminating portions of the display which are in diffusing state is scattered such that some of the light is allowed to escape total internal reflection, providing visibility of the display. Guided light illuminating portions of the display which are in non-diffusing state remains guided within the lightguide illuminator sheet. Combining multiple lightguide embedded displays can be used to provide a three-dimensional display. When a low refractive index cladding is applied to the surfaces of the lightguide embedded display, the display is robust in a dirty environment, and / or can be laminated to adjacent lightguide embedded displays. The use of one or more coupled light sources, such as light emitting diodes, provides color by combining one or more colored light sources or by time-sequentially driving one or more colored light sources. The lightguide illuminator embedded display may further be used as a content dependent active backlight for an LCD display panel to provide improved dynamic contrast.
Owner:POWELL KARLTON DAVID +1
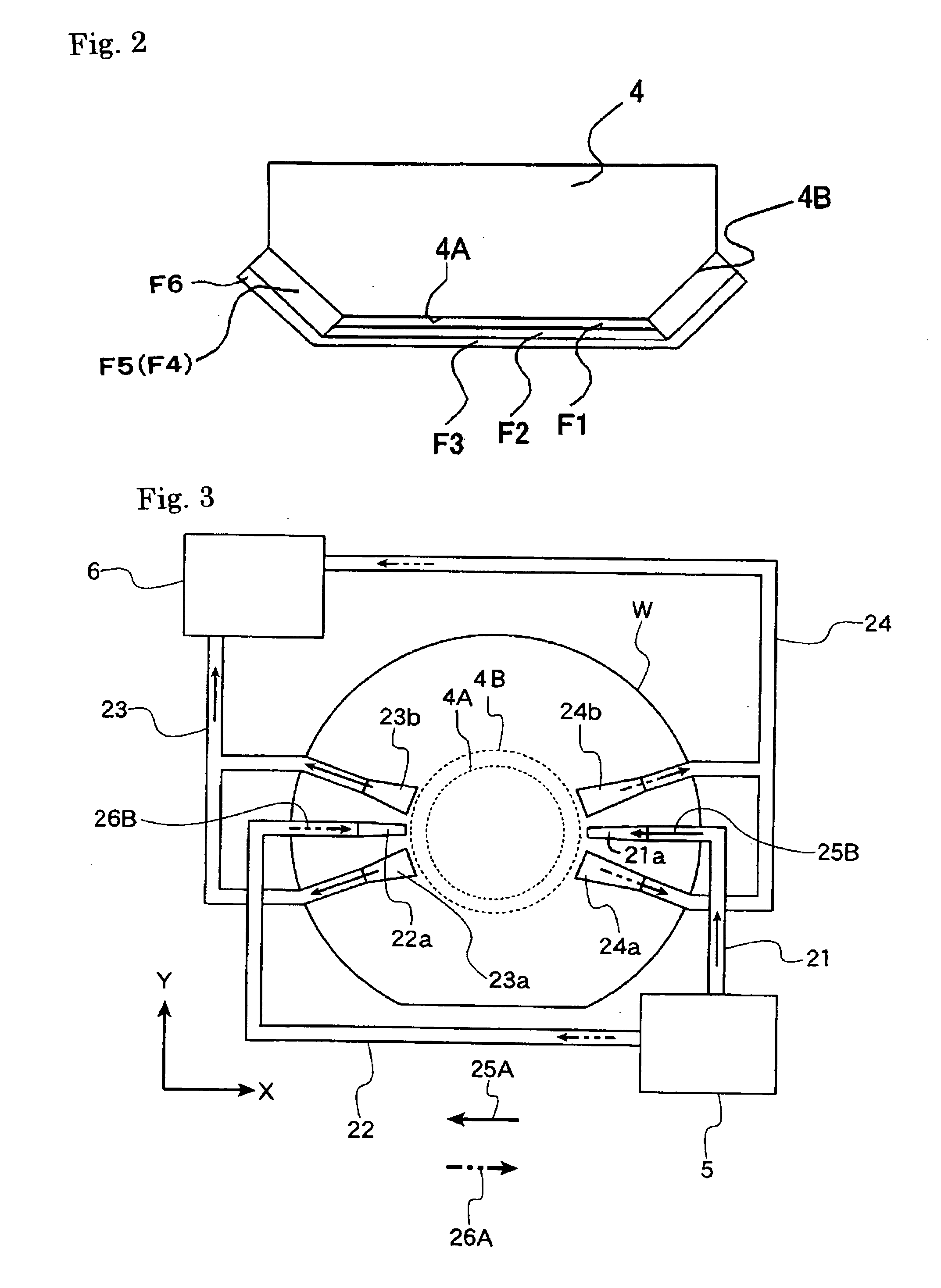
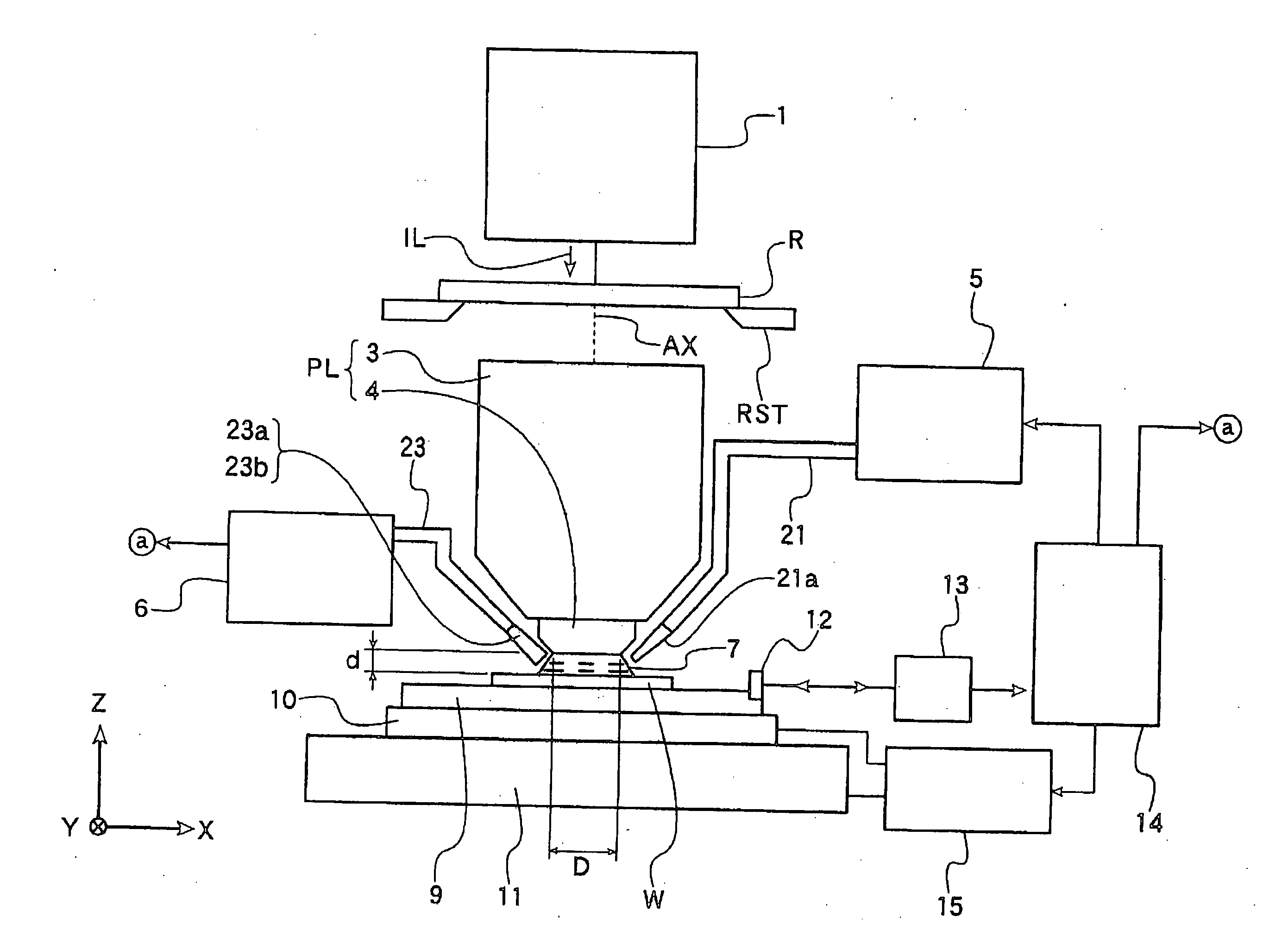
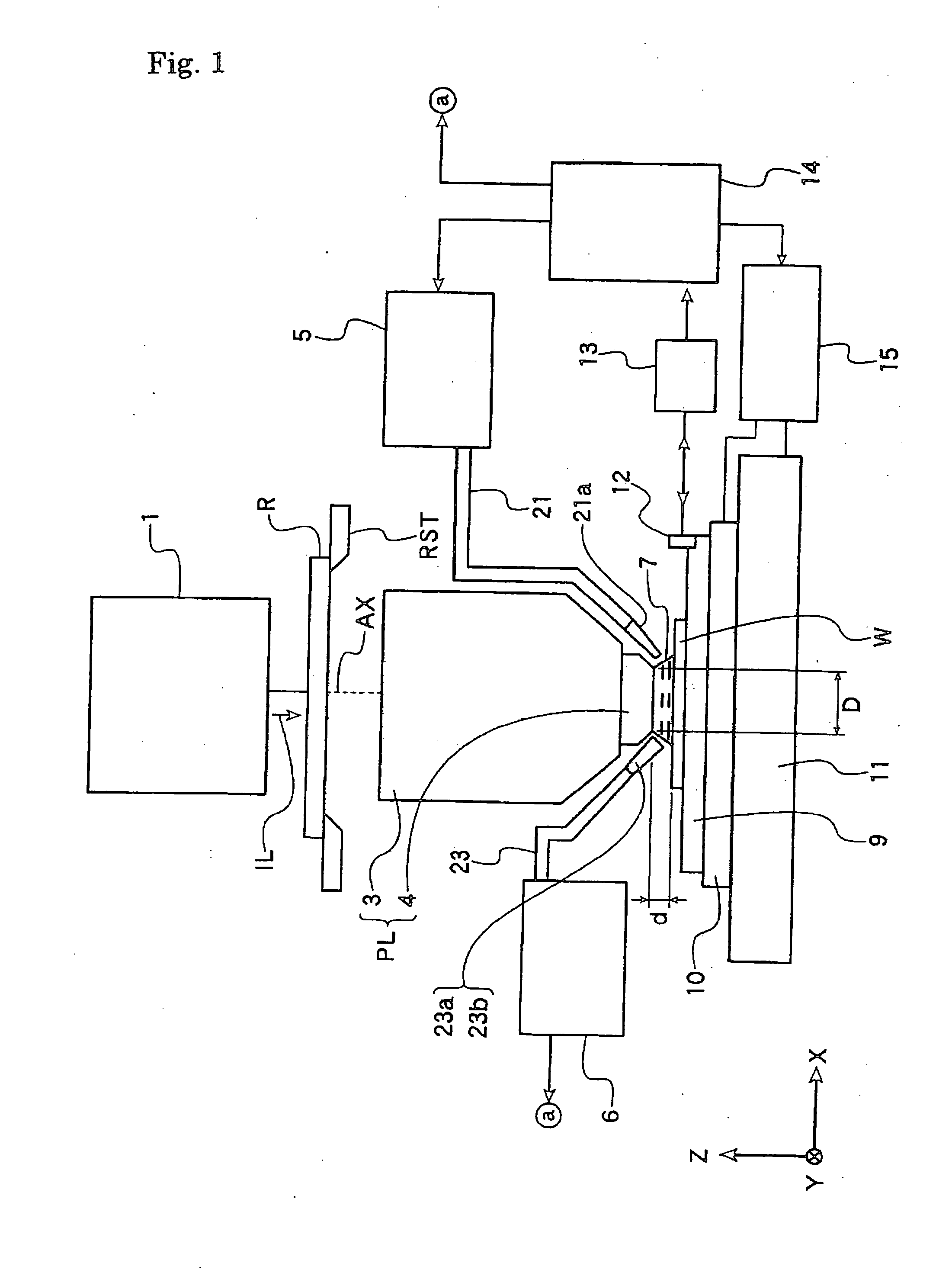
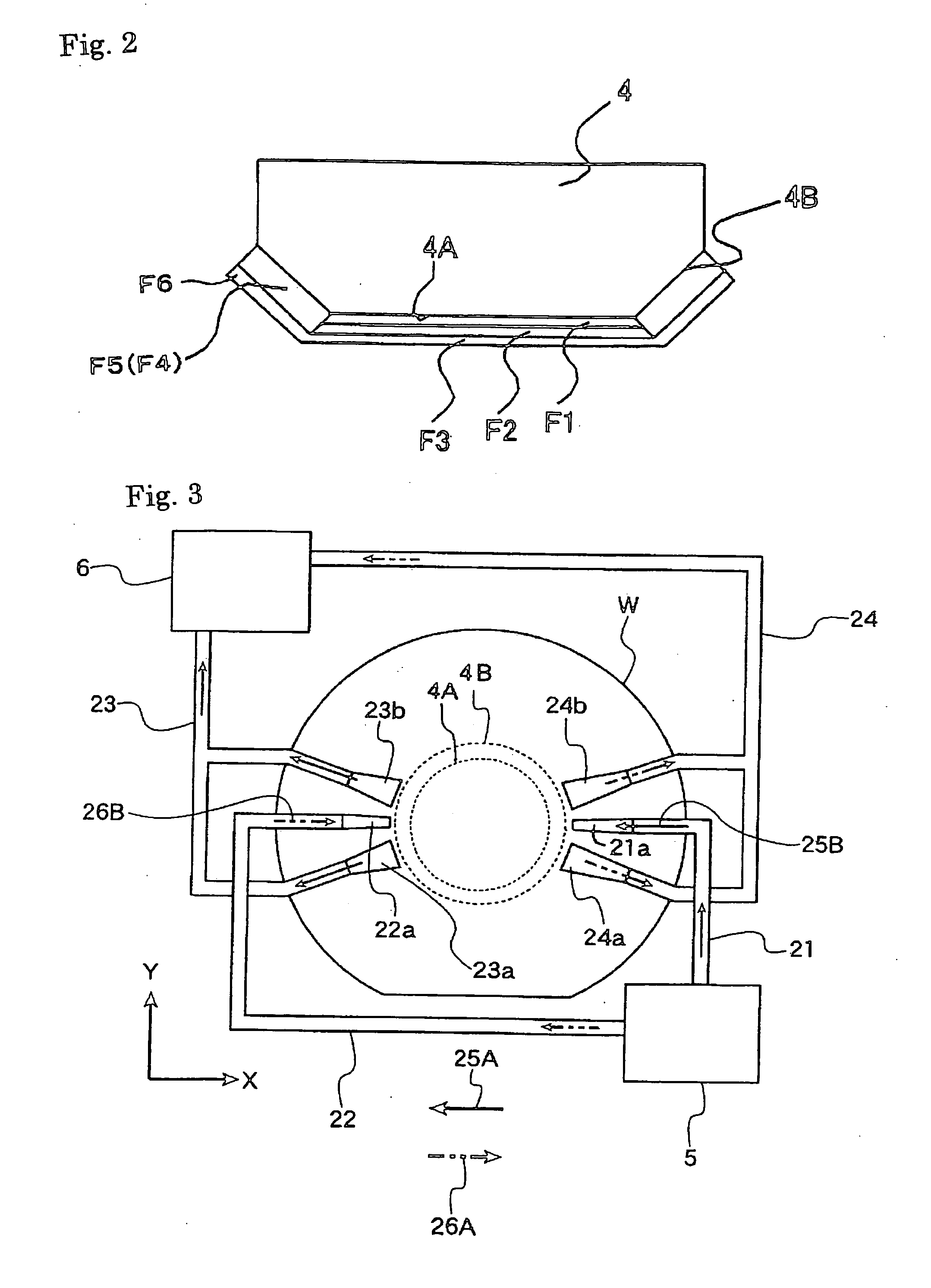
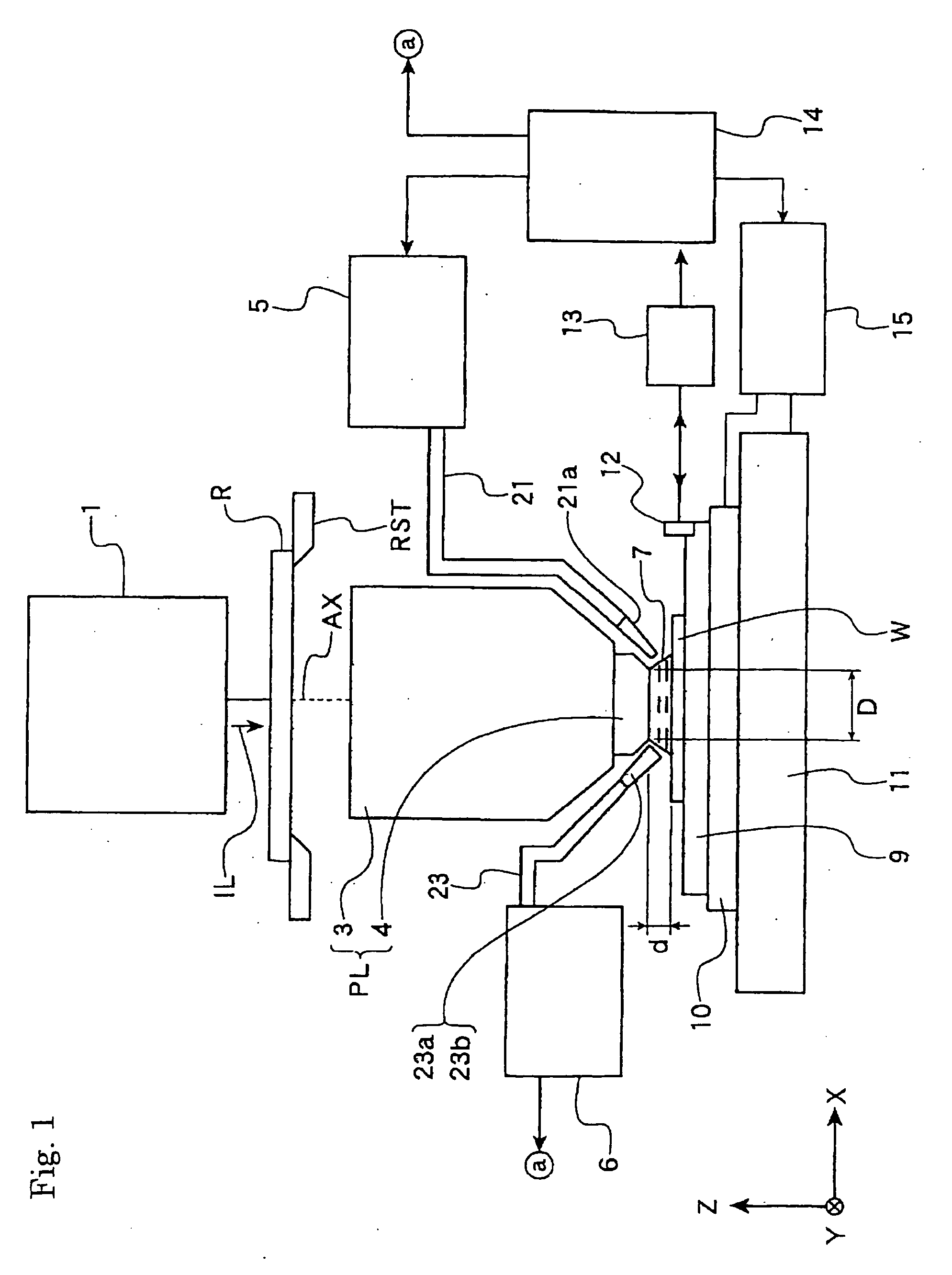
Optical element and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20060291060A1Prevent deterioration of sealingAvoid radiationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingLight beamDissolution
An optical element is used for an exposure apparatus which is configured to illuminate a mask with an exposure light beam for transferring a pattern on the mask onto a substrate through a projection optical system and to interpose a given liquid in a space between a surface of the substrate and the projection optical system. The optical element includes a first anti-dissolution member provided on a surface of a transmissive optical element on the substrate's side of the projection optical system.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Optical element and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20060203218A1Inhibition of dissolutionMaintain optical performancePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLight beamDissolution
An optical element is used for an exposure apparatus which is configured to illuminate a mask with an exposure light beam for transferring a pattern on the mask onto a substrate through a projection optical system and to interpose a given liquid in a space between a surface of the substrate and the projection optical system. The optical element includes a first anti-dissolution member provided on a surface of a transmissive optical element on the substrate's side of the projection optical system.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Imaging Lens
ActiveUS20090279188A1High melting pointGuaranteed Optical PerformanceOptical articlesLensCamera lensOptoelectronics
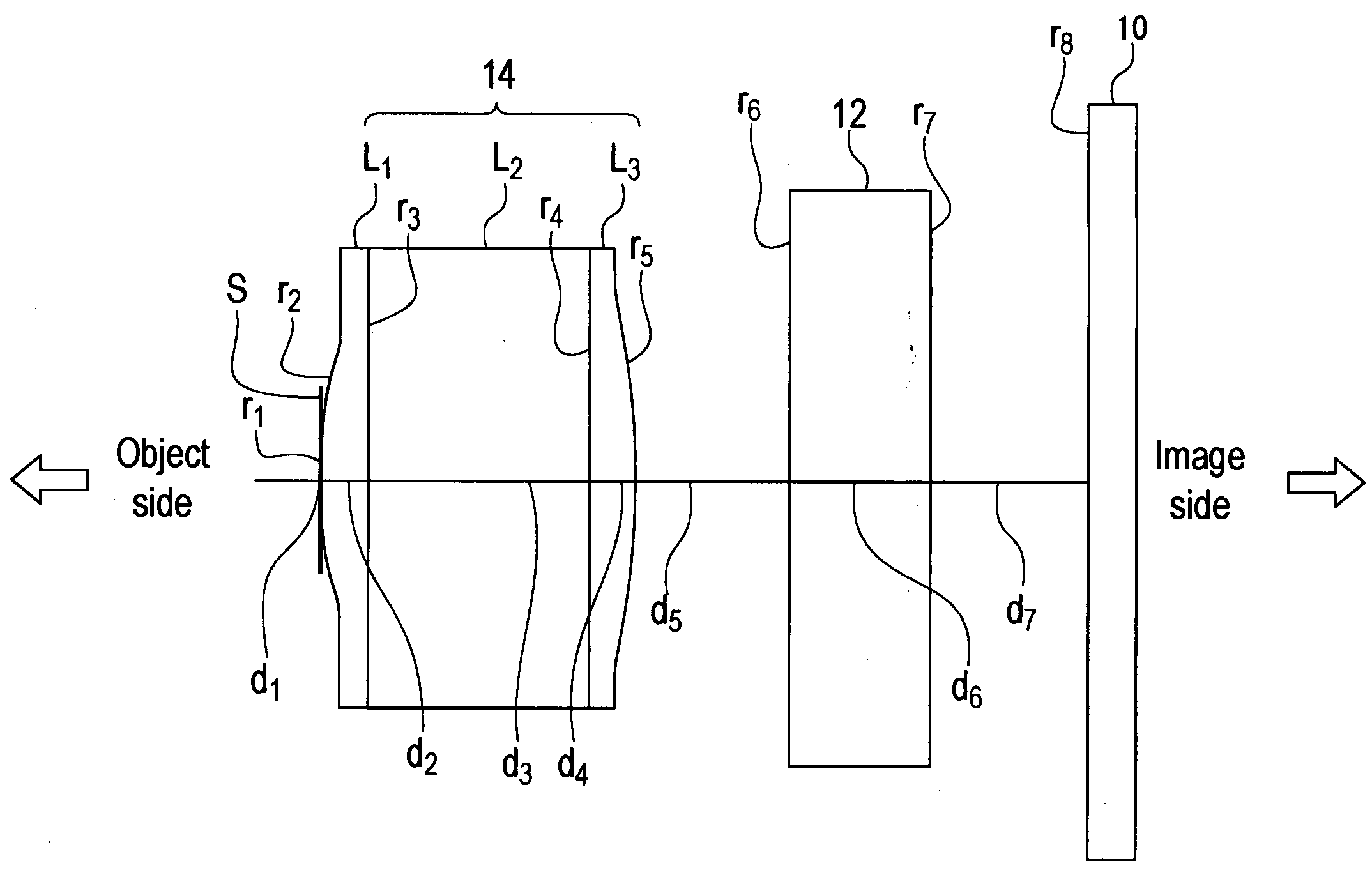
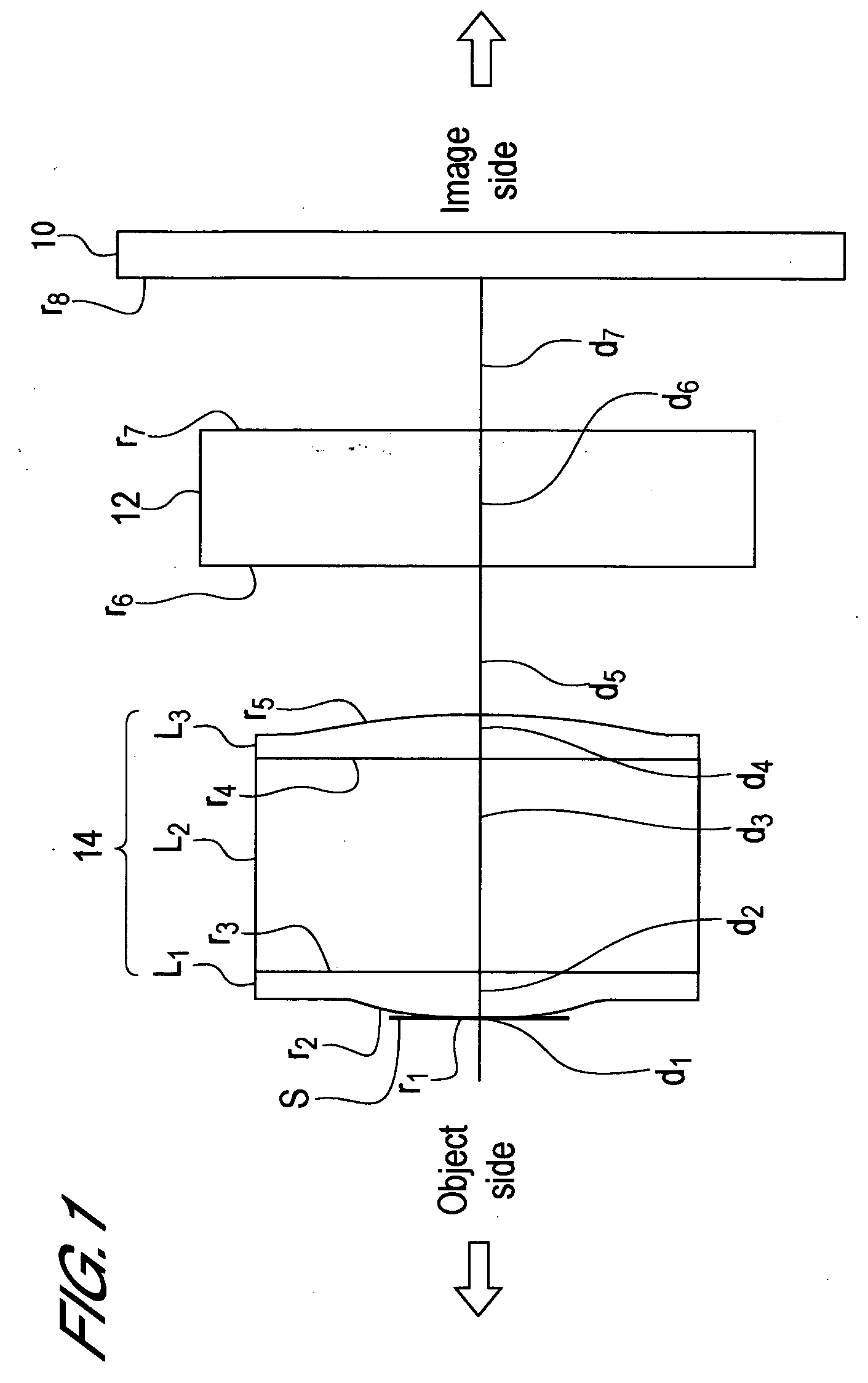
