Patents
Literature
388 results about "Desorption ionization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
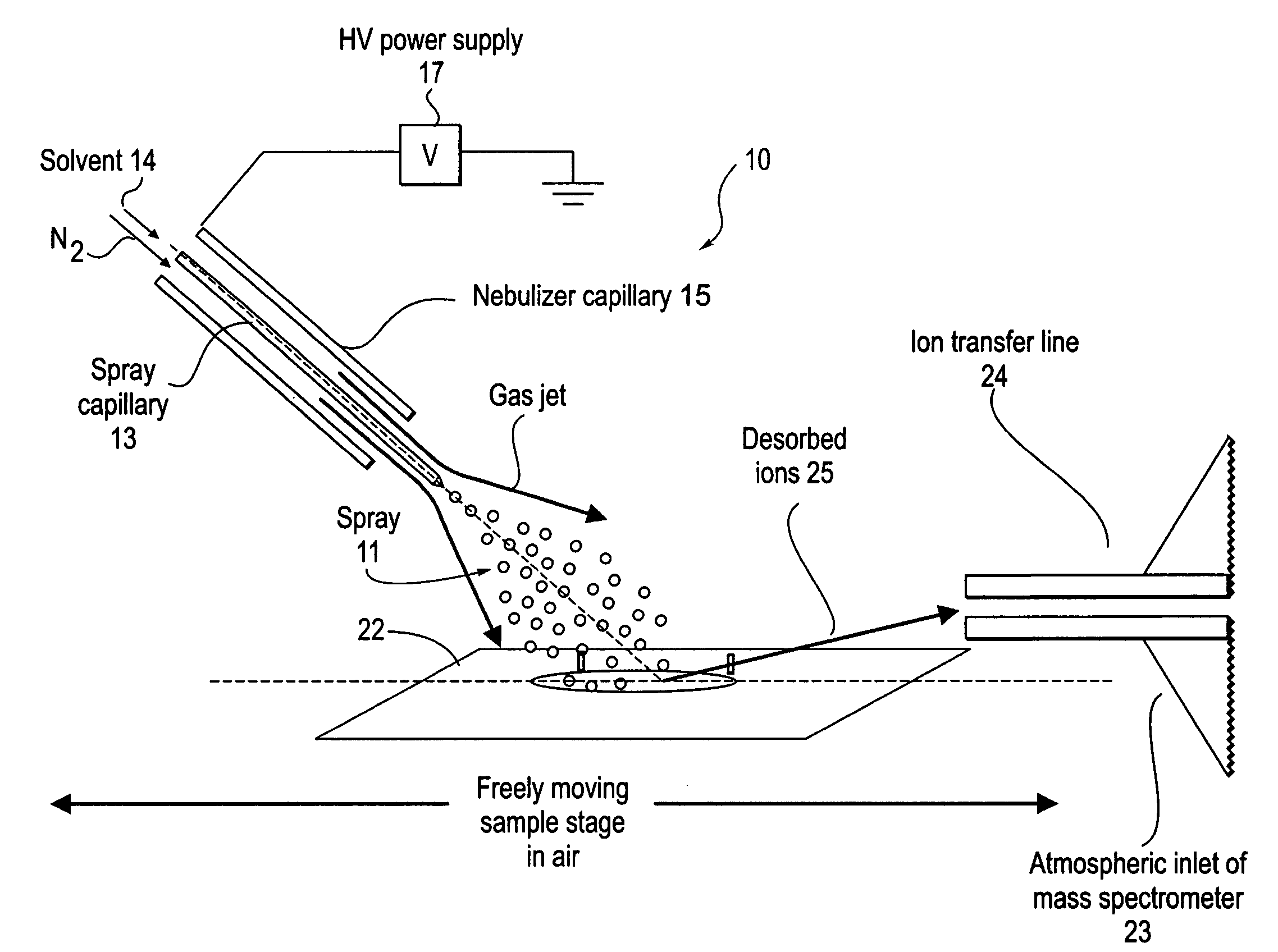
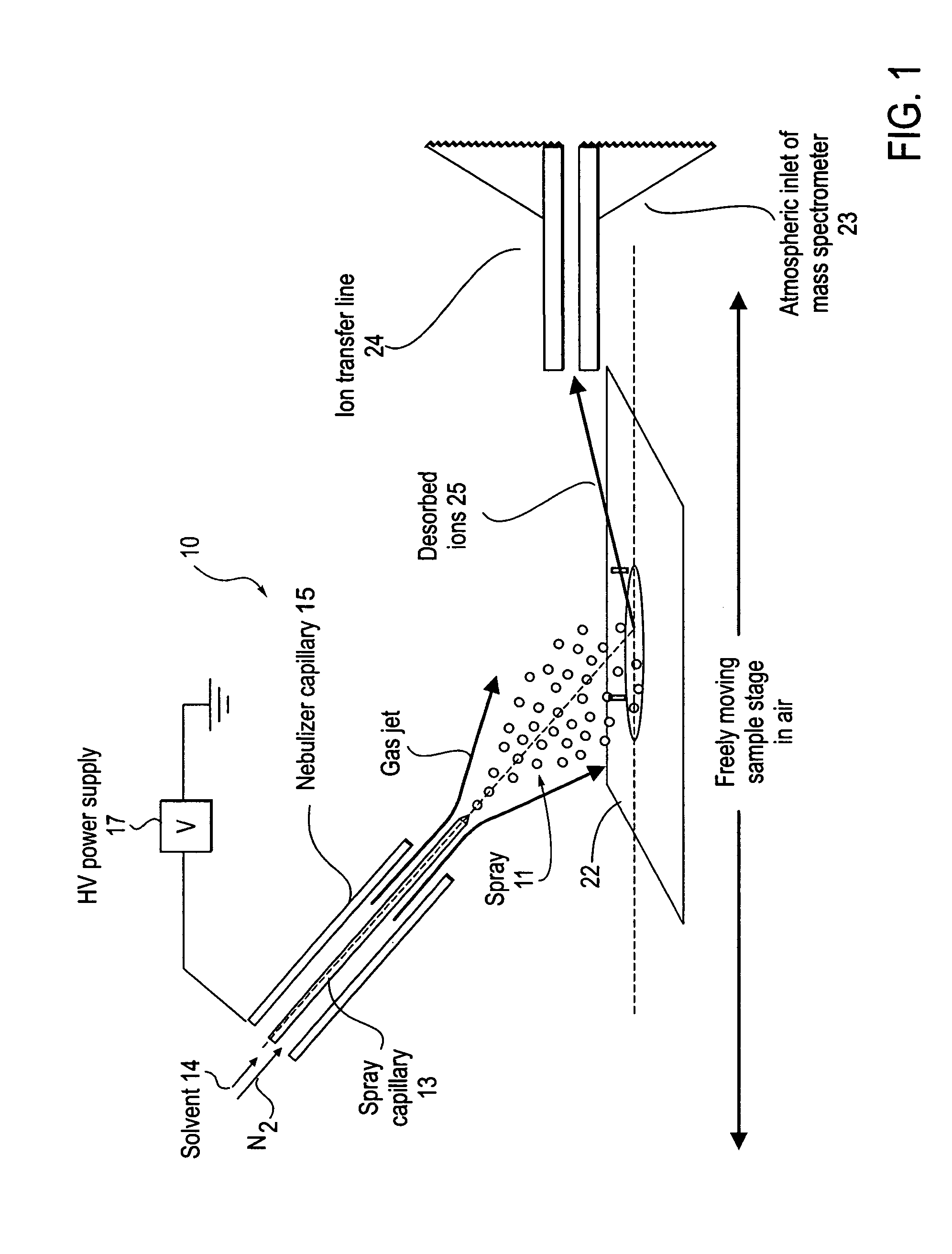
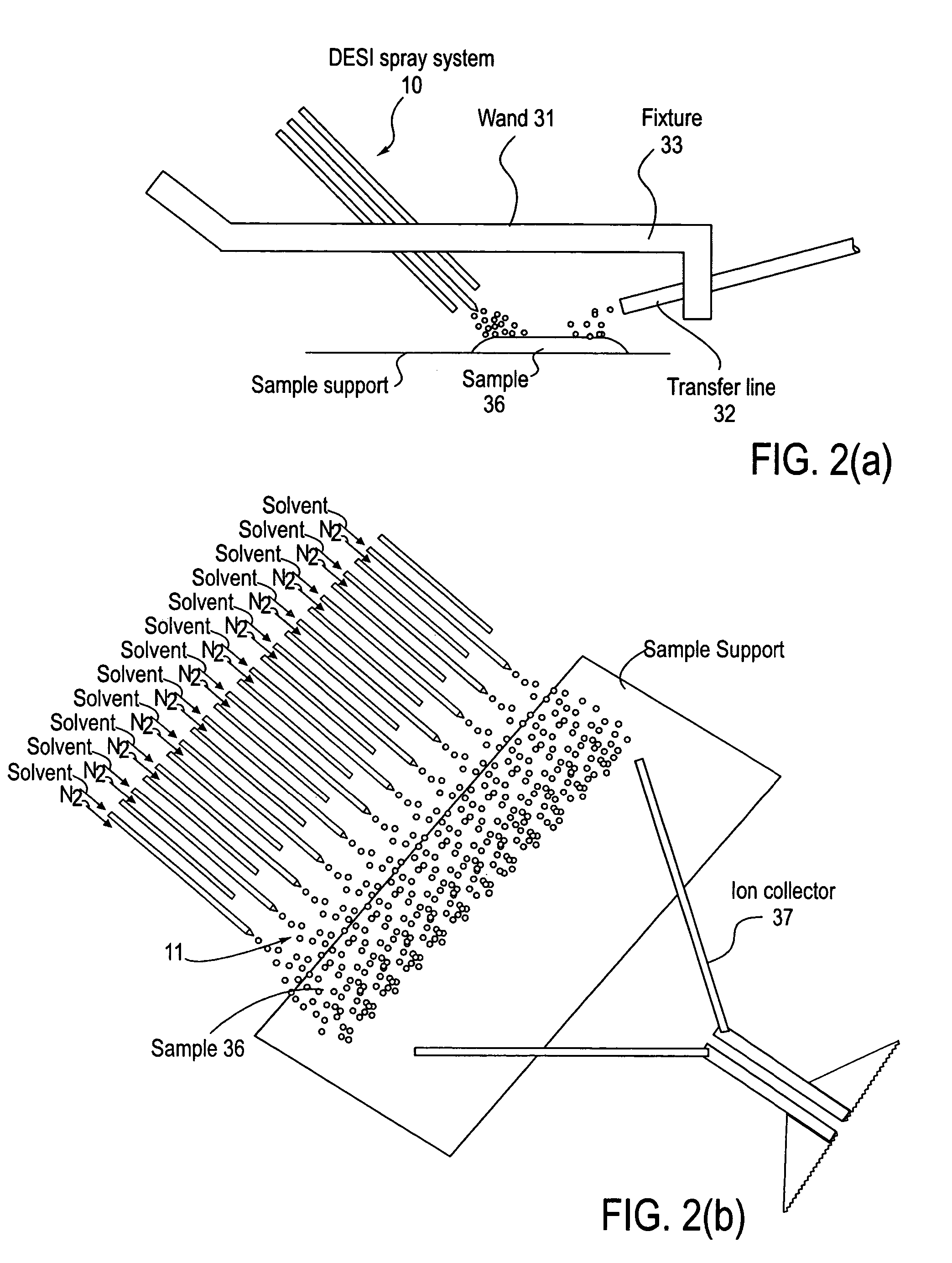
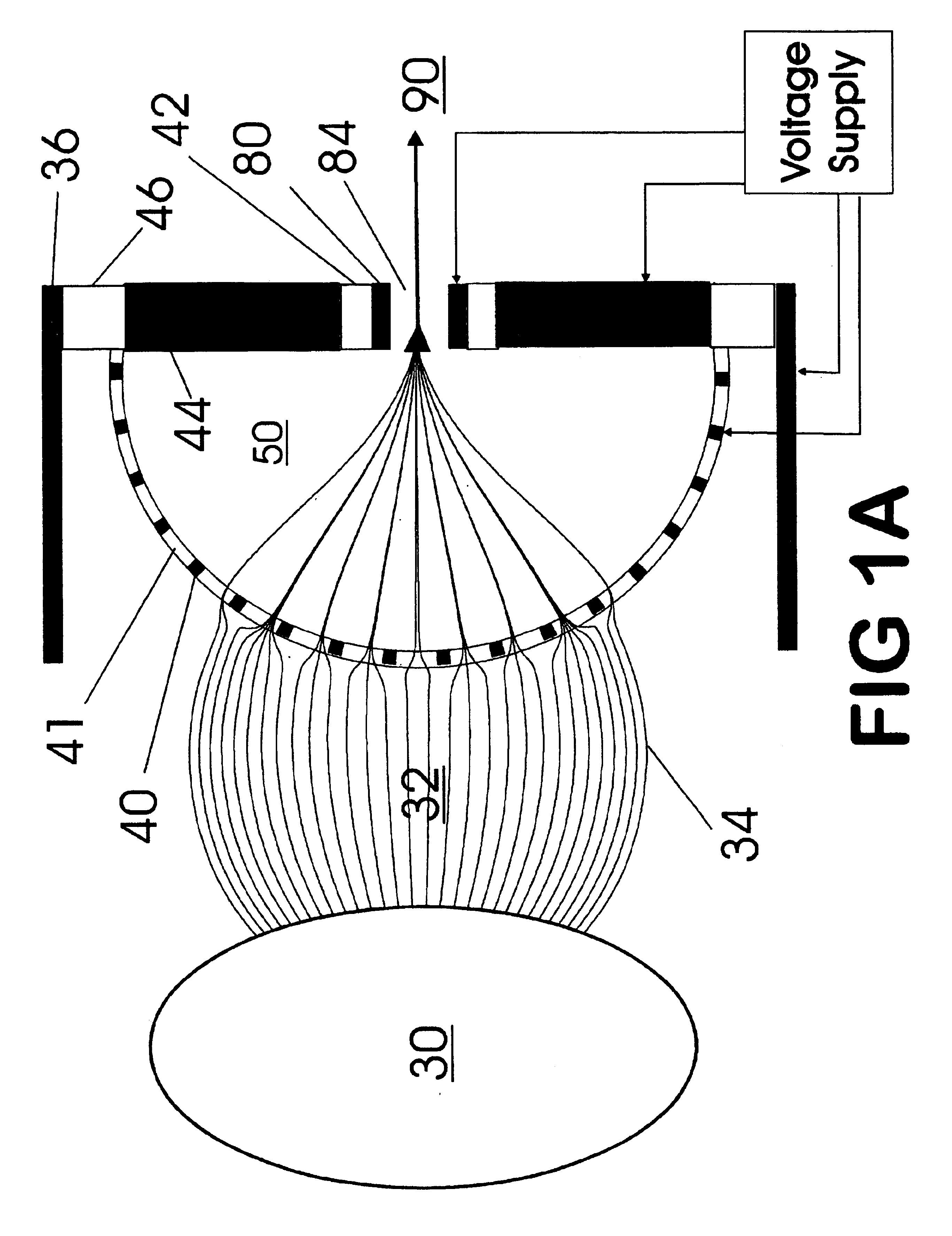
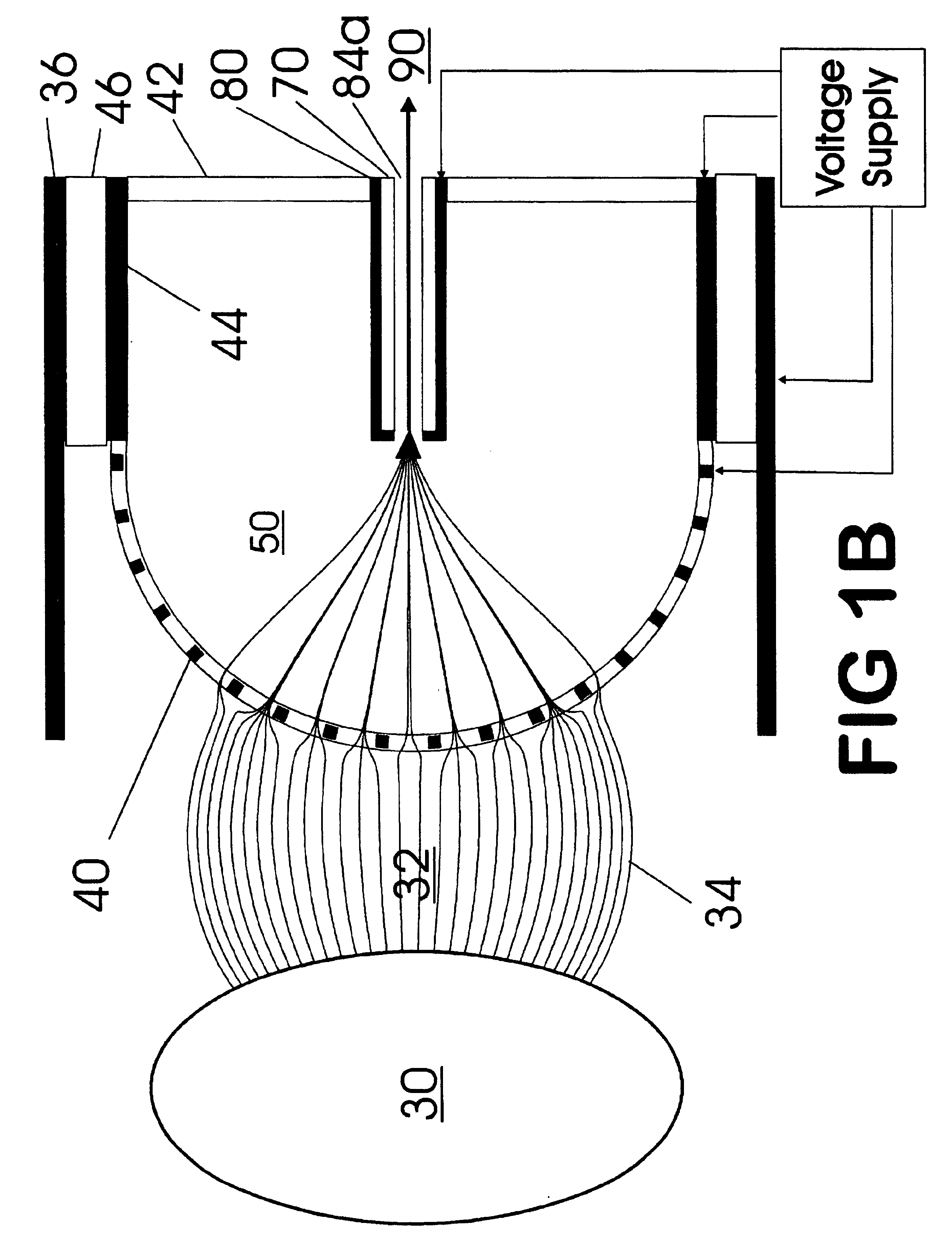
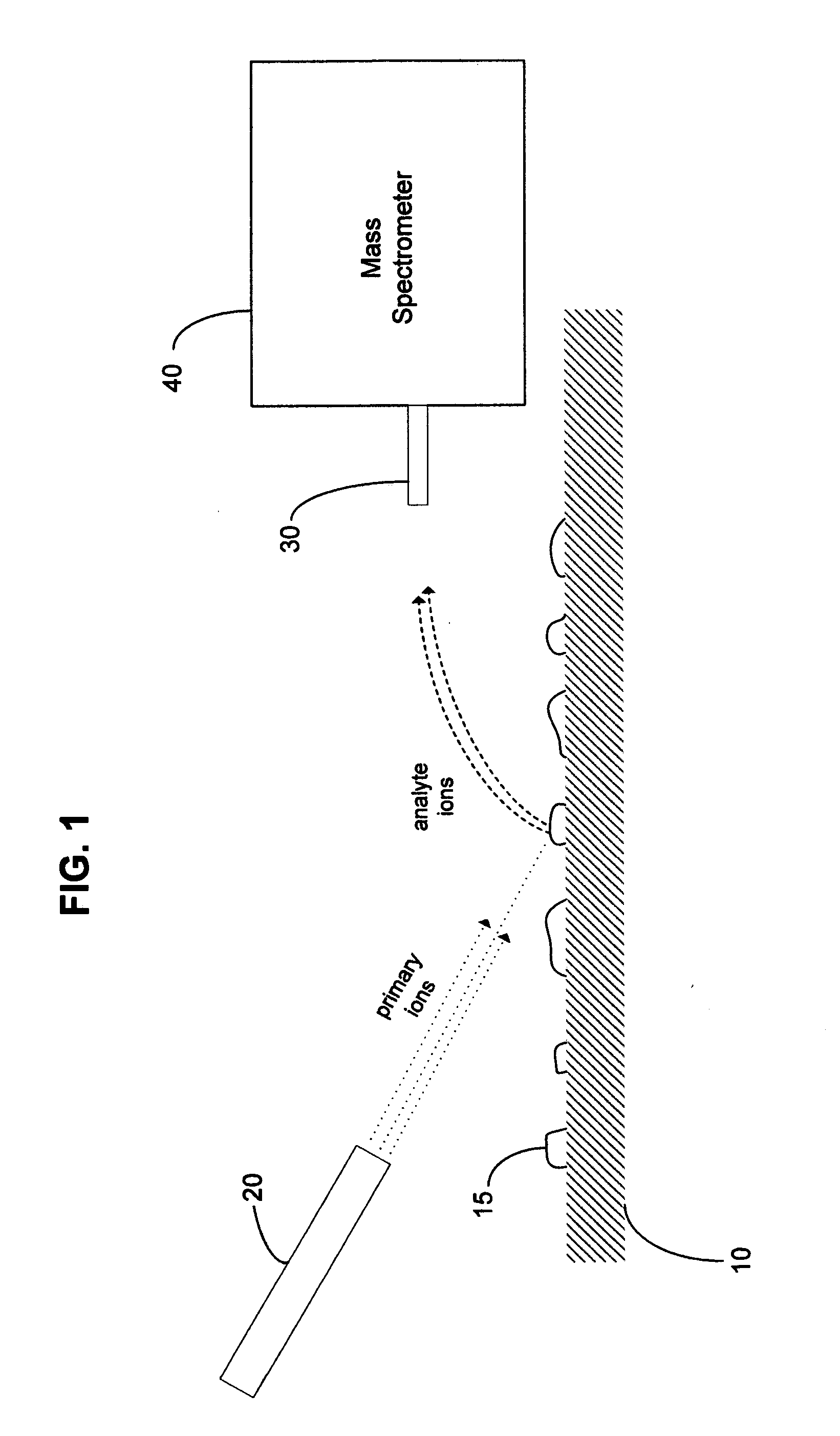
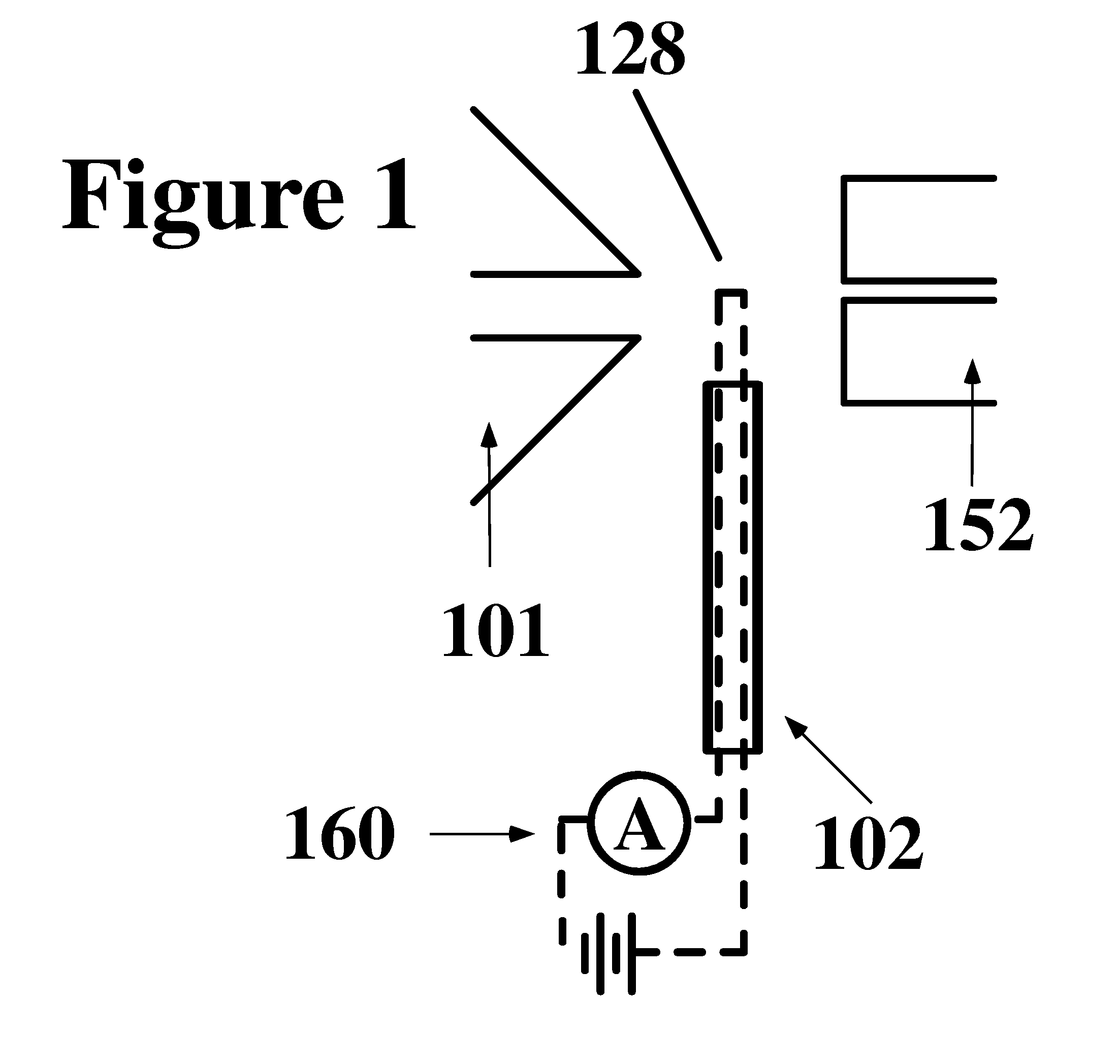
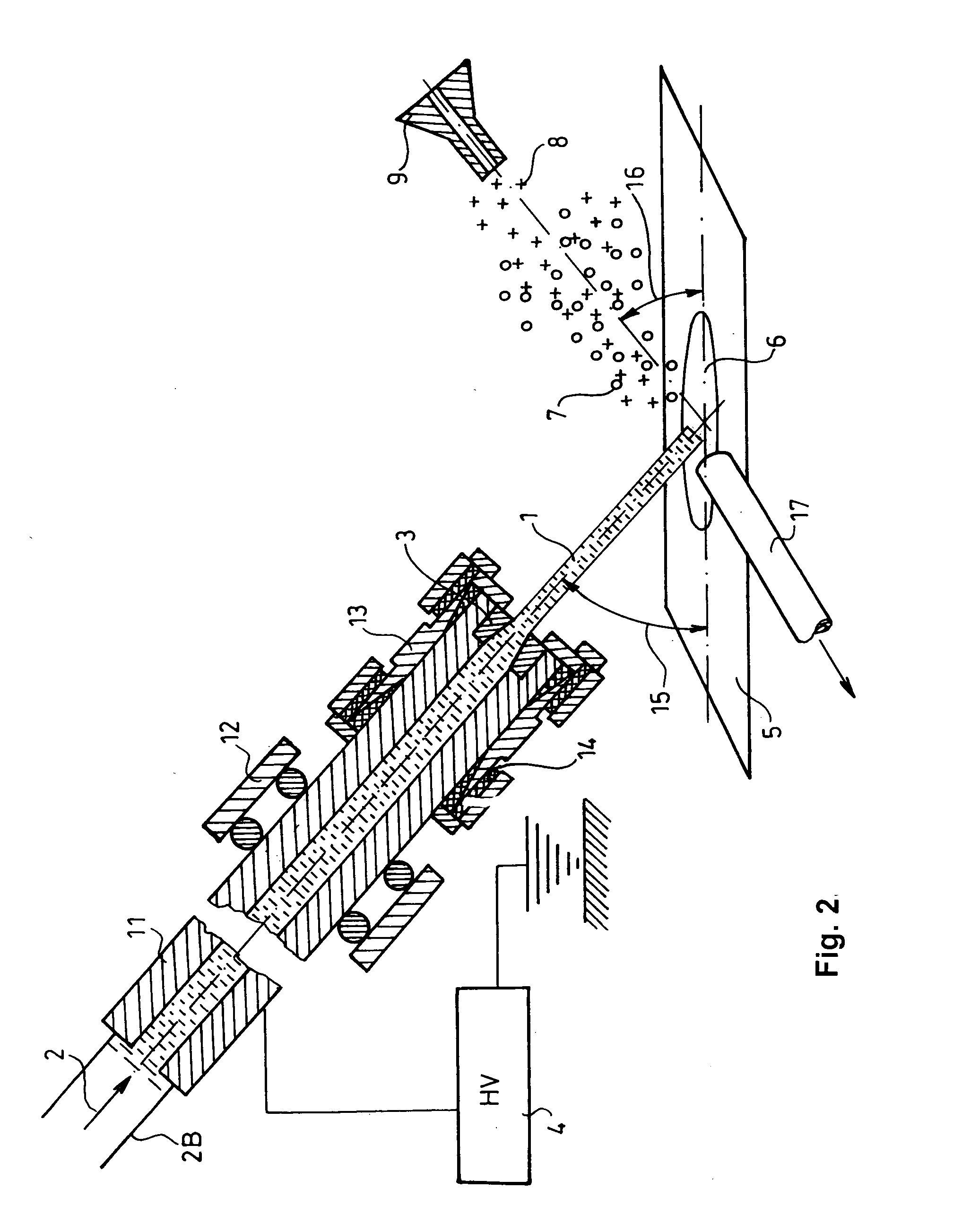
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
ActiveUS7335897B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLycopeneElectrospray ionization
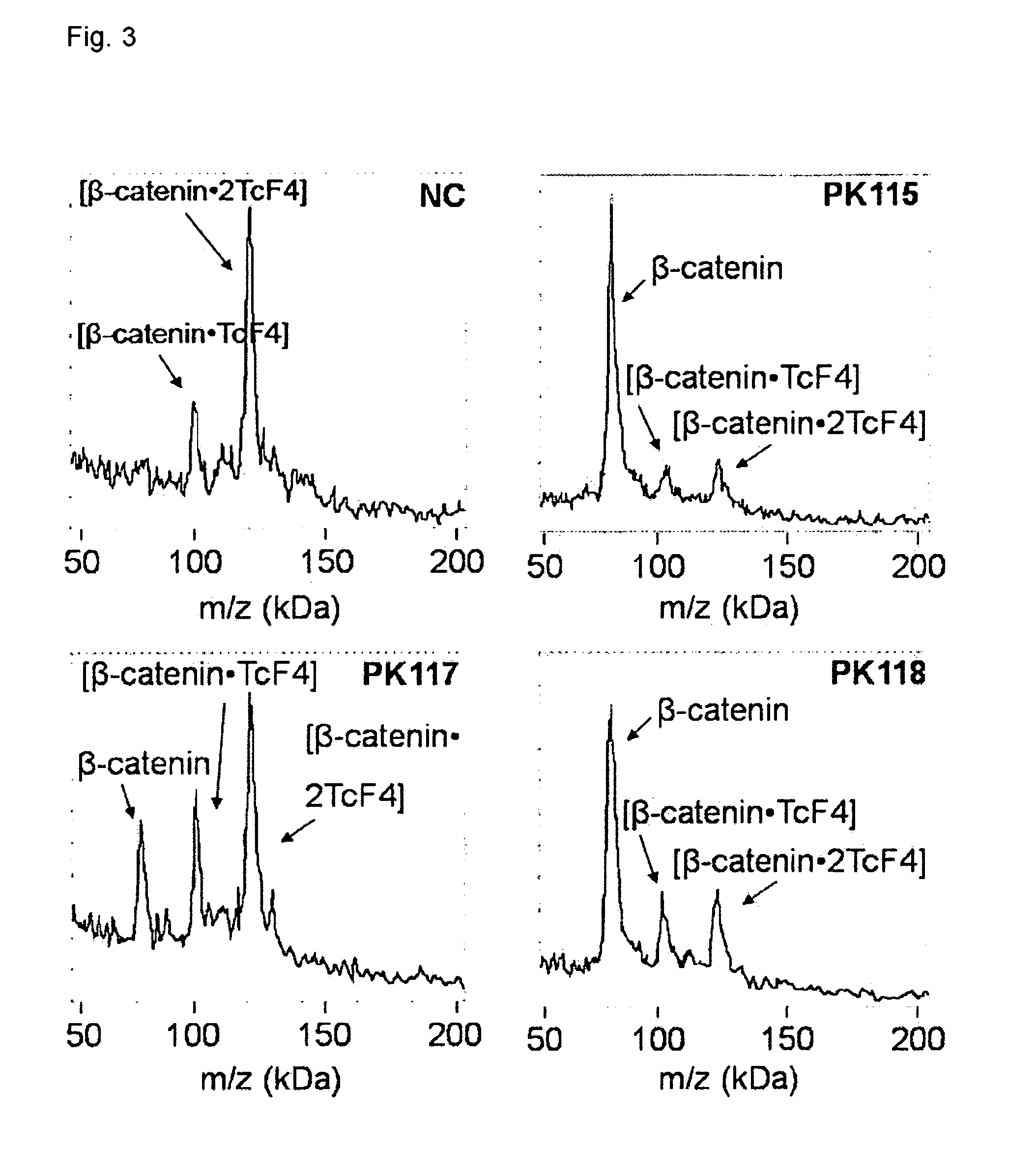
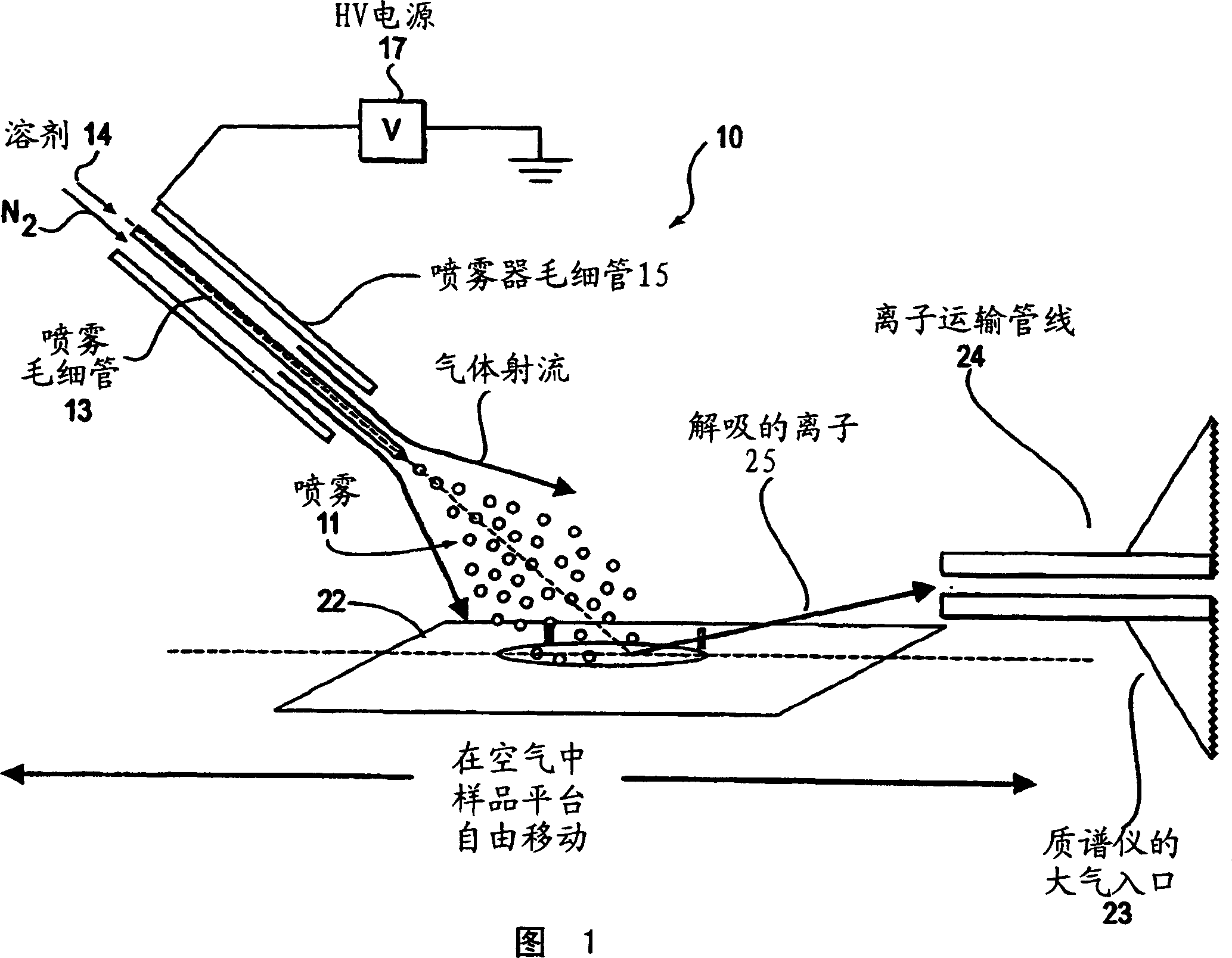
