Patents
Literature
202results about How to "Good torque transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
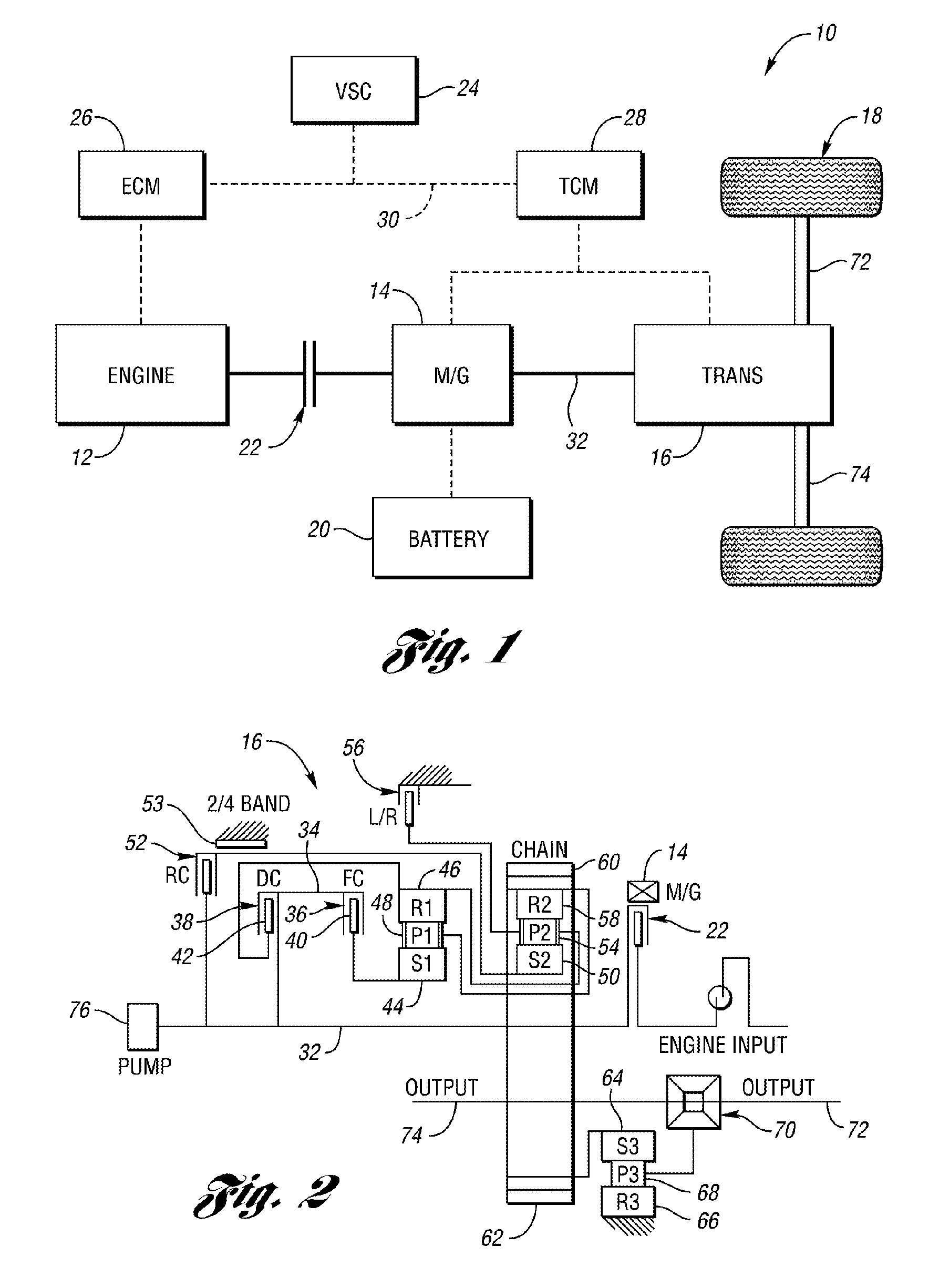
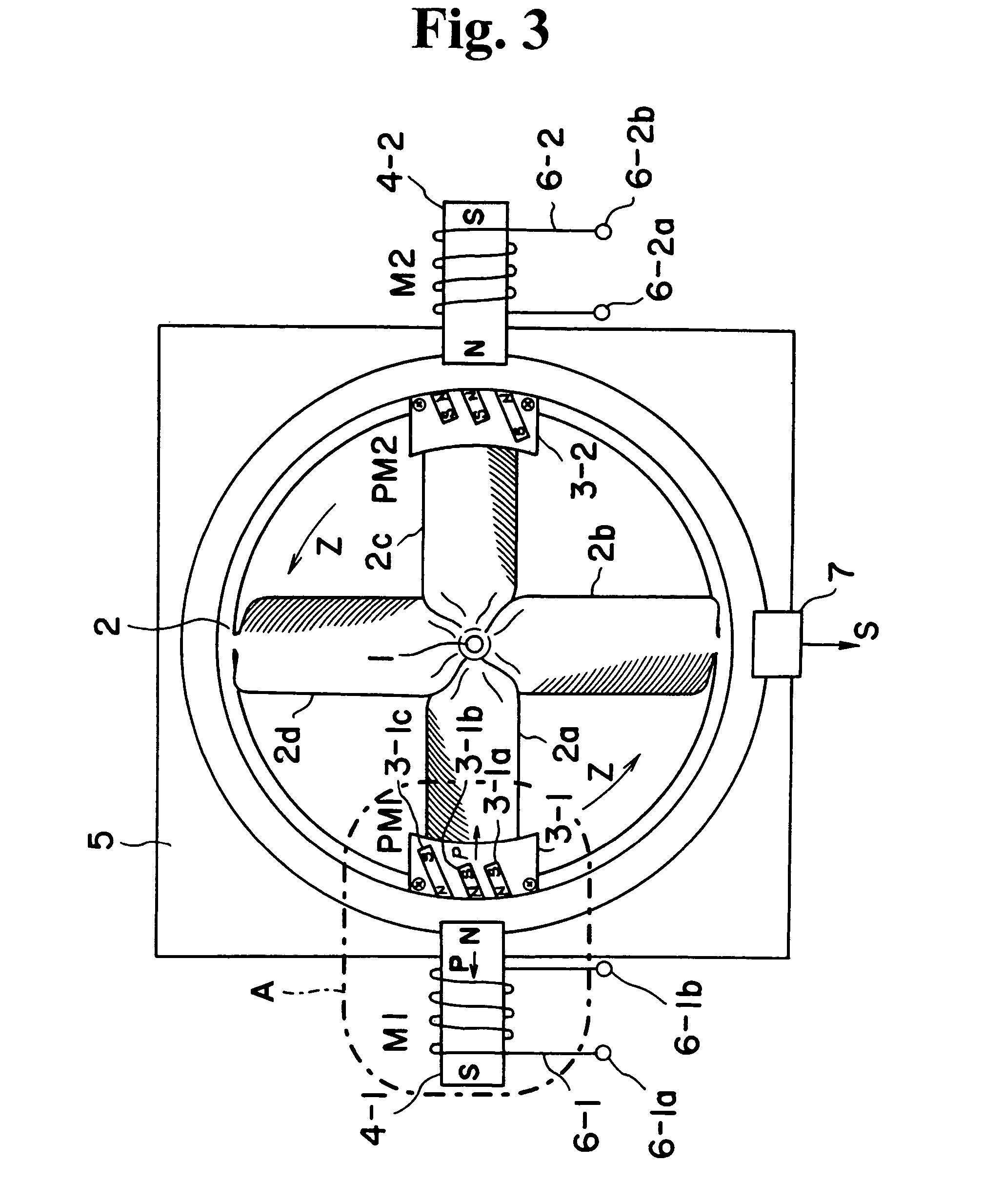
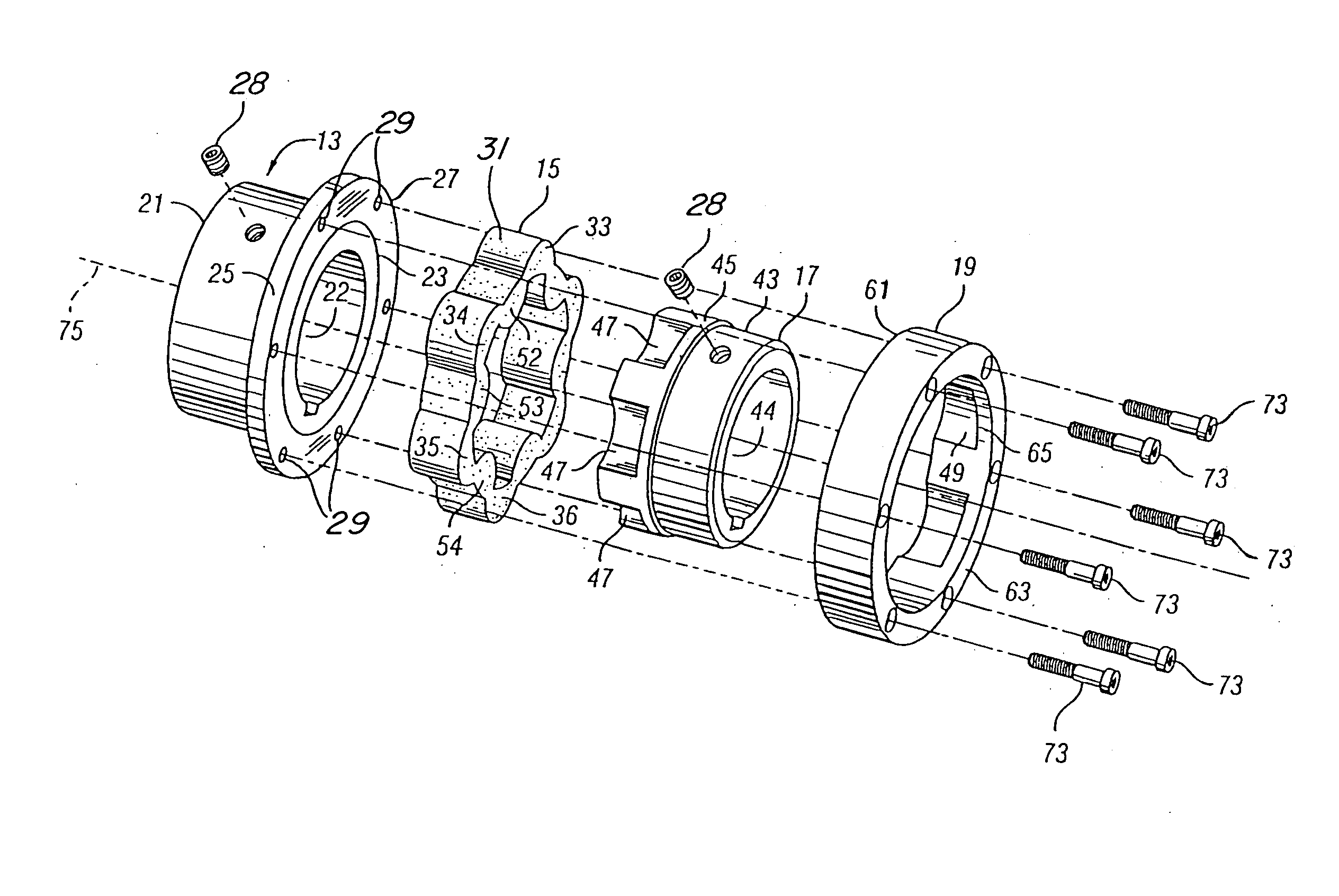
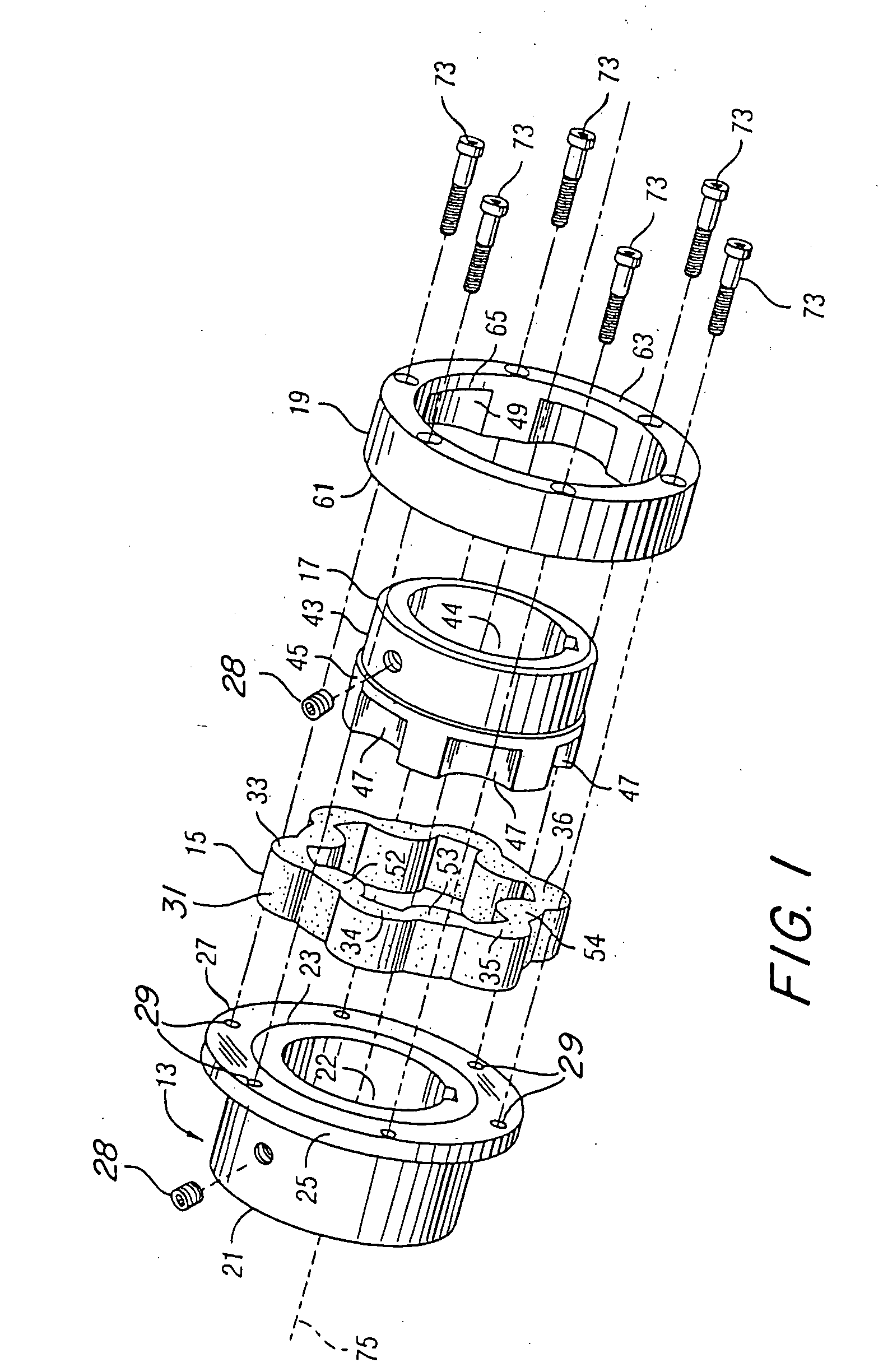
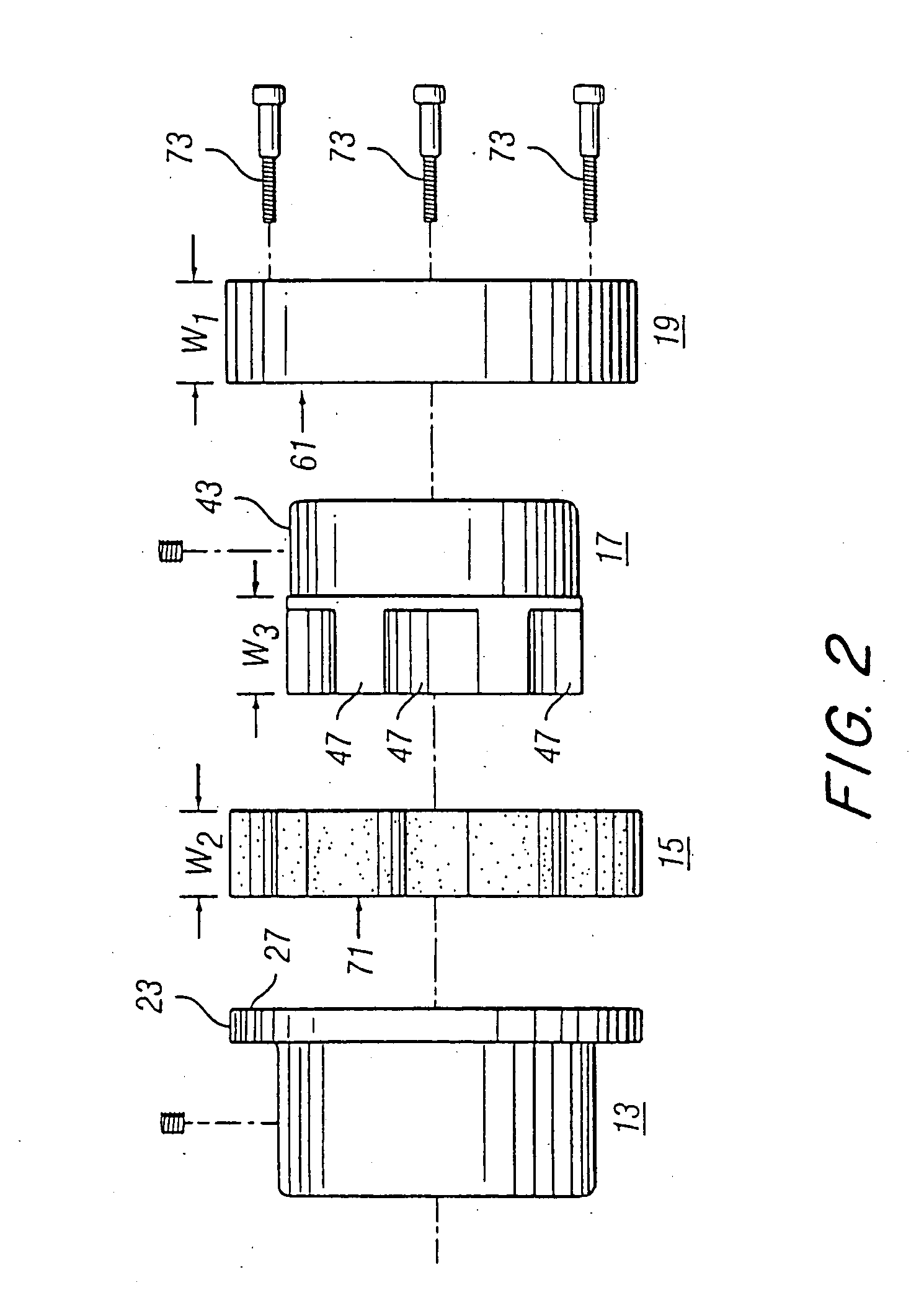
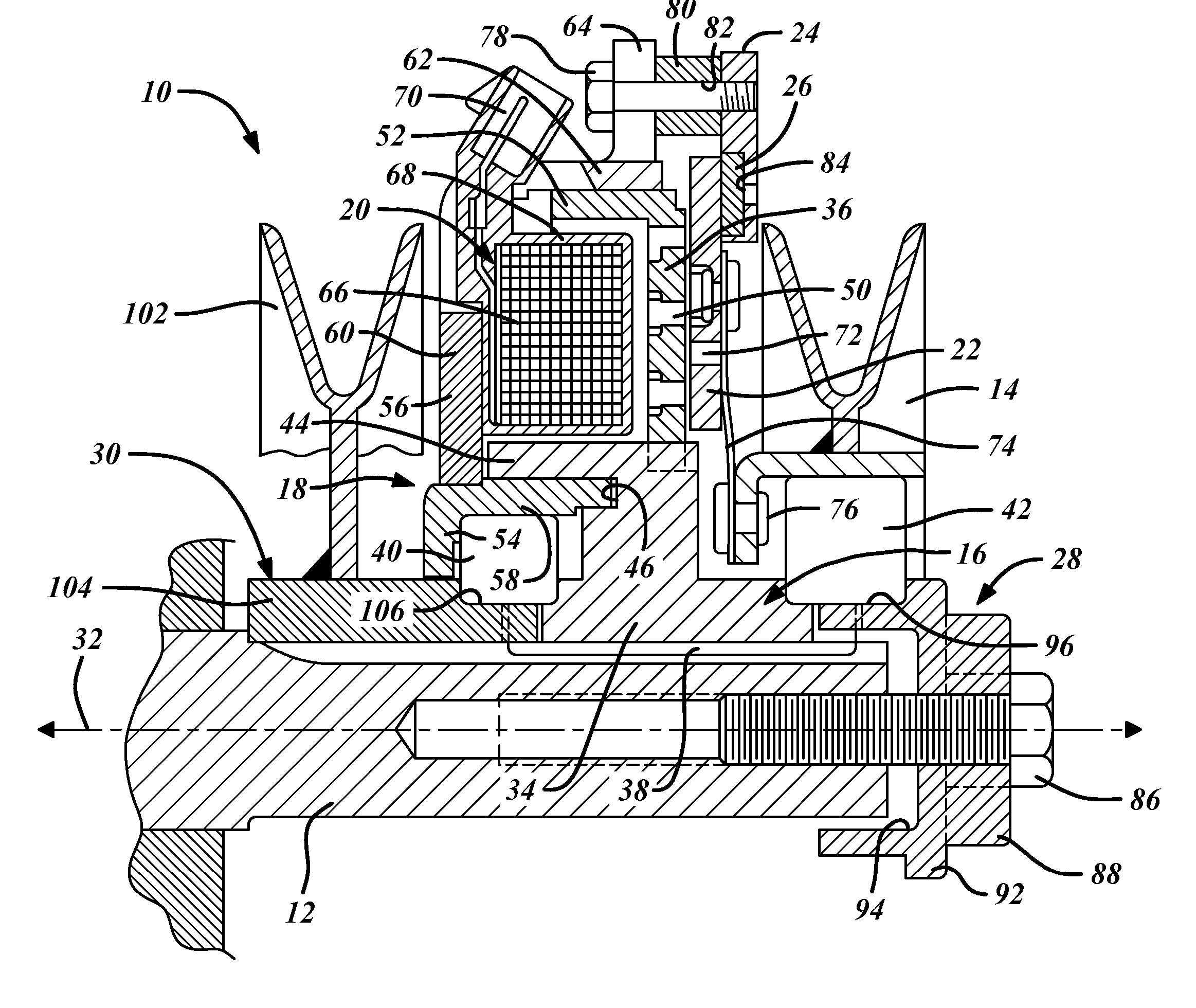
Hybrid-vehicle power train
ActiveUS7246672B2Achieve effectEfficient use ofElectric propulsion mountingElectric machinesClutchHybrid vehicle
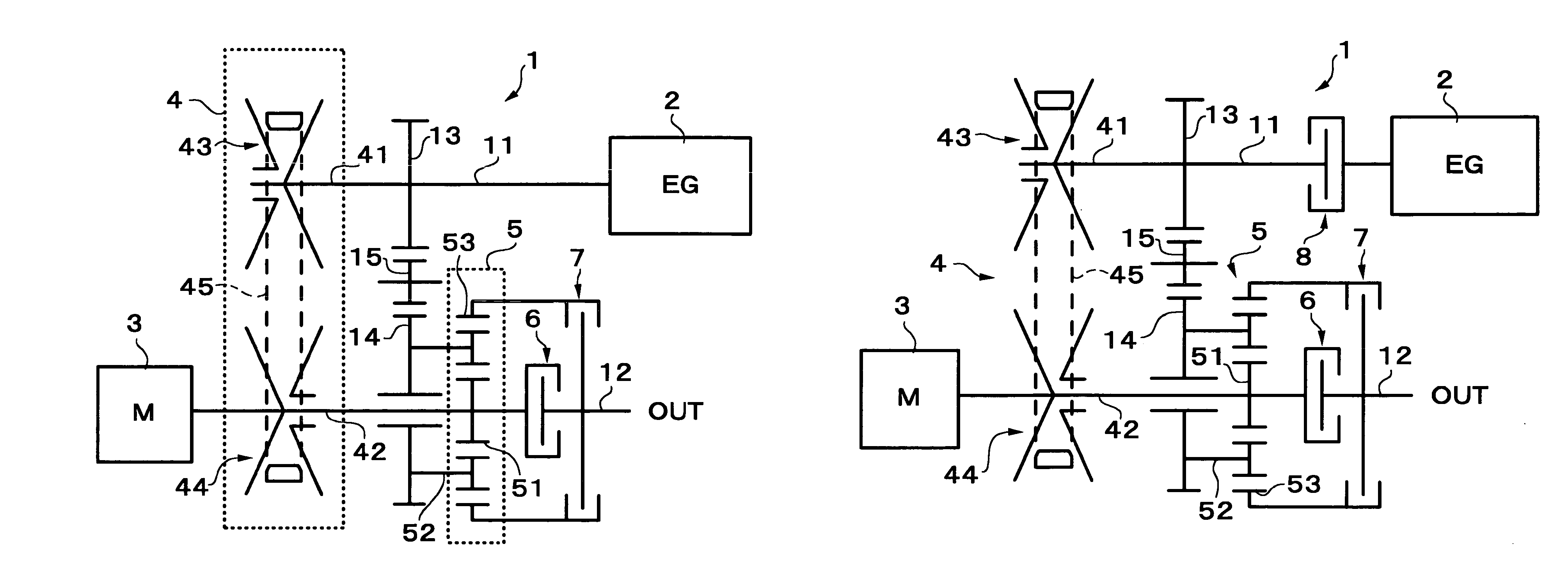
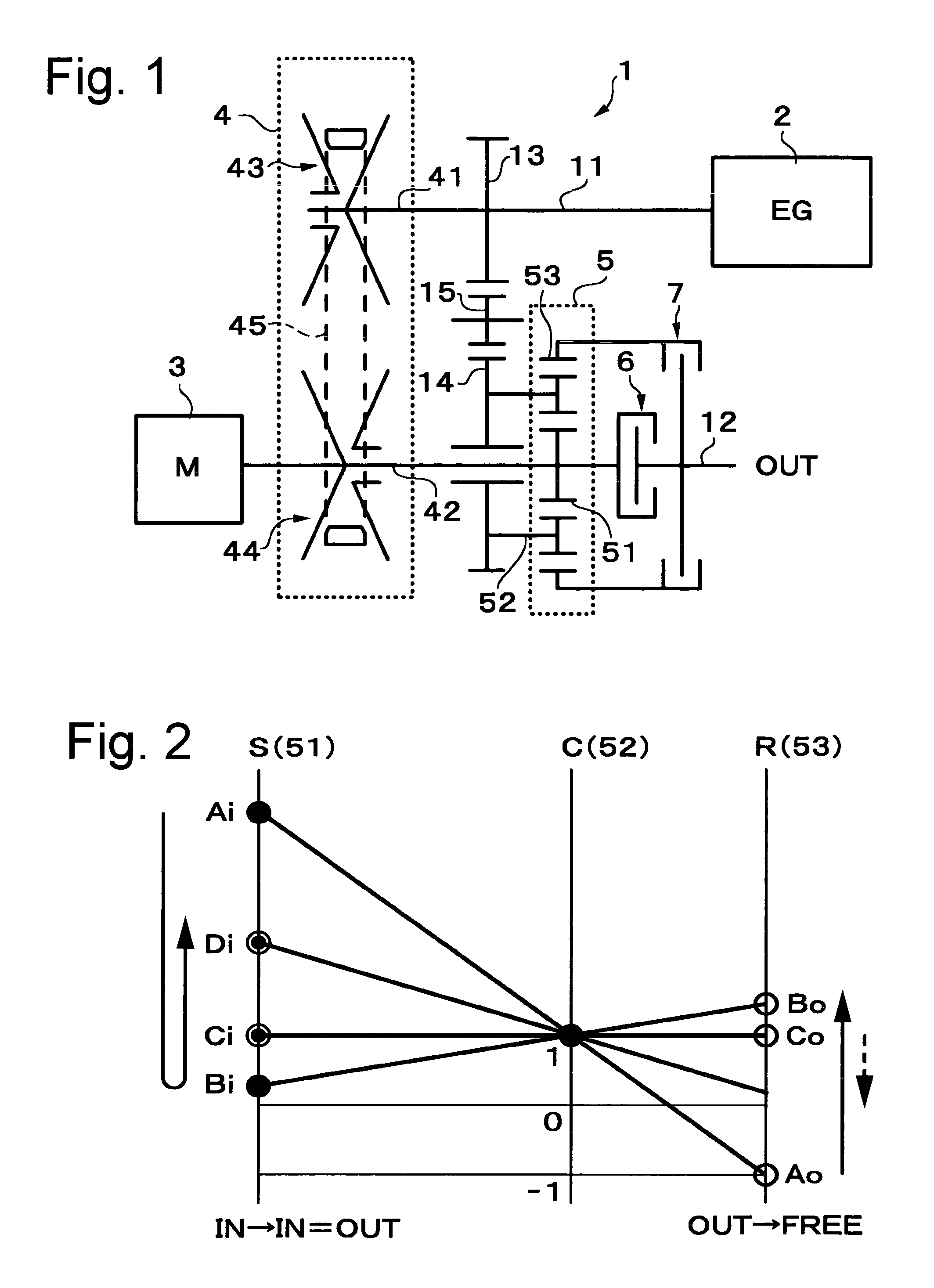
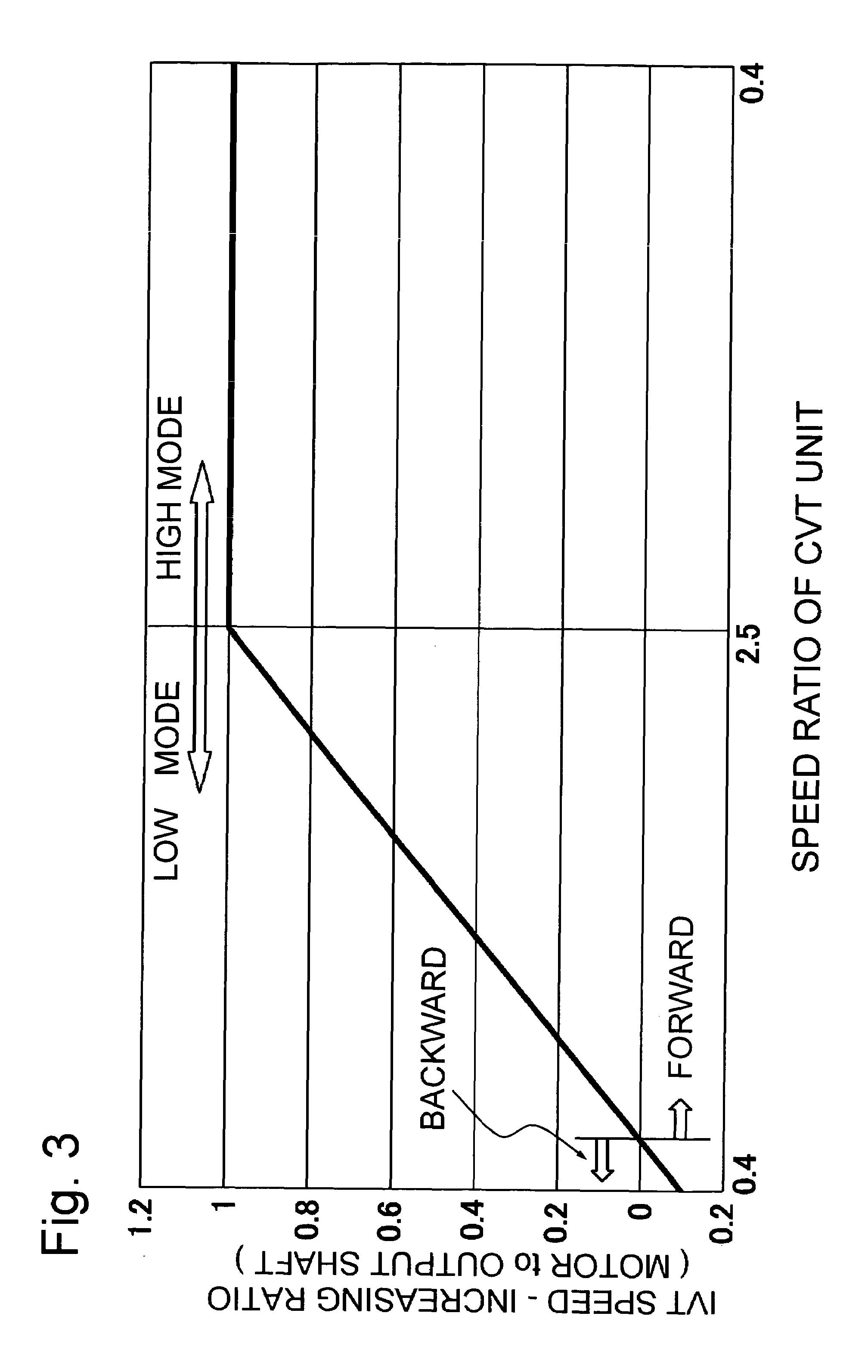
A hybrid-vehicle power train connected to an engine comprises a motor, a CVT unit, a planetary gear unit having at least two input elements, namely, first and second input elements and an output element, a first clutch for engaging / disengaging the first input element with / from a final shaft of the power train, and a second clutch for engaging / disengaging the output element with / from the final shaft of the power train. An input shaft of the CVT unit is connected to the engine and is drivingly connected to the second input element. An output shaft of the CVT unit is connected to the first input element. The motor is connected to the output shaft of the CVT unit. According this configuration, motor torque is amplified and transmitted to the final shaft when the first clutch is engaged, while motor torque is transmit directly to the final shaft when the second clutch is engaged.
