Patents
Literature
153 results about "Airborne exposure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anti-pathogenic air filtration media and air handling devices having protective capabilities against infectious airborne mircoorganisms
The present invention provides an anti-pathogenic air filtration medium comprising a fibrous substrate whose fibers are coated with coating comprising a polymer. The coating provides an environment that is destructive to airborne pathogens. In particular, the filter medium can be used in a building air handling system that both filters the air and eliminates pathogens. The filter medium also can be used to create a new bio-protective gas mask that not only offers protection against chemical warfare agents, but also provides protection against biological pathogens.
Owner:INNOVATIVE CONSTR & BUILDING MATERIALS
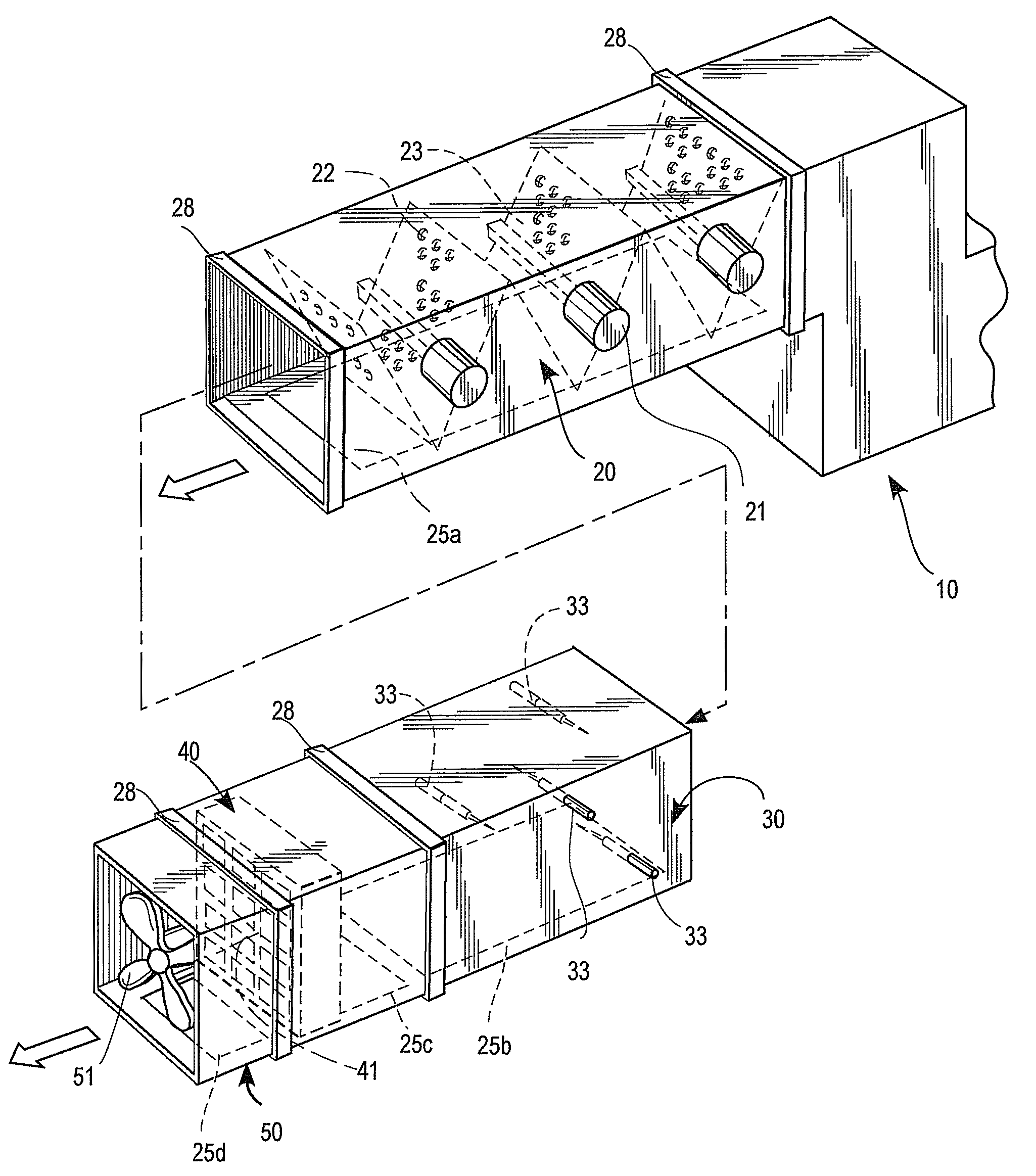
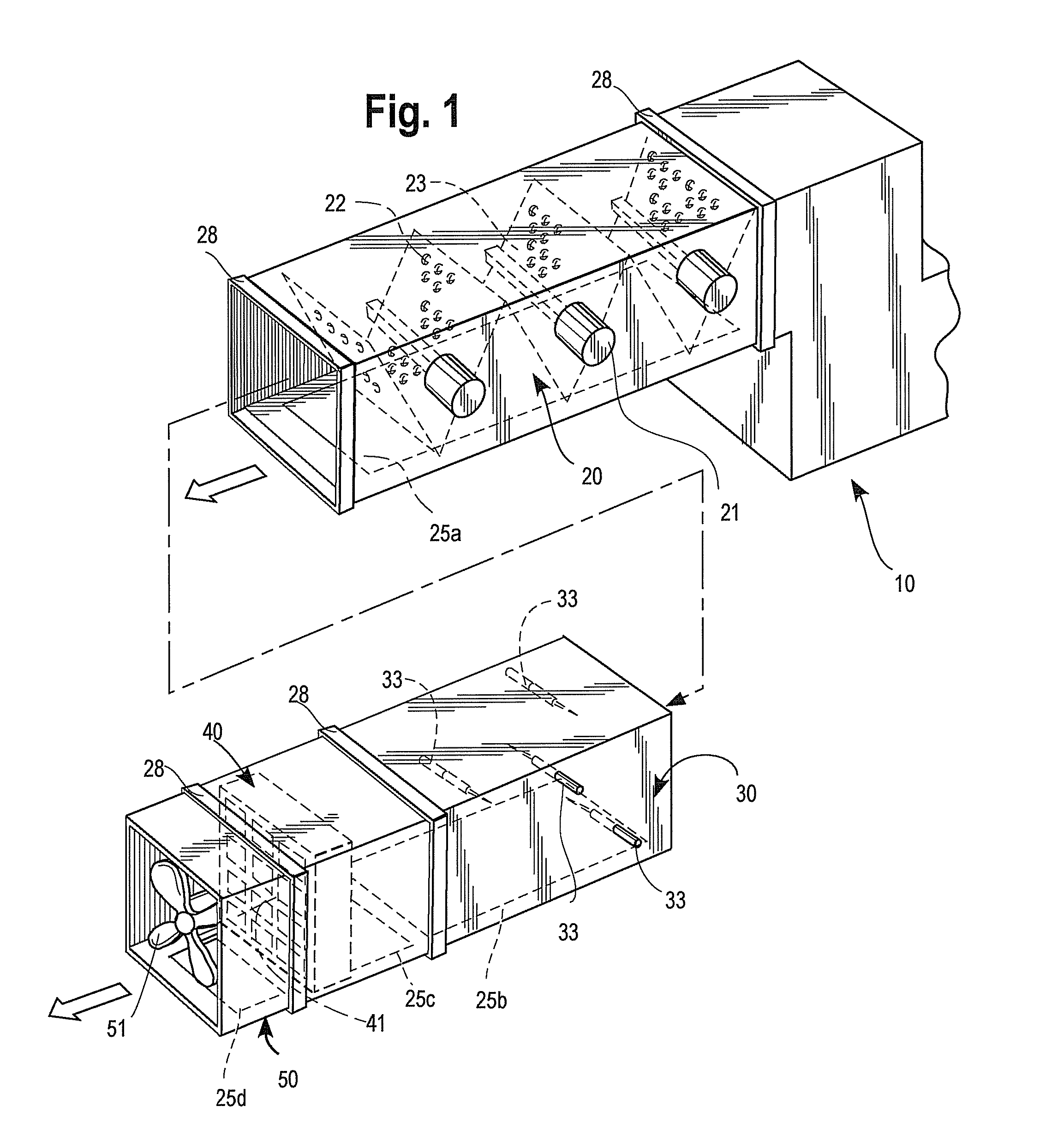
Modular Ductwork Decontamination Assembly
InactiveUS20080173178A1Little effortAvoid huge expensesCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesModularity
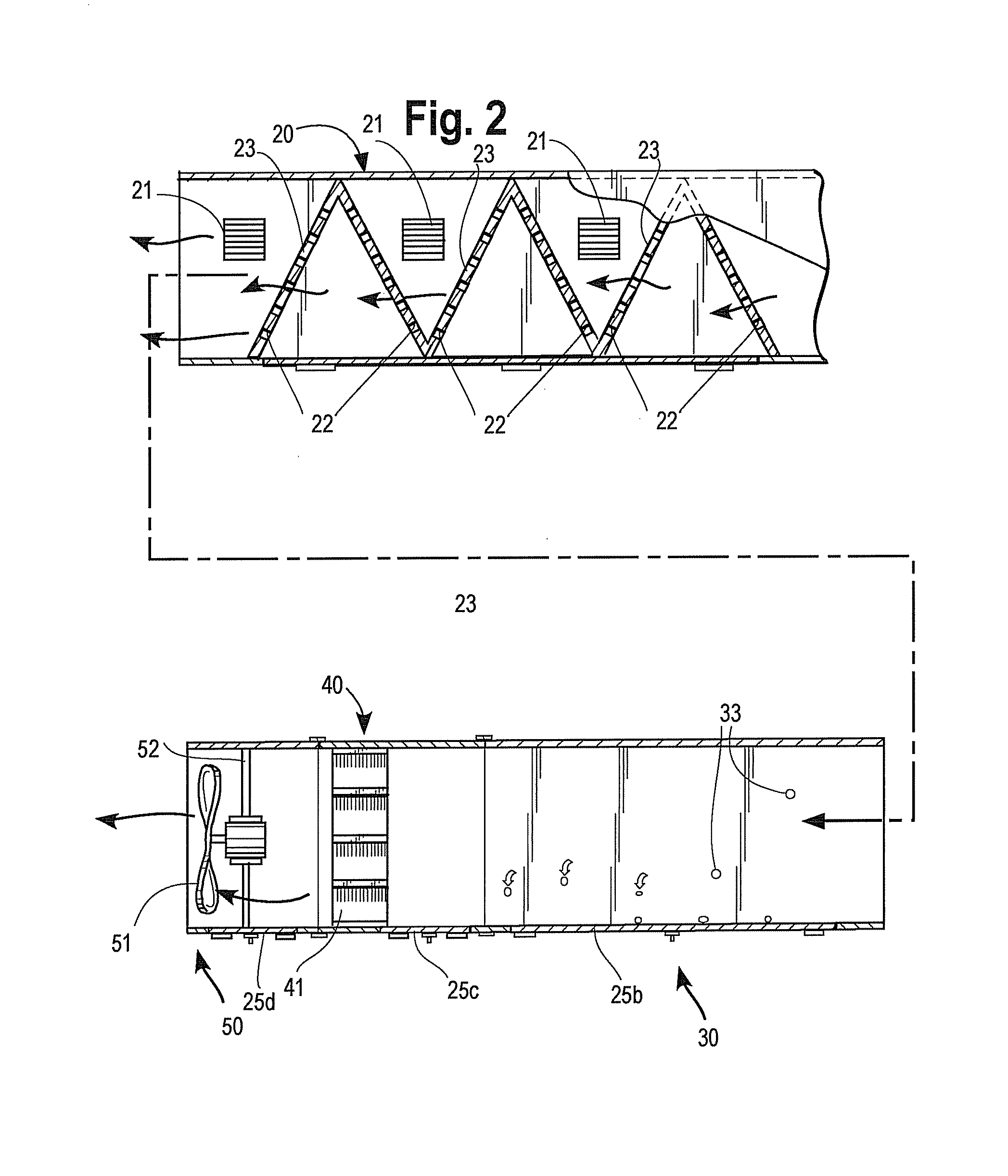
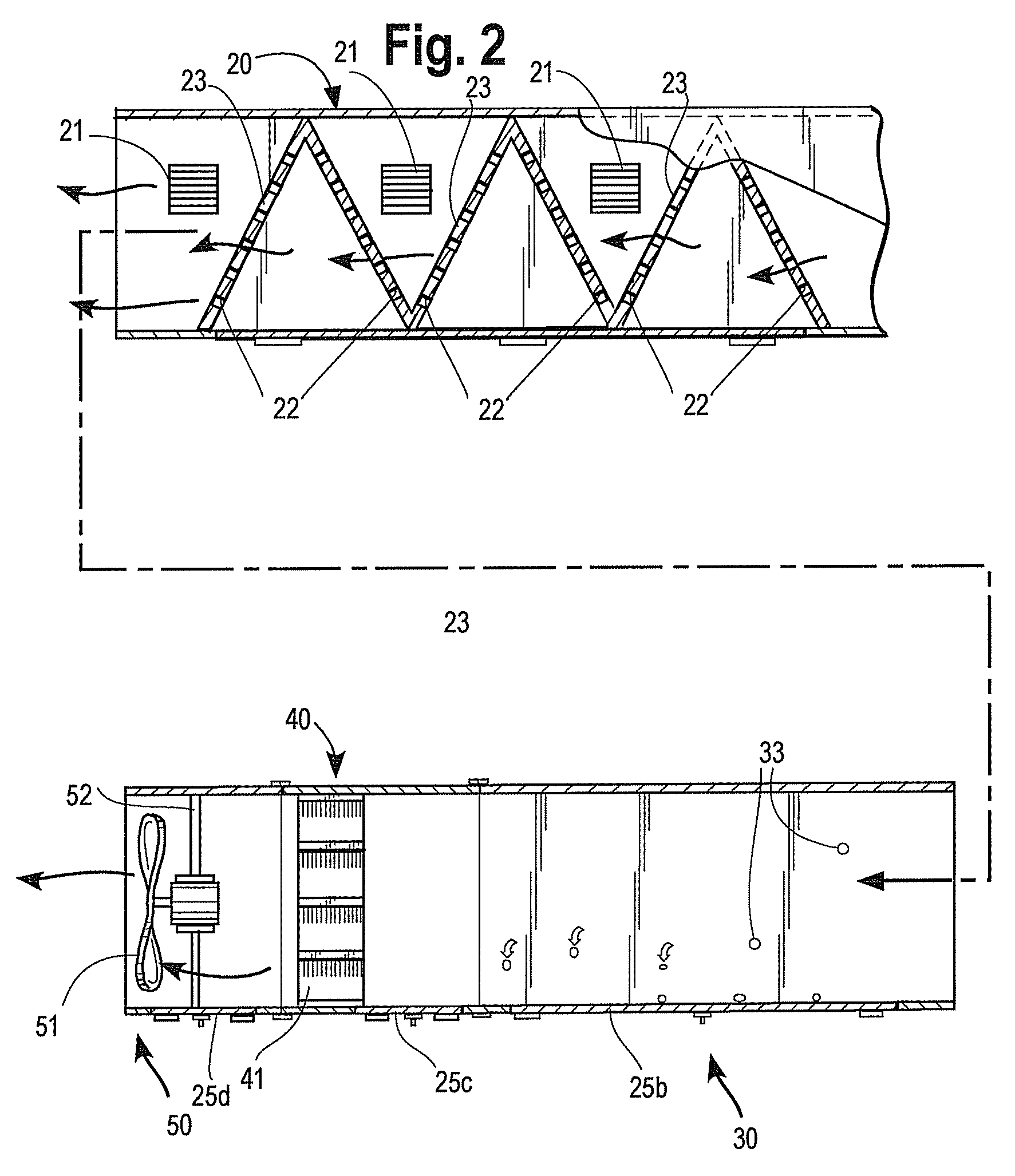
A modular ductwork assembly decontaminates an air stream circulating within an heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system. The assembly includes (a) an ionizing module for removing particulates from the air stream, (b) a sterilization module for neutralizing airborne pathogens present in the air stream, (c) an ozone treatment module for neutralizing odoriferous constituents or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) present in the air stream, optionally (d) baffles for slowing and disrupting the flow rate and promoting turbulence in the air stream traveling through the modules and optionally (e) a fan module for directing a treated air stream. Each of the modules is arranged substantially adjacent to at least one of the other modules.
Owner:METTEER KAREN
Cookery Air Purification and Exhaust System
InactiveUS20150226439A1Safely and efficiently removeAvoid operationLiquid surface applicatorsDomestic stoves or rangesPollutantUltra fine
