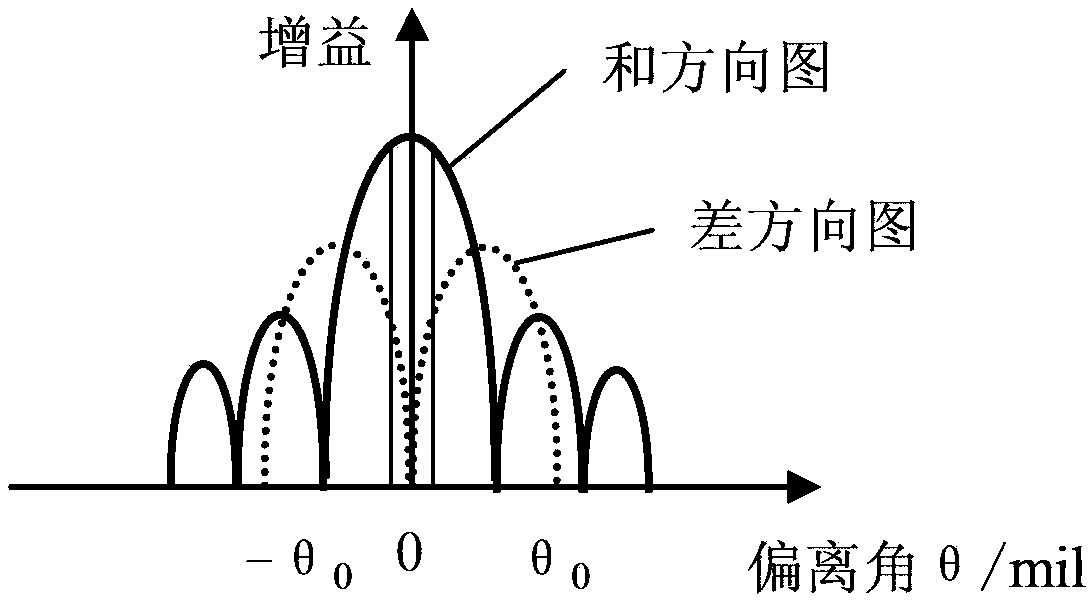
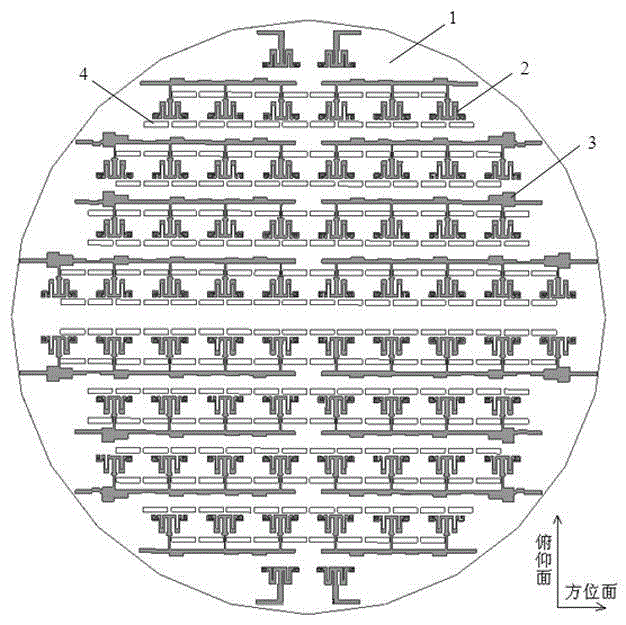
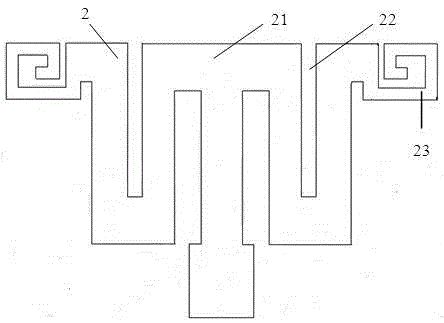
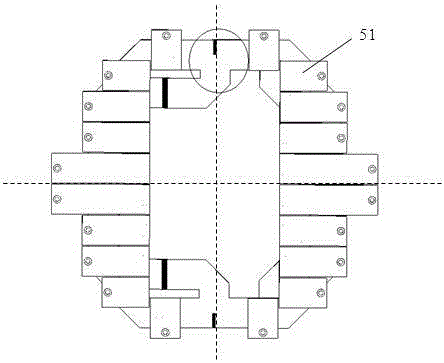
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Monopulse antennas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
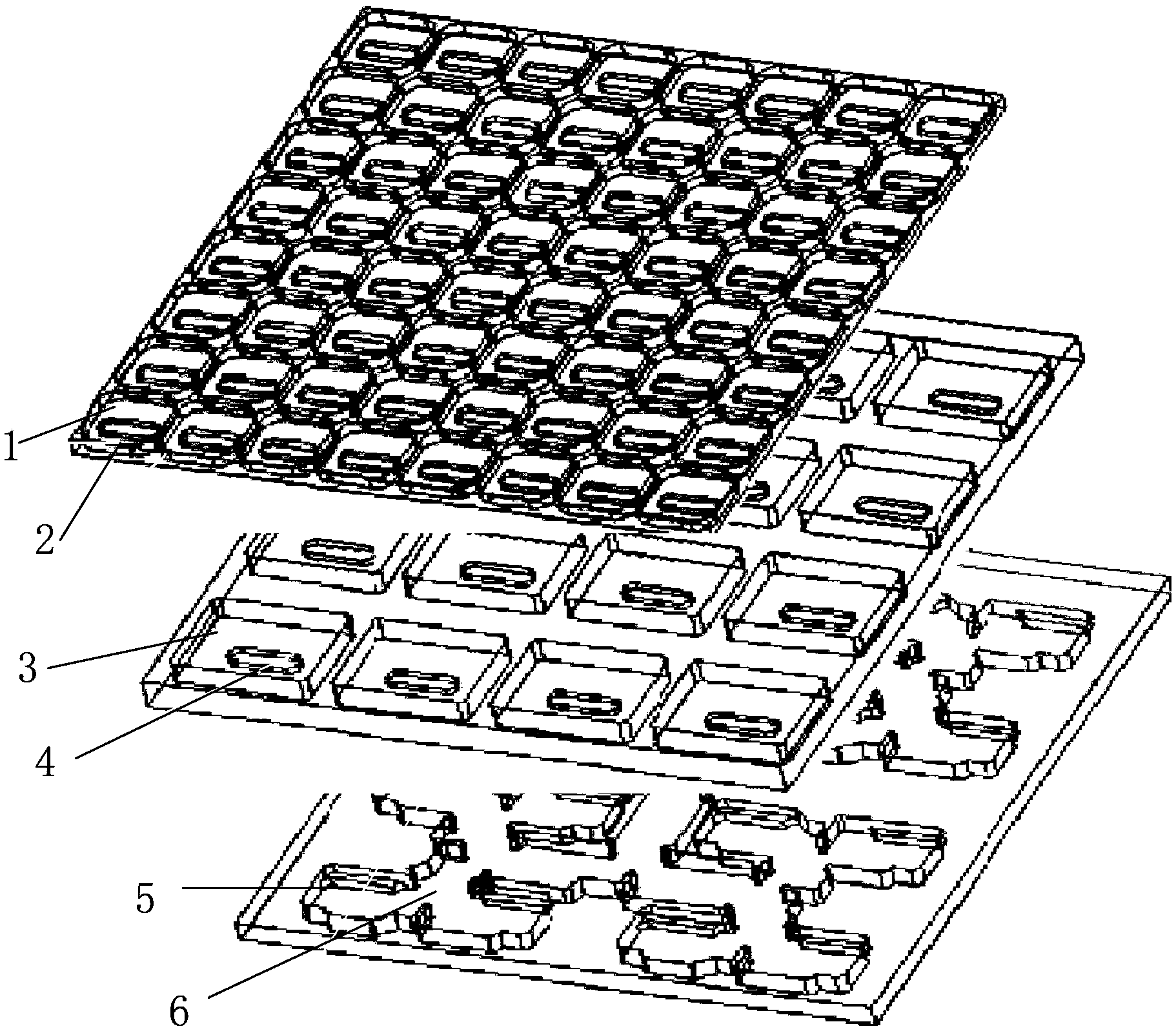
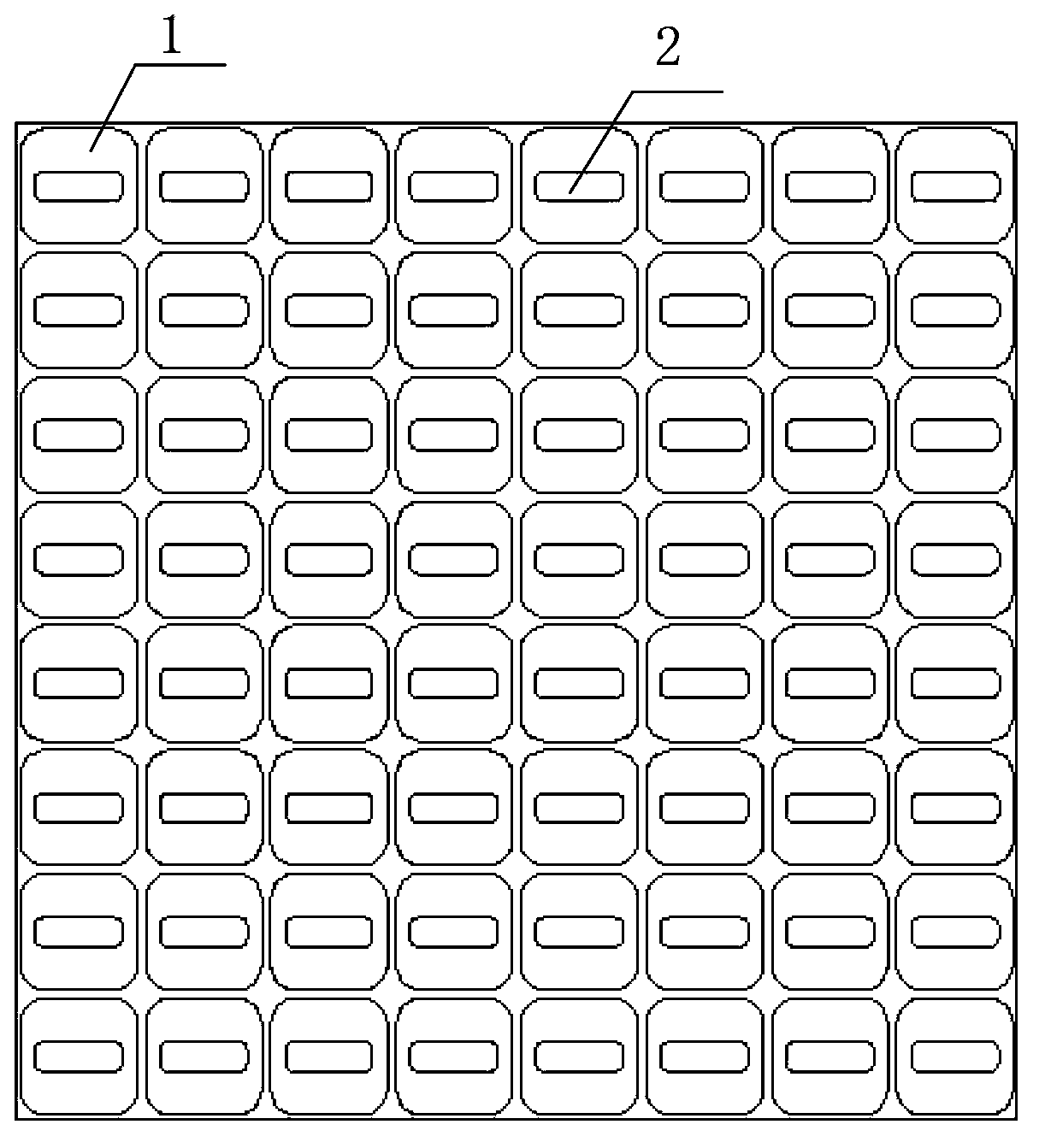
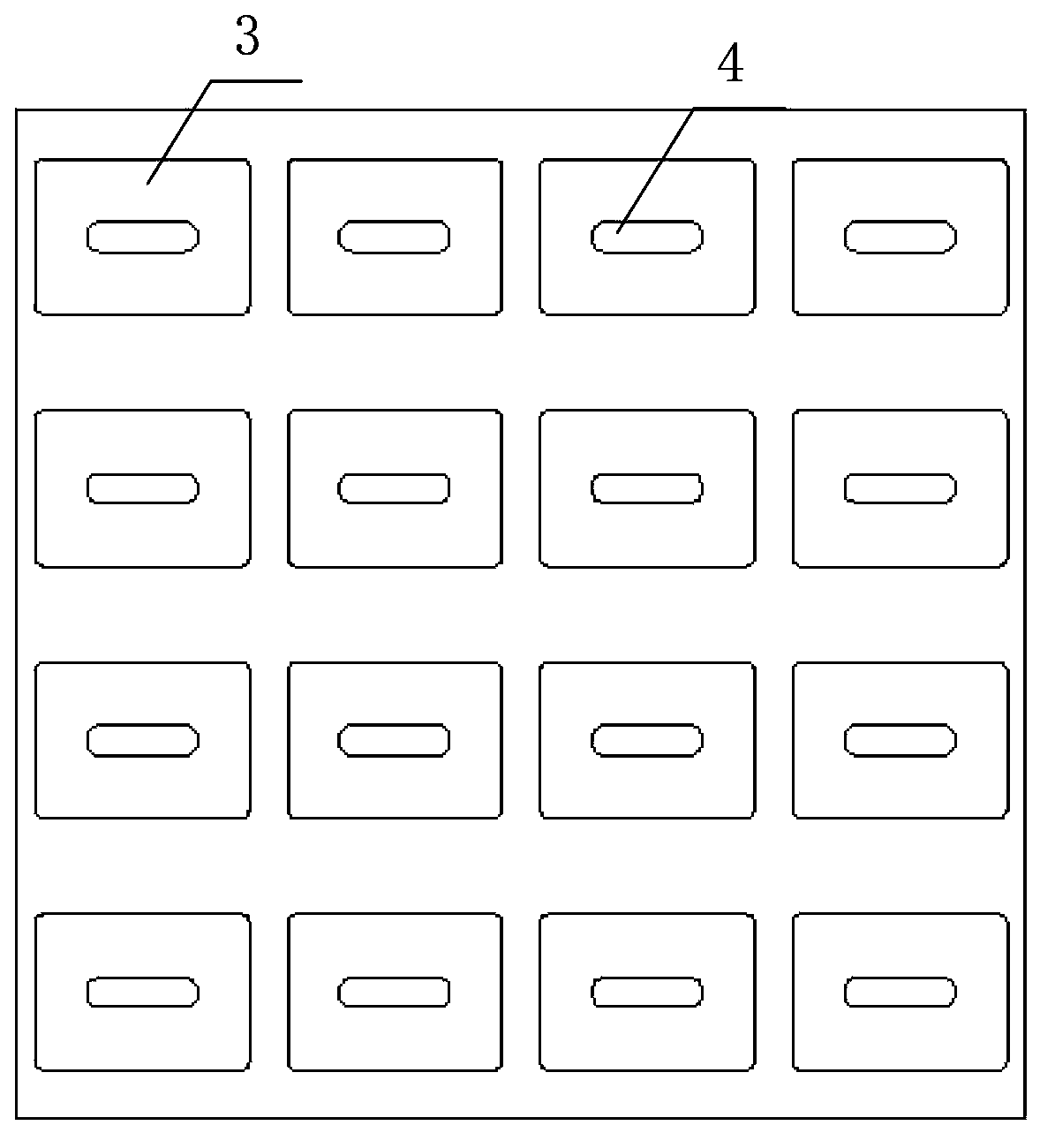
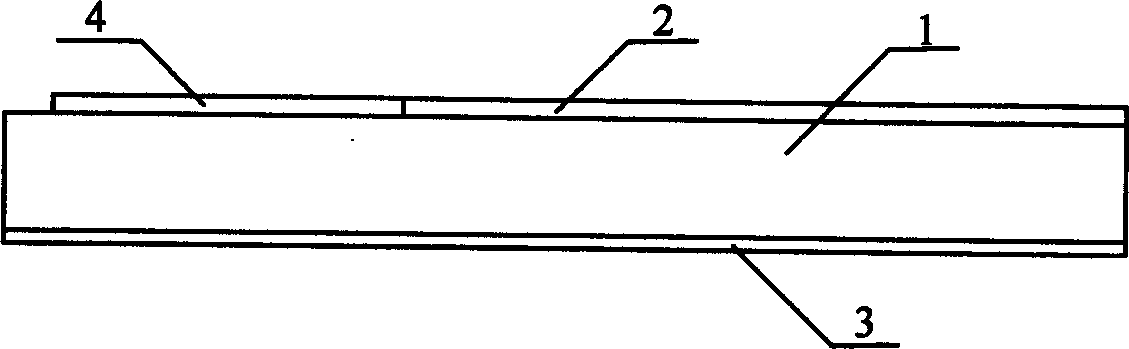
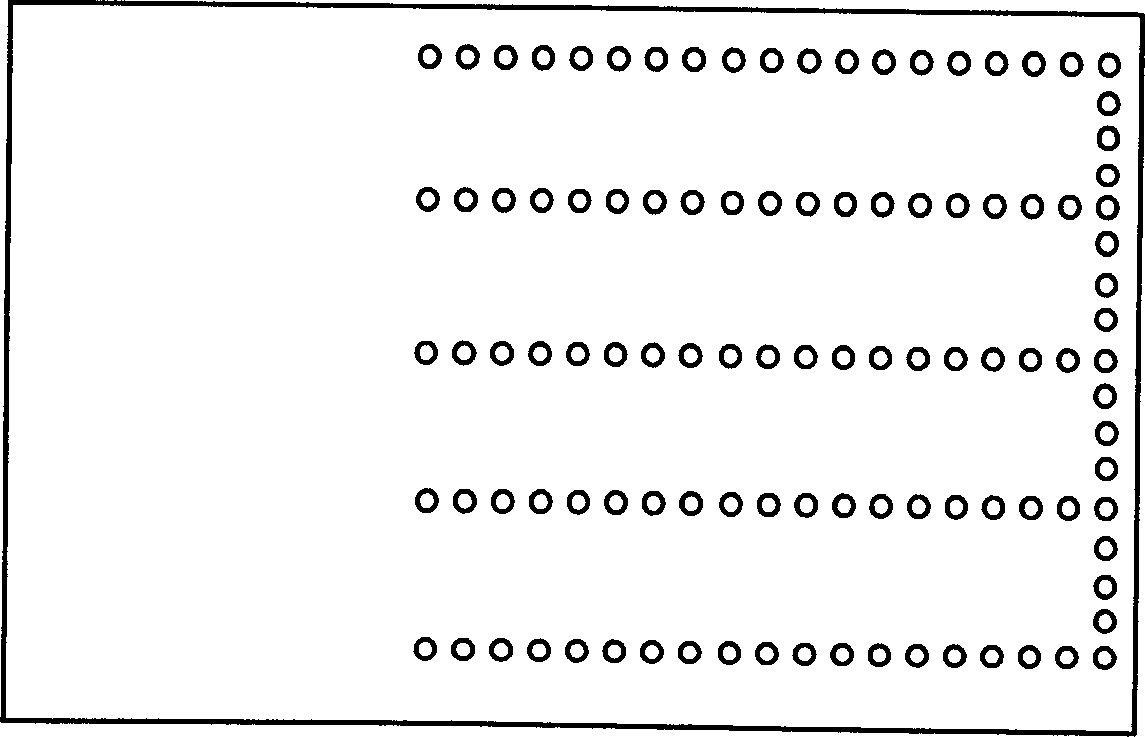
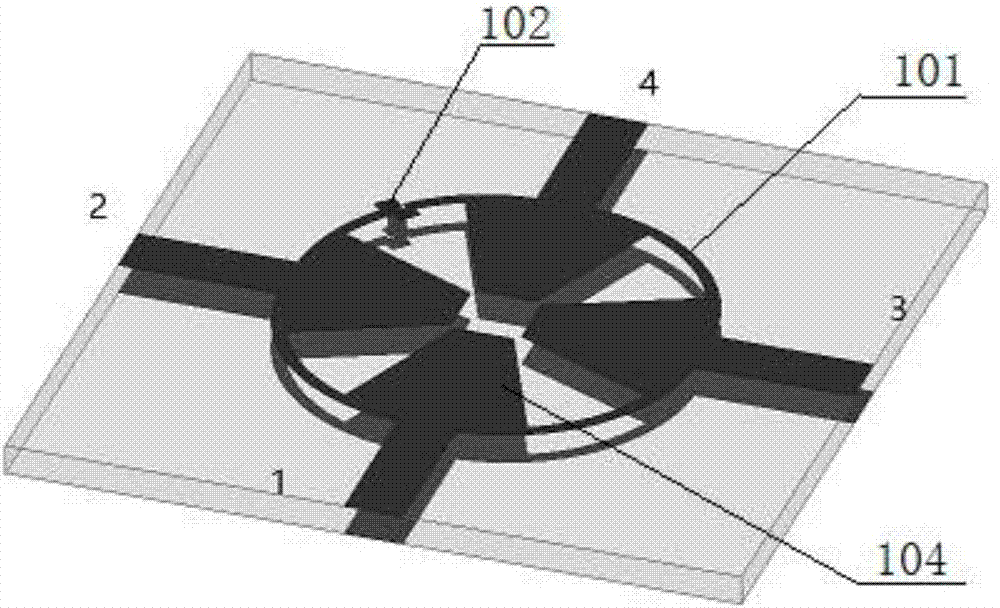
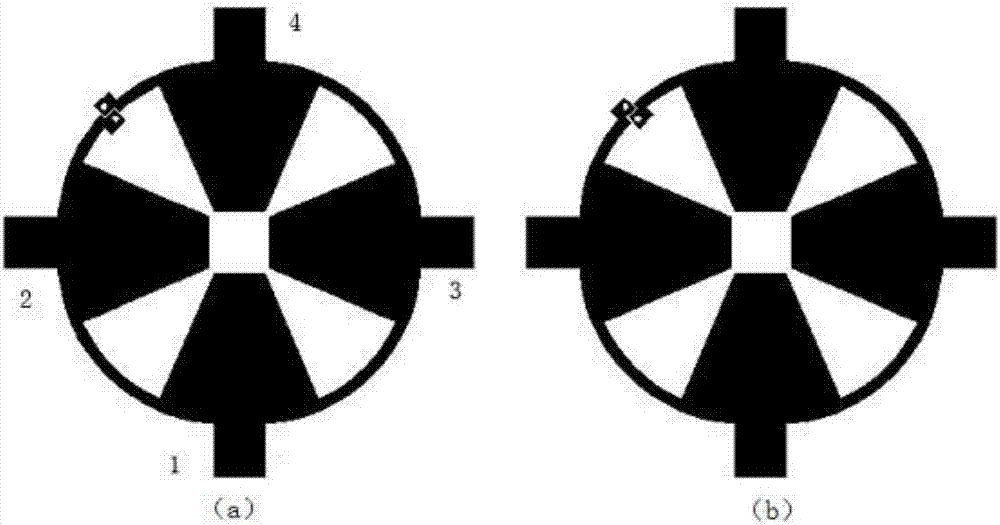
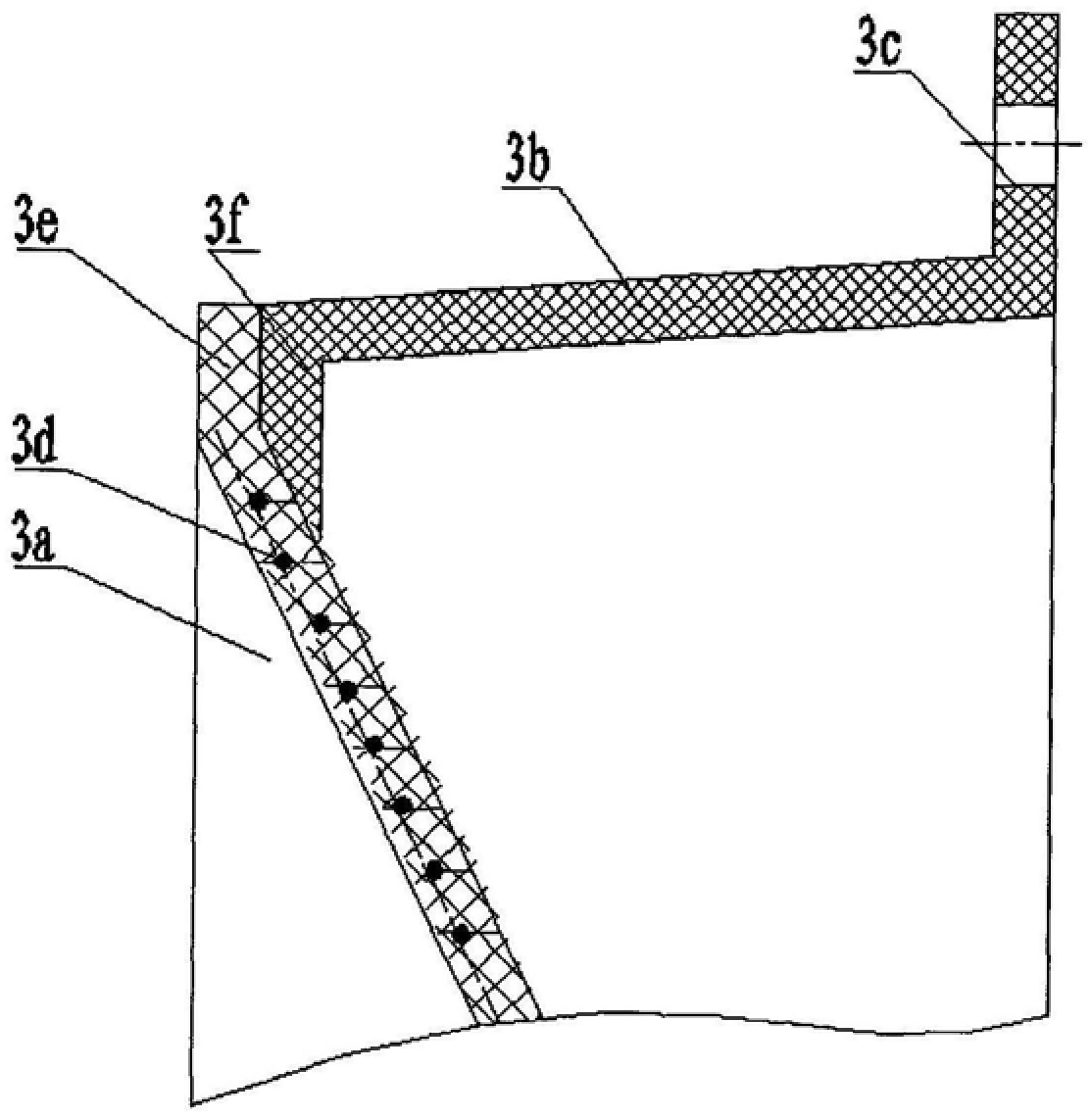
Wide band low profile flat plate slot array antenna
ActiveCN103414030AHigh formal efficiencyOvercome the disadvantage of narrow bandwidthAntenna arraysSlot antennasWide bandWaveguide
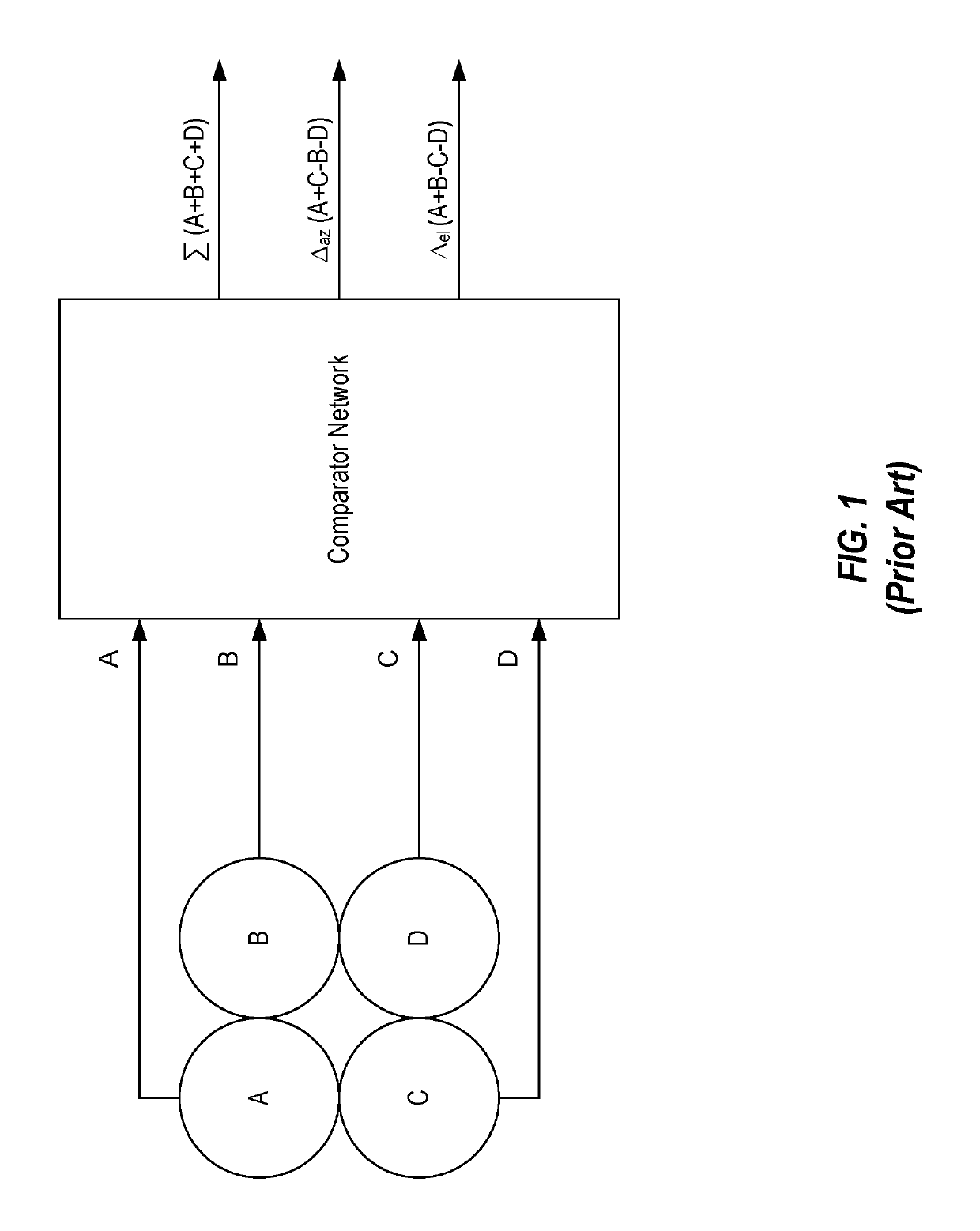
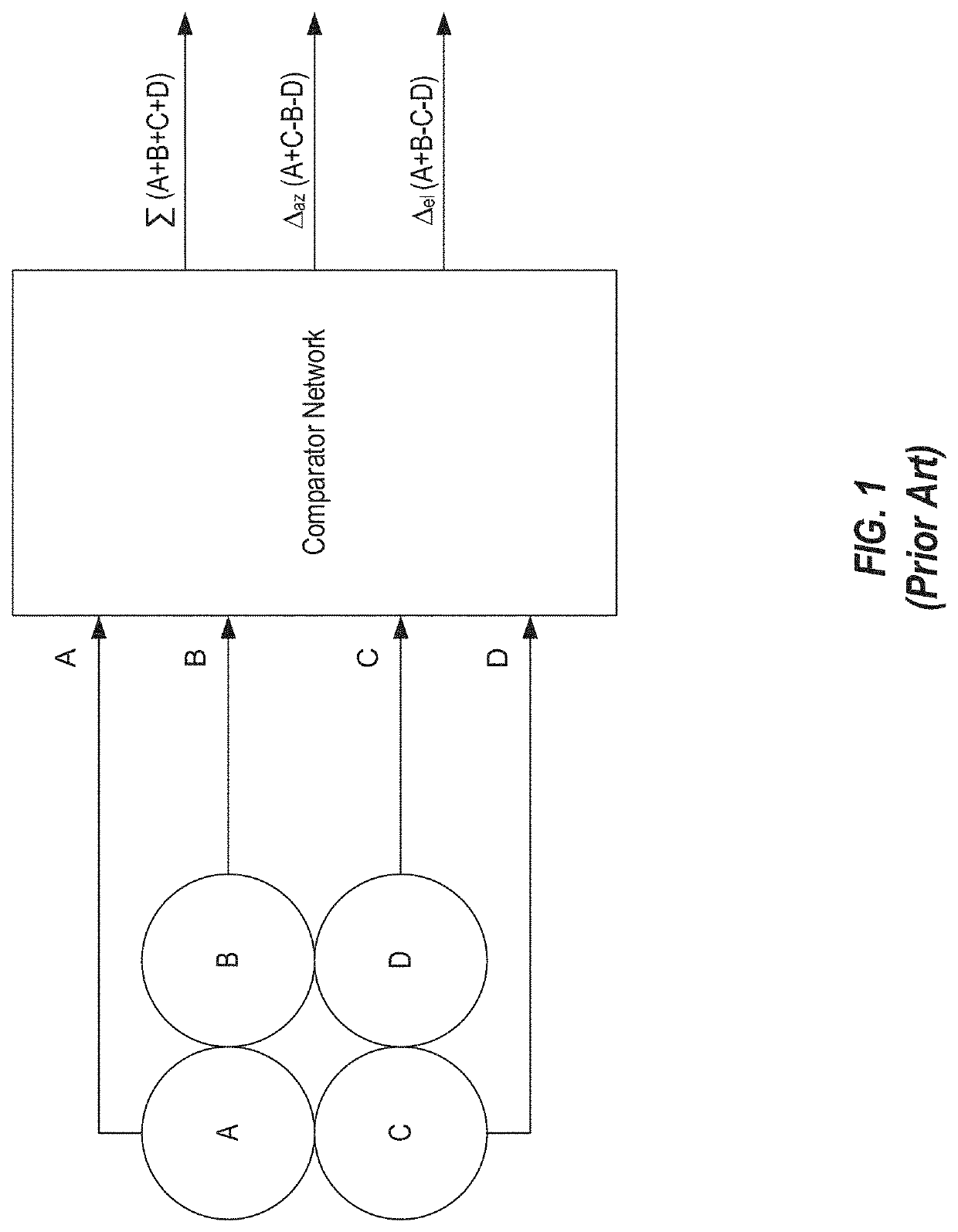
The invention discloses a wide band low profile flat plate slot array antenna which comprises wide band low profile flat plate slot antenna units and waveguide feed networks. Each wide band low profile flat plate slot antenna unit comprises a radiating square cavity, radiating slots, a stimulating waveguide cavity, a stimulating slot and a feed waveguide, wherein each waveguide feed network is composed of a plurality of equal-power-dividing and unequal-power-dividing waveguide H-T power dividers and connected with each power feeding waveguide, and the waveguide feed networks and the power feed waveguides are located in the same layer. Signals enter the feed waveguides through the waveguide feed networks and are transmitted to the stimulating waveguide cavities through the stimulating slots, the radiating slots enable the signals to be coupled out from the stimulating waveguide cavities, and then the signals are radiated to the free space through the radiating square cavities. The wide band low profile flat plate slot array antenna has the advantages of being wide in band, high in efficiency, low in profile and easy to machine, and is capable of being expanded to be a single pulse antenna after being combined with a comparator.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF TELEMETRY +1
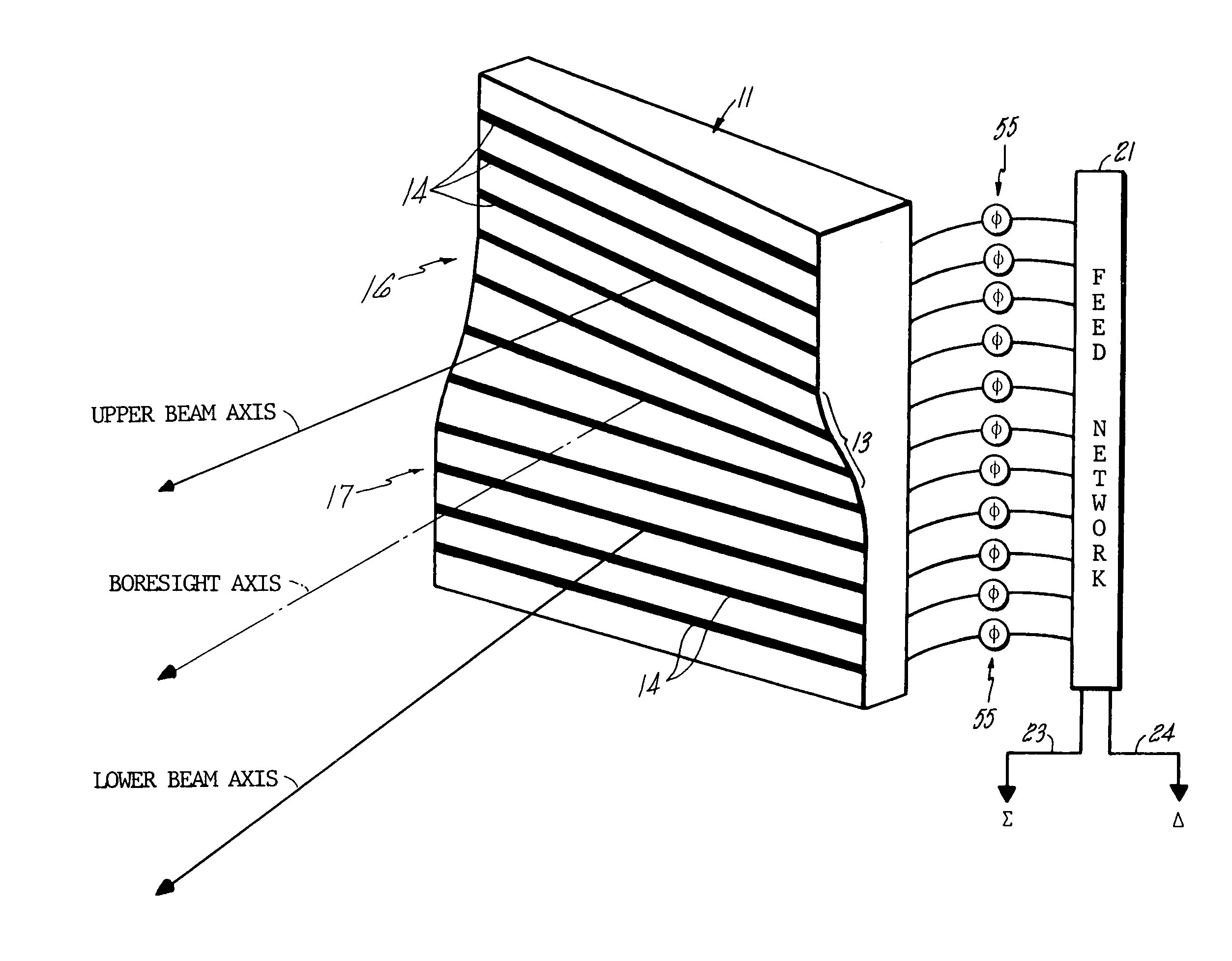
Warped plane phased array monopulse radar antenna
InactiveUS7038620B1Eliminate needAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElevation angleTarget analysis
