Patents
Literature
466 results about "High density storage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
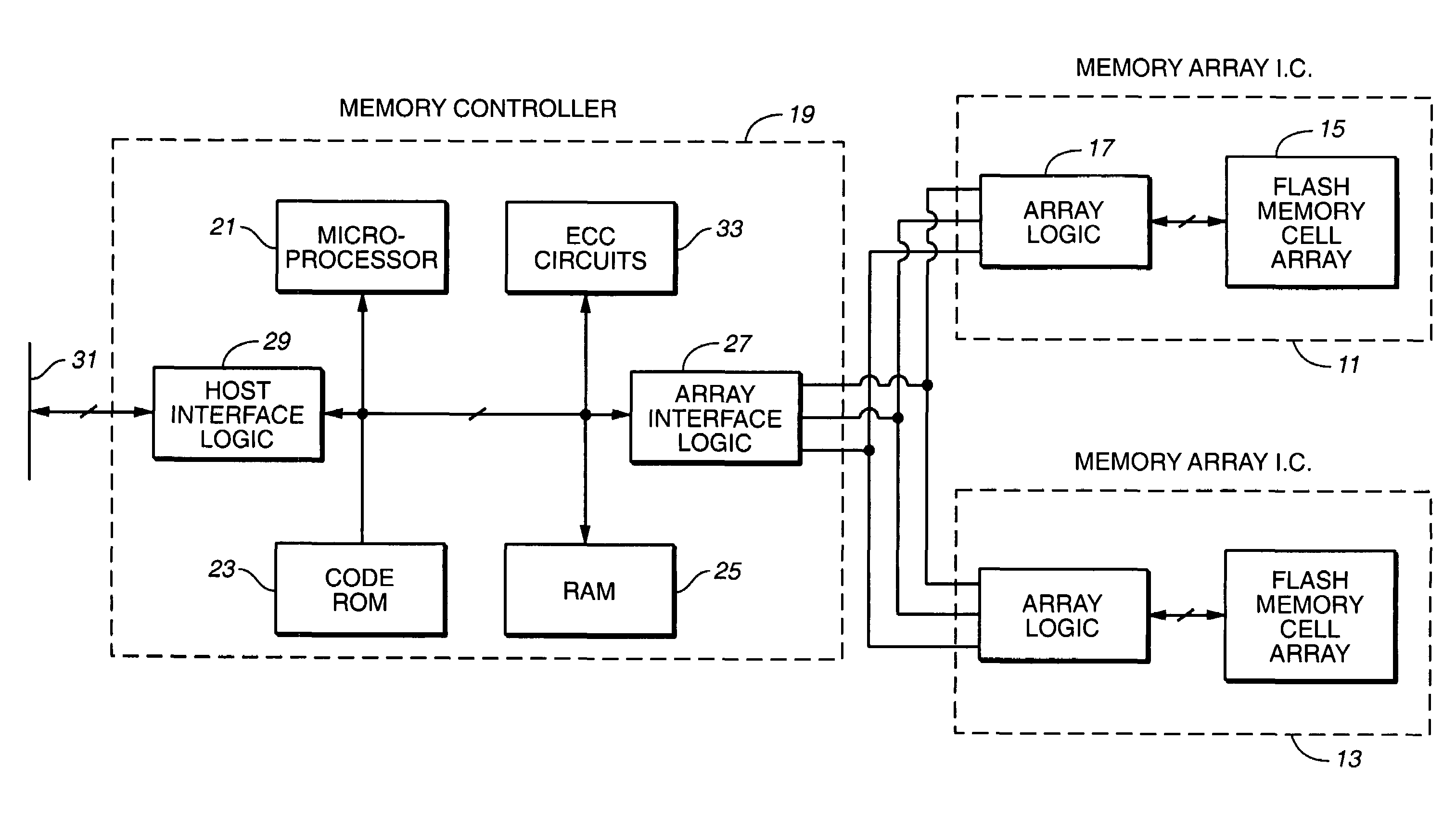
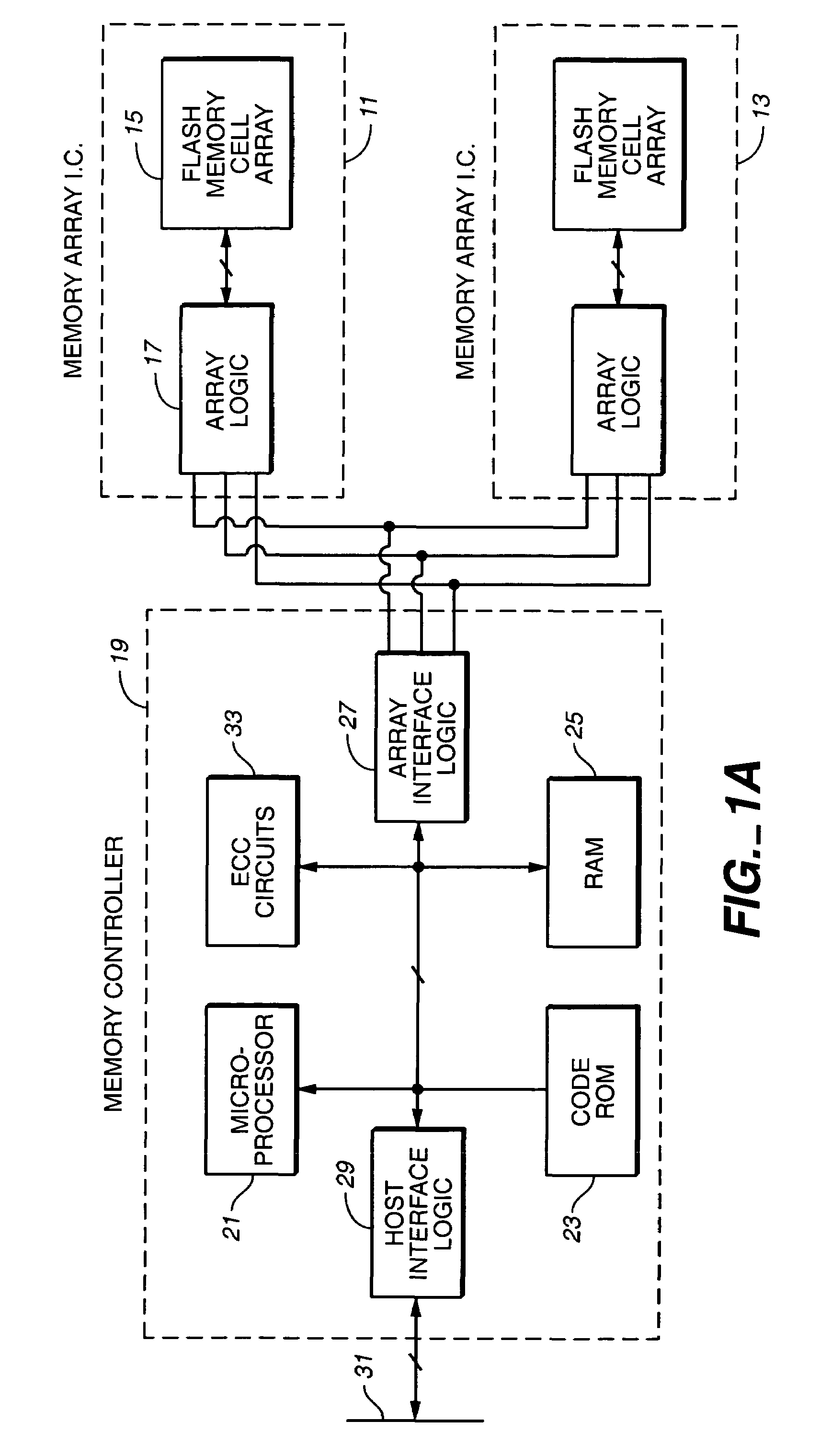
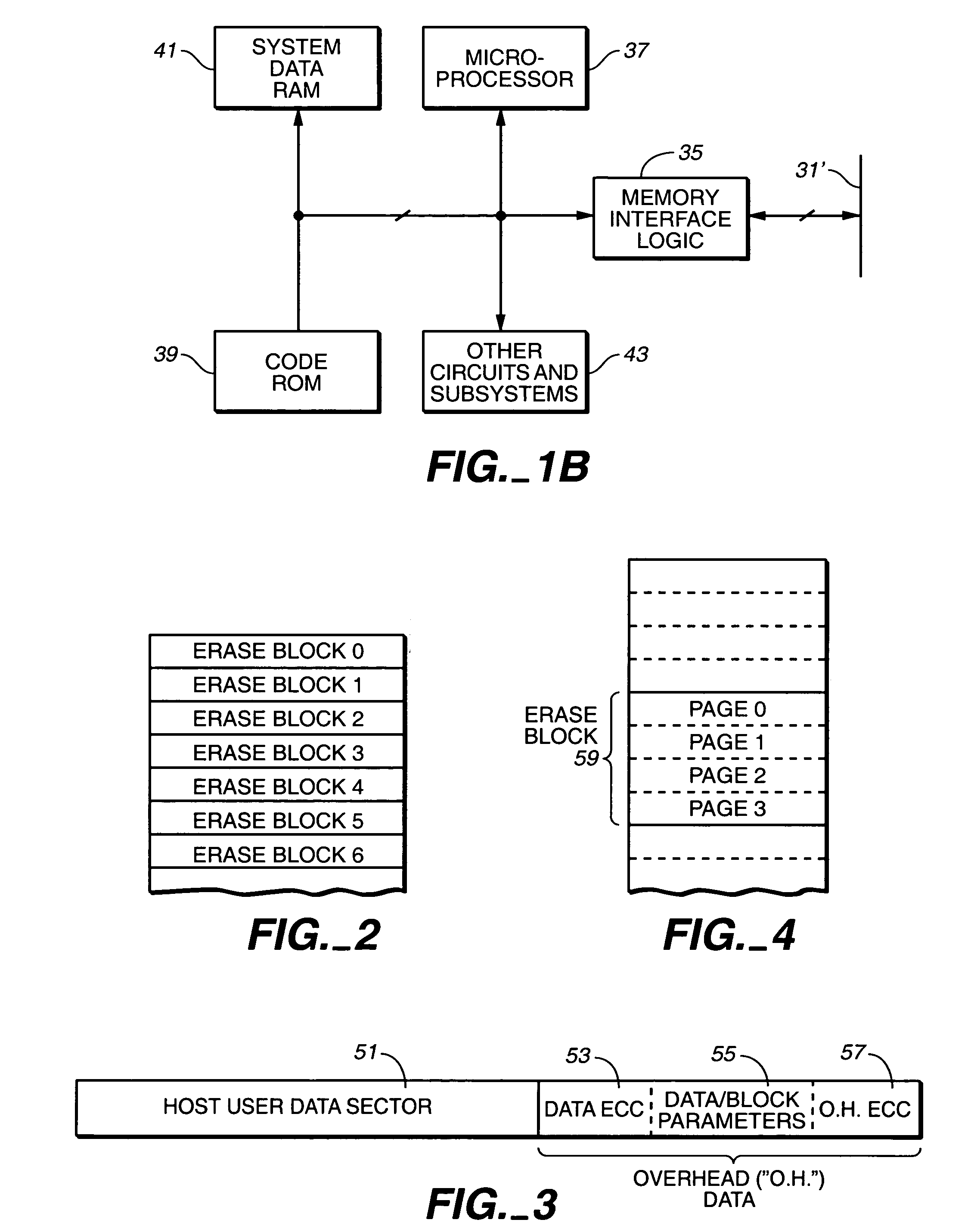
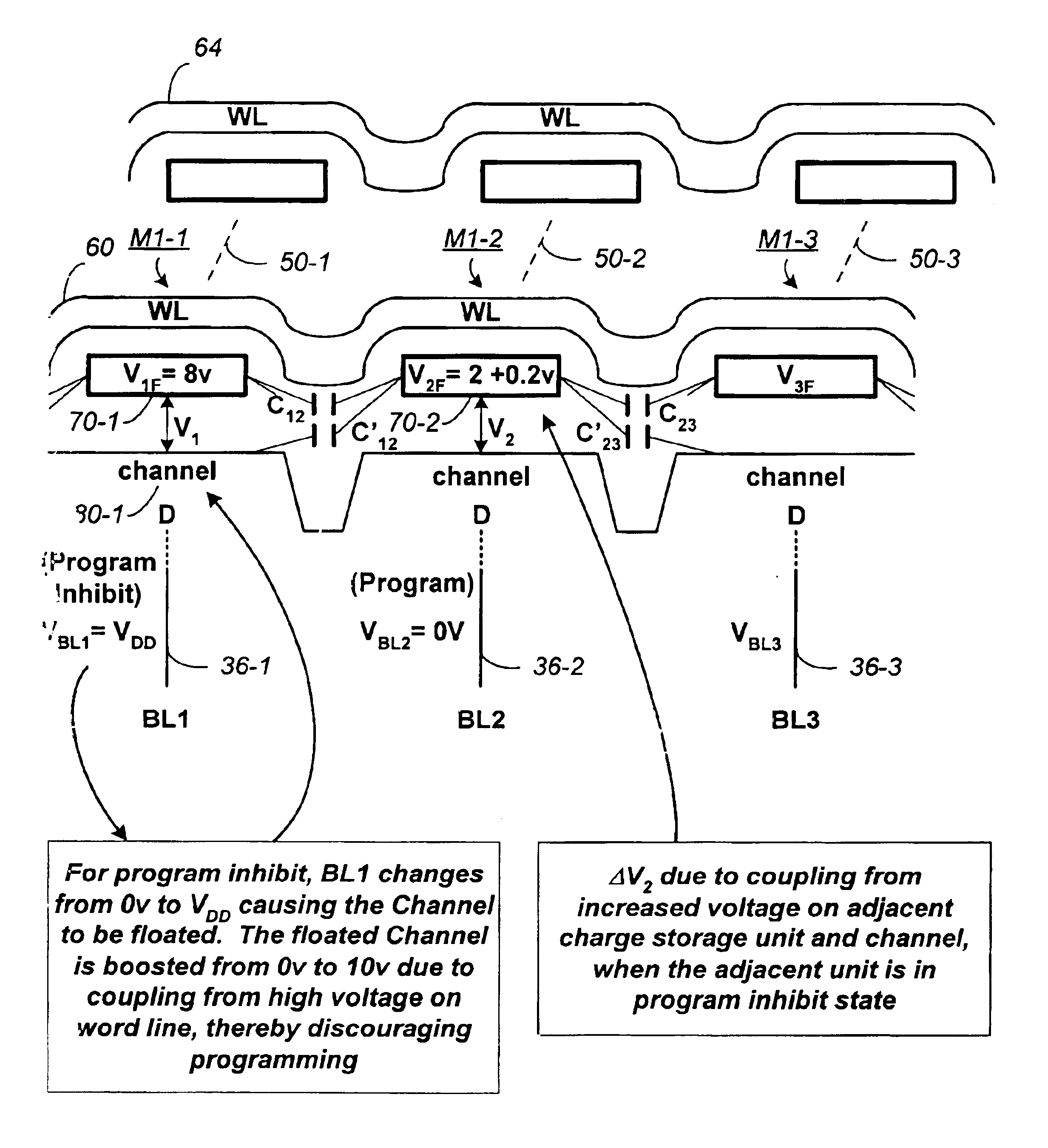
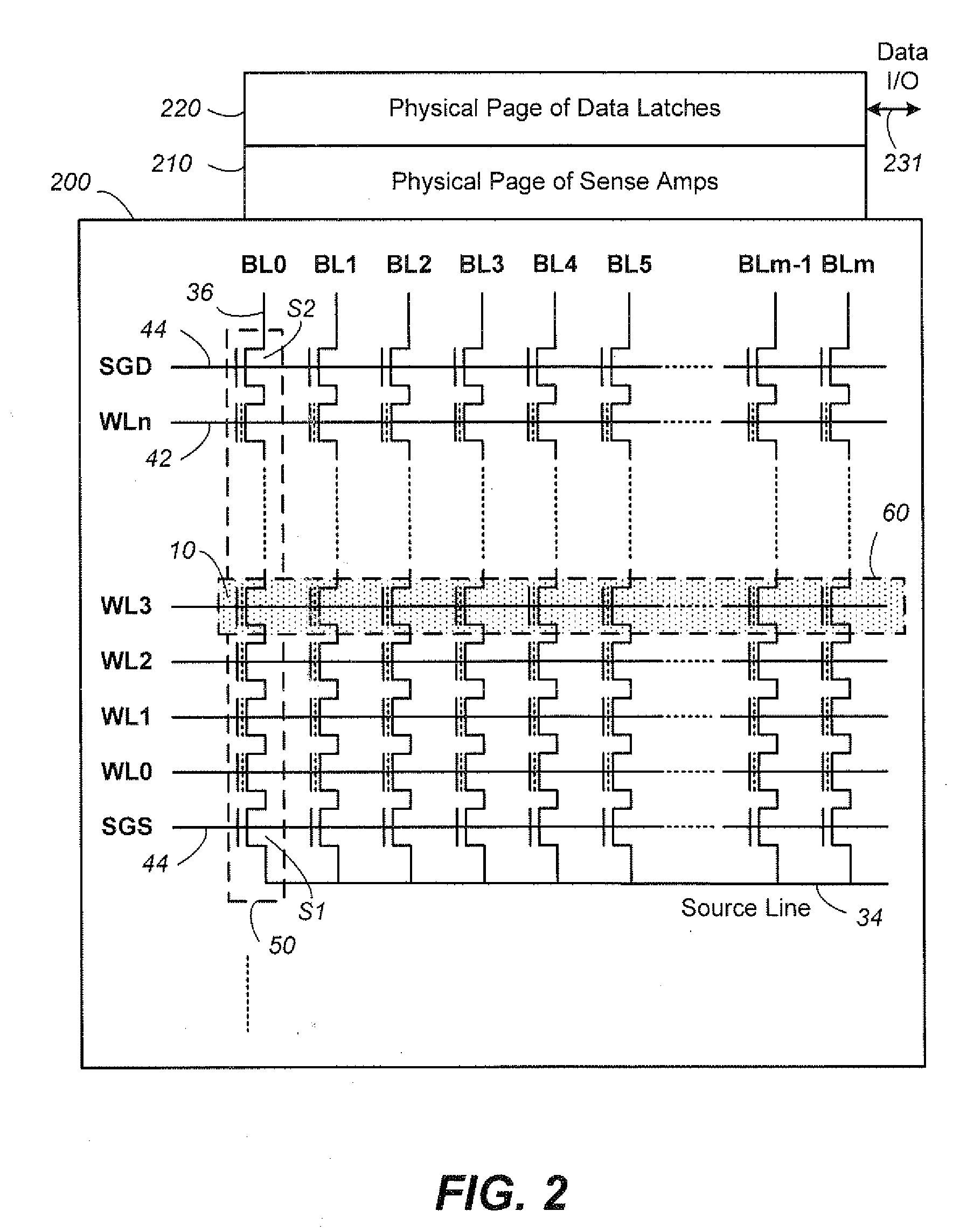
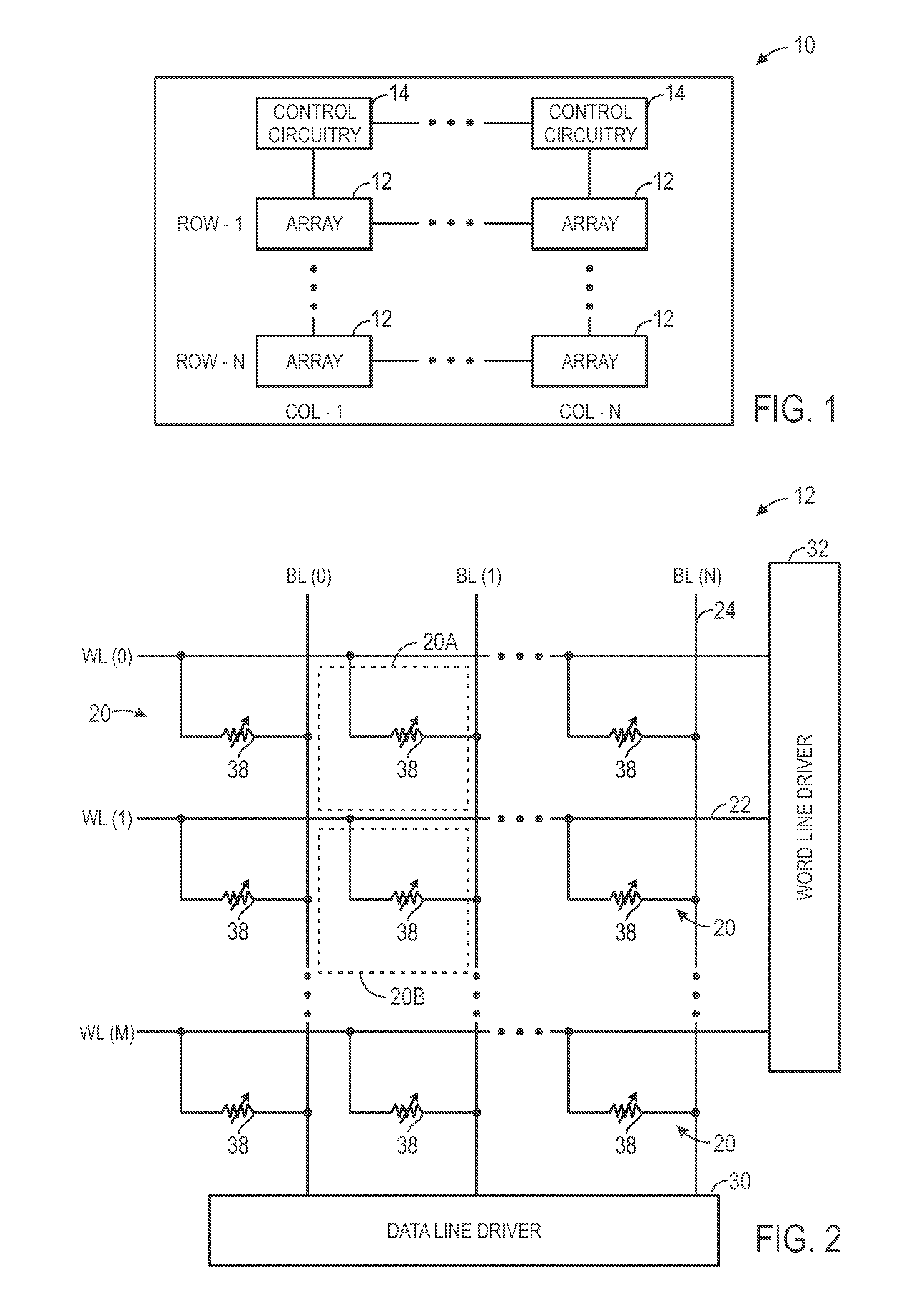
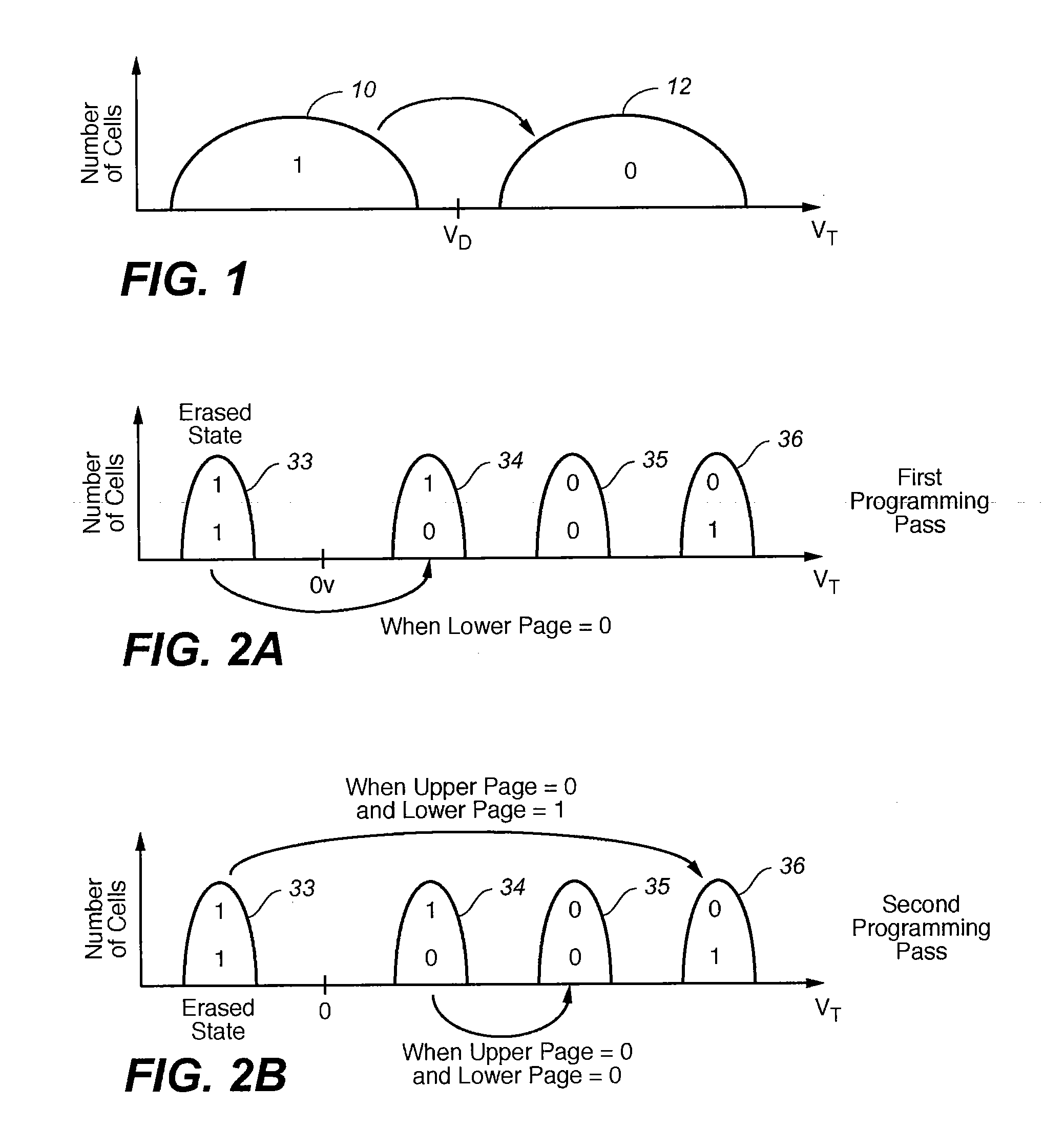
Non-volatile memory and method with bit line compensation dependent on neighboring operating modes
ActiveUS6956770B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineHigh density
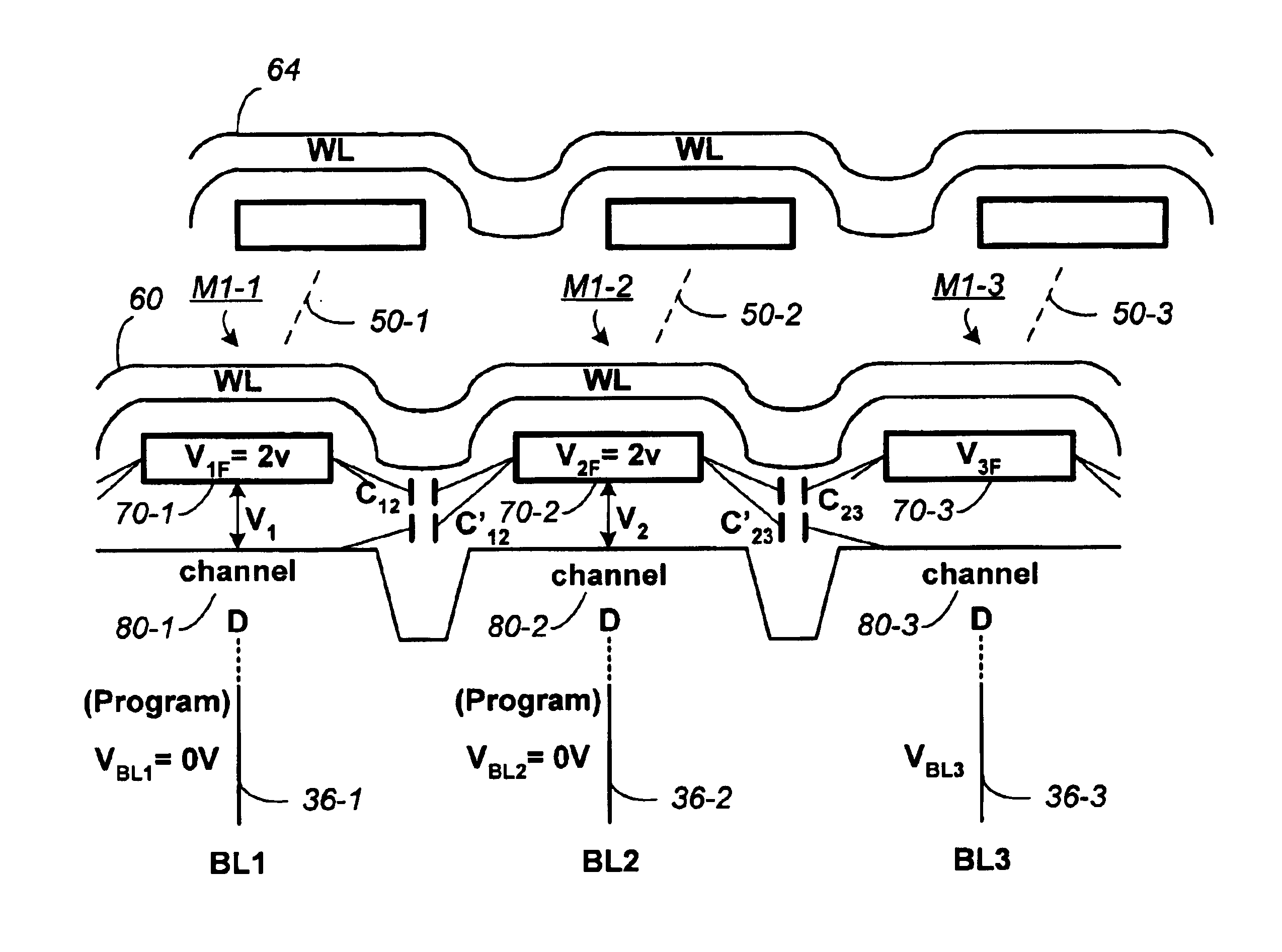
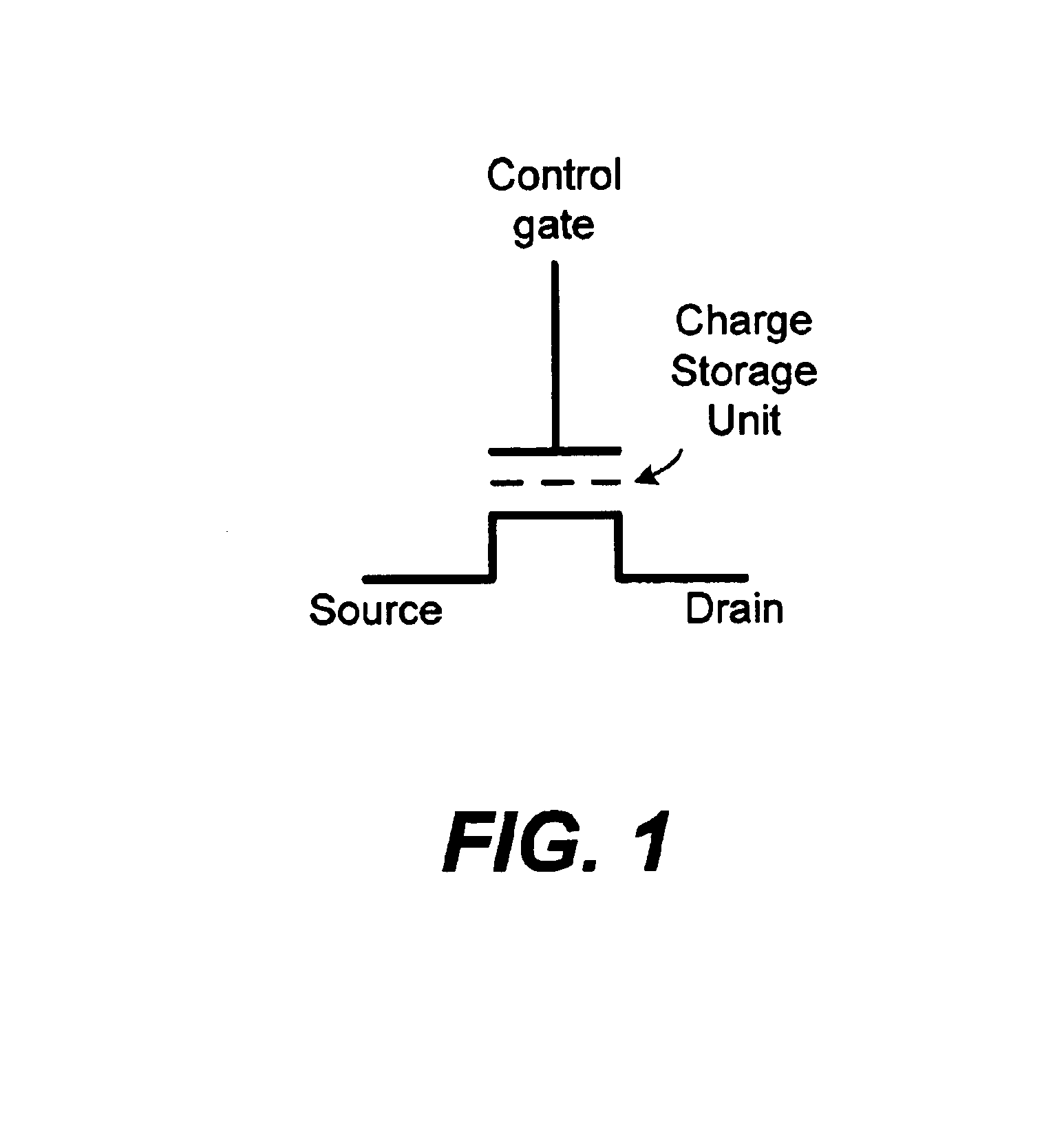
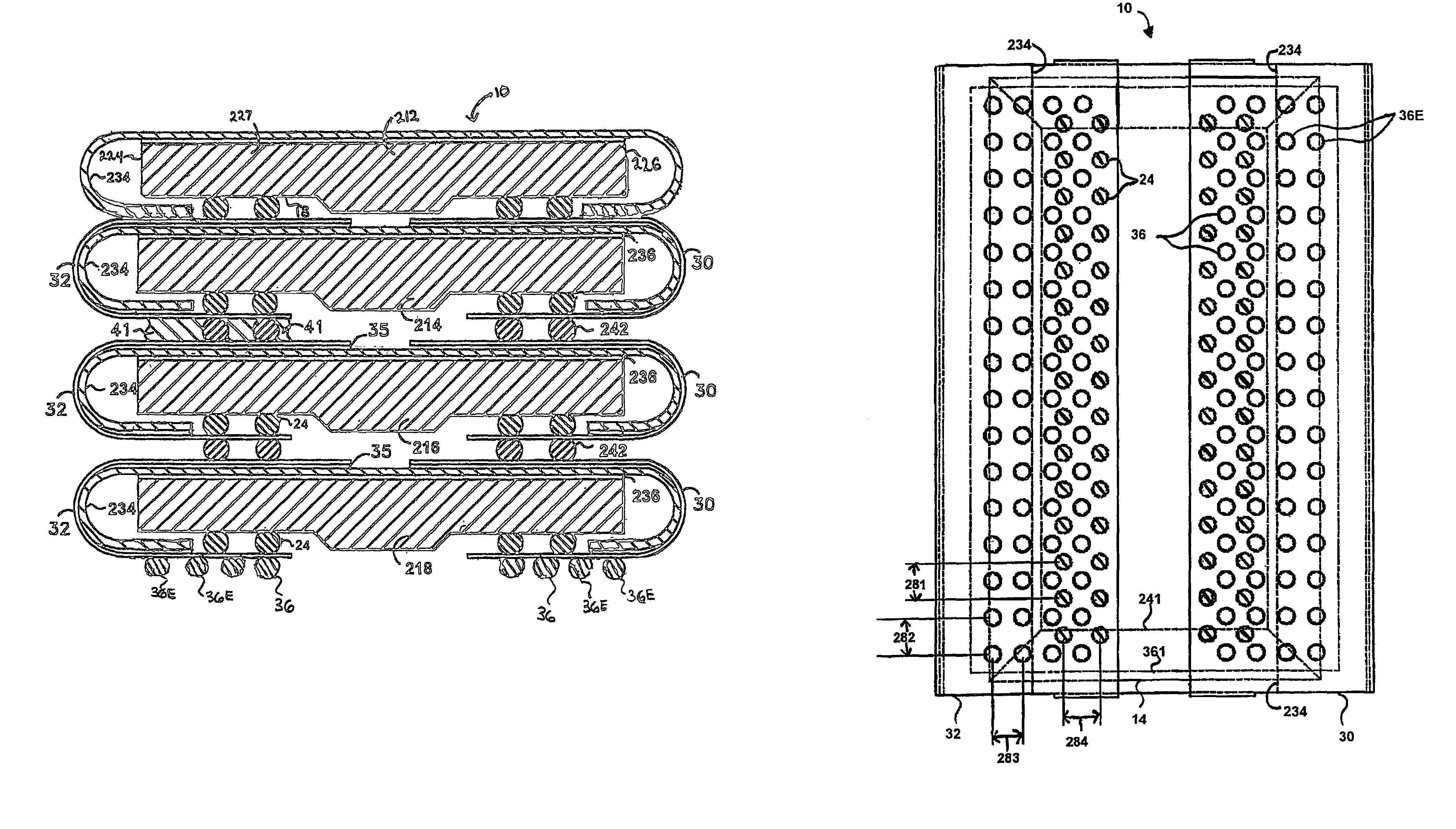
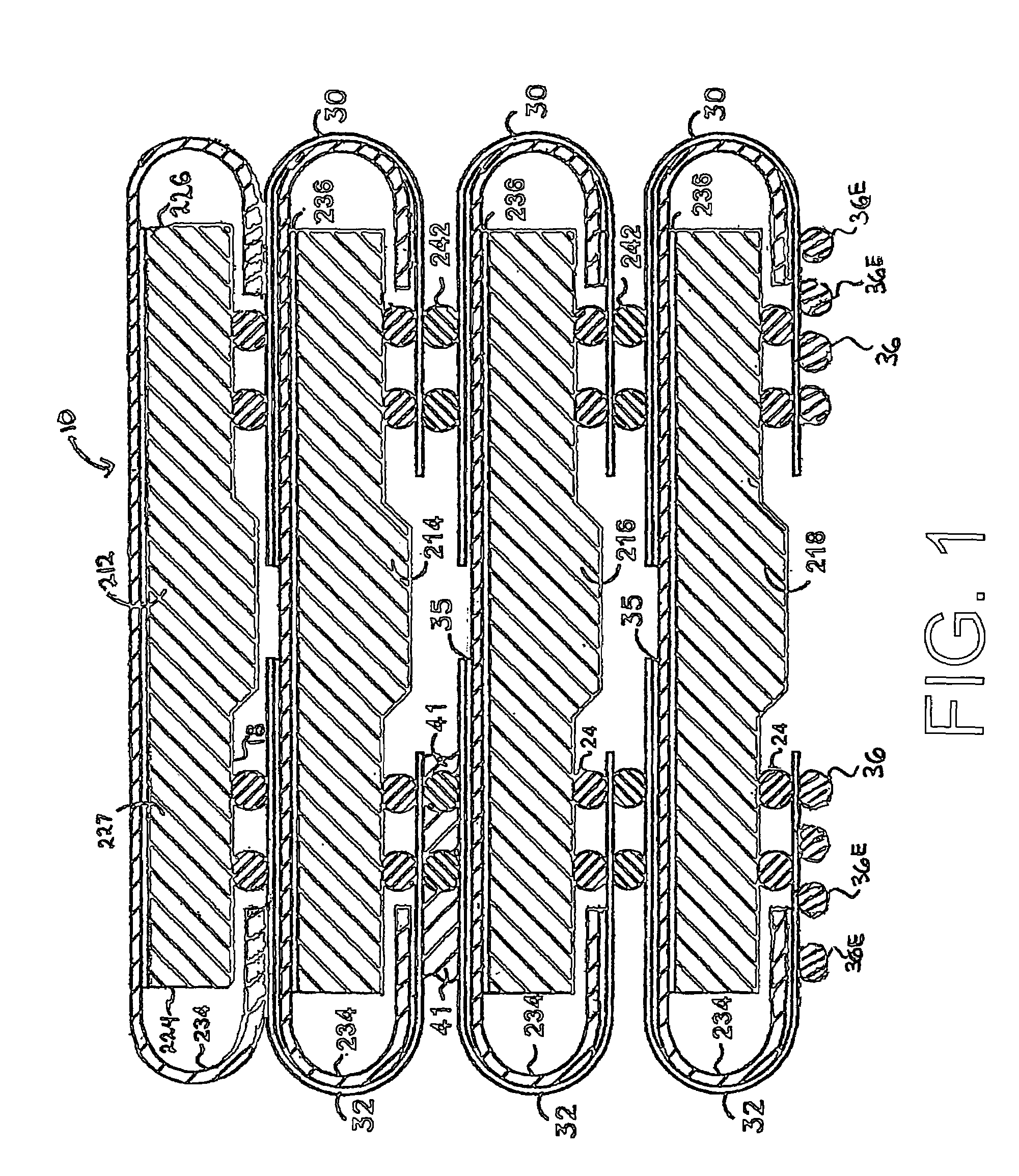
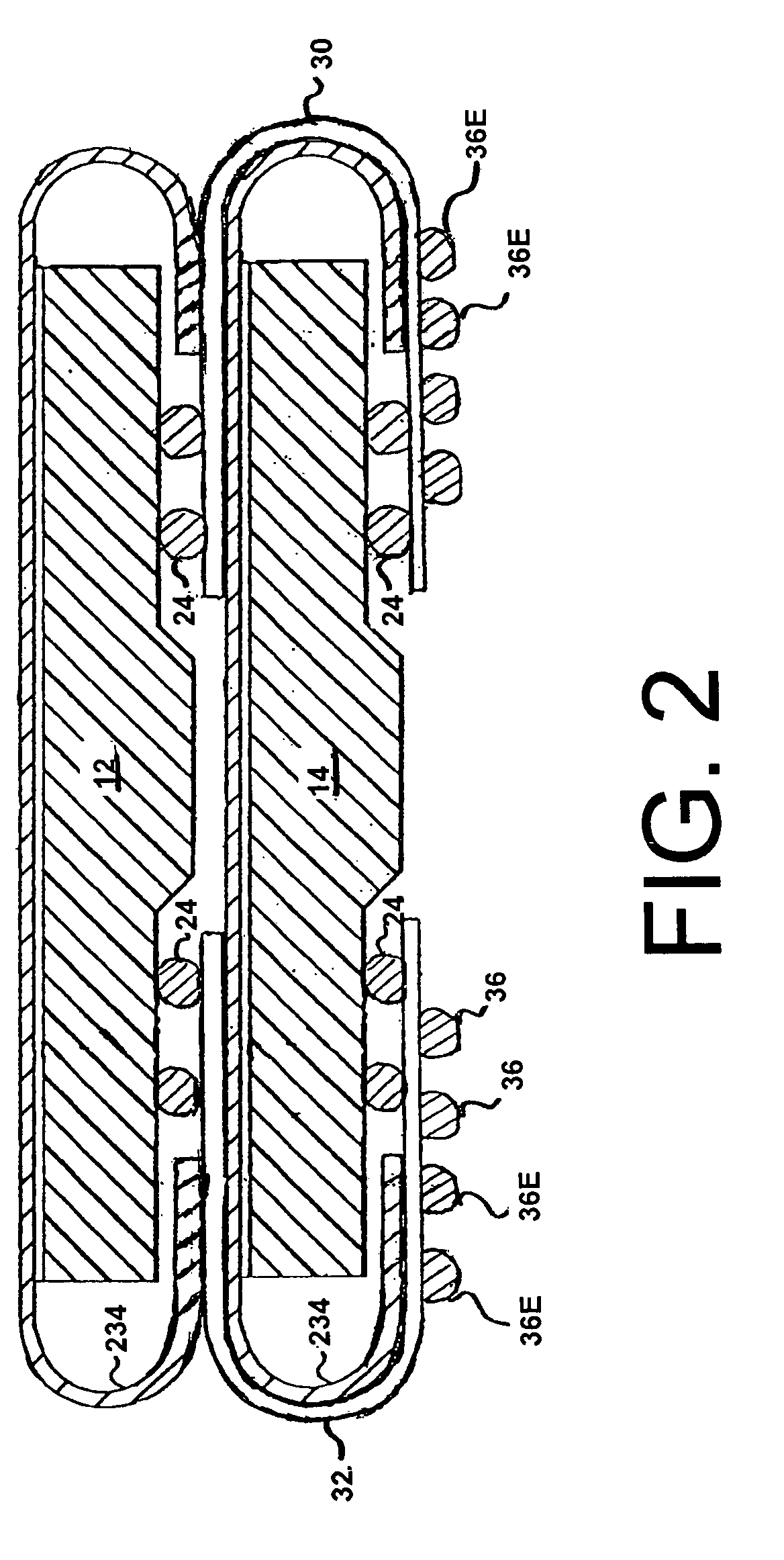
When programming a contiguous page of memory storage units, every time a memory storage unit has reached its targeted state and is program-inhibited or locked out from further programming, it creates a perturbation on an adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The present invention provides as part of a programming circuit and method in which an offset to the perturbation is added to the adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The offset is added as voltage offset to a bit line of a storage unit under programming. The voltage offset is a predetermined function of whether none or one or both of its neighbors are in a mode that creates perturbation, such as in a program inhibit mode. In this way, an error inherent in programming in parallel high-density memory storage units is eliminated or minimized.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
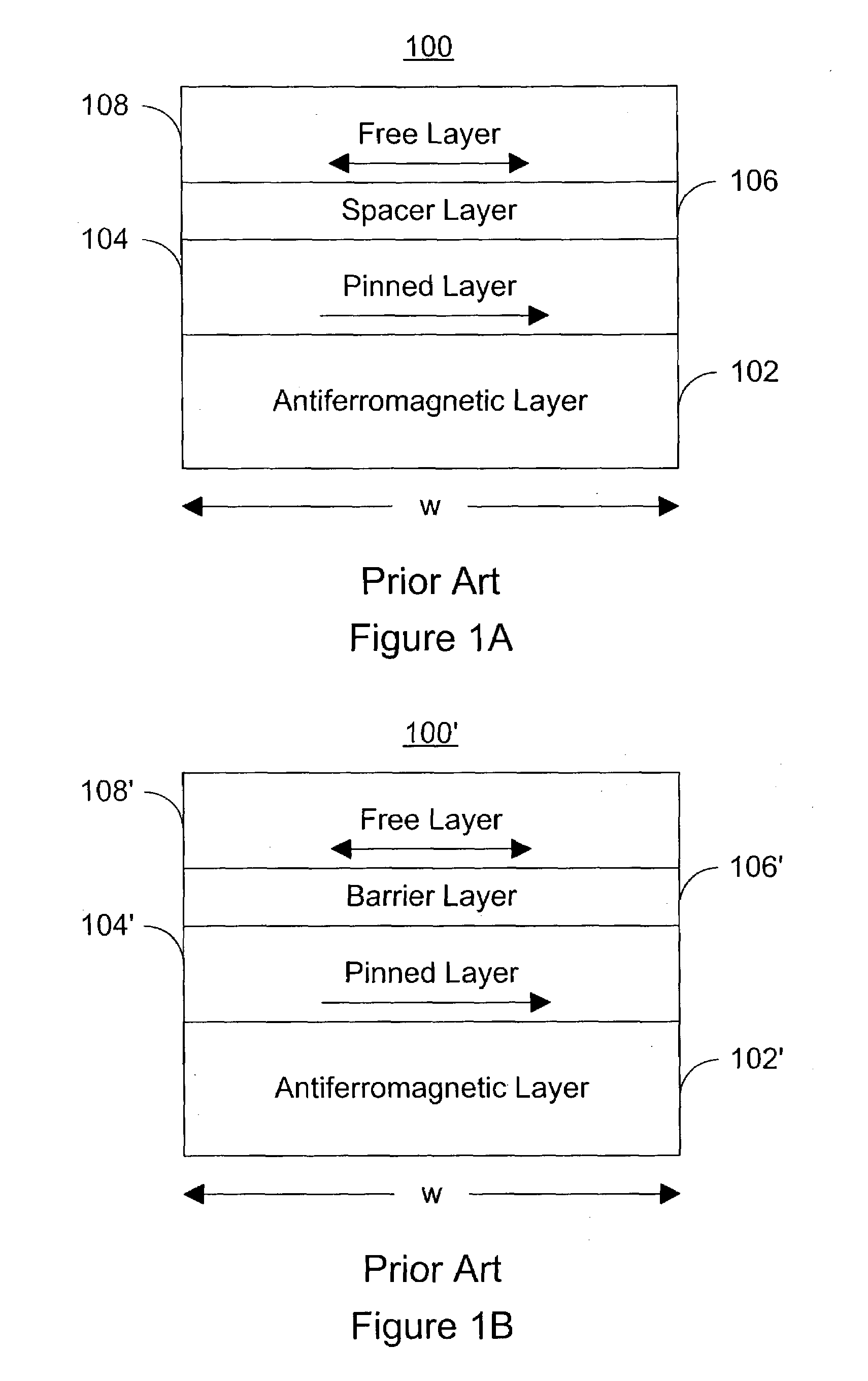
Spin-transfer multilayer stack containing magnetic layers with resettable magnetization
InactiveUS7190611B2Minimizing densityReduce process complexityGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesHigh densitySpin transfer
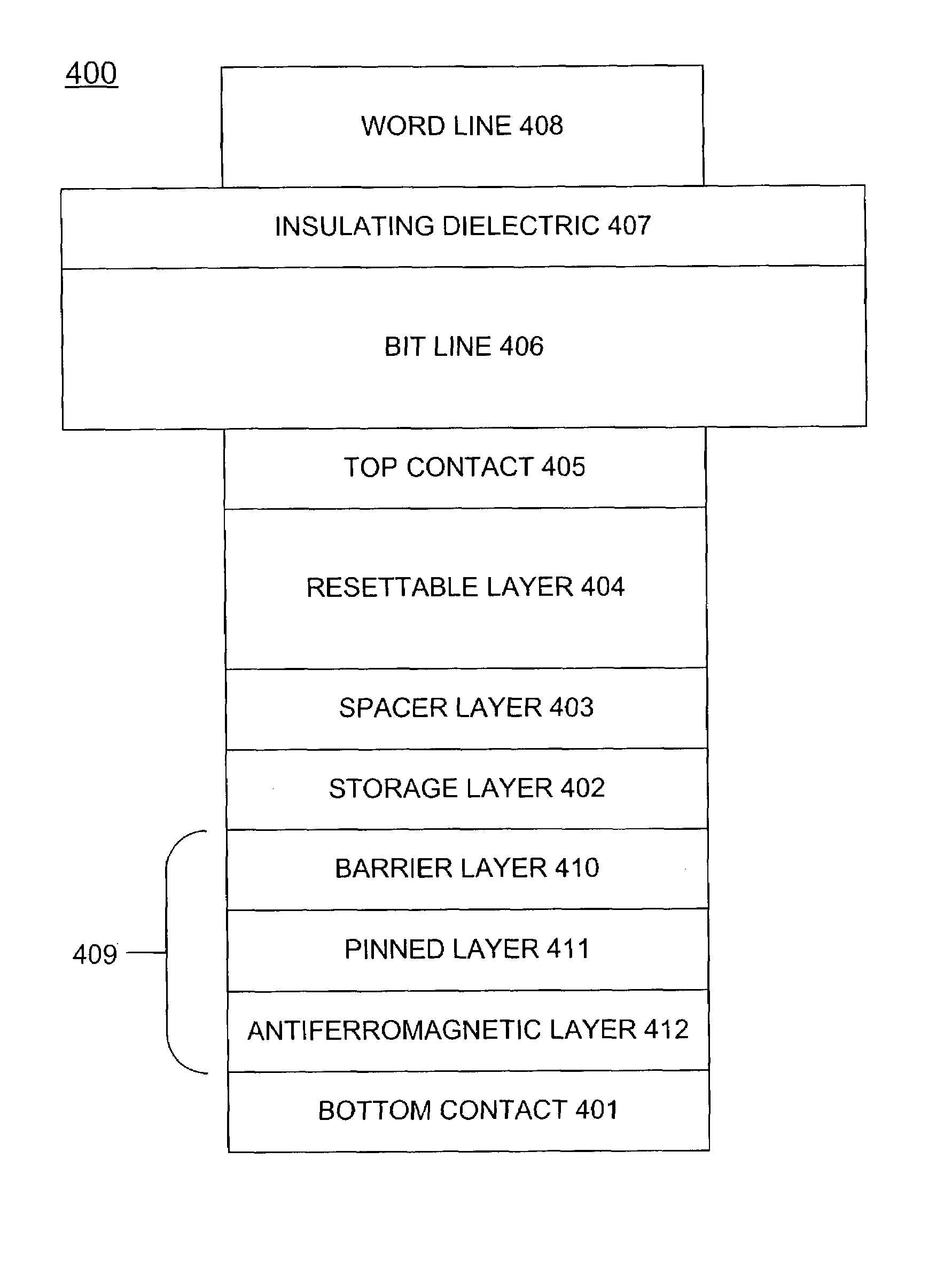
A magnetic element for a high-density memory array includes a resettable layer and a storage layer. The resettable layer has a magnetization that is set in a selected direction by at least one externally generated magnetic field. The storage layer has at least one magnetic easy axis and a magnetization that changes direction based on the spin-transfer effect when a write current