Patents
Literature
599results about "Generator control details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
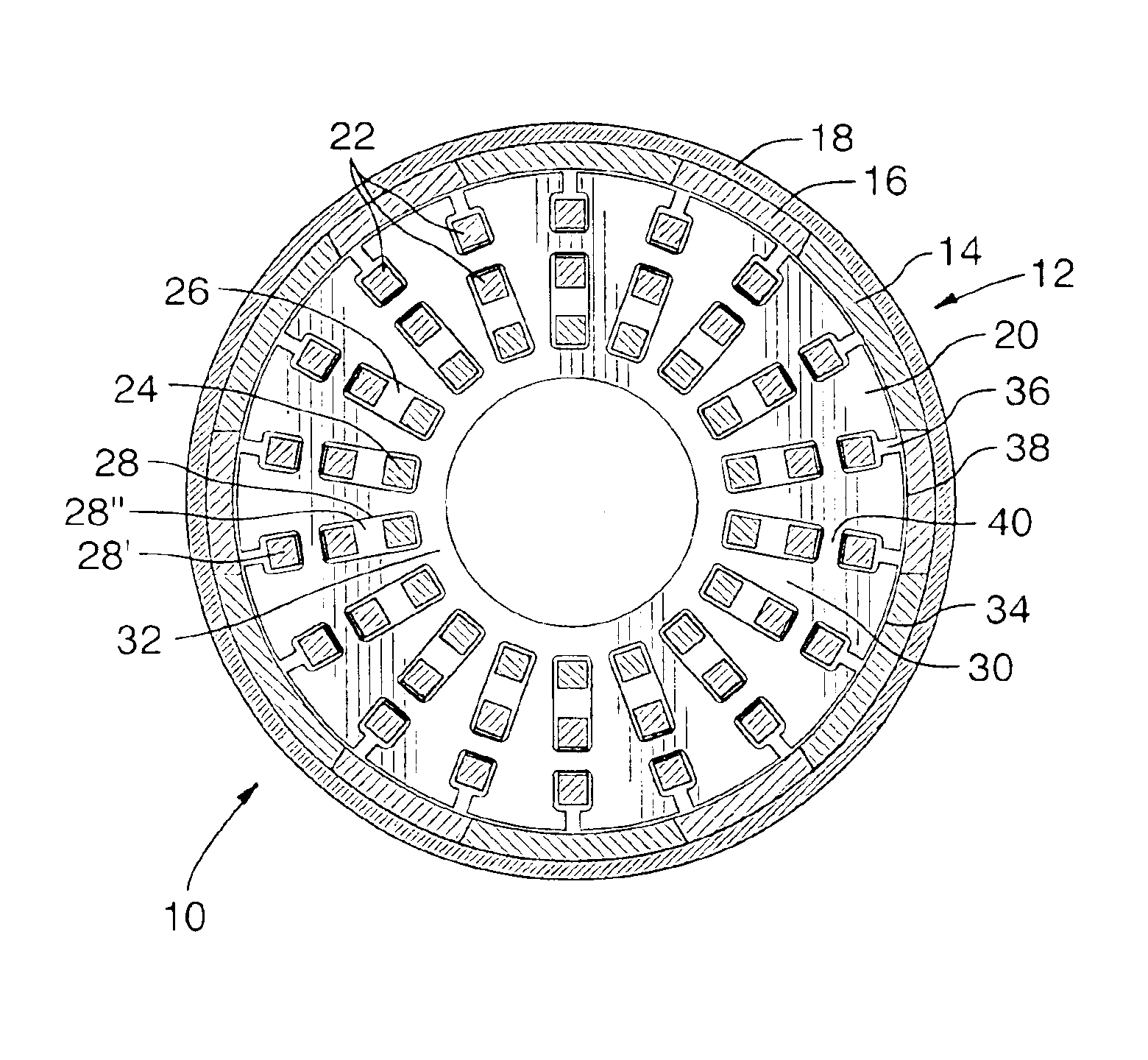
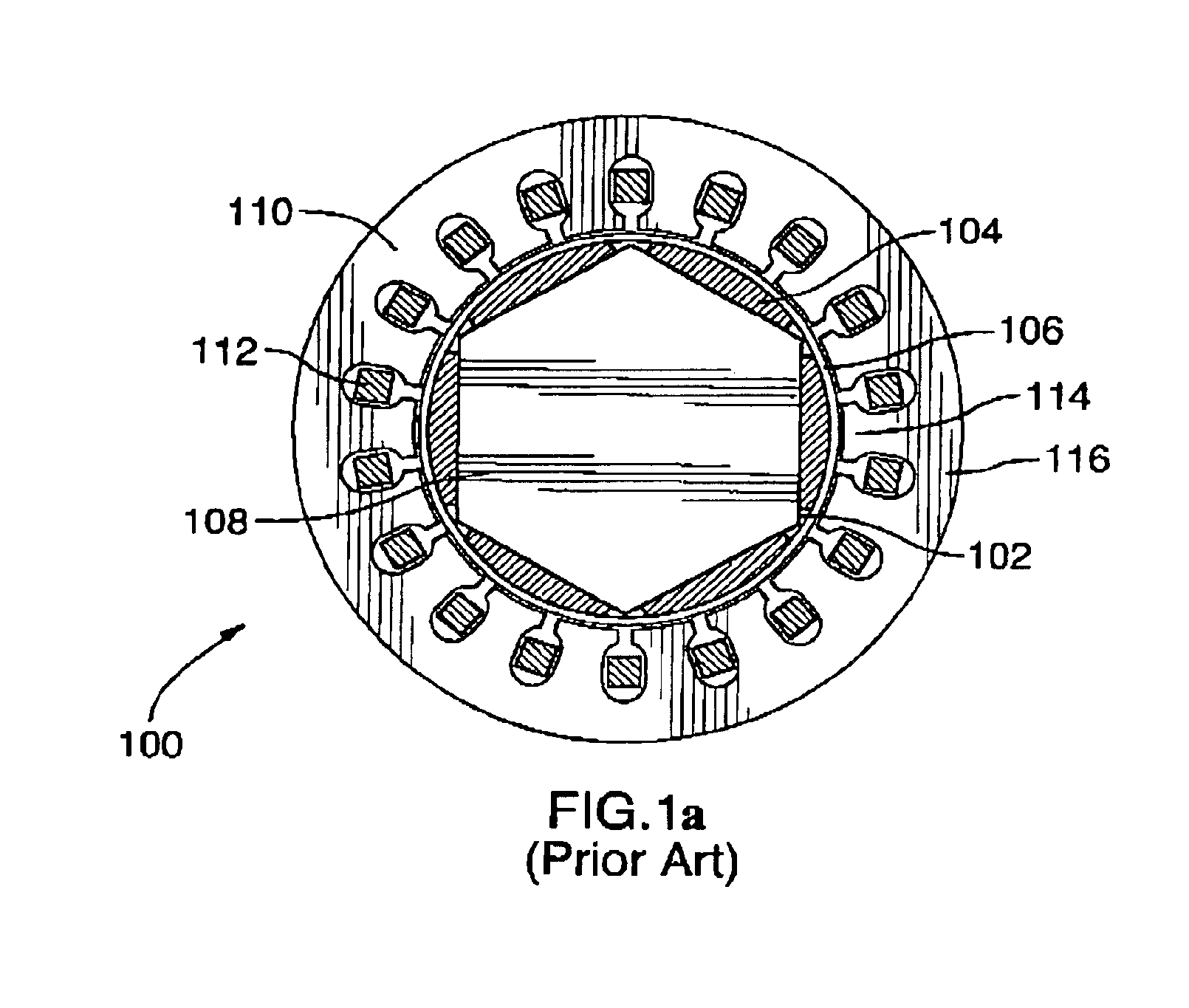
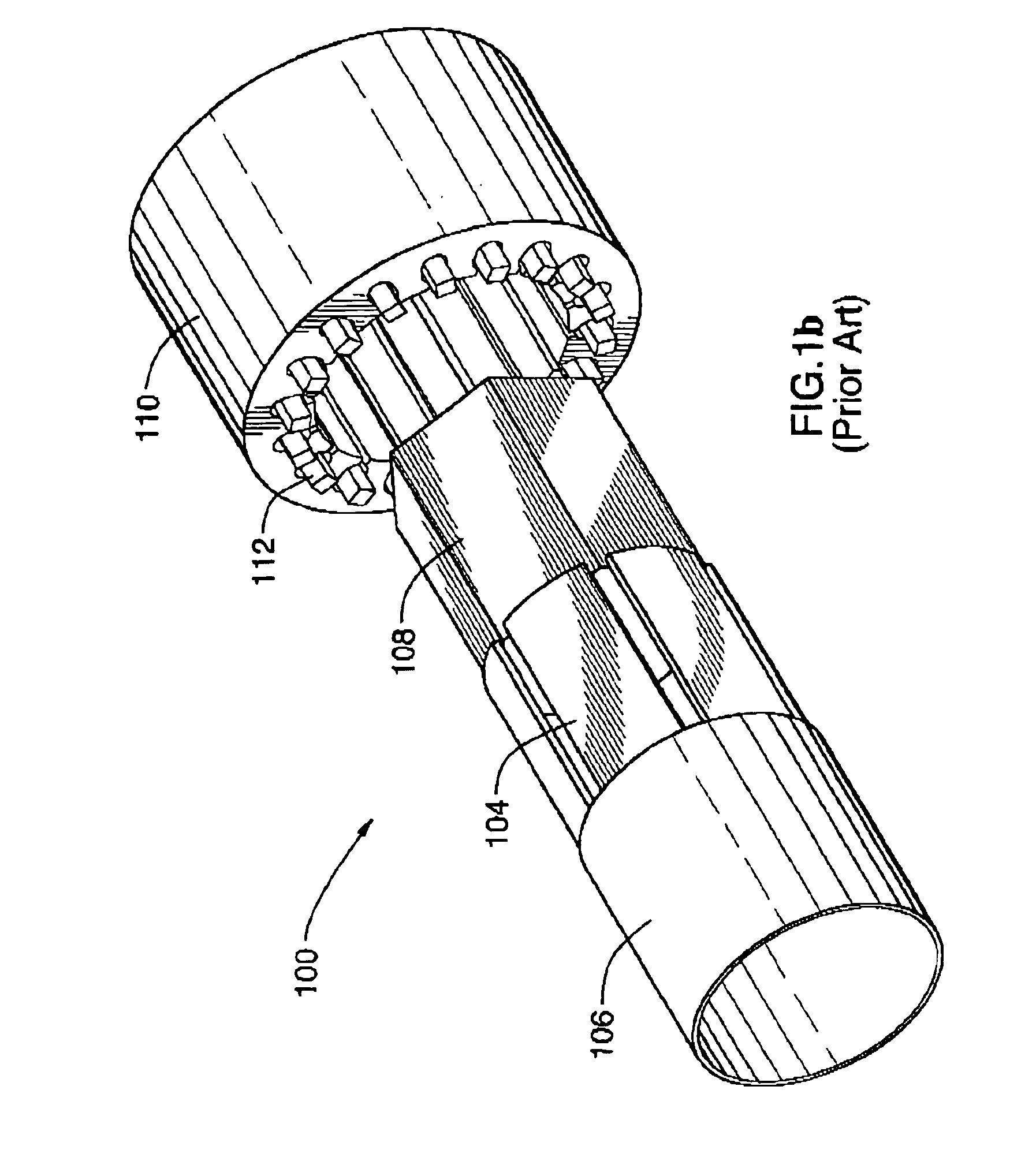
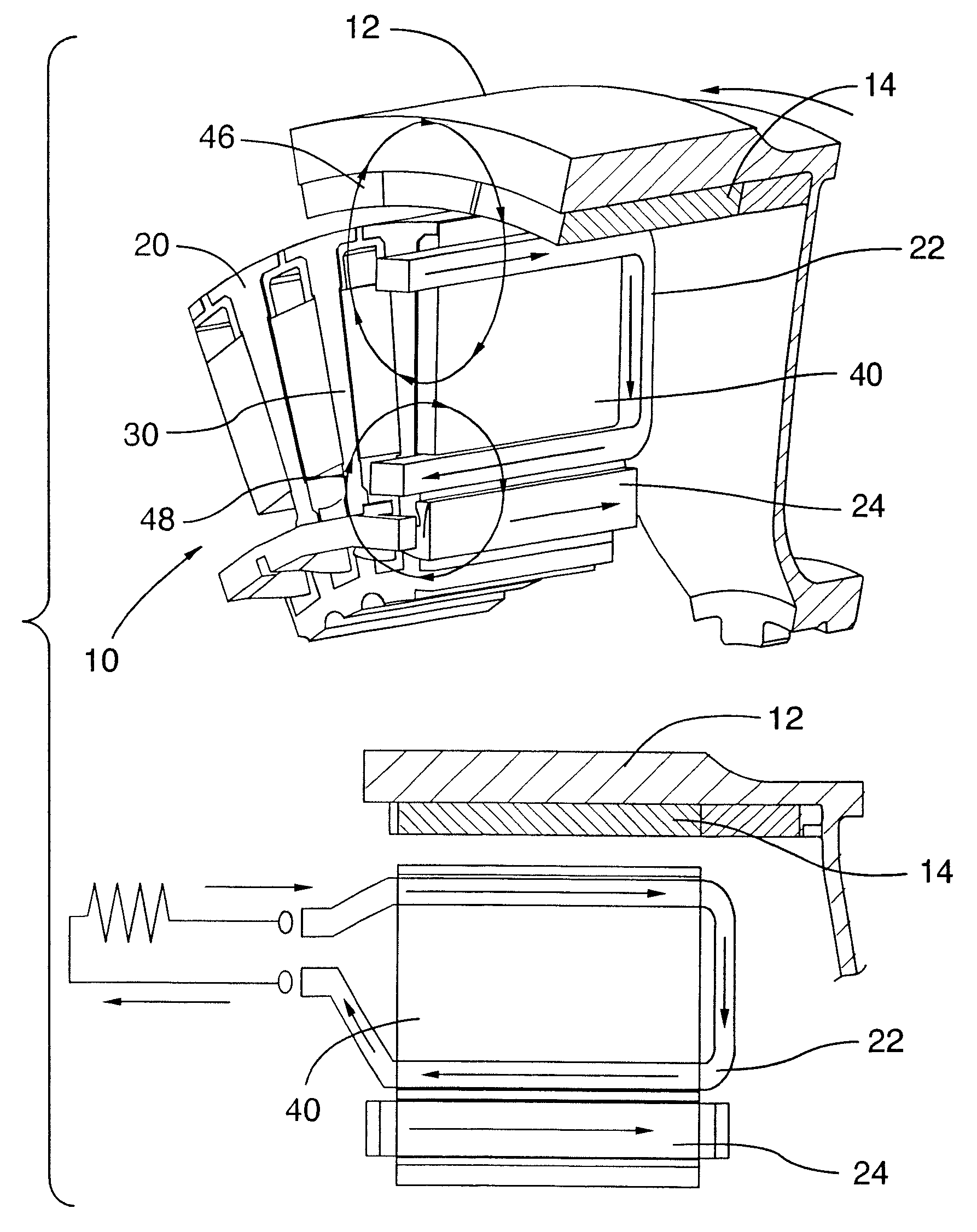
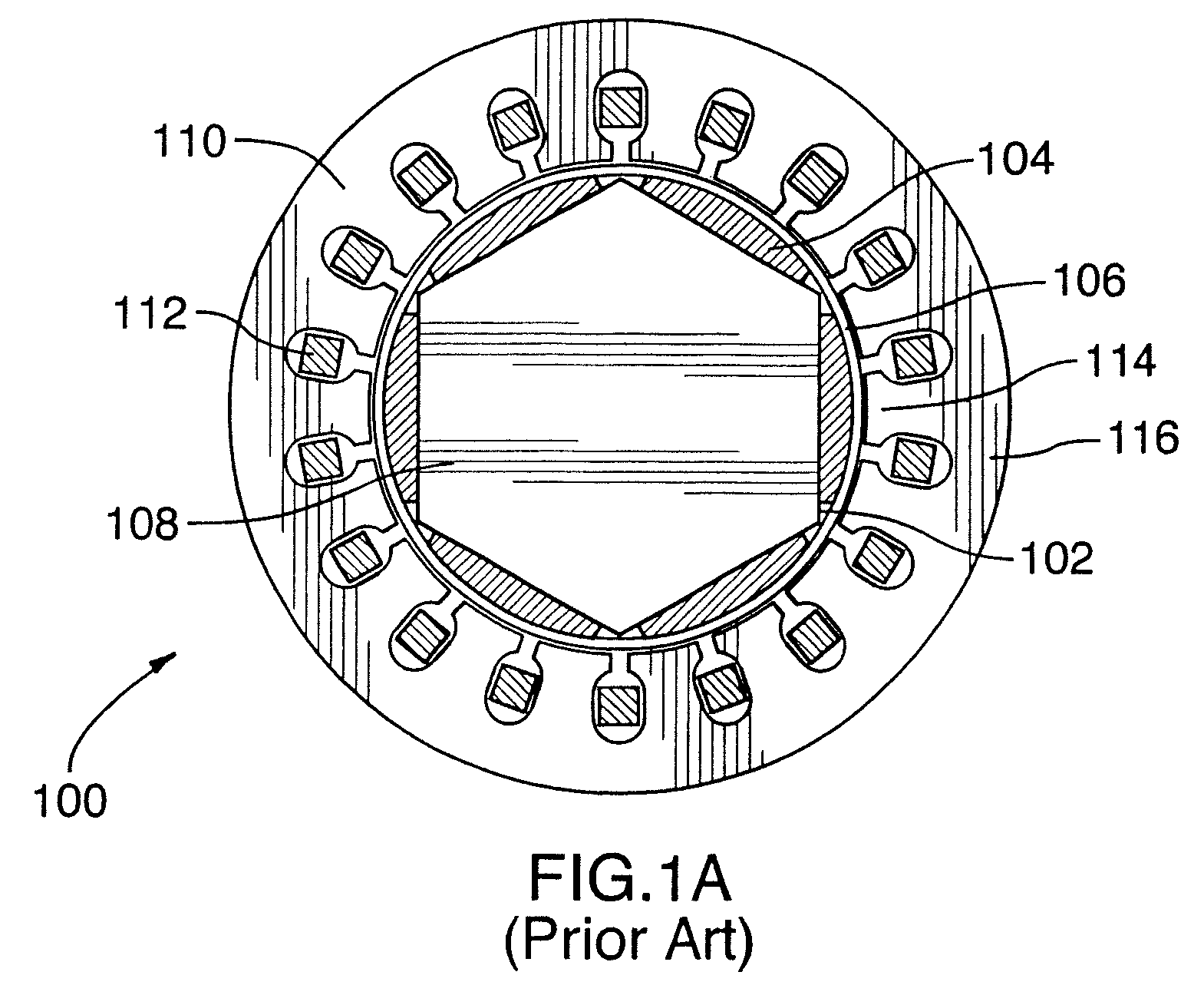
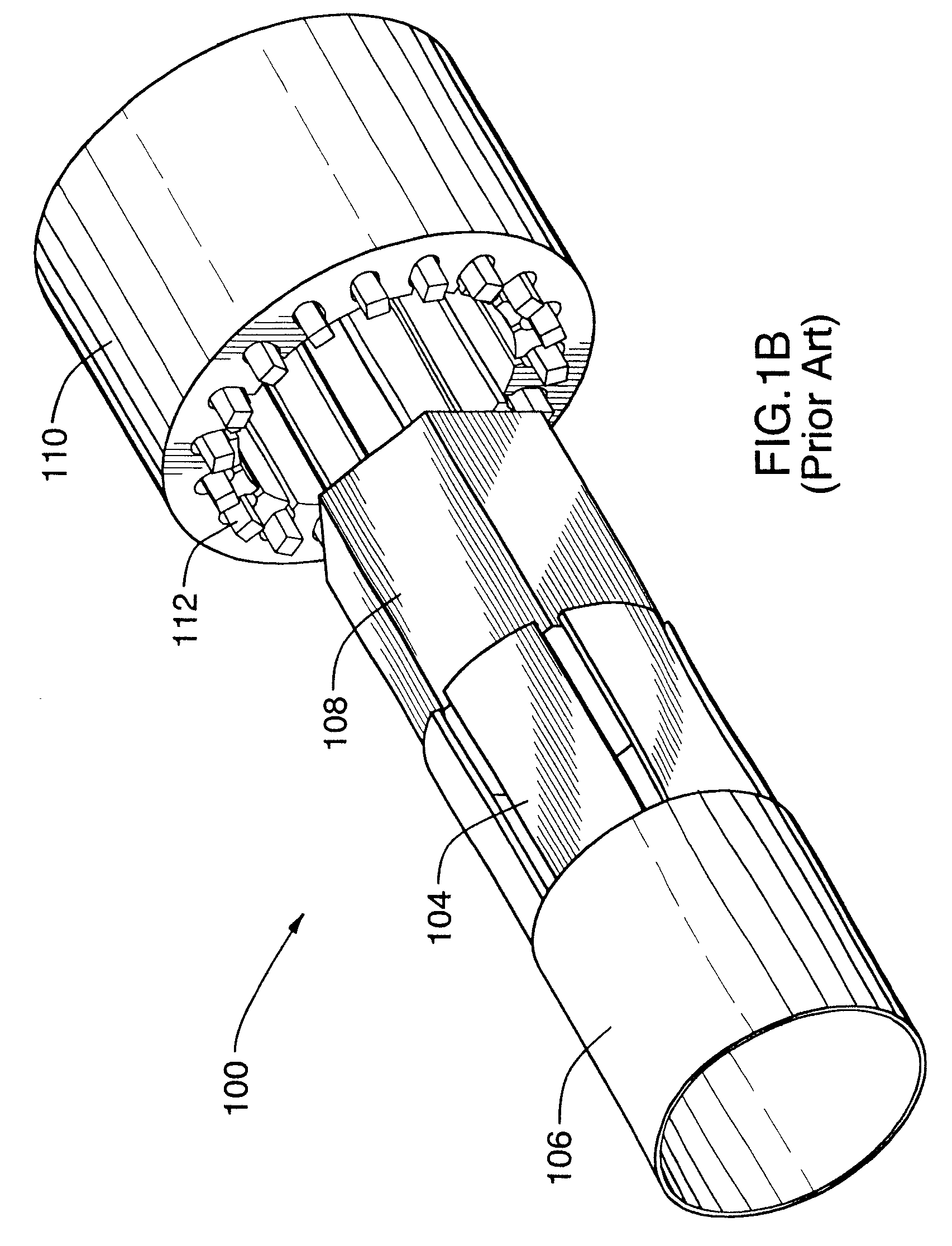
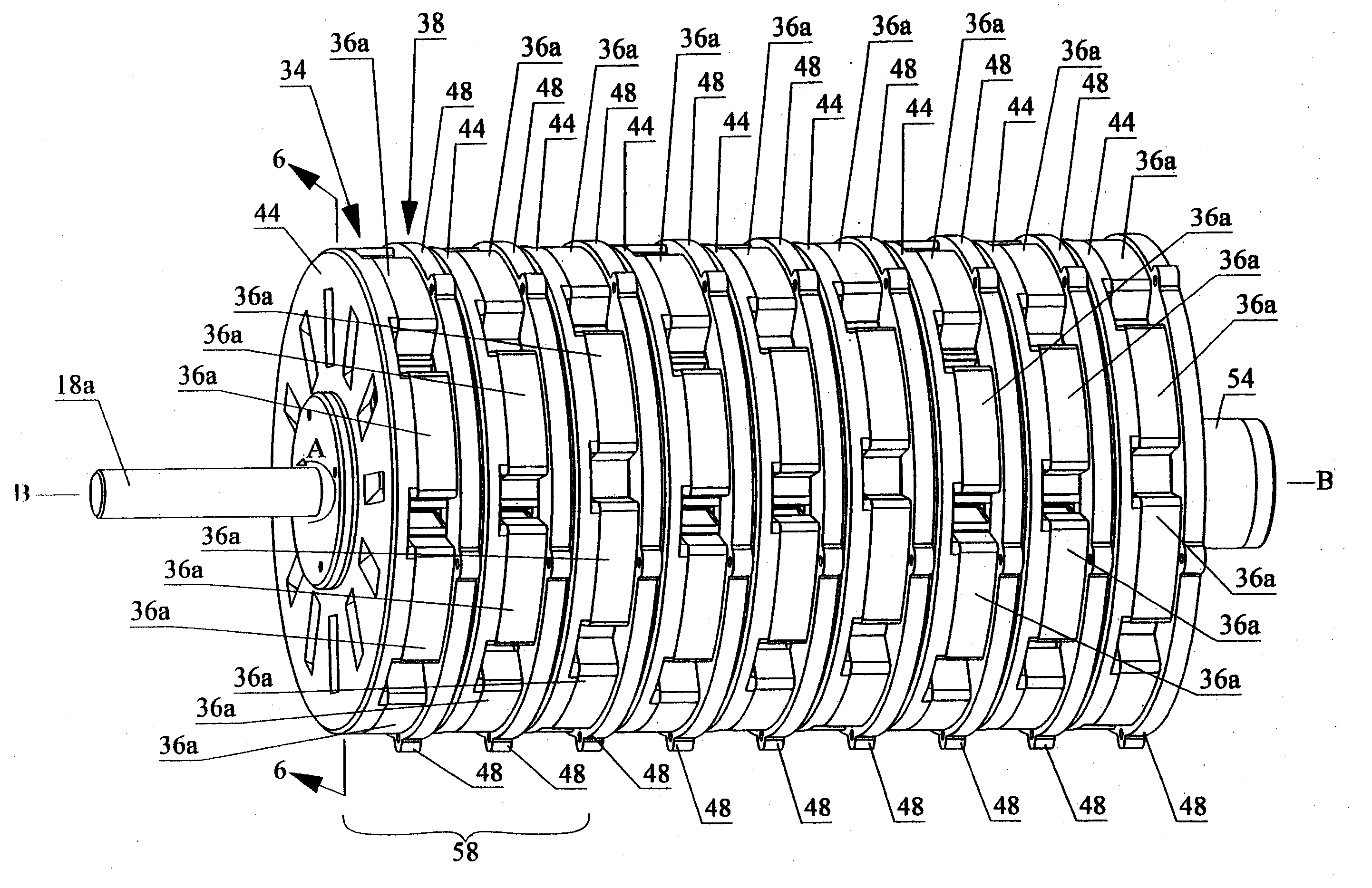
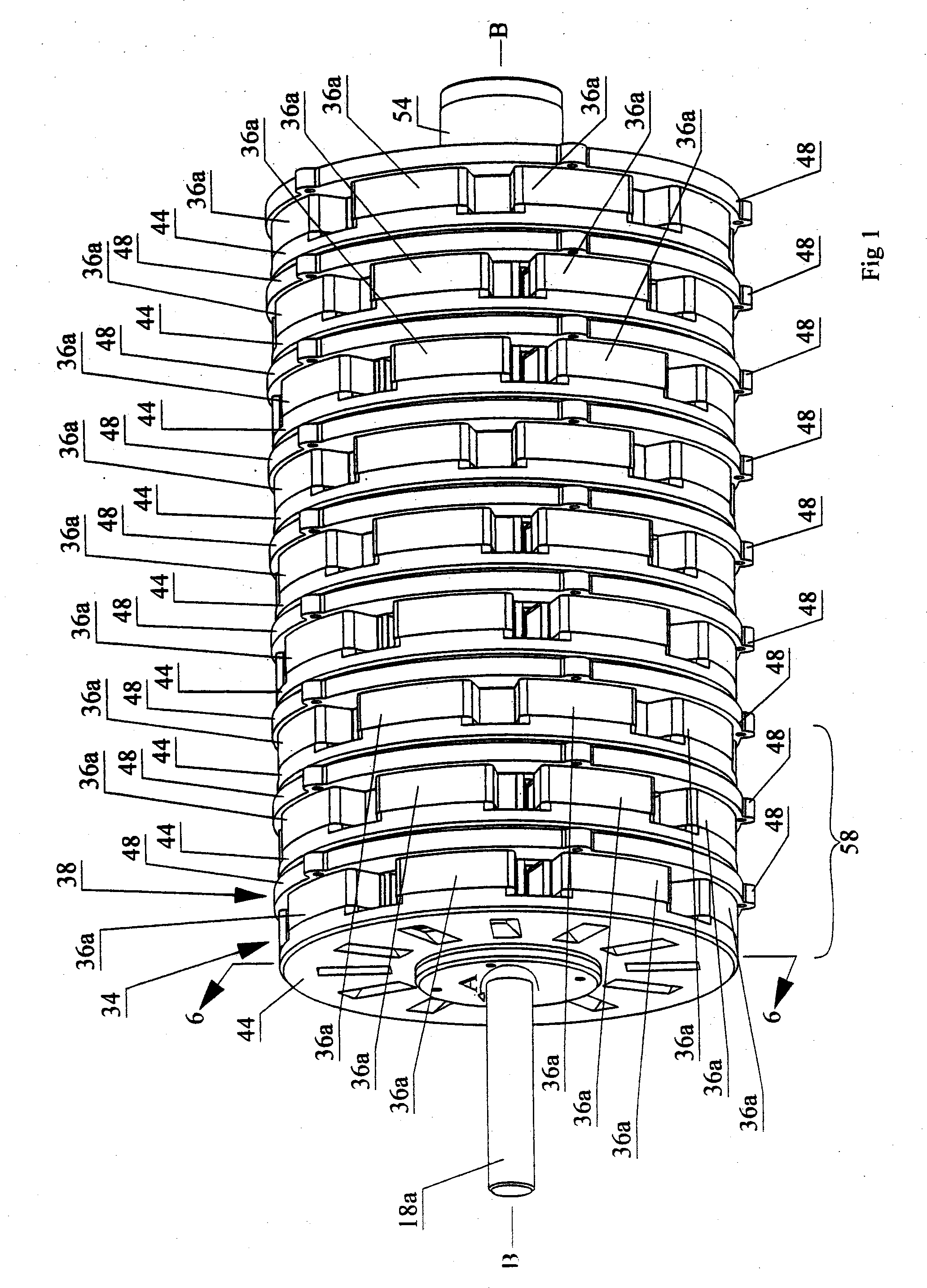
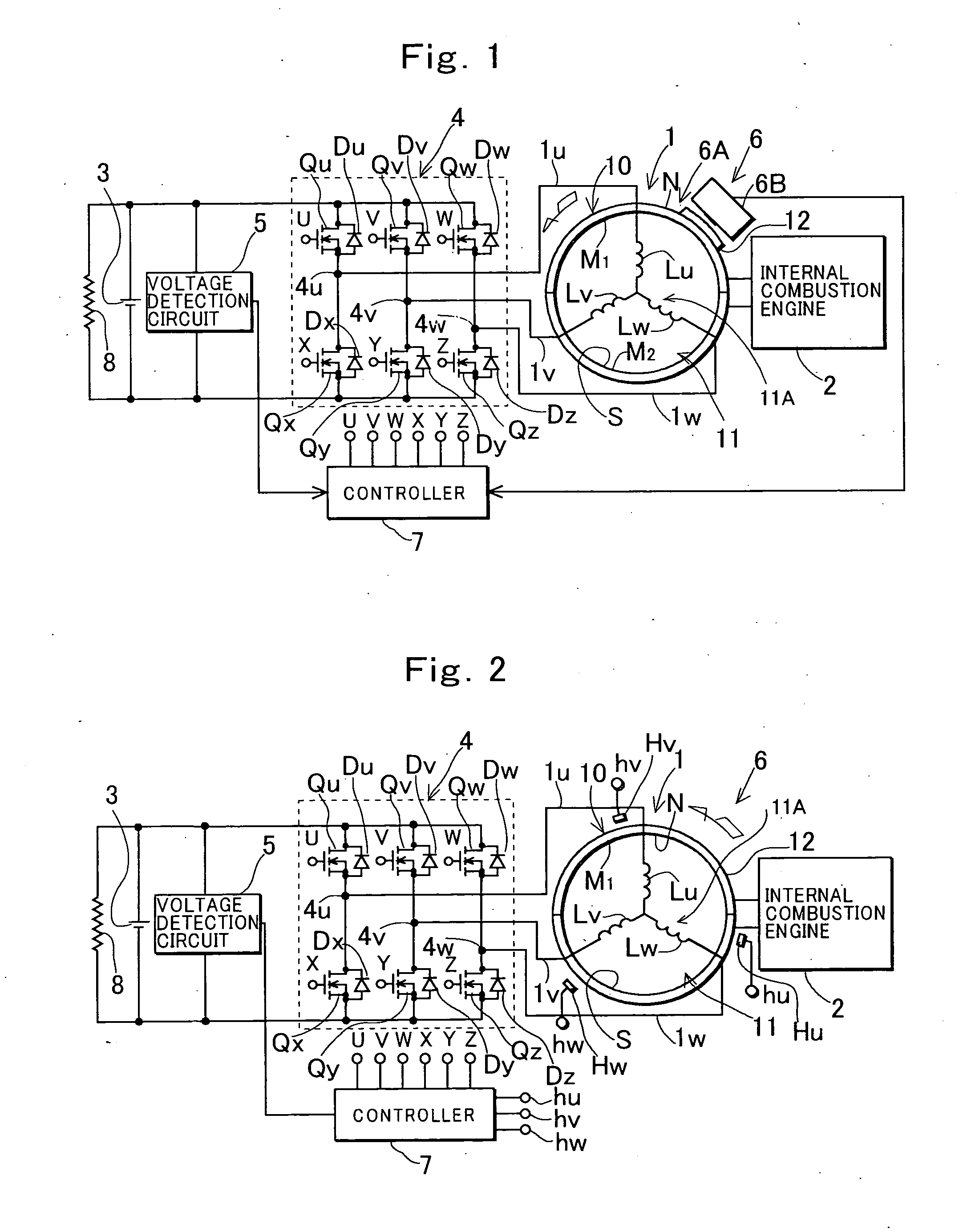
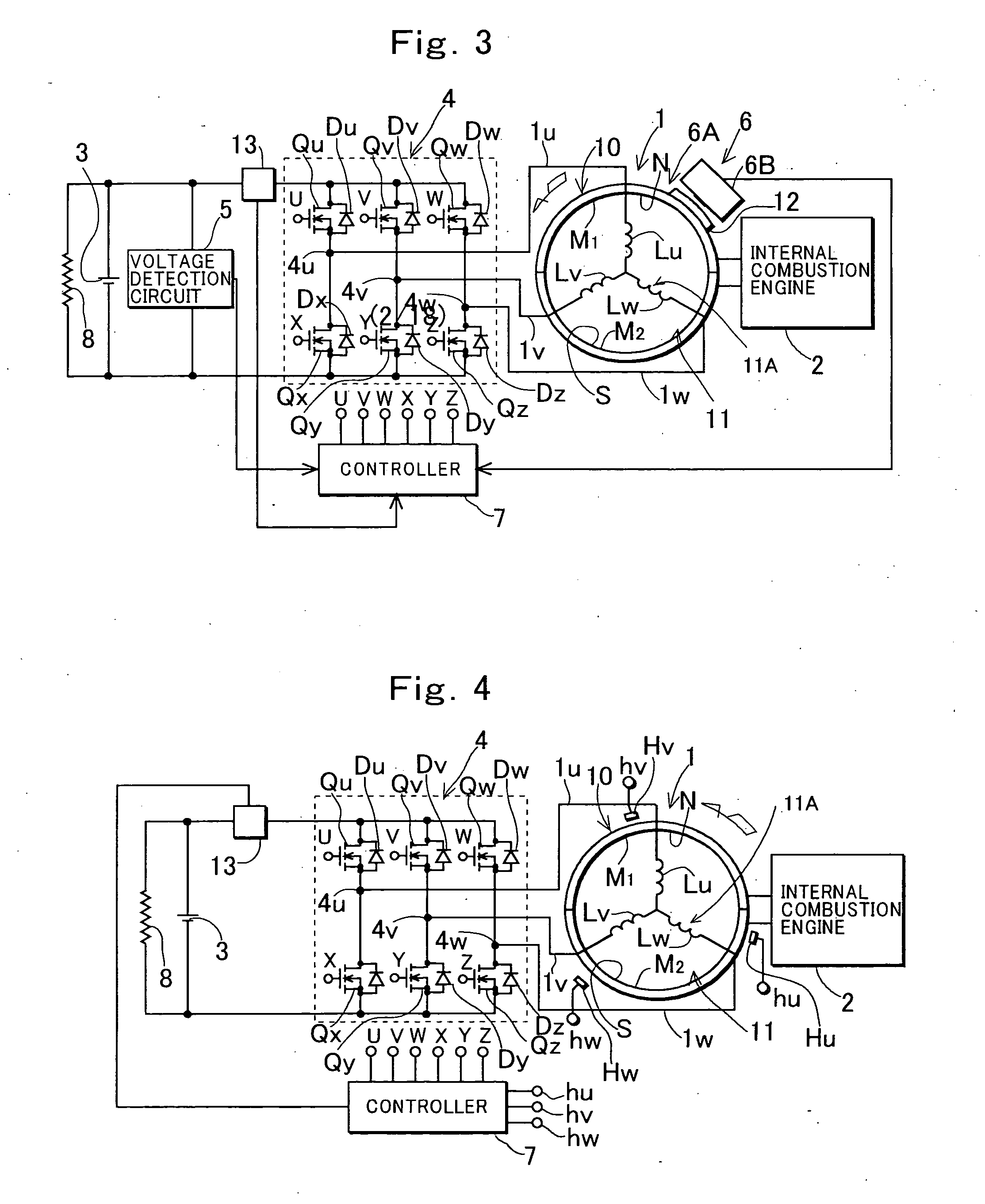
Electric machine having an integrally continuous stator winding and stator slot bridges
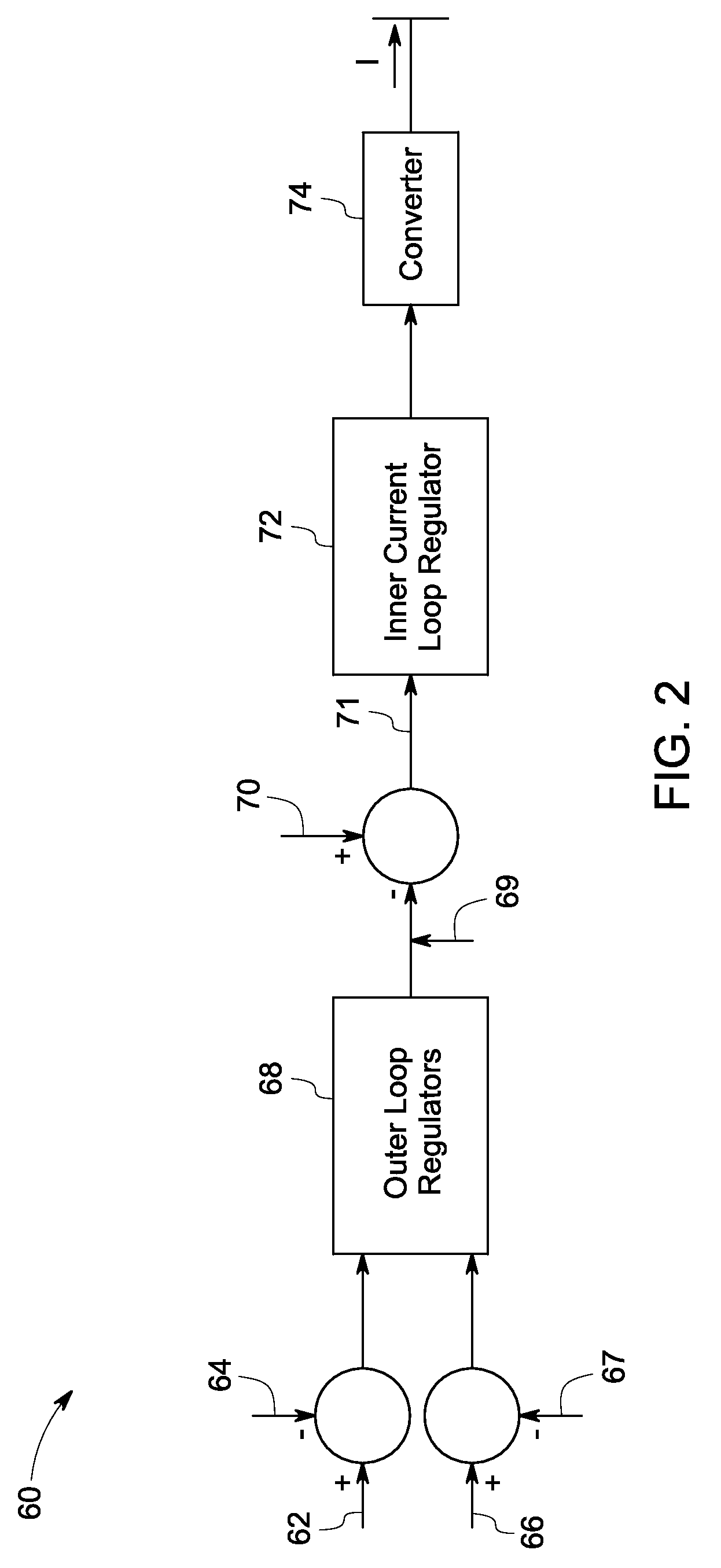
The invention includes an electric machine having a rotor, stator and at least one winding in the stator adapted to conduct a current, and a secondary winding, electrically isolated from the first winding and inductively coupled to the first winding, which may be used to control at least one of the output voltage and current of the first winding.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Architecture for electric machine
InactiveUS7583063B2Magnetic circuitEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityElectric machine
The invention includes an electric machine having a rotor, stator and at least one winding in the stator adapted to conduct a current, and a secondary winding, electrically isolated from the first winding and inductively coupled to the first winding, which may be used to control at least one of the output voltage and current of the first winding.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
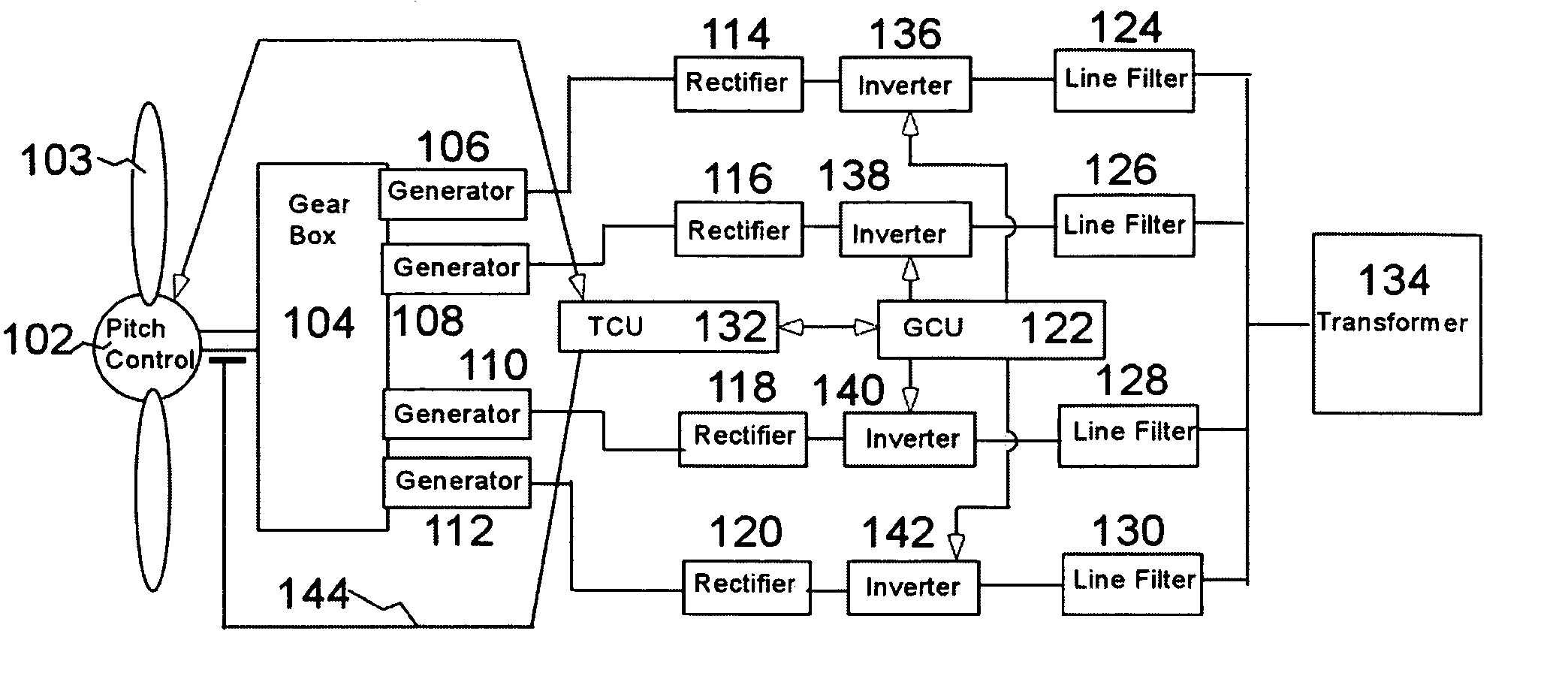
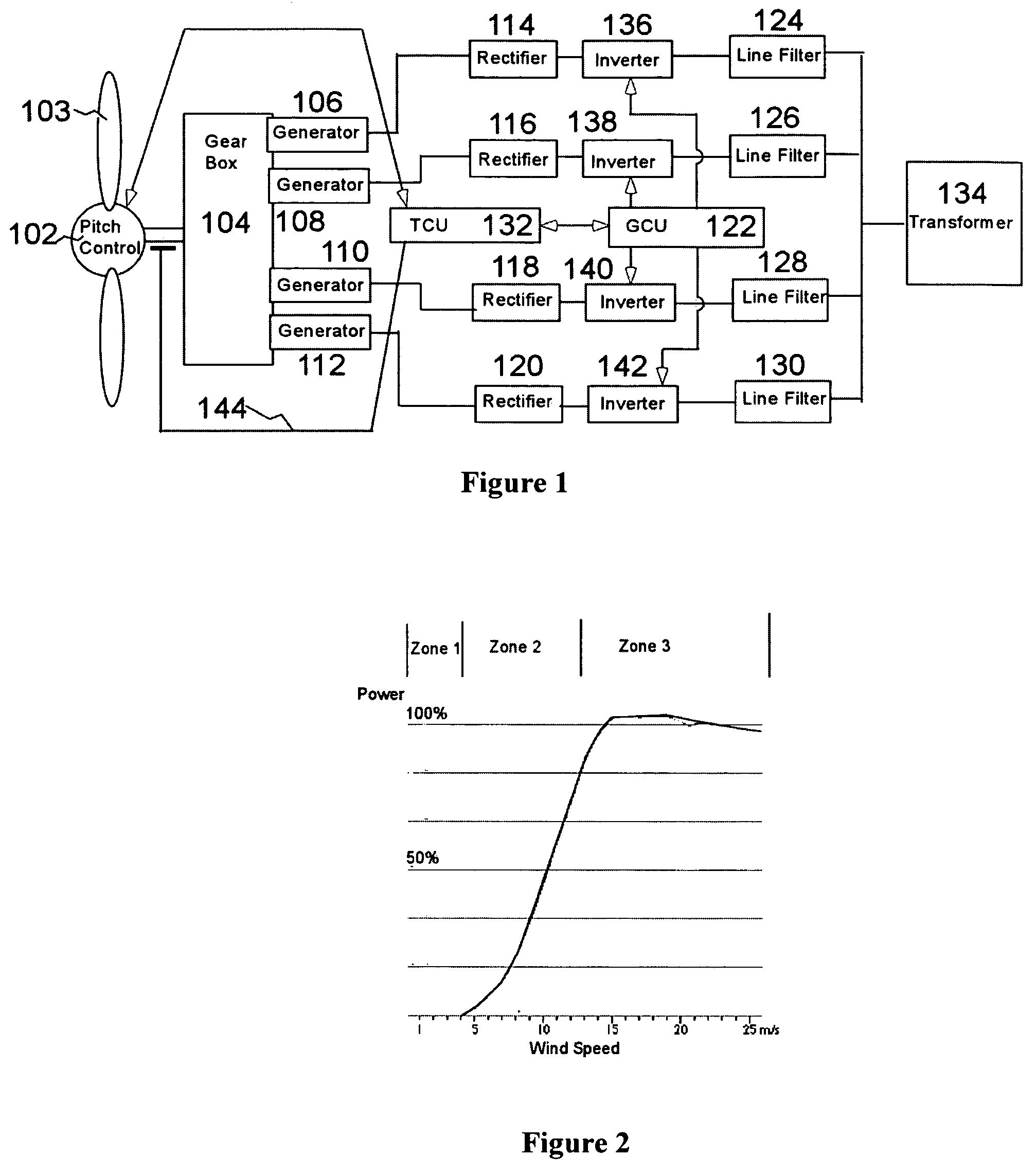
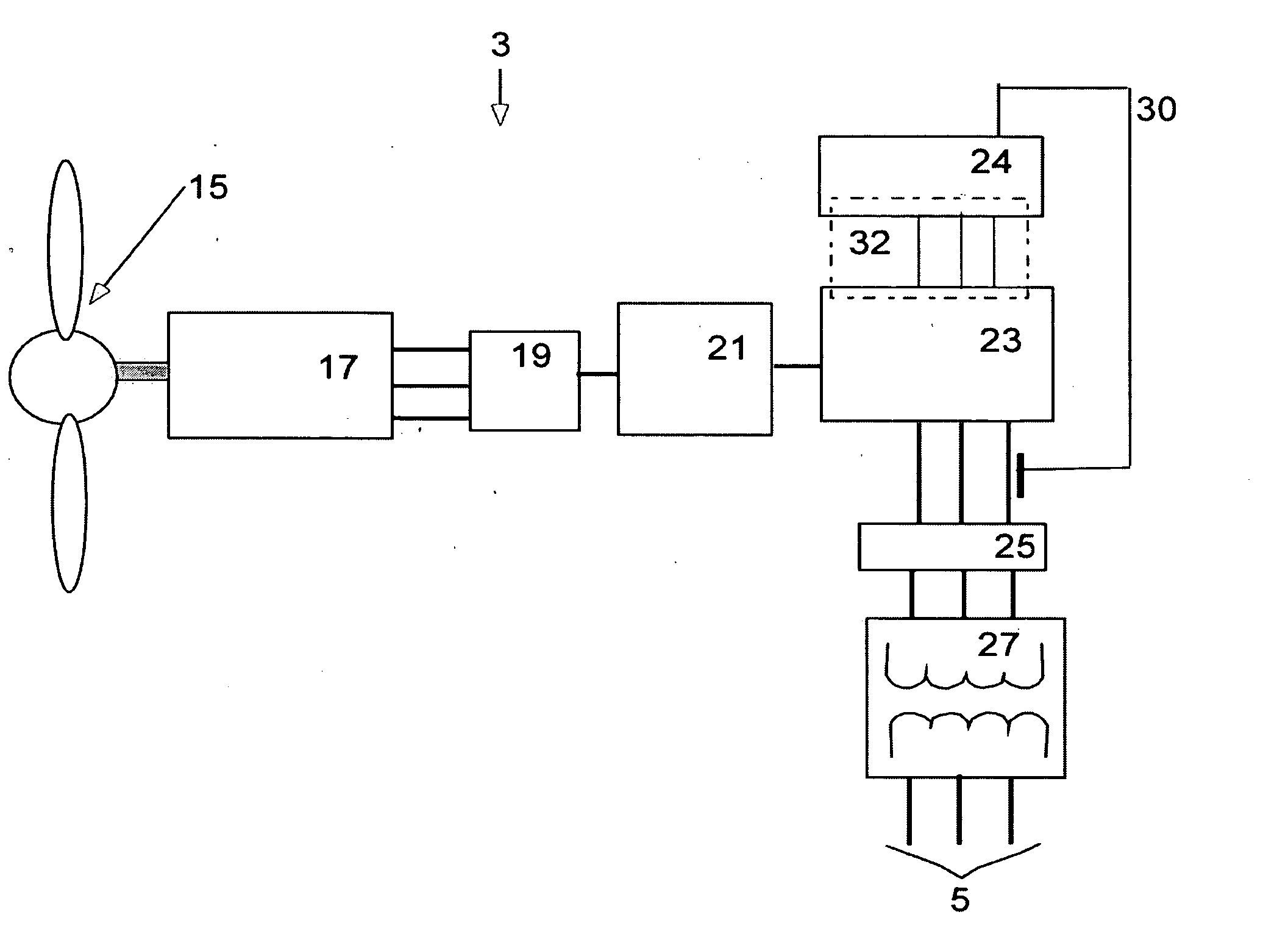
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS7042110B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPermanent magnet rotorDc current
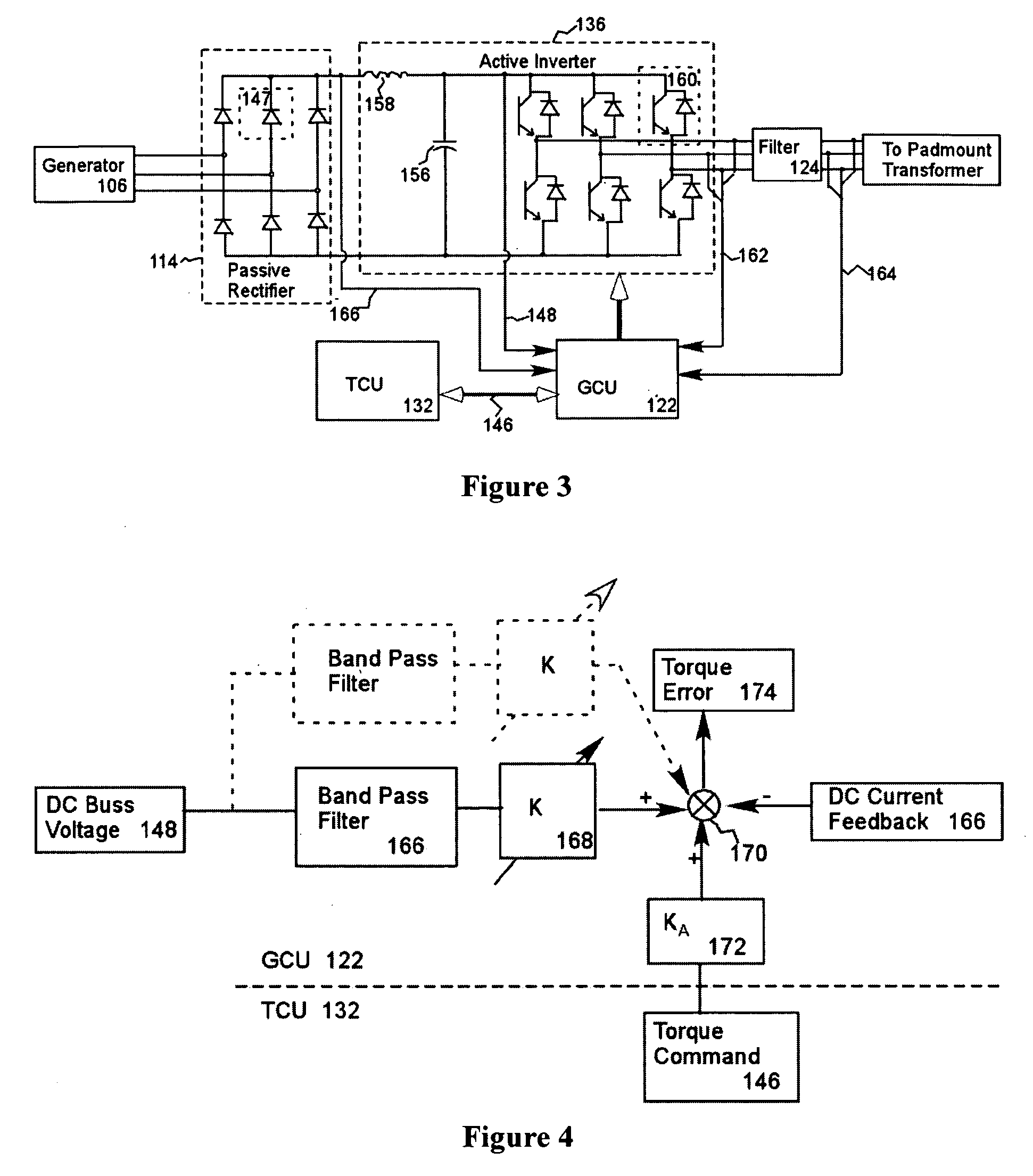
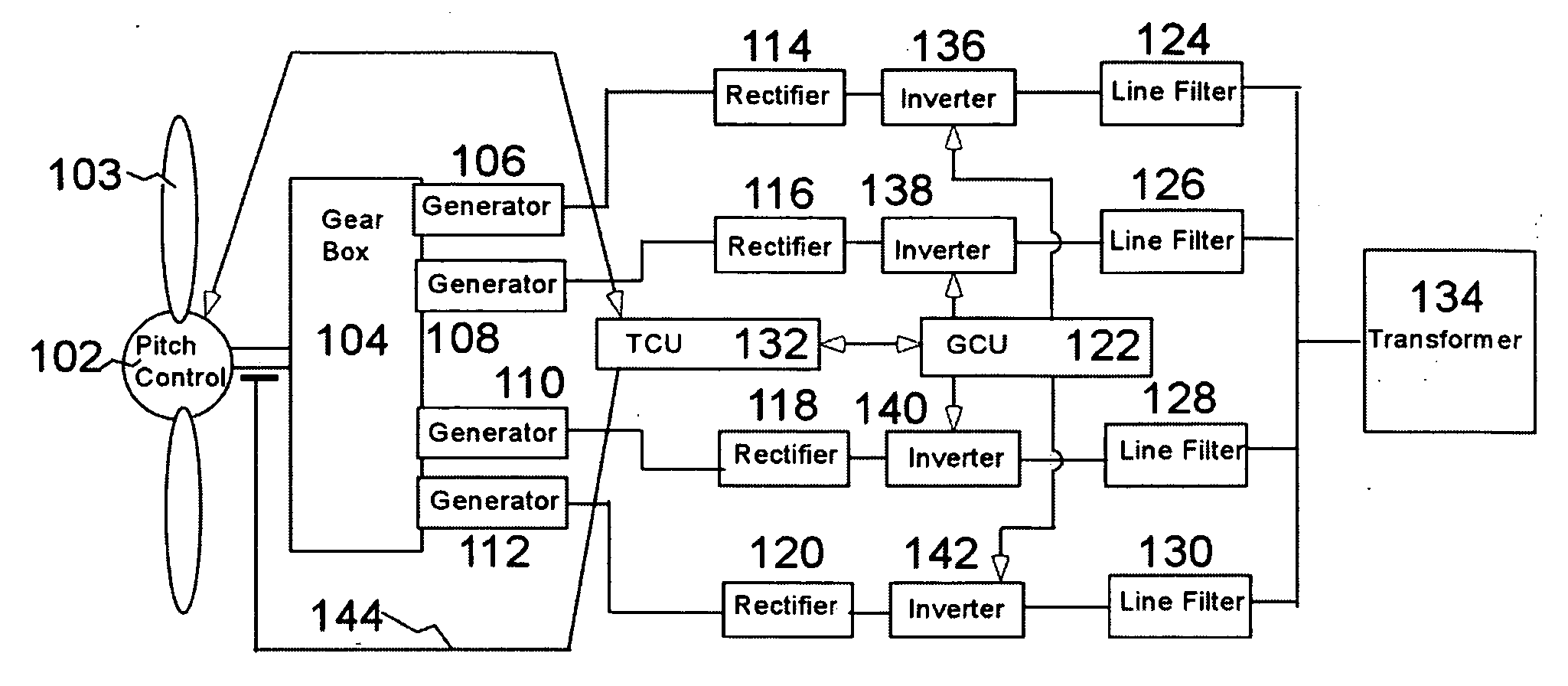
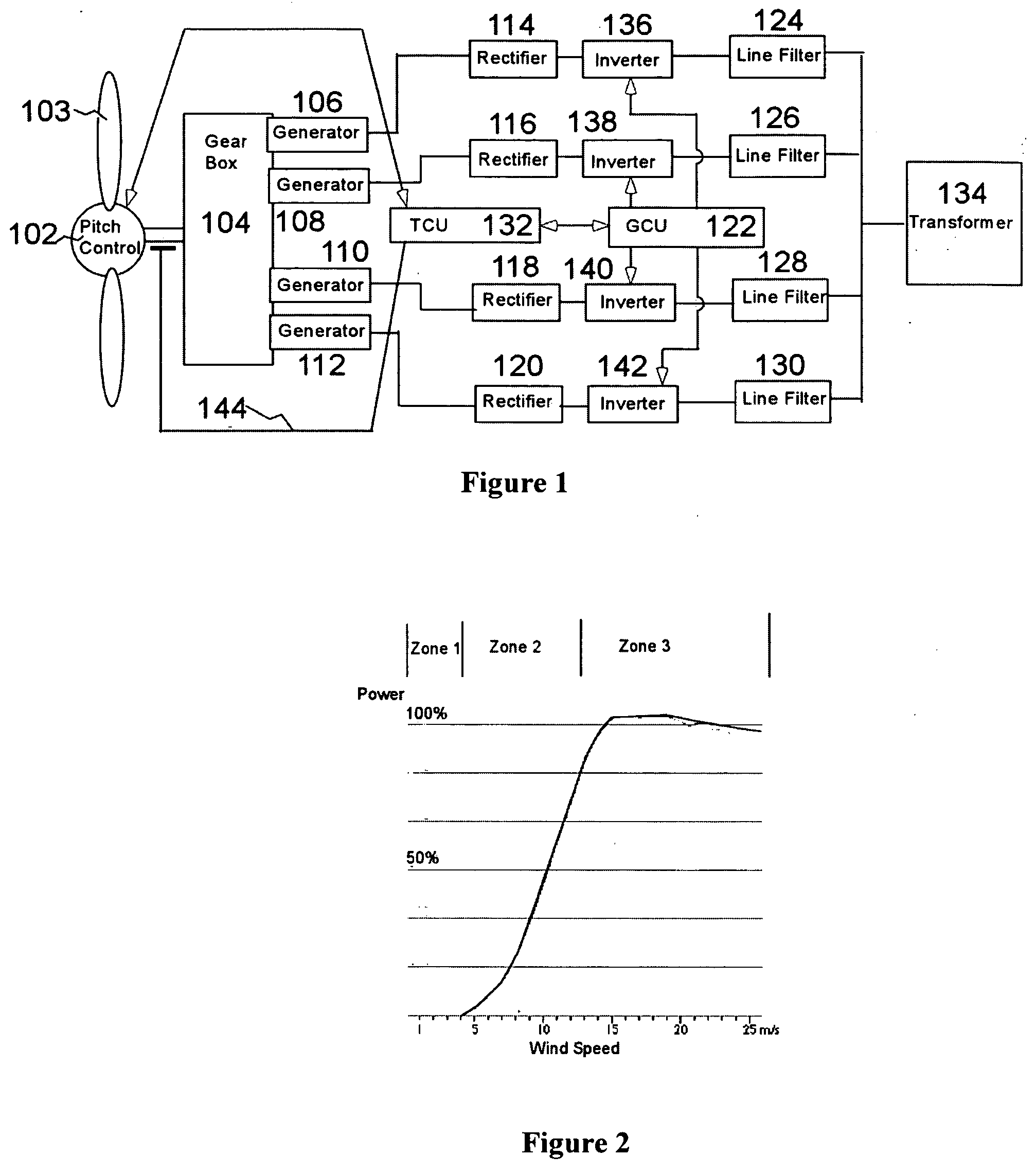
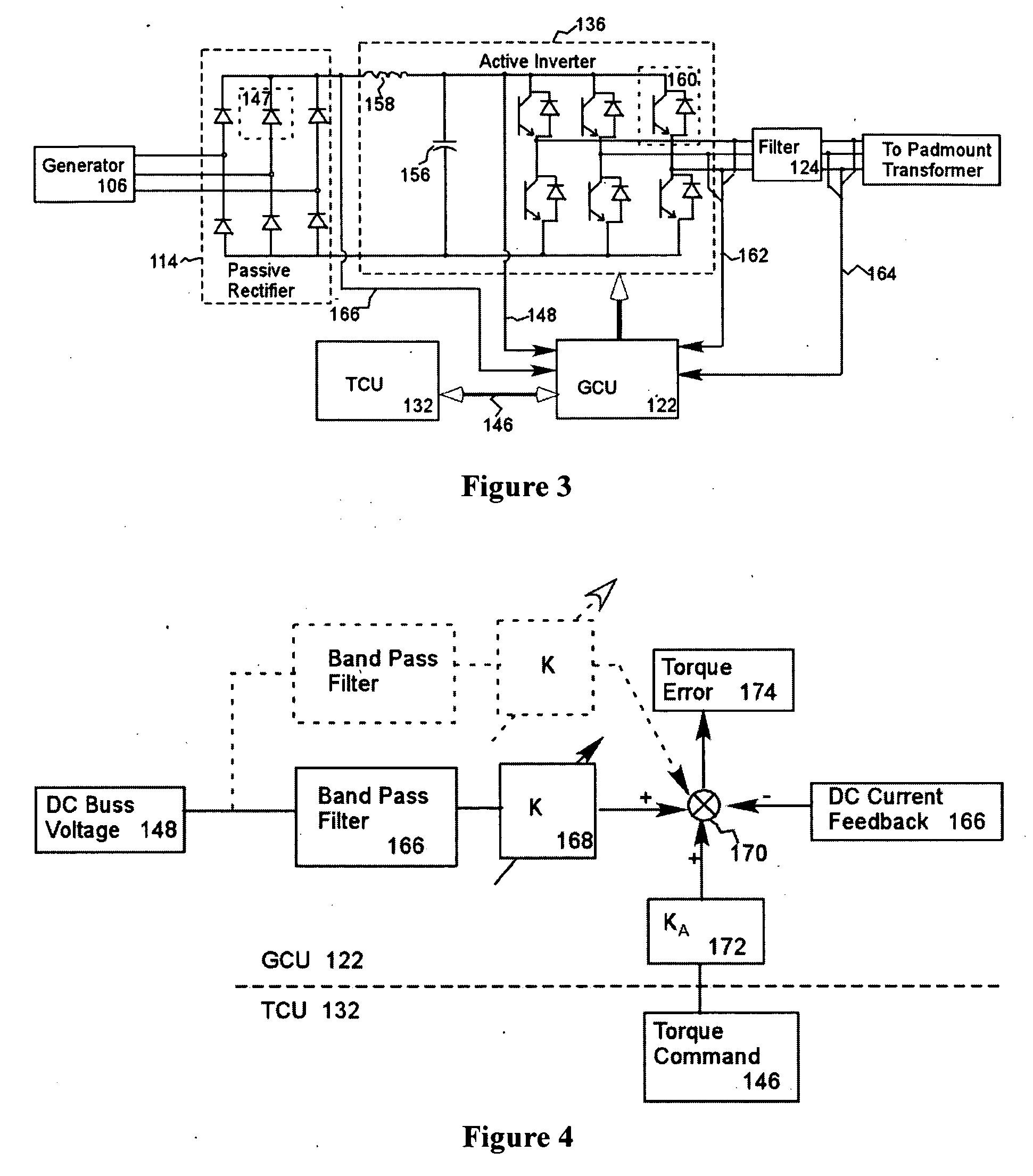
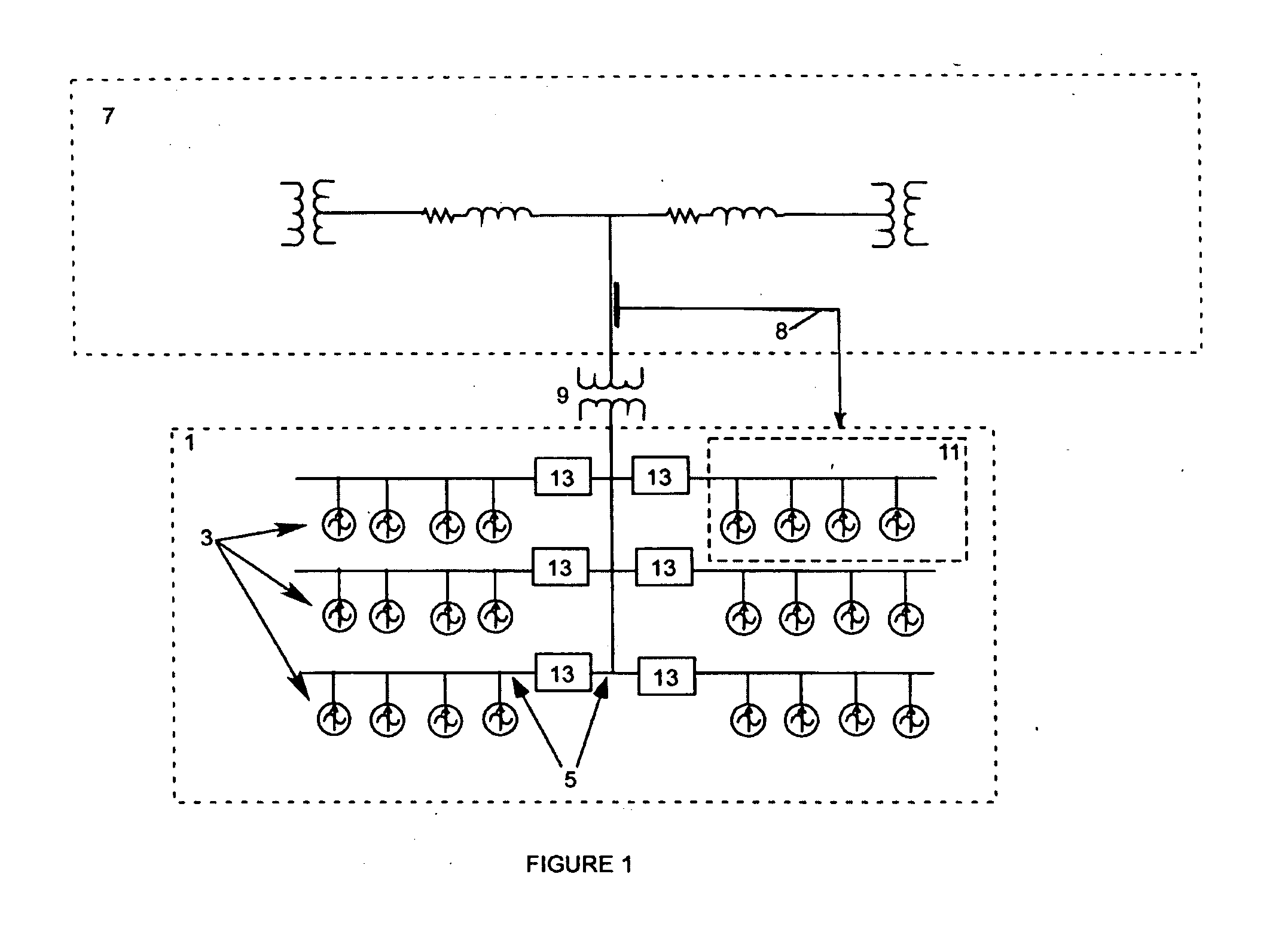
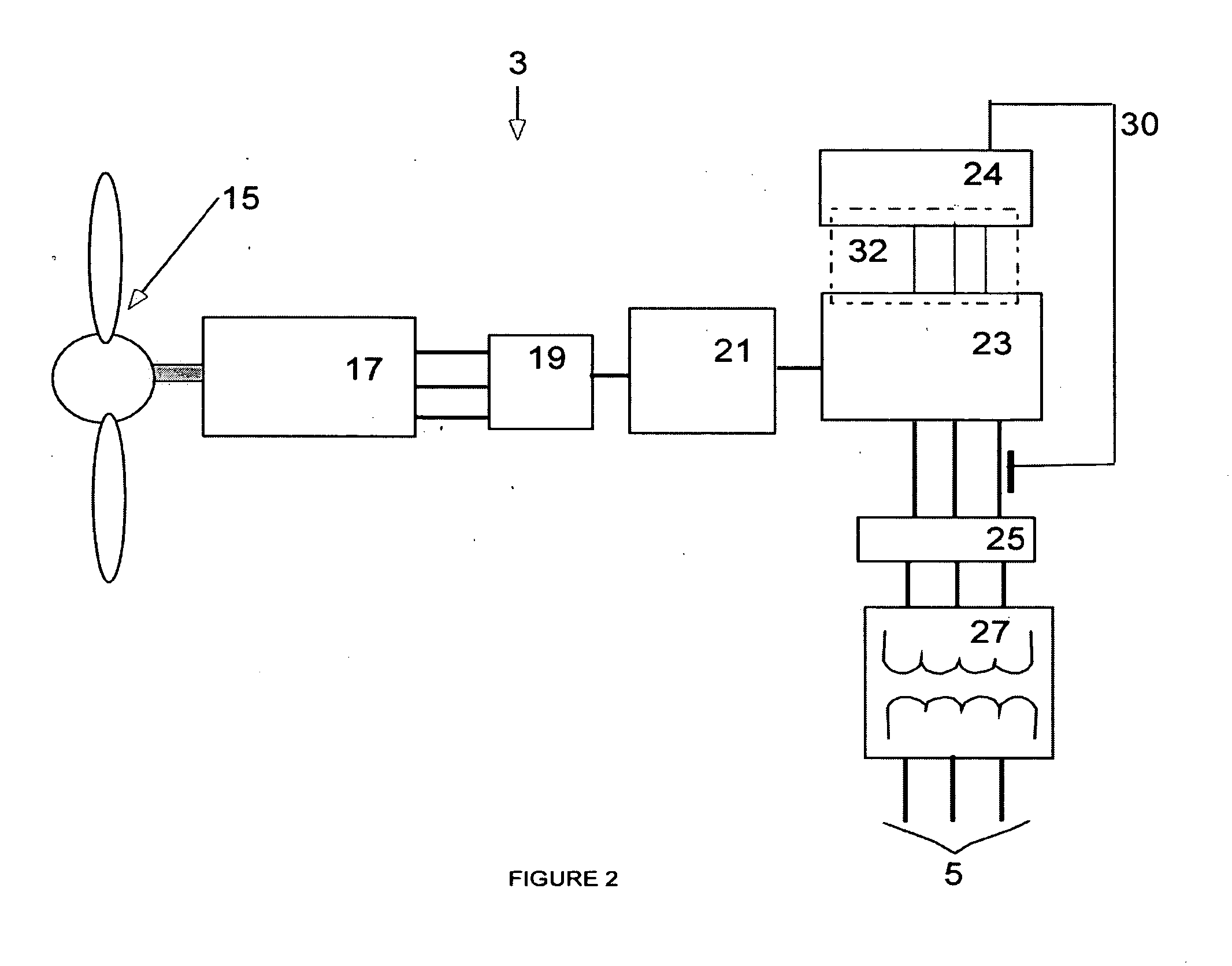
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS20050012339A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectric power transmissionPermanent magnet rotor
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