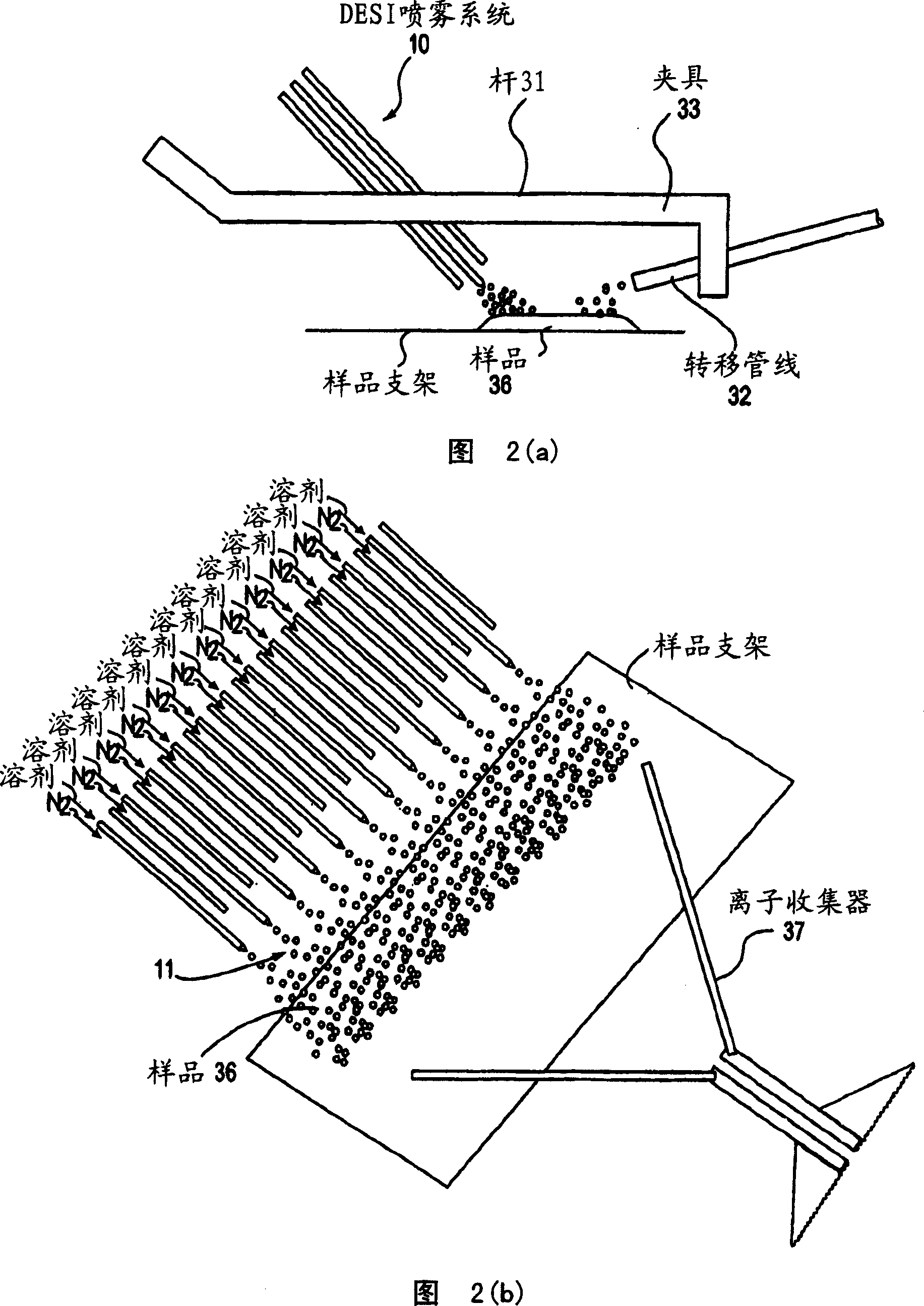
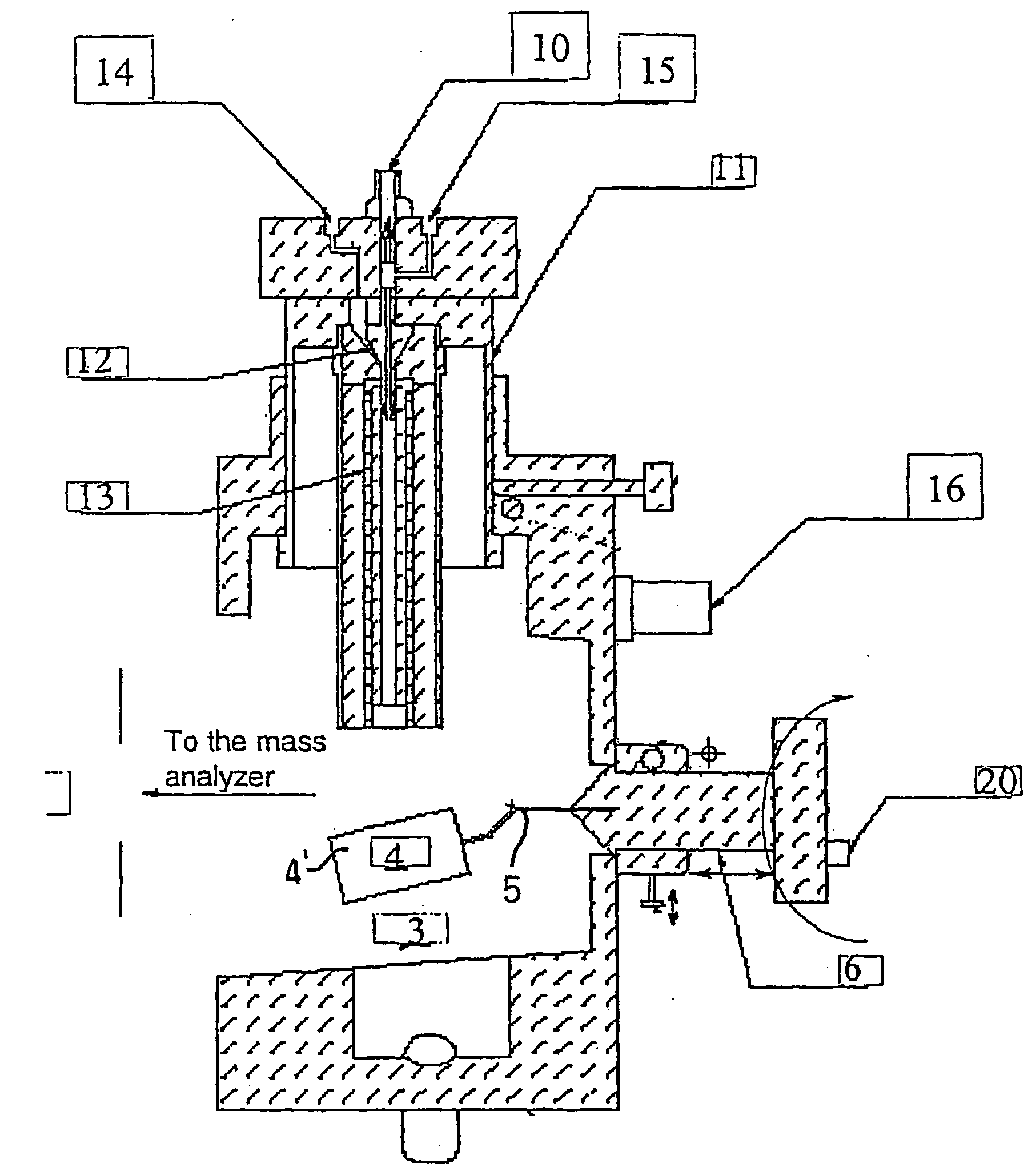
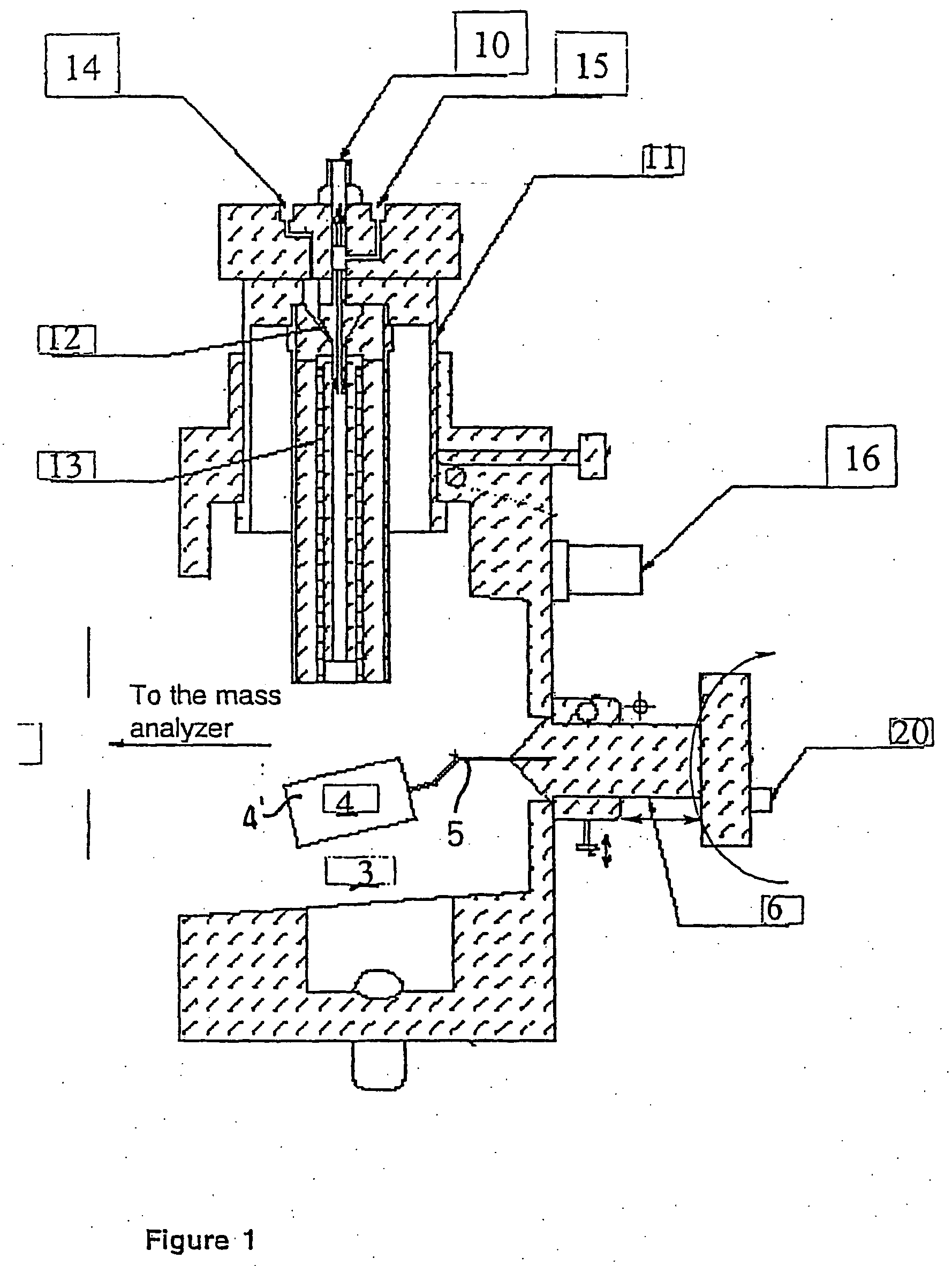
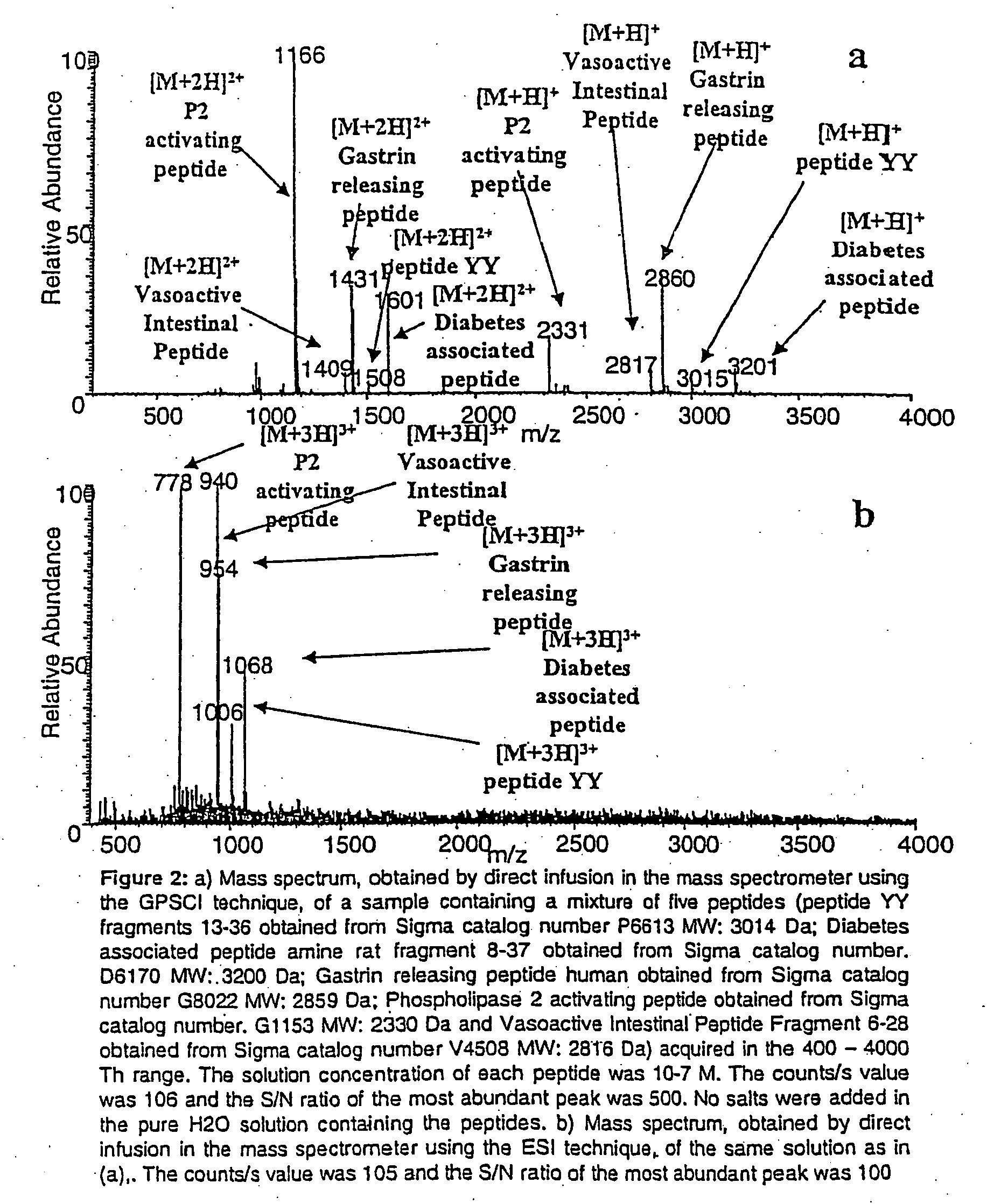
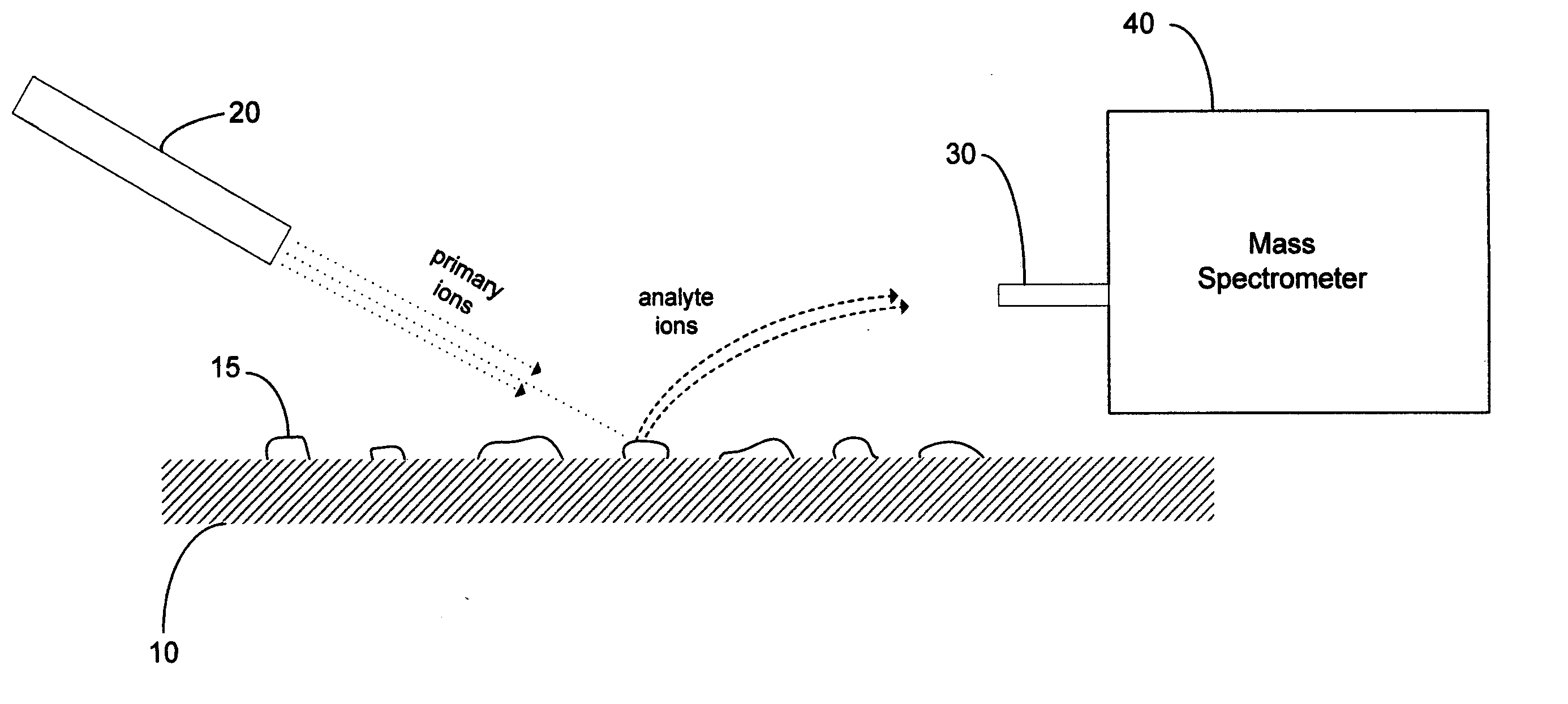
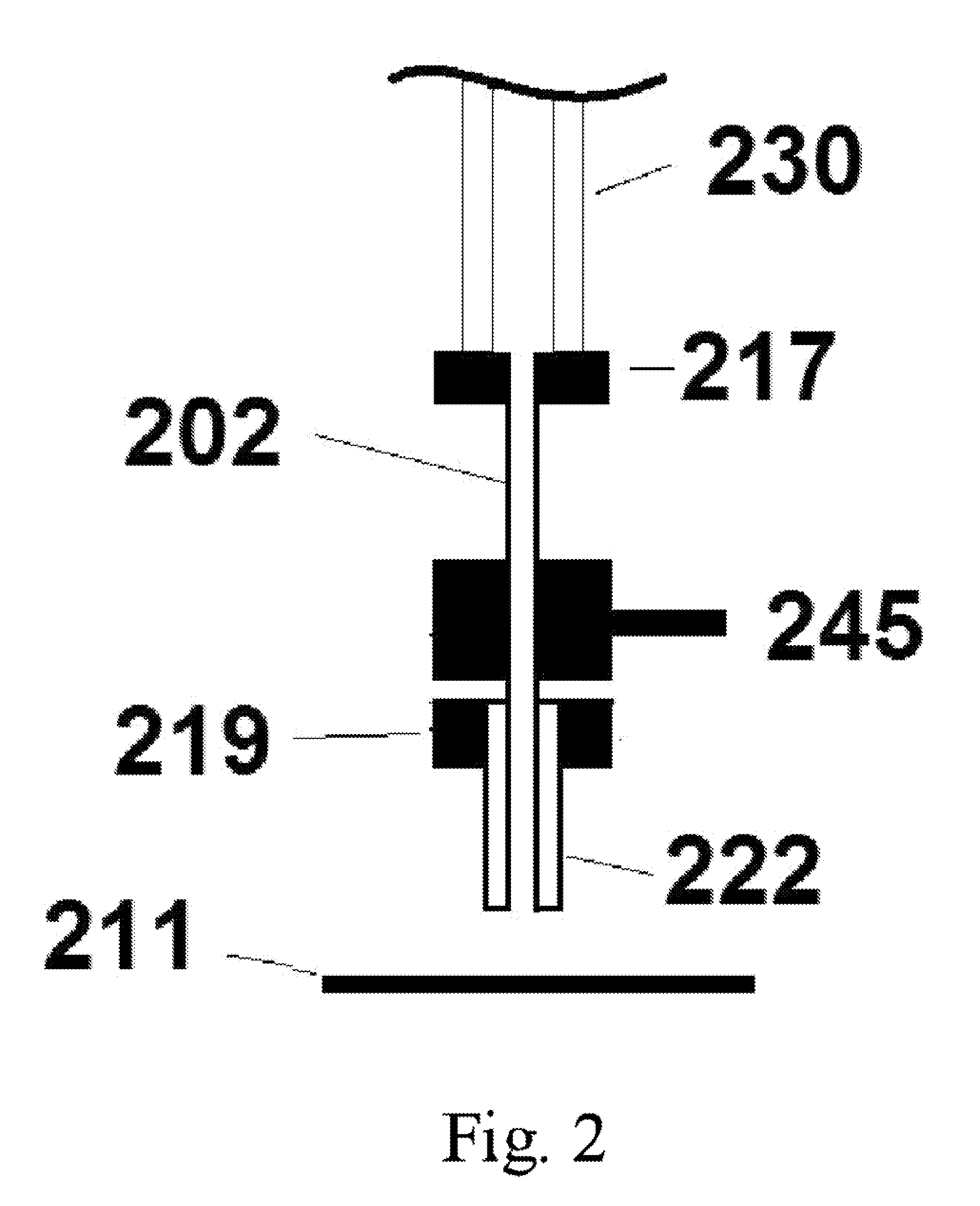
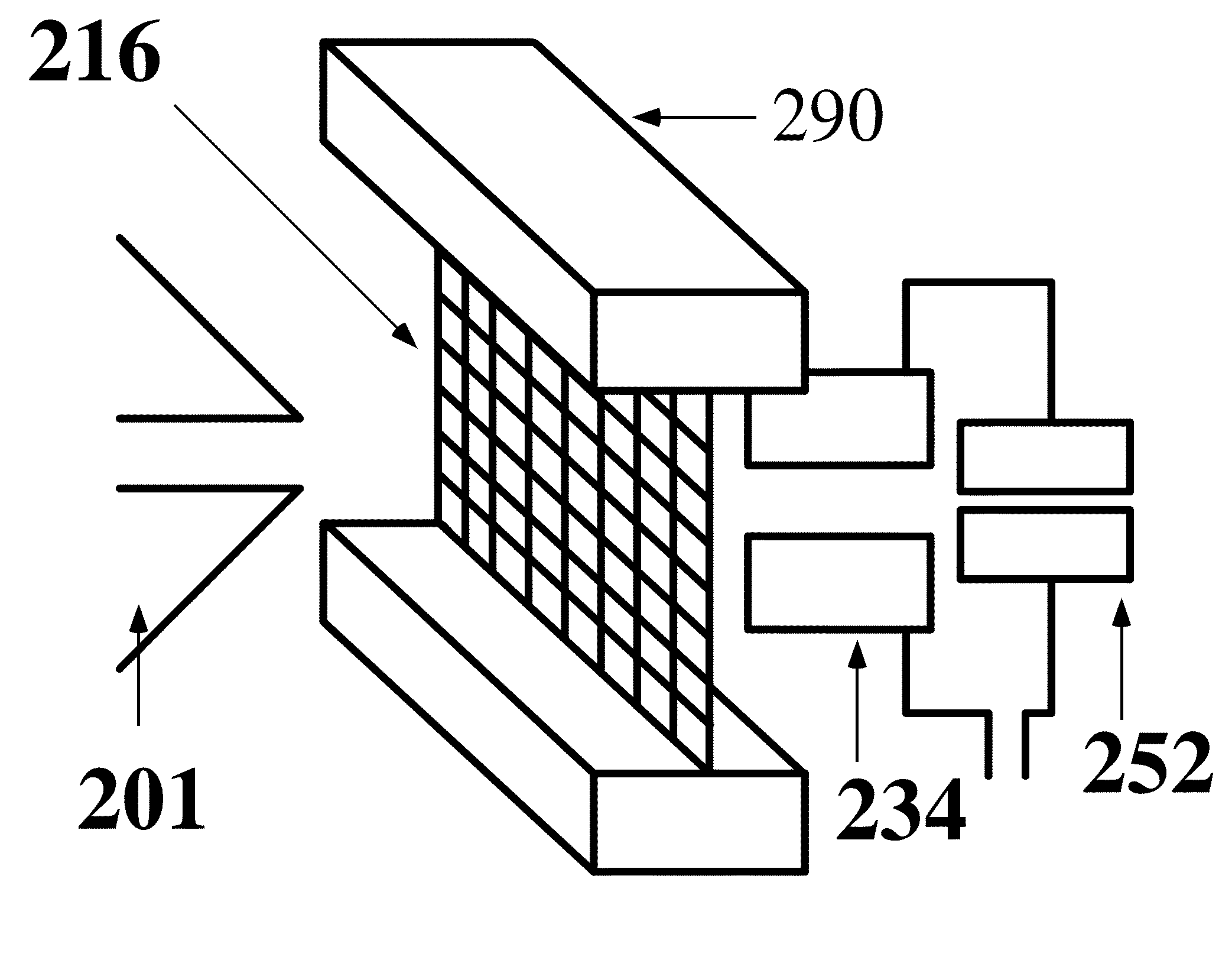
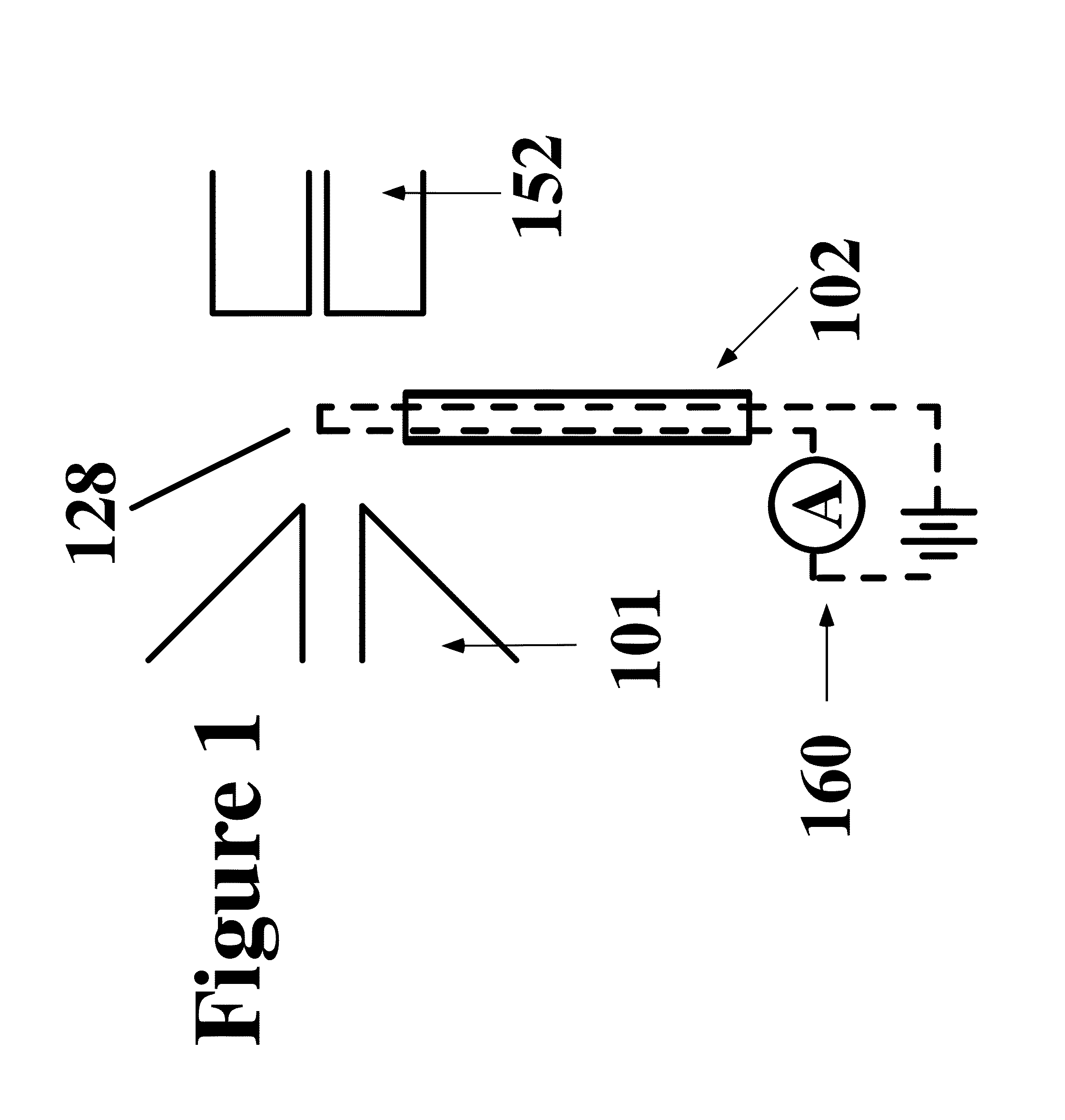
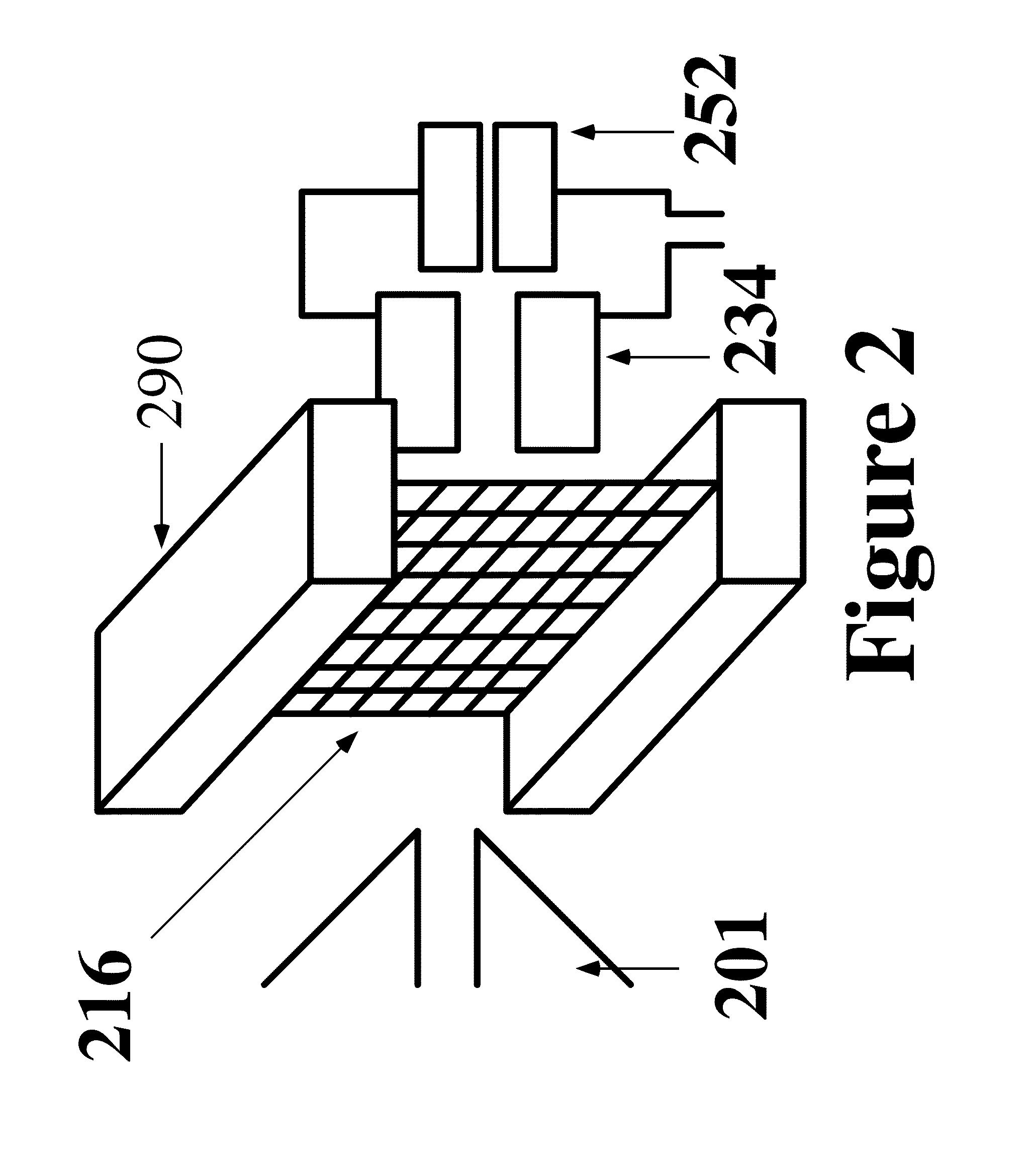
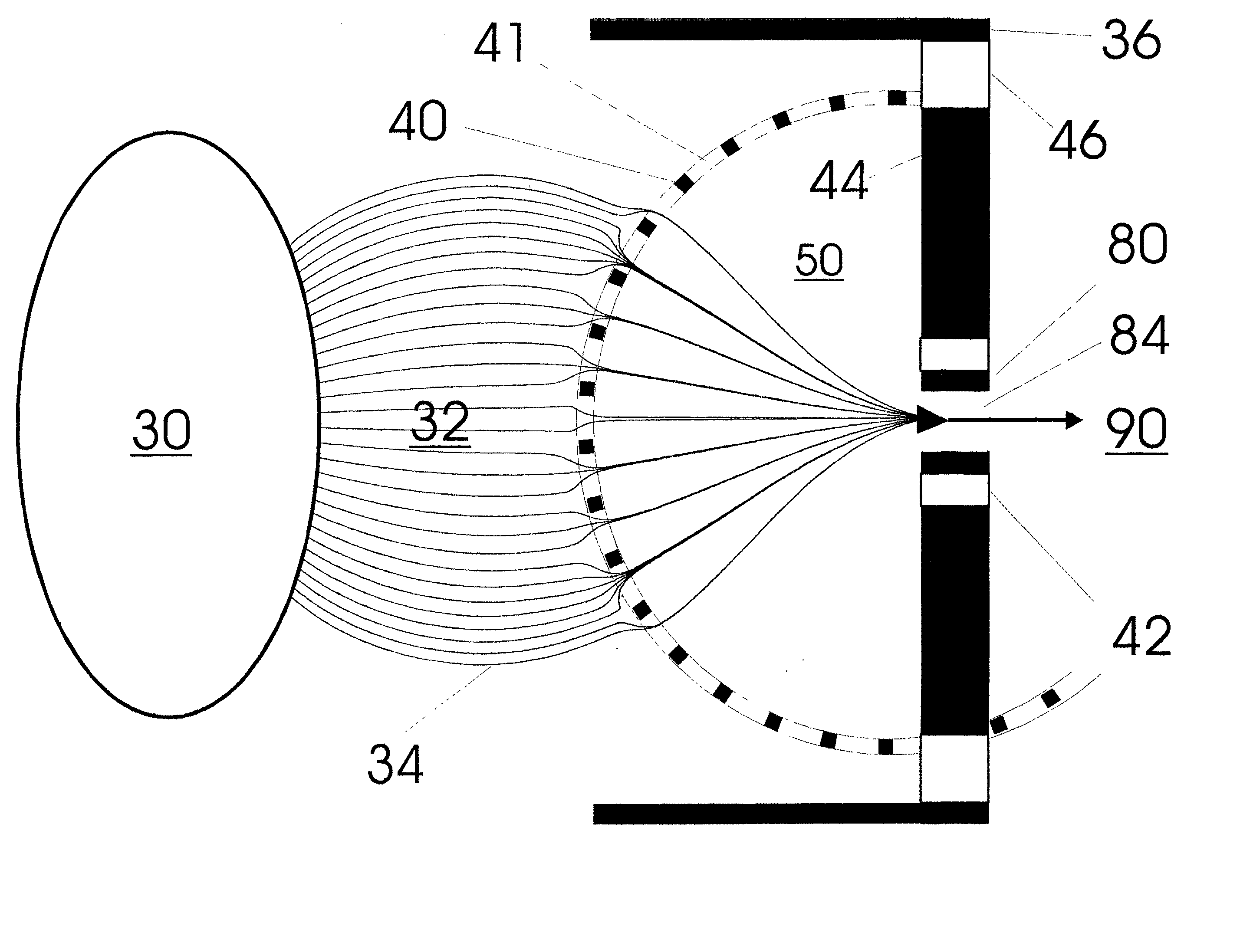
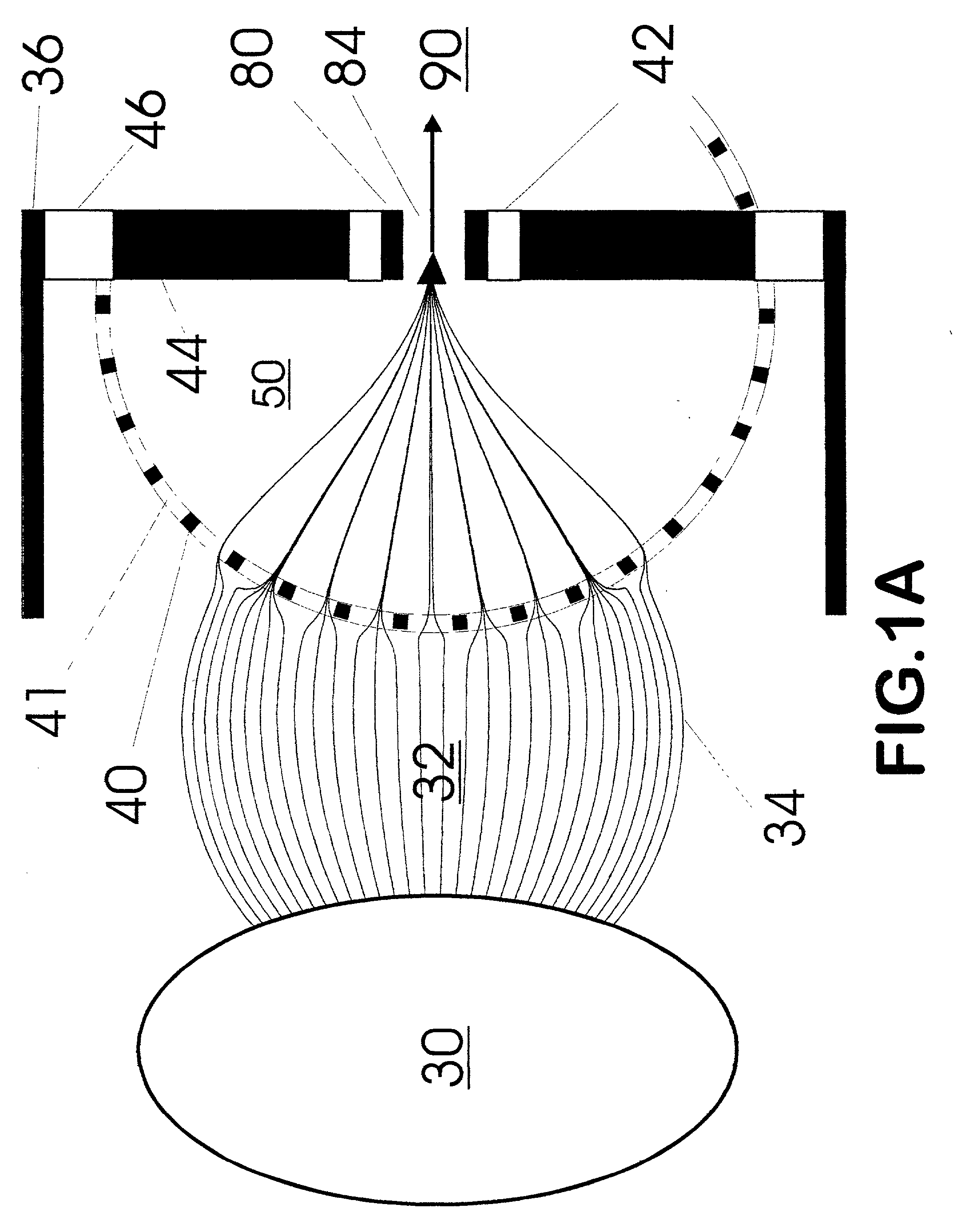
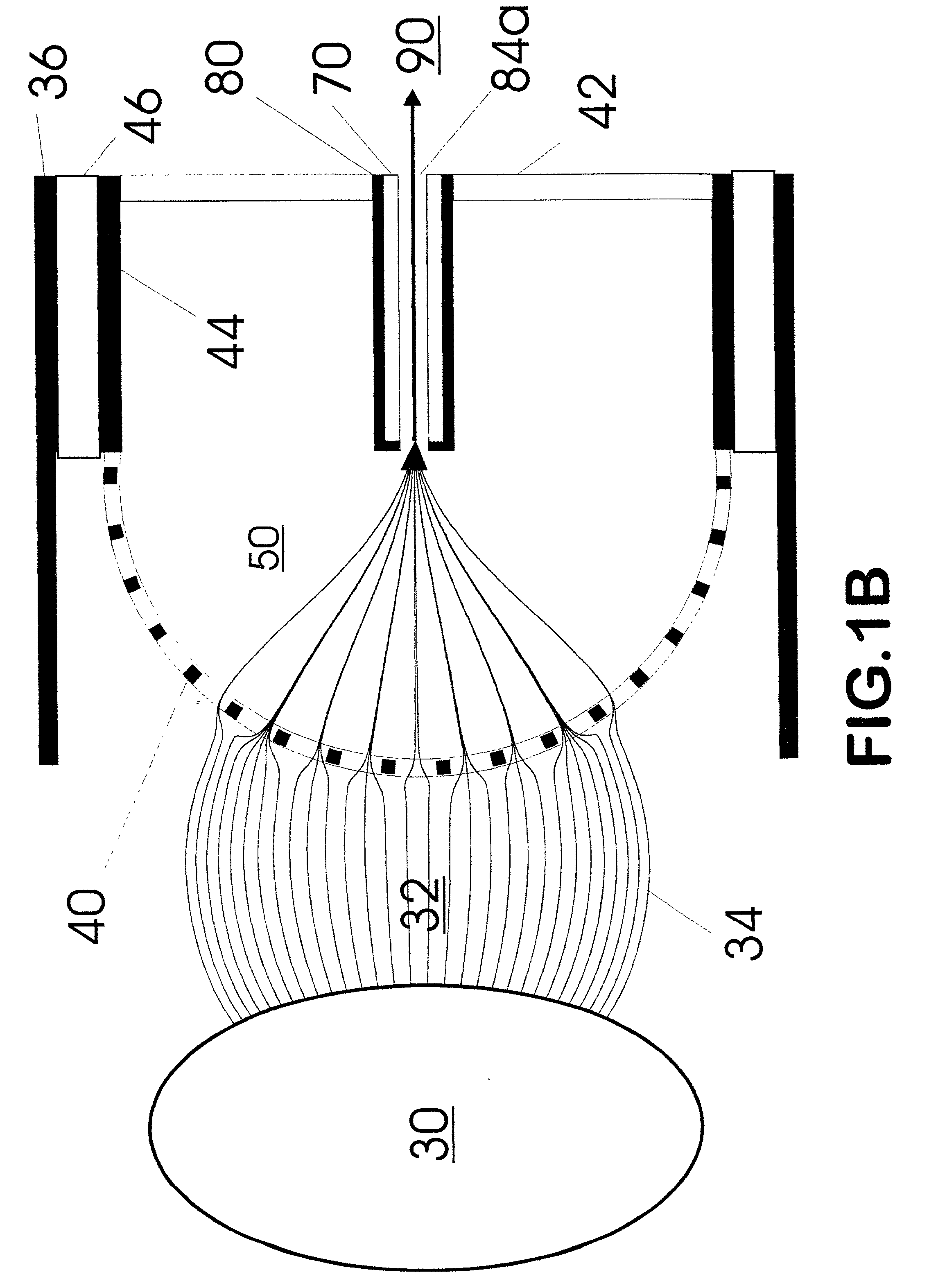
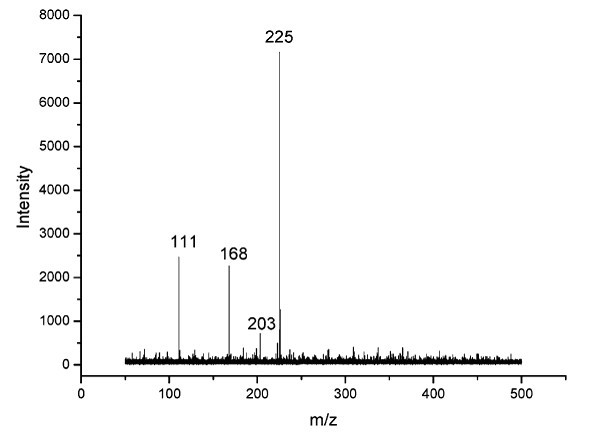
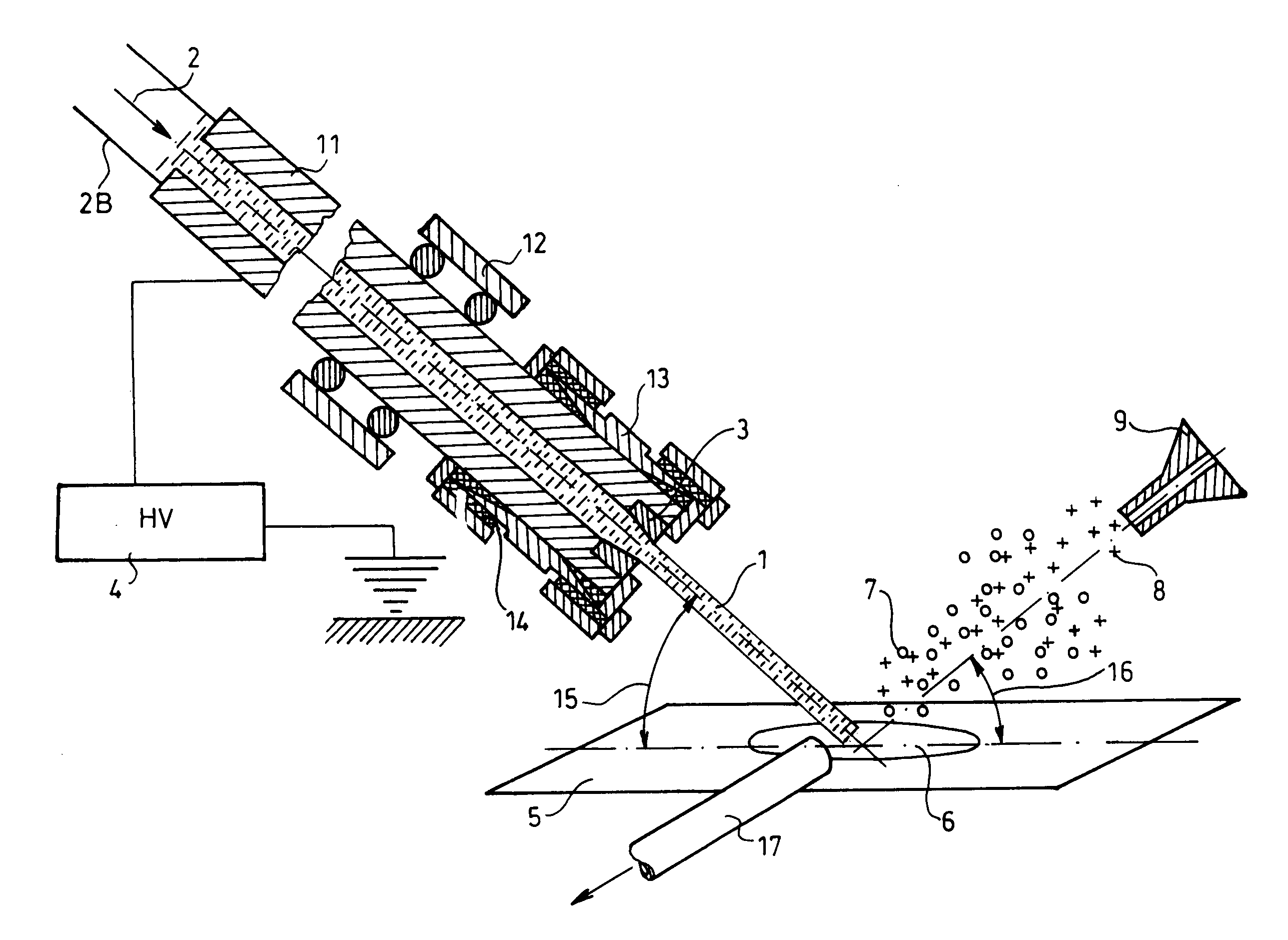
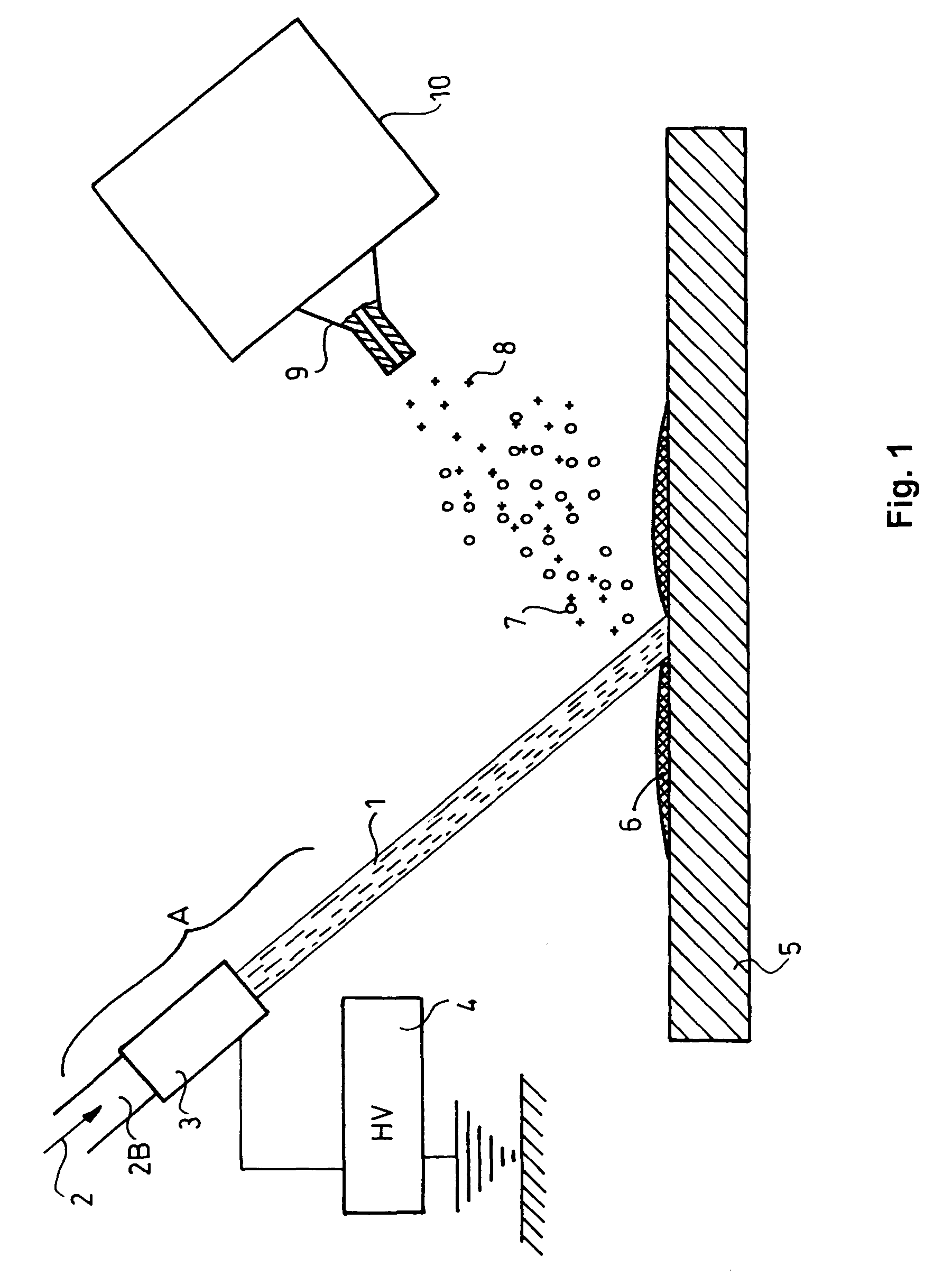
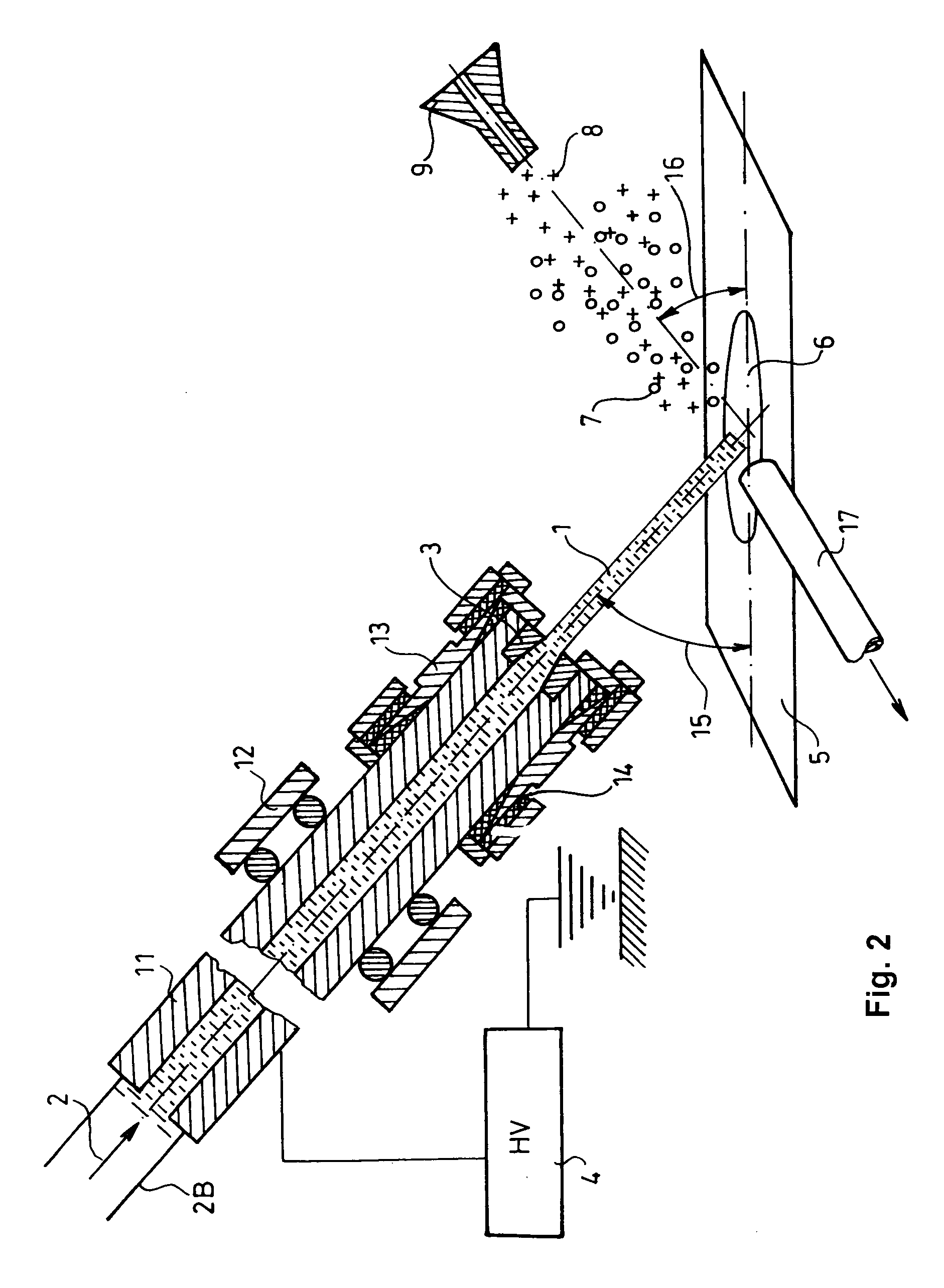
