Patents
Literature
202 results about "Transmission (telecommunications)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications, transmission (abbreviations: TX, Xmit) is the process of sending and propagating an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless.
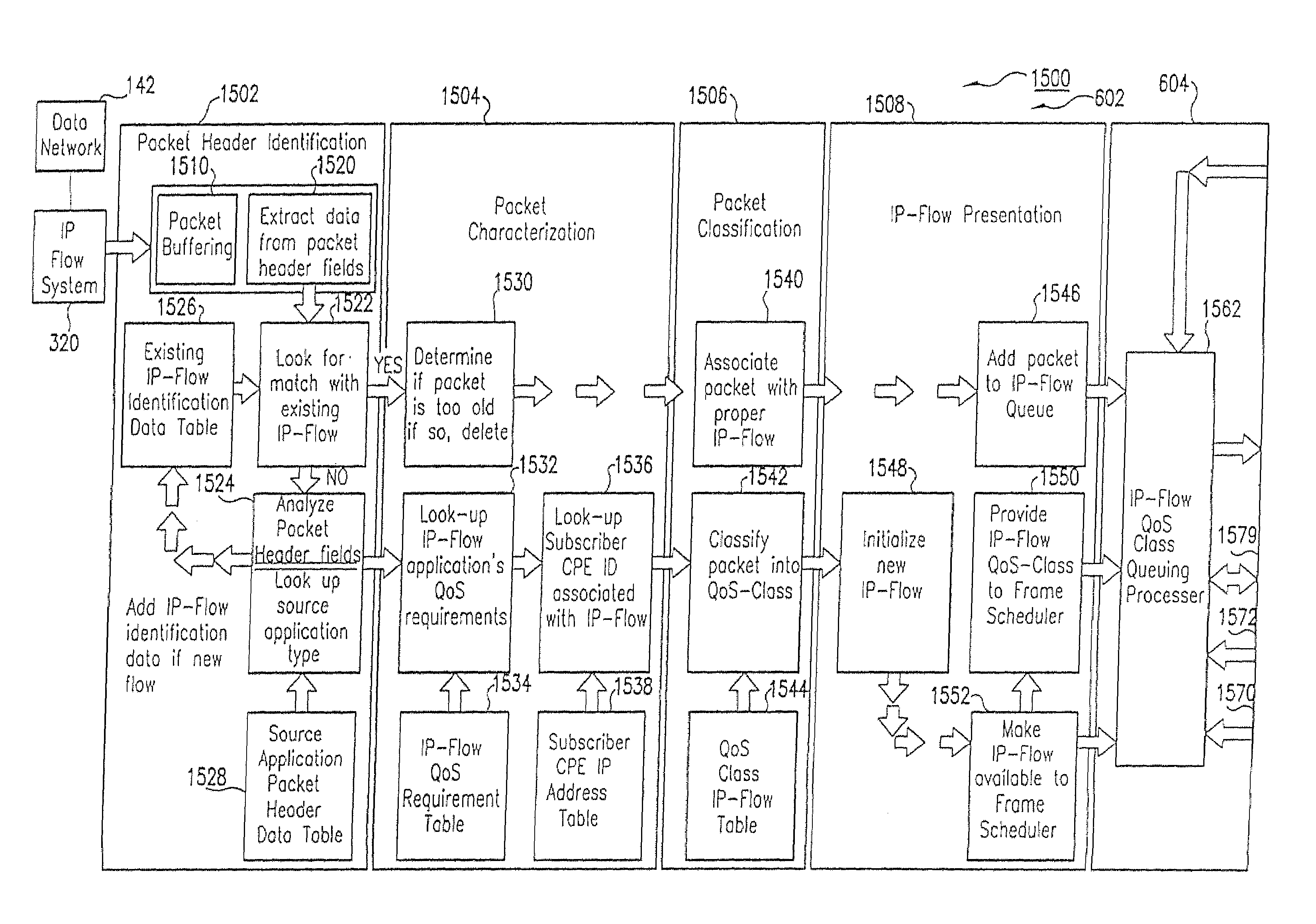
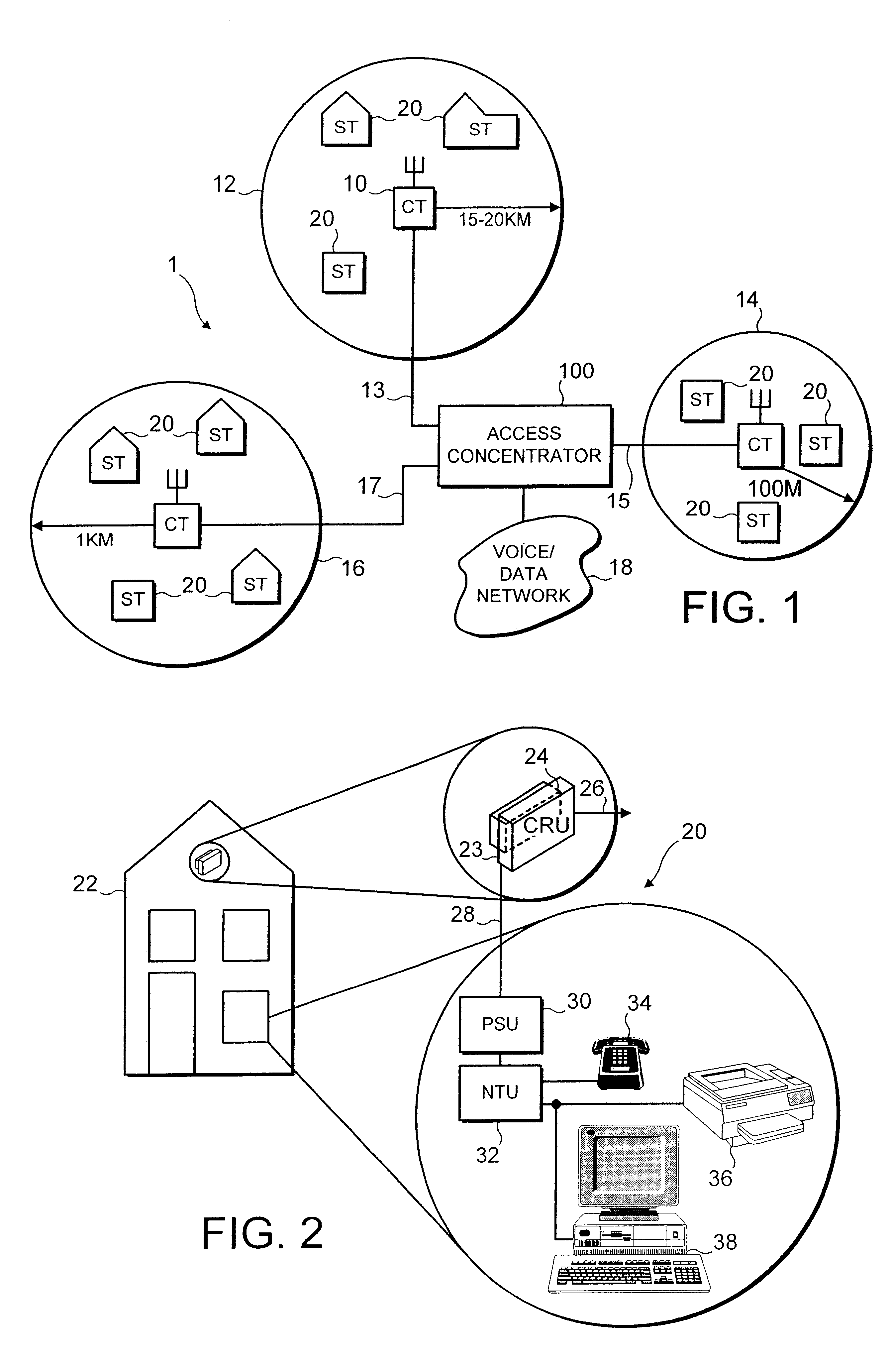
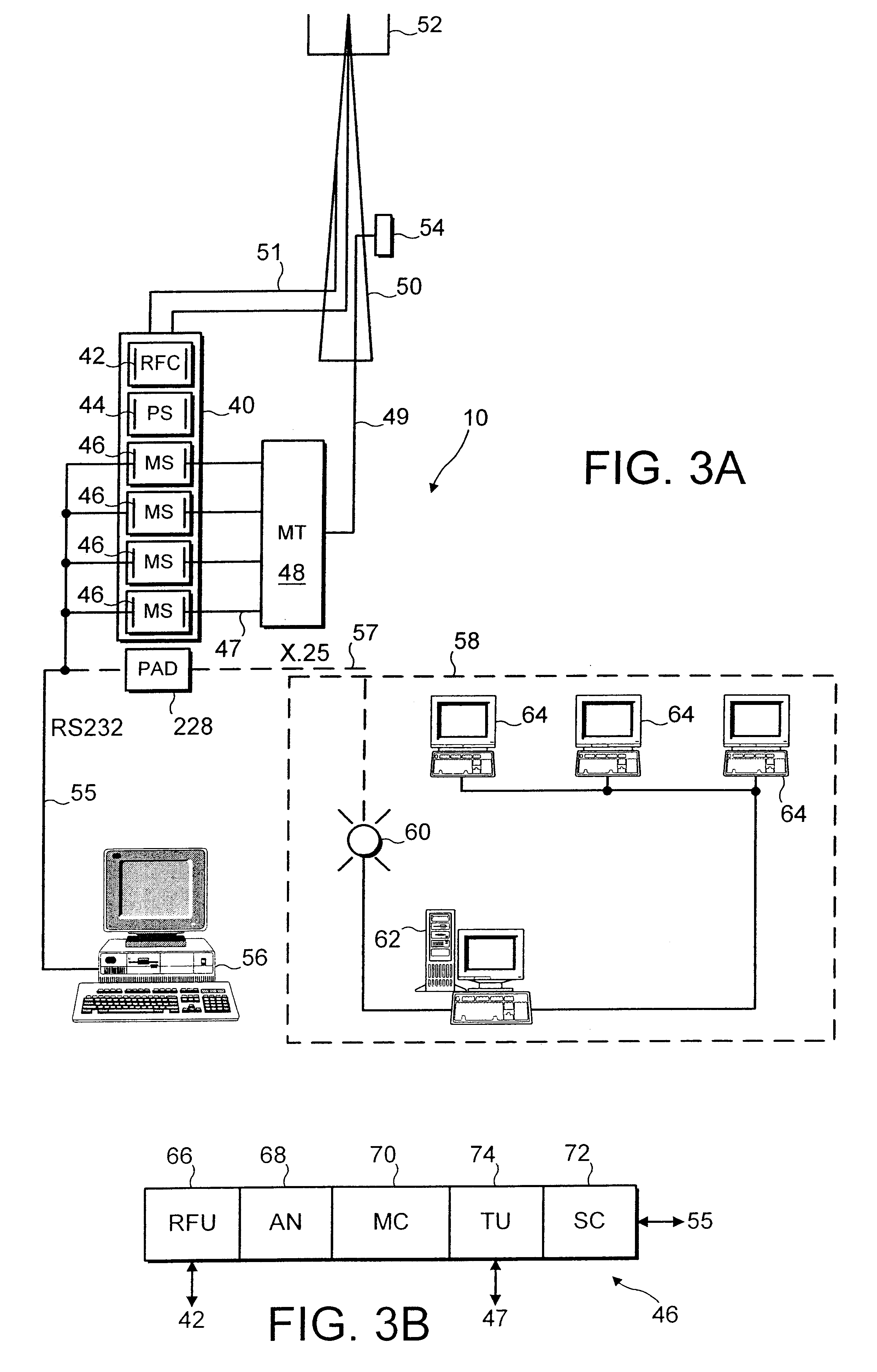
Method and computer program product for internet protocol (IP)-flow classification in a wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system
InactiveUS7251218B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceWireless access point
A system and method for Internet Protocol (IP) flow classification group IP flows in a packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system is disclosed. The method comprises analyzing an IP flow in a packet-centric manner, classifying the IP flow, scheduling the IP flow for transmission over a shared wireless bandwidth between a wireless base station and at least one subscriber customer premises equipment (CPE) station, allocating the shared wireless bandwidth to a communication of the IP flow between the wireless base station and a subscriber CPE station so as to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS) associated with the IP flow.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
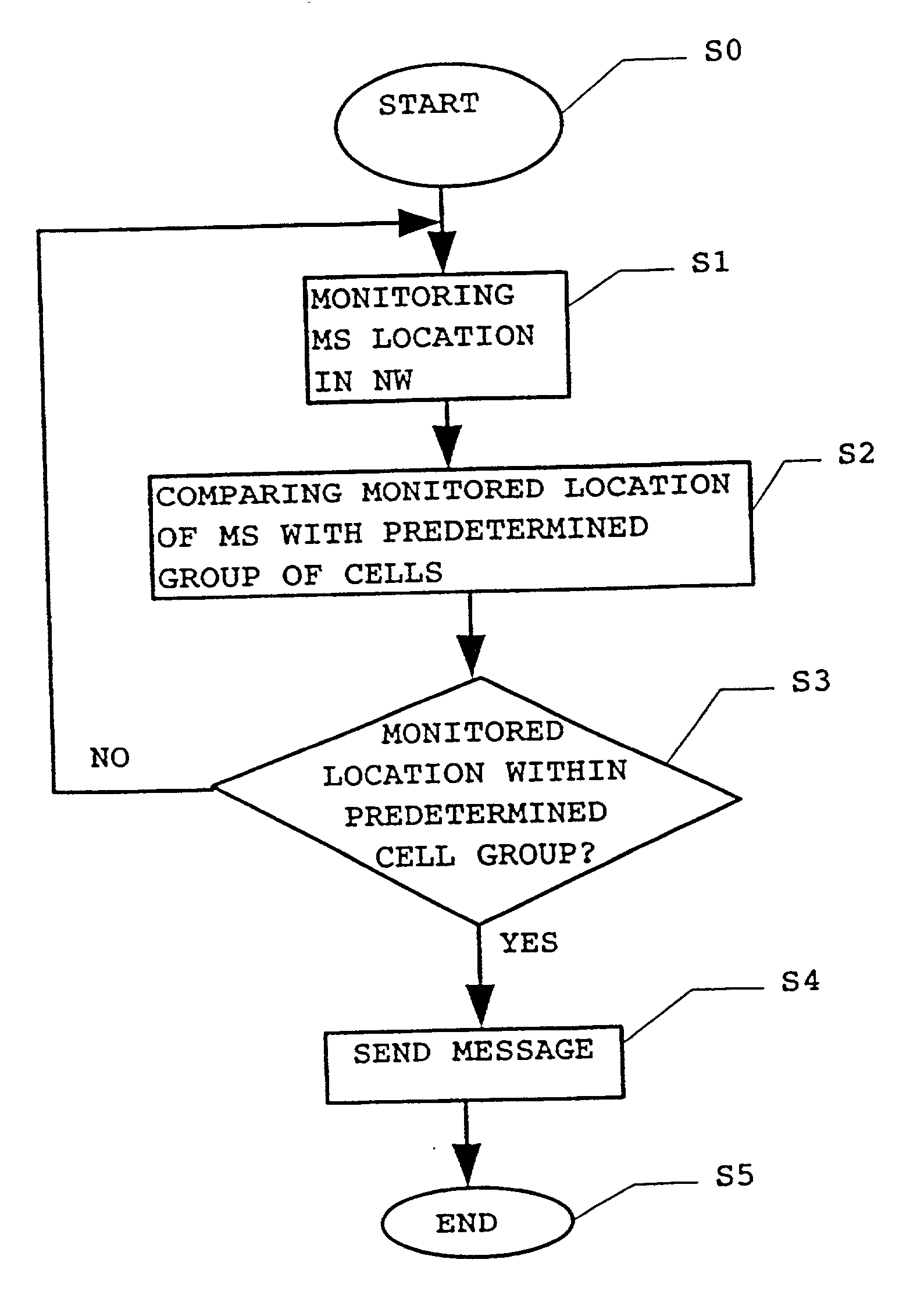
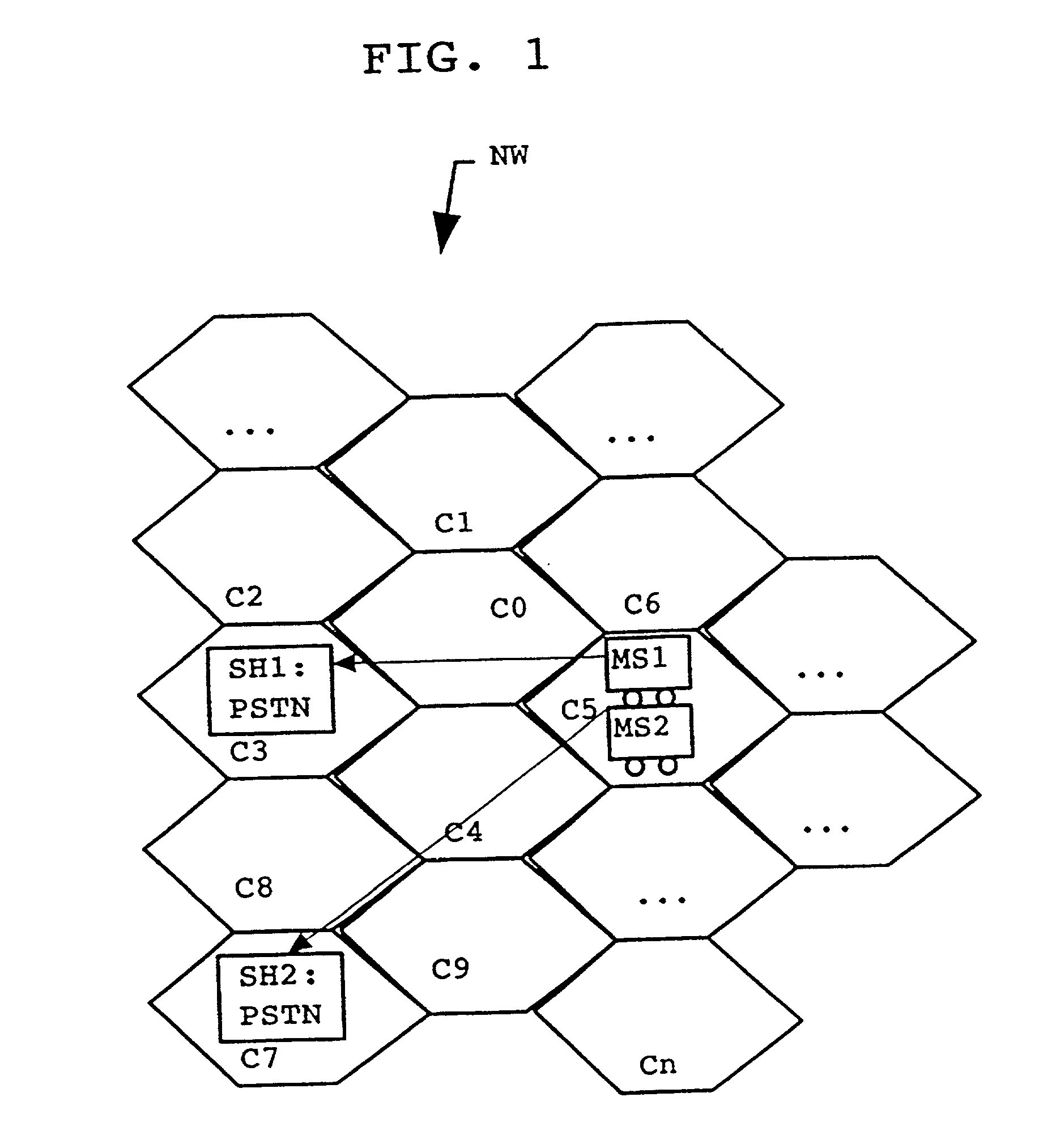
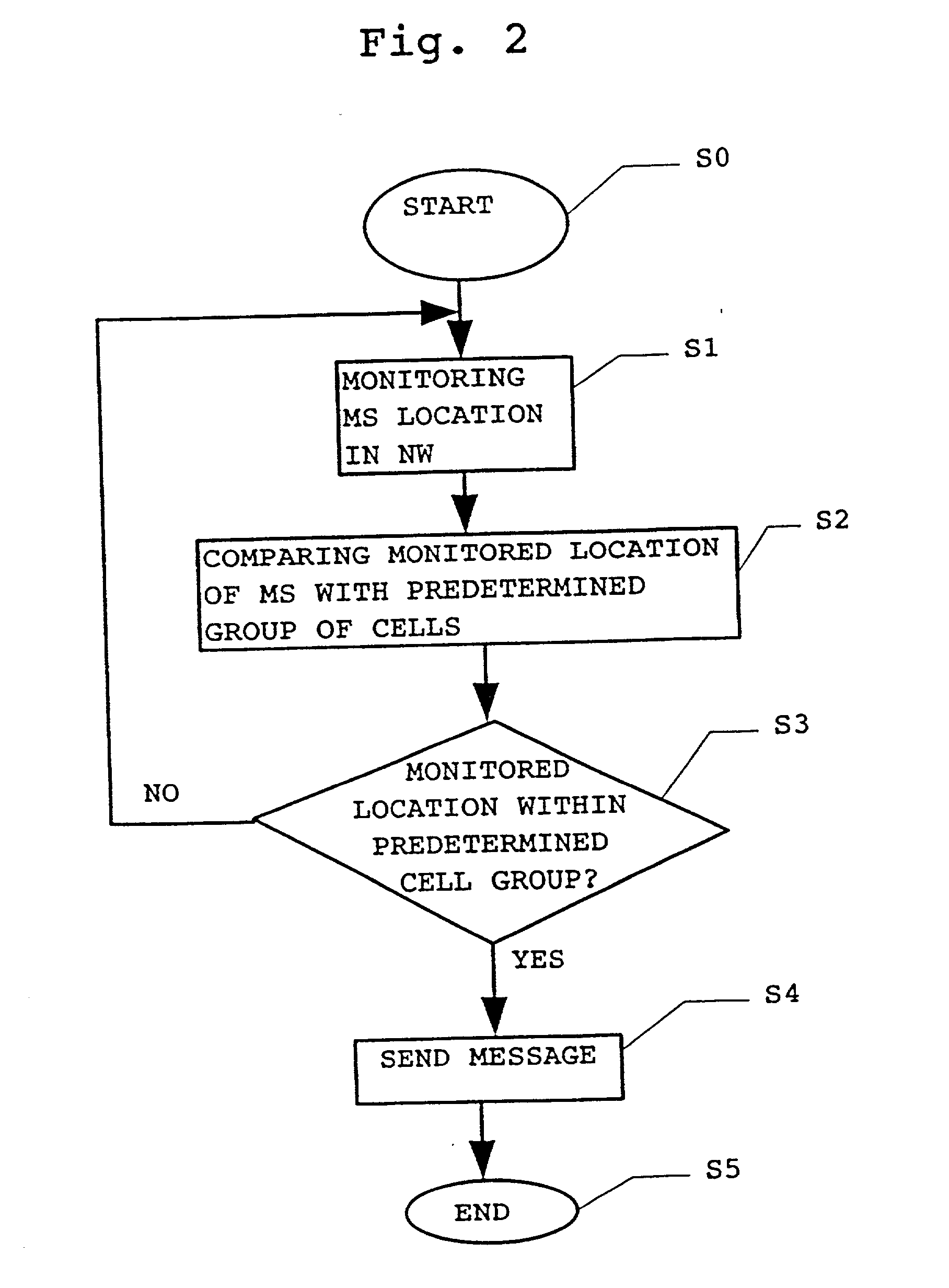
Method for generation and transmission of messages in a mobile telecommunication network
InactiveUS20020127997A1Improve comfortImprove securitySupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentTelecommunications networkTransmission (telecommunications)
The present invention proposes a method for generation and transmission of messages in a mobile telecommunication network, comprising the steps of monitoring the location of a mobile subscriber terminal within the mobile telecommunications network using location information available for said network; comparing the monitored location with a predetermined location within said network; judging whether the monitored location corresponds to said predetermined location, and if the result of judging is positive, sending a predetermined message from said network. Also, the present invention proposes an accordingly adapted telecommunication system as well as an accordingly adapted telecommunication network element.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
Method and system of retransmission
InactiveUS20050002412A1Increase profitEliminate and reduce delayError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemConnection control
The present invention relates to a method and system of transmissions and retransmissions of packet data in a communications system, where the communications system uses switched channels, switching between rates or channels of different characteristics, and connection control and management in such a system. Particularly, the invention relates to radio resource management in a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, UMTS, or WCDMA system allowing for use of compatible protocols for non-switched and switched channels.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Retransmission method with soft combining in a telecommunications system
InactiveUS6842445B2Save transmission resourcesLess complexError prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexAutomatic repeat requestTransmitter
An automatic repeat request mechanism (such as Type II / III hybrid ARQ) which includes (soft or hard) combining of initially transmitted and retransmitted versions of a packet, is provided for retransmission of erroneous packets. According to the present invention, in association with each retransmission, there is outband signaling from a transmitter to a receiver that unambiguously indicates when, e.g. the exact time or physical location, the first transmission of the packet was carried out, so that it is possible to combine the retransmitted version with the previous version(s) of the packet. Soft combining requires that the initial packet and the retransmitted packet be identical. In an embodiment of the invention, in order to overcome this problem, the information that needs to be changed between the initial transmission and the retransmission(s) of a packet is sent outband with other outband signaling information. Thus, the retransmitted packet can be maintained unchanged and the requirement for identical packets in soft combining is met.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and system for authorization, routing, and delivery of transmissions
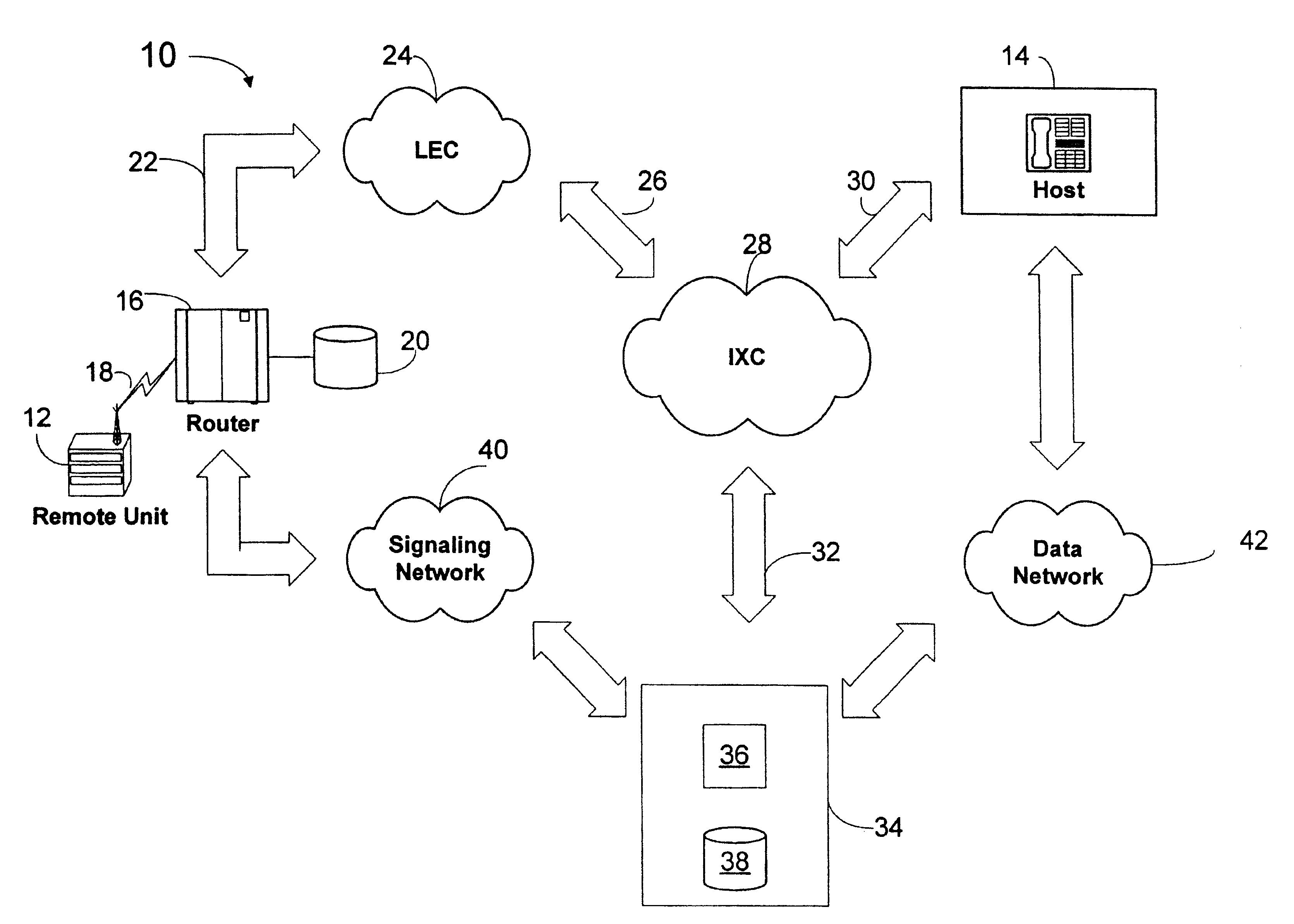
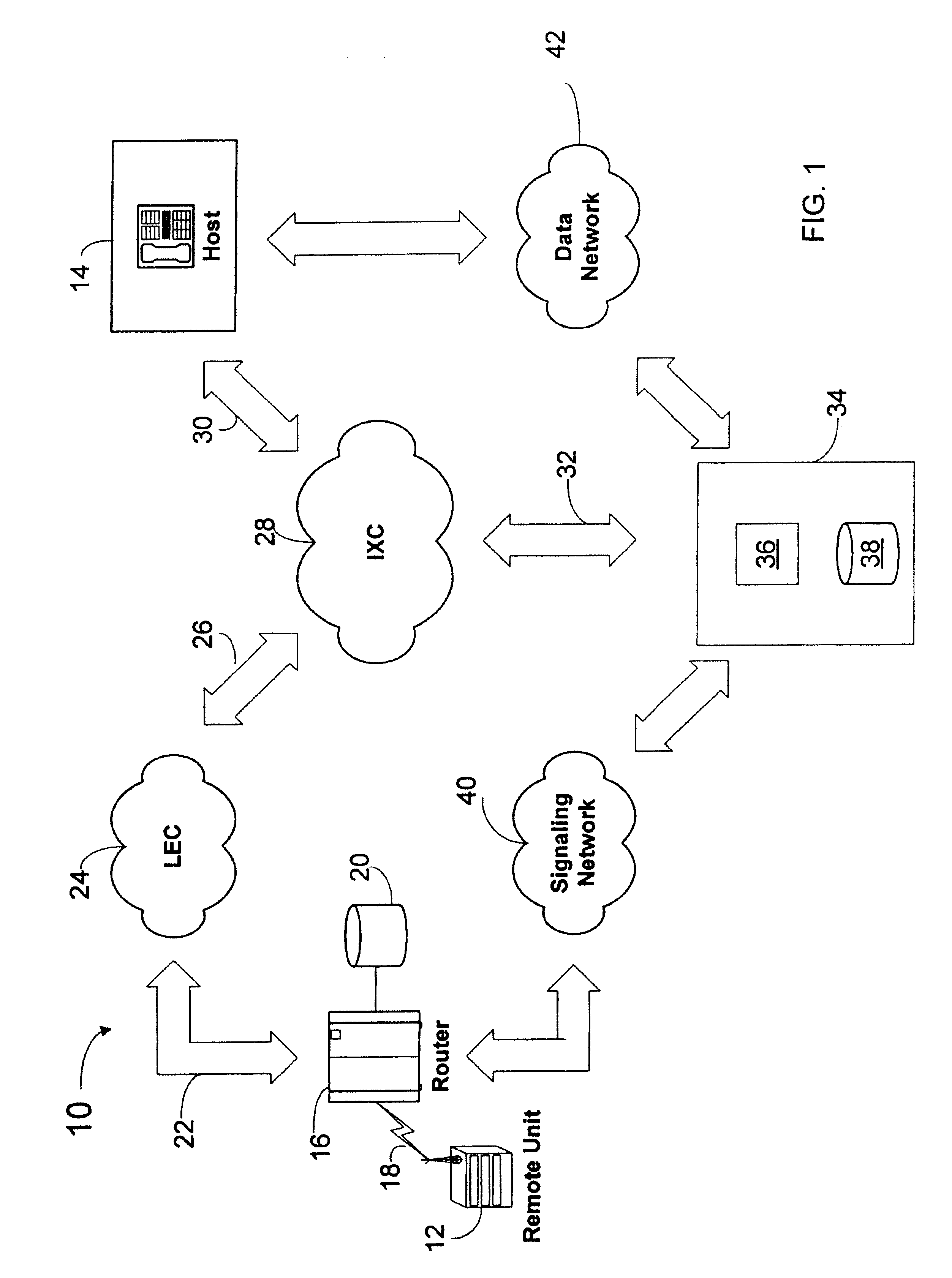
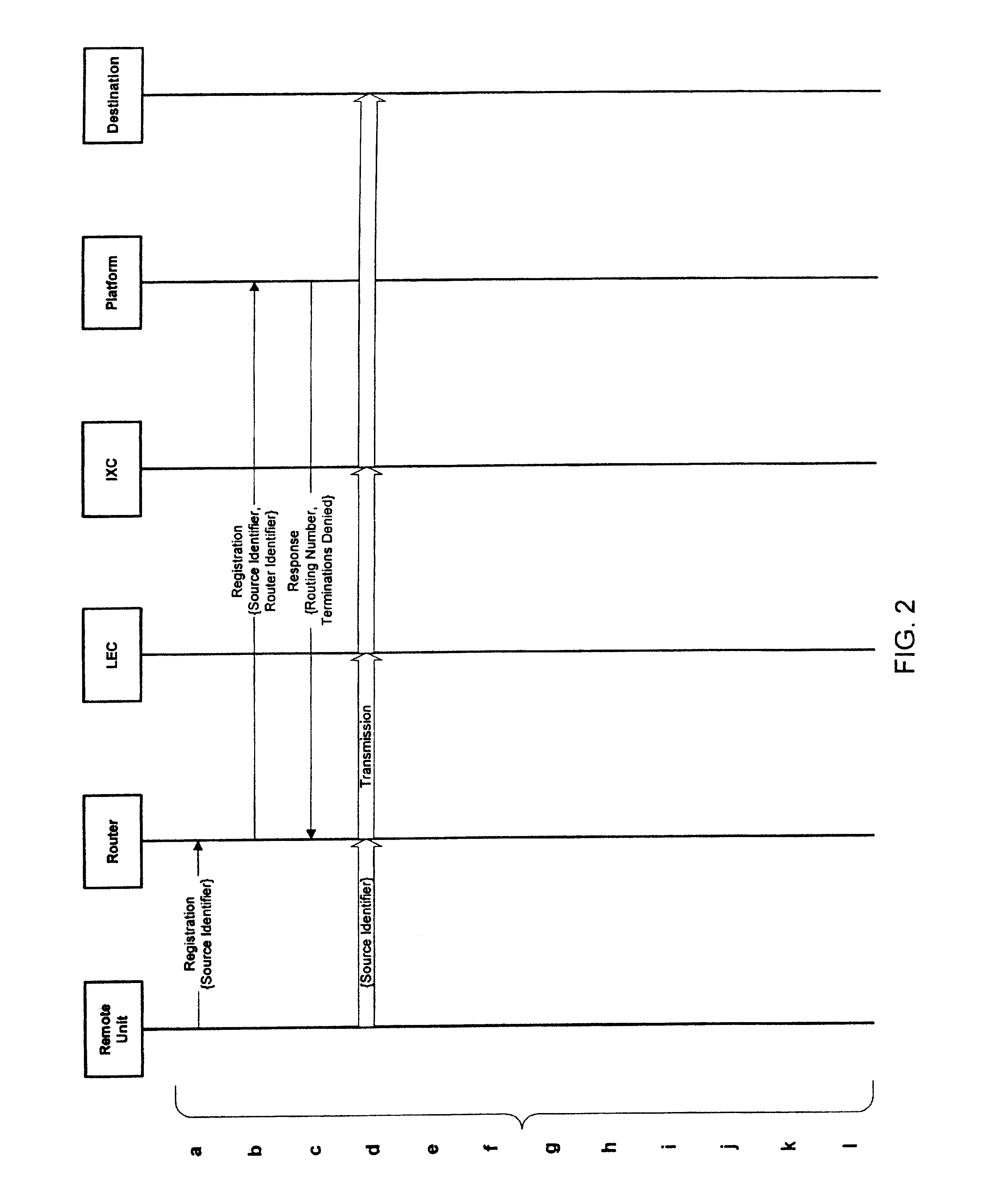
InactiveUS6963555B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsConnection managementStore and forwardTelecommunications network
In a telecommunications network, a platform is provided to perform authorization, routing, gathering, and delivery of transmissions between multiple remote units and host locations. In a controlled environment, remote units are authorized to initiate transmissions to and receive transmissions from a limited number of locations. The platform stores profile information for remote units in a database, including services authorized for remote units based on timing events. The platform determines the appropriate destination for a transmission from a remote unit based on the profile information stored in the database and identifiers associated with the remote unit and telecommunications router serving the remote unit. The platform authorizes a transmission to the destination based on the profile information, determines a routing number associated with the destination, and transmits the routing number to an appropriate point in the network to enable completion of the transmission. The platform also determines whether a transmission from a remote unit triggers an event or includes content that may be stored and forwarded to a host destination. Additionally, the platform authorizes and routes transmissions from a host to a remote unit.
