Patents
Literature
30 results about "Superconducting radio frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
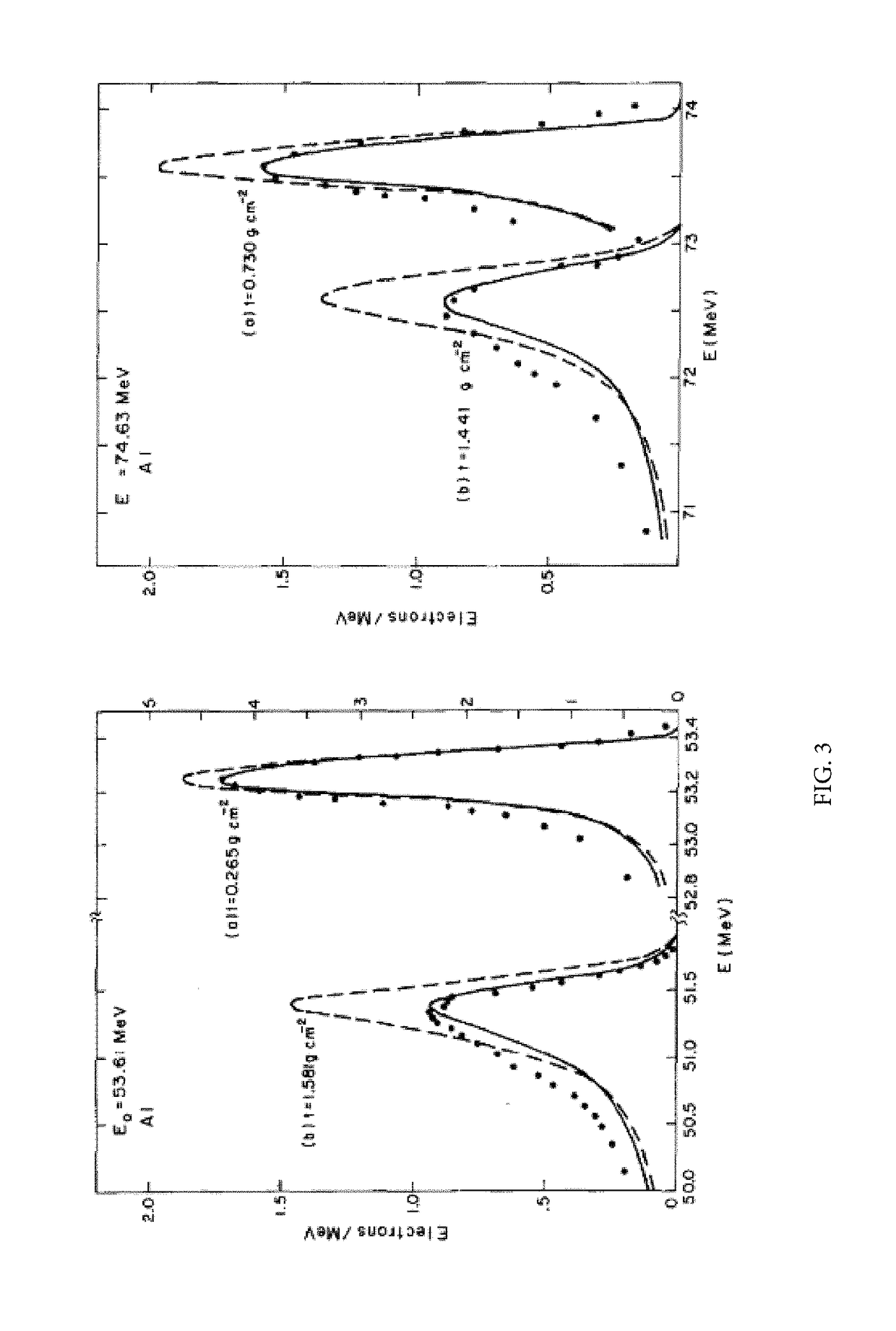
Superconducting radio frequency (SRF) science and technology involves the application of electrical superconductors to radio frequency devices. The ultra-low electrical resistivity of a superconducting material allows an RF resonator to obtain an extremely high quality factor, Q. For example, it is commonplace for a 1.3 GHz niobium SRF resonant cavity at 1.8 kelvins to obtain a quality factor of Q=5×10¹⁰. Such a very high Q resonator stores energy with very low loss and narrow bandwidth. These properties can be exploited for a variety of applications, including the construction of high-performance particle accelerator structures.
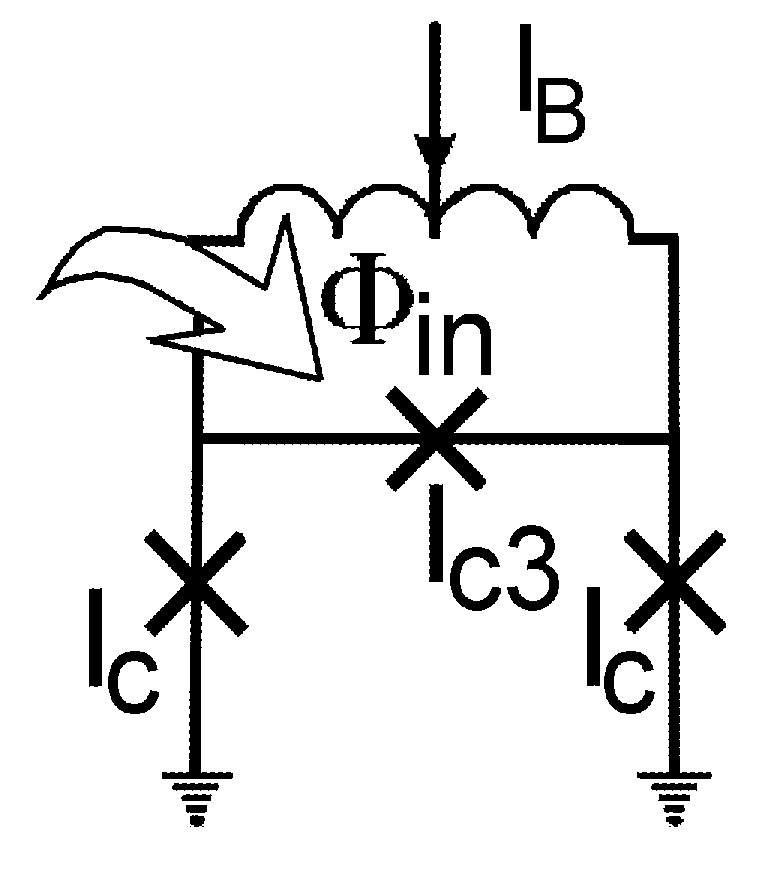
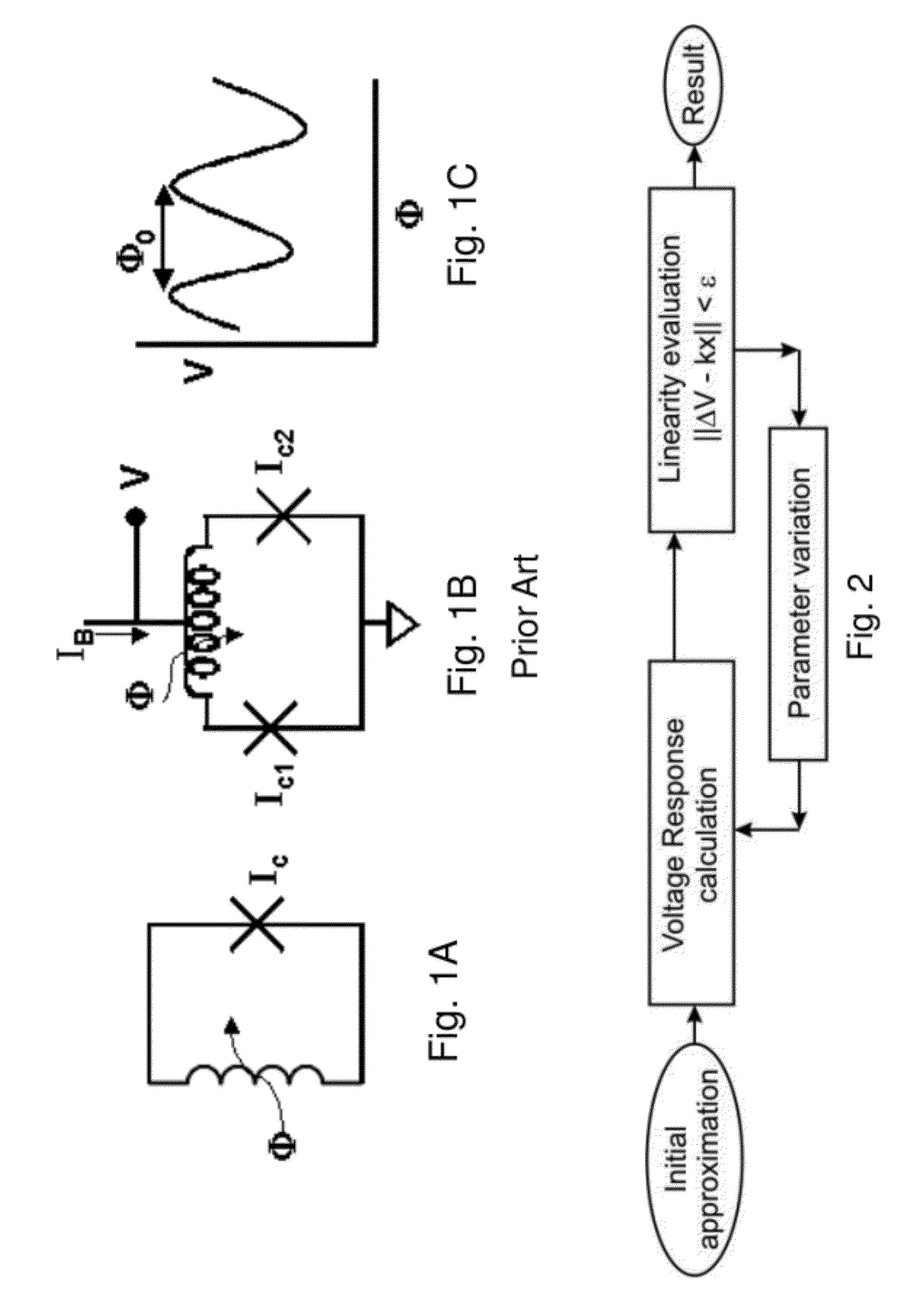
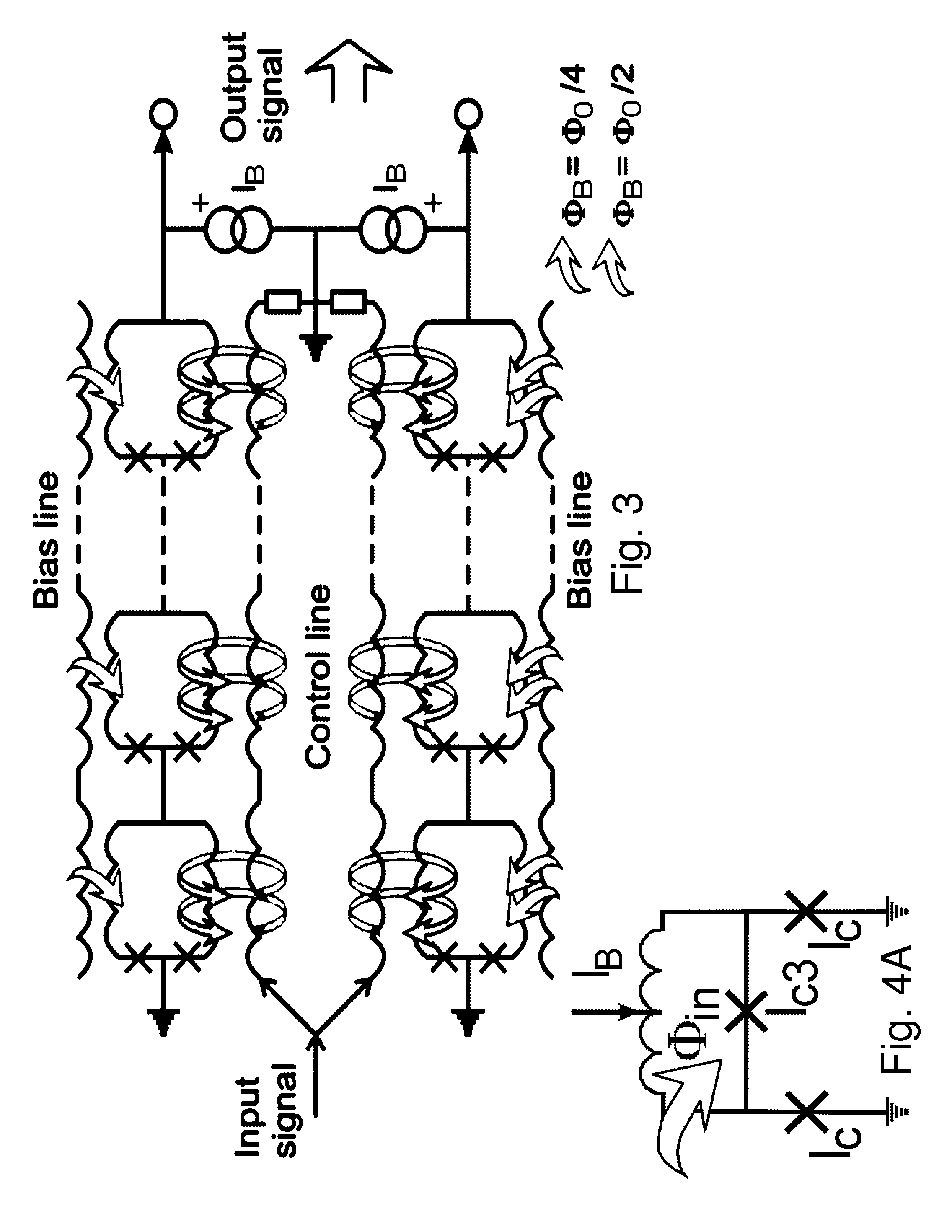
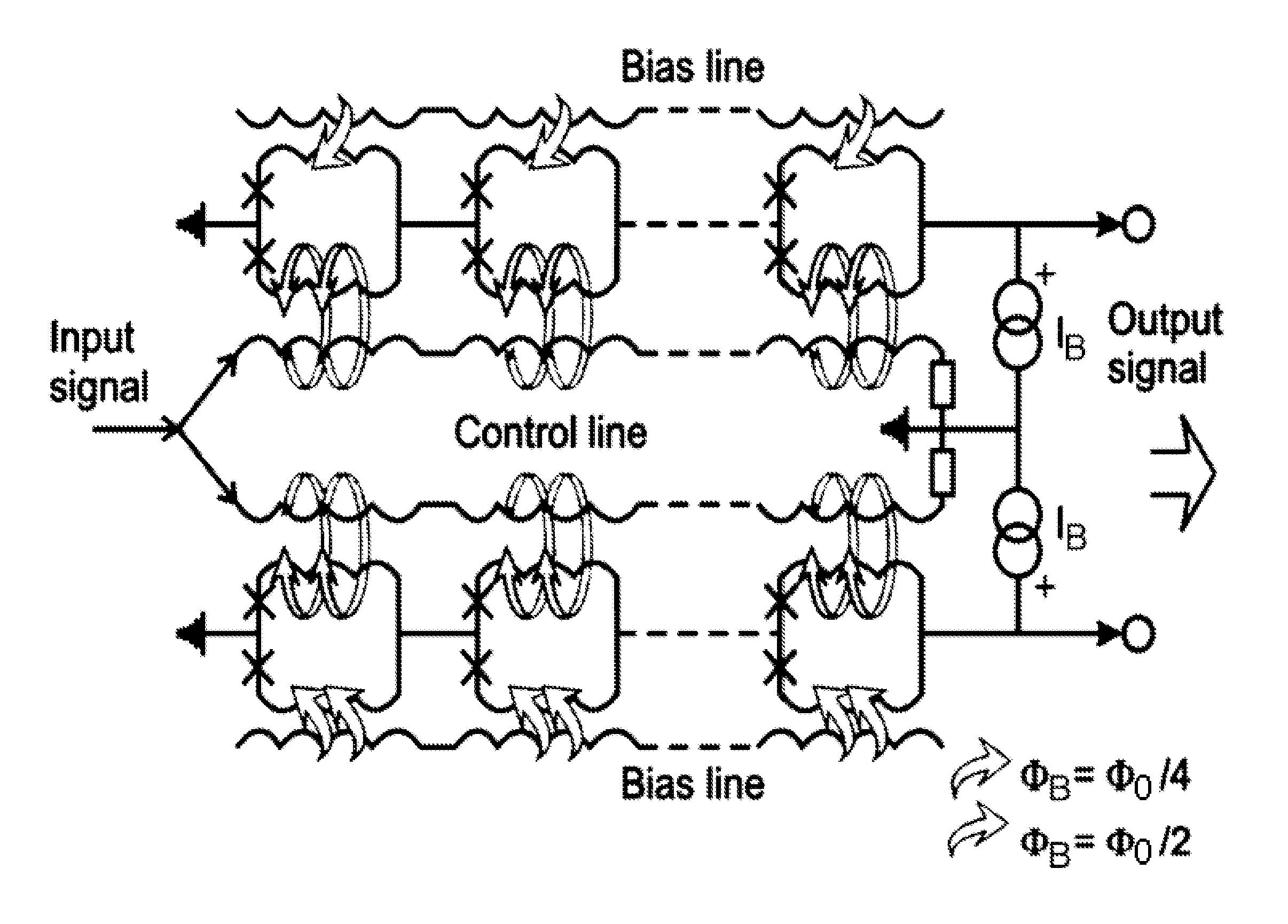
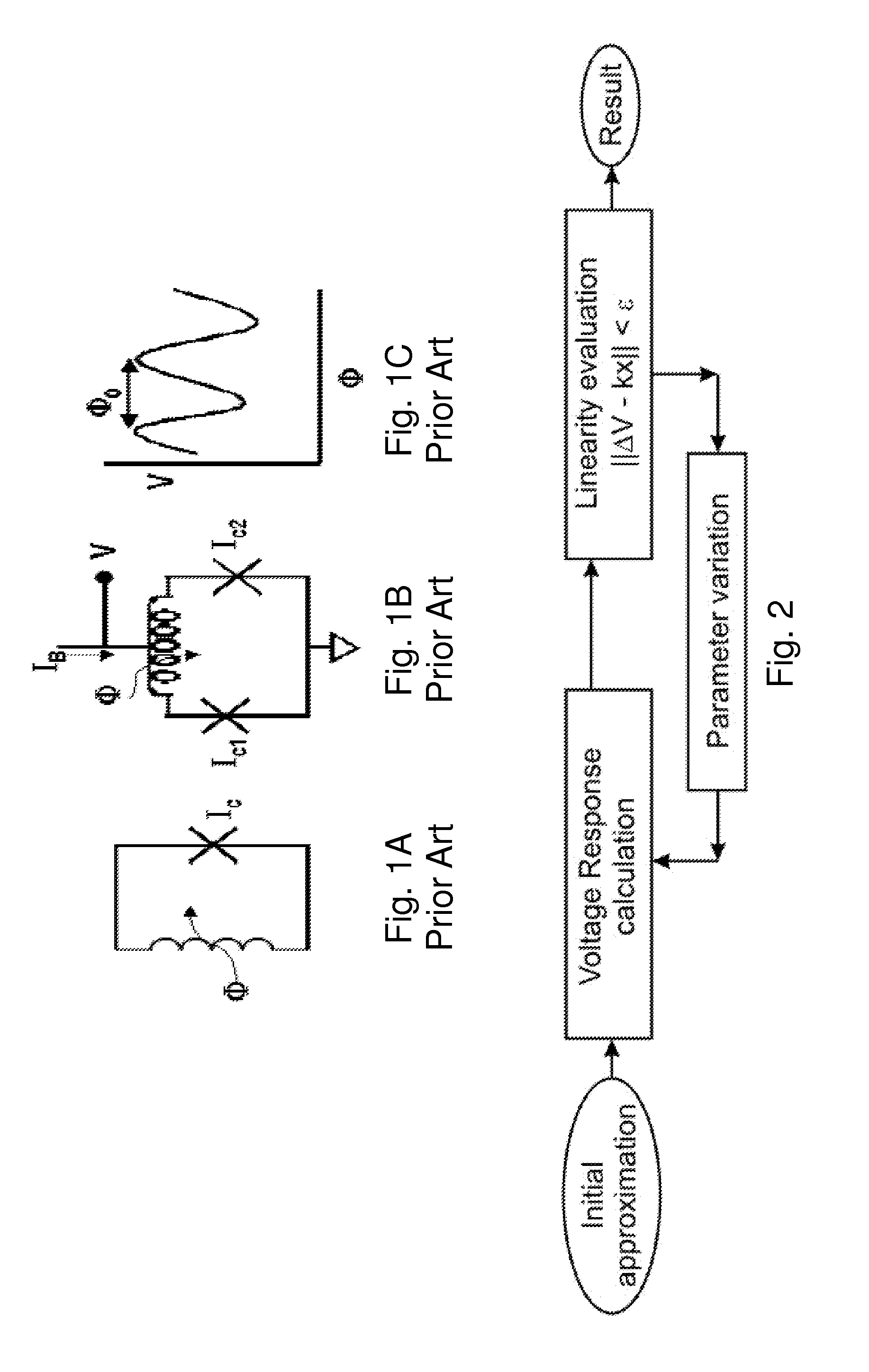
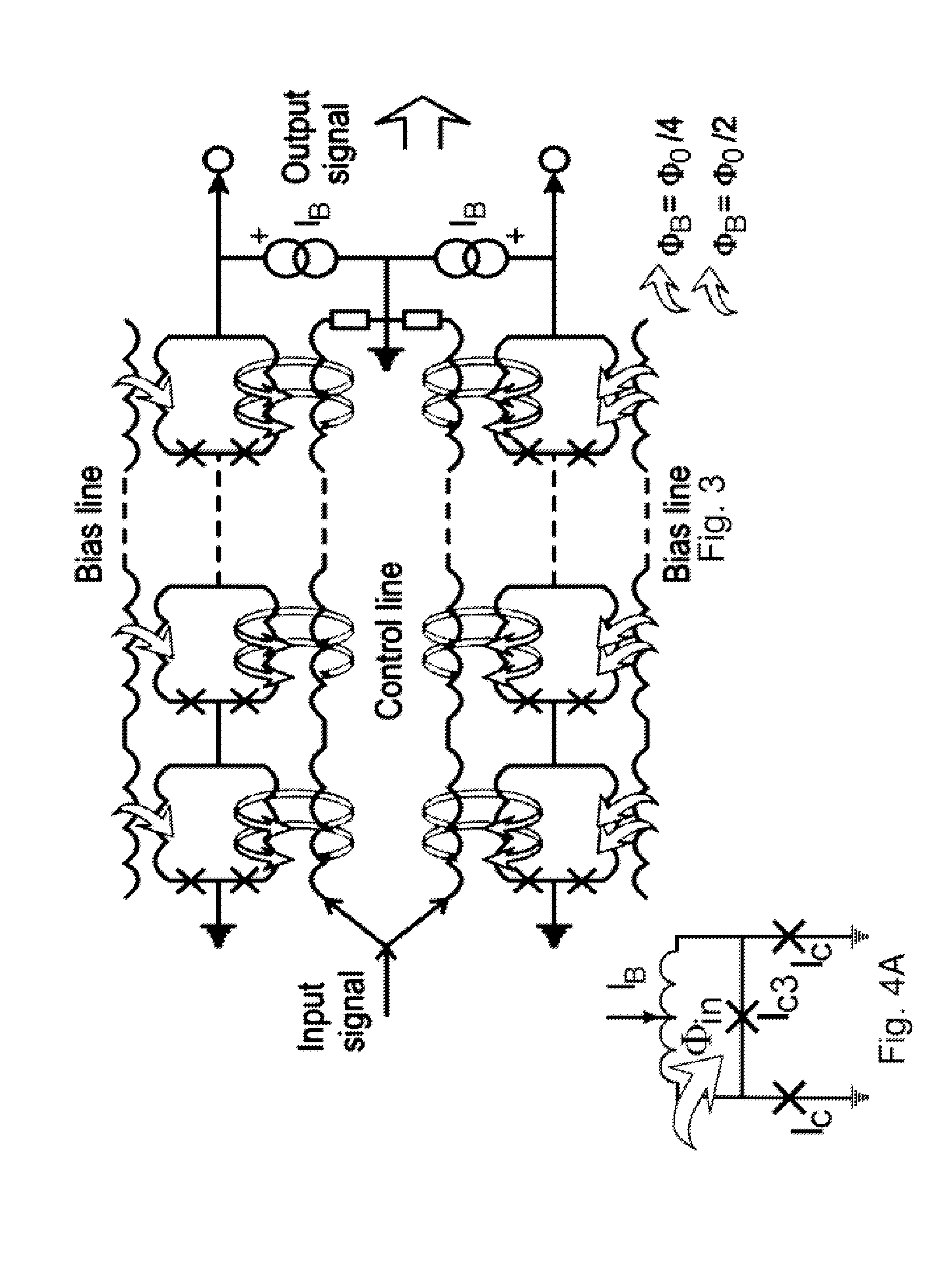
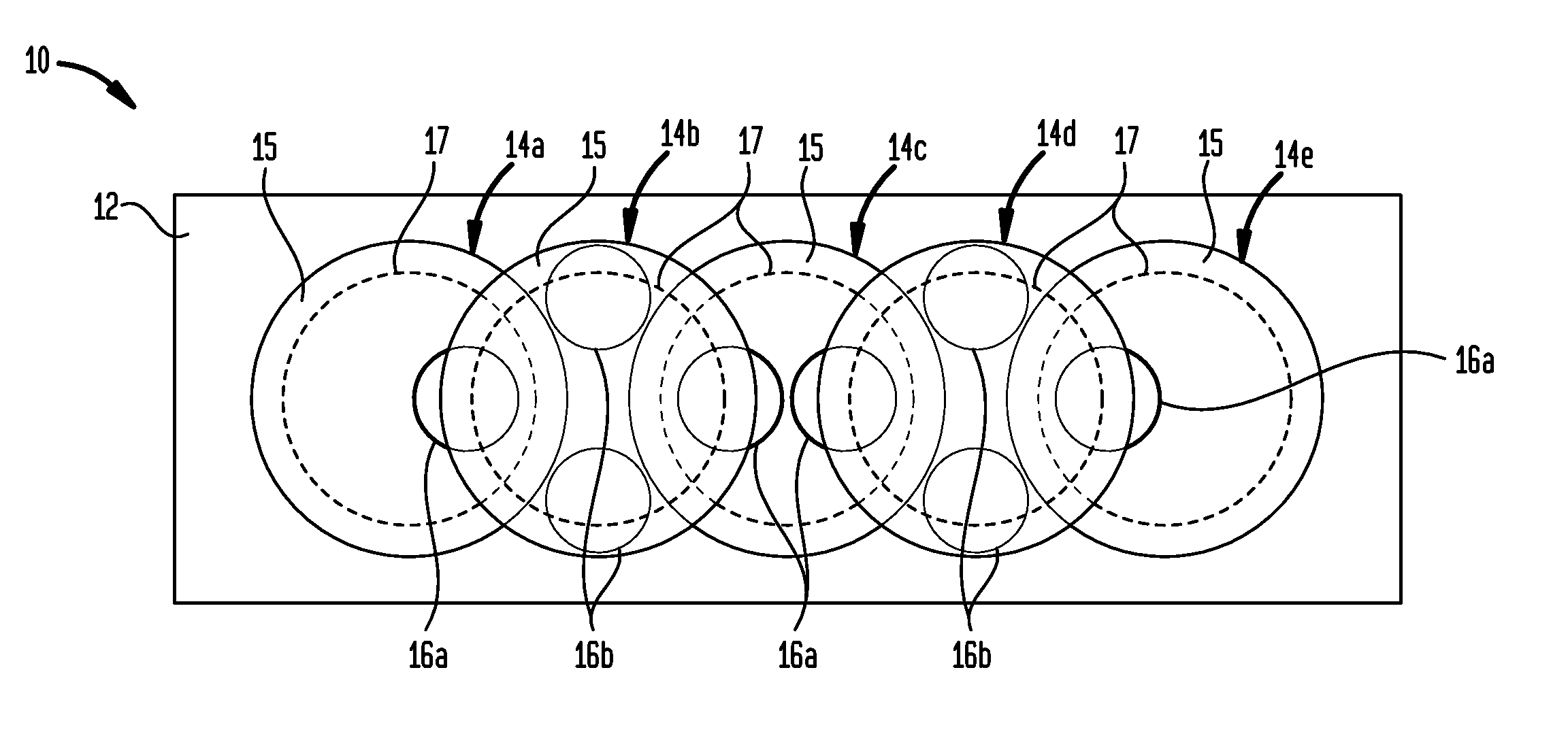
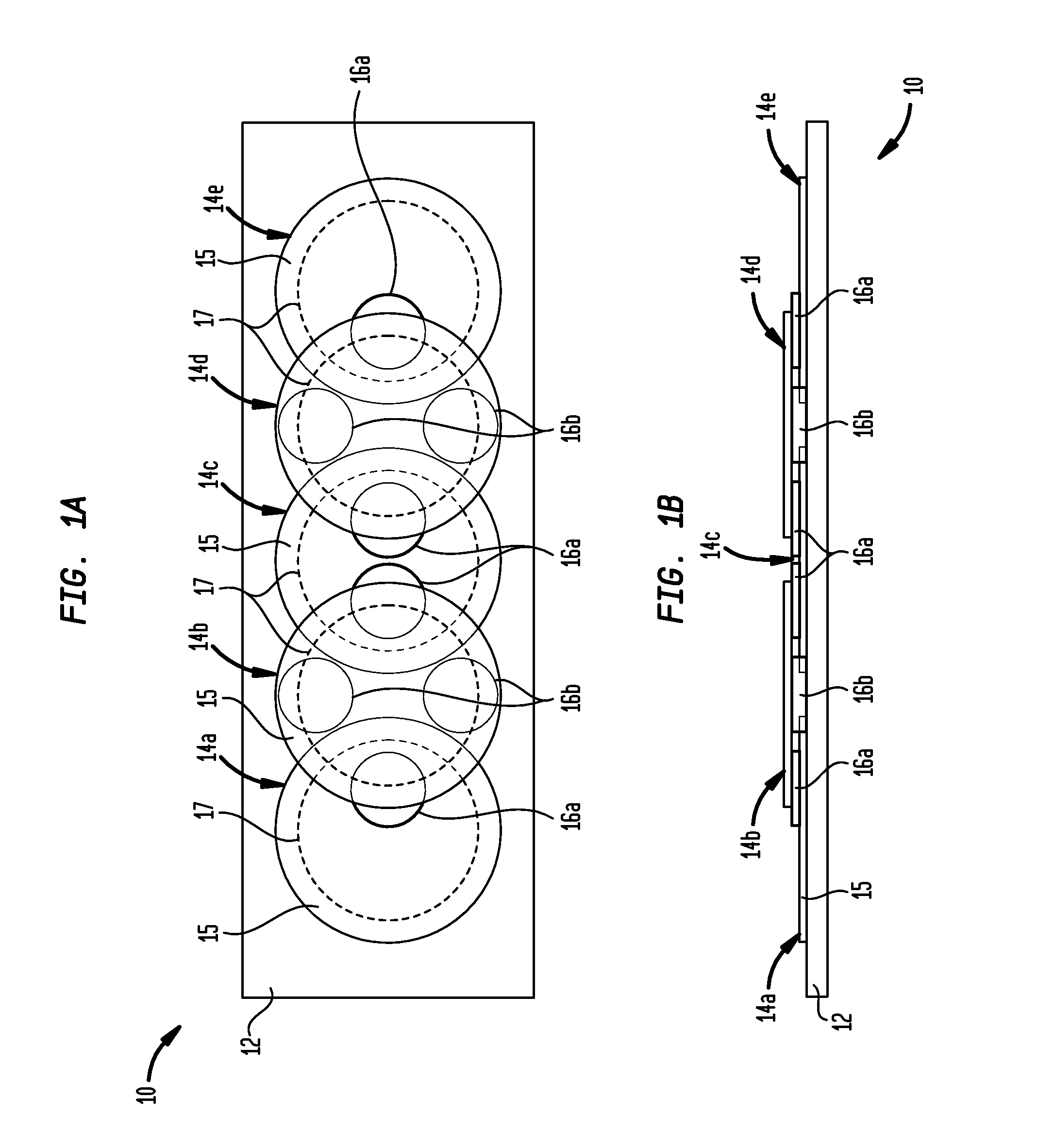
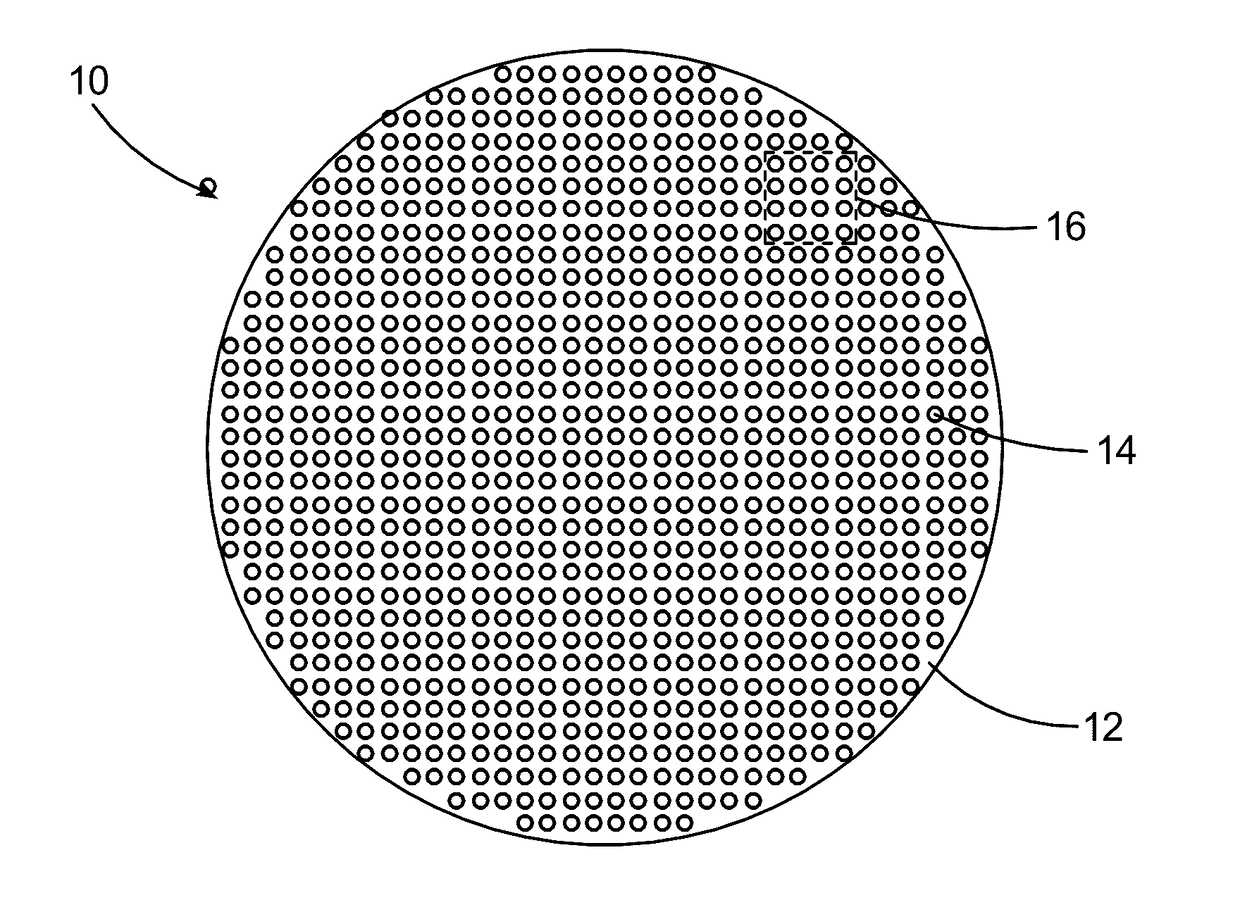
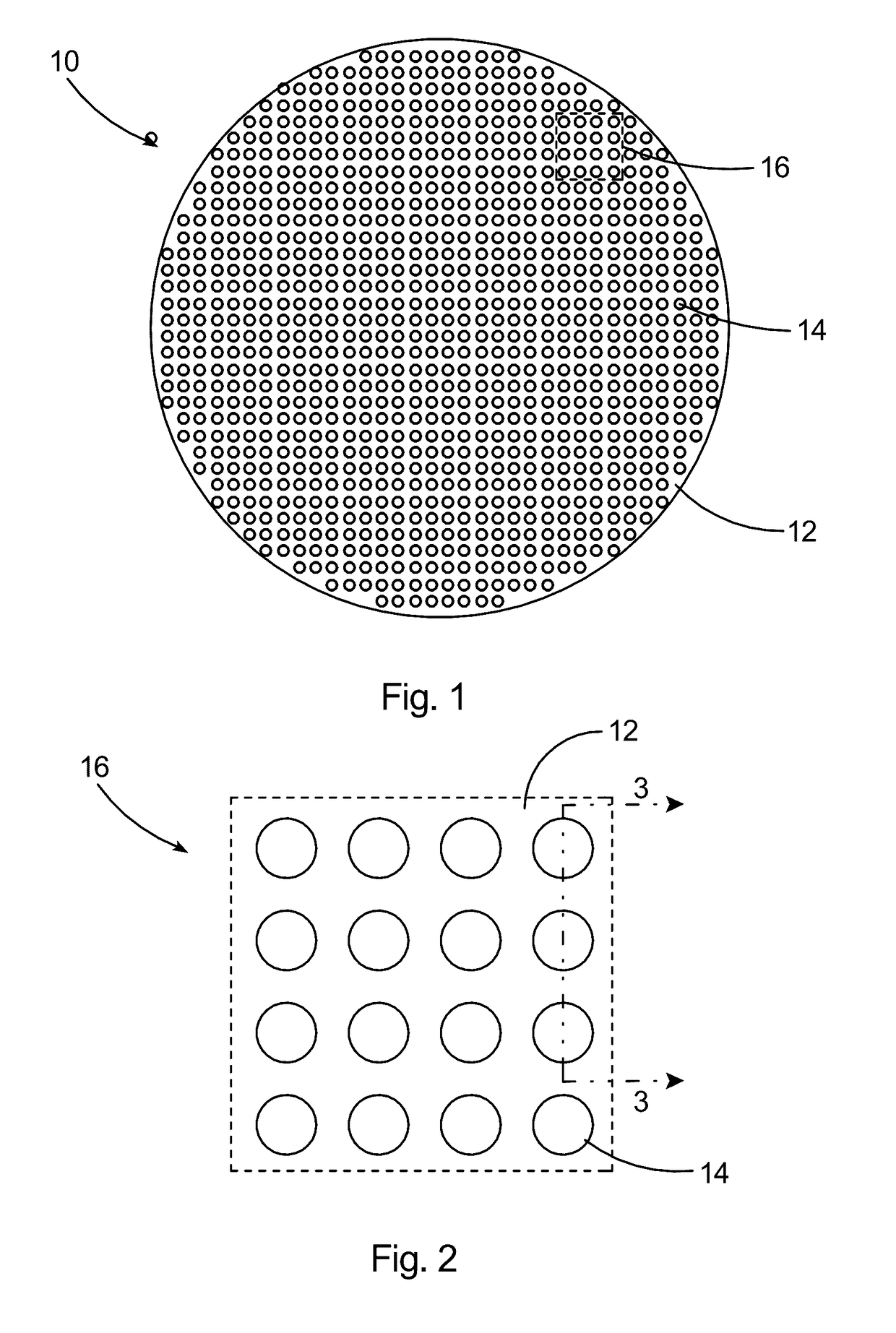
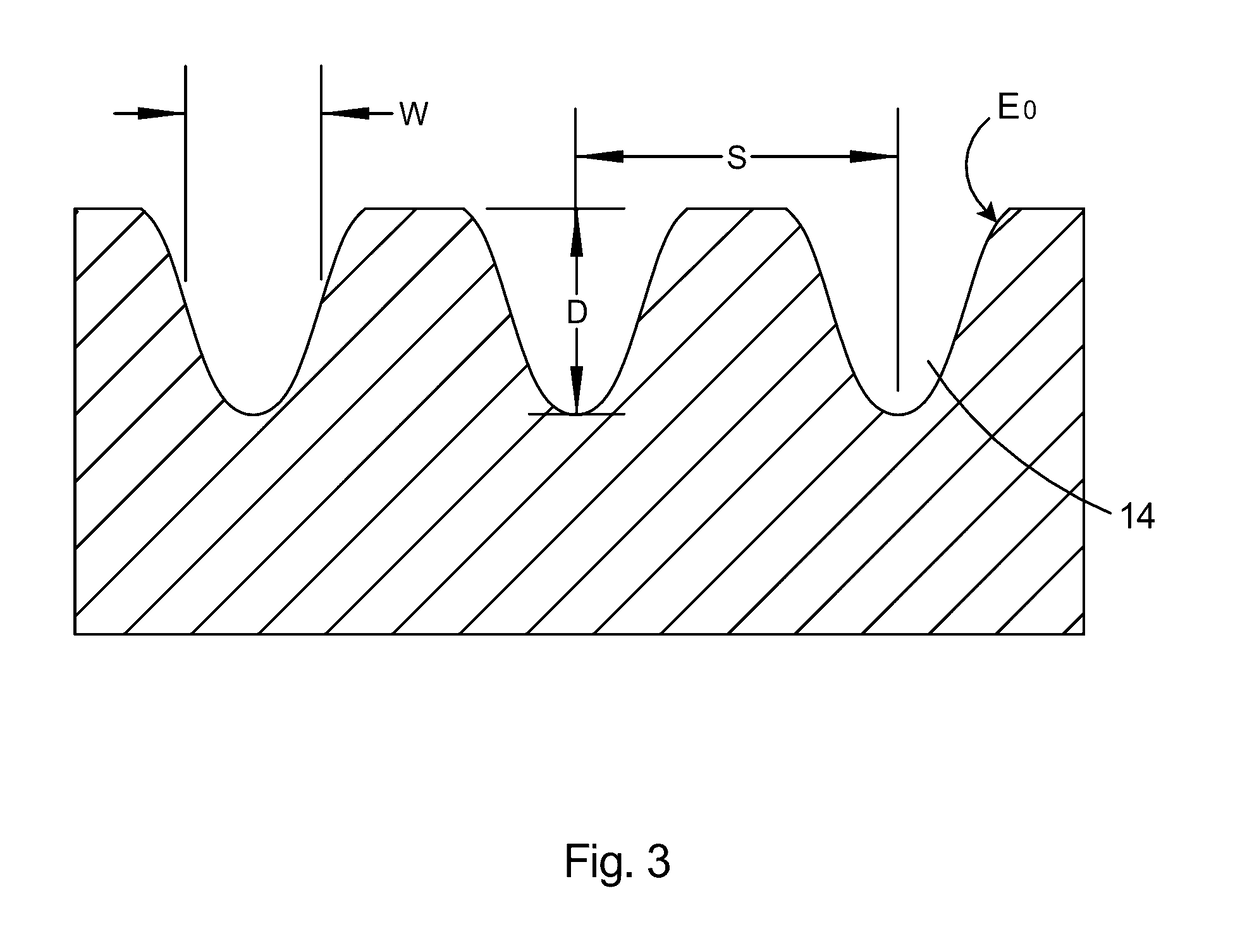
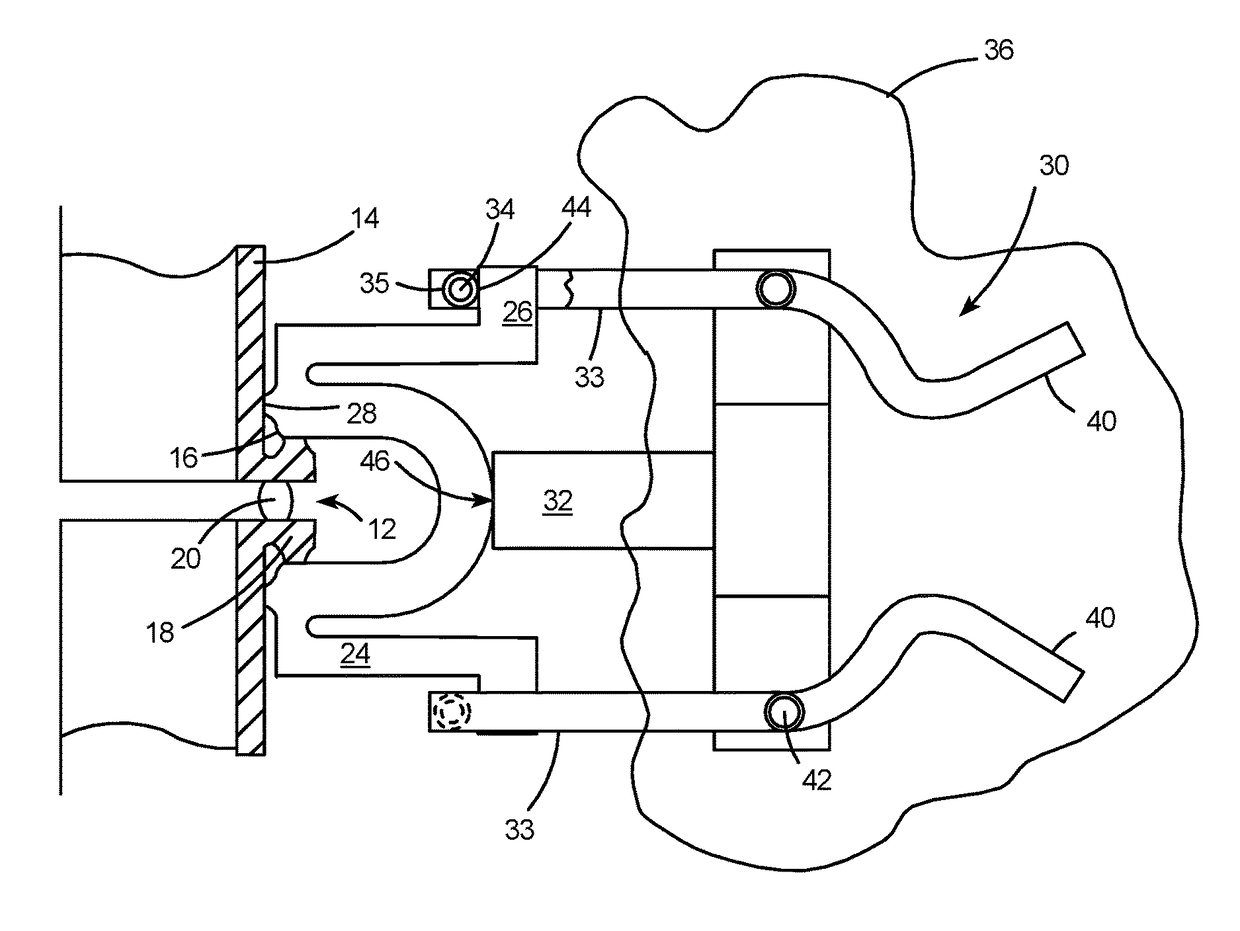
High linearity superconducting radio frequency magnetic field detector
ActiveUS8179133B1Total nonlinearities have been significantly reduced or eliminatedAvoid interferenceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectric pulse generatorTotal harmonic distortionRadio frequency
A superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUID) comprises a superconducting inductive loop with at least two Josephson junction, whereby a magnetic flux coupled into the inductive loop produces a modulated response up through radio frequencies. Series and parallel arrays of SQUIDs can increase the dynamic range, output, and linearity, while maintaining bandwidth. Several approaches to achieving a linear triangle-wave transfer function are presented, including harmonic superposition of SQUID cells, differential serial arrays with magnetic frustration, and a novel bi-SQUID cell comprised of a nonlinear Josephson inductance shunting the linear coupling inductance. Total harmonic distortion of less than −120 dB can be achieved in optimum cases.
Owner:SEEQC INC
High linearity superconducting radio frequency magnetic field detector
ActiveUS8933695B1Total nonlinearities have been significantly reduced or eliminatedAvoid interferenceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectric pulse generatorTotal harmonic distortionRadio frequency
A superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUID) comprises a superconducting inductive loop with at least two Josephson junction, whereby a magnetic flux coupled into the inductive loop produces a modulated response up through radio frequencies. Series and parallel arrays of SQUIDs can increase the dynamic range, output, and linearity, while maintaining bandwidth. Several approaches to achieving a linear triangle-wave transfer function are presented, including harmonic superposition of SQUID cells, differential serial arrays with magnetic frustration, and a novel bi-SQUID cell comprised of a nonlinear Josephson inductance shunting the linear coupling inductance. Total harmonic distortion of less than −120 dB can be achieved in optimum cases.
Owner:SEEQC INC