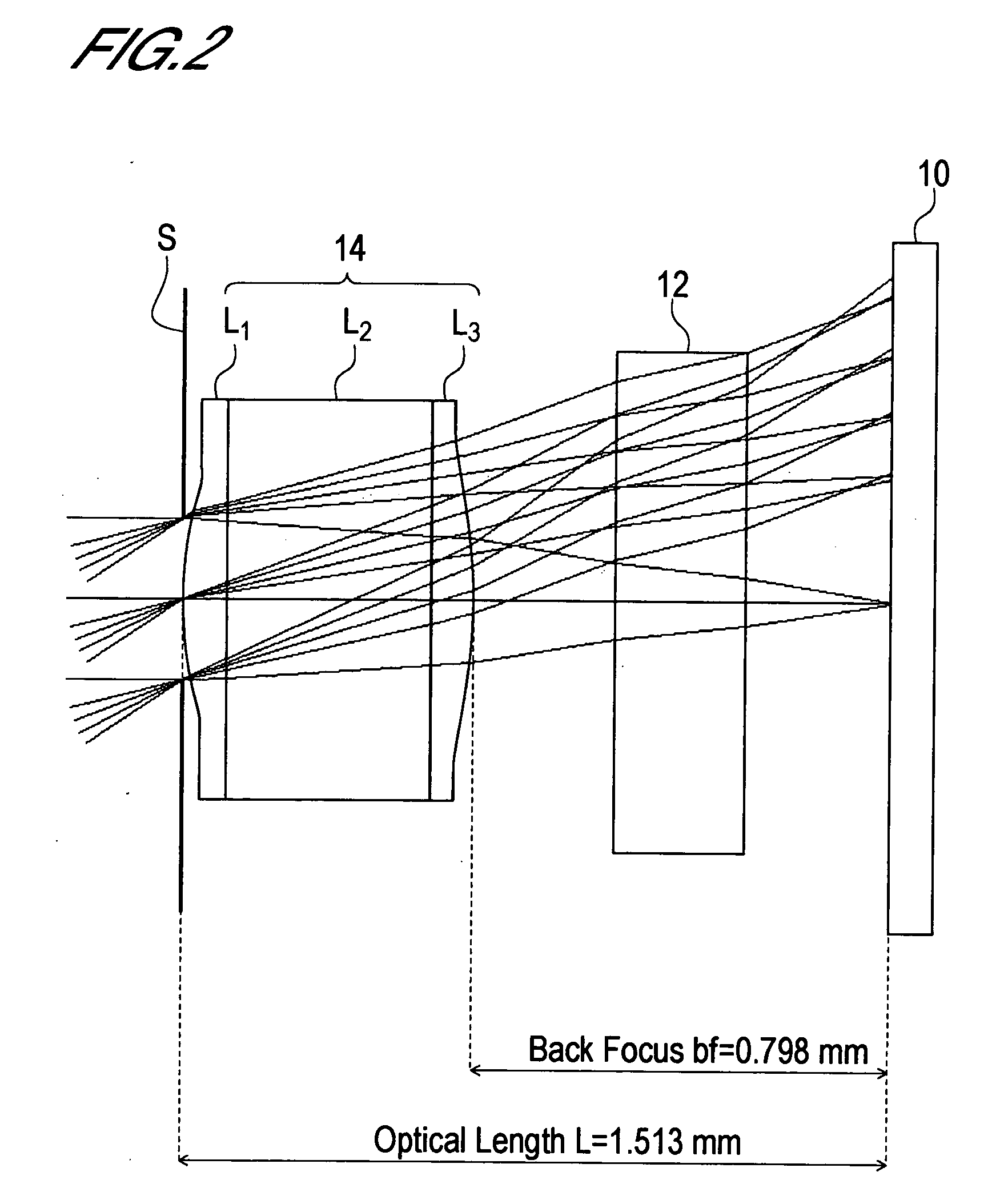
An imaging lens of which optical performance does not deteriorate even in a high temperature environment, various aberrations are well corrected, optical length is short, and back focus is sufficiently secured, comprising an aperture stop S and a junction type compound lens 14 having a positive refractive power, wherein the aperture stop and the junction type compound lens are arranged in this sequence from an object side to an image side. The junction type compound lens comprises a first lens L1, a second lens L2 and a third lens L3 arranged in this sequence from the object side to the image side. The first lens and the third lens are formed of a curable resin material, and the second lens is formed of an optical glass. The first lens and the second lens are directly bonded, and the second lens and the third lens are directly bonded. The object side face of the first lens and the image side face of the third lens are aspherical.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN +1
Optical element and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20090103070A1Inhibition of dissolutionMaintain optical performanceProjectorsVacuum evaporation coatingLight beamDissolution
An optical element is used for an exposure apparatus which is configured to illuminate a mask with an exposure light beam for transferring a pattern on the mask onto a substrate through a projection optical system and to interpose a given liquid in a space between a surface of the substrate and the projection optical system. The optical element includes a first anti-dissolution member provided on a surface of a transmissive optical element on the substrate's side of the projection optical system.
Owner:NIKON CORP
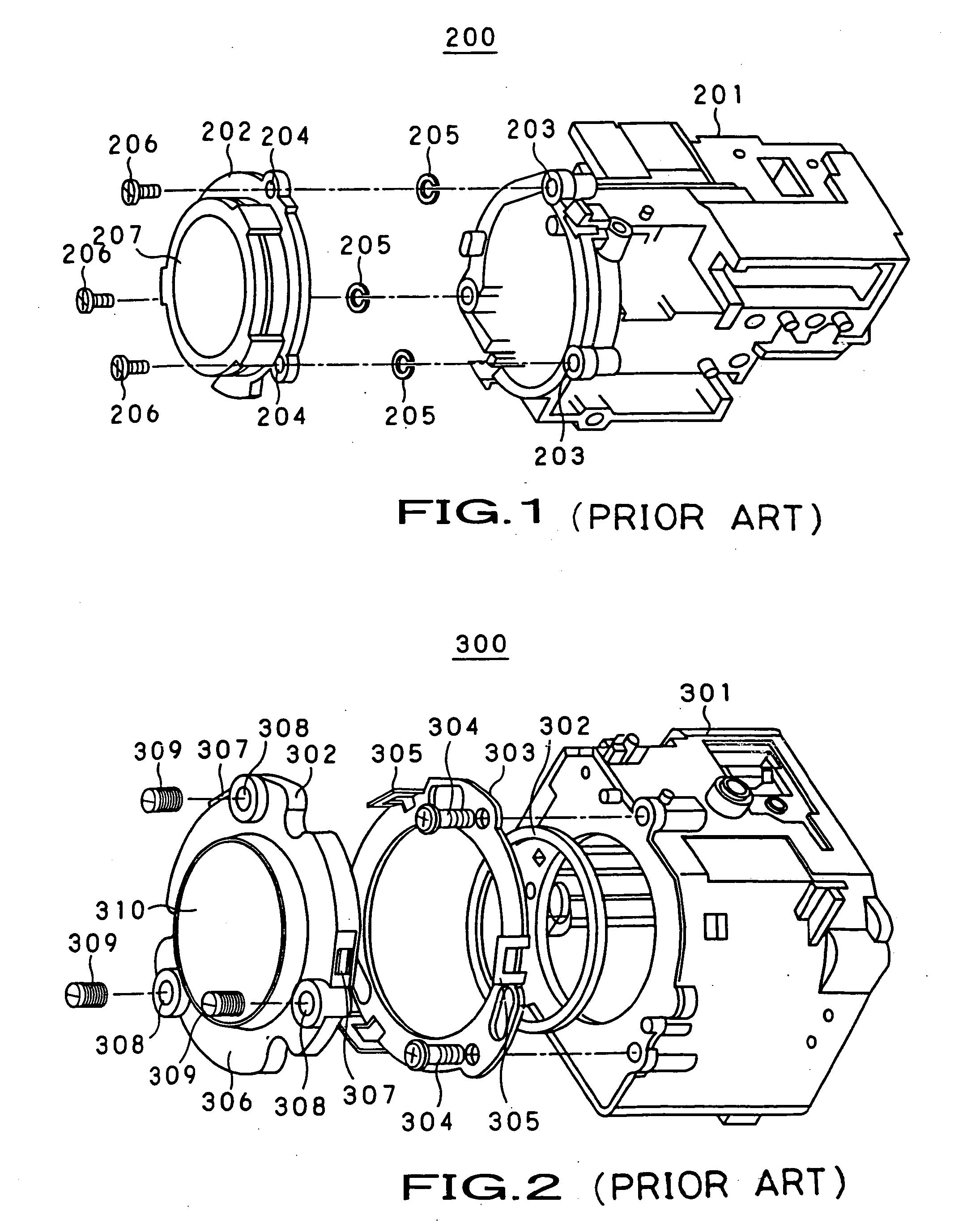
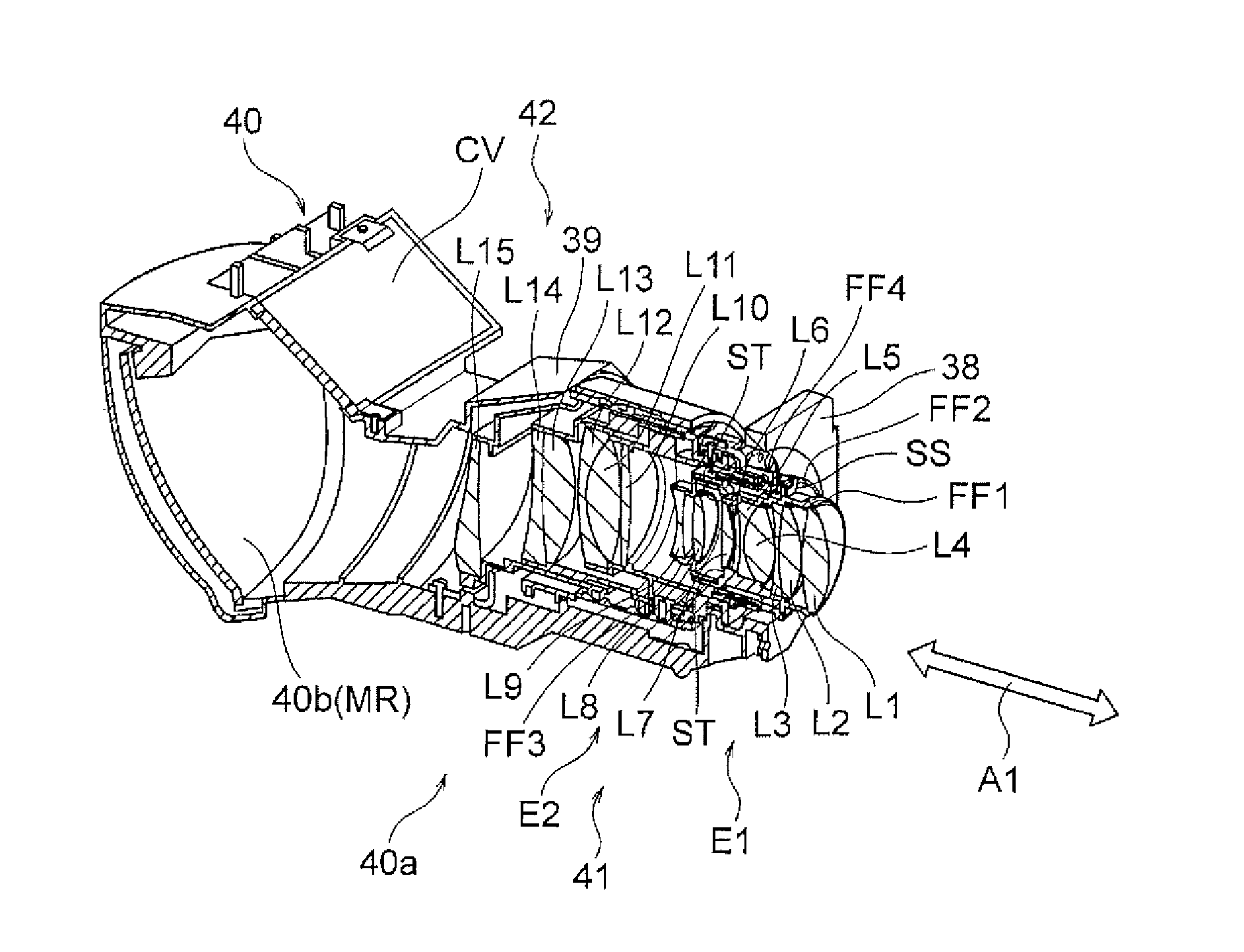
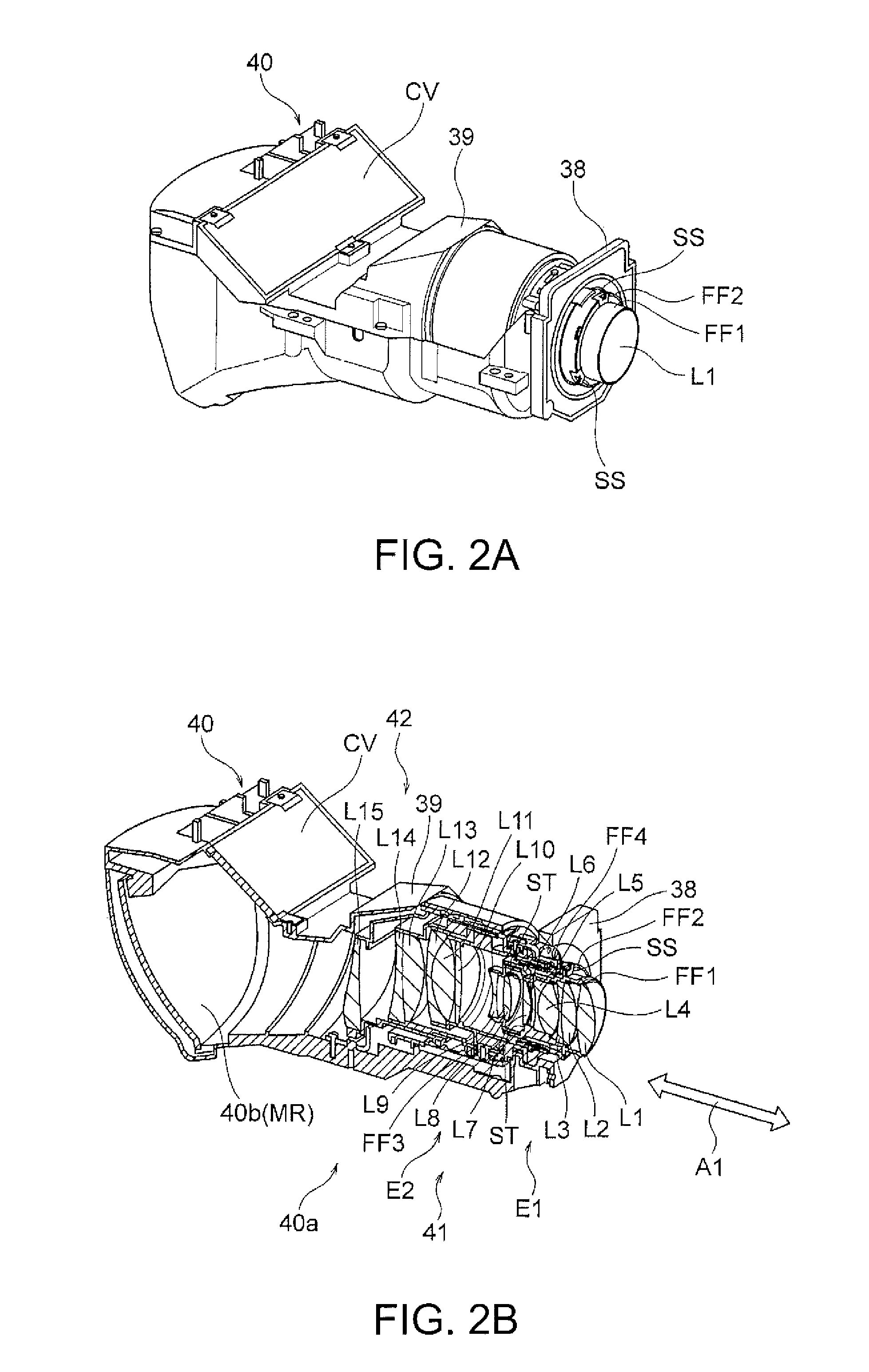
Lens centering mechanism, lens apparatus and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6909558B2Facilitated and optimized centeringLow costTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
A lens held by a lens holding member is centered easily and correctly by a mechanism in which a guide pin is inserted into a guide hole for positioning the lens holding member with respect to the main body unit of the lens barrel in a plane perpendicular to the optical axis of the lens and for mounting the lens holding member for movement in a direction along the optical axis. Adjustment pins are rotationally mounted on at least three sites on the outer peripheral surface of the main body unit of the lens barrel. If each adjustment pin is rotated, an offset portion of the adjustment pin which is relative to the center of rotation of the adjustment pin, is rotated, as the offset portion is engaged in an engagement hole of the lens holding member. In this way the lens holding member on each site is displaced in the direction along the optical axis to adjust the tilt of the lens held by the lens holding member.