Owner:GTE MOBILNET SERVICE +1
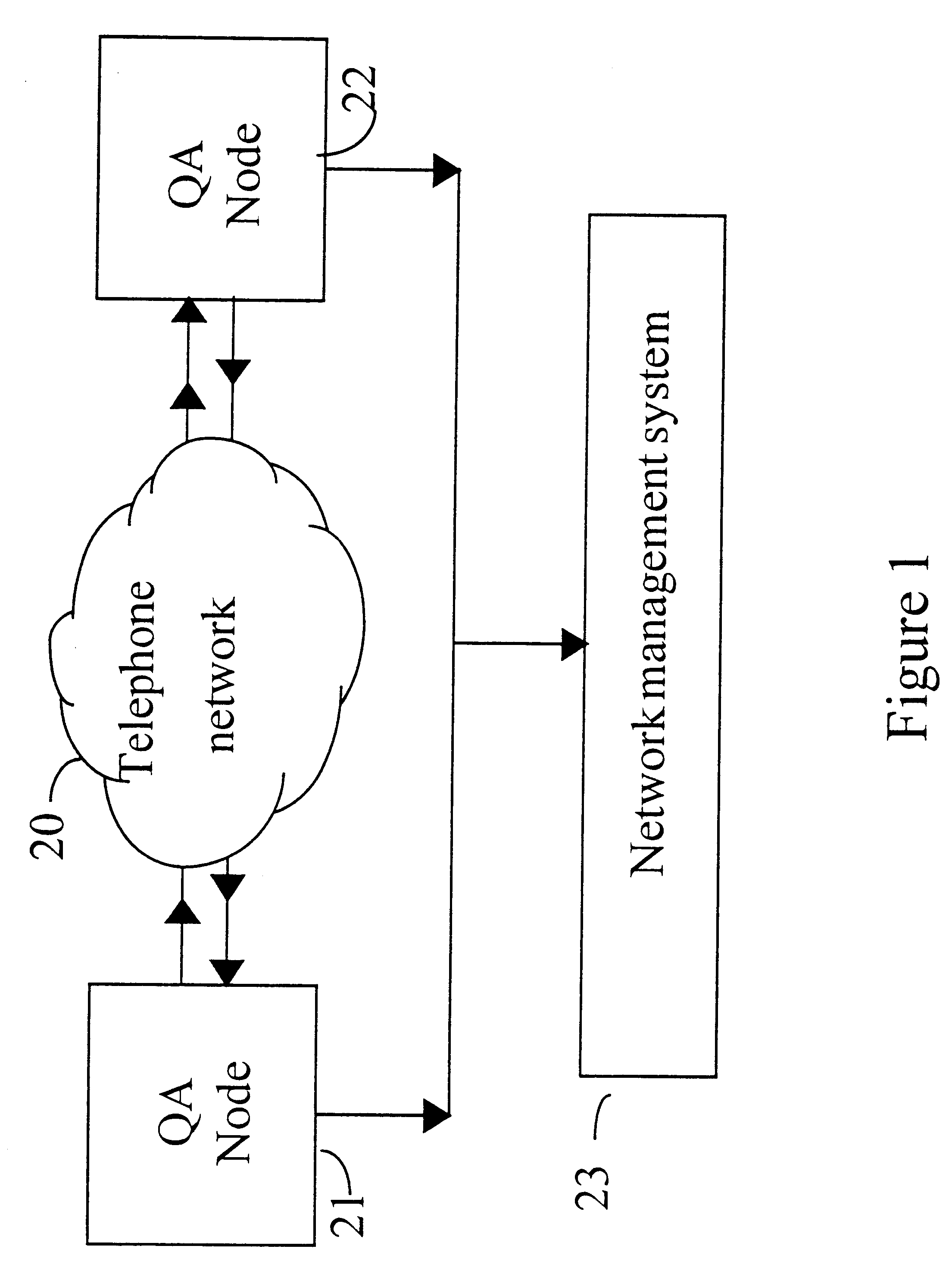
Measuring a talking quality of a telephone link in a telecommunications nework
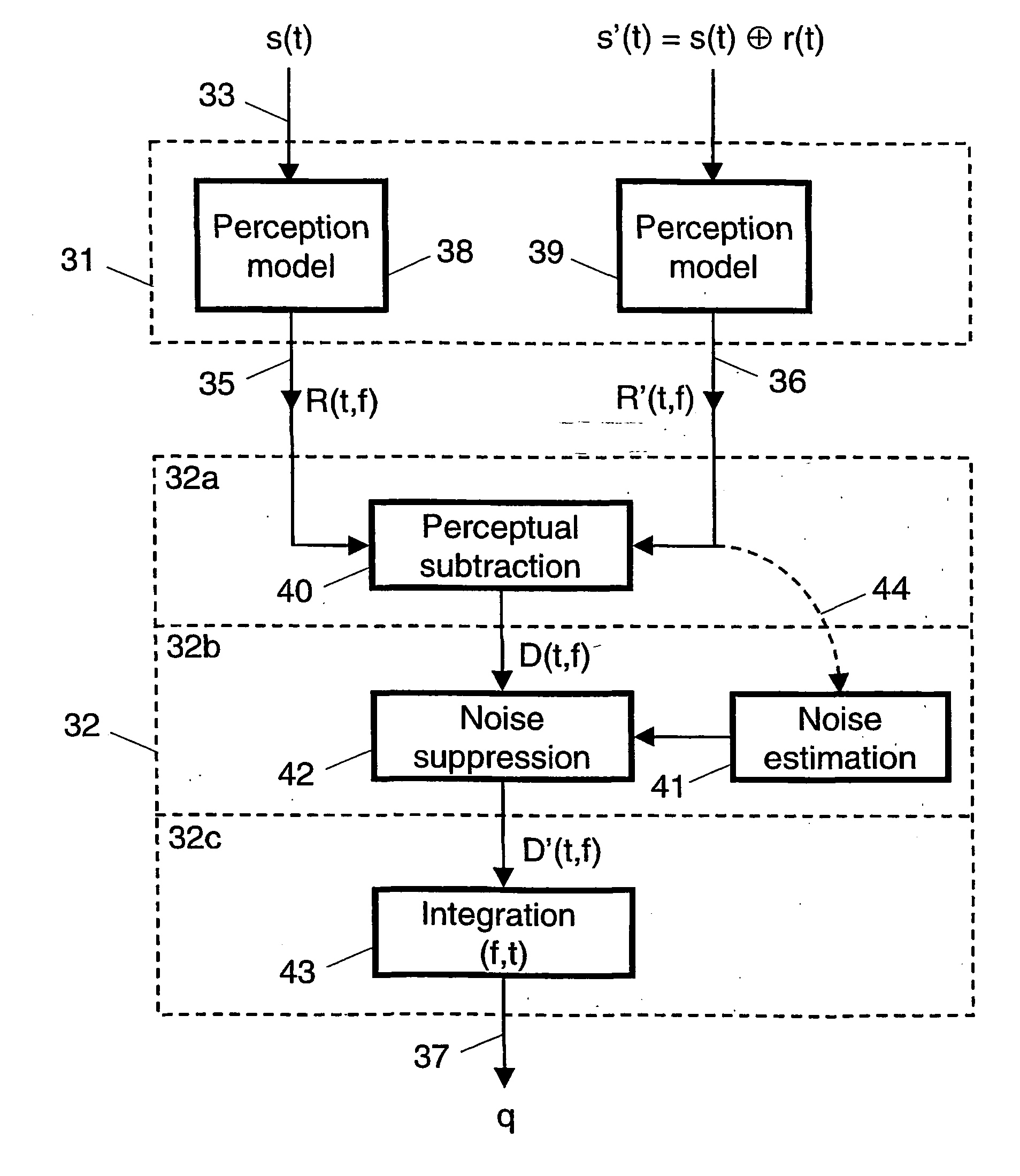
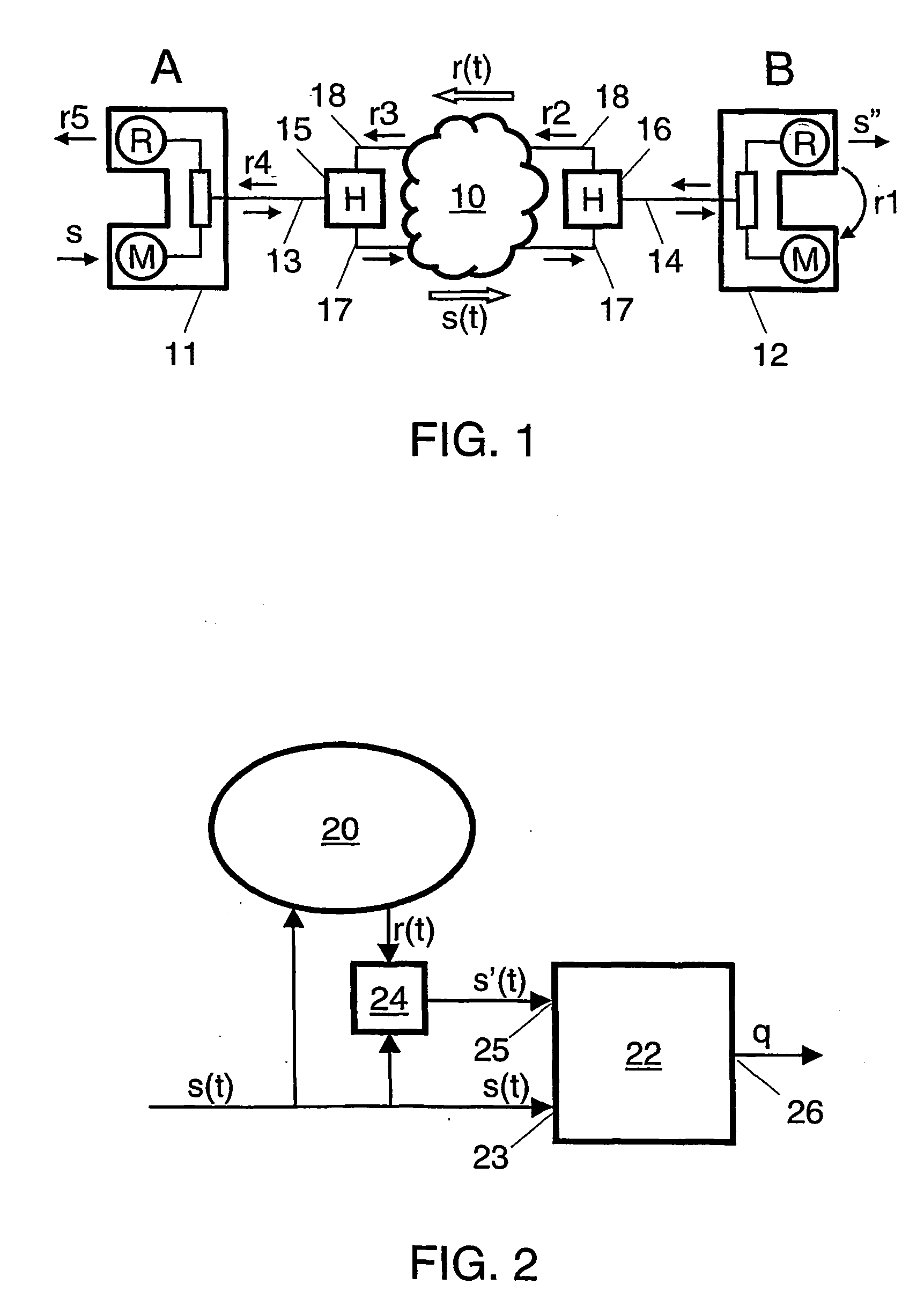
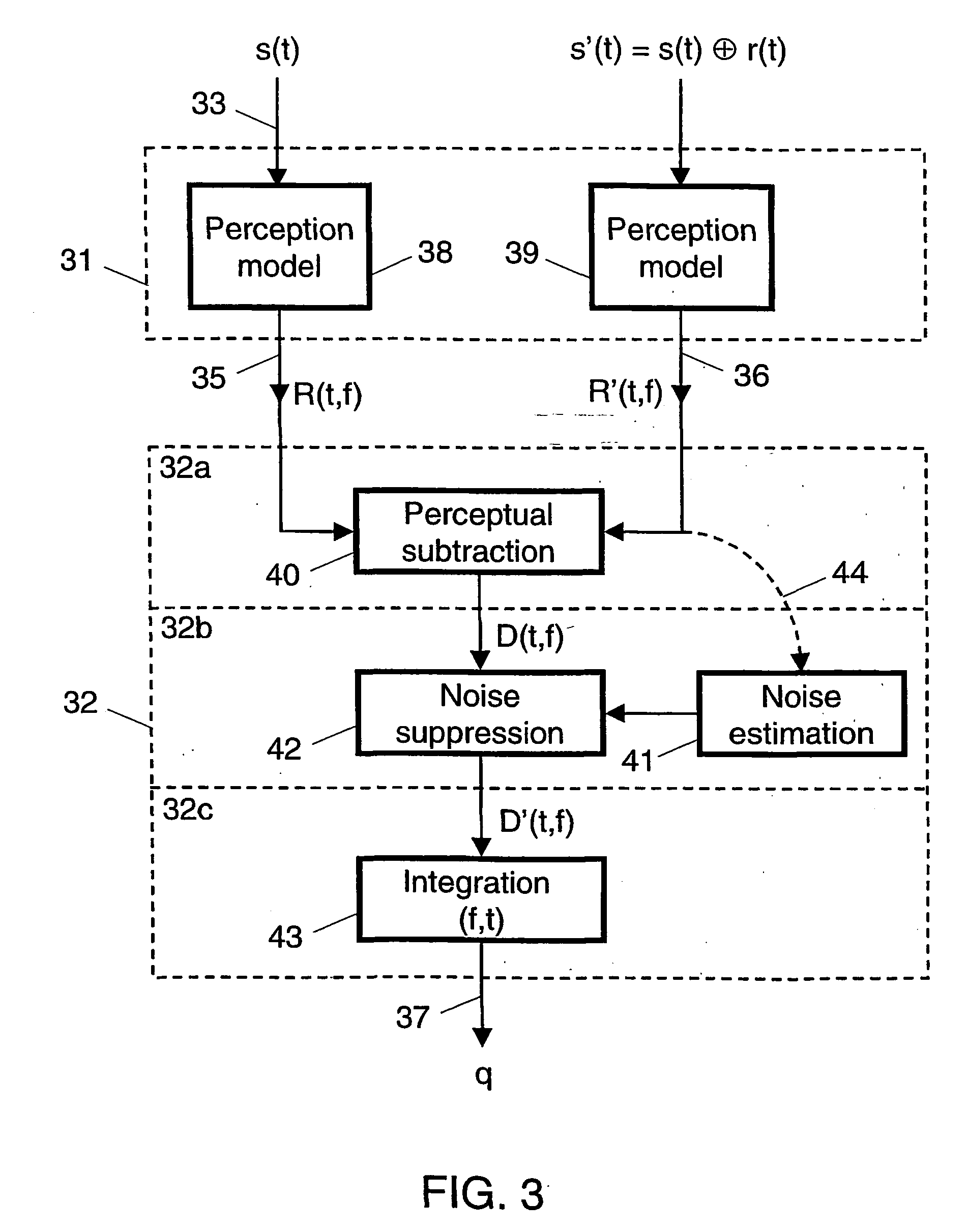
InactiveUS20040042617A1Improvement of subjectively perceived talking qualityMeasurement qualitySubstations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsTelecommunications networkObjective measurement
For measuring the influence of noise on the talking quality of a telephone link in a telecommunications network, a talker speech signal (s(t)) and a degraded speech signal (s'(t)) are fed to an objective measurement device (22) for obtaining an output signal (q) representing an estimated value of the talking quality. The degraded signal includes a returned signal (r(t)) originating from the network during transmission of the talker speech signal over the telephone link. The objective measurement carried out by the device is a modified PSQM-like measurement, which is modified as to include a modelling (32b) of masking effects in consequence of noise present in the returned signal. Preferably the modelling includes a noise suppression (42) carried out to a difference signal (D(t, f)) in the loudness density domain using a noise estimation (41).