Owner:EQUOS RES
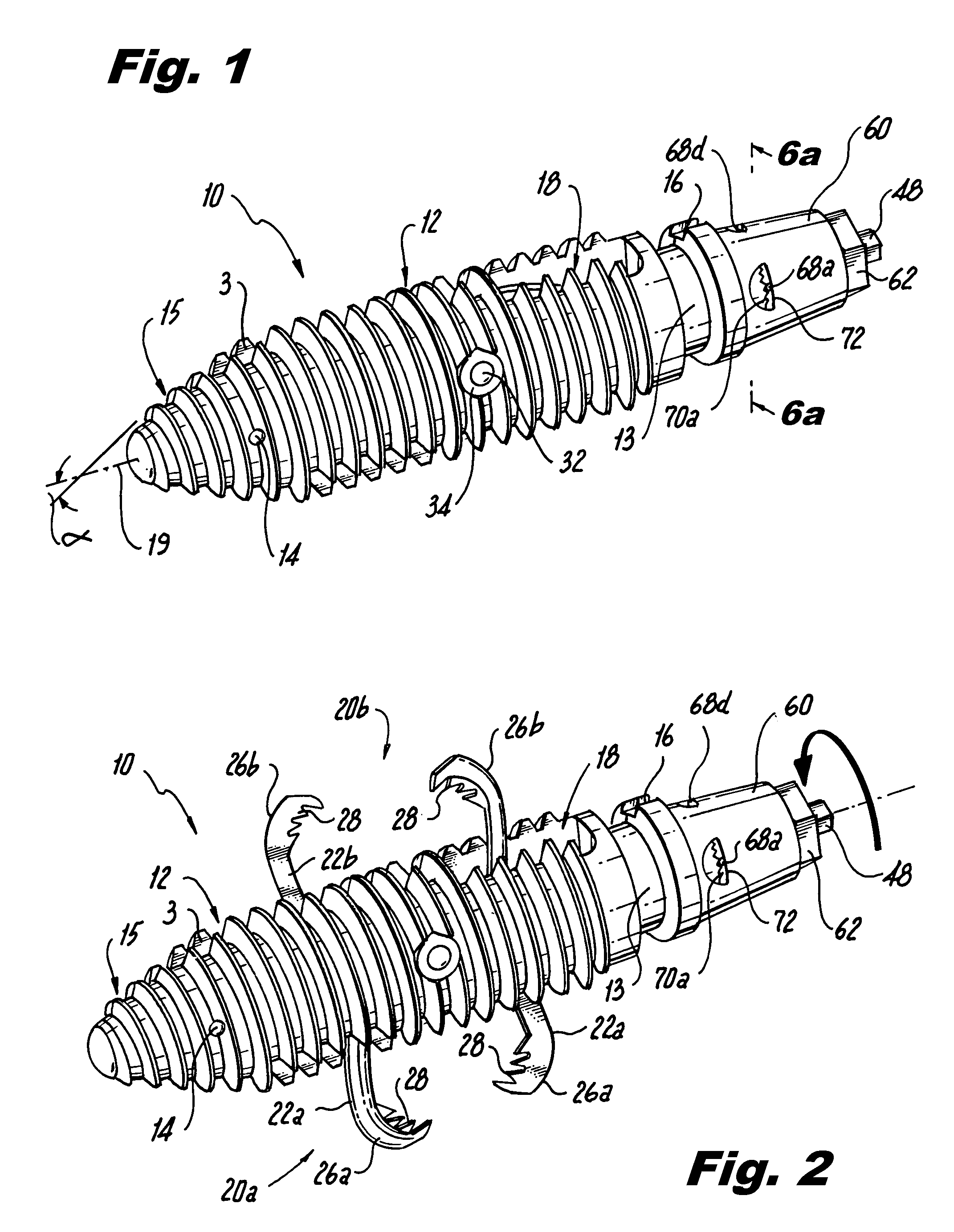
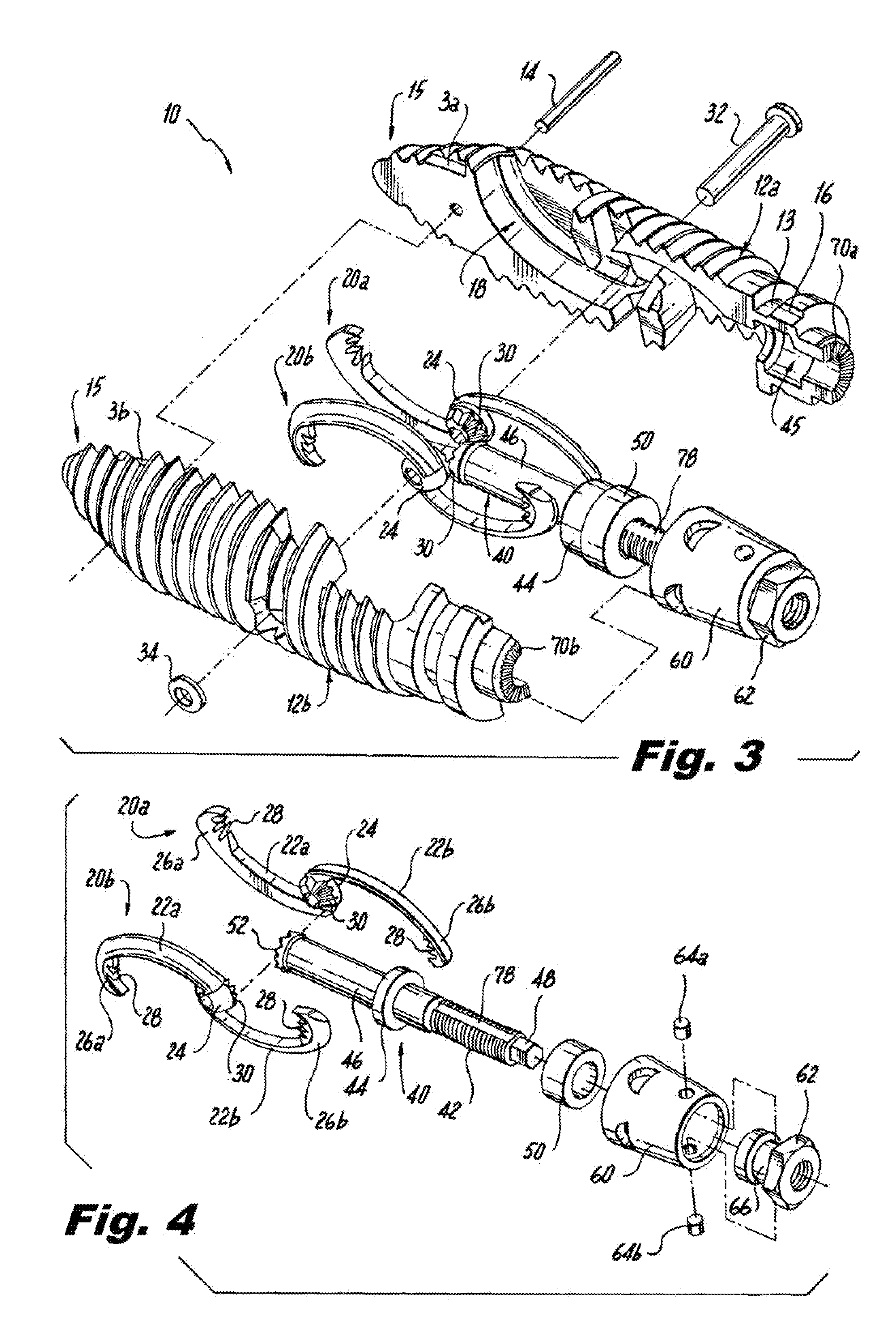
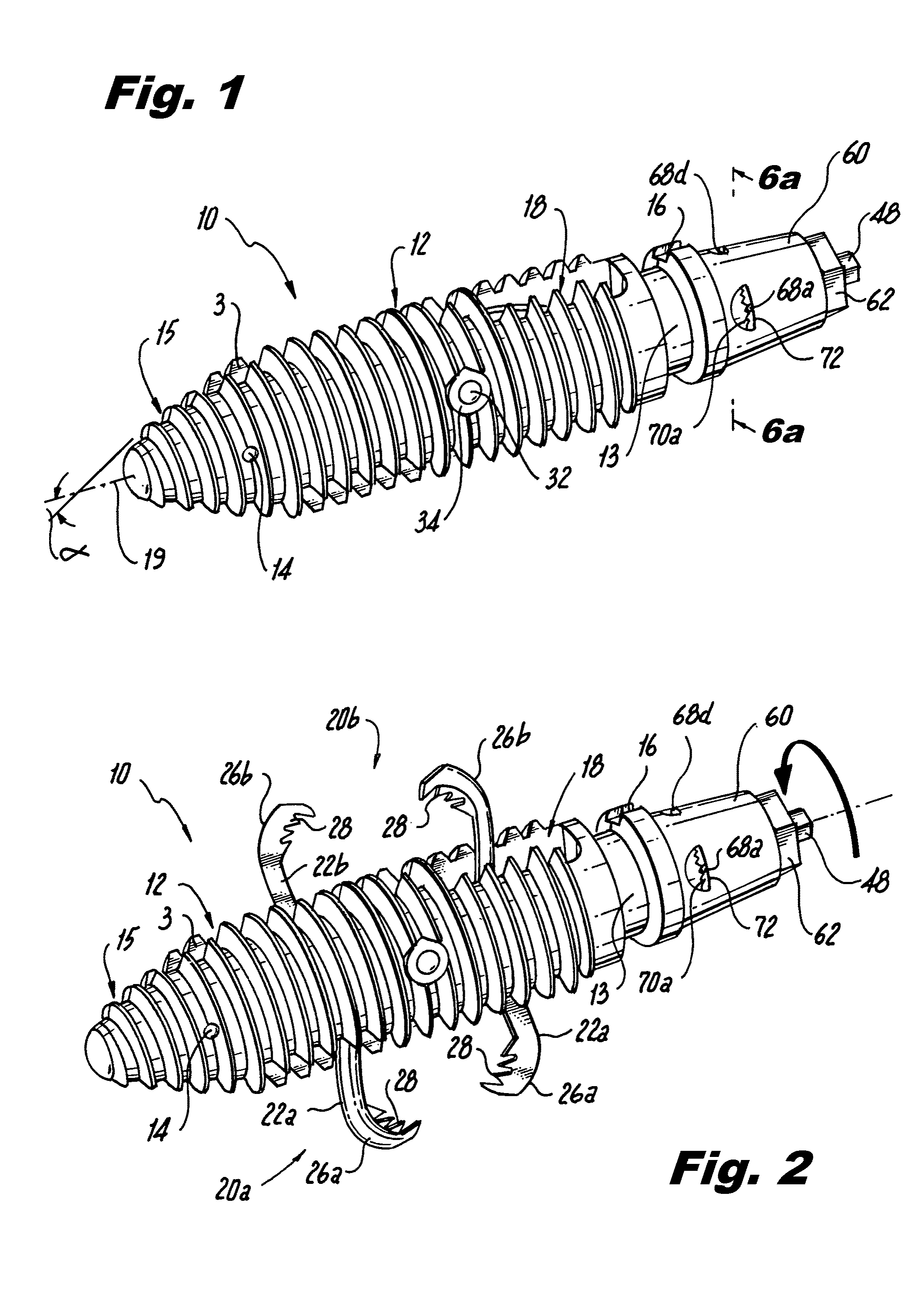
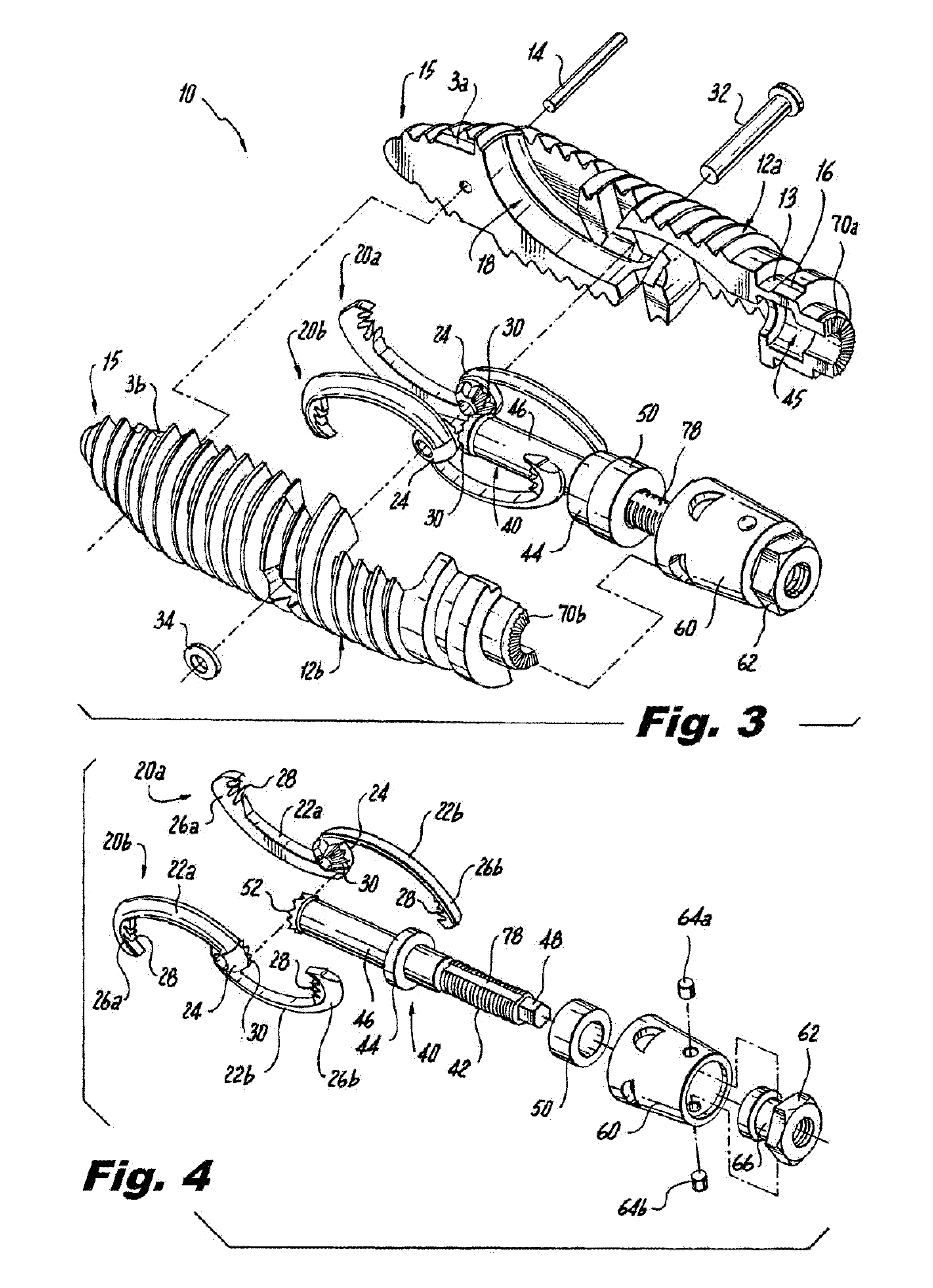
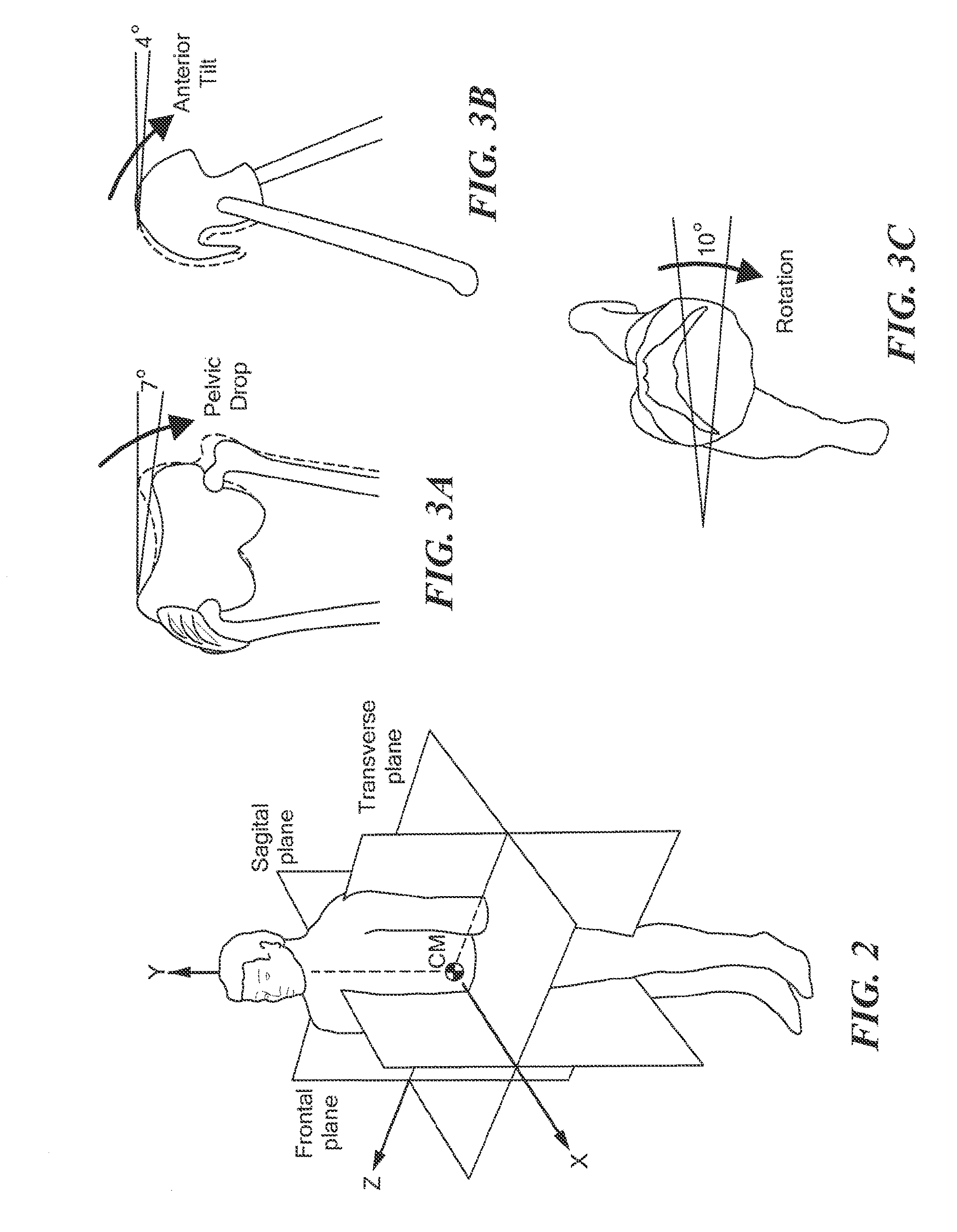
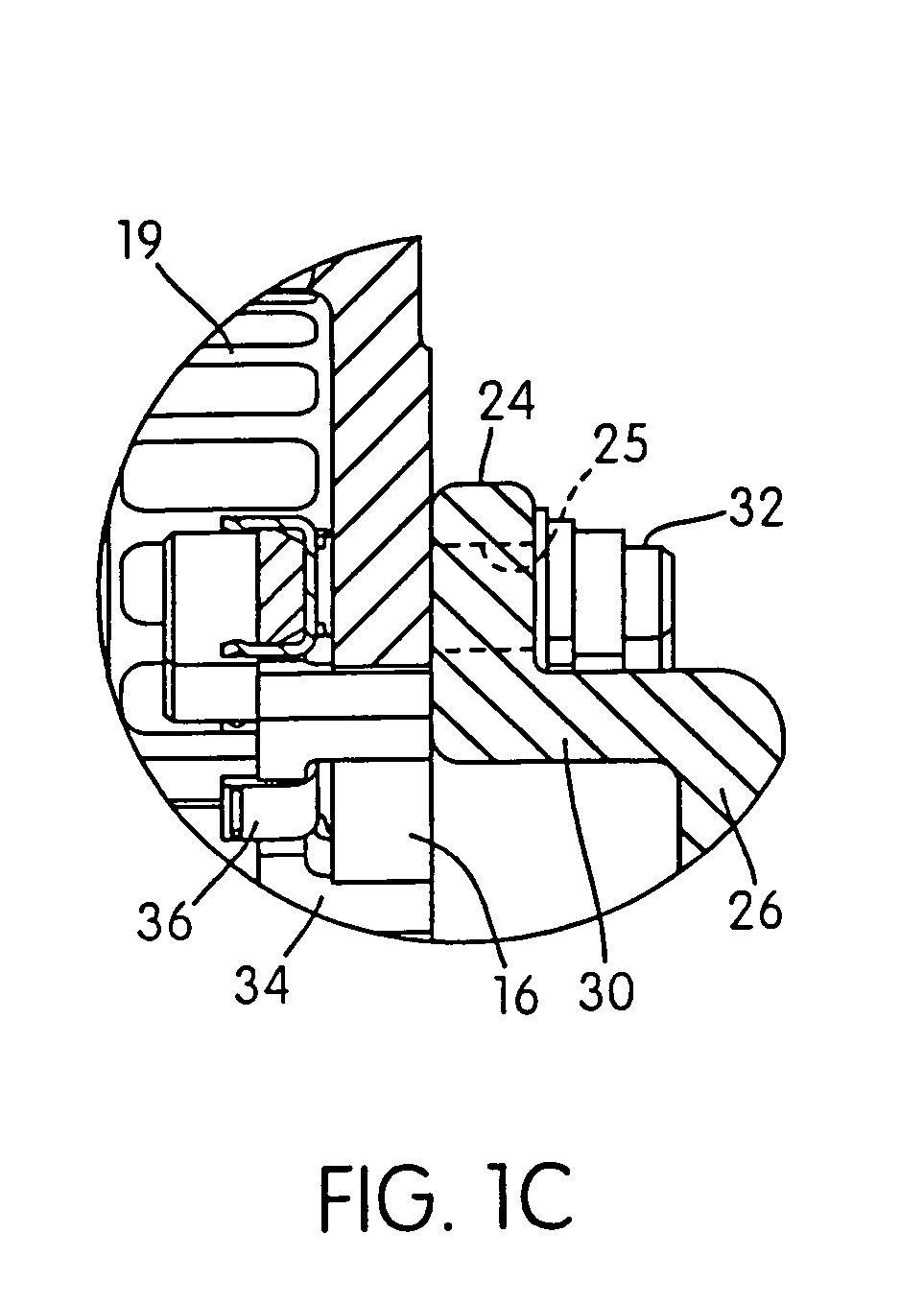
Interspinous process implants having deployable engagement arms
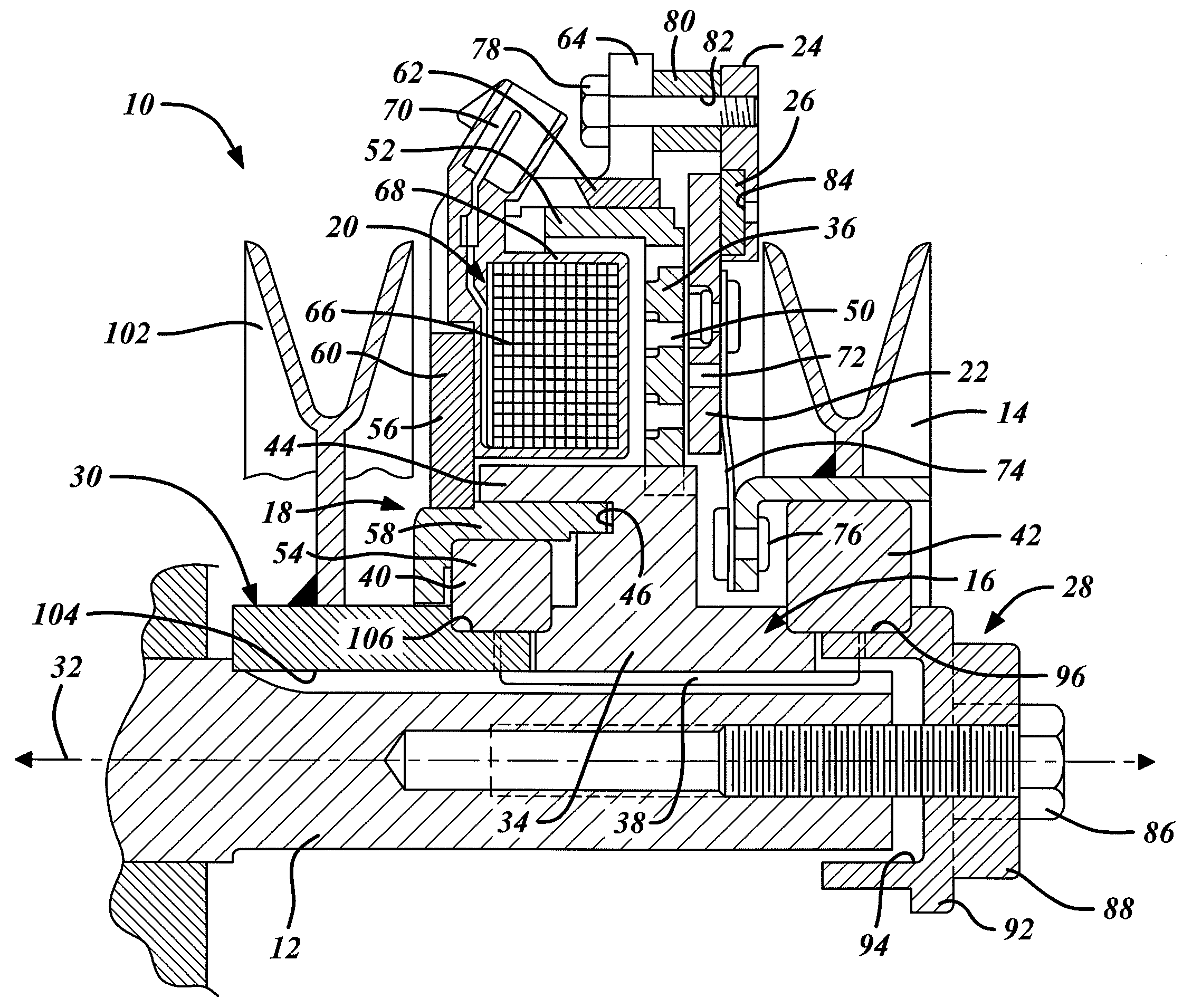
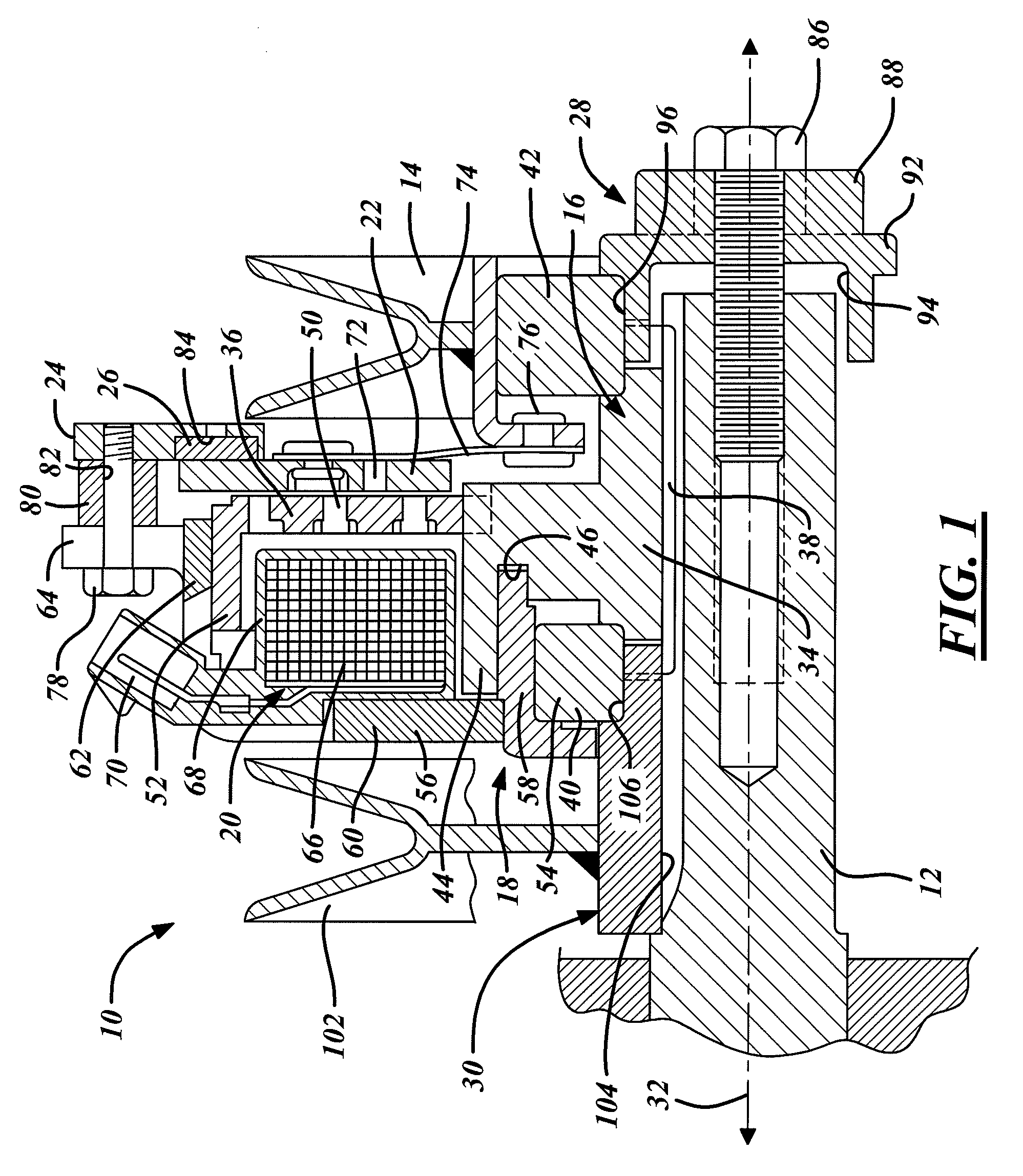
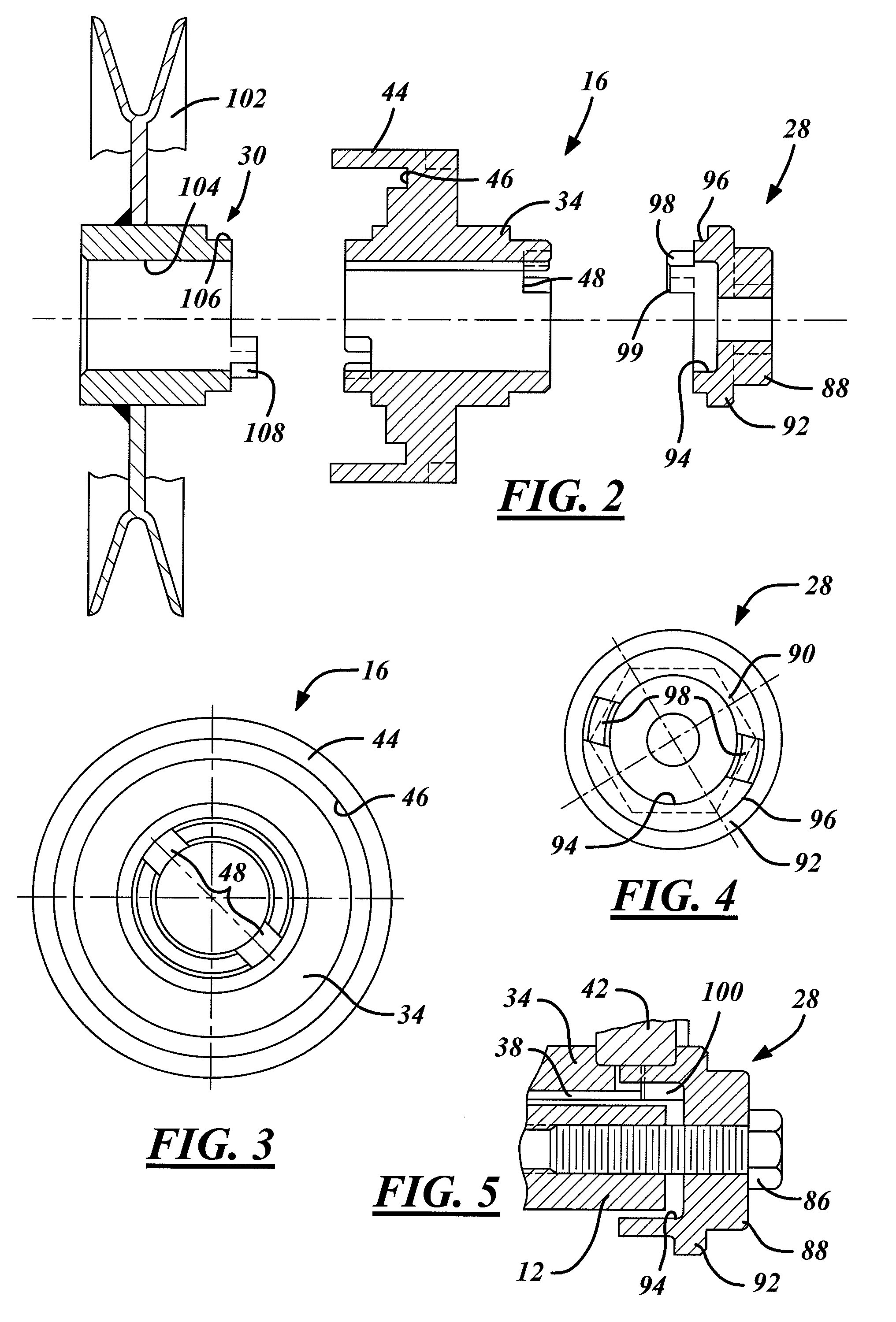
ActiveUS20090292316A1Good torque transmissionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionSpinal implant
Spinal implants include an elongated body portion dimensioned and configured for percutaneous introduction into a target interspinous process space, at which interspinous distraction and / or spinal fusion are desired. The body portion can include a threaded outer surface, or alternatively a smooth surface. The body portion can include one or more interior cavities, and can include deployable engagement members adapted and configured to move in tandem between a stowed position retracted within the interior cavity of the body portion and a deployed position extended from the interior cavity of the body for engaging adjacent spinous processes. An internal drive assembly for selectively moving the engagement members from the stowed position to the deployed position can be provided, as can a elements for locking the engagement members in a deployed position.