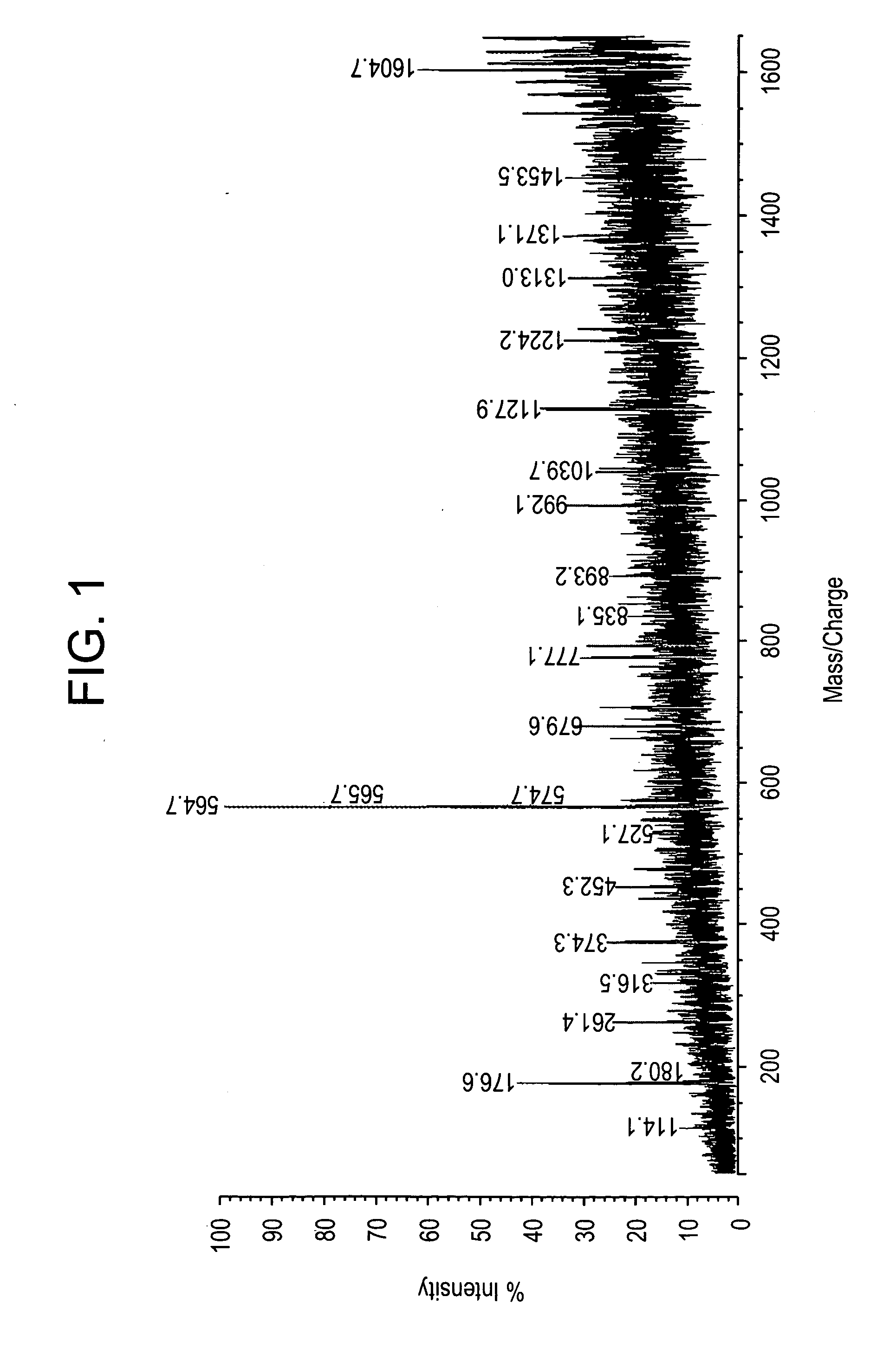
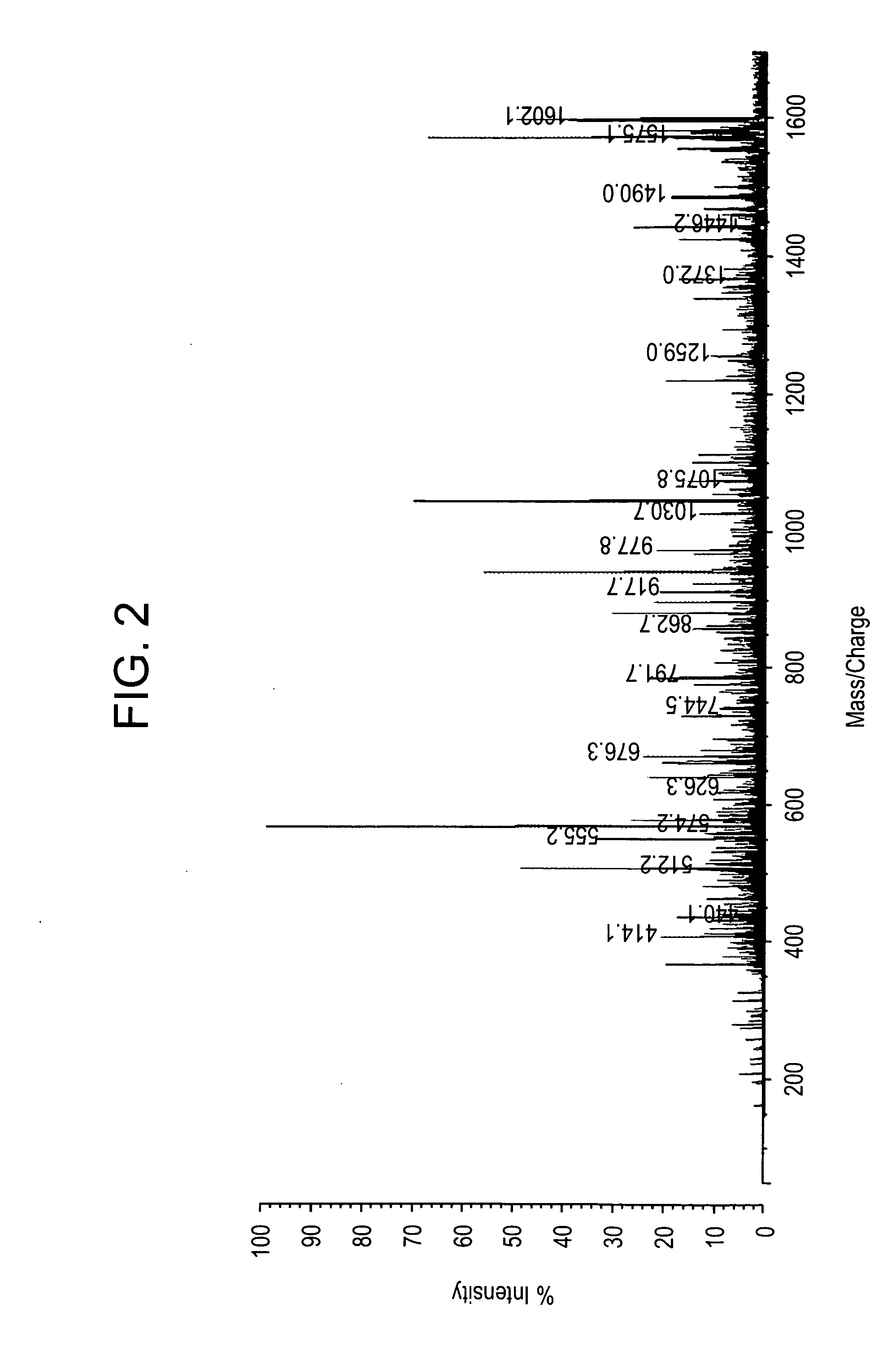
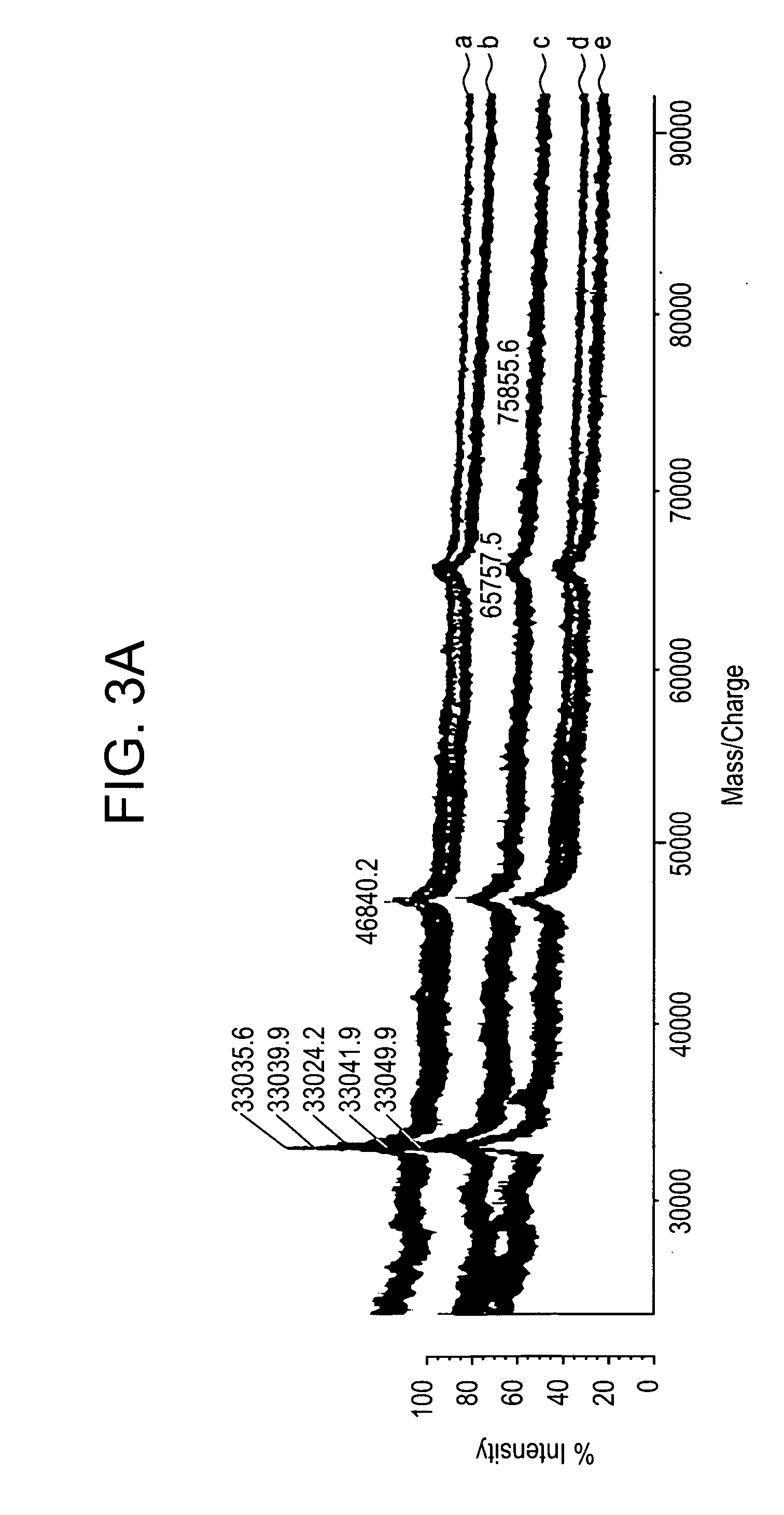
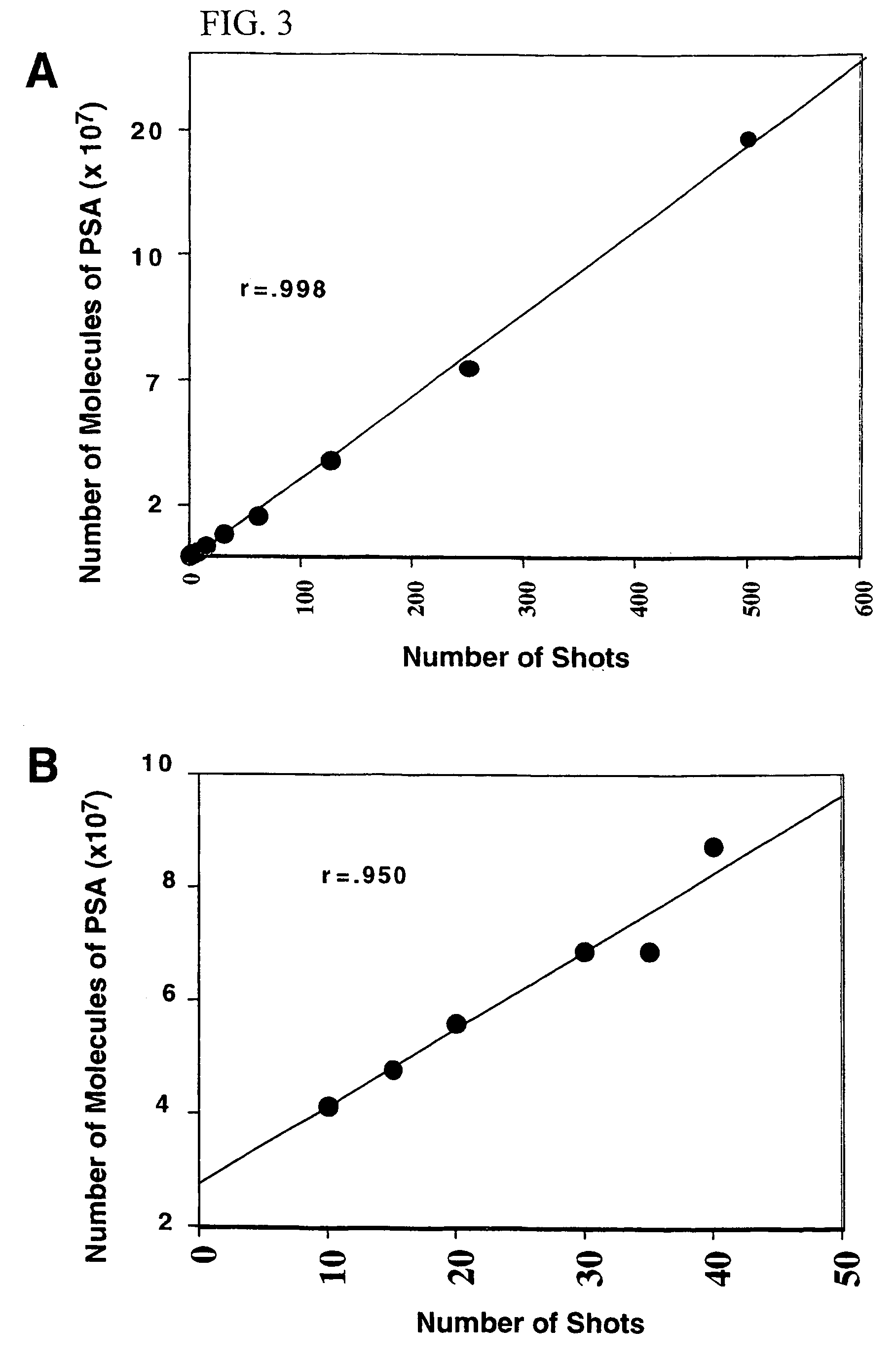
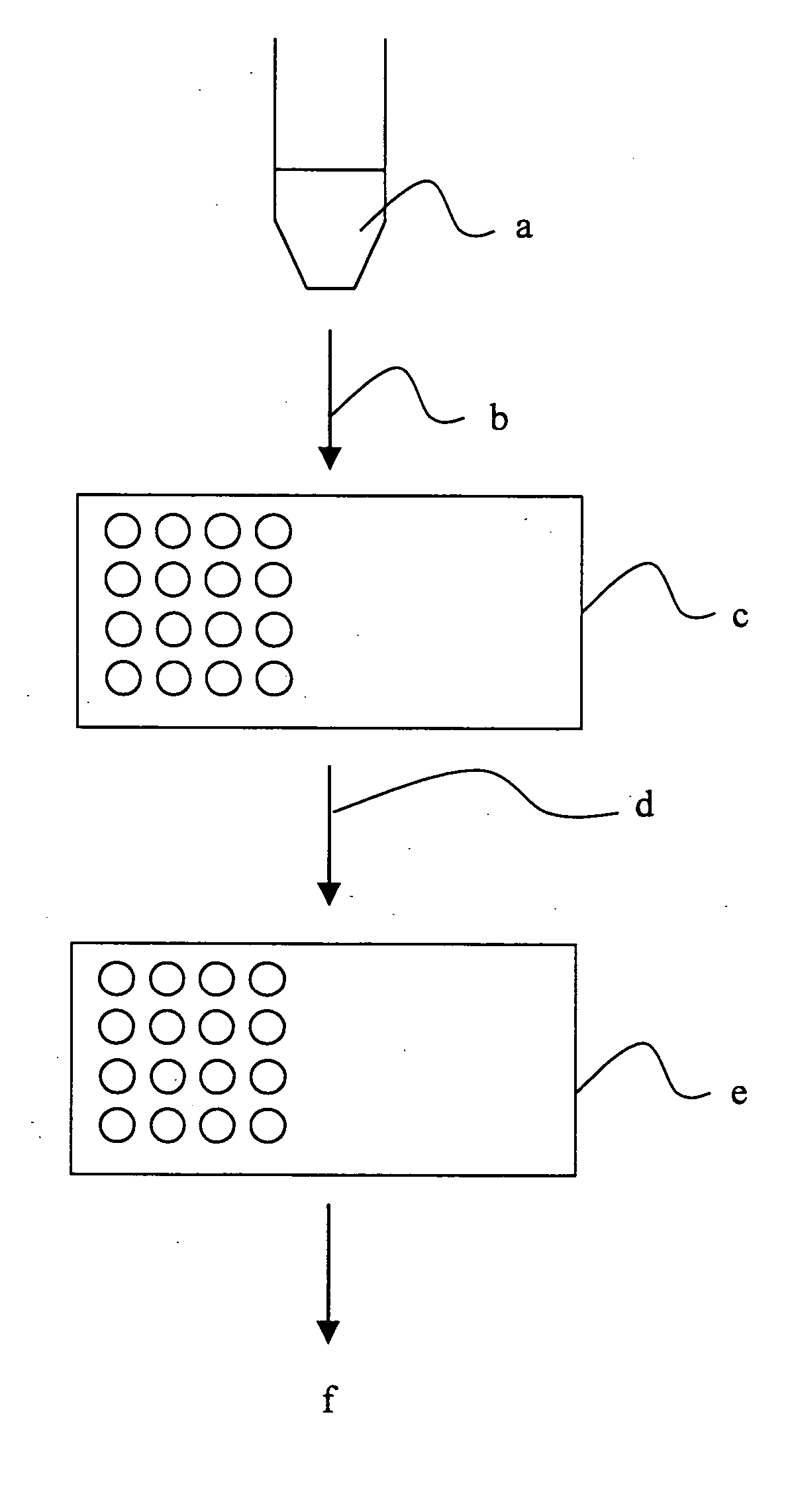
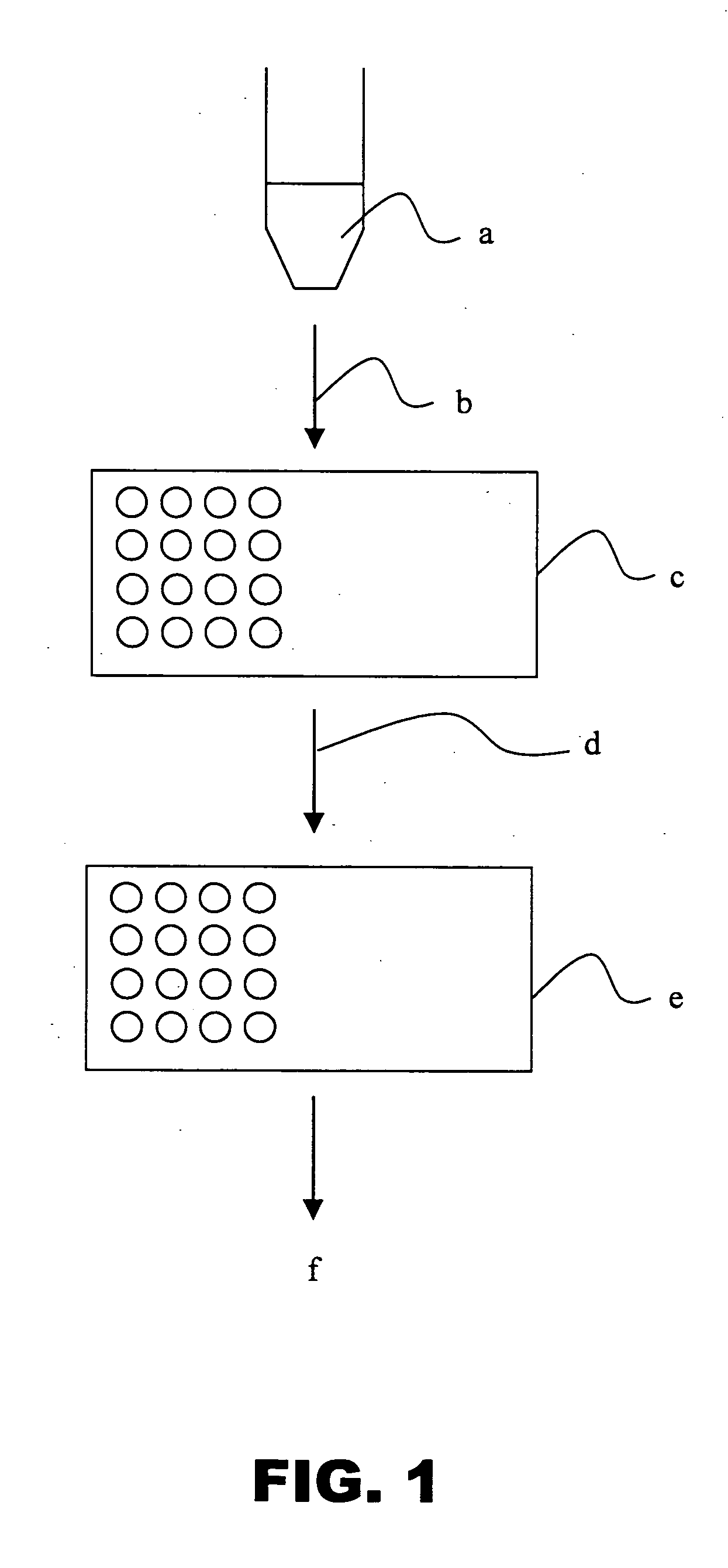
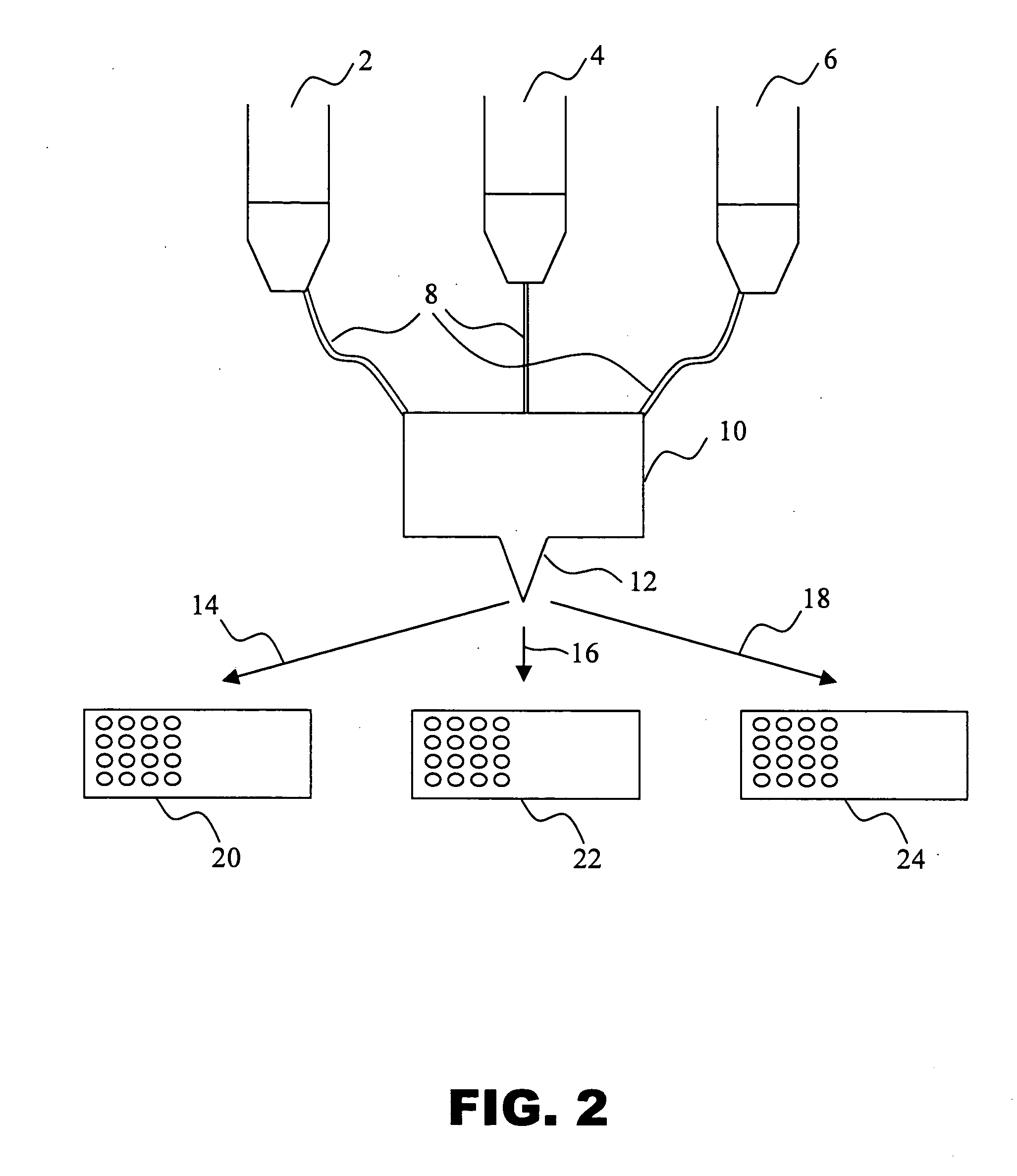
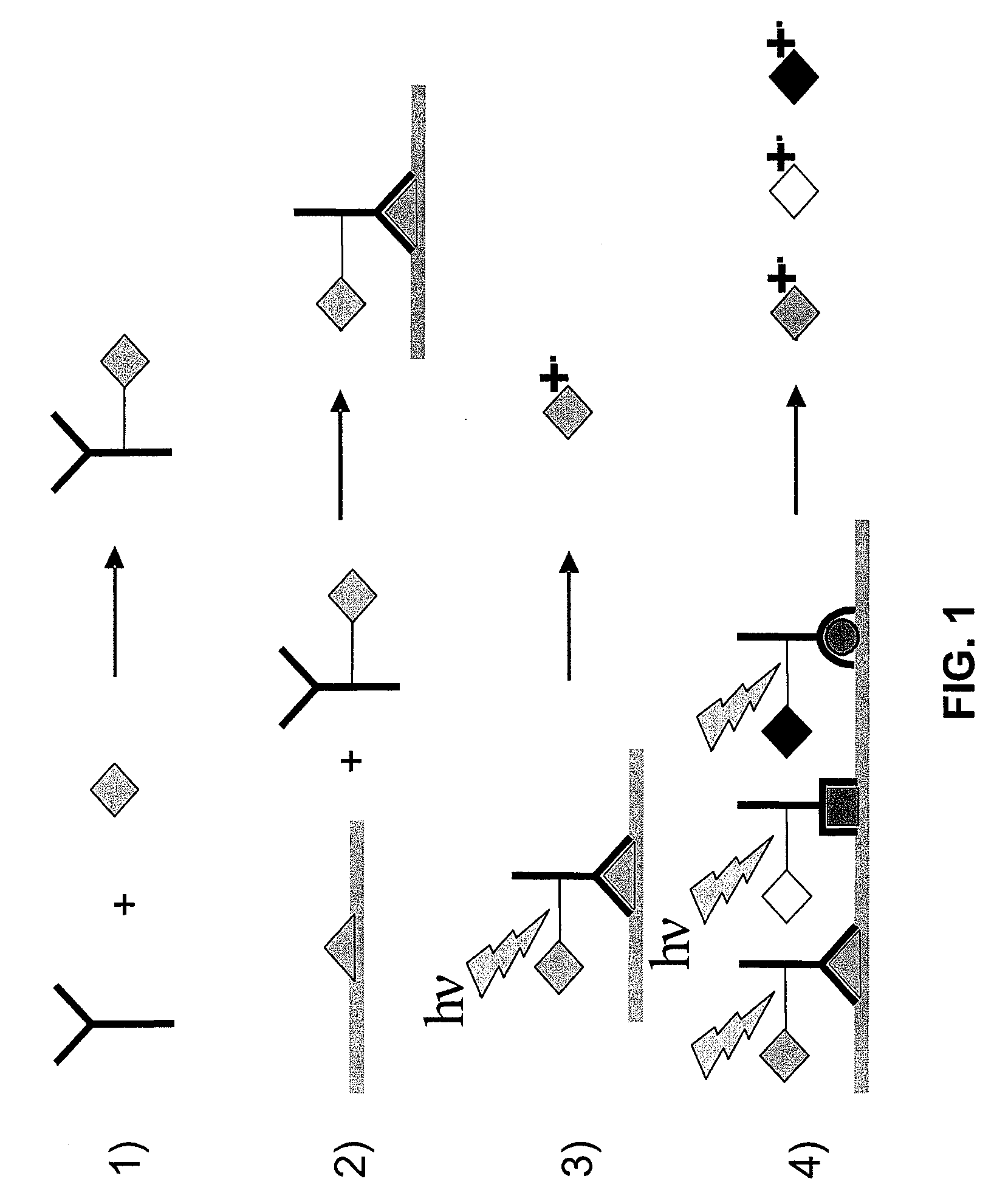
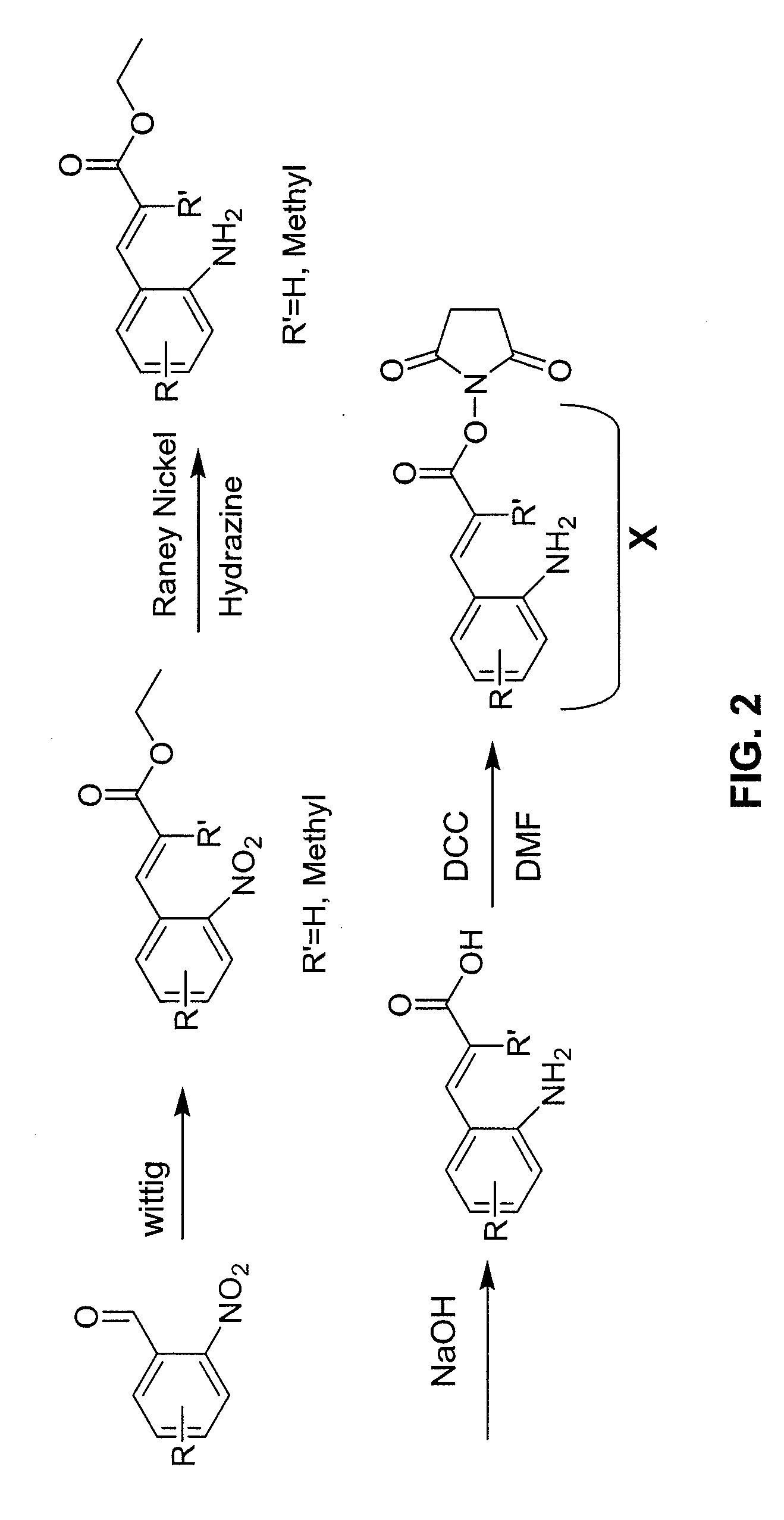
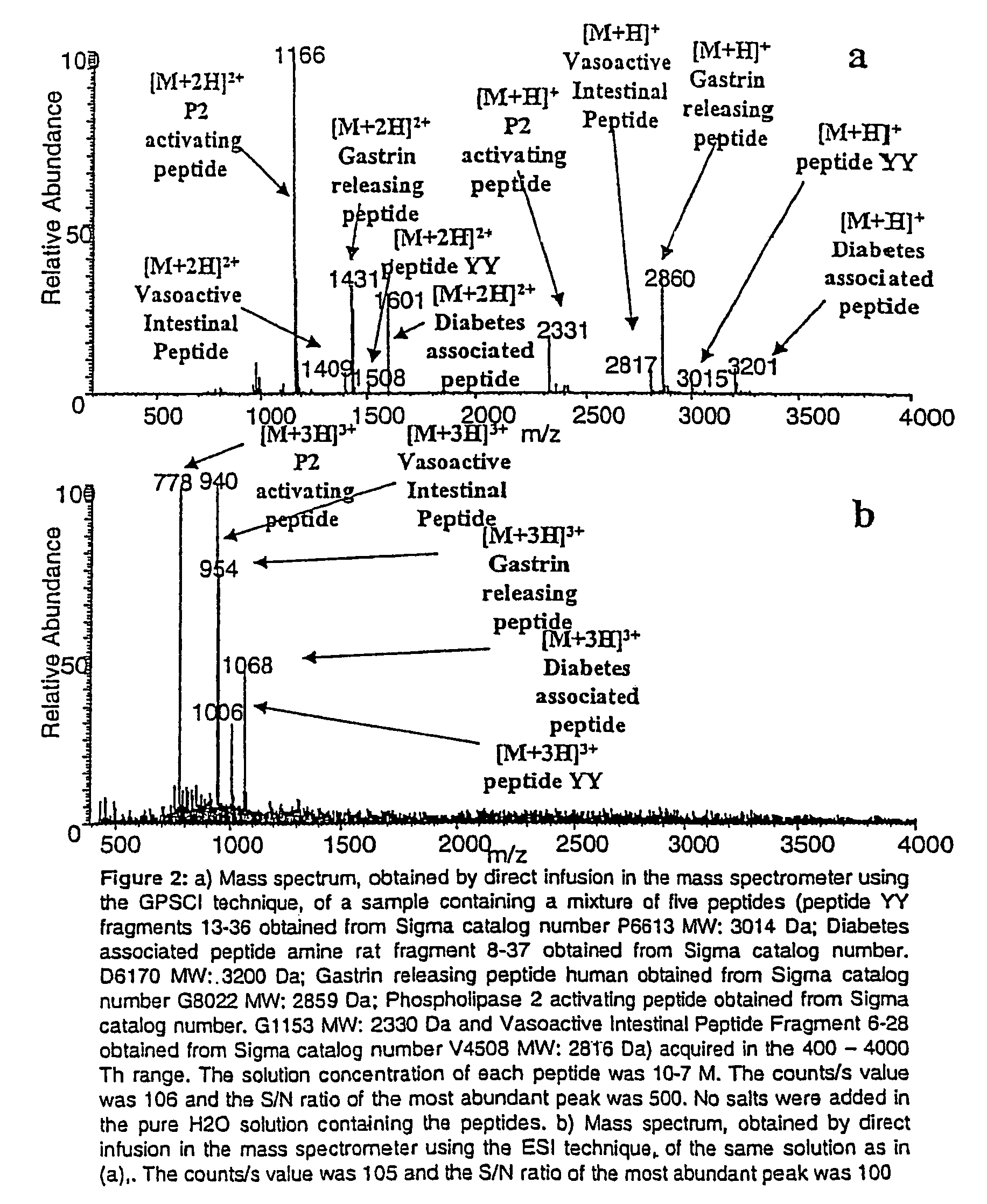
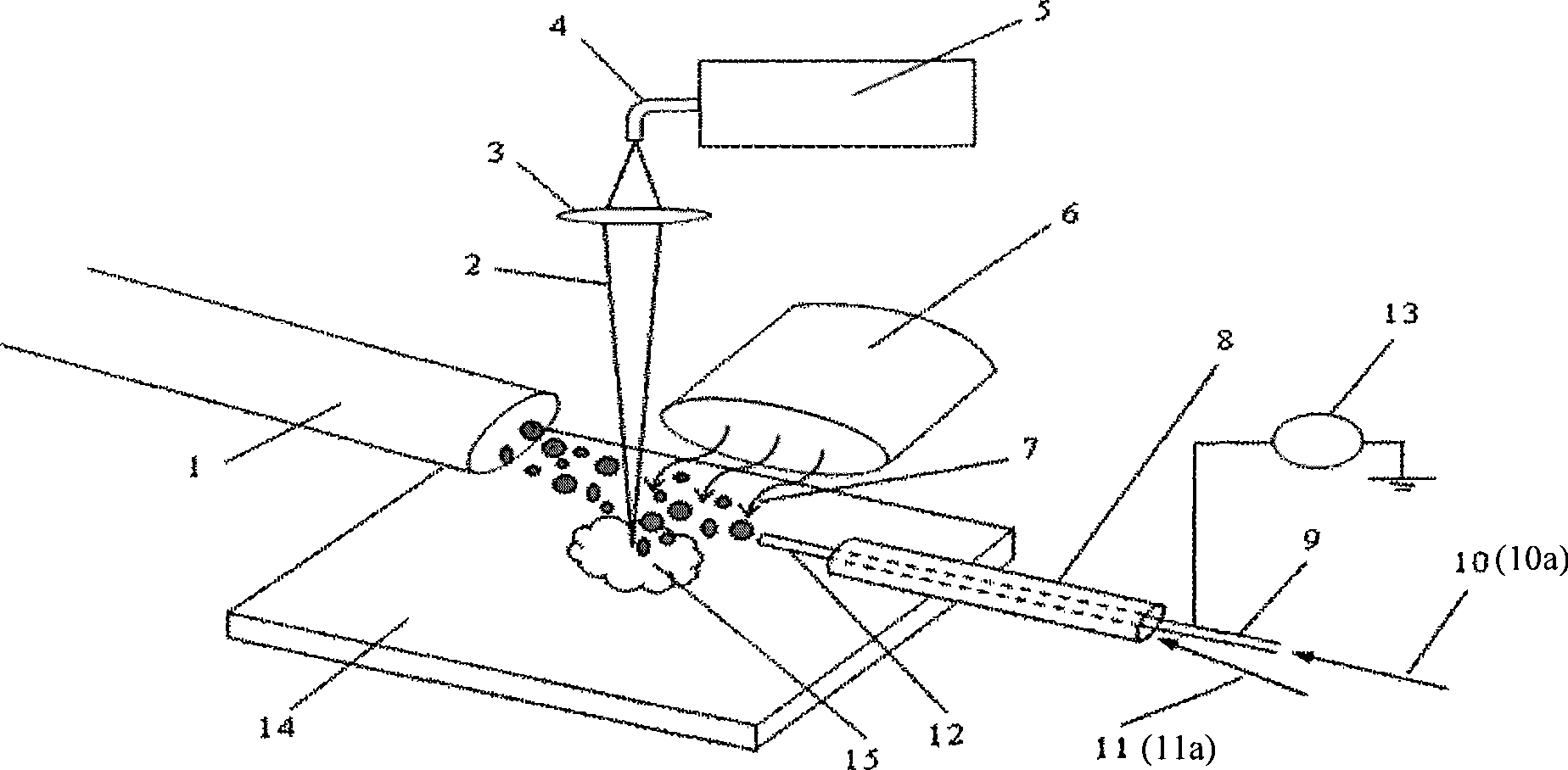
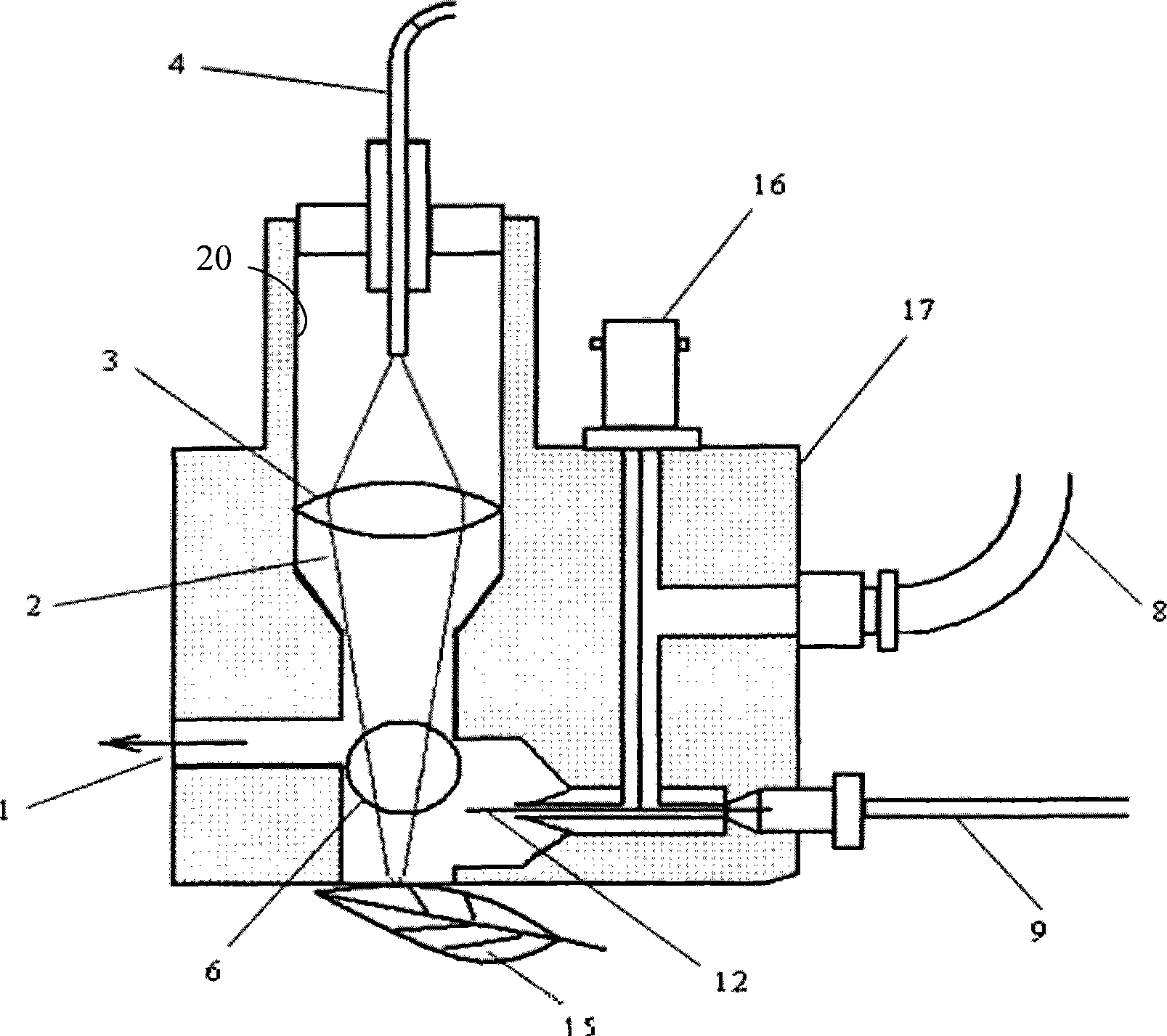
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs, through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
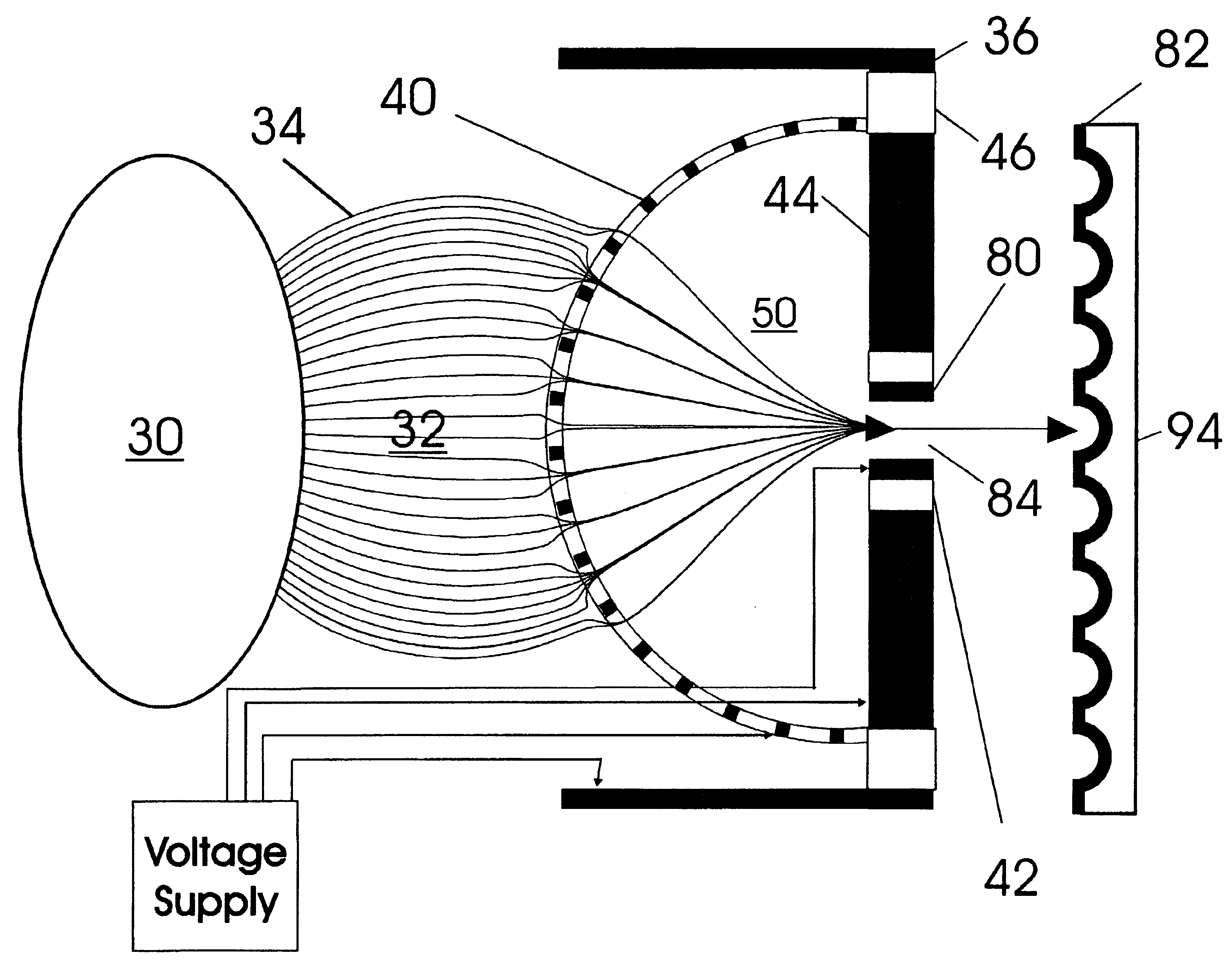
