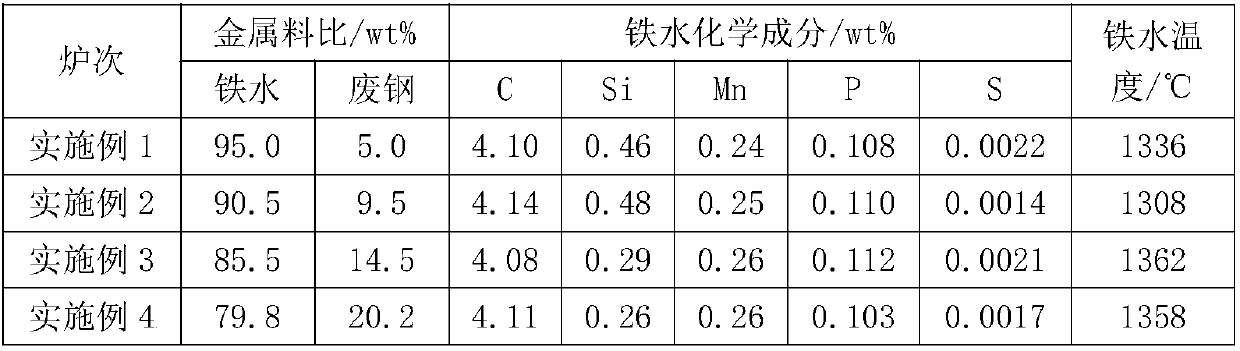
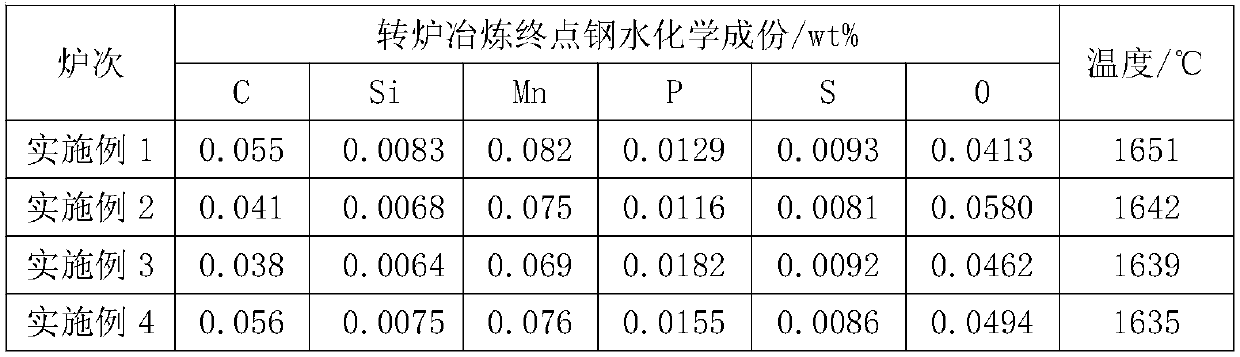
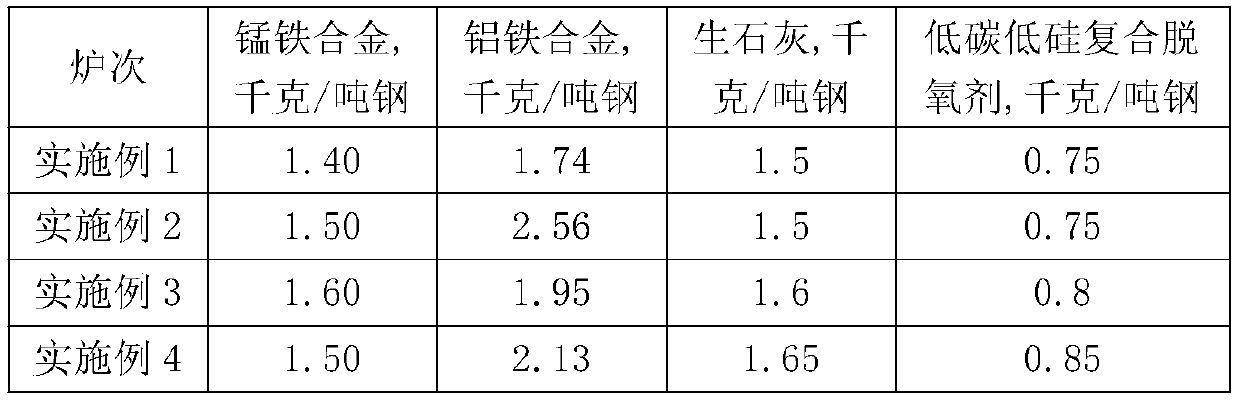
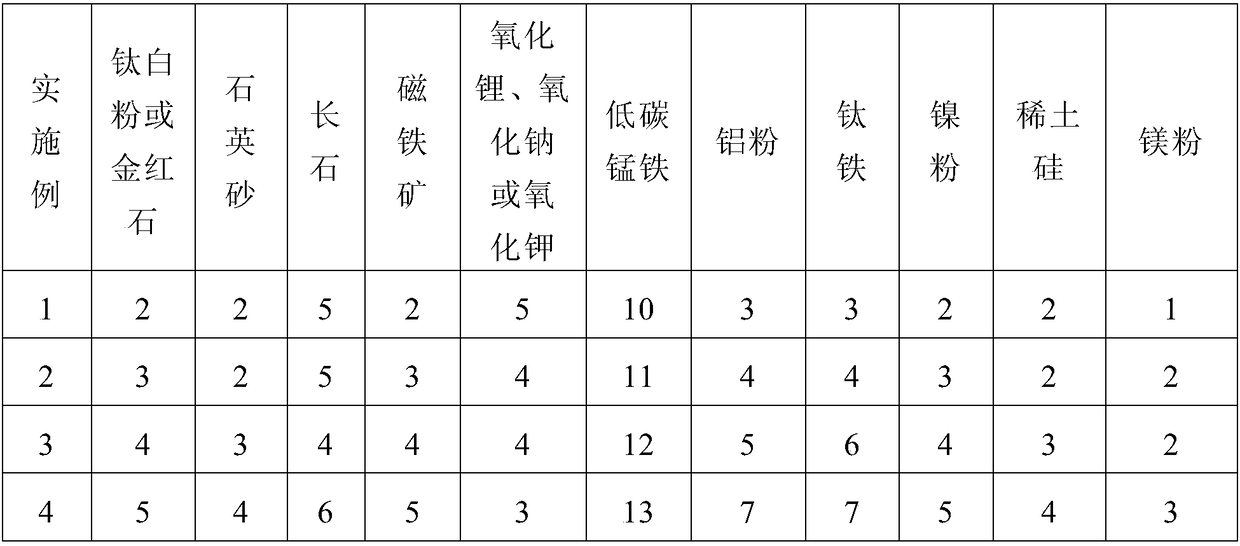
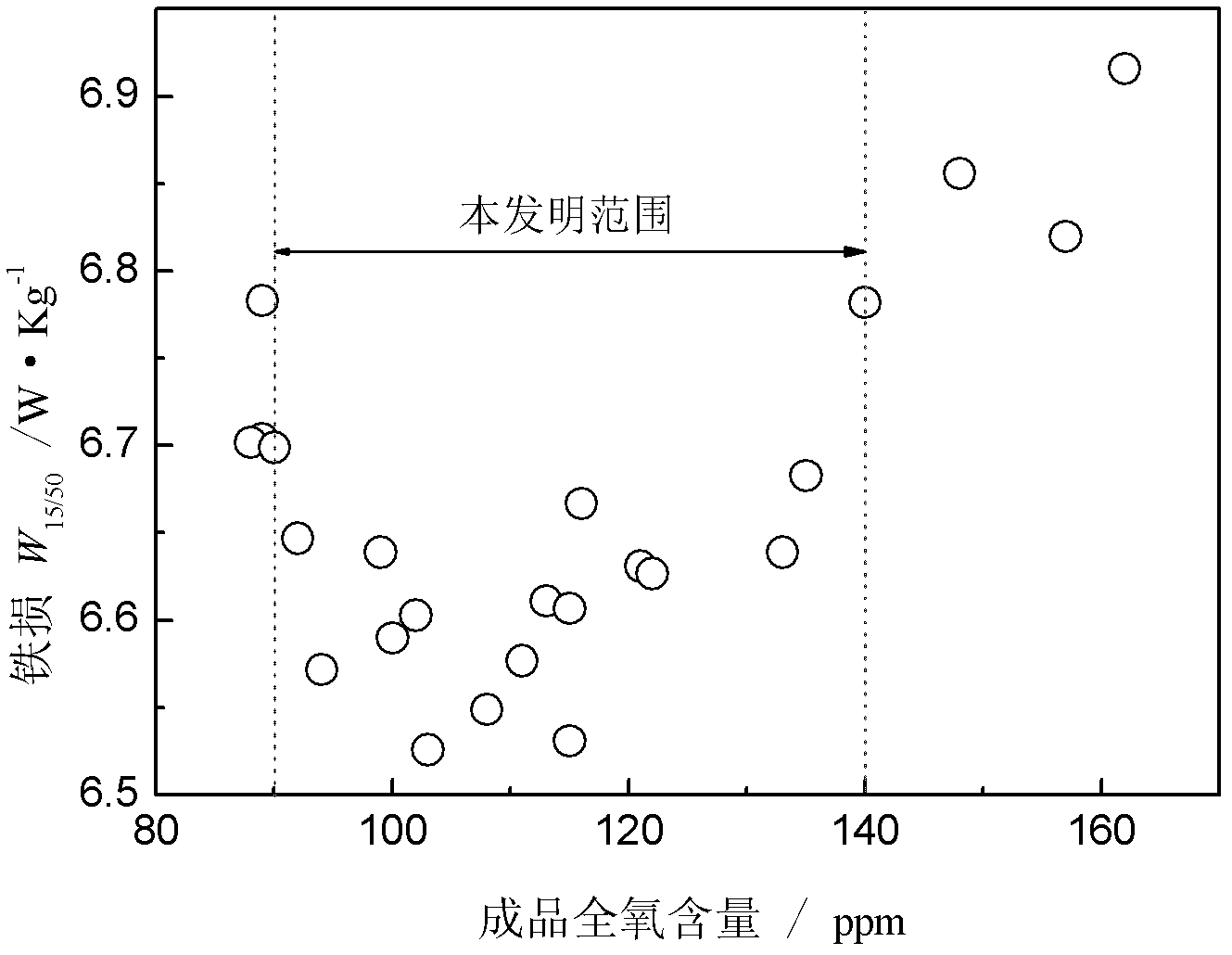
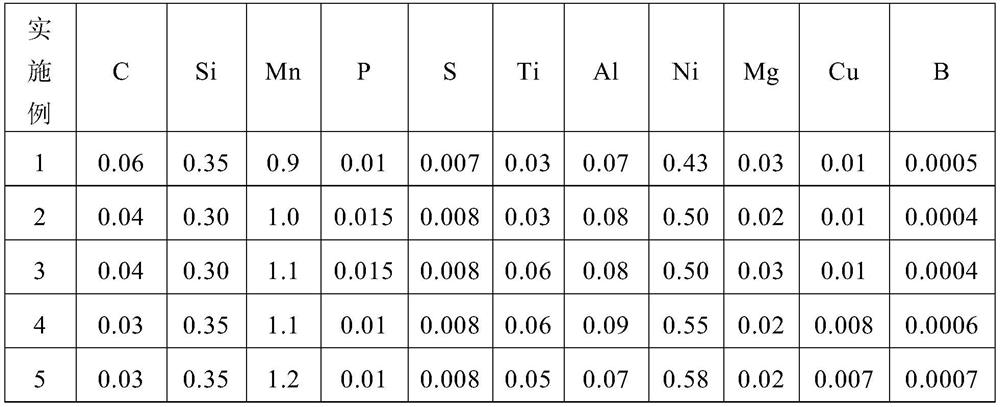
Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Reduce deoxygenation costs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-oriented electrical steel plate with extremely low content of Ti and smelting method for non-oriented electrical steel plate
ActiveCN102796948APrecise control of final deoxidation effectCause back TiManufacturing convertersElectrical steelSheet steel
The invention discloses a non-oriented electrical steel plate with extremely low content of Ti and a smelting method for the non-oriented electrical steel plate. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing hot metal pretreatment and converter smelting, namely smelting the following chemical components: less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of C, 0.1 to 1.6 weight percent of Si, 0.1 to 0.6 weight percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.2 weight percent of P, less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of S, less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of N, 0.005 to 0.02 weight percent of O, 0.0002 to 0.001 weight percent of Ti, and the balance of Fe and inevitable inclusions, and reducing the slag takeover by adopting slag stopping operation in a converter so as to ensure that the slag amount of the surfaces of steel ladles is less than or equal to 20kg in each ton of steel after the tapping of the converter is finished; and 2) performing Ruhrstahl-Heraeus (RH) refining, and weakly deoxidizing by using ferroaluminum and ferrosilicon sequentially after the decarburization of the RH refining is finished so as to ensure that the content of free oxygen of weakly deoxidized molten steel is 100 to 300ppm. The production of non-oriented electrical steel plates with extremely low content of Ti is realized by controlling the slag takeover of the tapping process of the converter, weakly deoxidizing by using the ferroaluminum and the ferrosilicon sequentially, and strictly controlling the content of oxygen in steel after the refining is finished.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Annealing-free low-carbon steel coil rod and production method thereof
InactiveCN102899554AReduce intensity to create conditionsIncrease oxygen activityManufacturing convertersMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionCarbonization
The invention provides an annealing-free low-carbon steel coil rod and a production method thereof. The annealing-free low-carbon steel coil rod comprises the following chemical components: 0.04-0.10% of C, 0.01-0.10% of Si, 0.20-0.35% of Mn, at most 0.015% of P, at most 0.010% of S, at most 0.0060% of N, 0.0030-0.0060% of total oxygen, 0.0020-0.0080% of total aluminum, at most 0.1% of inevitable impurity and the balance of iron. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of converter smelting, LF (ladle furnace) refining, continuous casting and rolling, wherein incomplete deoxidation occurs at the tapping side of a converter, the aluminum content of molten steel is reduced by using the high oxygen activity of the molten steel, the carbonization of the molten steel in the refining process is inhibited, bloom protection casting is performed, the temperature for double module input is controlled at 900-920 DEG C, the loop laying temperature is 870-900 DEG C, the speed of a roller way is 0.2-0.4 m / s, and a blower is closed. Thus, the vacuum treatment procedure is omitted, the technical process is shortened, the production cost is lowered, and the requirement of users for canceling the annealing technique in the drawing process is satisfied. For the annealing-free low-carbon steel coil rod produced according to the components and the production method provided by the invention, the grain size is controlled at 20-30 um, the tensile strength is no more than 350 MPa, and the reduction of area is no less than 75%.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Refined-smelting ladle furnace calcium carbide deoxidation method