Owner:SONY CORP
Photocuring composition and hard coating film
ActiveCN108753146AReduce surface tensionExcellent anti-fingerprint functionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesOligomerMicroparticle
Owner:宁波安特弗新材料科技有限公司
Lens centering mechanism, lens apparatus and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050180025A1Facilitated and optimized centeringLow costTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
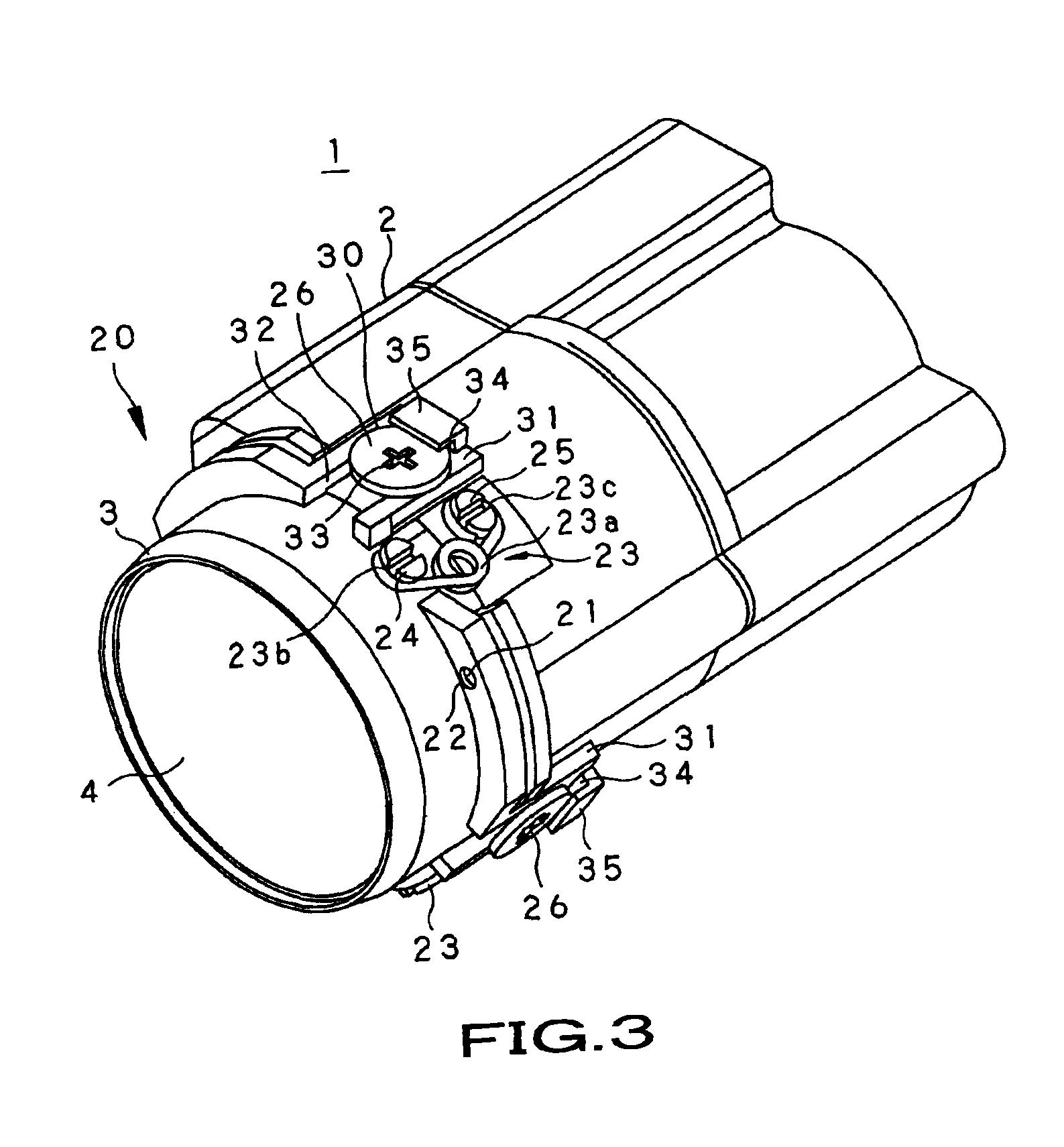
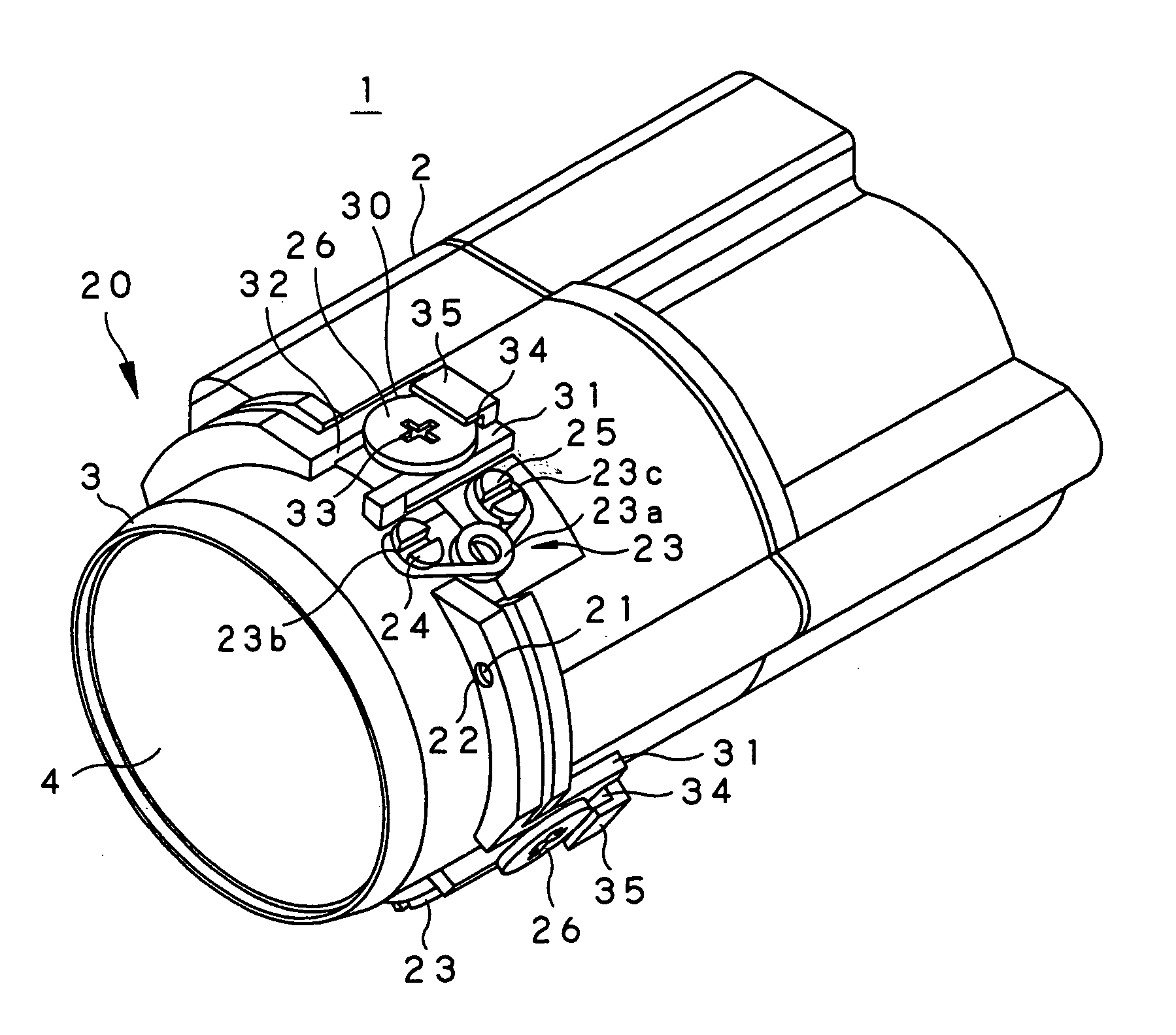
A lens held by a lens holding member is to be centered easily correctly. To this end, a guide pin 21 is inserted into a guide hole 22 for positioning the lens holding member 3 with respect to the main body unit of the lens barrel 2 in a plane perpendicular to the optical axis of the lens 4 and for mounting the lens holding member for movement in a direction along the optical axis. If, in this state, each of adjustment pins 26, rotationally mounted on at least three sites on the outer peripheral surface of the main body unit of the lens barrel 2, is rotated, an offset portion 29 of the adjustment pin, offset relative to the center of rotation of the adjustment pin, is rotated, as the offset portion is engaged in an engagement hole 32 of the lens holding member 3, so that the lens holding member 3 on each site is displaced in the direction along the optical axis to adjust the tilt of the lens 4 held by the lens holding member 3.
Owner:SONY CORP
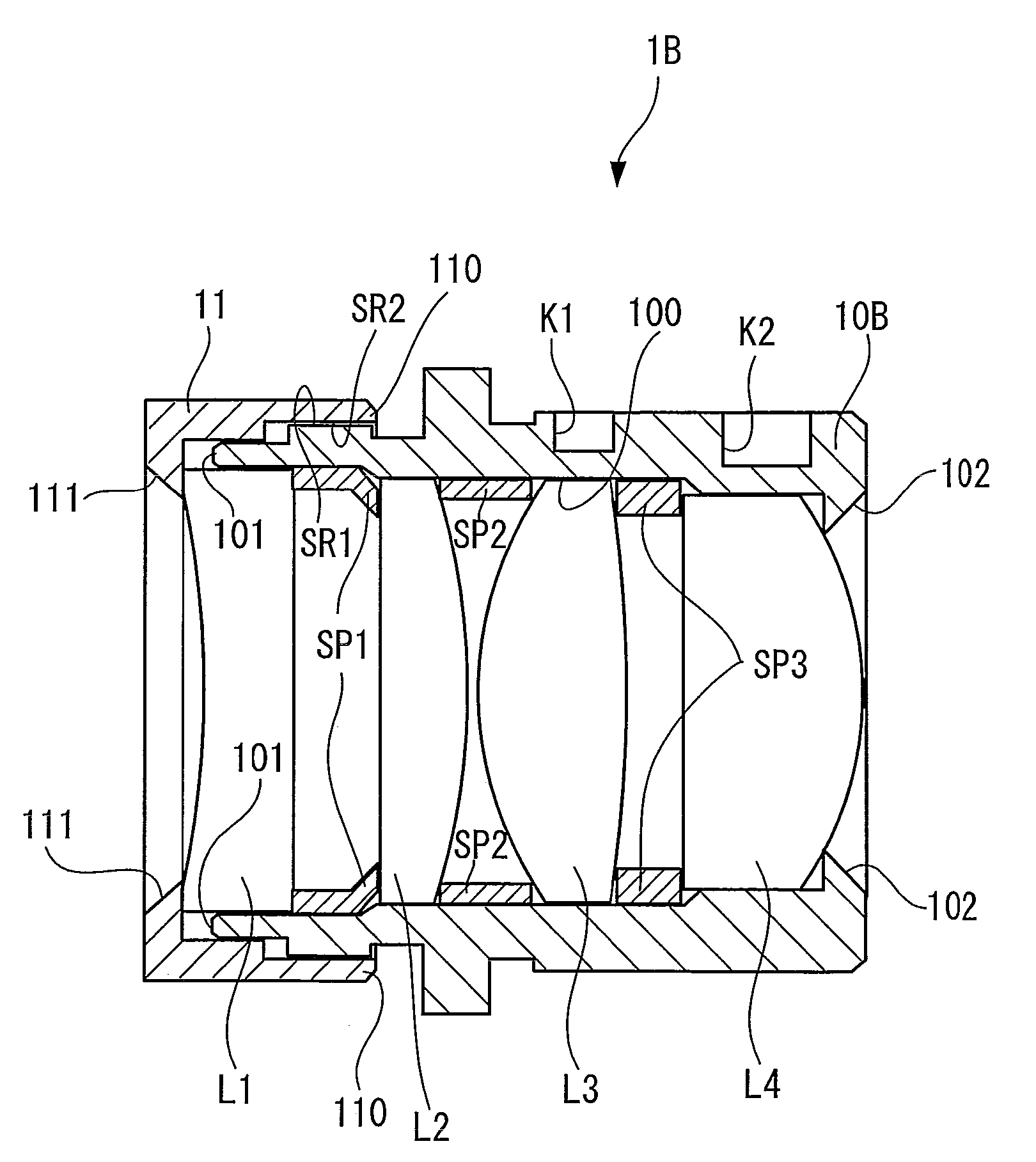
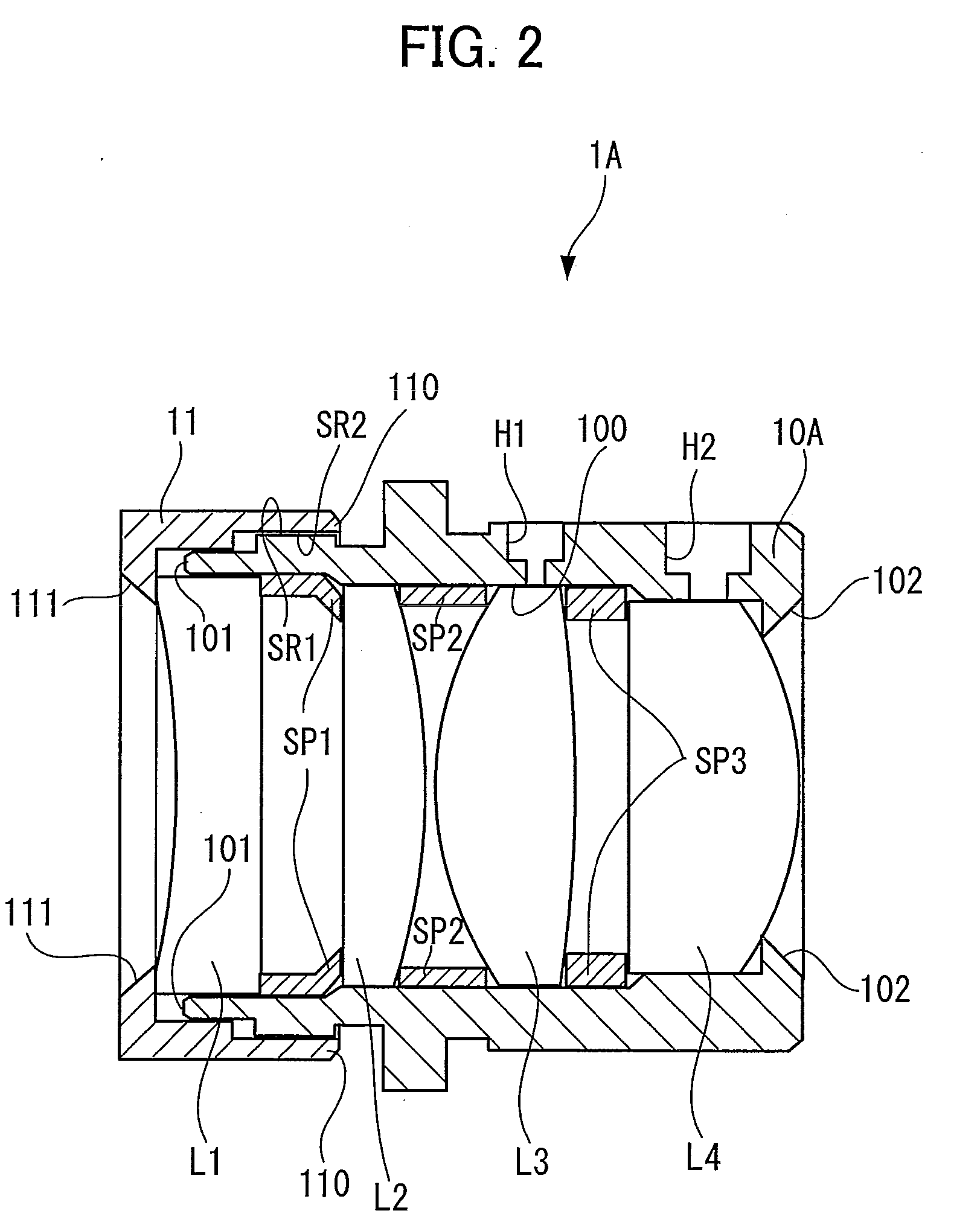
Lens barrel
A lens barrel for holding a lens system including at least a plastic lens disposed between two glass lenses separated from each other by a spacer ring comprises a cylindrical lens holding barrel fixedly holding the two glass and the plastic lenses, a cylindrical spacer ring fitted in the cylindrical lens holding barrel for elastically supporting the plastic lens therein and positioning the two glass lenses at a predetermined axial distance on opposite sides of the plastic lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Optical element and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS8149381B2Inhibition of dissolutionMaintain optical performancePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLight beamEngineering
An optical element is used for an exposure apparatus which is configured to illuminate a mask with an exposure light beam for transferring a pattern on the mask onto a substrate through a projection optical system and to interpose a given liquid in a space between a surface of the substrate and the projection optical system. The optical element includes a first anti-dissolution member provided on a surface of a transmissive optical element on the substrate's side of the projection optical system.
