Patents
Literature
113results about How to "Critical dimension reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
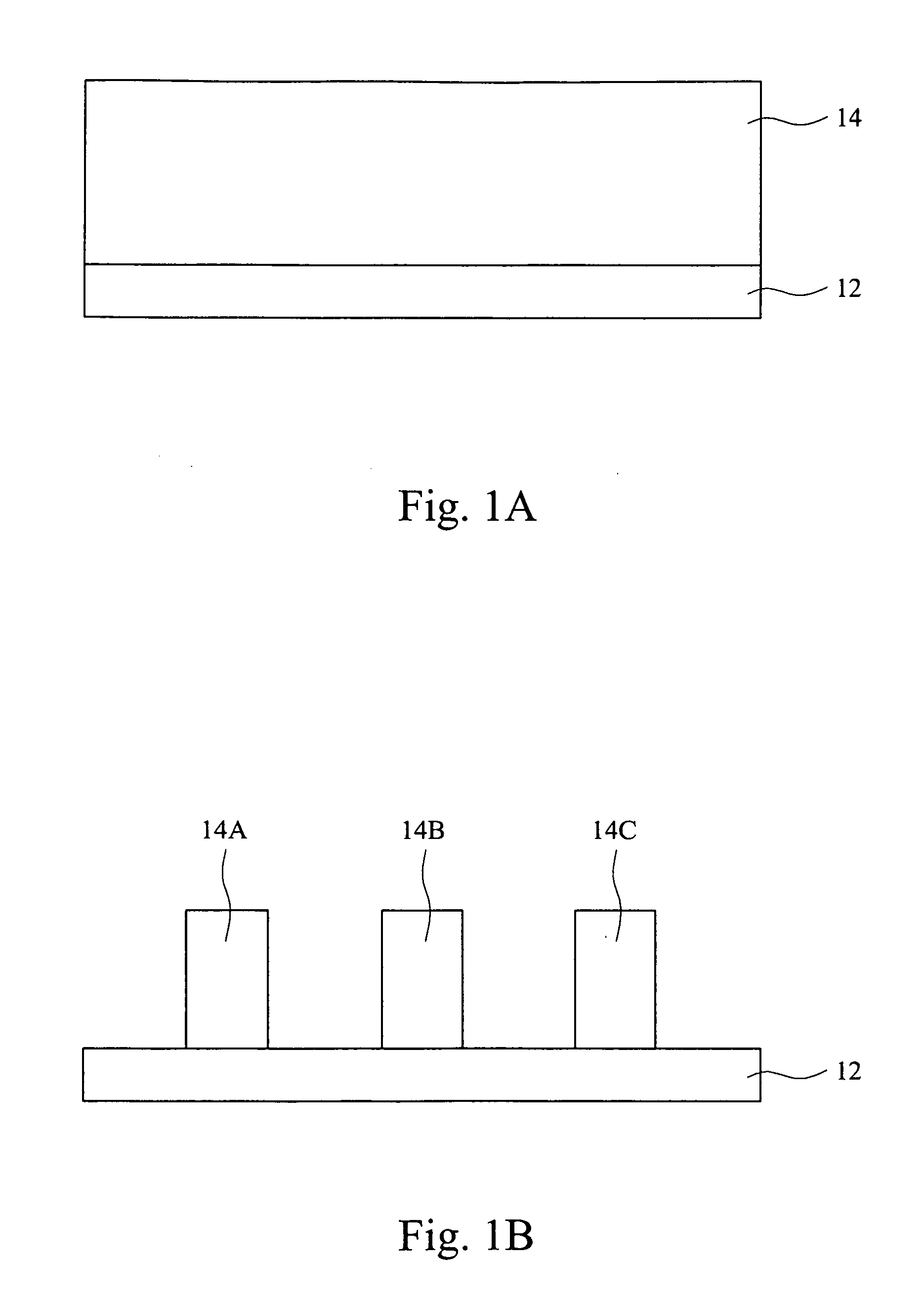
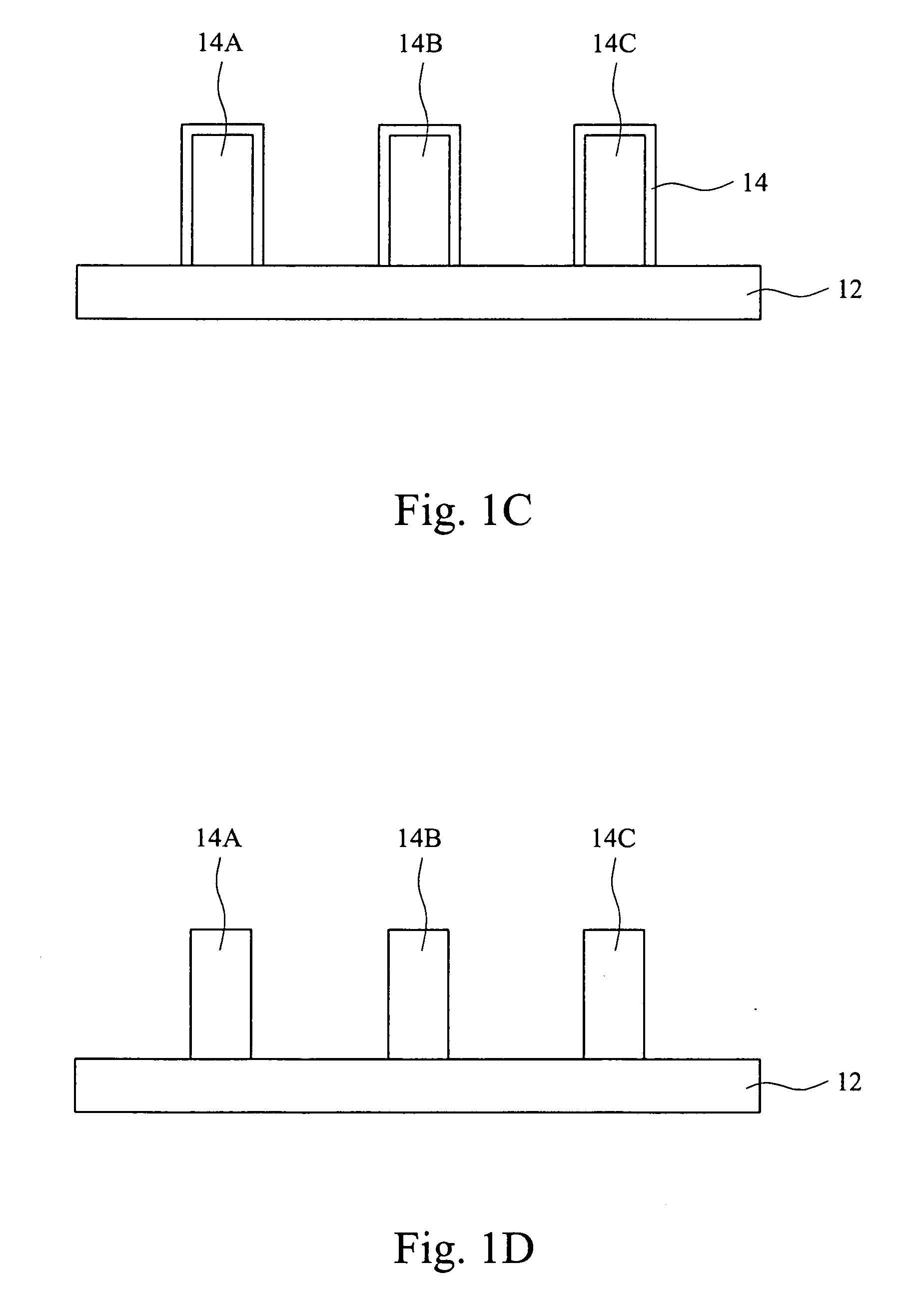
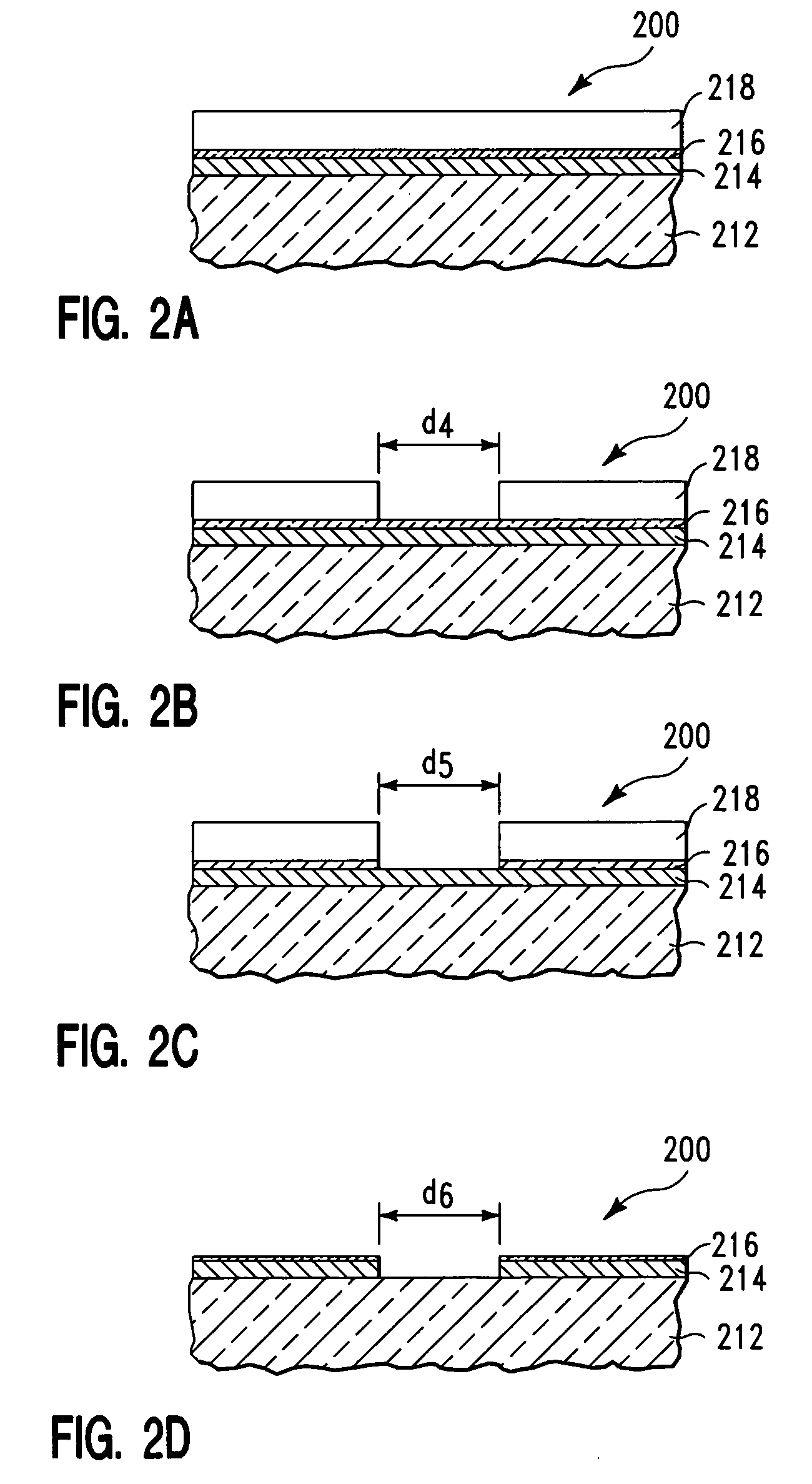
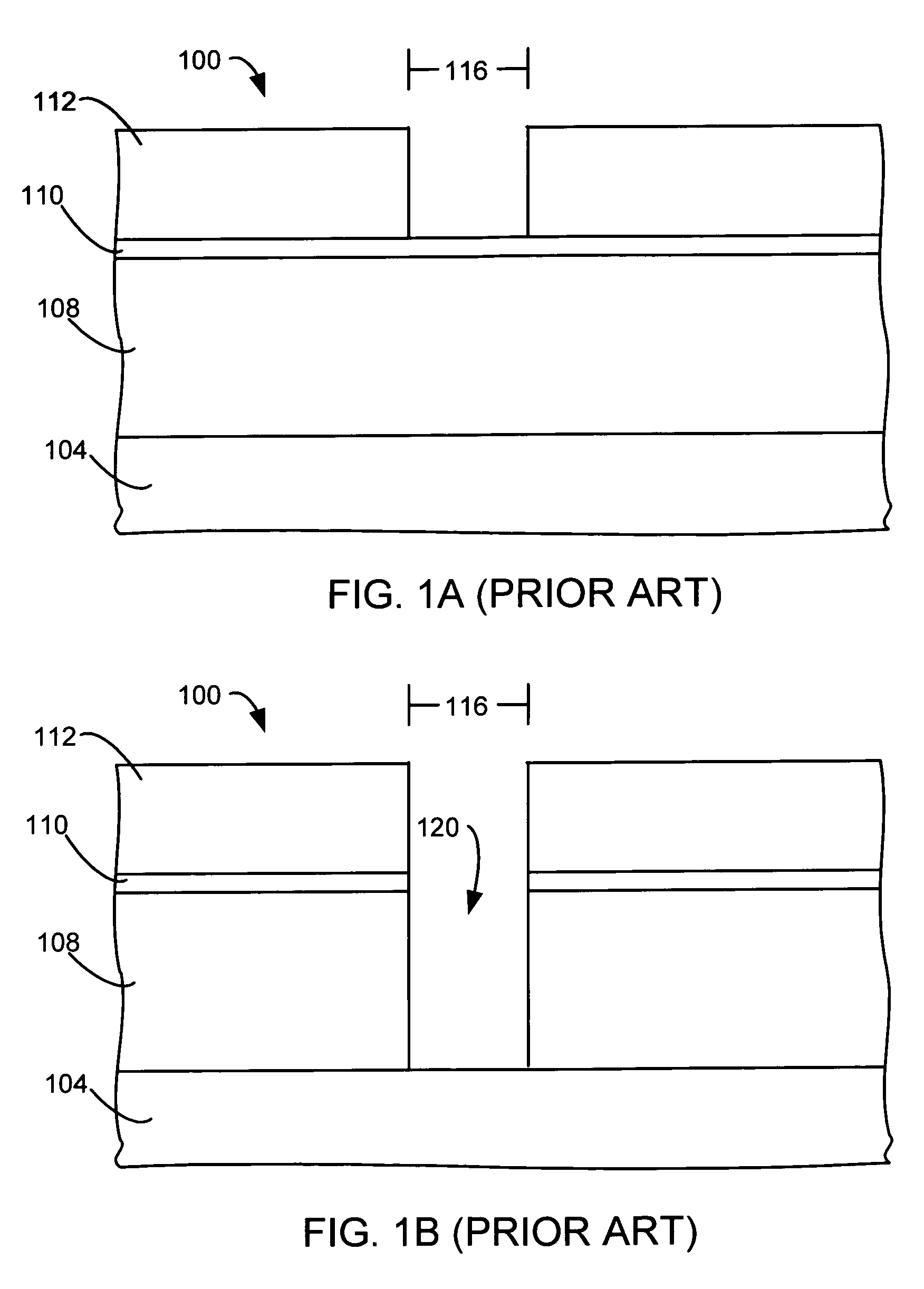
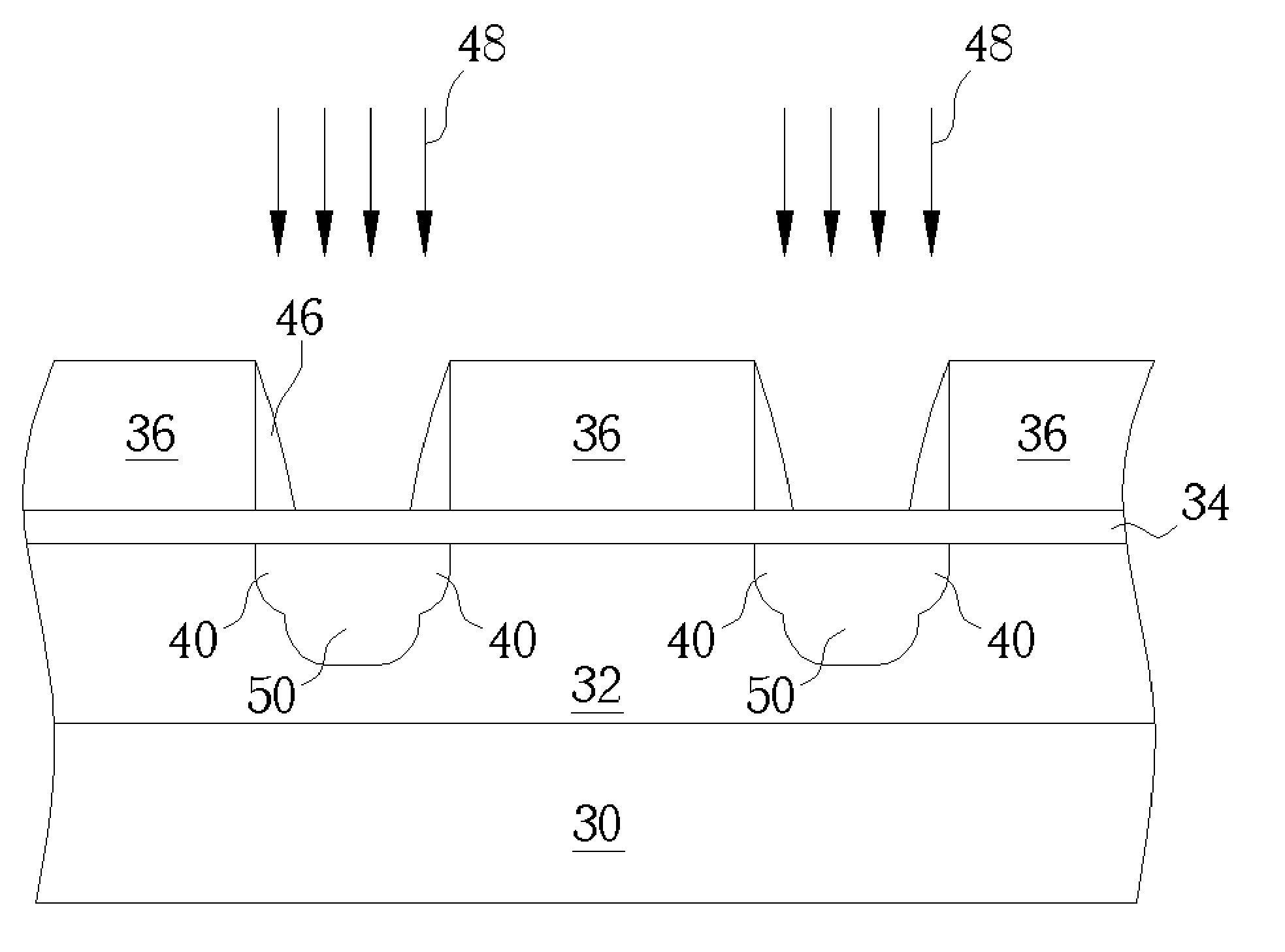
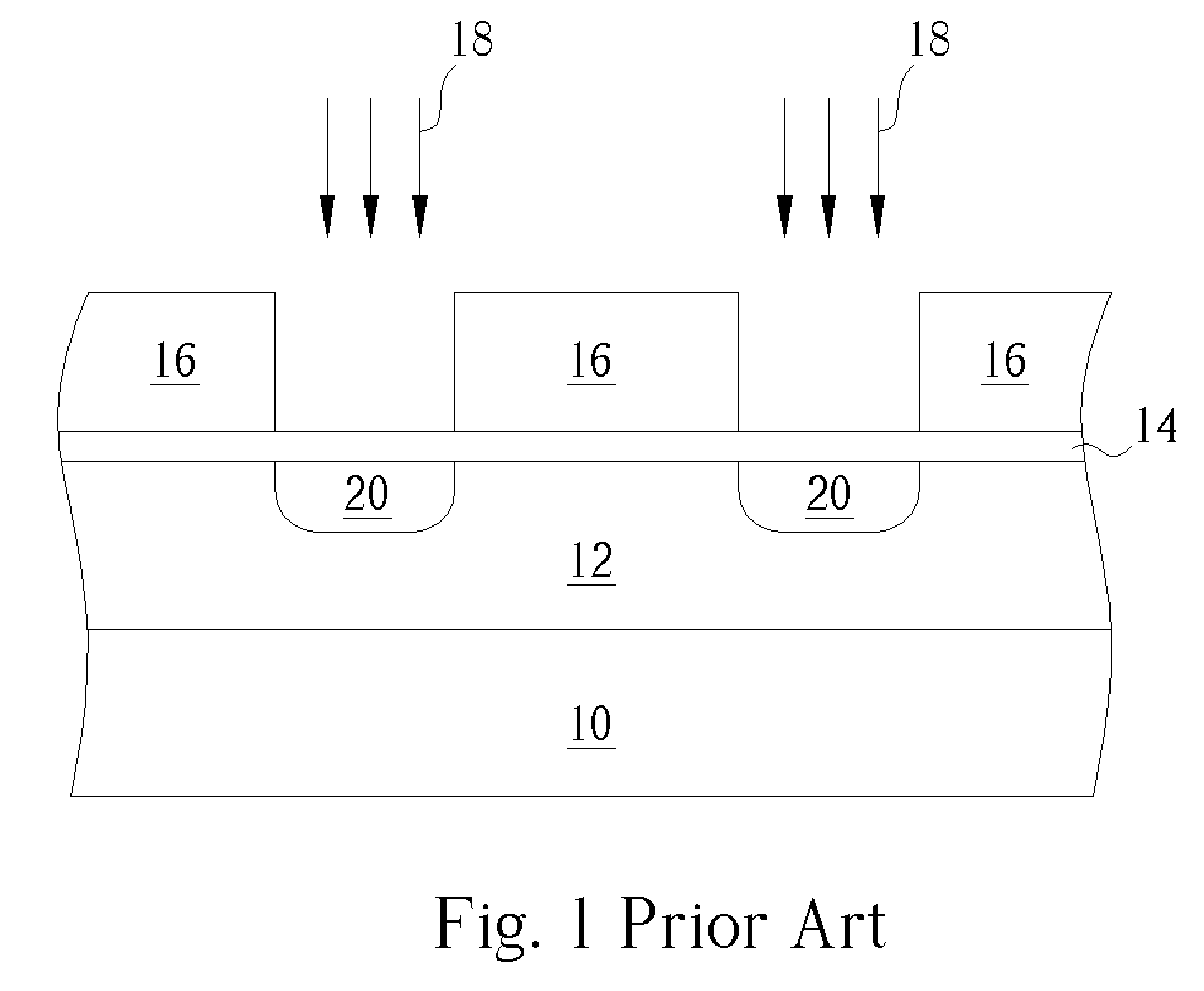
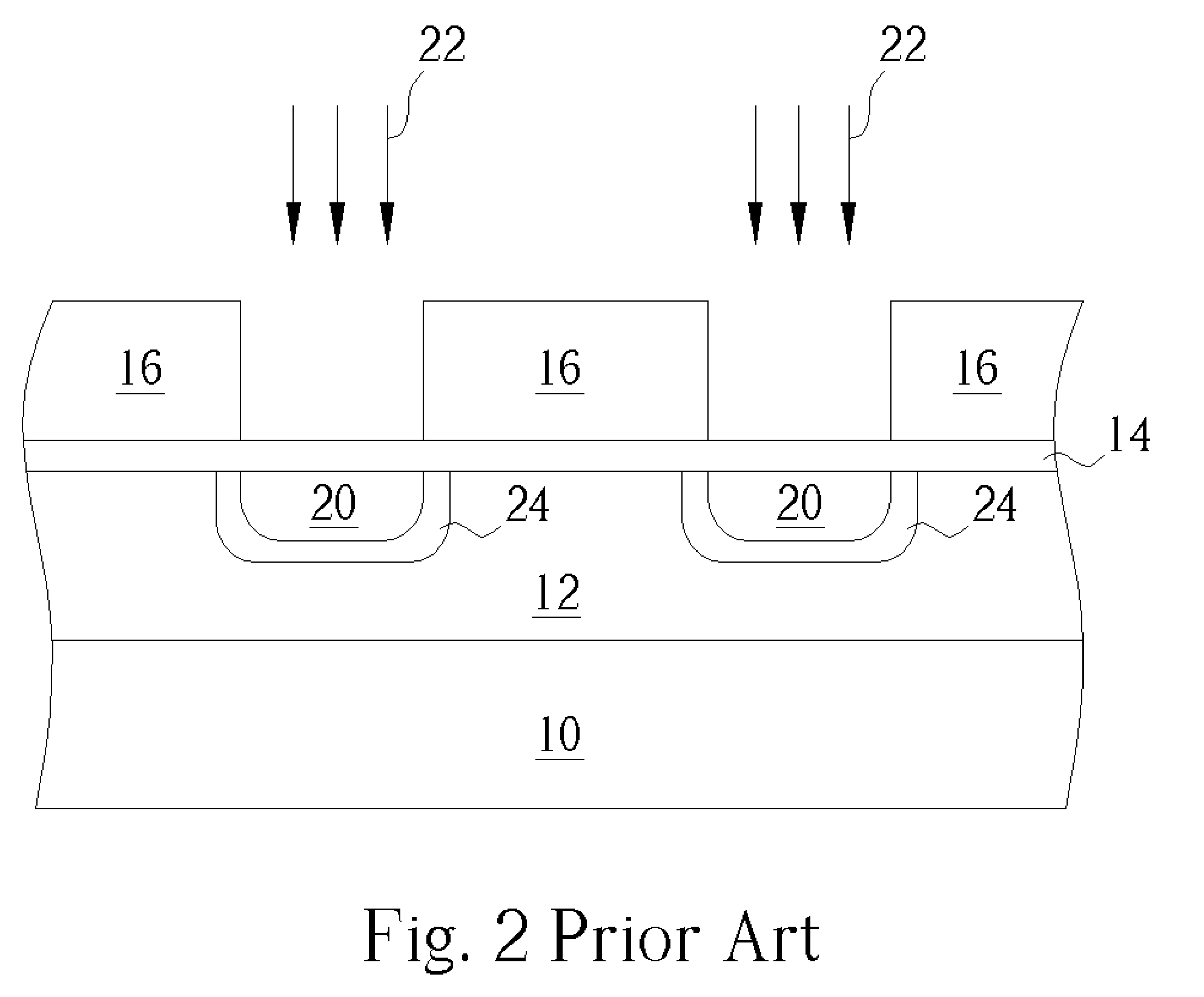
Method to reduce CD non-uniformity in IC manufacturing
ActiveUS7252909B2Narrow distribution rangeCritical dimension be reduceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIc manufacturingMask layer
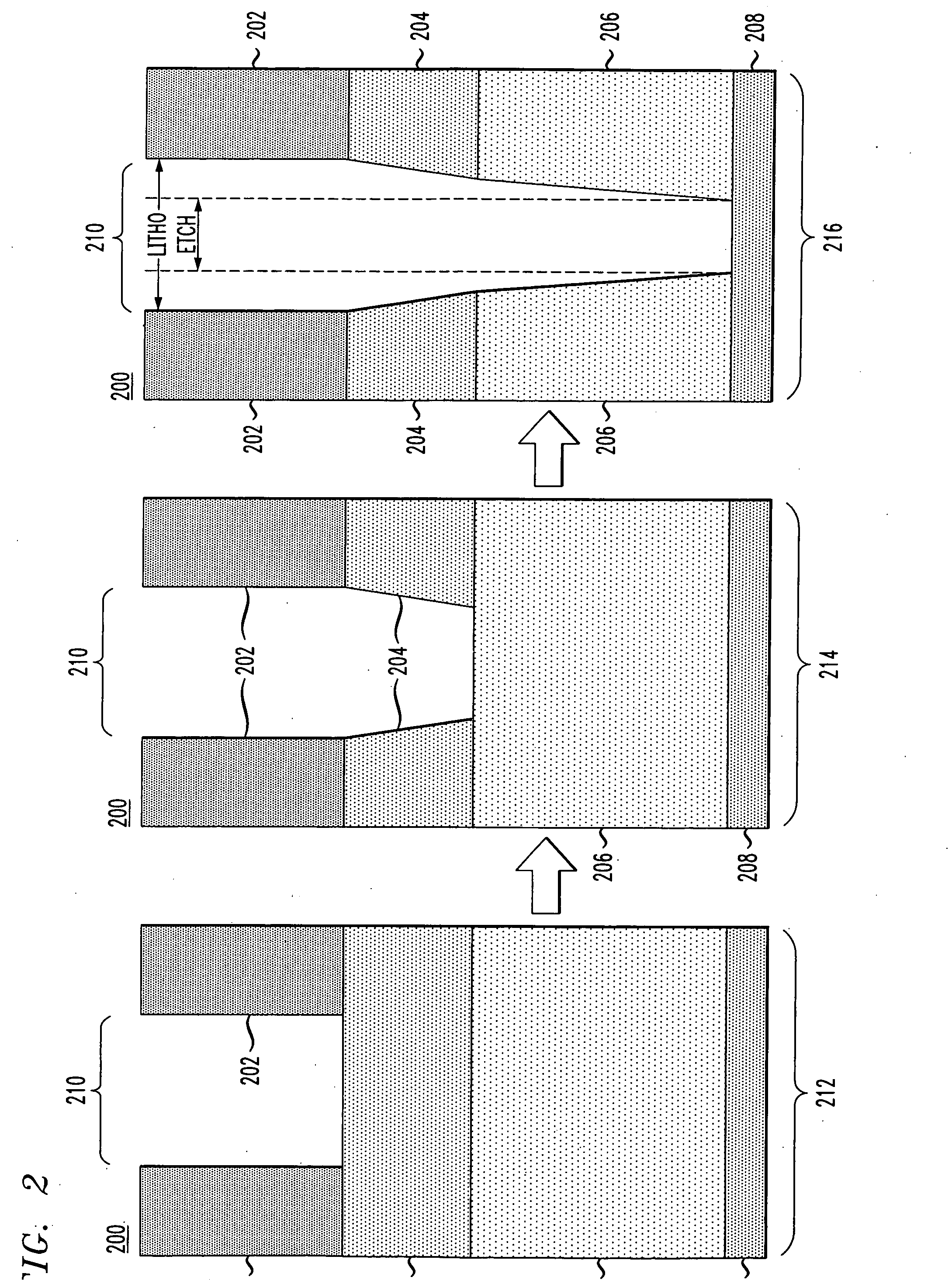
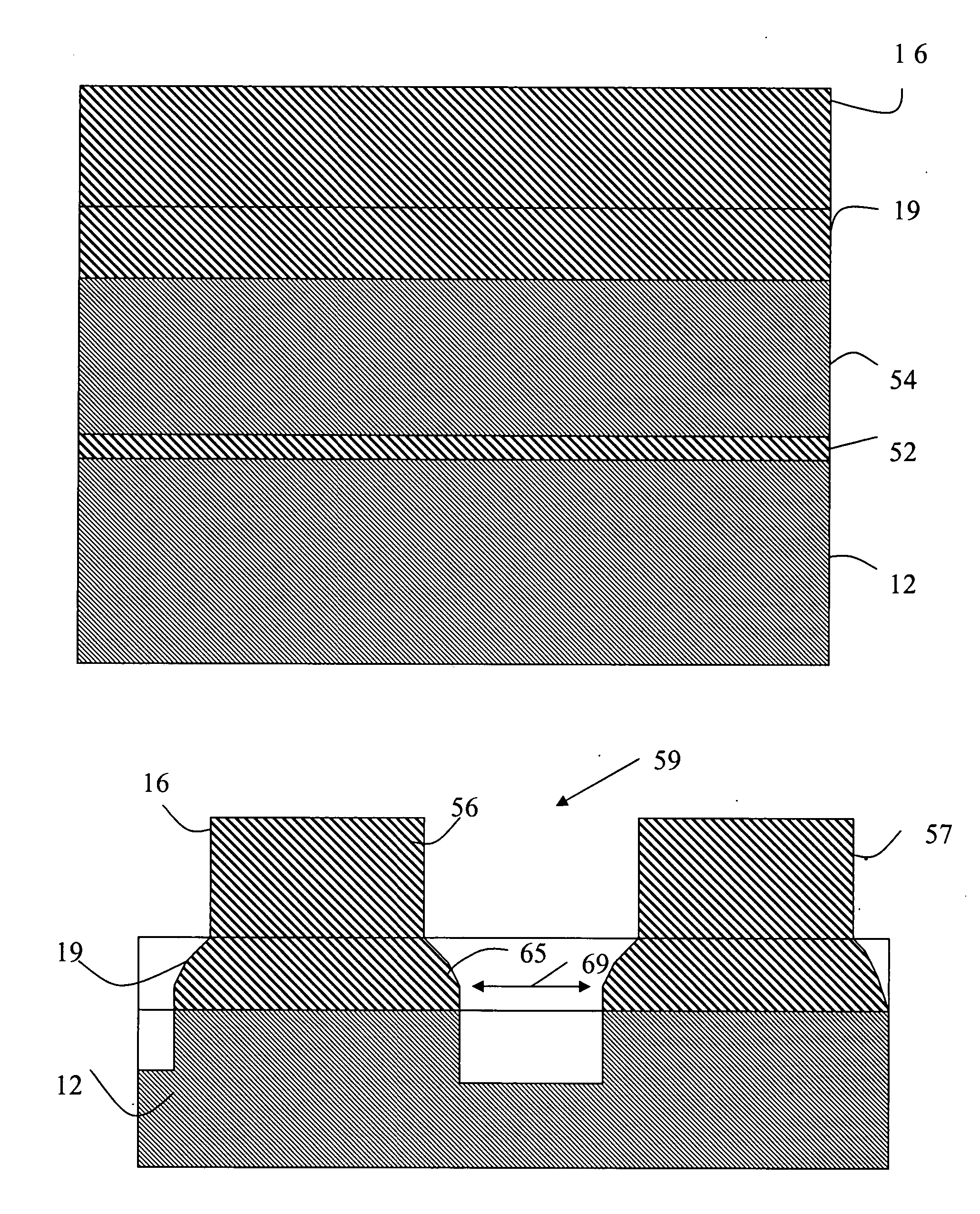
A method is provided for reducing Critical Dimension (CD) non-uniformity in creating a patterned layer of semiconductor material. Two masking layers are respectively created, the first masking layer comprising a main pattern, an isolated pattern and a dummy pattern, the second masking layer exposing the dummy pattern. Methods of compensating for optical proximity effects and micro-loading, as provided by the invention, are applied in creating the first masking layer. The patterned first masking layer is transposed to an underlying layer creating a first pattern therein. The second masking layer removes the dummy features from the transposed first pattern, creating a second pattern therein comprising a main pattern and an isolated pattern to which compensation for optical proximity effects and micro-loading have been applied. The second pattern serves for additional etching of underlying semiconductor material.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
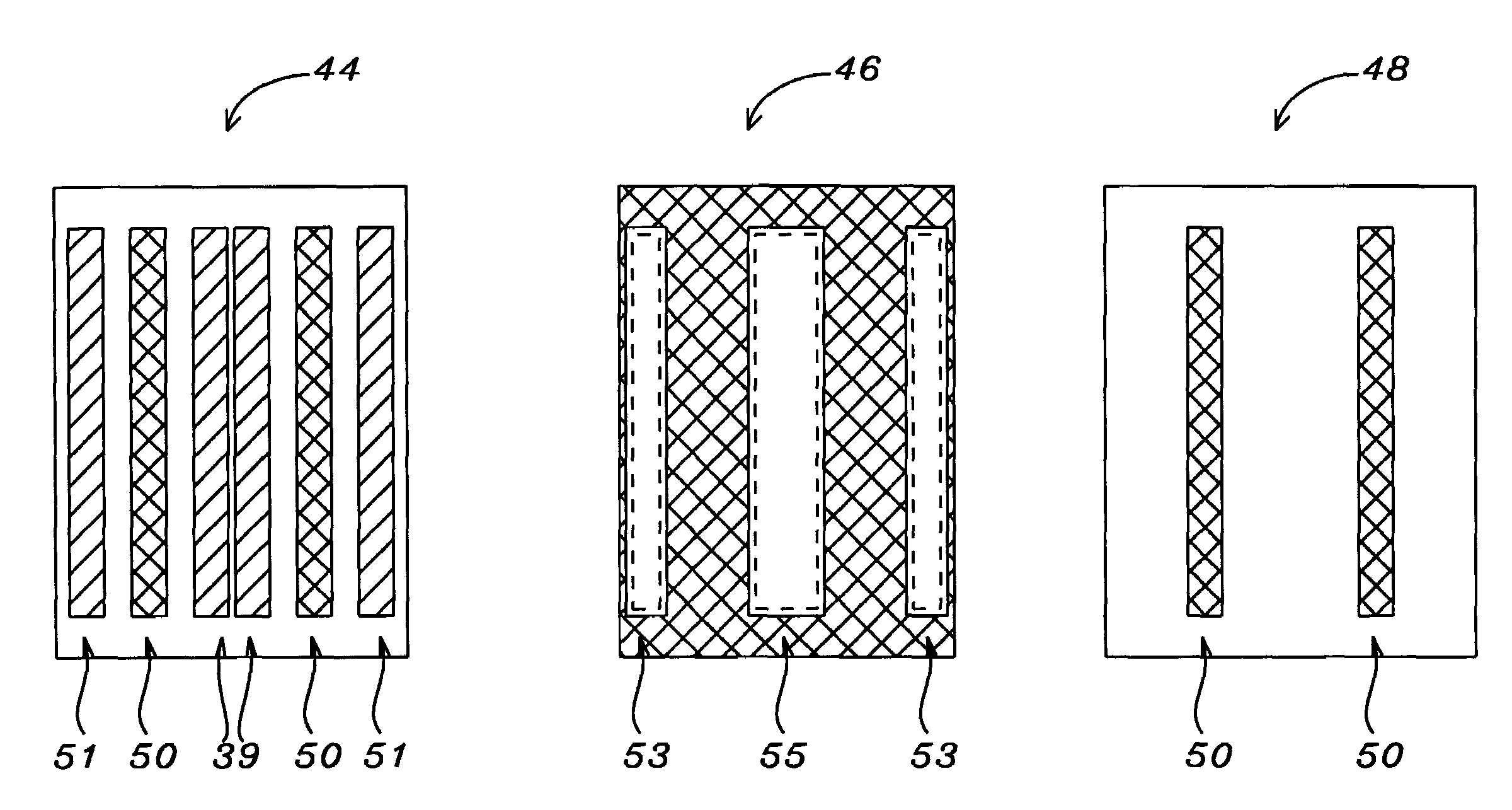
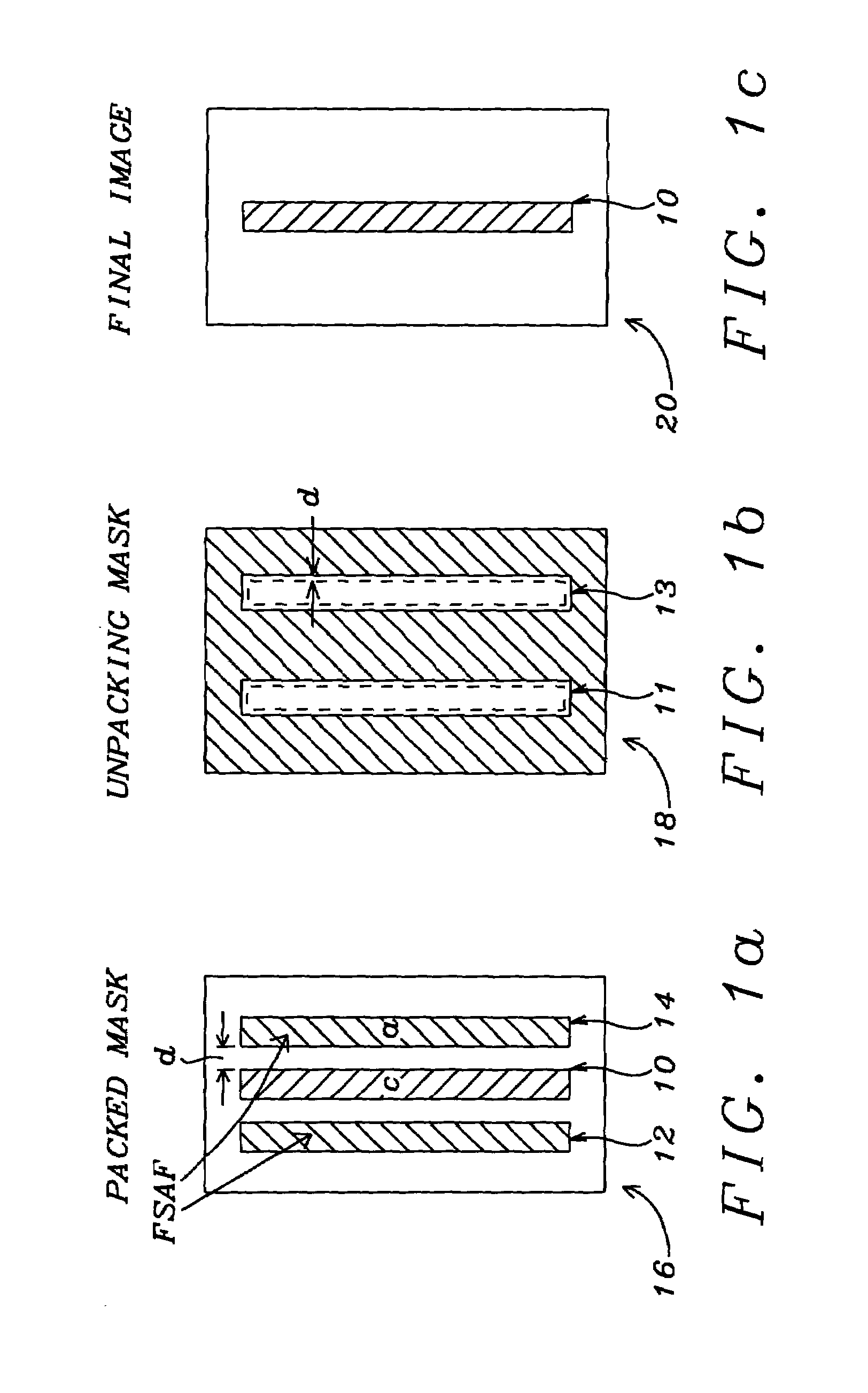
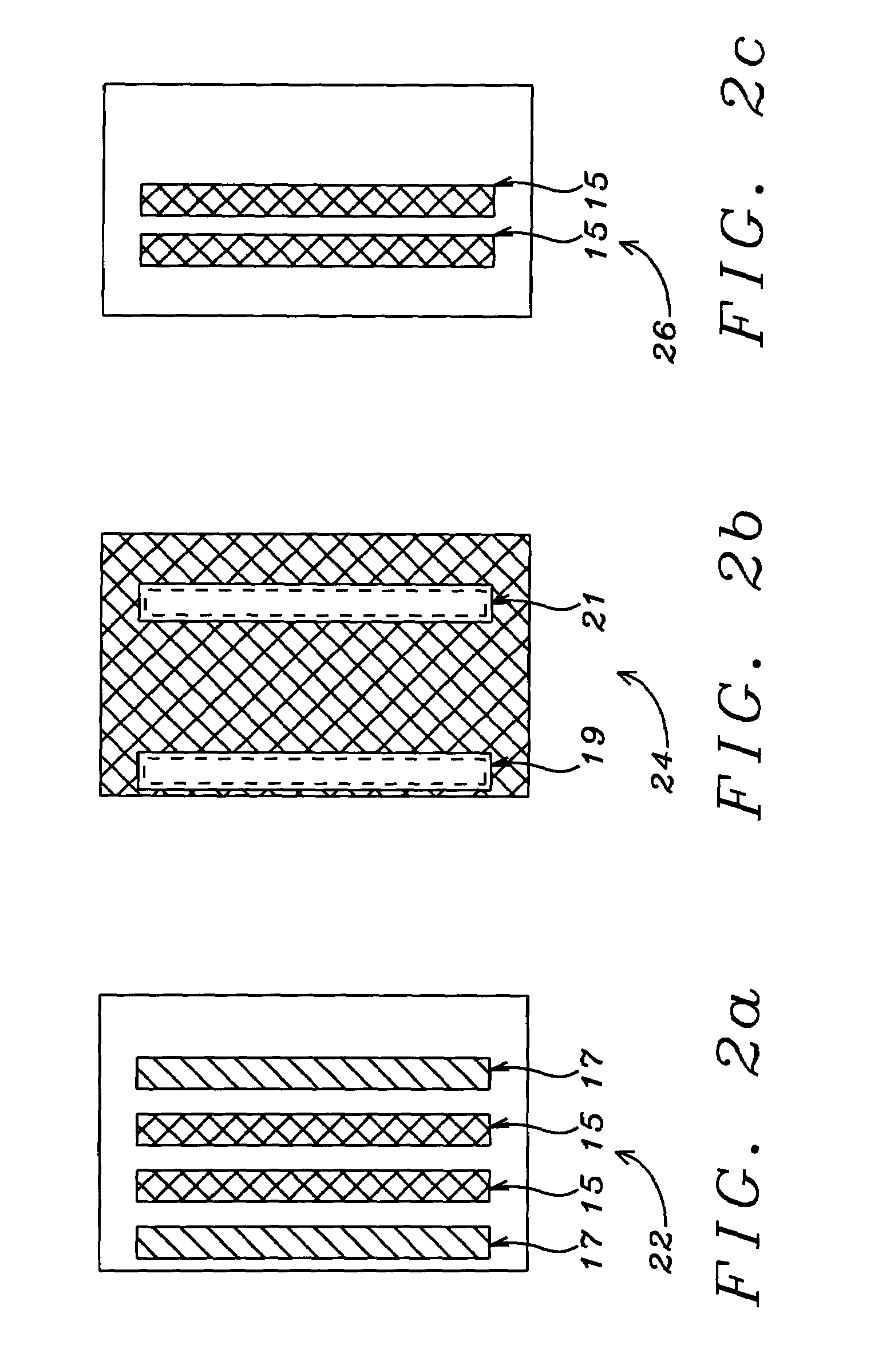
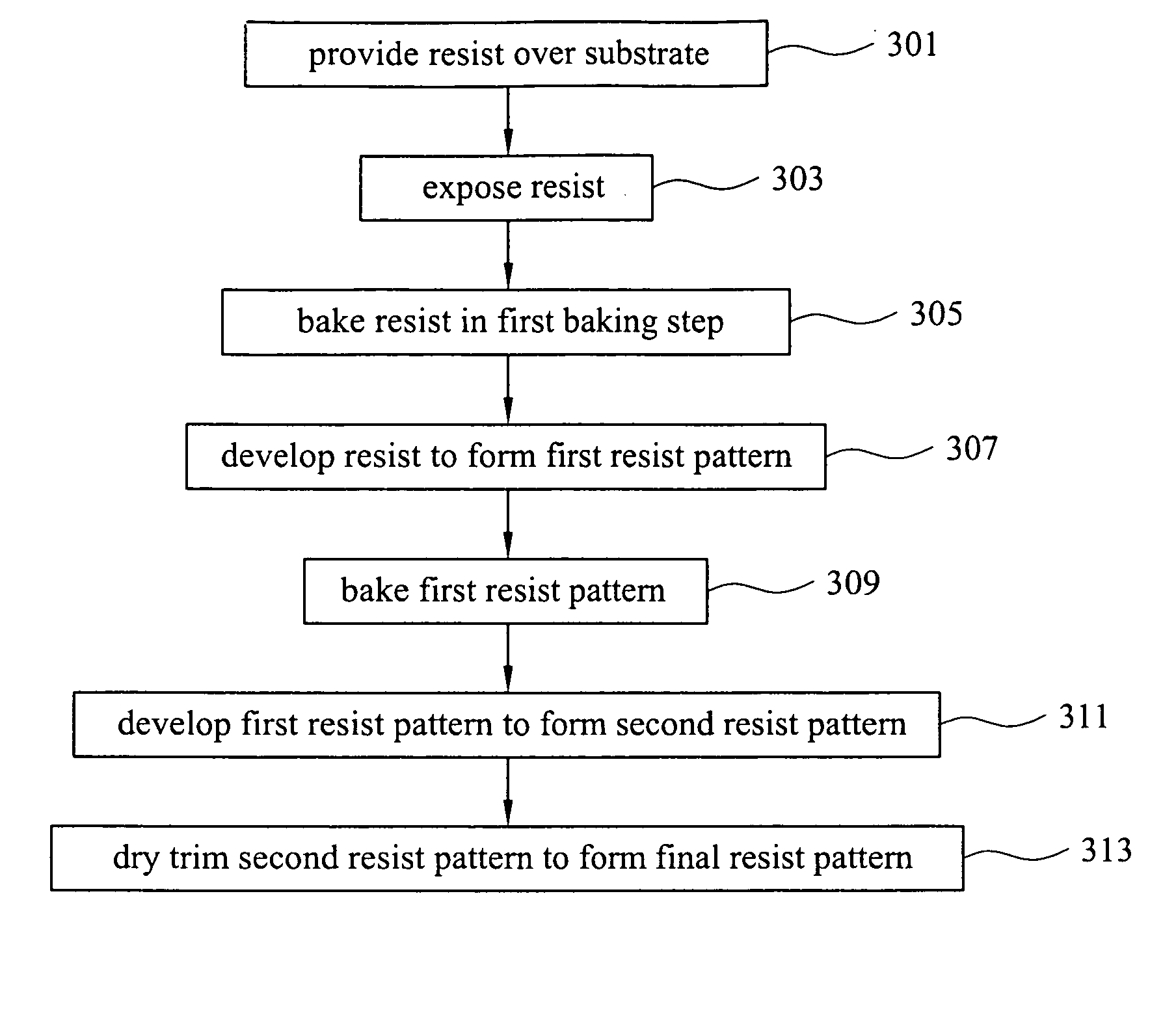
Method for forming a finely patterned resist
InactiveUS20060154185A1Critical dimension be reduceImprove spacingPhotosensitive material processingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResistPhotoresist
