Patents
Literature
52 results about "Multi element antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
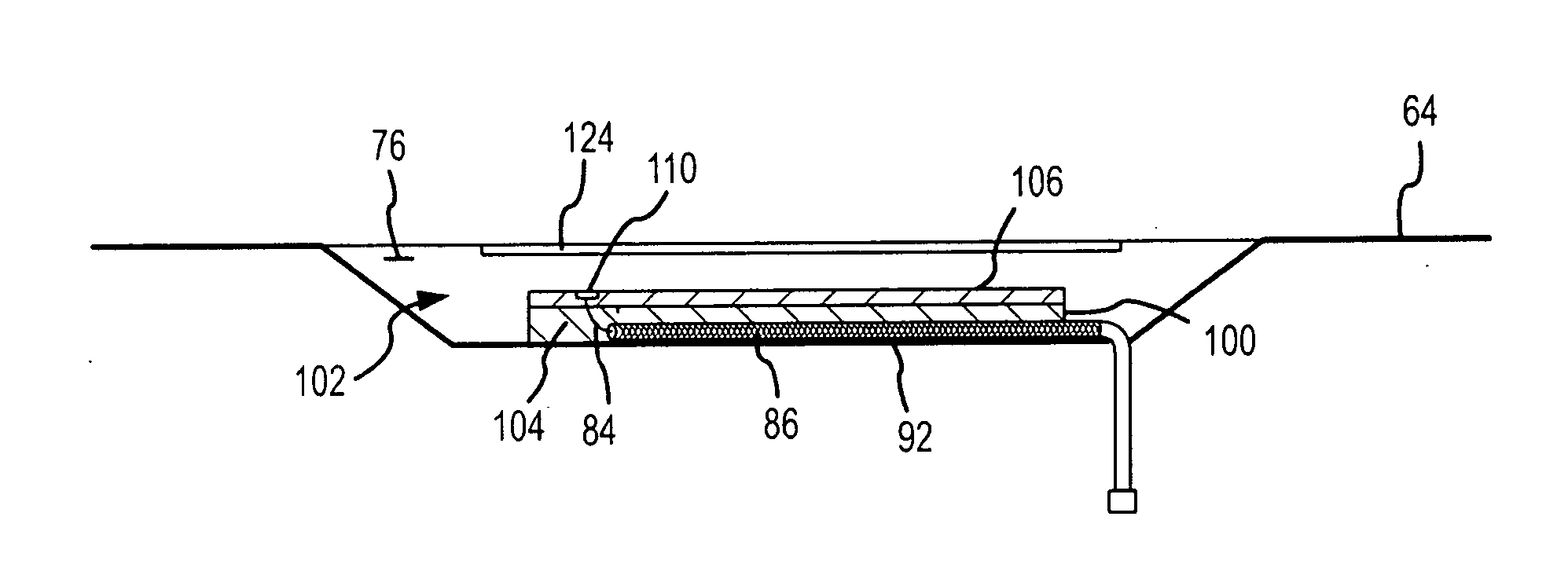
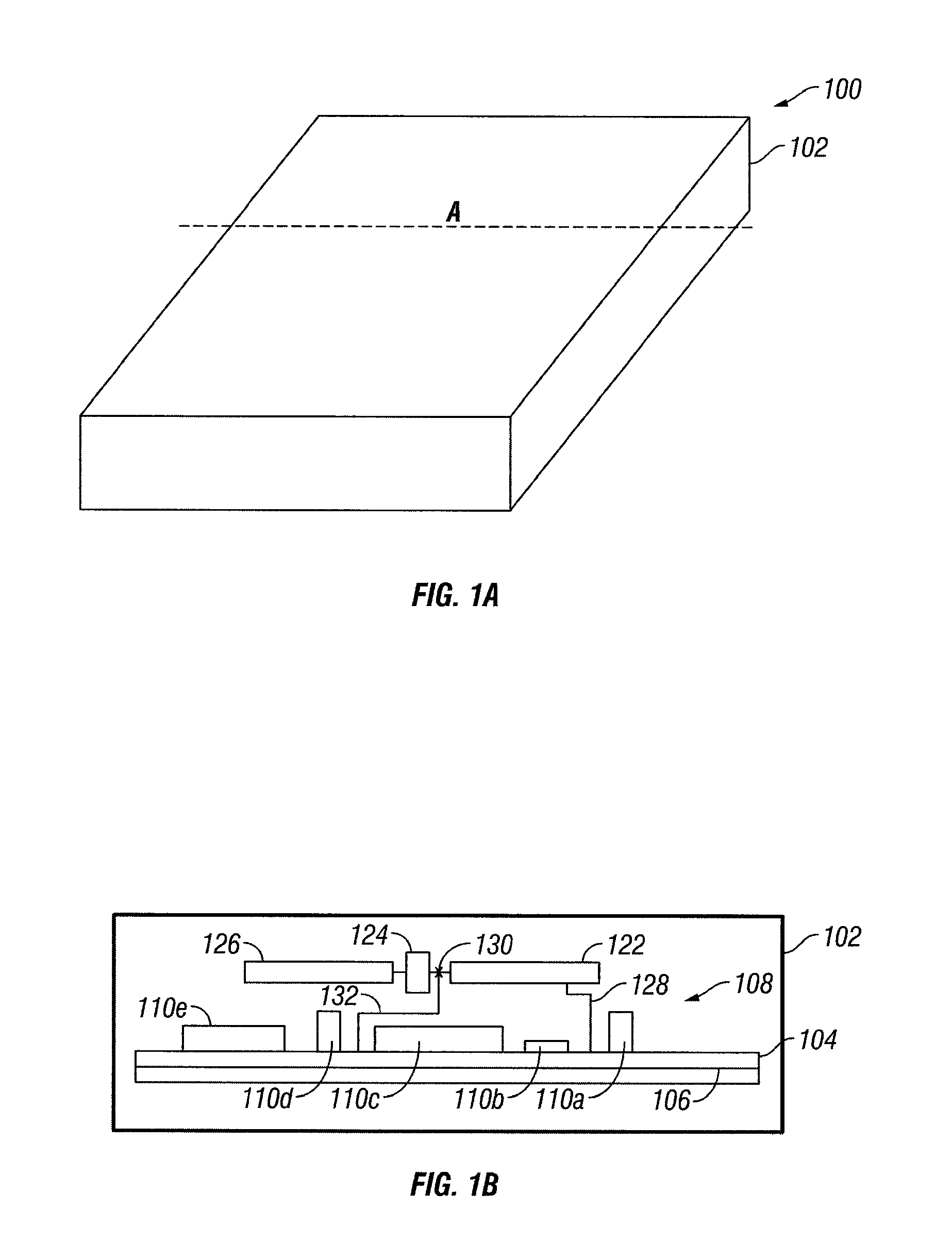
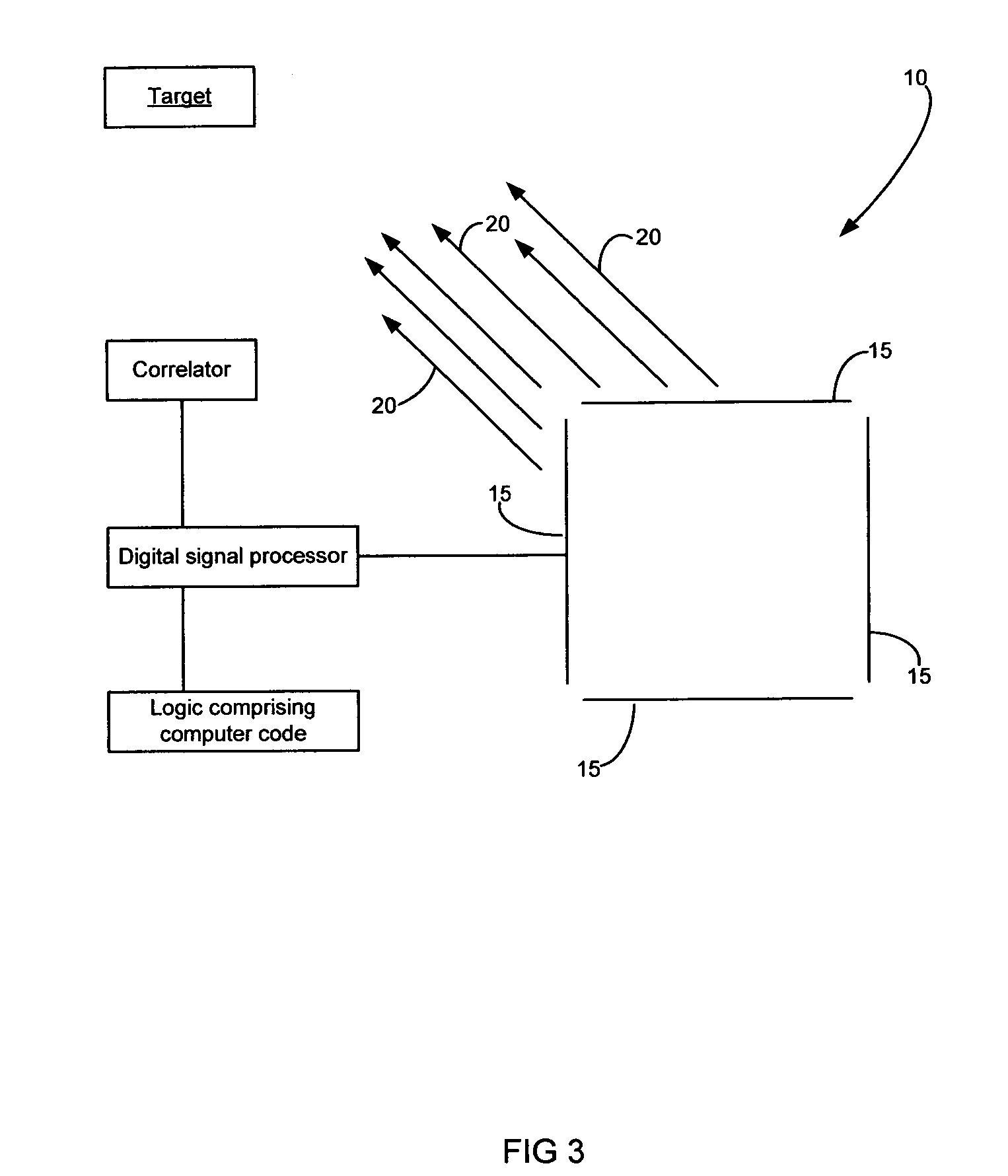
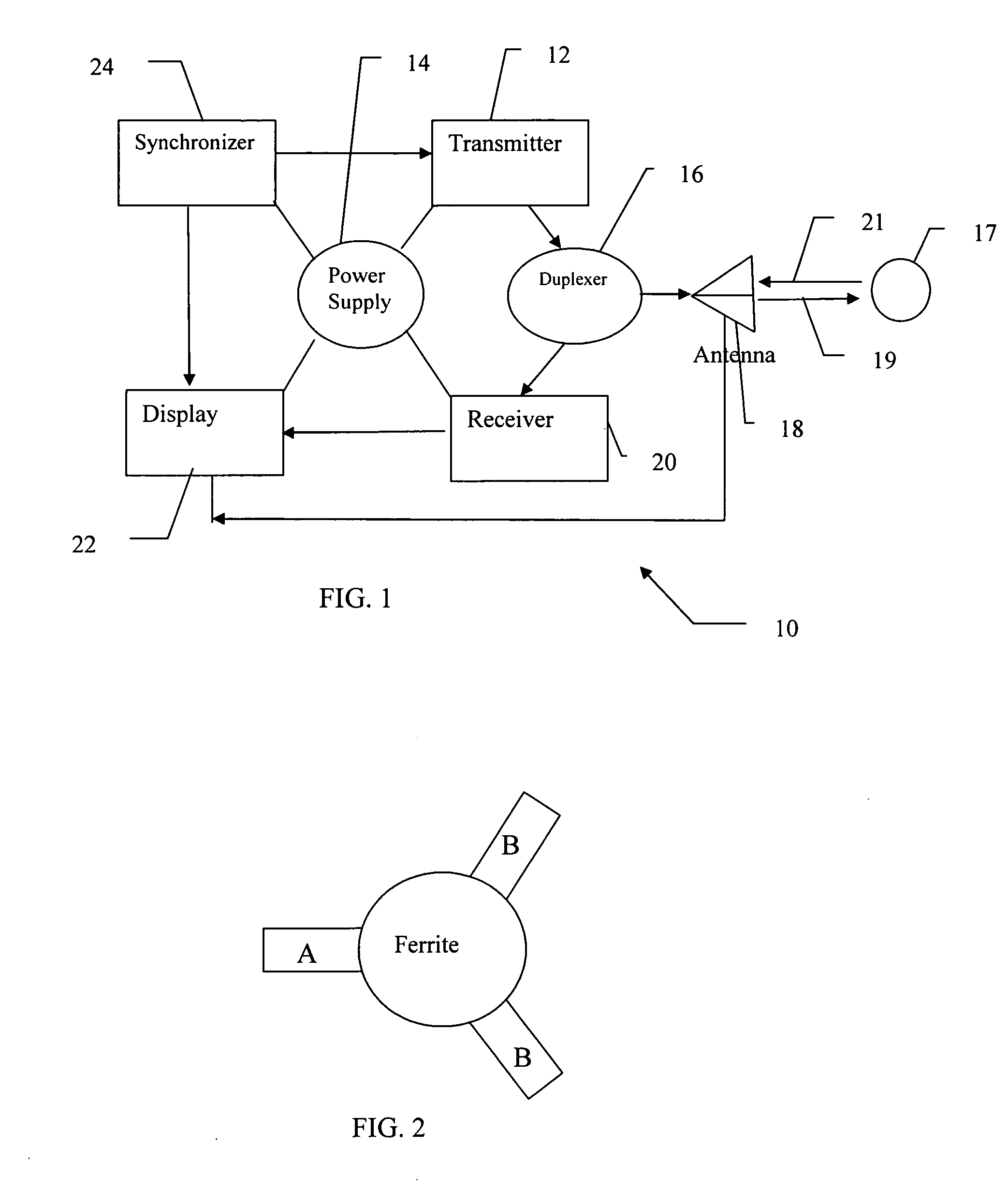
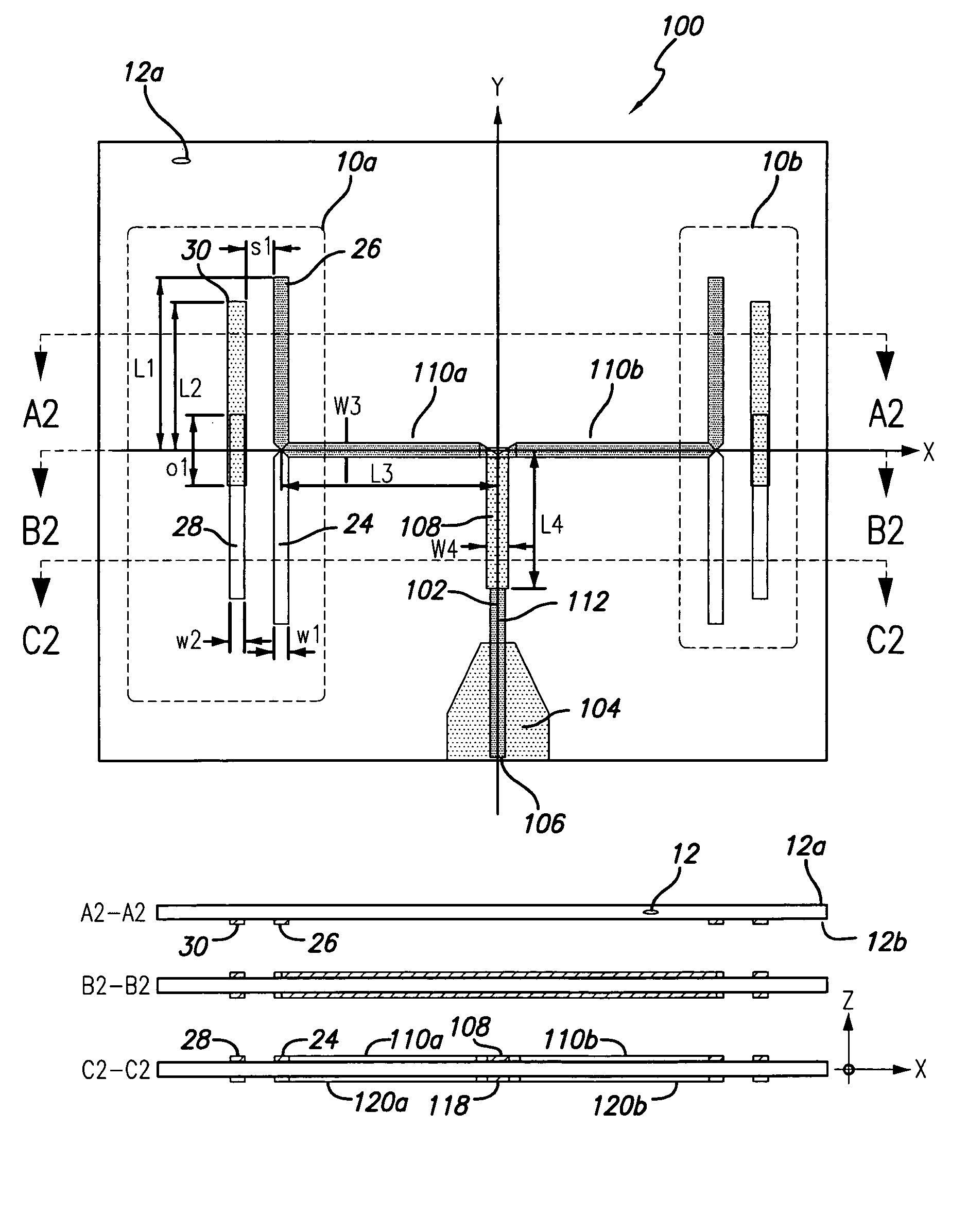
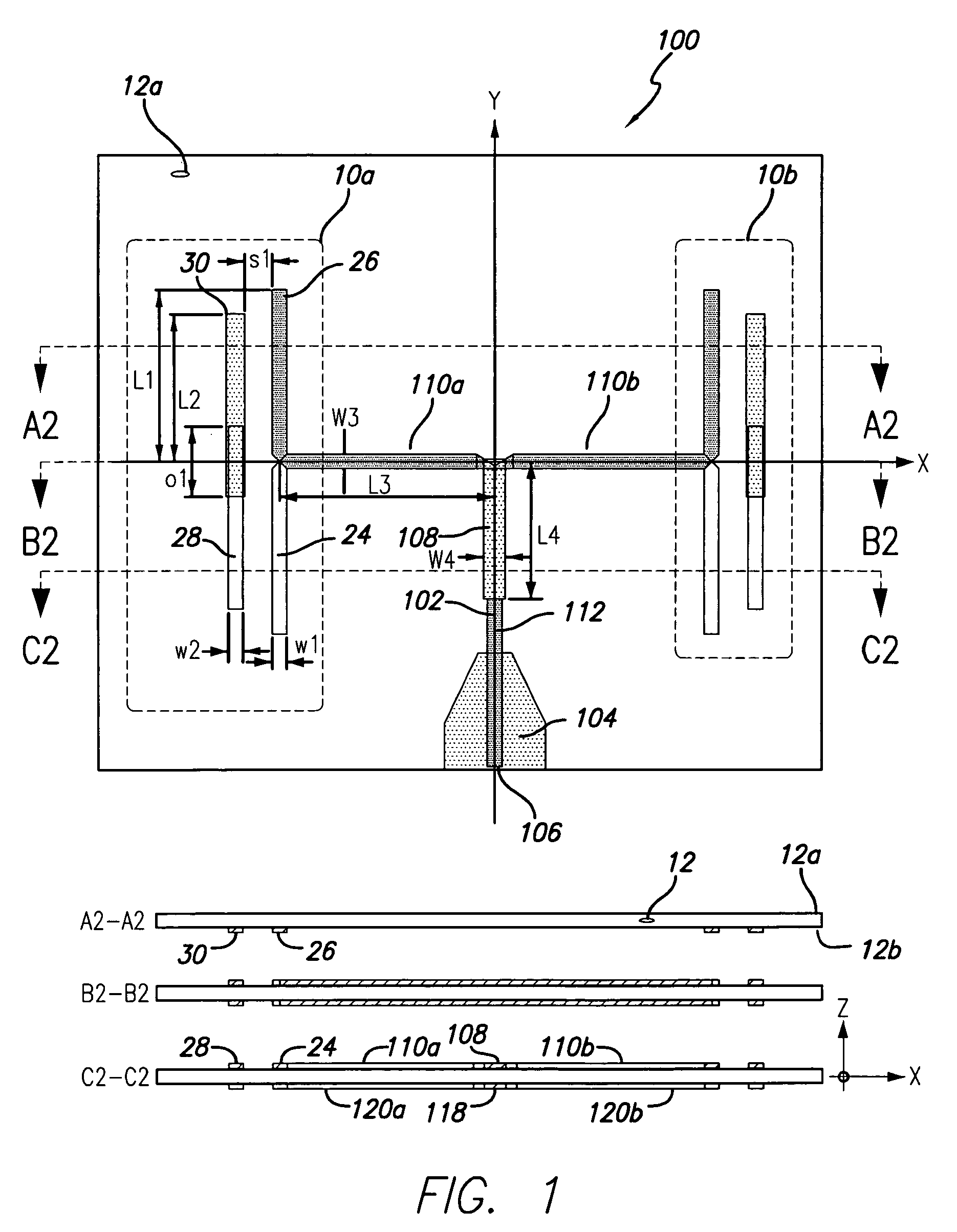
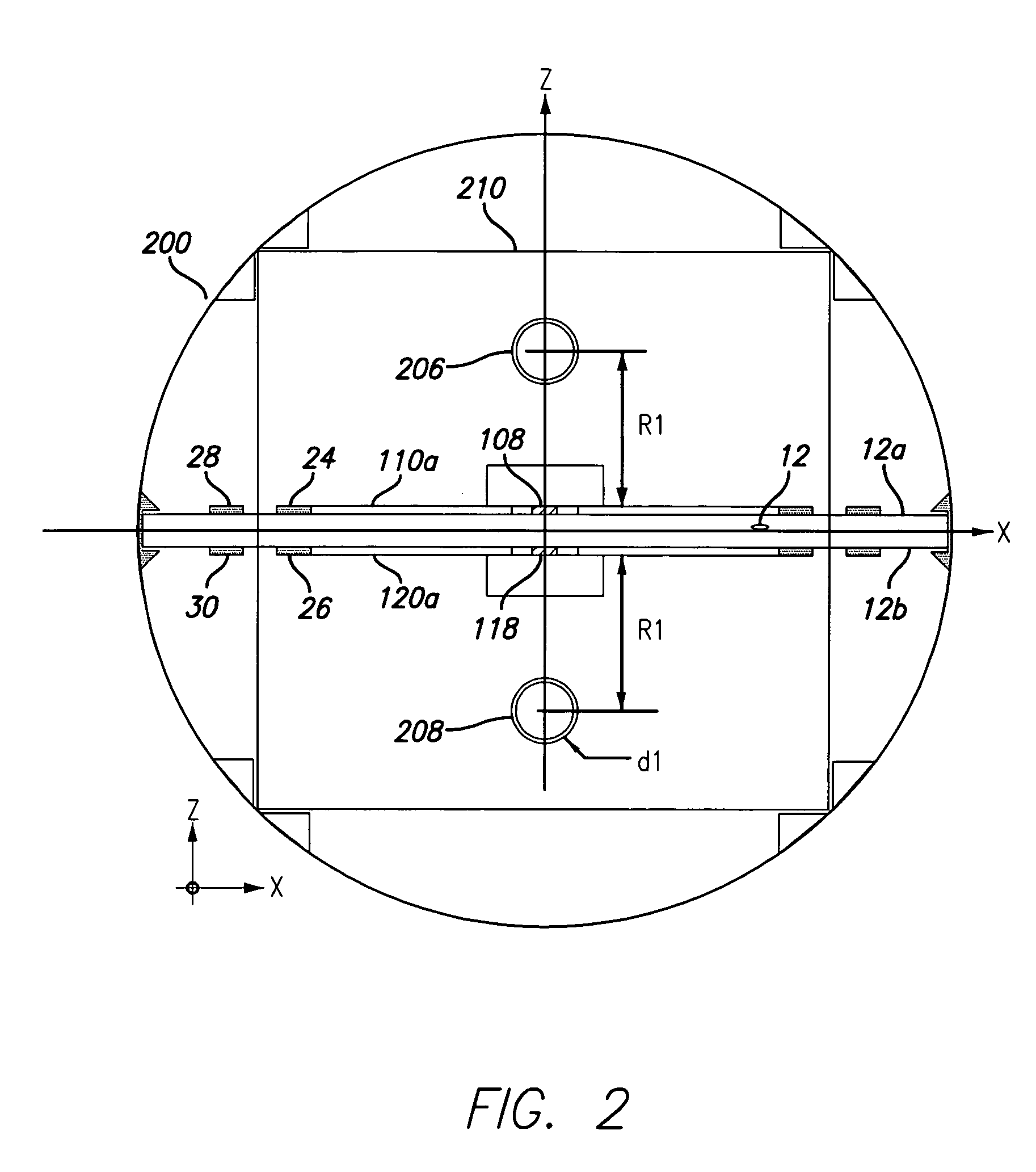
Compact, multi-element antenna and method
InactiveUS20060244663A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceTransceiver
An antenna is specially adapted for a portable electronic device, such as a hand-held computer or cell phone, having a conductive metal housing surrounding a radio transceiver. A rectangular recess is formed in one surface of the housing, and an elongated printed circuit board is placed along an inner wall of the housing. A coaxial cable coupled to the transceiver enters the housing, and an outer shield of the cable is connected to the inner wall of the housing along a substantial length of the cable. A center conductor of the cable is connected to a conductive layer of the printed circuit board. The recess is enclosed by a window that is substantially transparent to RF energy. RF energy radiated from the printed circuit board is capacitively coupled to a sheet of conductive material, and the RF energy is then radiated from the conductive sheet.