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
Antenna selection method
ActiveUS20060077935A1Power managementSpatial transmit diversityTelecommunications networkDiversity scheme
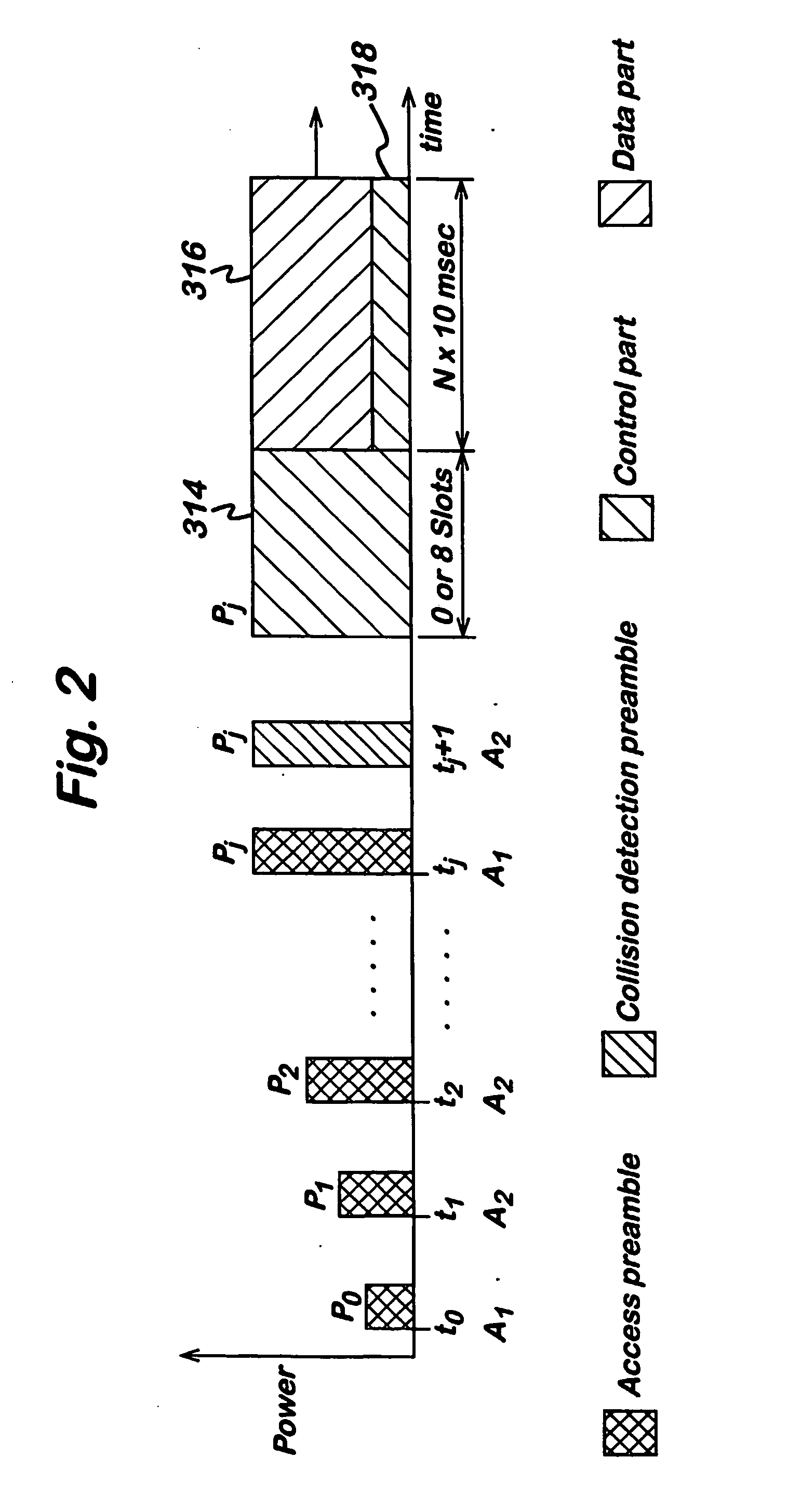
A method and apparatus for initiating a telecommunications uplink from a mobile terminal to a telecommunications network. A preamble signal is transmitted from the mobile terminal to the network in accordance with a transmission parameter of the mobile terminal. The parameter is changed and the preamble retransmitted until successful receipt in the network is confirmed. Changing the transmission parameter alters the signal diversity of one or more preambles as received by the base station.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Coding and packet distribution for alternative network paths in telecommunications networks
ActiveUS20070177579A1Improve service qualityReduce and even eliminate glitchNetwork connectionsQuality of serviceTelecommunications network
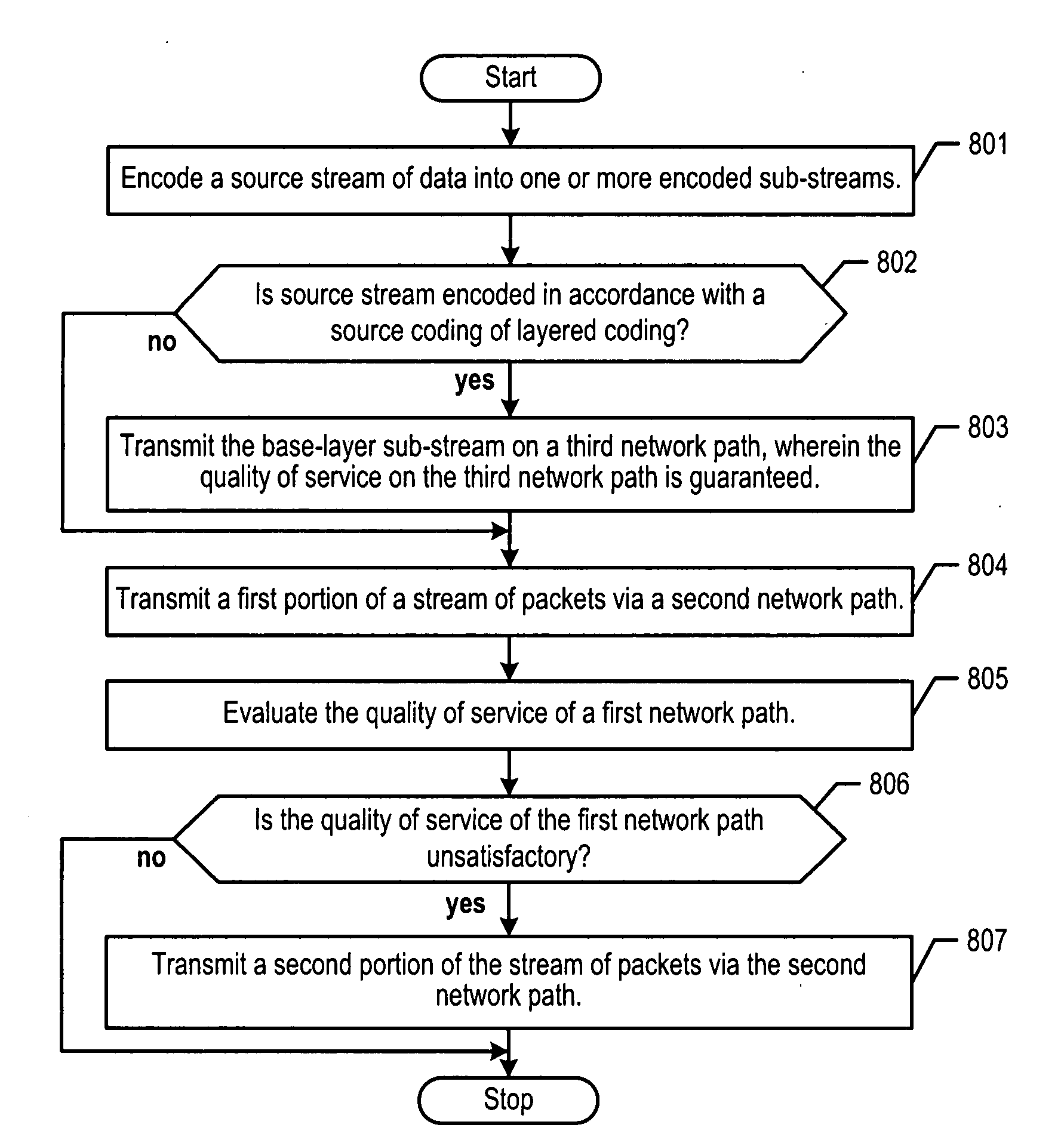
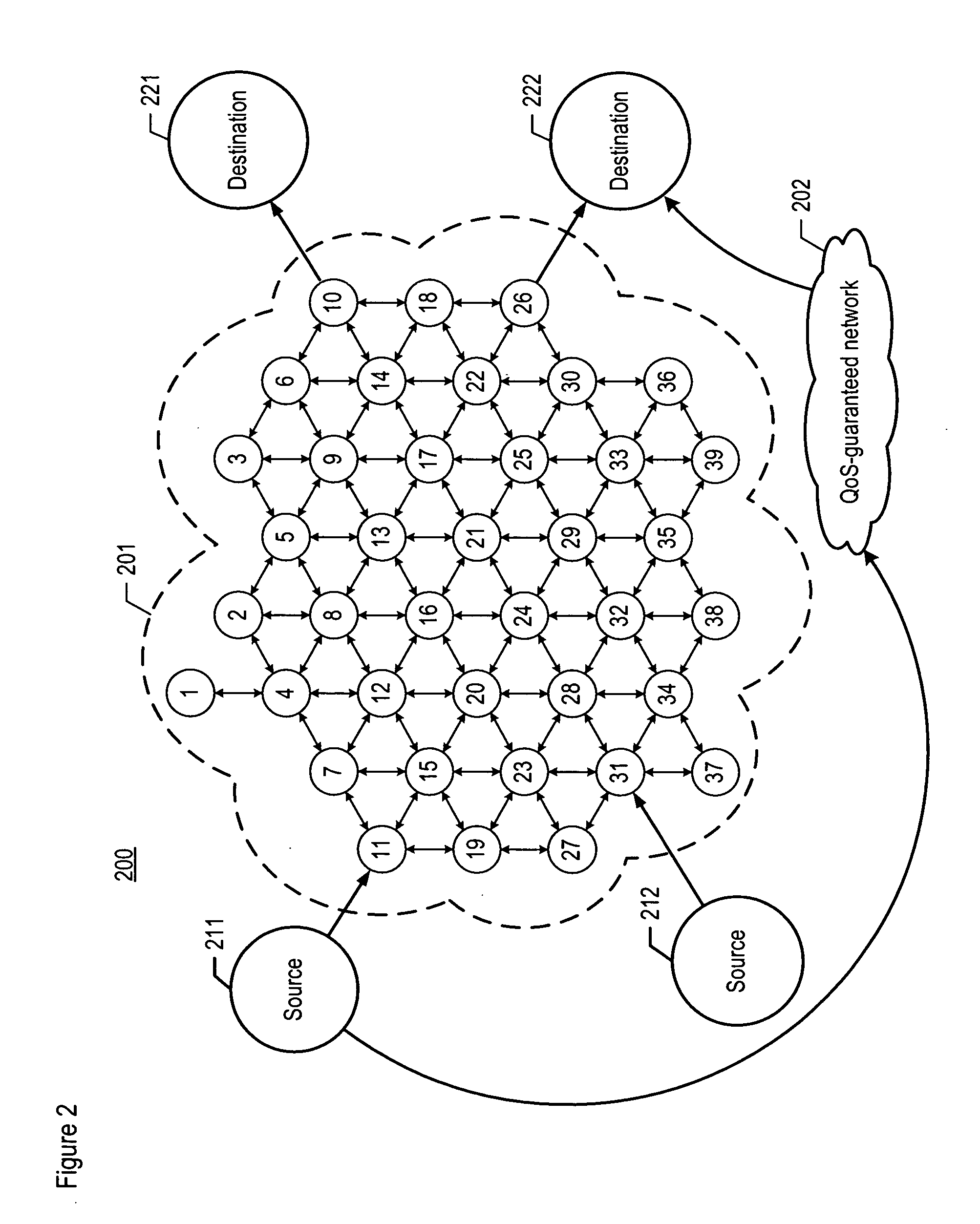
A method and apparatus are disclosed that seek to improve the quality of service that is experienced during the transmission of a stream of packets across one or more paths. In particular, a transmitting node encodes a source stream of data (e.g., audio, video, etc.) into one or more sub-streams, and distributes those sub-streams onto multiple network transmission paths. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment of the present invention, the transmitting node evaluates the quality of service of a first network path that fails to provide a quality-of-service guarantee. When the quality of service of the first network path becomes unsatisfactory, the coding of one or more sub-streams that are being transmitted on a second network path is adjusted. In other words, the coding on a second channel is adjusted in response to the changing conditions on a first channel.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Telecommunications network
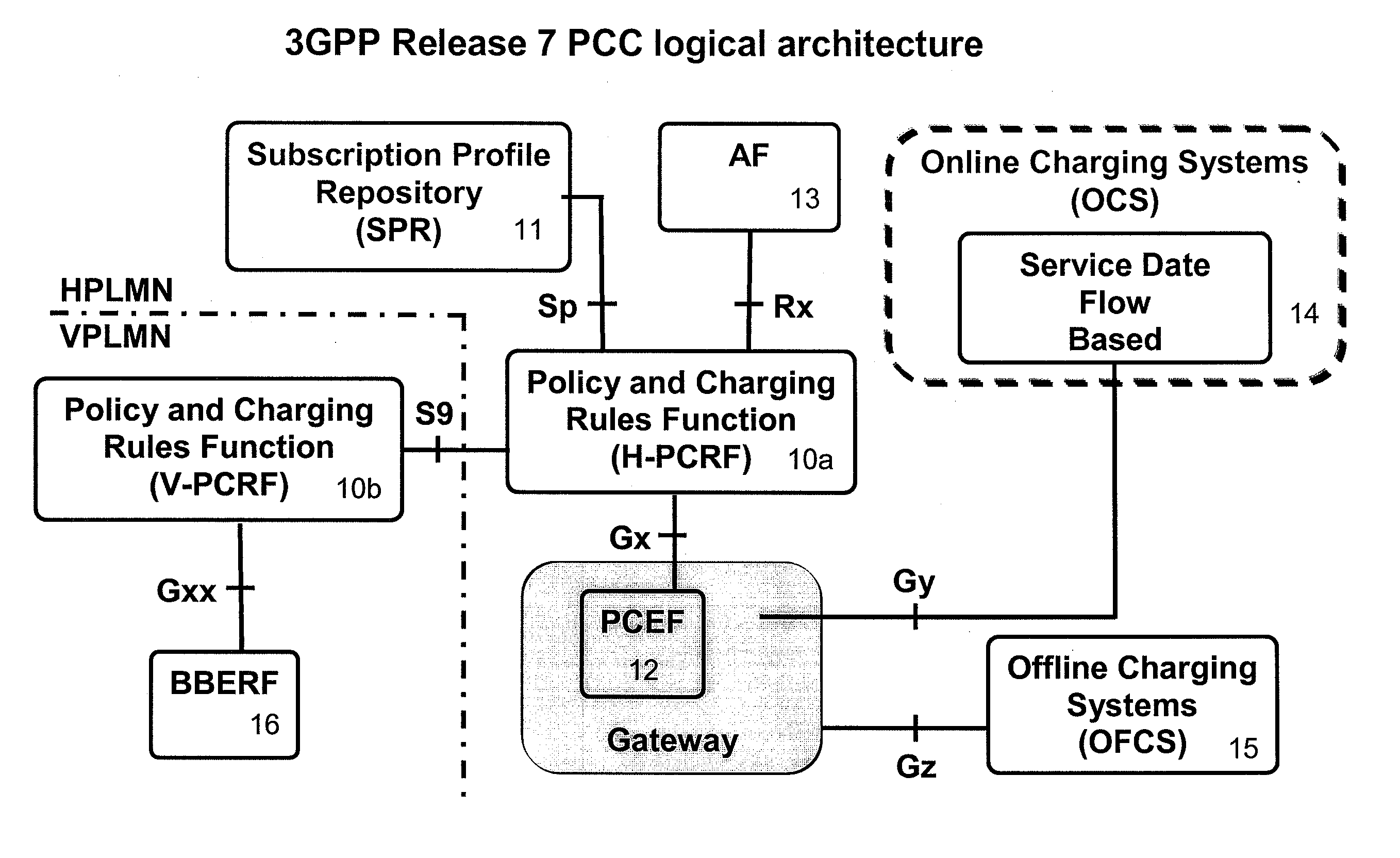
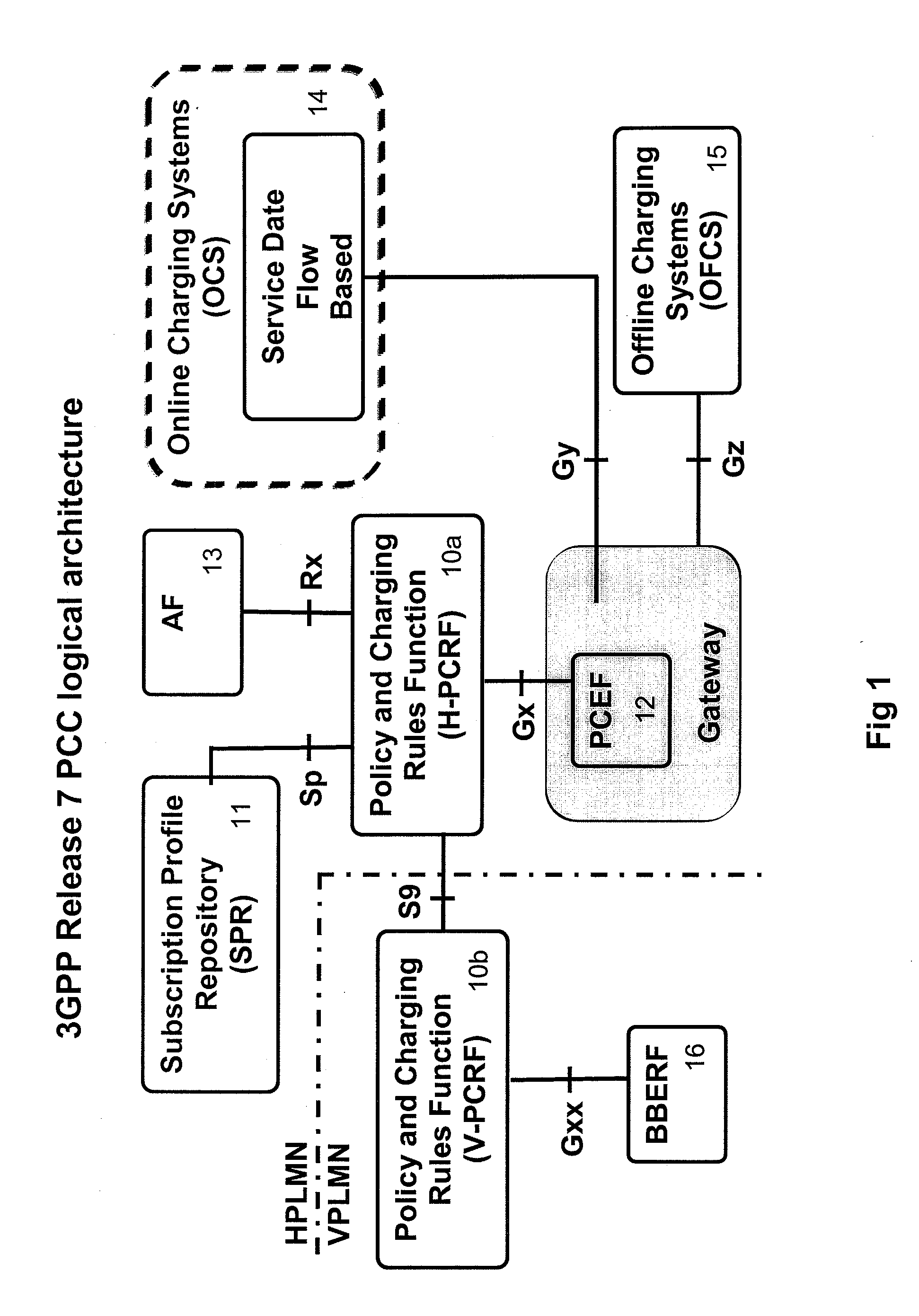
ActiveUS20110211465A1Accurate mechanismEnhance confidenceMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesNetwork elementDiameter protocol
In a telecommunications network including a gateway network element in communication with a control system and a user device, a system and method of controlling a data consumption rate of the user device including: a first control system node periodically transmitting a command to a second control system node, the message including information relating to a user's data usage, received from the gateway network node; in response to each command, the second control system node transmitting a reply message to the first control system node; controlling the transmission of the periodic commands according to a variable time interval; and the second control system node using the data usage information received in the periodic reply messages to control the data consumption of the user device. Preferably the control system conforms to a 3GPP Policy Charging Control Architecture and the first node is a PCEF and the second node is a PCRF. It is also preferable that the command is a DIAMETER protocol Accounting Request (ACR) command and the reply message is a DIAMETER protocol Accounting Answer (ACA) message.
Owner:VODAFONE GRP PLC
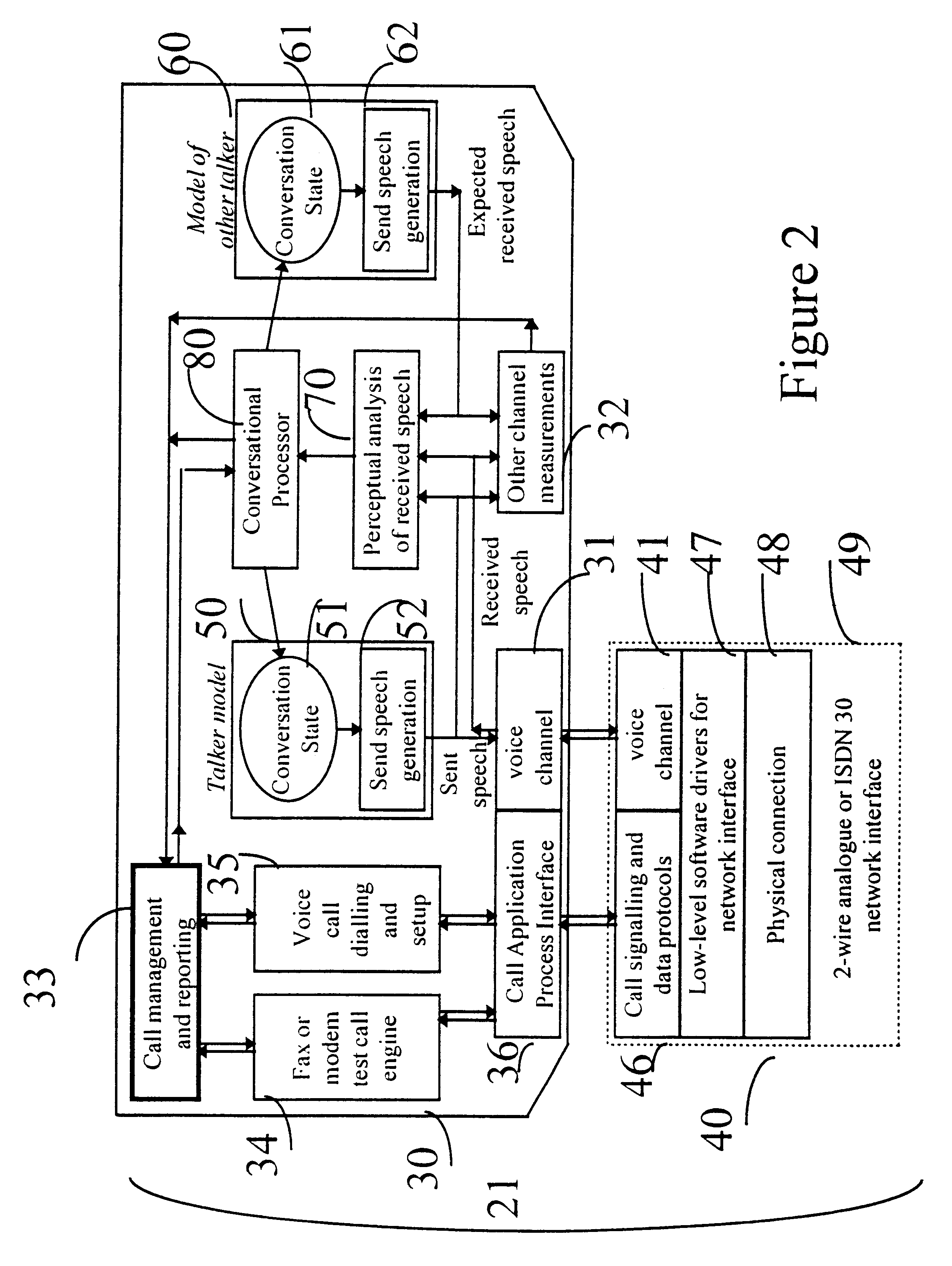
Testing telecommunications equipment
InactiveUS6304634B1Supervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentSignal qualityMeasurement device
A communications system is tested to simulate a realistic conversation. A first measurement device make a call, through the system it is testing, to a second measurement device and the two devices converse using predetermined speech generated dynamically by each device in response to the signals received from the other, to simulate aspects of conversation over non-perfect communications system link. The progress of the conversation will therefore take different courses according to the quality of the link. For example, if an expected signal is detected by one device, it transmits an appropriate predetermined response to the other device. However, if the expected signal is corrupted, or not received at all, different predetermined responses (or no response at all) are transmitted to the other device. This in turn may cause the other device to repeat the original signal. Because all the responses, including those to poor quality signals, are predetermined, each device can readily determine the quality of the signals received, because each signal received by one device form the other must be one of a limited number of possible responses to the last transmission made by the one device to the other. The devices perform measurements on the sounds they receive from each other, and monitor the progress of the conversation to compute parameters describing aspects of the received signal quality.
Owner:PSYTECHNICS
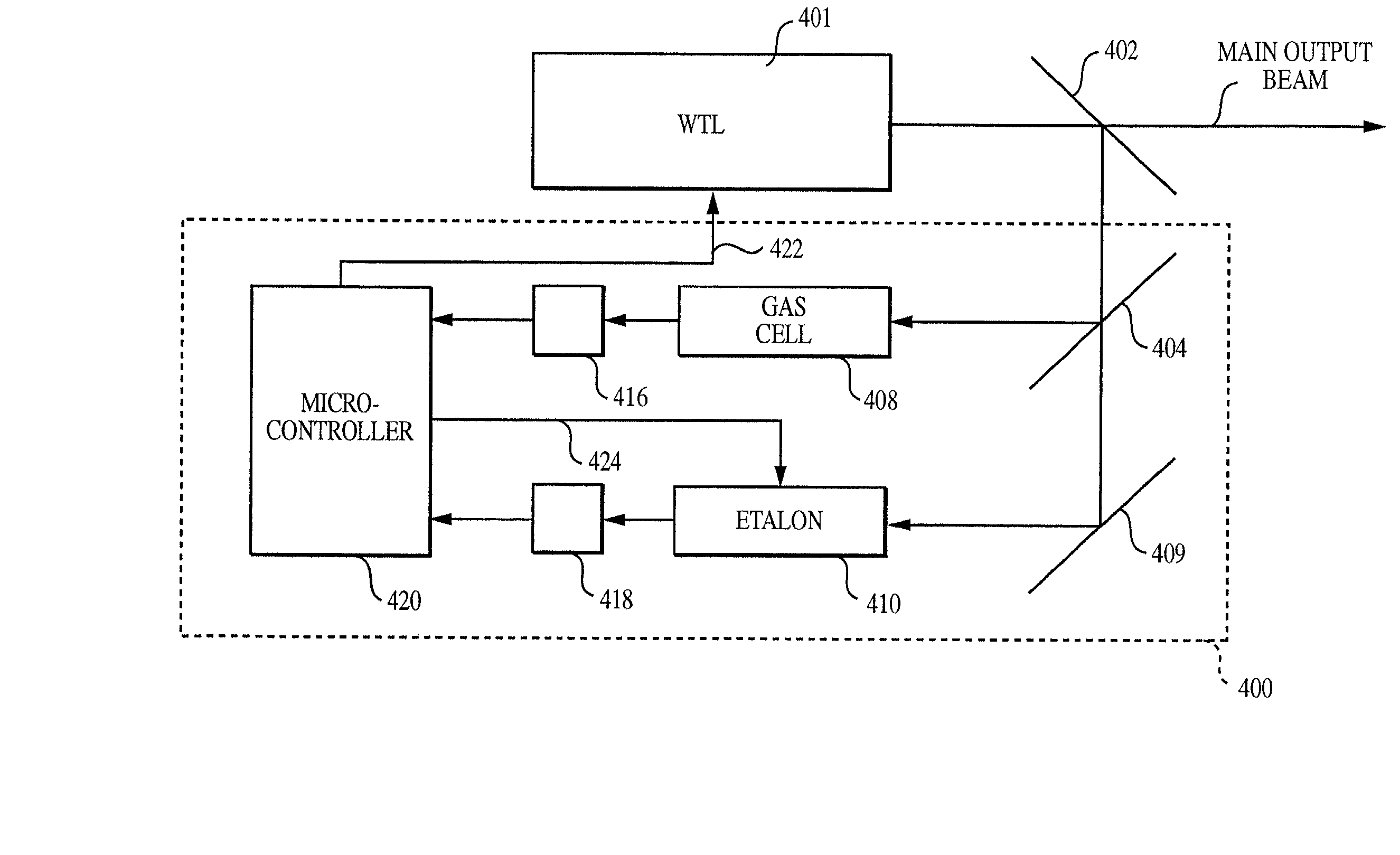
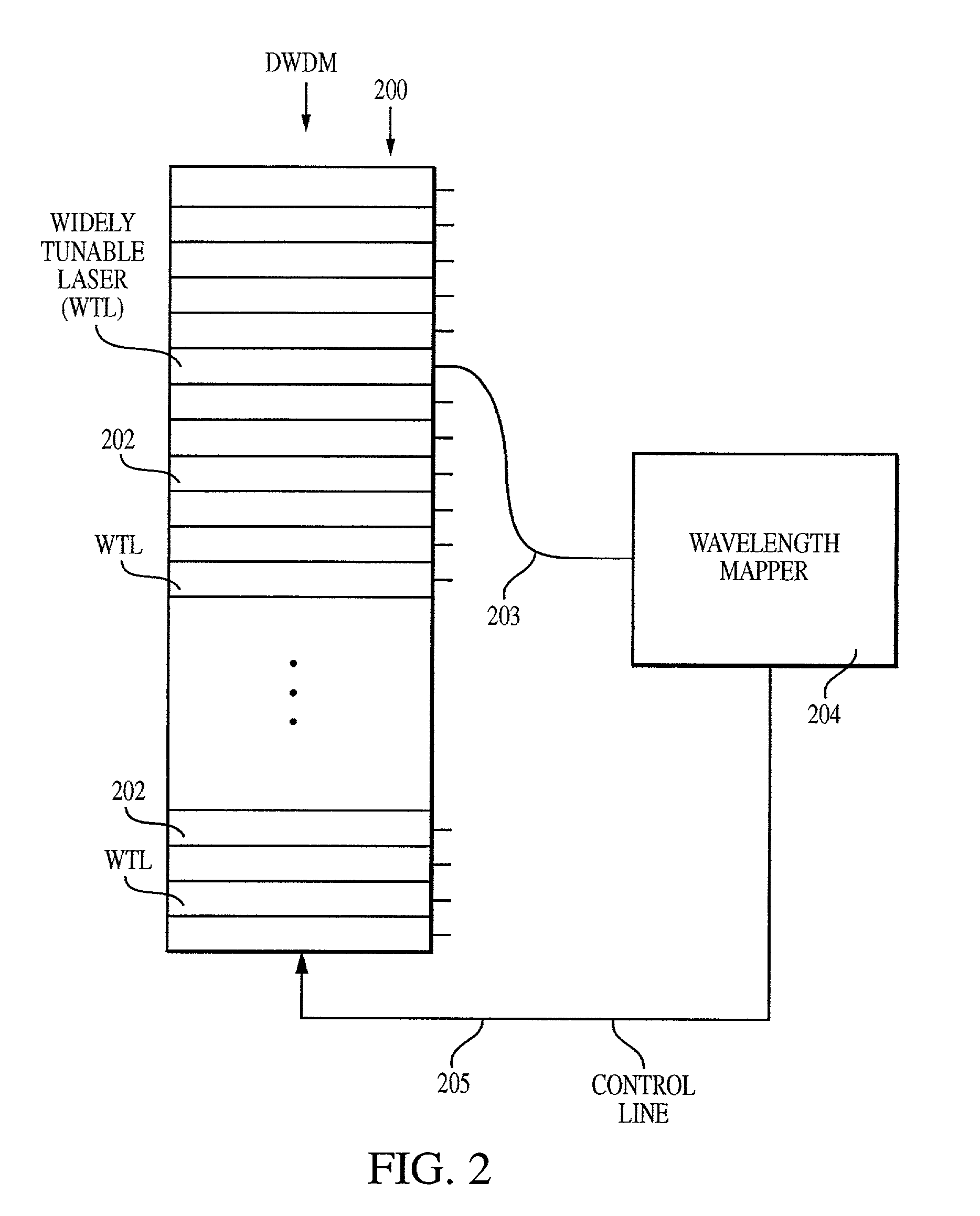
Method and system for locking transmission wavelengths for lasers in a dense wavelength division multiplexer utilizing a tunable etalon
InactiveUS20020041611A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsOptical resonator shape and constructionFiberMultiplexer
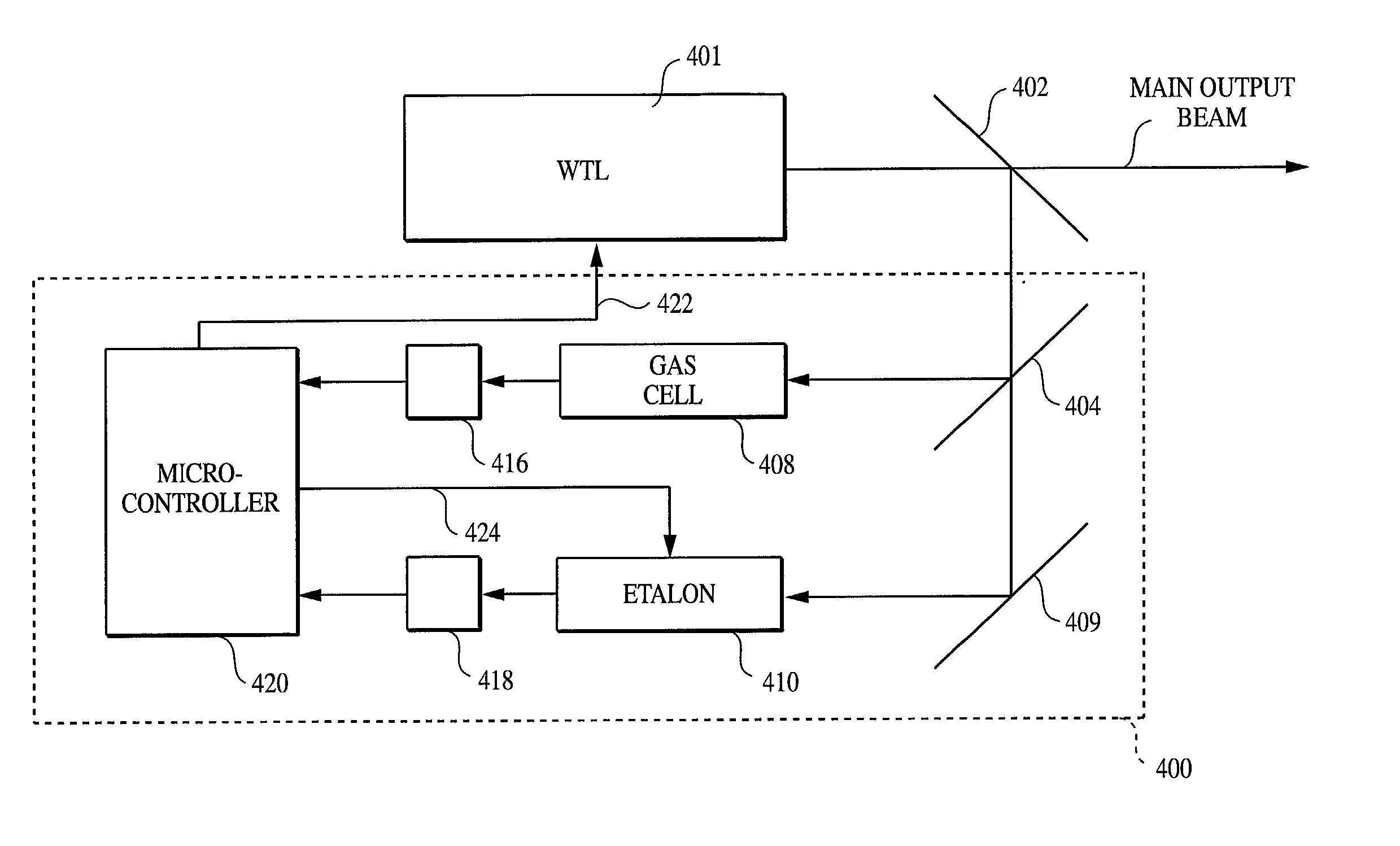
The method and system operate to calibrate a transmission laser of the dense wavelength division multiplexer (DWDM) and to lock the laser to a selected transmission wavelength. In one example, the transmission laser is a widely tunable laser (WTL) to be tuned to one of a set of International Telecommunications Union (ITU) transmission grid lines for transmission through an optic fiber. To lock the WTL to an ITU grid line, a portion of the output beam from the WTL is routed through the etalon to split the beam into a set of transmission lines for detection by an etalon fringe detector. Another portion of the beam is routed directly to a laser wavelength detector. A wavelength-locking controller compares signals from the two detectors and adjusts the temperature of the etalon to align the wavelength of one of the transmission lines of the etalon with the wavelength of the output beam, then controls the WTL in a feedback loop to lock the laser to the etalon line. The wavelength-locking controller thereafter monitors the temperature of the etalon and keeps the temperature constant to prevent any wavelength drift in the etalon. In one example, the optical components are aligned so that laser wavelength detector receives a portion of the laser beam directly from the laser so that phase characteristics of the laser beam are not affected by an intervening beamsplitter thereby permitting improved wavelength locking. In another embodiment, an etalon chirp filter is provided for reducing or eliminating optical frequency chirp, regardless of the particular ITU channel being used for transmission.
