Patents
Literature
238results about "By rectification and condensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
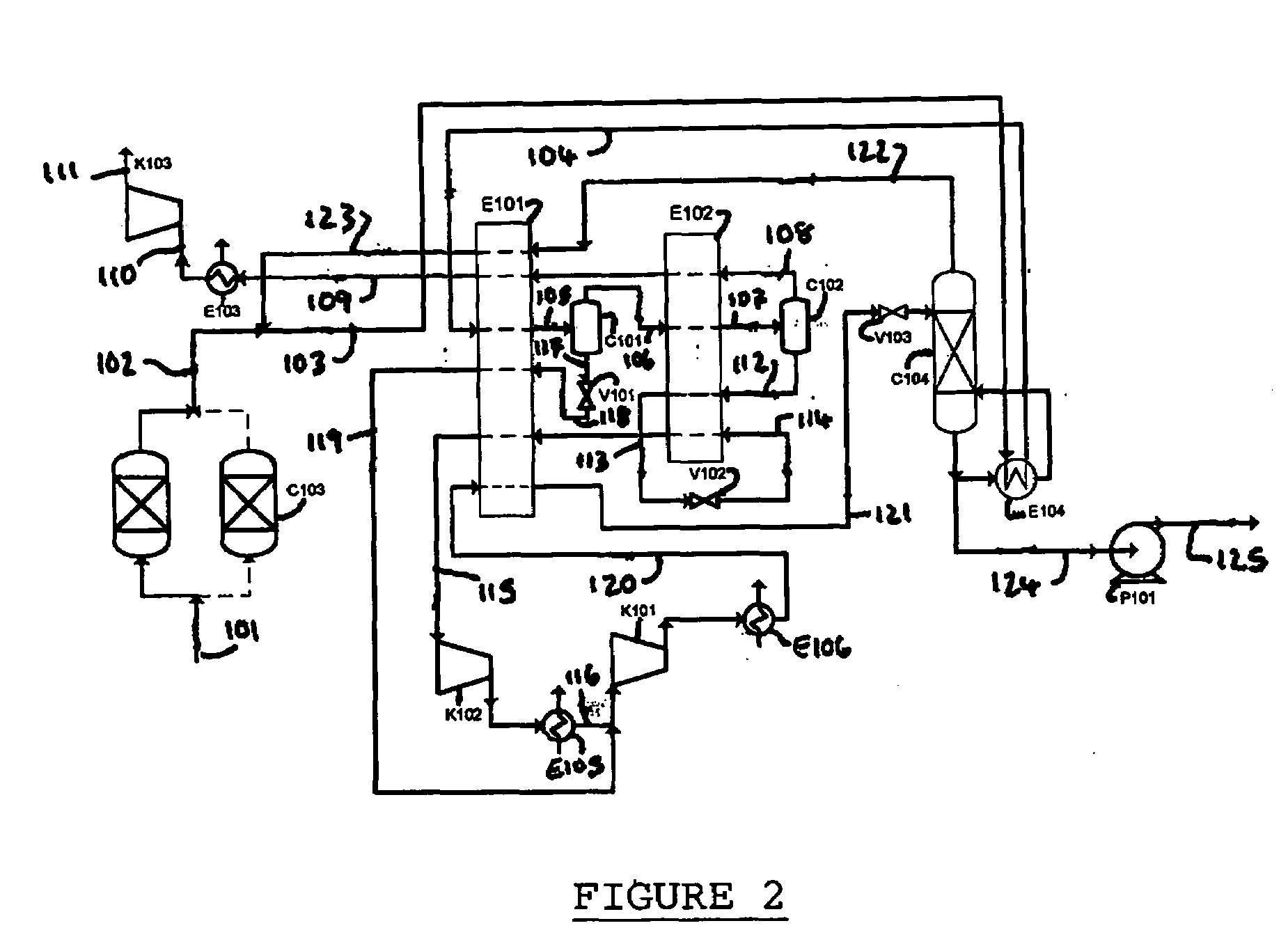
Apparatus for concentrating and diluting specific gas and method for concentrating and diluting specific gas
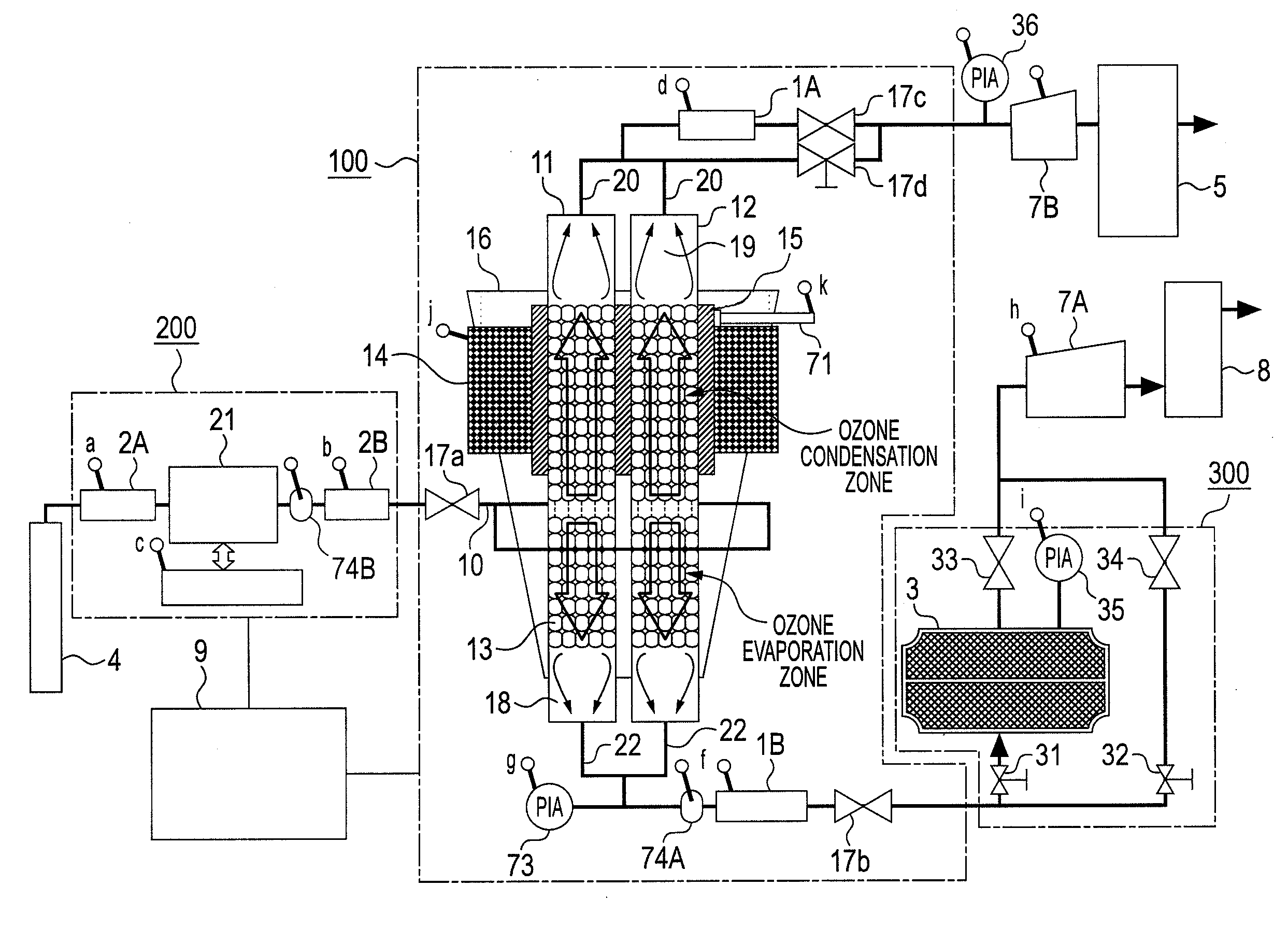
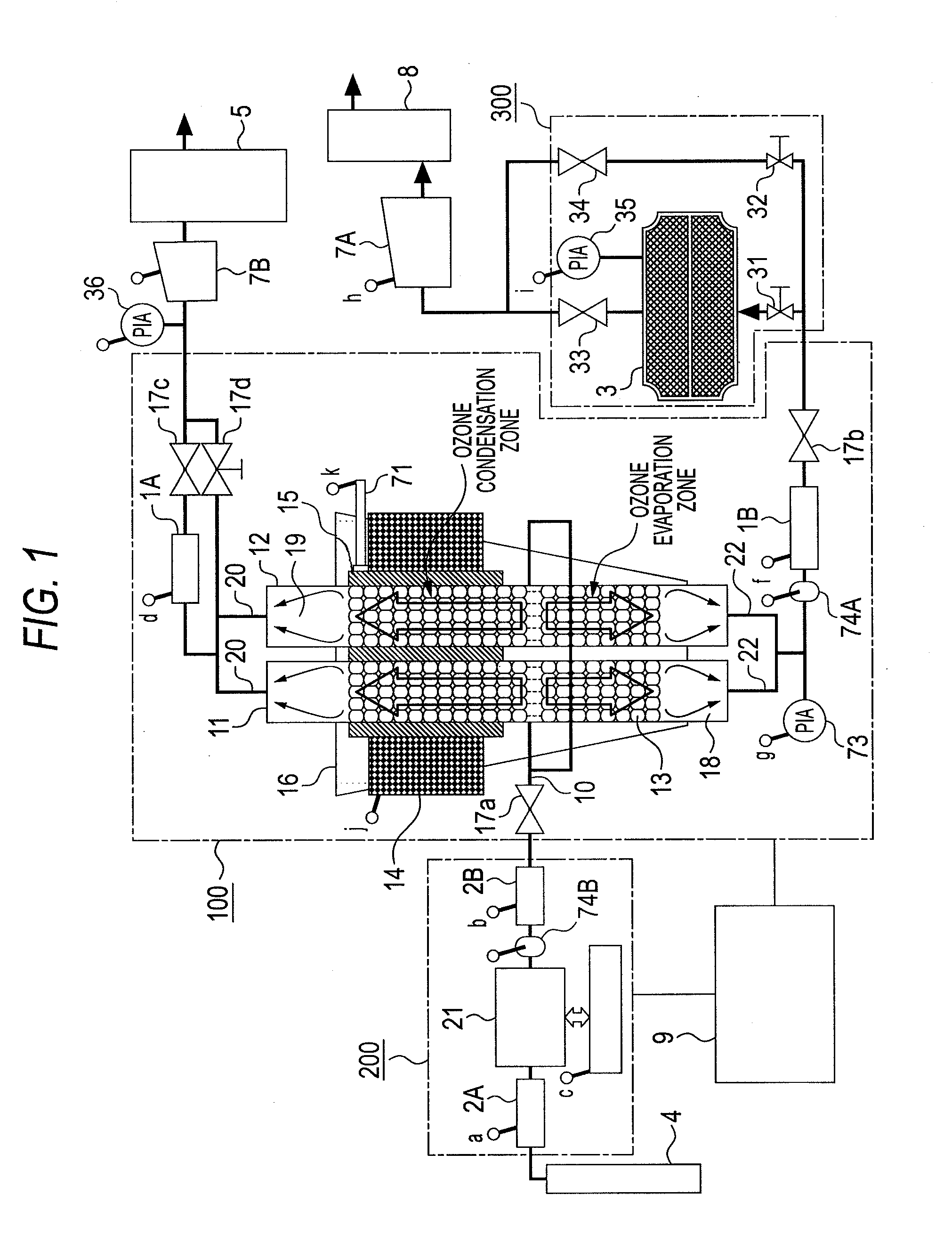
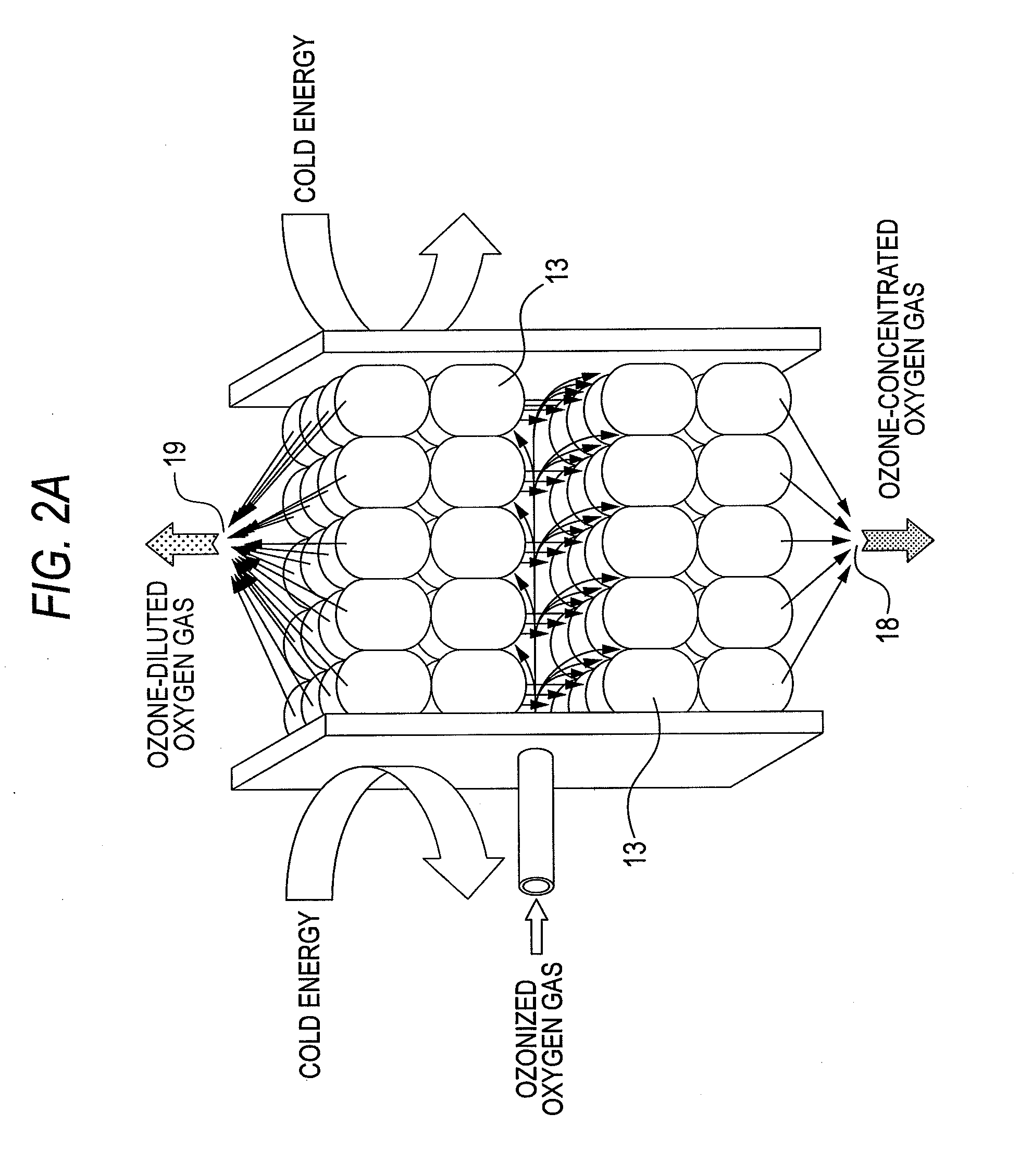
ActiveUS20100162752A1Improve processing efficiencySmall sizeSolidificationGas treatmentSpherical shapedVaporization
One ozone concentrating chamber is provided therein with a part of a cooling temperature range where ozone can be selectively condensed or an oxygen gas can be selectively removed by transmission from an ozonized oxygen gas, and a part of a temperature range where condensed ozone can be vaporized, and condensed ozone is vaporized by moving condensed ozone with flow of a fluid or by gravitation to the part where condensed ozone can be vaporized, whereby the ozonized oxygen gas can be increased in concentration. Such a constitution is provided that a particle material 13 for condensation and vaporization filled in the ozone concentrating chambers 11 and 12 has a spherical shape of a special shape with multifaceted planes on side surfaces, or an oxygen transmission membrane 130 capable of selectively transmitting an oxygen gas in an ozone gas is provided.
Owner:TOSHIBA MITSUBISHI-ELECTRIC IND SYST CORP
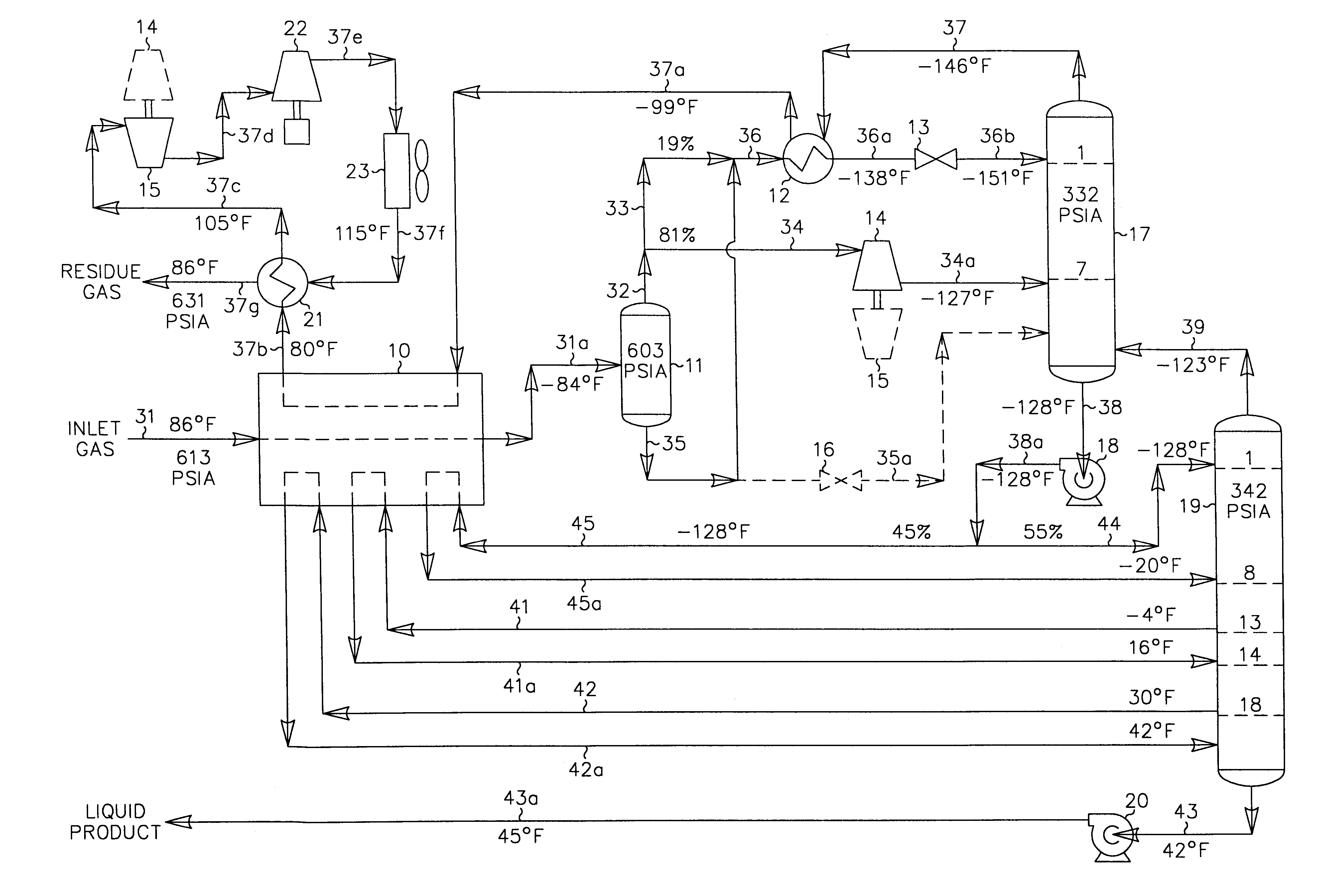
Hydrocarbon gas processing
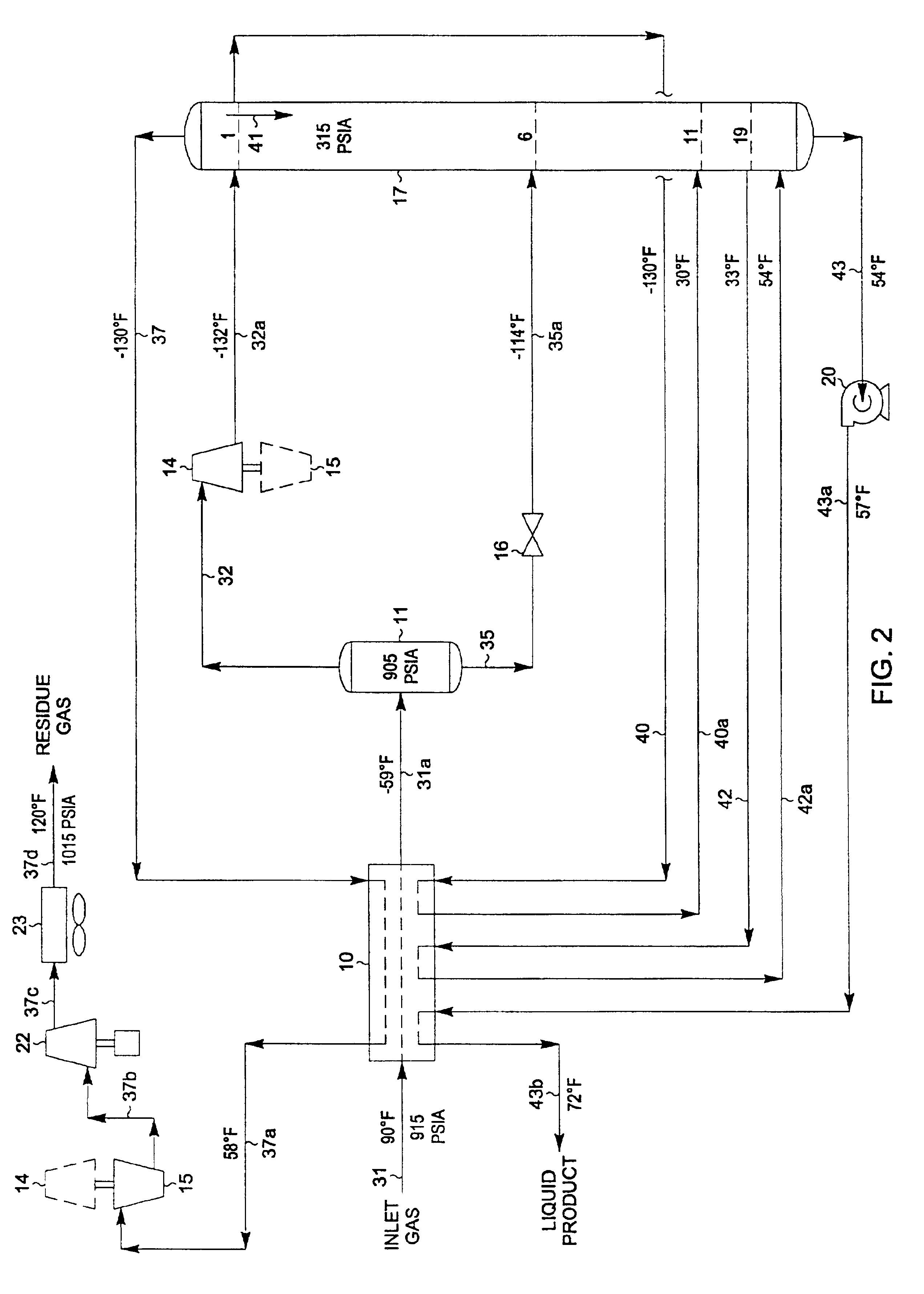
A process for the recovery of ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream is disclosed. In recent years, the preferred method of separating a hydrocarbon gas stream generally includes supplying at least portions of the gas stream to a fractionation tower having at least one reboiler, and often one or more side reboilers, to supply heat to the column by withdrawing and heating some of the tower liquids to produce stripping vapors that separate the more volatile components from the desired components. The reboiler and side reboilers (if any) are typically integrated into the feed stream cooling scheme to provide at least a portion of the refrigeration needed to condense the desired components for subsequent fractionation in the distillation column. In the process disclosed, the tower reboiling scheme is modified to use one or more tower liquid distillation streams from a point higher in the column than is used in the conventional reboiling scheme, providing colder stream(s) for the reboiler(s) that allow more effective cooling of the feed streams and thereby improve the efficiency with which the desired components are recovered. In addition, the tower liquid streams withdrawn from a higher point in the column contain larger quantities of the more volatile components, which when vaporized provide better stripping of undesirable components like carbon dioxide without reducing the recovery of the desired components. The heated distillation stream is returned to a lower point on the fractionation tower that is separated from the withdrawal point by at least one theoretical stage.
Owner:UOP LLC
Hydrocarbon gas processing
A process for the recovery of ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream is disclosed. In recent years, the preferred method of separating a hydrocarbon gas stream generally includes supplying at least portions of the gas stream to a fractionation tower having at least one reboiler, and often one or more side reboilers, to supply heat to the column by withdrawing and heating some of the tower liquids to produce stripping vapors that separate the more volatile components from the desired components. The reboiler and side reboilers (if any) are typically integrated into the feed stream cooling scheme to provide at least a portion of the refrigeration needed to condense the desired components for subsequent fractionation in the distillation column. In the process disclosed, the tower reboiling scheme is modified to use one or more tower liquid distillation streams from a point higher in the column than is used in the conventional reboiling scheme, providing colder stream(s) for the reboiler(s) that allow more effective cooling of the feed streams and thereby improve the efficiency with which the desired components are recovered. In addition, the tower liquid streams withdrawn from a higher point in the column contain larger quantities of the more volatile components, which when vaporized provide better stripping of undesirable components like carbon dioxide without reducing the recovery of the desired components. The heated distillation stream is returned to a lower point on the fractionation tower that is separated from the withdrawal point by at least one theoretical stage.
