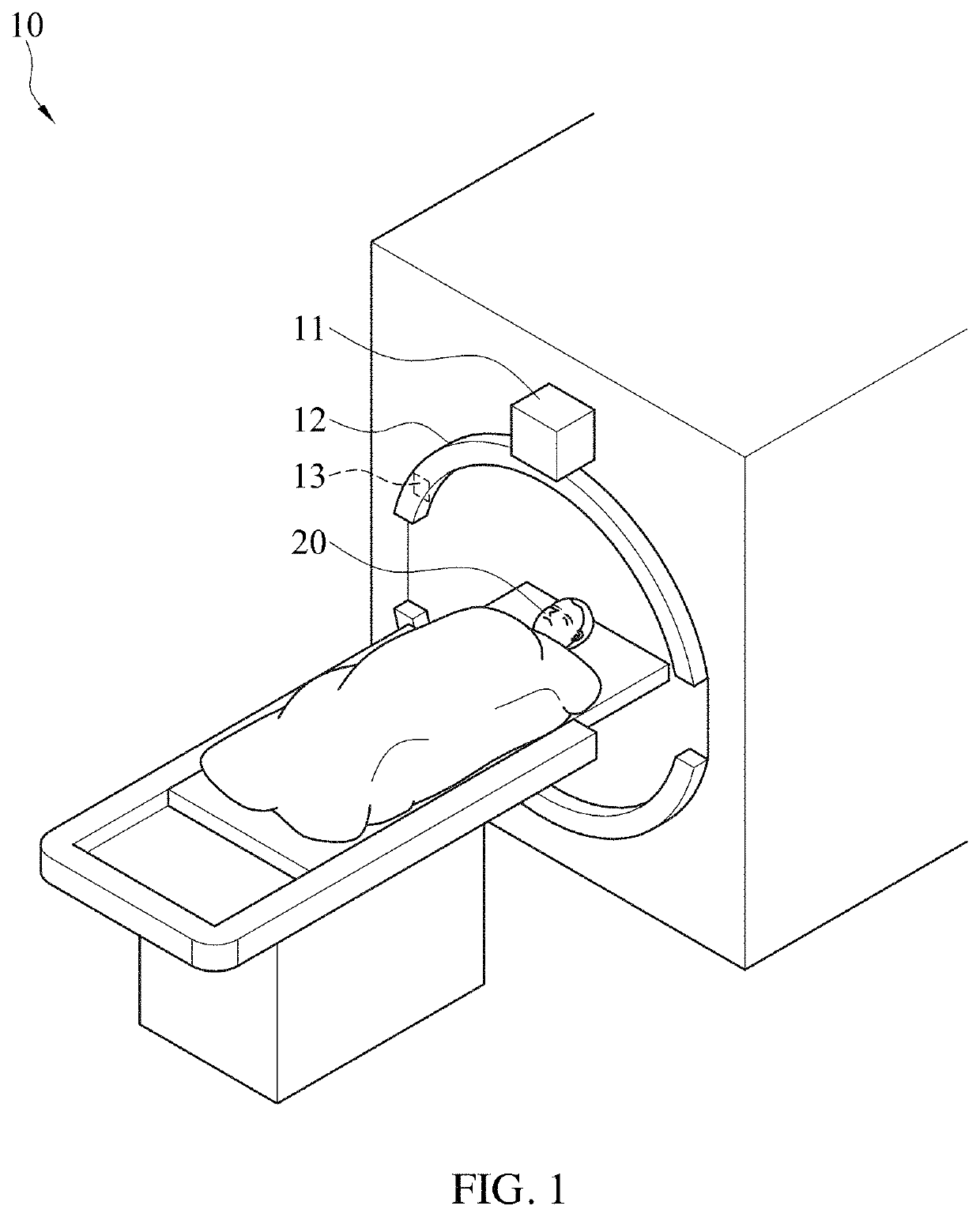
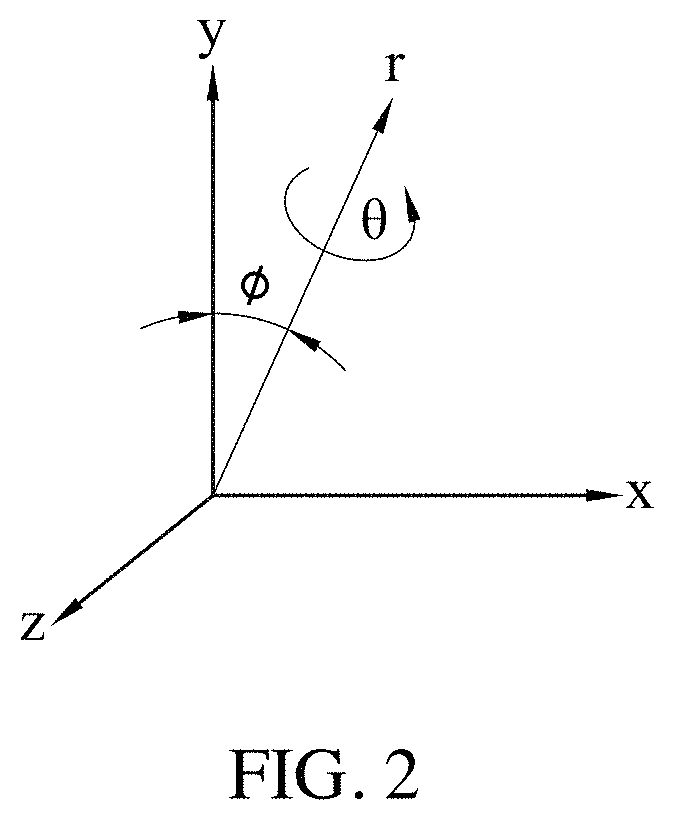
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Electron tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron tomography (ET) is a tomography technique for obtaining detailed 3D structures of sub-cellular macro-molecular objects. Electron tomography is an extension of traditional transmission electron microscopy and uses a transmission electron microscope to collect the data. In the process, a beam of electrons is passed through the sample at incremental degrees of rotation around the center of the target sample. This information is collected and used to assemble a three-dimensional image of the target. For biological applications, the typical resolution of ET systems are in the 5–20 nm range, suitable for examining supra-molecular multi-protein structures, although not the secondary and tertiary structure of an individual protein or polypeptide.
Extended electron tomography
ActiveUS20090283676A1High resolutionMicroscopic object acquisitionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationData setImage resolution
A method for improving image resolution of a three dimensional structure of at least one molecule conformation includes: determining a three dimensional structure of at least one conformation of a molecule in a sample from a first data set obtained from a series of 2D measurements of different geometrical projections of the molecule at a low electron beam dose in an electron microscope; producing a second data set including calculated two dimensional projections of the determined three dimensional structure of the at least one conformation of the same molecule; correlating data from a third data set obtained from at least one measurement of the same molecule using a higher electron beam dose with the second data set; and using the correlated data to improve the resolution of the three dimensional structure of the at least one conformation of the molecule by increasing the first data set with the correlated data and re-determining a three dimensional structure.
Owner:OKINAWA INST OF SCI & TECH PROMOTION CORP
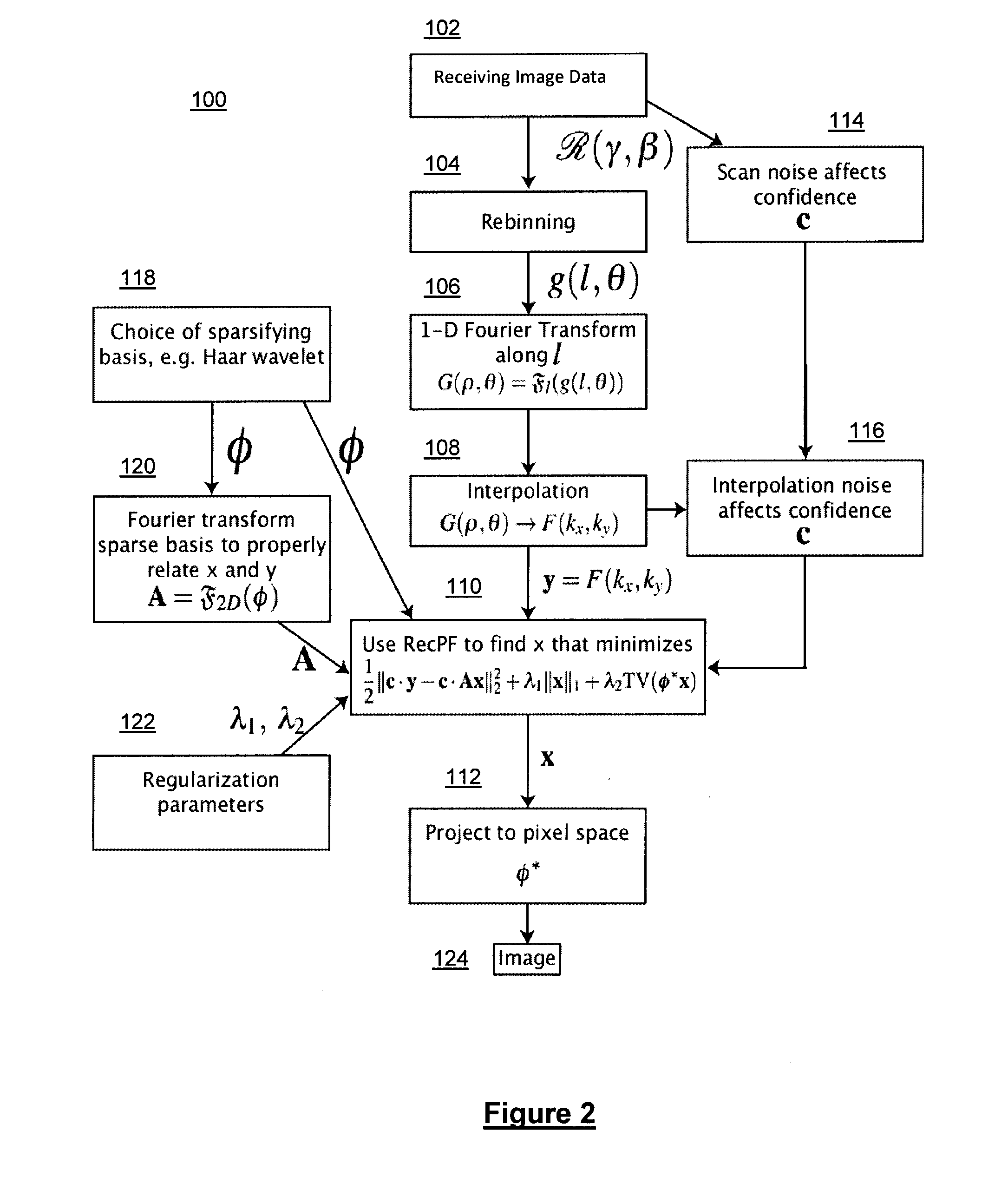
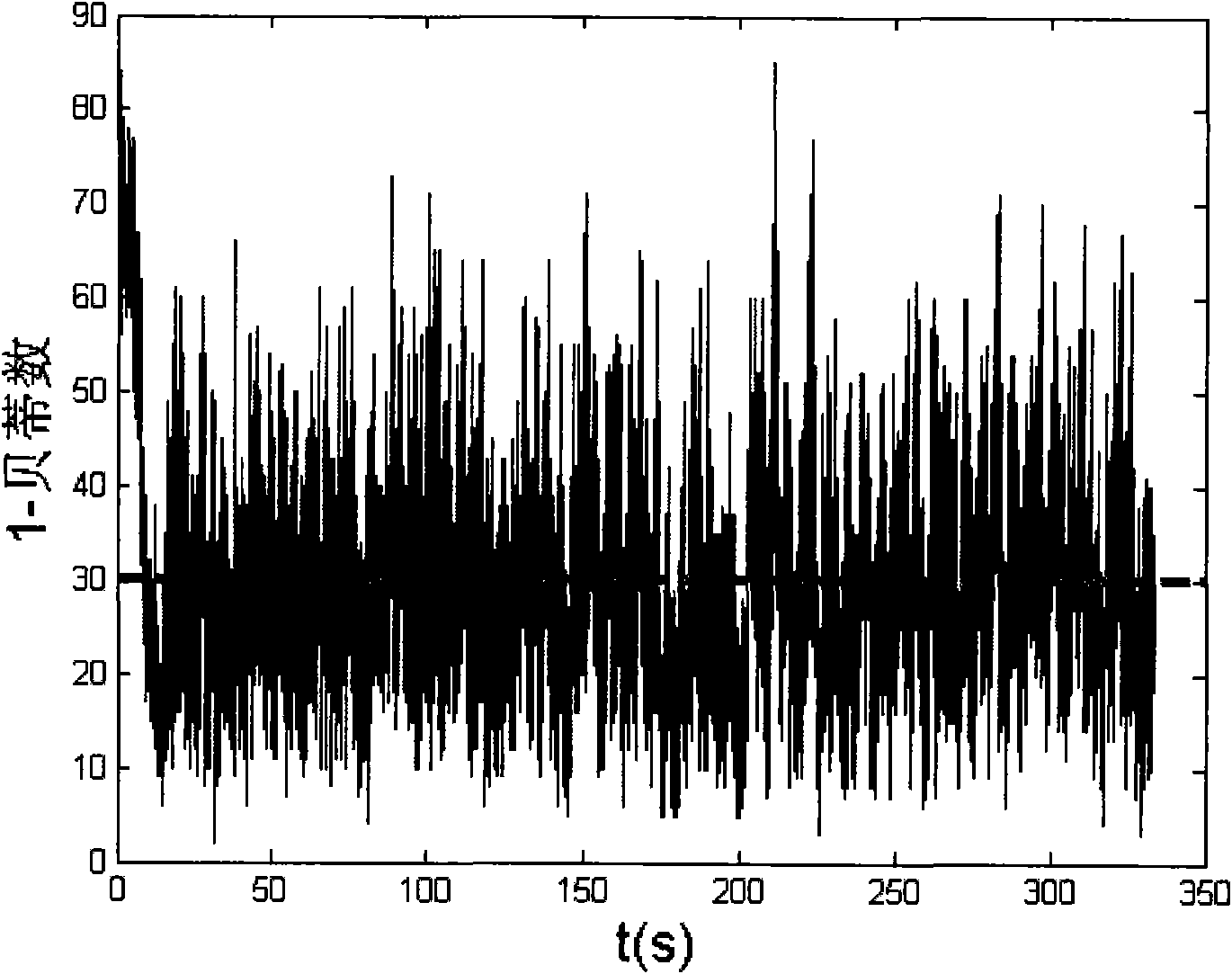
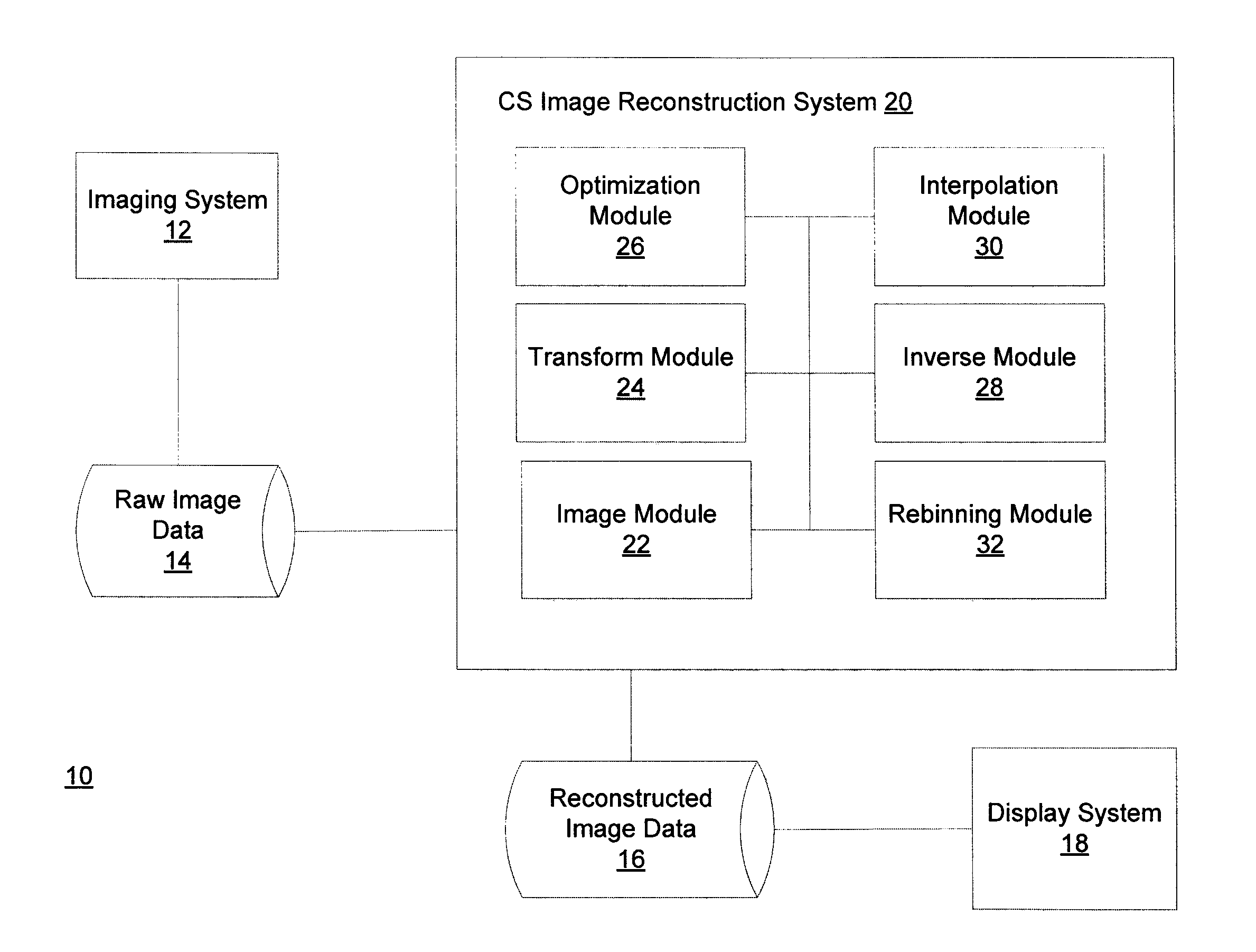
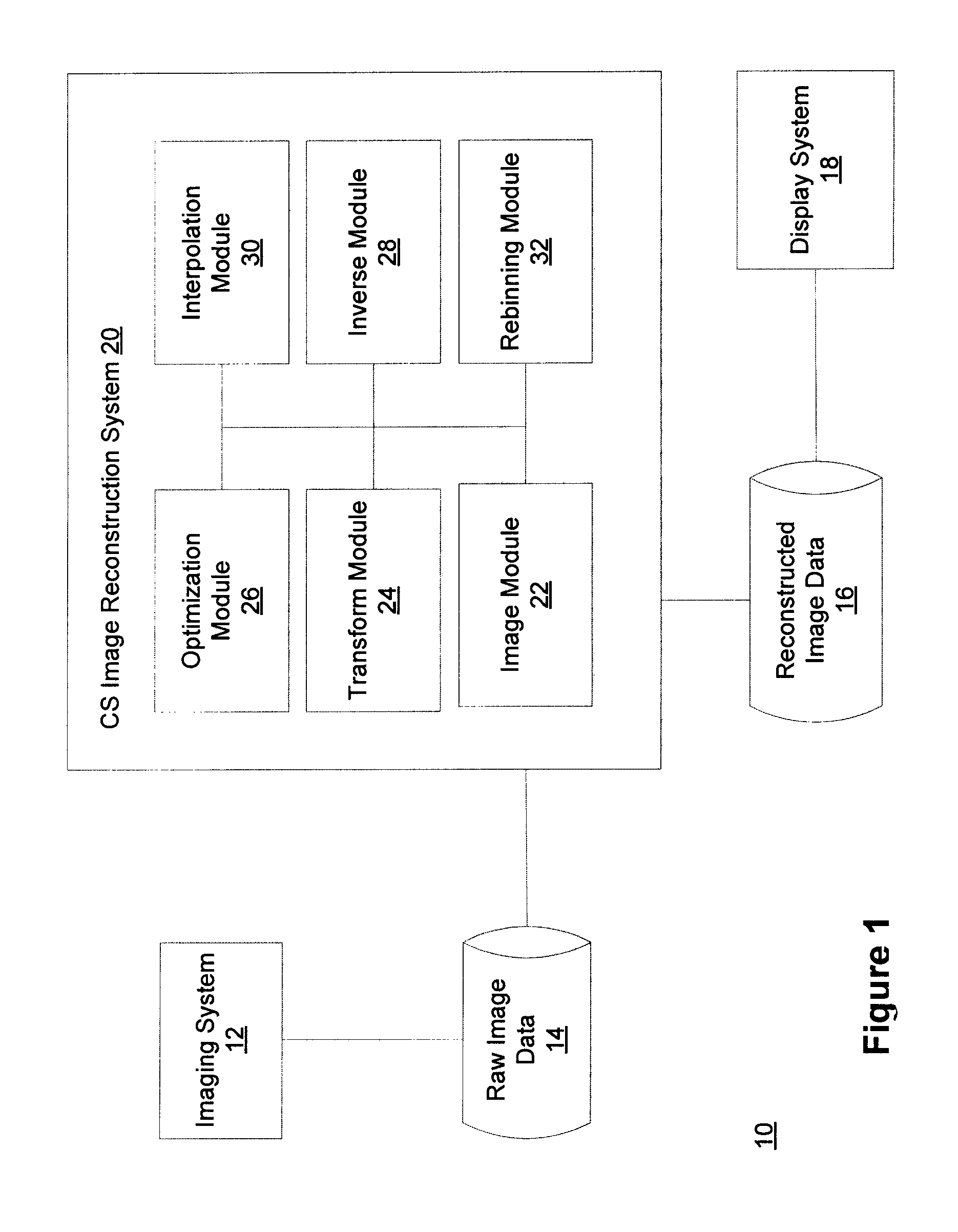
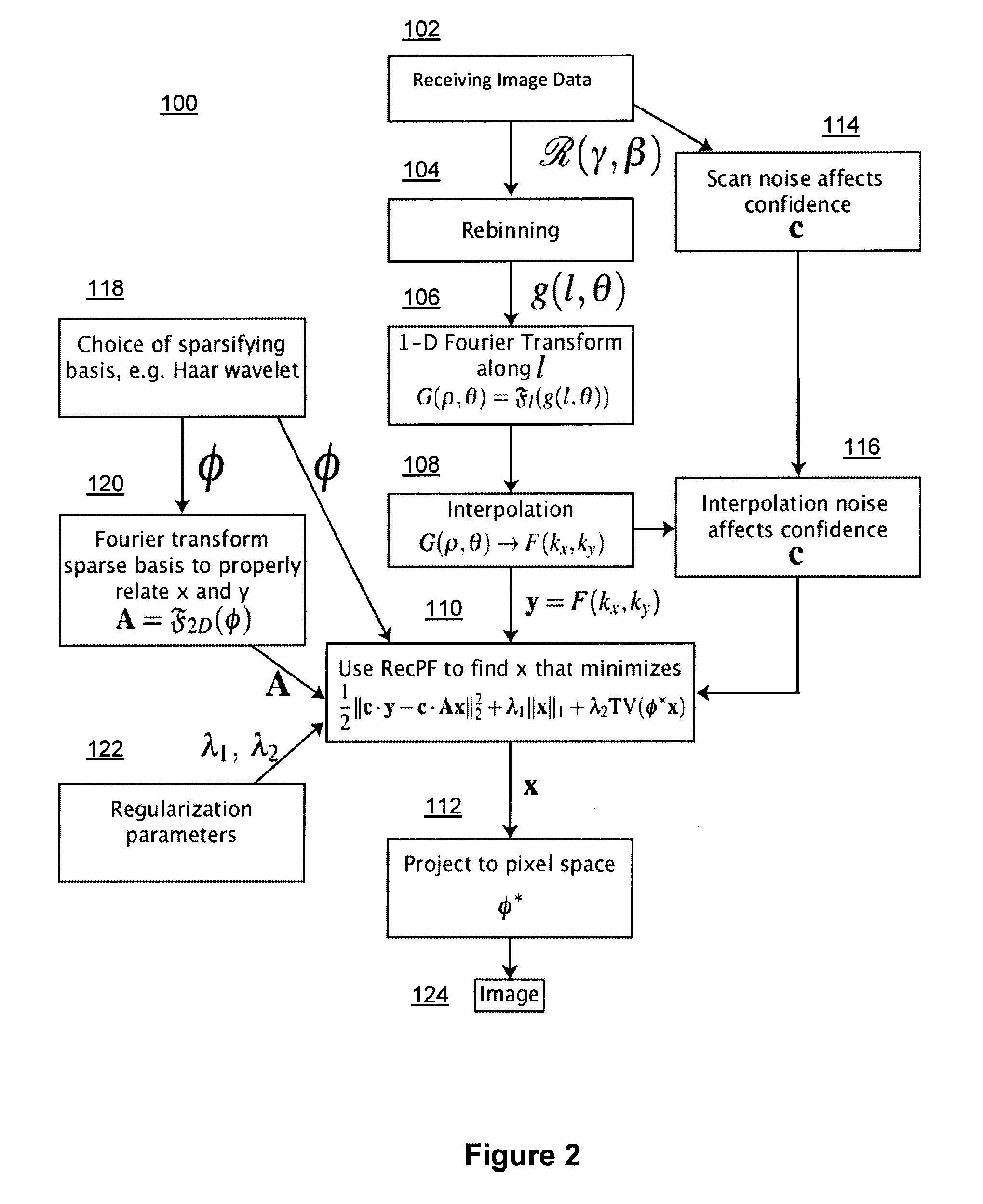
Method and system for compressed sensing image reconstruction
ActiveUS20150187052A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputation complexity
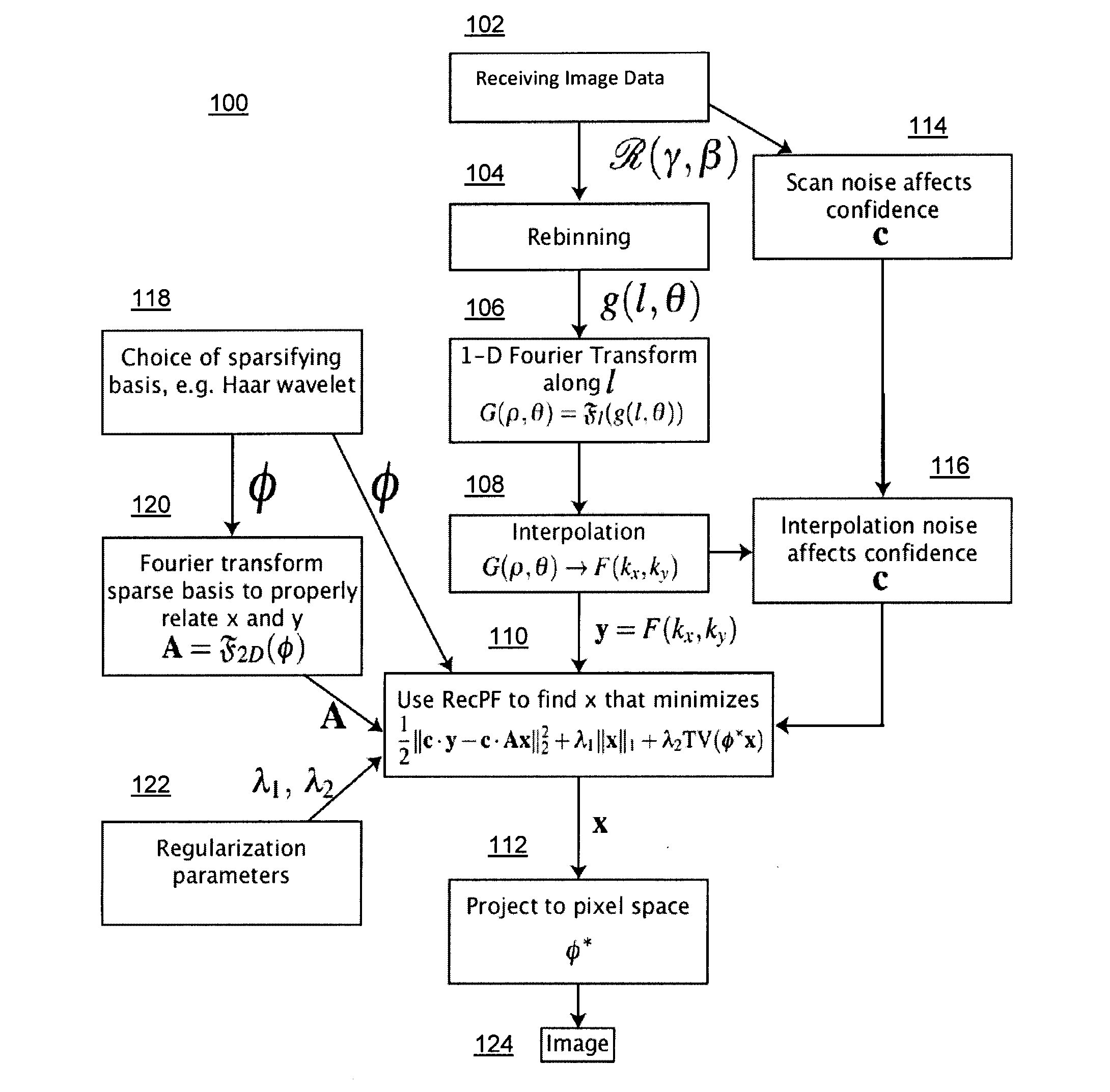
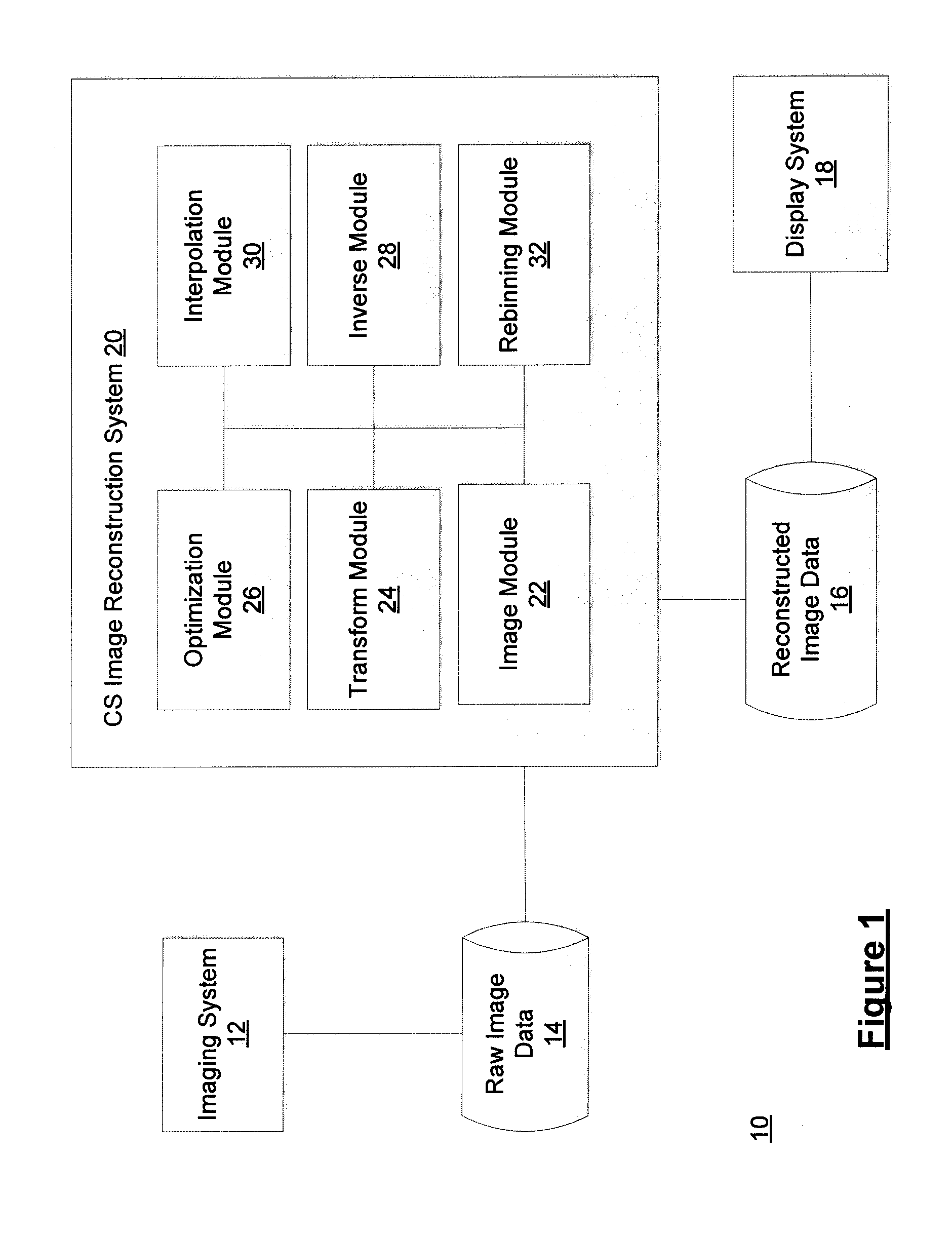
A Compressed Sensing (CS) based image reconstruction method and system is described herein which may be used to reduce the X-ray dose radiation in Computed Tomography (CT) or to decrease the scan duration in MR imaging (MRI). Methods and systems described herein may address problems that have hindered the clinical usage of CS, i.e. computation complexity and modeling problems. Using the described algorithm, high quality images may be recovered from undersampled data which may help to reduce the scan time and the exposed invasive radiations. Using the same set of data in conventional image reconstruction algorithms (e.g. Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in CT) may cause severe streak artifacts and may take significantly more time using Graphics Processing Units (GPU) and parallel clusters with the conventional CS-based methods. This method can be used other imaging modalities using Radon transform (such as C-Arm and electron tomography, for example).
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Parallel beam local tomography reconstruction method
InactiveUS20100054565A1Improve resolutionIncreasing effective informationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setReconstruction method
