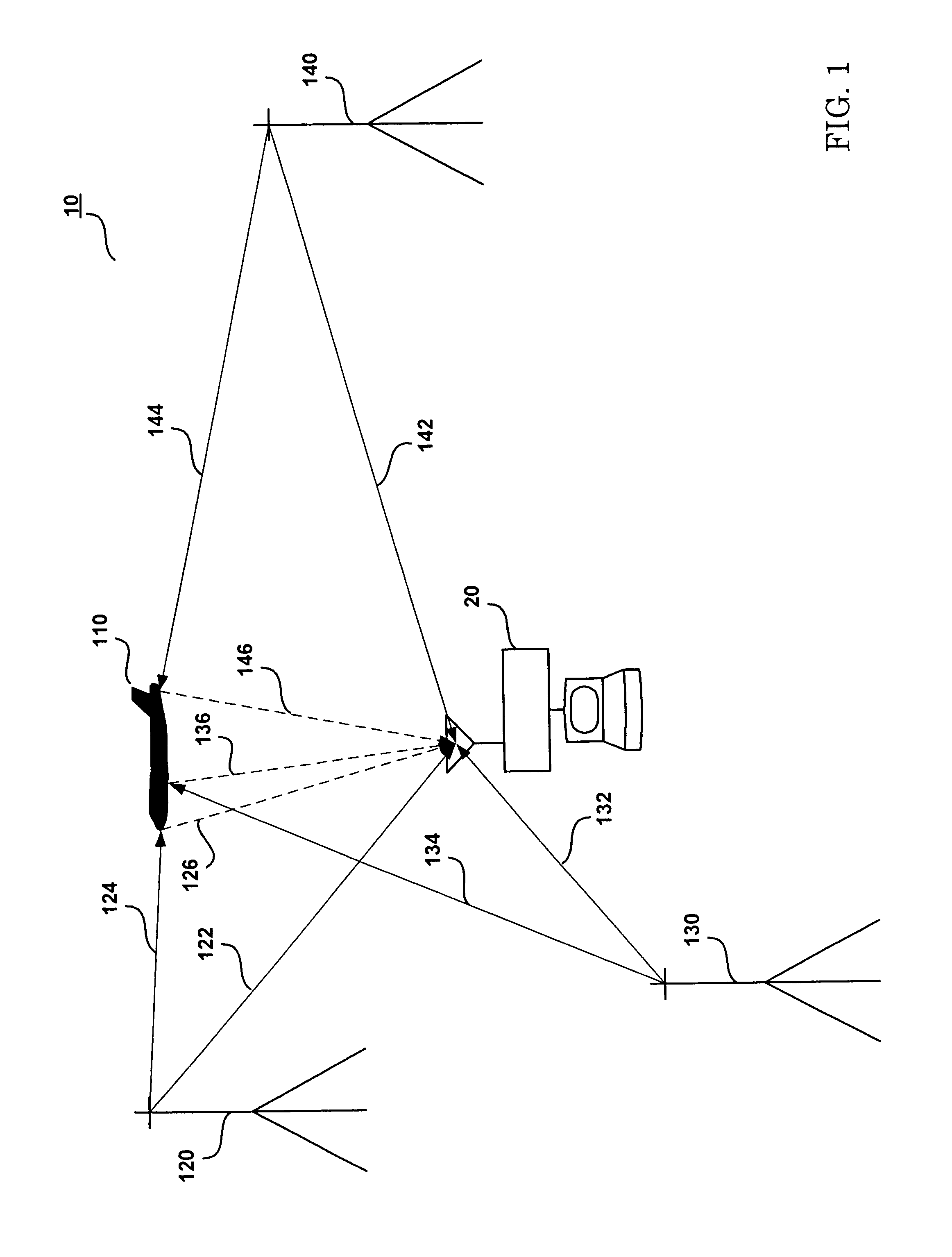
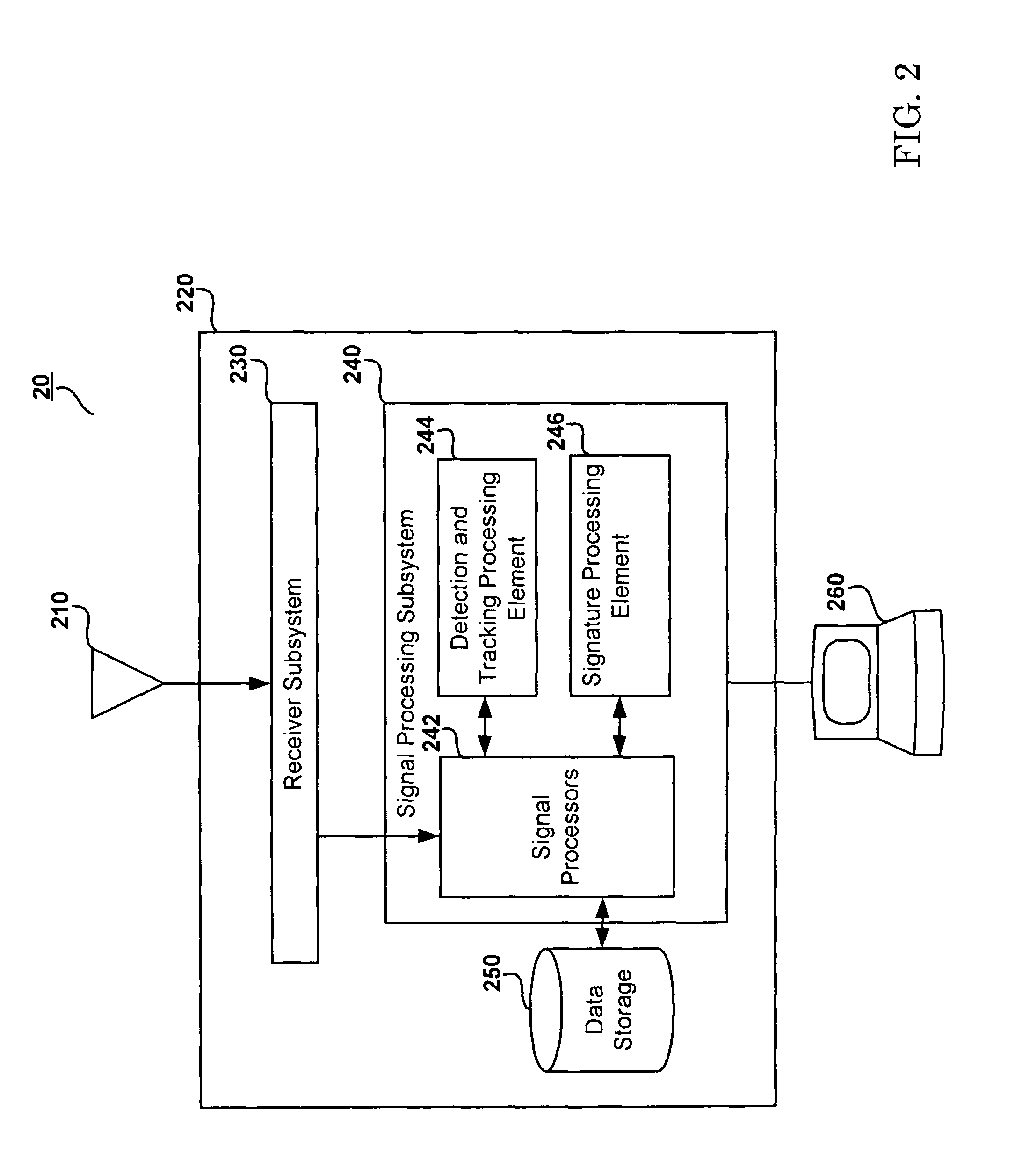
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Aspect angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
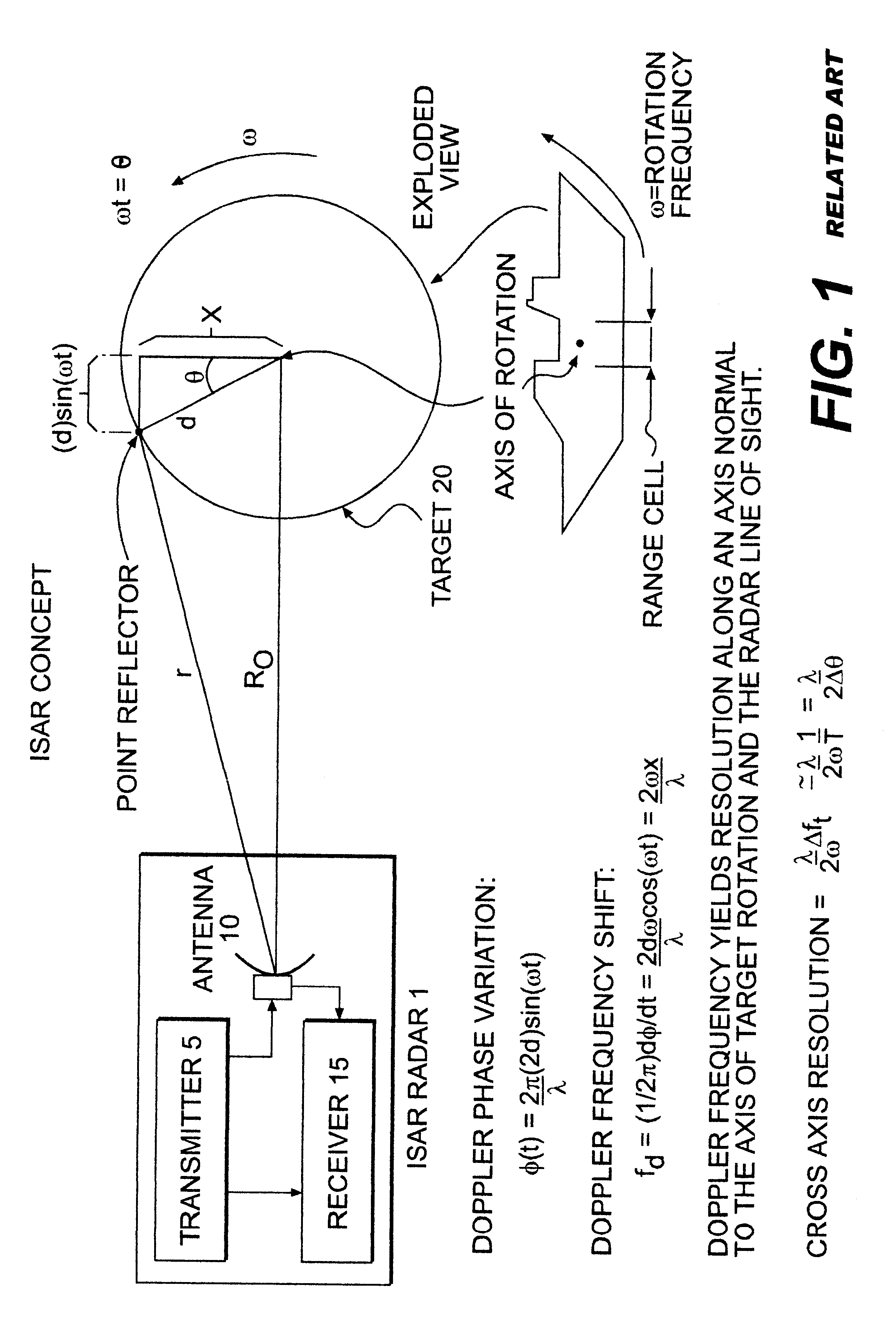
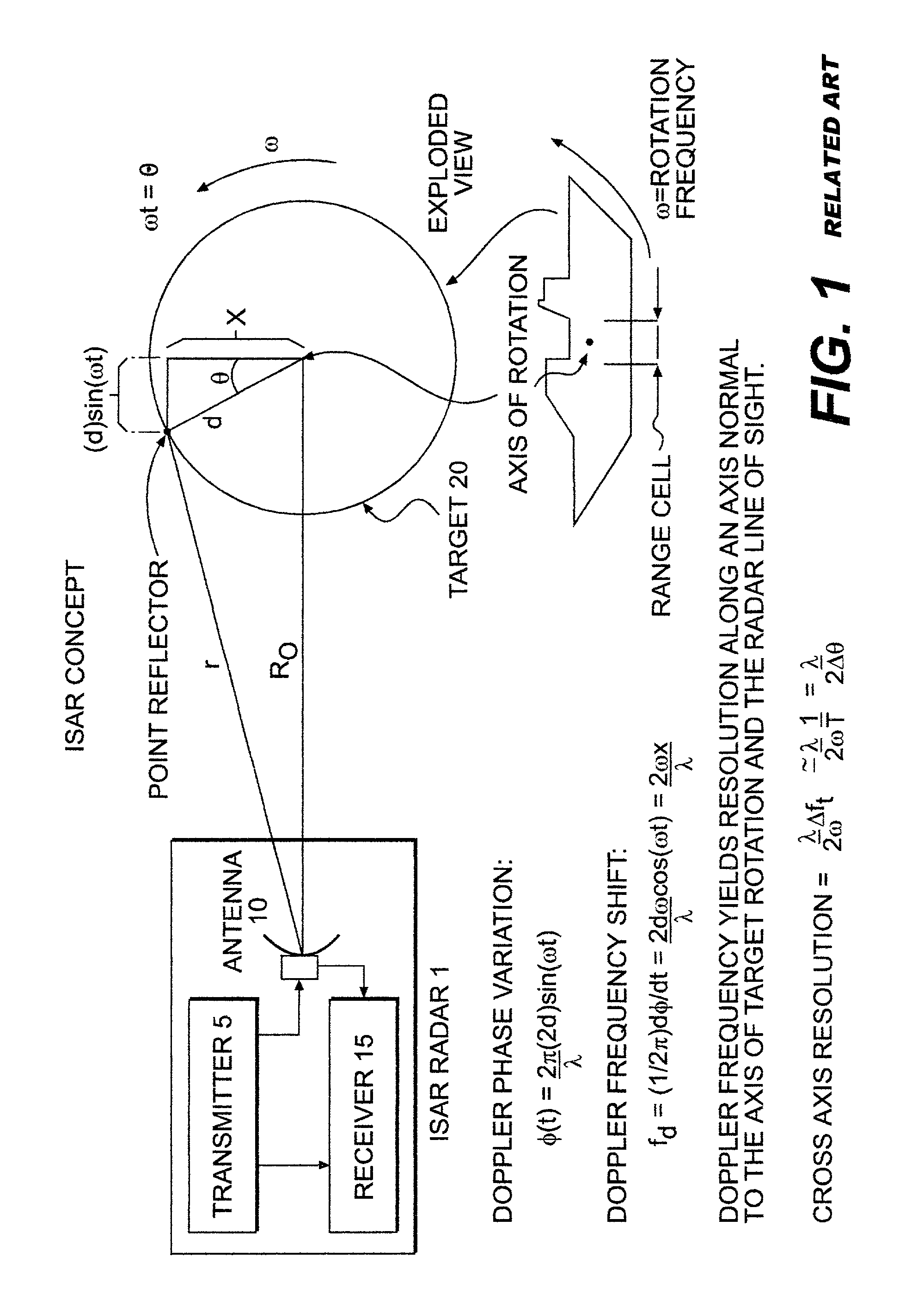
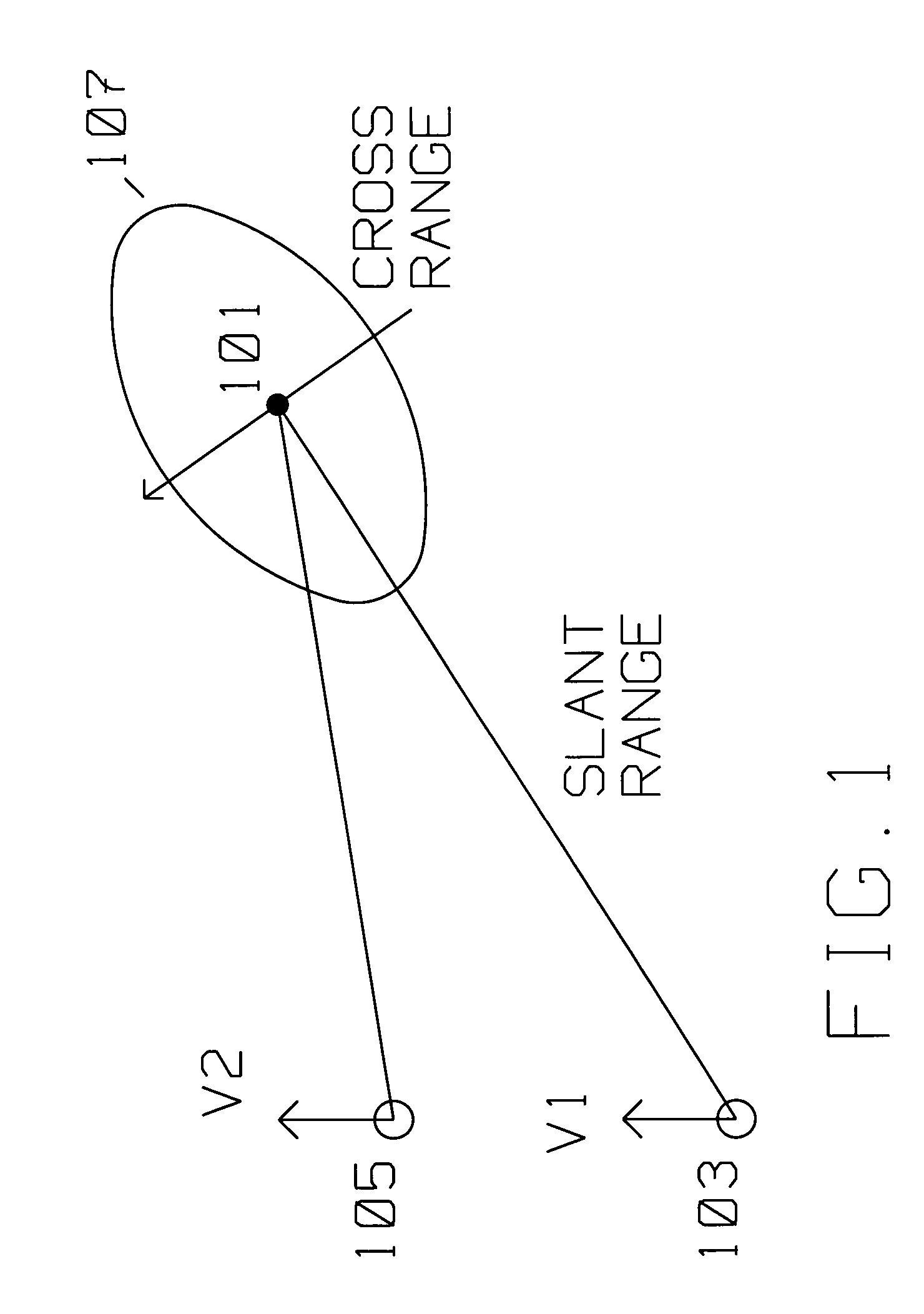
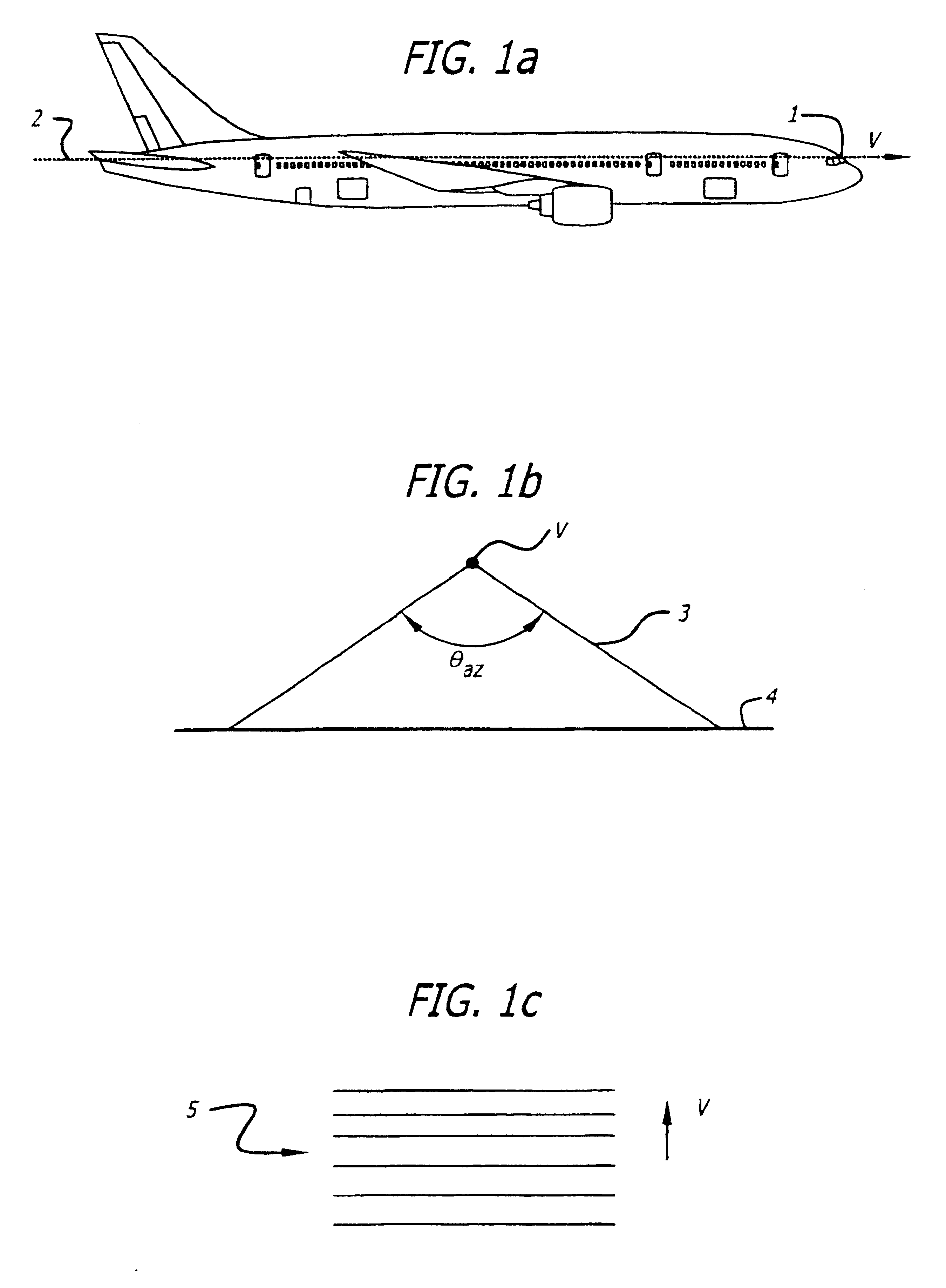
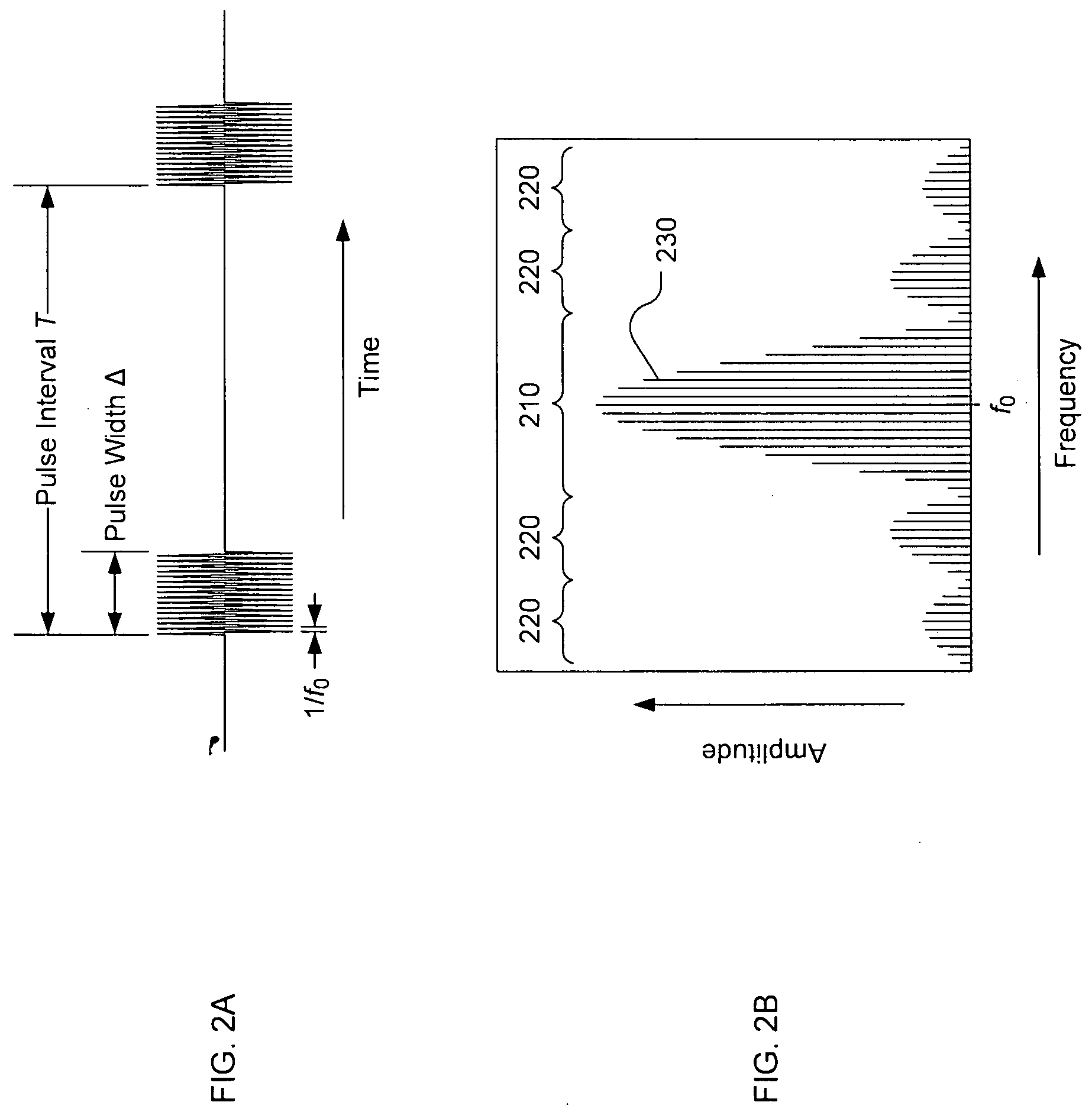
Aspect angle. [′a‚spekt ‚aŋ·gəl] (engineering) The angle formed between the longitudinal axis of a projectile in flight and the axis of a radar beam.