Owner:UOP LLC
Integrated enhanced oil recovery process
ActiveUS20110088896A1Enhanced overall recoveryIncrease productionSolidificationLiquefactionGeneration processMethane
The present invention relates to an enhanced oil recovery process that is integrated with a synthesis gas generation process, such as gasification or methane reforming, involving combined capture and recycle of carbon dioxide from both processes.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Purification of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is separated from a feed gas, preferably derived from flue gas from an oxyfuel combustion process, in a membrane separation system to produce separated carbon dioxide gas which is fed to the oxyfuel combustion process to improve the performance of the process.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Integrated enhanced oil recovery process
ActiveUS20110088897A1Increase productionEnhanced overall recoverySolidificationLiquefactionGeneration processCarbon dioxide
The present invention relates to an enhanced oil recovery process that is integrated with a synthesis gas generation process, such as gasification or methane reforming, involving combined capture and recycle of carbon dioxide from both processes.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Purification of carbon dioxide
Impure carbon dioxide (“CO2”) comprising a first contaminant selected from the group consisting of oxygen (“O2”) and carbon monoxide (“CO”) is purified by separating expanded impure carbon dioxide liquid in a mass transfer separation column system. The impure carbon dioxide may be derived from, for example, flue gas from an oxyfuel combustion process or waste gas from a hydrogen (“H2”) PSA system.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
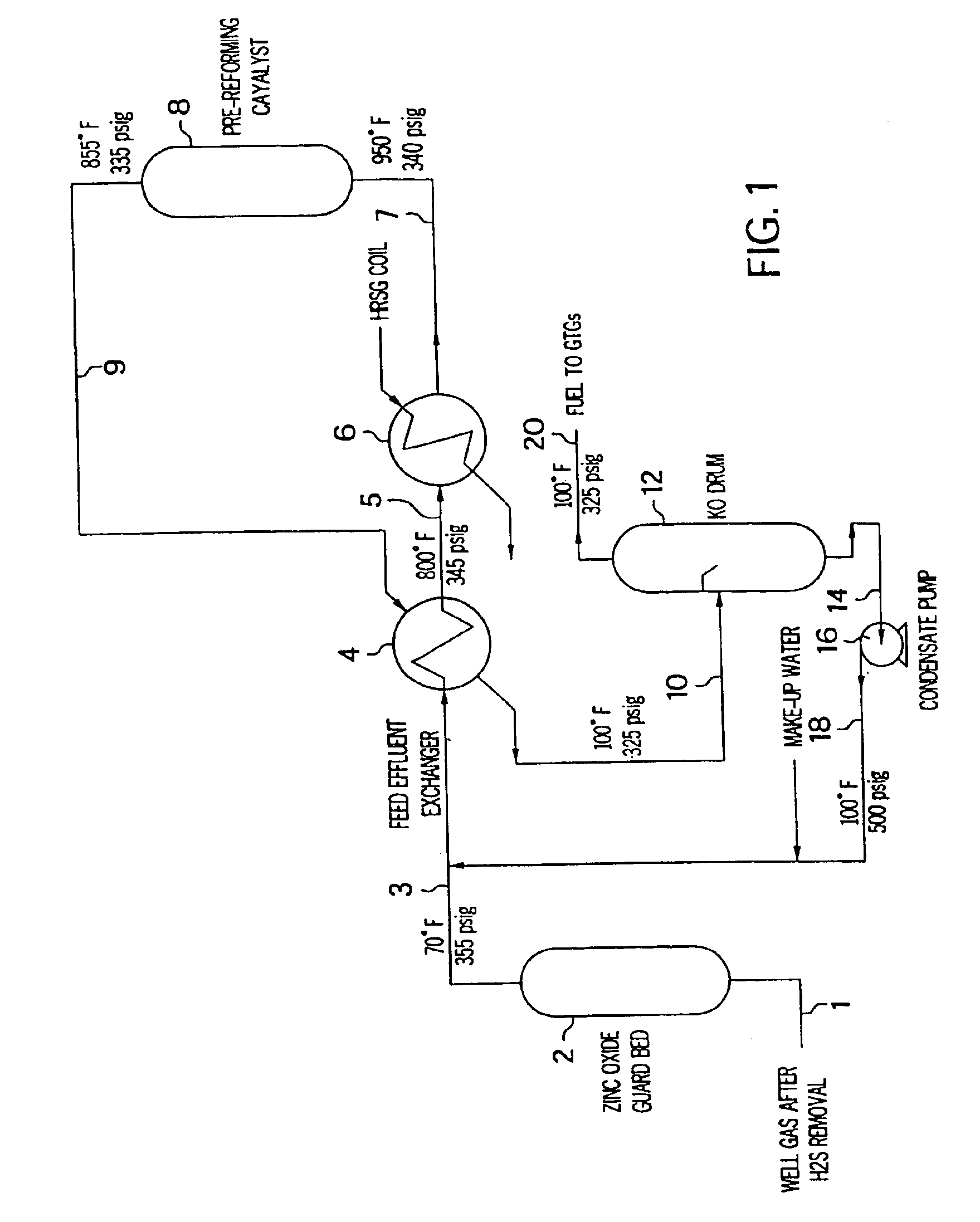
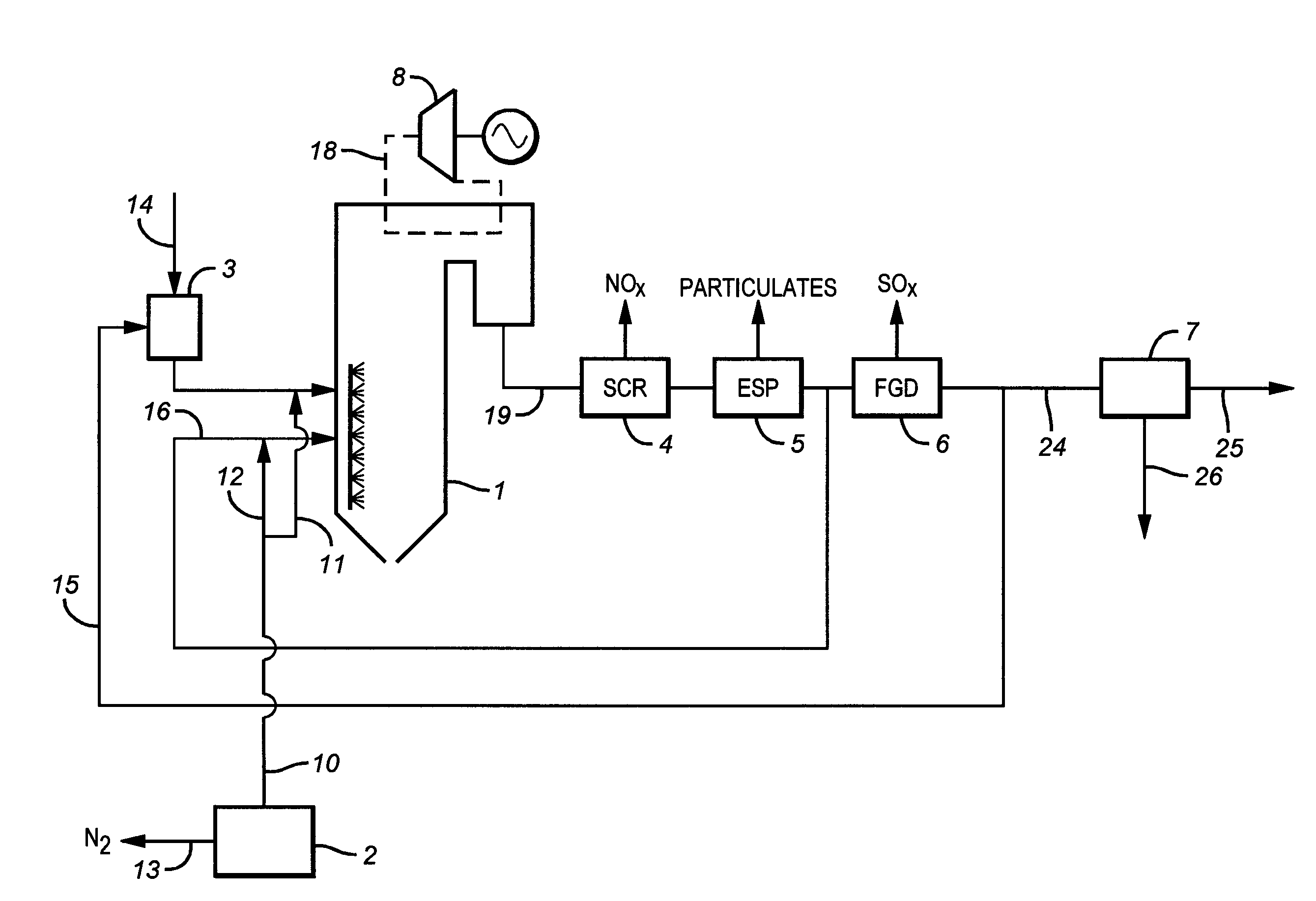
Method for utilizing gas reserves with low methane concentrations and high inert gas concentrations for fueling gas turbines
InactiveUS6907737B2Improve flammabilityLow costSolidificationLiquefactionProcess engineeringCurrent technology