Owner:SPINAL SIMPLICITY
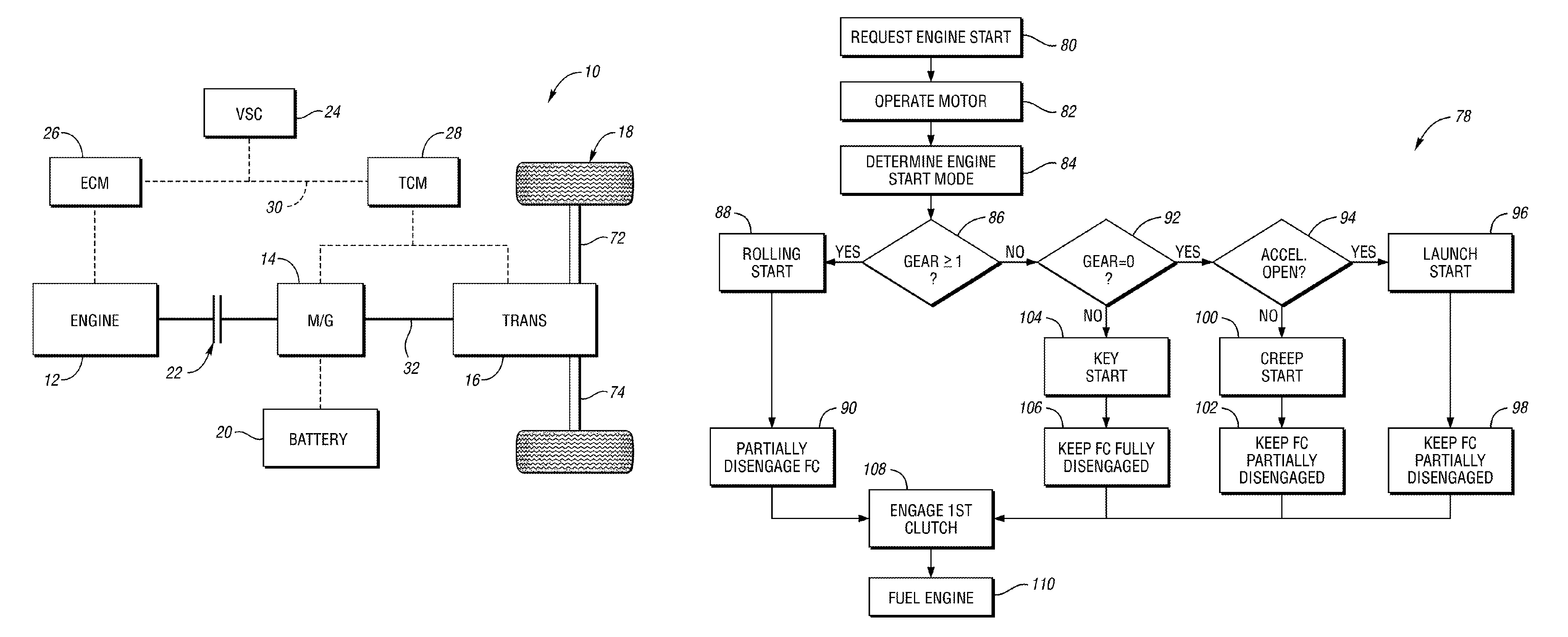
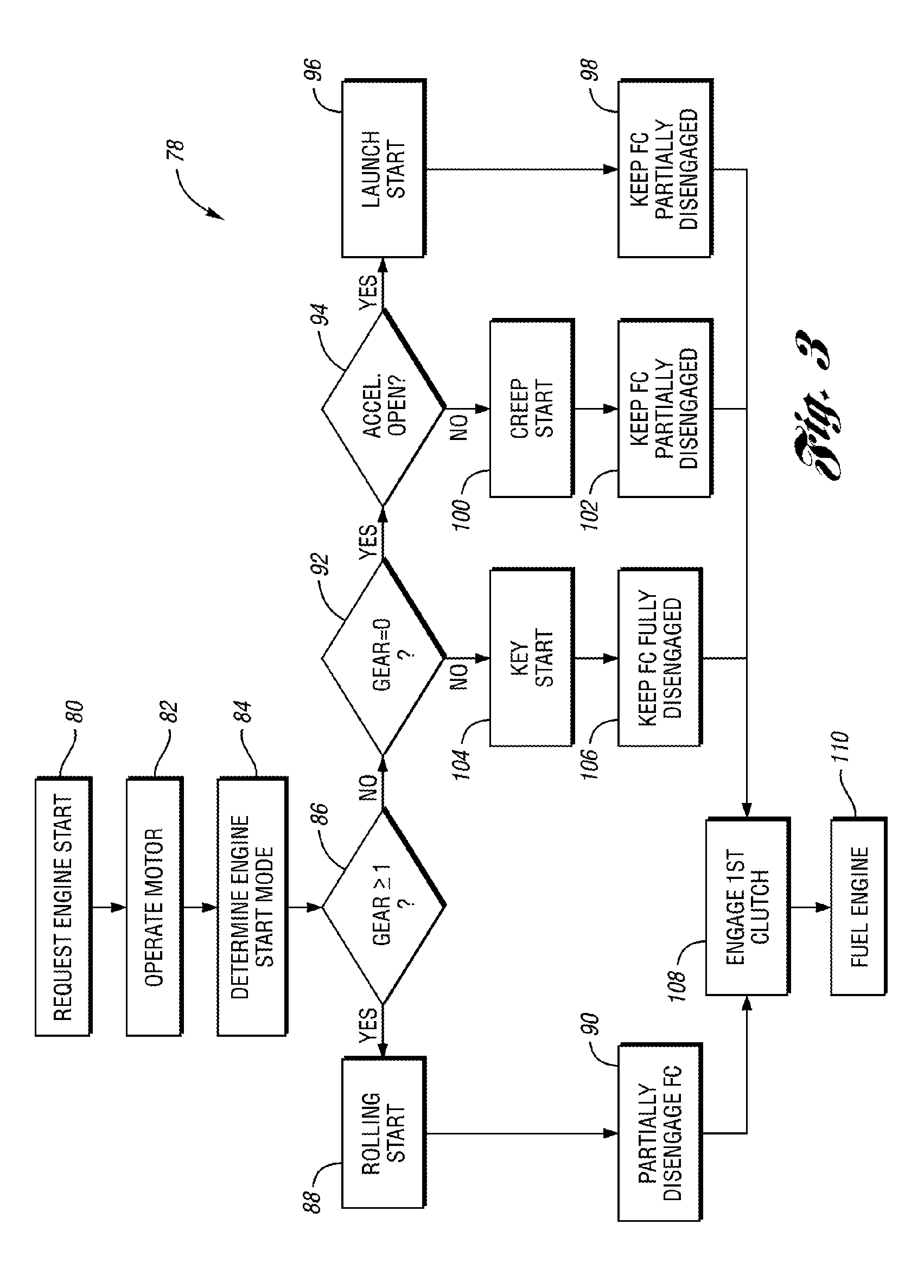
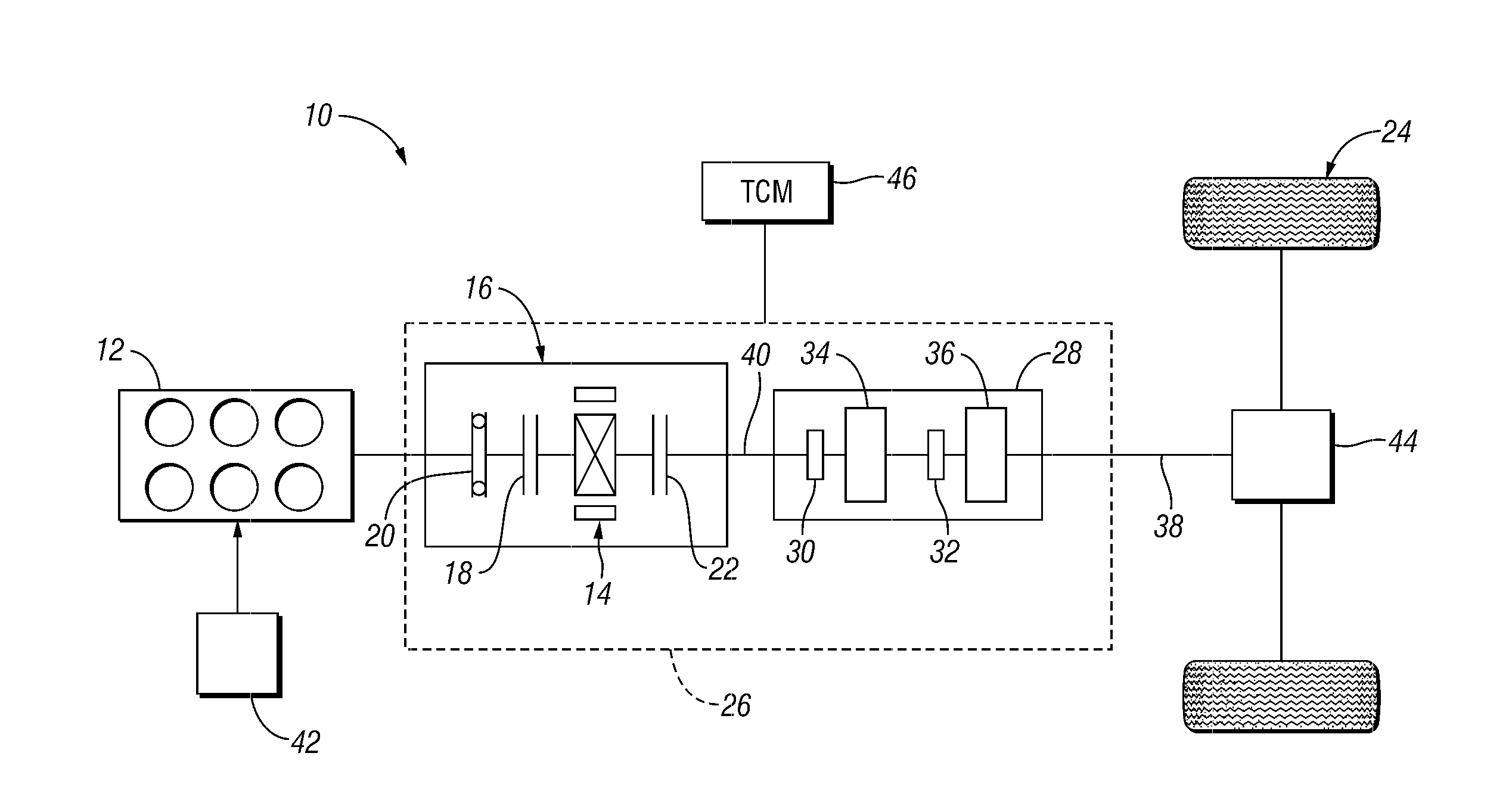
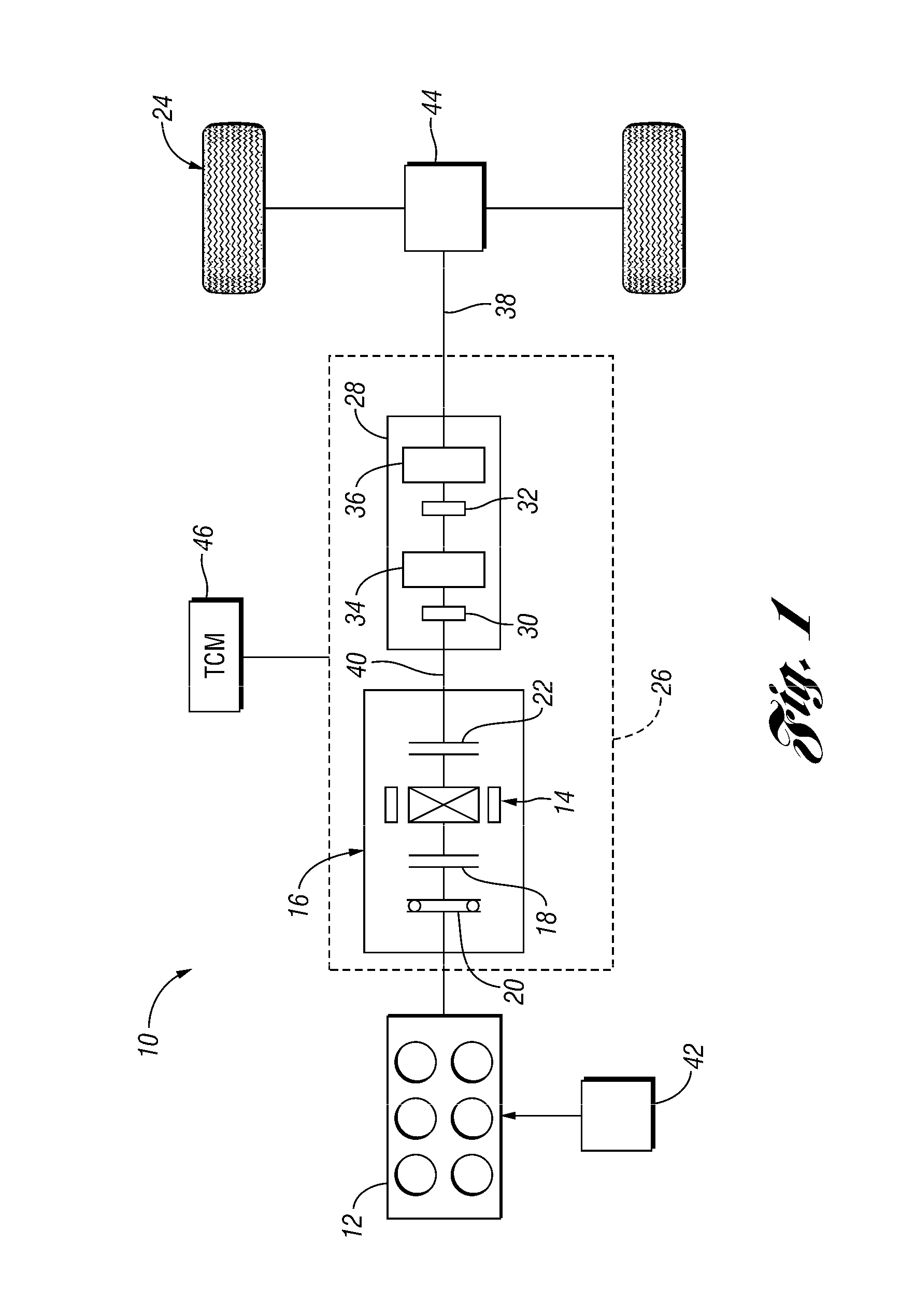
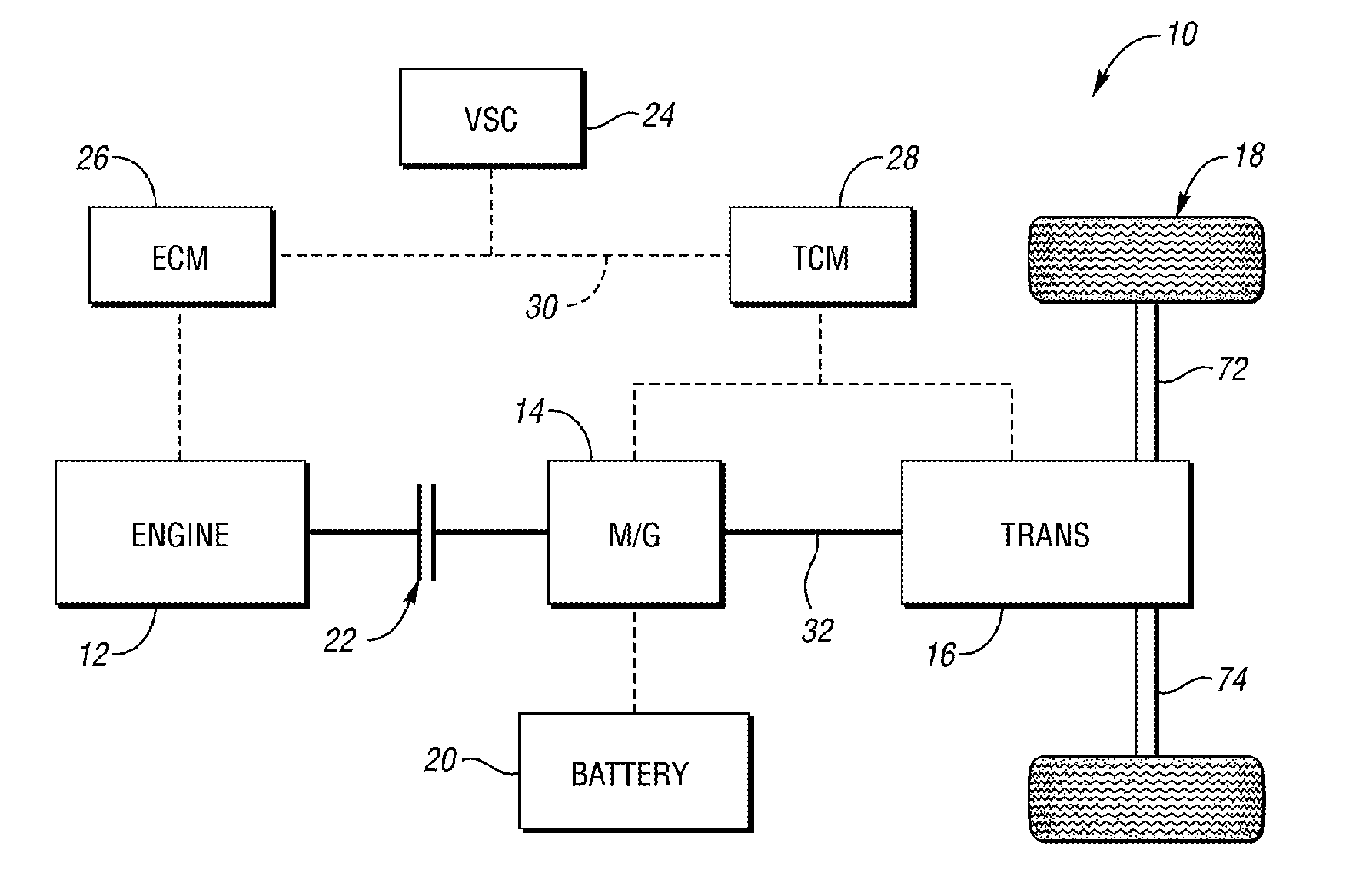
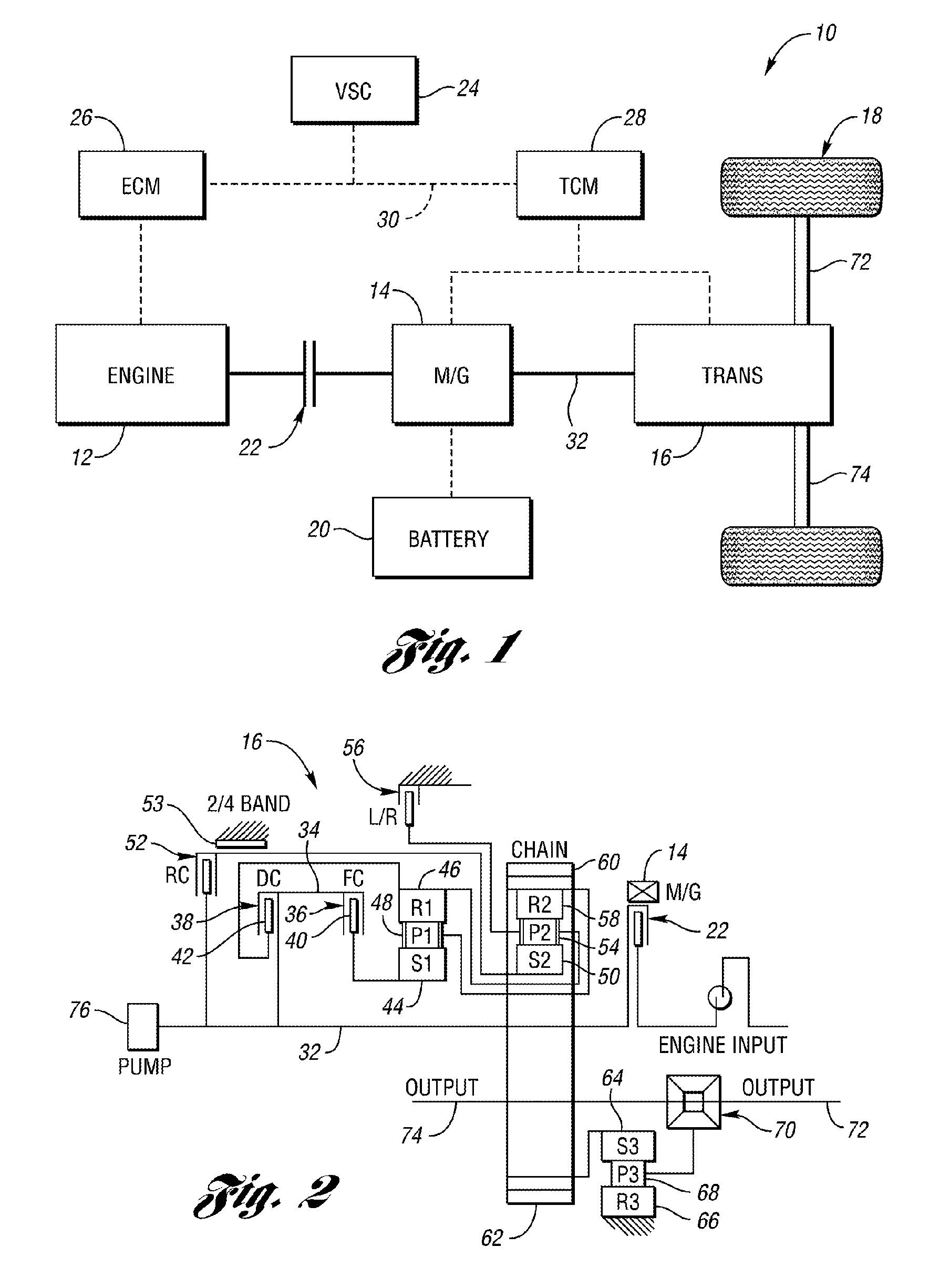
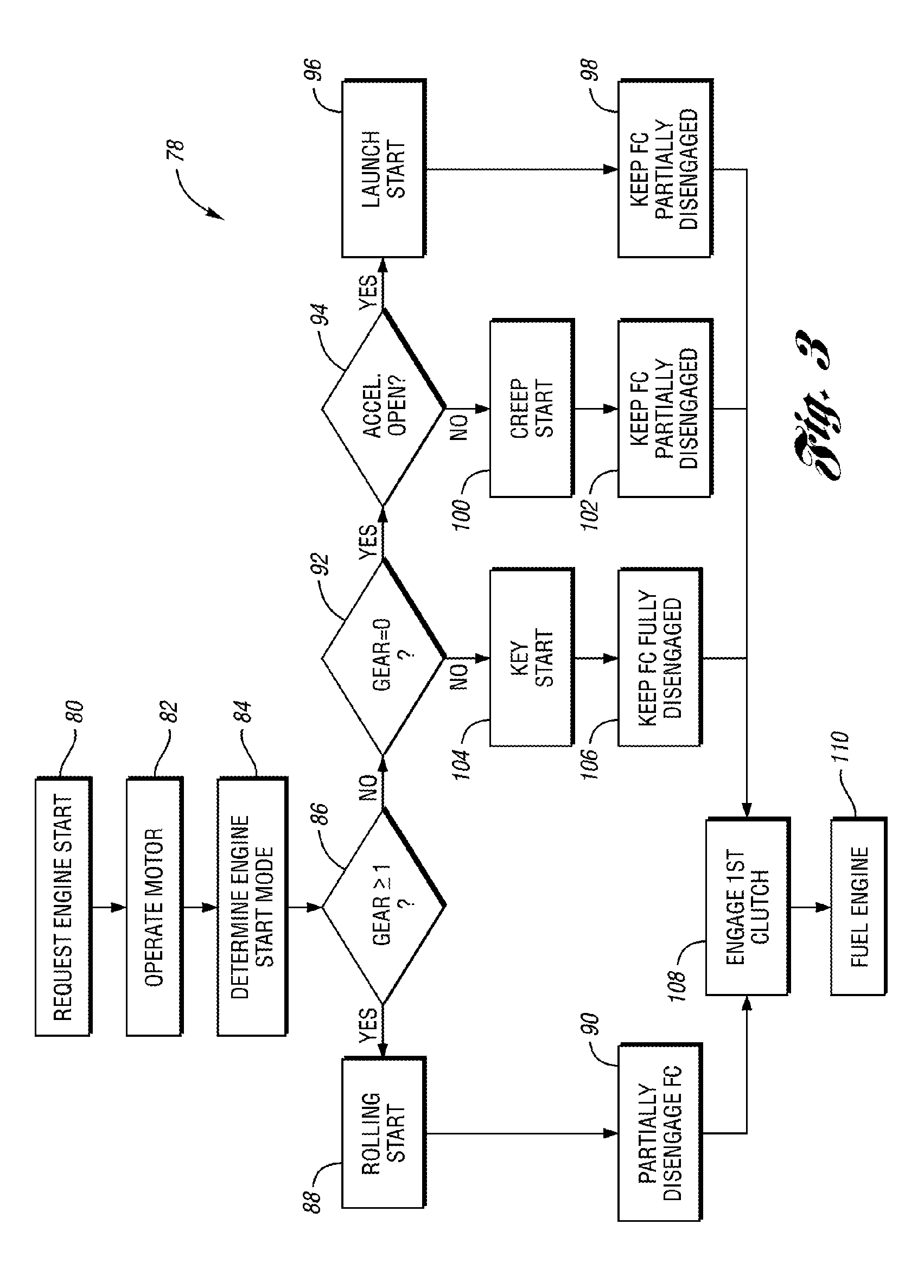
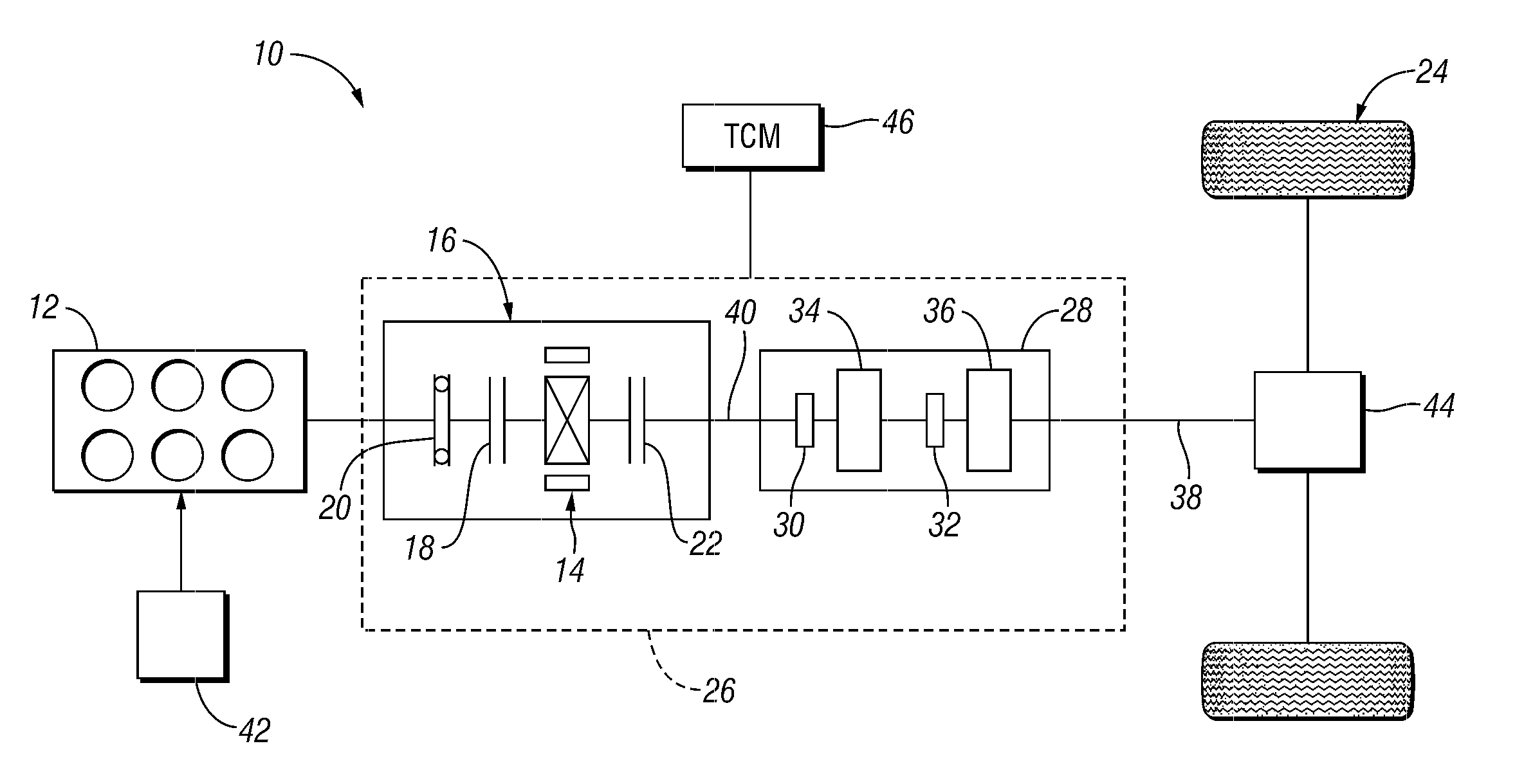
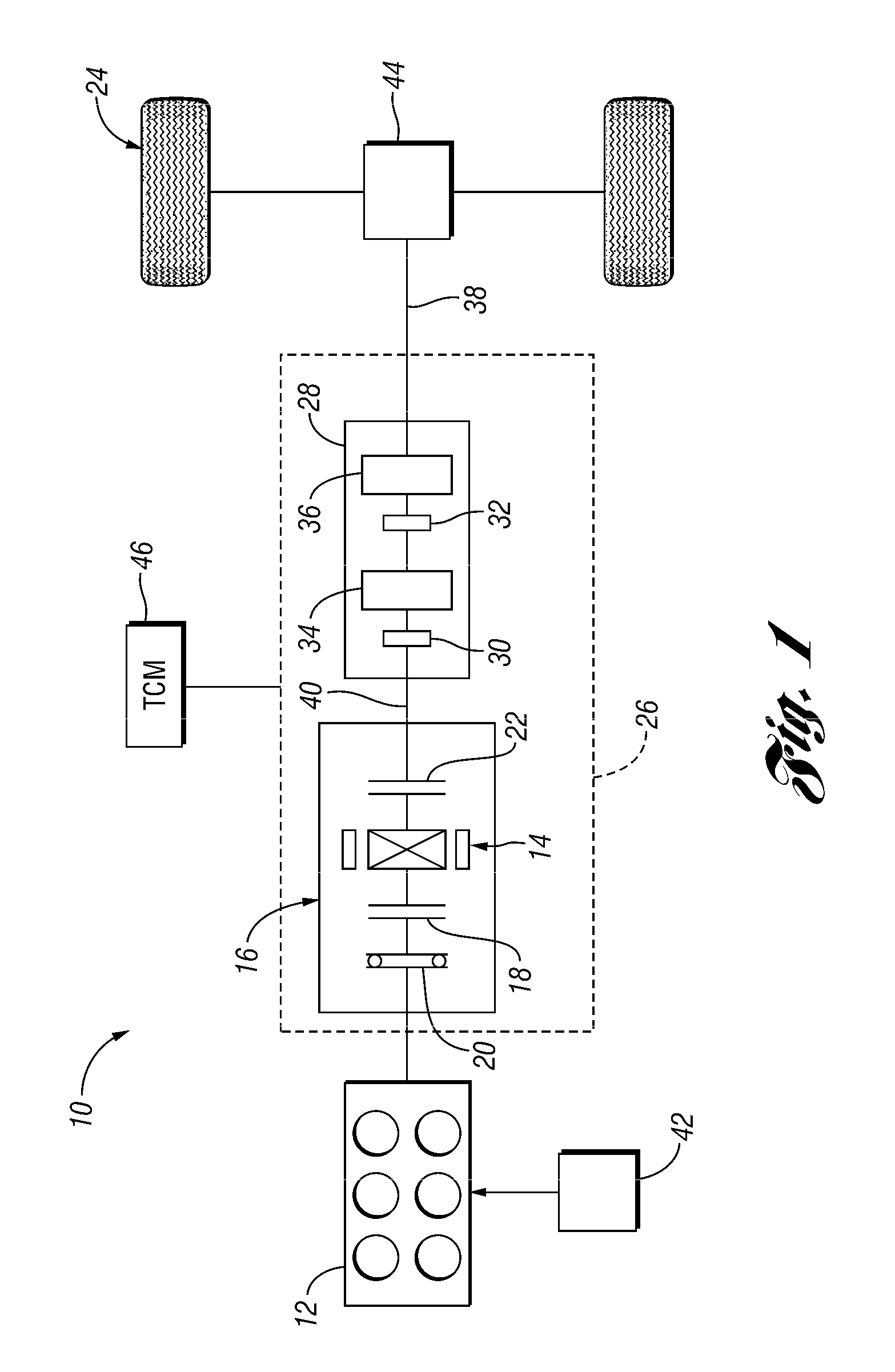
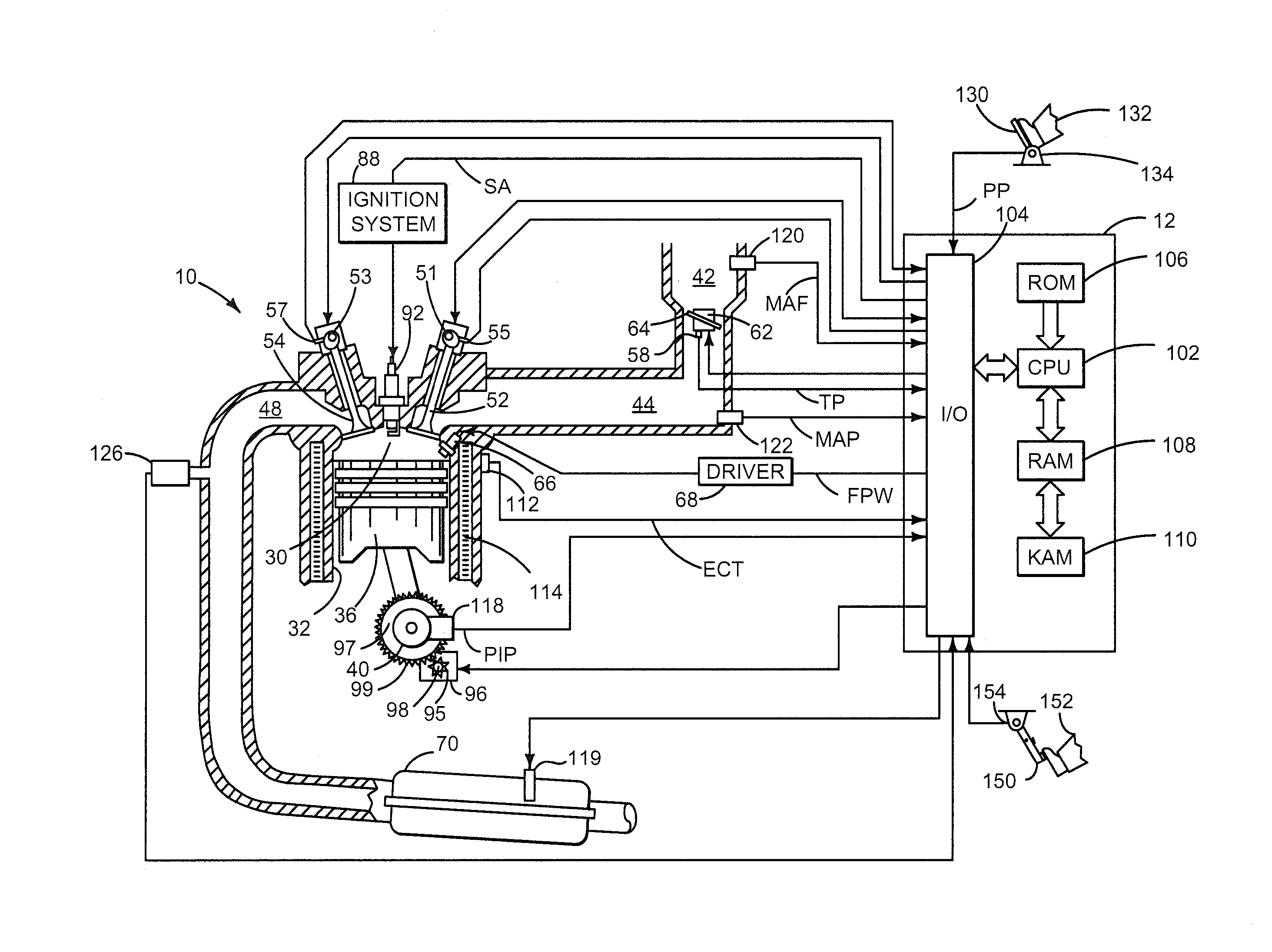
Vehicle and method for controlling engine start in a vehicle
ActiveUS7370715B2Reduce or eliminate driveline torque disturbances.Reduces or eliminates driveline torque disturbancesGas pressure propulsion mountingEngine controllersDrive wheelElectric generator
A vehicle includes a motor / generator, a disconnect clutch disposed between the engine and the motor / generator, and a transmission disposed between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. The transmission includes an input clutch which is selectively engagable for facilitating torque transfer between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. When an engine start is requested, the motor / generator is operated, and a start mode for the engine is determined based on a number of vehicle parameters. The transmission input clutch is partially disengaged to at least partially isolate the vehicle drive wheels from engine torque disturbances when the engine is started. The disconnect clutch is engaged, and the engine is fueled, thereby facilitating torque production by the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method of manufacturing a differentially heat treated catheter guide wire
InactiveUSRE36628E1Increase flexibilityIncrease the diameterGuide wiresDiagnostic recording/measuringTime conditionCoil spring
A catheter guide wire is provided for guiding a catheter into a body cavity such as a blood vessel. The base material constituting the wire is made of an elastic alloy wire and subjected to a heat treatment such that its flexibility is sequentially increased from its proximal to distal end portions. A thermoplastic resin or / and a coil spring can be applied to at least the distal end portion of the wire base material. A method of manufacturing the catheter guide wire is also provided. The method is characterized in that the leading end side of the base material is divided into a plurality of areas and subjected to a heat treatment by changing the heat treatment temperature and the time conditions in units of the areas so that the flexibility of the base material is sequentially increased from the proximal to distal end portions of the leading end side.