The invention relates to a calcium carbide oxidizing method of ladle fining furnace. The calcium carbide is completely substituted for aluminum for plain carbon steel, for low silicon aluminum killed steel and pipeline steel, according to the station of slag series, the aluminum of the weigh from 0.4 kg to 0.8 kg is added to the molten steel of per ton, milled on the flux of 500 L per minute of argon gas, then the calcium carbide of the weigh from 0.6 kg to 1.2 kg is also added to the molten steel of per ton, the calcium carbide is used for oxidizing, submerged-arcing and slagging. The method not only lessens the pollution of the lard of aluminum oxide for molten steel, forms foaming slag and benefits for ladle furnace submerged-arc slagging, but also reduces noise, shields the heat radiation of molten steel, saves the power use. At the same time, the method reduces the acid smelting aluminum, the use of calcium wire, enriching-lard, effectually prevents the phenomena of circumfluence from taking place and improves the inherent quality of the billet.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Production method of low-carbon low-silicon aluminum killed molten steel
InactiveCN110484681AReduce burning lossReduce deoxygenation costsManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementAluminiumMetal
The invention discloses a production method of low-carbon low-silicon aluminum killed molten steel. The production method mainly solves the technical problems of poor cleanliness and high deoxidationcost of the low-carbon low-silicon aluminum killed molten steel produced and smelted through a converter in the prior art. According to the technical scheme, the production method of the low-carbon low-silicon aluminum killed molten steel comprises the following steps that a top-bottom combined blowing converter is adopted for smelting, wherein metal main raw materials are composed of, in percentage by mass, 75%-100% of molten iron, and the balance waste steel; the smelting end point of the converter is controlled, and the w [ C ] and the temperature in the molten steel at the converter blowing end point are detected; molten steel tapping is immediately carried out after converter blowing is ended; the molten steel in a steel ladle is transported to an argon blowing station for molten steel temperature regulation and molten steel aluminum content regulation, and weak stirring is carried out on the molten steel with aluminum wires fed. The low-carbon low-silicon aluminum killed steel molten steel produced by the production method is high in cleanliness and low in deoxidation cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Large-heat input gas-electric vertical welding gas shielded flux-cored wire based on grain refinement mechanism
ActiveCN109128573AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove low temperature impact toughnessWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaLithium oxidePotassium
The invention provides a large-heat input gas-electric vertical welding gas shielded flux-cored wire based on a grain refinement mechanism. The large-heat input gas-electric vertical welding gas shielded flux-cored wire comprises a flux-cored wire outer skin and inner powder, wherein a low-carbon steel cold-rolled steel strip is adopted by the flux-cored wire outer skin, and the flux-cored wire comprises, by mass, less than 0.06% of C, less than 0.3% of Si, less than 0.8% of Mn, less than 0.02% of P, less than 0.01% of S, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities; the powder comprises, by mass, 1-5% of one or two of titanium dioxide or rutile, 2-6% of quartz sand, 3-8% of feldspar, 1-5% of magnetite, 2-5% of one or more of lithium oxide, sodium oxide or potassium oxide, 10-15% of low-carbon ferromanganese, 3-8% of aluminum powder, 3-8% of ferrotitanium, 2-6% of nickel powder, 2-6% of rare earth silicon, 1-3% of magnesium powder, and the balance reduced iron powder; and the powder accounts for 15-20% of the total mass of the flux-cored wire. The flux-cored wire can be used for 100kj / cm-300kj / cm large-heat input gas-electric vertical welding of a thick steel plate.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Pre-deoxygenation method and device for spraying blowing of carbon powder in tapping hole of converter