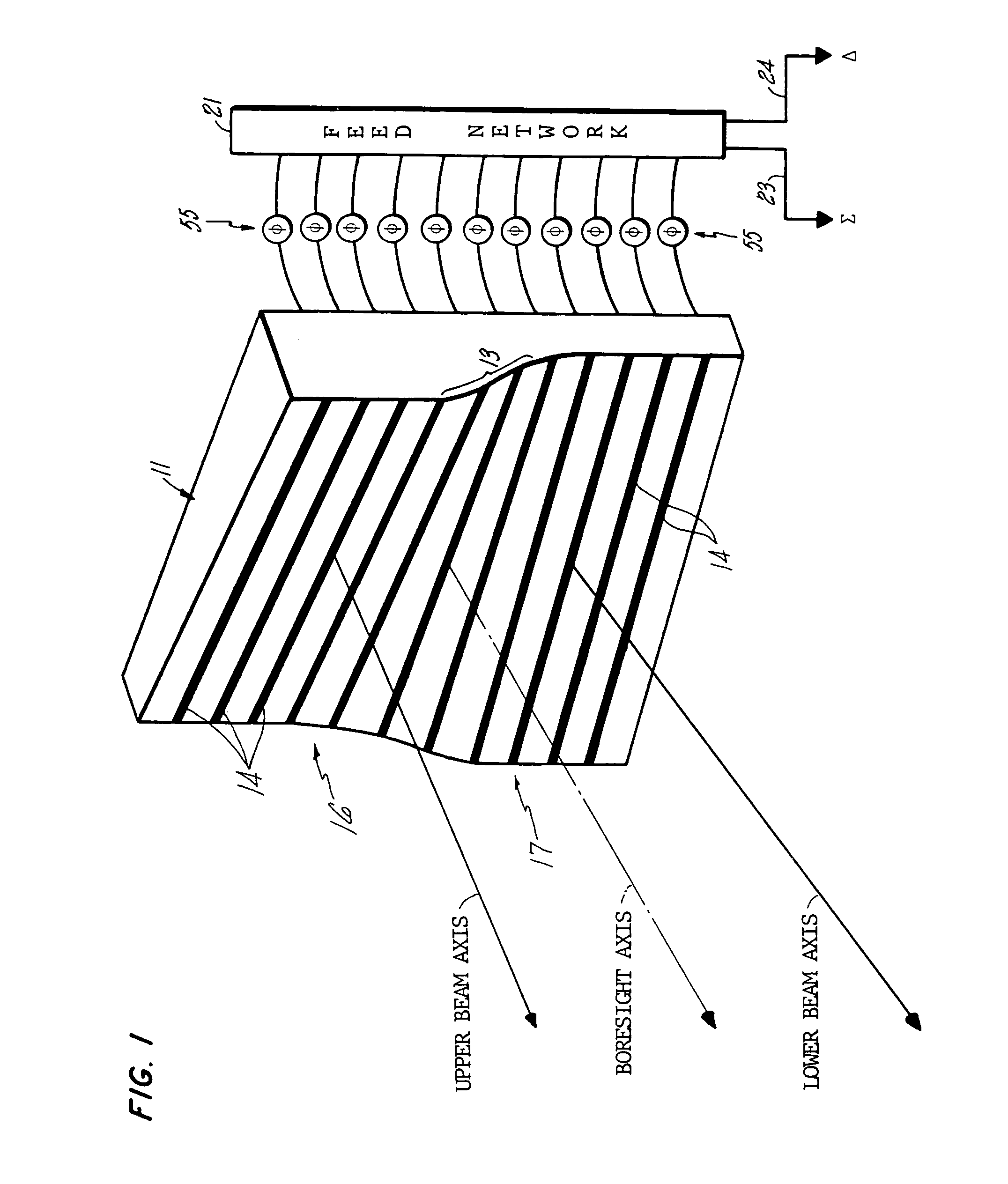
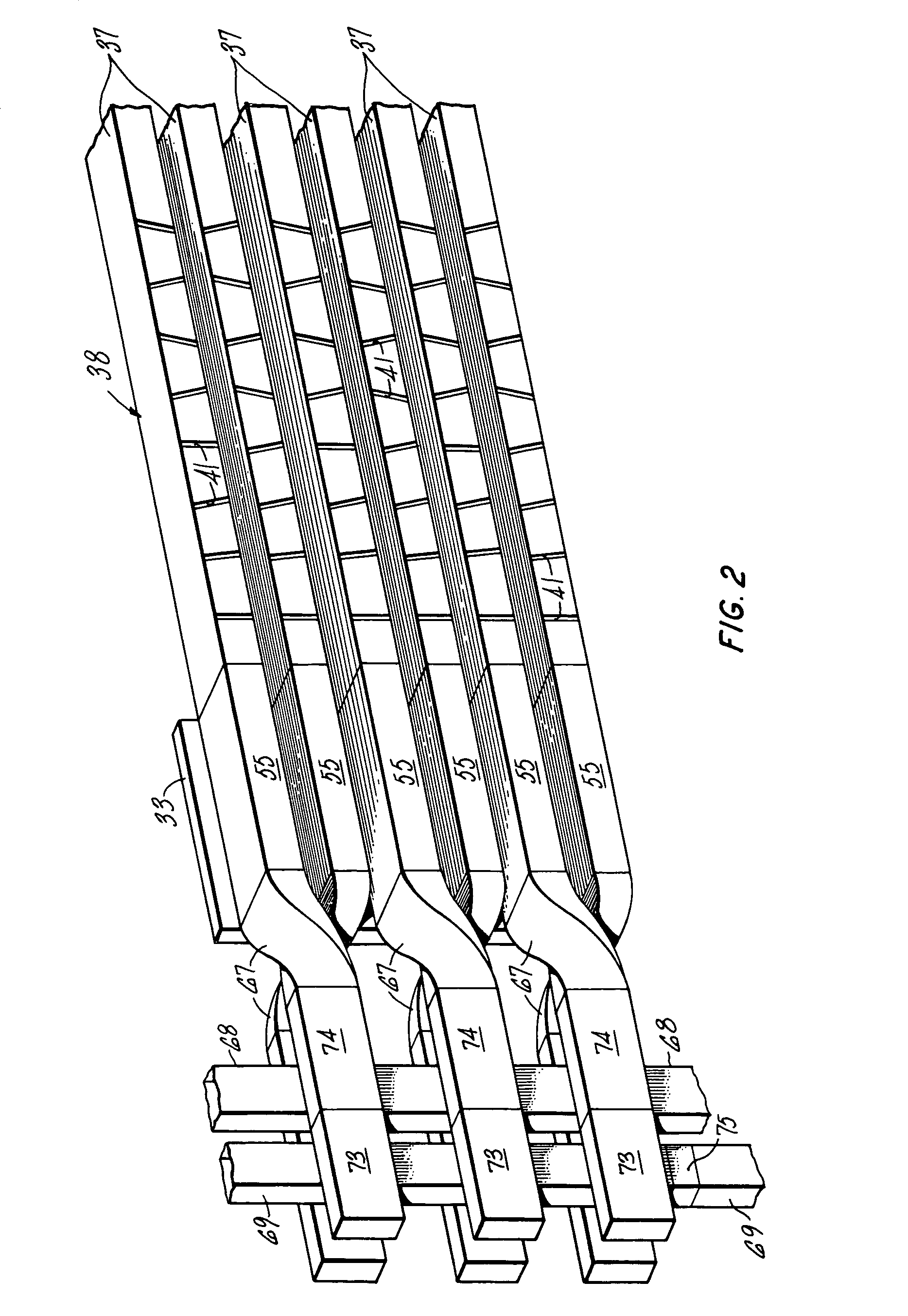
A phased array, phase-amplitude monopulse antenna arrangement for ground, shipboard or airborne radar systems. The phased array antenna is systematically warped and projects partially overlapping, separate beams from upper and lower regions of the array. A single set of phase-shifters is employed with a simplified feed structure to permit development of both azimuthal and elevation angle error signals in signal processing circuitry for target analysis.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
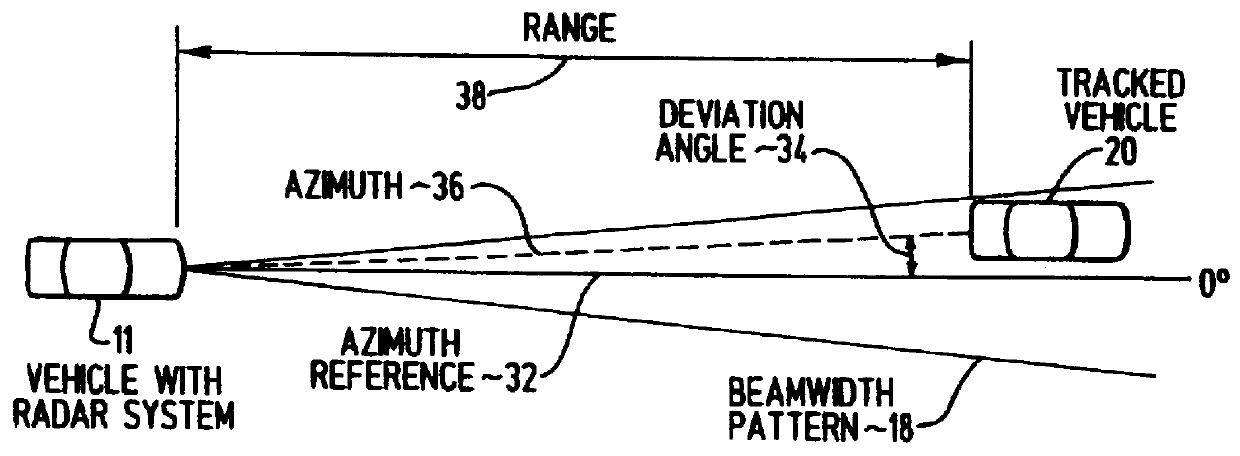
Monopulse azimuth radar system for automotive vehicle tracking
InactiveUSRE36819E1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionVehicle sub-unit featuresDigital signal processingRadar systems
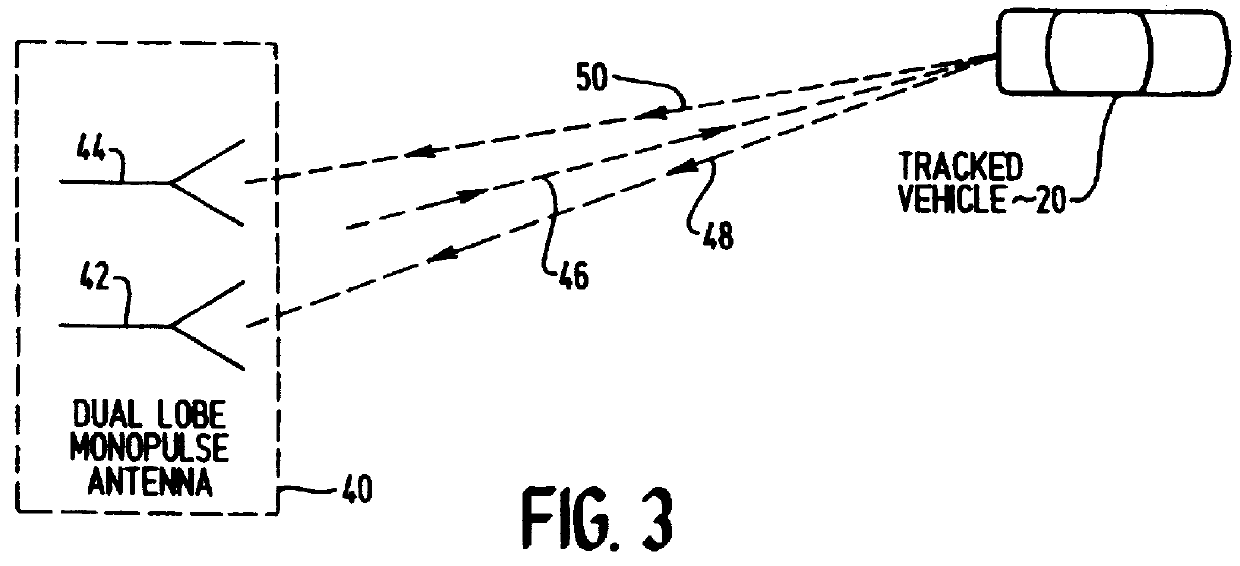
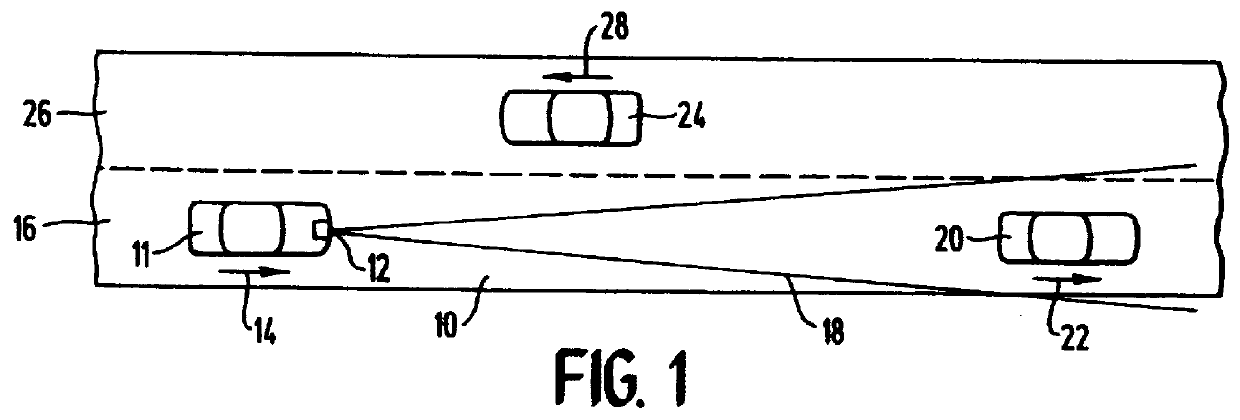
A monopulse vehicular radar system for tracking a target about an automotive vehicle senses a transmitted signal reflected back from the target and received at two different locations, determines the sum and the difference of the reflected signals sensed at the two locations, and compares the sum and difference to determine the deviation of the target from a reference azimuth. A source frequency provided by a Gunn diode is applied to and transmitted by a two-lobe monopulse antenna. The antenna lobes detect the reflected signals from the target by sensing them at the two different lobes. A hybrid junction provides sum and difference signals to mixers which homodyne the signals to produce sum and difference Doppler frequency signals using the source frequency. The Doppler frequency signals are amplified and then compared to determine the deviation of the target from the reference azimuth. The comparison process can be done digitally by converting the amplified frequency signals to digital signals which are then processed in a digital signal processor, or the comparison may be done in analog fashion using a phase / quotient detector. The range or distance of the target is determined by shifting the source frequency between two frequencies during transmission and frequency shifting the sum and difference Doppler frequency signals in similar fashion following reception by the antenna.