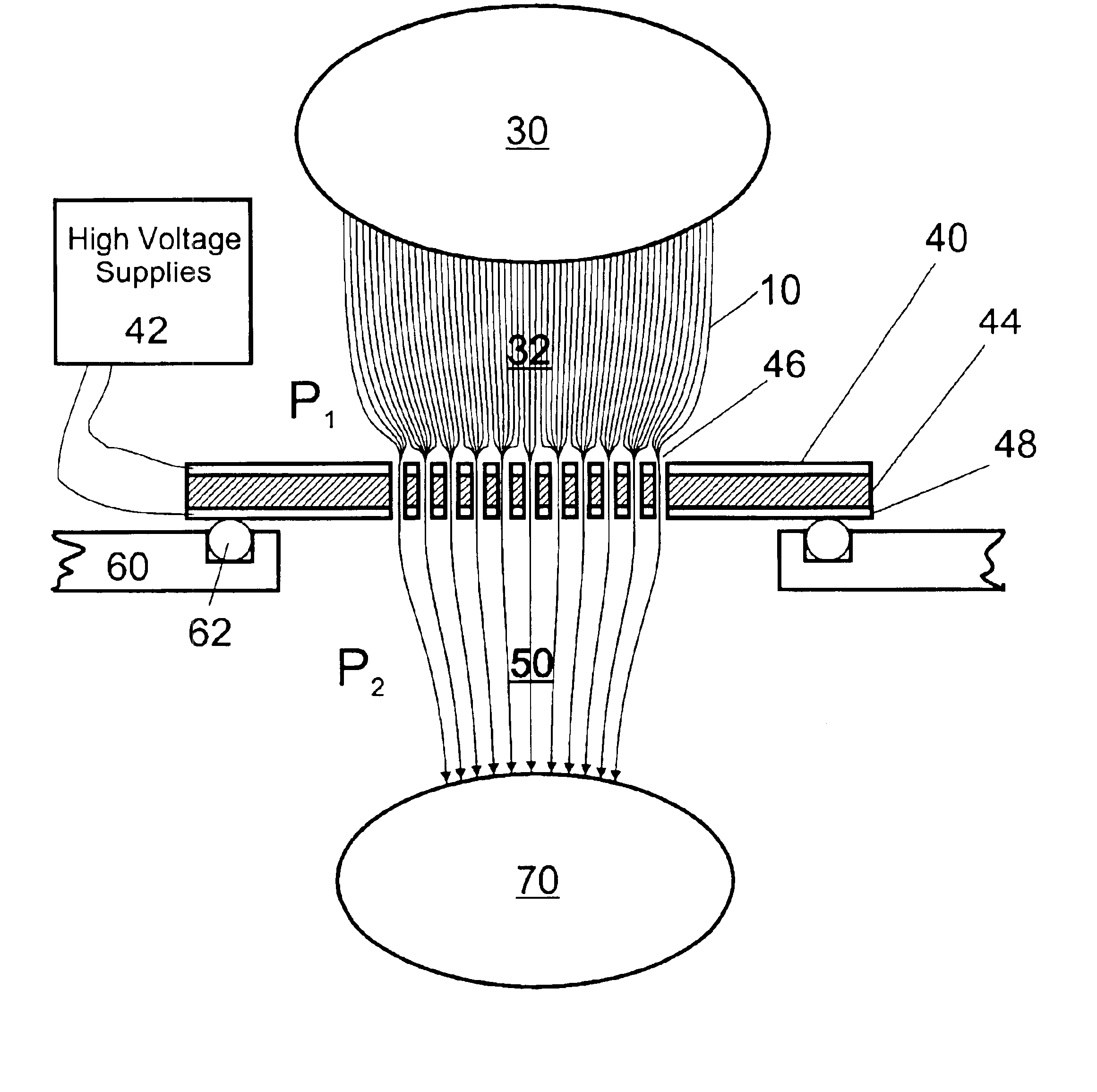
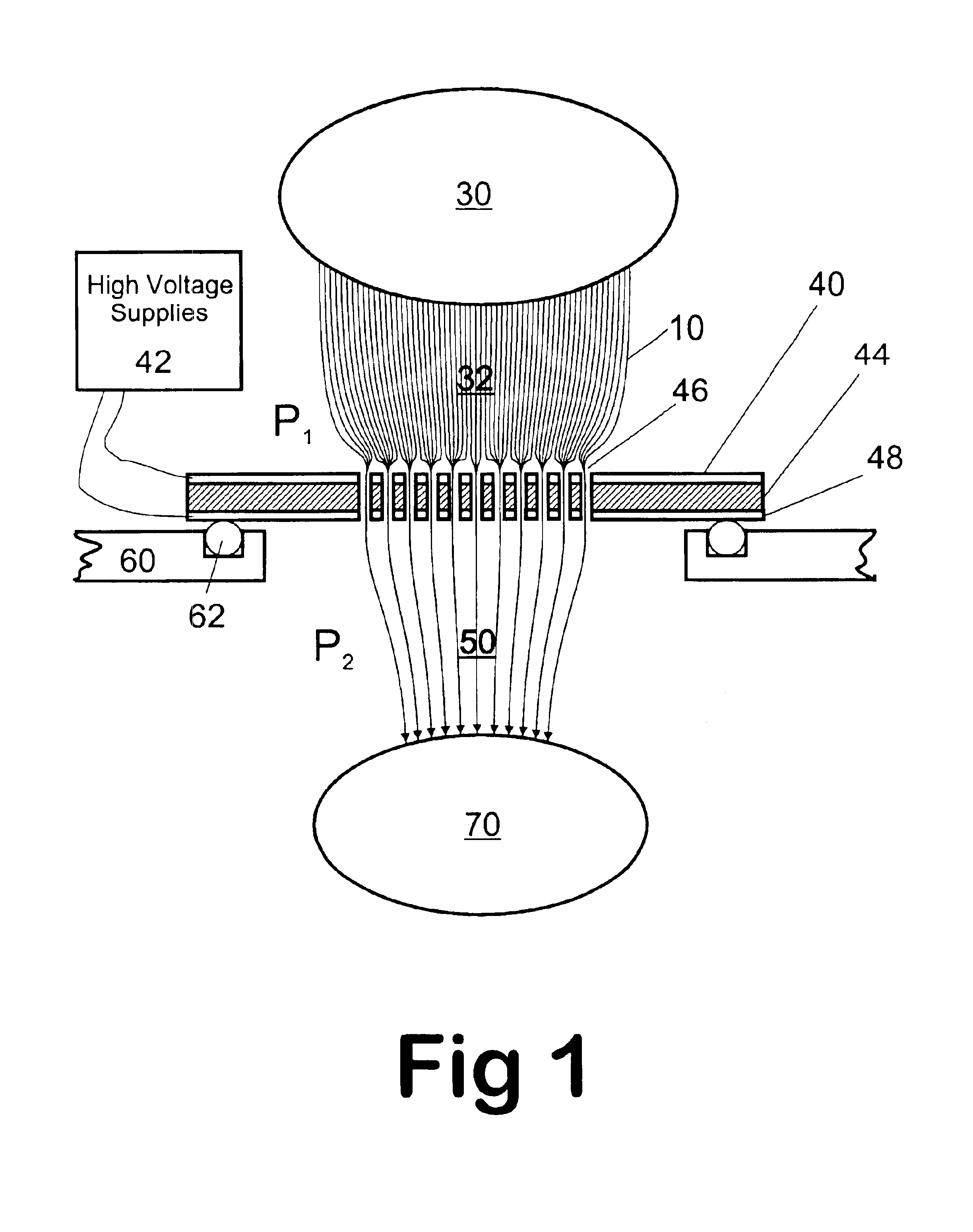
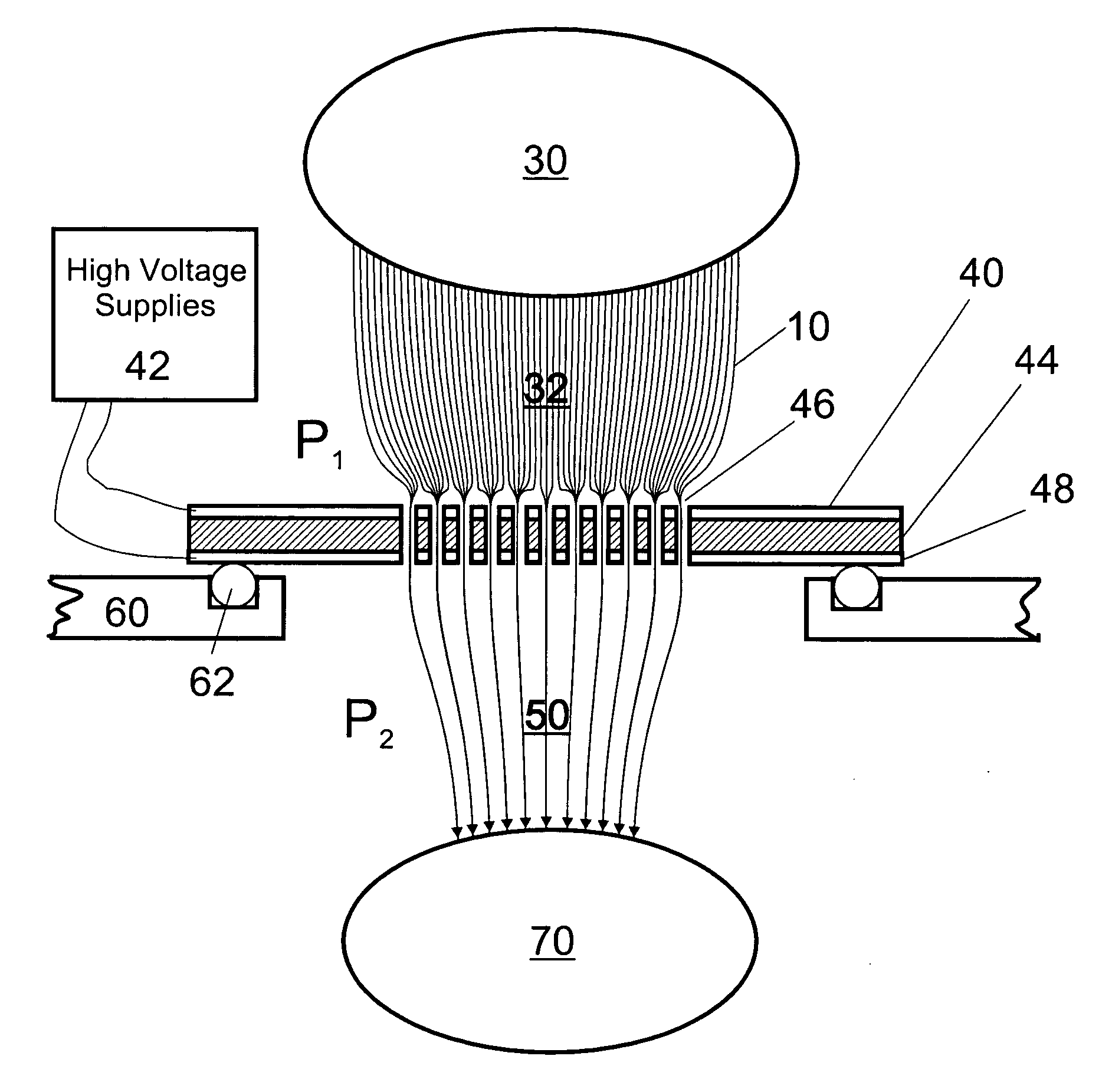
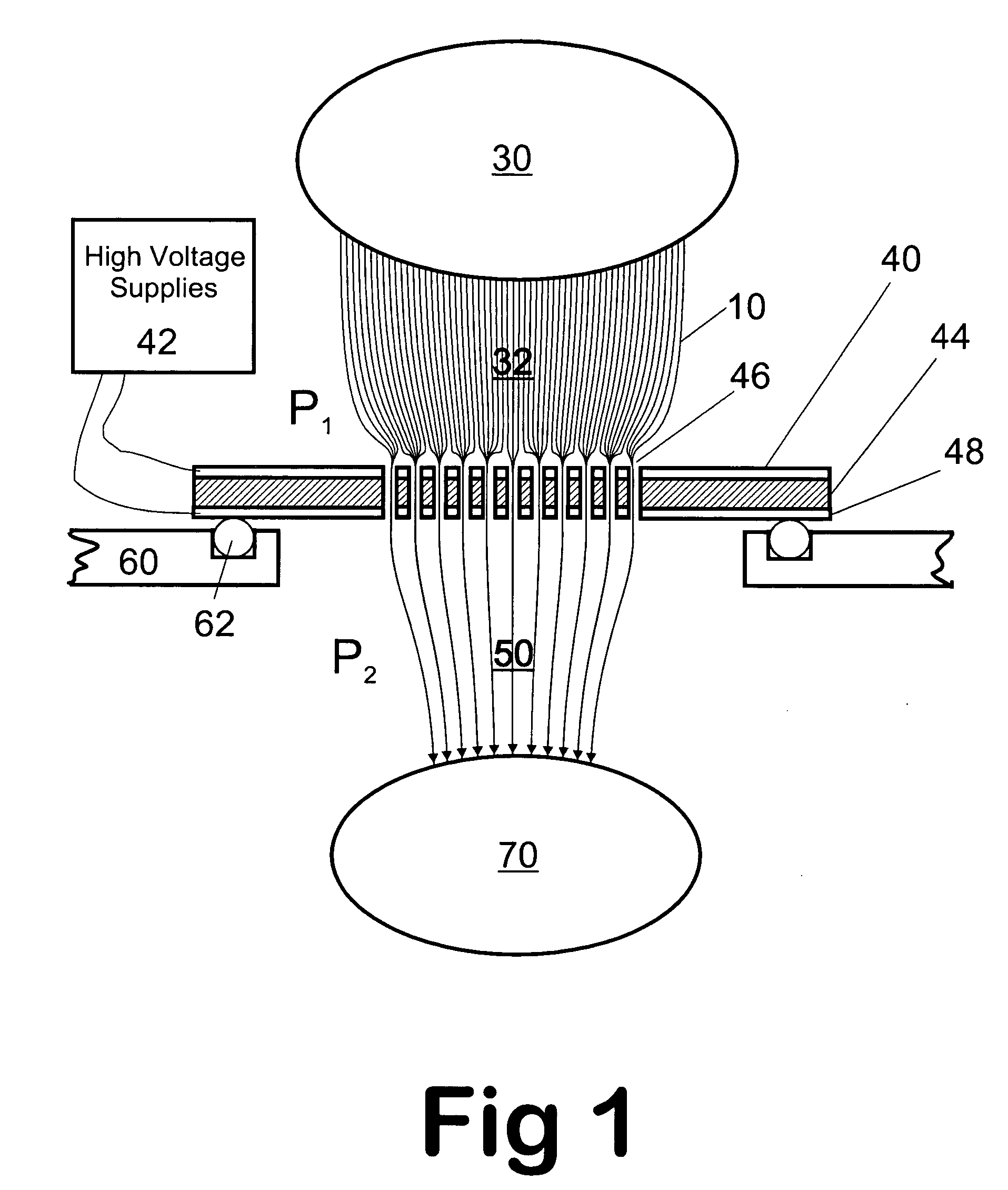
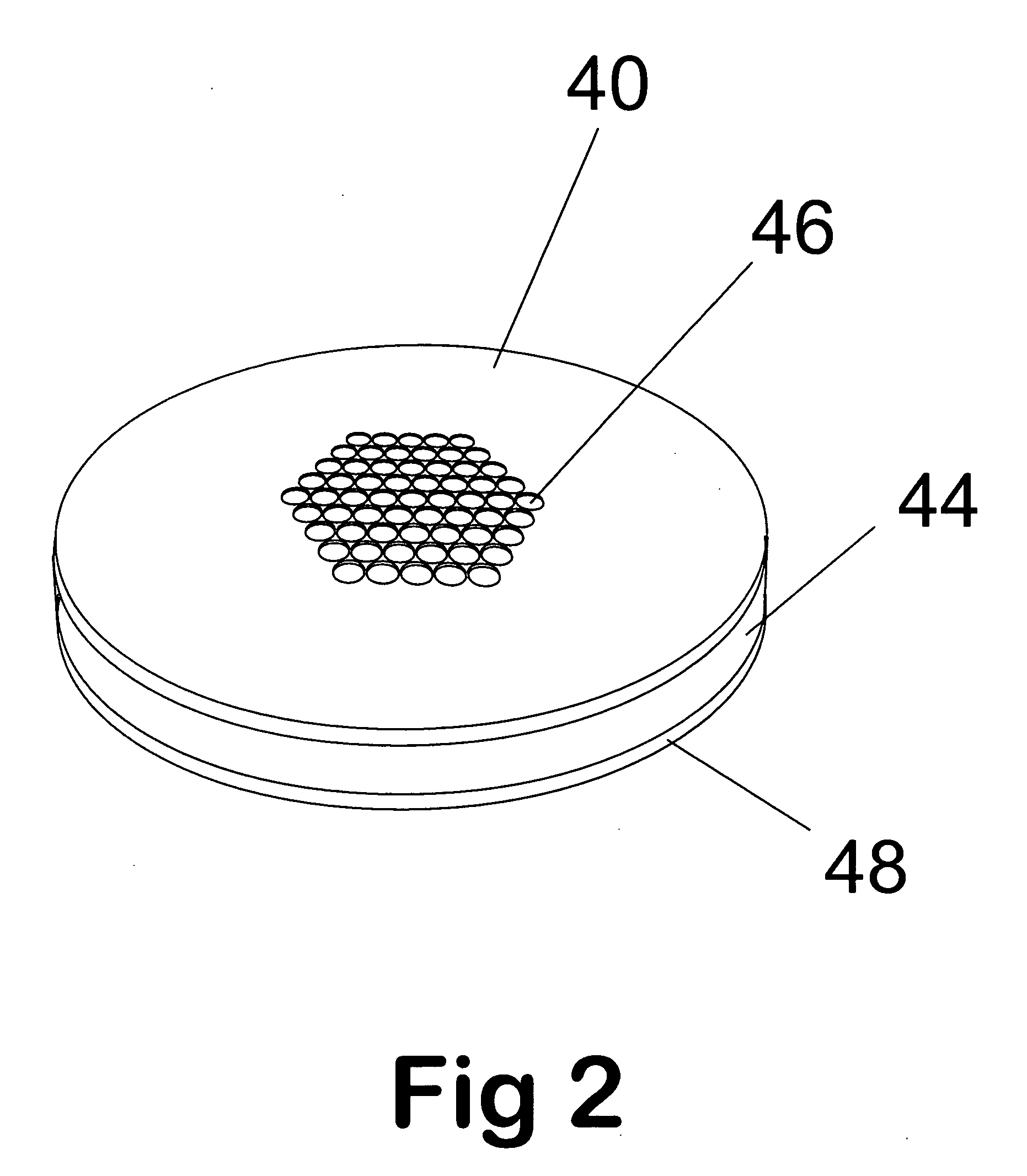
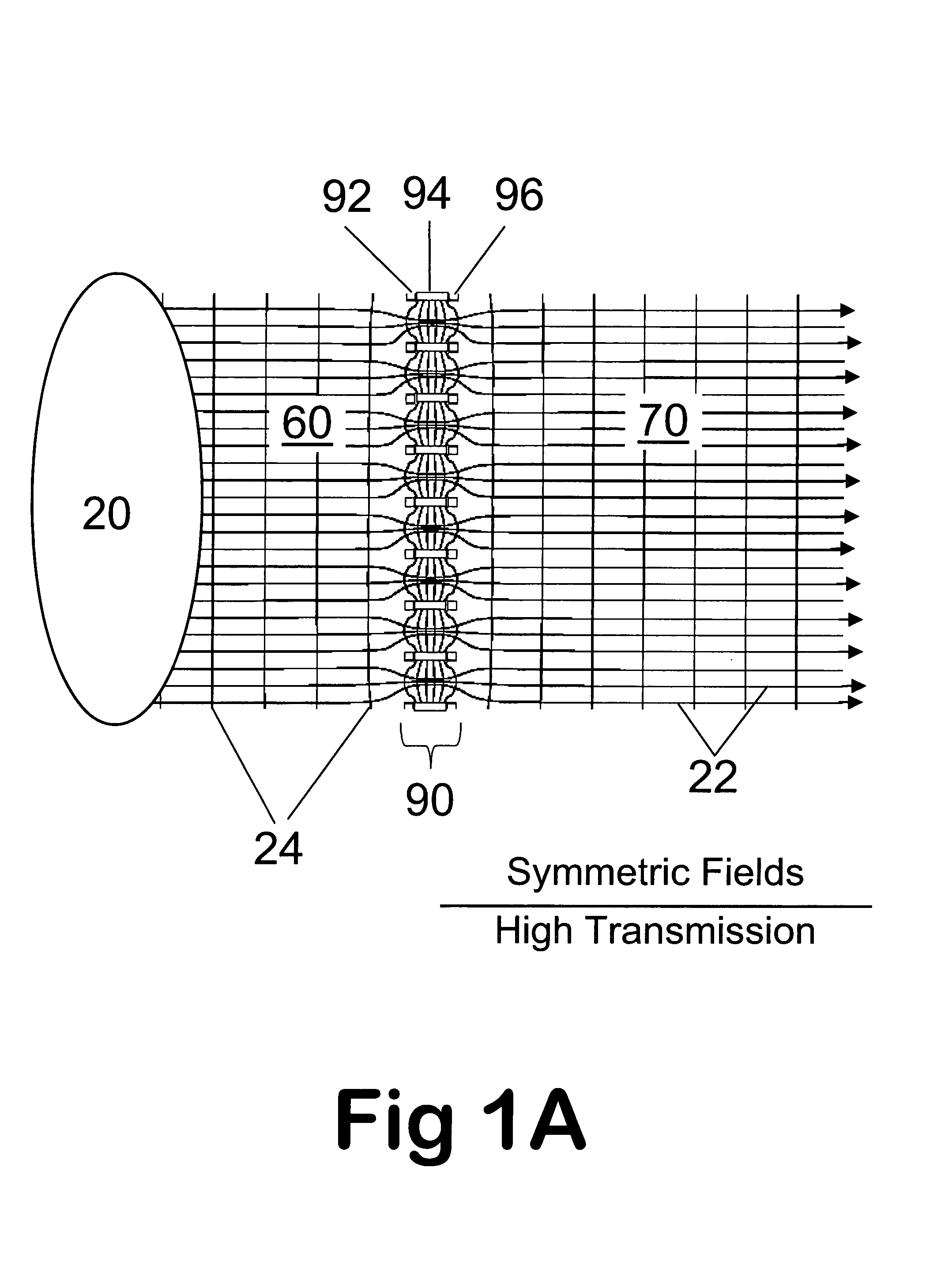
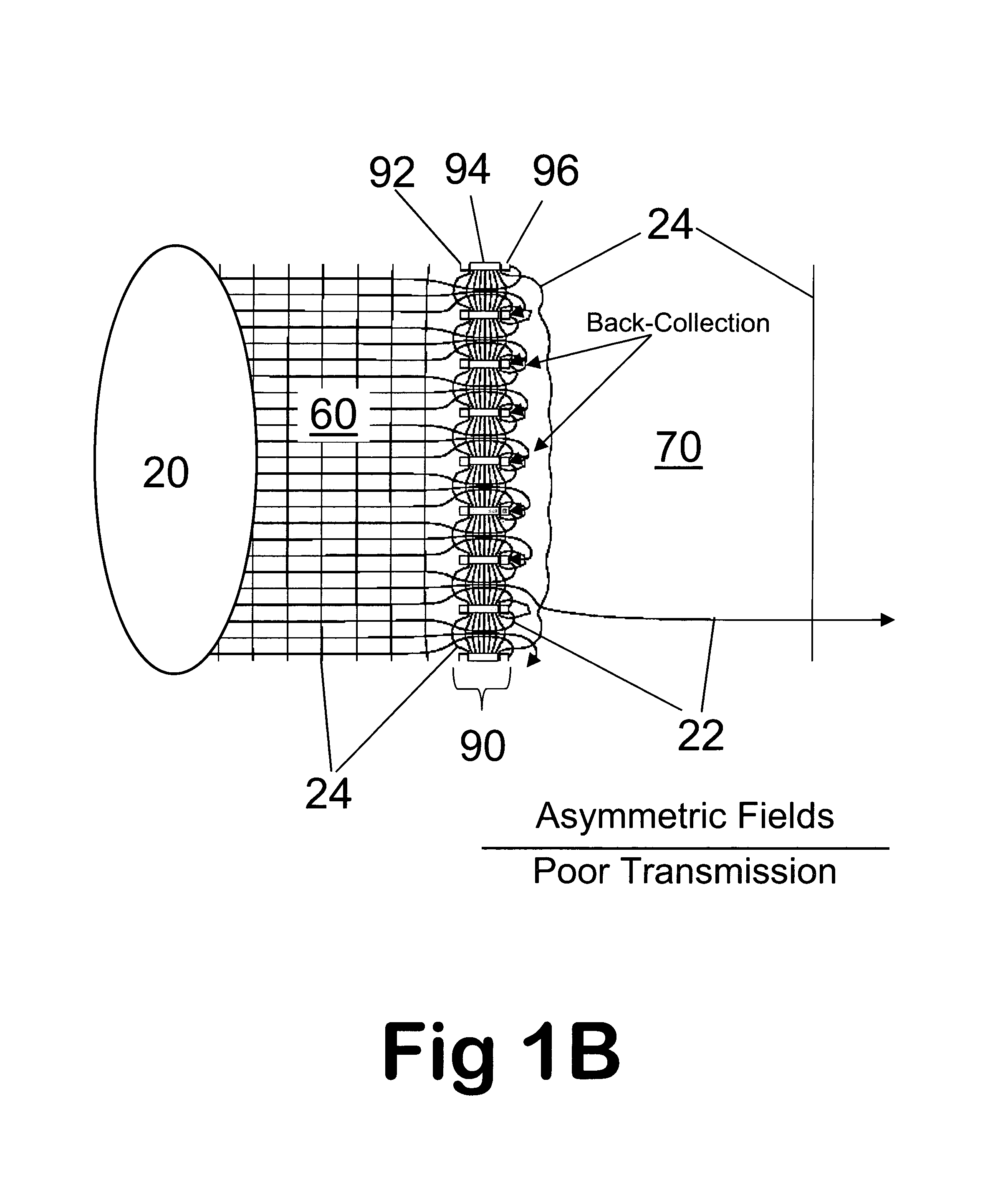
Apparatus and method for focusing ions and charged particles at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS6744041B2Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationInductively coupled plasmaElectrospray
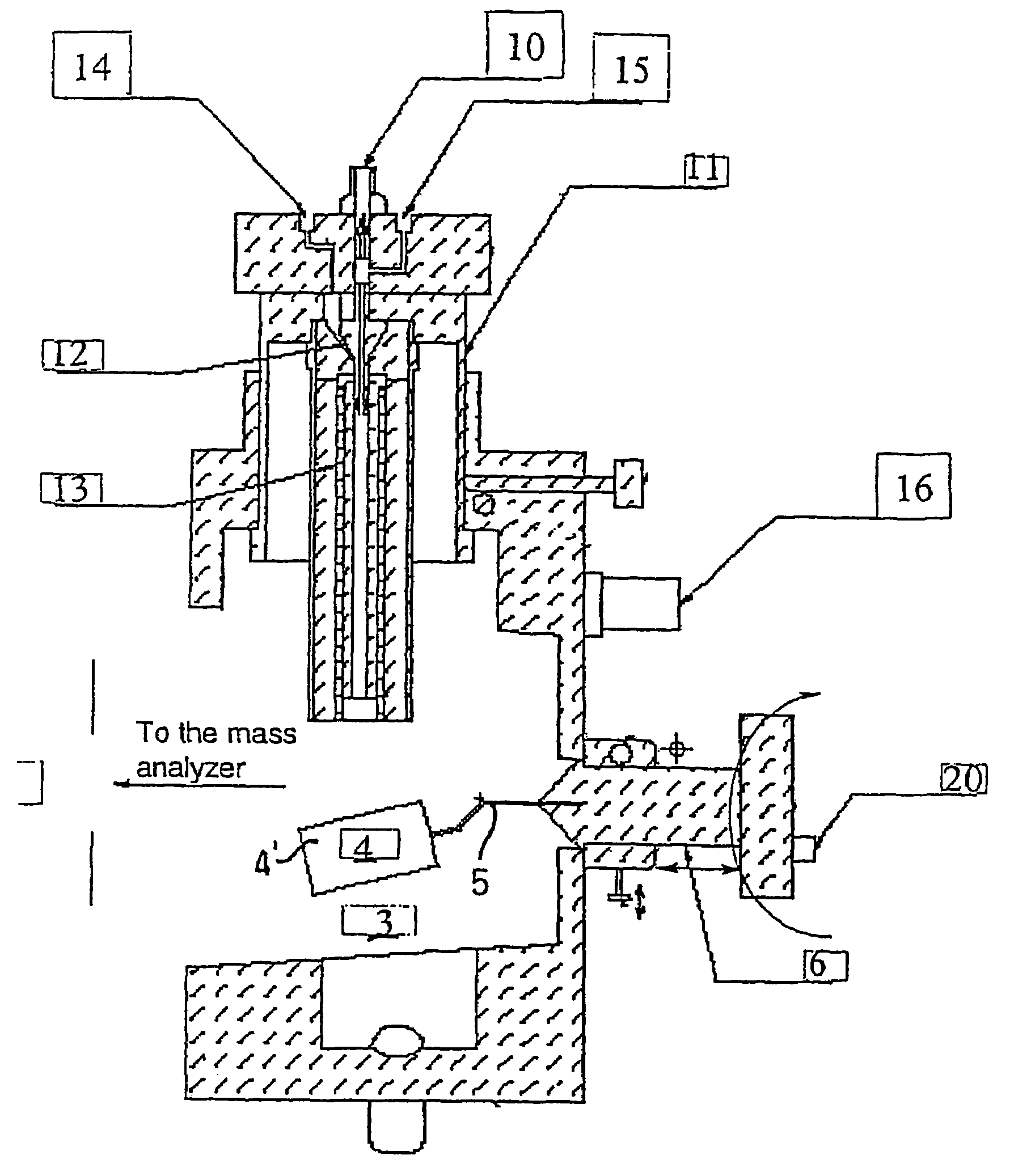
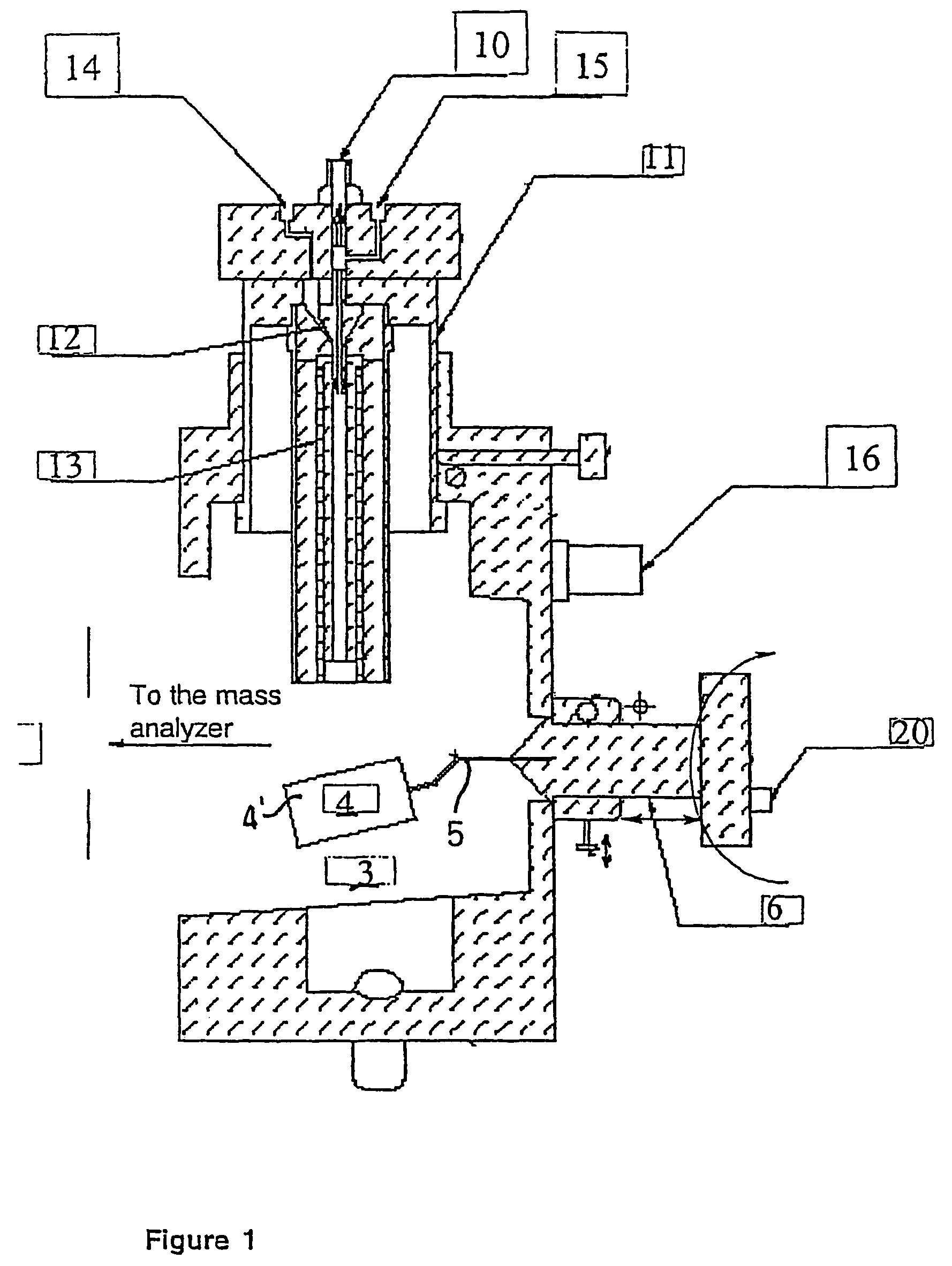
Improvements have been made for collection and focusing of ions generated from atmospheric pressure sources such as electrospray, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, inductively coupled plasma, discharge, photoionization and atmospheric pressure matrix assisted laser desorption ionization. A high transmission electro-optical surface is placed between the source regions and the focusing regions to optimize the field geometries and strengths in each respective region. Compression ratios of greater than 5000 are capable of transferring virtually all ions from large volume dispersive ion regions into ion beam cross-sections of less than 1 mm. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric pressure ionization sources.
