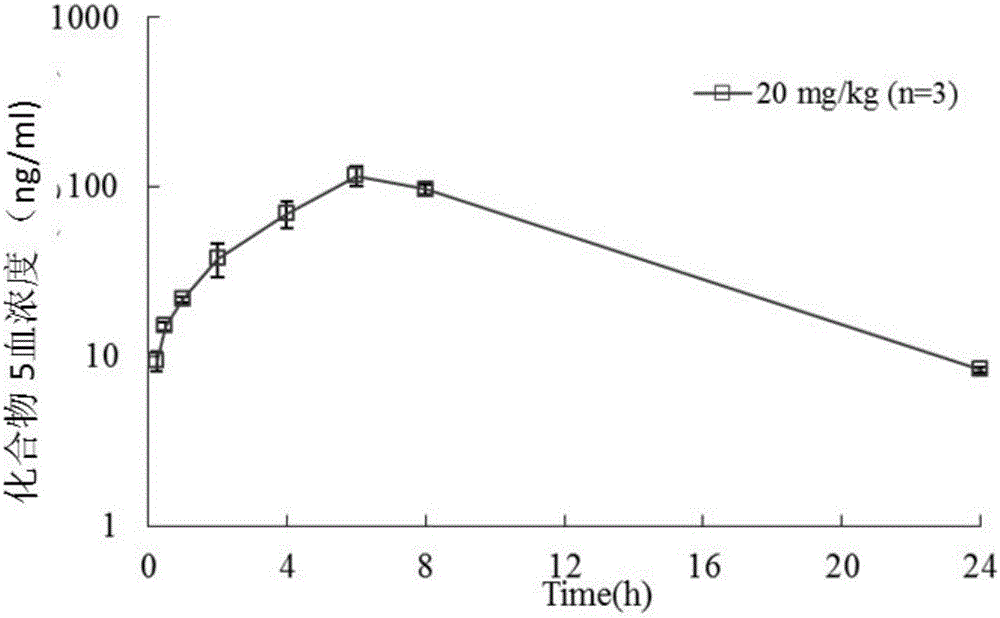
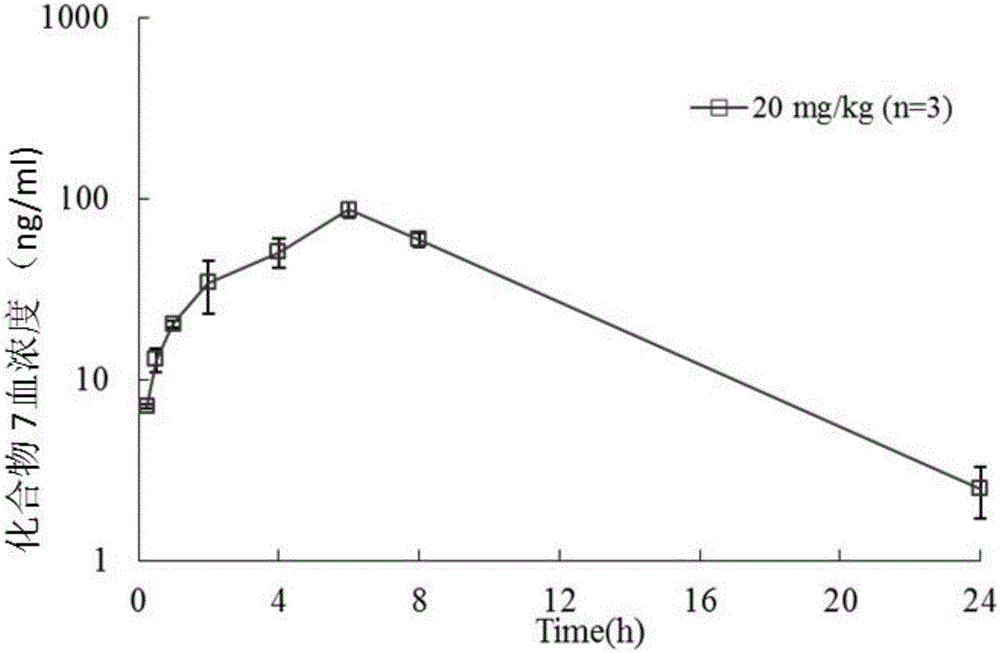
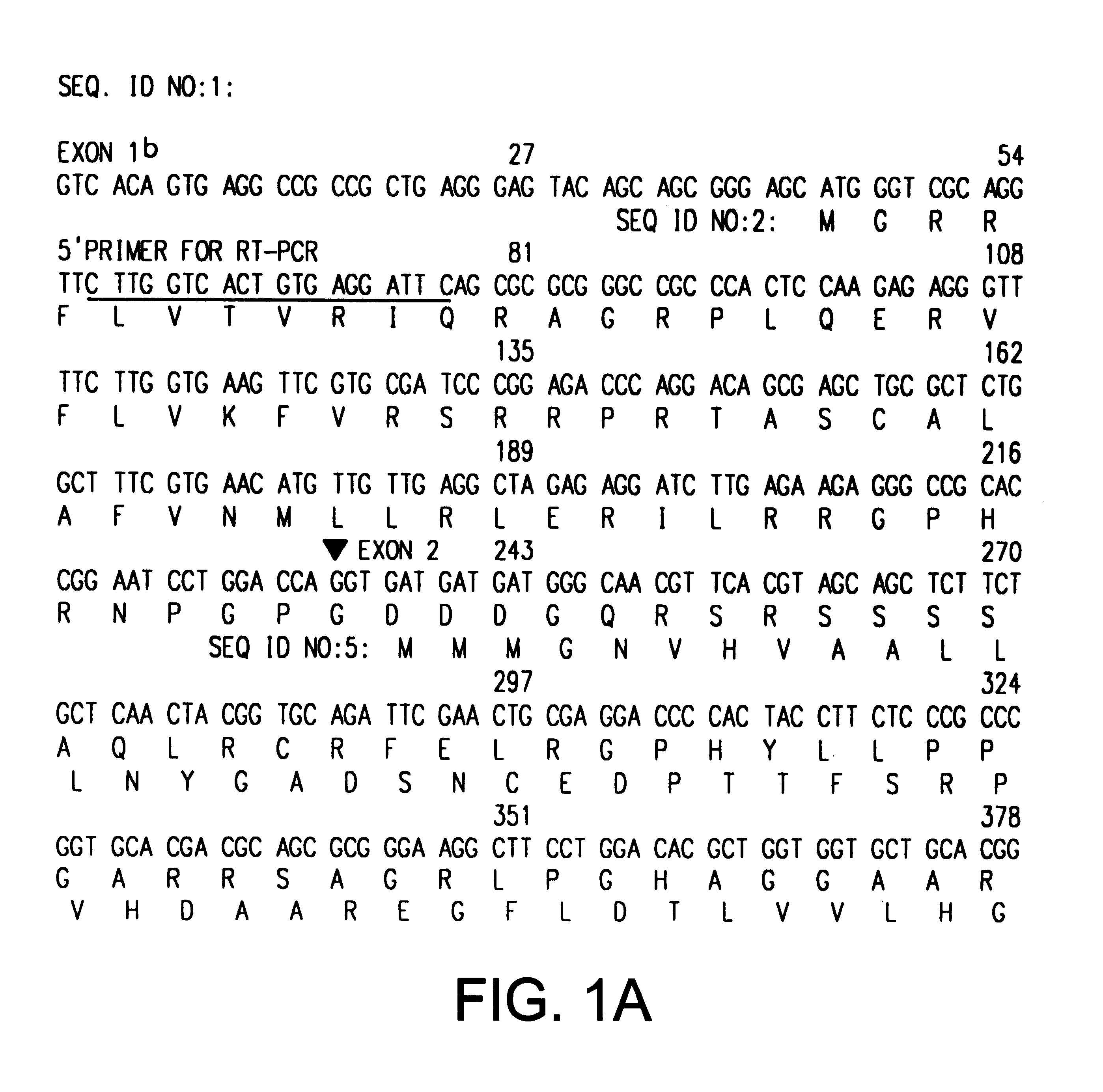
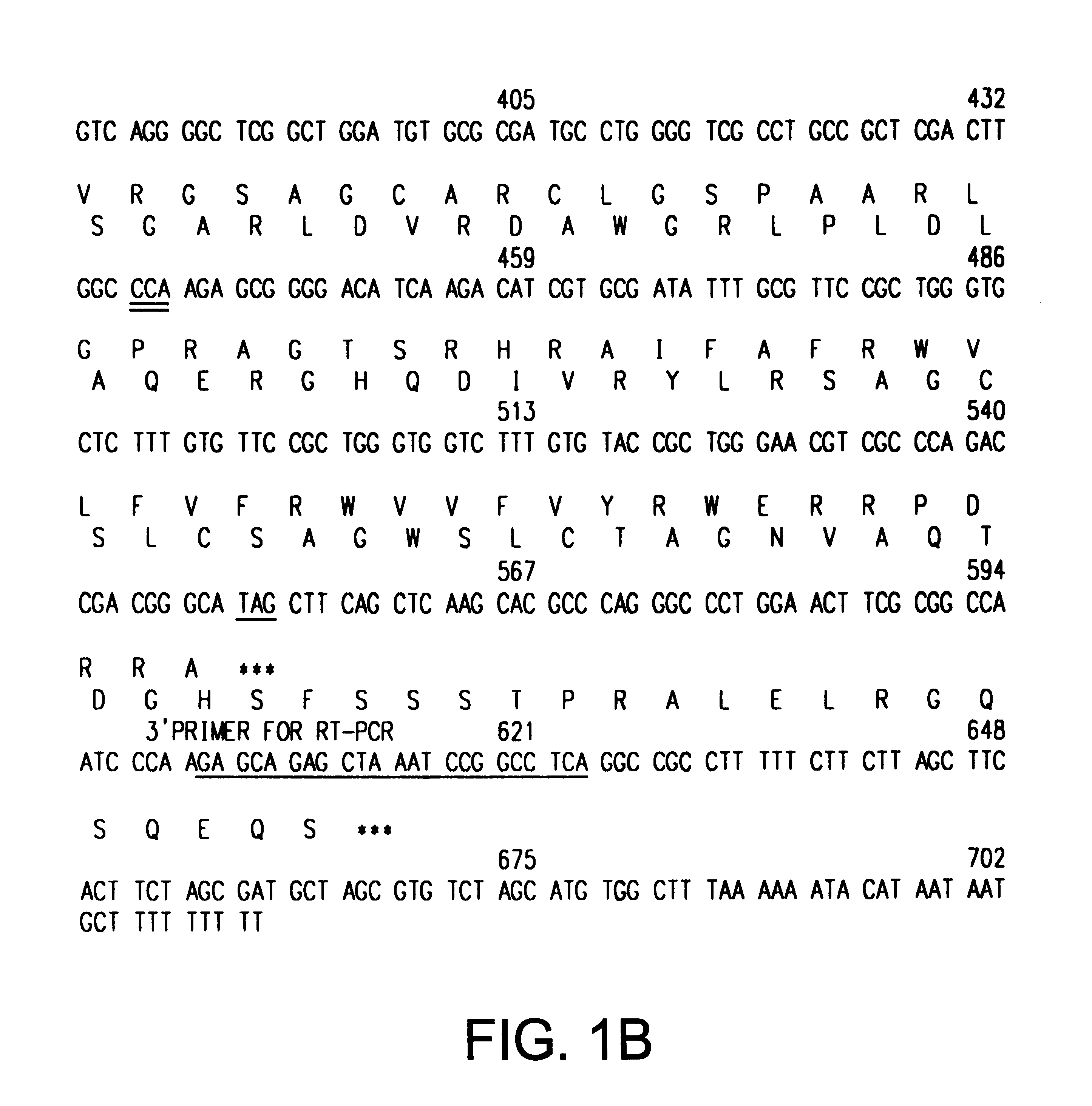
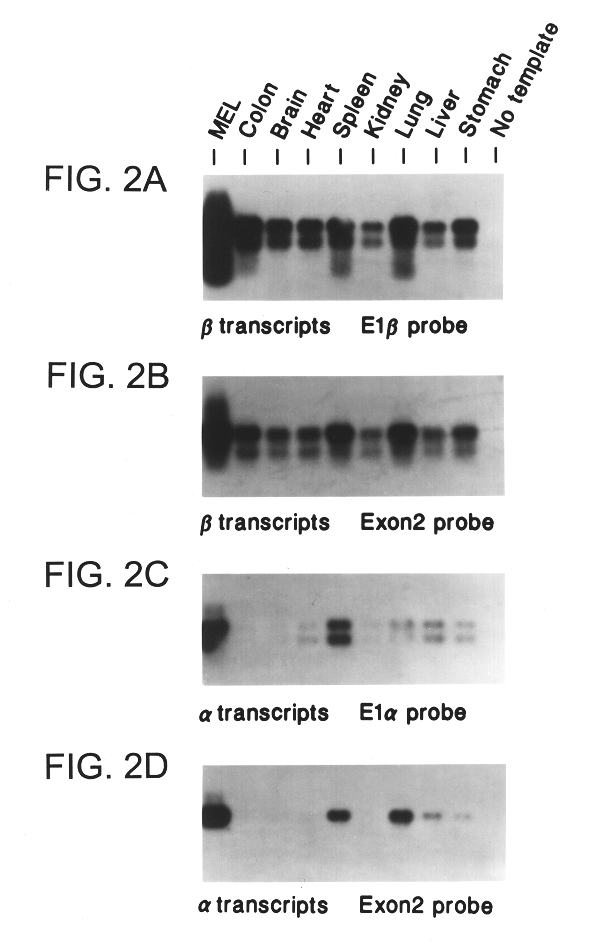
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Cell cycle control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
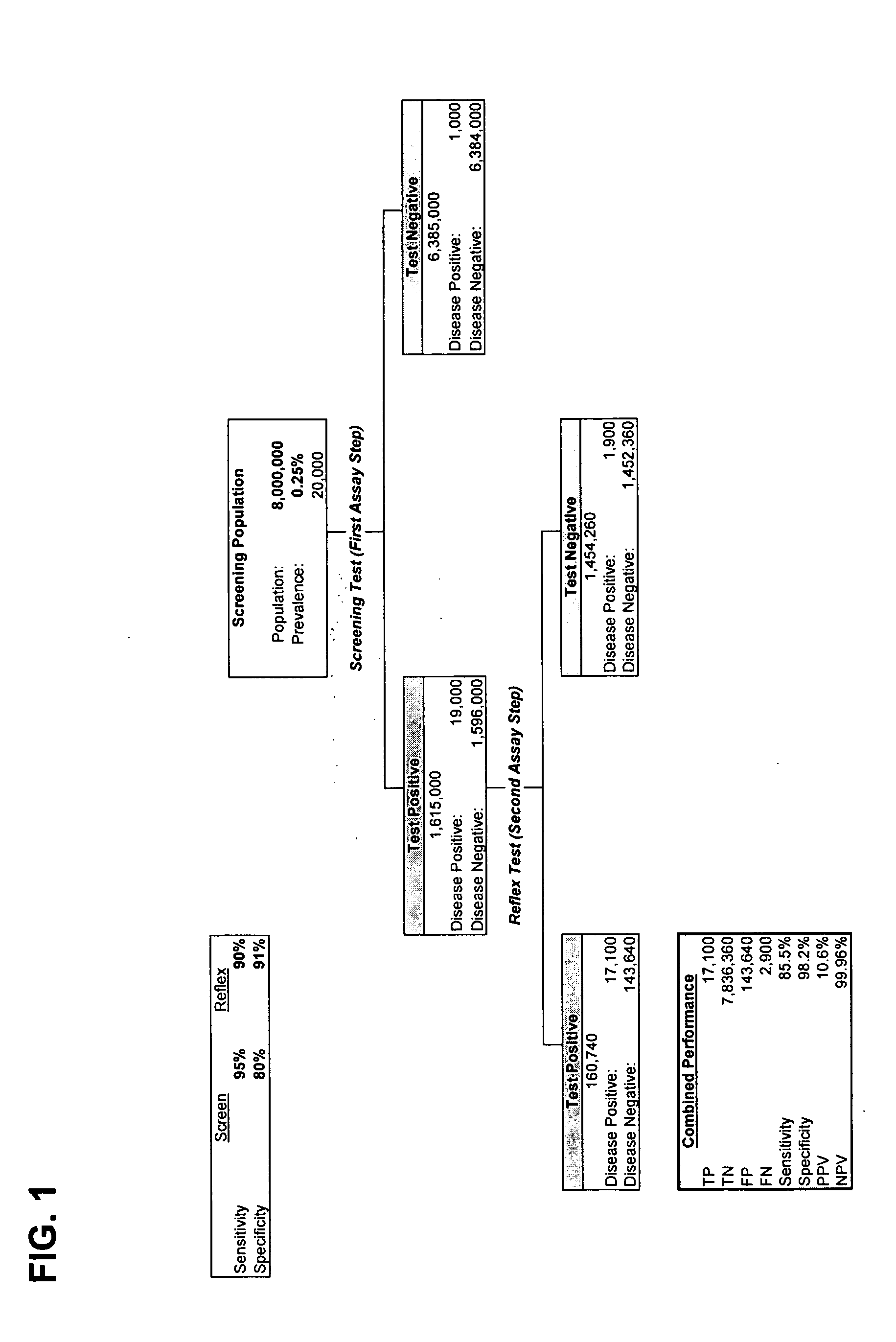
Control of Cell Cycle: The events of cell cycle are genetically controlled and highly conserved through evolution. The control mechanism operates in the same manner in yeast, plants and animals. Usually the cell cycle is controlled at three main checkpoints viz., G 1/S, G 2/M and spindle checkpoint (late metaphase).
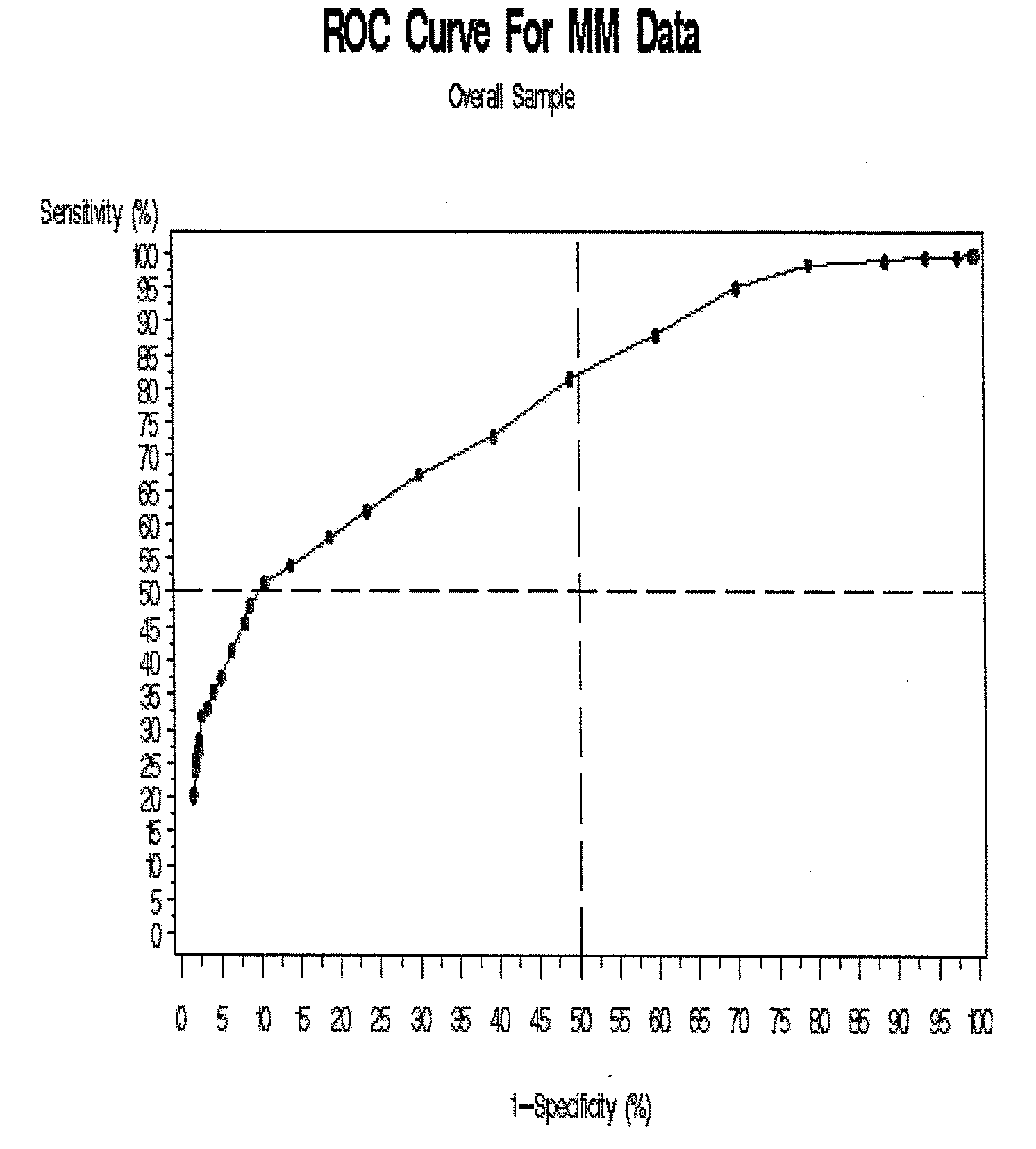
Methods for identifying patients with an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer and compositions therefor
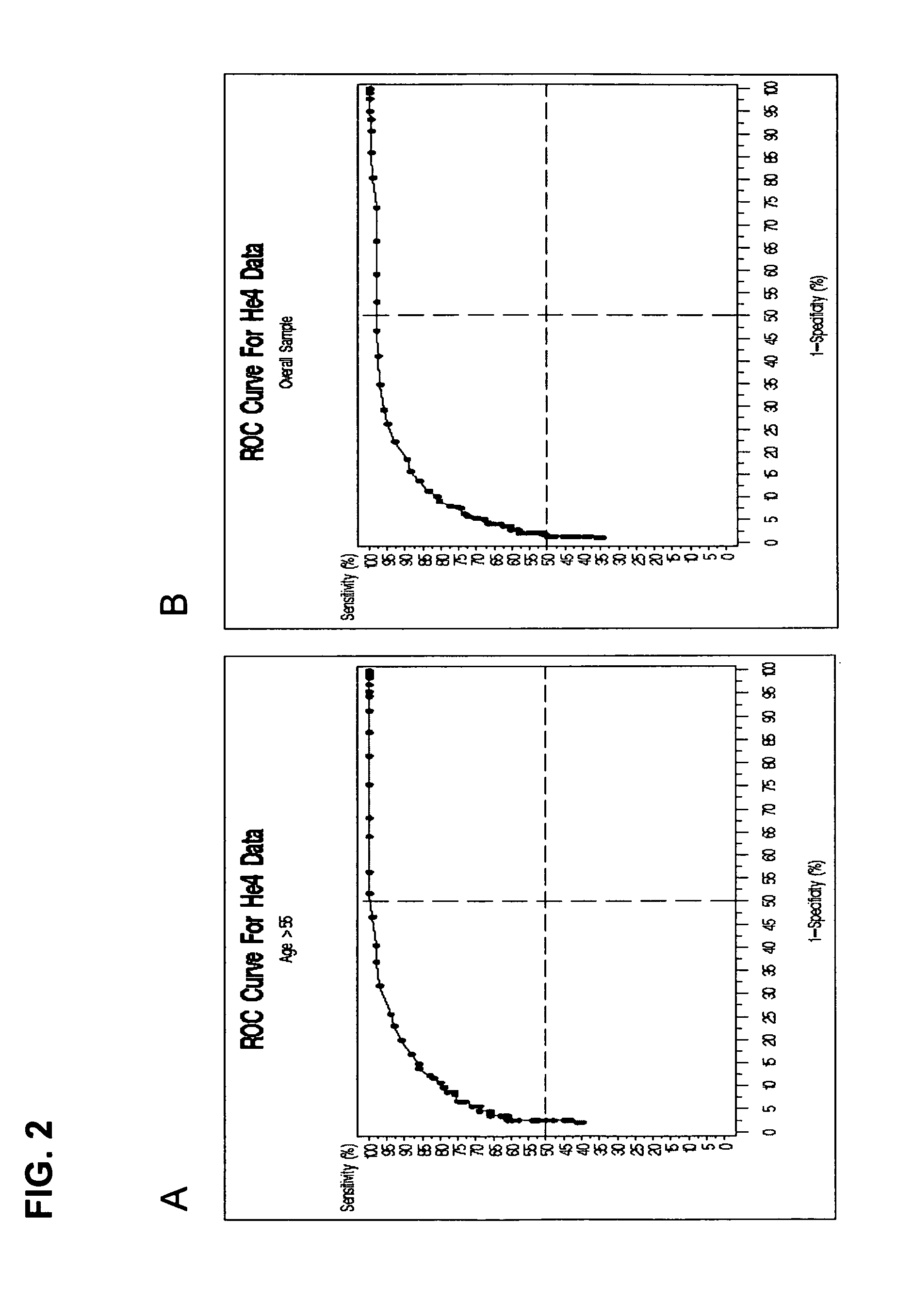
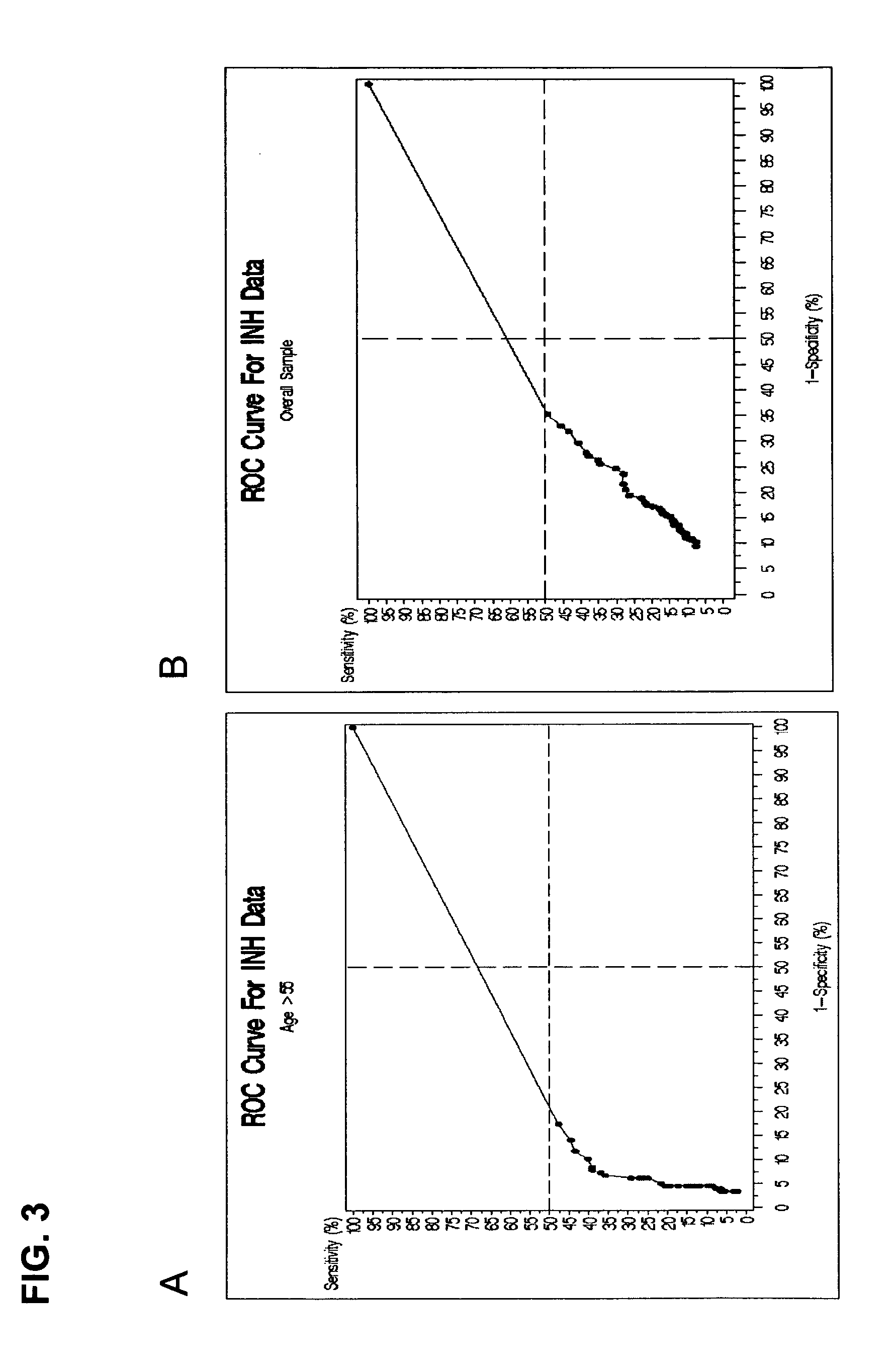
InactiveUS20070212721A1Easy to detectRaise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCancer cellMotility
Screening methods for identifying patients with an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer are provided. The screening methods involve the detection of expression of a plurality of biomarkers in a body sample, wherein overexpression of the biomarkers is indicative of an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer. The screening methods may further comprise a two-step analysis. Biomarkers of interest include genes and proteins that are, for example, involved in defects in DNA replication / cell cycle control, cell growth and proliferation, escape from apoptosis, angiogenesis or lymphogenesis, or the mechanisms of cancer cell motility and invasion. In some aspects of the invention, expression of a biomarker is detected at the protein level using a biomarker-specific antibody or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Methods for detecting ovarian cancer in patients are further disclosed herein. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
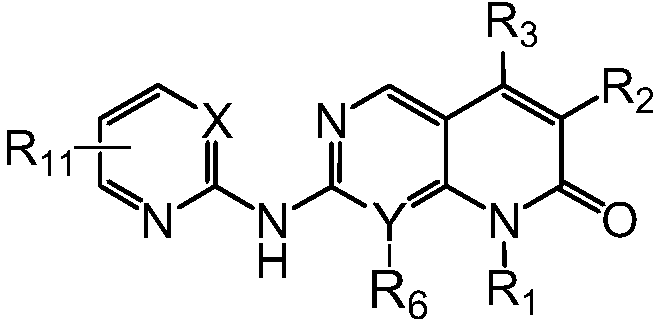
Pyridylpyrimidyl amine compounds or pyridylpyridyl amine compounds and application thereof
ActiveCN105153119AReduce phosphorylationApplicable treatmentOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAbnormal tissue growthDisease
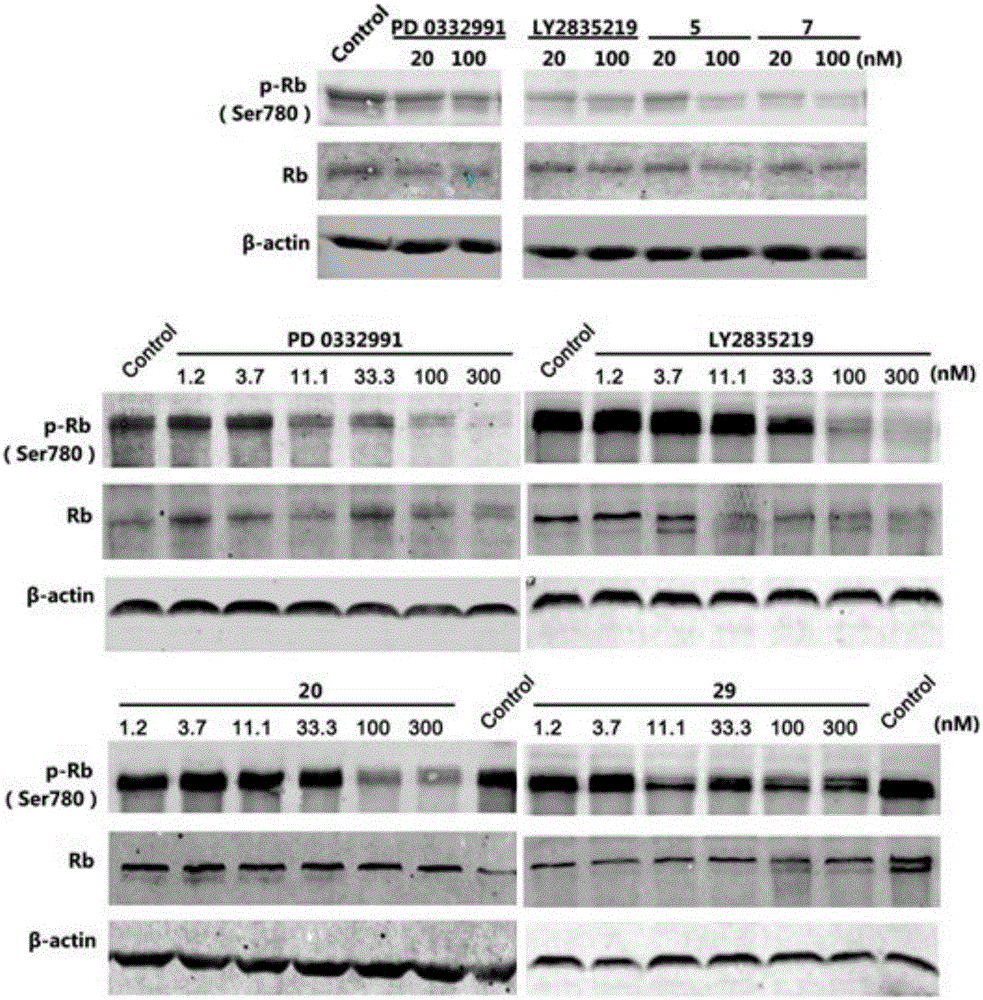
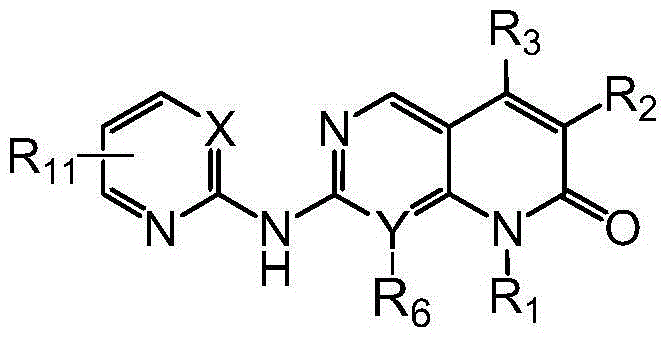
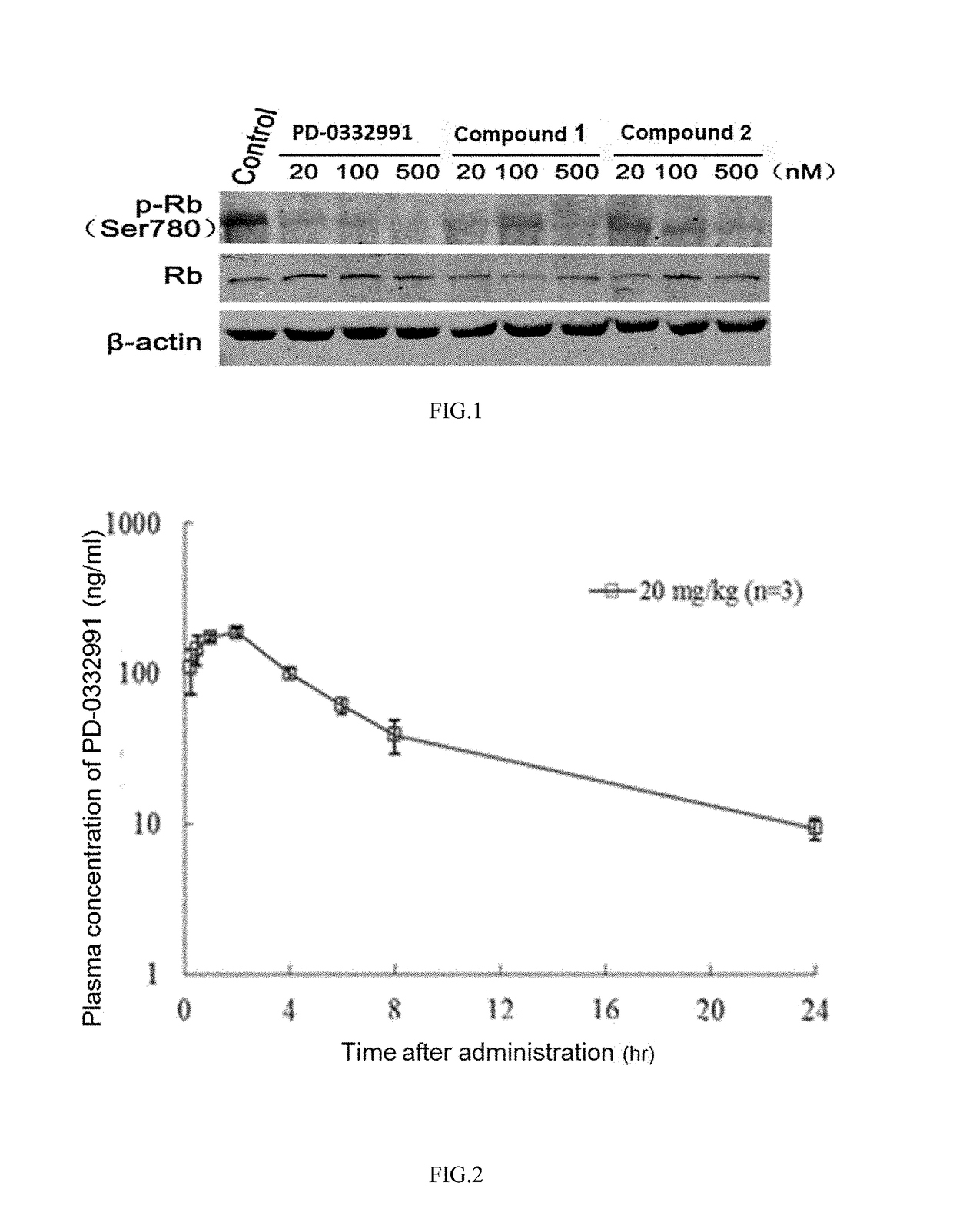
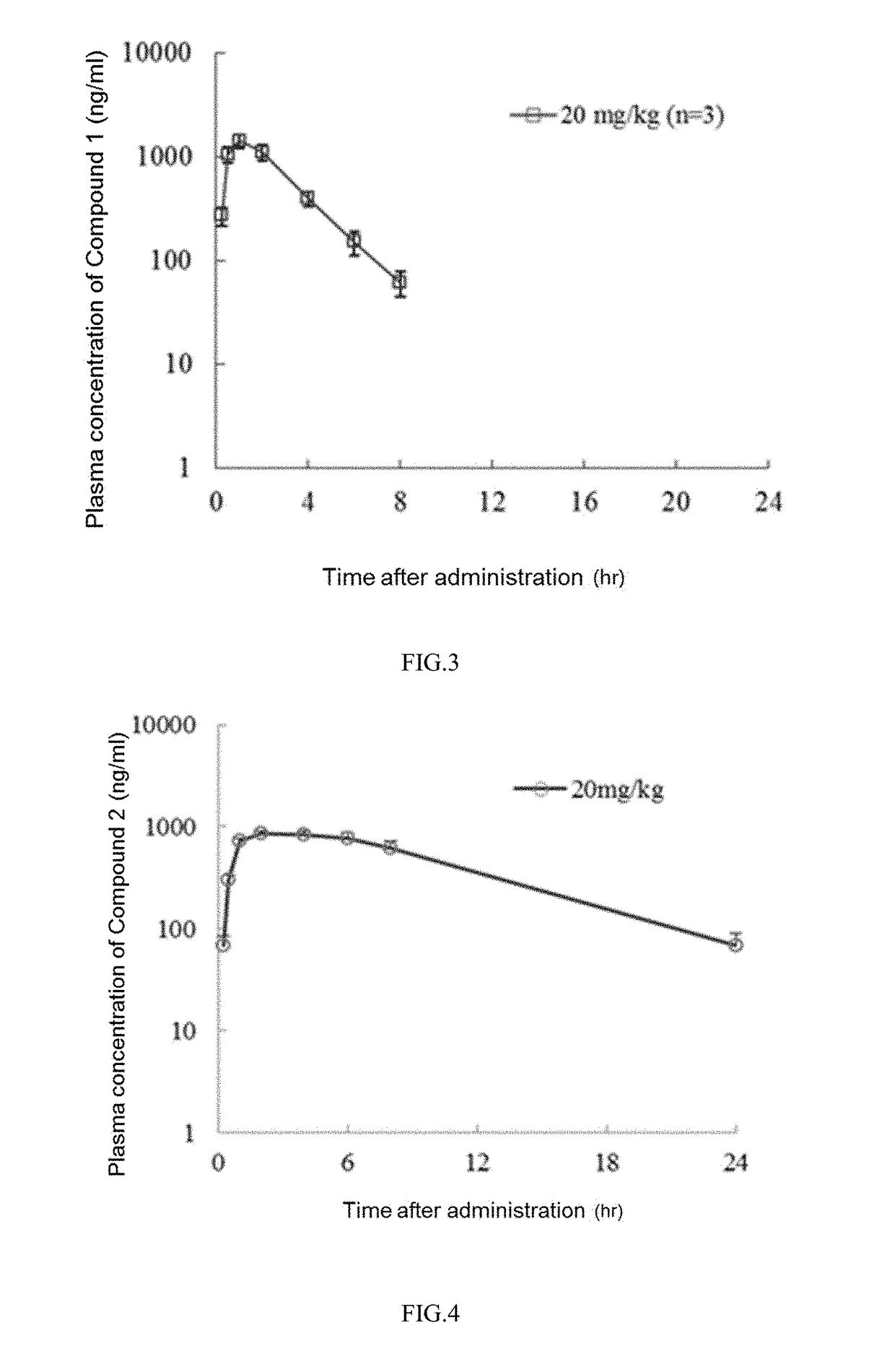
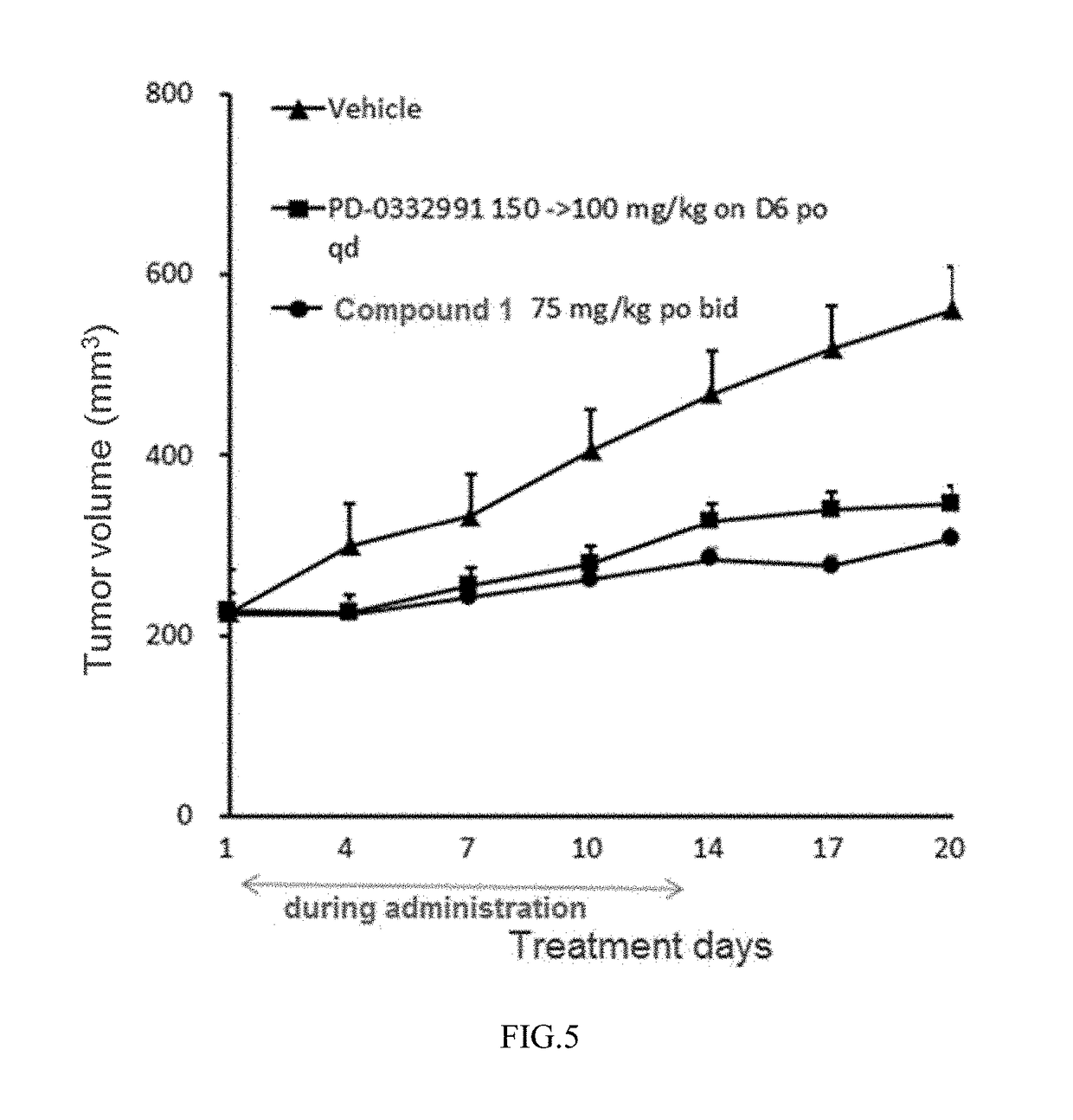
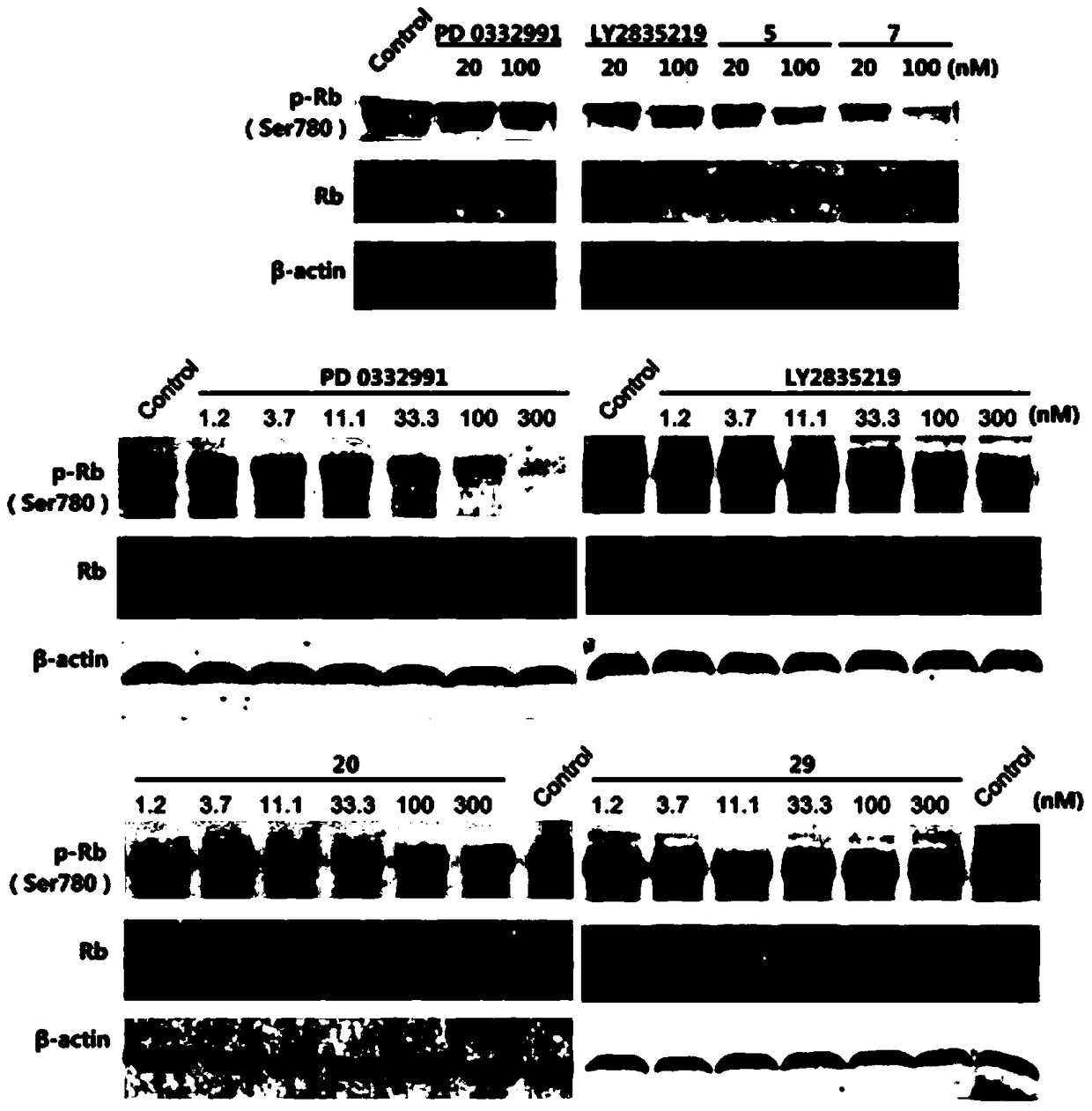
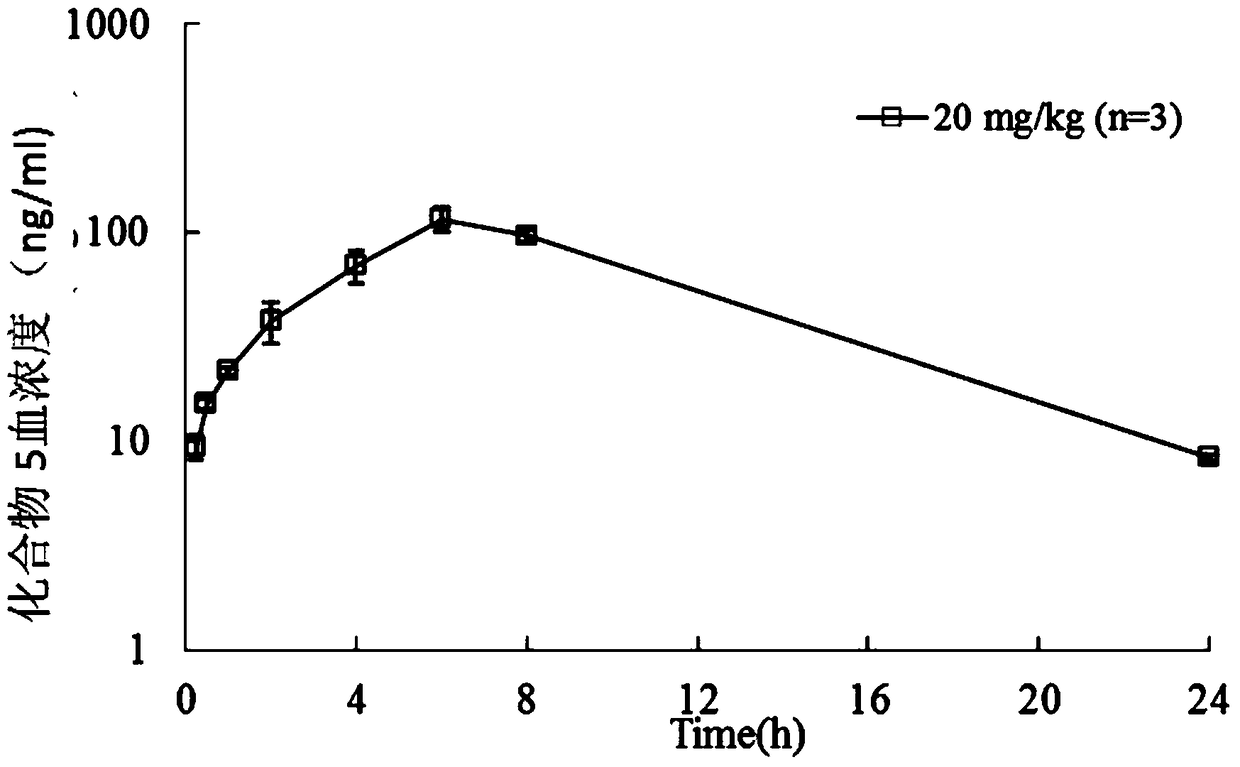
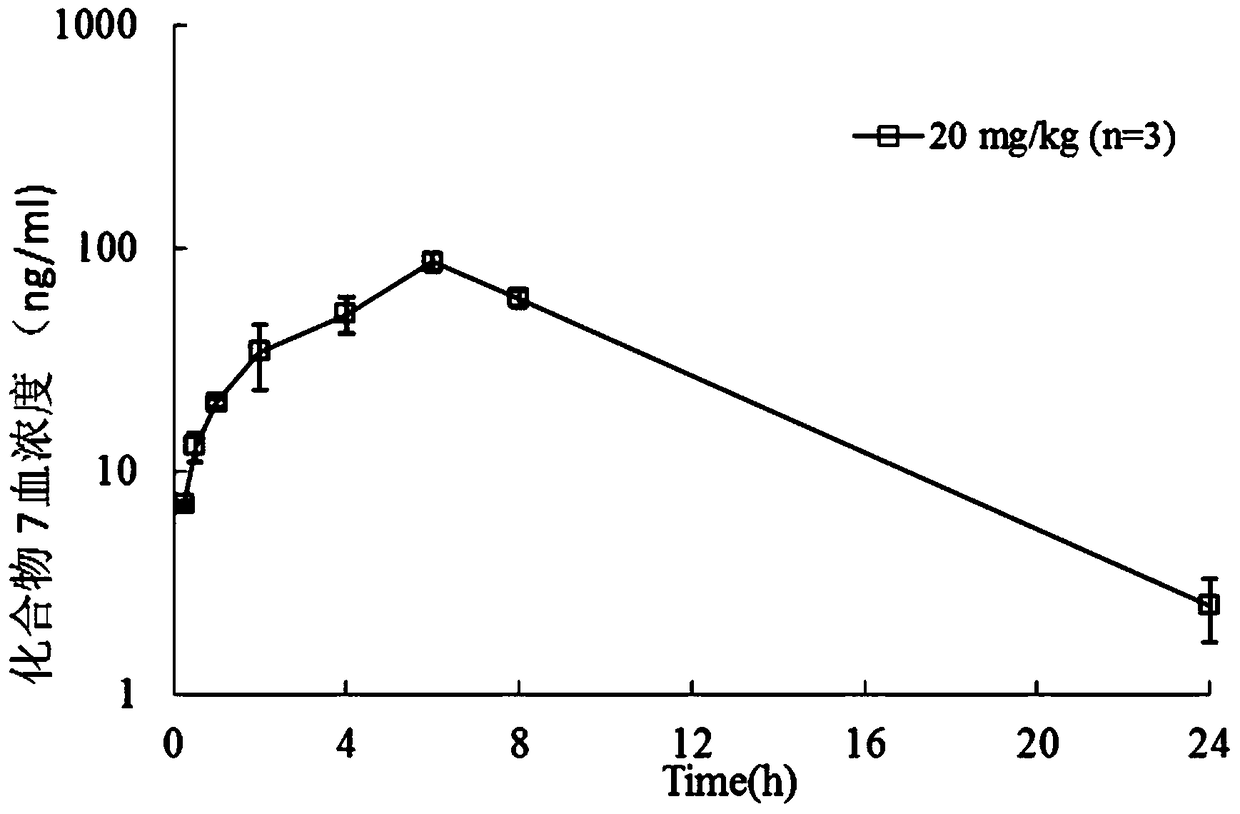