A method to image objects from local three-dimensional parallel beam tomographic data (line integrals) over lines parallel an arbitrary curve of directions on a sphere. Such data are used in electron microscopy, SPECT (with weighted integrals), and synchrotron tomography. The algorithm is adaptable to a number of data sets including single-axis and double-axis tilt electron tomography and truly three-dimensional curves of directions. The method stably gives pictures of the internal structure of objects and does not add strong singularities or artefacts. It is less influenced by objects outside the region of interest than standard non-local methods. The algorithm is combined with an electron microscope and computer to provide computer readable files showing the pictures of small objects such as molecules.
Owner:SIDEC TECH
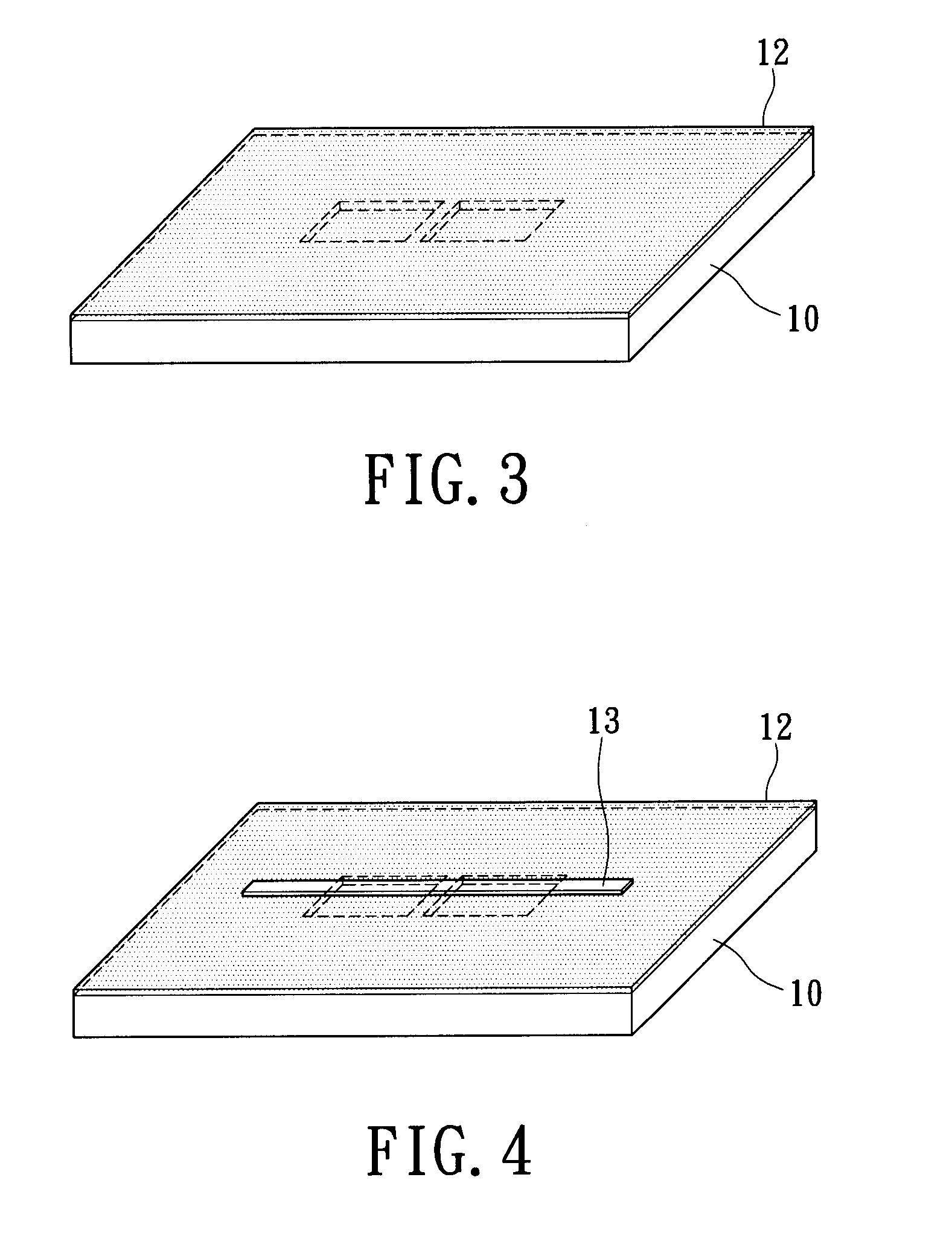
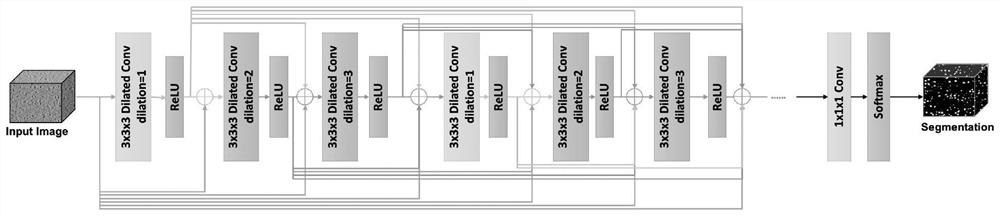
Preparation method for an electron tomography sample with embedded markers and a method for reconstructing a three-dimensional image
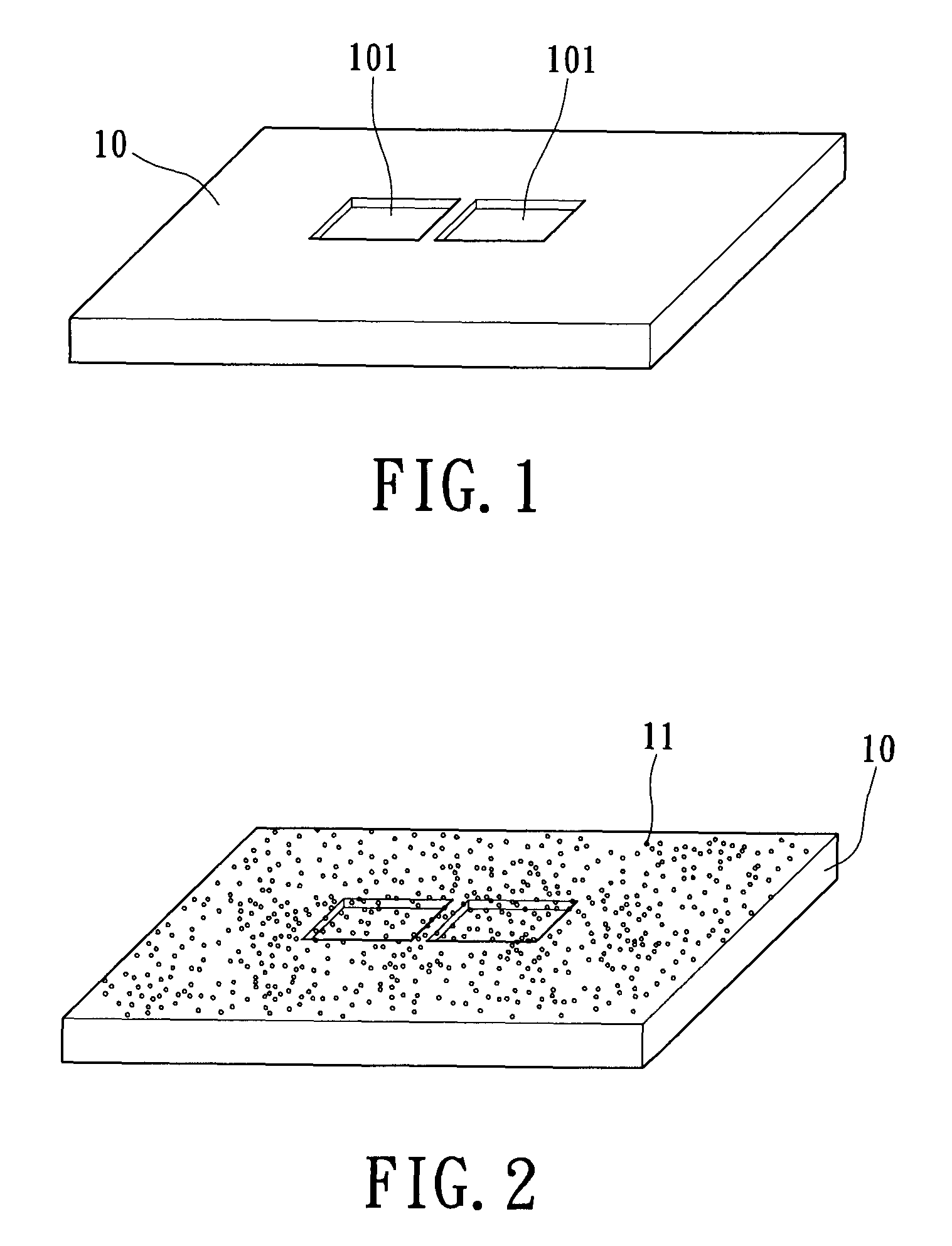
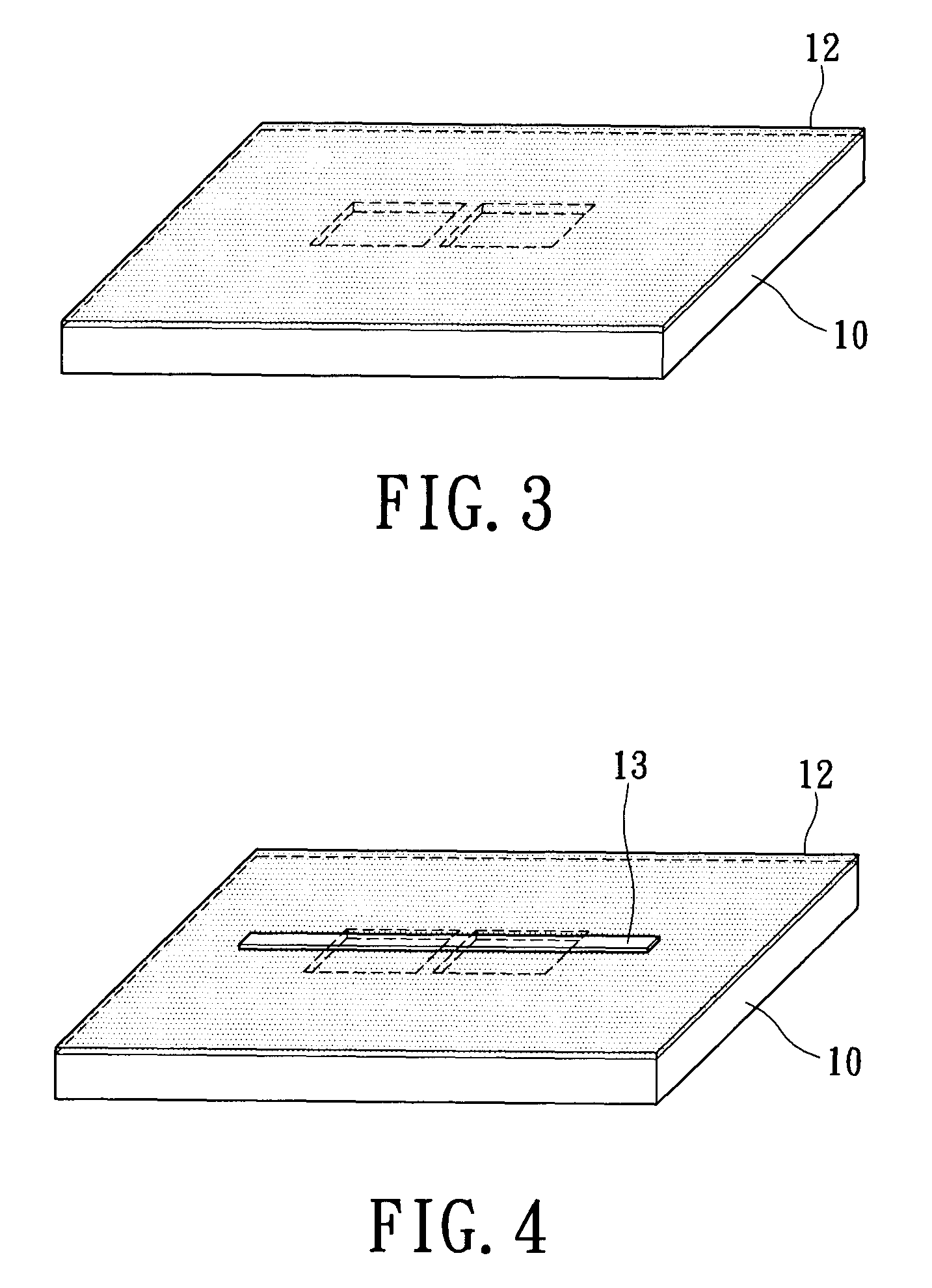
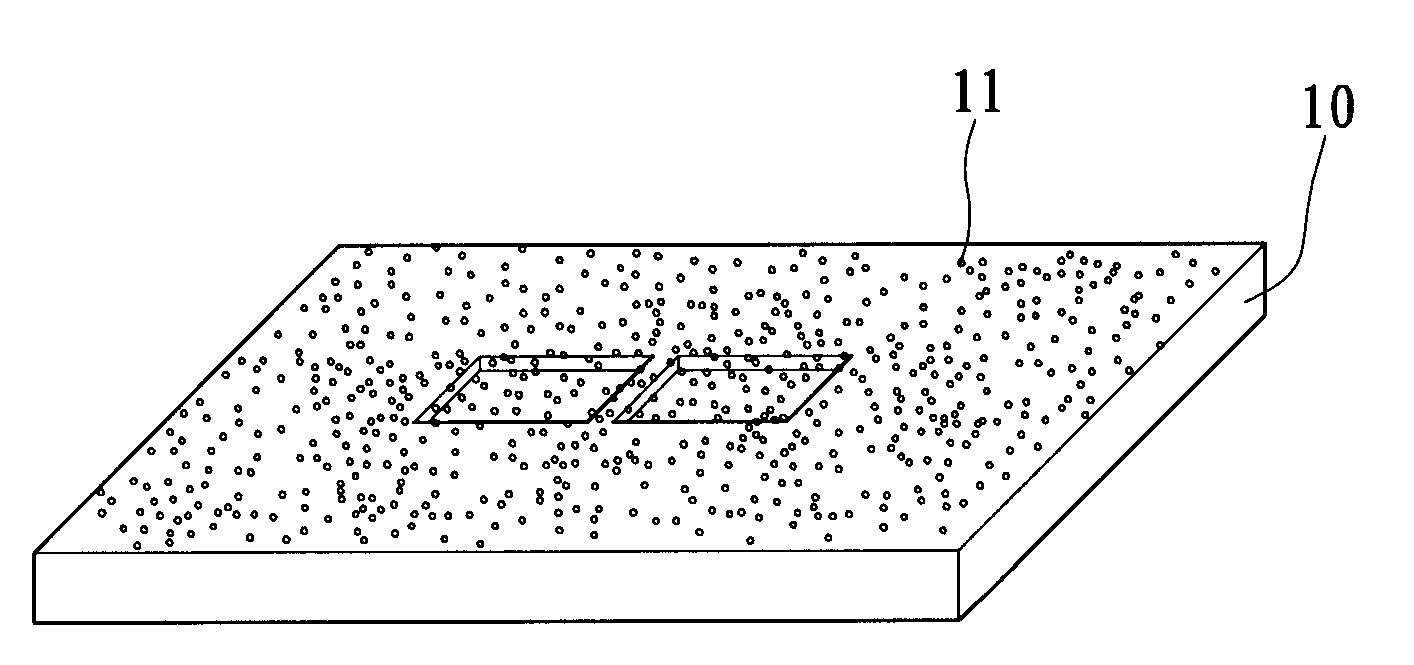
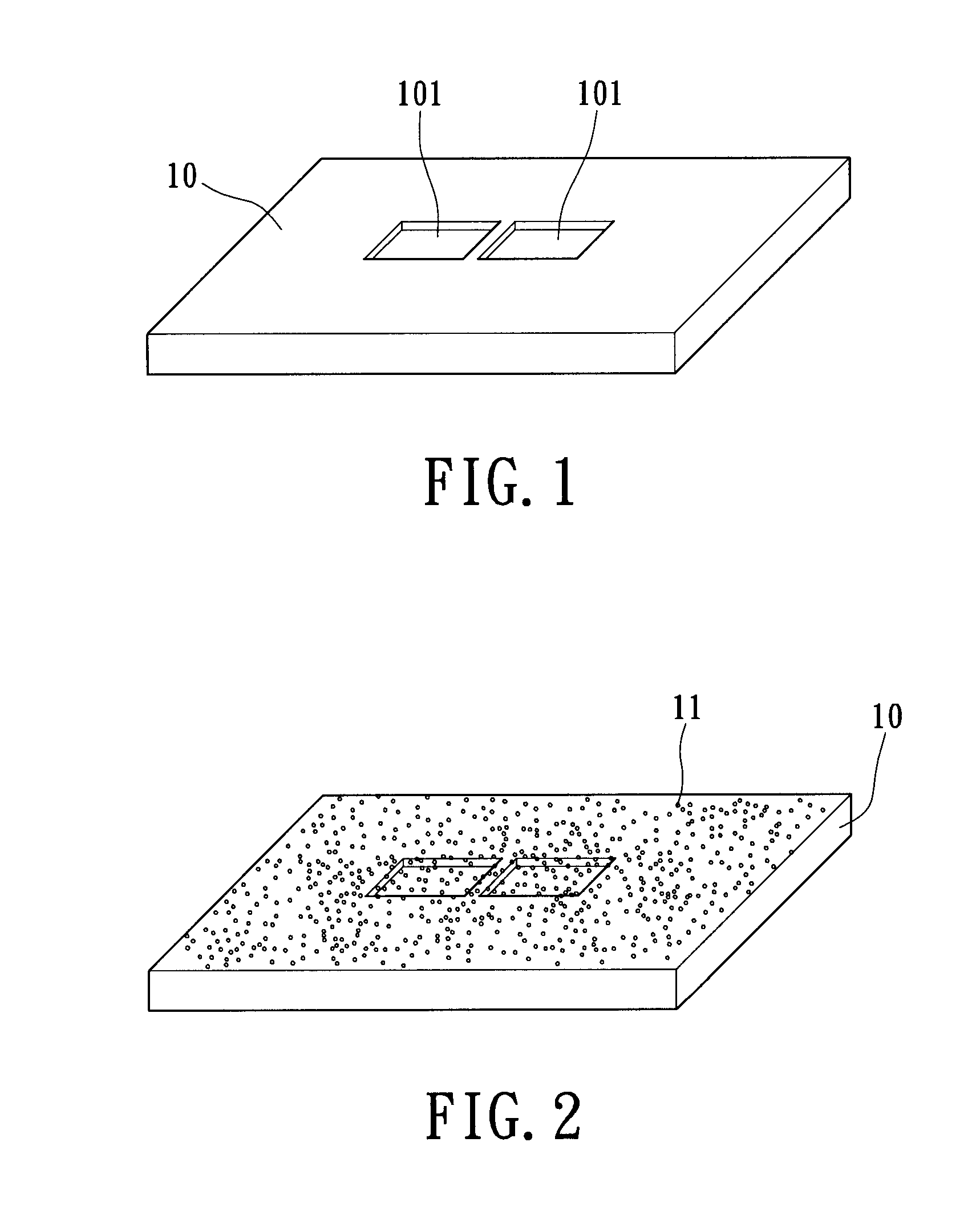
InactiveUS7939906B2Minimize blurringEasy to trackElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFeature trackingEngineering
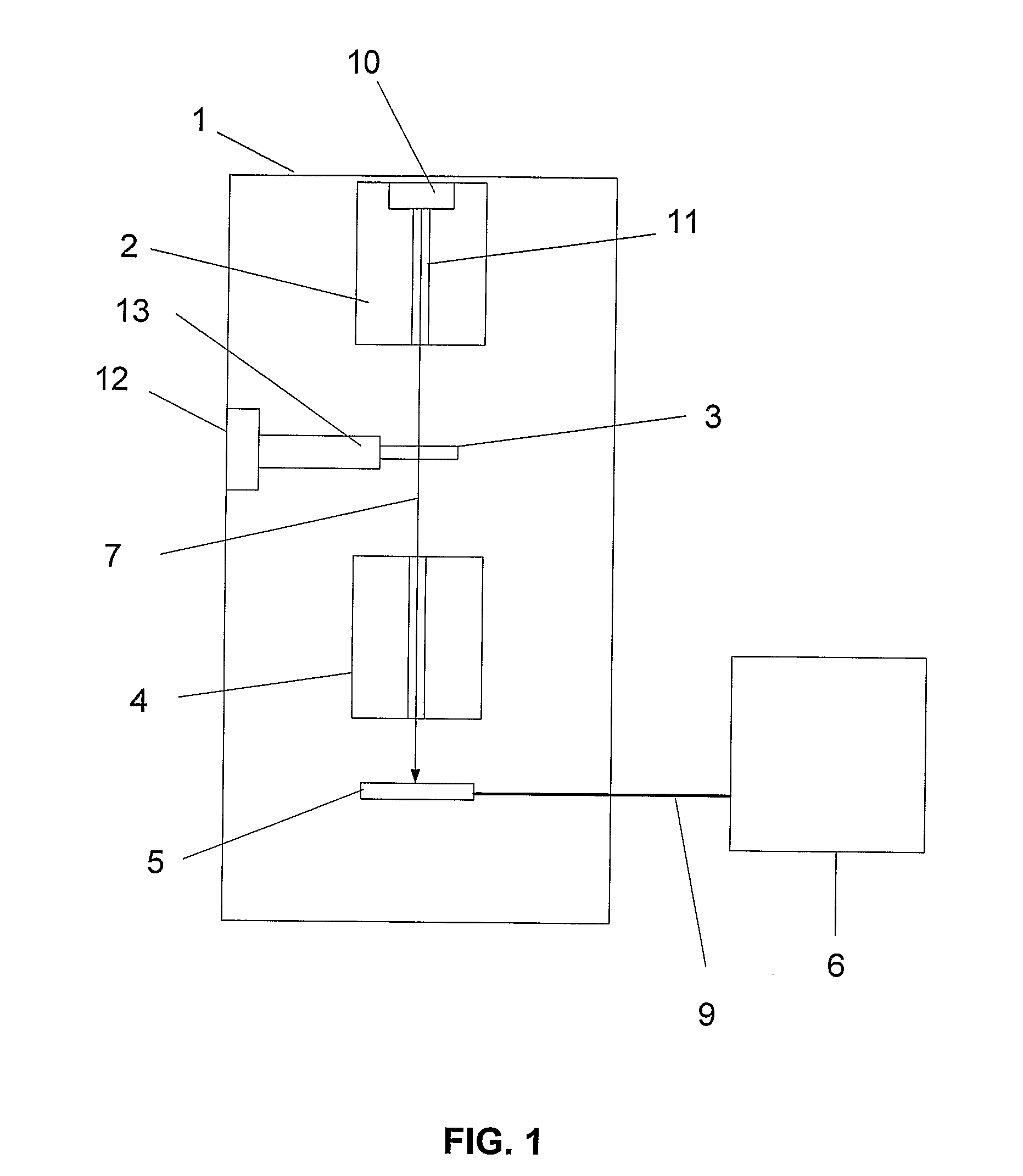
A manufacturing method for an electron tomography specimen with embedded fiducial markers includes the following steps. A chip of wafer is provided. The chip includes at least one inspecting area. At least one trench is produced beside the inspecting area. A liquid with the markers is filled into the trenches. A first protection layer is coated on the chip, and then a second protection layer is deposited on the first protection layer. Therefore, the markers can be embedded into the electron tomography specimen. The embedded markers can improve the alignment process, due to those embedded markers are easily tracked during feature tracking procedure. In addition, our novel invention also successfully provides a modified version of the technique to deposit gold beads onto TEM pillar samples for much improved 3D reconstruction.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Preparation method for an electron tomography sample with embedded markers and a method for reconstructing a three-dimensional image
InactiveUS20100084555A1Minimize blurringEasy to trackMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesFeature trackingEngineering
A manufacturing method for an electron tomography specimen with embedded fiducial markers includes the following steps. A chip of wafer is provided. The chip includes at least one inspecting area. At least one trench is produced beside the inspecting area. A liquid with the markers is filled into the trenches. A first protection layer is coated on the chip, and then a second protection layer is deposited on the first protection layer. Therefore, the markers can be embedded into the electron tomography specimen. The embedded markers can improve the alignment process, due to those embedded markers are easily tracked during feature tracking procedure. In addition, our novel invention also successfully provides a modified version of the technique to deposit gold beads onto TEM pillar samples for much improved 3D reconstruction.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
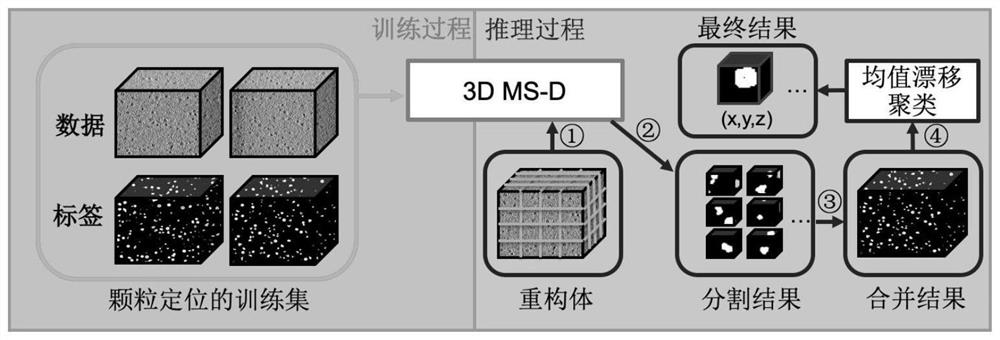
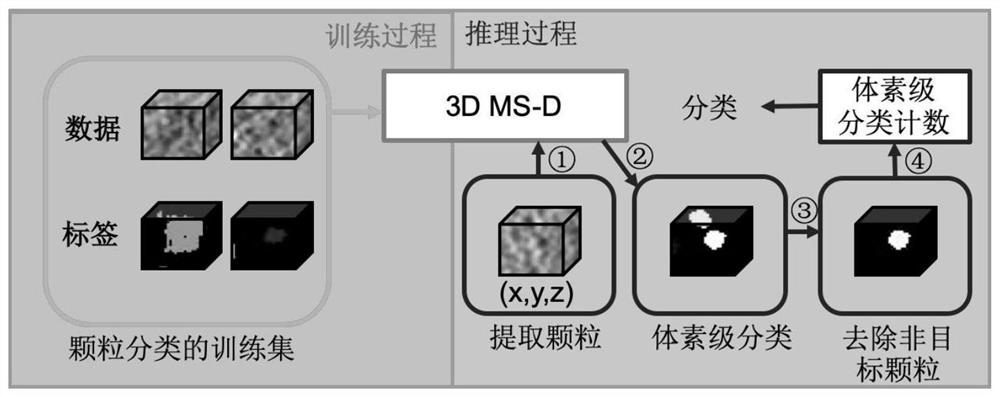
Three-dimensional particle category detection method and system based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN112001218AFew parametersImprove parametersNeural architecturesICT adaptationAlgorithm3d image