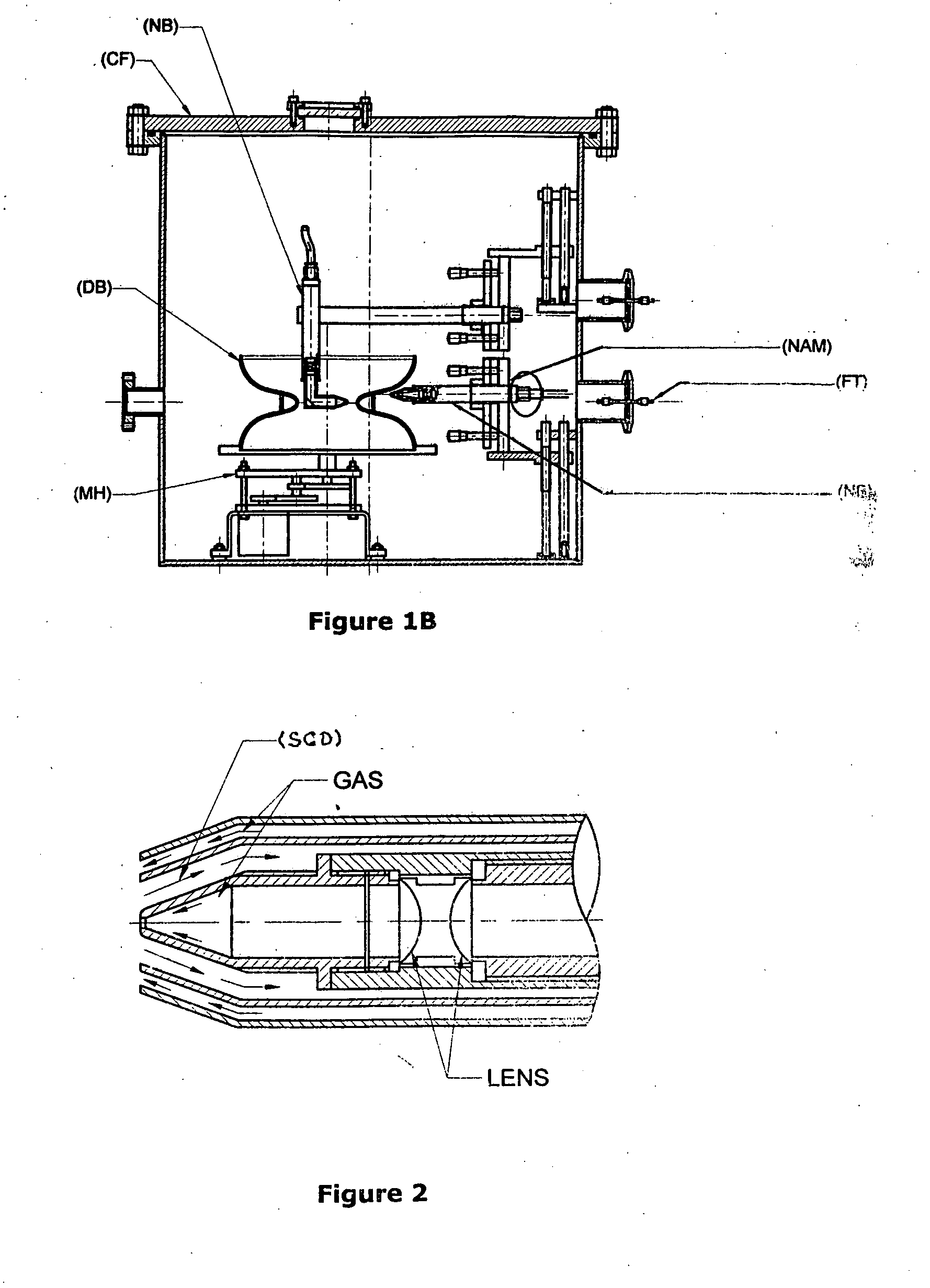
Niobium based superconducting radio frequency(SCRF) cavities comprising niobium components joined by laser welding, method and apparatus for manufacturing such cavities
InactiveUS20120094839A1Improve performanceIncrease costWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSuperconductor detailsSurface finishAlloy
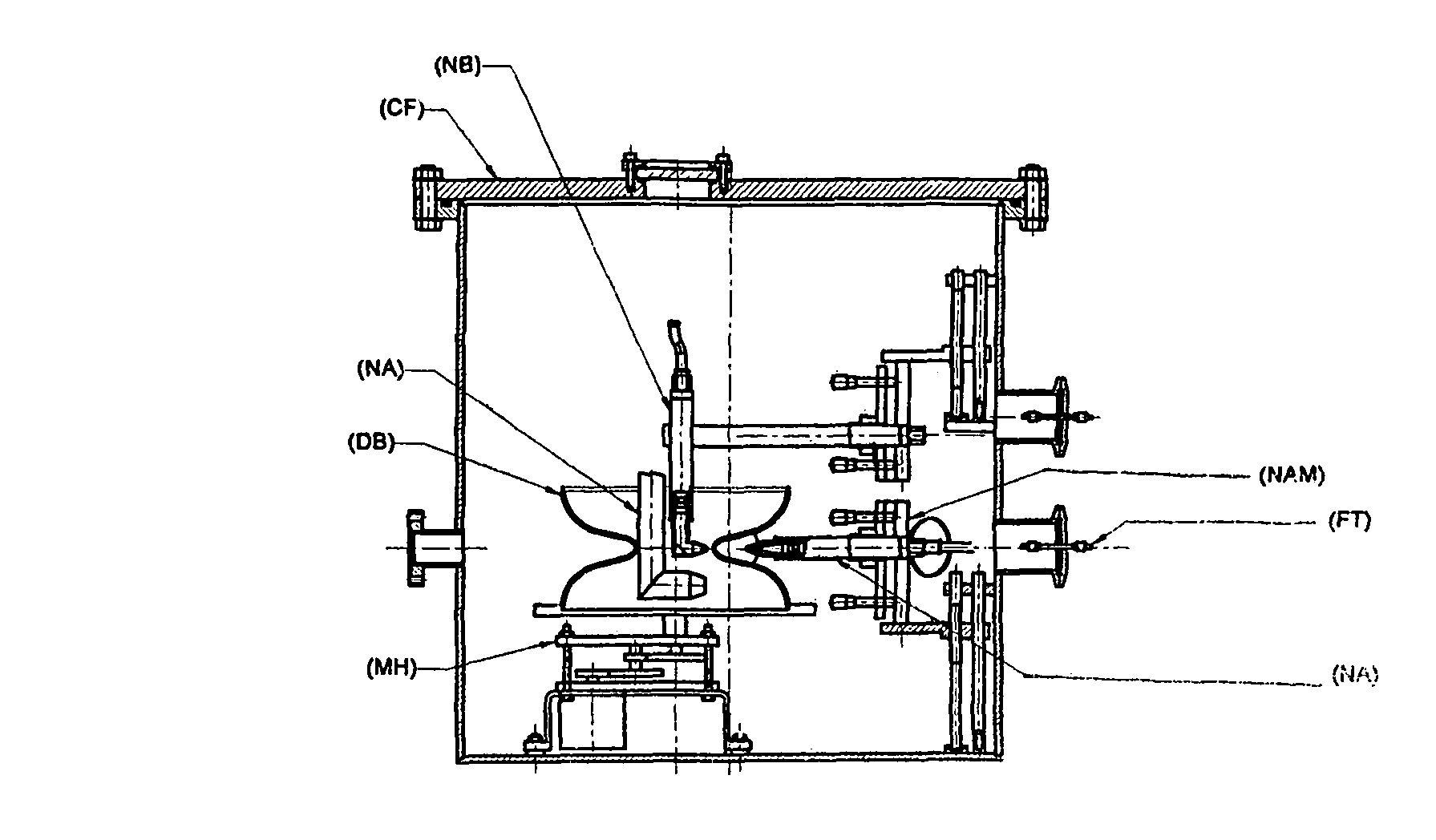
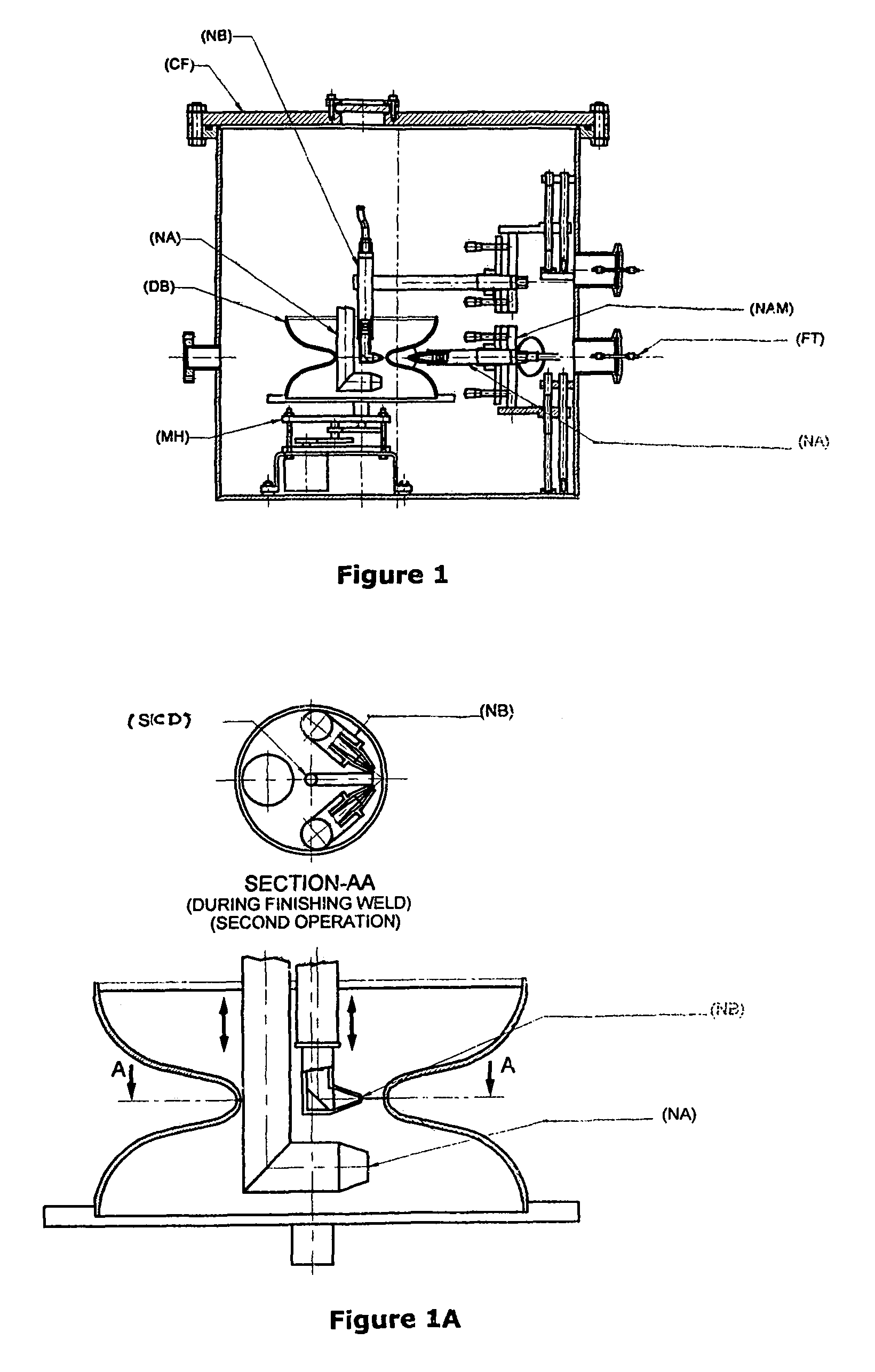
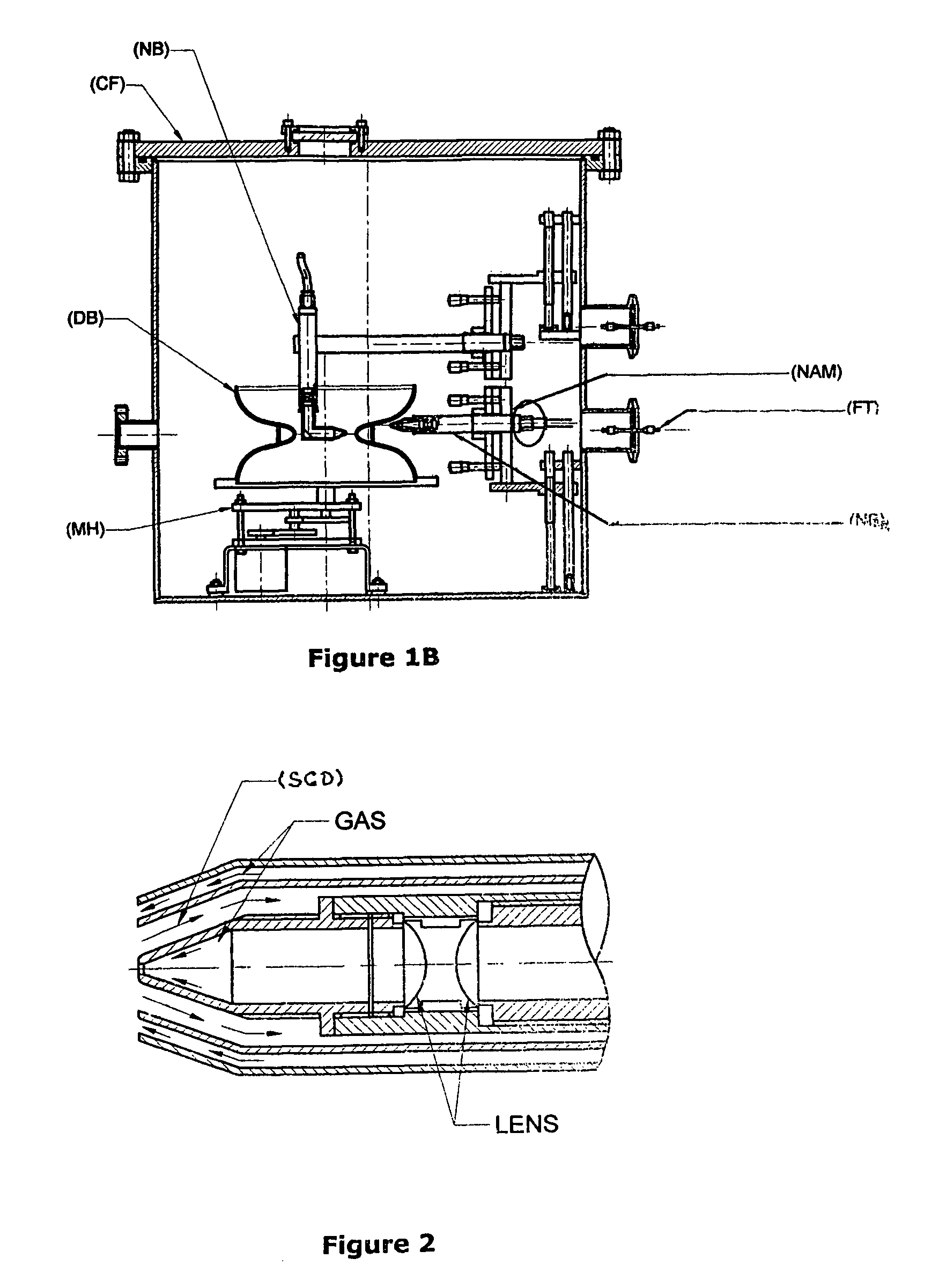
Niobium or its alloy based Superconducting Radio Frequency (SCRF) Cavities involving atleast one laser beam welded components in the SCRF cavity welded from inside surface of the wall of cavity directed to achieving more than half the thickness to full depth penetration with minimum HAZ, minimizing distortion and shrinkage. The method ensures improved weld quality and surface finish substantially free of any weld defects. Also disclosed is the welding nozzle system and welding rigs adapted to facilitate such laser welding of the Niobium or its alloy based Superconducting Radio Frequency (SCRF) Cavities. The invention is thus directed to enhancing productivity, ensuring consistent quality and reliability, enhanced weld penetration with minimum HAZ, smooth finish of weld joints at possible reduced costs.
Owner:SEC DEPT OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Nano-patterned superconducting surface for high quantum efficiency cathode
ActiveUS9589757B1Increase effective quantum efficiencyIncreases effective quantum efficiencyLapping machinesPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhotocathodeNiobium
A method for providing a superconducting surface on a laser-driven niobium cathode in order to increase the effective quantum efficiency. The enhanced surface increases the effective quantum efficiency by improving the laser absorption of the surface and enhancing the local electric field. The surface preparation method makes feasible the construction of superconducting radio frequency injectors with niobium as the photocathode. An array of nano-structures are provided on a flat surface of niobium. The nano-structures are dimensionally tailored to interact with a laser of specific wavelength to thereby increase the electron yield of the surface.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Niobium based superconducting radio frequency(SCRF) cavities comprising niobium components joined by laser welding, method and apparatus for manufacturing such cavities
InactiveUS9352416B2Improve performanceReduce functionWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSuperconductor detailsSurface finishAlloy
Niobium or its alloy based Superconducting Radio Frequency (SCRF) Cavities involving atleast one laser beam welded components in the SCRF cavity welded from inside surface of the wall of cavity directed to achieving more than half the thickness to full depth penetration with minimum HAZ, minimizing distortion and shrinkage. The method ensures improved weld quality and surface finish substantially free of any weld defects. Also disclosed is the welding nozzle system and welding rigs adapted to facilitate such laser welding of the Niobium or its alloy based Superconducting Radio Frequency (SCRF) Cavities. The invention is thus directed to enhancing productivity, ensuring consistent quality and reliability, enhanced weld penetration with minimum HAZ, smooth finish of weld joints at possible reduced costs.