The invention discloses pyridylpyrimidyl amine compounds or pyridylpyridyl amine compounds disclosed as Formula I and application thereof in preparing antineoplastic drugs, belonging to the technical field of drugs. The compounds can selectively inhibit CDK4 and CDK6, enable G1-period tumor cells to stop growth and G1-period tumor cells to reduce, can effectively lower the phosphorylation of the tumor inhibiting protein Rb in the Ser780 site, and thus, can be used for various diseases caused by cell cycle control maladjustment participated by CDK4 and CDK6. The compounds are especially suitable for treating malignant tumors, and have the characteristics of high selectivity, high activity and high tumor cell proliferation resistance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BEBETTER MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
ARF-P19, a novel regulator of the mammalian cell cycle
InactiveUS6407062B1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
The INK4A (MTS1, CDKN2) gene encodes a specific inhibitor (InK4a-p16) of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. InK4a-p16 can block these kinase from phosphorylating the retinoblastoma protein (pRb), preventing exit from the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Deletions and mutations involving the gene encoding InK4a-p16, INK4A, occur frequently in cancer cells, implying that INK4a-p16, like pRb, suppresses tumor formulation. However, a completely unrelated protein (ARF-p19) arises in major part from an alternative reading frame of the mouse INK4A gene. Expression of an ARF-p19 cDNA (SEQ ID NO:1) in rodent fibroblasts induces both G1 and G2 phase arrest. Economical reutilization of protein coding sequences in this manner is without precedent in mammalian genomes, and the unitary inheritance of INK4a-p16 and ARF-p19 may reflect a dual requirement for both proteins in cell cycle control.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN105622638AApplicable treatmentHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDrugs preparationsPyridine
The invention discloses a pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound shown in the formula I and its preparation method and use and belongs to the technical field of drug preparation. The pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound can efficiently and selectively inhibit cyclin-depedent kinase (Cdks) CDK4 and CDK6 activity and prevent tumor cell division through inhibiting CDK4 / CDK6. The pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound can be used for treating various diseases caused through imbalance of cell cycle control based on CDK4 and CDK6 and is especially suitable for cancer treatment.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BEBETTER MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Human autogenous siRNA sequence, its application and screening method
