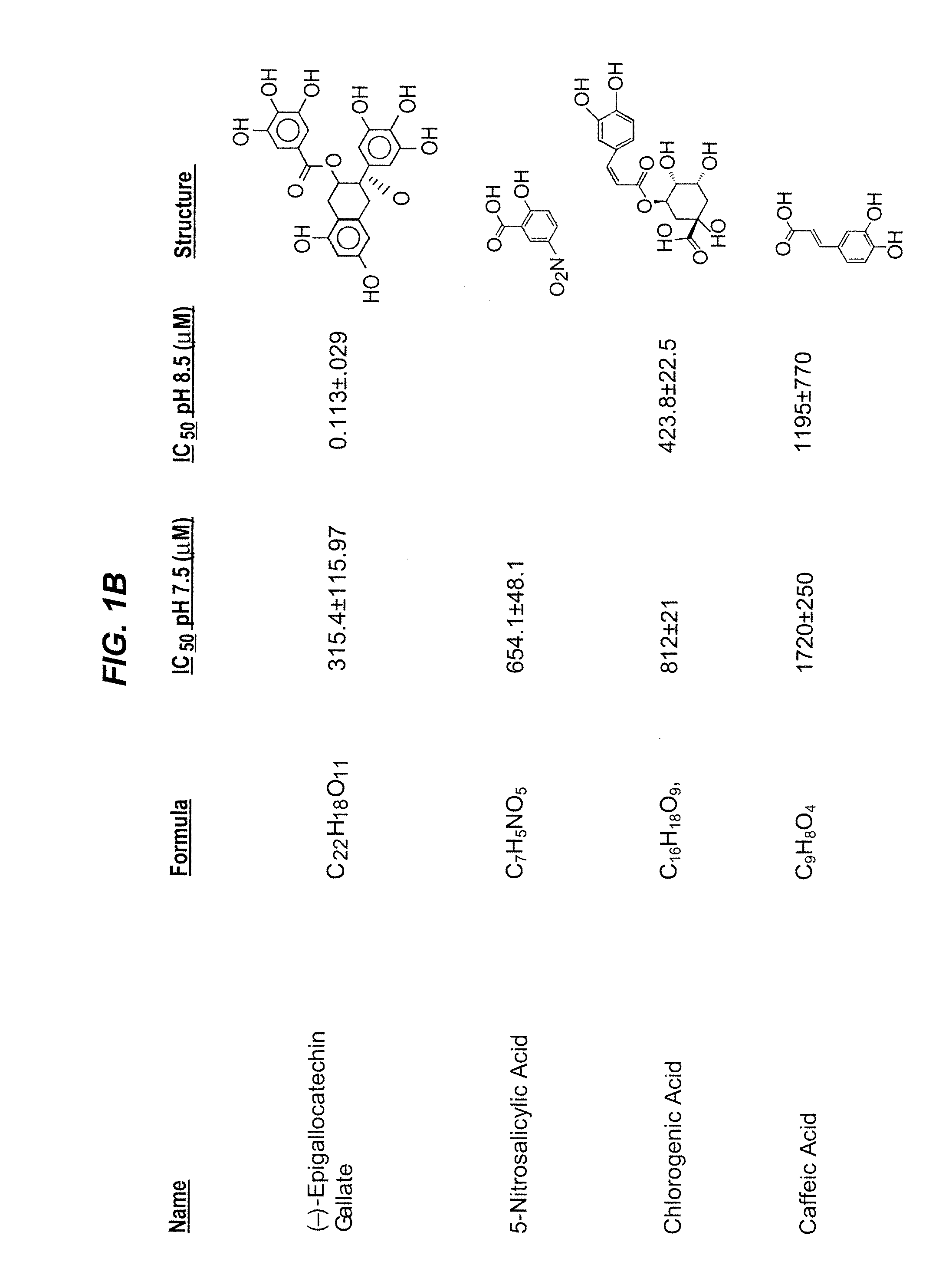
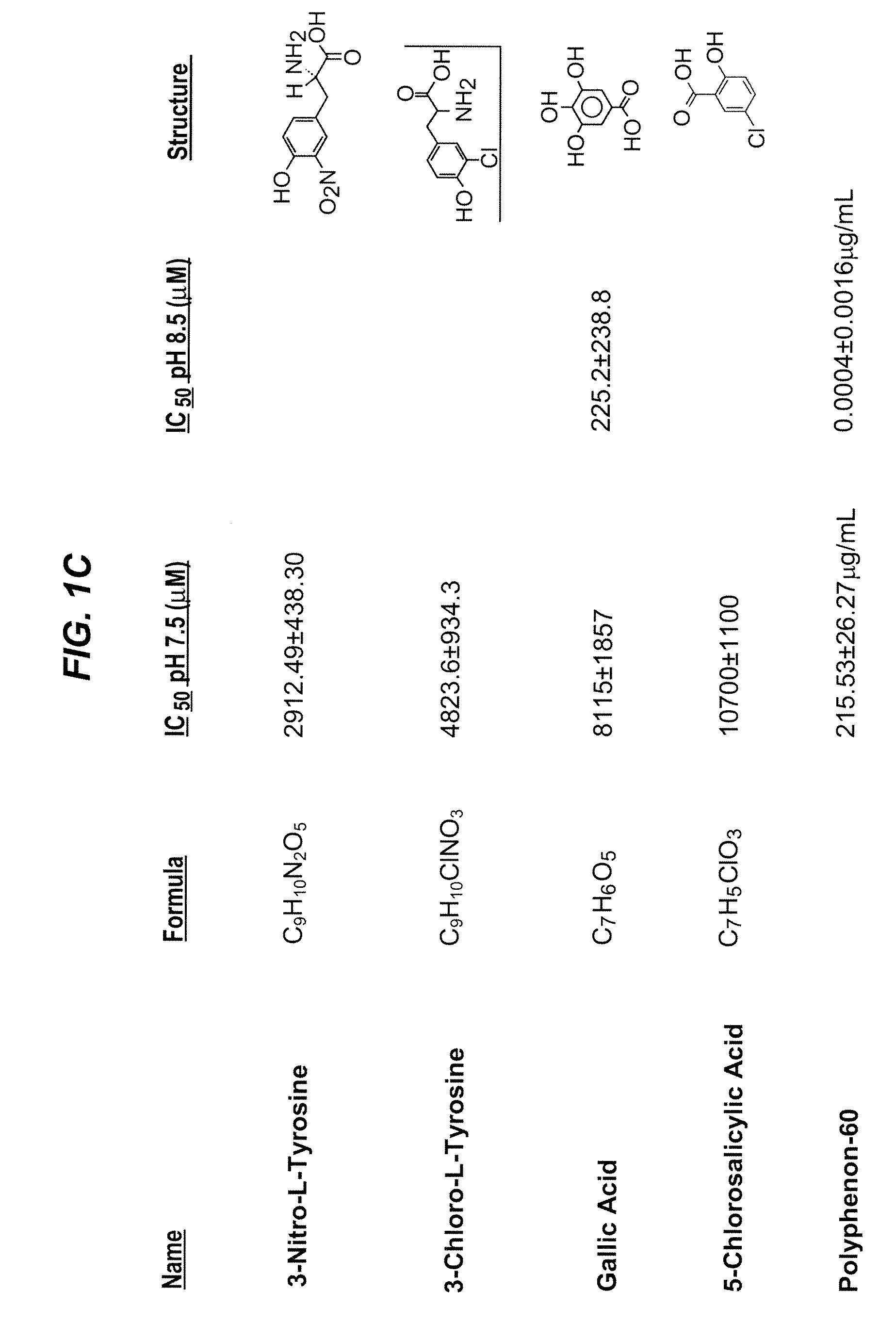
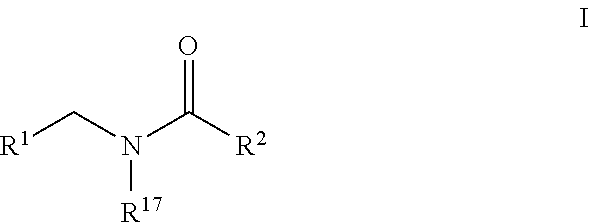
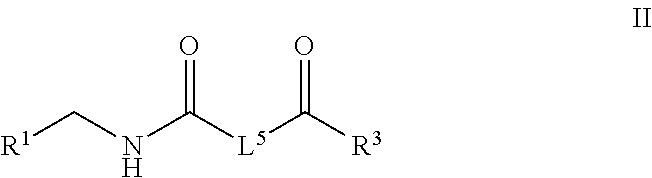
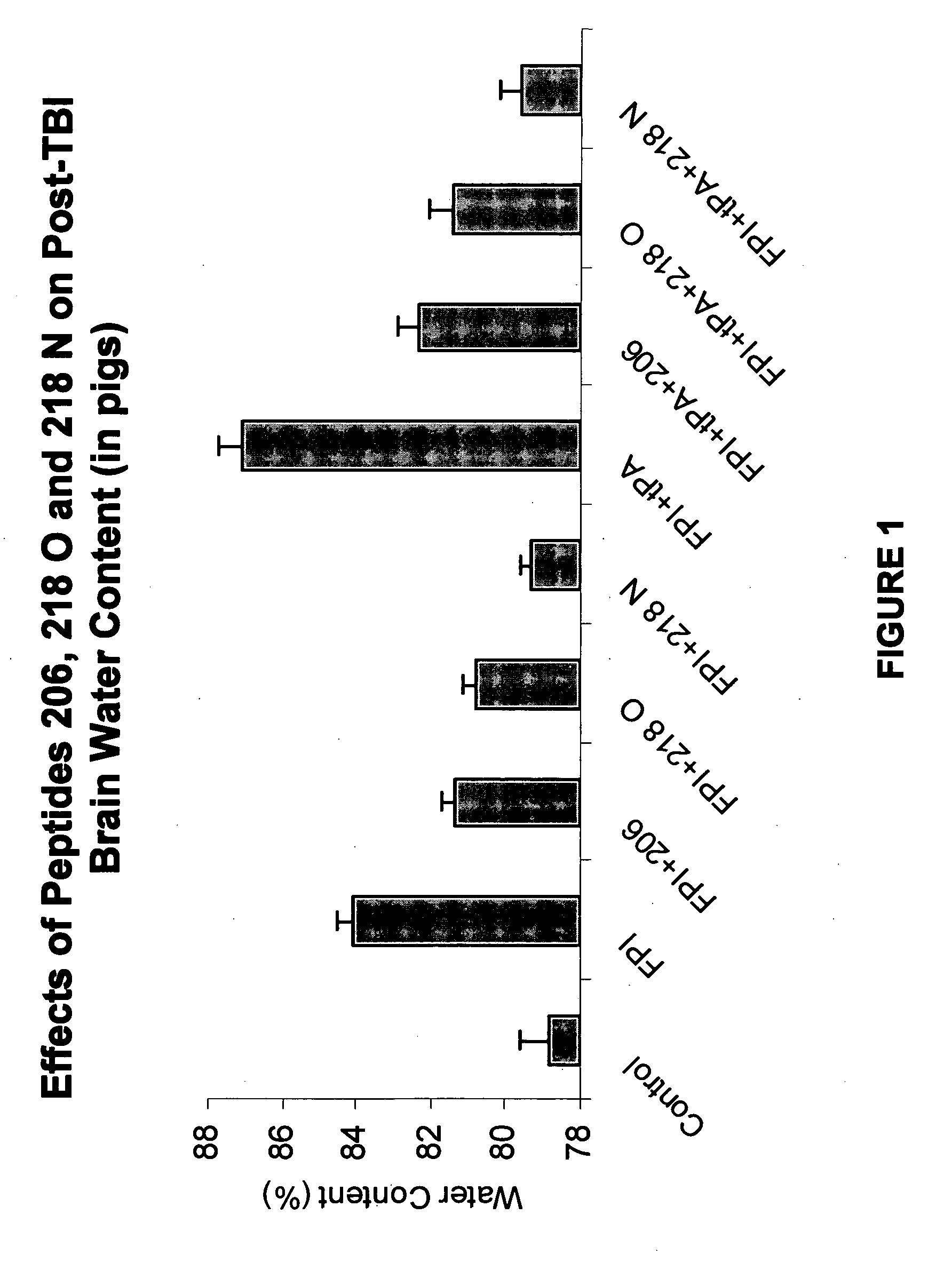
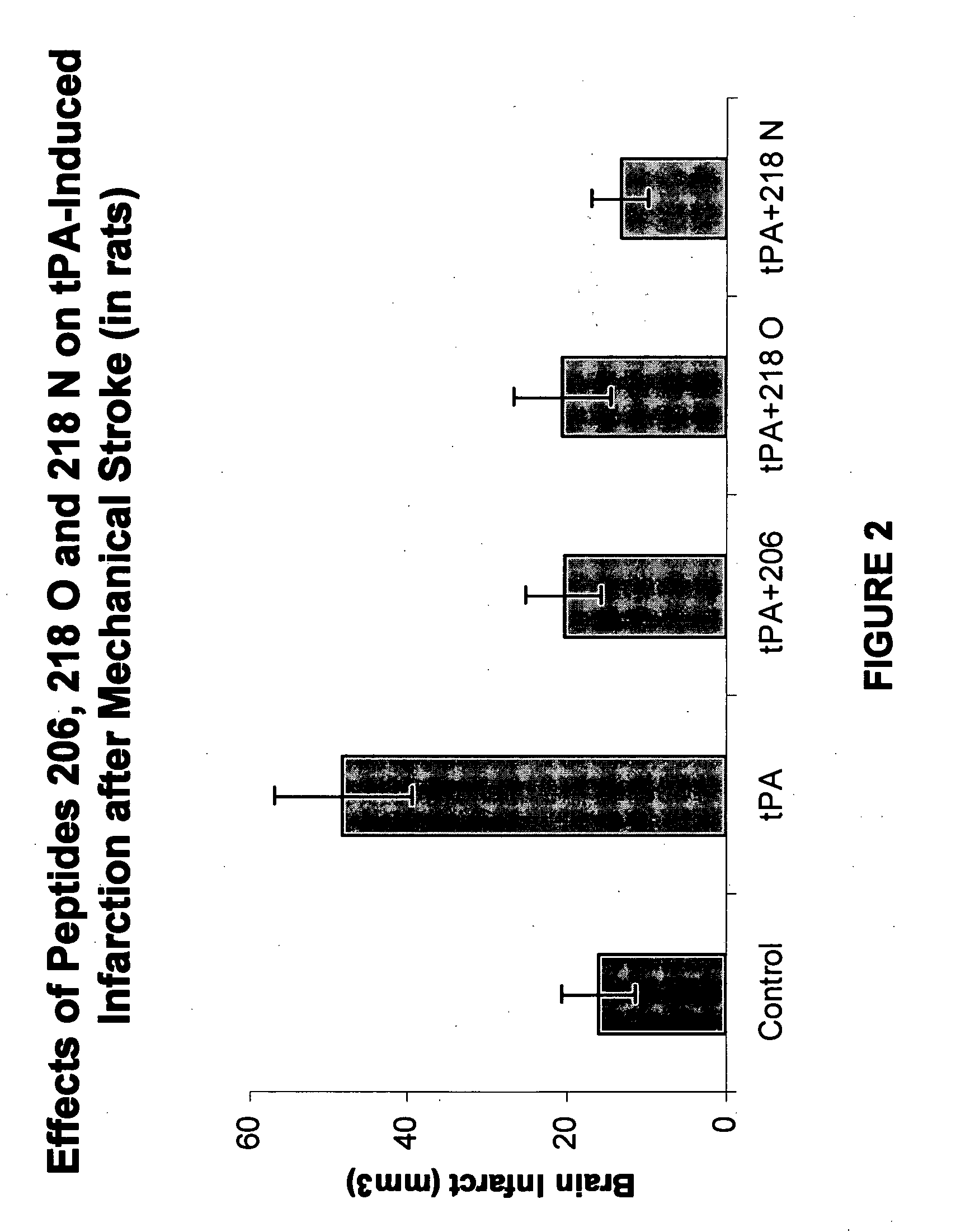
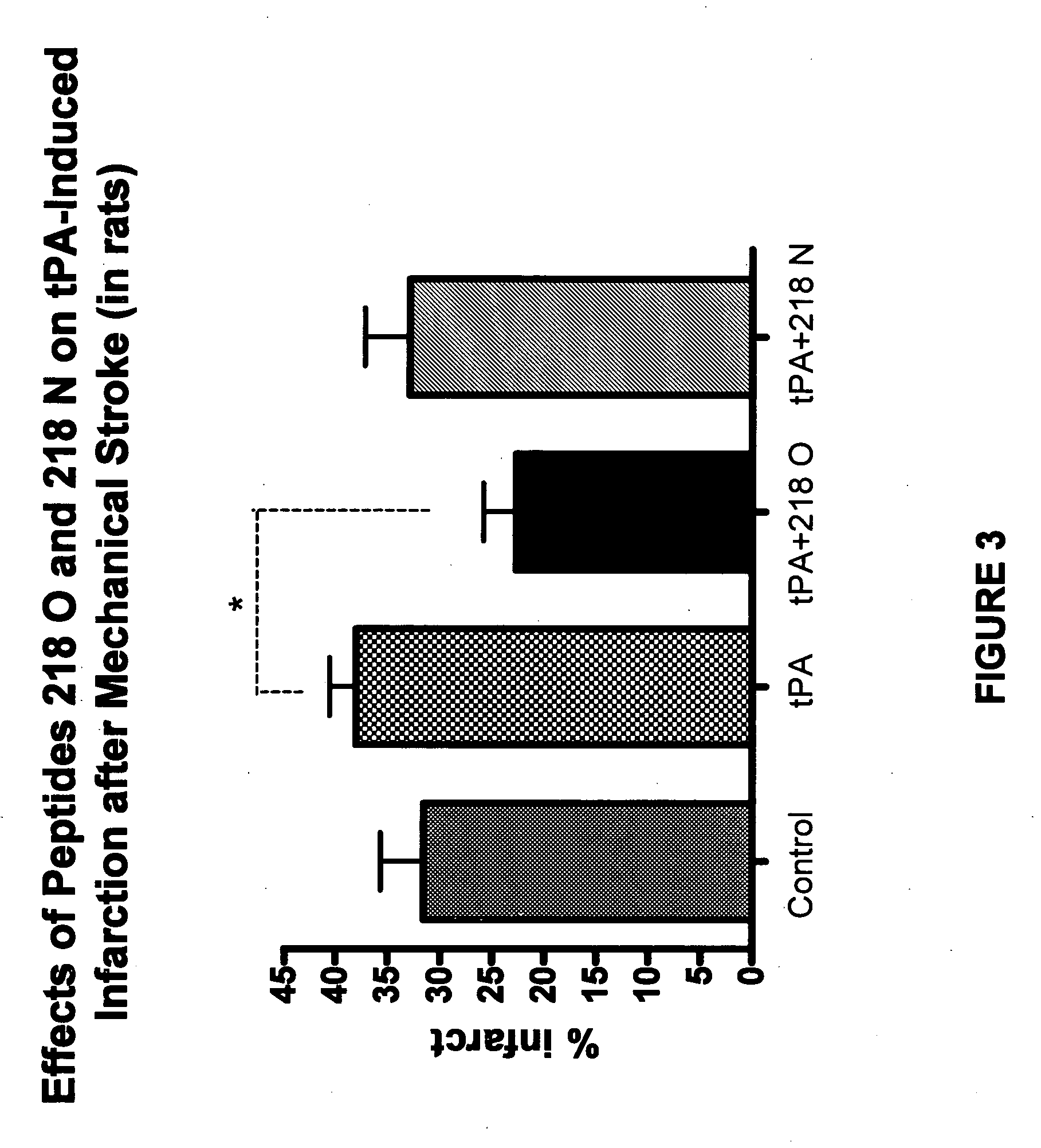
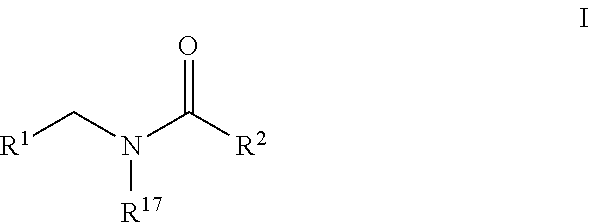
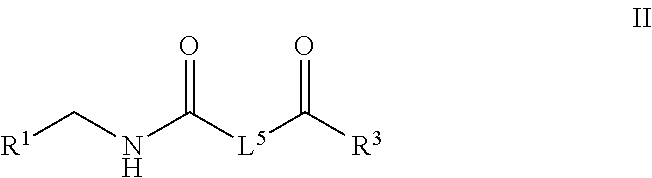
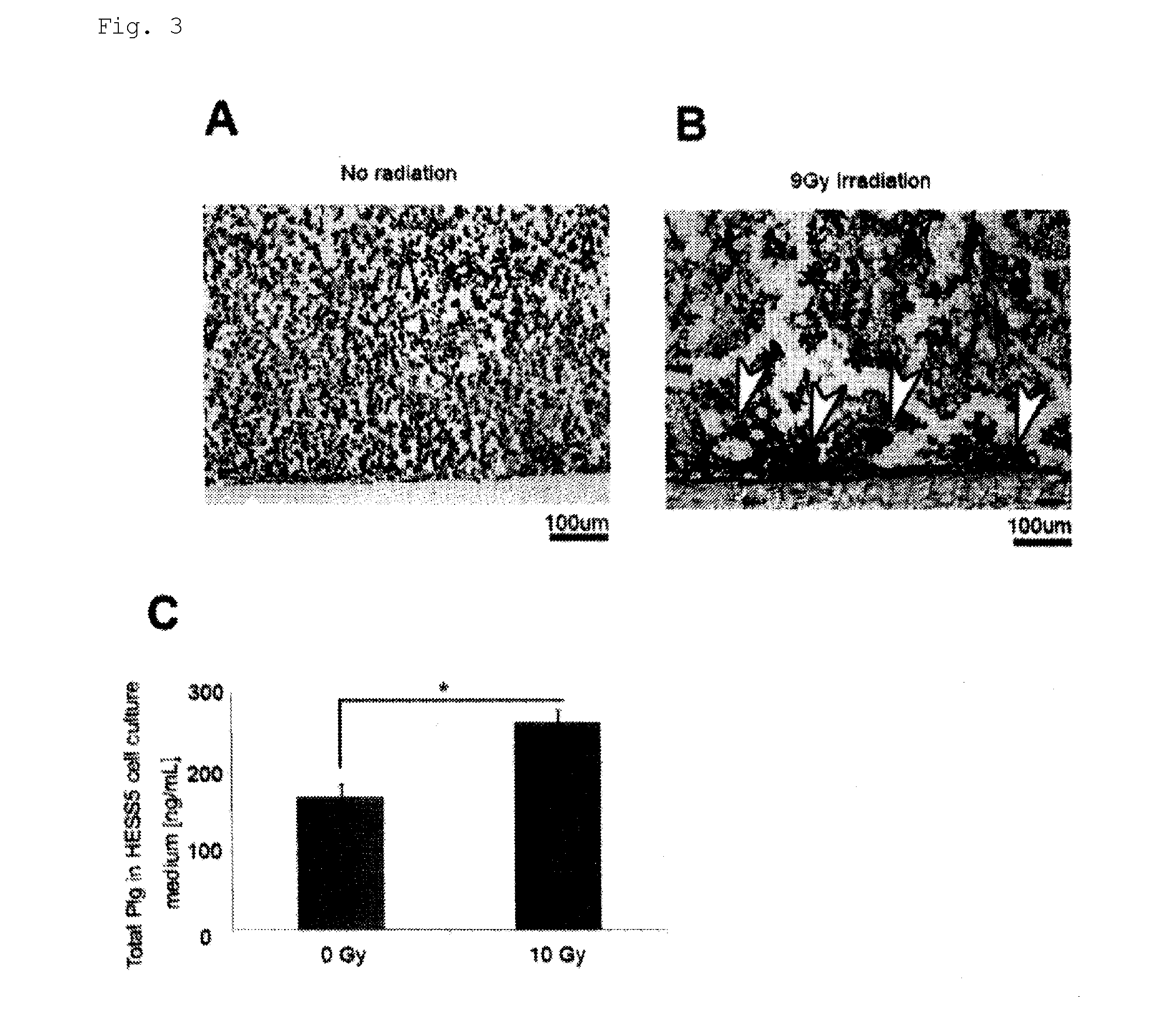
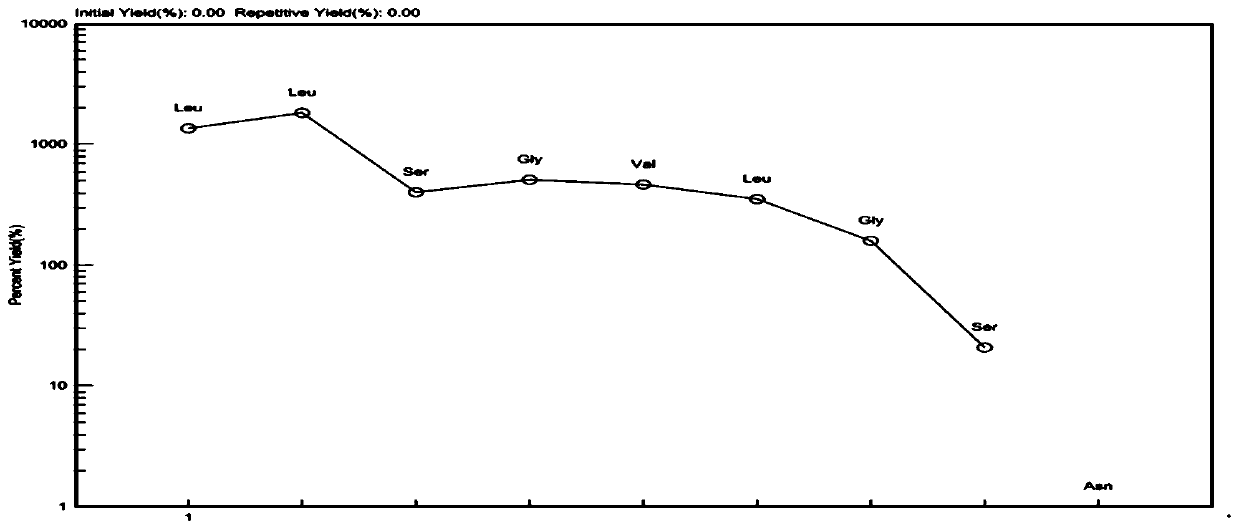
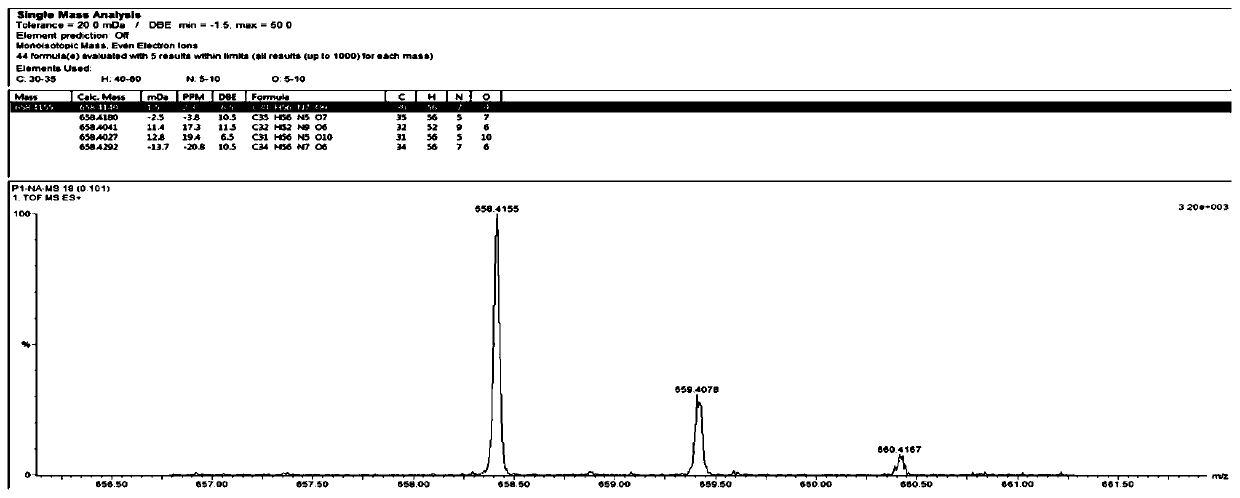
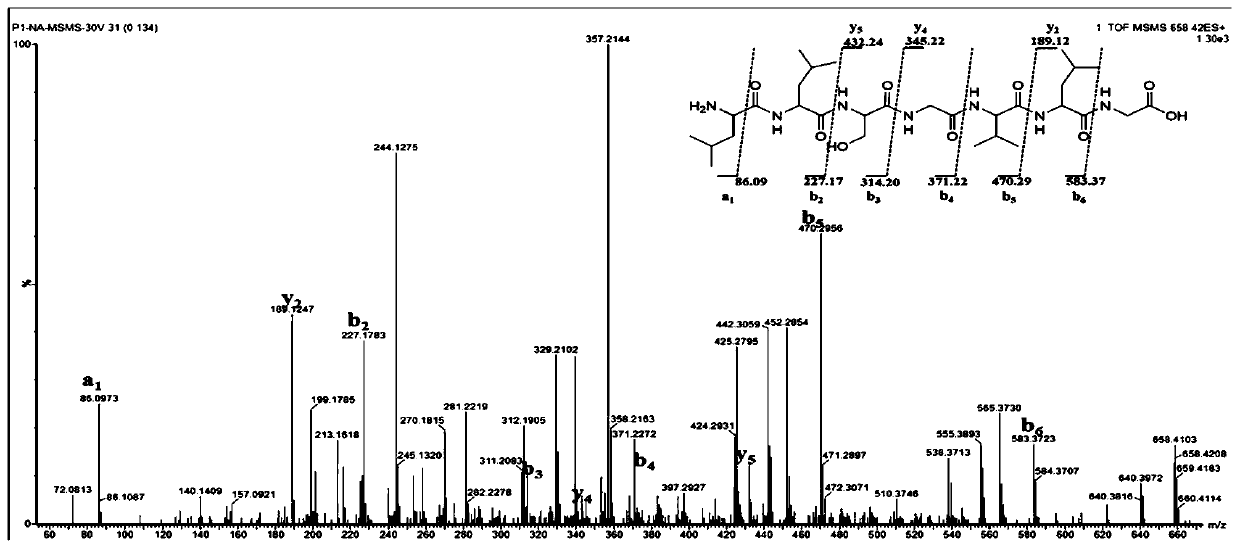
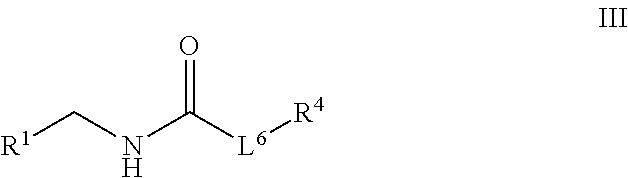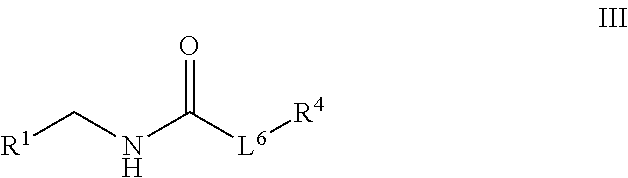Patents
Literature
52 results about "Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) also known as endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor or serpin E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINE1 gene. PAI-1 is a serine protease inhibitor (serpin) that functions as the principal inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase (uPA), the activators of plasminogen and hence fibrinolysis (the physiological breakdown of blood clots). It is a serine protease inhibitor (serpin) protein (SERPINE1).