An air filtration and exhaust system is described. The system comprises a microcontroller, a power supply, and a series of sensors that detect the presence of airborne contaminants such as ultra fine particles, smoke, natural gas and radon gas. In the presence of these airborne contaminants, the system is designed to inactivate and prevent operation of nearby food preparation appliances. Once these contaminants have been safely removed, the operation of these appliances is restored. In addition, the ventilation system may be equipped with a purification subassembly, which safely and efficiently removes such containments from the area. The system may also comprise an alarm that is activatable in the presence of these contaminants.
Owner:MIKULEC CONRAD S
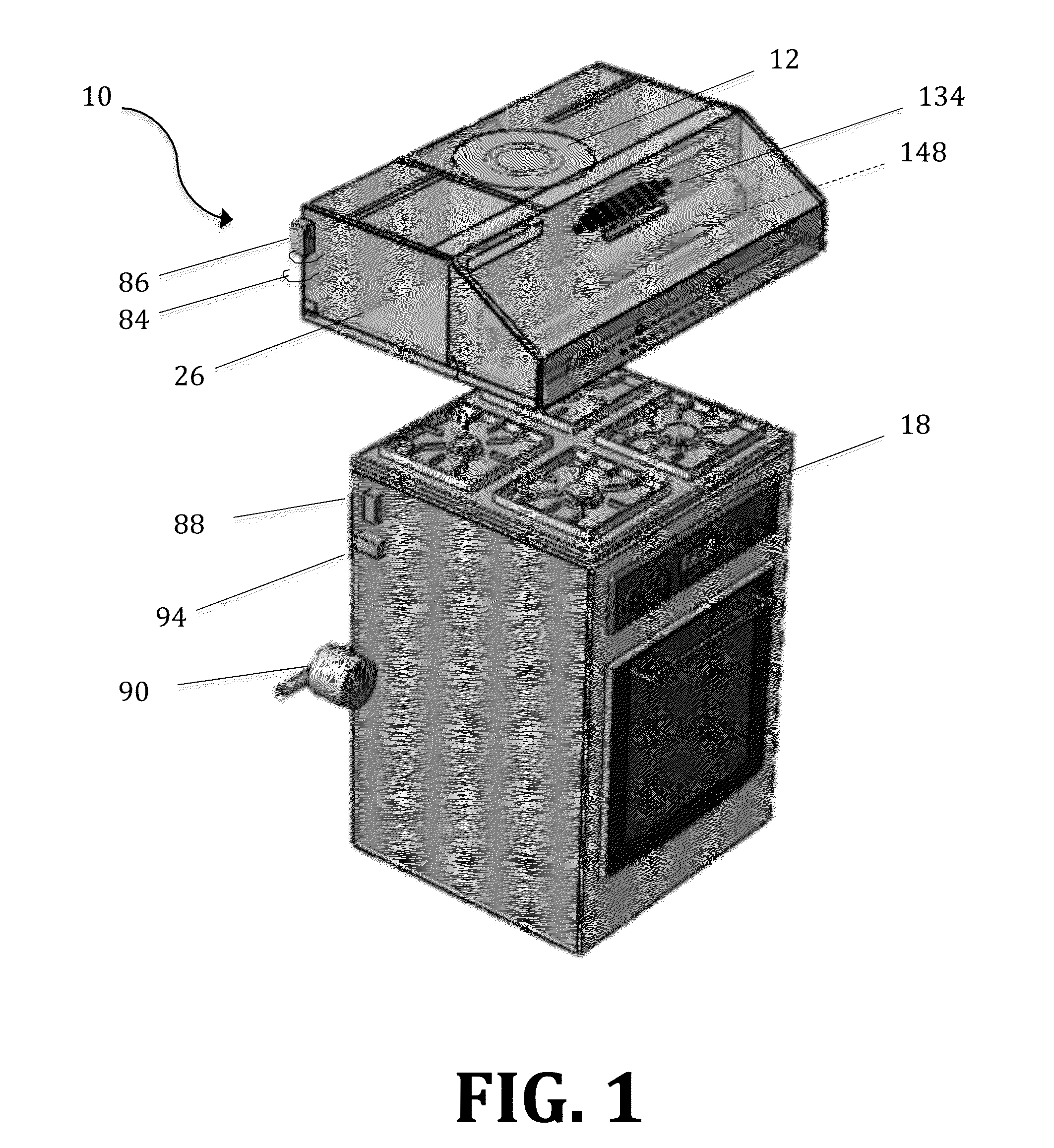
Integrated airborne substance collection and detection system
InactiveUS7633606B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBiological particles
A collection and detection system is configured as a detect to warn system in which the presence of specific types of particles are detected, and may or may not be identified. An air collection module intakes ambient air, detect the presence of one or more different types of airborne particles within the ambient air, and collect the airborne particles, such as within a fluid. A triggering mechanism is positioned to continuously monitor the airflow, to determine one or more characteristics of the airborne particles. If those measured characteristics match specific known characteristics, a trigger signal is generated. In response, a confirmation device performs a detection method on a fluid solution including the airflow particles to determine the presence of one or more different types of specific biological particles.
Owner:MICROFLUIDIC SYST
In-Line Smoke Attenuator
ActiveUS20090002182A1Constant ratioReduce concentrationDispersed particle filtrationWithdrawing sample devicesSmoke EmissionEngineering
In one form the present invention provides an apparatus in an airflow path before a particle detector, wherein the apparatus removes a substantially constant proportion of all sizes of airborne particles from the airflow over time. In an example the apparatus includes a flow splitting arrangement configured to divide a fluid flow into a plurality of sub-flows, the splitting arrangement 10 including means for defining a plurality of substantially identically dimensioned flow apertures configured to direct a portion of the fluid into a respective sub-flow.