Owner:VULCAN PORTALS
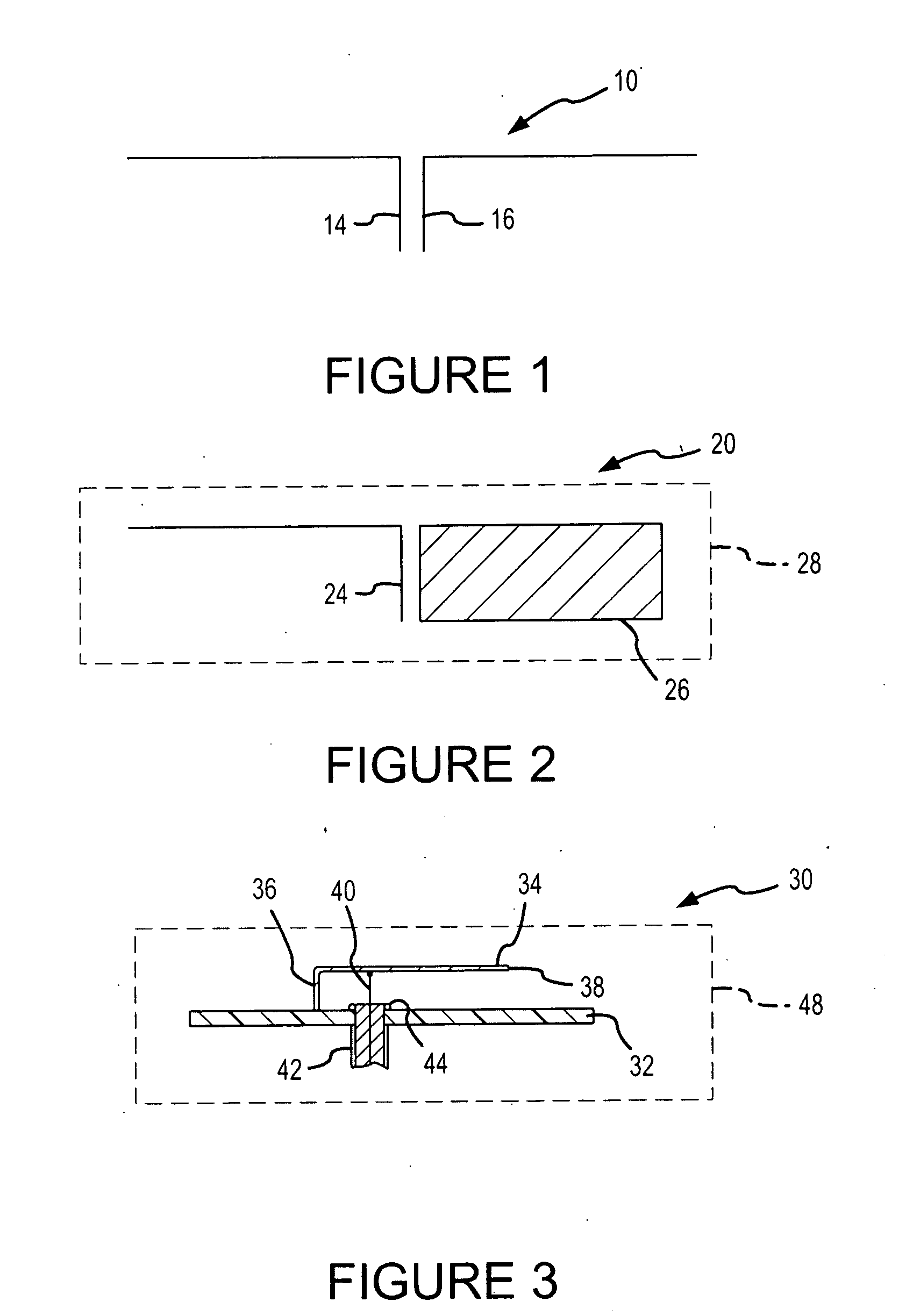
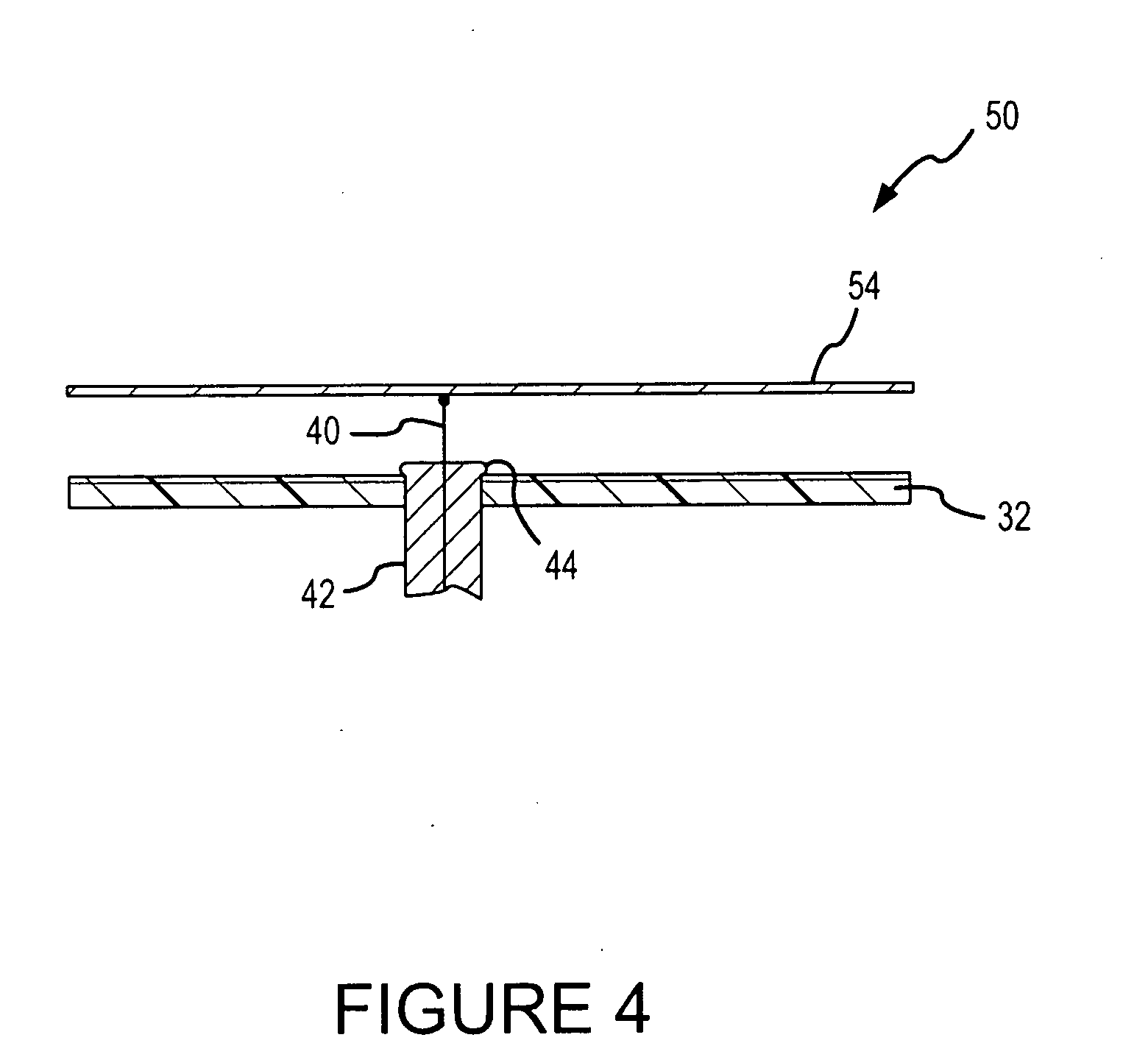
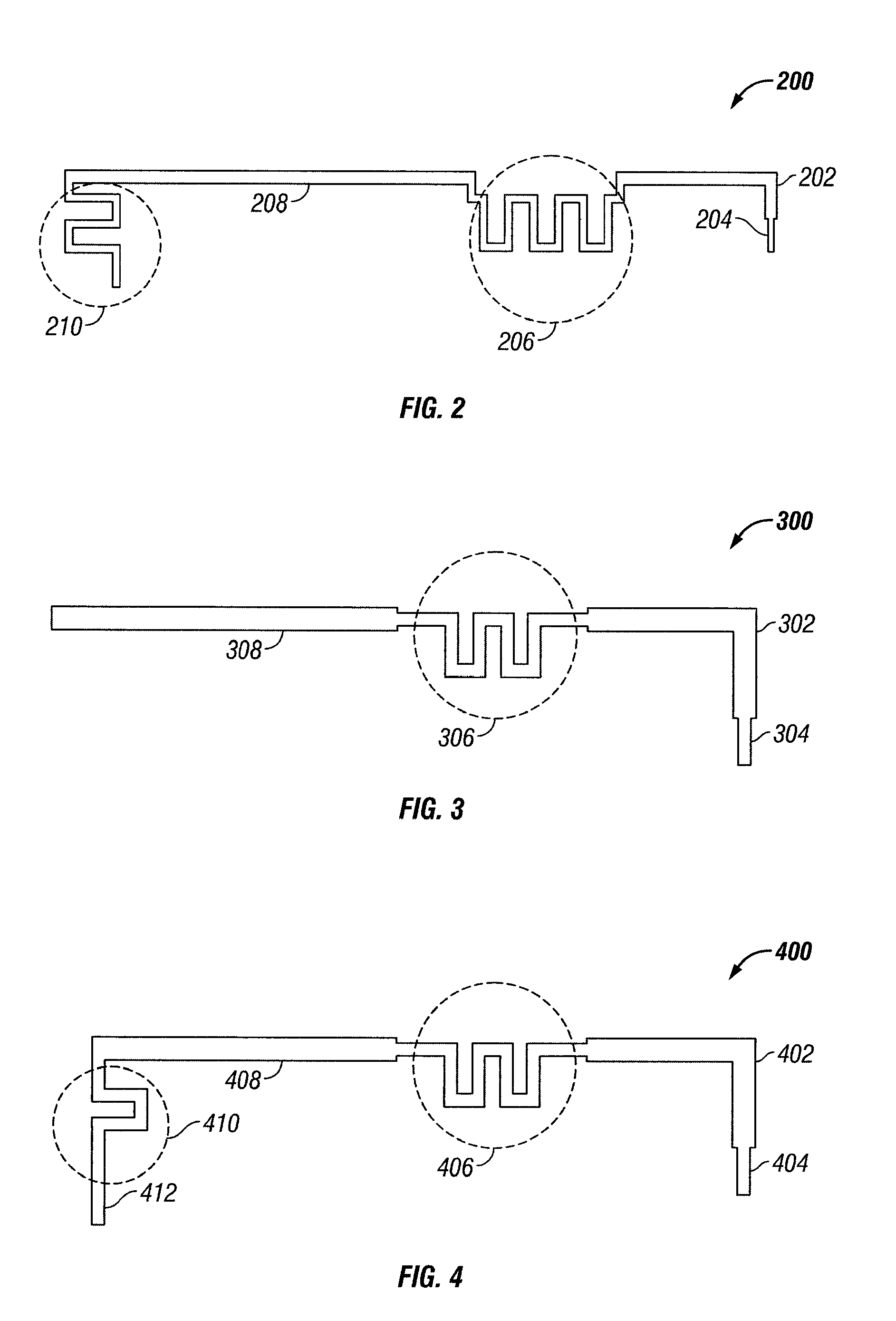
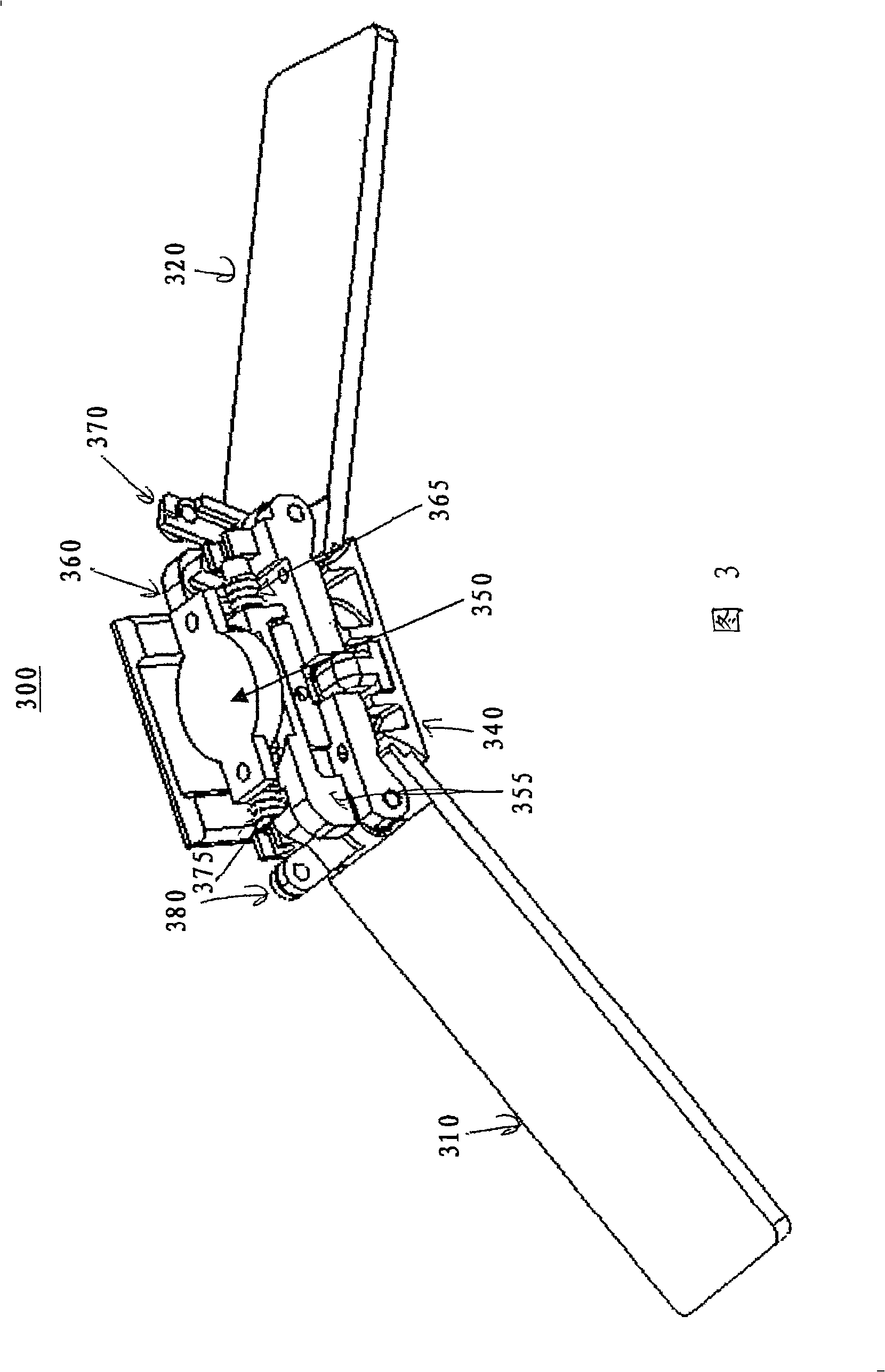
Compact multi-element antenna with phase shift
ActiveUS8310402B2High gainIncrease the lengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsPhase shiftedBeam pattern
A phased array antenna system includes a first radiation element that is made of a material and has a length selected to resonate at a desired frequency. A phase-shift element is coupled to one end of the first radiation element. A second radiation element is coupled to the end of the phase-shift element opposite the first radiation element, so that a radio signal passes through the first radiation element through the phase-shift element and through the second radiation element, the second radiation element is made of a material and has a length selected to resonate such that the first and second radiation elements cooperate to form a desired beam pattern from the antenna system.
Owner:AIRGAIN INC
Ultra-wideband antenna array
InactiveUS7042417B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncreased signal noiseSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityUltra-widebandSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
An ultra-wideband (UWB) antenna array is provided. One embodiment of the present invention employs a multi-element antenna for UWB beam forming and also for time-of-arrival vector processing to resolve multi-path problems in an UWB communication system. Another embodiment of the present invention recovers the energy contained in the multi-path reflections to increase signal-to-noise ratios of received UWB pulses.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
System and method of using absorber-walls for mutual coupling reduction between microstrip antennas or brick wall antennas
InactiveUS7427949B2Reduce signalingReduce horizontal sizeAntenna detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrostrip patch antennaBrick
A multi-element antenna with sufficiently small return loss and mutual coupling signals to allow the simultaneous transmission of powerful radar signals and the reception of faint target return signals. The microstrip patch antenna has radio frequency absorbing material place between neighboring antenna elements to reduce the mutual coupling leakage signals.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
Rf Power Amplifiers
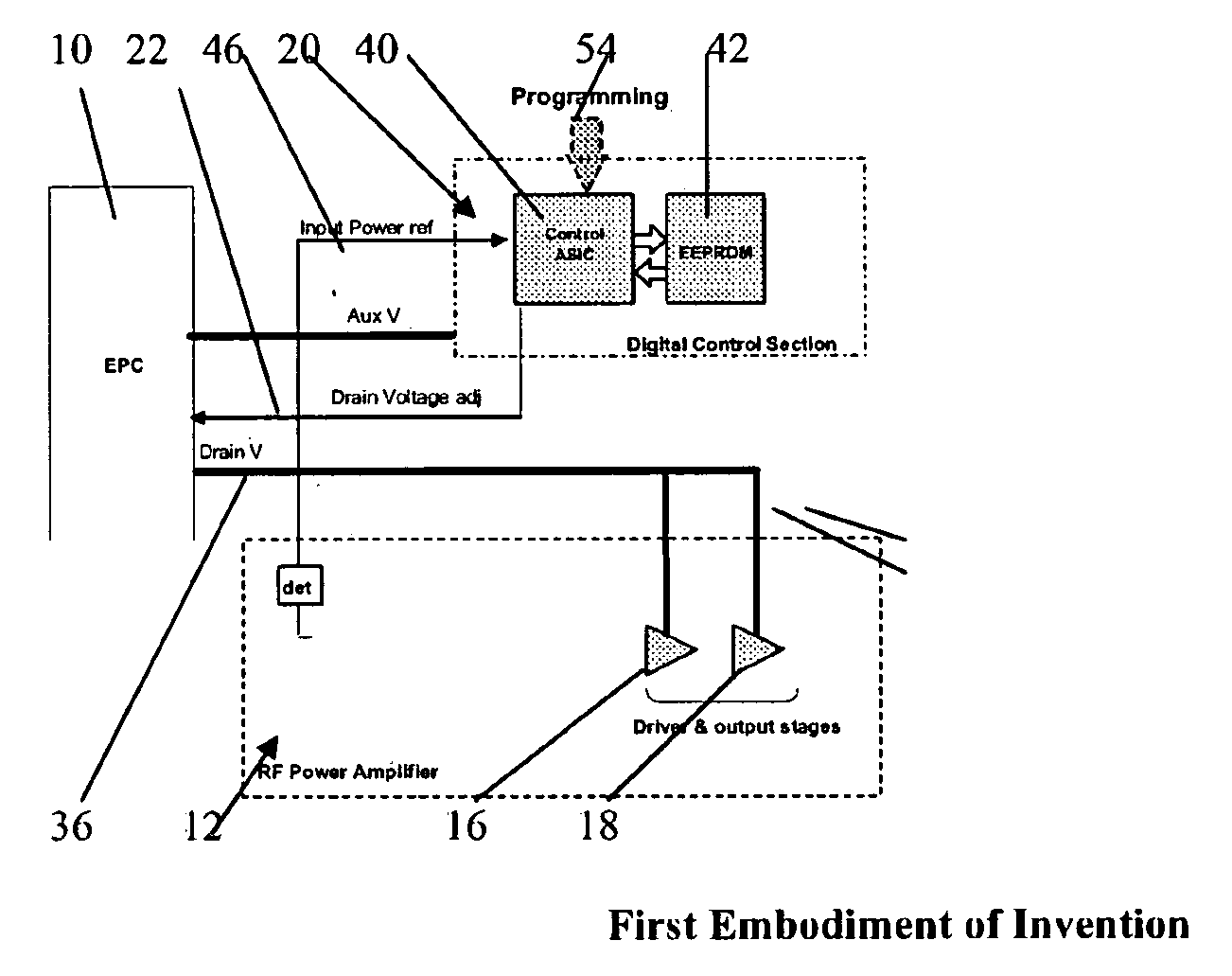
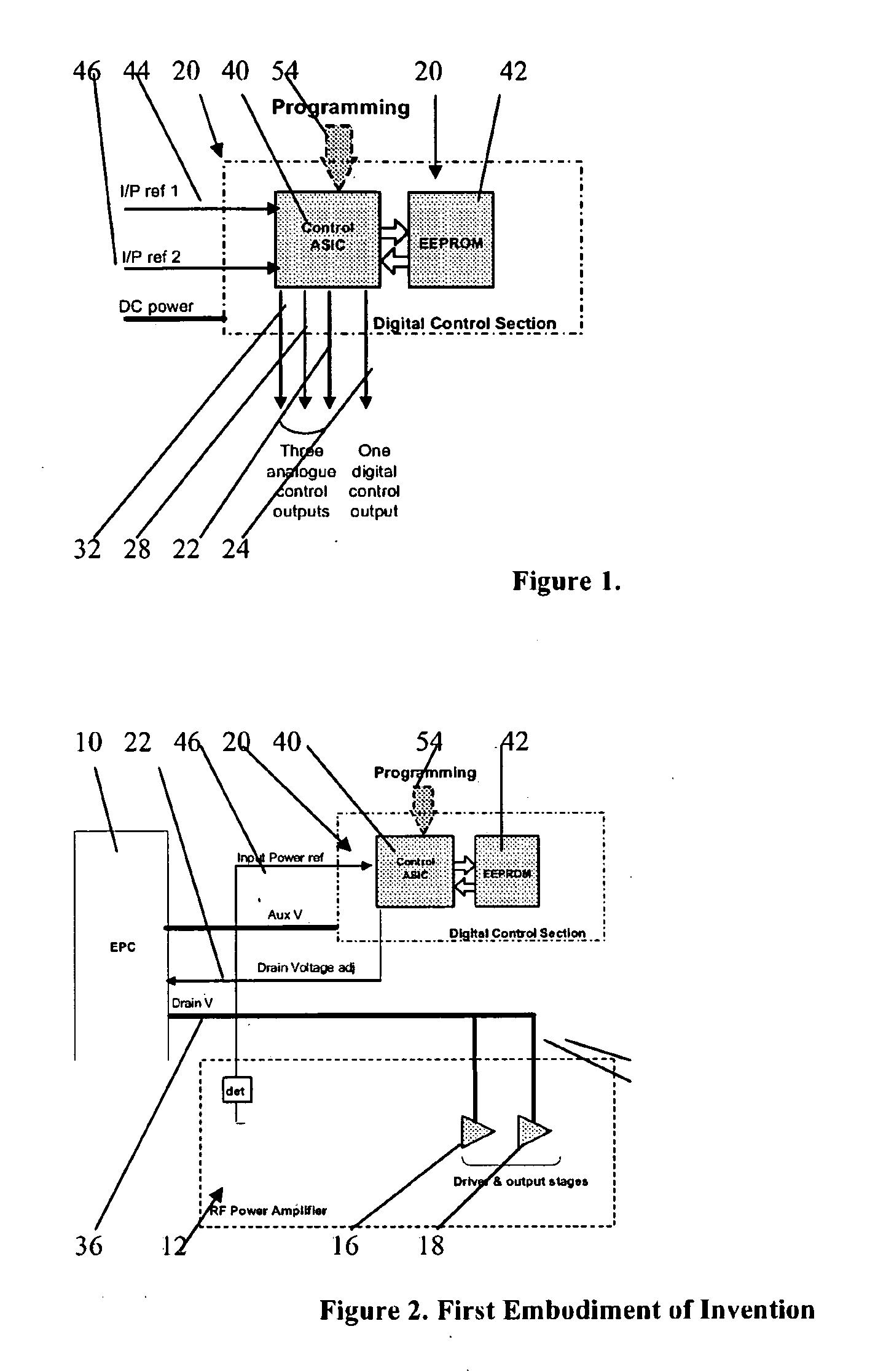
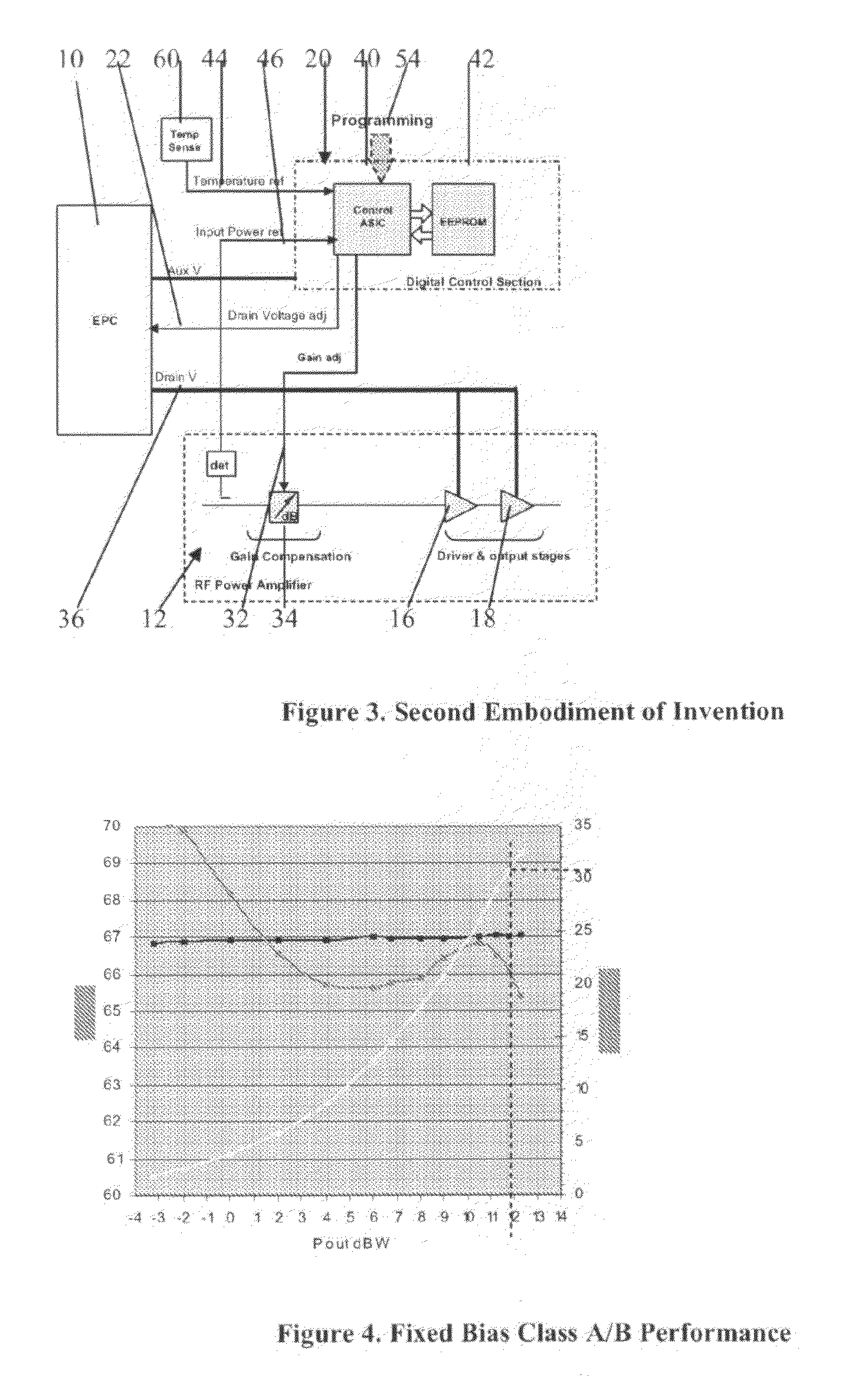
ActiveUS20080278236A1Improve featuresEliminating lossy and expensiveAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasControl signalGain compression