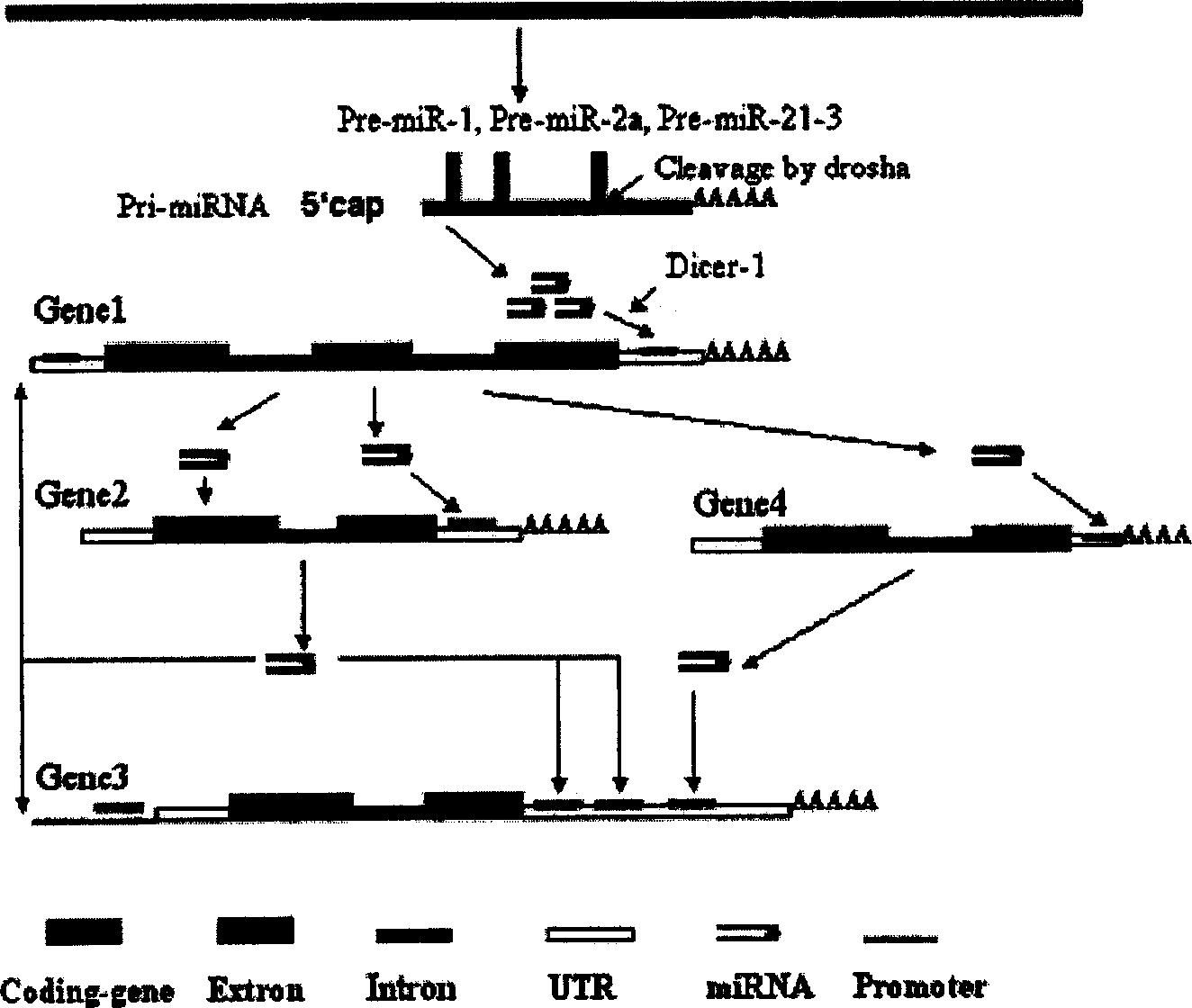
The invention relates to a computer algorithmic language and relative application software. It could rapidly select and predict internal source siRNA gene and siRNA molecule. Especially, it relates to an entire finding method for internal source siRNA gene and internal source siRNA molecule, and gaining 255 new siRNAs and target mRNAs from coding gene intron. The siRNA molecules could be used to research develop, differentiation and growth of cell, organization and organic, discuss the function and express adjusting network and discuss function of genes. It also could be used to develop medicines to prevent and cure kinds of disease.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Cancer immunotherapy
InactiveUS20060127408A1Eliminate the effects ofIncreasing breadth and hopefully potency of immune responseGenetic material ingredientsTissue cultureAntigenPolycomb-group proteins
The invention relates to the use of polycomb group proteins as a tumour-associated antigens. Polycomb group proteins are highly involved in body architecture development, haematopoiesis and cell cycle control. Aberrant expression of polycomb proteins has been linked with haematological malignancies, mainly lymphomas. This invention relates to the use of these polycomb group proteins as antigens for cancer immunotherapy. Immunological responses can be raised against these proteins and such responses are active against polycomb protein over-expressing tumour cells.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BIRMINGHAM
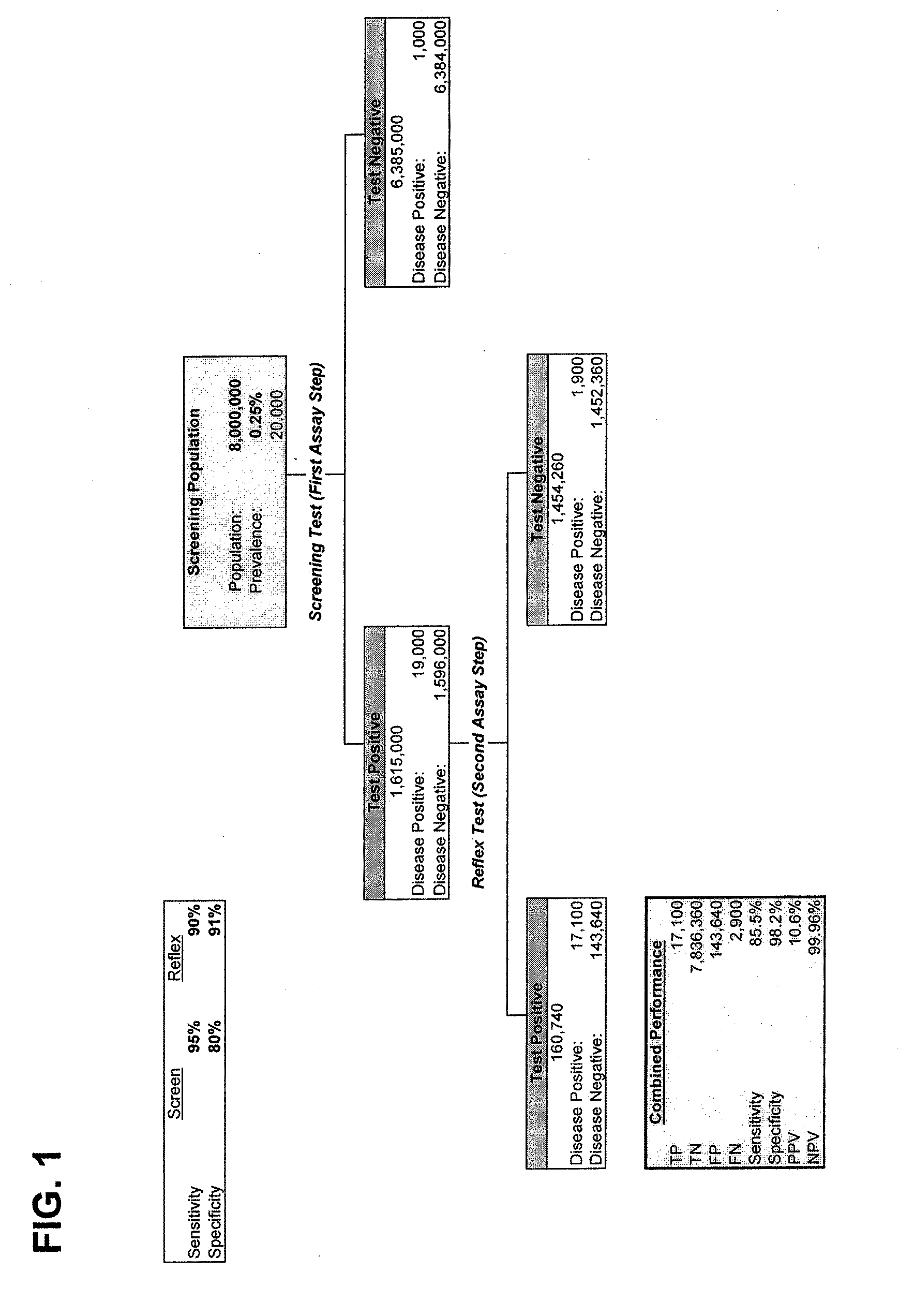
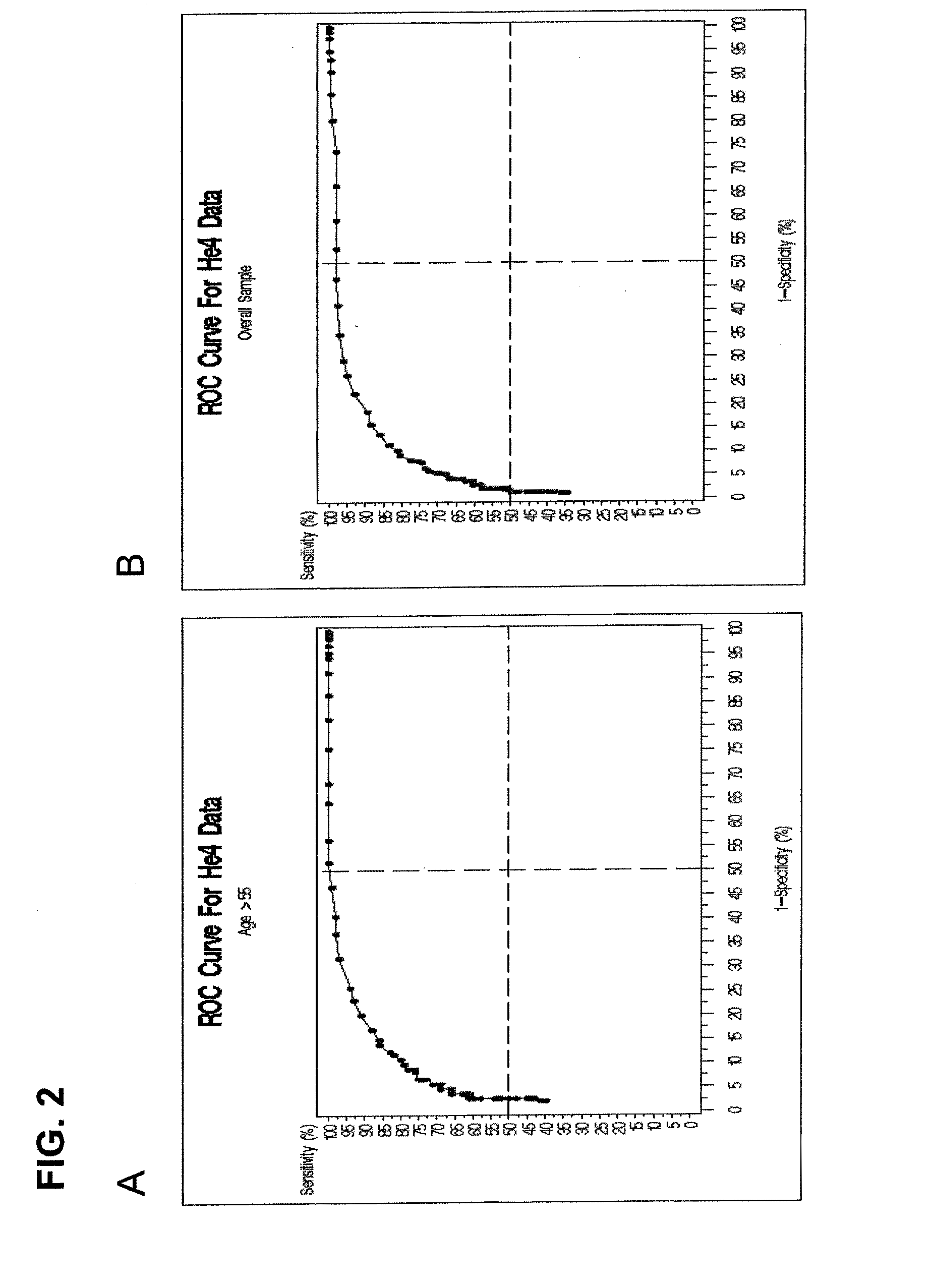
Approach to molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus-related diseases
ActiveUS7361460B2Accurate sensitive toolReduce in quantitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein markersSequential method
The present invention relates to an accurate, sensitive, and efficient sequential or concurrently sequential method for molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus (HPV)-based disease, where the method improves the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic and prognostic assessments of HPV-based disease. The method of the invention comprises a primary screen of a sample for HPV nucleic acids, followed by a secondary screen for molecular markers, such as proliferation and cell cycle control group protein markers. The sequential or concurrently sequential method significantly reduces the number of false positive results.
Owner:DIGENE CORP
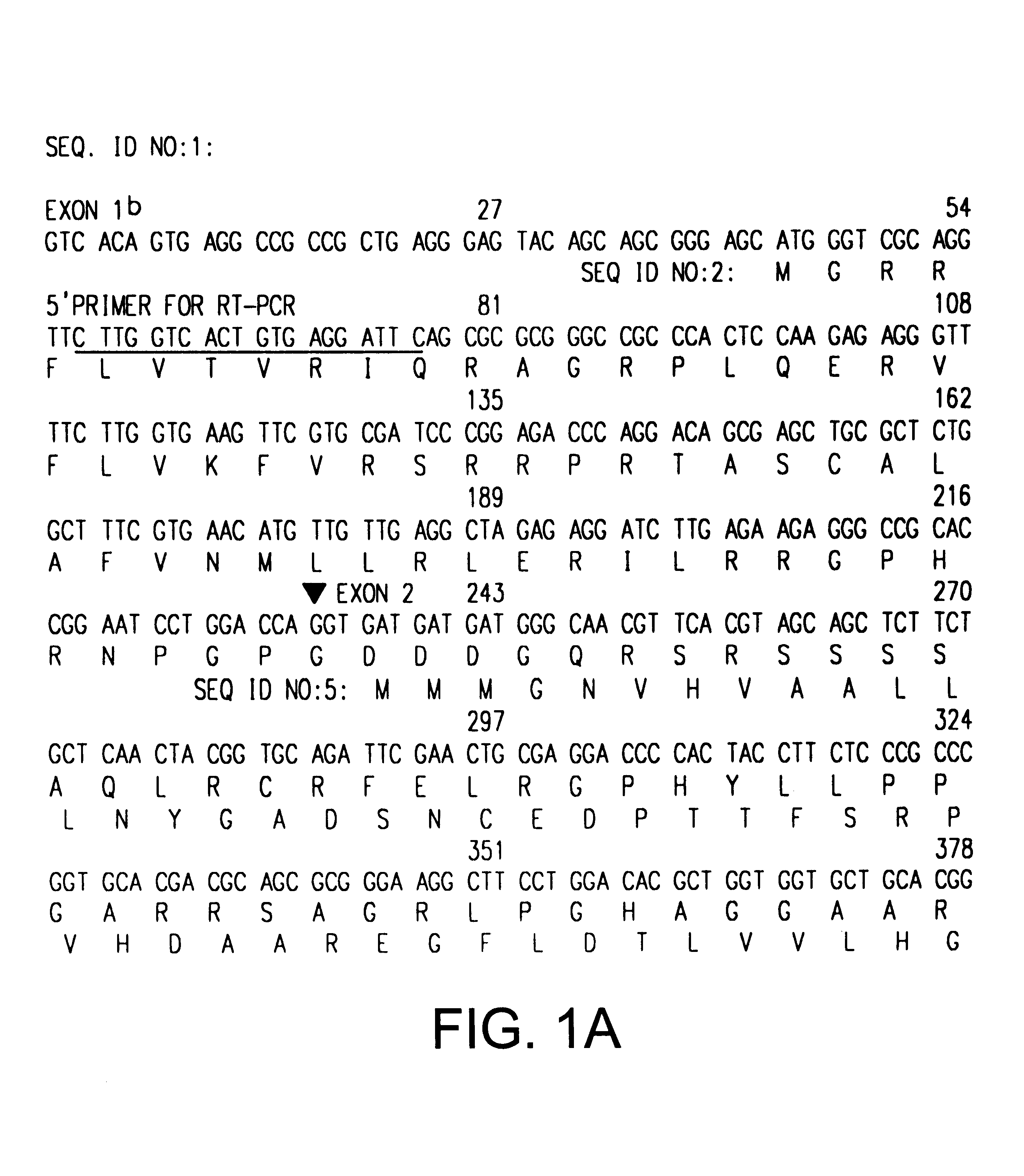
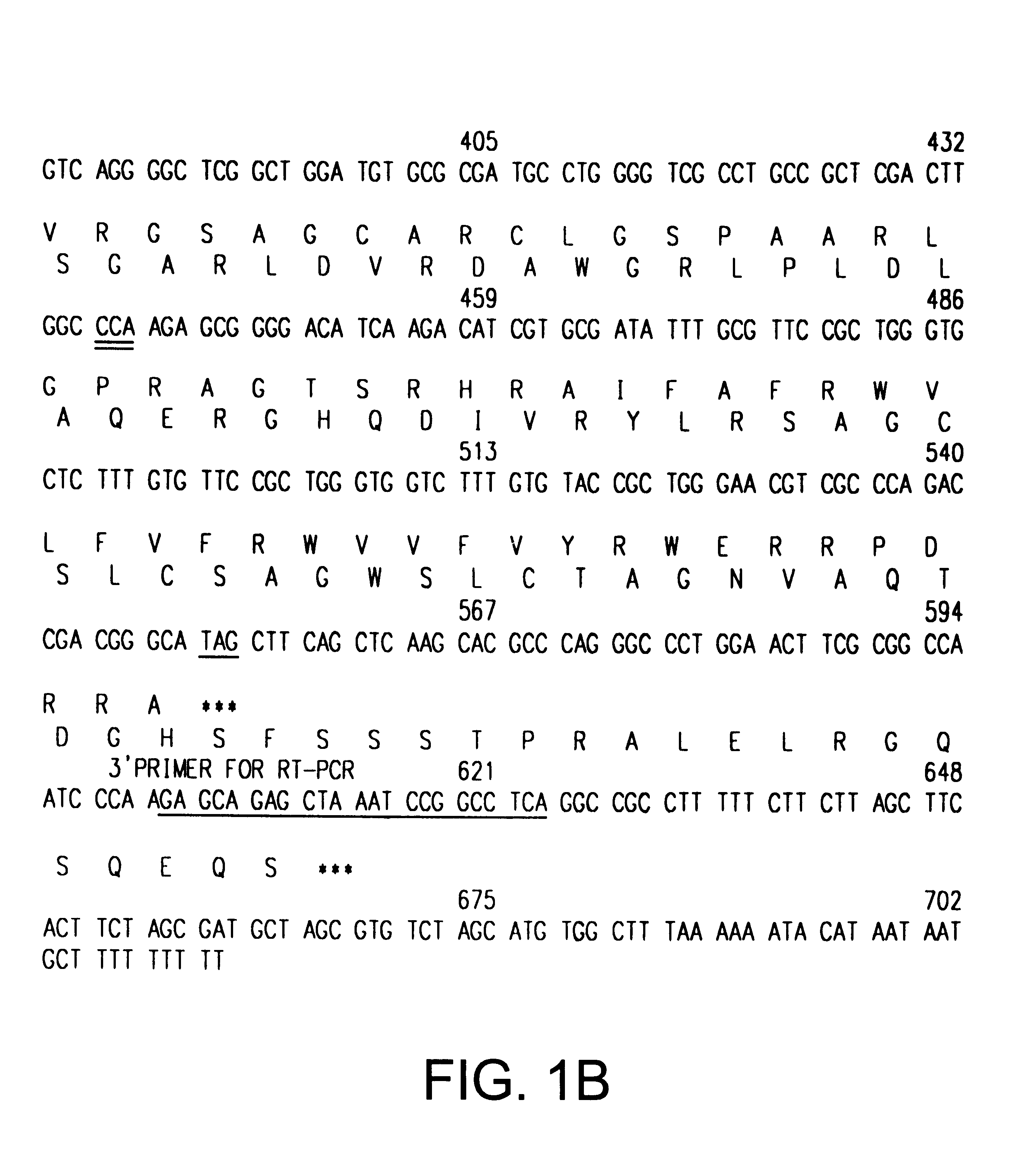
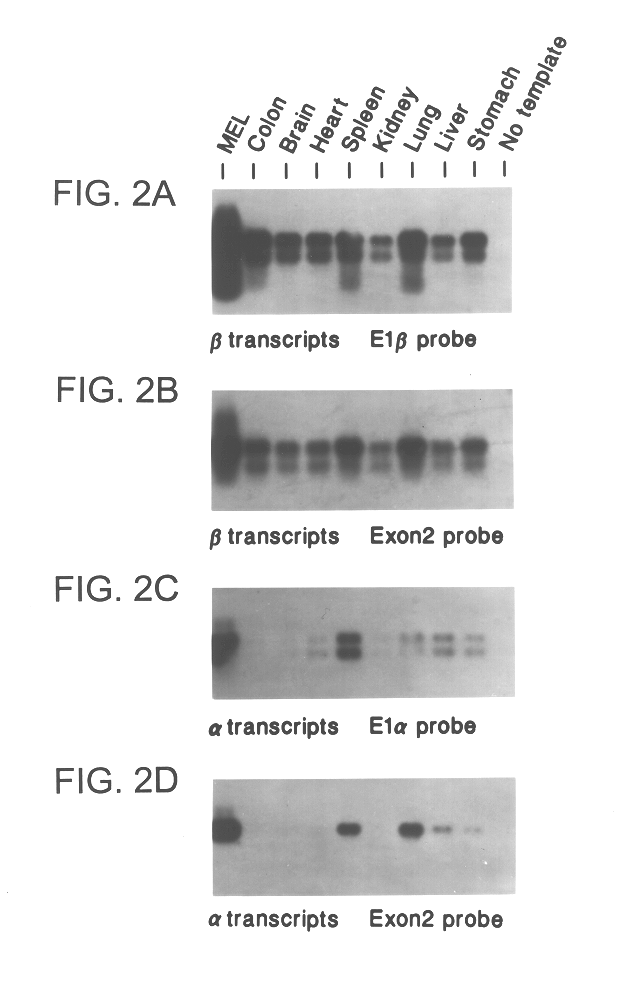
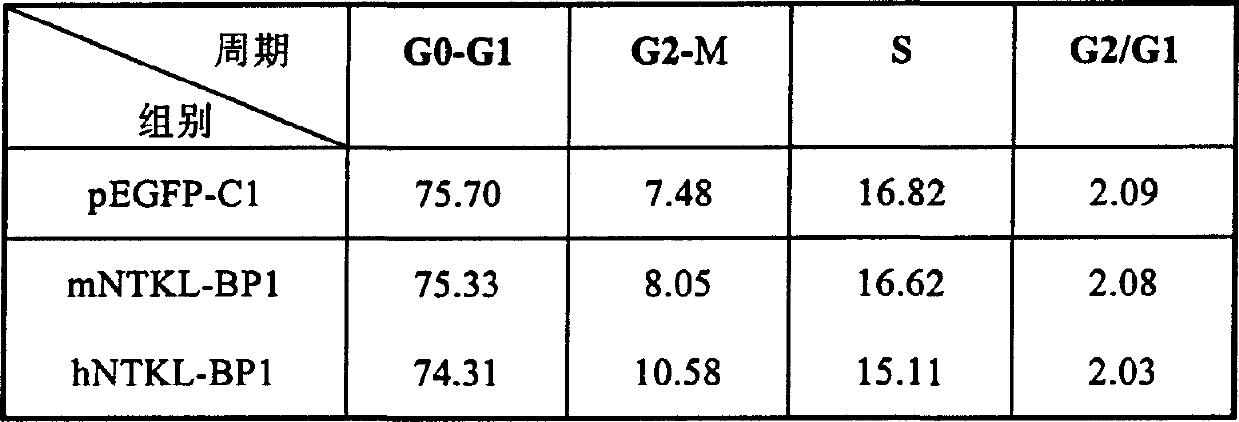