Owner:SEC DEPT OF ATOMIC ENERGY
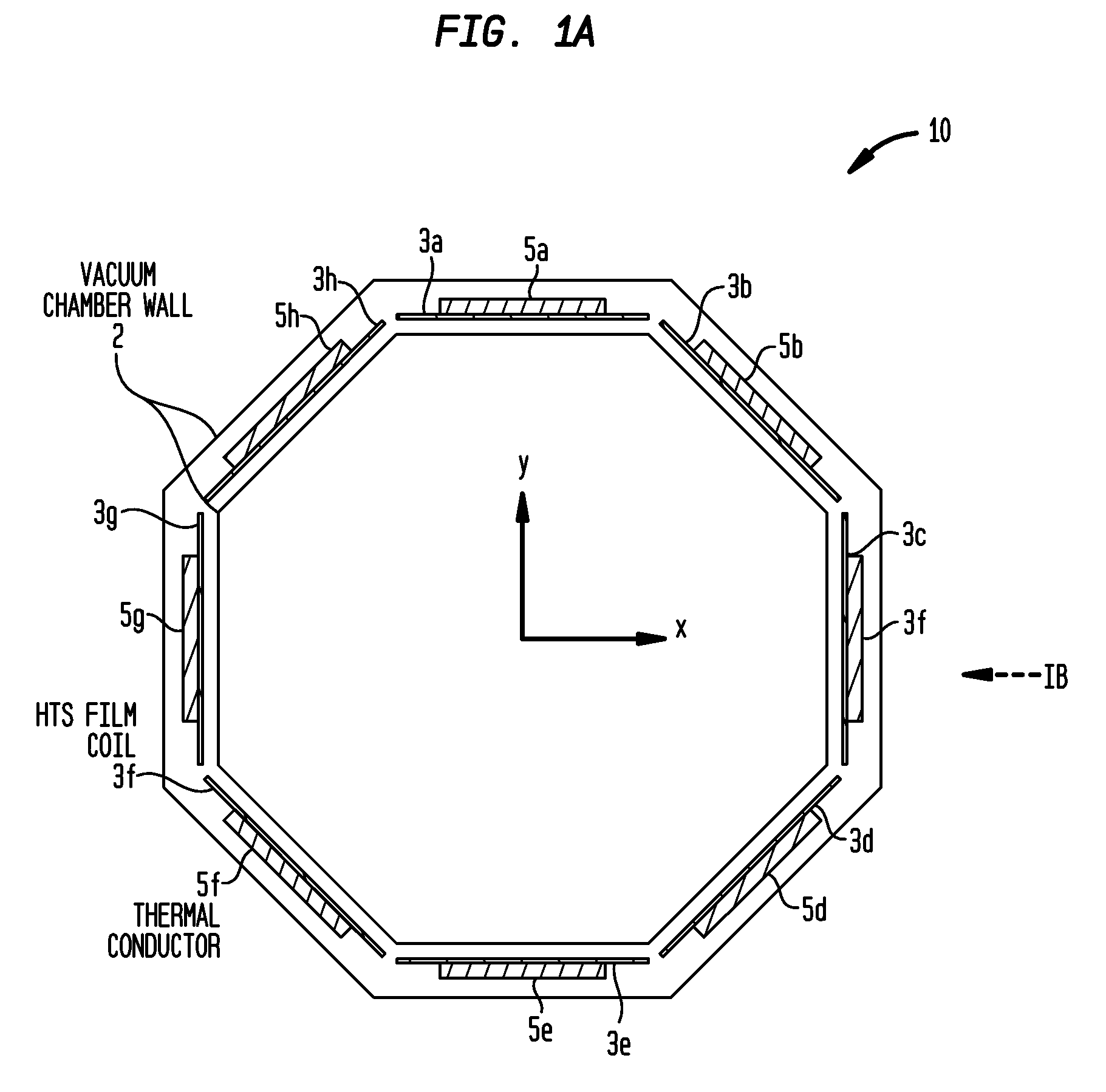
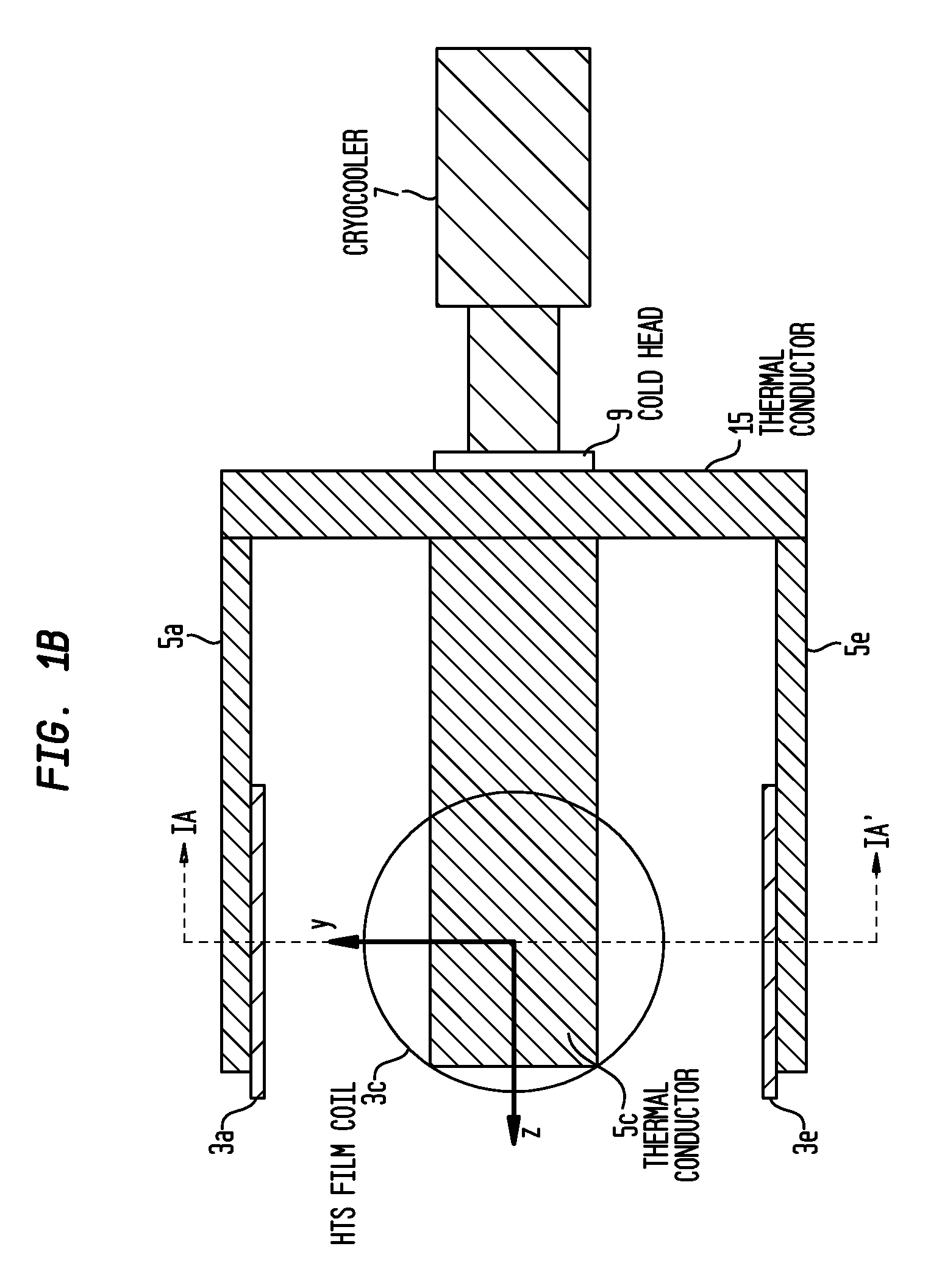
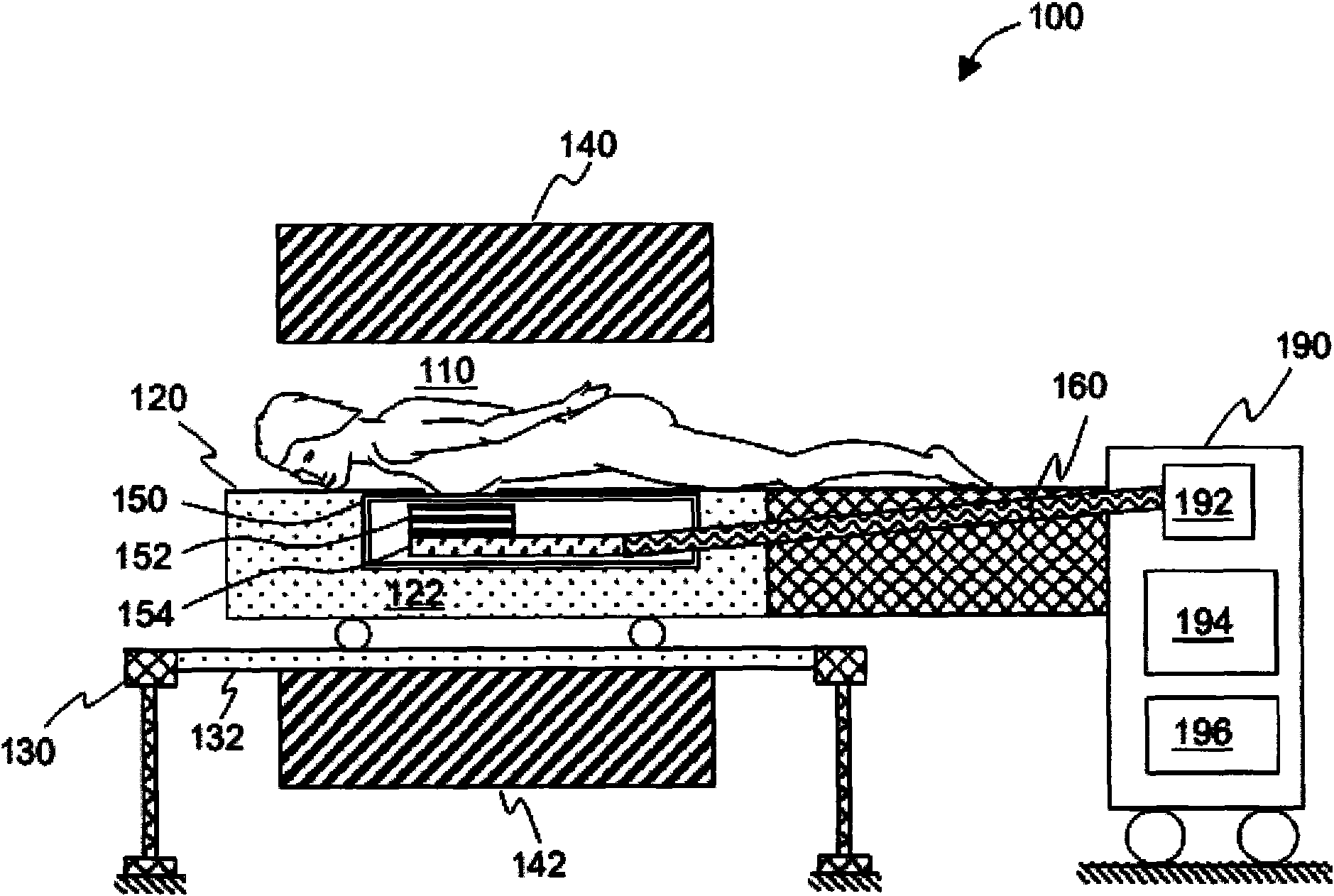
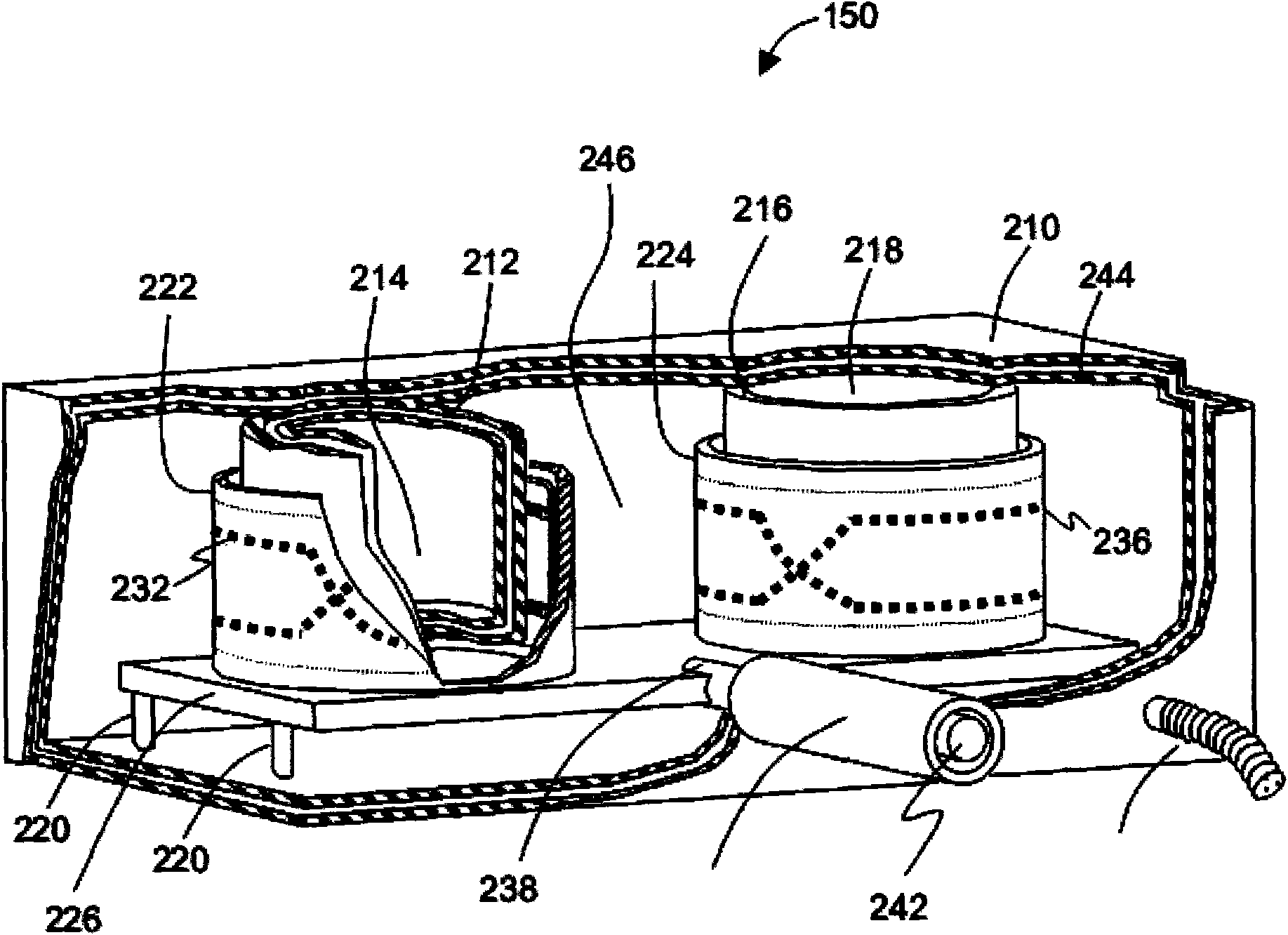
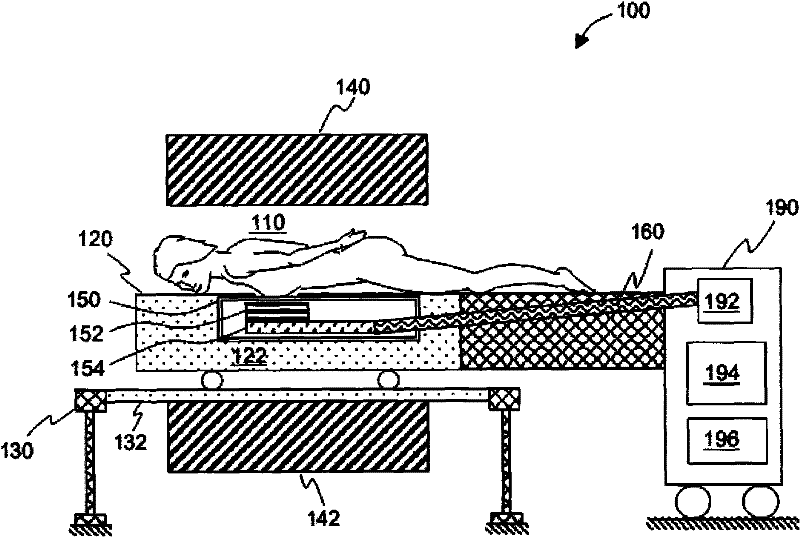
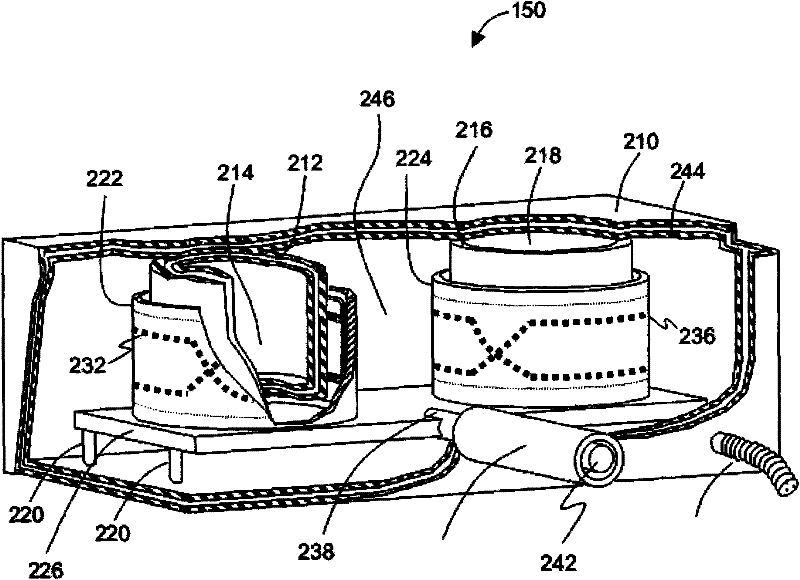
Cryogenically cooled superconductor RF head coil array and head-only magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system using same
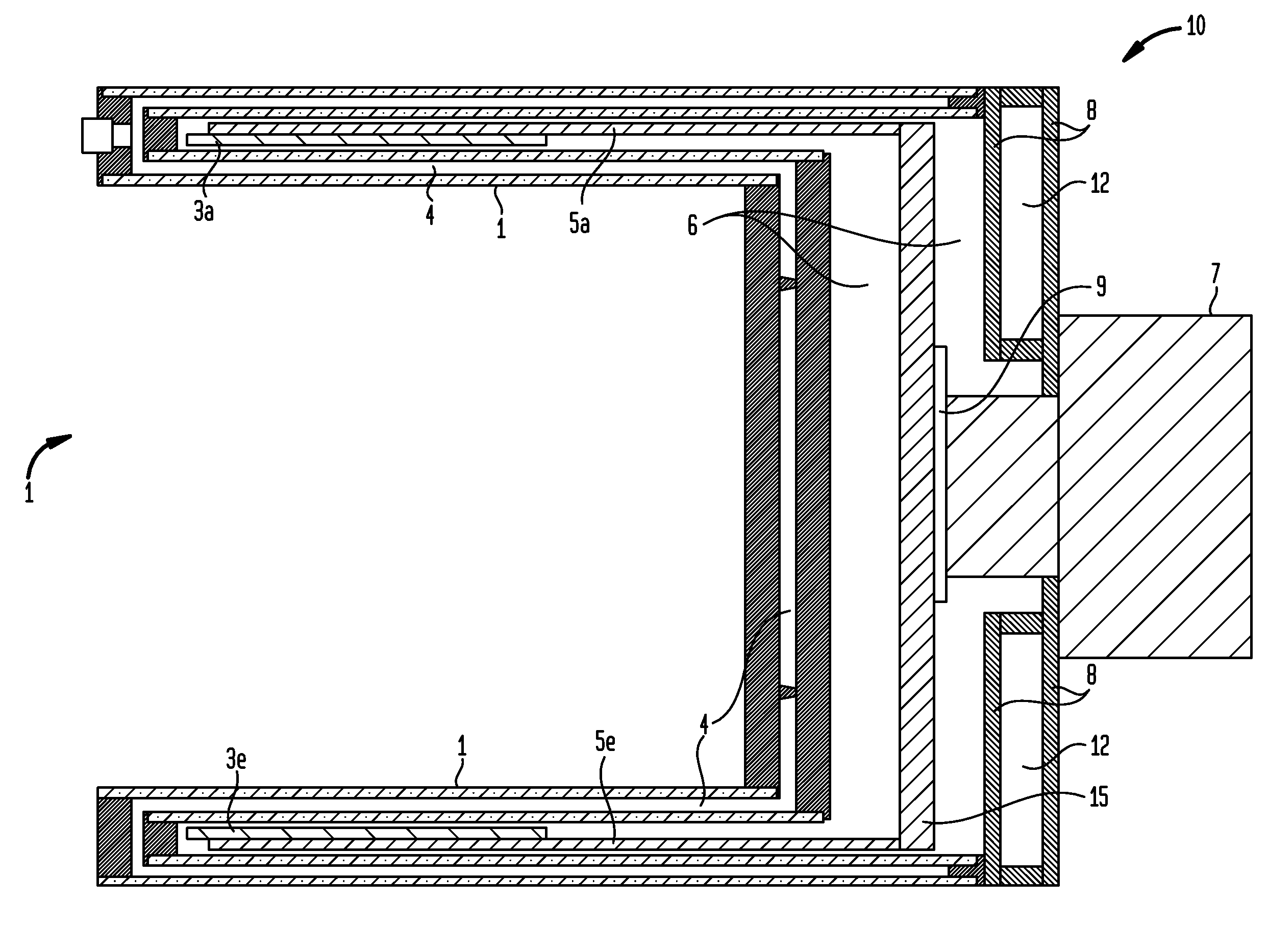
A cryogenically-cooled superconducting RF head-coil array which may be used in whole-body MRI scanners and / or in dedicated, head-only MRI systems. An RF head-coil array module may comprise a vacuum thermal isolation housing comprising a double wall hermetically sealed jacket that (i) encloses a hermetically sealed interior space under a vacuum condition, and (ii) substantially encloses an interior chamber region that is separate from the hermetically sealed interior space and is configured to be evacuated to a vacuum condition. A plurality of superconductor radiofrequency coils are disposed in the interior chamber region, and each radiofrequency coil is configured for at least one of generating and receiving a radiofrequency signal for at least one of magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. At least one thermal sink member may be disposed in the interior chamber region and in thermal contact with the superconductor radiofrequency coils. A port is configured for cryogenically cooling the thermal sink members.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
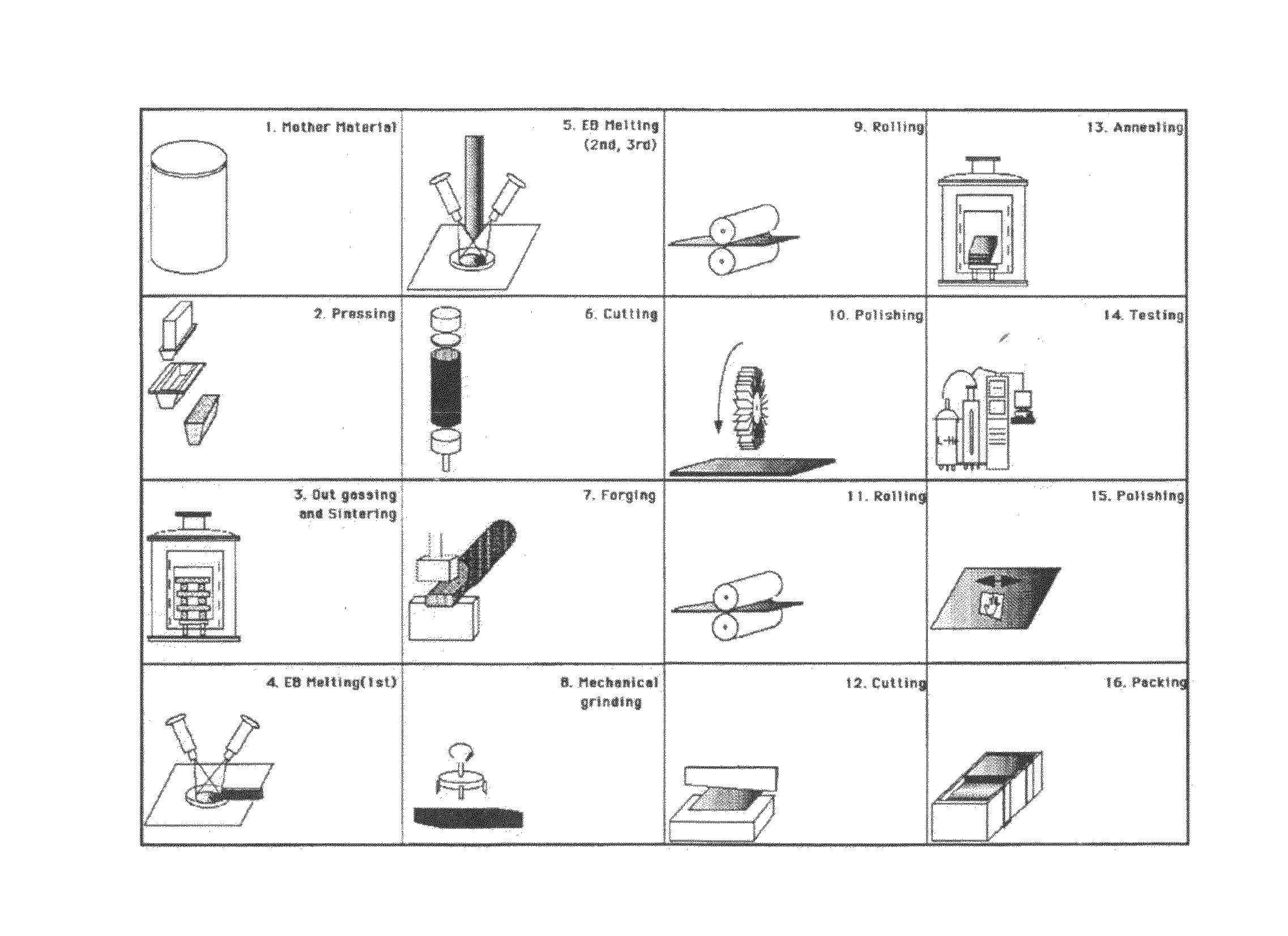
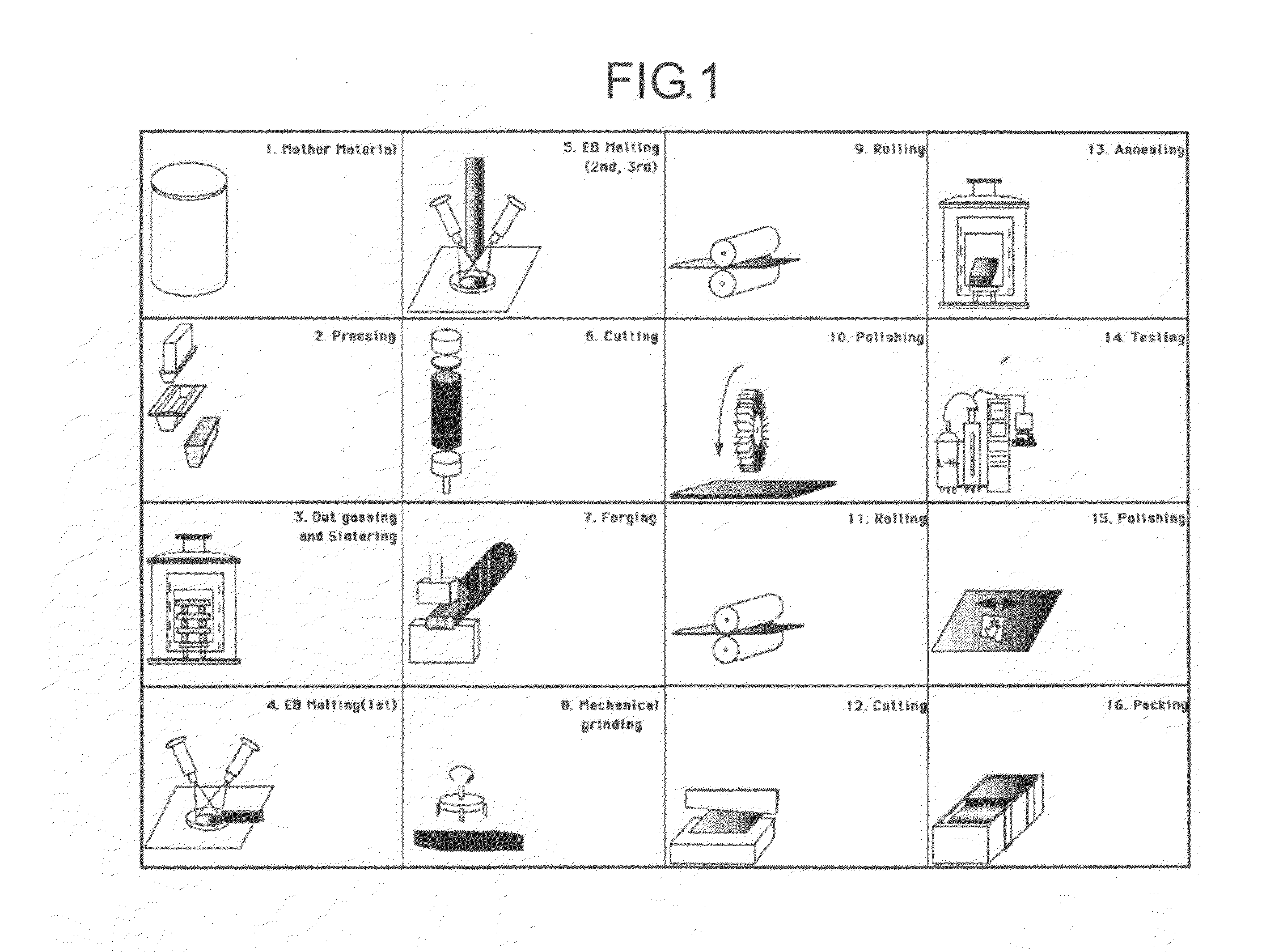
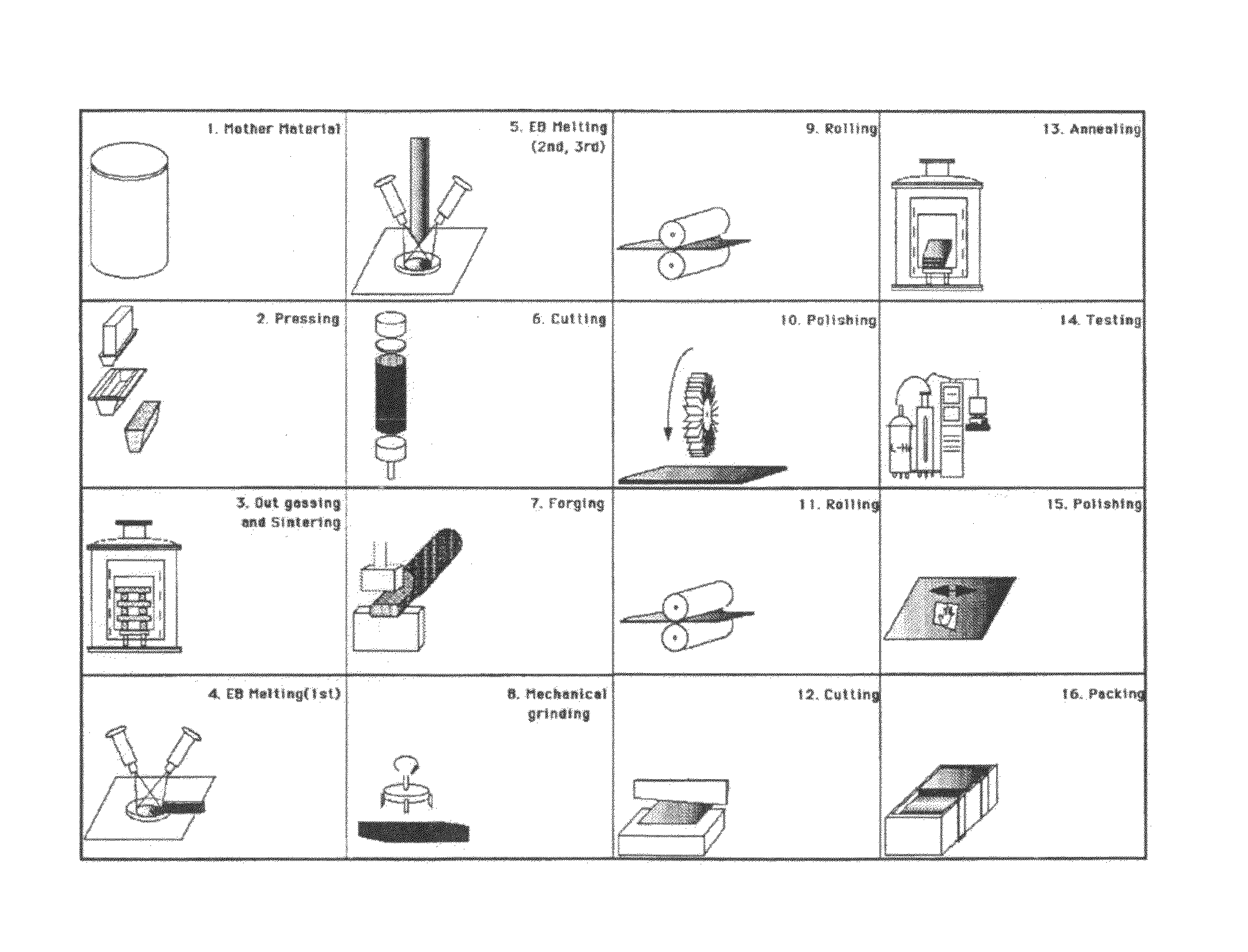
Method of manufacturing superconducting radio-frequency acceleration cavity
ActiveUS20110130294A1Reduce wasteImprove productivityDecorative surface effectsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentNiobiumIngot
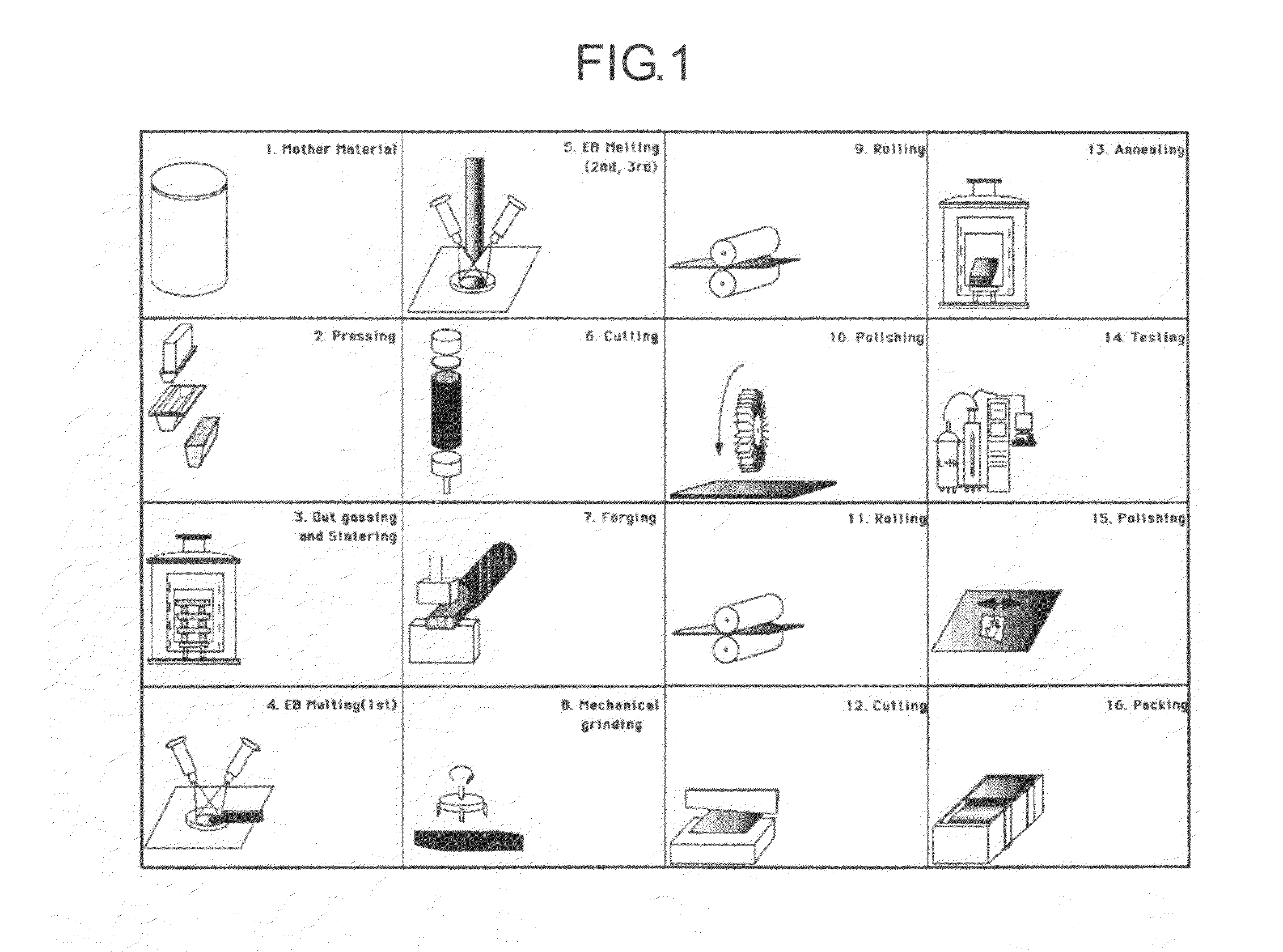
To provide a manufacturing method of a superconducting radio-frequency acceleration cavity used in a charged particle accelerator enabling the manufacturing with few waste amounts of the niobium material at low cost in a short time, the manufacturing method has each of the steps of (a) obtaining an ingot made from a disk-shaped niobium material, (b) slicing and cutting the niobium ingot into a plurality of niobium plates each with a predetermined thickness, by vibrating multiple wires back and forth while spraying fine floating abrasive grains with the niobium ingot supported, (c) removing the floating abrasive grains adhered to the sliced niobium plates, and (d) performing deep draw forming on the niobium plates and thereby obtaining a niobium cell of a desired shape.