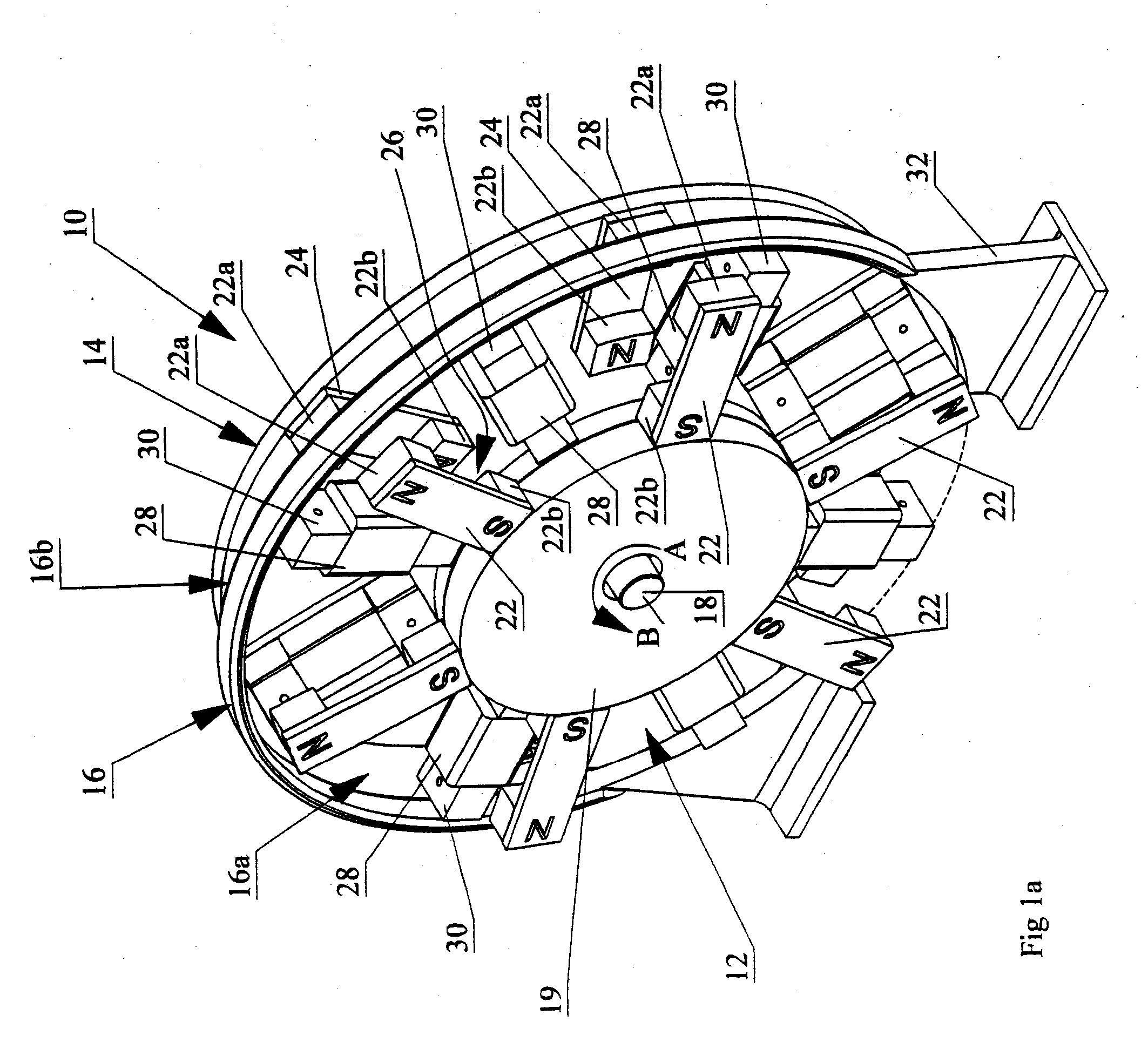
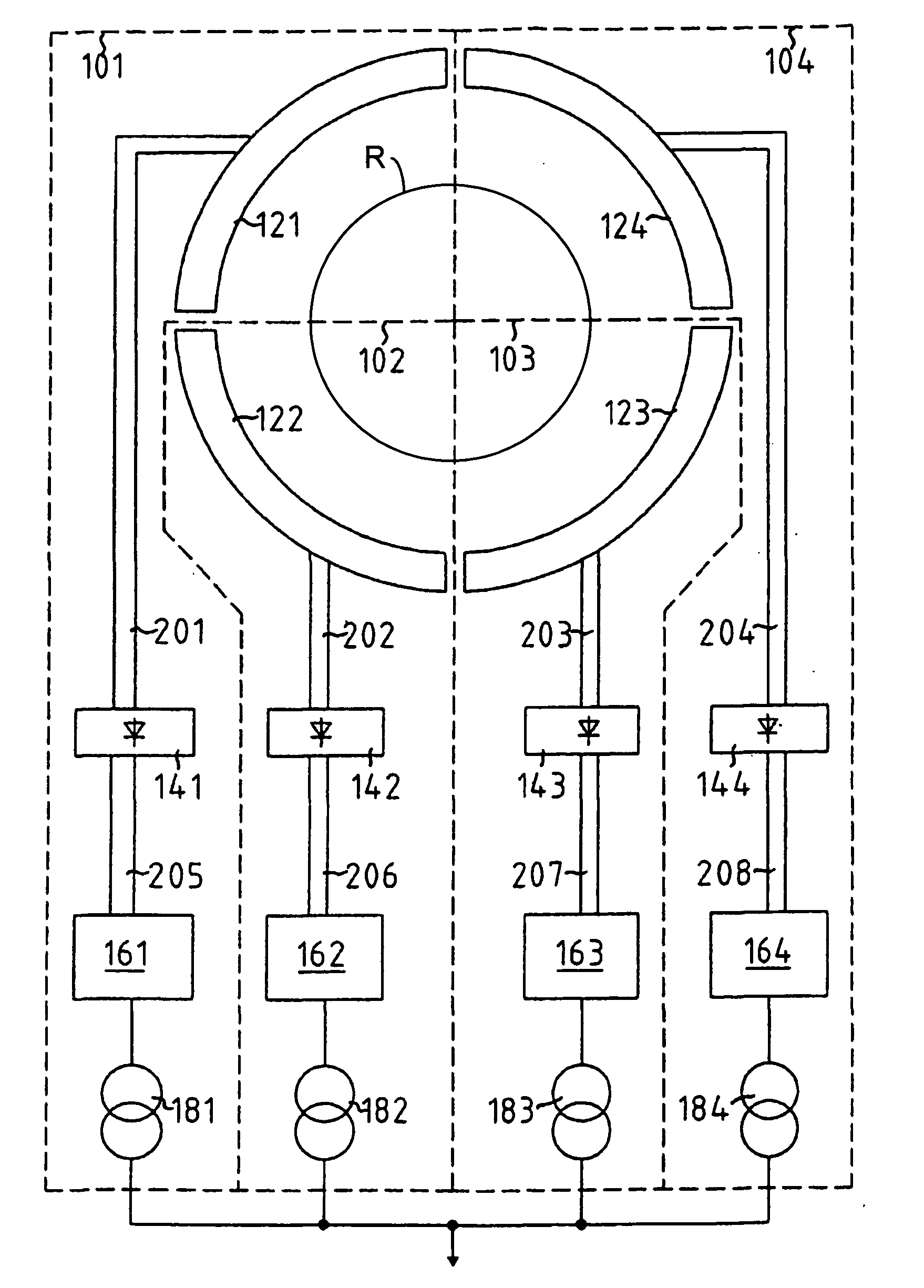
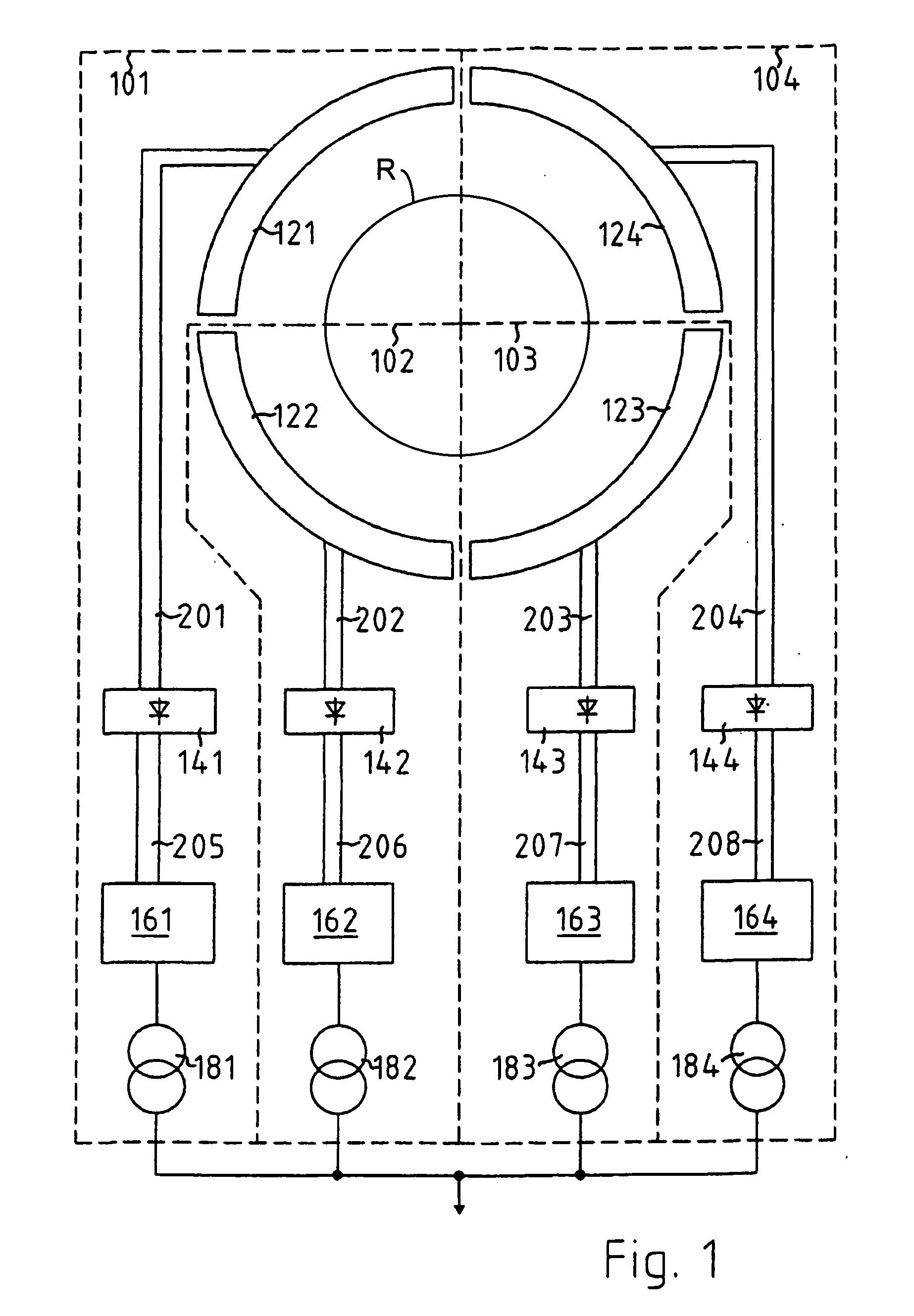
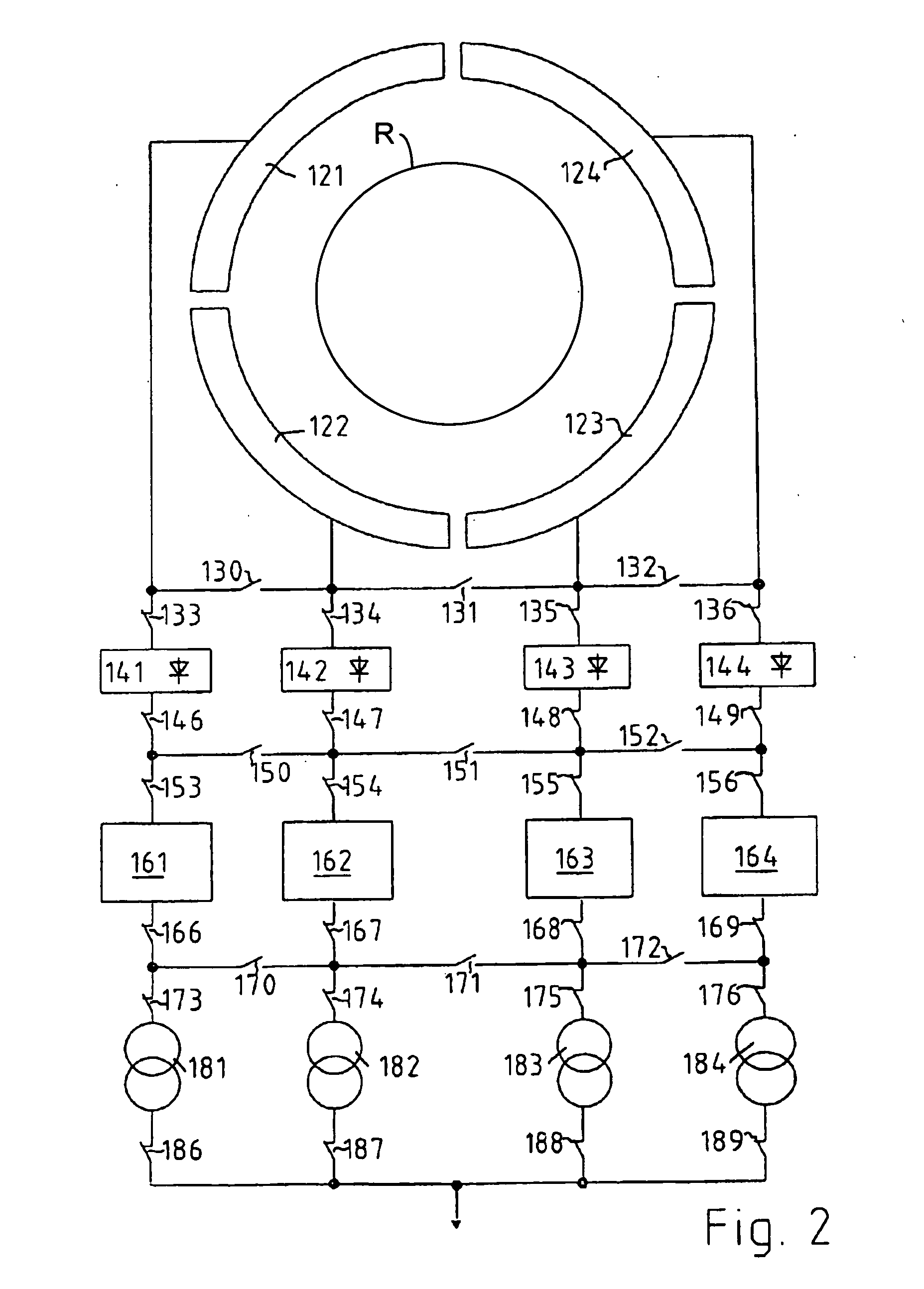
Poly-phasic multi-coil generator
InactiveUS20080088200A1Reduce negative impactReduce harmSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsAngular orientationMulti coil
Owner:RITCHEY JONATHAN
Generator with utility fault ride-through capability
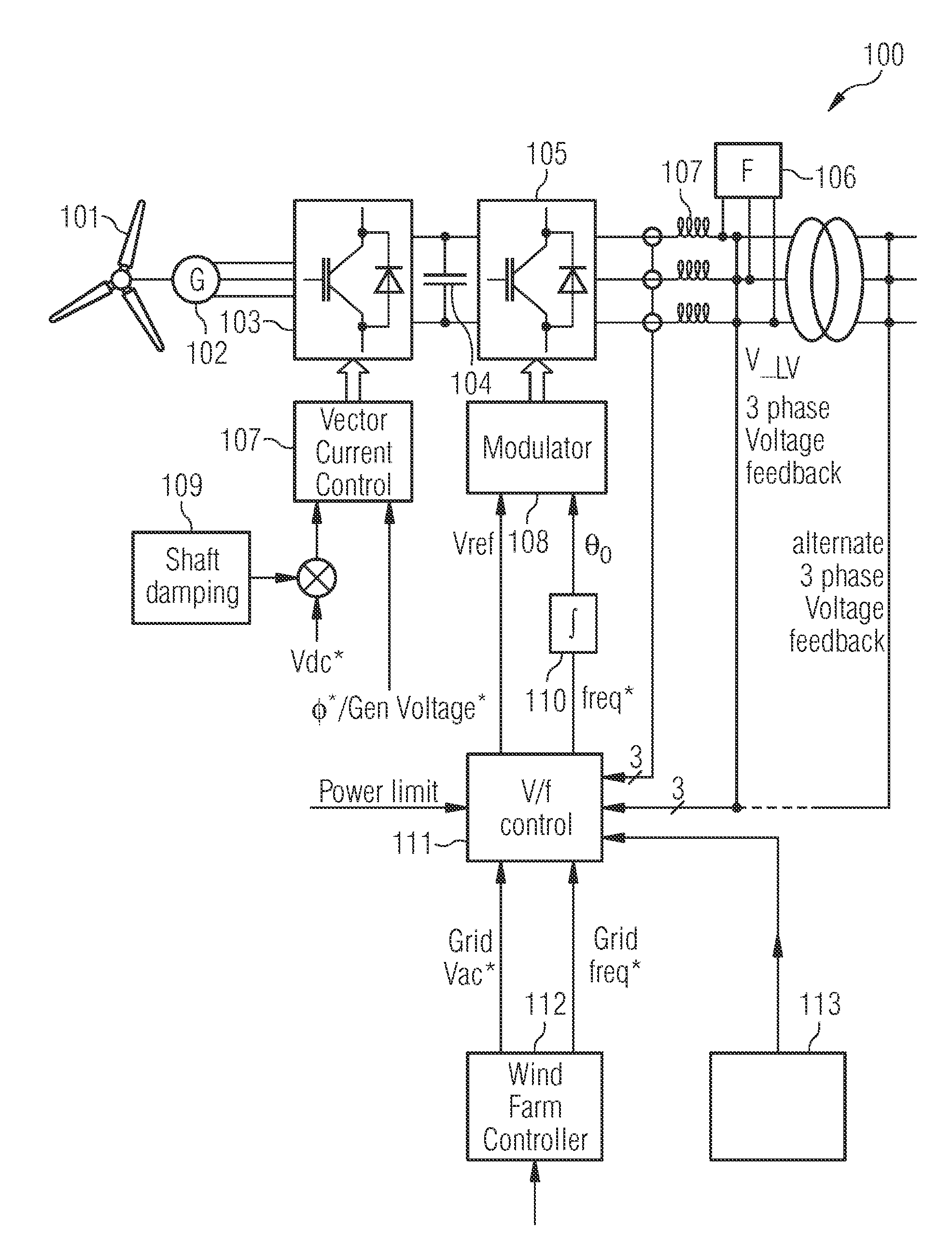
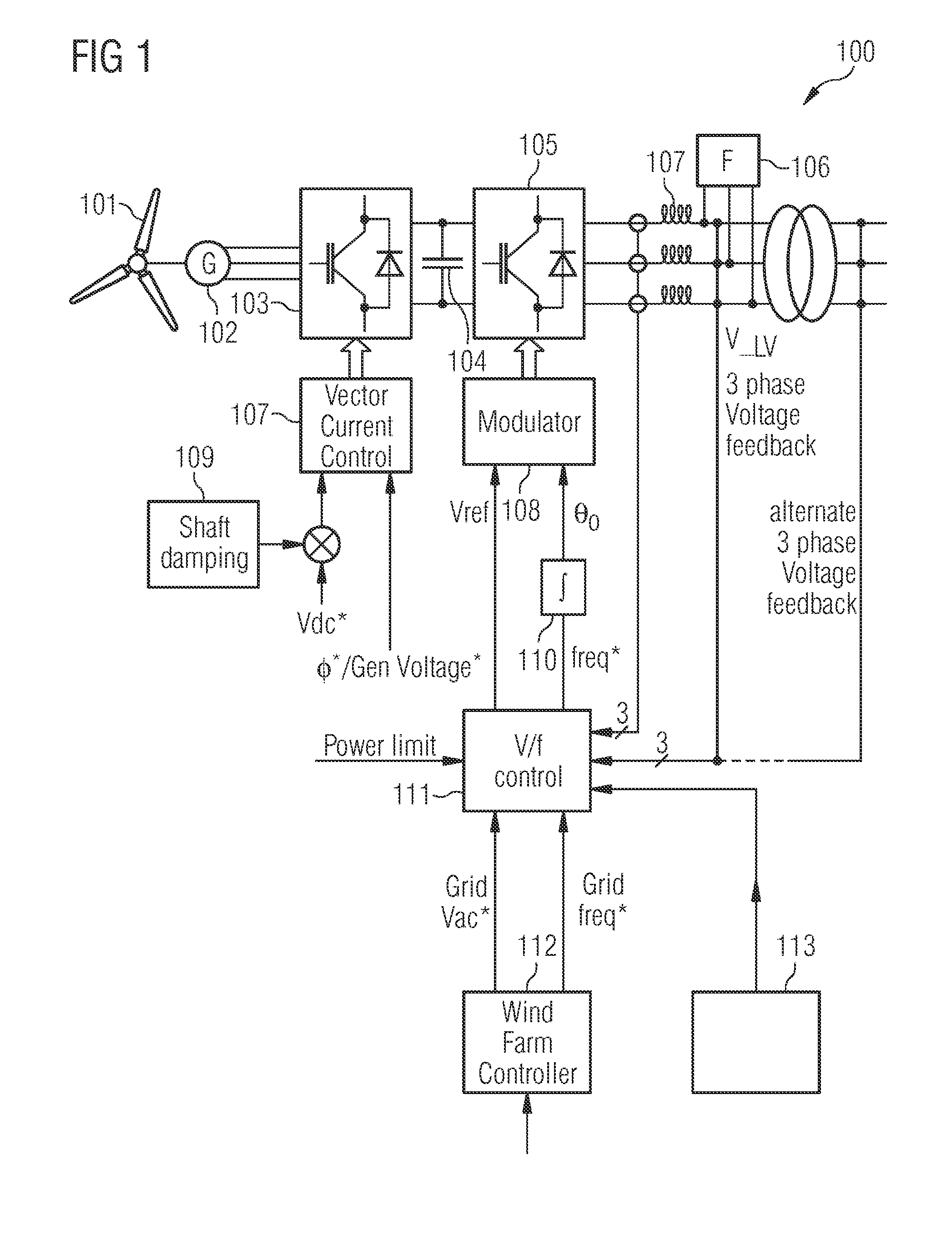
InactiveUS20050122083A1Simplified generator torque command approachPowerfulBatteries circuit arrangementsWind motor controlControl systemWave shape
A wind powered turbine with low voltage ride-through capability. An inverter is connected to the output of a turbine generator. The generator output is conditioned by the inverter resulting in an output voltage and current at a frequency and phase angle appropriate for transmission to a three-phase utility grid. A frequency and phase angle sensor is connected to the utility grid operative during a fault on the grid. A control system is connected to the sensor and to the inverter. The control system output is a current command signal enabling the inverter to put out a current waveform, which is of the same phase and frequency as detected by the sensor. The control system synthesizes current waveform templates for all three-phases based on a sensed voltage on one phase and transmits currents to all three-phases of the electrical system based on the synthesized current waveforms.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
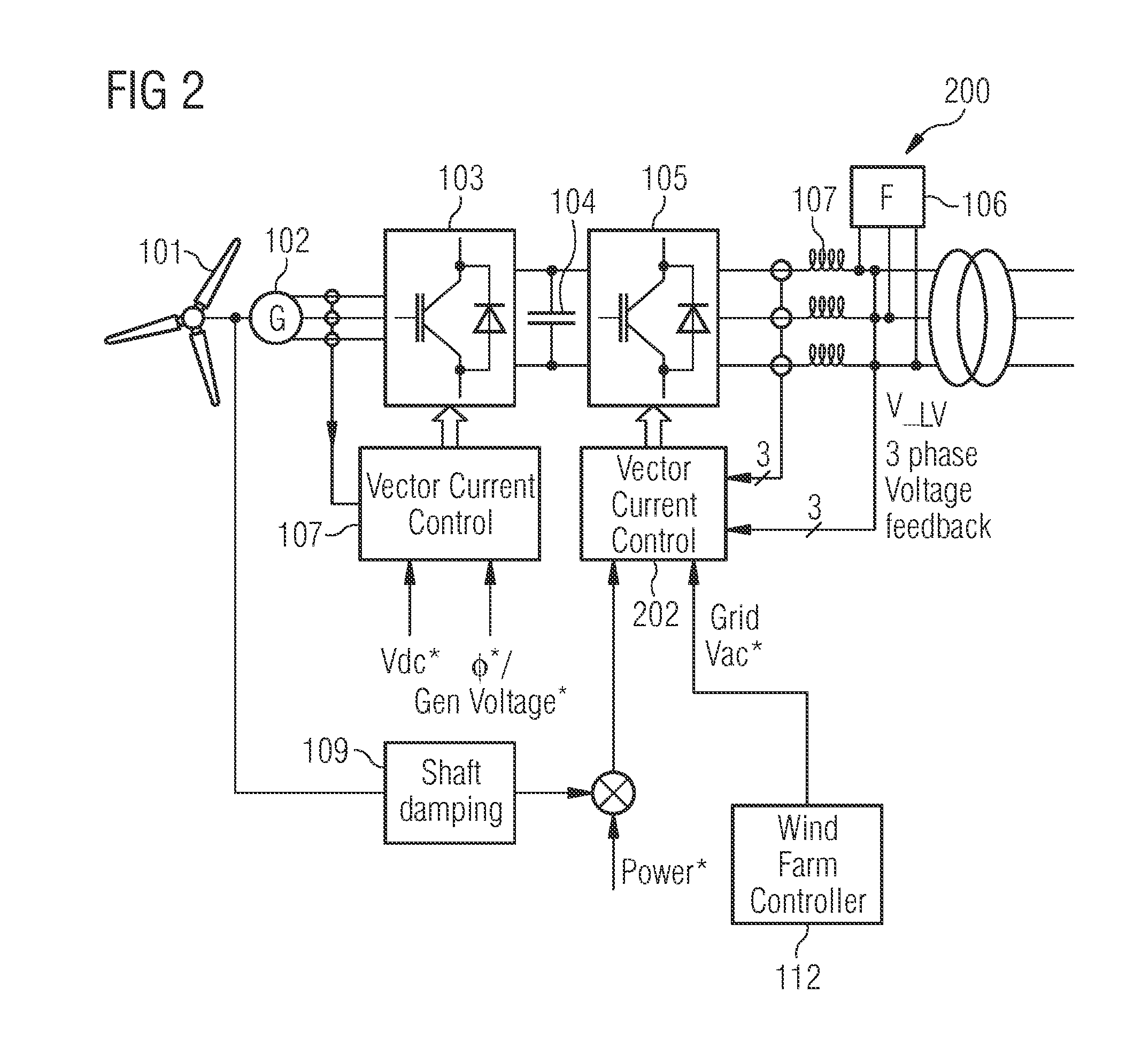
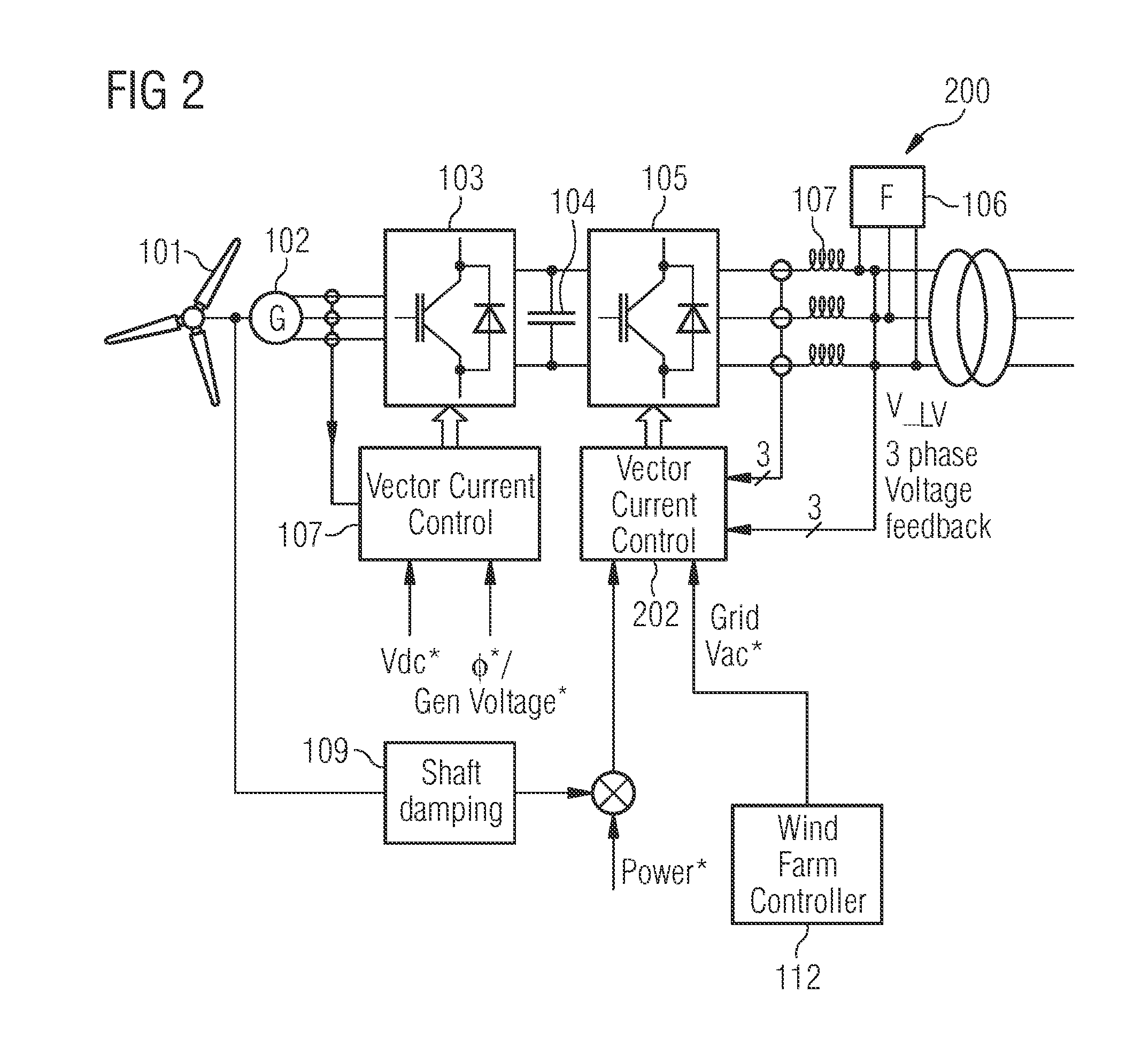
System and method for control of a grid connected power generating system
ActiveUS20100142237A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage amplitudePower grid
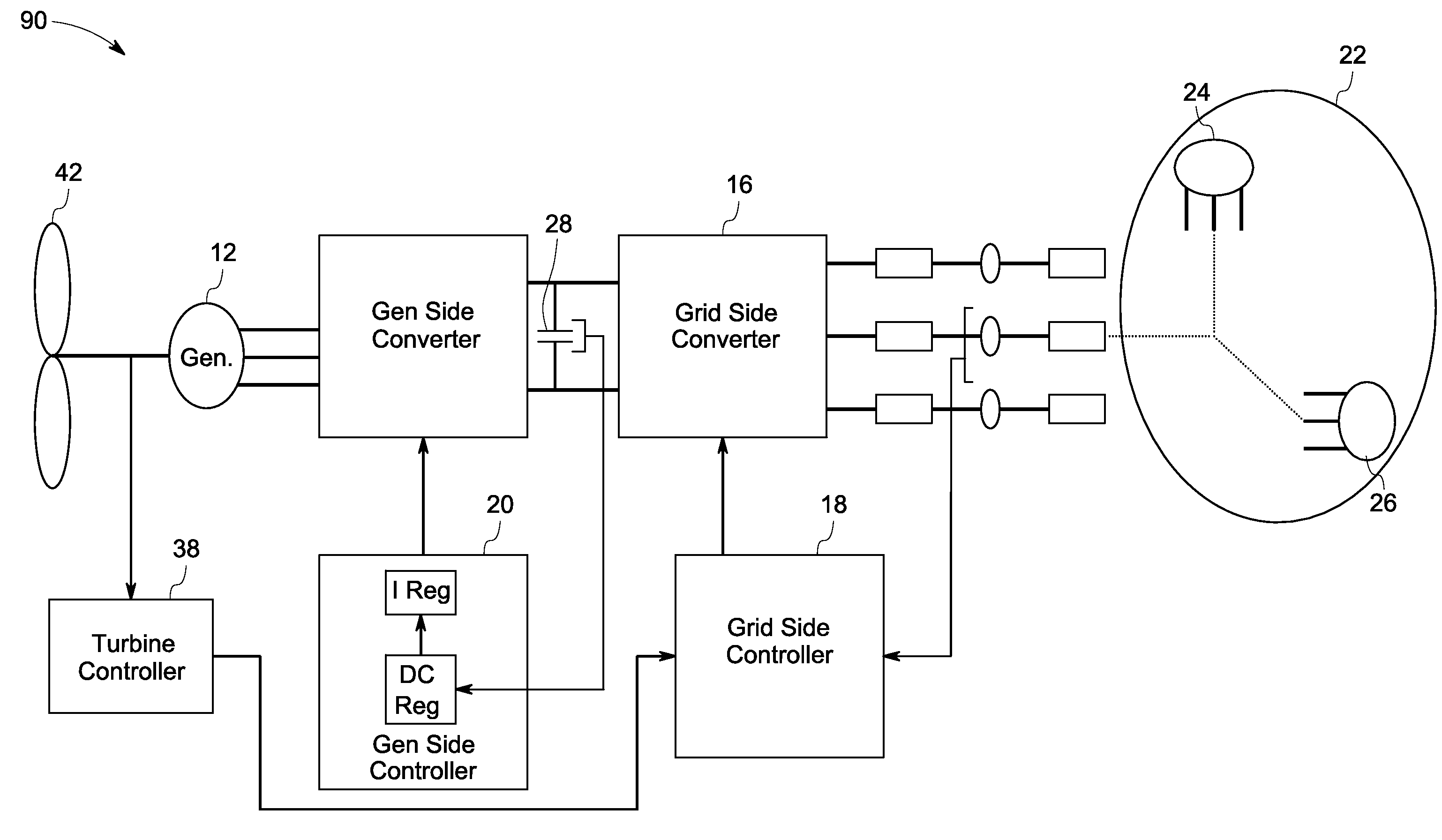
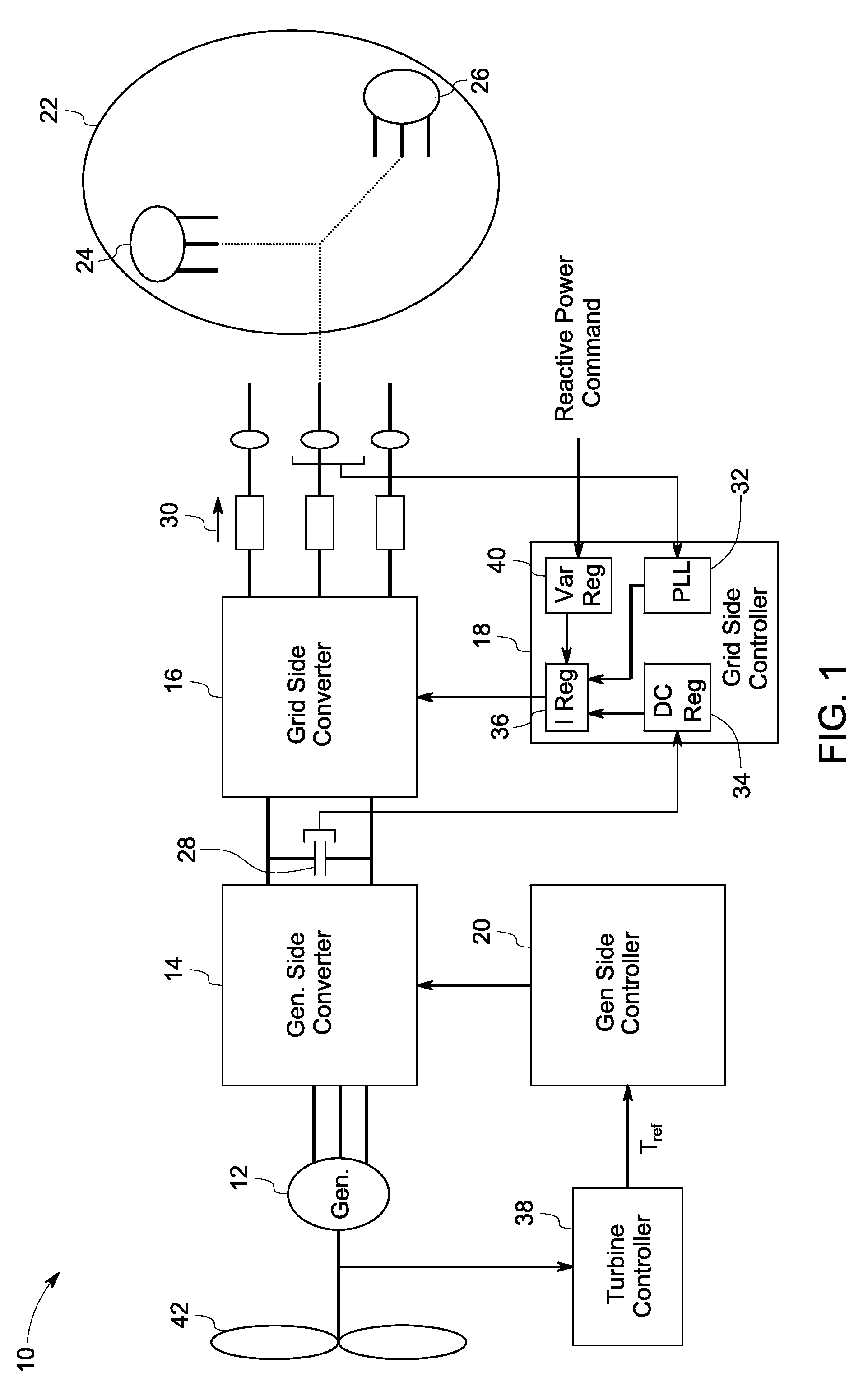
A system for controlling a grid connected power generating system is provided. The system includes a wind turbine, a converter, a first controller and a second controller. The wind turbine supplies electrical power to a power grid and the converter couples the wind turbine to the power grid. The first controller calculates voltage commands to emulate a phasor back electromotive