The invention is directed to a method of fueling gas turbines from natural gas reserves with relatively low methane concentrations. The invention uses such reserves to generate electric power. The invention permits the use of these reserves at significantly lower cost than by producing pipeline natural gas to fuel gas turbines to generate electric power. These reserves currently generally are used only after the removal of impurities to produce pipeline natural gas quality turbine fuel. The latter current technology is capital intensive, and at current natural gas prices, economically unattractive. The process of the invention can remove the impurities from the gas from the natural gas reserve necessary for protection of the environment, and leaves inert gasses in the fuel in an amount which will increase the output of a gas turbine for the generation of power by about 5 to about 20%.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
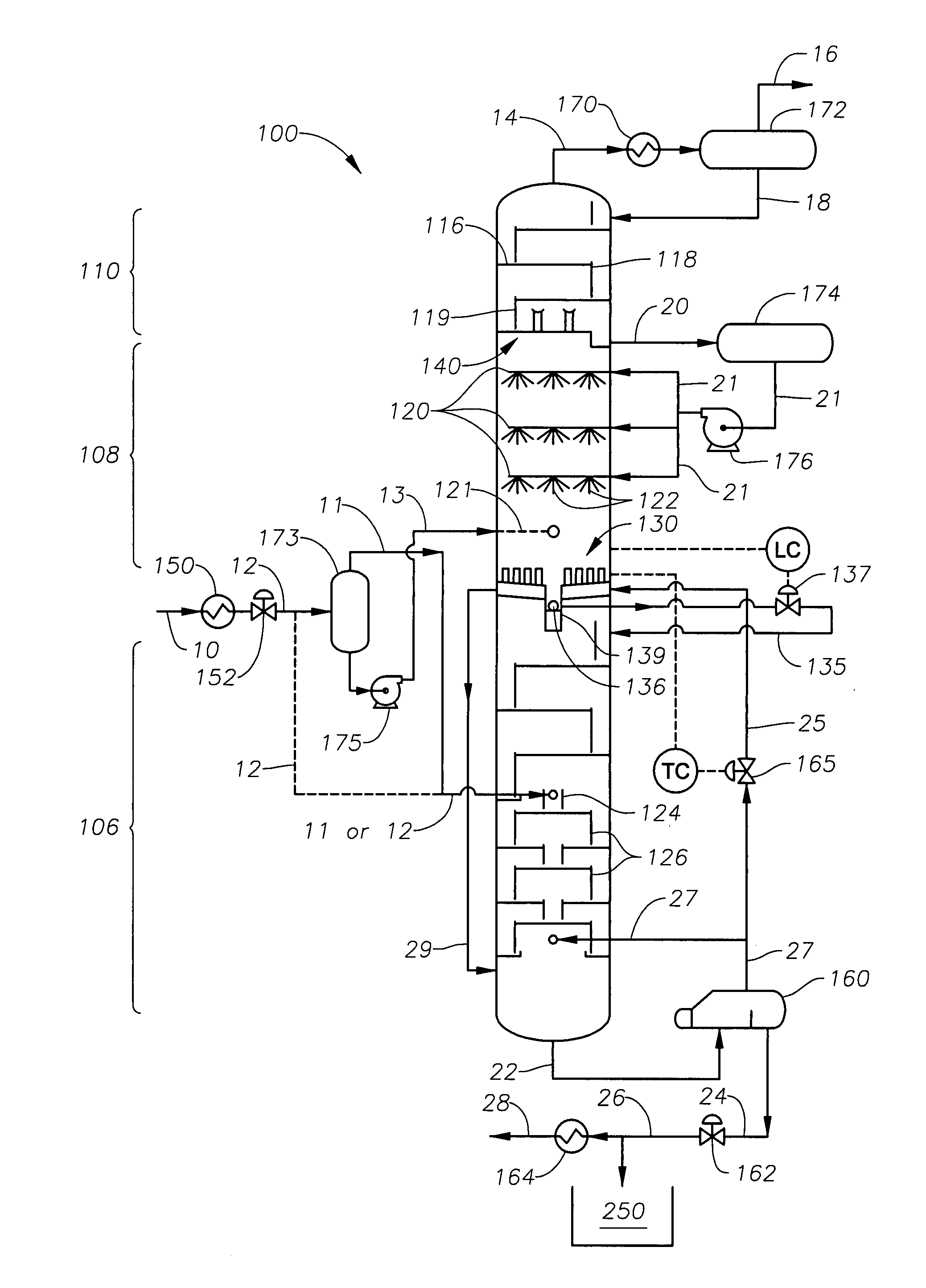
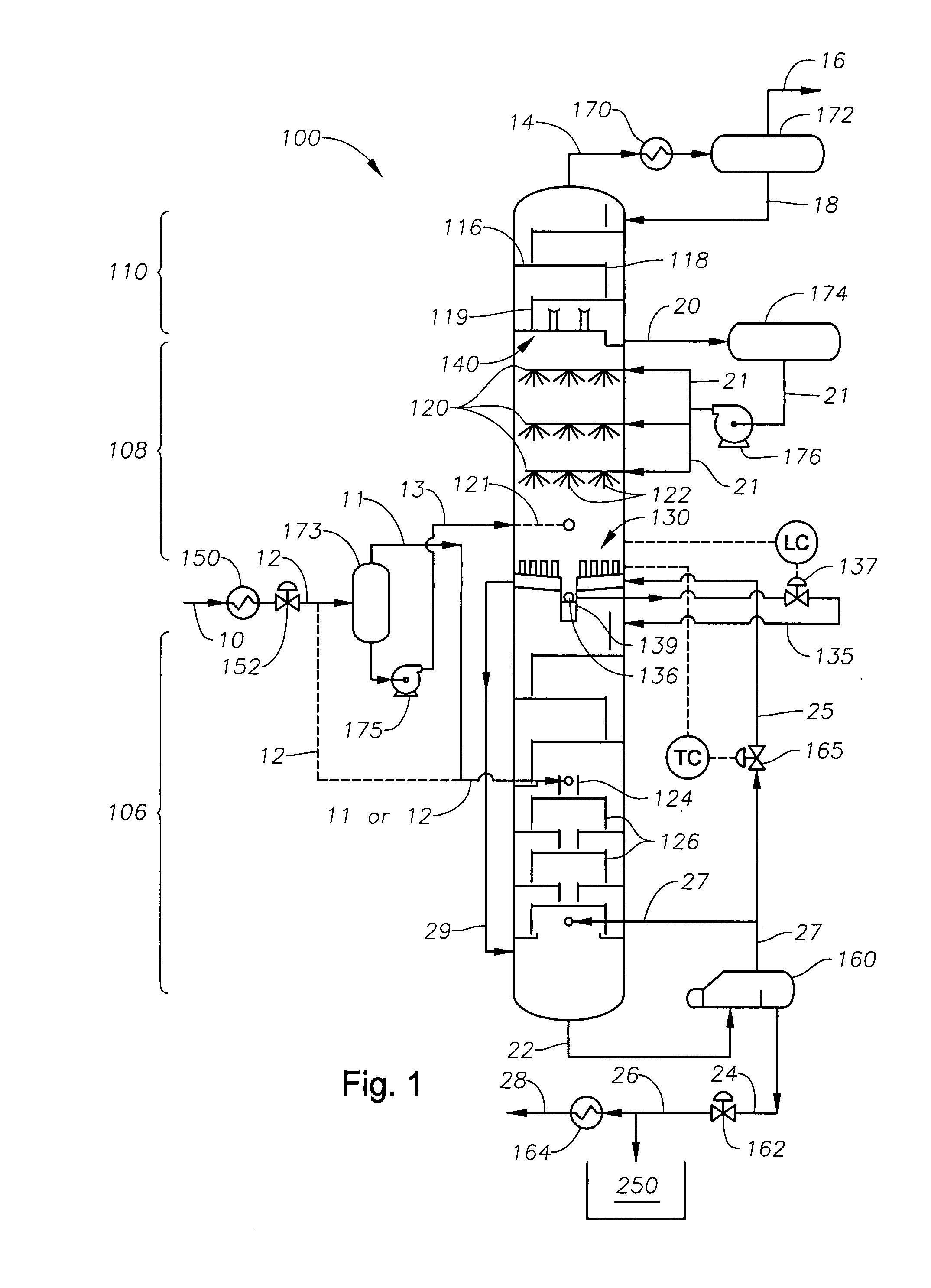
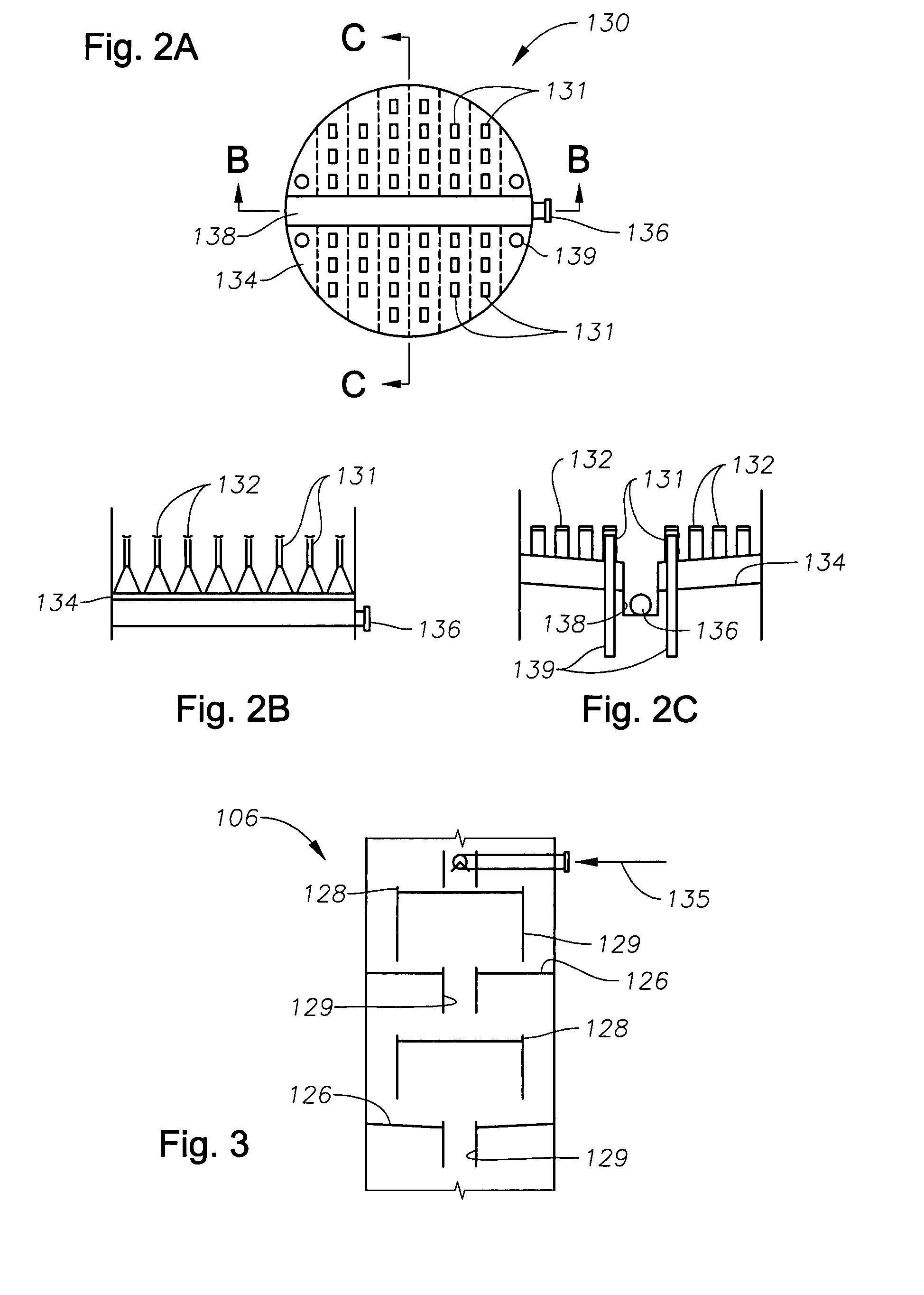
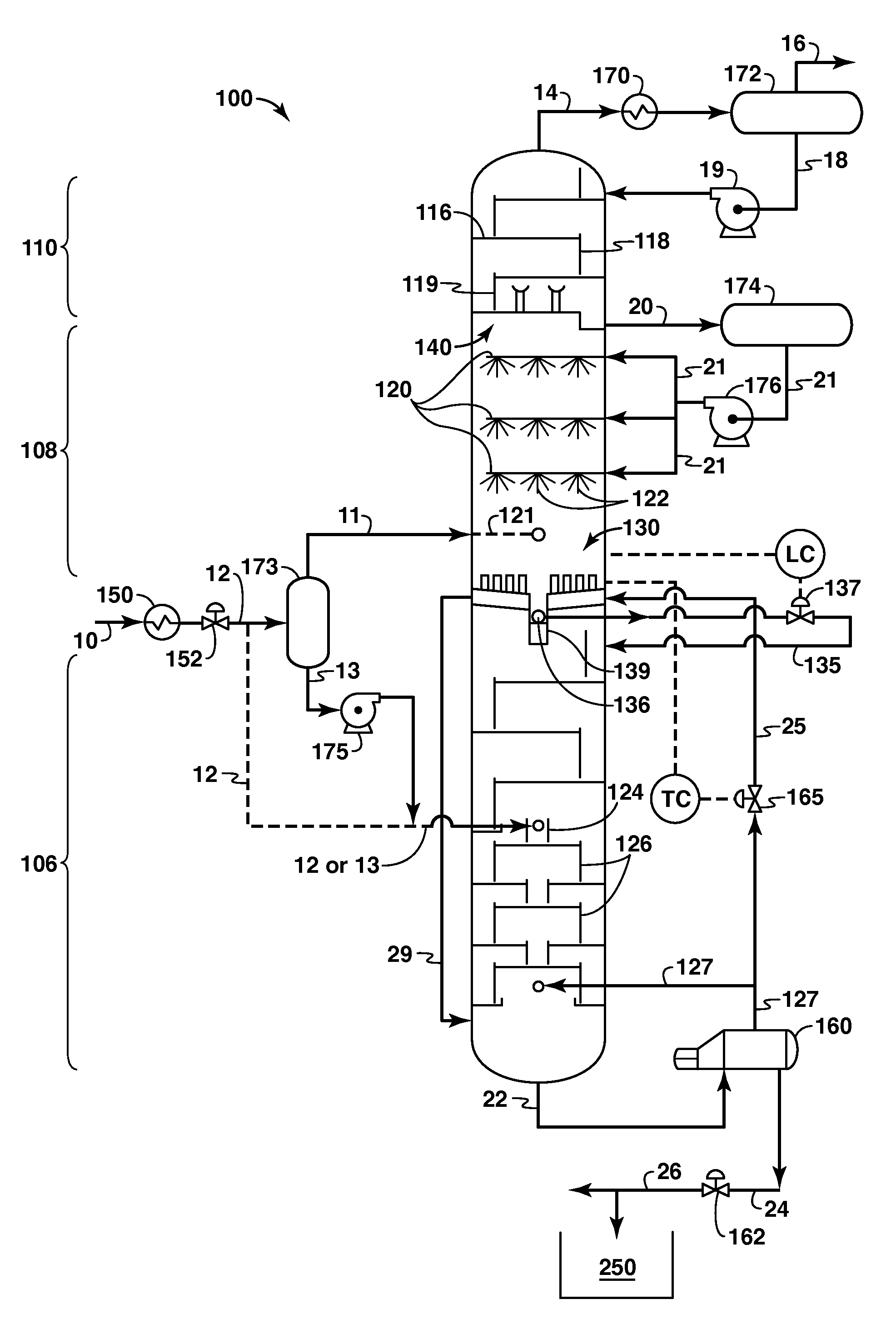
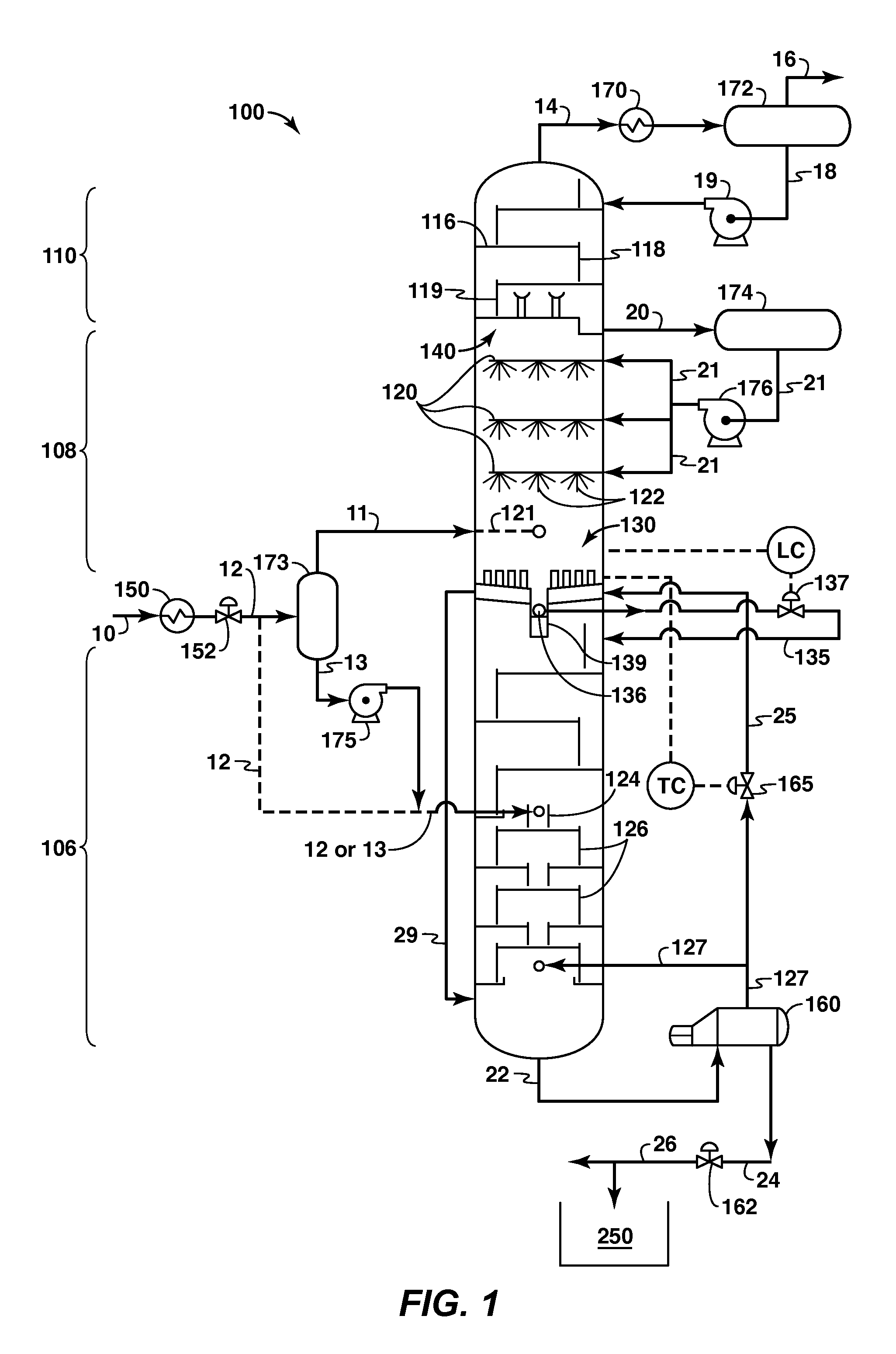
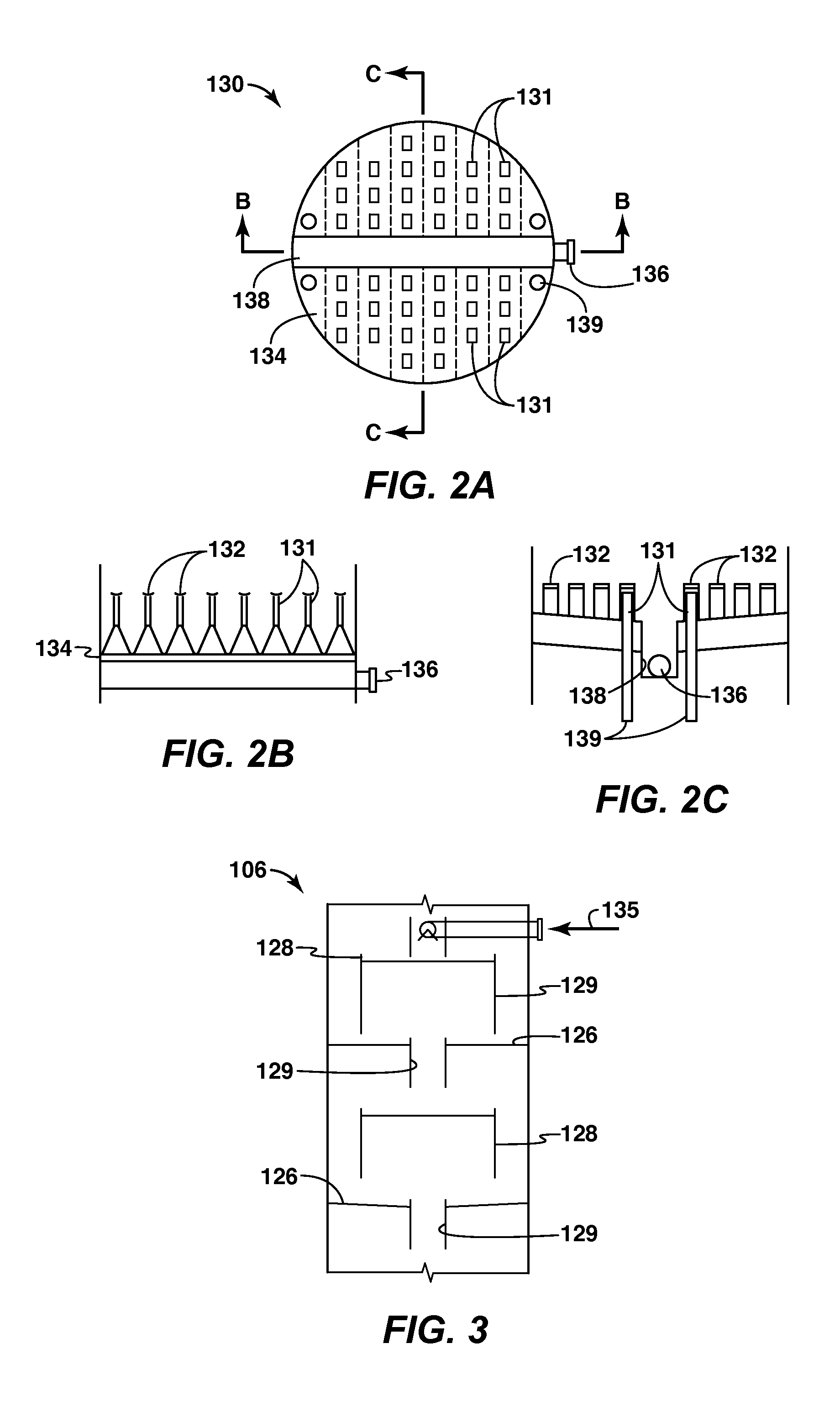
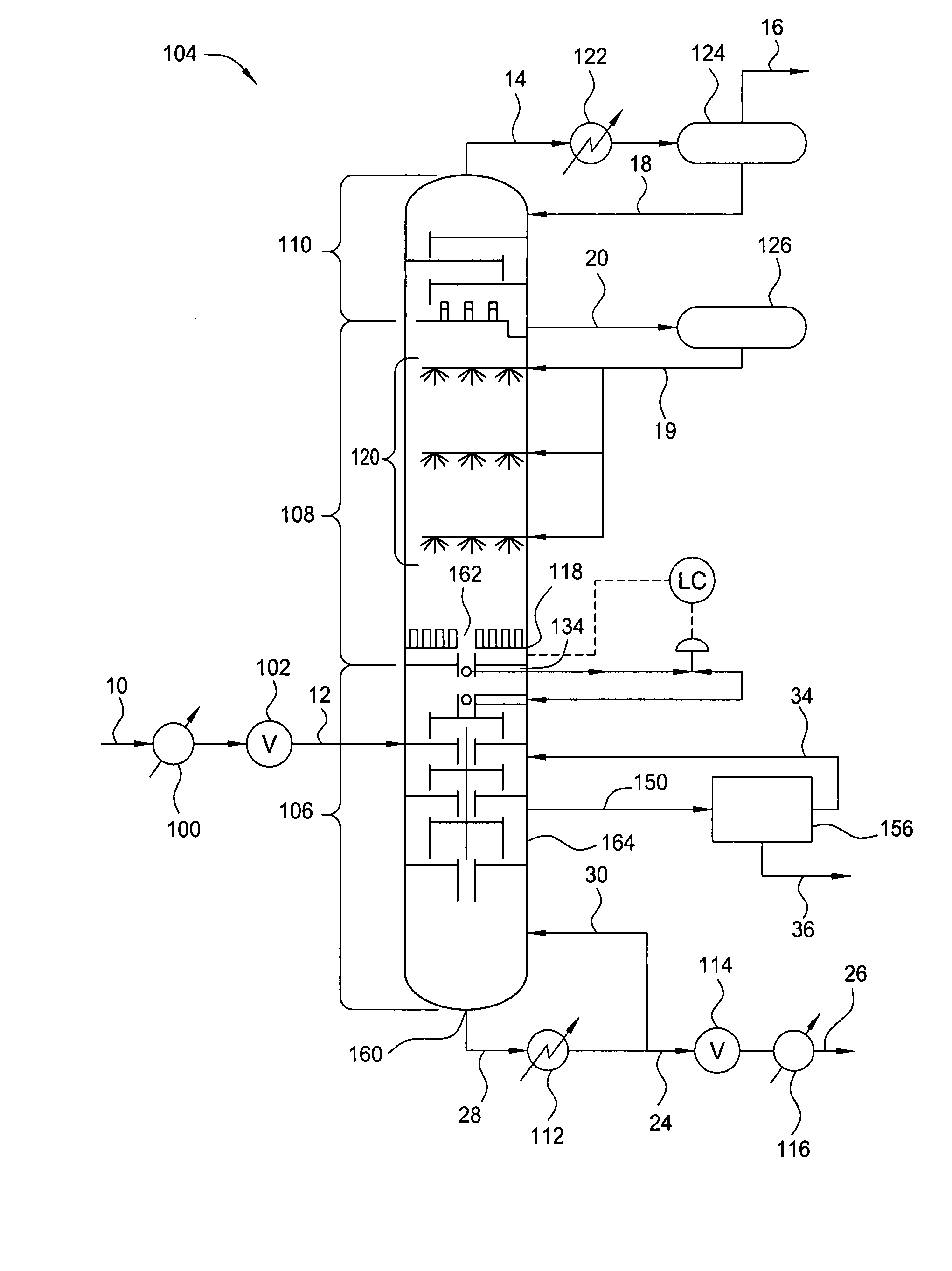
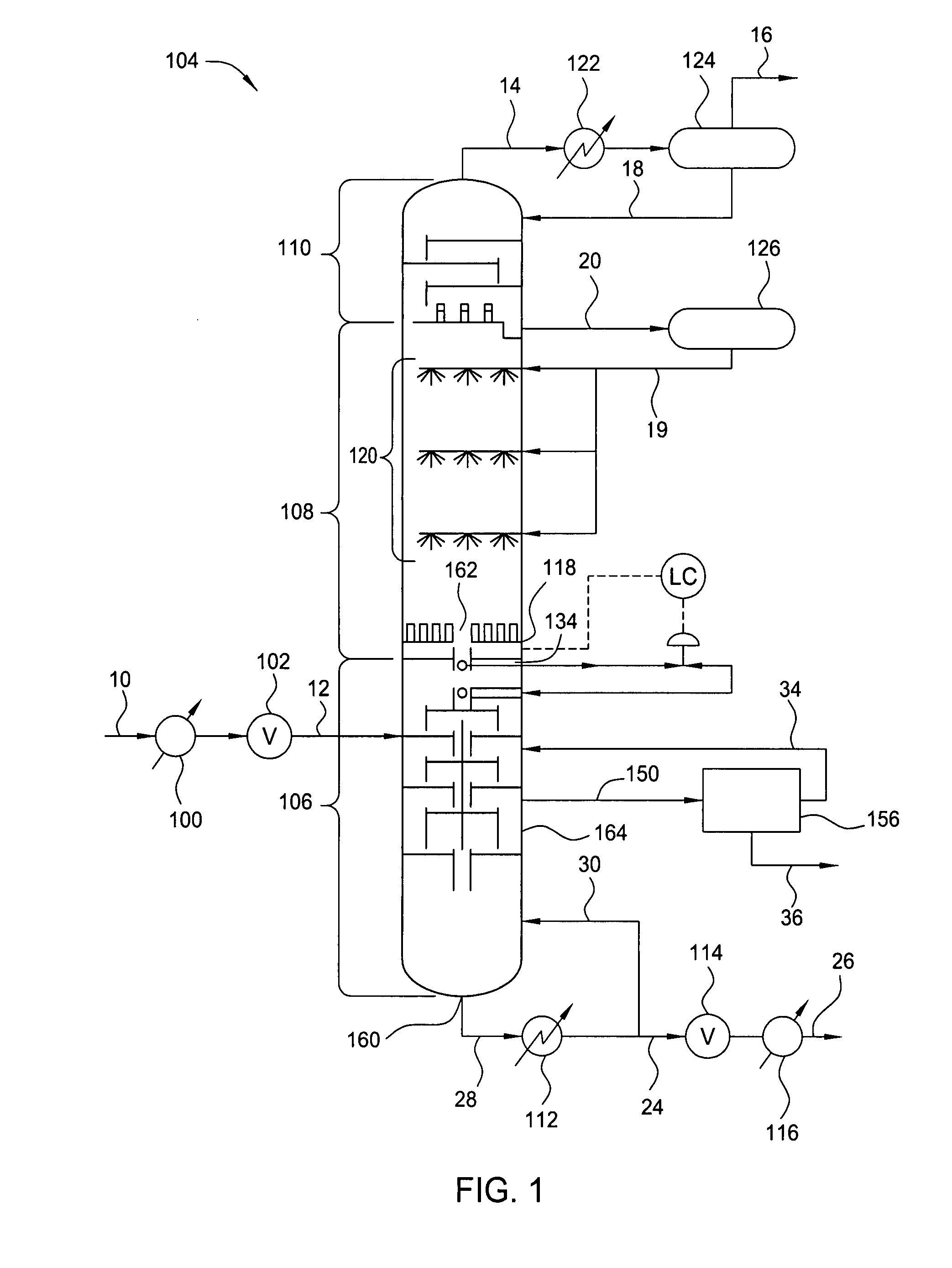
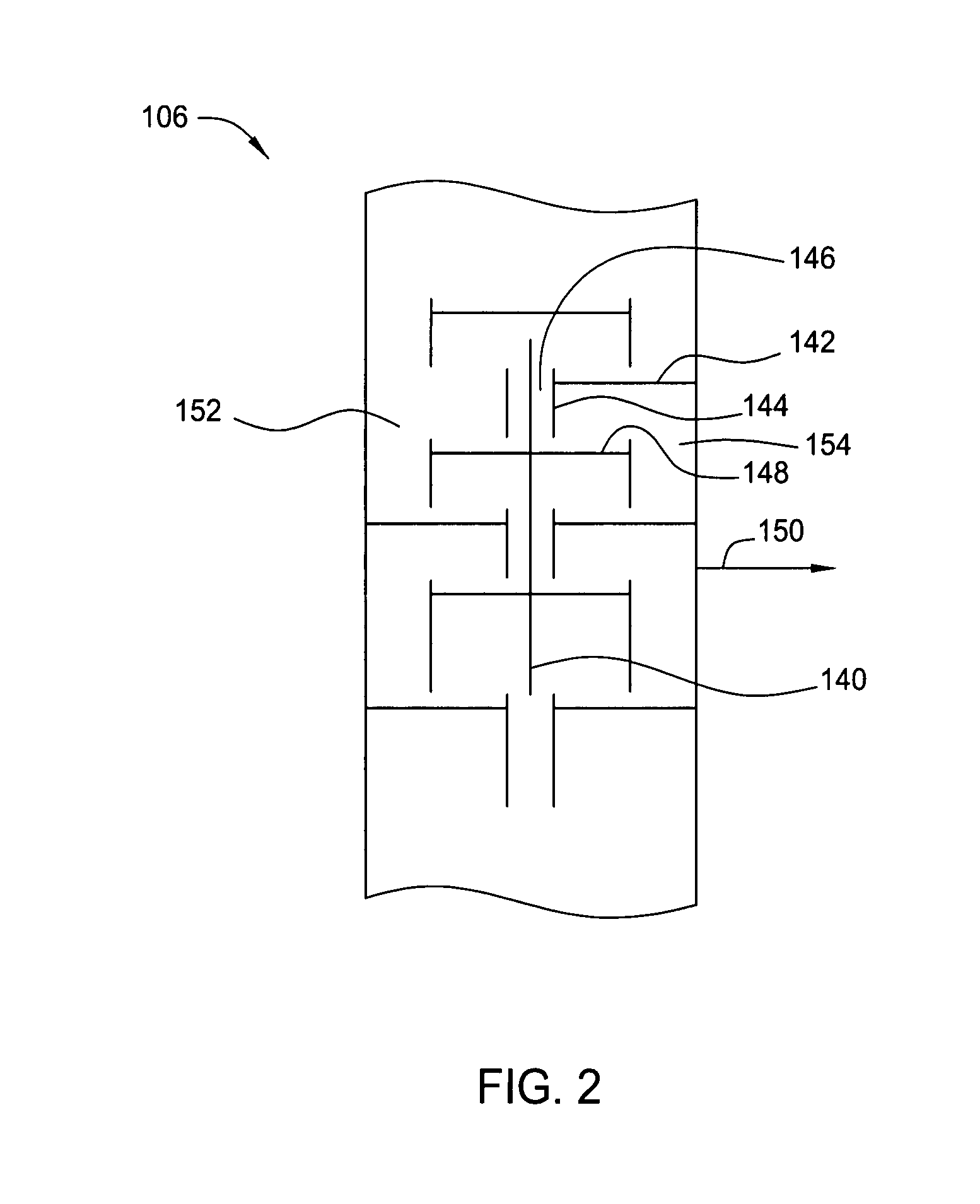
Controlled Freeze Zone Tower
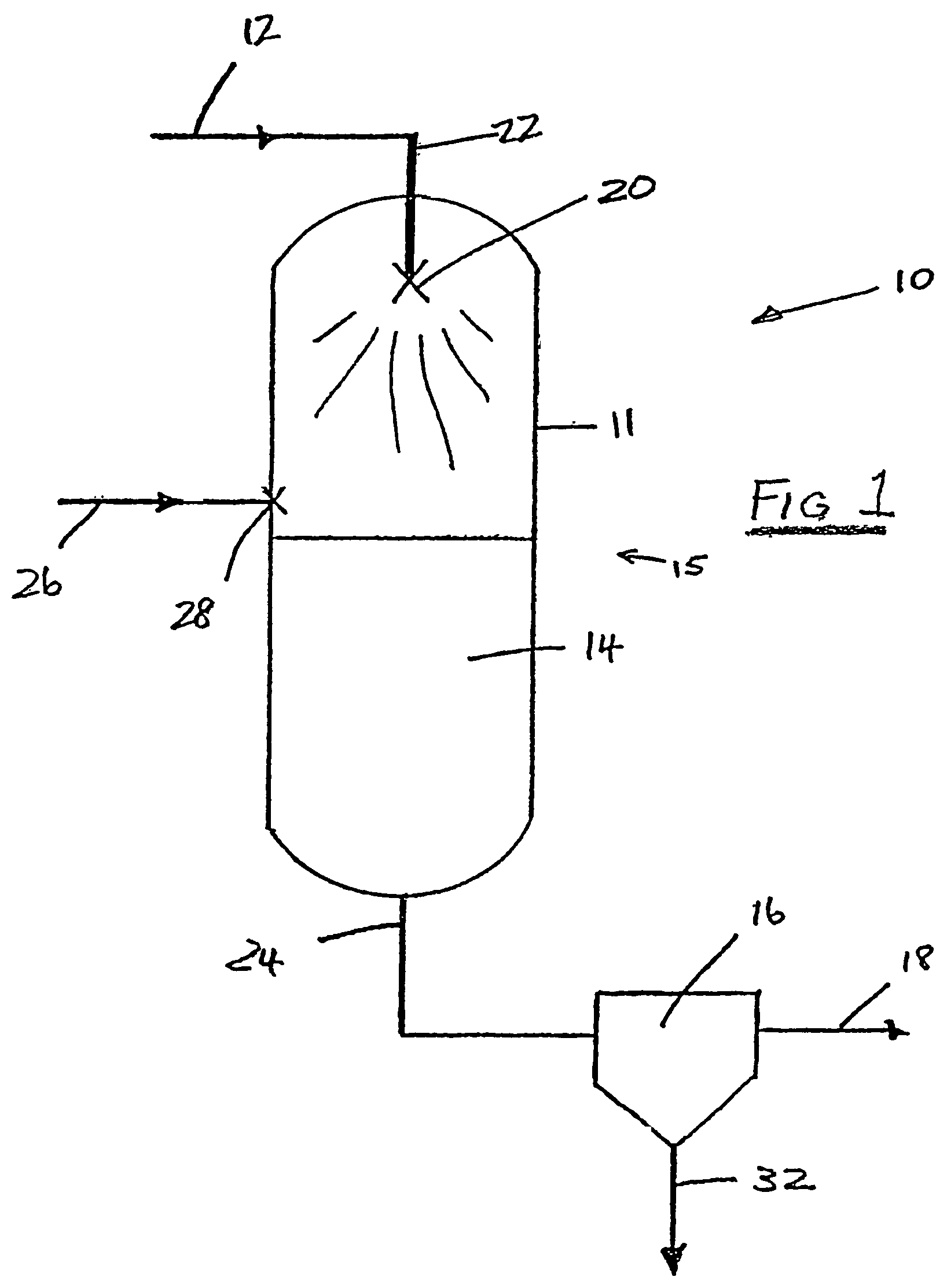
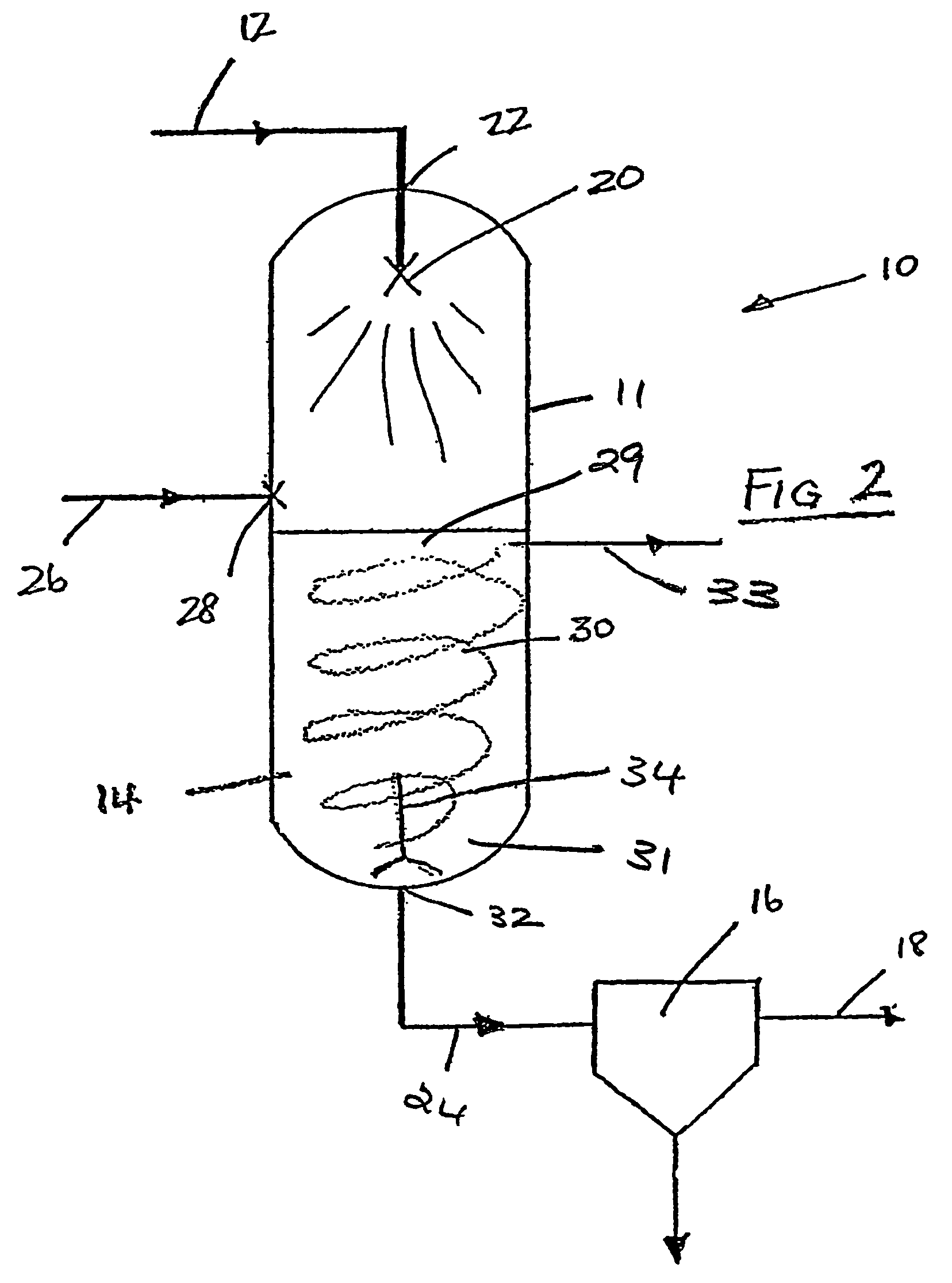
A cryogenic distillation tower is provided for the separation of a fluid stream containing at least methane and carbon dioxide. The cryogenic distillation tower has a lower stripping section, an upper rectification section, and an intermediate spray section. The intermediate spray section includes a plurality of spray nozzles that inject a liquid freeze zone stream. The nozzles are configured such that substantial liquid coverage is provided across the inner diameter of the intermediate spray section. The liquid freeze zone stream generally includes methane at a temperature and pressure whereby both solid carbon dioxide particles and a methane-enriched vapor stream are formed. The tower may further include one or more baffles below the nozzles to create frictional resistance to the gravitational flow of the liquid freeze zone stream. This aids in the breakout and recovery of methane gas. Additional internal components are provided to improve heat transfer and to facilitate the breakout of methane gas.