Peptide Inhibition of Lung Epithelial Apoptosis and Pulmonary Fibrosis
ActiveUS20090227515A1High expressionBlock bleo induced mouse lung fibrosisPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsIn vivoPulmonary fibrosis
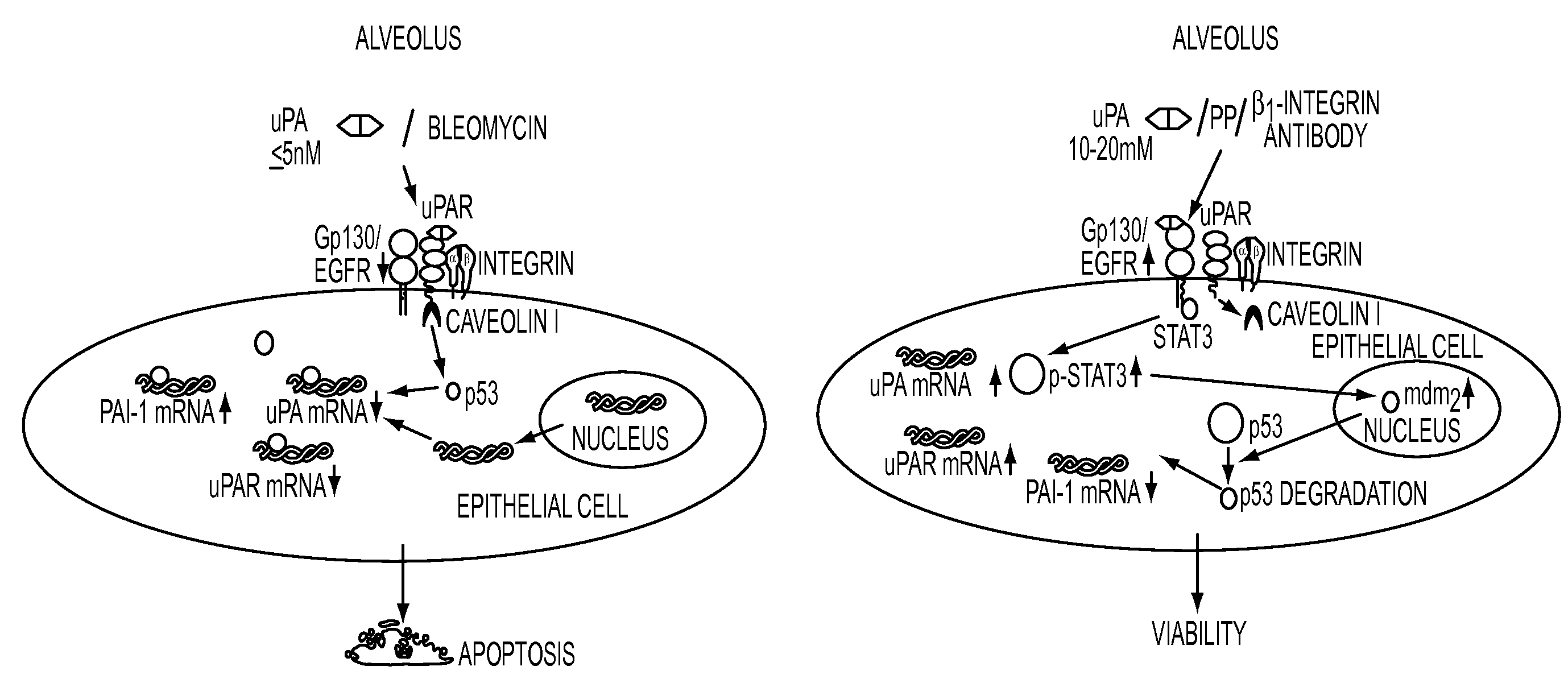
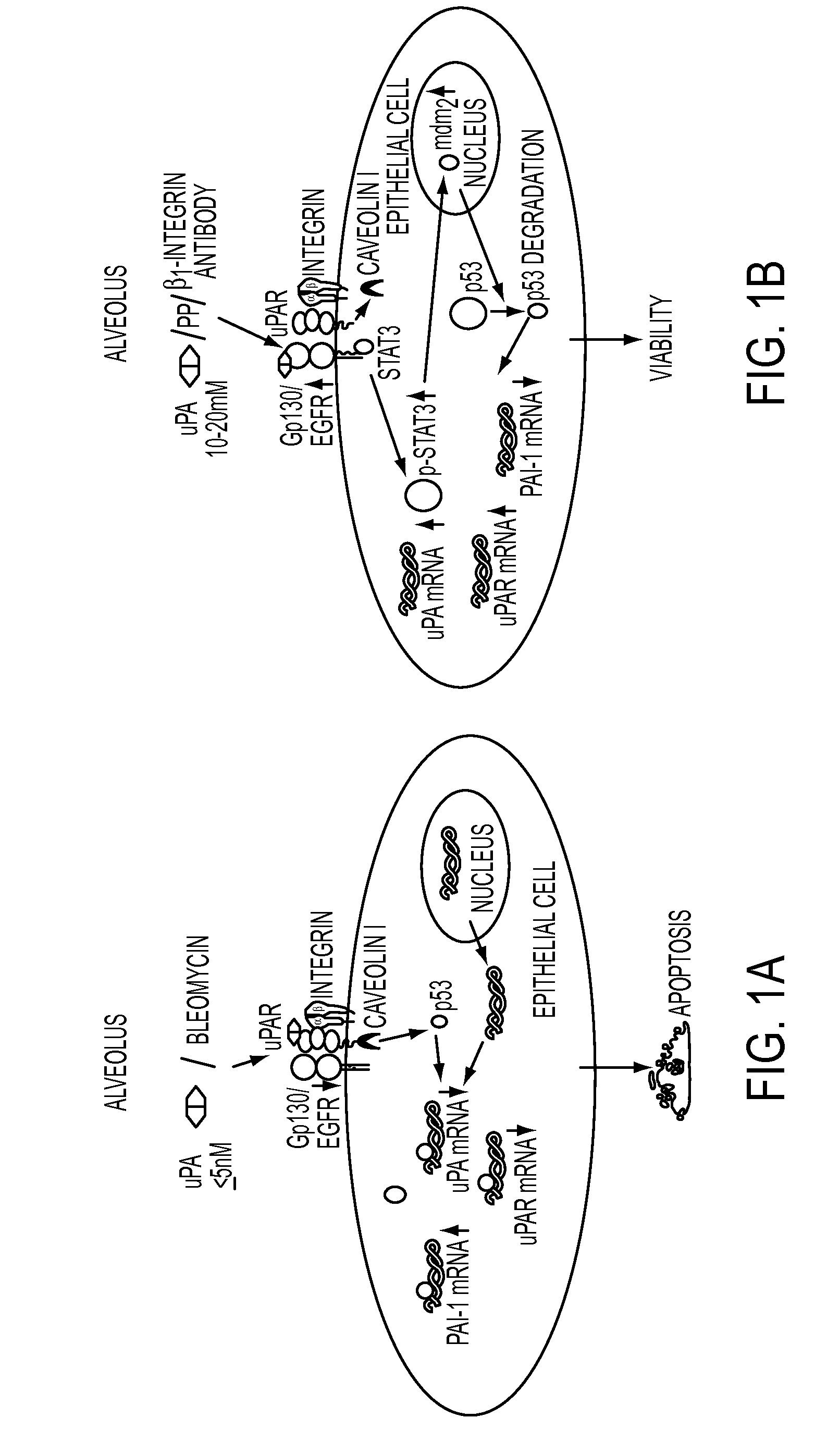
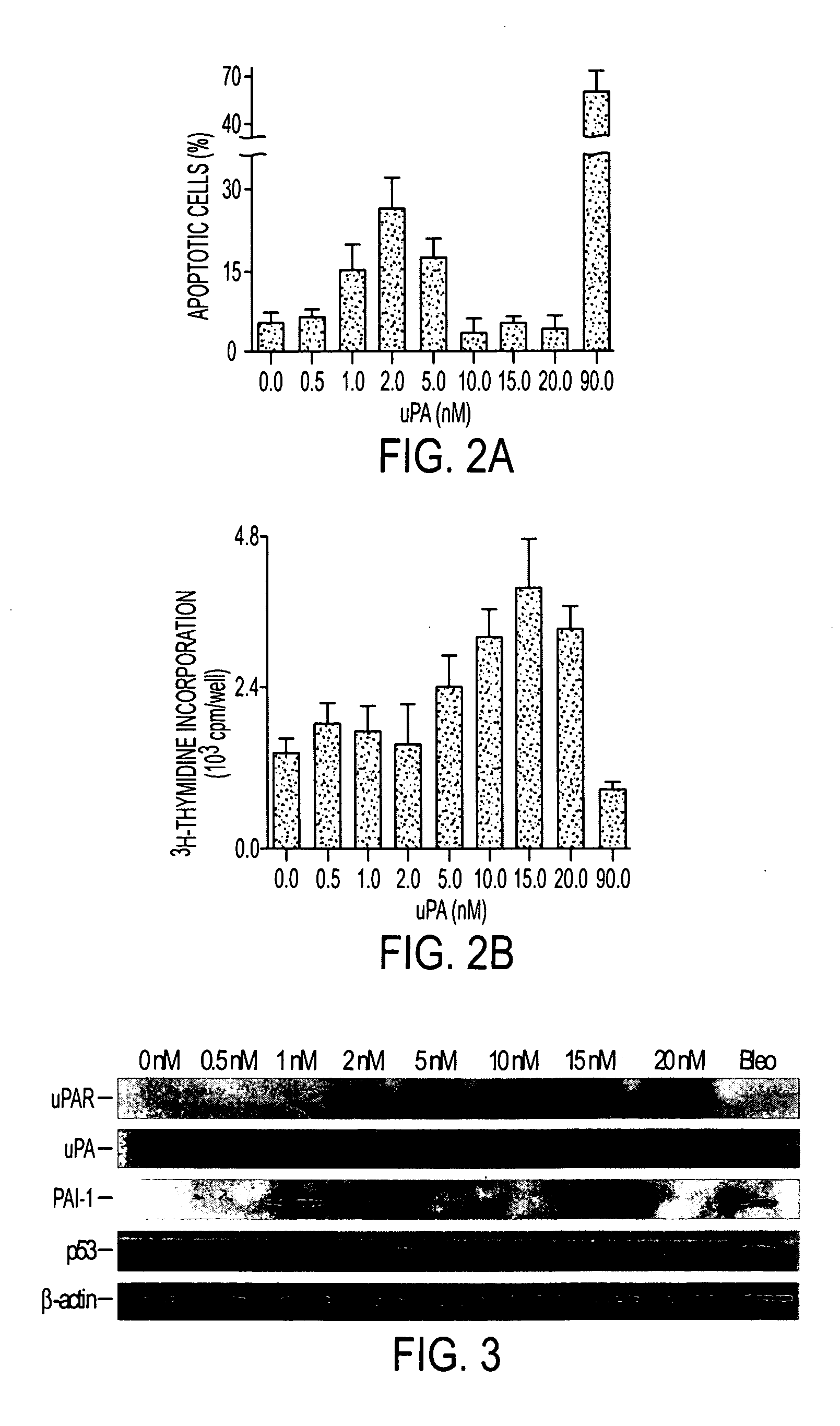
During lung injury, p53 expression increases, inducing plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) while inhibiting expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its receptor (uPAR), resulting in apoptosis of lung epithelial cells (LECs). In the bleomycin lung injury model, p53 and PAI-1 are induced while uPA and uPAR are inhibited. A 20 residue peptide DGIWKASFTTFTVTKYWFYR termed PP-1 (the Cav-1 scaffolding domain) or peptide NYHYLESSMTALYTLGH, termed PP-2, protected LECs from bleomycin-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo and prevented subsequent pulmonary fibrosis by attenuating lung epitheilial damage. Pharmaceutical compositions, peptide multimers and deliverable polypeptides comprising the above peptides are dislcosed. The peptides and functional variants, peptide multimers, cell-targeted polyepeptides and pharmaceutical compositions are used in methods for inhibiting apoptosis of injured or damaged lung epithelial cells and for treating acute lung injury and consequent pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Inhibitors And Methods Of Use Thereof To Modulate Lipid Metabolism
ActiveUS20090011055A1Efficient modulationModulate cholesterolBiocideCompound screeningDiseaseLipid formation
Owner:EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY +2
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors and methods of use thereof
The invention relates to plasminogen activator-1 (PAI-1) inhibitor compounds and uses thereof in the treatment of any disease or disorder associated with elevated PAI-1. The invention includes, but is not limited to, the use of such compounds to prevent or reduce thrombosis and fibrosis, to promote thrombolysis, and to modulate lipid metabolism and treat diseases or disorders associated with elevated PAI-1, cholesterol, or lipid levels.
Owner:EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY +1
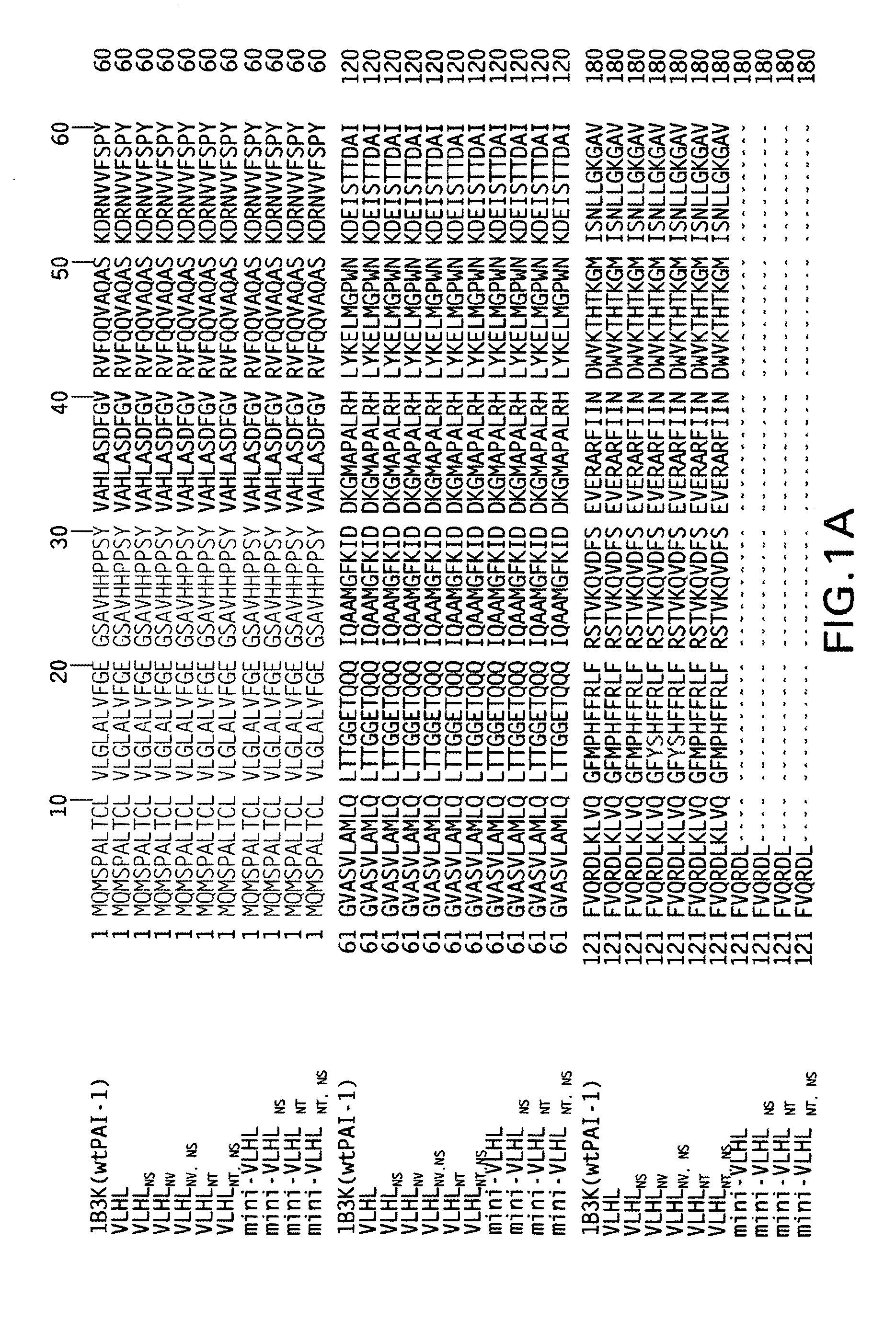
Modified plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 and methods based thereon
InactiveUS7592422B2Reduced activityExtended half-lifeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Peptides derived from plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100215636A1Higher neuroprotective activityReduce mortalityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPlasminogen activator inhibitor-1Peptide
The present invention relates to isolated 18-mer peptides corresponding to amino acid residues 369-386 of human plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) and fragments thereof, compositions that include such peptides, and uses of such compositions for treating thromboembolic diseases and pathological conditions associated with neurological damage.
Owner:D PHARMA LTD
Tissue-type plasminogen activator mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107760660AImprove the immunityPeptide/protein ingredientsRespiratory disorderDiseaseThrombus
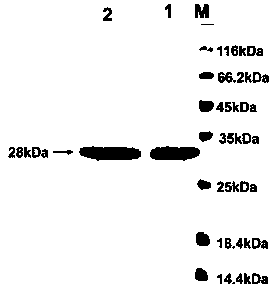
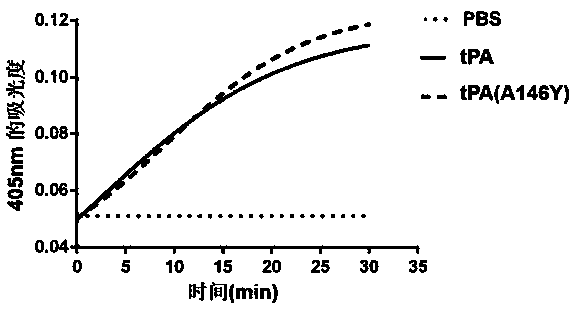
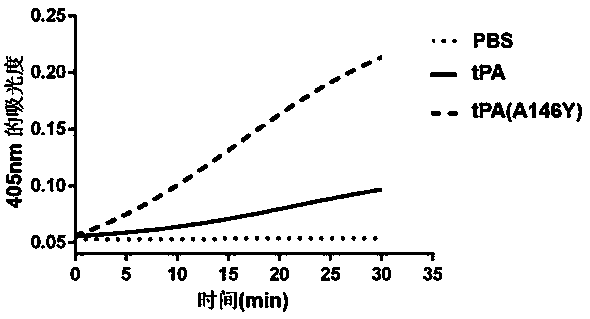
The invention provides a tissue-type plasminogen activator mutant and application thereof. The mutant comprises an A146 locus which is a brand new mutation site, referring to substitution, deletion oraddition of at least one or more amino acid residues comprising the A146. The mutant disclosed by the invention has the effects of obviously resisting ability inhibited by an endogenous inhibitor (PAI-1) (Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1) and enhanced ability of activating plasminogen. The mutant can be applied to preparing medicines for treating thrombotic diseases comprising acute myocardial infarction, acute pulmonary embolism, cerebral apoplexy, phlebothrombosis and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
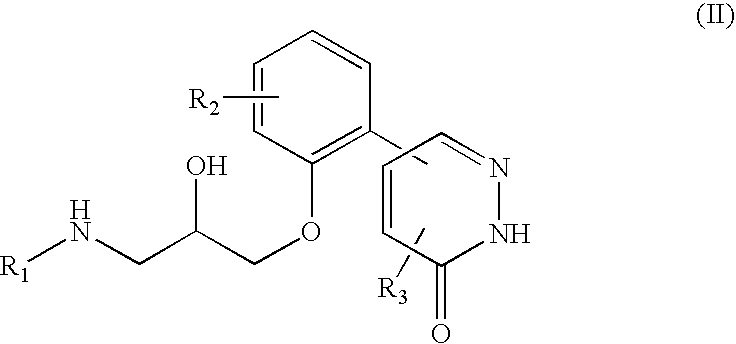
5-phenyl-3-pyridazinone derivative
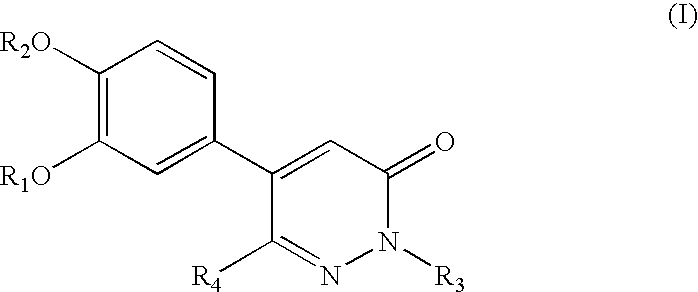
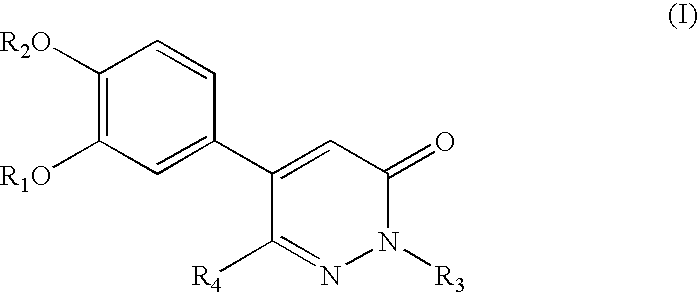
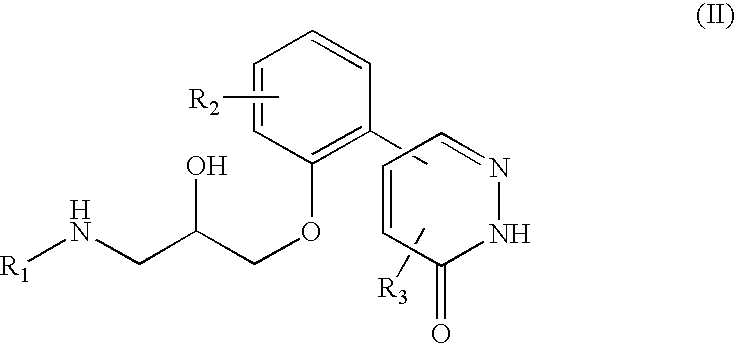
To find a compound having a tissue fibrinosis-inhibitory activity and a fibrinolytic activity, and to provide a novel compound that is useful for preventing and / or treating tissue fibrinosis diseases (pulmonary fibrosis, renal fibrosis etc.), diseases caused by pathological blood clots such as ischemic heart diseases (myocardial infarction, angina), intraatrial thrombus, pulmonary embolism, deep venous thrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, ischemic cerebral diseases (cerebral infarction, cerebral bleeding) and arteriosclerosis and the like. To provide a pharmaceutical drug comprising a 5-phenyl-3-pyridazinone derivative represented by the following general formula (I):and an optical isomer thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a hydrate or solvate thereof, useful for preventing and / or treating disease conditions or symptoms mediated by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Bionic affinity purification method of plasminogen activator
The invention relates to a plasminogen activator bionics and purifying method. It belongs to biotechnology field. It includes the following steps: basal chromatography medium reacts with tri-chlorine tri-nitrogen zin; they react with pair amino benzene formamidine to compound bionics and separating material; the upper material is made into affinity column; the sample of the plasminogen activator is flowed through the affinity column; then the former is absorbed in the latter; cleaning the latter; cleaning it again after changing buffer solution condition; purging the plasminogen activator to gain a purified one. The advantages of the invention are less purifying steps, low cost, high efficiency, and can realize volume produce.