Owner:BENDIX COMML VEHICLE SYST LLC
Monopulse antenna angle simulation tracking method
ActiveCN102722184ASelf Tracking NormalSelf-tracking stationaryControl using feedbackReduced modelIntermediate frequency
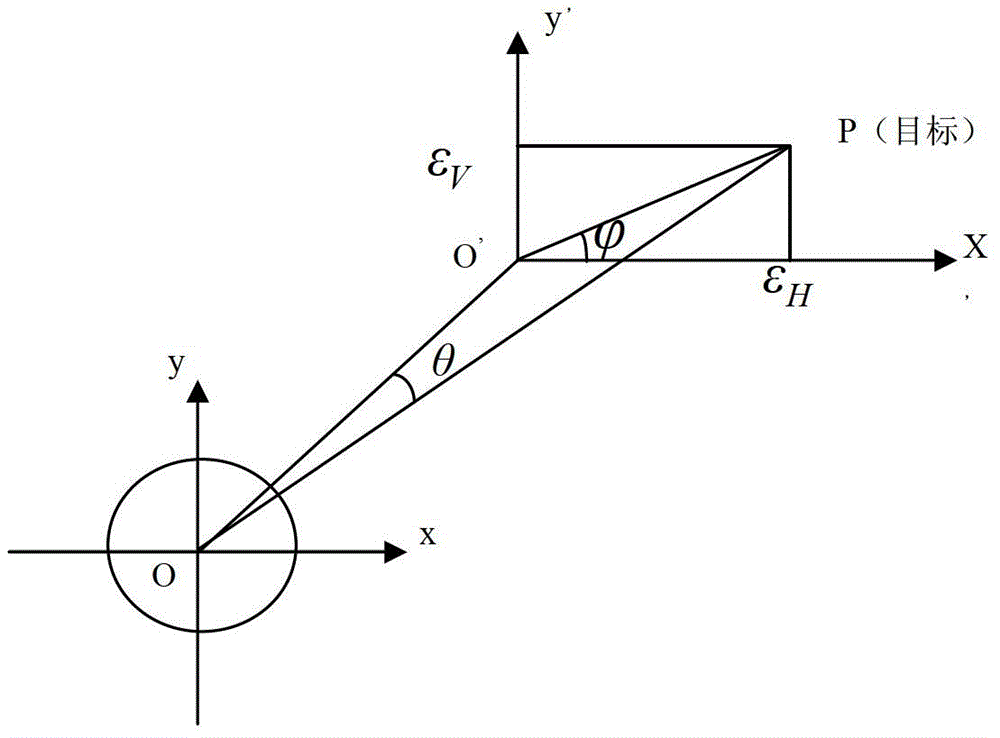
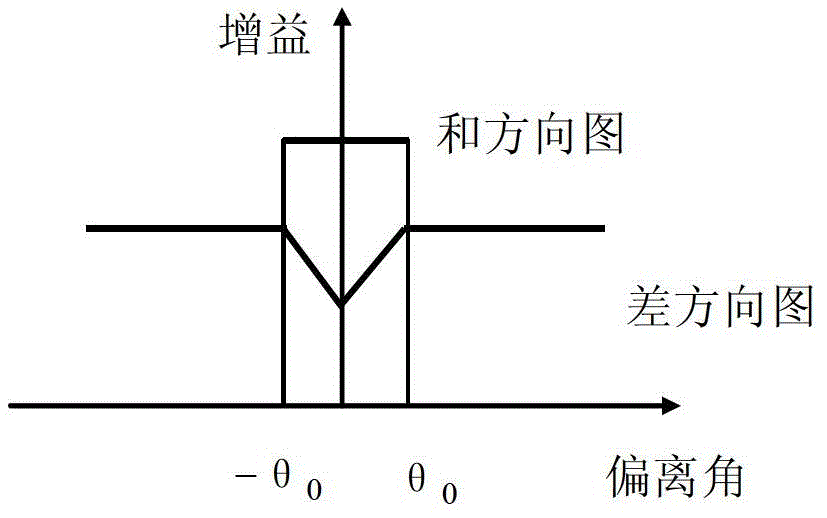
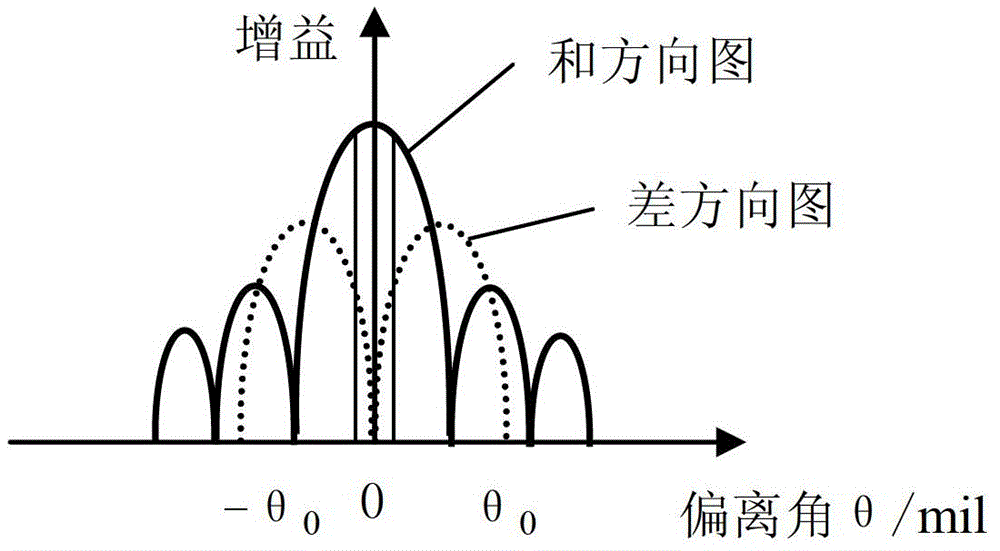
The invention provides a monopulse antenna angle simulation tracking method, which aims at providing an environment for inspecting and simulating equipment tracking performance at any time to a shooting range monitor system. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: establishing an XOY plane measurement coordinate system by taking the center of three axes of an antenna as an original point; constructing a simulation circuit according to an antenna pattern simplified model; drawing four calibration curves of a sum and different signal magnitude difference-deviation angle relationship, sum and difference signal amplitude different-error voltage relationship, deviation angle-error voltage relationship and deviation angle-AGC (automatic gain control) voltage relationship on each angle beyond the main beam of the antenna, and establishing a data mapping table; acquiring the controlled variable of an angle deviation control circuit and simulating to generate a radio frequency tracking signal according to a method of checking a signal amplitude mapping table; and demodulating and extracting an angle error signal by receiving link amplification and down-conversion in an intermediate frequency tracking receiver; and feeding position and pitch angle error voltage to an antenna control unit to complete angle closed-ring tracking.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
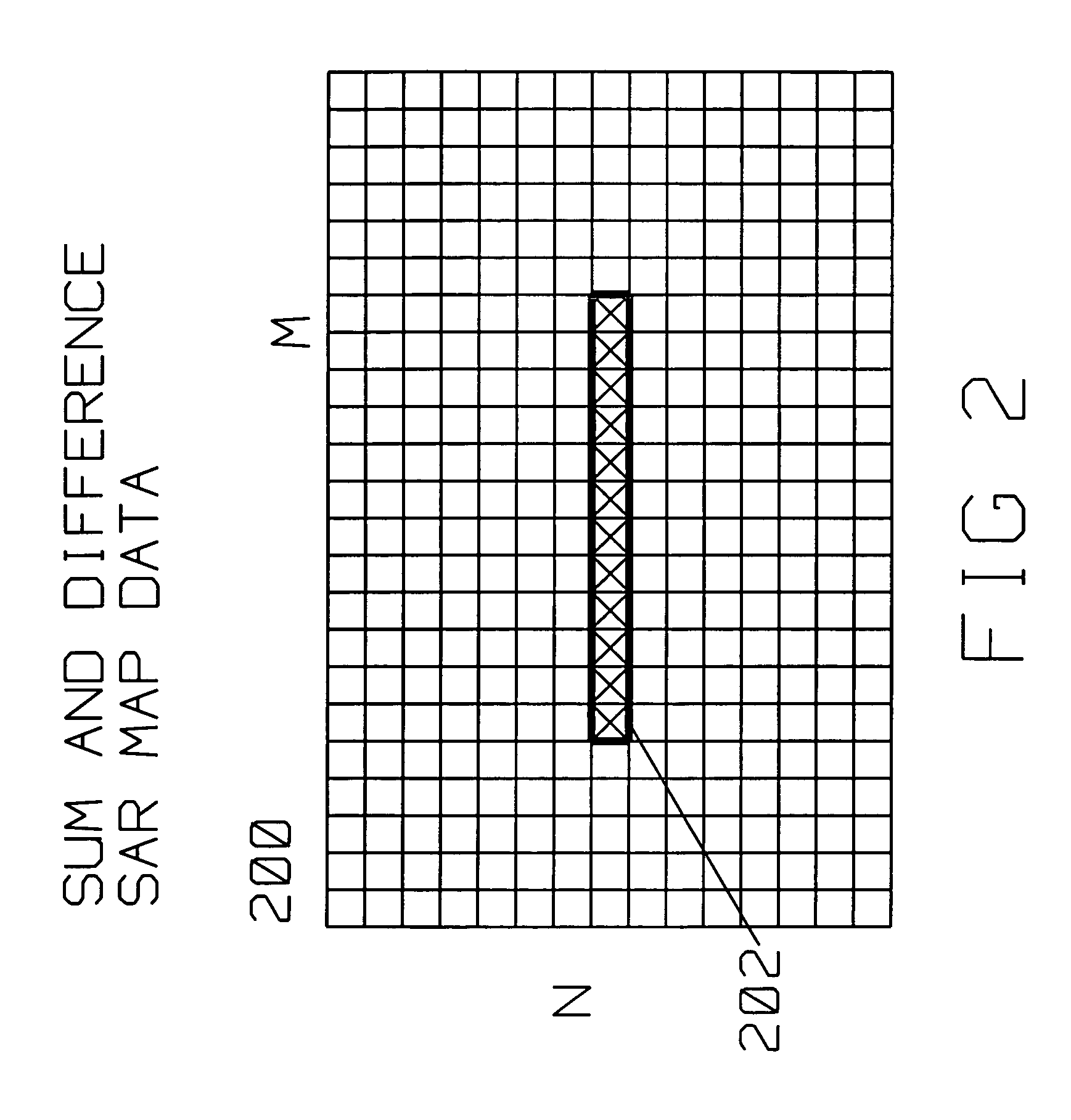
Inverse precision velocity update for monopulse calibration
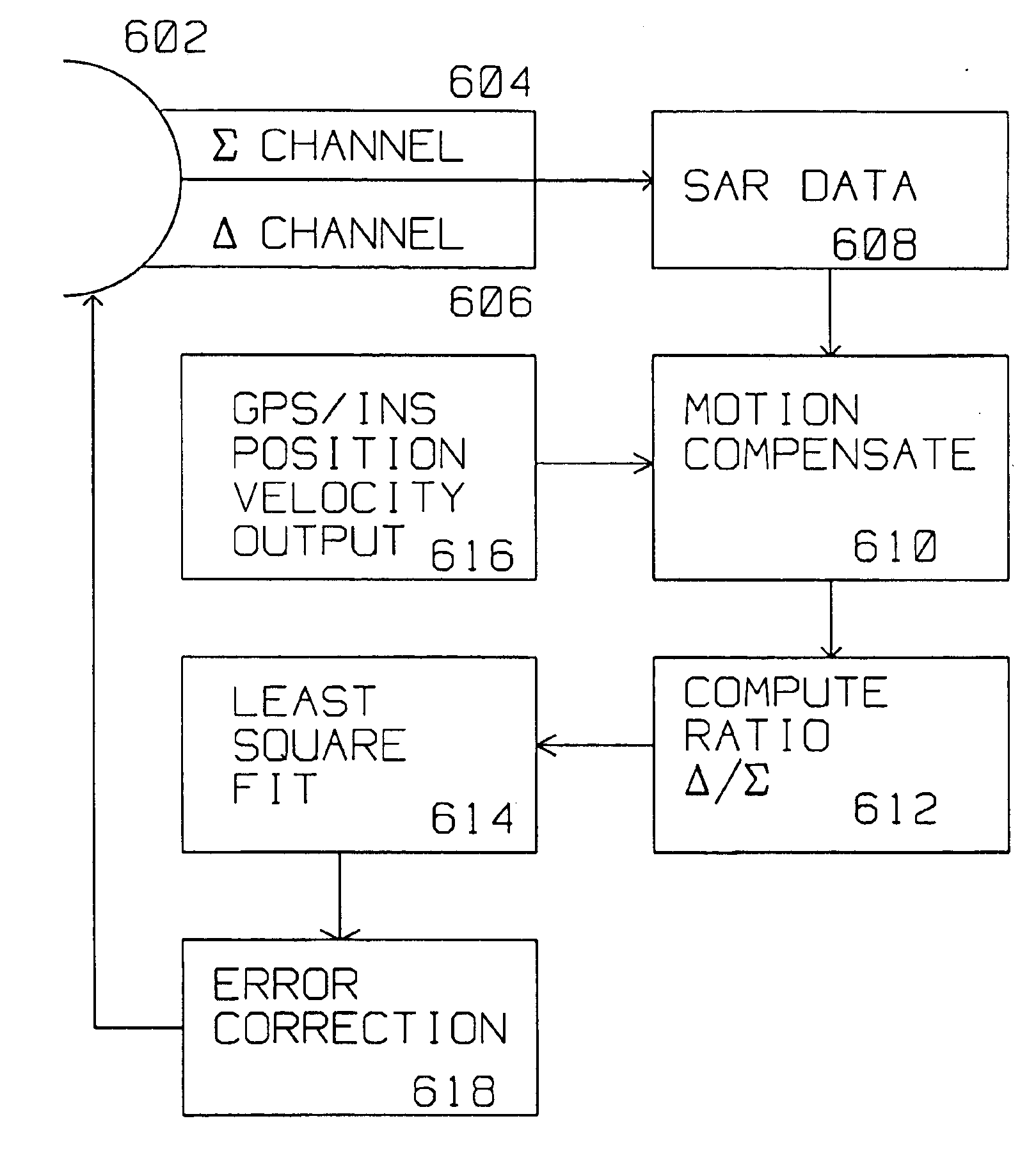
A radar system derives a correction for an actual boresight (311) of a radar monopulse antenna mounted on a moving platform from Σ data and Δ data generated with respect to an a priori known, calibrated boresight (309). The monopulse antenna (602) is coupled to a ground position measuring system (616) while acquiring data. The radar receiver acquires a Σ and Δ synthetic aperture map of the same radar scattering location with respect to the calibrated boresight. Σ SAR data and the Δ SAR data are motion compensated using the position and velocity supplied by the ground positioning system. A computer forms a ratio of the aligned Δ pixels to the aligned Σ pixels for each of a plurality of aligned Σ pixels located near the calibrated boresight. The correction for the location of the actual boresight of the monopulse antenna is computed by an analysis of the ratio of aligned Σ pixels and corresponding aligned Δ pixels over the radar scattering location. Typically, a least square fit analysis is used to plot the Δ / Σ ratio, and ascertain where the zero crossing of the monopulse angle=0 line is found thereby identifying the position of the actual boresight, and the correction from the a priori, calibrated boresight.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Electronically steered, dual-polarized, dual-plane, monopulse antenna feed
InactiveUS20100052987A1Reduce weight and costSmall sizePolarised antenna unit combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna feedElectron
A method and apparatus for electronically steering a RADAR beam across an array of feed horns by moving the phase center of the beam to different origination points on the array—each origination point being the phase center of a feed horn pair. Variations include polarized beams, polarized feed horns, dual-beam systems, dual direction steering, diagonal steering, and cross-polarized wire grids to control beamwidth.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
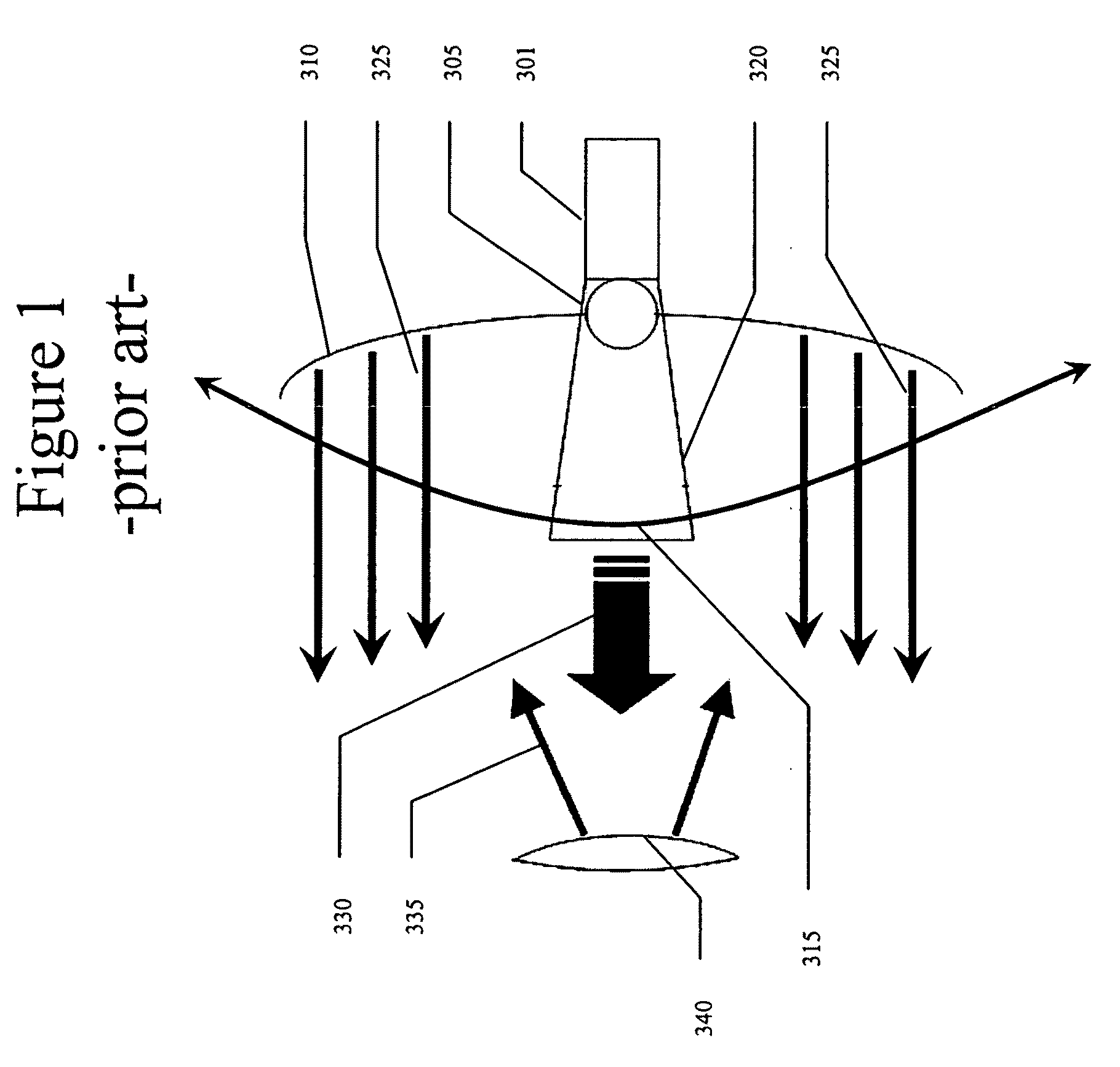
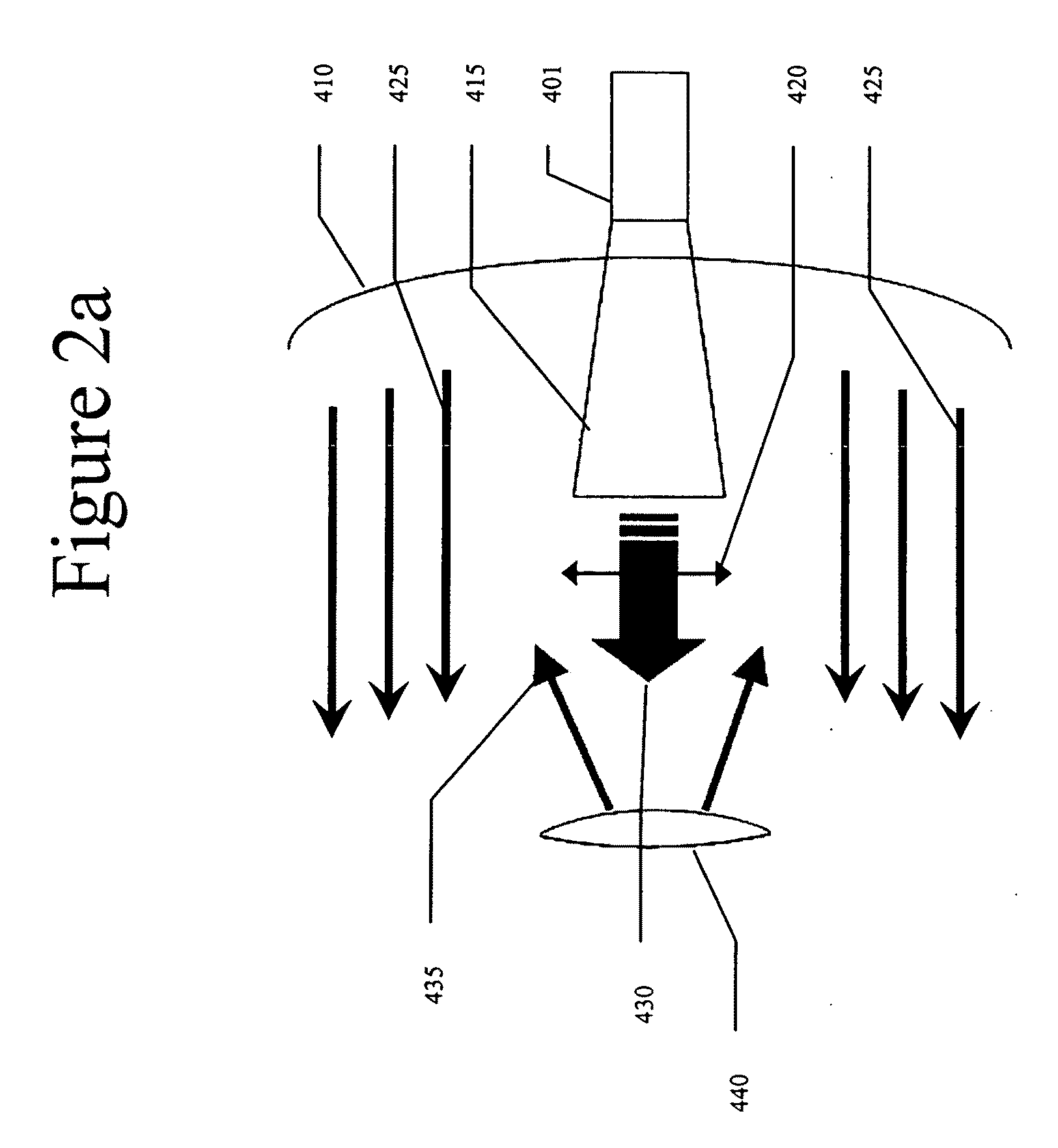
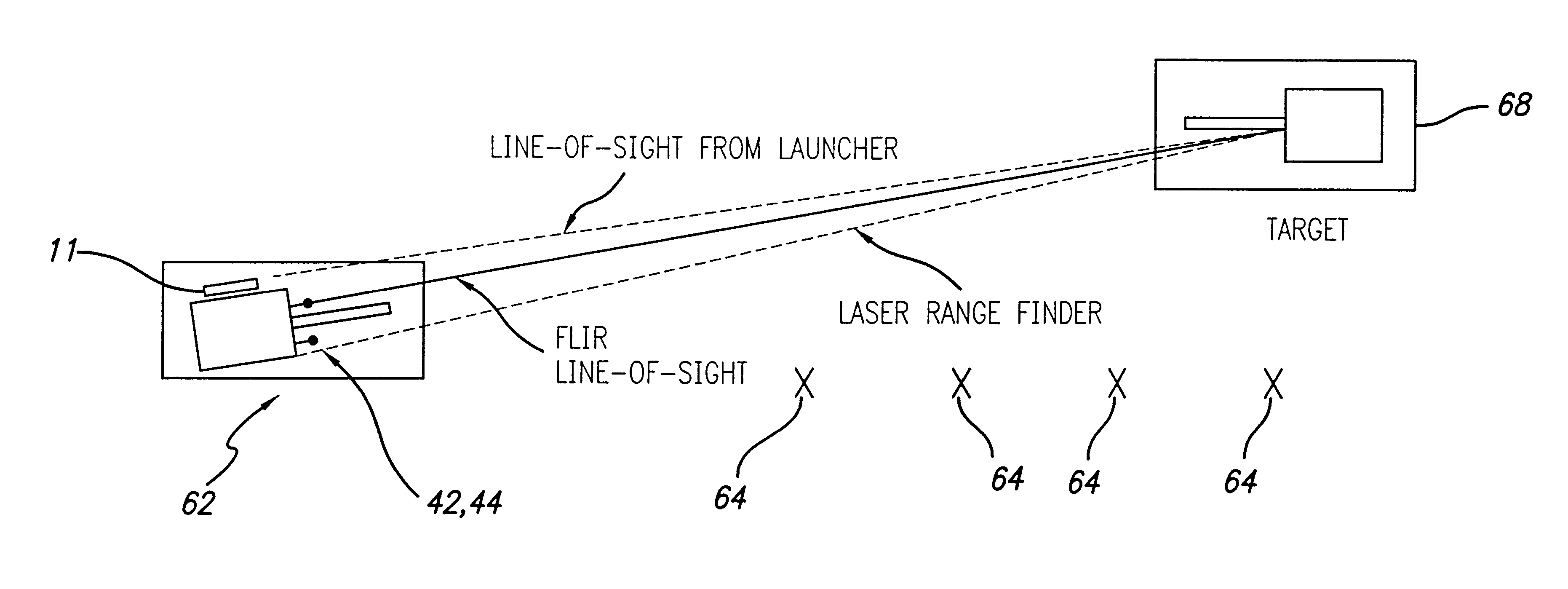
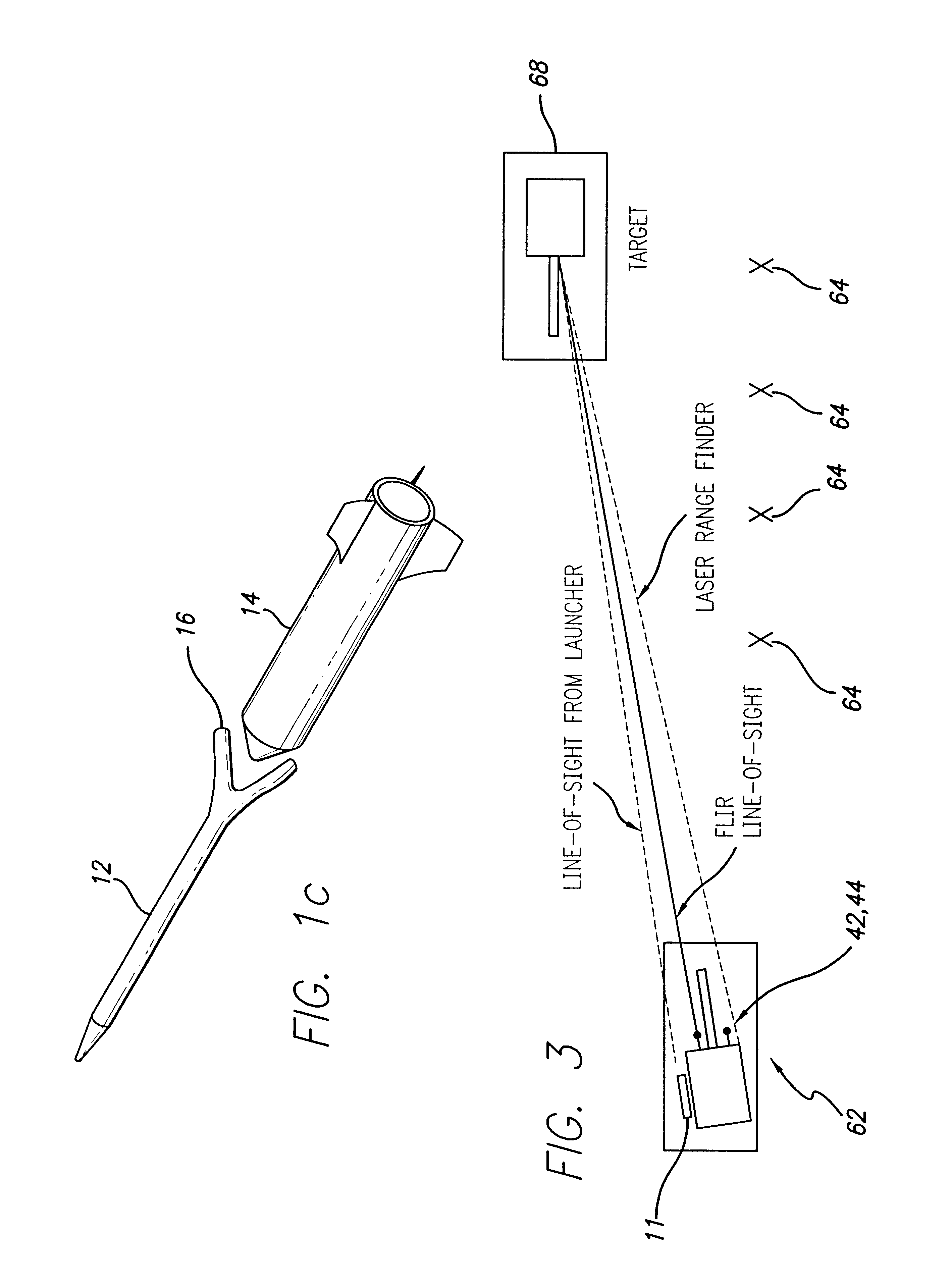
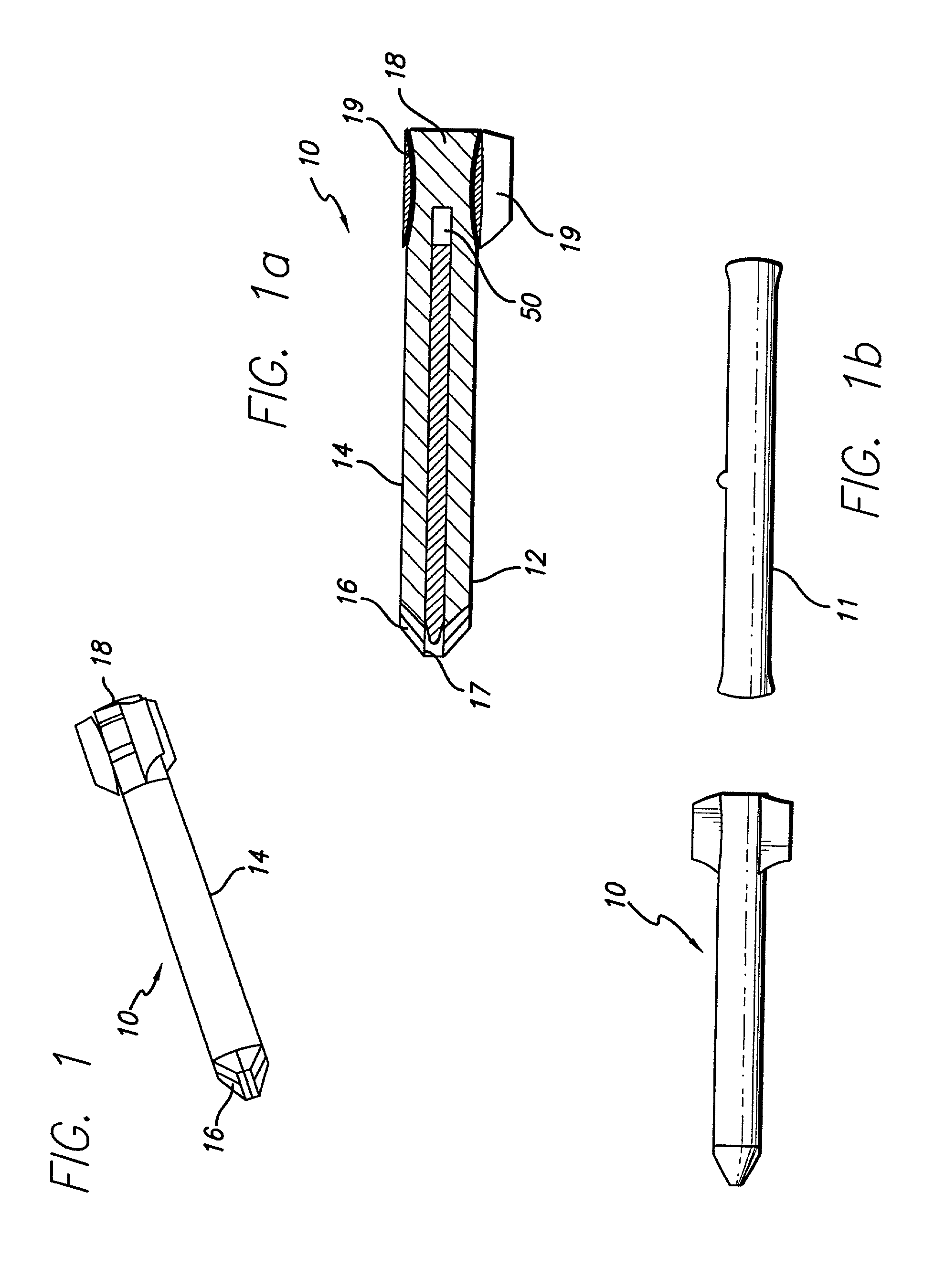
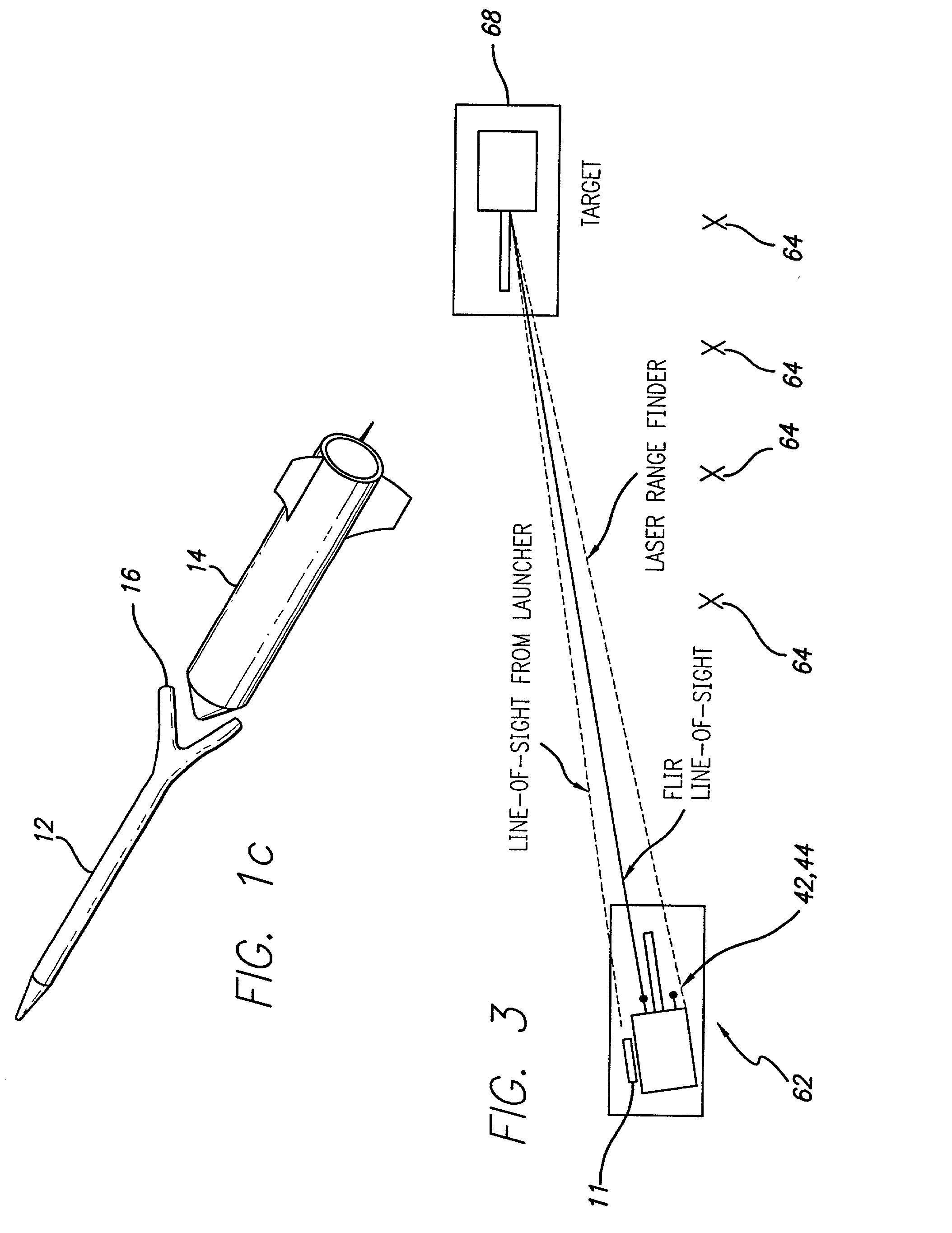
Precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system
A precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system. The inventive system includes a first subsystem for determining a target location and providing data with respect thereto. A second subsystem calculates trajectory to the target based on the data. The projectile is then launched and guided in flight along the trajectory to the target. In the illustrative application, the projectile is a tungsten rod and the first subsystem includes a forward-looking infrared imaging system and a laser range finder. The second subsystem includes a fire control system. The fire control system includes an optional inertial measurement unit and predicts target location. The projectile is mounted in a missile launched from a platform such as a vehicle. After an initial burn, the missile launches the projectile while in flight to the target. The missile is implemented with a rocket with a guidance system and a propulsion system. In accordance with the present teachings, the guidance system includes a transceiver system mounted on the projectile. The transceiver system includes a low-power continuous wave, millimeter wavelength wave emitter. A system is included at the launch platform for communicating with the projectile. The platform system sends a blinking command to the projectile and measures the round trip delay thereof to ascertain the range of the projectile. Velocity is determined by conventional Doppler techniques or differentiation. Azimuth and elevation are then determined by a monopulse antenna on the launch platform. As a consequence, the platform ascertains the location of the projectile and the impact point thereof. The platform generates a command to the projectile which is received by the projectile and used to actuate control surfaces to adjust the trajectory and impact point thereof as necessary.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Electronically steered, dual-polarized, dual-plane, monopulse antenna feed