Owner:SPECTRASENSORS INC
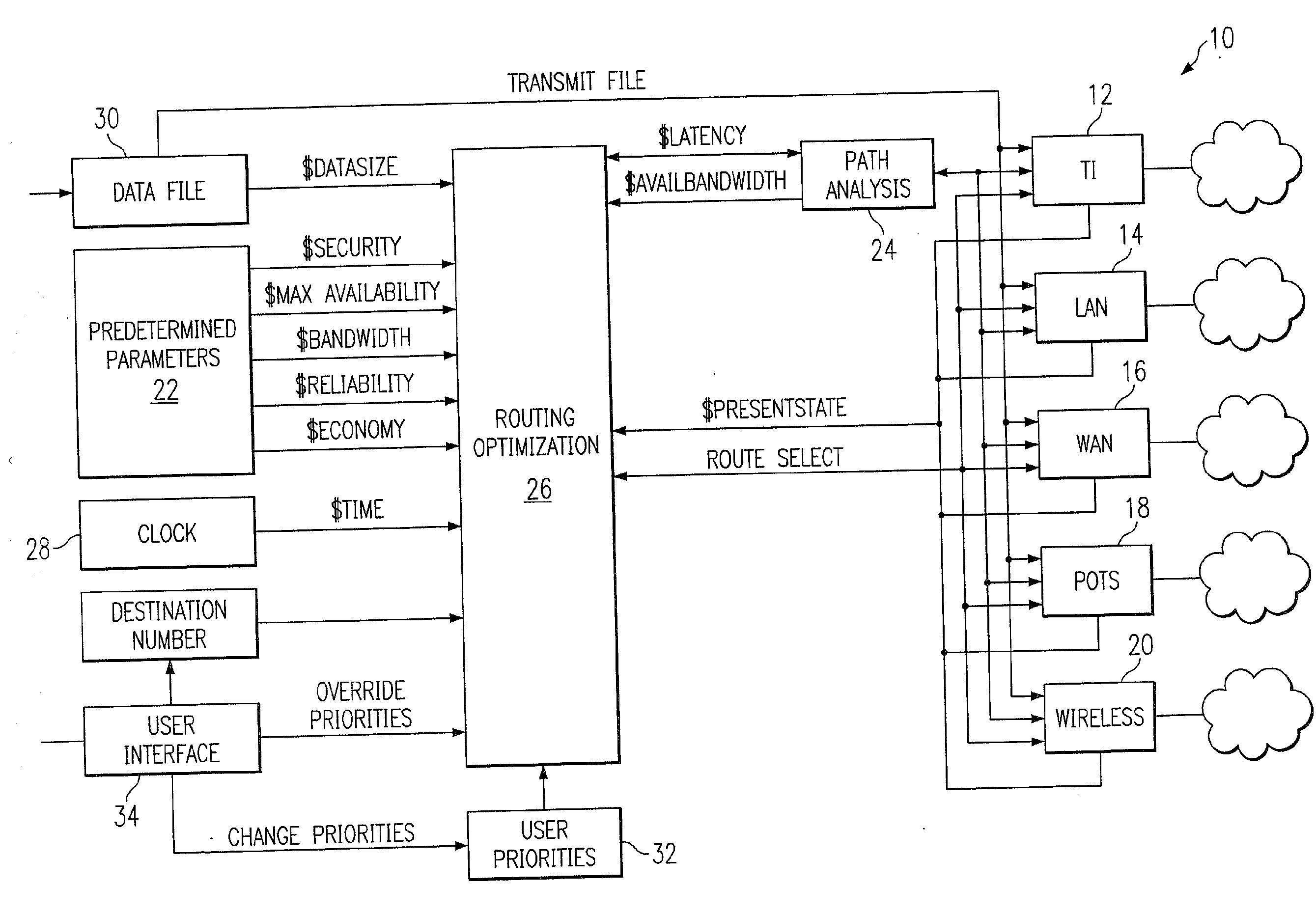
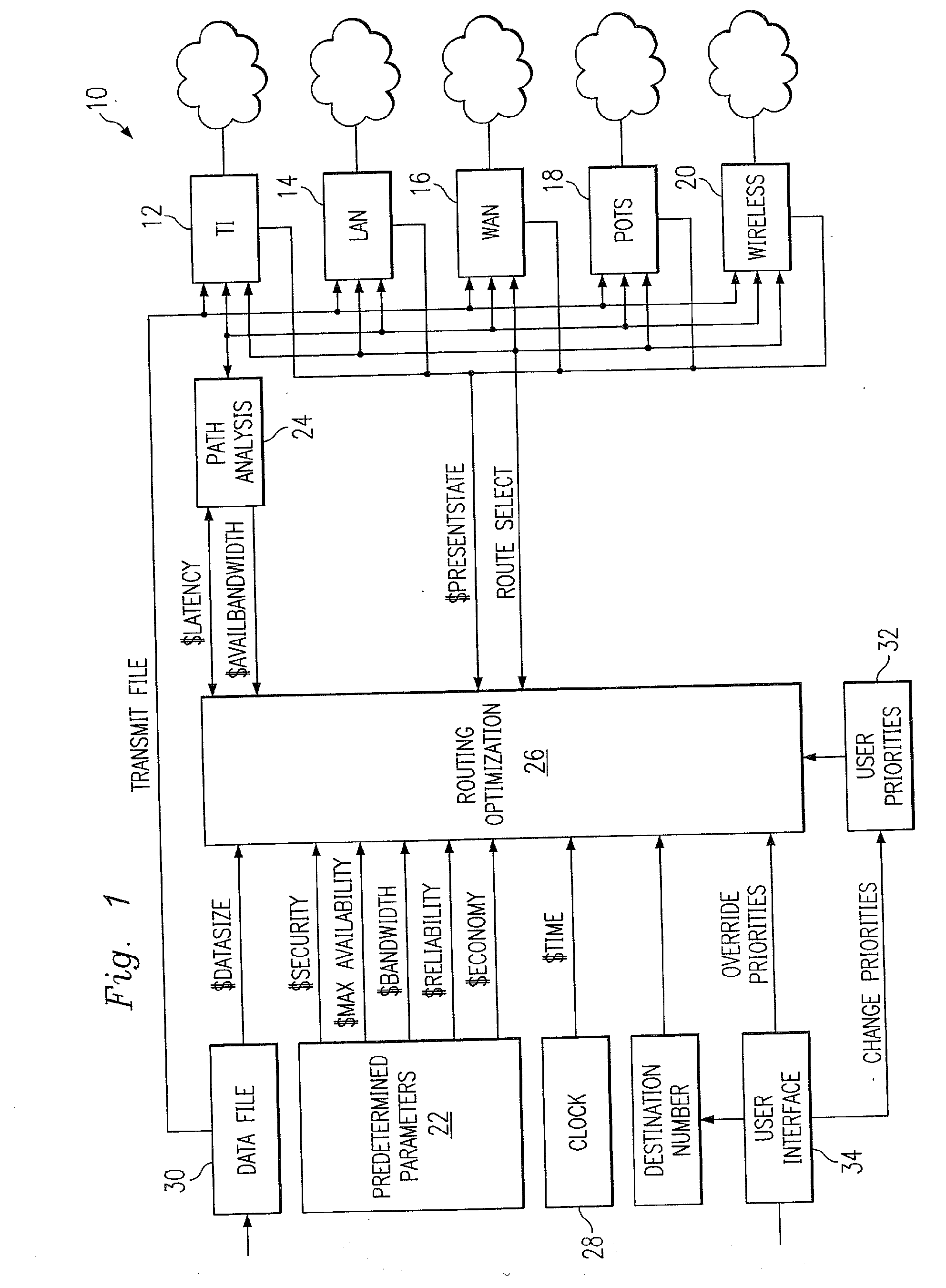
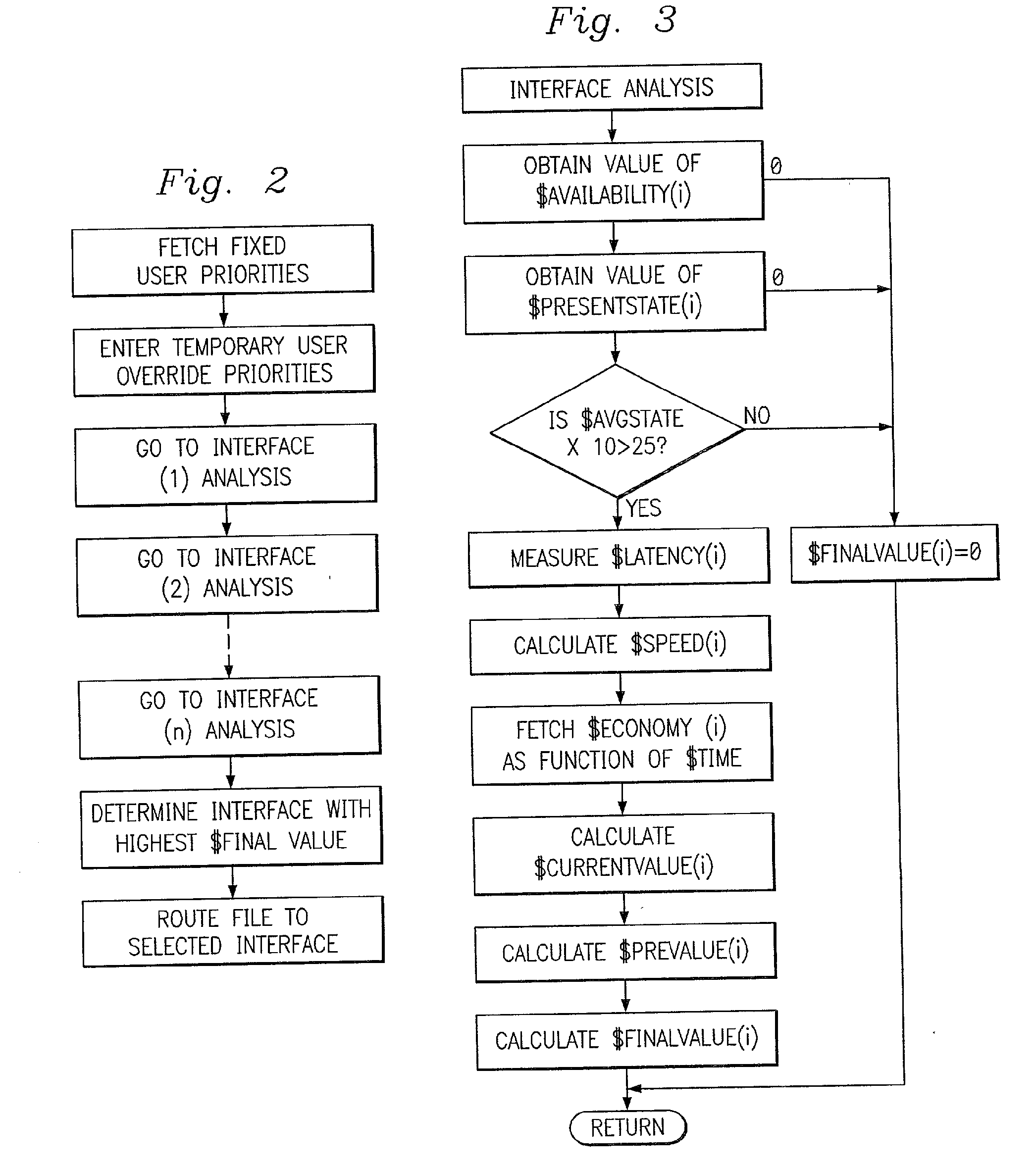
Multi-protocol telecommunications routing optimization
InactiveUS20080225832A1Interconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementData fileMulti protocol
A telecommunications switching system employing multi-protocol routing optimization which utilizes predetermined and measured parameters in accordance with a set of user priorities in determining the selection of a telecommunications path to be utilized for transmitting a data file to a remote destination. The switching system has a first memory for storing the data file to be transferred, a second memory for storing predetermined parameters such as cost data associated with each of the telecommunications paths, a third memory for storing a set of user priorities regarding the transmission of data files, and means for measuring the value of variable parameters such as file transfer speed associated with each of the telecommunications paths. Processor means are operatively associated with the second and third memories and the variable parameter measuring means for determining which of the plurality of telecommunications paths should be utilized for transferring the data file in accordance with the set of user priorities, the predetermined telecommunications path parameters, and the measured variable parameters. The switching system further comprises input means for allowing a user to change the user priorities in the third memory prior to transmitting a file.
Owner:PATENTMARKS COMM
Method and arrangement for the improved exploitation of technical resources between telecommunications networks and ip-networks
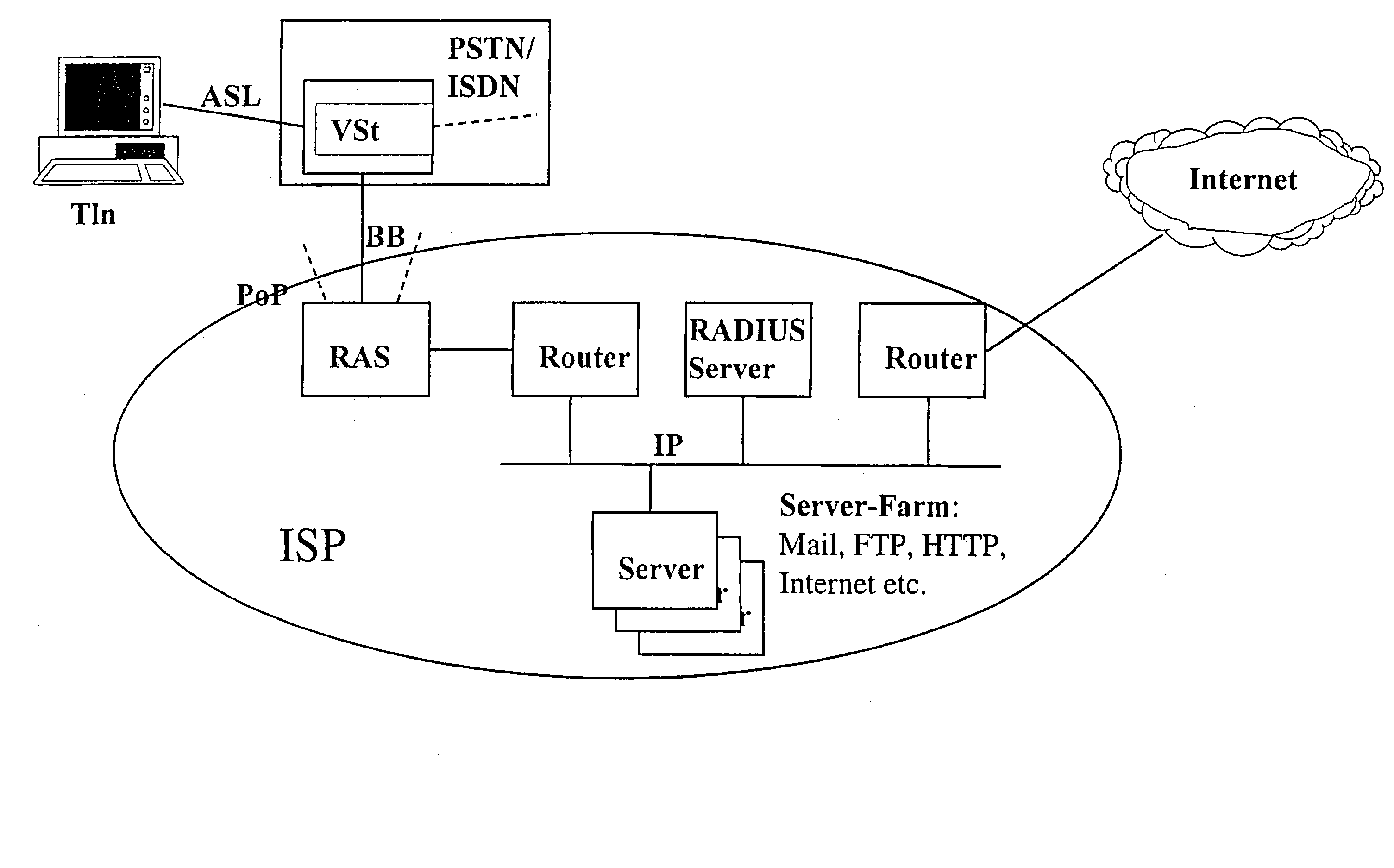
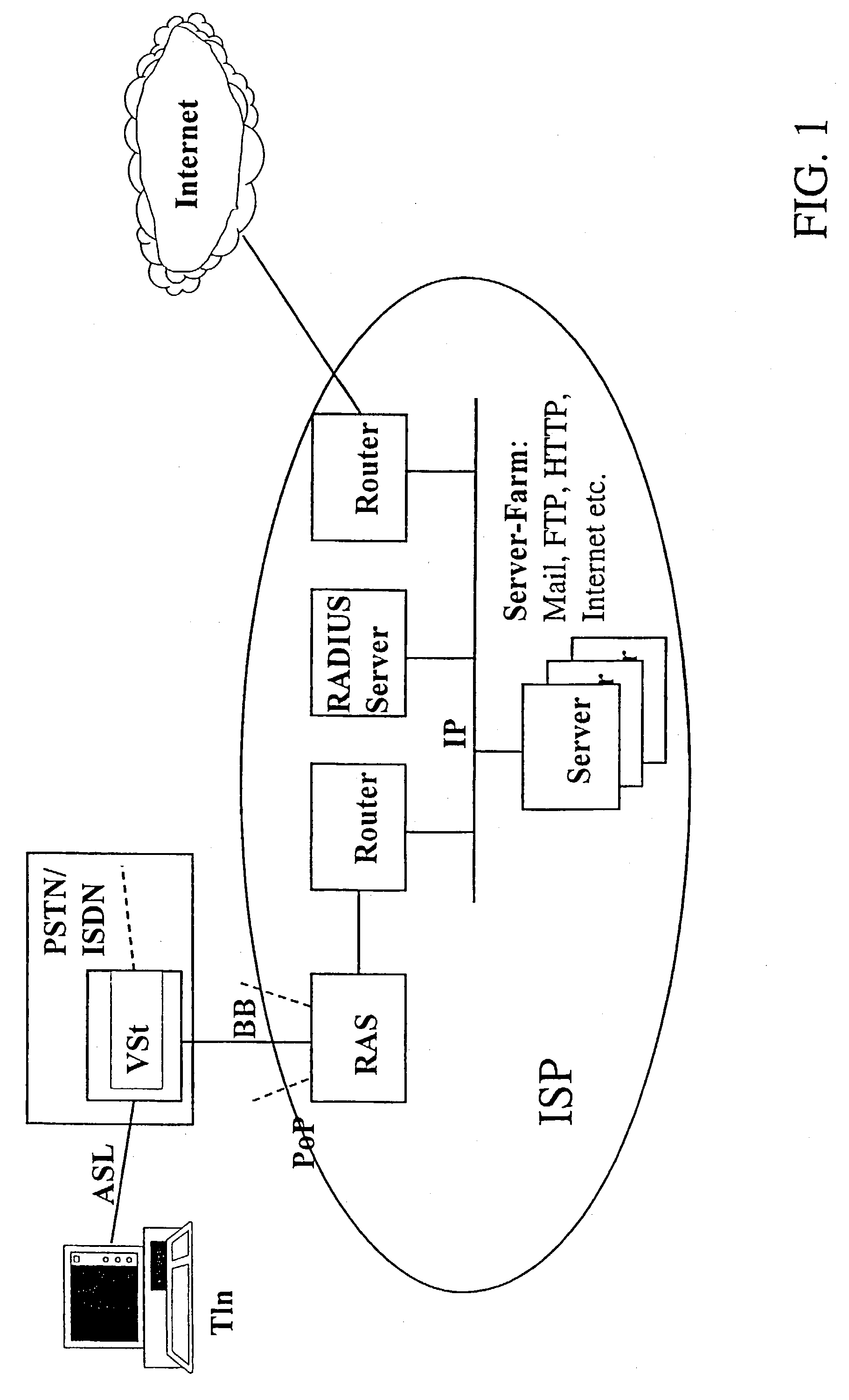
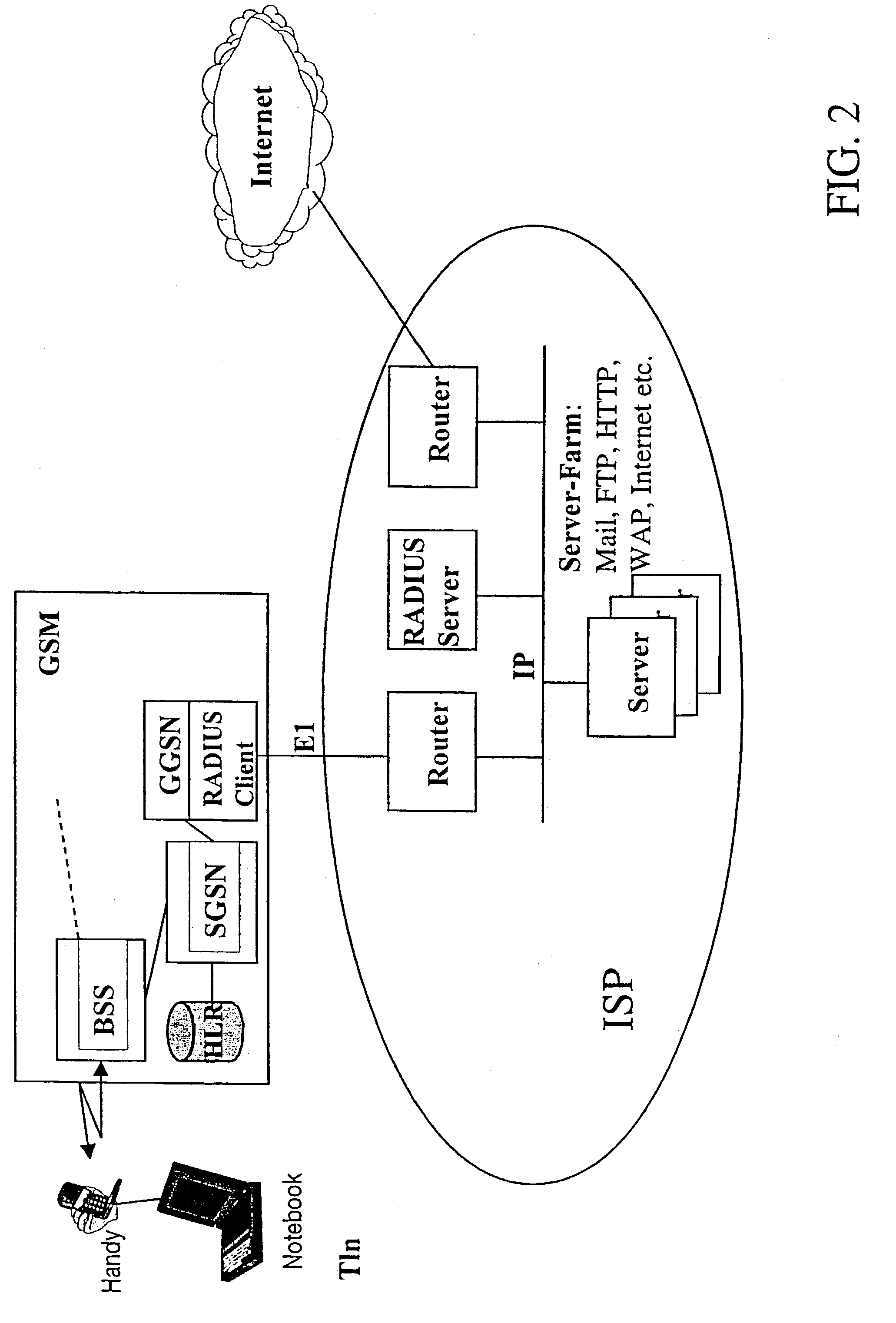
InactiveUS20030103506A1Effective connectionTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationRADIUSTelecommunications link
The invention relates to a method for the improved exploitation of resources between telecommunications networks and IP networks (for example, corporate LANs or the public Internet), for reducing the costs of permanent connections (always-on connections) and for optimsing IP address economy. According to said method an access, authentication and multiplex device ("RAMSES-client") replaces the usual RADIUS client. Said RC has an authentication device (RAC) which is connected to the ISP-specific authentication device and authenticates the ISP access of the subscriber. During the periods when there is no traffic, the RC deactivates the connection between the telecommunications network and the IP network, while the subscriber-side connection is maintained. When the subscriber has new data traffic, the RC automatically activates the IP connection concerned to the ISP with reversion to the stored authentication data. This makes a static use of the limited resources between the telecommunications and IP networks, such as dynamic IP addresses, PVCs, transmission channels, lines etc, possible. Additional RAMSES protocol elements allow the ISP-side activation of the partial connection for ISP-initiated e-mail delivery.