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
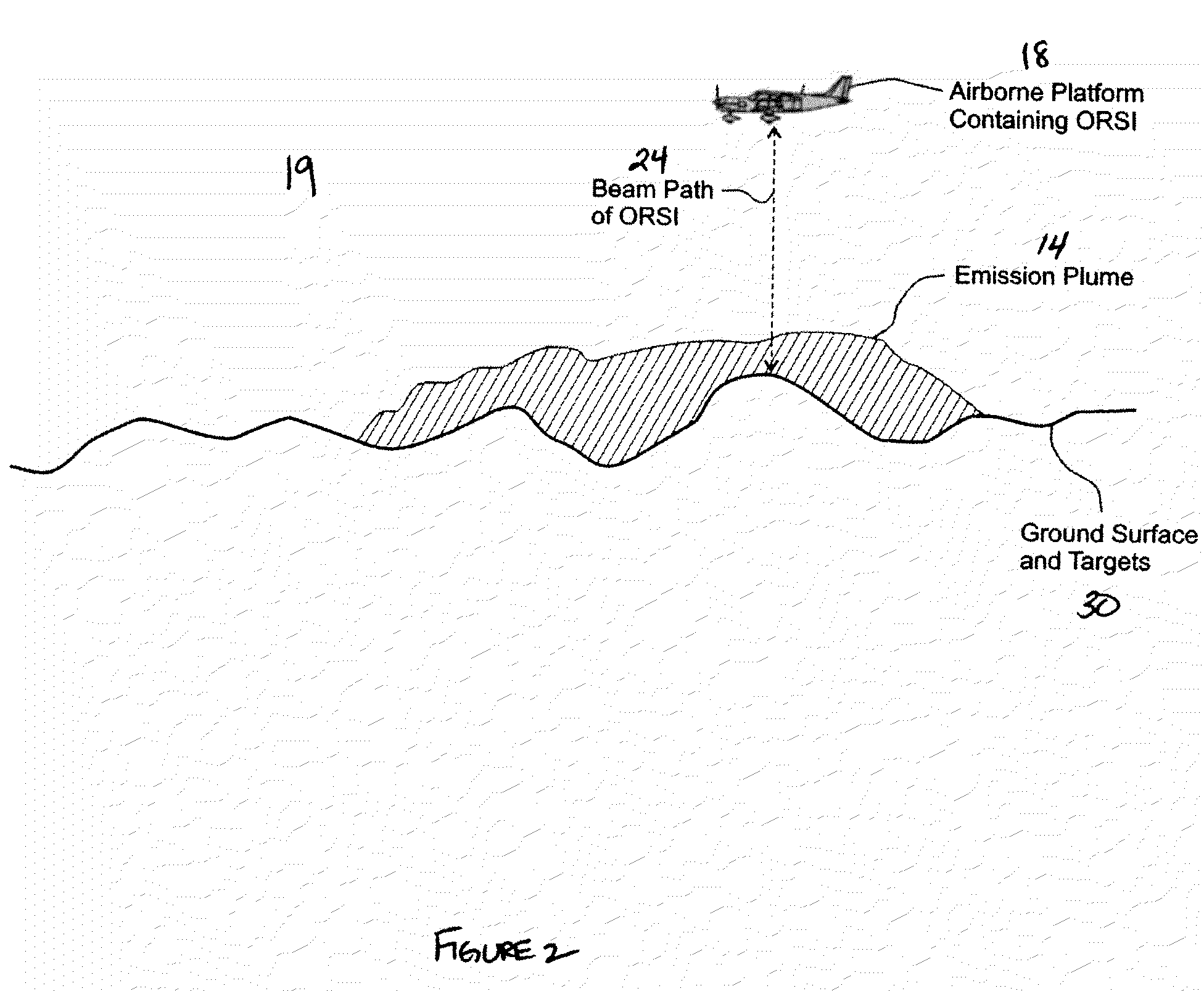
Fugitive emission flux measurement
A method of obtaining a fugitive emission flux measurement of airborne matter is provided. The method involves measuring the airborne matter along one or more than one measurement plane that spans the fugitive emission using two or more than two measurement beam paths where each of the two or more than two measurement beam paths are parallel to each other, or substantially parallel to each other, and determining a mass per unit length measurement for the measurement plane, determining a representative wind velocity at or near the one or more than one measurement plane, and calculating the fugitive emission flux of the airborne matter in mass per unit time using the mass per unit length determination and representative wind velocity.
Owner:GOLDER ASSOCIATES
Apparatus and Method to Monitor Particulates
InactiveUS20080297798A1Withdrawing sample devicesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationParticulatesProcess engineering
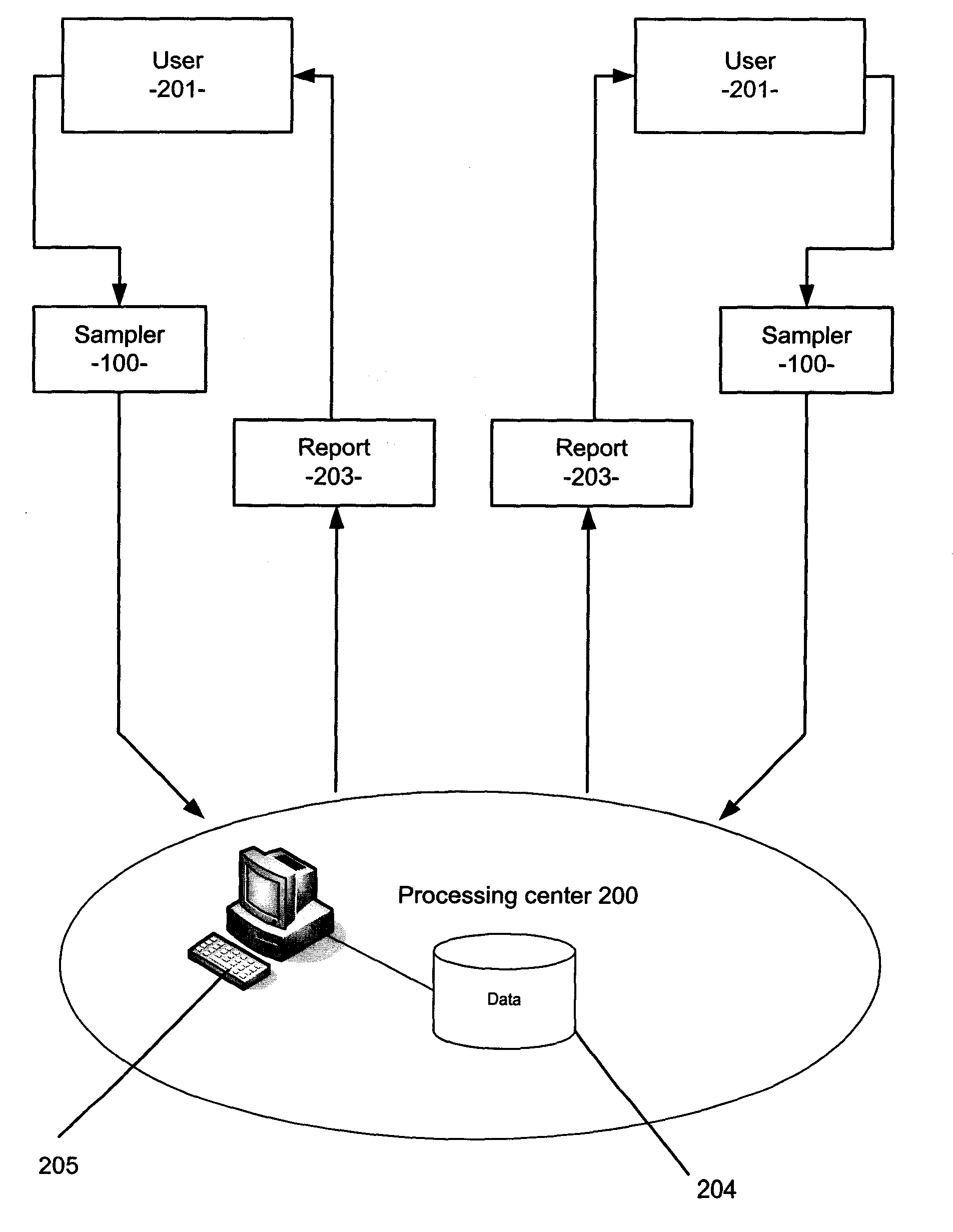
An apparatus, method and system for detecting and quantizing levels of specific airborne particle contamination in areas to be monitored for a plurality of users 201. Sealed particulate samplers 100 are distributed to a plurality of users 201. Samplers 100 are opened during a test period so that airborne particulate is pulled and affixed to surface 101 by means for attraction and affixing. After the test period, samplers 100 are sealed and sent to a processing center 200 where particulate affixed to surface 101 is analyzed using optical means and reports 203 generated and sent to users 201. Reports 203 compare test results with selected benchmark values from database 204.
Owner:WYSSEN HANS
Method for Particle Size and Concentration Measurement
ActiveUS20080037004A1High resolutionGood concentration sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisGaussian laser beamSignal mapping
The present invention provides method of particle size and concentration measurement that comprises the steps of: providing a focused, synthesized, non-Gaussian laser beam, causing the beam to interact with the particles, measuring the interaction signal and the number of interactions per unit time of the beam with the particles, and using algorithms to map the interaction signals to the particle size and the number of interactions per unit time to the concentration. The particles are fluid borne, airborne, or on a surface and have a size ranging from sub-micron to thousands of microns. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the focused, synthesized, non-Gaussian laser beam is a dark beam. The non-Gaussian beam can be generated by employing a mask over a Gaussian laser beam or by directly modifying the laser cavity or by combining the beams from several lasers. The measurements can be made using the duration of interaction with a scanning beam, including dark field. The invention further provides a system for particle size and concentration measurement.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Portable filter unit and methods for using same
InactiveUS6979359B2Avoid spreadingQuickly reconfiguredCombination devicesMechanical apparatusRadioactive agentFiltration
Portable, rapidly deployable filter unit for use in air filtering methods providing high efficiency filtration of airborne toxins. The filter unit includes a fan section and a filter section that are releasably attachable at their respective lateral ends permitting the filter unit to be reconfigurable to properly handle a variety of threat scenarios involving protecting the occupant(s) and equipment in an enclosure against an airborne release of toxic chemical, biological, or radiological agents that threaten to contaminate the air supply, or, alternatively, for decontaminating the air of an isolation room occupied by contaminated or contagiously ill persons or materials and protecting the occupants or equipment located outside the isolation room.