Owner:上海荣君生物医药科技有限公司
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors and methods of use thereof to modulate lipid metabolism
The invention relates to plasminogen activator-1 (PAI-1) inhibitor compounds and uses thereof in the treatment of any disease or condition associated with elevated PAI-1. The invention includes, but is not limited to, the use of such compounds to modulate lipid metabolism and treat conditions associated with elevated PAI-1, cholesterol, or lipid levels.
Owner:EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY +1
Modified plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 molecule and methods based thereon
InactiveUS20100184667A1Reduce cancer cell growthInhibit primaryPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorVitronectin
The present invention relates to a modified plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) molecule that displays CN an increased in vivo half-life of the active form of PAI-1, but is deficient in one or more functional activities as compared to the wild-type PAI-1 protein. The modified PAI-1 molecule that displays an increased half-life further displays at least one of the following funtional characteristics: (i) decreased binding activity to at least one of the following molecules: urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and vitronectin (Vn); and (ii) decreased specific activity against at least one of the following molecules: uPA, tPA and Vn. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising modified PAI-1 molecules and methods of using these pharmaceutical compositions for treatment.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
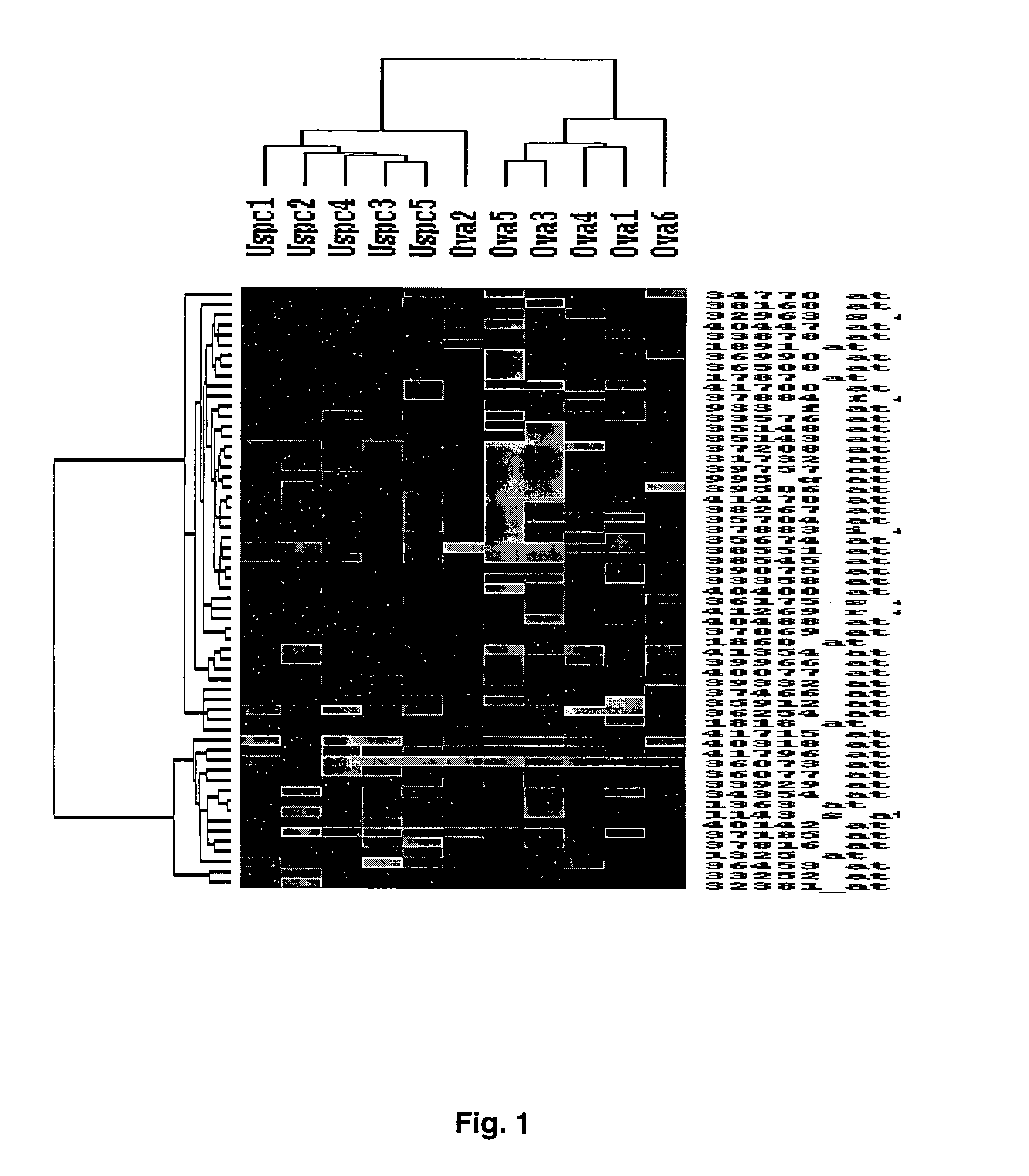
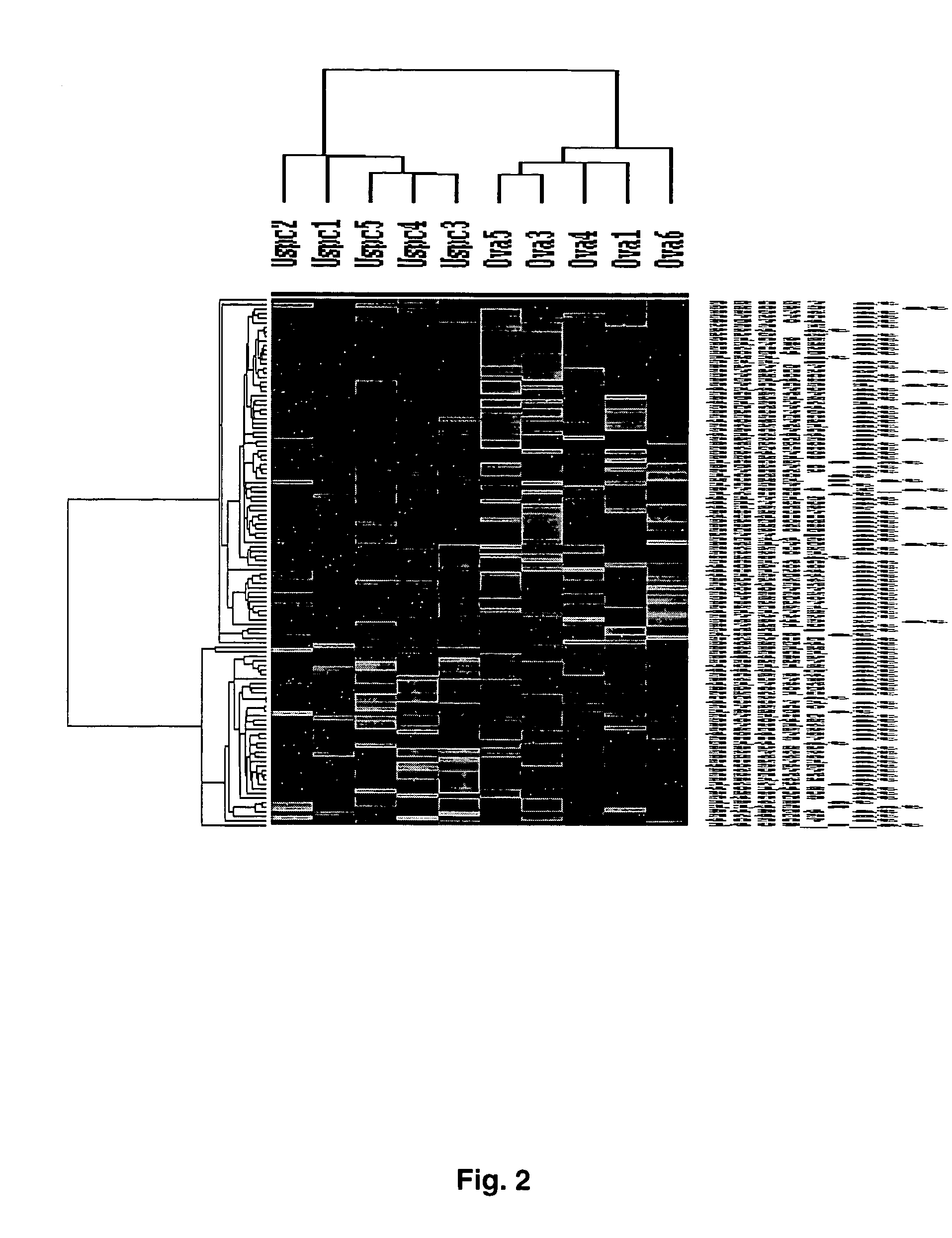
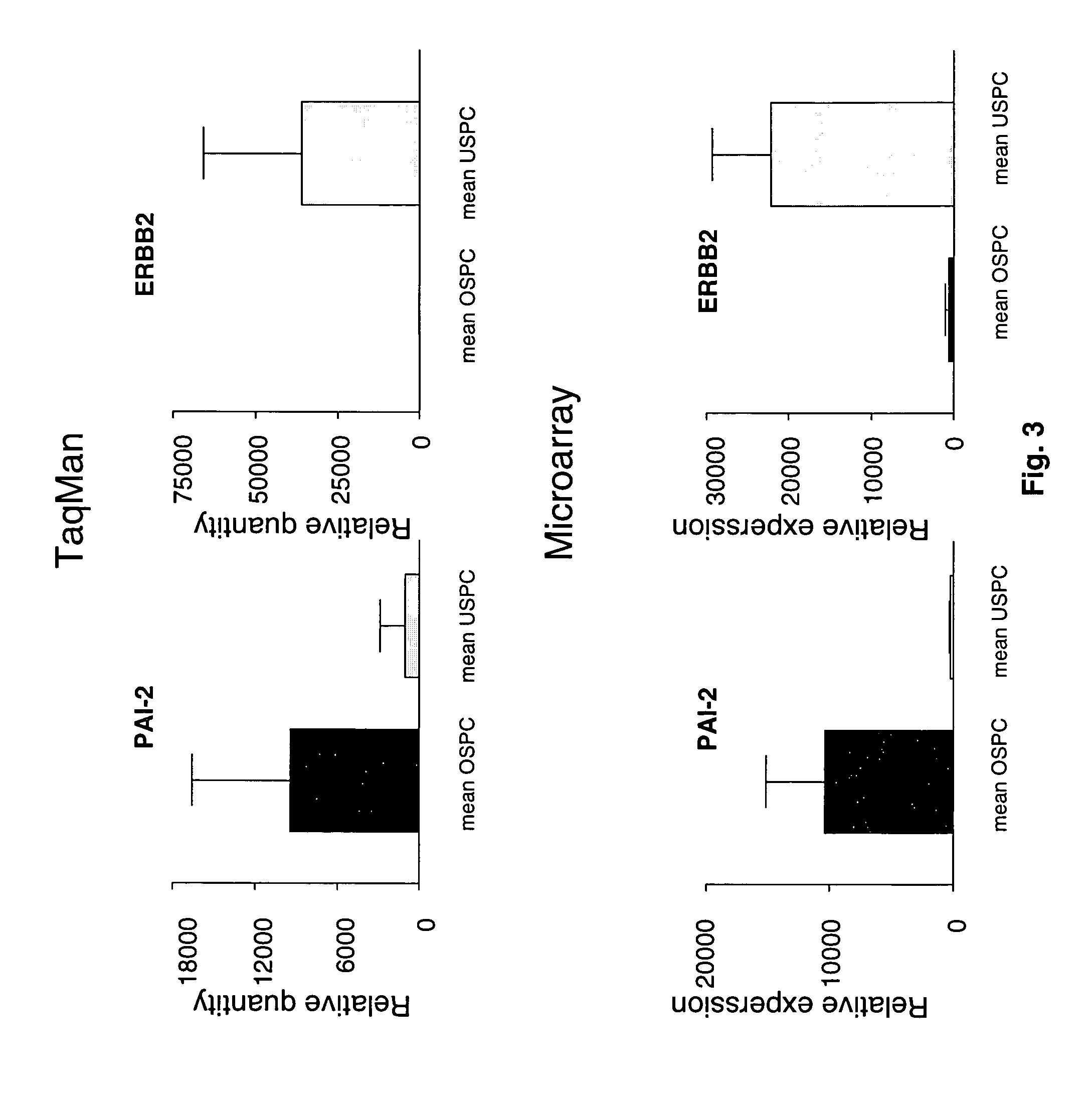
Gene expression profiling of uterine serous papillary carcinomas and ovarian serous papillary tumors
InactiveUS7659062B2Different responseEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPapillary carcinomaEndometrial epithelium
Oligonucleotide microarrays were used to profile and compare gene expression patterns between uterine serous papillary carcinoma and ovarian serous papillary carcinoma or normal endometrial epithelial cells. mRNA fingerprints readily distinguish the more biologically aggressive and chemotherapy resistant USPC from OSPC or NEC. Plasminogen activator inhibitor is the most highly up-regulated gene in OSPC relative to USPC, whereas the c-erbB2 gene product (HER-2 / neu) is strikingly overexpressed in USPC relative to OSPC and may therefore represent a novel diagnostic and therapeutic marker for this highly aggressive subset of endometrial tumors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Chimeric truncated and mutant variant of tissue plasminogen activator (t-pa) resistant to plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
InactiveUS20120058537A1Extended half-lifeHigh fibrin affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidasesTetrapeptidePlasminogen activator inhibitor-1
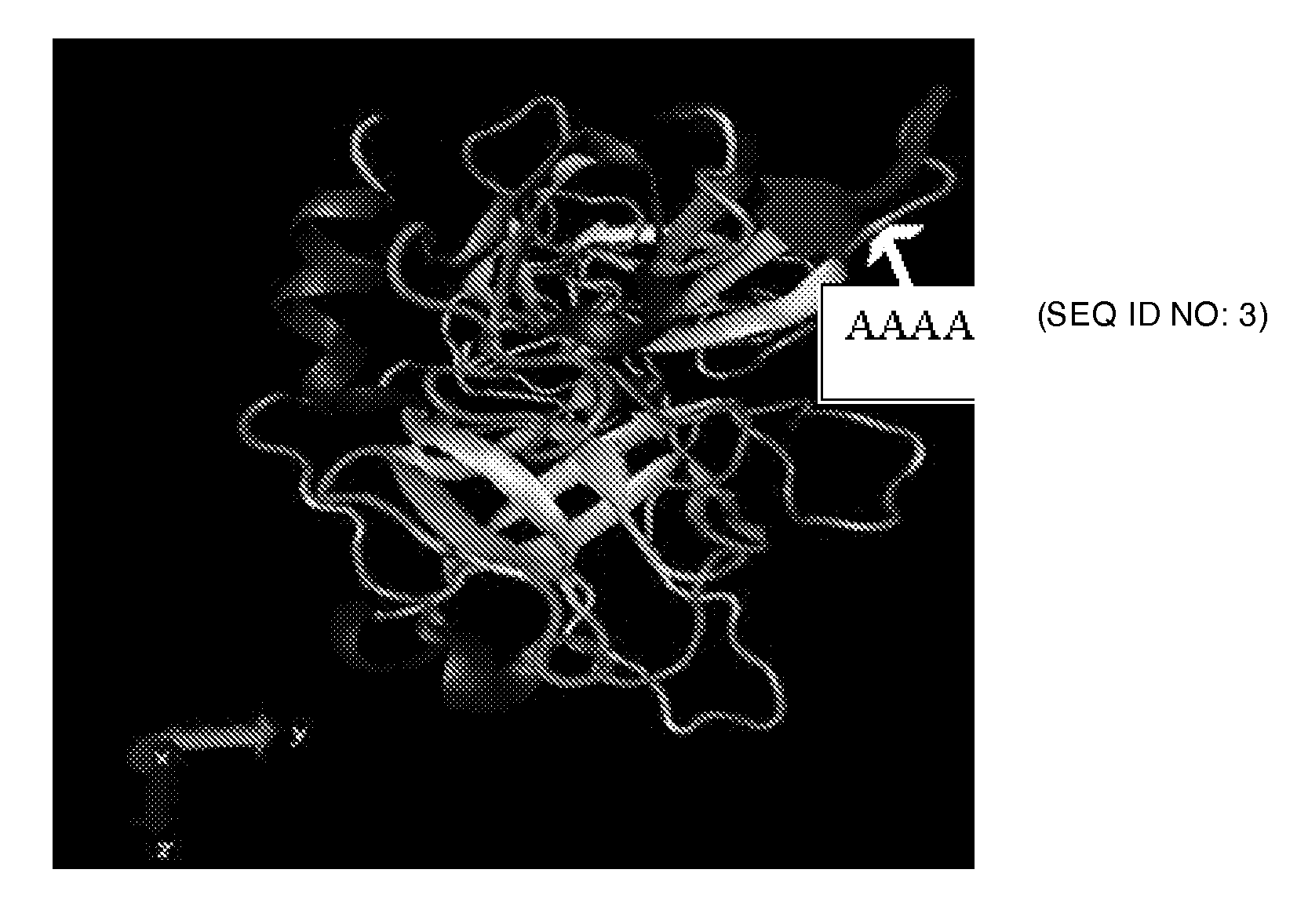
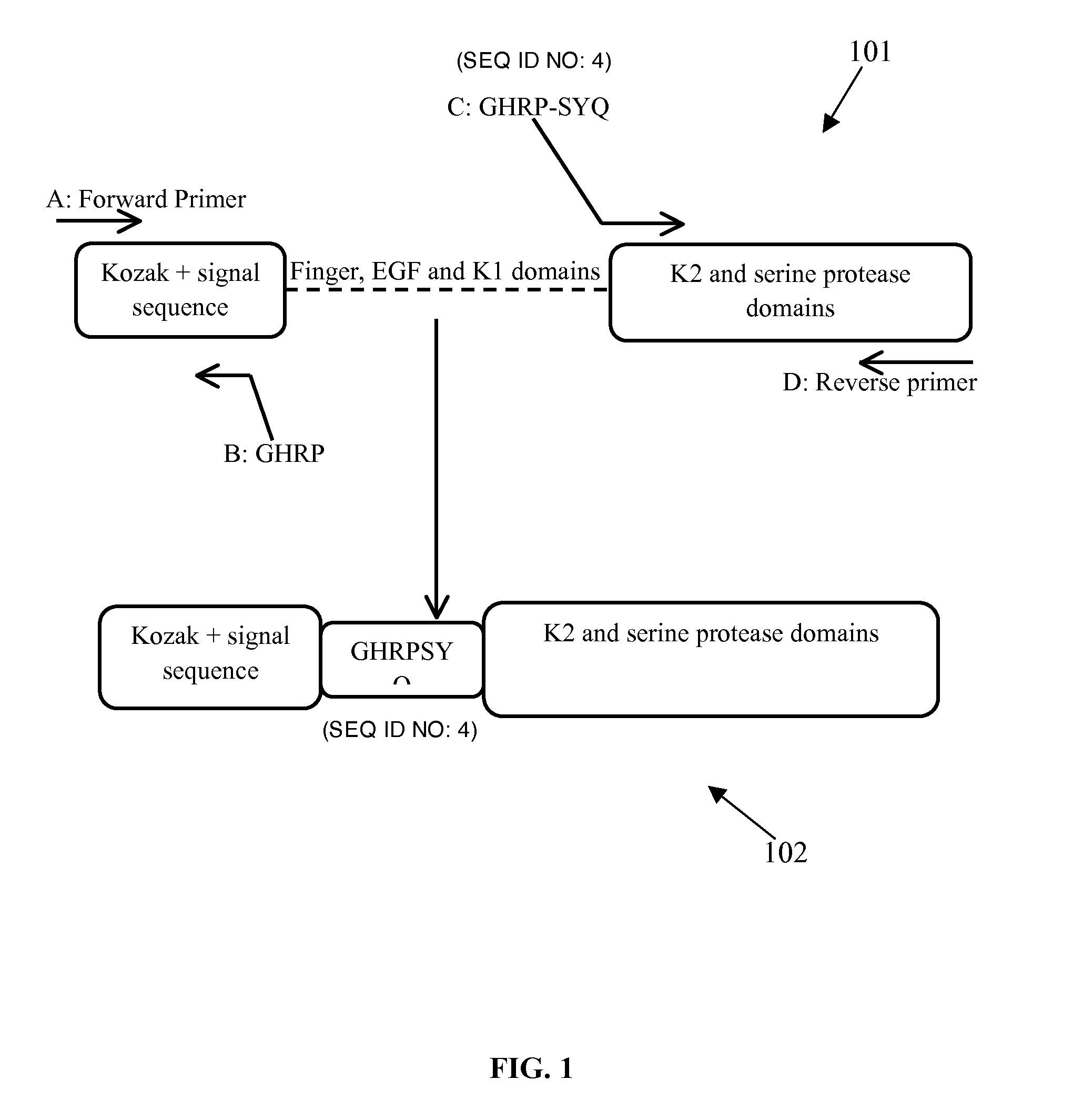
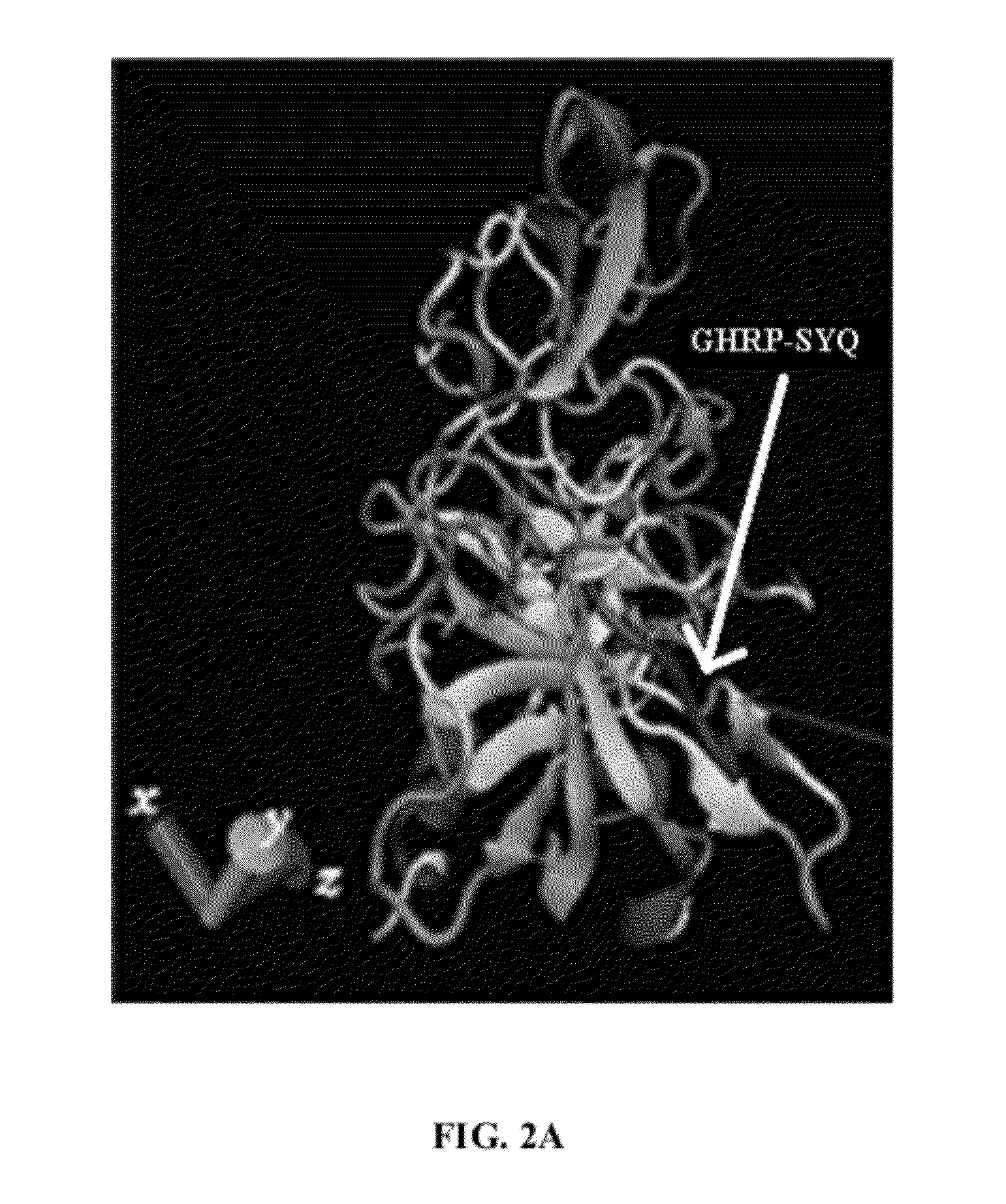