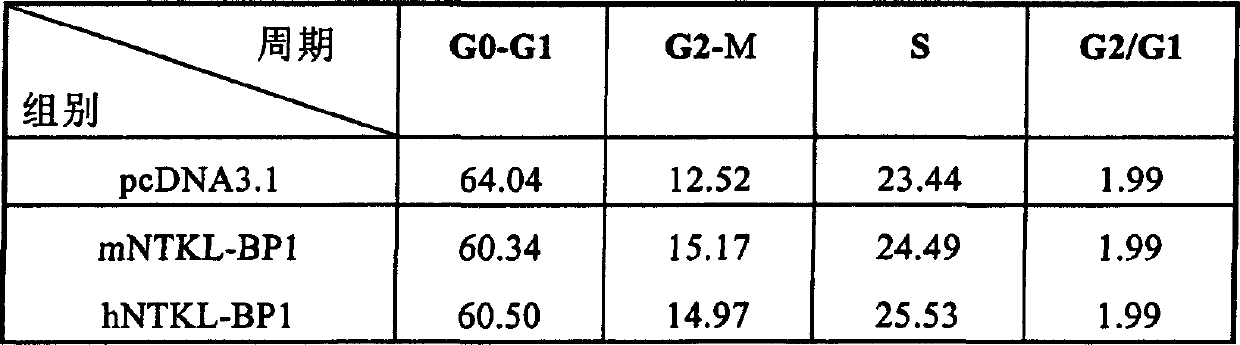
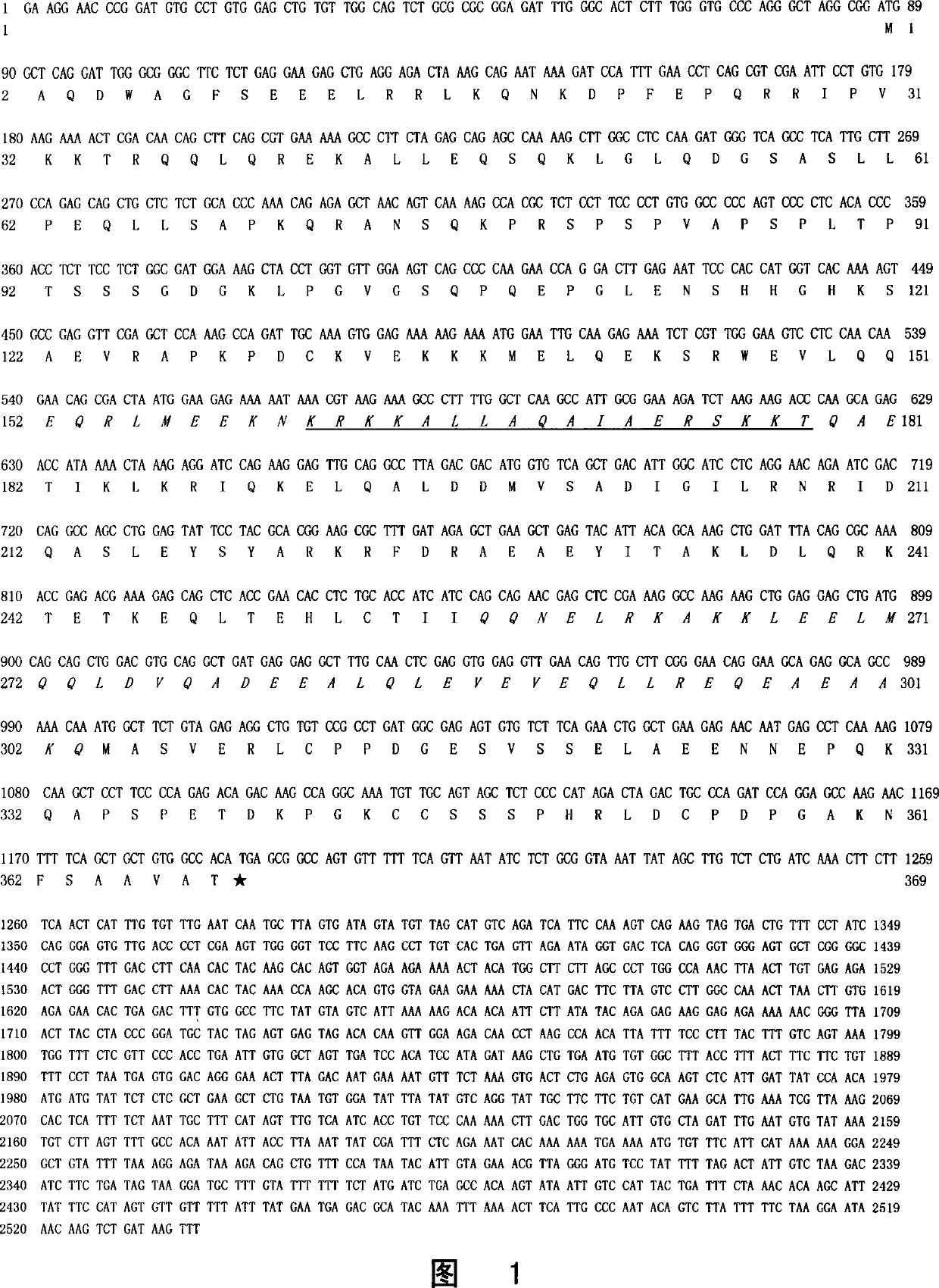
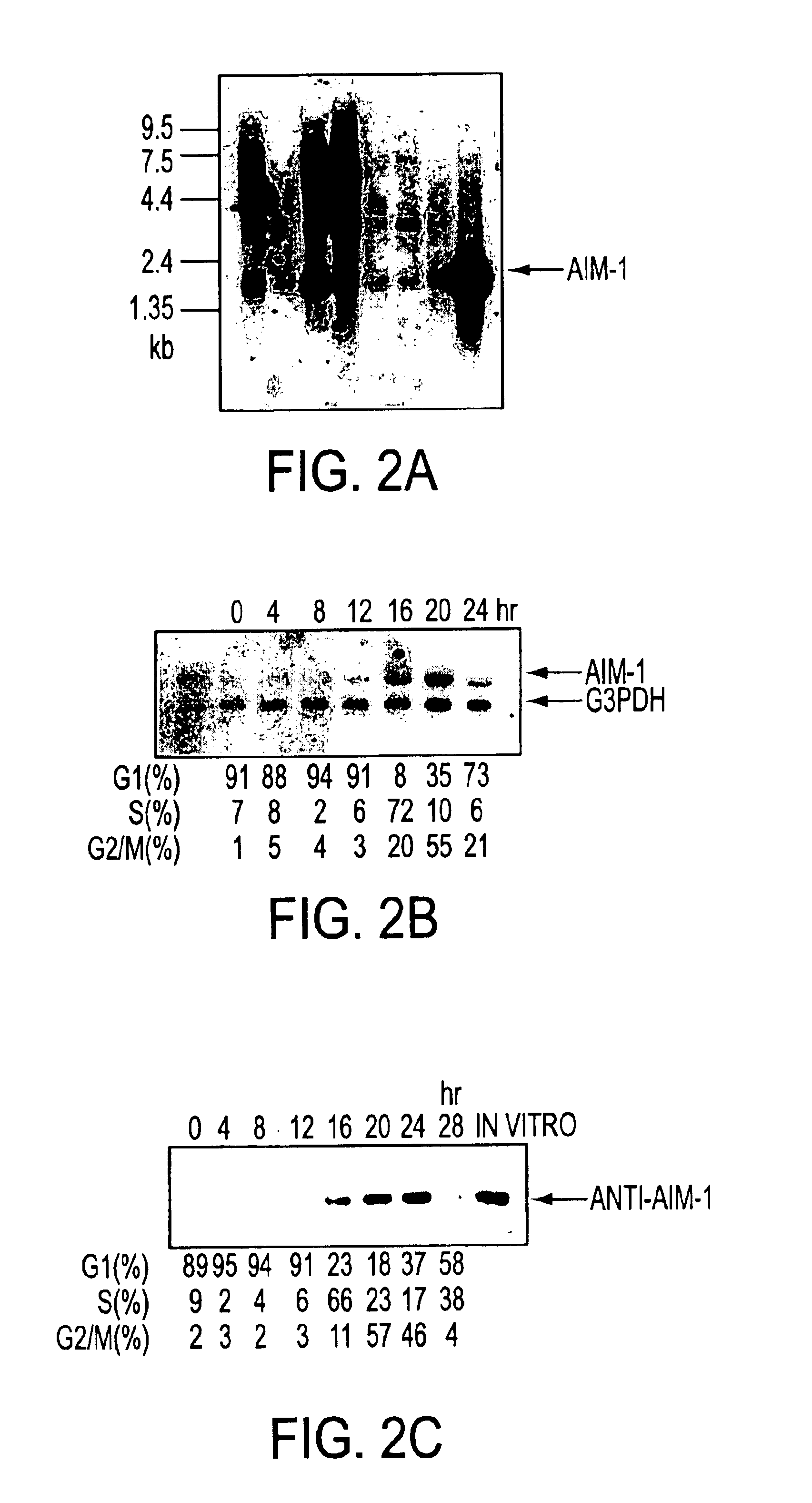
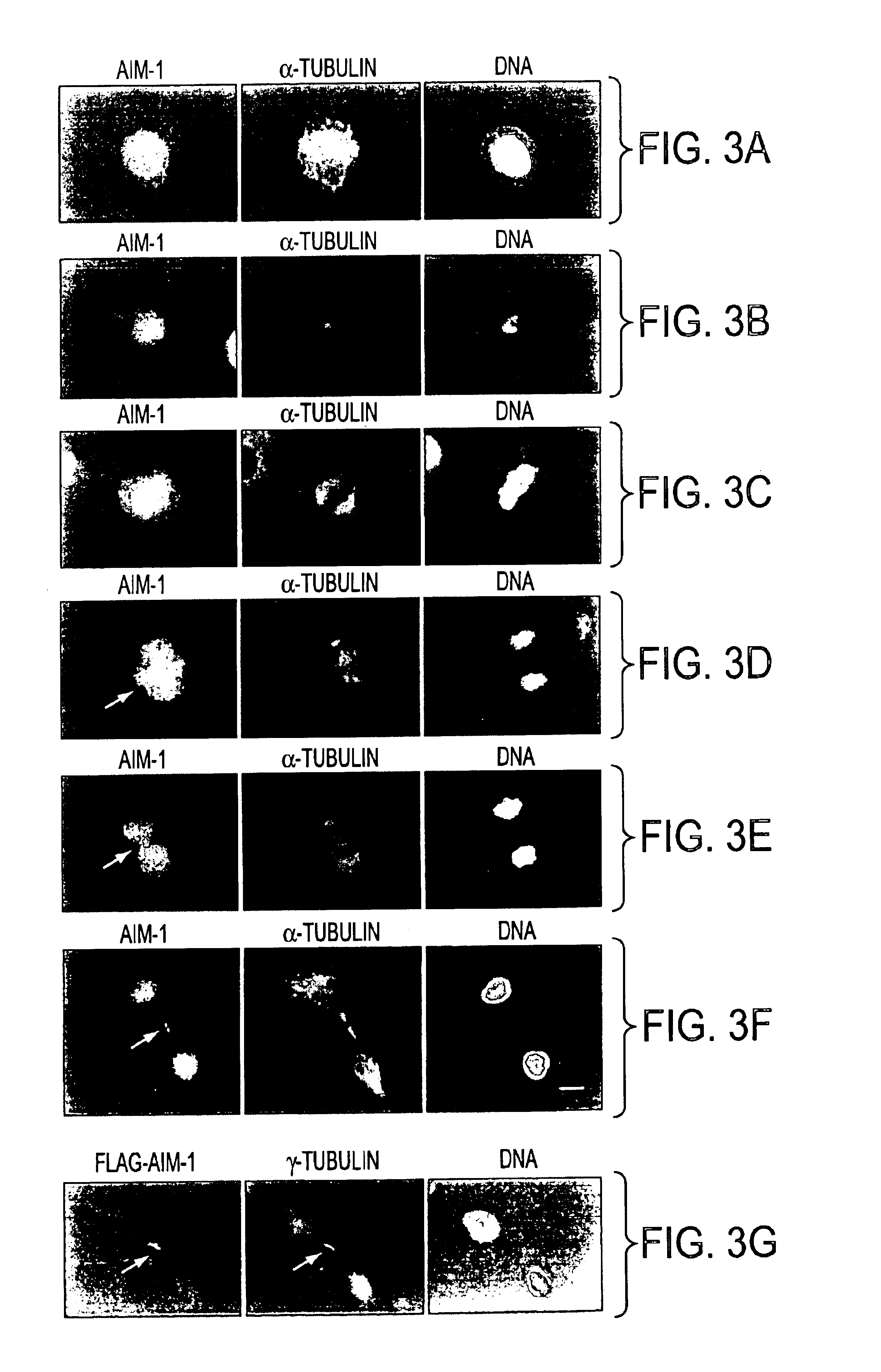
Cell cycle control protein
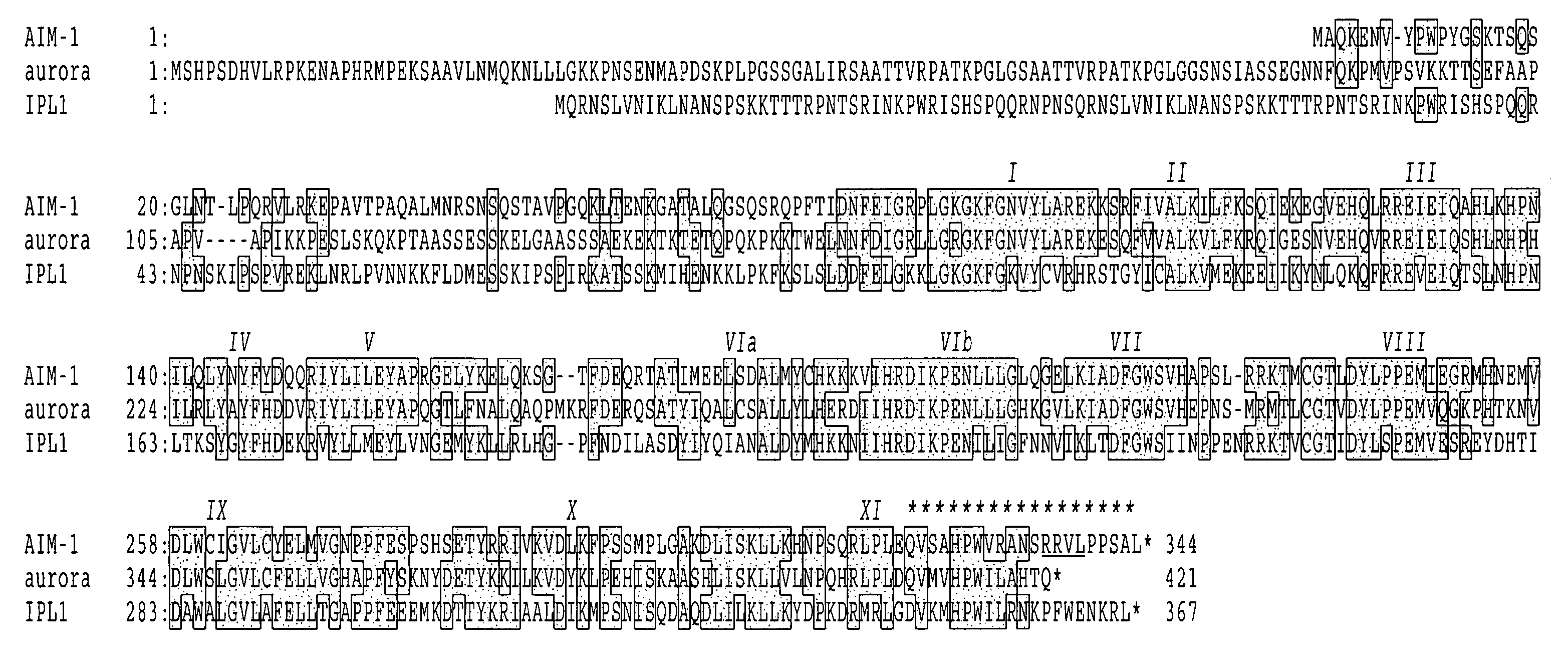
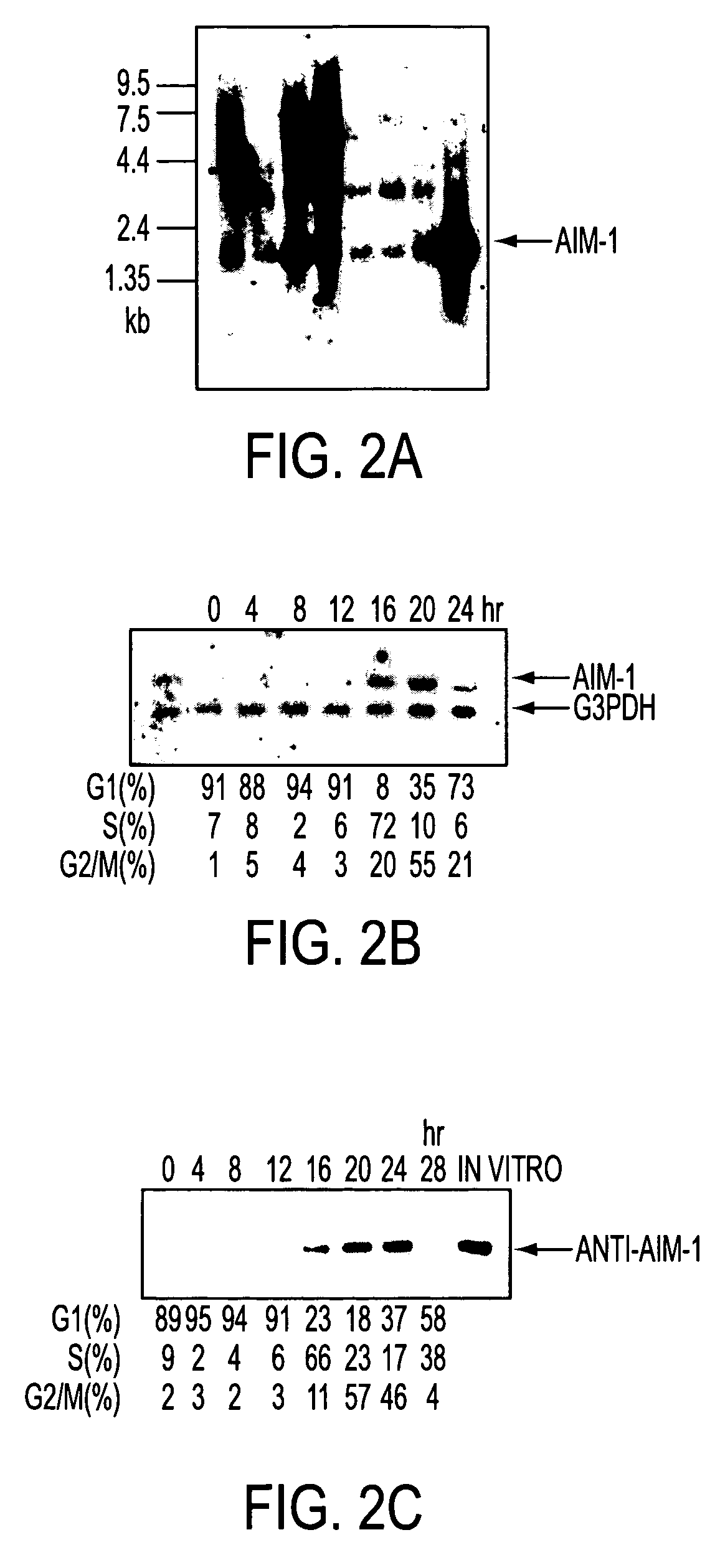
A DNA containing a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing, or a nucleotide sequence encoding a protein having the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing with partial substitution, deletion or addition and having cell cycle control activity, or a nucleotide sequence hybridizing to them; a recombinant vector containing said DNA; a cell transformed with said vector; a process for producing AIM-1 using said DNA; a recombinant AIM-1 protein obtained by said process; an oligonucleotide or peptide nucleic acid capable of specifically hybridizing to a nucleotide sequence encoding AIM-1 protein; an antibody recognizing AIM-1; a therapeutic agent for diseases associated with abnormal cell growth containing an inhibitor against AIM-1 protein; and a screening method for materials having serine-threonine inhibitory activity using AIM-1 gene or AIM-1 protein.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
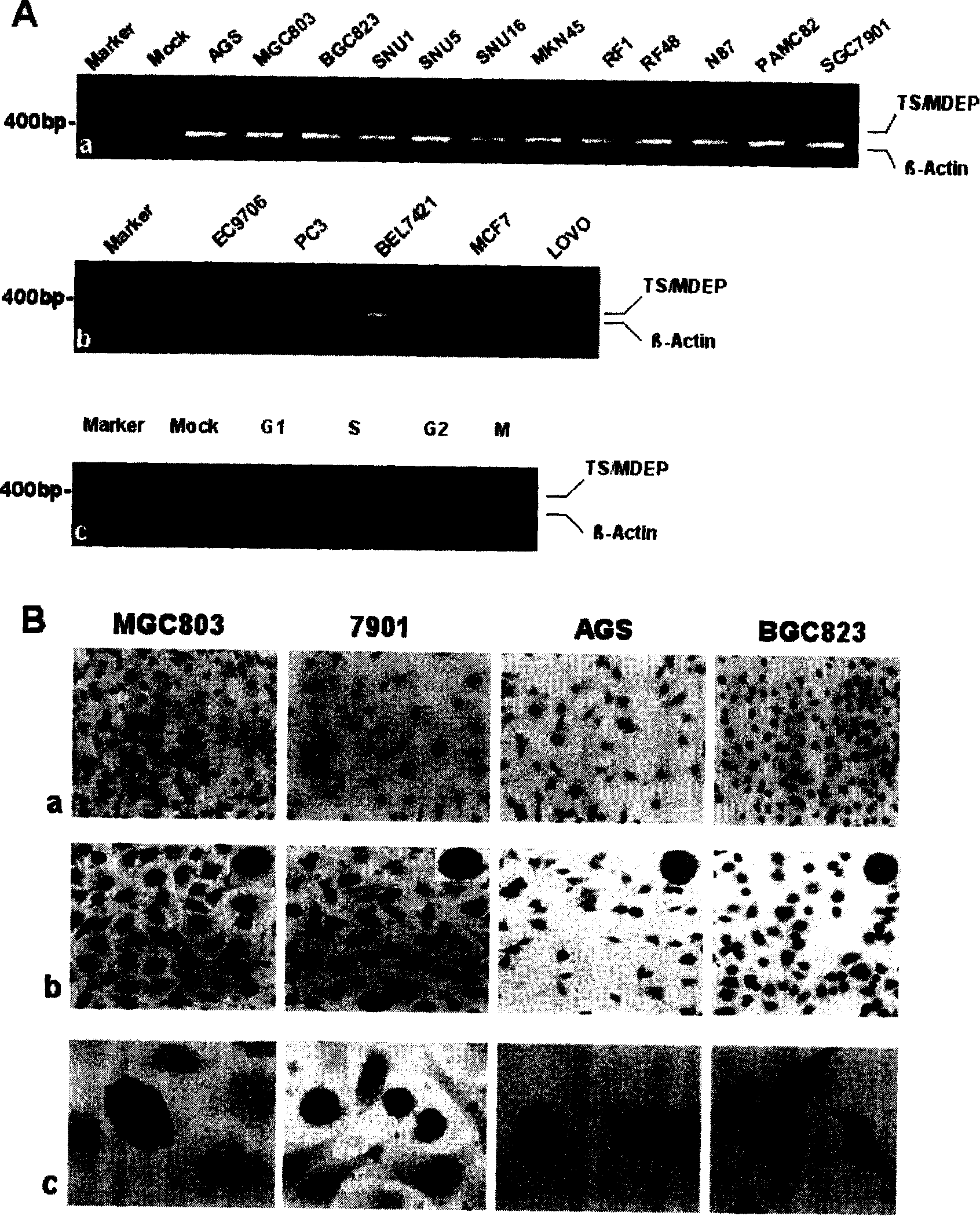
Preparation for antibody of antineoplastic specificity marker protein TS/MEDP and use thereof
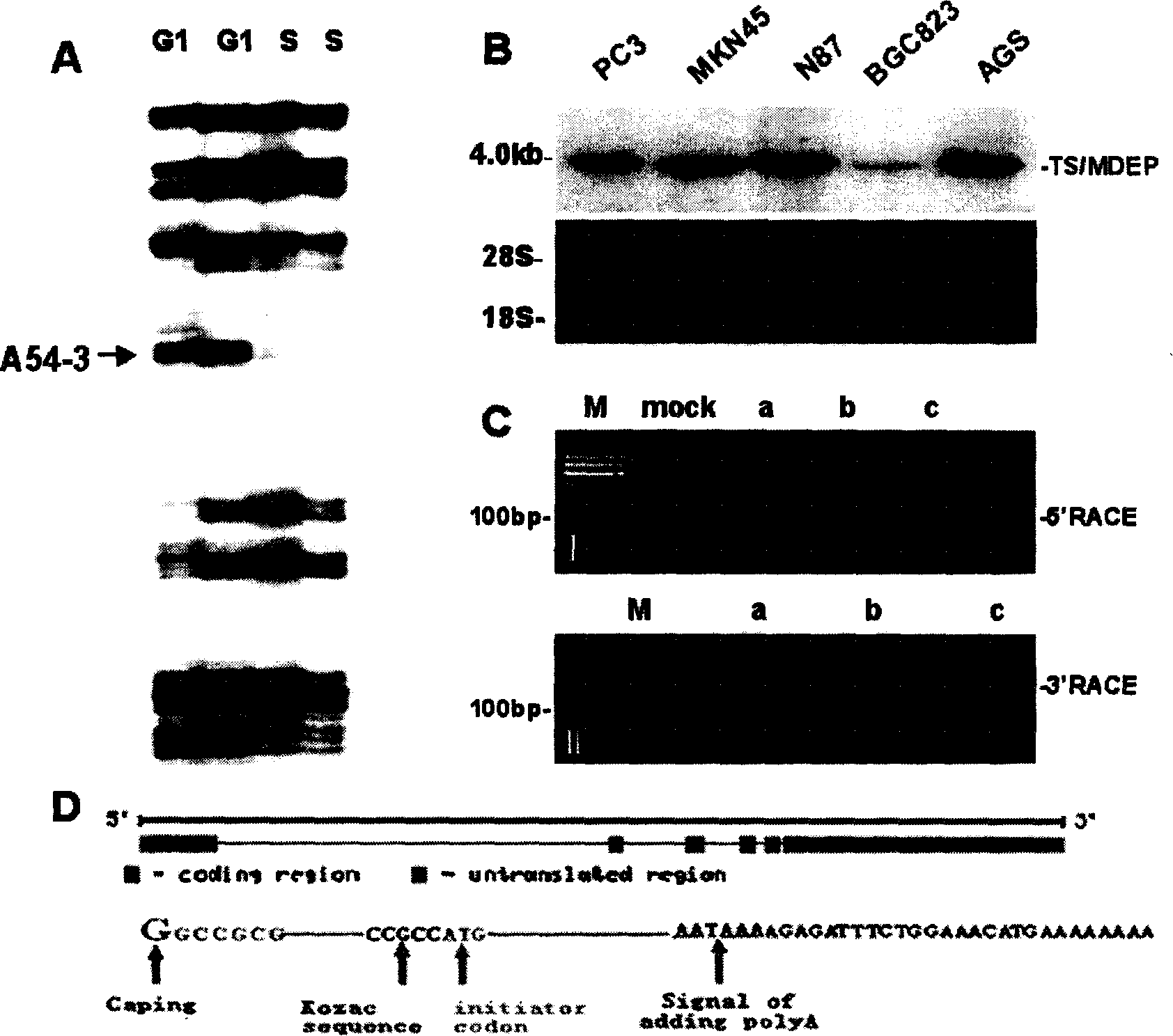
The invention discloses the specificity marker protein TS / MEDP antibody preparation and the purpose. The molecular biology technology is utilized, and a new gene is cloned in a stomach cancer cell and is named as TS / MDEP. A polyclonal antibody for preventing the TS / MDEP is prepared, and a high specificity antibody is acquired through the antibody purification technology. The expression characteristics of the TS / MDEP gene in a tumor cell line and a tumor cell tissue are verified from the mRNA and protein level, the expression in 14 tumor cell lines including the tumor cell line is determined, the dependance of cell cycle is assumed, the excess expression exists in stomach cancer, breast cancer and cervical cancer tissues, no expression is in the corresponding normal tissues, and the expression exists in an embryo tissue. The high expression of the TS / MDEP in the embryo tissue with exuberant cell proliferation is validated, after growing up, the gene is closed, and the high expression exists in the tumor cells. The TS / MDEP has the seasonal specificity expression to clew the occurrence and the development of the cell cycle control abnormity caused by the high expression of the TS / MDEP. The obtained antibody for preventing the TS / MDEP can be used to monitor the cell cycle advancement and the clinical biological behavior of the gastroenteric tumor.