A Solid State Power Amplifier (SSPA) for powering a single element of a multi-element antenna, the SSPA comprising:an RF amplifier, having a signal amplifying path that includes preamplifier, driver amplifier and a power output stage;an Electronic Power Conditioner (EPC) for providing a variable value of DC voltage for powering the power output stage of the RF amplifier;a control ASIC for receiving an input power signal of the RF amplifier for providing a voltage control signal to the EPC to determine the value of the DC voltage, the control ASIC addressing an EEPROM holding a collection of control words that define output values of a control output signal for varying values of said input power, such that the value of the DC voltage to the power output stage is varied so as to control the gain compression of the RF amplifier for varying values of input power in order to maintain constant amplifier linearity.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
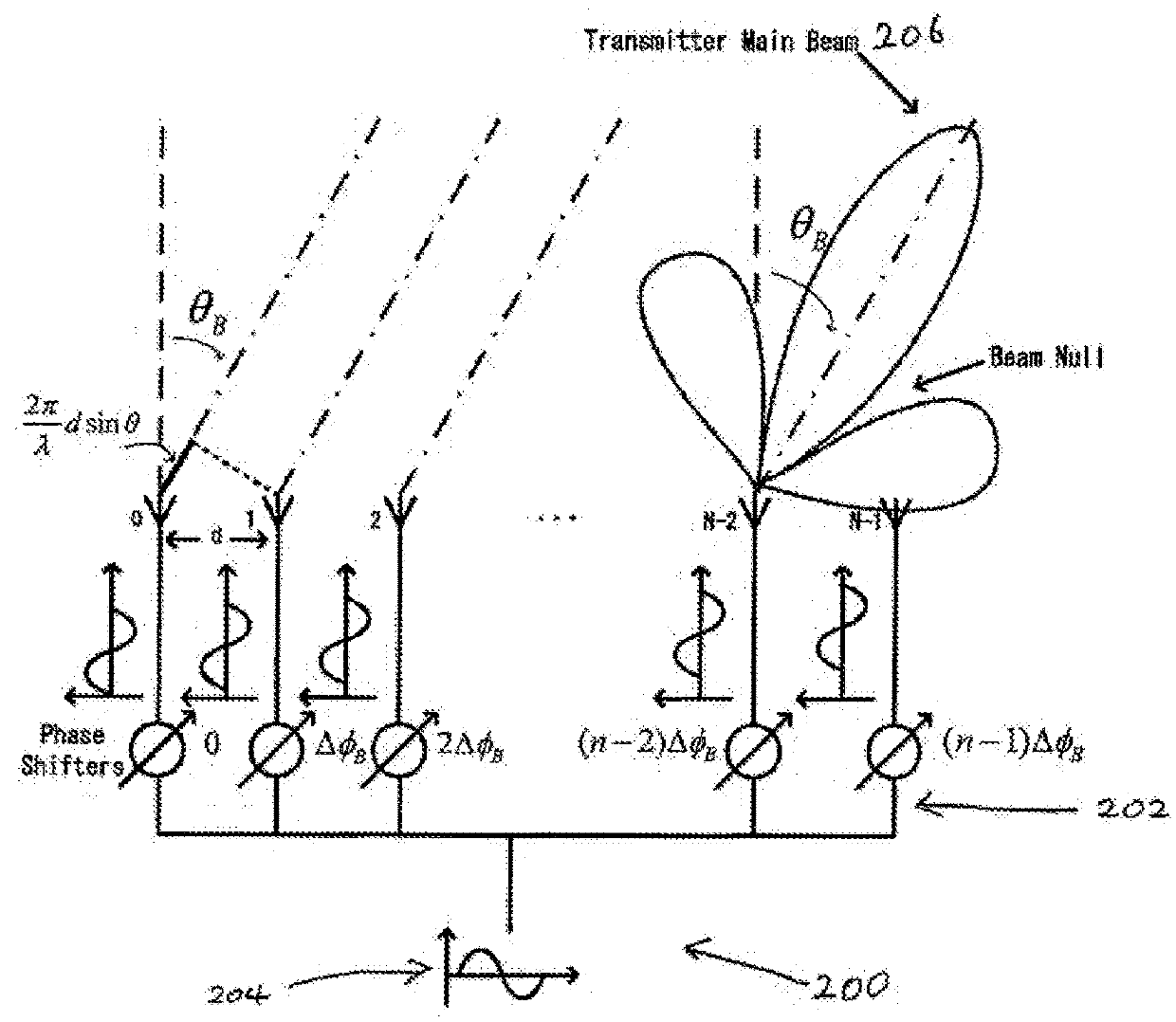
Methods and apparatus for implementing a wideband digital beamforming network
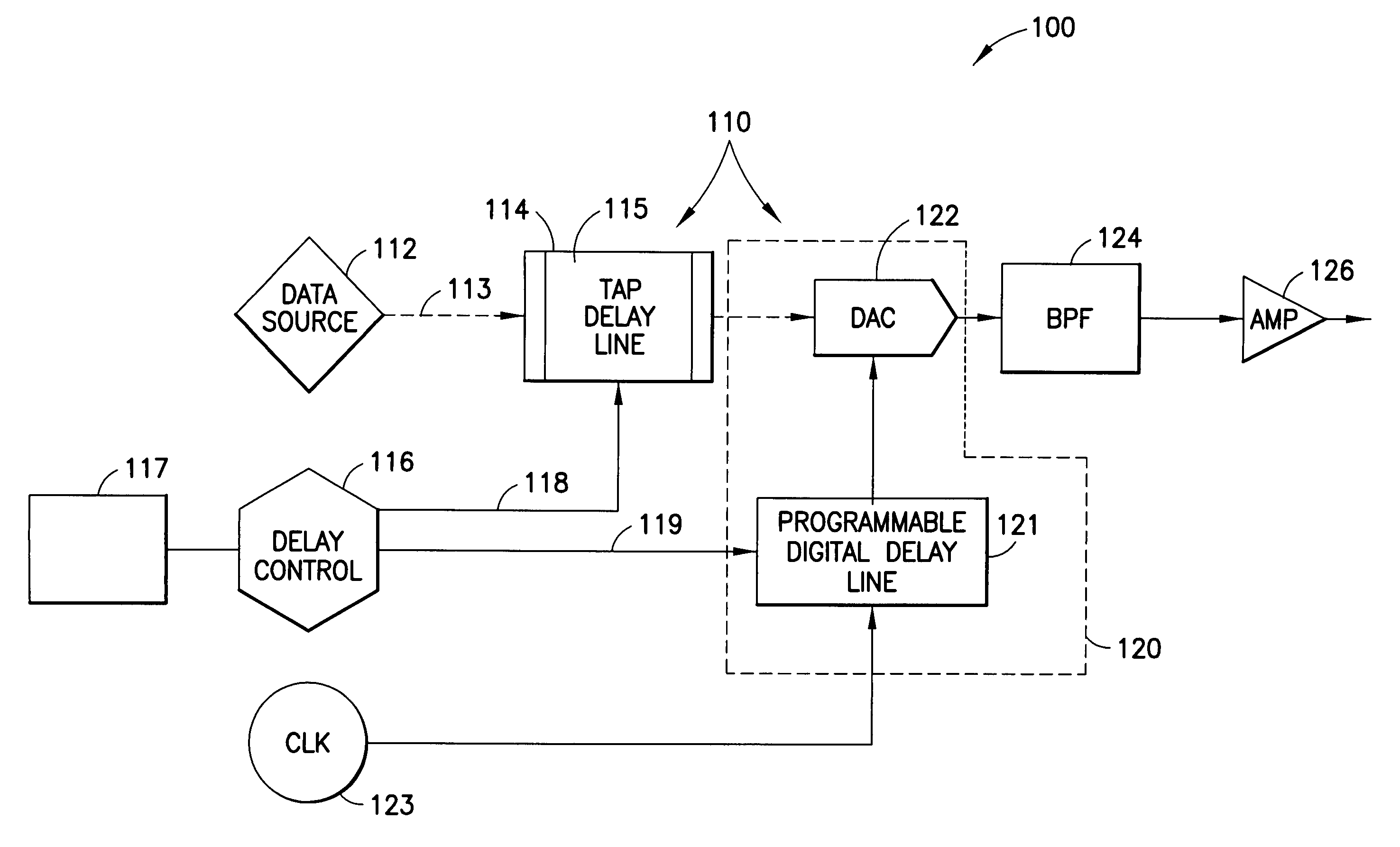
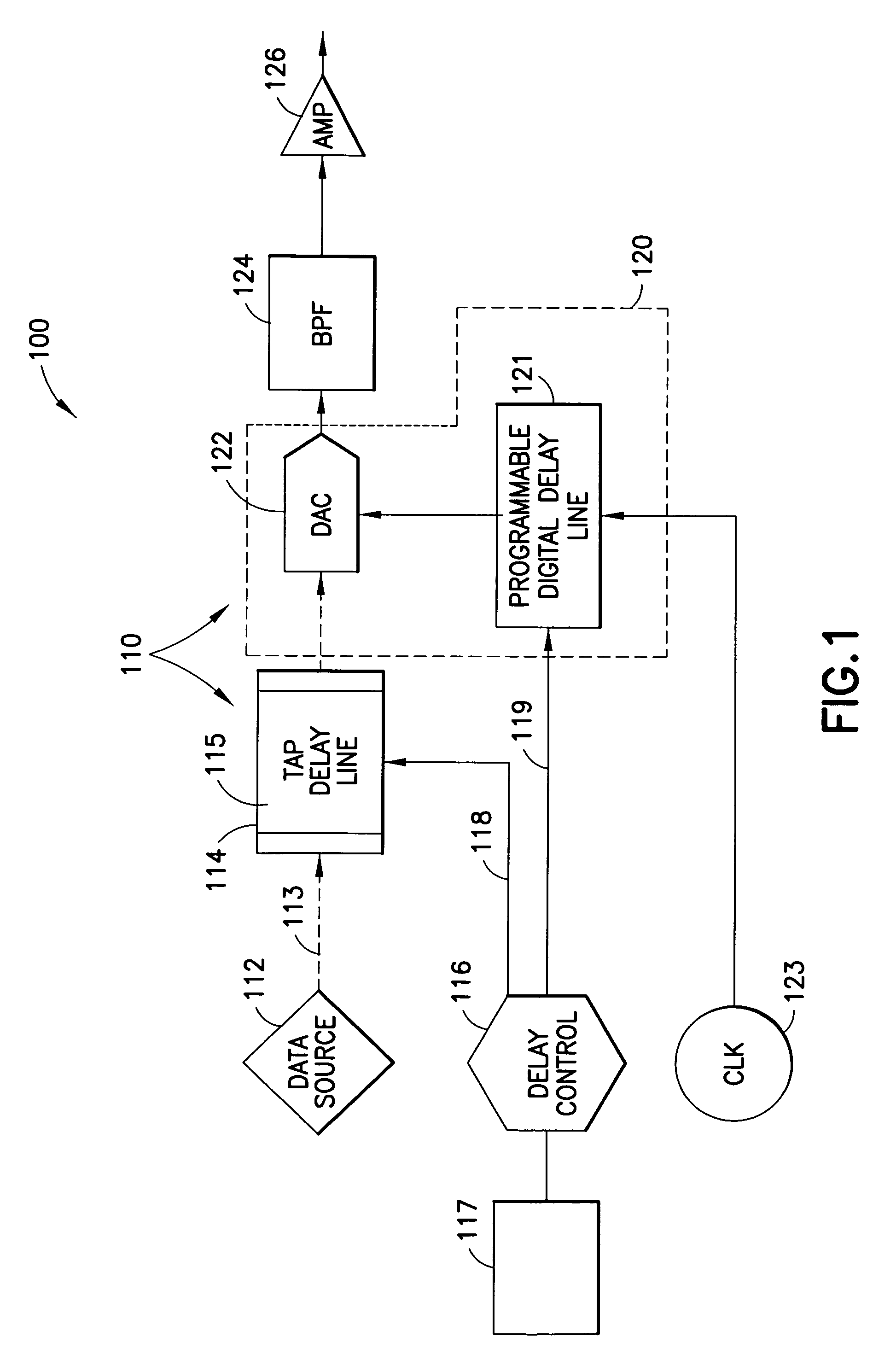
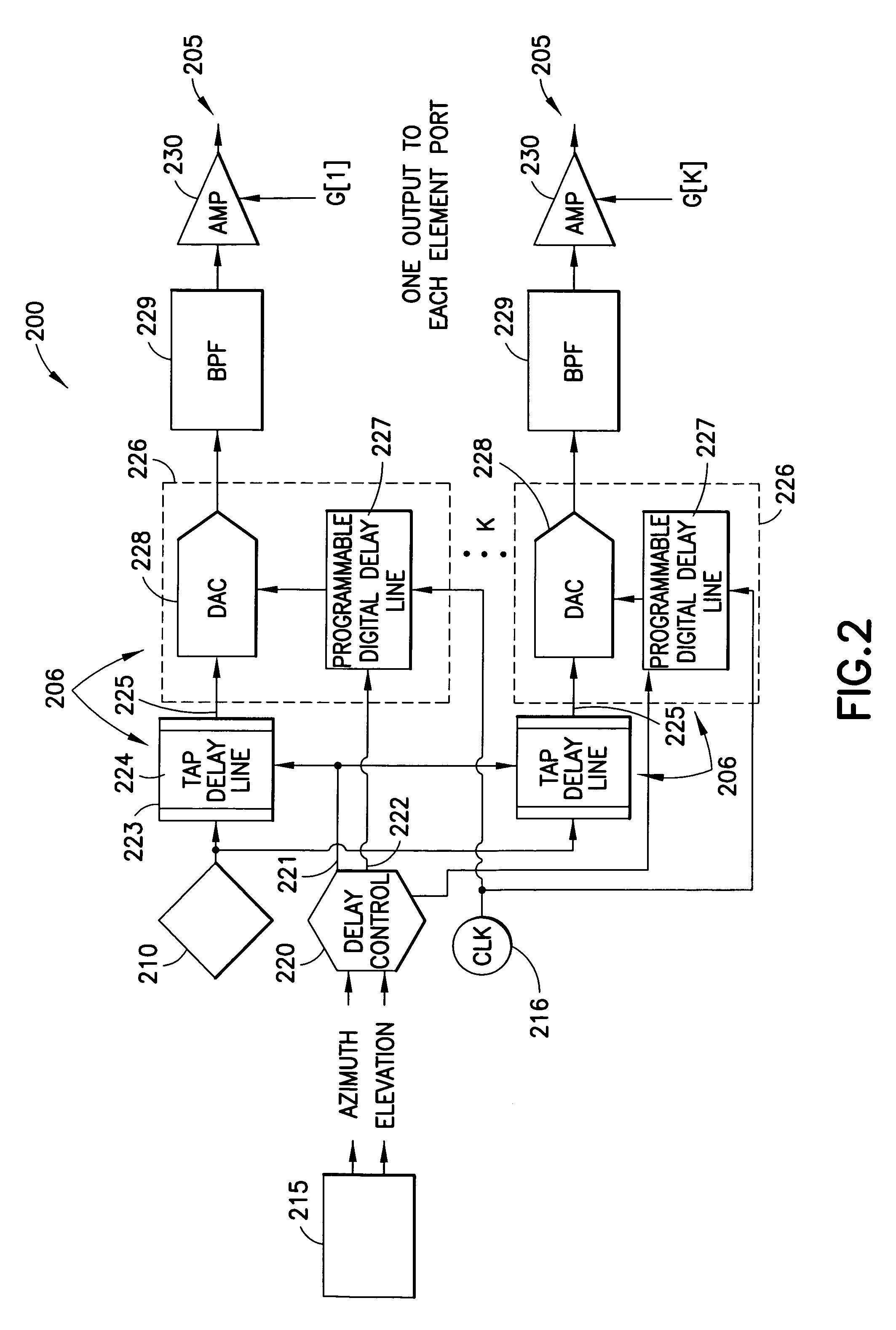
The present invention concerns methods and apparatus for implementing a true-time-delay wideband digital beamformer. In true-time-delay wideband digital beamformers of the present invention, improved control over beam properties formed by the combination of the beamformer and a multi-element antenna coupled to the beamformer is achieved through finer control of delays imparted to data signals. In beamformers of the present invention, data is delayed using a coarse control that provides a delay in whole increments of a clock cycle of a digital clock reference and a fine control that provides a delay corresponding to a fraction of a whole clock cycle of the digital clock reference. In the true time delay method of the present invention, transmission and reception across a wide frequency band is accommodated. In the true time delay method of the present invention, multiple simultaneous beams are formed independently, beam-to-beam, across a wide frequency band.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
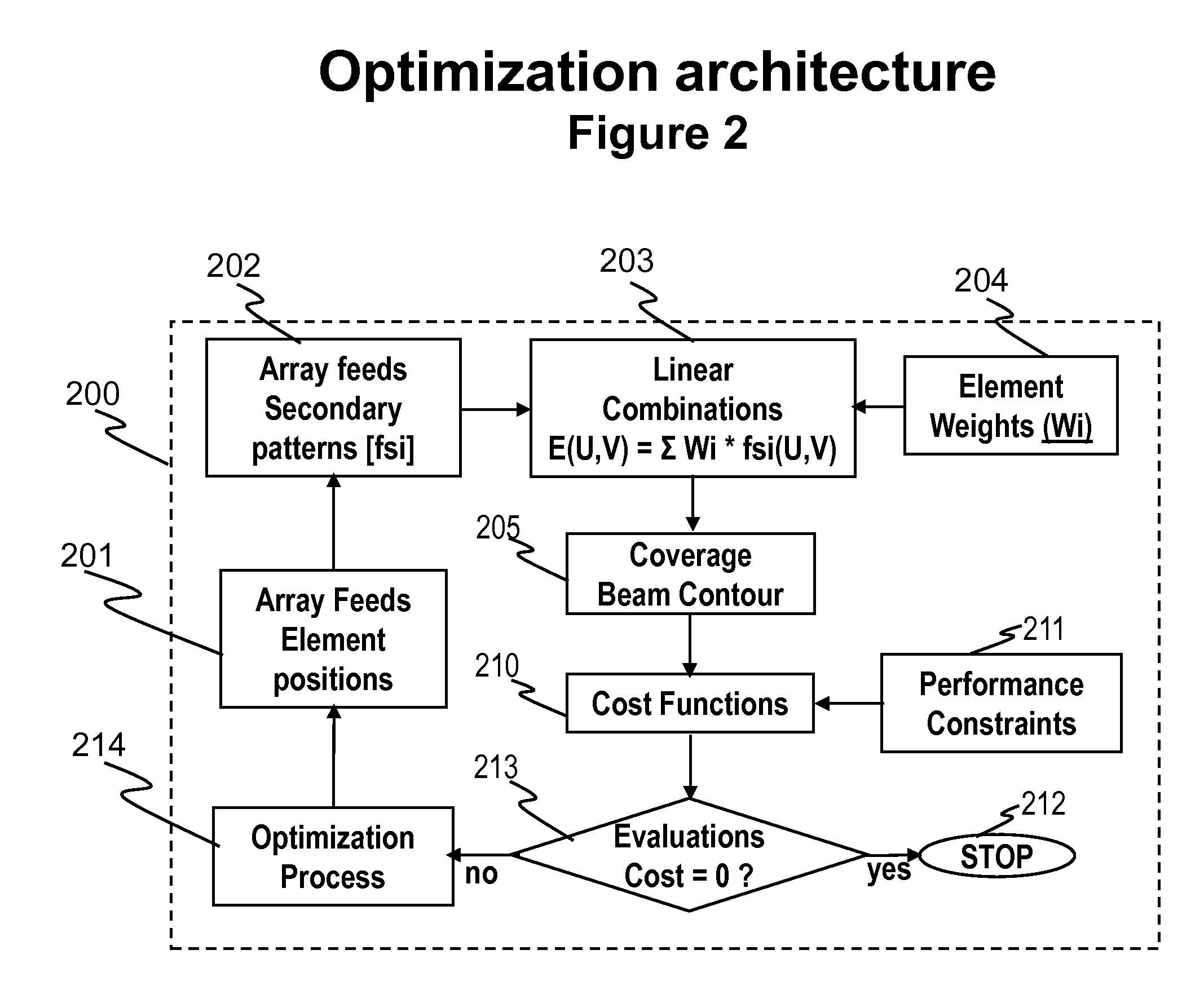
Architectures and Methods for Novel Antenna Radiation Optimization via Feed Repositioning
ActiveUS20110032173A1Complex antenna designCost-effective methodCollapsable antennas meansAntenna designSatellite antennas
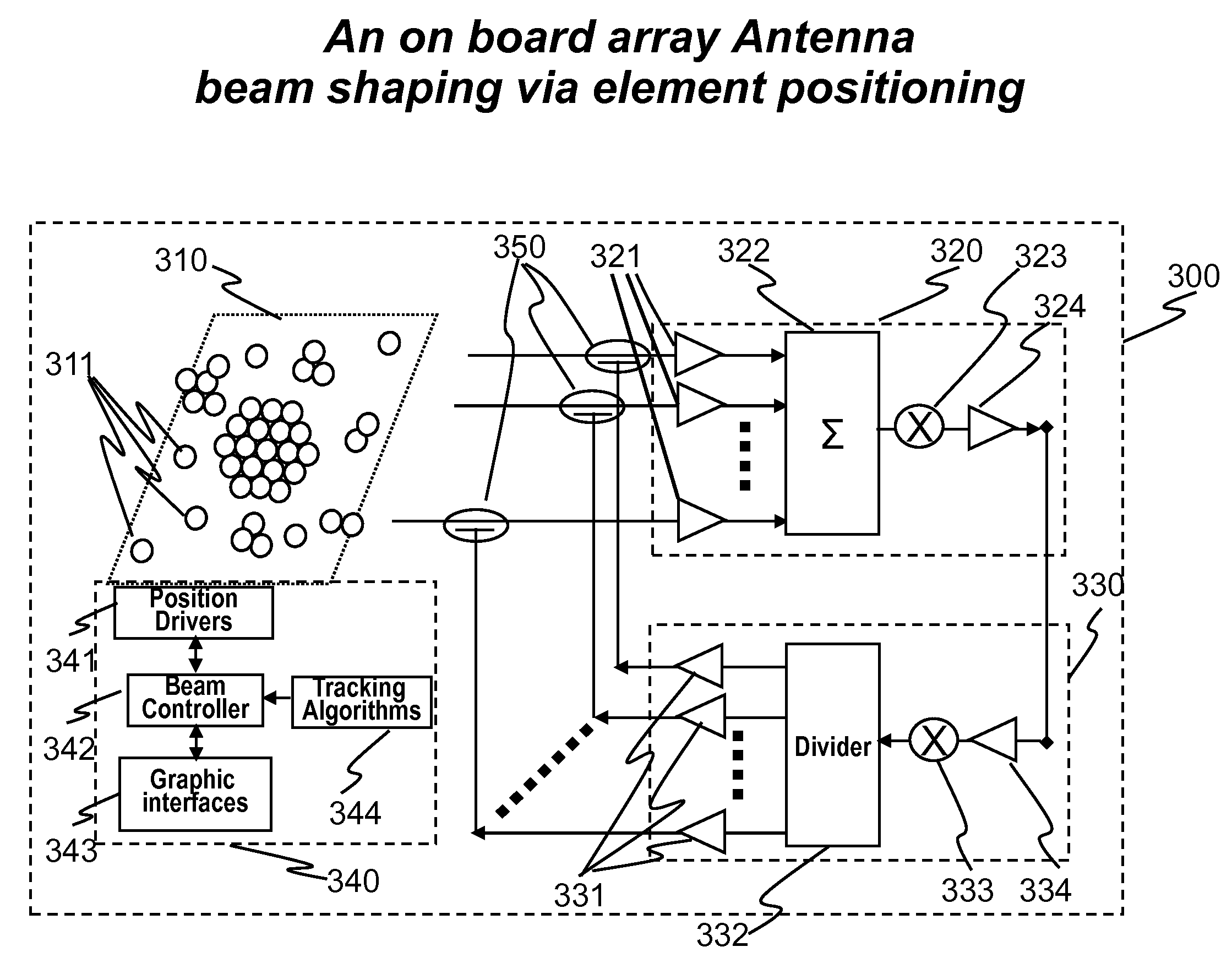
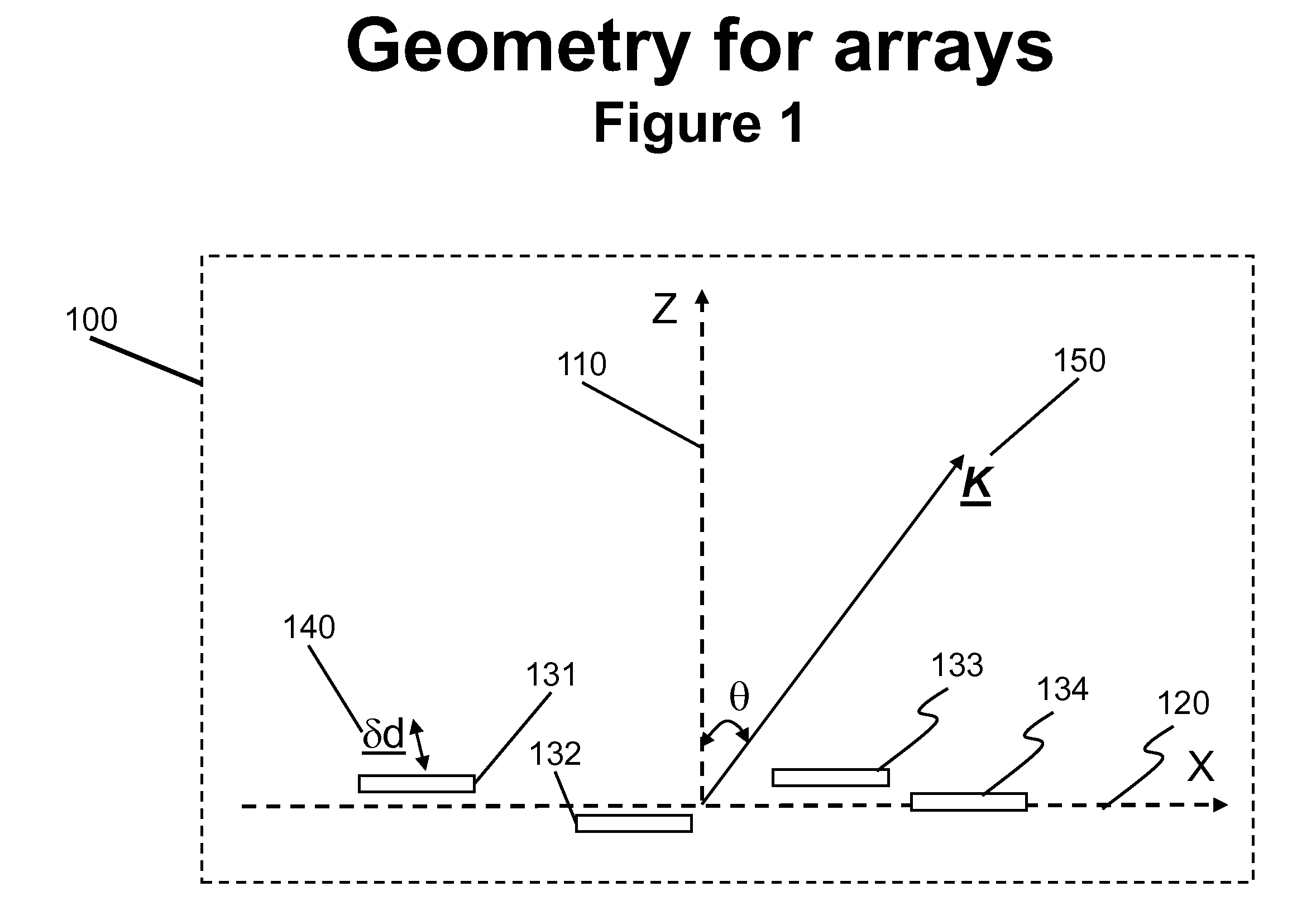