Owner:HIGH ENERGY ACCELERATOR RESEARCH ORGANIZATION +2
Superconducting magnetic resonance imaging machine used for breast disease diagnosis, and construction method and use thereof
ActiveCN101884533AQuality improvementImprove signal-to-noise ratioIndirect heat exchangersDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Heat conducting
The invention discloses a superconducting magnetic resonance imaging machine, and a construction method and a use thereof. The superconducting magnetic resonance imaging machine of the invention comprises imaging areas, at least one vacuum insulation cover, a main magnet and a low-temperature cooling system, wherein the main magnet generates magnetic fields in the imaging areas; the low-temperature cooling system is connected with the vacuum insulation cover; a low vacuum space is formed and a lower-temperature heat conducting plate and at least one high vacuum inner cover and high vacuum outer cover are arranged inside the vacuum insulation cover; the vacuum insulation cover at least provides one imaging area; at least one superconducting radio frequency coil is arranged inside the low vacuum space and connected with the low-temperature heat conducting plate; and the low-temperature heat conducting plate is connected with the low-temperature cooling system through a heat pipe to realize and maintain the lower temperature condition of the superconducting radio frequency coil. The construction of the vacuum insulation cover is suitable for the imaging of the following body parts: breasts, knees, wrists, feet, a neck and a head. The invention can improve the magnetic resonance imaging quality and achieve a high signal-to-noise ratio in the imaging areas.
Owner:美时医疗技术(上海)有限公司
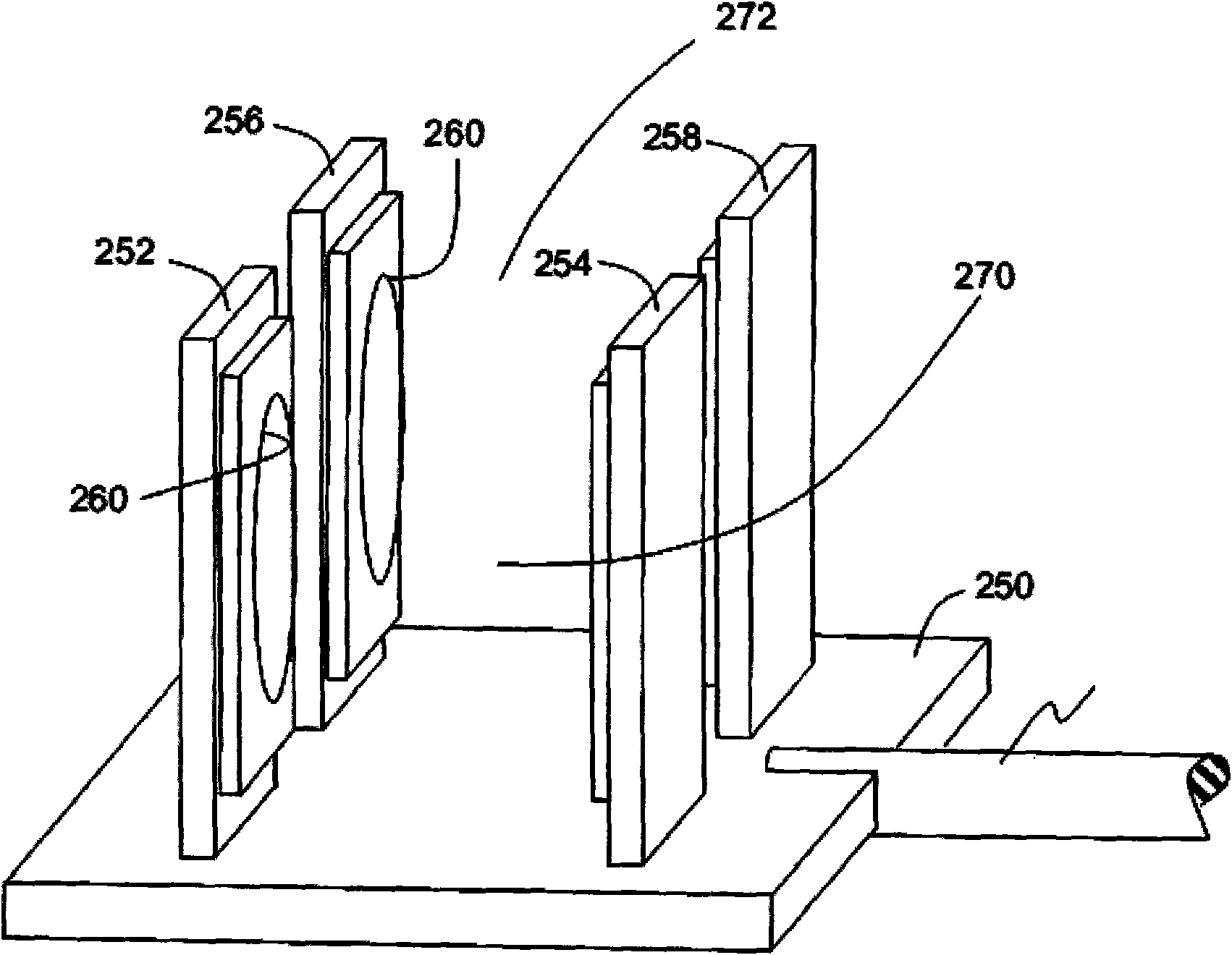
Superconductor RF coil array
A superconducting RF coil array which may be used in whole body MRI scanners and / or in dedicated MRI systems. Some embodiments provide a superconducting RF coil array for at least one of receiving signals from and transmitting signals to a sample during magnetic resonance analysis of the sample, the superconducting RF coil array comprising a thermally conductive member configured to be cryogenically cooled, and a plurality of coils elements comprising superconducting material, wherein each coil element is thermally coupled to the thermally conductive member and is configured for at least one of (i) receiving a magnetic resonance signal from a spatial region that is contiguous with and / or overlaps a spatial region from which at least one other of the plurality of coil elements is configured to receive a signal and (ii) transmitting a radiofrequency signal to a spatial region that is contiguous with and / or overlaps a spatial region to which at least one other of the plurality coil elements is configured to transmit a radiofrequency signal.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Method of manufacturing superconducting radio-frequency acceleration cavity
ActiveUS8324134B2Reduce wasteEasy to processDecorative surface effectsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentNiobiumIngot
Owner:HIGH ENERGY ACCELERATOR RESEARCH ORGANIZATION +2
High-current conduction cooled superconducting radio-frequency cryomodule
ActiveUS20190098741A1Reduce complexityLow costLinear acceleratorsNon-pressured vesselsNiobiumAverage current
A high-current, compact, conduction cooled superconducting radio-frequency cryomodule for particle accelerators. The cryomodule will accelerate an electron beam of average current up to 1 ampere in continuous wave (CW) mode or at high duty factor. The cryomodule consists of a single-cell superconducting radio-frequency cavity made of high-purity niobium, with an inner coating of Nb3Sn and an outer coating of pure copper. Conduction cooling is achieved by using multiple closed-cycle refrigerators. Power is fed into the cavity by two coaxial couplers. Damping of the high-order modes is achieved by a warm beam-pipe ferrite damper.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Method for producing superconducting radio-frequency acceleration cavity
Provided is a method for producing a superconducting radio-frequency acceleration cavity for use in a charged particle accelerator which can be produced in a short time at a low cost with a minimum amount of niobium material to be discarded. The method for producing a superconducting radio-frequency acceleration cavity comprises (a) a step for obtaining an ingot made of niobium material in the shape of a disk, (b) a step for slicing the niobium ingot into a plurality of niobium plates each having a predetermined thickness by vibrating a multiplex wire back and forth while blowing fine floating abrasive grains in a state where the niobium ingot is supported, (c) a step for removing the floating abrasive grains adhering to the niobium plates thus sliced, and a step (d) for forming a niobium cell of a desired shape by deep drawing the niobium plate.
Owner:HIGH ENERGY ACCELERATOR RESEARCH ORGANIZATION +2
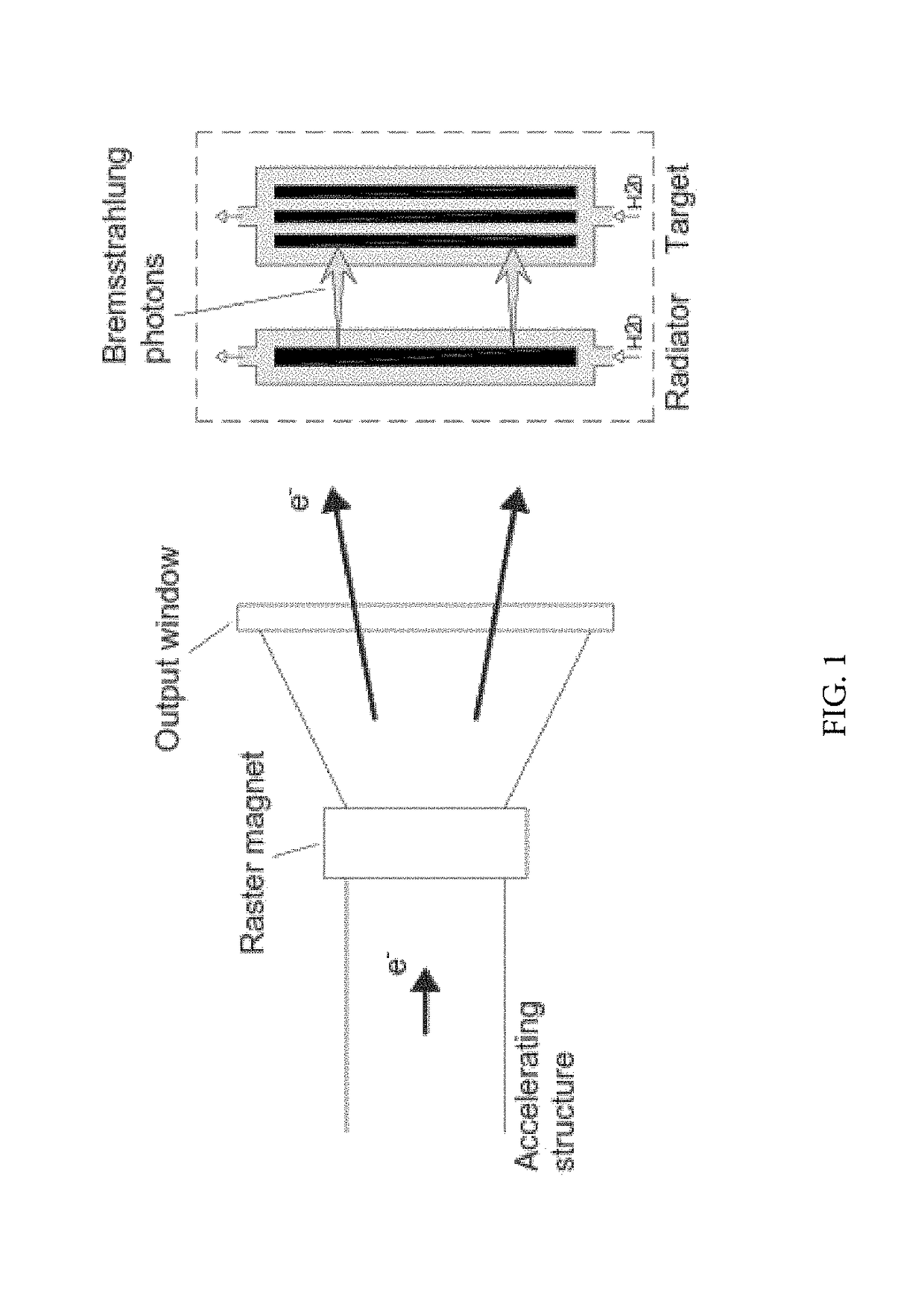
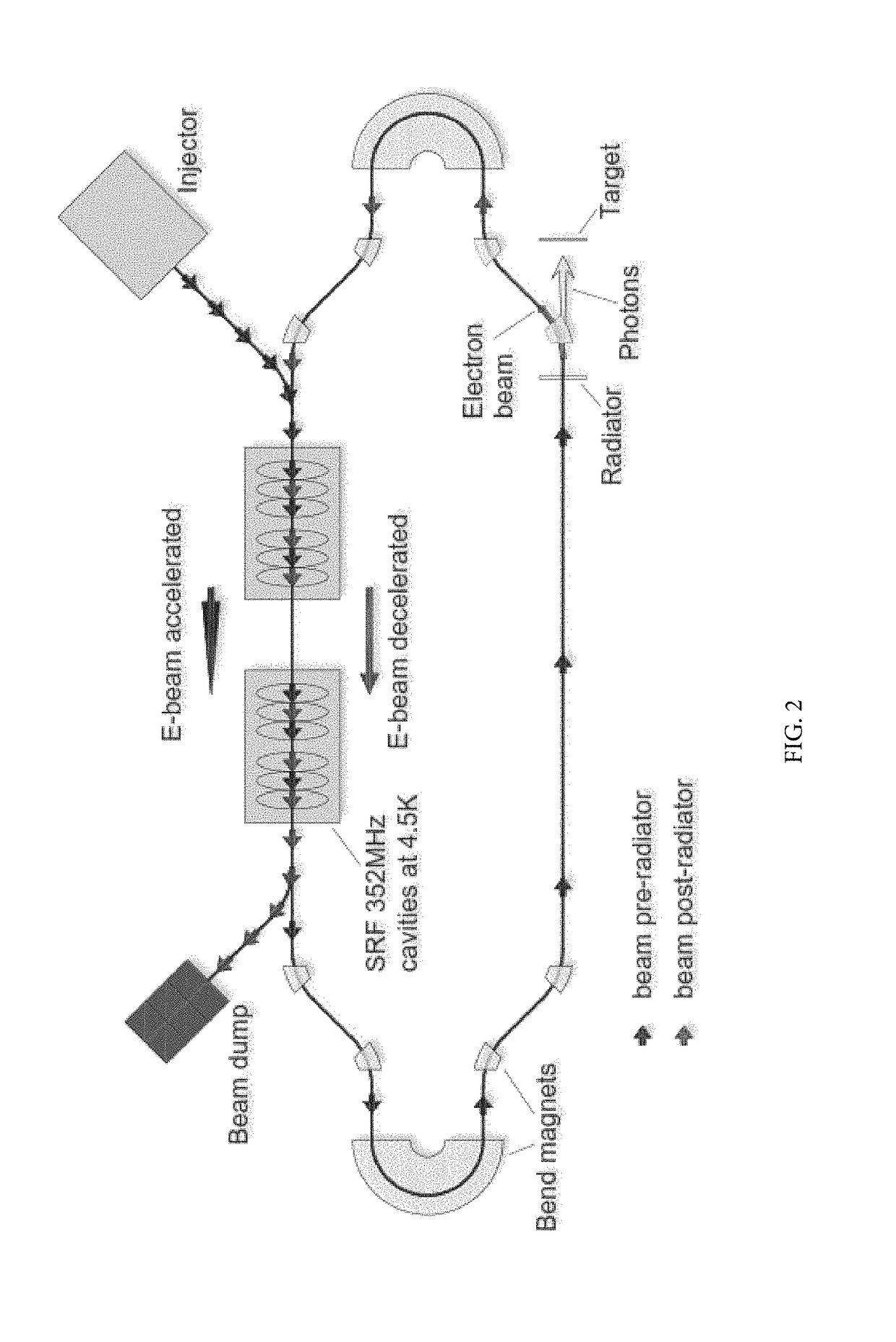
Synthesizing radioisotopes using an energy recovery linac
ActiveUS10236090B1Promote productionMinimizing overall energy requiredConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMagnetic resonance acceleratorsBeam energyBeam dump
An apparatus and method for the production of radioisotopes utilizing an energy recovery linac. The ERL system is composed of an electron beam source, multiple superconducting radio frequency cavities operating at 4.5 K, a thin radiator, a target material, and a beam dump. The accompanying method discloses the use of the ERL system to generate desired radioisotopes via target interaction with bremsstrahlung photons while allowing recovery of a substantial portion of the electron beam energy before the beam is extracted to the beam dump.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
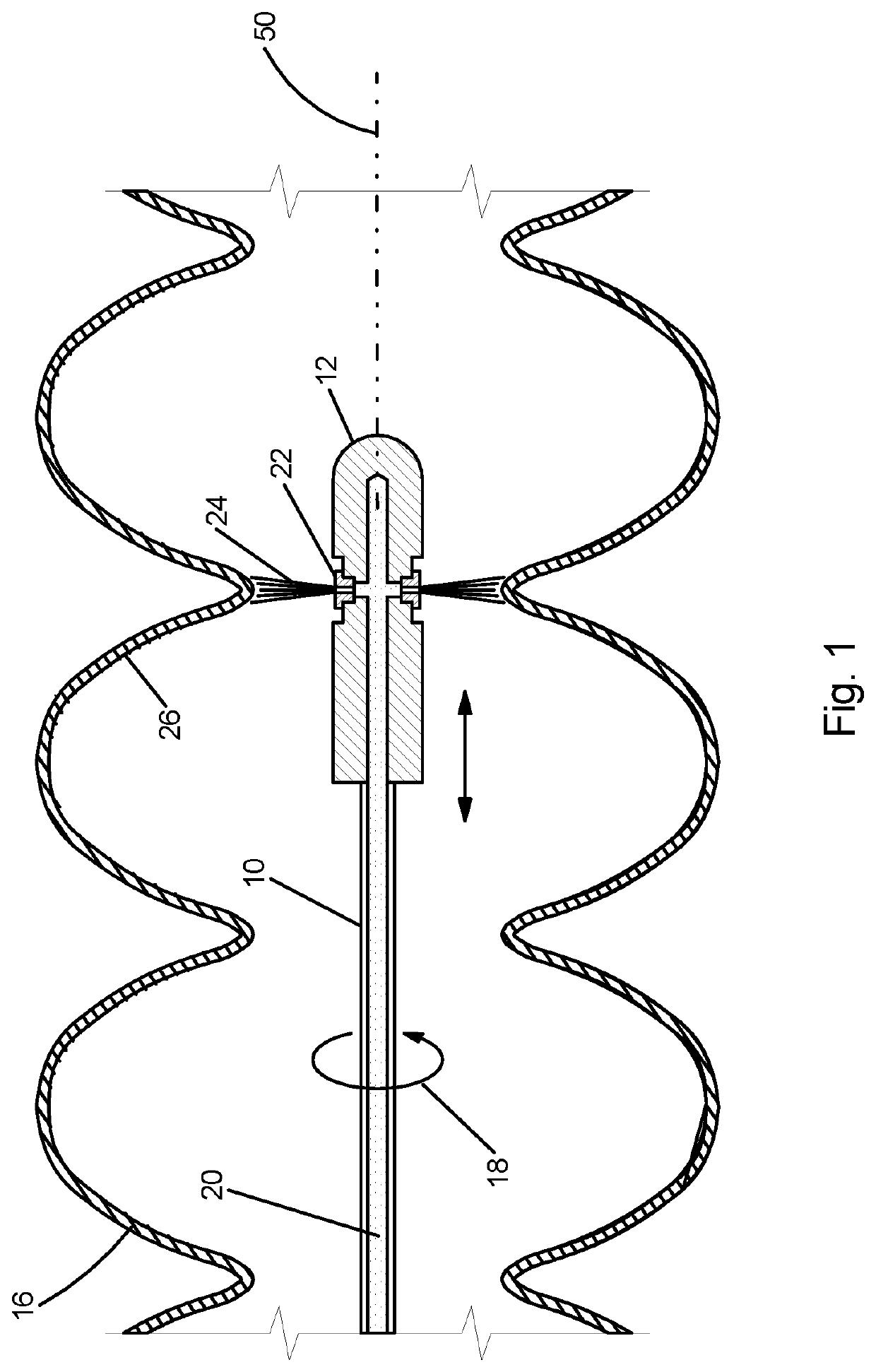
Method of tube-necking spinning and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20140102158A1Easy to shapeEfficient productionSuperconducting radio frequencyMechanical engineering
A two-step method and apparatus therefor provide cost-effective processing of tube-necking spinning for Superconducting Radio Frequency (SRF) cavities. A metal tube as a work piece may be rotated round its longitudinal axis; the target shape is obtained gradually in two steps by driving specially profiled rollers along roller paths moving in radial and axial directions. Alternatively, the rollers may rotate around a stationary work piece. To spin one cell, in the first step, a primary forming roller moves along a roller path to form a partial necking shape; then, in a second step, a secondary forming roller moves along a roller path to continue necking processing; and finally, the full cell is formed. To spin multi-cells, this two-step method is repeated for each cell. No additional equipment is required as rollers are mounted the same as in conventional spinning The cost is reduced by applying a rapid feeding rate, greatly shortening the length of the roller path, accurately controlling the spun profile and eliminating a complicated mandrel.