InactiveUS7834803B2Reduce weight and costSmall sizePolarised antenna unit combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna feedElectron
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Millimeter-wave radar antenna system and decoupling method
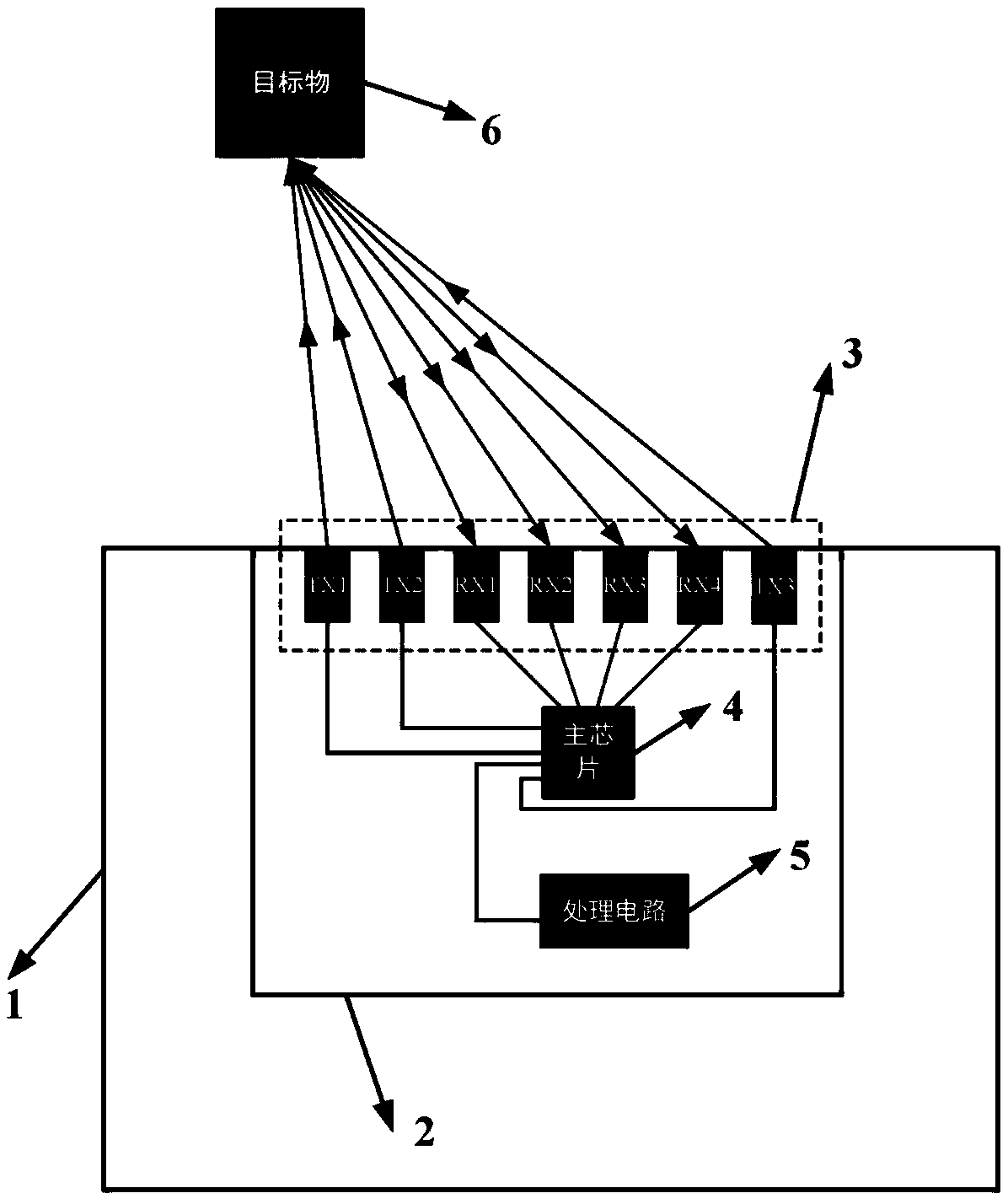
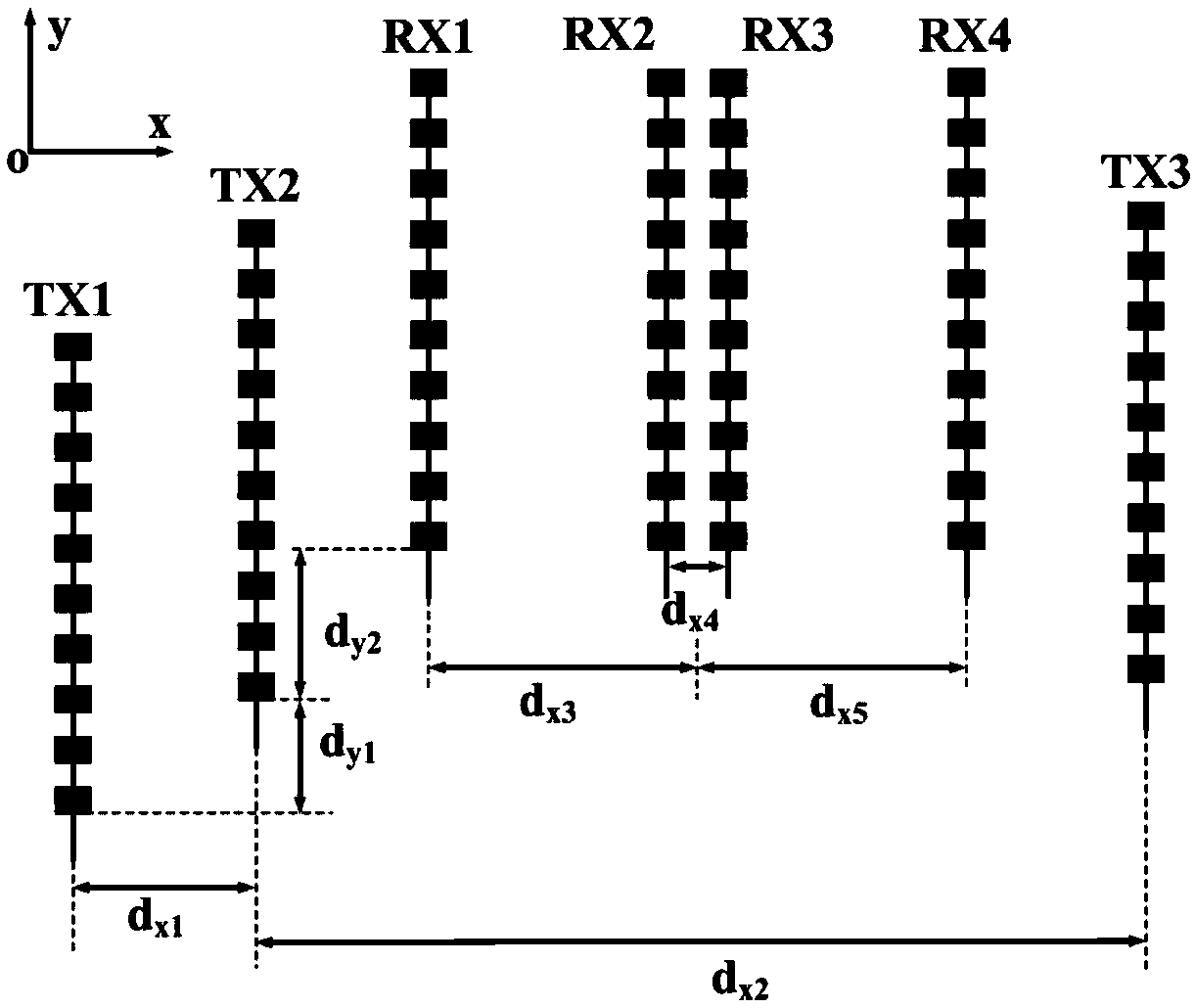
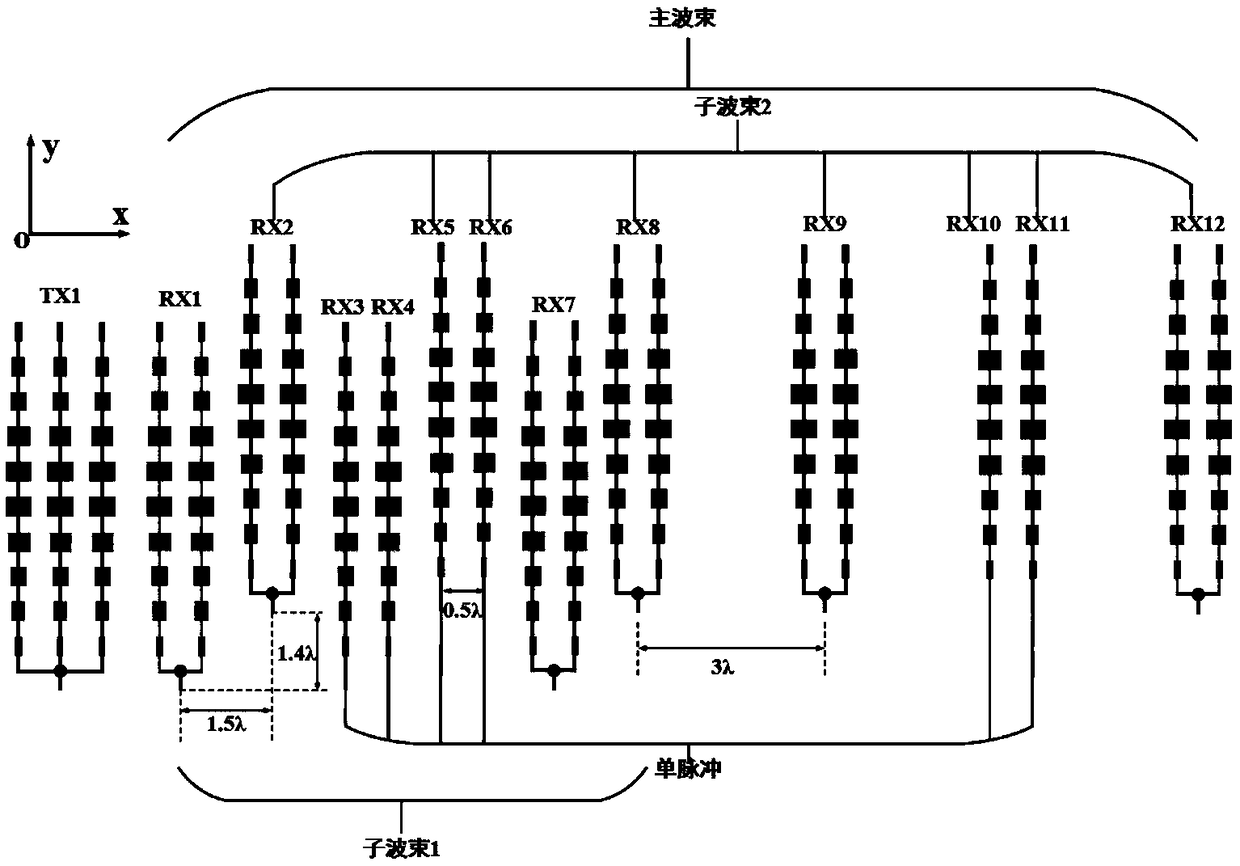
The invention discloses a millimeter-wave radar antenna system and a decoupling method. The antenna system comprises an antenna array, a main processor and a base band processing circuit, wherein theantenna array comprises at least two transmitting antennae and at least two receiving antennae, transmitting signals of the main processor are radiated to a target object through the transmitting antennae, the receiving antennae receive target reflected signals, the signals are mixed by the main processor to a base band, and the base band processing circuit analyzes and calculates target parameters. Compared with radar with the same performance, the antenna system adopts a single processing chip integration scheme, the cost is lower, and mainboard and antenna arrangement are more compact. By adopting the decoupling method, target azimuths and pitching angles can be calculated, the antenna system can produce more virtual receiving channels and improve the azimuth angle measurement resolution ratio according to the principle of a MIMO equivalent virtual array. By utilizing a mono-pulse antenna structure of the antenna system, the problem can be solved that main beamforming azimuth anglemeasurement is fuzzy when the separation distances of the receiving antennae are large.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LIBANG HEXIN INTELLIGENT BRAKING SYST CO LTD
Precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system
A precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system. The inventive system includes a first subsystem for determining a target location and providing data with respect thereto. A second subsystem calculates trajectory to the target based on the data. The projectile is then launched and guided in flight along the trajectory to the target. In the illustrative application, the projectile is a tungsten rod and the first subsystem includes a forward-looking infrared imaging system and a laser range finder. The second subsystem includes a fire control system. The fire control system includes an optional inertial measurement unit and predicts target location. The projectile is mounted in a missile launched from a platform such as a vehicle. After an initial burn, the missile launches the projectile while in flight to the target. The missile is implemented with a rocket with a guidance system and a propulsion system. In accordance with the present teachings, the guidance system includes a transceiver system mounted on the projectile. The transceiver system includes a low-power continuous wave, millimeter wavelength wave emitter. A system is included at the launch platform for communicating with the projectile. The platform system sends a blinking command to the projectile and measures the round trip delay thereof to ascertain the range of the projectile. Velocity is determined by conventional Doppler techniques or differentiation. Azimuth and elevation are then determined by a monopulse antenna on the launch platform. As a consequence, the platform ascertains the location of the projectile and the impact point thereof. The platform generates a command to the projectile which is received by the projectile and used to actuate control surfaces to adjust the trajectory and impact point thereof as necessary.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Ka-waveband cavity coupling feed circular polarized horn antenna
InactiveCN104518285AHigh precision of inquiryImprove anti-interference abilityWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysImpedance matchingWaveguide
The invention relates to a cavity coupling slot excited circular polarized horn antenna comprising a feed inclined slot (1), a coupling inclined slot (2), a coupling cavity (3), two pyramid horns (4) and feed waveguide (5). The coupling cavity is slotted by adopting coupling waveguide and then double slots are slotted on the coupling cavity for horn feed, wherein the coupling waveguide is internally provided with an adjusting column for adjusting impedance matching. Integration of the horn antenna and a circular polarized feed source is realized by the design. Electrical performance of the cavity coupling feed circular polarized pyramid horn antenna is not quite different from that of a previous wide-brimmed center inclined slot feed circular polarized horn antenna, and advantages are that the network is relatively simple, the feed structure after arraying is more compact and the tail end of a power dividing network is only provided with 14 ports. Now most of interrogation antennas are micro-strip antennas working in the L-waveband. The micro-strip antennas are liable to be affect by electromagnetic interference of the same frequency band, and the micro-strip type antennas also have the disadvantage of lower gain. The circular polarized horn antenna works in the Ka-waveband so that the characteristic of high gain of the horn antenna can be retained, circular polarization can also be realized, and thus the circular polarized horn antenna can act as an ideal mono-pulse antenna.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
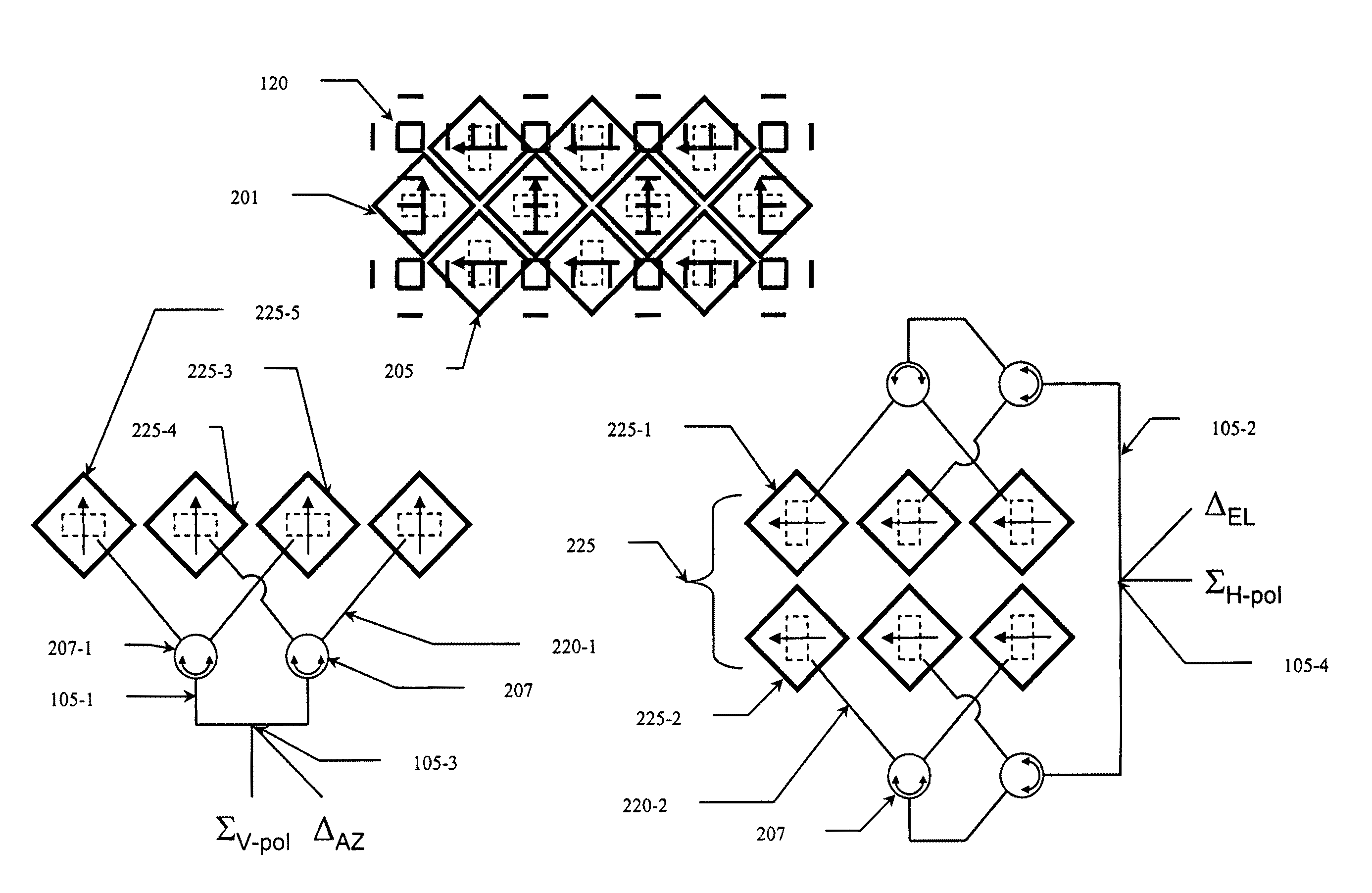
Split Aperture Monopulse Antenna System
ActiveUS20130027241A1Electromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElevation angleElectromagnetic electron wave
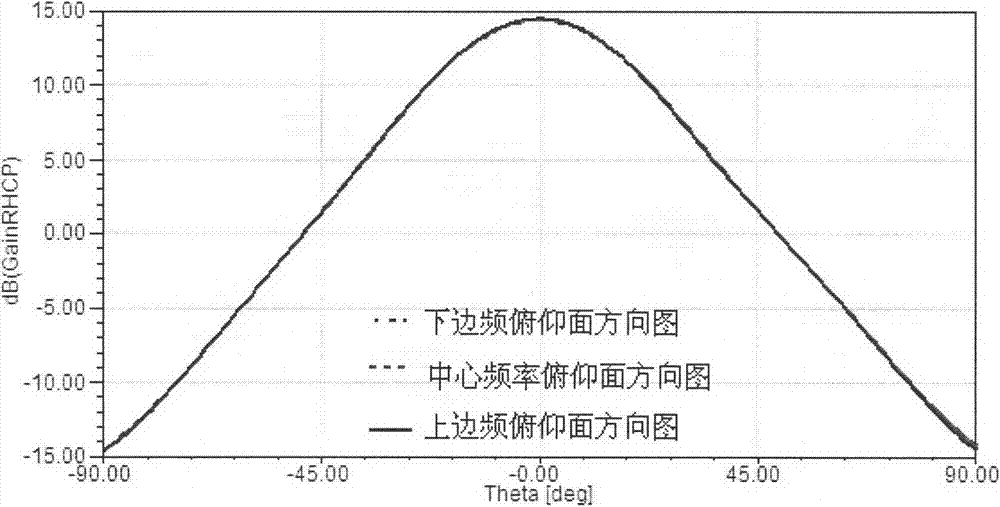
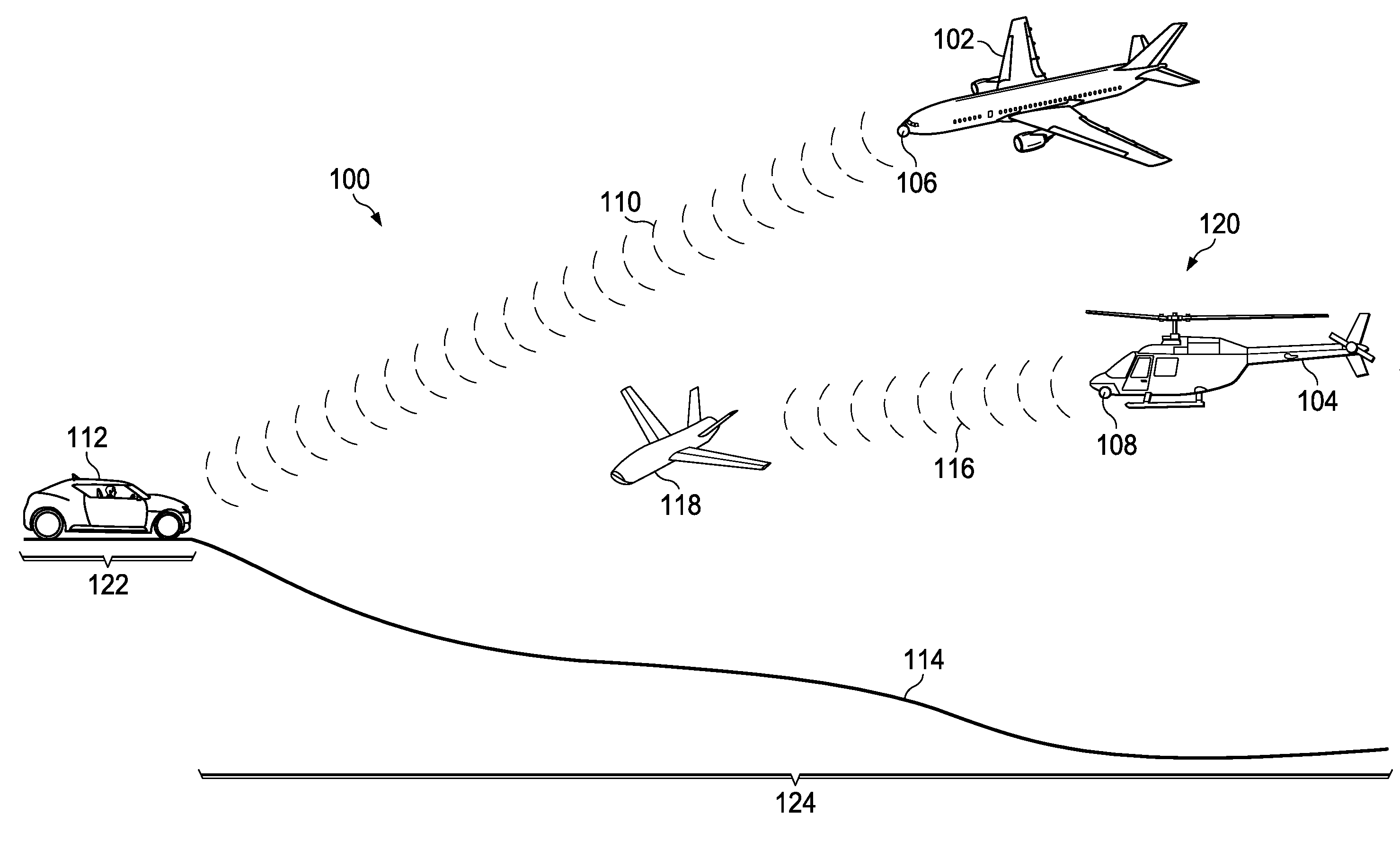
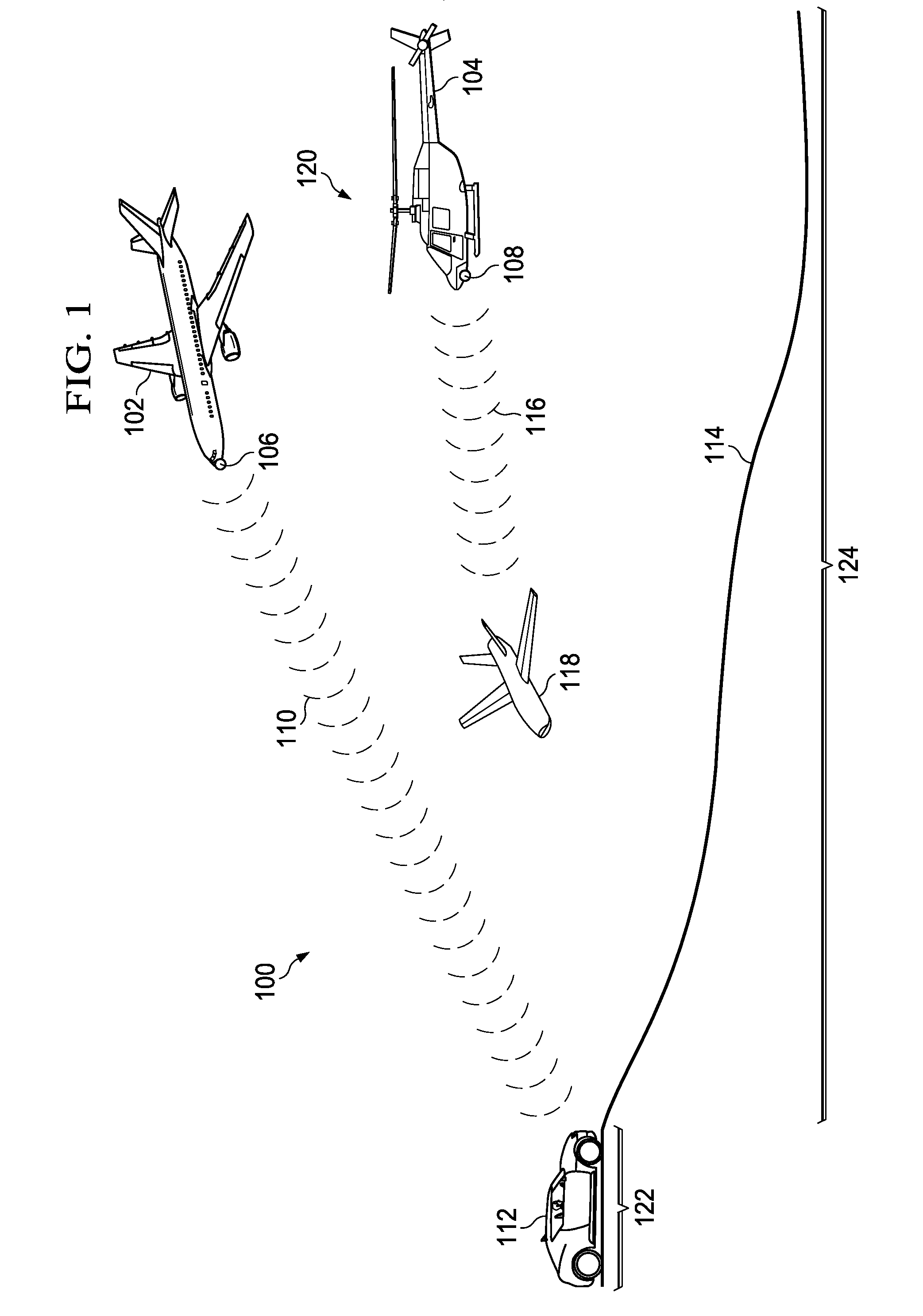
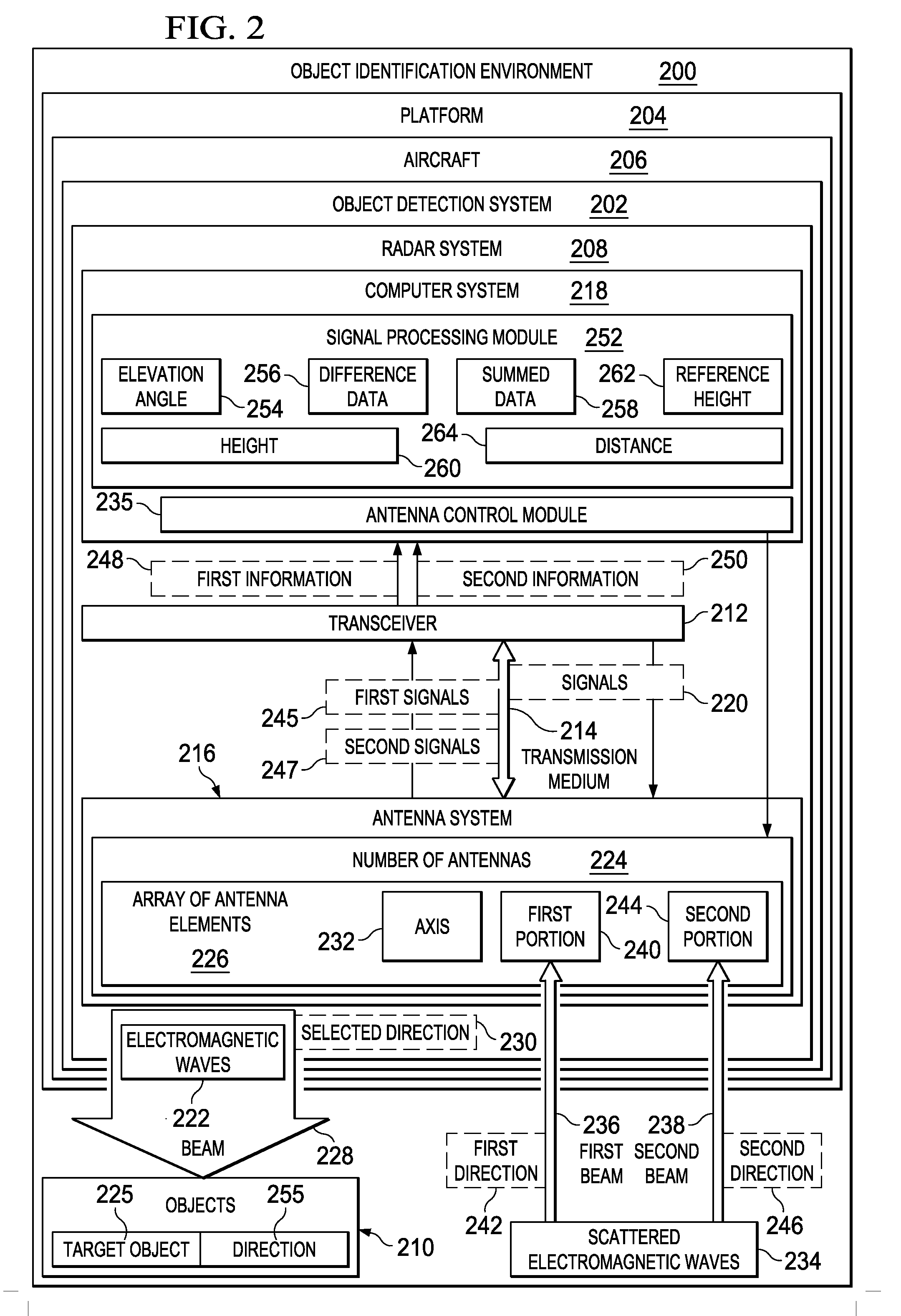