Owner:SHEEHAN EDWARD W +1
Methods of identification of biomarkers with mass spectrometry techniques
InactiveUS20060172429A1Avoid problemsReduce the impactDisease diagnosisBiological testingMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryDiagnoses diseases
The present invention provides methods for identifying various biological states. Methods for diagnosis of diseases, in particular cardiovascular and brain diseases, are provided herein. One aspect of the invention is the analysis of lipoprotein complexes with summary survey scan mass spectrum for the analysis of biological states. Another aspect of the invention is the use of matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometer to analysis lipoprotein complexes for the diagnosis of cardiovascular and brain diseases. Yet another aspect of the invention is a method of diagnosis of brain diseases by evaluating the characteristics of lipoprotein complexes.
Owner:INSILICOS
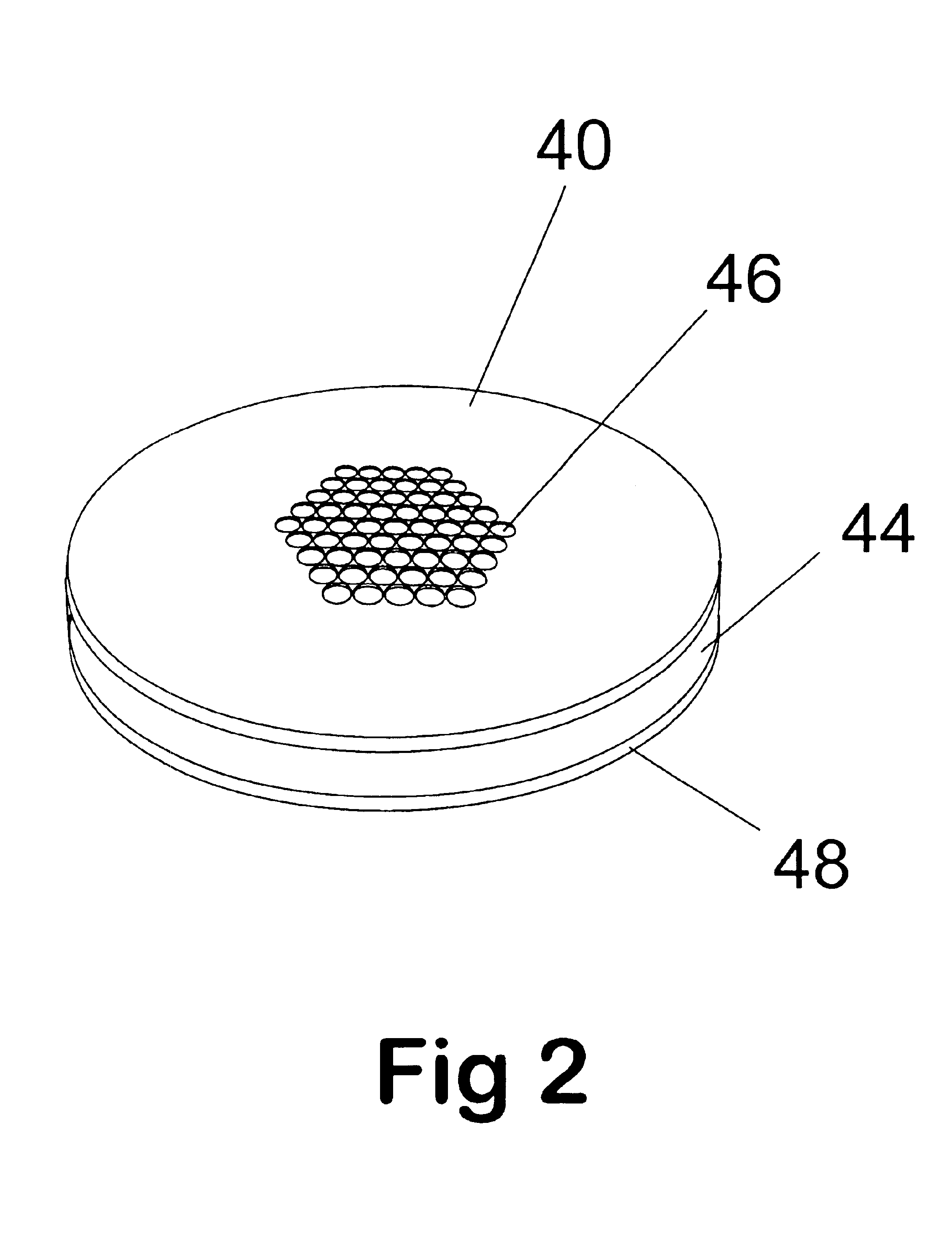
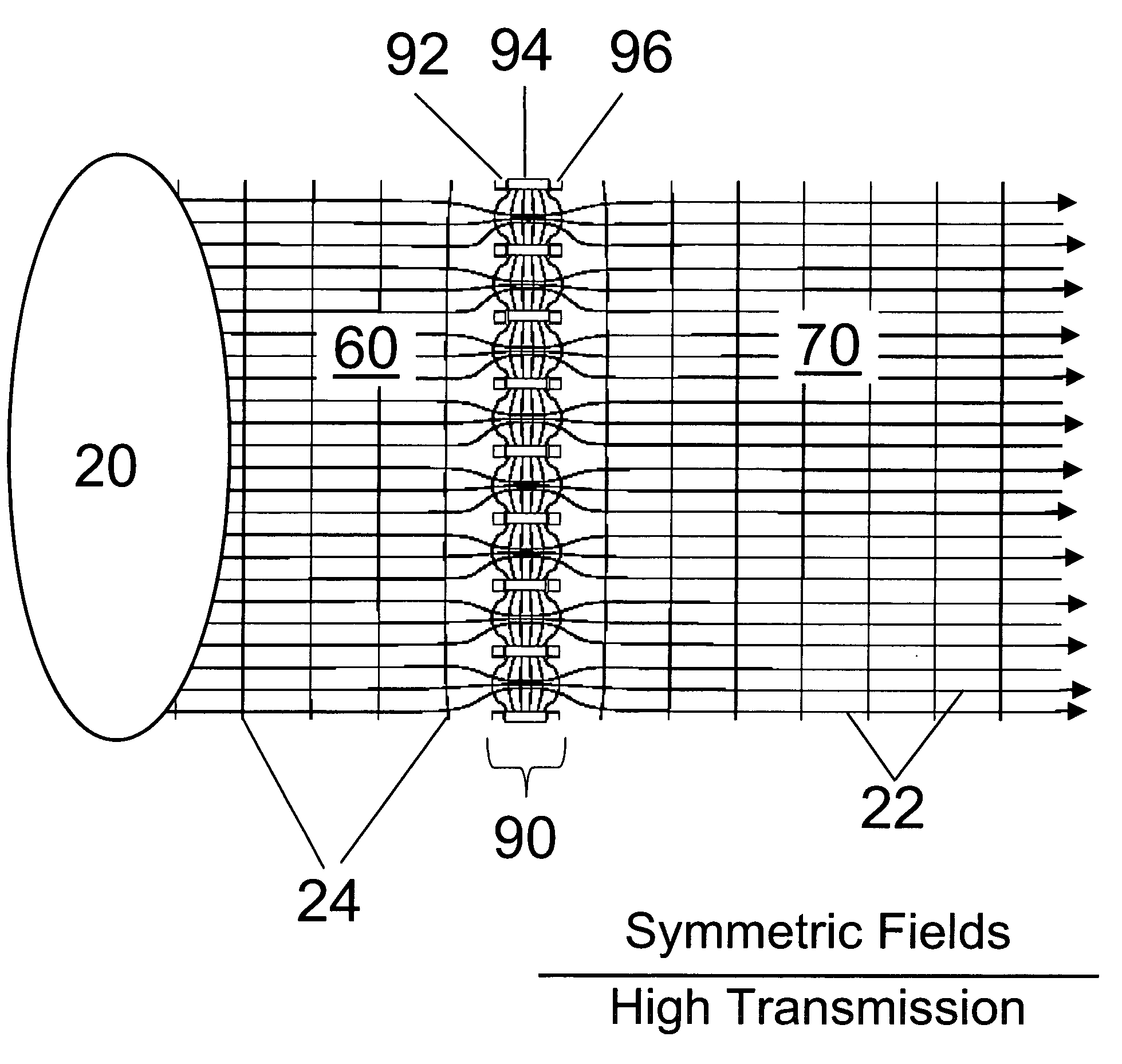
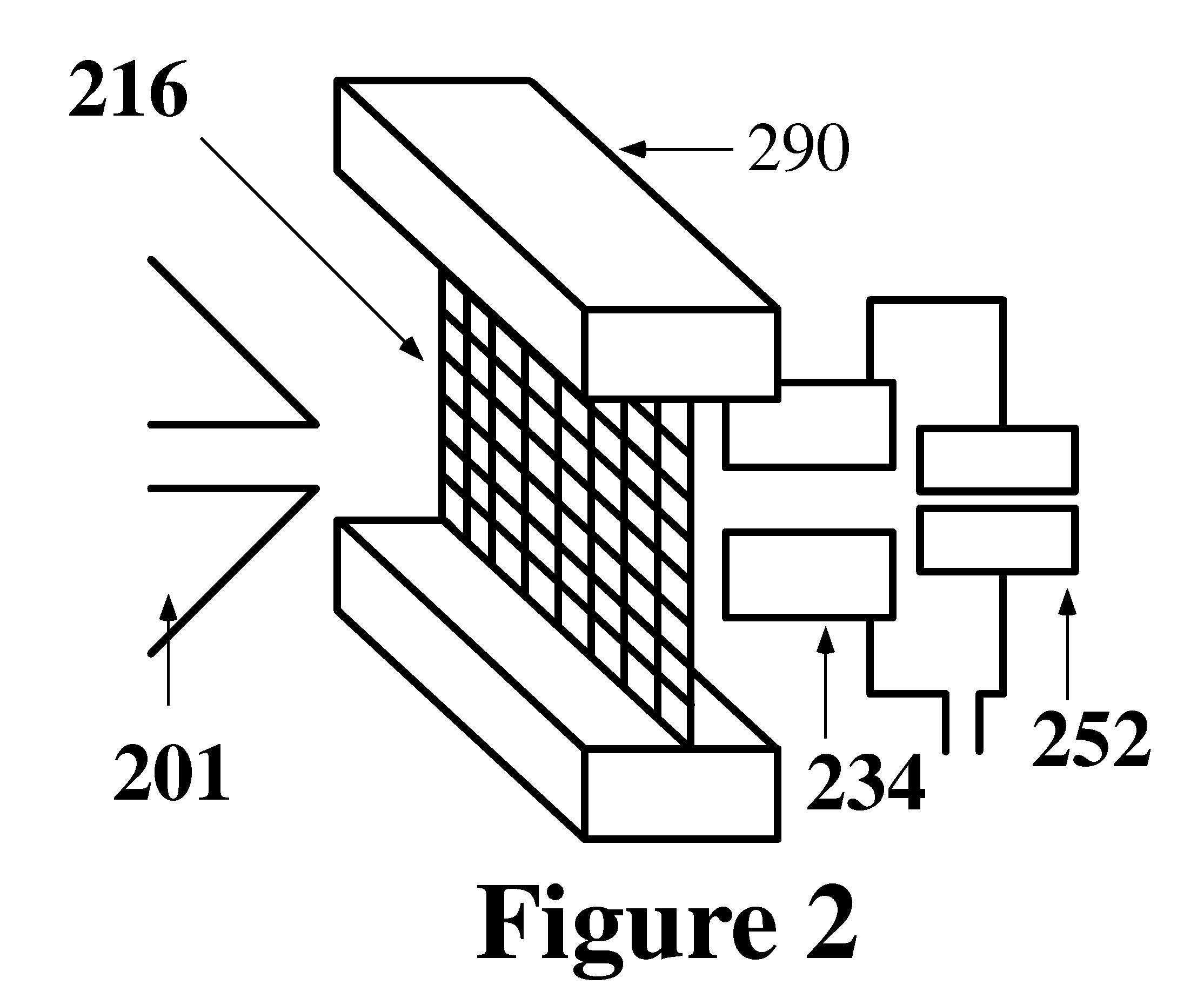
Ion enrichment aperture arrays
InactiveUS6914243B2Time-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsAtmospheric pressure dischargeInductively coupled plasma
Improvements have been made for collecting, focusing, and directing of ions and / or charged particles generated at atmospheric or near atmospheric pressure sources, such as but not limited to, electrospray; atmospheric pressure discharge ionization, chemical ionization, photoionization, and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization; and inductively coupled plasma ionization. A multiple-aperture laminated structure is place at the interface of two pressure regions. Electric fields geometries and strengths across the laminated structure and diameters of the apertures; all of which act to optimize the transfer of the ions from the higher pressure region into the lower pressure region while reducing the gas-load on the lower pressure region. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric, near atmospheric, or higher pressure ionization sources by reducing the gas-load on the vacuum system.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
Ion enrichment aperture arrays
InactiveUS20040245458A1Maximizes transmission of ionImprove transmittanceTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsAtmospheric pressure dischargeInductively coupled plasma
Improvements have been made for collecting, focusing, and directing of ions and / or charged particles generated at atmospheric or near atmospheric pressure sources, such as but not limited to, electrospray; atmospheric pressure discharge ionization, chemical ionization, photoionization, and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization; and inductively coupled plasma ionization. A multiple-aperture laminated structure is place at the interface of two pressure regions. Electric fields geometries and strengths across the laminated structure and diameters of the apertures; all of which act to optimize the transfer of the ions from the higher pressure region into the lower pressure region while reducing the gas-load on the lower pressure region. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric, near atmospheric, or higher pressure ionization sources by reducing the gas-load on the vacuum system.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
Laminated lens for focusing ions from atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS7081621B1Effective independenceUniform collectionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCurve shapeInductively coupled plasma
A thin laminated high transmission electro-optical lens populated with a plurality of apertures in communication with its laminates used to improve the collection, focusing, and selection of ions generated from atmospheric pressure sources, such as electrospray, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, inductively coupled plasma, discharge, photoionization and atmospheric pressure matrix assisted laser desorption ionization. The laminated lens is made of alternating layers of electrically insulating and metal laminates. The geometry of the lens may be planar or shaped into various curve shapes, any of which act to optimize both the direct current (DC) and alternate current (AC) electric field geometries and strengths across the lens for transferring virtually all the ions from the ion source into an ion-focusing region adjacent and upstream of a high pressure or atmospheric pressure interface to a mass spectrometer, ion mobility analyzer, or combination thereof. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to high pressure or atmospheric pressure ionization sources.
Owner:WILLOUGHBY ROSS CLARK +1
Direct mass spectrometric analysis of drug candidates targeting protein complexes
ActiveUS20100099200A1Improve throughputEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein targetProtein-protein complex
The invention relates to a method of using high mass matrix assisted laser desorption-ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the effect of drug candidates on protein complexes such as protein-protein interactions in purified samples or complex biological matrices, as well as to the use of this method for lead compound optimization, drug characterization, drug manufacturing processes, and drug quality control processes, including automated high throughput applications.
Owner:COVALX
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Ionization source for mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS20060145089A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansGas phaseMass analyzer
A new ionization source named Surface Activated Chemical Ionization (SACI) has been discovered and used to improve the sensitivity of the mass spectrometer. According to this invention the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer is heated and contains a physical new surface to improve the ionization process. The analyte neutral molecules that are present in gas phase are ionized on this surface. The surface can be made of various materials and may also chemically modified so to bind different molecules. This new ionization source is able to generate ions with high molecular weight and low charge, an essential new key feature of the invention so to improve sensitivity and reduce noise. The new device can be especially used for the analysis of proteins, peptides and other macromolecules. The new invention overcomes some of the well known and critical limitations of the Electrospray (ESI) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
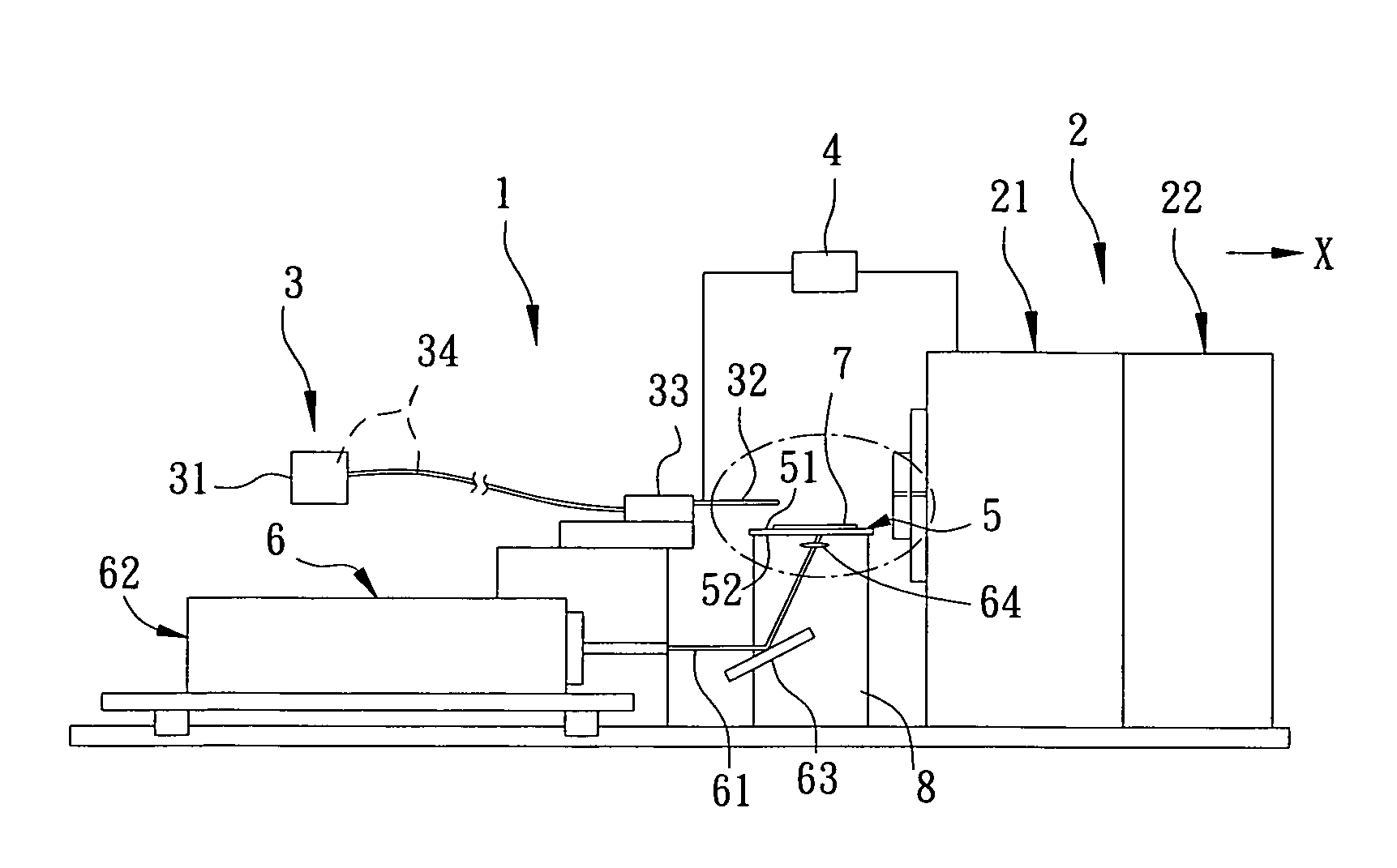
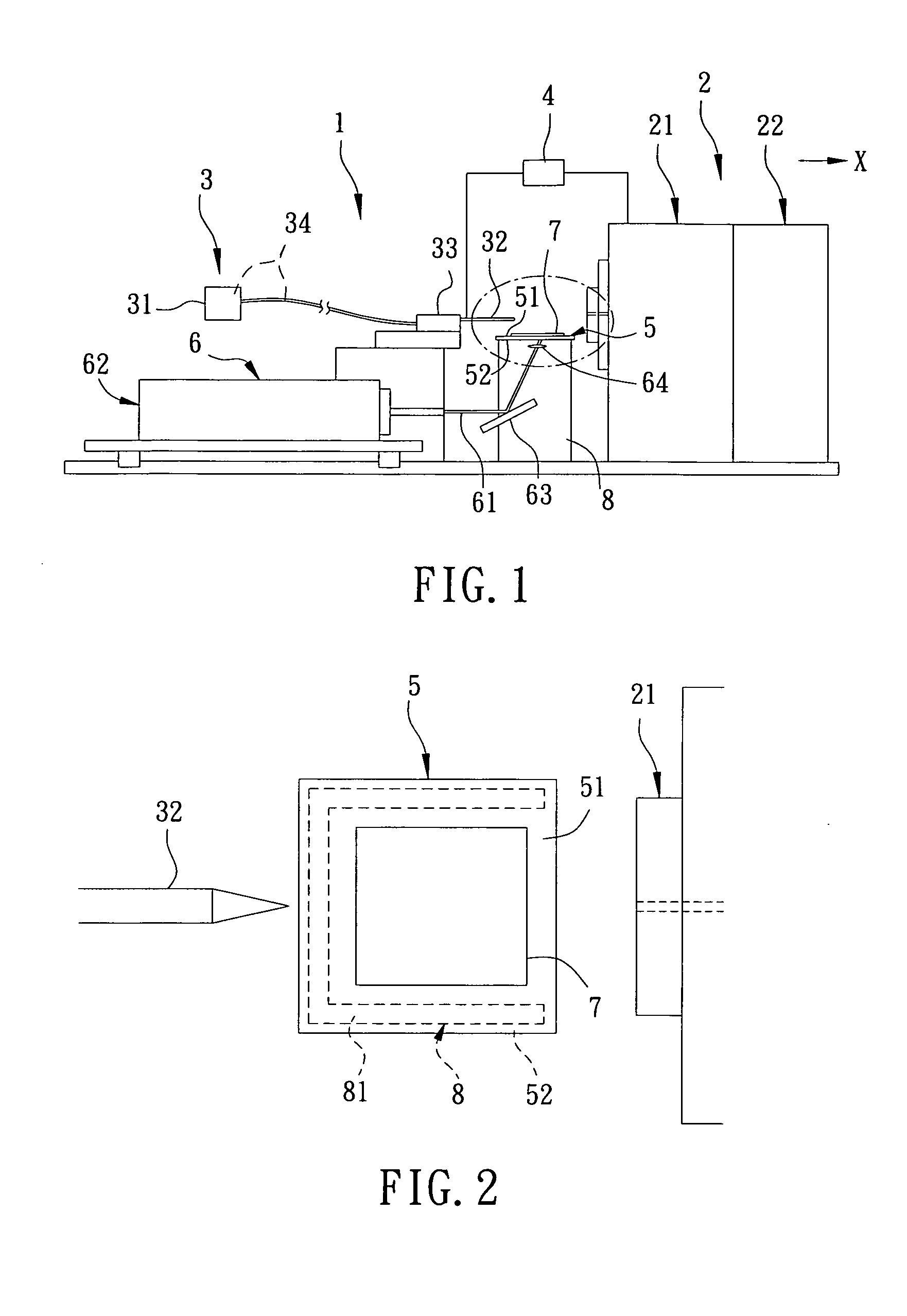
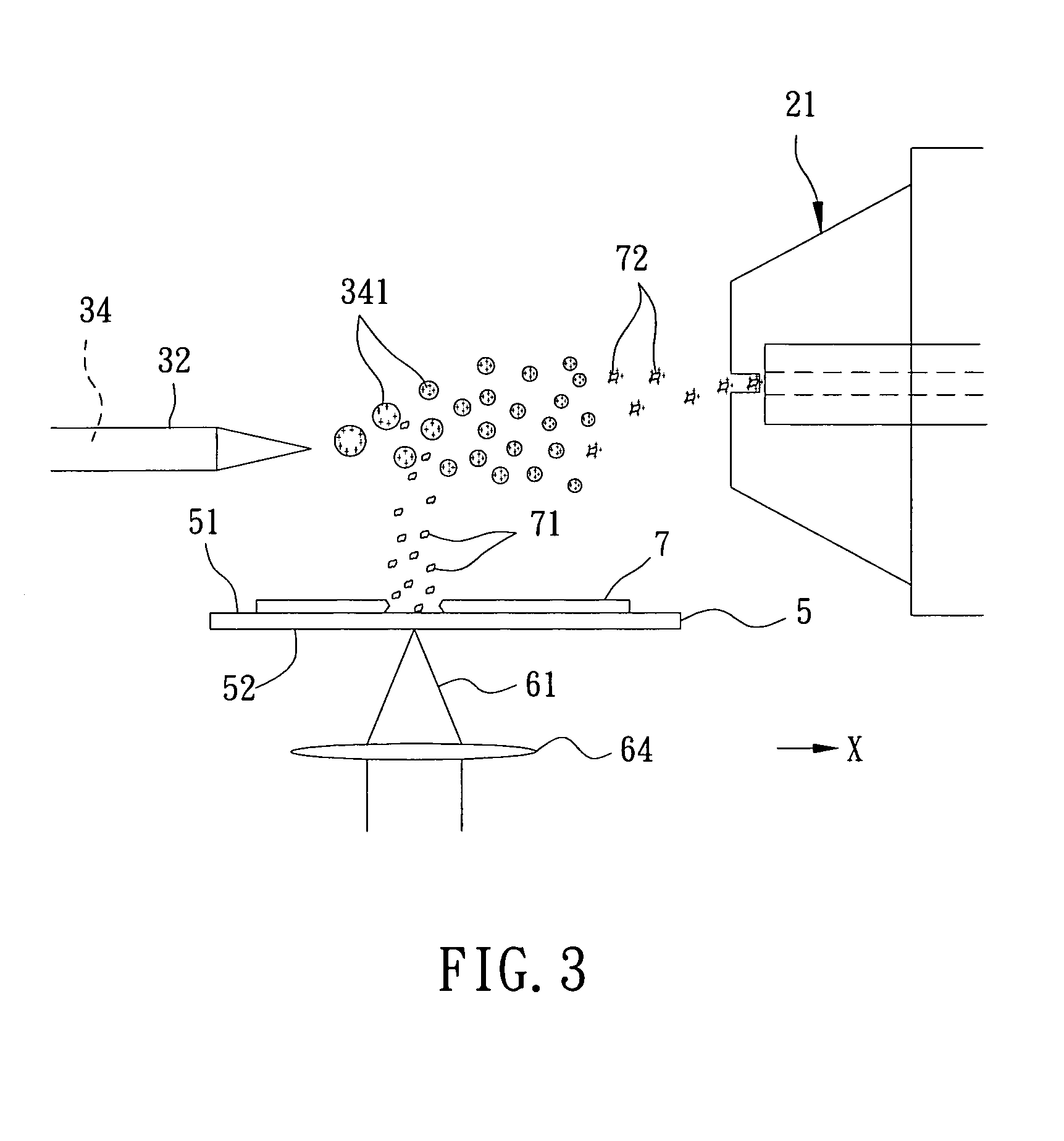
Method and apparatus for surface desorption ionization by charged particles
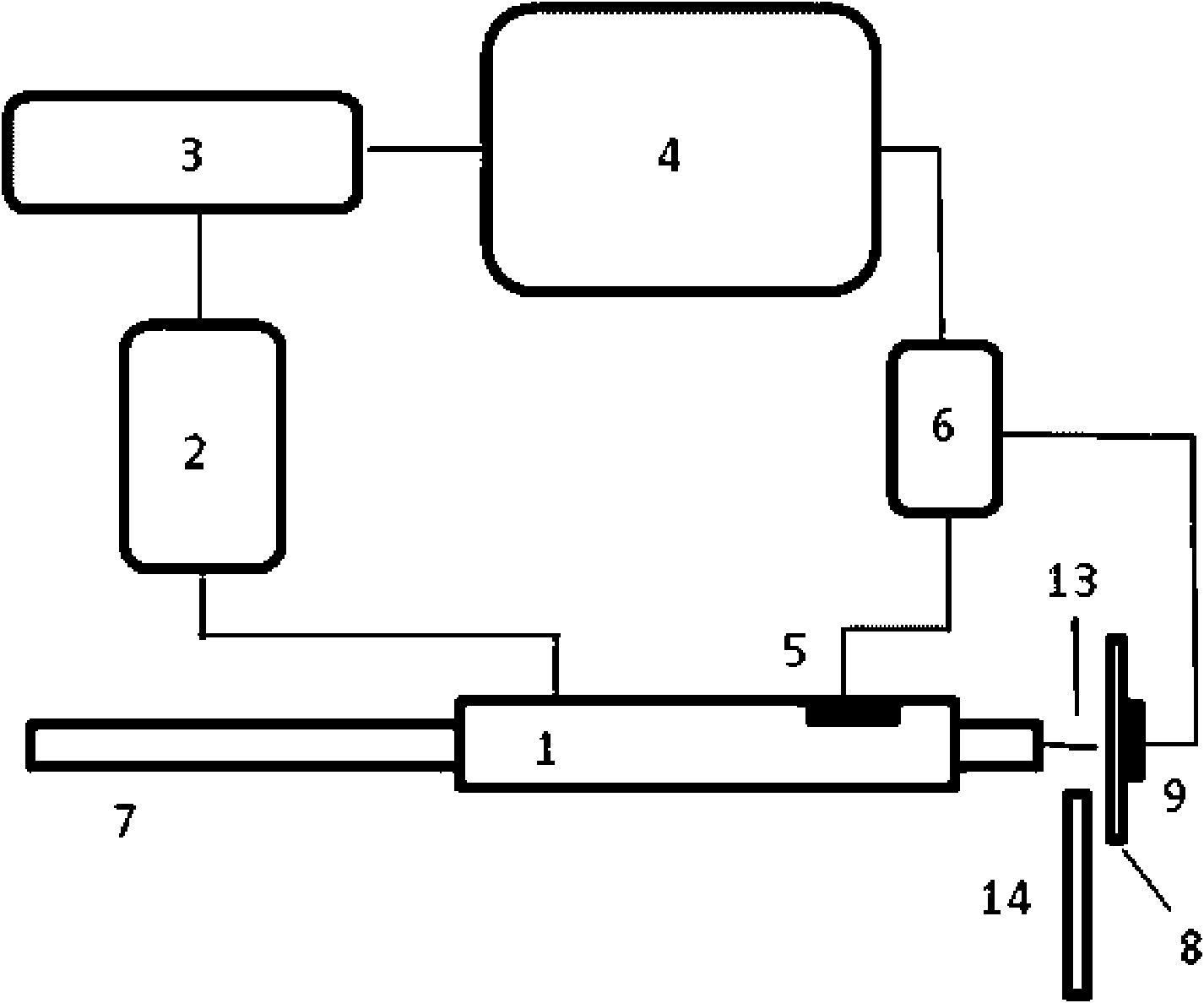
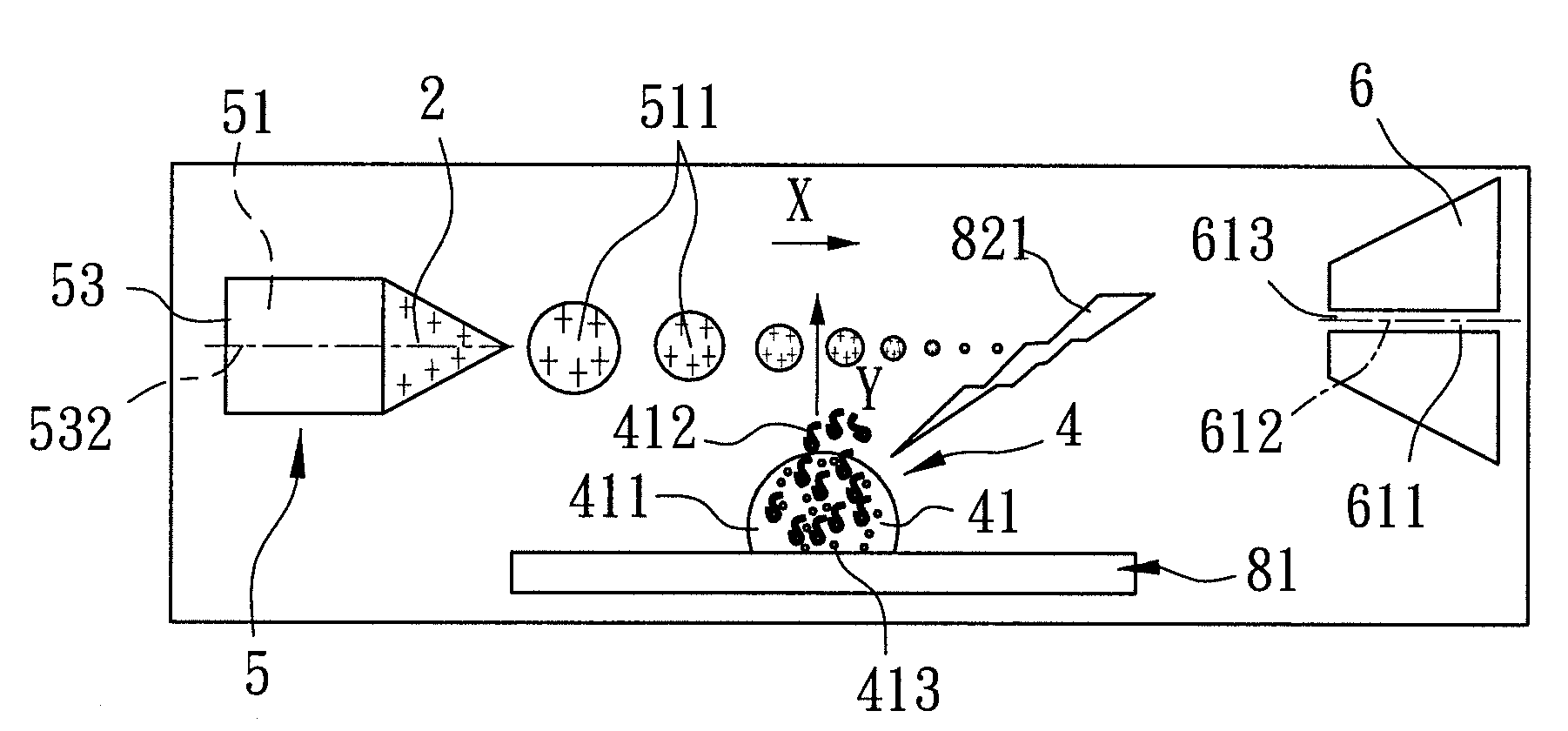
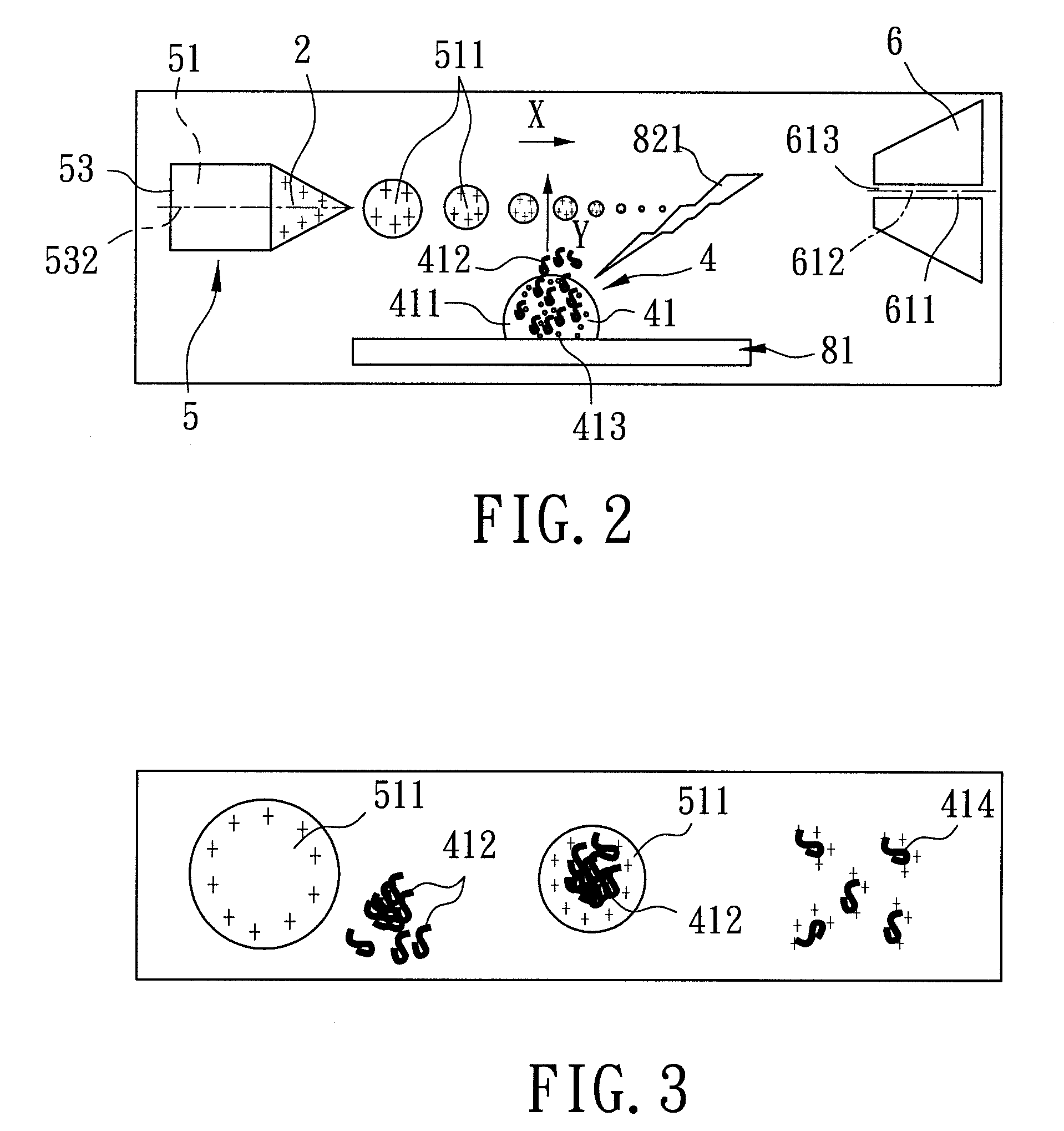
An apparatus and method for generating analyte ions from a sample. An ion generating device is provided having a chamber with an outlet and a surface having a material and means for applying a high velocity gas flow through the chamber toward the outlet such that charged particles are produced by physical interaction between the high velocity gas and the material. The charged particles then induce the generation of primary ions by interaction with molecules of the high velocity gas. The primary ions are emitted from the outlet of the ion generating device toward a sample-bearing surface and analyte ions are generated by impact of the primary ions on the analyte sample on the surface.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Flexible open tube sampling system for use with surface ionization technology
ActiveUS7705297B2Improve efficiencyStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersWide diameterSpectrometer
The present invention is a device to restrict the sampling of analyte ions and neutral molecules from surfaces with mass spectrometry and thereby sample from a defined area or volume. In various embodiments of the present invention, a tube is used to sample ions formed with a defined spatial resolution from desorption ionization at or near atmospheric pressures. In an embodiment of the present invention, electrostatic fields are used to direct ions to either individual tubes or a plurality of tubes positioned in close proximity to the surface of the sample being analyzed. In an embodiment of the present invention, wide diameter sampling tubes can be used in combination with a vacuum inlet to draw ions and neutrals into the spectrometer for analysis. In an embodiment of the present invention, wide diameter sampling tubes in combination with electrostatic fields improve the efficiency of ion collection.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
Apparatus and method for thermal assisted desorption ionization systems
ActiveUS8754365B2Raise transfer toHigh resolutionSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas phaseDesorption
The present invention is directed to a method and device to desorb an analyte using heat to allow desorption of the analyte molecules, where the desorbed analyte molecules are ionized with ambient temperature ionizing species. In various embodiments of the invention a current is passed through a mesh upon which the analyte molecules are present. The current heats the mesh and results in desorption of the analyte molecules which then interact with gas phase metastable neutral molecules or atoms to form analyte ions characteristic of the analyte molecules.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
Apparatus and method for focusing ions and charged particles at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS20020011560A1Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationInductively coupled plasmaElectrospray
Improvements have been made for collection and focusing of ions generated from atmospheric pressure sources such as electrospray, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, inductively coupled plasma, discharge, photoionization and atmospheric pressure matrix assisted laser desorption ionization. A high transmission electro-optical surface is placed between the source regions and the focusing regions to optimize the field geometries and strengths in each respective region. Compression ratios of greater than 5000 are capable of transferring virtually all ions from large volume dispersive ion regions into ion beam cross-sections of less than 1 mm. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric pressure ionization sources.