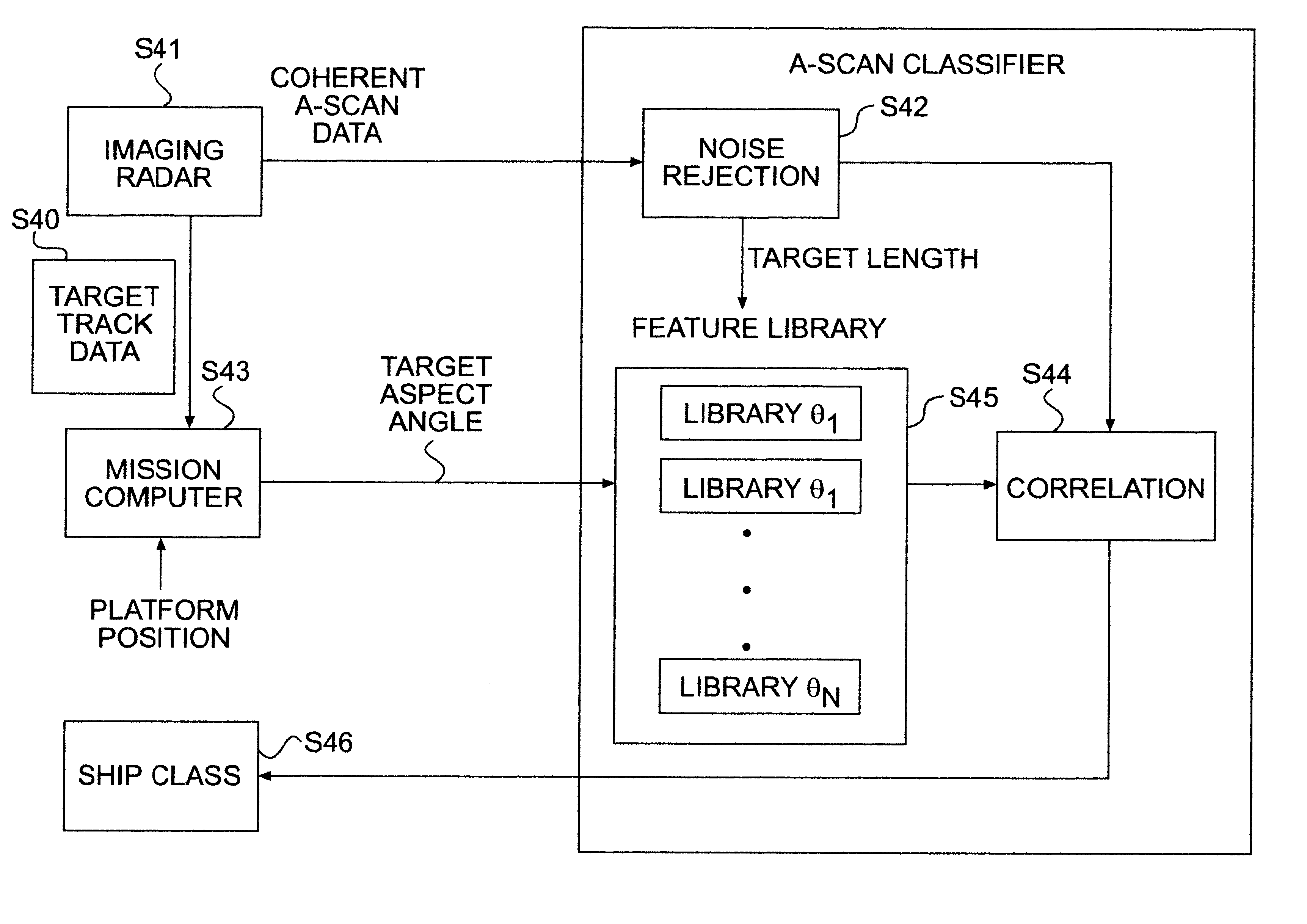
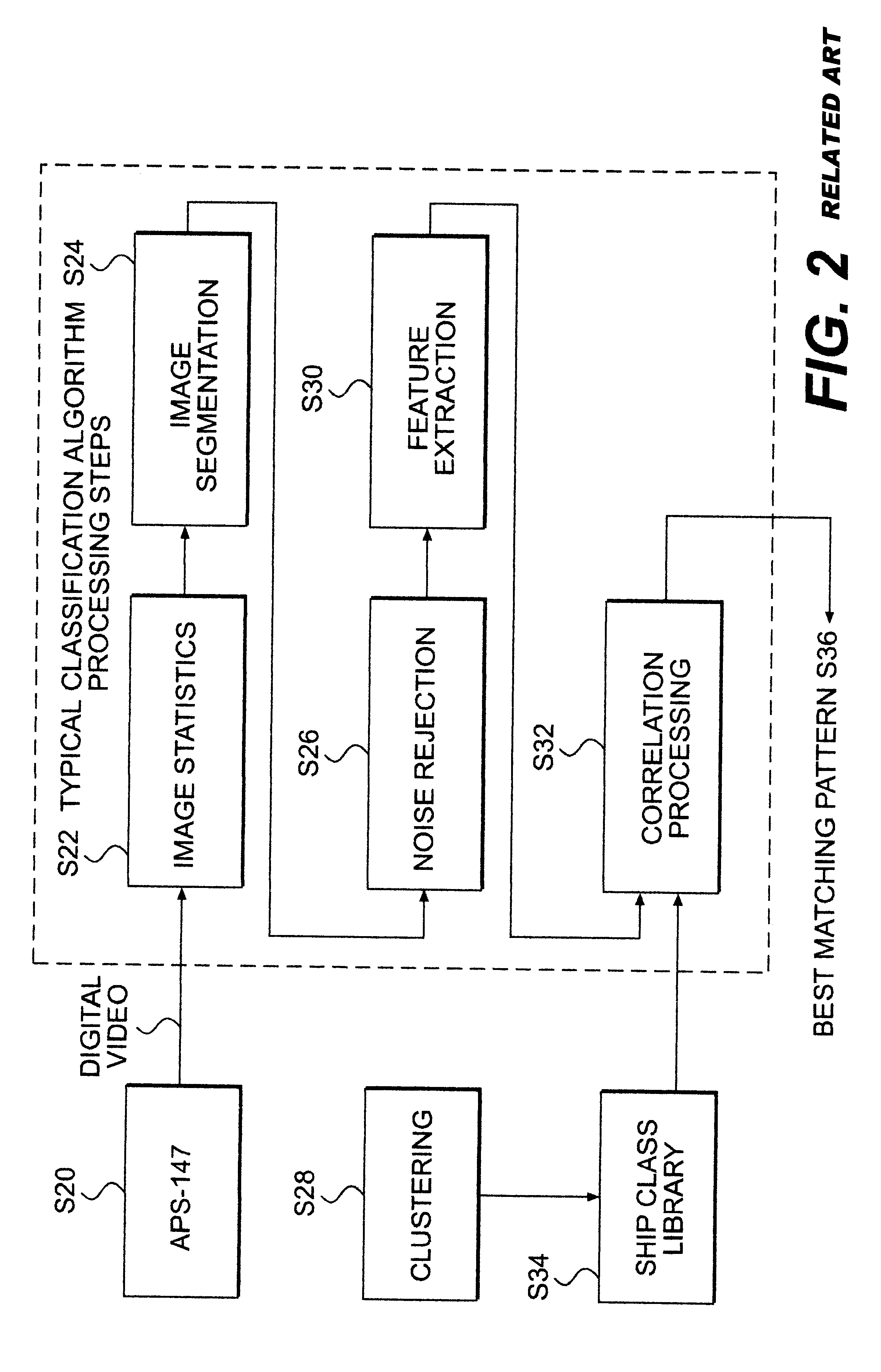
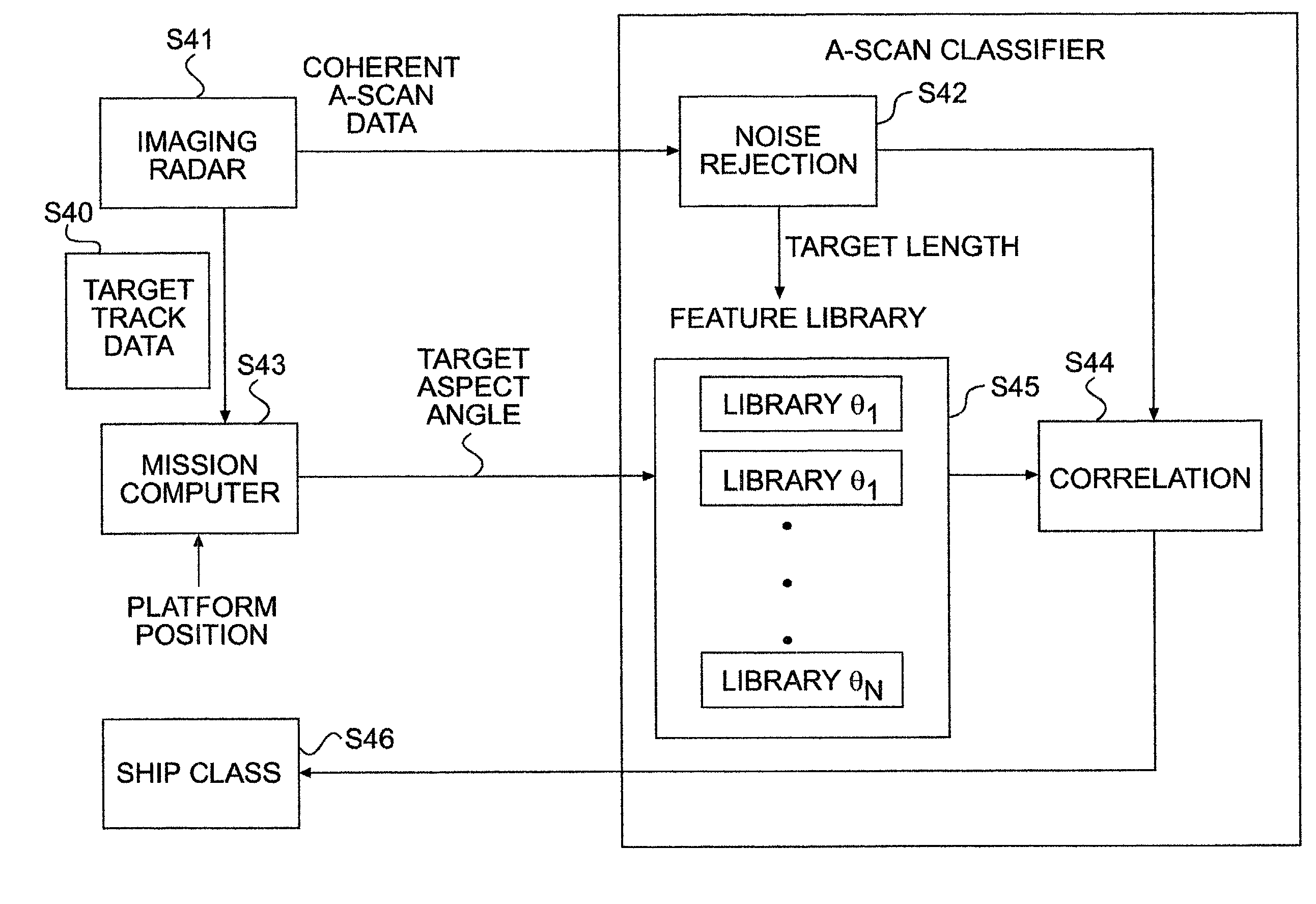
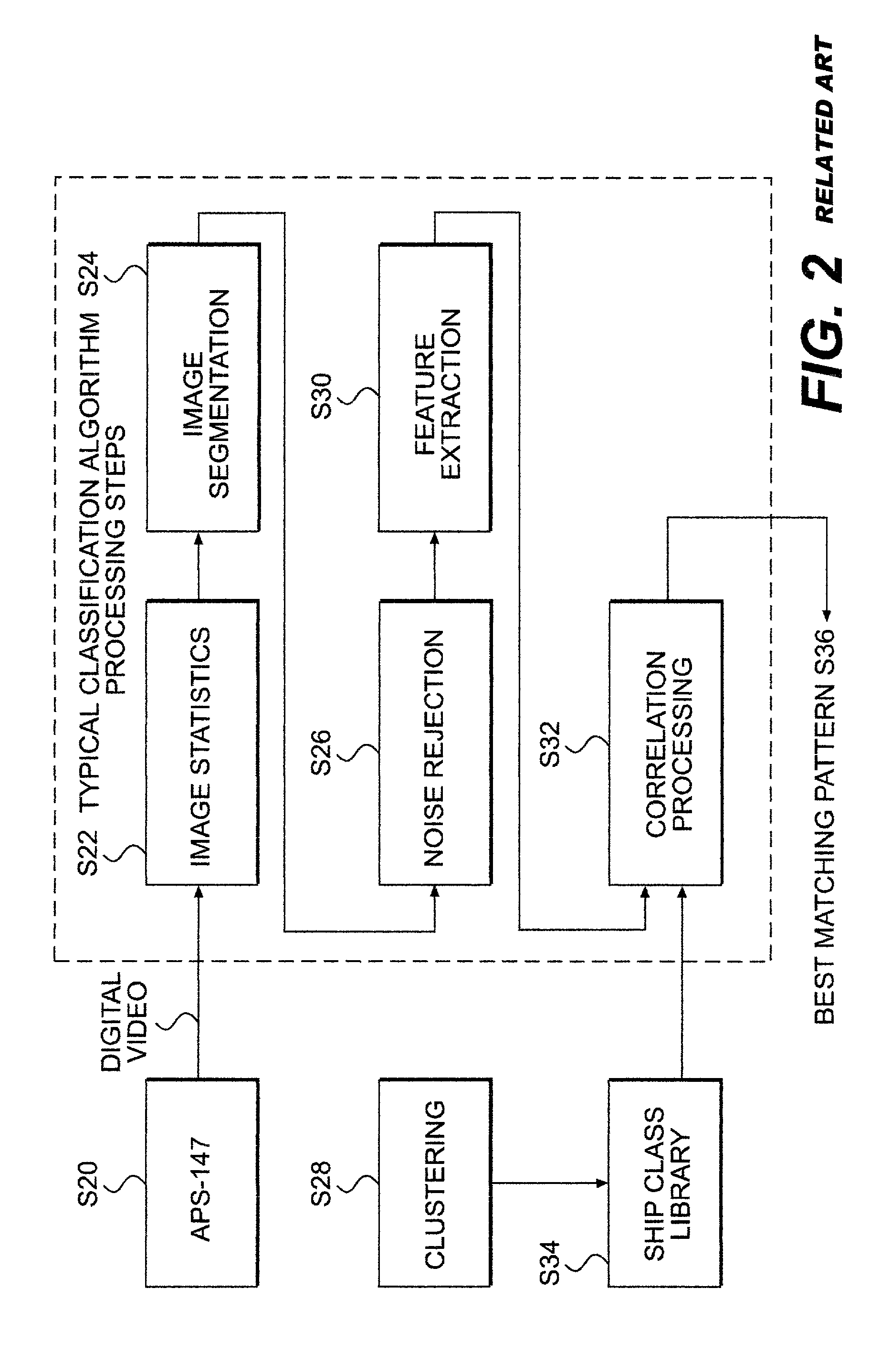
A-scan ISAR classification system and method therefor
InactiveUS6337654B1Character and pattern recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFeature vectorAspect angle
A target recognition system and method wherein only target amplitude data, i.e., coherent A-scan data, is interrogated for target recognition. Target aspect angle is ignored within the angular segmentation of the feature library without degrading classification performance. Observed signature characteristics are collected at various aspect angles and through unknown and arbitrary roll, pitch and yaw motions of each anticipated target and provided to a neural network as training sets. The neural network forms feature vectors for each target class which are useful for valid classification comparisons in all sea states, especially in calm and littoral waters. These feature vectors are useful for valid classification comparisons over at least 30 degrees of target aspect angle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
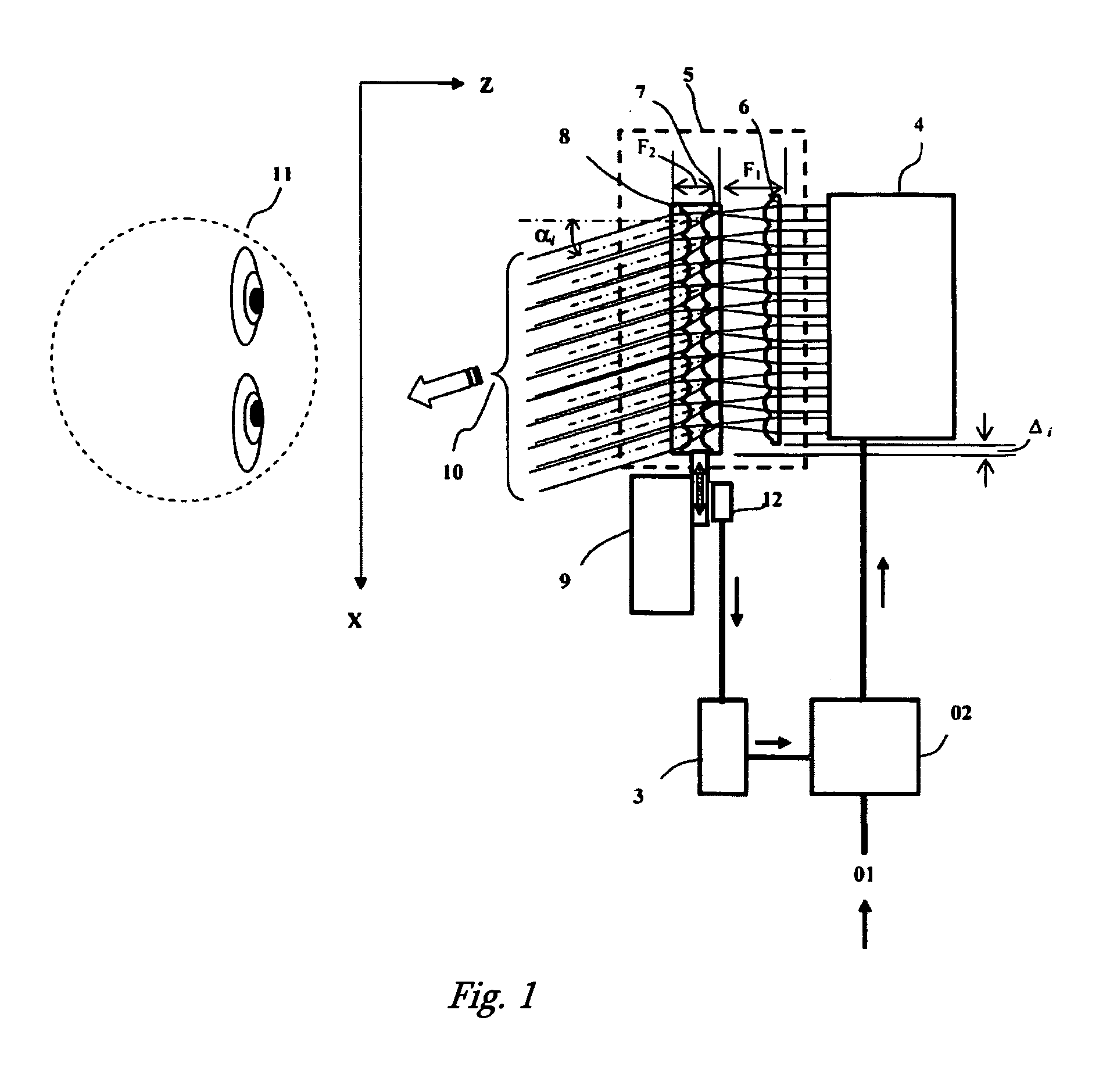
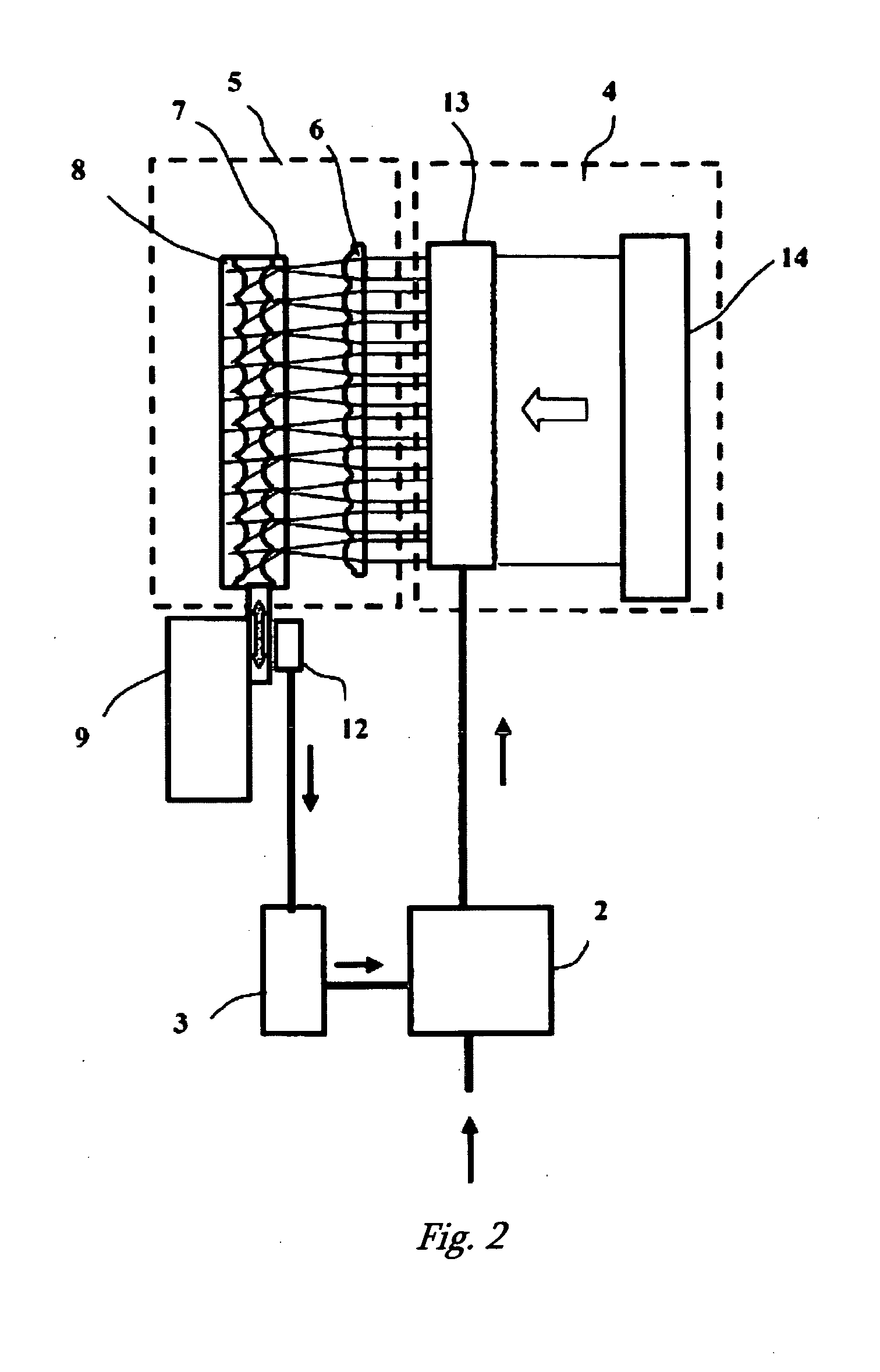
Apparatus and system for reproducing 3-dimensional images
InactiveUS20070165013A1Increase the number ofEasy constructionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsTelevision systemTelevision receivers
This invention relates to optical-electronic technology and can be used for building 3-dimensional displays for computers, television (TV) receivers and other devices, as well as for building systems for volumetric television. The technical result is an increase in the number of aspect angles with relatively simple construction and the use of presently available components. The equipment generates a 3-dimensional representation and contains a display component for 2-dimensional representation with digital inputs and a first 2-dimensional matrix of converging micro-lenses, in which each micro-lens is optically joined to the corresponding region of the display surface of the component for display of 2-dimensional representations. The equipment is equipped with second and third 2-dimensional matrices of micro-lenses, tightly connected to each other and coaxially placed and optically joined to the micro-lenses of the first matrix, forming in conjunction with the first matrix a matrix of scanning elements for sequential projection of 2-dimensional representations in the plane of their aspect angles, an adjustment mechanism of the matrices of micro-lenses, a positional sensor for adjustment of the micro-lenses and a controller connected to the adjustment mechanism through the digital input of the controller, providing the ability for synchronization of the frames of the representation of each 2-dimensional representation with the corresponding position of the matrix of micro-lenses, while the second matrix is arranged in the foreground focal plane of the third matrix, mixed with the background focal plane of the first matrix, and the first matrix or the combined second and third matrices can be adjusted in the plane in which they are installed, and moreover for the first, second and third matrices, the digital input of the display component is connected to the module of buffered memory, whose synchronization input is connected to the output of the controller. The described equipment can be used with a stereoscopic television system.
Owner:ZECOTEK MEDICAL SYST PTE LTD
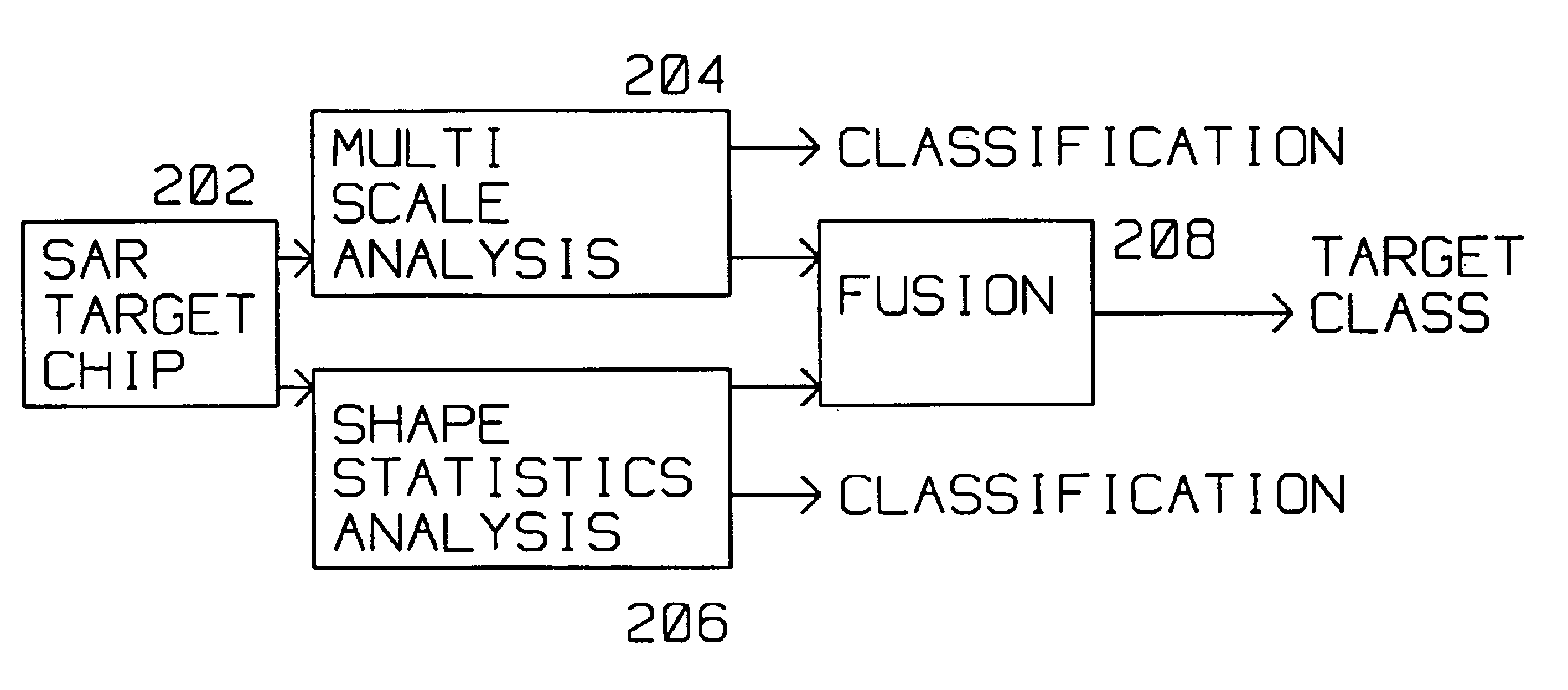
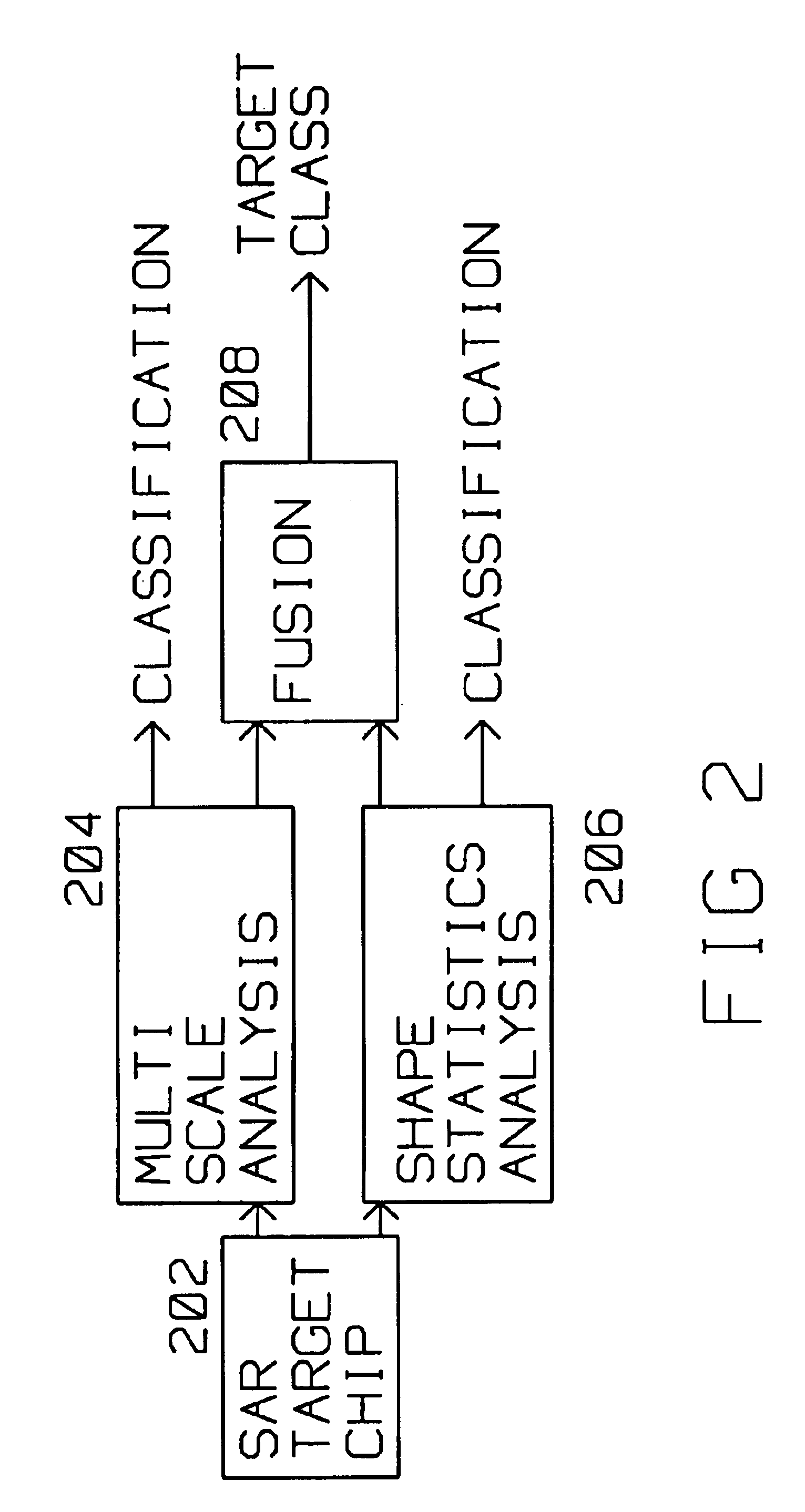
Fusion of shape and multiscale features for unknown target rejection
A plurality of image chips (202) (over 100), each of the chips containing the same, known target of interest, such as, for example an M109 tank are presented to the system for training. Each image chip of the known target is slightly different than the next, showing the known target at different aspect angles and rotation with respect to the moving platform acquiring the image chip.The system extract multiple features of the known target from the plurality of image chips (202) presented for storage and analysis, or training. These features distinguish a known target of interest from the nearest similar target to the M109 tank, for example a Caterpillar D7 bulldozer. These features are stored for use during unknown target identification. When an unknown target chip is presented, the recognition algorithm relies on the features stored during training to attempt to identify the target.The tools used for extracting features of the known target of interest as well as the unknown target presented for identification are the same and include the Haar Transform (404), and entropy measurements (410) generating coefficient locations. Using the Karhunen-Loeve (KL) transform 406, eigenvectors are computed. A Gaussian mixture model (GMM) (507) is used to compare the extracted coefficients and eigenfeatures from the known target chips with that of the unknown target chips. Thus the system is trained initially by presenting to it known target chips for classification. Subsequently, the system uses the training in the form of stored eigenfeatures and entropy coefficients fused with multiscale features to identify unknown targets.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Volumetric 3D x-ray imaging system for baggage inspection including the detection of explosives
InactiveUS20050025280A1Easy to detectMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionSoft x rayX-ray
A tomographic volumetric x-ray imaging system that uses either multiple x-ray sources in a fixed configuration or a single source that can be shifted to provide a plurality of incident aspect angles. A combination of volumetric x-ray image data and multi-energy image acquisition provides an effective method for high confidence explosives detection within baggage or parcels.