passes through the magnetic element. An alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure formed from a tunneling barrier layer, a pinned magnetic layer and an antiferromagnetic layer that pins the magnetization of the pinned layer in a predetermined direction. Another alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure that is formed from a tunneling barrier layer and a second resettable layer having a magnetic moment that is different from the magnetic moment of the resettable layer of the basic embodiment.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Process for making and programming and operating a dual-bit multi-level ballistic flash memory
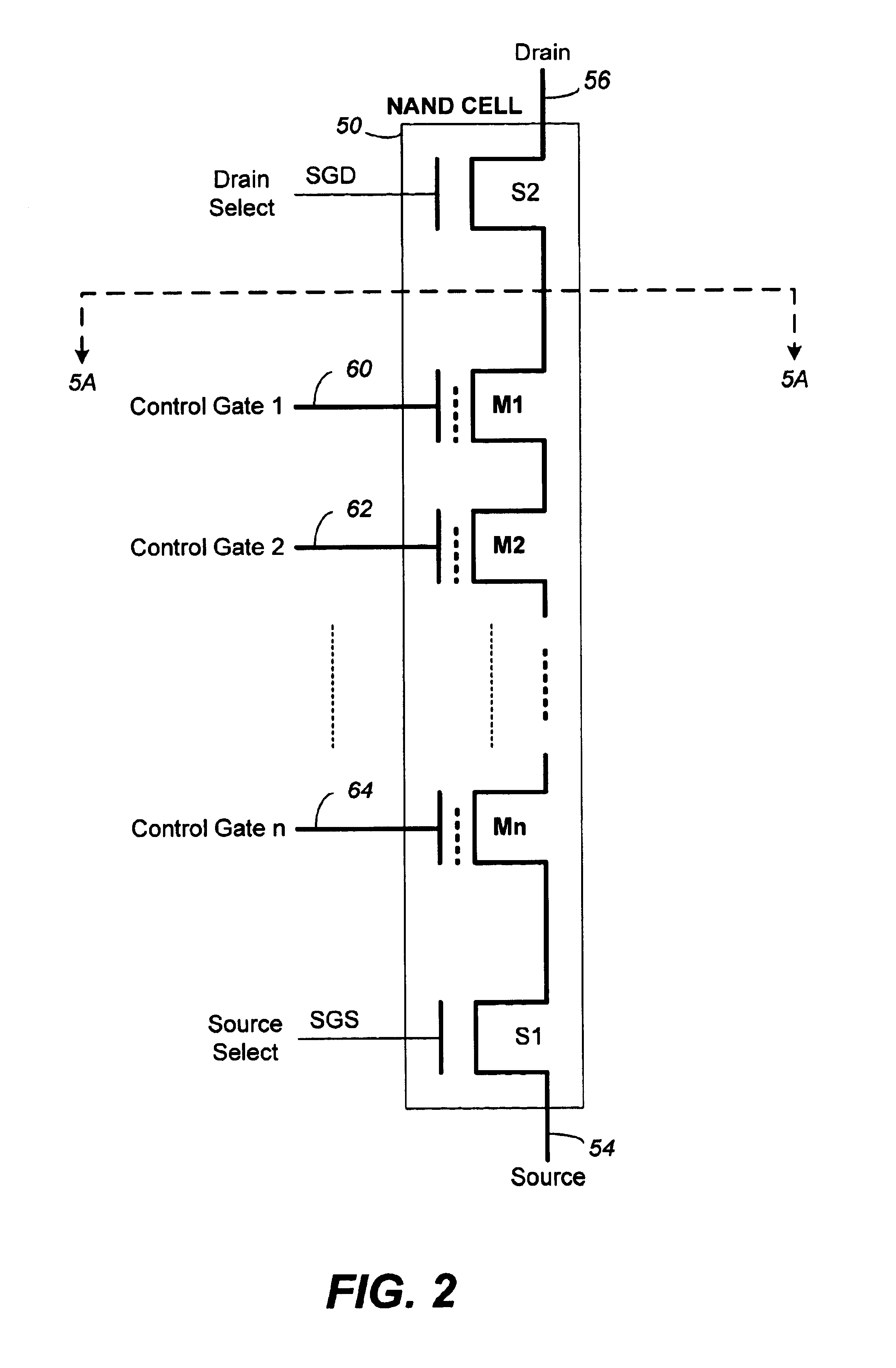
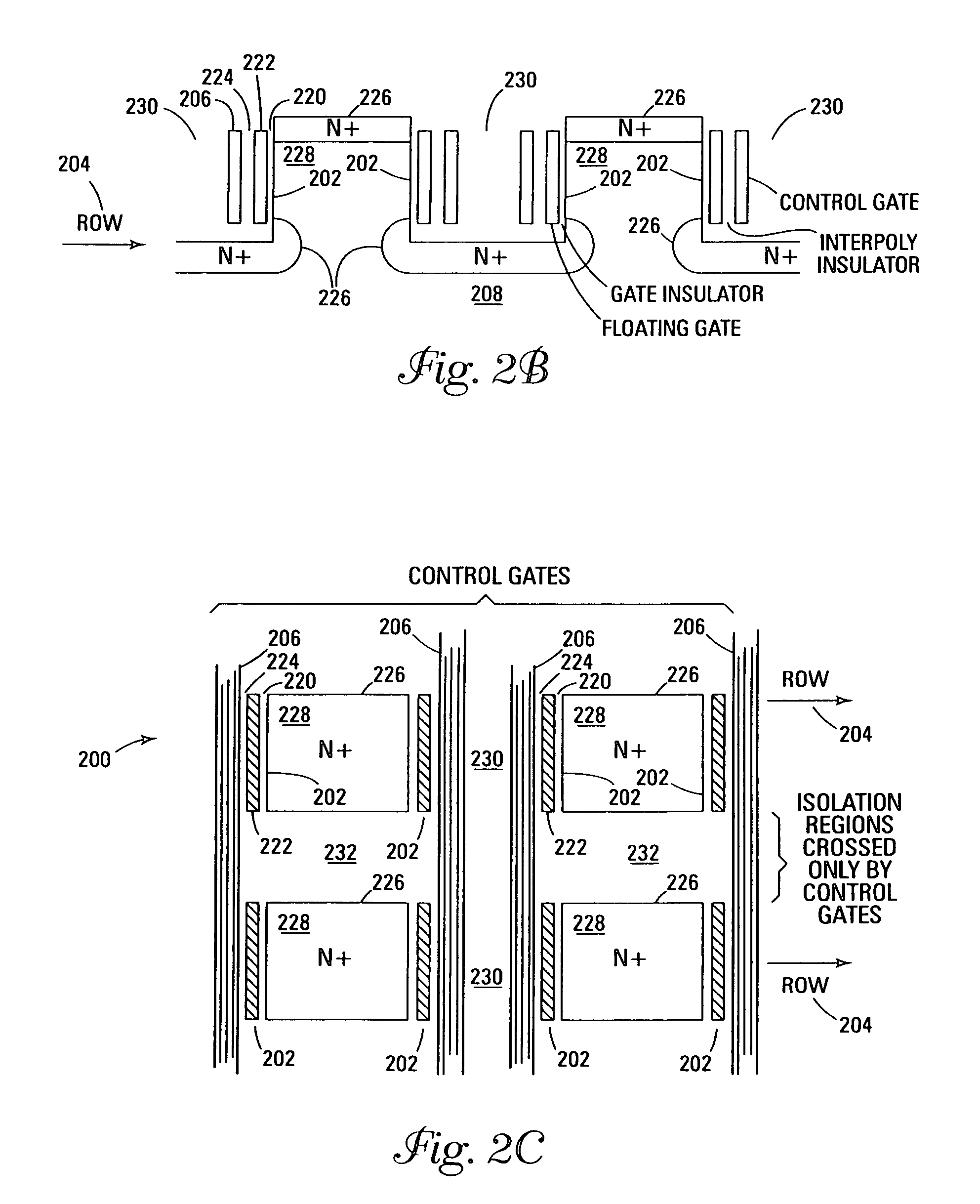
An fast program, ultra-high density, dual-bit, multi-level flash memory process, which can be applied to a ballistic step split gate side wall transistor, or to a ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor, which enables program operation by low voltage requirement on the floating gate during program is described. Two side wall floating gates are paired with a single word line select gate, and word lines are arranged to be perpendicular both the bit lines and control gate lines. Two adjacent memory cells on the same word line do not require an isolation region. Also, the isolation region between adjacent memory cells sharing the same bitline is defined by the minimum lithography feature, utilizing a self align fill technique. Adjacent memory cells on the same word line share bitline diffusion as well as a third poly control gate. Control gates allow program and read access to the individual floating gate. In addition to the dual-bit nature of the cell, density can be even further improved by multi-level storage. In one embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic step split gate side wall transistor. In a second embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor. Both types of ballistic transistors provide fast, low voltage programming. The control gates are used to override or suppress the various threshold voltages on associated floating gates, in order to program to and read from individual floating gates. The targets for this non-volatile memory array are to provide the capabilities of high speed, low voltage programming (band width) and high density storage.