The invention provides a three-dimensional particle category detection method and system based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a three-dimensional mixed-scale dense convolutional neural network comprising a mixed-scale three-dimensional extended convolutional layer, dense connection and a loss function, training the convolutional neural network by using a three-dimensional frozen electron tomography image marked with the particle coordinates to obtain a particle selection model, and training the convolutional neural network by using thethree-dimensional frozen electron tomography image marked with the particle category to obtain a particle classification model; acquiring the three-dimensional frozen electron tomography image through a sliding window to obtain to-be-detected three-dimensional reconstructed subareas, predicting each subarea through the particle selection model, and combining prediction results of the subareas toobtain coordinates of each particle in the three-dimensional frozen electron tomography image; and extracting a three-dimensional image of each particle according to the coordinate of each particle, and inputting the three-dimensional image of each particle into the particle classification model to obtain the category of each particle.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for building fractal dimension-based multi-phase mixed effect prediction model
ActiveCN101930501ATimely adjustmentTimely analysisSpecial data processing applicationsHigh rateTime delays
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring mixing effect of fluid
InactiveCN101650292ASimple methodReduce economic lossSurface/boundary effectSpecial data processing applicationsImaging techniqueMixing effect
The invention relates to a method for measuring the mixing effect of fluids and is mainly applied to judging the mixing effect of fluids and theoretically guiding the design of experiments in experiments of chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) utilizing a particle velometer (transparent or semi-transparent fluid mixing) and the electron tomography (nontransparent fluid mixing) to obtain a fluid mixing real-time pattern; (2) utilizing a written particular program to calculate a 0-dimension Betti number and a 1-dimension Betti number of the obtained real-time pattern; (3) judging the mixing effect through respectively calculating the evolvement of the 0-dimension Betti number and the 1-dimension Betti number of an integral region and the average value of the 0-dimension Betti number and the 1-dimension Betti number of a 4 region or a 16 region. The method is applied to the detection of the mixing effect of all fluids, is simple and convenient and has higherpractical value. The invention provides a reliable and practical measuring method for judging the mixing effects and theoretically guiding the design of experiments in experiments of chemical engineering.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for compressed sensing image reconstruction
ActiveUS9373159B2Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputation complexity
A Compressed Sensing (CS) based image reconstruction method and system is described herein which may be used to reduce the X-ray dose radiation in Computed Tomography (CT) or to decrease the scan duration in MR imaging (MRI). Methods and systems described herein may address problems that have hindered the clinical usage of CS, i.e. computation complexity and modeling problems. Using the described algorithm, high quality images may be recovered from undersampled data which may help to reduce the scan time and the exposed invasive radiations. Using the same set of data in conventional image reconstruction algorithms (e.g. Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in CT) may cause severe streak artifacts and may take significantly more time using Graphics Processing Units (GPU) and parallel clusters with the conventional CS-based methods. This method can be used other imaging modalities using Radon transform (such as C-Arm and electron tomography, for example).