The invention belongs to the technical field of steel and iron metallurgy, in particular to a pre-deoxygenation method and device for spraying blowing of carbon powder in a tapping hole of a converter. A plurality of carbon powder spraying pipes are installed in a tubular refractory material of the tapping hole of the converter, in the tapping process of the converter, the carbon powder is blow into tapping steel stream in a spraying manner, the carbon powder and dissolved oxygen [O] in molten steel have a reaction, and CO is generated. By means of the carbon powder spraying pipes in the tapping hole, the carbon powder is blown into the tapping steel stream in the spraying manner for deoxygenation, a deoxygenation product is CO, the gas state CO can escape from the tapping steel stream andis discharged into the atmosphere, no inclusion is left in the molten steel, and no harm is caused to the steel material quality. The carbon powder has large deoxygenation space and has very high deoxygenation capacity, and more than 40% of dissolved oxygen in the molten steel can be removed. Compared with deoxygenation performed through aluminum, about 90% of the deoxygenation cost can be savedby adopting the carbon powder; and compared with deoxygenation performed through silicon, about 80% of the deoxygenation cost can be saved by adopting the carbon powder.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Smelting method of electrode bar base material for non-protective-atmosphere electroslag remelting of H13 steel
The invention discloses a smelting method of an electrode bar base material for non-protective-atmosphere electroslag remelting of H13 steel, and belongs to the field of ferrous metallurgy. The smelting method of the electrode bar base metal for non-protective-atmosphere electroslag remelting of the H13 steel comprises the steps of electric furnace steelmaking, LF furnace refining, VD vacuum degassing, pouring and the like. According to the smelting method, by increasing the content of [Al] in the steel, adjusting the composition of the LF slag, and adjusting a VD argon soft blowing system to be proper, the content of inclusions in the molten steel can be effectively reduced, and the cleanliness of the electrode bar base material is improved. By the adoption of the electrode bar base material prepared through the method, secondary oxidation of molten steel in the electroslag remelting process can be avoided, so that the content of oxidation-system inclusions in the H13 steel manufactured through non-protective-atmosphere electroslag remelting is reduced, and the quality of steel obtained after non-protective-atmosphere electroslag remelting is improved. The problems that an existing electrode bar base material used for non-protective-atmosphere electroslag remelting of the H13 steel is low in cleanliness and prone to secondary oxidation in the non-protective-atmosphere electroslag remelting process can be effectively solved.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Non-oriented electrical steel plate with extremely low content of Ti and smelting method for non-oriented electrical steel plate
ActiveCN102796948BPrecise control of final deoxidation effectCause back TiManufacturing convertersElectrical steelSheet steel
The invention discloses a non-oriented electrical steel plate with extremely low content of Ti and a smelting method for the non-oriented electrical steel plate. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing hot metal pretreatment and converter smelting, namely smelting the following chemical components: less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of C, 0.1 to 1.6 weight percent of Si, 0.1 to 0.6 weight percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.2 weight percent of P, less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of S, less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.005 weight percent of N, 0.005 to 0.02 weight percent of O, 0.0002 to 0.001 weight percent of Ti, and the balance of Fe and inevitable inclusions, and reducing the slag takeover by adopting slag stopping operation in a converter so as to ensure that the slag amount of the surfaces of steel ladles is less than or equal to 20kg in each ton of steel after the tapping of the converter is finished; and 2) performing Ruhrstahl-Heraeus (RH) refining, and weakly deoxidizing by using ferroaluminum and ferrosilicon sequentially after the decarburization of the RH refining is finished so as to ensure that the content of free oxygen of weakly deoxidized molten steel is 100 to 300ppm. The production of non-oriented electrical steel plates with extremely low content of Ti is realized by controlling the slag takeover of the tapping process of the converter, weakly deoxidizing by using the ferroaluminum and the ferrosilicon sequentially, and strictly controlling the content of oxygen in steel after the refining is finished.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for reducing aluminum oxide inclusion in semi-steel steelmaking casting blank
ActiveCN107502704AReduce deoxygenation costsImprove billet qualityManufacturing convertersInlet temperatureSemi-steel