Owner:LAITI PETER J
Protective socket for use with a parallel optical transceiver module for protecting components of the module from airborne matter
A protective socket is provided for use with a parallel optical transceiver module. When the parallel optical transceiver module is seated within a receptacle of the protective socket, the side walls and bottom that define the receptacle of the protective socket protect the internal components of the parallel optical transceiver module from dirt, dust, gases, and other airborne matter.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
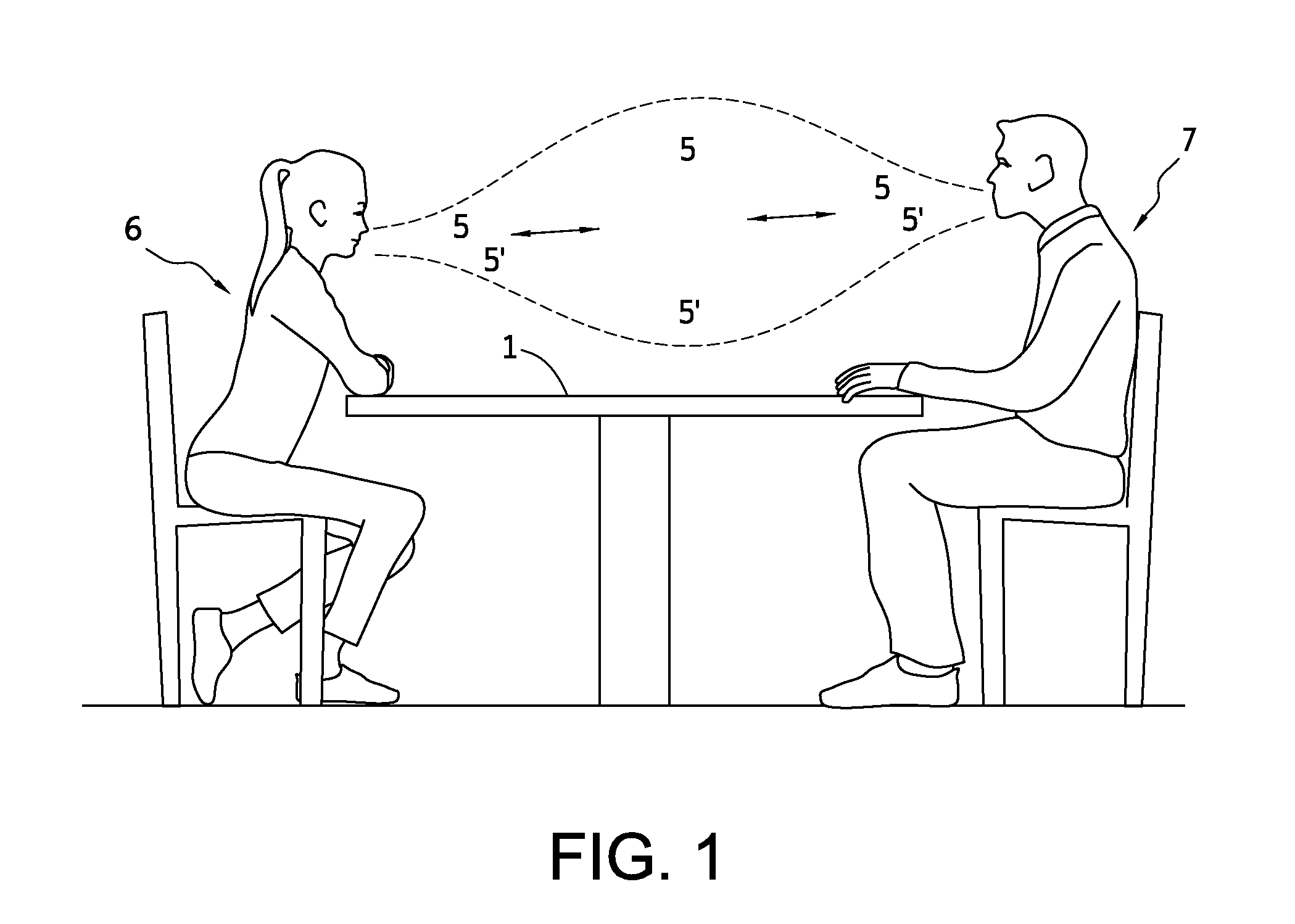
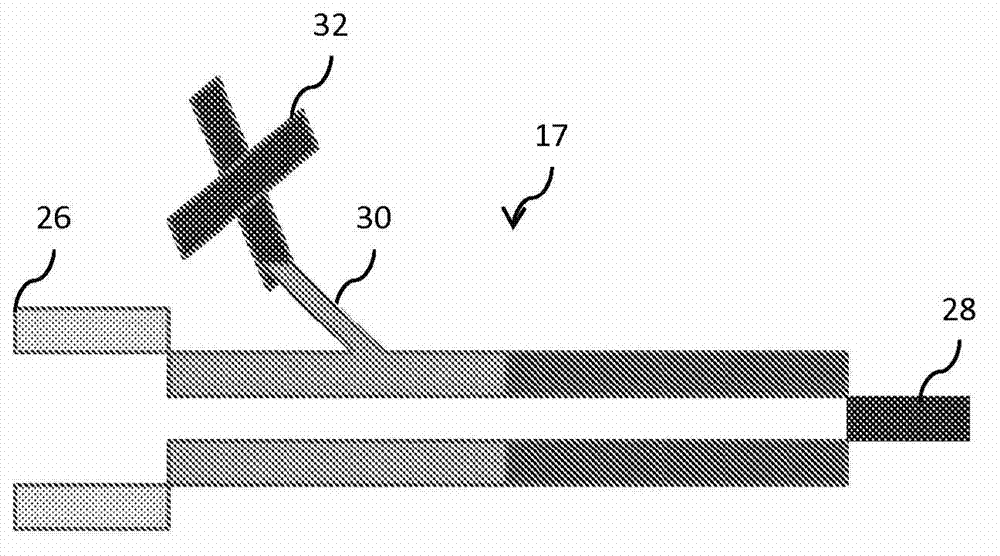
Close proximity airborne influenza/pathogen mitigator
Close proximity, including conversations at closer than three (3) feet apart, facilitates disease transfer via airborne pathogens. This transfer can be mitigated by the present invention, which is directed towards methods, systems and apparatuses to produce a predictably shaped and minimally intrusive air barrier that may comprise an airborne disinfectant, to divert and or render harmless and to divert and negate close proximity airborne pathogens, such as influenza and severe acute respiratory syndrome, etc., and other airborne particulates transferred from an infected person towards the face of an unfortunate recipient at normal conversational distances apart from each other, and / or to divert and render harmless such airborne particulates.
Owner:CARR PETER
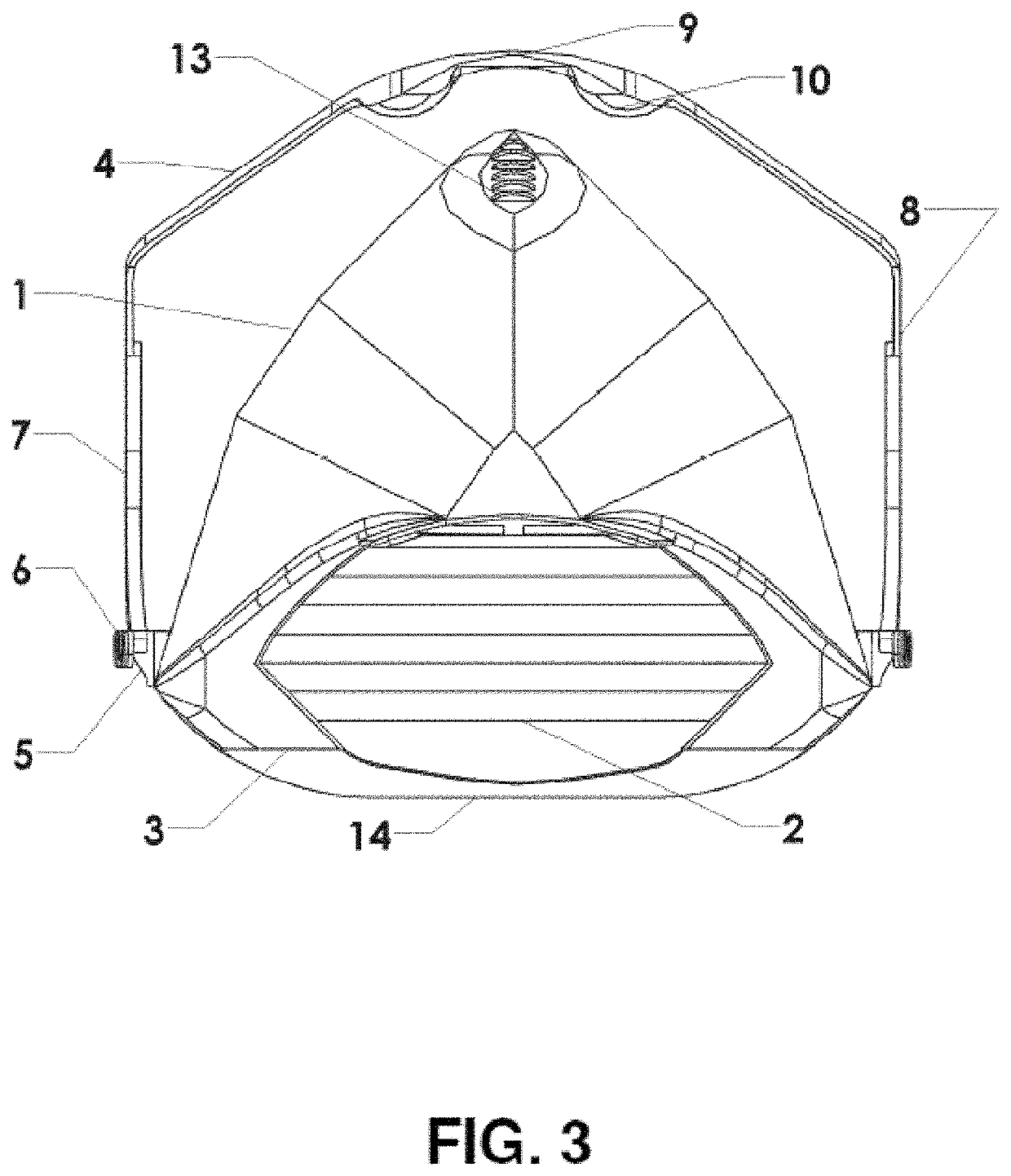
Facemask with filter insert for protection against airborne pathogens
A facemask assembly can include an interior air filter that is replaceable and / or contains biocidal elements. The filter can capture exhaled H2O to activate silver ions creating a biocidal environment. In some embodiments, at least part of the facemask is made via additive manufacturing. A facemask frame assembly can create a pleated filter to increase surface area and bring the filter material closer to the mouth and nose. The facemask can include a facial skirt customized to the facial geometry of the wearer. The facemask can have a permanently sealed filter than can withstand boiling and autoclaving temperatures so the mask system can be sterilized without disassembly. In some embodiments, the facemask has a visible display of how many times the facemask has been sterilized. In some embodiments, the mask includes a RFID device that can transmit how many times the facemask has been sterilized.
Owner:OCTO SAFETY DEVICES LLC
Pest control method and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20060021275A1Insect catchers and killersPoisonAgricultural scienceAgricultural engineering
A method and apparatus for controlling a pest by at least partially coating the pest with a particulate material that incorporates a killing or behavior-modifying agent. The method and apparatus involve drawing the pest sufficiently close to a surface bearing the particulate material, which is rendered airborne by movement of the pest in the region of the surface. The particulate material is electrostatically charged when rendered airborne, so as to be electrostatically attracted and attached to the pest.