Owner:BAILEY TOOL & MFG
Superconductor RF Coil Array
InactiveUS20150077116A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceWhole body mriCoil array
A superconducting RF coil array which may be used in whole body MRI scanners and / or in dedicated MRI systems. Some embodiments provide a superconducting RF coil array for at least one of receiving signals from and transmitting signals to a sample during magnetic resonance analysis of the sample, the superconducting RF coil array comprising a thermally conductive member configured to be cryogenically cooled, and a plurality of coils elements comprising superconducting material, wherein each coil element is thermally coupled to the thermally conductive member and is configured for at least one of (i) receiving a magnetic resonance signal from a spatial region that is contiguous with and / or overlaps a spatial region from which at least one other of the plurality of coil elements is configured to receive a signal and (ii) transmitting a radiofrequency signal to a spatial region that is contiguous with and / or overlaps a spatial region to which at least one other of the plurality coil elements is configured to transmit a radiofrequency signal.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
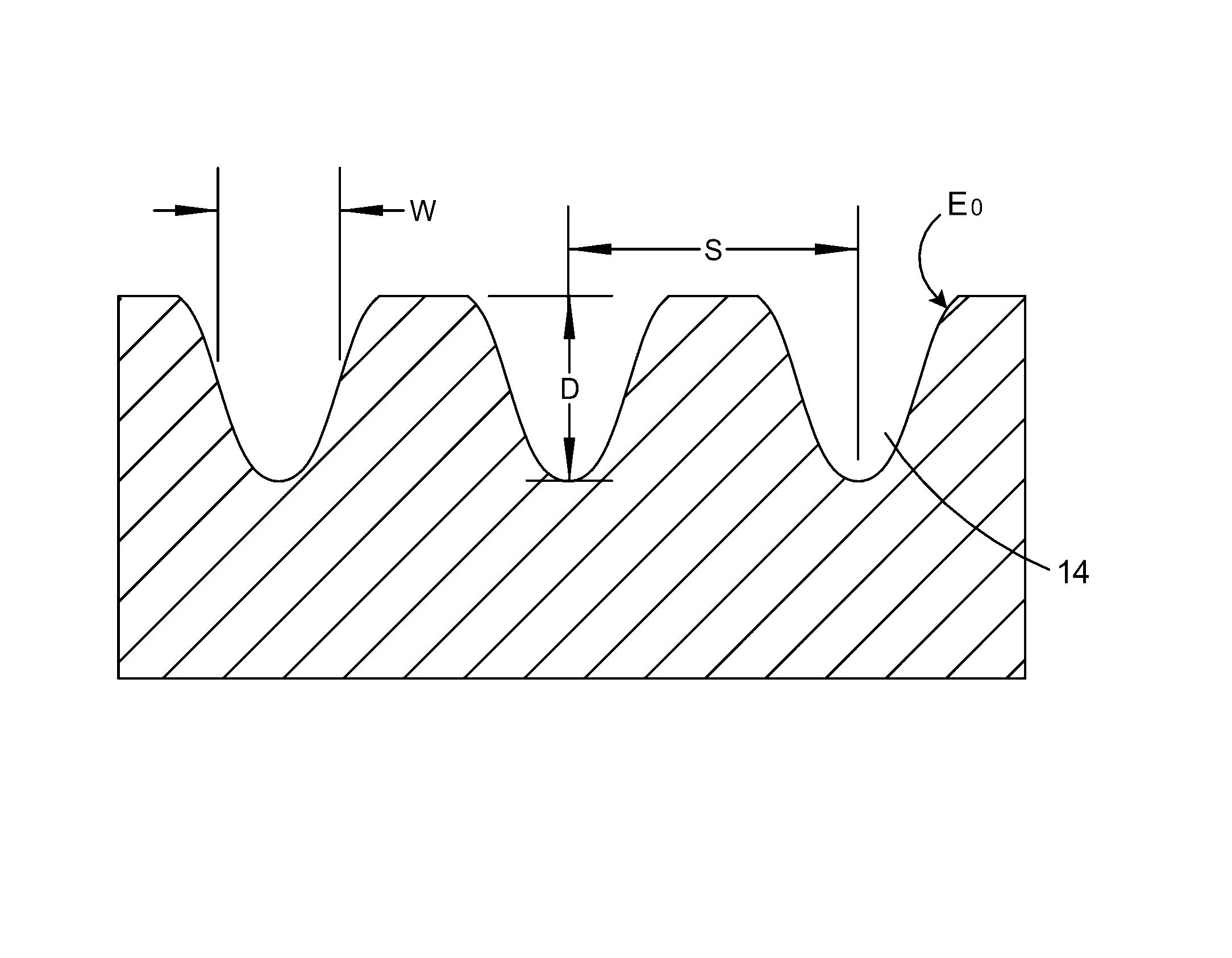
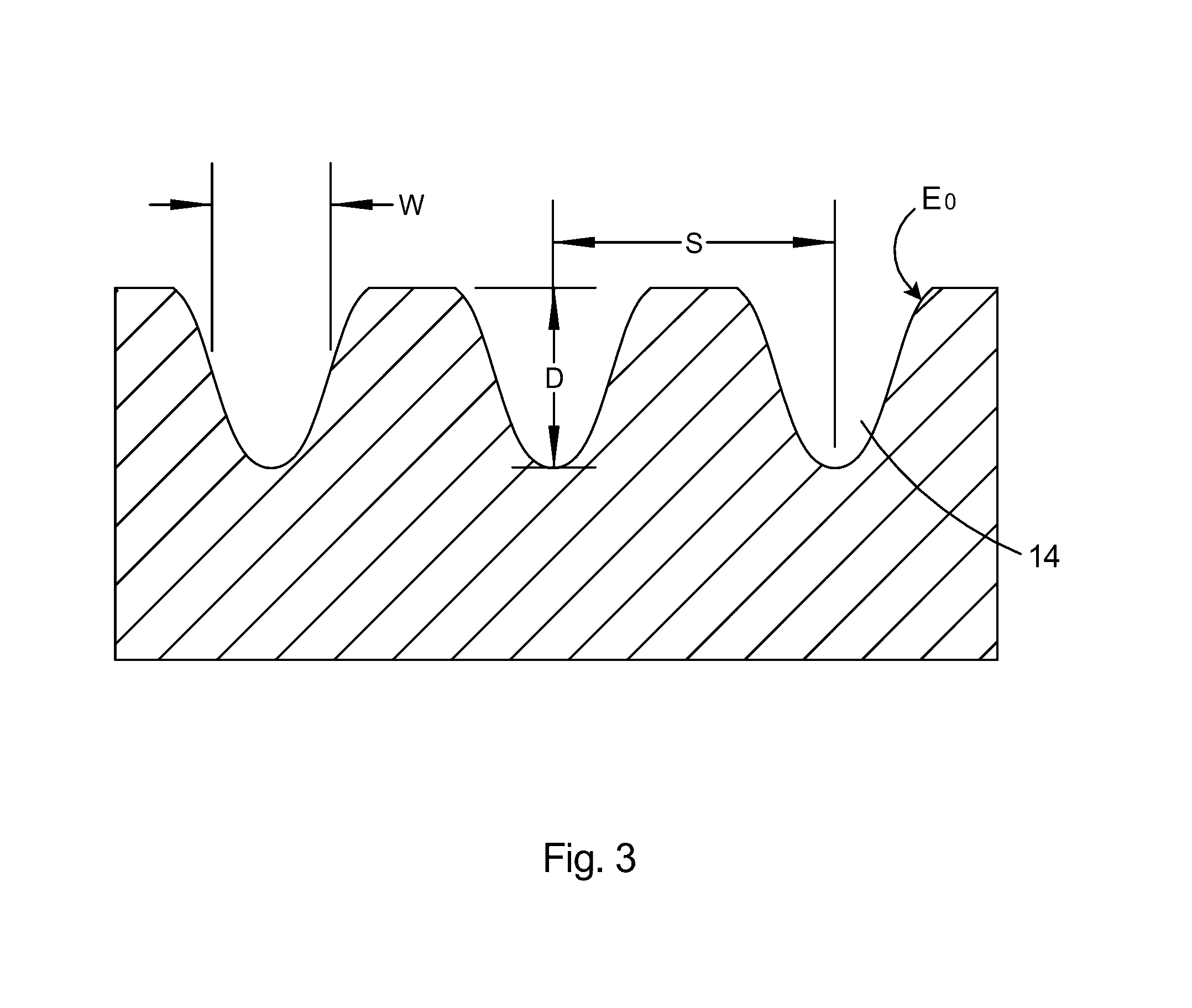
Nano-fabricated superconducting radio-frequency composites, method for producing nano-fabricated superconducting rf composites
ActiveUS8463342B2Elimination of elaborate cleaning and etching processAvoid pollutionMachines/enginesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsChemical compositionSuperconducting radio frequency
Superconducting rf is limited by a wide range of failure mechanisms inherent in the typical manufacture methods. This invention provides a method for fabricating superconducting rf structures comprising coating the structures with single atomic-layer thick films of alternating chemical composition. Also provided is a cavity defining the invented laminate structure.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
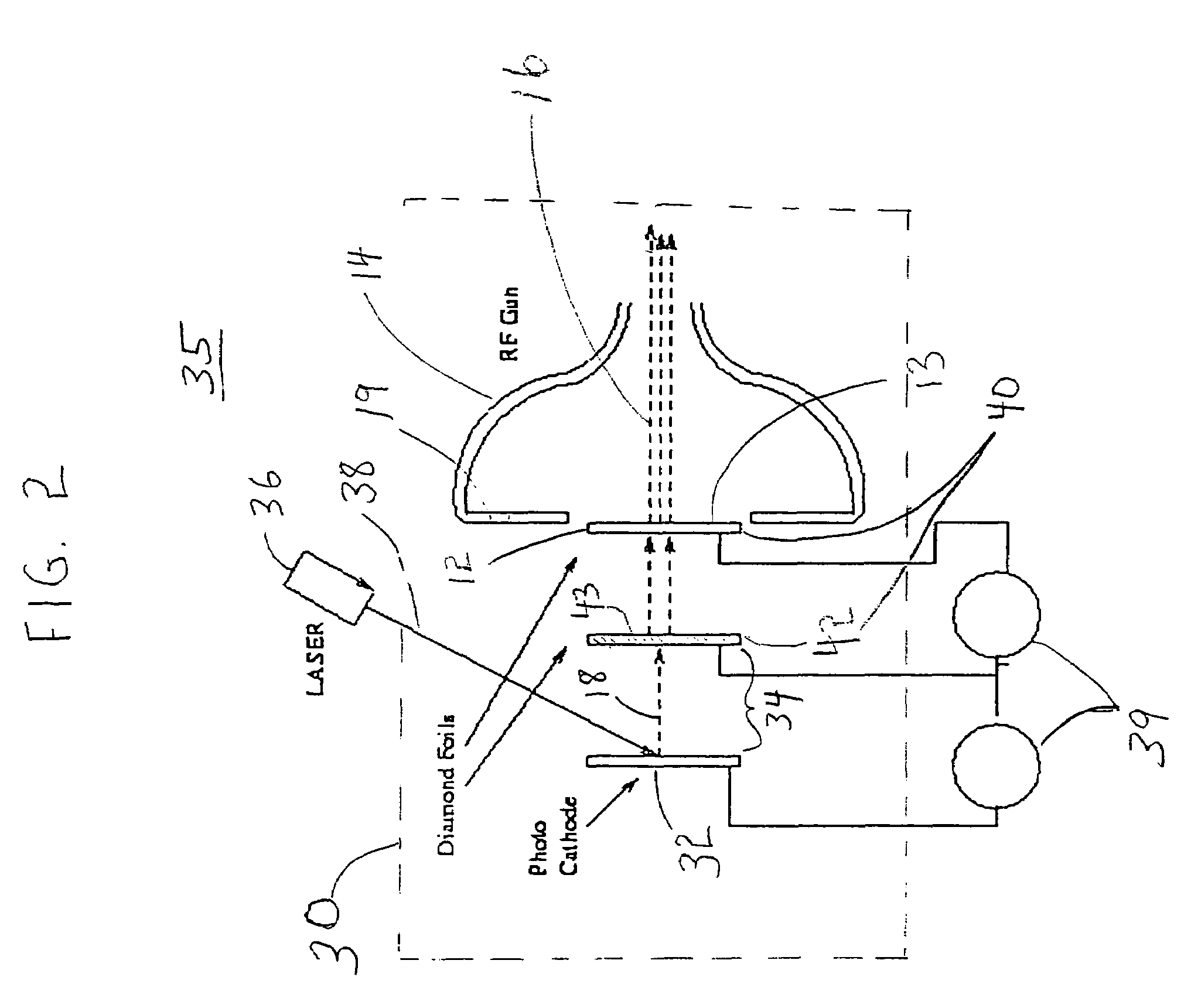
Secondary emission electron gun using external primaries
InactiveUS7227297B2Efficient and reliableImprove quantum efficiencyTransit-tube electron/ion gunsImage pickup tubesSecondary emissionPhotocathode
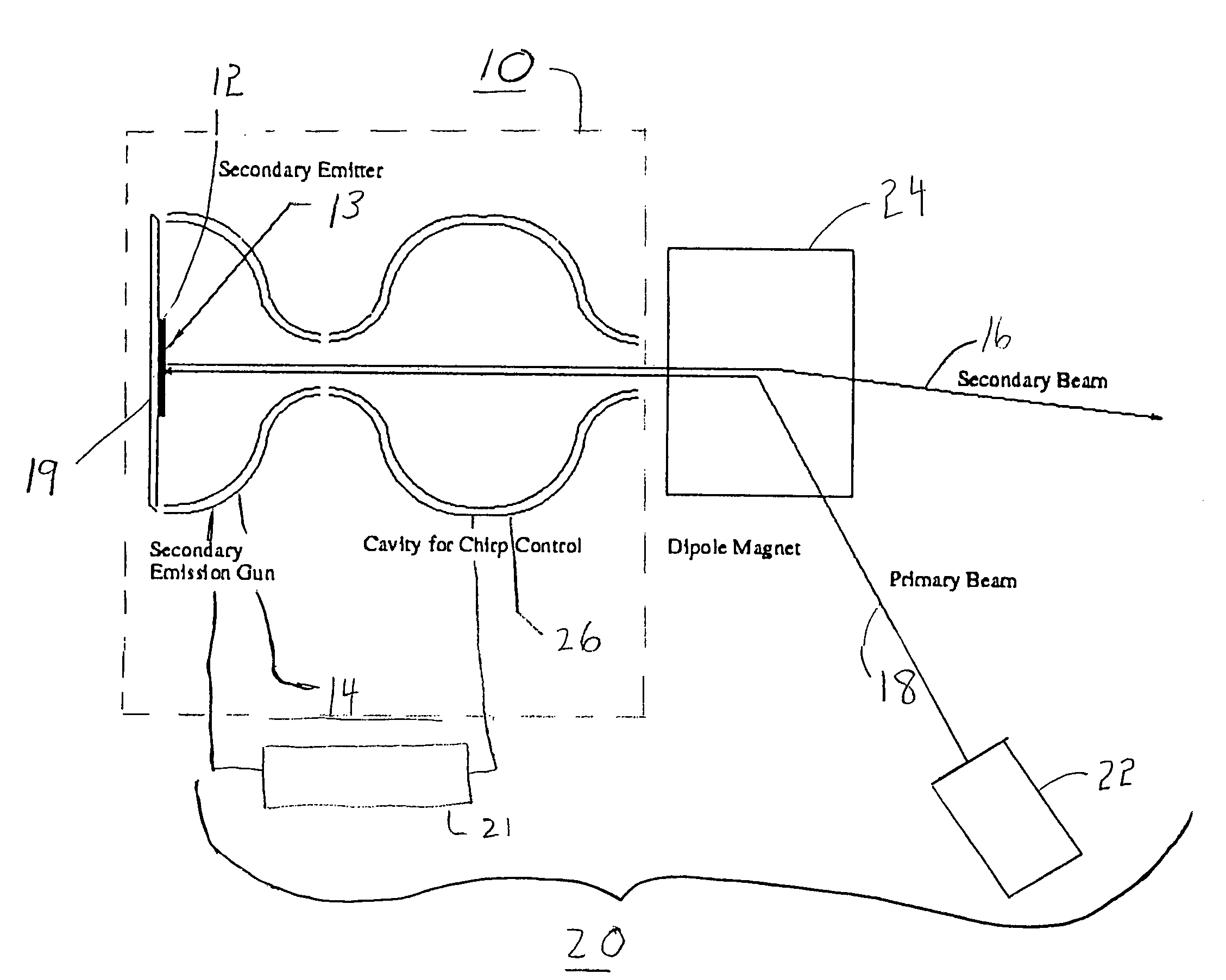
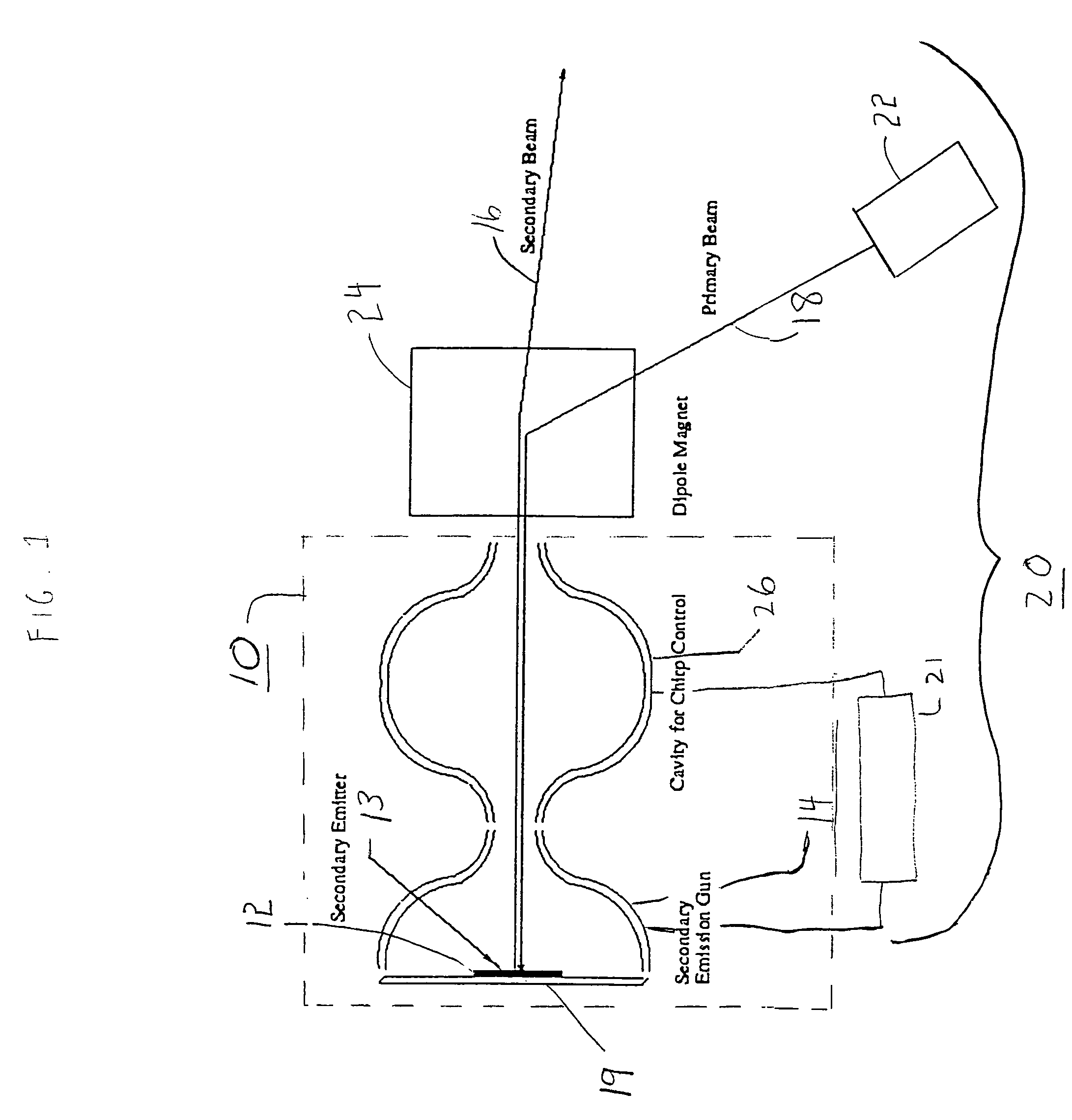
An electron gun for generating an electron beam is provided, which includes a secondary emitter. The secondary emitter includes a non-contaminating negative-electron-affinity (NEA) material and emitting surface. The gun includes an accelerating region which accelerates the secondaries from the emitting surface. The secondaries are emitted in response to a primary beam generated external to the accelerating region. The accelerating region may include a superconducting radio frequency (RF) cavity, and the gun may be operated in a continuous wave (CW) mode. The secondary emitter includes hydrogenated diamond. A uniform electrically conductive layer is superposed on the emitter to replenish the extracted current, preventing charging of the emitter. An encapsulated secondary emission enhanced cathode device, useful in a superconducting RF cavity, includes a housing for maintaining vacuum, a cathode, e.g., a photocathode, and the non-contaminating NEA secondary emitter with the uniform electrically conductive layer superposed thereon.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
An ion trap based on superconducting radio frequency accelerating electron
InactiveCN1972553AReduce volumeEasy to installElectric discharge tubesMagnetic induction acceleratorsHigh current densityHigh energy
This invention relates to one ion trap with static high charge based on superconductive radio frequency acceleration high energy electron and ion continuous collision and bonding, wherein, the laser generates photon and electron power cathode materials function in superconductive chamber to send electron speeding up by the radio field and compressed to form the electron beam with high energy and flow intensity; the electron enters float tube and attacks almost ion to peel off ion to high charge status.
Owner:朱晓峰 +1
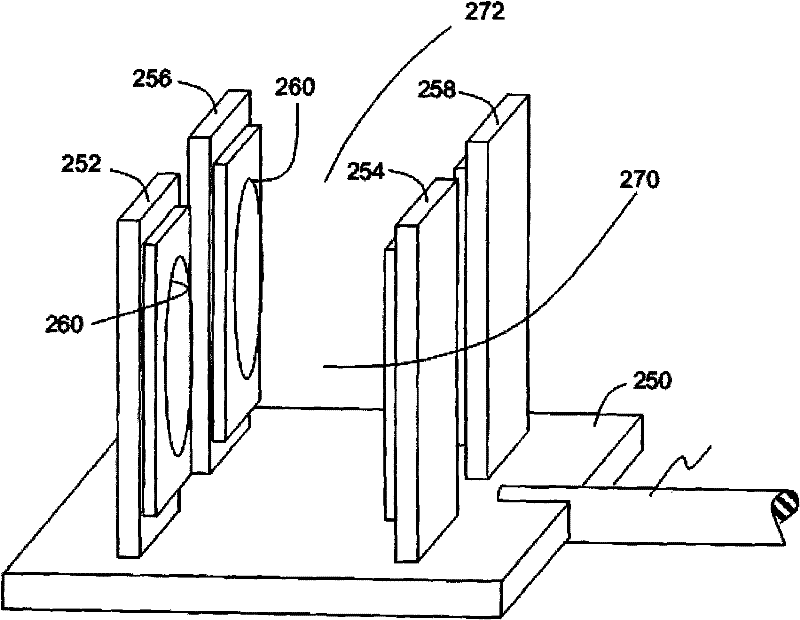
Flange joint system for srf cavities utilizing high force spring clamps for low particle generation
ActiveUS20150163895A1Minimize generation of particulateNegatively affect the performance of the particle acceleratorPipe elementsHose connectionsSuperconducting radio frequencyParticle generation
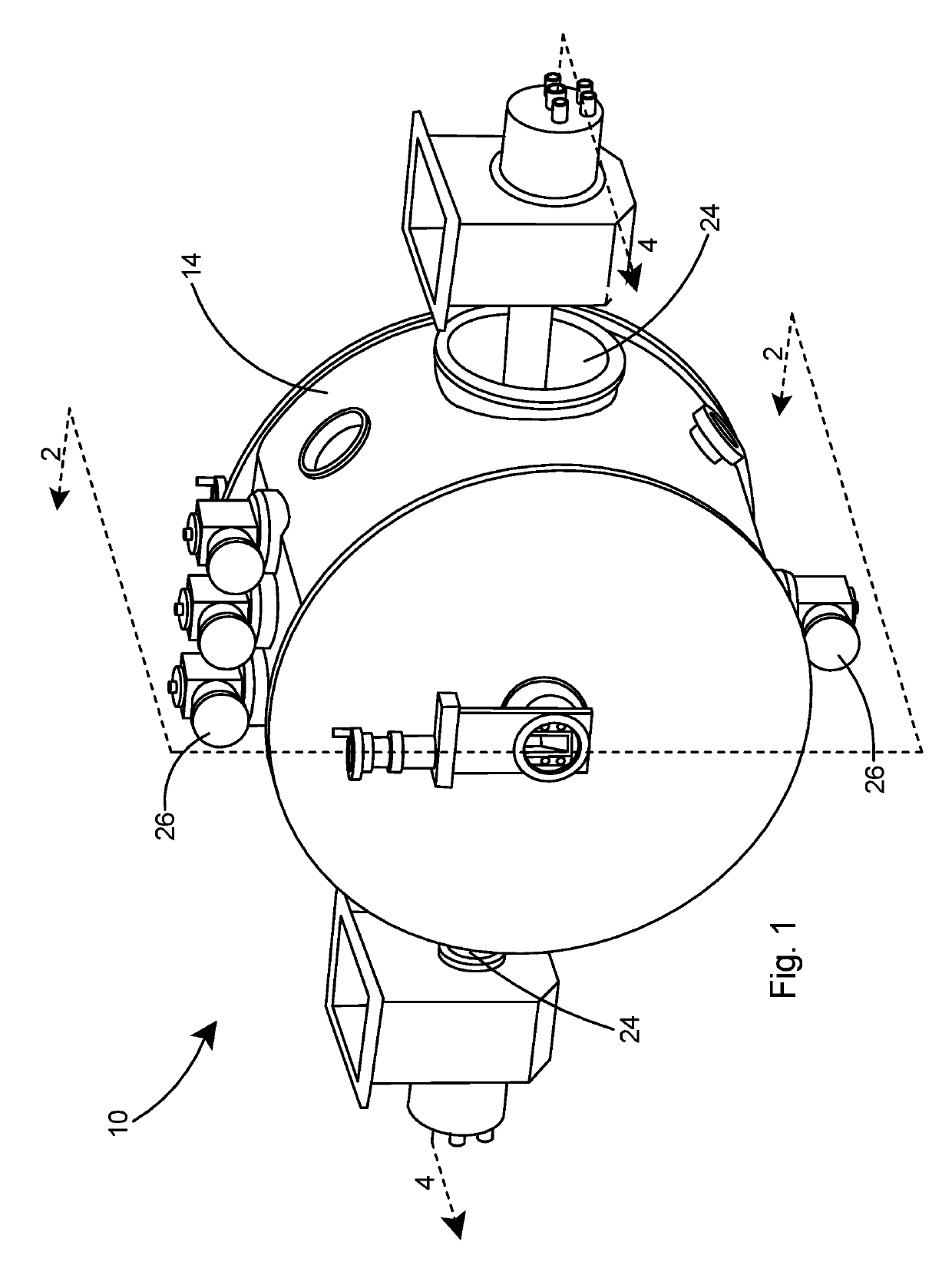
A flange joint system for SRF cavities. The flange joint system includes a set of high force spring clamps that produce high force on the simple flanges of Superconducting Radio Frequency (SRF) cavities to squeeze conventional metallic seals. The system establishes the required vacuum and RF-tight seal with minimum particle contamination to the inside of the cavity assembly. The spring clamps are designed to stay within their elastic range while being forced open enough to mount over the flange pair. Upon release, the clamps have enough force to plastically deform metallic seal surfaces and continue to a new equilibrium sprung dimension where the flanges remain held against one another with enough preload such that normal handling will not break the seal.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
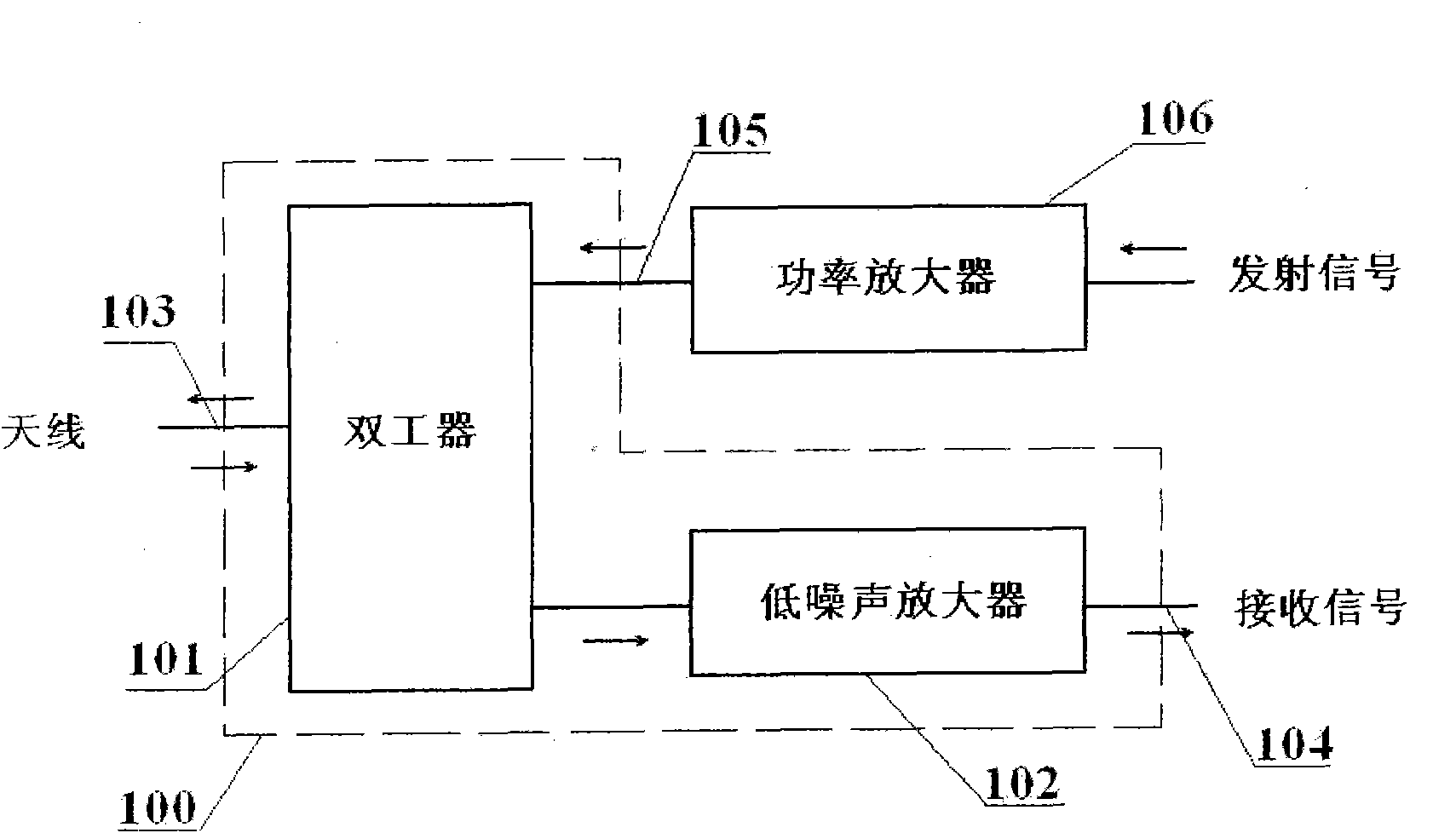
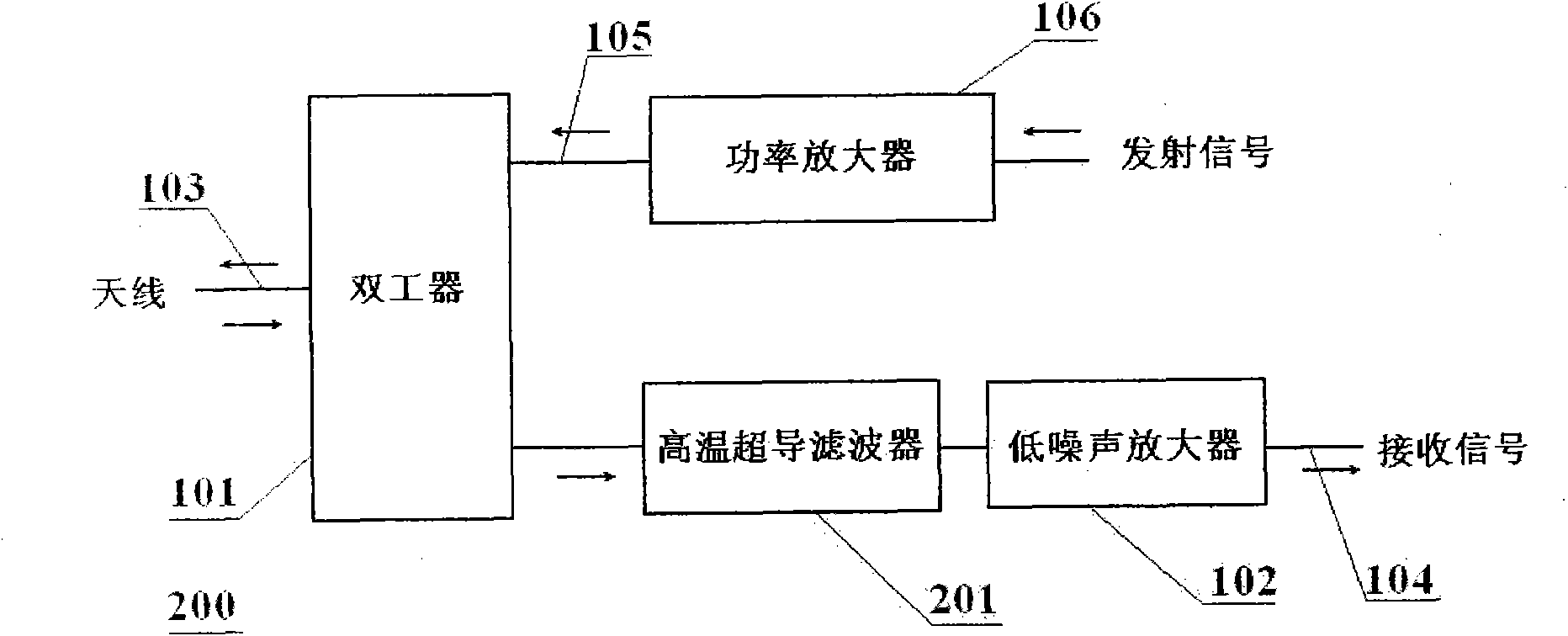
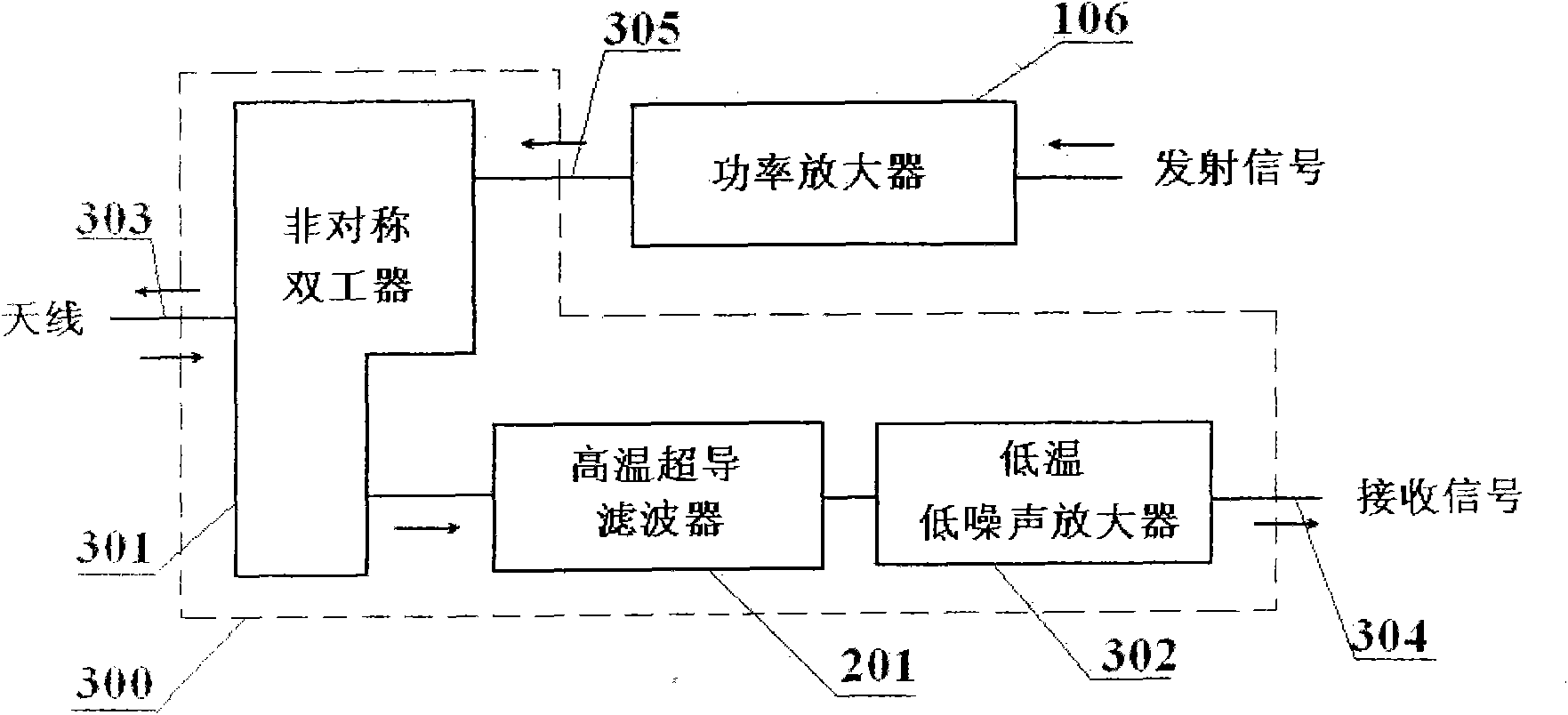
FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) high-temperature superconducting RF (Radio Frequency) front end subsystem
The invention relates to a FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) high-temperature superconducting RF (Radio Frequency) front end subsystem, which comprises a duplexer, a high-temperature superconducting filter and a low-temperature low-noise amplifier and is characterized in that the duplexer is an unsymmetrical duplexer. The invention has the advantages that the original emitting channel filter characteristics of a conventional RF front end are kept, a receiving channel integrates the advantages of high frequency selectivity of the superconducting filter and low noise of the low-temperature low-noise amplifier, and the FDD high-temperature superconducting RF front end subsystem has the advantages of compact structure, excellent technological indexes, rapidness in parallel networking, and the like.