A method for reducing a critical dimension of a photoresist pattern while improving a line spacing between distal end portions of pattern lines wherein the method includes providing a substrate including an overlying resist; exposing the resist to an activating light source; baking the resist in a first baking process followed by developing the resist in a first development process to form a first resist pattern; then baking the first resist pattern in a second baking process followed by developing the first resist pattern in a second development process to form a second resist pattern having reduced dimensions; and, then dry trimming the second resist pattern to form a final resist pattern with reduced dimensions compared to the second resist pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Etch pattern definition using a CVD organic layer as an anti-reflection coating and hardmask
InactiveUS20020086547A1Highly effective hard mask propertyHigh resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAnti-reflective coatingOrganic layer
A multilayer antireflective hard mask structure is disclosed. The structure comprises: (a) a CVD organic layer, wherein the CVD organic layer comprises carbon and hydrogen; and (b) a dielectric layer over the CVD organic layer. The dielectric layer is preferably a silicon oxynitride layer, while the CVD organic layer preferably comprises 70-80% carbon, 10-20% hydrogen and 5-15% nitrogen. Also disclosed are methods of forming and trimming such a multilayer antireflective hard mask structure. Further disclosed are methods of etching a substrate structure using a mask structure that contains a CVD organic layer and optionally has a dielectric layer over the CVD organic layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods of for forming ultra thin structures on a substrate
InactiveUS20090035944A1Critical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition processCritical dimension
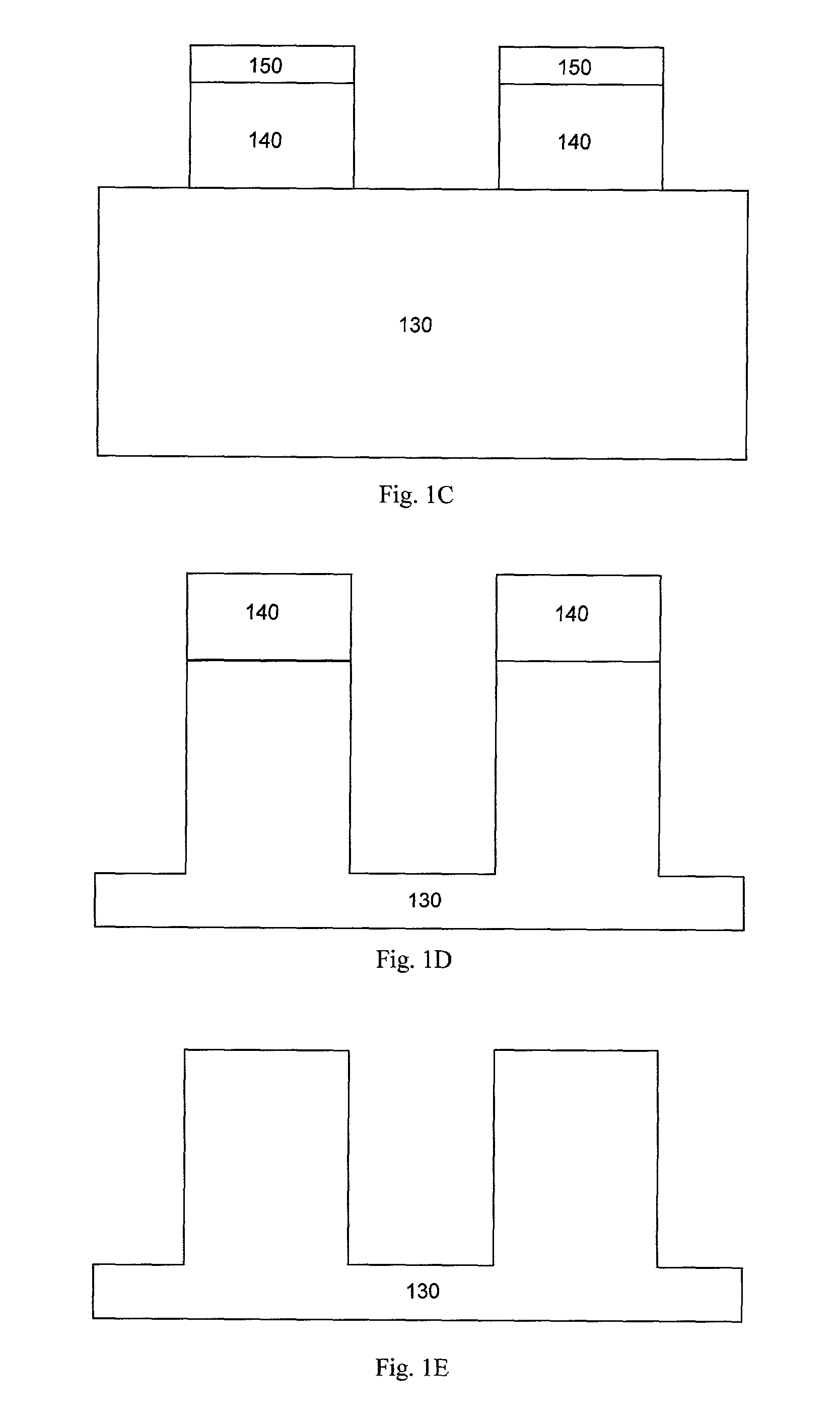
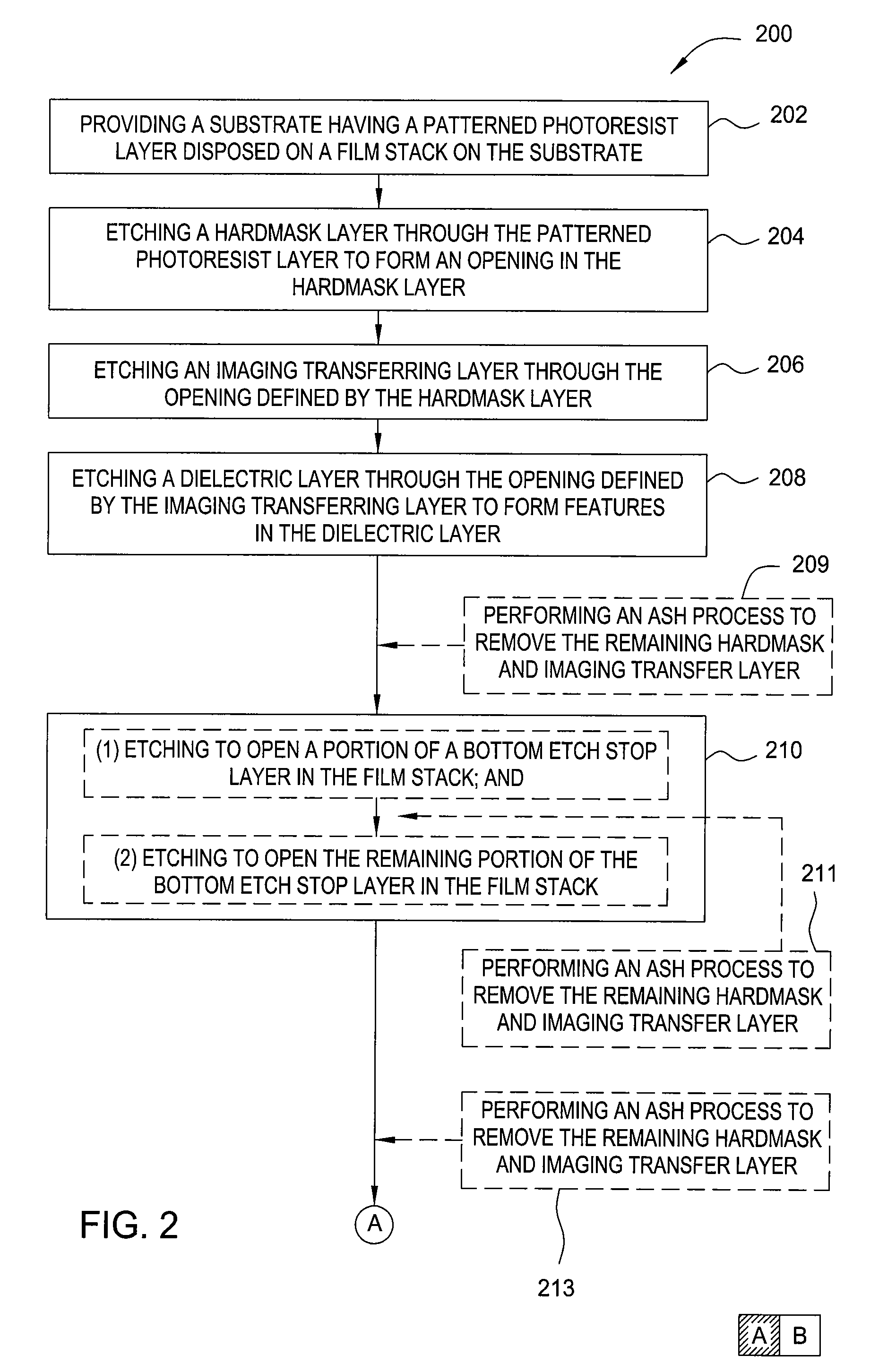
Methods for forming an ultra thin structure using a method that includes multiple cycles of polymer deposition of photoresist (PDP) process and etching process. The embodiments described herein may be advantageously utilized to fabricate a submicron structure on a substrate having a critical dimension less than 55 nm and beyond. In one