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Iterated variational regularization combined with componentwise regularization
ActiveUS20100005130A1Stable reconstructionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging analysisComputer science
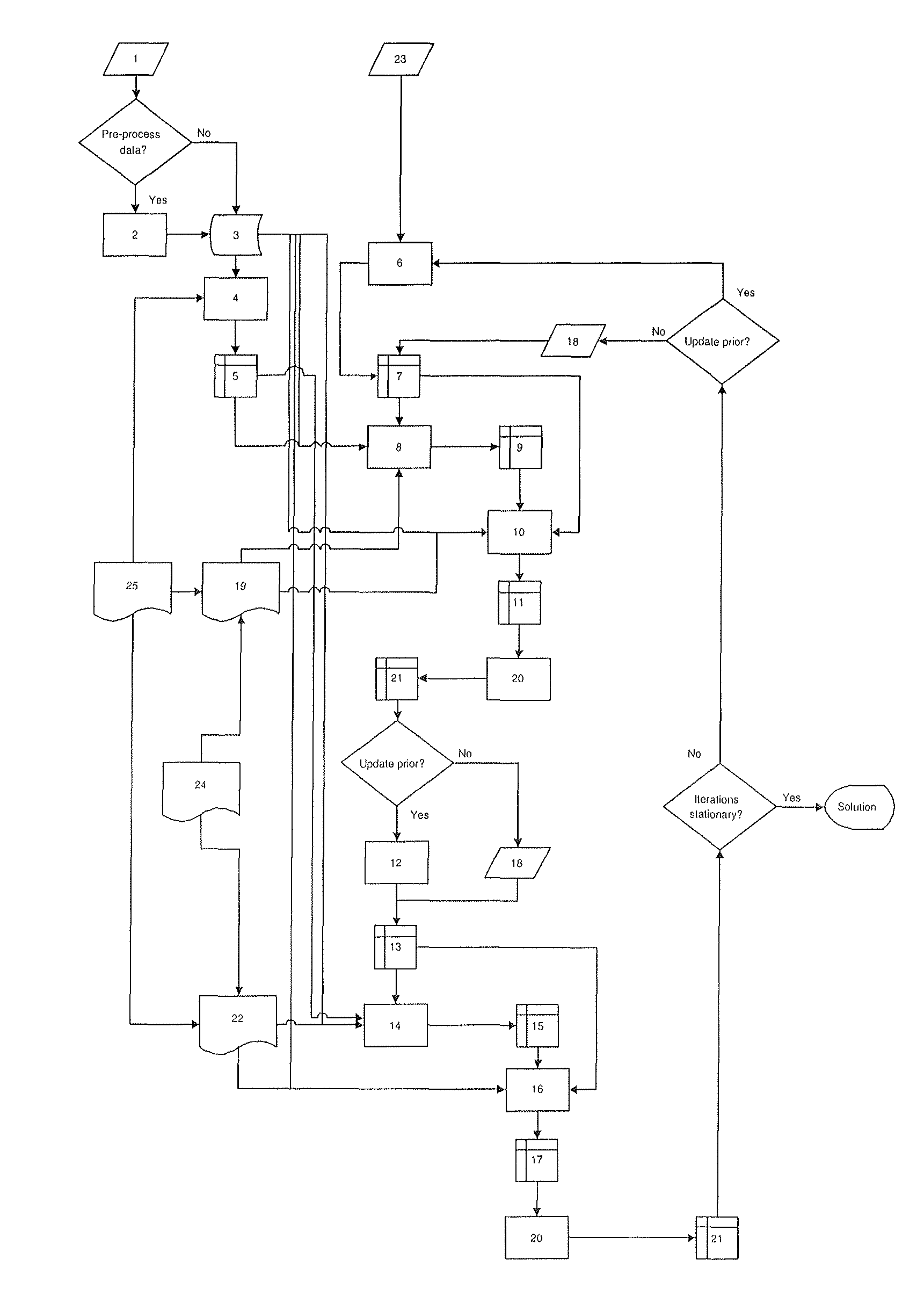
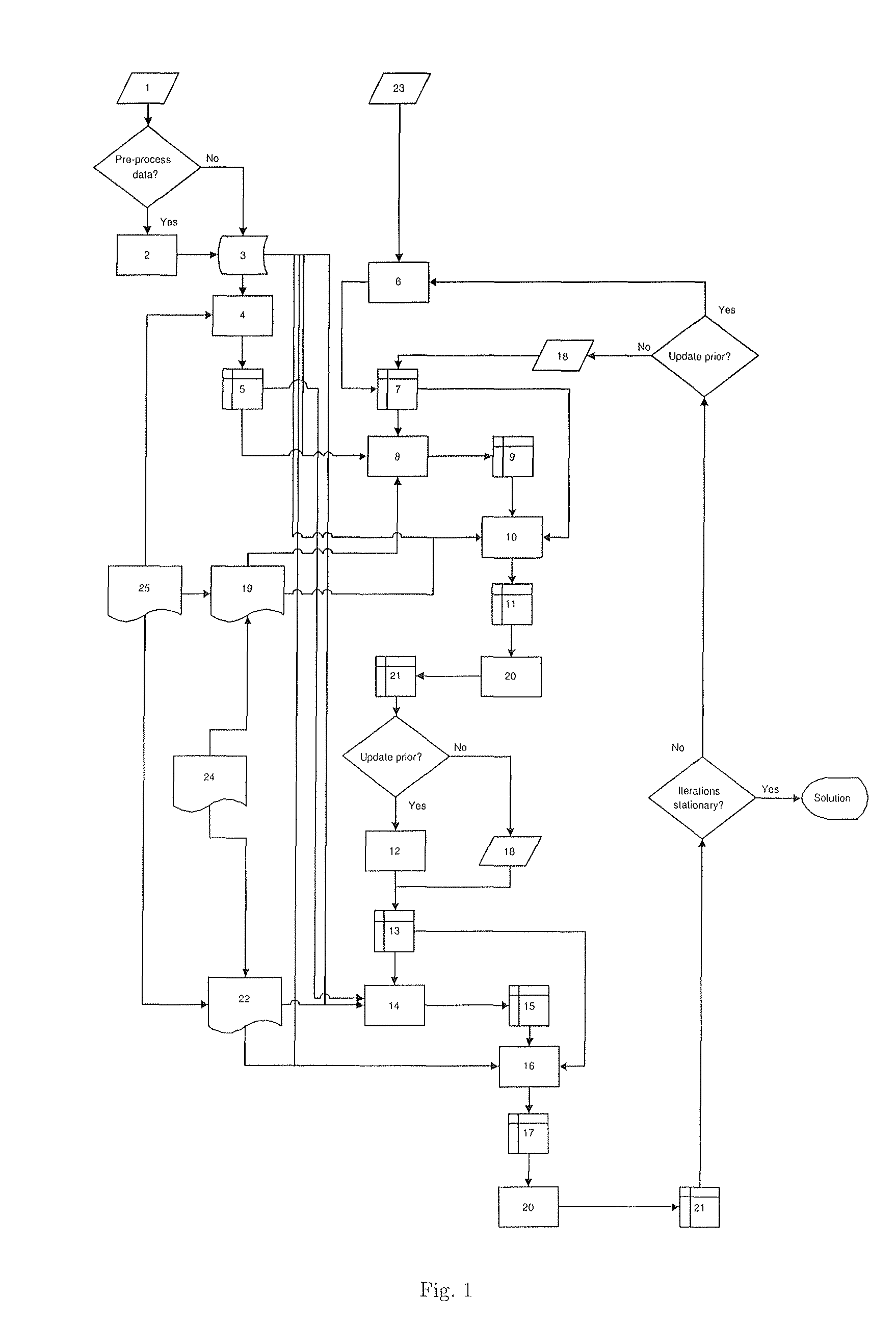
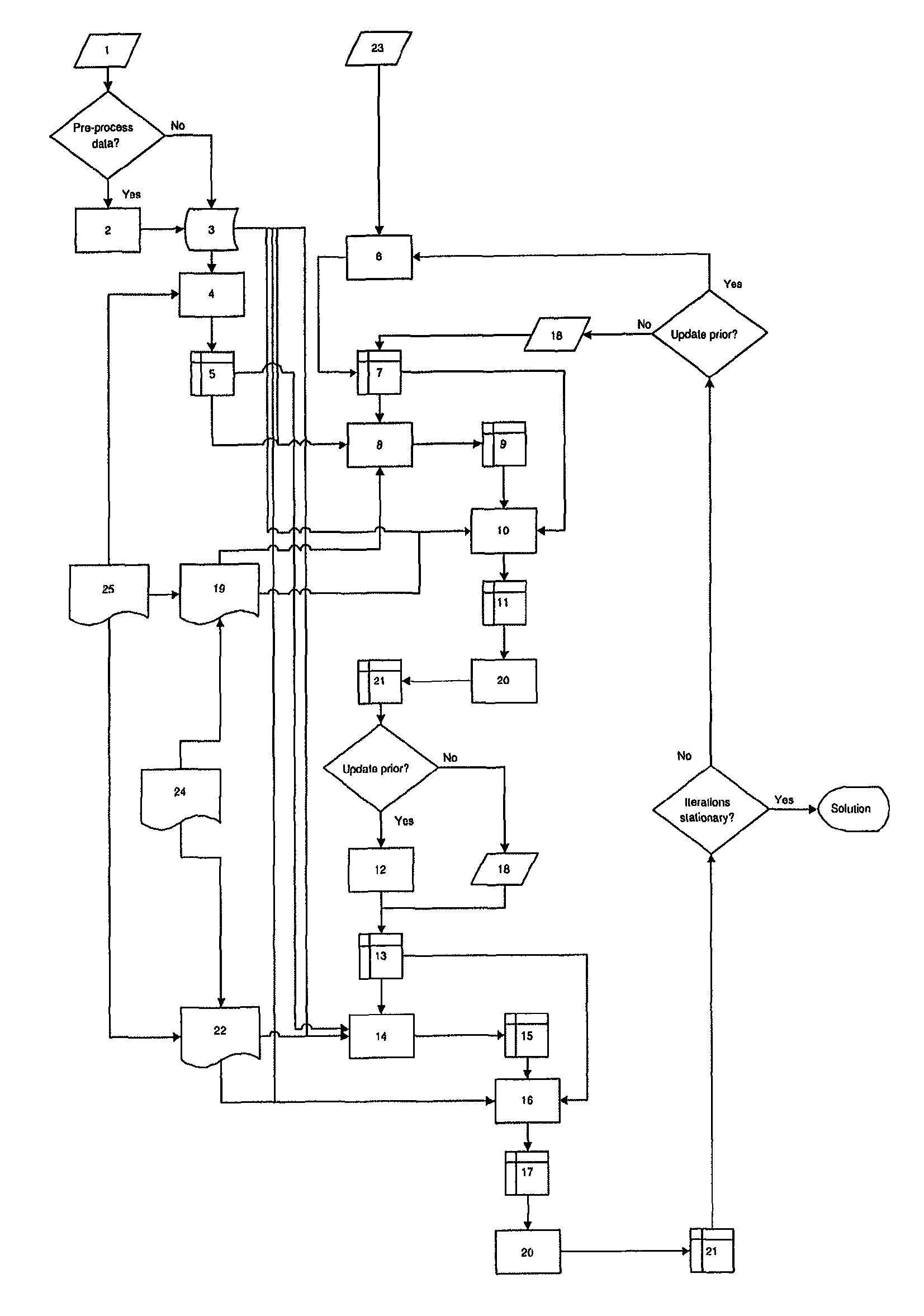
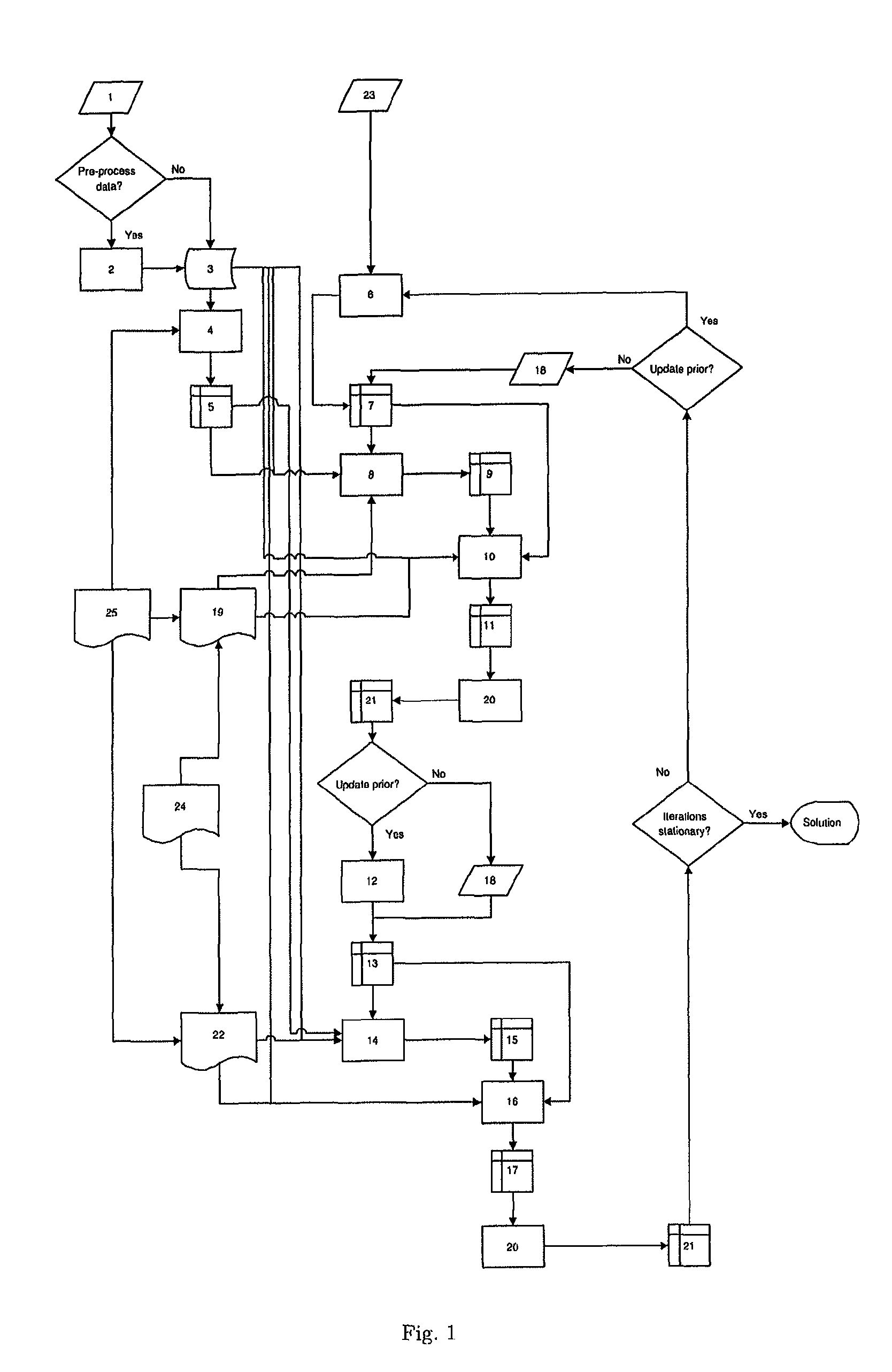
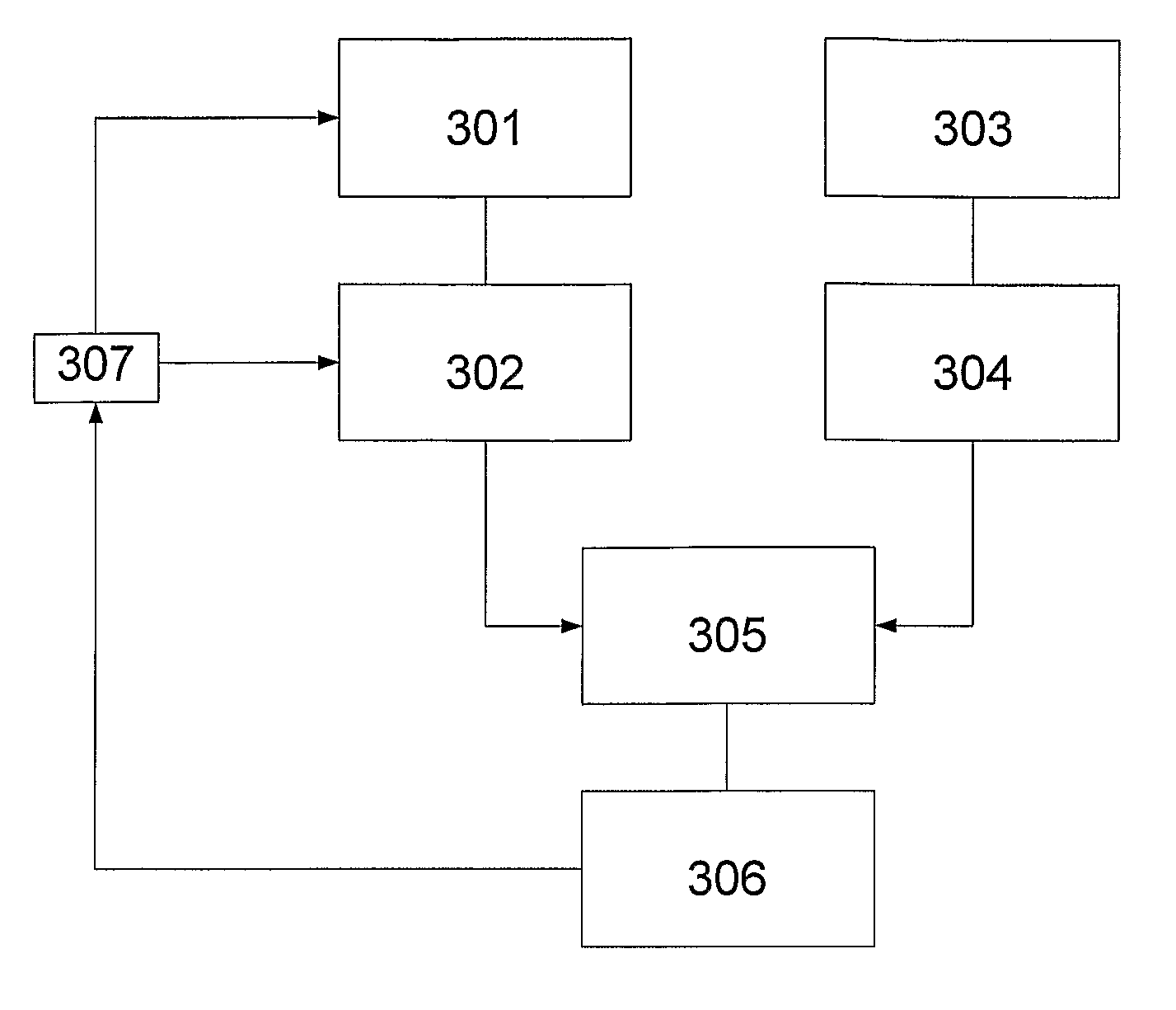
The present invention relates to a solution for solving an ill-posed inverse problem in image analysis, e.g. in an electron tomography application in order to recover a structure of a sample. The solution is provided for instance as a method comprising steps of determining reliable prior knowledge about the solution, determining initial guess for the solution and determining the corresponding forward operator, deciding upon model of stochasticity, deciding on suitable regularization method, deciding on updating scheme, and producing a sequence using the set configuration.
Owner:OKINAWA INST OF SCI & TECH PROMOTION CORP
Time sequence model and method for predicting multi-phase mixing uniformity
The invention discloses a method for establishing a time sequence model for predicting multi-phase mixing uniformity, and is mainly applicable to predicting fluid mixing effect and theoretically guiding and correcting experiment design in a chemical engineering experiment. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a multi-phase real-time stirring and mixing pattern by using electron tomography or a high-speed camera; (2) calculating the zeroth-dimension betti number of the acquired real-time pattern by using a written program; (3) acquiring related data at the beginning every certain time by using the method of the step (2) so as to obtain a corresponding time sequence; (4) calculating time delay variable, embedded dimension and bandwidth by a phase reconstruction method by using the time sequence obtained in the step (3); (5) linearly predicting the time sequence in the step (3) by using a one-step forward method and local weighting so as to obtain the complete time sequence; and (6) verifying prediction error by using an experimental method. The model is applied to the prediction of the mixing effect of all fluid; and the method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience and extremely high practical value.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for electron tomography
ActiveCN104224216AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesImproved methodTime-Consuming
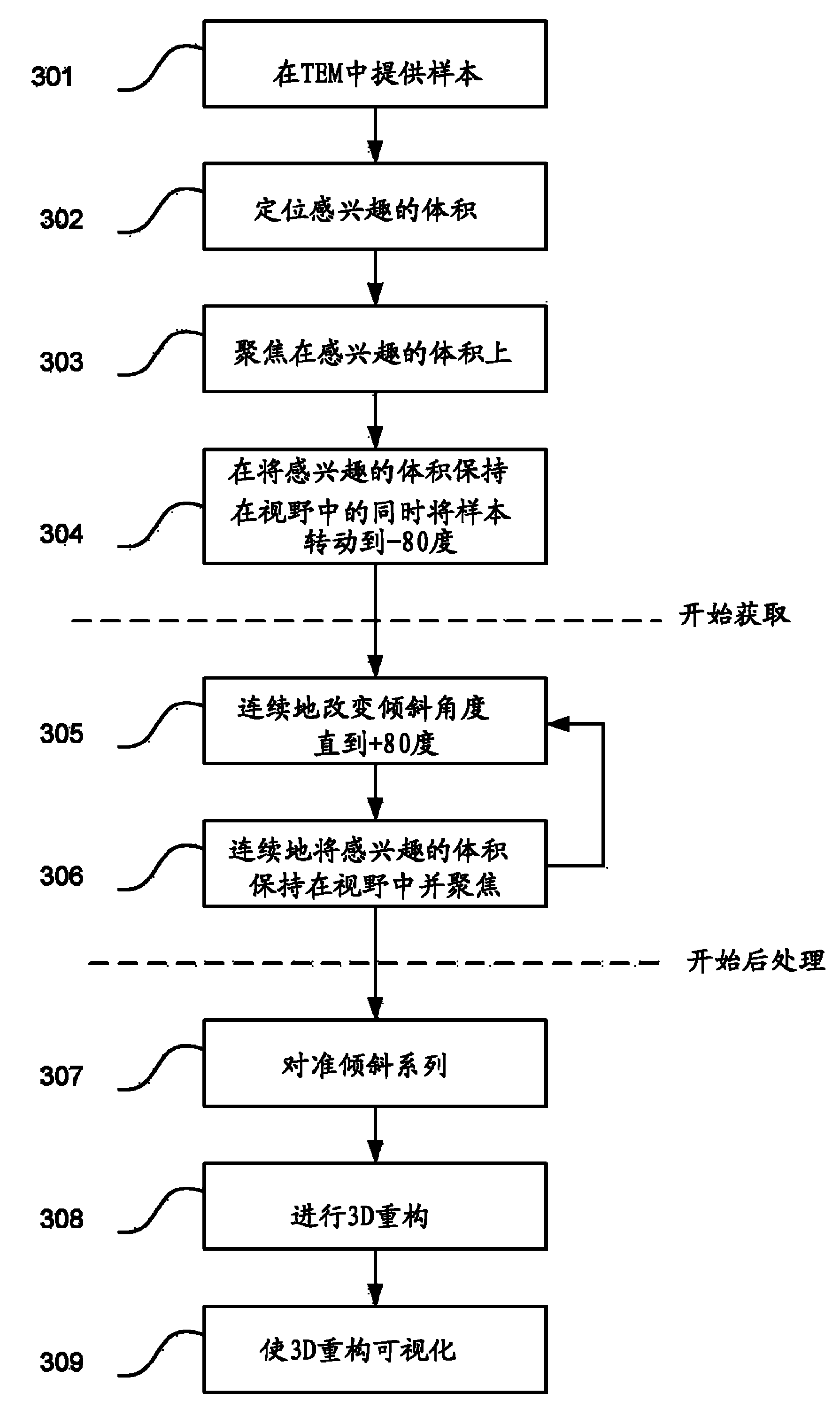
The invention relates to an improved method of electron tomography. Electron tomography is a time consuming process, as a large number of images, typically between 50-100 images, must be acquired to form one tomogram. The invention teaches a method to shorten the time needed to acquire this amount images much more quickly by tilting the sample continuously, instead of step-by-step. Hereby the time needed to reduce vibrations between steps is eliminated.