Owner:FIELER ELEANOR R +3
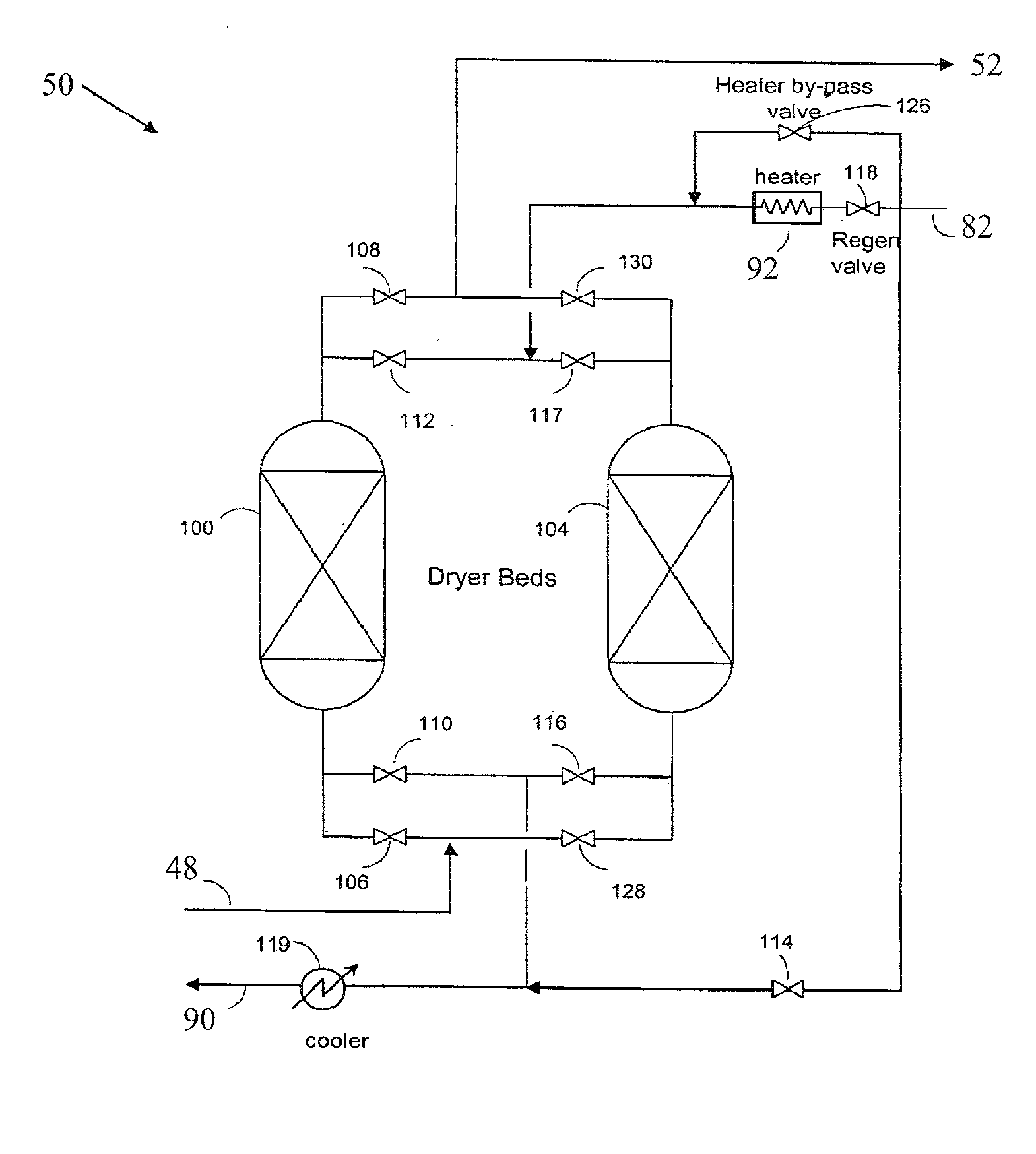
Recovery of carbon dioxide from flue gas
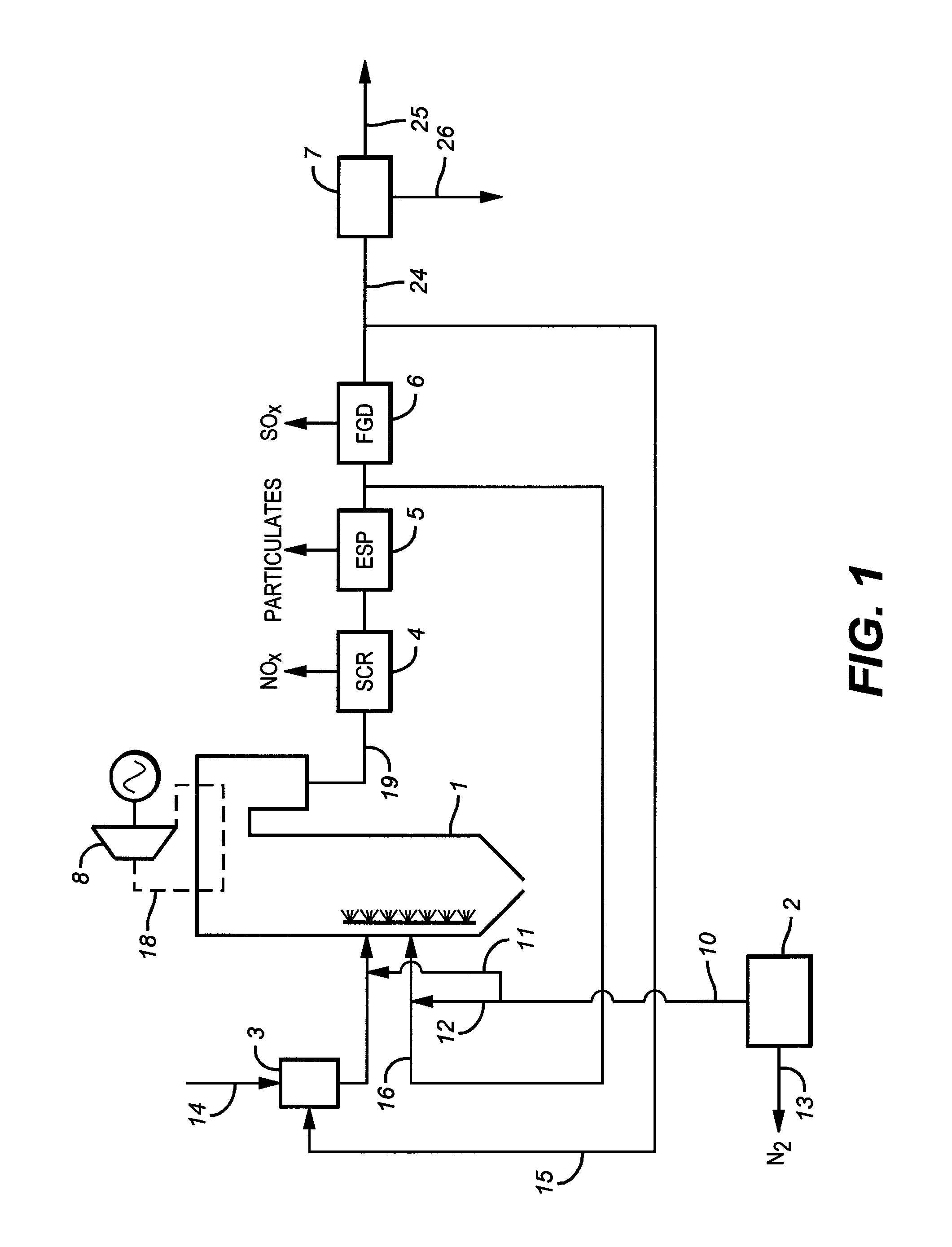
Carbon dioxide-containing gas such as flue gas and a carbon dioxide-rich stream are compressed and the combined streams are then treated to desorb moisture onto adsorbent beds and then subjected to subambient-temperature processing to produce a carbon dioxide product stream and a vent stream. The vent stream is treated to produce a carbon dioxide-depleted stream which can be used to desorb moisture from the beds, and a carbon dioxide-rich stream which is combined with the carbon dioxide-containing gas.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Carbon dioxide production method
ActiveUS20070232706A1Increased hydrogen recoveryPromote recoverySolidificationLiquefactionVacuum pressureCarbon dioxide production
A method of producing a carbon dioxide product stream from a synthesis gas stream formed within a hydrogen plant having a synthesis gas reactor, a water-gas shift reactor, located downstream of the synthesis gas reactor to form the synthesis gas stream and a hydrogen pressure swing adsorption unit to produce a hydrogen product recovered from the synthesis gas stream. In accordance with the method the carbon dioxide from the synthesis gas stream by separating the carbon dioxide from the synthesis gas stream in a vacuum pressure swing adsorption system, thereby to produce a hydrogen-rich synthesis gas stream and a crude carbon dioxide stream and then purifying the crude carbon dioxide stream by a sub-ambient temperature distillation process thereby to produce the carbon dioxide product. A hydrogen synthesis gas feed stream to the hydrogen pressure swing adsorption unit is formed at least in part from the hydrogen rich stream.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Carbon dioxide purification method
InactiveUS20070231244A1Lower energy requirementsLess refrigerationSolidificationLiquefactionPurification methodsRefrigeration
Method of purifying a feed stream containing carbon dioxide wherein the feed stream after having been compressed and dried is partly cooled and then used to reboil a stripping column. Thereafter, the feed stream is further cooled and expanded to a lower operational temperature of the stripping column. A carbon dioxide product stream composed of the liquid column bottoms of the stripping column is expanded at one or more pressures to generate refrigeration, then fully vaporized within the main heat exchanger and compressed by a compressor to produce a compressed carbon dioxide product. Refrigeration is recovered in the main heat exchanger from a column overhead stream extracted from the stripping column within the main heat exchanger either directly or indirectly by auxiliary processing in which carbon dioxide is further separated and optionally recycled back to the main compressor used in compressing the feed stream.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Process to remove nitrogen and/or carbon dioxide from methane-containing streams
A process for the removal of inert gases, such as nitrogen and carbon dioxide, from methane-containing gases, such as natural gas, including a first stage removal which lowers the total combined inert content to about less than 30% and a second stage removal utilizing a pressure swing adsorption process comprising one or more adsorbent beds comprising contracted titanosilicate-1 adsorbent, wherein the purified methane-containing gas contains less than about 6% total combined inerts.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC +1
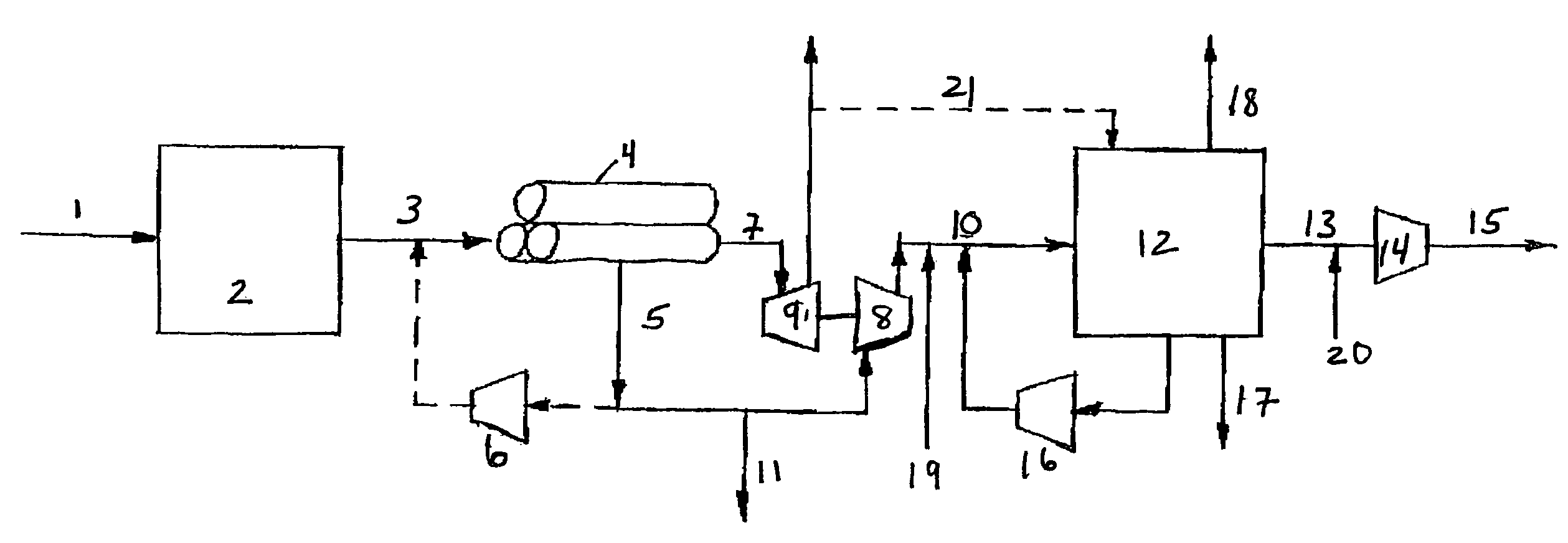
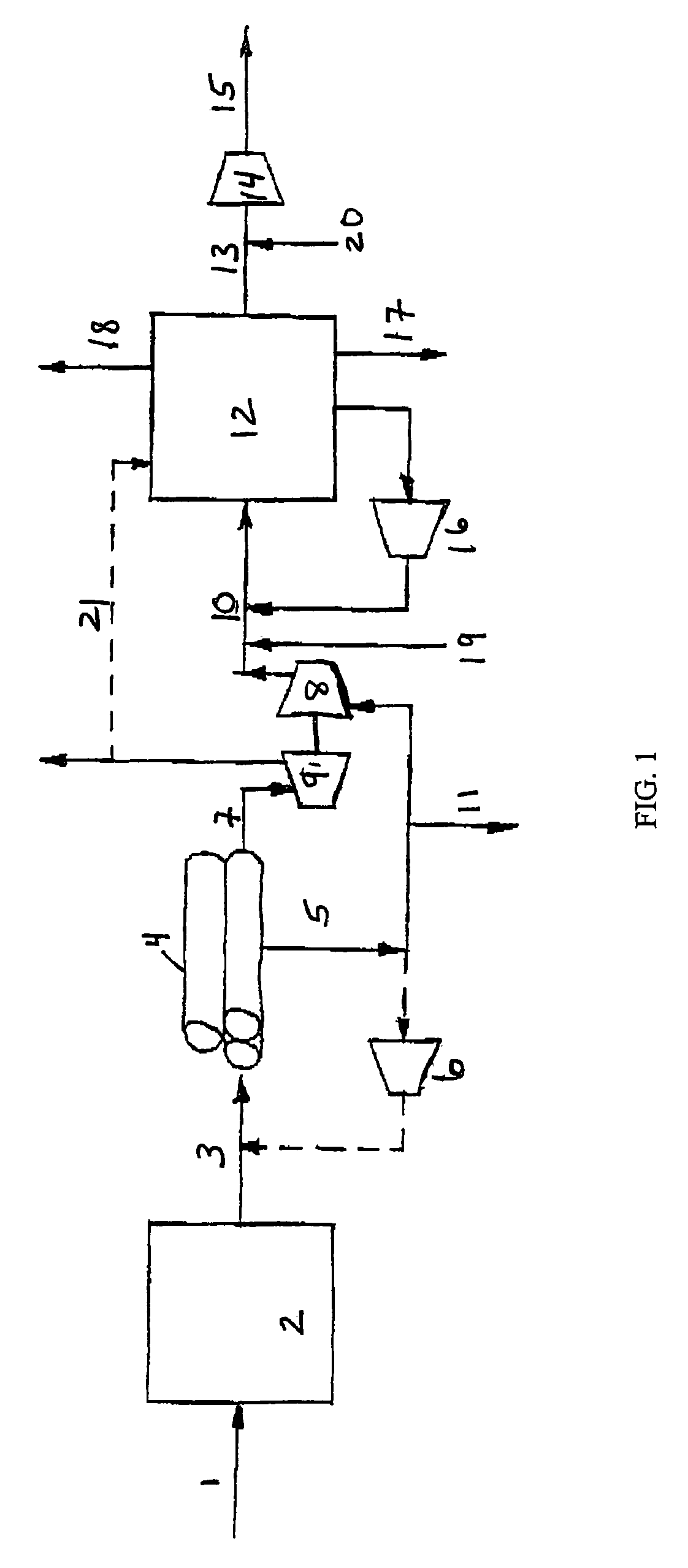
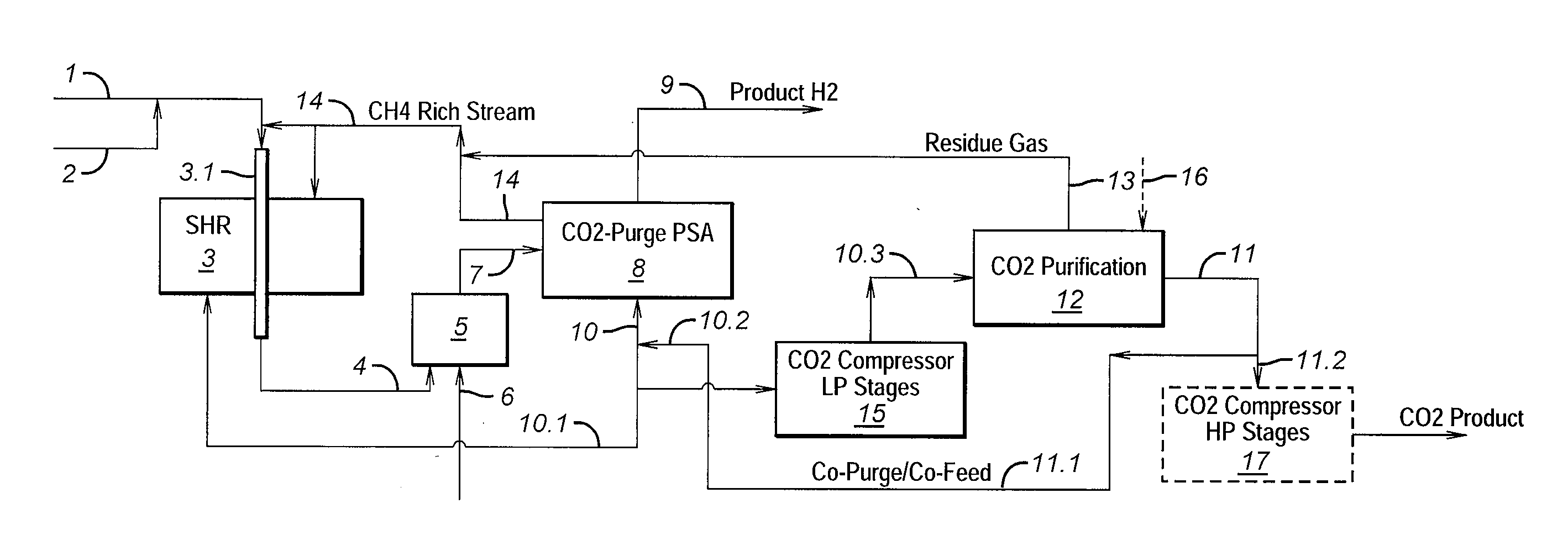
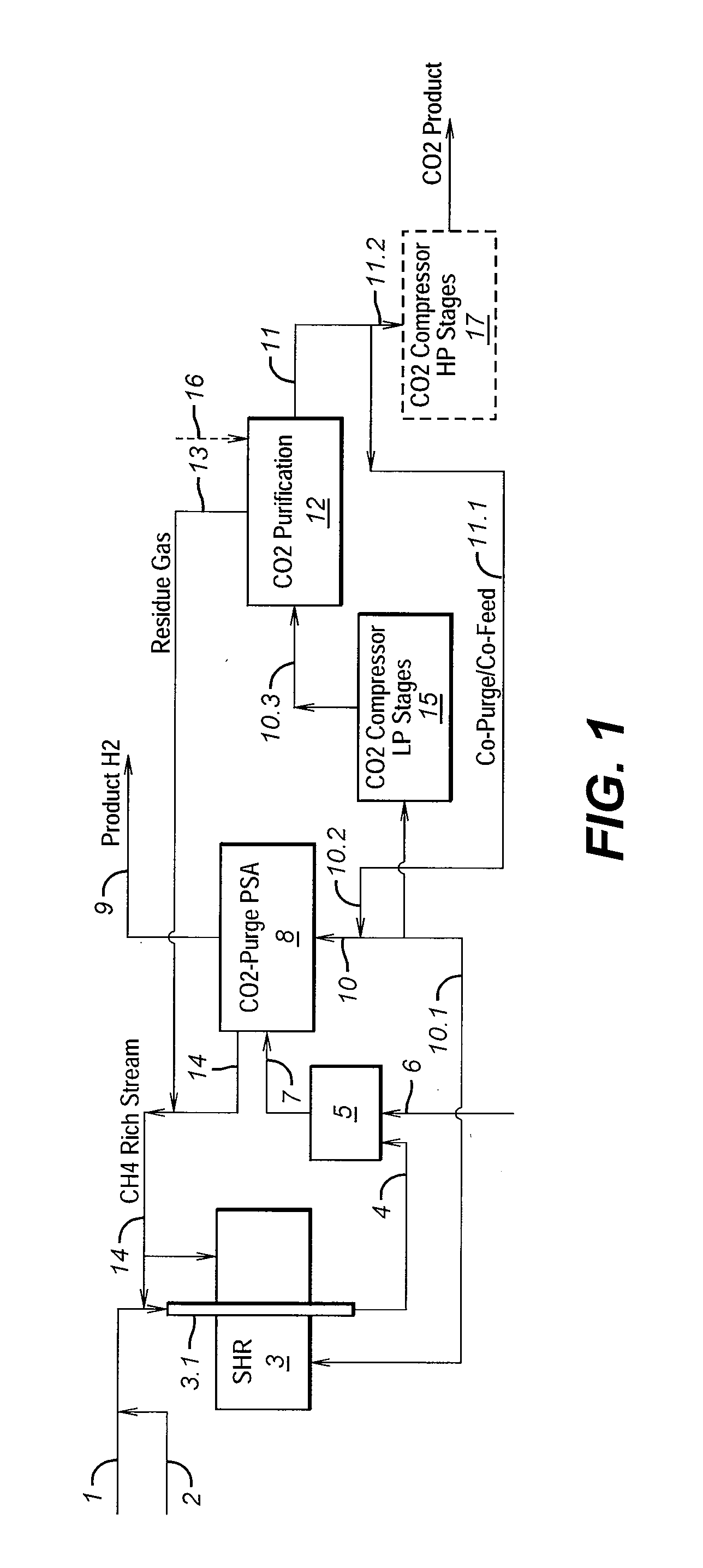
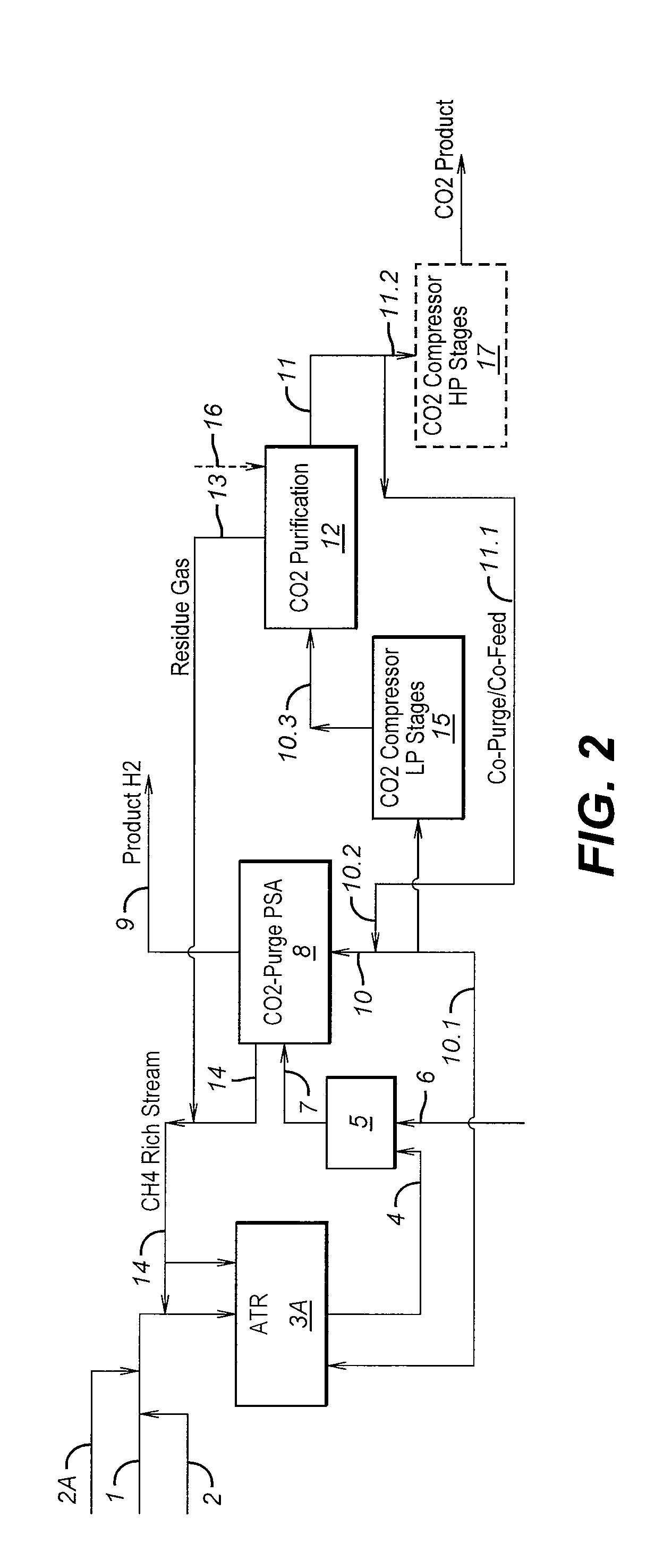
Process For The Production Of Carbon Dioxide Utilizing A Co-Purge Pressure Swing Adsorption Unit
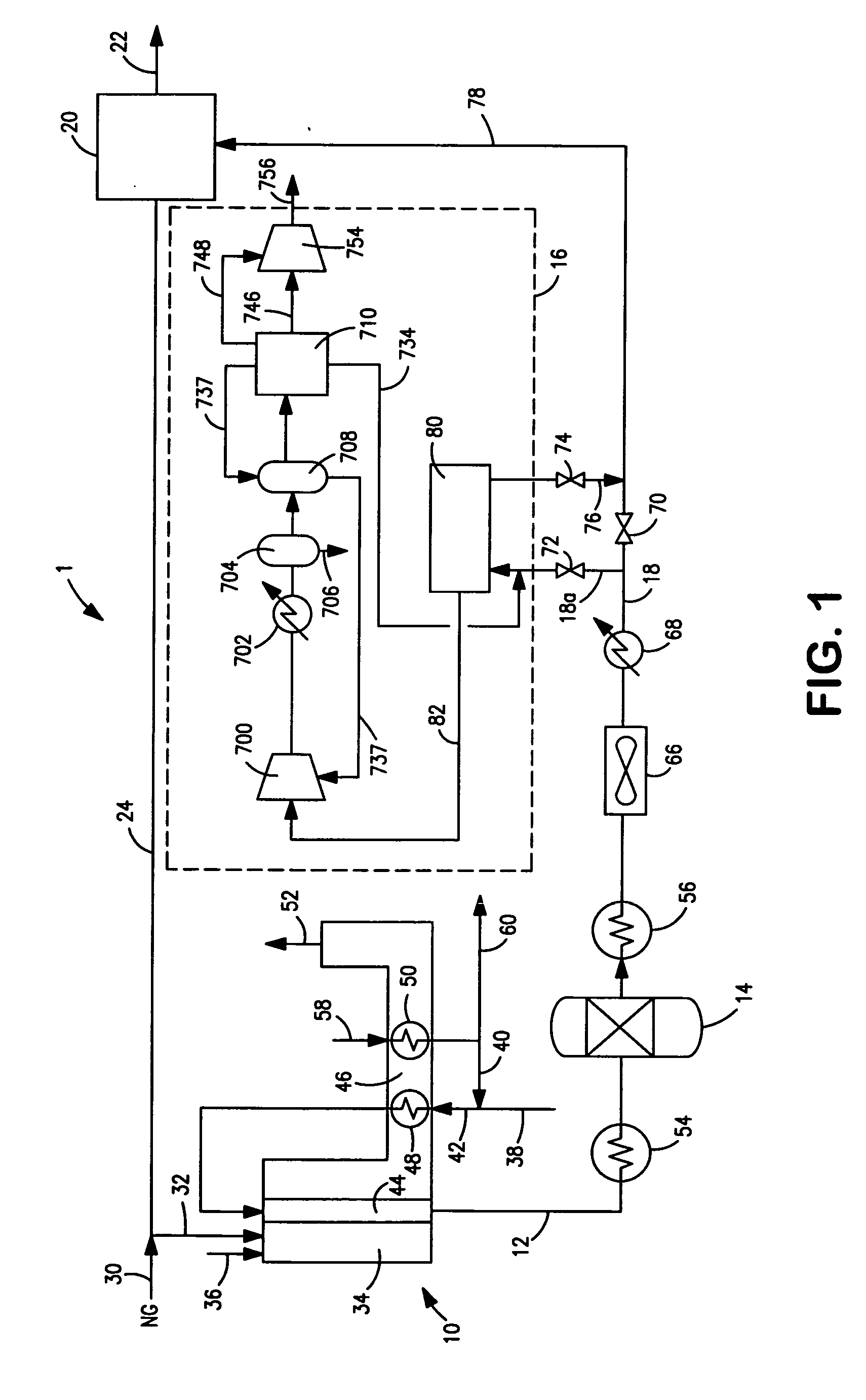
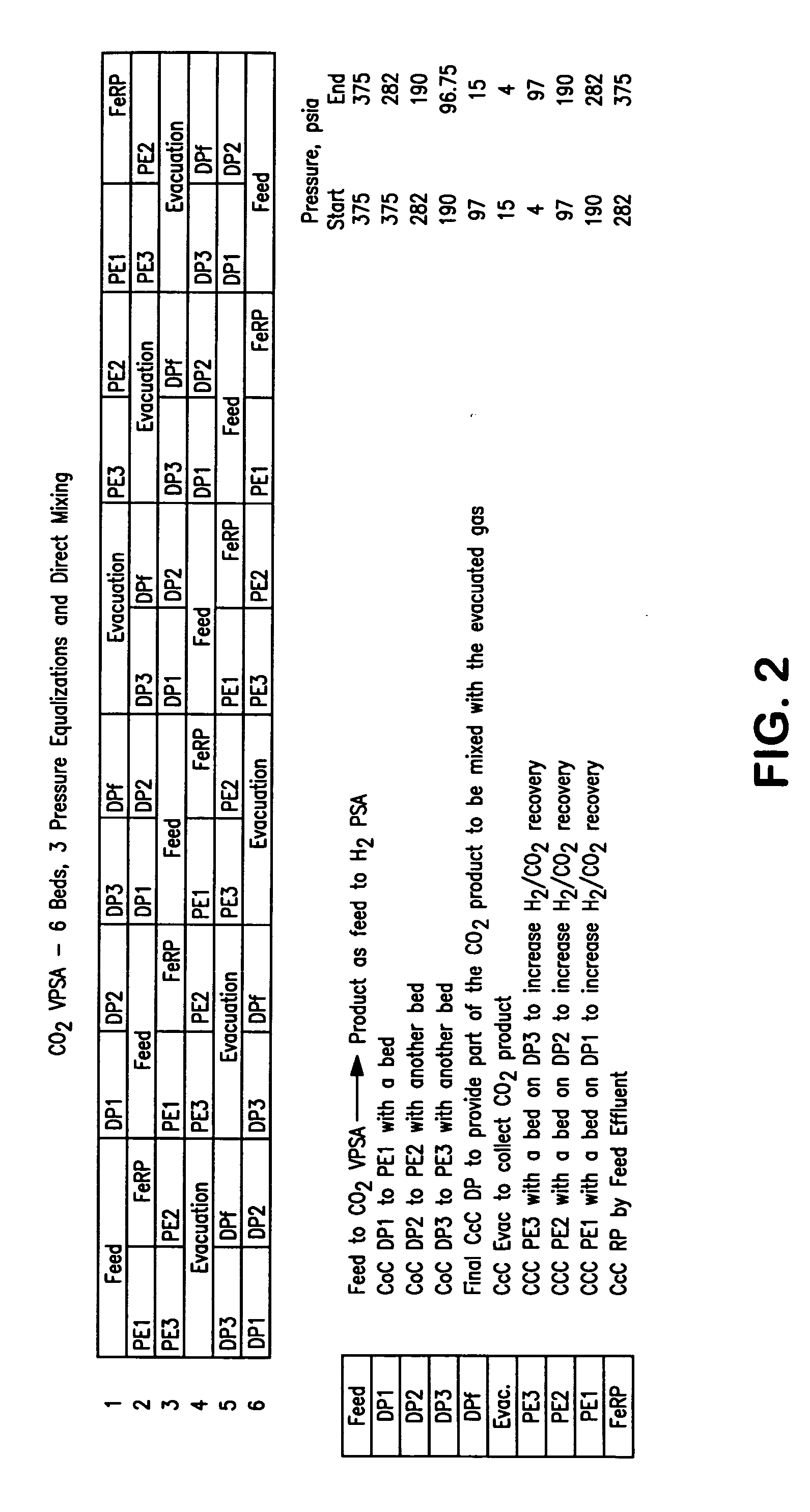
The present invention provides a process for recovering gaseous hydrogen and gaseous carbon dioxide from a mixture of hydrocarbons by utilizing a system that includes a reformer unit, an optional water gas shift reactor, and a pressure swing adsorption unit in conjunction with a carbon dioxide purification unit such as a cryogenic purification unit or a catalytic oxidizer. In this process, purified CO2 from the CO2 purification unit is used as a co-feed / co-purge in the pressure swing adsorption unit in order to produce a CO2 tail gas that includes a higher concentration of CO2.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Purification of carbon dioxide
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Systems and Methods for Removing Heavy Hydrocarbons and Acid Gases From a Hydrocarbon Gas Stream
A system for removing acid gases from a sour gas stream is provided. The system includes an acid gas removal system and a heavy hydrocarbon removal system. The acid gas removal system receives the sour gas stream and separates the sour gas stream into an overhead gas stream comprised primarily of methane, and a bottom acid gas stream comprised primarily of acid gases such as carbon dioxide. The heavy hydrocarbon removal system may be placed upstream or downstream of the acid gas removal system or both. The heavy hydrocarbon removal system receives a gas stream and separates the gas stream into a first fluid stream comprising heavy hydrocarbons and a second fluid stream comprising other components. The components of the second fluid stream will depend on the composition of the gas stream. Various types of heavy hydrocarbon removal systems may be utilized.