embodiment, a method of forming a submicron structure on a substrate may include providing a substrate having a patterned photoresist layer disposed on a film stack into an etch chamber, wherein the film stack includes at least a hardmask layer disposed on a dielectric layer, performing a polymer deposition process to deposit a polymer layer on the pattered photoresist layer, thus reducing a critical dimension of an opening in the patterned photoresist layer, and etching the underlying hardmask layer through the opening having the reduced dimension.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
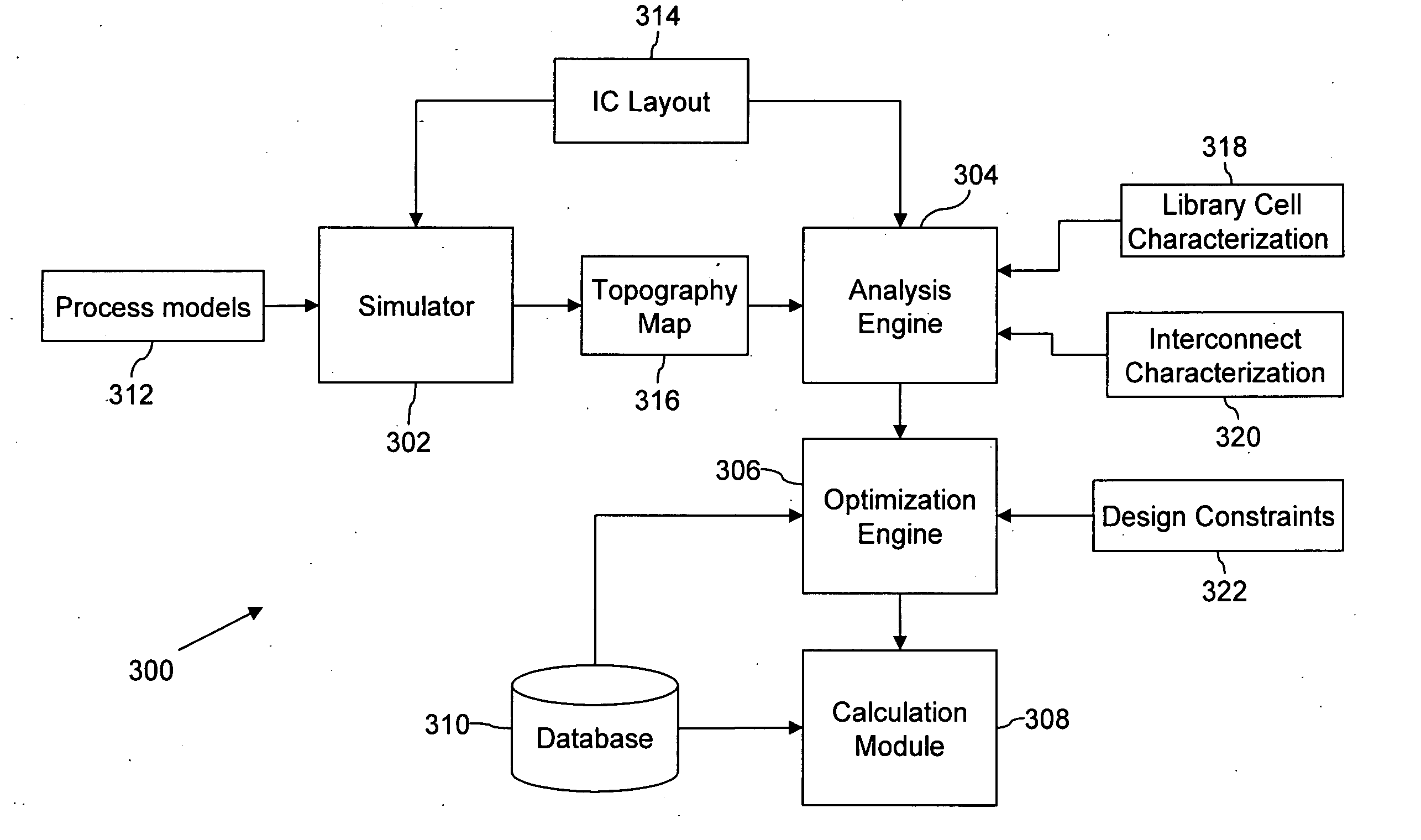
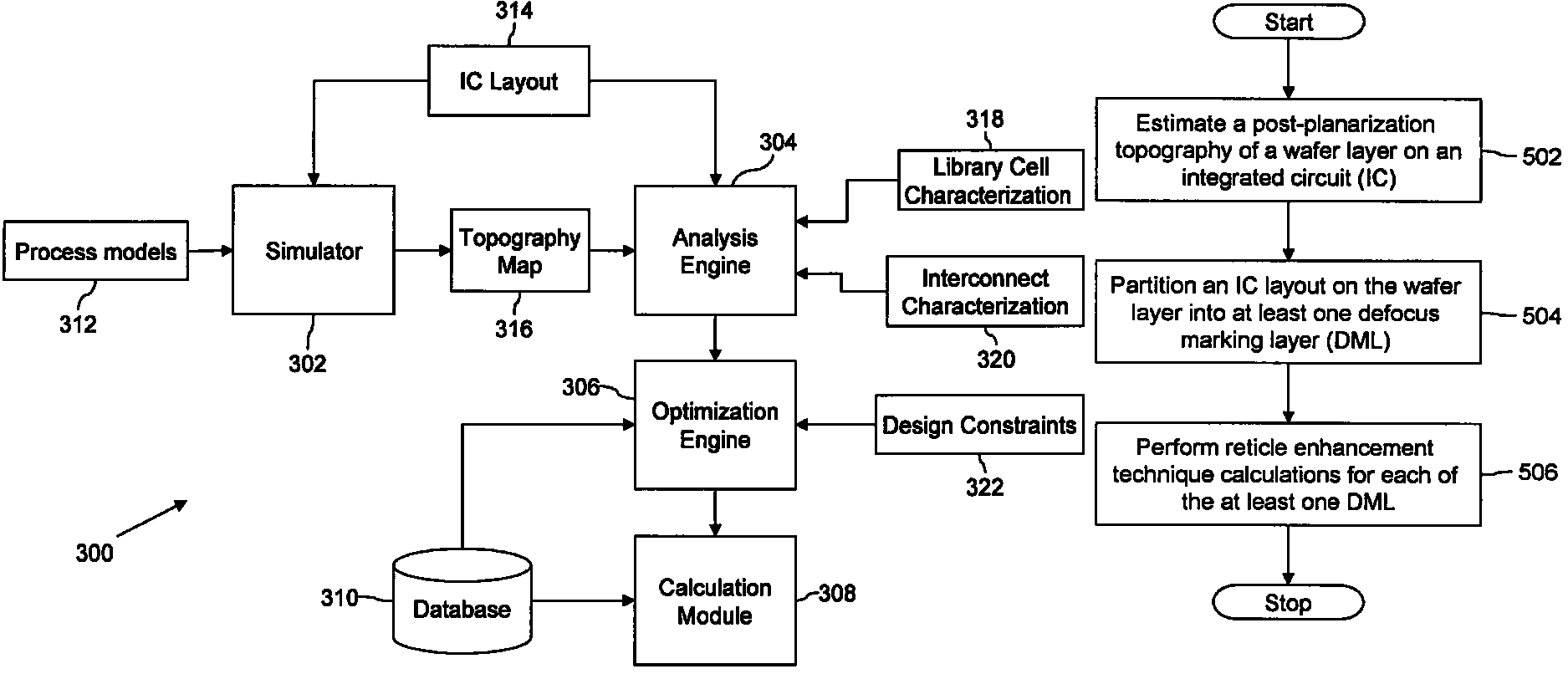
Method and system for topography-aware reticle enhancement
InactiveUS20060110837A1Simple designReduce errorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesEngineeringLandform
The present invention provides a method and system for improving reticle enhancement calculations during manufacture of an integrated circuit (IC). The reticle enhancement calculations are improved by incorporating post-planarization topography estimates. A planarization process of a wafer layer is simulated to estimate the post-planarization topography. RET calculations, such as sub-resolution assist feature insertion, optical proximity corrections and phase shifting are then performed based on the post-planarization topography of the wafer layer.
Owner:RPX CORP
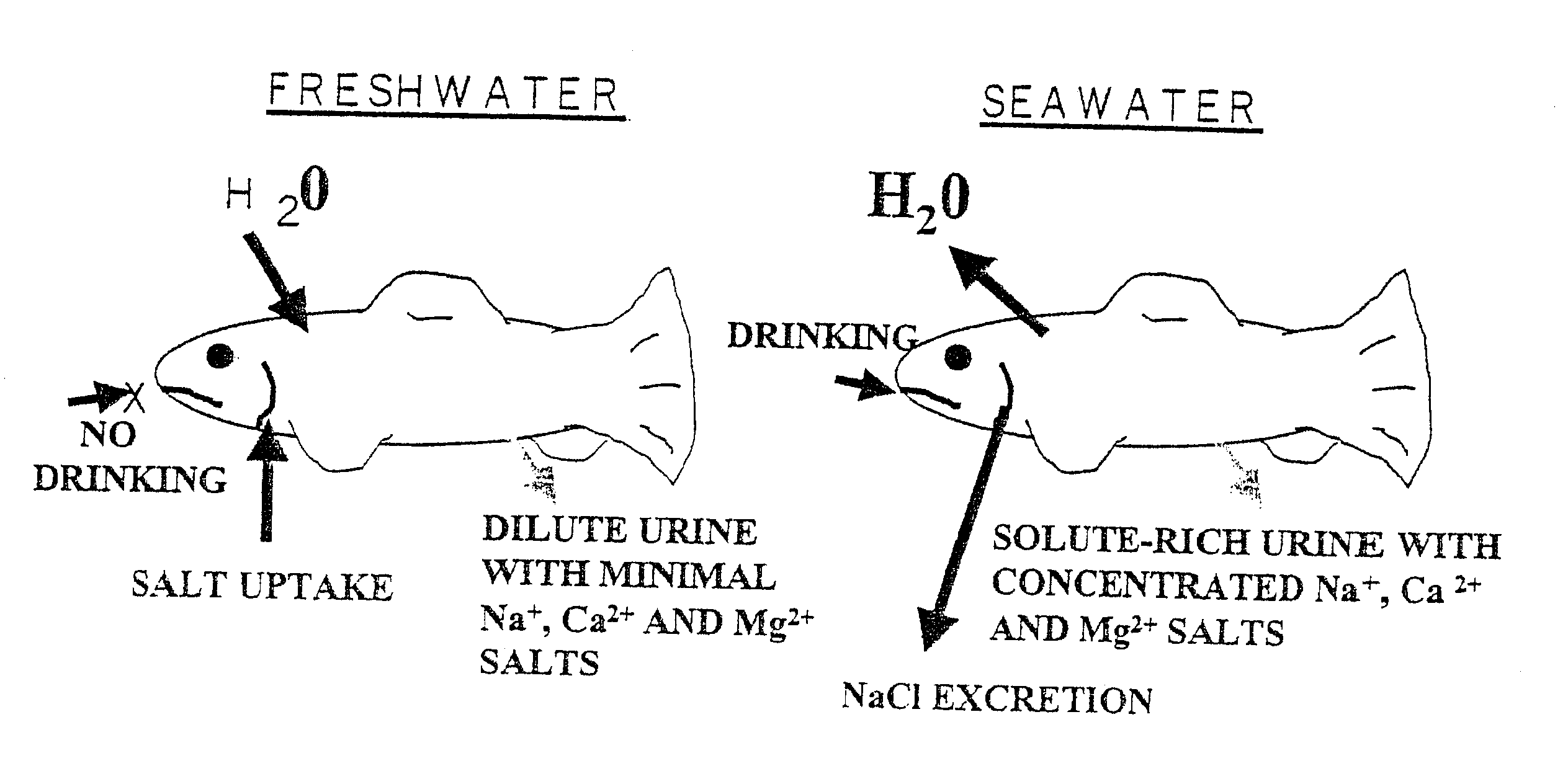
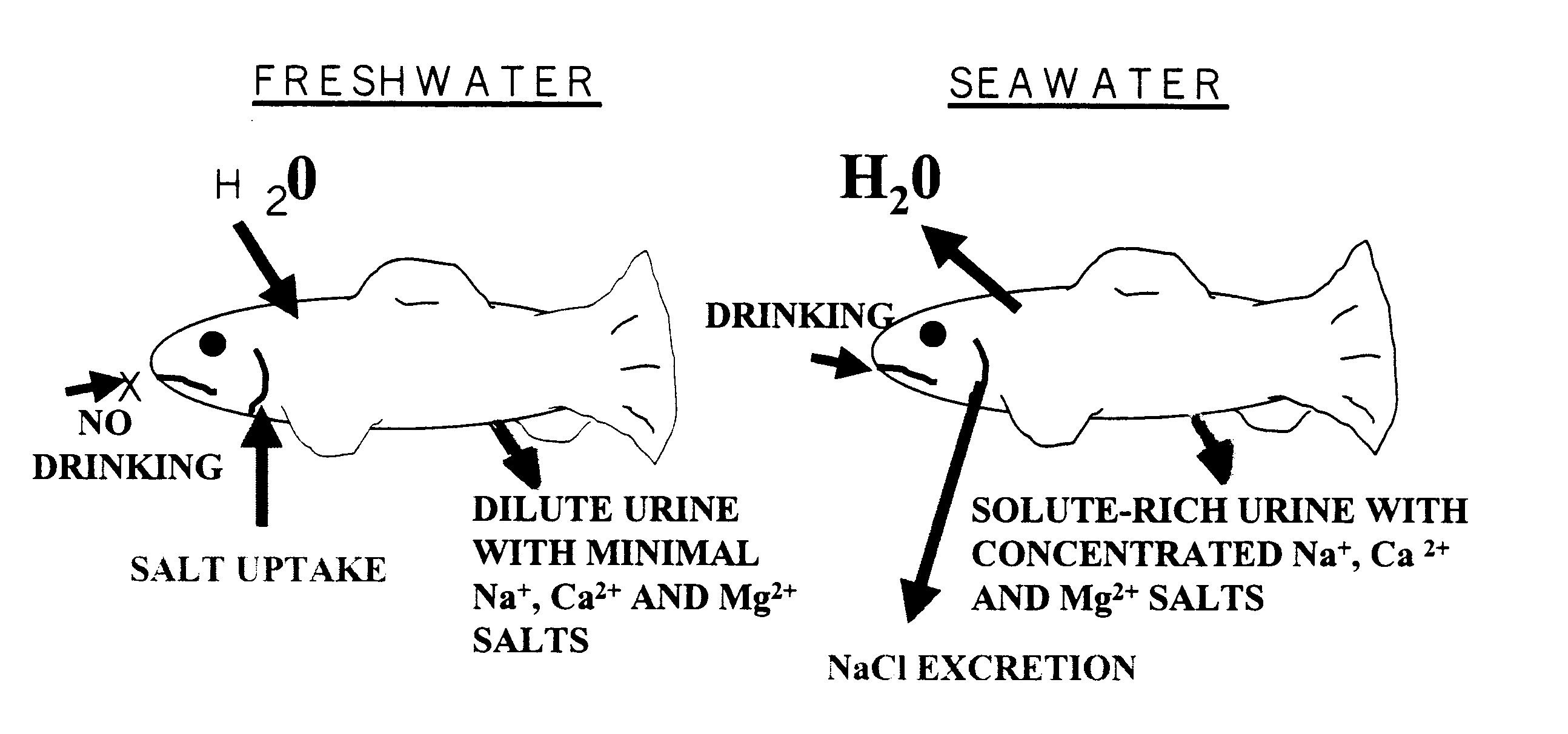
Methods for raising pre-adult anadromous fish
InactiveUS6564747B2Improves the osmoregulatory capabilitiesReductions in the "critical siAnimal feeding stuffTissue cultureFresh water organismFishery
Owner:MARICAL
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20170012000A1Highly integratedCritical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
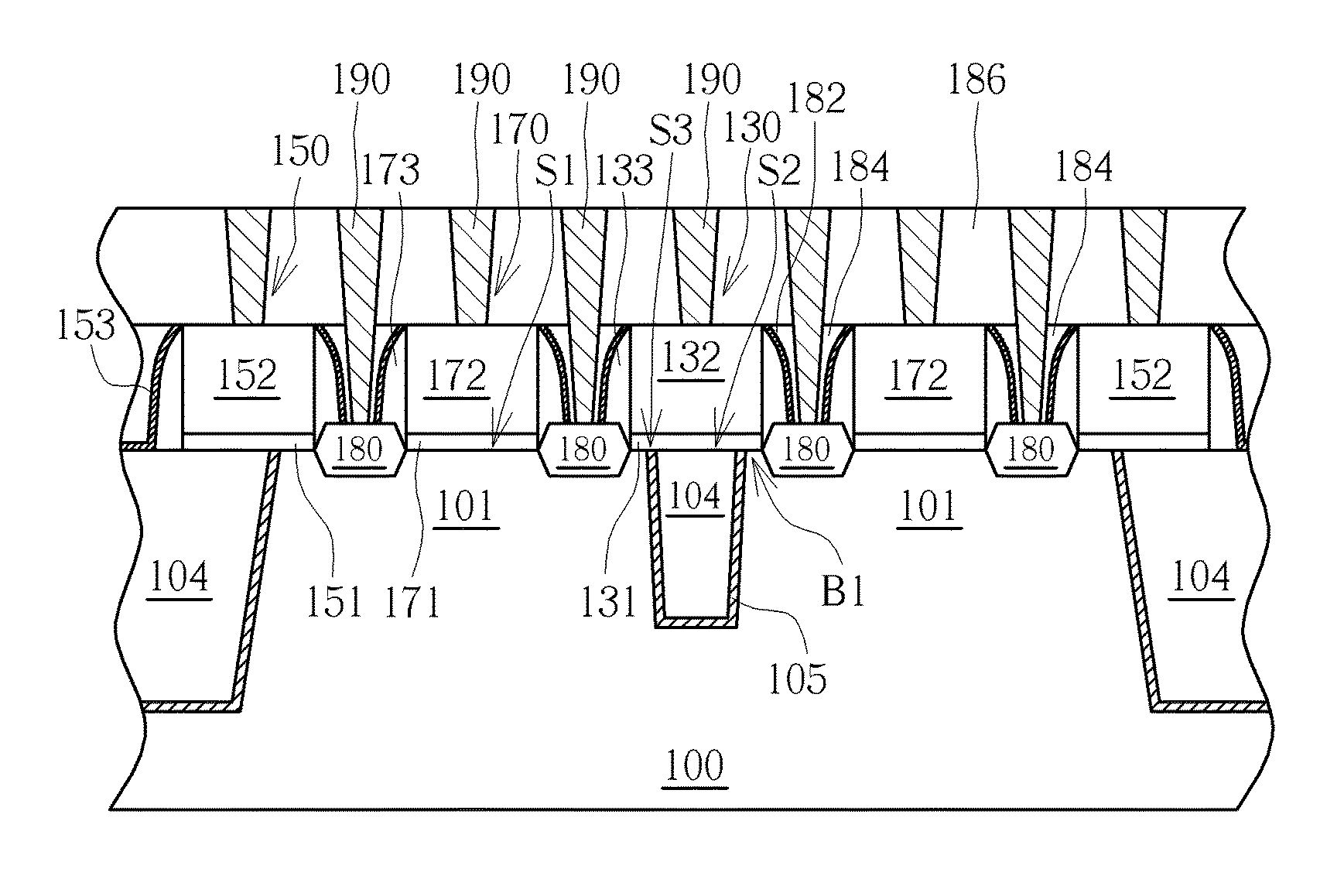
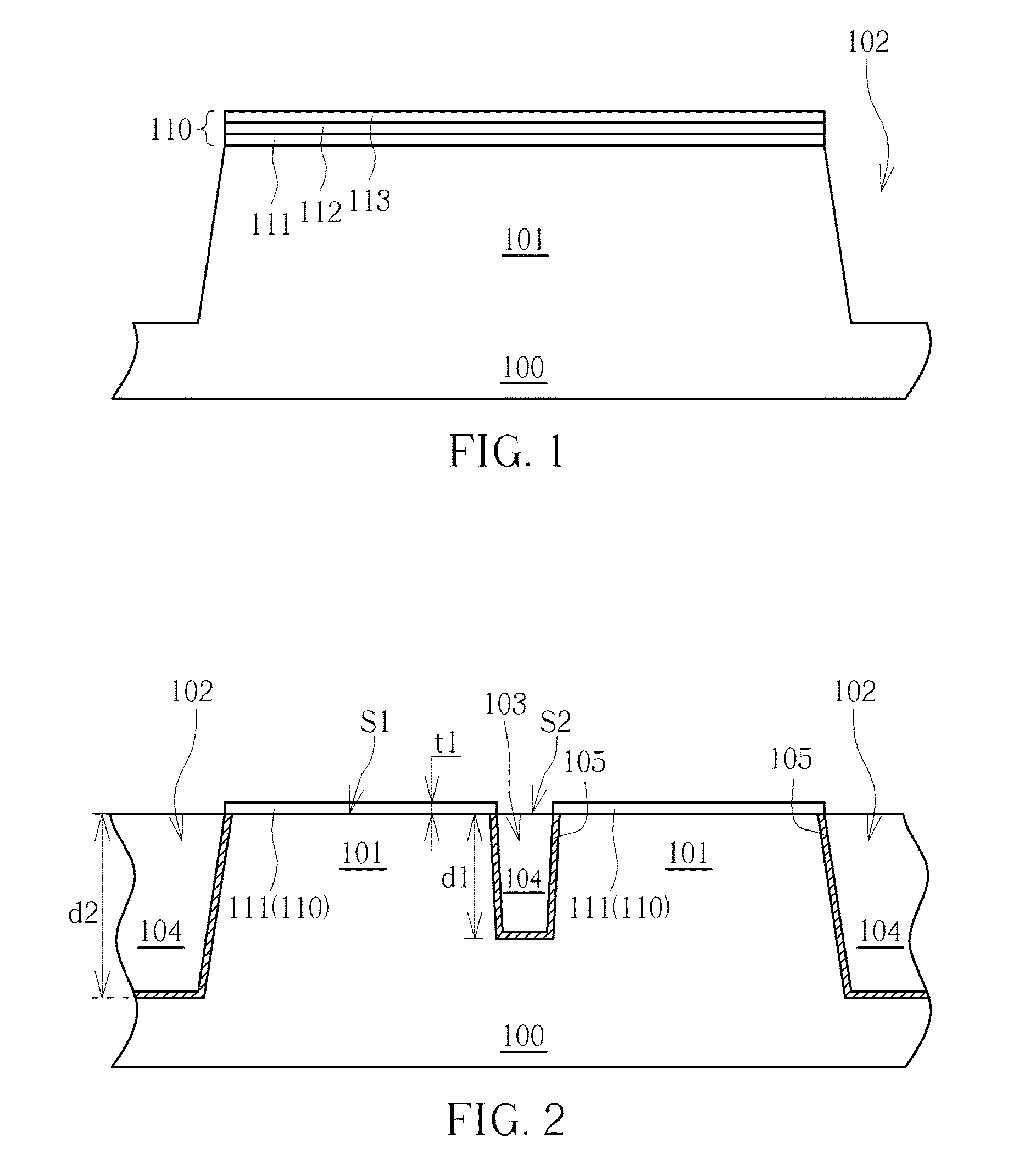
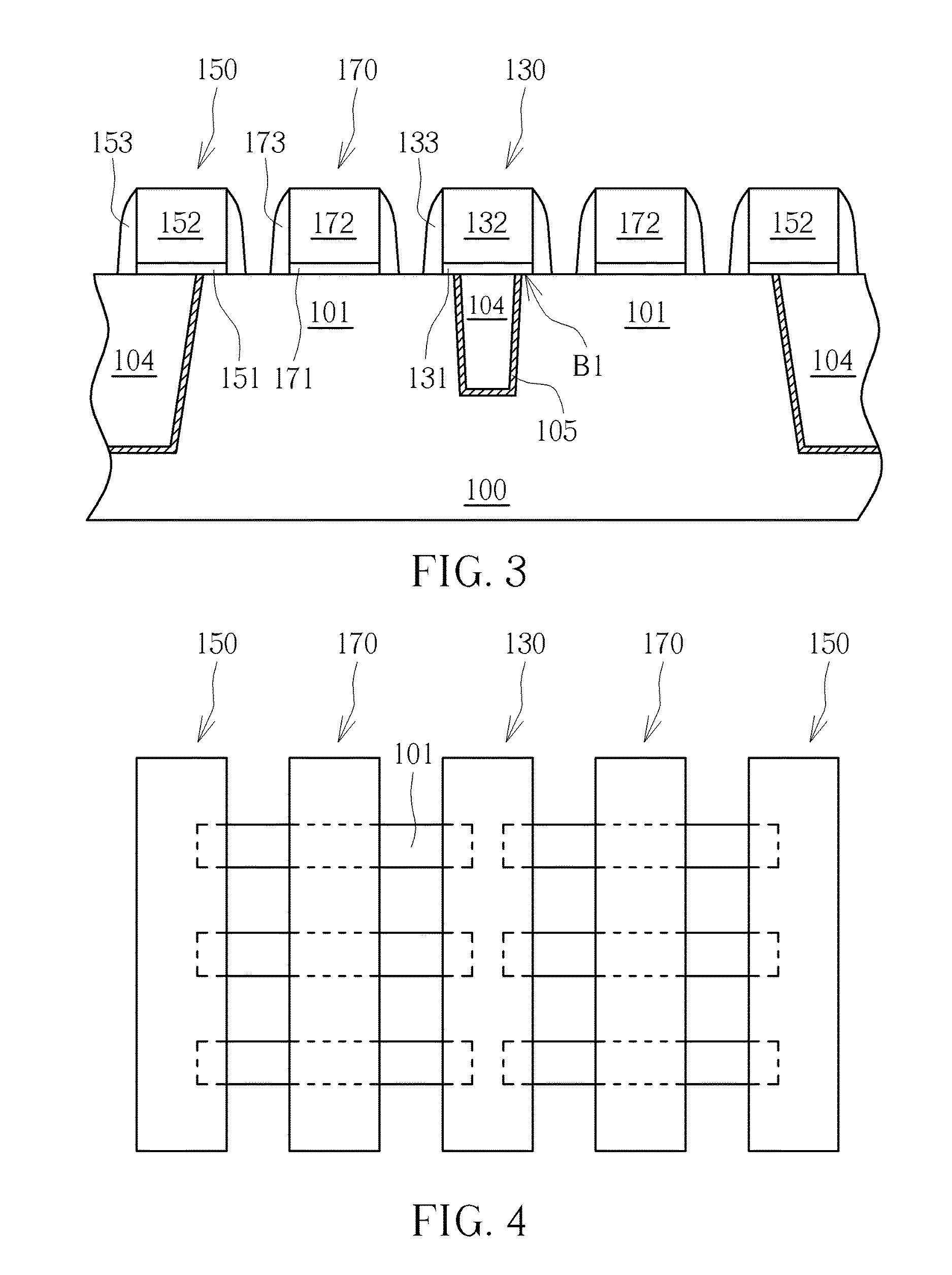