Owner:SHEEHAN EDWARD W +1
Apparatus and method for thermal assisted desorption ionization systems
ActiveUS20120199735A1Easy to analyzeHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionPower flowDesorption
The present invention is directed to a method and device to desorb an analyte using heat to allow desorption of the analyte molecules, where the desorbed analyte molecules are ionized with ambient temperature ionizing species. In various embodiments of the invention a current is passed through a mesh upon which the analyte molecules are present. The current heats the mesh and results in desorption of the analyte molecules which then interact with gas phase metastable neutral molecules or atoms to form analyte ions characteristic of the analyte molecules.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
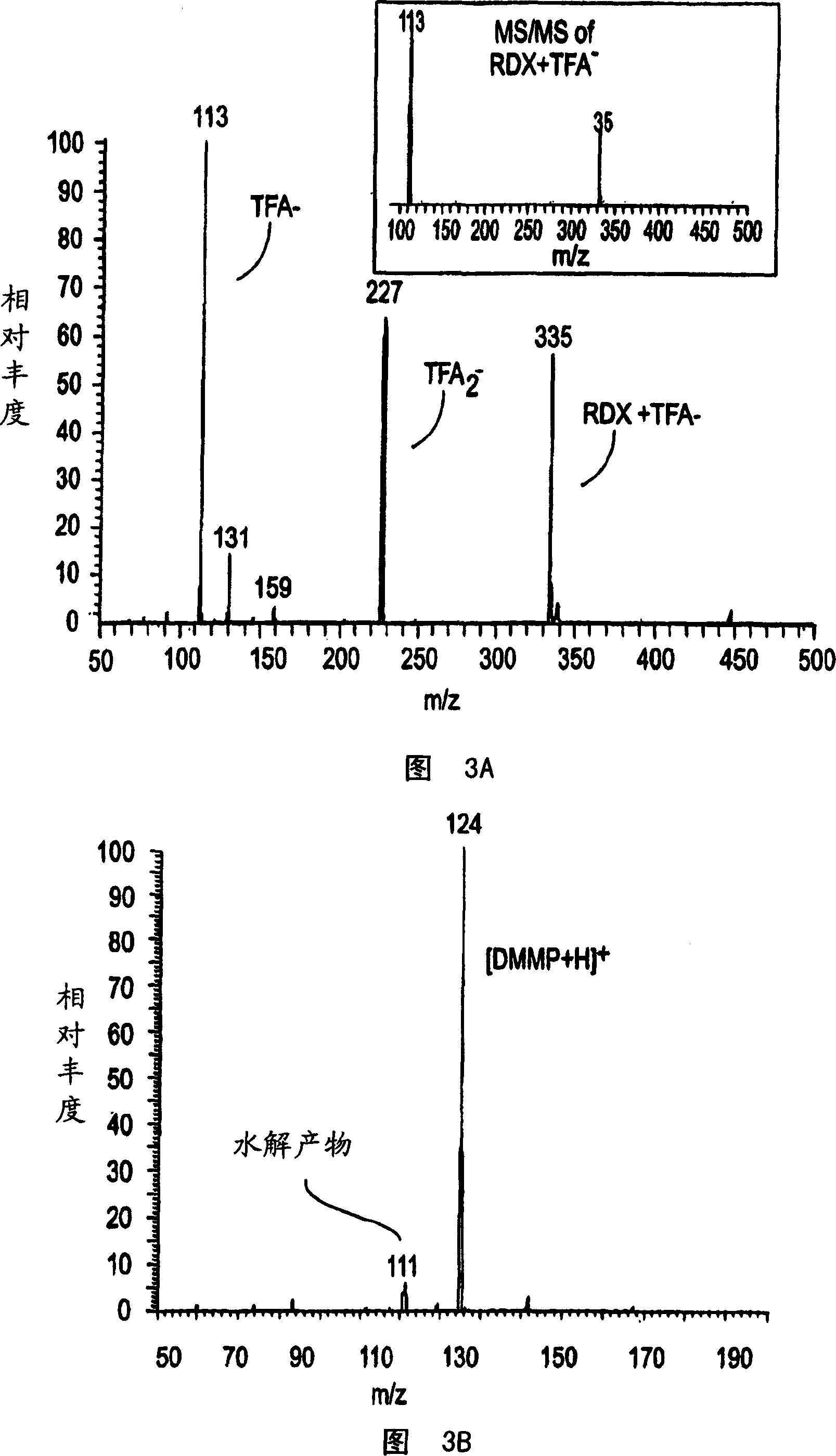
Method and device for desorption ionization by liquid jet
ActiveUS20090302211A1Sufficient energyImprove efficiencySamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementLiquid jetJet flow
The invention relates to method and apparatus for production of gaseous ions from components of a condensed phase sample and analysis thereof, wherein one or more liquid jet(s) is / are directed to the surface of the sample to be investigated, where the impact of the liquid jet on the sample surface produces droplets carrying sample particles which are turned into gaseous ions via the evaporation of liquid or, if desired, by a subsequent ionization after the evaporation and the obtained sample particles are analyzed by a known method.
Owner:SEMMELWEIS EGYETEM
Method and device for producing ions used for analysis under low pressure
The invention relates to a method and device for producing ions used for analysis, in particular to an ionization method and device for producing ions through multiple modes under the lower pressure and enabling multiple ion sources to be compounded and used. According to the method and device, an electrospray ion source and other desorbing / ionization devices (such as laser desorbing ion sources) are placed in the same vacuum cavity and act on sample molecules in the vacuum cavity independently or commonly, and the irons produced by ionization are fed into an ion analyzer to be analyzed through an ion focusing device.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Graphene matrix and application of graphene matrix in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight-mass spectrometry detection
InactiveCN102426187AUnique physical propertiesUnique chemical propertiesPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMetaboliteNucleotide
The present invention discloses a graphene matrix and an application of the graphene matrix in matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization-time of flight-mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) detection. According to the present invention, in the MALDI-TOF-MS, the graphene is adopted as an assisted matrix, such that the analysis and the detection of the materials including from the small molecule compounds to the biological macromolecules can be efficiently and rapidly achieved; importantly the background interference of the molecular ion peak of the traditional organic matrix can be effectively eliminated so as to achieve the analysis and the detections of amino acids, lipid compounds, peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides, and other structural molecules; the MALDI-TOF-MS adopting the graphene as the matrix is the desorption ionization method, which does not require addition of any organic matrixes, such that the decomposition of the analyte can be avoided, and good reproducibility and high salt tolerance are provided; the efficient and rapid detection method is provided for the natural products and the biological metabolites; the method further can be used for the detection of the common biological macromolecules, and can be popularized and applied in all the MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry so as to achieve the deep application of the graphene.
Owner:程金生
Method and device for desorption ionization by liquid jet
ActiveUS8314382B2Improve efficiencyOverall light weightSamplingParticle separator tubesLiquid jetPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to method and apparatus for production of gaseous ions from components of a condensed phase sample and analysis thereof, wherein one or more liquid jet(s) is / are directed to the surface of the sample to be investigated, where the impact of the liquid jet on the sample surface produces droplets carrying sample particles which are turned into gaseous ions via the evaporation of liquid or, if desired, by a subsequent ionization after the evaporation and the obtained sample particles are analyzed by a known method.
Owner:SEMMELWEIS EGYETEM
Sample supporting body and method of manufacturing sample supporting body
ActiveUS20170358436A1Easy to handleEasy to obtainSamples introduction/extractionPreparing sample for investigationPhysicsSurface-assisted laser desorption/ionization
A sample support according to an aspect is a sample support for a surface-assisted laser desorption / ionization method, and includes: a substrate in which a plurality of through-holes passing from one surface thereof to the other surface thereof are provided; and a conductive layer that is formed of a conductive material and covers at least the one surface. The through-holes have a width of 1 to 700 nm, and the substrate has a thickness of 1 to 50 μm.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
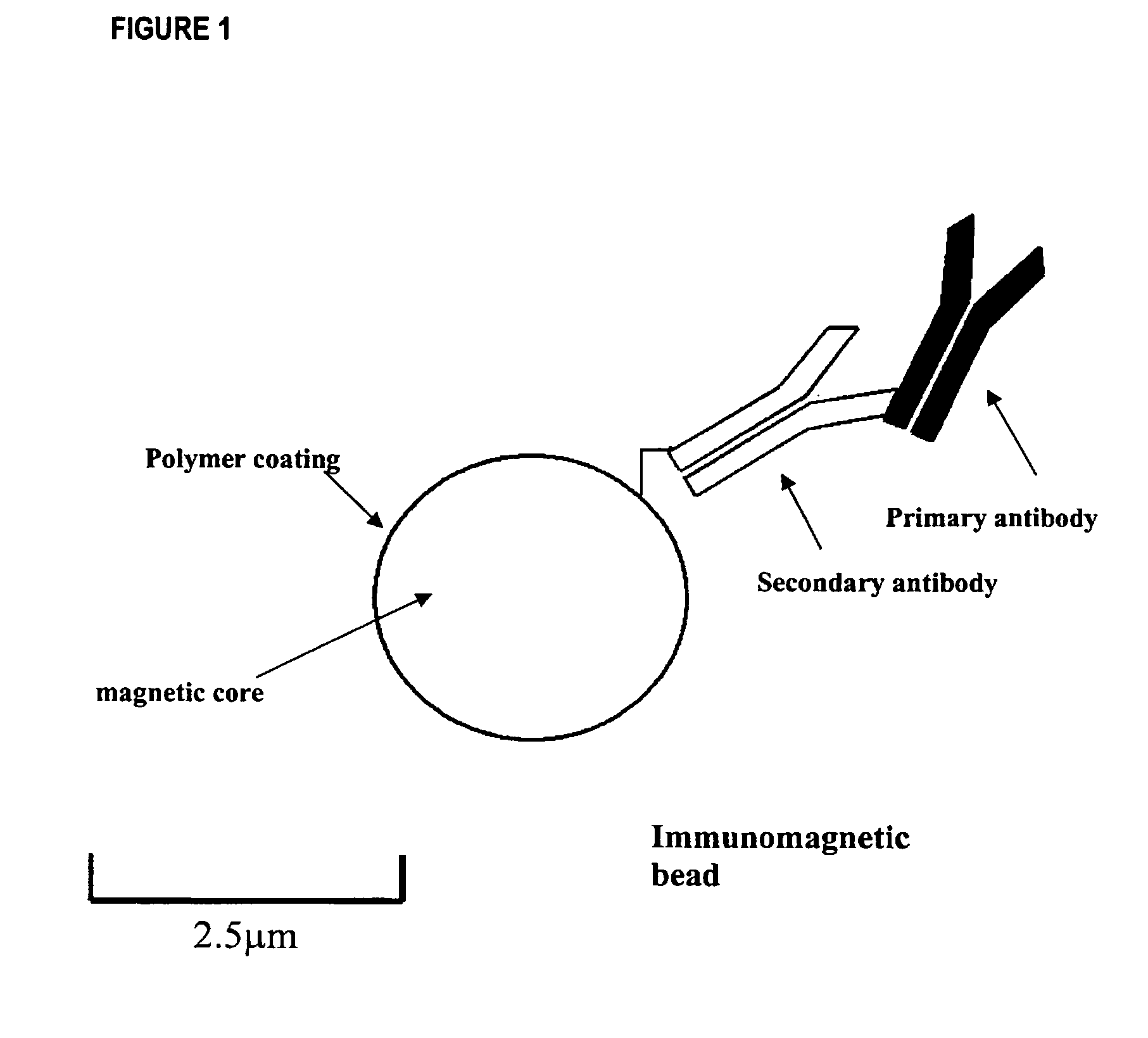
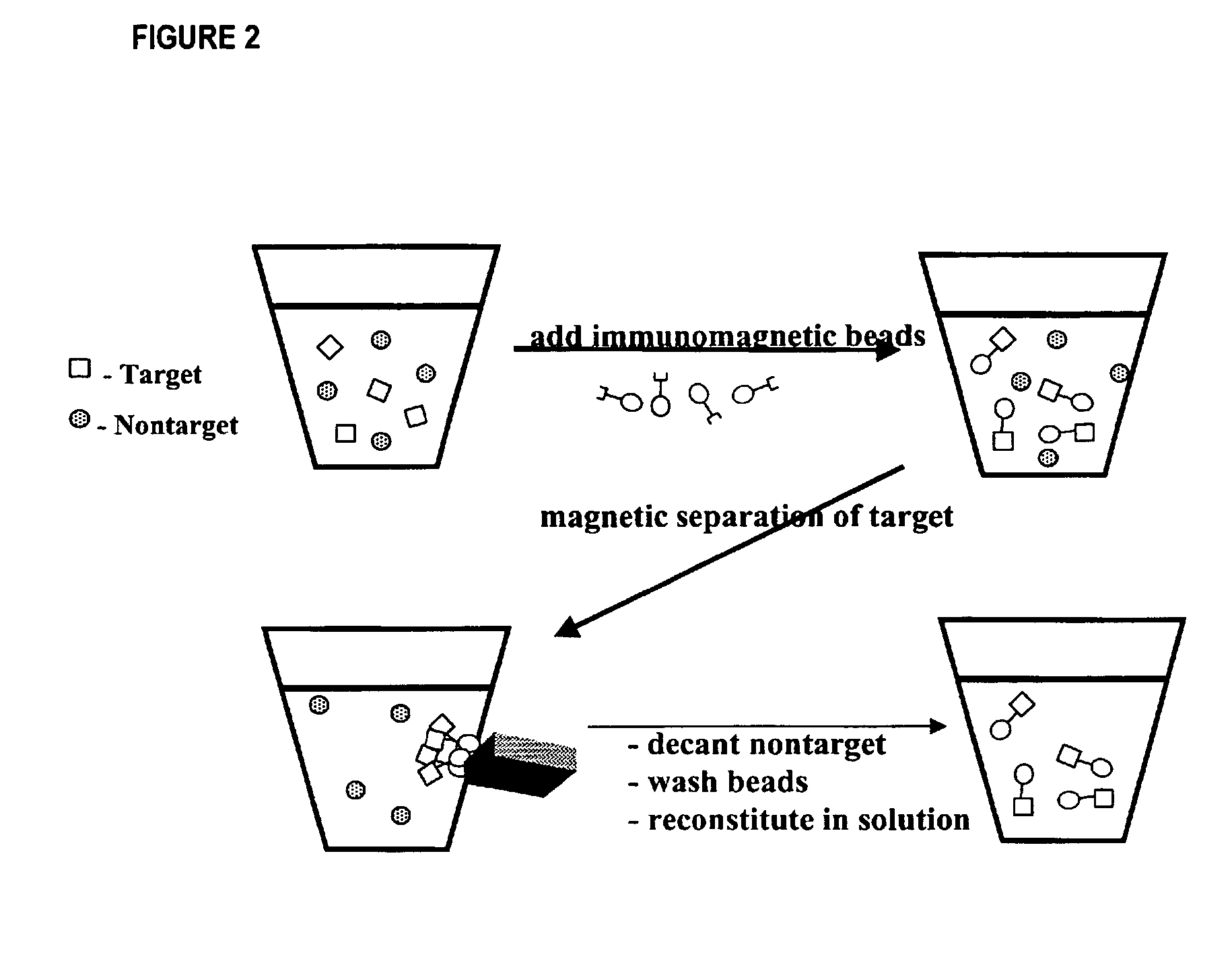
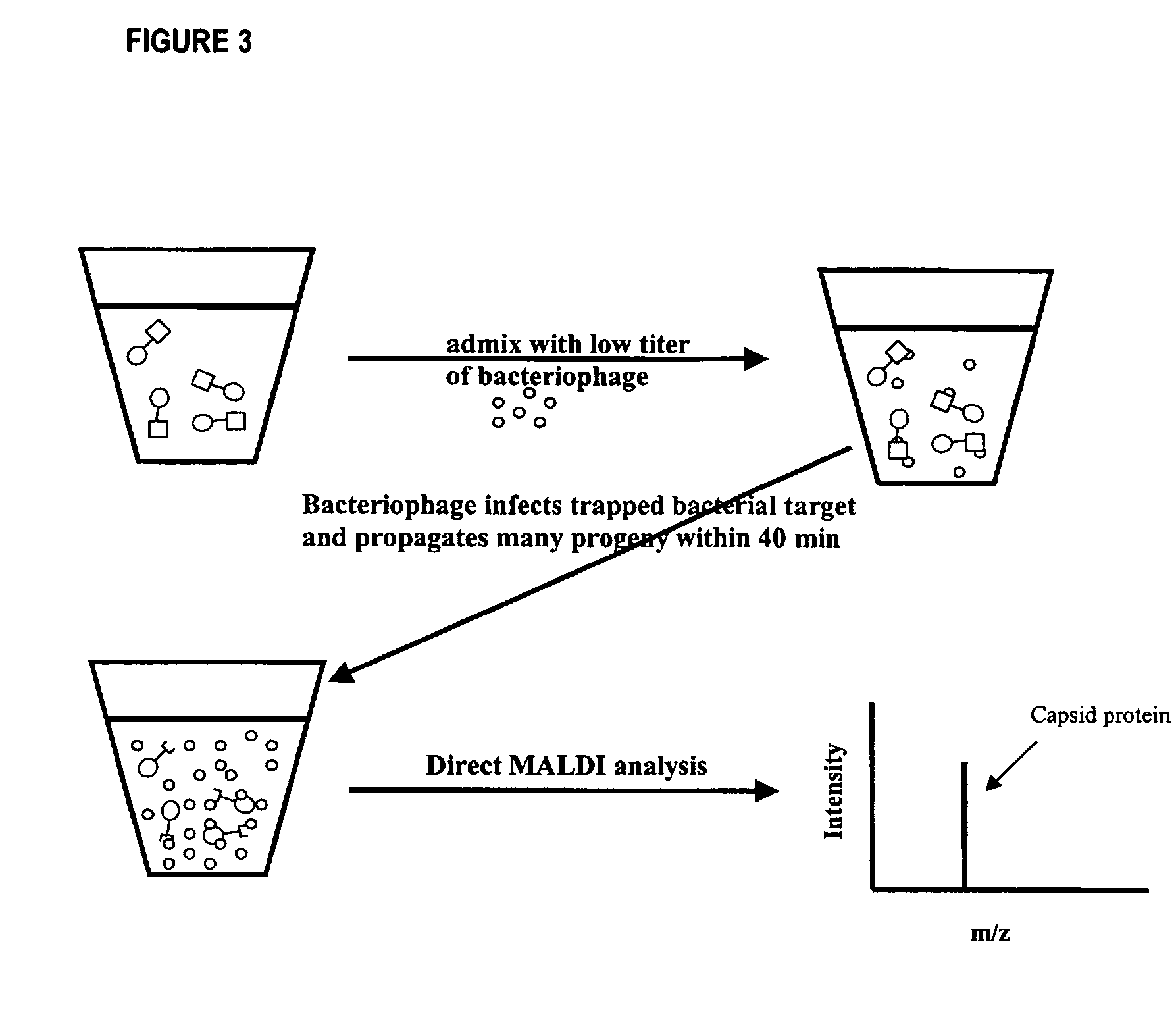
Method for detecting low concentrations of a target bacterium that uses phages to infect target bacterial cells
InactiveUS7166425B2Reduce concentrationBiocideComponent separationTime-of-flight mass spectrometryBacteriophage
The invention is directed to a method for detecting low concentrations of bacteria in liquid solution that may or may not be complex liquid solutions. In one embodiment, immunomagnetic separation (IMS) is used to separate target bacterium that may be in a liquid mixture from other constituents in the mixture. A low concentration of a bacteriophage for the target bacteria is subsequently used to infect target bacterial cells that have been captured using the IMS technique. If at least a certain concentration of target bacterium are present, the bacteriophage will multiply to a point that is detectable. Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization / time-of-flight-mass spectrometry (MALDI / TOF-MS) is then used to produce a mass spectrum that is analyzed to determine if one or more proteins associated with the bacteriophage are present, thereby indirectly indicating that target bacterium were present in the liquid mixture.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
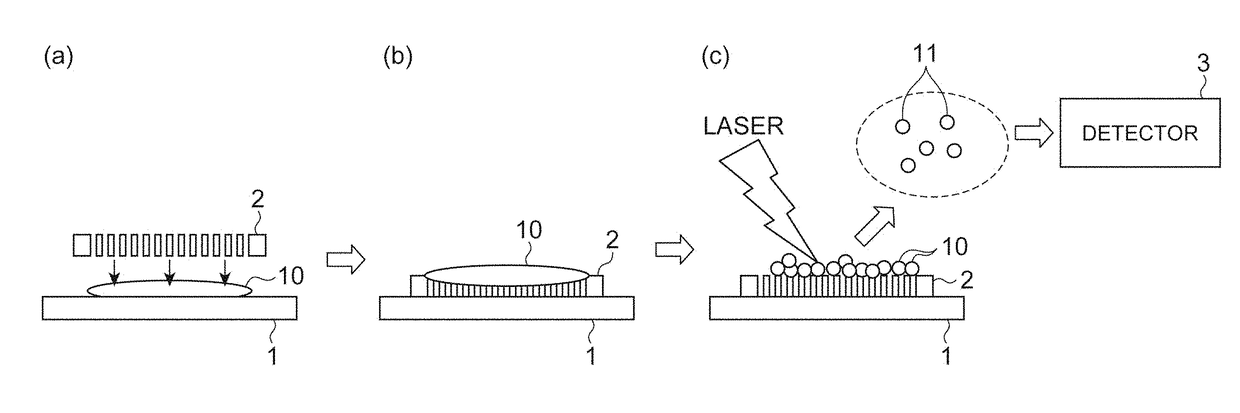
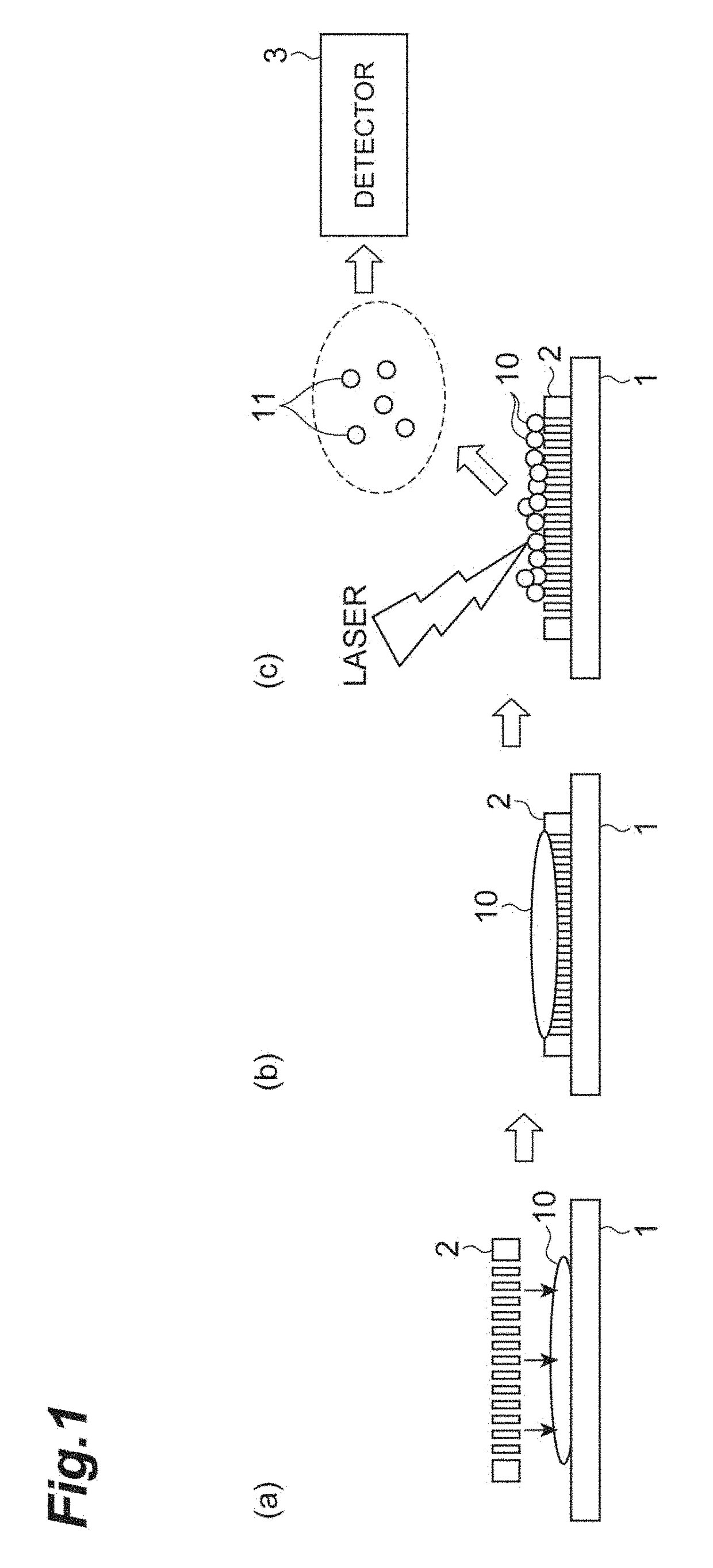
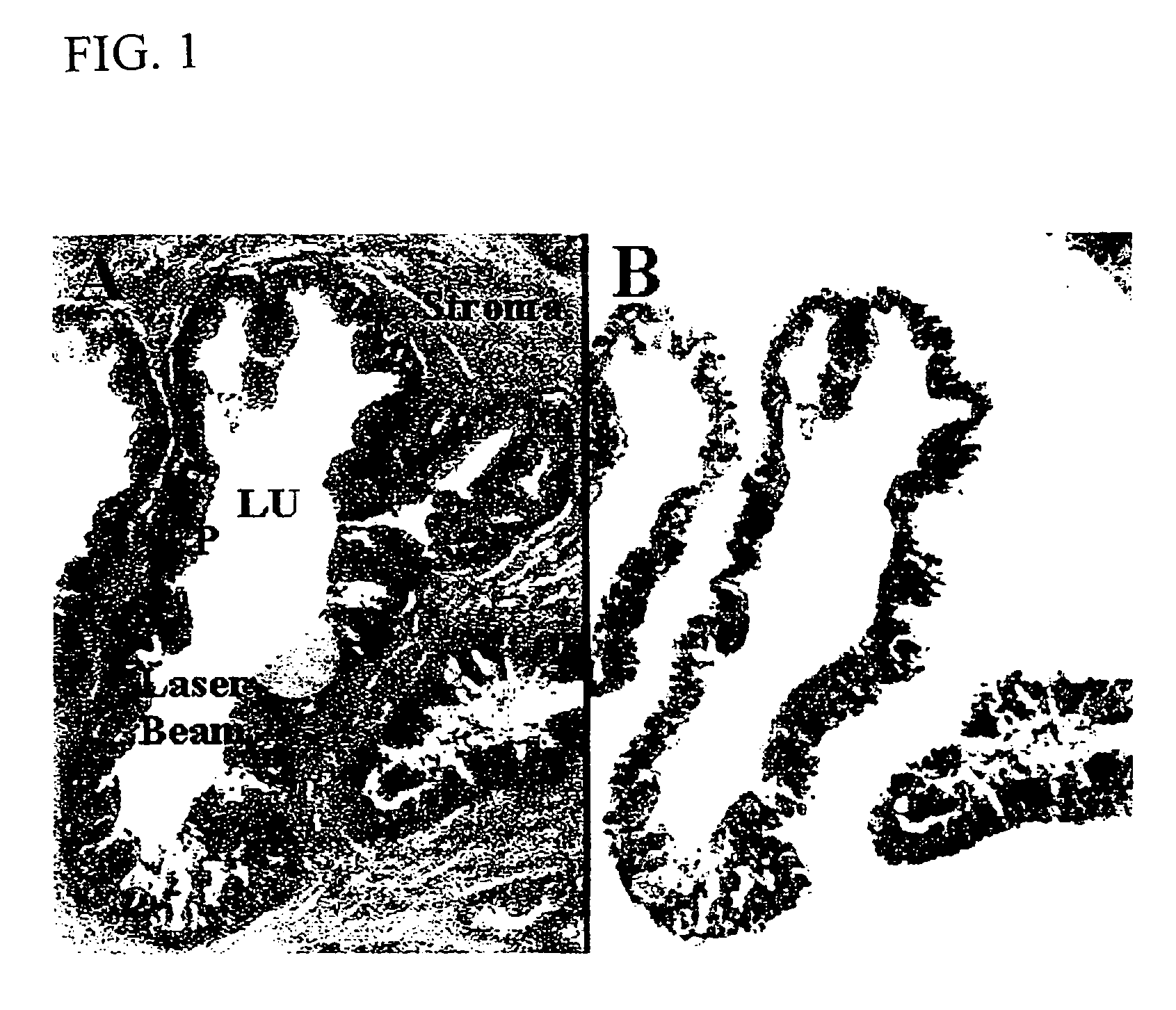
Methods for direct biomolecule identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20070114375A1Particle separator tubesIsotope separationLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention relates to the use of post source decay (PSD) or collision induced dissociation (CID) direct tissue (DT) MALDI-TOF or DT-MALDI-TOF-TOF mass spectrographic identification of biological molecules in a tissue or cellular sample without the need for further protein extraction. This method provides for studying cells or tissues by direct tissue MALDI (DT-MALDI), thereby substituting in situ protein release for further protein extraction. Mass / intensity data was processed with Mascot© software interrogation of the NCBI database. These results are proof of principle that DT-MALDI, combined with bioinformatics, can directly identify proteins in cells and tissues from their mass spectra.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
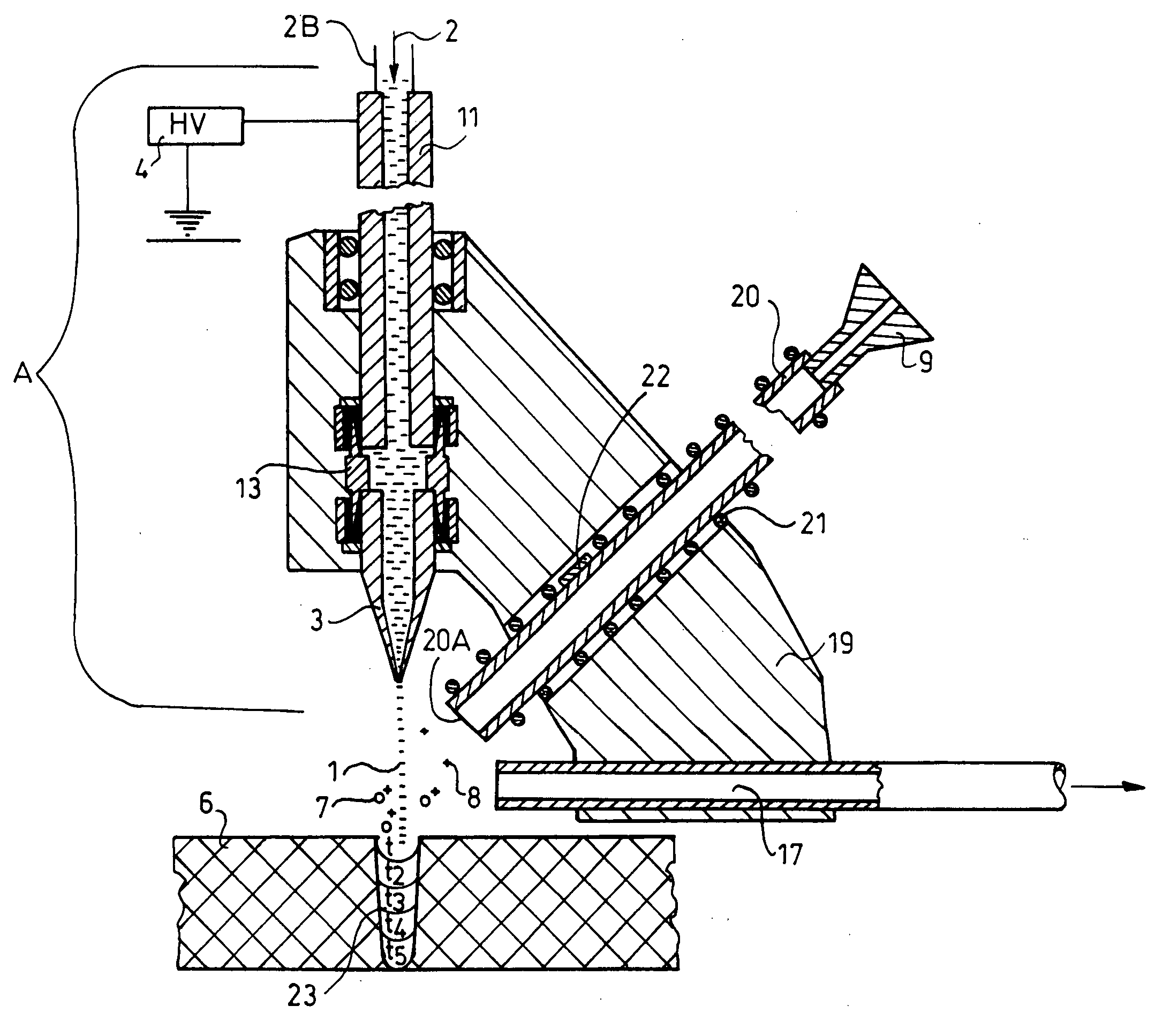
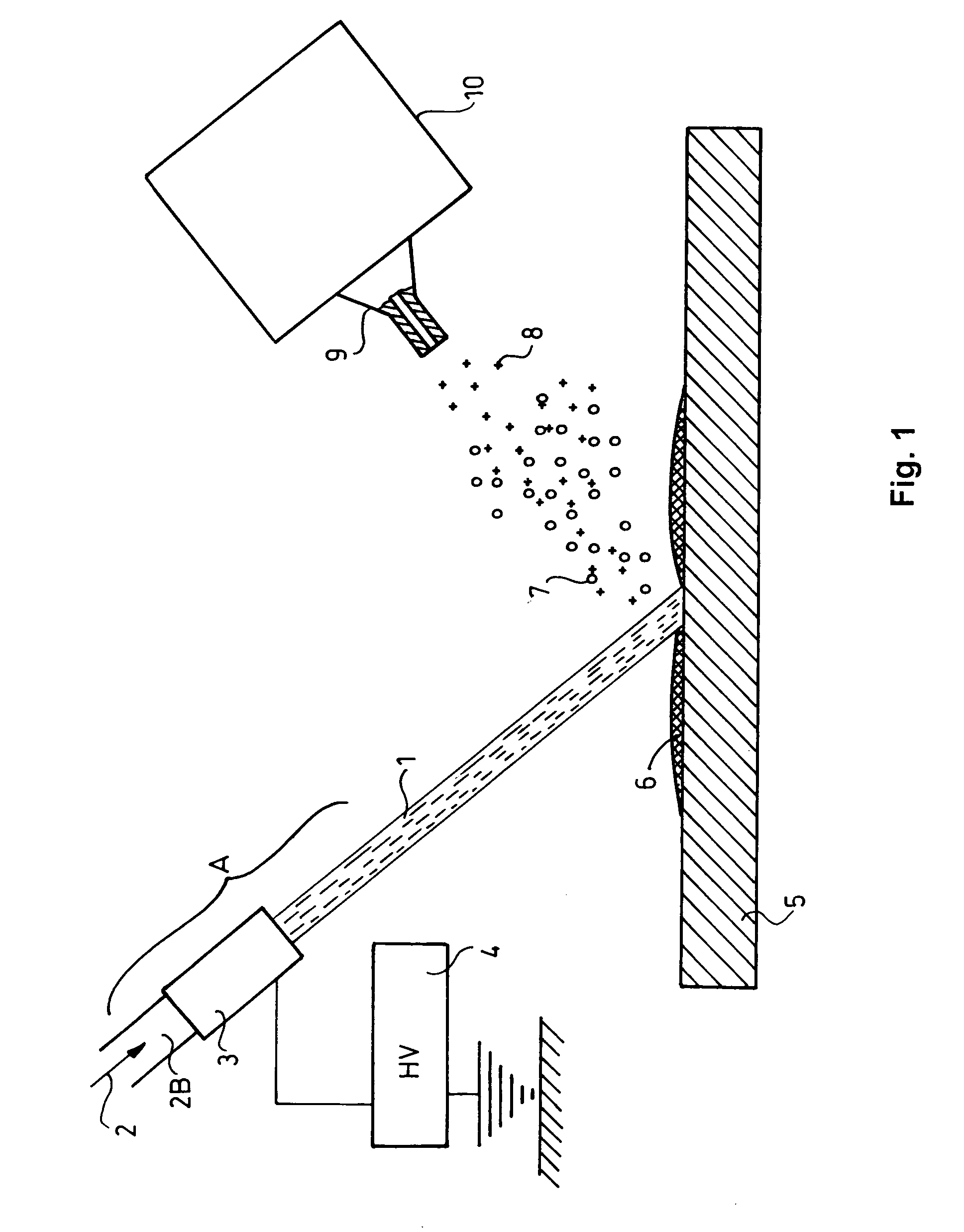
Electrospray-assisted laser-induced acoustic desorption ionization mass spectrometer and a method for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20080308722A1Particle separator tubesIsotope separationAnalyteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A mass spectrometer includes: an electrospray unit for forming liquid drops of an electrospray medium; a voltage supplying member disposed to allow the liquid drops to be laden with a plurality of charges for heading toward a receiving unit along a traveling path; a substrate having a sample surface for placement of a sample and an irradiated surface opposite to the sample surface; and a laser transmission mechanism for irradiating the irradiated surface. The substrate permits propagation of laser energy therethrough such that laser energy is passed on to at least one analyte in the sample via the substrate so that the analyte is desorbed to fly along a flying path intersecting the traveling path to enable occlusion of the analyte in the liquid drops. As a result of dwindling in size of the liquid drops, charges will pass on to the analyte to form a corresponding ionized analyte.