Owner:DIGITOME CORP
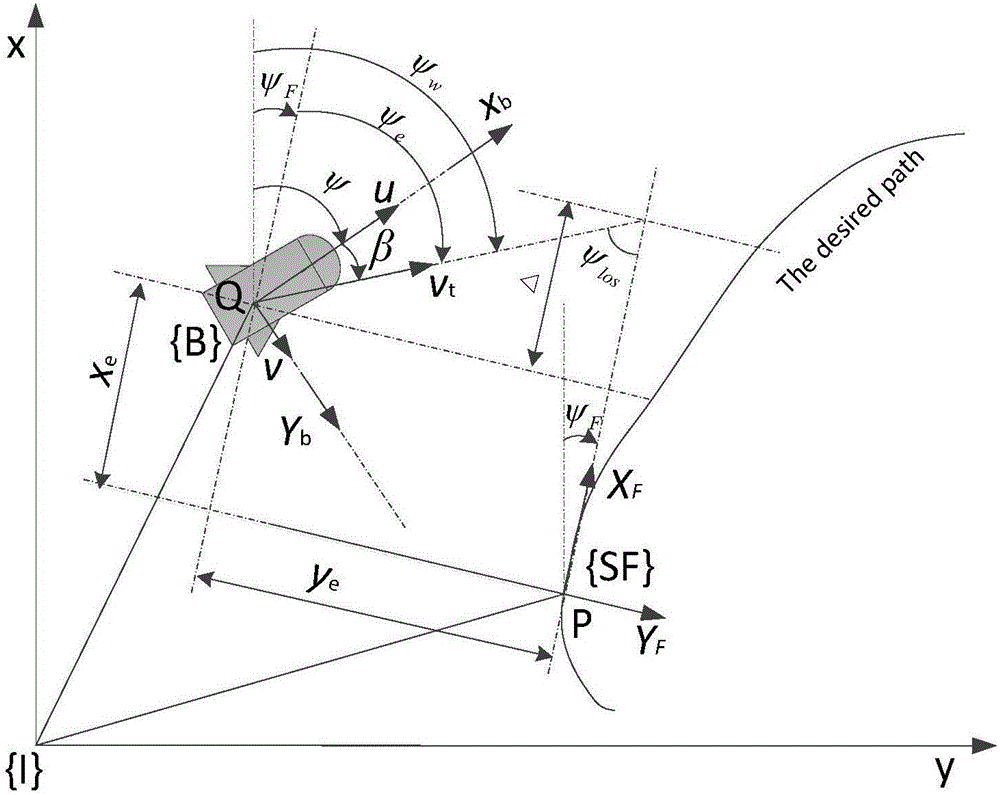
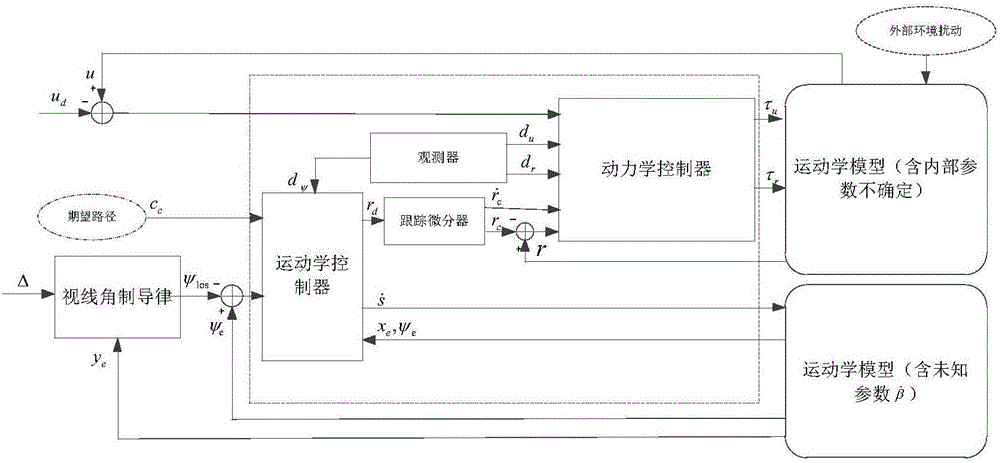
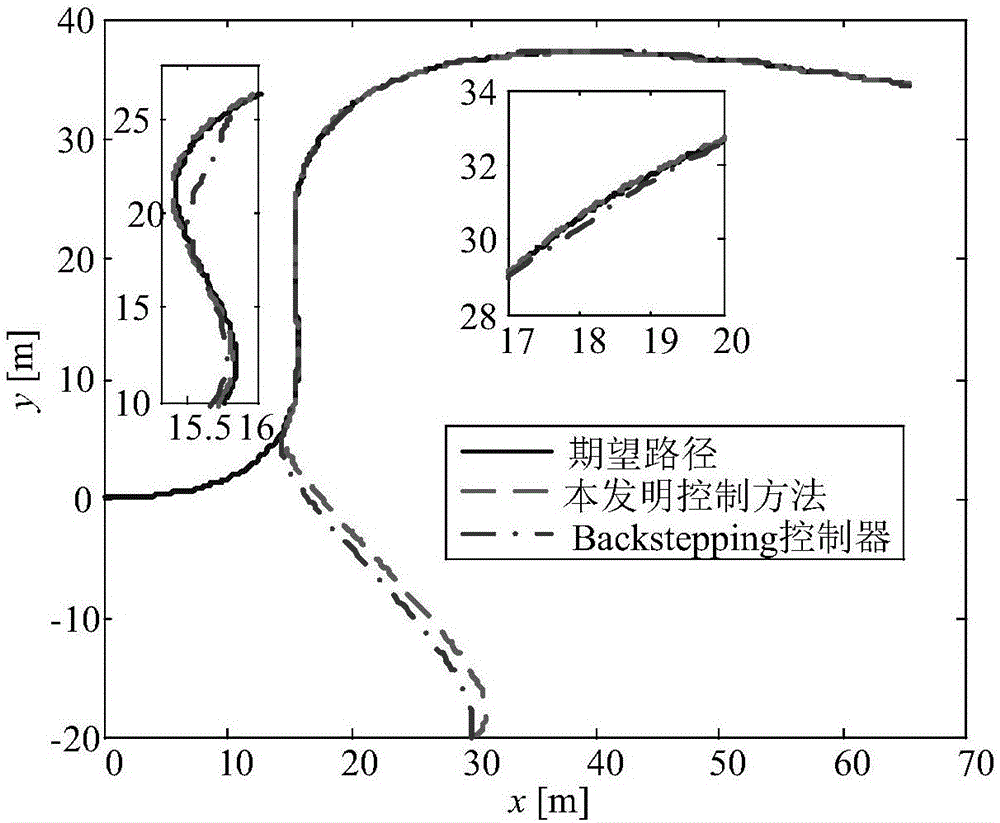
High-accuracy nonlinear path tracking control method for under-actuated marine vehicle
ActiveCN106773713AAchieve precise tracking controlApplicable Engineering PracticeTarget-seeking controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsKinematicsDifferentiator
The invention provides a high-accuracy nonlinear path tracking control method for an under-actuated marine vehicle. According to the method, the change rate of the sideslip angle of the vehicle is regarded as an uncertain item, the parameter uncertainty in a dynamic model, unmodeled dynamics and external environmental disturbances are regarded as lumped uncertainty, and an observer is adopted to conduct real-time observation on kinematic uncertainty and dynamic uncertainty; a traditional aspect-angle guiding method is adopted to calculate an expected aspect angle; a nonlinear path tracking controller based on the observer is designed, and the kinematic and dynamic uncertainty are compensated; a tracking differentiator is adopted to simplify the controller to make the controller more suitable for engineering application. According to the method, the influences of the parameter uncertainty in the dynamic model, the unmodeled dynamics and the external environmental disturbances on path tracking are eliminated, and the accurate tracking control over an expected path of the vehicle is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A-Scan ISAR classification system and method therefor
InactiveUS20020057216A1Character and pattern recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFeature vectorGoal recognition
A target recognition system and method wherein only target amplitude data, i.e., coherent A-scan data, is interrogated for target recognition. Target aspect angle is ignored within the angular segmentation of the feature library without degrading classification performance. Observed signature characteristics are collected at various aspect angles and through unknown and arbitrary roll, pitch and yaw motions of each anticipated target and provided to a neural network as training sets. The neural network forms feature vectors for each target class which are useful for valid classification comparisons in all sea states, especially in calm and littoral waters. These feature vectors are useful for valid classification comparisons over at least 30 degrees of target aspect angle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
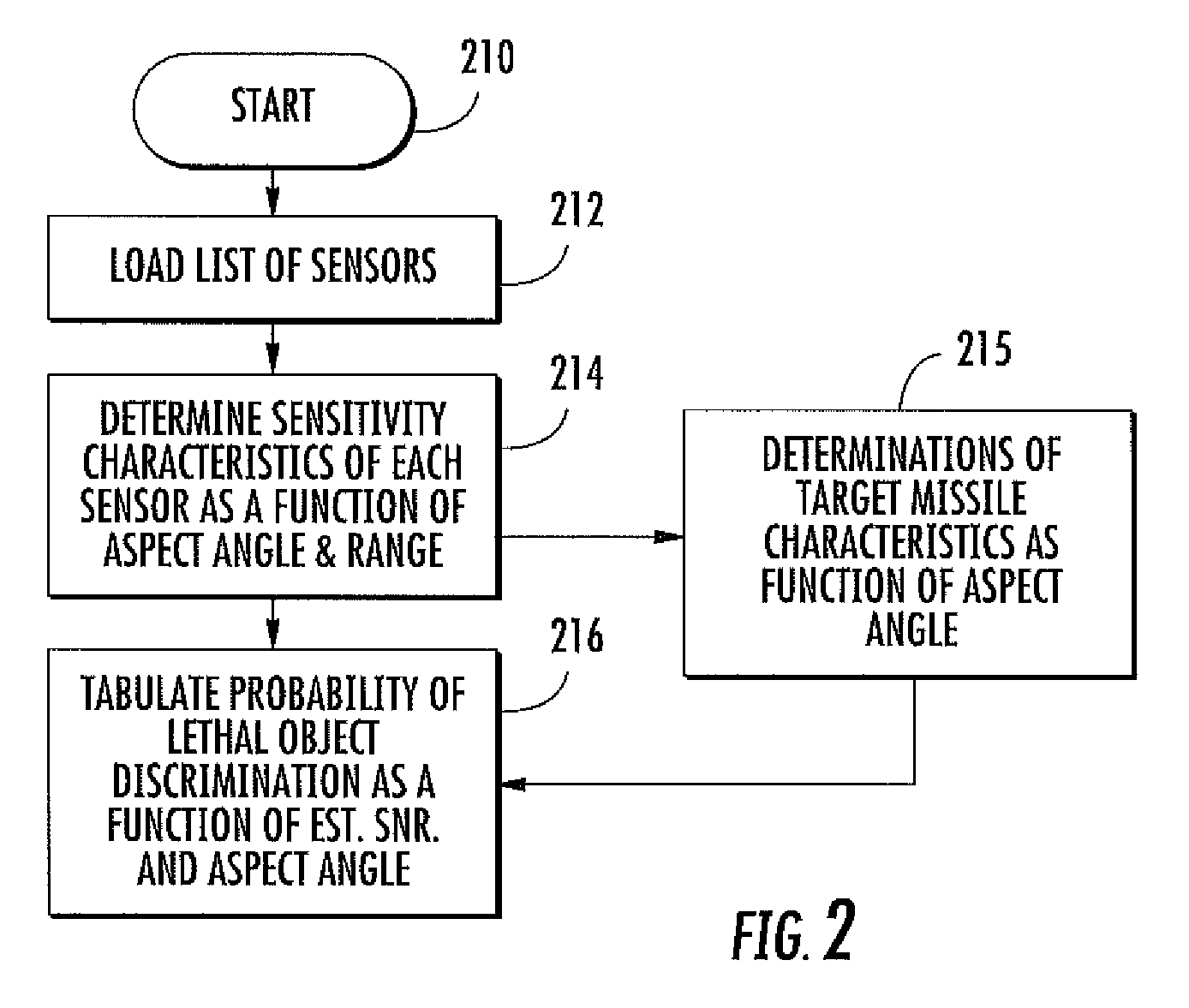
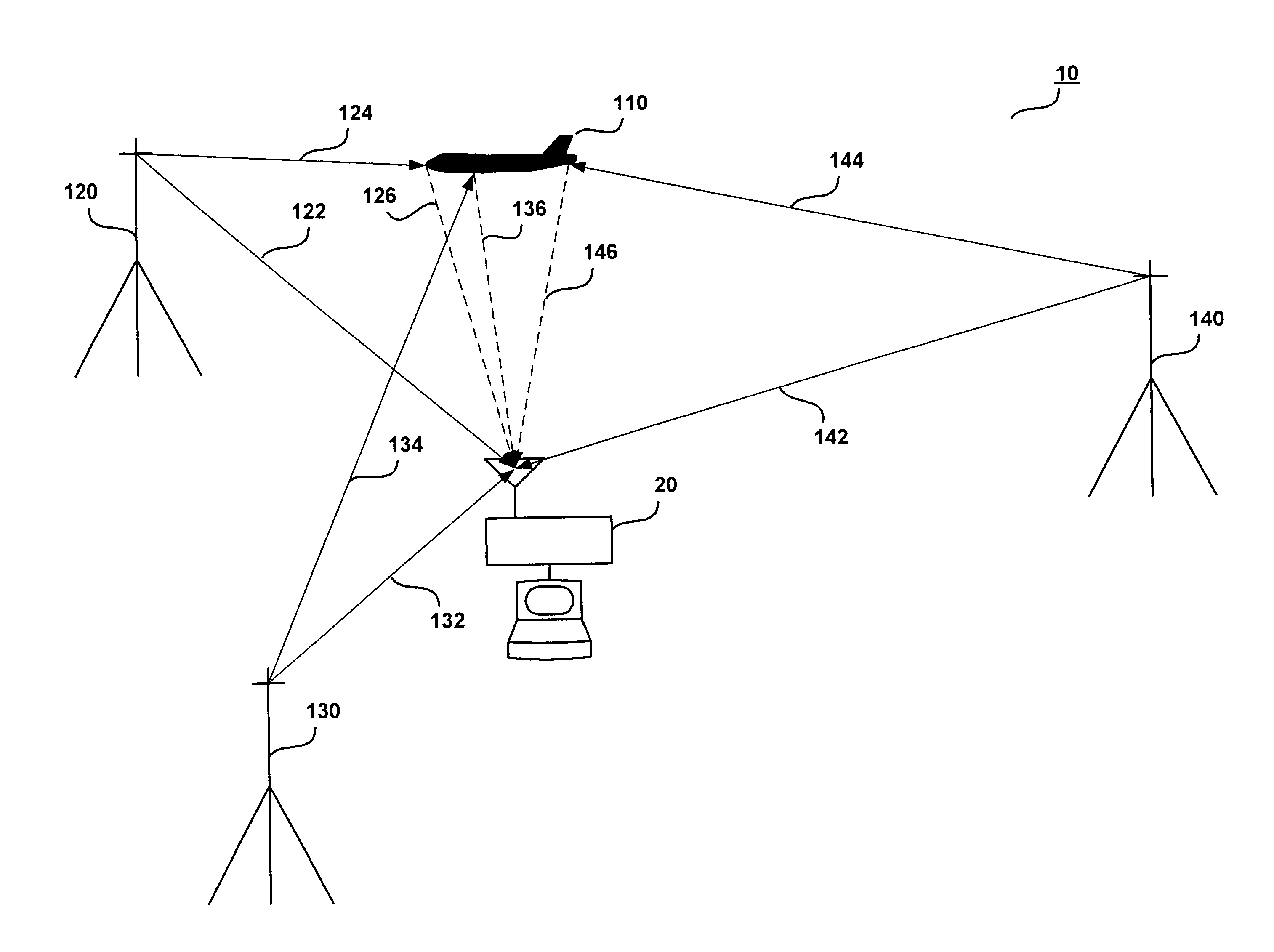
Missile tracking with interceptor launch and control
InactiveUS7875837B1Direction controllersAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Data signal
A method for engaging a hostile missile with an interceptor missile includes mathematically dividing an estimated target trajectory into portions, the junction of each portion with the next defining a possible intercept point. The engagement for each possible intercept point is modeled, to generate a probability of lethal object discrimination which is processed to generate a probability of intercept for each of the possible intercept points. The intercept point having the largest probability of intercept defines a selected intercept point from which intercept missile launch time is calculated, interceptor missile guidance is initialized, and the interceptor is launched at the calculated launch time and under the control of the interceptor missile guidance. Also, a method for estimating discrimination performance of a system of sensors includes generating sensor data signal-to-noise ratio and an aspect angle between the sensor and a lethal object. A table of probability of lethal object discrimination is generated as a function of the signal-to-noise ratio and aspect angle. The signal-to-noise ratio and the aspect angle are quantized into bins and the table with at least the signal-to-noise ratio and the aspect angle is entered to determine the probability of lethal object discrimination.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
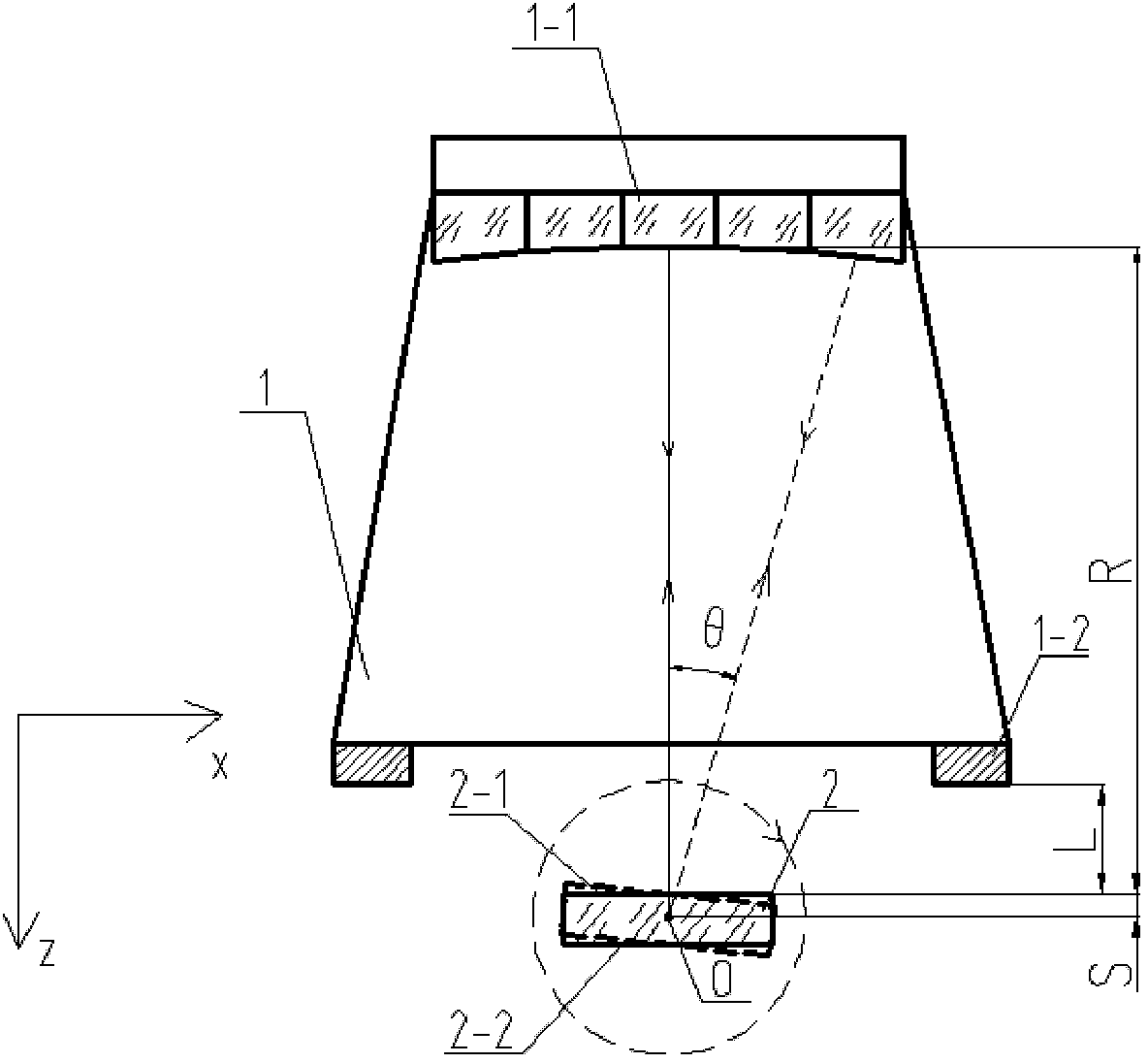
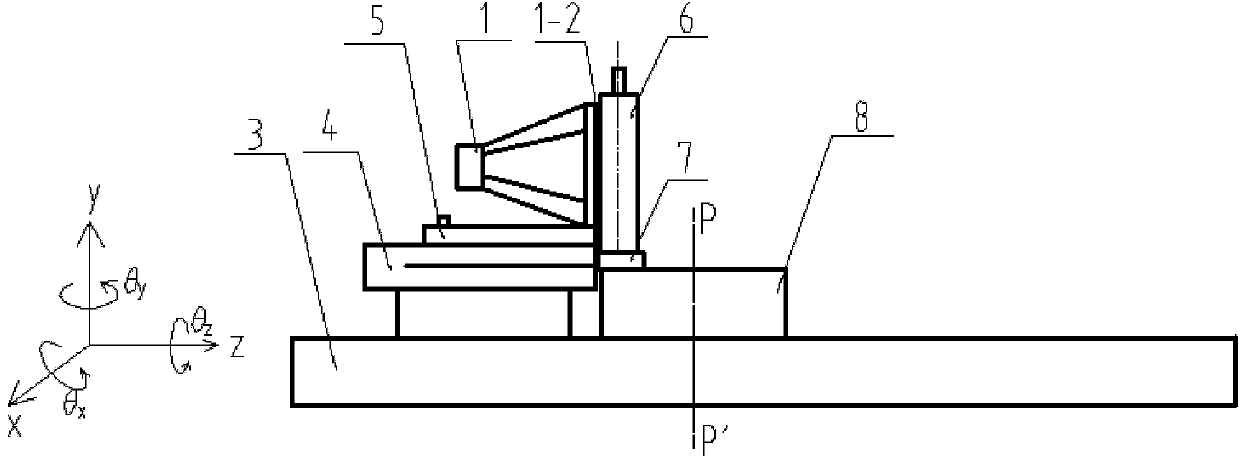
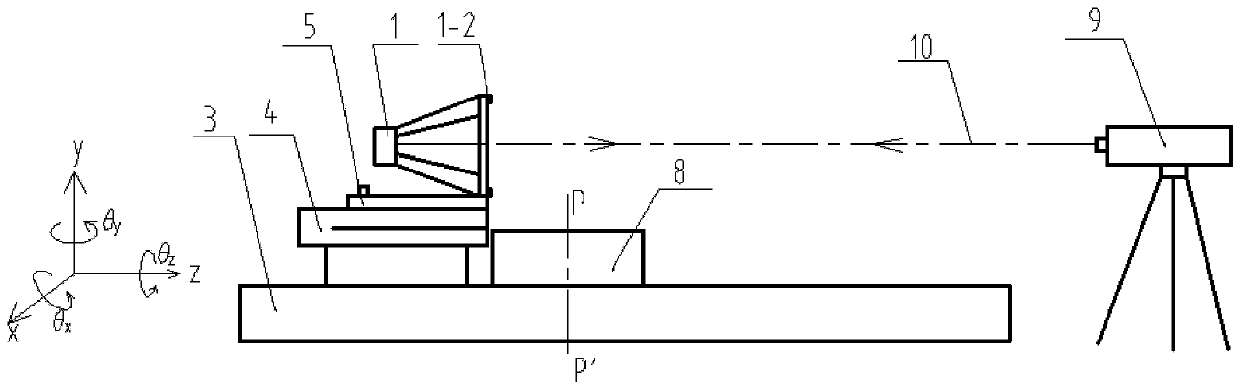
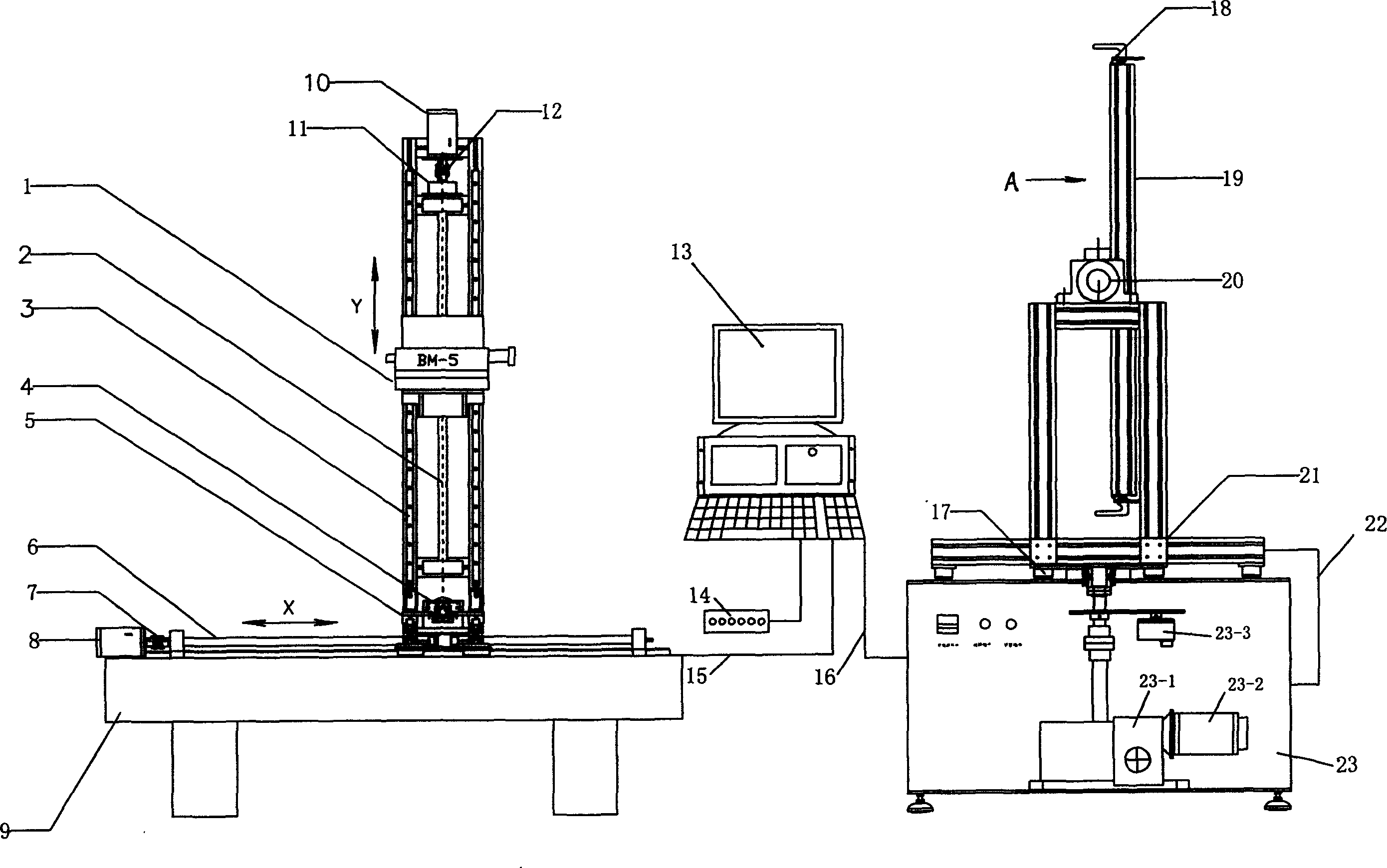
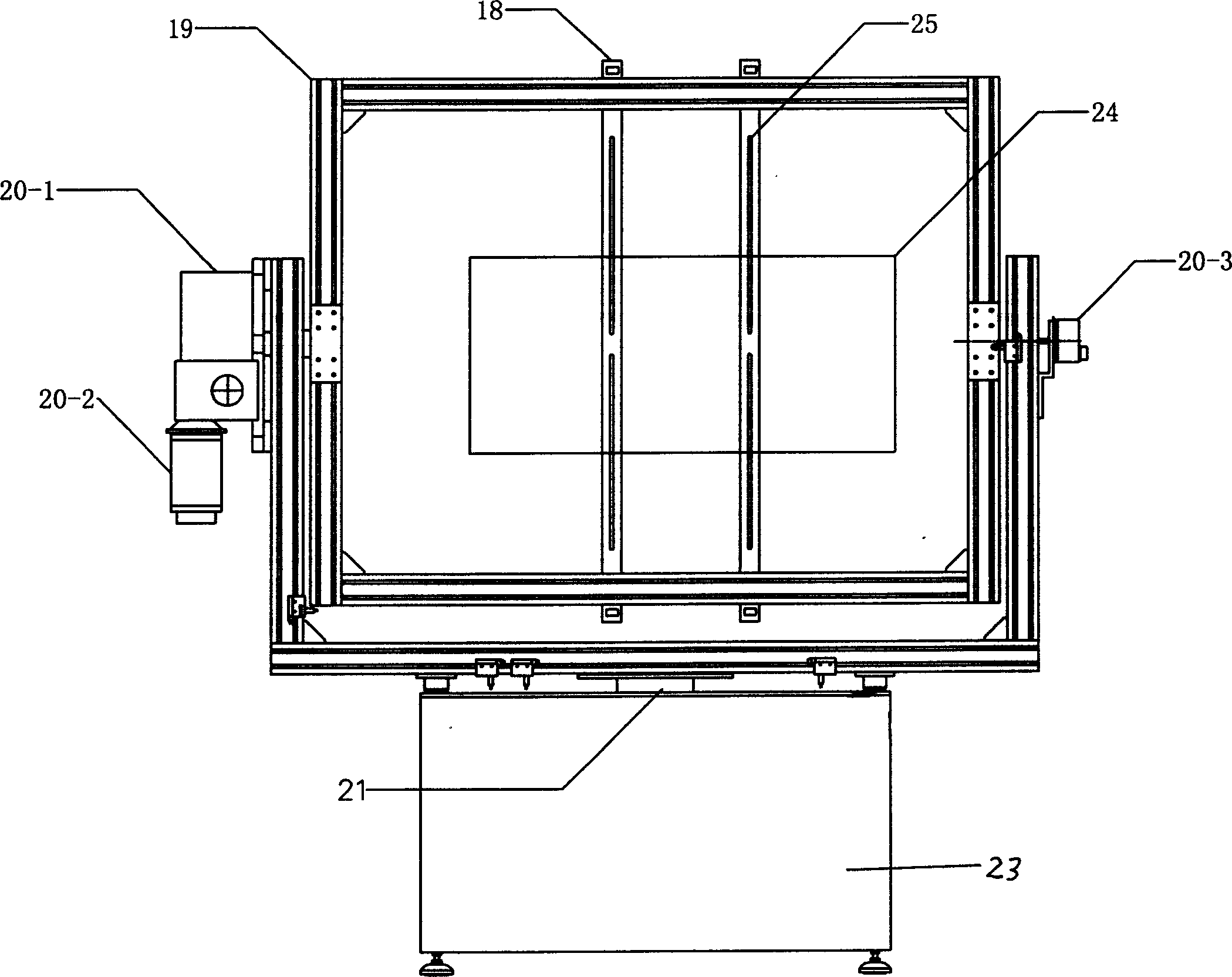
Angle measurement precision detecting device of aspect angle monitor for satellite