A method and apparatus for processing electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves are transmitted in a selected direction toward a target object from a first array of antenna elements. Scattered electromagnetic waves generated from the electromagnetic waves are received at a first portion of a second array of antenna elements configured to receive the scattered electromagnetic waves in a first direction with respect to the selected direction and at a second portion of the second array of antenna elements configured to receive the scattered electromagnetic waves in a second direction with respect to the selected direction. First information in the scattered electromagnetic waves received by the first portion is subtracted from second information in the scattered electromagnetic waves received by the second portion to form difference data. An elevation angle is identified between a direction of the target object and the selected direction using the difference data.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
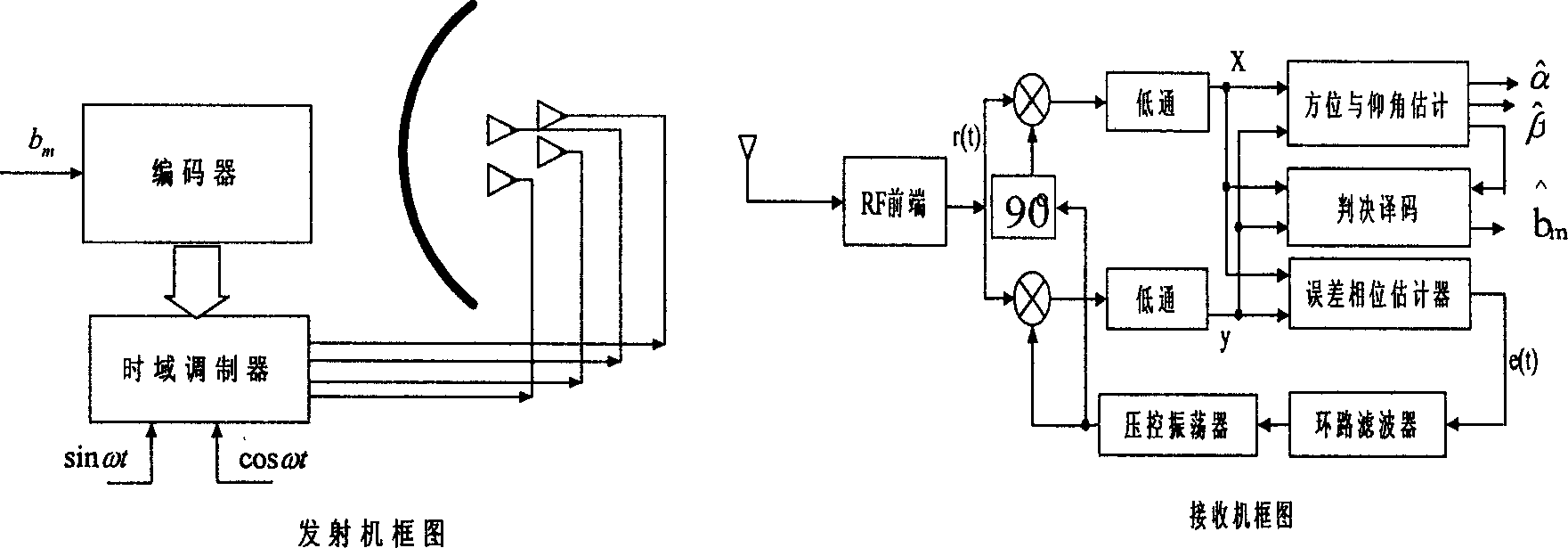
Single pulse antenna time-space modulating method and device with position and elevation information
The method comprises: 1) designing a multiple antenna transmitting drive signal; 2) two dimensional modulation designing is made for said signal; 3) encoding the message to be transmitted; 4) the signal is modulated and transmitted; 5) making carrier extraction and coherent demodulation for the received signal. The invention not only has PSK and QPSK digital communication capacity, but also can make high accuracy direction finding like mono-pulse radar, and is a new architecture of bistatic radar or multistatic radar.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
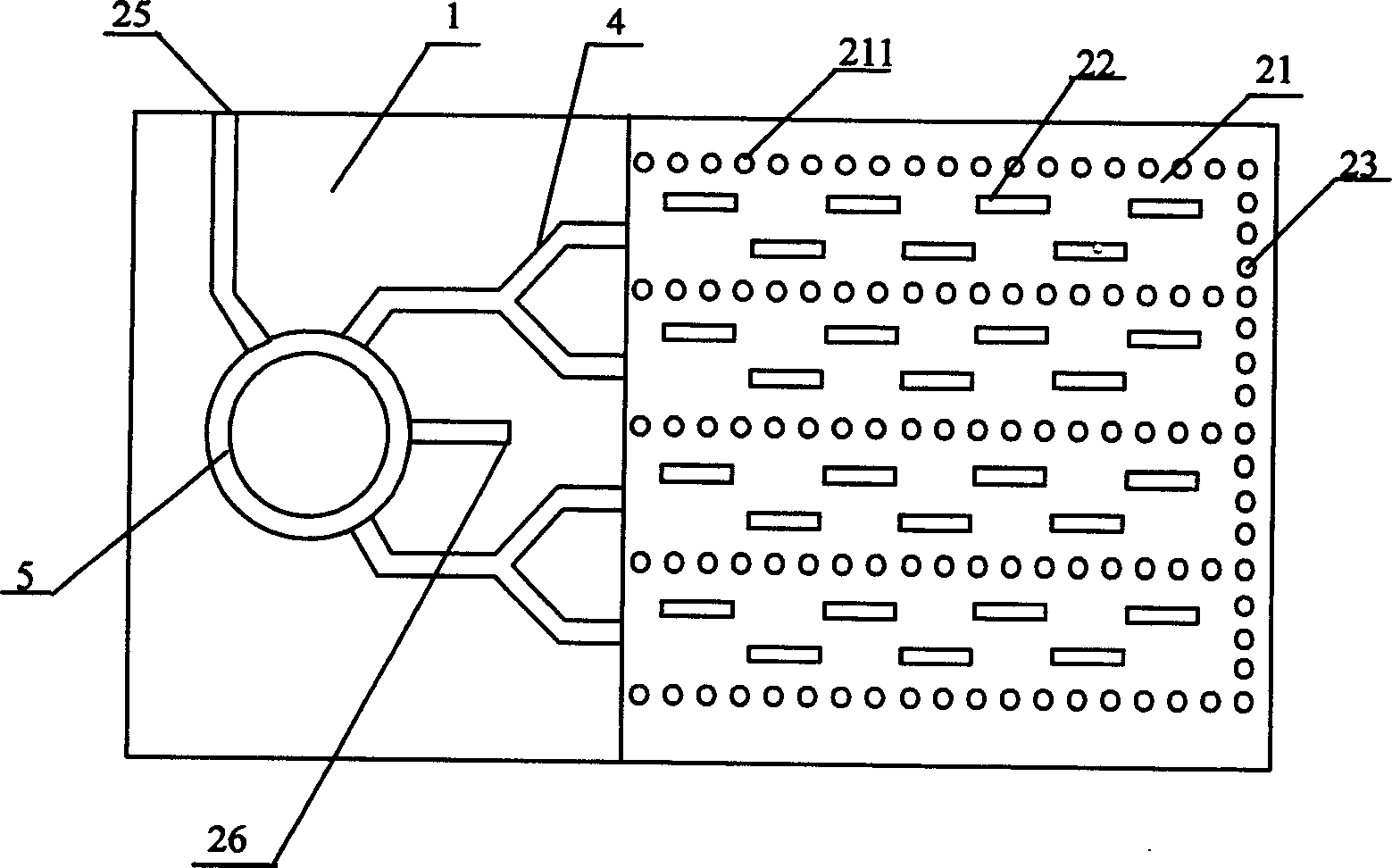
Dielectric substrate integrated single pulse antenna
InactiveCN1719662AHigh gainHigh angle sensitivityAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsMetallic foilDielectric substrate
This invention discloses a dielectric substrate integrated single pulse antenna including a dielectric substrate board set with metallic foils at the positive and negative sides, a slit array, a microstrip power divider and a combiner are etched on one side of the foil, the slit array unit is connected with one end of the microstrip power divider, the other end of which is connected with the combiner, interconnected metallized through holes are set on the substrate board and the foil arrayed in U shape enclosing the slit array.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
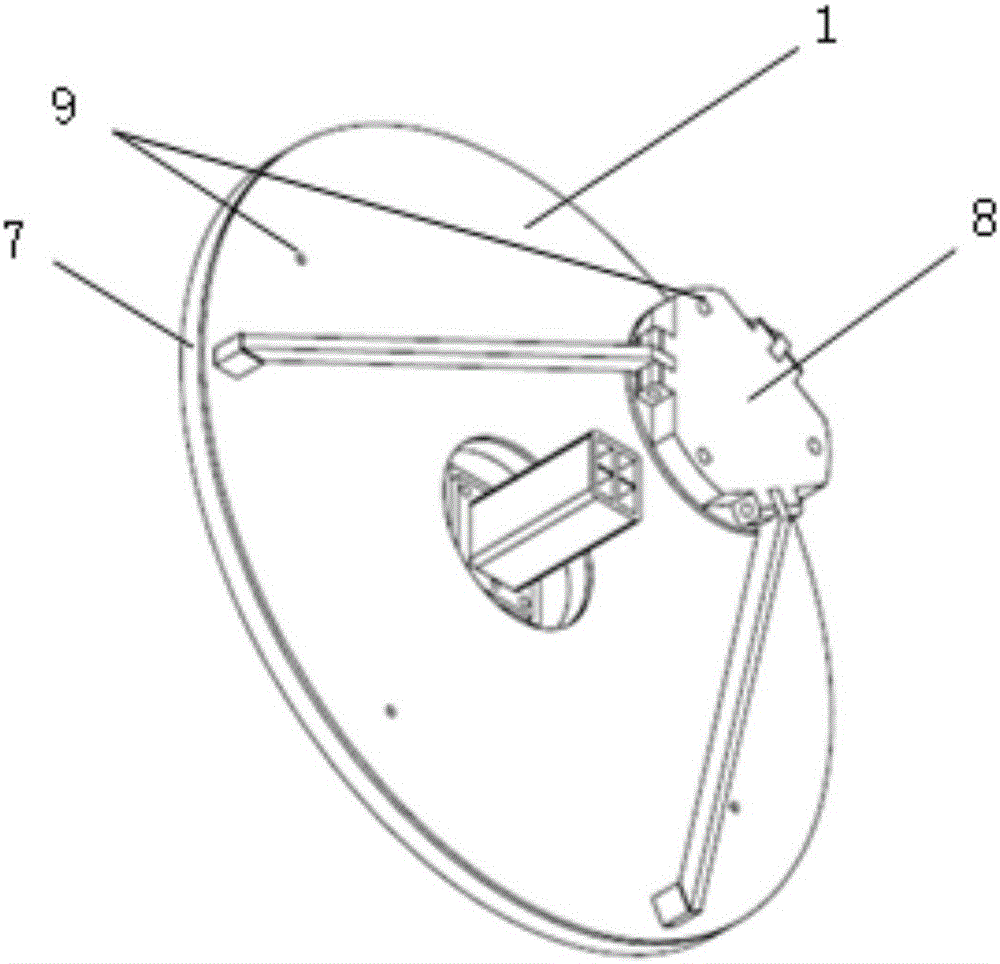
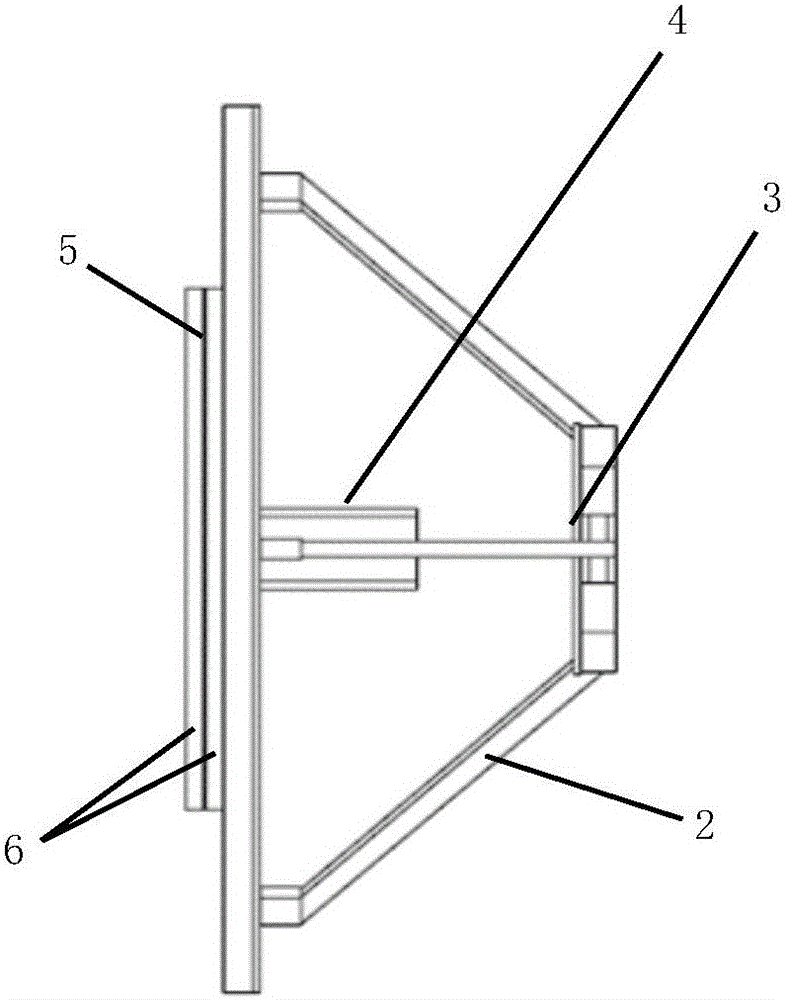
Compact type millimeter-wave monopulse antenna
InactiveCN106159462AReduce volumeReduce weightWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysMillimetre waveMonopulse antennas
The invention discloses a compact type millimeter-wave monopulse antenna and belongs to the technical field of antennas. The compact-type millimeter-wave mmonopulse antenna comprises a feed source, a main reflecting surface, an auxiliary reflecting surface, a supporting structure and a sum-difference network. Both the main reflecting surface and the auxiliary reflecting surface adopt plane reflection array antennas, and the sum-difference network is of a plane structure. Compared with a traditional monopulse antenna, the compact type millimeter-wave monopulse antenna has the advantages of small size, light weight and proneness to connection with other integrated high-frequency components.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
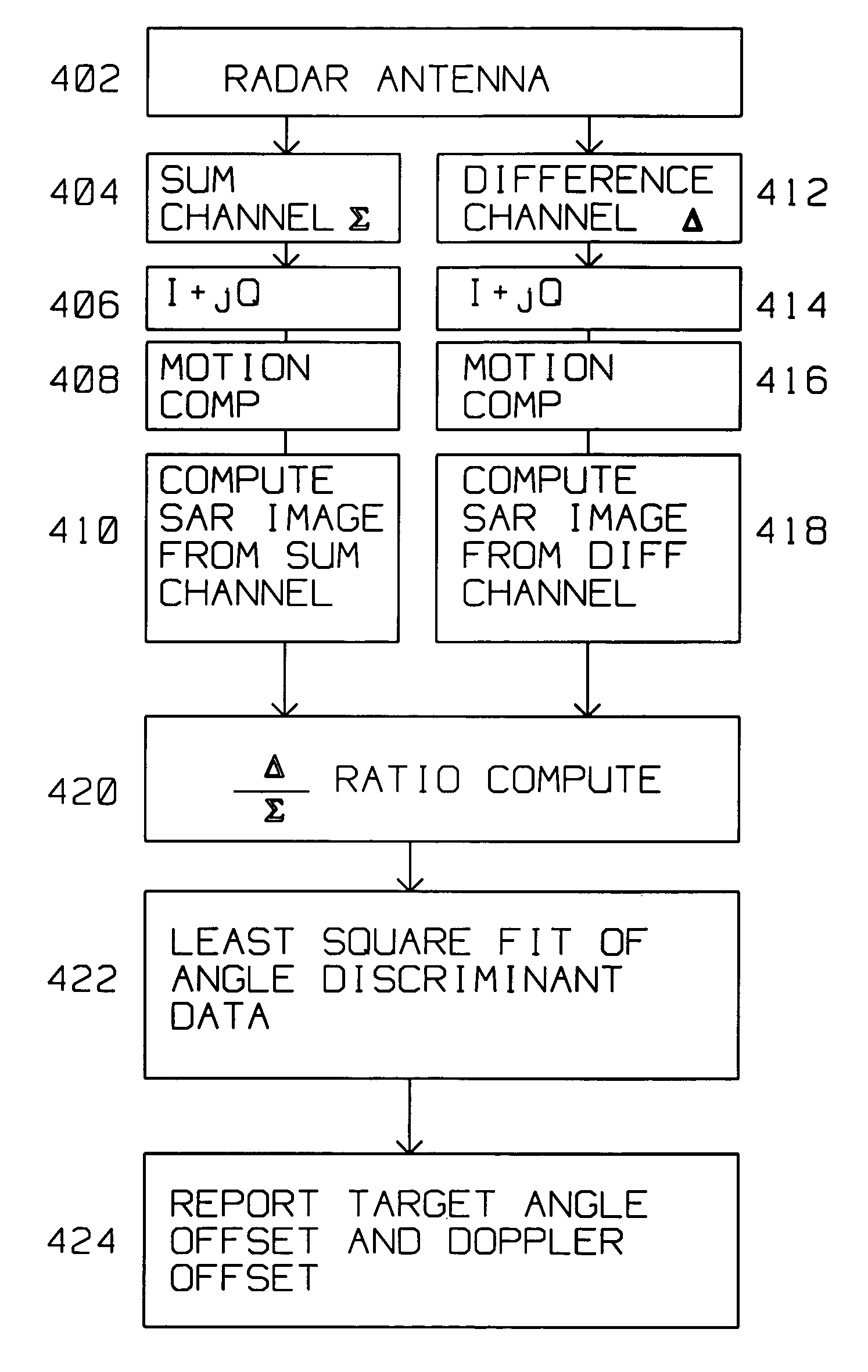
Robust detection technique of fixed and moving ground targets using a common waveform
ActiveUS20060152402A1Easy to detectReduce restrictionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDiscriminantRadar
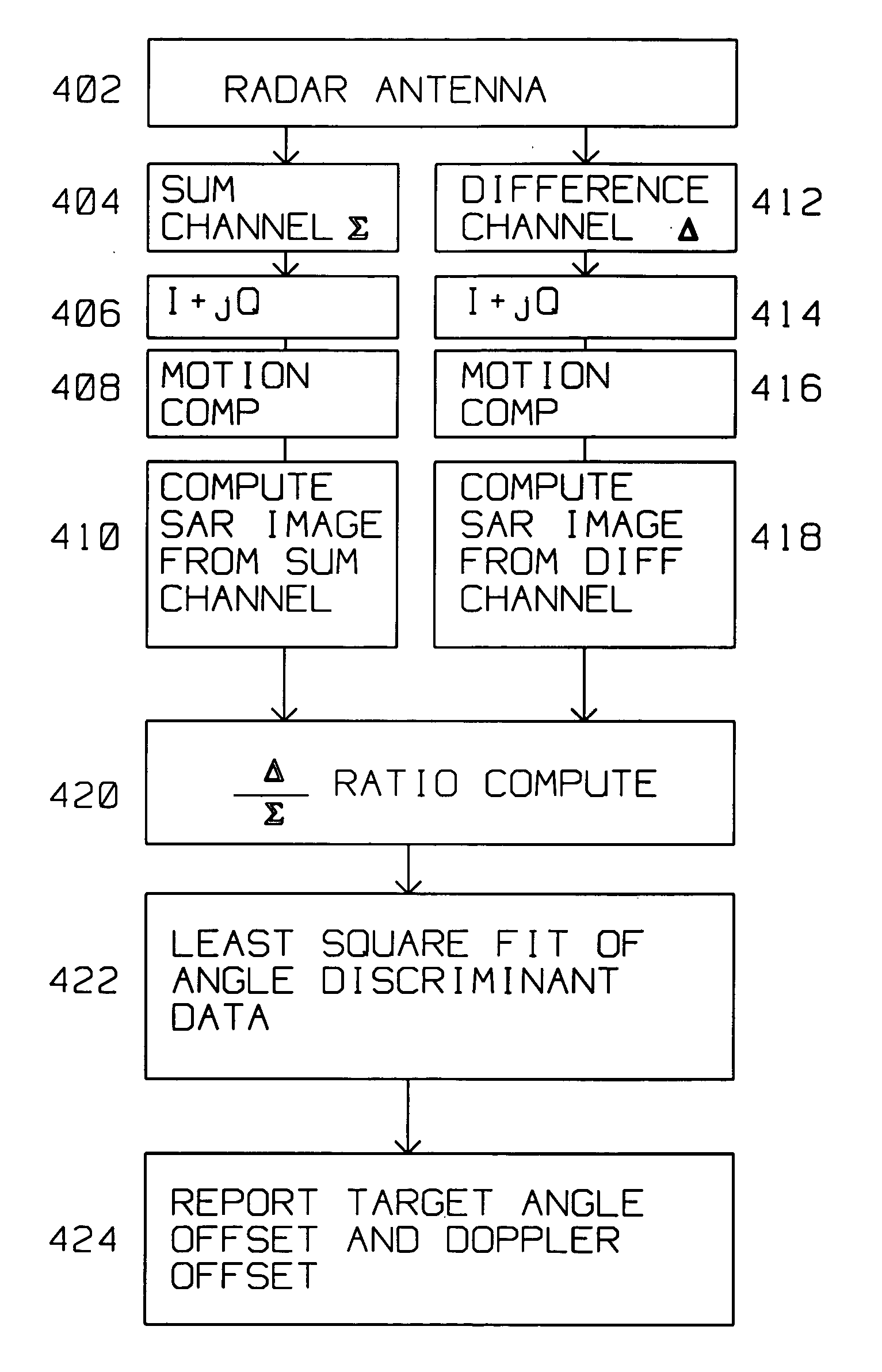
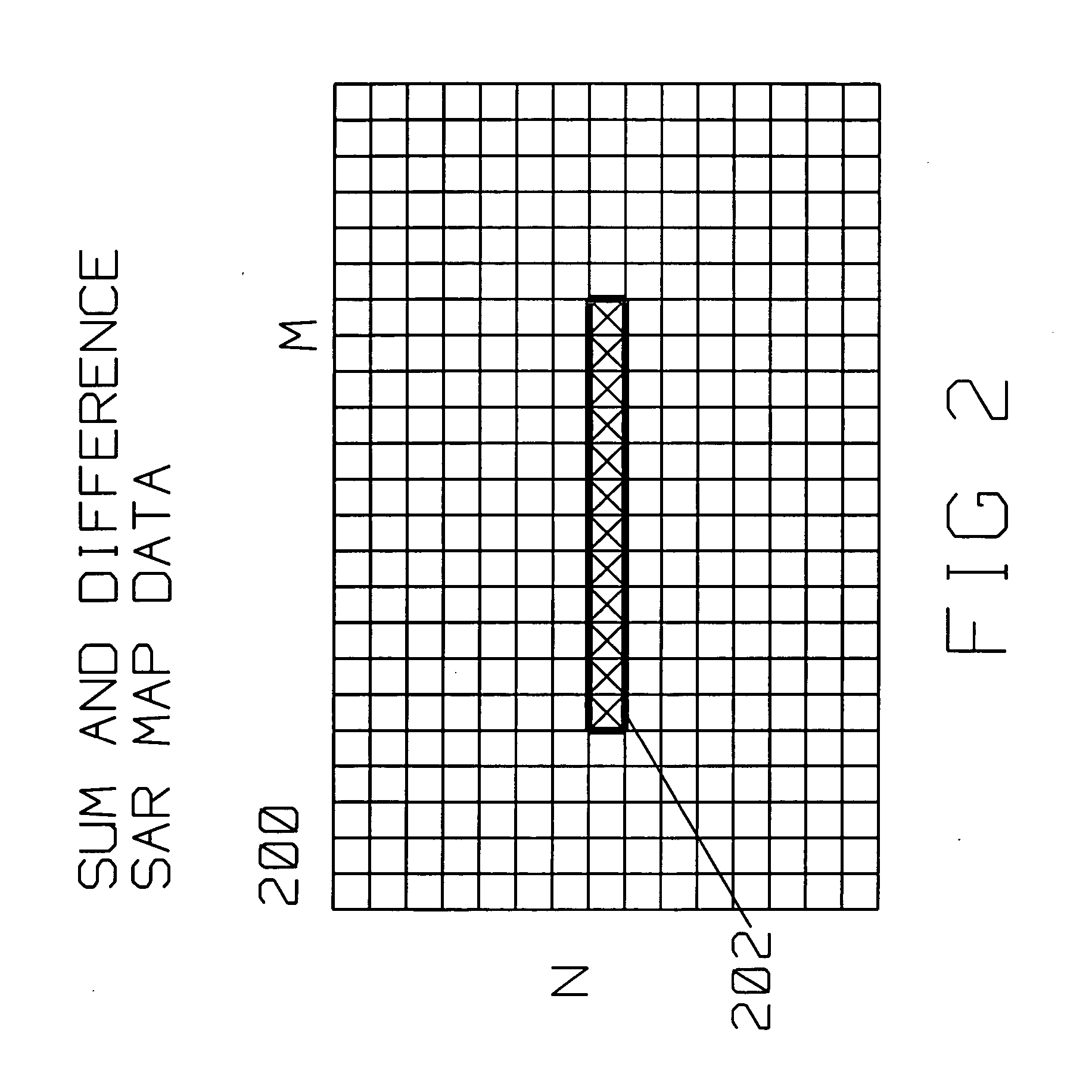
Detection of moving targets in SAR images is improved by a radar on a moving platform for generating a focused synthetic aperture image of a scene The scene contains a target described by pixels within the SAR image. The radar has a monopulse antenna having a sum channel output and a difference channel output feeding analog to digital converters for converting the sum channel output and difference channel output into respective digital streams concurrently. The digital streams generate a difference channel SAR image and a sum channel SAR image. Target ratios are computed for those pixels descriptive of a target within the scene. Background ratios are computed for pixels around the target. Target ratios and background ratios define respective least square fit of angle discriminants. Comparing the target least square fit of angle discriminant with the background least square fit angle discriminant identifies an angle offset and a Doppler offset of the target with respect to the background. The background least square fit of angle discriminant using background ratios is computed for a region around the target. A 20 by 20 sum synthetic aperture pixels is evaluated as a background around the target.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
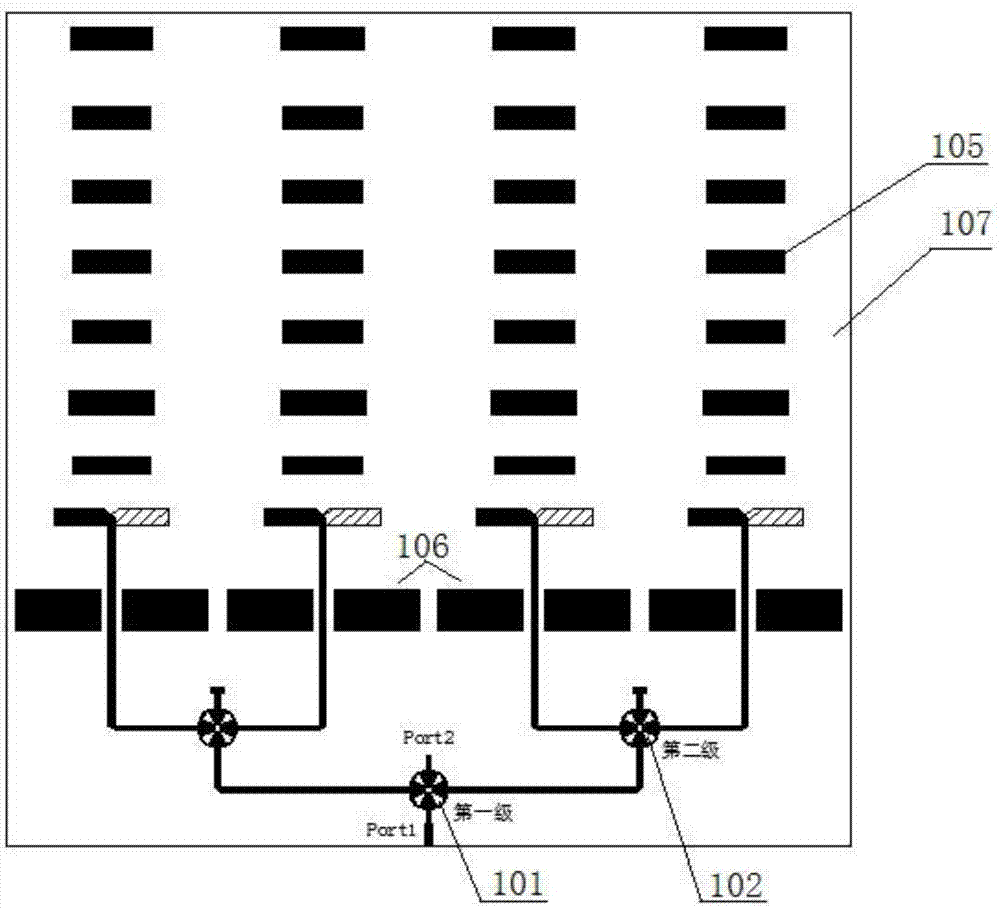
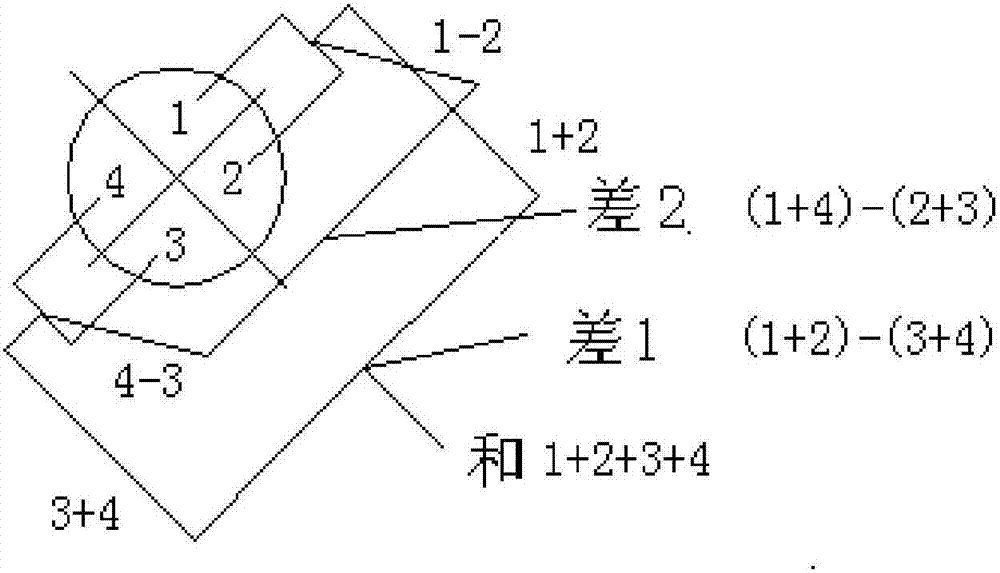
Planar waveguide sum-and-difference network
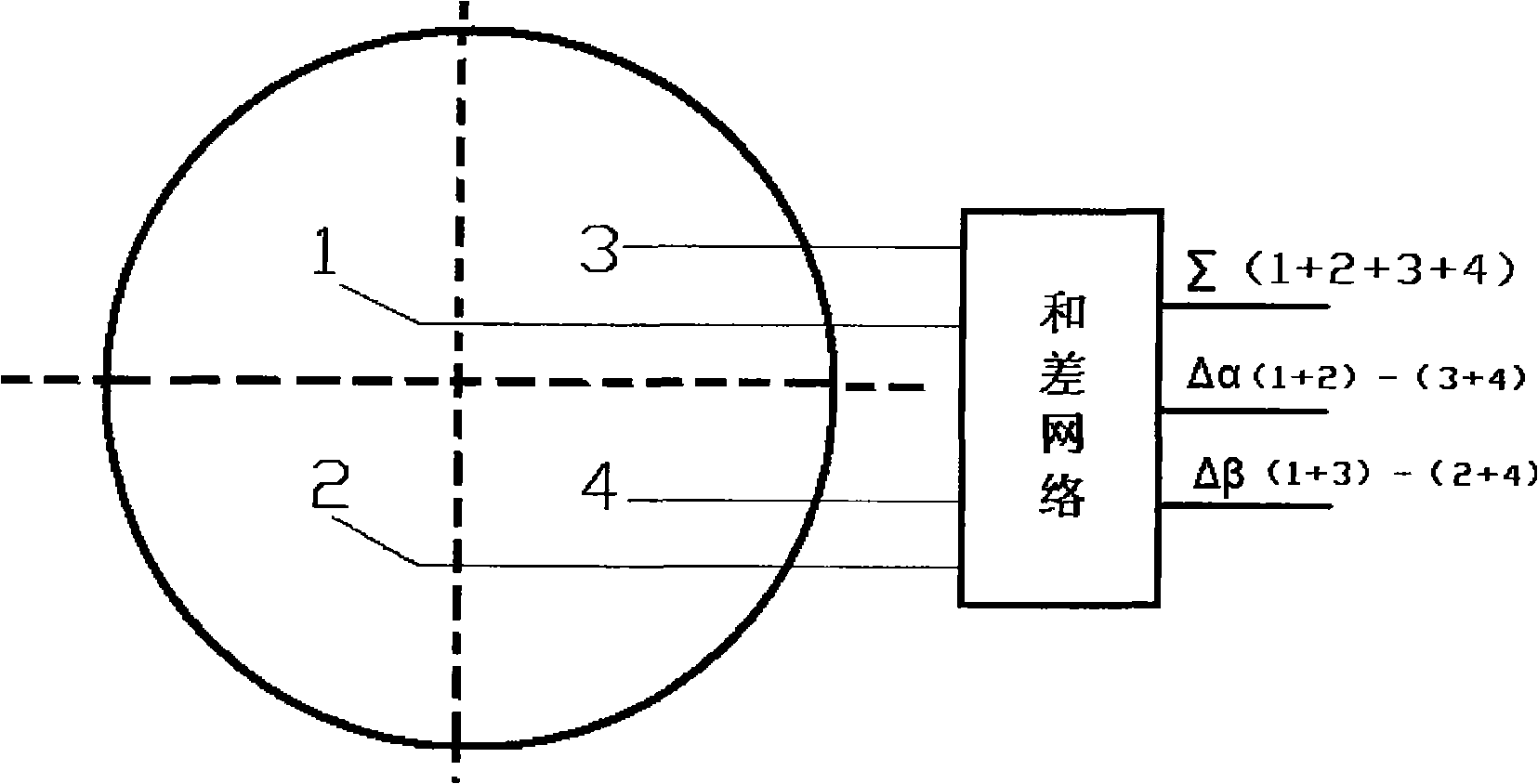
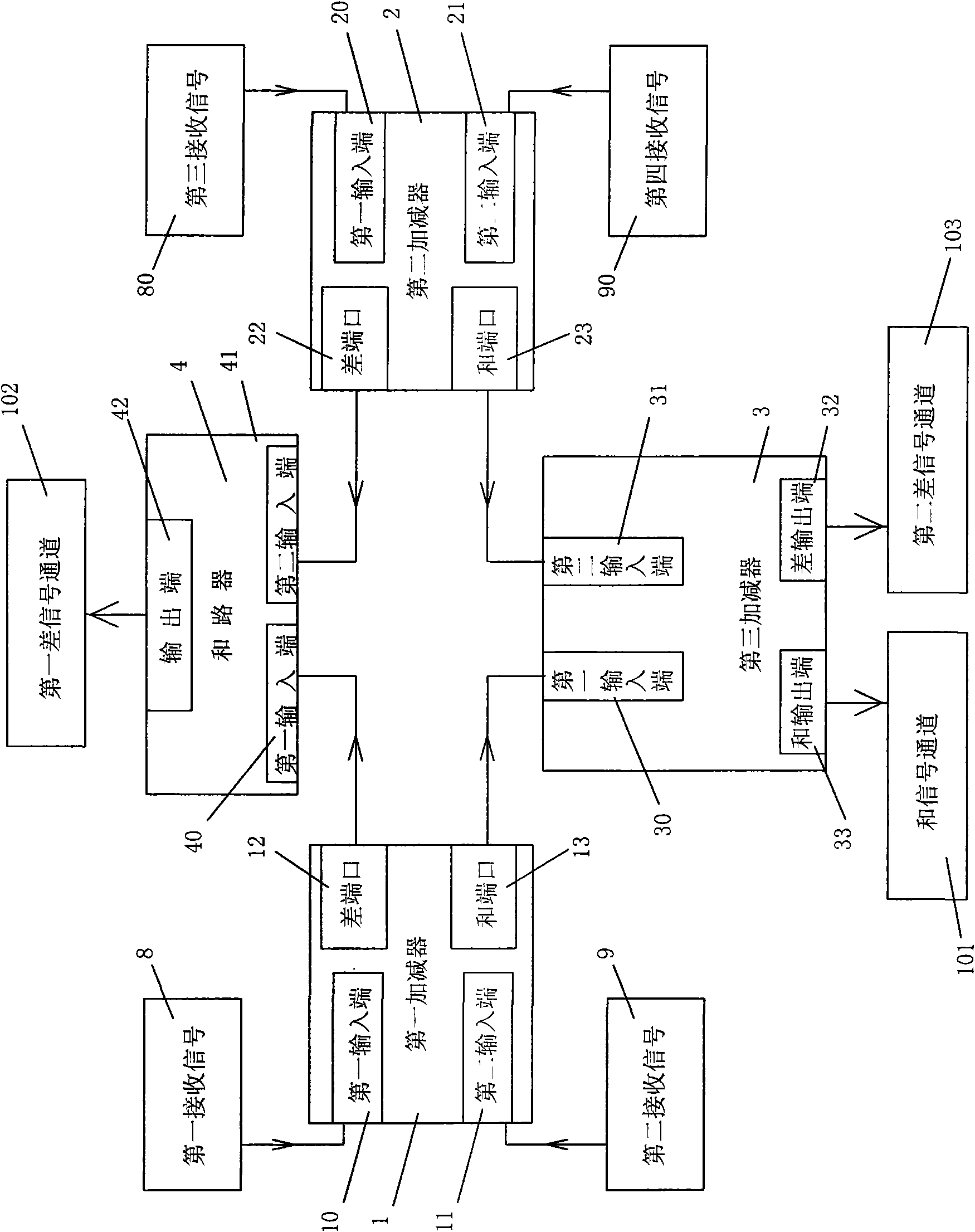
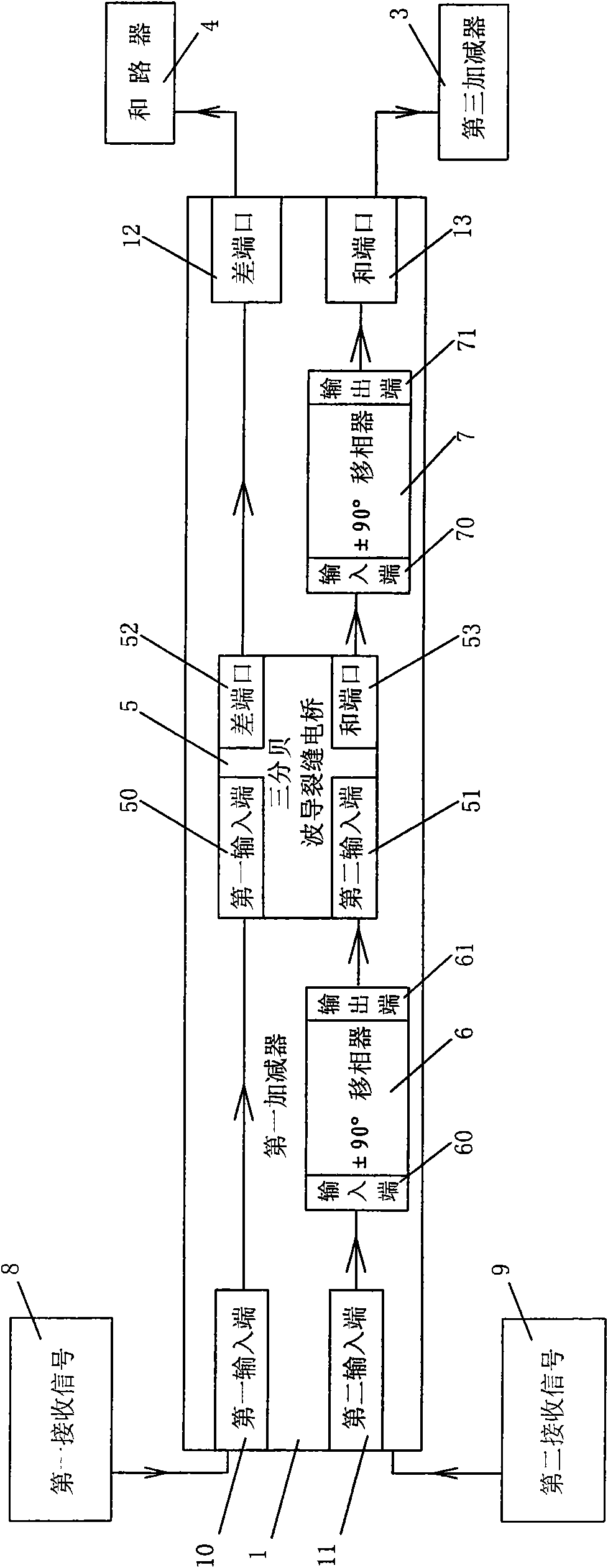
The present invention discloses a planar waveguide sum-and-difference network which relates to an antenna feed network device of a single-pulse system radar system. The planar waveguide sum-and-difference network changes four receiving signals of the single-pulse antenna to a azimuth difference signal, a trim difference signal and a sum signal. The planar waveguide sum-and-difference network is composed three high-frequency waveguide adder-substracter and a combiner. The planar waveguide sum-and-difference network of the invention has the characteristics of low section, compact structure and excellent electrical property. The planar waveguide sum-and-difference network of the invention is particularly suitable for designing and manufacturing the high-efficiency single-pulse radar antenna sum-and-difference network.