The various embodiments herein provide a chimeric truncated and mutant variant of a tissue plasminogen activator (t-pa) and a method for preparing the same. According to an embodiment herein, the mutant variant comprises a signal sequence domain, followed by a chimeric tetrapeptide, followed by a tripeptide, followed by a kringle 2 domain, followed by a serine protease domain and a substituted amino acids at position 128-131. The substituted amino acids are AAAA (SEQ ID NO: 3) amino acids. The chimeric tetrapeptide is Gly-His-Arg-Pro (SEQ ID NO: 1). The chimeric tetrapeptide is at a position of 36 to 39 amino acid of the mutant variant. The tripeptide is Ser-Tyr-Glu. According to an embodiment herein, a chimeric truncated and mutant variant of a tissue plasminogen activator comprises a native t-pa deleted with Finger domain, a Growth Factor domain and a Kringle 1 domain, a chimeric tetrapeptide and a substituted amino acids at a position of 128-131.
Owner:MAHBOUDI FEREIDOUN +3
Methods for modulating angiogenesis via VEGF
InactiveUS7241446B2Peptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAngiogenesis growth factorApoptosis
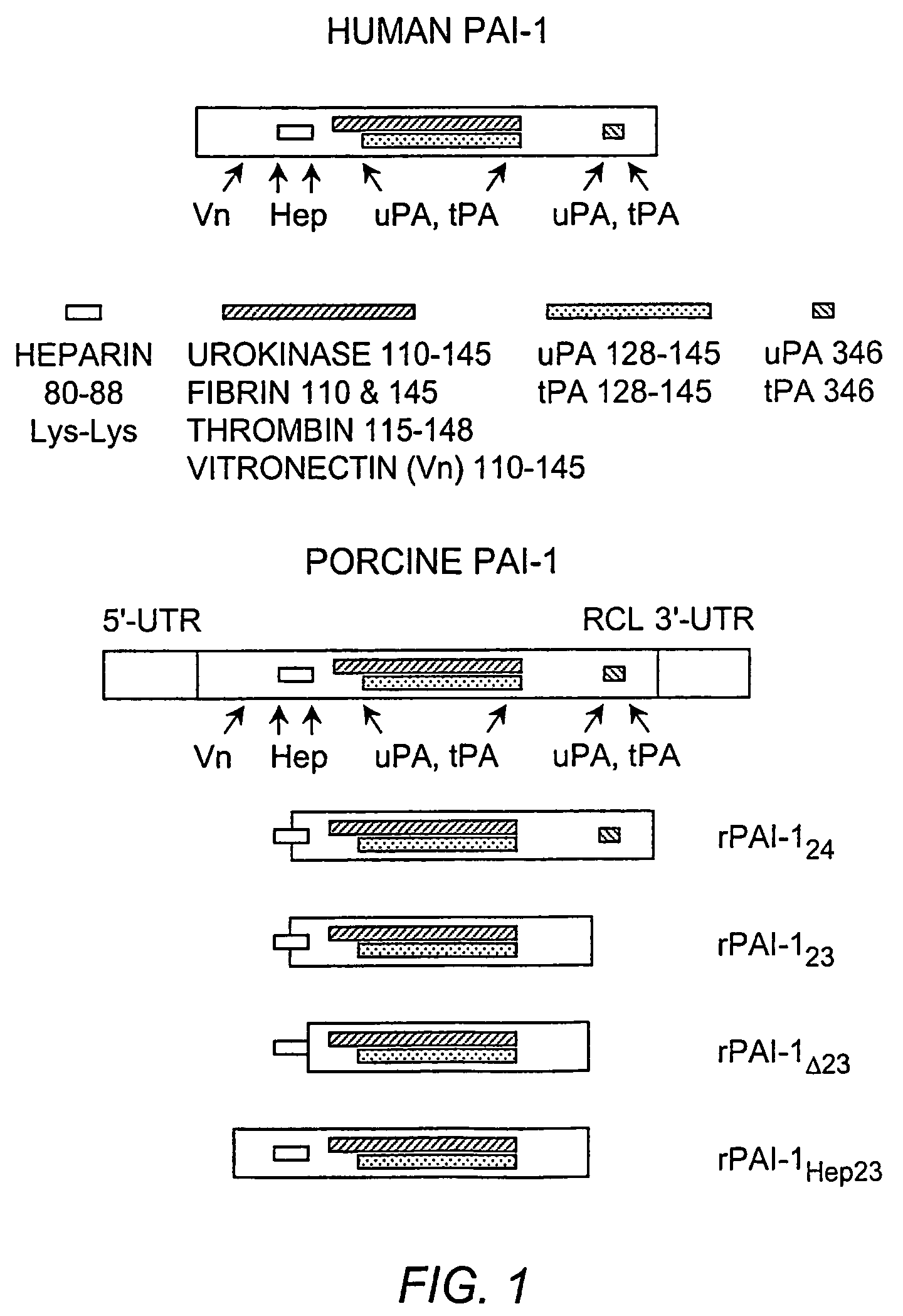
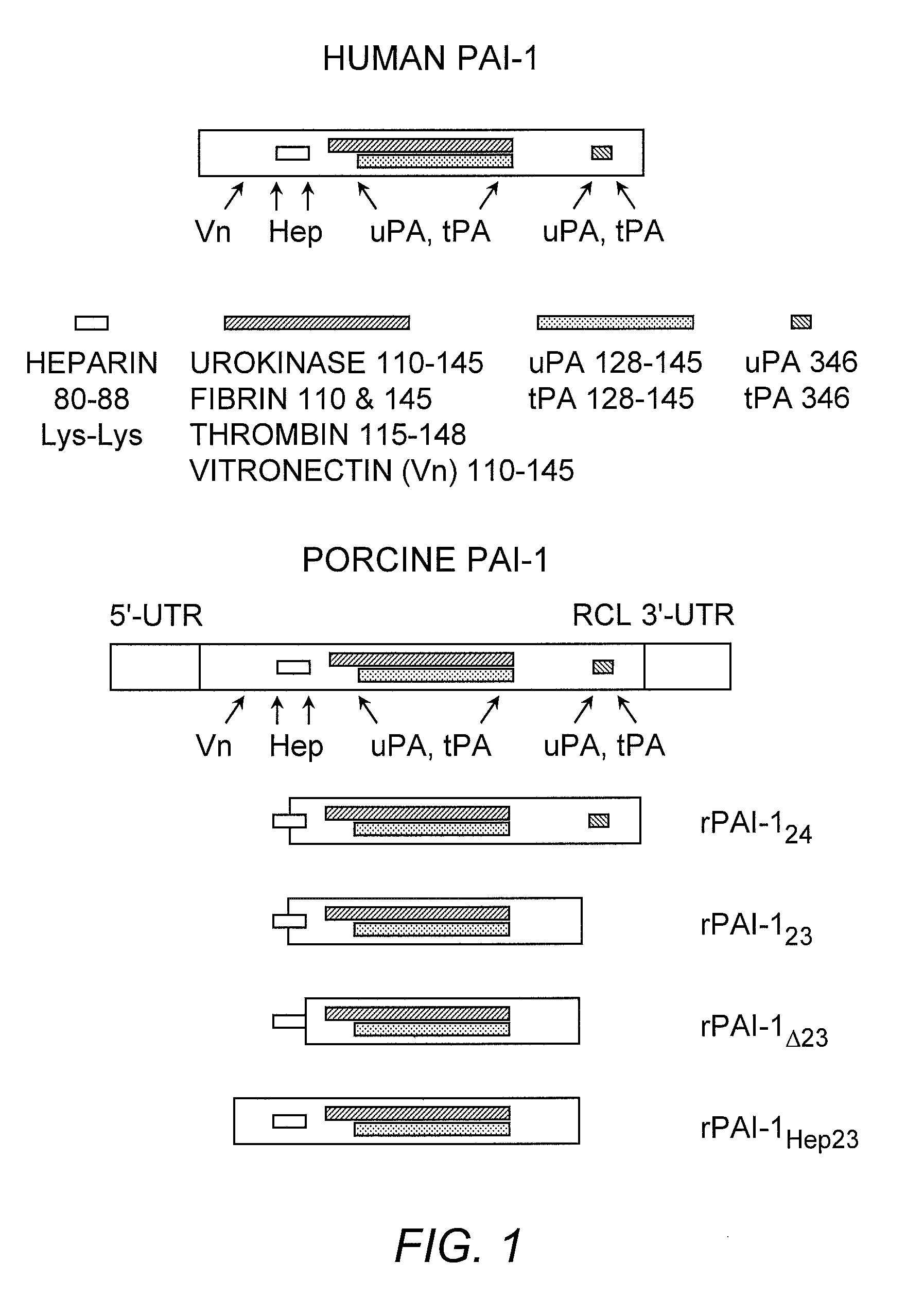
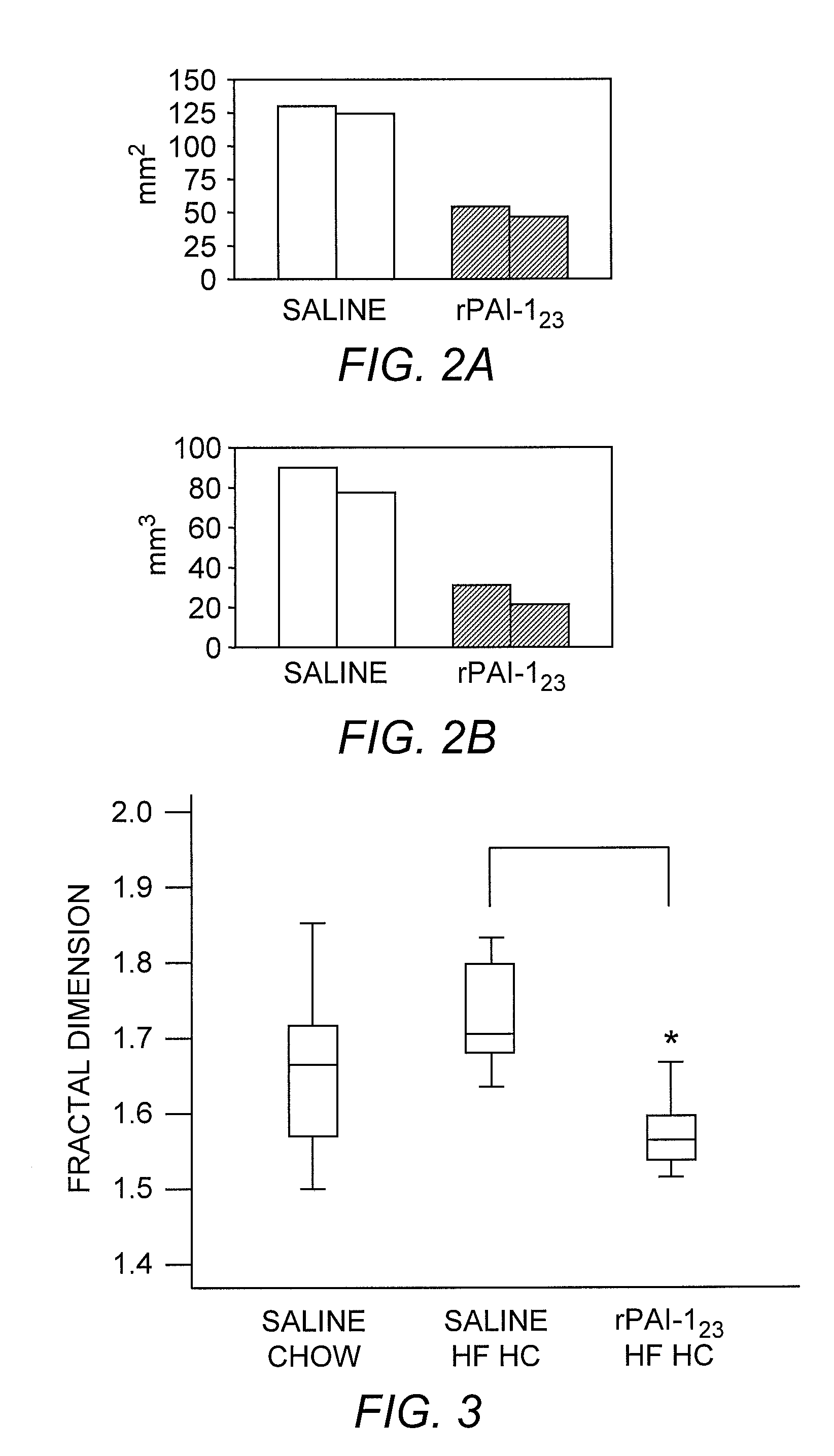
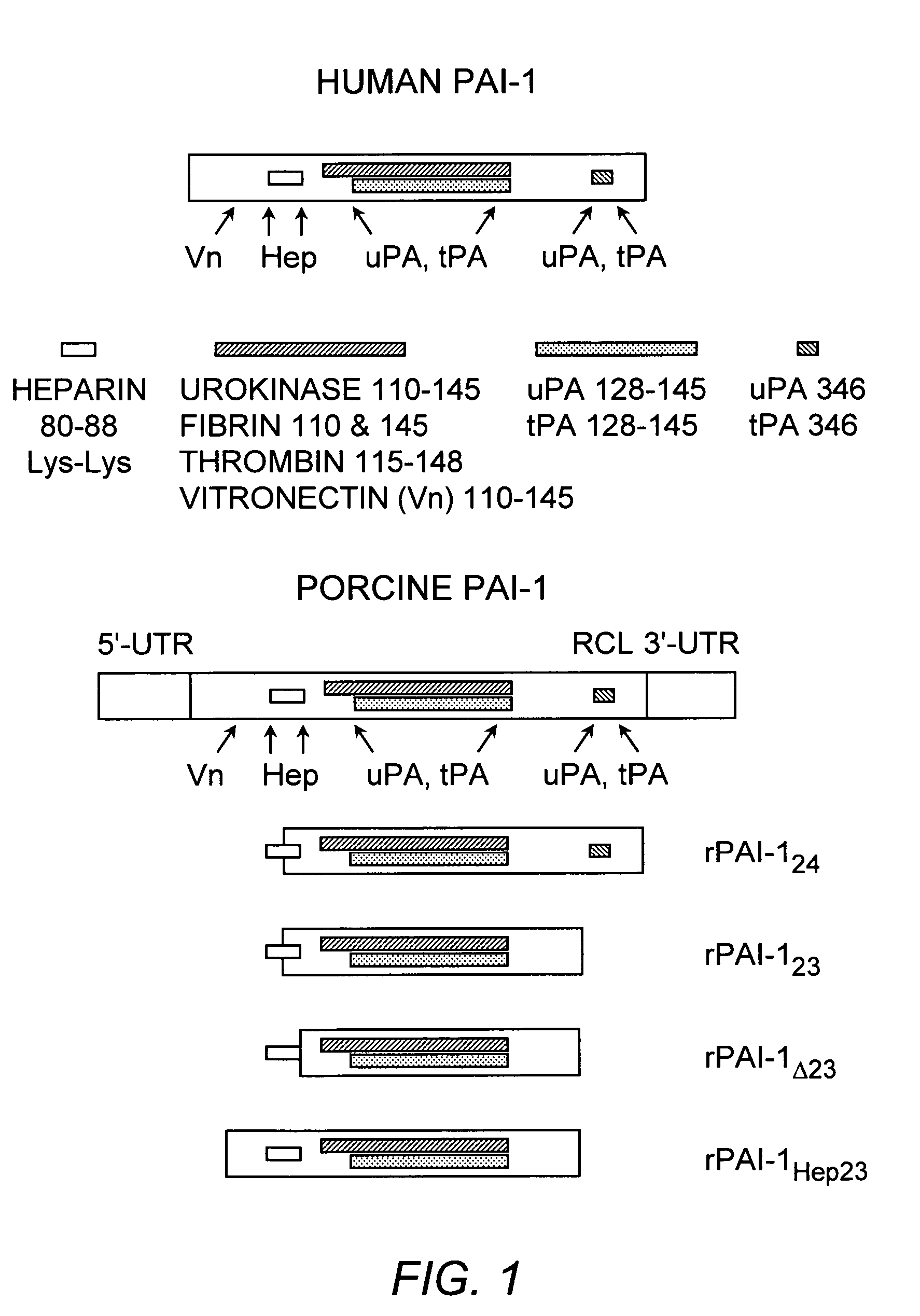
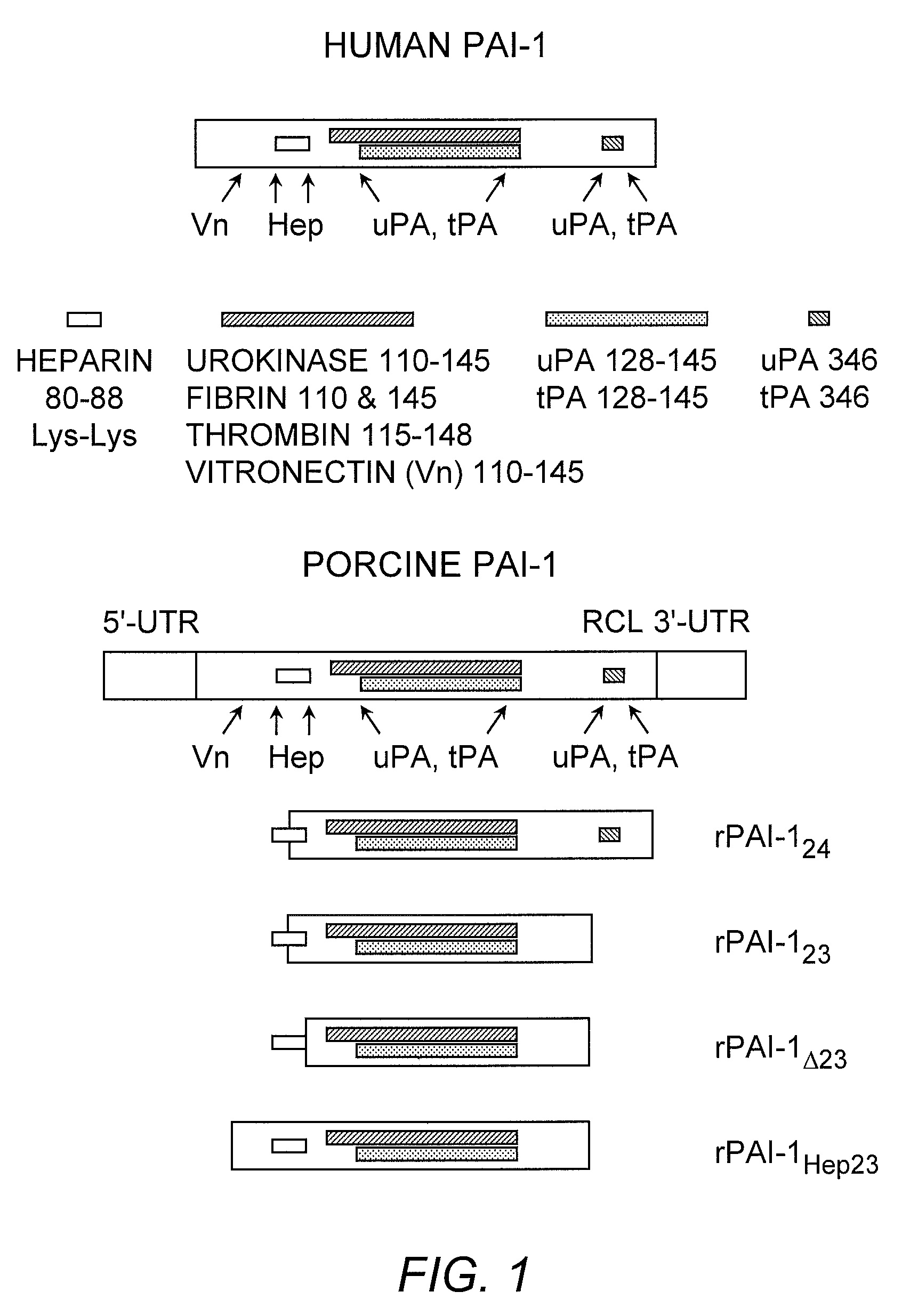
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1–3 and kringles 1–4.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Methods for modulating angiogenesis
InactiveUS20070191277A1Stimulating and inhibiting angiogenesisPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAngiostatinAngiogenesis growth factor
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore, the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1-3 and kringles 1-4. A truncated proteolytic plasmin protein of 34 kDa is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Peptides derived from plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and uses thereof
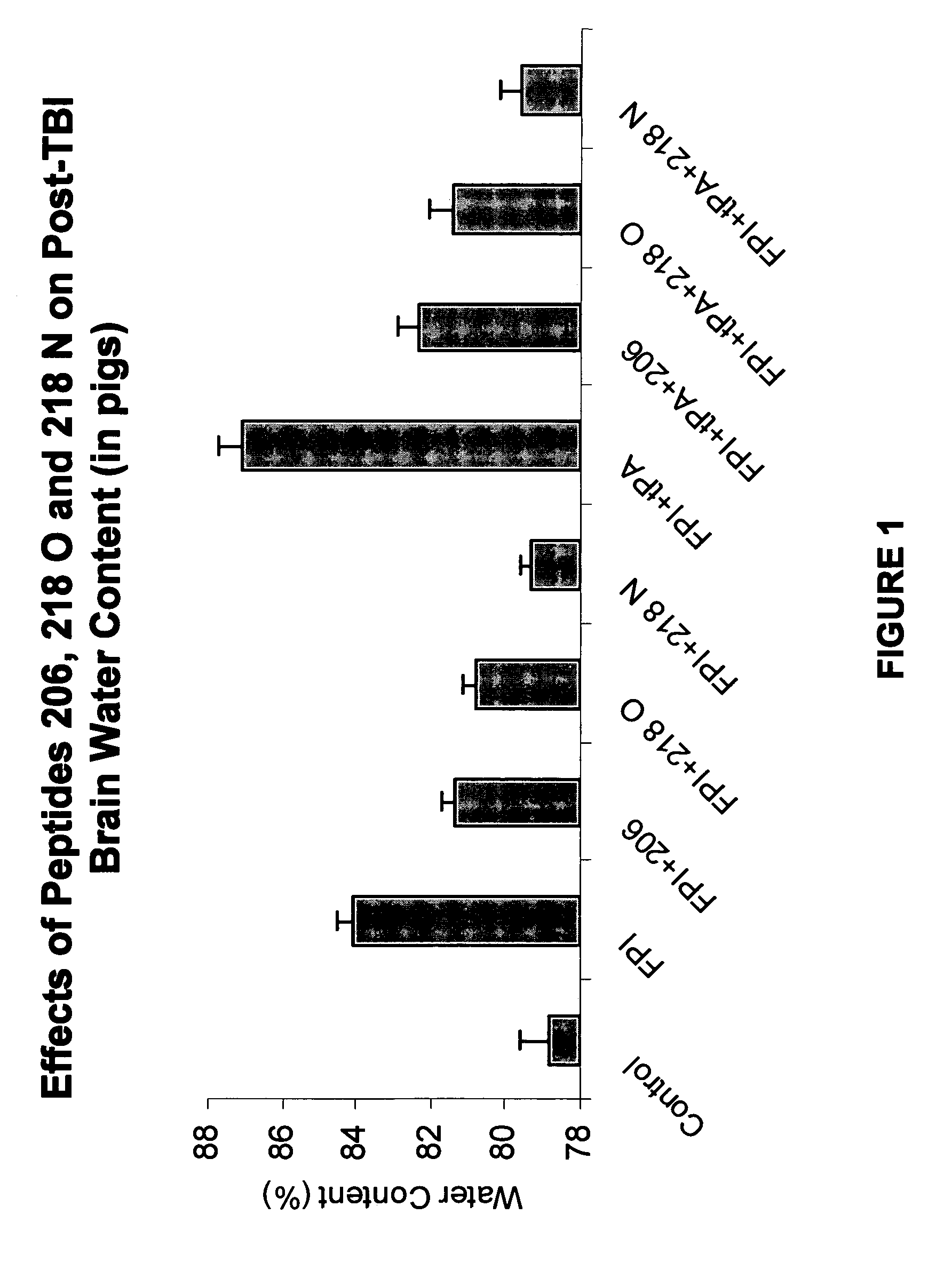
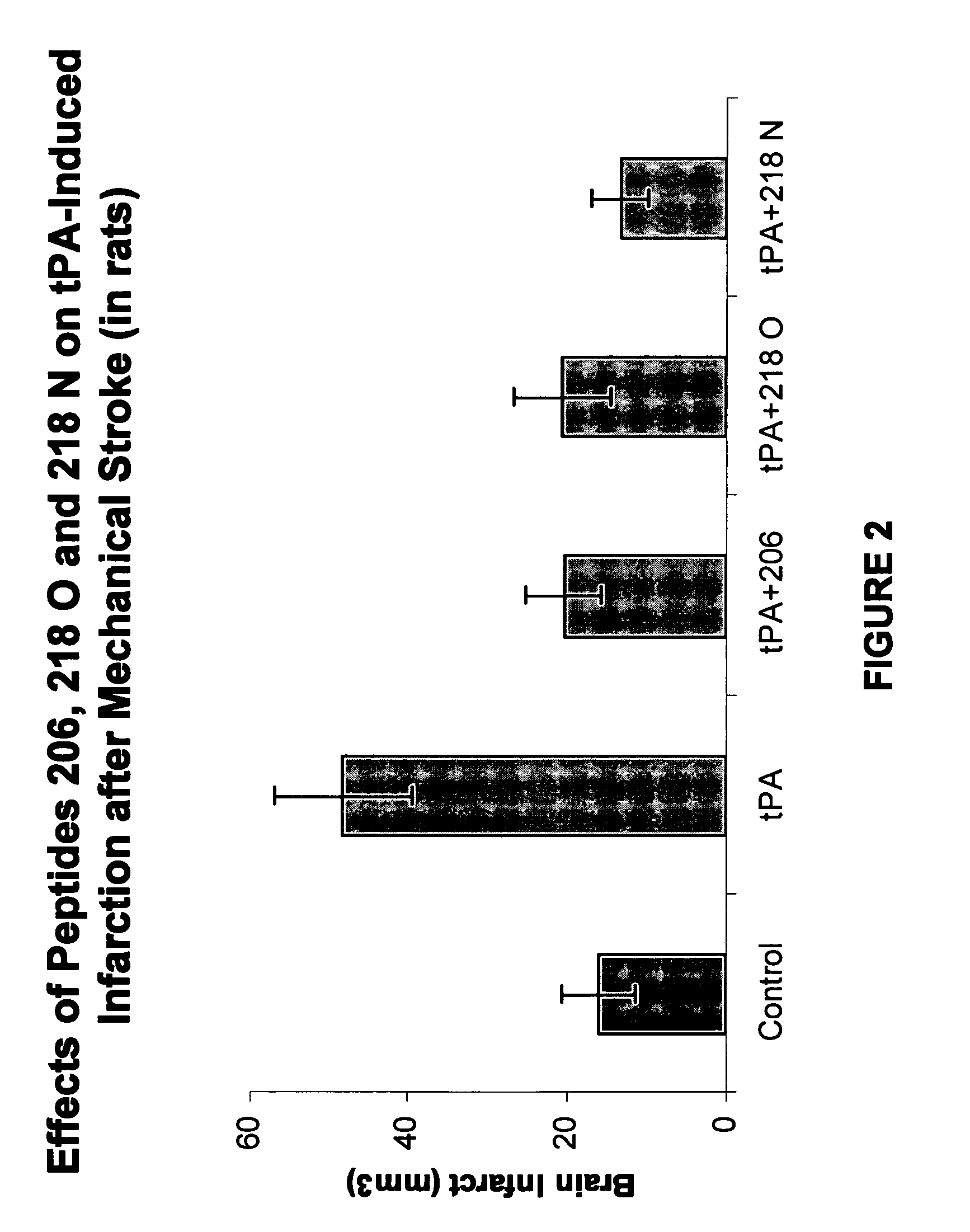
InactiveUS8507436B2Reducing tPA-induced brain edemaReduce mortalityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPlasminogen activator inhibitor-1Plasminogen Activator Inhibitors
Owner:D PHARMA LTD
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors and methods of use thereof to modulate lipid metabolism
Owner:EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY +2
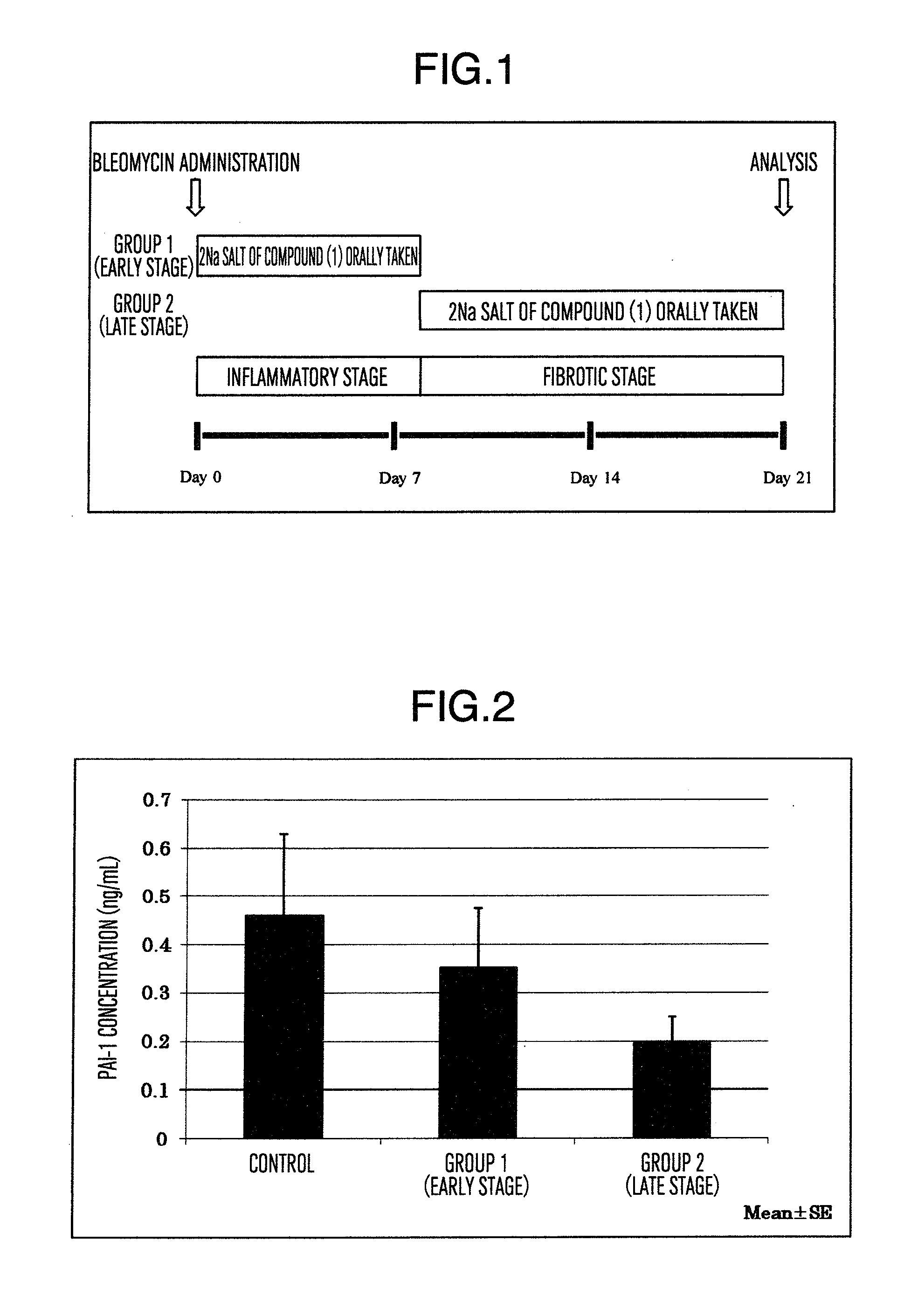
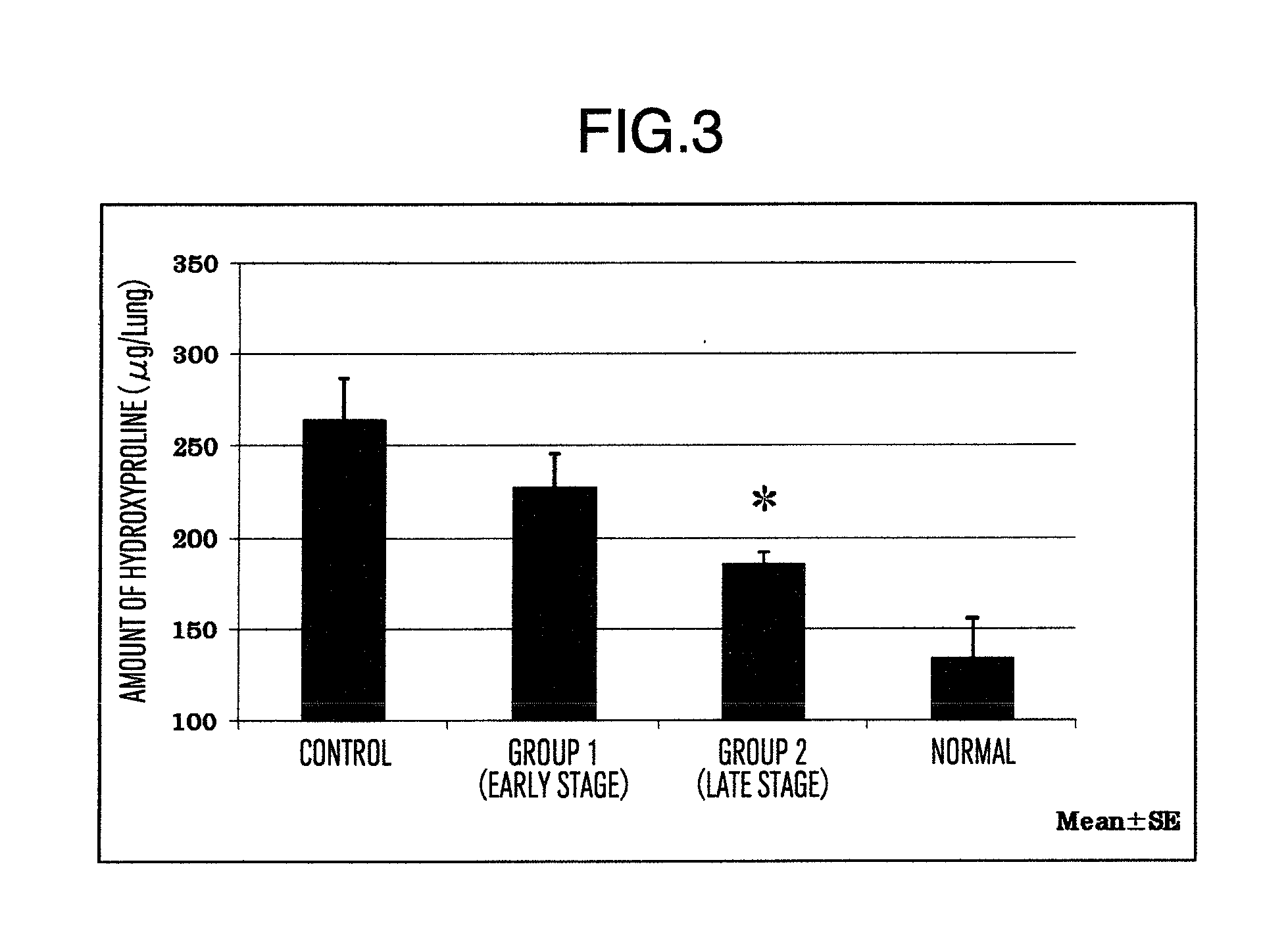
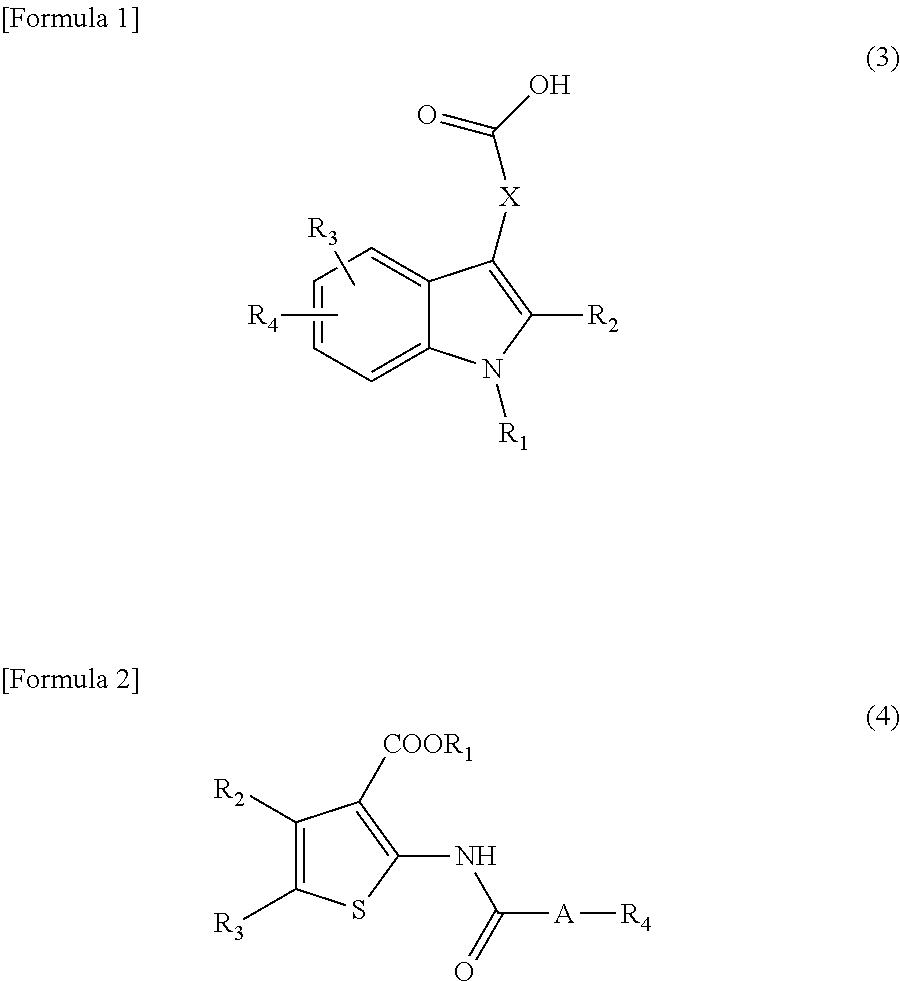
Prophylactic or therapeutic agent for pulmonary fibrosis
InactiveUS20120059020A1Suppression problemGood effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHydrogen atomPhenyl group
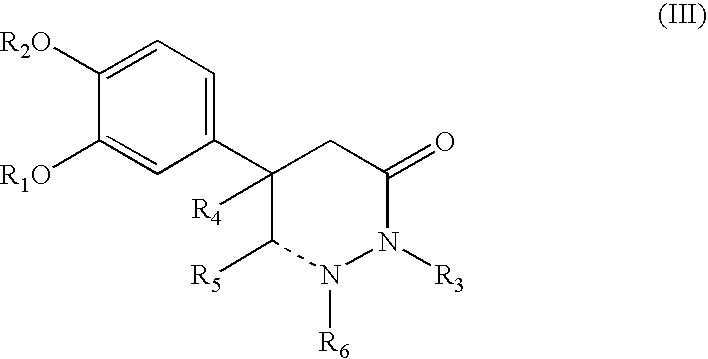
Disclosed is a compound which has an inhibitory activity on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and has a propanedioic acid structure represented by formula (1) [wherein R1 and R2 independently represent a hydrogen atom or a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; R3 represents a cyclohexyl group or a phenyl group (provide that the phenyl group may be substituted by a substituent selected from a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and a halogen atom); R4 represents a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms or a phenyl group (provide that the phenyl group may be substituted by a substituent selected from a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and a halogen atom); and n represents an integer of 1 to 8]. The compound is useful as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:SHIZUOKA KAFUEIN INDSSHIYO