The invention provides a method for reducing aluminum oxide inclusion in a semi-steel steelmaking casting blank. The method comprises the steps that molten iron pretreatment, top-bottom combined blowing converter smelting, vacuum circulating degassing refining and continuous casting are sequentially conducted, and the casting blank is obtained, wherein carbon deoxidization is conducted at the inlet temperature ranging from 1,595 DEG C to 1,620 DEG C in the vacuum circulating degassing refining process. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the vacuum circulating degassing refining procedure is conducted in the semi-steel smelting process, deoxidization is conducted by controlling the inlet temperature in the vacuum circulating degassing refining process, aluminum-iron deoxidization does not need to be adopted in the top-bottom combined blowing converter smelting process, and therefore the deoxidization cost is reduced; in addition, by adopting the method, the Al2O3 inclusion in the casting blank can be reduced, and the quality of the casting blank can be improved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Deoxidation method of aluminum-killed silicon-containing steel
InactiveCN113215360AQuality improvementImprove purityManufacturing convertersSmelting processMolten steel
The invention discloses a deoxidation method of aluminum-killed silicon-containing steel. The deoxidation method comprises a converter smelting process, an LF furnace refining process and a refining process, wherein the converter process specifically involves that a silicon-containing deoxidizer is adopted for deoxidation in a converter tapping process, after tapping is completed, a top slag modifier is added to the surface of molten steel, 400 + / -25 kg of the top slag modifier per converter is added, the top slag modifier comprises of, in percentage by mass, 9% + / -1% of Al2O3, 27.5% + / -1.5% of CaO, 3% + / -1% of SiO2, 50% + / -2% of Al, and 7% + / -1% of CaF2; and the refining process spedifically involves that deoxidizing and slagging are conducted by adopting an aluminum deoxidizer. According to the deoxidation method, through the two-step deoxidation process, the deoxidation cost is greatly reduced, meanwhile, the molten steel quality is improved, and as inclusions formed in the molten steel by silicon deoxidation are easier to float upwards compared with aluminum deoxidation, the purity of the molten steel is also improved, and the molten steel quality is improved.
Owner:HANDAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
Converter steel-smelting technique
InactiveCN101168786AIncrease productivityEfficient removalManufacturing convertersSlagMaterial consumption
The invention relates to a new technology for revolving furnace steel making. The technology comprises the smelting steps in a converter, and the invention is characterized in that steel and steel slag are discharged in a mixed way when the steel is discharged from the converter, liquid steel is discharged completely, the slag removal is performed after the liquid steel is poured into a steel ladle, harmful foreign impurities such as phosphorus and silicon can be effectively removed, the slag is rebuilt after the slag removal, and aluminum powder spraying is adopted to perform deoxygenation. The invention can simplify the original technological process, save the productive time, reduce the production energy consumption and the material consumption, and enhance the production efficiency of steel and iron smelting. The technology is in particular suitable for the smelting of low silicon and low phosphorus steel type.
Owner:孙中强
Deoxidation method for converter smelted steel
The invention discloses a deoxidation method for converter smelted steel, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgical production processes and methods. The deoxidation method for converter smelted steel is relatively low in deoxidation cost, convenient to construct and implement and relatively good in deoxidation effect. The deoxidation method is adopted at the initial converter smelted steel discharge stage. When the liquid level in a steel ladle reaches 18-22% height of the steel ladle, carburant low in cost and low in deoxidizing capacity is adopted for deoxidation; when the liquid level in the steel ladle is increased to be 30-35% the height of the steel ladle, manganese alloy moderate in cost and relatively strong in deoxidation capacity is adopted for deoxidation, and then steel grade alloy control is carried out; after converter smelted steel is completely discharged out of a converter, bottom argon blowing is carried out on the steel ladle not shorter than 3 min; an aluminum wire for deoxidation with the length of 80-150 m is fed into the steel ladle according to the final C content in the converted smelted steel. Accordingly, the converter smelted steel is deoxidized one time.