Owner:HALO LSI DESIGN & DEVICE TECH
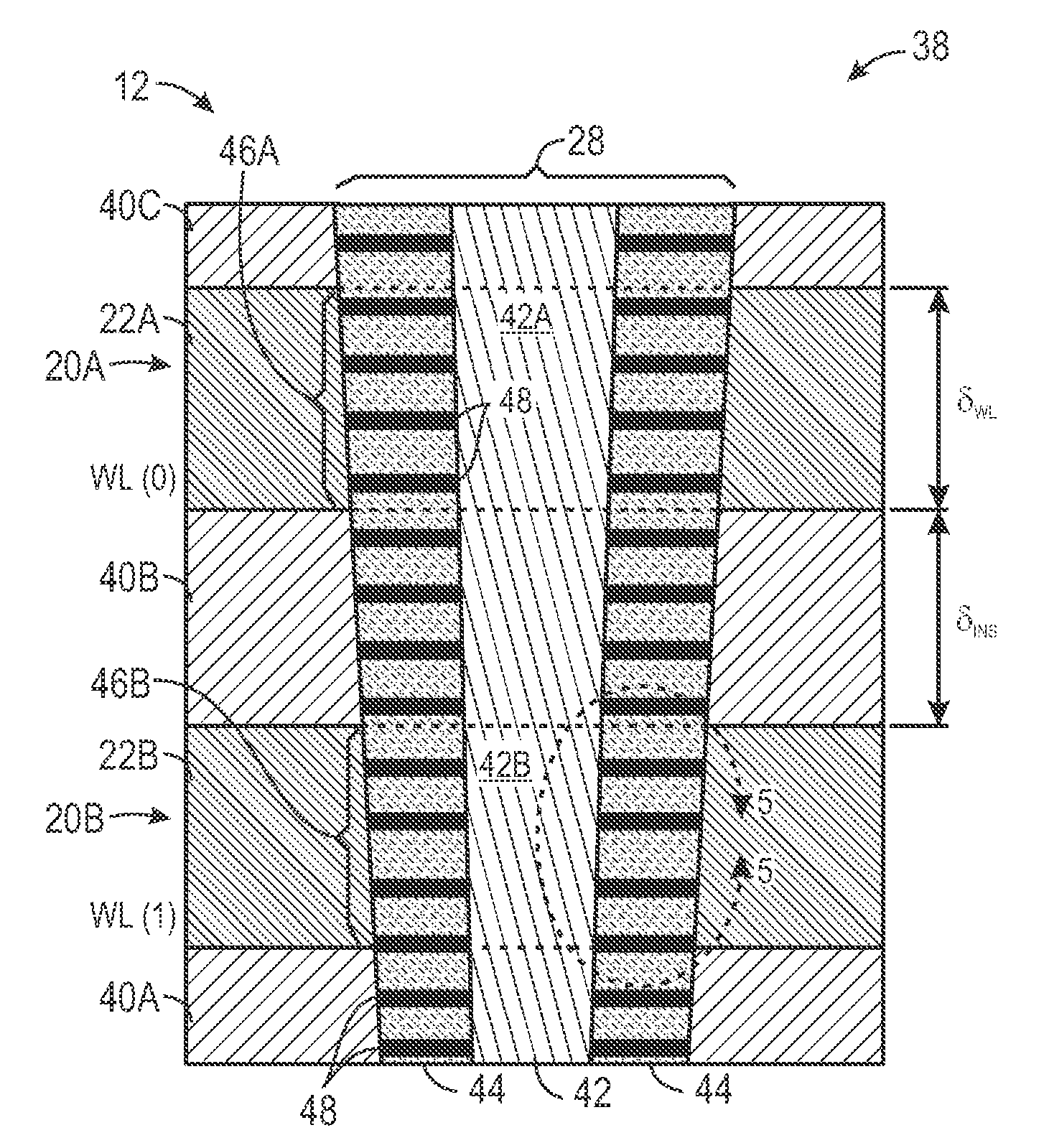
Three-dimensional memory device incorporating segmented bit line memory array
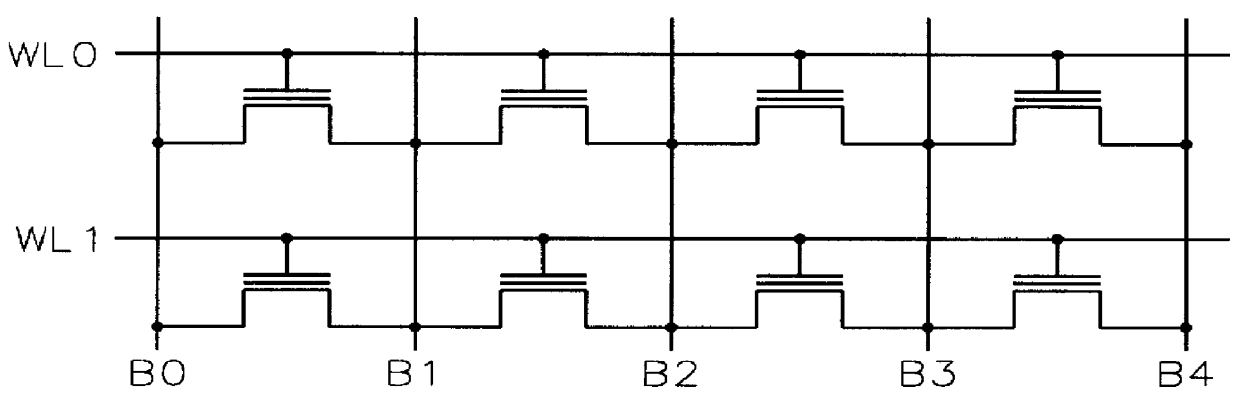
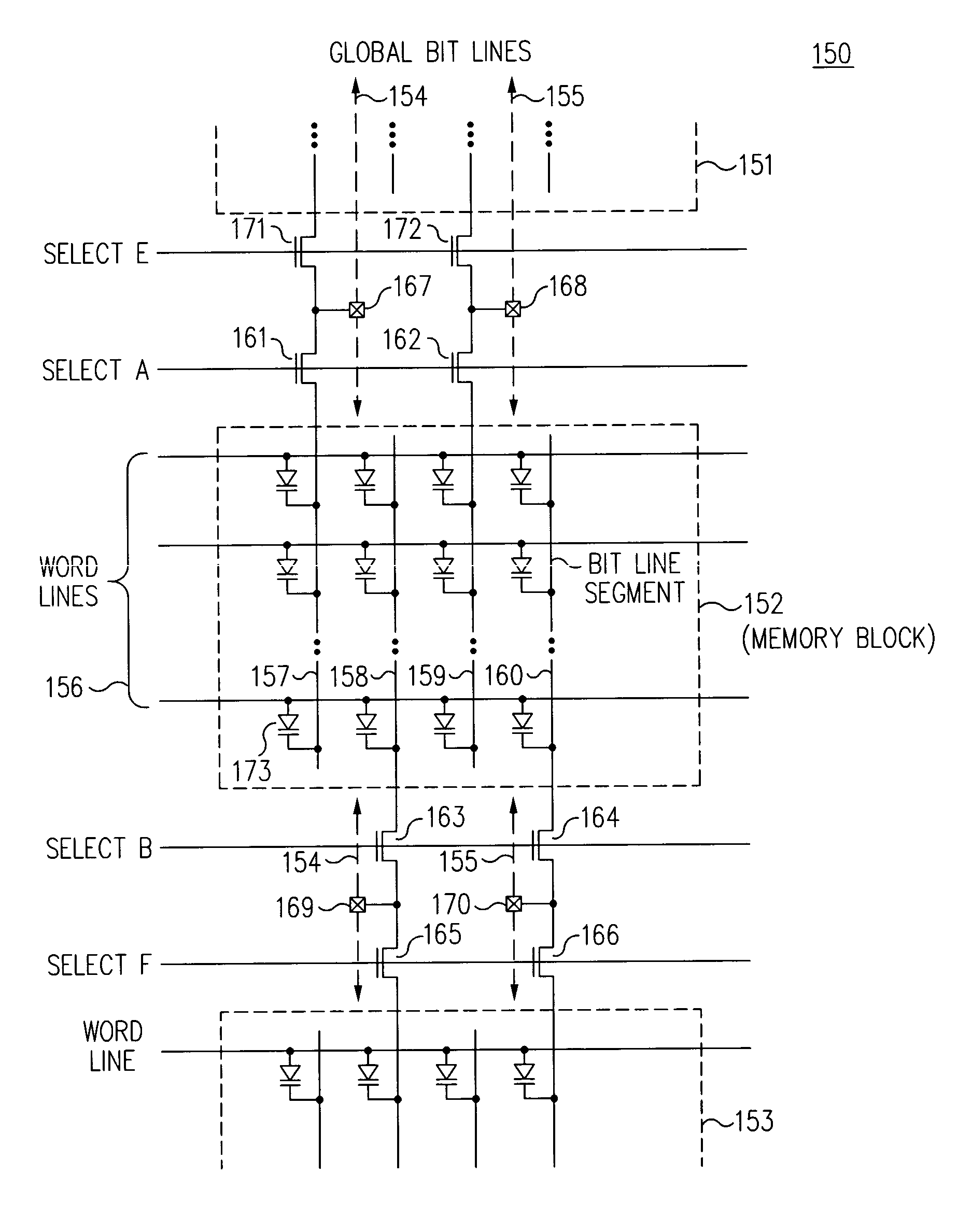
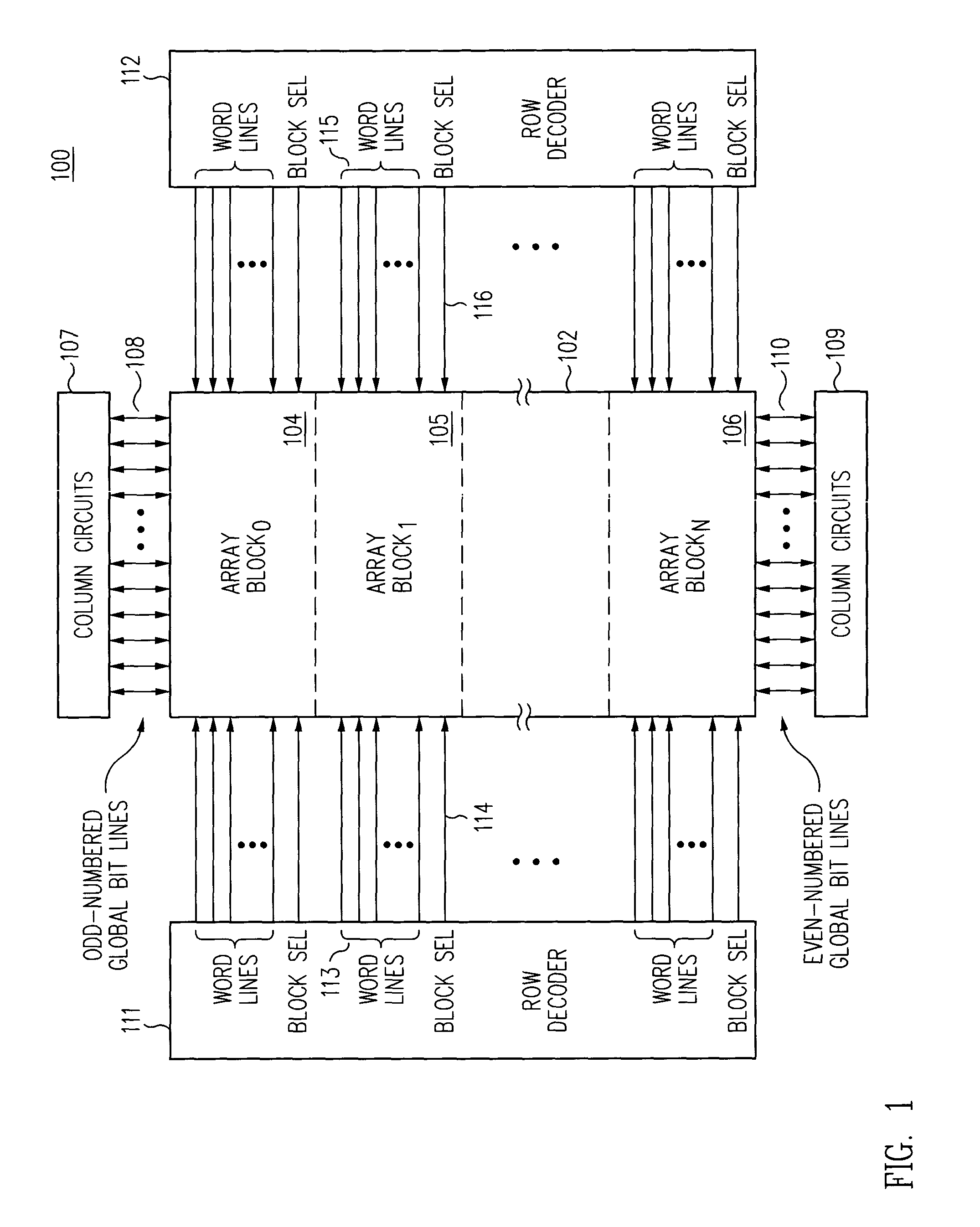
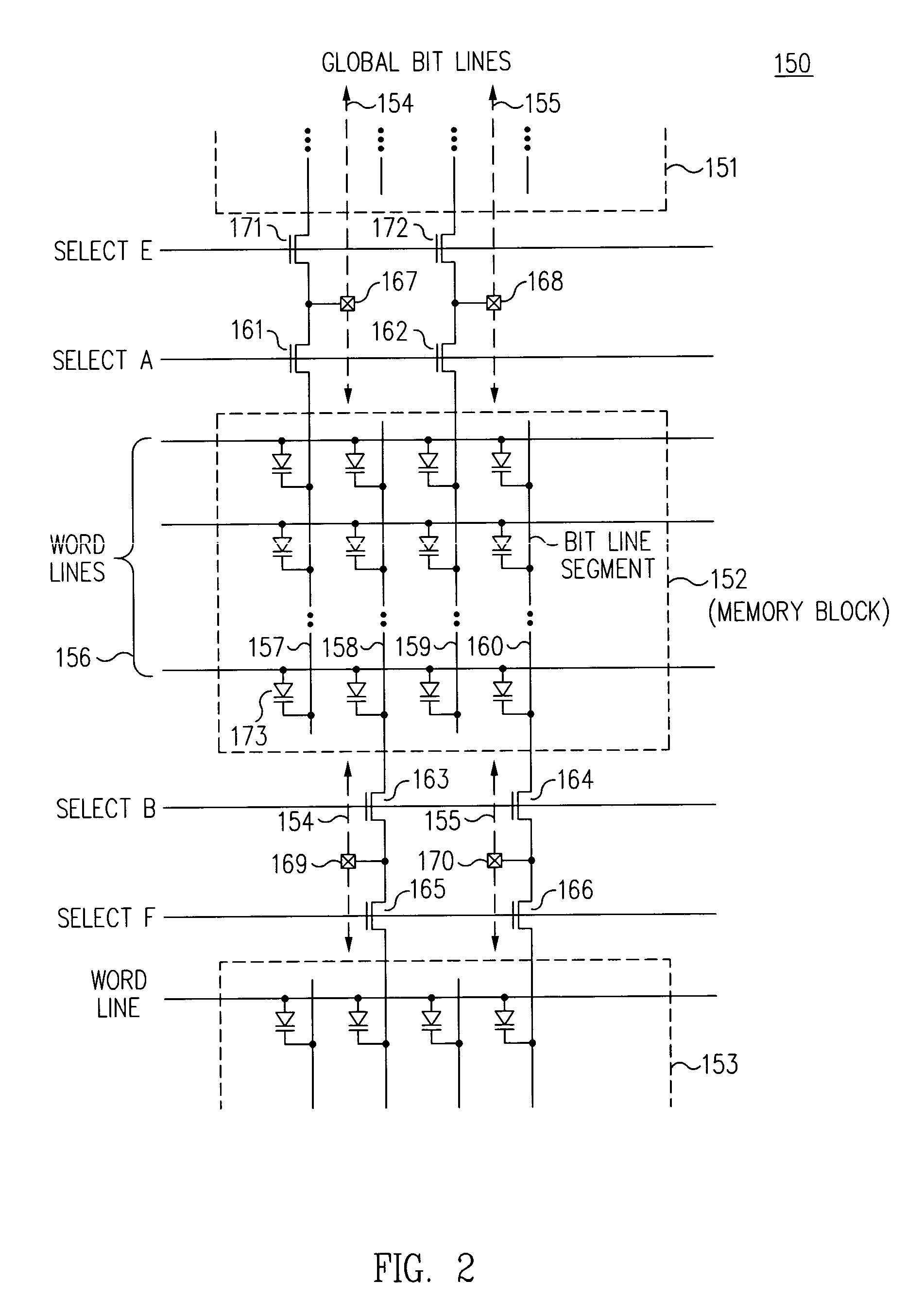
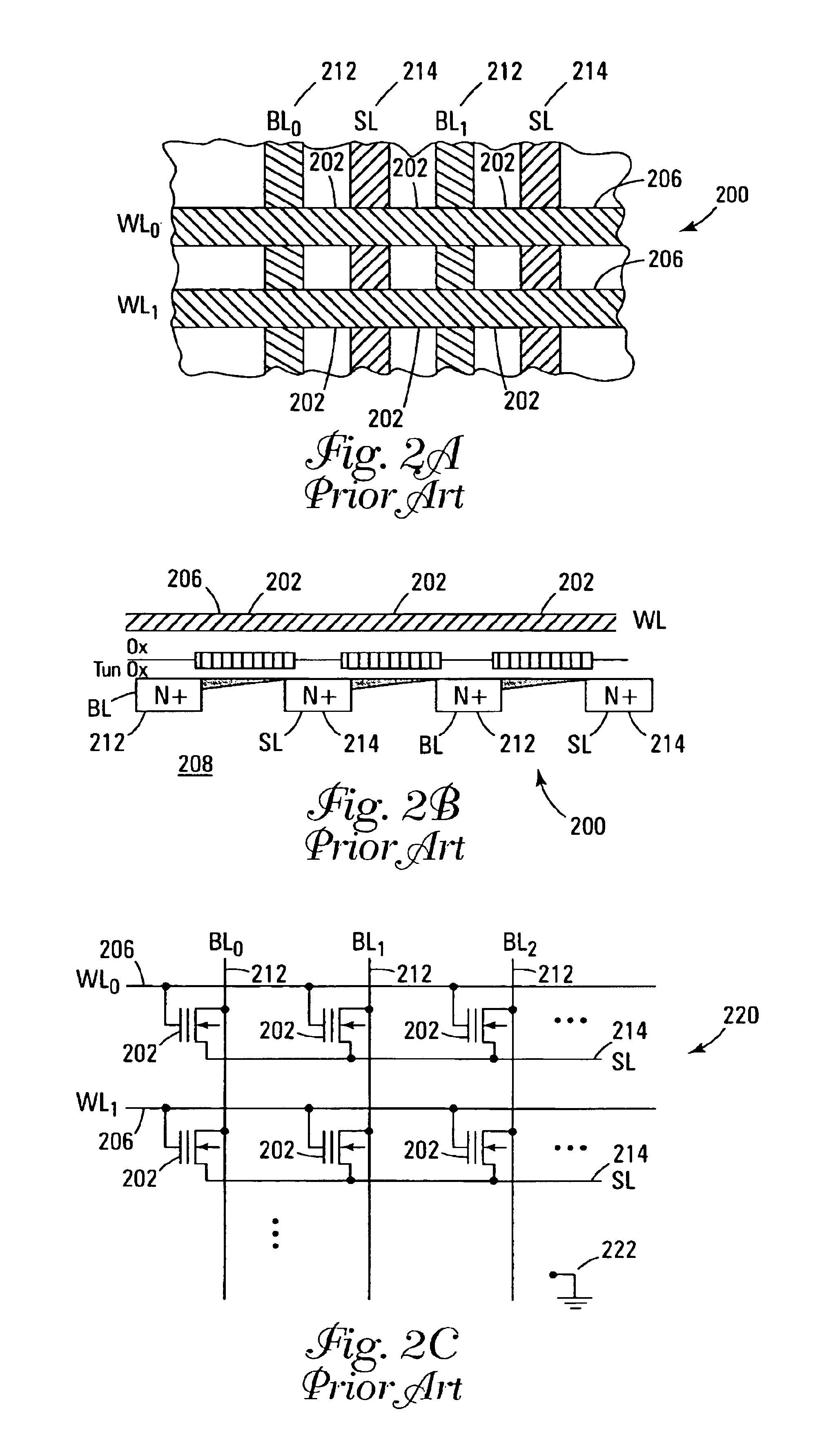
InactiveUS7233024B2Reduce capacitanceShorten overall length of unitSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineHigh density
A three-dimensional (3D) high density memory array includes multiple layers of segmented bit lines (i.e., sense lines) with segment switch devices within the memory array that connect the segments to global bit lines. The segment switch devices reside on one or more layers of the integrated circuit, preferably residing on each bit line layer. The global bit lines reside preferably on one layer below the memory array, but may reside on more than one layer. The bit line segments preferably share vertical connections to an associated global bit line. In certain EEPROM embodiments, the array includes multiple layers of segmented bit lines with segment connection switches on multiple layers and shared vertical connections to a global bit line layer. Such memory arrays may be realized with much less write-disturb effects for half selected memory cells, and may be realized with a much smaller block of cells to be erased.