force behind an inductance. The controller further generates converter switching commands from the voltage commands. The voltage commands include a voltage magnitude reference and an internal frequency reference calculated from a power imbalance between an active power reference and the electrical power. The second controller is used to limit a converter current.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for providing low voltage 3-phase power in a vehicle
ActiveUS7521814B2Synchronous generatorsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsLow voltageConductor Coil
A vehicle including a principal power unit that includes a generator coupled to a prime mover. The generator includes at least first and second sets of windings to generate power. The first set of windings is configured to generate power at a first voltage and the second set of windings is configured to generate power at a second voltage that is different from the first voltage.
Owner:OSHKOSH CORPORATION
Vehicle motor-generator apparatus utilizing synchronous machine having field winding
InactiveUS20020074803A1Improve the level ofImprove efficiencyCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingMaximum torquePower inverter
A vehicle motor-generator apparatus based on a field winding type of synchronous machine coupled to a power inverter and a battery, wherein the synchronous machine is controlled to operate as a motor to perform engine starting and thereafter be driven by the engine as an electrical generator, wherein during a short time interval at the commencement of engine starting, the armature winding of the synchronous machine is driven by a current such that magnetic flux is produced by the armature winding acting in the same direction as magnetic flux produced by the field winding, to thereby achieve increased torque during the time when maximum torque is required. In addition, the supplied field current is set at a maximum value during only an initial period when engine starting begins, until the first compression stroke of the engine has been completed, and thereafter set to a reduced value until the completion of engine starting, thereby reducing the amount temperature rise within the field winding during engine starting, while ensuring a sufficiently high value of initial torque.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Vehicle motor-generator apparatus utilizing synchronous machine having field winding