5-phenyl-3-pyridazinone derivative
InactiveUS8106053B2Strong inhibitory activityBiocideOrganic chemistryDisseminated coagulopathyCerebral Bleeding
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Methods for modulating angiogenesis
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore, the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1-3 and kringles 1-4. A truncated proteolytic plasmin protein of 34 kDa is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Methods for modulating angiogenesis
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore, the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1-3 and kringles 1-4. A truncated proteolytic plasmin protein of 34 kDa is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Anti-blood stasis syndrome application of scirpusin A component in Rhizoma Sparganii
ActiveCN108926566ASignificant anti-blood stasis effectImprove liver indexOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderThromboxane B2Medicine
The invention discloses an anti-blood stasis syndrome application of a scirpusin A component in Rhizoma Sparganii. It is firstly proved that the scirpusin A has a significant anti-blood stasis drug effect, and can be used to prepare drugs for treating blood stasis syndromes. Pharmacological experiments prove that the scirpusin A can significantly reduce the Thromboxane B2 (TXB2) level, the fibrinogen (FIB) level, the tissue plasminogen inhibitor-1 (Active Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, PAI-1) level and the endothelin (ETo-1) level in serum of a blood stasis model mouse, can improve the thymus index (TI), the spleen index (SI) and the hepatic index (HI) index of the mouse, and has high clinical application values and a broad development prospect in the treatment of blood stasis syndromes.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors and methods of use thereof
The invention relates to plasminogen activator-1 (PAI-1) inhibitor compounds and uses thereof in the treatment of any disease or disorder associated with elevated PAI-1. The invention includes, but is not limited to, the use of such compounds to prevent or reduce thrombosis and fibrosis, to promote thrombolysis, and to modulate lipid metabolism and treat diseases or disorders associated with elevated PAI-1, cholesterol, or lipid levels.
Owner:EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY +1
Pharmaceutical composition for treatment of thrombosis-related diseases comprising a fragment of prolactin (PRL)-growth hormone (GH)-placental lactogen (PL)-family protein
The present disclosure relates to a pharmaceutical composition for use in the preventive and / or therapeutic treatment of thrombosis-related diseases or conditions relating to high level of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) expression, which composition comprises: A) a fragment of a polypeptide or protein of prolactin (PRL)-growth hormone (GH)-placental lactogen (PL)-family and homologous derivatives thereof, which fragment comprises from 6 to 14 consecutive amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence having general formula (I); or B) a peptide or a recombinant protein comprising said peptide, wherein the peptide is from 6 to 50 amino acids in length and has the activity to inhibit PAI-1, said peptide comprising from 6 to 14 consecutive amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence of general formula (I); or C) a polynucleotide encoding said fragment of a polypeptide or protein of A) or said peptide or recombinant protein of B).