The invention discloses an angle measurement precision detecting device of an aspect angle monitor for a satellite. A small plane mirror is connected to a mounting base plane position of the aspect angle monitor; the aspect angle monitor for the satellite is arranged on a two-dimension inclined platform and is placed on a two-dimension translation platform; a double-faced simulation swing mirror is arranged on a three-dimension adjusting platform and is placed on a digital display turntable; a first autocollimator and a second autocollimator are placed on a lifting support; the two-dimension translation platform, the digital display turntable and the lifting support are placed on a table top of a detection platform; a central spindle is sleeved in a central hole of the digital display turntable; a standard circular device is placed on a standard block and is close to the central spindle; laser beams emitted by a laser align with a central prism of a five-mirror reflector to form a detection standard optical axis; a dial indicator is fixed on the detection platform; a gauge block is placed above the digital display turntable and between the aspect angle monitor for the satellite and the double-faced simulation swing mirror; one face of the gauge block is close to the mounting base plane of the aspect angle monitor for the satellite; and the other face of the gauge block is close to a first optical surface of the double-faced simulation swing mirror.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for guiding input constraining differential game based on self-adaptive dynamic planning
InactiveCN106647287ASolve problemsAvoid the disadvantages of offline computingAdaptive controlDynamic planningCountermeasure
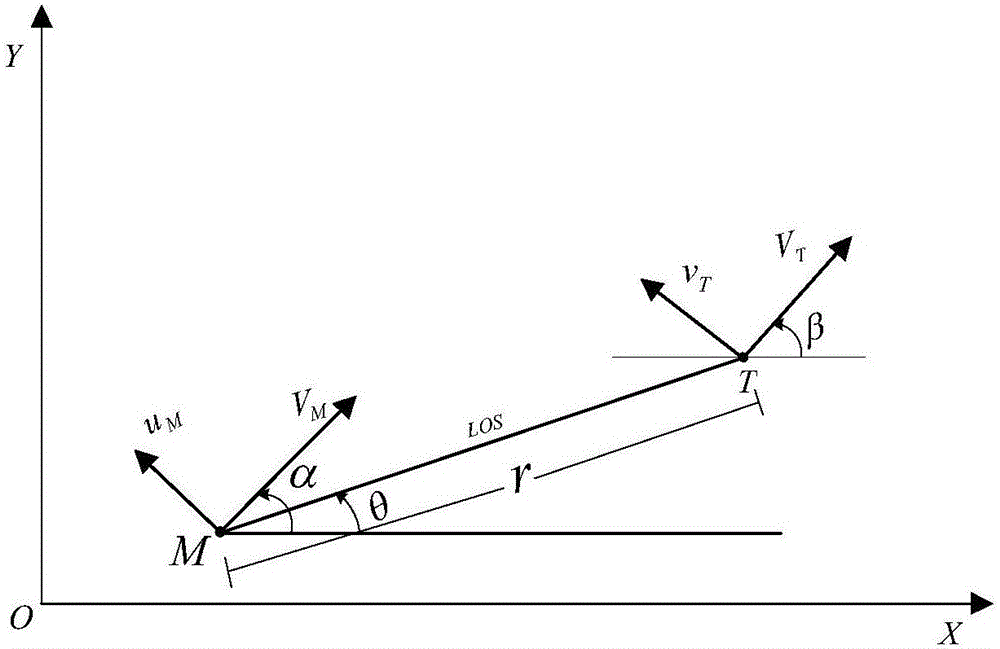
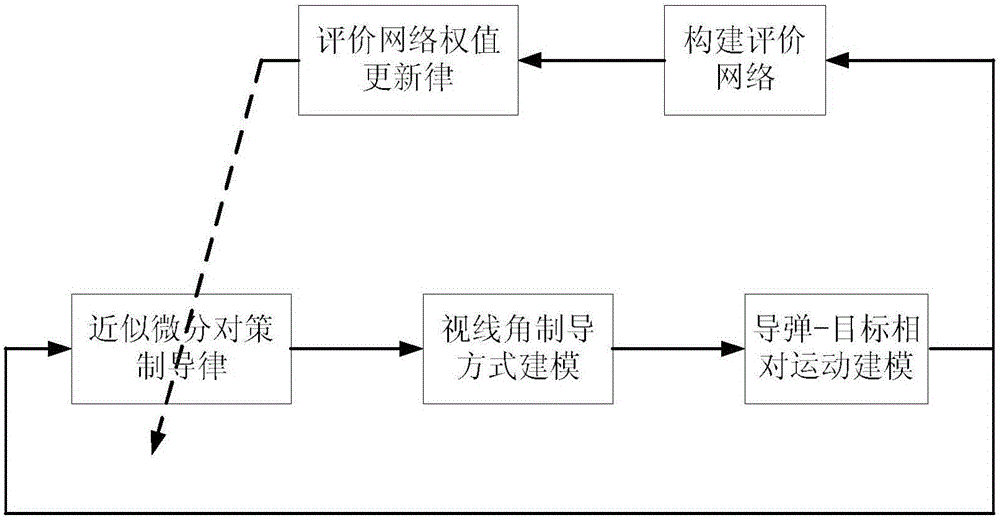
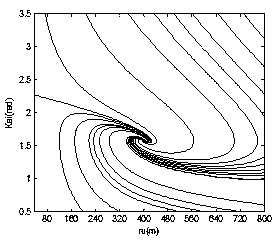
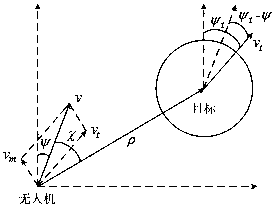
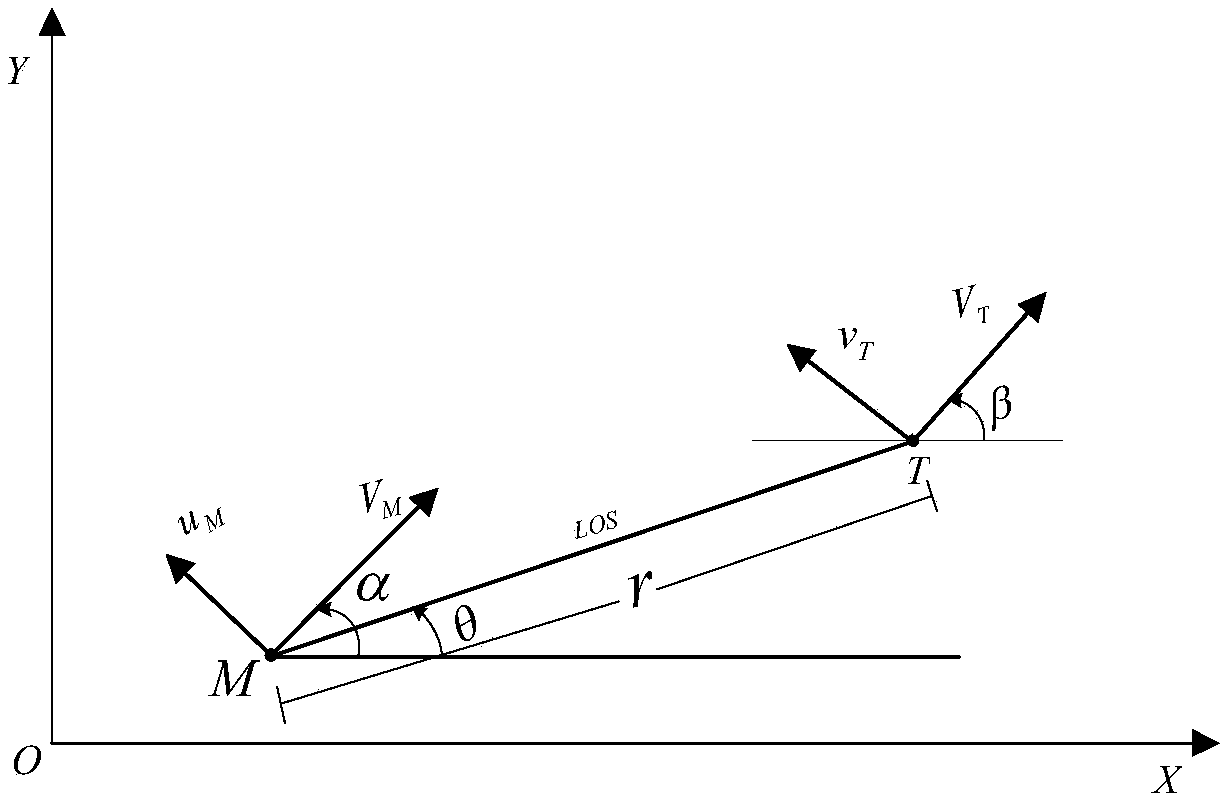
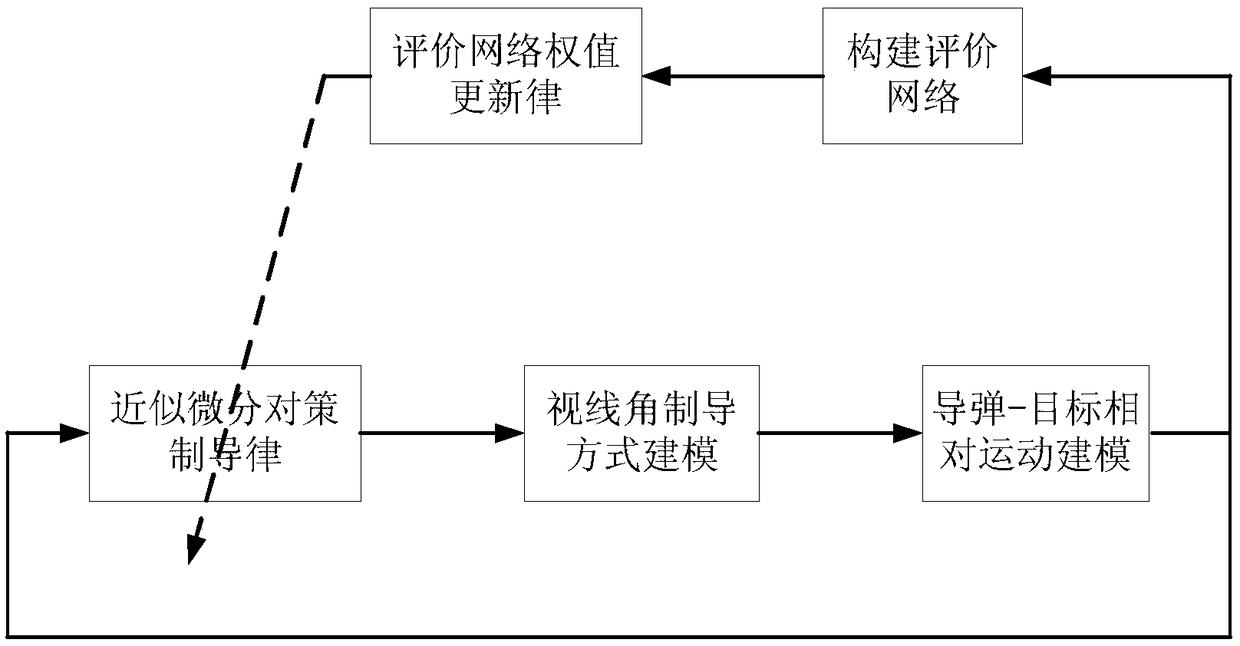
The invention discloses a method for guiding an input constraining differential game based on self-adaptive dynamic planning. According to the method, a solving problem of an HJI equation and an input saturation problem in a nonlinear differential game problem are solved; an input constraining solving problem of the nonlinear differential game is solved by virtue of a self-adaptive dynamic planning technique, and a neural network and a Lyapunov method are combined so as to obtain a guidance control volume; and an input constraining differential game guidance law can be online obtained in real time based on an evaluation network updating law, and the aspect angle velocity in a guided missile-target relative motion relation tends to 0, so that the successful interception is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
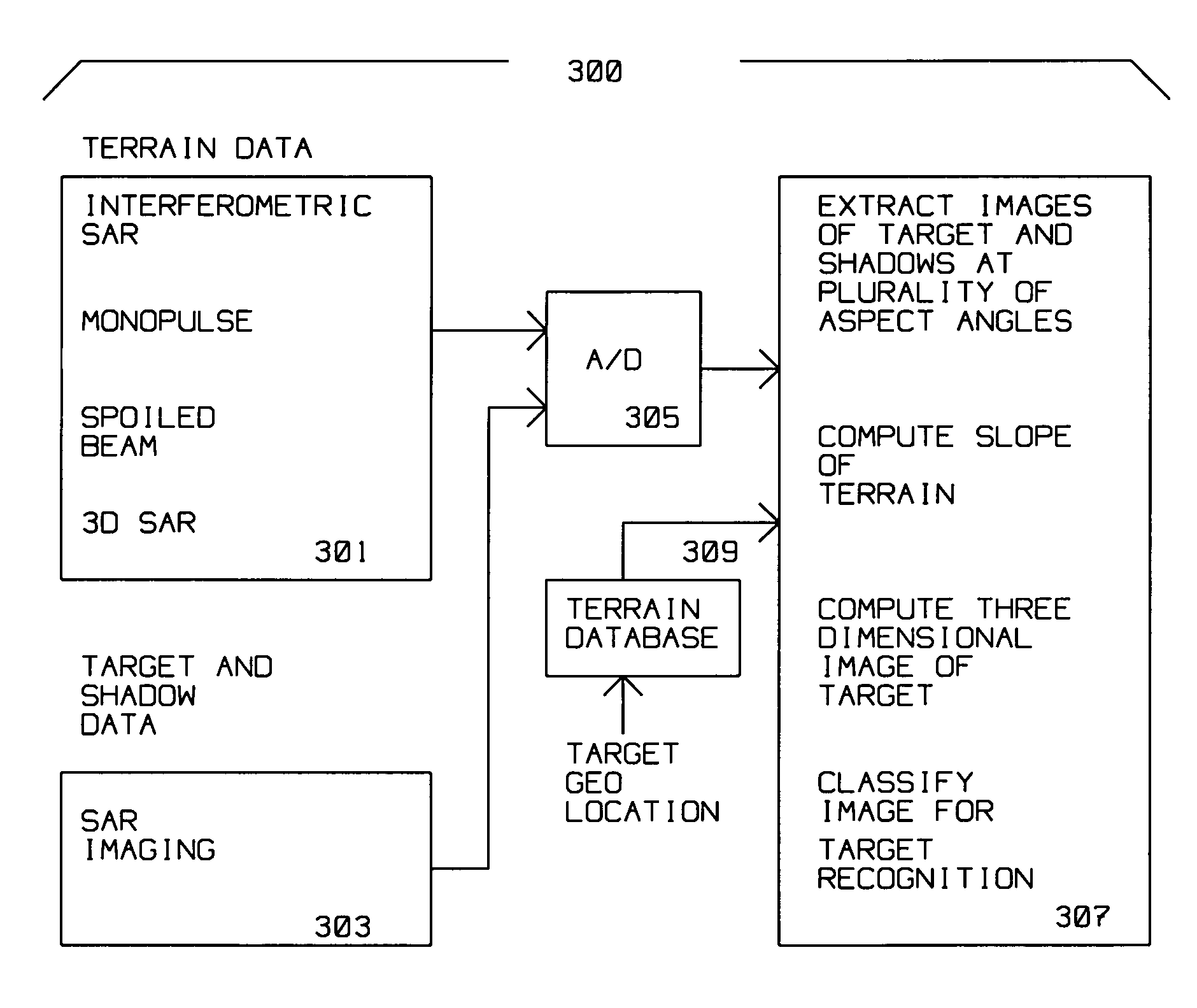
Technique for low grazing angle 3D SAR target recognition
ActiveUS20060273946A1Reducing pluralityHigh gainRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital dataTerrain
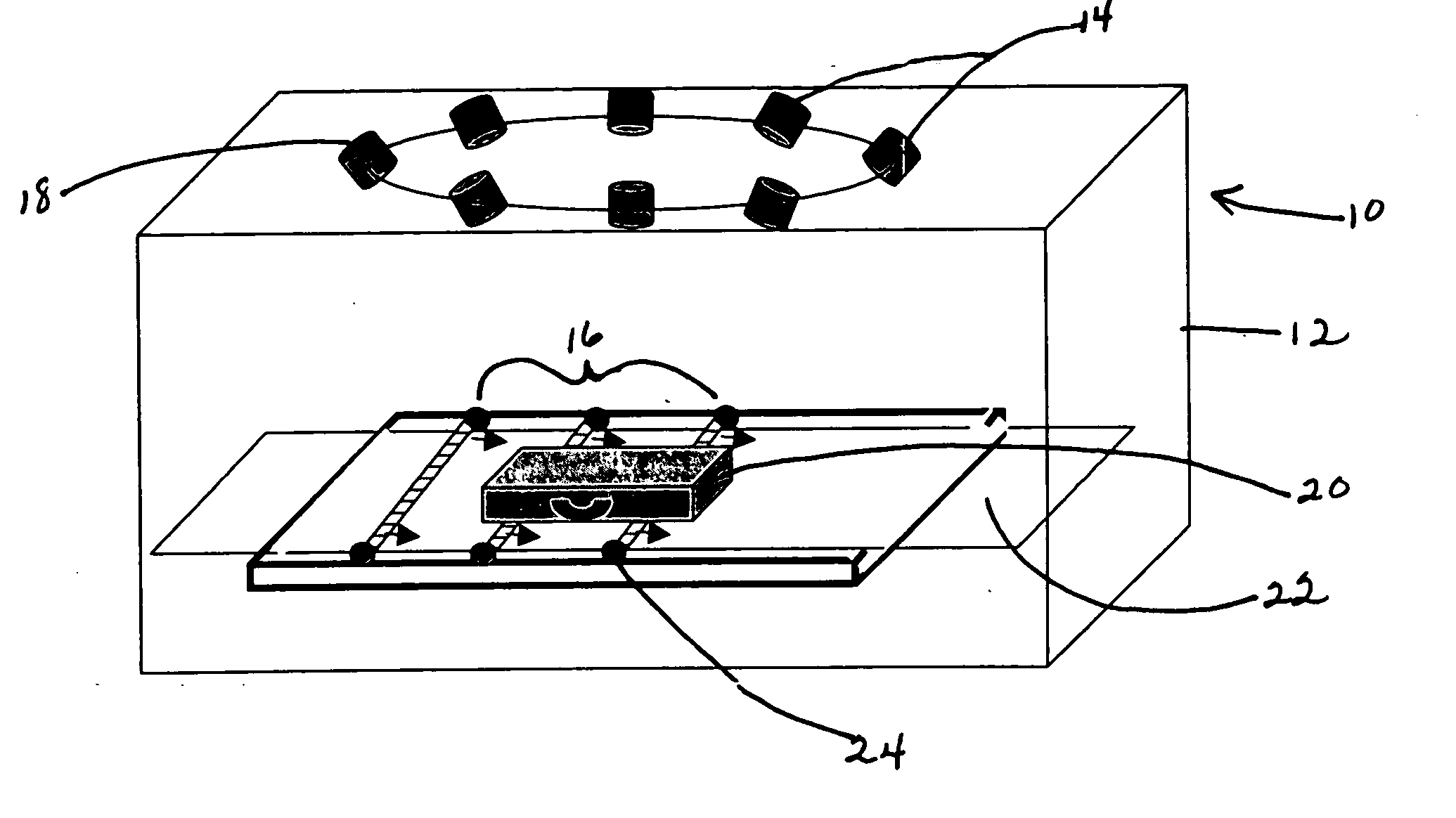
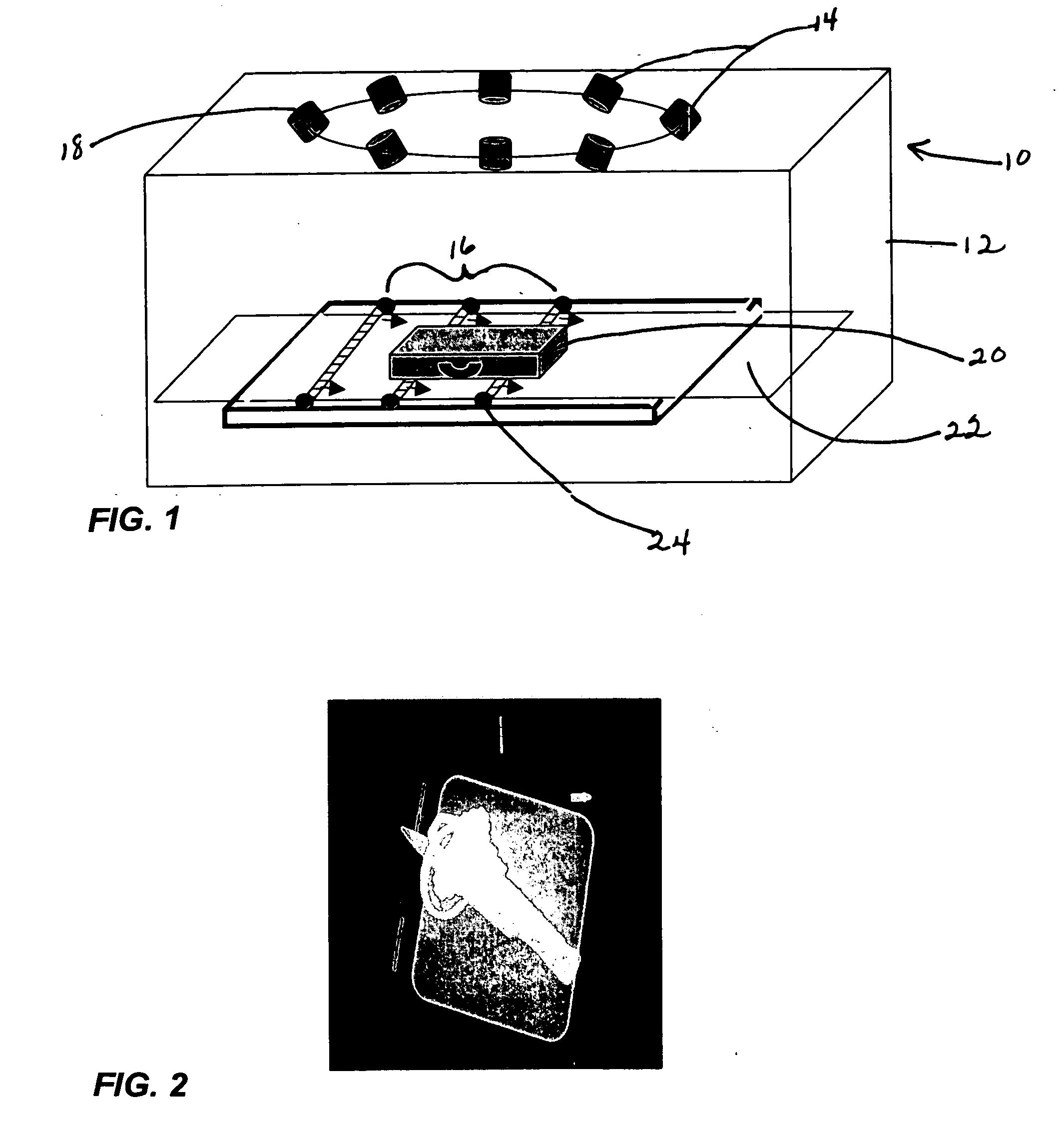
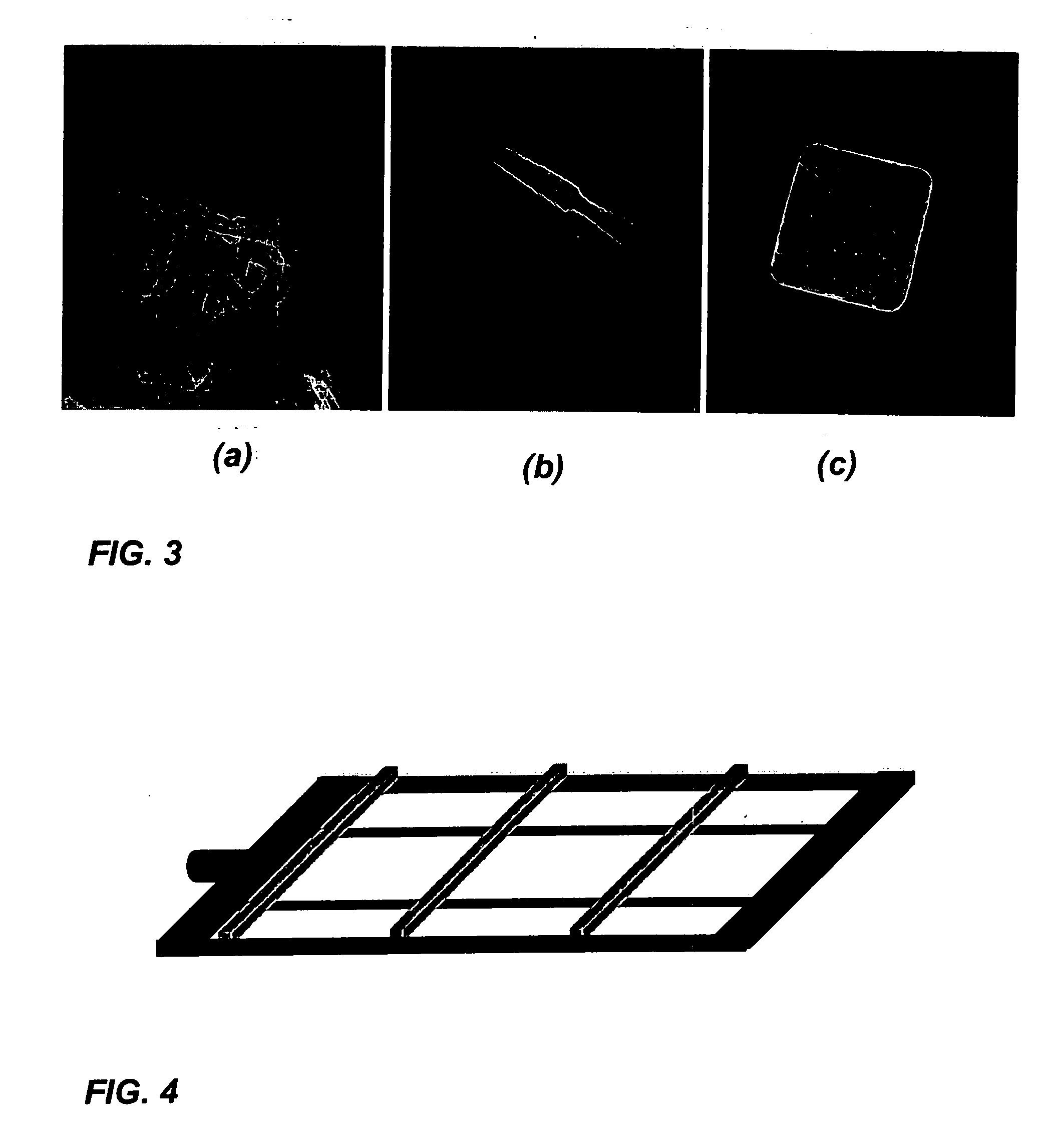
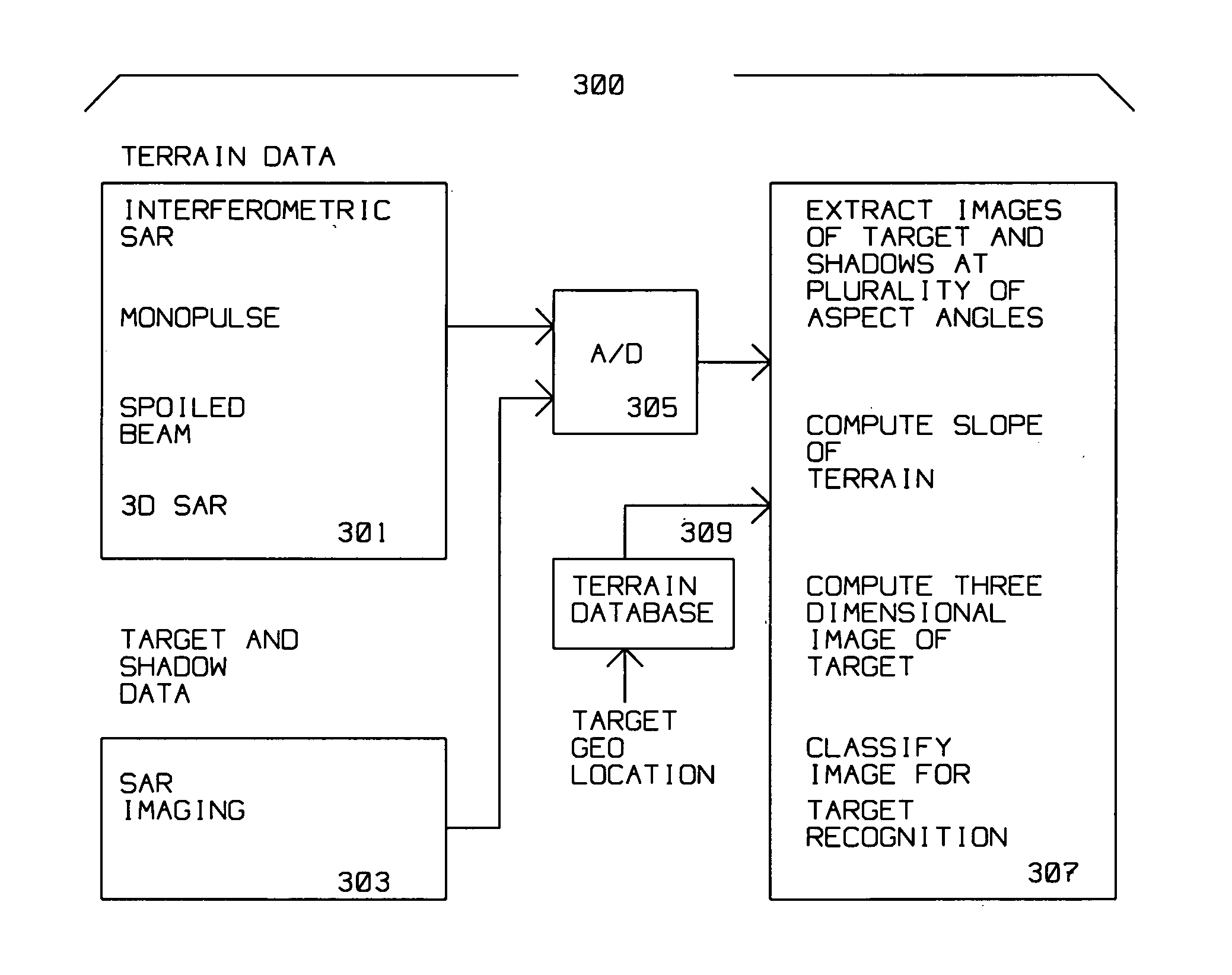
A radar on a moving platform for three dimensional target recognition of a target on a flat or sloping terrain is described. The target is illuminated from a plurality of locations to generate images at many aspect angles. The radar is positioned at a low grazing angle with respect to the target for generating a shadow of the target on the flat or sloping terrain for each aspect angle of the plurality of aspect angles. The radar comprises an analog to digital converter for converting reflections from the target induced by radar illumination into target digital data and for converting reflections induced by the illumination from the flat or sloping terrain into terrain digital data. The radar further comprises a computer for extracting radar images of the target and its shadow(s) at the plurality of aspect angles at low grazing angles; computing the slope of the terrain from the terrain digital data; correlating a plurality of the radar images to compute a three dimensional image of the target from the shadow of the target upon the flat or sloping terrain; and classifying the three dimensional image for target recognition using a target recognition algorithm.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
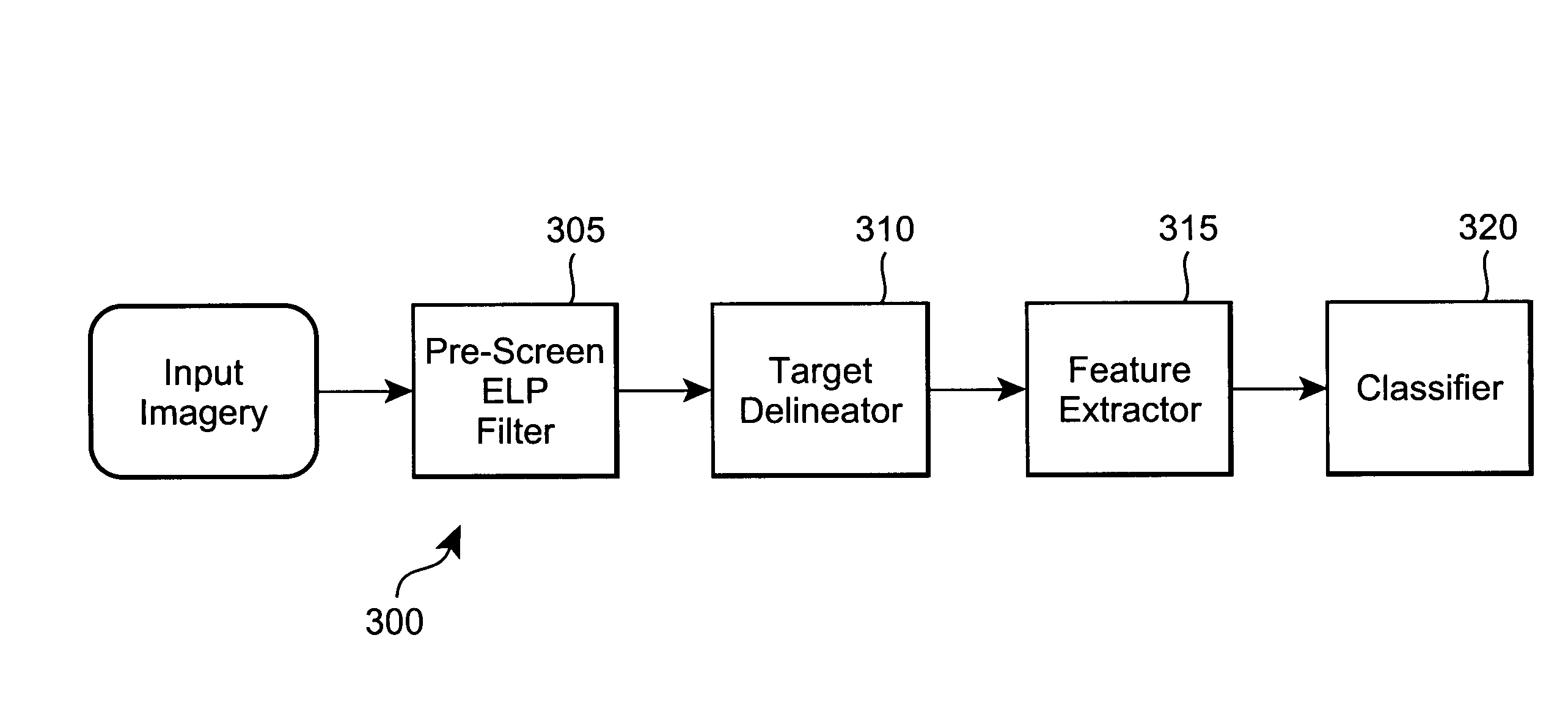
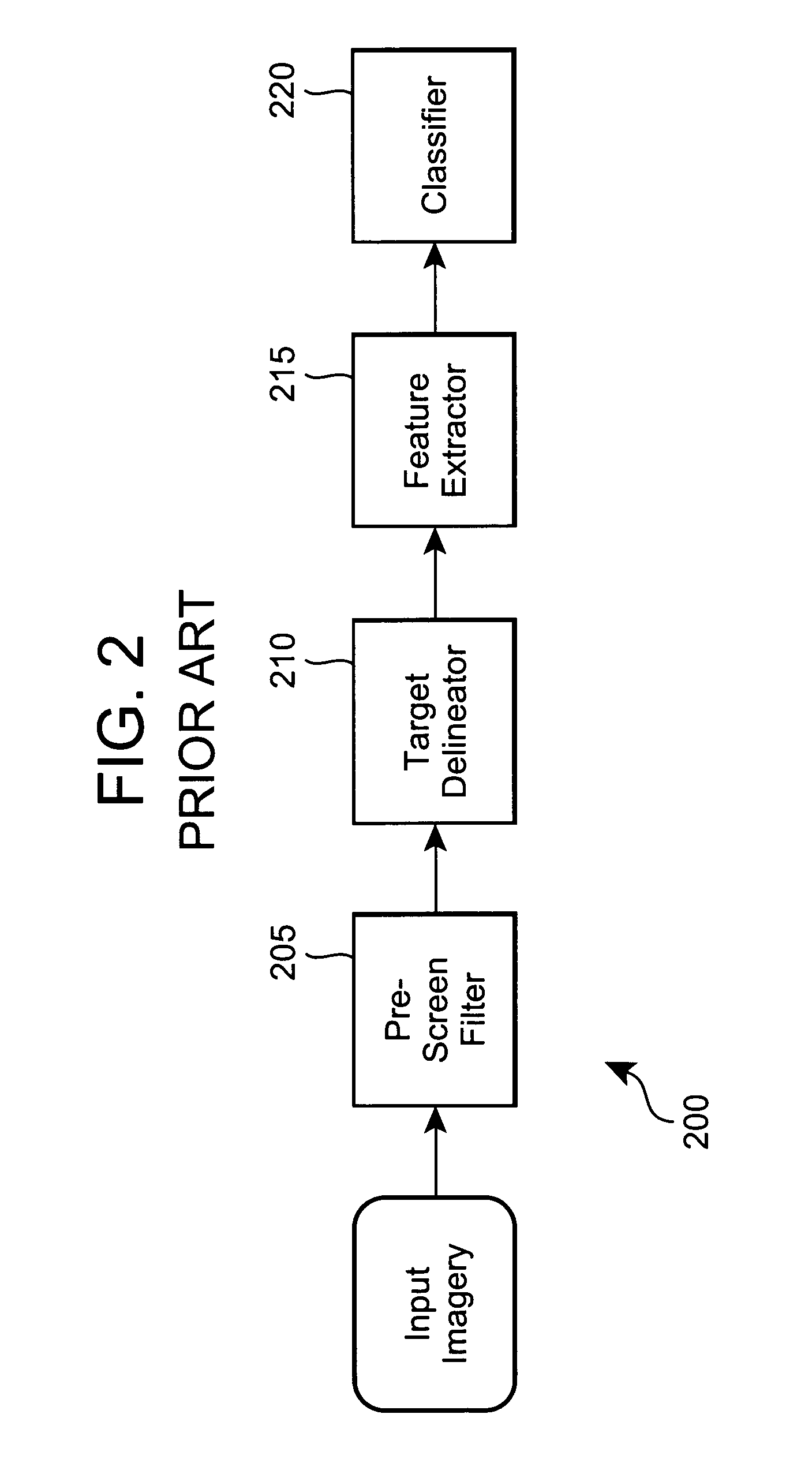
Automatic target recognition system with Elliptical Laplacian Pyramid filter
InactiveUS7274801B2High Pd : Pfd ratioEfficiently effectively identifyingTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionEllipse
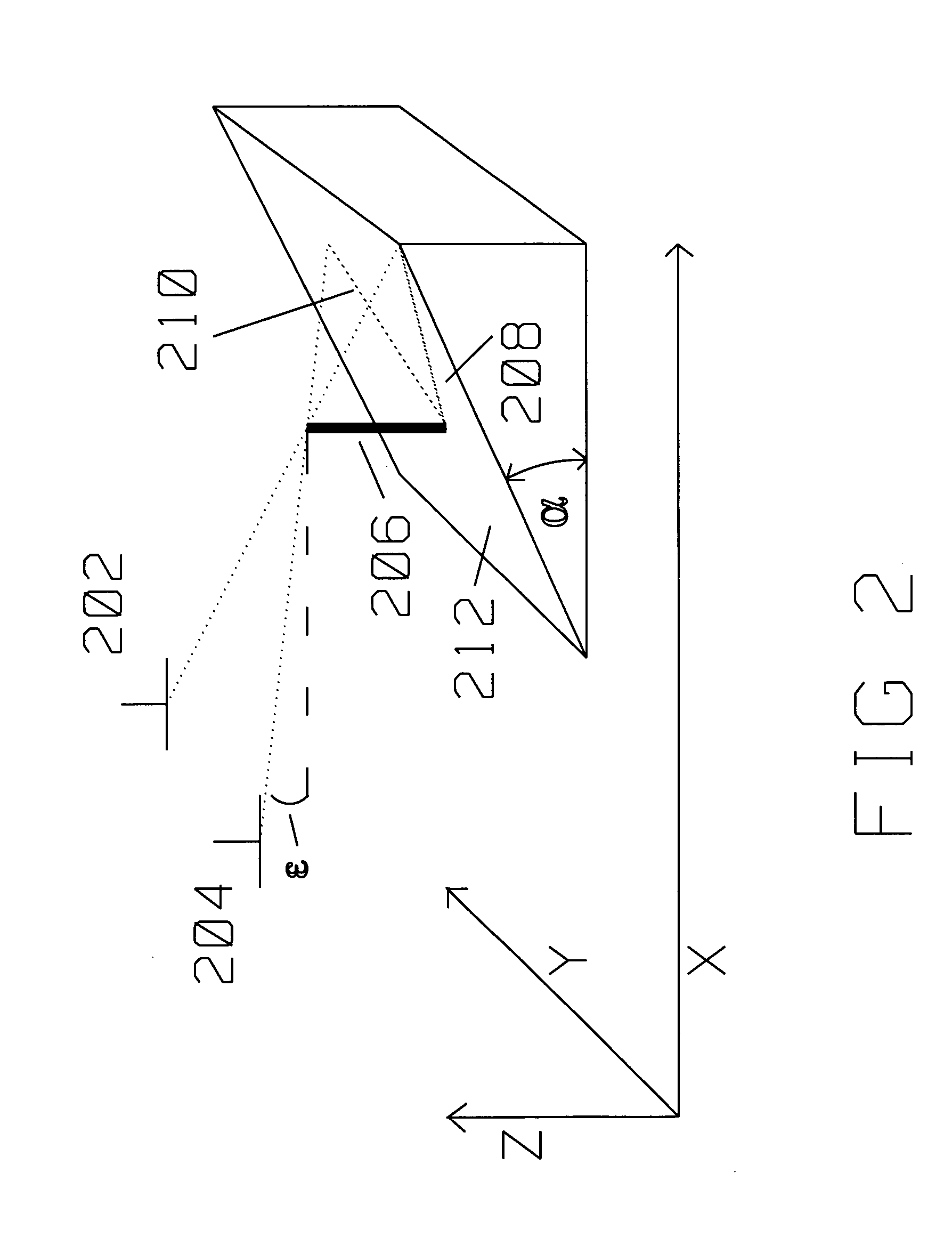
Automatic target recognition system and / or method which employs an elliptical Laplacian pyramid based pre-screen image data filter. The filter is a resolution sequence matched filter, where the elliptical Laplacian operator reflects the size, spatial characteristics and image intensity level of prospective, candidate targets embedded in the image data. Targets which exhibit a rectangular or elliptical shape at various aspect angles are more therefore more effectively and efficiently identified and located.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ELECTRONICS & MISSILES +1
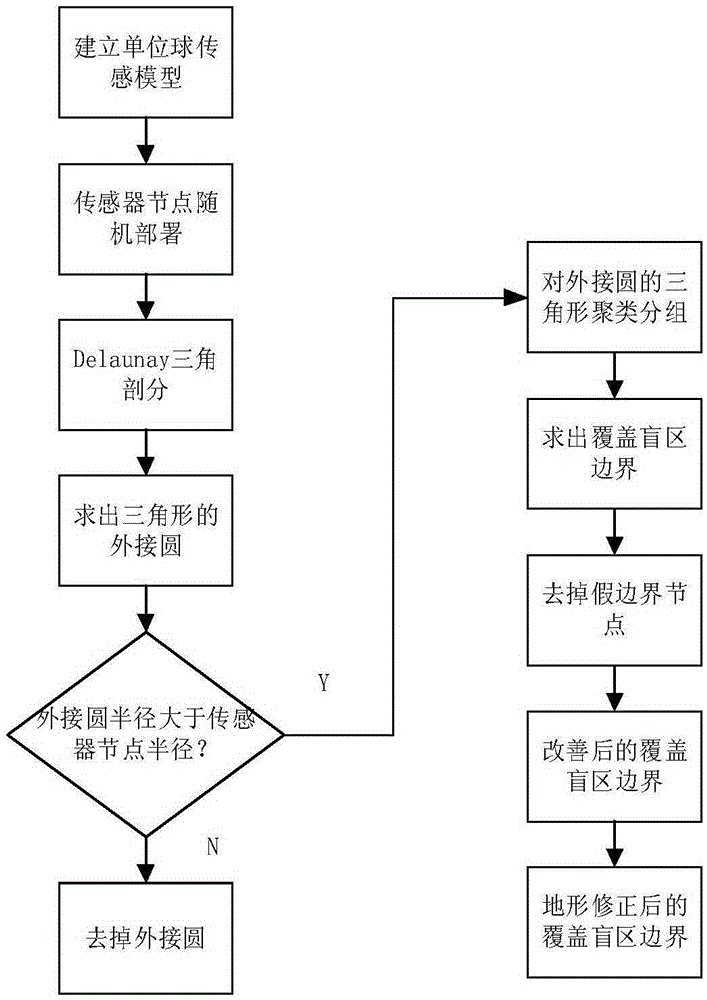
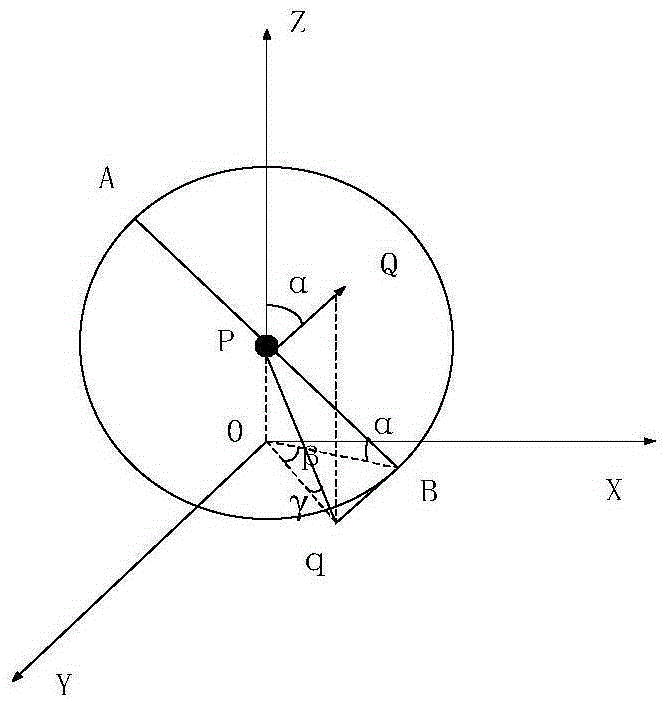
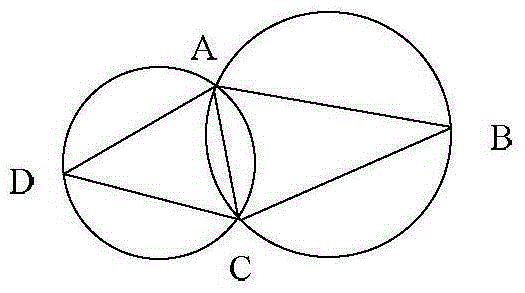
WSN coverage blind zone detection method based on three-dimensional terrain correction