The present invention relates to antenna architectures and methods on re-configurable multi-element antennas via feed re-positioning for various optimized radiation contours, including beam forming (or shaping) and / or null steering on contoured beams, spot beams, and orthogonal beams. The feed re-positioning techniques can also be used in radiation pattern optimization processing during antennas designing phases for fixed beams. The techniques are applicable for satellite communications. For satellite antennas, the beam shaping capability via element repositioning can be utilized for (1) optimized geometries on satellite antennas for given desired coverage areas, (2) re-optimizing radiation contours for reconfigurable antenna on board satellites in operation, (3) additional flexibility for satellite antennas using ground based beam forming (GBBF). As to satellite ground terminals, the same techniques are applicable for both fixed and mobile satellite terminals featuring either single beam or multiple beams. For fixed terminals, are applicable for terrestrial based communications; such as retrofitting existing antennas eliminating interference radiations coming from fixed or slow varying directions.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
Antenna array including virtual antenna elements
A method and associated system for effectively increasing the number of antenna elements within a multi-element antenna system through computation of a response of “virtual” antenna elements located along an antenna array. The physical elements of the array are positioned sufficiently near each other to enable synthesis of a polynomial or other mathematical expression characterizing the response of the array to receipt of an incident waveform. Values of the responses associated with the virtual antenna elements of the array may then be determined through evaluation of the synthesized polynomial or other expression. The resultant array response values associated with the virtual and physical elements of the array are then provided to an associated receiver for processing.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
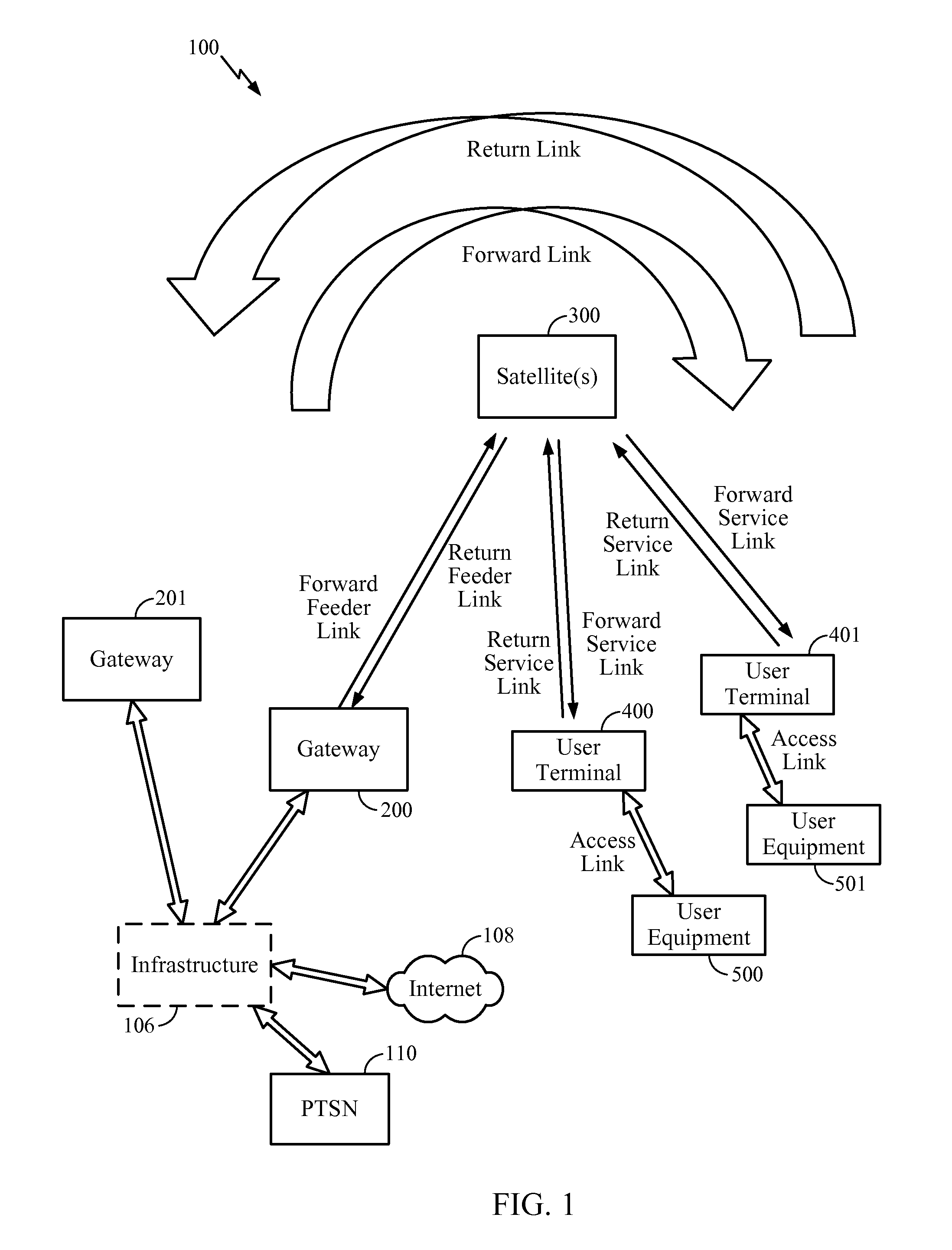
Transmitting service advertisements
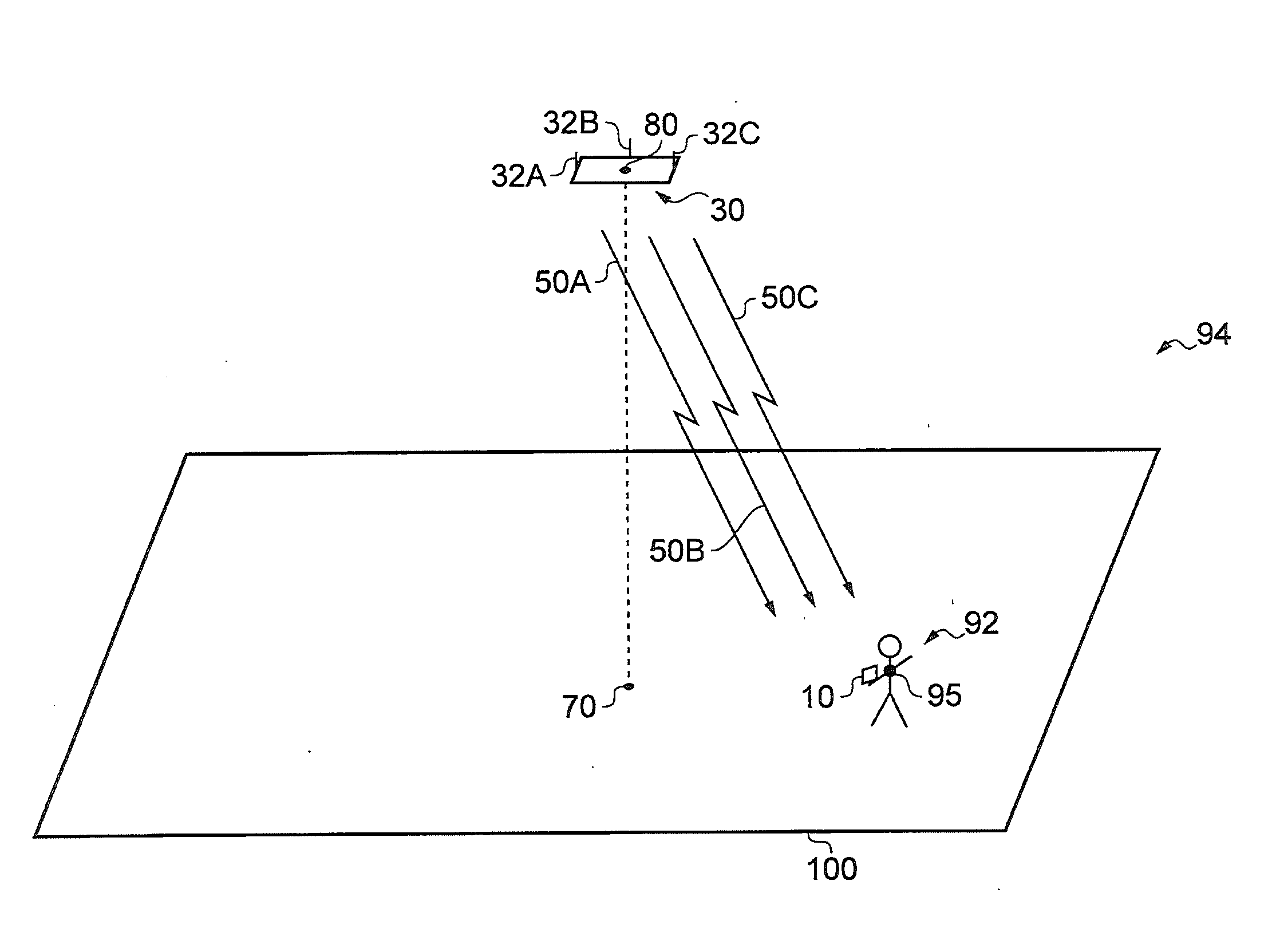
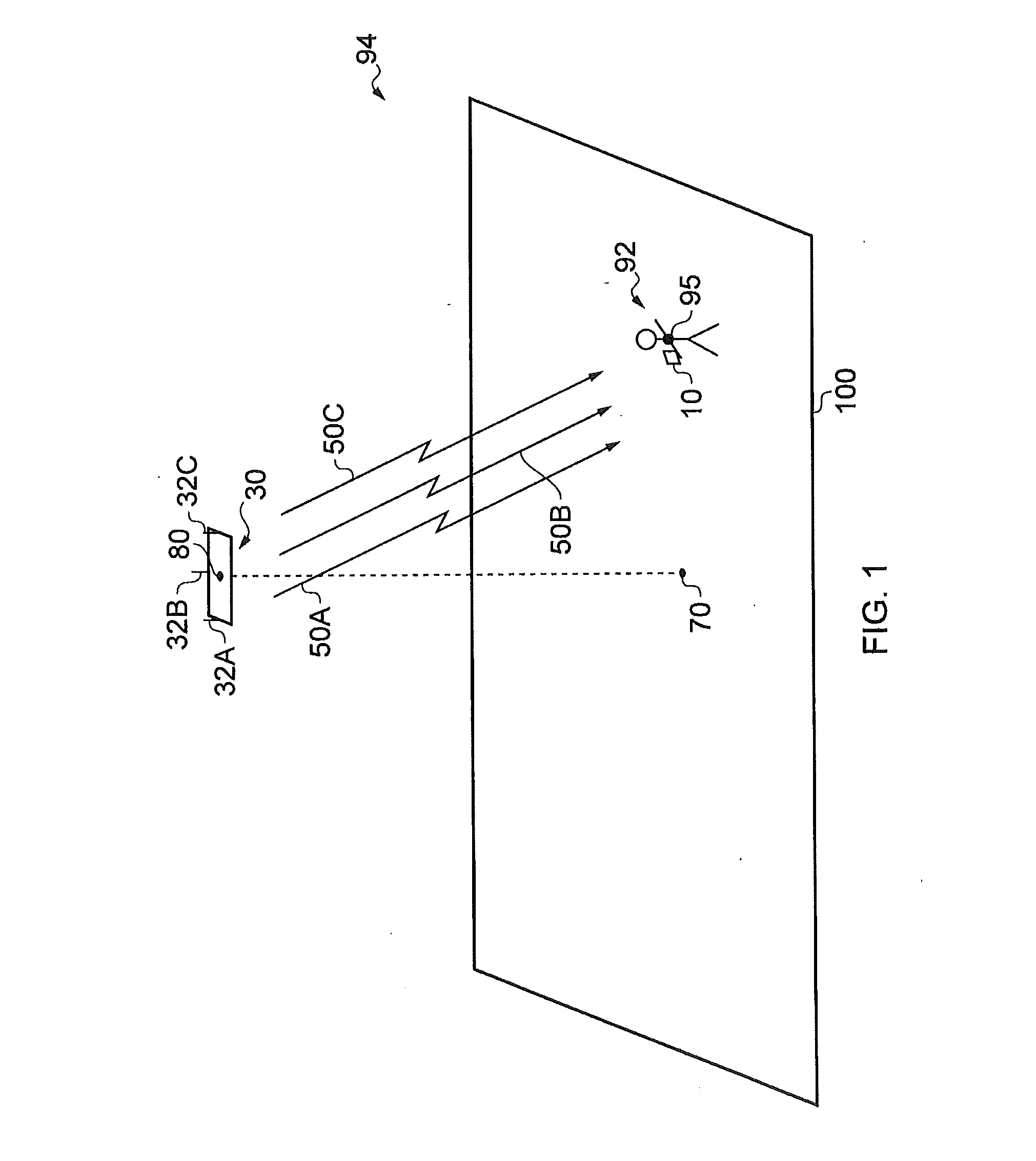
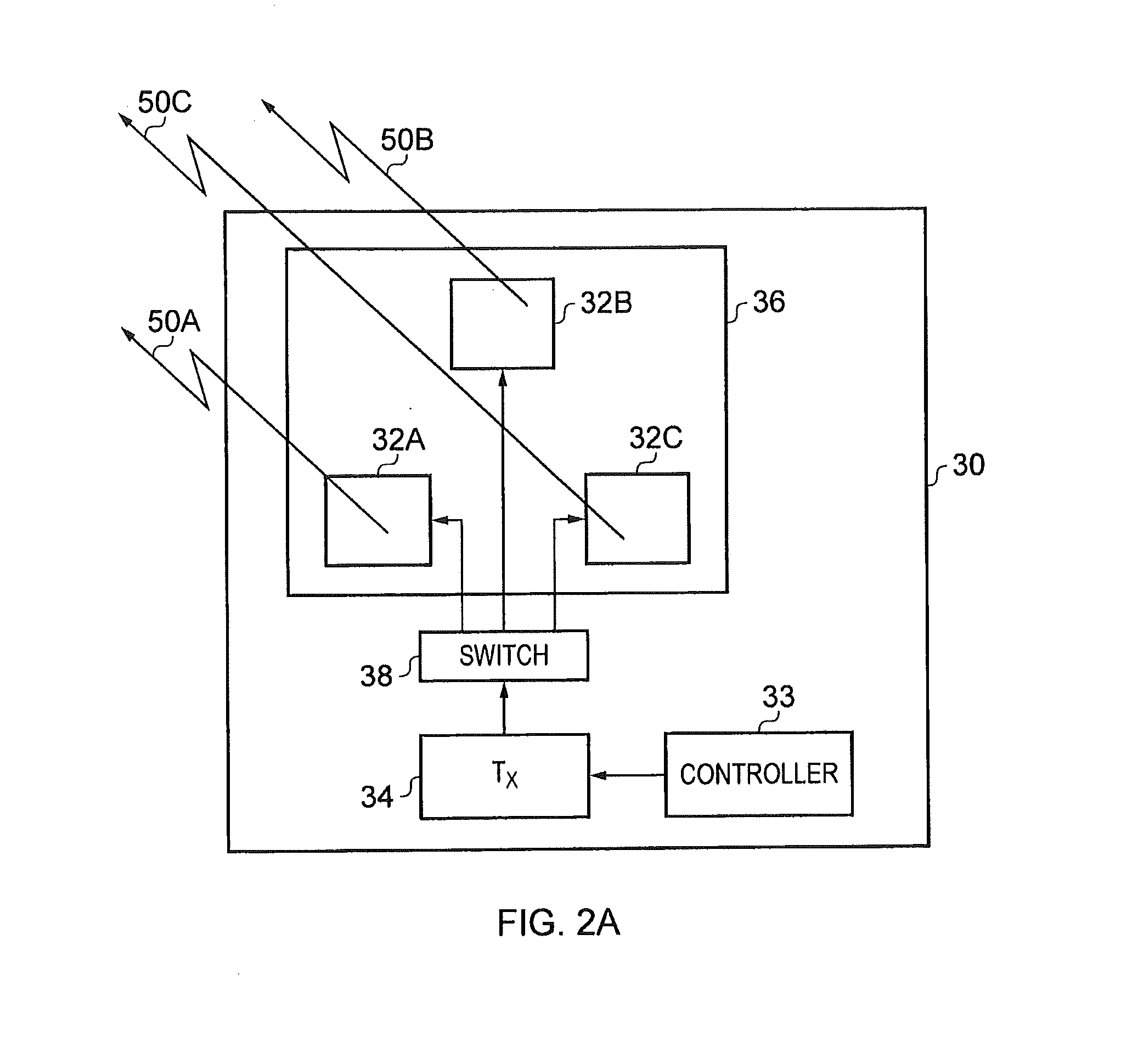
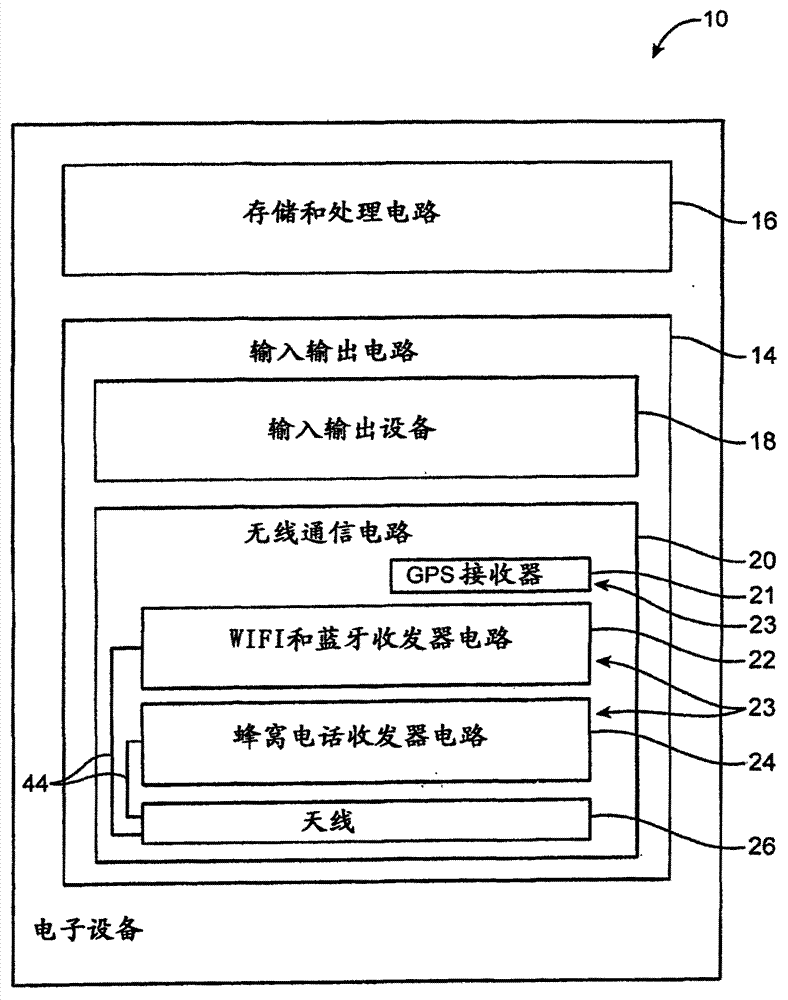
Apparatus (30) comprises a battery power supply, a radio-frequency transceiver, a multi-element antenna, and processor and memory. Software causes the apparatus (30): when in an idle mode, to broadcast positioning service advertisements and to refrain from broadcasting positioning packets, when in a positioning mode to broadcast positioning packets from each of the elements of the antenna (32A-C) such as to allow a mobile device (10) to determine a bearing to the mobile device (10) from the apparatus (30), and to transition from the idle mode to the positioning mode in response to receiving either a) a wake-up command or b) a positioning packet, from another apparatus including a multi-element antenna. The apparatus (30) may comprise a Bluetooth Low Energy transceiver; and software that causes the apparatus (30): to transmit advertisements for positioning services on a first channel; and to broadcast positioning packets on a second channel such as to allow a mobile device (10) to determine a bearing to the mobile device (10) from the apparatus (30), wherein the first and second channel are on different frequencies.