Owner:TERUMO KK
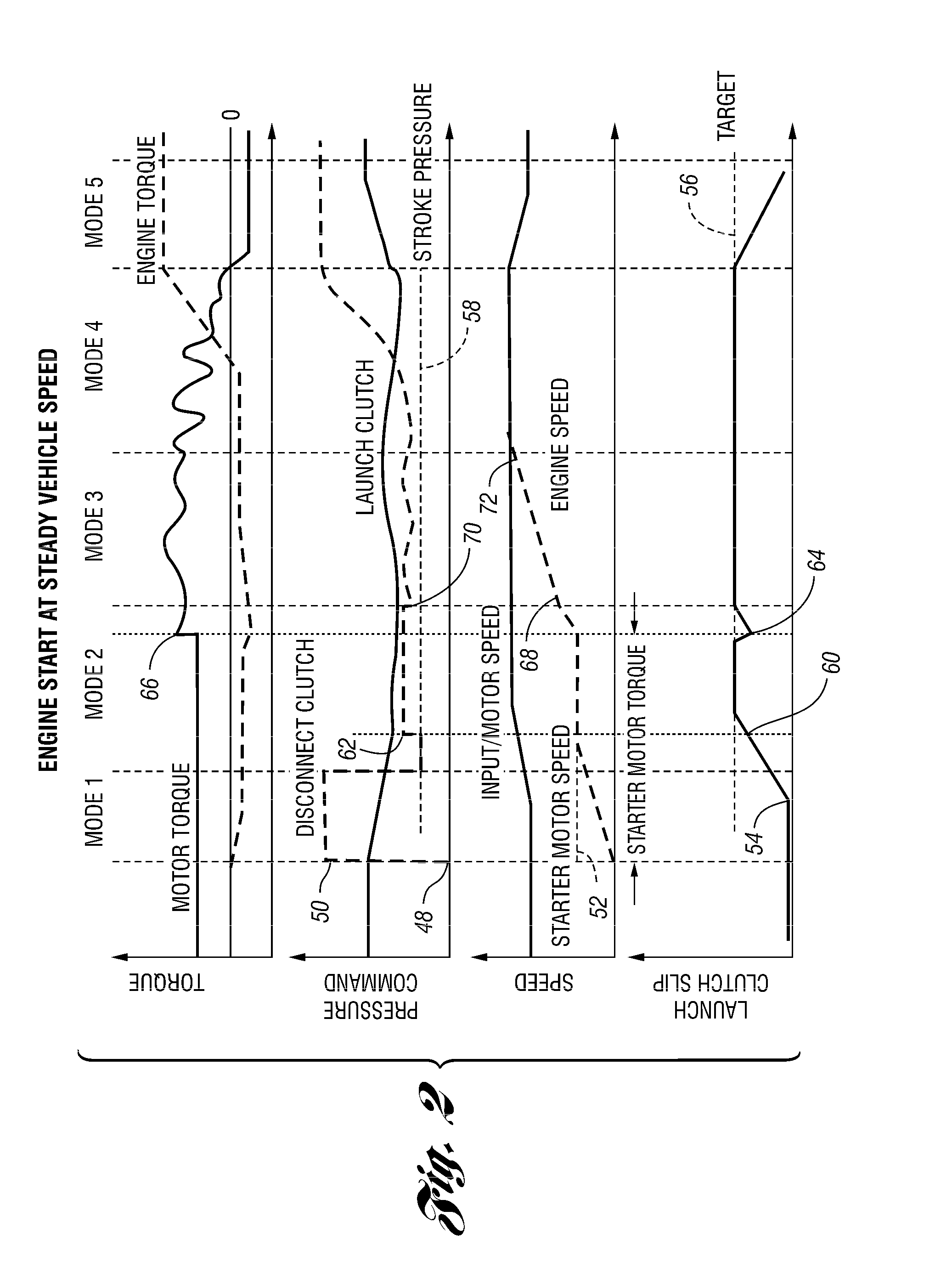
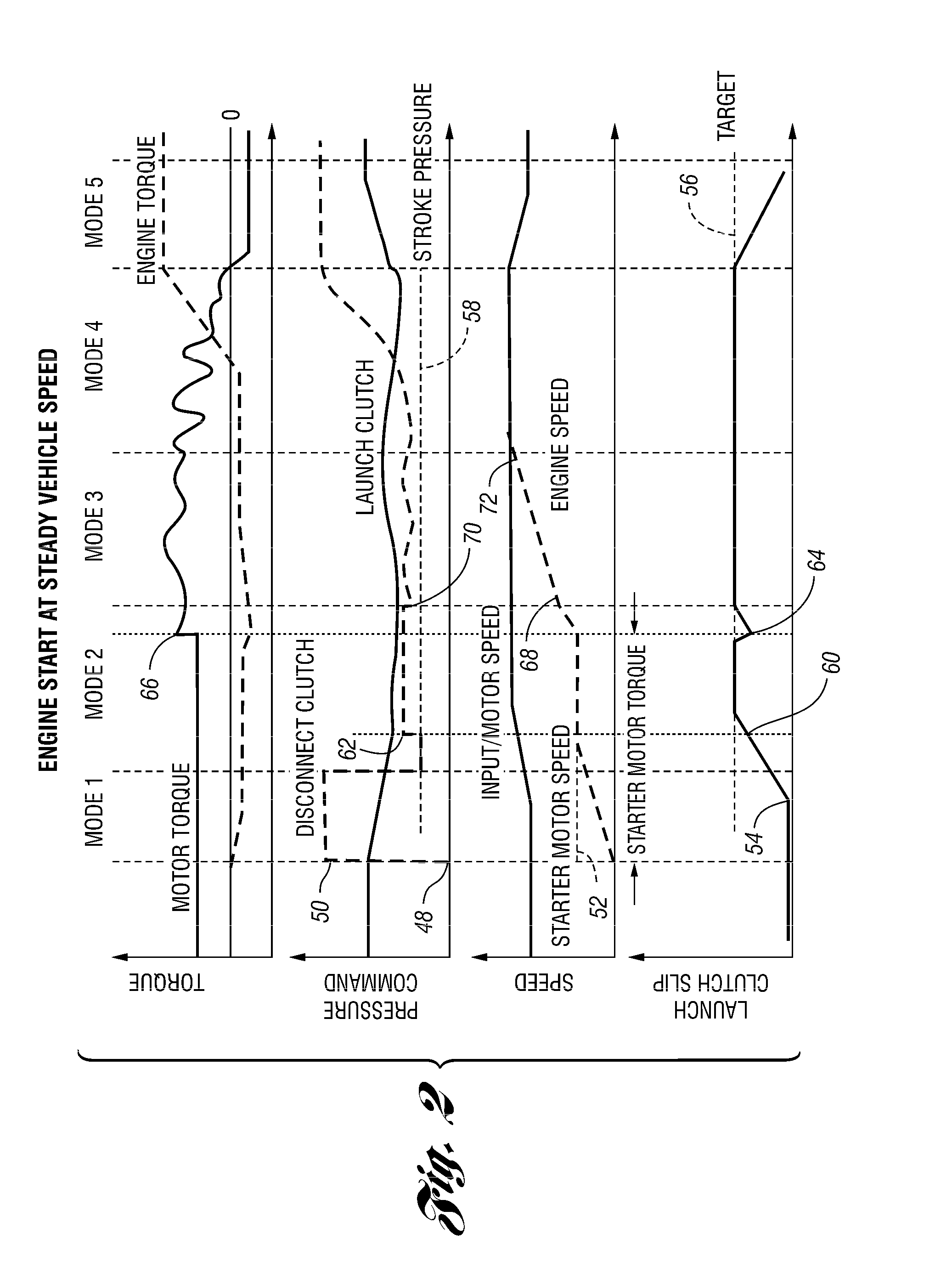
Vehicle And Method For Controlling Engine Start In A Vehicle
ActiveUS20110118078A1Driveline torque disturbances are reduced or eliminatedReduce transferPower operated startersEngine controllersDrive wheelDrivetrain
A vehicle includes a motor / generator, a starter motor, a disconnect clutch disposed between the engine and the motor / generator, and at least one clutch disposed between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. When an engine start is requested, various parameters are controlled to ensure a smooth engine start wherein driveline torque disturbances are minimized. The starter motor is used to crank the engine at the lowest engine speeds when the engine-required torque is the highest. This reduces the amount of torque necessary to be supplied from the motor / generator, and further helps to reduce torque disturbances in the driveline. If the motor / generator is producing torque to propel the vehicle at the time the engine start is requested, a launch clutch or one or more transmission clutches can be controlled to provide slip between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels to further reduce torque disturbances in the driveline.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Interspinous process implants having deployable engagement arms
ActiveUS8142479B2Good torque transmissionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionSpinal implant
Spinal implants include an elongated body portion dimensioned and configured for percutaneous introduction into a target interspinous process space, at which interspinous distraction and / or spinal fusion are desired. The body portion can include a threaded outer surface, or alternatively a smooth surface. The body portion can include one or more interior cavities, and can include deployable engagement members adapted and configured to move in tandem between a stowed position retracted within the interior cavity of the body portion and a deployed position extended from the interior cavity of the body for engaging adjacent spinous processes. An internal drive assembly for selectively moving the engagement members from the stowed position to the deployed position can be provided, as can a elements for locking the engagement members in a deployed position.
Owner:SPINAL SIMPLICITY
Robotic gait rehabilitation training system with orthopedic lower body exoskeleton for torque transfer to control rotation of pelvis during gait
InactiveUS20140213951A1Facilitates robotic gaitGood torque transmissionDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesRoboticsControl system
A robotic gait rehabilitation (RGR) training system is provided to address secondary gait deviations such as hip-hiking. An actuation assembly follows the natural motions of a user's pelvis, while applying corrective moments to pelvic obliquity. A human-robot interface (HRI), in the form of a lower body exoskeleton, is provided to improve the transfer of corrective moments to the pelvis. The system includes an impedance control system incorporating backdrivability that is able to modulate the forces applied onto the body depending on the patient's efforts. Various protocols for use of the system are provided.
Owner:SPAULDING REHABILITATION HOSPITAL CORP +1
Vehicle and method for controlling engine start in a vehicle
ActiveUS20060137921A1Reduce or eliminate driveline torque disturbancesReduces or eliminates driveline torque disturbancesGas pressure propulsion mountingEngine controllersDrive wheelEngineering
A vehicle and a method for starting an engine in a vehicle are provided. The vehicle has a motor / generator, a disconnect clutch disposed between the engine and the motor / generator, and a transmission disposed between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. The transmission includes an input clutch which is selectively engagable for facilitating torque transfer between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. When an engine start is requested, the motor / generator is operated, and a start mode for the engine is determined based on a number of vehicle parameters. The transmission input clutch is partially disengaged to at least partially isolate the vehicle drive wheels from engine torque disturbances when the engine is started. The disconnect clutch is engaged, and the engine is fueled, thereby facilitating torque production by the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Vehicle and method for controlling engine start in a vehicle
ActiveUS8192324B2Driveline torque disturbances are reduced or eliminatedReduce transferPower operated startersElectric motor startersDrive wheelDrivetrain
A vehicle includes a motor / generator, a starter motor, a disconnect clutch disposed between the engine and the motor / generator, and at least one clutch disposed between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. When an engine start is requested, various parameters are controlled to ensure a smooth engine start wherein driveline torque disturbances are minimized. The starter motor is used to crank the engine at the lowest engine speeds when the engine-required torque is the highest. This reduces the amount of torque necessary to be supplied from the motor / generator, and further helps to reduce torque disturbances in the driveline. If the motor / generator is producing torque to propel the vehicle at the time the engine start is requested, a launch clutch or one or more transmission clutches can be controlled to provide slip between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels to further reduce torque disturbances in the driveline.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
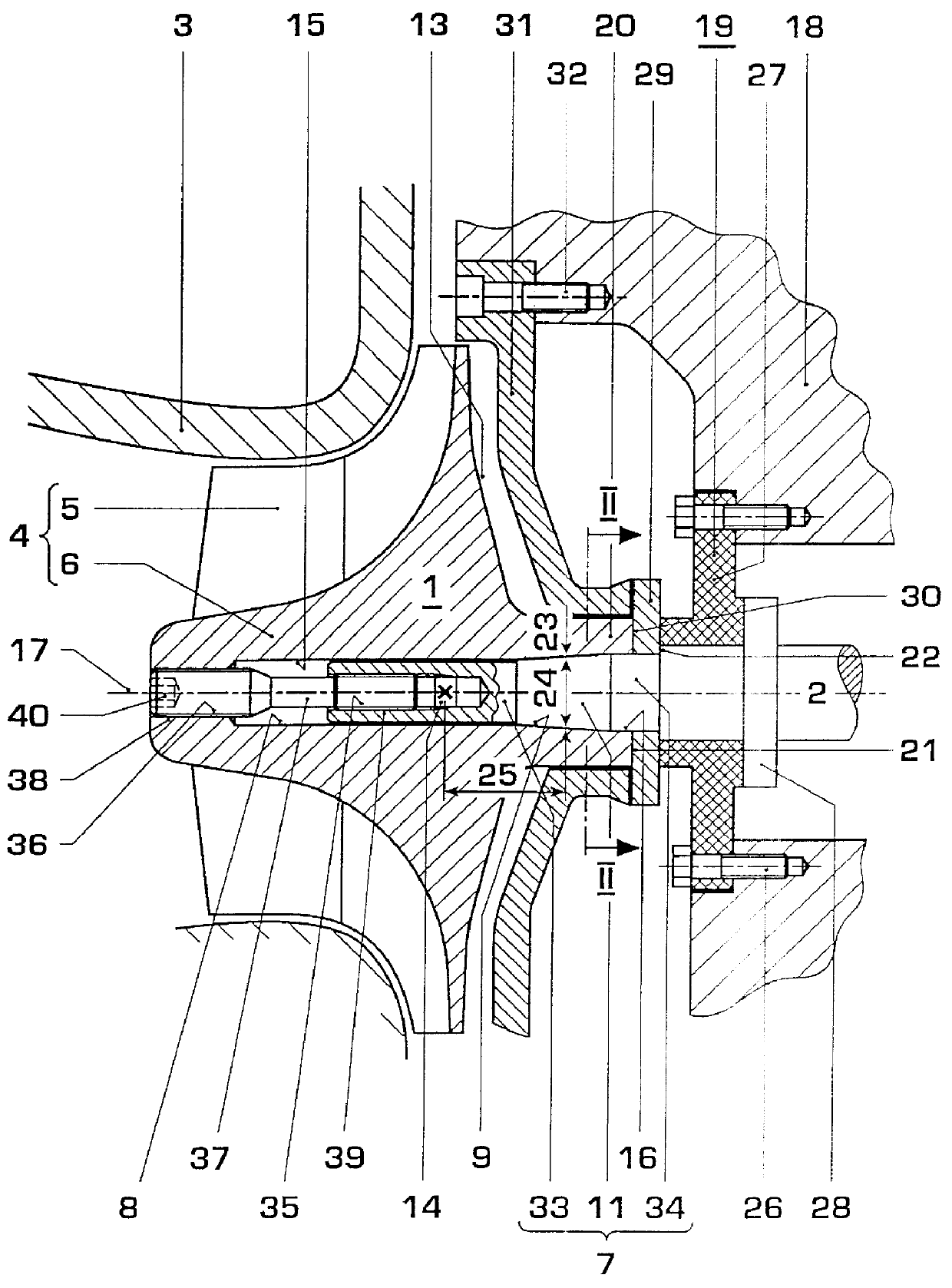
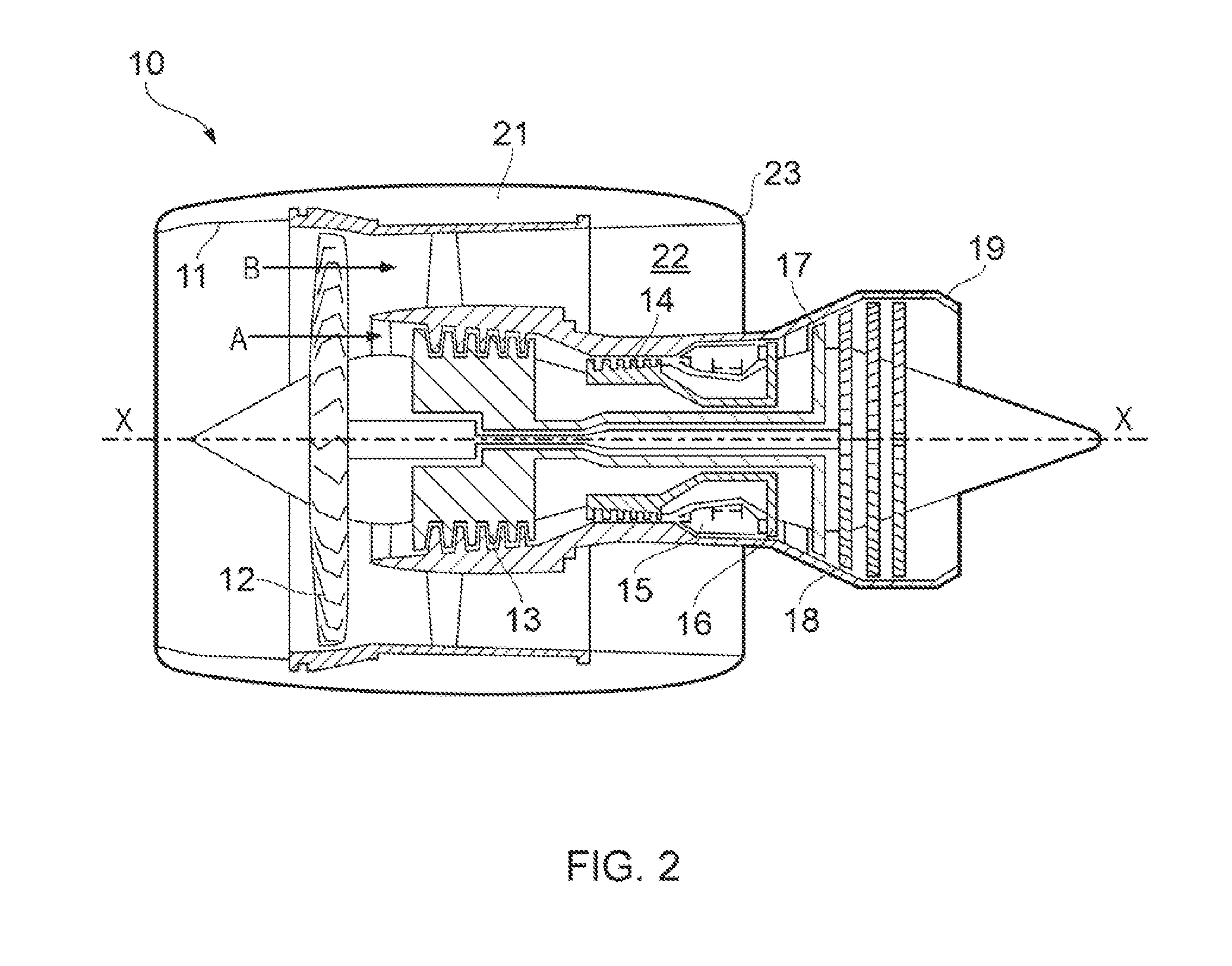
Compressor impeller fastening for high speed turboengines
InactiveUS6012901ALess stressShorten the axial lengthPump componentsRotary propellersMean diameterImpeller
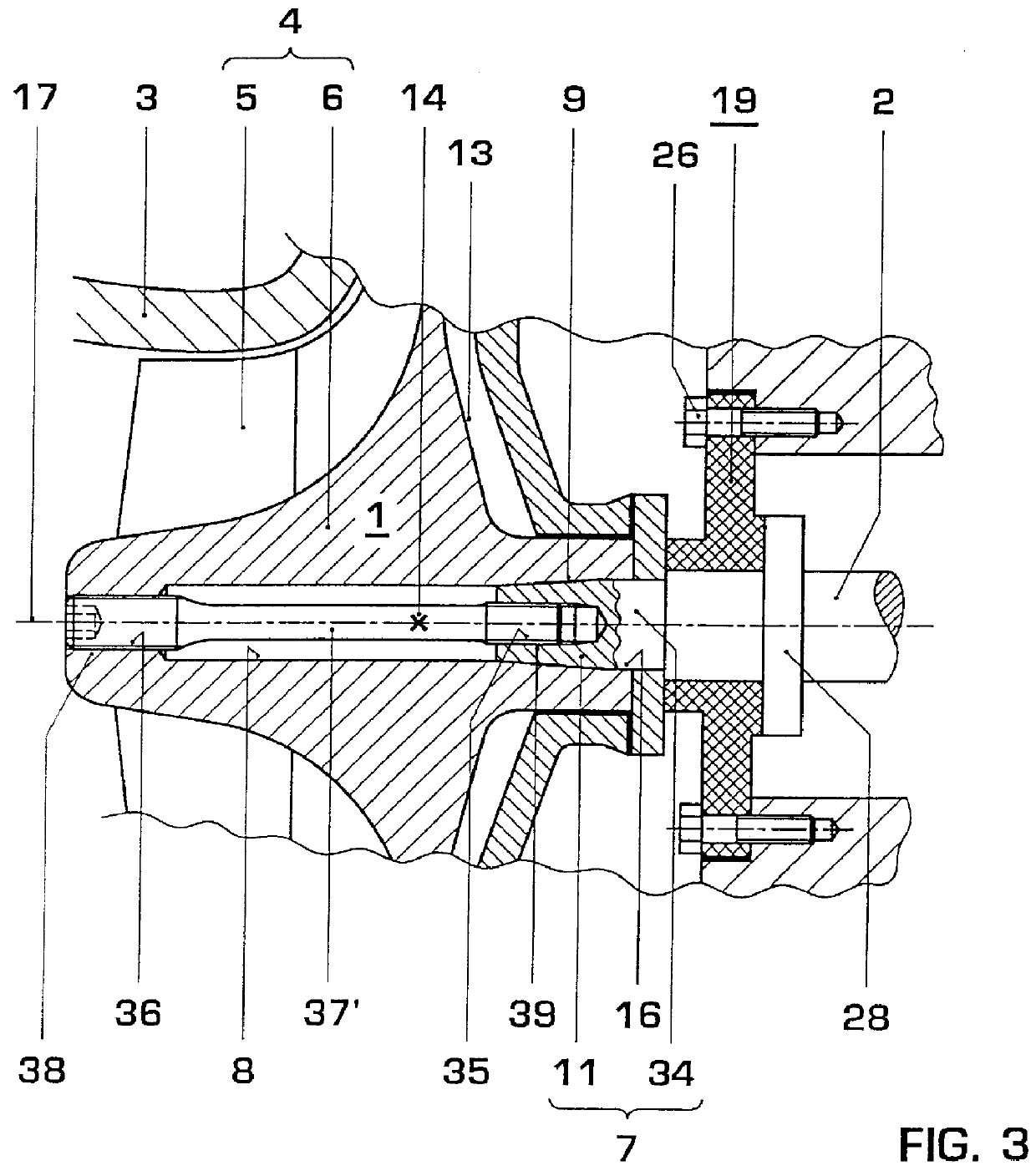
The object of the invention is to provide a safe and reproducible compressor impeller fastening for high speed turboengines, which, moreover, possesses more accurate concentricity. This is achieved, according to the invention, in that both the hub cone (9) and the shaft cone (11) each have a mean diameter (23, 24) and these mean diameters (23, 24) are arranged at an axial distance (25) from the mass center of gravity (14) of the compressor impeller (4), said distance corresponding at least to half the mean diameters (23, 24). On the shaft side of the hub cone (9), the through bore (8) of the hub (6) is designed at least partially as a cylindrical bore (16).
Owner:ABB TURBO SYST
Method of and apparatus for detecting friction heat of a clutch and regulating the clutch
InactiveUS6152275AExtended service lifeGood torque transmissionFluid actuated clutchesEngine controllersMobile vehicleTorque transmission
There are disclosed a method of and an apparatus for regulating the operation of a friction clutch or another torque transmission system in the power train of a motor vehicle. The regulation is such that the operator of the vehicle is informed of a prevailing or impending condition which entails or is about to entail damage to the system or to the entire power train. Such situation can arise in response to excessive and / or prolonged slip of abutting friction surfaces in a friction clutch, overheating of one or more parts of the system for any other reason(s), as a result of improper selection of the transmission speed for starting of the vehicle and / or due to excessive wear upon the friction linings and / or other parts. The remedial undertaking can include such regulation of the system that the ride become uncomfortable to the occupant(s) of the vehicle and / or automatic elimination of the cause(s) of unsatisfactory torque transmission.