The invention discloses a WSN coverage blind zone detection method based on three-dimensional terrain correction. The WSN coverage blind zone detection method comprises the steps of: deploying sensor nodes in a target region randomly, and carrying out Delaunay triangular subdivision; drawing a circumcircle of each Delaunay triangle, and showing boundary of a coverage blind zone through adopting a minimum polygon capable of containing the coverage blind zone; judging false boundary nodes among the boundary nodes, and showing the improved coverage blind zone boundary through adopting a minimum polygon capable of containing the coverage blind zone again after removing the false boundary nodes; and calculating an actual detection radius by utilizing a slope and a slope aspect angle, and finally calculating the corrected coverage blind zone boundary by using a detection algorithm. The WSN coverage blind zone detection method has the beneficial effects that the detection algorithm of the coverage blind zone can be applied to terrain surface with large fluctuation.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Technique for low grazing angle 3D SAR target recognition
A radar on a moving platform for three dimensional target recognition of a target on a flat or sloping terrain is described. The target is illuminated from a plurality of locations to generate images at many aspect angles. The radar is positioned at a low grazing angle with respect to the target for generating a shadow of the target on the flat or sloping terrain for each aspect angle of the plurality of aspect angles. The radar comprises an analog to digital converter for converting reflections from the target induced by radar illumination into target digital data and for converting reflections induced by the illumination from the flat or sloping terrain into terrain digital data. The radar further comprises a computer for extracting radar images of the target and its shadow(s) at the plurality of aspect angles at low grazing angles; computing the slope of the terrain from the terrain digital data; correlating a plurality of the radar images to compute a three dimensional image of the target from the shadow of the target upon the flat or sloping terrain; and classifying the three dimensional image for target recognition using a target recognition algorithm.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Automatic measuring system for visual angle of liquid crystal display
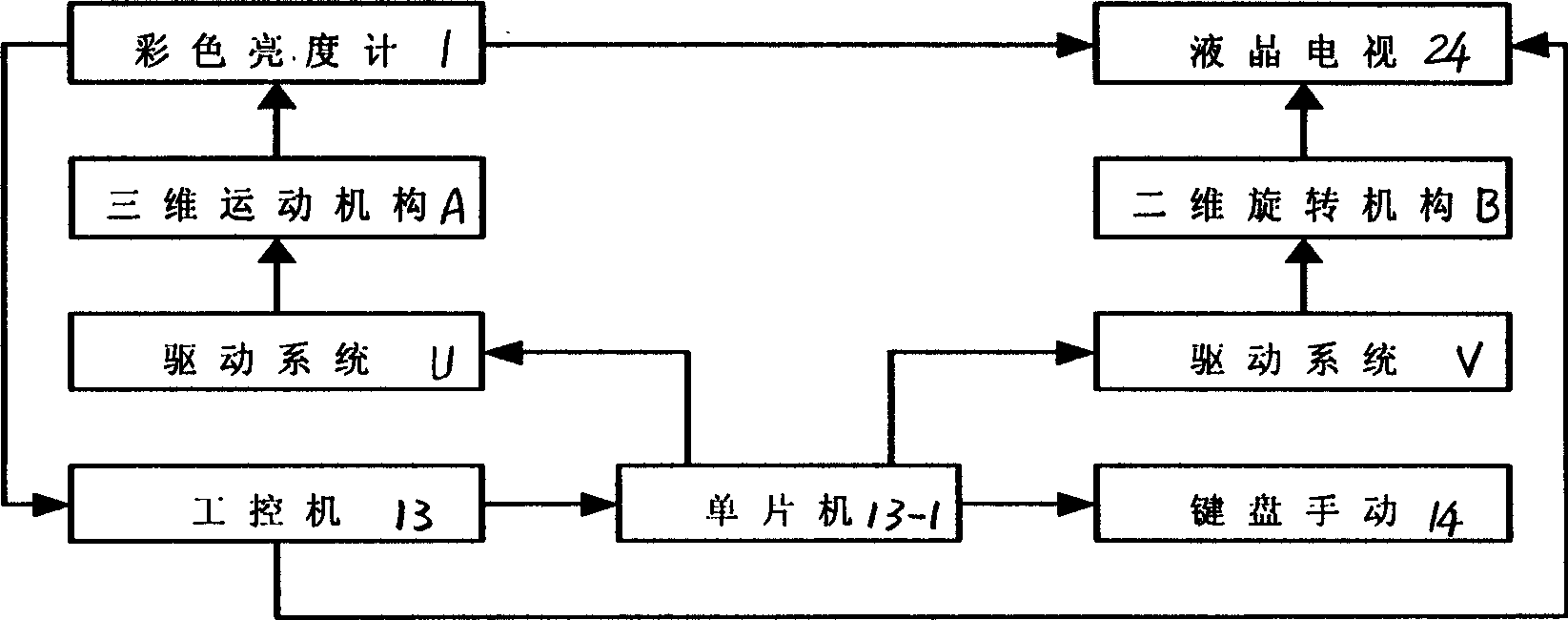
InactiveCN1664535AEasy to measureImprove work efficiencyElectrical testingOptical apparatus testingLinear motionEngineering
The invention relates to a system of measuring the aspect angle of the liquid crystal display automatically, which can measure the aspect angle, uniformity of luminance, uniformity of chromaticity. The technical project is: 1) controlling machine for the whole system and provide the signal for measuring; 2) driving system(U) and three-dimensional motion device(A), which can be used for linear motion of front and rear, left and right, up and down;3) driving system(V),which realize the motion of pitching and rotating; 4)color brightness meter, which is fixed on the vertical moving channel and measures the color coordinate and brightness of the liquid crystal display. The invention can be used in the fields of manufacturing and measuring the liquid crystal display.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Synthetic aperture radar systems and methods
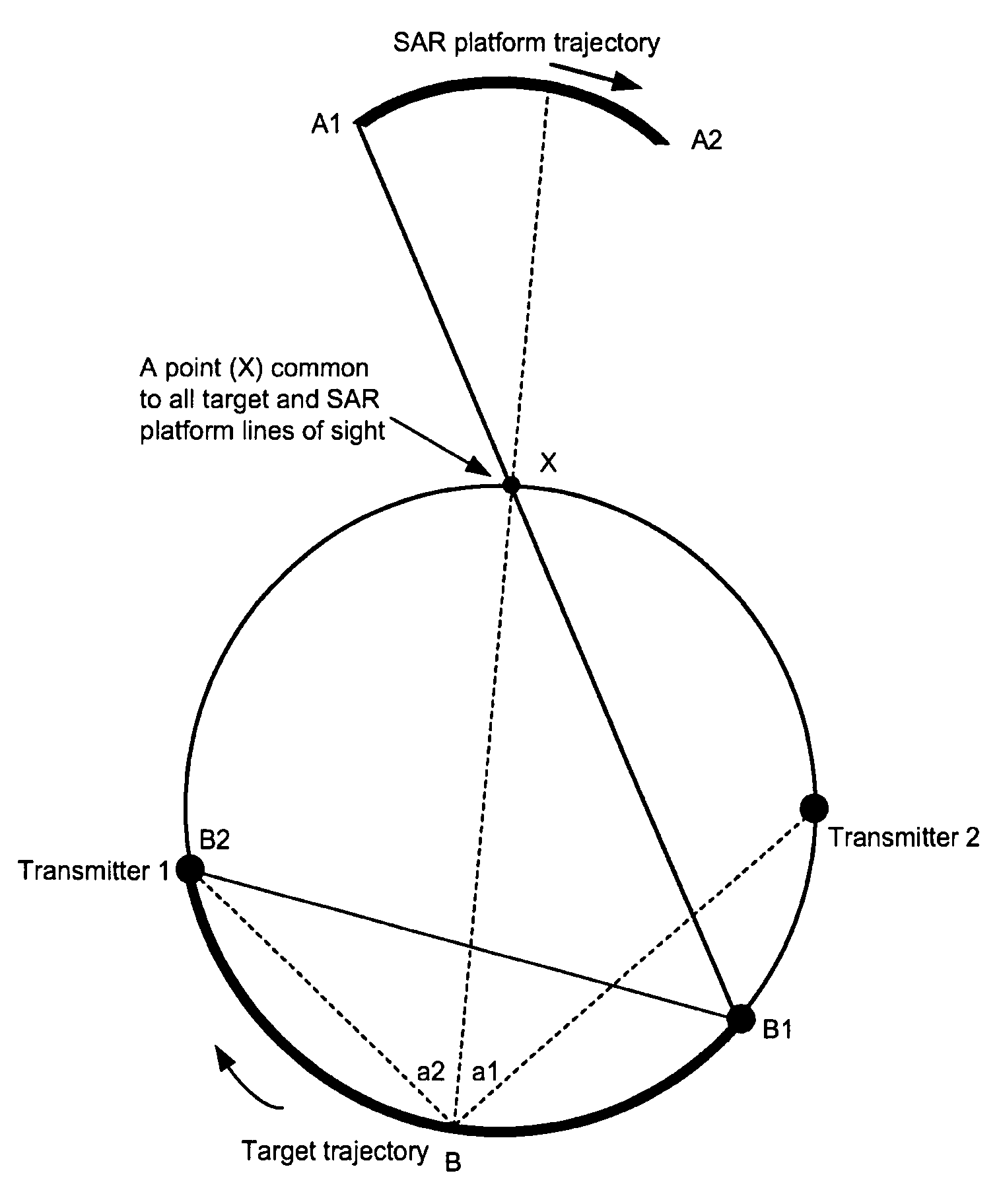
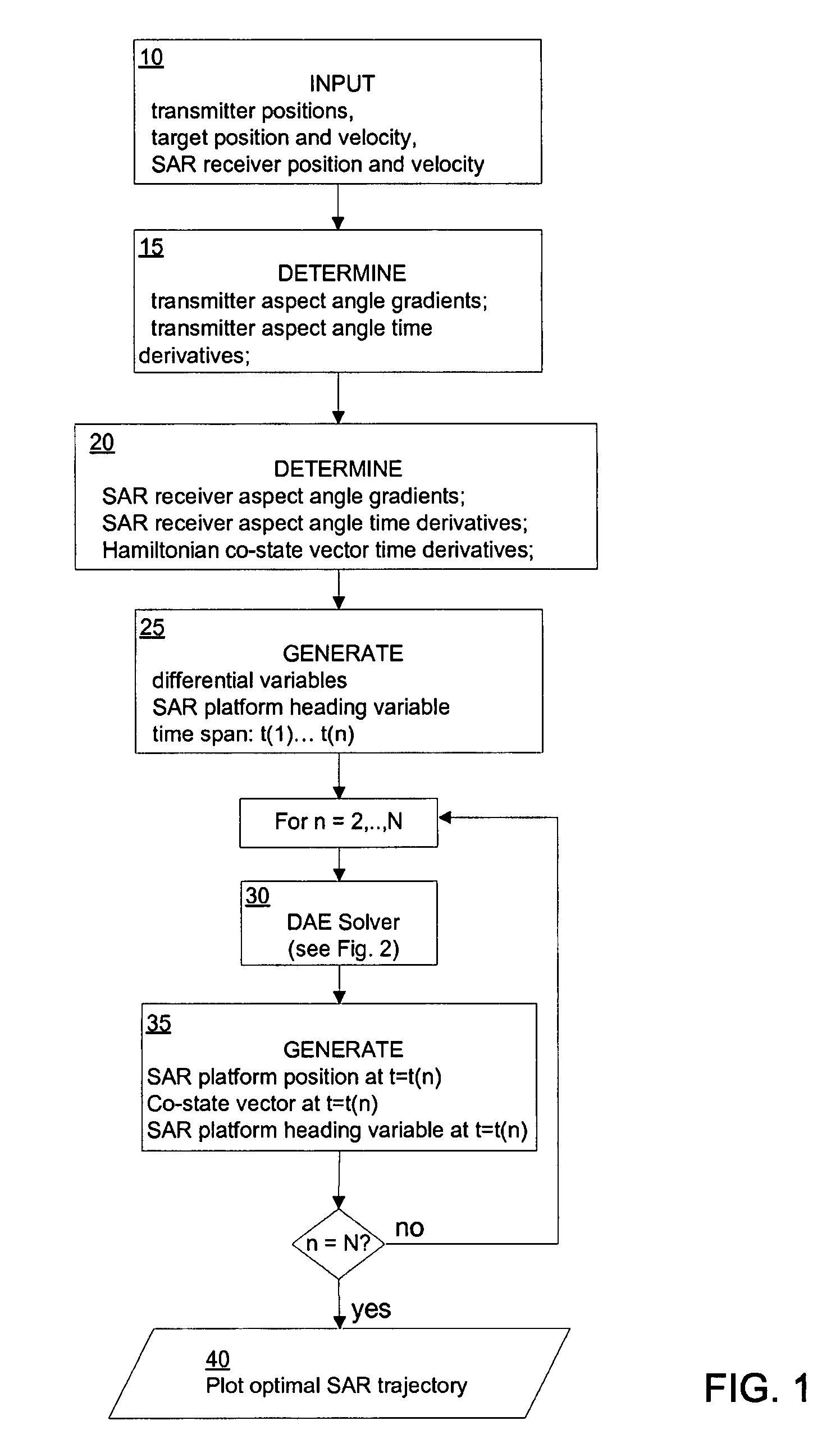
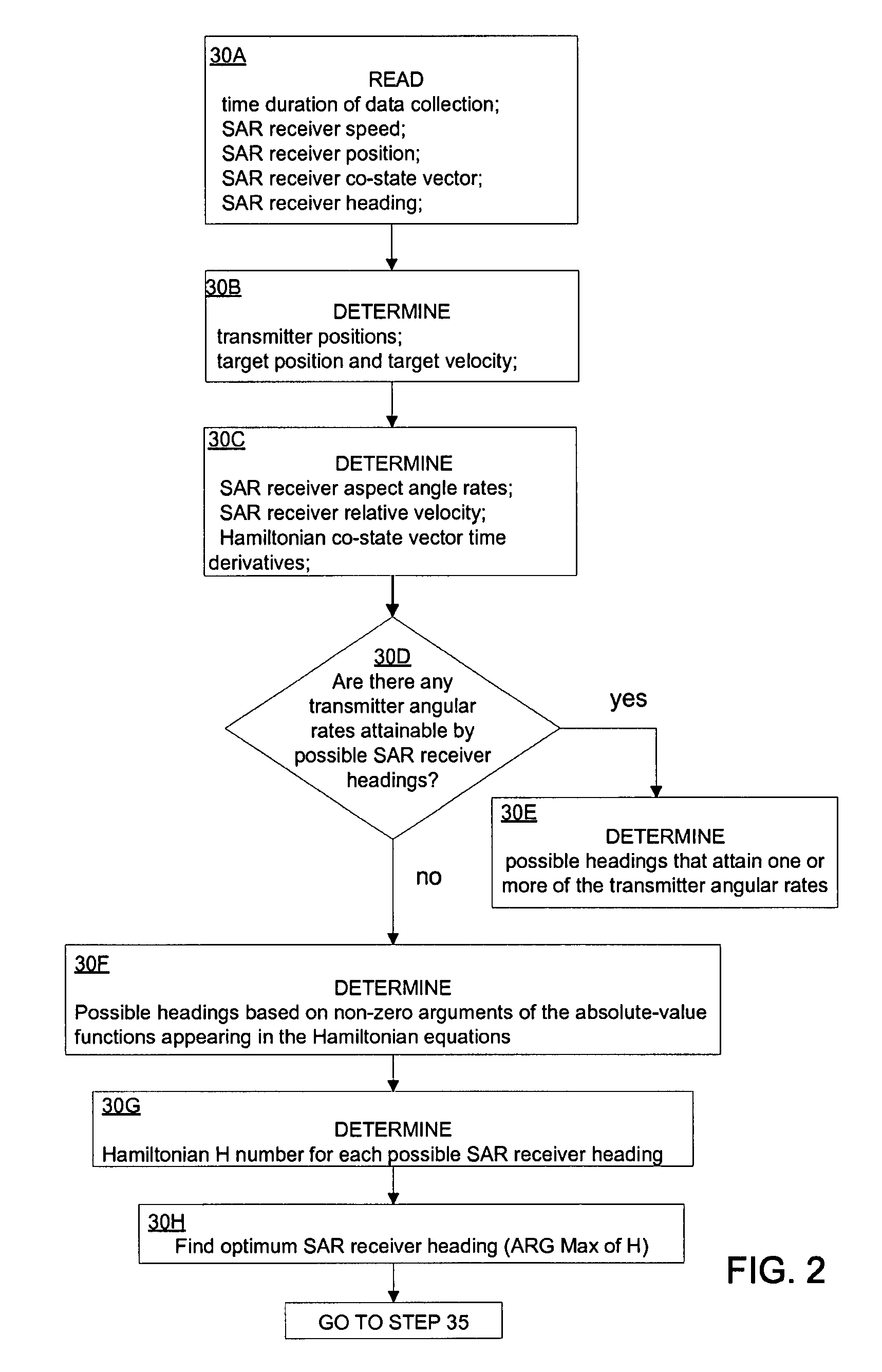
A method of determining a radar receiver path, comprising the steps of: obtaining a transmitter position; obtaining a target position and velocity; obtaining a radar receiver position and velocity; determining a transmitter aspect angle gradient, a transmitter aspect angle time derivative and a transmitter co-state vector time derivative; determining a target aspect angle gradient, a target aspect angle time derivative and a target co-state vector time derivative; generating a radar platform heading variable, and a group of differential variables over a defined time span; inputting the group of differential variables into a differential equation solver; receiving a group of possible headings for the radar receiver path; and finding an optimum radar receiver path from the group of possible headings.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
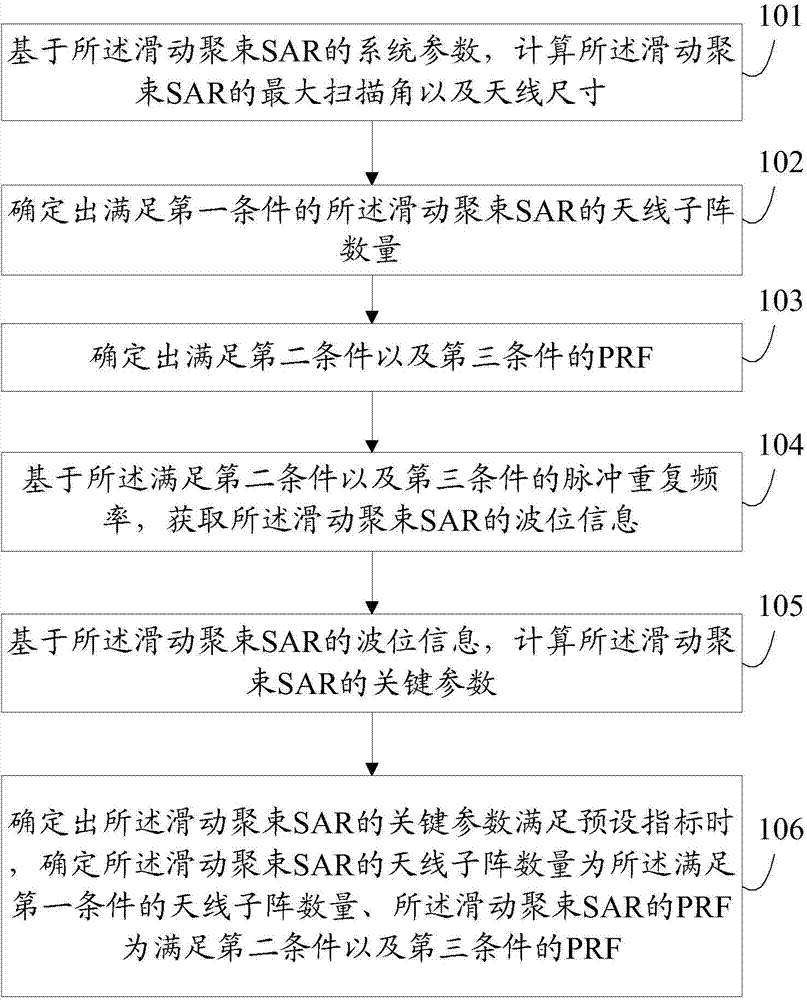
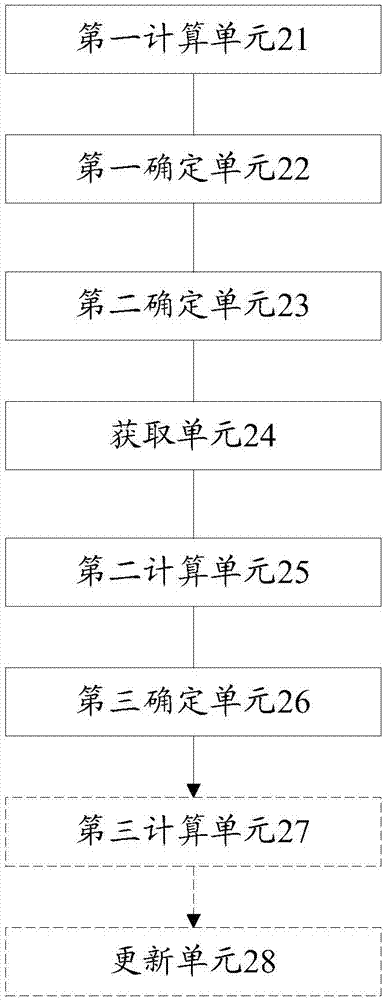
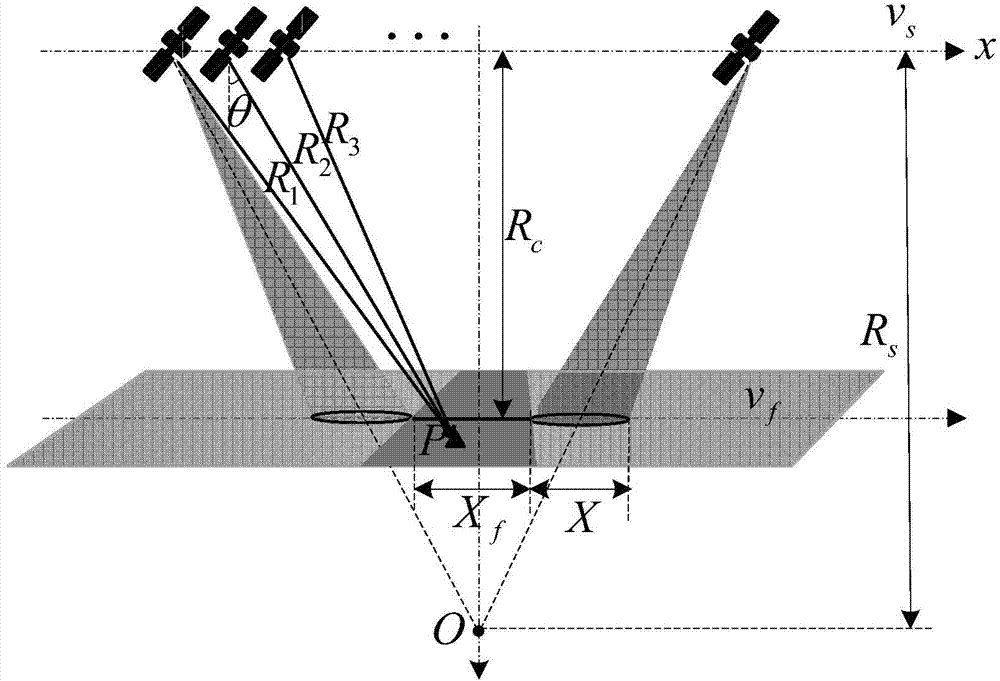
Sliding spotlight SAR (synthetic aperture radar) as well as implementing method and device thereof