Owner:NORTHROP PAUL SCOTT +4
Process and apparatus for the separation of a gaseous mixture
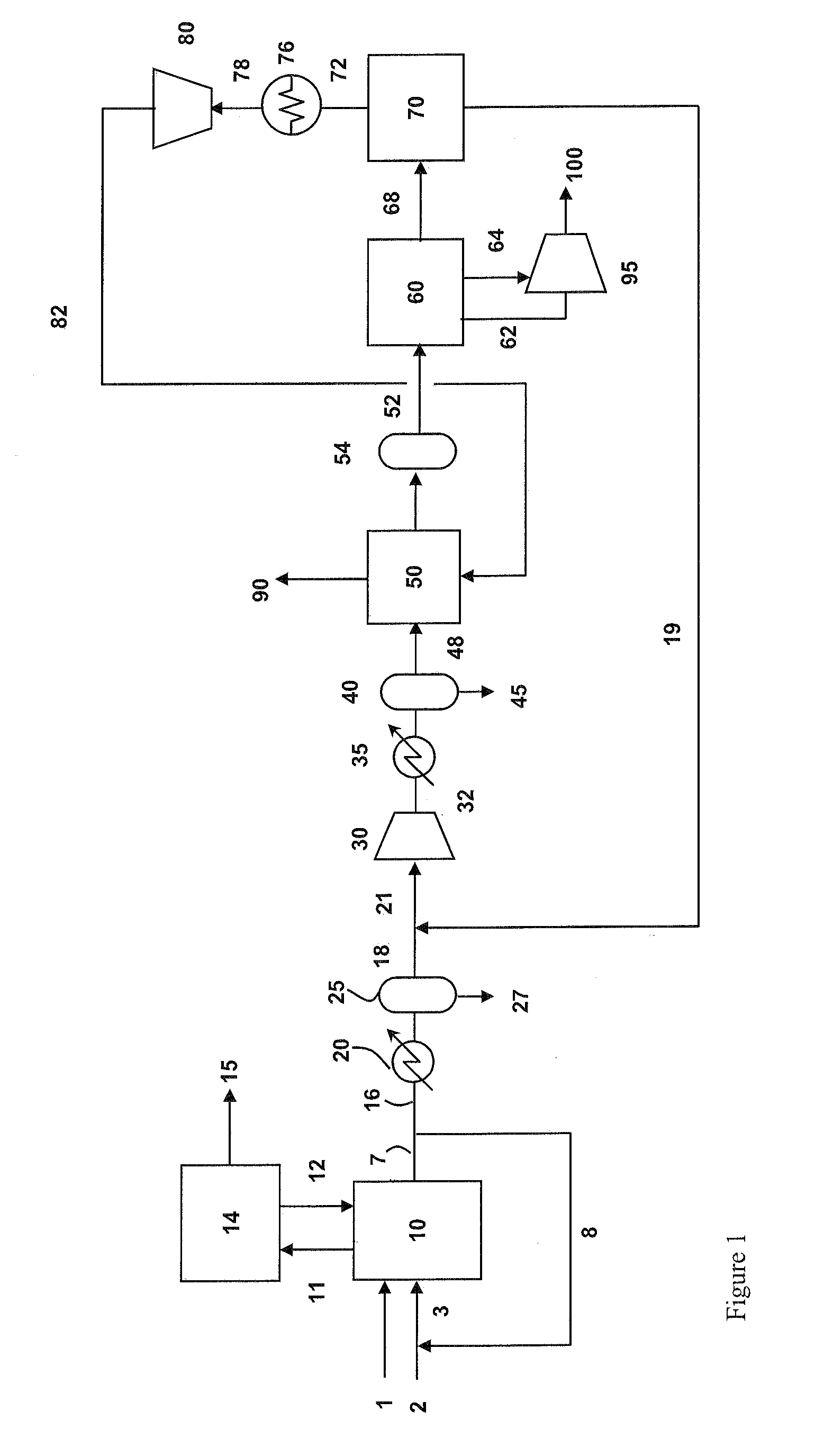
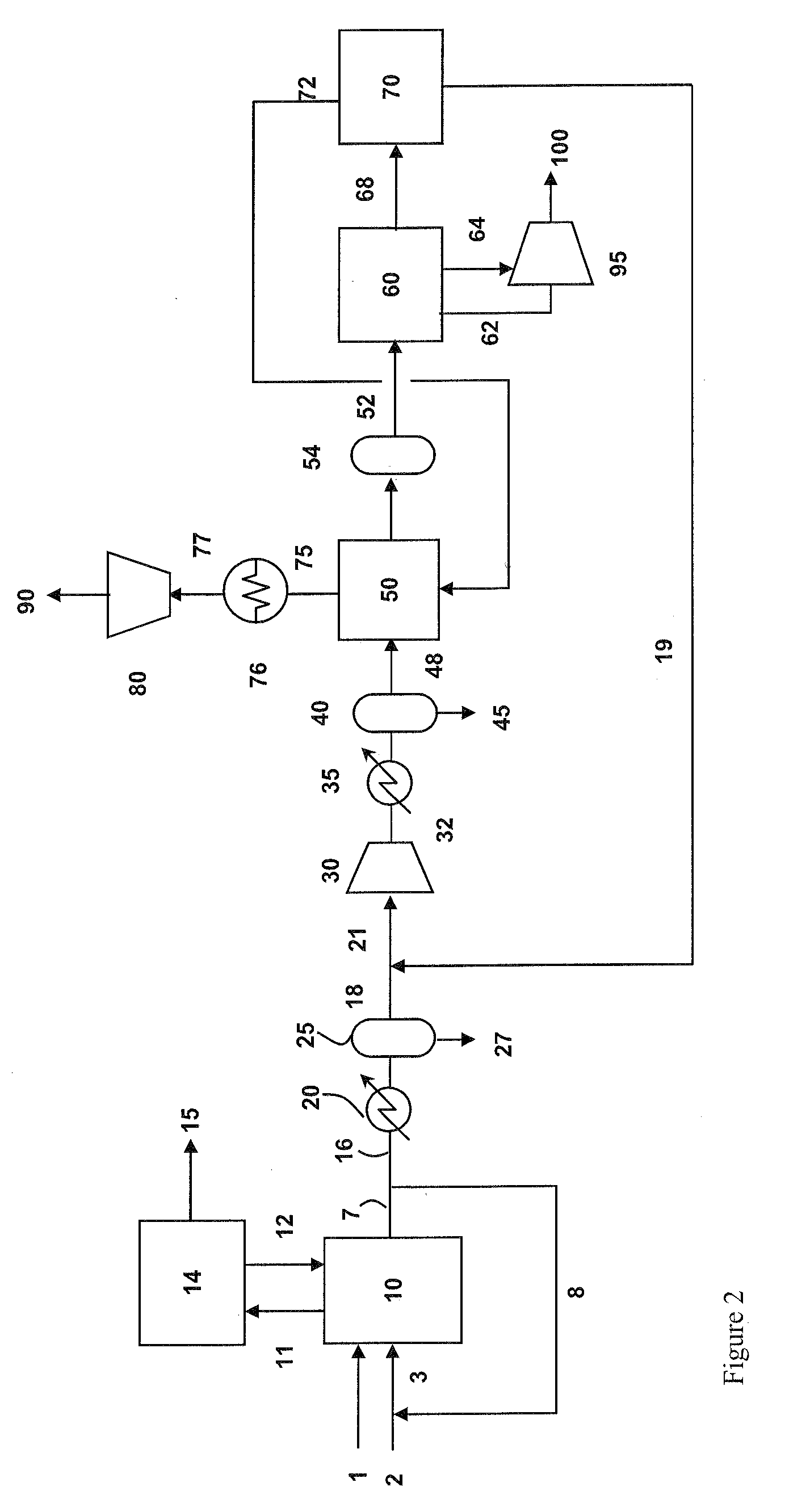
A process for separating carbon dioxide from a compressed, dried and cooled carbon dioxide containing fluid comprises separating the fluid into at least a carbon dioxide enriched stream, and a carbon dioxide depleted stream, expanding at least part of the carbon dioxide lean stream in an expander, compressing a process stream wherein the power for the compression step is at least in part provided by the power generated by the expander.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE PROCESS & CONSTRUCTION INC
Carbon Dioxide Removal Process
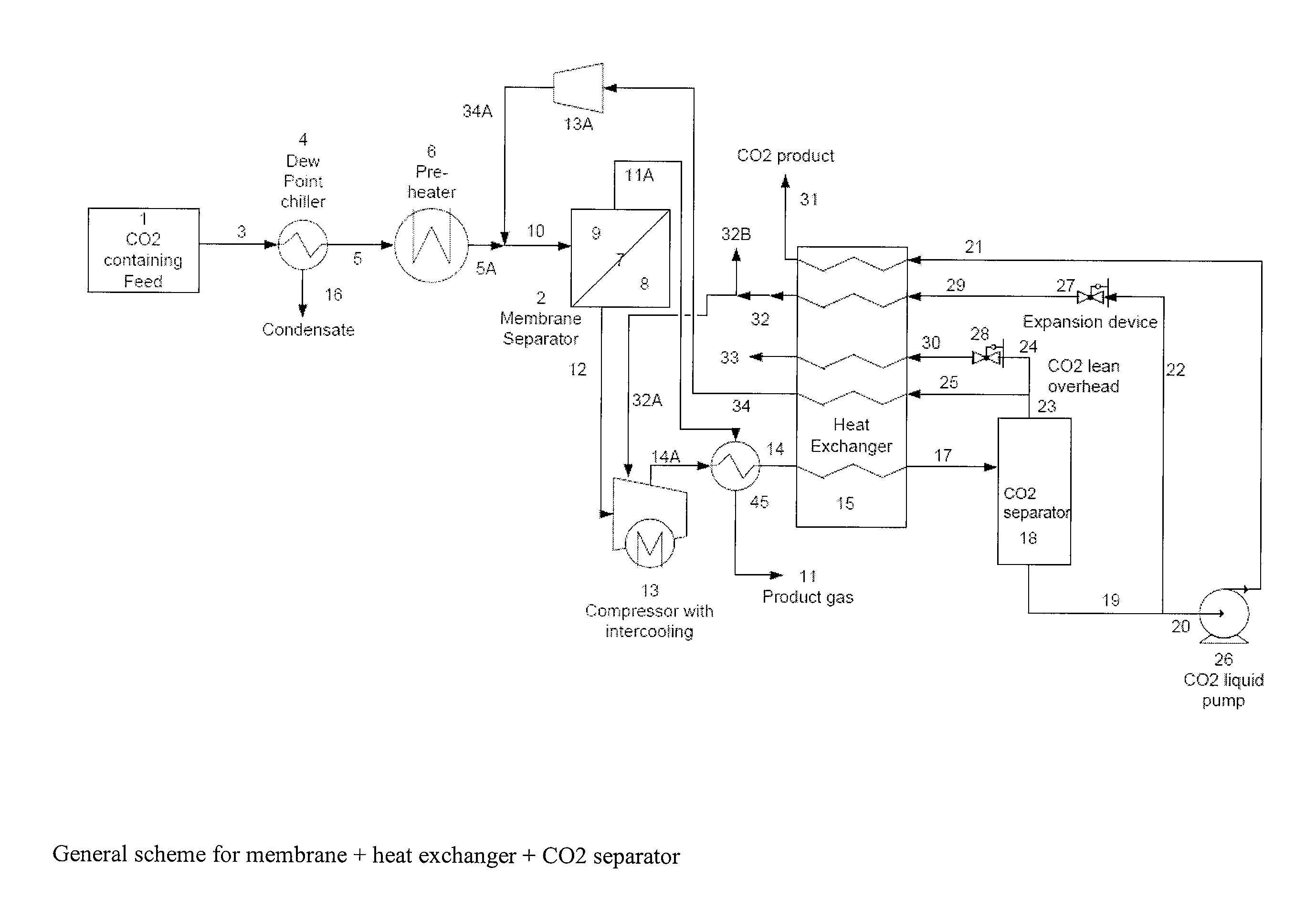
ActiveUS20120111051A1Reduce lossesIncrease pressureSolidificationLiquefactionCooling effectHydrocarbon
A process for efficiently removing carbon dioxide from a hydrocarbon containing feed stream utilizing a membrane separation unit in conjunction with a heat exchanger and a carbon dioxide separation unit wherein the streams obtained in the carbon dioxide separation unit are utilized to provide the cooling effect in the heat exchanger.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Plant and process for removing carbon dioxide from gas streams
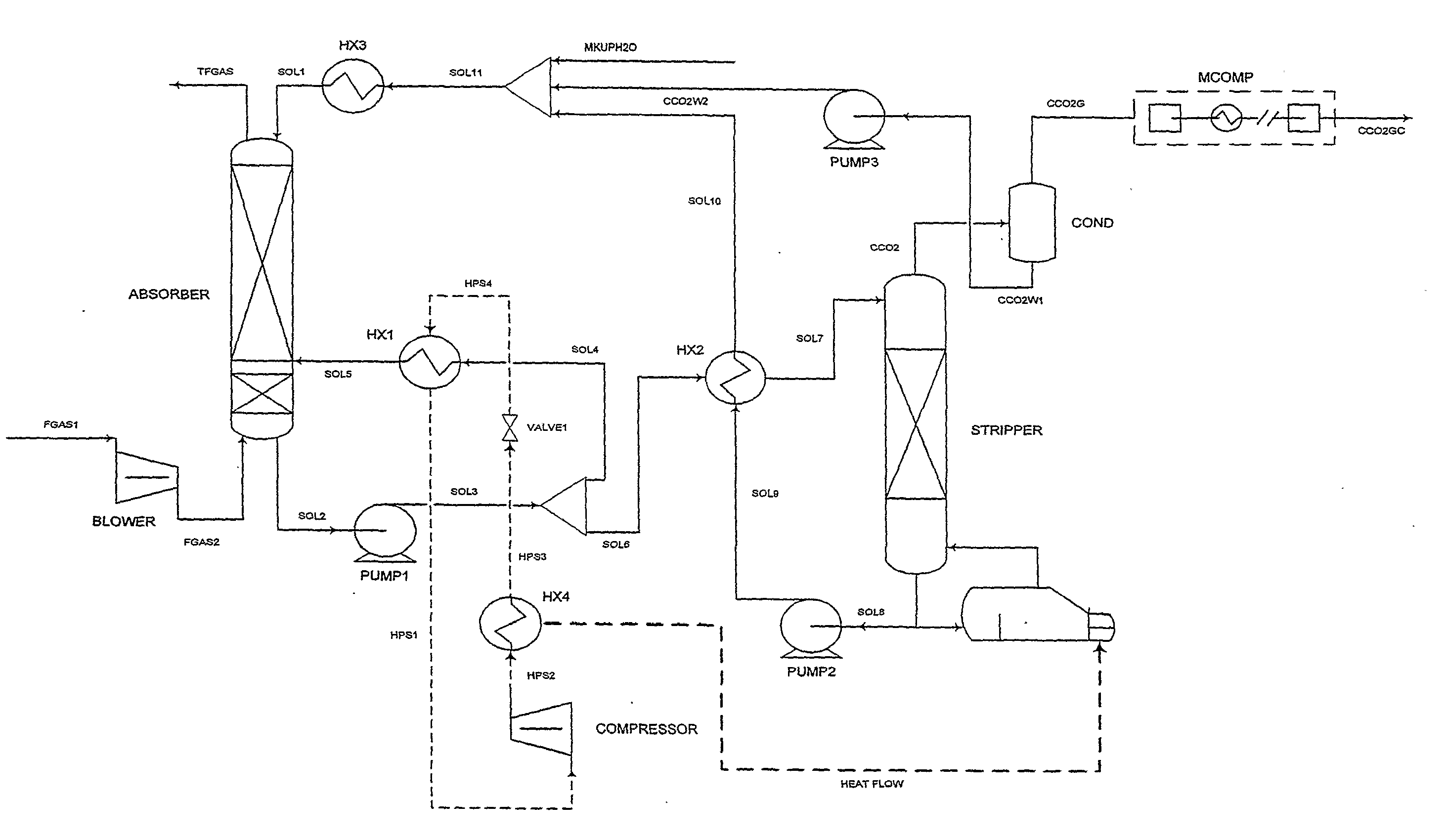
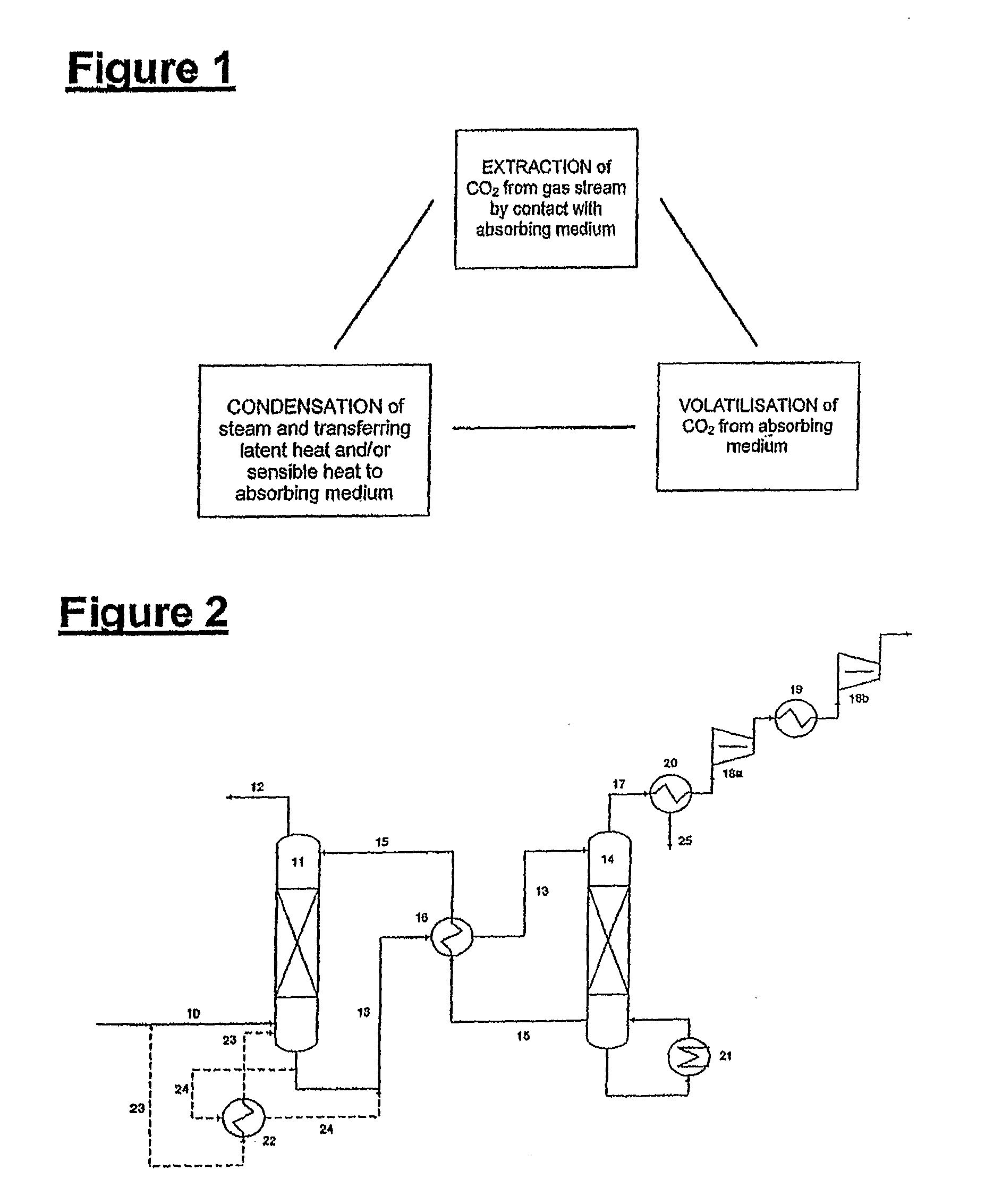
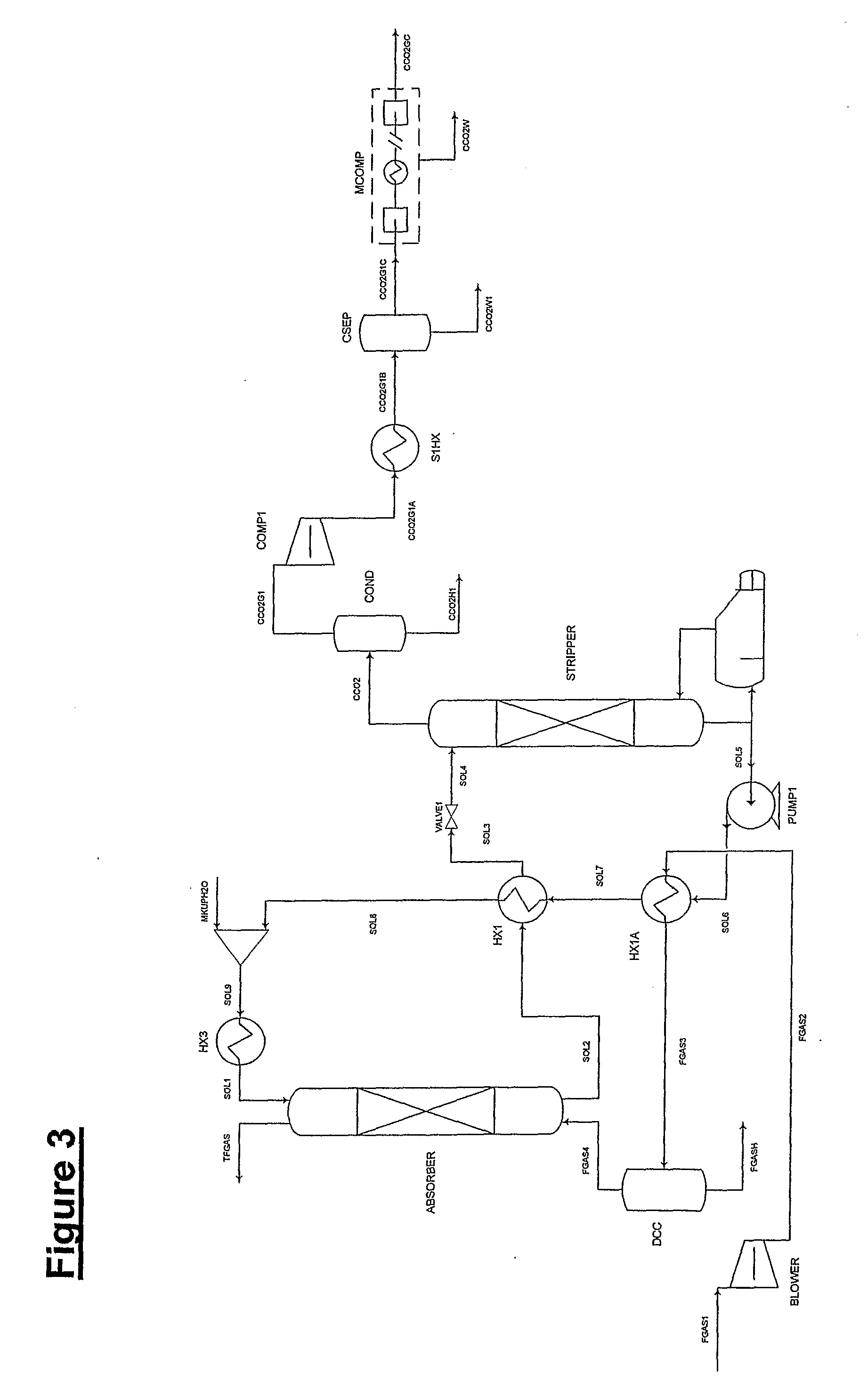