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for avoiding exceeding interference limits for a non-geostationary satellite system
ActiveUS20170019814A1Reduce the required powerNetwork traffic/resource managementAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesGeosynchronous satelliteLong axis
A non-geosynchronous satellite system, where each satellite has an antenna (perhaps a multi-element antenna) to form a beam pattern comprising a set of beams in the footprint of the satellite, where in one implementation each beam is substantially elliptical in shape having a minor axis and a major axis, where the minor axes are substantially collinear and the major axes are substantially oriented east to west. For a satellite, power is reduced or turned off for a subset of the set of beams, wherein each beam in the subset is reduced at or below a corresponding power level such that when a beam is powered above its corresponding power level an equivalent power flux-density (EPFD) exceeds a limit at some point on the Earth's surface.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
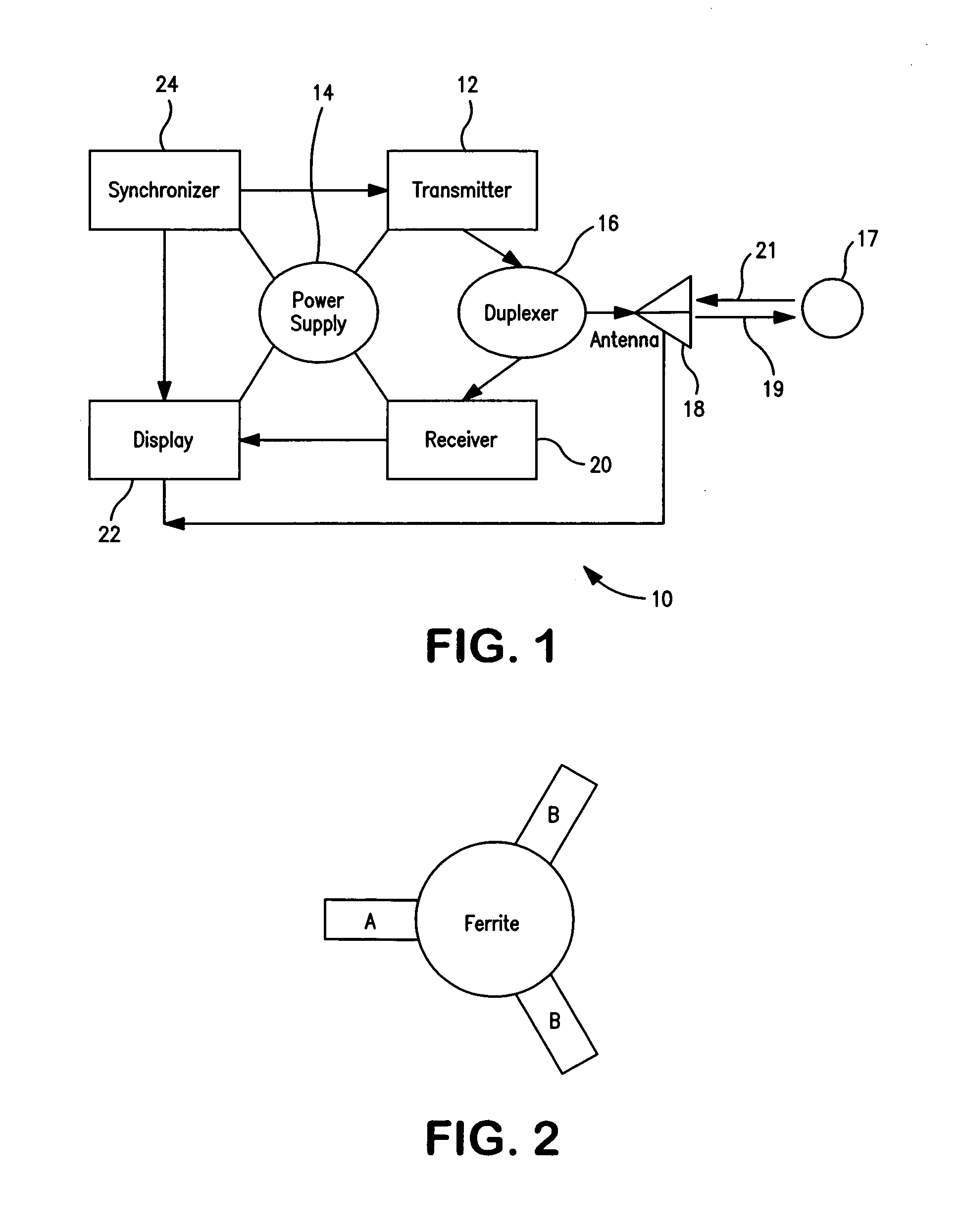
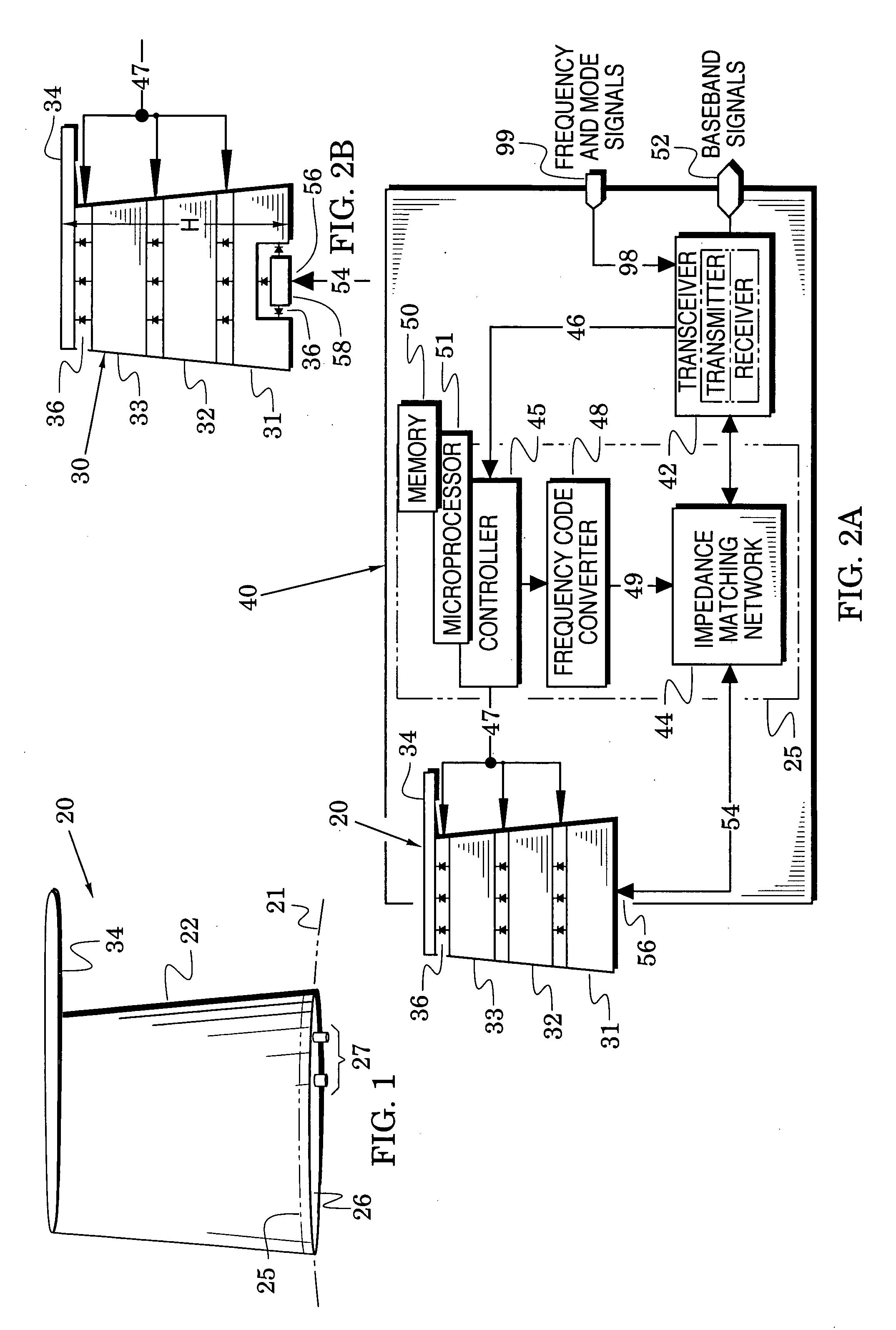
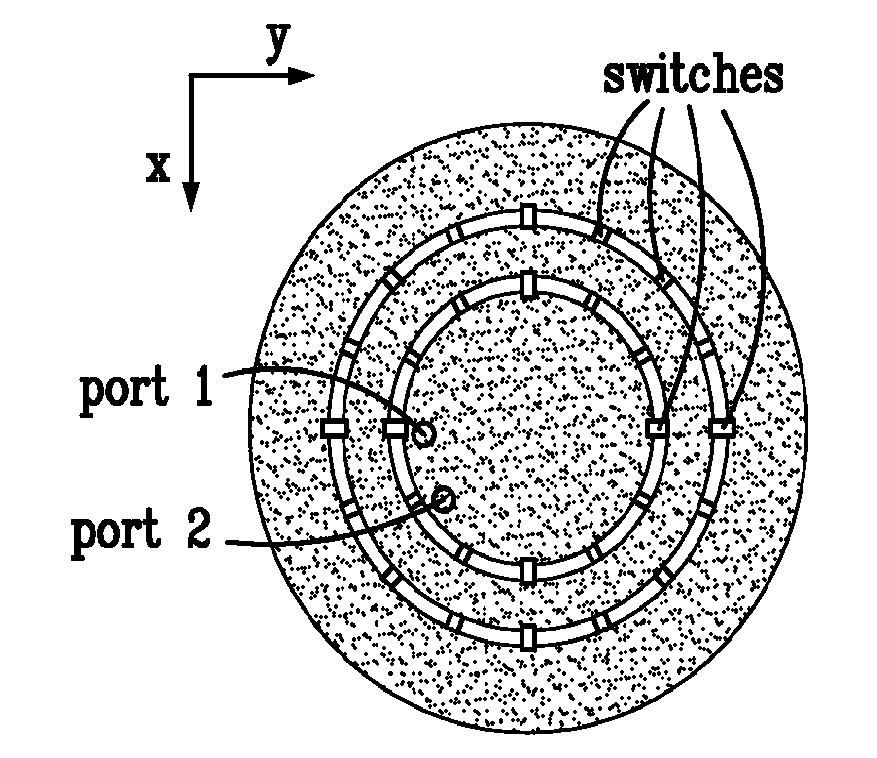
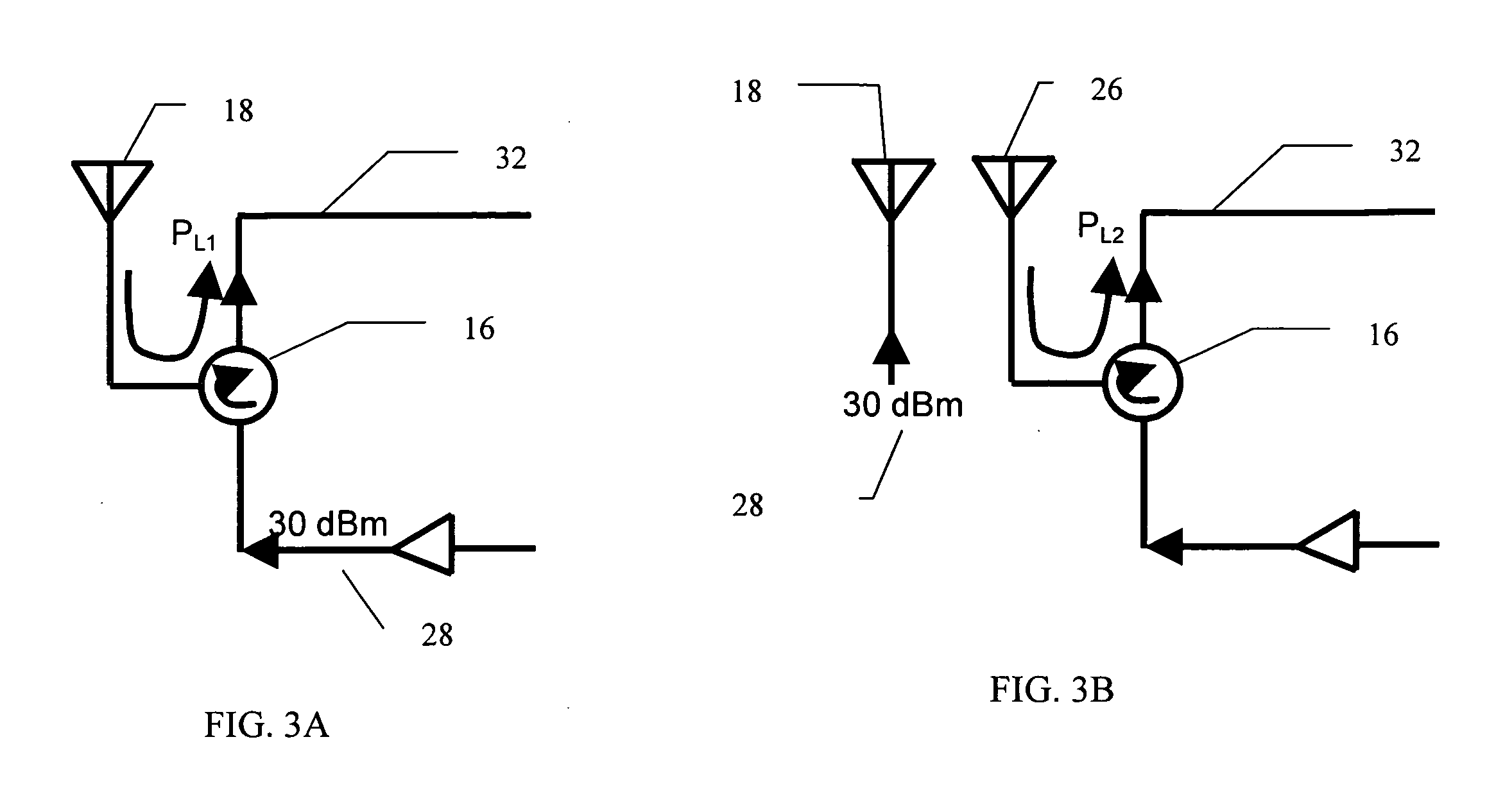
Broadband tunable antenna and transceiver systems
InactiveUS20050088362A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesTransceiverEngineering
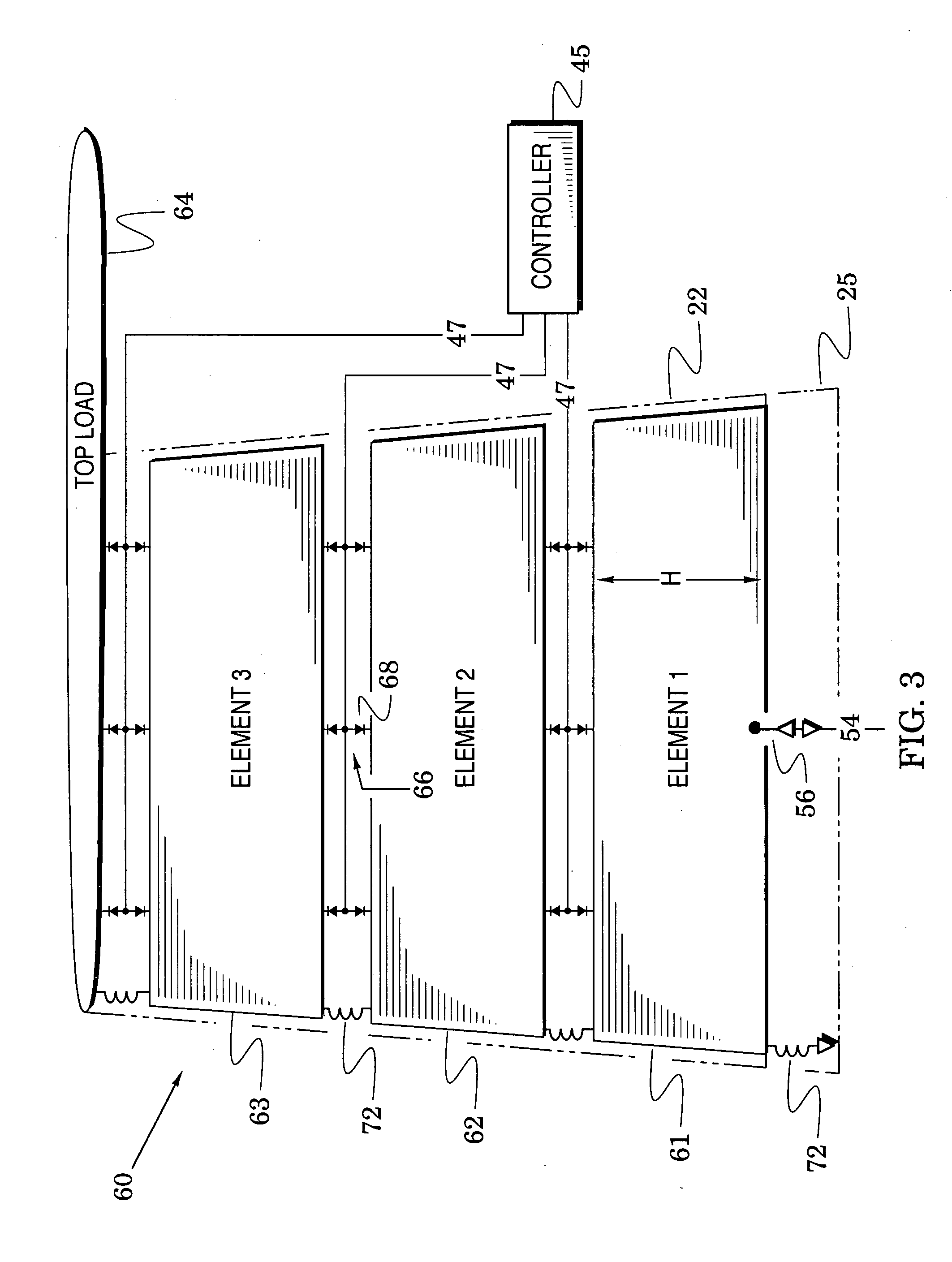
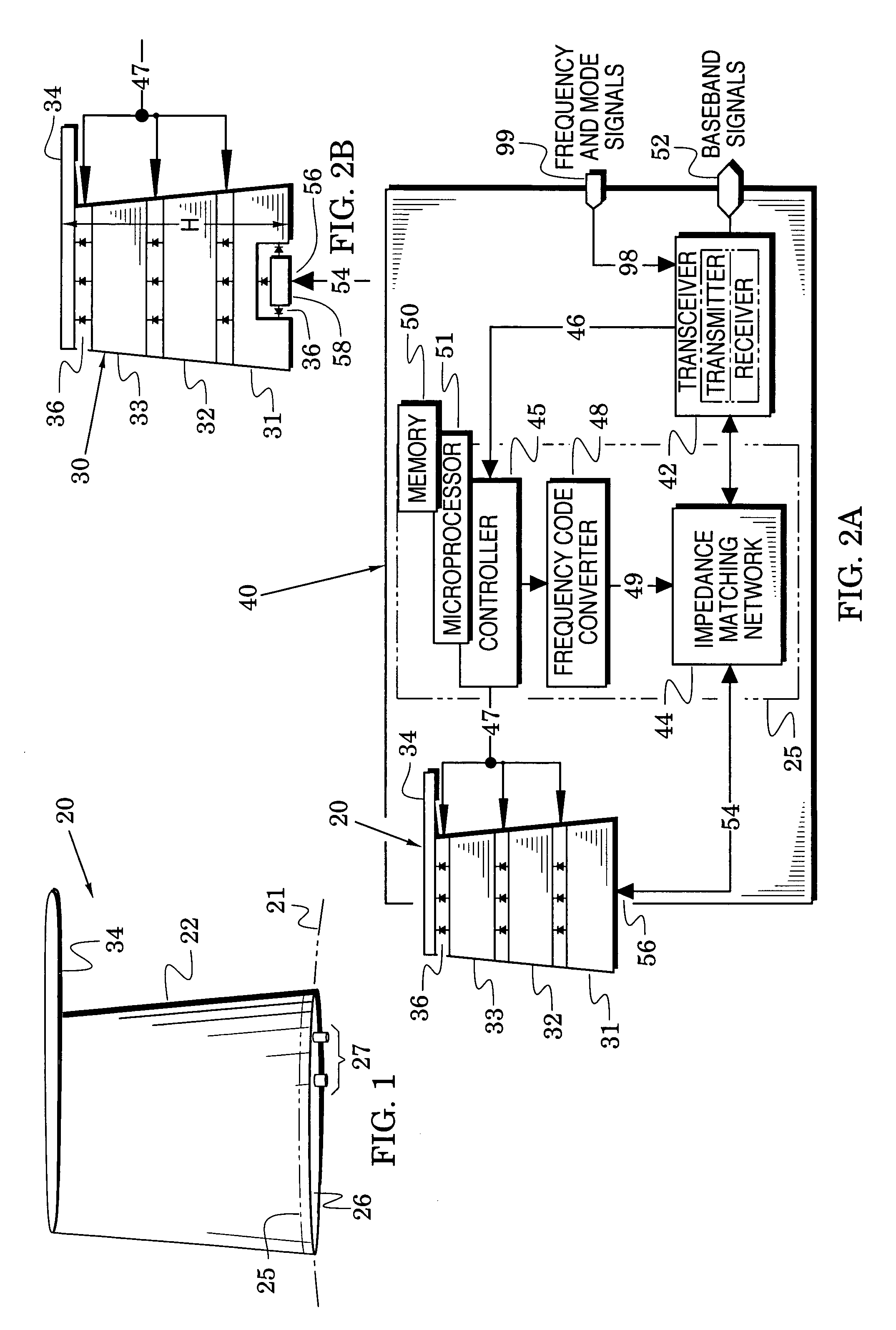
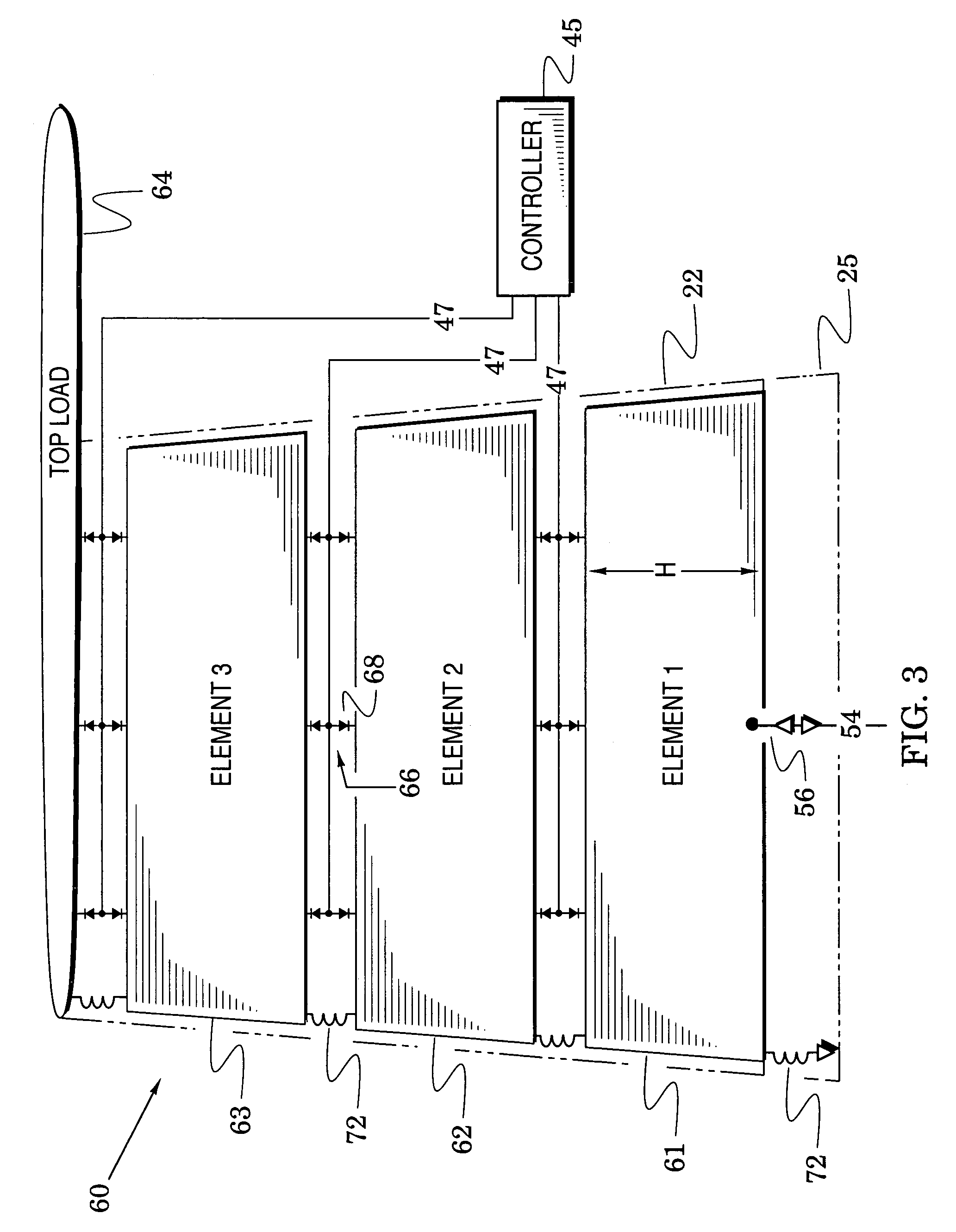
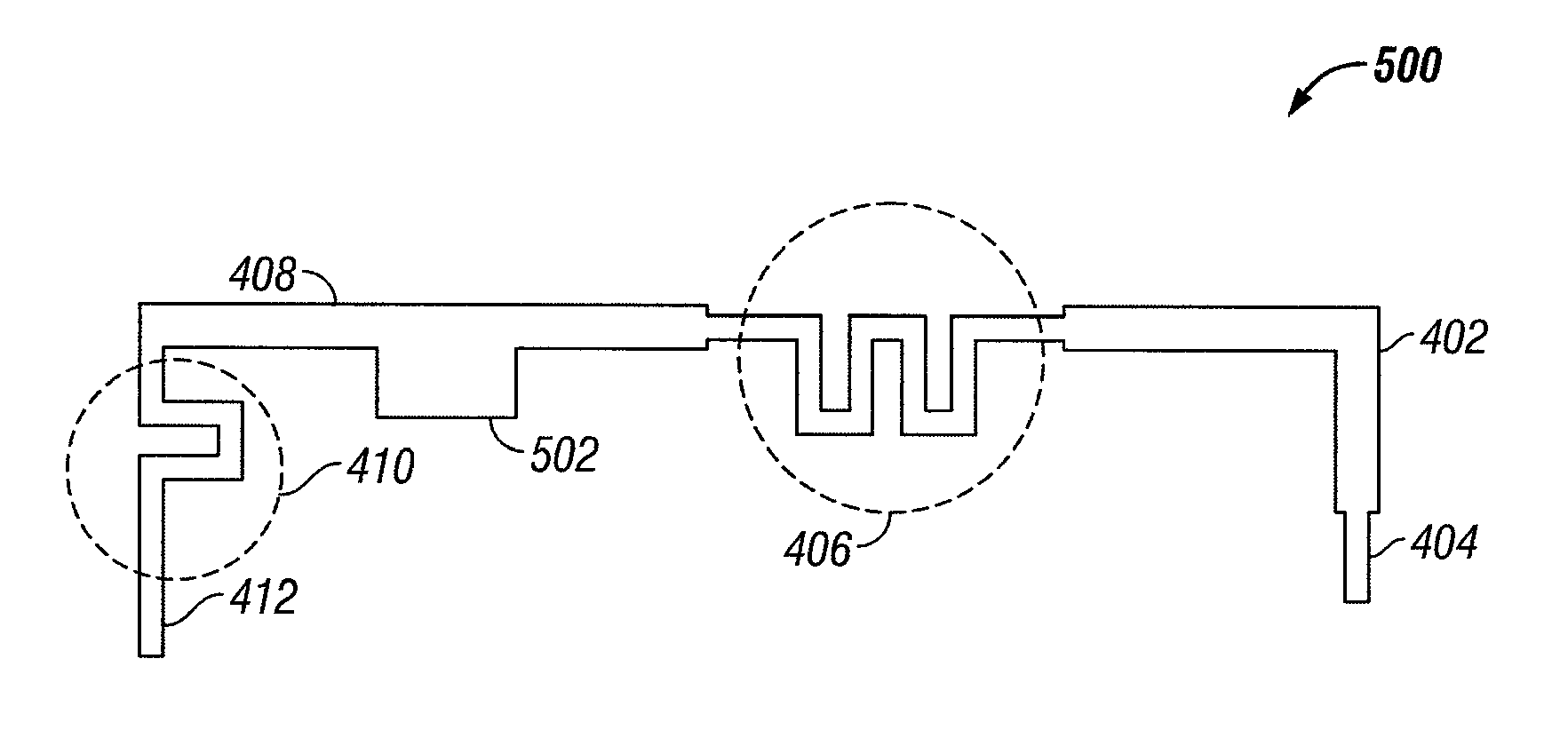
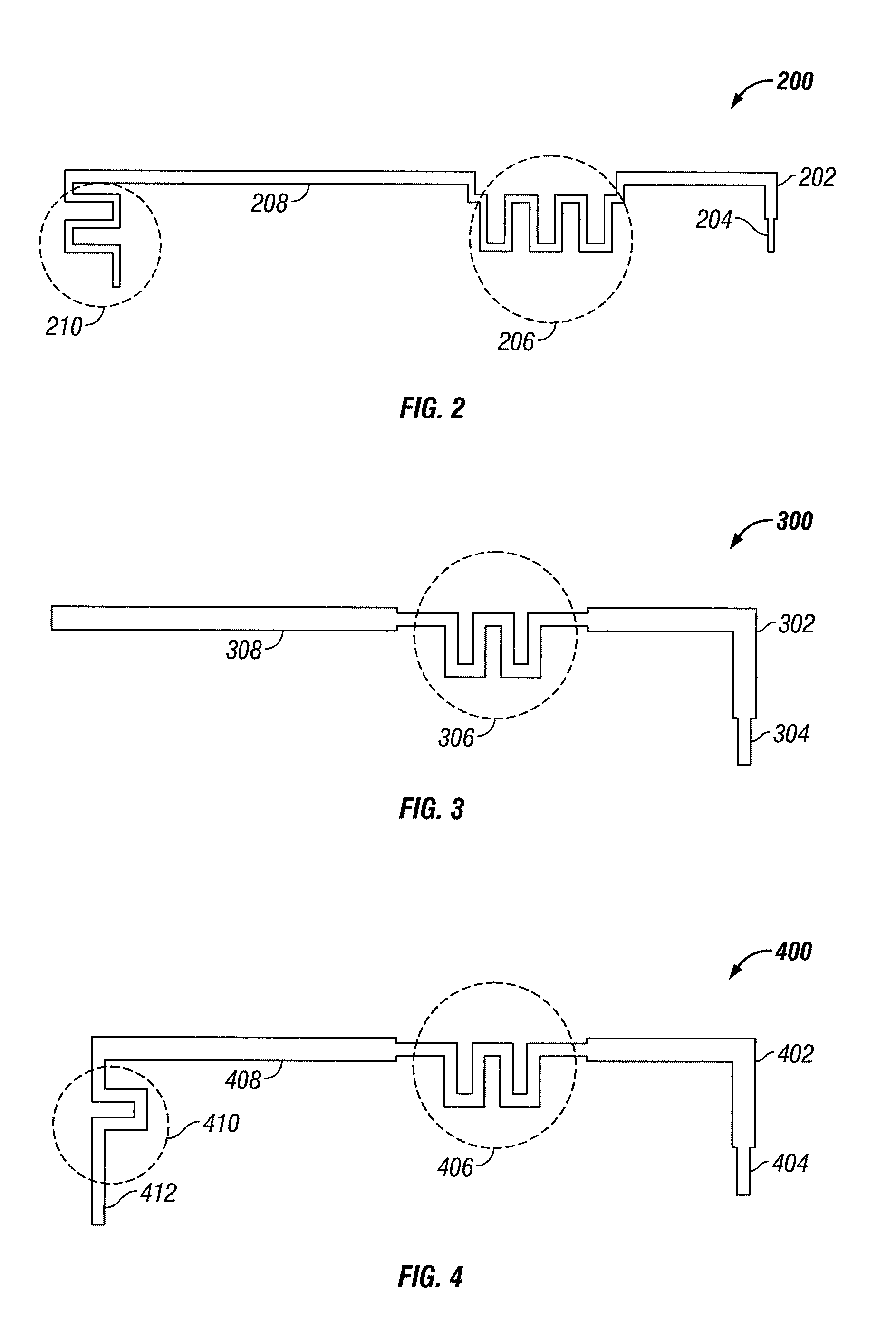
The present invention is directed to multi-element antennas that include, for each adjacent pair of antenna elements, at least one switch arranged to selectively connect that pair to thereby selectively alter an antenna dimension. Accordingly, a multi-element antenna can be configured to enhance its gain at different operational frequencies while a corresponding impedance matching network can enhance the impedance match (i.e., reduce reflected signal energy) between the antenna and a corresponding system (e.g., a transceiver system). The antenna and system can thus be effectively tuned across a wide operational band. The antenna and impedance matching network are configured with switch command signals and match command signals that are provided in response to each of a plurality of frequency codes.