A semiconductor device and a method of fabricating the same, the semiconductor device including a fin structure, a first liner, a first insulating layer and a dummy gate structure. The fin structure is disposed on a substrate, where the fin structure has a trench. The first liner disposed in the trench. The first insulating layer disposed on the first liner. The dummy gate structure is disposed on the first insulating layer and disposed above the trench, where a bottom surface of the dummy gate and a top surface of the fin structure are on a same level.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Device and method for anisotropically plasma etching of a substrate, particularly a silicon body
InactiveUS20050126710A1Increase etch rateImprove the level ofDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic plasmaSilicon
A method and device for implementing the method for anisotropically plasma etching a substrate (e.g., silicon body). The device has a chamber and plasma source for generating a high-frequency electromagnetic alternating field and a reaction region for generating a plasma having reactive species, within the chamber, that is generated by the action of the alternating field on etching gas and passivation gas introduced at the same time but spatially separated from it. An arrangement defines at least one first zone acted on by the etching gas and at least one second zone acted on by the passivation gas in the reaction region. The device has a mixing region downstream of the reaction region in which the reactive species generated from the etching gas in the first zone and the reactive species generated from the passivation gas in the second zone are blended before they act on the substrate.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
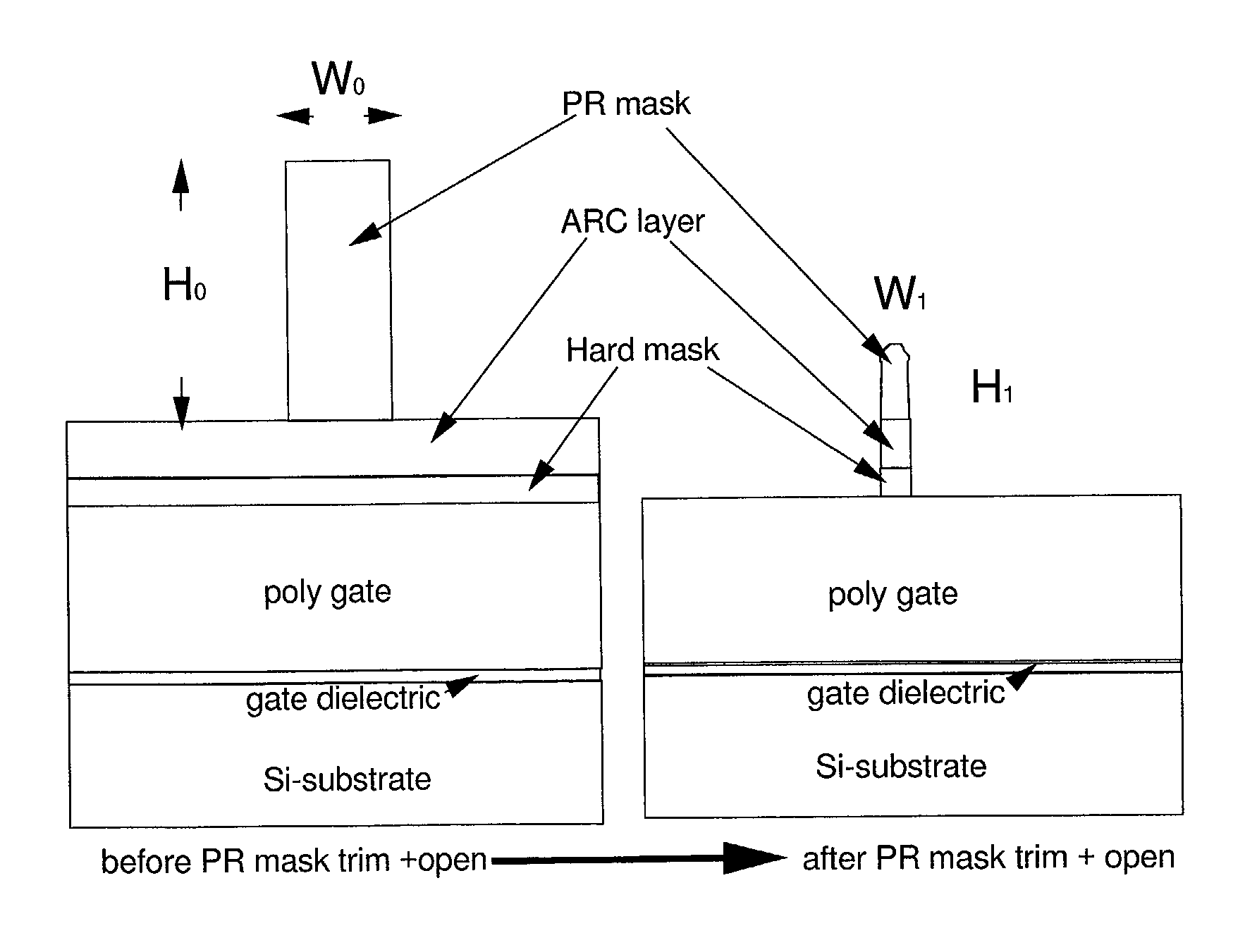
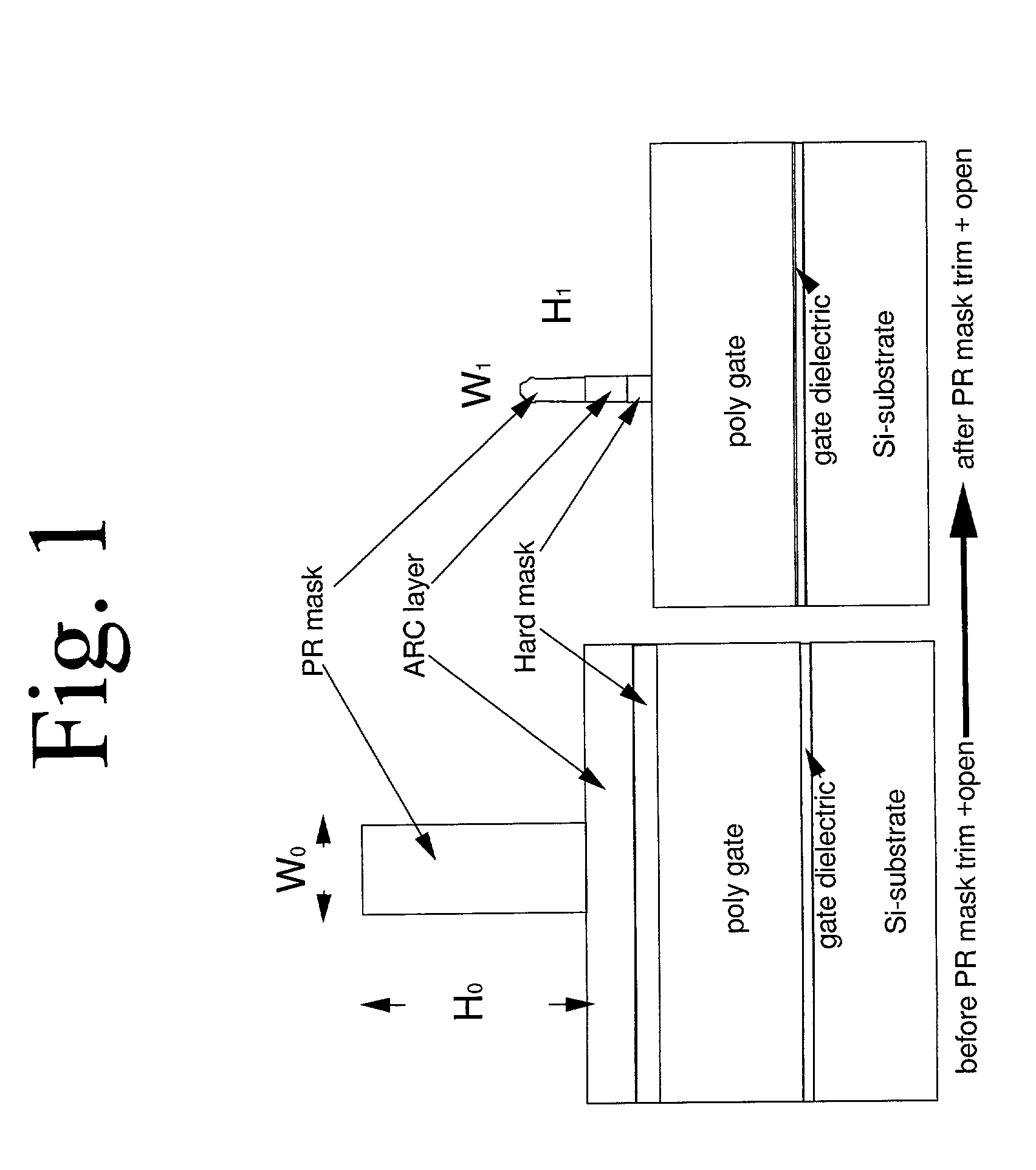
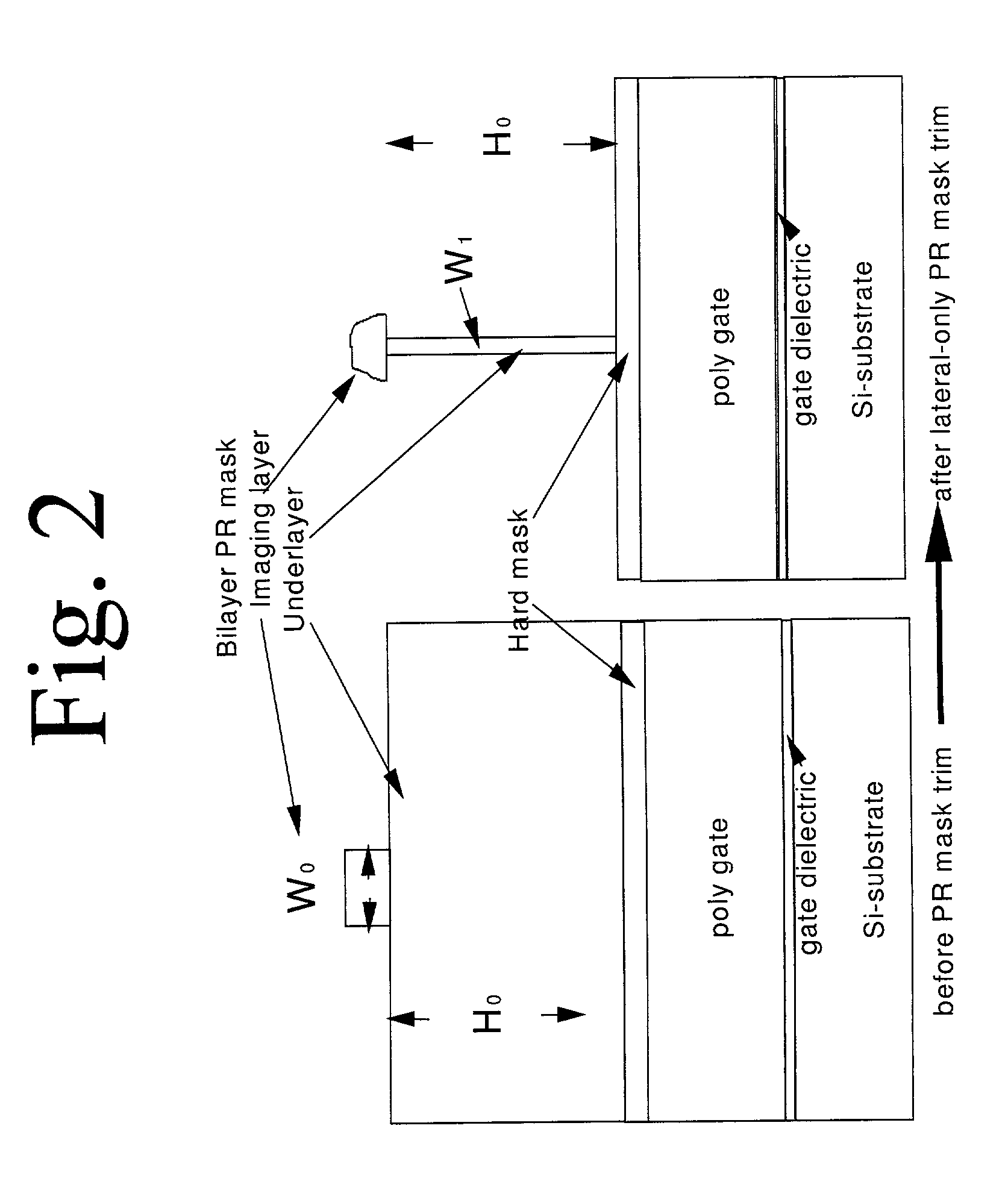
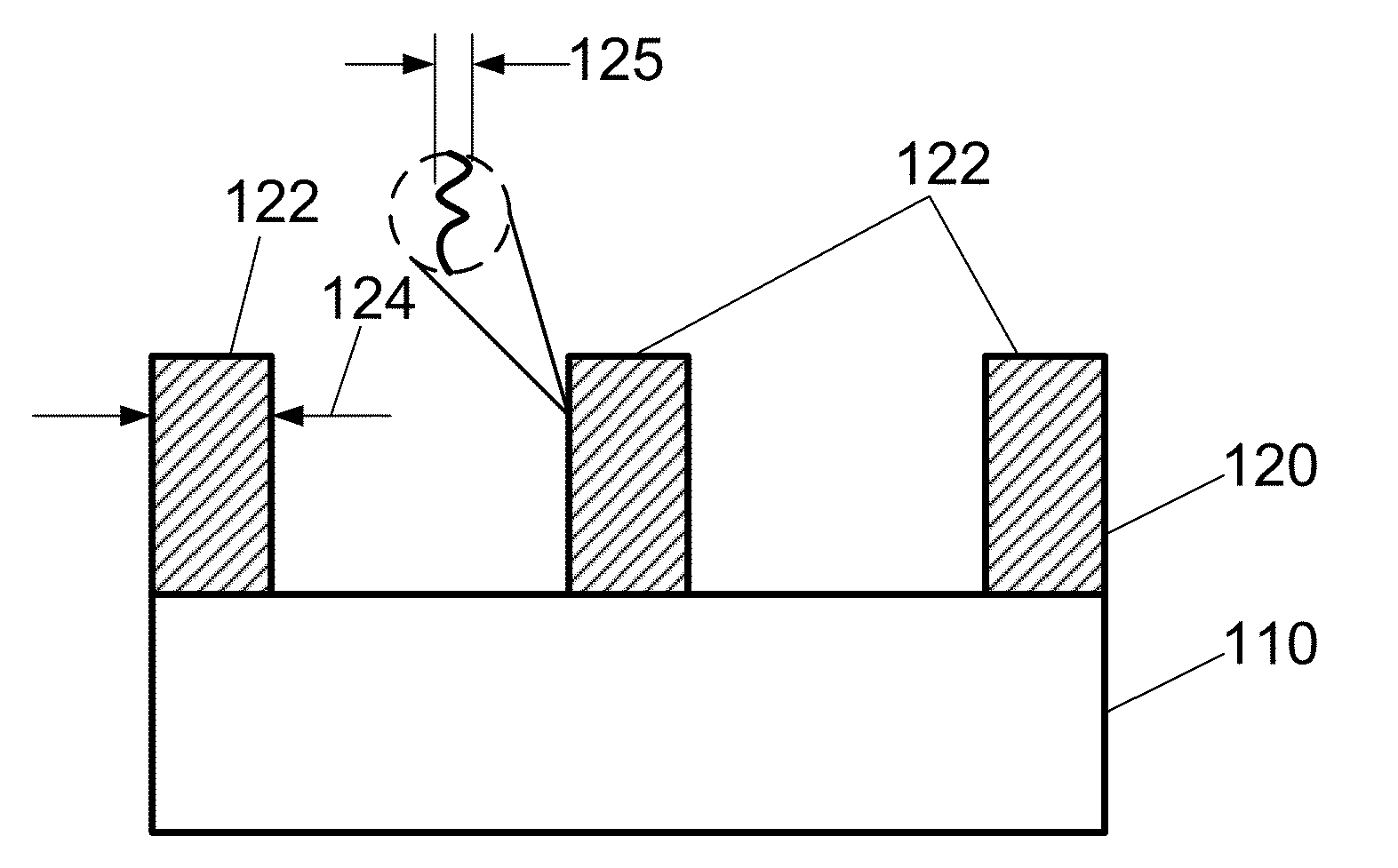
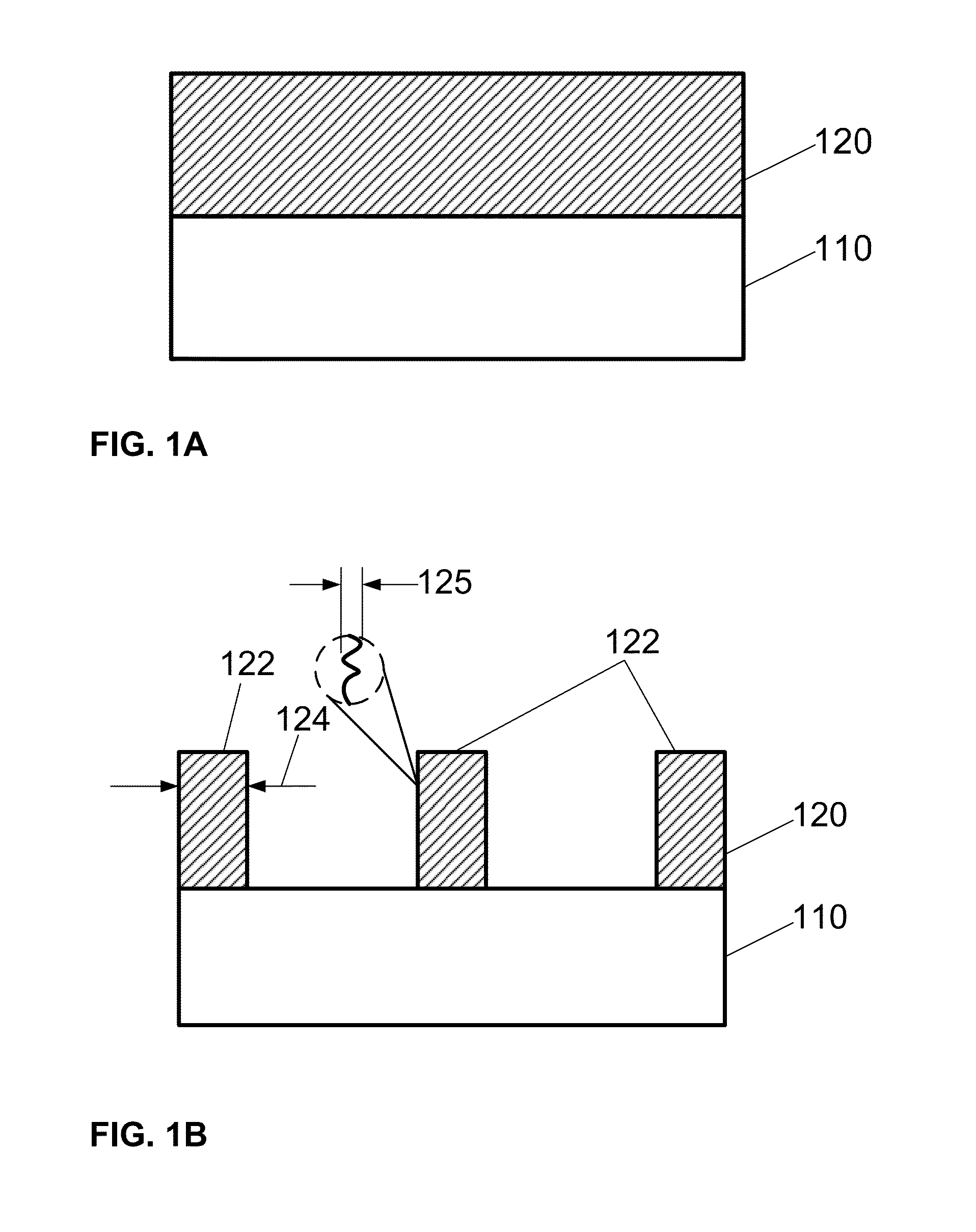
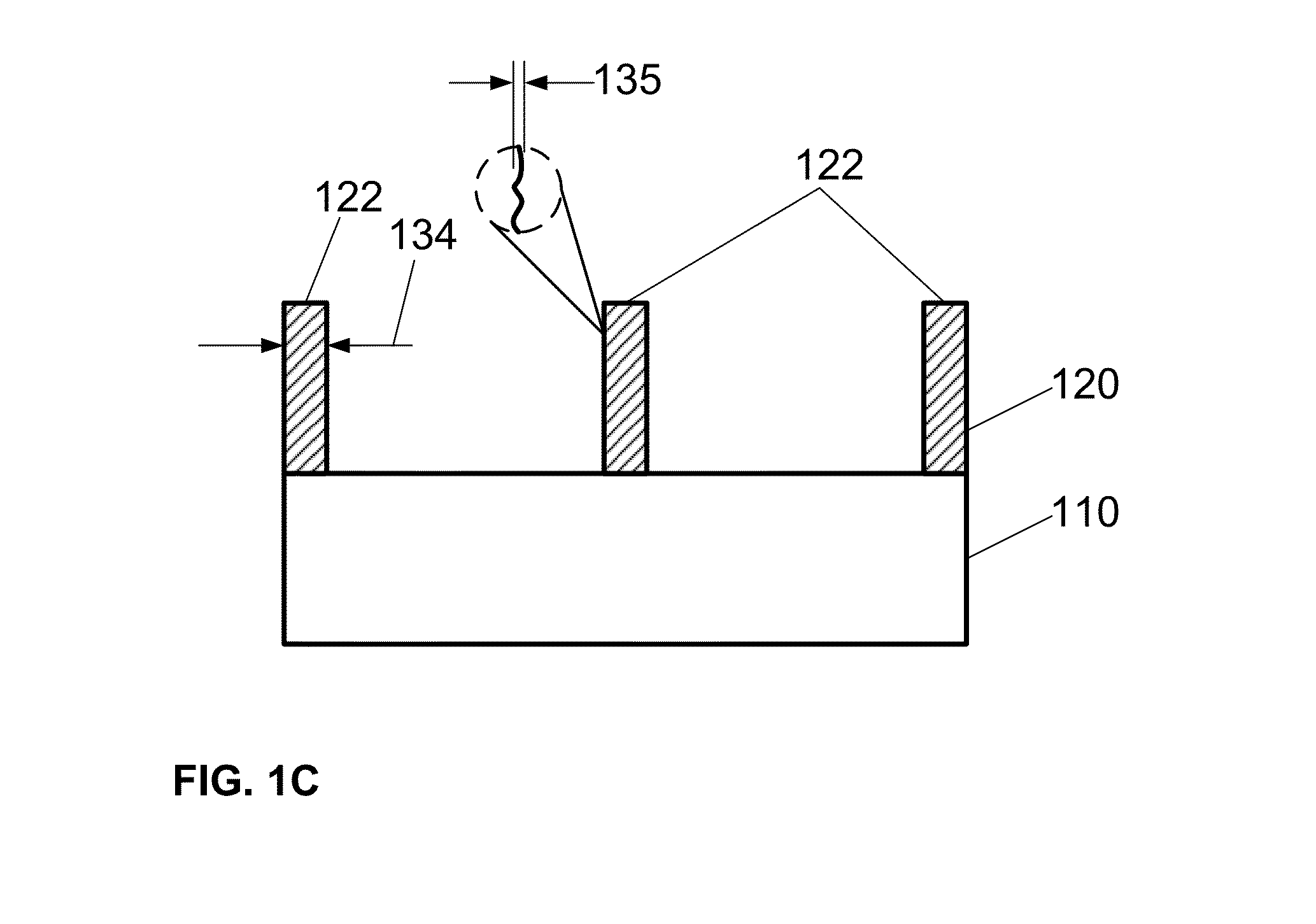
Lateral-only photoresist trimming for sub-80 nm gate stack
InactiveUS20030017711A1Significant retentionCritical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistLithographic artist