Owner:LUK GETRIEBE SYST
Twisting bifurcation delivery system
A catheter system comprises a catheter having an elongate catheter shaft such that a portion of the catheter shaft proximal a stent retaining region defines at least one bend that is bent around the longitudinal axis of a vessel. The catheter also has a side branch guidewire housing, defining a side branch guidewire lumen, and a side branch guidewire that extends through the side branch guidewire lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Handle with vibration-reducing device
InactiveUS20070143966A1Eliminate aforesaid disadvantageMaximum transmissionTravelling carriersHoldersElastic vibrationHand held
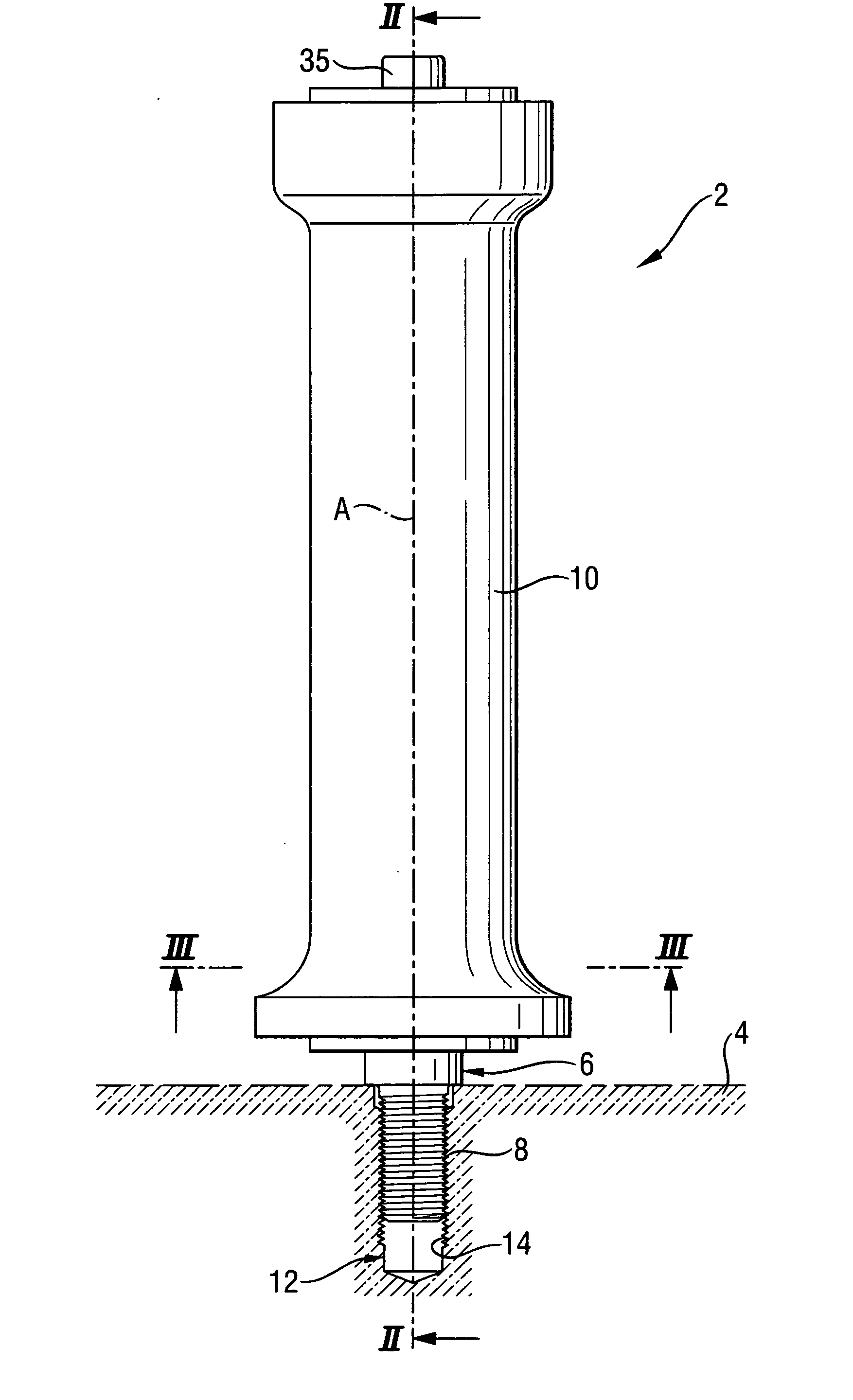
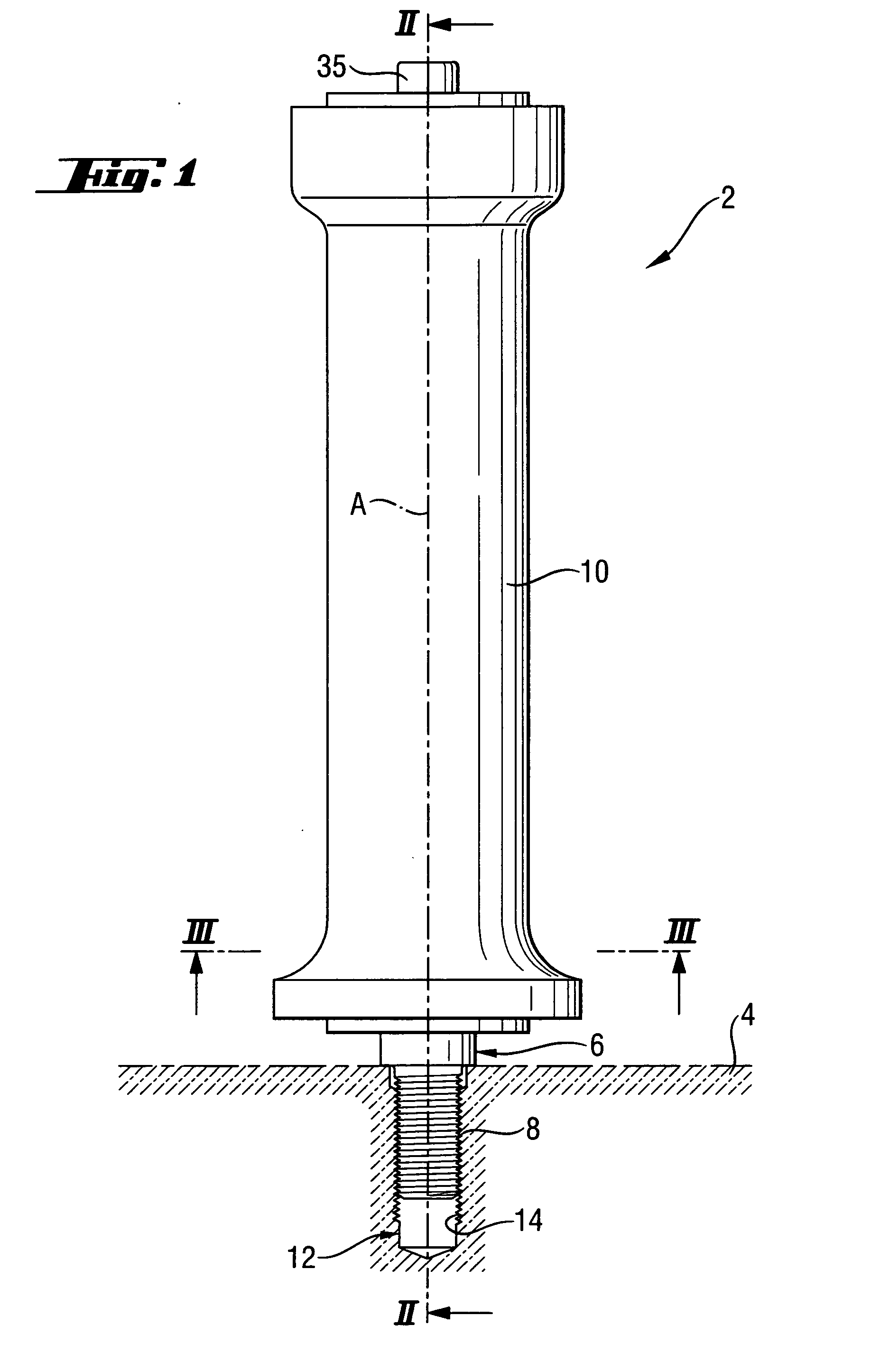
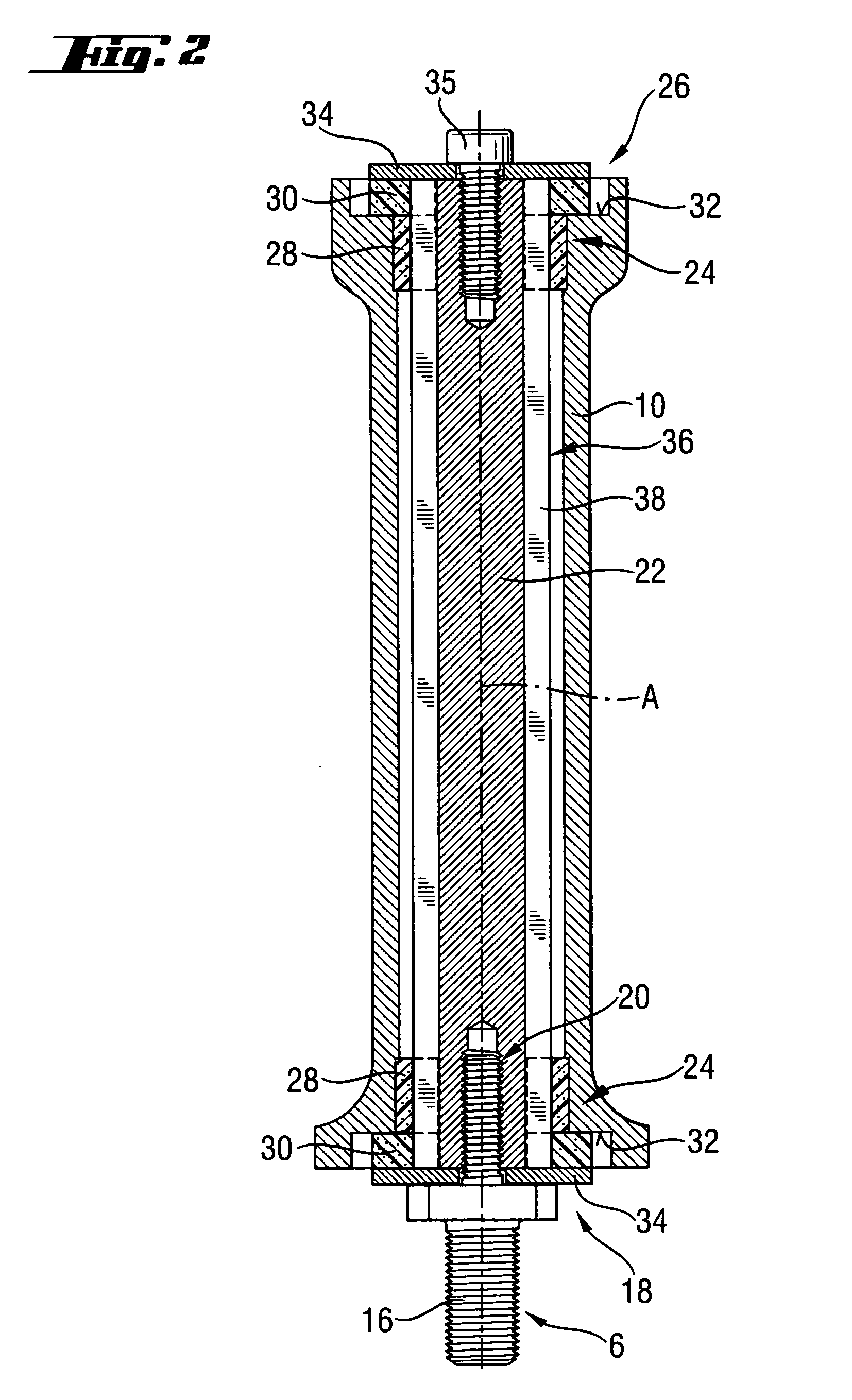
A handle (2) of a hand-held power tool (4), includes an outer sleeve (10) to be gripped by a user, a support element (22) extending at least partially within the outer sleeve (10) along a longitudinal axis (A), a pivot attachment element (6) which at least partially is rotatable with the support element (22) and can be fixed via the handle (2) on the hand-held power tool (4), an elastic vibration-reducing device (24) which encompasses support element (22) and holds the outer sleeve (10) in a radially spaced relationship relative to the support element (22) which has an outer profile (36) with radial outer profile elevations (38) which, at least at the axial height of the vibration-reducing device (24), are arranged at a level of the radial inner profile elevations (44) of an inner profile (50) of the outer sleeve (10).
Owner:HILTI AG
Drill adapter for a power screwdriver
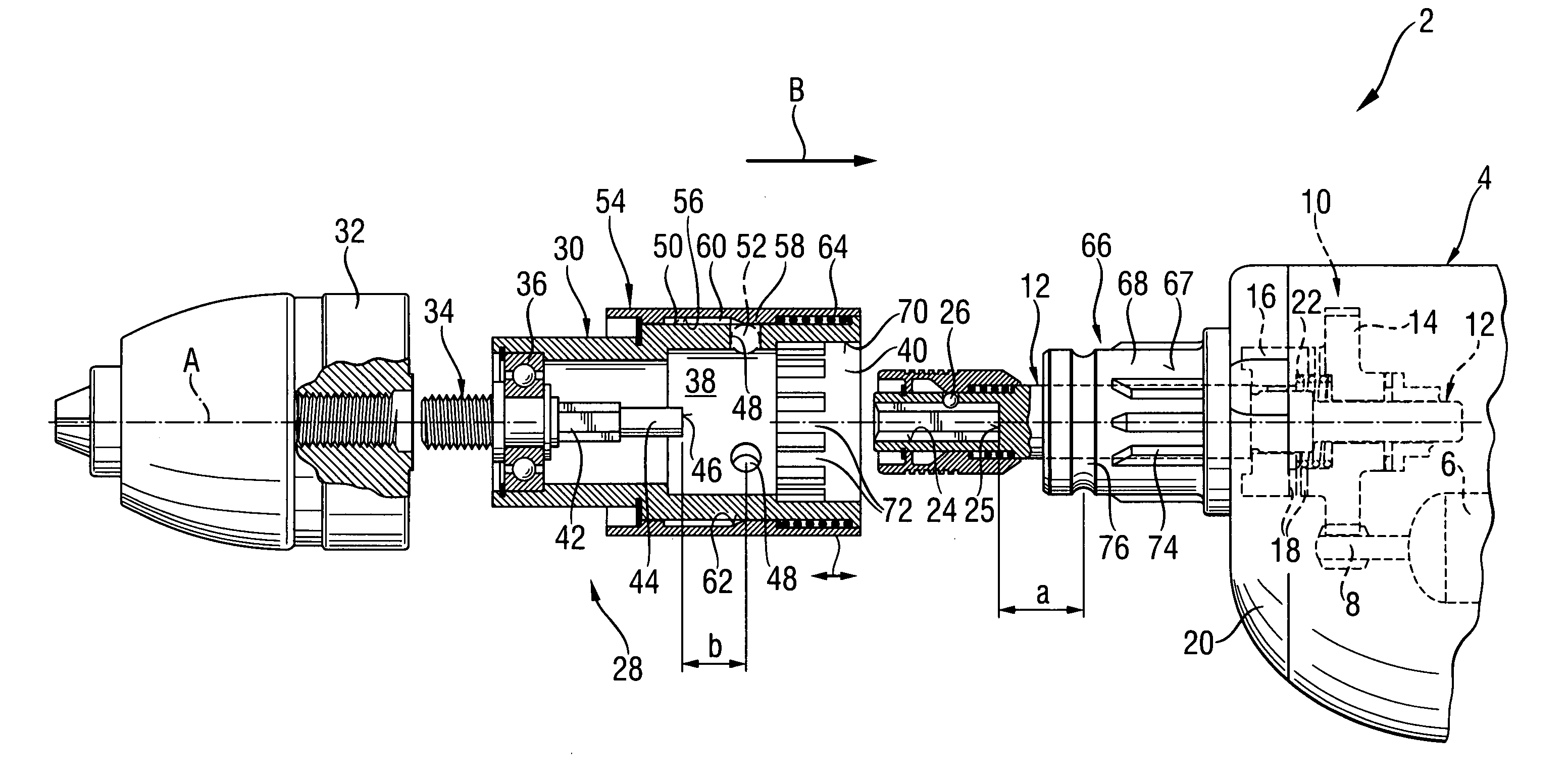
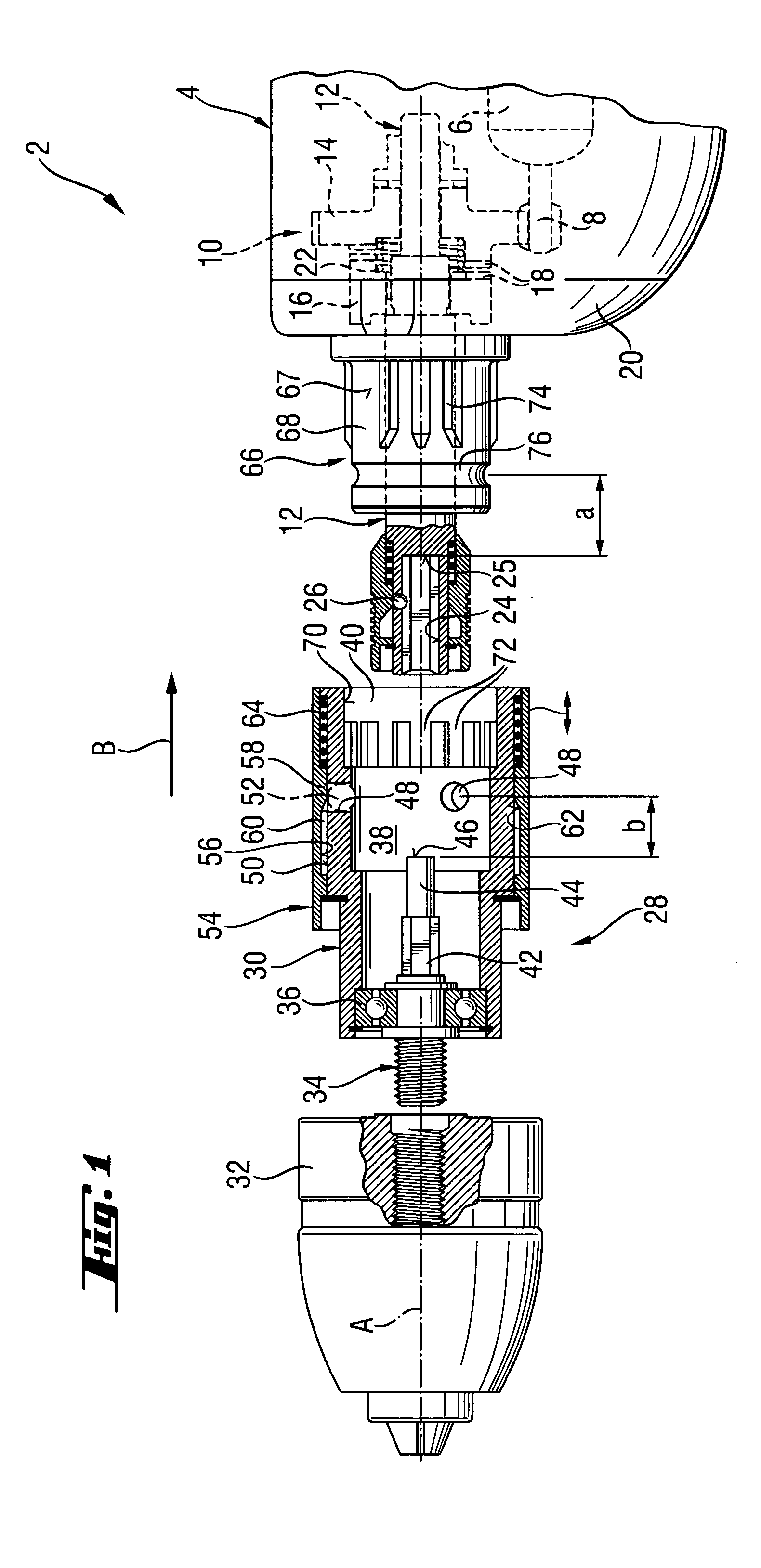
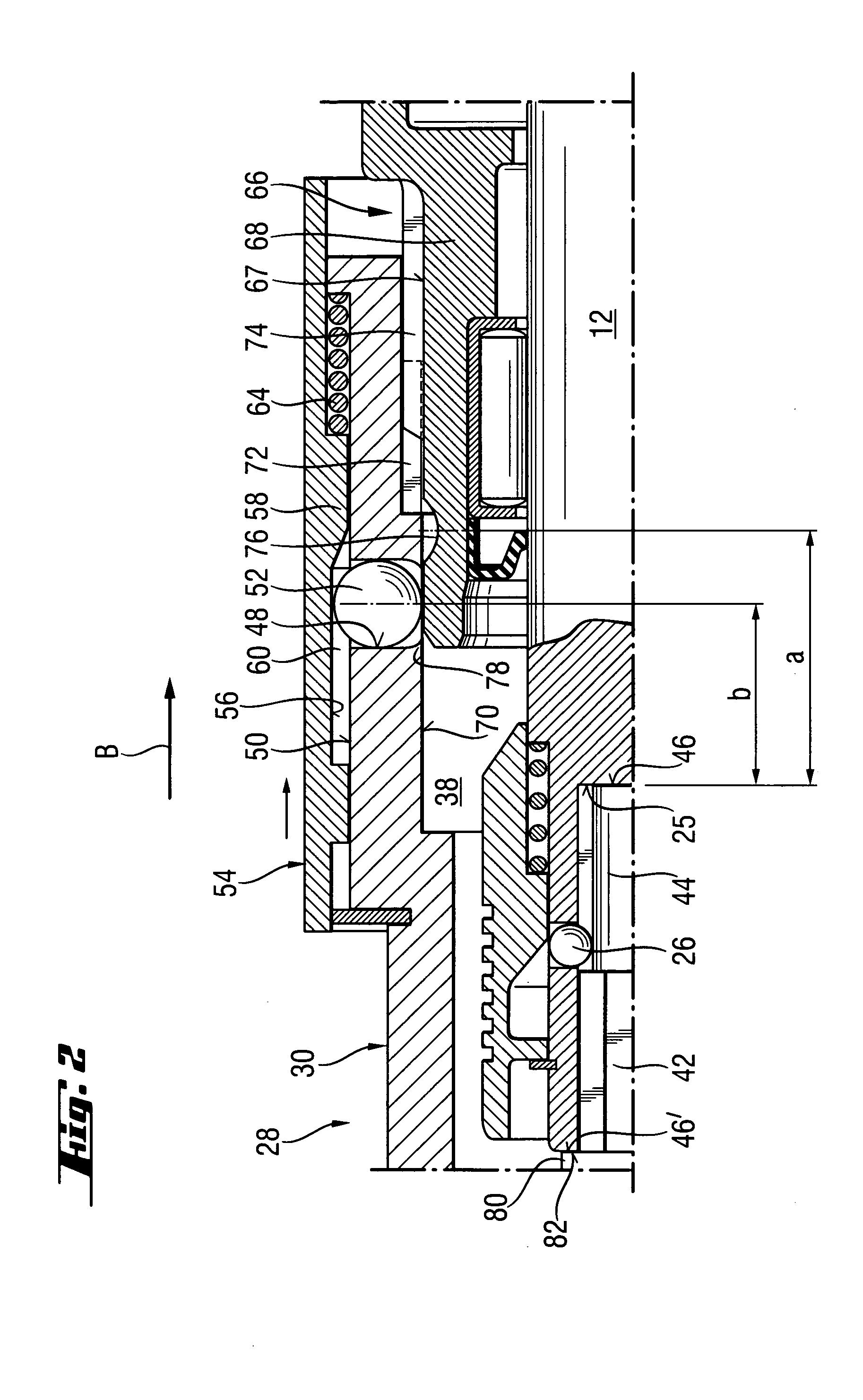
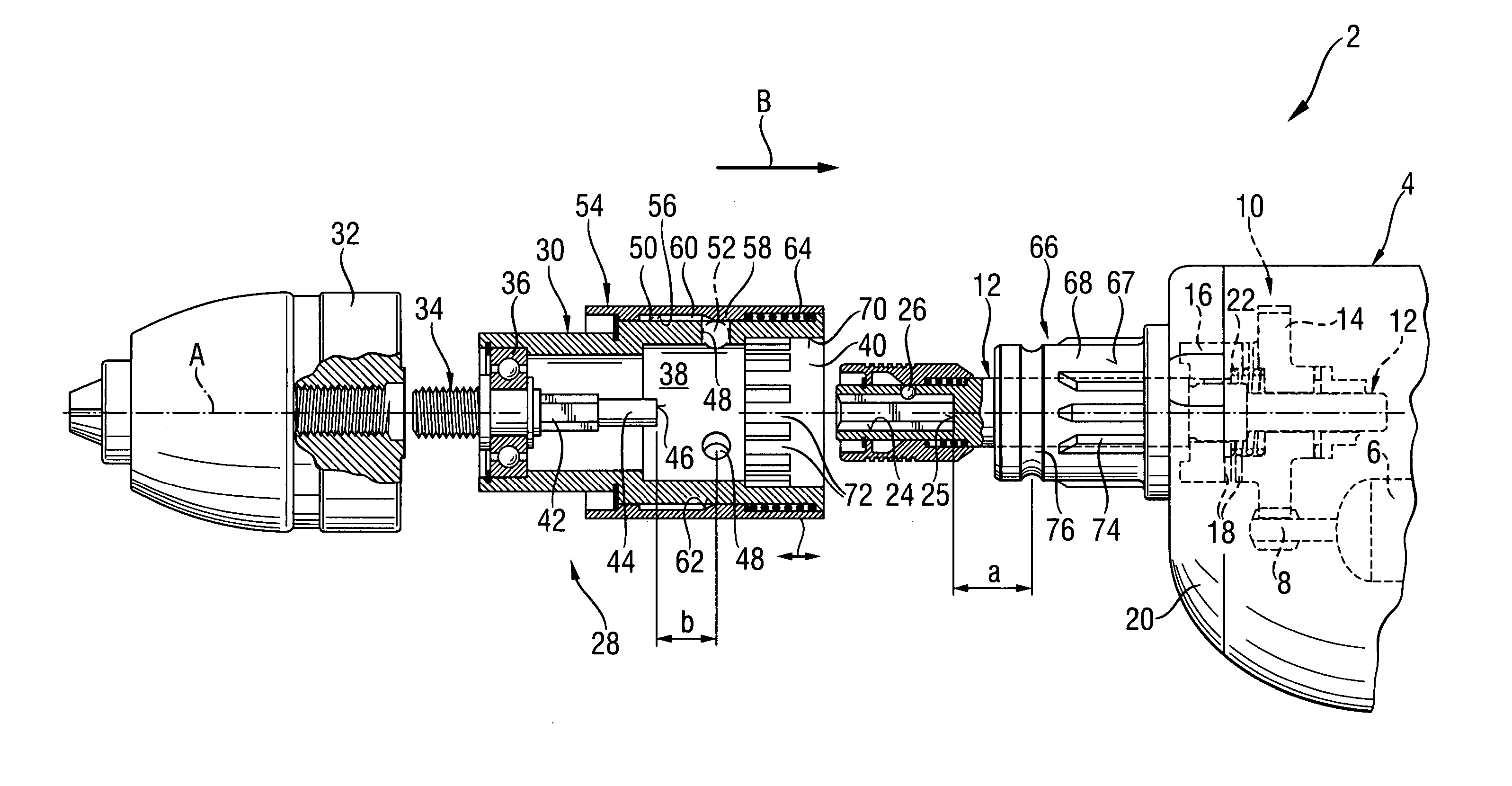
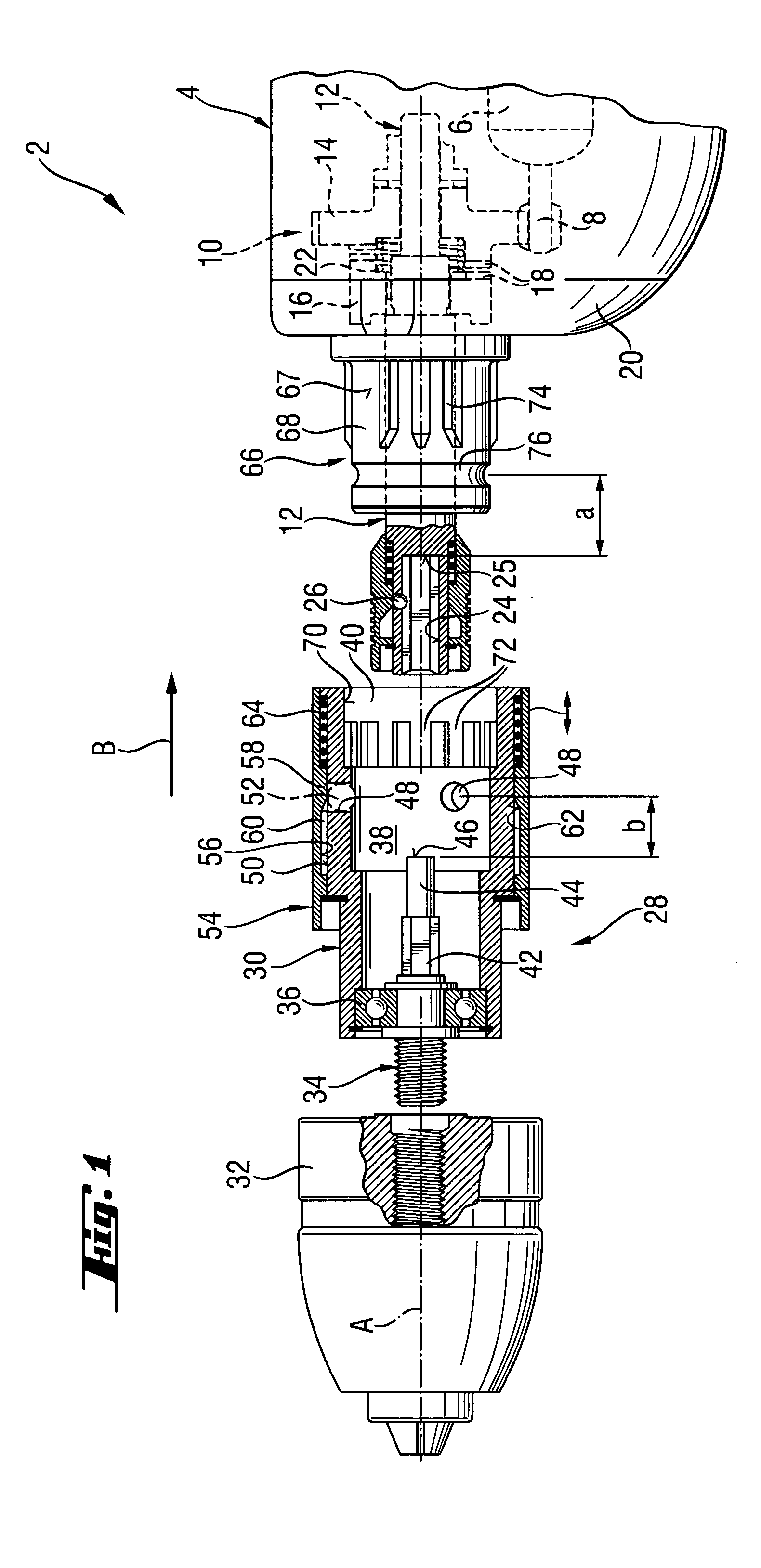
InactiveUS7331738B2Easy to useDrive directlySleeve/socket jointsTransportation and packagingEngineeringClutch
A drill adapter for a power screwdriver and including a locking device for releasably securing the drill adapter (28) on the support region (66) of the screwdriver (4) and having a push-on sleeve (30) supportable on the support region (66) and at least one engagement member (52) for releasably securing the push-on sleeve (30) on the support region, and an element for actuating the drive clutch (10) of the screwdriver (4) via the tool spindle (12) and projecting into a receiving space (38), which is partially limited by the push-on sleeve (30) and is open at one side, and having an axial stop (46) for engaging the tool spindle (12), with the at least one engagement member (52) projecting, in its locking position, beyond an inner surface (70) of the push-on sleeve (30) for establishing an axial formlocking connection between the push-on sleeve (30) and the support region (66) of the screwdriver (4) and which provides for actuation of the drive clutch (10) with actuating element.