InactiveUS6713888B2Improve the level ofIncrease power generationCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingPower inverterMaximum torque
A vehicle motor-generator apparatus based on a field winding type of synchronous machine coupled to a power inverter and a battery, wherein the synchronous machine is controlled to operate as a motor to perform engine starting and thereafter be driven by the engine as an electrical generator, wherein during a short time interval at the commencement of engine starting, the armature winding of the synchronous machine is driven by a current such that magnetic flux is produced by the armature winding acting in the same direction as magnetic flux produced by the field winding, to thereby achieve increased torque during the time when maximum torque is required. In addition, the supplied field current is set at a maximum value during only an initial period when engine starting begins, until the first compression stroke of the engine has been completed, and thereafter set to a reduced value until the completion of engine starting, thereby reducing the amount temperature rise within the field winding during engine starting, while ensuring a sufficiently high value of initial torque.
Owner:DENSO CORP
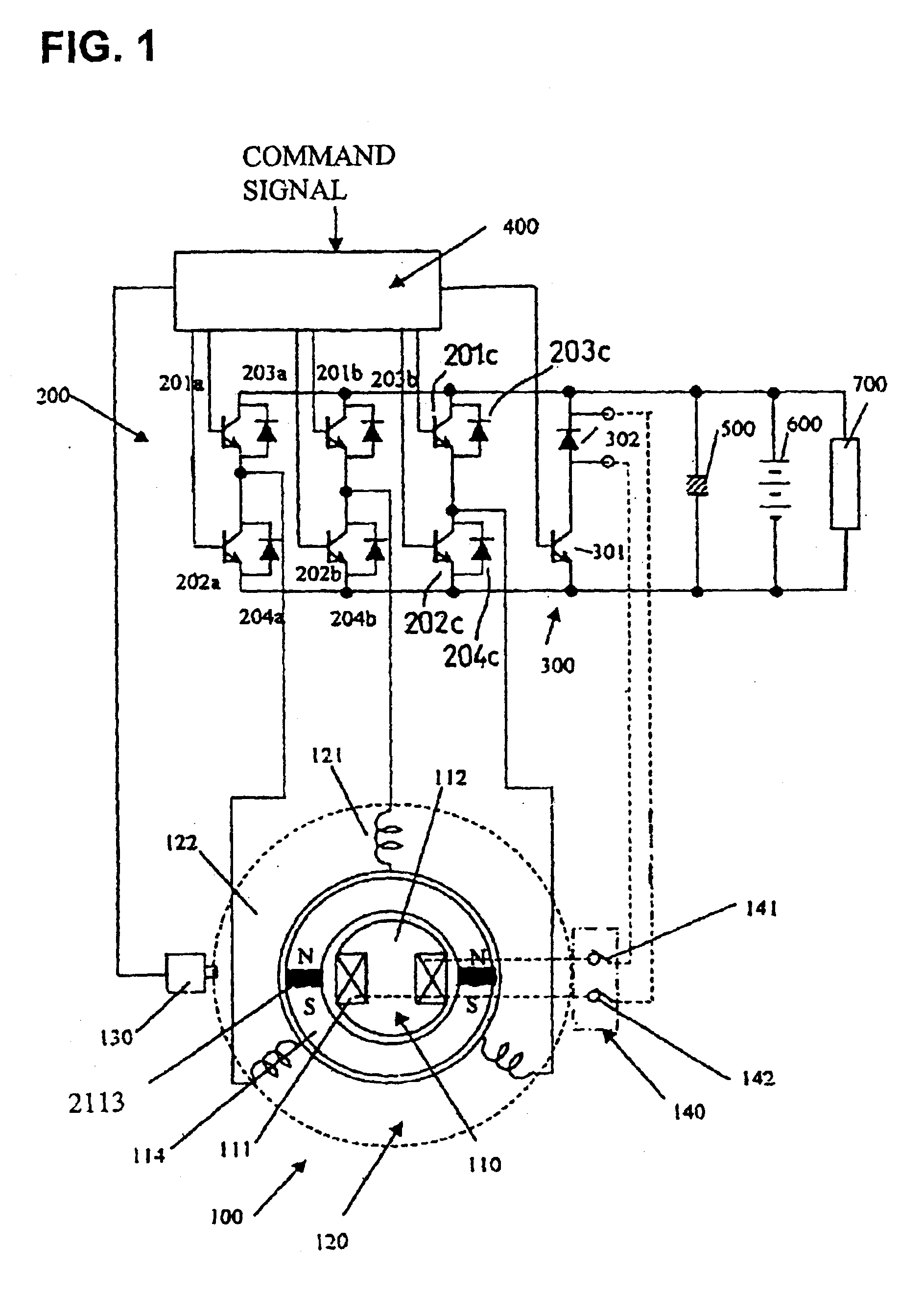
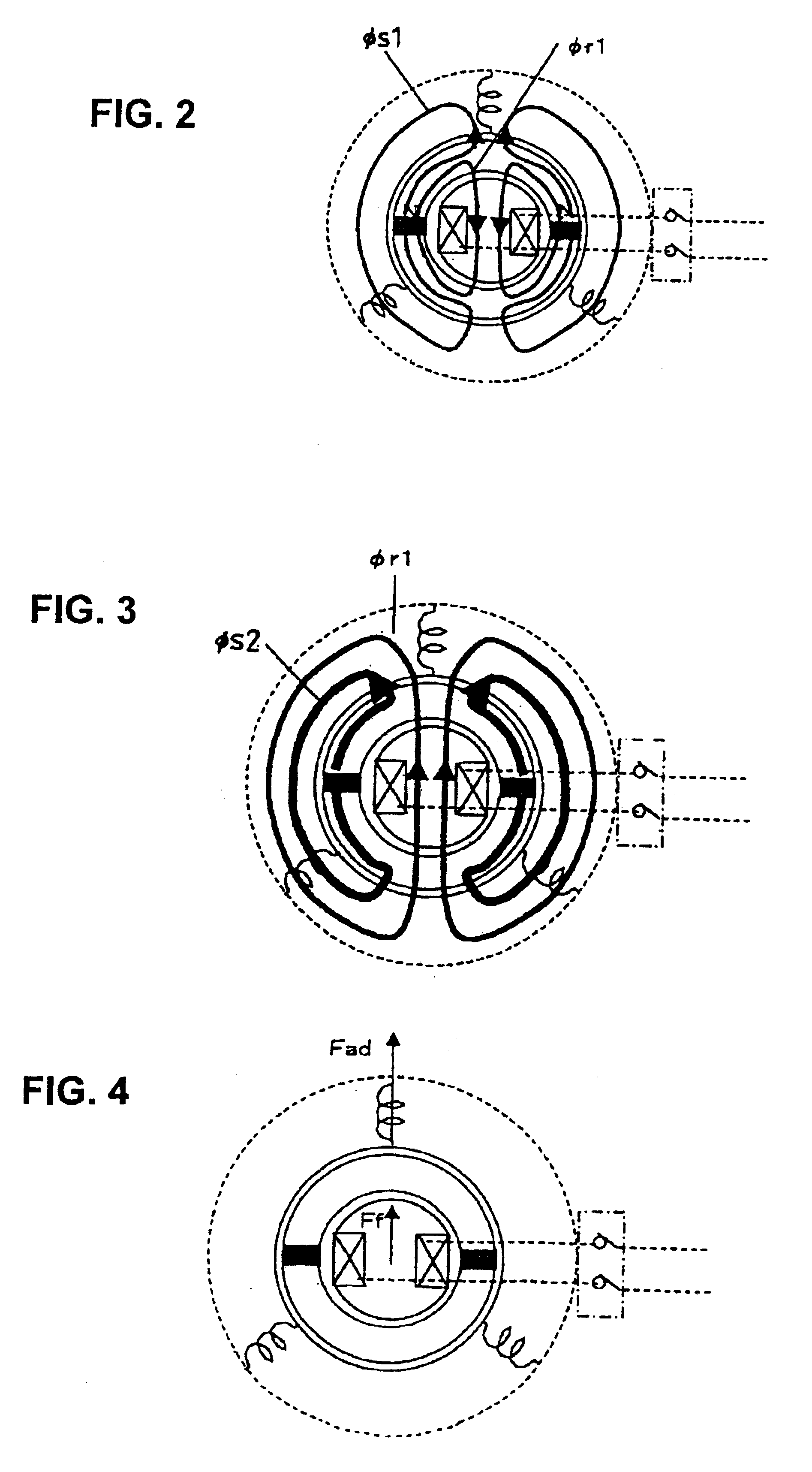
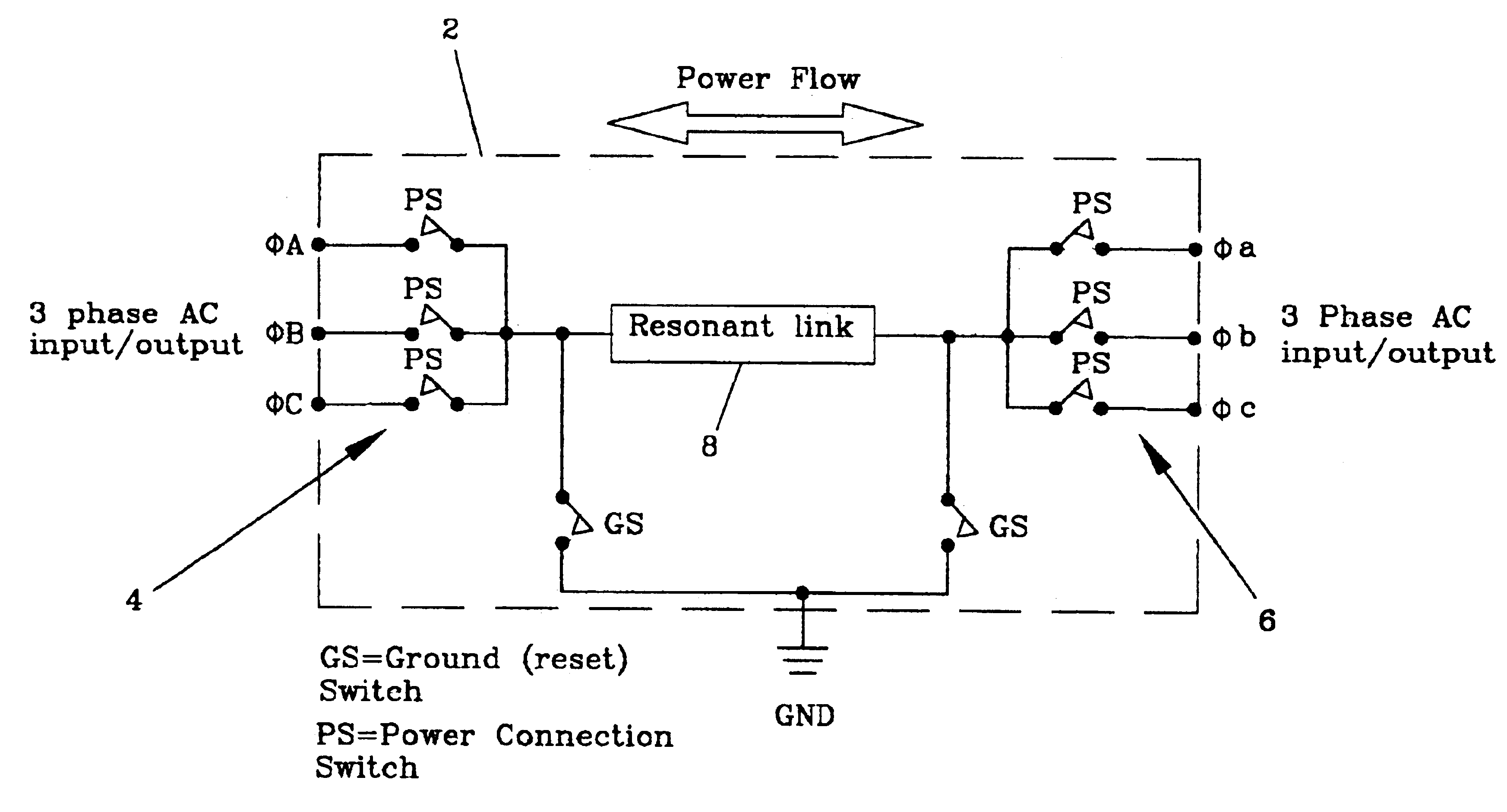
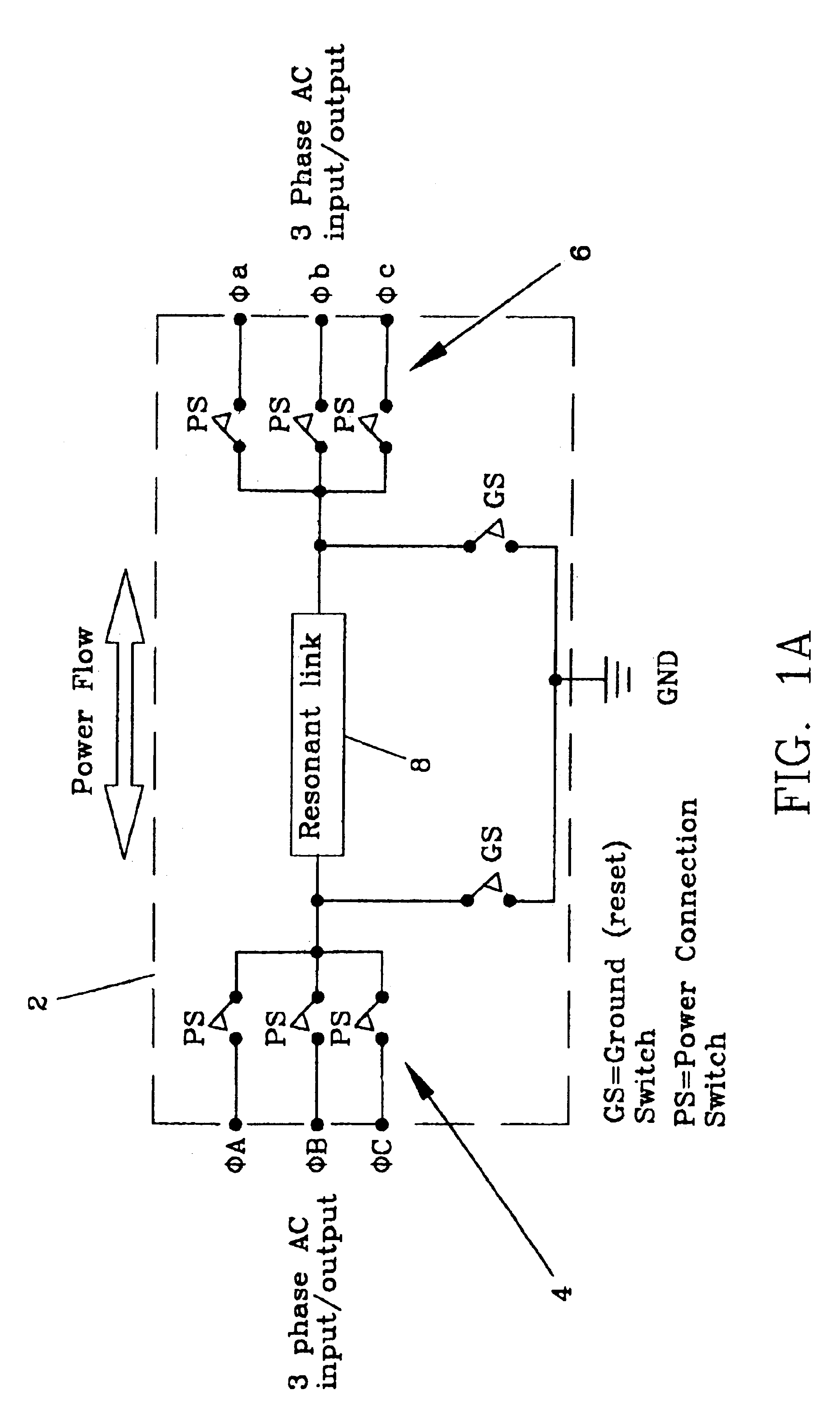
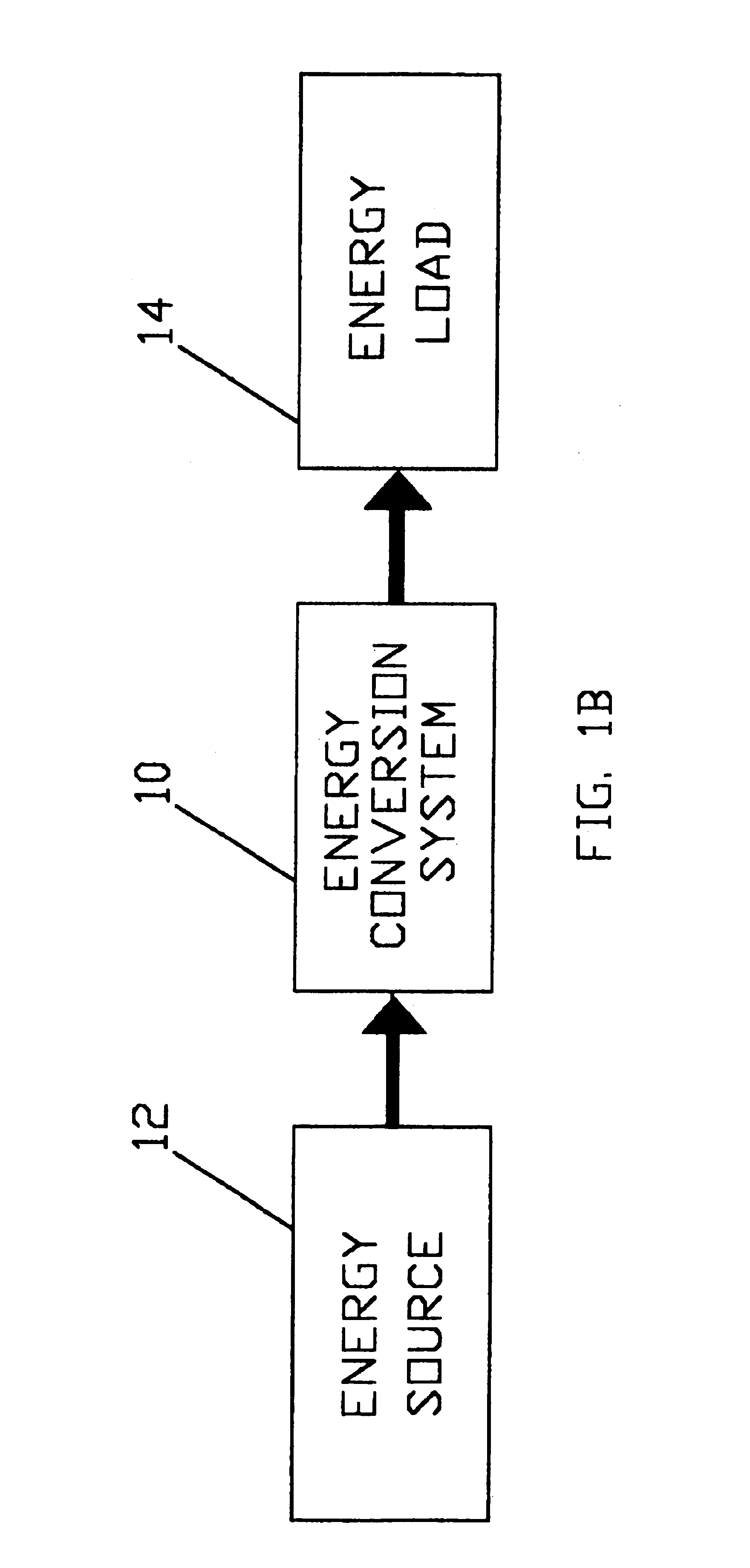
Electro-mechanical energy conversion system having a permanent magnet machine with stator, resonant transfer link and energy converter controls
ActiveUS6984897B2Raise the ratioImprove efficiencyAC motor controlWind motor controlEnergy transferMultiplexer
An electro-mechanical energy conversion system coupled between an energy source and an energy load comprising an energy converter device including a permanent magnet induction machine coupled between the energy source and the energy load to convert the energy from the energy source and to transfer the converted energy to the energy load and an energy transfer multiplexer to control the flow of power or energy through the permanent magnetic induction machine.