Owner:FEI CO
Method for making customized acetabular prosthesis and auxiliary method for total hip replacement arthroplasty
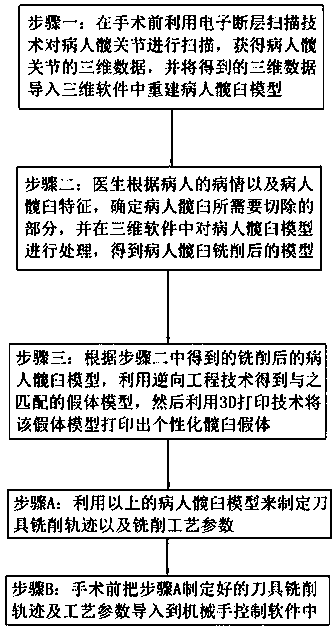
ActiveCN110251277APlace stableLow surgical repair rateJoint implantsHip jointsSoftwareReverse engineering
The invention relates to a method for making customized acetabular prosthesis and an auxiliary method for total hip replacement arthroplasty, which relate to the technical field of the total hip replacement arthroplasty. The method comprises the followings steps: scanning the hip joint of a patient by using an electron tomography technique before an operation, obtaining three-dimensional data of the hip joint of the patient, and introducing the obtained three-dimensional data into the three-dimensional software to reconstruct an acetabular model of the patient; processing the patient's acetabular model in the three-dimensional software to obtain the acetabular model of the patient after milling; using a reverse engineering technique to obtain a prosthetic model matching the above model, and then using a 3D printing technology to print the prosthetic model to the customized acetabular prosthesis, and using the patient acetabular model to formulate a tool milling trajectory and the milling process parameters; before the operation, introducing the tool milling trajectory and the process parameters into the robot control software, and using a robot for doctor to mill the patient's acetabulum, wherein the customized acetabular prosthesis is provided for the doctor to mount the acetabulum of the patient after milling. The method can reduce the doctor's surgical burden and improve the quality of milling.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Thermoplastic resin composition, process for producing the same and molding
This invention relates to a thermoplastic resin composition comprising a thermoplastic resin (A) and a reactive functional group-containing thermoplastic resin (B), which has a specific structure in the morphology of the resin composition observed by transmission electron tomography, and the relaxation time T1C of each carbon nucleus by the solid NMR measurement of the thermoplastic resin composition containing a polyamide resin is kept in a specific range. The composition is excellent in the balance between contradictory properties such as impact resistance and heat resistance, remarkably exhibits a peculiar viscoelastic behavior not observed in the conventional polymeric materials, and is remarkably excellent in impact energy absorbing performance and vibration energy absorbing performance at the time of high-speed deformation.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Iterated variational regularization combined with componentwise regularization
ActiveUS8468189B2Stable reconstructionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging analysisComputer science
The present invention relates to a solution for solving an ill-posed inverse problem in image analysis, e.g. in an electron tomography application in order to recover a structure of a sample. The solution is provided for instance as a method comprising steps of determining reliable prior knowledge about the solution, determining initial guess for the solution and determining the corresponding forward operator, deciding upon model of stochasticity, deciding on suitable regularization method, deciding on updating scheme, and producing a sequence using the set configuration.
Owner:OKINAWA INST OF SCI & TECH PROMOTION CORP
Extended electron tomography
ActiveUS7880142B2High resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesData setImage resolution
A method for improving image resolution of a three dimensional structure of at least one molecule conformation includes: determining a three dimensional structure of at least one conformation of a molecule in a sample from a first data set obtained from a series of 2D measurements of different geometrical projections of the molecule at a low electron beam dose in an electron microscope; producing a second data set including calculated two dimensional projections of the determined three dimensional structure of the at least one conformation of the same molecule; correlating data from a third data set obtained from at least one measurement of the same molecule using a higher electron beam dose with the second data set; and using the correlated data to improve the resolution of the three dimensional structure of the at least one conformation of the molecule by increasing the first data set with the correlated data and re-determining a three dimensional structure.
Owner:OKINAWA INST OF SCI & TECH PROMOTION CORP
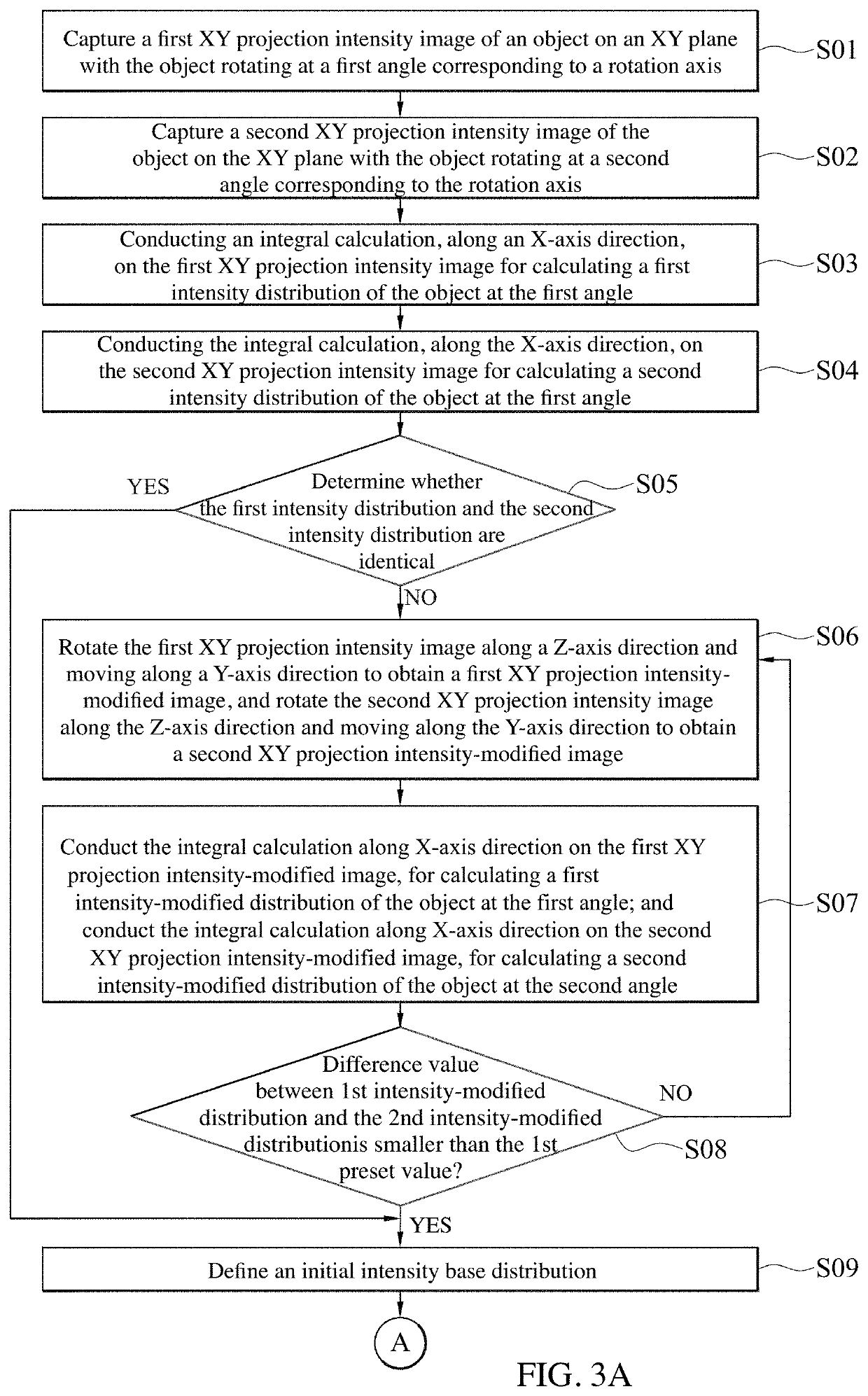
Fast projection matching method for computed tomography images
ActiveUS20190156523A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionComplex event processing3D projection
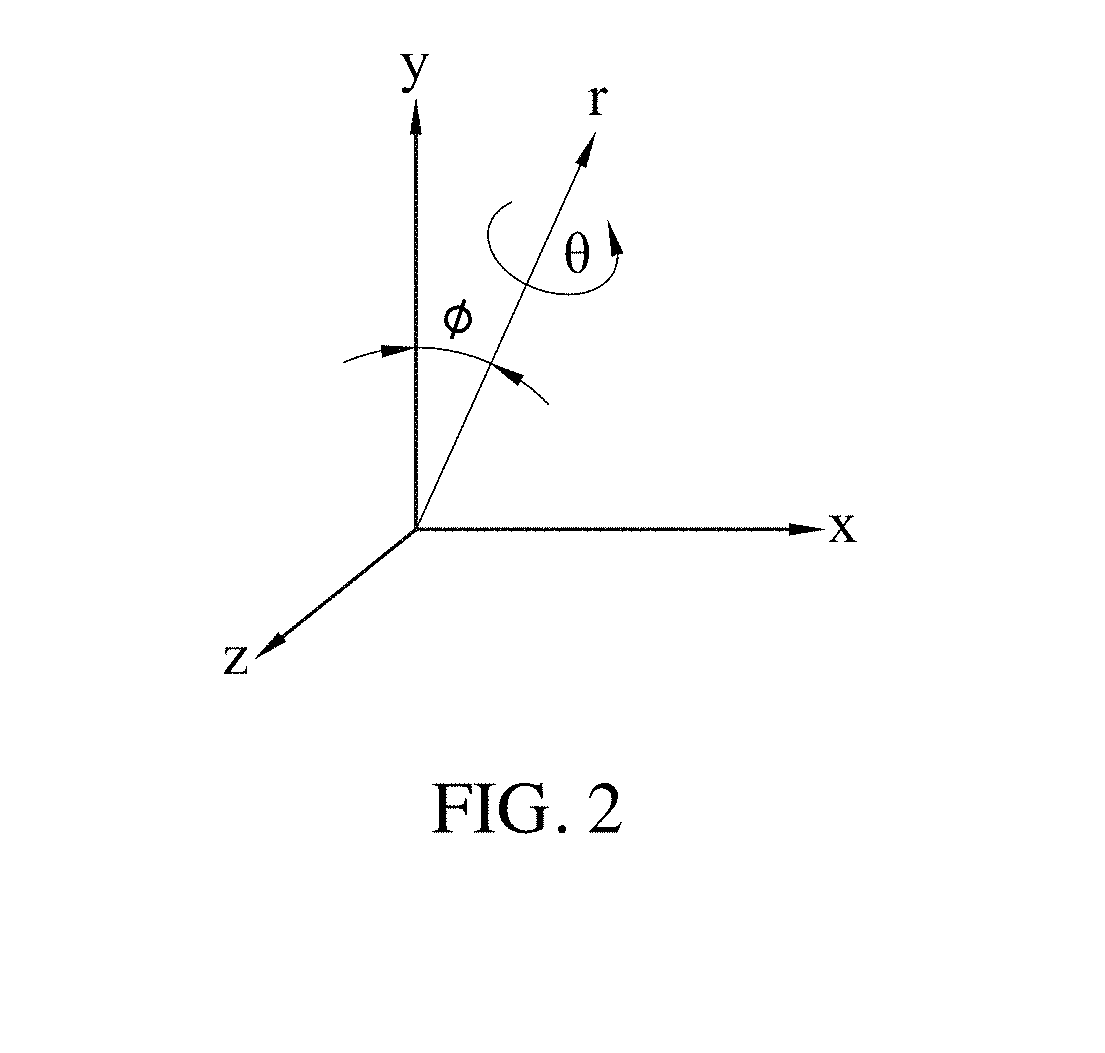
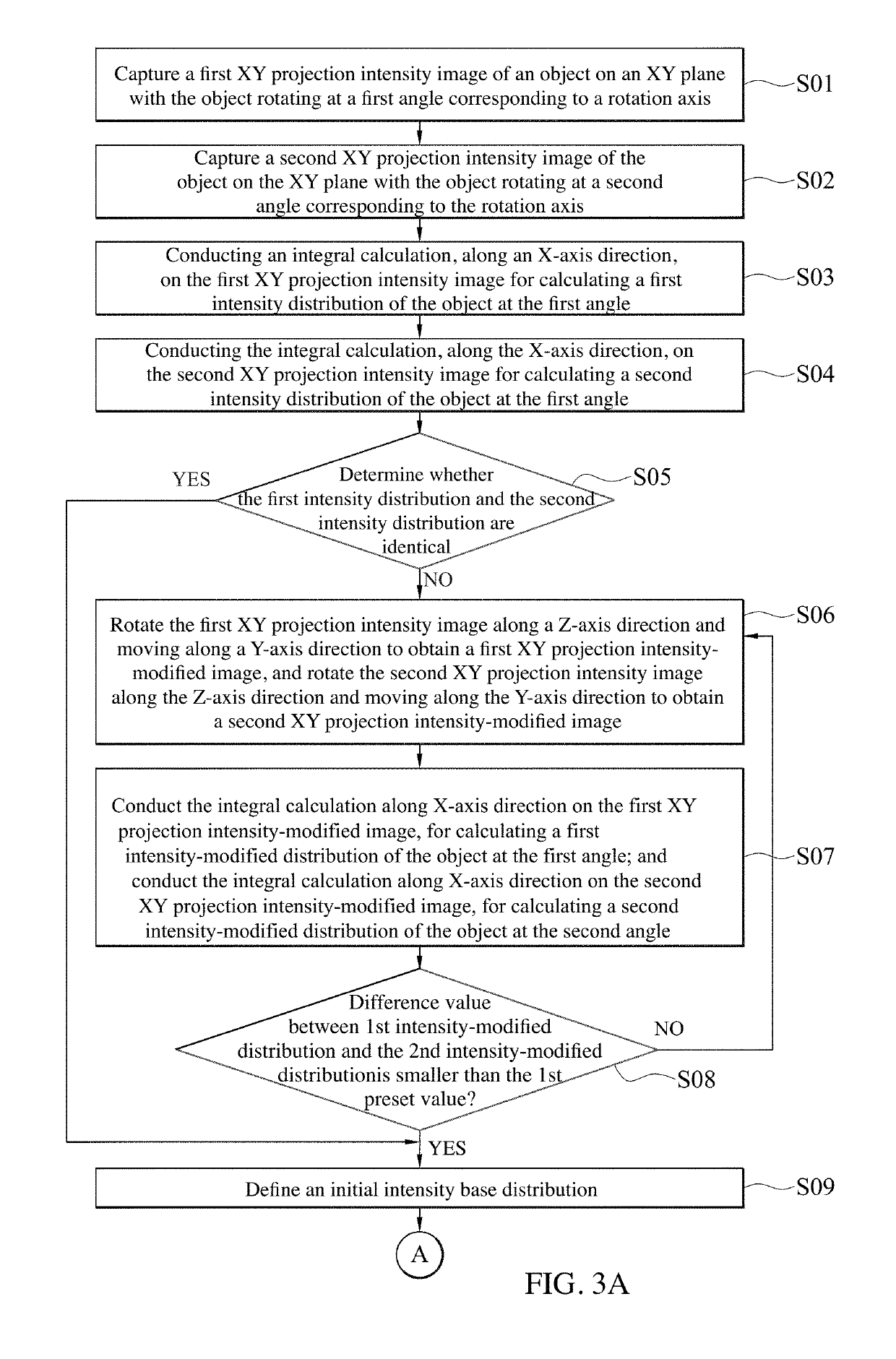
A fast projection matching method for computed tomography (CT) images is provided. The method mainly bases on an iterative algorithm. The algorithm simplifies a traditional issue of three-dimensional projection matching into a two-dimensional projection-matching problem by pre-correcting the Y-axis offset and ϕ shift of each projection intensity image using common-line concept, thereby making the complex CT alignment processing faster and more reliable. This majorly reduces the hardware requirements for CT and data processing, which facilitates the applications in other three dimensional tomographic techniques, such as X-ray micro-CT or electron tomography.