Owner:天津海泰超导电子有限公司
Nano-patterned superconducting surface for high quantum efficiency cathode
ActiveUS20170084416A1Effective efficiencyPromote absorptionLapping machinesPhotoelectric discharge tubesNano structuringPhotocathode
A method for providing a superconducting surface on a laser-driven niobium cathode in order to increase the effective quantum efficiency. The enhanced surface increases the effective quantum efficiency by improving the laser absorption of the surface and enhancing the local electric field. The surface preparation method makes feasible the construction of superconducting radio frequency injectors with niobium as the photocathode. An array of nano-structures are provided on a flat surface of niobium. The nano-structures are dimensionally tailored to interact with a laser of specific wavelength to thereby increase the electron yield of the surface.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Flange joint system for SRF cavities utilizing high force spring clamps for low particle generation
ActiveUS9756715B2Minimize generation of particulateNegatively affect the performance of the particle acceleratorAcceleratorsEngineeringSuperconducting radio frequency
A flange joint system for SRF cavities. The flange joint system includes a set of high force spring clamps that produce high force on the simple flanges of Superconducting Radio Frequency (SRF) cavities to squeeze conventional metallic seals. The system establishes the required vacuum and RF-tight seal with minimum particle contamination to the inside of the cavity assembly. The spring clamps are designed to stay within their elastic range while being forced open enough to mount over the flange pair. Upon release, the clamps have enough force to plastically deform metallic seal surfaces and continue to a new equilibrium sprung dimension where the flanges remain held against one another with enough preload such that normal handling will not break the seal.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