Owner:BEIJING CANCER HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV CANCER HOSPITAL
Novel approach to molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus-related diseases
ActiveUS20070243552A1Accurate sensitive toolReduce in quantitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein markersHuman papillomavirus
The present invention relates to an accurate, sensitive, and efficient sequential or concurrently sequential method for molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus (HPV)-based disease, where the method improves the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic and prognostic assessments of HPV-based disease. The method of the invention comprises a primary screen of a sample for HPV nucleic acids, followed by a secondary screen for molecular markers, such as proliferation and cell cycle control group protein markers. The sequential or concurrently sequential method significantly reduces the number of false positive results.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG
Integrated Analyses of Breast and Colorectal Cancers
InactiveUS20100136560A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCellular pathwaysIntracellular signalling
Genome-wide analysis of copy number changes in breast and colorectal tumors used approaches that can reliably detect homozygous deletions and amplifications. The number of genes altered by major copy number changes—deletion of all copies or amplification of at least twelve copies per cell—averaged thirteen per tumor. These data were integrated with previous mutation analyses of the Reference Sequence genes in these same tumor types to identify genes and cellular pathways affected by both copy number changes and point alterations. Pathways enriched for genetic alterations include those controlling cell adhesion, intracellular signaling, DNA topological change, and cell cycle control. These analyses provide an integrated view of copy number and sequencing alterations on a genome-wide scale and identify genes and pathways that are useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for identifying patients with an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer and compositions therefor
InactiveUS20090068690A1Improved prognosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellMotility
Screening methods for identifying patients with an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer are provided. The screening methods involve the detection of expression of a plurality of biomarkers in a body sample, wherein overexpression of the biomarkers is indicative of an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer. The screening methods may further comprise a two-step analysis. Biomarkers of interest include genes and proteins that are, for example, involved in defects in DNA replication / cell cycle control, cell growth and proliferation, escape from apoptosis, angiogenesis or lymphogenesis, or the mechanisms of cancer cell motility and invasion. In some aspects of the invention, expression of a biomarker is detected at the protein level using a biomarker-specific antibody or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Methods for detecting ovarian cancer in patients are further disclosed herein. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
ARF-P19, a novel regulator of the mammalian cell cycle
The INK4A (MTS1, CDKN2) gene encodes a specific inhibitor (InK4a-p16) of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. InK4a-p16 can block these kinase from phosphorylating the retinoblastoma protein (pRb), preventing exit from the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Deletions and mutations involving the gene encoding InK4a-p16, INK4A, occur frequently in cancer cells, implying that INK4a-p16, like pRb, suppresses tumor formulation. However, a completely unrelated protein (ARF-p19) arises in major part from an alternative reading frame of the mouse INK4A gene. Expression of an ARF-p19 cDNA (SEQ ID NO:1) in rodent fibroblasts induces both G1 and G2 phase arrest. Economical reutilization of protein coding sequences in this manner is without precedent in mammalian genomes, and the unitary inheritance of INK4a-p16 and ARF-p19 may reflect a dual requirement for both proteins in cell cycle control.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