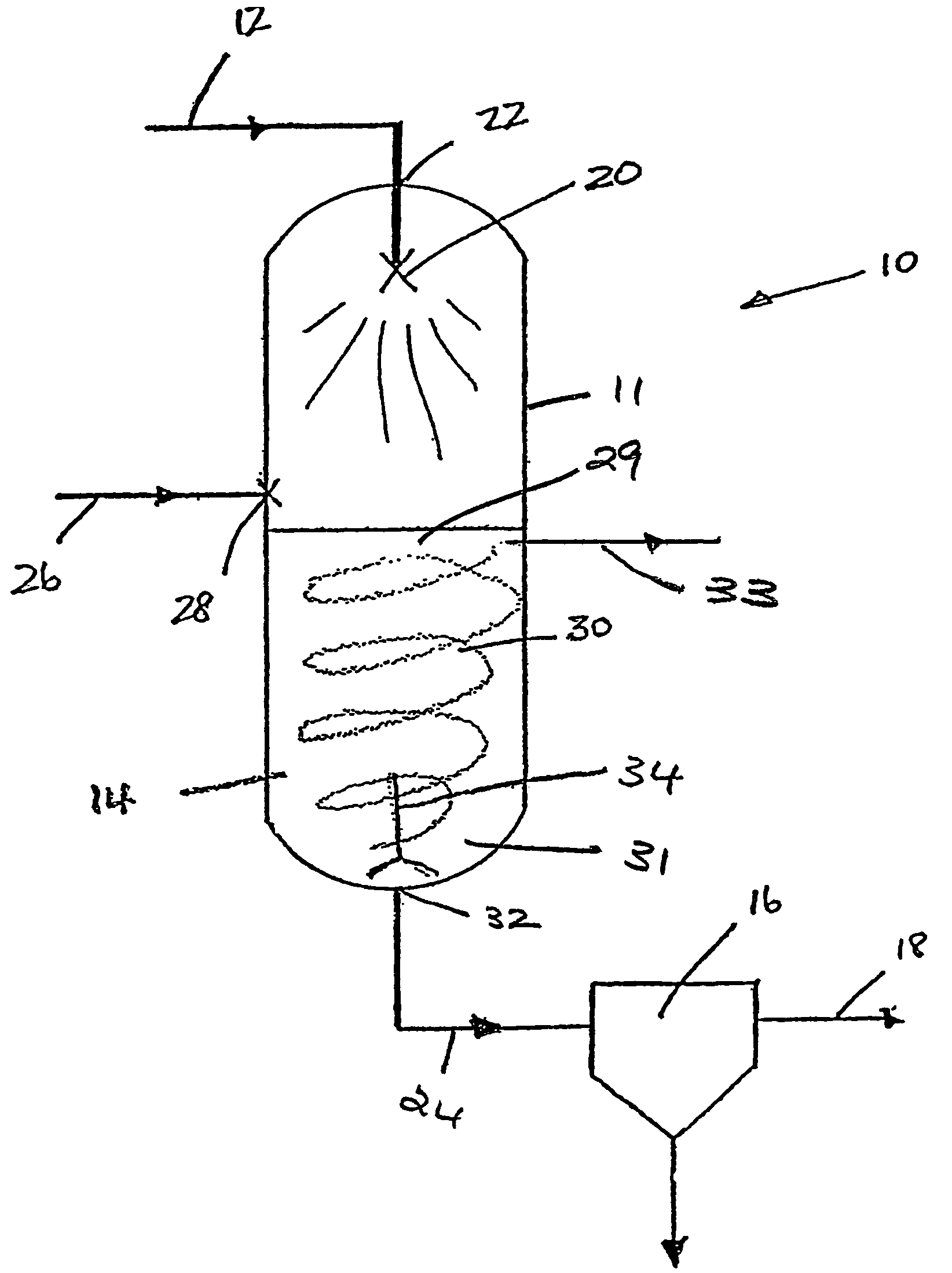
ActiveUS7976803B2Minimizing overall energy requiredAssist in volatilizationFluidized bed combustionIndirect heat exchangersComponents of crude oilCoal
Owner:KC8 CAPTURE TECH LTD
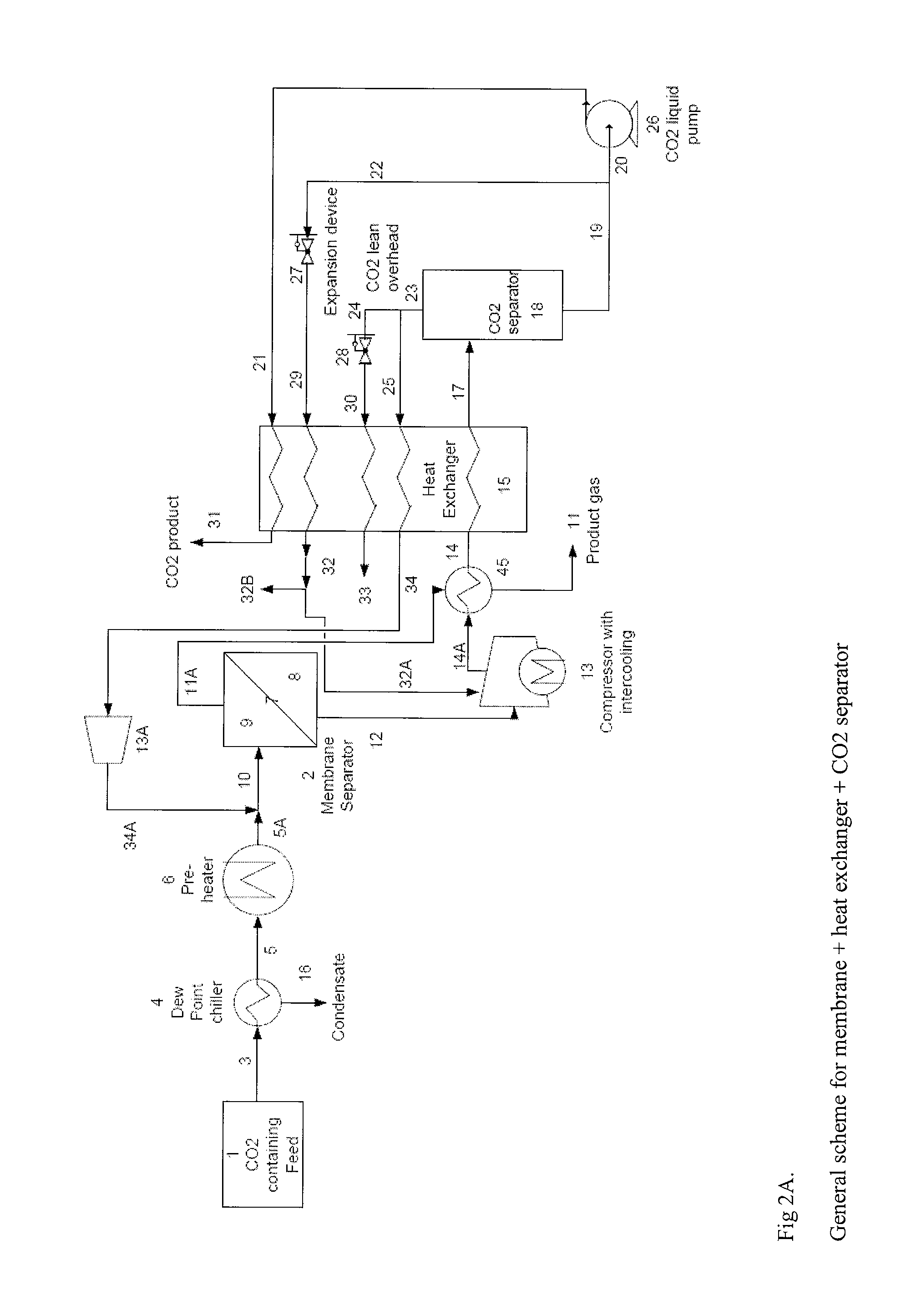
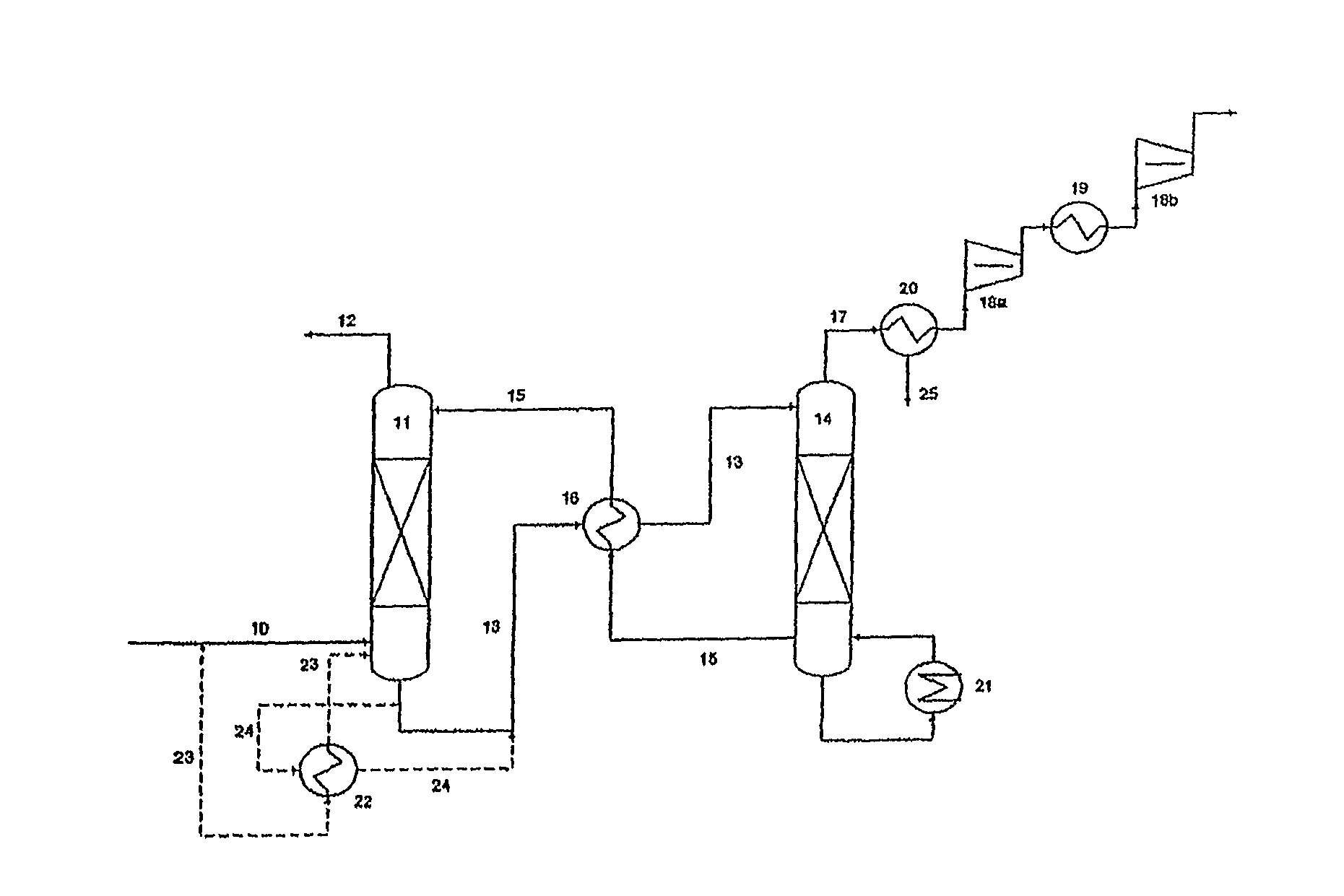
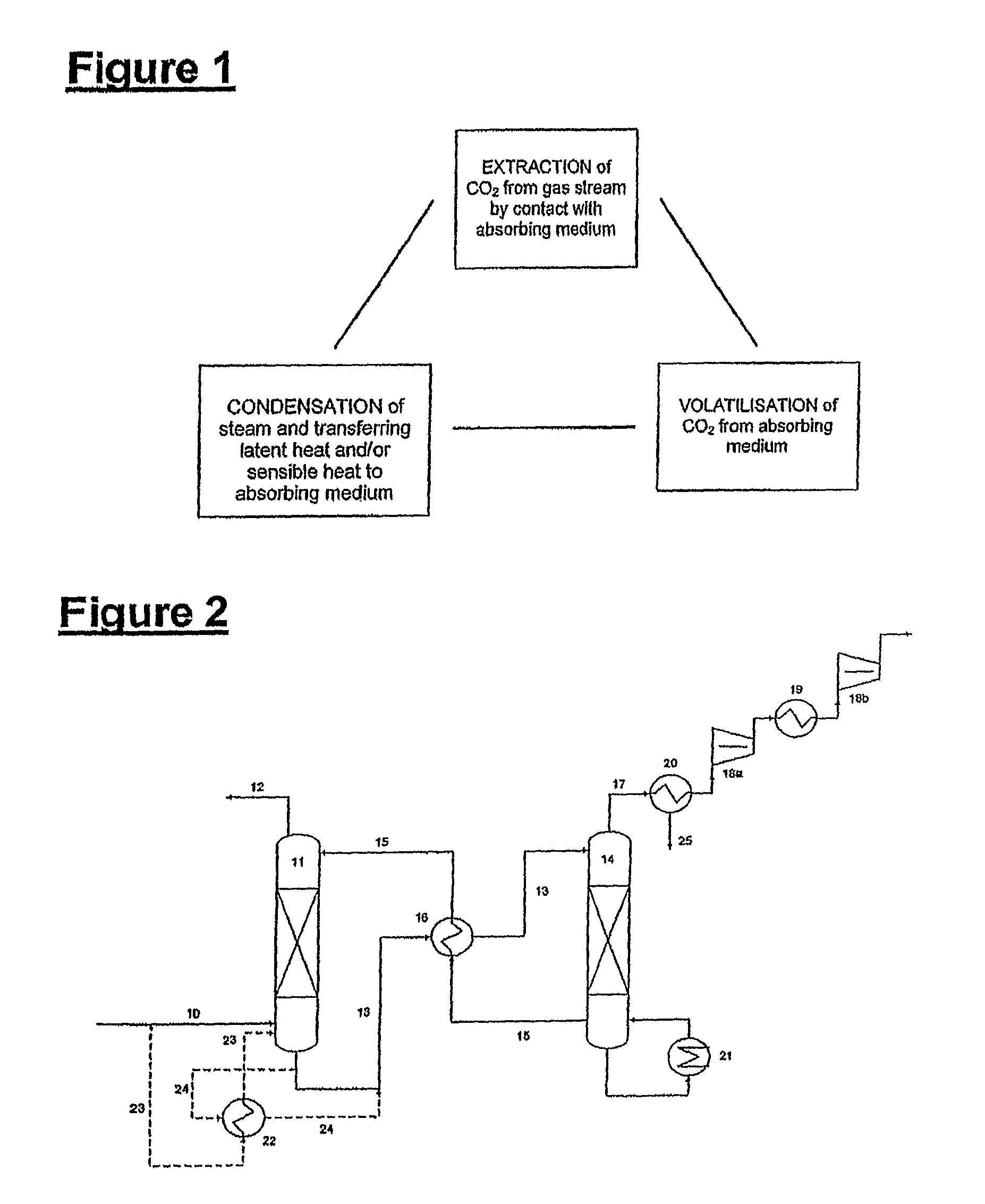
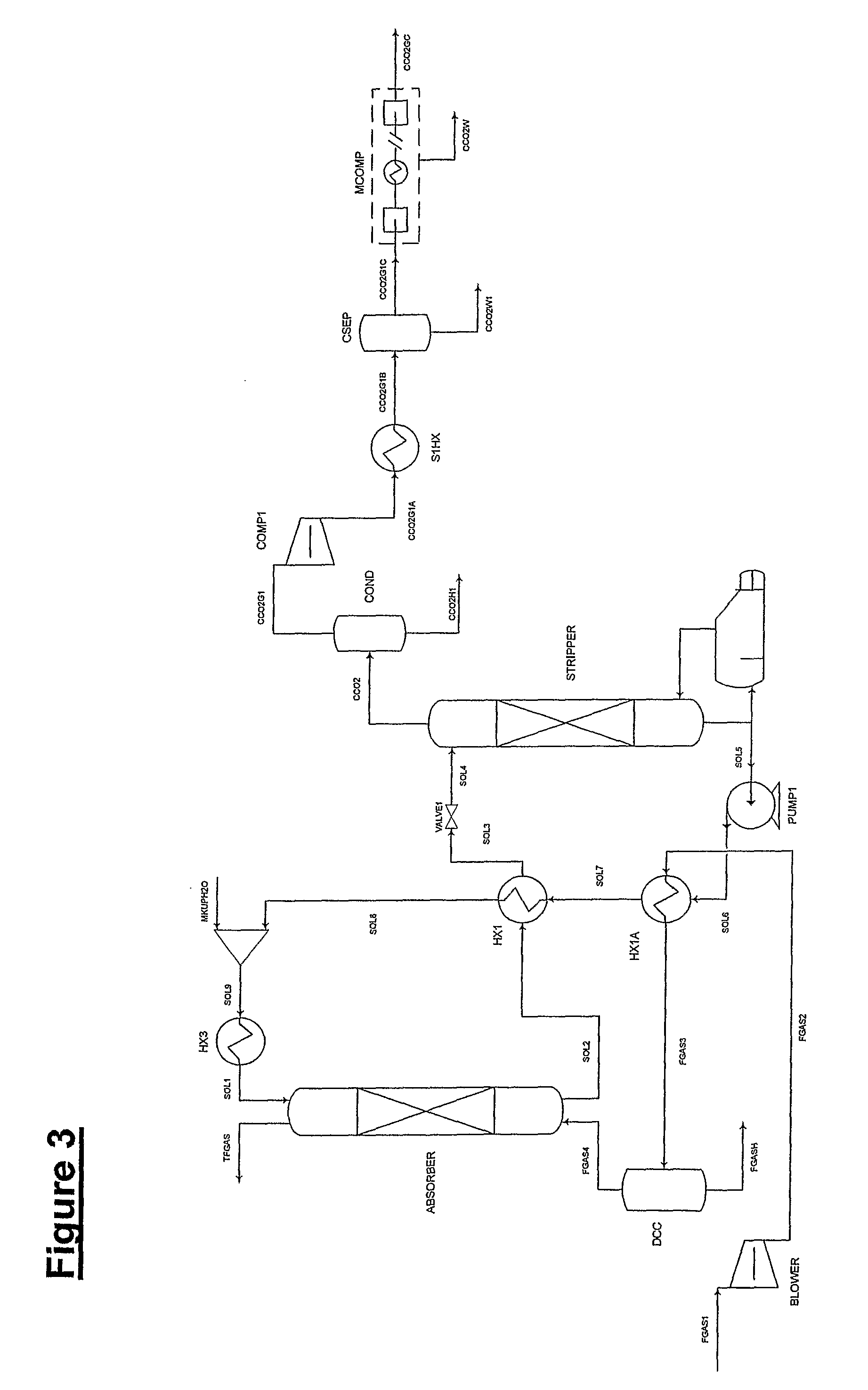
Plant And Process For Removing Carbon Dioxide From Gas Streams
ActiveUS20080317651A1Minimizing overall energy requiredAssist in volatilizationExhaust apparatusDispersed particle separationBy-productChemistry
The present invention is based on the realization that the carbon dioxide component of industrial gas streams also containing steam can be processed so to utilize either as latent and / or sensible heat the heat available from the steam component to assist in separating carbon dioxide from the remainder of the gas stream. For example, flue gases produced by power stations burning brown coal, black coal or natural gas inherently contain a useful amount of energy that can be harnessed according to the present invention. According to particular preferred forms of the invention, nitrogen and sulphur constituent such as SOx and NOx, H2S and other nitrogen containing compounds may also be removed from the gas stream through direct contact with the absorbing medium and used to produce by-products such as fertiliser material.