Owner:PANGANG GRP PANZHIHUA STEEL & VANADIUM
Multielement aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a multielement aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of smelting. The multielement aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer is composed of the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 30.0-35.0% of Al, less than 0.35% of C, 15.0-18.0% of Si, 4.0-6.0% of Mn, 3.0-3.5% of Ca, 4.0-4.5% of Ba, 3.5-3.8% of Mg, 0.5-0.8% of RE, 1.2-1.5% of Zn, less than 0.02% of S, less than 0.03% of P and the balance of Fe. The deoxidizer adopts a crucible melt resistance furnace and an induction furnace to simultaneously perform smelting, and is injected into one casting ladle and cast into a cast iron mold to obtain the aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer block material. The multielement aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer has excellent deoxidizing effect.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Production method of low-aluminum carbon structural molten steel
The invention discloses a production method of low-aluminum carbon structural molten steel. The production method mainly solves the technical problems that existing carbon structural steel produced by a slab continuous casting machine is poor in cleanliness and high in deoxidation cost. According to the technical scheme, the production method of the low-aluminum carbon structural molten steel comprises the following steps that a top-bottom combined blowing converter is adopted for smelting, and 80%-100% of molten iron is added by mass percent; controlling a converter smelting end point, and detecting w [C] and molten steel temperature in molten steel at the converter smelting end point; tapping immediately after converter blowing is finished, and blowing argon at the bottom of a steel ladle in the converter tapping process; molten steel in the steel ladle is conveyed to an argon blowing station for molten steel temperature regulation and final deoxidation; and carrying out weak stirring on the molten steel fed with the aluminum wire. The low-aluminum carbon structural steel produced by the method disclosed by the invention is low in deoxidation cost, and the deoxidation cost per ton of steel is reduced by 12-22 yuan; and the cleanliness of the steel is high, and the total oxygen weight content in tundish molten steel is 0.0015-0.0025%.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Silicon deoxidizing process for silicon-contained steel grades
The invention provides a silicon deoxidizing process for silicon-contained steel grades. The silicon deoxidizing process includes the following steps that a silicon iron deoxidizing agent is added when converter tapping is conducted by 1 / 5, then an aluminum iron deoxidizing agent is added when converter tapping is conducted by 2 / 3, and for the steel grades, not including the rectangular billet steel grades, requiring the silicon content in steel to be larger than 0.10% by mass fraction, the addition quantity of the silicon iron deoxidizing agent is that 100 kg of the silicon iron deoxidizing agent is added in every 175 tons of steel, and the addition quantity of the aluminum iron deoxidizing agent is that 100-200 kg of the aluminum iron deoxidizing agent is added in every 175 tons of steel; and for the steel grades requiring the silicon content in steel to be 0.06%-0.10% and requiring the manganese content to be lower than 1.00%, the addition quantity of the silicon iron deoxidizing agent is that 30 kg of the silicon iron deoxidizing agent is added in every 175 tons of steel, and the addition quantity of the aluminum iron deoxidizing agent is that 200-300 kg of the aluminum iron deoxidizing agent is added in every 175 tons of steel. According to the silicon deoxidizing process, by adjusting the manner and sequence of deoxidizing alloying, the molten steel quality is improved whole the deoxidizing cost is substantially reduced. The deoxidizing method is good in deoxidizing effect and free of other bad influences; and meanwhile, because compared with aluminum deoxidizing, inclusions formed in molten steel through silicon deoxidizing are easier to float, the nozzle blockage and flow stop probability of the continuous casting working procedure is also decreased.