The invention discloses a sliding spotlight SAR (synthetic aperture radar) as well as an implementing method and a device thereof. The implementing method of the sliding spotlight SAR comprises steps as follows: the maximum aspect angle and the antenna dimension of the sliding spotlight SAR are calculated on the basis of system parameters of the sliding spotlight SAR; the quantity of antenna subarrays, meeting the requirement of a first condition, of the sliding spotlight SAR is determined; a PRF (pulse repetition frequency) which meets requirements of a second condition and a third condition is determined; wave position information of the sliding spotlight SAR is acquired on the basis of the PRF meeting the requirements of the second condition and the third condition; key parameters of the sliding spotlight SAR are calculated on the basis of the wave position information of the sliding spotlight SAR; and when the key parameters of the sliding spotlight SAR meet the requirements of preset indexes, the quantity of the antenna subarrays of the sliding spotlight SAR is the quantity of the antenna subarrays meeting the requirement of the first condition, and the PRF of the sliding spotlight SAR is the PRF meeting the requirements of the second condition and the third condition. With the adoption of the technical scheme, the key parameters of the sliding spotlight SAR can be effectively designed, so that the sliding spotlight SAR can have higher resolution ratio and larger azimuth width.
Owner:中科卫星山东科技集团有限公司
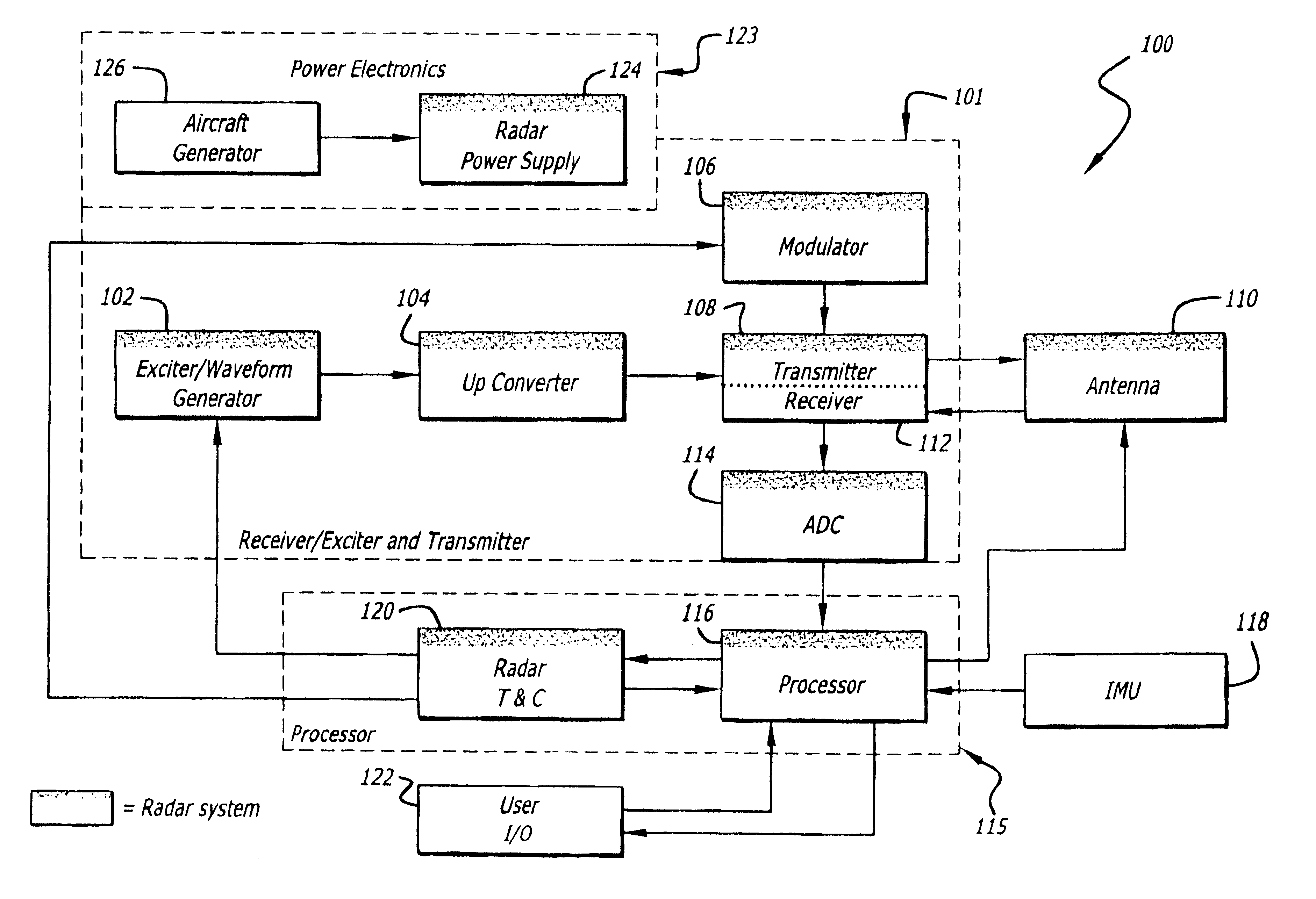
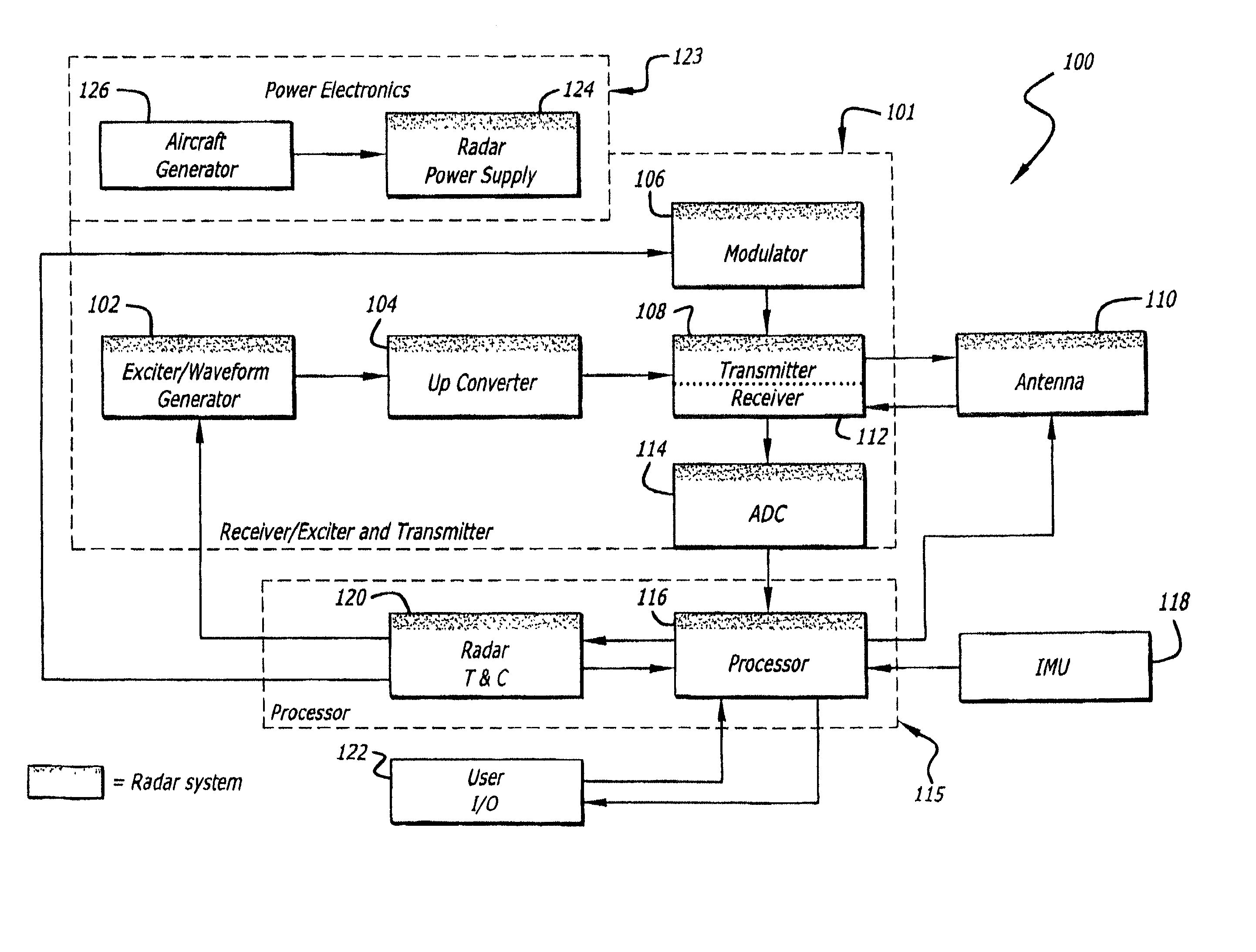
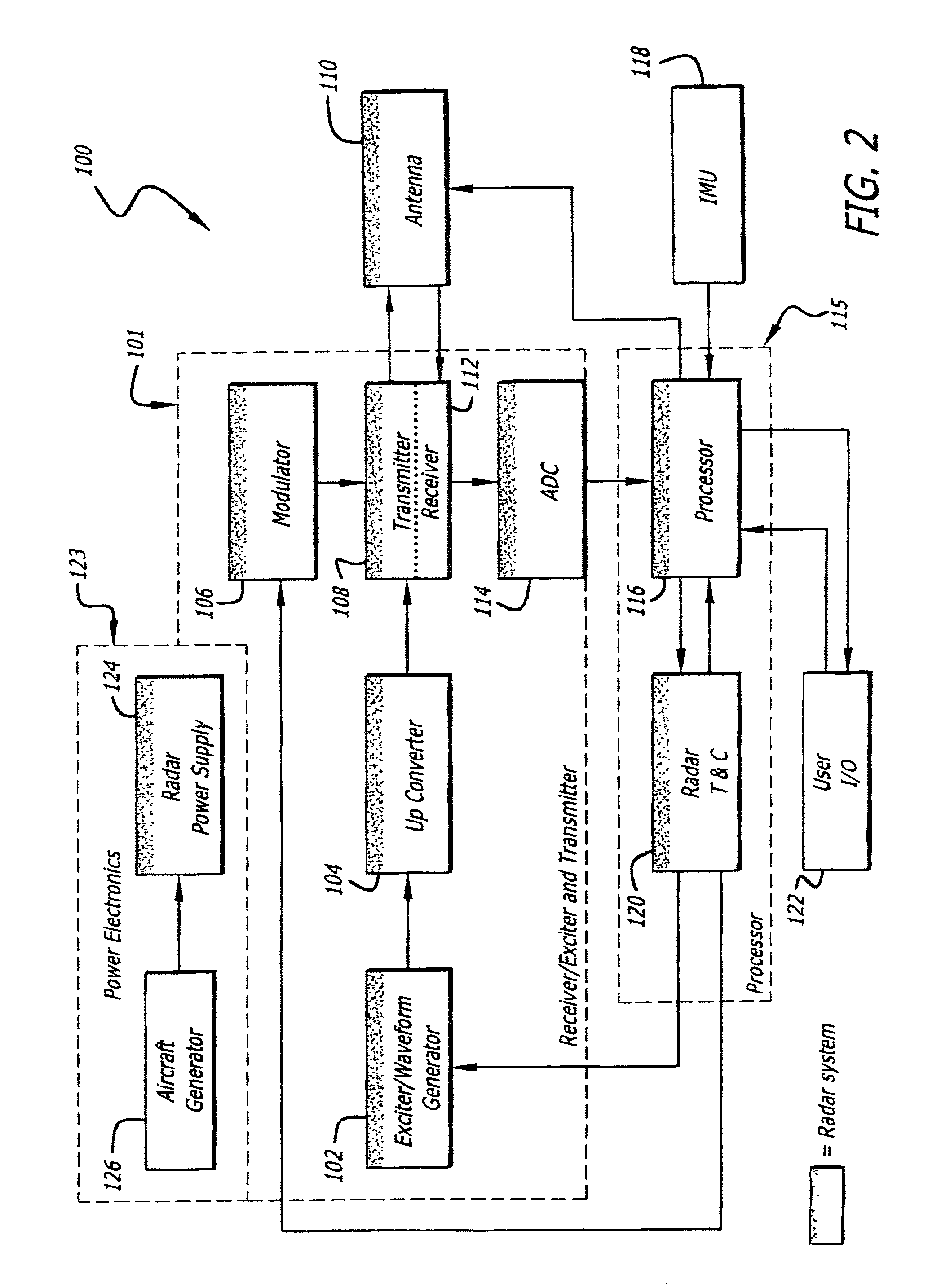
Radar imaging system and method
An imaging system and method. The invention provides an intra-pulse repetition interval (PRI) agile beam technique for enhanced resolution that can be used at aspect angles near the velocity vector of a host vehicle. It is particularly useful at small scan angles where beam sharpening array times become large. At these scan angles, the bandwidth of the clutter is narrower than at higher scan angles and allows large PRIs without degradation from Doppler ambiguities. In accordance with the present teachings, sequential illumination is performed within a PRI to multiple beam locations using an agile beam. The interleaving of beams reduces map formation times compared to conventional techniques using sequential arrays. The inventive system is adapted for use with an electronically scanned (e.g., synthetic aperture array radar) antenna. The inventive method includes the steps of activating the antenna to generate a beam of electromagnetic energy; causing the beam to scan over a predetermined scan volume consisting of a predetermined range of scan angles relative to a reference vector; and generating multiple simultaneous beams of electromagnetic energy over a subset of the predetermined range of scan angles.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Mirror Image Target Detection and Recognition
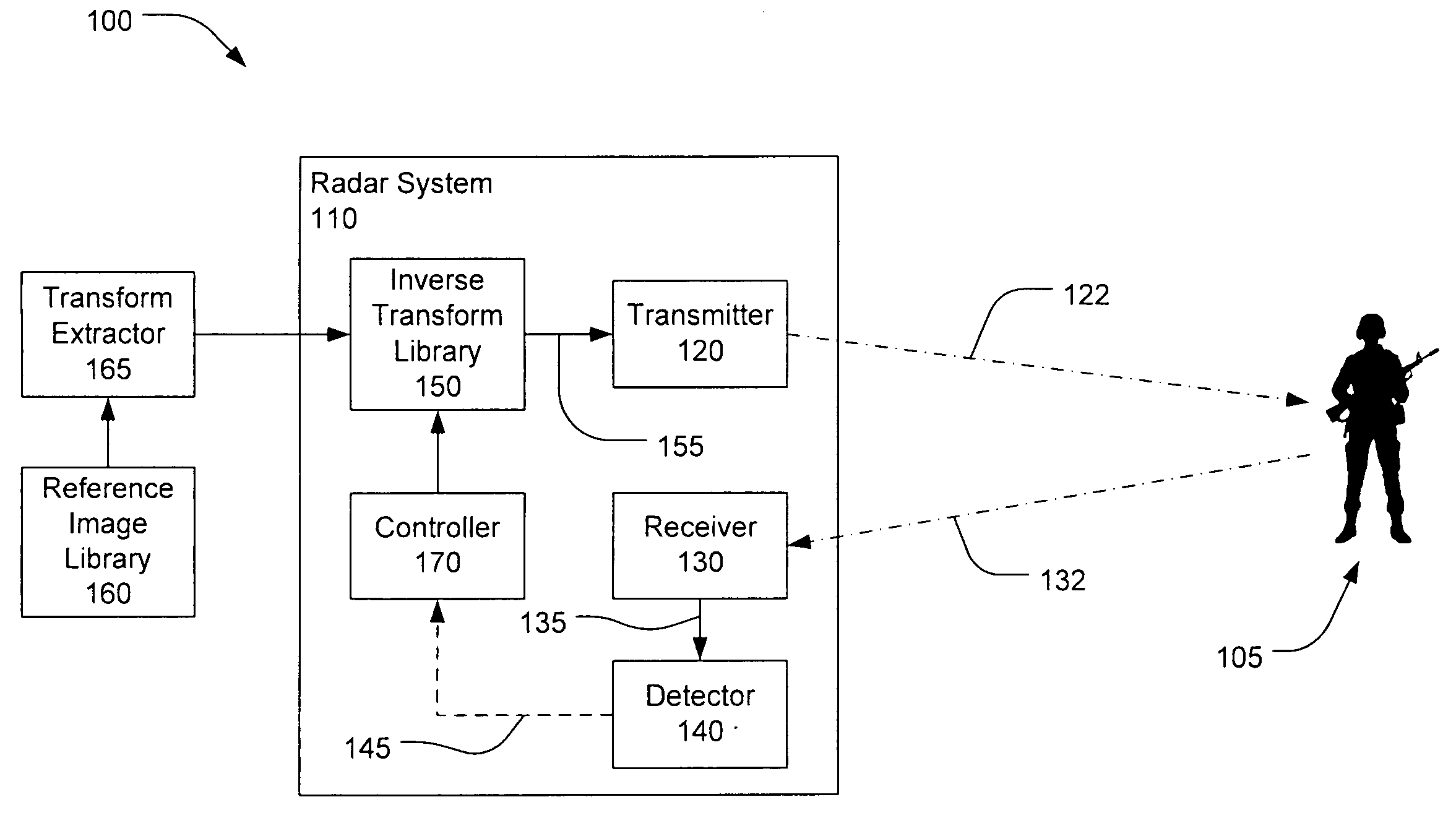
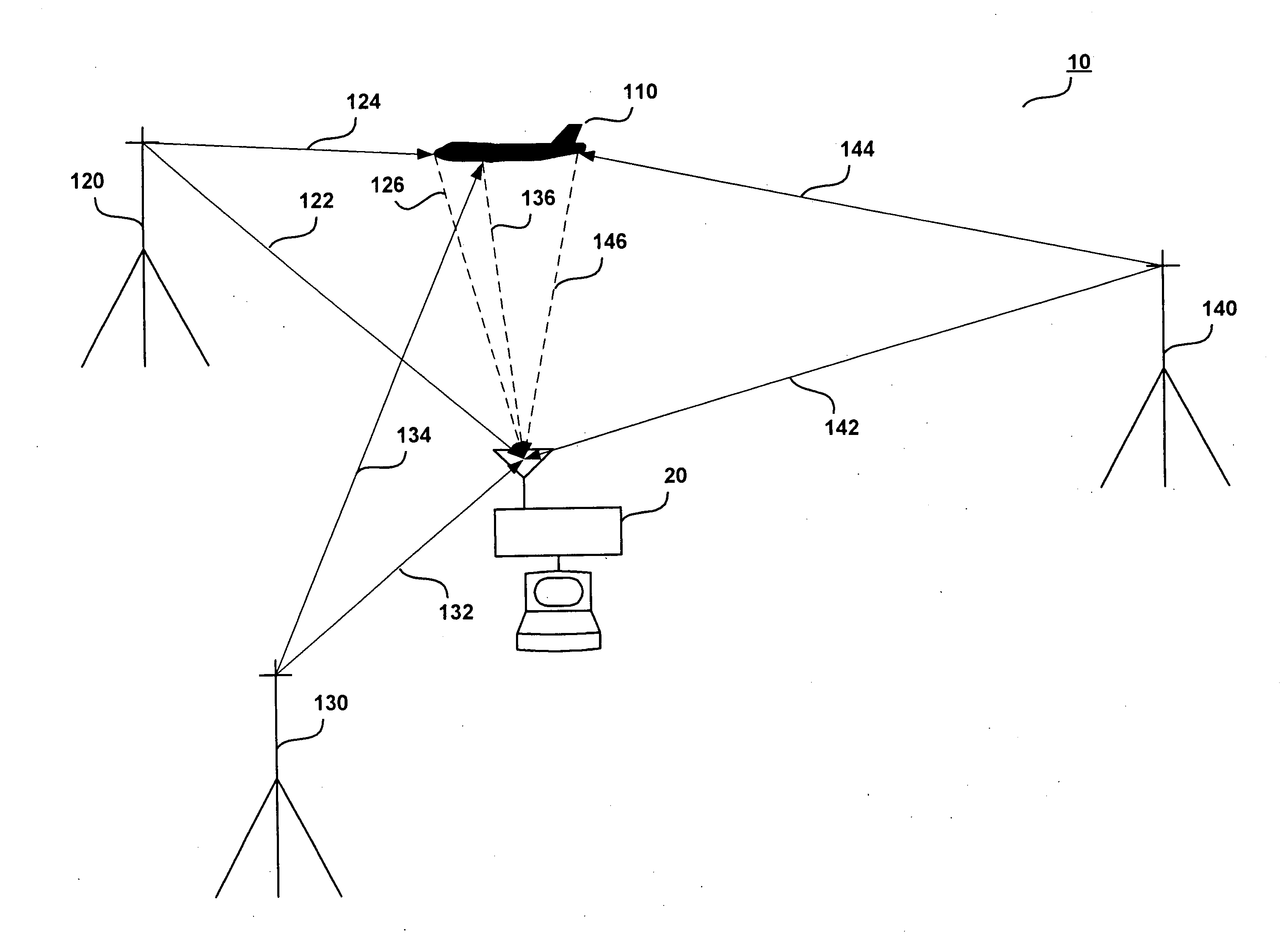
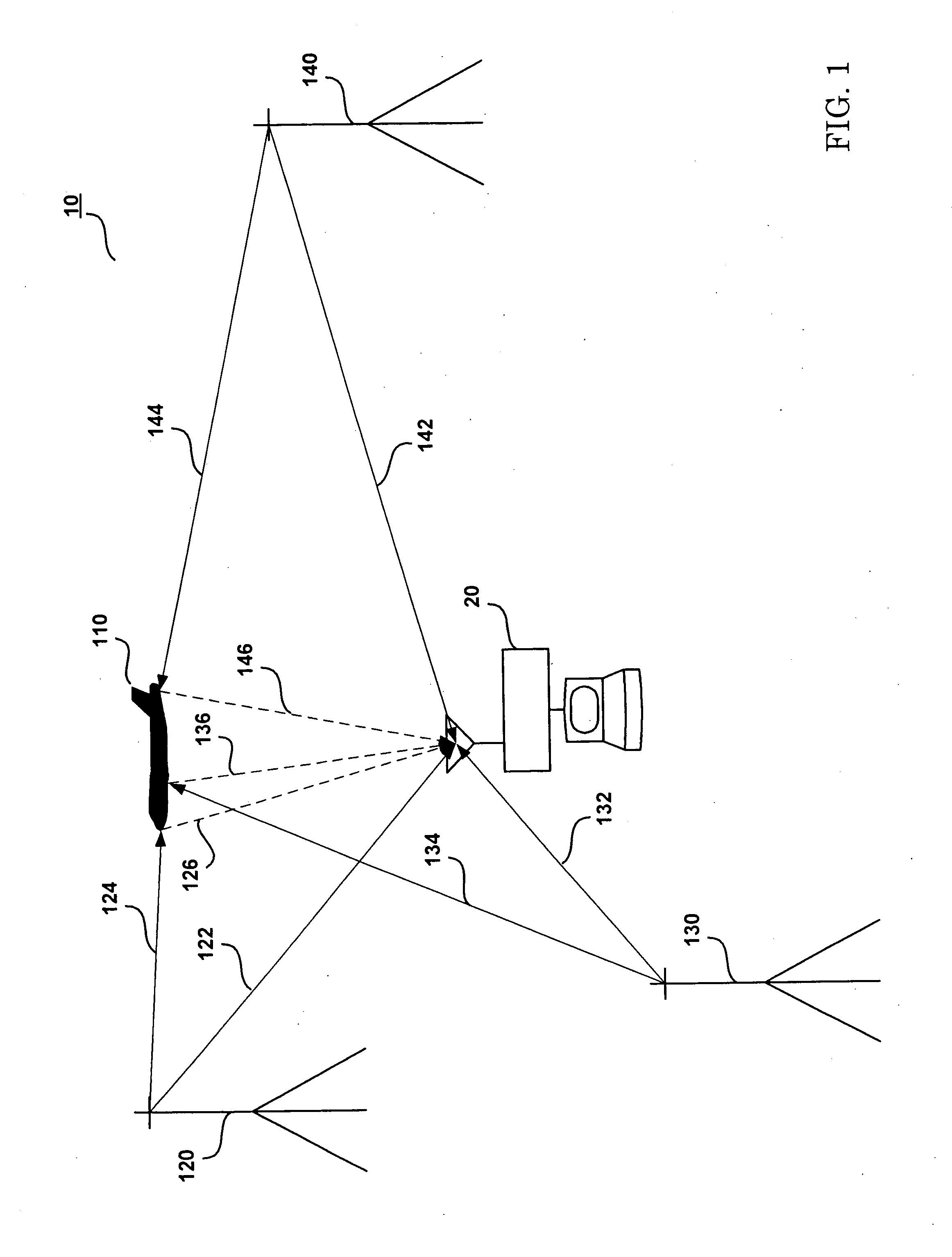
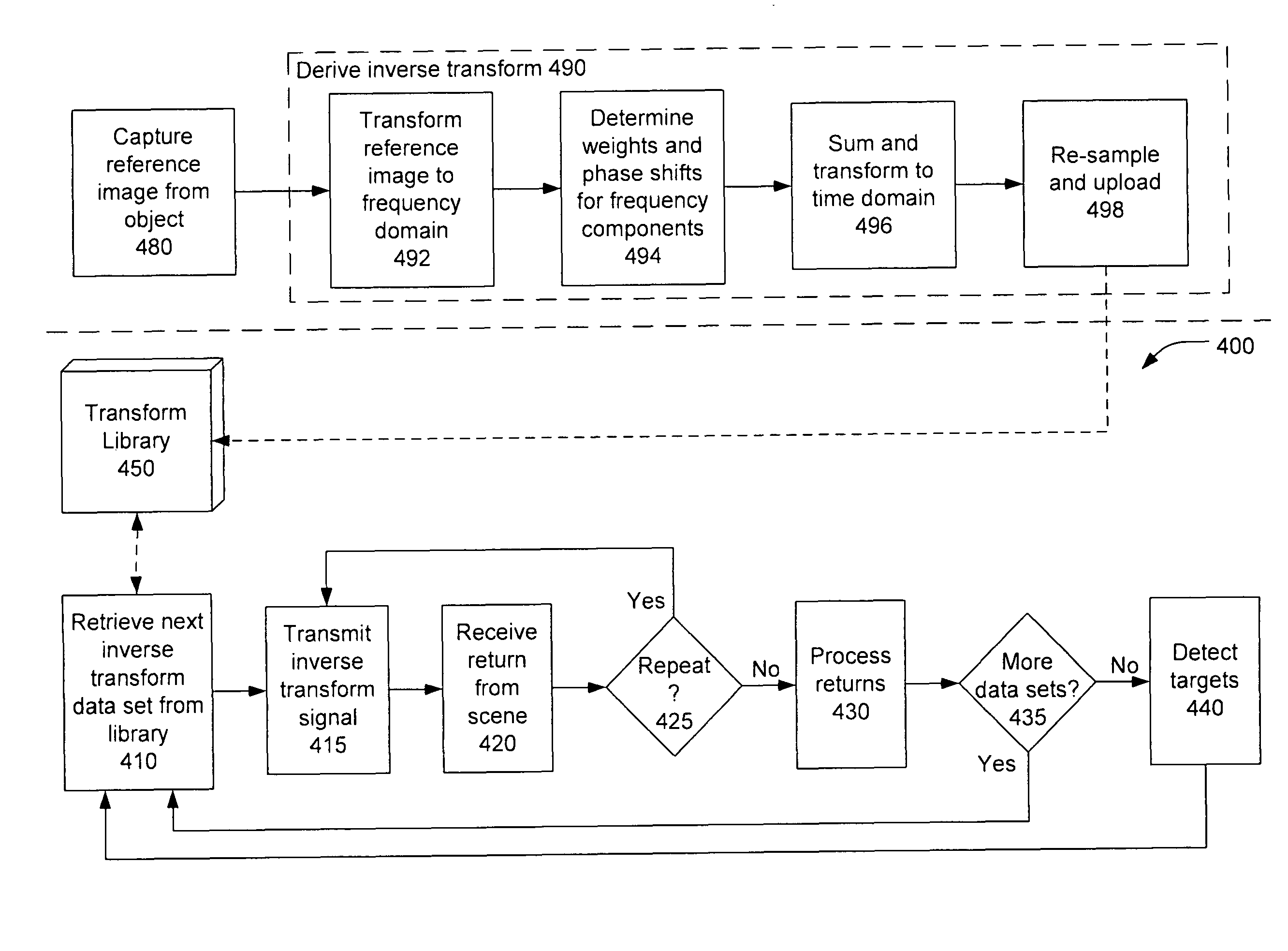
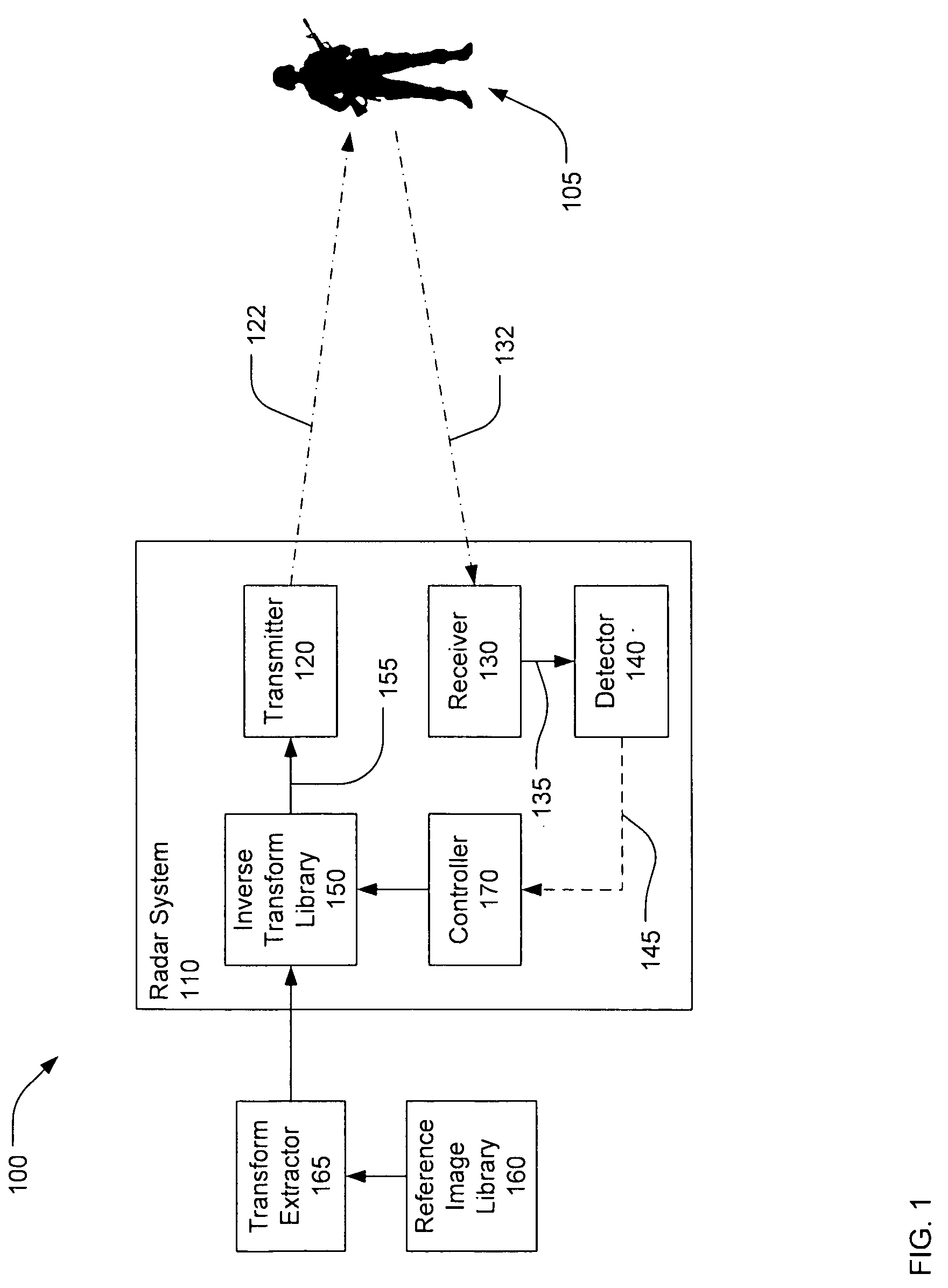
There is disclosed a system and method for detecting targets. A transmitter may transmit a first inverse transform signal, the first inverse transform signal derived from a reference image of a first reference target at a first aspect angle. A receiver may receive a return signal reflected from a scene. A detector may determine, based on the return signal, if an object similar to the first target at the first aspect angle is detected within the scene.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
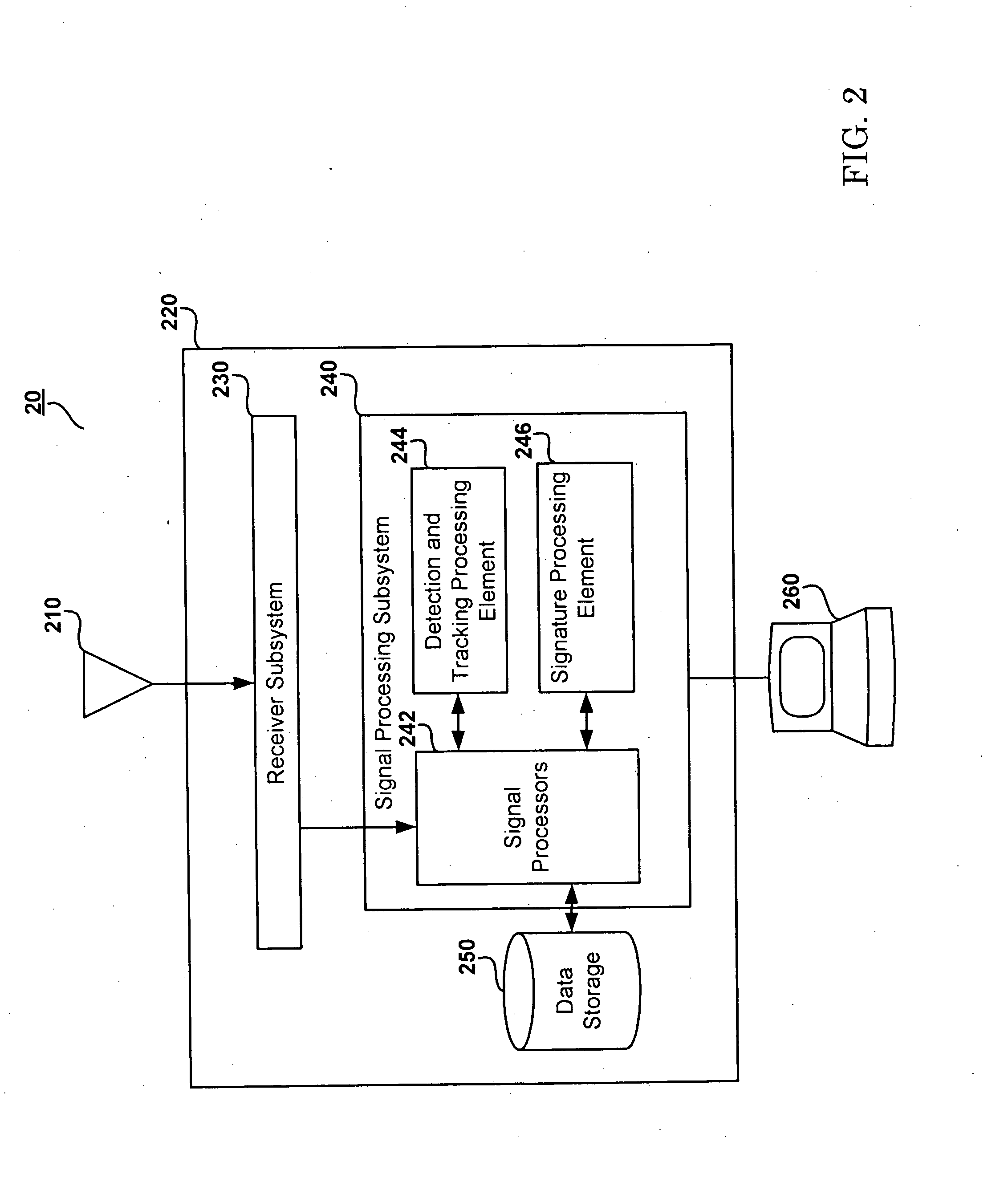
System and method for target signature calculation and recognition
ActiveUS20110210885A1Easy to detectHigh energy of signalRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFeature DimensionTarget signature
The present invention is directed to a system and method for the identification of a target object in PCL radar applications. The disclosed embodiments describe the systems and methods used in the identification of a target object from the collection of data representing specific target object features, such as velocity, altitude, fuselage length, wing length, or wing sweepback angle, and the comparison of selected target object features with a database of known aircraft features. The present invention also provides for the calculation of feature dimensions, such as the fuselage length, wing length, or wing sweepback angle from measurements associated with a peak signal lobe as a function of a bistatic aspect angle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
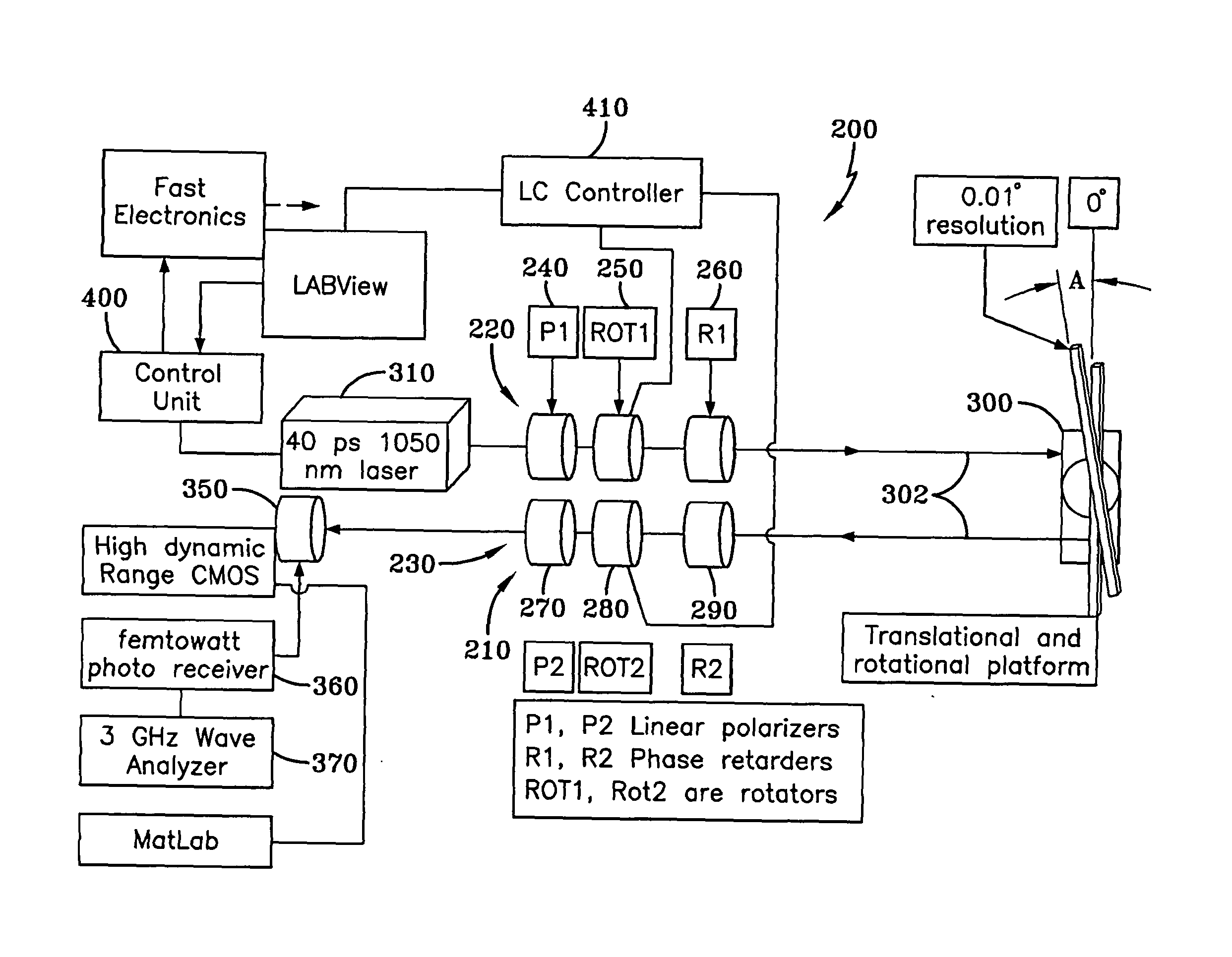
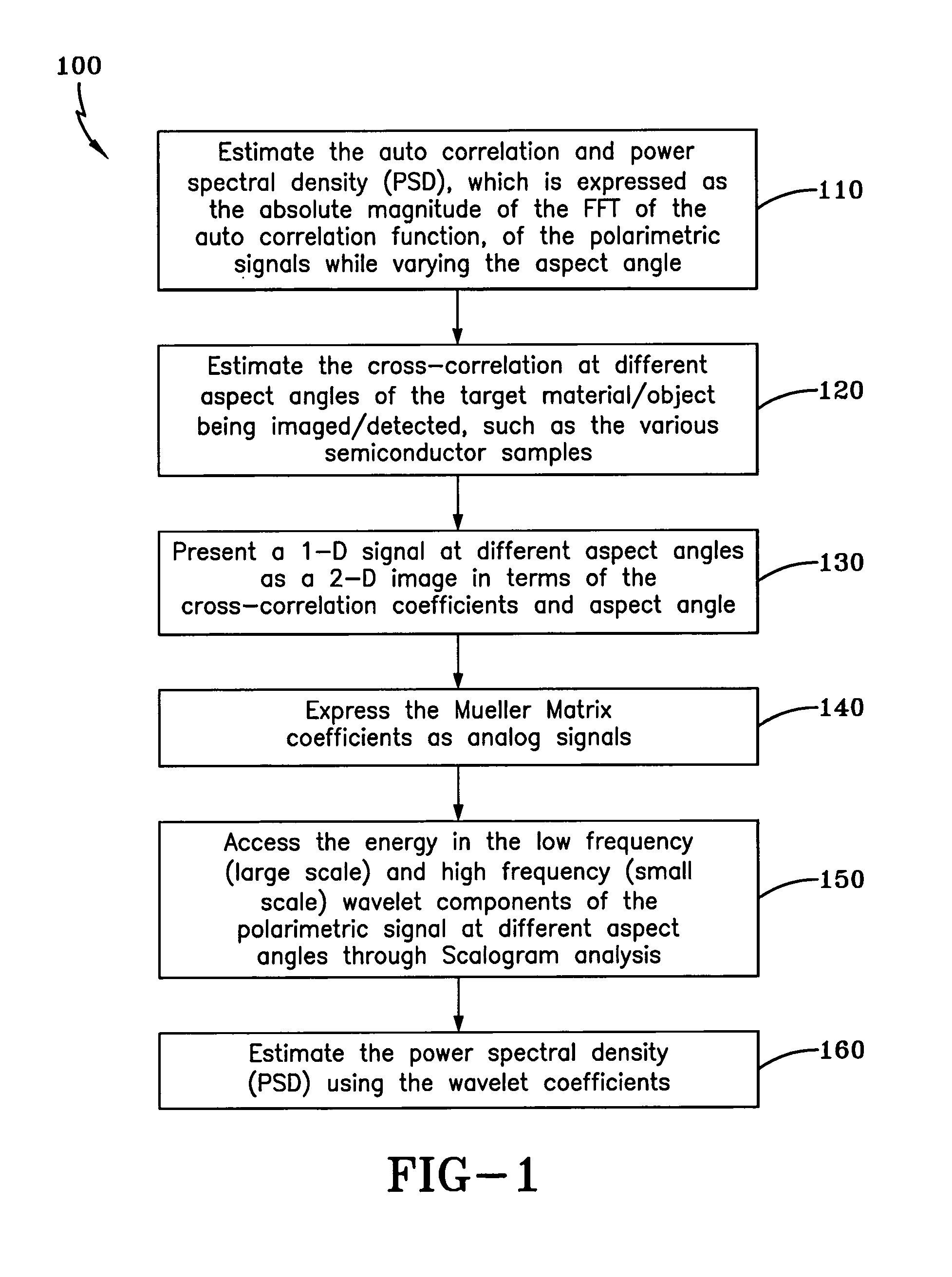
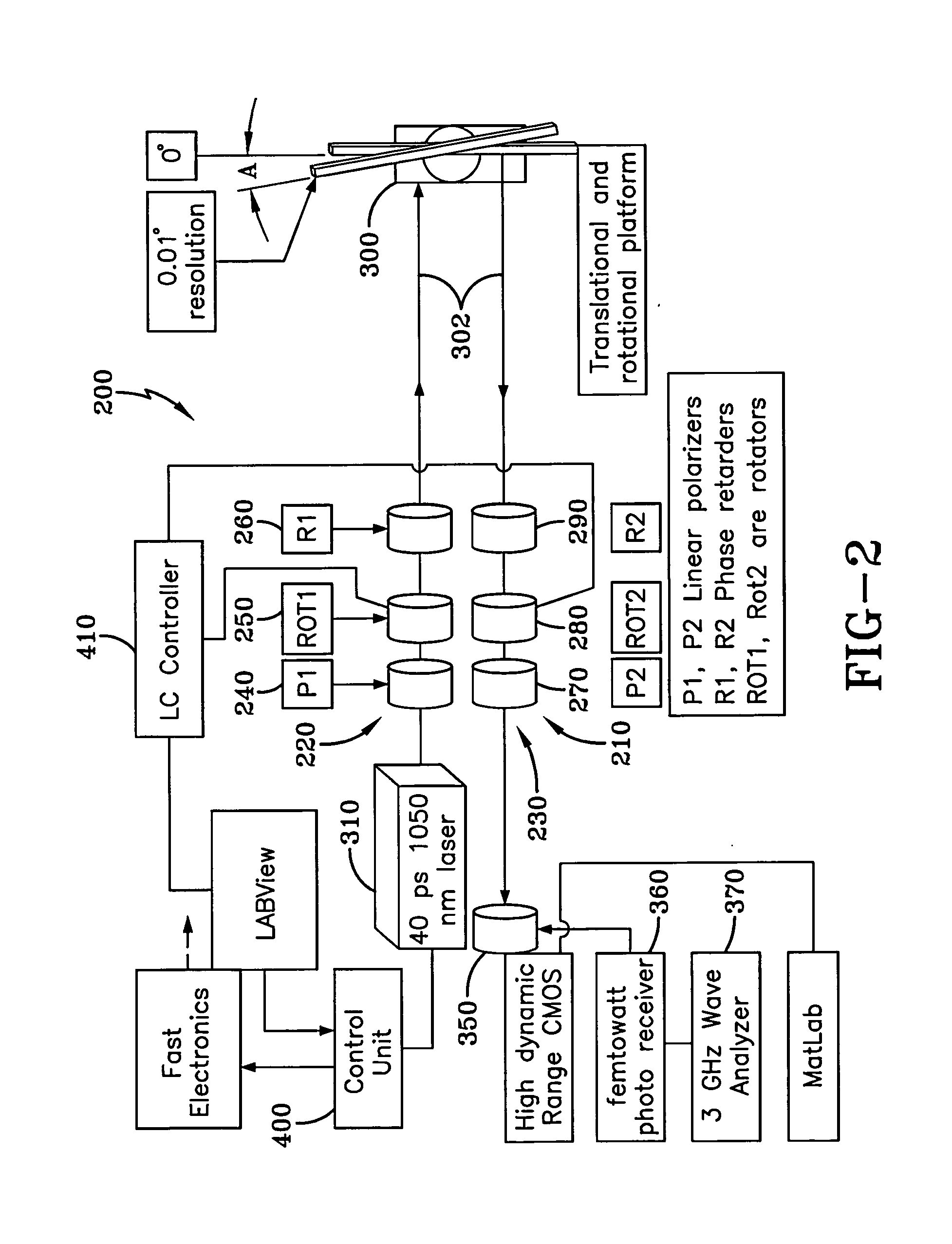
System and method for polarimetric wavelet fractal detection and imaging
InactiveUS20130308132A1Enhanced signal detectionEasy to trackMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementNeurofuzzy networksComputer science
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Liquid crystal display device with optical compensation