Owner:EXOSECT
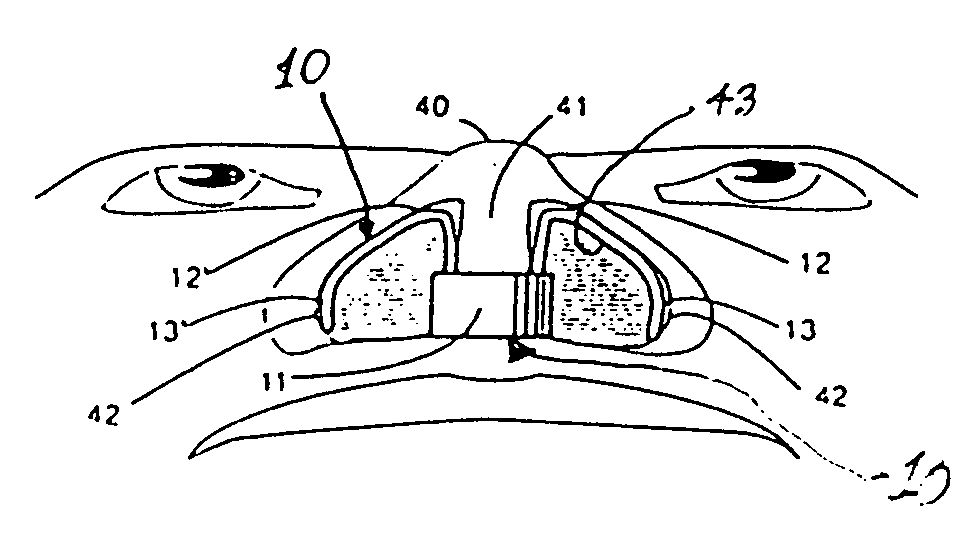
Nose airway for aromatherapy and detecting airborne pathogens
InactiveUS20050199245A1Controlling and limiting projectionEasy and inexpensive to manufactureFire rescueInvestigating presence of gasesAromatherapyMedicine
A nasal airway for insertion in the nose for the delivery of volatile compositions into air entering the nose or, in a second embodiment, for the detection of targeted airborne pathogenic organisms present in the respirated airstream. The volatile compositions include aromatherapeutic compositions and scents.
Owner:BRENNAN H GEORGE
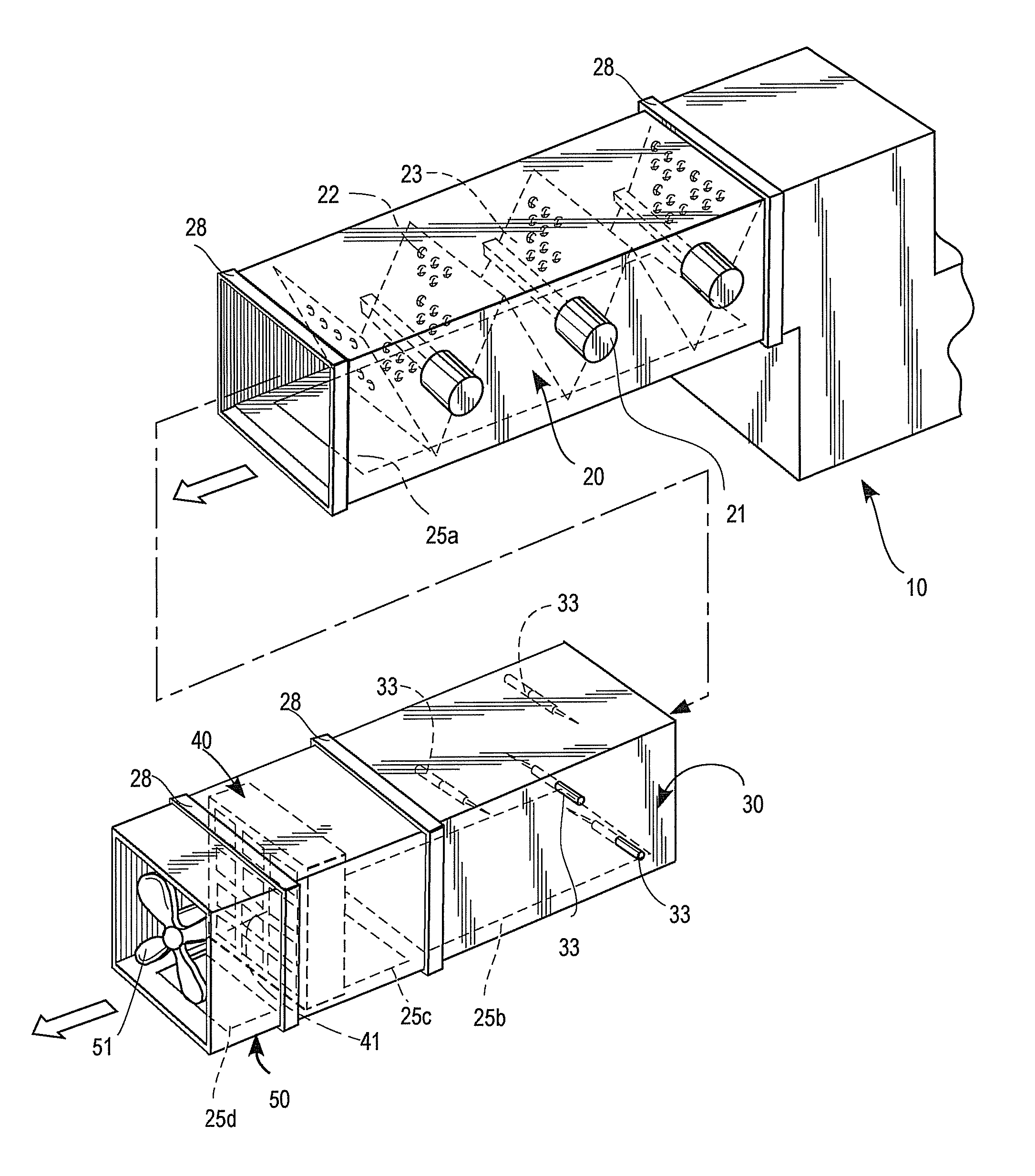
Modular ductwork decontamination assembly
InactiveUS20130183214A1Little effortAvoid huge expensesSpace heating and ventilationUsing liquid separation agentParticulatesModularity
A modular ductwork assembly decontaminates an air stream circulating within a heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system. The assembly includes one or more of (a) an ionizing module for removing particulates from the air stream, (b) a sterilization module for neutralizing airborne pathogens present in the air stream, (c) an ozone treatment module for neutralizing pathogens or odoriferous or gaseous constituents or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) present in the air stream, optionally (d) baffles for slowing and disrupting the flow rate and promoting turbulence in the air stream traveling through the modules, optionally (e) a fan module for directing a treated air stream, optionally (f) an ozone sensor, optionally (g) a monitoring or ozone control means, and optionally (h) a means of delivering and repurposing generated ozone. Each of the modules is arranged substantially adjacent to at least one of the other modules.
Owner:METTEER KAREN
Fugitive emission flux measurement
A method of obtaining a fugitive emission flux measurement of airborne matter is provided. The method involves measuring the airborne matter along one or more than one measurement surface that spans the fugitive emission using two or more than two measurement beam paths where each of the two or more than two measurement beam paths are parallel to each other, or substantially parallel to each other, and determining a mass per unit length measurement for the measurement surface, determining a representative wind velocity at or near the one or more than one measurement surface, and calculating the fugitive emission flux of the airborne matter in mass per unit time using the mass per unit length determination and representative wind velocity.
Owner:GOLDER ASSOCIATES
Modular ductwork decontamination assembly
InactiveUS7740686B2Little effortAvoid huge expensesCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesModularity
A modular ductwork assembly decontaminates an air stream circulating within an heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system. The assembly includes (a) an ionizing module for removing particulates from the air stream, (b) a sterilization module for neutralizing airborne pathogens present in the air stream, (c) an ozone treatment module for neutralizing odoriferous constituents or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) present in the air stream, optionally (d) baffles for slowing and disrupting the flow rate and promoting turbulence in the air stream traveling through the modules and optionally (e) a fan module for directing a treated air stream. Each of the modules is arranged substantially adjacent to at least one of the other modules.
Owner:METTEER KAREN
Compositions and methods for protecting against airborne pathogens and irritants
PendingUS20170246262A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBacilliPathogen
The present disclosure features methods and compositions for enhancing the ability of the respiratory membranes to filter airborne pathogens and protect a subject from respiratory infections that result from inhalation of such pathogens. In particular, the disclosure provides antimicrobial compositions that prevent and treat respiratory infections caused by bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Owner:APPLIED BIOLOGICAL LAB INC
Ultrasonic-assisted liquid manipulation
ActiveUS11098951B2Drying solid materials with heatDrying solid materials without heatUltrasonic assistedAcoustic energy
A phased array of ultrasonic transducers may create arbitrary fields that can be utilized to manipulate fluids. This includes the translation of drops on smooth surfaces as well speeding the evaporation of fluids on wetted hands. Proposed herein is the use airborne ultrasound focused to the surface of the hand. The risk is that coupling directly into the bulk of the hand may cause damage to the cellular material through heating, mechanical stress, or cavitation. Using a phased array, the focus may be moved around, thus preventing acoustic energy from lingering too long on one particular position of the hand. While some signaling may penetrate into the hand, most of the energy (99.9%) is reflected. Also disclosed are methods to couple just to the wetted surface of the hand.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
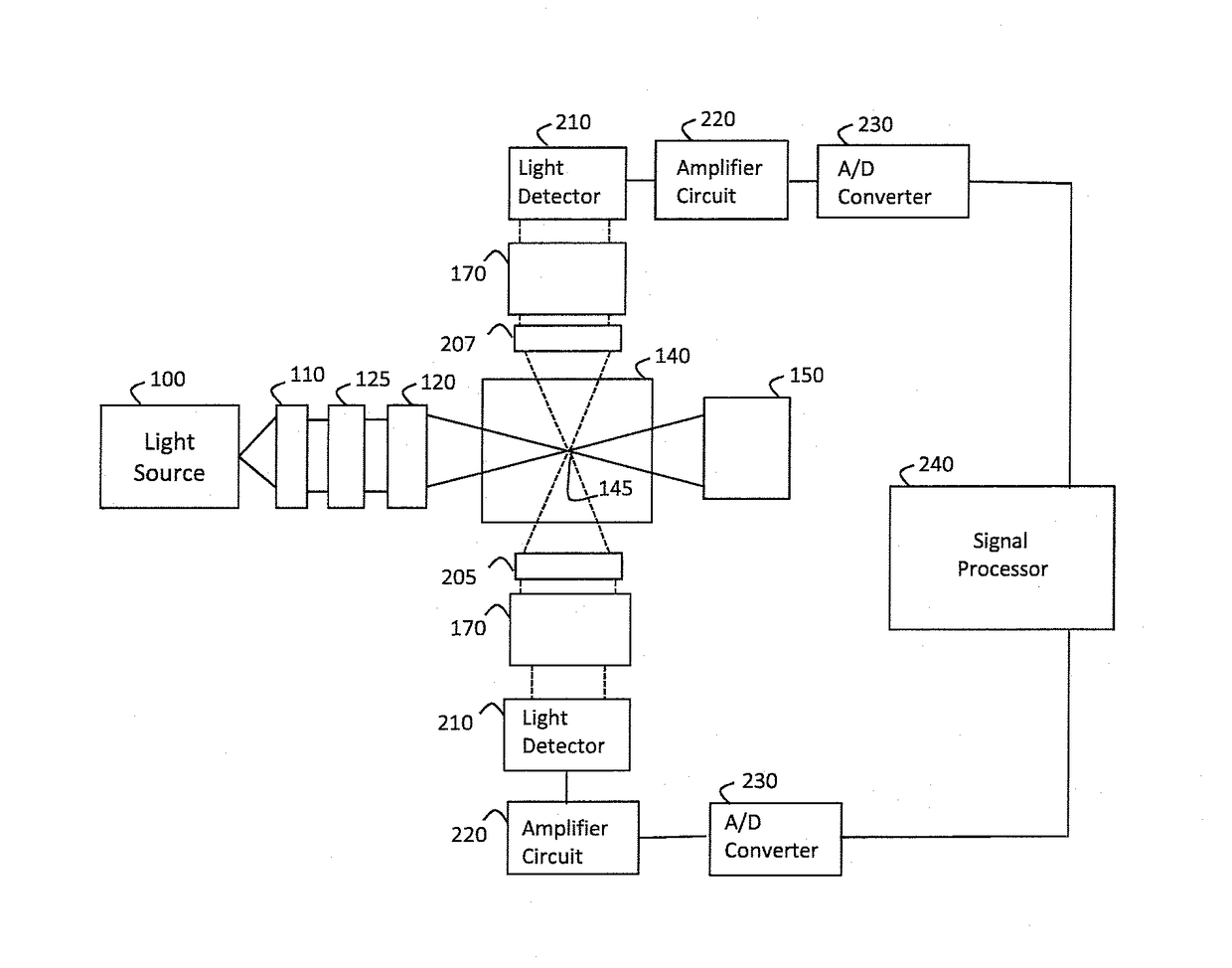
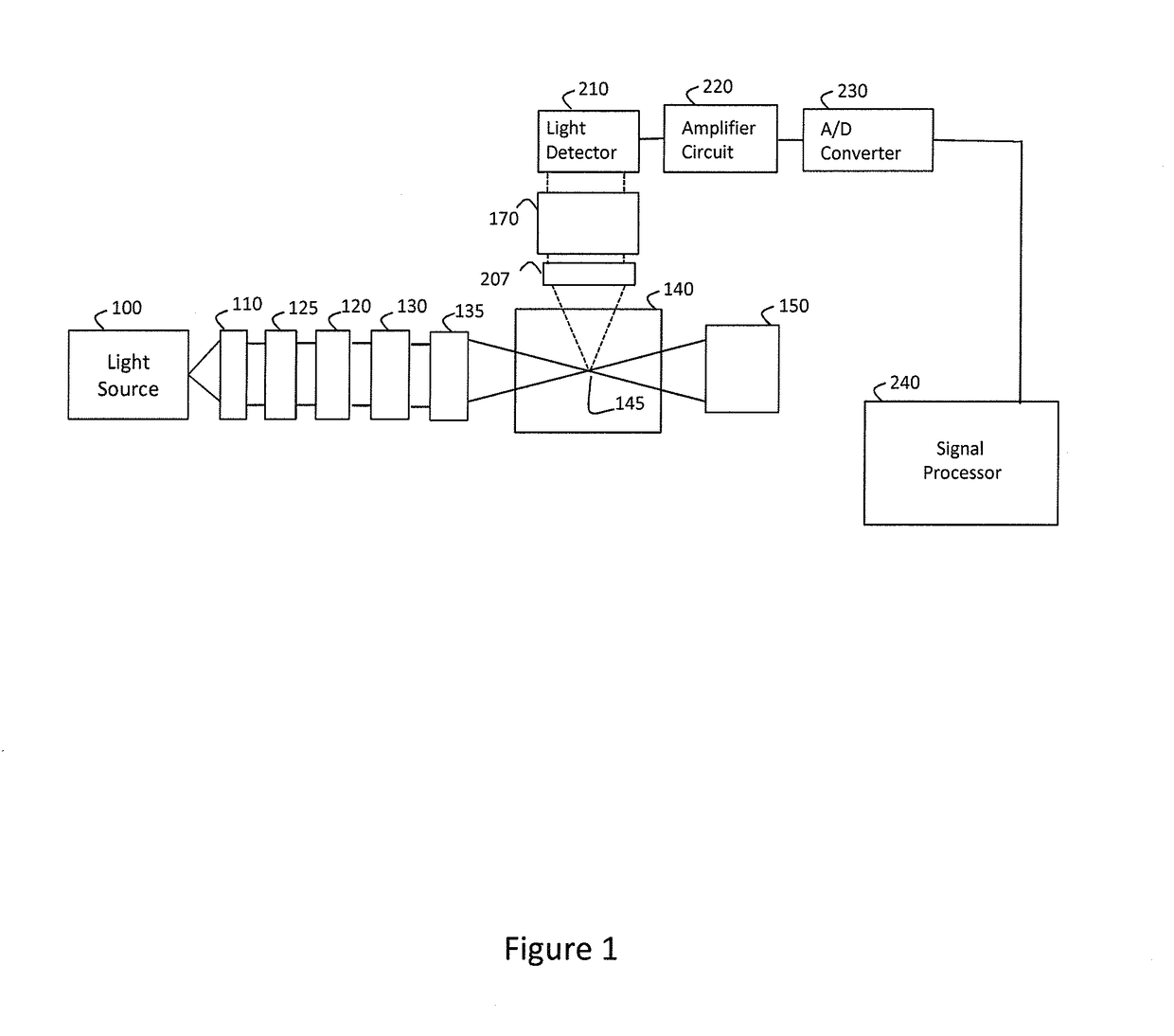
Method and instrumentation for measuring fluorescence spectra of individual airborne particles sampled from ambient air
InactiveUS6947134B2Reliable and rapid fluorescence spectrum detectionRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectrometerInstrumentation
A Fluorescence Particle Spectrometer (FPS) performs real-time measurement of the fluorescence spectra of aerosol particles in the size range 1-10 μm diameter. The FPS has a sufficiently high sample rate (estimated to be a few liters / min) to measure aerosol within buildings (from 1 up to 600 particle fluorescence spectra per minute) at practical rates. A virtual impactor first concentrates aerosol particles, which are then drawn under negative pressure through an aerodynamic focusing nozzle in the inlet of the instrument, through the sample region, providing further concentration. The rate of particle spectra measured by the FPS increases significantly when the particle inlet is within a few meters of some common sources of indoor biological particles.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Method and apparatus for inhibiting accretion of airborne material on a surface of an aircraft
An apparatus for inhibiting accretion of airborne material on a surface of an aircraft. The apparatus comprises a film adapted to overlie at least a portion of the aircraft surface and a driver mechanism coupled to the film. The driver mechanism is operative to slideably move the film relative to the aircraft surface, such that airborne material impinging on the film detaches itself and breaks away therefrom. In a particular example of implementation, the apparatus is adapted and used for inhibiting accretion of airborne material on an airfoil leading edge.
Owner:BOMBARDIER AERONAUTIQUE
Air sampler module for enhancing the detection capabilities of a chemical detection device or system
ActiveUS20080007728A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRadiation pyrometryTransceiverSpectroscopy
An air sampler module is provided for use with a detection device that monitors liquids and / or solids on a surface using spectroscopy techniques. The air sampler module comprises a housing, an intake port for collecting air containing airborne threats to be analyzed by the detection device, and a port to permit communication of an optical transceiver of the detection device into the housing to permit analysis of the collected air. Thus, the capabilities of a spectroscopy detection system are expanded to include the ability to analyze airborne threats.
Owner:PERATON INC
Aerosol collection apparatus and methods
InactiveUS7767150B1Increase airflowReduce stressBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalyteCompound (substance)
Apparatus and methods for detecting the presence of an airborne chemical or biological analyte utilise:a substantially gas- and liquid-impermeable container; means for introducing a substantially analyte-free collection liquid into said container; means for rapidly sampling ambient air and transferring said analyte therefrom into said collection liquid, said sampling means comprising an air intake means and and an air venting means; and-means for removing from said container an analyte-enriched collection liquid; wherein said volume of air passes through a substantially horizontal air inlet and upwardly through a substantially vertical collector electrode tube with means for applying an electric field between said tube and a co-axial spiked wire- or rod-shaped discharge electrode.
Owner:ZAROMB SOLOMON +2
System for airborne bacterial sample collection and analysis
InactiveCN103119417AEasy to understandMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesBacteriaBiological organism
An aerosol biological collector / analyzer, and method of collecting and analyzing an aerosol sample for diagnosis is provided. In particular, the current invention is directed to an airborne aerosol collection and bacterial analysis system and method, capable of collecting an airborne aerosol sample and preparing it for analysis via aerodynamic shock in a single-step.
Owner:DETON
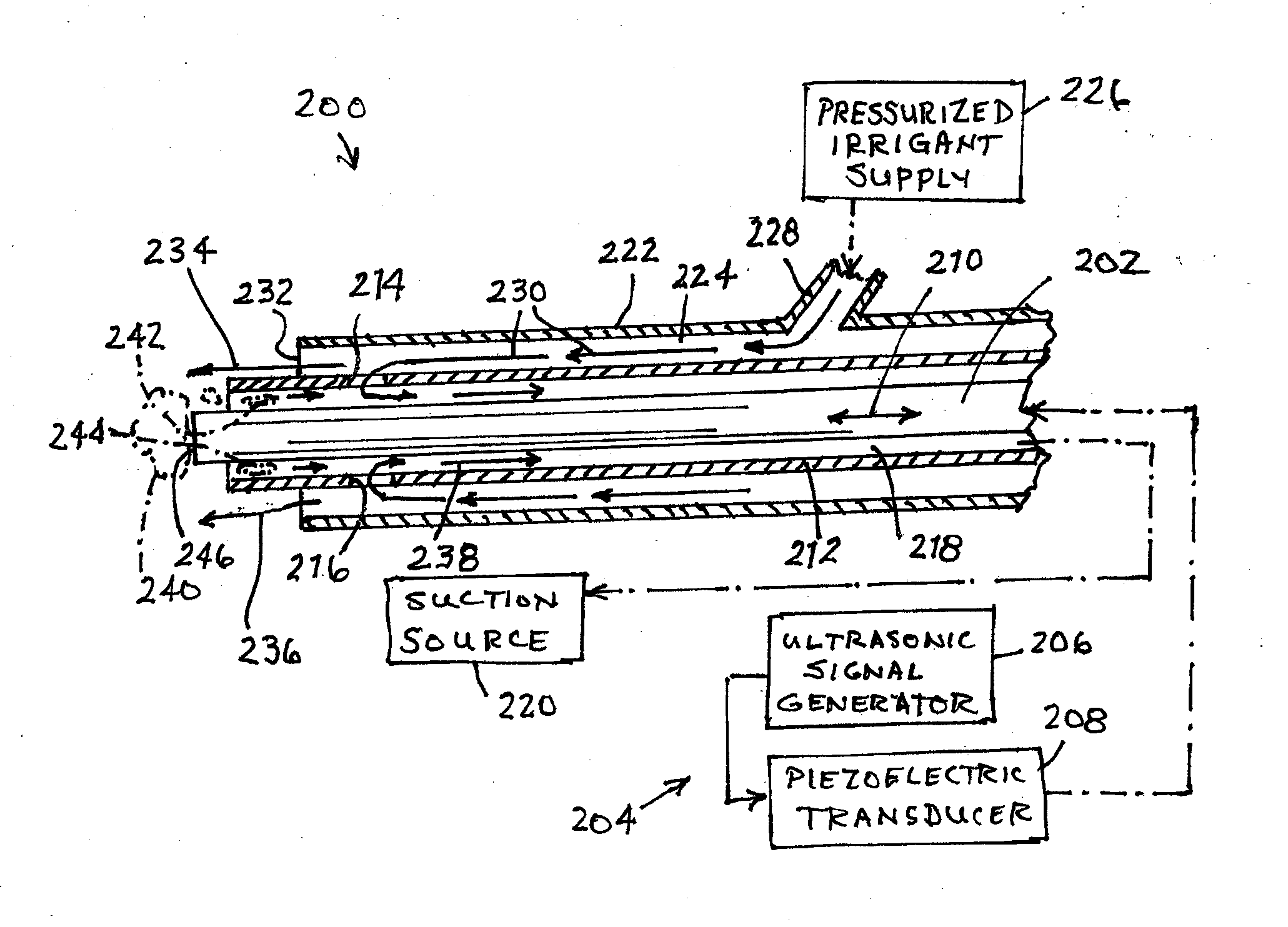
Method for reducing biofilm formation
ActiveUS20160128708A1Reduce the possibilityEasy to placeSurgeryMedical devicesBiofilmSurgical treatment
A two phase method for reducing the formation of biofilm includes an evacuation of ambient air from a region about the surgical or treatment site, to extract airborne or aerosolized bacteria ejected from the site by the treatment. The extracted bacteria are prevented from settling back onto the cleansed tissue surface, thus at least reducing colonial bacteriological growth and concomitantly exuded biofilm material. A second phase involves the attachment of one or more ultrasonic transducers to the patient over or near a surgical treatment site after the surgery is terminated. Each applied ultrasonic transducer is used to vibrate the patient's tissues at the treatment site to disrupt biofilm formation.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Realtime optical method and system for detecting and classifying biological and non-biological particles
ActiveUS20170315045A1Material analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisRefractive indexParticle physics
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for detecting and classifying individual airborne biological and non-biological particles, in real time, based on particle size and polarized elastic scatter. Auto-fluorescence content may also be used along with particle size and polarized elastic scatter for further orthogonal classification. With polarized elastic scattering, the degree of linear or circular depolarization produced from particle morphology, refractive index, internal asymmetric structures and molecular optical activity can be used for classifying individual airborne particles. Alternatively, circular intensity differential scattering (CIDS) or linear intensity differential scattering (LIDS) can be used to discriminate individual particles.