Owner:SPELLMAN HIGH VOLTAGE ELECTRONICS
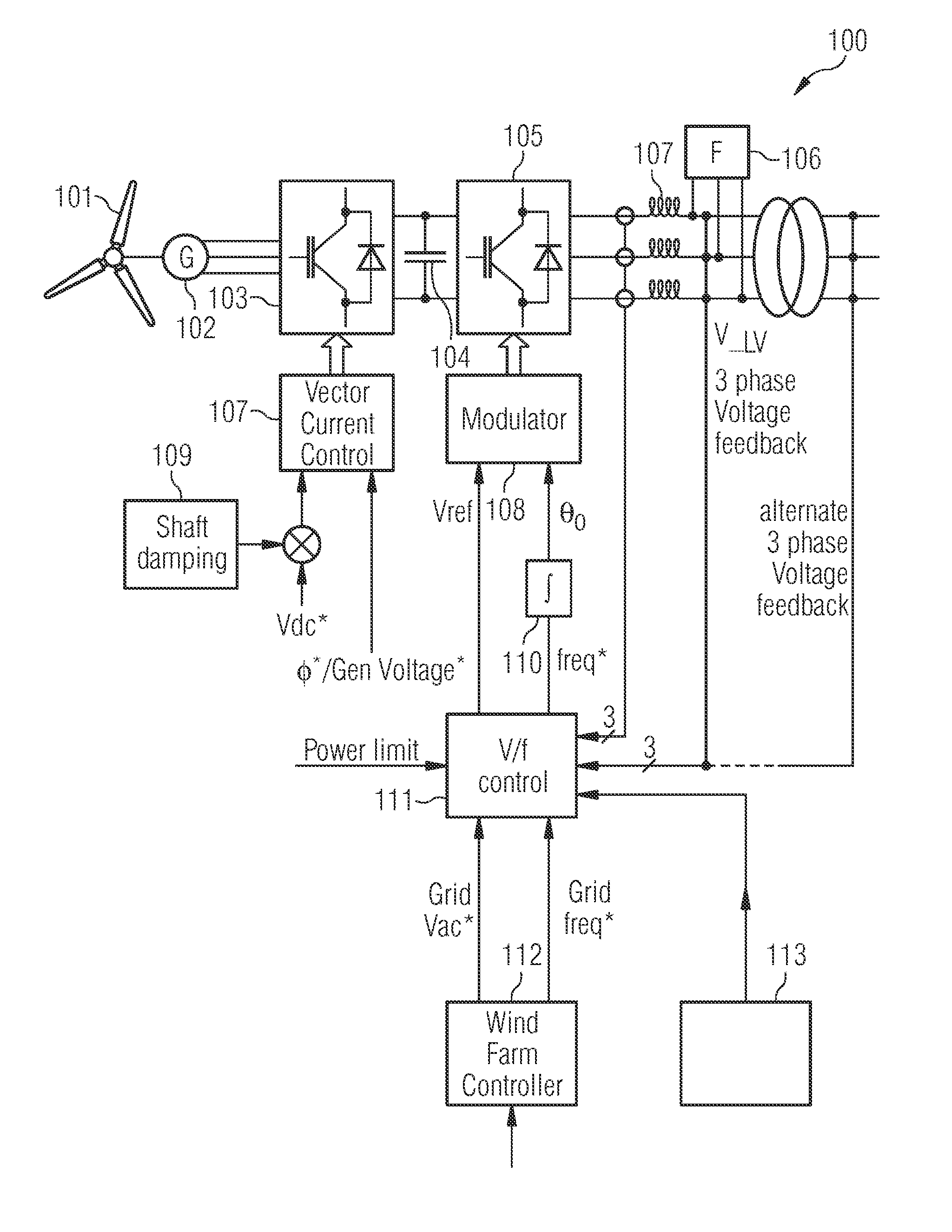
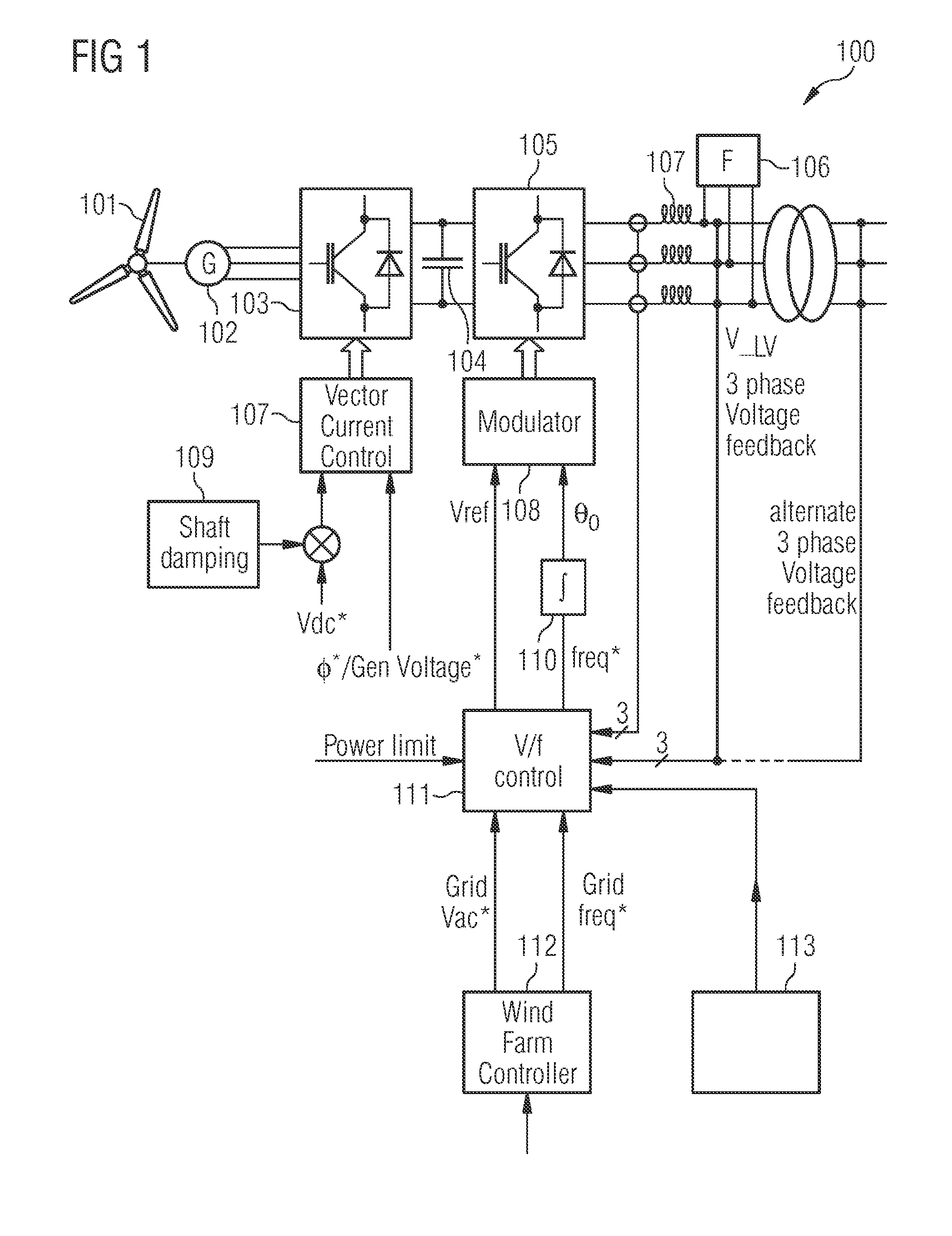
Controller for controlling a power converter
ActiveUS9270194B2Reduce loadActive power filteringEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl powerTransverter
A controller is provided for controlling a power converter that converts electrical input power of a wind turbine into electrical output power provided to a grid. The power converter includes grid-side and turbine-side converter parts. The controller comprises an input terminal for receiving a voltage reference signal associated with a predefined grid voltage and a frequency reference signal associated with a predefined grid frequency, and a network bridge controller adapted to control power conversion of the grid-side converter part. The network bridge controller includes a modulator for modulating gate drive command signals in the grid-side converter part based on a reference voltage and a reference angle derived from the voltage reference signal and the frequency reference signal. The modulator is adapted to modulate the gate drive command signals to maintain the predefined grid voltage and the predefined grid frequency in the power converter in case of failure within the grid.
Owner:INNOMOTICS GMBH
Generator with utility fault ride-through capability
A wind powered turbine with low voltage ride-through capability. An inverter is connected to the output of a turbine generator. The generator output is conditioned by the inverter resulting in an output voltage and current at a frequency and phase angle appropriate for transmission to a three-phase utility grid. A frequency and phase angle sensor is connected to the utility grid operative during a fault on the grid. A control system is connected to the sensor and to the inverter. The control system output is a current command signal enabling the inverter to put out a current waveform, which is of the same phase and frequency as detected by the sensor. The control system synthesizes current waveform templates for all three-phases based on a sensed voltage on one phase and transmits currents to all three-phases of the electrical system based on the synthesized current waveforms.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Generating device having magneto generator
ActiveUS20050093520A1Increase in sizeIncrease productionAssociation with control/drive circuitsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringControl switch
A generating device that includes an AC / DC conversion unit having a rectifier circuit that rectifies an output of a magneto rotor and applies the output to a battery, and an inverter circuit that converts a voltage of the battery into an AC control voltage and applies the AC control voltage to an armature coil of the magneto generator, performs chopper control that controls switch elements of the inverter circuit so as to interrupt an output current of the magneto generator to control the output of the magneto generator when a rotational speed of the magneto generator is lower than a set speed, and performs drive control that applies the AC control voltage from the battery through the inverter circuit to the armature coil when the rotational speed becomes higher than the set speed, and changes a phase angle of the AC control voltage to control the output of the magneto generator.
Owner:MAHLE INT GMBH
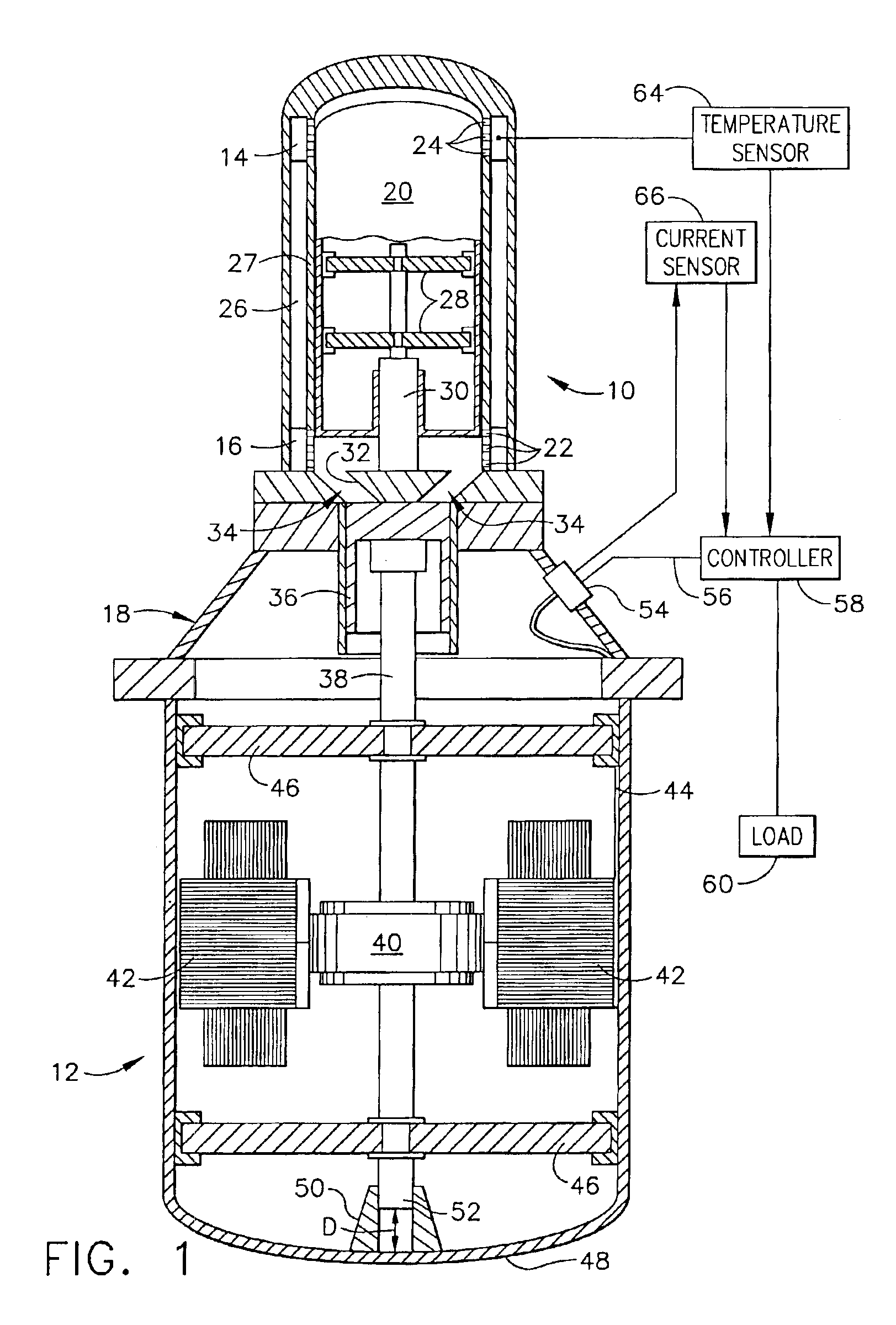
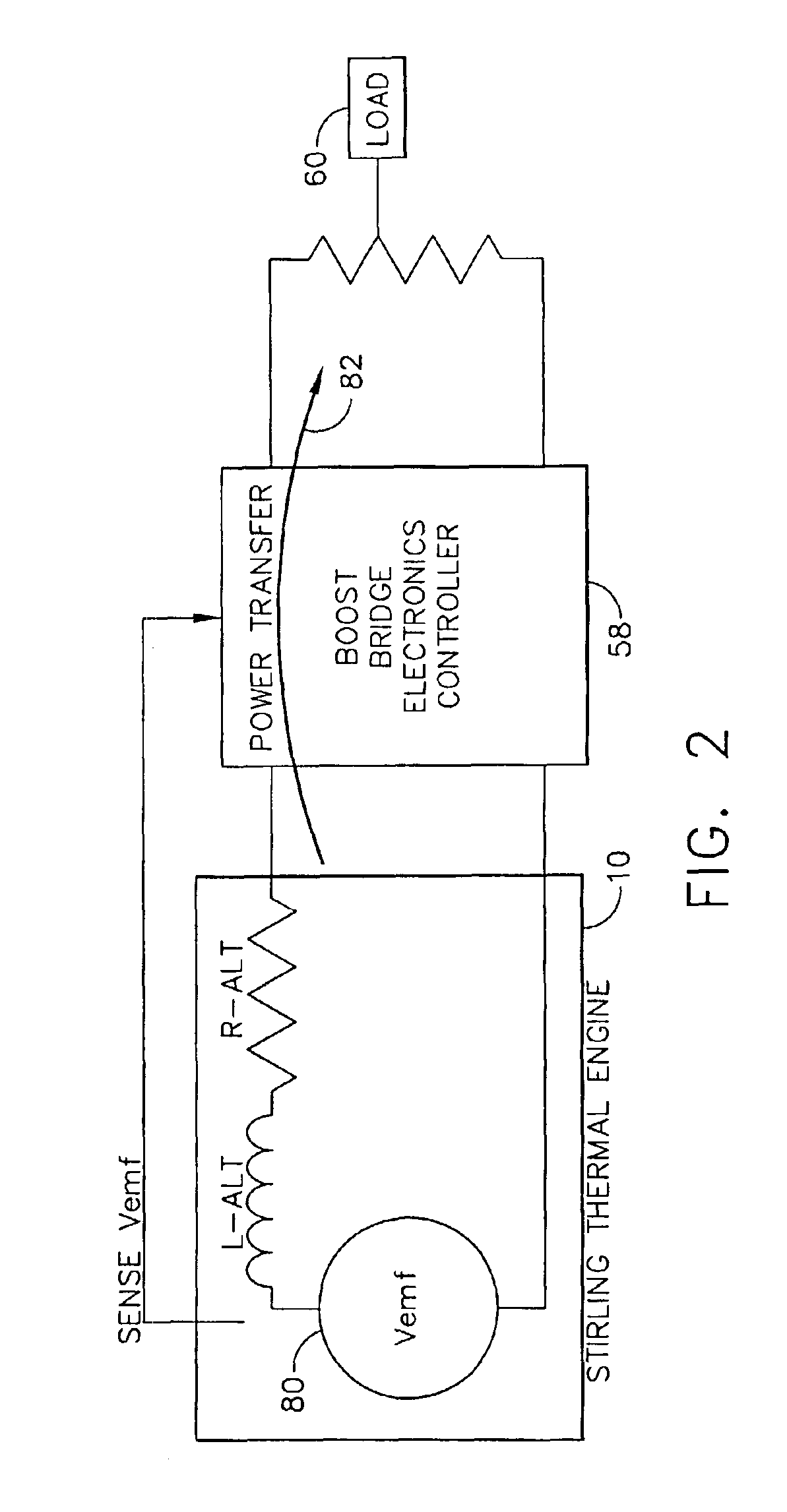
Thermal cycle engine boost bridge power interface
InactiveUS6871495B2Good power deliveryLarge power factorAC motor controlClosed-cycle gas positive displacement engine plantCurrent loadAlternator
A system and method for controlling a thermal dynamic cycle engine, such as a Stirling engine. The system includes a controller able to execute a program to alter certain aspects of the system to provide for a maximum power transfer and substantially stall free start up of the thermal dynamic cycle engine. Generally the controller is able to alter the current load to achieve a selected stroke length, pattern or temperature of a heater head of the engine. The system allows for generally stall free start-up and continuous control for maximum power (with maximum power factor) transfer from the thermal cycle engine or the associated alternator.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Wind power installation
InactiveUS20060103137A1Prevent overloadDistributed loadWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesElectricityWind power generation
A wind power installation having external and / or internal redundancy derived by multiple, independent power generating systems arranged in parallel, but switchably interconnected to allow substantial continued operation in the event of a critical component failure.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
Series hybrid electric vehicle
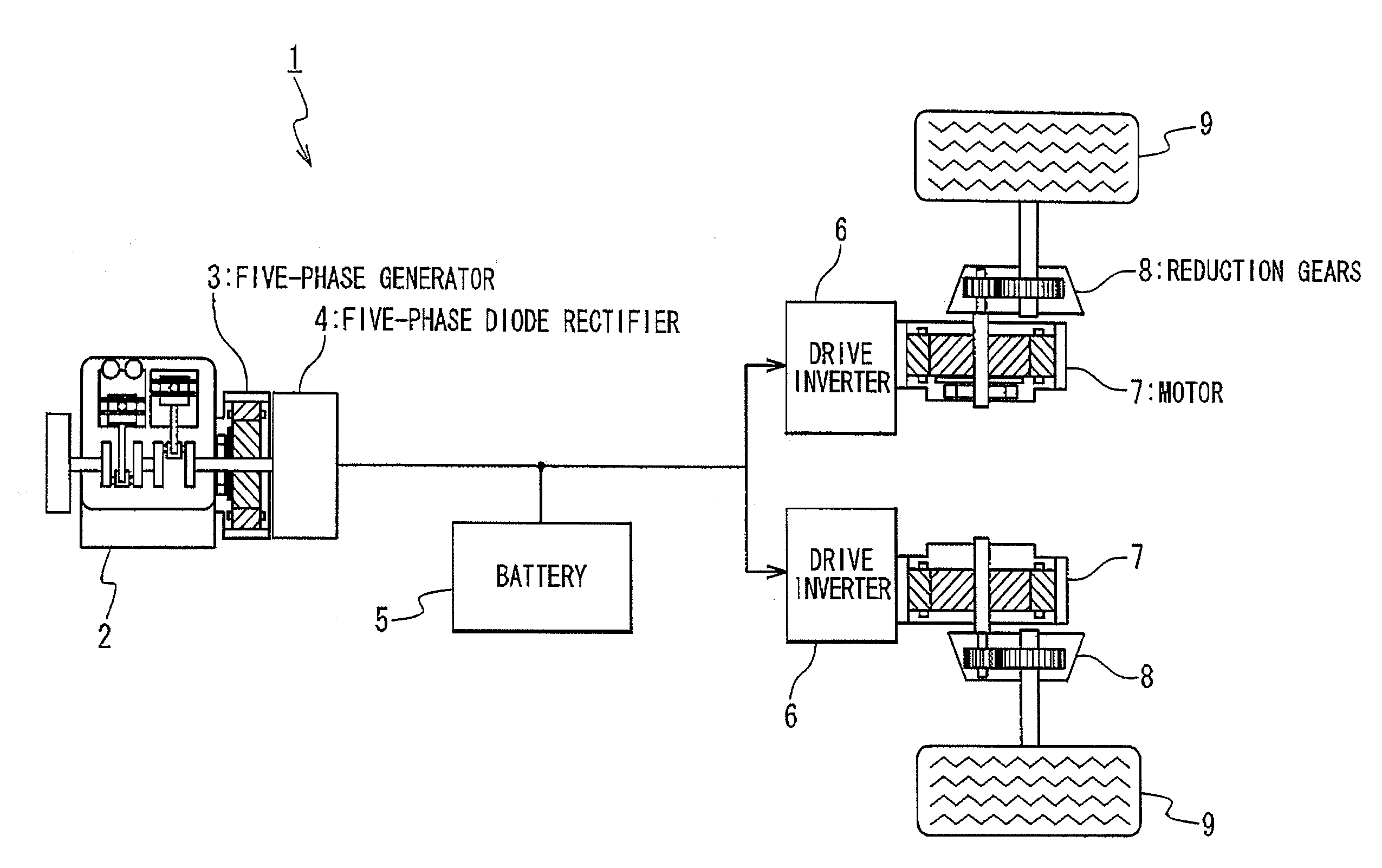
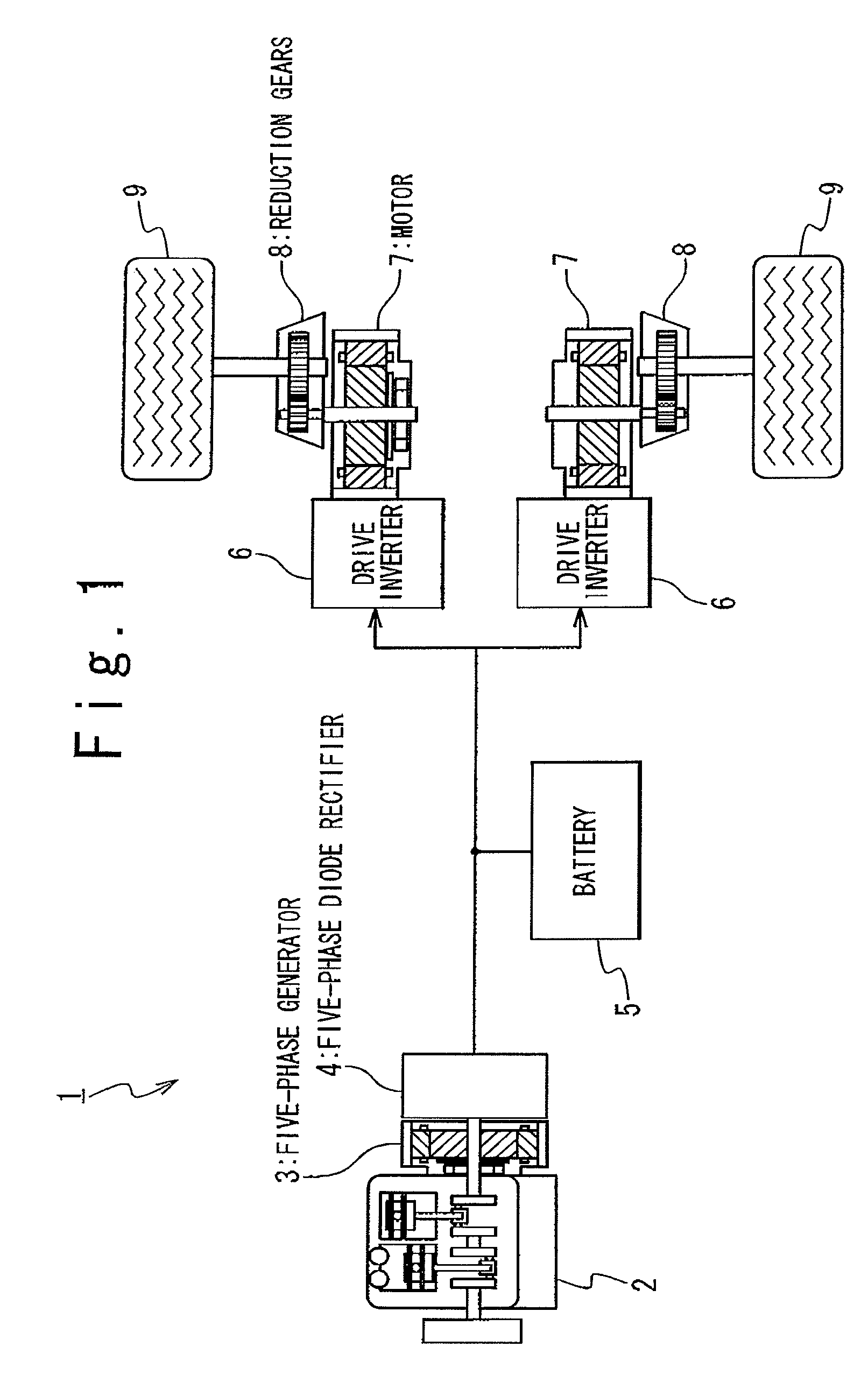