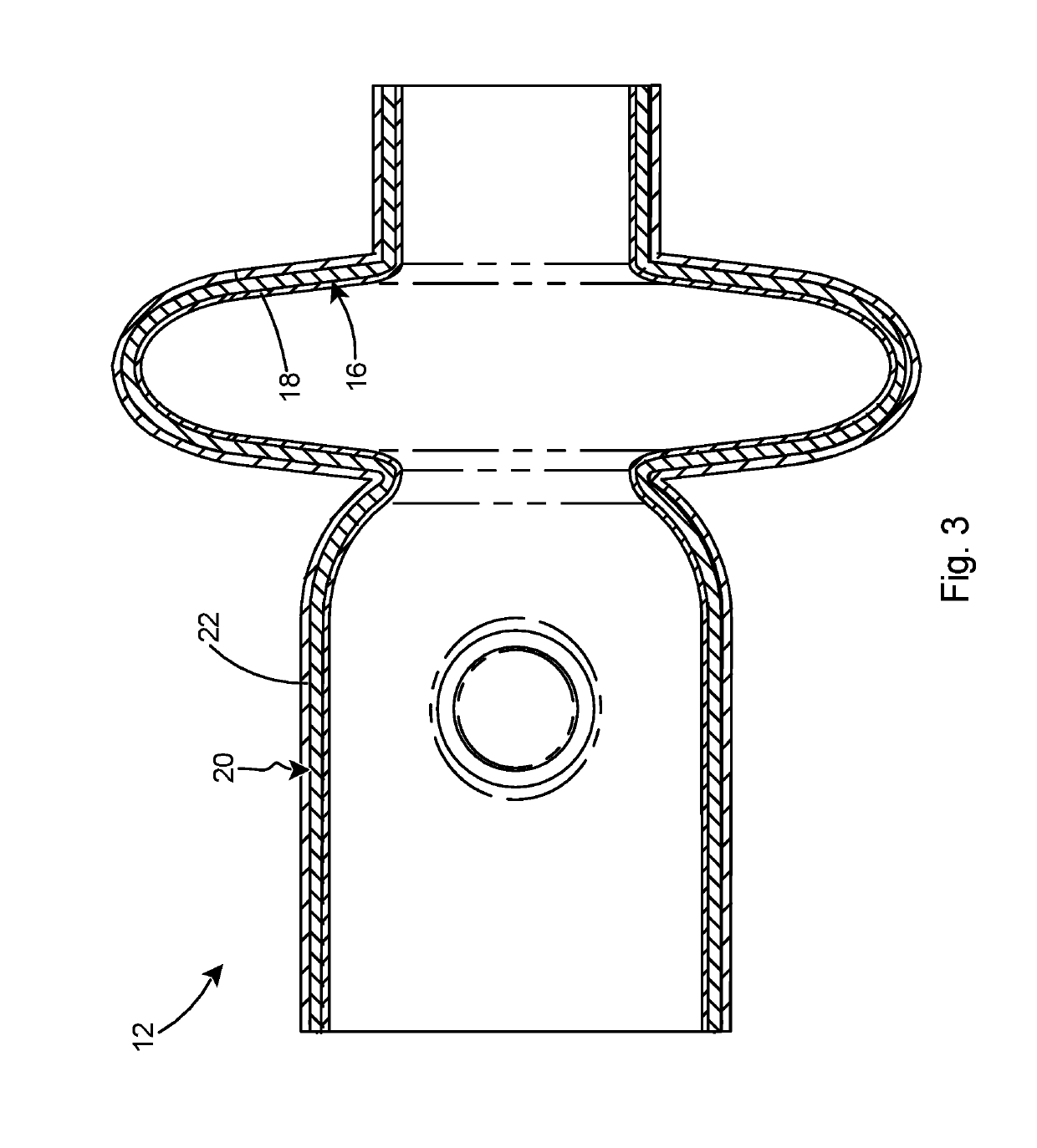
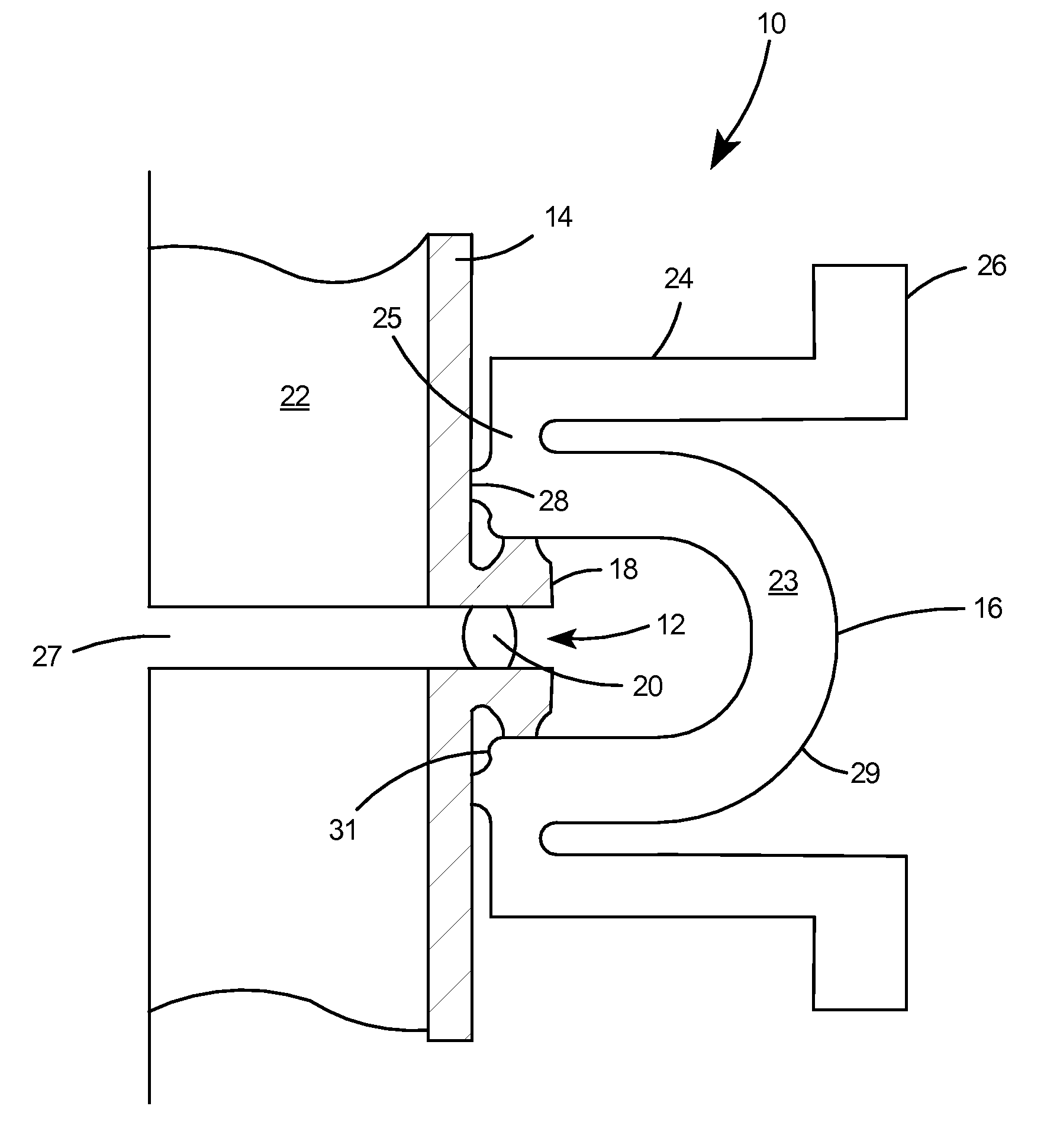
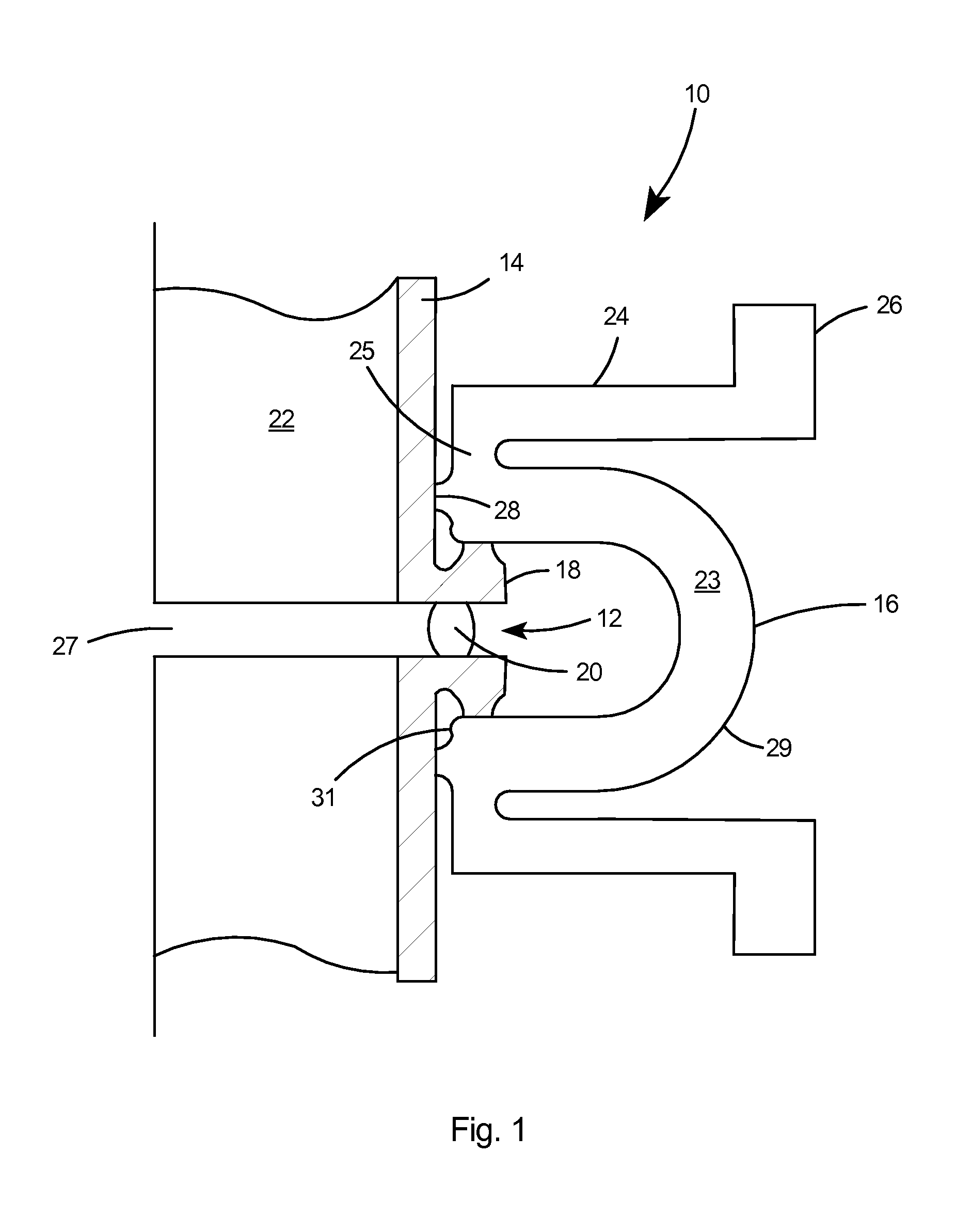
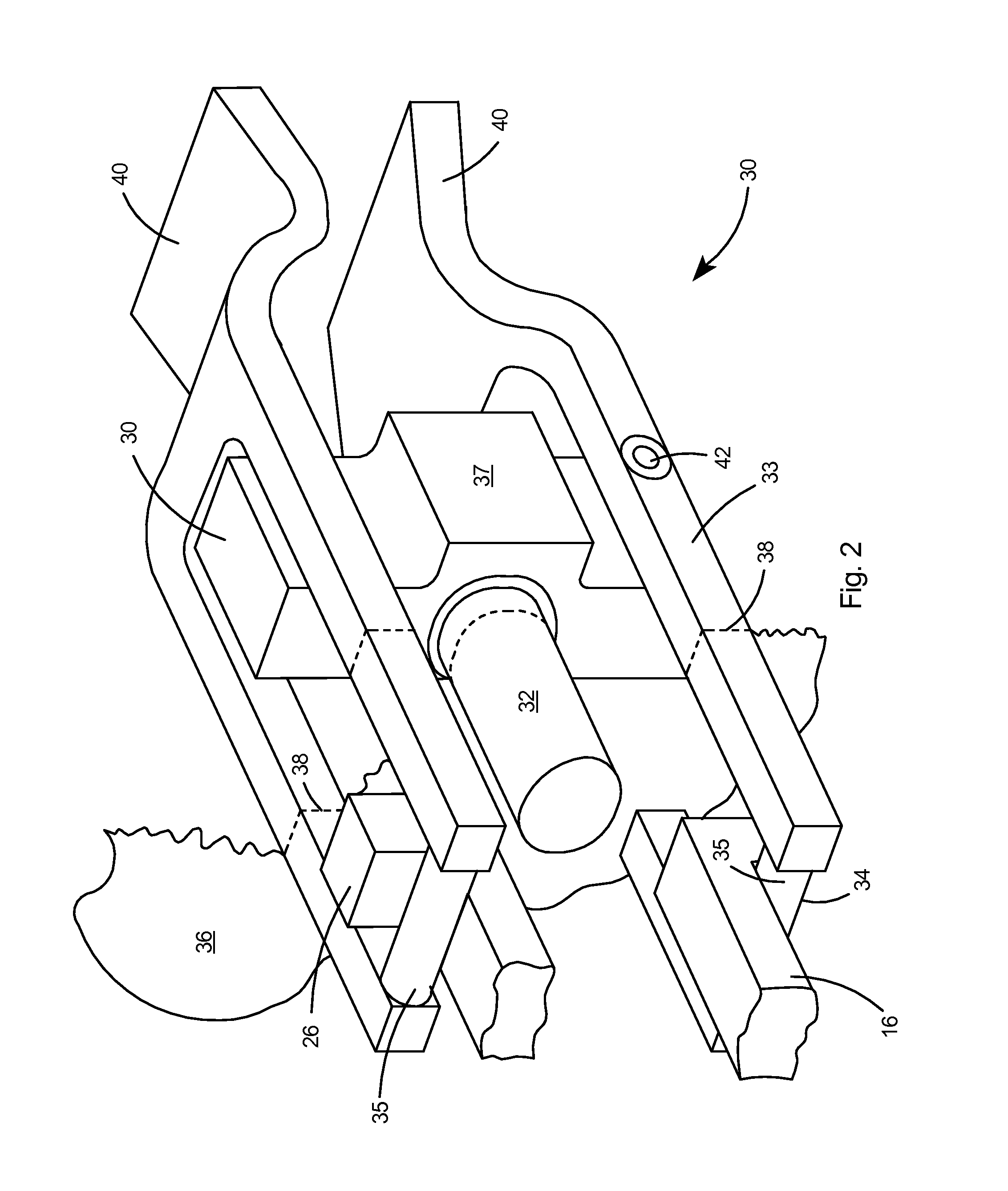
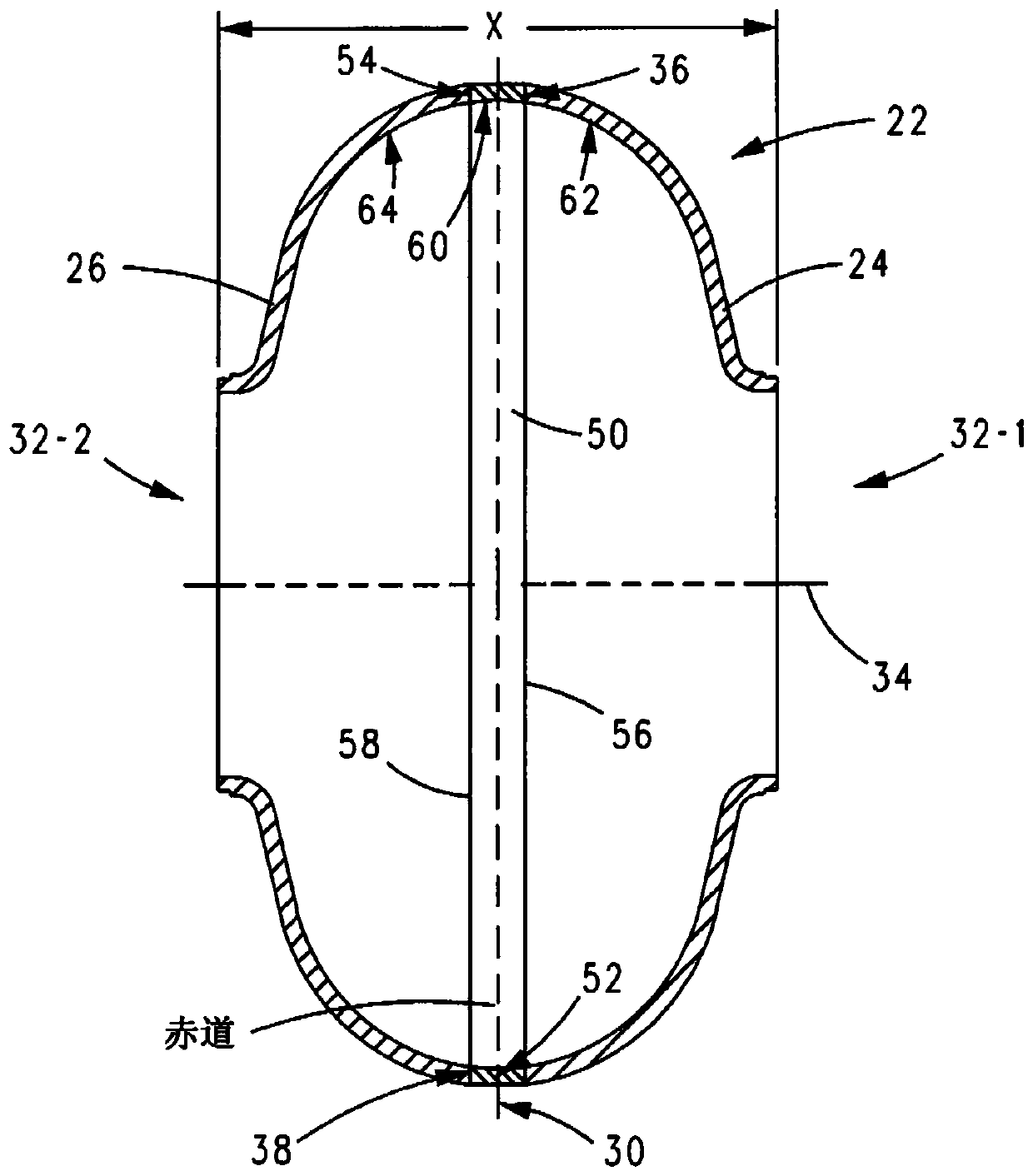
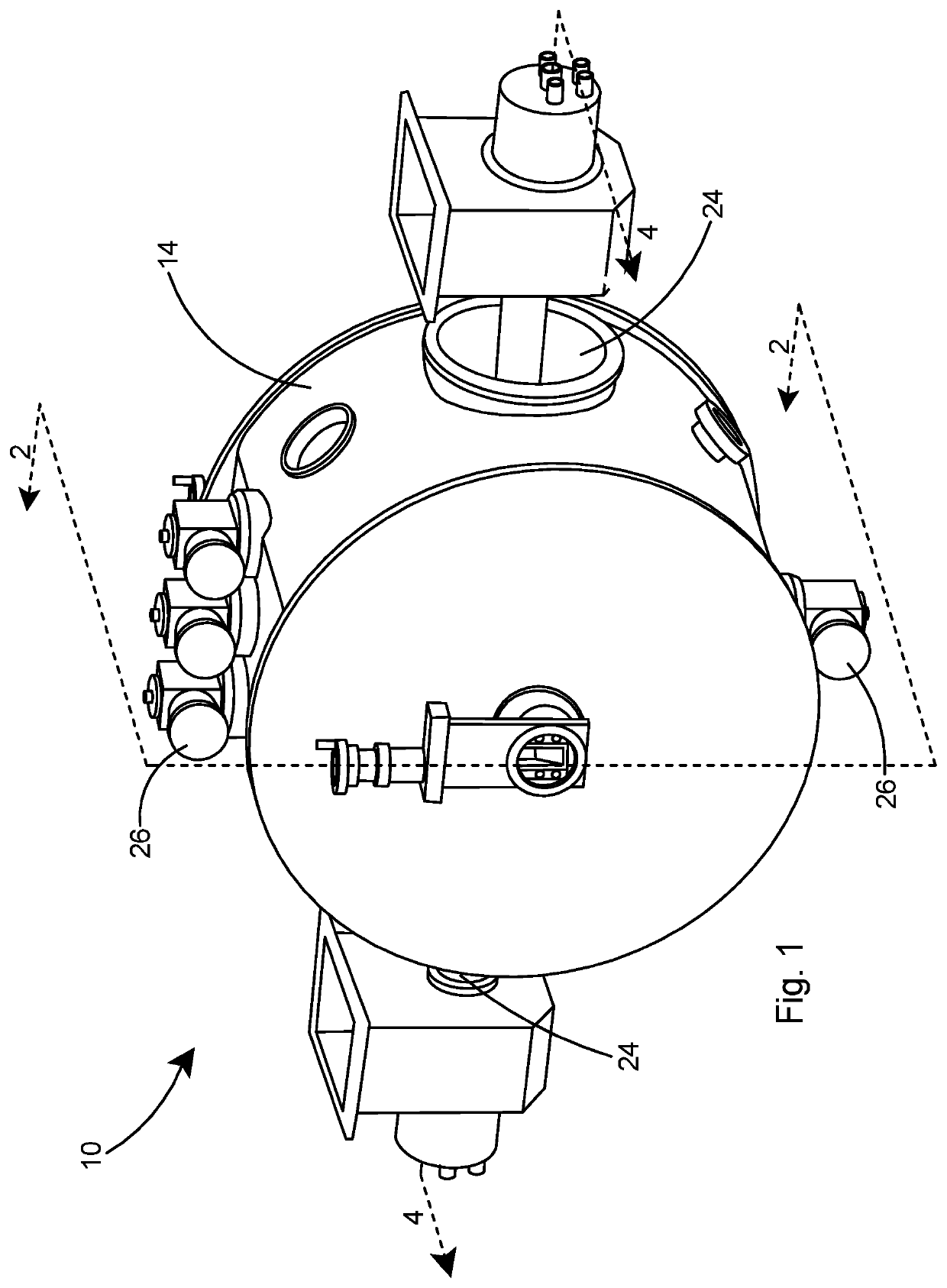
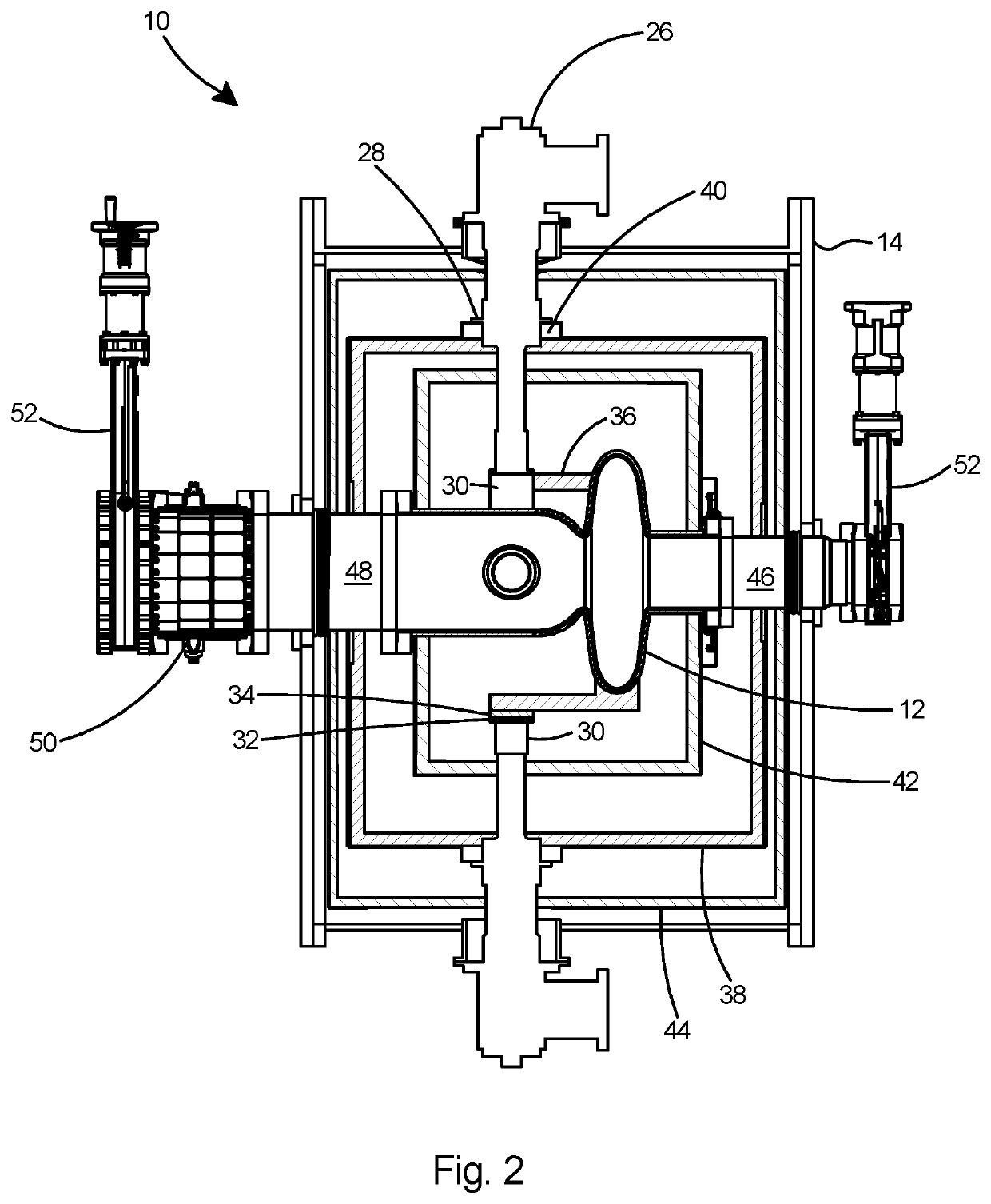
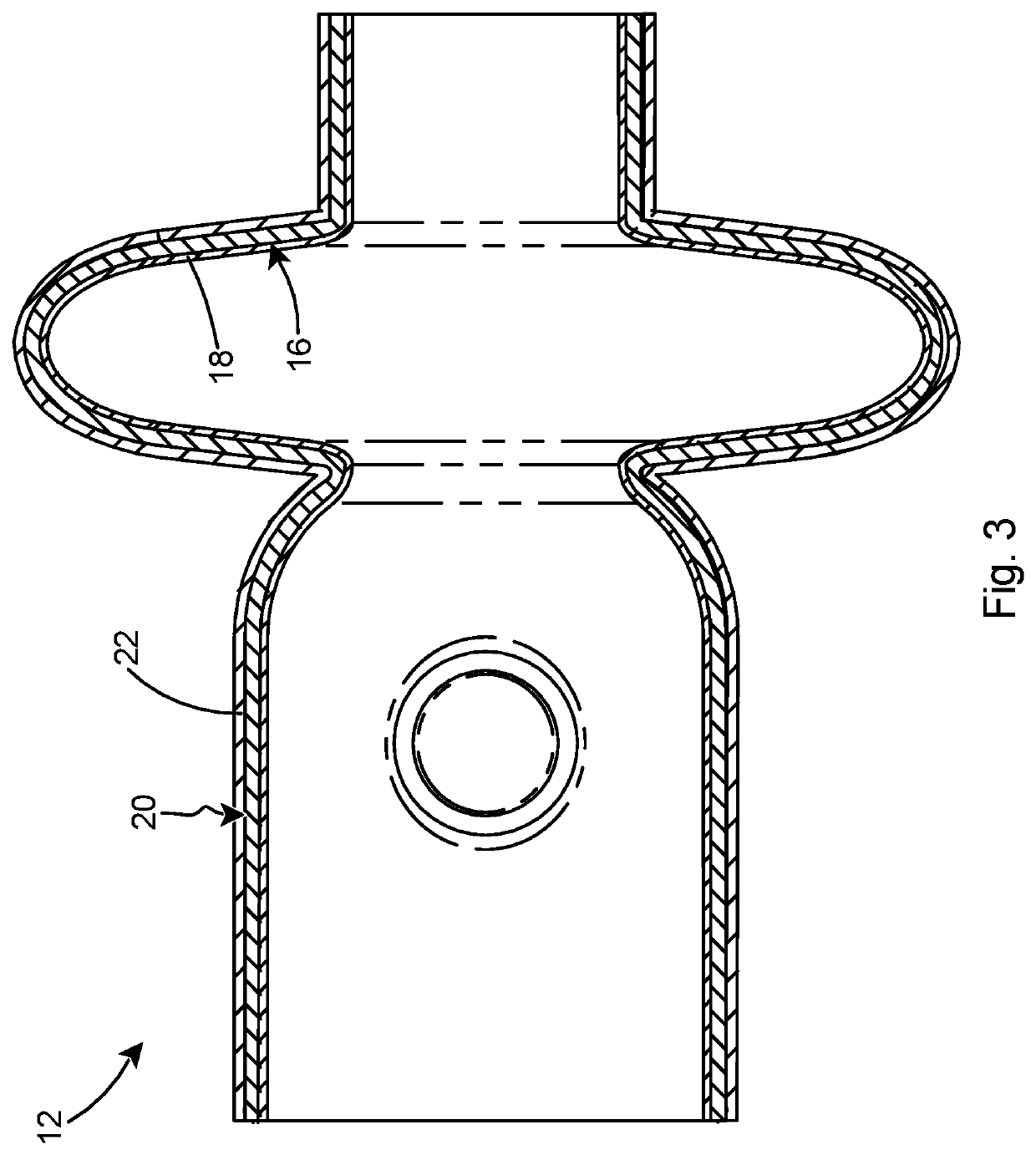
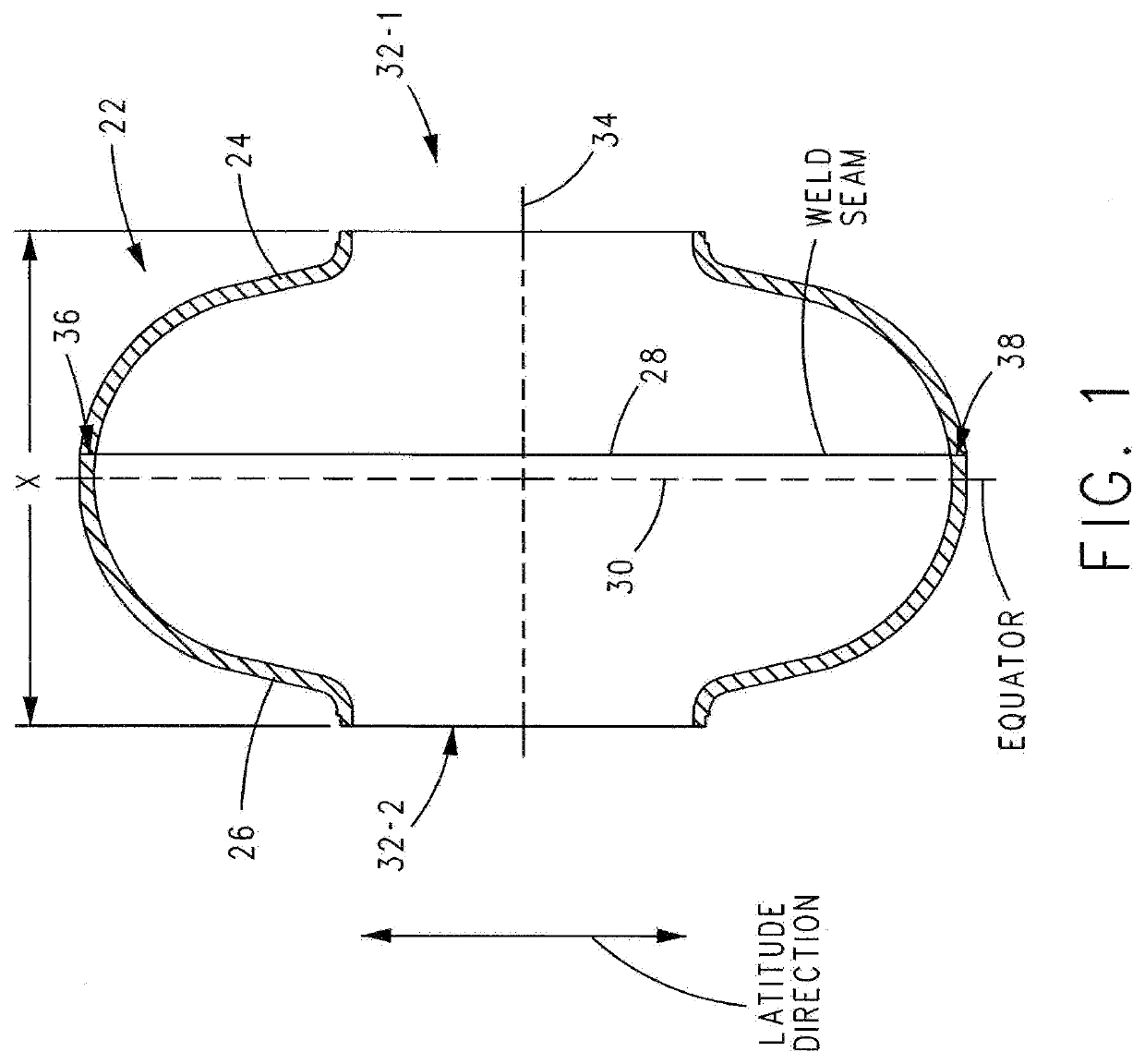
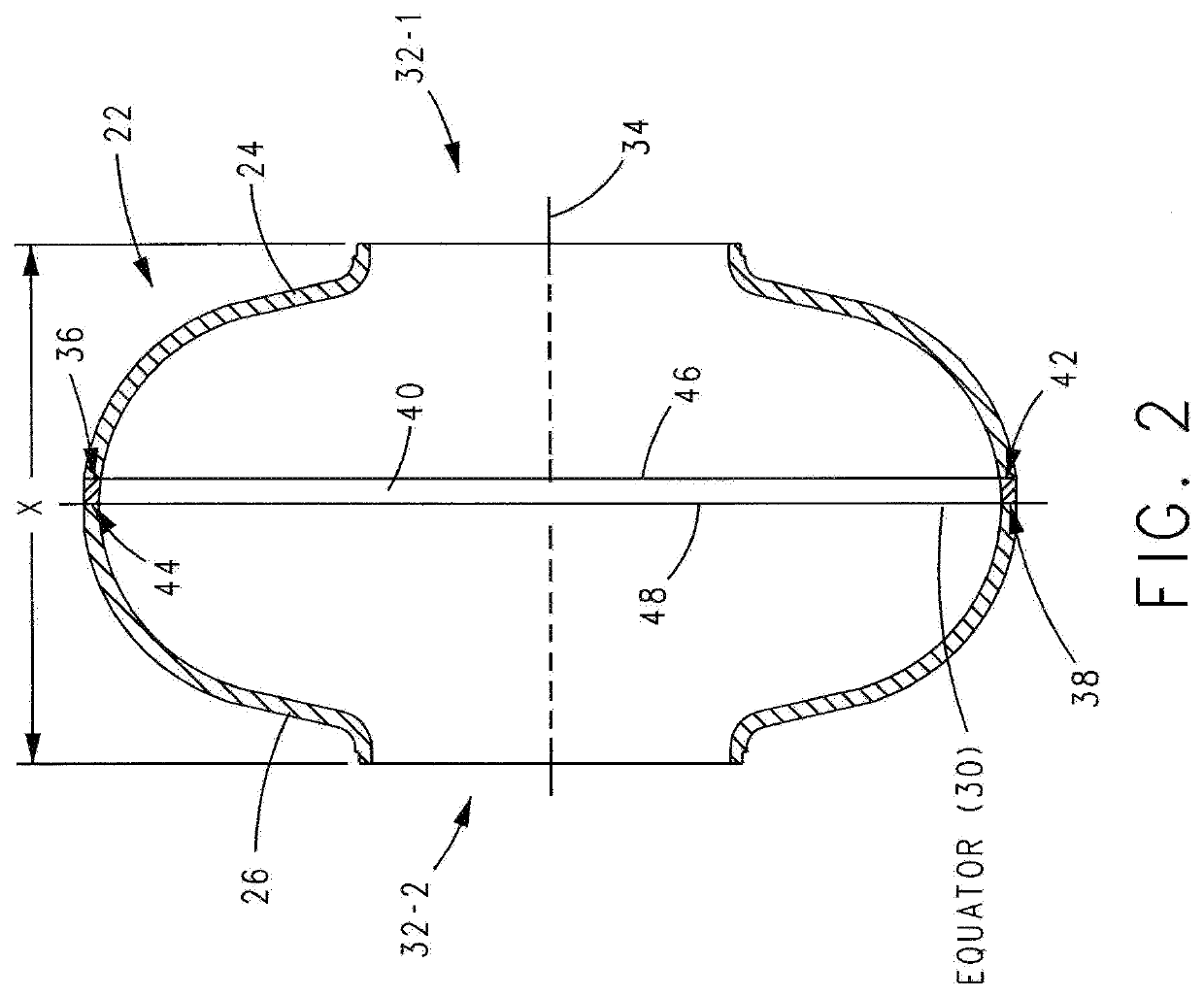
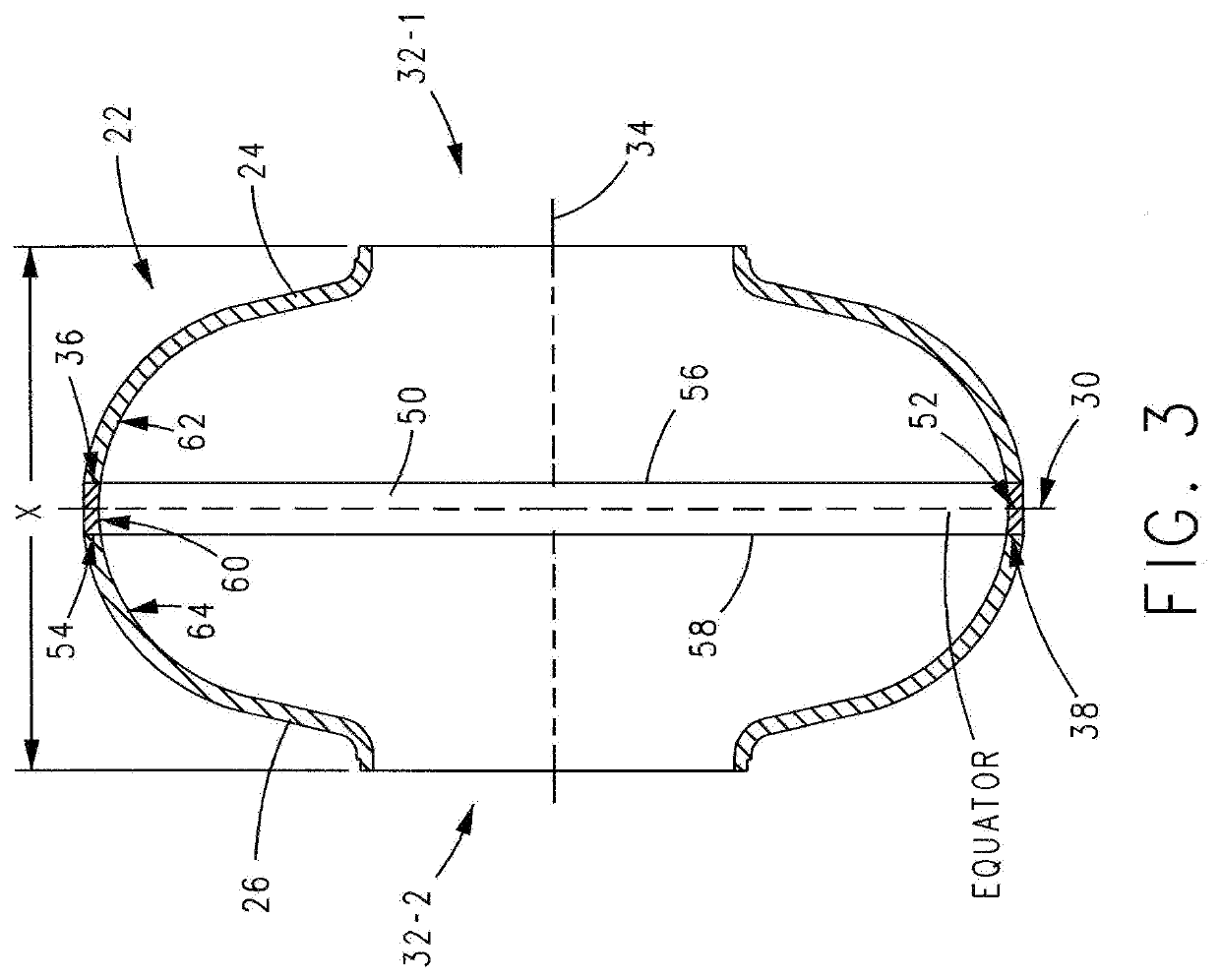
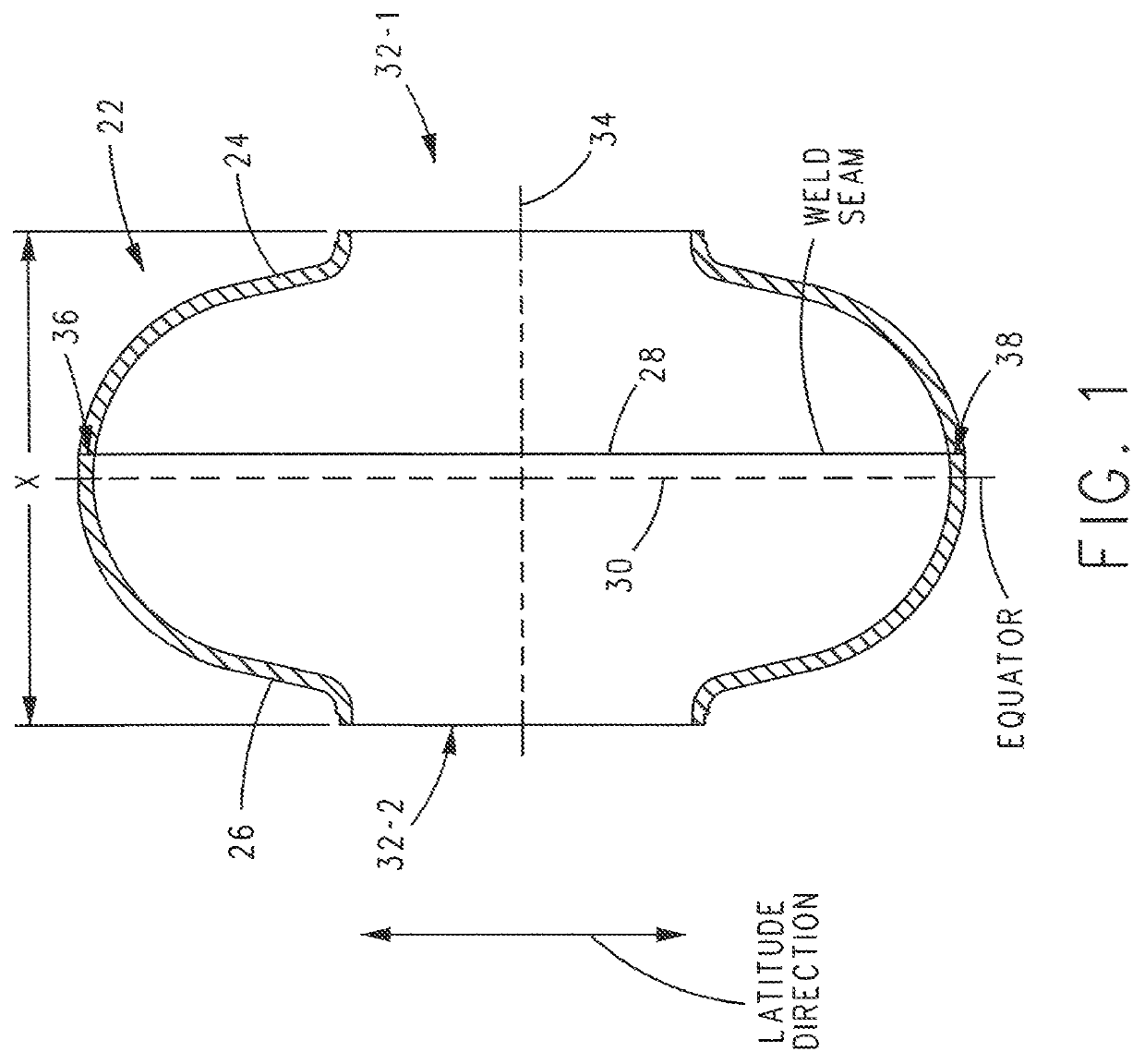
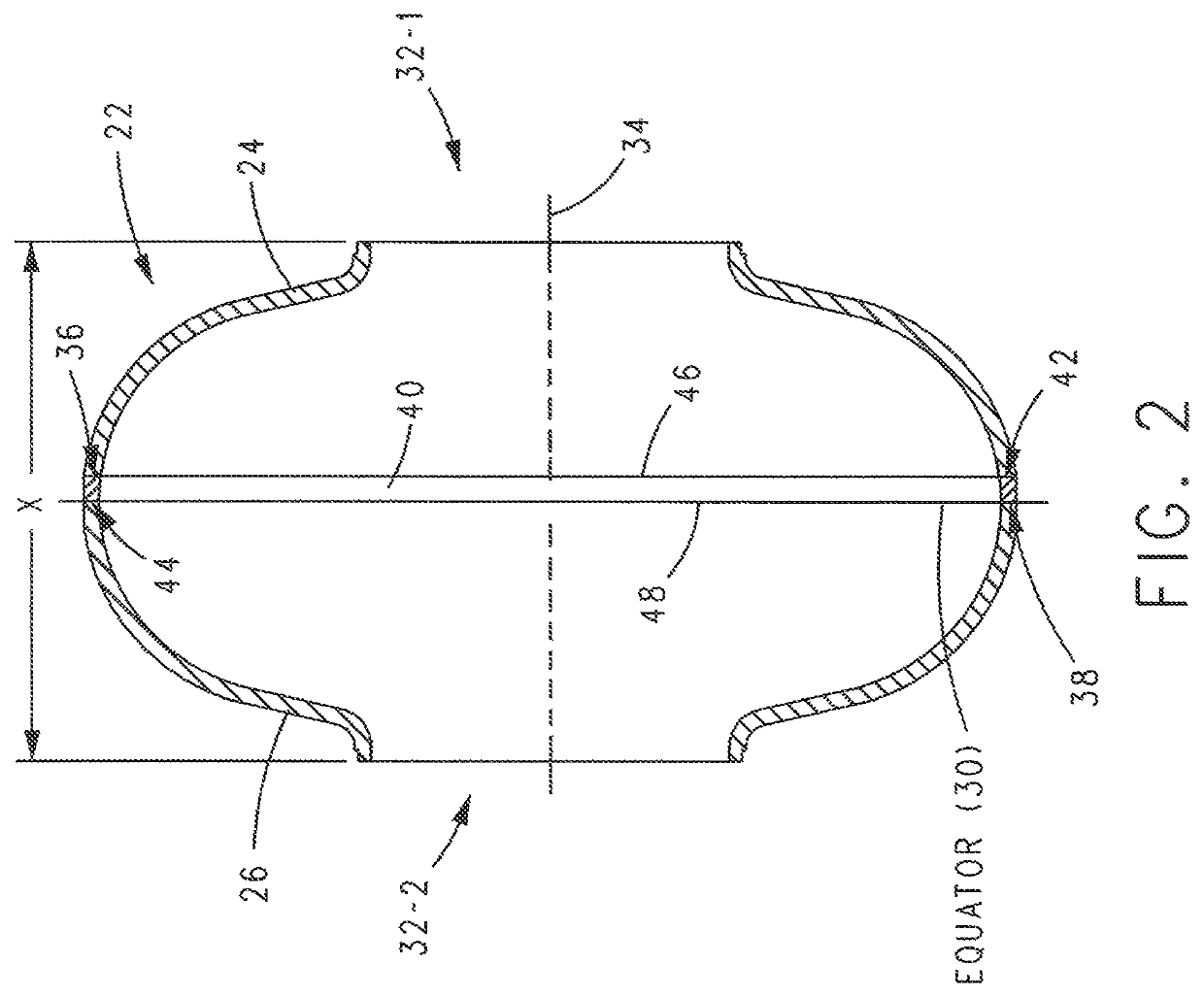
Superconducting resonating cavity and method of production thereof
PendingCN110505748AEasy to weldWays to Improve WeldsResonatorsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesResonant cavityWeld seam
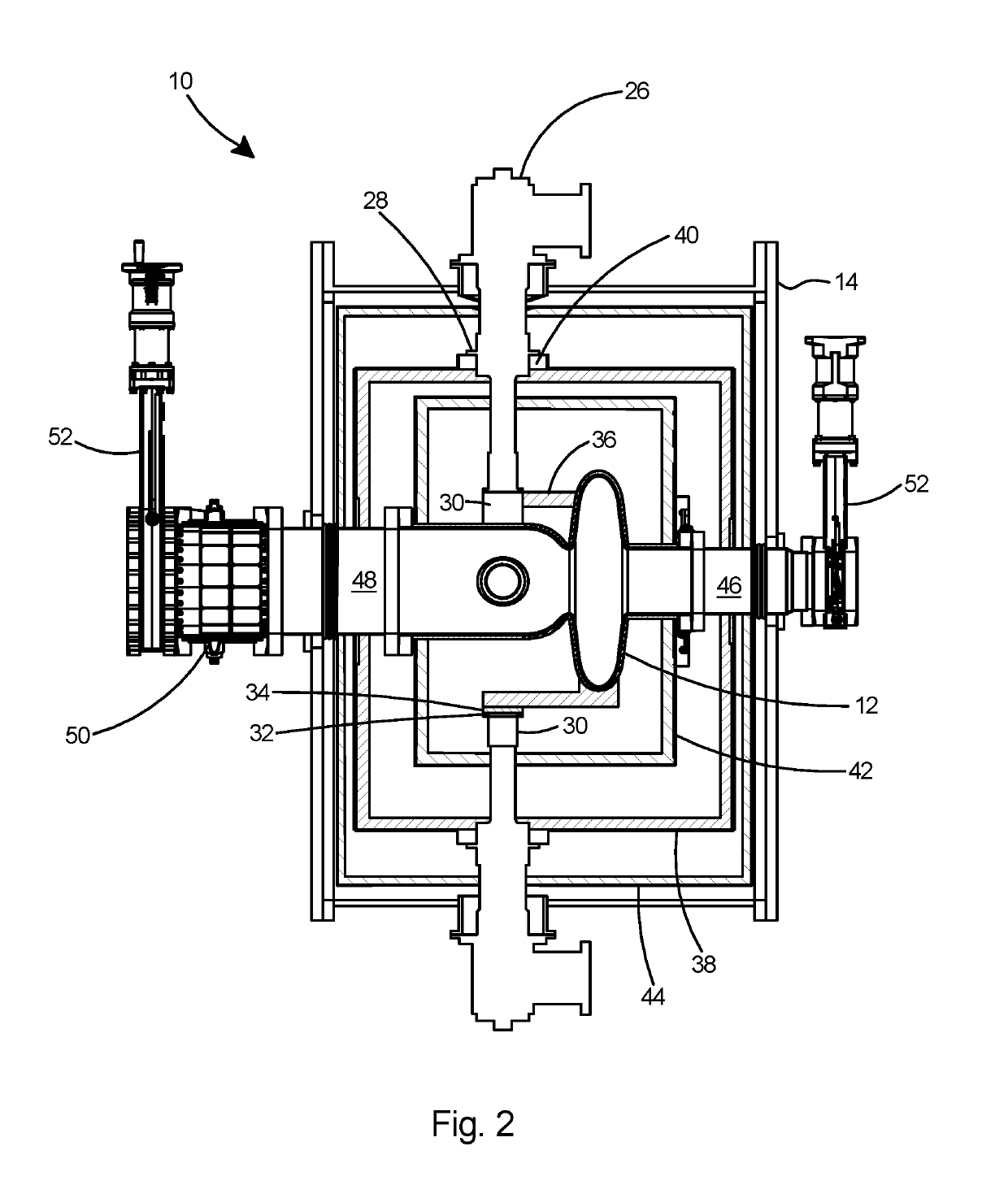
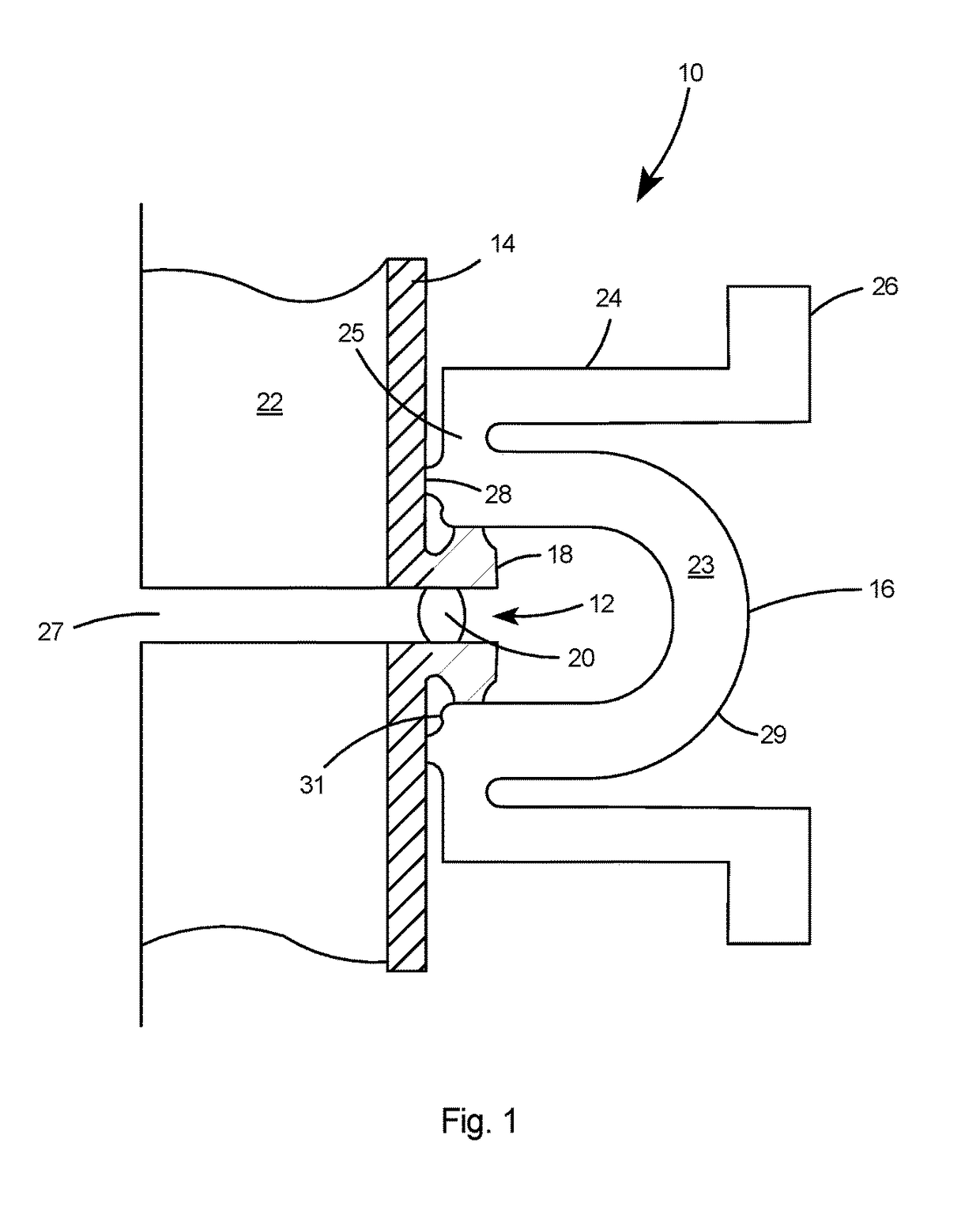
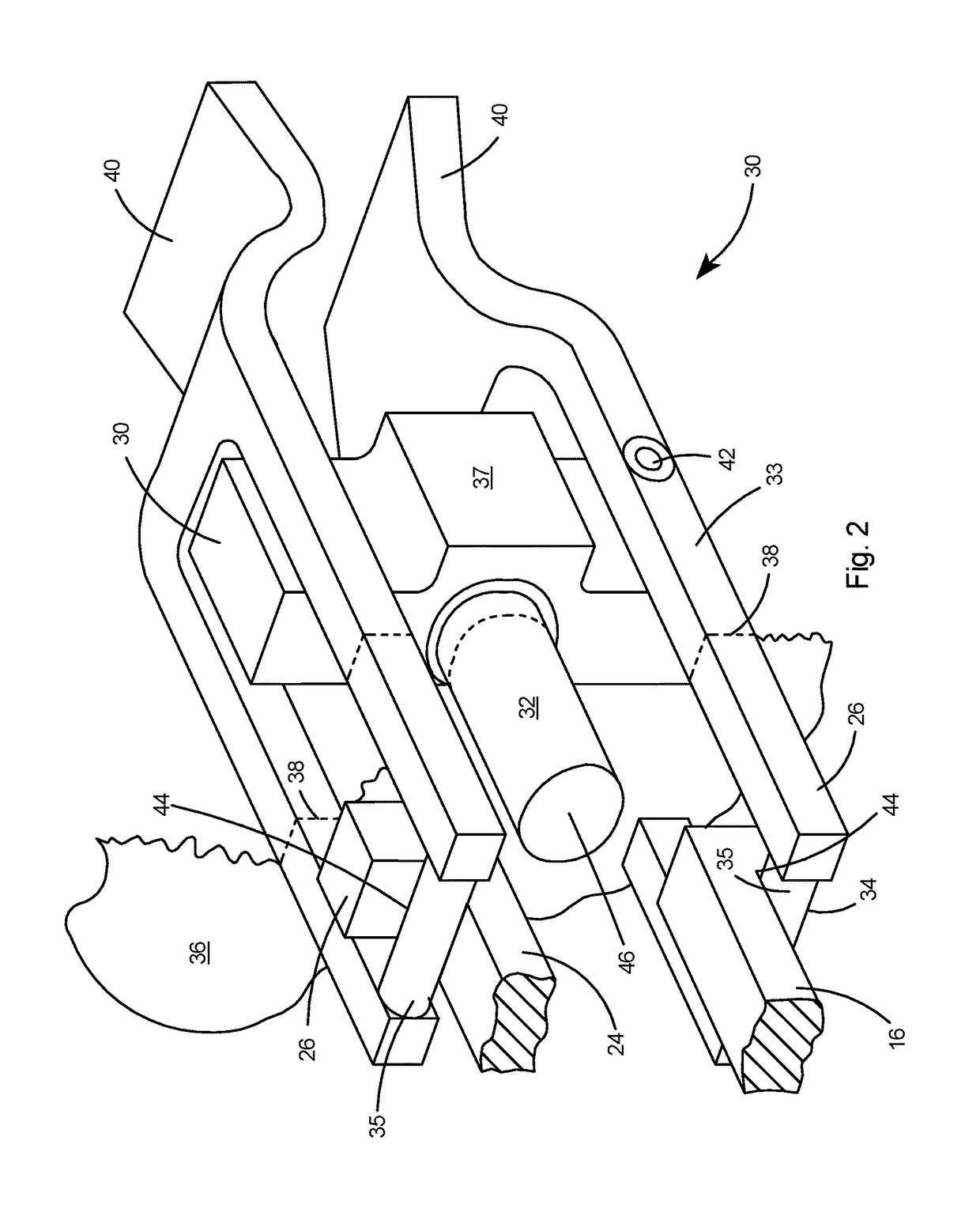
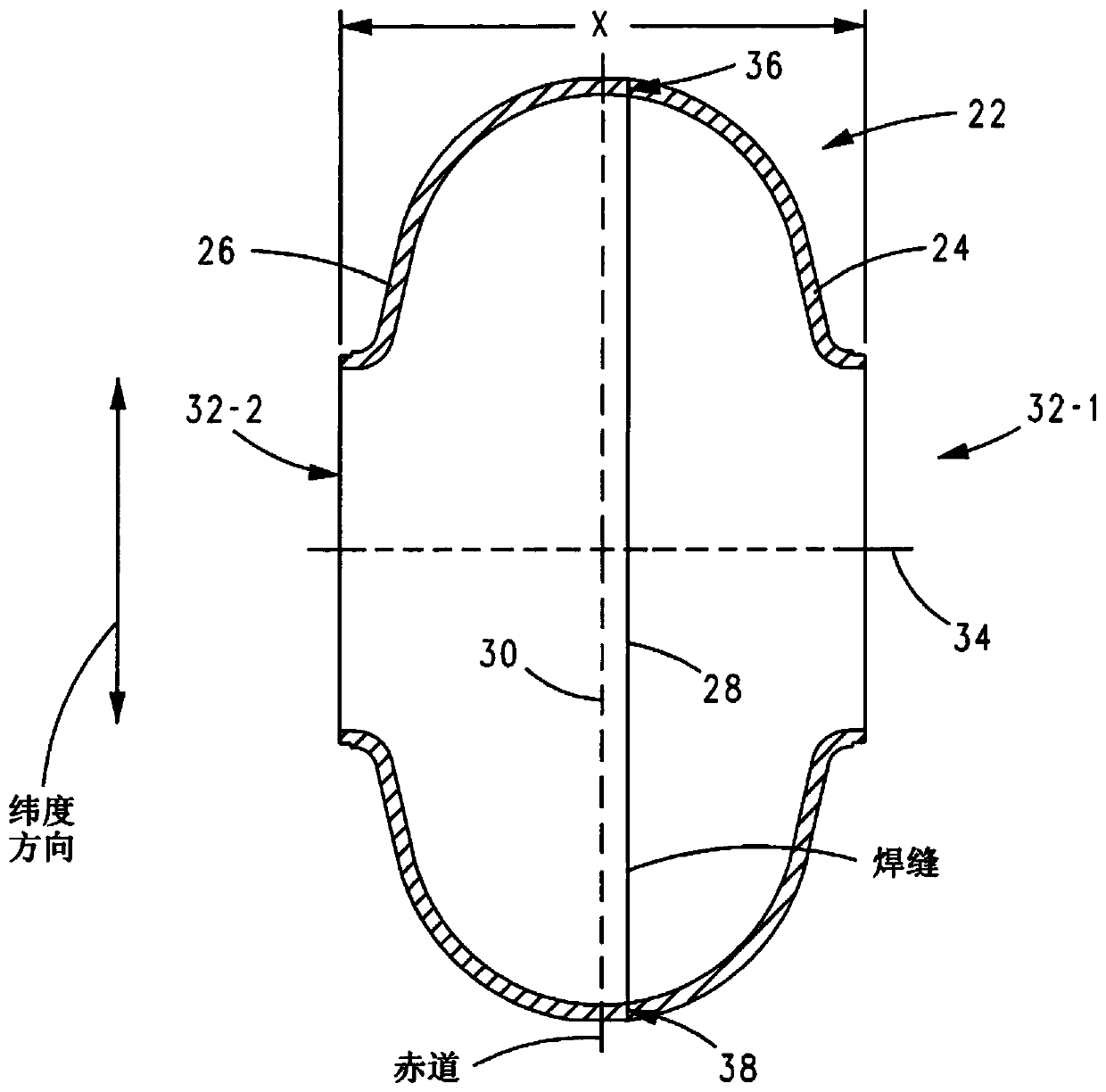
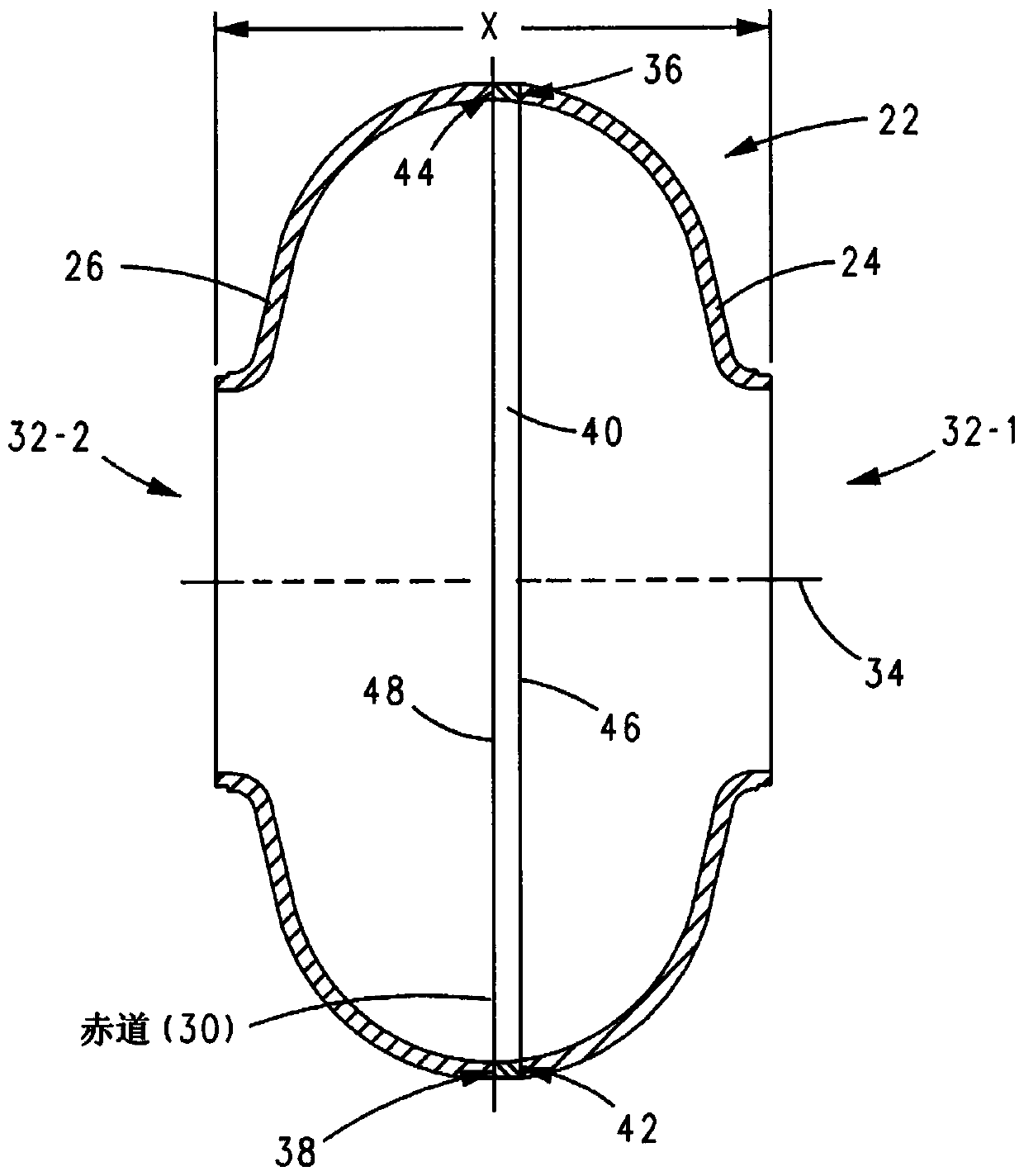
The invention reveals a superconducting radio frequency unit. The superconducting radio frequency unit includes a body defining a hollow cavity, the body having first and second apertures, an axis atopposite ends of the body, and an equator extending between the first and second apertures, and surrounding the axis between the first and second apertures. The body includes at least a first weld that surrounds the axis at a location on the body spaced apart from the equator. Each of the weld seams extends through the body and has opposite sides terminating near the inside and outside of the body, and each of the weld seams includes a first conductive weld portion formed on one side of the weld seam and a second weld portion formed on the opposite side of the weld seam. The second weld may bea conductive weld, a piercing weld, or a transition weld.