Owner:BENGANG STEEL PLATES
Low-cost composite pre-deoxidation method for molten steel
The invention discloses a low-cost composite pre-deoxidation method for molten steel, which comprises the following steps that: when 1 / 3 of molten steel is tapped from a converter, coke powder is added, so that the coke powder reacts with oxygen in the molten steel in the tapping process, and a deoxidation alloy is added 1-2 minutes after the coke powder is added; before the molten steel reaches a treatment position of an LF refining furnace, 20-30 kg of coke powder is added to the slag surface, argon bottom blowing is started, stirring is conducted, and oxygen in the slag is de-oxidized; when the molten steel reaches the treatment position of the LF refining furnace, 20-40 kg of calcium carbide is added to the slag surface, and slag deoxidation is conducted through stirring; and 20-40kg of calcium carbide is added again to deoxidize the oxygen in the furnace slag again if the furnace slag is blackened in the slagging process of the LF refining furnace. Part of materials used in the method are coking tailings and can partially replace deoxidation alloy; and meanwhile, the deoxidation product is carbon monoxide or carbon dioxide, so that the cleanliness of the molten steel can be effectively promoted, and good conditions are provided for improving the product quality.
Owner:SD STEEL RIZHAO CO LTD
A high heat input gas-electric vertical welding gas-shielded flux-cored wire based on grain refinement mechanism
ActiveCN109128573BPromote high melting point interstitial phaseNucleation refinementWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaLithium oxideMagnetite
A high heat input gas-electric vertical welding gas-shielded flux-cored wire based on a grain refinement mechanism, including a flux-cored wire sheath and its inner drug powder, wherein the flux-cored wire sheath is made of low-carbon steel cold-rolled steel strip, which The mass percentage of the composition is: C<0.06%, Si<0.3%, Mn<0.8%, P<0.02%, S<0.01%, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities; the mass percentage of the composition of the powder is: titanium dioxide Or one or both of rutile: 1-5%, quartz sand: 2-6%, feldspar: 3-8%, magnetite: 1-5%, lithium oxide, sodium oxide or potassium oxide One or more: 2-5%, low-carbon ferromanganese: 10-15%, aluminum powder: 3-8%, titanium iron: 3-8%, nickel powder: 2-6%, rare earth silicon: 2- 6%, magnesium powder: 1-3%, and the rest is reduced iron powder; and the powder accounts for 15-20% of the total mass of the flux-cored wire. The welding wire of the invention can be used for gas-electric vertical welding of thick steel plate with large heat input of 100kJ / cm-300kJ / cm.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A method for reducing aluminum oxide inclusions in semi-steelmaking steelmaking slabs
ActiveCN107502704BReduce inclusionsReduce deoxygenation costsManufacturing convertersSteelmakingSmelting process
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Production process for low-cost and highly-clean X80 pipeline steel
ActiveCN103388041BLow costReduce deoxygenation costsManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSlagFerrosilicon
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
A low-cost converter steelmaking deoxidation process
ActiveCN105695664BImprove control effectGood deoxidation effectManufacturing convertersSteelmakingNon-metallic inclusions
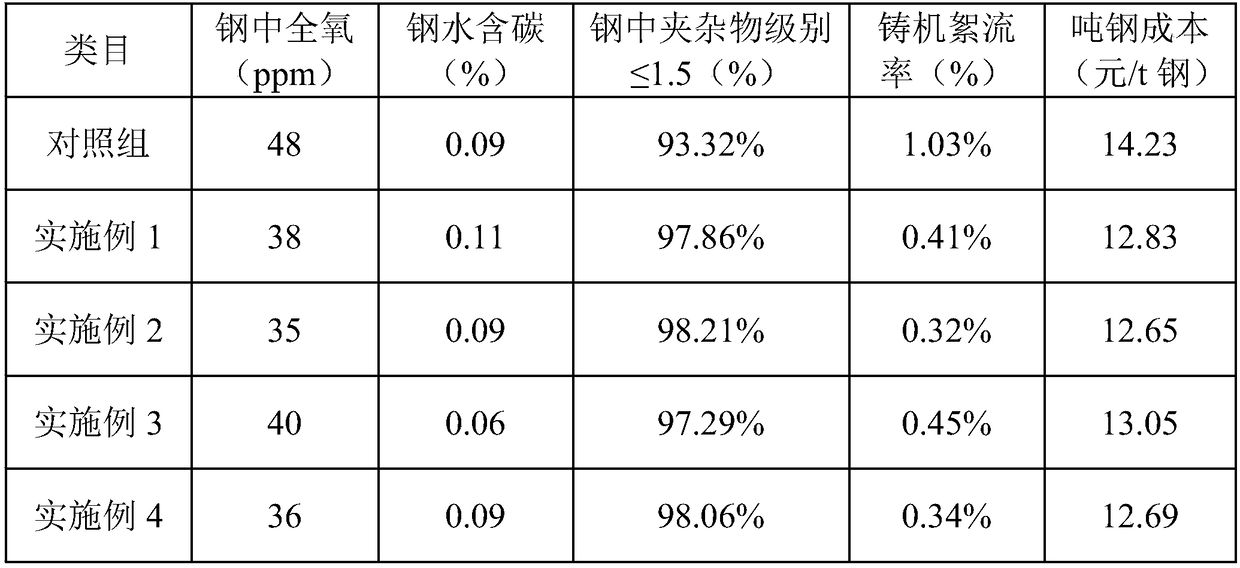
The invention discloses a low-cost converter steelmaking deoxidization process. The process is characterized in that in the converter steel tapping process, carbon powder and a composite deoxidization agent are added for segmented deoxidization, the content of total oxygen in molten steel is reduced by controlling the deoxidization occasion and optimizing the steel tapping deoxidization operation process, the low-price carbon powder and the composite deoxidization agent are used for replacing a traditional aluminum and iron deoxidization agent, deoxidization cost can be greatly reduced, and meanwhile, non-metallic inclusion is reduced. By means of the deoxidization process, the ratio of inclusion, with the level smaller than or equal to 1.5, in steel is increased to 98.21%, the continuous casting fluctuation flow rate is reduced to 0.32%, the deoxidization cost of each ton of steel is reduced by 1.58 RMB yuan, and profit margin is increased for enterprises while steel quality is improved.