The invention relates generally to lithographic patterning of very small features. In particular, the invention relates generally to patterning of semiconductor circuit features smaller than lithographically defined using either conventional optical lithography or next generation lithography techniques. The invention relates more particularly, but not by way of limitation, to lateral trimming of photoresist images.
Owner:IBM CORP
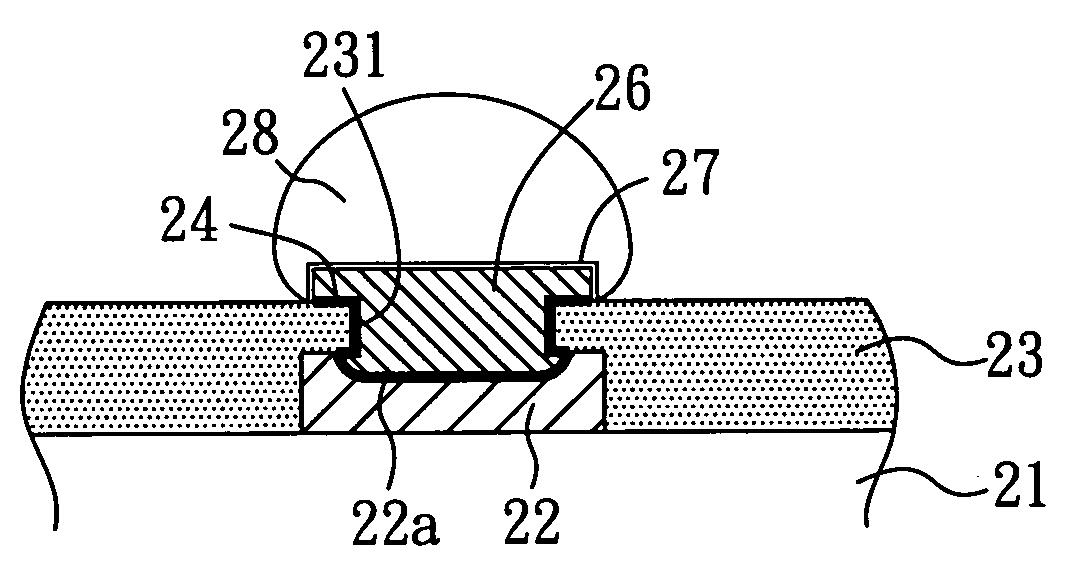
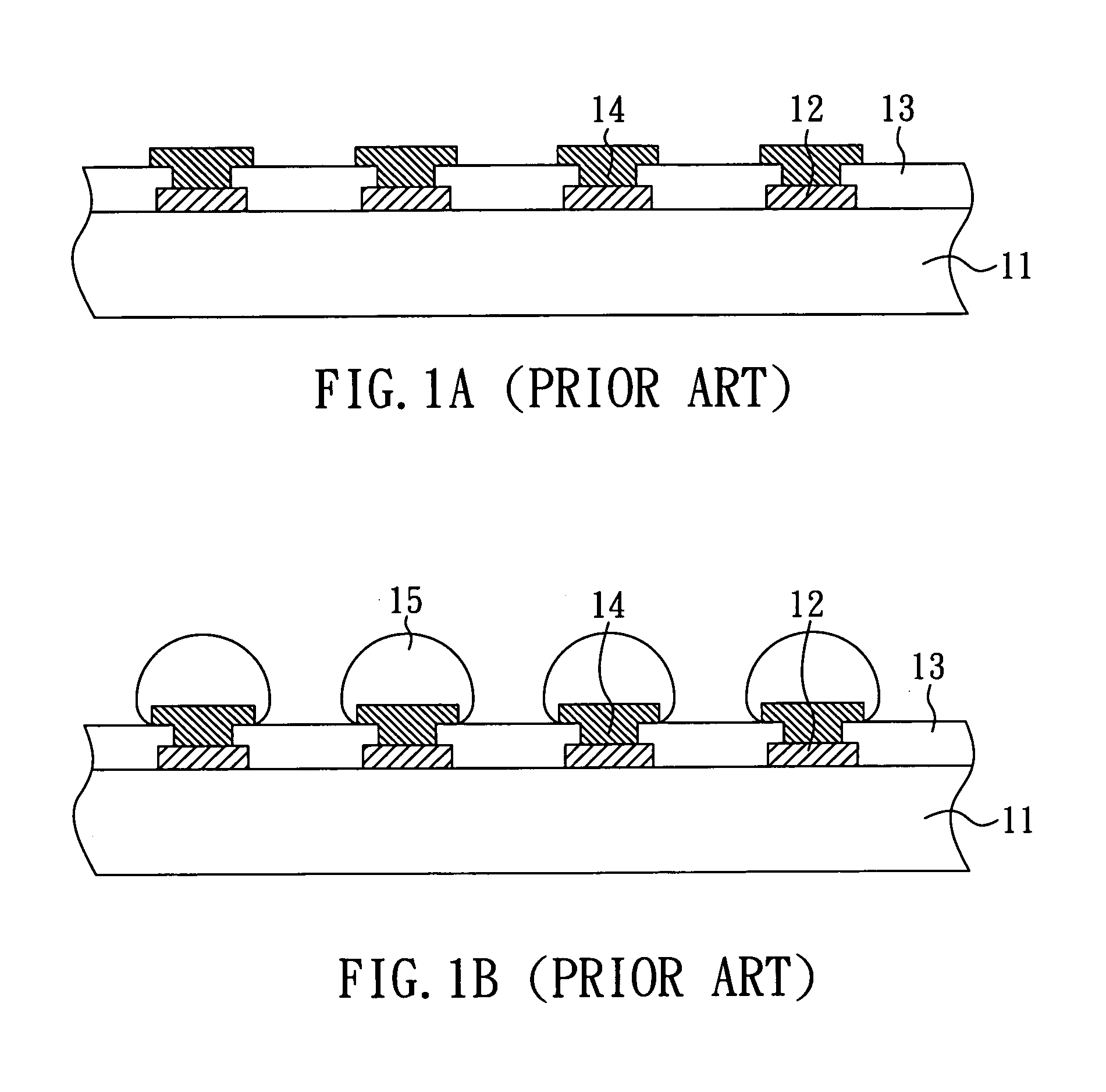
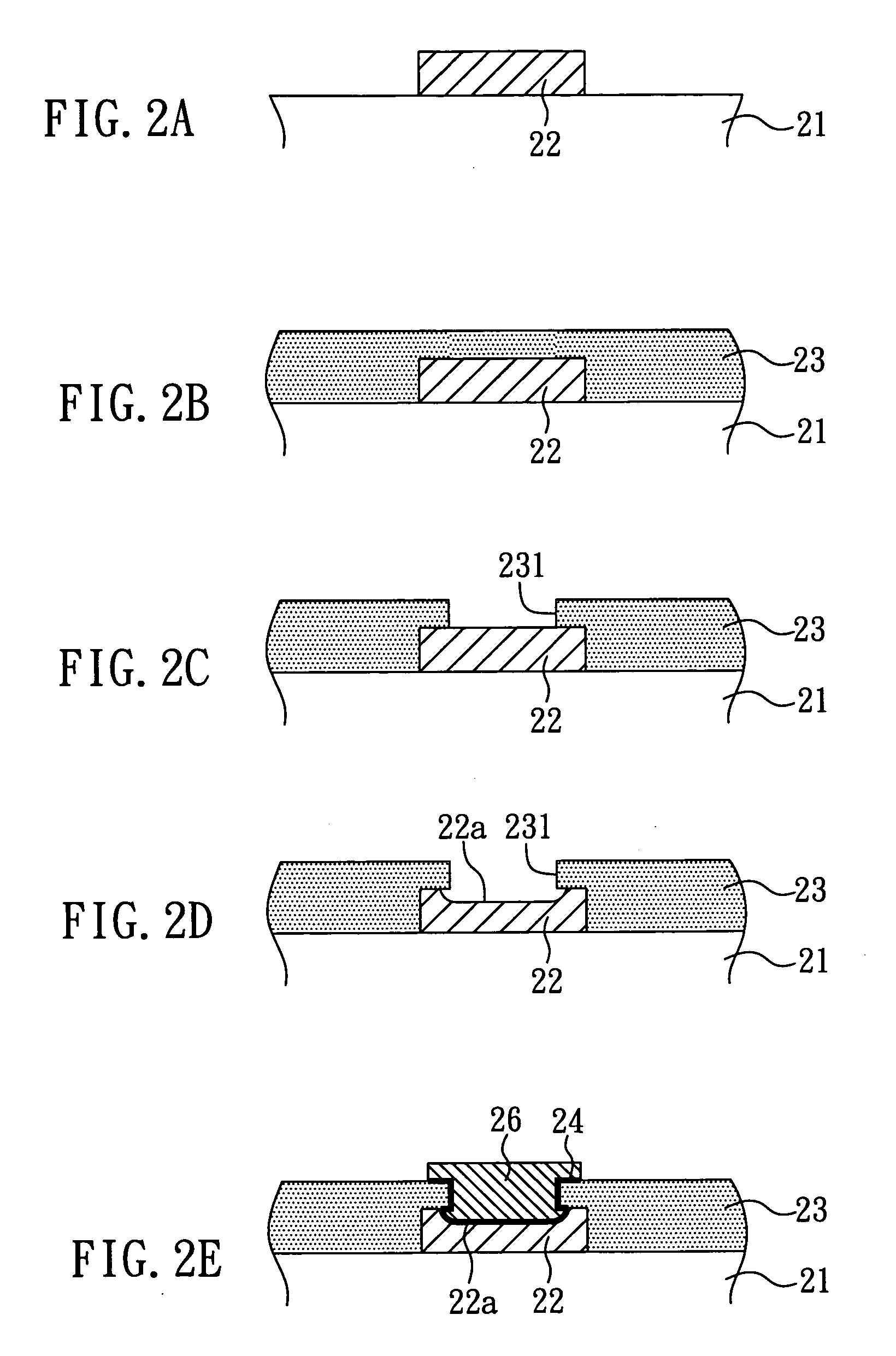
Packaging substrate and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080257595A1Increase joint surface areaAvoid joint crackingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsSolder maskEngineering
The present invention relates to a packaging substrate and a method for manufacturing the same. The packaging substrate includes: a substrate body, having a plurality of conductive pads on the surface thereof, wherein the top surfaces of the conductive pads have a concave each; a solder mask, disposed on the surface of the substrate body and having a plurality of openings to correspondingly expose the concaves of the conductive pads each; and a plurality of metal bumps, disposed correspondingly in the openings of the solder mask and over the concaves of the conductive pads. The present invention increases the joint surface area between the metal bumps and the conductive pads so as to inhibit the joint crack and improve the reliability of the conductive structure of the packaging substrate.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
Methods for raising pre-adult anadromous fish
InactiveUS6463883B1Improves the osmoregulatory capabilitiesReductions in the "critical siClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceFishery
The invention relates to methods, compositions and kits for improving the raising of pre-adult anadromous fish, or preparing pre-adult anadromous fish for transfer to seawater. The methods involve adding at least one Polyvalent Cation Sensing Receptor (PVCR) modulator to the freshwater in an amount sufficient to increase expression and / or sensitivity of at least one PVCR; and adding feed for fish consumption to the freshwater, wherein the feed comprises an amount of NaCl sufficient to contribute to a significantly increased level of the PVCR modulator in serum of the pre-adult anadromous fish.