Owner:HILTI AG
Drill adapter for a power screwdriver
InactiveUS20050191139A1Wide range of applicationsEasy to handleSleeve/socket jointsTransportation and packagingClutchDrill bit
A drill adapter for a power screwdriver and including a locking device for releasably securing the drill adapter (28) on the support region (66) of the screwdriver (4) and having a push-on sleeve (30) supportable on the support region (66) and at least one engagement member (52) for releasably securing the push-on sleeve (30) on the support region, and an element for actuating the drive clutch (10) of the screwdriver (4) via the tool spindle (12) and projecting into a receiving space (38), which is partially limited by the push-on sleeve (30) and is open at one side, and having an axial stop (46) for engaging the tool spindle (12), with the at least one engagement member (52) projecting, in its locking position, beyond an inner surface (70) of the push-on sleeve (30) for establishing an axial formlocking connection between the push-on sleeve (30) and the support region (66) of the screwdriver (4) and which provides for actuation of the drive clutch (10) with actuating element.
Owner:HILTI AG
Handle-Driven Torque Transfer Wrench having Pivotable Head
InactiveUS20120297939A1Smooth rotationGood torque transmissionSpannersWrenchesUniversal jointTorque transmission
Disclosed is a torque transfer device, comprising a body section, a rotary head section and an internal driveshaft within the body section for coupling rotational input through the body to the head section at an angle with respect to the drive direction. The body section comprises a rotational drive input that connects to an internal driveshaft. The body section terminates, allowing the driveshaft to continue into a universal pivot joint, which further connects to the head section having an internal rotary ratchet transmission and socket-accepting inner portion. As the input is rotated, the driveshaft rotates the ratchet head, providing a tool that allows directional variation with regard to input and output torque transmission. The universal joint allows the head section to be further rotated with respect to the body section for improved torque input onto fastener heads in enclosed or shrouded locations.
Owner:SPATA JOSEPH
Torsion vibration damper and damping device and torque transmission device
InactiveUS20120190462A1Increase installation spaceReduce mechanical frictionVibration suppression adjustmentsMechanical hybrid vehiclesMobile vehicleTorque transmission
A torsion vibration damper for a drive train of a motor vehicle, in particular a drive train of a hybrid vehicle, comprising: a spring support and a force transmission flange configured rotatable relative to the spring support, wherein at least one compression spring is provided between the spring support and the force transmission flange for transferring a mechanical torque, wherein a housing of the spring support is configured so that in a radial direction of the torsion vibration damper, at least one longitudinal end of the compression spring is supported at / in the spring support housing and / or a clearance remains between windings of a center section of the compression spring and a wall of the spring support.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Spindle unit with switchable gear, and method for using the spindle unit
ActiveUS7063173B2Maintain support effectGood torque transmissionDrilling rodsTransmission elementsInterference fitMotor drive
A system and a method are described that facilitate gear switching of a motor-driven spindle. A spindle head shaft is driven by a drive shaft via a gear mechanism in a first gear position. The drive shaft, including a rotor, can be switched from the first gear position to a second gear position where the spindle head shaft is connected by interference fit directly with the drive shaft without the interposed gear mechanism. The spindle head shaft can then be directly driven by the drive shaft in the second gear position. This eliminates the need to dismantle an anterior spindle from the drive unit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Direct-driven magnetic rotating apparatus
ActiveUS7075200B2Reduce size and costIncrease power consumptionSynchronous generatorsWindingsEngineeringMagnet
Rotating-force transmission means is omitted by mounting permanent magnet plates directly to a rotational body which is rotated by magnetic repulsive force, thereby achieving a high-efficiency compact low-cost direct-driven magnetic rotating apparatus.
Owner:FOREST PINE ELECTRIC
Multifilar flexible rotary shaft and medical instruments incorporating the same
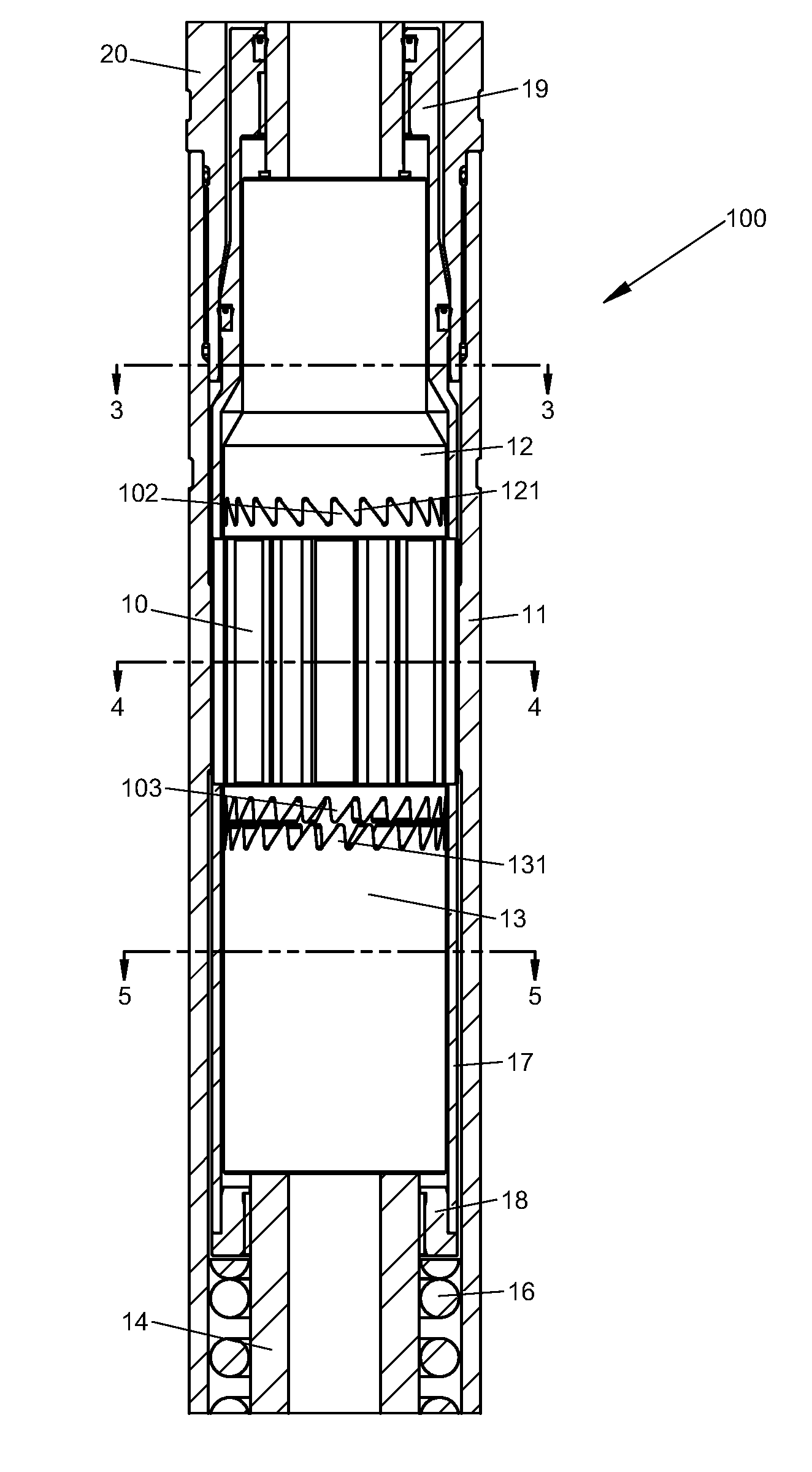
InactiveUS7276067B2Reduce hysteresisGood torque transmissionCatheterExcision instrumentsHysteresisEngineering
A multifilar flexible rotary shaft includes a plurality of individual filaments which are not wound around each other or around a central core, a loose ensemble of filaments. The input ends of each filament are coupled to each other and the output ends of each filament are coupled to each other. Preferably all of the filaments are identical. A loose ensemble of N filaments can transmit N times the torque of a single filament, and will have N times the torsional stiffness of a single filament, while retaining the minimum radius of operation of a single filament. Since a loose ensemble of filaments does not have any appreciable contact forces among the filaments (because they are not forcibly twisted together), there is no appreciable internal friction or hysteresis. In order to appreciably eliminate all the hysteresis in such an ensemble of filaments, the filaments should be no more than loosely twisted together, if at all. The only reason for loosely twisting the wires together is to allow the ensemble to be easily handled and to insure that the individual wire filaments follow the same general curved path from one end to the other. Several practical applications of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Flexible couplings
A flexible coupling including a first hub having an inner face, a flexible insert having a plurality of exterior lobes and a plurality of interior lobes, a retainer ring having an interior which engages the exterior lobes of the flexible insert, and a second hub having an exterior surface contoured to engage the interior lobes of the flexible insert.
Owner:ATR SALES
Rotational Coupling Device
ActiveUS20070227853A1Big gapGood torque transmissionMagnetically actuated clutchesFriction clutchesEngineeringClutch
A rotational coupling device for use as a clutch and / or brake is provided having a construction enabling improved torque transfer characteristics. The device includes a rotor rotatably coupled to an input shaft and an armature coupled to an output member and configured for selective engagement with the rotor. The rotor includes a hub having a central bore into which the input shaft extends. A support member, such as a spacer or pulley hub is coupled to the rotor hub using an axially projecting lug and notch construction. The structure of the device provides greater clearance for the input shaft and may eliminate the need for keys on the support member.
Owner:WARNER ELECTRIC TECH
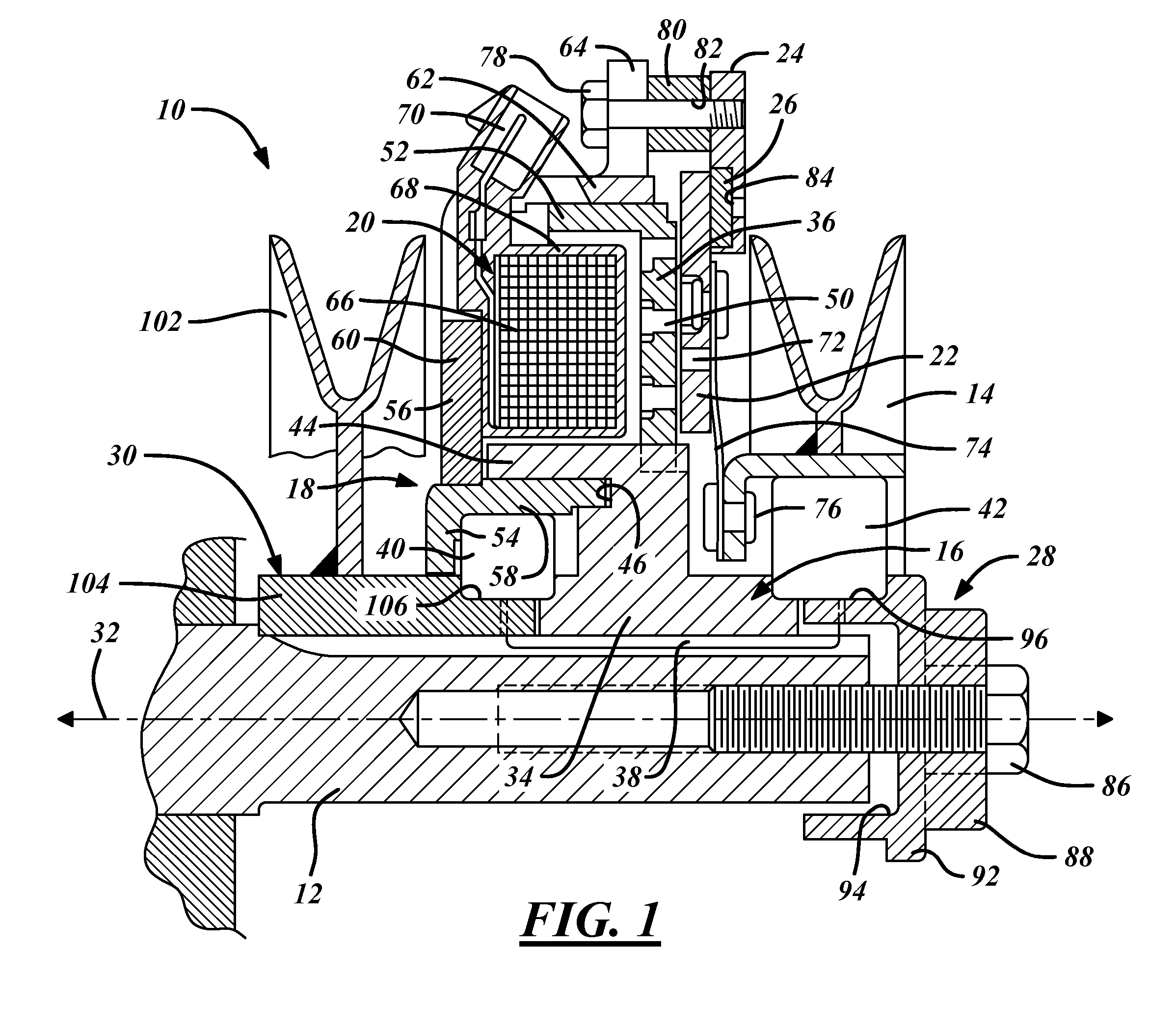
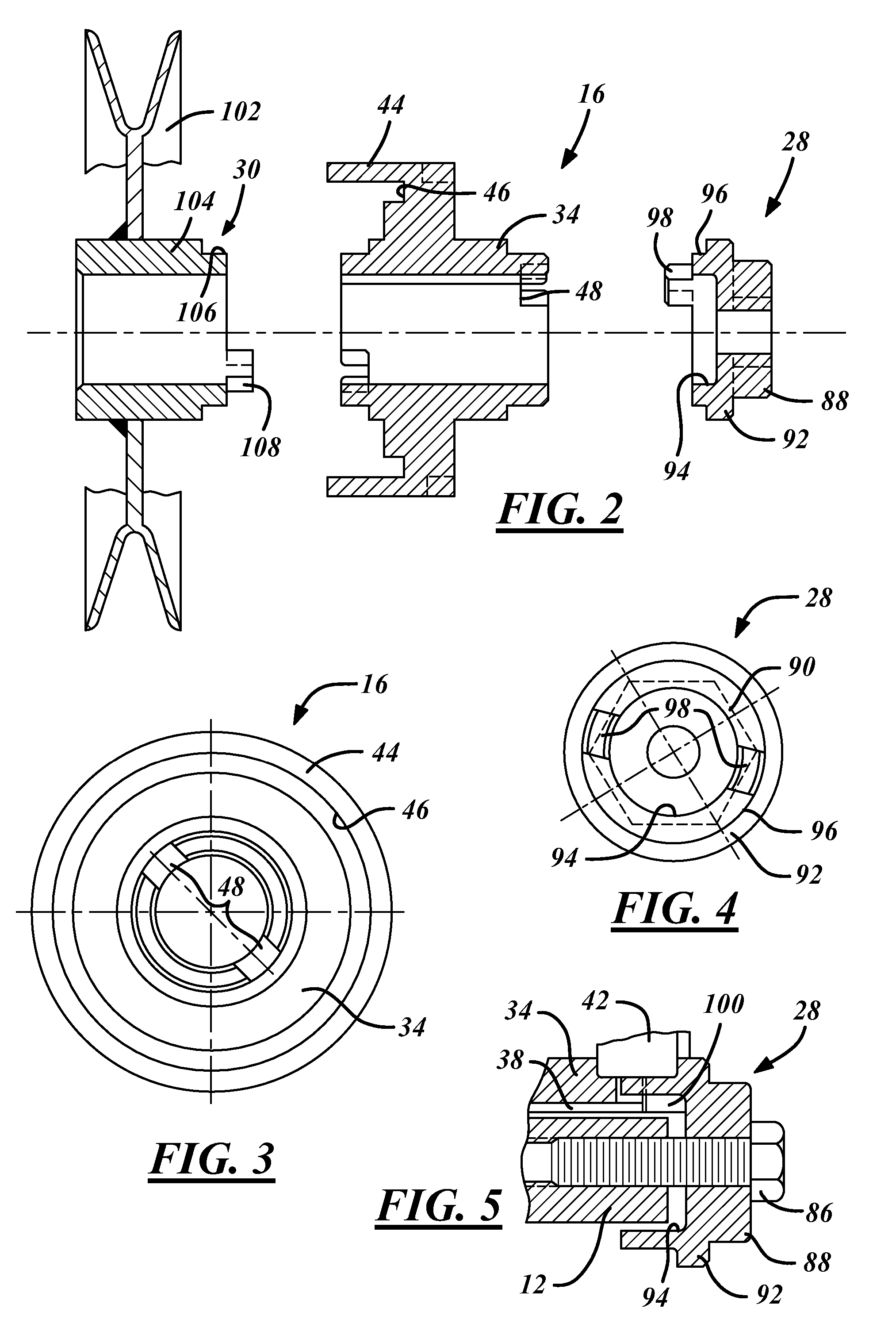
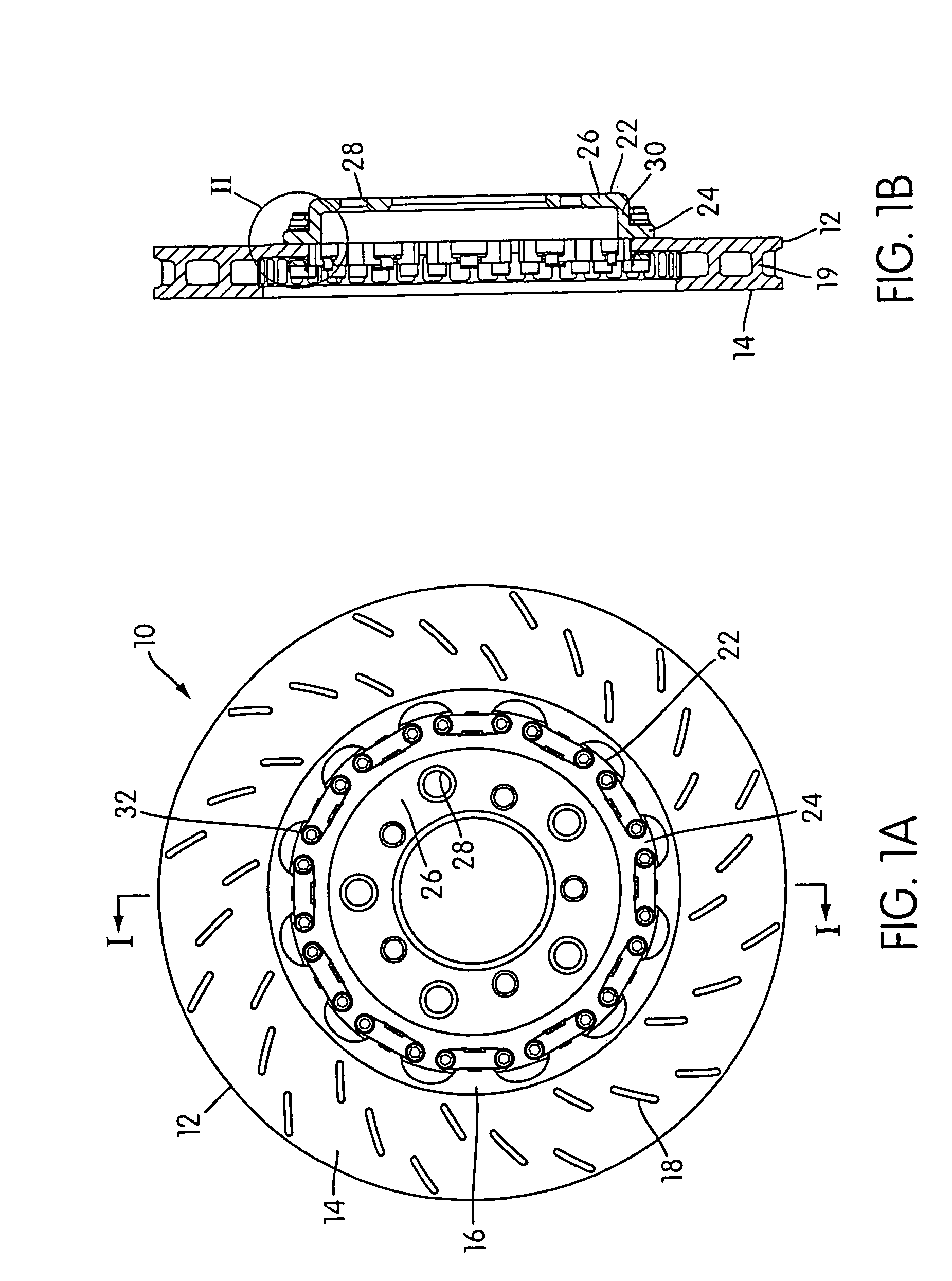
Brake rotor attachment assembly that promotes in plane uniform torque transfer distribution
InactiveUS7077247B2Eliminate concentrationEliminate fatigueBraking element arrangementsBraking drumsIn planeBobbin
A brake assembly for use on vehicles includes a rotor and a wheel mount, formed as a hat portion, fastened to the rotor with a bobbin assembly. The rotor has a flange formed as a series of spaced tabs, and the bobbin assembly is bolted to the hat portion with the rotor flange clamped therebetween. A spring clip can be used with the bobbin to accommodate thermal expansion of the rotor and eliminate rotor rattling. The bobbin has a binocular shape that receives a pair of bolts. A crush zone can be provided between the rotor and the bobbin yields to accommodate machining tolerances of the rotor and promote uniform torque transfer distribution to the hub. Torque is transferred from the brake rotor to the hat portion in a common plane to prevent twisting in the fastener connection.