Owner:KC8 CAPTURE TECH LTD
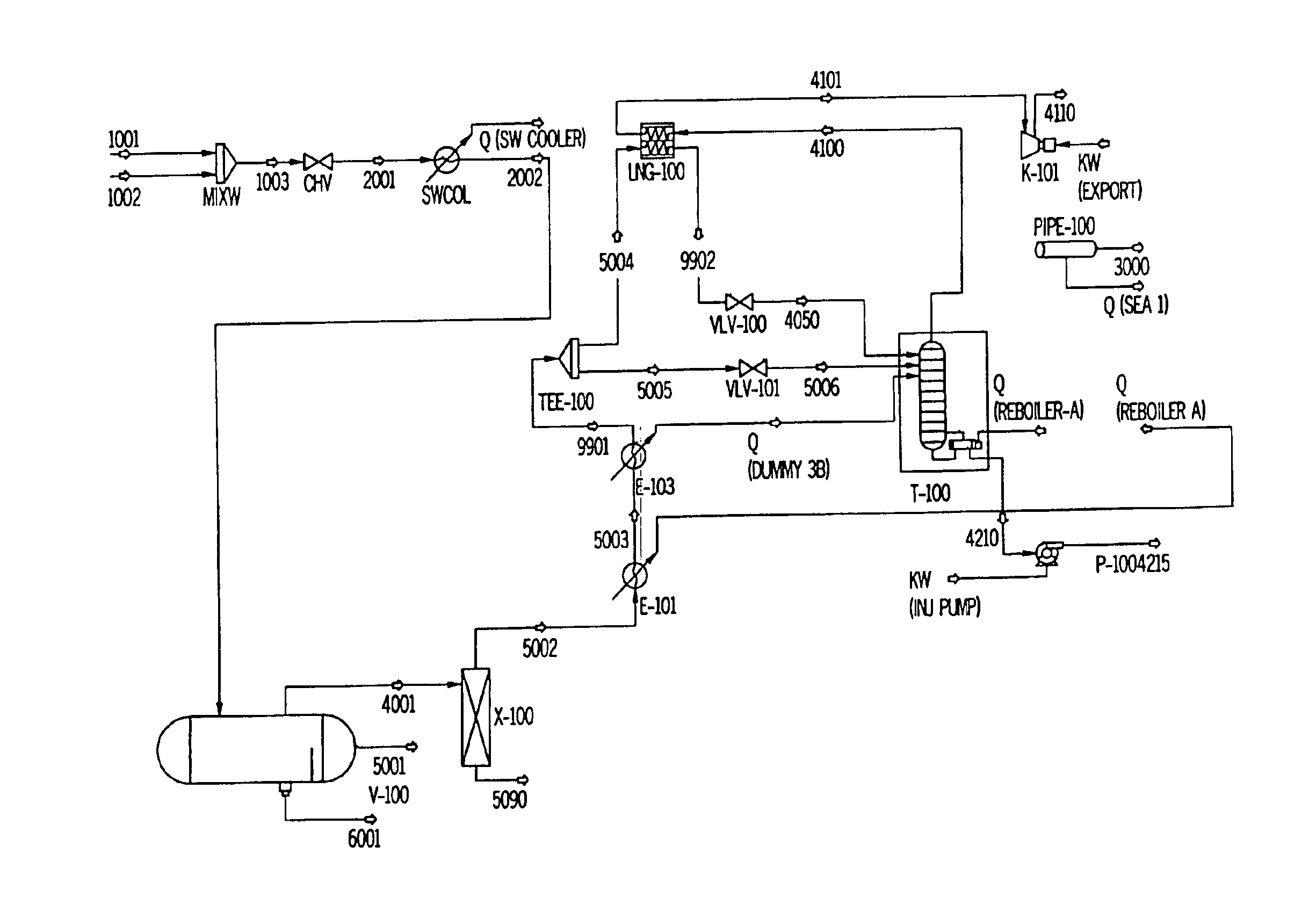
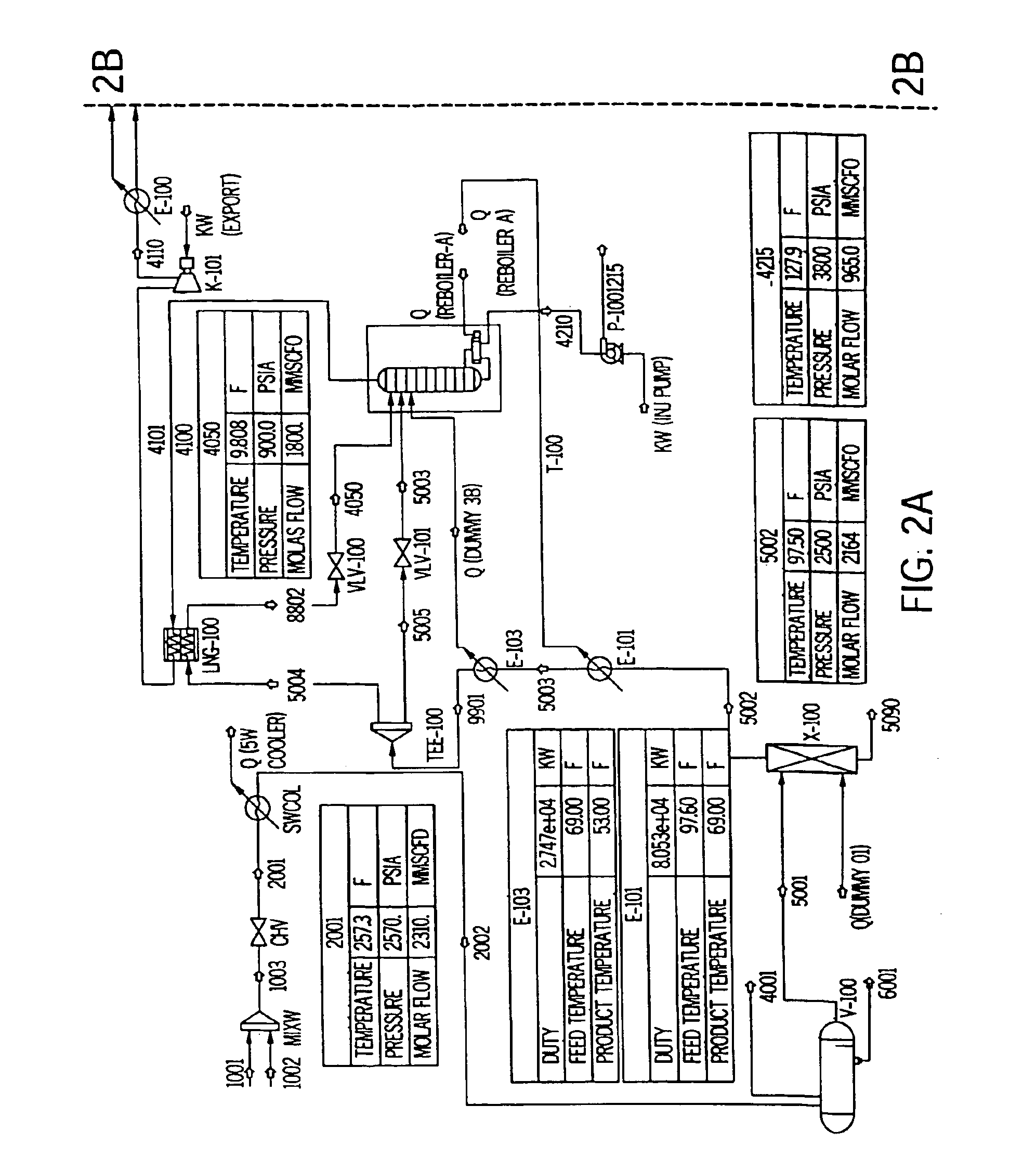
Process and device for production of LNG by removal of freezable solids
ActiveUS7325415B2Reducing and eliminating foulingSolidificationLiquefactionWorking pressureAmount of substance
Novel processes and devices for the removal of freezable species such as carbon dioxide, water and heavy hydrocarbons from a natural gas feed stream during liquefaction to produce LNG are disclosed. The freezable species are able to be removed as a solid, avoiding the costly step of pretreatment to remove the freezable species from the natural gas feed stream prior to the liquefaction stage. The freezable species may be removed on a continuous basis being separated as solids following liquefaction of the natural gas feed stream with subsequent separation of the solids. The solid freezable species may then be liquefied on a continuous basis if required with natural gas recycled to the process. Continuous removal of the freezable species from the natural gas feed stream is achievable by maintaining cooling and separation apparatus at the same working pressure. Advantageously, at least part of the cooling vessel is constructed from a material having a low thermal conductivity which discourages formation of the solids of the freezable species on the walls of the cooling vessel.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Recycle TSA regen gas to boiler for oxyfuel operations
NO2 may be removed from a carbon dioxide feed gas comprising NOx and at least one “non-condensable” gas as contaminants by passing the feed gas at a first elevated pressure through a first adsorption system that selectively adsorbs at least NO2 to produce at least substantially NO2-free carbon dioxide gas. The adsorption system is at least partially regenerated using a carbon dioxide-rich gas recovered from the substantially NO2-free carbon dioxide gas after purification. The invention has particular application in removing NOx and water from flue gas generated by oxyfuel combustion.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
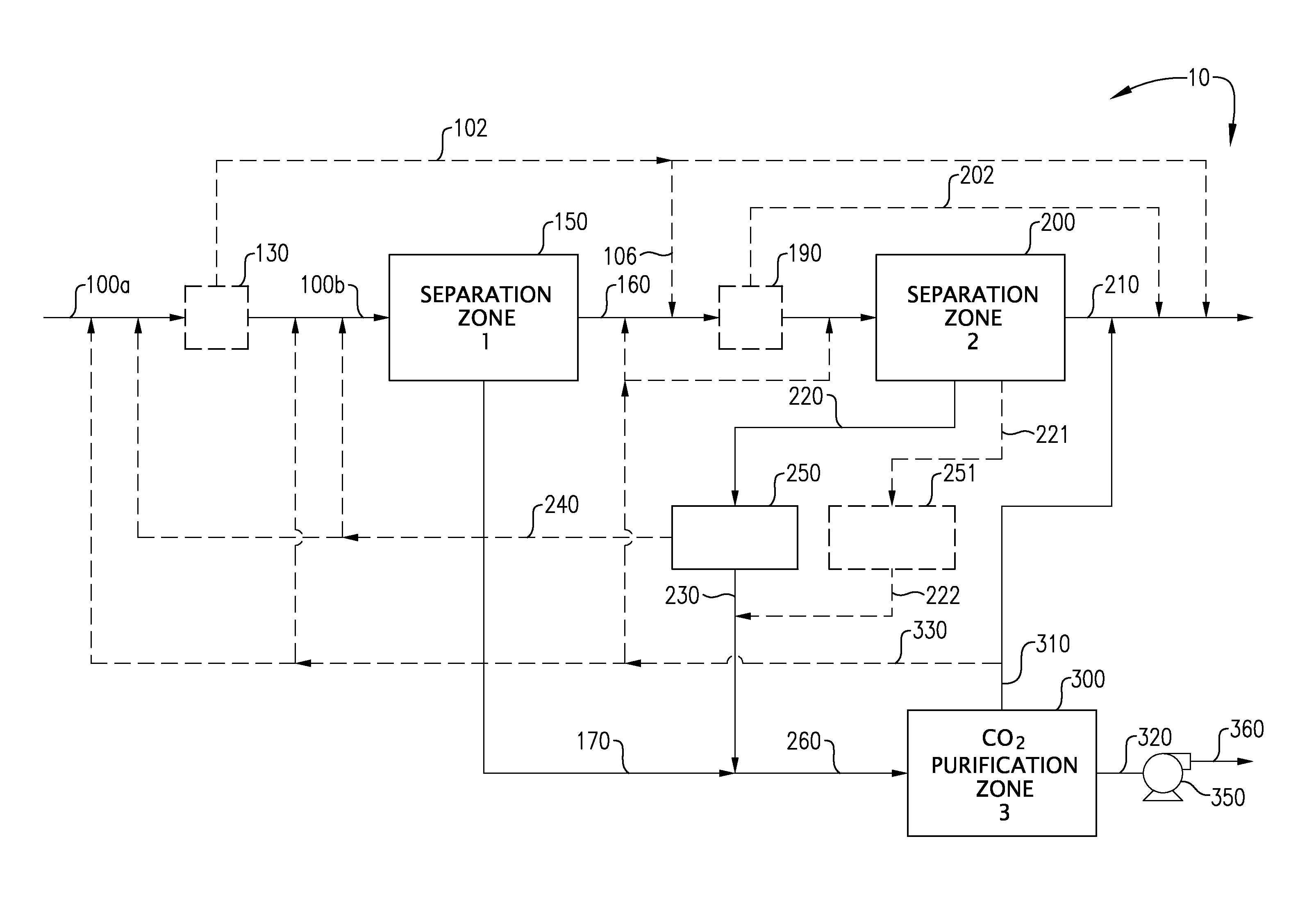
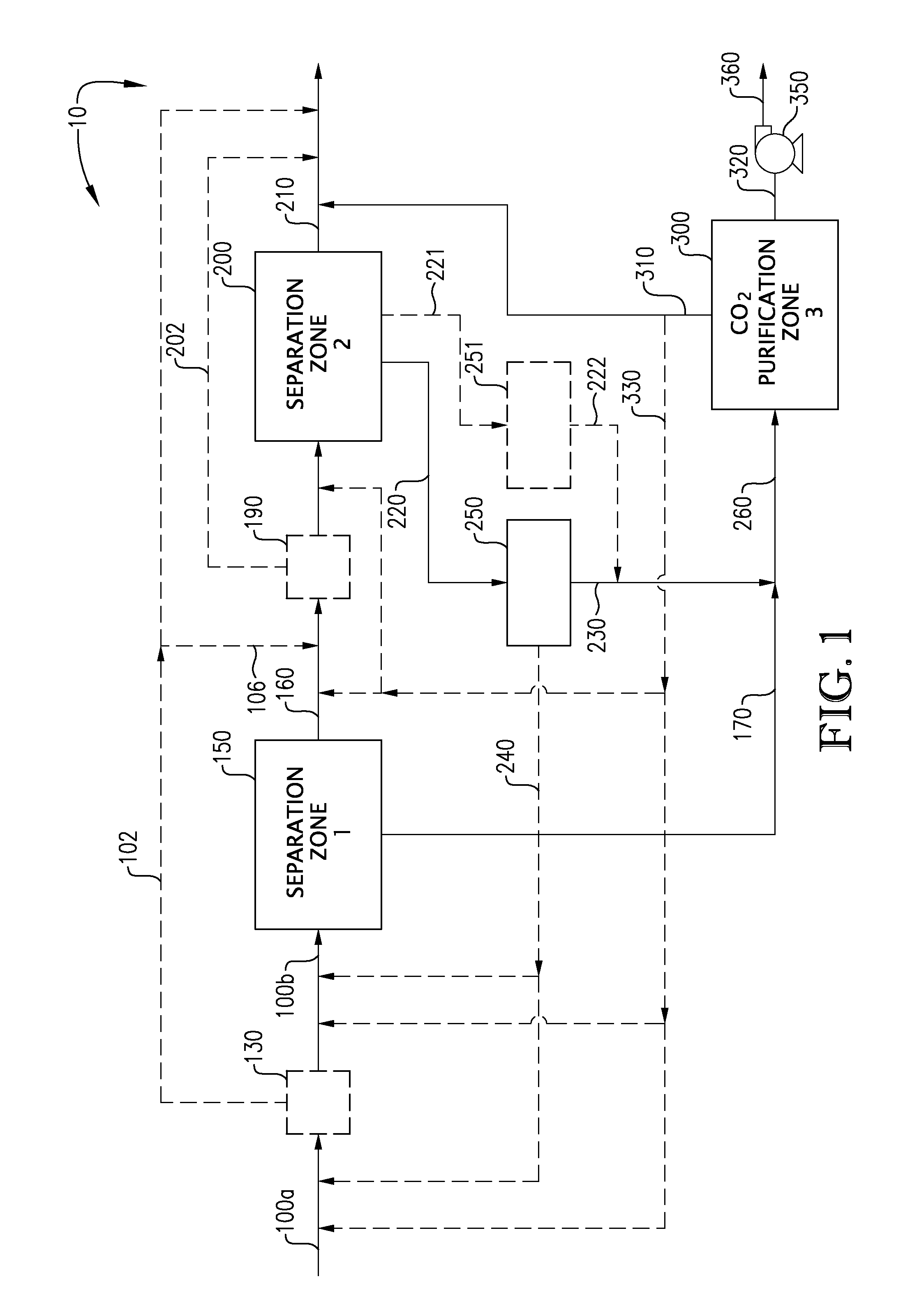
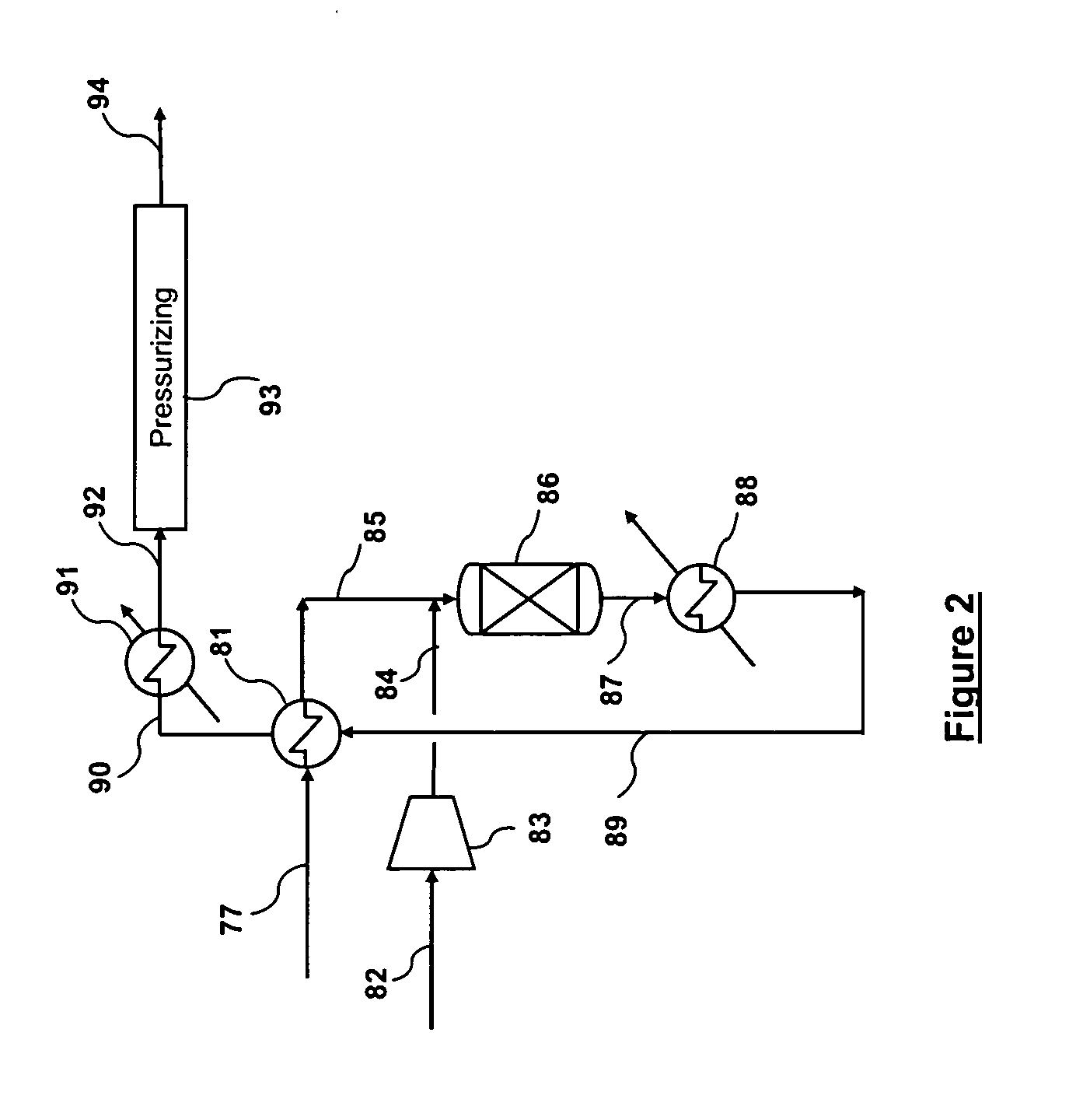
Carbon dioxide capture and liquefaction
ActiveUS20120006054A1Big advantageMinimize energy consumptionSolidificationLiquefactionLiquid stateHigh pressure
An energy-efficient method of recovering carbon dioxide (CO2) in a high-pressure liquid state from a high-pressure gas stream. The method includes cooling, condensing, and / or separating CO2 from a high-pressure gas stream in two or more separation zones and further purifying the resulting sub-critical pressure liquid CO2 streams in a third purification zone to thereby provide purified CO2. The purified liquid CO2 may be pumped to above the critical pressure for further utilization and / or sequestration for industrial or environmental purposes.
Owner:KELLER ARNOLD
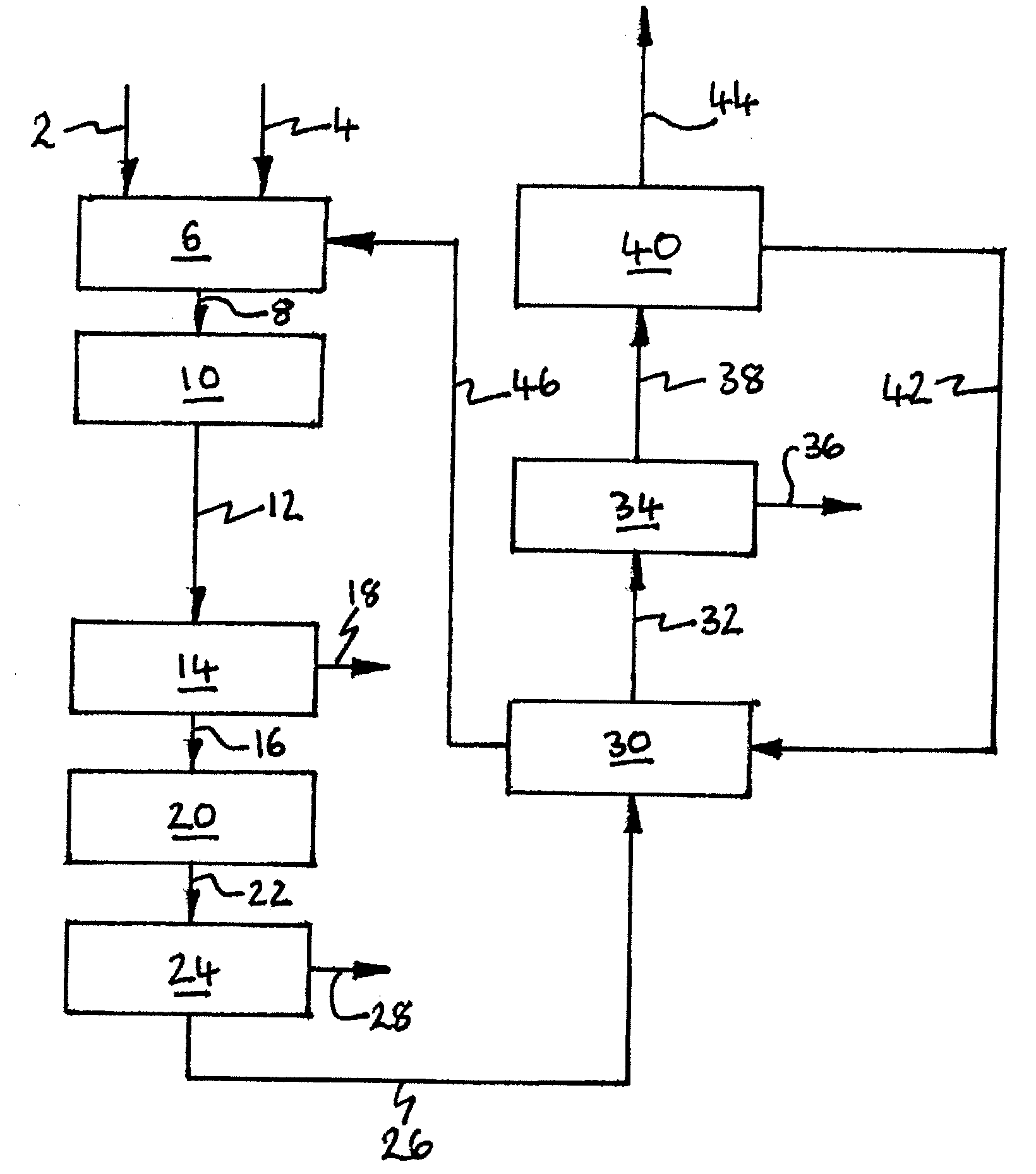
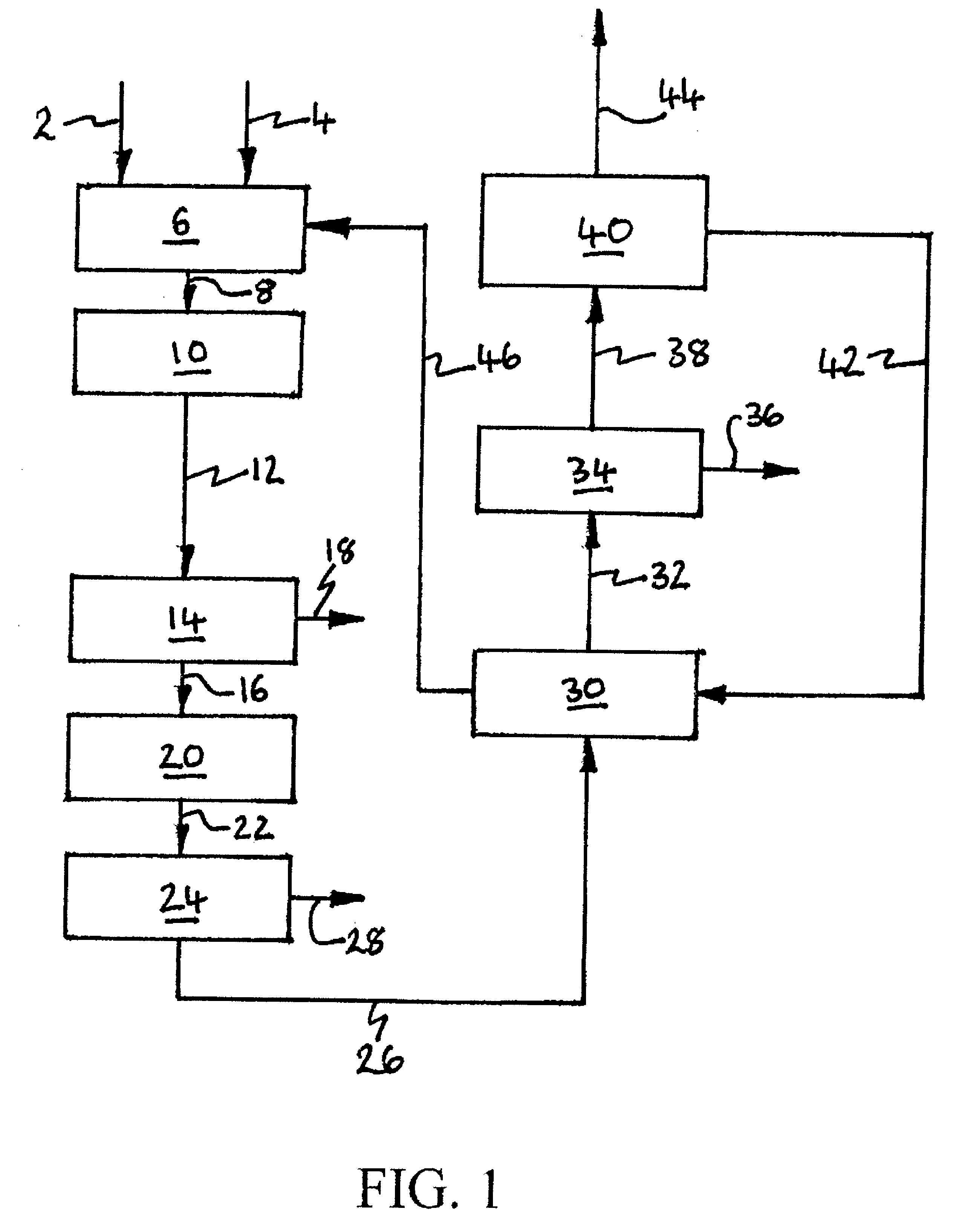
Integrated Controlled Freeze Zone (CFZ) Tower and Dividing Wall (DWC) for Enhanced Hydrocarbon Recovery
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for the operation of a distillation tower containing a controlled freezing zone and at least one distillation section. The process and tower design are utilized for the additional recovery of hydrocarbons from an acid gas. In this process, a separation process is utilized in which a multi-component feedstream is introduced into an apparatus that operates under solids forming conditions for at least one of the feedstream components. The freezable component, although typically CO2, H2S, or another acid gas, can be any component that has the potential for forming solids in the separation system. A dividing wall is added to at least a portion of the lower distillation section of the apparatus to effect the separation of at least some fraction of the hydrocarbons in that portion of the tower.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
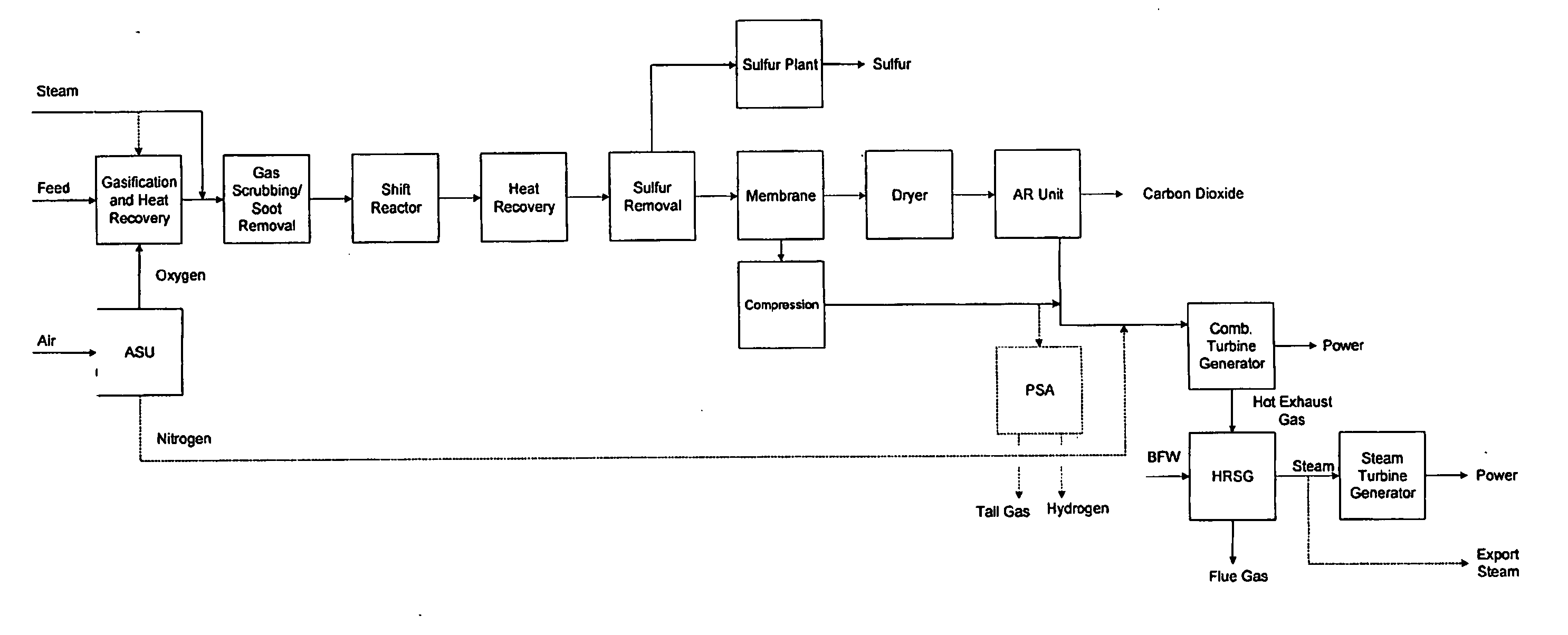
Configurations and methods of carbon capture
An IGCC plant has a precombustion decarbonization unit in which acid gas is removed from a combustion gas before the combustion gas enters a combustion turbine. In one preferred configuration, a sulfur removal unit removes hydrogen sulfide from a feed gas before the desulfurized feed gas enters an autorefrigeration unit in which carbon dioxide is removed. In another preferred configuration, hydrogen sulfide is converted to carbonyl sulfide in a dryer, and the carbonyl sulfide is absorbed in the liquid carbon dioxide that is prepared from the feed gas using autorefrigeration.