Owner:NAT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
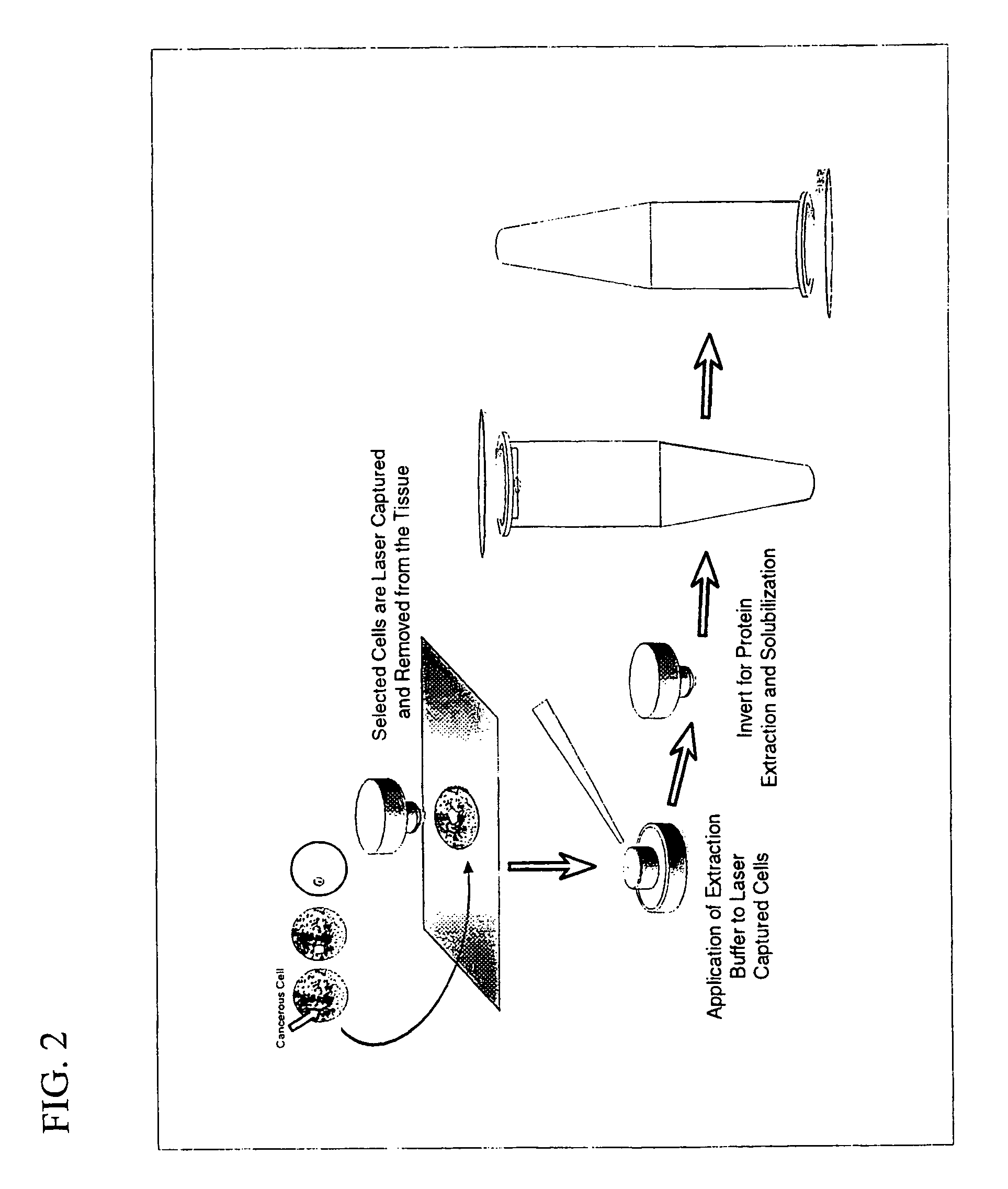
Methods for the isolation and analysis of cellular protein content
InactiveUS6969614B1Rapid and reliable to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesLymphatic SpreadPresent method
The present invention describes devices and methods for performing protein analysis on laser capture microdissected cells, which permits proteomic analysis on cells of different populations. Particular disclosed examples are analysis of normal versus malignant cells, or a comparison of differential protein expression in cells that are progressing from normal to malignant. The protein content of the microdissected cells may be analyzed using techniques such as immunoassays, 1D and 2D gel electrophoresis characterization, Western blotting, liquid chromatography quadrapole ion trap electrospray (LCQ-MS), Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization / Time of Flight (MALDI / TOF), and Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption Ionization Spectroscopy (SELDI). In addition to permitting direct comparison of qualitative and quantitative protein content of tumor cells and normal cells from the same tissue sample, the methods also allow for investigation of protein characteristics of tumor cells, such as binding ability and amino acid sequence, and differential expression of proteins in particular cell populations in response to drug treatment. The present methods also provide, through the use of protein fingerprinting, a rapid and reliable way to identify the source tissue of a tumor metastasis.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
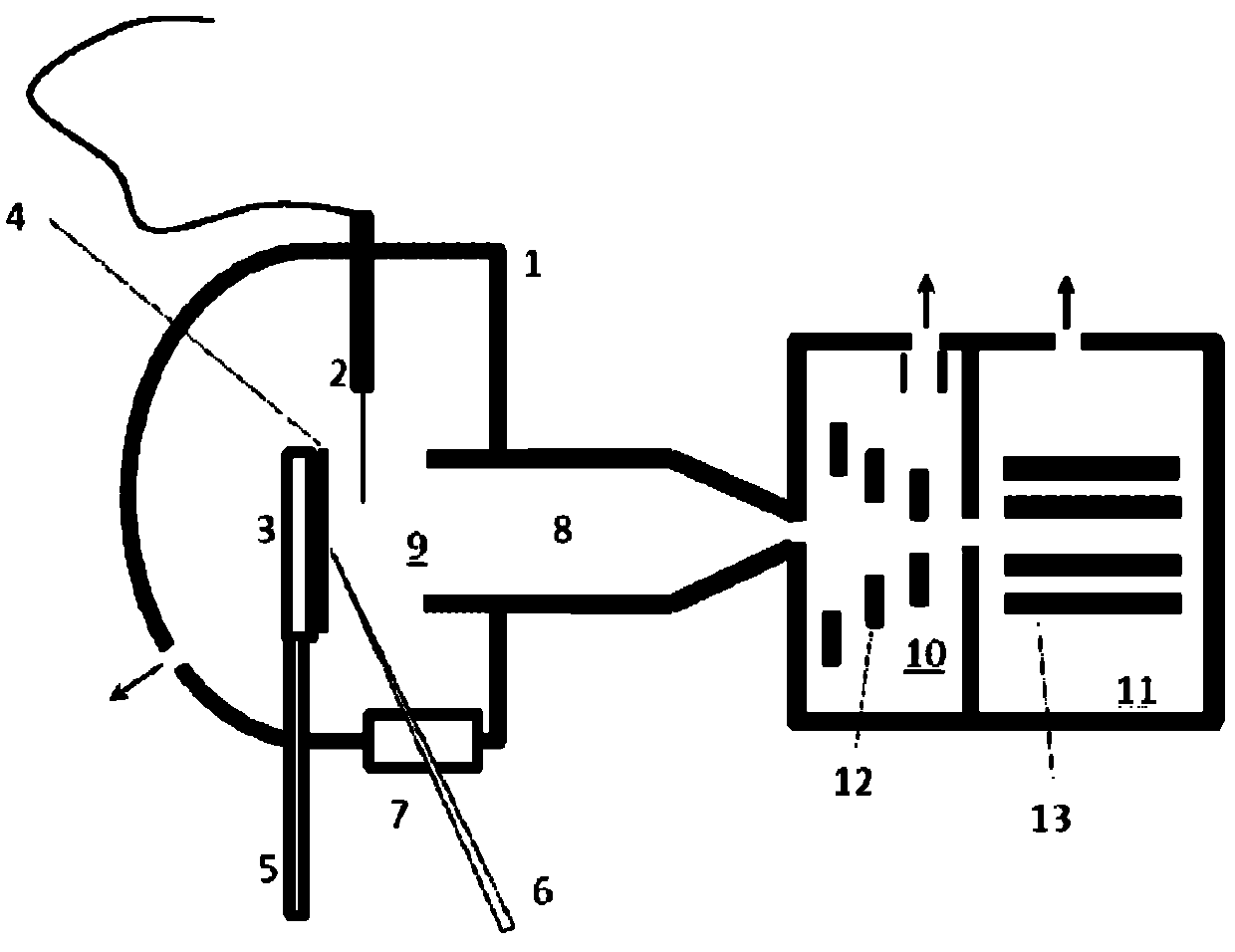
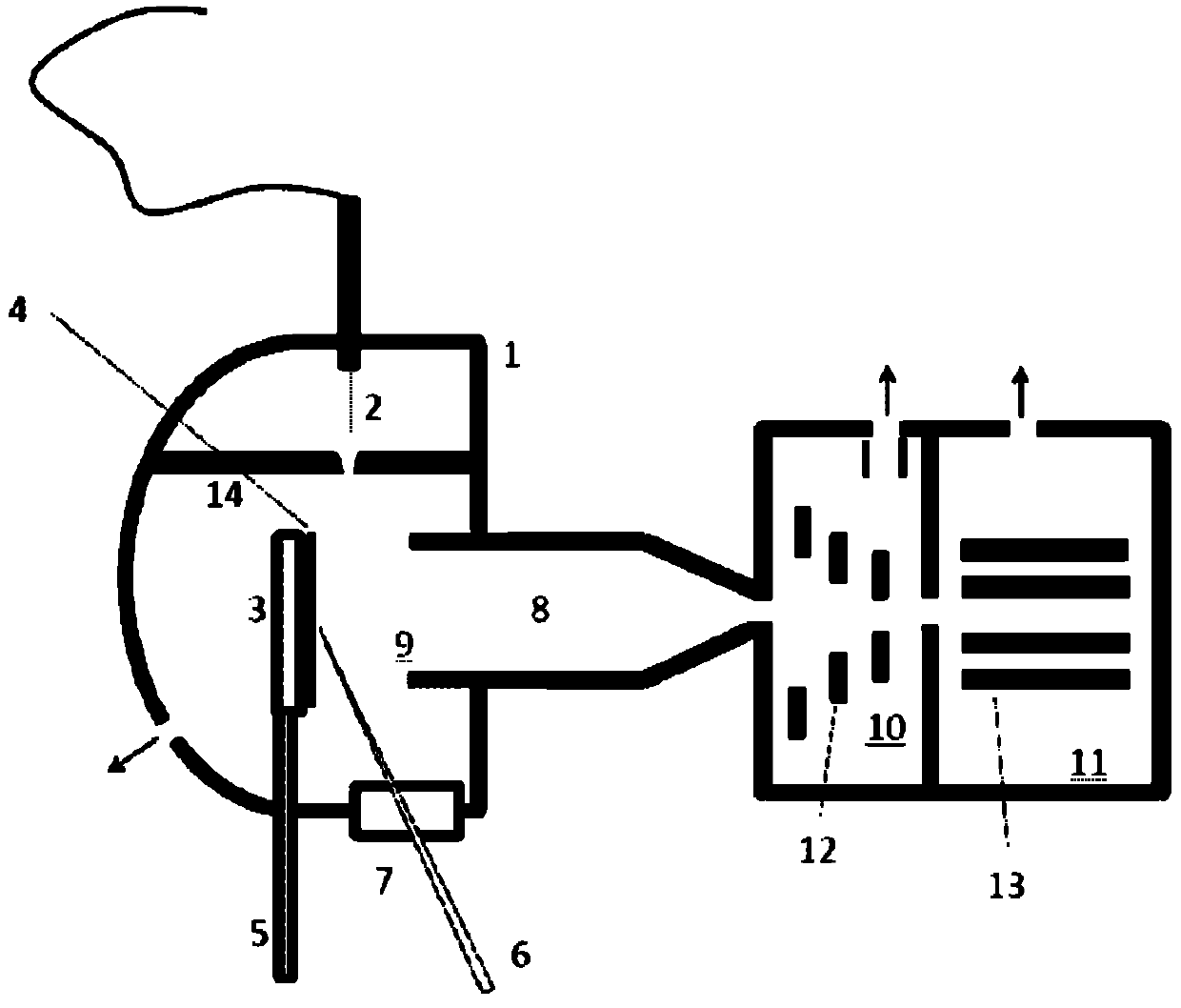
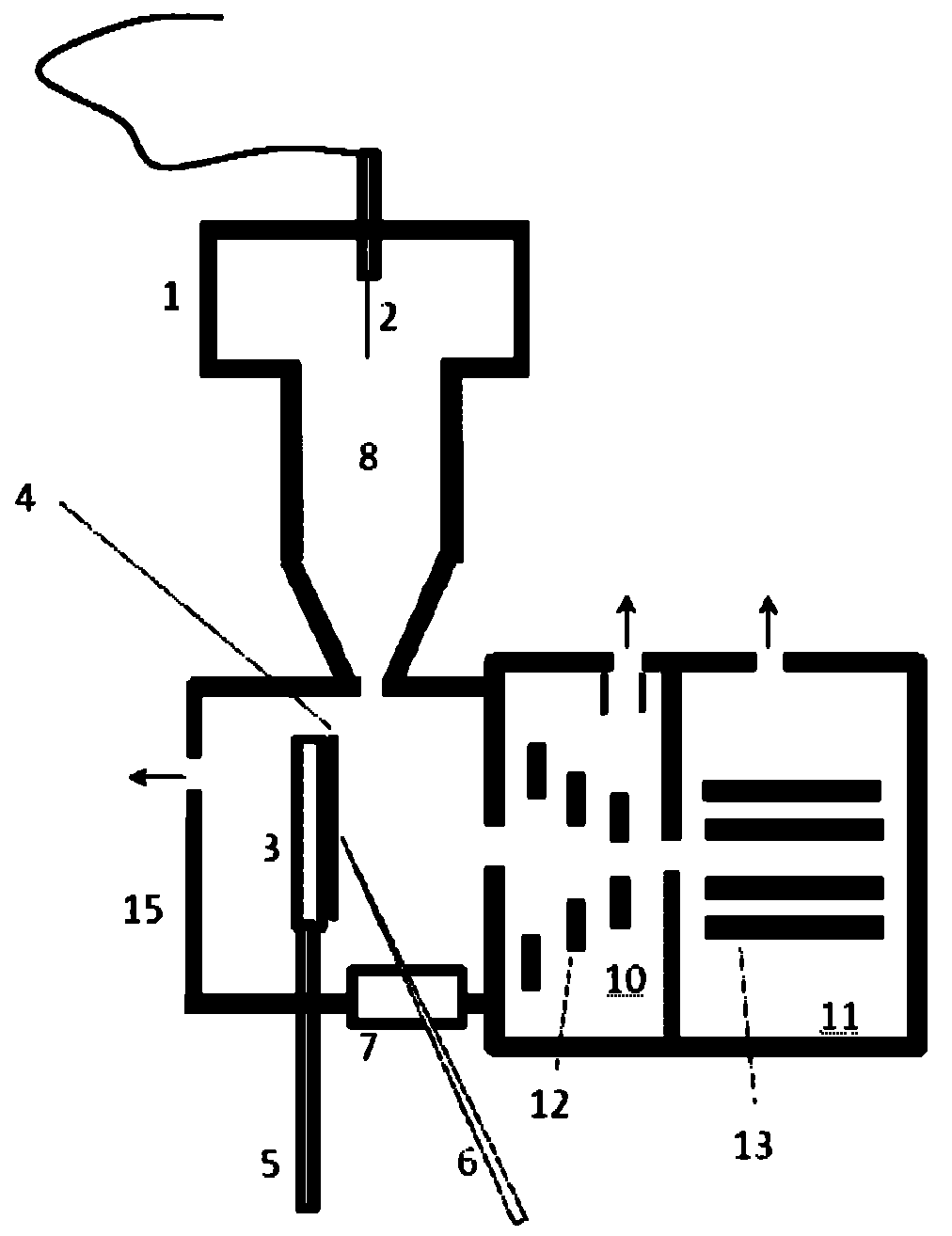
Method and device thereof for desorption ionization
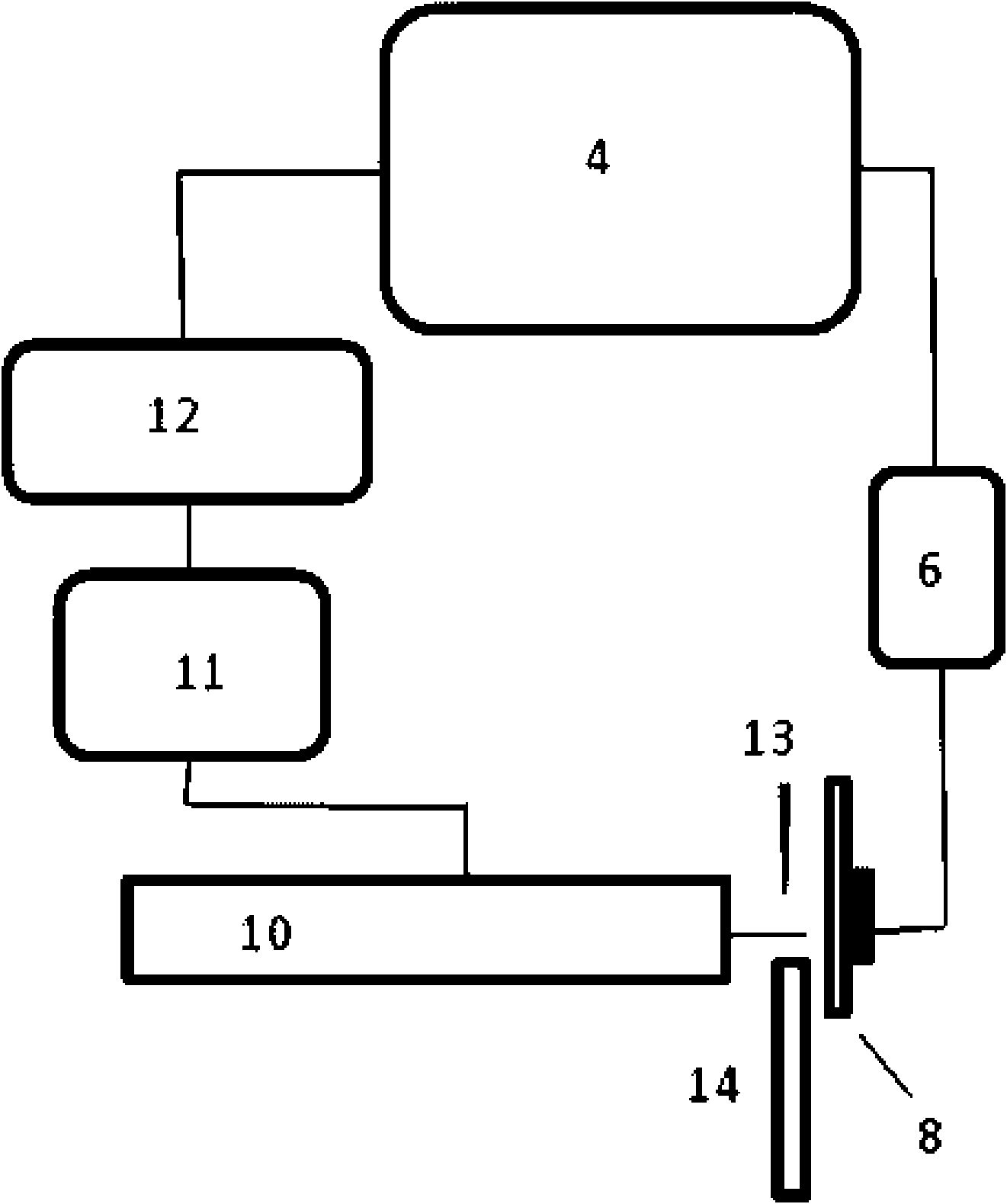
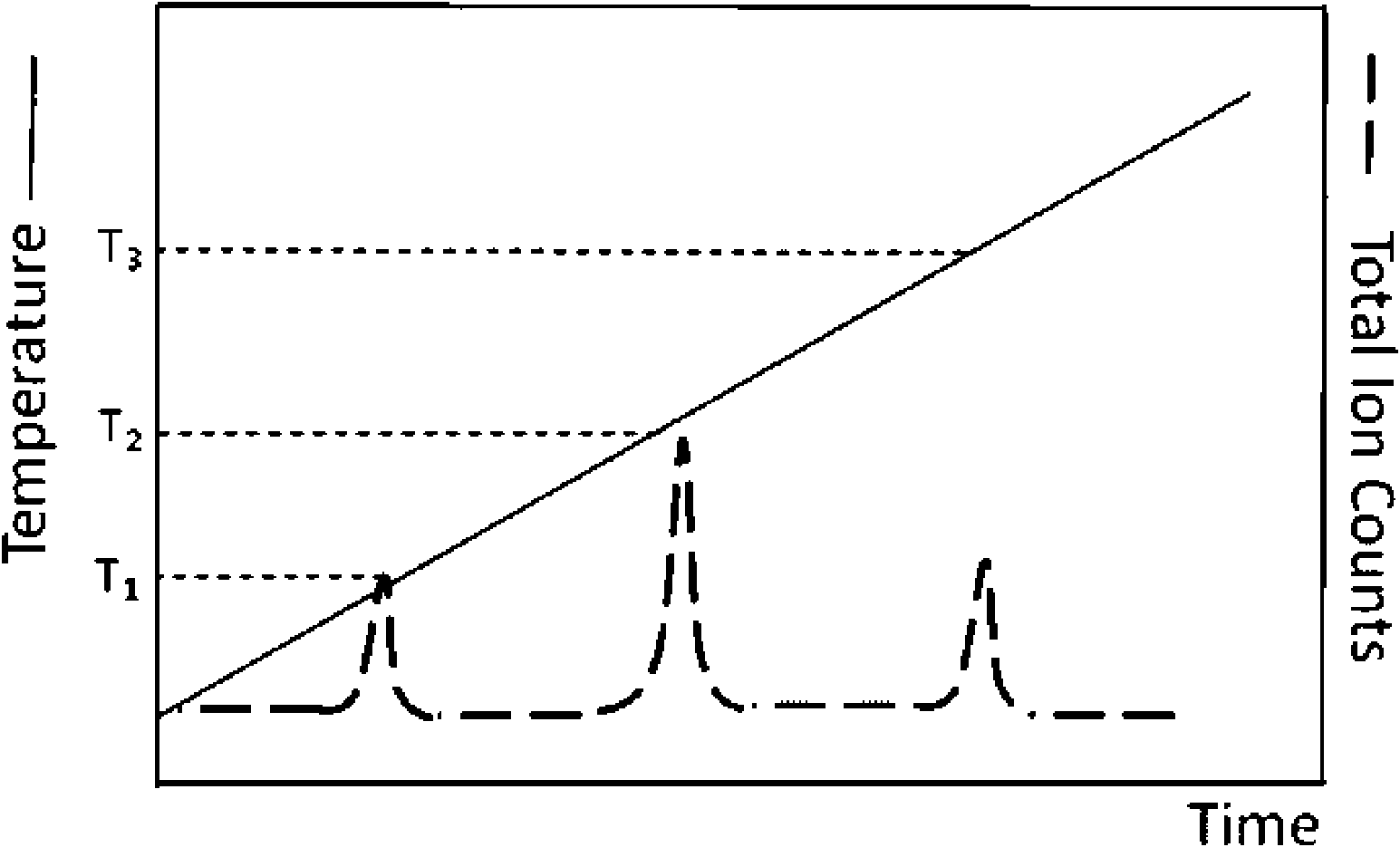
InactiveCN101871914AReduce difficultyImprove detection efficiencySamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBoiling pointData acquisition
The invention relates to a method and a device thereof, which adopt a mode of rising the temperature gradually under normal pressure to carry out desorption ionization in sequence on mixed objects to be tested on the solid surface and carry out continuous and multiple data acquisition in the process of desorption ionization gradually. The invention leads the objects to be tested with different thermal desorption capabilities to be desorbed out of the surface of the solid object to be tested by rising the temperature of at least one part of samples gradually, thus providing a means for pre-separating mixed samples so as to reduce the difficulty for subsequent mass spectrometric detection. Simultaneously, the invention acquires mass spectrometric data for multiple times for objects to be tested with various boiling points in the process of rising temperature so as to lead the objects to be tested with low boiling point not to be consumed completely quickly due to high temperature, thus improving the detection efficiency of the objects to be tested with lower boiling points.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB SHANGHAI
Methods and compositions for assessing a sample by maldi mass spectrometry
The invention provides methods for preparing a sample for matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI). In general, the methods involve: binding analytes in a sample to capture agents that are bound to matrix that is present in a plurality of wells of a multi-well sample plate, washing any unbound analytes from the matrix, cleaving any bound analyte / capture agent complexes with a MALDI cleavage agent, and depositing the cleavage products on a multi-sample MALDI sample plate. Kits and other compositions are provided for performing the subject methods. The subject invention finds use in methods of simultaneously assessing the presence of several analytes in a single sample, and, as such, the invention finds use in a variety of different medical, research and proteomics applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Molecular detection by matrix free desorption ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20080113875A1High sensitivityLibrary screeningBiological testingMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMolecular binding
The present invention provides methods for obtaining information of a plurality of target molecules by matrix free LDI MS. Mass tagged complexes for detection of target molecules comprise a target molecule binding domain, and a mass tag separated by a cleavable linker. Methods of the invention may be used for example to analyze the distribution of a multiple target molecules in a complex sample, such as a tissue section.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Ionization source for mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS7368728B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryGas phase
A new ionization source named Surface Activated Chemical Ionization (SACI) has been discovered and used to improve the sensitivity of the mass spectrometer. According to this invention the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer is heated and contains a physical new surface to improve the ionization process. The analyte neutral molecules that are present in gas phase are ionized on this surface. The surface can be made of various materials and may also chemically modified so to bind different molecules. This new ionization source is able to generate ions with high molecular weight and low charge, an essential new key feature of the invention so to improve sensitivity and reduce noise. The new device can be especially used for the analysis of proteins, peptides and other macromolecules. The new invention overcomes some of the well known and critical limitations of the Electrospray (ESI) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
Laser desorption device, mass spectrometer assembly, and method for ambient liquid mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20080116366A1Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansDesorptionEngineering
An electrospray-assisted laser desorption ionization device includes: an electrospray unit including a nozzle; a voltage supplying member disposed to establish between the nozzle and a receiving unit a potential difference such that liquid drops of the electrospray medium formed at the nozzle are laden with charges, and such that the liquid drops are forced to leave the nozzle toward the receiving unit along a traveling path; a laser desorption unit adapted to irradiate a sample such that, upon irradiation, analytes contained in the sample are desorbed to fly along a flying path which intersects the traveling path so as to enable the analytes to be occluded in the liquid drops, and such that as a result of dwindling in size of the liquid drops when moving along the traveling path, charges of the liquid drops will pass on to the analytes occluded therein to form ionized analytes.
Owner:NAT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Desorption ionization device used in mass spectrometer
ActiveCN101520432AAtmospheric pressure direct analysis technology is perfectImprove the ionization effectMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometersDesorptionUltraviolet
The invention relates to a desorption ionization device which carries out desorption to a measured object with a solid surface at atmospheric pressure by laser and then carries out ionization to the object after desorption by utilizing vacuum-ultraviolet light. The device comprises a laser generating laser beams, an optical laser system used for converging the laser beams on the surface of the measured object so as to lead the measured object in the sample to be desorbed or gasified, and an ultraviolet lamp which is arranged near the desorbed or gasified part and gives off ultraviolet rays soas to lead molecules of at least one part of the desorbed or gasified object to be ionized. Being combined with a spraying apparatus, the desorption ionization device has higher ionization efficiencyto nonpolar or low-polar micromolecules. The desorption ionization device can be applicable to fast sync analysis of complex mixtures with different polarities and molecular weights by utilizing vacuum-ultraviolet light / electron spray. Meanwhile, the design of the multichannel chamber structural keeps the local concentration of each component in an ion source effectively when a test is carried out, thereby improving the ionization efficiency.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB SHANGHAI
Application for analyzing micromolecules with irradiating nanometer carbon spots serving as matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix
InactiveCN102645481AOvercoming the inability to efficiently analyze small molecule samplesReduce processing requirementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectroscopyBiomarker discovery
The invention discloses application for analyzing micromolecules with irradiating nanometer carbon spots serving as a matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix. The carbon spots serve as an analysis method of the MALDI matrix and are suitable to mass spectrum analysis for the micromolecules with the m / z between 150-1000. Suitable molecule types comprise amino acid, polypeptide, beta-exhilarant, fatty acid, polymer and the like. When the method is used for detecting the molecule with the m / z between 150-1000, background peaks hardly exist to produce background interference. The method can be effectively used in the fields of organic and biomass spectrometry, spectrometry imaging, protein spectroscopy, metabonomics, biomarker discovery, environment analysis and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com