InactiveCN1790135ARapid responseReduce dark state light leakageStatic indicating devicesPolarising elementsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The invention discloses a LCD of optical compensation, which comprises the following parts: first base plate, second base plate, liquid crystal layer, the first-phase compensating plate, second-phase compensation plate, optical compensation film, first polarizing plate and second polarizing plate, wherein the liquid crystal array pattern of liquid crystal layer displays optical compensation bent pattern; the first-phase compensating plate is set on the exterior of the first base plate; the second-phase compensation plate is set on the exterior of second base plate; multilayer non-cylinder liquid crystal is contained in the first-phase compensation plate and second-phase compensation plate, which reduces the dark mesh-light of liquid crystal layer; the optical compensation film adapts the single-axle extension delaying-piece on the exterior of the first-phase compensation plate, which reduces the incidence mesh-light of two pieces of orthogonal polarizing plate. The invention improves the LCD comparison and aspect angle effectively.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
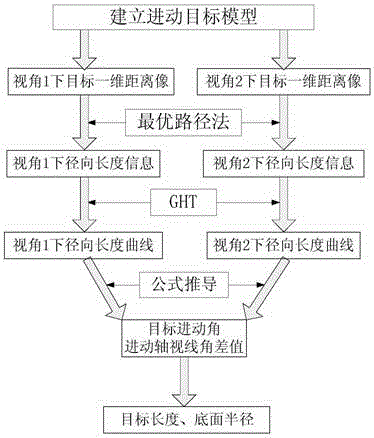
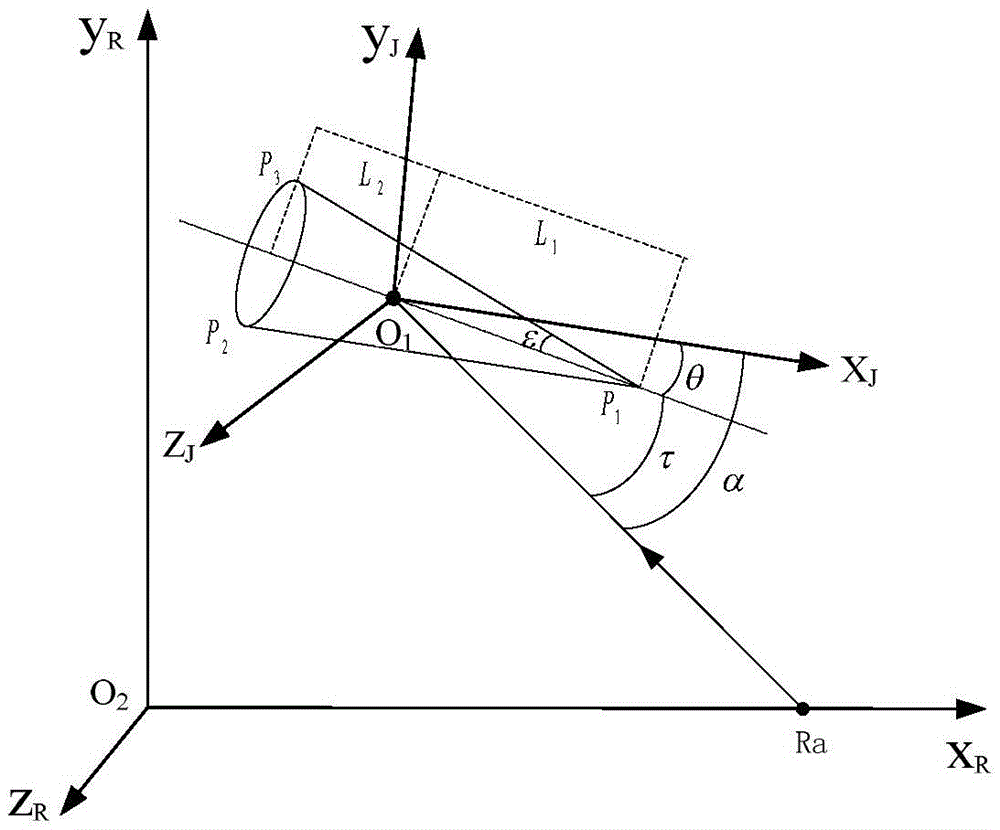
Parameter extraction method for precession target structure
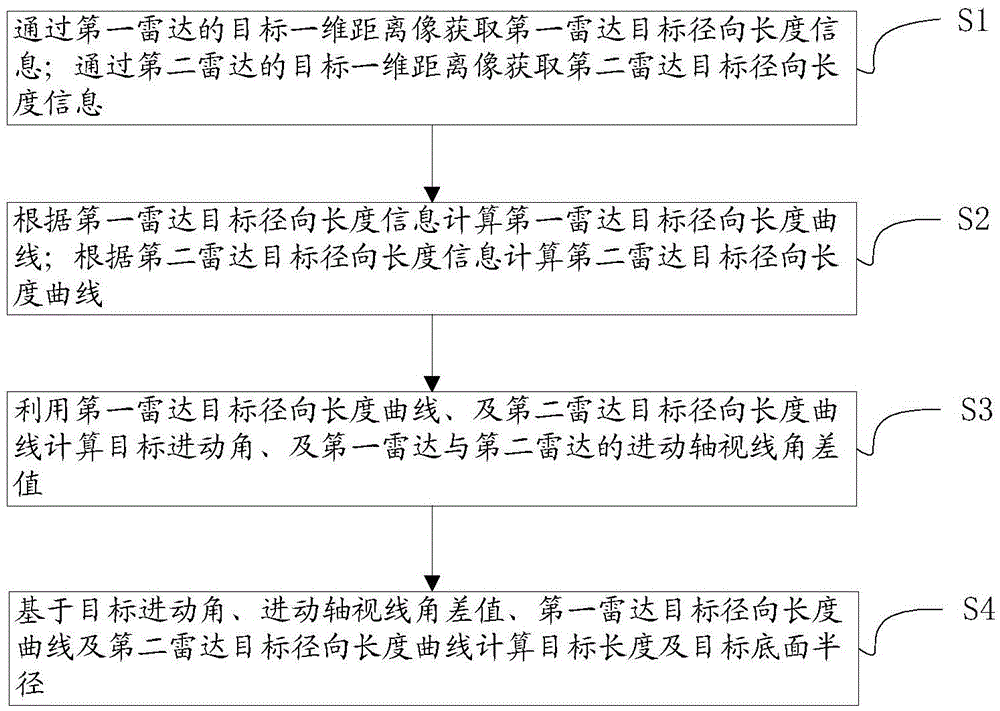
ActiveCN105676200AShorten observation timeAccurate extractionWave based measurement systemsPrecession angleComputer science
The present invention discloses a parameter extraction method for a precession target structure. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of respectively acquiring the target radial length information of two radars based on the target one-dimensional range profiles of the two radars; according to the target radial length information, calculating the target radial length curves of the two radars; according to the target radial length curves of the two radars, calculating the target precession angles and the precession axis aspect angle difference of the two radars; according to the target precession angles, the precession axis aspect angle difference of the two radars and the target radial length curves of the two radars; calculating a target length and a target bottom-surface radius. Compared with the prior art, the structure parameters and the precession angles of cooperative targets and non-cooperative targets can be extracted at a relatively accuracy error. Meanwhile, the observation time required for extracting precession characteristics is greatly shortened.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
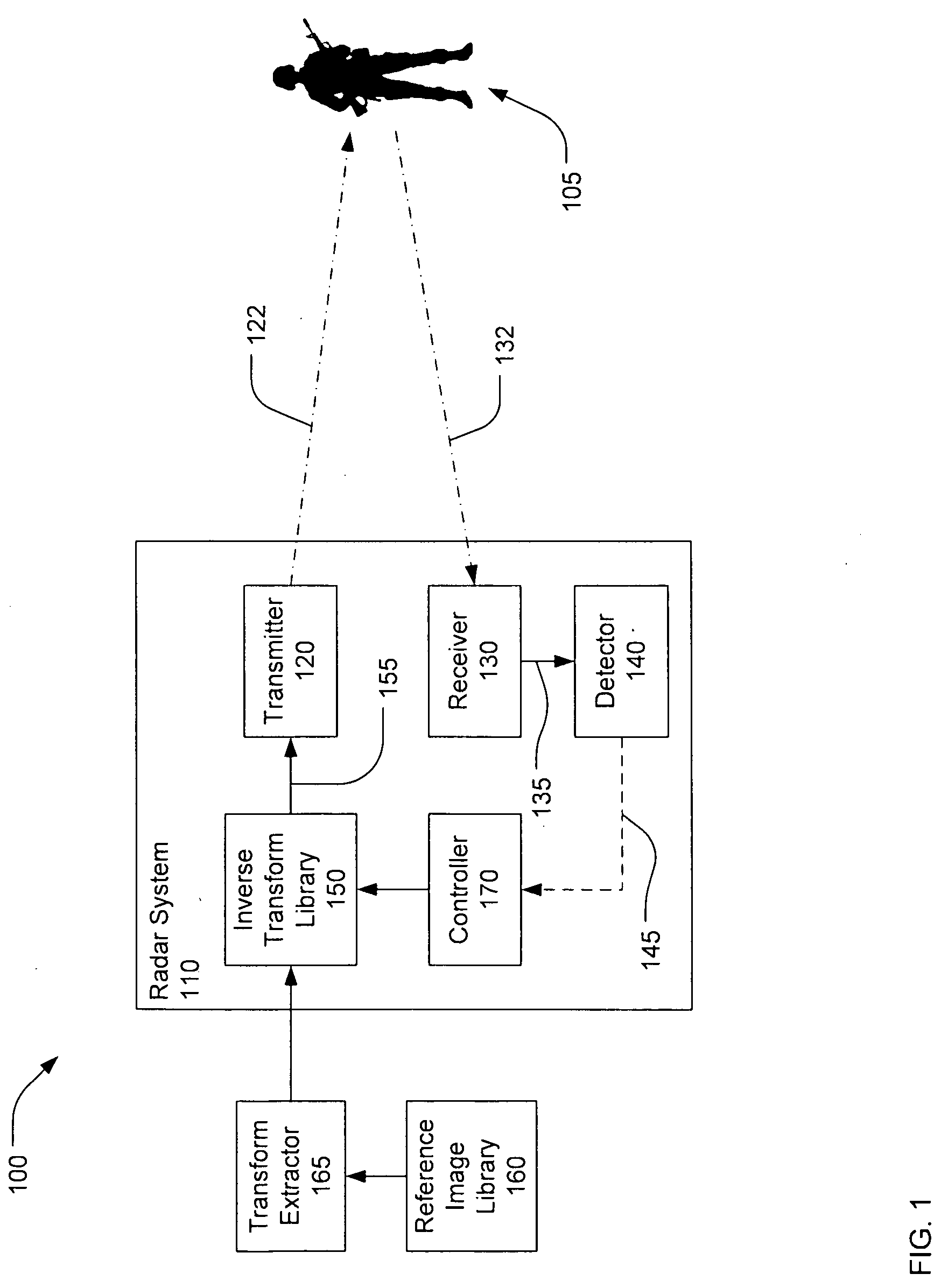
Mirror image target detection and recognition
There is disclosed a system and method for detecting targets. A transmitter may transmit a first inverse transform signal, the first inverse transform signal derived from a reference image of a first reference target at a first aspect angle. A receiver may receive a return signal reflected from a scene. A detector may determine, based on the return signal, if an object similar to the first target at the first aspect angle is detected within the scene.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
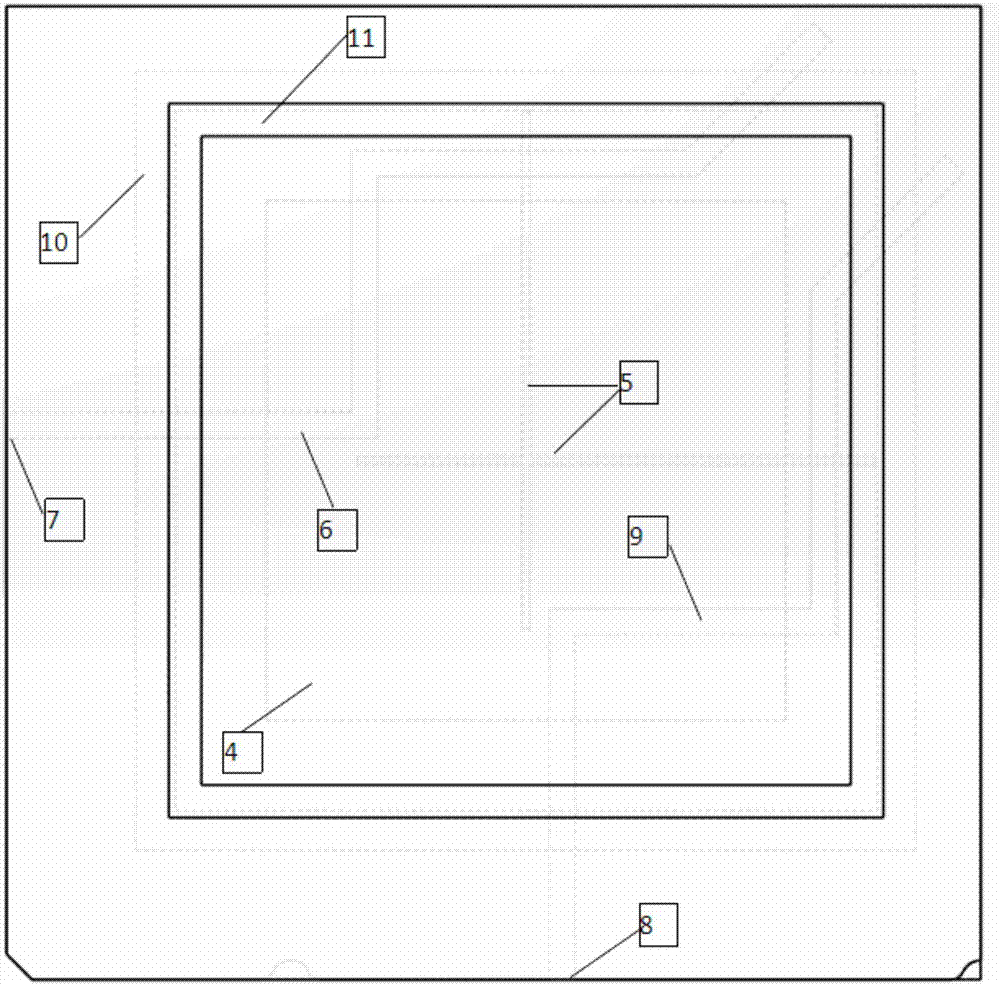
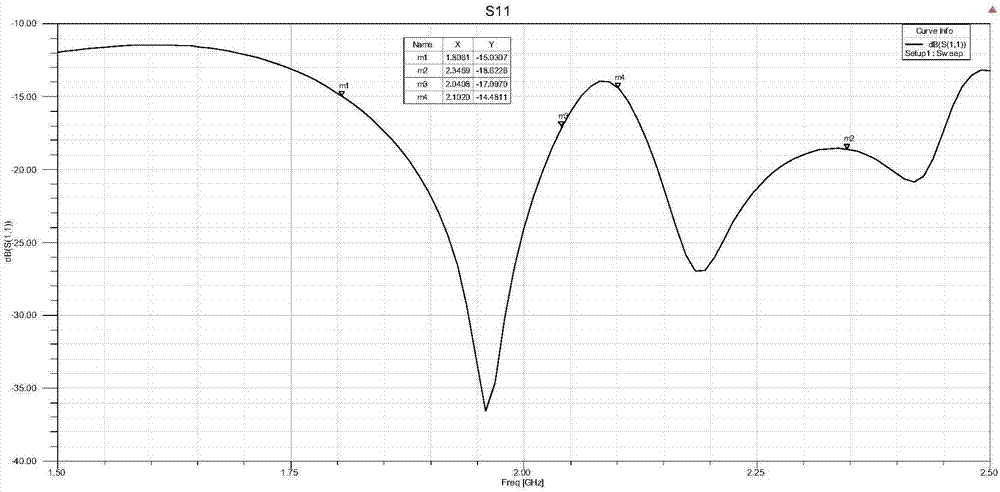
Wide-aspect-angle S-band dual-circular-polarization microstrip antenna for phased array, and phased array
PendingCN107978865AFulfillment requirementsHigh bandwidthIndividually energised antenna arraysSubstantially flat resonant elementsAxial ratioDielectric layer
The invention relates to a wide-aspect-angle S-band dual-circular-polarization microstrip antenna for a phased array, and the phased array. The microstrip antenna comprises a top dielectric layer, a central dielectric layer, a bottom dielectric layer, an annular structure located above the top dielectric layer, a rectangular paster and an annular structure which are located on the central dielectric layer, a gap on a ground plate, a first feed line and a second feed line which are located below the bottom dielectric layer. Two ends of the microstrip antenna are respectively connected with a left-hand circular polarization port and a right-hand circular polarization port, wherein the left-hand circular polarization is obtained through the port, and the right-hand circular polarization is obtained through the port. The microstrip antenna has the scanning range of + / -70 degrees, is wide in bandwidth, is large in beam width, is low in width-angle axial ratio, and is simple in structure. The microstrip antenna has two ports, thereby facilitating the free selection of the left-hand circular polarization mode or the right-hand circular polarization mode. The microstrip antenna can be extended to form a large-scale phased array with a random number of antennas.
Owner:BEIJING HUAMETA TECH CO LTD
System and method for target signature calculation and recognition
ActiveUS8130136B2Easy to detectHigh energyRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFeature DimensionAngular degrees
The present invention is directed to a system and method for the identification of a target object in PCL radar applications. The disclosed embodiments describe the systems and methods used in the identification of a target object from the collection of data representing specific target object features, such as velocity, altitude, fuselage length, wing length, or wing sweepback angle, and the comparison of selected target object features with a database of known aircraft features. The present invention also provides for the calculation of feature dimensions, such as the fuselage length, wing length, or wing sweepback angle from measurements associated with a peak signal lobe as a function of a bistatic aspect angle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Dynamic three-dimensional-scene virtual-landform visual rapid discrimination method