Owner:NIKON CORP
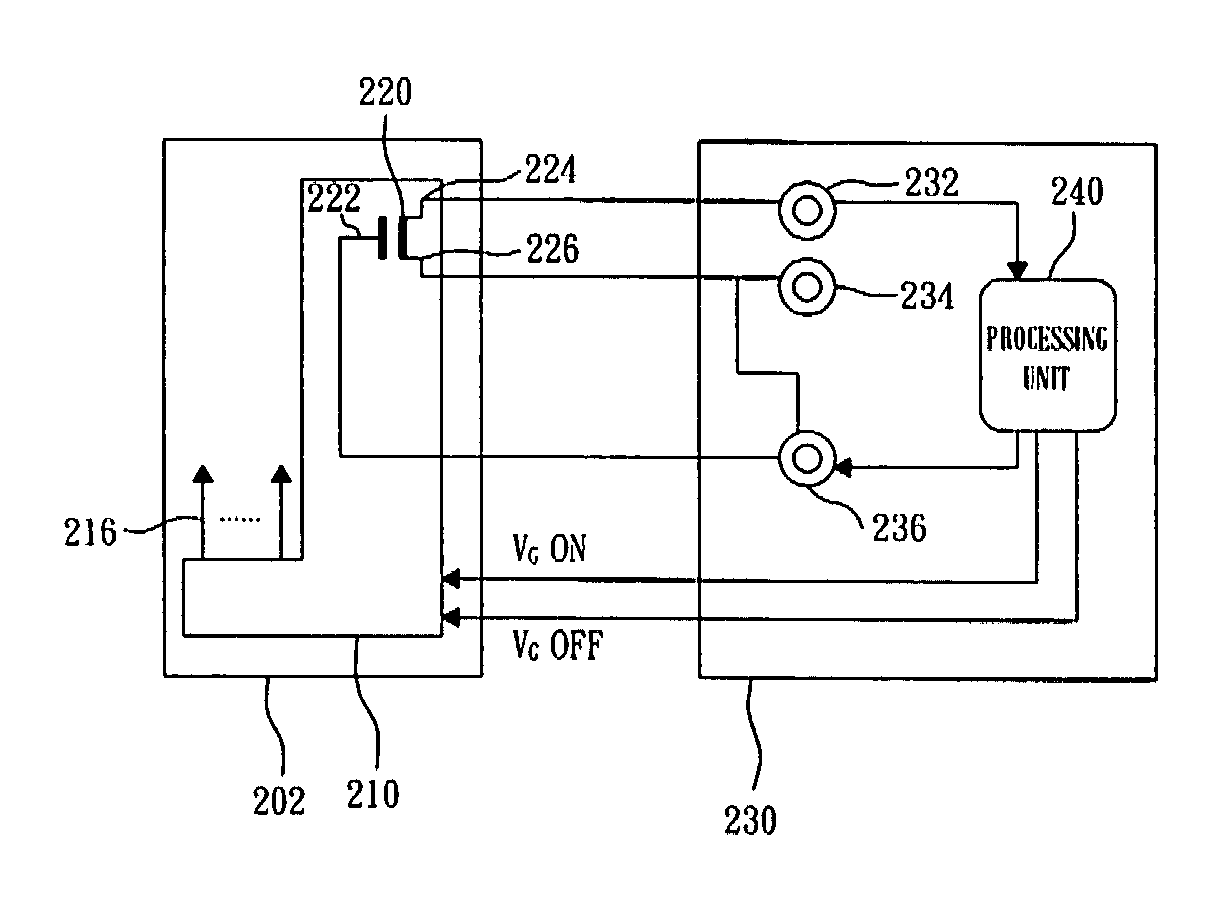
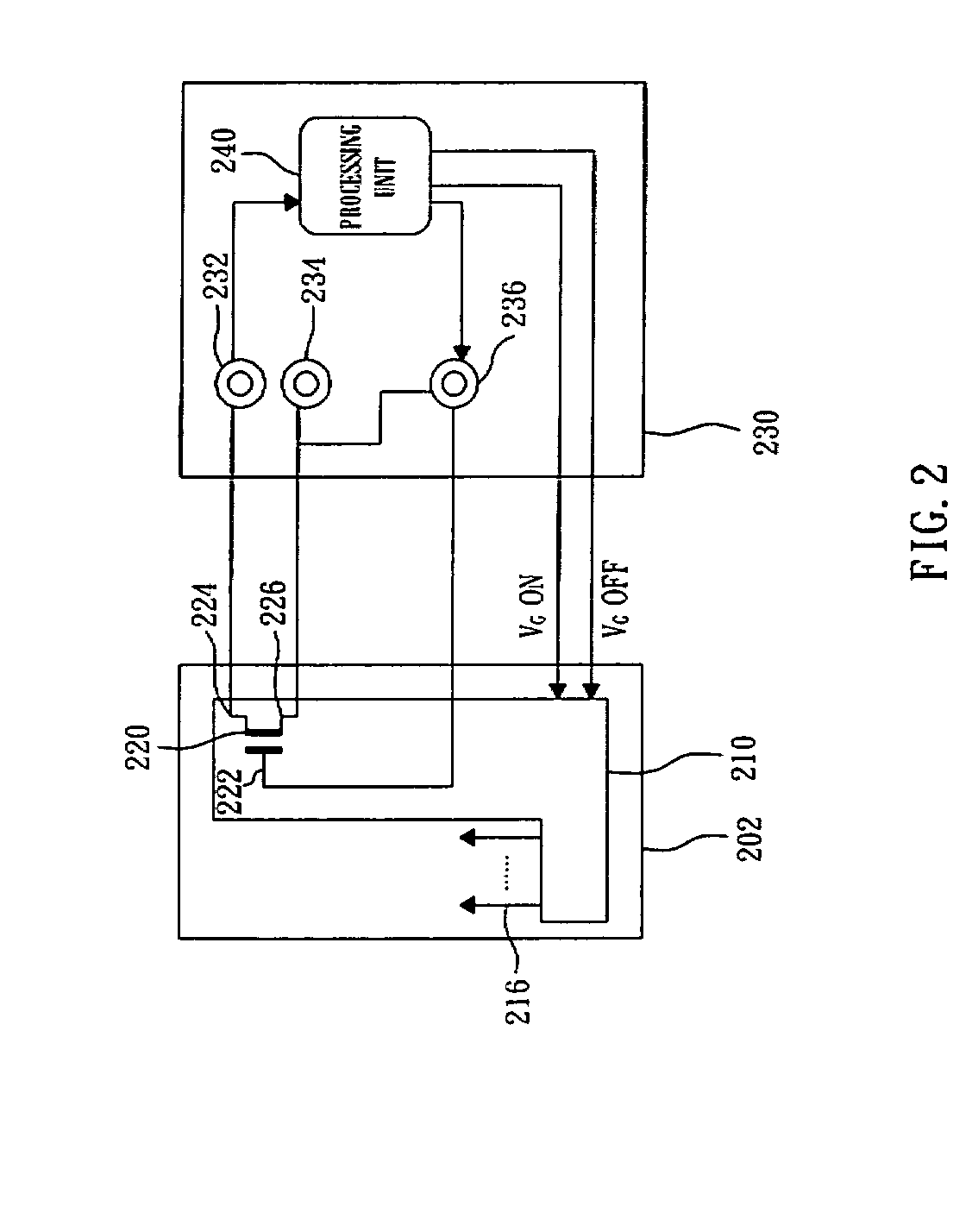
Display device comprising an integrated gate driver
InactiveUS20080079684A1Maintain optical performanceMaintain performanceStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitActive matrix
Owner:TPO HONG KONG HLDG
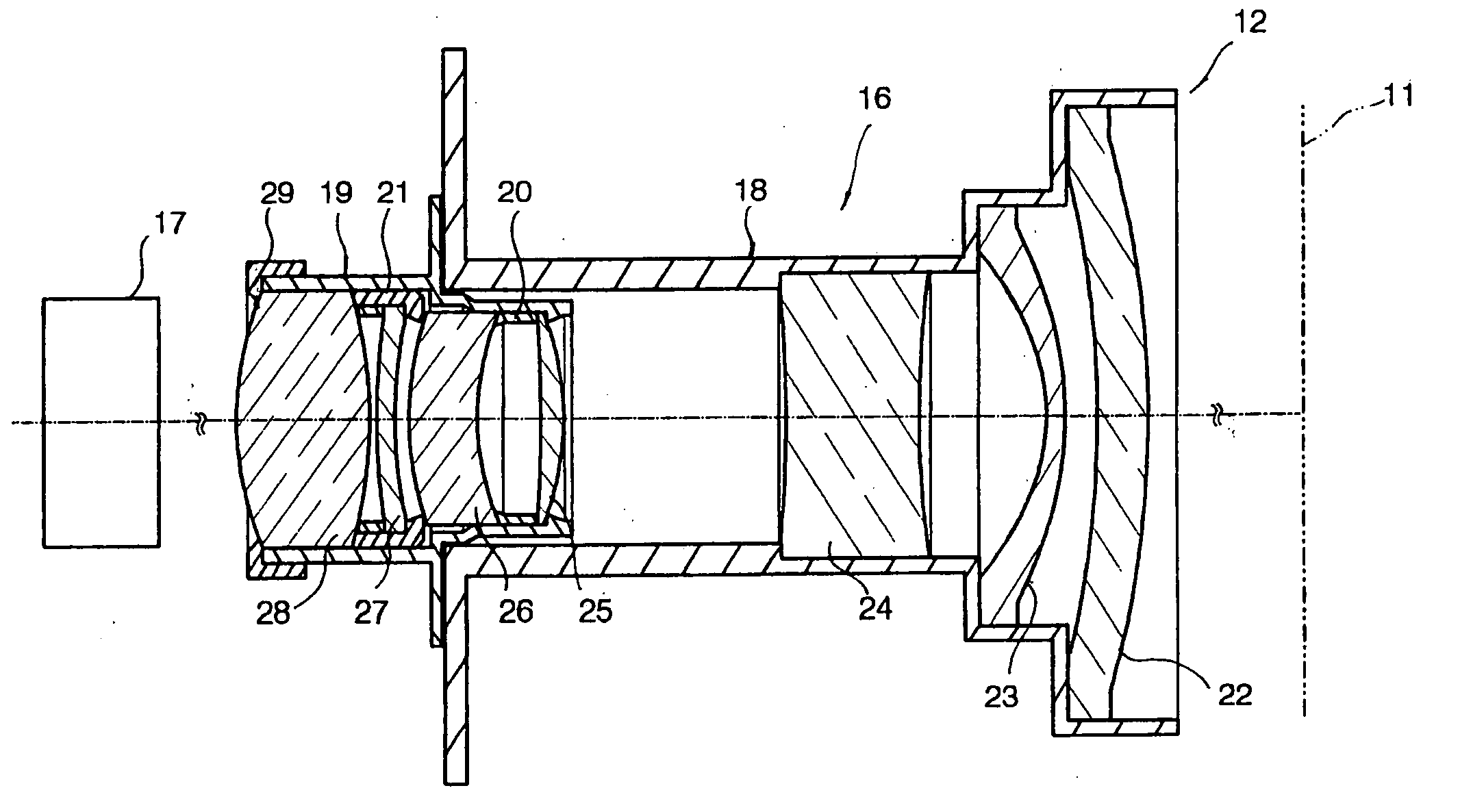
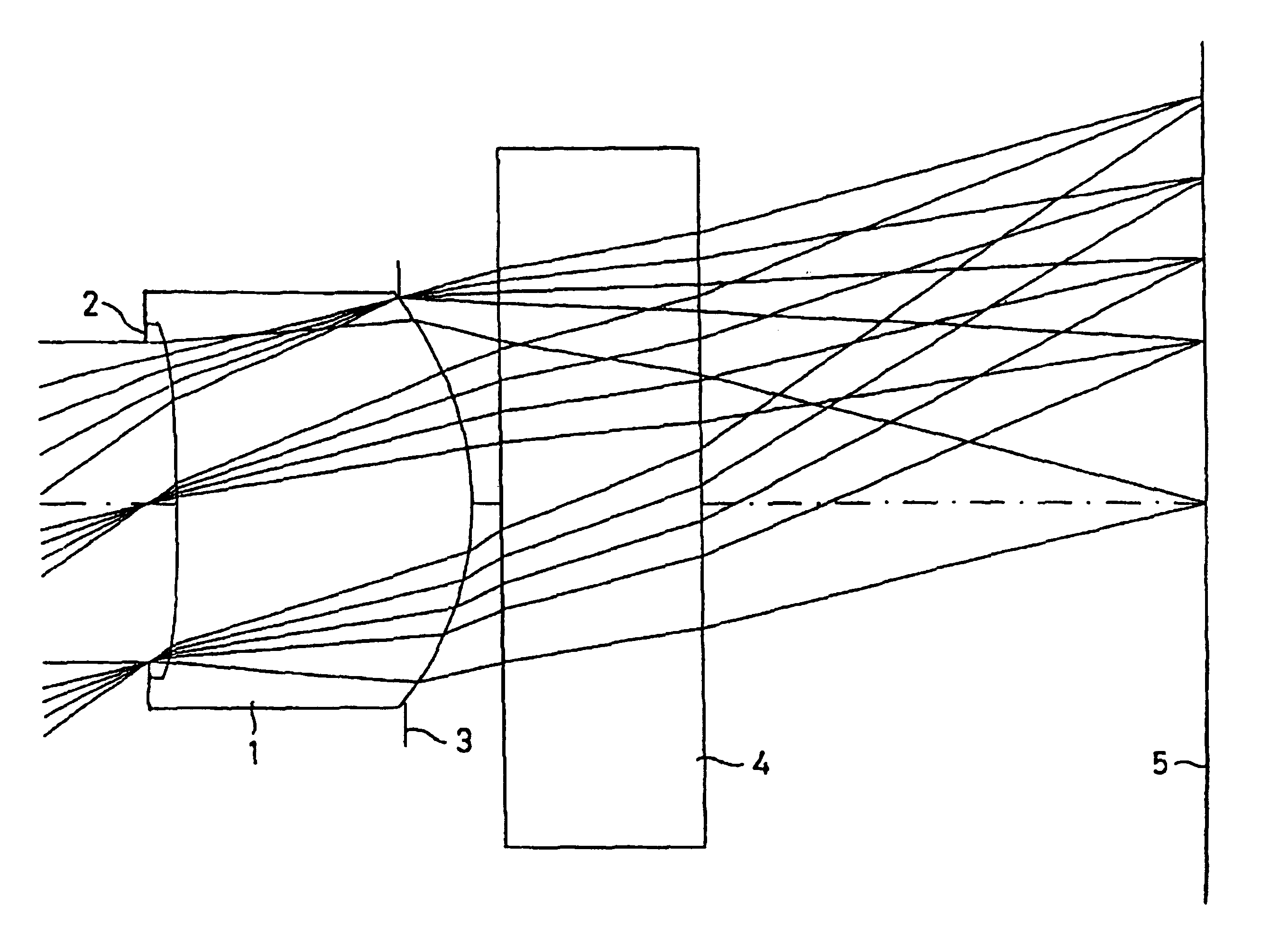
Image pickup lens system
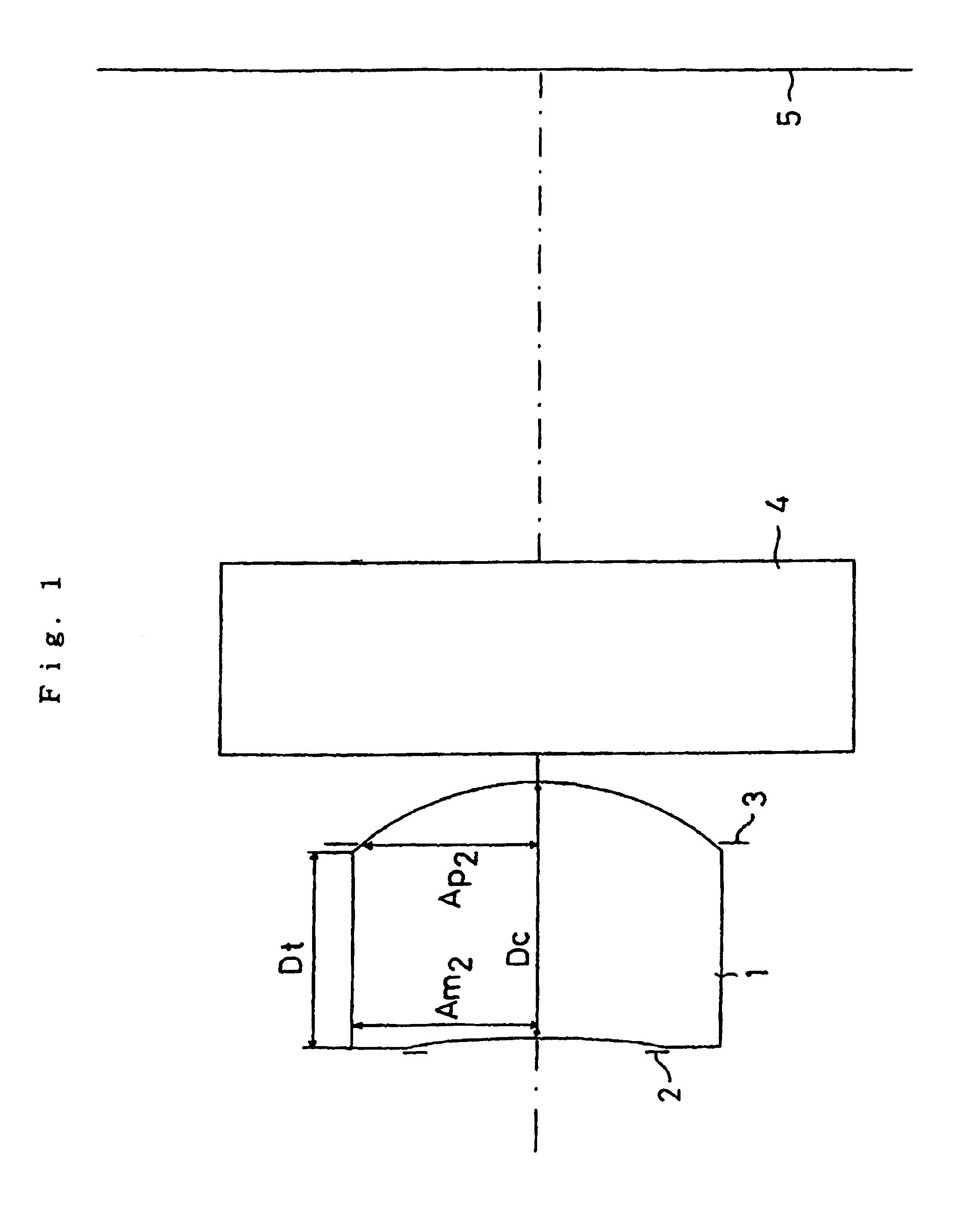
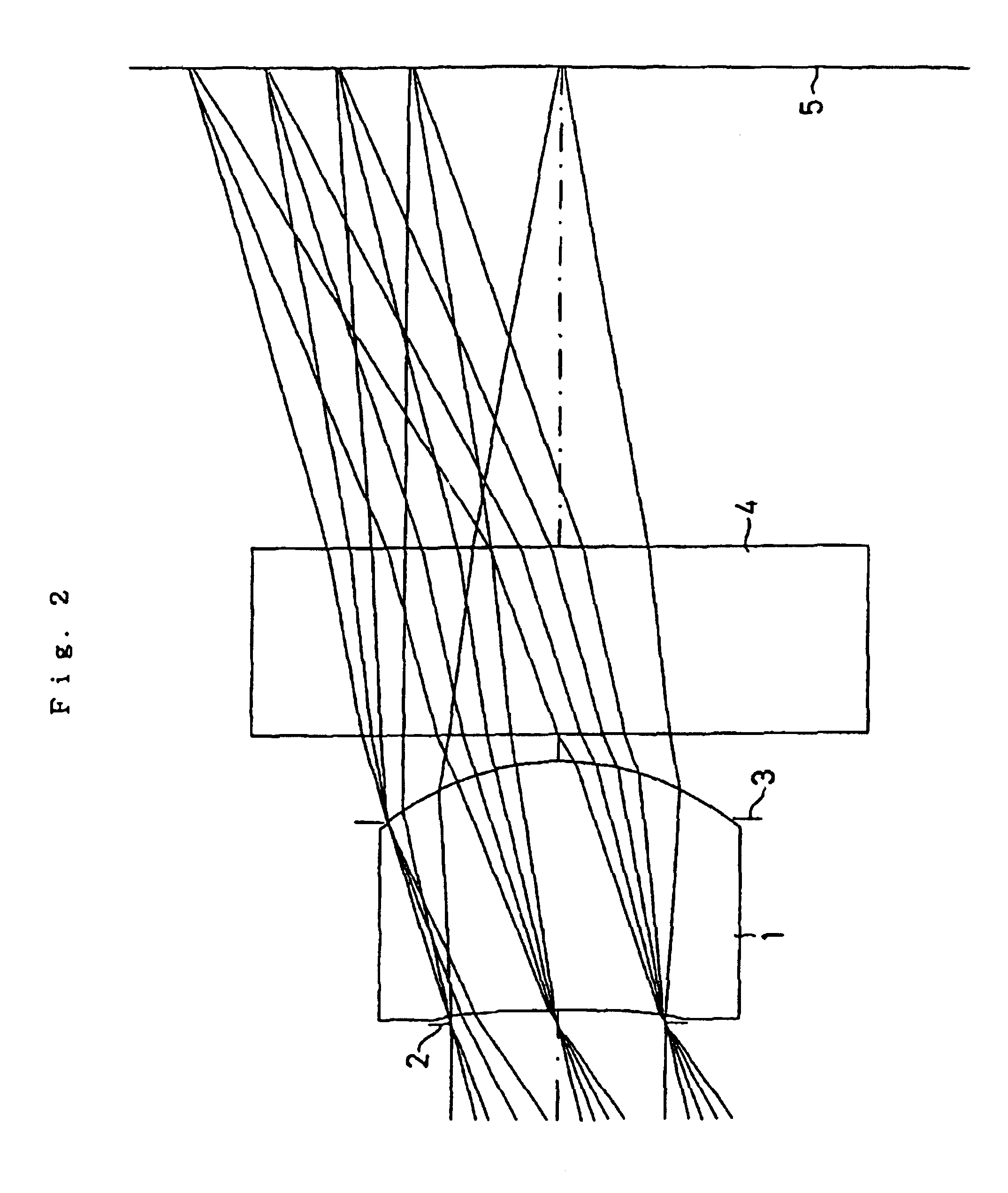
InactiveUSRE40638E1Easy to produceMaintain optical performanceRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansPhysicsCamera lens
An image pickup lens system includes a lens 1 of a meniscus shape having a first face as a convexconcave face, and a diaphragm 2 disposed on an object side of the lens 1. The lens 1 meets the following conditions: Y′ / fl equal to or larger than 0.6; Dt / Dc is equal to or smaller than 0.9 and equal to or larger than 0.5; and Ap2 / Am2 is equal to or larger than 0.9. Thus, even when an image pickup element is of a reduced size, a desired optical performance can be maintained, and it is possible to produce a lens easily with a back focal length ensured.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Lens barrel
A lens barrel for holding a lens system including at least a plastic lens disposed between two glass lenses separated from each other by a spacer ring comprises a cylindrical lens holding barrel fixedly holding the two glass and the plastic lenses, a cylindrical spacer ring fitted in the cylindrical lens holding barrel for elastically supporting the plastic lens therein and positioning the two glass lenses at a predetermined axial distance on opposite sides of the plastic lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
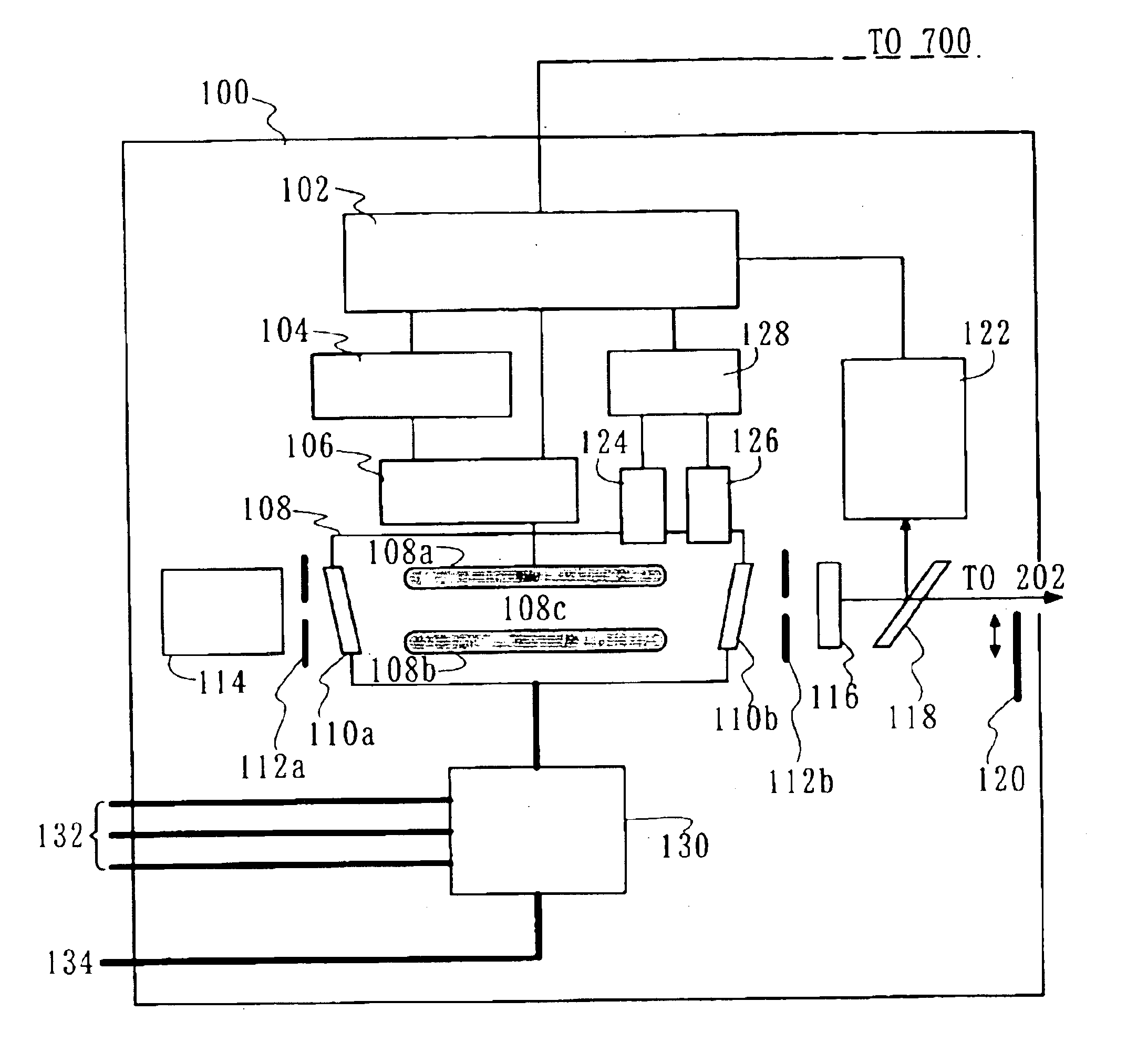
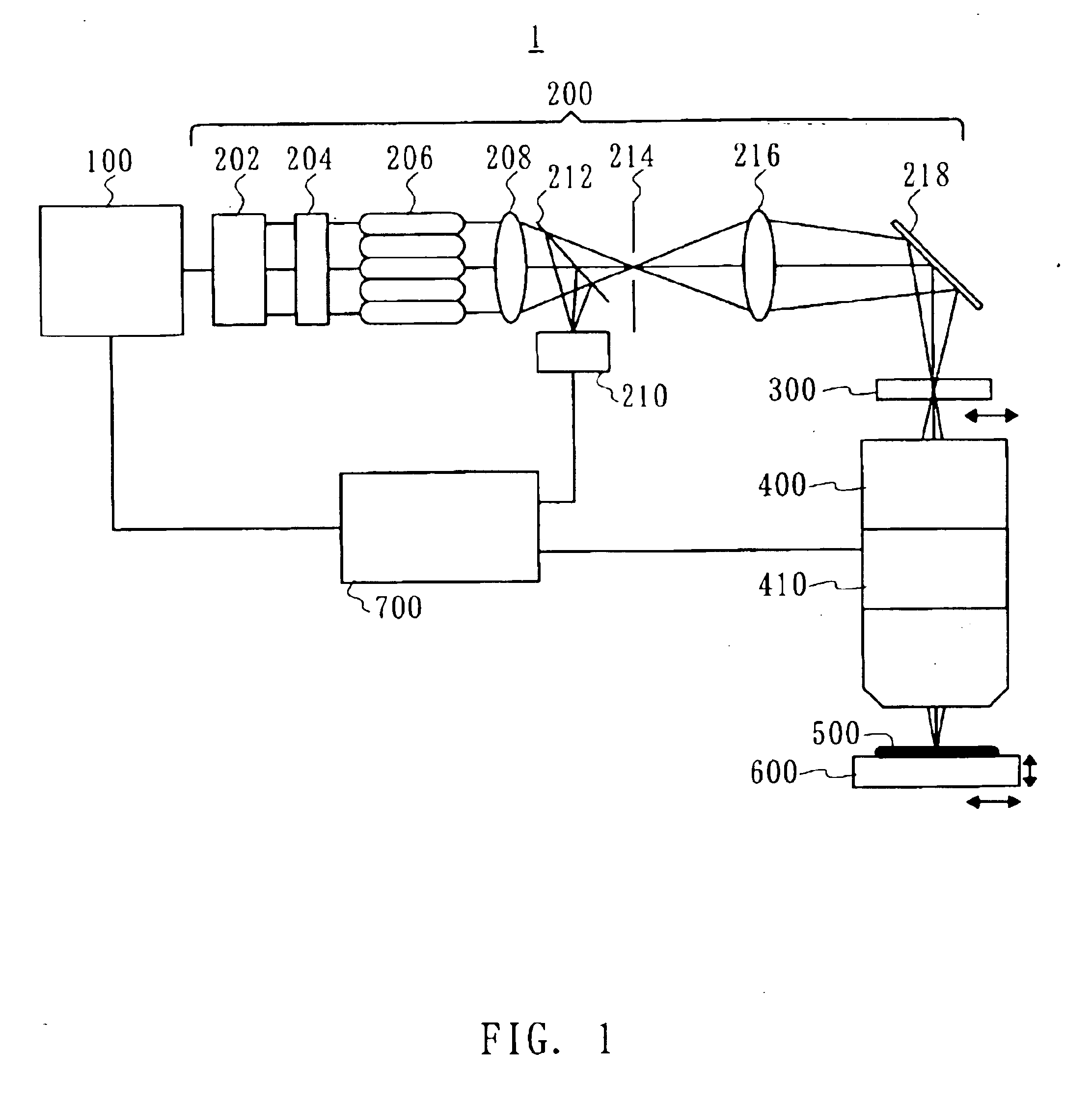
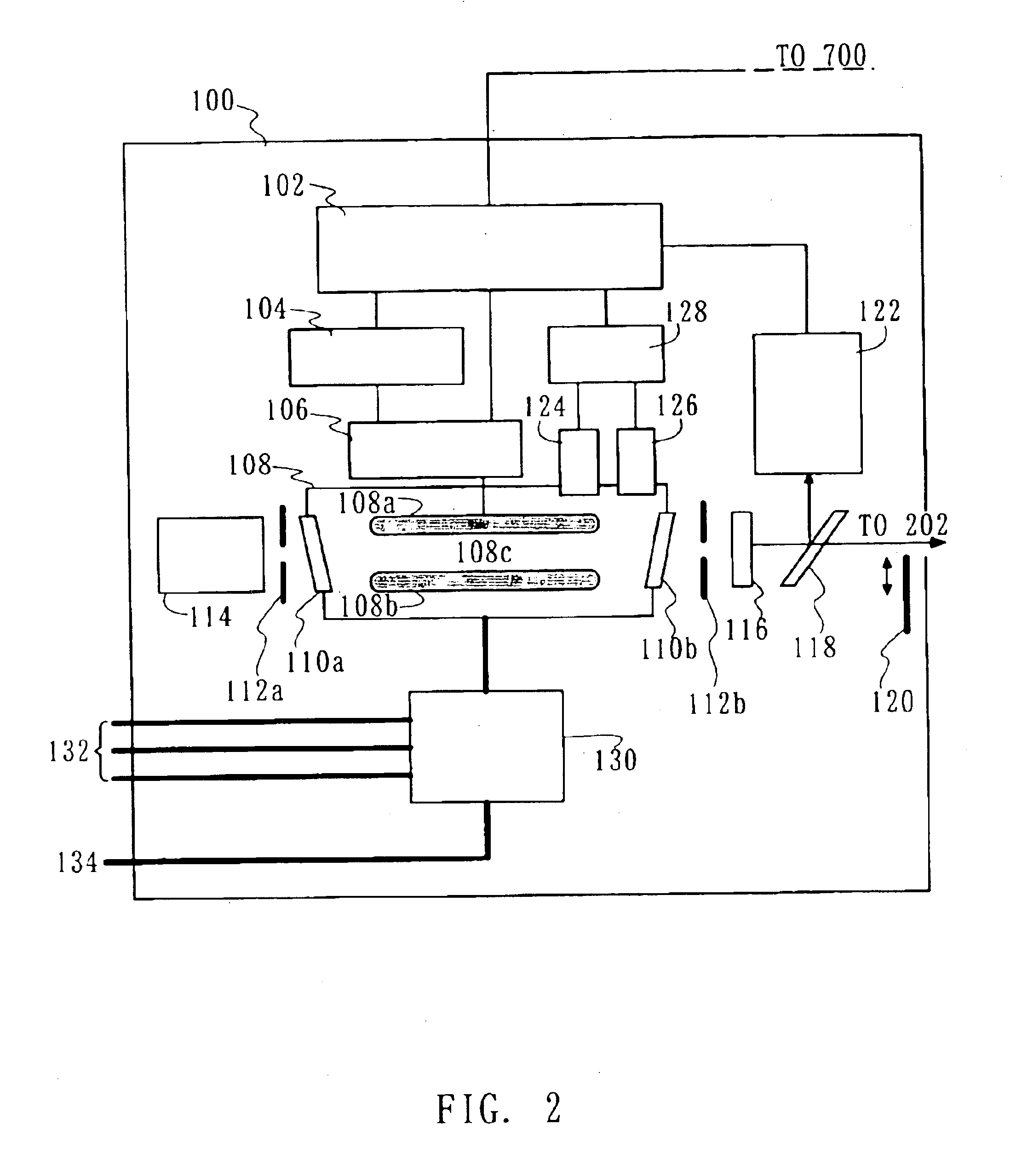
Laser apparatus, exposure apparatus and method
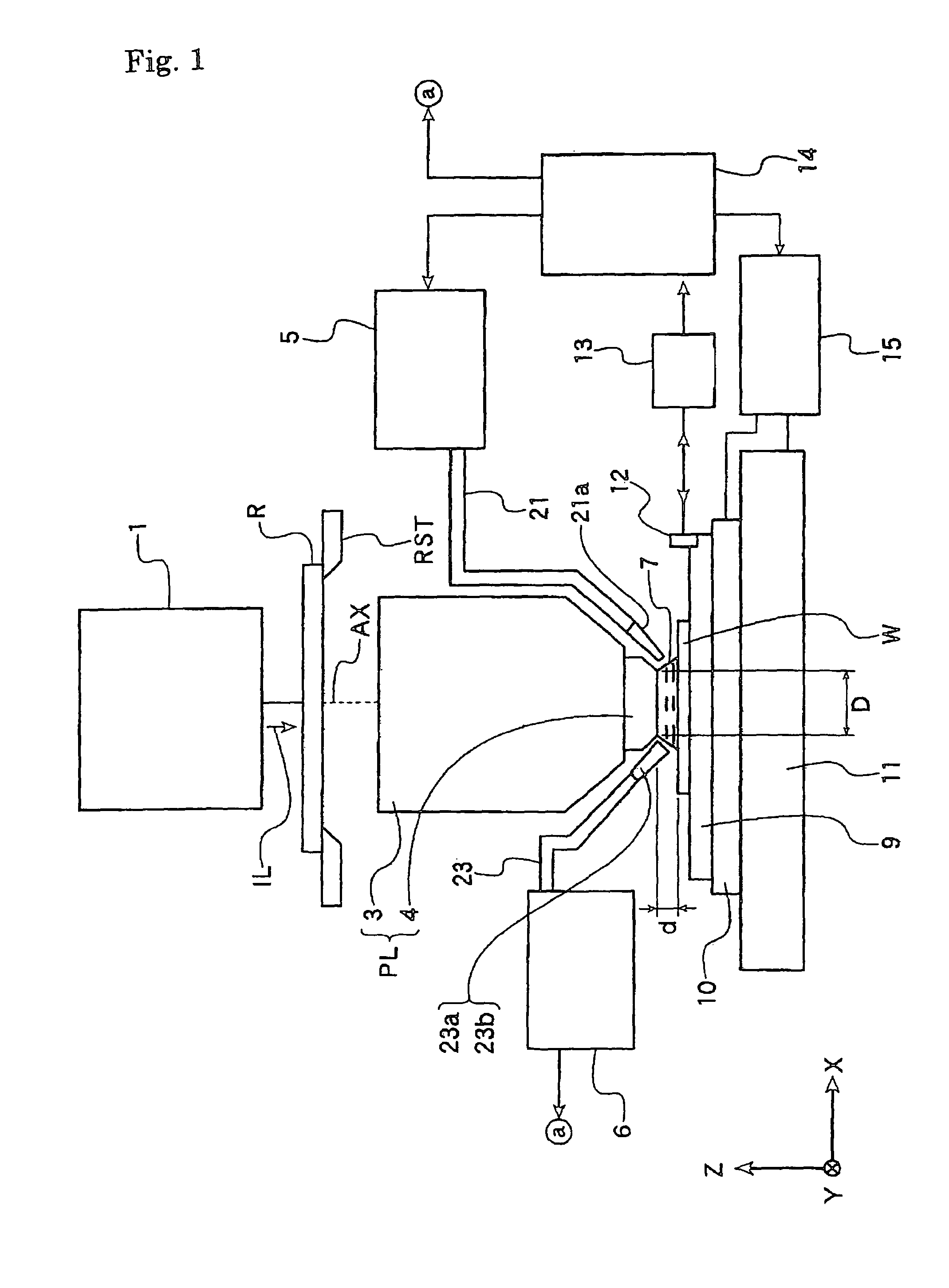
InactiveUS7085302B2Detect changeMaintain optical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive medium materialLight beamLength wave
There is to provide a laser apparatus that emits a laser beam by exciting gas enclosed in a chamber, including a gas characteristic detecting mechanism for detecting a characteristic of the gas in the chamber, and a calculation mechanism for calculating an oscillation wavelength and / or a wavelength spectral bandwidth of the laser beam based on a detected result by the gas characteristic detecting mechanism.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection system and projector