Owner:II VI特拉华公司
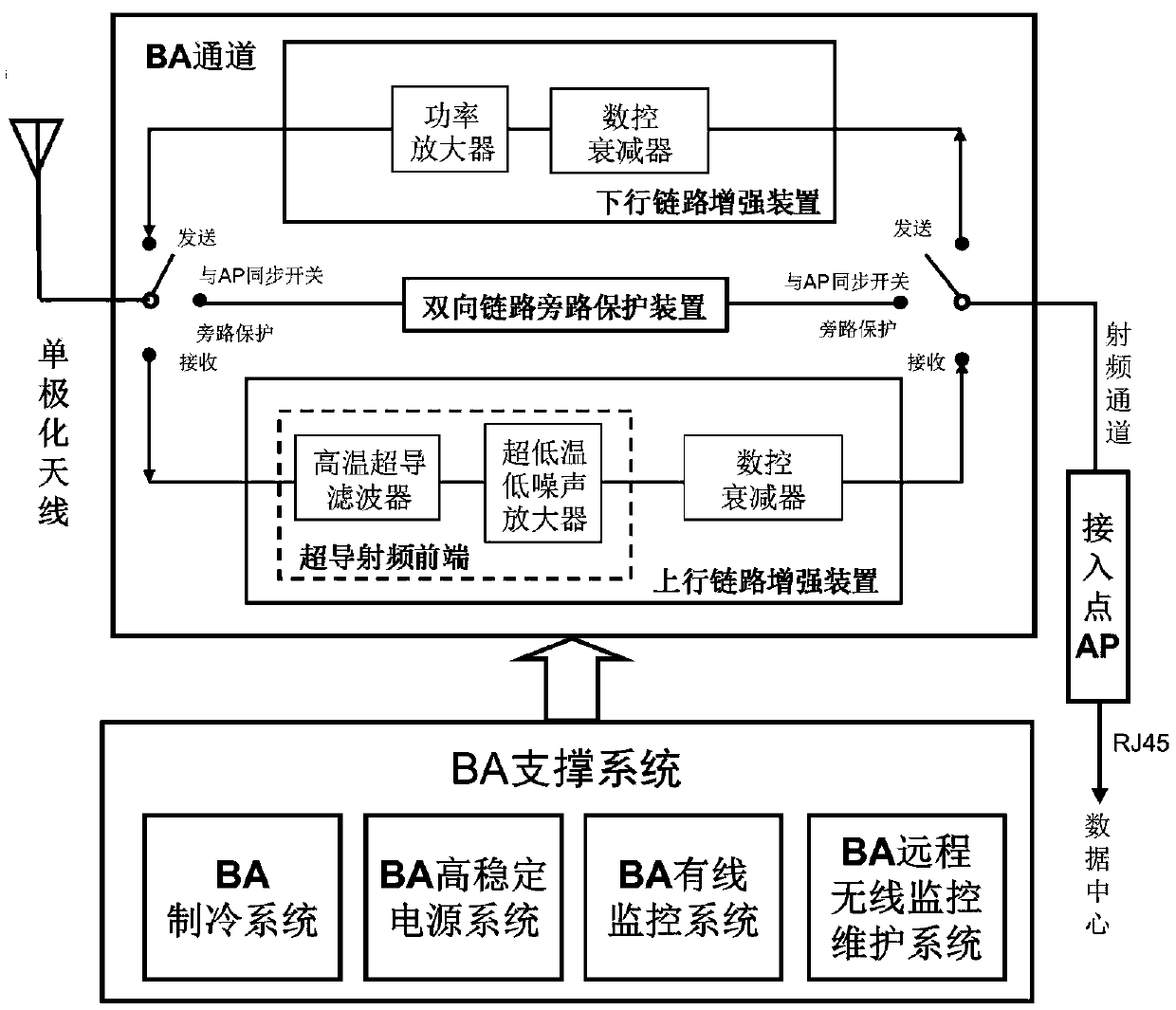
Intelligent monitoring system for ap wireless system with superconducting radio frequency front end
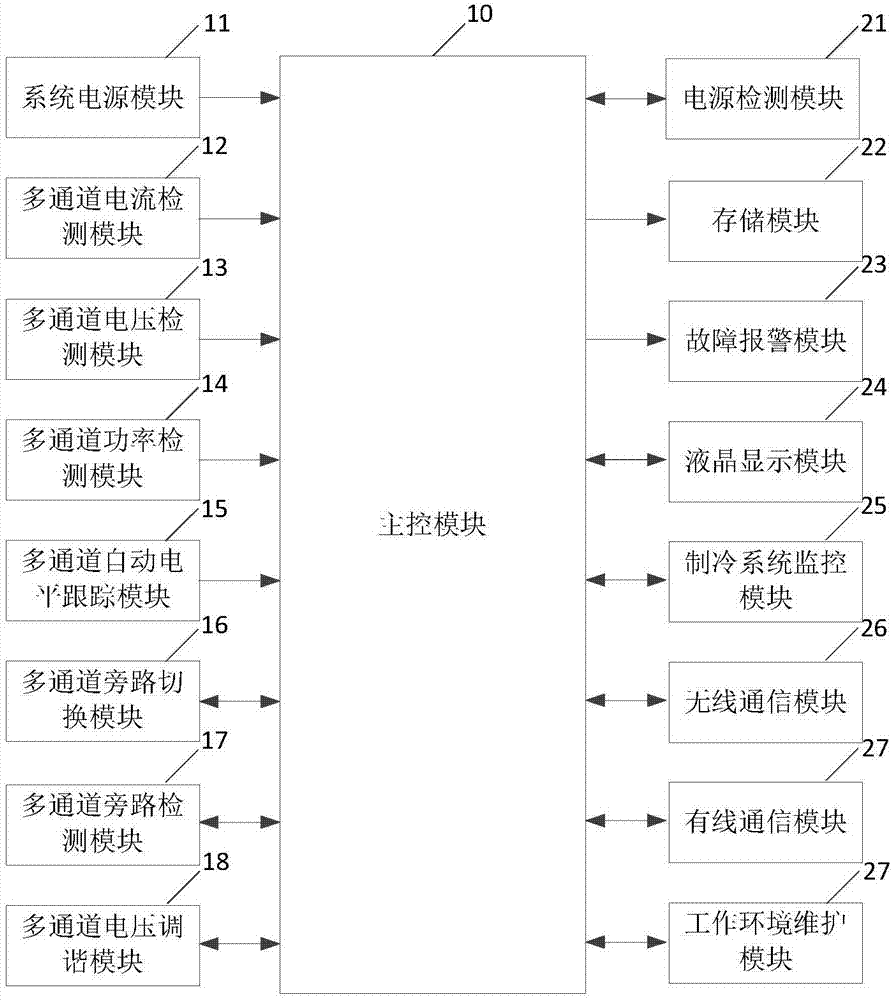
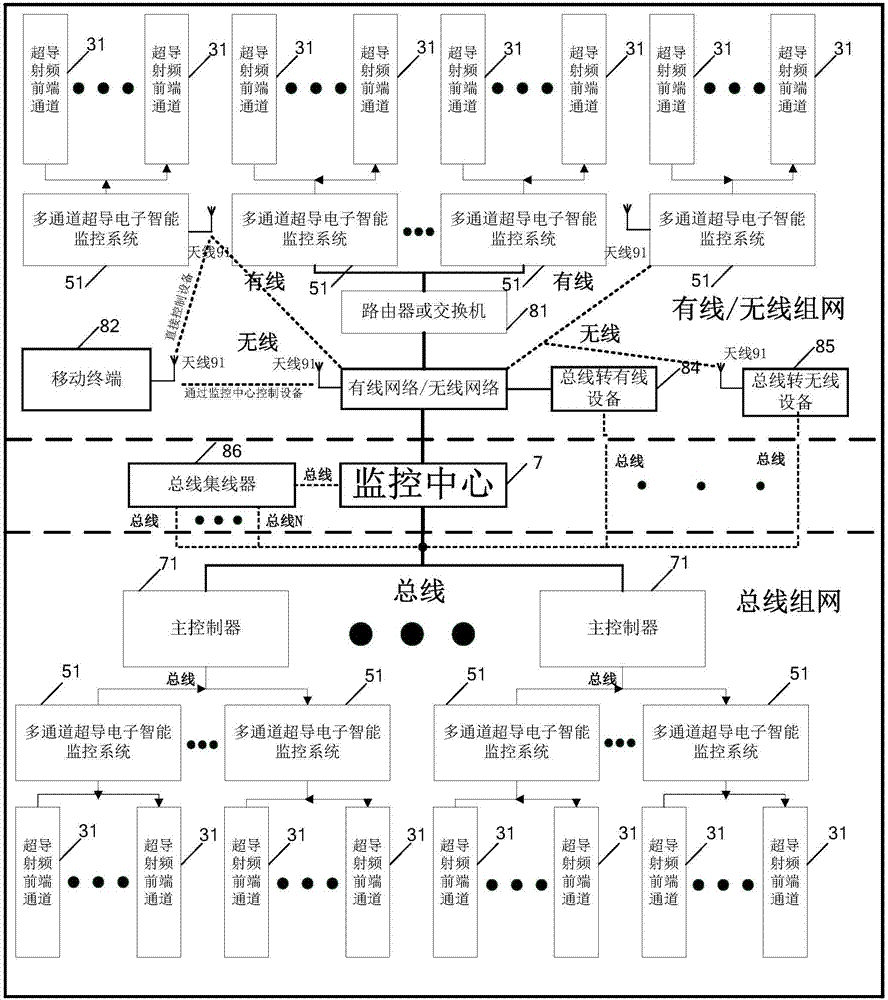
ActiveCN107179727BImprove reliabilityHigh precisionProgramme controlComputer controlSystem maintenanceData acquisition
The invention discloses an intelligent monitoring system of a superconducting access system, wherein the intelligent monitoring system is applied to the superconducting access system to realize real-time remote monitoring, control and maintenance so as to guarantee normal work of the superconducting access system. The intelligent monitoring system is composed of a main control module, a power supply detection module, a current detection module, a voltage detection module, a refrigeration system monitoring module, a case temperature monitoring module, a power monitoring module, a storage module, a liquid crystal display module, a fault warning module and a remote monitoring module. According to the intelligent monitoring system disclosed by the invention, with an ARM architecture processor with high performance and low power consumption, data acquisition, warning, controlling, processing, information recording and system maintenance are carried out on a BA channel of the superconducting access system, a BA refrigeration system and a BA high-stability power system in real time, so that reliability of the superconducting access system and network transmission can be improved. The intelligent monitoring system has advantages of powerful function, high precision, wide range, fast speed, low power consumption and simple control in fields of monitoring, controlling, and maintenance.
Owner:广州特信网络技术有限公司
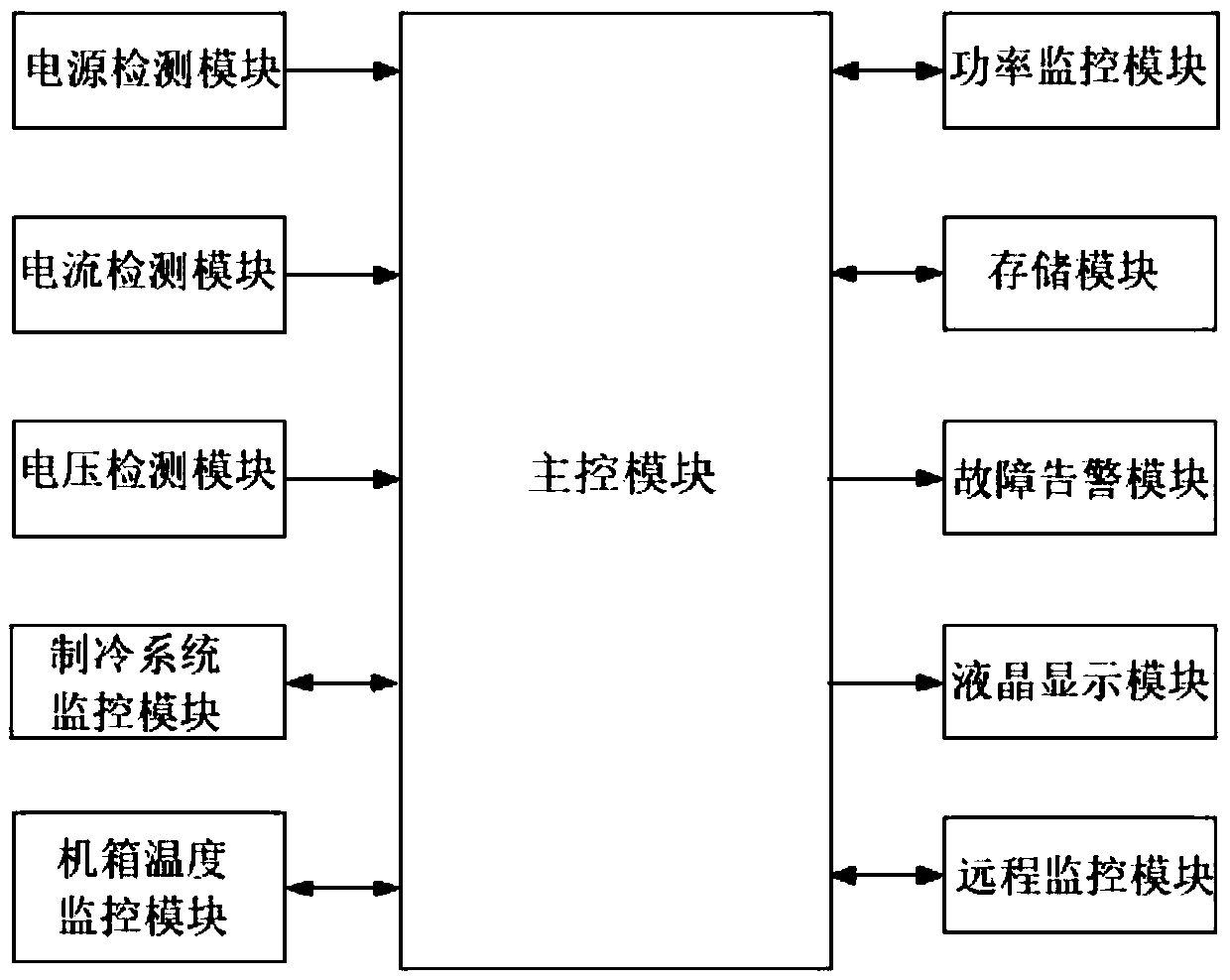
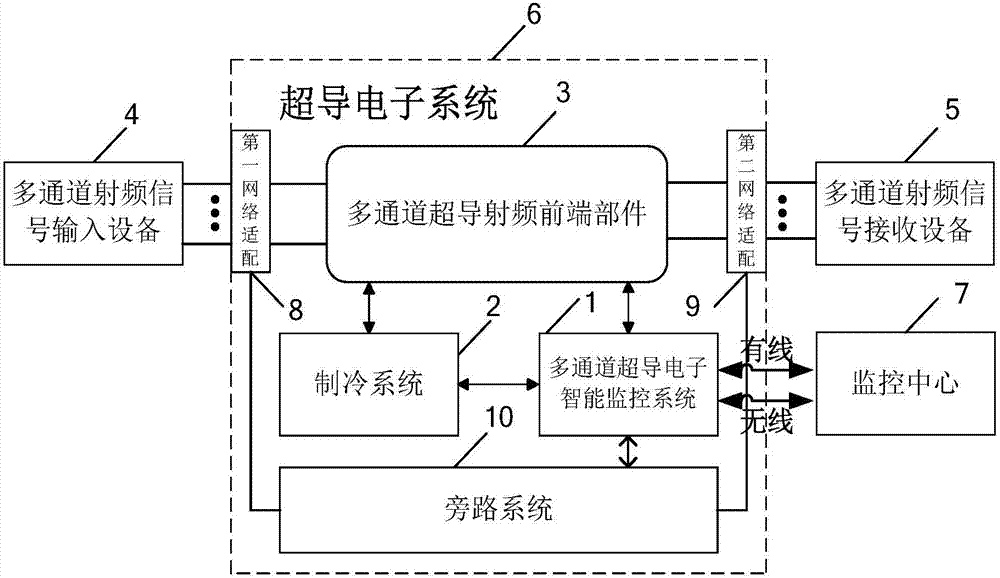
Multi-channel superconducting electronic intelligent monitoring system
InactiveCN107367977AImprove reliabilityIncrease speedProgramme controlComputer controlSystem maintenanceEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-channel superconducting electronic intelligent monitoring system, which is applied to a superconducting electronic system to realize multi-channel remote monitoring, control and maintenance, and forms the control of a monitoring network to ensure the normal operation of the superconductive electronic system. The multi-channel superconducting electronic intelligent monitoring system comprises a main control module, a multi-channel current detection module, a multi-channel voltage detection module, a refrigeration system monitoring module, a multi-channel power detection module, a fault alarm module and a vacuum degree maintenance module. A superconducting electronic system monitoring network is formed through a bus and wired and wireless connection. The system of the invention adopts a high-speed, high-performance, high-integration and low-power ARM architecture processor to perform real-time data acquisition, alarming, control, processing, information recording and system maintenance on a superconducting radio frequency front-end system, a refrigeration system and a high-stability power system of the superconducting electronic system to improve the reliability of the superconducting electronic system and network transmission. The system of the invention has the advantages of high-precision, high-speed, high-reliability, low-power monitoring, controlling and maintenance control and simple operation and control.
Owner:广东特信超导技术有限公司
Superconducting magnetic resonance imaging machine used for breast disease diagnosis, and construction method and use thereof
ActiveCN101884533BQuality improvementImprove signal-to-noise ratioIndirect heat exchangersDiagnostic recording/measuringNoise (radio)Heat conducting
The invention discloses a superconducting magnetic resonance imaging machine, and a construction method and a use thereof. The superconducting magnetic resonance imaging machine of the invention comprises imaging areas, at least one vacuum insulation cover, a main magnet and a low-temperature cooling system, wherein the main magnet generates magnetic fields in the imaging areas; the low-temperature cooling system is connected with the vacuum insulation cover; a low vacuum space is formed and a lower-temperature heat conducting plate and at least one high vacuum inner cover and high vacuum outer cover are arranged inside the vacuum insulation cover; the vacuum insulation cover at least provides one imaging area; at least one superconducting radio frequency coil is arranged inside the low vacuum space and connected with the low-temperature heat conducting plate; and the low-temperature heat conducting plate is connected with the low-temperature cooling system through a heat pipe to realize and maintain the lower temperature condition of the superconducting radio frequency coil. The construction of the vacuum insulation cover is suitable for the imaging of the following body parts: breasts, knees, wrists, feet, a neck and a head. The invention can improve the magnetic resonance imaging quality and achieve a high signal-to-noise ratio in the imaging areas.
Owner:美时医疗技术(上海)有限公司
High-current conduction cooled superconducting radio-frequency cryomodule
ActiveUS10932355B2Reduce complexityLow costLinear acceleratorsNon-pressured vesselsAverage currentEngineering
A high-current, compact, conduction cooled superconducting radio-frequency cryomodule for particle accelerators. The cryomodule will accelerate an electron beam of average current up to 1 ampere in continuous wave (CW) mode or at high duty factor. The cryomodule consists of a single-cell superconducting radio-frequency cavity made of high-purity niobium, with an inner coating of Nb3Sn and an outer coating of pure copper. Conduction cooling is achieved by using multiple closed-cycle refrigerators. Power is fed into the cavity by two coaxial couplers. Damping of the high-order modes is achieved by a warm beam-pipe ferrite damper.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
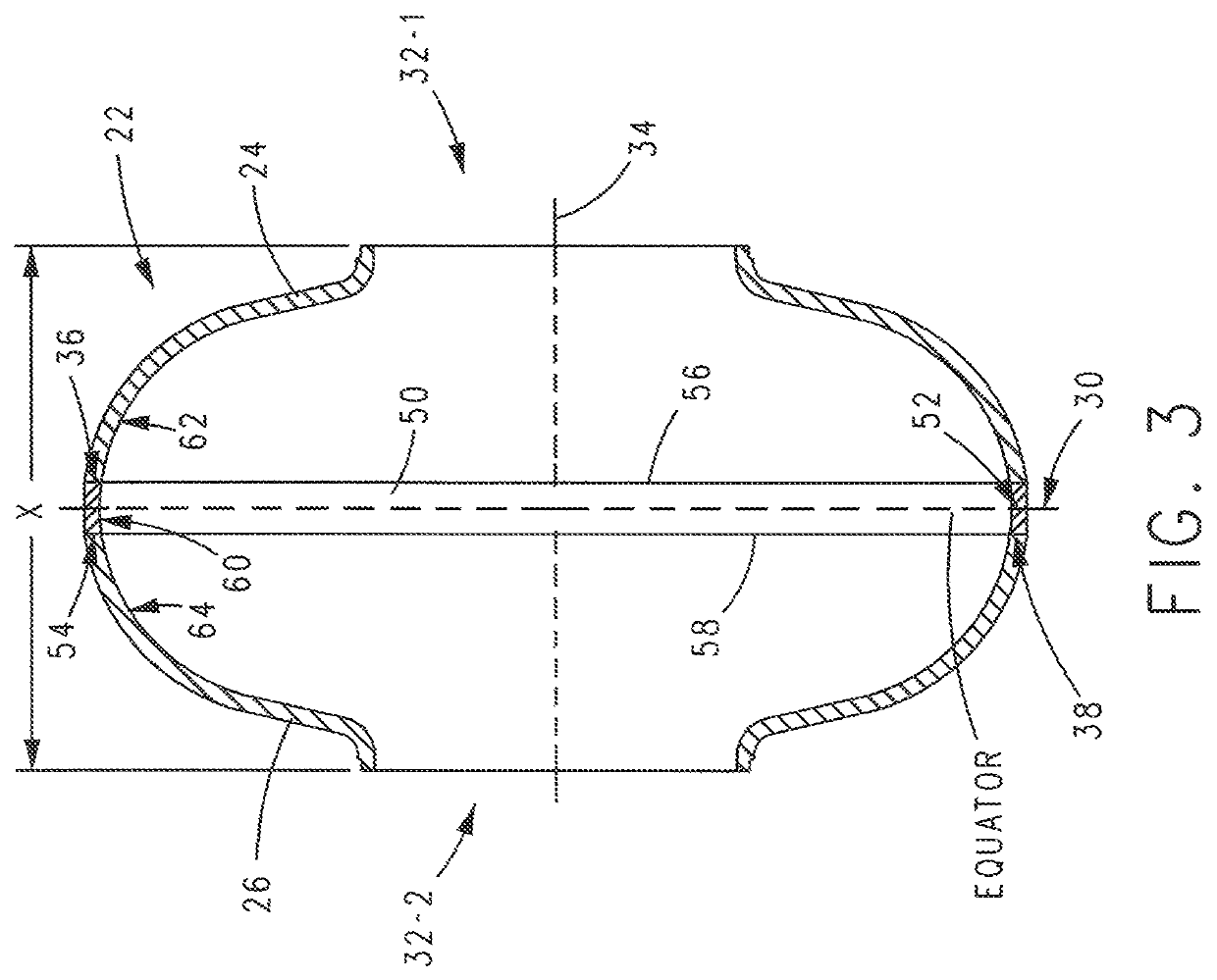
Superconducting resonating cavity with laser welded seam and method of formation thereof
ActiveUS20190357344A1Convenient treatmentResonatorsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesEngineeringWeld seam
A superconducting radio frequency cell includes a body defining a hollow cavity having a first iris and second iris at opposite ends of the body, an axis that extends between the first and second irises, and an equator around the axis between the first and second irises. The body includes at least a first weld seam around the axis at a location on the body spaced from the equator. Each weld seam extends through the body and has opposite sides terminating proximate an interior and an exterior of the body, and each weld seam includes a first, conduction weld formed on one side of the weld seam and a second weld formed on the opposite side of the weld seam. The second weld can be a conduction weld, a keyhole weld, or a transition weld.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Superconducting resonating cavity and method of production thereof
A superconducting radio frequency (SRF) cell includes a body defining a hollow cavity having a first iris at a first end of the body, a second iris at a second end of the body, an axis that extends between the first and second irises and an equator around the axis between the first and second irises. The body includes a first weld seam around the axis at a location on the body spaced from the equator. A method for producing the SRF cavity includes: (a) providing a first-partial cell including a first cell welding edge; (b) providing a second-partial cell including a second cell welding edge; (c) positioning the first- and second-partial cells with the first and second cell welding edges facing toward each other; and (d) welding the first- and second-partial cells together at a position other than the equator of the body.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
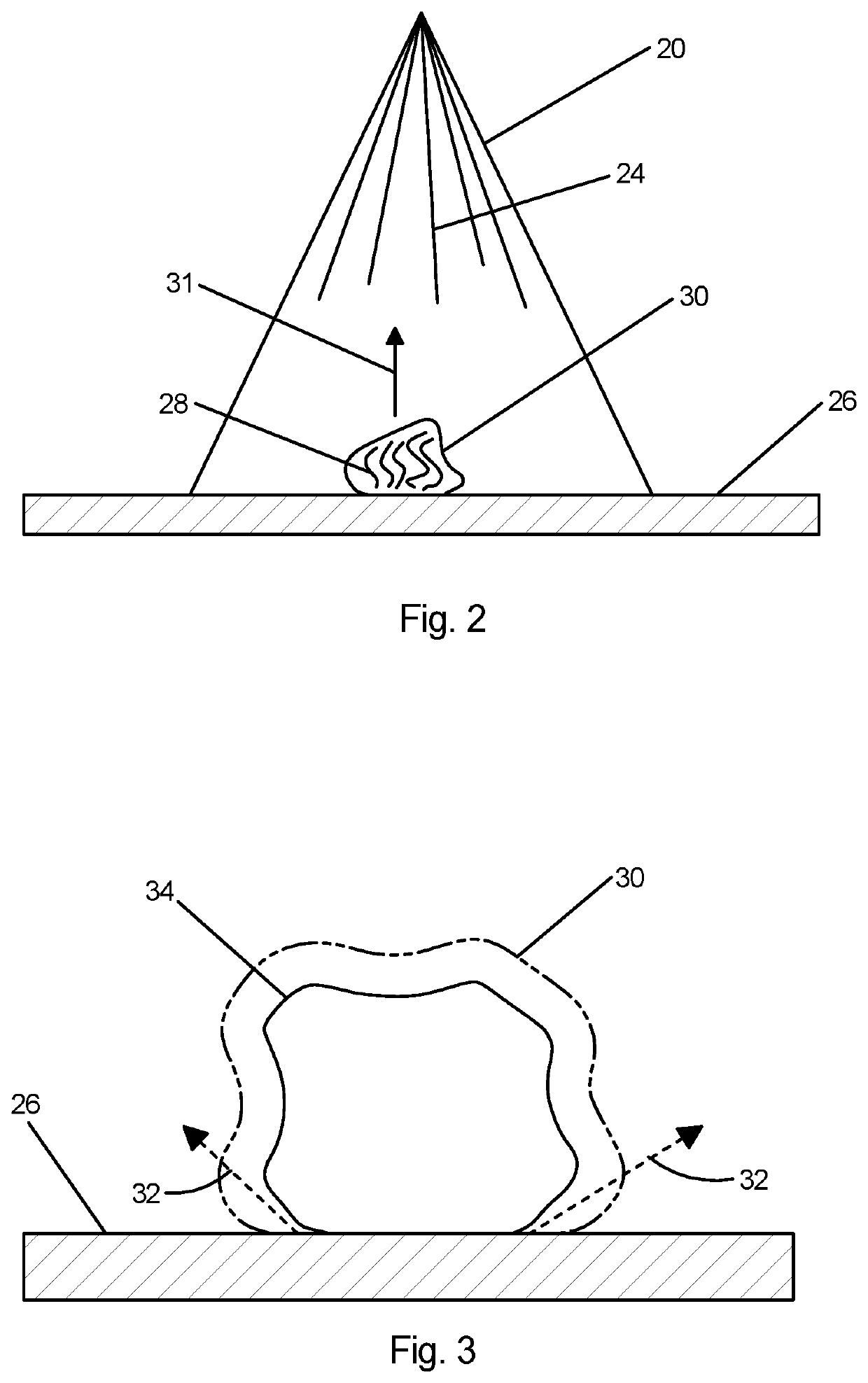
Method and apparatus for removal of microscopic contaminant particulates from superconducting radio frequency cavities and cavity strings
PendingUS20210316340A1Suppresses field emissionIncrease of usable accelerating gradientHollow article cleaningCleaning using liquidsParticulatesNuclear engineering
A method and apparatus for removing microscopic contaminant particulates by high pressure liquid nitrogen jet cleaning from the inner surface of a superconducting radio frequency cavity or a string of multiple cavities and transporting the removed particulates out of the inner space enclosed by the cleaned surfaces. The cleaning method of the invention suppresses field emission, resulting in an increase of the usable accelerating gradient of the cavities and a reduction of the activated radioactivity in accelerator components around cavities.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com