Owner:SENSOR SYST
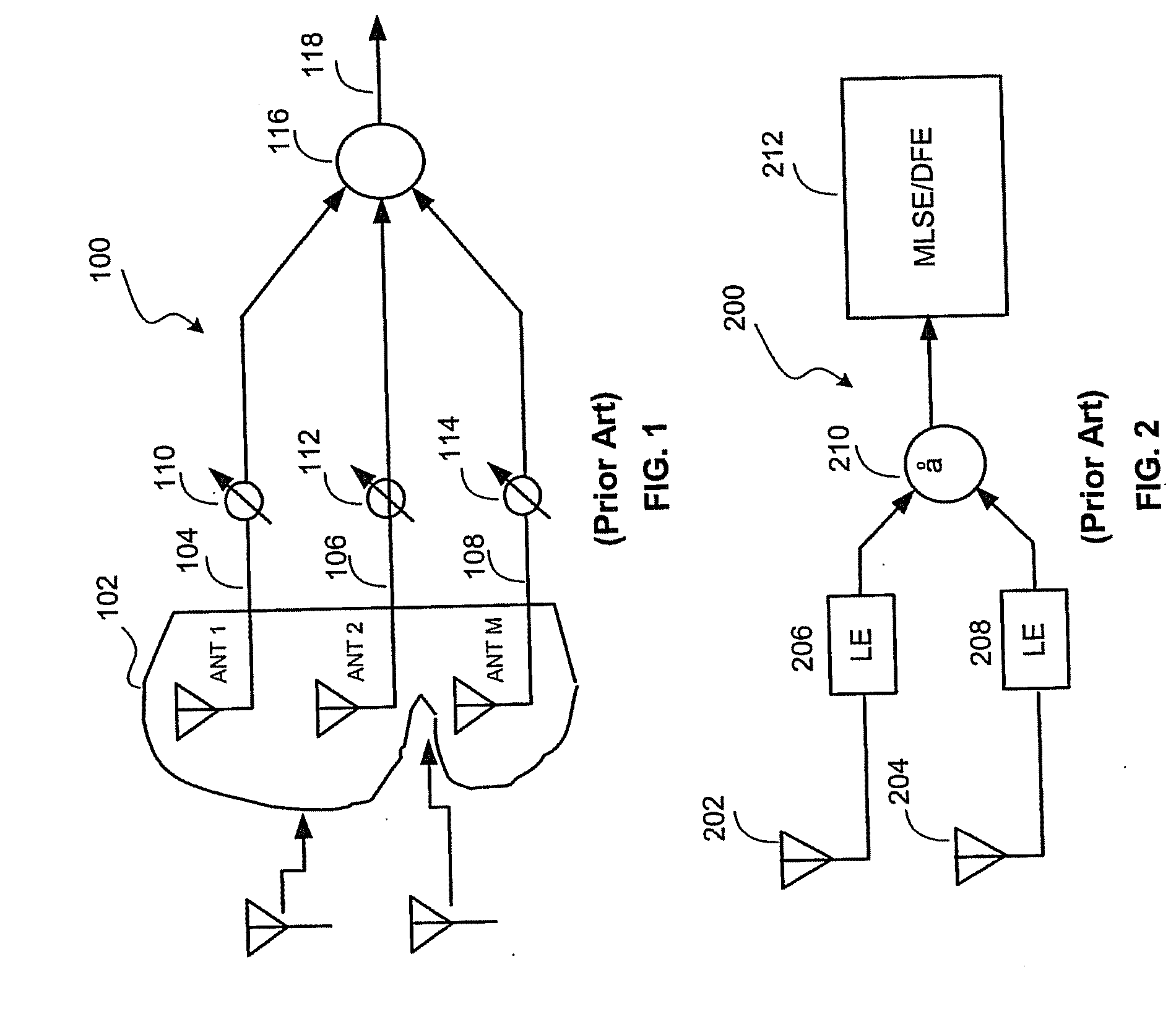
Determining channel characteristics in a wireless communication system that uses multi-element antenna
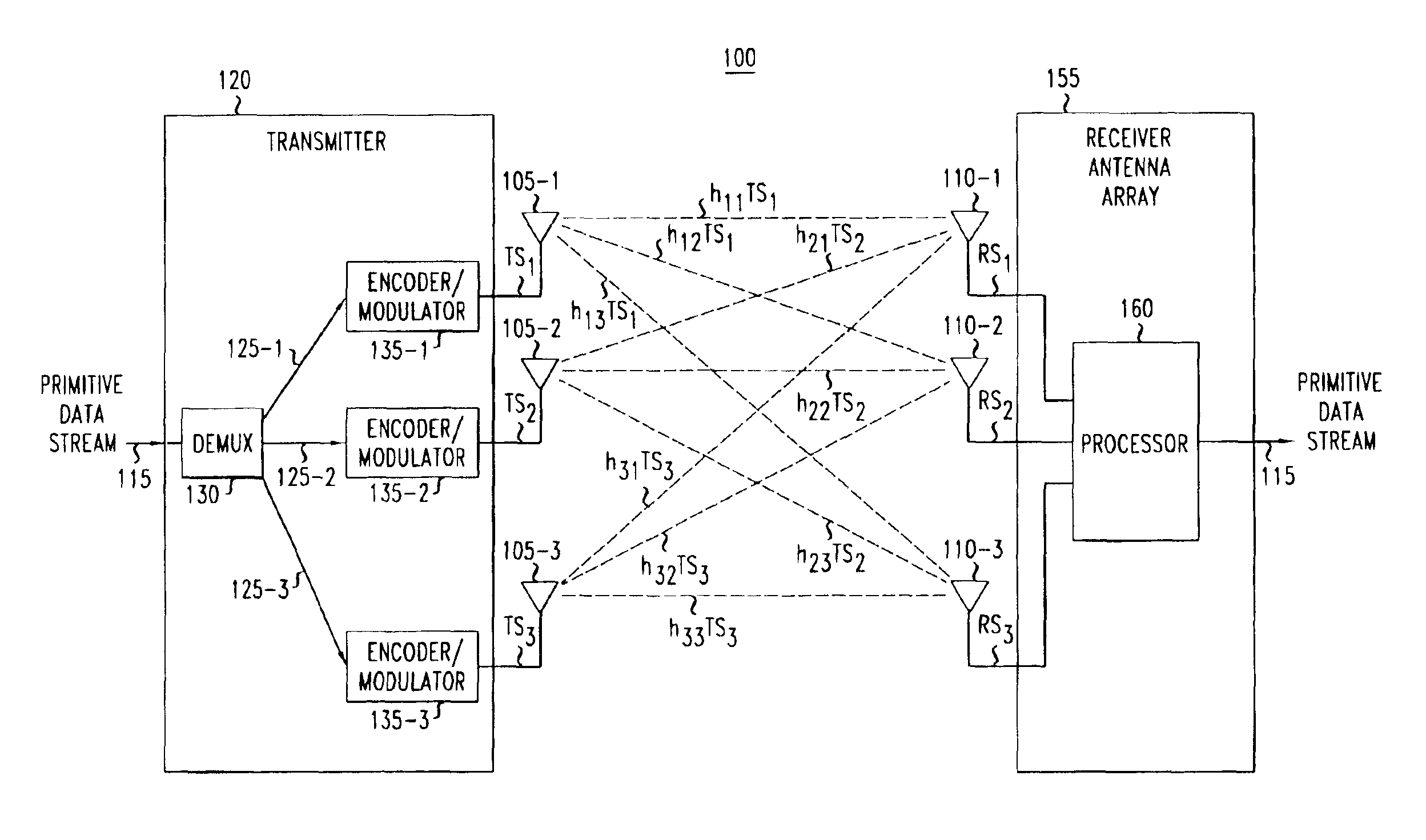
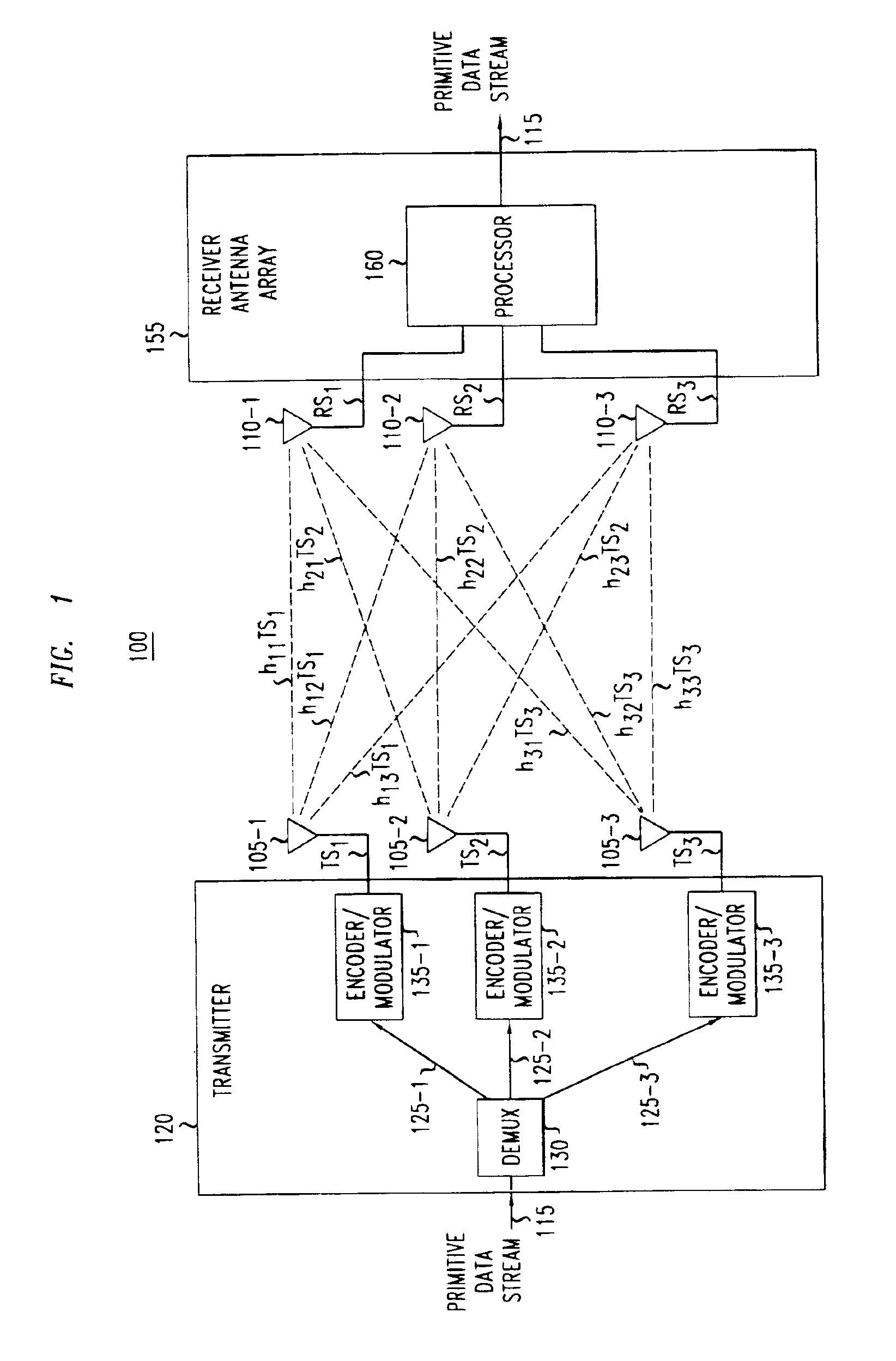
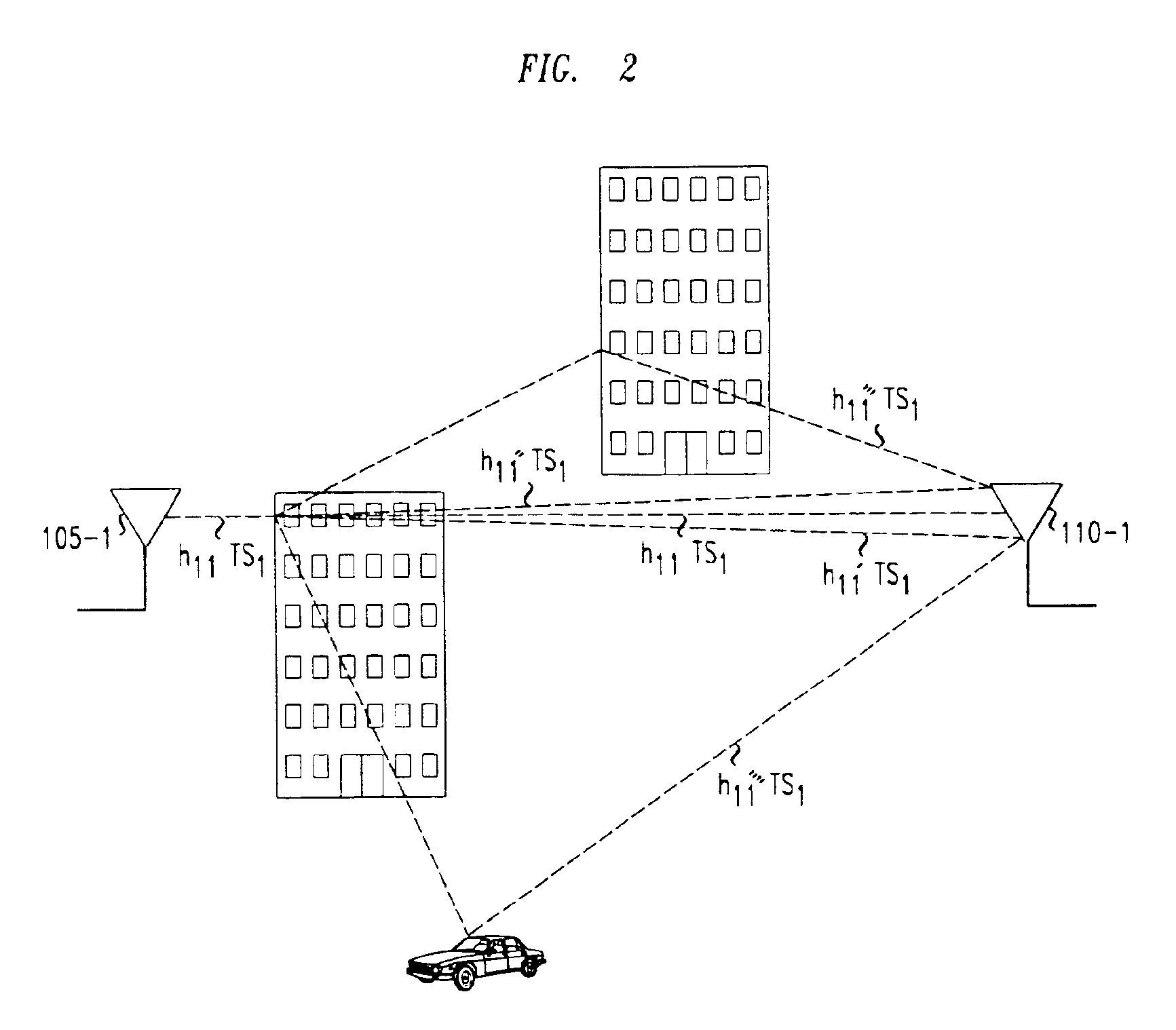
InactiveUS6925131B2High data rateReduce Intersymbol InterferenceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsConjugate transposeCommunications system
A method and apparatus for increasing in the data rate of a multiple-input and / or multiple-output system that has frequency selective fading by using training sequences with both low normalized auto-correlation and low normalized cross-correlation. Both 1) the sum of the square of the normalized auto-correlation of each training sequence over an auto-correlation window and 2) the sum of the square of the normalized cross-correlation of each pair of the training sequences over a cross-correlation window, are significantly less than unity. In one embodiment of the invention the training sequences are shifted versions of each other, and the low normalized cyclic-auto-correlation of cyclic sequences is significantly less than unity, with each cyclic sequence being N′, N′=N−L+1, symbols of one of the at least two training sequences. In another embodiment, the training sequences are ones where the trace of the inverse of the product of the matrix of training sequences' symbols and the conjugate transpose of this matrix is low. The matrix is a function of the number of symbols over which multipaths of significant power can arrive, the number of training sequences, and the number of symbols in a training sequence. More particularly the matrix is a block-toeplitzmatrix composed of the training symbols.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
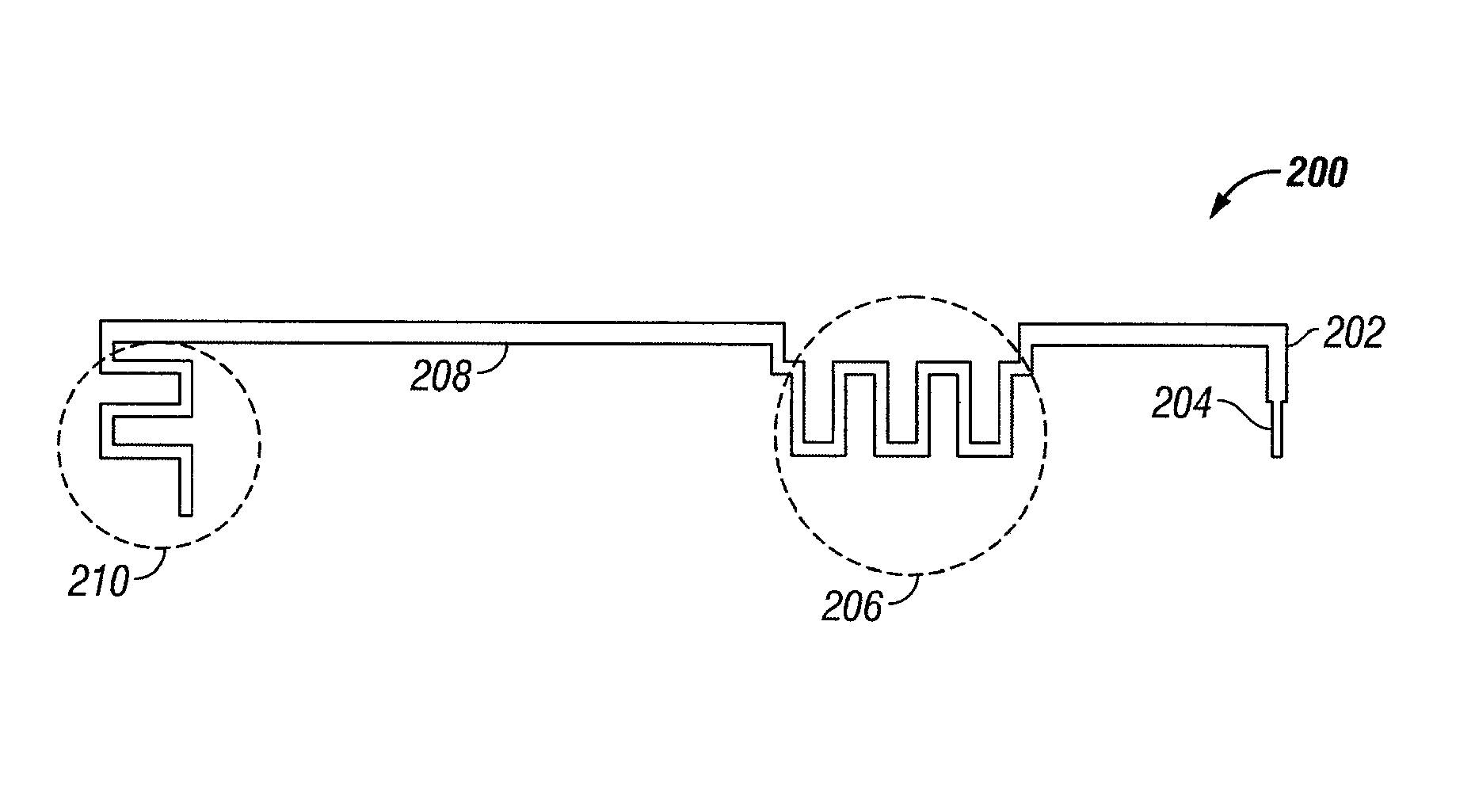
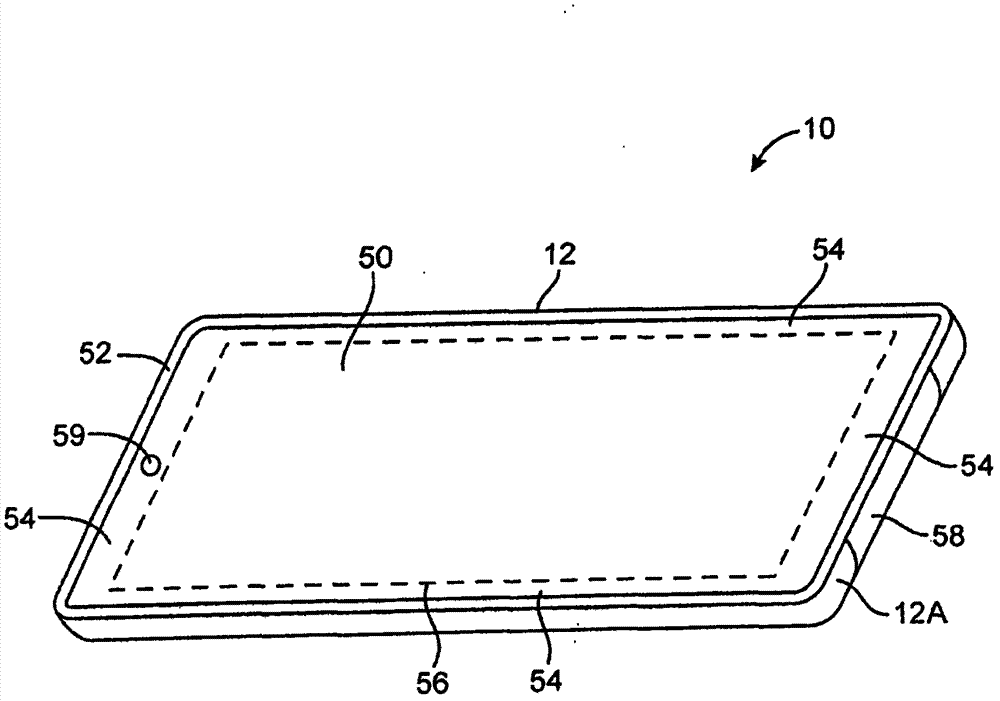
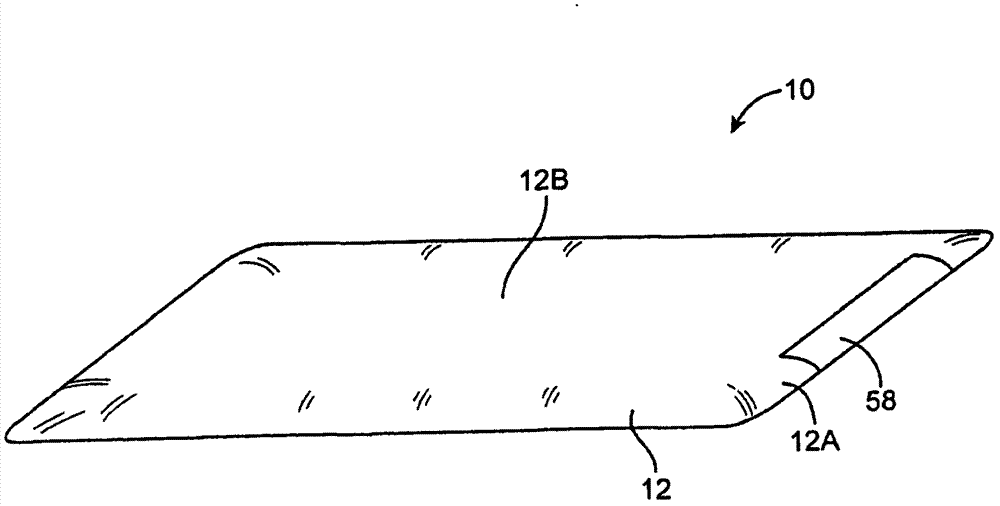
Multi-element antenna structure with wrapped substrate
Antennas are provided for electronic devices such as portable computers. Multiple resonating elements may be formed on a flexible antenna resonating element substrate. The flexible antenna resonating element substrate may have a first antenna resonating element at one end and a second antenna resonating element at an opposing end. The flexible antenna resonating substrate may be wrapped around a dielectric carrier and mounted within an electronic device under an inactive display region and above a dielectric housing window. Conductive structures such as conductive housing structures may form antenna ground. The resonating elements and antenna ground may form first and second antennas. A parasitic antenna resonating element may form part of the first antenna.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems and methods for selecting reconfigurable antennas in MIMO systems
ActiveUS20120106613A1Full Coverage GuaranteedAffecting shapeRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringConfiguration selectionAntenna radiation patterns
A method allows reconfigurable multi-element antennas to select the antenna configuration in MIMO, SIMO and MISO communication system. This selection scheme uses spatial correlation, channel reciprocal condition number, delay spread and average Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) information to select the antenna radiation pattern at the receiver. Using this approach, it is possible to achieve capacity gains in a multi-element reconfigurable antenna system without modifying the data frame of a conventional wireless communication system. The capacity gain achievable with this configuration selection approach is calculated through numerical simulations using reconfigurable circular patch antennas at the receiver of a MIMO system that employs minimum mean square error receivers for channel estimation. Channel capacity and Bit Error Rate (BER) results show the improvement offered relative to a conventional antenna selection technique for reconfigurable MIMO systems.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO
Antenna system for interference supression
ActiveUS20130135162A1Improved signal to noise ratio (SNR) performanceEnhanced signalResonant antenna detailsAntenna detailsTransceiverTelecommunications link
An antenna system is capable of optimizing communication link quality with one or multiple transceivers while suppressing one or multiple interference sources. The antenna provides a low cost, physically small multi-element antenna system capable of being integrated into mobile devices and designed to form nulls in the radiation pattern to reduce interference from unwanted interferers. The antenna system operates in both line of sight and high multi-path environments by adjusting the radiation pattern and sampling the received signal strength to reduce signal levels from interferers while monitoring and optimizing receive signal strength from desired sources.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
System and method of using absorber-walls for mutual coupling reduction between microstrip antennas or brick
InactiveUS20070126620A1Reduce signalingReduce horizontal sizeAntenna detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrostrip patch antennaBrick
A multi-element antenna with sufficiently small return loss and mutual coupling signals to allow the simultaneous transmission of powerful radar signals and the reception of faint target return signals. The microstrip patch antenna has radio frequency absorbing material place between neighboring antenna elements to reduce the mutual coupling leakage signals.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
Code assignment algorithm for synchronous DS-CDMA links with SDMA using estimated spatial signature vectors
InactiveUS7050480B2Increase system capacityAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemParallel computing
A method is disclosed for operating a synchronous space division multiple access, code division multiple access communications system. The method operates, within a coverage area of a base station (BS) or radio base unit (RBU) having a multi-element antenna array, for estimating a SSV for individual ones of a plurality of active subscriber stations (SSs) and assigns a spreading code to a subscriber station (SS) that minimizes the similarity of the determined SSVs of the SSs in a spreading code set. A metric used to measure the similarity of the spatial signature vectors of the SSs comprises the squared sum of the inner products of same code SSs' SSV with a current SS's SSV. The step of assigning includes calculating the magnitude of the squared inner product of the SSVs of all pairs of active SSs; using the calculated values for determining ξn(c) for each spreading code that is not already used some specified maximum number of times; and assigning to a SS the spreading code with a minimum ξn(c).