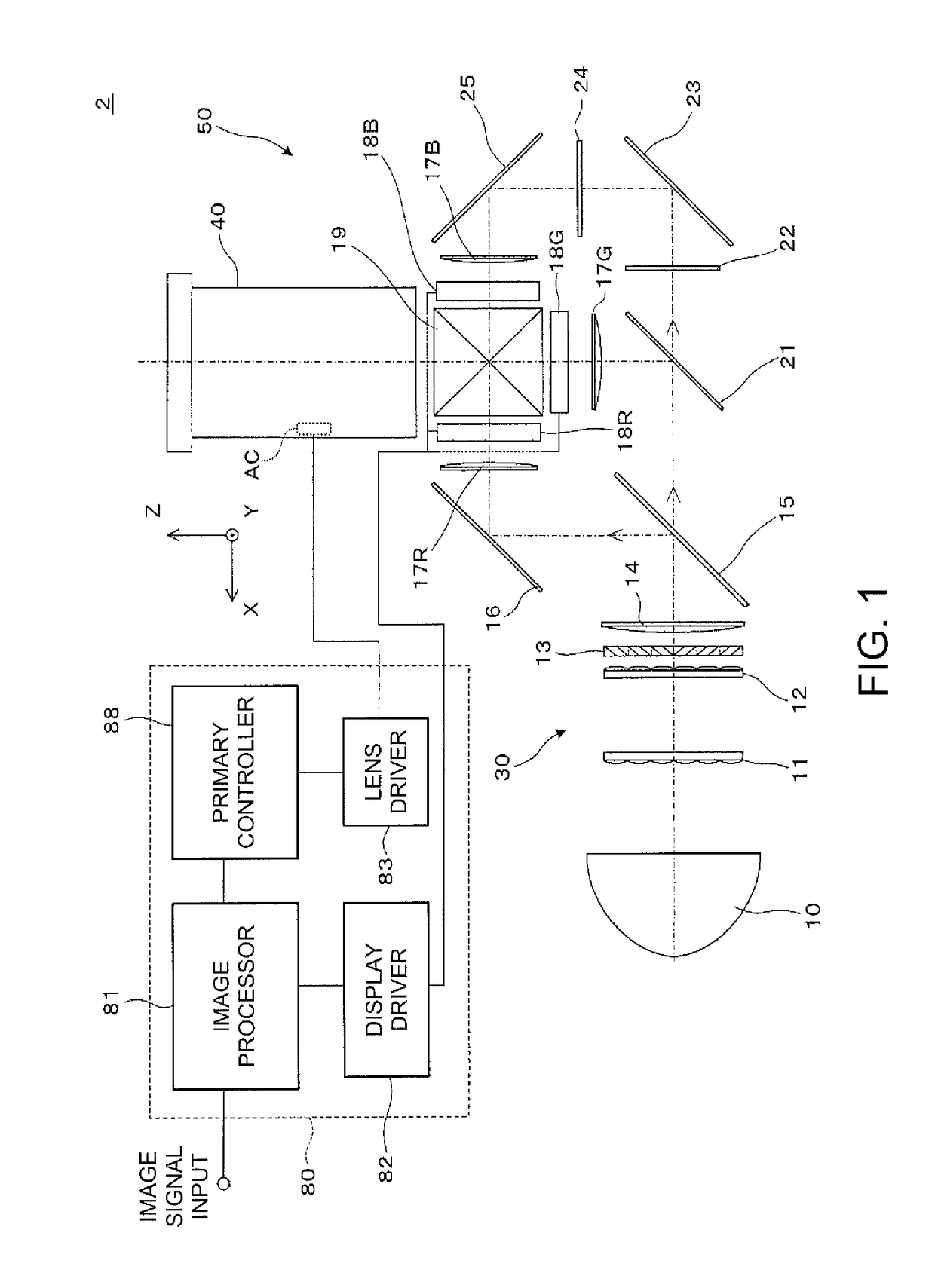
ActiveUS20160370691A1Centering can be readilyEasy to implementProjectorsMountingsEngineeringProjection system
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
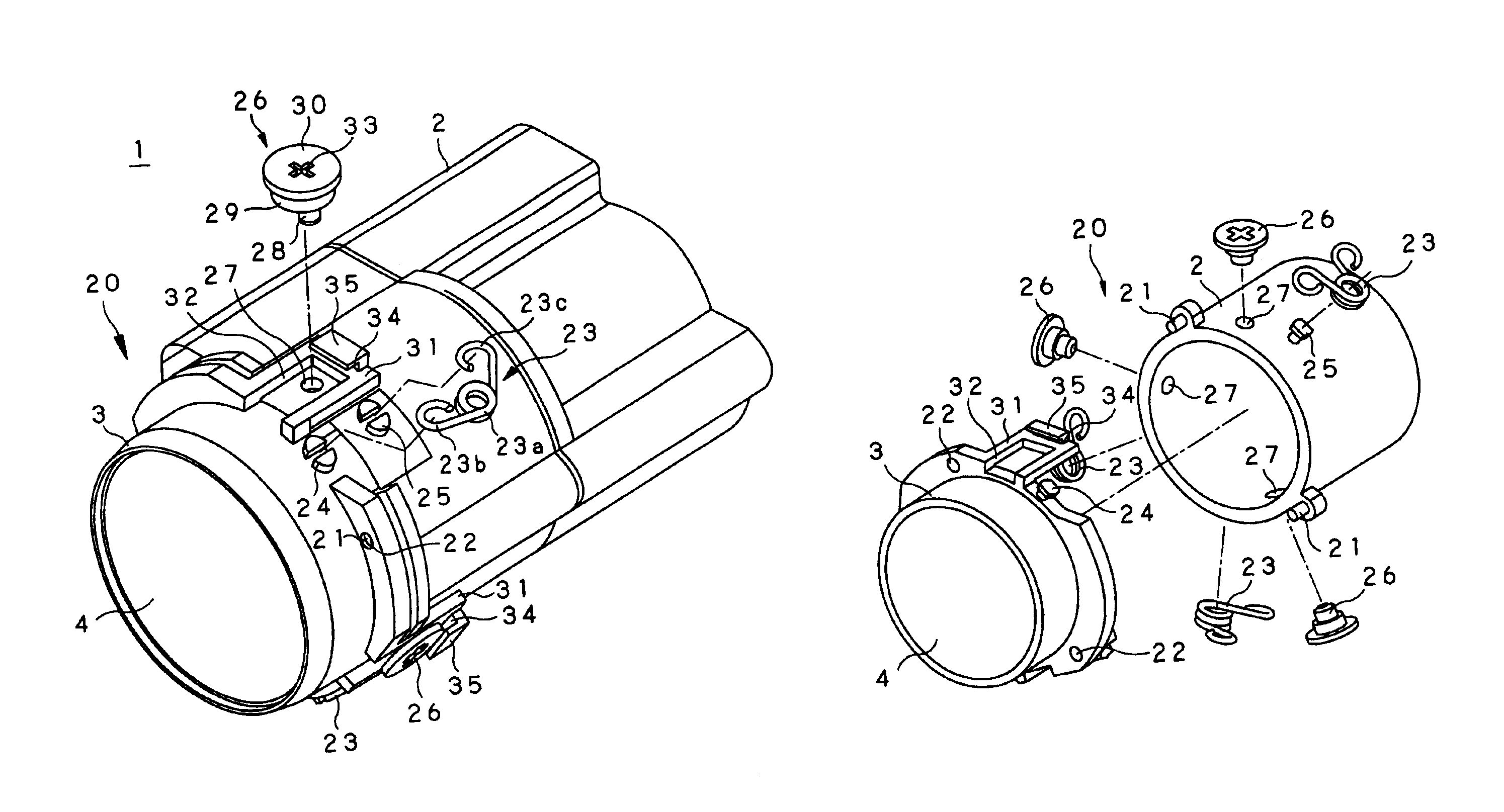
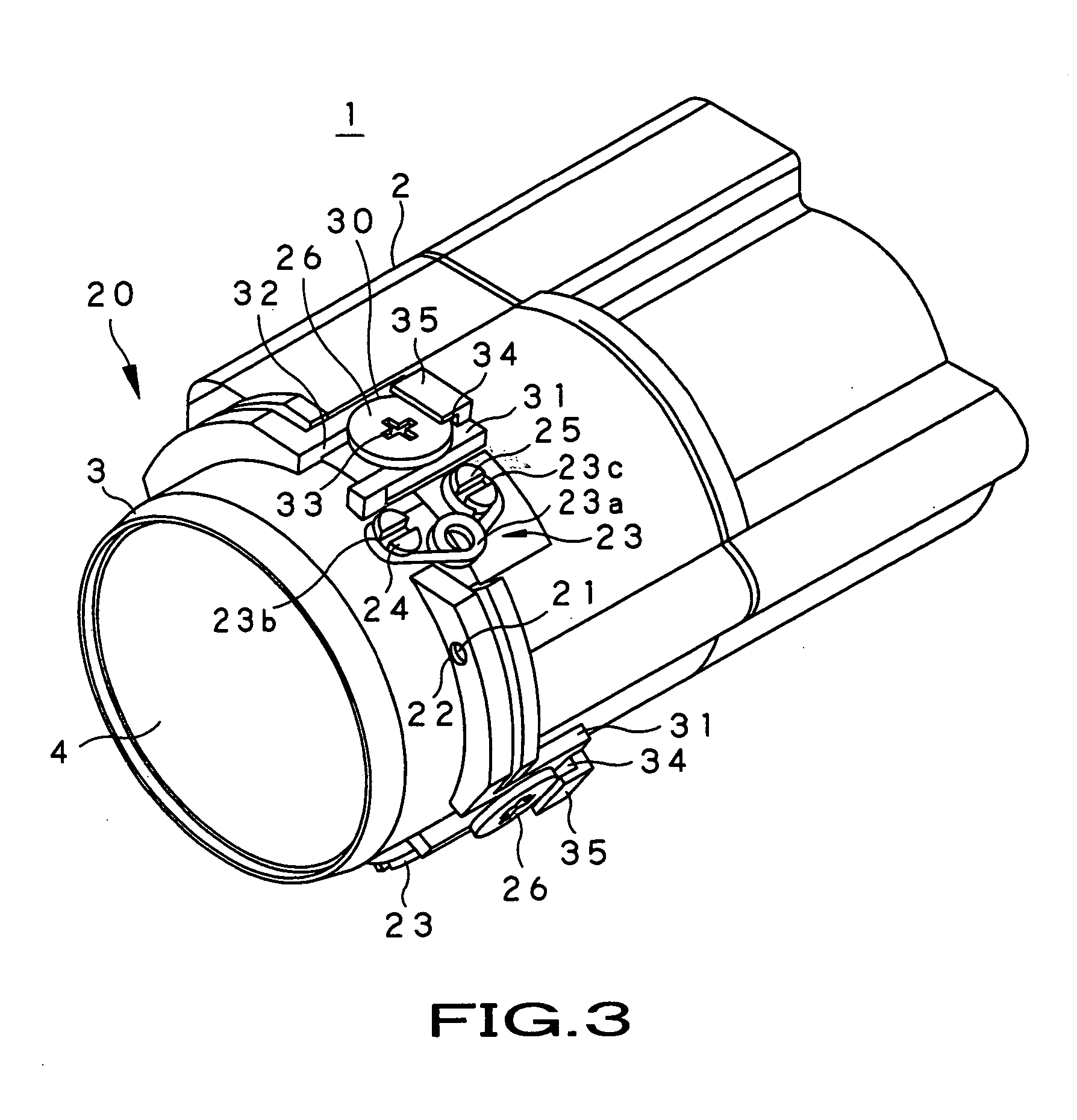
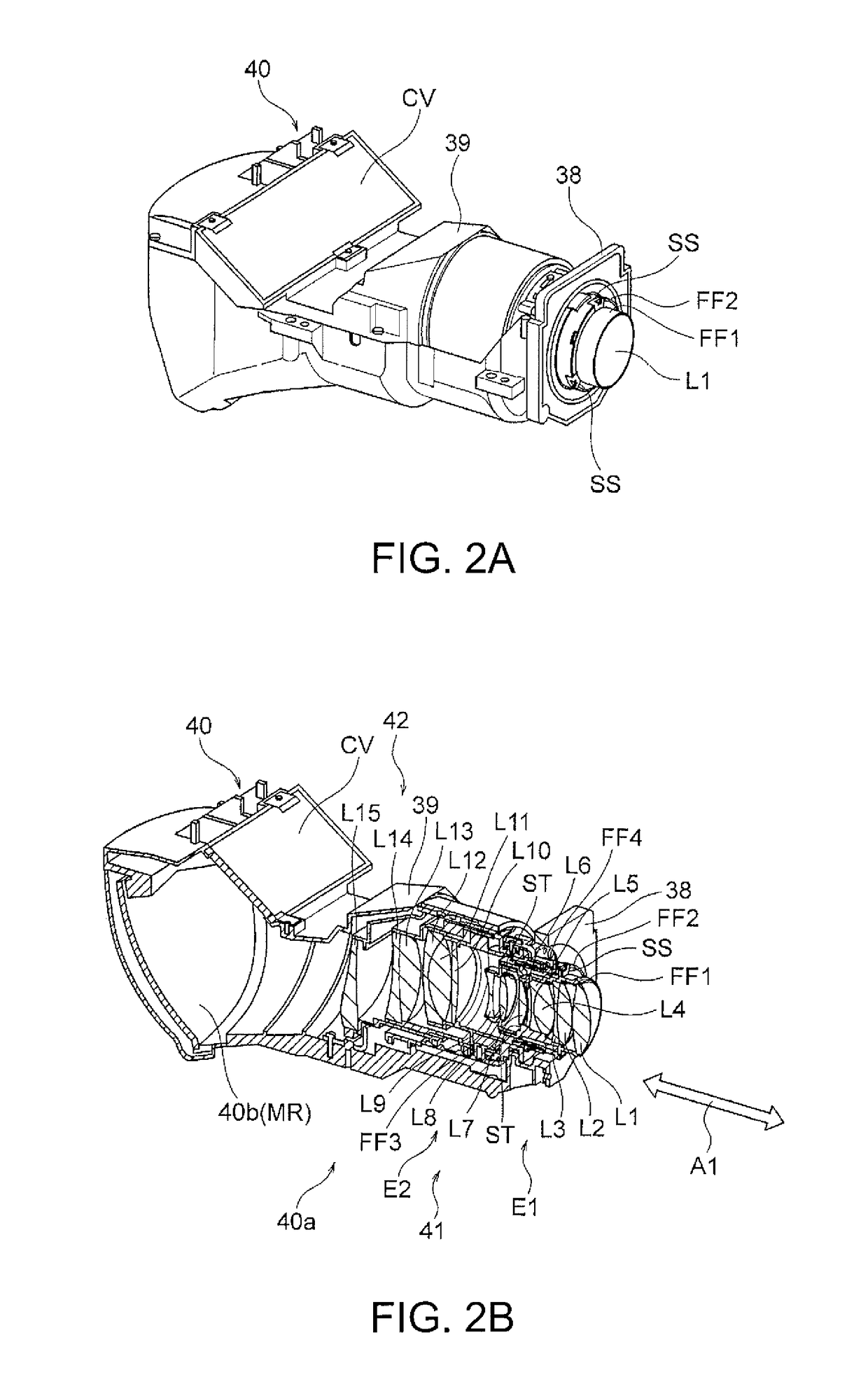
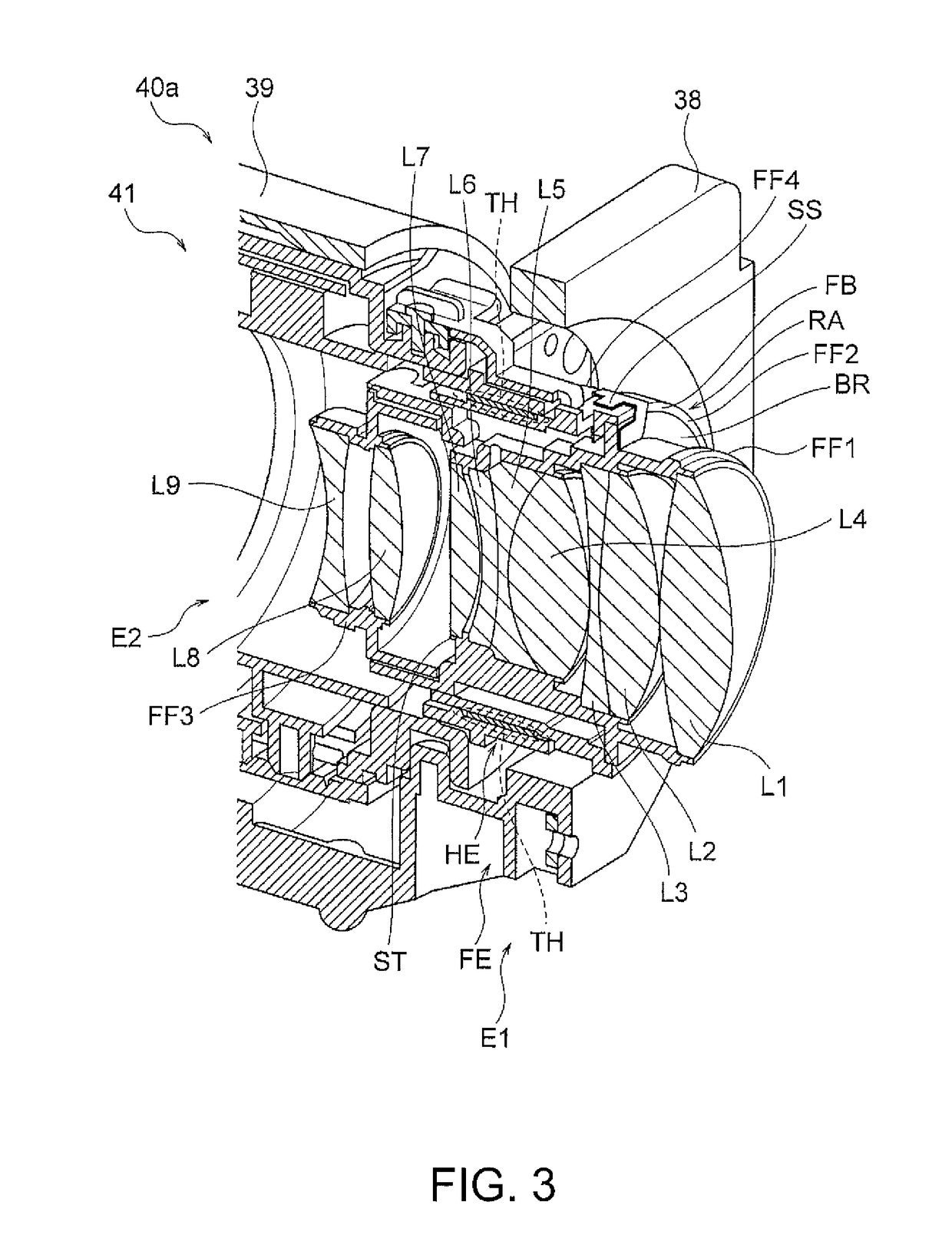
Lens frame, lens assembly and image-taking apparatus
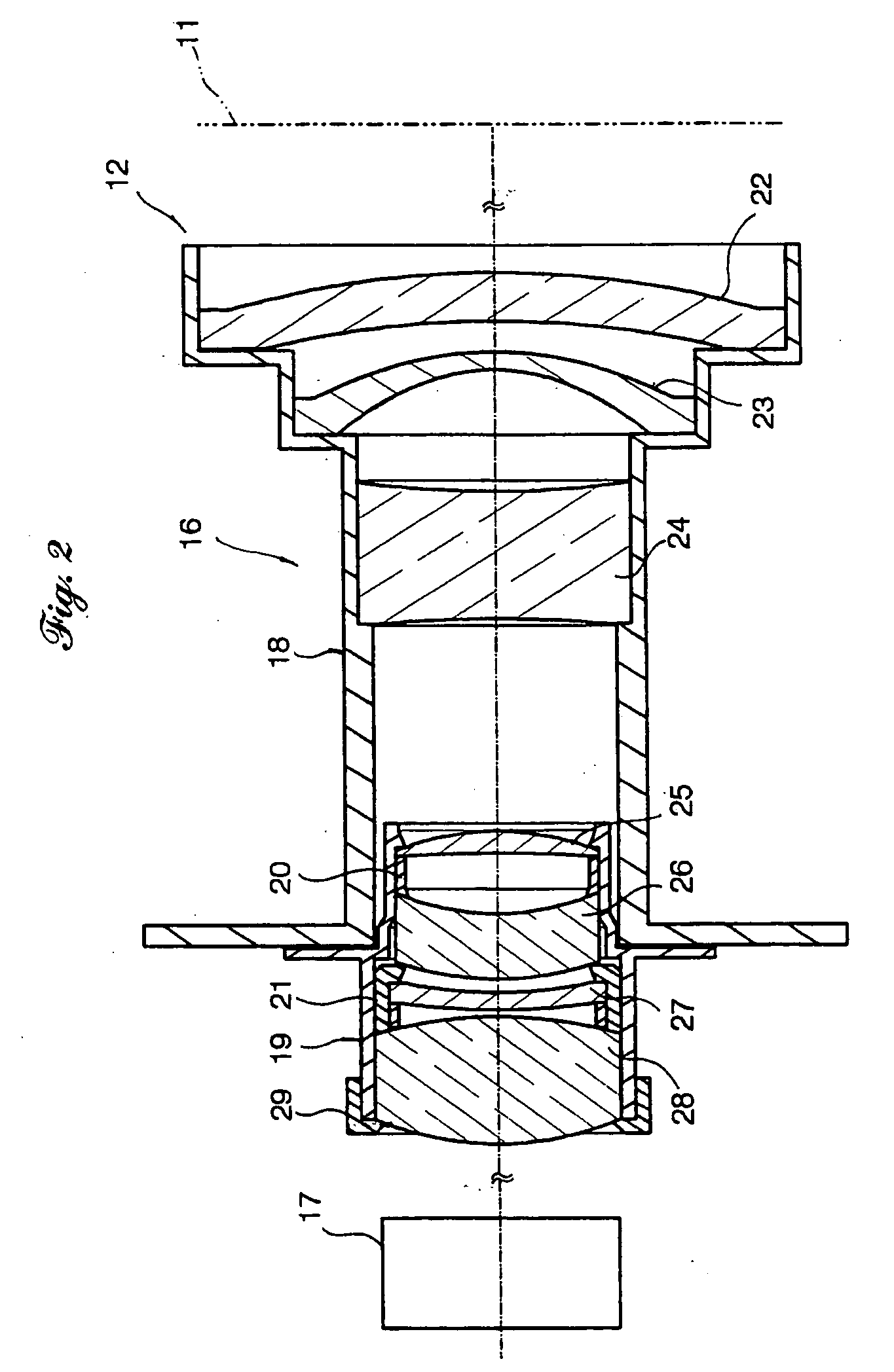
ActiveUS8025450B2Maintain optical performancePrevent movementTelevision system detailsProjector film strip handlingAdhesiveEngineering
A lens assembly made of porous ceramic is provided with concave sections into which an adhesive for fixing lenses inserted into a lens frame is injected. Each of the concave sections has an outward opening and a spacing wall provided between a hollow part of the lens frame and the opening. The adhesive injected into the concave sections passes through multiple pores in the lens frame made of porous ceramic, and reaches the periphery of each of the lenses, thereby fixing the lenses to an inner wall of the hollow part of the lens frame.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Lens frame, lens assembly and image-taking apparatus
ActiveUS20100080552A1Prevent movementMaintain optical performanceTelevision system detailsProjector film strip handlingCamera lensAdhesive
A lens assembly made of porous ceramic is provided with concave sections into which an adhesive for fixing lenses inserted into a lens frame is injected. Each of the concave sections has an outward opening and a spacing wall provided between a hollow part of the lens frame and the opening. The adhesive injected into the concave sections passes through multiple pores in the lens frame made of porous ceramic, and reaches the periphery of each of the lenses, thereby fixing the lenses to an inner wall of the hollow part of the lens frame.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Light-diffusive methacrylic resin light guide and surface light source device comprising the same
InactiveUS20090269008A1Improve image qualityImprovement of screen image qualityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideLight guideImaging quality