Owner:NAT SYNCHROTRON RADIATION RES CENT
Apparatus and methods for depth-of-interaction positron tomography detector using dichotomous sensing
InactiveUS10466371B2High resolutionReduce manufacturing costComputerised tomographsTomographyDepth of interactionTomography
Apparatus and methods for depth-of-interaction (DOI) positron tomography detection are disclosed herein. Certain embodiments utilize dichotomous sensing to obtain DOI information.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Bulk Synthesis of Nanoporous Palladium and Platinum Powders
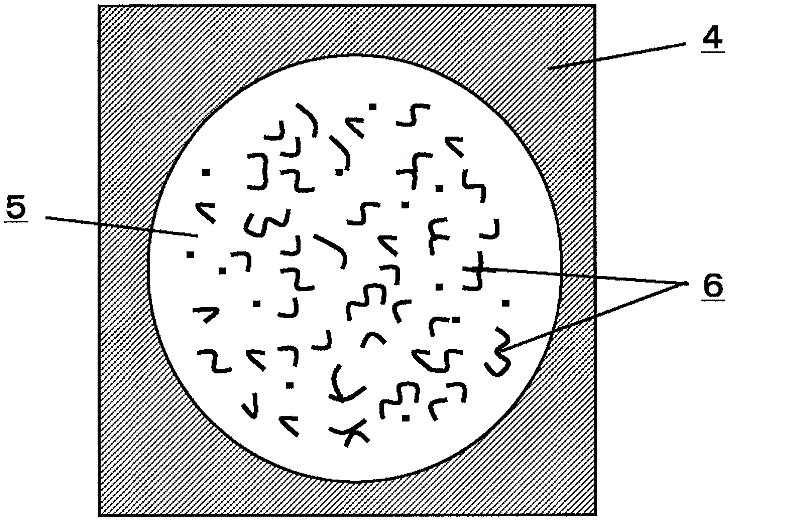
Disclosed is a method for providing nanoporous palladium and platinum powders. These materials were synthesized on milligram to gram scales by chemical reduction of tetrahalo-complexes with ascorbate in a concentrated aqueous surfactant at temperatures between −20° C. and 30° C. The prepared particles have diameters of approximately 50 nm, wherein each particle is perforated by pores having diameters of approximately 3 nm, as determined by electron tomography. These materials are of potential value for hydrogen and electrical charge storage applications.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope) three-dimensional reconstruction sample rod capable of carrying nanometer needle tip sample and automatically rotating 360 degrees
PendingCN114300327AEasy to operateGuaranteed coaxialityElectric discharge tubesControl systemElectron microscope
The invention relates to a TEM three-dimensional reconstruction sample rod capable of carrying a nanometer needle tip sample and automatically rotating 360 degrees. The sample rod specifically comprises a sample rod main body, a nano needle tip sample clamping device, a 360-degree rotation control device and a touch screen control system. According to the invention, the clamping mode of the nano needle tip sample is optimized, and the high coaxiality of the nano needle tip sample and the sample rod is ensured; under the control of the servo motor, the sample autorotation completely avoids the defect that the tilt angle of the traditional TEM sample rod is limited by an angle measuring table of an electron microscope, and meanwhile, the danger that the sample rod touches a pole shoe in the tilt process is greatly reduced. The data is collected by rotating the sample by 360 degrees, so that the problem of information loss in the electron tomography process is completely eliminated, and the resolution limit of three-dimensional reconstruction of the transmission electron microscope is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
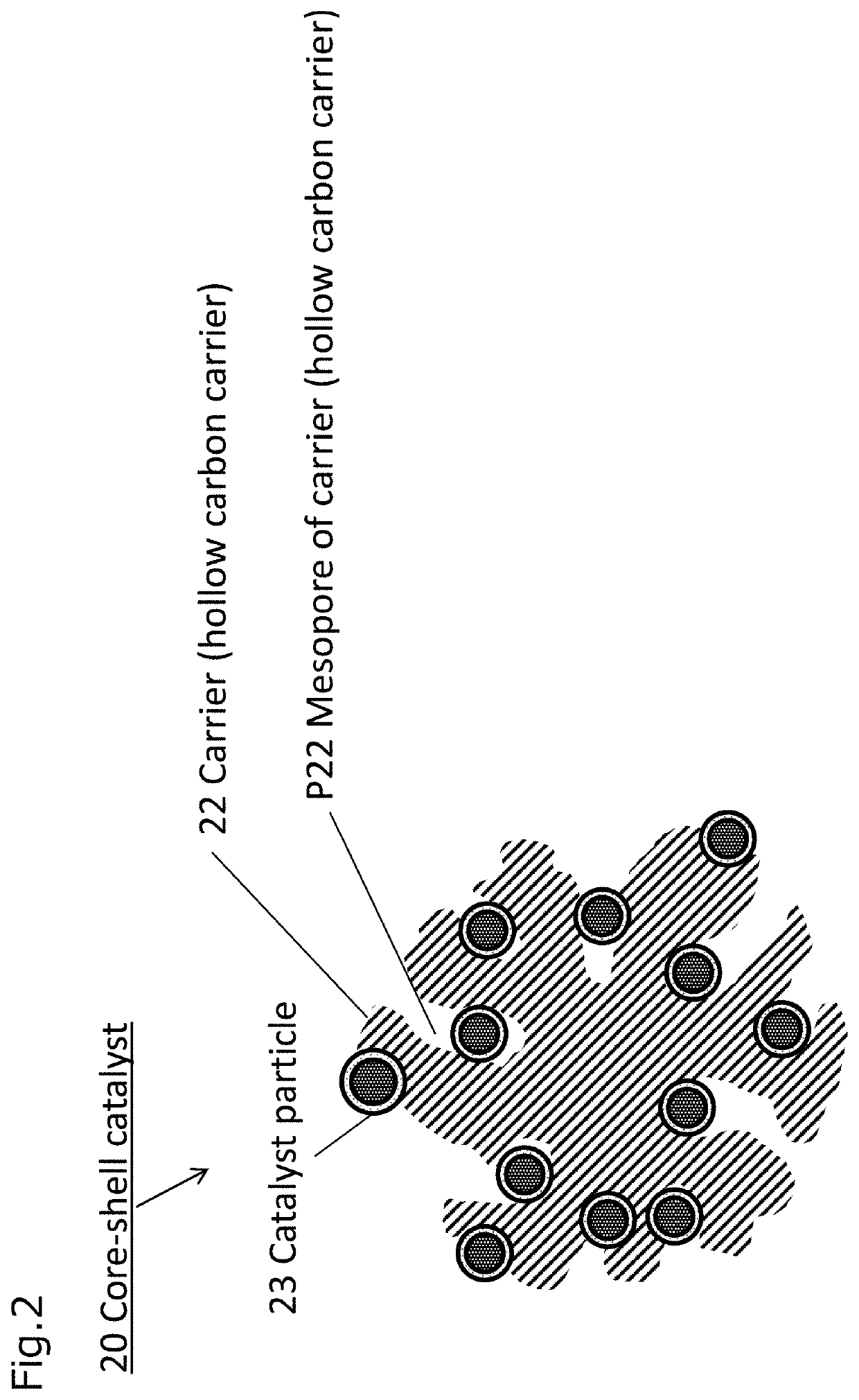
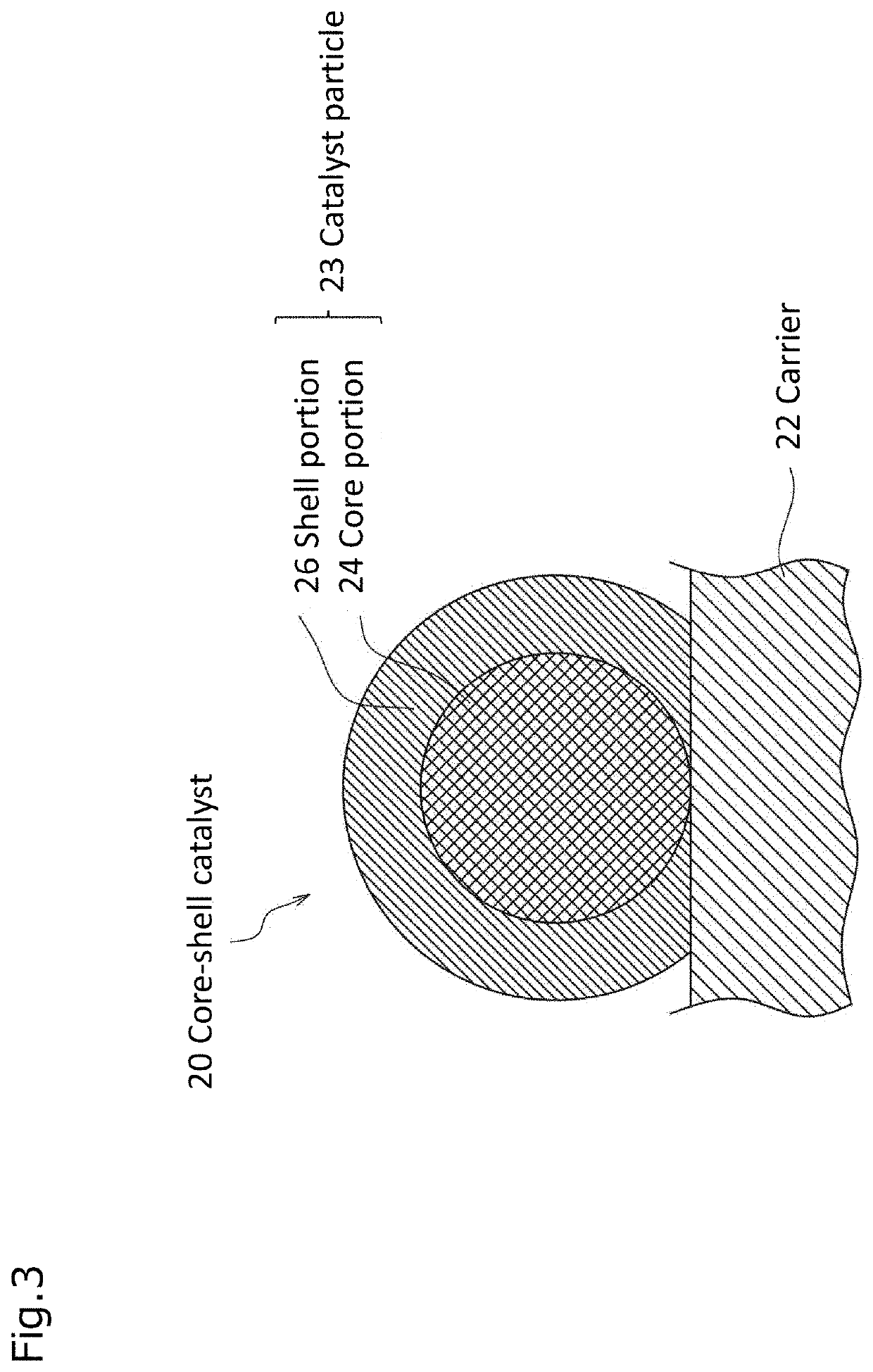
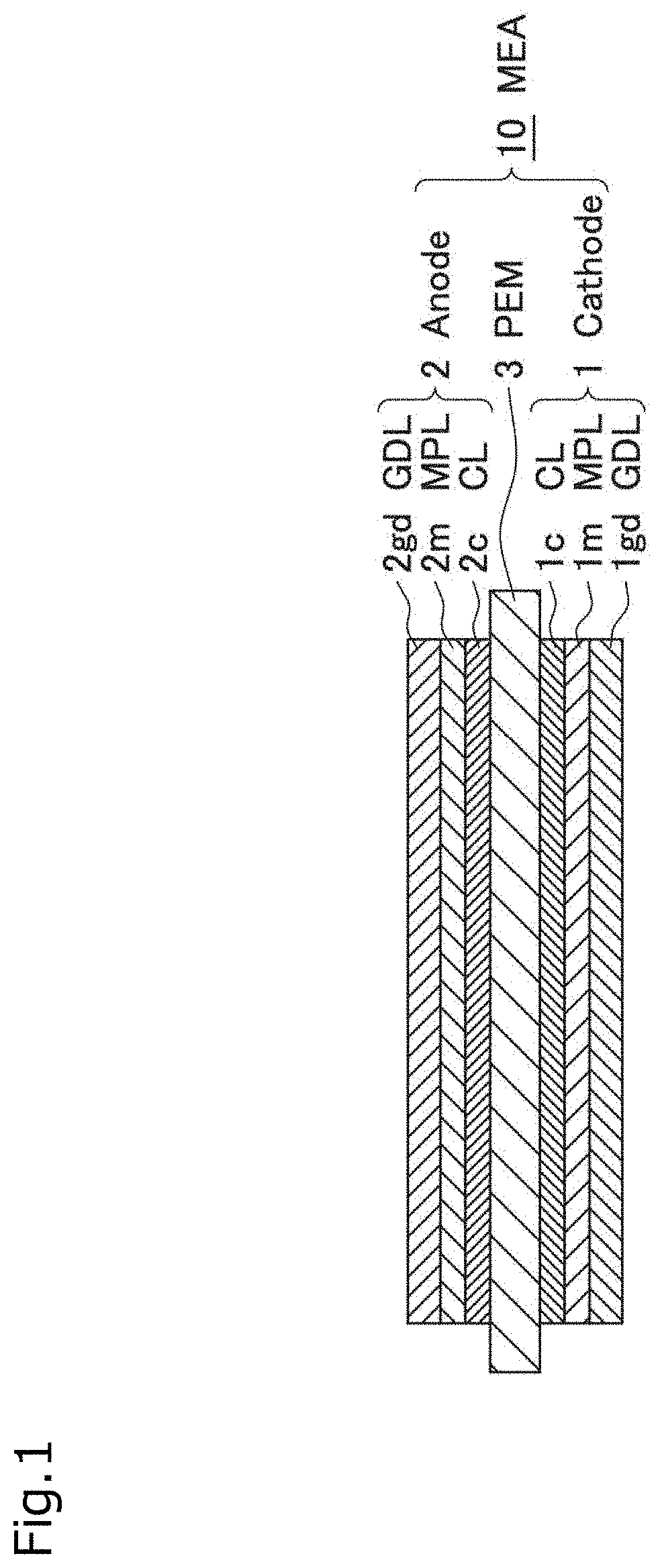
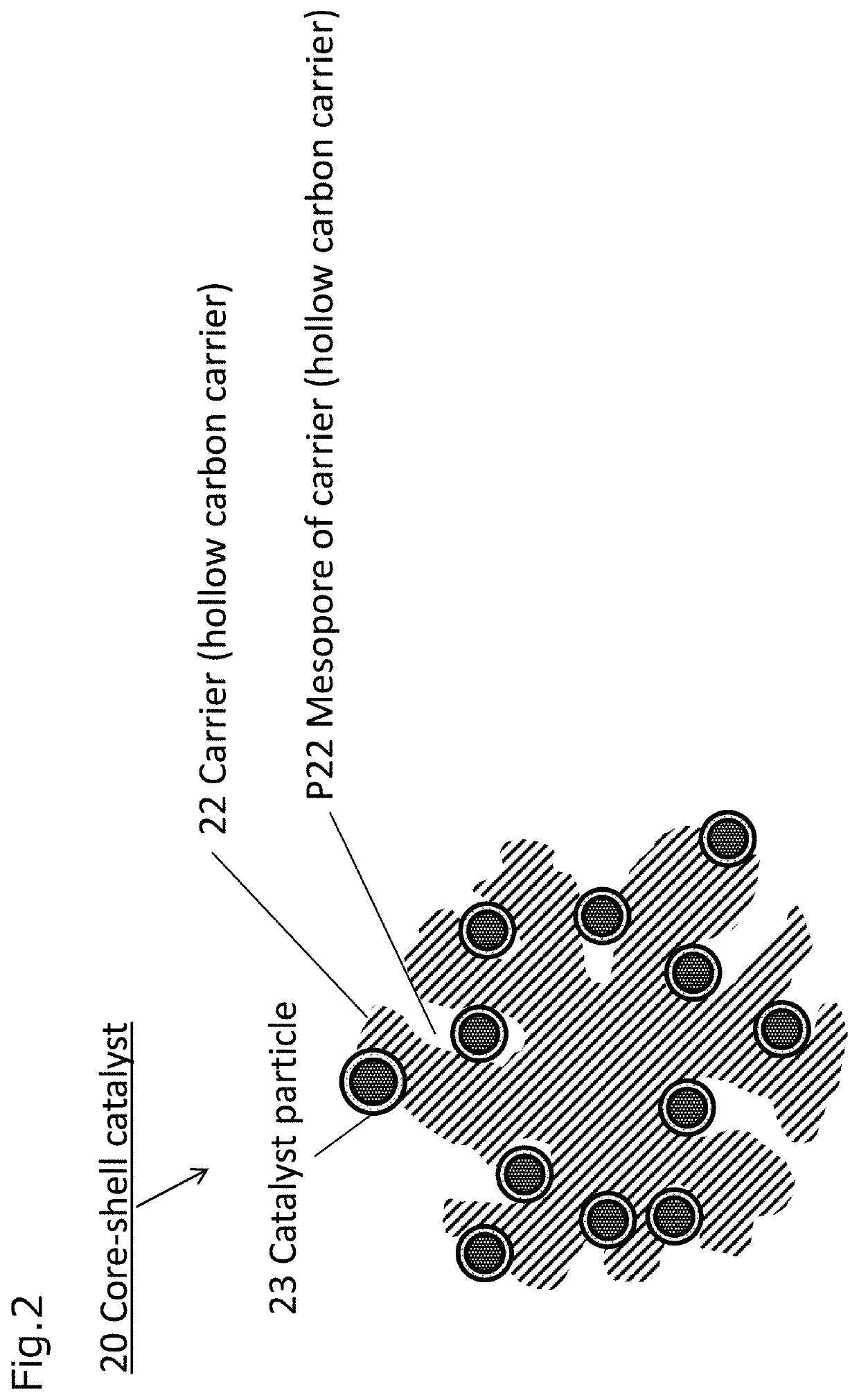
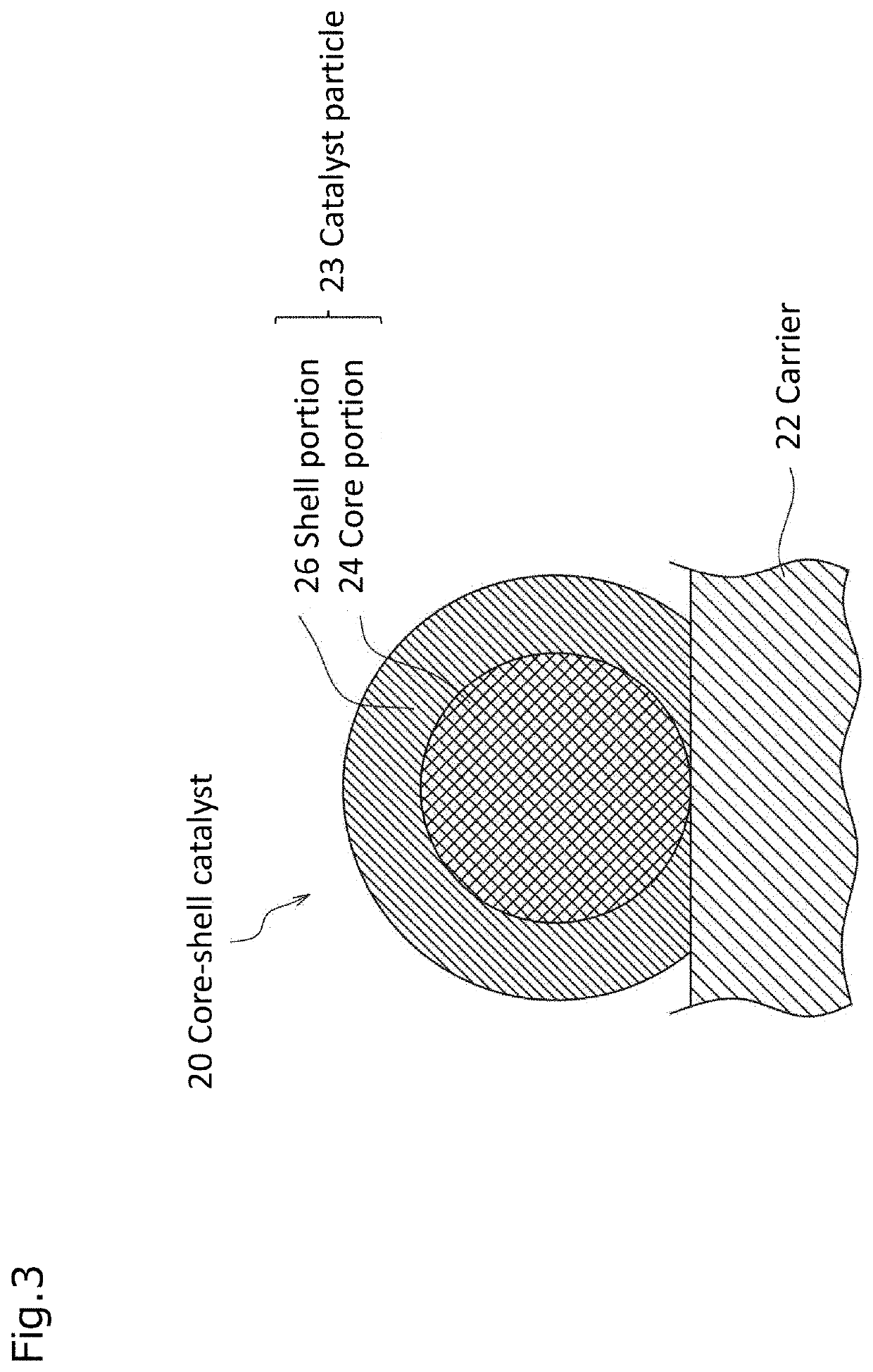
Electrode catalyst, composition for forming gas diffusion electrode, gas diffusion electrode, membrane electrode assembly and fuel cell stack
ActiveUS20210184228A1High catalytic activityLow costSolid electrolytesPositive electrodesPtru catalystFuel cells
Provide an electrode catalyst with excellent catalytic activity that can contribute to cost reduction of PEFC. The electrode catalyst includes a hollow carbon carrier with mesopores with a pore size of 2 to 50 nm and a catalyst particle supported on the carrier. The catalyst particle is supported on both inside and outside the mesopores of the carrier, and have a core portion formed on the carrier and a shell portion covering at least a part of the surface of the core portion. Pd is included in the core portion, and Pt is included in the shell portion, and when the analysis of the particle size distribution of the catalyst particles using the three dimensional reconstructed image obtained by electron beam tomography (electron tomography) measurement using an STEM is performed, the ratio of the catalyst particles supported inside the mesopore is 50% or more.
Owner:N E CHEMCAT
[*F] fluoraro-marked purine compound, its production and use
ActiveCN100506822CHigh aggregation valueHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersPurineCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a [18F]fluorine-labeled purine compound, which is 2-amino-6-[18F]fluoro-9-(4-hydroxyl-3-hydroxymethylbutyl ) Purine. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the above-mentioned [18F] fluorine-labeled purine compound and its application as a molecular probe for positron electron tomography (PET) of reporter gene HSV1-tk.