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
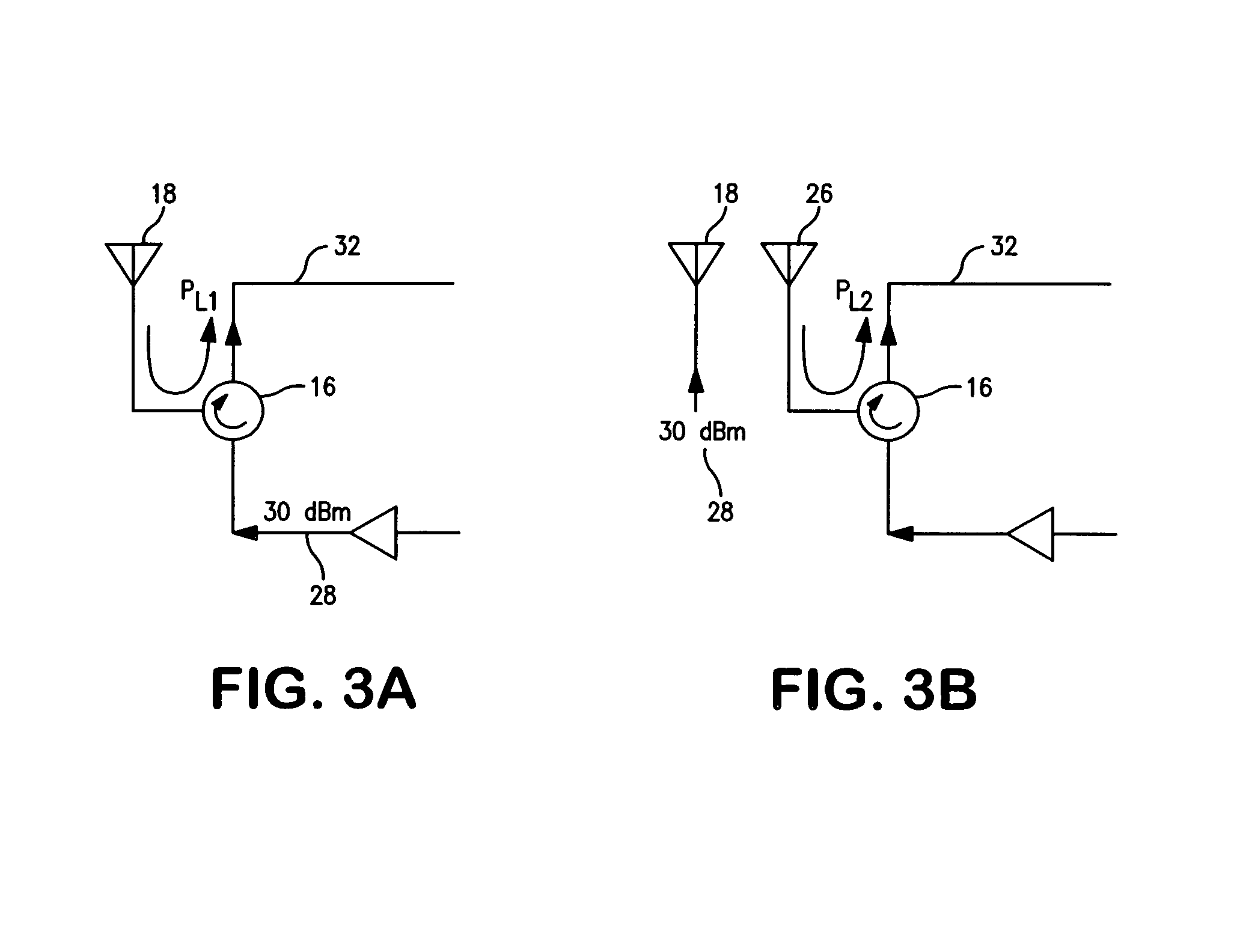
Indented antenna array for transmitter to receiver isolation
ActiveUS20170207532A1High antenna isolationImprove antenna isolationAntenna arraysAntenna earthingsRadio communicationsTransmitter
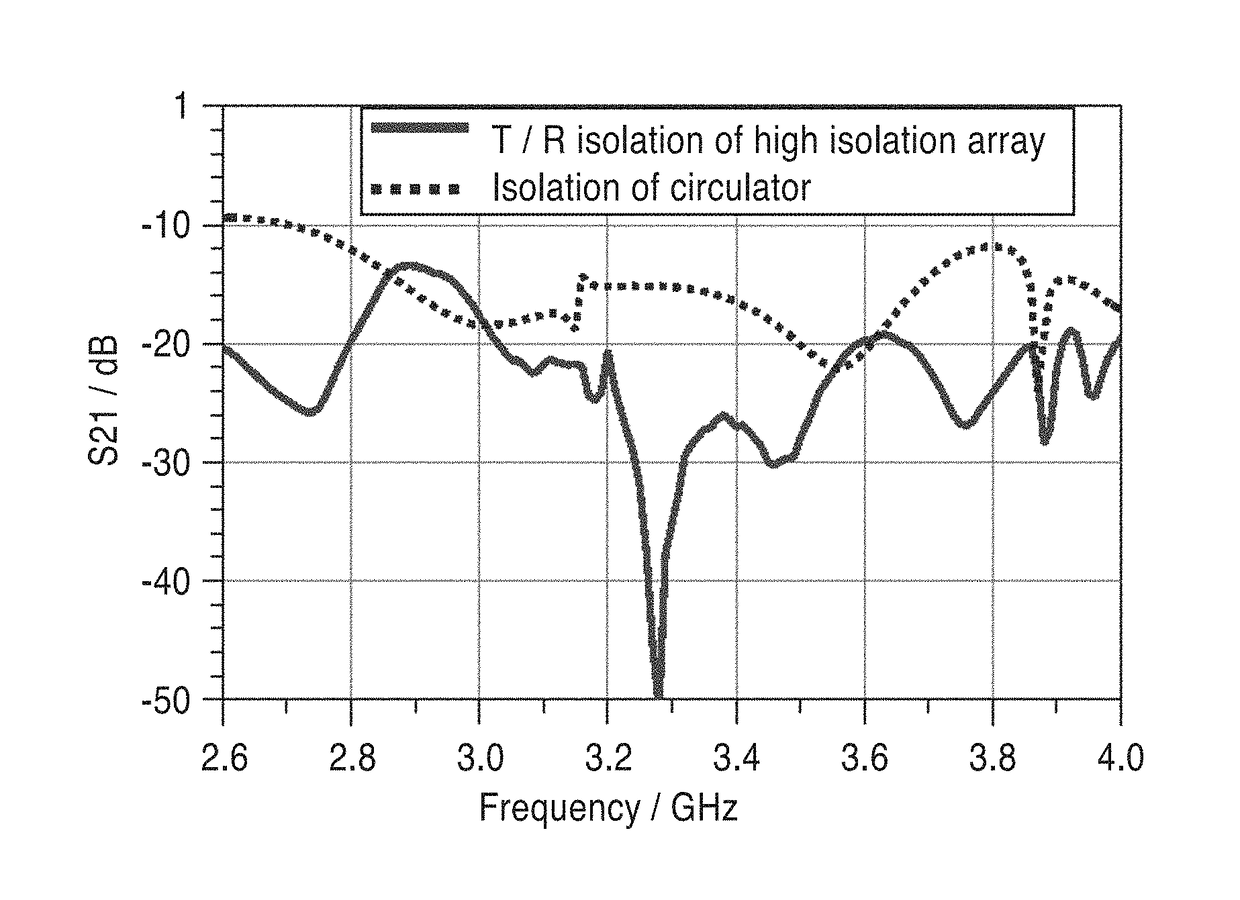
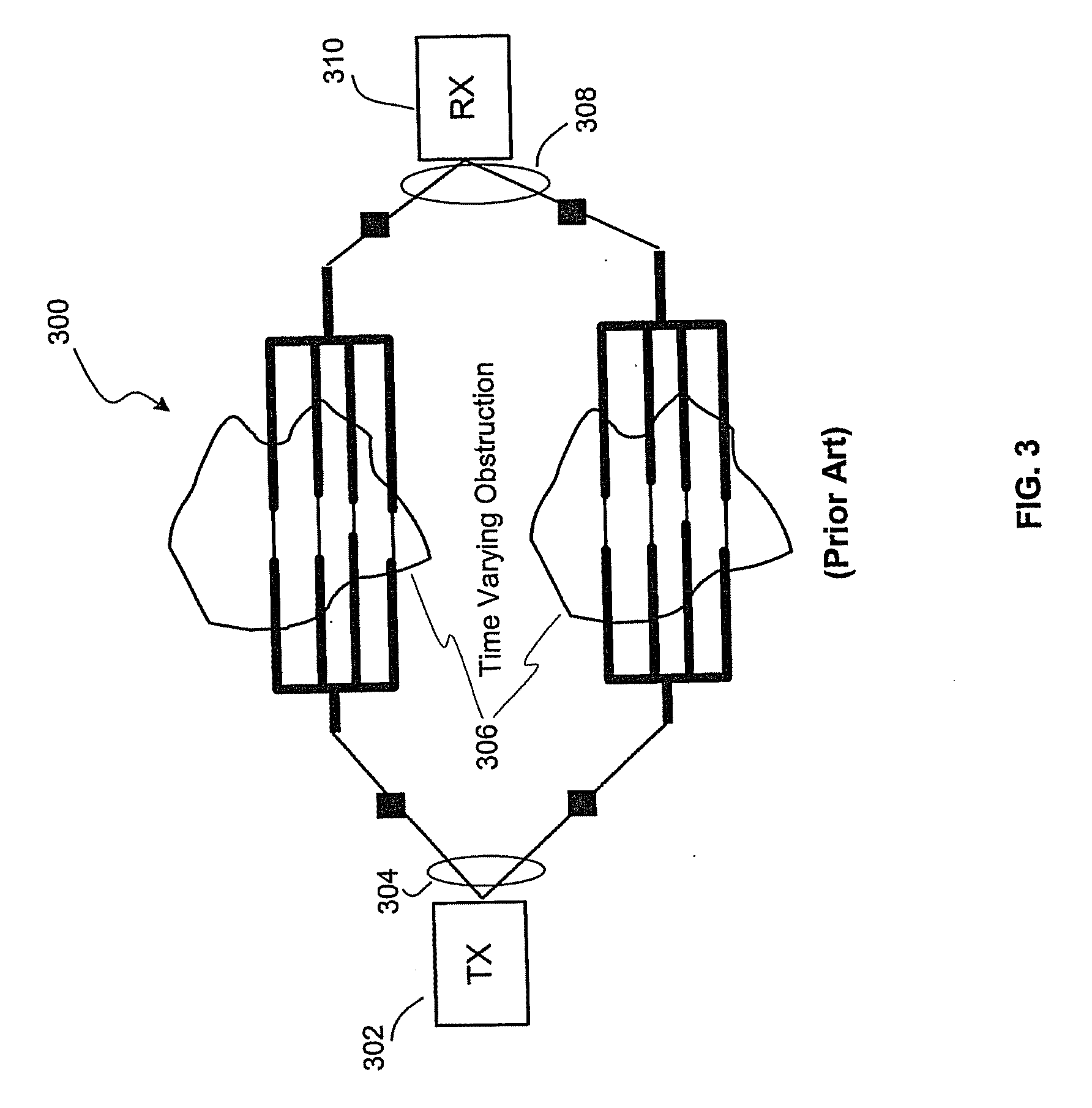
An apparatus and method for enhancing full-duplex radio communications using an indented transmitter and receiver antenna. A multi-element antenna array is configured with each antenna coupled to a circulator that has connections to both a transmission path and a receiving path. The apparatus is configured with indentations that provide a tilting of the array from its broadside to create a progressive phase delay between adjacent pairs of elements. Transmitted and received waves travel a single trip through the indention, while antenna reflection or circulator leakage travels a round trip through indention, so that these signal components can be readily separated to achieve high levels of isolation during full-duplex transmitting and receiving.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
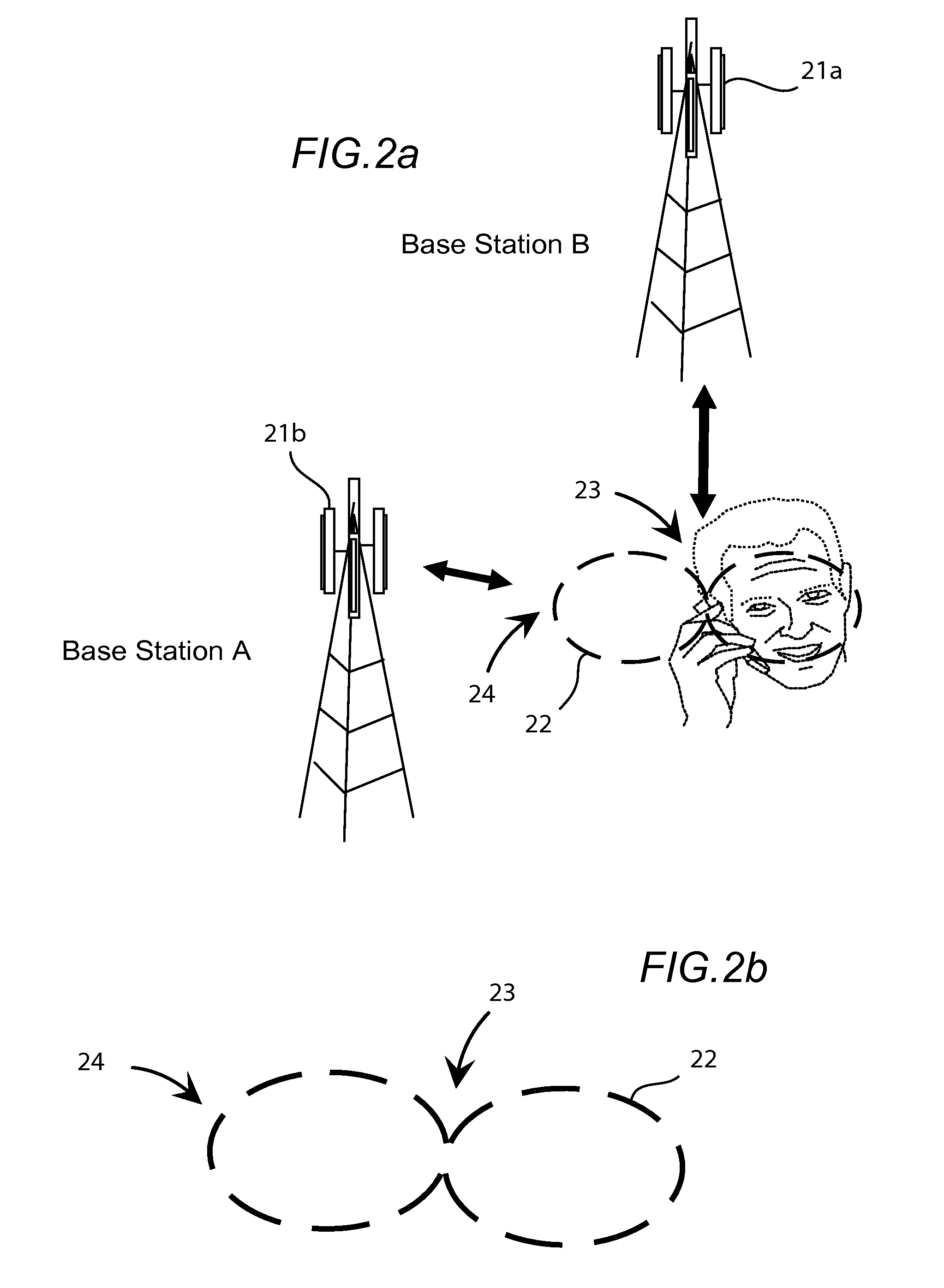
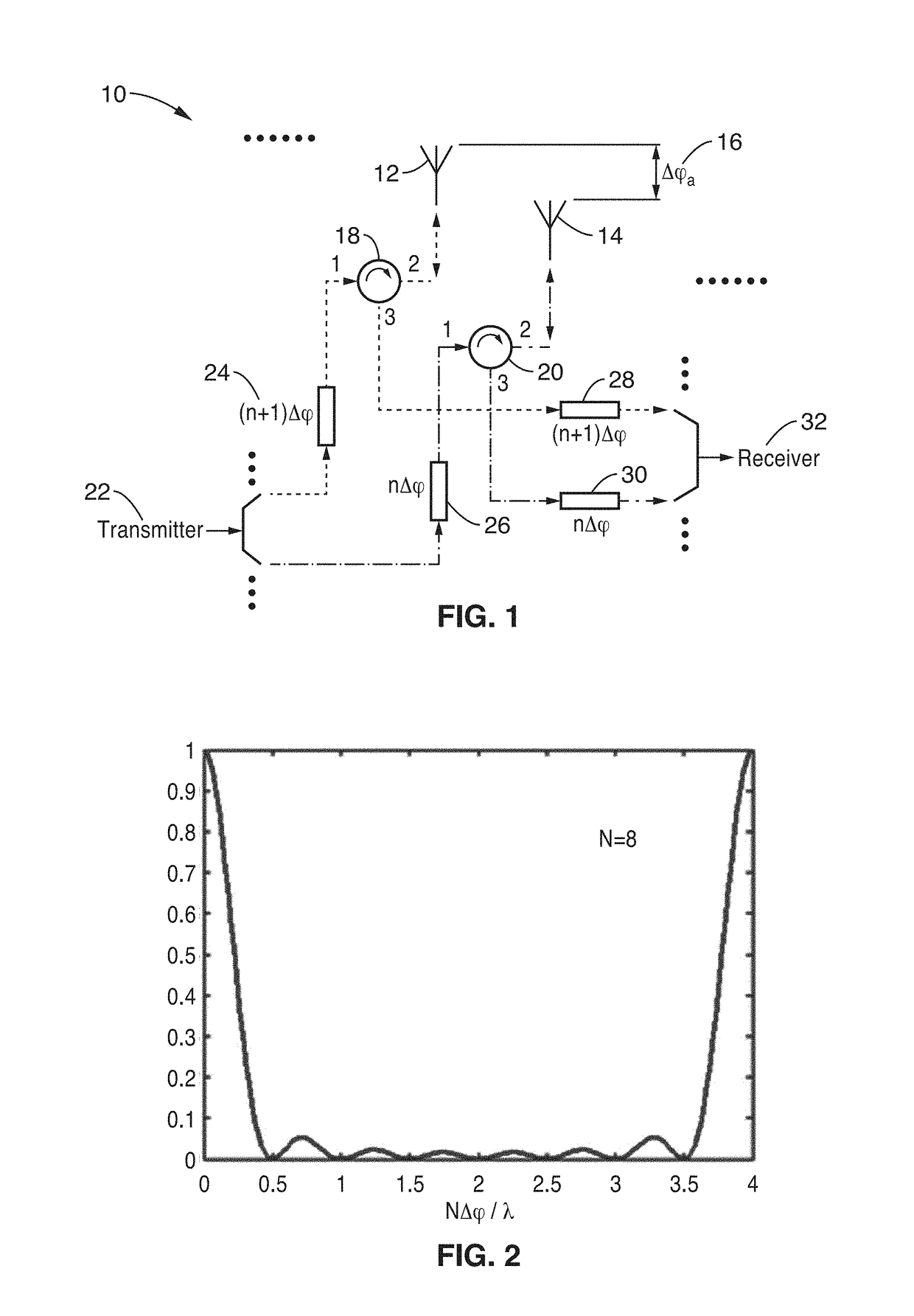
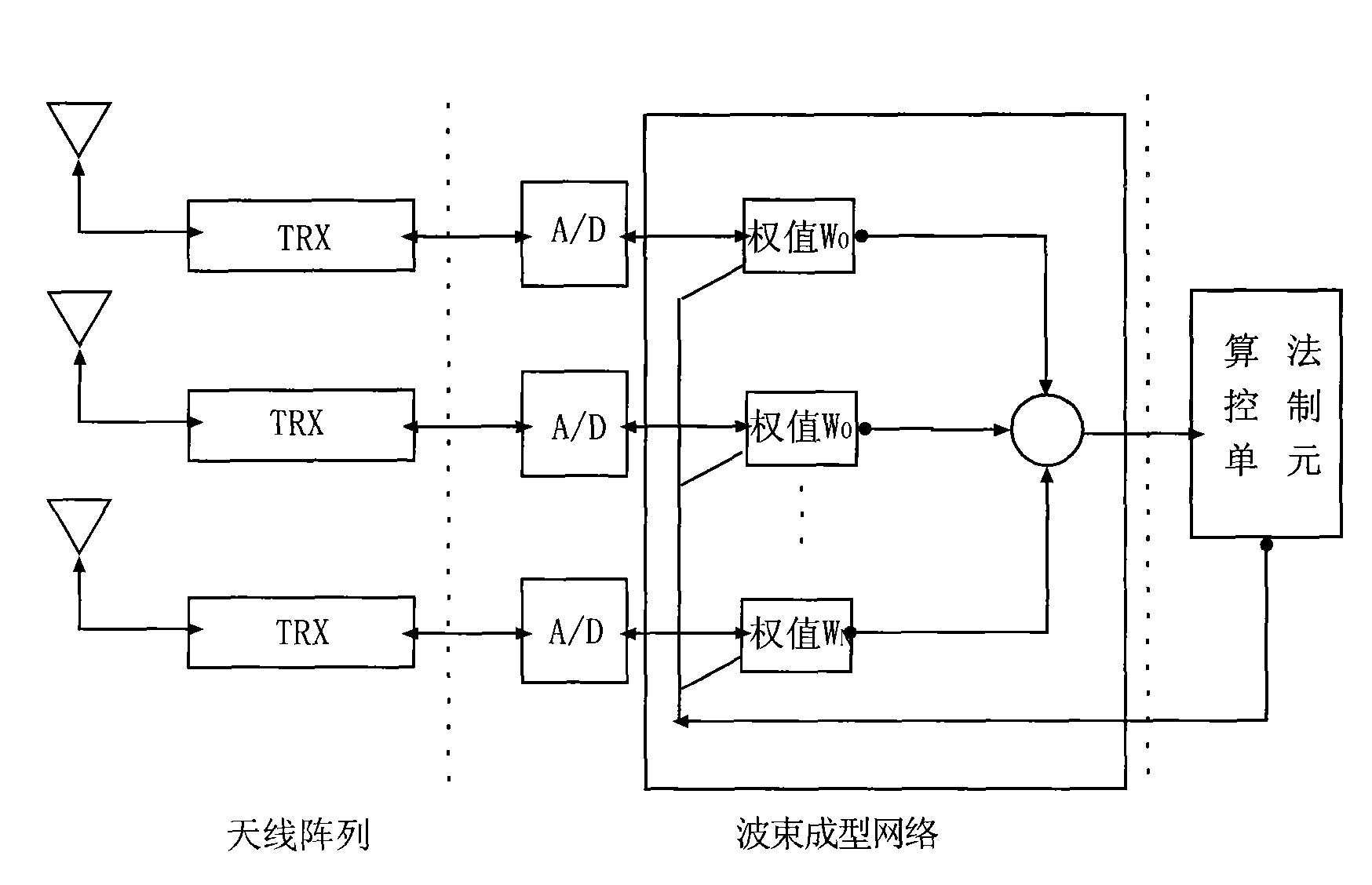
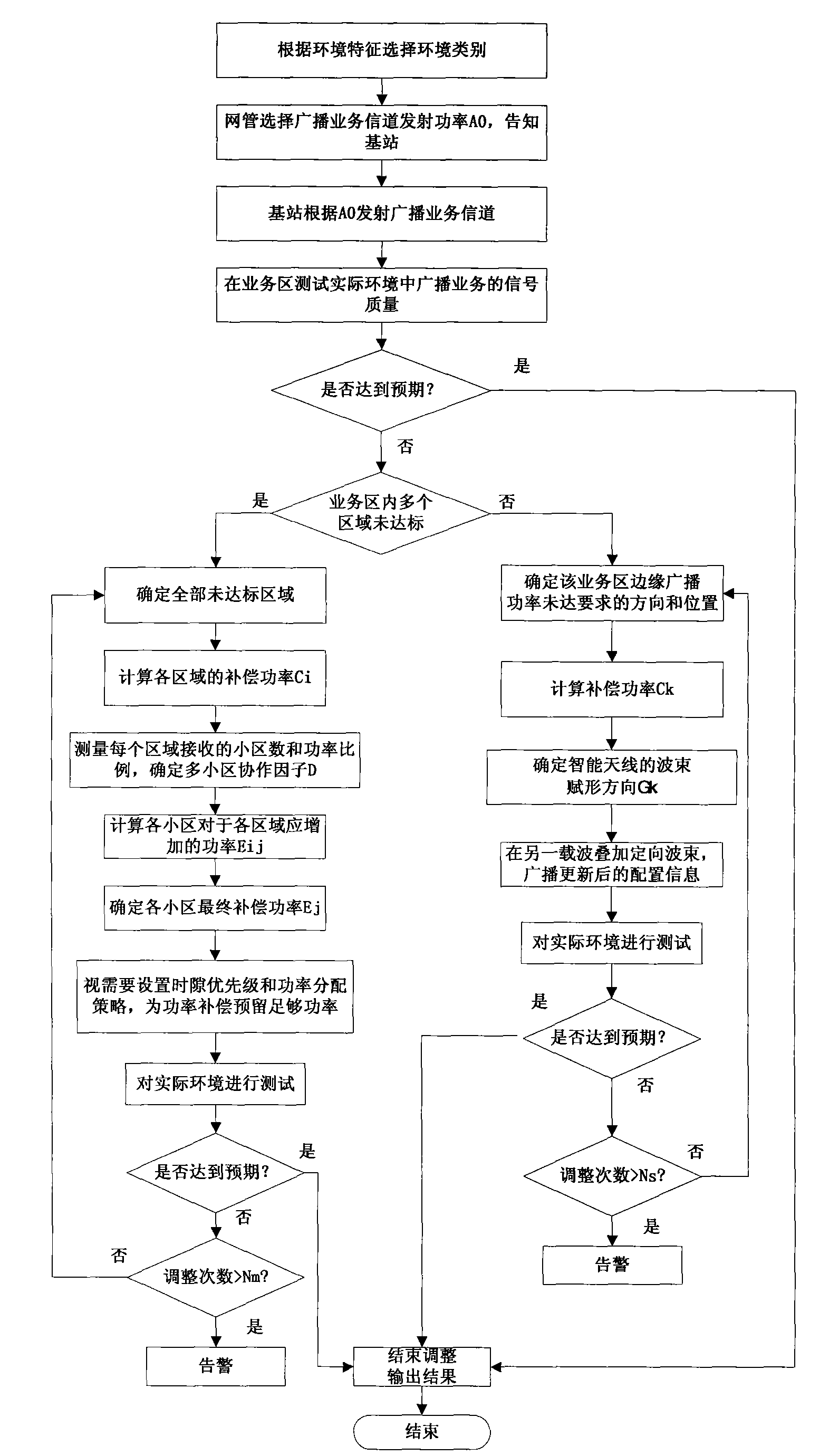
Method for improving quality of broadcasting service in mobile communication network
ActiveCN101651481AImprove performance lossAdd supportSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingQuality of servicePower compensation
The invention provides a method for improving the quality of a broadcasting service in a mobile communication network, which is invented to solve the problem that the quality of the broadcasting service in the prior cellular mobile communication network cannot be guaranteed. The method comprises the following steps: testing the received power strength of a broadcasting service channel in a service coverage region, and determining the location of a region in which the received power strength of the broadcasting service channel does not reach an expected value; if the region not reaching the expected value is positioned on the edge of the service region, superposing a beamformed broadcasting service channel with a different frequency or a different time slot which bears the same service on the basis of the prior signals in the service coverage region; and if the region not reaching the expected value is not positioned on the edge of the service region, performing joint adjustment of thepower of the broadcasting service channels of a plurality of cells in the service coverage region. The method can select different adjusting modes according to the location characteristics of the region not reaching the standard and improves broadcasting service signals by power compensation or multi-element antenna beamforming.