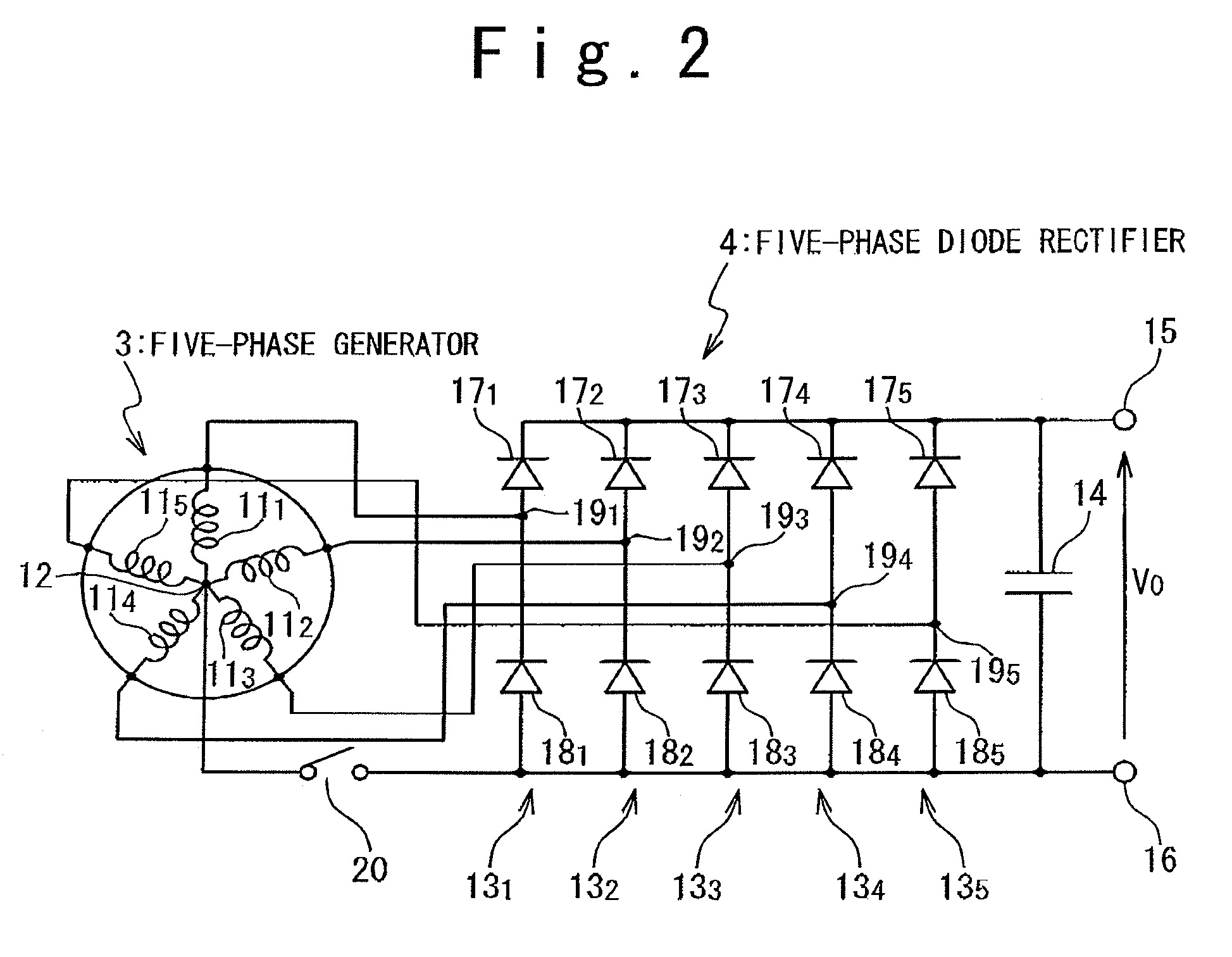
There is provided a technique for improving the efficiency of a generation system of a series hybrid electric vehicle The series hybrid electric vehicle is composed of: an engine; an n-phase generator driven by the engine; a rectifier generating a DC voltage from an n-phase AC voltage received from the n-phase generator; a battery charged with the DC voltage generated; a motor driving drive wheels; an inverter driving the motor on the DC voltage received from the rectifier and / or a DC voltage supplied from the battery; and a switch. The n-phase generator has n armature windings each having one end connected to a common neutral point. The rectifier has a negative terminal, a positive terminal on which a higher potential is generated than on the negative terminal, and n rectifying arms. Each of the n rectifying arms includes; a first diode connected between an intermediated node connected to the other end of the corresponding armature windings and the negative terminal; and a second diode connected between the intermediate node and the positive terminal. The switch is connected between the neutral point and the negative terminal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
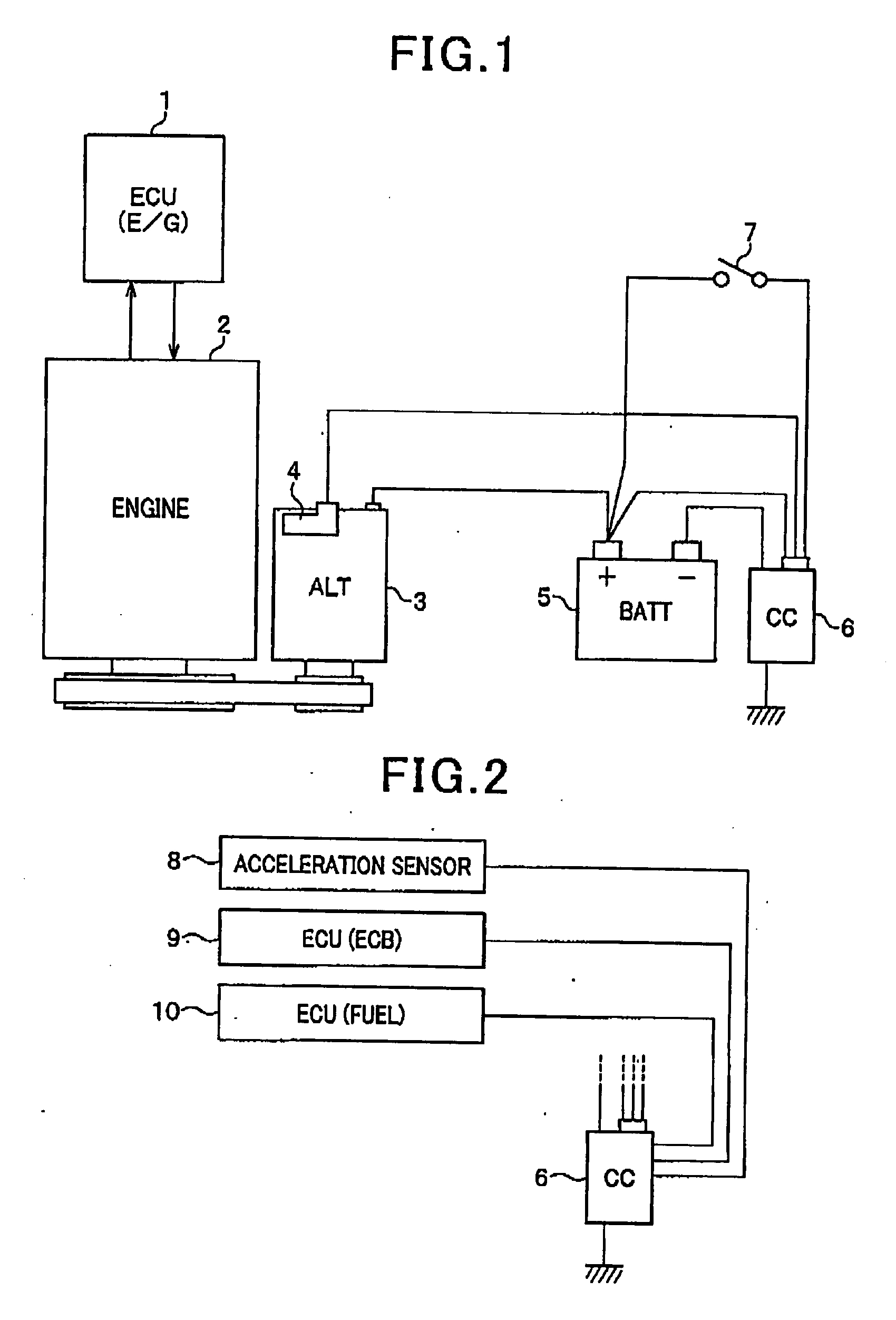
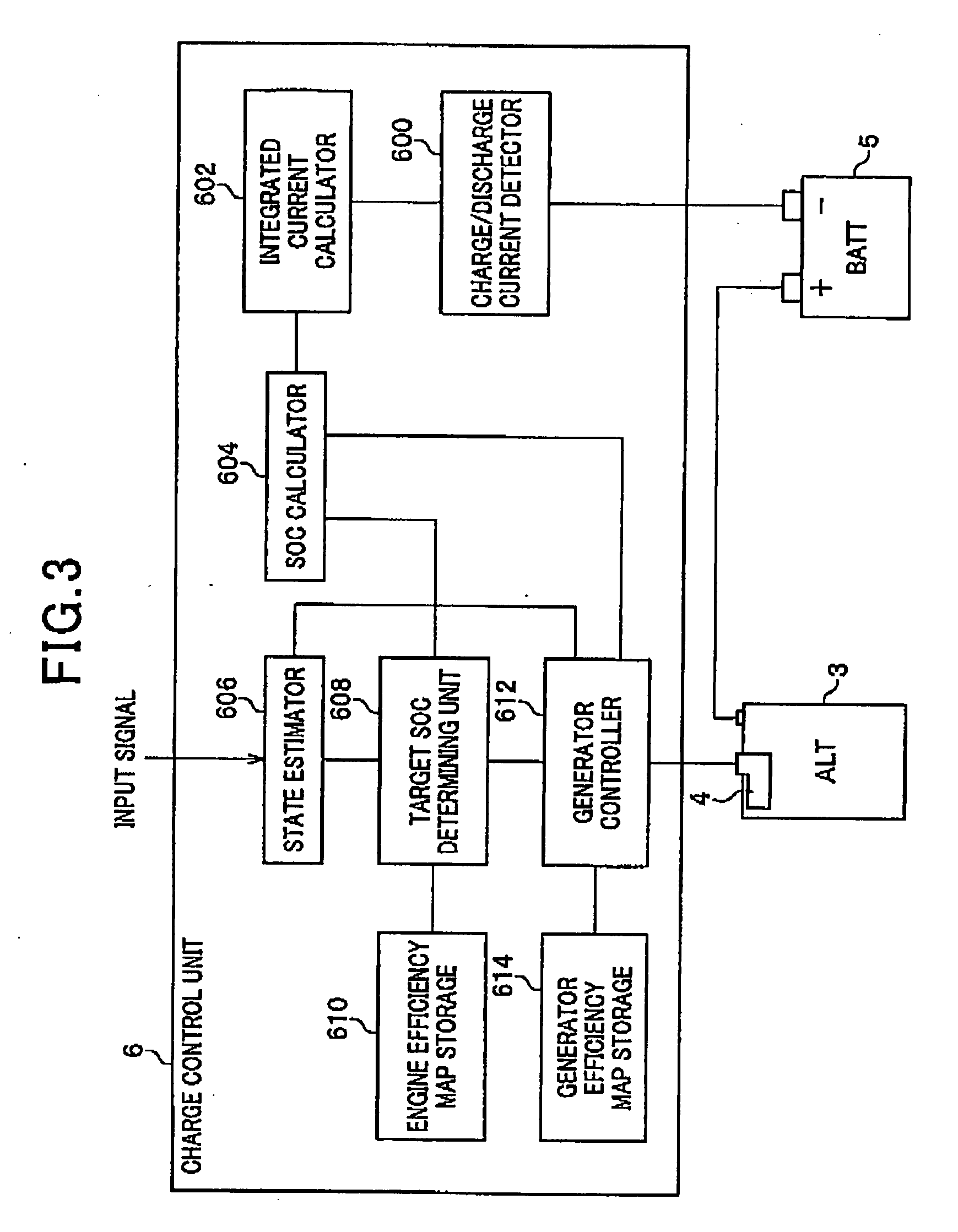
Method and apparatus for controlling charging operations for battery
ActiveUS20080093851A1Reduce processing loadSuppress useless fuel consumptionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingElectrical batteryState of charge
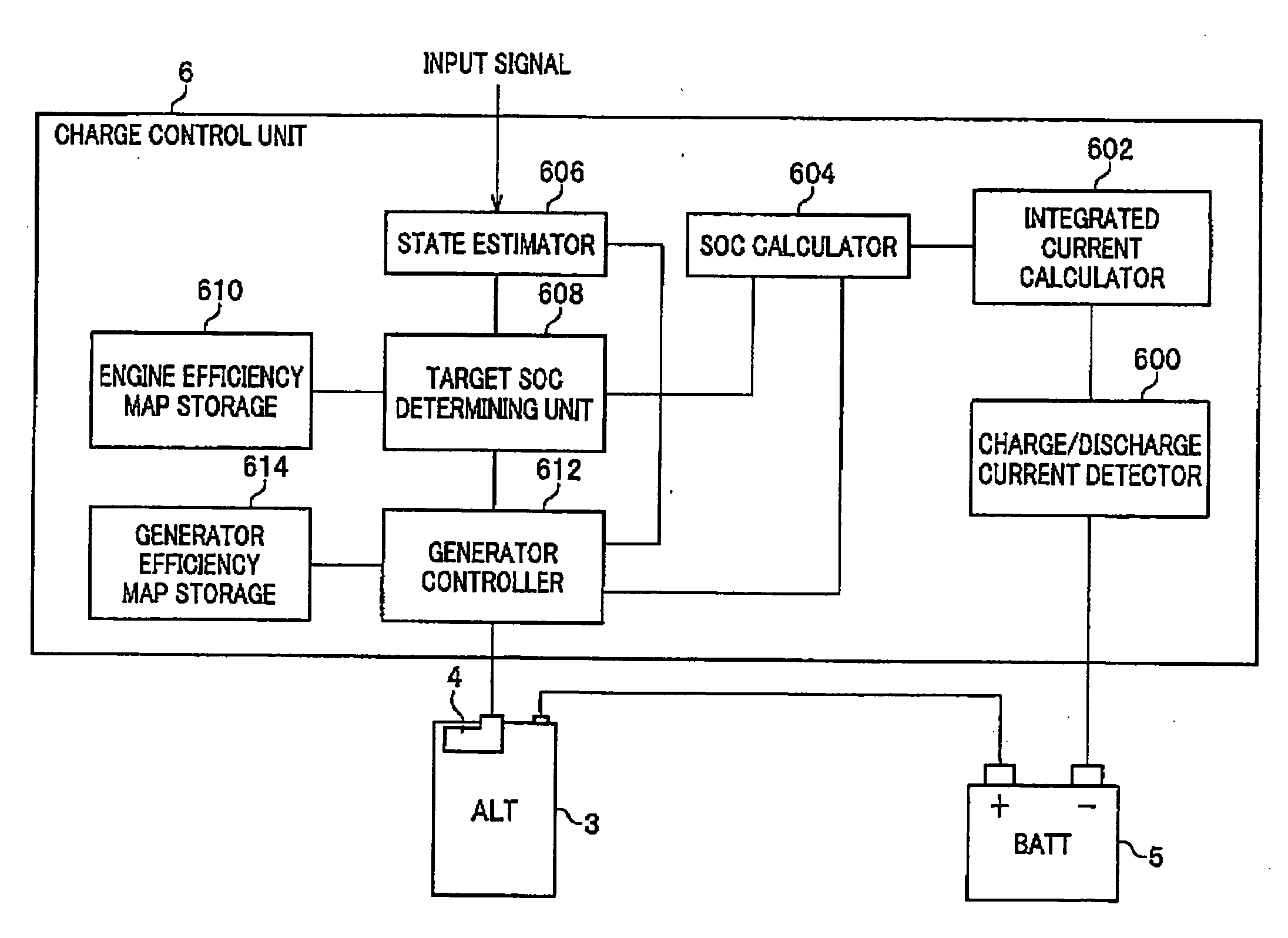
An apparatus controls a state of charge (SOC) of a battery mounted on a vehicle provided with an internal combustion engine driving a generator mounted on the vehicle. The generator charges the battery. In the apparatus, a setting unit sets a target value directed to controlling the SOC of the battery such that the target value is higher as an efficiency of the internal combustion engine depending on the number of rotations of the engine is higher. A determining unit determines whether the vehicle is in a decelerated state. A controlling unit controls a state of rotation of the generator to enable the generator i) to perform regeneration when it is determined that the vehicle is in the decelerated state and ii) to perform generation to enable the SOC of the battery to be the target value when it is determined that the vehicle is not in the decelerated state.
Owner:DENSO CORP
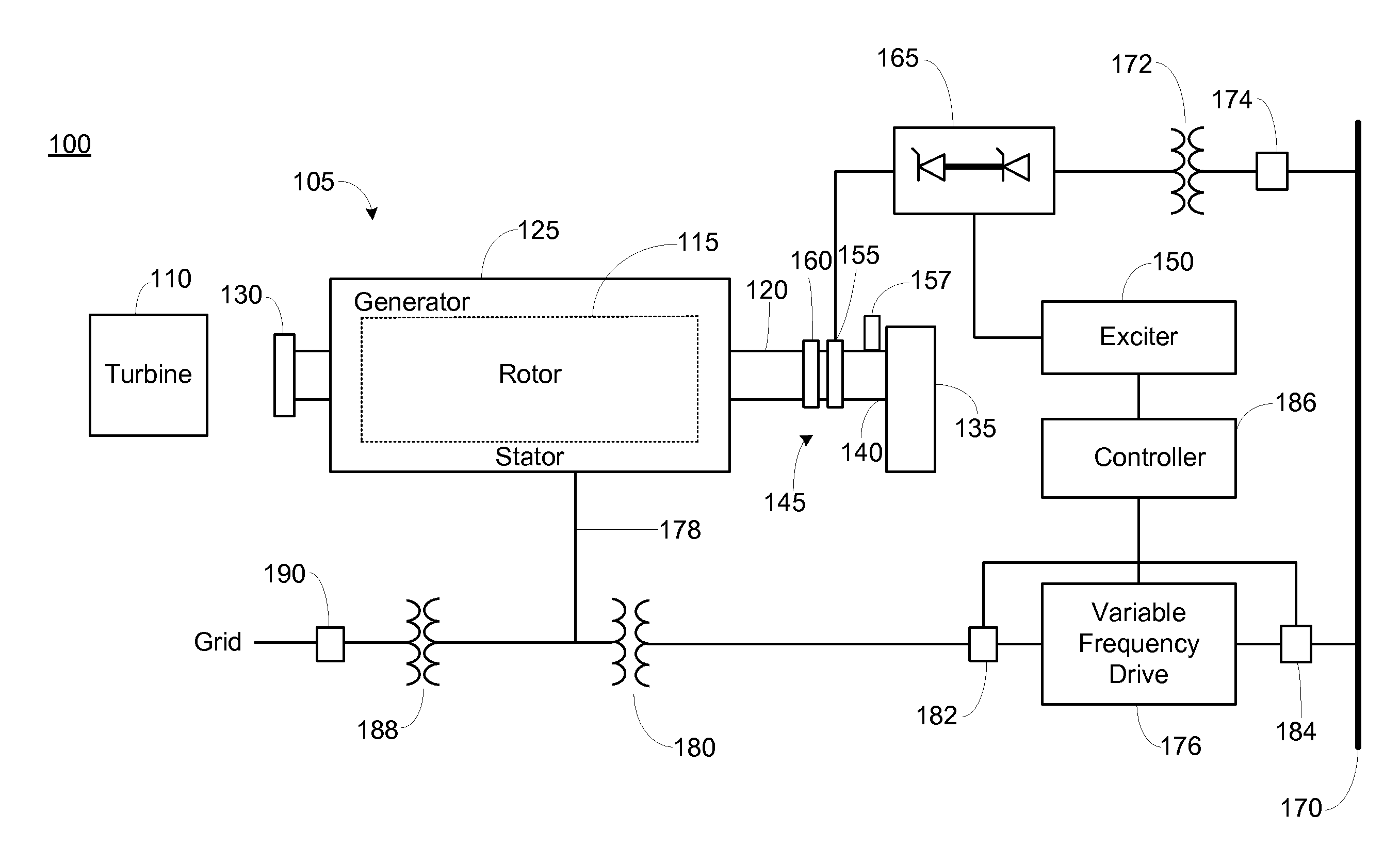
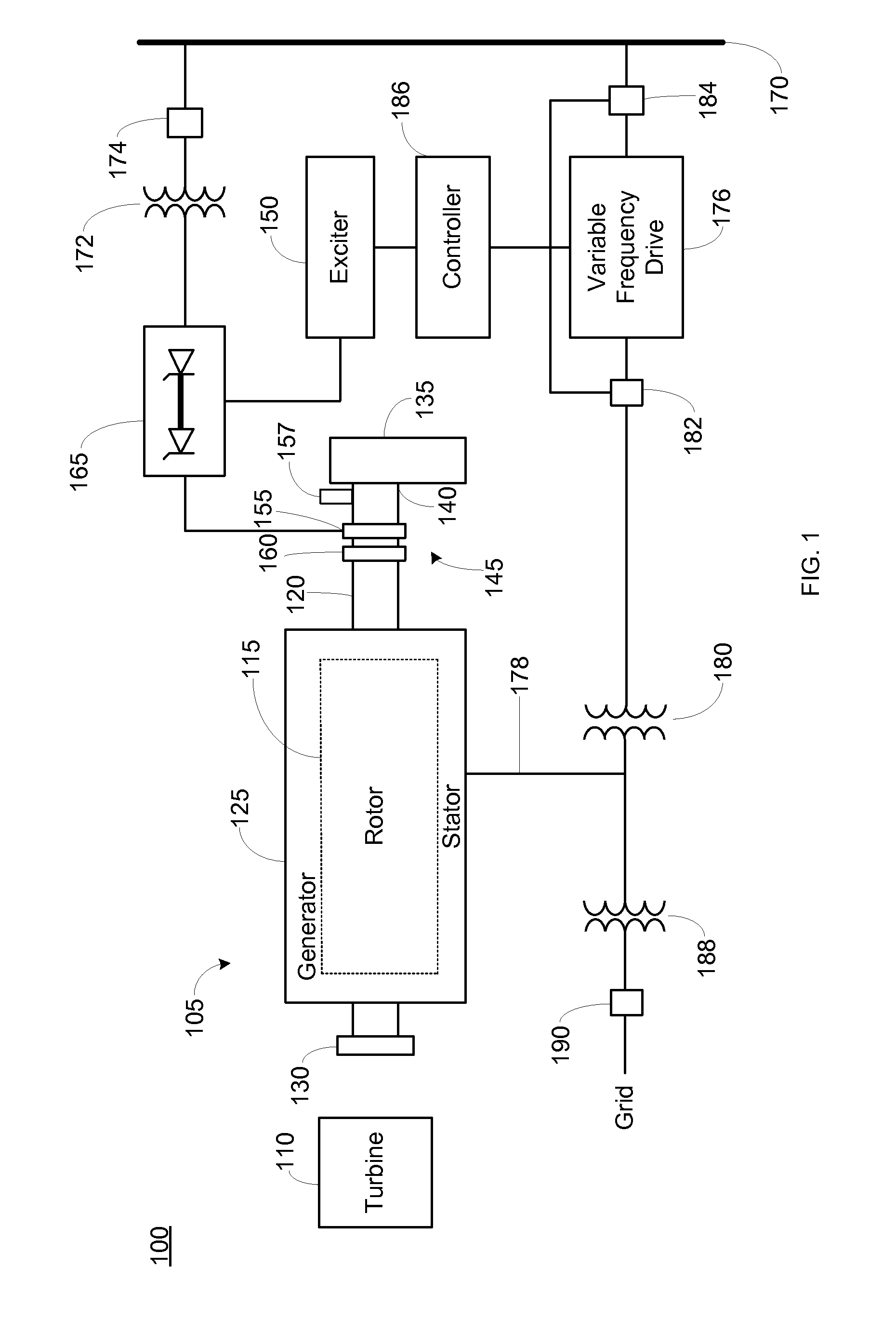
Conversion of synchronous generator to synchronous condenser
ActiveUS20120306458A1Easy injectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlSynchronous condenserEngineering
An approach for converting a synchronous generator to a synchronous condenser is disclosed. In one aspect, a variable frequency driver is used to provide a starting power source to accelerate a synchronous generator decoupled from a turbine to an operational speed to act as a synchronous condenser. In another aspect, the synchronous condenser can be recoupled back to the turbine to form the synchronous generator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
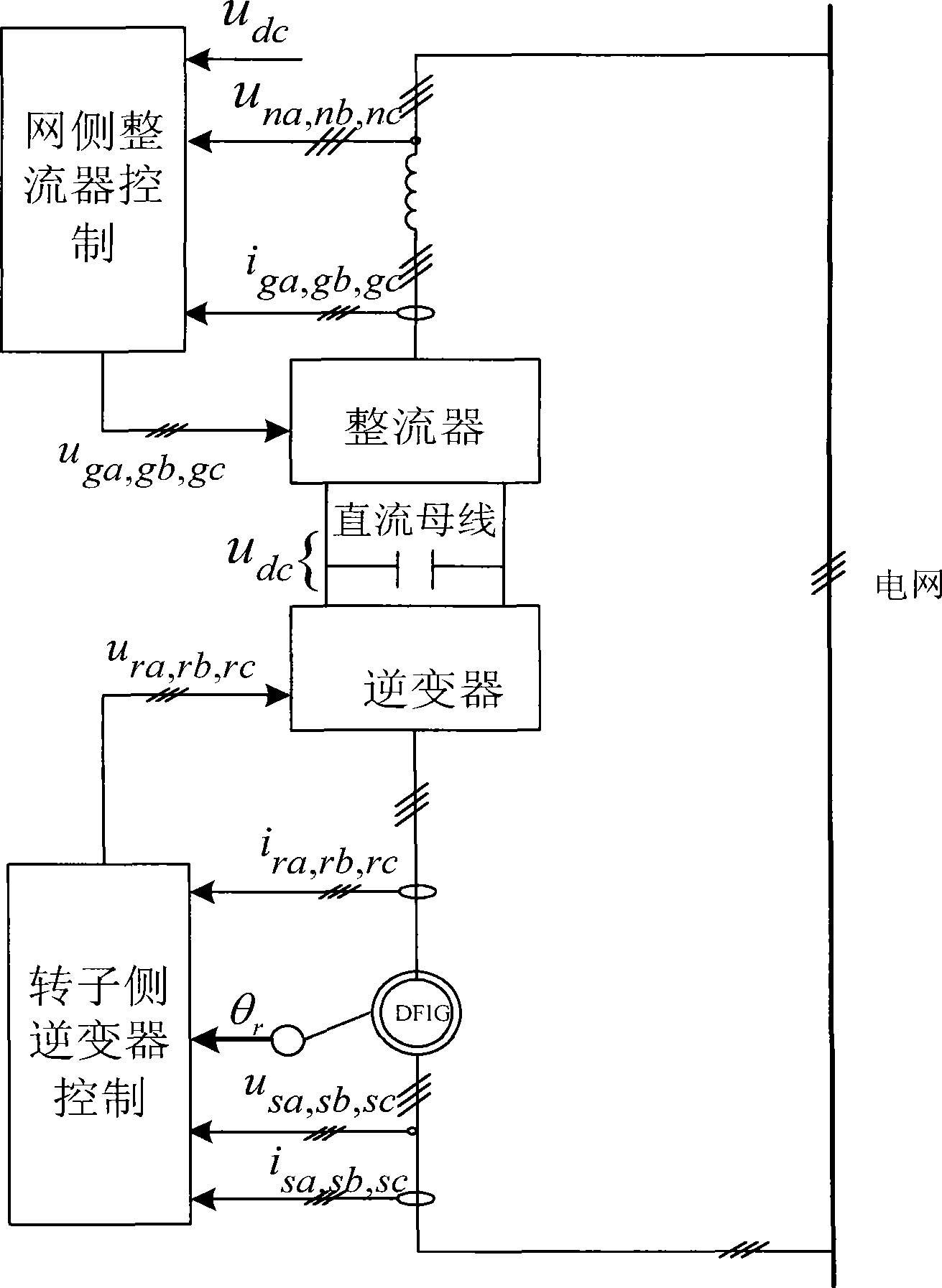
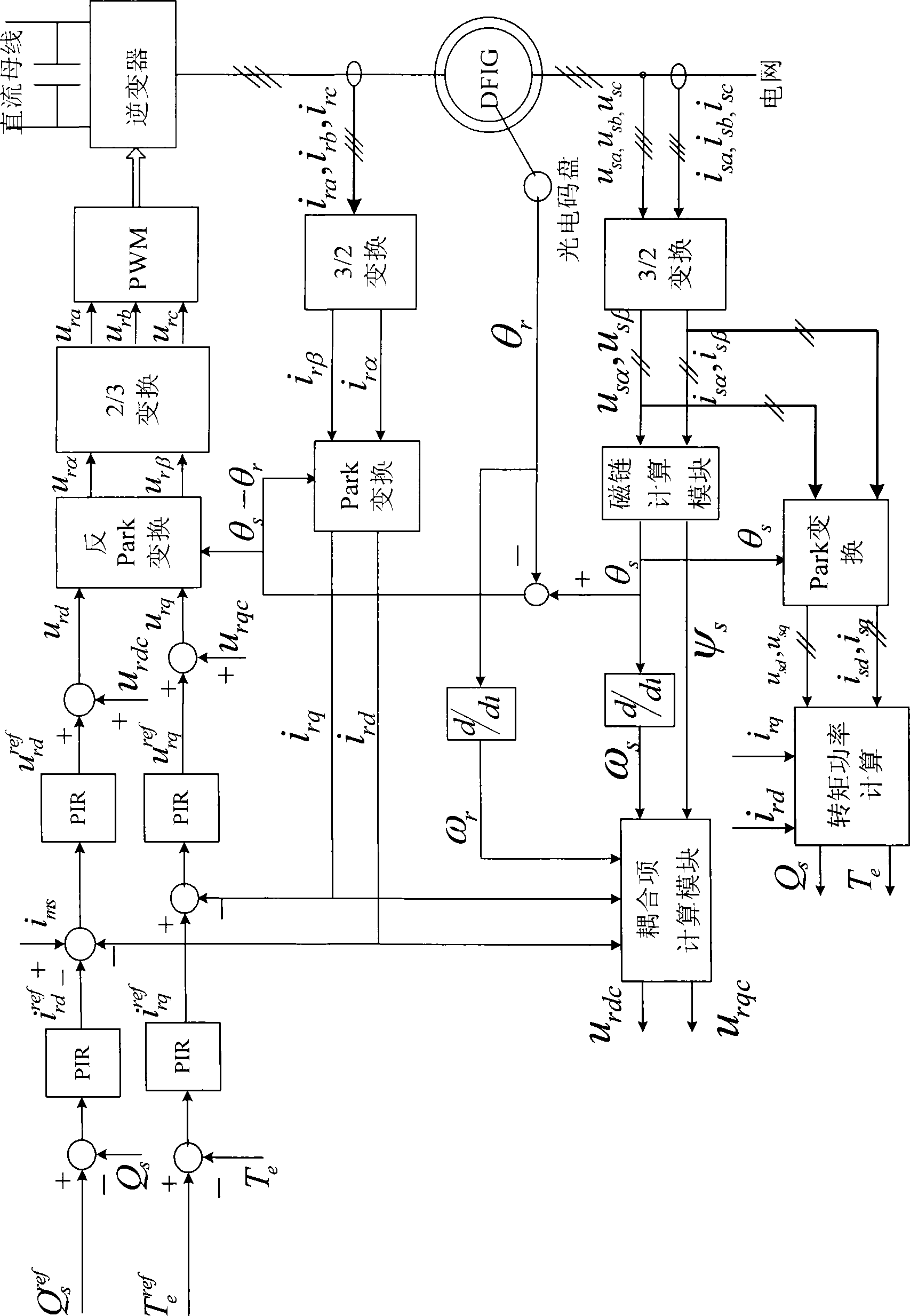
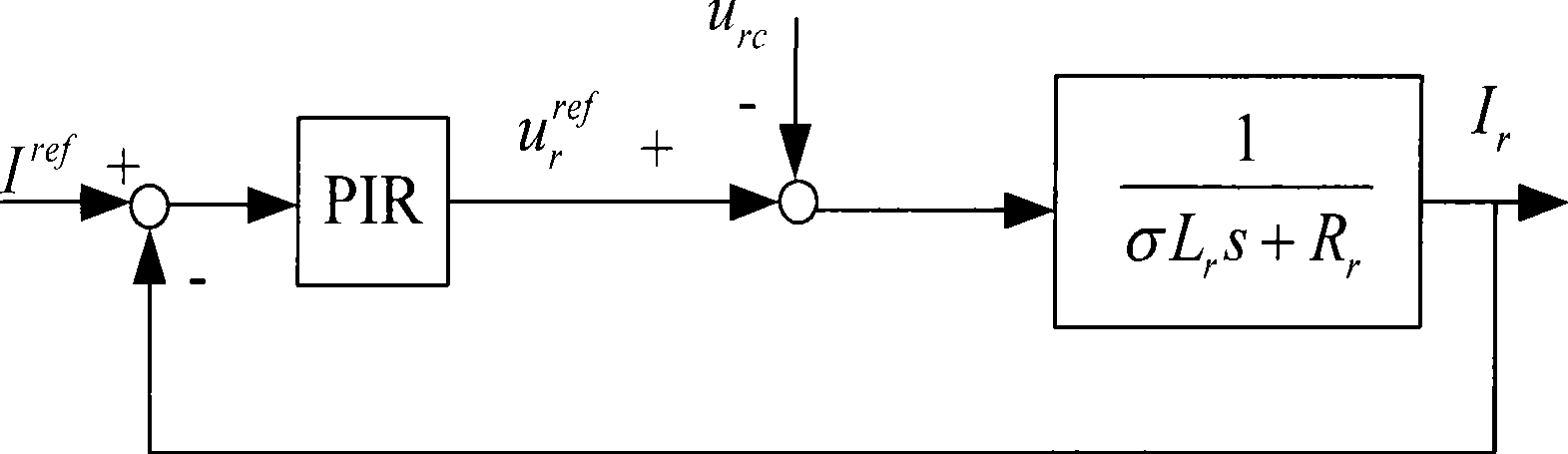
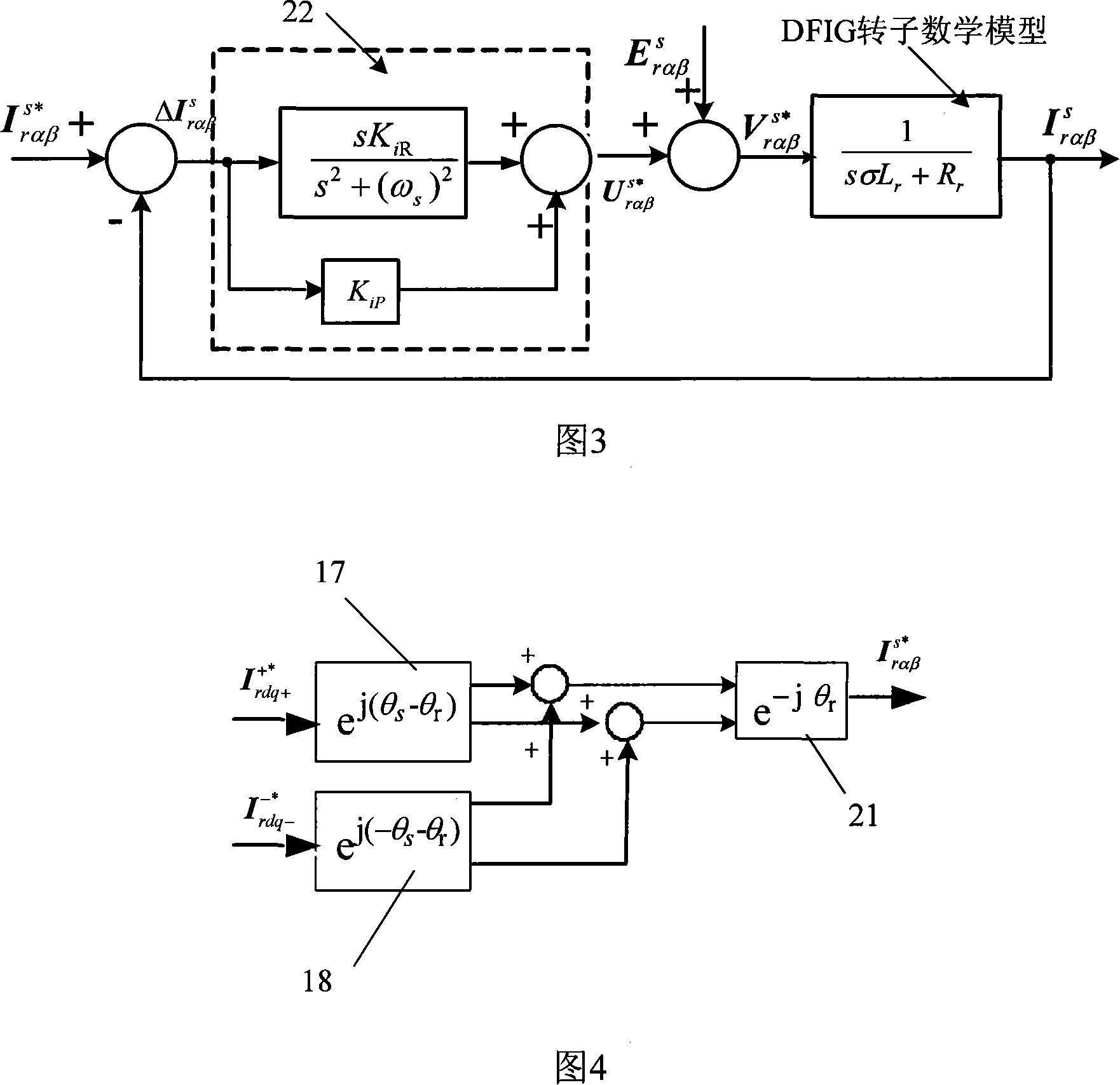
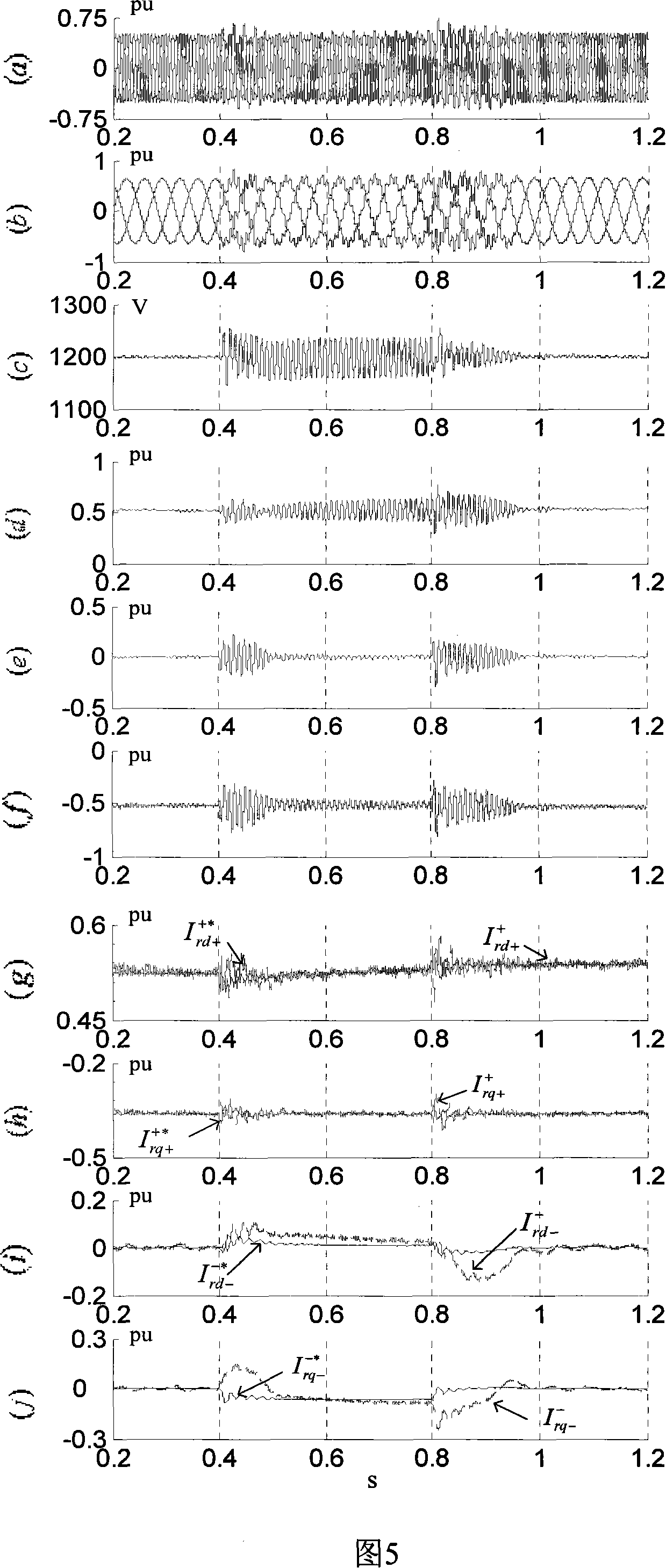
Dual feedback asynchronous wind power generator rotor side inverter control method under unbalanced electric grid voltage
InactiveCN101478283ASuppresses the DC componentSuppression of double frequency componentsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsEngineeringConductor Coil
The invention designs a control method of an inverter on a rotor side of a double fed wind induction generator. In the control method, a traditional PI adjustor is changed into a PIR adjustor, and a setting frequency Omega c in the PIR adjustor is set as a bisynchronous revolution angular speed Omega s, that is, a double frequency negative sequence component in disturbance quantity can be restrained completely, so the situation that power outputted to a power grid oscillates caused by impulsive motion of the electromagnetic torque of an engine because of unequal power grid voltage can be avoided. At the same time, the PIR adjustor can track a positive sequence component with frequency being zero and the double frequency negative sequence component in the forward path which are input in an astatic manner, thereby avoiding that unequal voltage aggravates the imbalance of stator current to cause a stator winding to heat because of serious imbalance. In addition, the control method realizes the control of the inverter on the rotor side of the generator under the condition of the unequal power grid voltage only through the replacement of the adjustor, the alteration thereof is simple, the effect is obvious, the design of complex elements is not involved, and the actualization is easy.