Owner:PERFORMANCE FRICTION
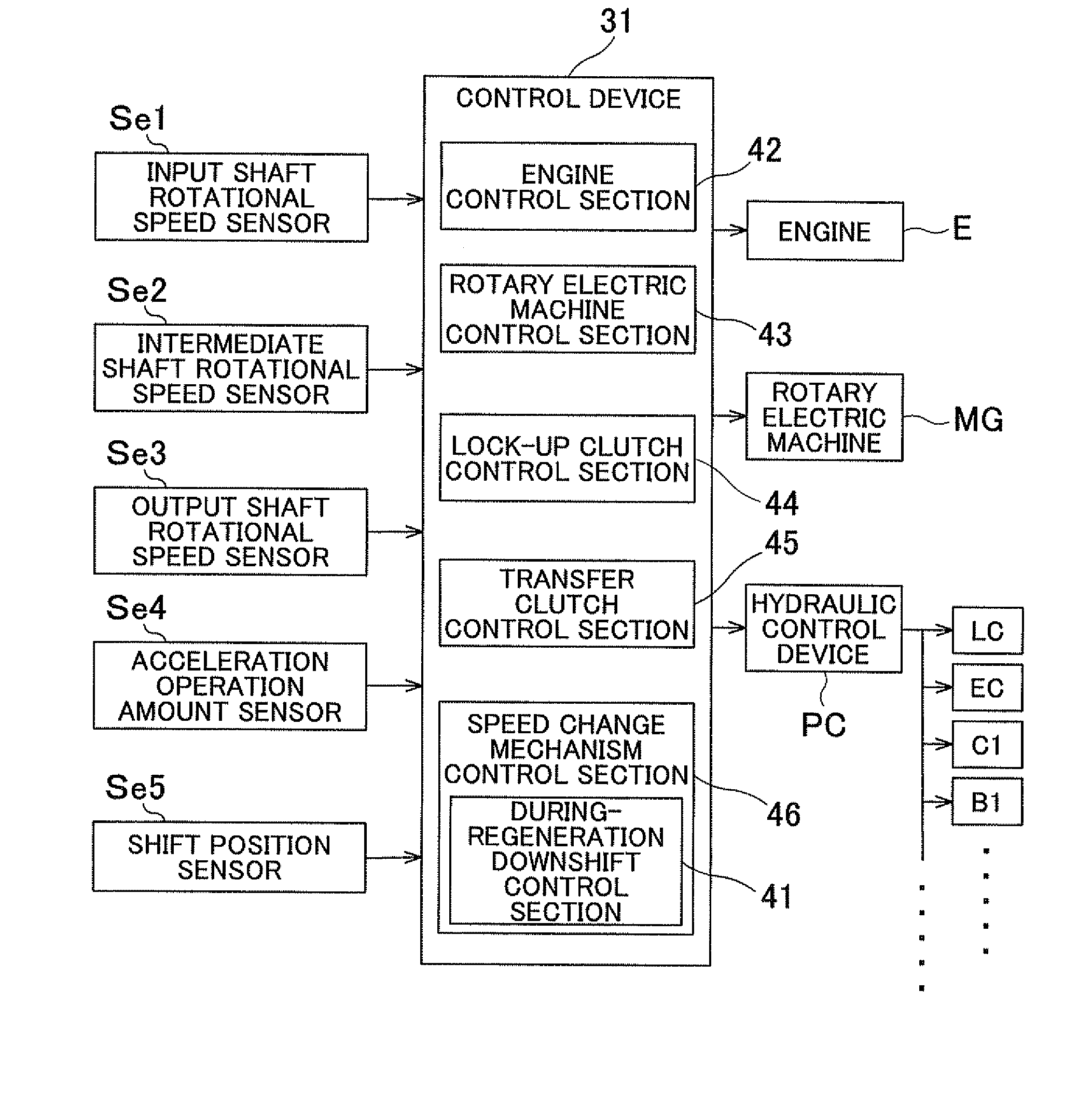
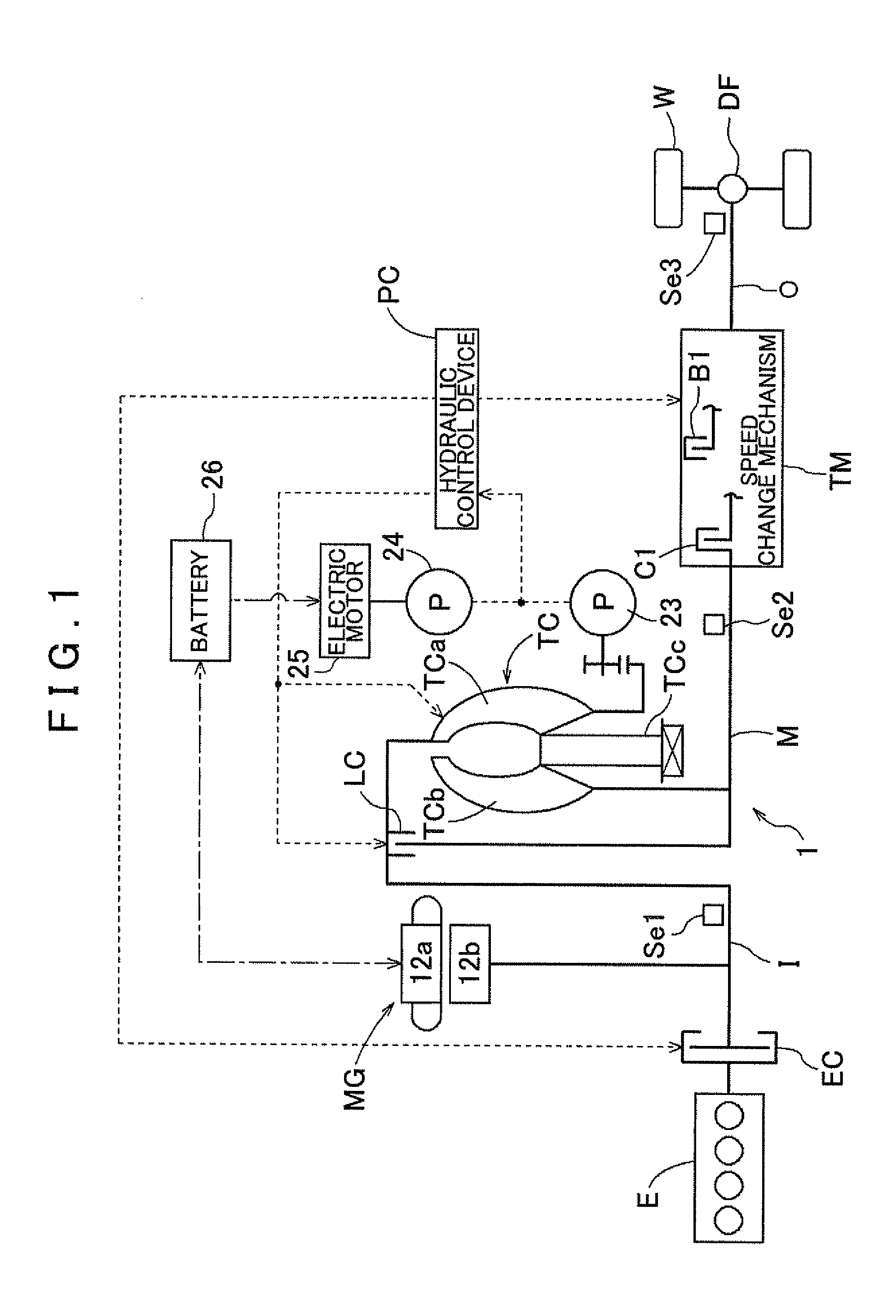
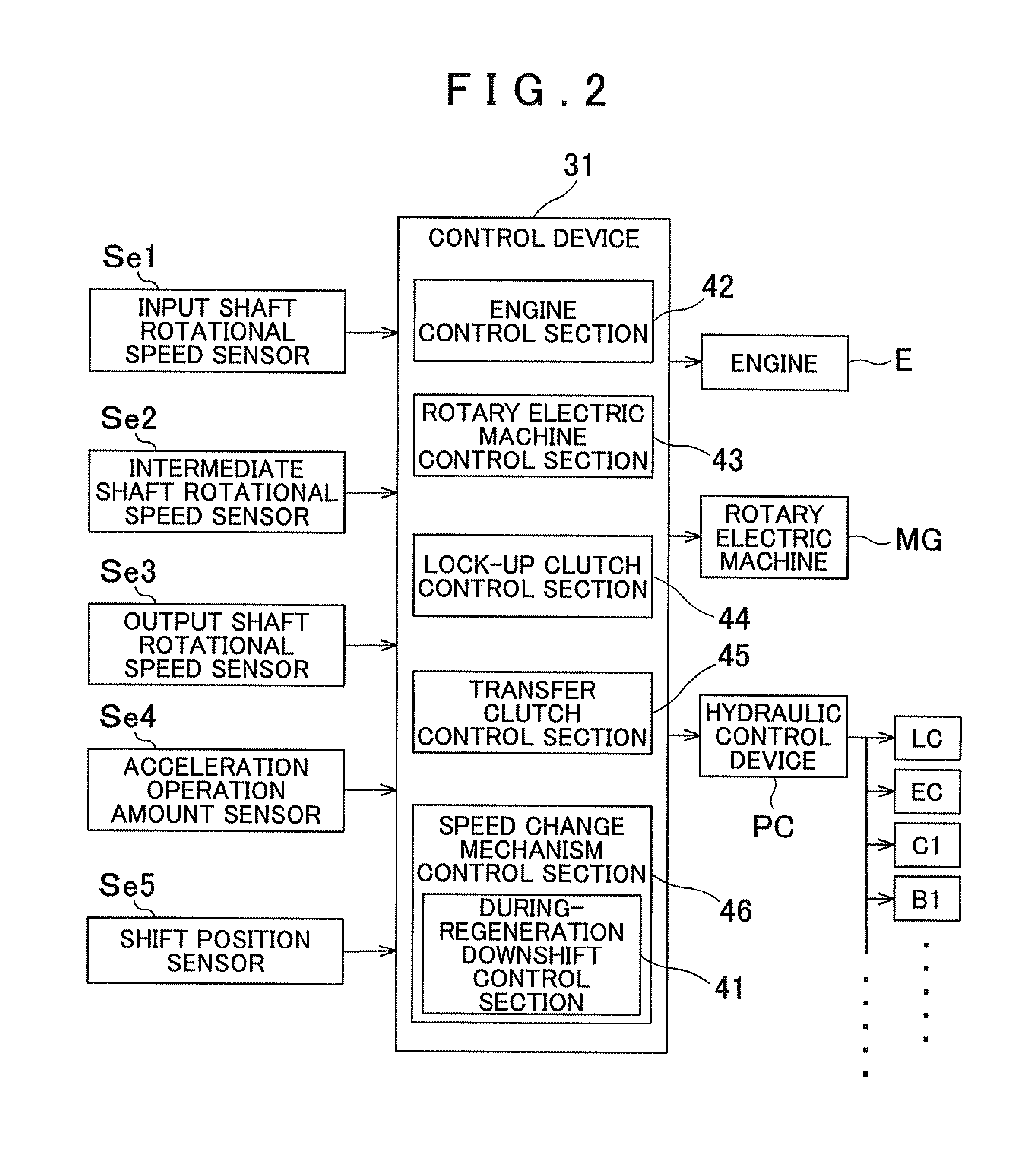
Vehicle transmission device
ActiveUS20120290163A1Inhibit transferAppropriately transferredDigital data processing detailsElectrodynamic brake systemsElectric machineInternal combustion engine
A vehicle transmission device includes an input member coupled to a combustion engine and a rotary electric machine; an output member coupled to wheels; a speed change mechanism with a plurality of friction engagement elements and that provides a plurality of shift speeds; and a control device that controls the speed change mechanism. When a during-regeneration downshift is performed while the rotary electric machine is outputting regenerative torque, the control device sets a target increase capacity, which is a target value of a transfer torque capacity of an engagement-side element to be engaged after an increase, increases the transfer torque capacity of the engagement-side element to the target increase capacity over a predetermined torque capacity increase period, and decreases a transfer torque capacity of a disengagement-side element, which is to be disengaged, over a predetermined torque capacity decrease period that at least partially overlaps the torque capacity increase period.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Fan disc
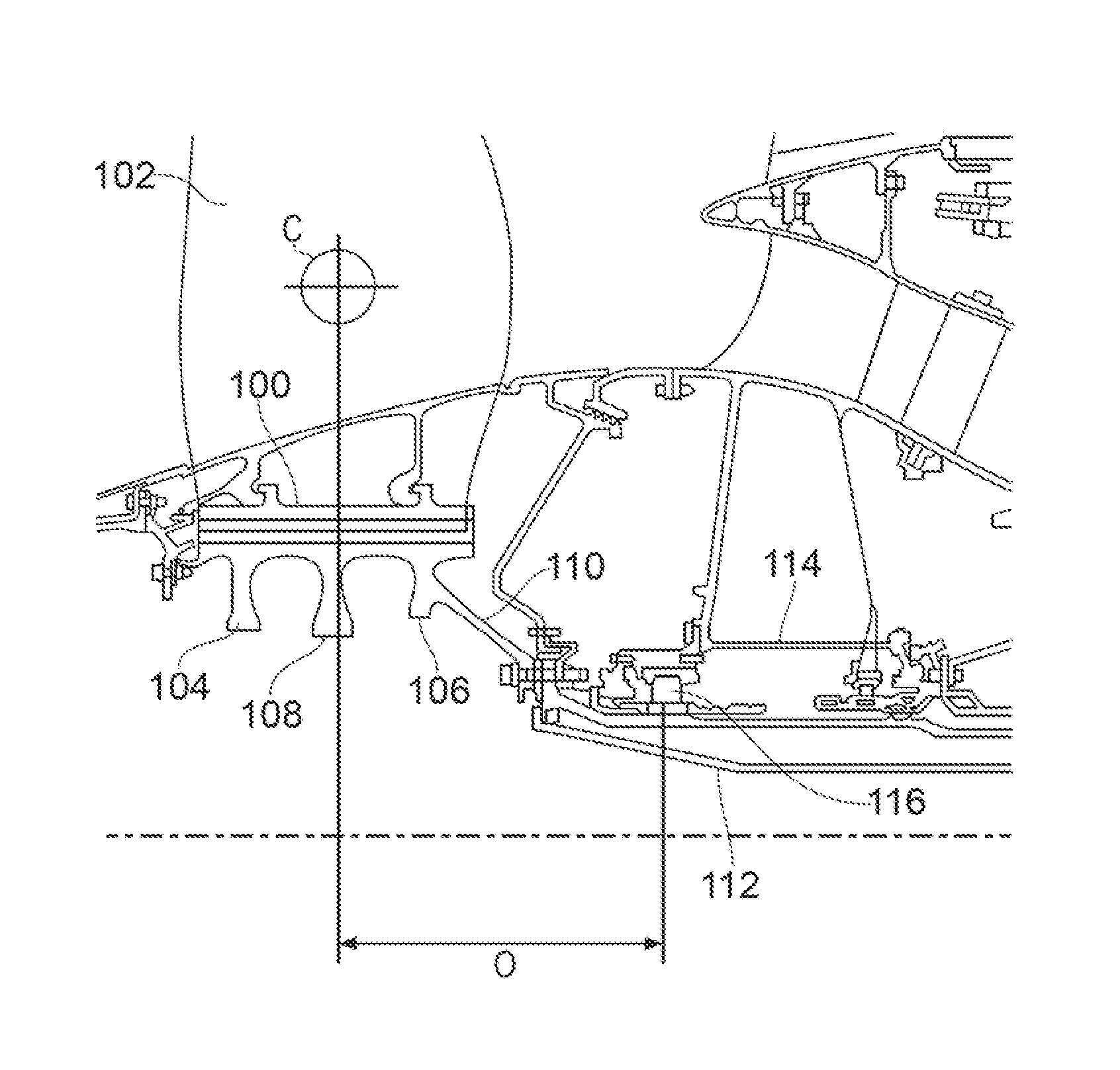
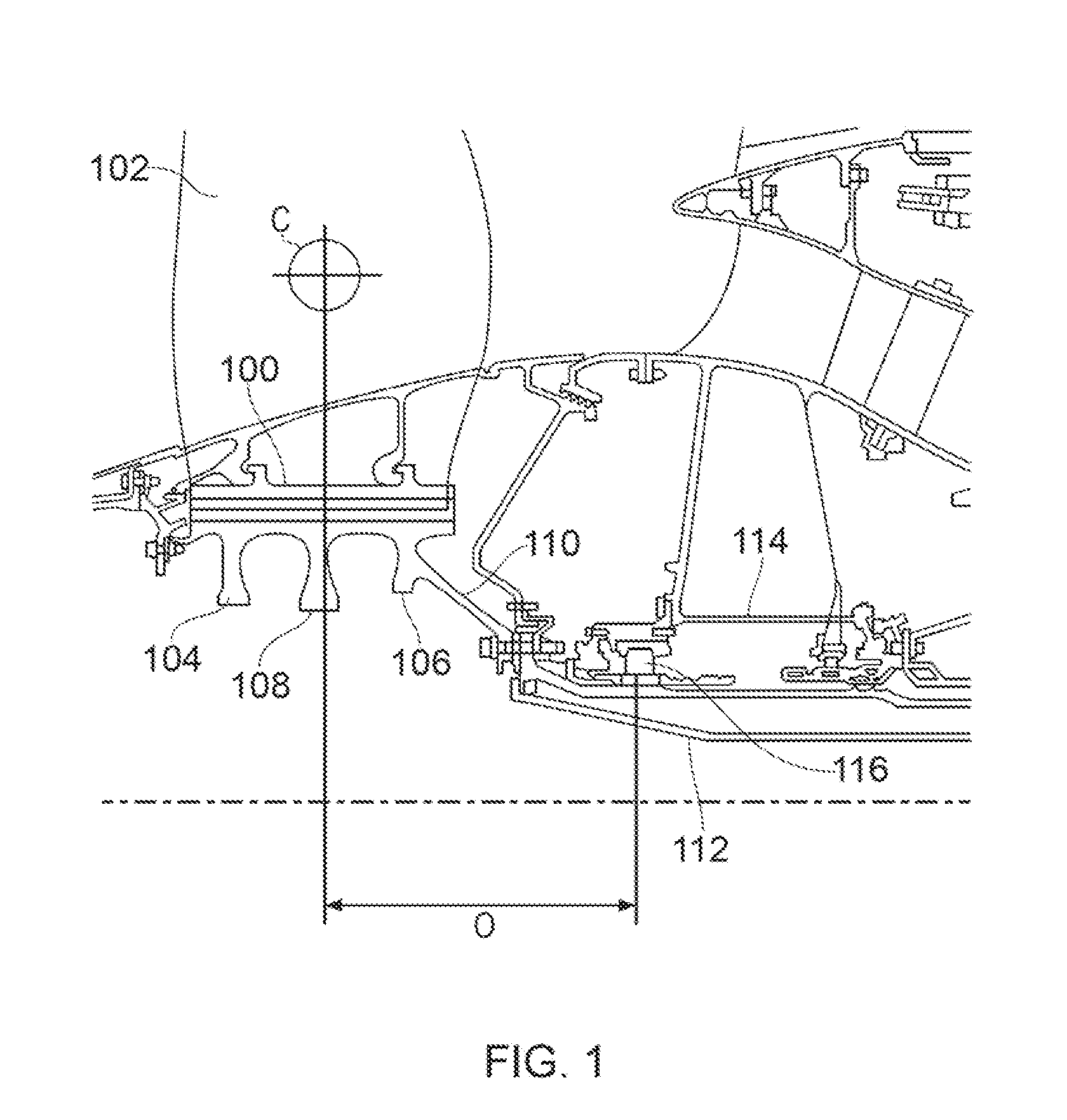
InactiveUS20150377027A1Good torque transmissionHigh temperature capabilityPropellersPump componentsDrive shaftEngineering
A fan disc is provided for supporting fan blades of a gas turbine engine. The fan disc has a disc body having axially extending slots for receiving, in use, dovetail root fixings of a circumferential row of fan blades. The fan disc further has an annular drive arm which extends radially inwardly from a forward portion of the disc body to a connector for engaging, in use, with a corresponding connector portion of a drive shaft of the engine. The fan disc further has a hoop stiffening ring which is removably mounted to a rear portion of the disc body, the stiffening ring being axially spaced from the drive arm to increase the torsional stiffness of the fan disc.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Method and system for torque control
ActiveUS20150047607A1Engine speed can be slowedSmooth transmission shiftHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlControl theoryDirect torque control
Methods and systems are provided for enabling a smooth transmission shift in a hybrid vehicle configured with a motor hybrid transmission. During an initial part of a transmission upshift, spark timing may be advanced from MBT to expedite torque reduction. Once engine speed has sufficiently reduced, and is within a threshold range of the desired engine speed, spark timing may be retarded until the transmission shift is completed.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Brake rotor attachment assembly that promotes in plane uniform torque transfer distribution
InactiveUS6997292B2Eliminate concentrationEliminate fatigueBraking element arrangementsBraking drumsIn planeBobbin
A brake assembly for use on vehicles includes a rotor and a wheel mount, formed as a hat portion, fastened to the rotor with a bobbin assembly. The rotor has a flange formed as a series of spaced tabs, and the bobbin assembly is bolted to the hat portion with the rotor flange clamped therebetween. A spring clip can be used with the bobbin to accommodate thermal expansion of the rotor and eliminate rotor rattling. The bobbin has a binocular shape that receives a pair of bolts. A crush zone between the rotor and the bobbin yields to accommodate machining tolerances of the rotor and promote uniform torque transfer distribution to the hub. Torque is transferred from the brake rotor to the hat portion in a common plane to prevent twisting in the fastener connection.
Owner:PERFORMANCE FRICTION
Torque-transmitting, variably-flexible, corrugated insertion device and method for transmitting torque and variably flexing a corrugated insertion device
A torque-transmitting, variably-flexible, corrugated insertion device includes a hollow body having a proximal end with an entrance for receiving an instrument and a distal end with a tip for protrusion of the instrument. A vacuum-activated device transitions the hollow body between a relatively flexible condition and a relatively stiff condition. A corrugated tube transmits torque from the proximal end toward the distal end. A method for transmitting torque and variably flexing an insertion device for receiving an instrument includes providing a hollow body, transmitting torque along the hollow body with a corrugated tube, applying suction to create a vacuum in the hollow body for placing the hollow body in a relatively stiff condition, and relieving the vacuum for placing the hollow body in a relatively flexible condition.
Owner:SYNTHEON
Rotational coupling device
ActiveUS7527134B2Big gapGood torque transmissionMagnetically actuated clutchesFriction clutchesEngineeringPulley
A rotational coupling device for use as a clutch and / or brake is provided having a construction enabling improved torque transfer characteristics. The device includes a rotor rotatably coupled to an input shaft and an armature coupled to an output member and configured for selective engagement with the rotor. The rotor includes a hub having a central bore into which the input shaft extends. A support member, such as a spacer or pulley hub is coupled to the rotor hub using an axially projecting lug and notch construction. The structure of the device provides greater clearance for the input shaft and may eliminate the need for keys on the support member.
Owner:WARNER ELECTRIC TECH
Mechanism for providing controllable angular orientation while transmitting torsional load
InactiveUS20110073372A1Control displacementRelieve pressureSurveyDerricks/mastsEngineeringAngular orientation
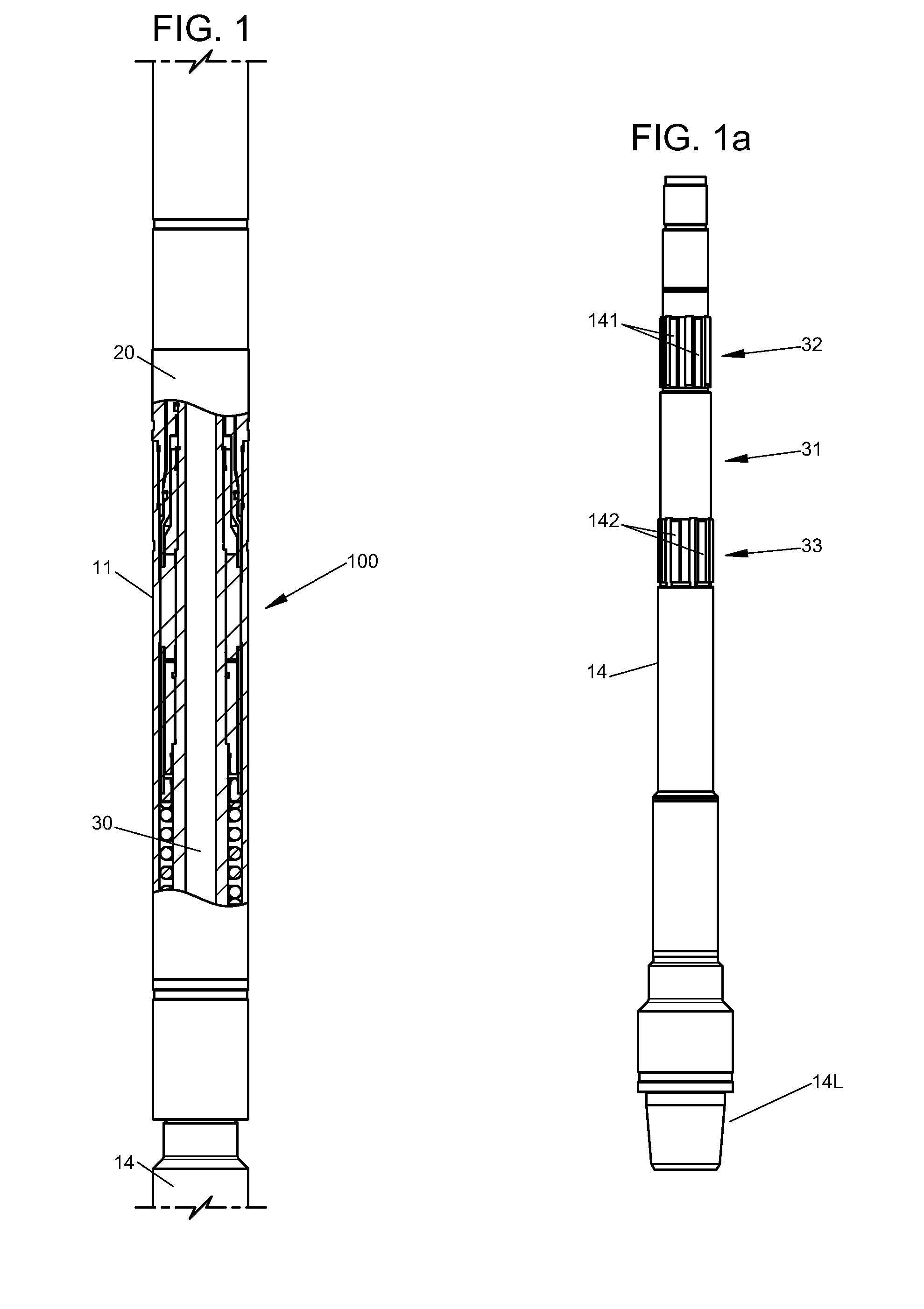
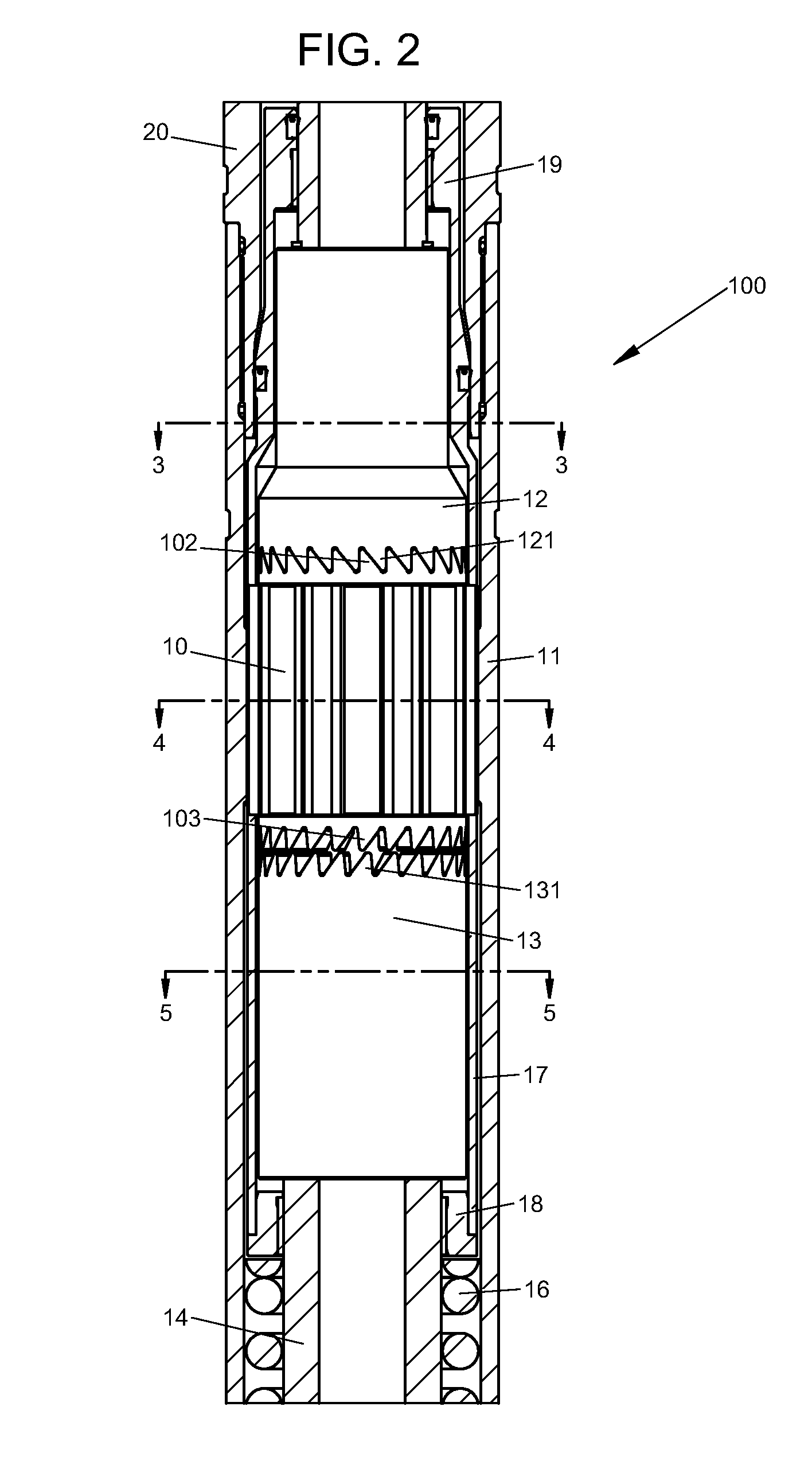
A mechanism for adjusting the relative angular orientation of two coaxial components includes a mandrel having a cylindrical central section between upper and lower splined sections, a sleeve rotatably and slidably disposed around the mandrel's central section, and generally cylindrical upper and lower ratchet members positioned, respectively, about the mandrel's upper and lower splined sections. The ratchet members have internal grooves which receive the mandrel splines for torsional load transfer while permitting limited rotation relative to the mandrel, but their axial positions relative to the mandrel are fixed. The upper and lower ends of the sleeve have circumferentially-arrayed ratchet teeth engageable, respectively, with corresponding teeth on the upper and lower ratchet members. The central sleeve has torque-transferring external splines slidable within matching grooves on the inner surface of a cylindrical tool housing enclosing the mechanism. The mandrel is rotatable relative to the housing, but its axial position is fixed. The teeth of the sleeve and ratchet members are configured such that movement of the sleeve from a position engaging the upper ratchet member to a position engaging the lower ratchet member, or vice versa, will effect an incremental angular shift of the mandrel relative to the tool housing, while maintaining effective transfer of torsional loads therebetween.
Owner:DRECO ENERGY SERVICES ULC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com