Owner:UNIV LIEGE
Novel use for pai-1 inhibitor
ActiveUS20160158188A1Efficient killingImproved prognosisBiocideAnimal repellantsTumor chemotherapyBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Provided is a novel use of a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitor (PAI-1 inhibitor) that is used as an active ingredient of an agent for controlling a tumor stem cell, an agent for enhancing the antitumor effect of an antitumor agent, an agent for tumor chemotherapy, a stem-cell protecting drug, or a hematopoietic disorder improving agent.
Owner:RENASCI
Hirudo polypeptide with functions of antithrombus and brain nerve cell protection and application of hirudo polypeptide
ActiveCN110437307AGood plasma stabilityLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesDiseaseAdjuvant therapy
The invention discloses hirudo polypeptide with functions of antithrombus and brain nerve cell protection and application of the hirudo polypeptide, and relates to the fields of traditional Chinese medicine, natural medicine and health care products. The structure of the hirudo polypeptide is presented as a formula I, human umbilical vein endothelial cell expressing vascular hemophilia factor (vWF) and a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(PAI-1) can be significantly lowered at the low concentration of the hirudo polypeptide, the survival rate of nerve cells after oxygen and glucose deprivationis increased, platelet aggregation in vitro is inhibited, the plasma recalcification time is prolonged, formation of thrombi in vivo is reduced, neurobehavior after cerebral infarction of a rat is improved, encephaledema is relieved, the area of cerebral infarction is reduced, the toxicity is low, good application prospects are achieved, and the hirudo polypeptide can be used for preparing medicine or health care products for treating or adjuvant therapy of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, thrombi and cerebral post-stroke nerve function deficit. The formulaI is NH2-Leu-D-Leu-Ser-Gly-Val-R whitmantide A: R=D-Leu-Gly-COOHwhitmantide B: R=D-Leu-Gly-Gly-COOH whitmantide C: R=COOH.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting procoagulant genetic and metabolic conditions associated with, and potentially predispositional for, activation of the coagulation response
InactiveUS20050069969A1Low levelTreated more effectivelyFibrinogenPeptide/protein ingredientsWarfarinResponse method
Methods for diagnosing and identifying genetic and metabolic factors associated with a physiologic procoagulant predisposition for and concurrent activation of the coagulation response in patients suffering from conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, Gulf War illness and cardiovascular disease are disclosed. Diagnostic assays utilized in the methods include measurement of blood levels of Protein C, Protein S, antithrombin, activated protein C resistance, prothrombin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, lipoprotein (a) and homocysteine. Treatment regimens include anticoagulant therapies comprising administering warfarin or heparin as needed.