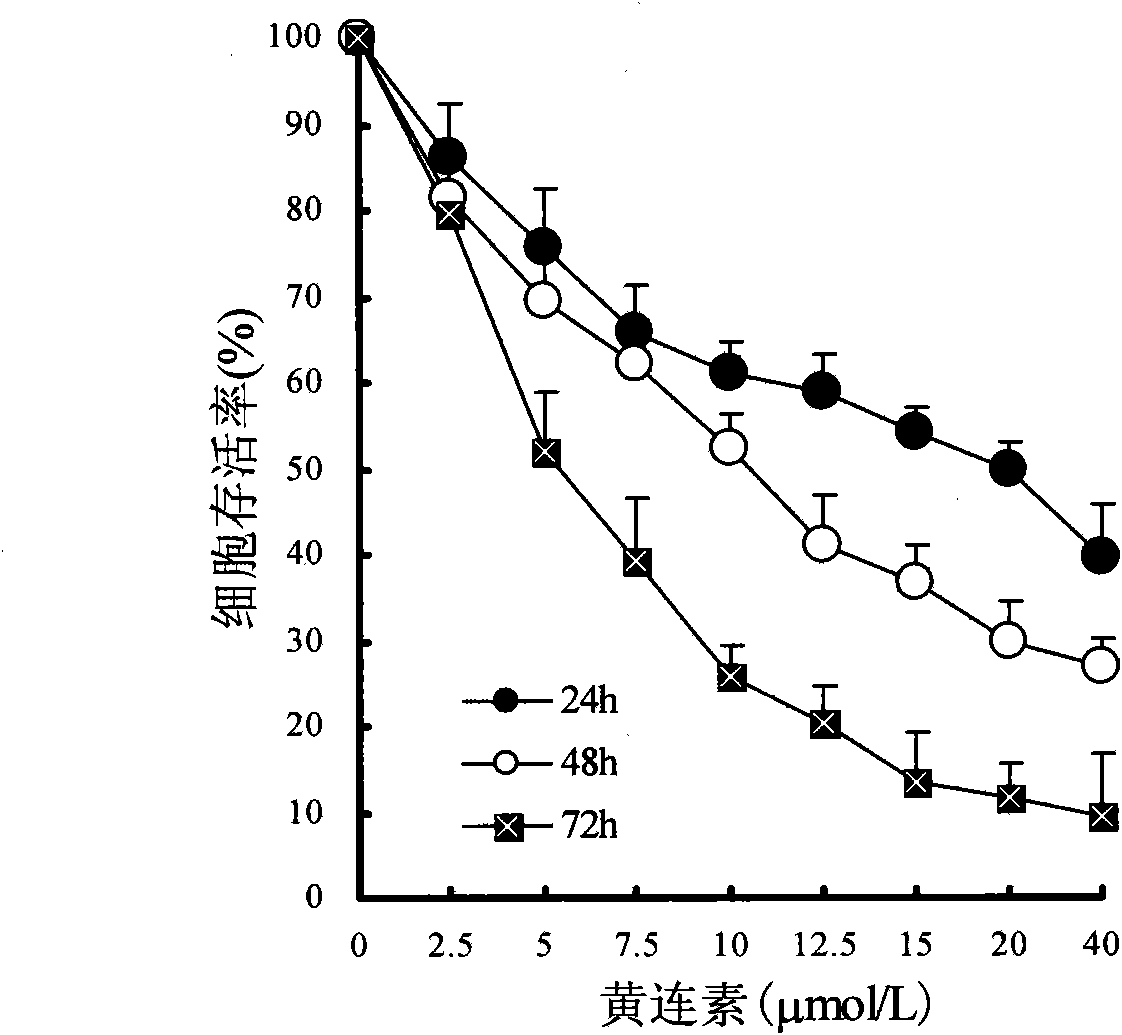
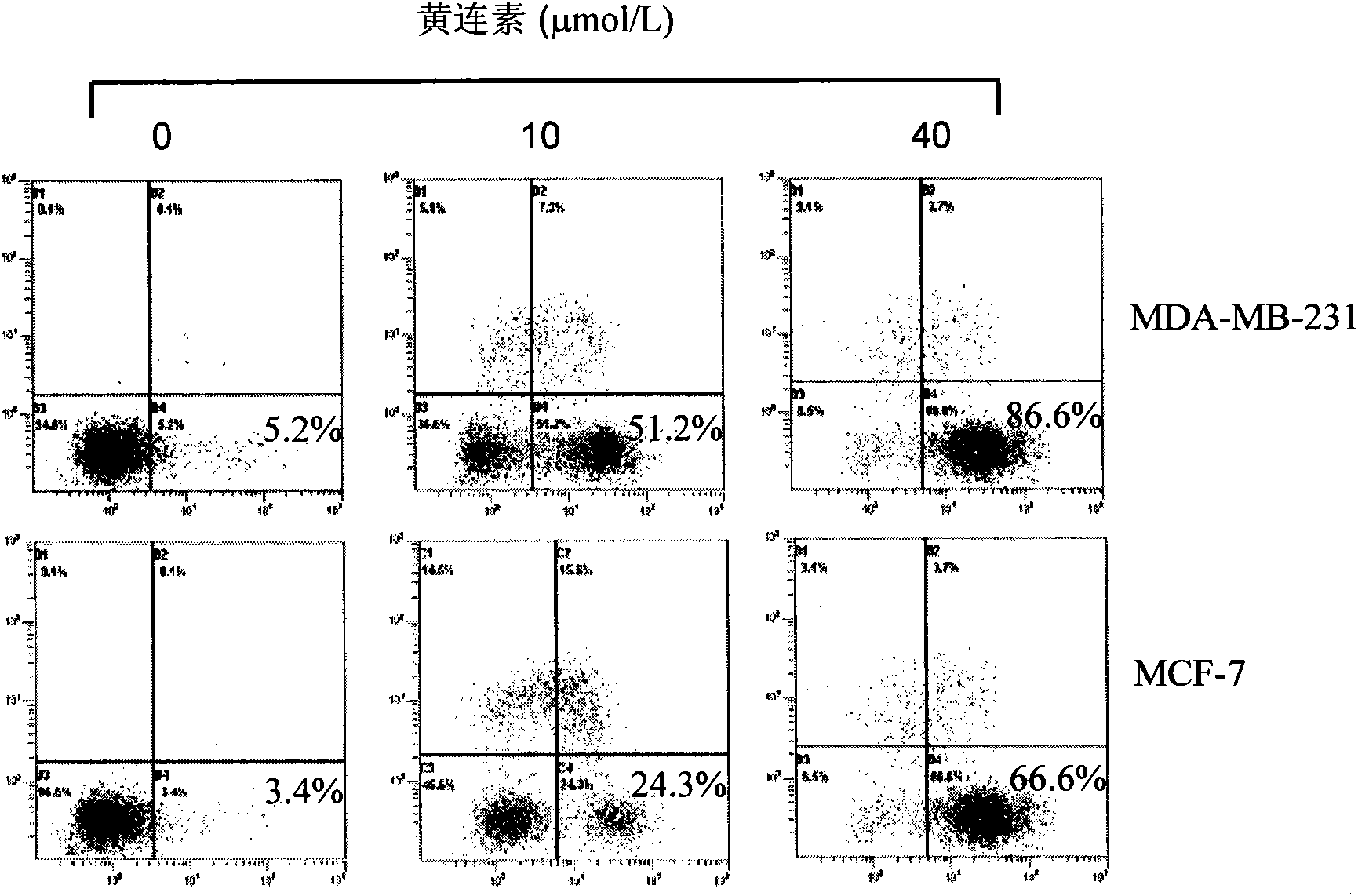
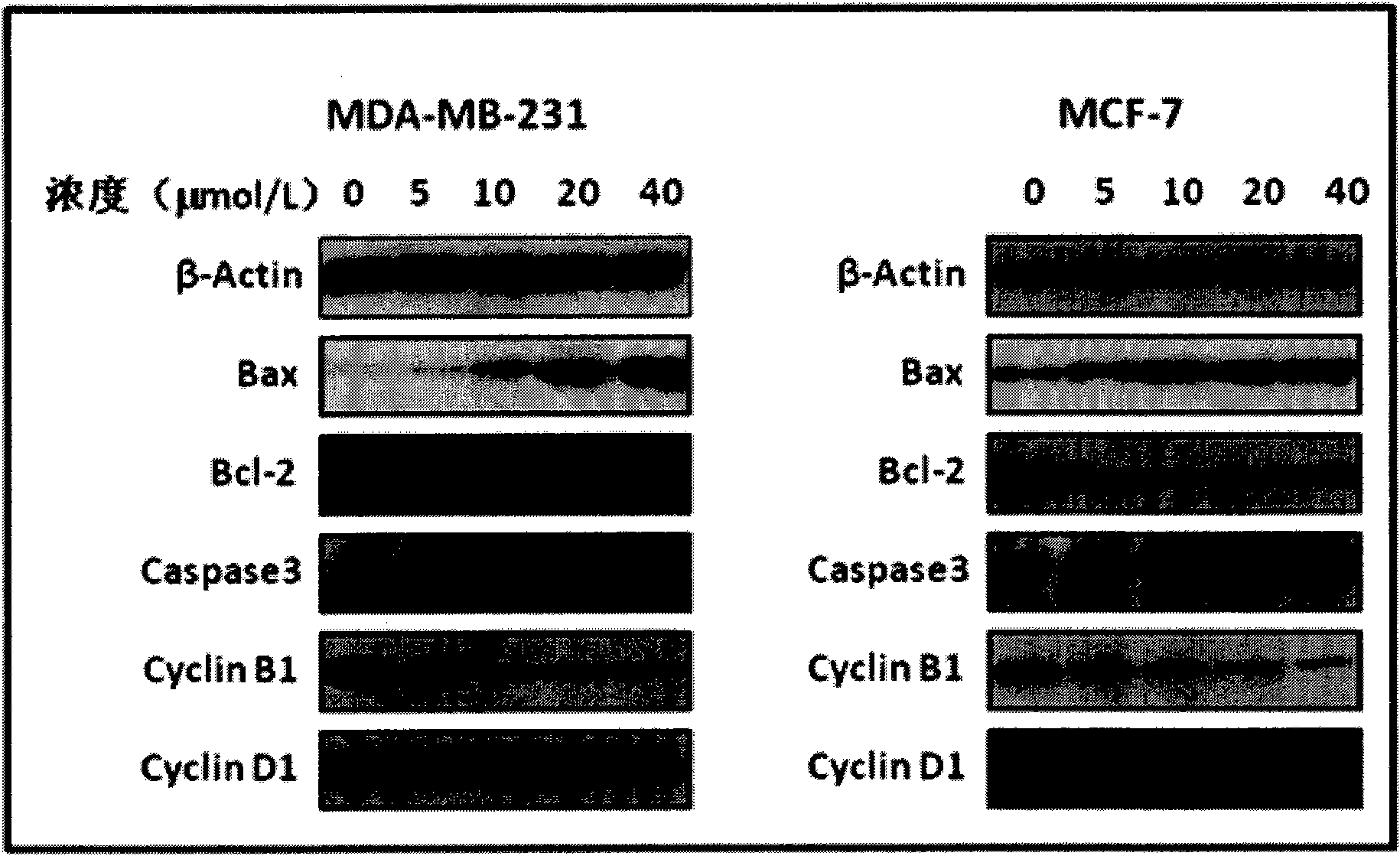
Application of berberine in preparing tumor radio sensitization medicine
InactiveCN101816653AGood treatment effectReduce radiation doseOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a tumor radio sensitization medicine which has an active component of berberine. Proved by research: the berberine has the following efficacy of: 1, breast cancer cells are treated by berberine, which can induce dose-dependently G0 / G1 stage cell retardation and apoptosis; 2, the berberine remarkably reduces the expression level of cell cycle control associated protein cyclin B and apoptosis resisting protein Bcl-2 and increases the expression level of apoptins Bax and caspase-3; and 3, the breast cancer cells treated by the berberine remarkably improve the sensitiveness of the cells to radiotherapy. The tumor radio sensitization medicine can improve the treatment effect of tumor radiotherapy, lower the exposure dose of the radiotherapy of a tumor patient, and lower the toxic and side effects brought by the radiotherapy, thereby improving the living quality of patients.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
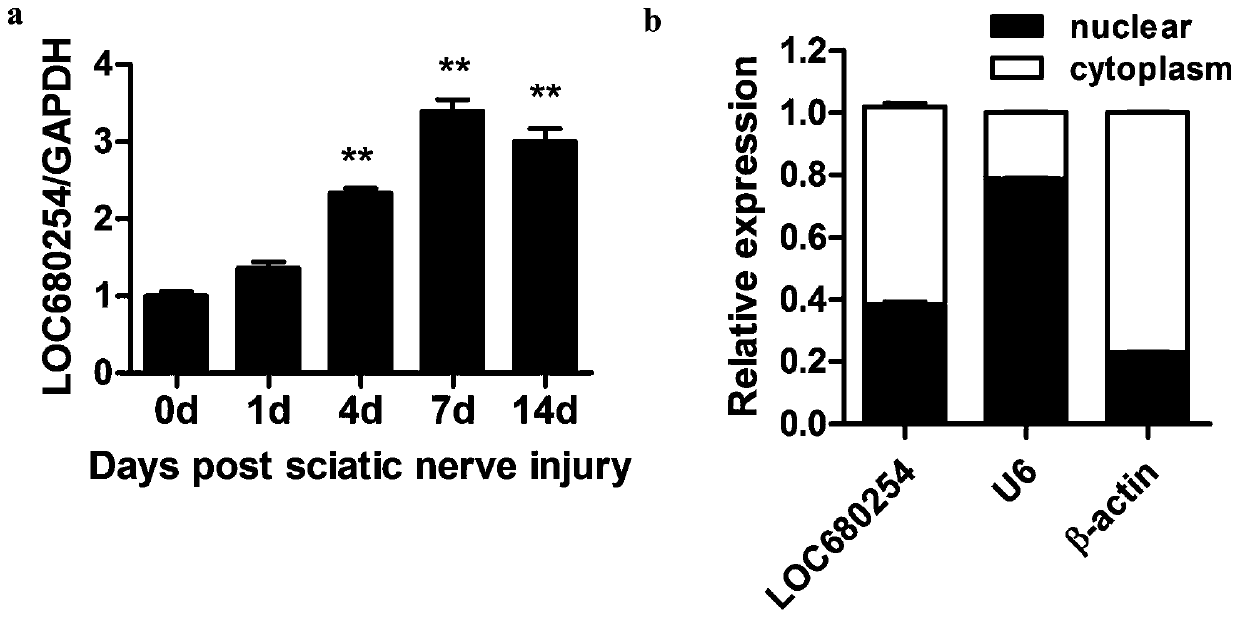
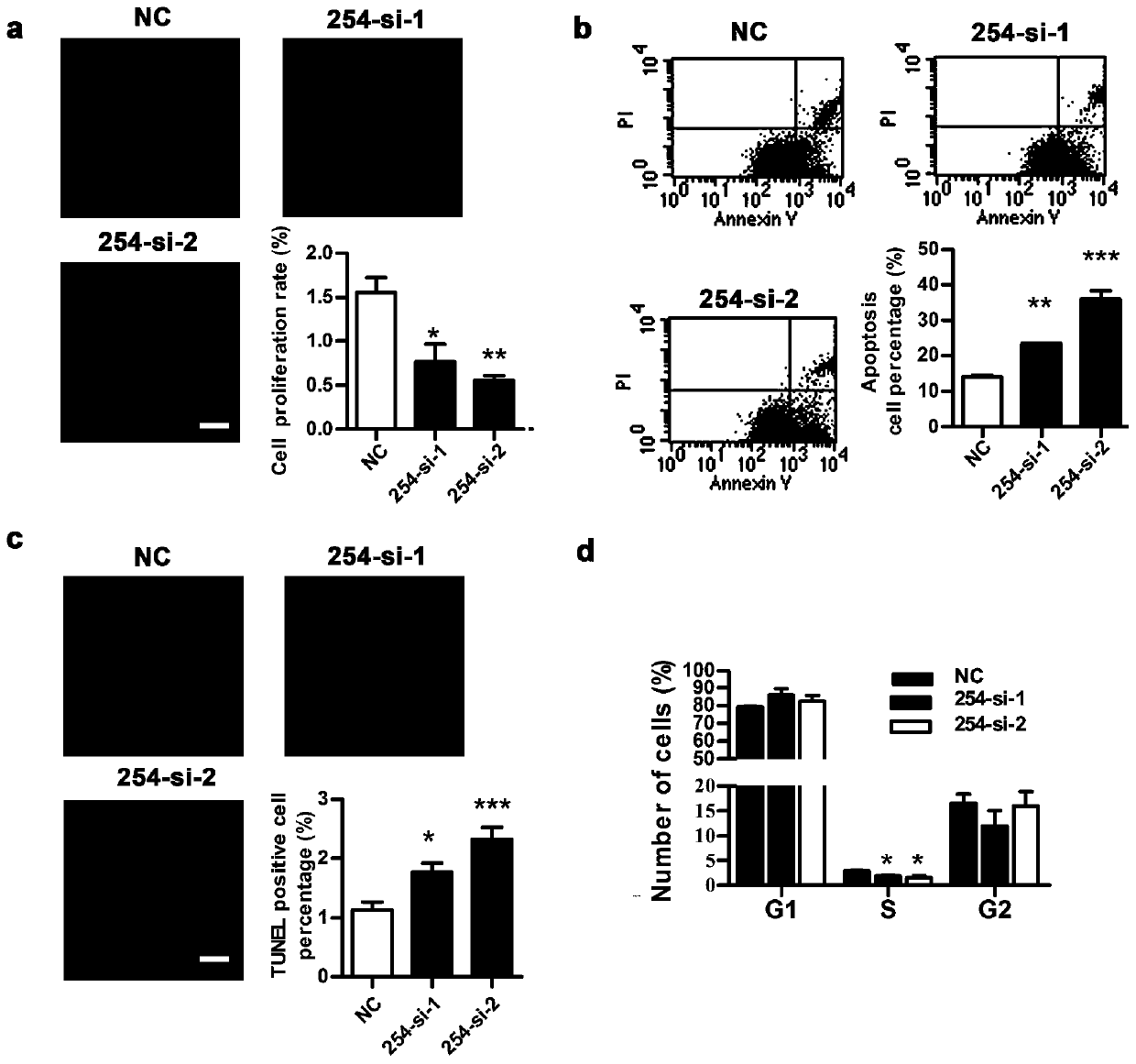
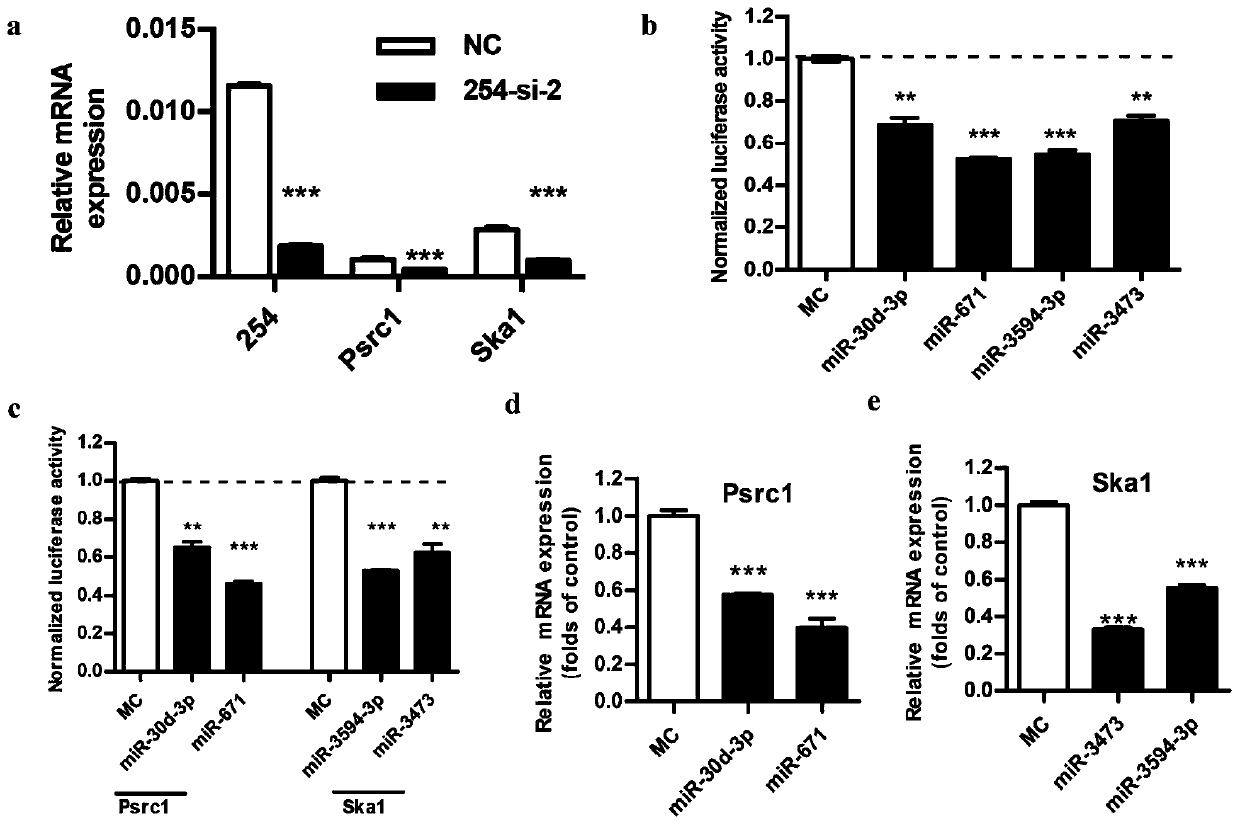
Long-chain non-coding RNA and application thereof
ActiveCN109897853APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisNervous disorderAntipyreticNon-coding RNAGene
The invention relates to long-chain non-coding RNA and an application thereof. LncRNA LOC680254 related to cell proliferation and cell cycle control is obtained by analyzing different LncRNAs in different time point samples after sciatic nerve injury of SD rats by use of RNA-seq and can be used as miRNA molecular sponge to specifically bind miR-30d-3p, miR-671, miR-3594-3p or miR-3473 so as to resist miRNA functions and promote expression of Psrc1 and Ska1, and cell proliferation is promoted.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Tumor suppressor, coded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN1566148AGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAbnormal tissue growthDisease
The invention discloses a human and mice tumor suppressor and coded protein, wherein the gene relates to the regulation and control for encoded proteins and cell cycles, thus is closely related to the occurrence of tumors, the gene, the encoded protein and their derivatives can be used for diagnosis and treatment for tumor diseases caused by cell cycle control imbalance and medicament screening.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
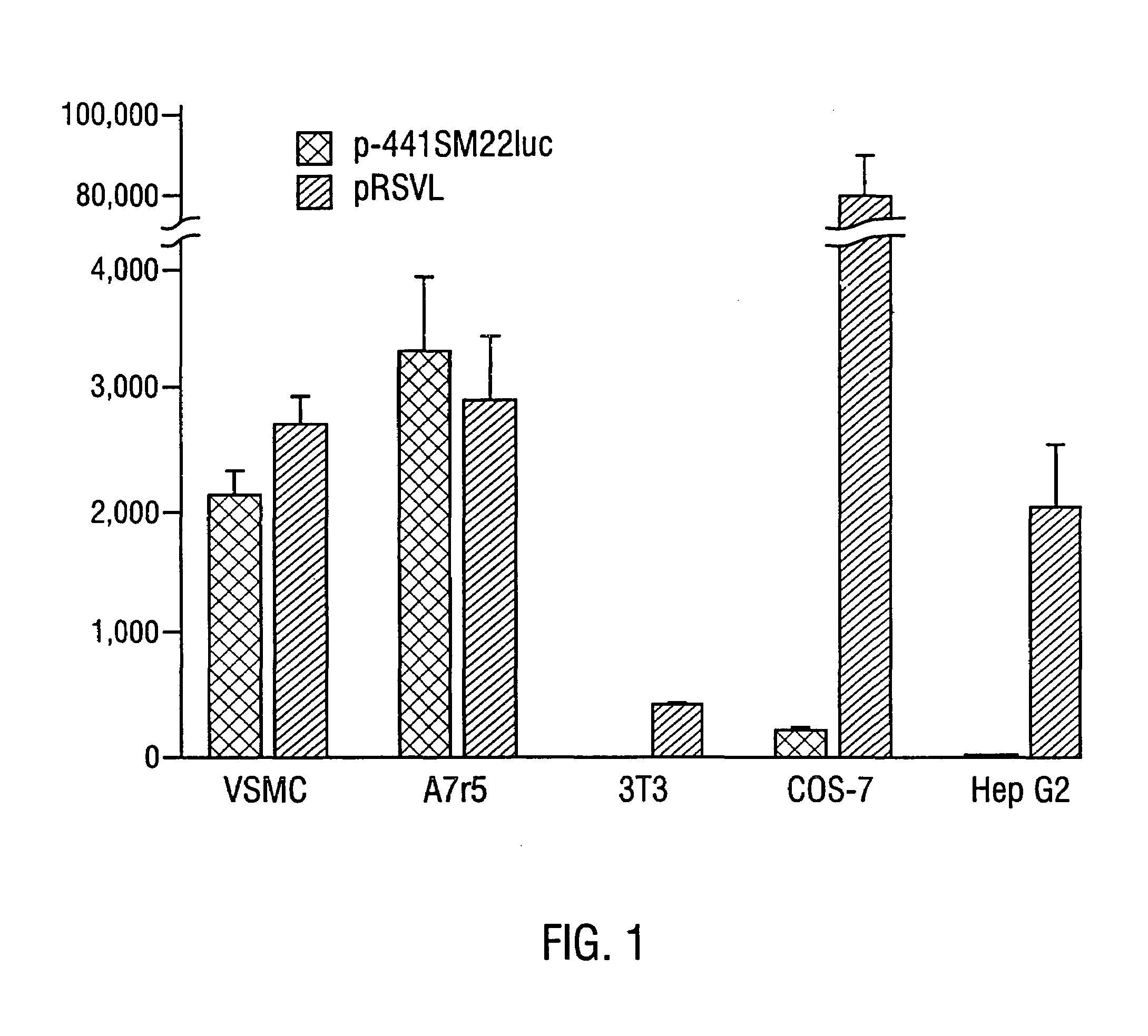
Promoter for smooth muscle cell expression
InactiveUS7169764B1Promoting transcriptionPromote angiogenesisOrganic active ingredientsTissue cultureCell specificPercent Diameter Stenosis
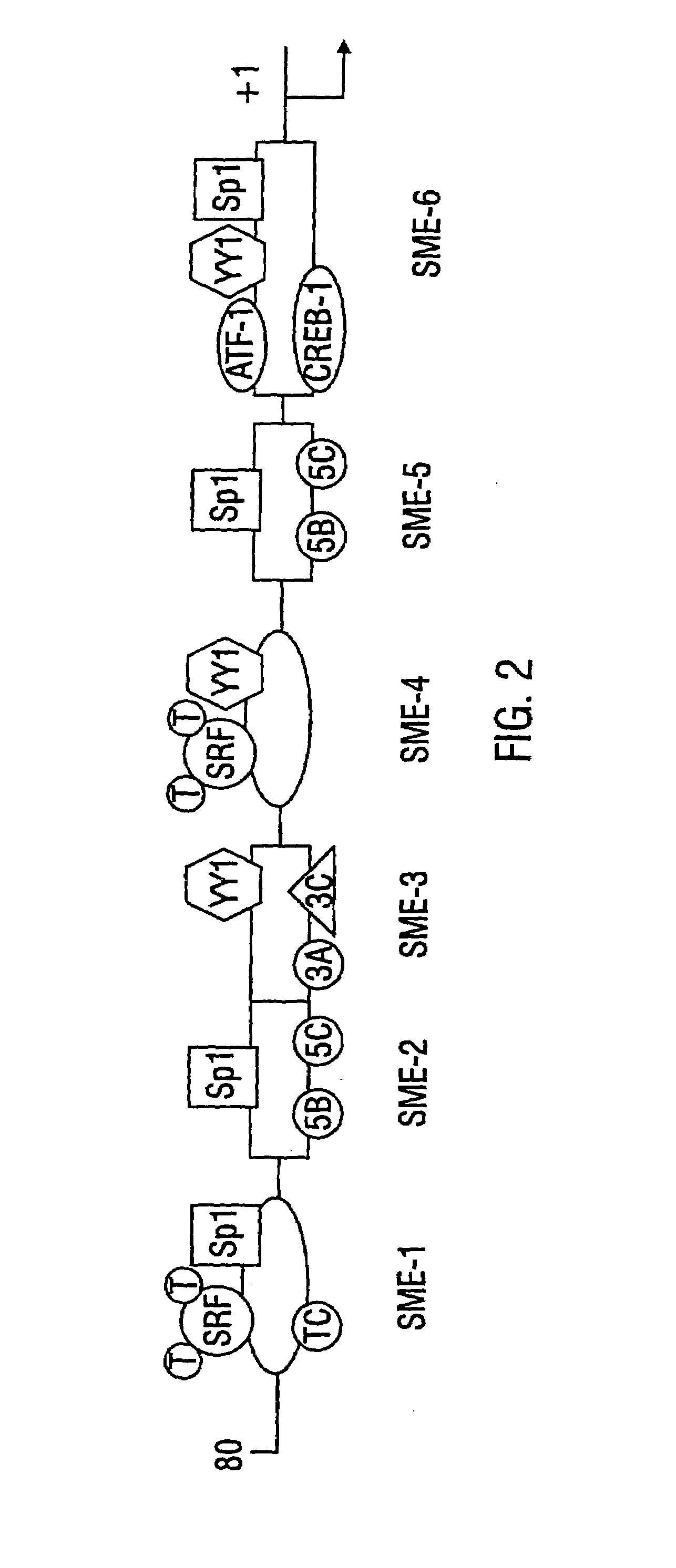
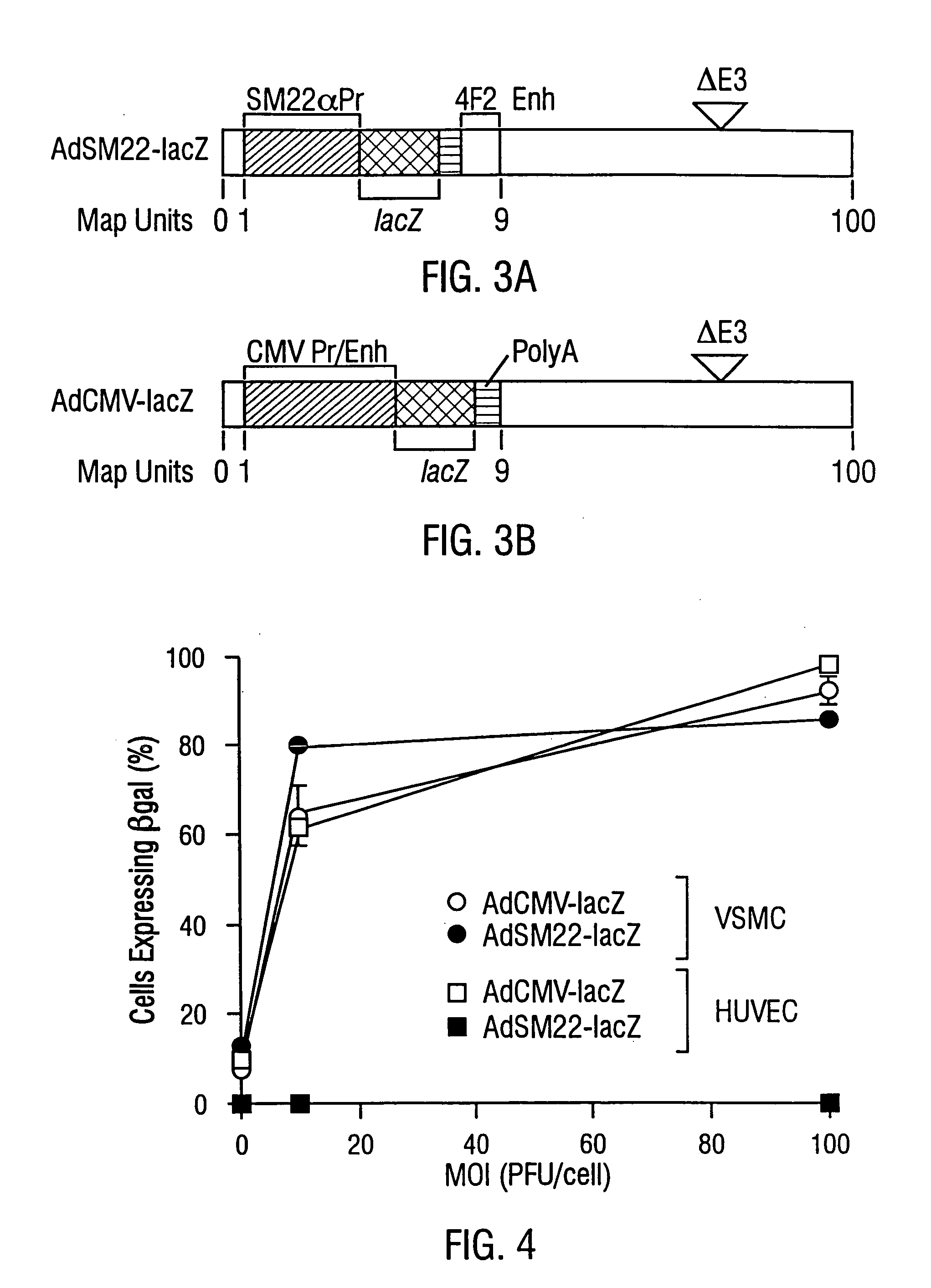
Disclosed is a smooth muscle cell specific promoter, the SM22α gene promoter as well as the murine cDNA and genomic SM22α nucleic acid sequences. Also disclosed are methods of preventing restenosis following balloon angioplasty and methods of treating asthma based on inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation by expressing cell cycle control genes, or contraction inhibiting peptides in smooth muscle cells, under the control of the SM22α promoter.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Rec 2 kinase
The invention includes a method of phosphorylating a serine containing substrate by incubating the substrate with ATP and an enzyme that is hsRec2 or muRec2 or a derivative thereof. The natural substrates of the kinase activity of Rec2 are the cell cycle control proteins such as p53 and cyclin E. The over expression of Rec2 is known to cause cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis and the invention discloses that these effects are kinase mediated. Accordingly, the invention provides a method of assessing antagonists and agonists of Rec2, which antagonists and agonists would have pharmacological activity. The invention further discloses that there is specific binding between hsRec2 and at least three cell cycle control proteins: p53, PCNA and cdc2.