Owner:WODEN TECH INC
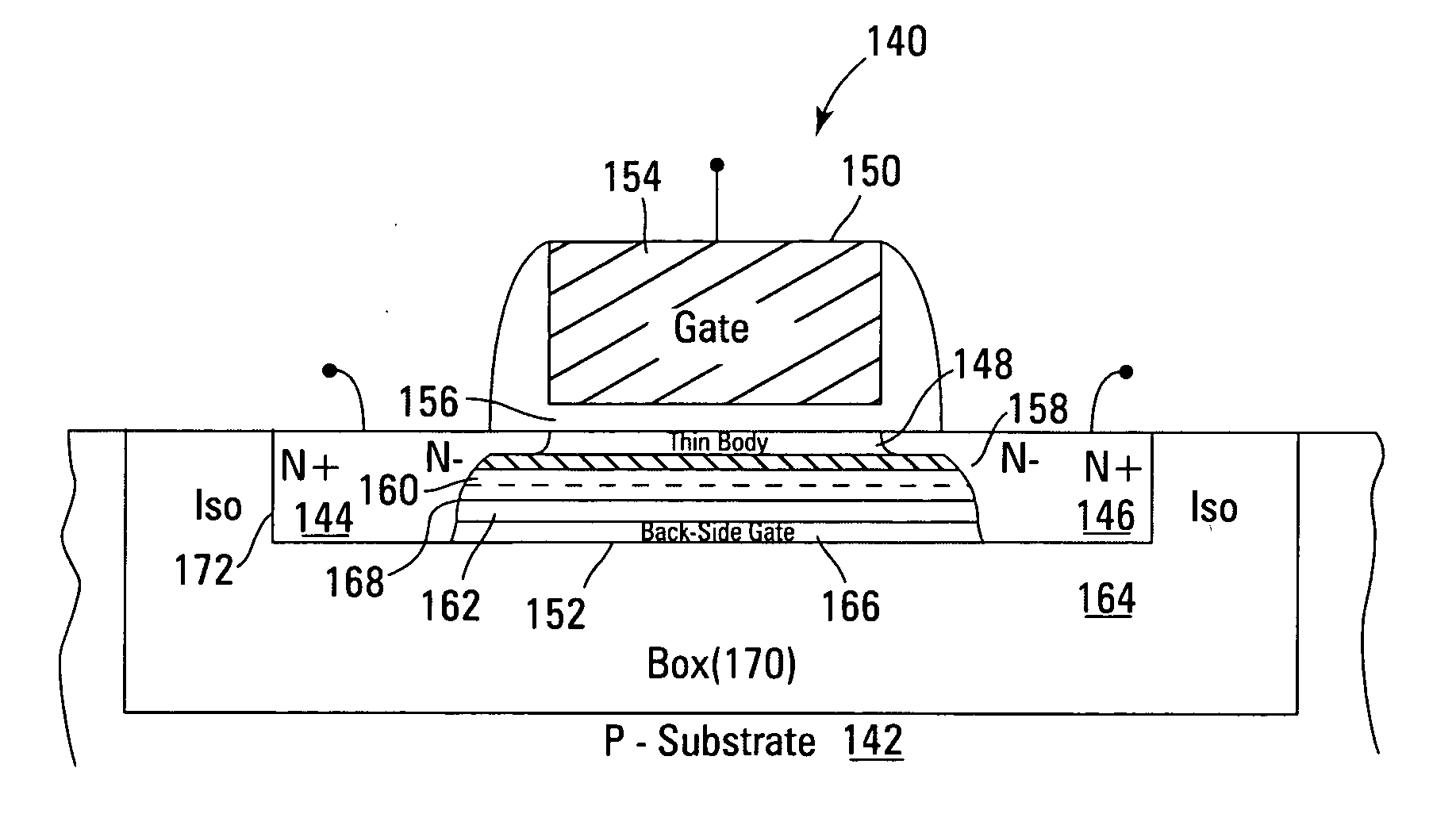
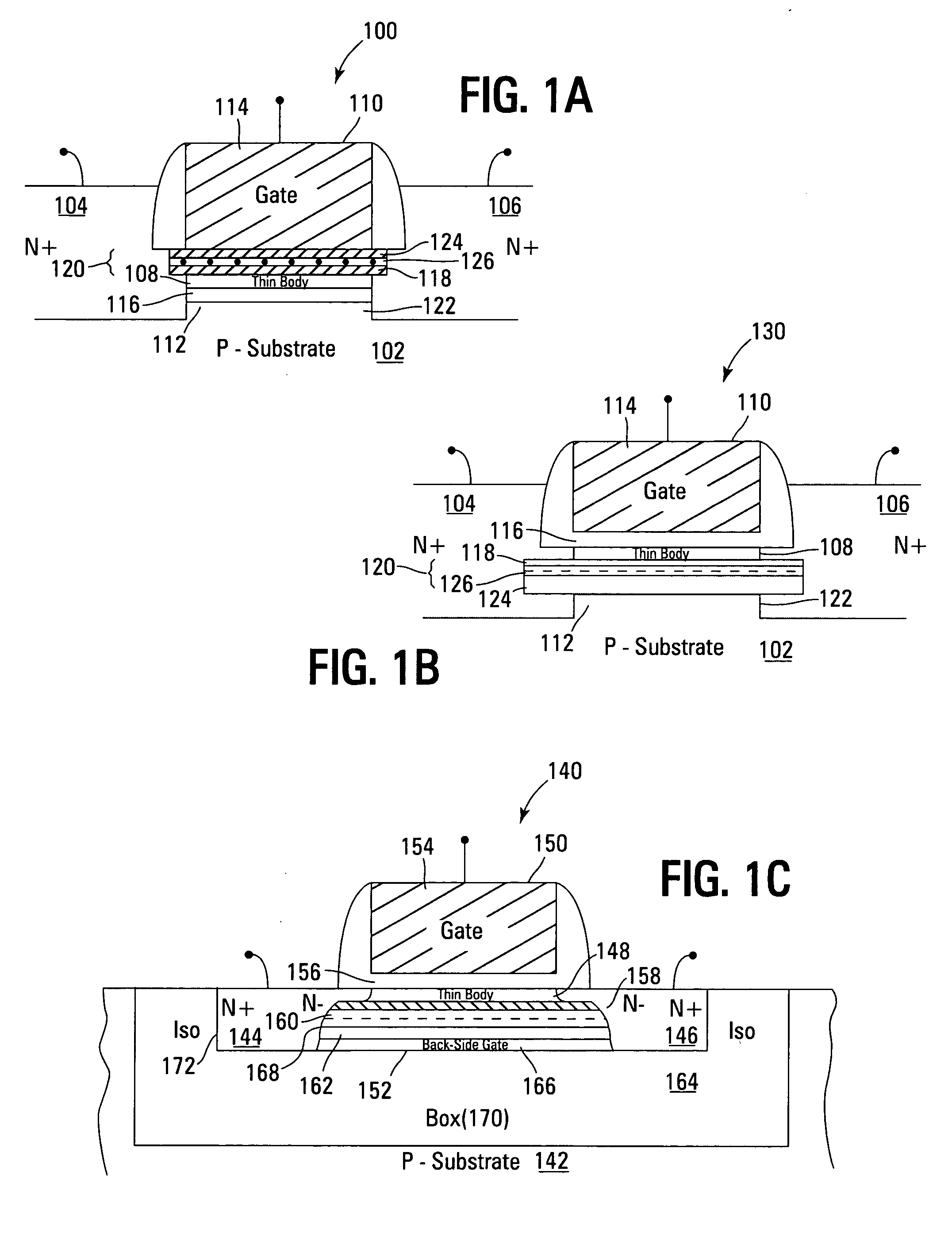
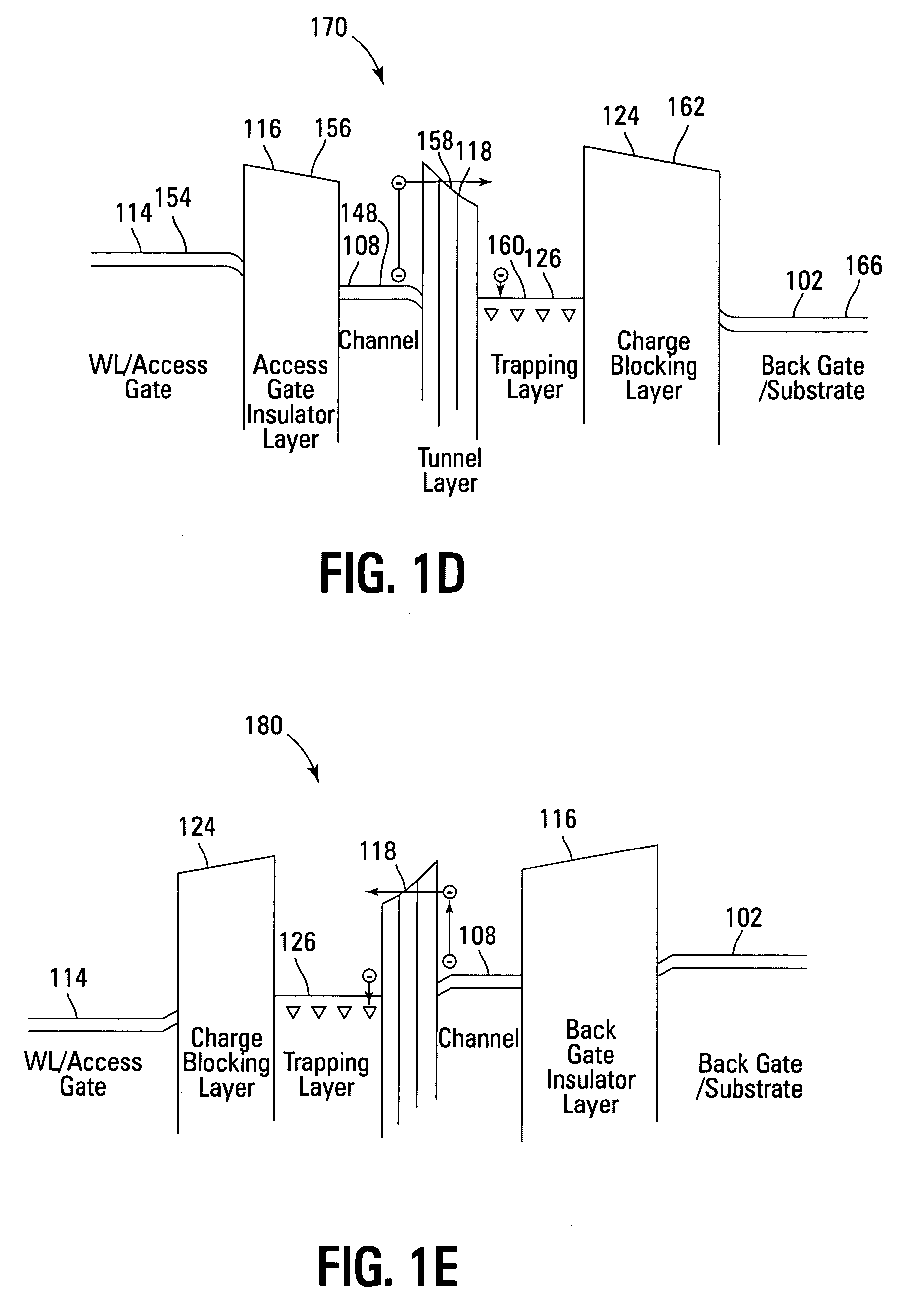
High density NAND non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS20070012988A1Efficient eraseReduce harmSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionLow voltage
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize dual gate (or back-side gate) non-volatile memory cells with band engineered gate-stacks that are placed above or below the channel region in front-side or back-side charge trapping gate-stack configurations in NAND memory array architectures. The band-gap engineered gate-stacks with asymmetric or direct tunnel barriers of the floating node memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and efficient erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The memory cell architecture also allows for improved high density memory devices or arrays with the utilization of reduced feature word lines and vertical select gates.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
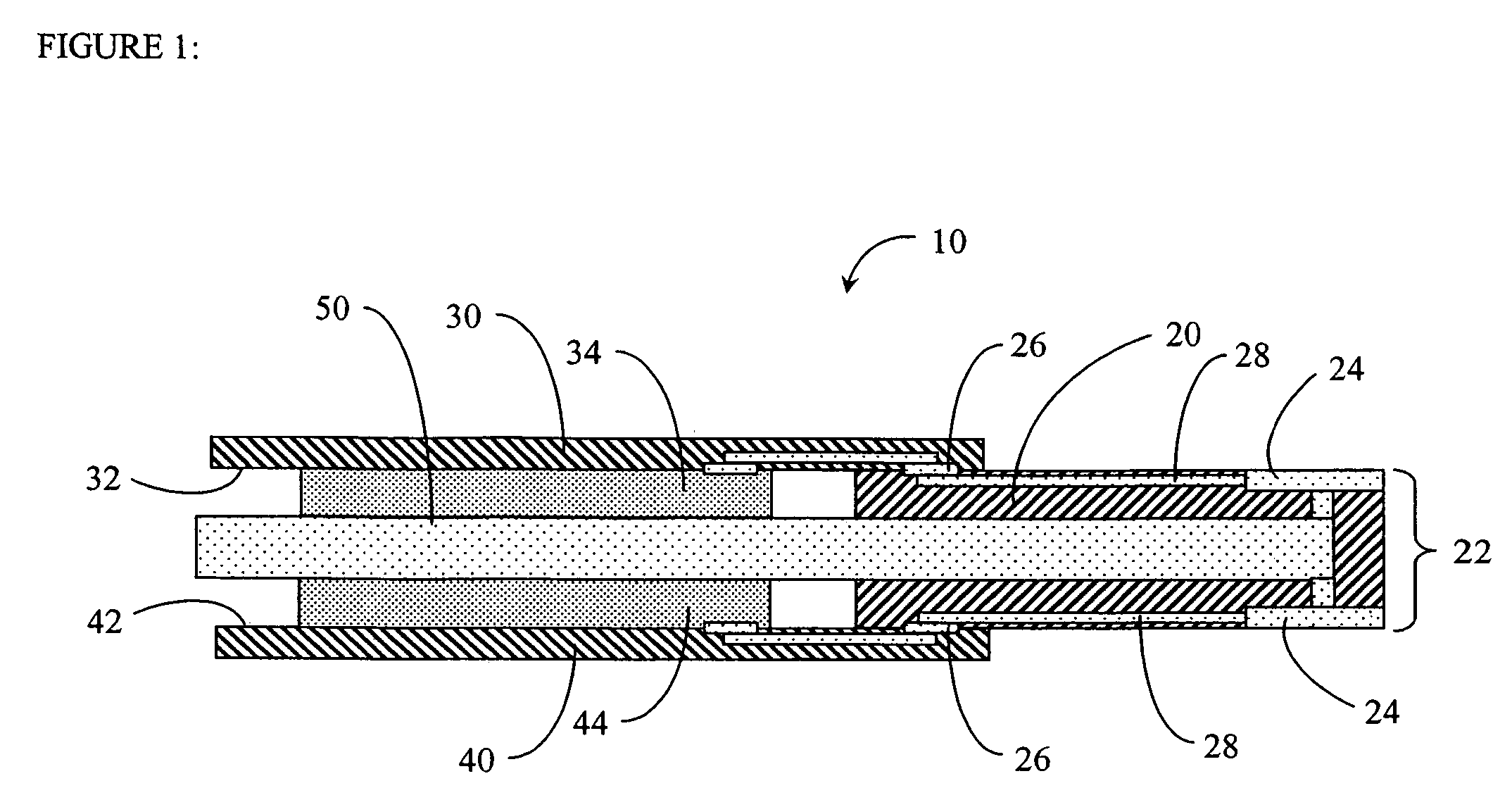
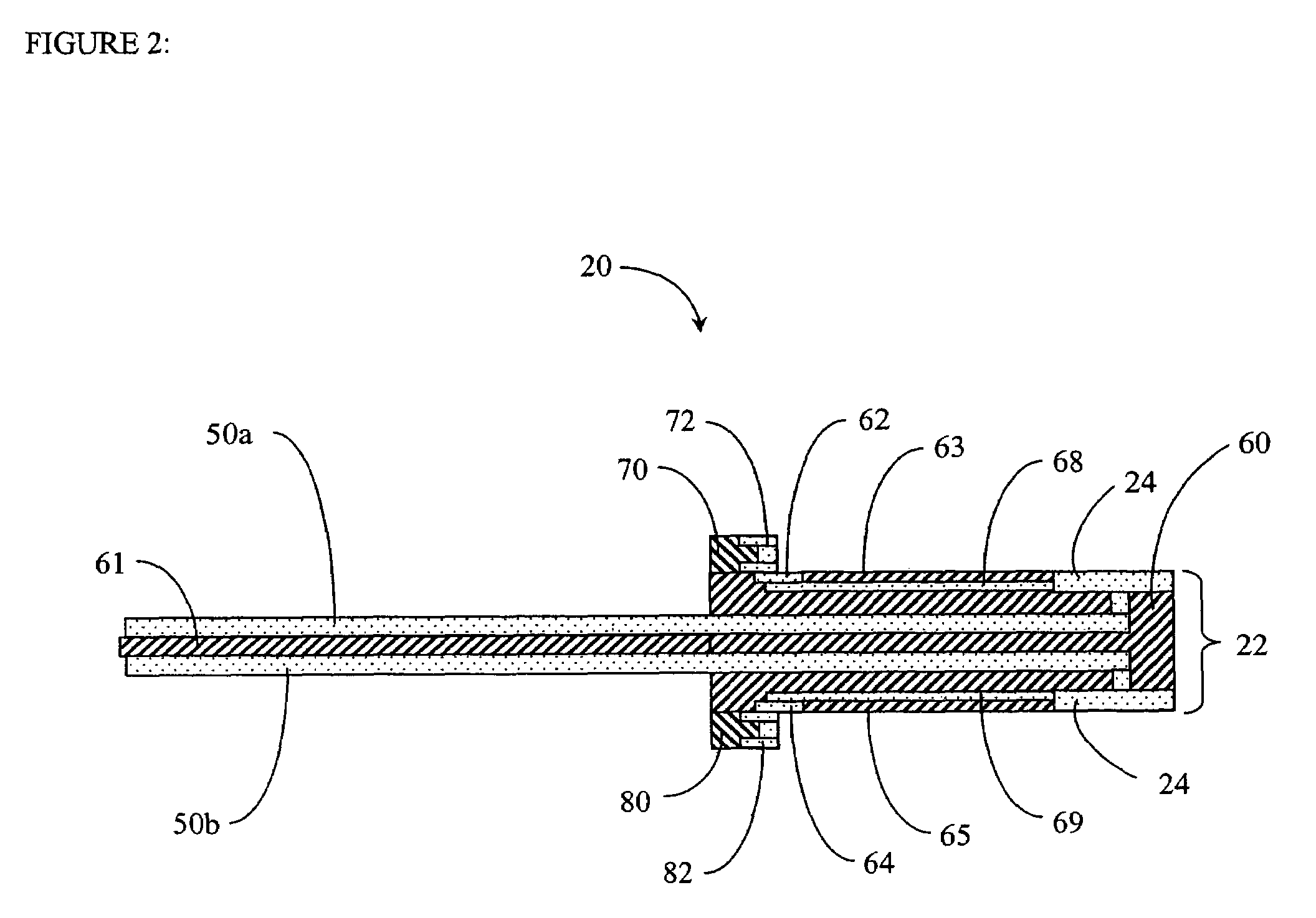
High density memory module using stacked printed circuit boards
ActiveUS7254036B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsHigh densityComputerized system
Owner:NETLIST INC
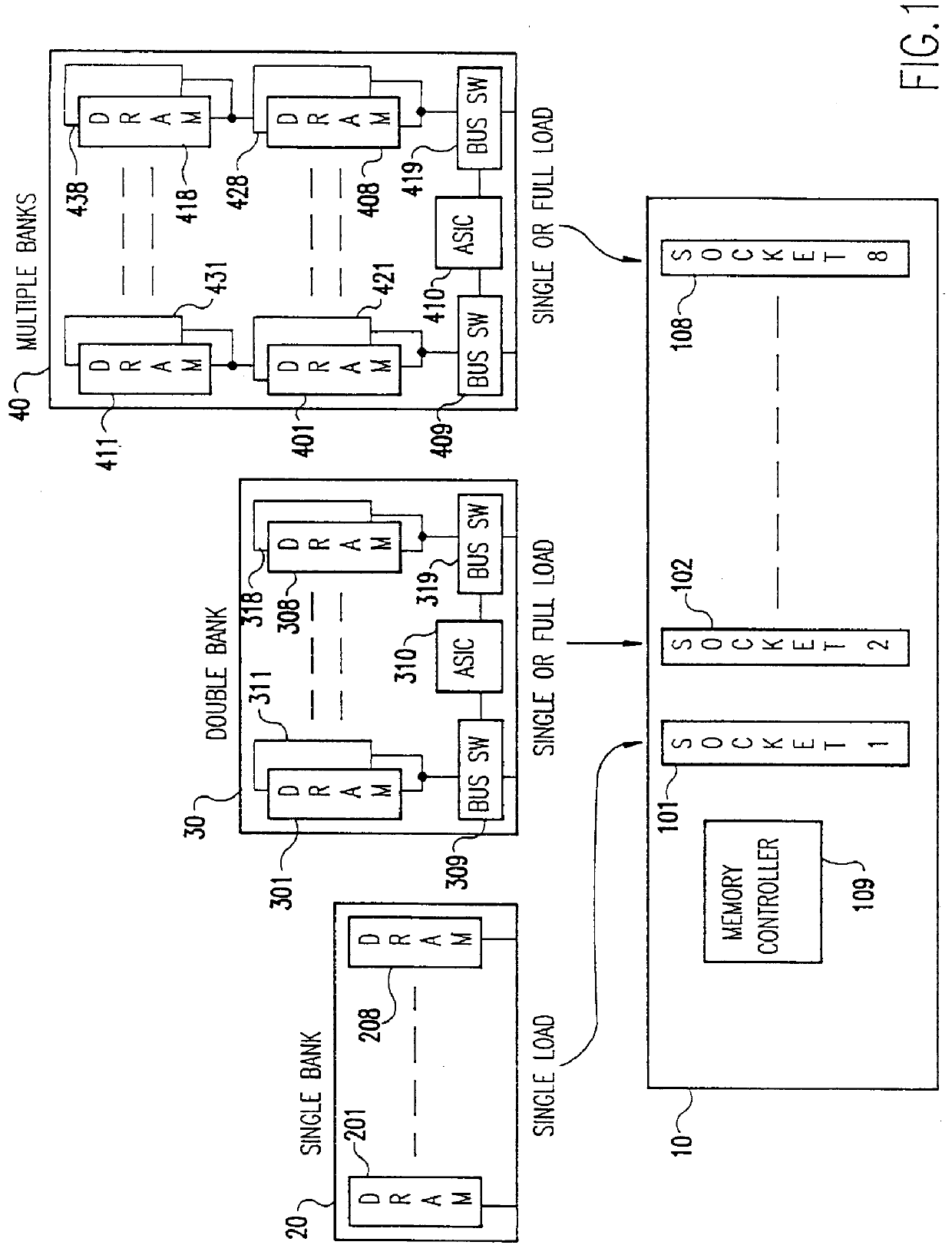
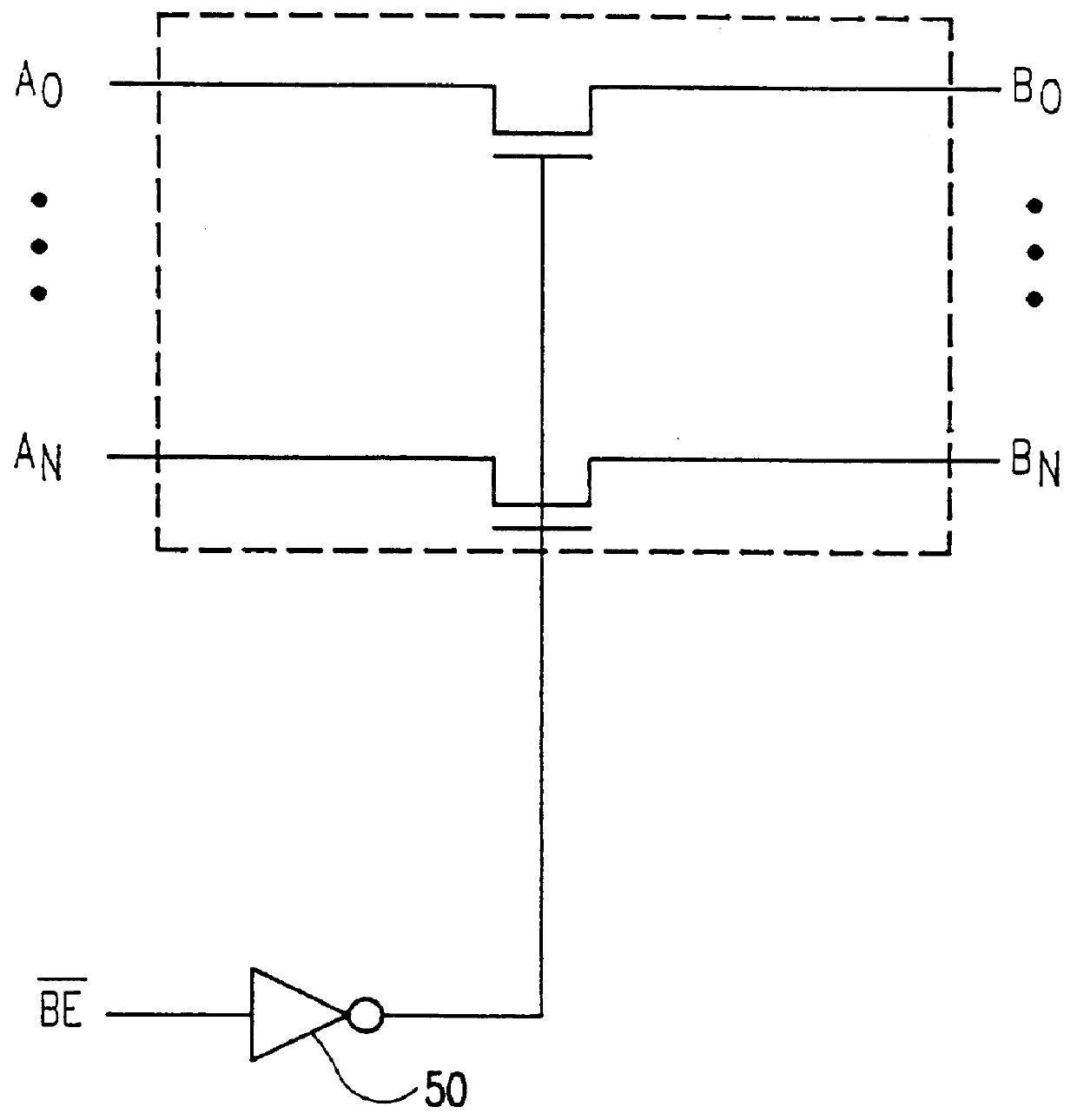
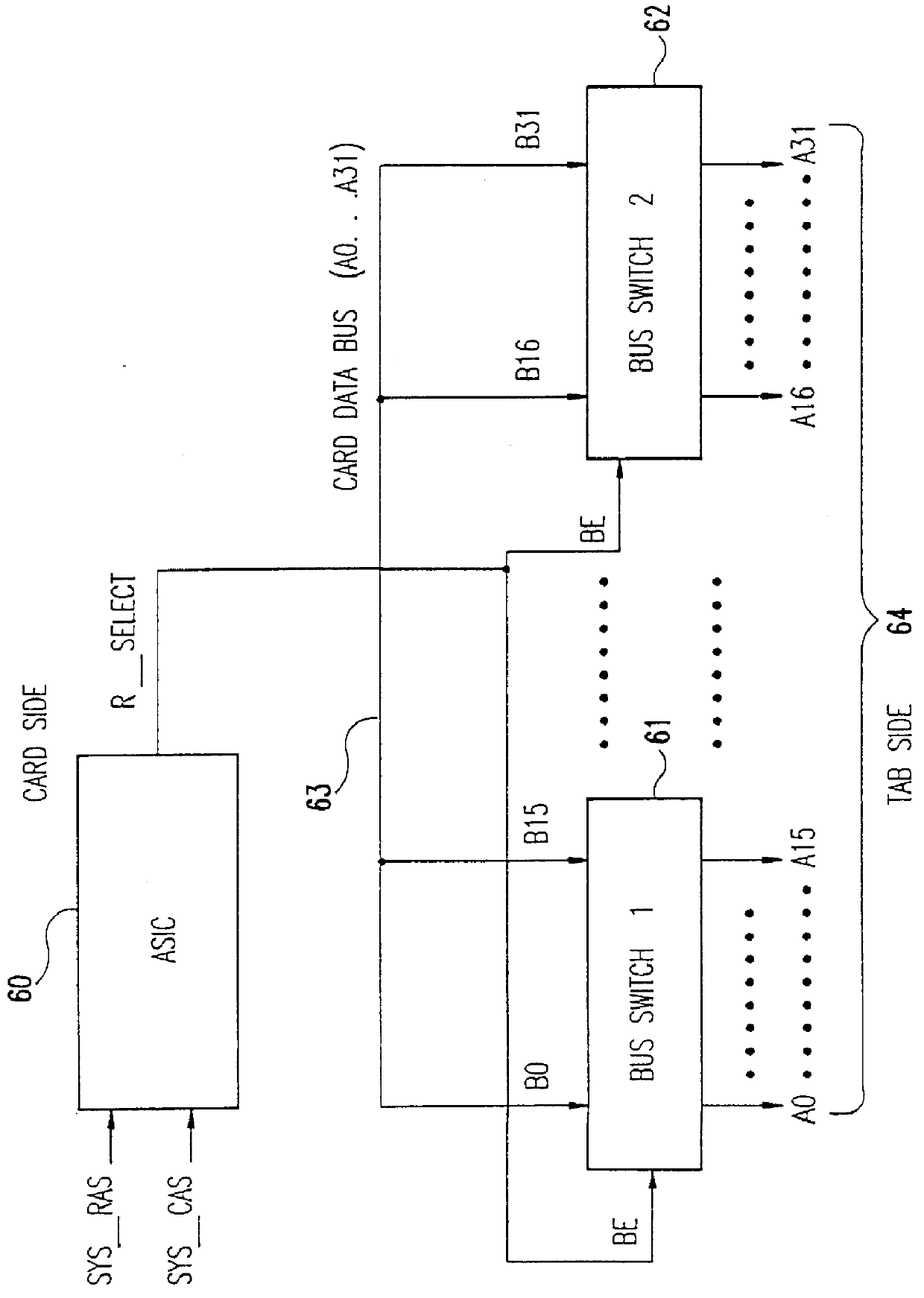
High density memory module with in-line bus switches being enabled in response to read/write selection state of connected RAM banks to improve data bus performance
InactiveUS6070217AMaximize memory densityReduce signal reflectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-state devicesCapacitanceBiological activation
Data line loading on high density modules with multiple DRAMs is minimized permitting the maximum memory density of systems of otherwise limited density to be increased without an ensuing performance degradation due to data line capacitive loading. First the single or dual in-line memory module (SIMM or DIMM) includes in-line bus switches. The bus switches are between the SIMM or DIMM module tabs (system) and random access memory devices (RAM) and are either in a high impedance (off) or active state depending on the READ / WRITE state of the RAM. When in the high impedance state, the effective loading of the module is that of the bit switch device. The logic for determining the READ / WRITE state may be embedded in an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that monitors bus activity and controls activation of the bus switches, be provided by a memory controller or, generated by the RAM itself. The bus switches are active when the RAM is performing a read or a write and inactive otherwise. The RAM is Fast Page Mode (FPM) and Extended Data Output (EDO) or Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM).