Owner:BERG DAVID E +2
Methods for selecting treatment regimens and predicting outcomes in cancer patients
InactiveUS20180282822A1Improve survivalEfficaciousMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgeryNODALAdjuvant
The present invention relates to methods for determining a treatment regimen beyond surgical removal of tumor tissue for node negative or node positive breast cancer patient. The method comprises measuring the levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in a subject, preferably a tumor; and, based upon the values, predicting the expected benefit including disease-free survival and / or overall survival for the patient without treatment (beyond the surgical removal of tumor tissue) or with a particular treatment and using that information to select a treatment regimen for the subject. High risk subject is identified by high levels of both uPA and PAI-1, high level of uPA and low level of PAI-1 or, low level of uPA and high level of PAI-1. Treatment options for high risk subjects include, but are not limited to, adjuvant CMF chemotherapy, adjuvant non-CMF chemotherapy, adjuvant endocrine therapy, adjuvant anthracyclin-containing chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and gene therapy. Treatment options for low risk subjects include, but are not limited to, no treatment, radiation, and adjuvant endocrine therapy.
Owner:BIOMEDICA DIAGNOSTICS INC
Modified plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 and methods based thereon
InactiveUS20100137209A1Reduced activityExtended half-lifeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsLymphatic SpreadHalf-life
The present invention is based upon the discovery that modified plasminogen activator inhibitor type-I (PAI-1) in which two or more amino acid residues that do not contain a sulfhydryl group have been replaced with amino acid residues that contain a sulfhydryl group and, therefore, forms intramolecular disulfide bonds, have increased in vivo half-life. Also disclosed are the modified PAI-1 proteins, derivatives and analogs thereof, specific antibodies, nucleic acid molecules and host cells. Methods for producing modified PAI-1, derivatives and analogs are also provided. The invention further relates to Therapeutics, pharmaceutical compositions and method of using the composition for treatment. The invention may be used to inhibit angiogenesis in a subject, thereby treating diseases or conditions associated with undesired angiogenesis and cell proliferation. Such conditions include psoriasis, chronic inflammation, tumor invasion and metastasis and conditions in which angiogenesis is pathogenic. The modified PAI-1 molecules of the present invention are useful for the treatment, prophylaxis, management and amelioration of cardiovascular diseases such as, but not limited to those that are related to hyperfibrinolysis, hemophilia, and vessel leakage syndrome.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Biomarkers
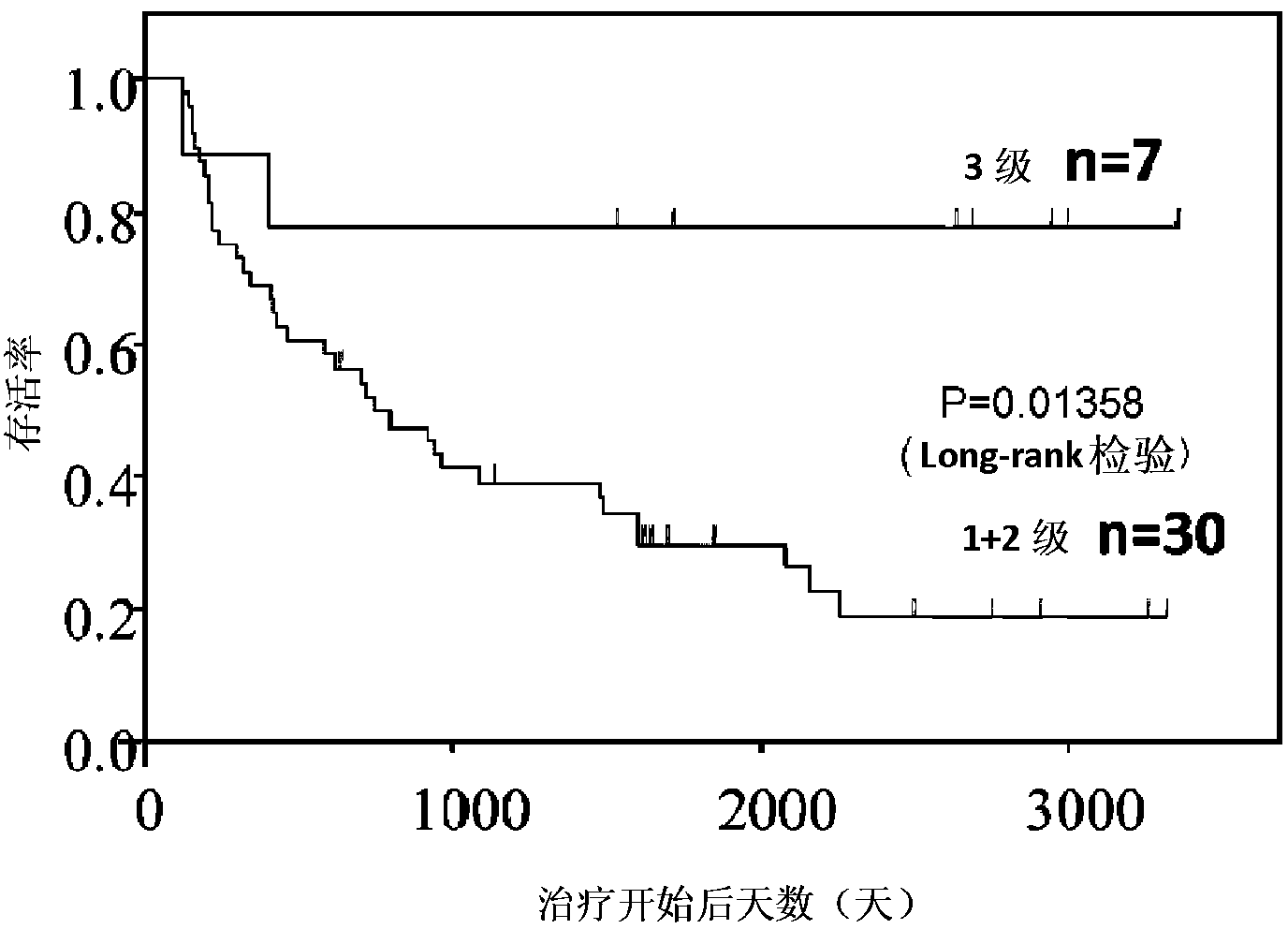
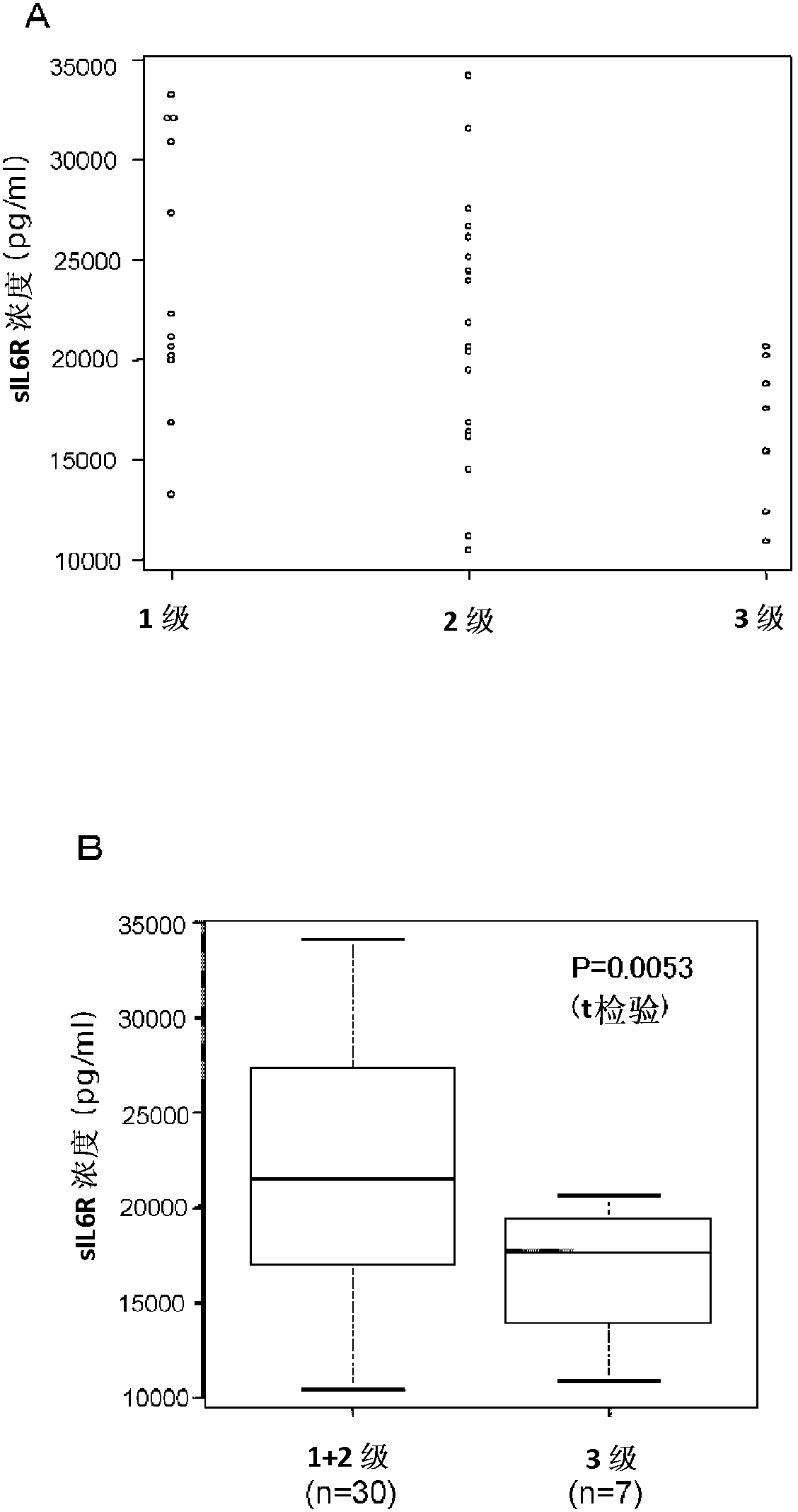
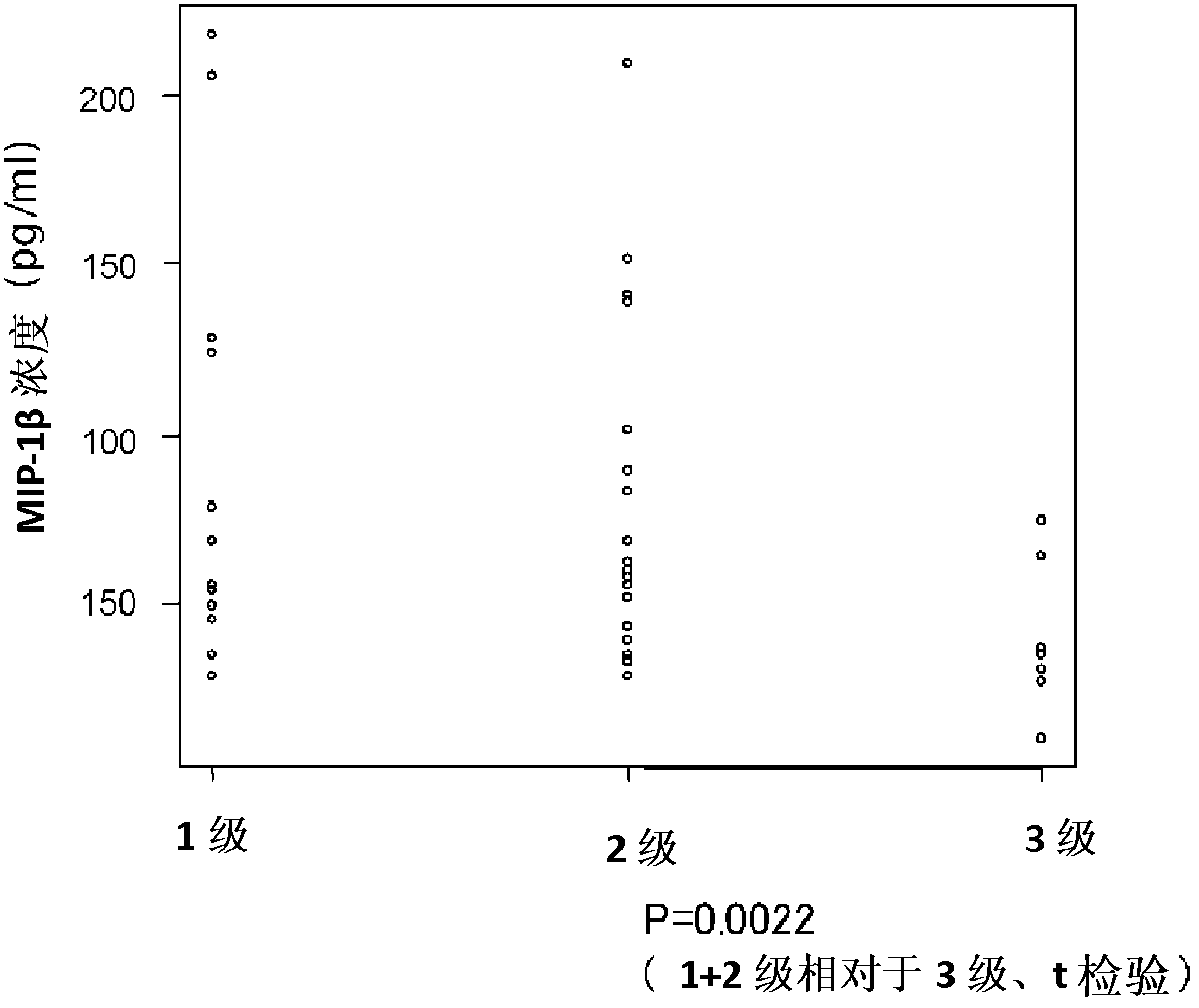
InactiveCN102985824ADisease diagnosisBiological testingSoluble Interleukin 6 ReceptorTherapeutic effect
Provided are biomarkers for predicting the therapeutic effect of a chemoradiotherapy treatment for cancer and predicting the prognosis of a cancer patient, and a method for measuring the biomarkers. The therapeutic effect of a chemoradiotherapy treatment on cancer in a cancer vertebrate individual can be predicted by measuring the concentrations of soluble interleukin 6 receptor, MIP-1[beta] and activated plasminogen activator inhibitor in the blood that has been collected from the vertebrate before the initiation of the chemoradiotherapy treatment. By measuring the concentration of soluble interleukin 6 receptor in the blood, the prognosis of said vertebrate can be evaluated.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT
Carboxilic acid derivatives
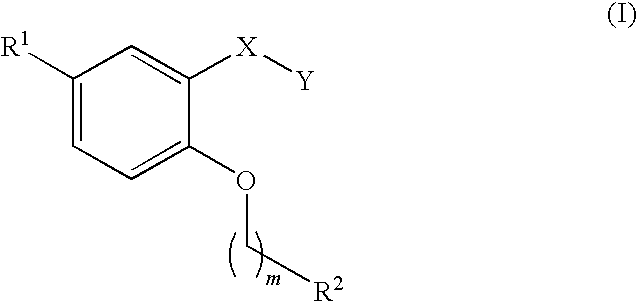
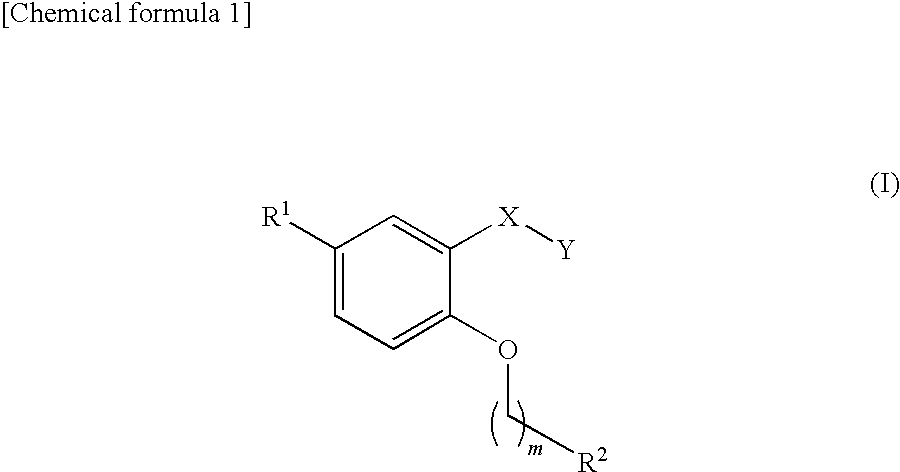
A compound represented by the following general formula (I) or a salt thereof, or a hydrate thereof or a solvate thereof having an inhibitory action against plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1):wherein R1 represents a C6-10 aryl group; or a substituted C6-10 aryl group, R2 represents a C6-10 aryl group; or a C6-10 aryl group substituted with a group or groups selected from the group consisting of a halogen atom, nitro group, a C1-6 alkyl group, a halogenated C1-6 alkyl group, a C1-6 alkoxy group, a halogenated C1-6 alkoxy group, a phenyl group and carboxy group, X represents —CH2—, —CH2CH2—, —CH═CH— or —N(R3)—C(═O)—, Y represents carboxy group or a bioisostere of carboxy group, R3 represents hydrogen atom, a C1-4 alkyl group or a C7-12 aralkyl group, m represents 0 or 1.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL MOLECULAR DESIGN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com