Owner:SHANGHAI ATOM KEXING PHARMA +1
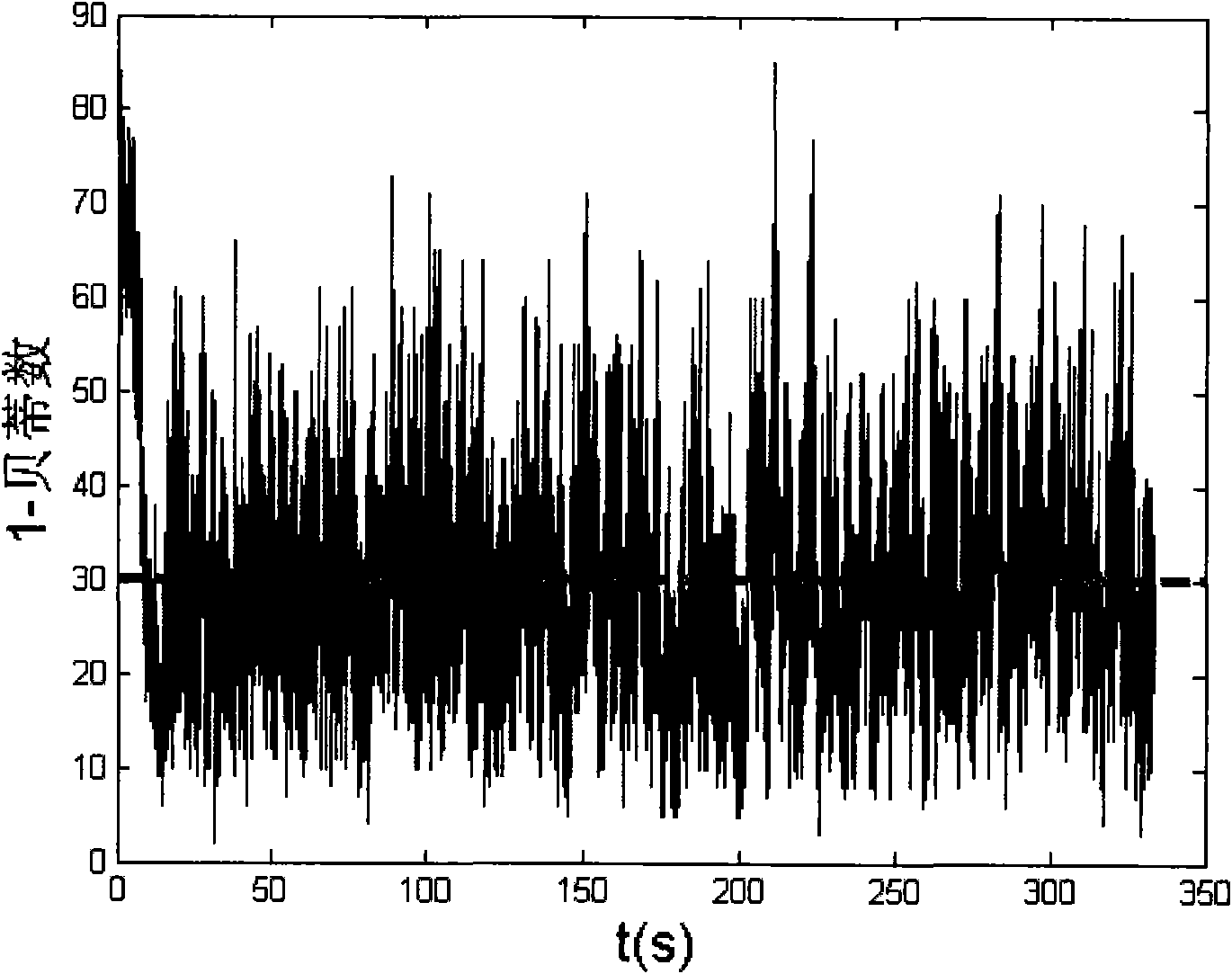
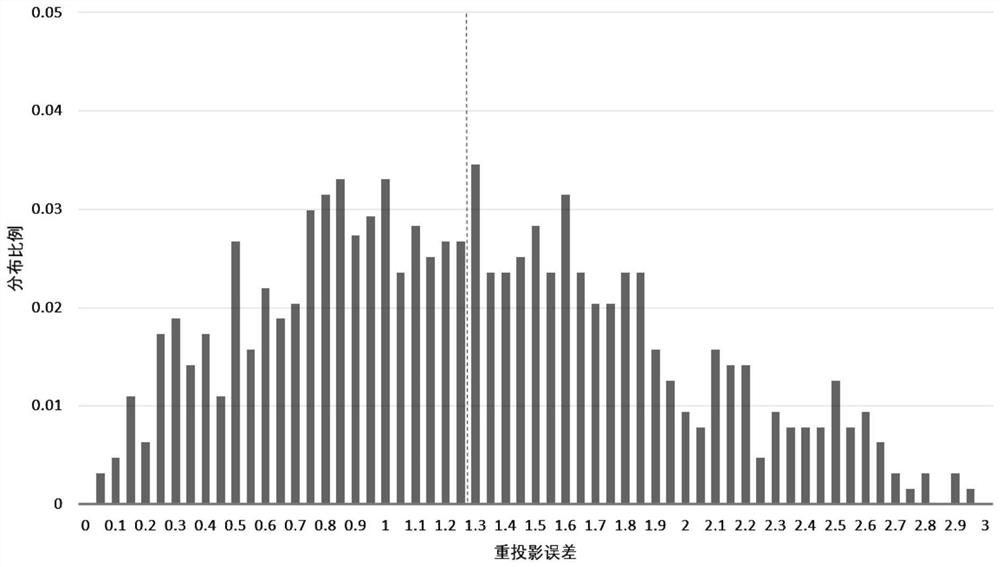
Freeze electron cross-sectional image-oriented mismatching removal method
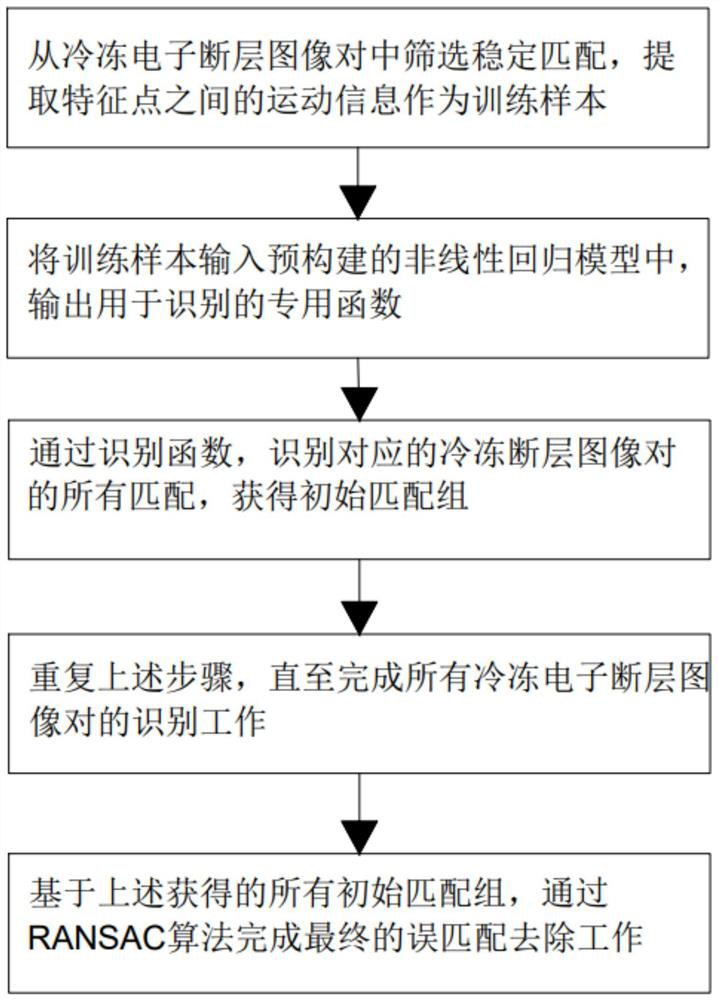
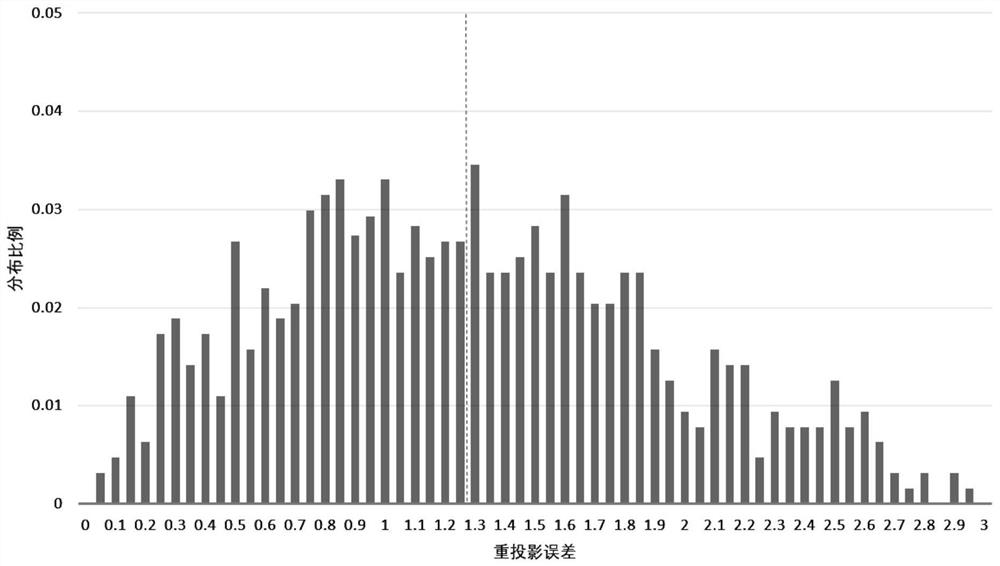
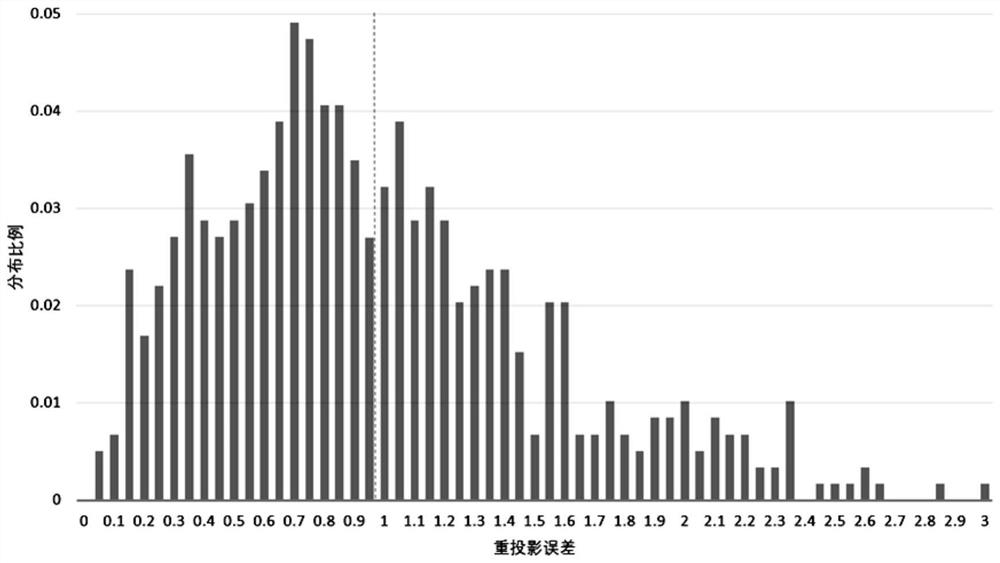
PendingCN114359593AImprove the accuracy of mismatch removalGuaranteed correctnessCharacter and pattern recognitionProjection imageComputational physics
The invention discloses a frozen electron cross-sectional image-oriented mismatching removal method, which comprises the following steps of: S1, screening stable matching from a group of frozen electron cross-sectional image pairs, and extracting motion information between feature points as a training sample; s2, inputting the training sample obtained in the S1 into a pre-constructed nonlinear regression model, and fitting an identification function for calculating all matching correctness probabilities of the frozen electron cross-sectional image pair through training; s3, an identification function is obtained based on training fitting in the S2, and the frozen electron cross-sectional image pair is calculated to obtain an initial matching group; s4, repeating S1, S2 and S3 until an initial matching group of all the frozen electron cross-sectional image pairs is obtained; and S5, on the basis of all the initial matching groups, finishing final mismatching removal work through an RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) algorithm. According to the method, the wrong matching is removed by using the motion consistency between the electron tomography projection image sequences, so that the correct matching between the images is effectively kept, and meanwhile, the accuracy of the alignment result is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
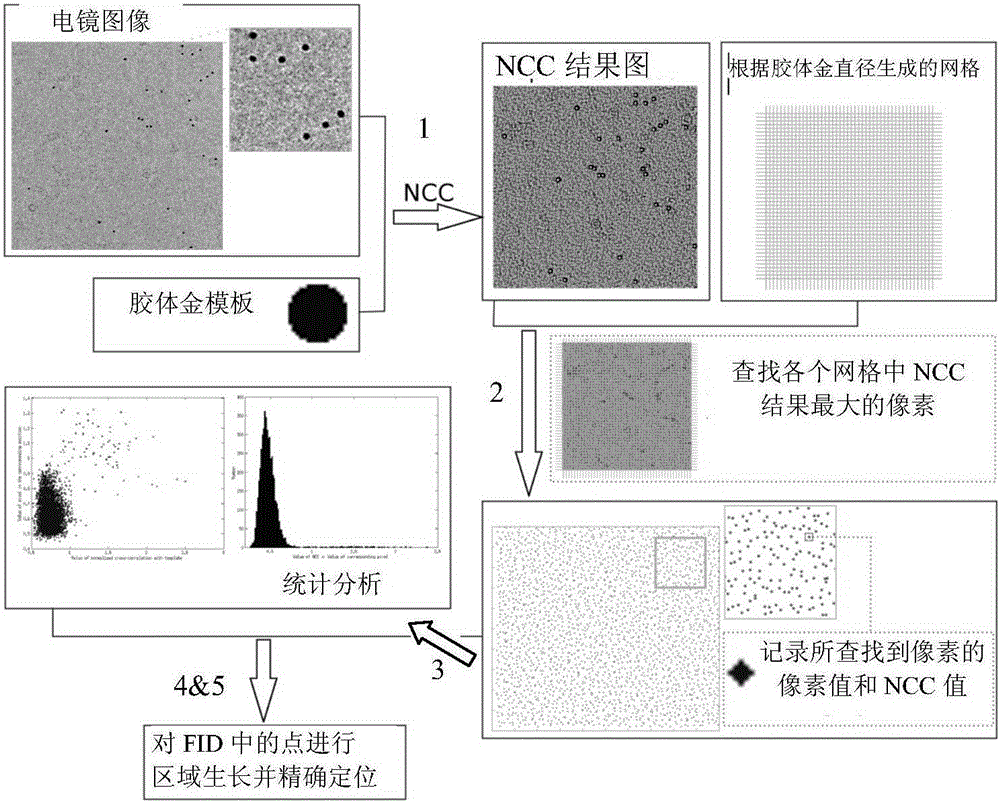
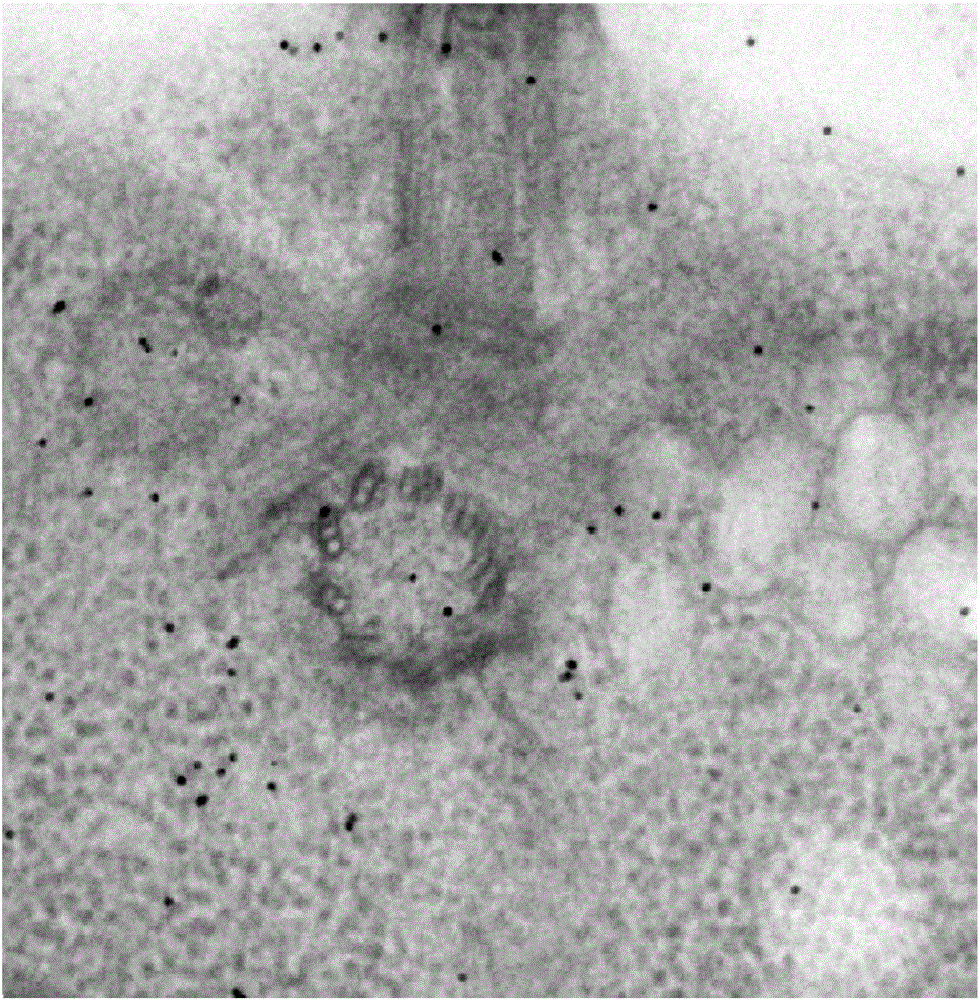
Diameter estimation and automatic identification methods for colloidal gold in electron tomography image
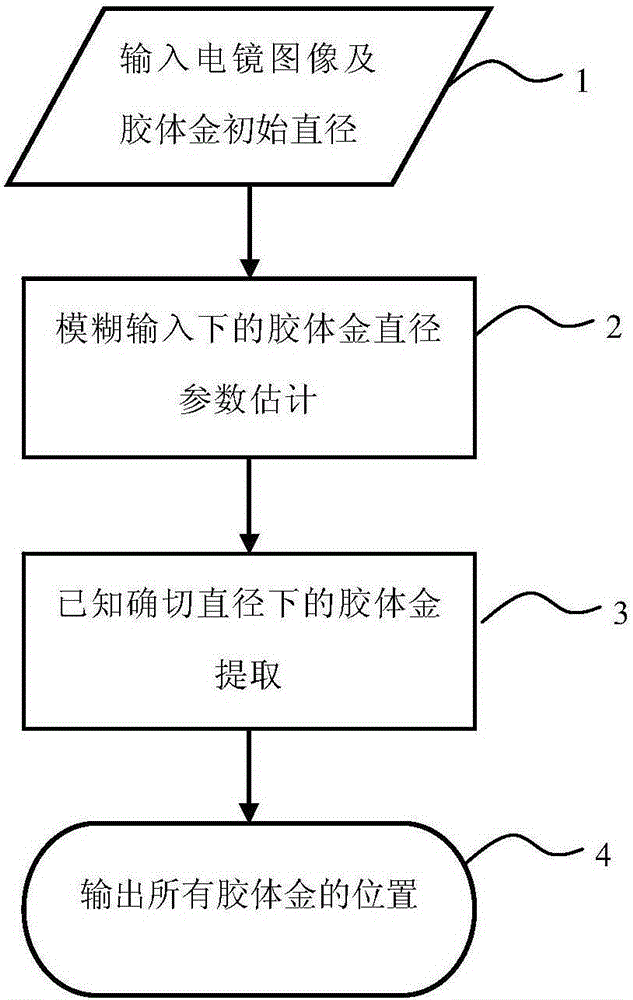
ActiveCN105205840AReduce dependenceImprove recognition rateImage analysis2D-image generationTemplate matchingCorrelation coefficient
The invention provides a diameter estimation method for colloidal gold in an electron tomography image. The diameter estimation method comprises that 1) a series of estimation diameters are obtained within the value range close to the diameter of original colloidal gold; 2) the cross correlation coefficient between a manual template and an average template is calculated under each estimation diameter and serves as a template matching cross correlation coefficient, the manual template is a colloidal gold template directly generated according to the estimation diameter, and the average template is a colloidal gold template obtained by extracting colloidal gold according to the estimation diameter and averaging images in the extracted colloidal gold area; and 3) the accurate diameter of the colloidal god is determined according to template matching cross correlation coefficients corresponding to the different estimation diameters. The invention also provides a corresponding automatic identification method for colloidal gold. Methods of the invention are less dependent on parameters as the diameter and amount of the colloidal gold, and the identification rate is higher.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fast projection matching method for computed tomography images
ActiveUS10565745B2Image enhancementReconstruction from projection3D projectionThree dimensional tomography
A fast projection matching method for computed tomography (CT) images is provided. The method mainly bases on an iterative algorithm. The algorithm simplifies a traditional issue of three-dimensional projection matching into a two-dimensional projection-matching problem by pre-correcting the Y-axis offset and ϕ shift of each projection intensity image using common-line concept, thereby making the complex CT alignment processing faster and more reliable. This majorly reduces the hardware requirements for CT and data processing, which facilitates the applications in other three dimensional tomographic techniques, such as X-ray micro-CT or electron tomography.
Owner:NAT SYNCHROTRON RADIATION RES CENT
Electrode catalyst, composition for forming gas diffusion electrode, gas diffusion electrode, membrane electrode assembly and fuel cell stack
ActiveUS11271219B2High catalytic activityLow costSolid electrolytesPositive electrodesPtru catalystFuel cells
Provide an electrode catalyst with excellent catalytic activity that can contribute to cost reduction of PEFC. The electrode catalyst includes a hollow carbon carrier with mesopores with a pore size of 2 to 50 nm and a catalyst particle supported on the carrier. The catalyst particle is supported on both inside and outside the mesopores of the carrier, and have a core portion formed on the carrier and a shell portion covering at least a part of the surface of the core portion. Pd is included in the core portion, and Pt is included in the shell portion, and when the analysis of the particle size distribution of the catalyst particles using the three dimensional reconstructed image obtained by electron beam tomography (electron tomography) measurement using an STEM is performed, the ratio of the catalyst particles supported inside the mesopore is 50% or more.