Owner:IBM CORP
Non-volatile memory and method with bit line compensation dependent on neighboring operating modes
ActiveUS20050057967A1Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineHigh density
When programming a contiguous page of memory storage units, every time a memory storage unit has reached its targeted state and is program-inhibited or locked out from further programming, it creates a perturbation on an adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The present invention provides as part of a programming circuit and method in which an offset to the perturbation is added to the adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The offset is added as voltage offset to a bit line of a storage unit under programming. The voltage offset is a predetermined function of whether none or one or both of its neighbors are in a mode that creates perturbation, such as in a program inhibit mode. In this way, an error inherent in programming in parallel high-density memory storage units is eliminated or minimized.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
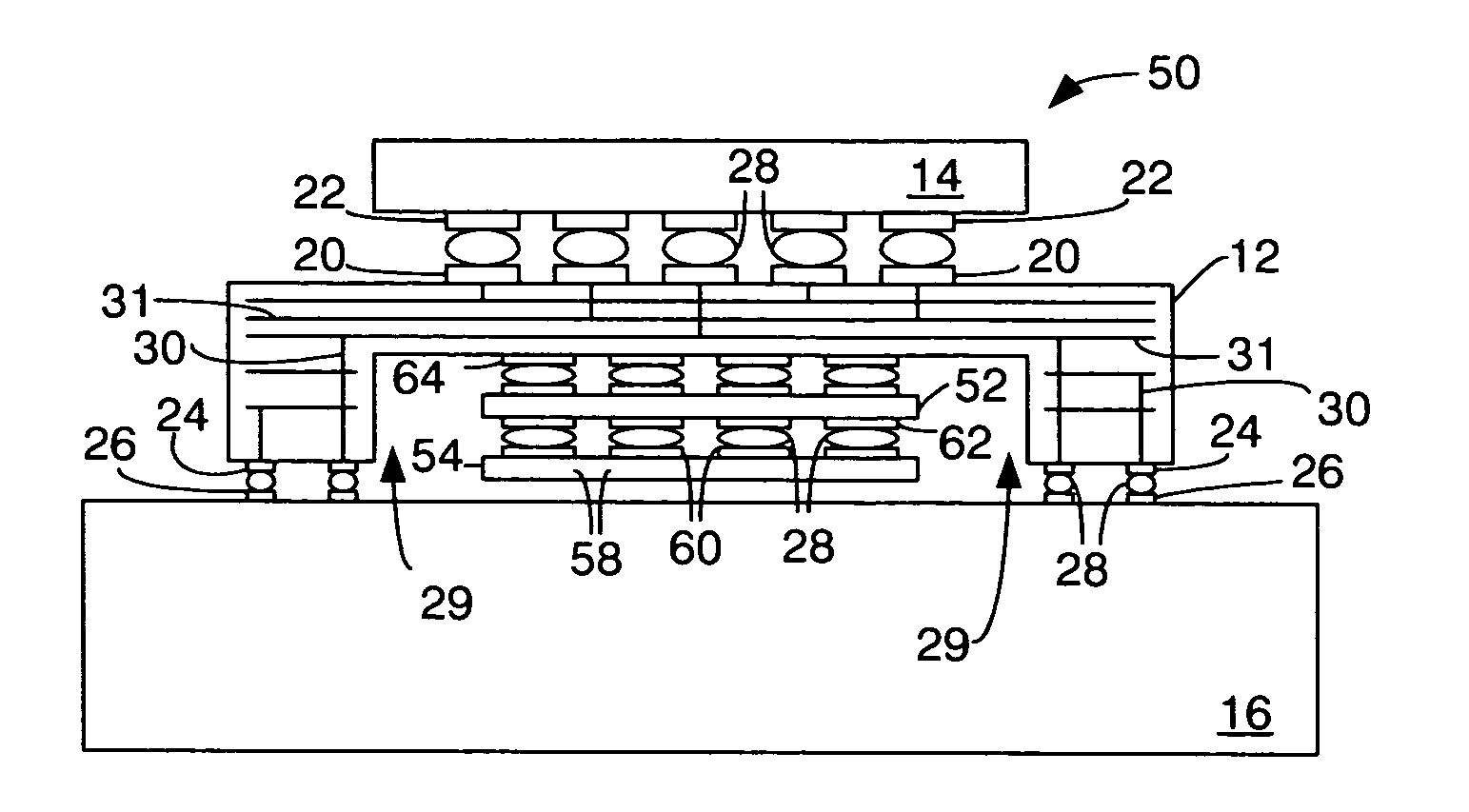
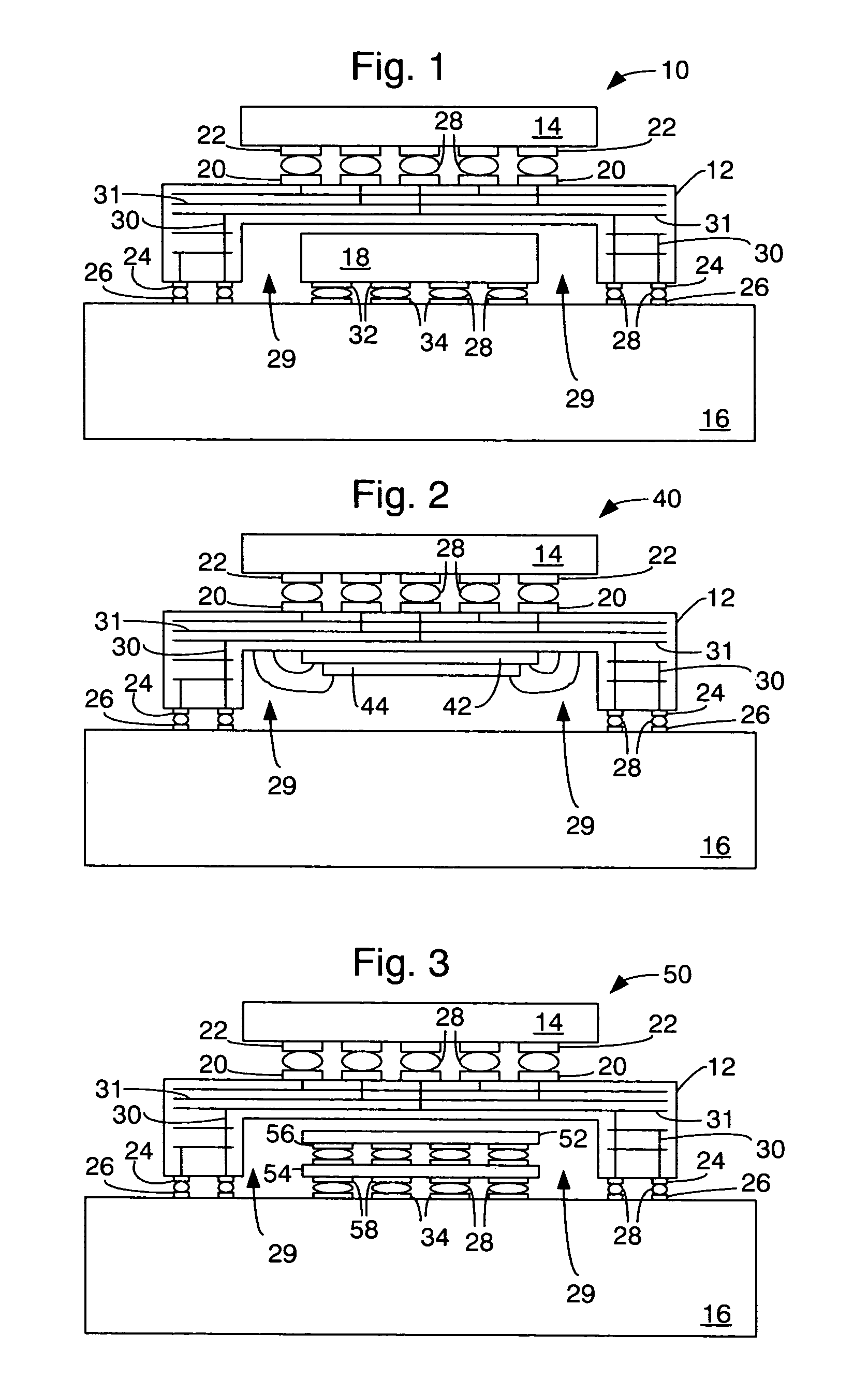
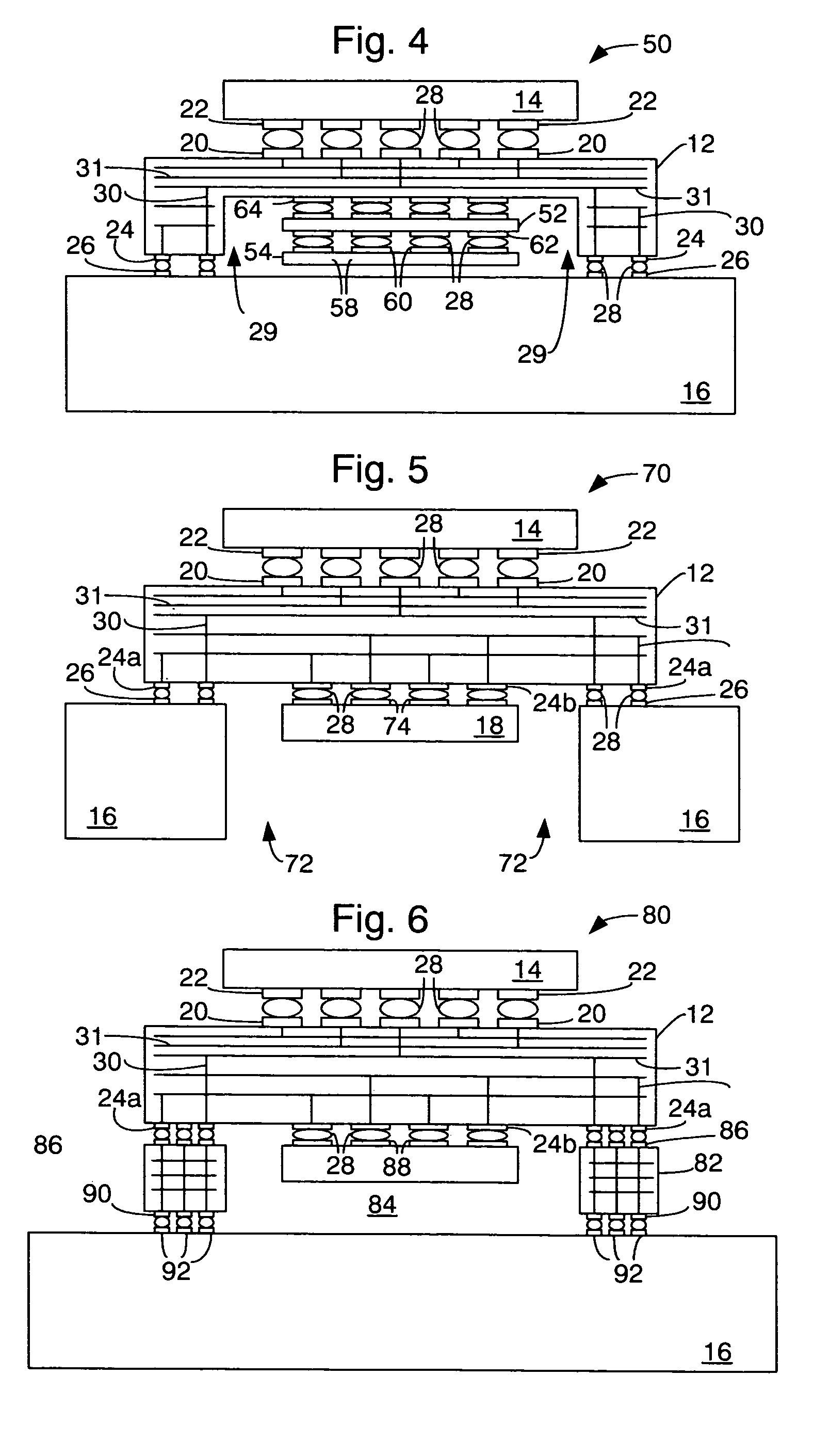
Pitch change and chip scale stacking system
InactiveUS7053478B2Printed circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh densityFlexible circuits
The present invention stacks integrated circuits into modules that conserve board surface area. In a two-high stack or module devised in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a pair of integrated circuits is stacked, with one integrated circuit above the other. The two integrated circuits are connected with a pair of flexible circuit structures. Each of the pair of flexible circuit structures is partially wrapped about a respective opposite lateral edge of the lower integrated circuit of the module. The flex circuit pair connects the upper and lower integrated circuits and provides a thermal and electrical path connection path between the module and its application environment. The module has a ballout pattern with a different pitch and / or supplemental module contacts devised to allow combined signaling to the integrated circuits through contacts having a desired ballout footprint. The present invention may be employed to advantage in numerous configurations and combinations of integrated circuits in modules provided for high-density memories or high capacity computing.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Scratch pad block
ActiveUS7315916B2Improve performanceWrite efficientlyMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesHigh densityHigh velocity
In a memory array having a minimum unit of erase of a block, a scratch pad block is used to store data that is later written to another block. The data may be written to the scratch pad block with a low degree of parallelism and later written to another location with a high degree of parallelism so that it is stored with high density. Data may be temporarily stored in the scratch pad block until it can be more efficiently stored elsewhere. This may be when some other data is received. Unrelated data may be stored in the same page of a scratch pad block.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS20090194839A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsBit lineHigh density
Owner:NANTERO
High Density Storage System
InactiveUS20080030945A1Reducing temperature influence on carrierEnergy efficient ICTTime segmentCooling fluid
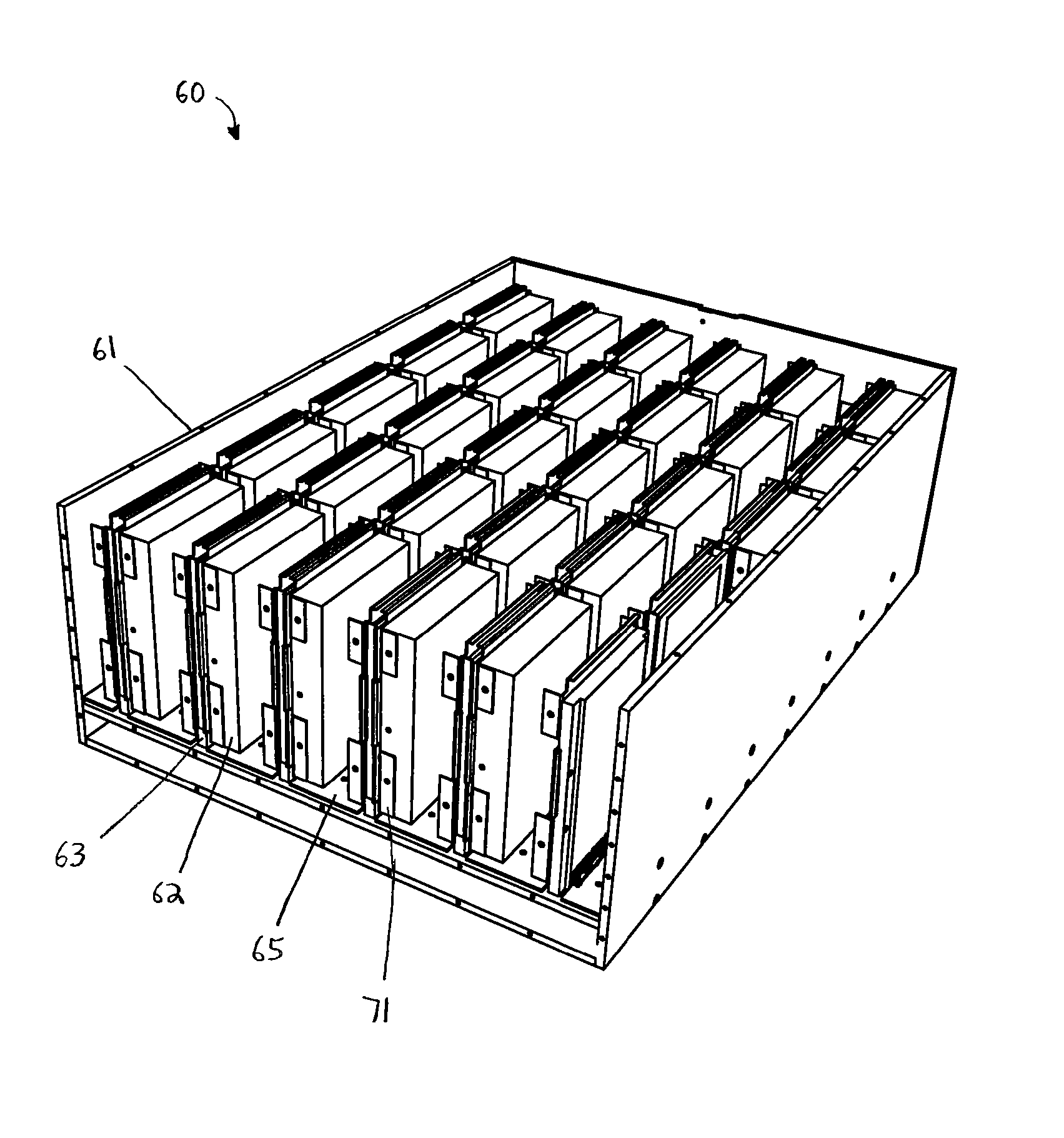
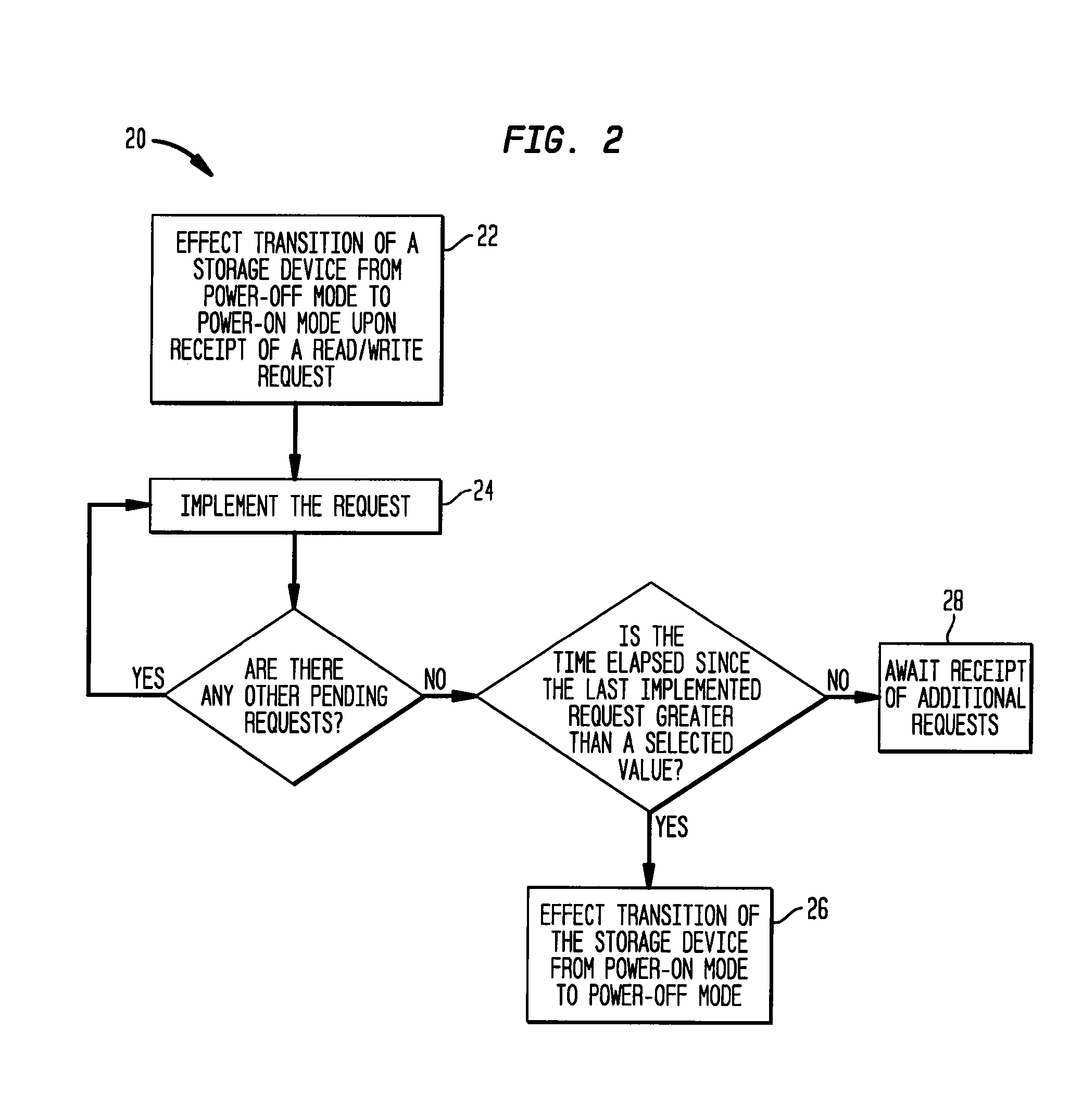
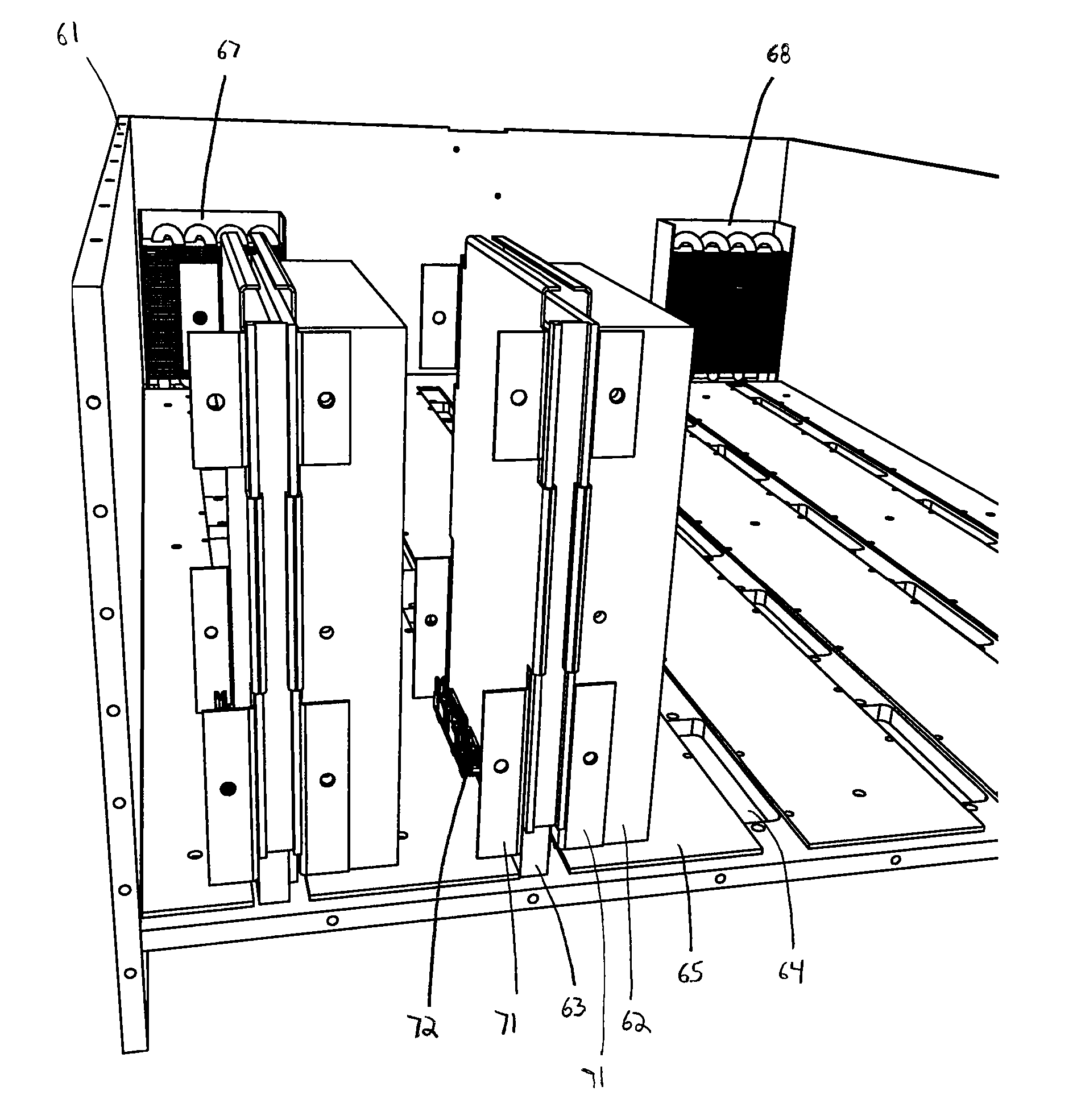
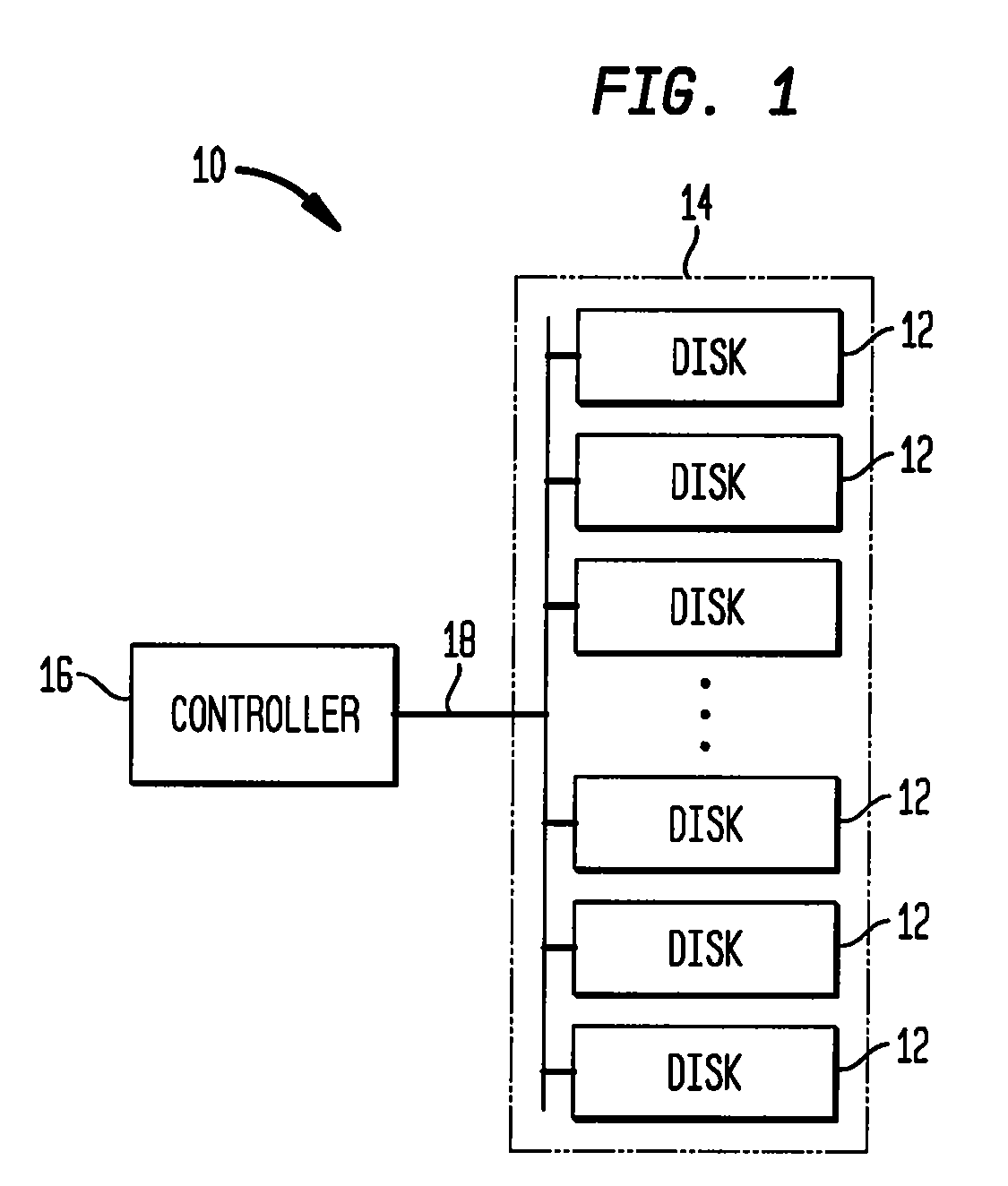
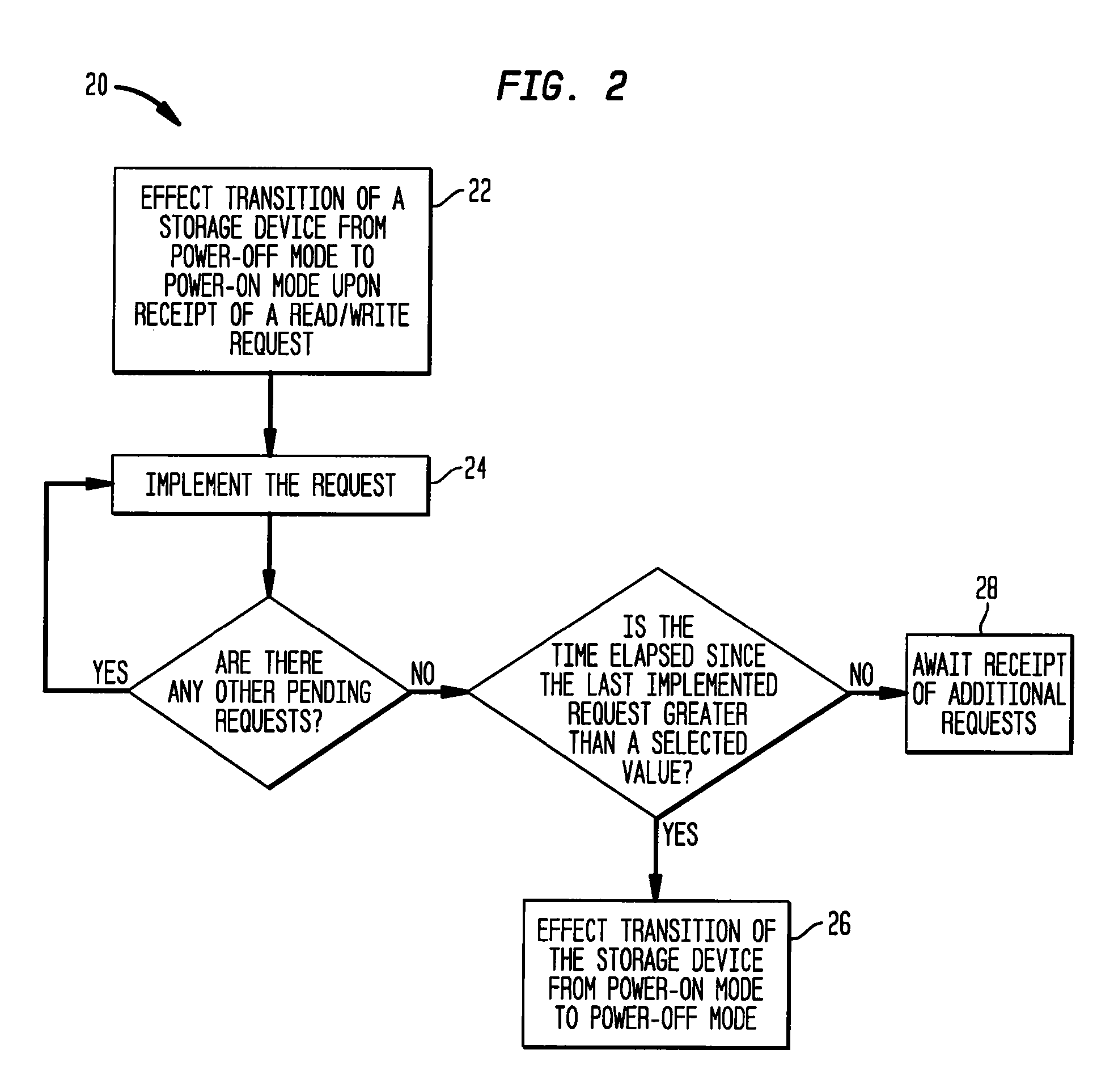
The present invention provides methods and systems for storage of data. In one aspect, the invention provides a data storage system that includes a plurality of storage devices, such as, disks, for storing data, and a controller that implements a policy for managing distribution of power to the storage devices, which are normally in a power-off mode. In particular, the controller can effect transition of a storage device from a power-off mode to a power-on mode upon receipt of a request for reading data from or writing data to that storage device. The controller further effects transition of a storage device from a power-on mode to a power-off mode if no read / write request is pending for that storage device and a selected time period, e.g., a few minutes, has elapsed since the last read / write request for that storage device. In another aspect, the present invention provides a data storage system that includes a plurality of cooling plates, each with one or more storage devices thermally coupled thereto. More specifically, for example, a cooling plate can have a storage device thermally coupled to each of two opposed cooling surfaces. A heat exchanging device can be thermally coupled to the cooling plates, e.g., via fluid channels carrying a cooling fluid, for dissipating heat generated by the storage devices.