Owner:T-MOBILE DEUTSCHLAND
Automatic repetition request mechanism in a radio access network
InactiveUS20020094814A1Facilitate transmissionReduce needError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkReliable transmission
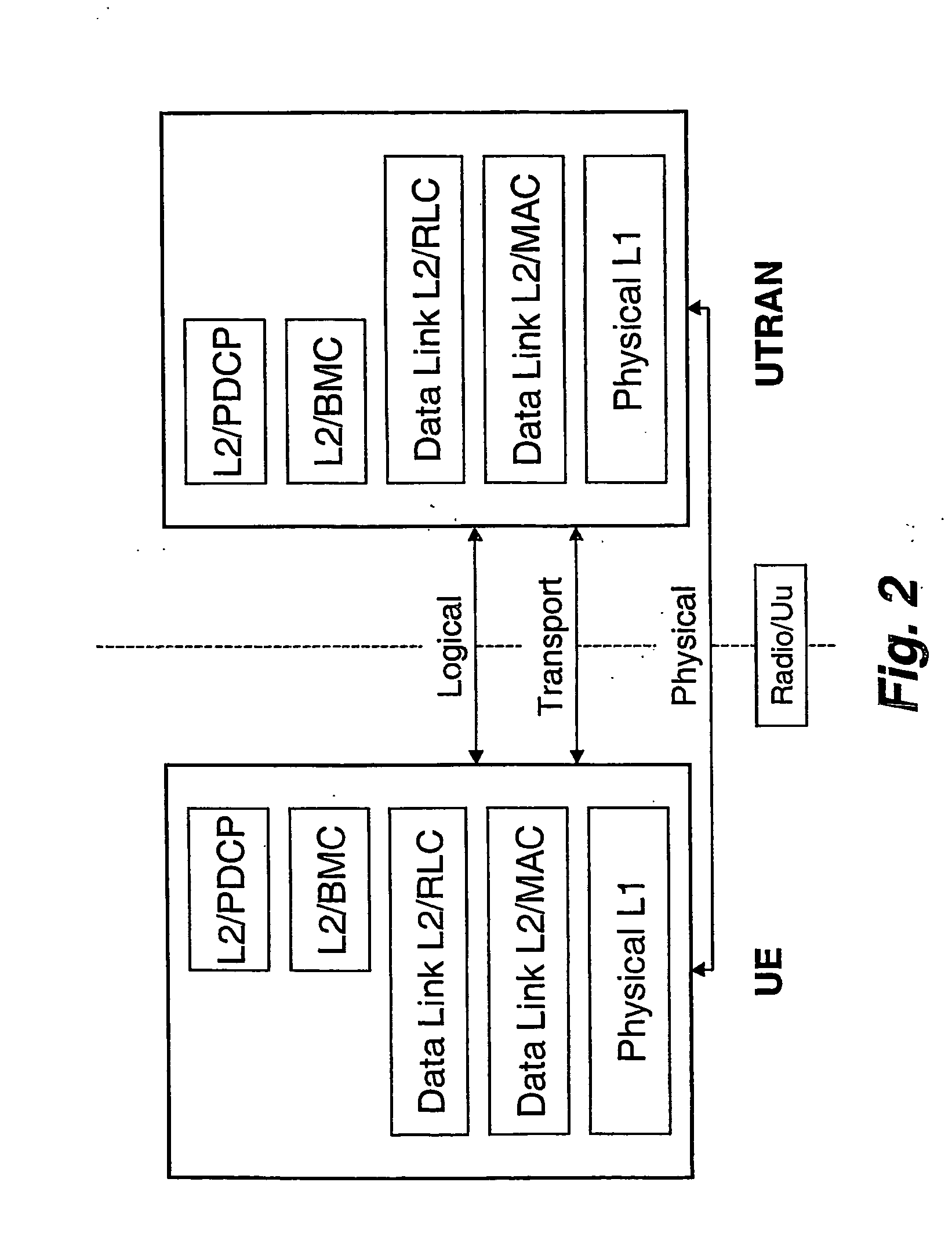
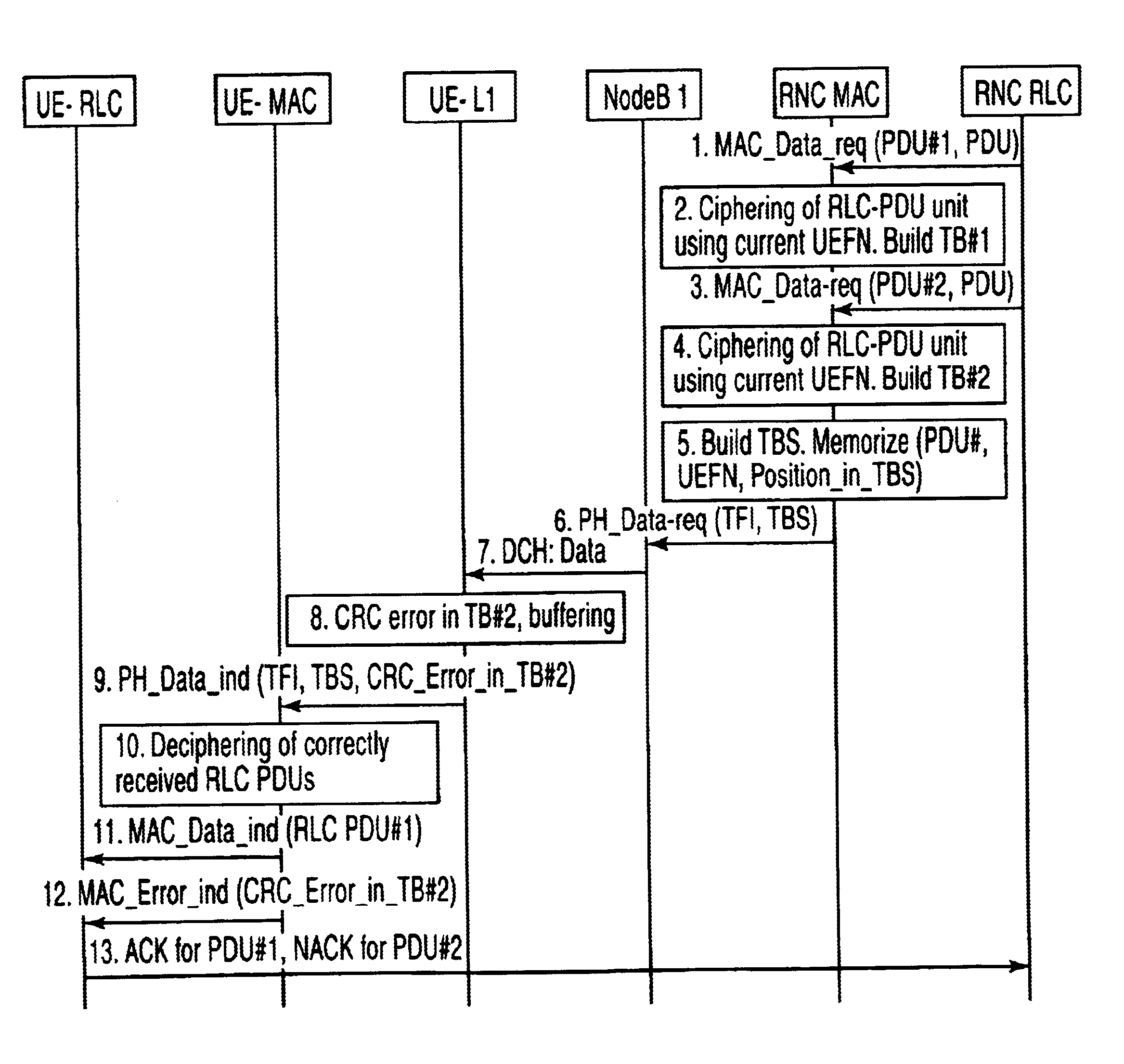
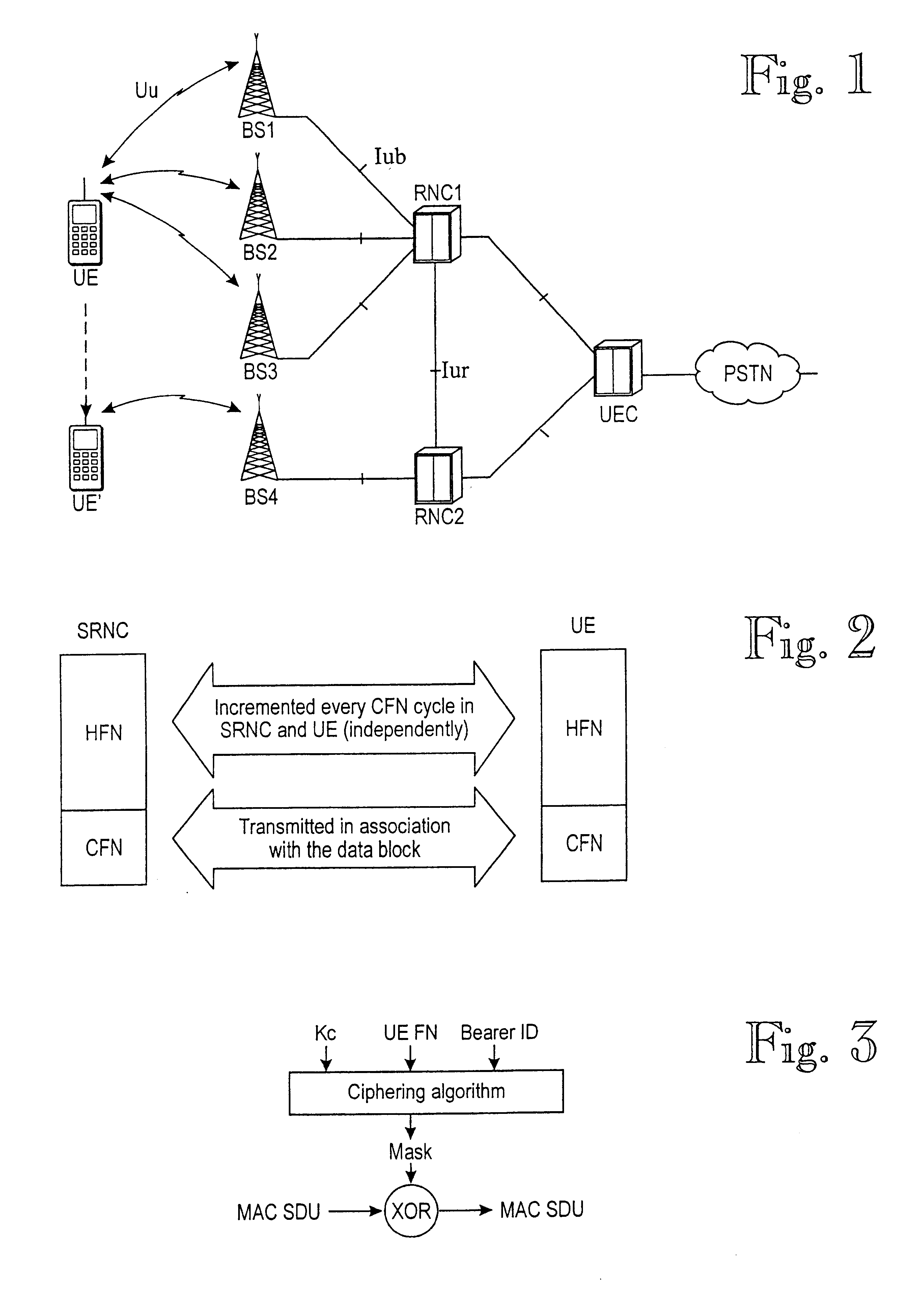
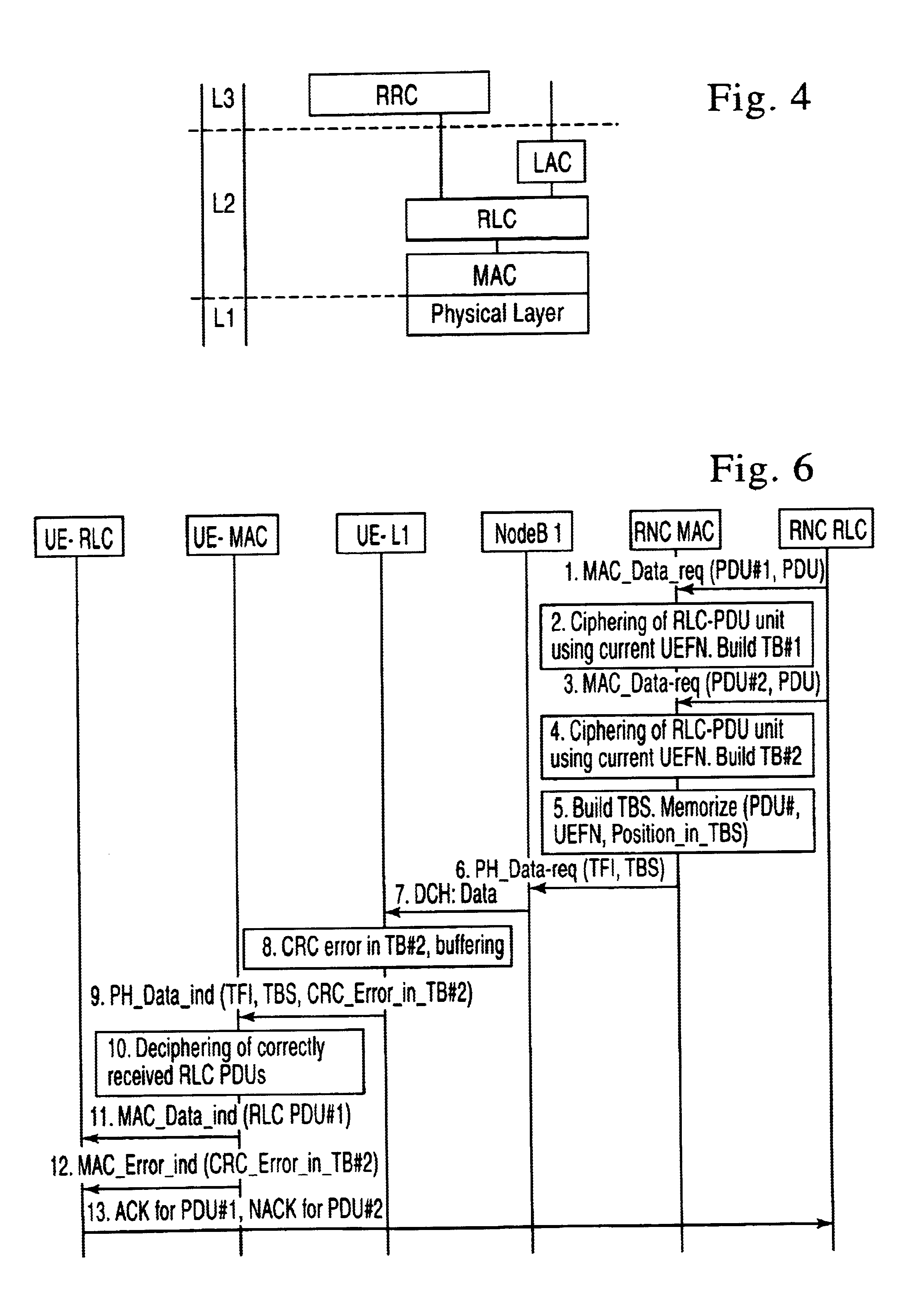
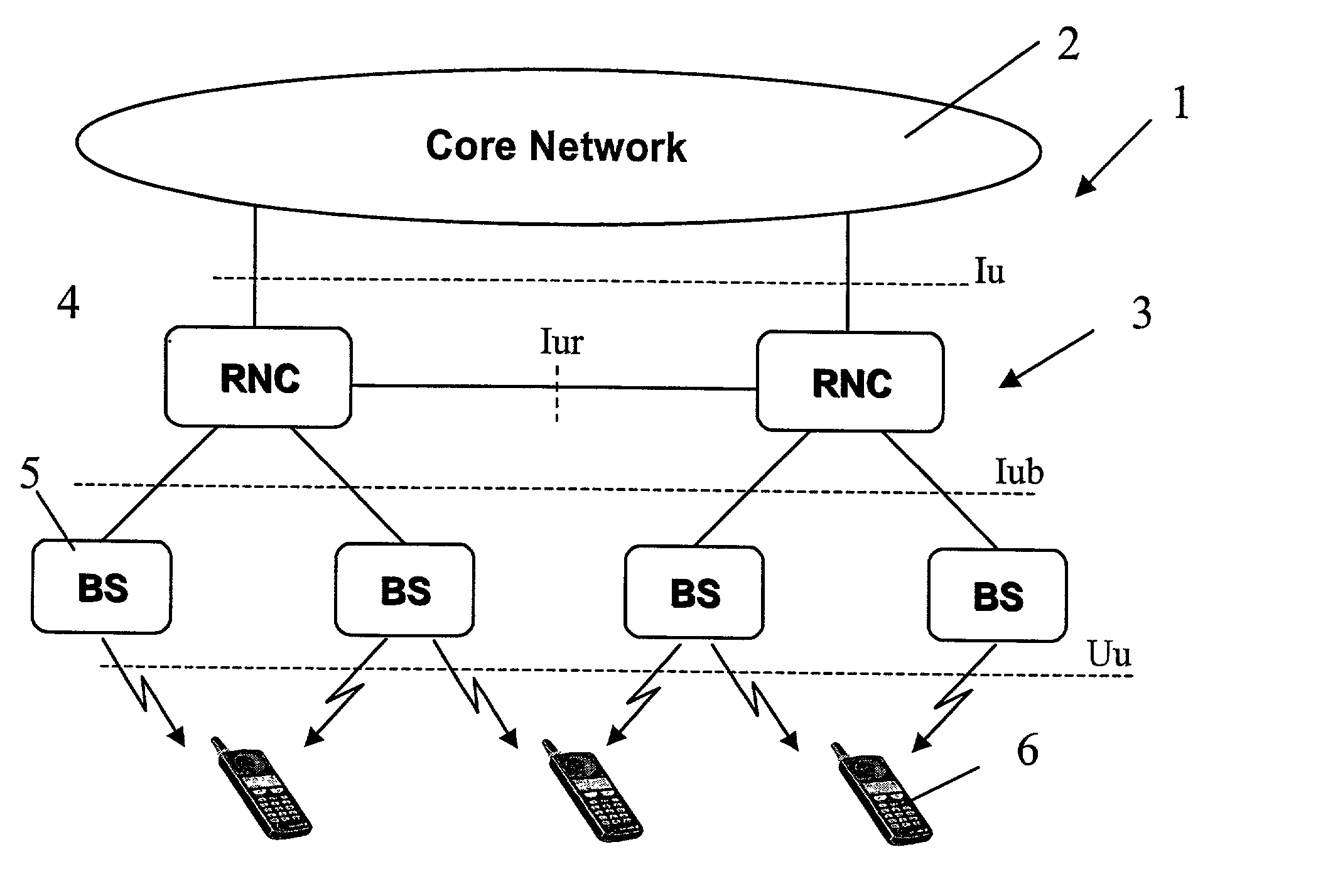
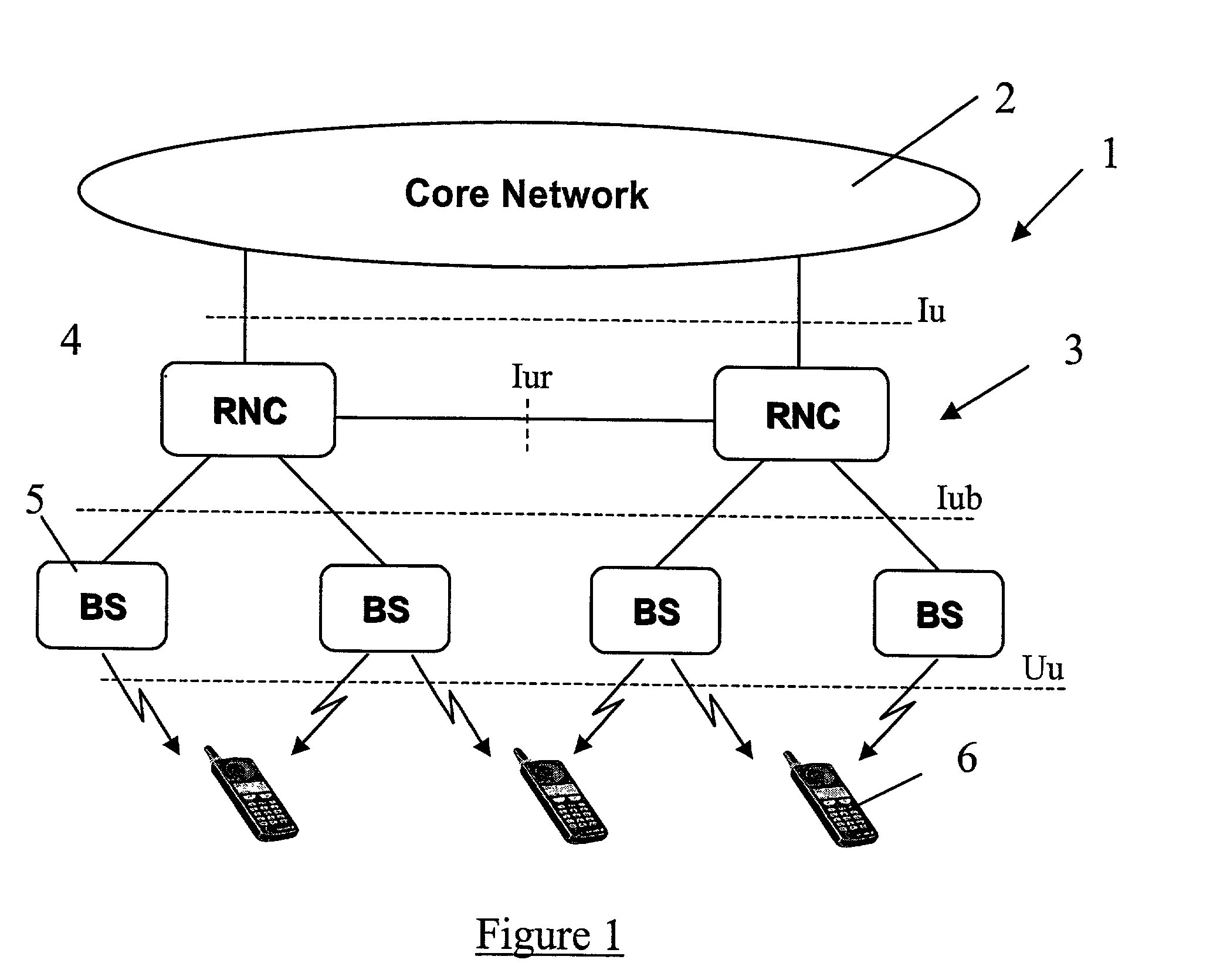
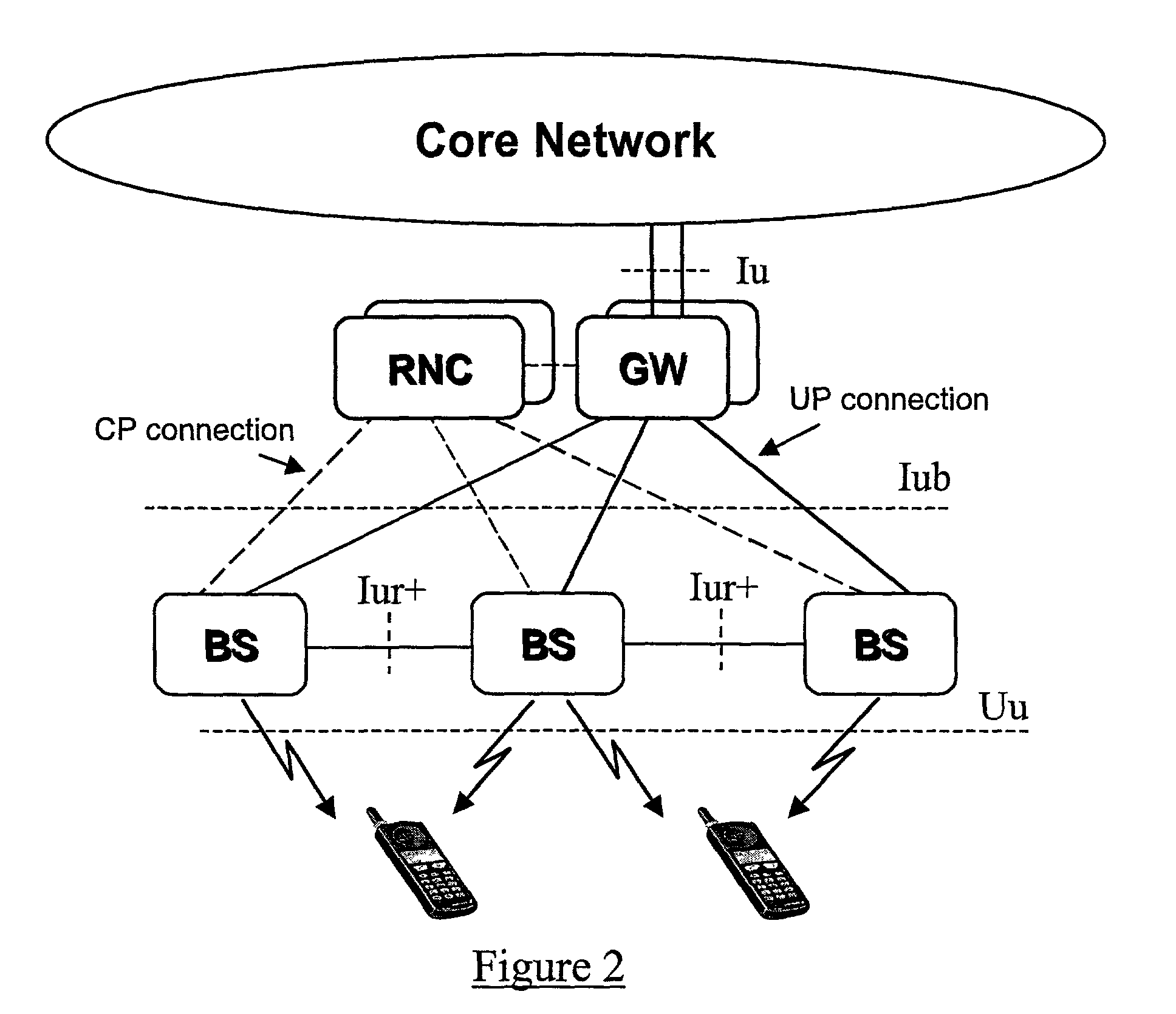
A method of handling the transmission of RLC PDUs from a Radio Access Network (RAN) of a mobile telecommunications system to User Equipment (UE). At a Gateway (GW) of the UTRAN, RLC SDUs are segmented into RLC PDUs for transmission to one or more Base Stations (BSs) of a set of BSs belonging to a handover link set, and RLC PDUs received from one or more of those BSs into RLC SDUs are combined for transmission to a core network of the system. At the or each said BS, RLC PDUs received from the GW and or the UE are buffered. An ARQ mechanism is implemented at the or each BS to facilitate reliable transmission of RLC PDUs between the UE and the GW.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
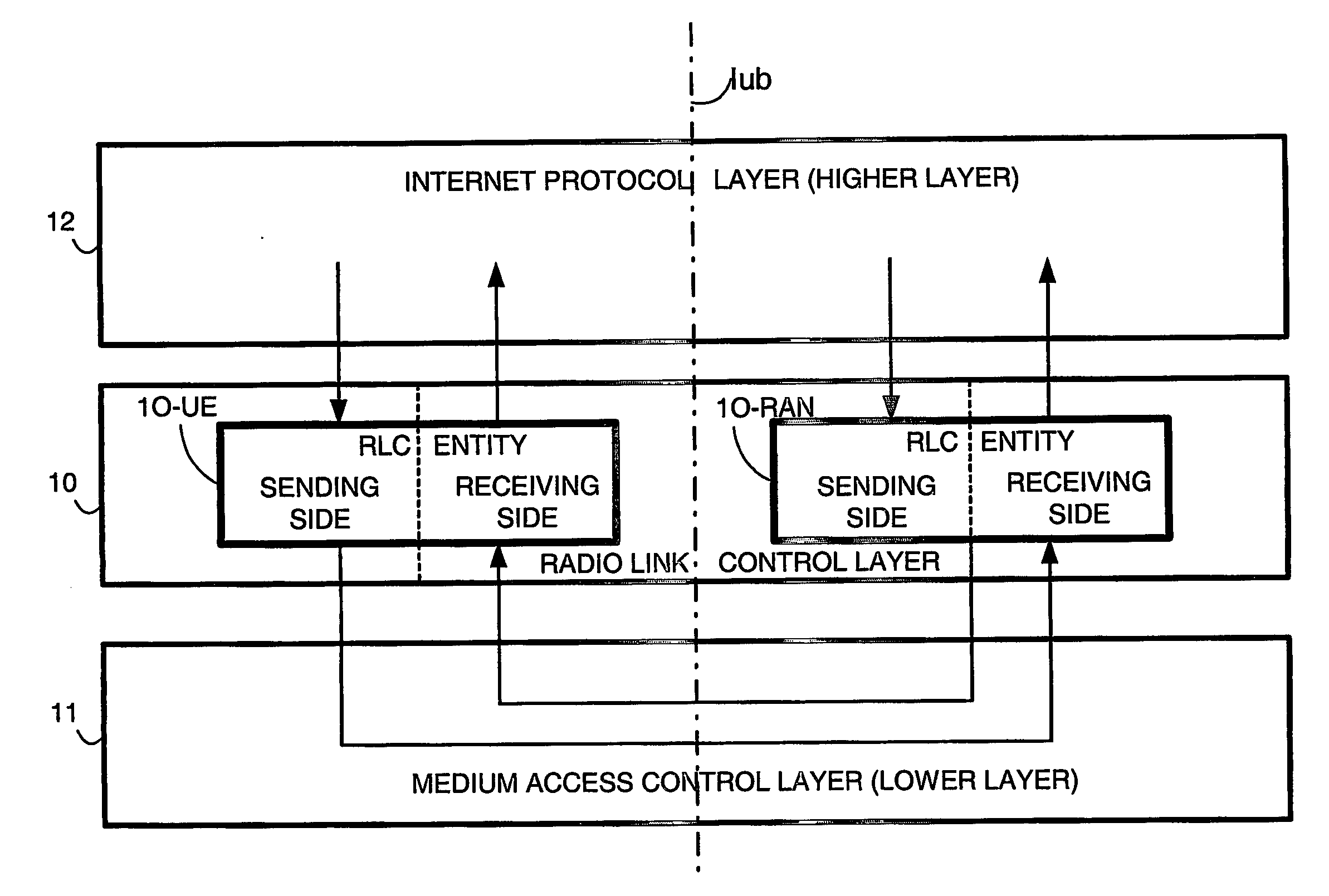
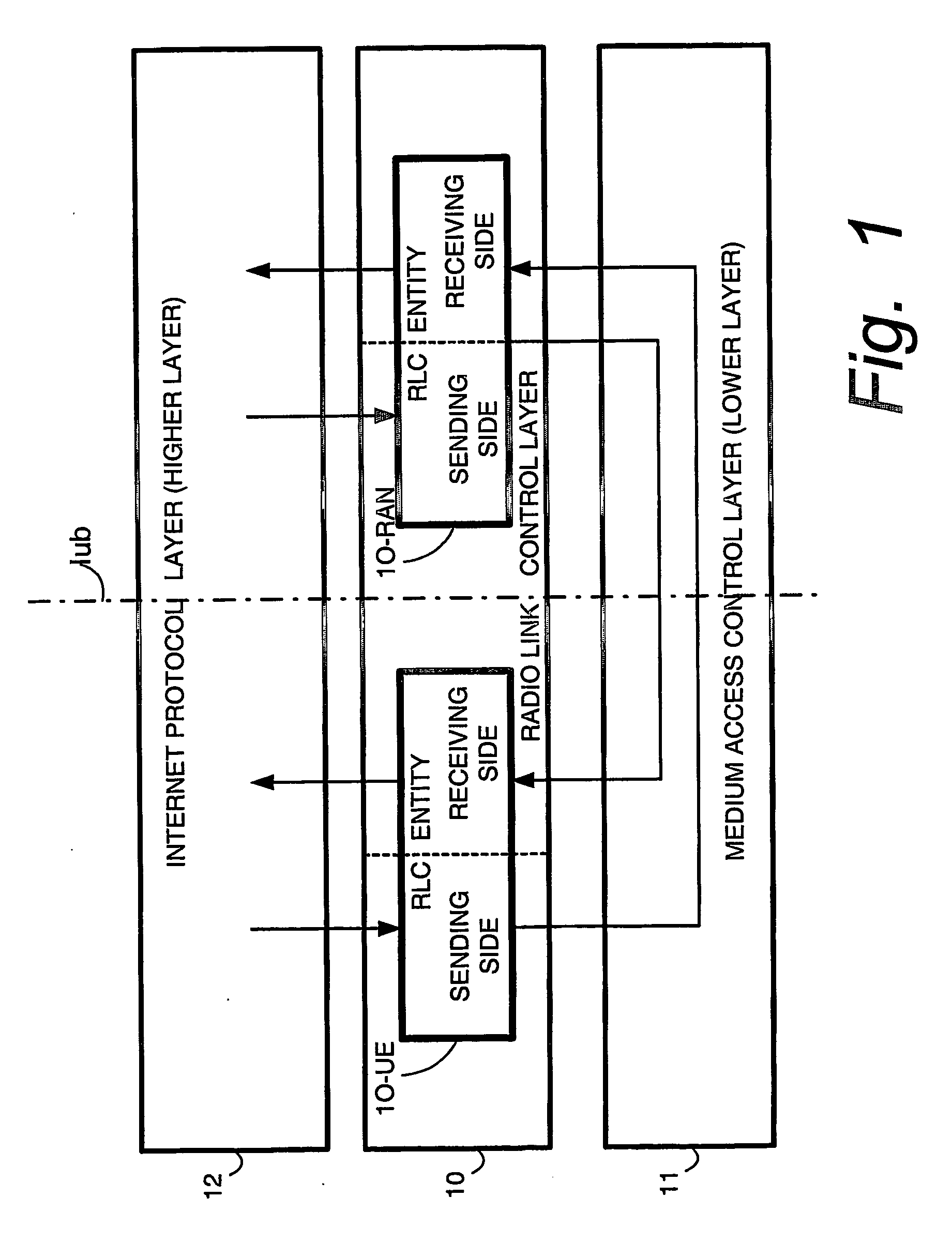
RLC Window Size Reconfiguration
ActiveUS20090221242A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTransceiverAir interface
A telecommunications device comprises a transceiver (33); a radio link control entity (50); and, a radio link control (RLC) buffer memory (150). The transceiver (33) which enables the device to communicate over an air interface (32). The radio link control entity (50) forms uplink RLC protocol data units (PDUs) for transmission over the air interface (32) and receives downlink RLC protocol data units (PDUs) over the air interface (32). The radio link control (RLC) buffer memory (150) is configured to include a transmitter buffer for storing the uplink RLC protocol data units (PDUs) and a receiver buffer for storing the downlink RLC protocol data units (PDUs). The radio link control entity includes RLC reconfiguration logic means (200) which reconfigures at least one of a size of a transmitter buffer window and a size of a receiver buffer window. In performing the reconfiguration, the RLC reconfiguration logic means implements a strategy for handling at least one of (1) downlink RLC protocol data units (PDUs) which are outside a new receiver buffer window; and (2) uplink RLC protocol data units (PDUs) which are either outside a new transmitter window or whose receipt by the radio access network has not been positively acknowledged.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Aligning Radio Base Station Node Transmission Timing on Multiple Transmit Paths
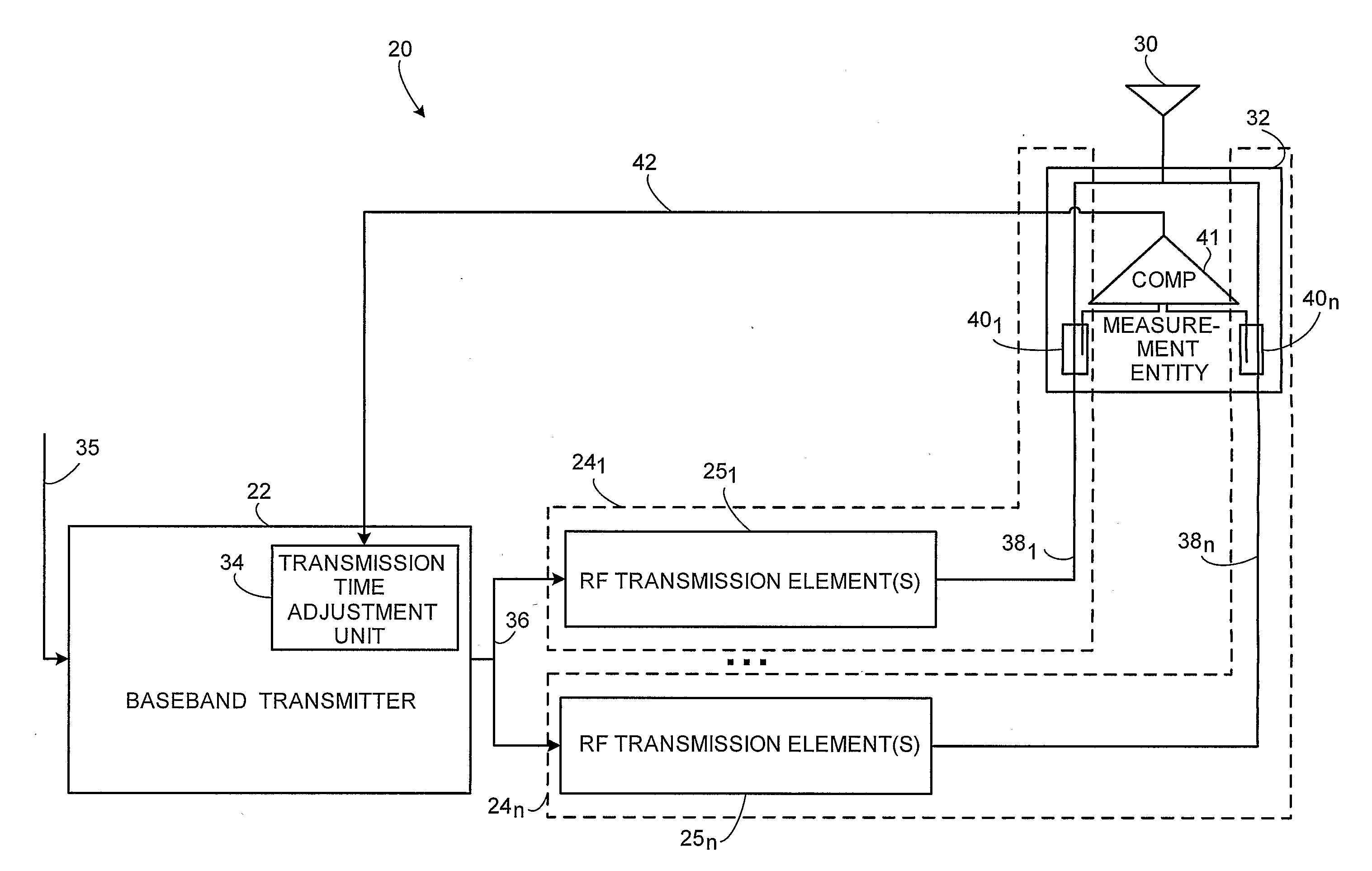
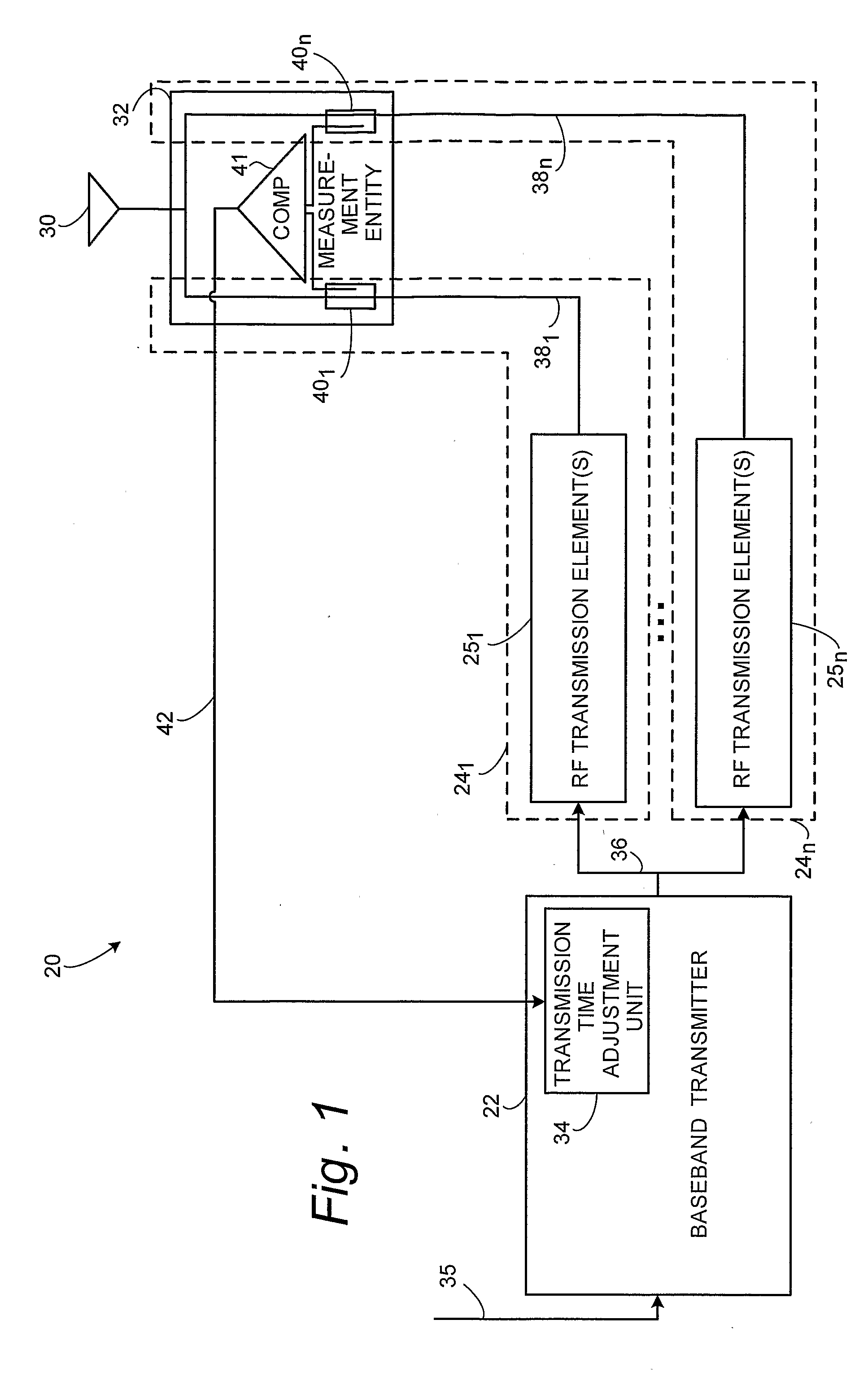
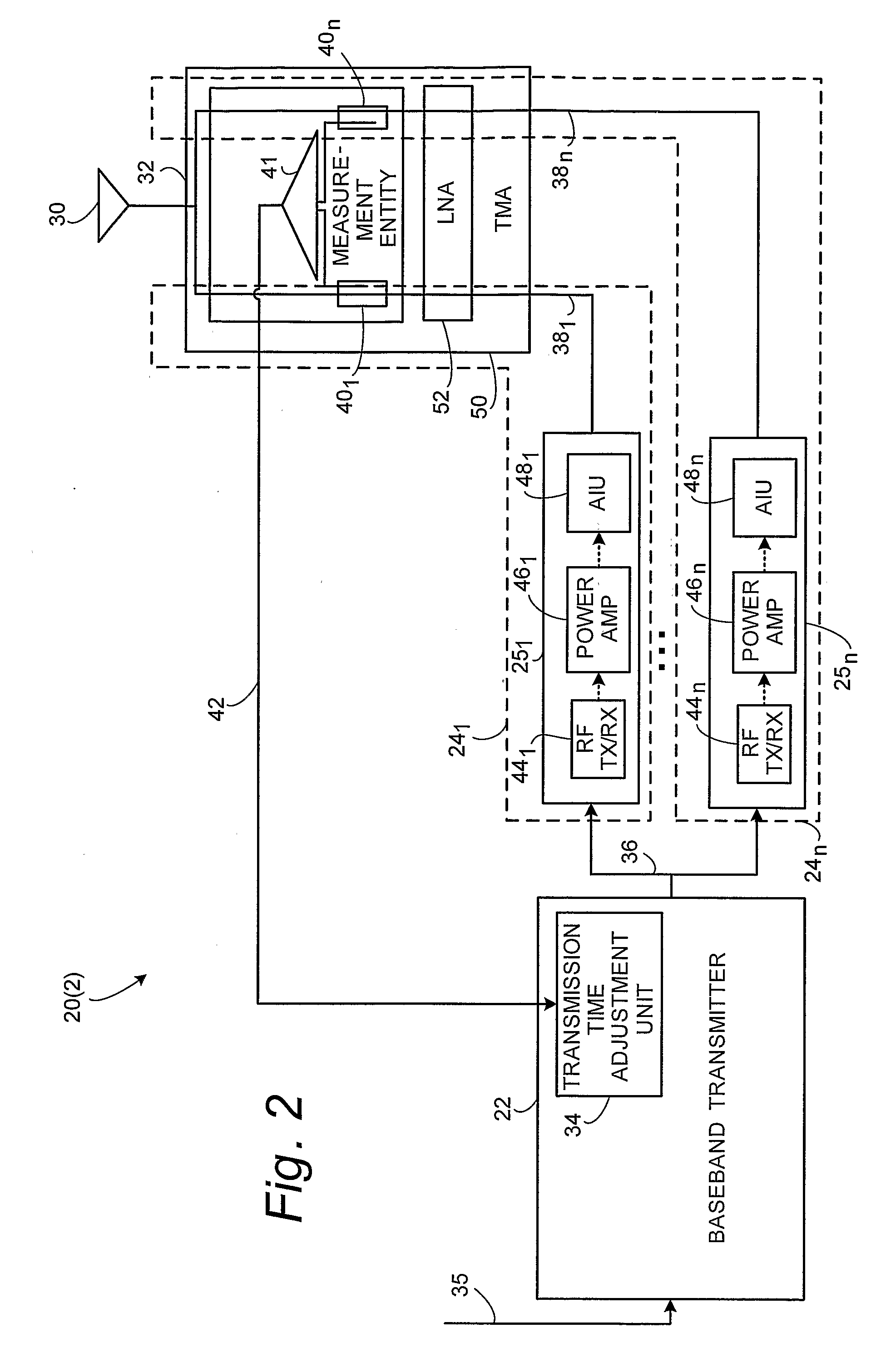
ActiveUS20080300003A1Reduce the required powerSufficient accuracyTransmitters monitoringSubstation equipmentPower modulationTelecommunications network
A radio base station node (20) of a telecommunications network comprises a baseband transmitter (22) and plural radio frequency (RF) paths (24) between the baseband transmitter (22) and an antenna system (30). A measurement entity (32) is provided, preferably near the antenna system (30), for making a measurement or comparison of a time of detecting of a power modulation for each of plural RF transmission paths (24), e.g., a time of detecting of a power modulation for a first of the plural RF transmission paths and a time of detection of a power modulation for a second of the plural RF transmission paths. A transmission timing adjustment unit (34) uses the power modulation measurement or comparison for adjusting timing of transmission of signals for the plural RF transmission paths for obtaining a desired time alignment for the plural RF transmission paths.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and device in a telecommunications system