Owner:RIZHAO BAOHUA NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Multi -aluminum iron alloy de -oxygen and preparation methods
The invention relates to a multielement aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of smelting. The multielement aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer is composed of the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 30.0-35.0% of Al, less than 0.35% of C, 15.0-18.0% of Si, 4.0-6.0% of Mn, 3.0-3.5% of Ca, 4.0-4.5% of Ba, 3.5-3.8% of Mg, 0.5-0.8% of RE, 1.2-1.5% of Zn, less than 0.02% of S, less than 0.03% of P and the balance of Fe. The deoxidizer adopts a crucible melt resistance furnace and an induction furnace to simultaneously perform smelting, and is injected into one casting ladle and cast into a cast iron mold to obtain the aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer block material. The multielement aluminum-iron alloy deoxidizer has excellent deoxidizing effect.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Deoxidation method of naphtha raw material
InactiveCN107964422AReduce deoxygenation costsTreatment with plural serial refining stagesHydrocarbon oils refiningRefluxNaphtha
The invention discloses a deoxidation method of a naphtha raw material. The method comprises the following flows: (1) the raw material naphtha is heated by a heater and enters a deoxygenation tower, and in the raw material heater, the raw material naphtha is heated by a low temperature heat source; (2) reformed PSA desorbed gas is introduced into the deoxygenation tower, light components in the raw material naphtha and oxygen dissolved in the naphtha are evaporated to a tower top together, the oxygen is cooled at the tower top, formed light component condensate liquid is pumped into the towerfor forming total reflux, noncondensable gas enters a low pressure gas system, and the noncondensable gas comprises reformed PSA desorbed gas which is injected into the deoxygenation tower, oxygen desorbed from the naphtha, and light components which are not condensed; deoxidized naphtha formed after deoxidation enters the reforming prehydrogenation system. The deoxidation method employs a low temperature heat source as a heating source of naphtha, and at the same time, partial pressure of the naphtha is reduced, oxygen in the naphtha is easy to overflow from naphtha, so that deoxidation costof the naphtha is effectively reduced.
Owner:PANJIN NORTHERN ASPHALT FUEL
A kind of killed steel deoxidation method
The invention discloses a killed steel deoxygenation method and belongs to the technical field of ladle refining. The killed steel deoxygenation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of slag washing, refining, slag electrification, deoxygenation, acceleration of steel slag interface reactions and soft blowing. According to the deoxygenation step, a deoxidizing agent comprises silicon carbide and calcium carbide, 70% of silicon carbide is added firstly, then calcium carbide is added, and then 30% of silicon carbide is added. Compared with the prior art, the killed steel deoxygenation method has the characteristics of being good in product deoxygenation effect, greatly reducing the deoxygenation cost and being stable in product quality.
Owner:RIZHAO STEEL HLDG GROUP
Double-layer explosion-proof power distribution cabinet
InactiveCN109687314AAvoid explosionSimplified deoxygenation stepsGas treatmentSubstation/switching arrangement cooling/ventilationAir pumpEngineering
The invention provides a double-layer explosion-proof power distribution cabinet. The double-layer explosion-proof power distribution cabinet comprises a mounting board, a power distribution cabinet body and a power distribution cabinet door, wherein one side of the power distribution cabinet body is provided with an air inlet, the other side of the power distribution cabinet body is provided withan air outlet, the air inlet is connected to one end of an electric air pump, the power distribution cabinet door is hinged to one side of the power distribution cabinet body, the power distributioncabinet body and the power distribution cabinet door are both of double-layered structures, and the inner-layer structures are oxygen removal layers. The double-layer explosion-proof power distribution cabinet has the advantages of simple structure, low use cost, wide application range, high safety factor and higher market application value.