Owner:BIOTRONIX INC
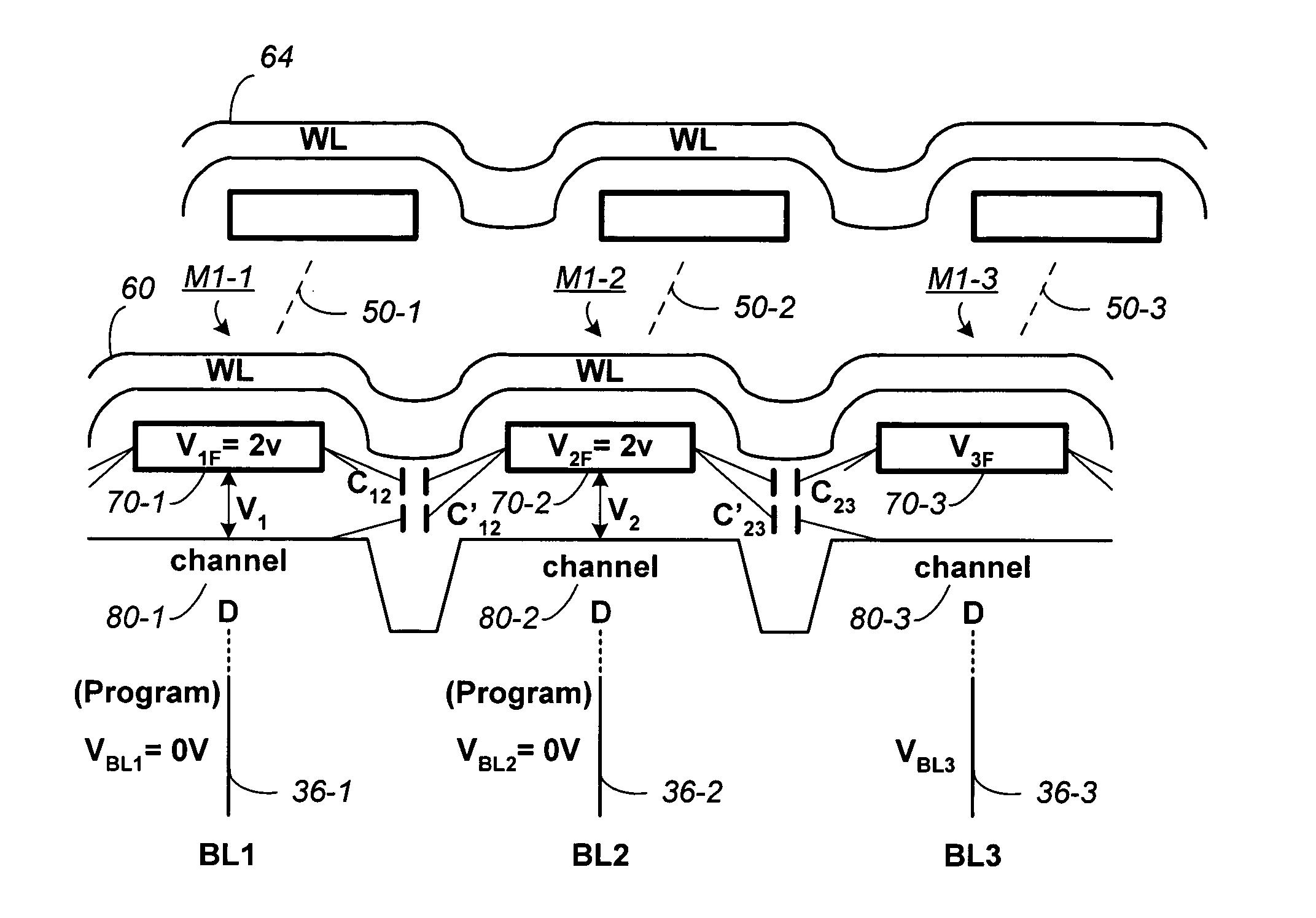
Non-volatile memory and method with bit line coupled compensation
InactiveUS7064980B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineHigh density
When programming a contiguous page of memory storage units, every time a memory storage unit has reached its targeted state and is program-inhibited or locked out from further programming, it creates a perturbation on an adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The present invention provides as part of a programming circuit and method in which an offset to the perturbation is added to the adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The offset is added by a controlled coupling between the adjacent bit lines of the program-inhibited memory storage unit and the still under programming memory storage unit. In this way, an error inherent in programming in parallel high-density memory storage units is eliminated or minimized.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
Owner:NANTERO
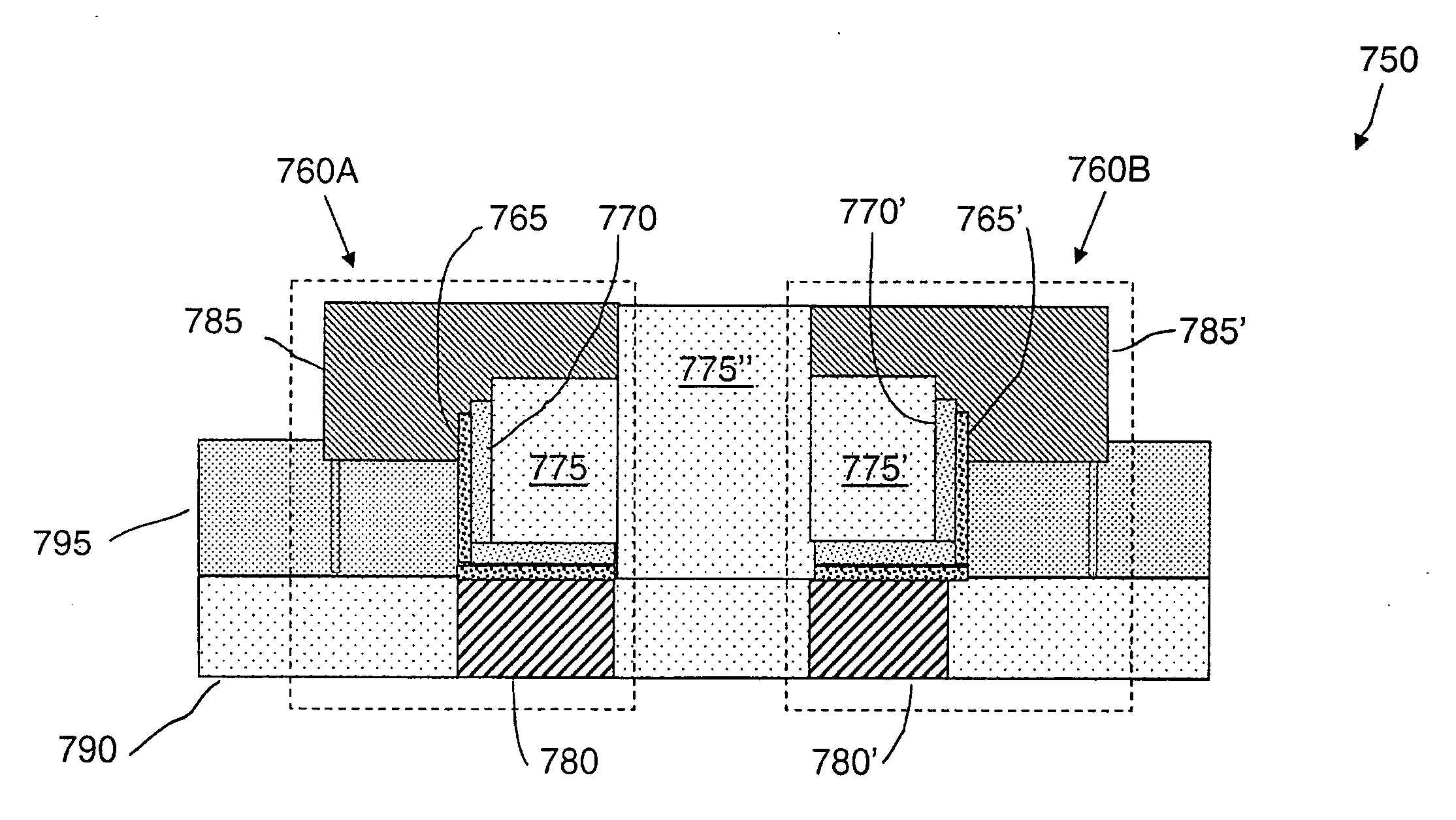
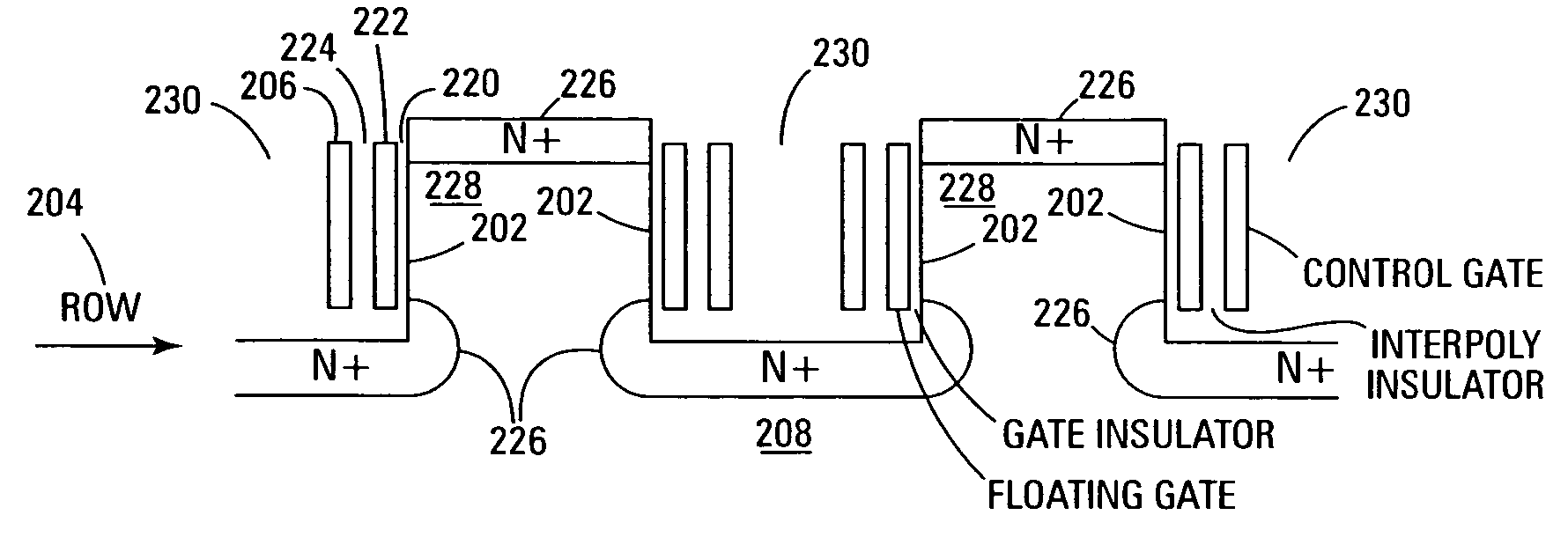
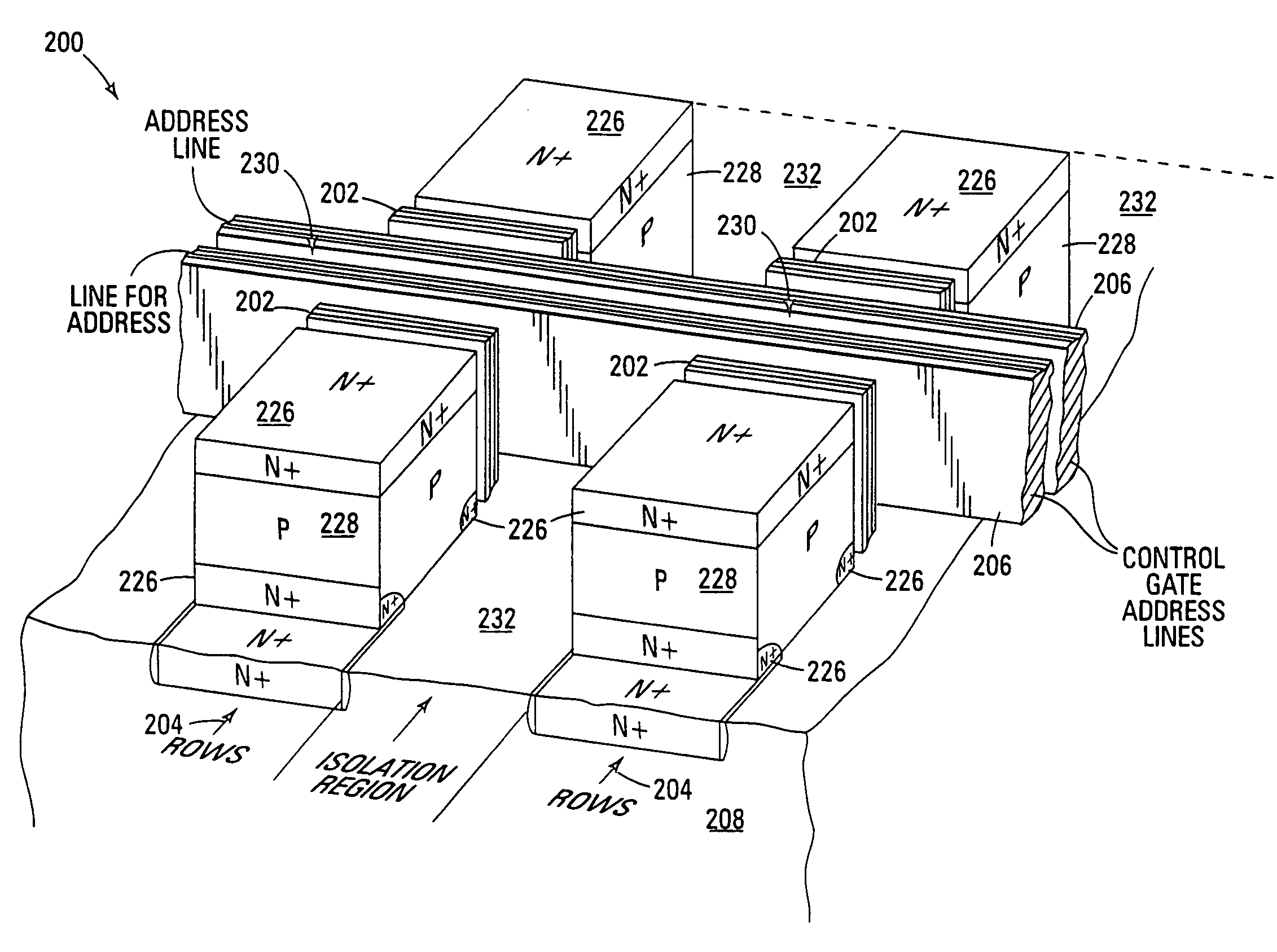
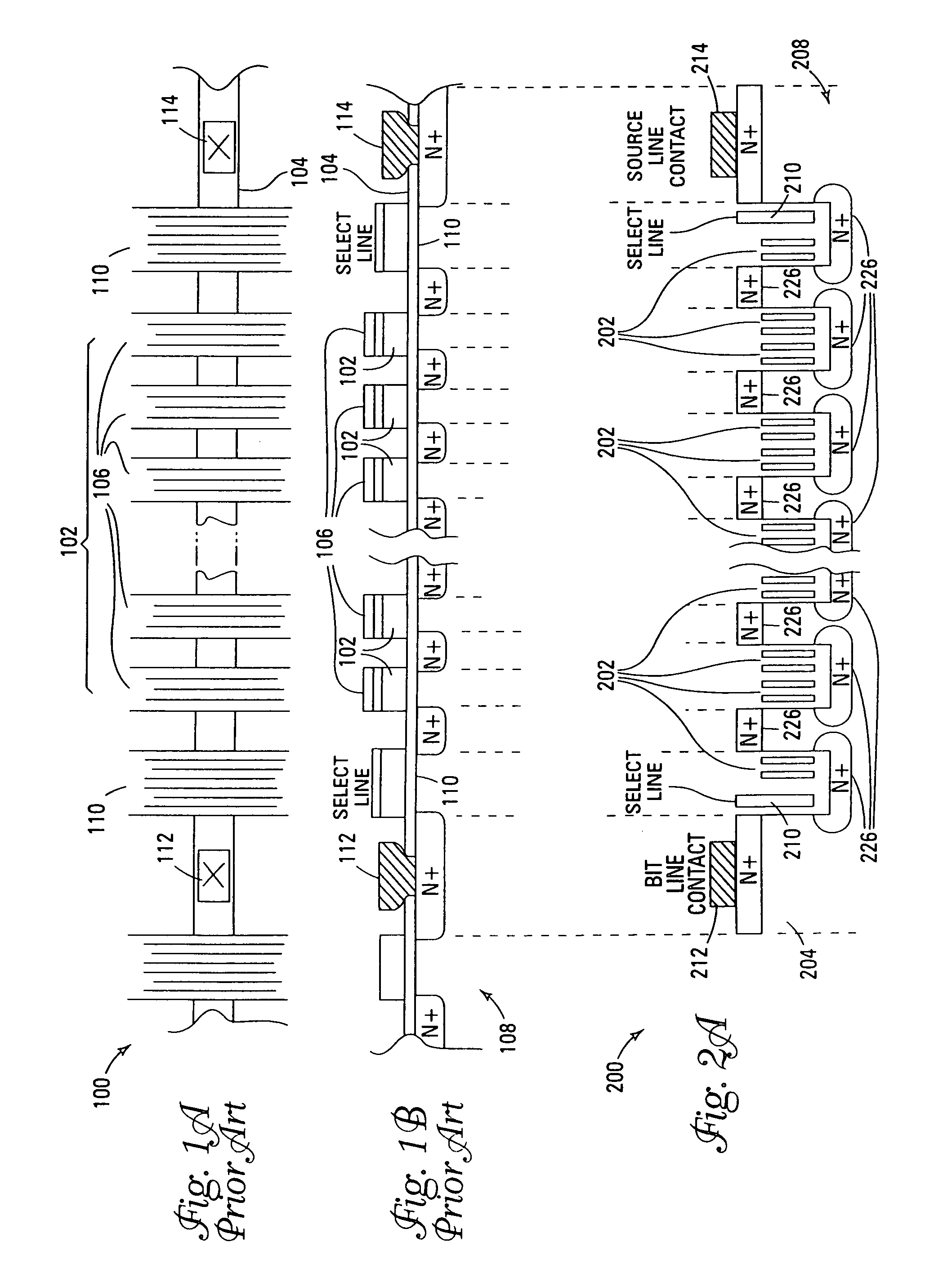
Vertical device 4F2 EEPROM memory
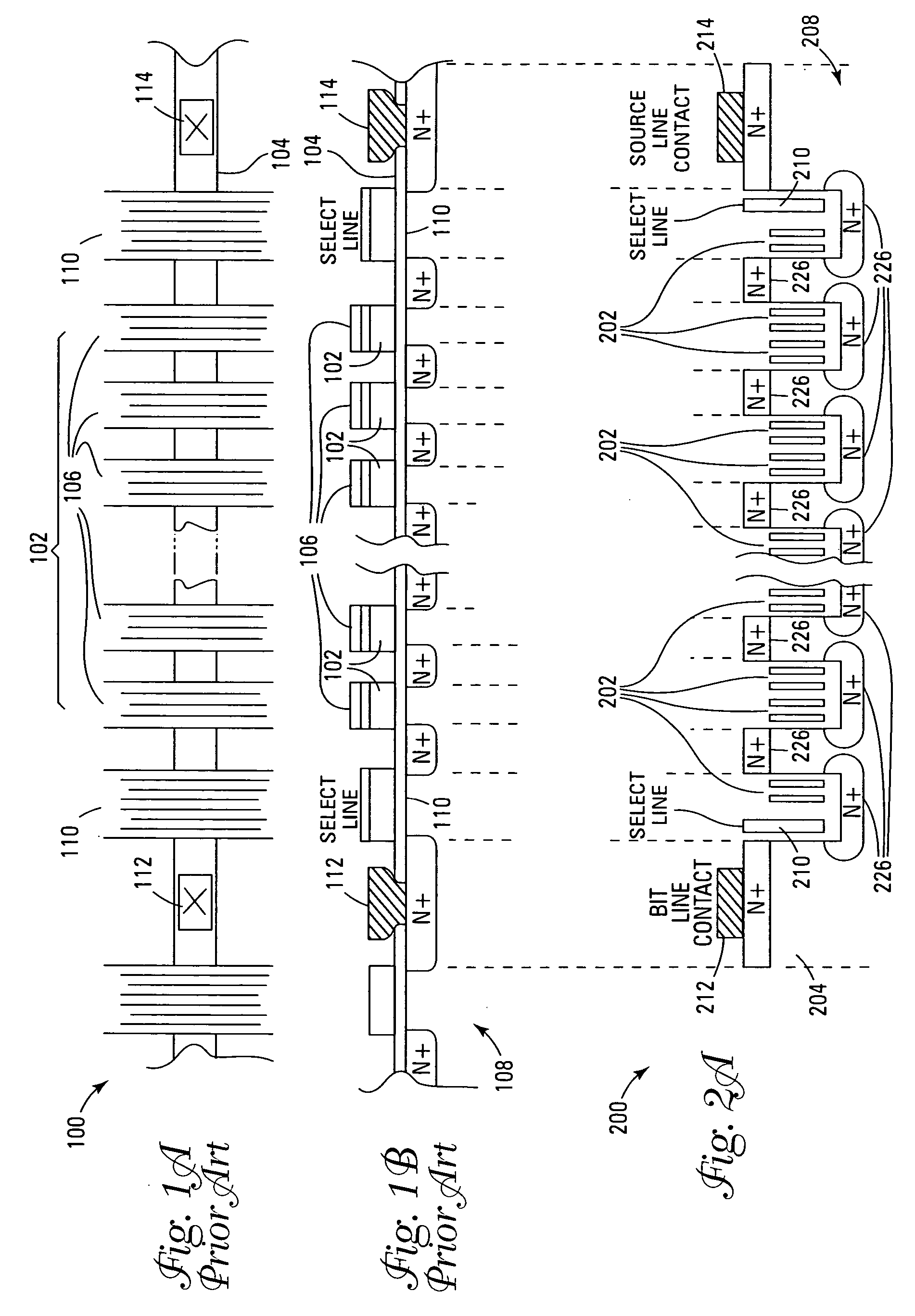
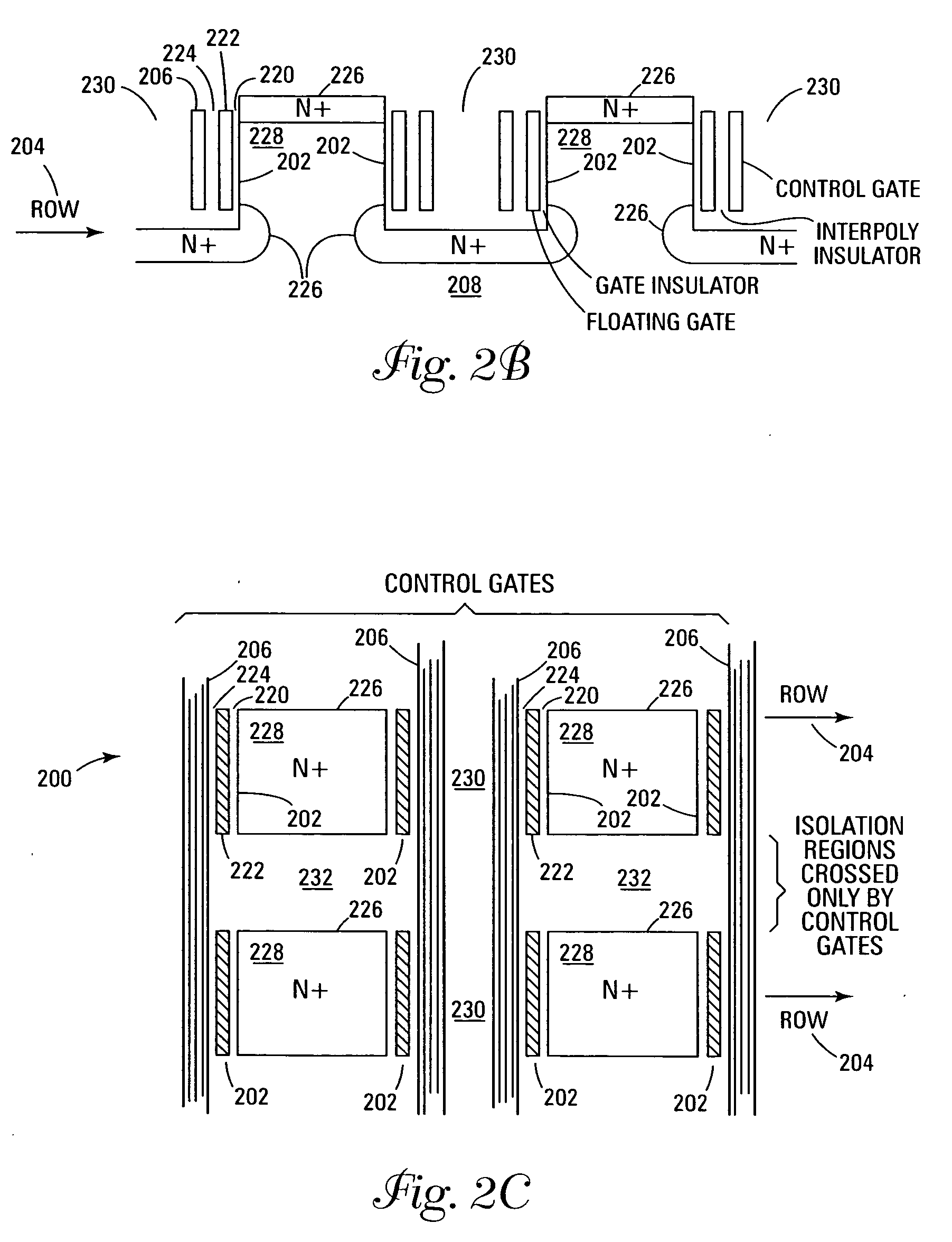
ActiveUS6878991B1Promotes its utilizationImproved high density memory deviceTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineHigh density
EEPROM memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of vertical floating gate memory cells and select gates in NOR or NAND high density memory architectures. Memory embodiments of the present invention utilize vertical select gates and floating gate memory cells to form NOR and NAND architecture memory cell strings, segments, and arrays. These memory cell architectures allow for improved high density memory devices or arrays with integral select gates that can take advantage of the features semiconductor fabrication processes are generally capable of and allow for appropriate device sizing for operational considerations. The memory cell architectures also allow for mitigation of disturb and overerasure issues by placing the floating gate memory cells behind select gates that isolate the memory cells from their associated bit lines and / or source lines.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High density memory card assembly
ActiveUS7317250B2Increasing overall height and area consumedHigh density arrangementPrinted electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh densityDigital storage
A high density memory card assembly having application for USB drive storage, flash and ROM memory cards, and similar memory card formats. A cavity is formed through a rigid laminate substrate. First and second digital memory devices (e.g., TSOP packages or bare semiconductor dies) are located within the cavity so as to be recessed relative to the top and bottom of the substrate. The recessed first and second memory devices are arranged in spaced, face-to-face alignment with one another within the cavity. The first and second memory devices are covered and protected by respective first and second memory packages that are located on the top and bottom of the substrate. By virtue of the foregoing, the memory package density of the assembly can be increased without increasing the height or area consumed by the assembly for receipt within an existing external housing.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
Stack package for high density integrated circuits
InactiveUS7217994B2Small sizeEasy to use3D rigid printed circuitsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMemory chipHigh density
A stack package for a high density memory module includes at least one memory chip, an ASIC and an interposer, wherein the interposer comprises a first surface having contacts arranged in electrical communication with corresponding contacts on the ASIC and a second, substantially opposite surface including contacts arranged in electrical communication with corresponding contacts on a PCB. The at least one memory chip is dimensioned to fit within a cutout section in the interposer.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Vertical NAND flash memory array
ActiveUS20050133851A1Improve utilizationEasy to optimizeTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densityParallel computing
Memory devices, arrays, and strings are described that facilitate the use of vertical floating gate memory cells in NAND architecture memory strings, arrays, and devices. NAND Flash memory strings, arrays, and devices in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, include vertical Flash memory cells to form NAND architecture memory cell strings and memory arrays. These vertical memory cell NAND architecture strings allow for an improved high density memory devices or arrays that can take advantage of the feature sizes semiconductor fabrication processes are generally capable of and still allow for appropriate device sizing for operational considerations.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
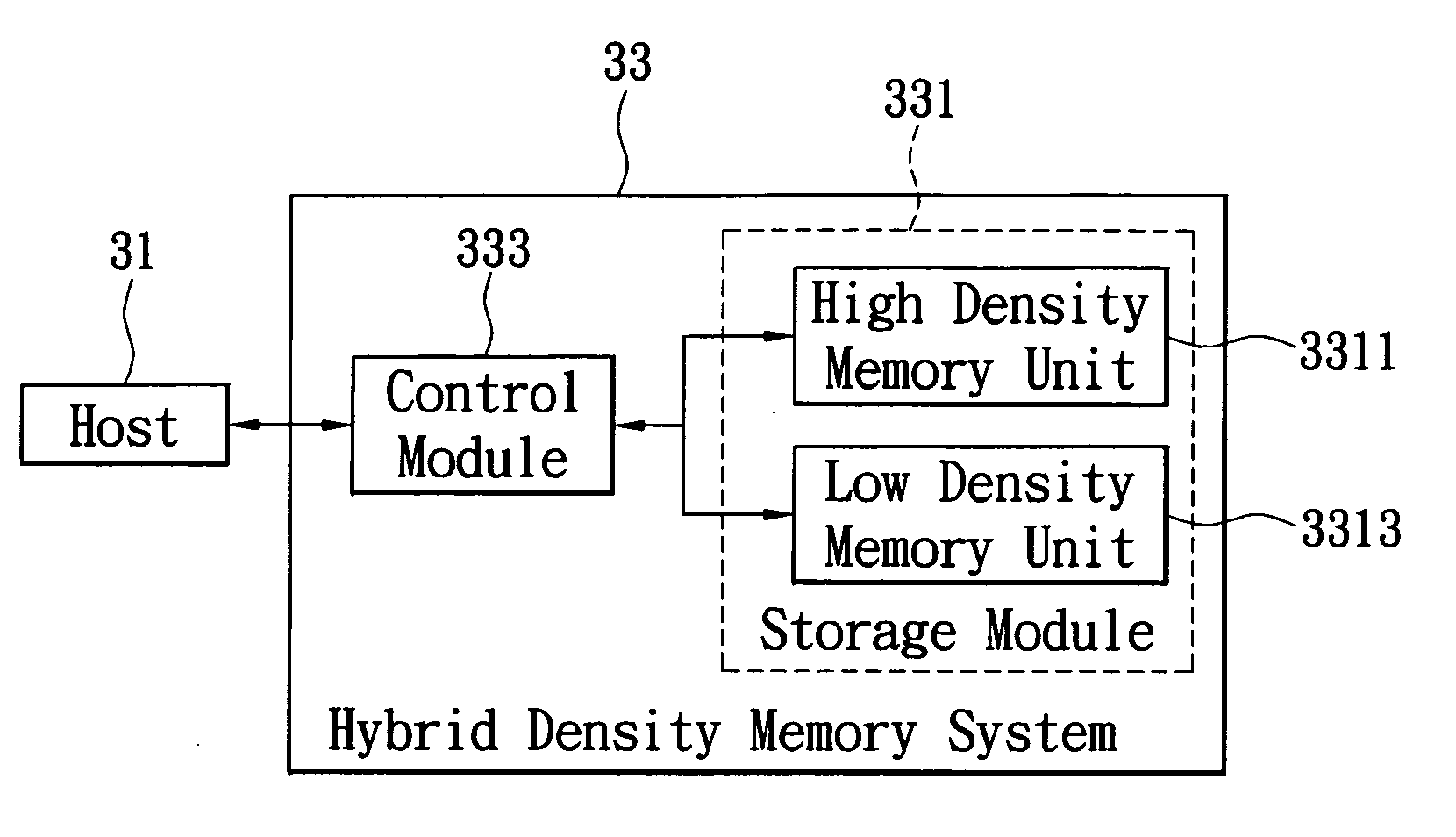
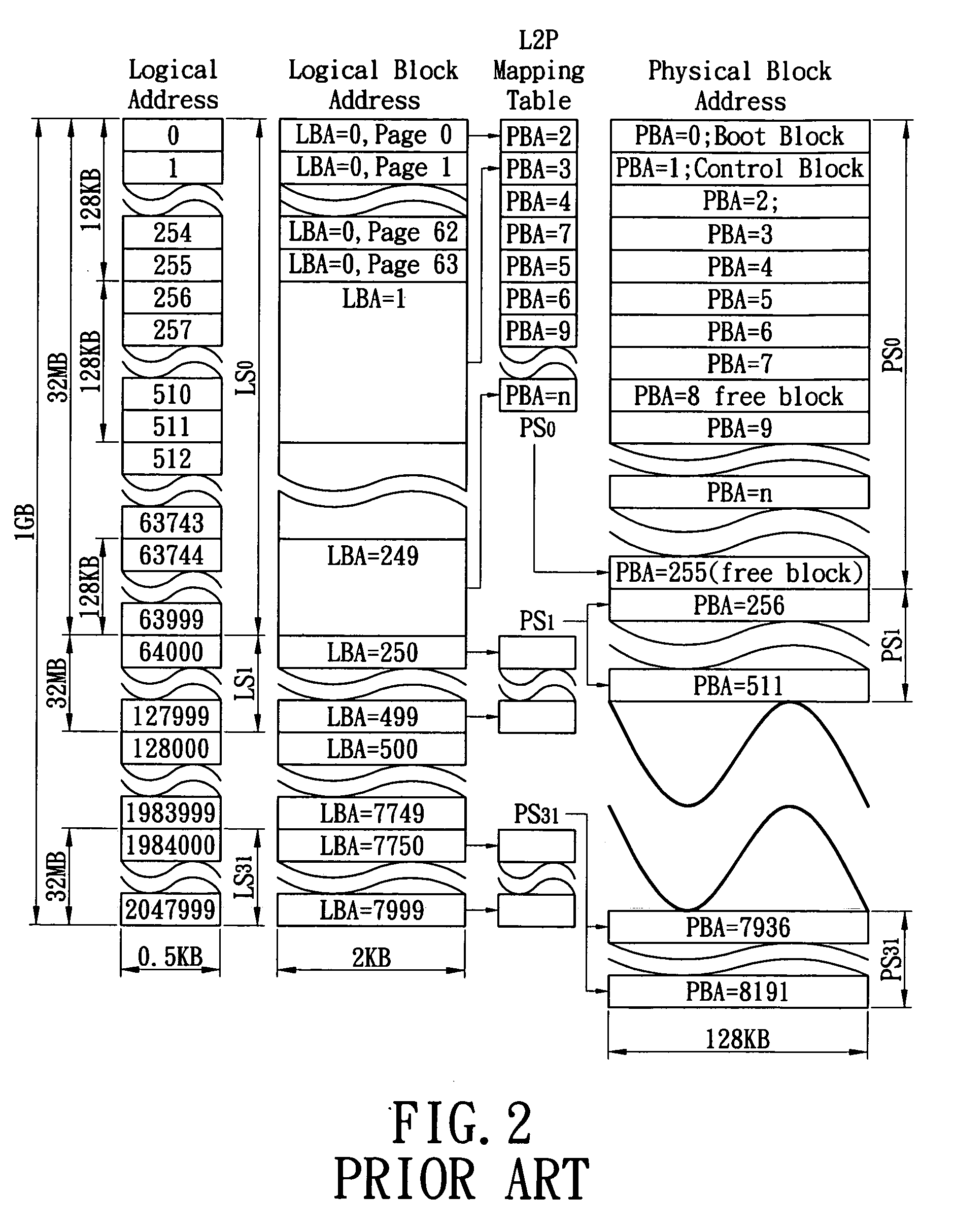
Hybrid density memory system and control method thereof
InactiveUS20100082883A1Extend your lifeEfficient managementMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHigh densityParallel computing
A control method of a memory system for accessing an updated data between a host and the memory system is provided. The host has storage space which is divided into a plurality of logical segments to access the data. The system includes a high density memory and a low density memory, and the high density memory includes a plurality of physical segments to access the data. The control method includes the following steps: first, providing a LDM table in the memory system to indicate the allocation information of the low density memory; finally, deciding where the data is written to is according to its properties and the LDM table.