InactiveUS6038439ASimple interfaceSimplicity and stability in interfaceAccounting/billing servicesTelephonic communicationAccess networkWireless transmission
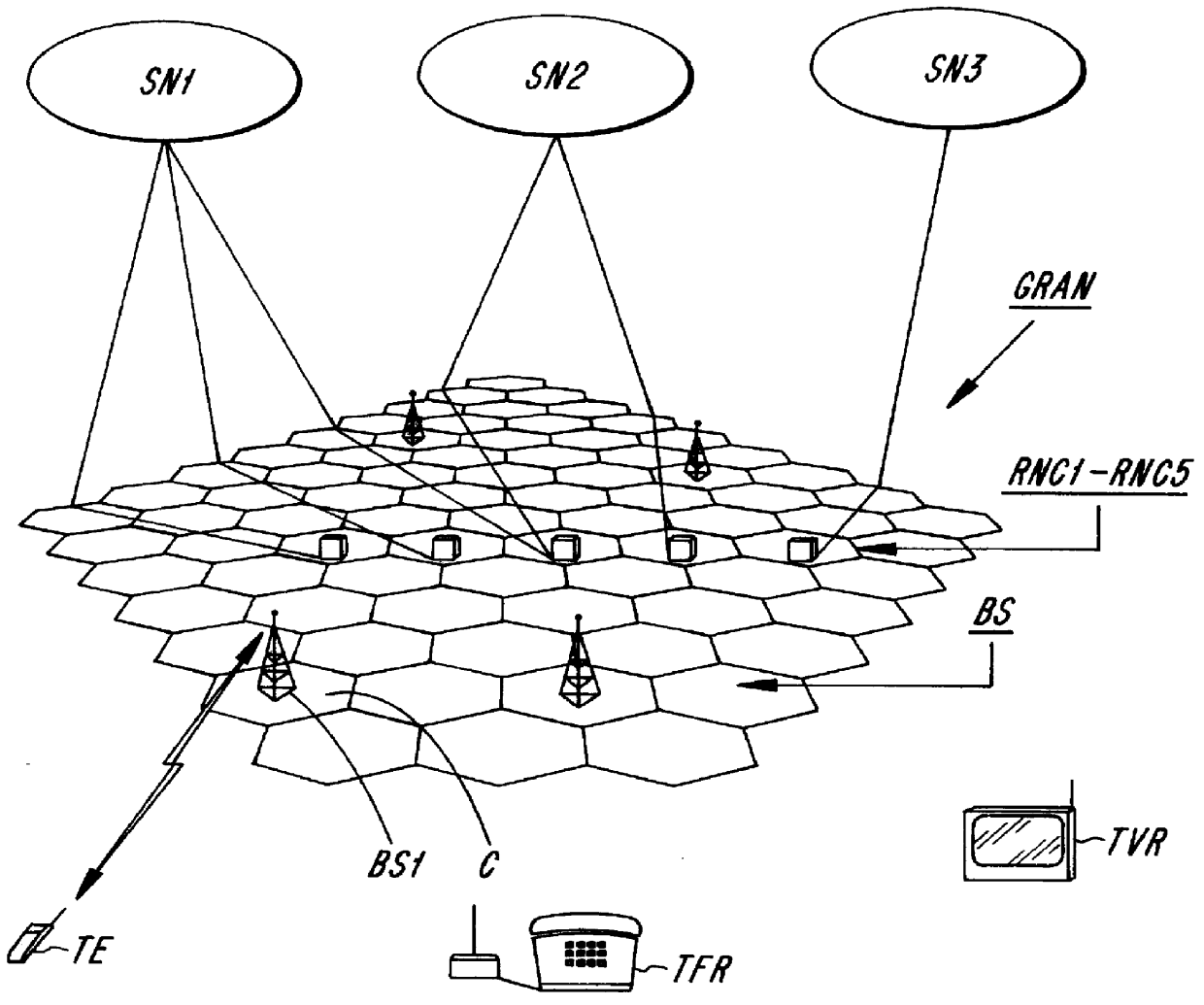
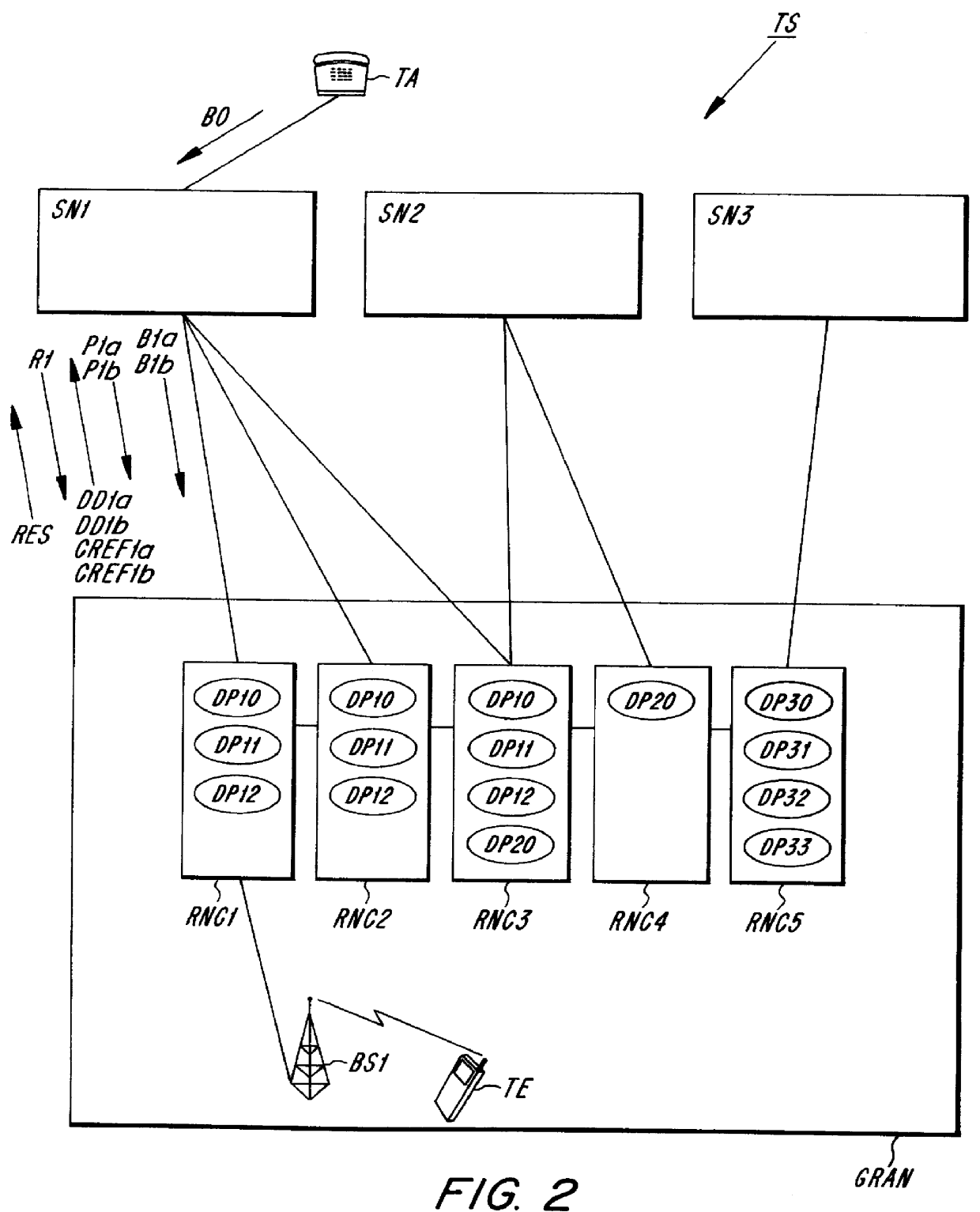
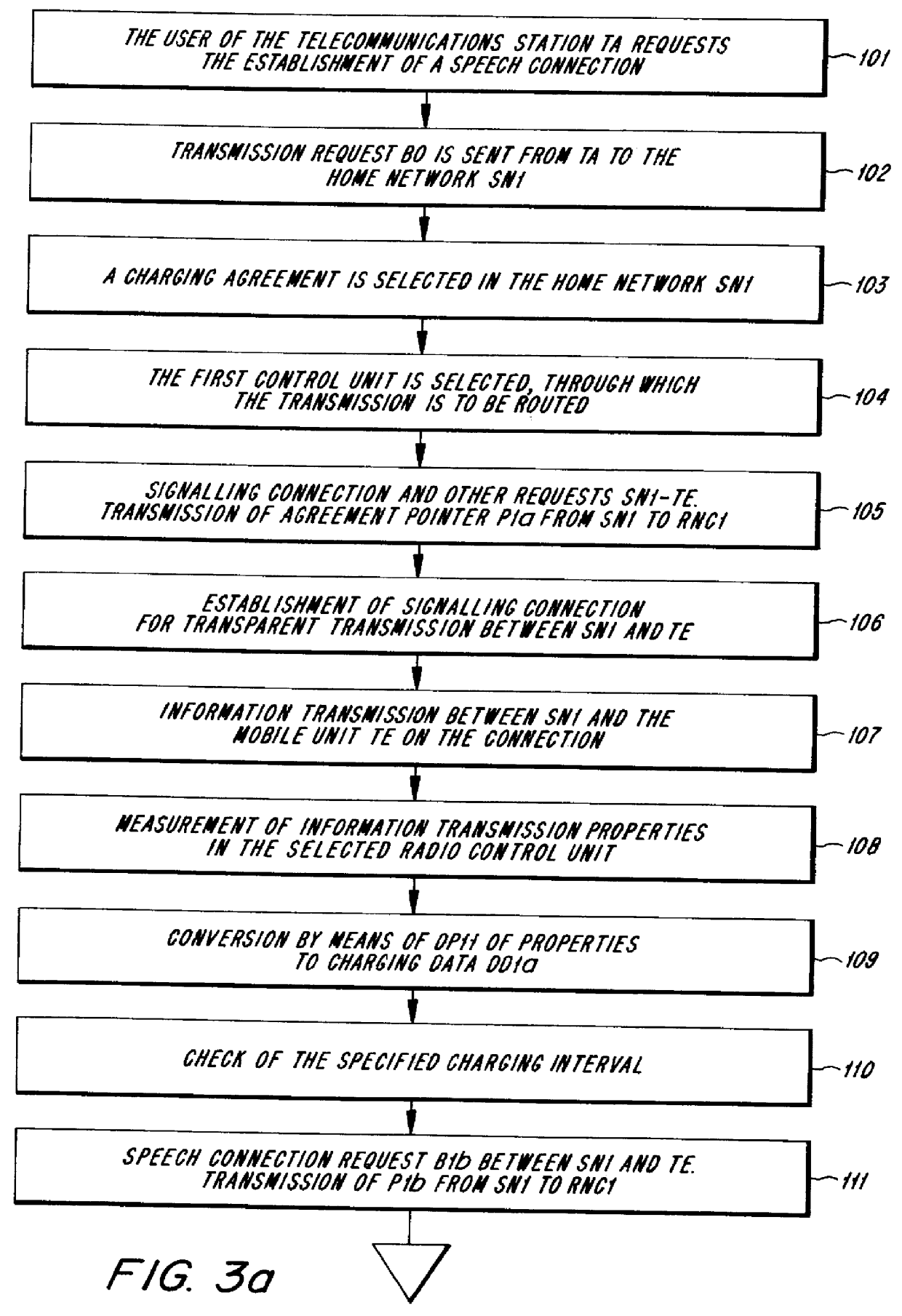
The present invention relates to a charging method in a telecommunications system (TS) when information is being transmitted in a generic radio based access network (GRAN) to which two or more service networks (SN1, SN2, SN3) with different specified standards are connected. The access network comprises radio control units (RNC1-RNC5), each of which constitutes a connection point between the access network (GRAN) and at least one of the service networks (SN1-SN3). Charging parameters (DP10-DP12, DP20, DP30-DP33) representing charging agreements for the service networks' (SN1-SN3) utilization of the access network (GRAN) are stored in the radio control units. The method also comprises the following additional steps: A transmission request (B0) for information transmission is sent from the telecommunications station (TA) to the home network (SN1). A charging agreement for the requested information transmission is selected in the home network (SN1). Transmission of a connection request (B1a) for the establishment of a connection to the mobile unit (TE) from the home network (SN1) to a first radio control unit (RNC1) constituting a connection point between the access network (GRAN) and the home network (SN1); Transmission of a charging agreement pointer (P1a) from the home network (SN1) to the first radio transmission unit (RNC1). The pointer (P1a) points out charging parameters (DP11) representing the selected charging agreement.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Link adaptation in a wireless telecommunications system
ActiveUS20100323739A1Reduce amountNetwork traffic/resource managementCode division multiplexLink adaptationComputer science
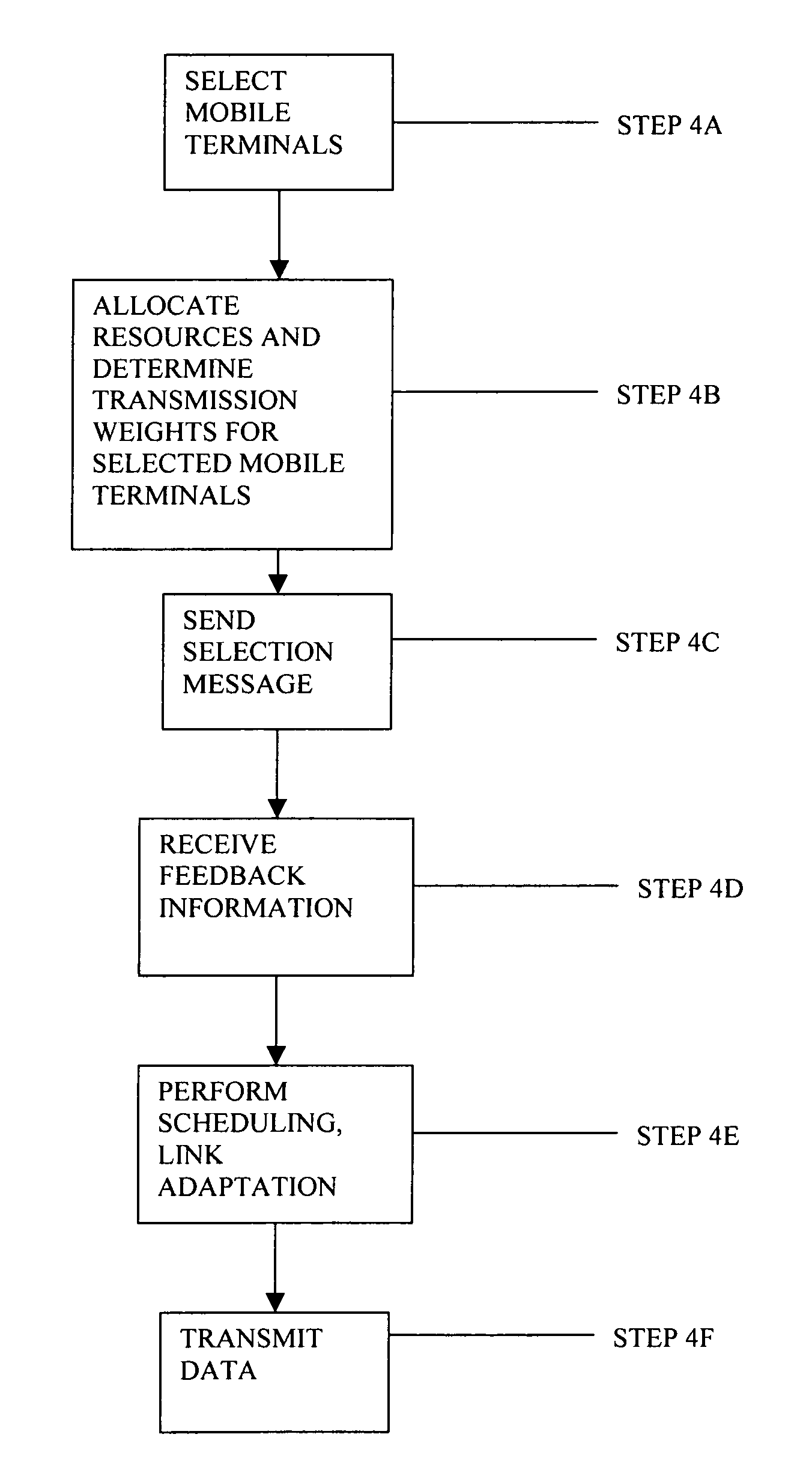
The invention relates to control of link resources in a wireless telecommunications system, in which instant channel feedback information is transmitted from a mobile terminal in response to receipt of a selection message from a basestation, and the instant channel feedback information is used for real-time resource allocation and adaptation at the basestation. The feedback information includes channel quality information derived from pilot signals and from pre-allocated transmission weights.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Billing scheme for a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6016340AReduce chanceEasy to implementTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunications linkTelecommunications service
A billing scheme for a telecommunications network is described in which a billing record for a call including at least a plurality of data bytes is generated in a switch (10), each billing record is duplicated, and check information is generated from each data byte of a billing record and associated with each said data byte to form a protected billing record. Each protected billing record of a duplicated pair is transmitted via two independent transmission lines to processing means (40, 50) in which the associated check information is generated byte-for byte from each received billing record and the generated check information is compared byte-for-byte with the transmitted check information in parity checking circuits (60, 61). If for any one byte of a billing record, the generated check information does not agree with the received check information, that billing record is discarded. If there is no inconsistency between the received and generated check information for both billing records of a duplicated pair, the two billing records of the pair are compared bit-for-bit in a comparator (70). If any difference is found between the billing records of the pair, both billing records are discarded. Otherwise the received billing records are stored in non-volatile memory (75).