This invention provides a methyl methacrylate resin light guide for use in a surface light source device. The methyl methacrylate resin light guide can reduce the occurrence of dark lines and can improve the screen image quality of a surface light source device. The light guide characterized by including a methyl methacrylate resin and fine particles. Herein, not less than 0.01 parts by mass and not more than 0.5 parts by mass of the fine particles are dispersed in 100 parts by mass of the methyl methacrylate resin. In addition, the absolute value of a difference in refractive index between the fine resin particles and the methyl methacrylate resin is not less than 0.001 and not more than 0.02, the fine resin particles have an average particle size of not less than 1 μm and not more than 10 μm.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
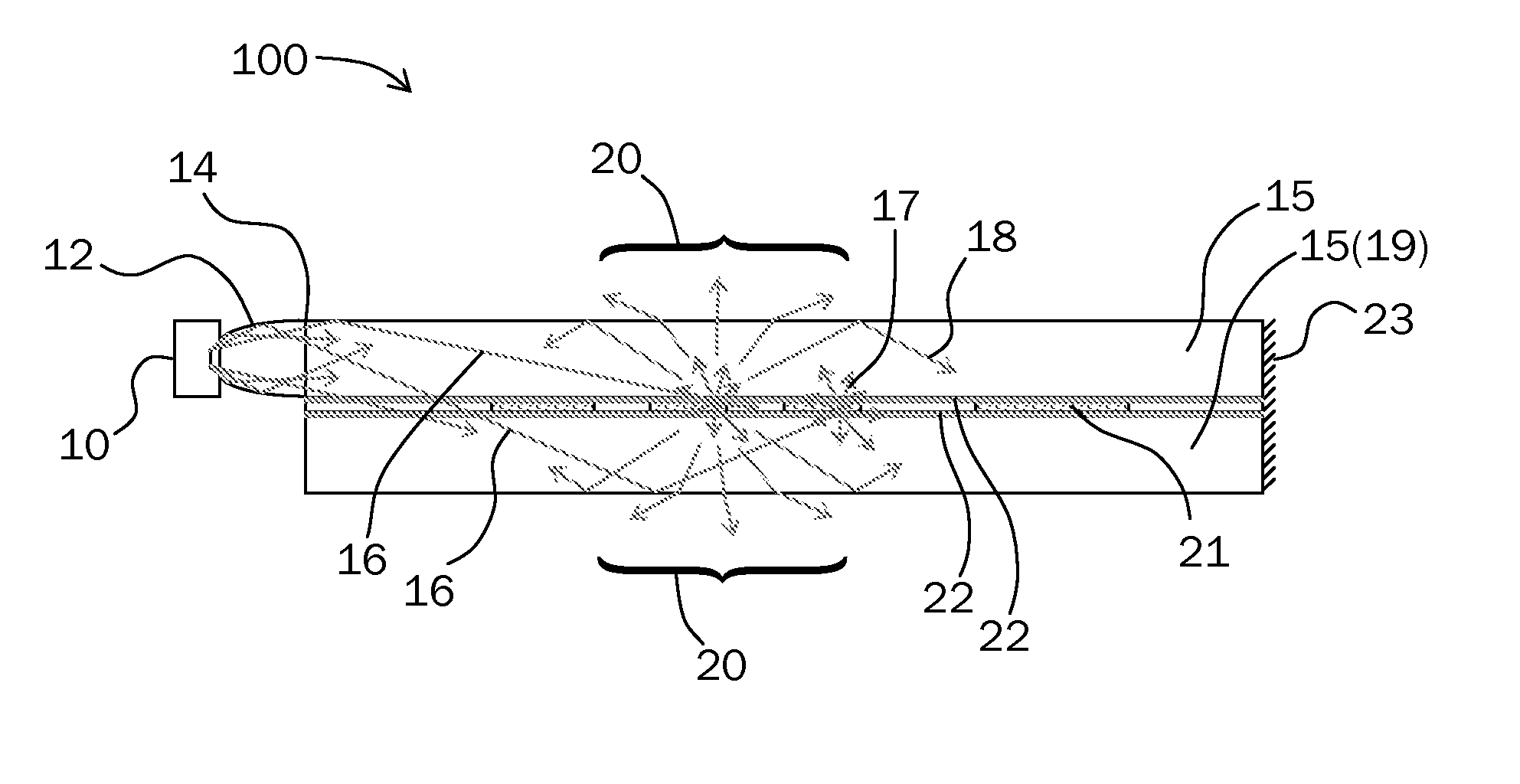
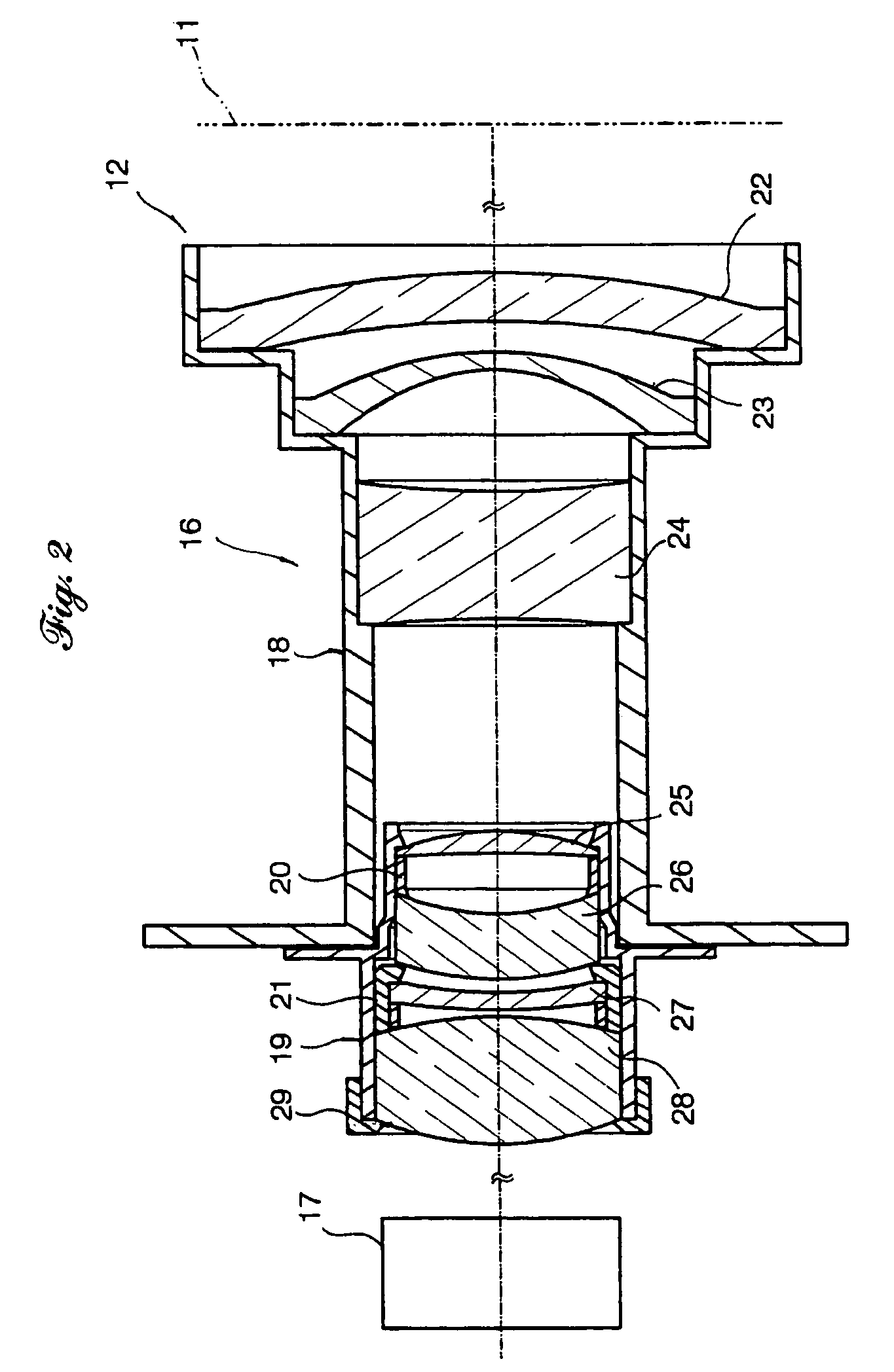
Armored fiber optic cable having a centering element and methods of making
Armored fiber optic cables and methods for making are disclosed that include an armor layer generally surrounding a fiber optic cable that includes at least one optical waveguide and a cable jacket. The cable jacket has an outer diameter and armor layer has an inner surface, wherein a gap exists between the outer diameter of the cable jacket and the inner surface of the armor layer. The armored fiber optic cable further includes a centering element disposed in the gap between the fiber optic cable and the armor layer. The centering element generally inhibits the fiber optic cable from moving away from a middle of the armored fiber optic cable towards the inner surface of the armor layer during winding of the armored fiber optic cable, thereby inhibiting wavy armor and / or preserving the optical performance of the at least one optical waveguide.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC
Plastic optical element, nest structure, die, optical scan apparatus and image formation apparatus
ActiveUS7898739B2Increase productivityLess optically harmful externalOptical articlesMountingsImage formationEngineering
A plastic optical element is provided, which includes an optical element body having a transfer surface which includes at least one laser beam incident portion of a concave shape, and a support portion connected with the optical element body, in which the support portion is disposed in a direction of a tangent line at an end of the transfer surface, and the optical element body and a part of the support portion are molded in the same nest structure.