Owner:HAMILTON ASSOCS
Apparatus and Method for Reducing Contamination of Surgical Sites
ActiveUS20100280436A1Effective and inexpensive and easy to implementPrevent bacterial invasionRestraining devicesOperating tablesSurgical site infectionMedicine
Apparatus and methods for protecting a patient from surgical site infection from airborne microbes during surgery. A sterile gas flow conditioning emitter for affixation onto an anatomical surface of a patient adjacent a site of incision is anatomically shape conforming for attaching a unidirectional coherent non-turbulent flow field of sterile gas substantially anatomically levelly on that anatomical surface and flowing the flow field in the direction of that site while essentially preventing ambient airborne particles from entering the interior of the flow field under the emitter to maintain the gas essentially sterile during passage over the site.
Owner:MIZUHO ORTHOPEDIC SYST
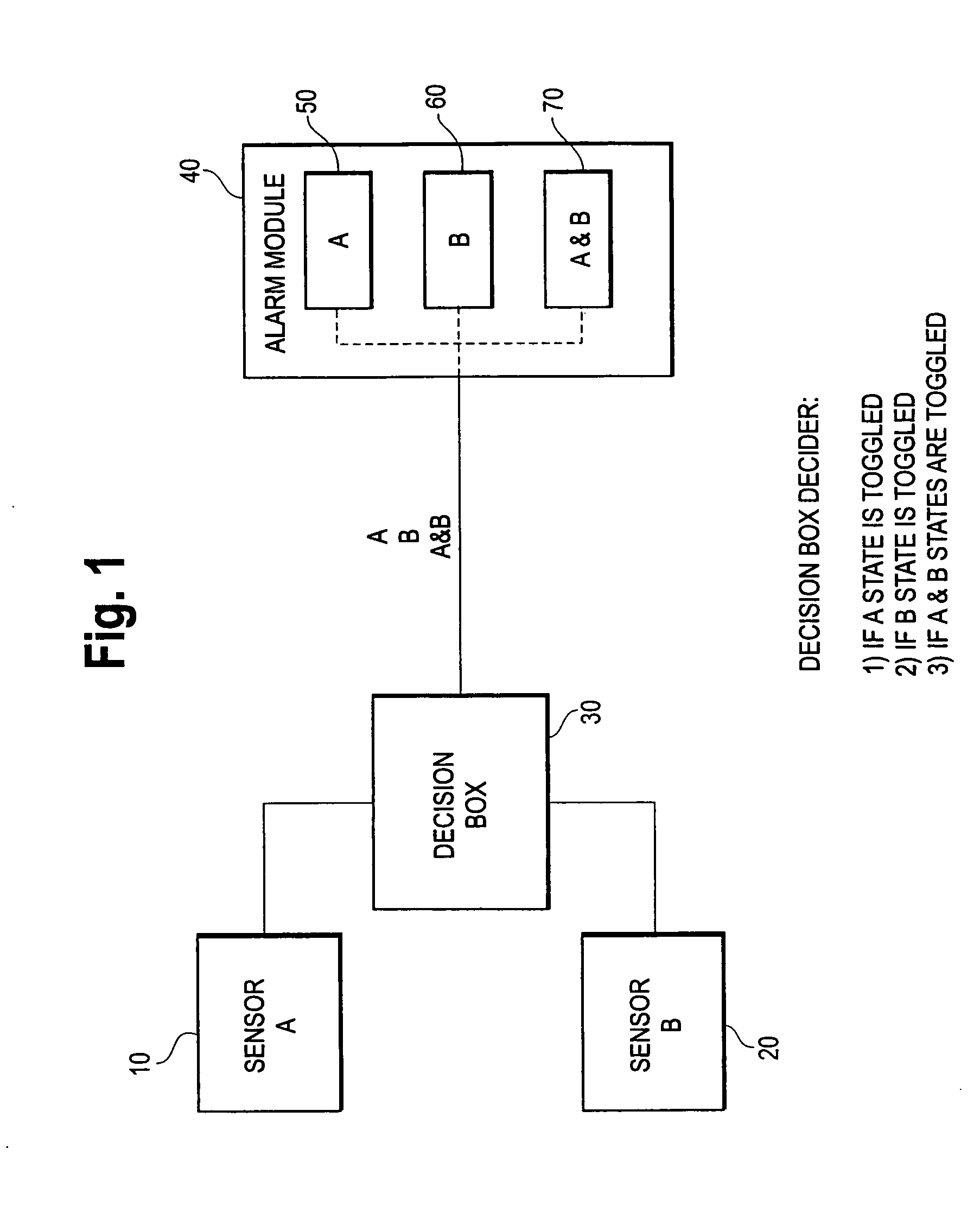
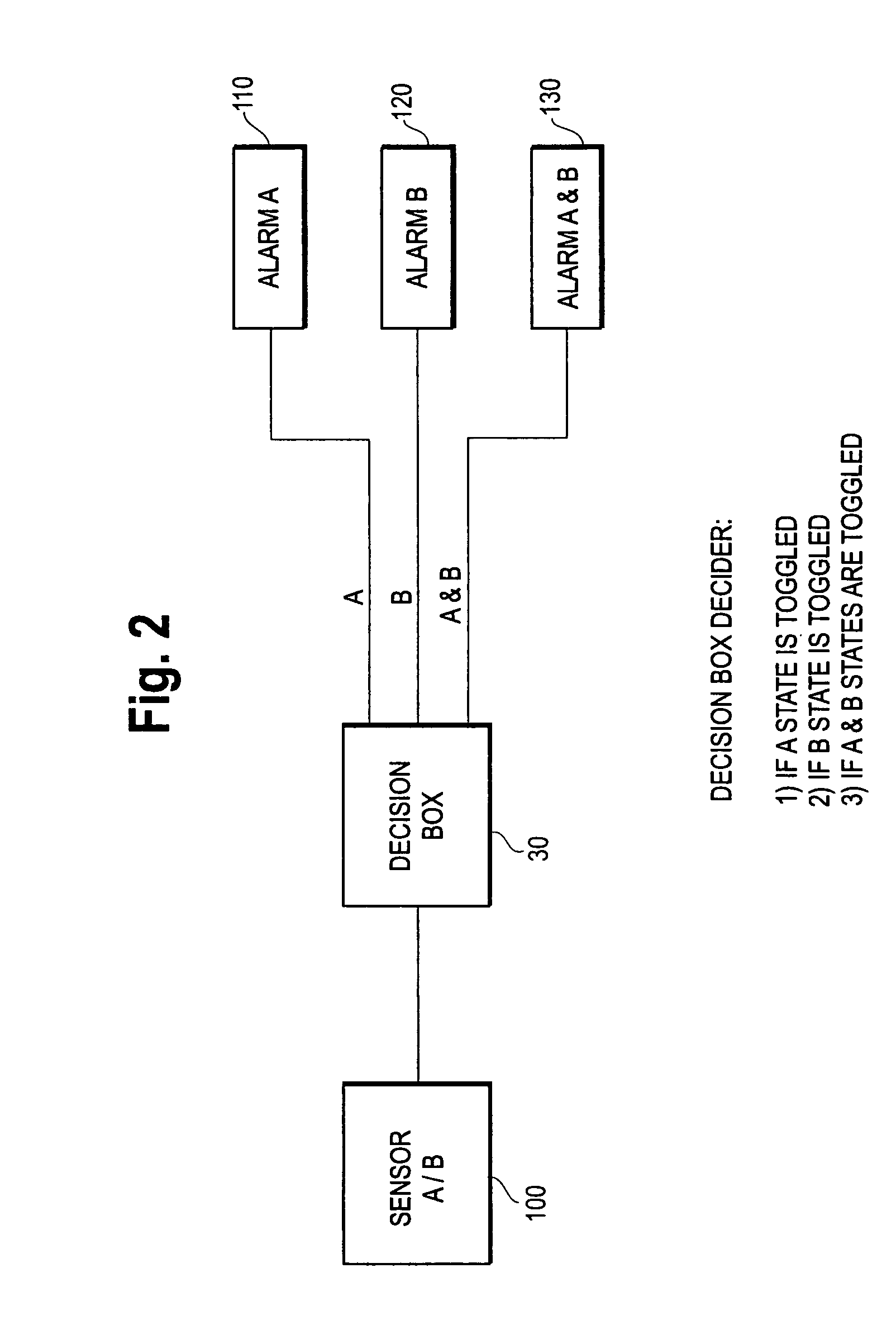
Combination airborne substance detector
ActiveUS7248156B2Biological testingSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringAmount of substance
A combination airborne substance detection apparatus includes an enclosure, a first module disposed within the enclosure for detecting the presence of a quantity of a first airborne substance, a second module disposed within the enclosure for detecting the presence of a quantity of a second airborne substance, and an alarm module for producing a first perceivable emission when the first substance is detected and for producing a second perceivable emission when the second substance is detected. The first perceivable emission includes at least one of an audible and a visible emission that is distinguishable from the second perceivable emission. The first and second detector modules are each capable of independently and continuously detecting the first and second substances, respectively.