Owner:北京清能华福风电技术有限公司
Polyphasic multi-coil generator
ActiveUS20100090553A1Improve power generation efficiencySynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsAngular orientationMulti coil
A polyphasic multi-coil generator includes a driveshaft, at least first and second rotors rigidly mounted on the driveshaft so as to simultaneously synchronously rotate with rotation of the driveshaft, and at least one stator sandwiched between the first and second rotors. The stator has an aperture through which the driveshaft is rotatably journalled. A stator array on the stator has an equally circumferentially spaced-apart array of electrically conductive coils mounted to the stator in a first angular orientation about the driveshaft. The rotors and the stator lie in substantially parallel planes. The first and second rotors have, respectively, first and second rotor arrays.
Owner:DPM TECH INC
Variable speed constant frequency dual-feed asynchronous wind power generator rotor current non-delay control method
InactiveCN101141110AEnhanced Control ObjectivesImprove uninterrupted operation (traversal) capabilityGenerator control detailsConstant frequencyVoltage reference
The invention discloses a nondelay control method for the current of the rotor of the variable speed constant frequency double feed nonsynchronous aerogenerator(DFIG). The switch of the rotational coordinate is finished by collecting three phase rotor current signal so as to obtain the rotor current feedback amount in the static frame of axes to compare with the rotor current command in the stator static frame of axes, the difference signal is input into the proportion-resonance regulator for comparison, the rotor voltage reference value in the stator static fame of axes is obtained after feedback compensation decoupling. The rotor voltage reference value is then transformed into reference signals for space vector pulse width regulation in the rotor frame axes to generate switch signals of the power components of the converter of the rotor to control the synchronize and close operation of the generator. The invention is needless of the break down of the positive and negative sequence of current of the EFIG rotor no matter the electric net voltage is balance or not without introducing break down delay. The invention can realize strengthened control of the generating system in imbalanced electric net, effectively improve non-stop operation of the aerogenerator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
DC electric motor/generator with enhanced permanent magnet flux densities
ActiveUS20130249343A1Reduces and eliminates undesired effect and lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesMagnetic tension forceEngineering
This disclosure relates in general to a new and improved electric motor / generator, and in particular to an improved system and method for producing rotary motion from a electro-magnetic motor or generating electrical power from a rotary motion input by concentrating magnetic forces due to electromagnetism or geometric configurations.
Owner:LINEAR LABS
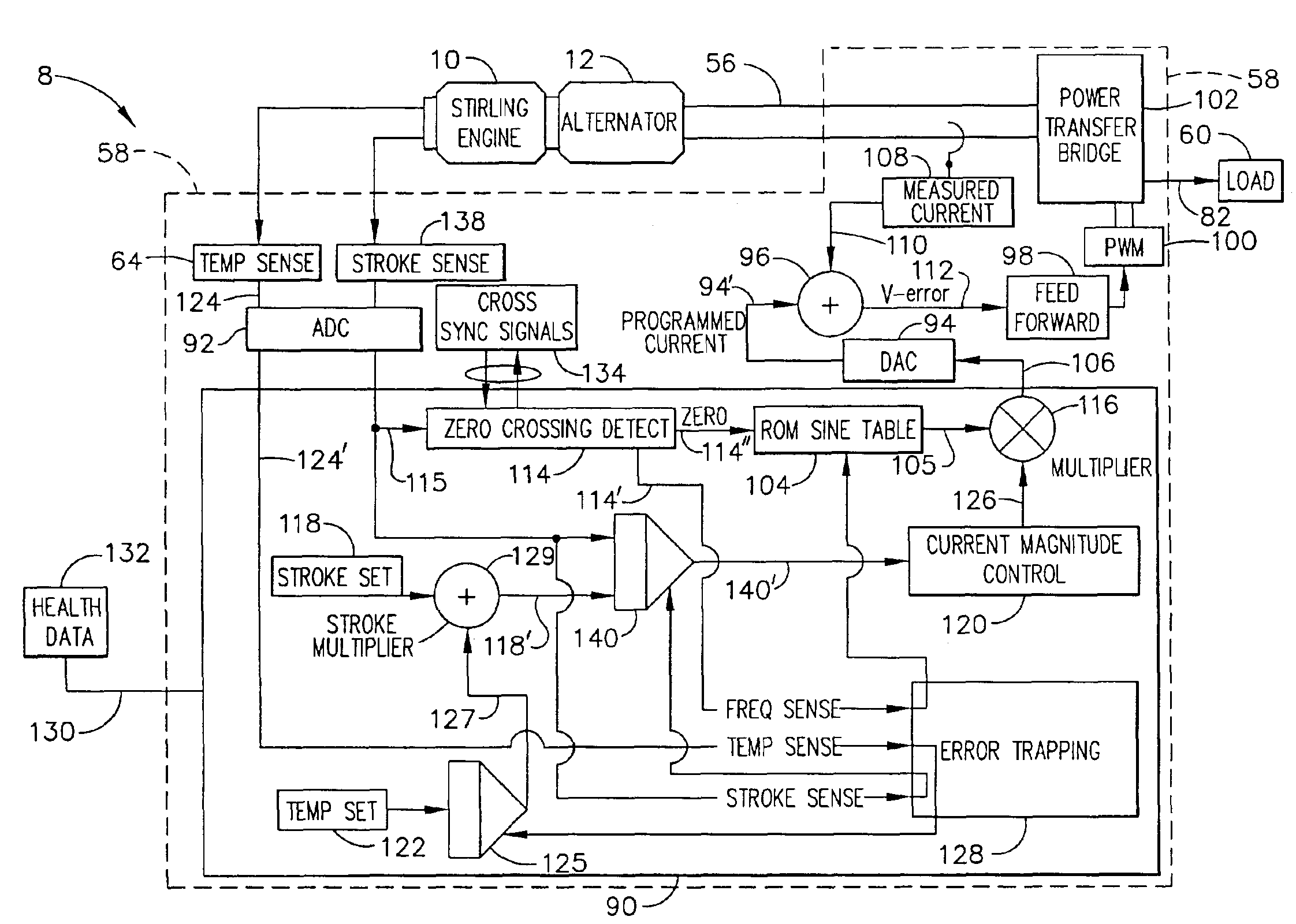
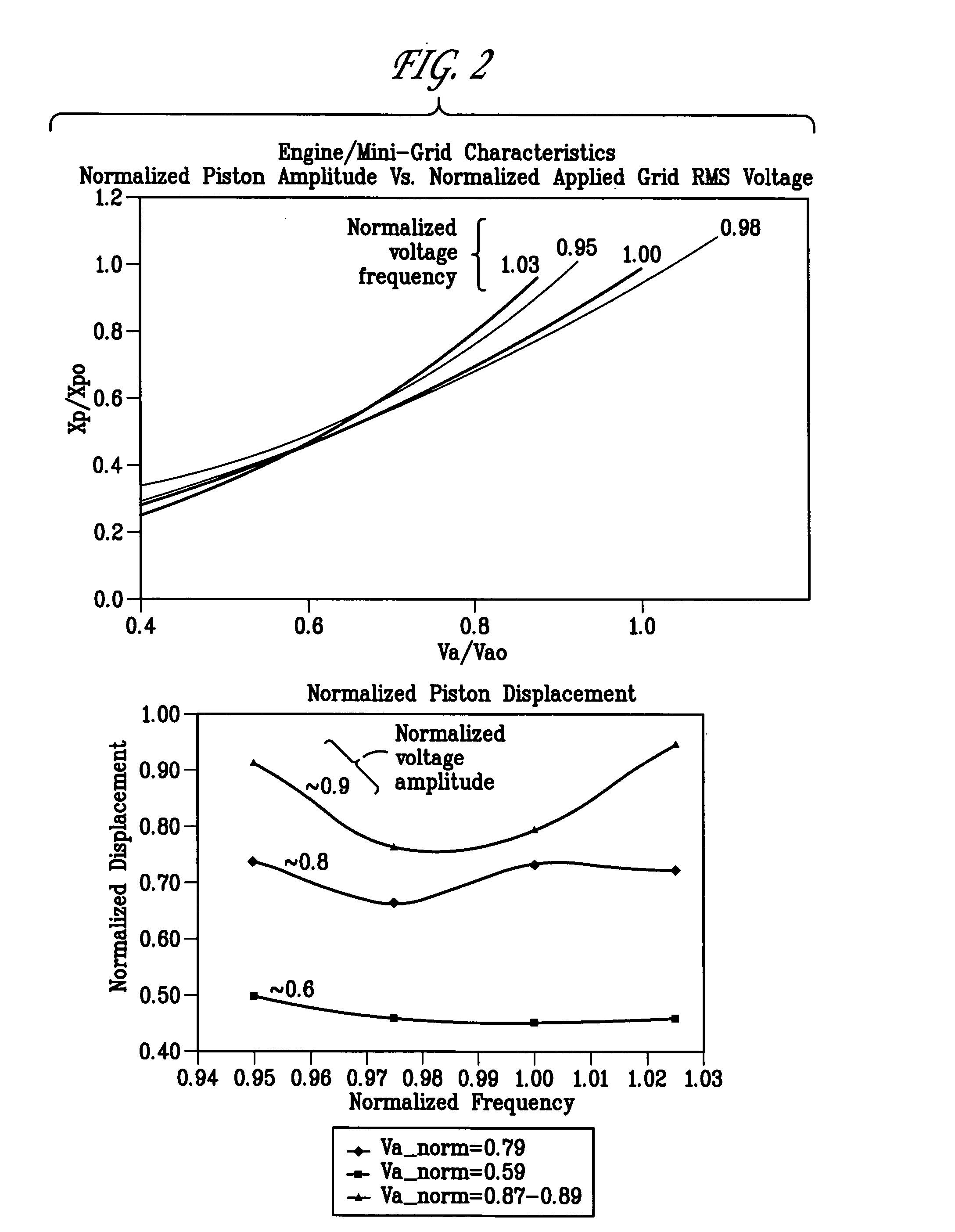
Free piston Stirling engine control
InactiveUS20050028520A1Large and heavy and expensiveAC motor controlEngine componentsVoltage amplitudeElectric power system
A control system for a Stirling engine including the use of a synchronous power converter (“SPC”) which is connected to the terminals of the alternator in a linear alternator / FPSE power system. According to the teachings of the present invention, the attached SPC is small and portable and further ensures that piston and displacer excursion within the system remain within design limits. The system and method are designed such that it is possible to adjust both the voltage amplitude and the waveform frequency at the terminals of the linear alternator. By controlling these operational aspects, both the speed and the range of travel associated with the piston and the displacer in the FPSE can be controlled.
Owner:TIAX LLC
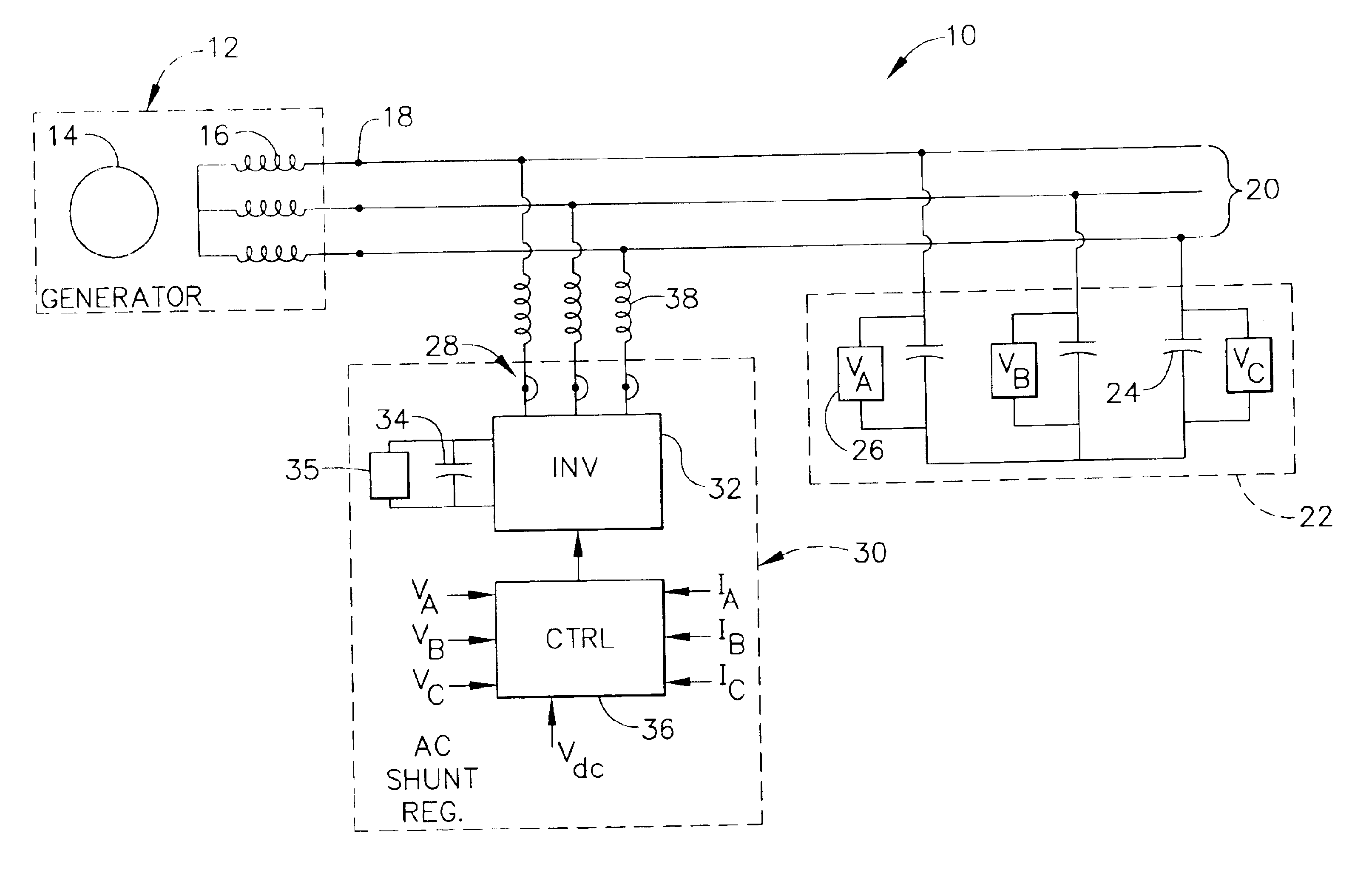
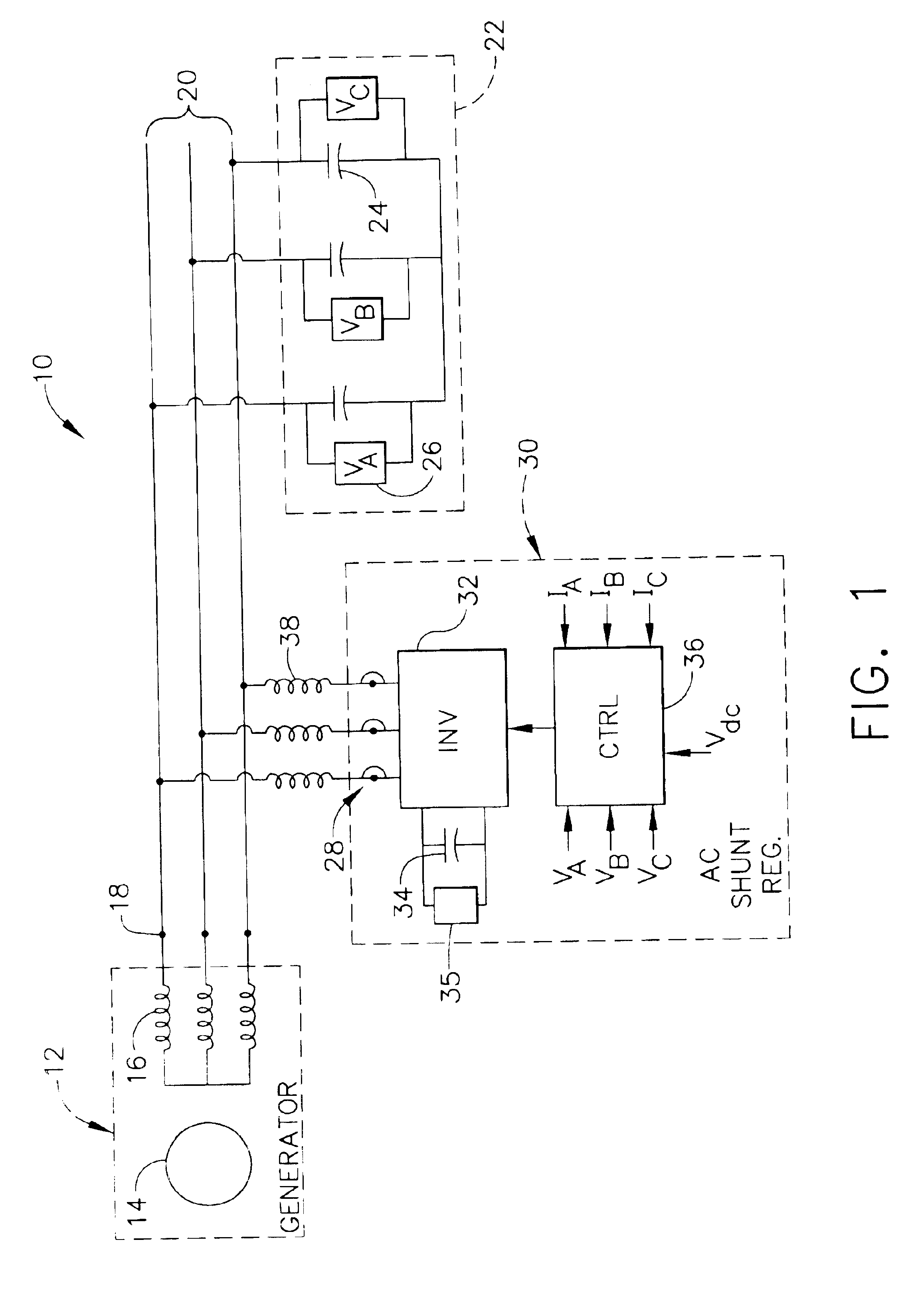
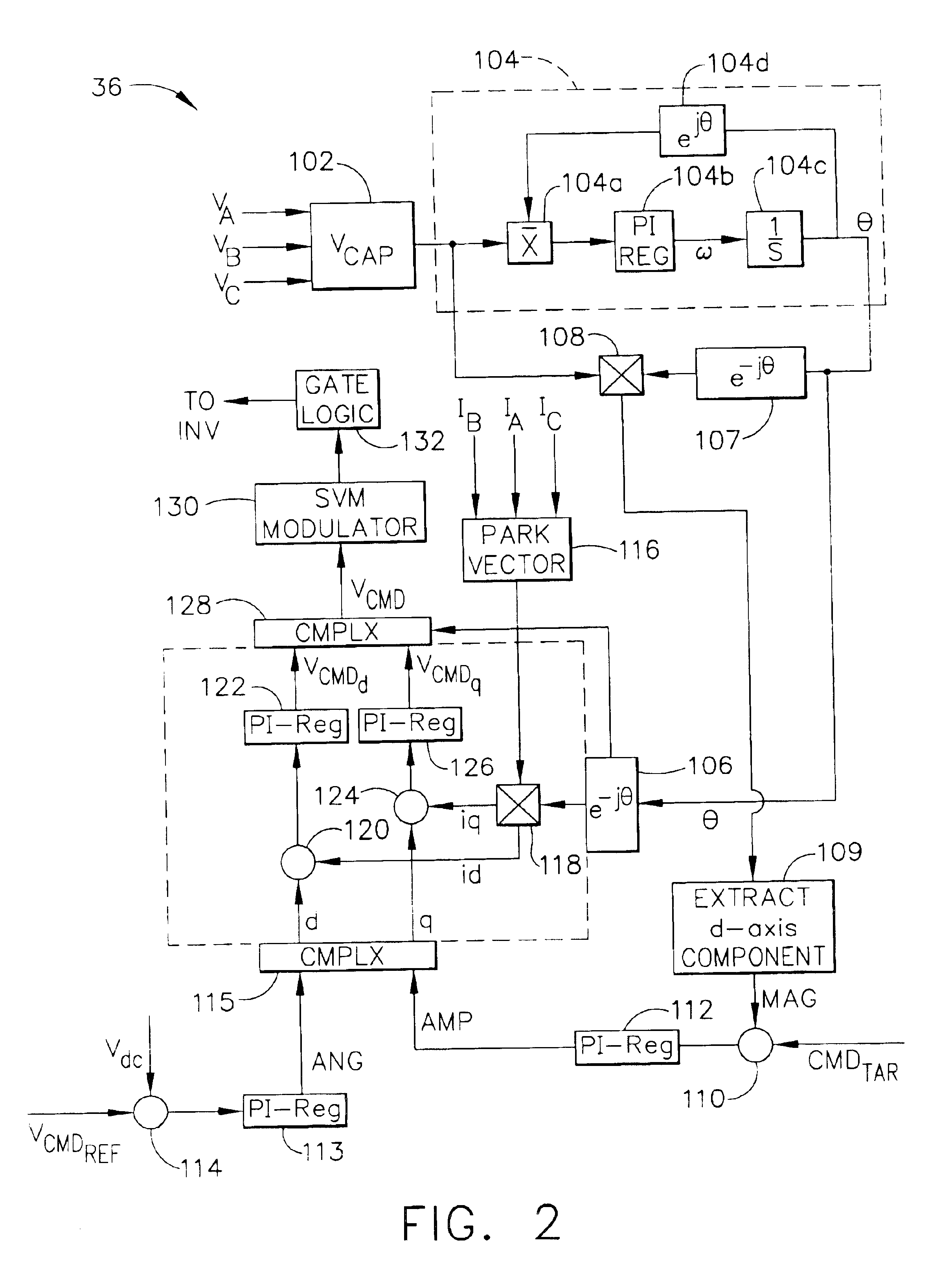
Power generating system including permanent magnet generator and shunt AC regulator
InactiveUS6838860B2Active power filteringEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDistribution systemPermanent magnet synchronous generator
An electrical power distribution system includes permanent magnet generator, and an ac regulator. The ac regulator includes an inverter shunt-connected to the permanent magnet generator, and an inverter control for causing the inverter to regulate voltage at output terminals of the generator by providing reactive power (either leading or lagging) that circulates between the inverter and the generator.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Resonant commutation system for exciting a three-phase alternator
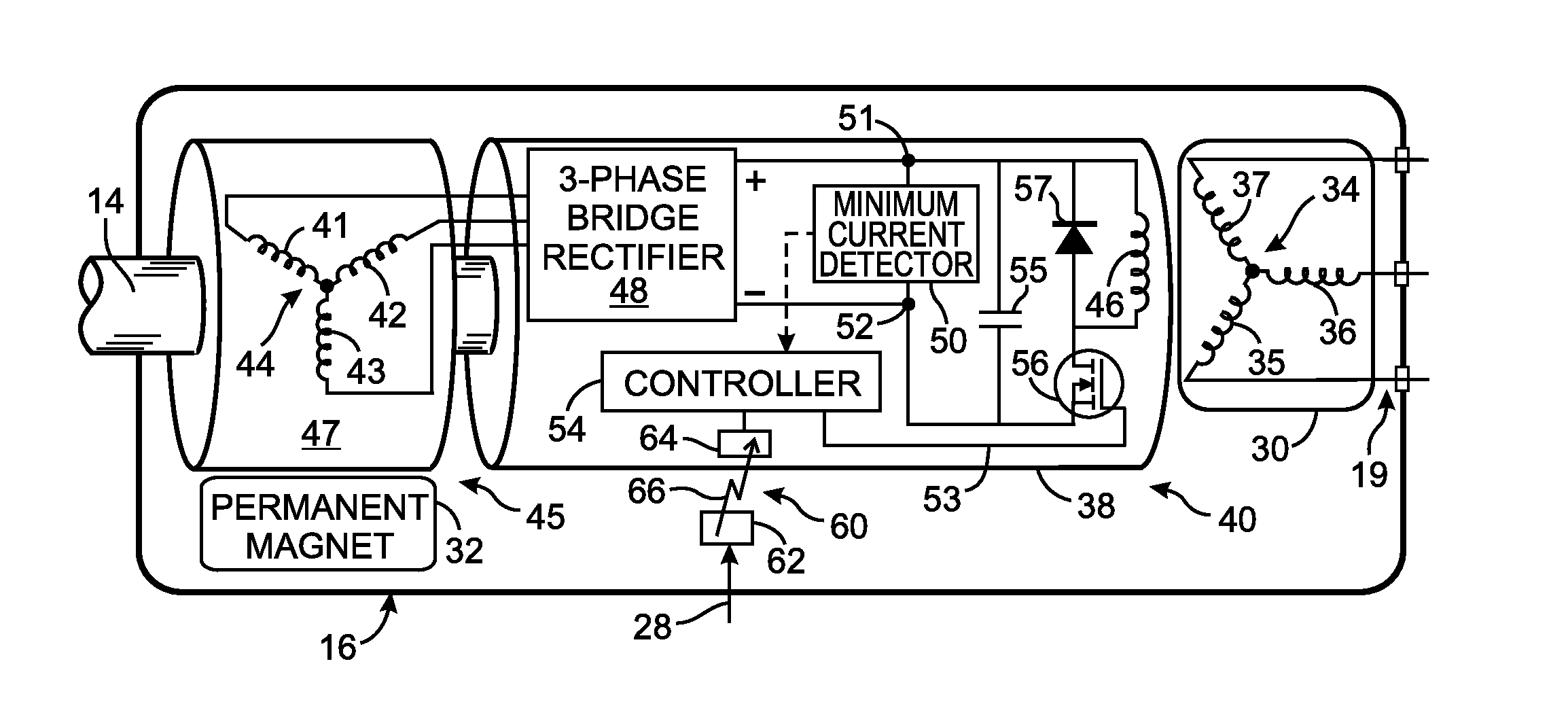
InactiveUS20120153904A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlCapacitanceControl signal
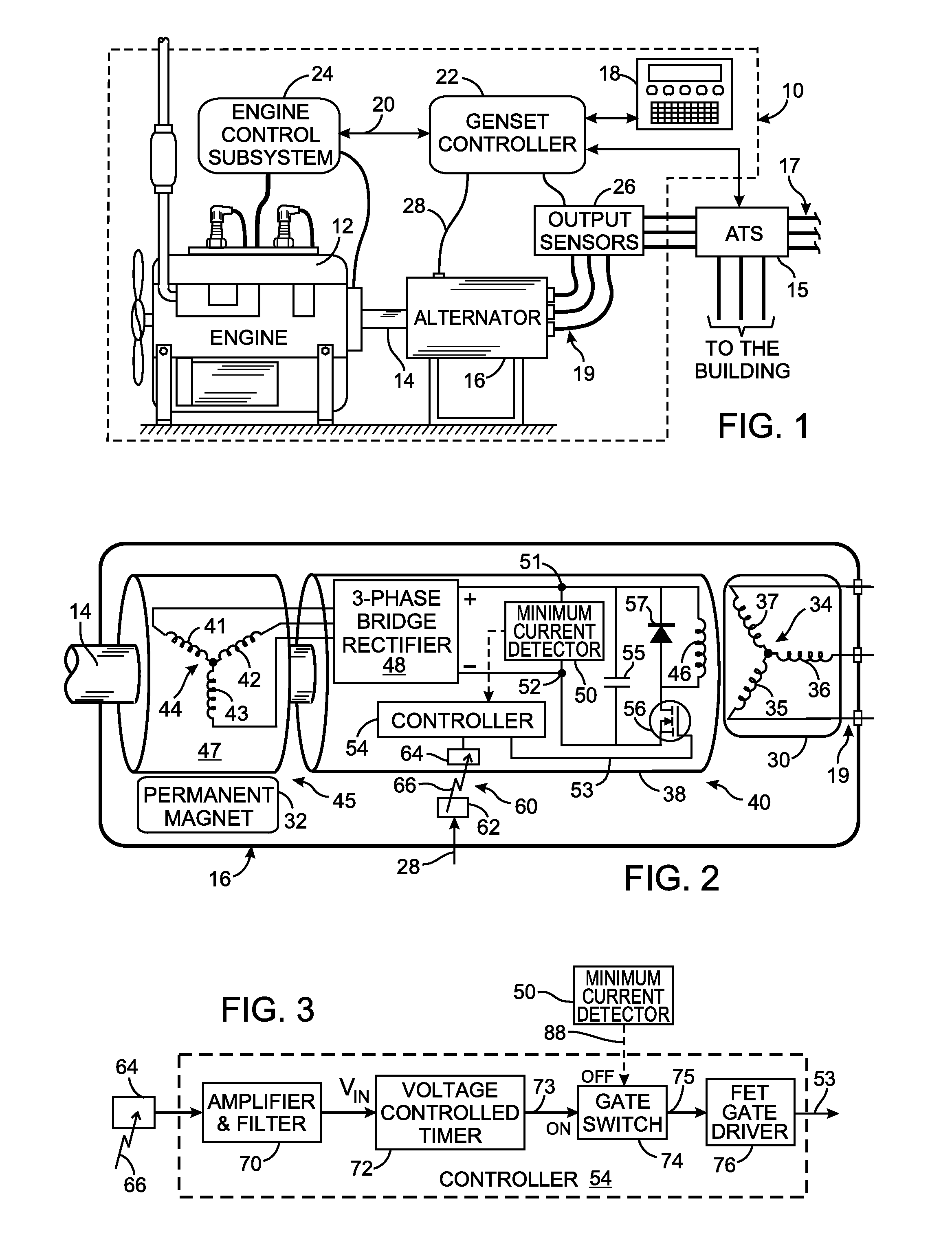
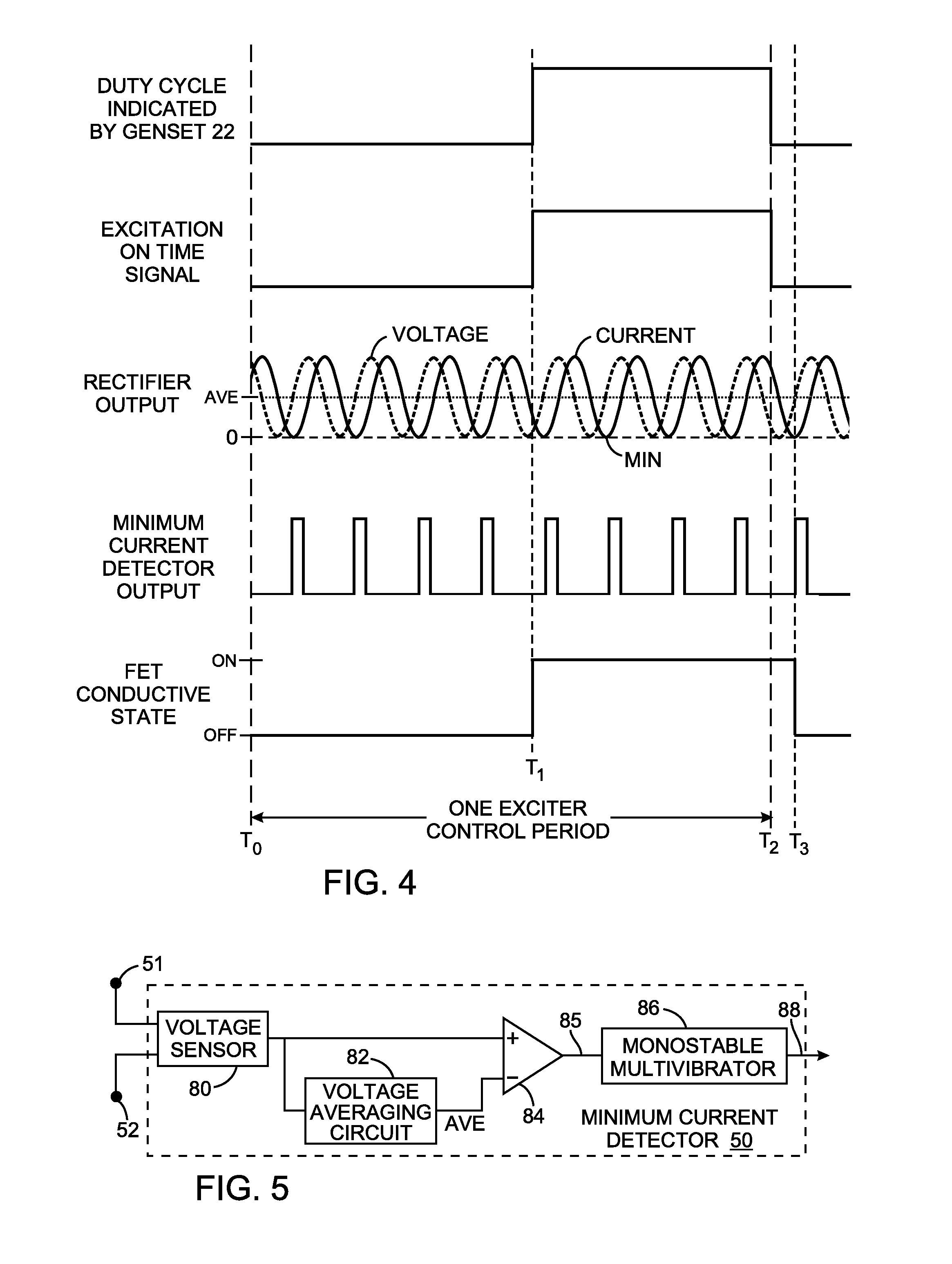
An alternator has a field coil that produces a magnetic field which induces electricity in an coil arrangement. A field coil excitation system includes a generator with an output coil assembly for producing alternating electricity. A rectifier converts the alternating electricity into voltage and direct current at two nodes. A capacitor, between the nodes, has capacitance that forms a resonant circuit with inductance of the output coil assembly. Due to that resonant circuit, the voltage and direct current oscillate in a predefined phase relationship. A switch and the field coil are connected in series between the nodes. A controller renders the switch conductive for a time period specified by a received control signal. The switch is rendered non-conductive at the first occurrence of a minimum current level after the time period ends. The predefined phase relationship enables the minimum current level to be detected by sensing the voltage.