Owner:ADATA
Multi-bit high-density memory device and architecture and method of fabricating multi-bit high-density memory devices
ActiveUS20080001176A1ThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor materialsHigh density
A structure, memory devices using the structure, and methods of fabricating the structure. The structure includes: an array of nano-fins, each nano-fin comprising an elongated block of semiconductor material extending axially along a first direction, the nano-fins arranged in groups of at least two nano-fins each, wherein ends of nano-fins of each adjacent group of nano-fins are staggered with respect to each other on both a first and a second side of the array; wherein nano-fins of each group of nano-fins are electrically connected to a common contact that is specific to each group of nano-fins such that the common contacts comprise a first common contact on the first side of the array and a second common contact on the second side of the array; and wherein each group of nano-fins has at least two gates that electrically control the conductance of nano-fins of the each group of nano-fins.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
High density storage system
InactiveUS7573715B2Reducing temperature influence on carrierEnergy efficient ICTTime segmentHybrid storage system
The present invention provides methods and systems for storage of data. In one aspect, the invention provides a data storage system that includes a plurality of storage devices, such as, disks, for storing data, and a controller that implements a policy for managing distribution of power to the storage devices, which are normally in a power-off mode. In particular, the controller can effect transition of a storage device from a power-off mode to a power-on mode upon receipt of a request for reading data from or writing data to that storage device. The controller further effects transition of a storage device from a power-on mode to a power-off mode if no read / write request is pending for that storage device and a selected time period, e.g., a few minutes, has elapsed since the last read / write request for that storage device. In another aspect, the present invention provides a data storage system that includes a plurality of cooling plates, each with one or more storage devices thermally coupled thereto. More specifically, for example, a cooling plate can have a storage device thermally coupled to each of two opposed cooling surfaces. A heat exchanging device can be thermally coupled to the cooling plates, e.g., via fluid channels carrying a cooling fluid, for dissipating heat generated by the storage devices.
Owner:BIOTRONIX INC
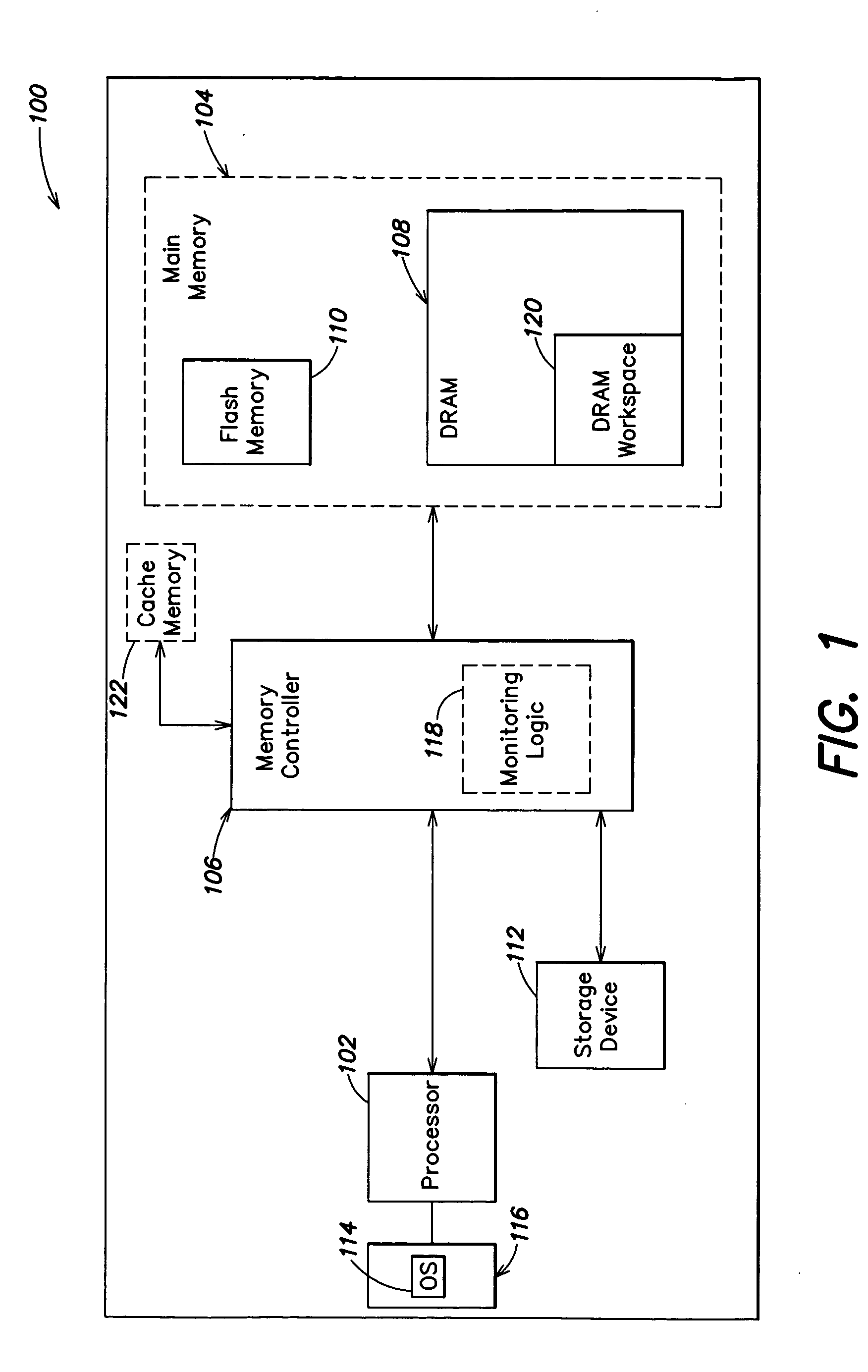
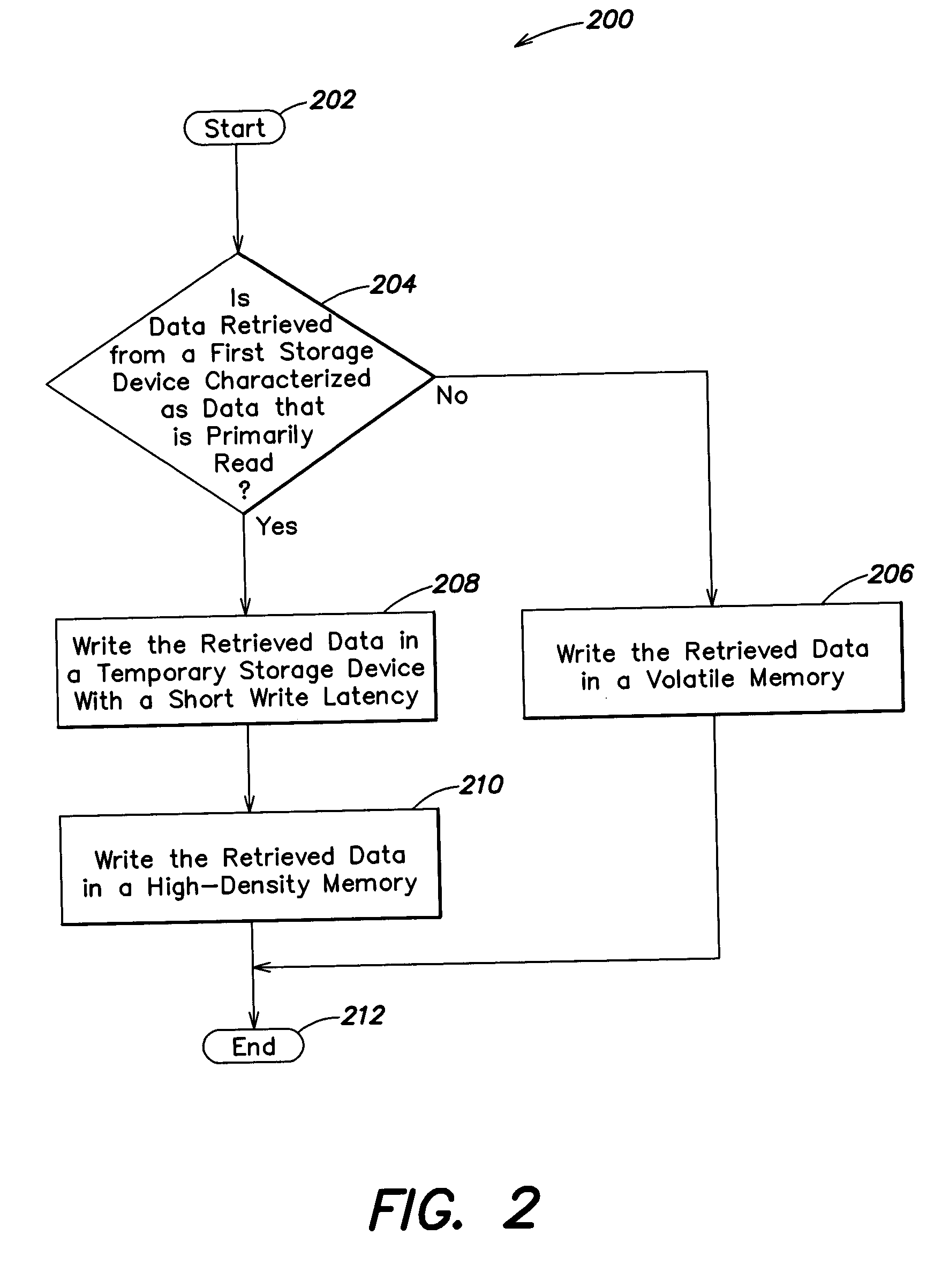
Methods and apparatus for efficient memory usage
ActiveUS20060106984A1Efficient memory usageReduce write latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTHigh densityParallel computing
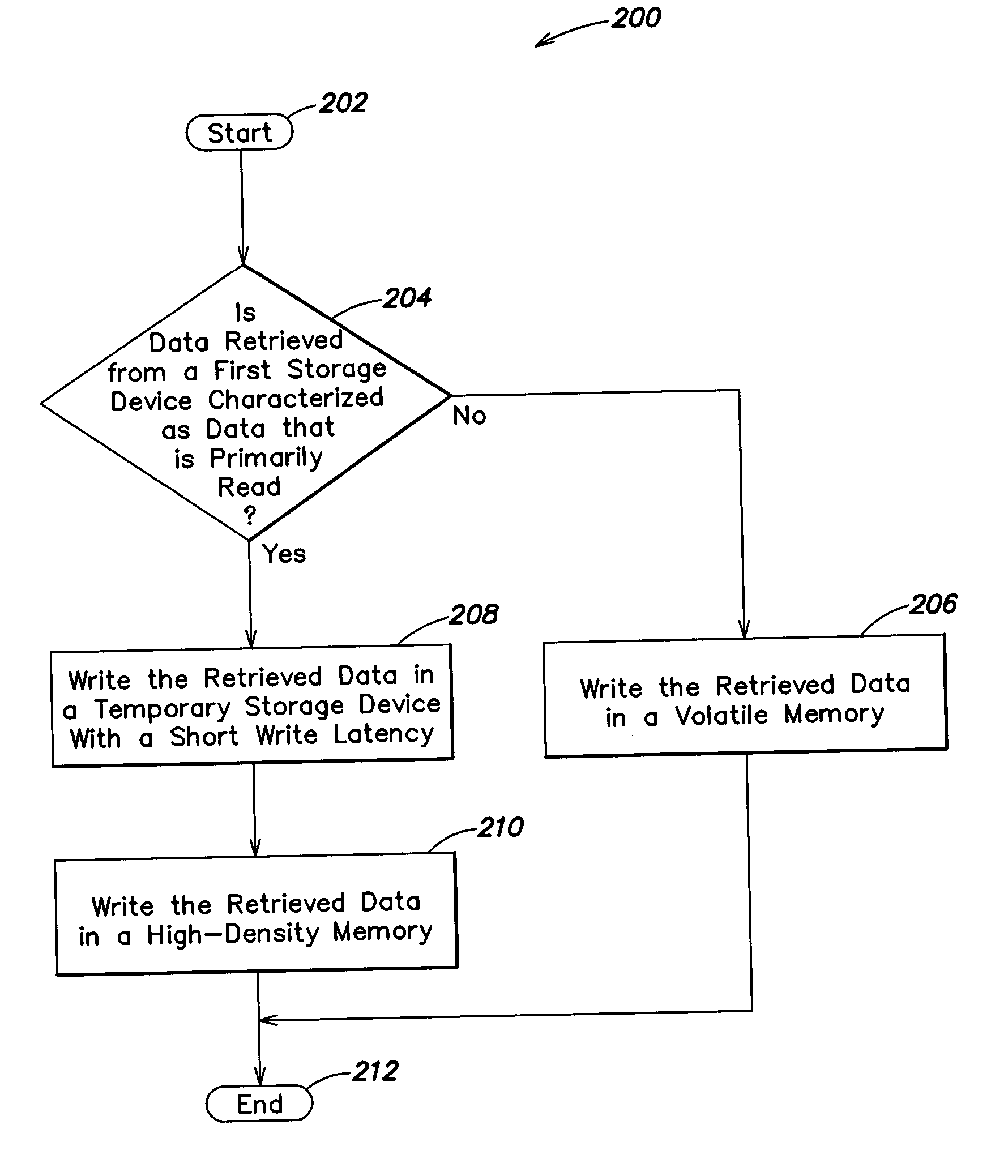
In a first aspect, a first method is provided for efficient memory usage. The first method includes the steps of (1) determining whether data retrieved from a first storage device is characterized as data that is primarily read; and (2) if data retrieved from the first storage device is characterized as data that is primarily read (a) writing the retrieved data in a temporary storage device with short write latency; and (b) writing the retrieved data in a high-density memory. Numerous other aspects are provided.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
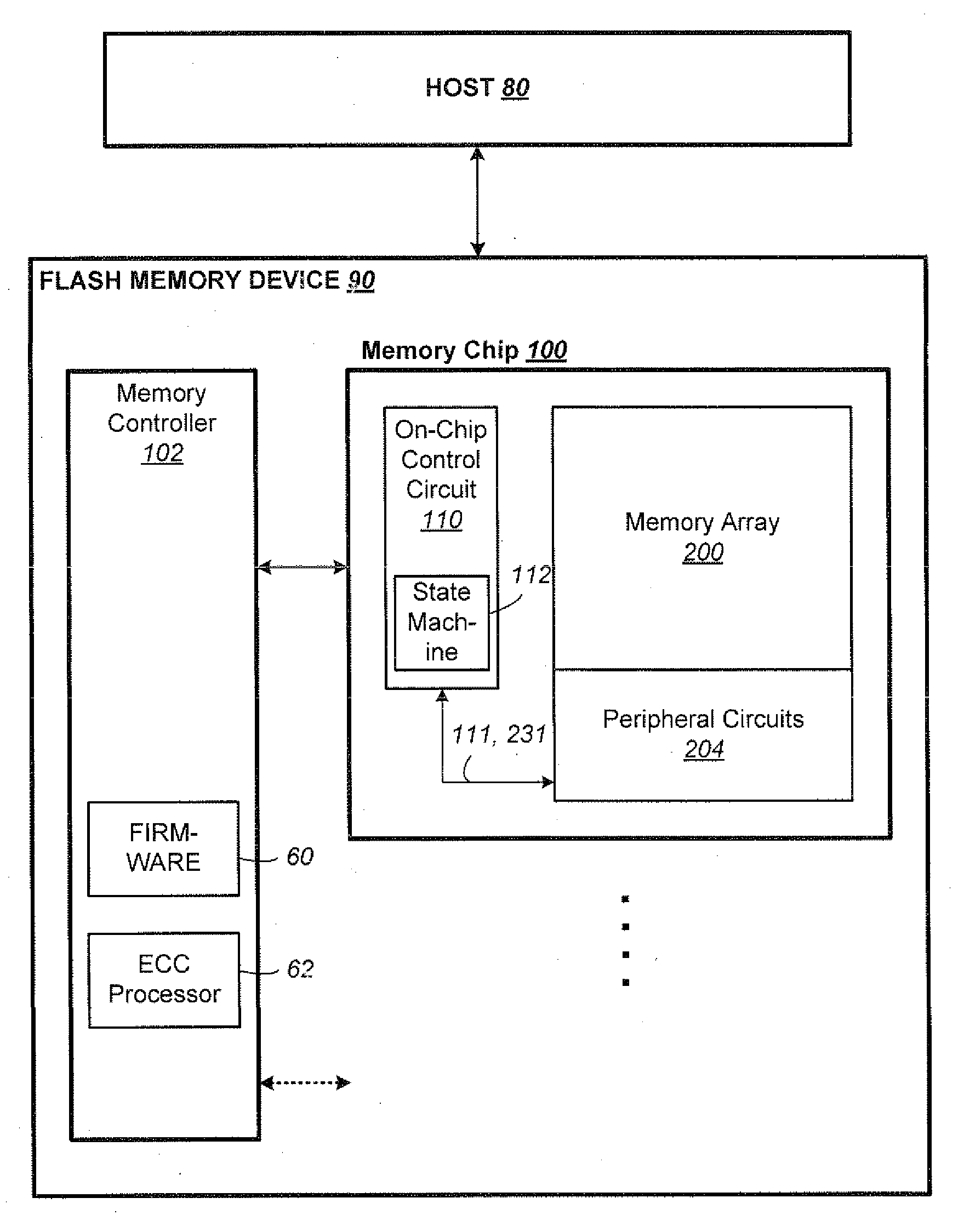
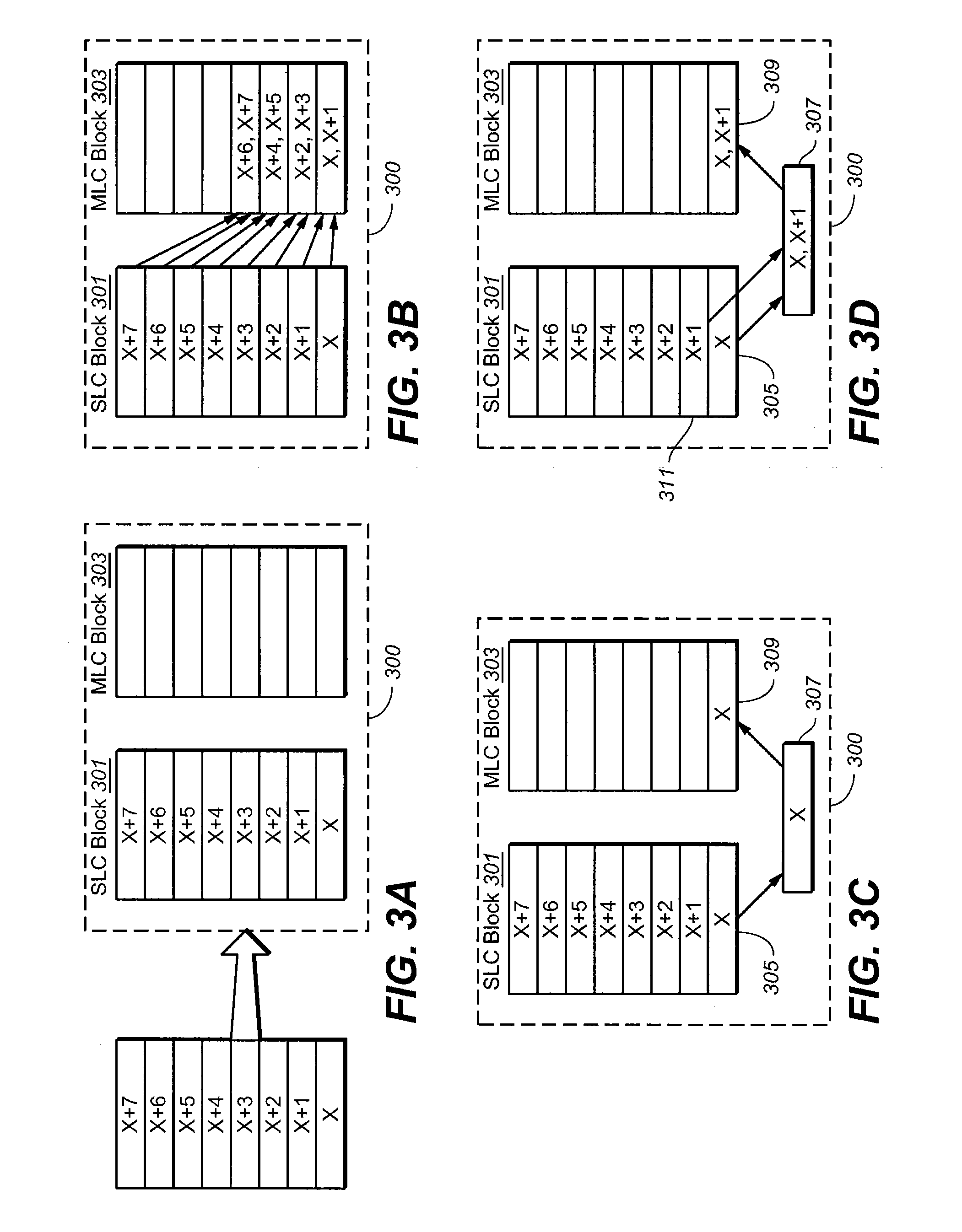
Non-Volatile Memory and Method Having Efficient On-Chip Block-Copying with Controlled Error Rate
A non-volatile memory chip having SLC blocks acting as a write cache for MLC blocks for high density storage requires constant copying or folding of SLC blocks into MLC blocks. To avoid the time-consuming toggling out and in of the pages of the entire SLC block for ECC checking by a controller chip, only a small sample is checked. An optimal read point for reading the memory cells in the sample of the SLC block is dynamically determined by trying different read points so that the data is read within an error budget. Once the optimal read point is determined, it is used to read the entire SLC block without further error checking. Then the SLC block can be copied (blind folded) to the MLC block with the confidence of being within the error budget.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
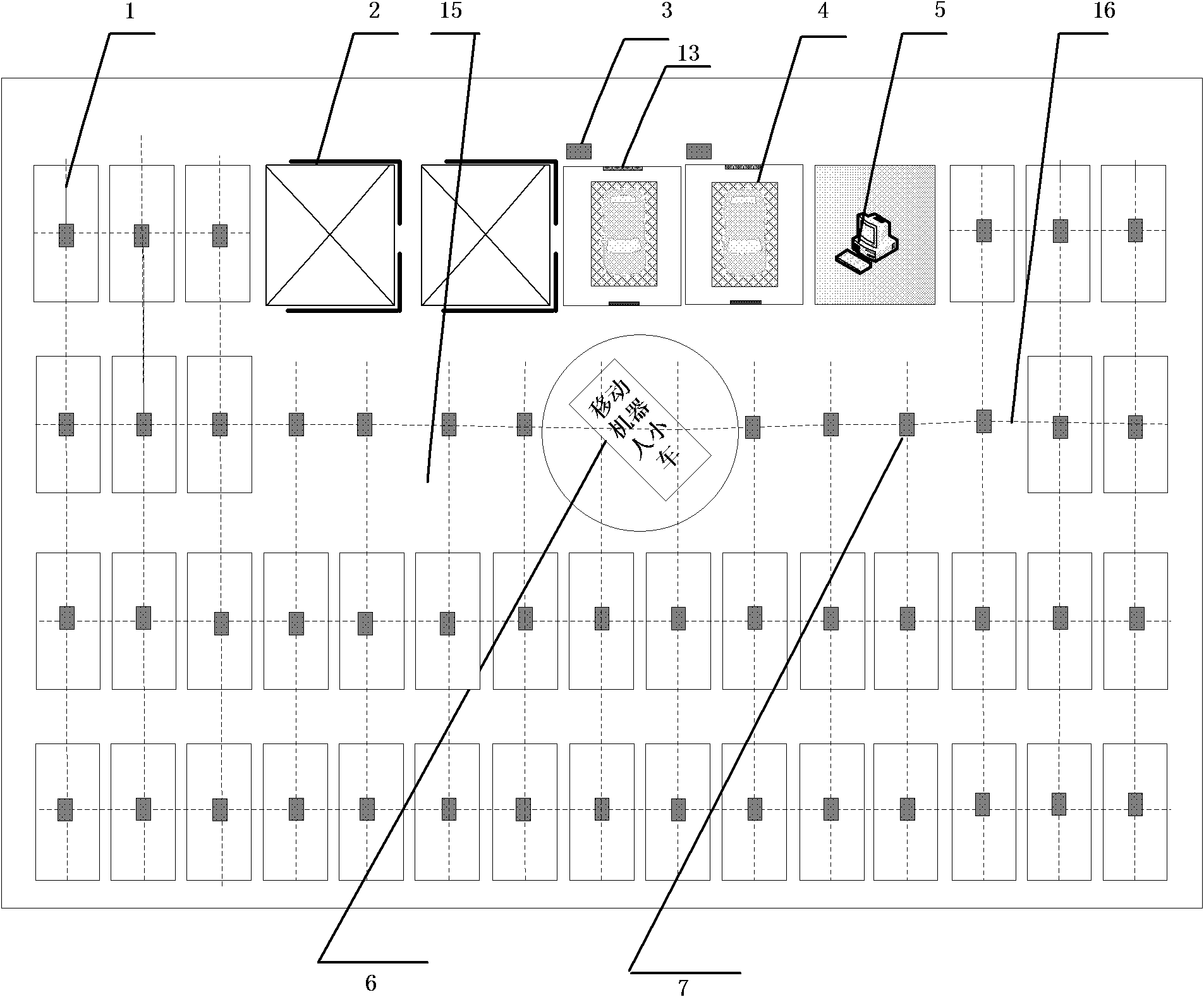
Automatic parking system based on mobile robot trolley
ActiveCN102535915ARealize the access functionSmall auxiliary space areaParkingsParking areaParking space
The invention relates to an automatic parking system based on a mobile robot trolley. The automatic parking system is mainly and technically characterized by comprising a parking lot, the mobile robot trolley and a parking lot intelligent control system, wherein a plurality of rows of parking spaces, a plurality of lines of parking spaces and mobile robot trolley rotating spaces are arranged on the ground of the parking lot, a non-rail type vehicle guide device is paved on the ground of the parking lot, a vehicle access chamber and a center control chamber are arranged in the parking lot, the parking lot intelligent control system is arranged in the center control chamber and is connected with the mobile robot trolley and the vehicle access chamber, and the mobile robot trolley supports vehicles to be accessed for realizing the vehicle access through being controlled by the parking lot intelligent control system. The automatic parking system has the advantages that the design is reasonable, and the flexible dispatching on the vehicles to be accessed and the flexible vehicle access can be carried out through the mobile robot trolley and the corresponding control system, so the functions of high-density storage, fast response and safe service are realized, and the automatic parking system has the characteristics that the building and maintenance cost is low, the access is convenient, the energy is saved, the environment is protected, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN PUZHILIANKE ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Vertical memory cell for high-density memory