Owner:FLUOR TECHSE CORP
Process and apparatus for the separation of a gaseous mixture
A process for separating carbon dioxide from a carbon dioxide containing fluid comprises the steps of: compressing the fluid in a compressor to form a compressed fluid, drying at least part of the compressed fluid to form a compressed and dried fluid, cooling at least part of the compressed and dried fluid to form a compressed, dried and cooled fluid, separating the compressed, dried and cooled fluid at a temperature lower than 0° C. into a carbon dioxide rich stream, a carbon dioxide lean stream and at least one intermediate purity liquid stream having a carbon dioxide purity lower than that of the carbon dioxide rich stream and higher than that of the carbon dioxide lean stream, expanding at least one intermediate purity liquid stream to produce at least one expanded stream using at least one expanded stream to cool the compressed and dried fluid and recycling at least part of the expanded stream.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Hydrocarbon gas processing
A cryogenic natural gas liquids recovery process which includes the use of a demethanizer and a deethanizer includes a step of recycling a portion of the deethanizer overhead to the demethanizer.
Owner:TREBBLE MARK A
Removing contaminants from natural gas
A process for removing contaminants from a natural gas feed stream including water and sour species is provided, which process comprises the steps of cooling the natural gas feed stream in a first vessel (12) to a first operating temperature at which hydrates are formed and removing from the first vessel (12) a stream of dehydrated gas (34); and cooling the dehydrated gas in a second vessel (14) to a second operating temperature at which solids of the sour species are formed or at which the sour species dissolve in a liquid and removing from the second vessel (14) a stream of dehydrated sweetened gas (62).
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
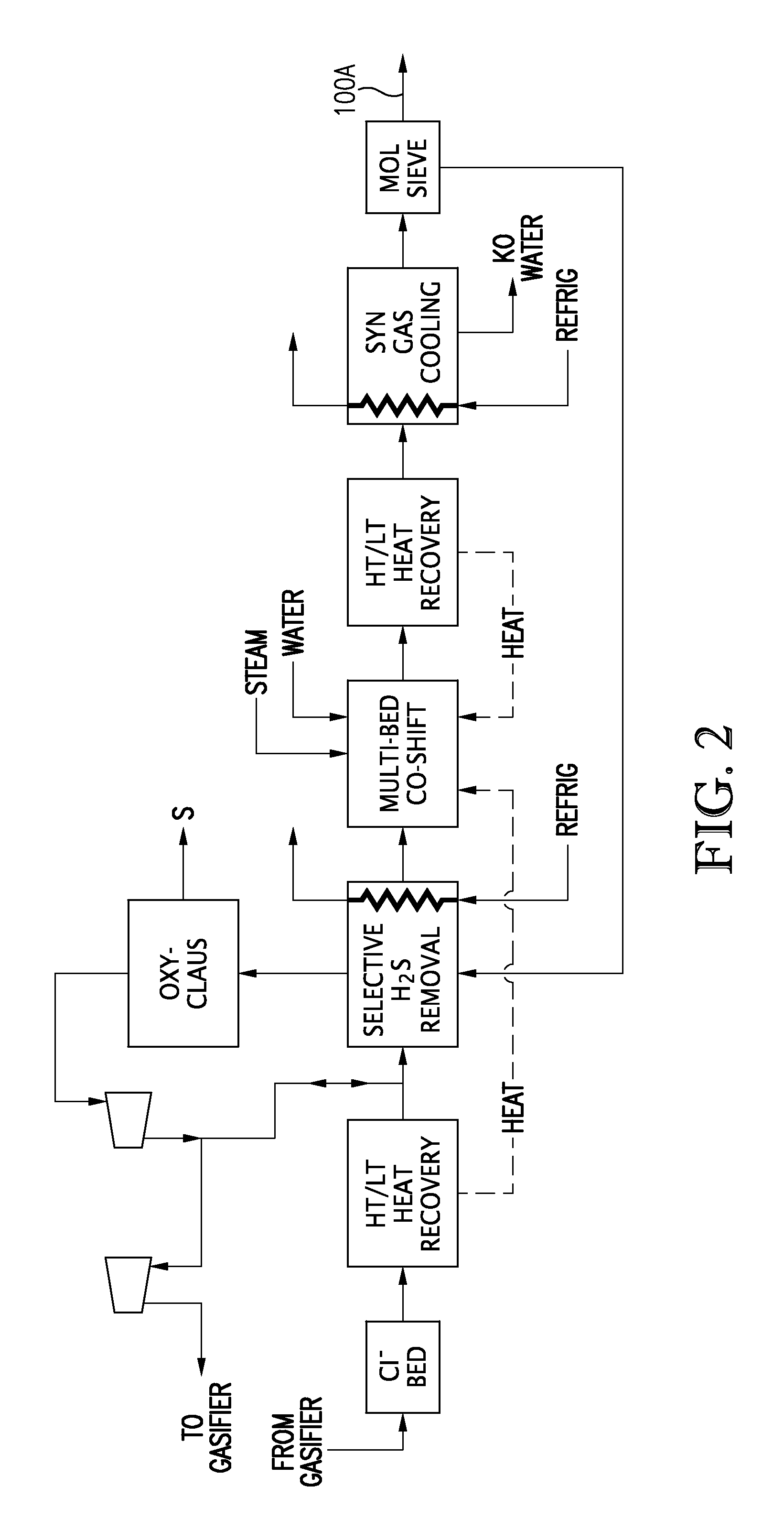
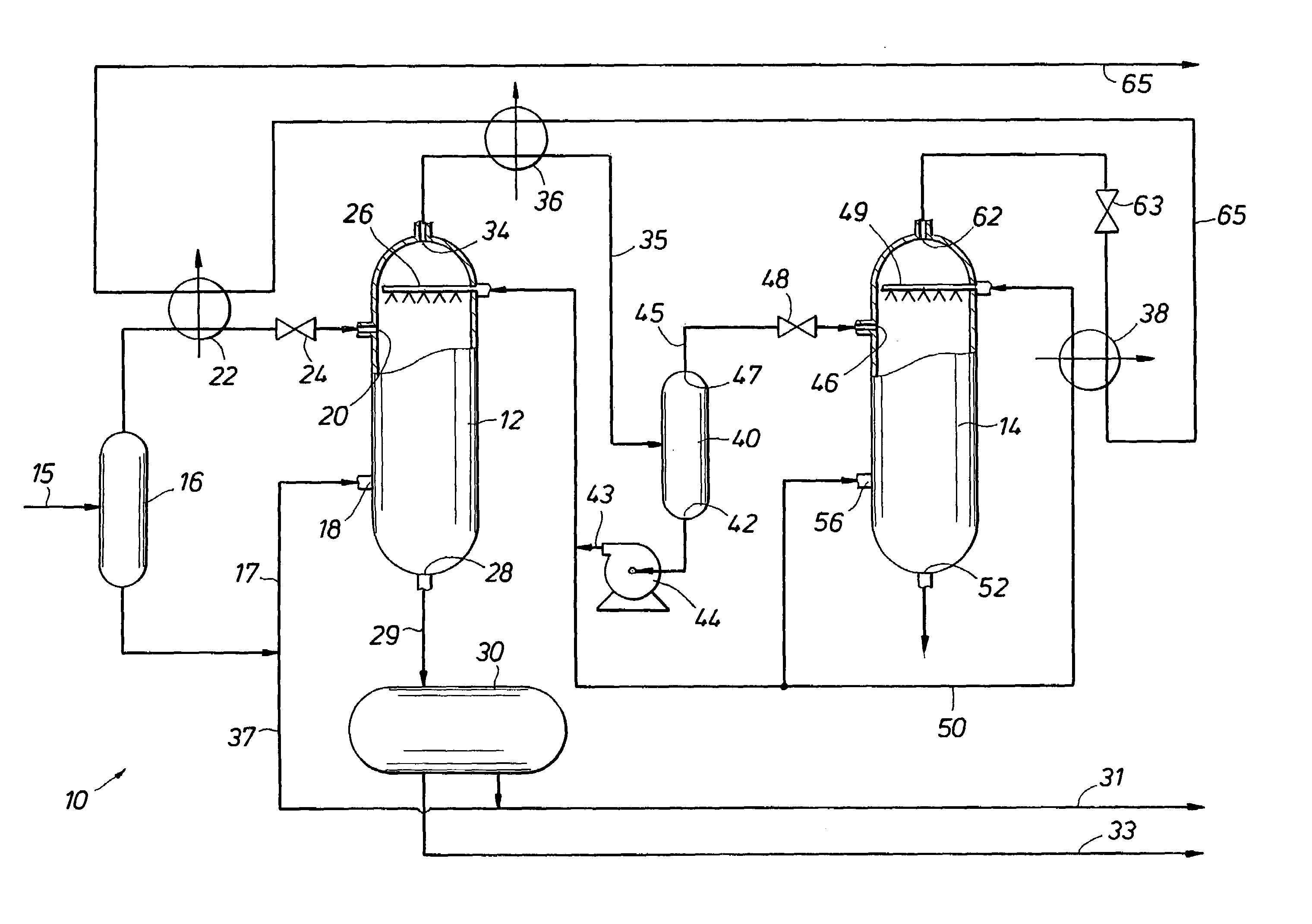
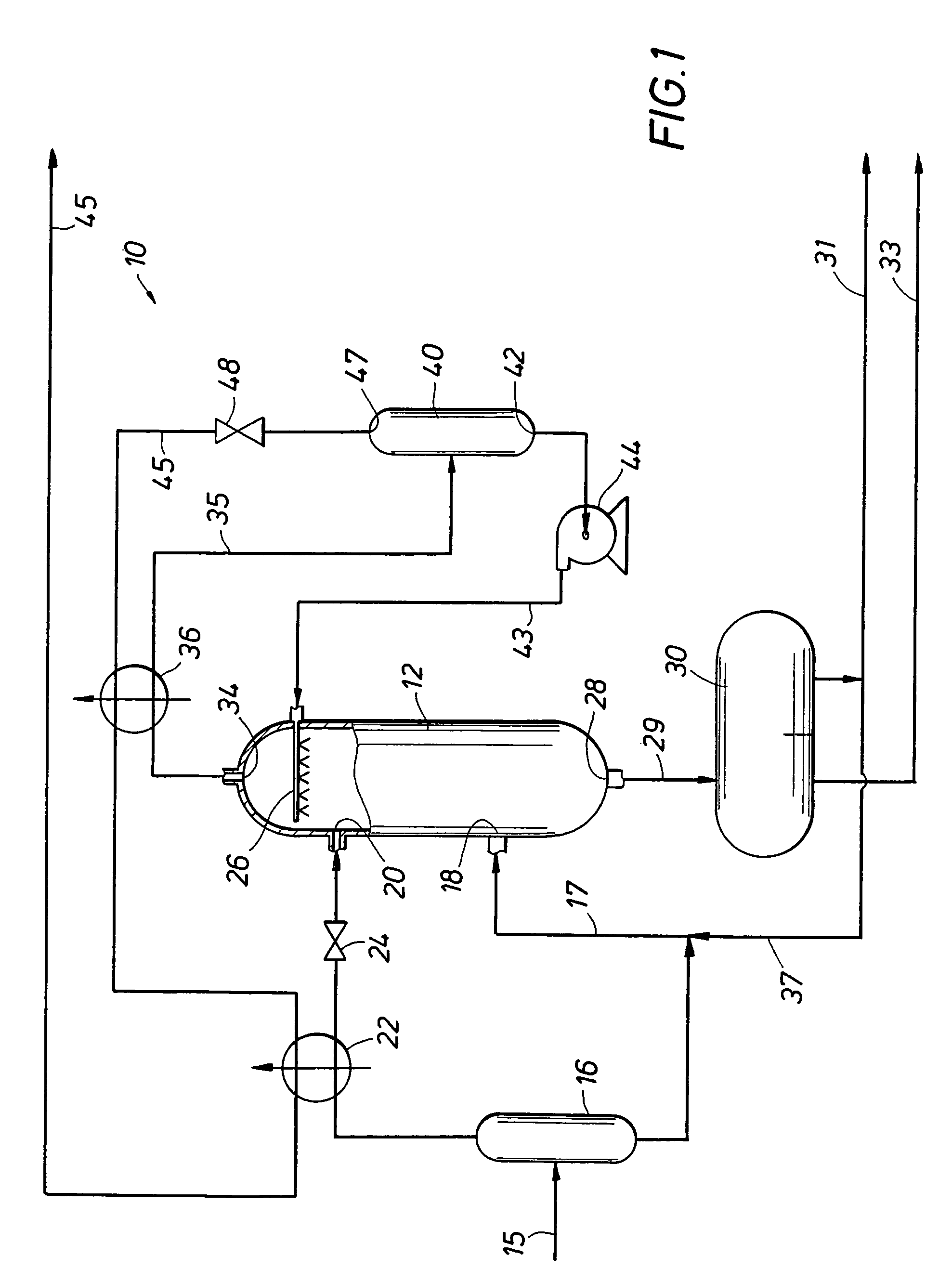
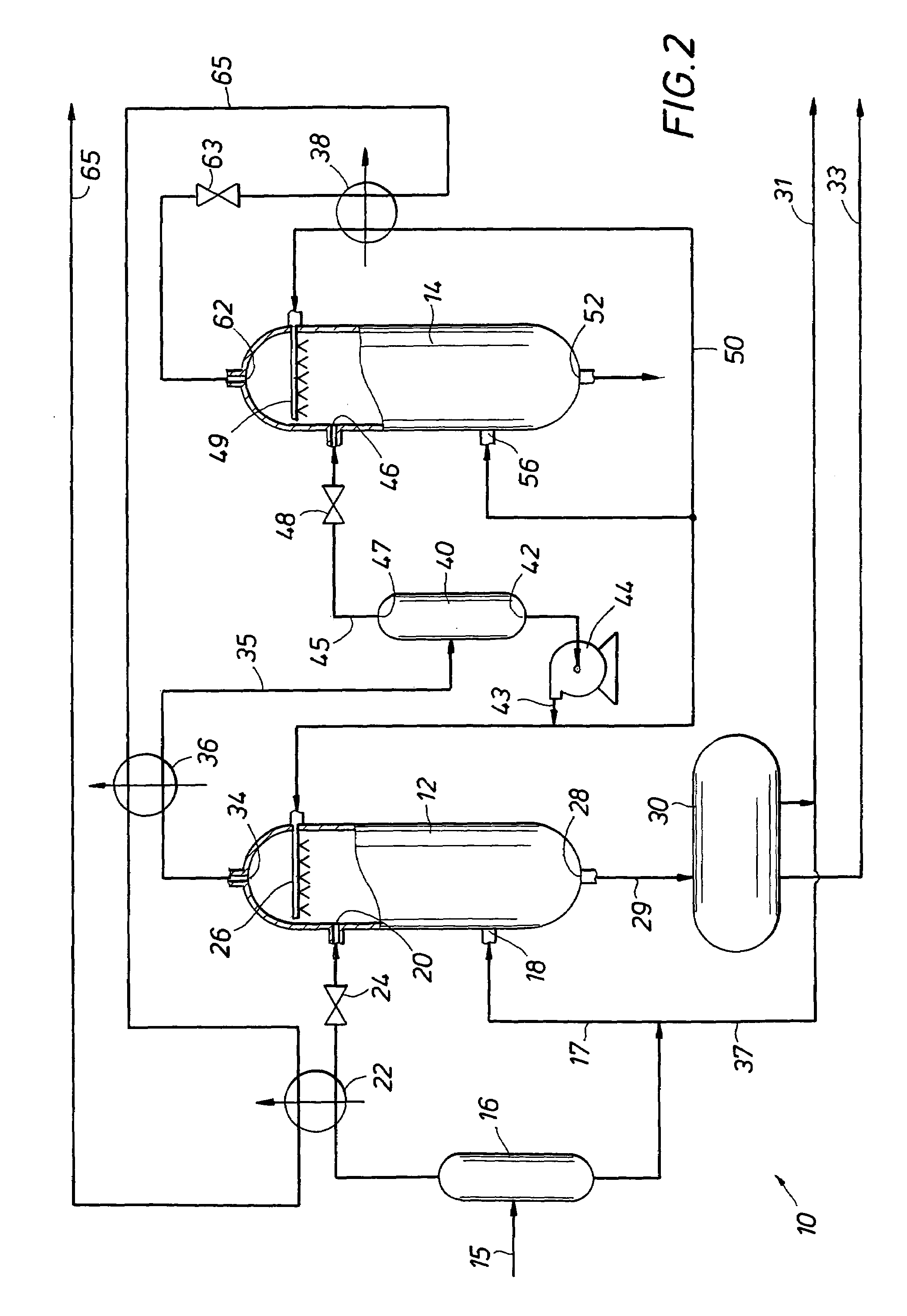
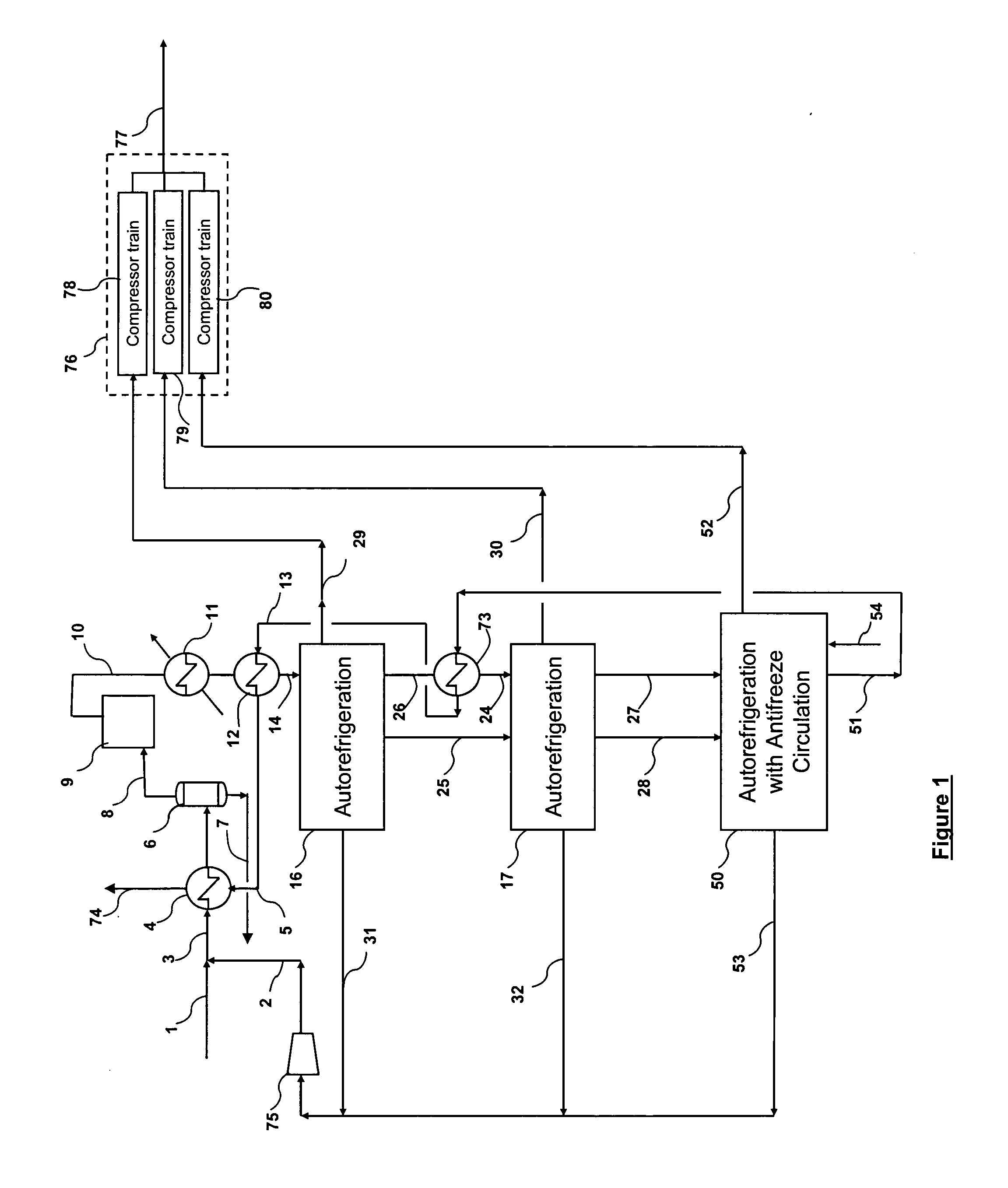
Multi-stage cryogenic acid gas removal
InactiveUS20070221541A1Alleviate power needsIncrease the number ofSolidificationLiquefactionPetroleumPetroleum coke
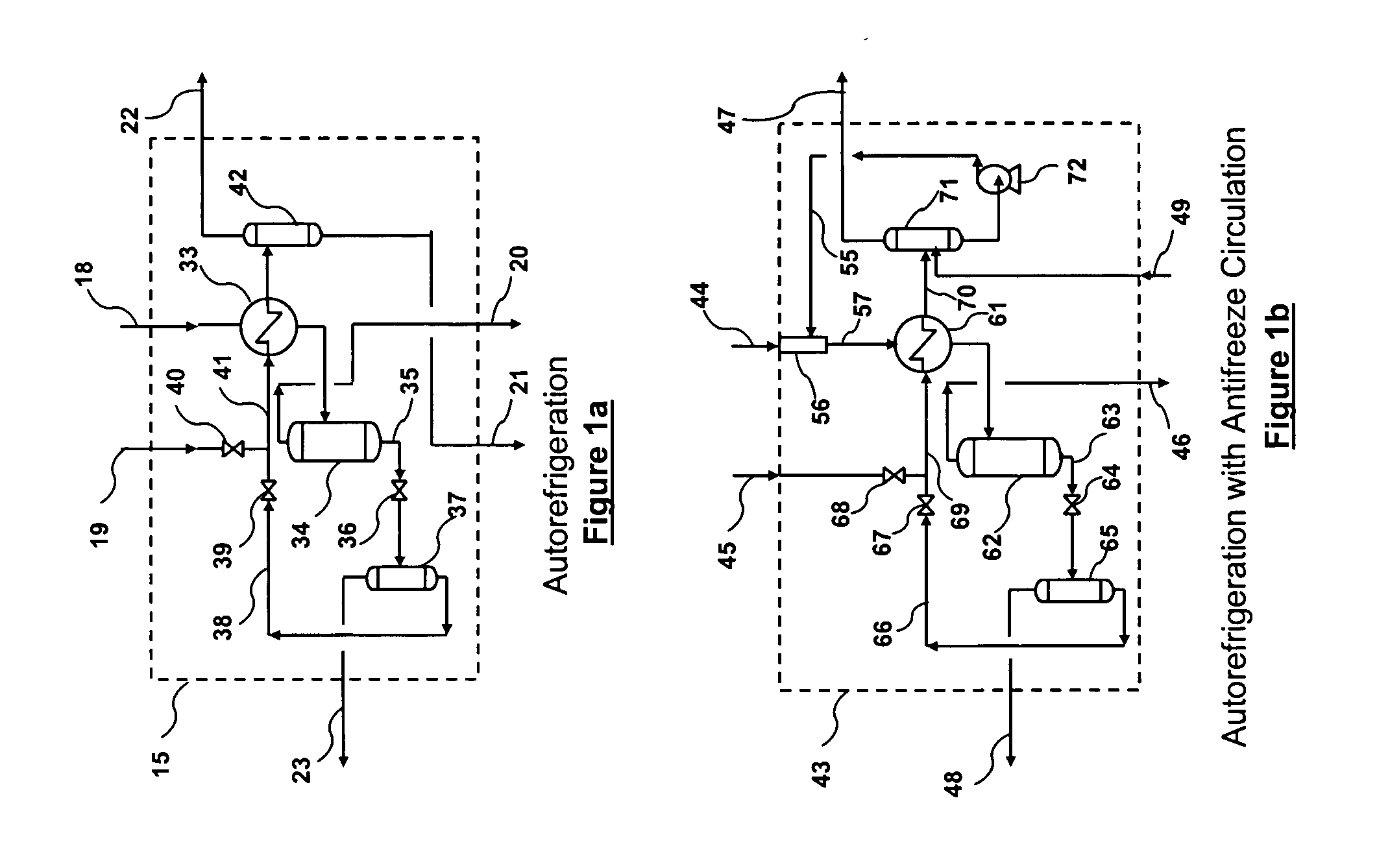
A relatively simple and energy efficient multiple stage cryogenic process for the purification of a hydrogen-rich stream by the removal of acid gases, mainly CO2 and H2S, by method of autorefrigeration and delivering or producing those acid gases, mainly CO2, at pressure sufficiently high for disposal by containment, commonly known as sequestration. Autorefrigeration is comprised of (a) condensing acid gases from the syngas stream by cooling the syngas, (b) separating the liquefied acid gases from the syngas, and (c) evaporating the liquefied acid gases at a pressure lower than that of the syngas to provide cooling. The process is composed of multiple autorefrigeration stages to generate multiple acid gas product streams with a pressure as high as practical in each stream so as to lessen the power needed to pressurize the acid gas streams for sequestration. The final autorefrigeration stage utilizes an antifreeze liquid that allows the final stage to operate below the freezing point of CO2; thus allowing more acid gas removal. The antifreeze liquid is an alcohol or a mixture of alcohols with a freezing point lower than about minus 110 degrees F. and a boiling point higher than about 100 degrees F. The process includes hydrogen recovery and recycle as well as recovery of the energy contained in the sulfur bearing compounds. The process is especially well suited for CO2 removal / sequestration from a coal (or petroleum coke) gasification process.
Owner:TENNESSEE VALLEY AUTHORITY
Process for removing gaseous contaminants from a feed gas stream comprising methane and gaseous contaminants
InactiveUS20100107687A1Energy efficiencyGood removal effectCombination devicesSolidificationGas phaseDistillation
A process for removing gaseous contaminants from a feed gas stream that comprises a gaseous product and gaseous contaminants, comprising: providing the feed gas stream, cooling the feed gas stream to a temperature at which liquid phase contaminant is formed as well as a gaseous phase rich in gaseous product, separating the two phases by means of a gas / liquid separator, and introducing the gaseous phase rich in gaseous product into a cryogenic separation device that comprises a freezing zone and a distillation zone positioned below the freezing zone, and removing from the cryogenic separation device a bottom stream rich in liquid phase contaminant and lean in gaseous product, and a top stream rich in gaseous product and lean in gaseous contaminant. The invention further includes a device for carrying out the present process, the purified gas stream, and a process for liquefying a feed gas stream.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com