Owner:VALIGEN US
Productivity and Bioproduct Formation in Phototropin Knock/Out Mutants in Microalgae
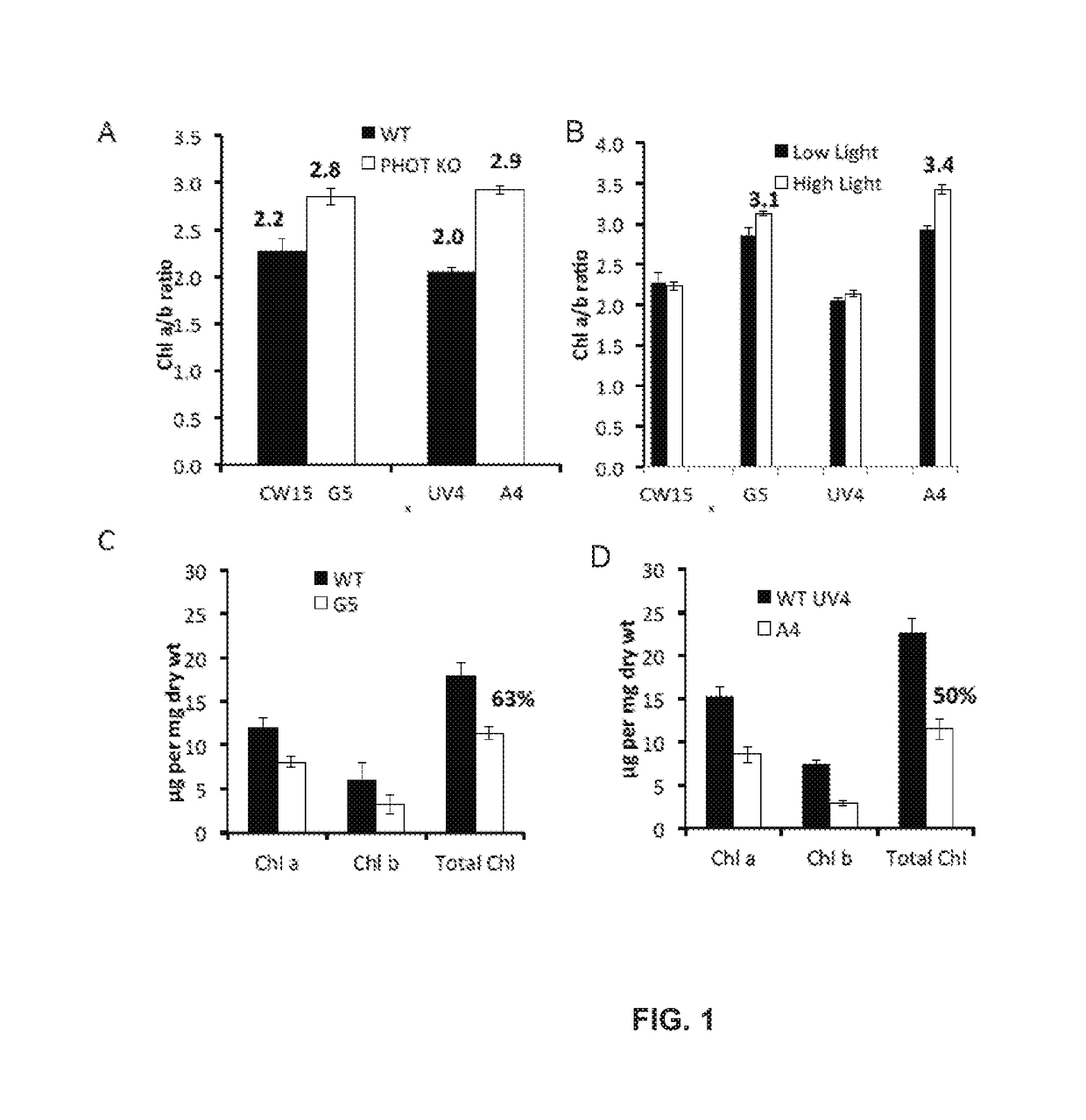
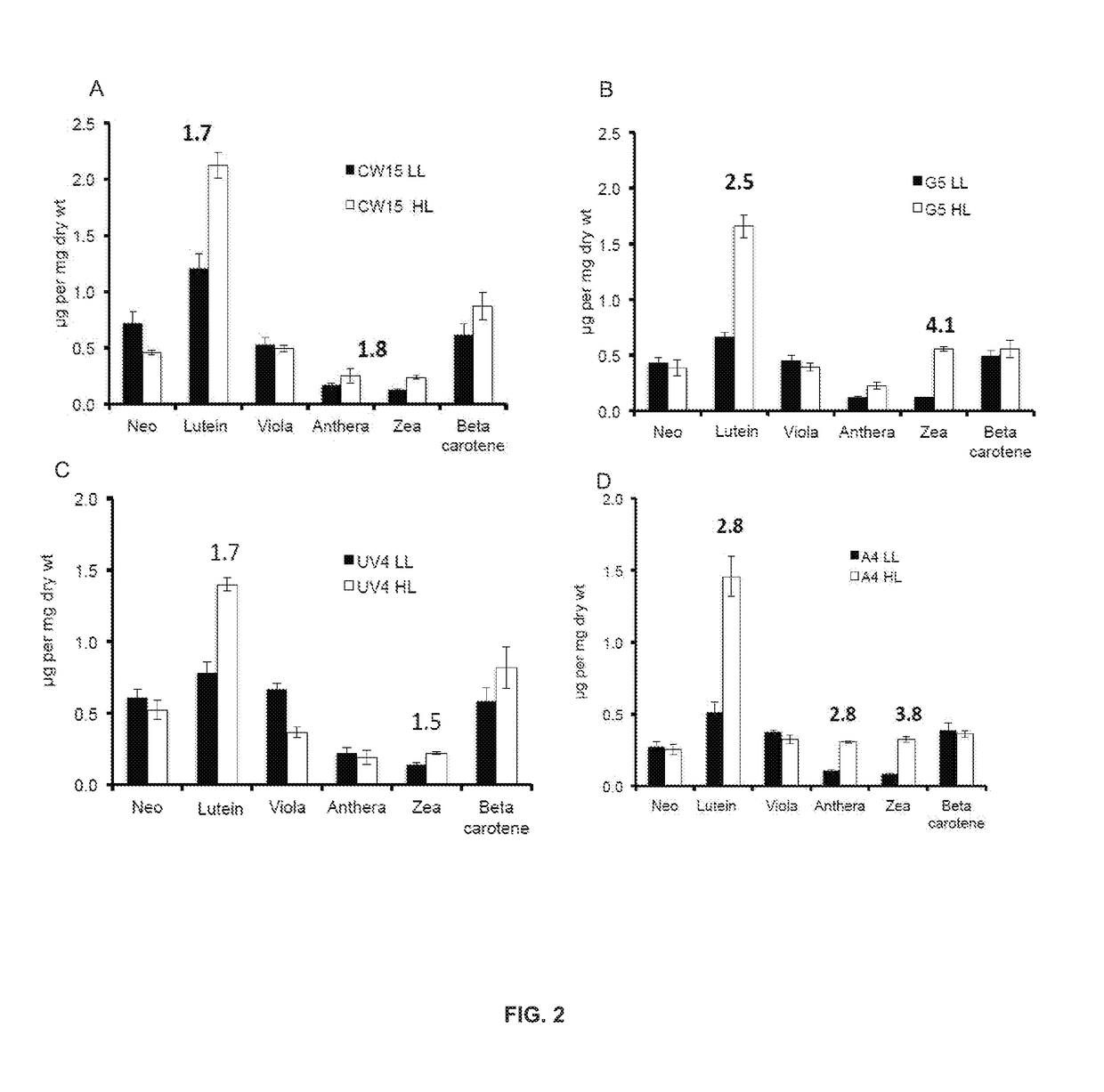
ActiveUS20180187170A1Reduced PHOT expressionHigh genetic stabilityHydrolasesUnicellular algaeElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
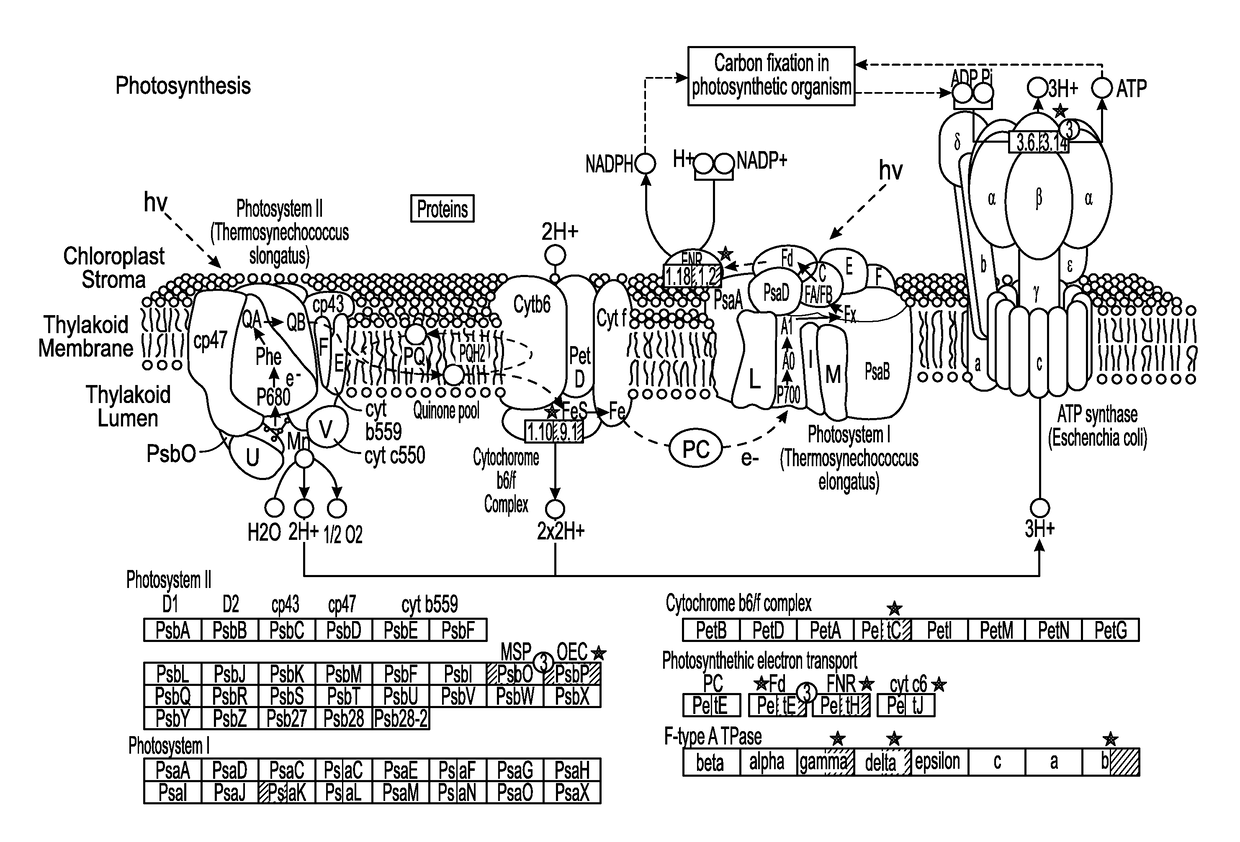
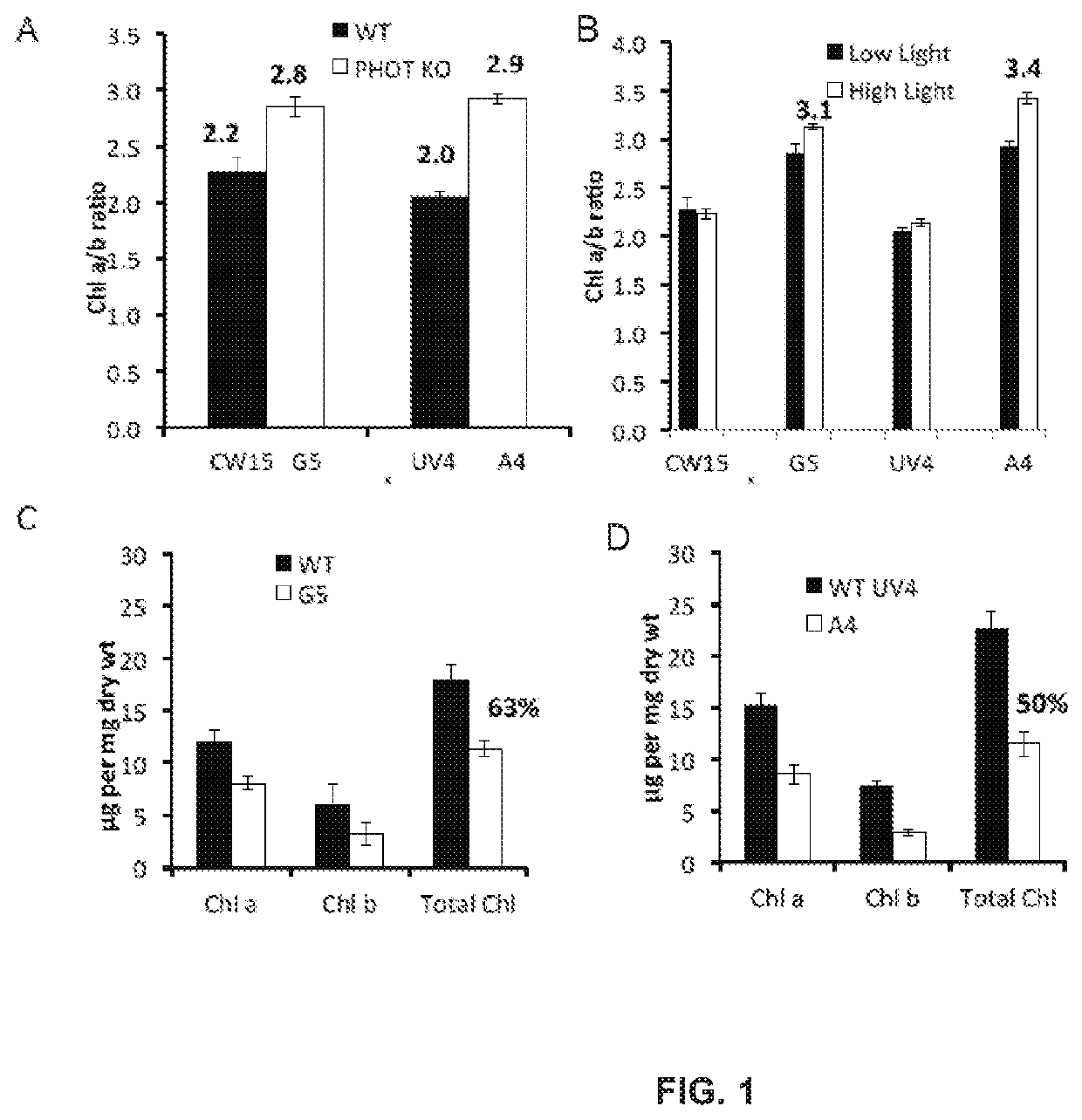
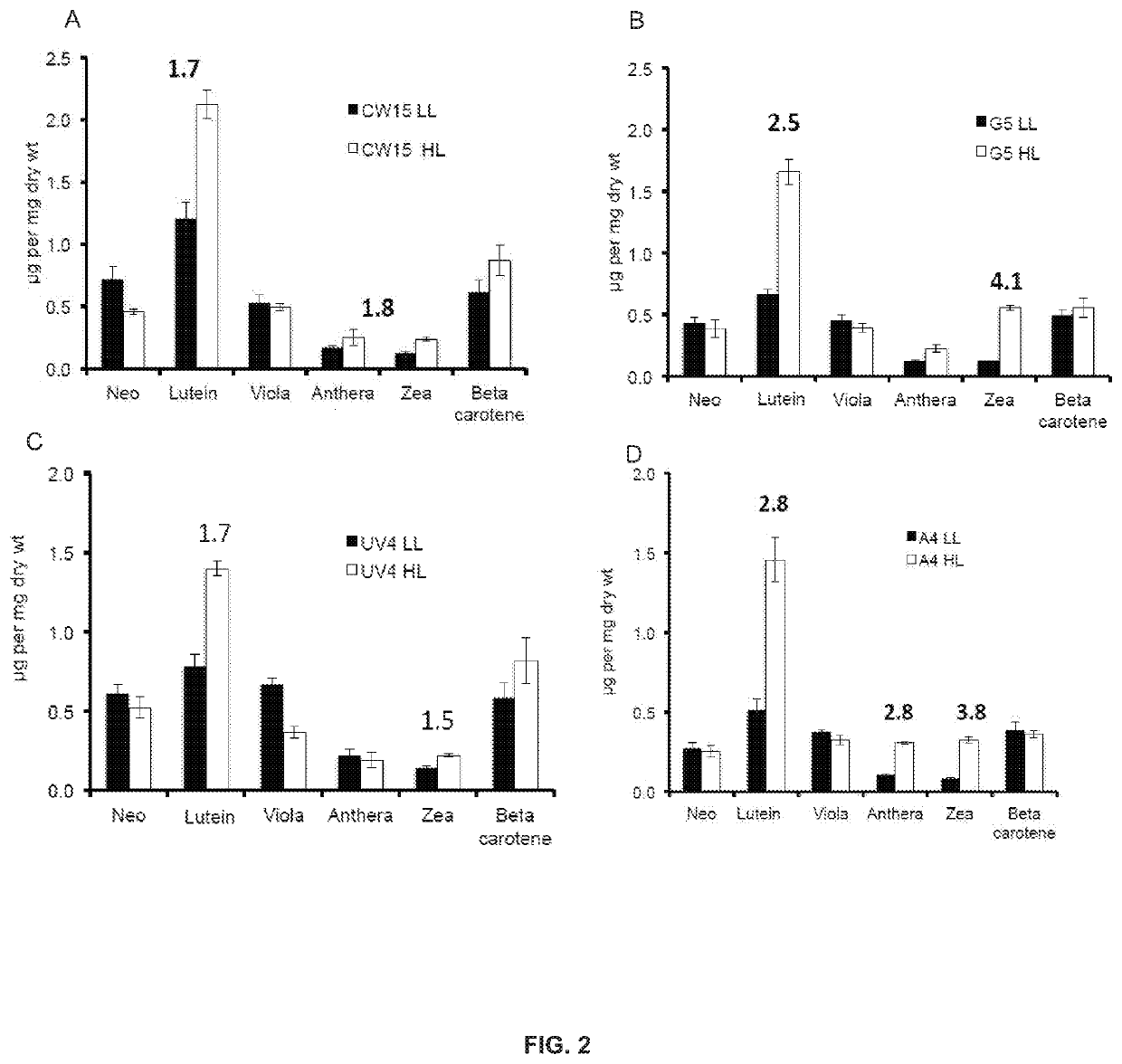
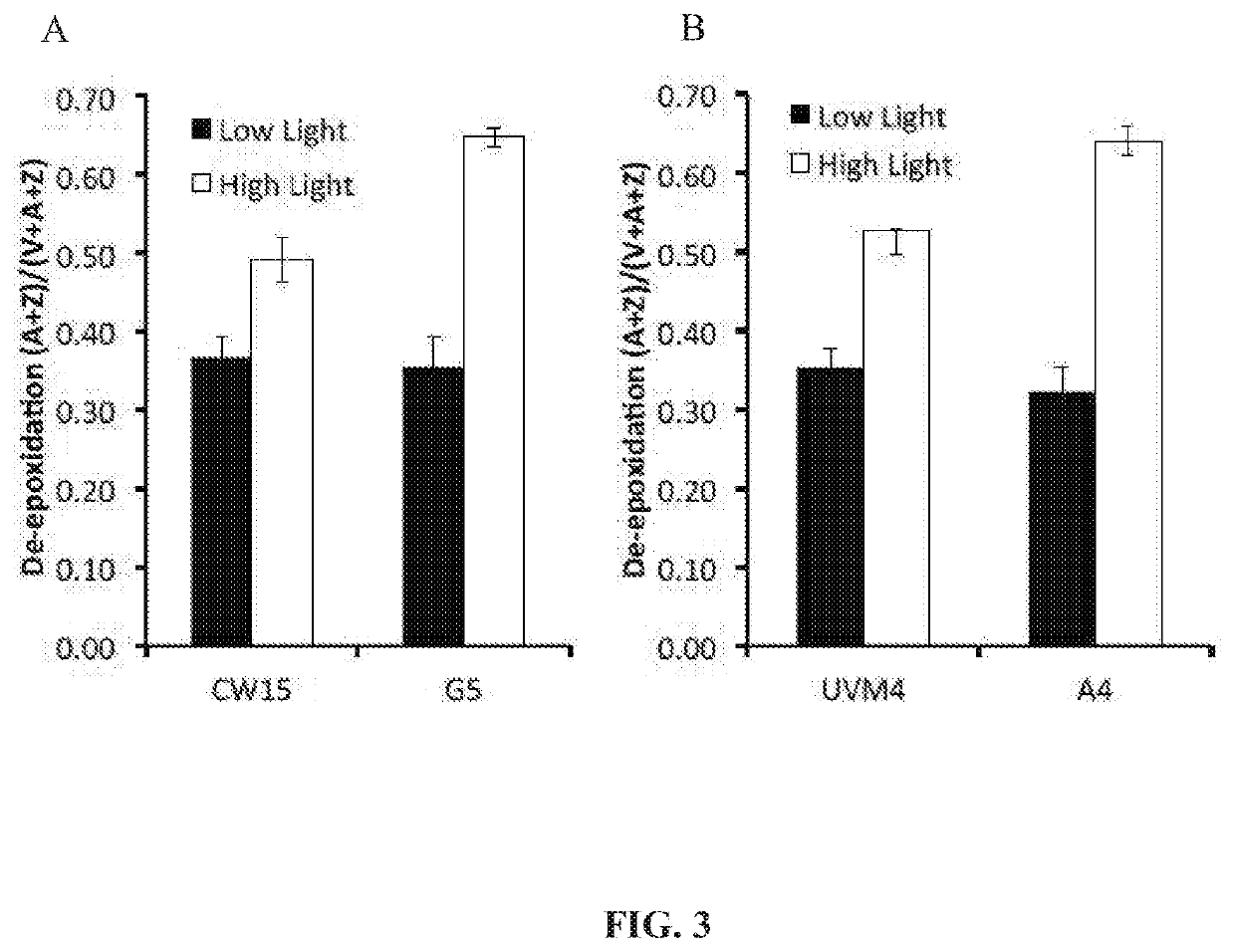
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2 s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:NMC INC +1
Cell cycle-regulating proteins
A DNA containing a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing, or a nucleotide sequence encoding a protein having the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing with partial substitution, deletion or addition and having cell cycle control activity, or a nucleotide sequence hybridizing to them; a recombinant vector containing said DNA; a cell transformed with said vector; a process for producing AIM-1 using said DNA; a recombinant AIM-1 protein obtained by said process; an oligonucleotide or peptide nucleic acid capable of specifically hybridizing to a nucleotide sequence encoding AIM-1 protein; an antibody recognizing AIM-1; a therapeutic agent for diseases associated with abnormal cell growth containing an inhibitor against AIM-1 protein; and a screening method for materials having serine-threonine inhibitory activity using AIM-1 gene or AIM-1 protein.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
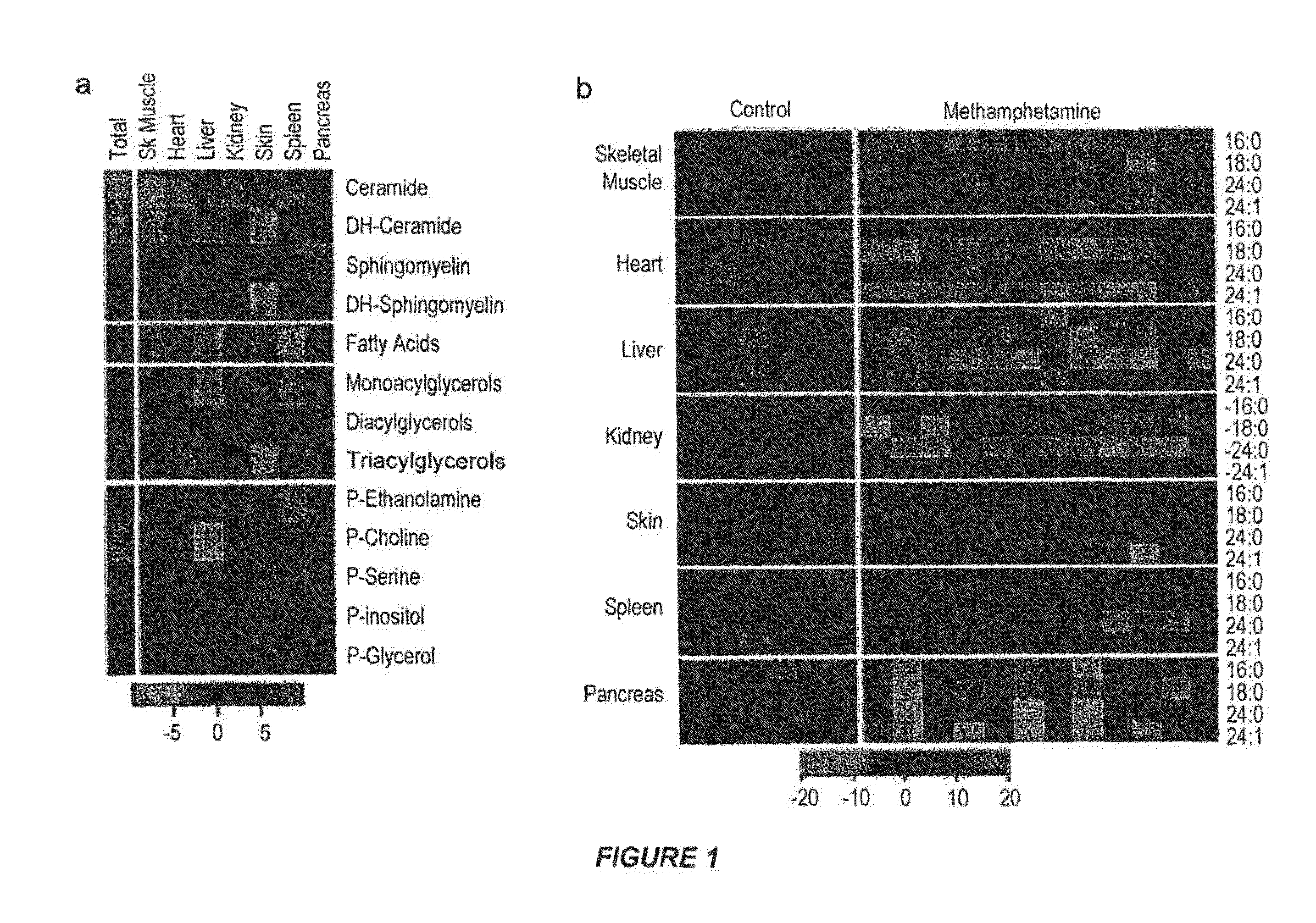
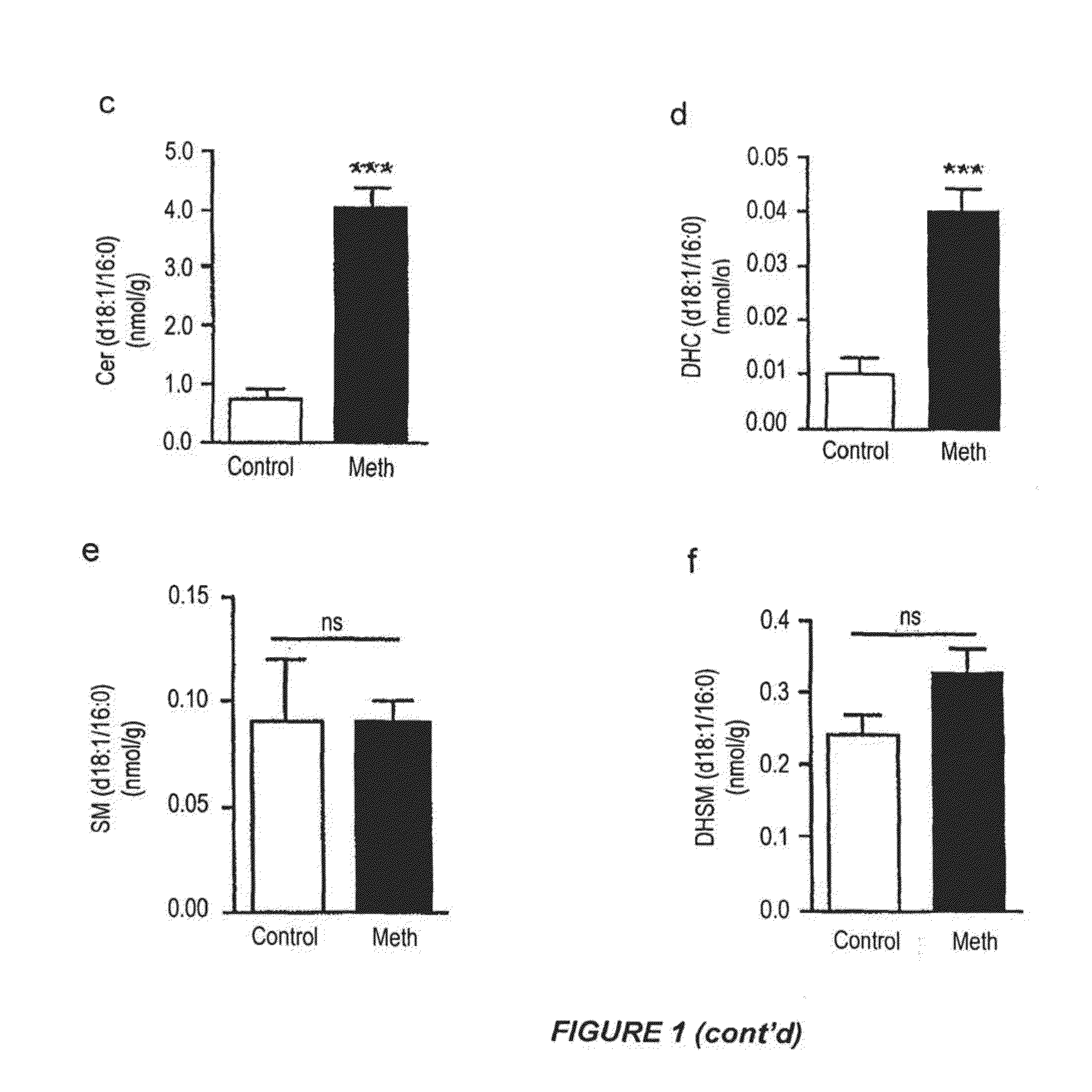
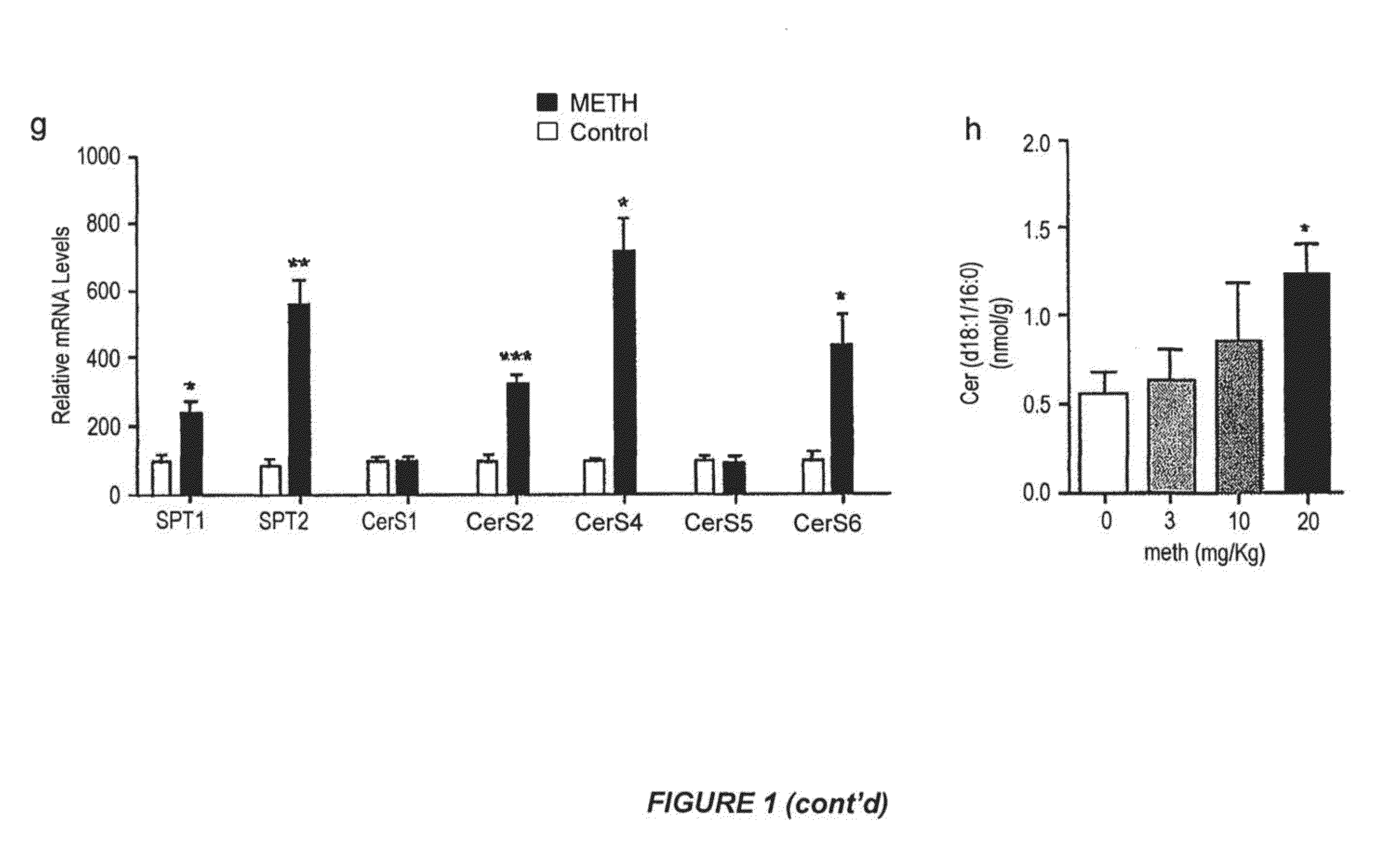
Methods of treatment, diagnosis and monitoring for methamphetamine toxicity which target ceramide metabolic pathways and cellular senescence
InactiveUS20150148387A1Reduce morbidityReduce toxic effectsBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsCeramide formationCeramide biosynthesis
Owner:FOND INST ITAL DI TECH +1
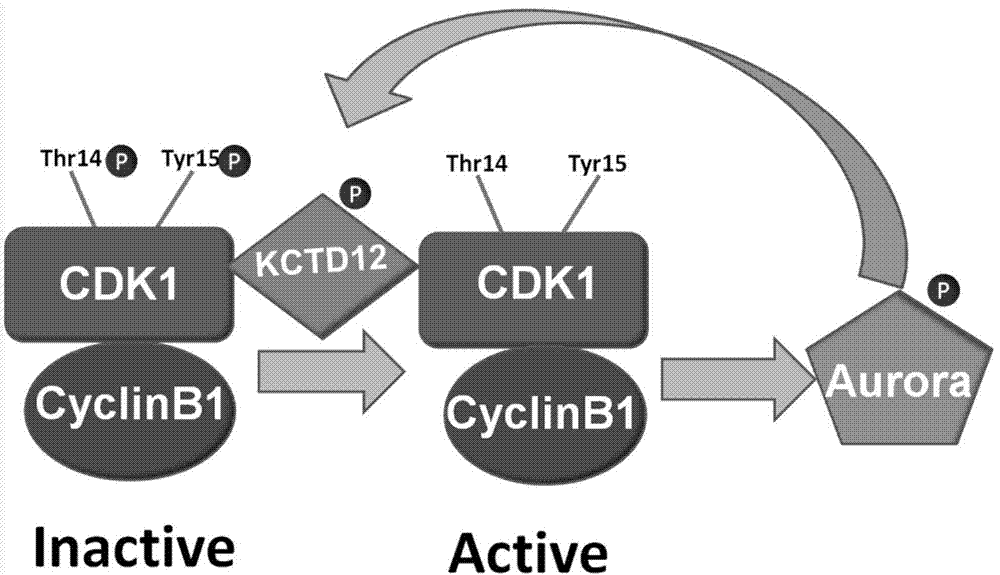
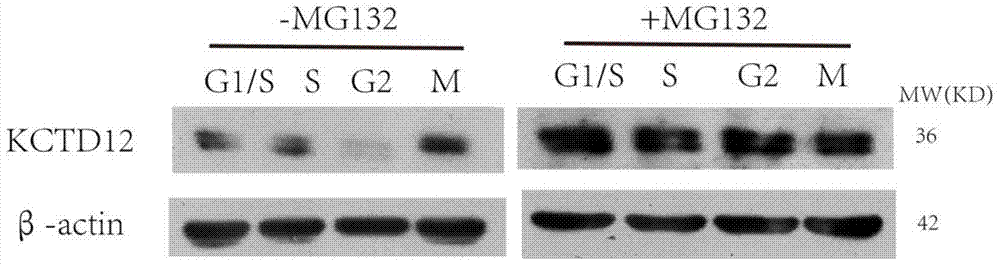
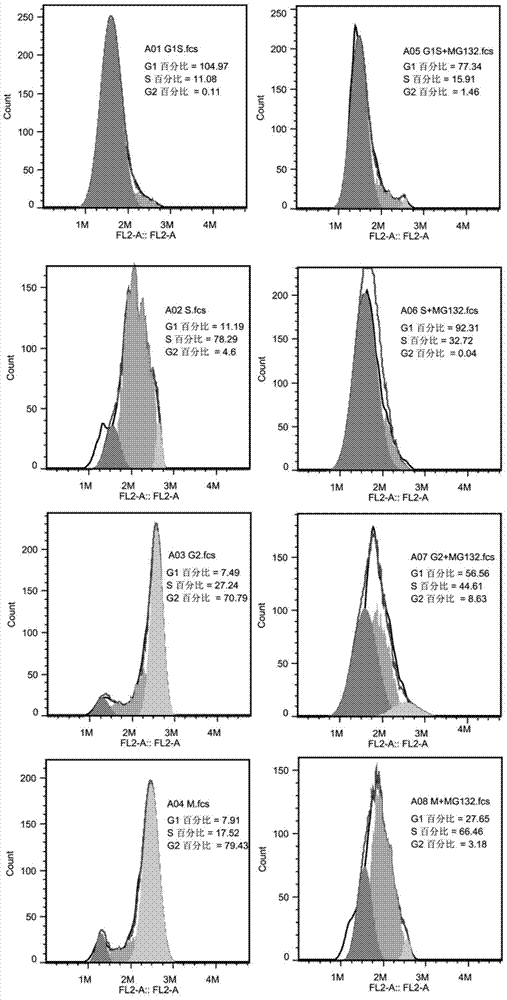
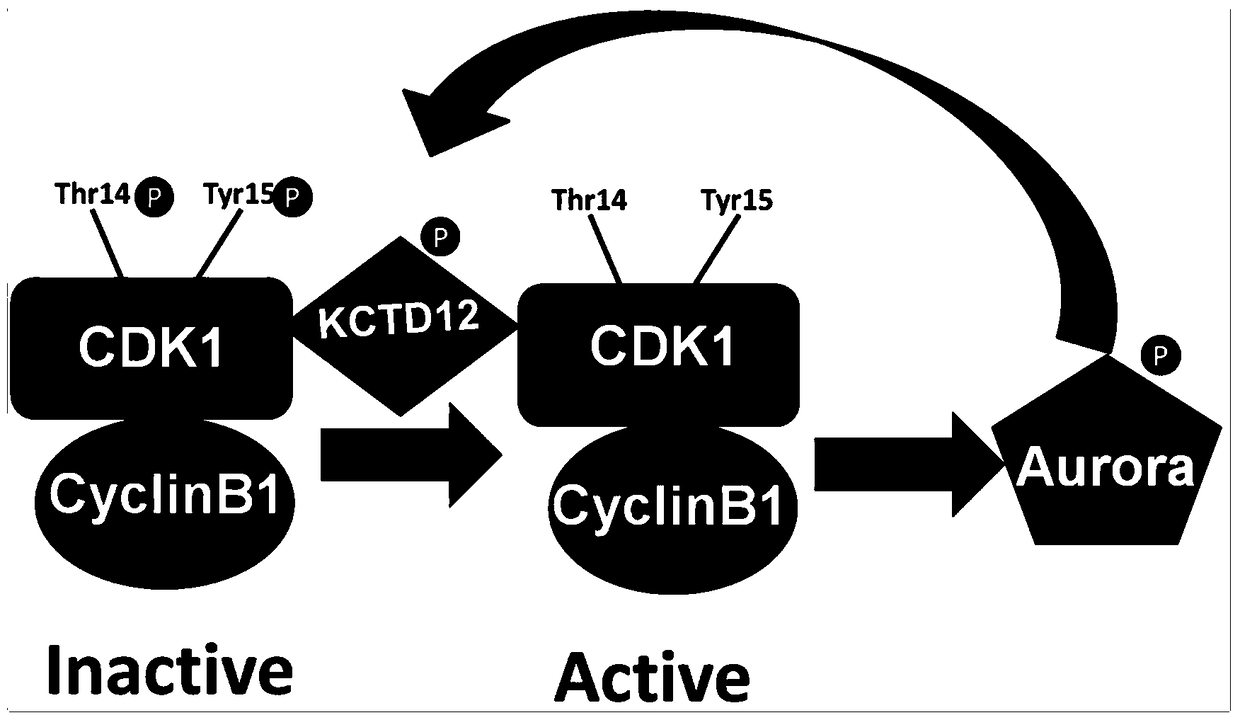
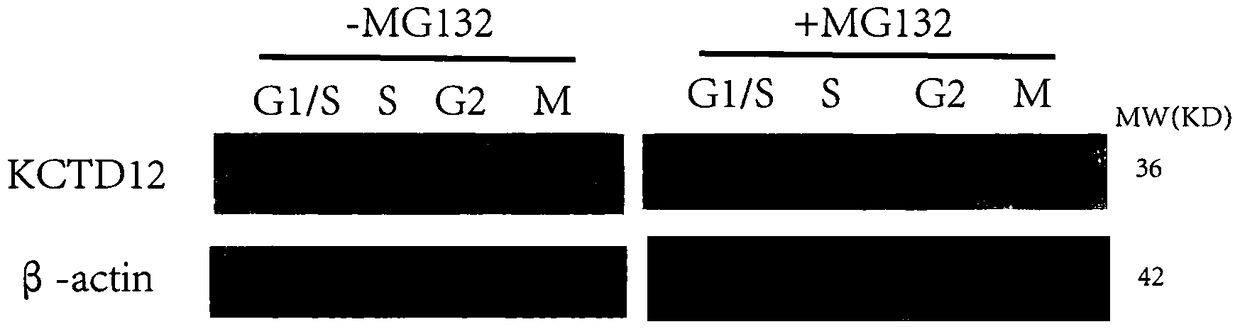
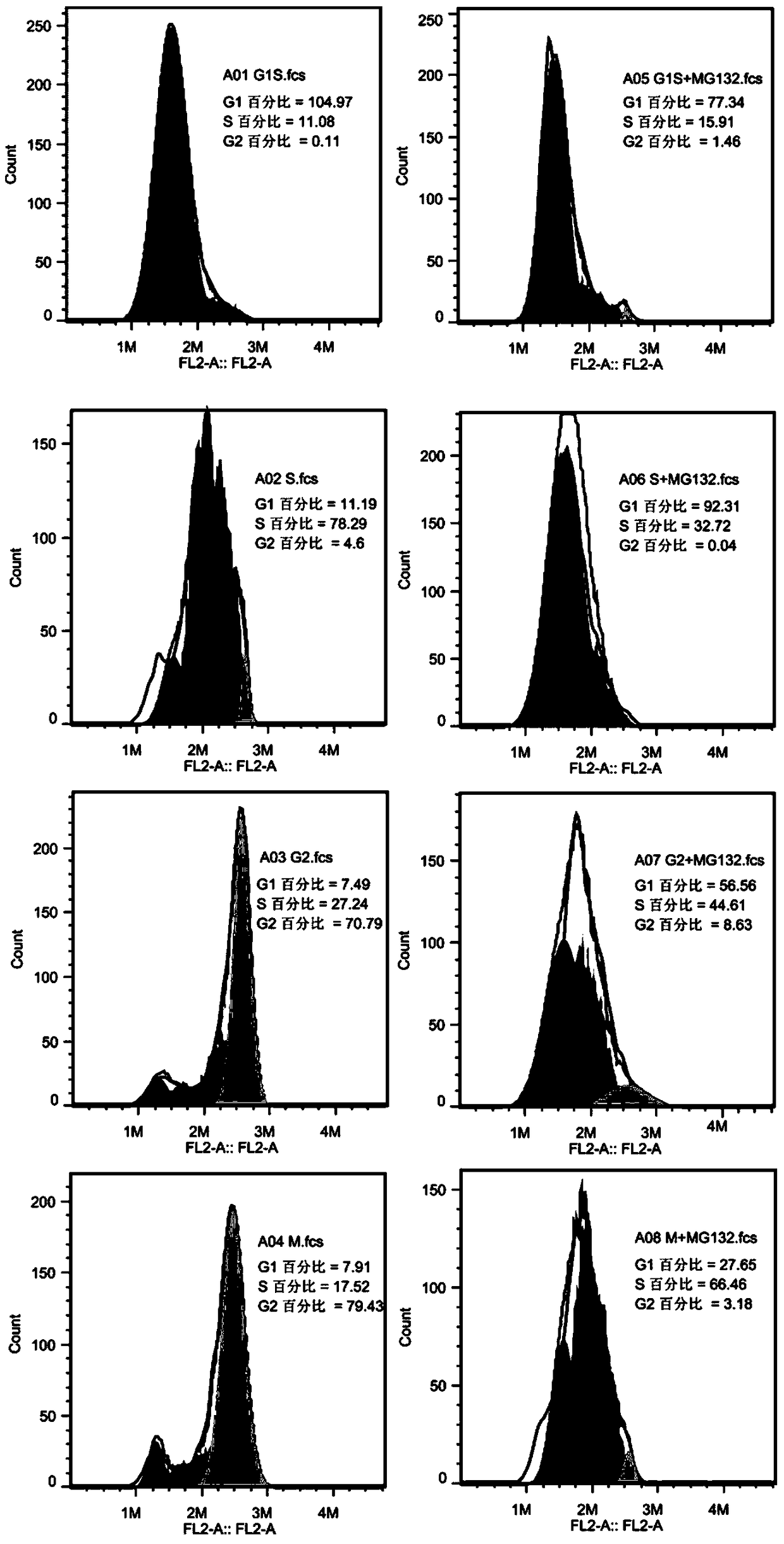
Novel application of KCTD12 protein in cell cycle control
ActiveCN104844705AAdjustable periodRegulates the cell cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsProtein SciencesPhosphorylation
The present invention, belonging to the technical field of protein science, particularly discloses a new application of KCTD12 protein in cell cycle control. The KCTD12 protein cell control cycle is achieved via the following steps: regulating and controlling a cell cycle by controlling a degeneration degree of KCTD12 protein in an S period; or, regulating and controlling a cell cycle by controlling phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of KCTD12 protein in an M period; or, regulating and controlling a cell cycle by regulating interaction of the KCTD12 protein and CDK1 protein in an M period. The KCTD12 protein can serve as a new target of cancer cell proliferation regulation and control, and is favorable for developing more anti-cancer drugs.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
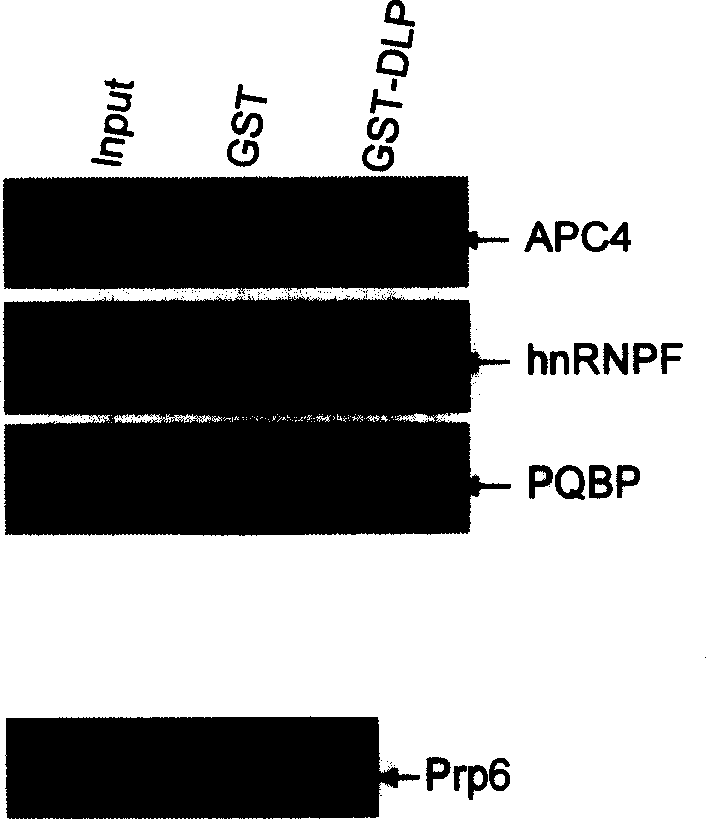
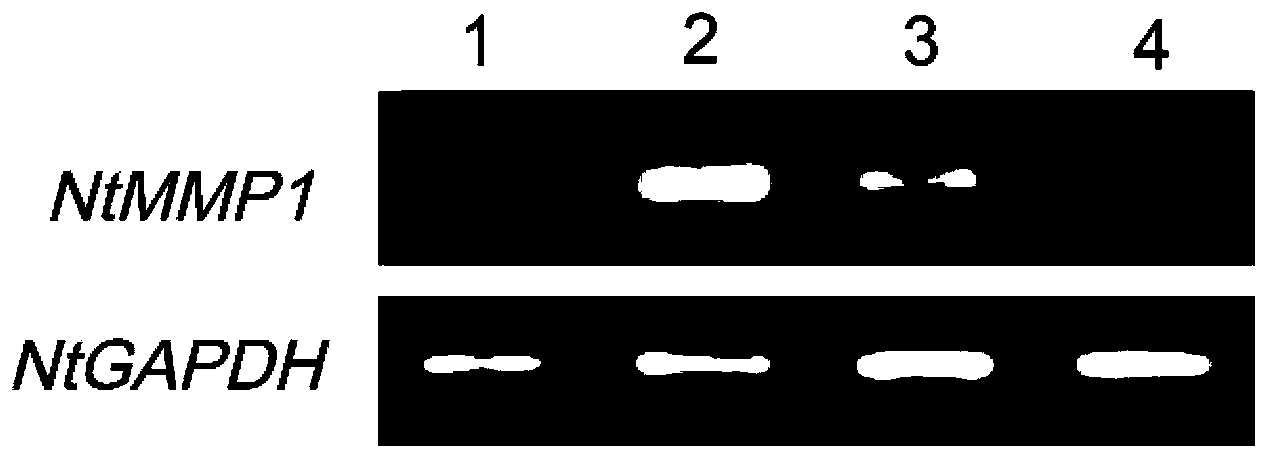
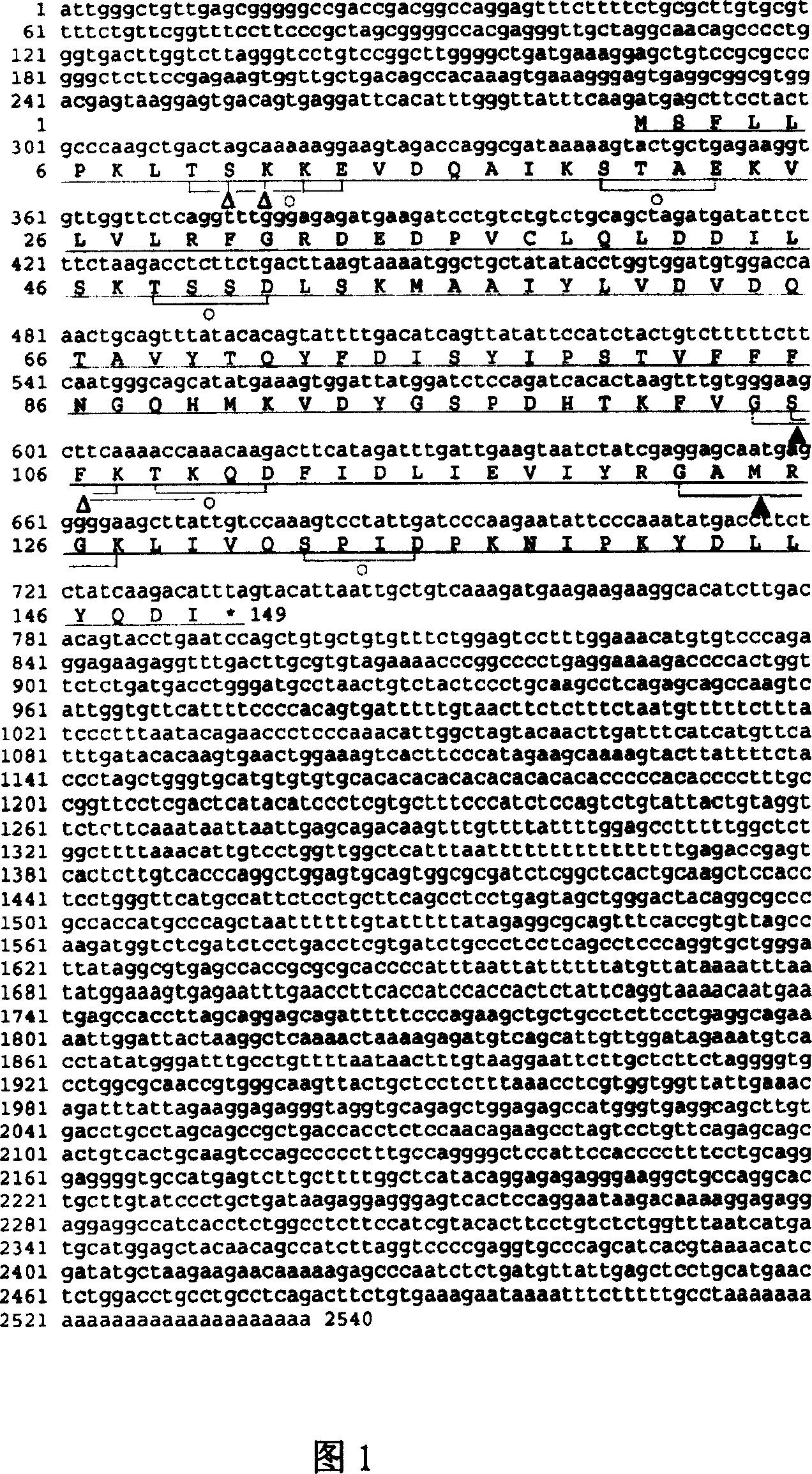
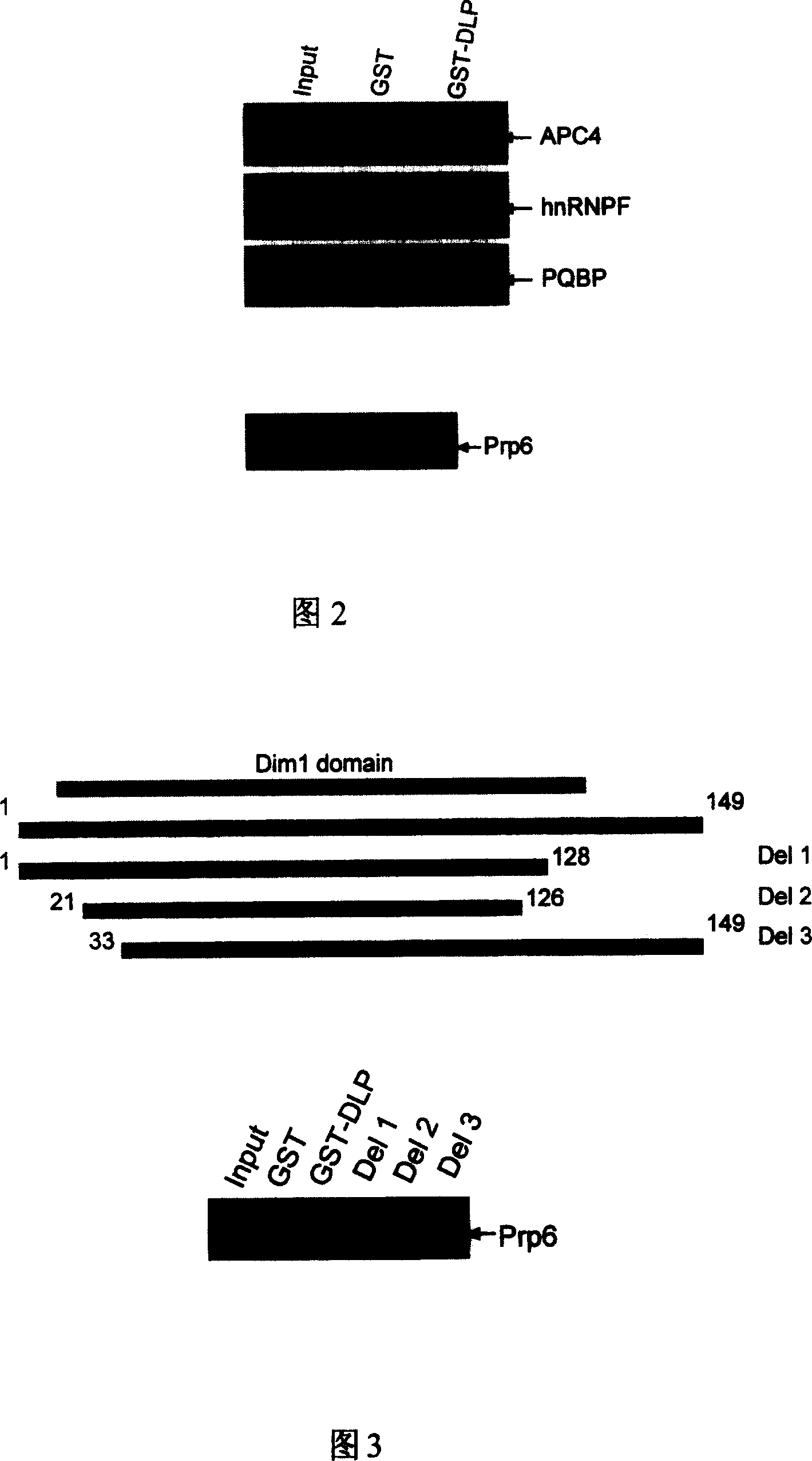
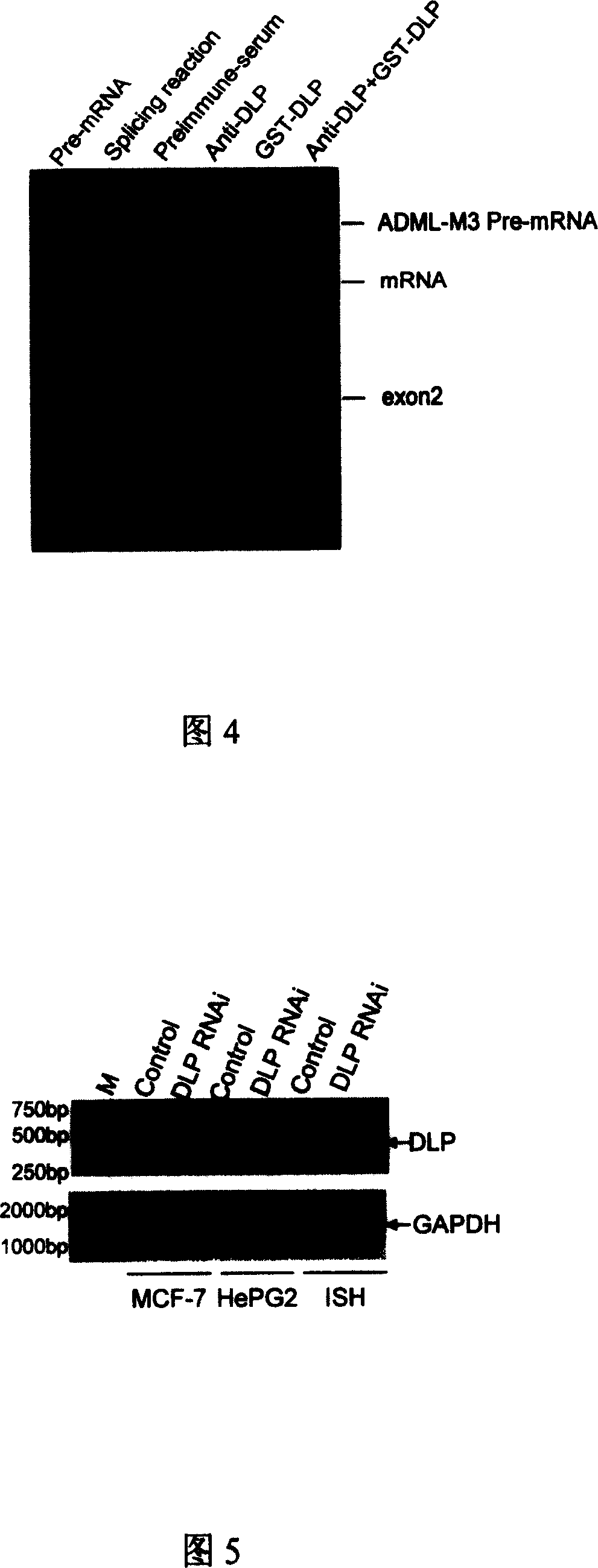
Use of DLP in Pre-mRNA splicing and cell cycle control
InactiveCN1631899AGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMedicinePrecursor mRNA