Owner:BEIJING HUADA ZHIBAO ELECTRONICS SYST
High-order mode single-pulse antenna based on substrate integrated waveguide
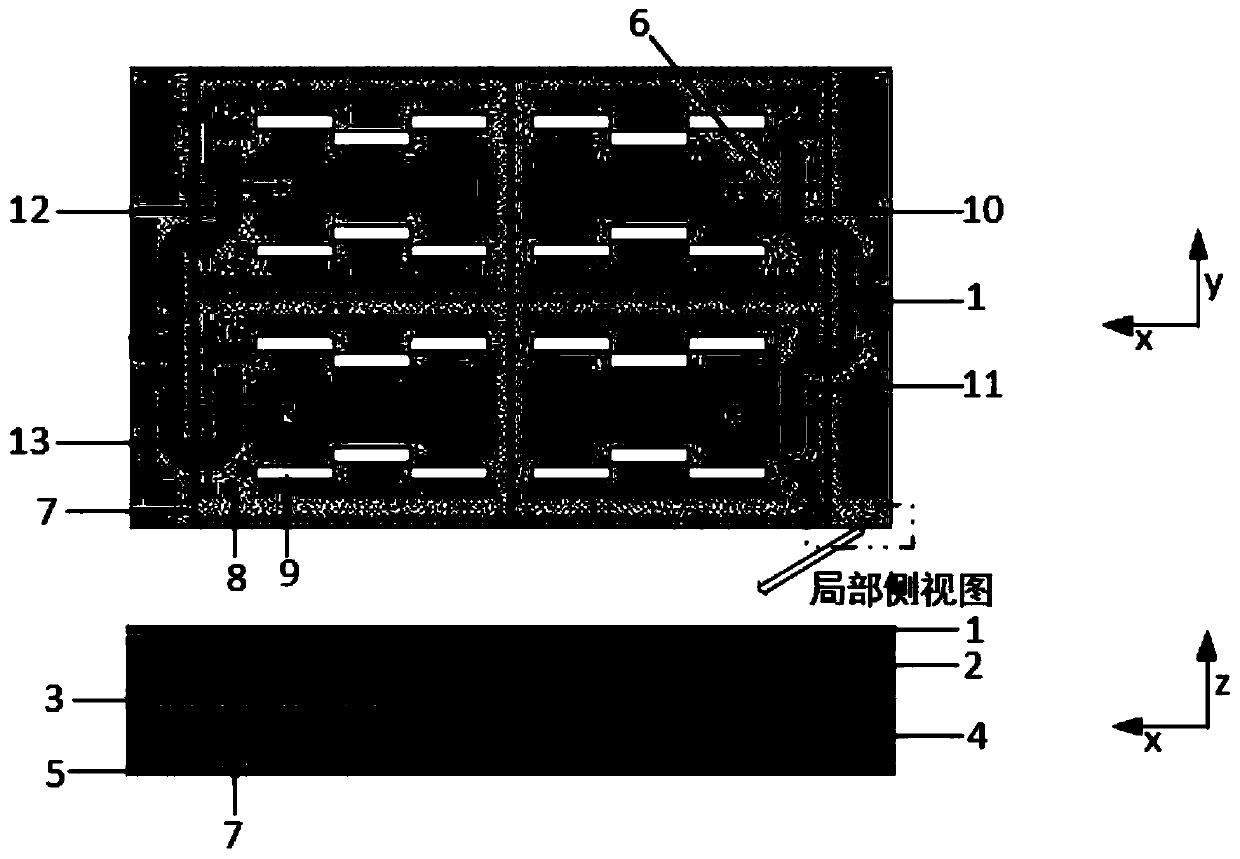
ActiveCN110504546ASimple feed structureSmall footprintAntennas earthing switches associationWaveguidesElectricityChinese characters
The invention discloses a high-order mode single-pulse antenna based on substrate integrated waveguide. A feed network, an upper layer medium base plate and a substrate integrated waveguide cavity aresequentially arranged from top to bottom. The feed network comprises a difference port network and a port network respectively arranged at two ends of an antenna; the substrate integrated waveguide cavity is divided into four independent symmetrical sub waveguide cavities through a first metal through hole in a shape like a Chinese character 'tian'; the difference port network and the port network respectively correspond to two sub waveguide cavities and respectively correspond to one row of second metal through holes; 180-degree phase differences are formed in the sub waveguide cavity corresponding to the difference port network, so that difference beams are obtained; and sum beams are obtained in the sub waveguide cavity corresponding to the port network. The single-pulse antenna provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, high radiation efficiency and low profile. The feed network design of the single-pulse antenna is greatly simplified.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
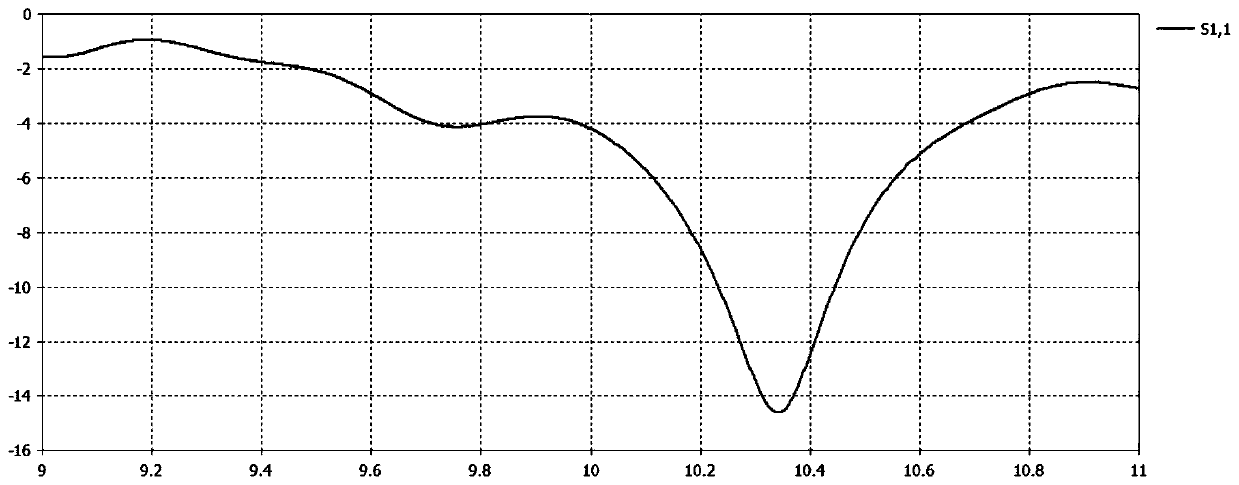
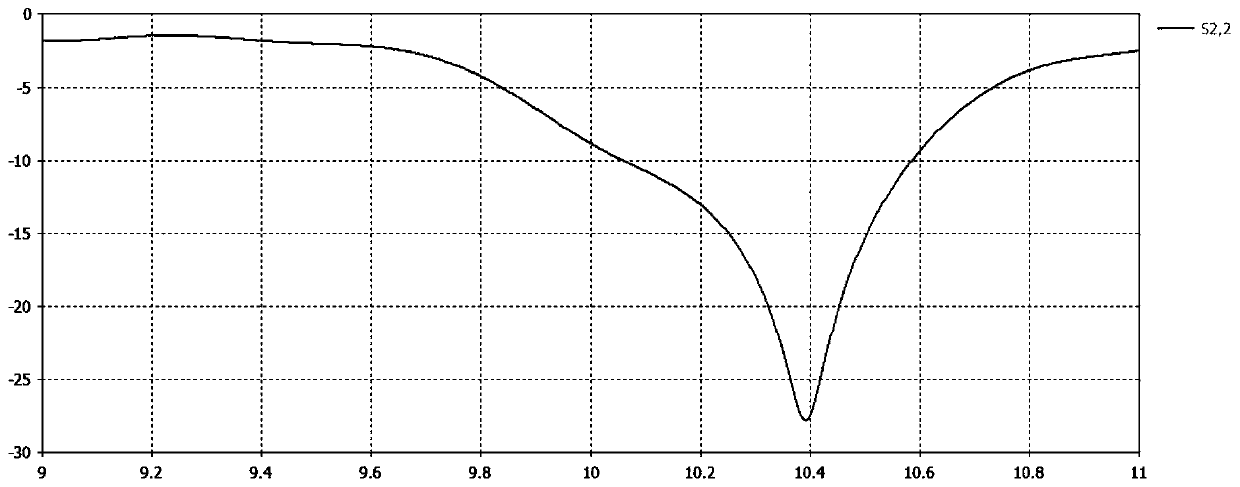
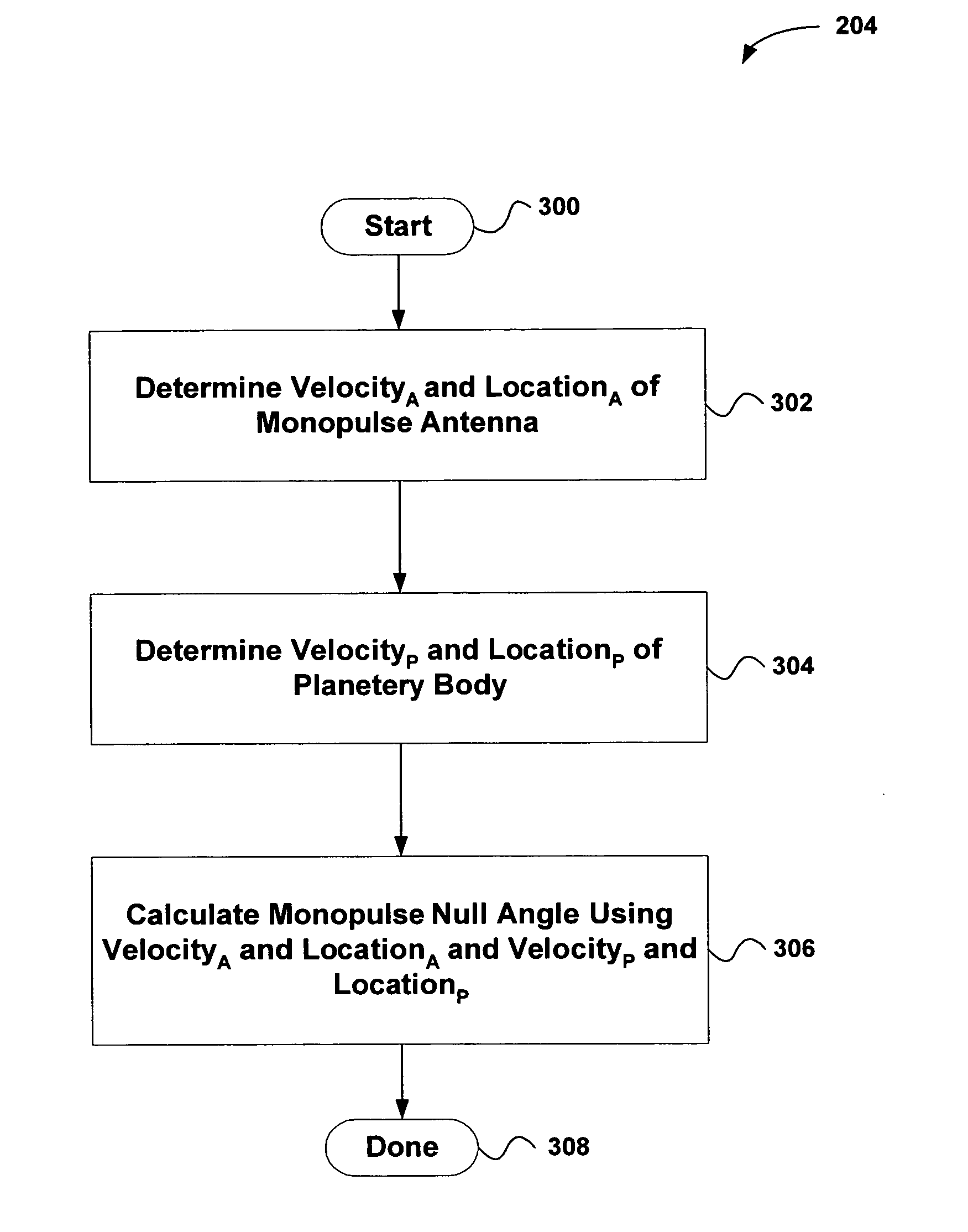
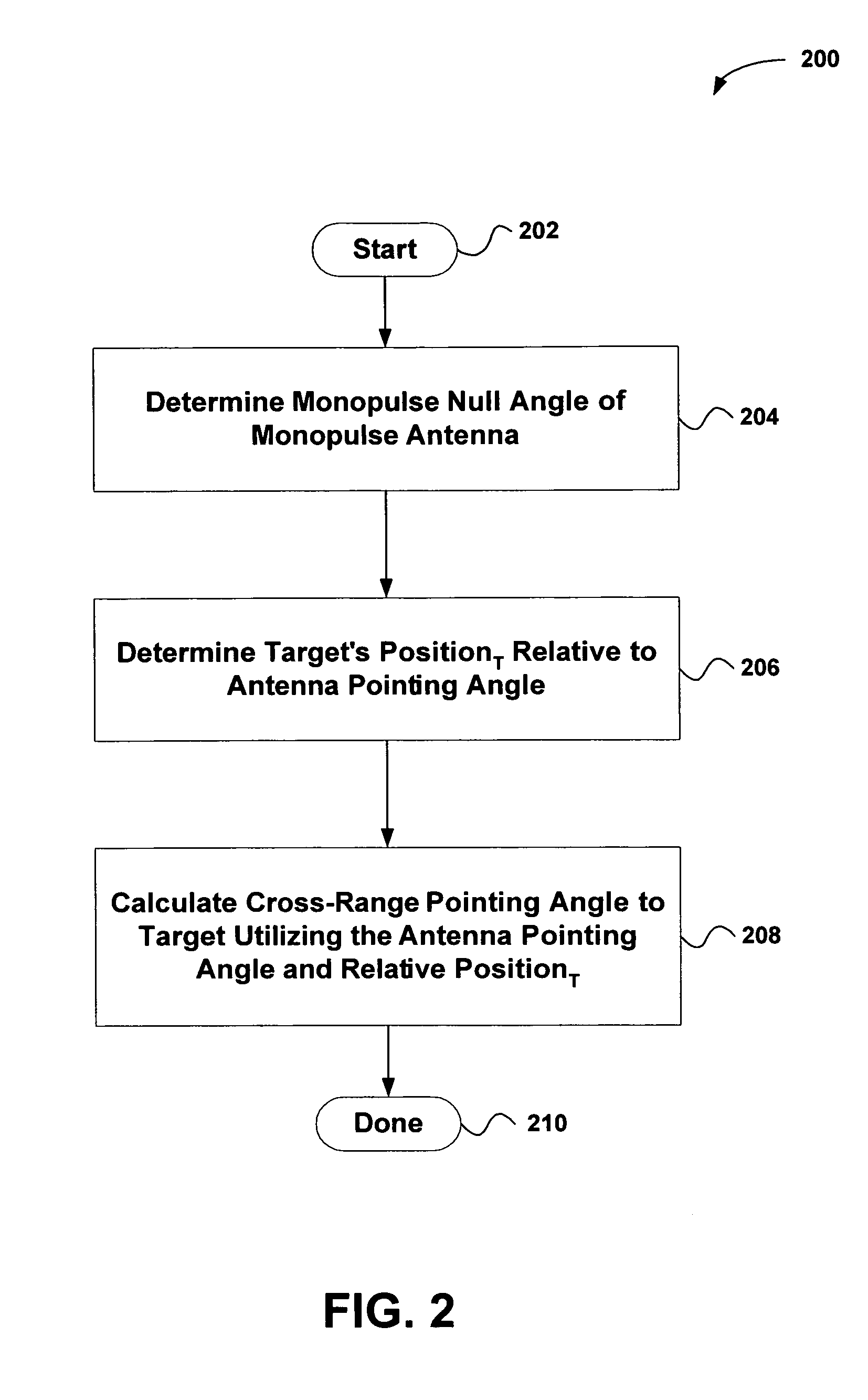
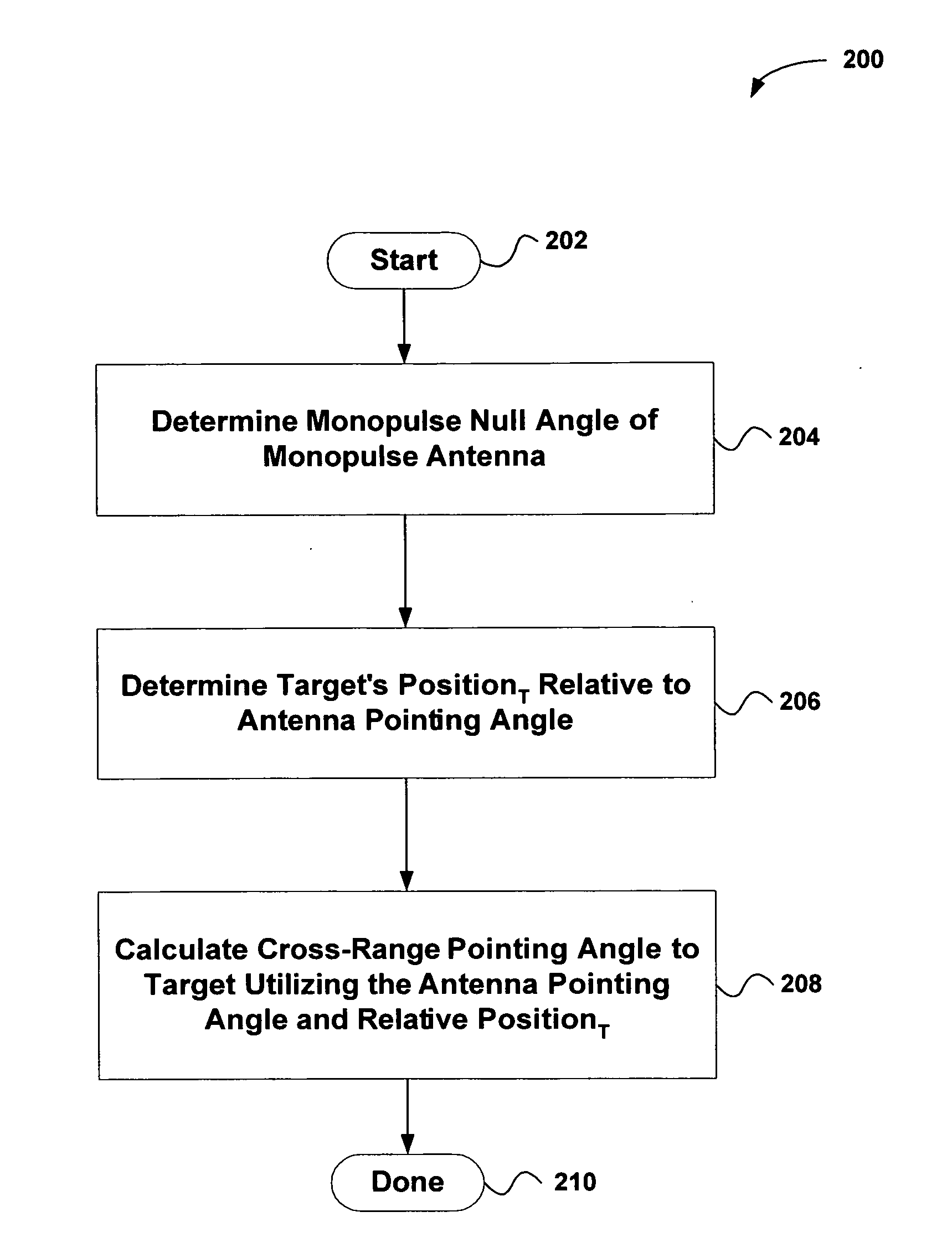
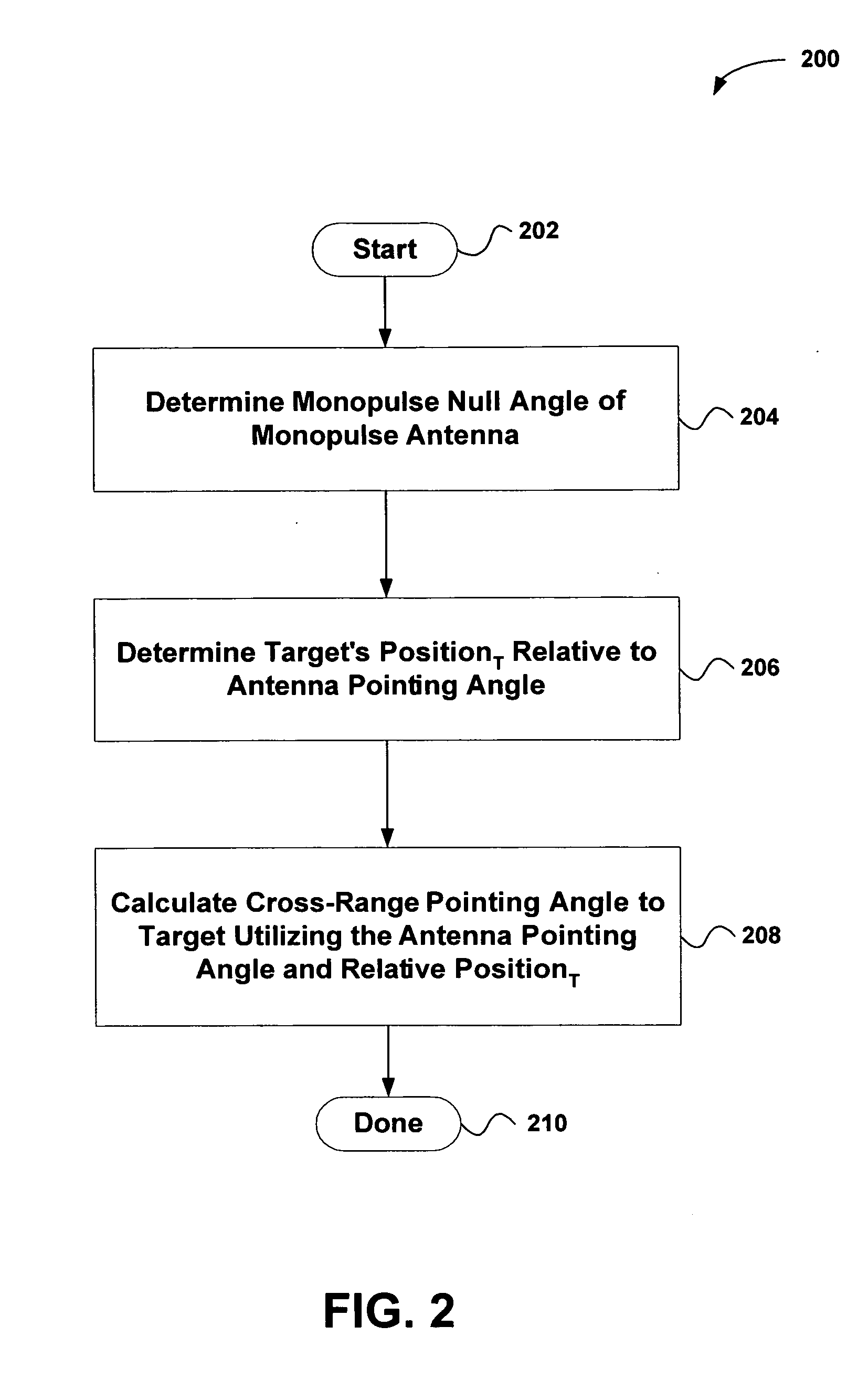
System and method for estimating the azimuth pointing angle of a moving monopulse antenna
An invention is provided for determining the azimuth pointing angle of a moving monopulse antenna. Pulses of energy are broadcast at the surface of a planetary body. Reflected signals are received from the surface of the planetary body using a plurality of feeds. A monopulse ratio is then calculated based on a sum pattern and a difference pattern. The sum pattern is based on the sum of the reflected signals received using the feeds, and the difference pattern is based on a difference of the reflected signals received using the feeds. An azimuth pointing angle of a monopulse antenna is then calculated using the monopulse ratio.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Robust detection technique of fixed and moving ground targets using a common waveform
Detection of moving targets in SAR images is improved by a radar on a moving platform for generating a focused synthetic aperture image of a scene The scene contains a target described by pixels within the SAR image. The radar has a monopulse antenna having a sum channel output and a difference channel output feeding analog to digital converters for converting the sum channel output and difference channel output into respective digital streams concurrently. The digital streams generate a difference channel SAR image and a sum channel SAR image.Target ratios are computed for those pixels descriptive of a target within the scene. Background ratios are computed for pixels around the target. Target ratios and background ratios define respective least square fit of angle discriminants. Comparing the target least square fit of angle discriminant with the background least square fit angle discriminant identifies an angle offset and a Doppler offset of the target with respect to the background.The background least square fit of angle discriminant using background ratios is computed for a region around the target. A 20 by 20 sum synthetic aperture pixels is evaluated as a background around the target.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
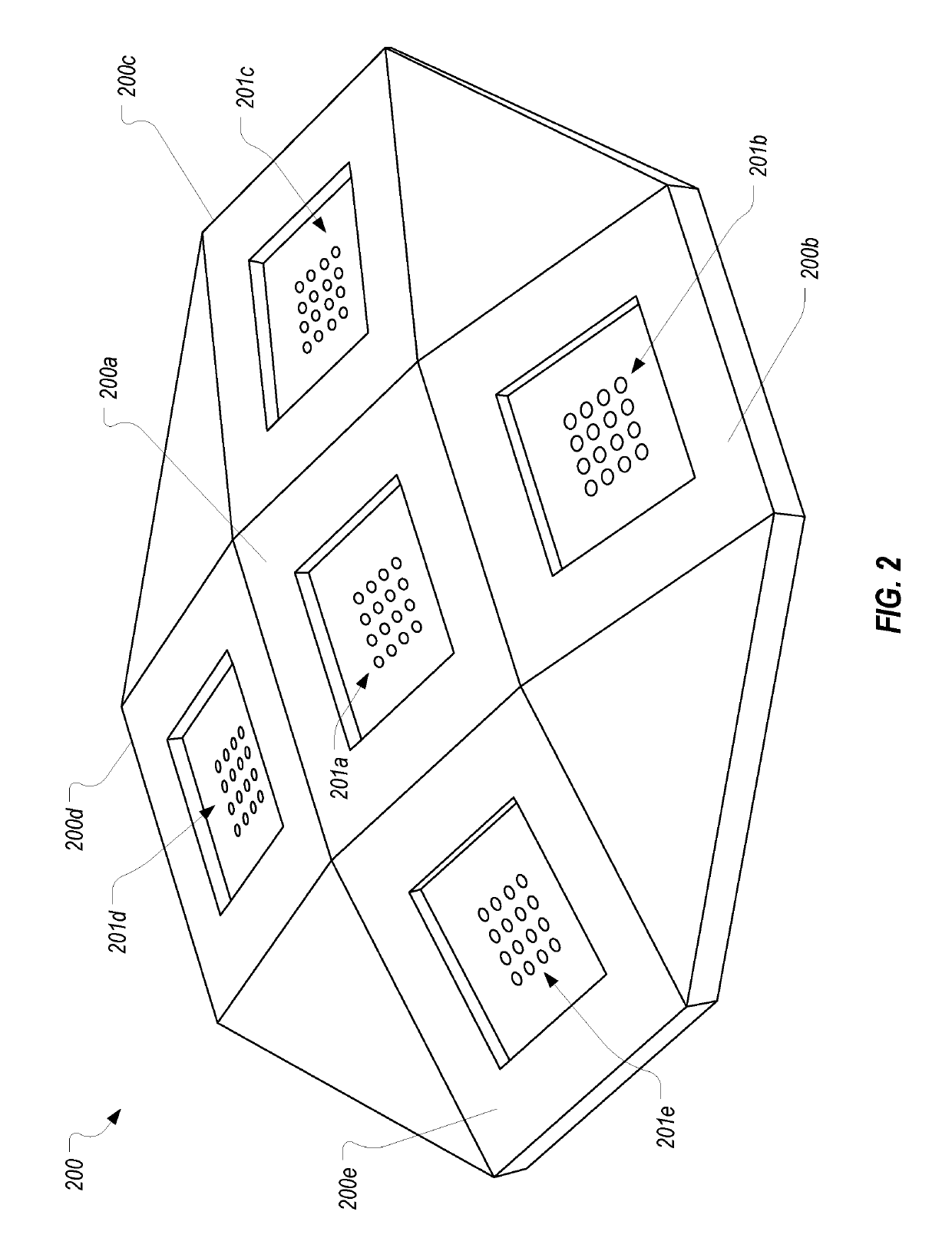
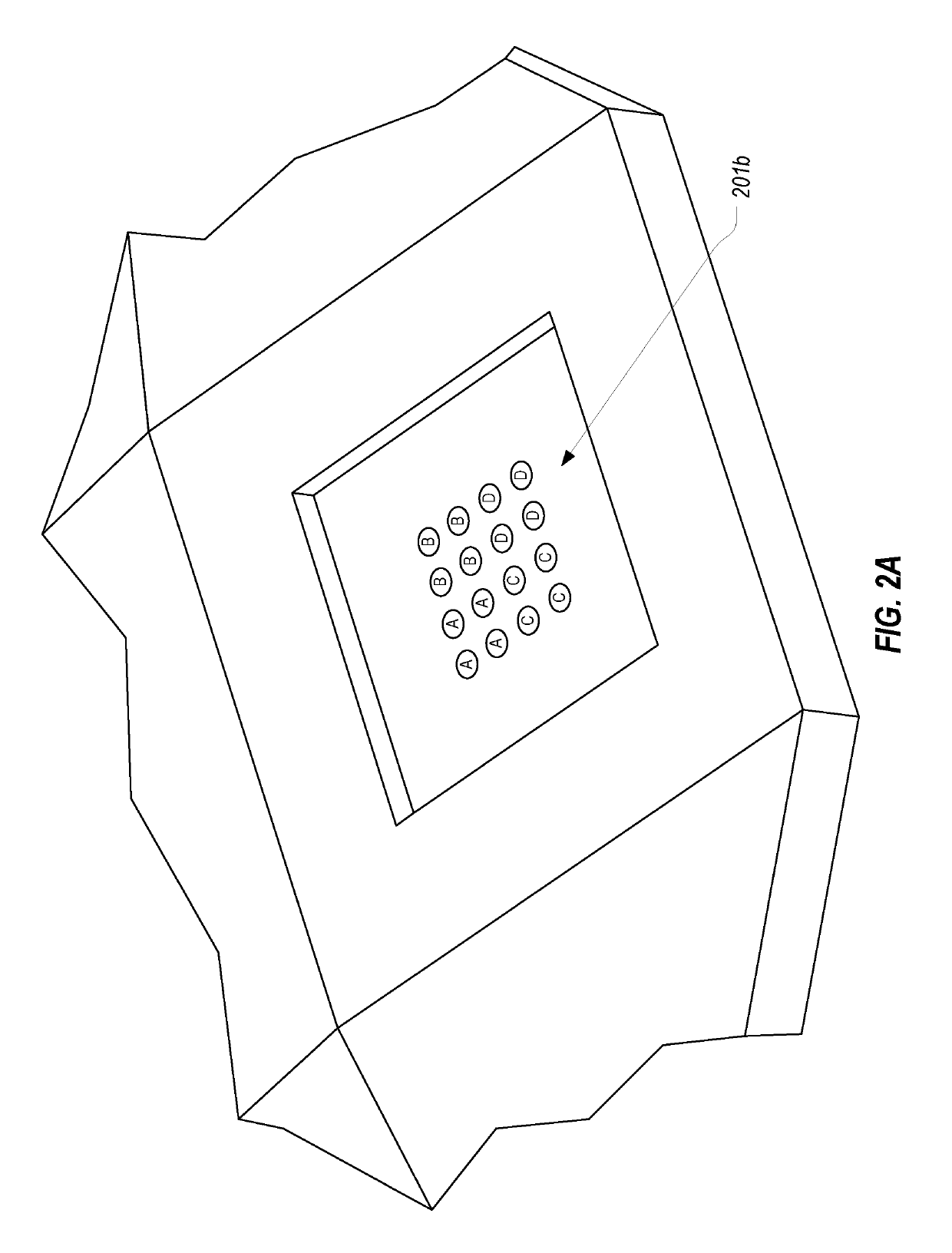
Low-profile monopulse tracker
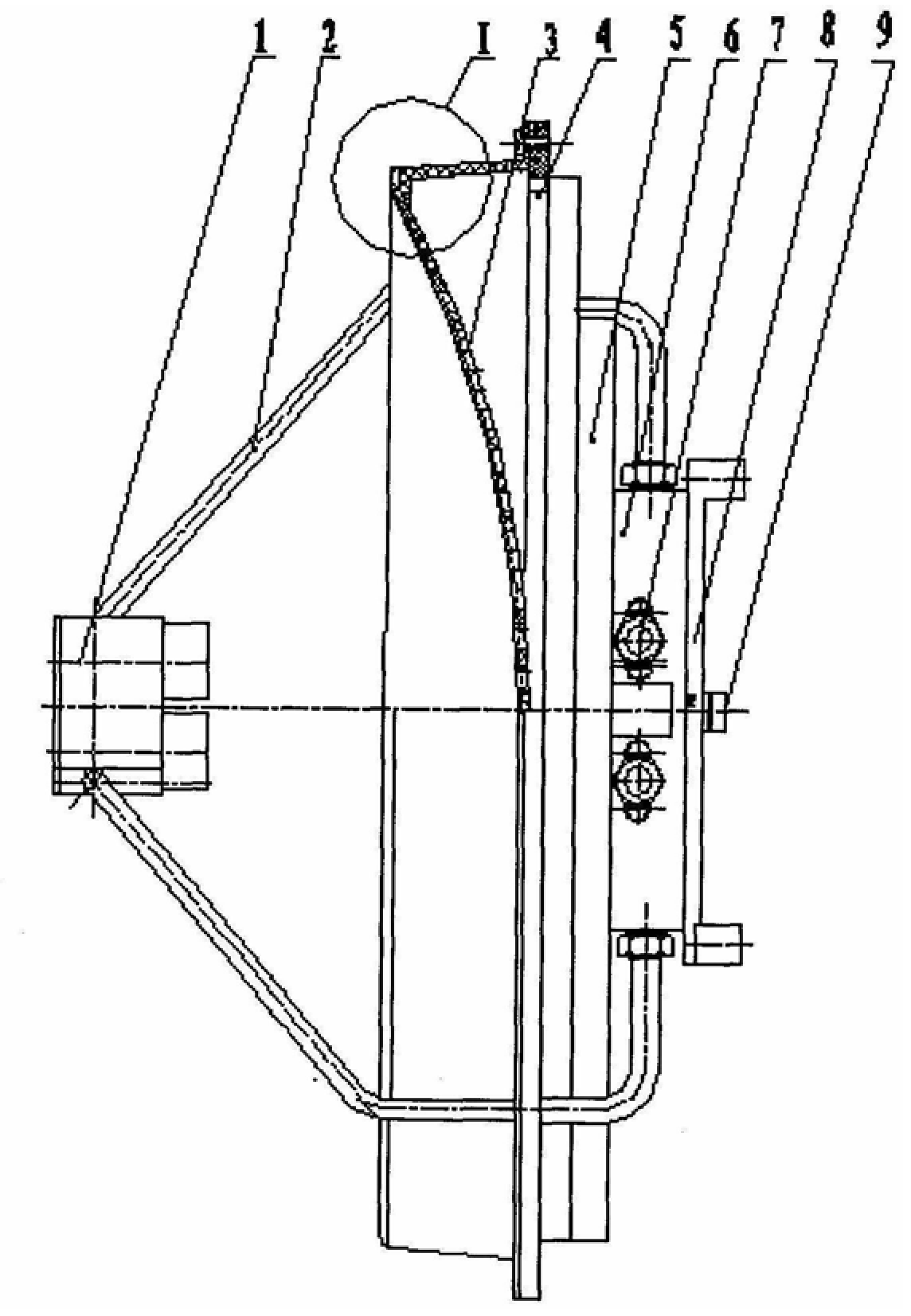
A monopulse tracker includes multiple dual-axis monopulse antenna systems that are angled with respect to one another. The orientations of the monopulse antenna systems create a much larger field of view for the monopulse tracker to eliminate the need to steer the monopulse tracker. The monopulse tracker can be configured to estimate a position of an object based on tracking information received from more than one monopulse antenna system therefore increasing the accuracy of the estimated position. The multiple monopulse antenna systems can be arranged in a low-profile housing to facilitate use of the monopulse tracker on aircraft.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Monopulse antenna array of integrated broadband miniaturization and difference phase comparison network
ActiveCN107464993AHigh bandwidthSolve the problem of narrowbandAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsElectricityRadar systems