Owner:N E CHEMCAT
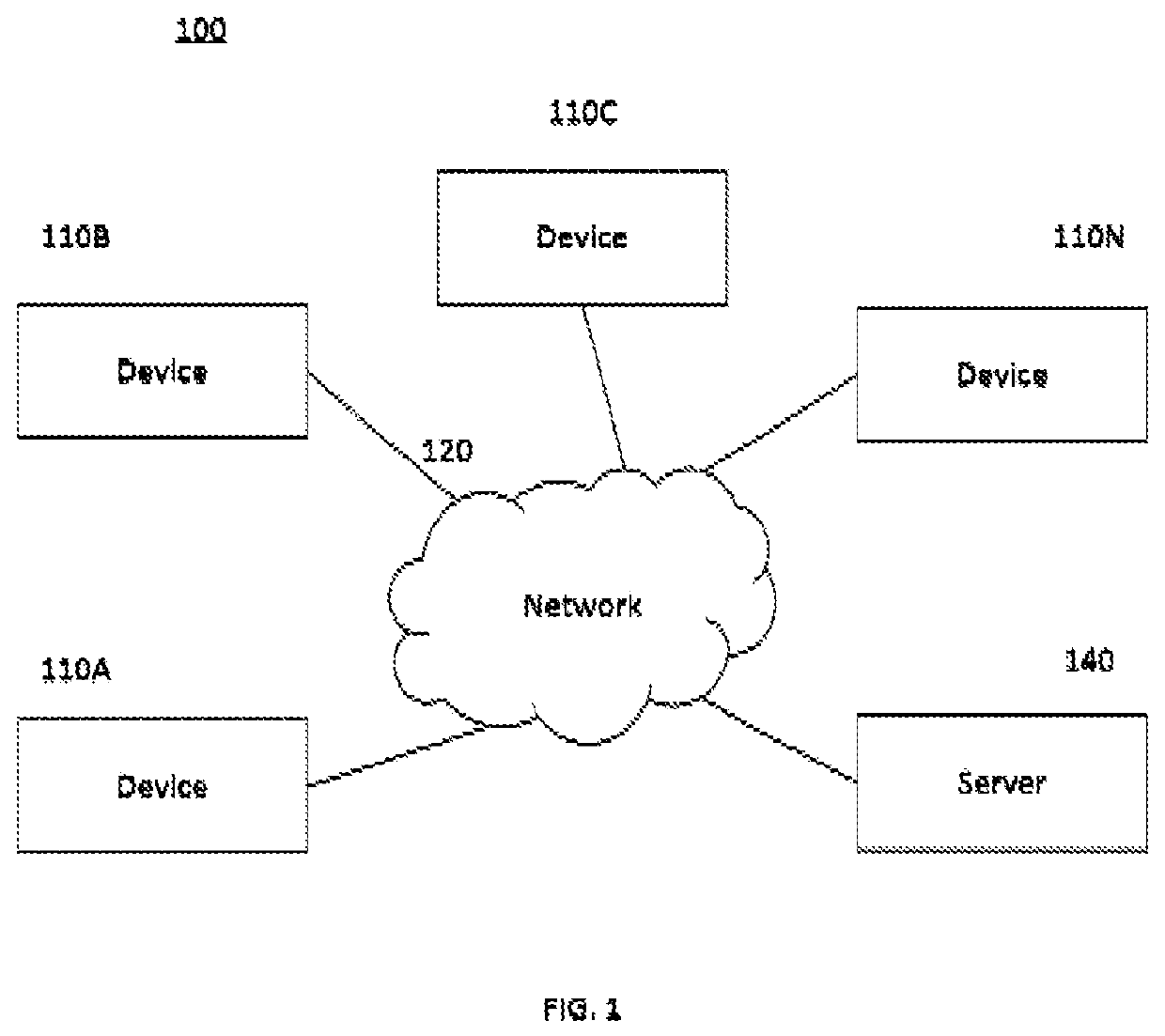
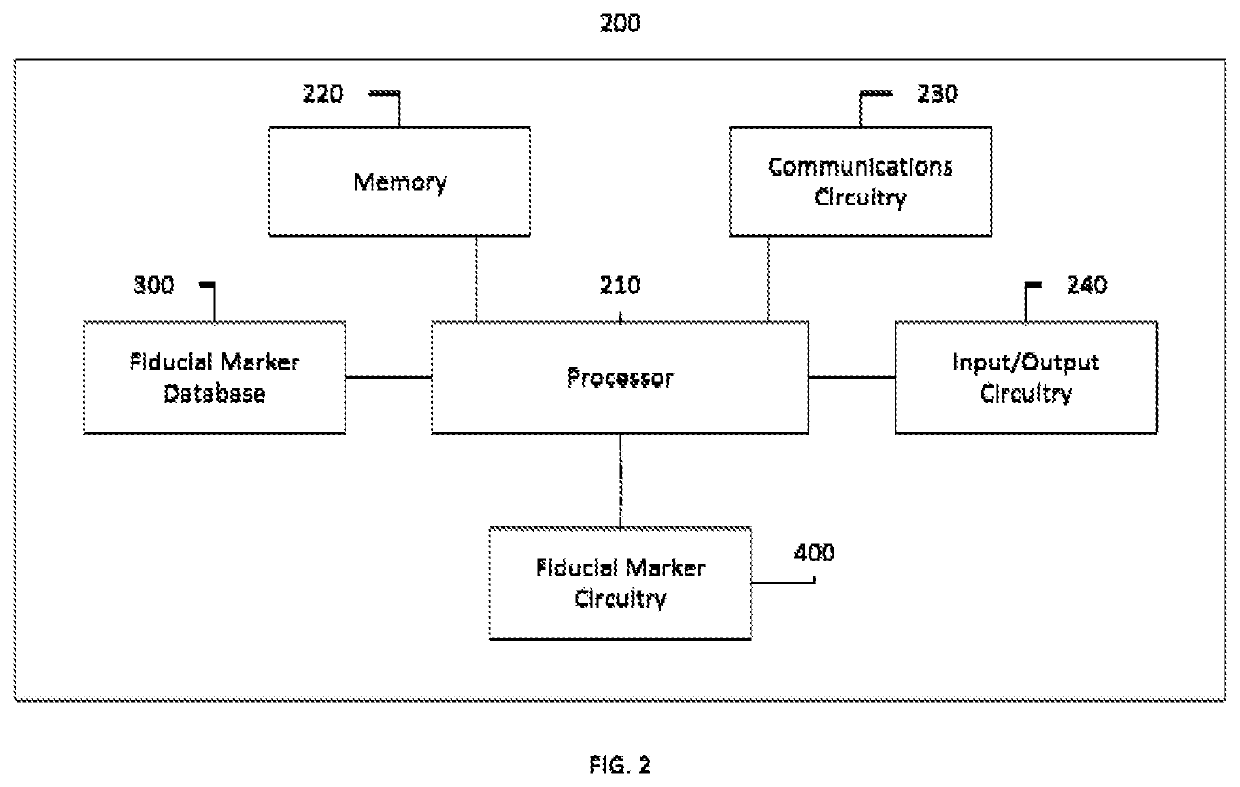
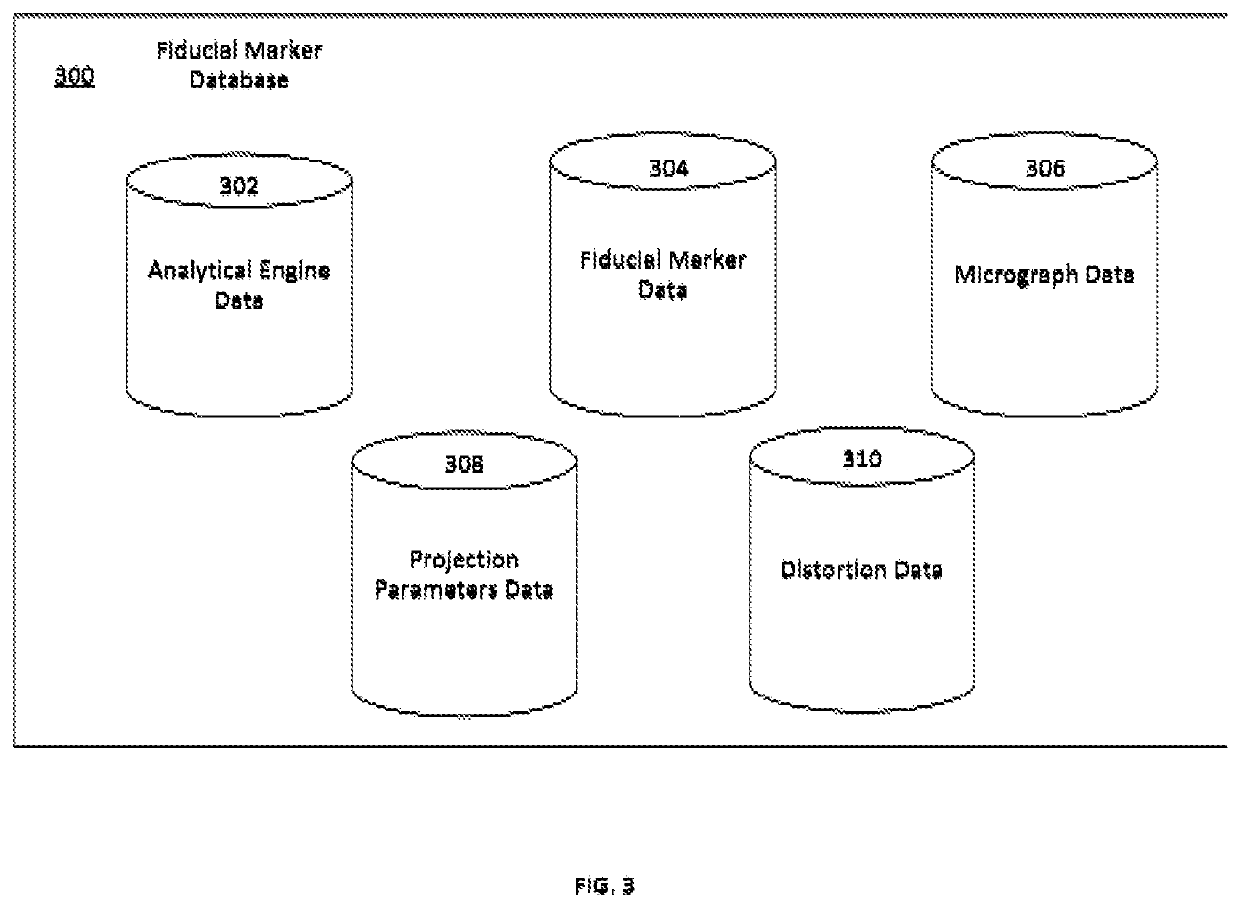
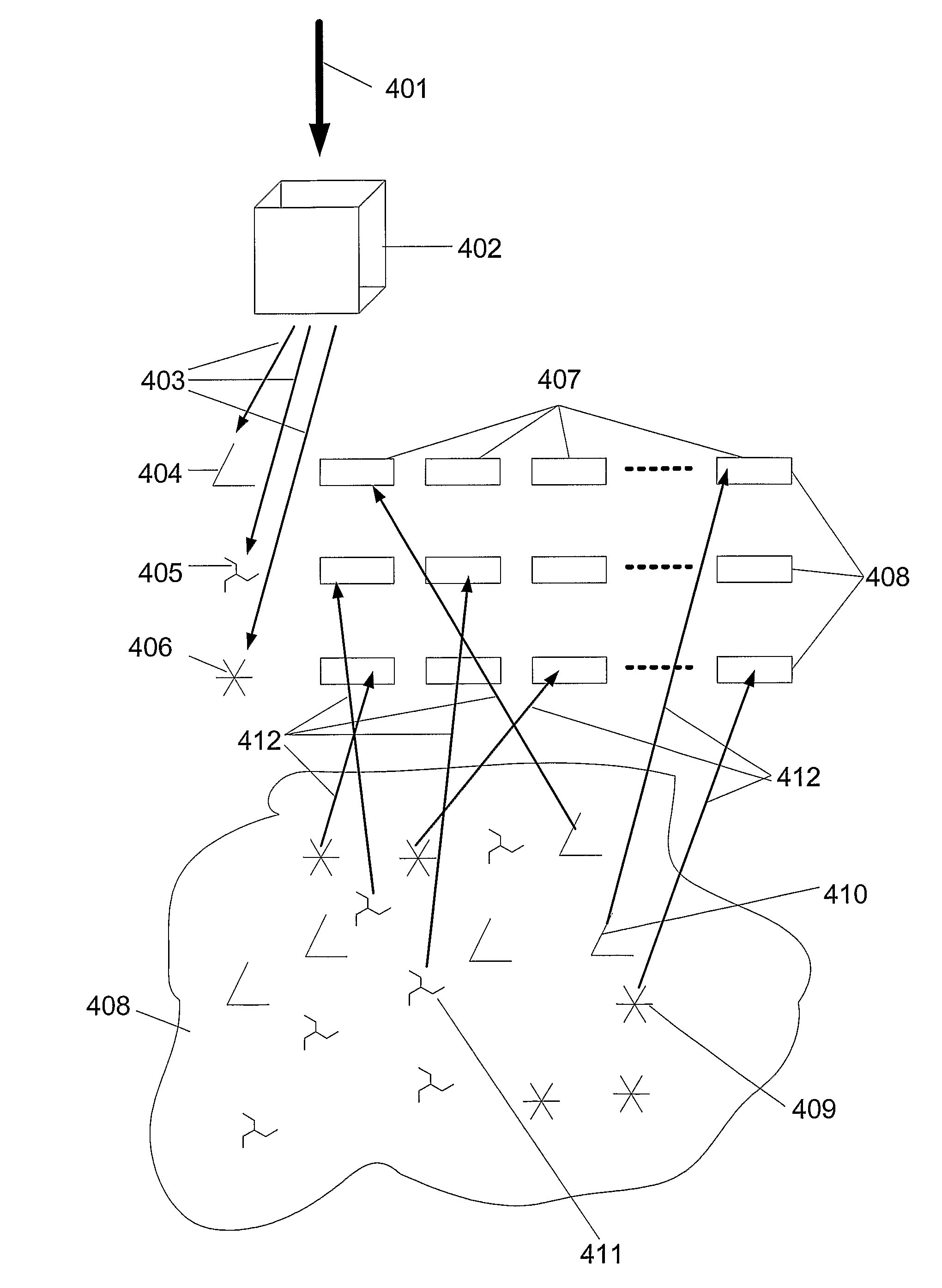
Apparatus and method for fiducial marker alignment in electron tomography
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring mixing effect of fluid
InactiveCN101650292BSimple methodReduce economic lossSurface/boundary effectSpecial data processing applicationsImaging techniqueMixing effect
The invention relates to a method for measuring the mixing effect of fluids and is mainly applied to judging the mixing effect of fluids and theoretically guiding the design of experiments in experiments of chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) utilizing a particle velometer (transparent or semi-transparent fluid mixing) and the electron tomography (nontransparent fluid mixing) to obtain a fluid mixing real-time pattern; (2) utilizing a written particular program to calculate a 0-dimension Betti number and a 1-dimension Betti number of the obtained real-time pattern; (3) judging the mixing effect through respectively calculating the evolvement of the 0-dimension Betti number and the 1-dimension Betti number of an integral region and the average value of the 0-dimension Betti number and the 1-dimension Betti number of a 4 region or a 16 region. The method is applied to the detection of the mixing effect of all fluids, is simple and convenient and has higher practical value. The invention provides a reliable and practical measuring method for judging the mixing effects and theoretically guiding the design of experiments in experiments of chemical engineering.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
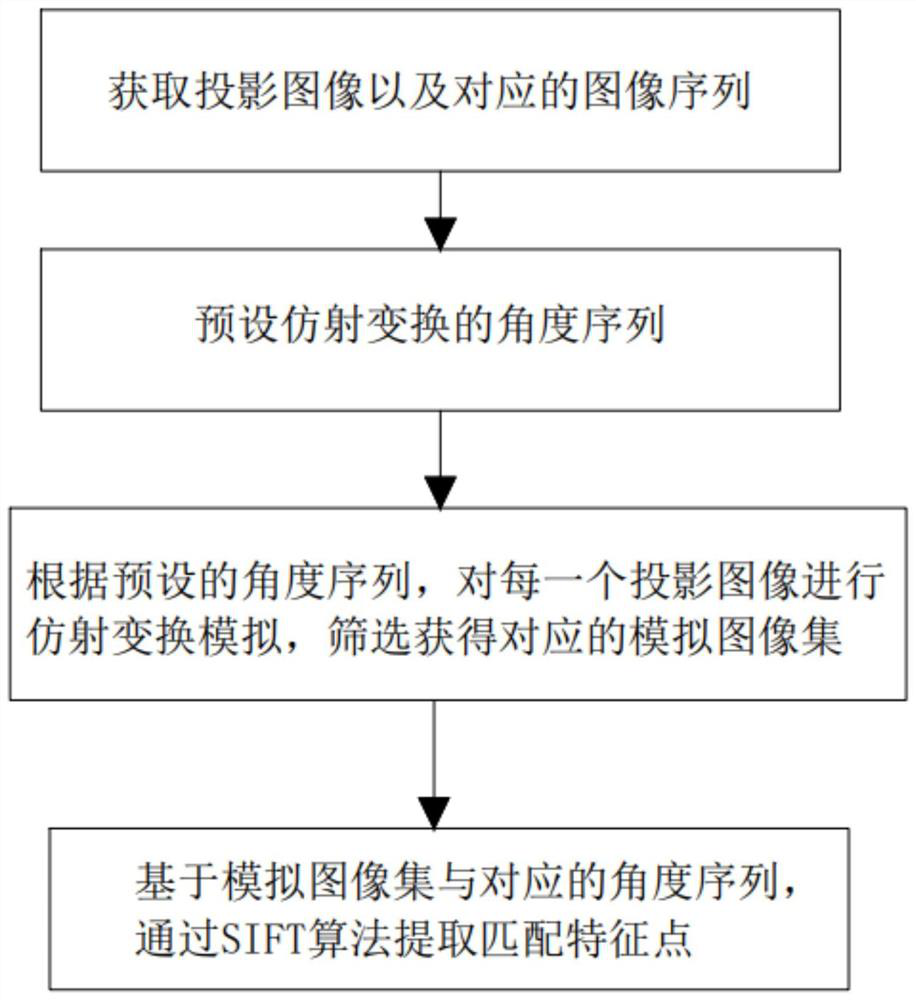
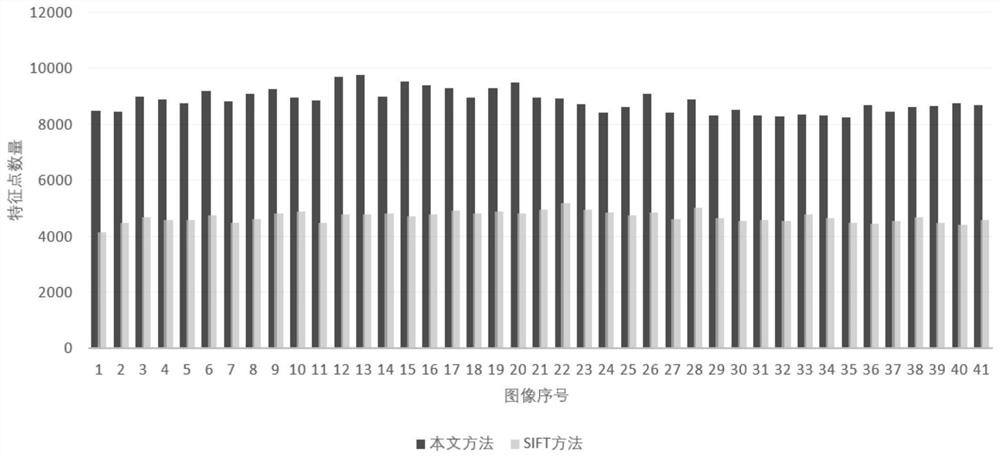
Feature extraction method for frozen electron cross-sectional image
PendingCN114359581AClear angle of rotationAvoid spatial movement errorsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a feature extraction method for a frozen electron cross-sectional image. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring a projected image of a frozen electron cross-sectional image and a corresponding image sequence; s2, presetting an angle sequence of affine transformation simulation; s3, according to a set angle sequence, affine transformation simulation is carried out on the projection image of each frozen electron tomography, and a corresponding simulation image set is obtained after screening; and S4, according to the analog image set obtained in the S3 and the corresponding angle sequence, extracting and obtaining matched feature points. According to the method, through the simulated image set and the corresponding angle sequence, the interference on the spatial position of the sample during manual tilting is solved, and the extraction quality of the feature points is improved, so that a high-quality frozen electron three-dimensional reconstruction model is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
An apparatus and method for fiducial marker alignment in electron tomography
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

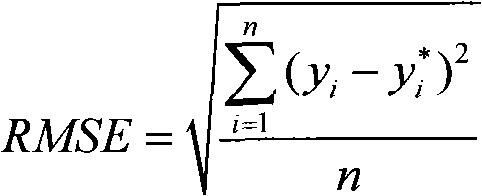

![[*F] fluoraro-marked purine compound, its production and use [*F] fluoraro-marked purine compound, its production and use](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ff99111-4694-44ca-b99a-dd0b23c6a2fb/C200710103614E00171.png)
![[*F] fluoraro-marked purine compound, its production and use [*F] fluoraro-marked purine compound, its production and use](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ff99111-4694-44ca-b99a-dd0b23c6a2fb/C200710103614E00172.png)
![[*F] fluoraro-marked purine compound, its production and use [*F] fluoraro-marked purine compound, its production and use](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ff99111-4694-44ca-b99a-dd0b23c6a2fb/C200710103614E00181.png)