Owner:广东求精电气有限公司
A kind of smelting method of high phosphorus if steel with high cleanliness
ActiveCN113736949BWarming slows downReduce oxygen intensityManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementCarbide siliconSmelting process
The invention discloses a smelting method for high-phosphorus IF steel with high cleanliness, and belongs to the technical field of high-phosphorus steel smelting. It includes the following steps: the oxygen supply in the converter reaches 200m 3 ‑500m 3 In the first stage, add the first batch of materials, wherein the first batch of materials includes lime and magnesium balls, and the lime in the first batch of materials is 70% of the total amount of lime added; the oxygen supply in the converter reaches 2500m 3 ‑2800m 3 In the second stage, add the second batch of materials, wherein the second batch of materials includes lime, and the lime in the second batch of materials is 20% of the total amount of lime added; the oxygen supply in the converter reaches 6000m 3 ‑6300m 3 In the third stage, the third batch of materials is added, wherein the third batch of materials includes lime and silicon carbide, and the lime in the third batch of materials is 10% of the total amount of lime added. In view of the existing technical problems, it is necessary to study a smelting method of high-phosphorus IF steel with high cleanliness, which can effectively ensure that high-phosphorus IF steel does not splash during the smelting process, and has low oxygen content at the end point and high cleanliness.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Explosion-proof power distribution cabinet
InactiveCN109616883AAvoid explosionSimplified deoxygenation stepsSubstation/switching arrangement cooling/ventilationSubstation/switching arrangement casingsPetrochemicalOxygen
The invention provides an explosion-proof power distribution cabinet. The explosion-proof power distribution cabinet comprises a mounting plate, a power distribution cabinet, an electric air pump anda dust removal and oxygen removal device. The problem that a power distribution cabinet is prone to generating a safety accident in flammable and explosive places such as petrochemical engineering places and the like is solved. The explosion-proof power distribution cabinet is simple in structure and low in use cost, wide in application range, high in safety coefficient and relatively high in market application value.
Owner:广东求精电气有限公司
Method for reducing converter semi-steel-making deoxidization cost
The invention provides a method for reducing the converter semi-steel-making deoxidization cost. The method comprises the steps that aluminum-iron alloy is added into molten steel for deoxidization at first, and aluminum wires are added into the deoxidized material to continue to carry out deoxidization, wherein the mass ratio of the aluminum-iron alloy to the aluminum wires is (2-4):1. Compared with the prior art, the deoxidization method for semi-steel making is provided, the aluminum-iron alloy is adopted for carrying out primary deoxidization on molten steel, then, the aluminum wires are adopted for carrying out further deoxidization on the molten steel, the consumption ratio of the aluminum-iron alloy to the aluminum wires is reasonably controlled, and the deoxidization cost is reduced on the condition of ensuring the good deoxidization effect under the cooperation effect of the aluminum-iron alloy and the aluminum wires.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Low-cost arc furnace tapping deoxidization technique
InactiveCN101157965BReduce the cost of steel deoxidationReduce deoxygenation costsElectric arc furnaceFerrosilicon
The invention discloses a low-cost tapping deoxidizing technique of an electric-arc furnace, which is characterized in that the low-cost carbon power is used for predeoxidizing in the prophase of tapping, the cheap ferrosilicon is used for shallow-deoxidizing in the metaphase of tapping, the aluminum block with strong deoxidizing ability is used for deep-deoxidizing in the anaphase of tapping, thereby the molten steel becomes to the aluminum killed steel finally, the oxygen activity of the molten steel is controlled to the control range of the clean steel. The invention has the technical proposal that: (1) by optimizing the operating process of tapping deoxidizing, the deoxidization is controlled, the acieration is eliminated and the air-breathing is lessened, (2) the low-cost carbon powerand ferrosilicon substituting for part of expensive aluminum are used for controlling the tapping deoxidizing , the cost of tapping deoxidizing of electric-arc furnace is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PEARL RIVER STEEL & IRON
Damping explosion-proof power distribution cabinet
InactiveCN109546542ASimple stepsReduce deoxygenation costsSubstation/switching arrangement cooling/ventilationSubstation/switching arrangement casingsOxygen monitoringElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention provides a damping explosion-proof power distribution cabinet, and the cabinet comprises a power distribution cabinet body, a power distribution cabinet door, an oxygen monitoring and alarm device, damping legs and a fixed device. One side of the power distribution cabinet is provided with an air inlet, and the other side is provided with a one-way air outlet valve. The air inlet isconnected with one end of an electric air pump, and the other end of the electric air pump is connected with an air dust removing and deaerator. The damping legs and the fixed device are fixed at thebottom of the power distribution cabinet body. The power distribution cabinet of the invention has the advantages of simple structure, low use cost, wide application range, high safety factor and goodmarket application value.
Owner:广东求精电气有限公司
ASTM4130 steel and production method thereof
ActiveCN114645190ALow elongationReduce contentProcess efficiency improvementMetal rolling arrangementsSlagAluminium
The invention discloses ASTM4130 steel and a production method thereof. The disclosed ASTM4130 steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.28-0.33% of C, 0.17-0.30% of Si, 0.45-0.60% of Mn, 0.85-1.05% of Cr, 1t of Al, 0.20-0.30% of Cr, 0.20-0.30% of Mo, 0.20-0.30% of Mo, 0.20-0.30% of Mo, 0.20-0.30% of Mo, 0.20- The steel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.01% of Fe, less than or equal to 0.0015% of O, less than or equal to 0.020% of P, less than or equal to 0.012% of According to the disclosed production method, a low-alkalinity refining slag system and an aluminum-free deoxidation process are adopted in the LF external refining process, the alkalinity of refining slag does not exceed 3.0, and the ASTM4130 steel with the tensile strength larger than or equal to 760 MPa and the ductility A larger than or equal to 17.5% is finally produced and obtained and can be used as a cold-drawn material subsequently.
Owner:BAOTOU IRON & STEEL GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com