ActiveUS20120261638A1Solid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesHigh densityUnit structure
This disclosure provides embodiments for the formation of vertical memory cell structures that may be implemented in RRAM devices. In one embodiment, memory cell area may be increased by varying word line height and / or word line interface surface characteristics to ensure the creation of a grain boundary that is suitable for formation of conductive pathways through an active layer of an RRAM memory cell. This may maintain continuum behavior while reducing random cell-to-cell variability that is often encountered at nanoscopic scales. In another embodiment, such vertical memory cell structures may be formed in multiple-tiers to define a three-dimensional RRAM memory array. Further embodiments also provide a spacer pitch-doubled RRAM memory array that integrates vertical memory cell structures.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
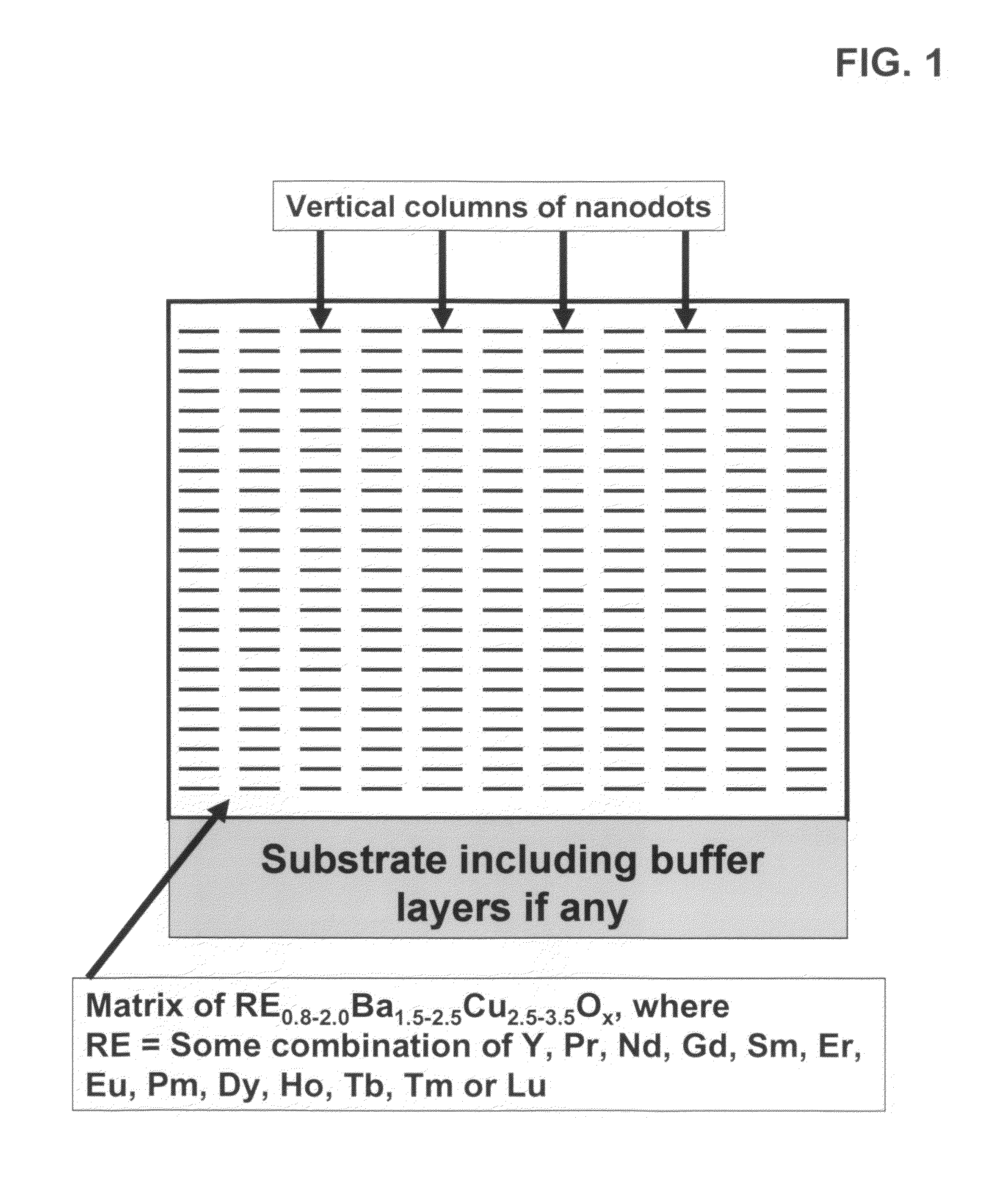
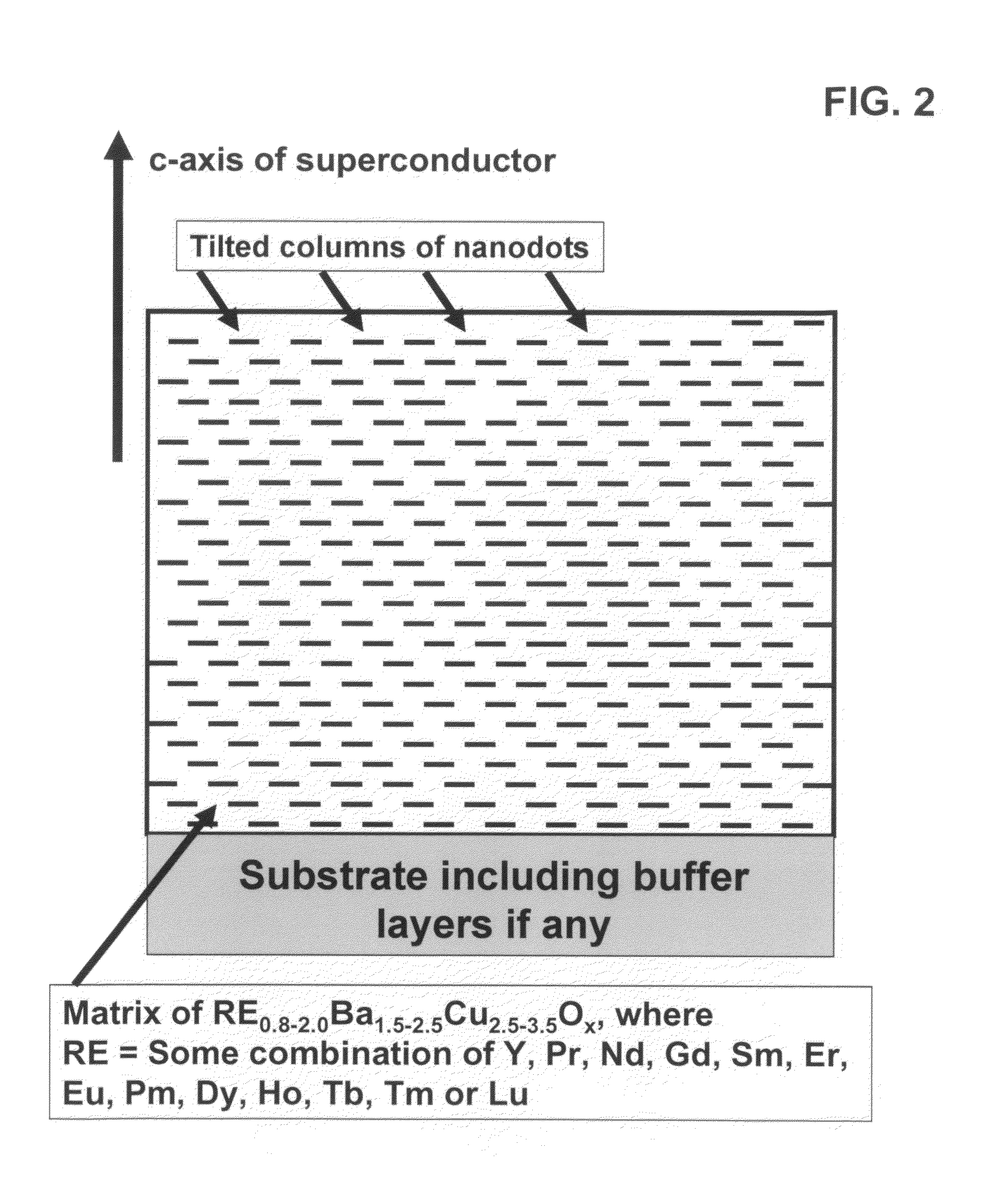
High performance devices enabled by epitaxial, preferentially oriented, nanodots and/or nanorods
ActiveUS20080176749A1Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionNanodotPhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate same with self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods of a single or multicomponent material within another single or multicomponent material for use in electrical, electronic, magnetic, electromagnetic, superconducting and electrooptical devices is disclosed. Self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods are ordered arrays wherein ordering occurs due to strain minimization during growth of the materials. A simple method to accomplish this when depositing in-situ films is also disclosed. Device applications of resulting materials are in areas of superconductivity, photovoltaics, ferroelectrics, magnetoresistance, high density storage, solid state lighting, non-volatile memory, photoluminescence, thermoelectrics and in quantum dot lasers.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
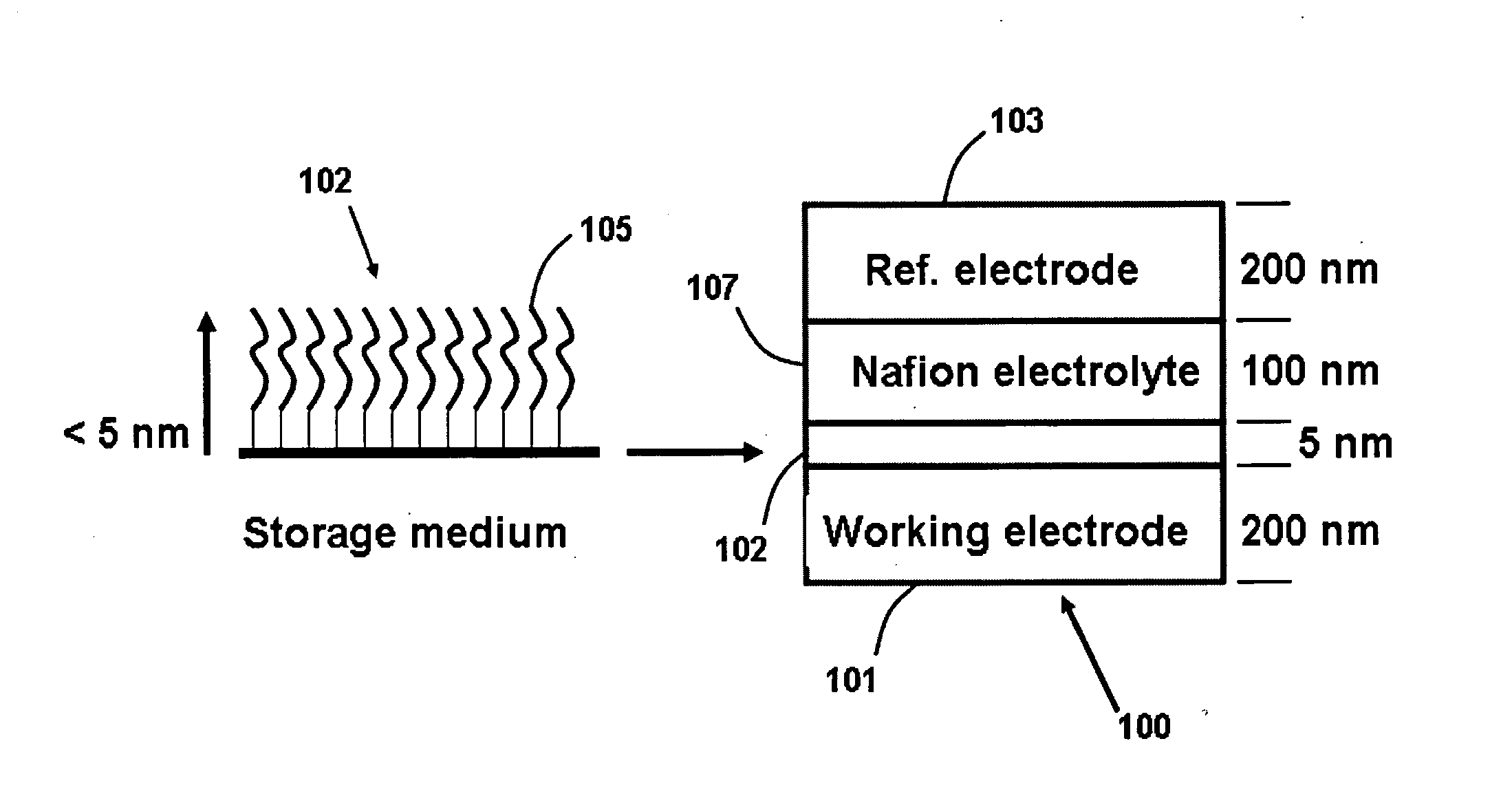
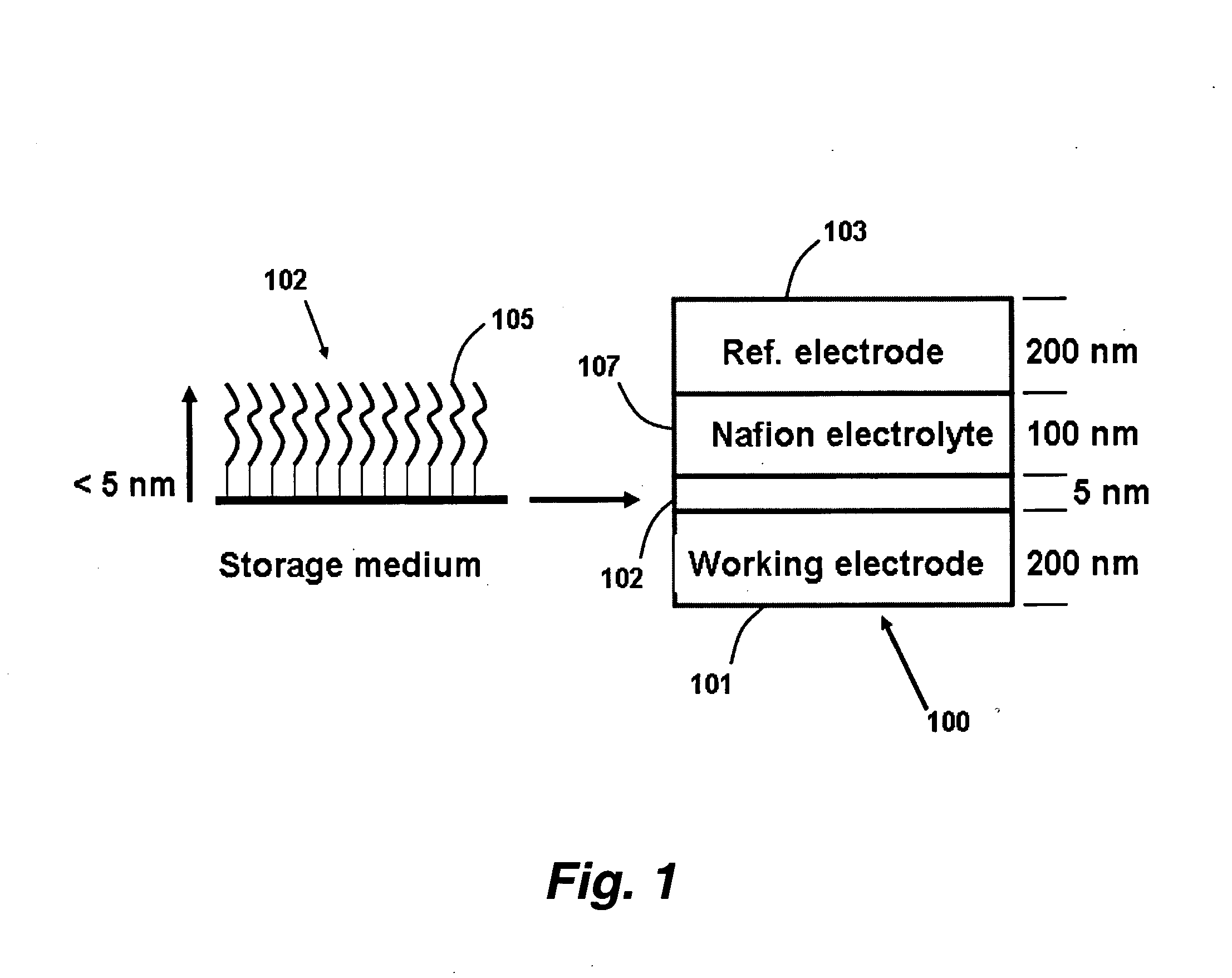
High density non-volatile memory device
InactiveUS20050041494A1Suitable mechanical propertyPrevent charge leakageNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesChemical synthesisFault tolerance
This invention provides novel high density memory devices that are electrically addressable permitting effective reading and writing, that provide a high memory density (e.g., 1015 bits / cm3), that provide a high degree of fault tolerance, and that are amenable to efficient chemical synthesis and chip fabrication. The devices are intrinsically latchable, defect tolerant, and support destructive or non-destructive read cycles. In a preferred embodiment, the device comprises a fixed electrode electrically coupled to a storage medium having a multiplicity of different and distinguishable oxidation states wherein data is stored in said oxidation states by the addition or withdrawal of one or more electrons from said storage medium via the electrically coupled electrode.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Embedded semiconductor memory devices and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080145985A1High density data storageEasy to useNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesGate dielectricSemiconductor
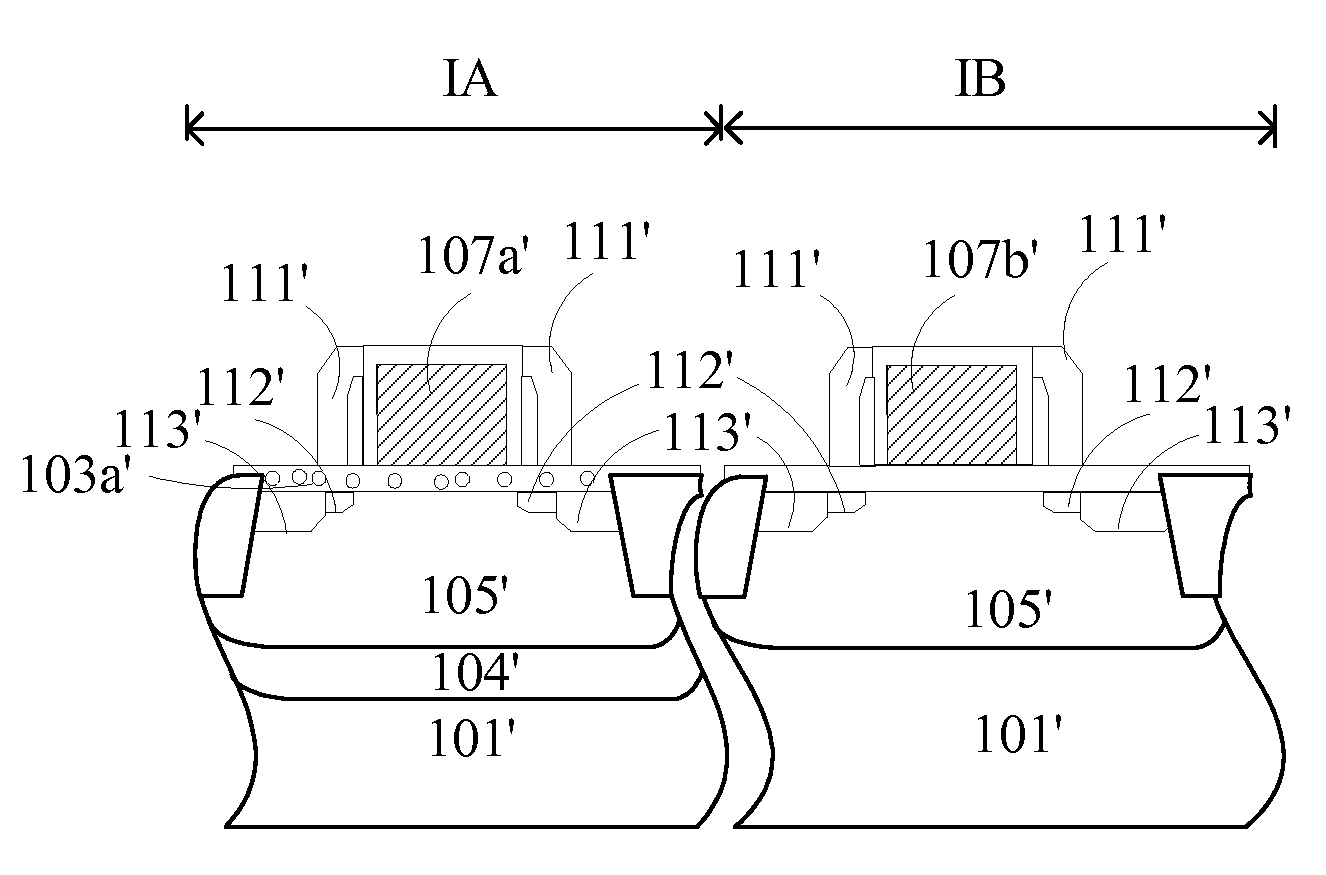
The invention discloses a method for fabricating an embedded semiconductor memory device, comprising: preparing a semiconductor substrate comprising a region IA and a region IB; forming gate dielectric layers and gate structures sequentially on the semiconductor substrate, with the gate dielectric layer in region IA being a charge trap region, and the gate dielectric layer in region IB being a non-charge trap region; forming source / drain extension regions in region IA and region IB of the semiconductor substrate; and forming source / drain regions in region IA and region IB of the semiconductor substrate. There is provided correspondingly an embedded semiconductor memory device. The invention also provides an embedded semiconductor memory device and a method for fabricating the same. A two-bit storage operation can be enabled for the embedded semiconductor memory device according to the invention so as to achieve high-density storage. Furthermore, the process for forming a logic circuit can be compatible with that for forming a memory device circuit according to the invention.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
Methods of programming multilevel cell nonvolatile memory
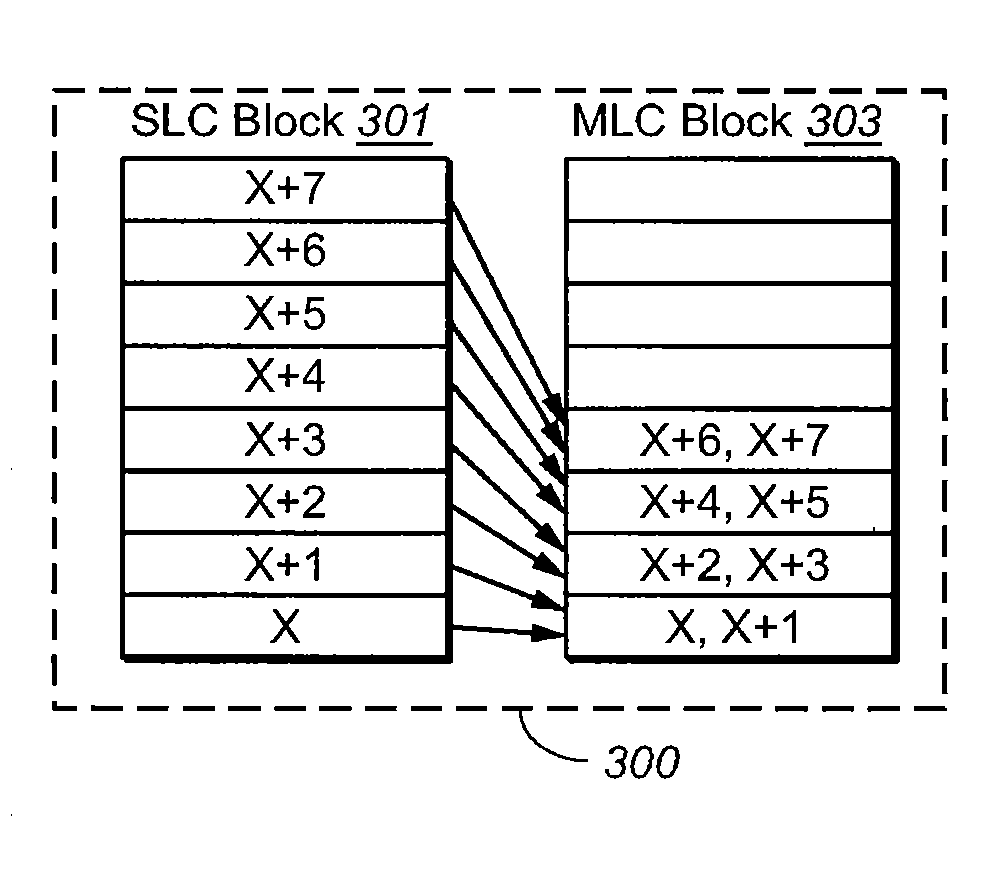
A memory system includes a first block in which data is stored with a low density and a second block in which data is stored with a high density. When data is received it is written to the first block, and in parallel some of the data is written to the second block, so that the second block is partially programmed. The second block is later fully programmed by copying additional data from the first block.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Vertical NAND flash memory device
ActiveUS20050269626A1Promotes its utilizationHigh densityTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densityParallel computing
Memory devices, arrays, and strings are described that facilitate the use of vertical floating gate memory cells in NAND architecture memory strings, arrays, and devices. NAND Flash memory strings, arrays, and devices in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, include vertical Flash memory cells to form NAND architecture memory cell strings and memory arrays. These vertical memory cell NAND architecture strings allow for an improved high density memory devices or arrays that can take advantage of the feature sizes semiconductor fabrication processes are generally capable of and still allow for appropriate device sizing for operational considerations.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com