Owner:MARINE TECH
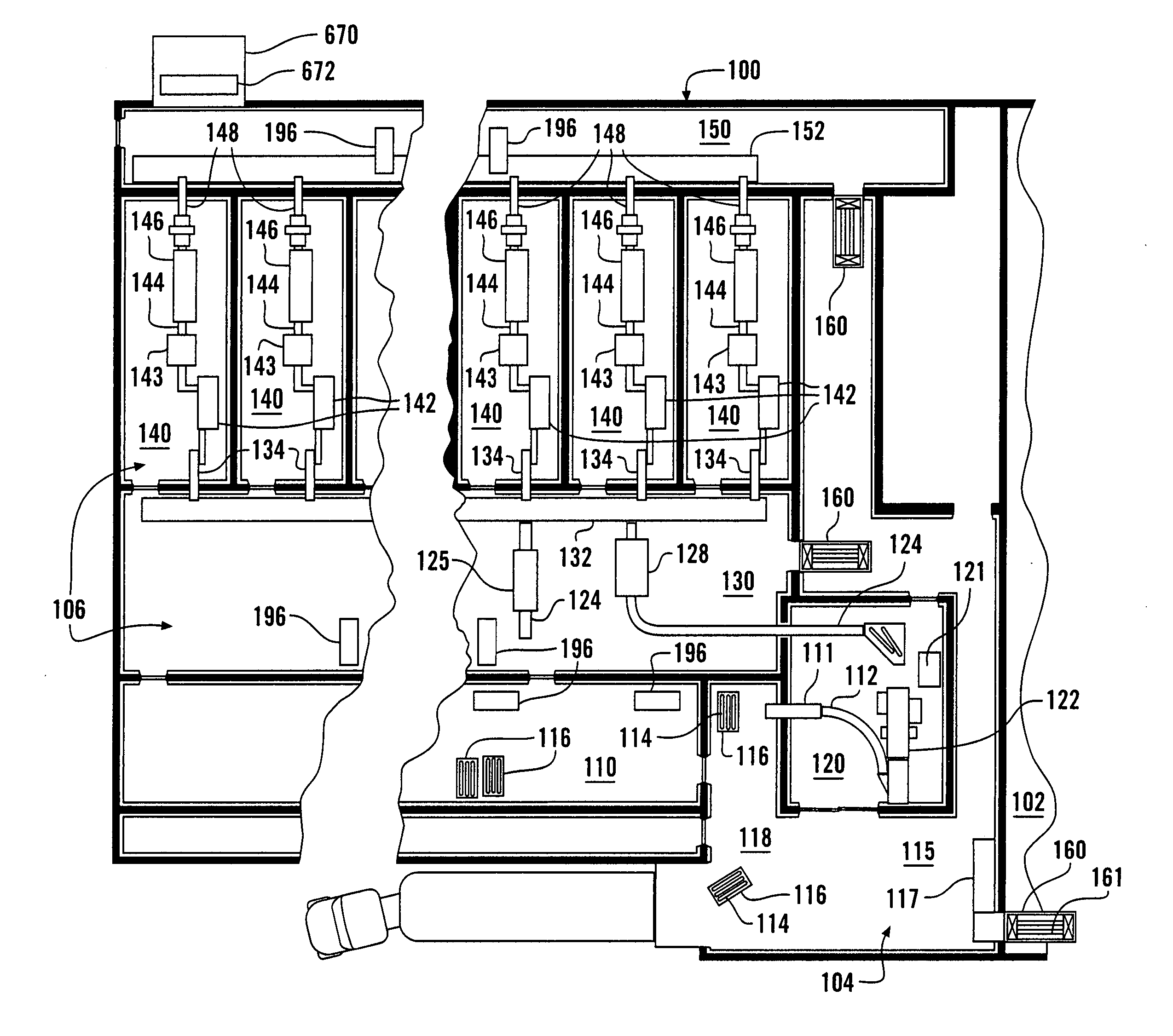
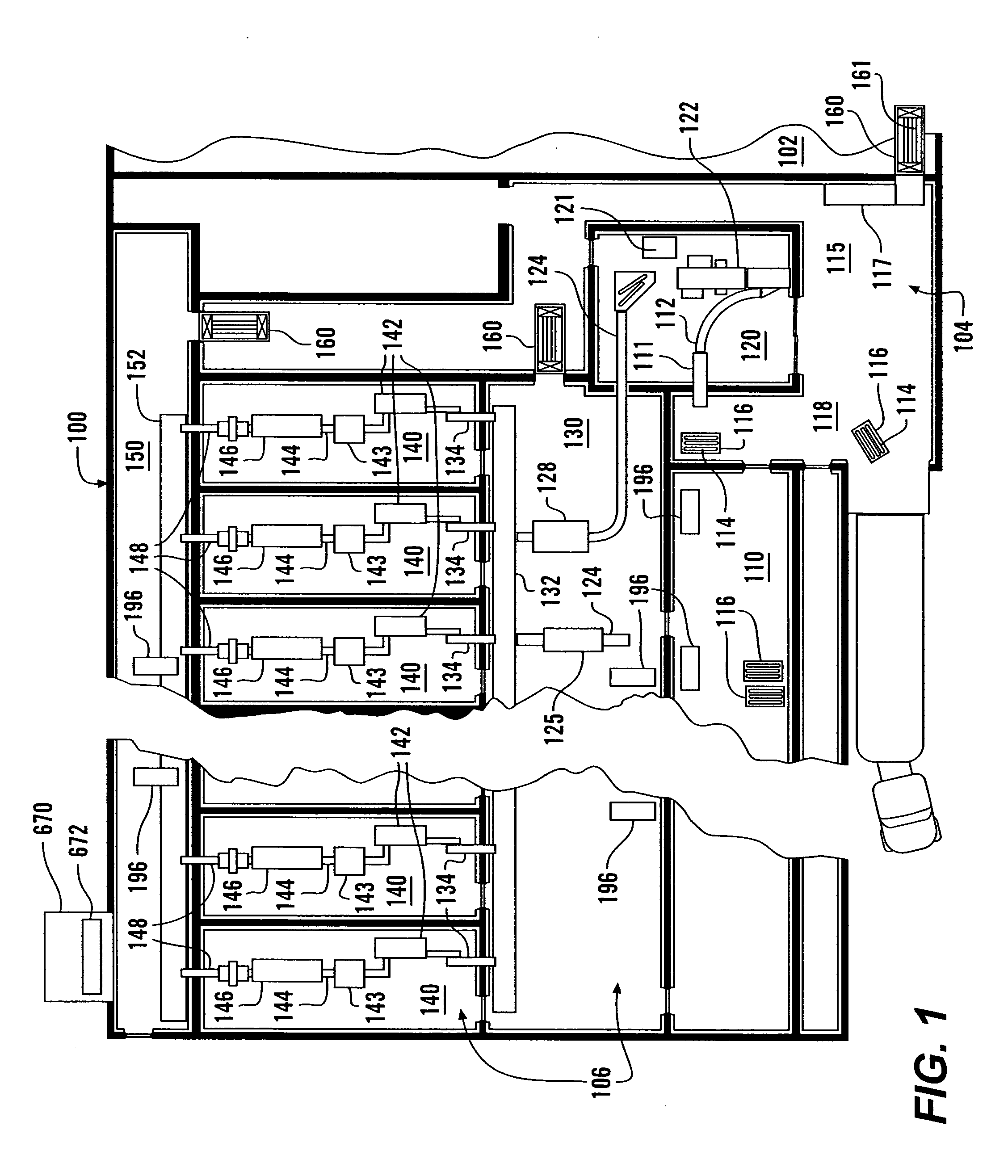
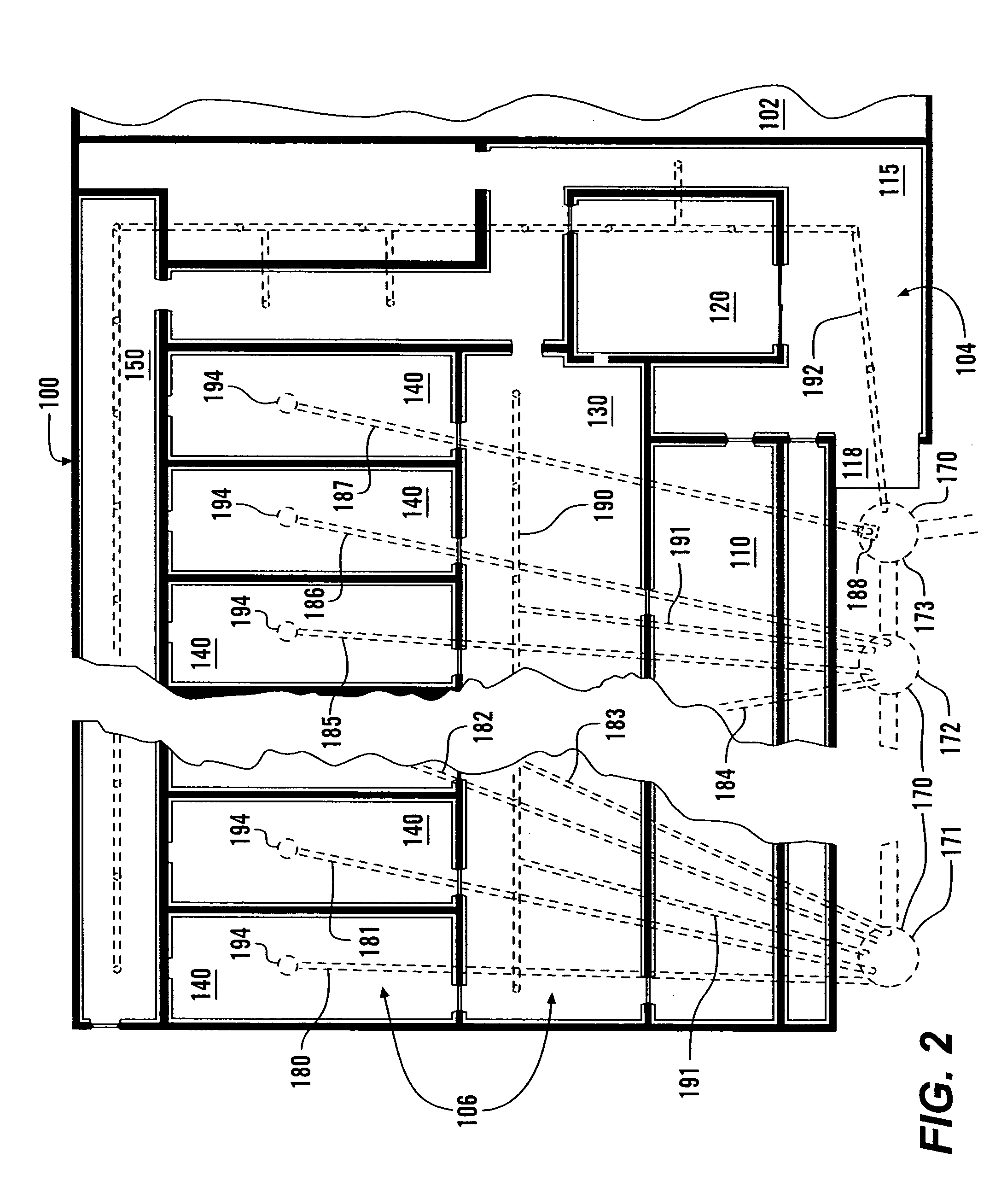
Clean room food processing systems, methods and structures
Some food pathogens are not well controlled by lethality treatments followed by refrigeration. A food processing facility according to this invention reduces the likelihood that food pathogens will be able to enter the food processing facility, or spread should they be able to enter. The food processing facility is divided into a plurality of area, with different areas having different allowed actions that can be taken on the food product, different rules and / or procedures for persons who are allowed entry, and / or different levels of cleanliness. The food processing facility includes a plurality of separate rooms for processing the food product, each including separate food processing machines, air handling systems, drain systems and / or often-used supplies and tools. Different air pressures within different areas limit the possible movement of airborne food pathogens. Sanitizing stations are placed between various ones of the different areas.
Owner:WEST LIBERTY FOODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com