Owner:MARICAL
Lateral-only photoresist trimming for sub-80 nm gate stack
InactiveUS6869899B2Significant retentionCritical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLithographic artistNext-generation lithography
The invention relates generally to lithographic patterning of very small features. In particular, the invention relates generally to patterning of semiconductor circuit features smaller than lithographically defined using either conventional optical lithography or next generation lithography techniques. The invention relates more particularly, but not by way of limitation, to lateral trimming of photoresist images.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method of manufacturing flash memory device
InactiveUS7037785B2Critical dimension reductionIncrease surface areaTransistorSolid-state devicesPolycrystalline siliconOxide
Disclosed is a method of manufacturing the flash memory device. The method comprises the steps of sequentially forming a tunnel oxide film, a first polysilicon film and a hard mask film on a semiconductor substrate, etching portions of the hard mask film, the first polysilicon film, the tunnel oxide film and the semiconductor substrate through a patterning process to form a trench within the semiconductor substrate, depositing an oxide film to bury the trench and then polishing the oxide film by means of a chemical mechanical polishing process until the hard mask film is exposed, removing the hard mask film, implementing a cleaning process so that a protrusion of the oxide film is recessed to an extent that the sidewall bottom of the first polysilicon film is not exposed, depositing a second polysilicon film on the results in which the protrusion of the oxide film is recessed and then polishing the second polysilicon film until the protrusion of the oxide film is exposed, forming a dielectric film on the second polysilicon film, and forming a control gate on the dielectric film.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor structure and method for making the same
InactiveUS20120086054A1Deteriorated operational performanceHigh currentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureEngineering
A semiconductor structure is disclosed. The semiconductor structure includes a gate structure disposed on a substrate, a source and a drain respectively disposed in the substrate at two sides of the gate structure, a source contact plug disposed above the source and electrically connected to the source and a drain contact plug disposed above the drain and electrically connected to the drain. The source contact plug and the drain contact plug have relatively asymmetric element properties.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
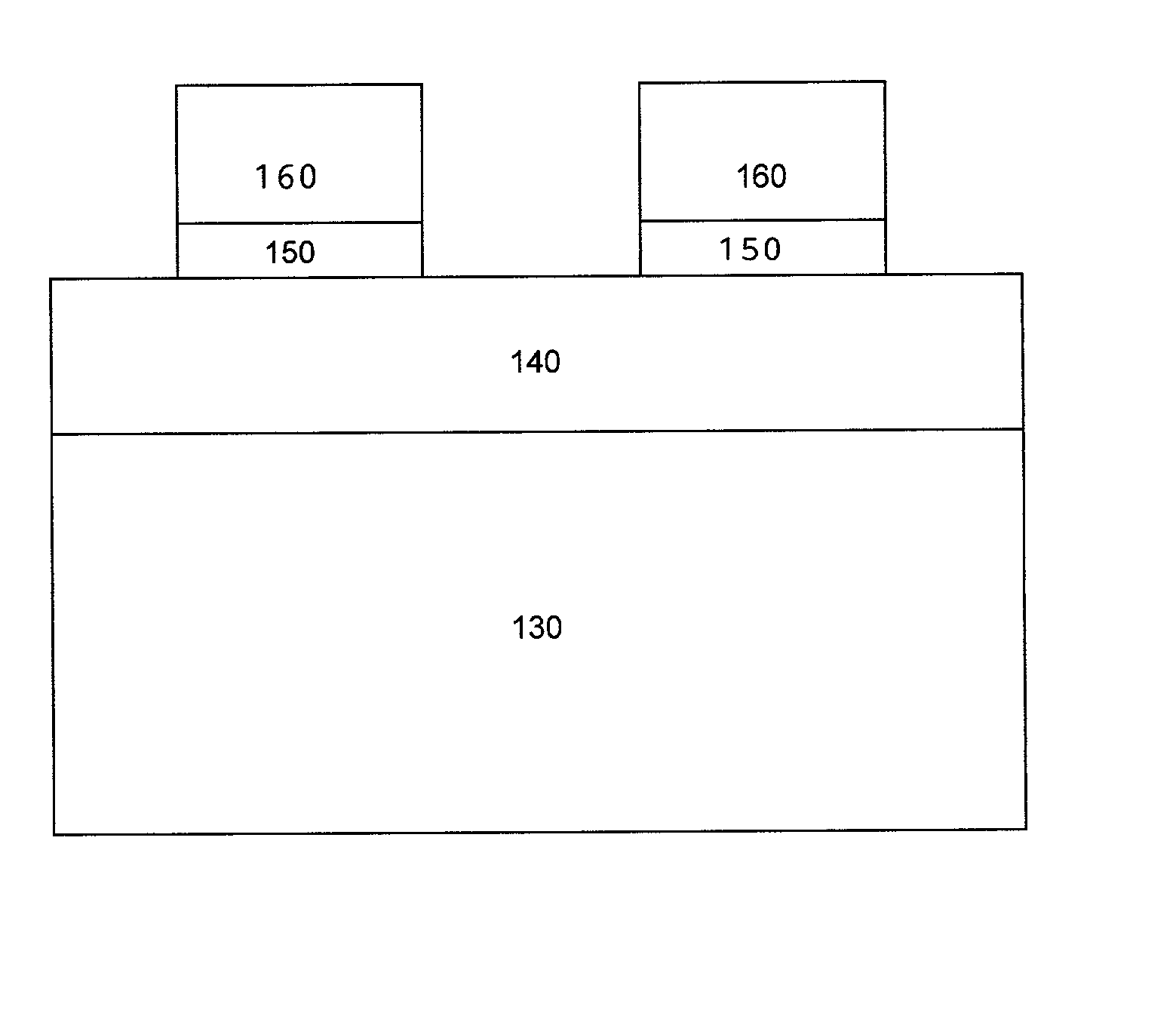
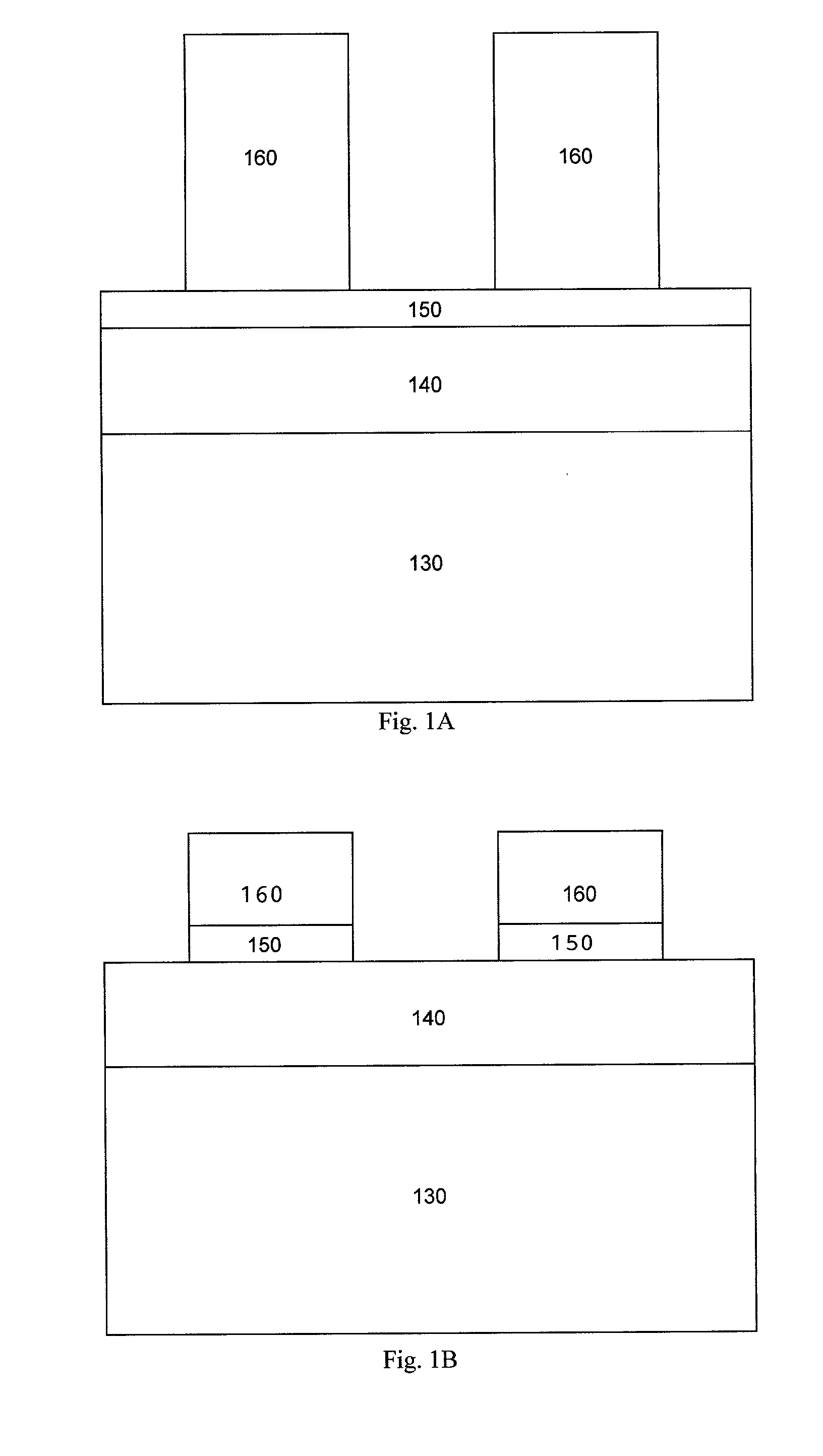
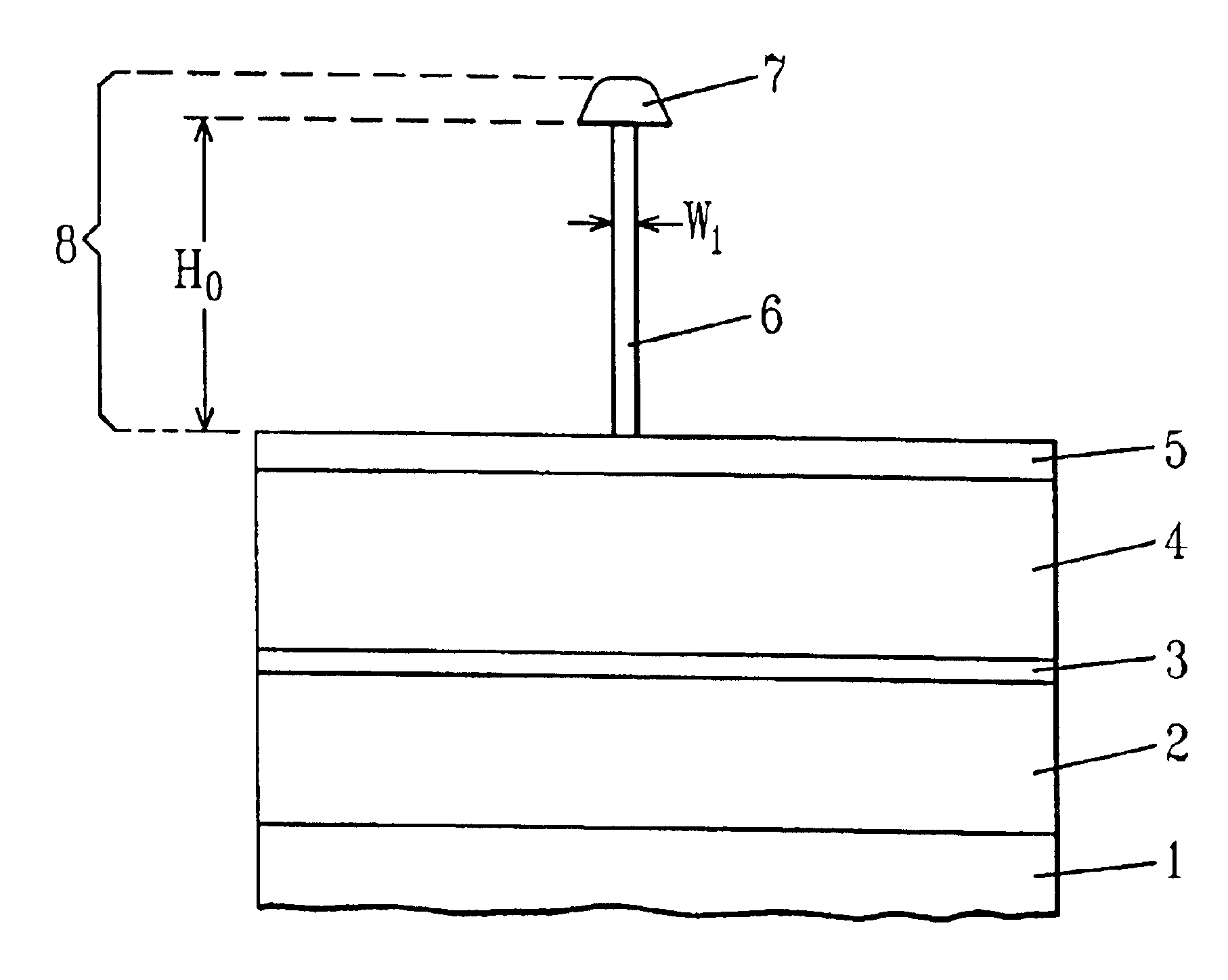
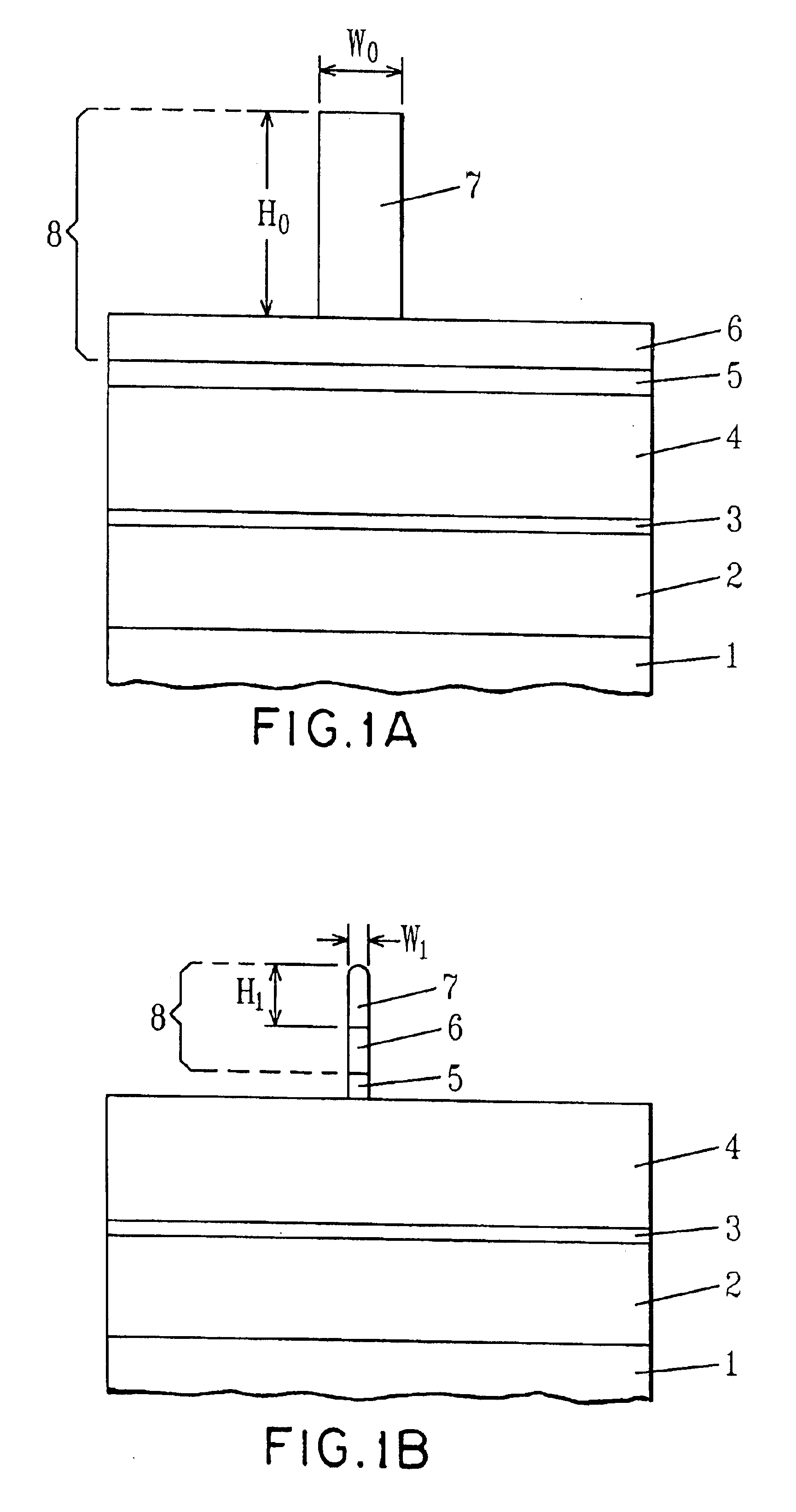
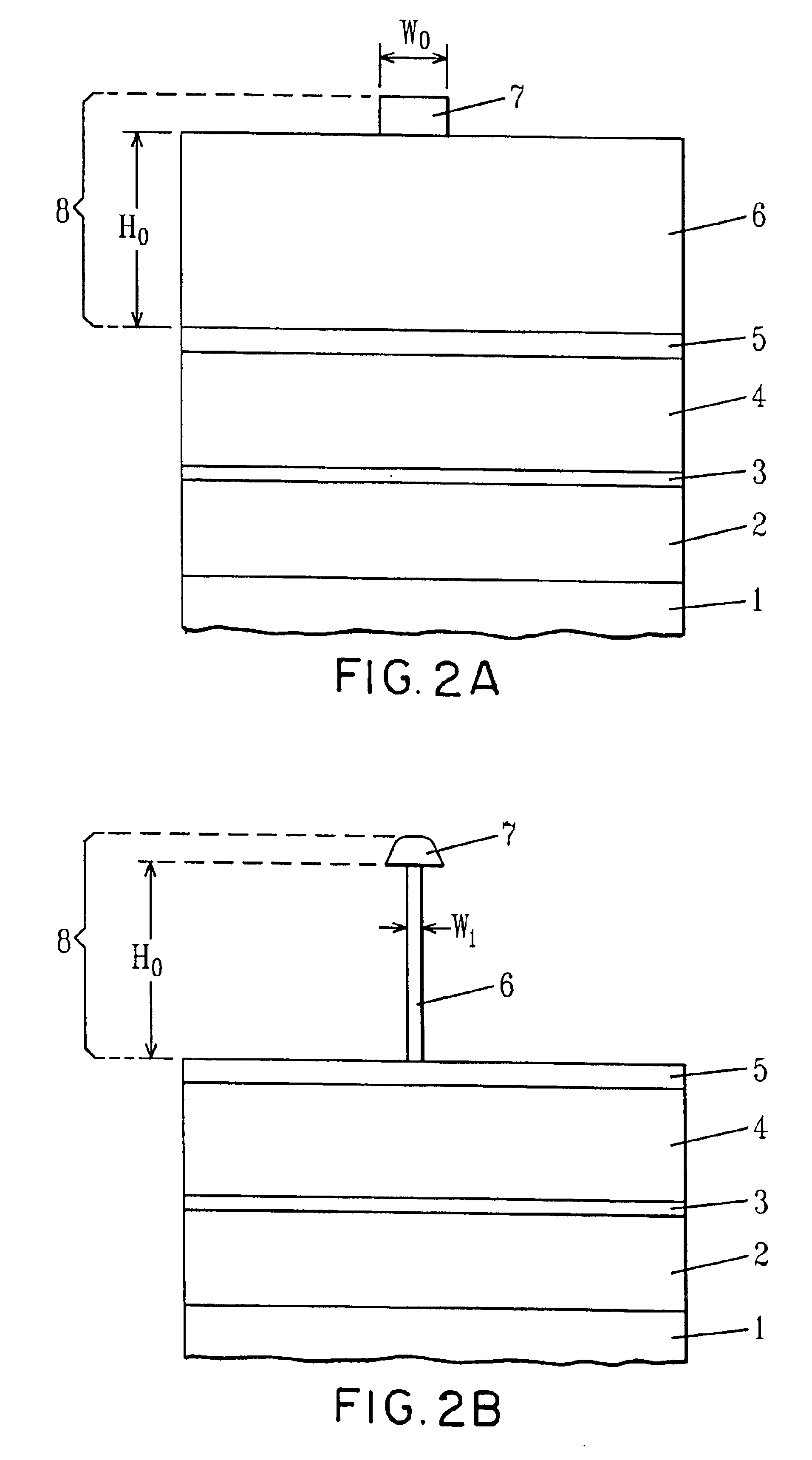
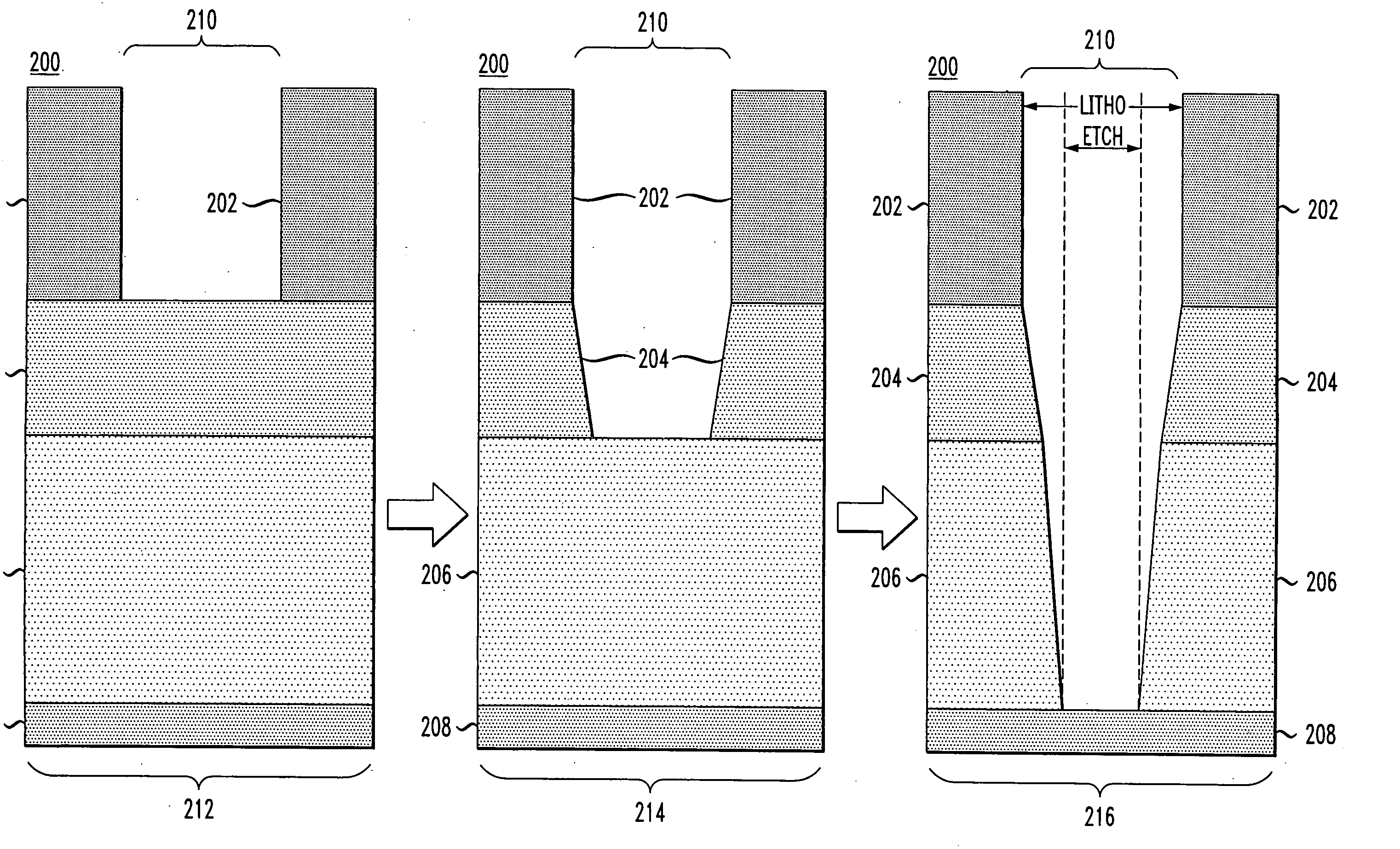
Reticle fabrication using a removable hard mask
InactiveUS20050170655A1Reduced critical dimension biasCritical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistDevice material
We have reduced the critical dimension bias for reticle fabrication. Pattern transfer to the radiation-blocking layer of the reticle substrate essentially depends upon use of a hard mask to which the pattern is transferred from a photoresist. The photoresist pull back which occurs during pattern transfer to the hard mask is minimalized. In addition, a hard mask material having anti-reflective properties which are matched to the reflective characteristics of the radiation-blocking layer enables a reduction in critical dimension size and an improvement in the pattern feature integrity in the hard mask itself. An anti-reflective hard mask layer left on the radiation-blocking layer provides functionality when the reticle is used in a semiconductor device manufacturing process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Vapor treatment process for pattern smoothing and inline critical dimension slimming
ActiveUS20130171571A1Reducing roughness of patternCritical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptoelectronicsCritical dimension