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Packet mode telecommunications method and system in which calls can be handed over from one path to another
InactiveUS6690935B1Reduce transfer timeEasy to implementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationDigital dataPath switching
The invention concerns a method of transmitting non-dated digital data between a transmitter and a receiver in which the data can take at least two different paths between the transmitter and the receiver and handover from one path to another occurs during transmission. In the transmitter, packets intended for the second path are transmitted only after the last packet intended for the first path has been transmitted and in the transmitter and in the receiver packets on the first or second path are delayed in order for packets on the second path to arrive after packets on the first path. It is therefore not necessary to transmit signaling to differentiate the two paths at the receiver, which can include a single demodulator.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
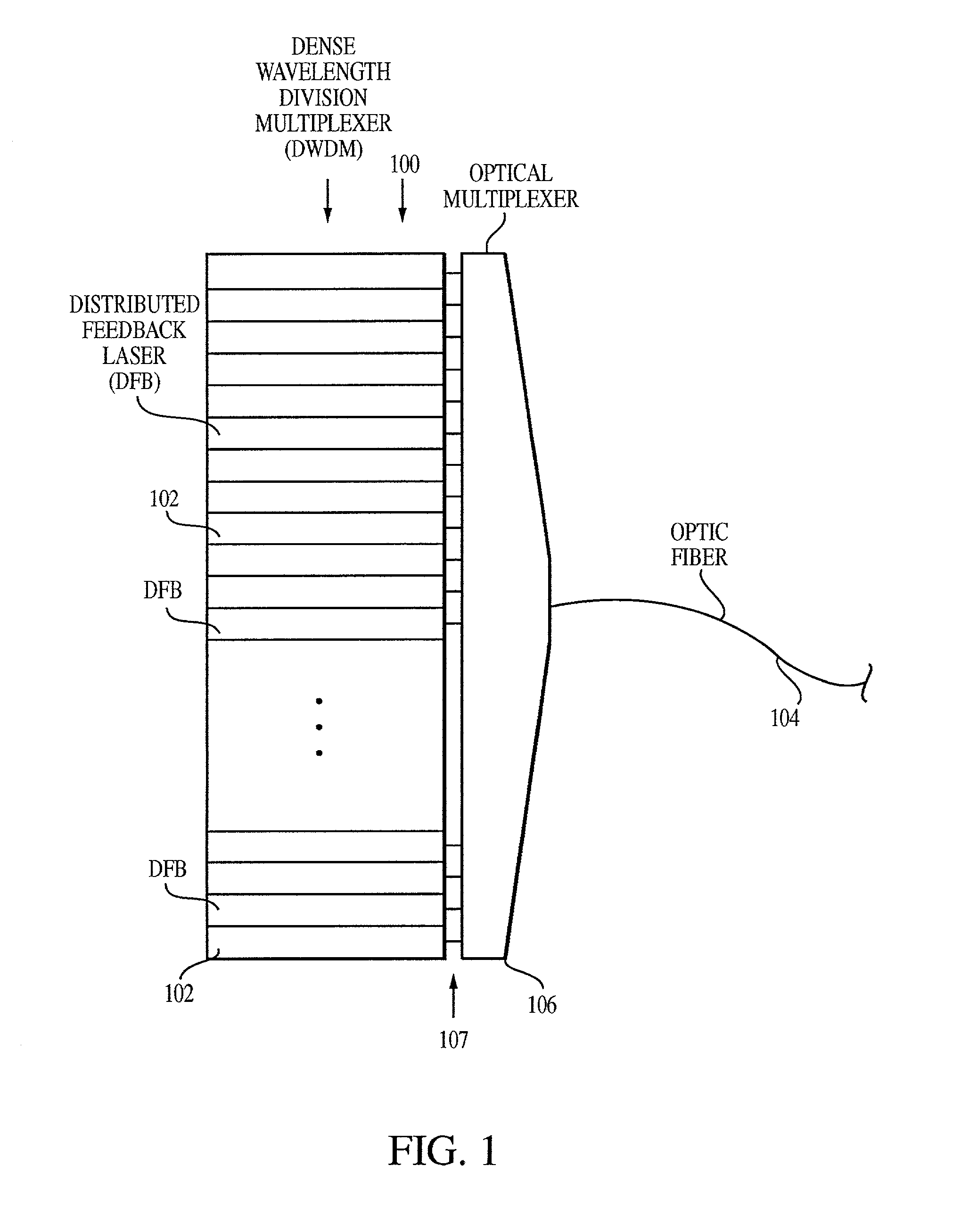
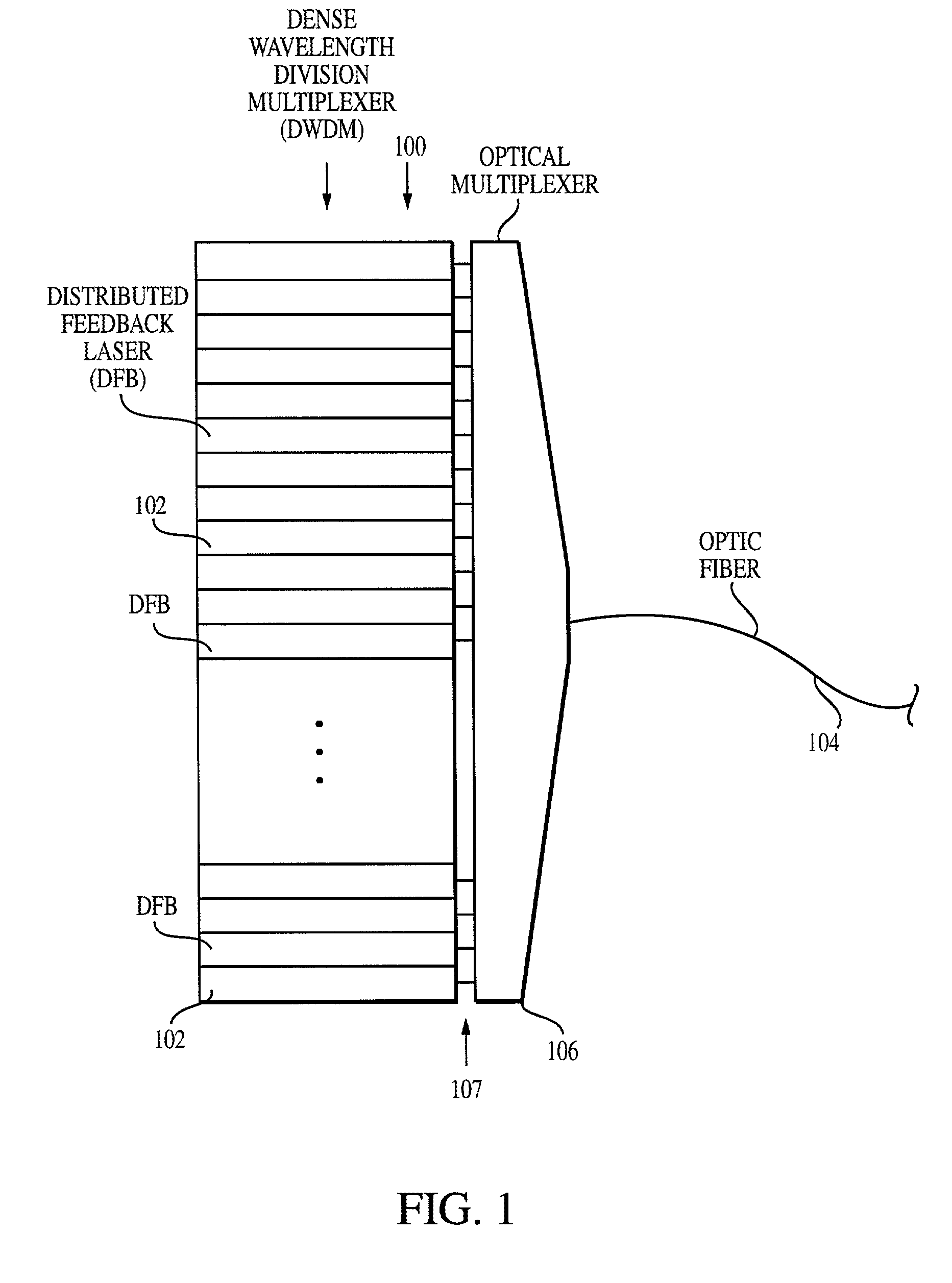
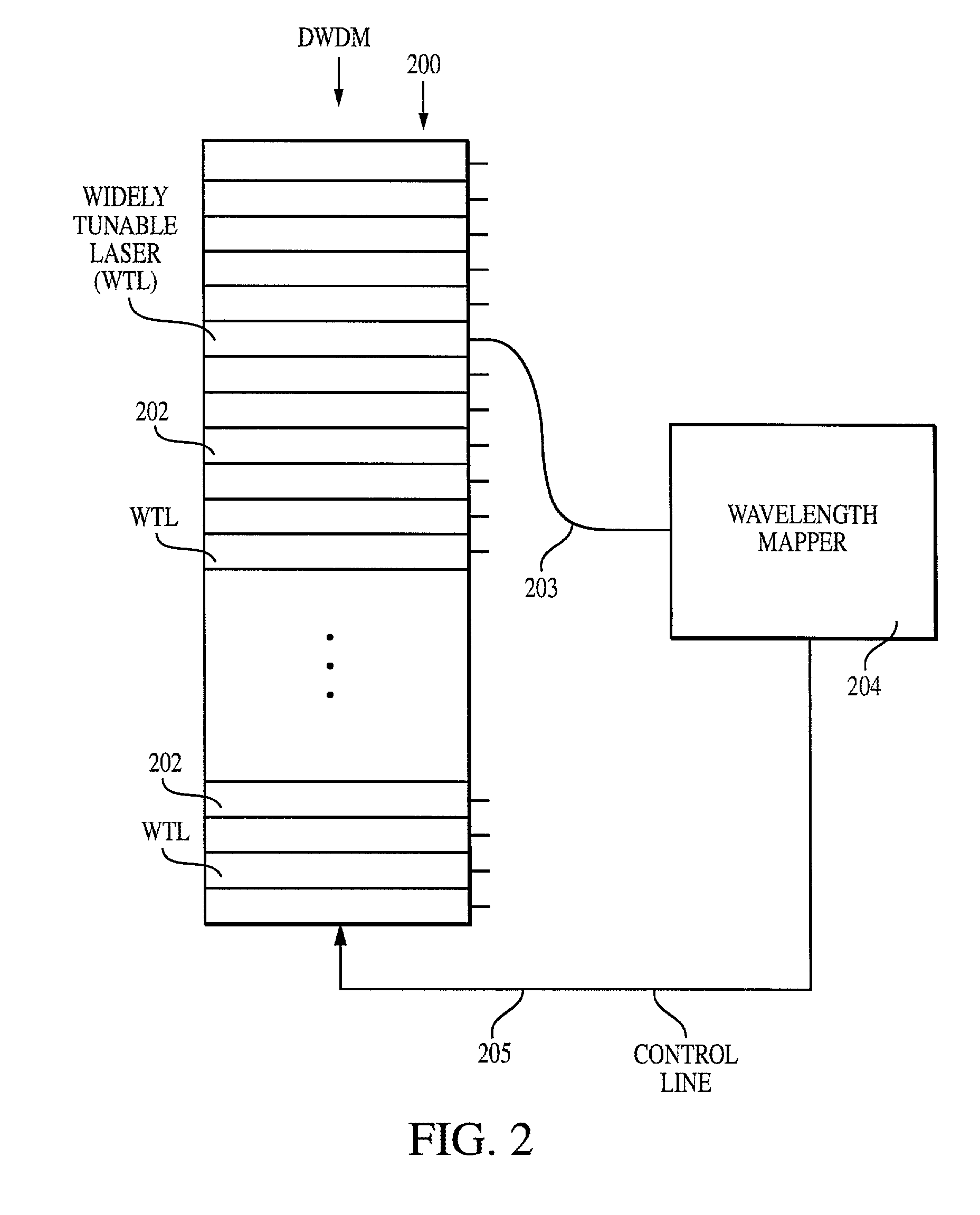
Method and system for locking transmission wavelengths for lasers in a dense wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS20020163650A1Heat is lostChange in refractive indexSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlFiberFinesse
Owner:SPECTRASENSORS INC
Measurement technique for a radio access telecommunications terminal
InactiveUS20030228890A1Reduce power consumptionReduce the amount of noiseEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplexPower modePeak value
A frequency division duplex radio access telecommunications terminal comprises a transmitter for transmitting a transmission signal at a first frequency. The transmitter is arranged to switch between a peak power mode in which the transmission signal is transmitted at a peak power level, and a reduced power mode. A receiver receives a reception signal at a second frequency different from the first frequency. A detector measures the signal strength of the reception signal. A controller is arranged to cause the detector to measure the signal strength of the reception signal whilst the transmitter is operating in the reduced power mode, and at a predetermined time before the transmitter switches to the peak power mode.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
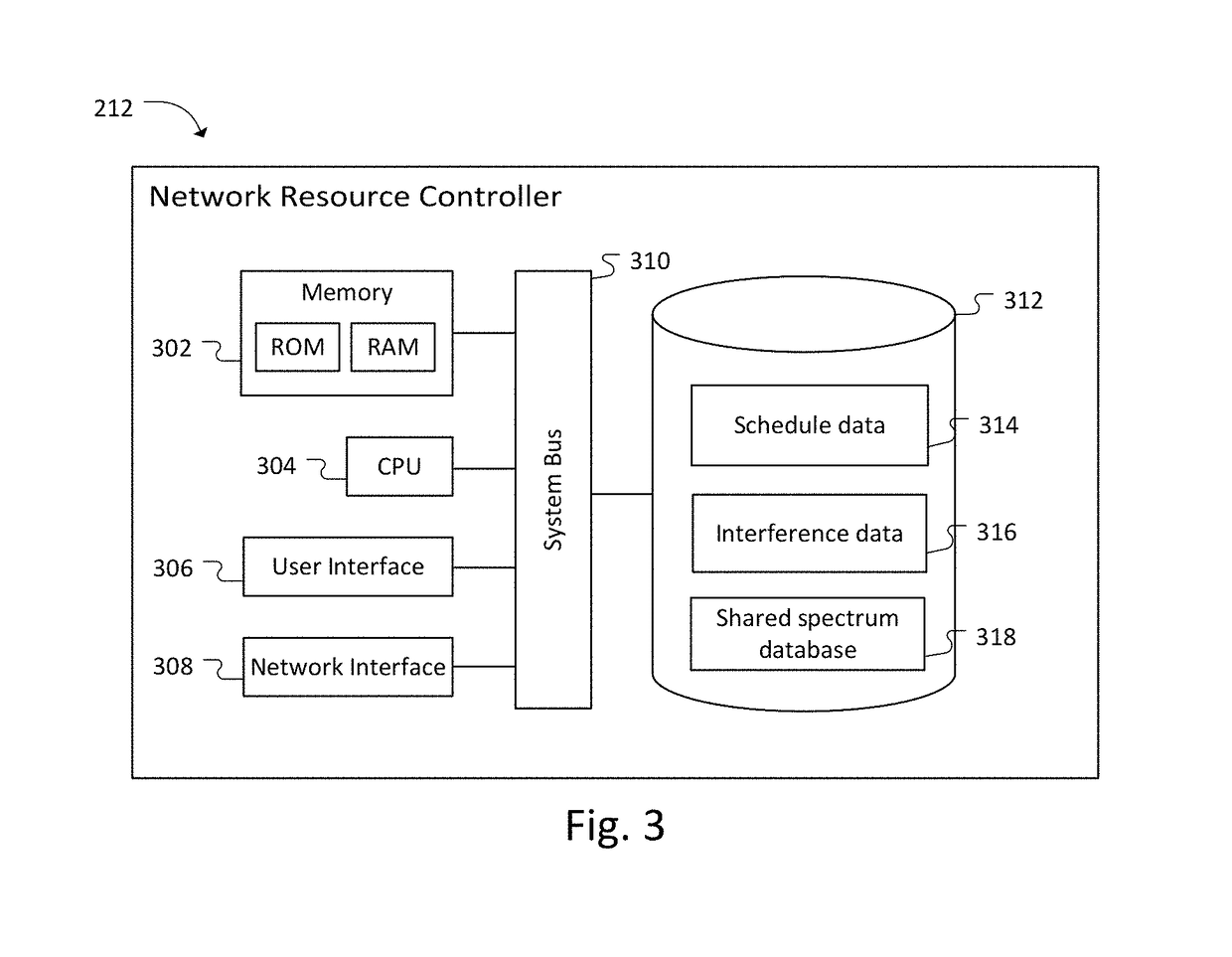
Carrier aggregation using shared spectrum
ActiveUS10194324B2Function increasePromote aggregationNetwork planningFrequency spectrumTelecommunications network
A method for performing Carrier Aggregation (CA) using spectrum shared between an incumbent user and a telecommunications network includes establishing a primary cell (PCell) for the secondary user in a portion of radio spectrum that is exclusively licensed to the telecommunications network, establishing a secondary cell (SCell) for the telecommunications network in a portion of the shared spectrum that is shared with the incumbent user, receiving schedule data for the incumbent user at a controller in communication with the incumbent user and a transmitter for the PCell and the SCell, scheduling transmissions for the PCell and the SCell to avoid interference to the incumbent user, and transmitting the scheduled transmissions through the PCell and the SCell using Carrier Aggregation (CA). Accordingly, one or more SCell in shared spectrum may be aggregated with a PCell in dedicated spectrum.
Owner:SPECTRUM EFFECT
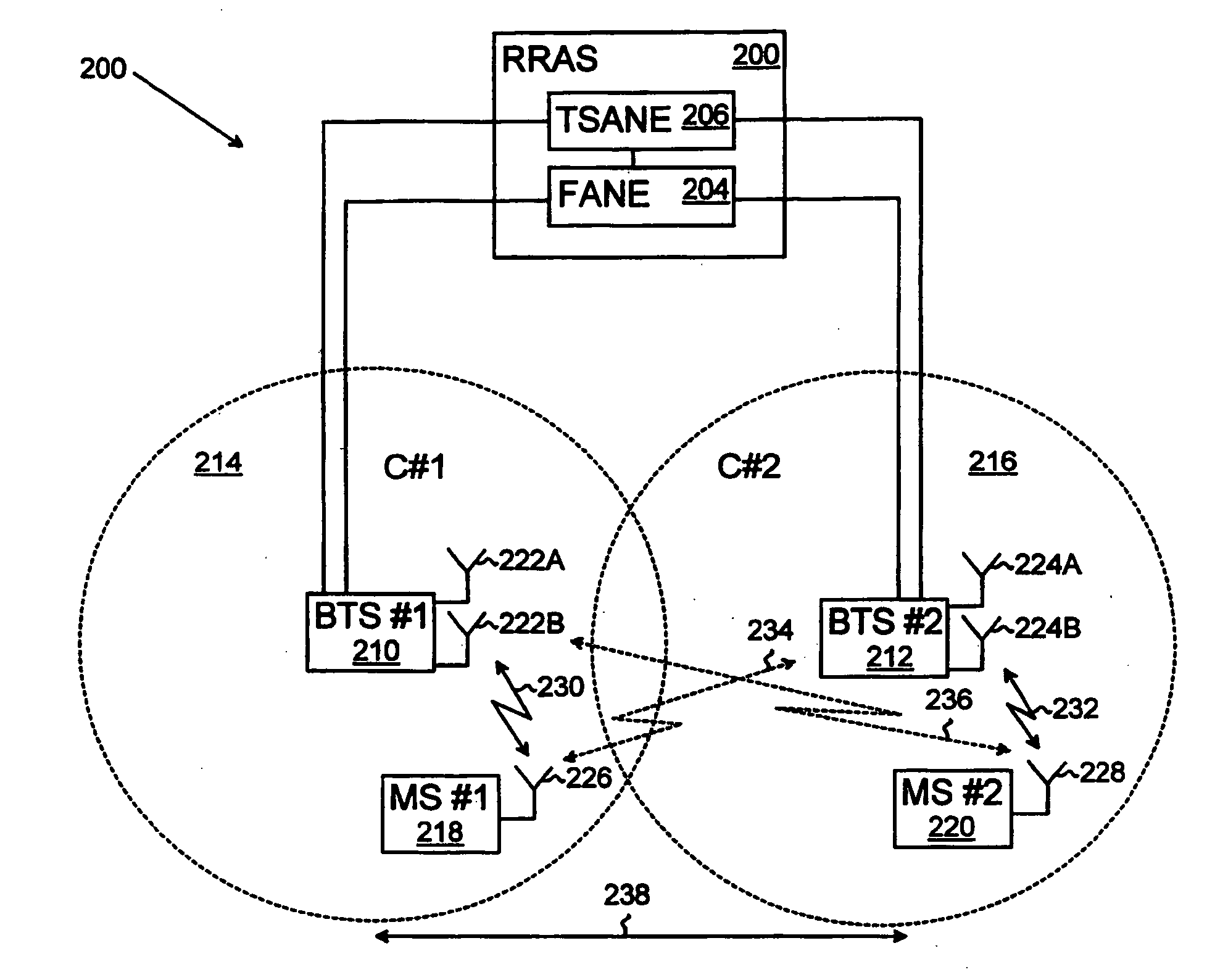
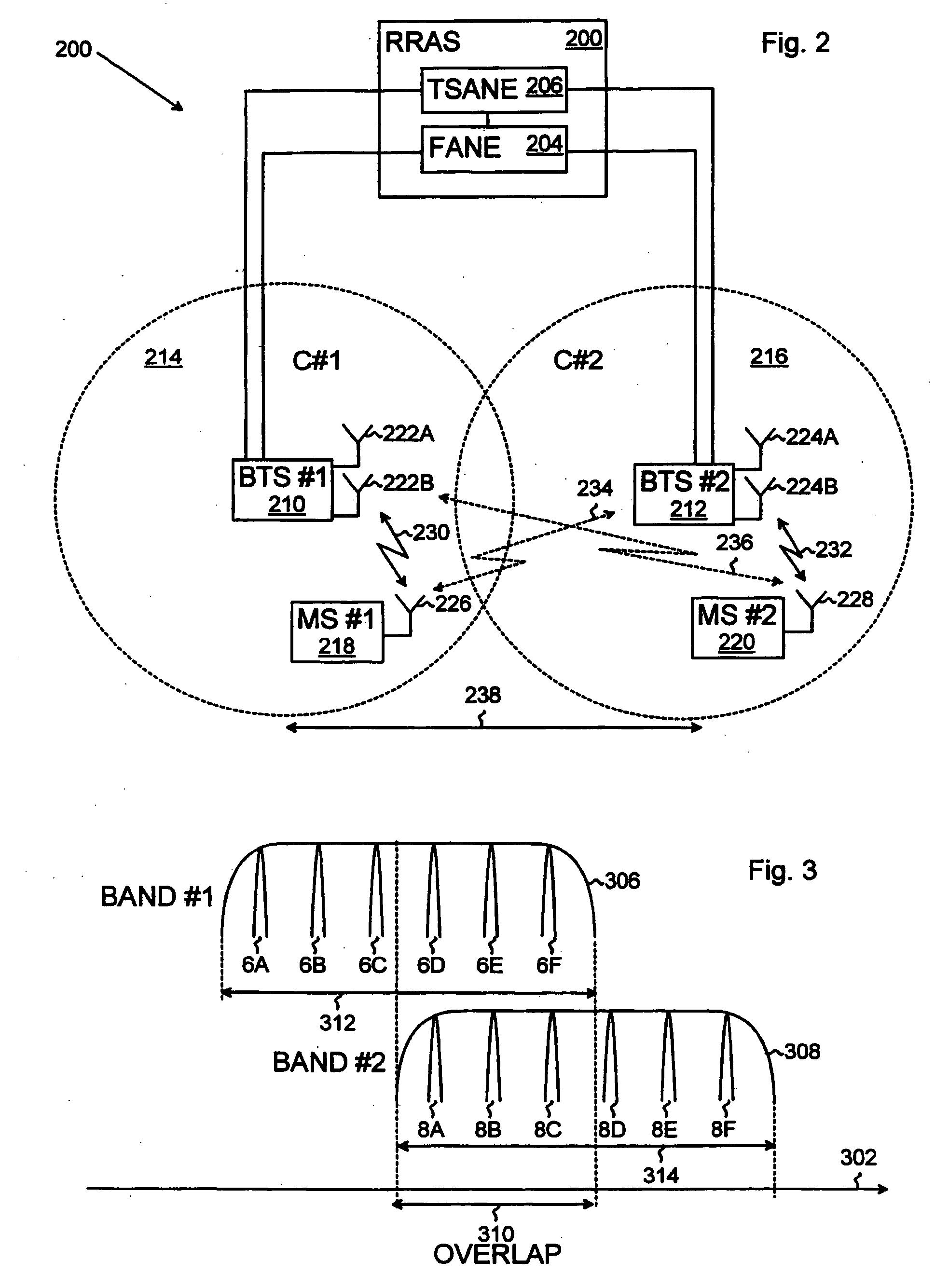
Method, system, and computer program for allocating radio resources in TDMA cellular telecommunications system
InactiveUS20050181797A1Increase the maximum capacityExpand coverageNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesCell specificFrequency reuse
A method, a computer program and a system for allocating radio resources are provided for a TDMA cellular telecommunications system which applies spatial diversity and cell-specific radio frequency bands. The system for allocating the radio resources includes a frequency allocating network element for allocating radio frequency bands to at least two radio cells located within a reuse distance from each other, at least one overlap region being formed between the radio frequency bands, the at least one overlap region being reserved for a simultaneous use in the same transmission direction of the at least two radio cells. The invention provides a frequency reuse capability for radio cells located within a reuse distance from each other.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method and system for planning the power of carriers in a cellular telecommunications network
ActiveUS20070026886A1Eliminate disadvantagesOptimised effective bit rateRadio transmissionNetwork planningUltrasound attenuationTelecommunications network
A system allowing reuse of one same frequency on all the cells of a network. It includes means storing data characteristic of the network and a computing module provided with means to associate carriers of a transmitter with service areas to distribute the traffic to be handled in the sector over N shares of traffic in N complementary areas determined in relation to their radio attenuation, and a determined frequency with each service area, the different carriers used being respectively associated with a single service area of a sector. With the system it is possible to adjust the transmission power of each carrier in relation to the determination made by the computing module to share the power of transmitter between the carriers of one same sector.