Owner:THE RES INST OF TELECOMM TRANSMISSION MIIT +1
Code assignment algorithm for synchronous DS-CDMA links with SDMA using channel scanning
InactiveUS7031290B2Increase system capacityAntenna supports/mountingsSecret communicationCommunications systemSpace-division multiple access
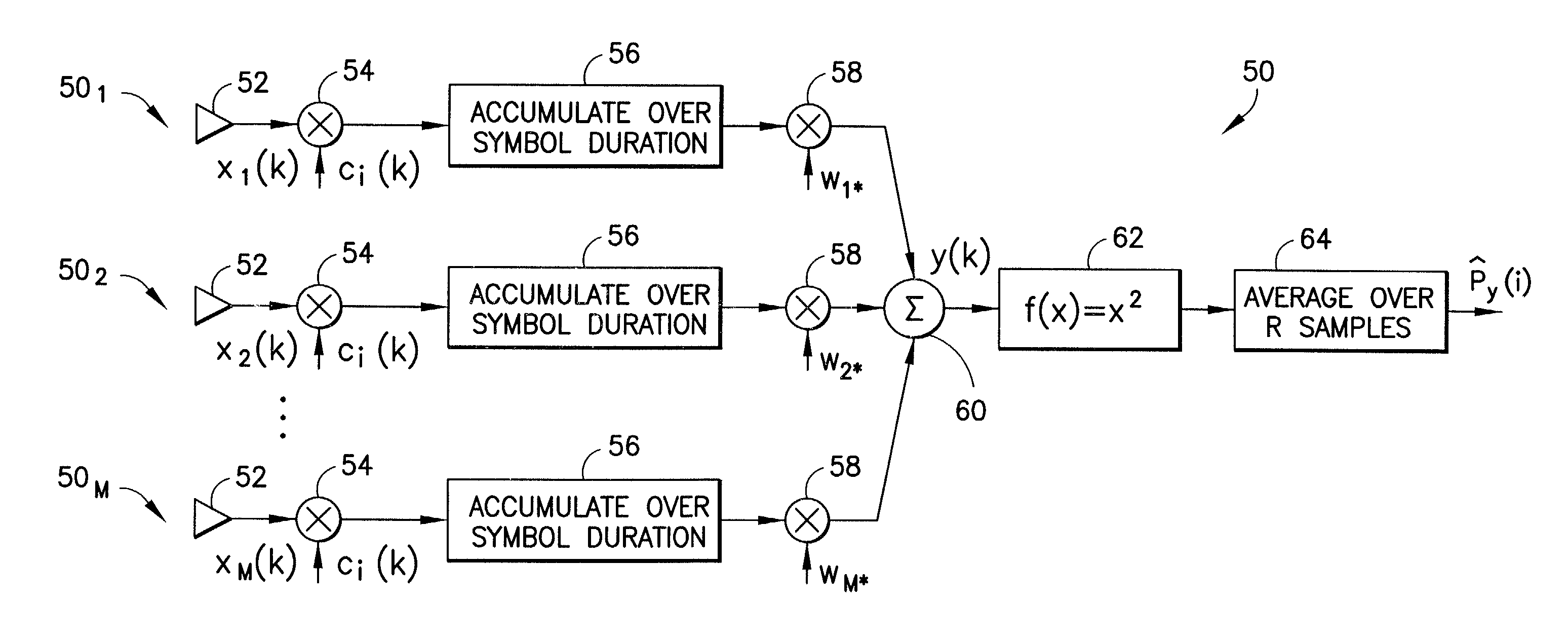
A method is disclosed for operating a synchronous space division multiple access, code division multiple access communications system. The method operates, within a coverage area of a base station (BS) or radio base unit (RBU) having a multi-element antenna array, to assign spreading codes to users. The method estimates a spatial signature vector (SSV) for a current subscriber station; uses the estimated SSV as a weight vector when determining the output power that is correlated with each of a plurality of spreading code sequences and assigns a spreading code to the current subscriber station that is determined to have the minimum output power. The step of determining the output power includes steering a beamformer toward the current subscriber station by setting the weight vector equal to the SSV, and also determines the average squared value of the antenna array output that has been despread using a code i. The multi-element antenna array has M elements, and the step of determining the output power operates an M-branch receiver to despread a signal received on each element with a spreading code i, to accumulate the despread signal over a symbol duration, to scale the accumulated signal by the weight vector, to sum all of the scaled values and to square the result, and to average the squared result over R samples to determine the output power for code i for the current subscriber station. R may have a value in the range of about 16 symbols to about 64 symbols, and may be fixed or variable.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
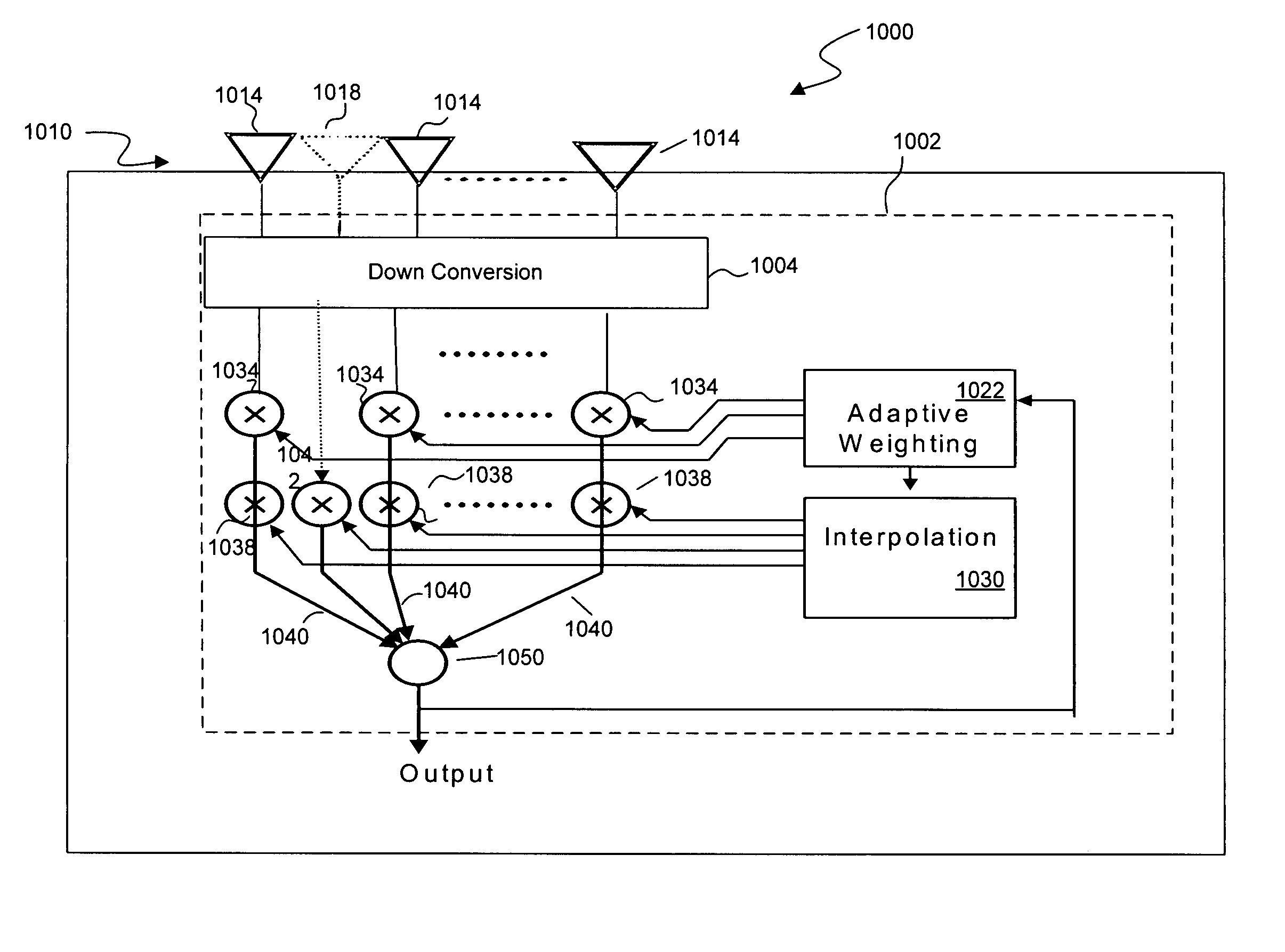
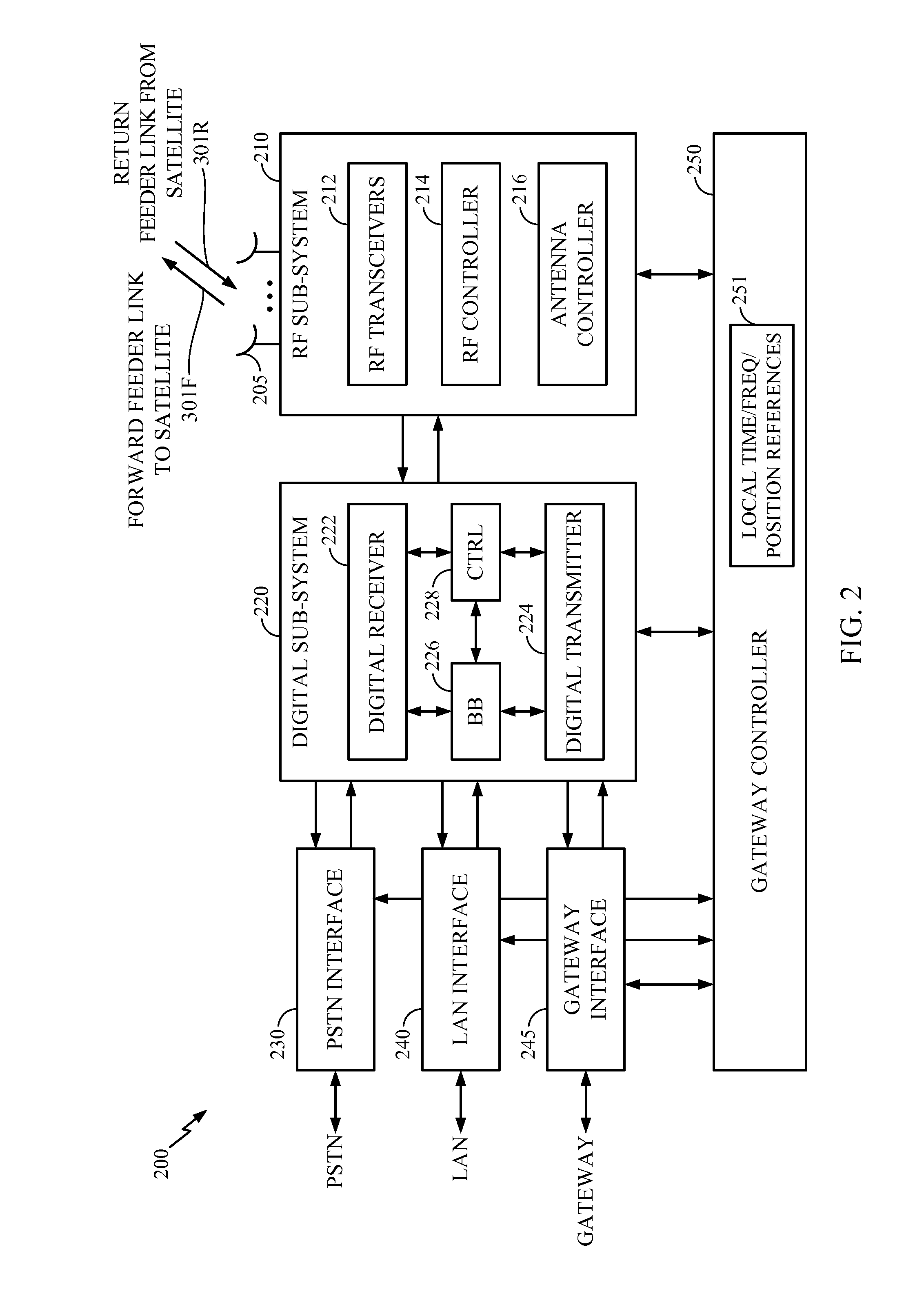
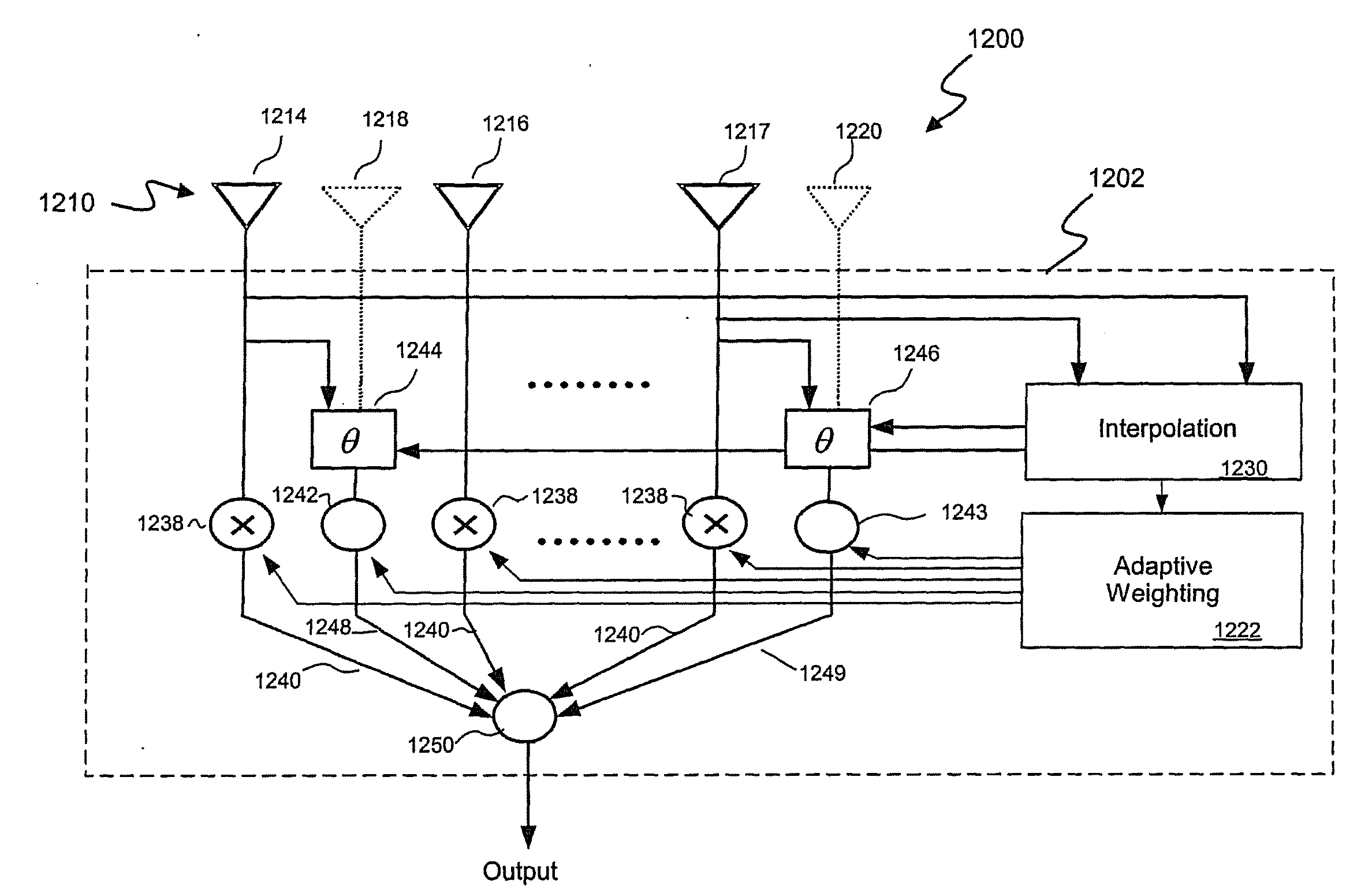
Multi-Element antenna Calibration Technique
Antenna system having an antenna array with multiple sub-arrays, each having one or more antenna elements, is calibrated using a distributed calibration antenna element, such as a leaky coaxial cable, that spans across at least two and possibly all of the sub-arrays. To calibrate the transmit (TX) paths of the sub-arrays, TX calibration test signals are transmitted by the sub-arrays, captured by the distributed calibration element, and processed by a corresponding calibration radio. To calibrate the receive (RX) paths of the sub-arrays, an RX calibration test signal is generated by the calibration radio, transmitted by the distributed calibration element, captured by the sub-arrays, and processed by their corresponding radios. Cross-correlation between the calibration and captured signals is performed to derive the complex gain of each sub-array transmitter and receiver, which provides information for aligning the gain, phase, and delay of the different TX and RX paths of the antenna array.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
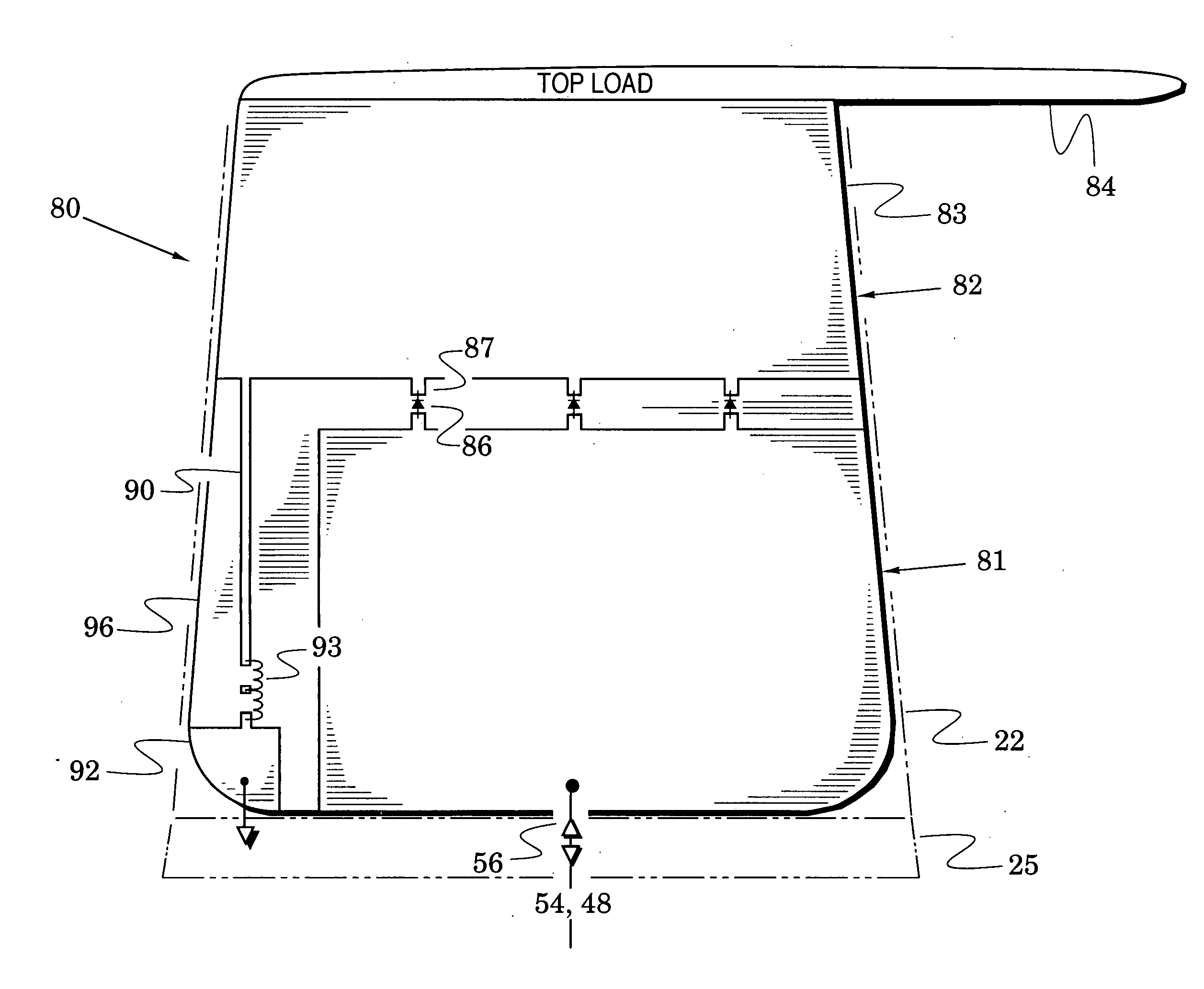
Articulating dual antenna
A method and apparatus for deploying a multi-element antenna system on a portable television signal processing apparatus. The system utilizes a plurality of spring loaded racks engaged in a pinion restrained by a rotational damper and a manual release mechanism. Each individual rack is attached to a rotational mechanism used to rotate an antenna element around an axis. The springs are compressed when the antenna is in its stored state and released via the manual release mechanism. The released rack and pinion system biases a plurality of rotational mechanisms which respectively extend the antenna elements into their deployed configuration.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Phased array, a coherent source array, an antenna array and a system for controlling thereof
ActiveUS9966661B2Low costAchieve synchronizationPulse automatic controlAntennasPhase controlEngineering
A system for controlling a multi-element antenna array comprising a plurality of elements each arranged to receive a signal from a signal source, wherein each of the plurality of elements includes a frequency locking module arranged to lock the frequency of the signal received by each of the elements, and, a phase control module being in communication with each of the frequency locking modules to control the phase of the signal received by each of the elements.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
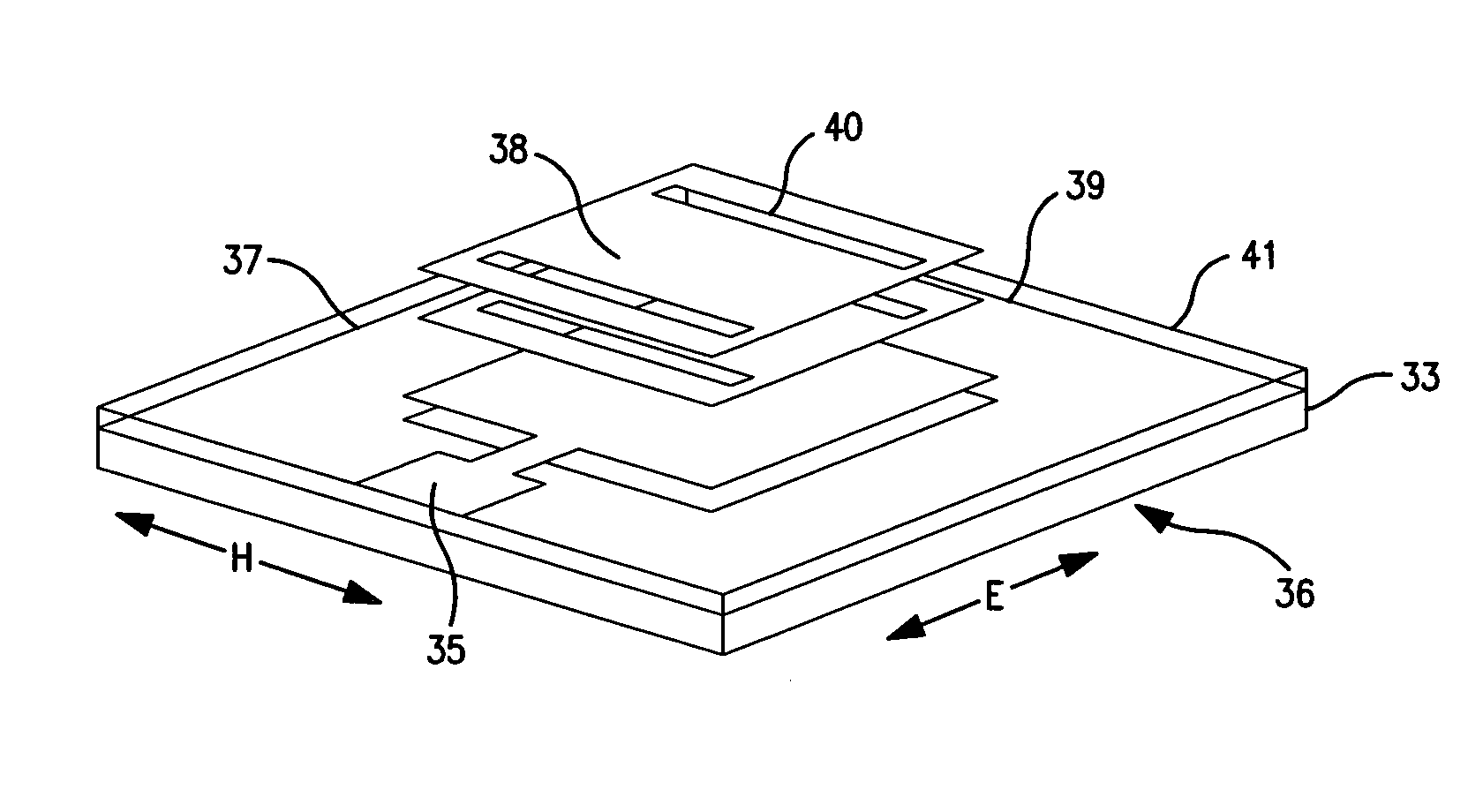
Omni directional broadband coplanar antenna element
ActiveUS8199064B2Antenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricOmni directional
The present invention provides an omni-directional antenna element configuration having a compensated radiation pattern. Broadband antenna elements are coplanarly disposed on a suitable planar dielectric material. A single element omni-directional antenna comprises a pair of balanced fed radiating microstrip elements symmetrically disposed about the centerline of a balanced signal feed network. Additionally, a pair of pattern augmentation rods are positioned on each side of and proximate to the planar dielectric material running longitudinally to the centerline axis of a balanced feed network. Disposed proximate to each radiating element are partially coplanar, frequency bandwidth expanding microstrip lines. The combination of radiating elements together with pattern augmentation rods provides a broad bandwidth omni-directional radiating element suitable for use in multi-element antenna arrays.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Broadband tunable antenna and transceiver systems
InactiveUS7129907B2Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsTransceiverImpedance matching
The present invention is directed to multi-element antennas that include, for each adjacent pair of antenna elements, at least one switch arranged to selectively connect that pair to thereby selectively alter an antenna dimension. Accordingly, a multi-element antenna can be configured to enhance its gain at different operational frequencies while a corresponding impedance matching network can enhance the impedance match (i.e., reduce reflected signal energy) between the antenna and a corresponding system (e.g., a transceiver system). The antenna and system can thus be effectively tuned across a wide operational band. The antenna and impedance matching network are configured with switch command signals and match command signals that are provided in response to each of a plurality of frequency codes.
Owner:SENSOR SYST
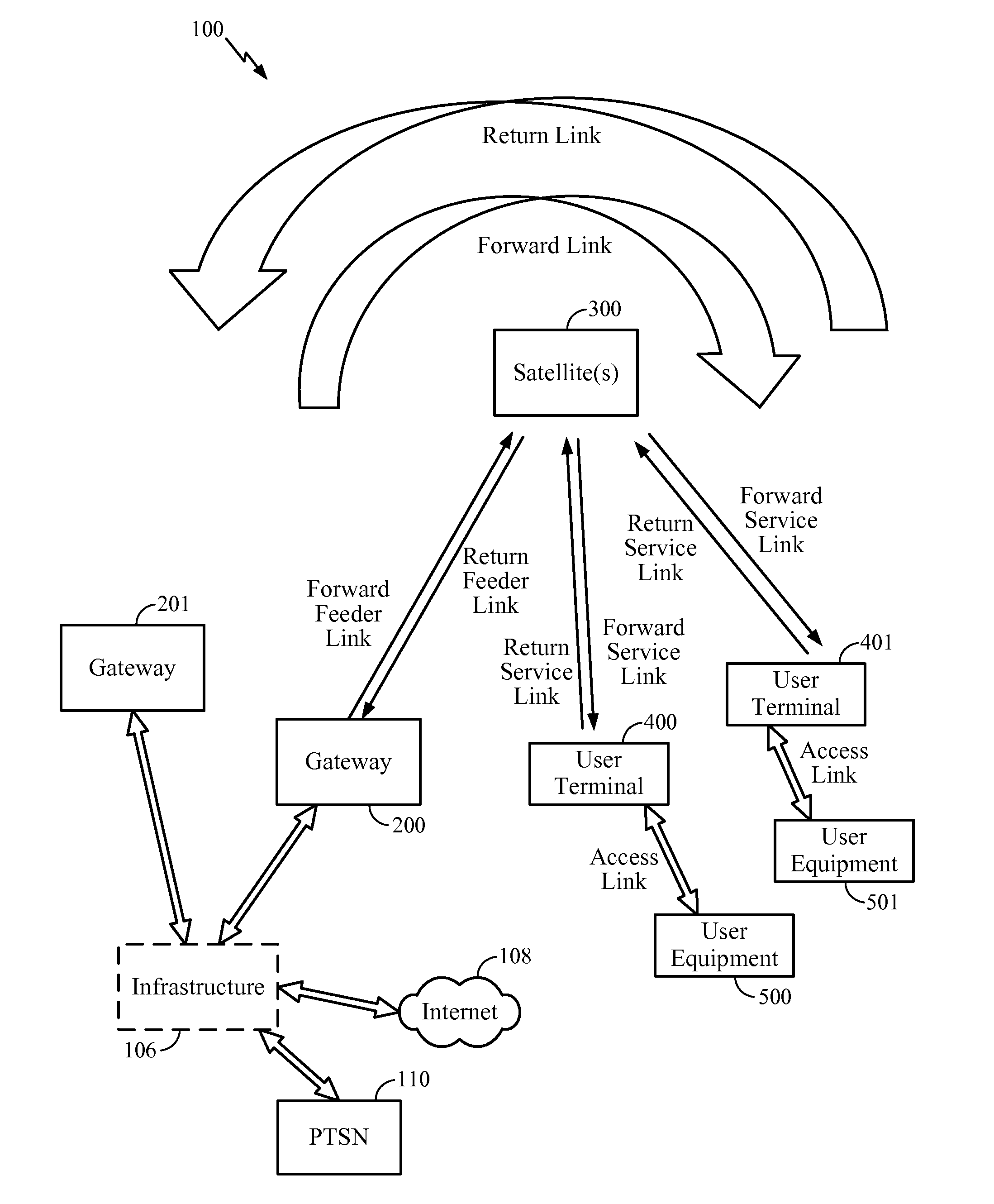
Communication system
ActiveUS20180123707A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityBase station identity codeCommunications system
A signal is transmitted and received between a base station device and a communication terminal device that are included in a communication system, through a multi-element antenna including a plurality of antenna elements. At least one of the base station device and the communication terminal device includes a PHY processing unit that is a calibration unit that performs calibration of phases and amplitudes of beams formed by the antenna elements when the signal is transmitted and received. The PHY processing unit obtains a correction value for the phases and the amplitudes of the beams in the respective antenna elements so that the phases and the amplitudes of the beams are identical among the antenna elements, and performs the calibration based on the obtained correction value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Compact Multi-Element Antenna With Phase Shift
ActiveUS20120086604A1High gainReduce negative impactSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsPhase shiftedBeam pattern
A phased array antenna system includes a first radiation element that is made of a material and has a length selected to resonate at a desired frequency. A phase-shift element is coupled to one end of the first radiation element. A second radiation element is coupled to the end of the phase-shift element opposite the first radiation element, so that a radio signal passes through the first radiation element through the phase-shift element and through the second radiation element, the second radiation element is made of a material and has a length selected to resonate such that the first and second radiation elements cooperate to form a desired beam pattern from the antenna system.
Owner:AIRGAIN INC
Antenna array including virtual antenna elements
InactiveUS20070109191A1Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringAntenna element
A method and associated system for effectively increasing the number of antenna elements within a multi-element antenna system through computation of a response of “virtual” antenna elements located along an antenna array. The physical elements of the array are positioned sufficiently near each other to enable synthesis of a polynomial or other mathematical expression characterizing the response of the array to receipt of an incident waveform. Values of the responses associated with the virtual antenna elements of the array may then be determined through evaluation of the synthesized polynomial or other expression. The resultant array response values associated with the virtual and physical elements of the array are then provided to an associated receiver for processing.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Systems and methods for multi-element antenna arrays with aperture control shutters
InactiveUS7756471B2Easy to implementProduction toleranceResonant long antennasPosition fixationCommunications systemBeam direction
Embodiments include systems and methods for controlling beam direction of an array of antenna elements in a wireless communications system. In one embodiment, aperture control shutters substantially cover each radiating antenna element. Each aperture control shutter is selectively turned on or off to control the direction of a beam of the antenna array.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Transmitting service advertisements
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com