Owner:RICOH KK
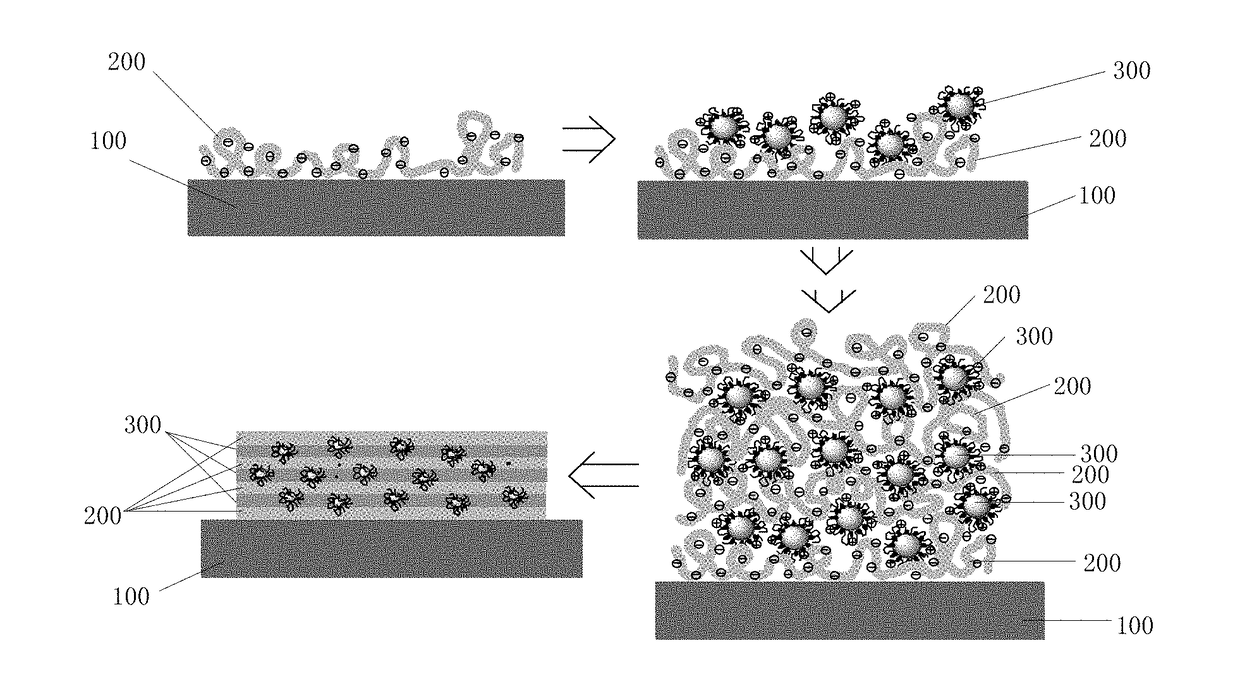
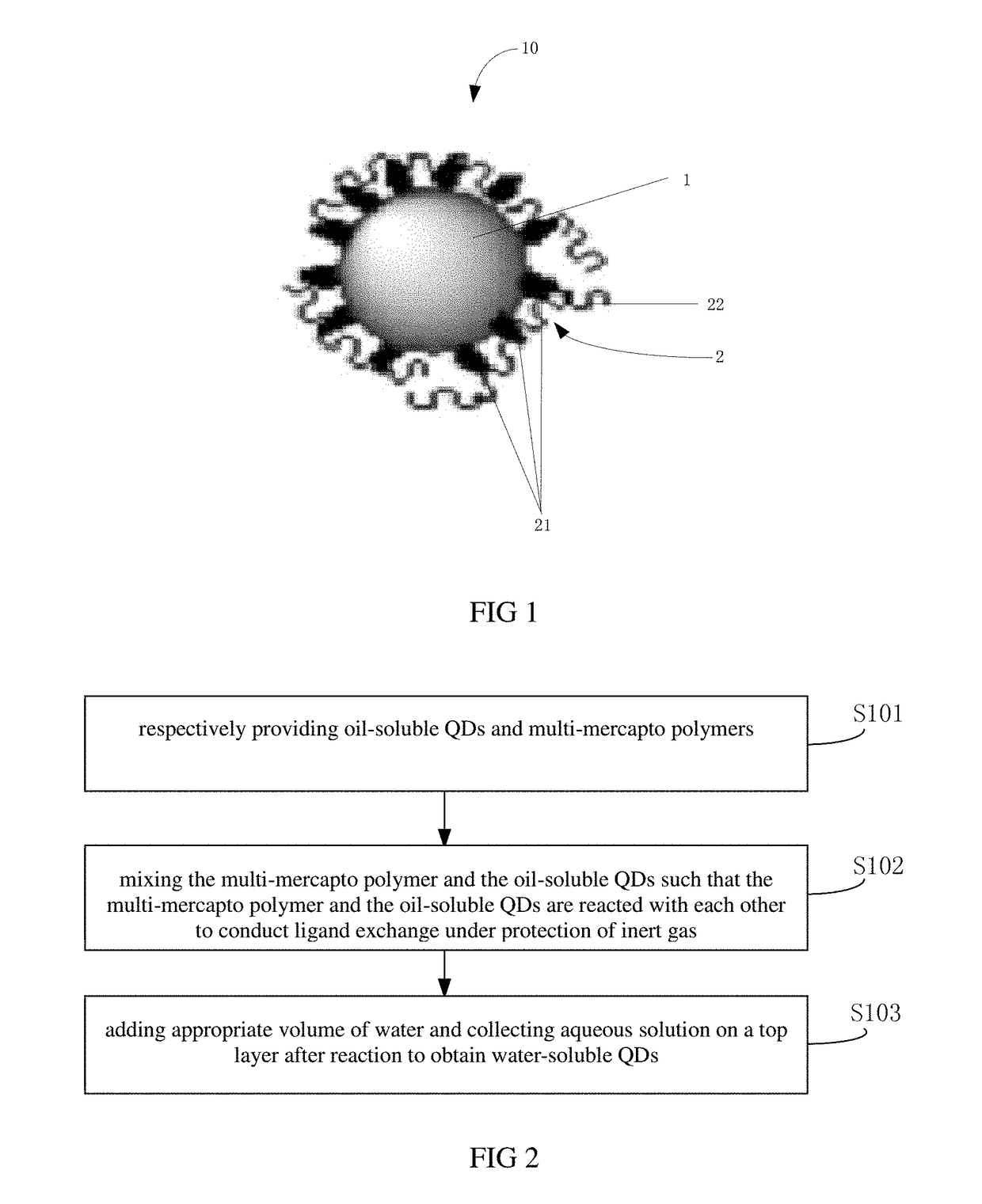
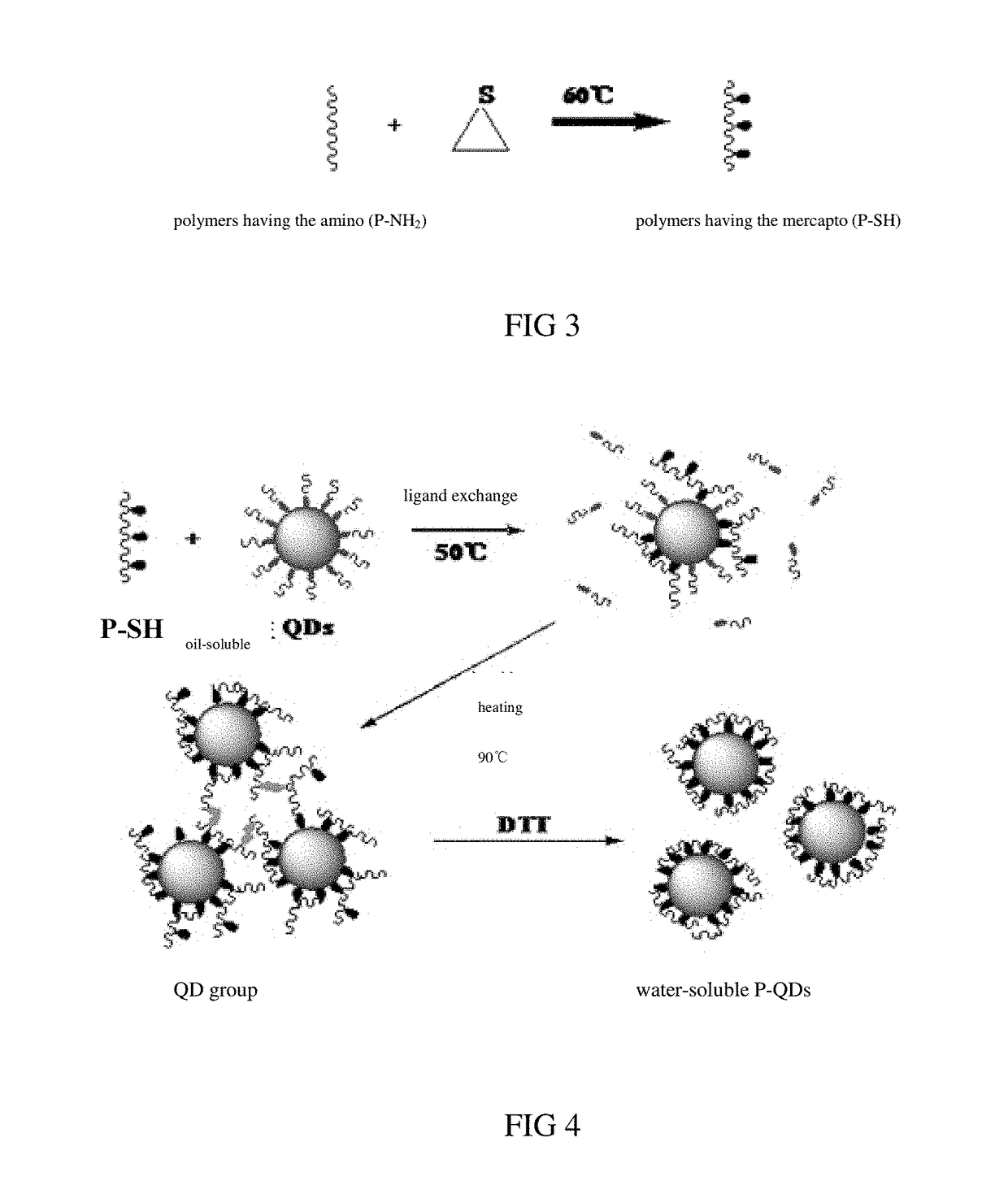
Water-soluble quantum dot (QD) and manufacturing methods of the water-soluble qd and the qd films
ActiveUS20180171219A1Improve adhesionStable water-solubleMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsQuantum dotWater soluble
The present disclosure relates to a water-soluble QD, and manufacturing methods of the water-soluble QDs and the QD films. The manufacturing method includes respectively providing oil-soluble QDs and multi-mercapto polymers, mixing the multi-mercapto polymer and the oil-soluble QDs such that the multi-mercapto polymer and the oil-soluble QDs are reacted with each other to conduct ligand exchange under protection of inert gas, and adding appropriate volume of water and collecting aqueous solution on a top layer after reaction to obtain water-soluble QDs. By adopting the above method, stable water-soluble QDs may be obtained, and the optical performance of the QDs may be maintained. In addition, the water-soluble QDs carrying the electrical charges may be adopted to prepare the QD film via the LBL method.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Eyepiece lens group of a riflescope system
An eyepiece lens group in a riflescope system comprises, from a front, eye side to a rear, object side, a glass lens and a plastic lens. The plastic lens has an aspherical surface and a diffractive surface, wherein the diffractive surface is on the front surface of the plastic lens and the aspherical surface is on the rear surface of the plastic lens. The aspherical surface of the plastic lens is utilized to abate the aberration. The diffractive surface of the plastic lens is utilized to abate the chromatic aberration. Therefore, the total numbers of lenses of the eyepiece lens group in the riflescope system could be reduced and the weight of the riflescope system could be reduced.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
Virtual image display device
InactiveUS20190079299A1Suppress generationReduce weightPolarising elementsMagnifying glassesImaging qualityDisplay device
By removing part of a lens effective diameter range in a cut lens, a lens is reduced in size and weight in an HMD that trends toward a larger device size. At this time, by making an area to be removed within the lens effective diameter range to be an area on a nose side, reductions in size and weight can be achieved while considering influence on image quality or fitting to a human face.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Remotely coated fluorescent powder plate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107425096AHigh hardnessMaintain physical propertiesSemiconductor devicesFluorescenceSilica gel
The invention discloses a remotely coated fluorescent powder plate and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of 1, design and manufacturing of a mold: designing and manufacturing a glass mold provided with a groove and a positioning through hole and matched with a dispensing device; 2, deploying and dispensing of fluorescent colloid: mixing fluorescent powder with silica gel, then stirring uniformly, and defoaming to acquire the fluorescent colloid; uniformly spraying a releasing agent to the inner wall and the bottom of the groove of the glass mold, and then dispensing the colloid; 3, solidification: after colloid is dispensed, standing horizontally, and after the colloid flows flat, placing the glass mold into an oven for baking so as to solidify the fluorescent colloid in the groove; and 4, demolding: scraping the solidified fluorescent colloid away from the inner wall of the groove to acquire the remotely coated fluorescent powder plate. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, the silica gel with rigidity of Shore hardness D40 which is higher than the rigidity of common COB packaging silica gel, so that the prepared remotely coated fluorescent powder plate is prone to shape and demold, good in shape retentivity, and is applicable to integrated lamps, with good photoelectric index.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN INST OF MODERN IND TECH SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
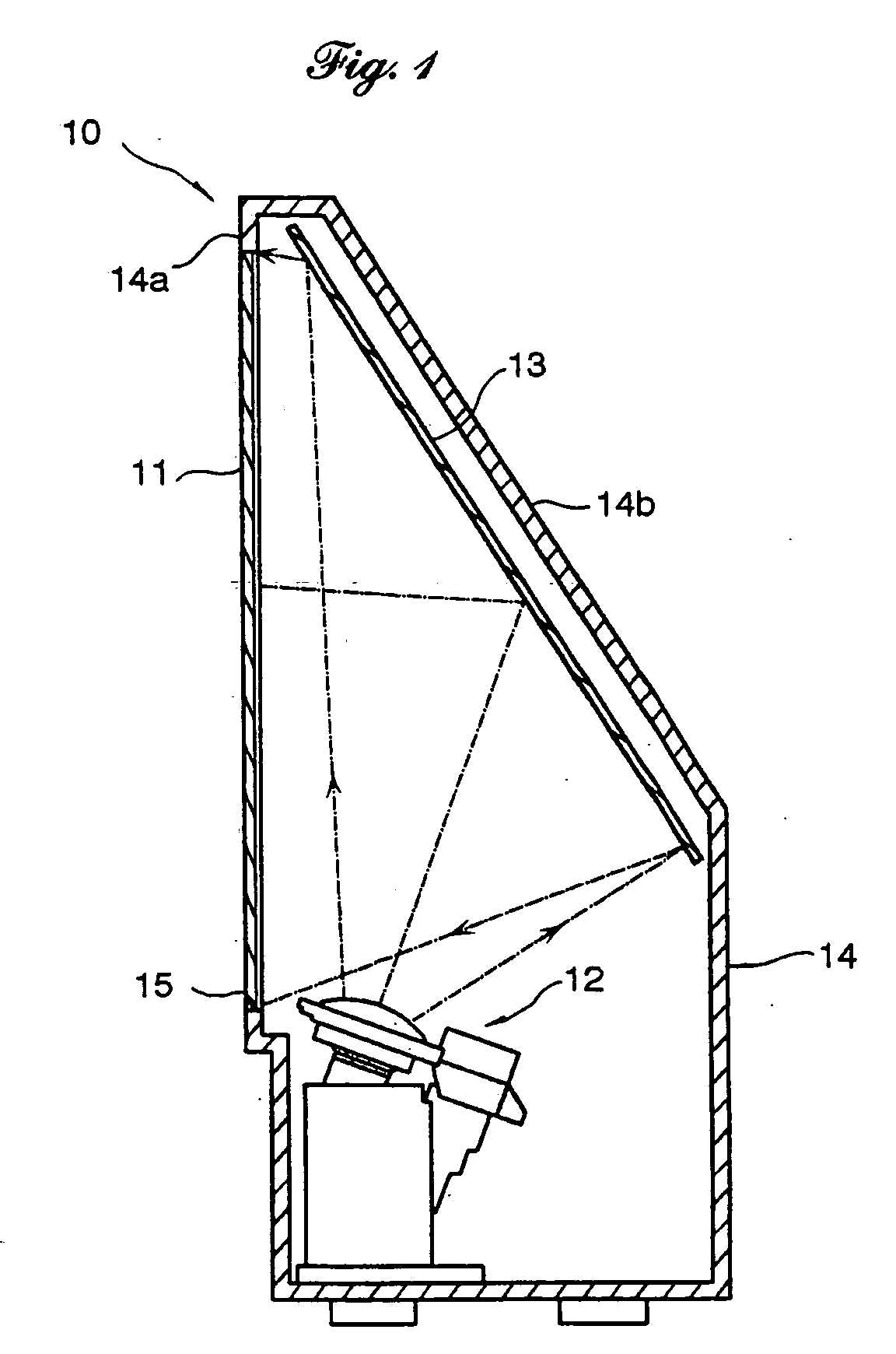