The invention discloses a monopulse antenna array of an integrated broadband miniaturization and difference phase comparison network. The monopulse antenna array comprises a miniaturized broadband plane and difference phase comparison network and a plane yagi array antenna; the miniaturized broadband plane and difference phase comparison network is composed of a double-faced parallel strip line, and comprises a first-level network and a second-level network, the first-level network comprises a first-level network and a second-level network, the first-level network comprises a first-level annular coupler, the second-level network comprises two second-stage annular couplers, a phase inverter is arranged at the annular part of the couplers, and electrical connection is formed between the upper layer and the lower layer of the phase inverter through a metallized through hole. The bandwidth of the integrated broadband miniaturization and difference phase comparison network is increased, the monopulse antenna array has smaller structure size and is smaller than the size of a general T-shaped power dividing feed network, and a transition structure between the feed network and the antenna is not needed; by adopting a plane structure, the integral construction is greatly simplified, the processing difficulty is low, and the monopulse antenna array is easy to large-scale production, is easy to be integrated with other plane circuits, is particularly suitable for integration in radar systems, and is extremely convenient to install and debug.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System and method for estimating the azimuth pointing angle of a moving monopulse antenna
ActiveUS20060109172A1Antenna detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMonopulse antennasPlanetary body
An invention is provided for determining the azimuth pointing angle of a moving monopulse antenna. Pulses of energy are broadcast at the surface of a planetary body. Reflected signals are received from the surface of the planetary body using a plurality of feeds. A monopulse ratio is then calculated based on a sum pattern and a difference pattern. The sum pattern is based on the sum of the reflected signals received using the feeds, and the difference pattern is based on a difference of the reflected signals received using the feeds. An azimuth pointing angle of a monopulse antenna is then calculated using the monopulse ratio.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Dual-polarized monopulse antenna based on substrate integrated waveguide and strip line feed
ActiveCN114006172ASimple feeding methodHigh gainDisturbance protectionSubstantially flat resonant elementsEngineeringPerpendicular polarization
The invention discloses a dual-polarized monopulse antenna based on substrate integrated waveguide and strip line feed. A square patch layer, a first substrate integrated waveguide cavity layer shaped like a Chinese character ''tian'', a first cross-shaped slot layer, a second substrate integrated waveguide cavity layer shaped like a Chinese character ''tian'', a second cross-shaped slot layer, a substrate integrated waveguide comparator layer, a vertical slot layer, a strip line layer and a metal bottom plate are sequentially arranged from top to bottom. An electromagnetic field forms a vertical polarization electromagnetic field after passing through the second cross-shaped slot layer, the vertical polarization electromagnetic field is coupled to the first cross-shaped slot layer to form a high-order mode, is finally coupled to the square patch layer, and is radiated to a free space by the square patch layer to form a vertical polarization wave beam; the strip line layer excites the vertical slot layer to generate a horizontal polarization electromagnetic field, and the horizontal polarization electromagnetic field is coupled to a square patch through a second cross-shaped slot and a first cross-shaped slot and radiated to a free space by the square patch to form a horizontal polarization beam. The dual-polarized monopulse antenna is simple in structure, high in gain and relatively deep in zero depth; and dual polarization of the monopulse antenna is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
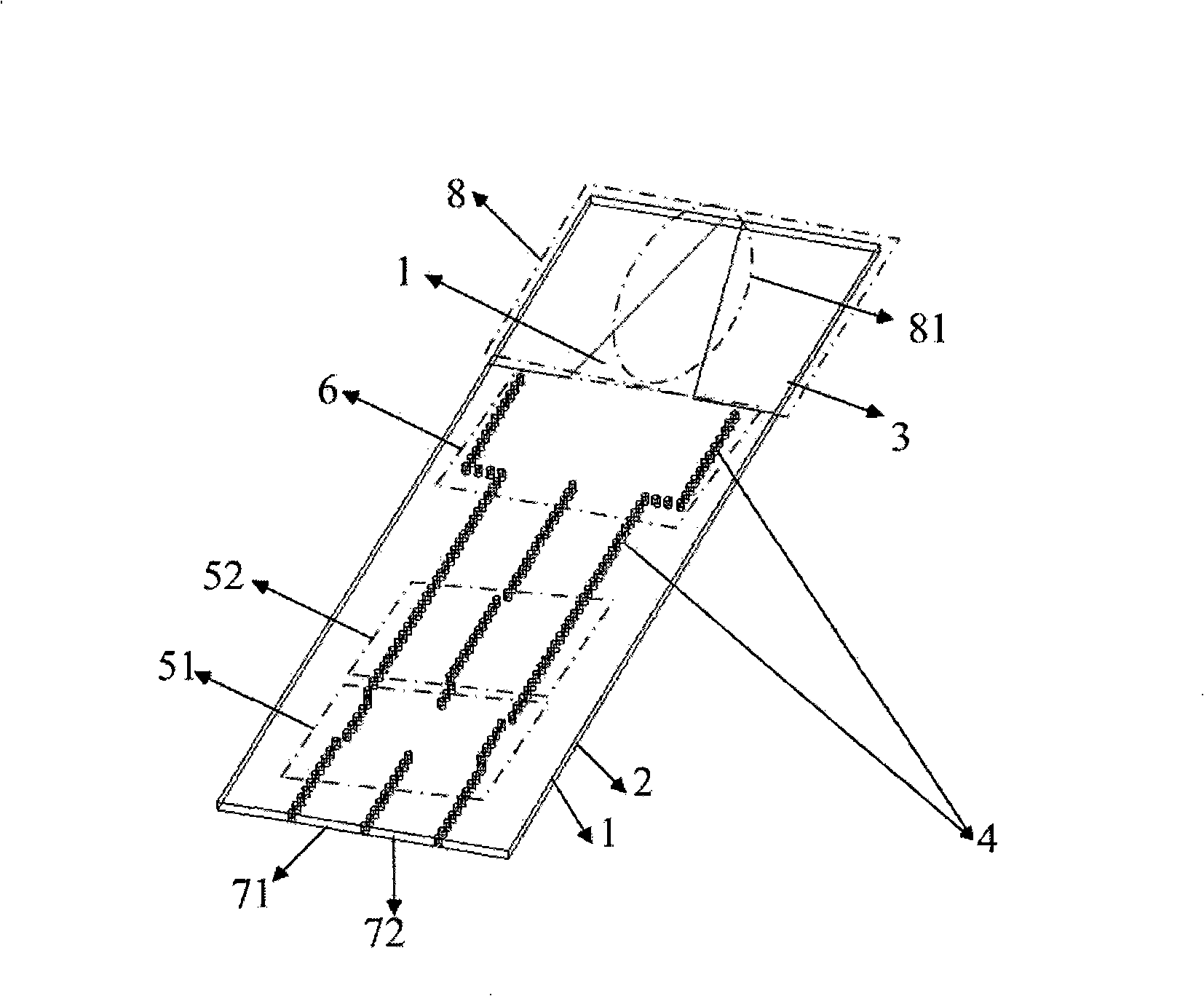
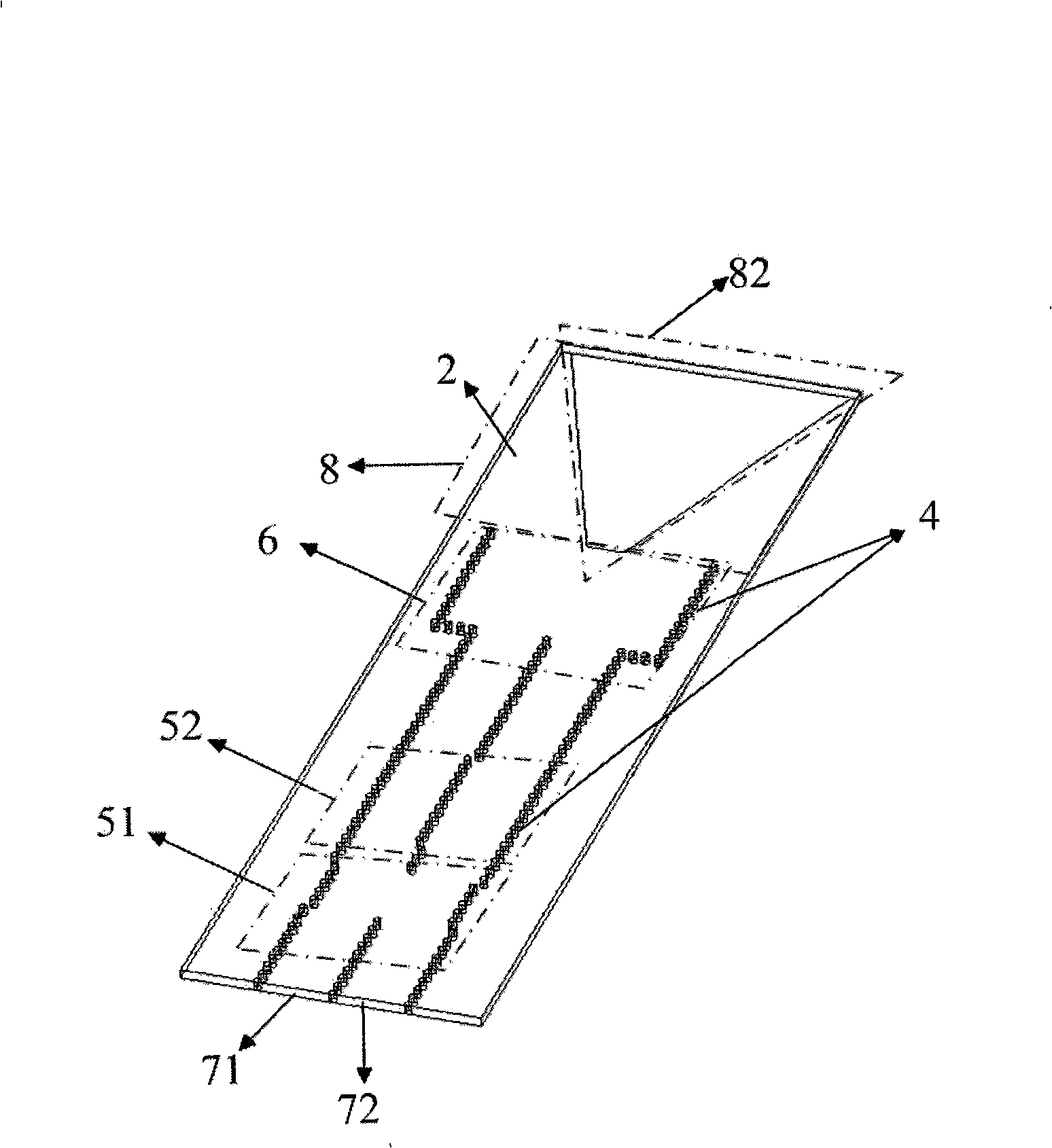
Single pulse antenna with double V shaped linear gradually changing slot
InactiveCN101340021AHigh gainHigh Q valueAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateWaveguide
A double V-shaped linear tapered slot monopulse antenna can be applicable to the systems of tracking, detection, communication, measurement, astronomical observation, etc. The antenna comprises an upper layer metal copper bonded surface (1), a lower layer metal copper bonded surface (2), a dielectric substrate (3), a metallized through hole (4), a substrate integrated waveguide 90-degree directional coupler (51), a 90-degree phase shifter (52), a substrate integrated waveguide H-plane wave generator (6), an input port (71), an output port (72), a double V-shaped linear tapered slot antenna (8), an upper surface triangular metallic cladding (81) and a lower surface triangular slot (82); a multimode substrate integrated waveguide is adopted for feeding to form a monopulse antenna. The double V-shaped linear tapered slot monopulse antenna works at the millimeter wave frequency band, can be directly applied to the integrated circuit design, and is characterized by low consumption, small volume, low cost and being easy for mass production, etc.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Monopulse antenna angle simulation tracking method
ActiveCN102722184BRealize sidelobe simulation functionFriendly human-computer interfaceControl using feedbackReduced modelIntermediate frequency
The invention provides a monopulse antenna angle simulation tracking method, which aims at providing an environment for inspecting and simulating equipment tracking performance at any time to a shooting range monitor system. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: establishing an XOY plane measurement coordinate system by taking the center of three axes of an antenna as an original point; constructing a simulation circuit according to an antenna pattern simplified model; drawing four calibration curves of a sum and different signal magnitude difference-deviation angle relationship, sum and difference signal amplitude different-error voltage relationship, deviation angle-error voltage relationship and deviation angle-AGC (automatic gain control) voltage relationship on each angle beyond the main beam of the antenna, and establishing a data mapping table; acquiring the controlled variable of an angle deviation control circuit and simulating to generate a radio frequency tracking signal according to a method of checking a signal amplitude mapping table; and demodulating and extracting an angle error signal by receiving link amplification and down-conversion in an intermediate frequency tracking receiver; and feeding position and pitch angle error voltage to an antenna control unit to complete angle closed-ring tracking.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