InactiveCN106960464AImprove dynamic update efficiency3D-image renderingGeometric primitiveIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a dynamic three-dimensional-scene virtual-landform visual rapid discrimination method. The method is characterized in that the method comprises three portions; in a first portion, aiming at an initial virtual landform, an agent bounding box is formed; a visibility function is designed; local maximum and minimum values of a basic point of a geometric graphic element are randomly extracted; and through the visibility function, a test wire used for approximation detection is intersected with a virtual landform. In the method, through designing one agent bounding box of the virtual landform, an intersection point of the test wire and a scene is rapidly detected; and through designing a phase-type parallel height field scanning algorithm, a maximum aspect angle of any one point in the scene is pre-calculated so that complexity of a traditional scanning method is effectively reduced and point-to-point visibility discrimination efficiency of the virtual landform in a three-dimensional virtual scene is increased.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Radar imaging system and method
An imaging system and method. The invention provides an intra-pulse repetition interval (PRI) agile beam technique for enhanced resolution that can be used at aspect angles near the velocity vector of a host vehicle. It is particularly useful at small scan angles where beam sharpening array times become large. At these scan angles, the bandwidth of the clutter is narrower than at higher scan angles and allows large PRIs without degradation from Doppler ambiguities. In accordance with the present teachings, sequential illumination is performed within a PRI to multiple beam locations using an agile beam. The interleaving of beams reduces map formation times compared to conventional techniques using sequential arrays. The inventive system is adapted for use with an electronically scanned (e.g., synthetic aperture array radar) antenna. The inventive method includes the steps of activating the antenna to generate a beam of electromagnetic energy; causing the beam to scan over a predetermined scan volume consisting of a predetermined range of scan angles relative to a reference vector; and generating multiple simultaneous beams of electromagnetic energy over a subset of the predetermined range of scan angles.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Stereoscopic digital camera and imaging display method
InactiveCN100458559CEasy to take anytimeStrong sense of realityCamerasImage data processing detailsCamera lensEyewear
This invention relates to an apparatus and method for acquiring and observing the space image by the digital cameral. Its main principle are the following: to shoot the image pictures with different aspect angle and same view point by a digital cameral with two lens and transmit them to the computer and after procession of relevant software to simultaneously generate synchronous drive signals; and to let relevant lens at different working statuses to make the two eyes can see the images with different aspect angle and same view point to form the space image sense. At the same time the software can color filter the images acquired and through directly wearing relevant complementary color glasses to observe the relevant complementary space image.
Owner:辜进荣
A guidance method for automatic tracking of ground targets for unmanned aerial vehicles
ActiveCN105425819BSimple structureReduce the calculation burdenTarget-seeking controlUncrewed vehicleComputer science
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
An Input Constrained Differential Game Guidance Method Based on Adaptive Dynamic Programming
InactiveCN106647287BSolve problemsAvoid the disadvantages of offline computingAdaptive controlDynamic planningCountermeasure
The invention discloses a method for guiding an input constraining differential game based on self-adaptive dynamic planning. According to the method, a solving problem of an HJI equation and an input saturation problem in a nonlinear differential game problem are solved; an input constraining solving problem of the nonlinear differential game is solved by virtue of a self-adaptive dynamic planning technique, and a neural network and a Lyapunov method are combined so as to obtain a guidance control volume; and an input constraining differential game guidance law can be online obtained in real time based on an evaluation network updating law, and the aspect angle velocity in a guided missile-target relative motion relation tends to 0, so that the successful interception is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com