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Pyrimidine or pyridopyridone compound and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN105622638BApplicable treatmentHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDrugs preparationsPyridine
The invention discloses a pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound shown in the formula I and its preparation method and use and belongs to the technical field of drug preparation. The pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound can efficiently and selectively inhibit cyclin-depedent kinase (Cdks) CDK4 and CDK6 activity and prevent tumor cell division through inhibiting CDK4 / CDK6. The pyrimido or pyridopyridone compound can be used for treating various diseases caused through imbalance of cell cycle control based on CDK4 and CDK6 and is especially suitable for cancer treatment.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BEBETTER MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Pyrimidine or pyridopyridone compound and application thereof
ActiveUS20180297995A1High selectivityStrong anti-proliferation effectOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsKinasePyridine
The present invention discloses a pyrimidine or pyridopyridone compound as shown in formula (I) and an application thereof relating to the technical field of medicament preparation. The compound can selectively suppress cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) CDK4 and CDK6 with almost no suppression of the activity of the kinase CDK2. Thus, the compound can be used for various diseases caused by cell cycle control disorders involving CDK4 and CDK6, and particularly in the treatment of malignant tumors.
Owner:BEBETTER MED INC
Pyridine pyrimidine amine compound or pyridine pyridine amine compound and application thereof
ActiveCN105153119BReduce phosphorylationApplicable treatmentOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseasePhosphorylation
Owner:GUANGZHOU BEBETTER MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Productivity and Bioproduct Formation in Phototropin Knock/Out Mutants in Microalgae
InactiveUS20200208125A1Reduced PHOT expressionHigh genetic stabilityUnicellular algaeTransferasesElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Application of kctd12 protein in cell cycle regulation
ActiveCN104844705BAdjustable periodRegulates the cell cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsProtein SciencesPhosphorylation
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for determining the action factor of microbial preparations in reducing protein content in tobacco leaves
InactiveCN103308627BComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for measuring effect factors of a microorganism preparation for reducing the protein content in tobaccos. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting metabolites of a microorganism, performing sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS)-preview and graphics editing (PAGE) or dimensional electrophoresis after-cut adhesive tape or digging enzymolysis, and performing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry / mass spectrometry (LC-MS / MS) analysis on an enzymolysis adhesive tape or a glue point; by multiple comparison treatment, performing chip hybridization on the treated tobaccos, and measuring a gene up-regulation expression and a gene down-regulation expression which are related to plant defense response, endogenous hormone metabolism, cell cycle control and enzyme control. The method has the beneficial effects that metabolic components capable of degrading the proteins in the tobaccos in the microorganism preparation from the molecule level and the change of the gene level of the tobaccos applied with the preparation can be analyzed, so that a mechanism of the microorganism preparation for degrading the proteins in the tobaccos can be comprehensively and clearly defined; theoretical basis is laid for further application of the biological preparation.
Owner:CHONGQING CHINA TOBACCO IND CO LTD +1
Use of DLP in Pre-mRNA splicing and cell cycle control
InactiveCN100360560CGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMedicinePrecursor mRNA
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com