Owner:SOC FR DU RADIOTELEPHONE SFR
Transfer of different data types in a telecommunications system
InactiveUS6816726B2Improve efficiencyImprove data throughputWave amplification devicesSpecial service for subscribersData typeResource allocation
Owner:AIRSPAN IP HOLDCO LLC
Carrier aggregation using shared spectrum
ActiveUS20160050690A1Function increaseFacilitate carrier aggregationWireless commuication servicesNetwork planningInterference (communication)Telecom network
A method for performing Carrier Aggregation (CA) using spectrum shared between an incumbent user and a telecommunications network includes establishing a primary cell (PCell) for the secondary user in a portion of radio spectrum that is exclusively licensed to the telecommunications network, establishing a secondary cell (SCell) for the telecommunications network in a portion of the shared spectrum that is shared with the incumbent user, receiving schedule data for the incumbent user at a controller in communication with the incumbent user and a transmitter for the PCell and the SCell, scheduling transmissions for the PCell and the SCell to avoid interference to the incumbent user, and transmitting the scheduled transmissions through the PCell and the SCell using Carrier Aggregation (CA). Accordingly, one or more SCell in shared spectrum may be aggregated with a PCell in dedicated spectrum.
Owner:SPECTRUM EFFECT
Method and a system for delivering messages
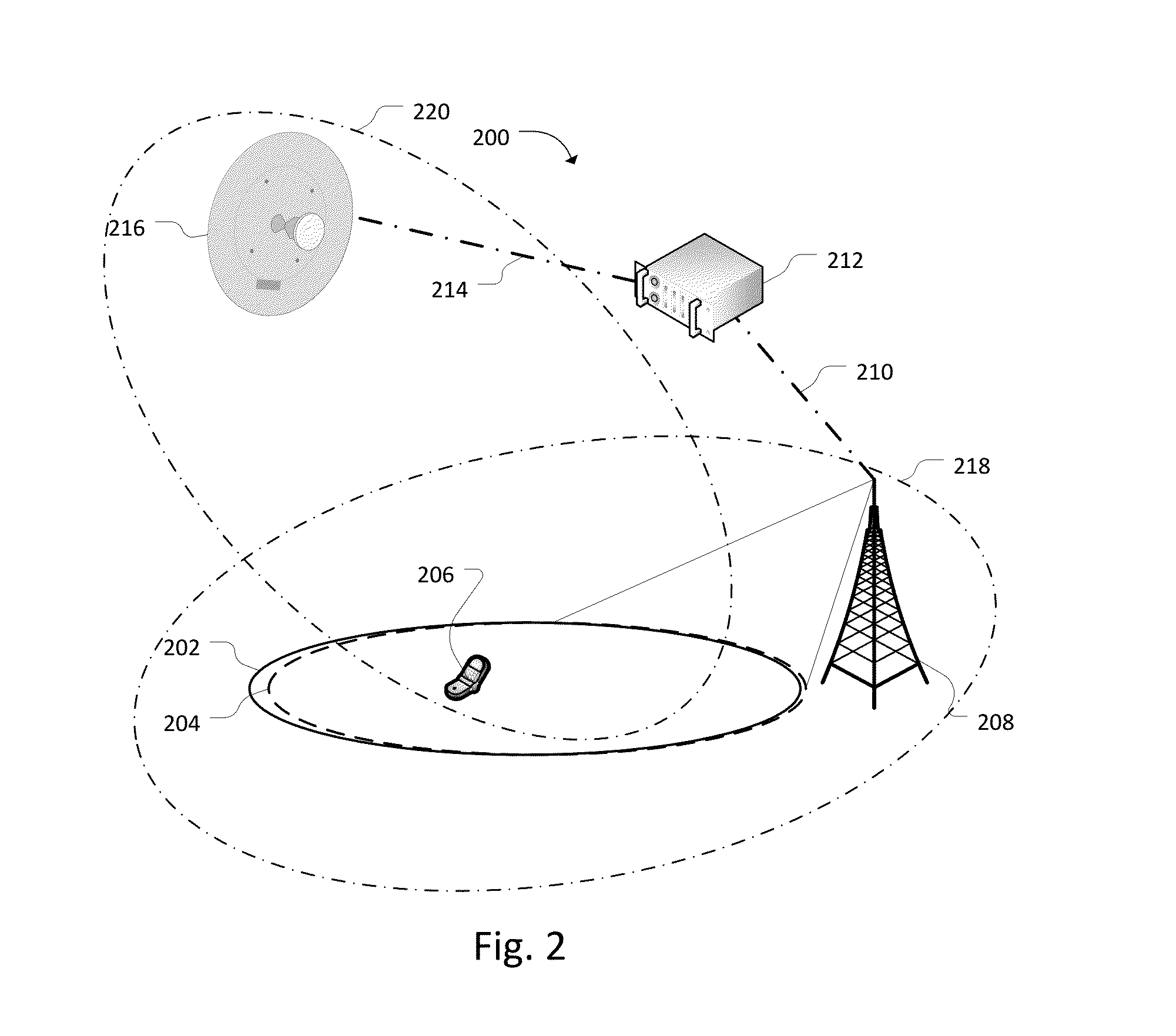
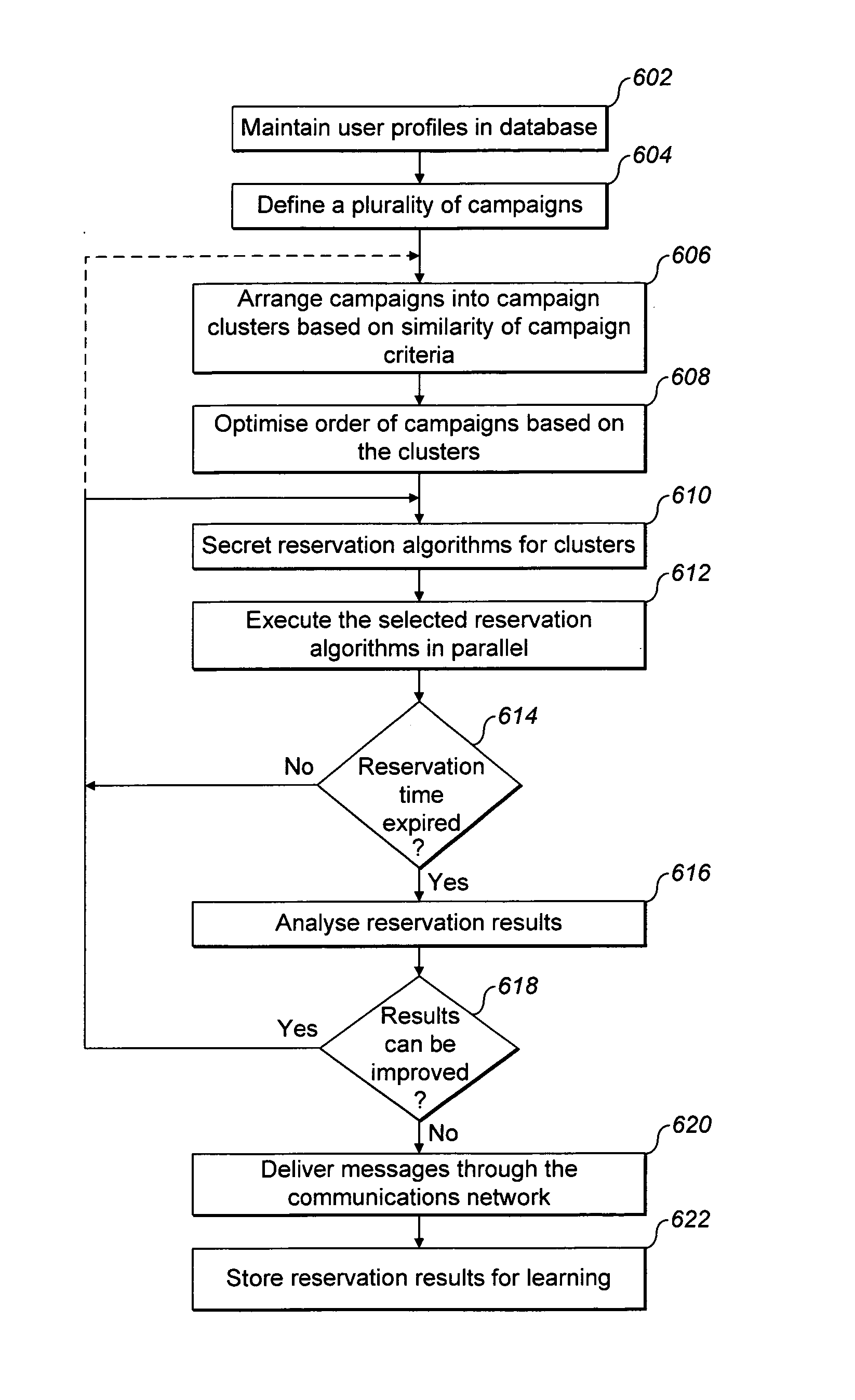
ActiveUS20080312948A1Effective resourcesEffective distributionResourcesMarketingTelecommunications networkMessage delivery
A system for generating a schedule for use in triggering transmission of message content in a telecommunications network is provided. The system comprises a store for storing profiles of a plurality of recipients, and a plurality of message delivery campaigns with one or more criteria. The campaigns to be executed in relation to a given inventory, which may relate to a predetermined time period, may be arranged into one or more campaign clusters. A suitable allocation method may be used individually for each of said plurality of campaign clusters to allocate, among the plurality of recipients, target recipients for each of the campaign clusters based on campaign criteria and the profiles. The allocation process may be repeated to obtain, for example as high a number of messages as possible with the network resources available without exceeding a predetermined maximum number of messages per any given recipient. After the allocation process is completed, the campaign messages are delivered to the allocated target recipients via a communications network.
Owner:APPLE INC
Data Distribution in a Distributed Telecommunications Network
A technique is disclosed that enables a set of information to be represented by data packets, where those data packets can then be distributed as needed throughout the telecommunications system that uses the data. The data packet of the illustrative embodiment is an autonomous encapsulation of data, a subsection of a data model at a certain time in relation to other data in the system at another time. The data packet is identified at a particular time and value with a globally unique identifier. Relationships of the data packet to other data packets are made known by using references to the other packets. As a result, referenced data packets are retrieved throughout the system based on their relationships to each other. Whenever a data packet is transmitted or received, each node involved in the transmission applies rules that determine where the data has to be transmitted to and what to do with the data when received.
Owner:AVAYA INC
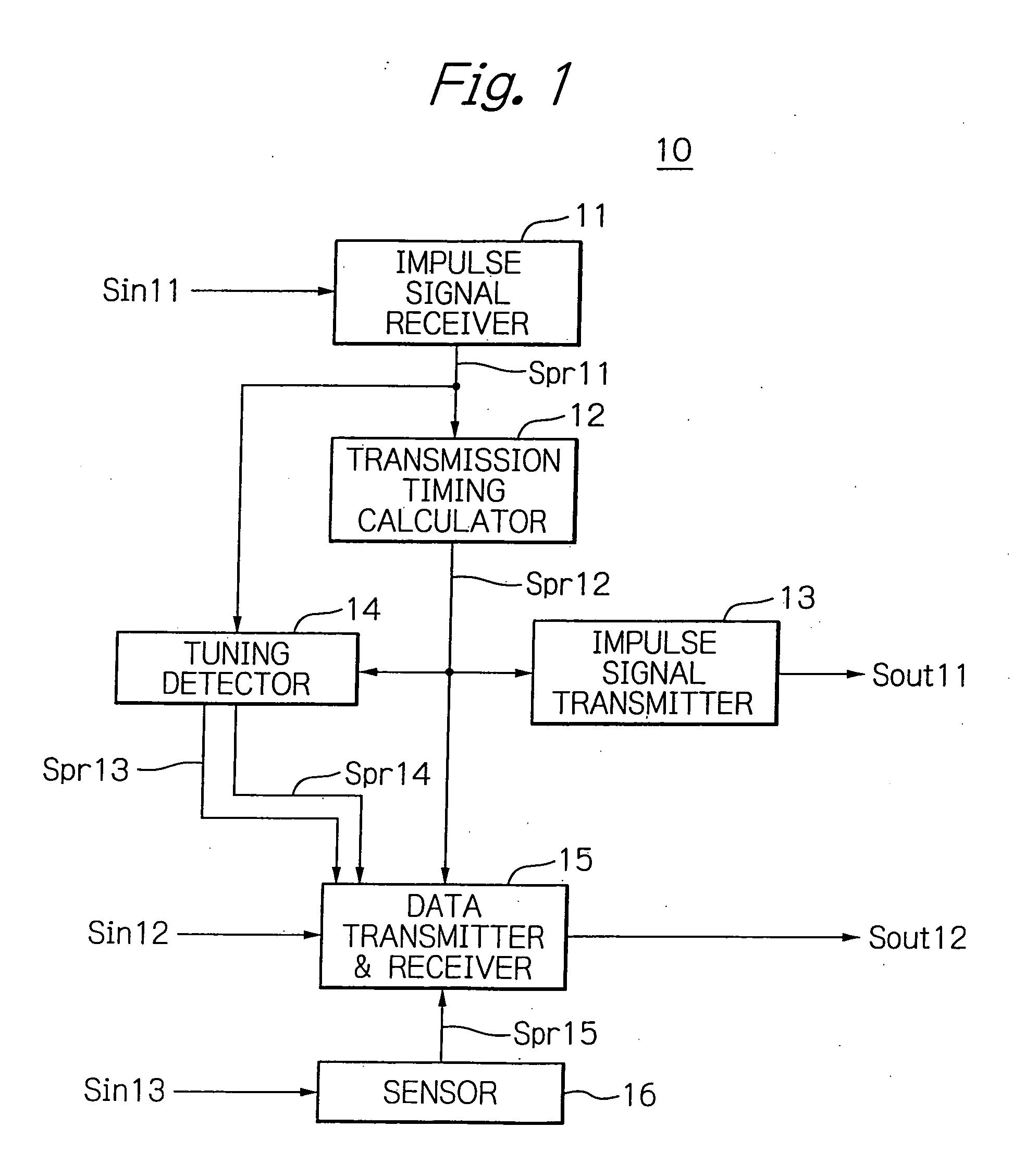
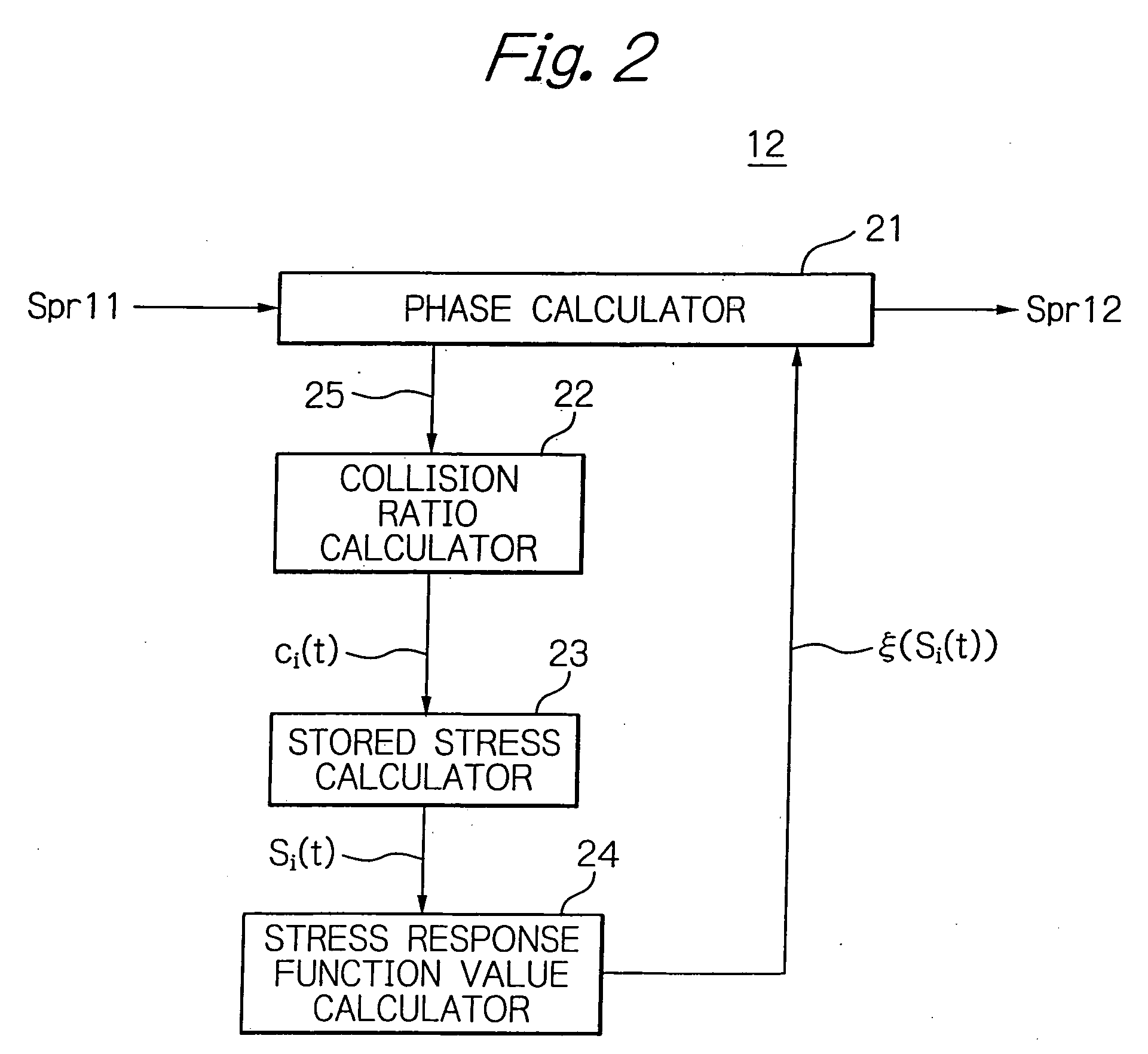
Apparatus for controlling data transmission timing responsively to a calculated collision ratio
InactiveUS20060050826A1Flexible controlSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTelecommunications networkControl data
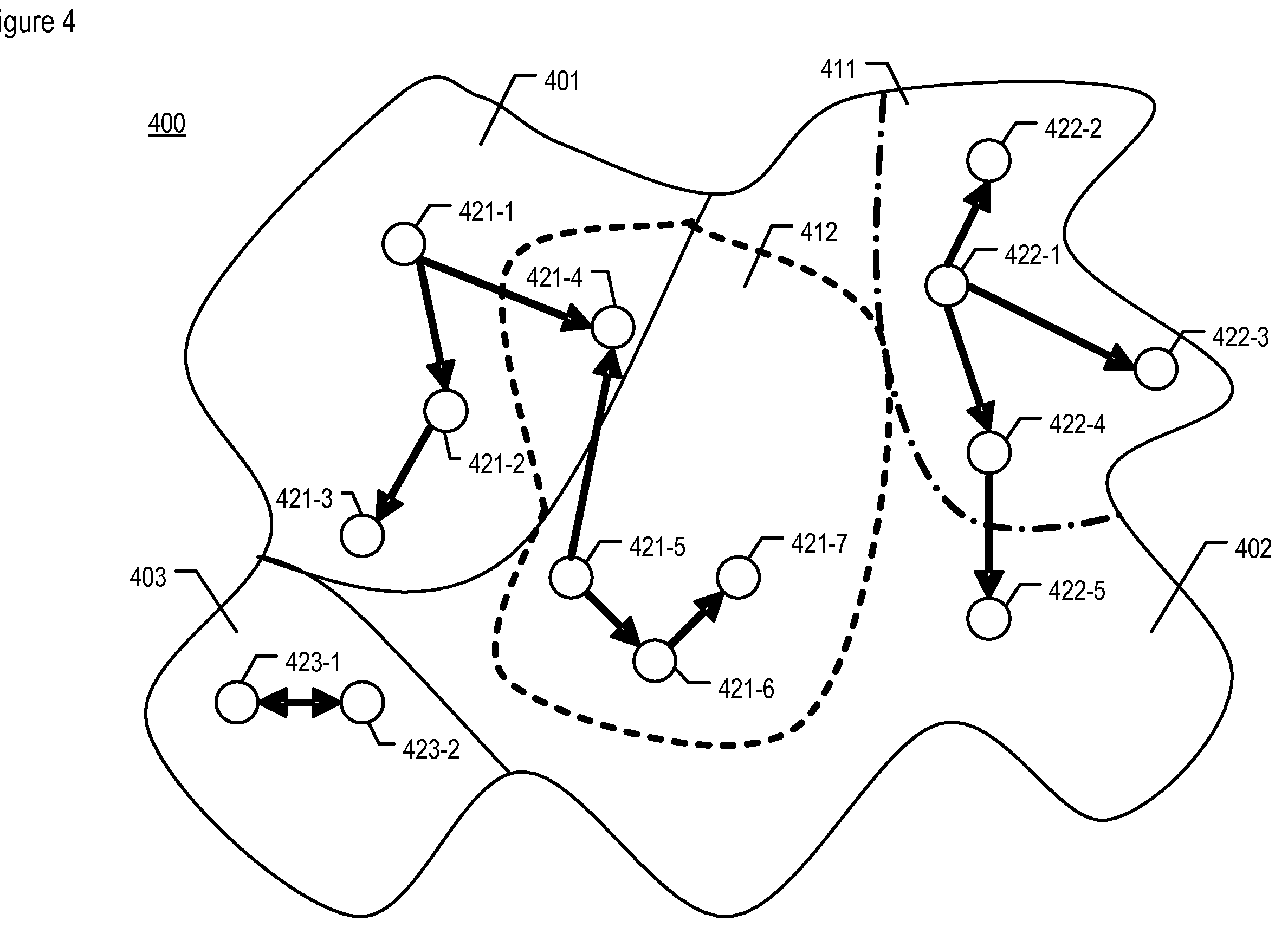
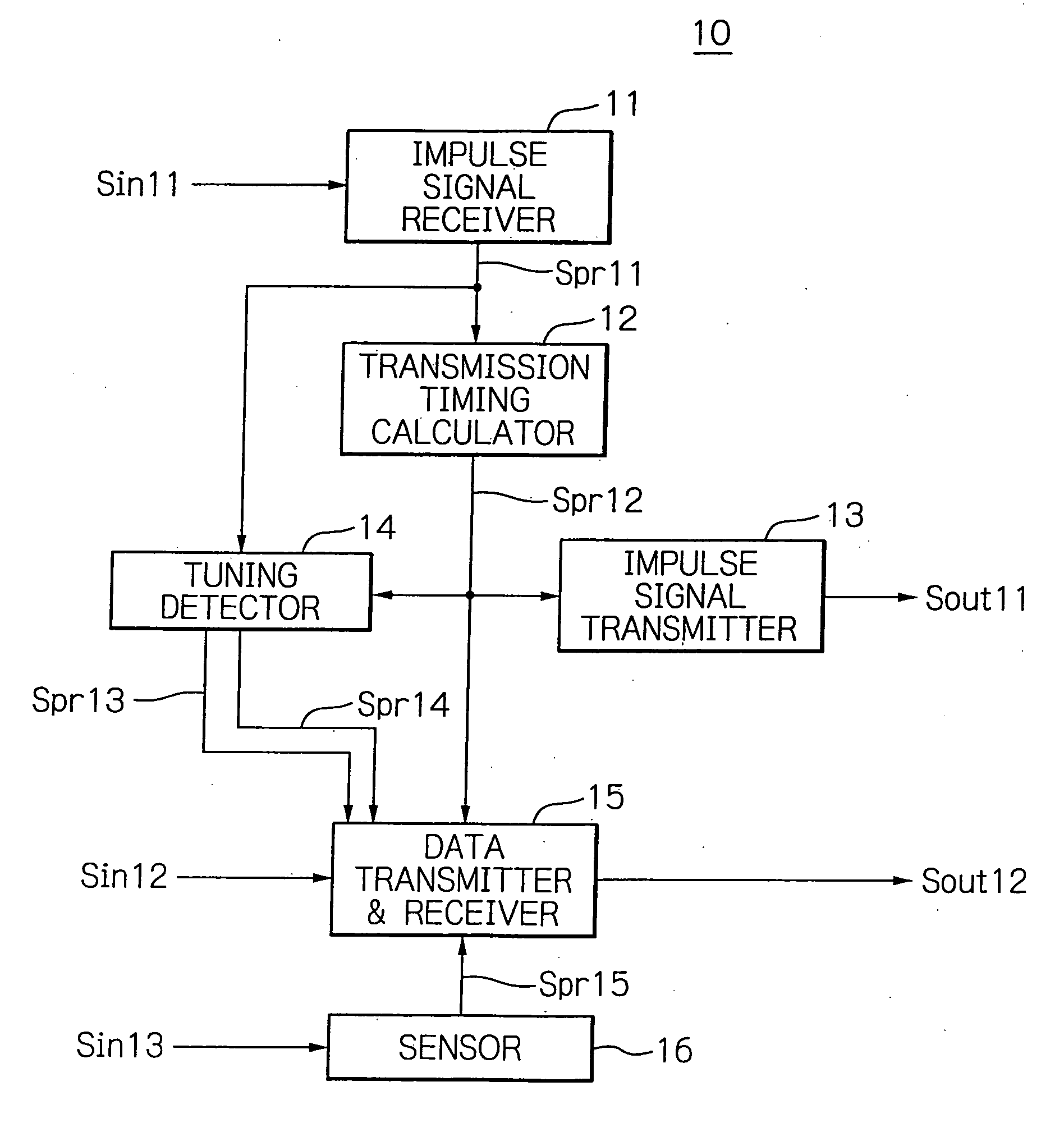
Communication control apparatus provided in nodes forming a telecommunications network includes a transmission timing calculator responsive to the state of the phase of the own node to determine a timing at which the node transmits data. The calculator is responsive to a state variable signal transmitted by a neighboring node and reflecting the phase of the neighboring node to change the state of the phase of the own node in accordance with a time development rule. The calculator monitors a phase difference of the own node against the neighboring node to calculate, based on the difference, the ratio of collision on data transmission timing between the own and neighboring nodes. The stress value corresponding to the collision ratio is stored time-serially. A stress response function value is generated such that the stored stress value causes the time development rule to shift the phase with its value made at random.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com