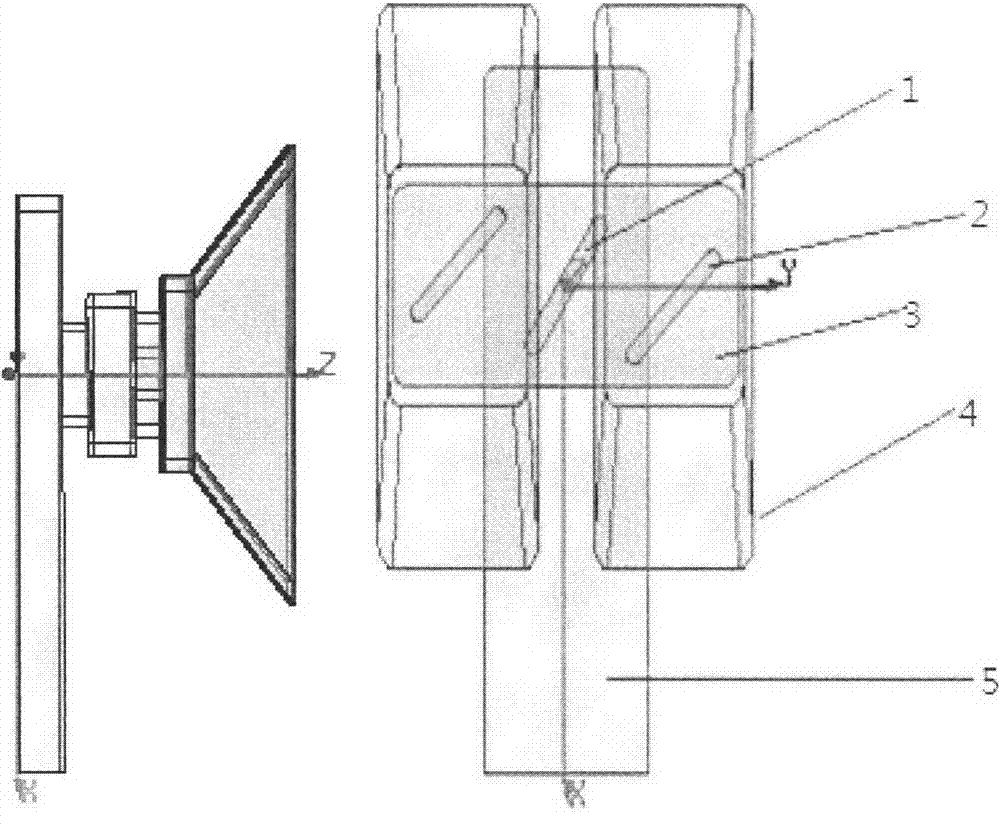
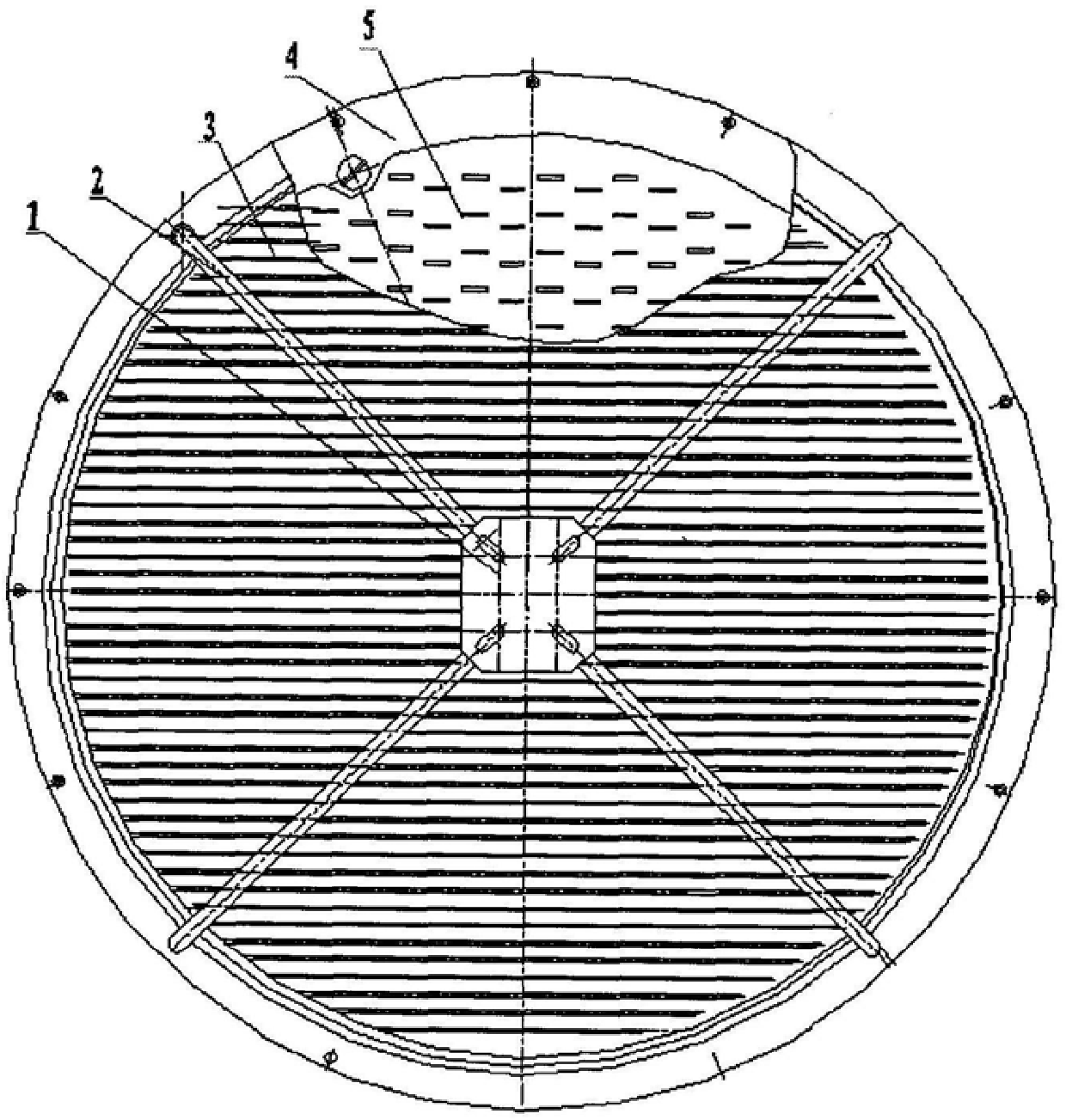
Miniature dual-frequency-band coplanar composite monopulse array antenna
ActiveCN105071053AClever layoutReduce coupling effectSeparate antenna unit combinationsLow frequency bandDouble frequency
A miniature dual-frequency-band coplanar composite monopulse array antenna comprises the components of a circular metal reflecting plate which is uniformly divided into four sector-shaped areas; a low-frequency-band radiating array plane which is arranged at the frontmost end of the monopulse array antenna and comprises a plurality of microstrip antenna arrays that are arranged above the metal reflecting plate; a low-frequency-band pitching surface waveguide power synthesizing network which is arranged below the low-frequency-band radiating array plane and is connected with the low-frequency-band radiating array plane; a high-frequency-band radiating array plane which is arranged below the low-frequency-band radiating array plane and comprises a plurality of waveguide opening antenna arrays that are arranged below the metal reflecting plate; and a high-frequency-band waveguide power synthesizing network which is arranged below the high-frequency-band radiating array plane and is connected with the high-frequency-band radiating array plane. The miniature dual-frequency-band coplanar composite monopulse array antenna is advantageous in that relatively low minor lobes and a radiating efficiency which is equivalent with that of a single-frequency single-pulse antenna; furthermore a coupling effect of two frequency bands is reduced; the miniature dual-frequency-band coplanar composite monopulse array antenna has characteristics of small size and double frequencies; ingenious layout is realized and a requirement for combining and being compatible between the antenna arrays in two frequency bands of the space can be satisfied; and furthermore the miniature dual-frequency-band coplanar composite monopulse array antenna has high practicability and wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
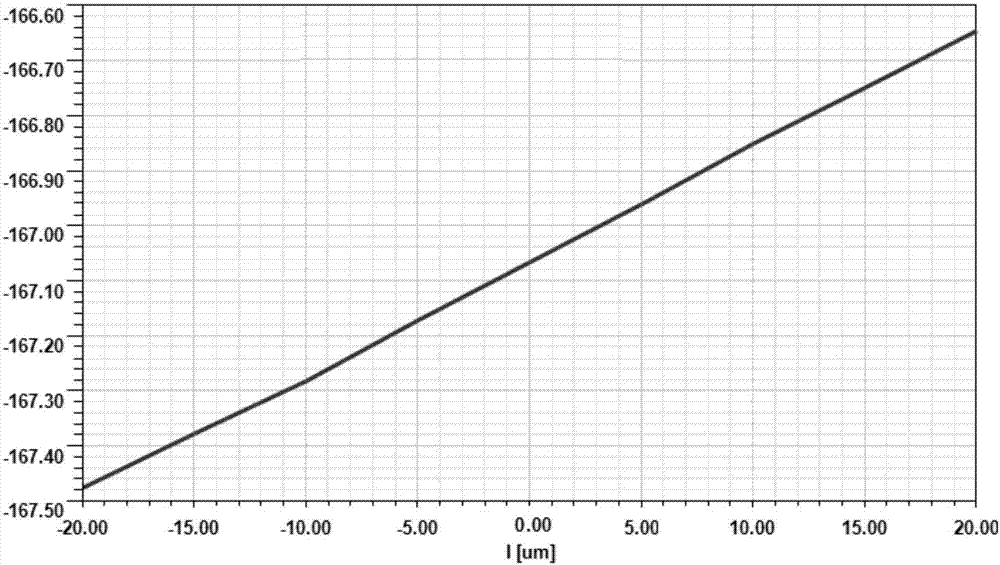
Adaptive discovery and correction of phase alignment errors in monopulse antenna systems
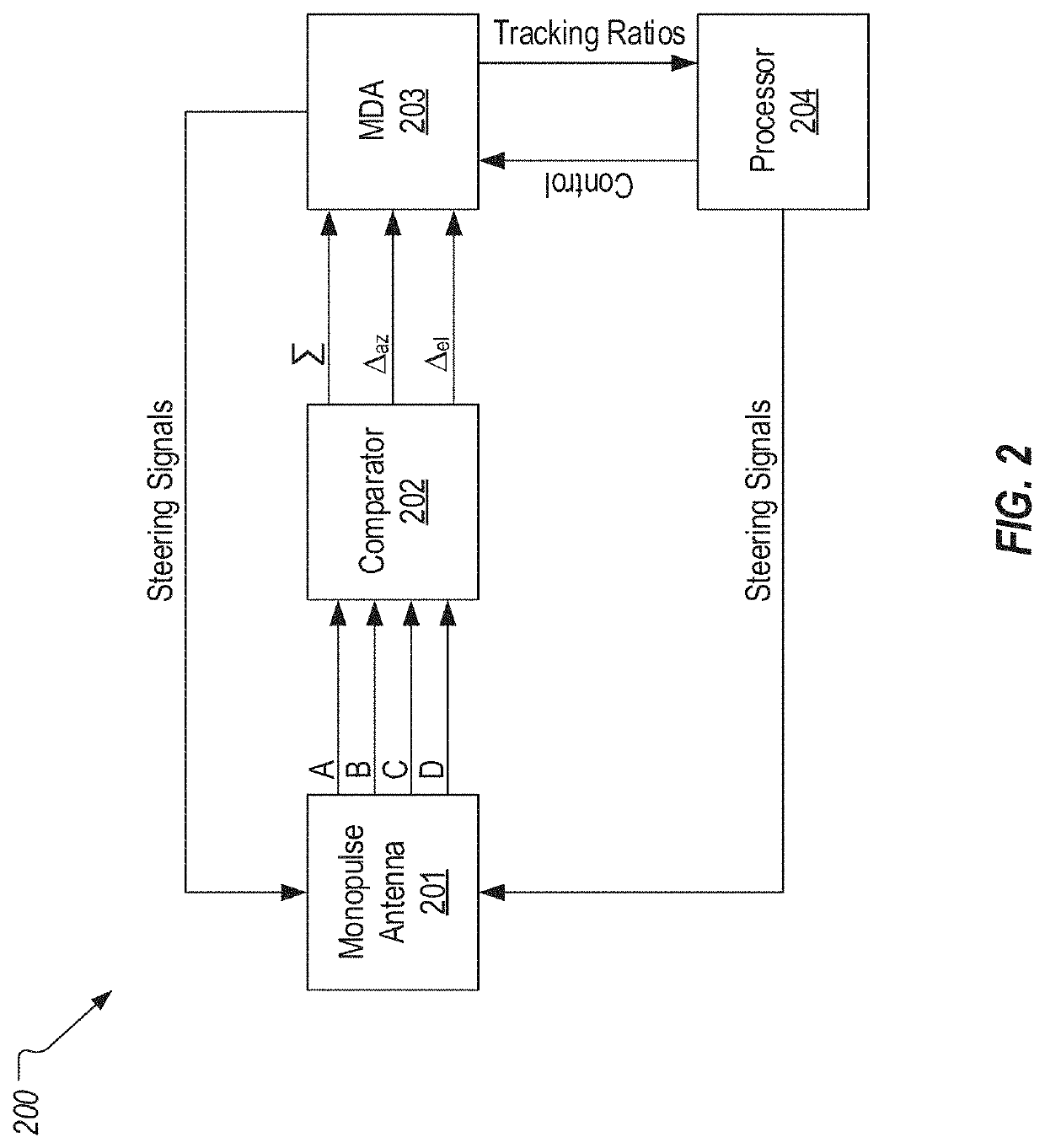
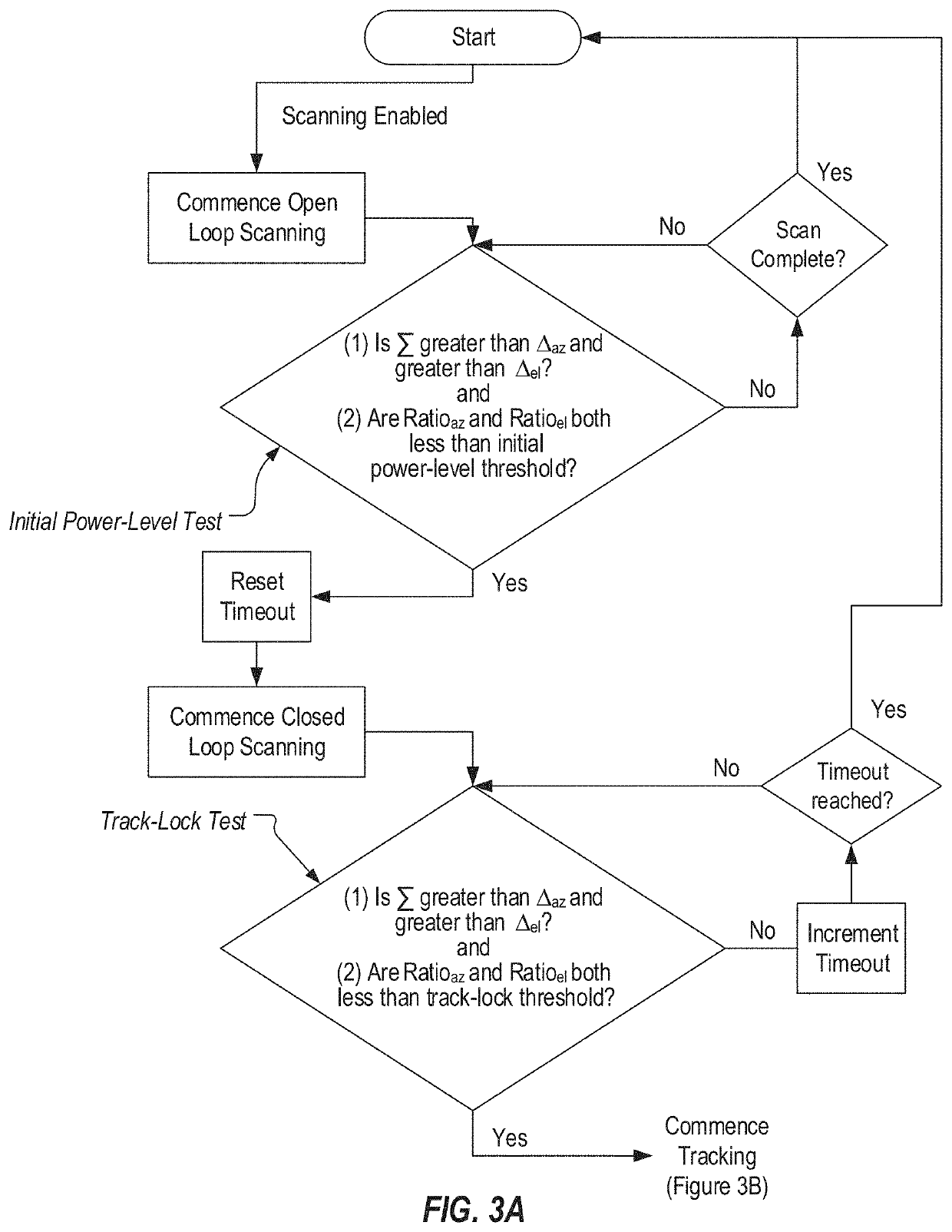
A mainlobe detection process can include a number of tests that are performed to define when the monopulse antenna system will transition from open loop scanning to closed loop scanning and then to tracking. A hybrid tracking technique is also provided which adaptively discovers and corrects for phase alignment error. Magnitude-only tracking can be performed initially to locate the nulls in the azimuth and elevation ratios and to identify the magnitudes of these ratios at these nulls. Phase tracking can be then performed. During phase tracking, phase corrections can be repeatedly applied to the azimuth and elevation difference channels to correct any phase error that may exist. During this process, the magnitudes of the ratios can be used to determine how the phase corrections should be adjusted. Once the hybrid tracking process is complete, the monopulse antenna system is properly phase-aligned and phase tracking will be correctly employed.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Active and passive radar seeker composite antenna
ActiveCN106342376BHigh gainEliminate occlusionIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsSlot antennasPassive radarAntenna gain
The active and passive radar seeker composite antenna of the invention belongs to the antenna technology and relates to the improvement of the active and passive radar seeker composite antenna. It includes a waveguide slotted array monopulse antenna with high gain and low sidelobe working in the Ka band. Slit Array Monopulse Antenna A common-aperture parabolic four-horn monopulse antenna working in the X-band. The gain of the active and passive antennas of the invention is relatively high, which greatly increases the working distance.
Owner:CHINA AIR TO AIR MISSILE INST
Method for easily adjusting overlapping of electric axes of multiple antennas
ActiveCN107544554AImproving Impedance MatchingSimple structureControl using feedbackAntenna radiation diagramsPhase shiftedImpedance matching
The invention relates to a method for easily adjusting the overlapping of the electric axes of multiple antennas. The method configures electric axis regulators which separately correspond to a plurality of zones of multiple antennas so as to perform phase adjustment, and the electric axes of the antennas are adjusted by the electric axis regulators, such that the adjusted electric axes of the antennas overlap a mechanical axis. According to the invention, the method herein, by adding electric axis regulators or replacing electric axis regulators at different phases, can adjust the electric axis of a monopulse antenna until the electric axis and the mechanical axis completely overlap. By adding metal adjusting blocks on the broad face of a waveguide, the method herein can increase or decrease signal transmission paths, adjusts signal phase, designs the structure of wide phase shift of the electric axis regulator, and achieves impedance matching. According to the invention, the method therein has the advantages of simple structure, easy implementation, wide adjustment range, and high integration, and is suitable for adjusting the electric axes of multiple antennas of any specification.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com