Owner:KOHLER CO
Digital Excitation Control System Utilizing Self-Tuning PID Gains and an Associated Method of Use
InactiveUS20090195224A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlElectricitySelf-tuning
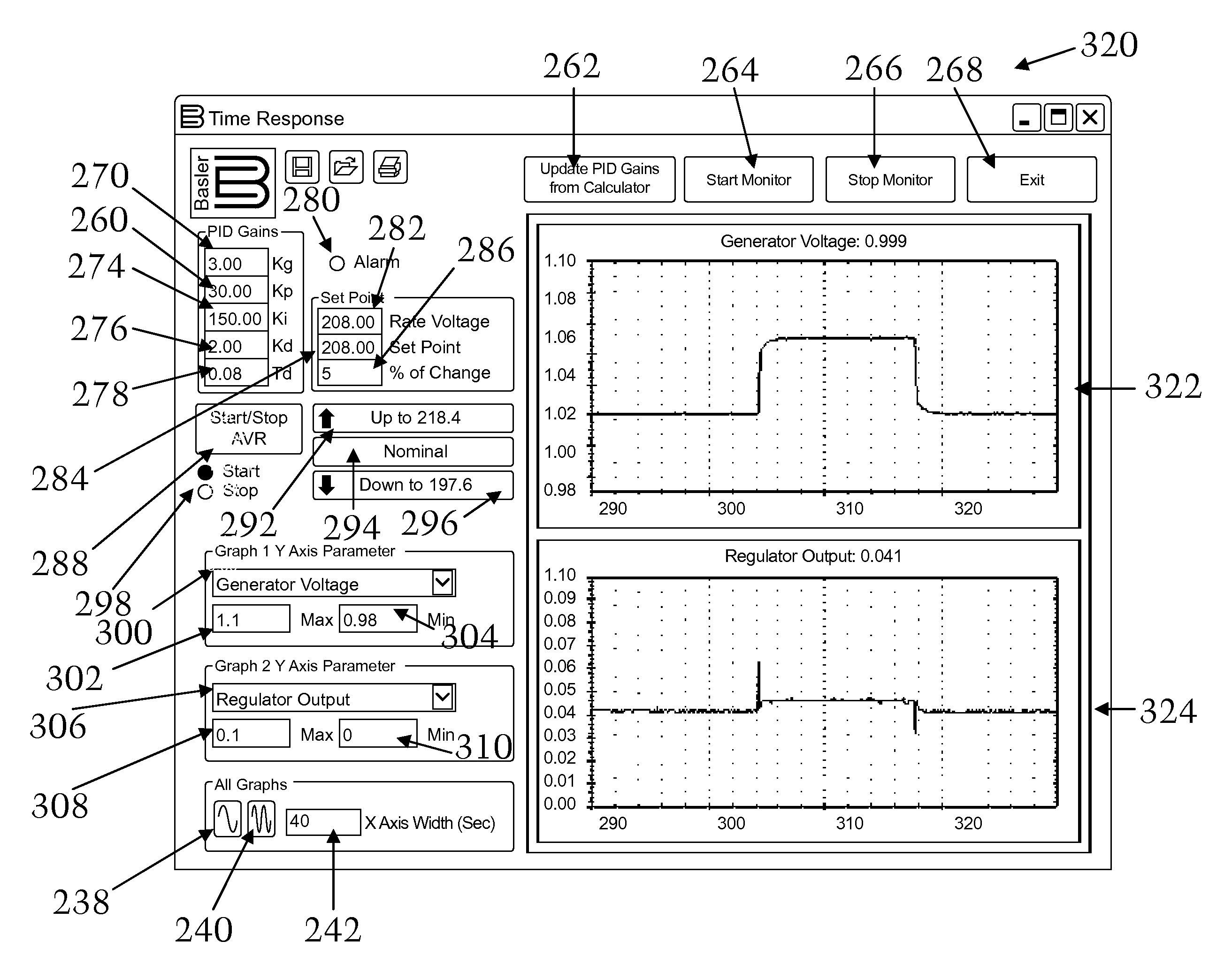
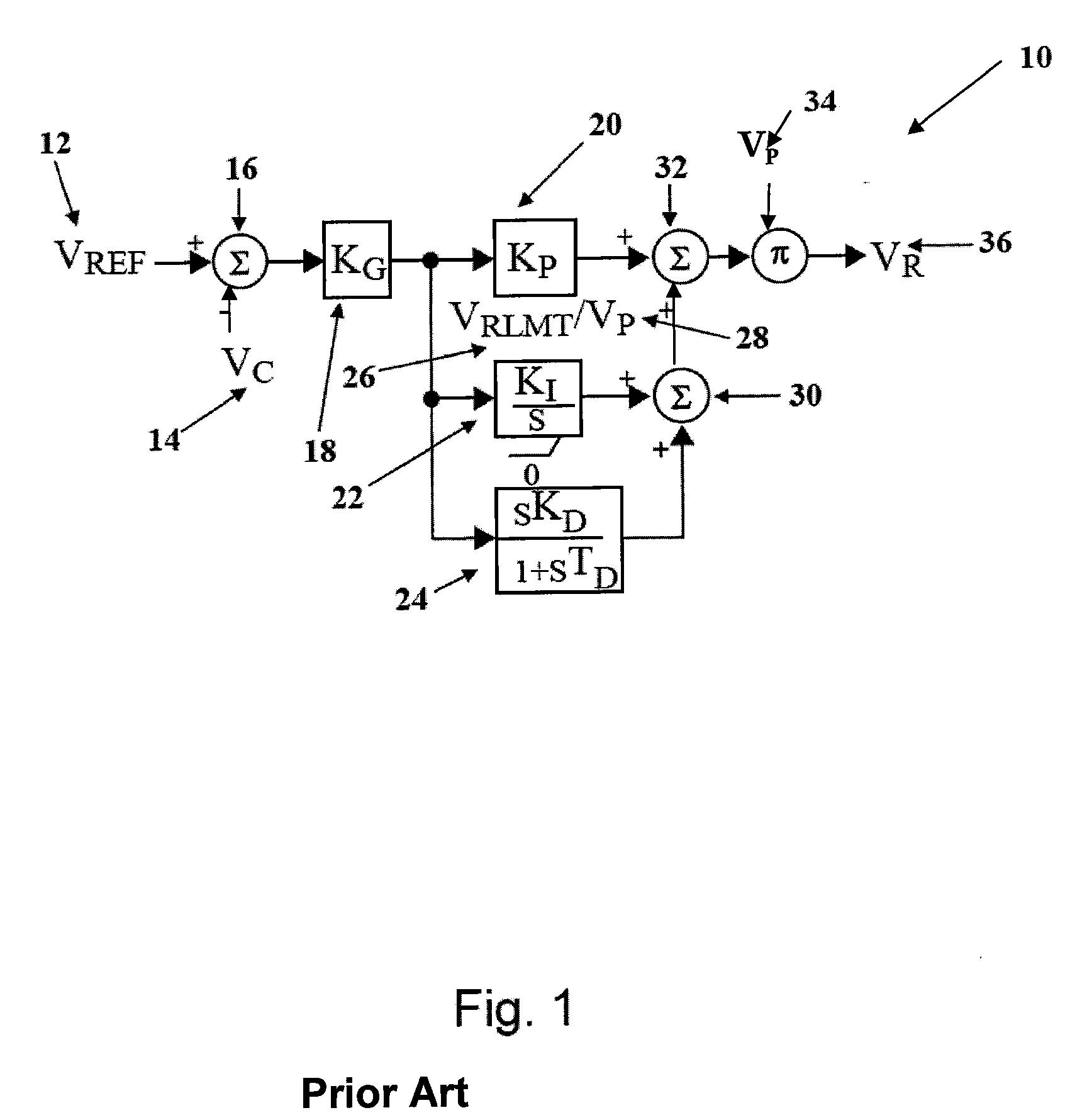
A system and method for self-tuning a PID controller utilized with an exciter and generator, which includes a power source, an exciter electrically connected to the power source, a generator that is electrically energized by the exciter, and a processor that provides a PID controller that calculates system gain an estimated exciter time constant and an estimated generator time constant with a recursive least square with forgetting factor algorithm, wherein the estimated exciter time constant and the estimated generator time constant are utilized to calculate PID gains by the processor, wherein the processor includes a random input generator that is summed with the output of the PID controller as input to determine the PID gains using the estimated exciter time constant and the estimated generator time constant and the processor compares a digital value of rms generator voltage against a reference voltage as input into the PID controller.
Owner:BASLER ELECTRIC
Series hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS20070137908A1Avoids excessive increase in output voltageReduce speedAuxillary drivesAC motor controlDrive wheelMotor drive
There is provided a technique for improving the efficiency of a generation system of a series hybrid electric vehicle The series hybrid electric vehicle is composed of: an engine; an n-phase generator driven by the engine; a rectifier generating a DC voltage from an n-phase AC voltage received from the n-phase generator; a battery charged with the DC voltage generated; a motor driving drive wheels; an inverter driving the motor on the DC voltage received from the rectifier and / or a DC voltage supplied from the battery; and a switch. The n-phase generator has n armature windings each having one end connected to a common neutral point. The rectifier has a negative terminal, a positive terminal on which a higher potential is generated than on the negative terminal, and n rectifying arms. Each of the n rectifying arms includes; a first diode connected between an intermediated node connected to the other end of the corresponding armature windings and the negative terminal; and a second diode connected between the intermediate node and the positive terminal. The switch is connected between the neutral point and the negative terminal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Controller for controlling a power converter
ActiveUS20140307488A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionReduce loadActive power filteringElectric power transfer ac networkControl powerPower grid
A controller is provided for controlling a power converter that converts electrical input power of a wind turbine into electrical output power provided to a grid. The power converter includes grid-side and turbine-side converter parts. The controller comprises an input terminal for receiving a voltage reference signal associated with a predefined grid voltage and a frequency reference signal associated with a predefined grid frequency, and a network bridge controller adapted to control power conversion of the grid-side converter part. The network bridge controller includes a modulator for modulating gate drive command signals in the grid-side converter part based on a reference voltage and a reference angle derived from the voltage reference signal and the frequency reference signal. The modulator is adapted to modulate the gate drive command signals to maintain the predefined grid voltage and the predefined grid frequency in the power converter in case of failure within the grid.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
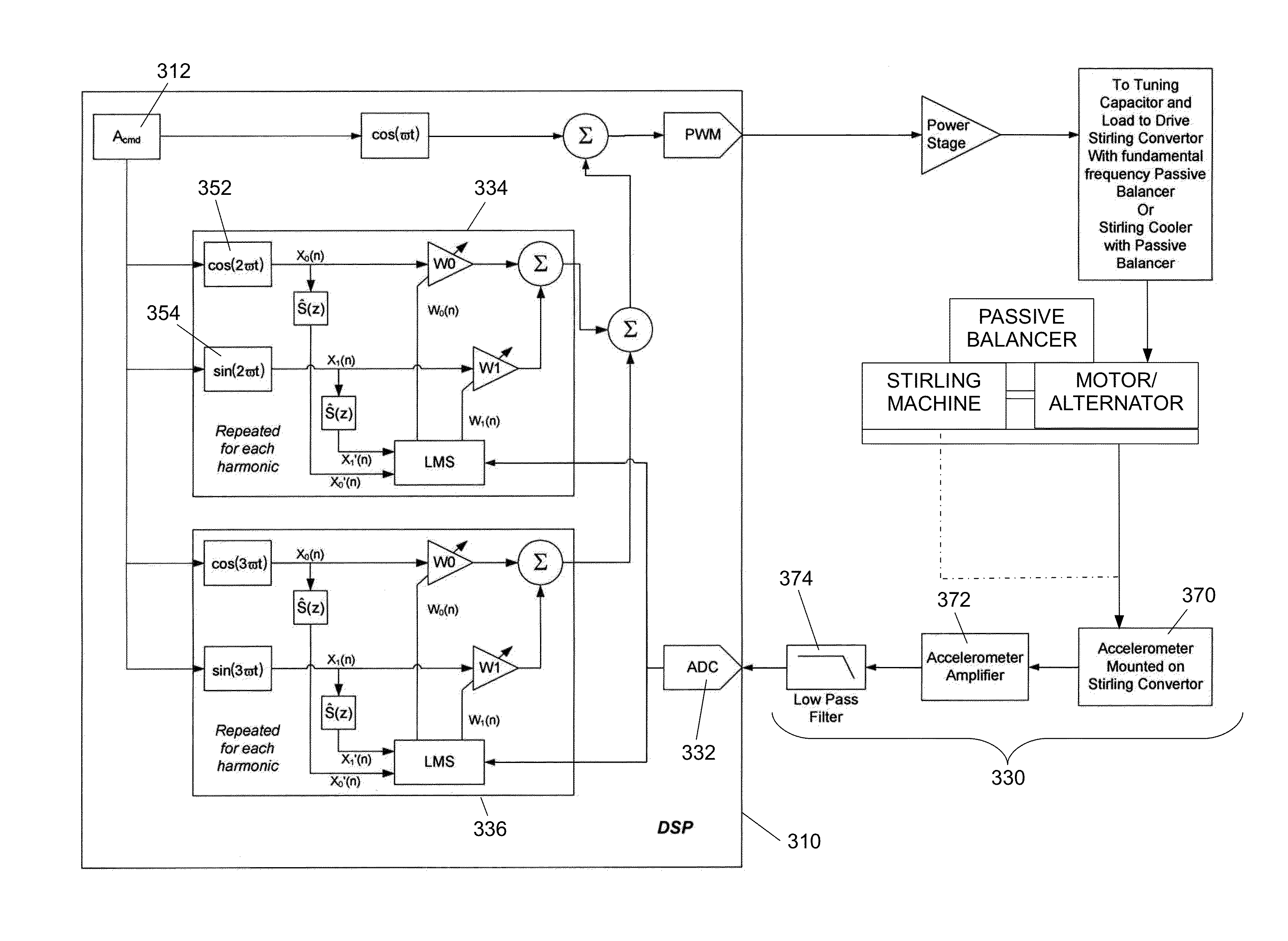
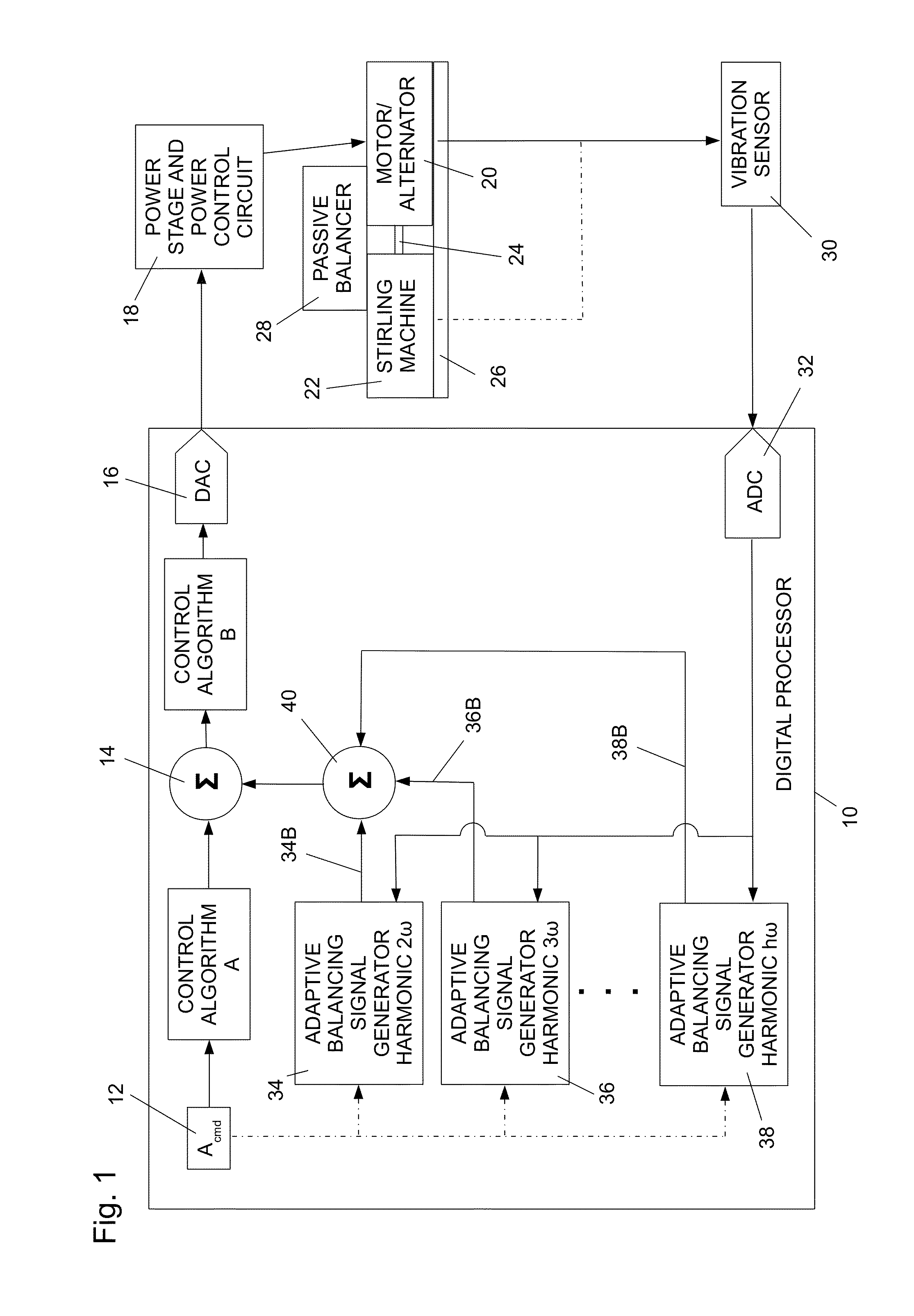
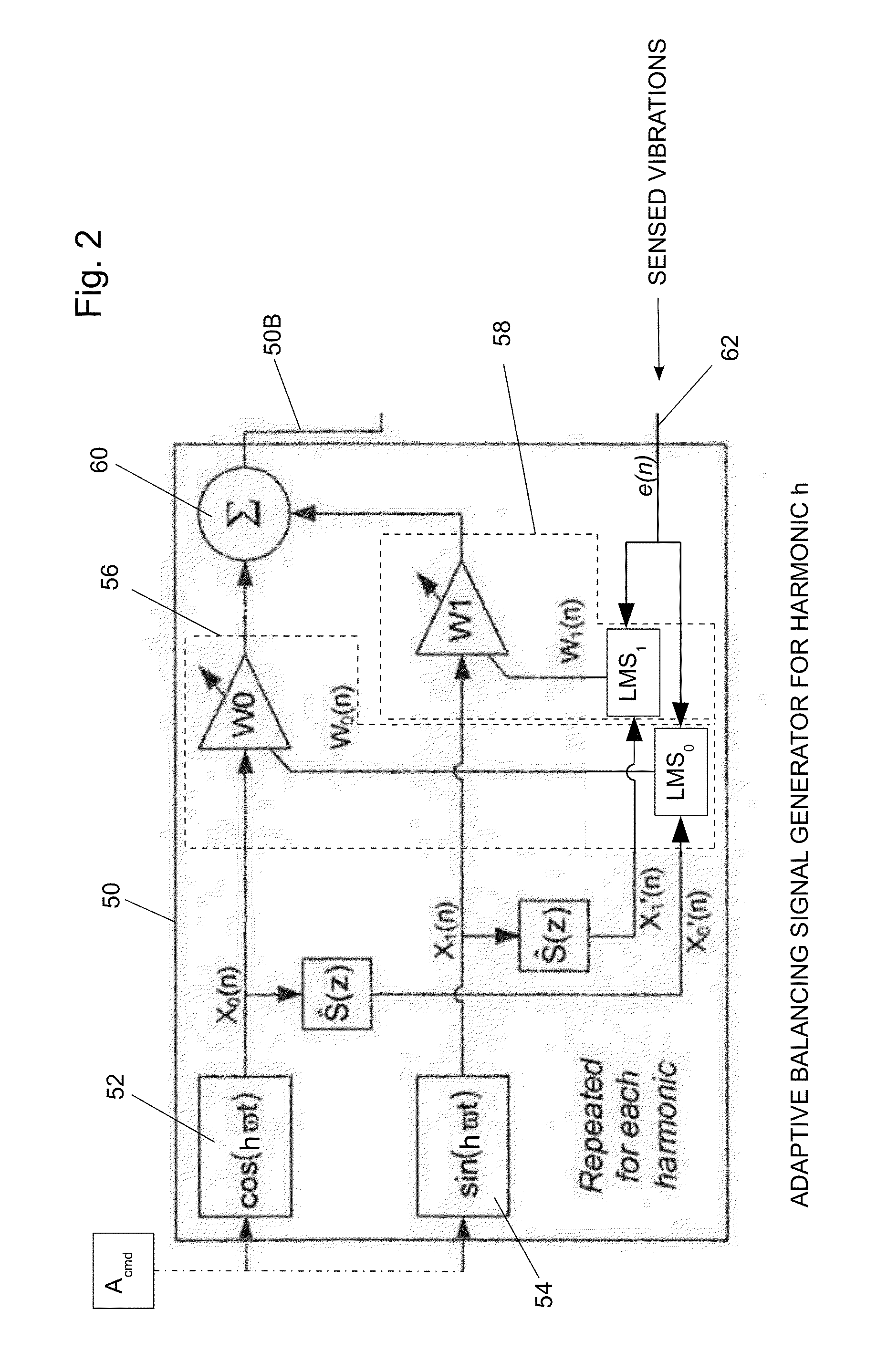
Balancing Vibrations At Harmonic Frequencies By Injecting Harmonic Balancing Signals Into The Armature Of A Linear Motor/Alternator Coupled To A Stirling Machine
ActiveUS20140015497A1Vibration minimizationMechanical oscillations controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAdaptive filtering algorithmMachining vibrations
Vibrations at harmonic frequencies are reduced by injecting harmonic balancing signals into the armature of a linear motor / alternator coupled to a Stirling machine. The vibrations are sensed to provide a signal representing the mechanical vibrations. A harmonic balancing signal is generated for selected harmonics of the operating frequency by processing the sensed vibration signal with adaptive filter algorithms of adaptive filters for each harmonic. Reference inputs for each harmonic are applied to the adaptive filter algorithms at the frequency of the selected harmonic. The harmonic balancing signals for all of the harmonics are summed with a principal control signal. The harmonic balancing signals modify the principal electrical drive voltage and drive the motor / alternator with a drive voltage component in opposition to the vibration at each harmonic.
Owner:SUNPOWER
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com