Compact projector with high optical performance
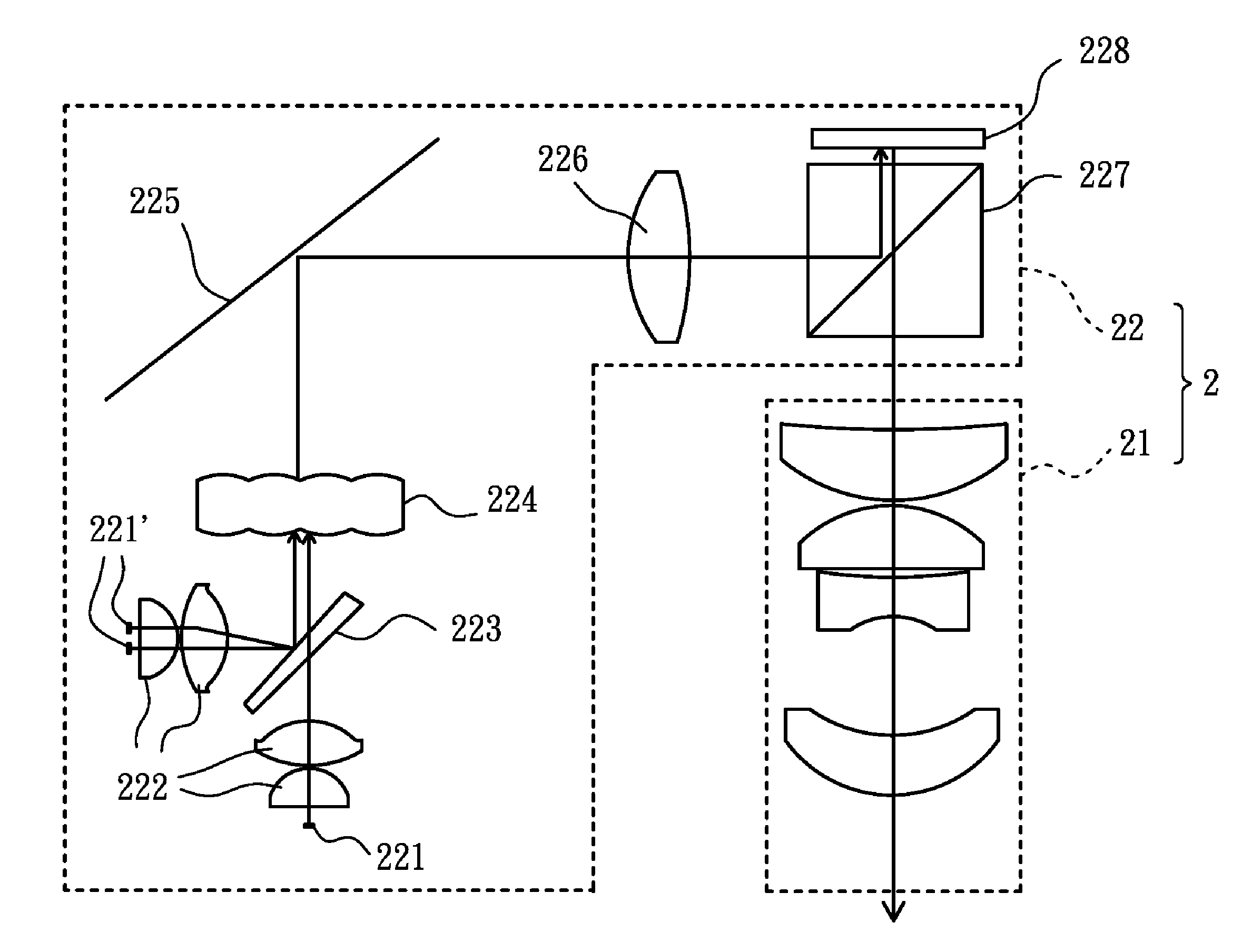
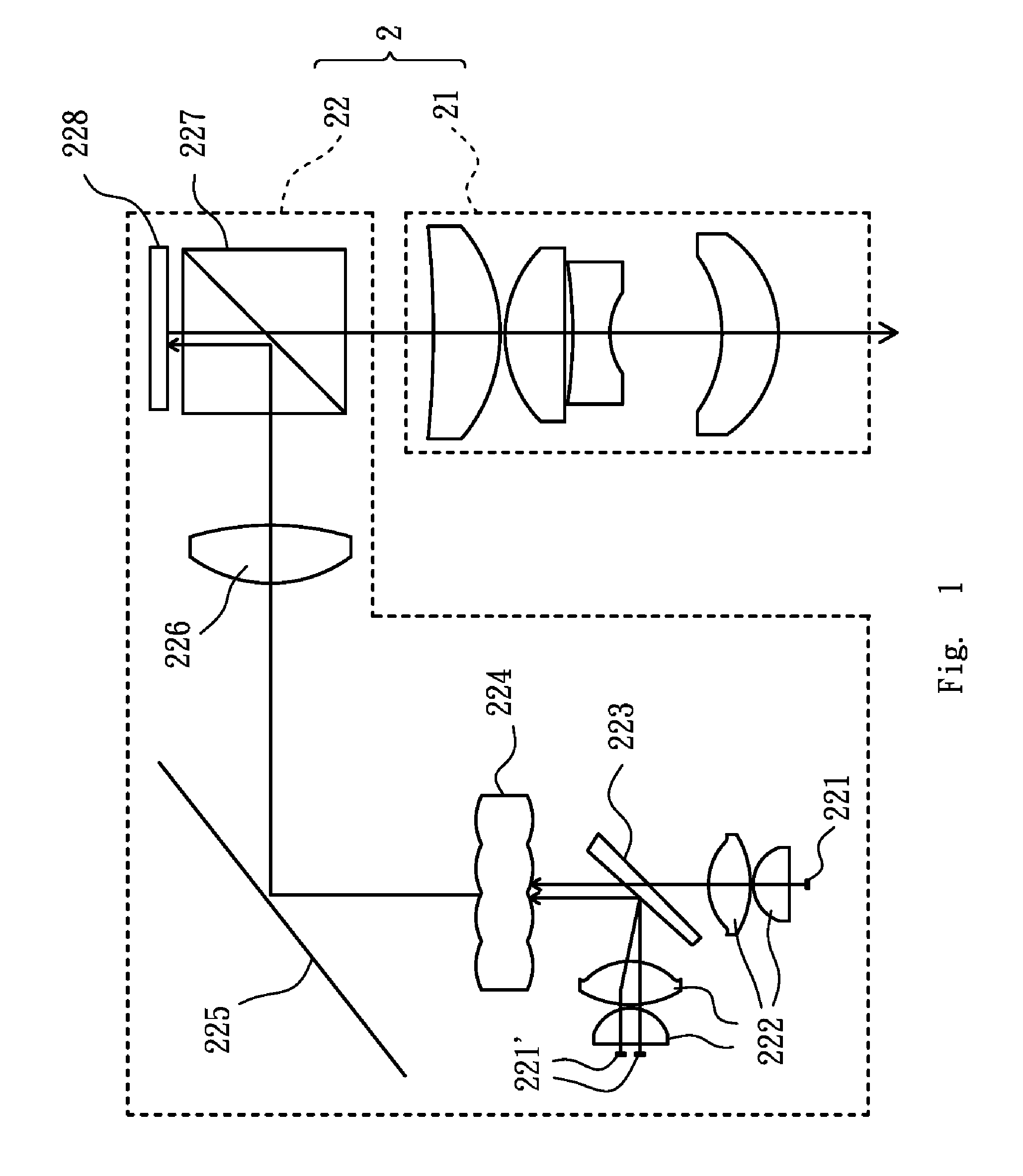
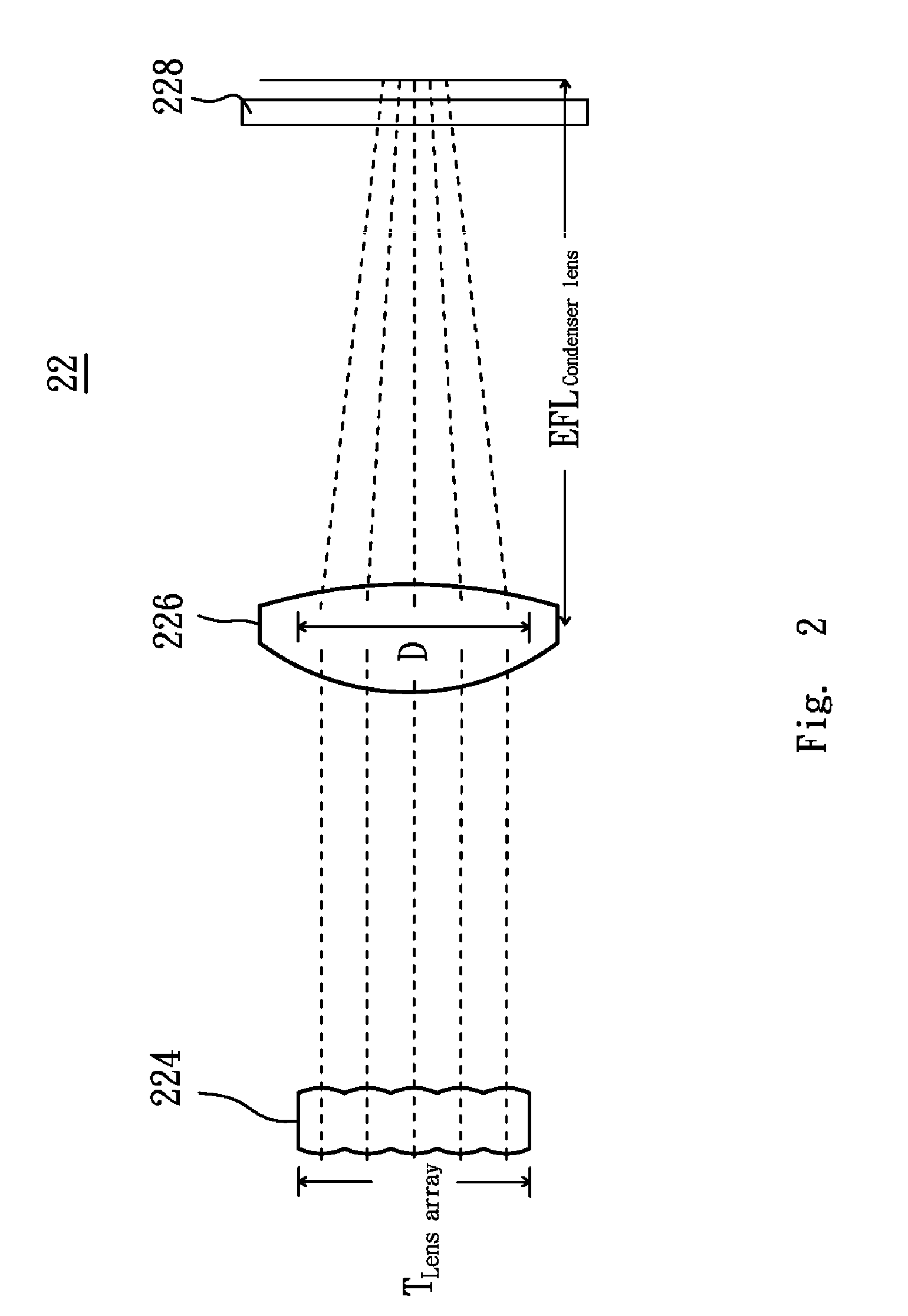
ActiveUS9081191B2Maintain optical performanceLower the volumeProjectorsColor photographyComputer moduleLight beam
A projector includes an illuminating system and an imaging system. The illuminating system includes a light source module, a lens array, a condenser lens and a display panel, in which light beams are generated by the light source module, uniformly dispersed by the lens array, condensed by the condenser lens, and reflected by the display panel to obtain image light, and the condenser lens has an effective focal length substantially equal to a product of an f-number of the illuminating system and a thickness of the lens array. The imaging system outwardly projects the image light.
Owner:SINTAI OPTICAL SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
A kind of photocurable composition and hard coating film
ActiveCN108753146BReduce surface tensionExcellent anti-fingerprint functionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPolymer scienceOligomer
The invention relates to the field of UV photocuring coating, in particular to a photocuring composition and a hard coating film. In order to solve the problem that the conventional hard coating filmhas bad comprehensive performance, the invention provides the photocuring composition and the hard coating film. The photocuring composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20 to 40 parts of high-functionality polyurethane acrylate oligomer, 10 to 20 parts of low-functionality fluorinated acrylate oligomers, 5 to 30 parts of high-functionality active monomers, 0.5 to 6 partsof a photoinitiator, 0.1 to 1 part of a leveling agent, 0.5 to 5 parts of an anti-fouling agent, 0.5 to 3 parts of conductive particles and 25 to 50 parts of a solvent. The hard coating film is formed by the photocuring composition provided by the invention; and the hard coating film has the characteristics of anti-fouling property, anti-static property, high wear resistance, low haze and the like, and also has high forming property and excellent comprehensive property.
Owner:宁波安特弗新材料科技有限公司
Polyamide film, cover window comprising same, and display device
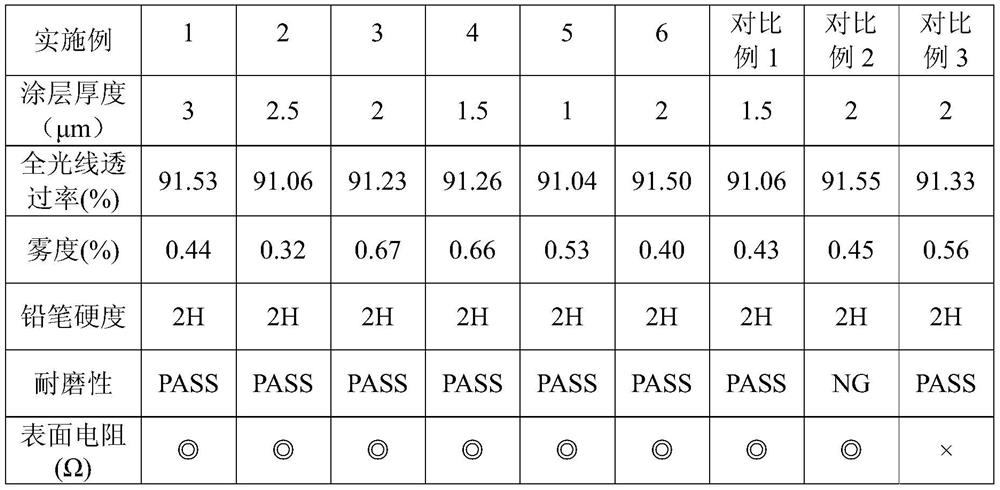
PendingCN114479072AGood optical performanceImprove mechanical propertiesIdentification meansPolymer scienceOptical property
The present embodiment relates to a polyamide film having excellent optical properties, mechanical properties, and processability, and a cover window and a display device comprising the same. The polyamide membrane includes a polyamide-based polymer in which the dipolar solvent compatibility represented by Formula 1 is 18.5 to 24. [In formula 1, [sigma] d is the value of the dispersion component in the surface energy of the polyamide film, [sigma] p is the value of the polar component in the surface energy of the polyamide film, [delta] 1d is the value of the dispersion component in the Hansen solubility parameter of the dipole solvent, and [delta] 1p is the value of the dipole component in the Hansen solubility parameter of the dipole solvent.
Owner:爱思开迈克沃有限公司
Laser scanning unit
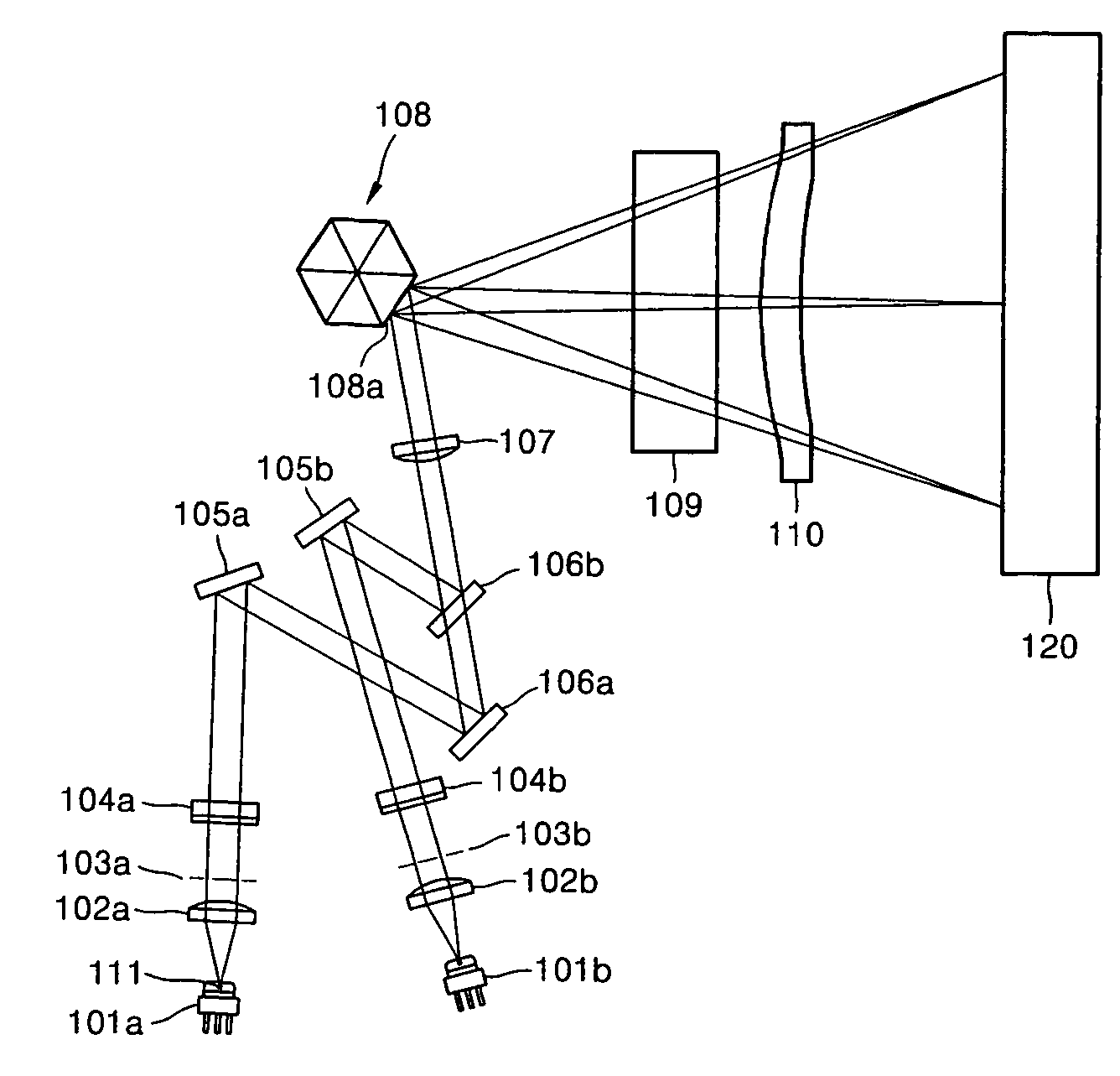
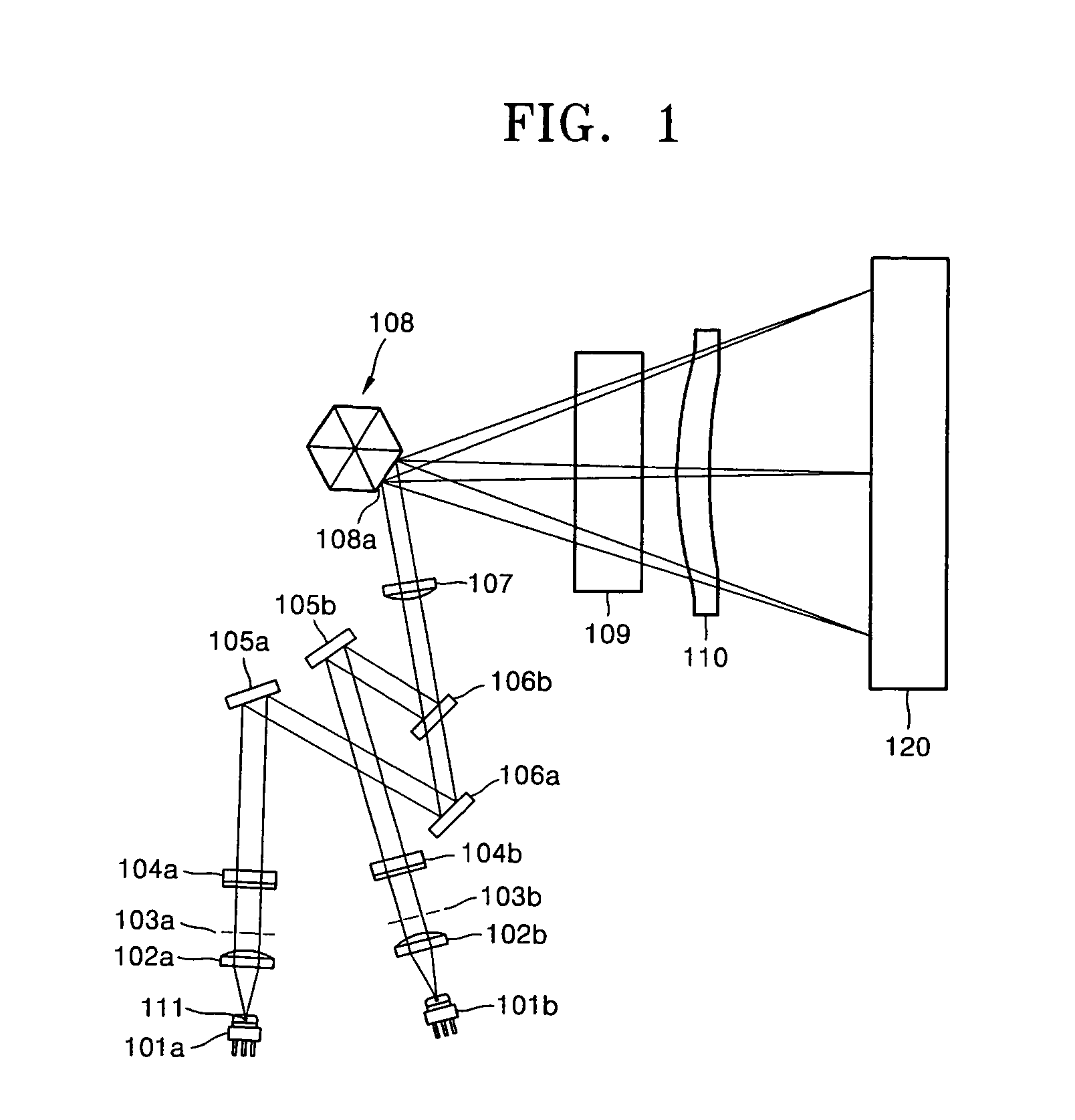
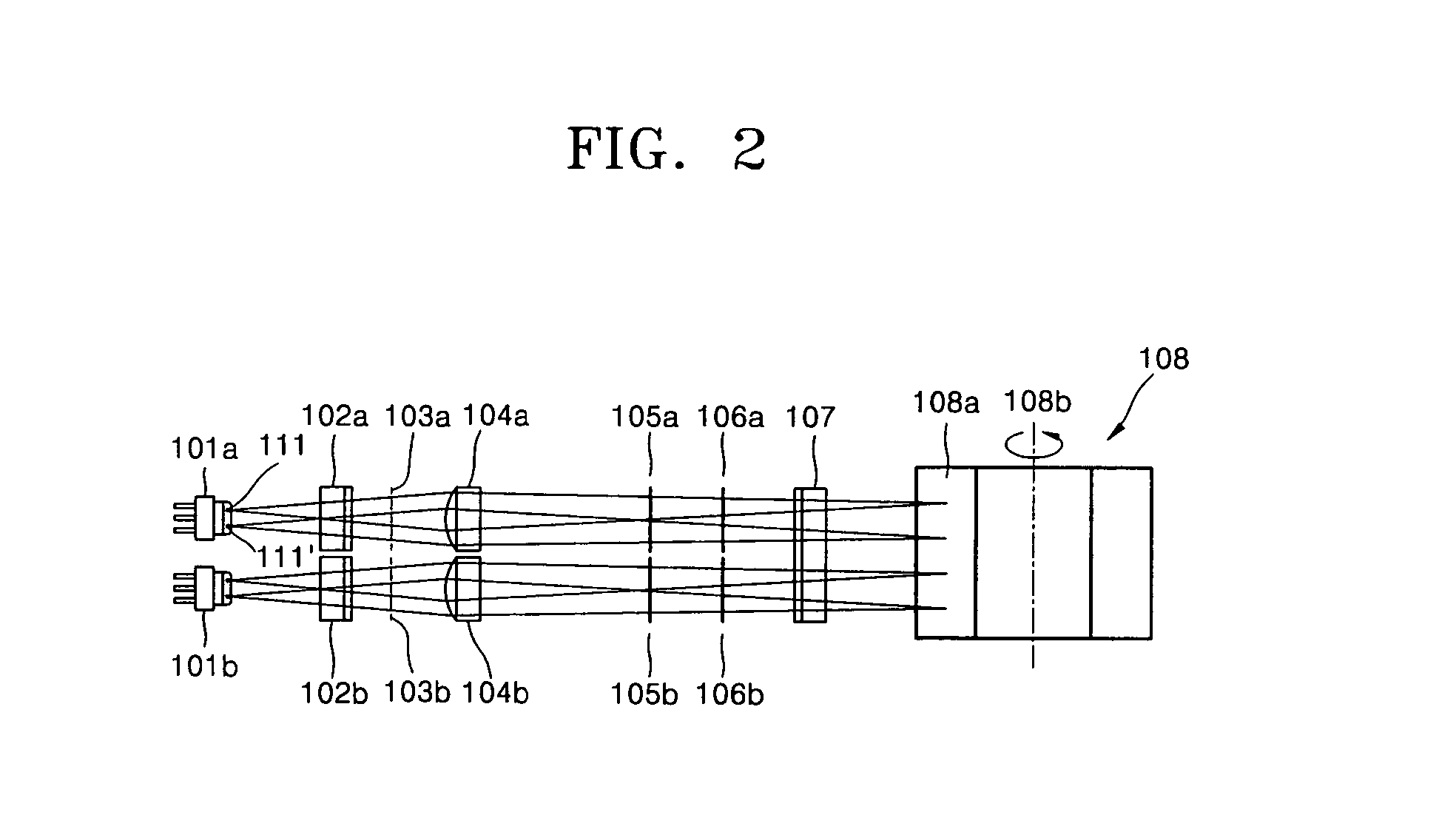
InactiveUS6958838B2Corrects linearity errorPrevents focal distance changeElectrographic process apparatusPrintingLight beamLaser scanning
A laser scanning unit is provided comprising a polygon mirror that deflects light beams respectively emitted by a plurality of light sources, an image focusing system that respectively focuses an image corresponding to each light beam deflected from the polygon mirror onto a surface of a plurality of photoconductive drums, and an incident optical system disposed between the light sources and the polygon mirror. The incident optical system comprises an infinite optical system along a main scanning direction and a finite optical system along a sub-scanning direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Projection system and projector
ActiveUS10146109B2Centering can be readilyEasy to implementProjectorsMountingsEngineeringProjection system
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com