A method for patterning a substrate is described. The method includes forming a layer of radiation-sensitive material on a substrate, and preparing a pattern in the layer of radiation-sensitive material using a lithographic process, wherein the pattern is characterized by a critical dimension (CD) and a roughness. Following the preparation of the pattern in the layer of radiation-sensitive material, the method further includes performing a CD slimming process to reduce the CD to a reduced CD, and performing a vapor smoothing process to reduce the roughness to a reduced roughness.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Device and method for anisotropic plasma etching of a substrate, a silicon body in particular
InactiveUS7285228B2Increase etch rateImprove the level ofDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic plasmaReaction zone
A method and device for implementing the method for anisotropically plasma etching a substrate (e.g., silicon body). The device has a chamber and plasma source for generating a high-frequency electromagnetic alternating field and a reaction region for generating a plasma having reactive species, within the chamber, that is generated by the action of the alternating field on etching gas and passivation gas introduced at the same time but spatially separated from it. An arrangement defines at least one first zone acted on by the etching gas and at least one second zone acted on by the passivation gas in the reaction region. The device has a mixing region downstream of the reaction region in which the reactive species generated from the etching gas in the first zone and the reactive species generated from the passivation gas in the second zone are blended before they act on the substrate.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
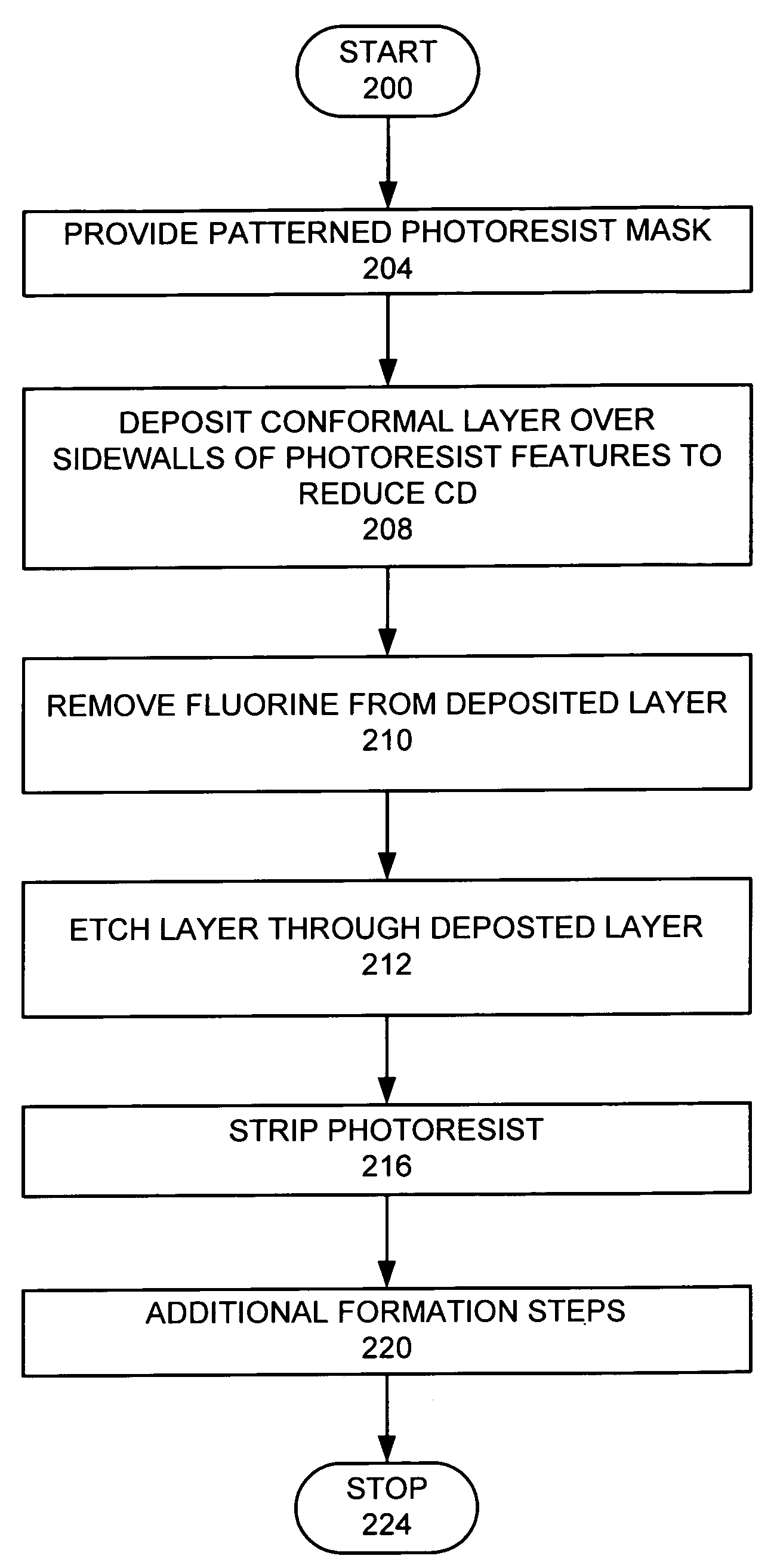
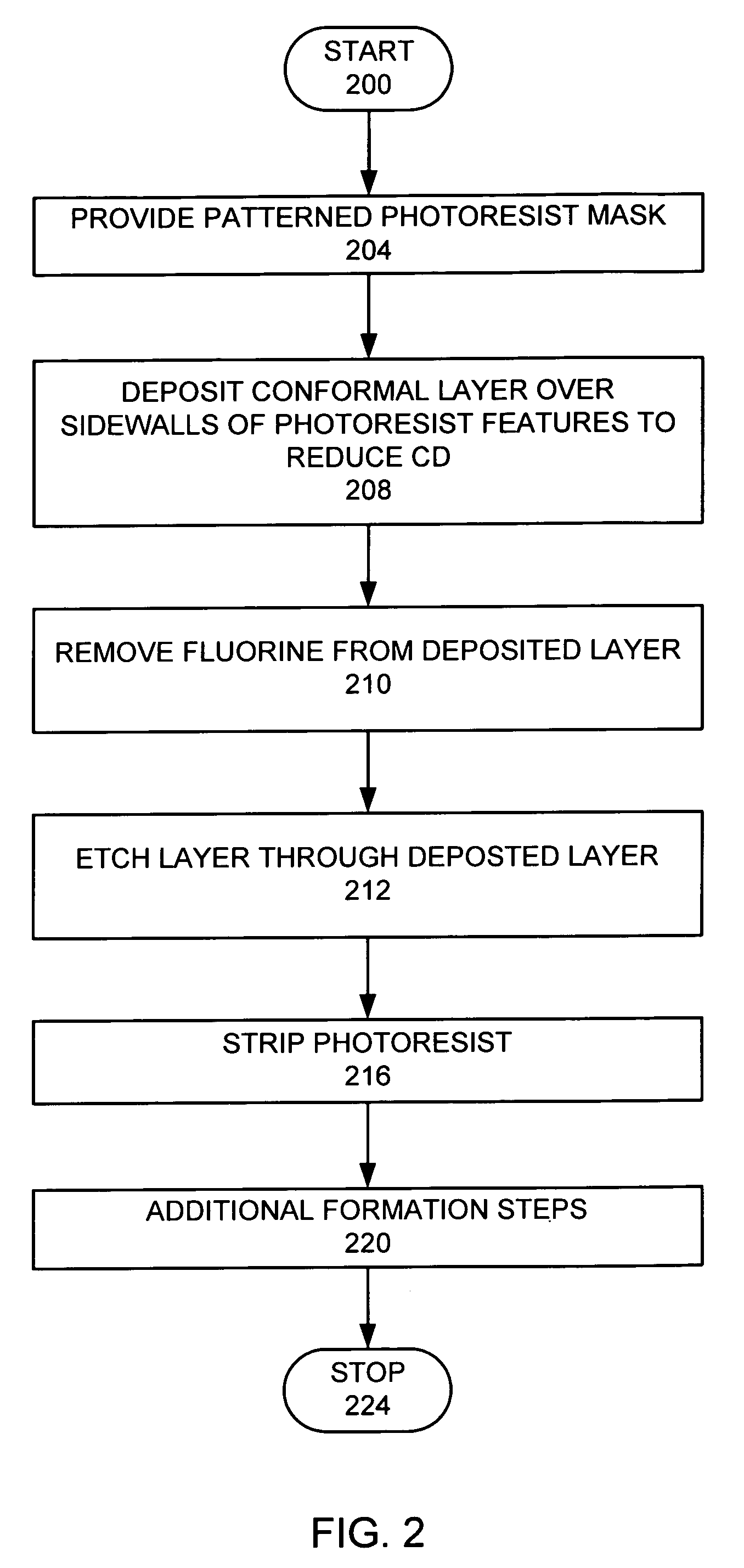
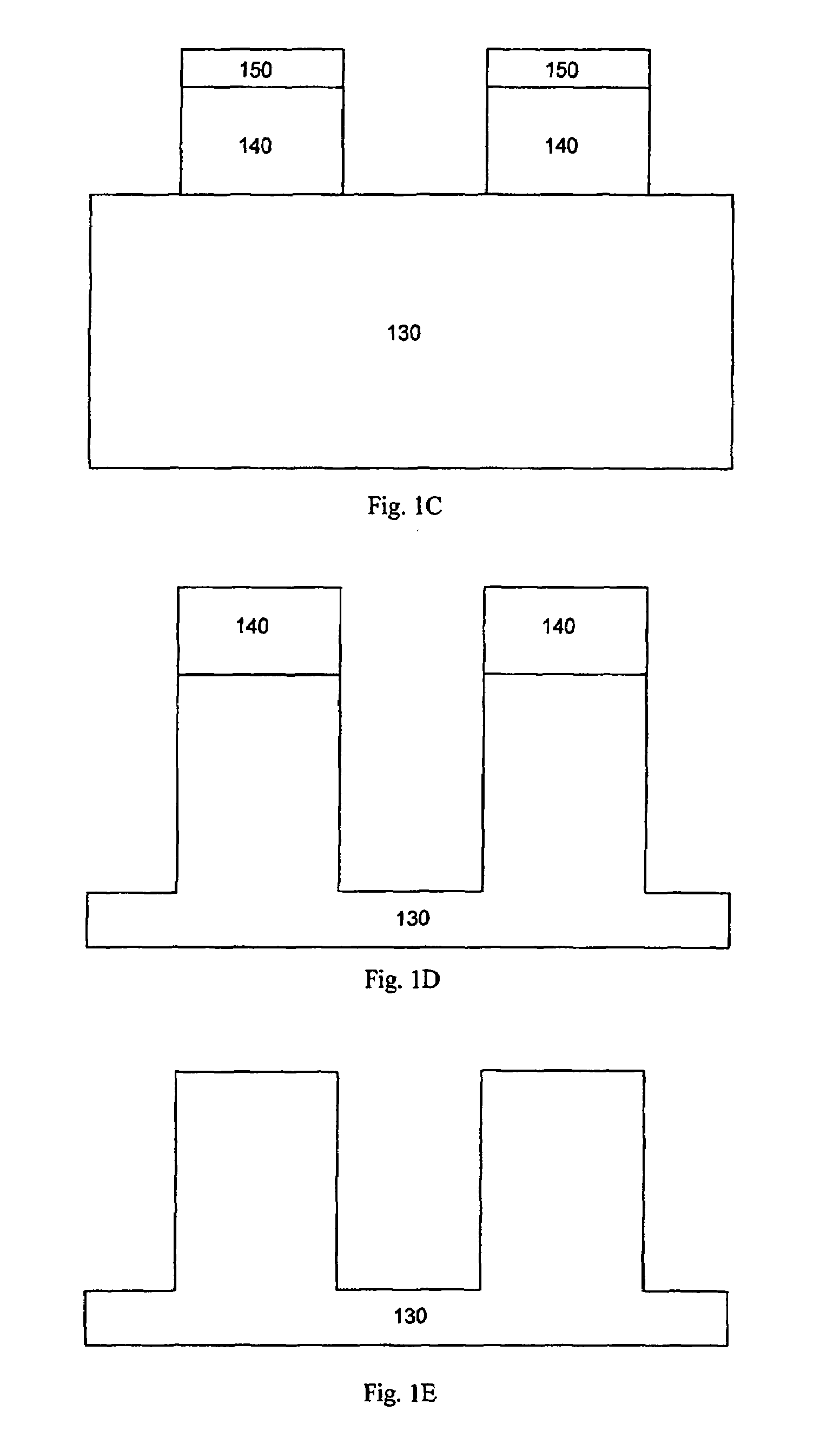
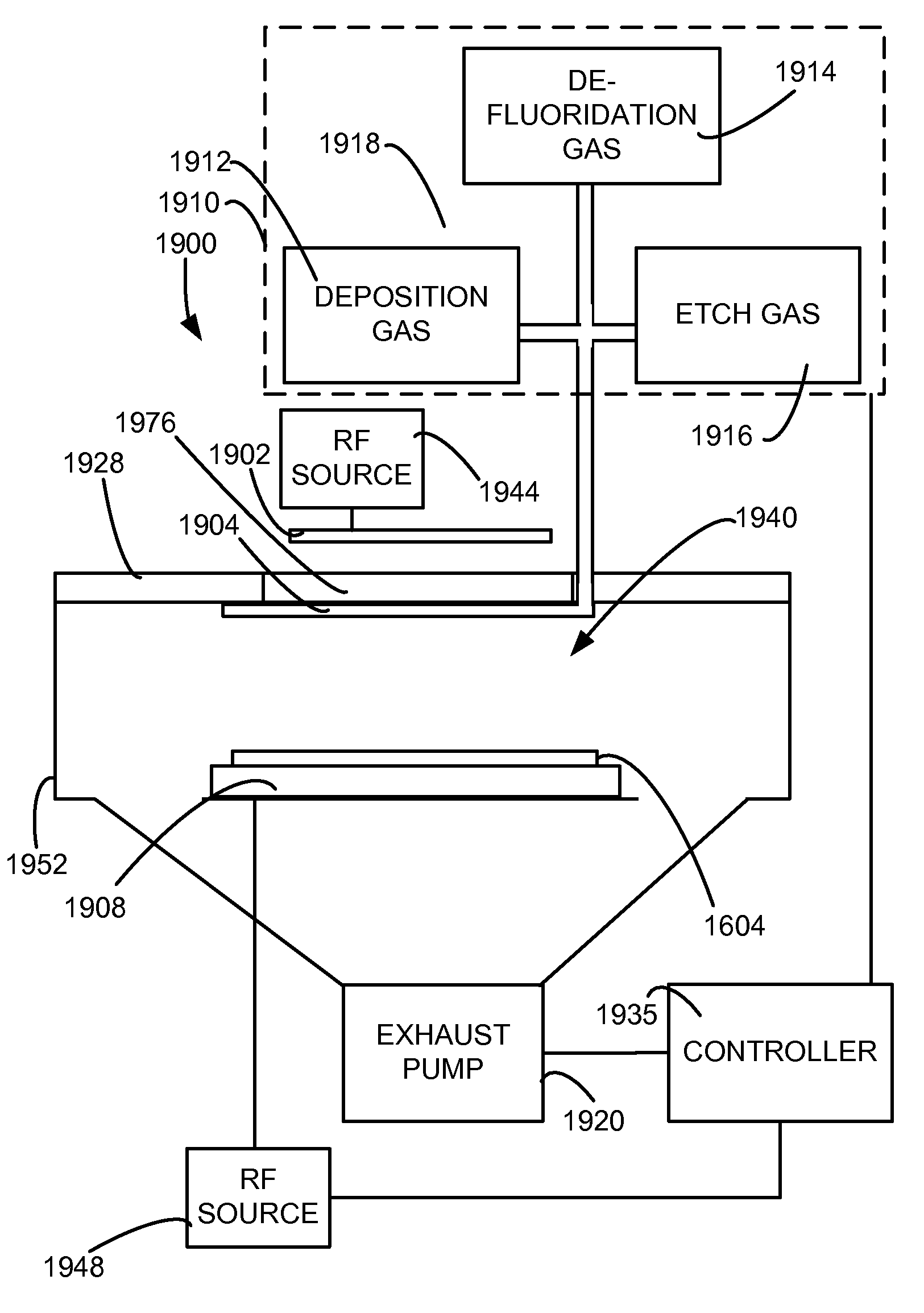
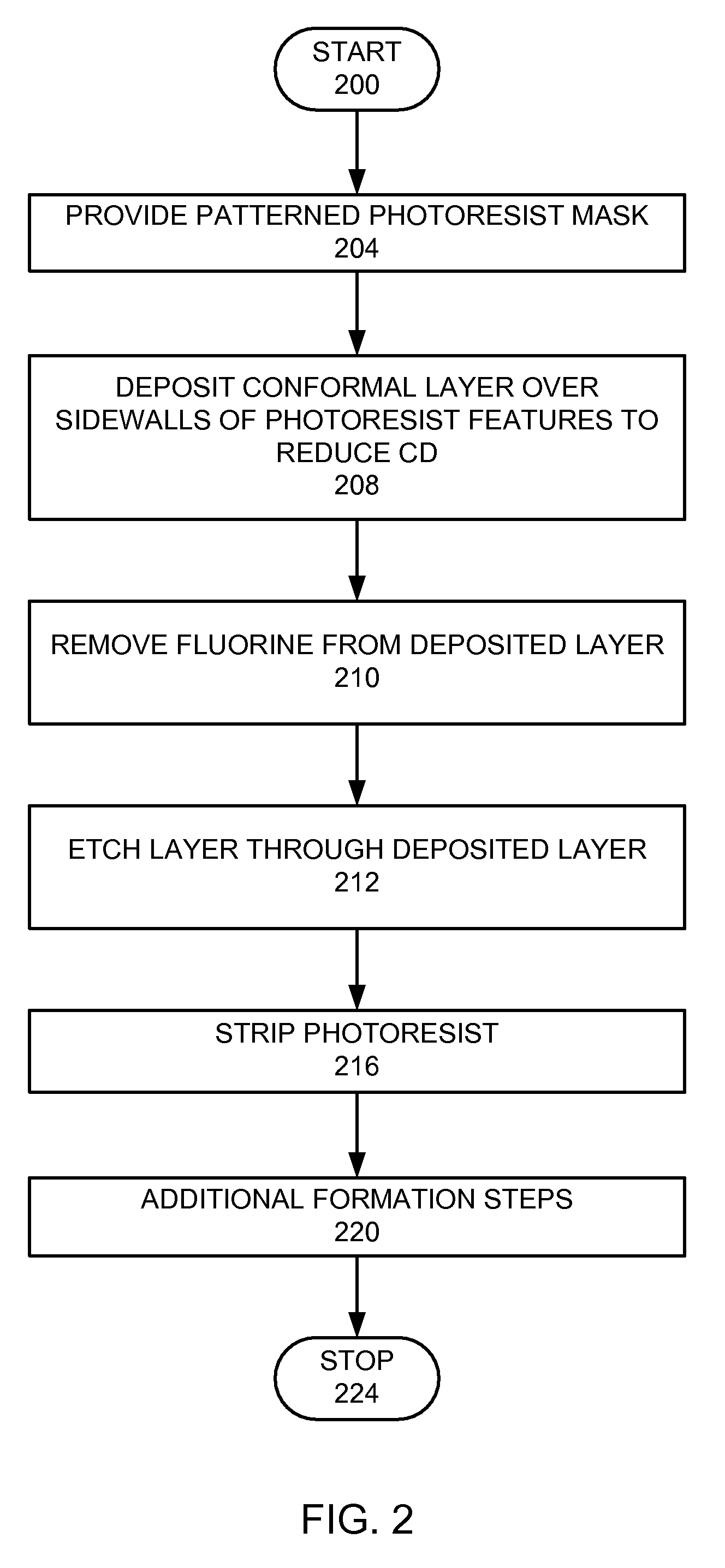
De-fluoridation process
ActiveUS7309646B1Critical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistCritical dimension
A feature in a layer is provided. A photoresist layer is formed over the layer. The photoresist layer is patterned to form photoresist features with photoresist sidewalls, where the photoresist features have a first critical dimension. A fluorine-containing conformal layer is deposited over the sidewalls of the photoresist features to reduce the critical dimensions of the photoresist features. Fluorine is removed from the conformal layer, while the remaining conformal layer is left in place. Features are etched into the layer, wherein the layer features have a second critical dimension, which is less than the first critical dimension.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Techniques for patterning features in semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20050056823A1Critical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanotechnologyCritical dimensionComputer science
Techniques for semiconductor processing are provided. In one aspect, a method for patterning one or more features in a semiconductor device comprises the following step. At least one critical dimension of the one or more features is reduced during etching of the antireflective material. A lithographic structure is also provided.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method and system for topography-aware reticle enhancement
InactiveUS7814456B2Critical dimension reductionIncrease parametric yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesTopographyReticle
The present invention provides a method and system for improving reticle enhancement calculations during manufacture of an integrated circuit (IC). The reticle enhancement calculations are improved by incorporating post-planarization topography estimates. A planarization process of a wafer layer is simulated to estimate the post-planarization topography. RET calculations, such as sub-resolution assist feature insertion, optical proximity corrections and phase shifting are then performed based on the post-planarization topography of the wafer layer.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method for fabricating a mask ROM
ActiveUS20060014348A1Critical dimension be reduceEasily removeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoresistSemiconductor
The present invention discloses a method for fabricating a buried bit line of a mask ROM. The method includes providing a semiconductor substrate with a photoresist layer, and patterning the photoresist layer to form a photoresist pattern. A first ion implantation process is performed to form a first doped region in the semiconductor substrate not covered by the photoresist pattern. Then, an organic layer is coated on the photoresist pattern and the semiconductor substrate and an etching process is performed to form an organic spacer at two sides of the photoresist pattern. Finally, a second ion implantation process forms a second doped region in the semiconductor substrate not covered by the photoresist pattern and the organic spacer. Finally, the photoresist pattern and the organic spacer are removed.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
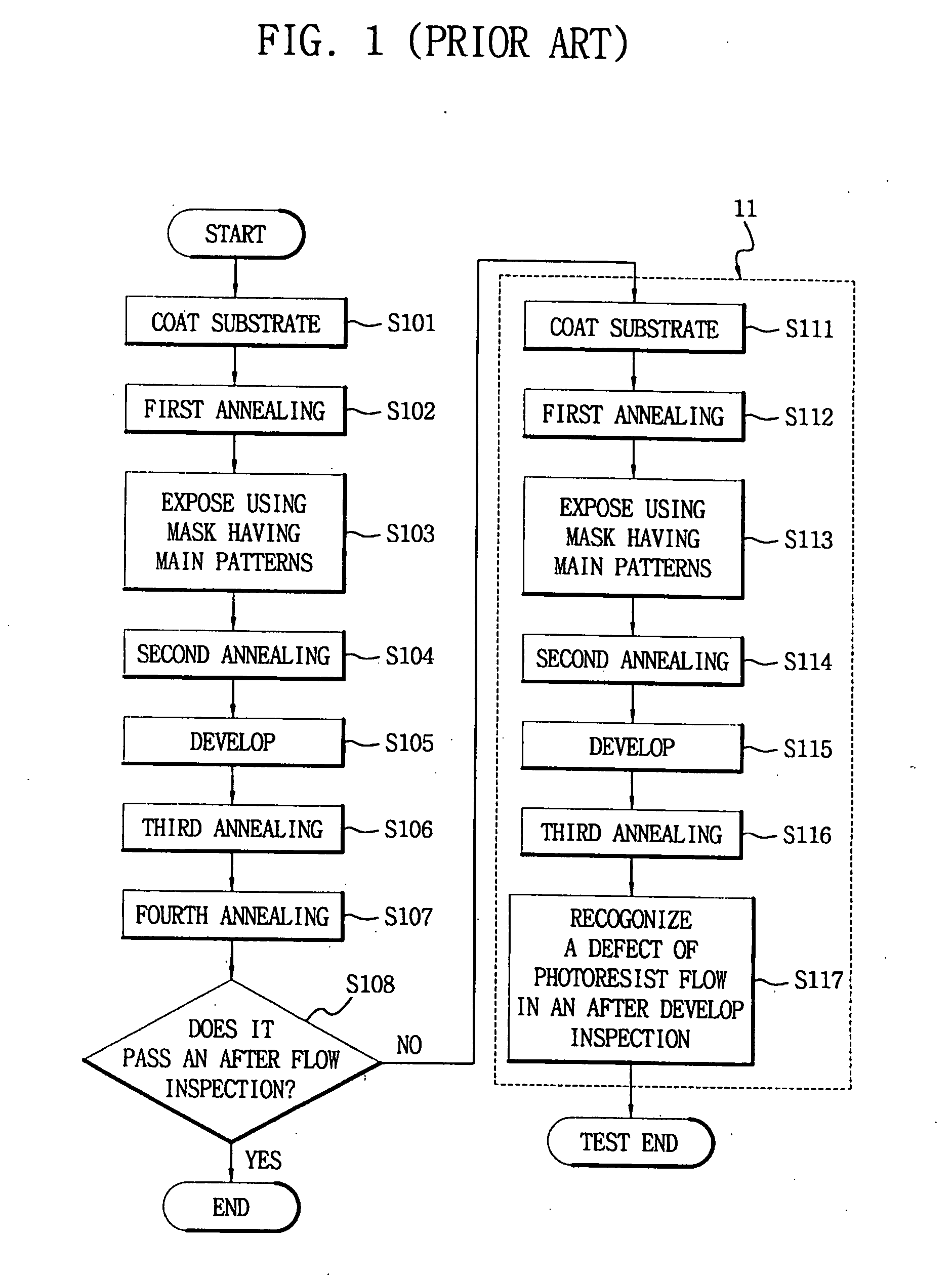
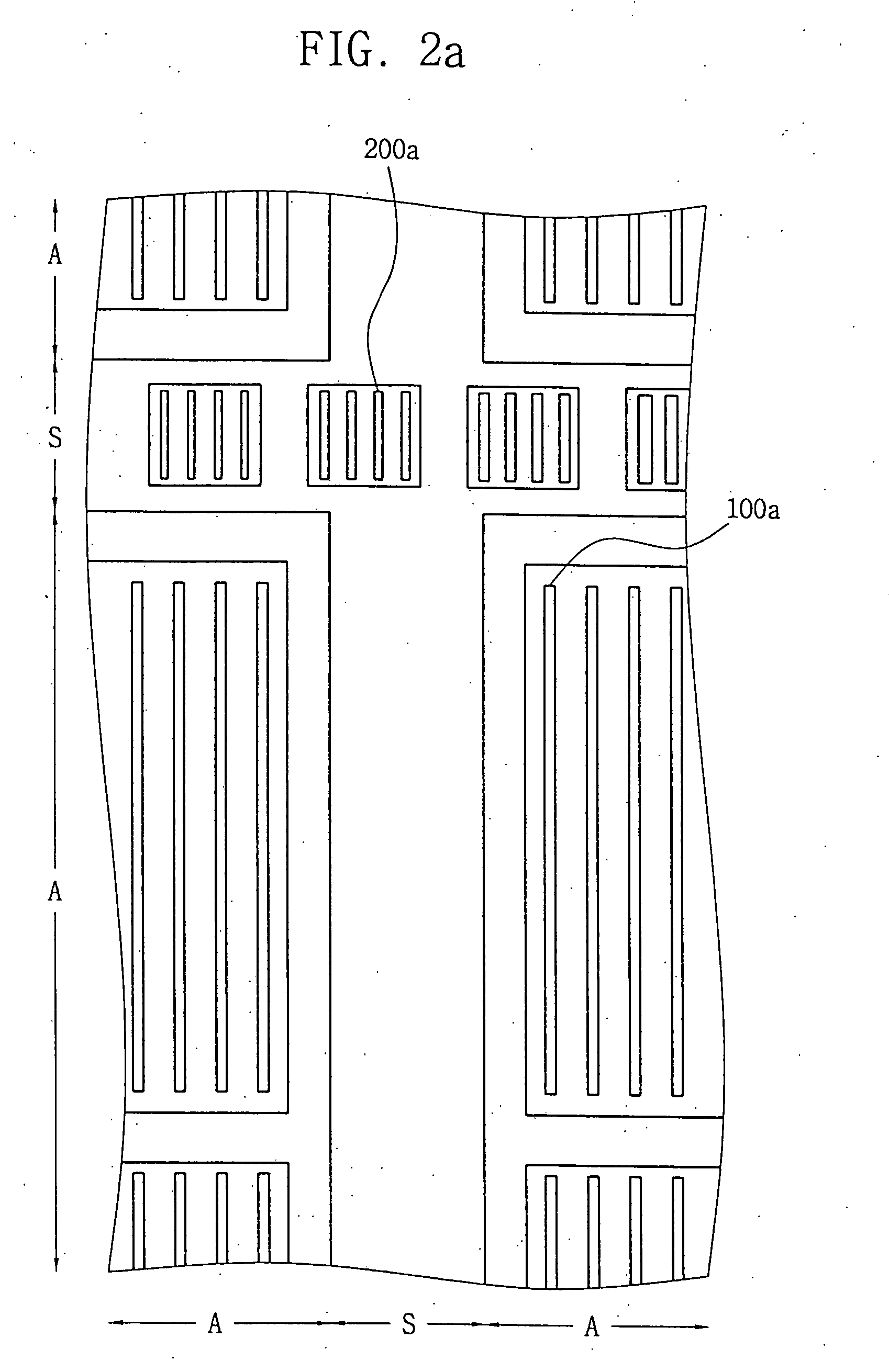
Photoresist pattern, method of fabricating the same, and method of assuring the quality thereof
InactiveUS20050153466A1Critical dimension reductionQuick identificationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLithography processDevice form
A photoresist pattern and a method of fabricating the same make it easy to quickly identify a particular portion of a photolithography process that is responsible for causing process defects. The method of fabricating the photoresist pattern includes forming main patterns having a predetermined critical dimension in device-forming regions of a semiconductor substrate, and forming a plurality of test patterns in scribe regions of the substrate. The scribe regions are defined alongside the device-forming regions and separate the device-forming regions from one another. The test patterns have shapes similar to that of the main patterns. Also, one of the test patterns has a critical dimensions similar to that of the main patterns, and other test patterns have respective critical dimensions that are different from the critical dimension of the main patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
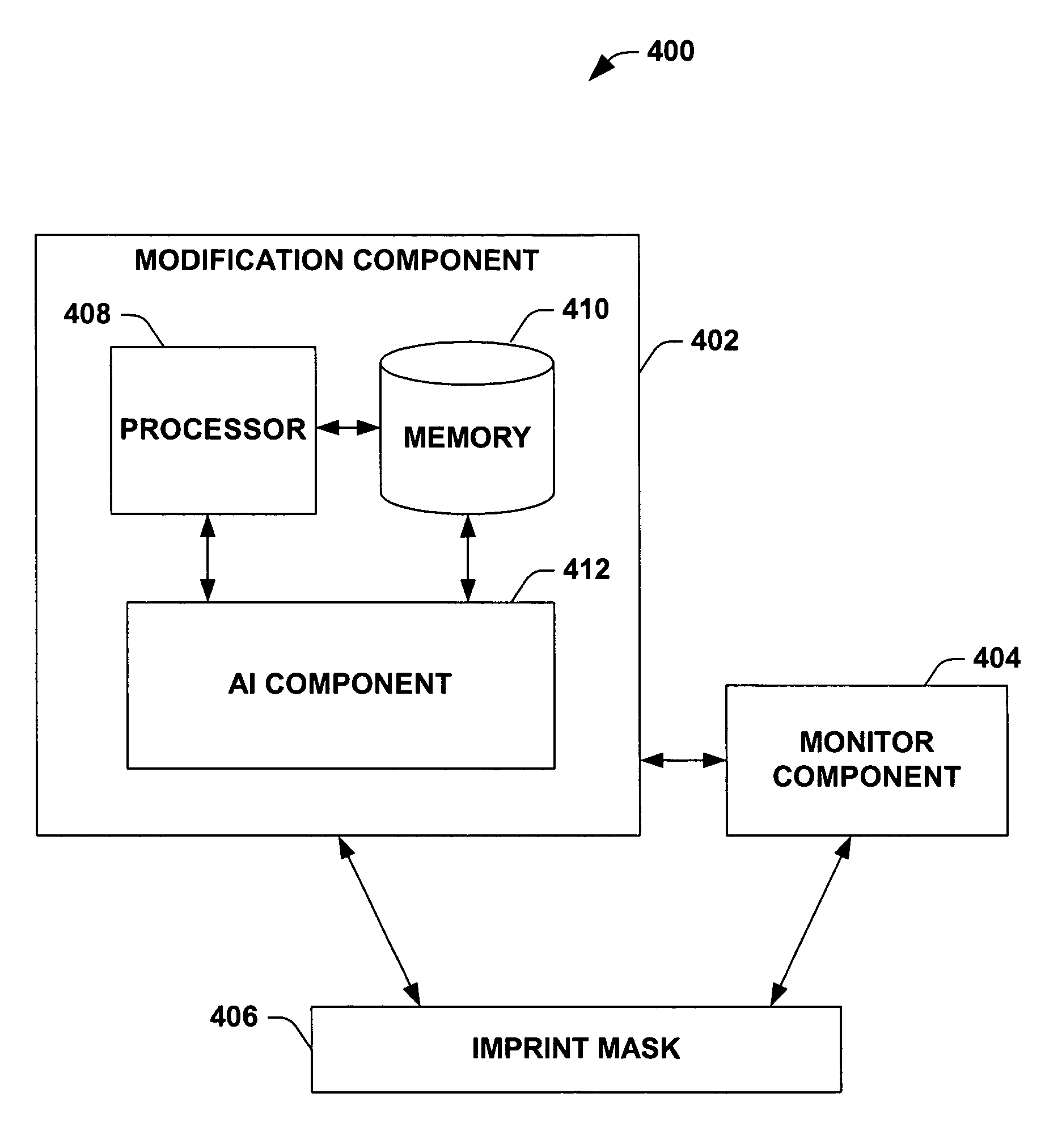
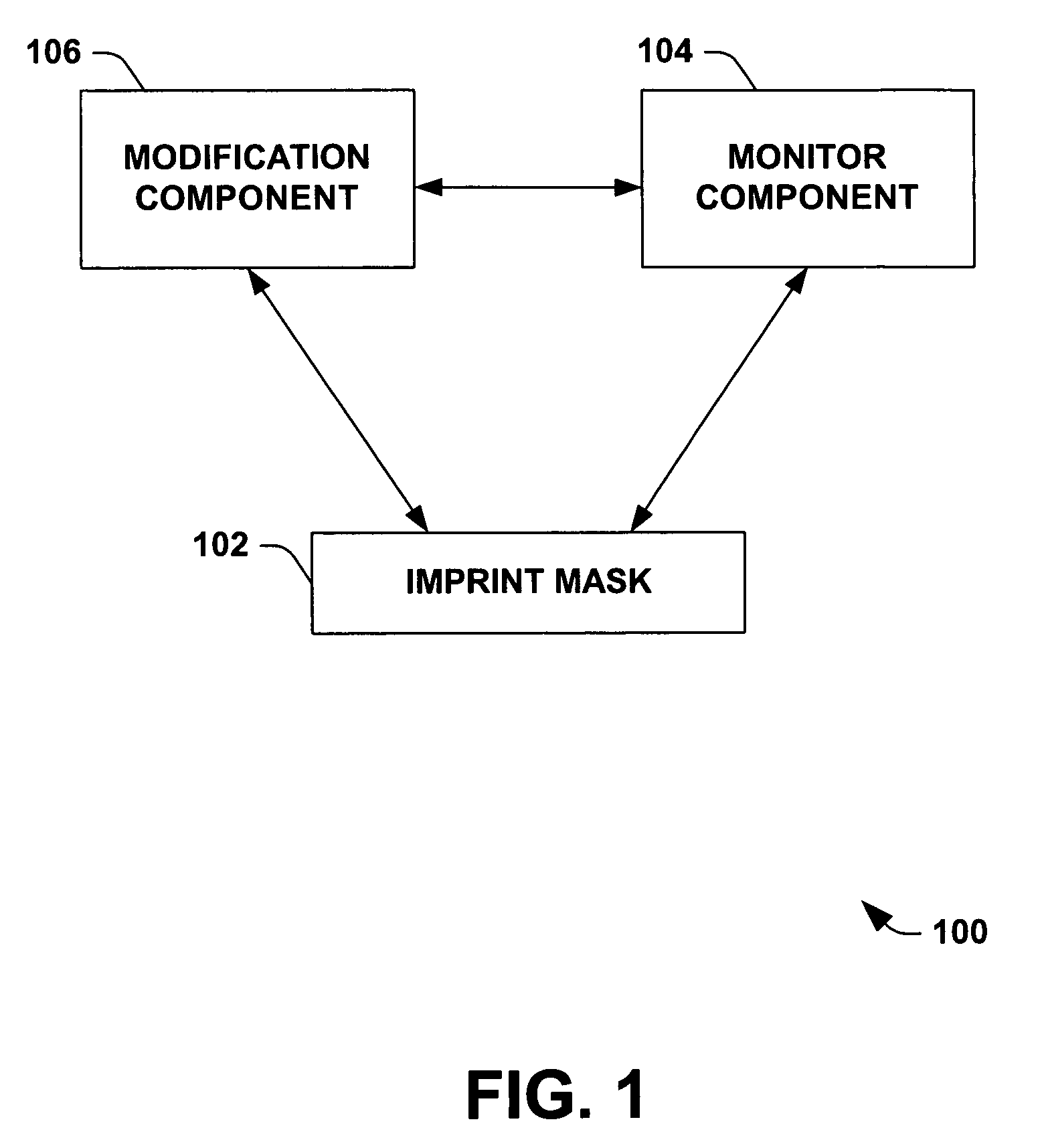
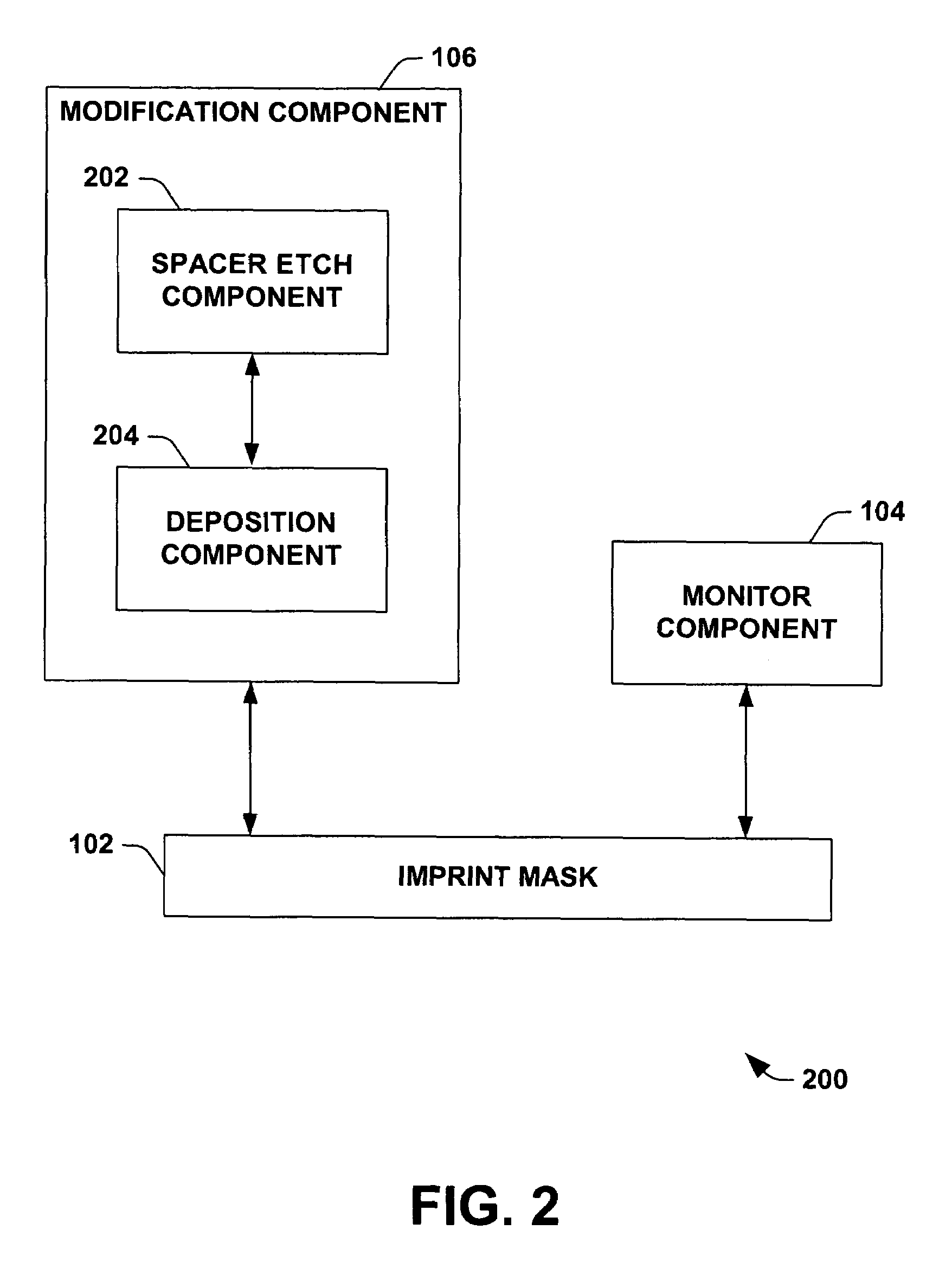
Post fabrication CD modification on imprint lithography mask
InactiveUS7386162B1Improve efficiencyGood economic benefitsNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringCritical dimension
The present invention relates generally to photolithographic systems and methods, and more particularly to systems and methodologies that facilitate compensating for imprint mask critical dimension error(s). An aspect of the invention generates feedback information that facilitates control of imprint mask critical dimension via employing a scatterometry system to detect imprint mask critical dimension error, and mitigating the error via a spacer etchback procedure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Etching method and method for forming contact opening
ActiveUS20060281313A1Reducing after-etching-inspection (AEI)Reducing the after-etching-inspection (AEI) CDSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCritical dimensionMaterials science
An etching method is described, including a first etching step and a second etching step. The temperature of the second etching step is higher than that of the first etching step, such that the after-etching-inspection (AEI) critical dimension is smaller than the after-development-inspection (ADI) critical dimension.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Process for separation of oxygen from an oxygen containing gas using oxygen selective sorbents
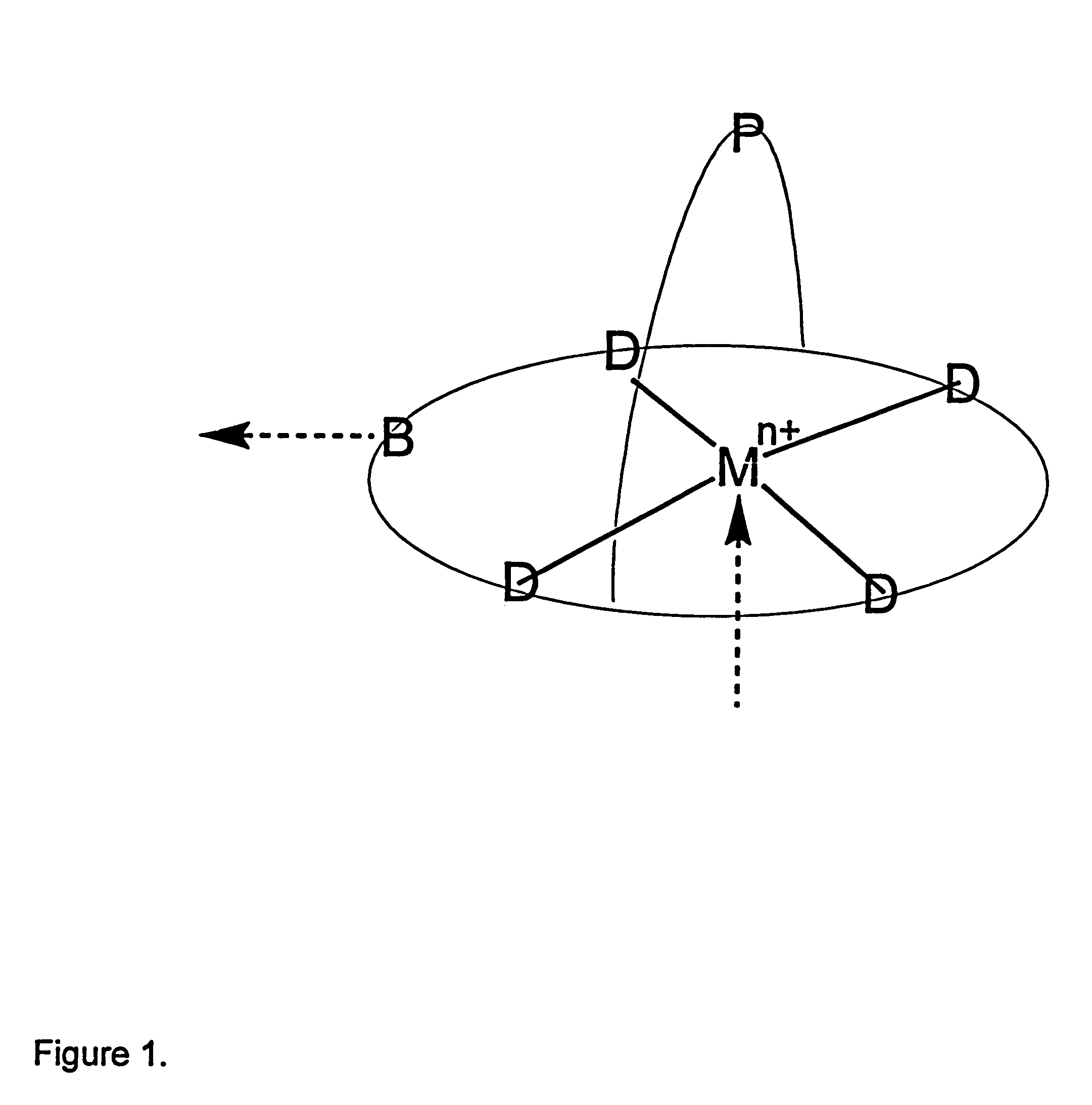
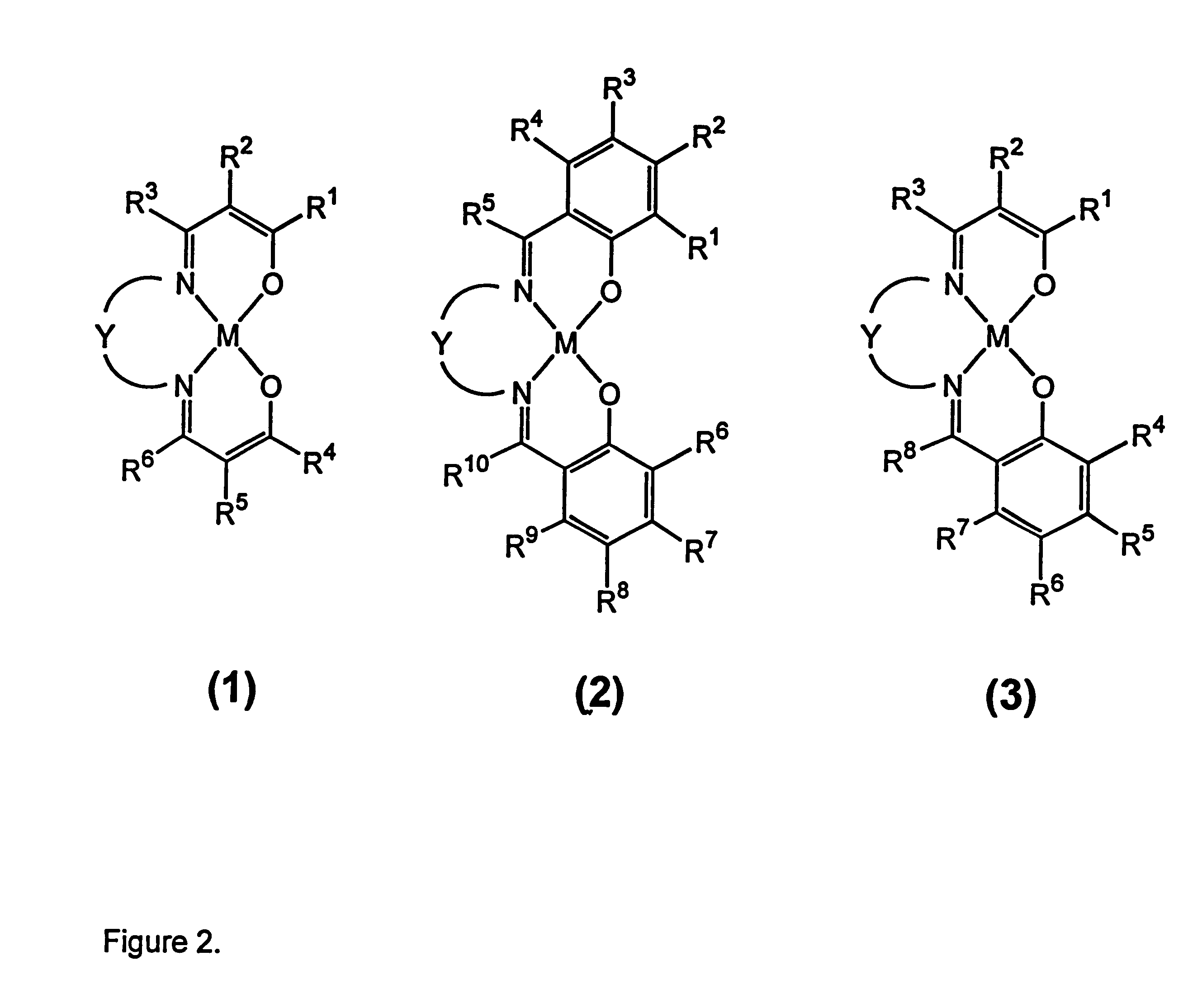
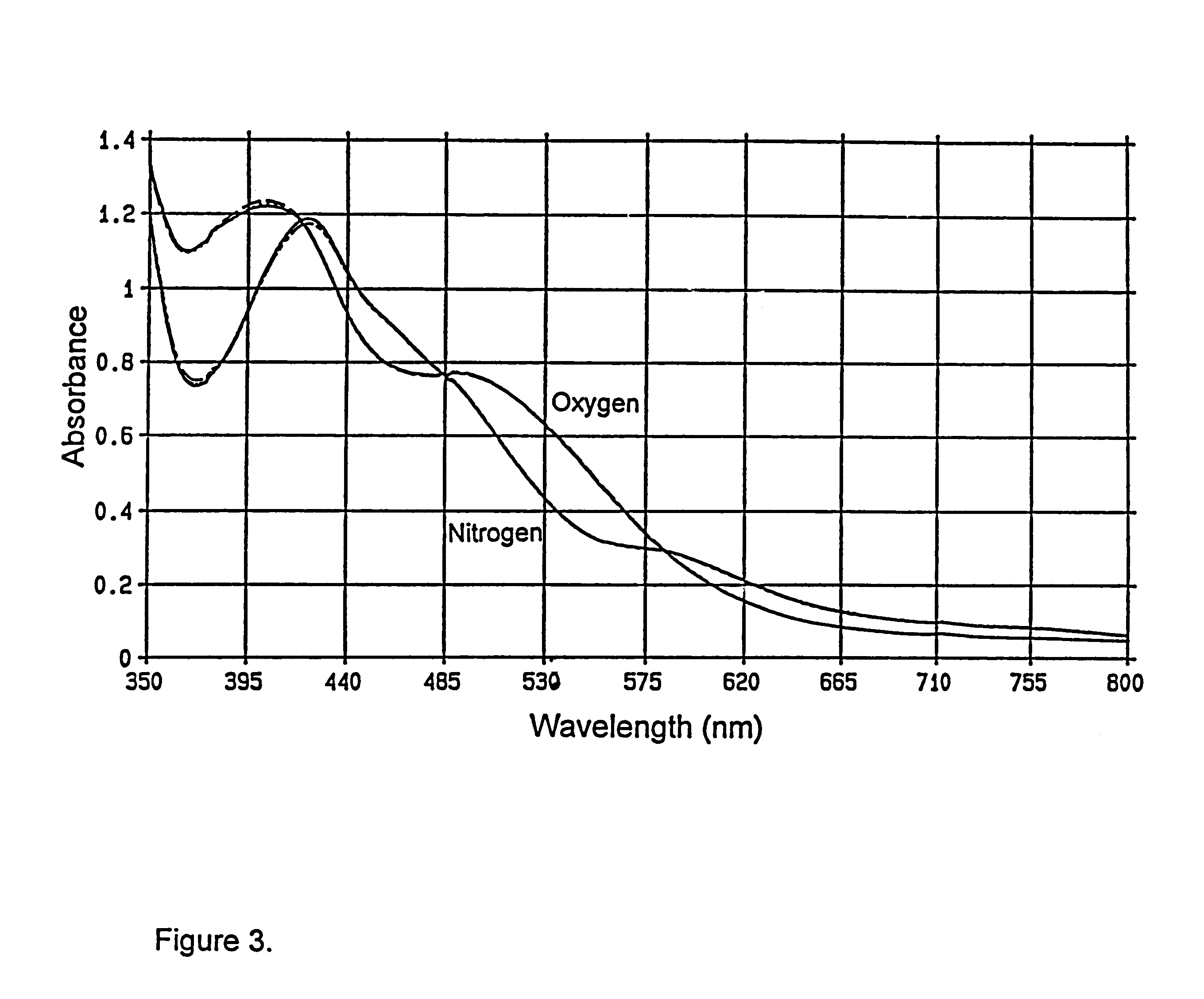
InactiveUS6183709B1Easy to synthesizeStructural versatilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCobalt organic compoundsIonComputational chemistry
The invention is directed to a process for the separation of oxygen from an oxygen containing gas using an oxygen selective material comprising a transition element complex comprising a first transition element ion and one or more chelating ligands, wherein:i) said first transition element ion is capable of accepting intermolecular donation;ii) said chelating ligand or ligands provides up to four intramolecular donor sites to said transition element ion;iii) said chelating ligand or ligands provides an intermolecular donor site to a second transition element ion which is contained in second discrete transition element complex; andiv) said chelating ligand or ligands contains at least one substituent that inhibits mu-peroxo dimer formation on said sorbent;wherein when said material is in deoxy form, the total number of donor sites to said first transition element ion is five.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
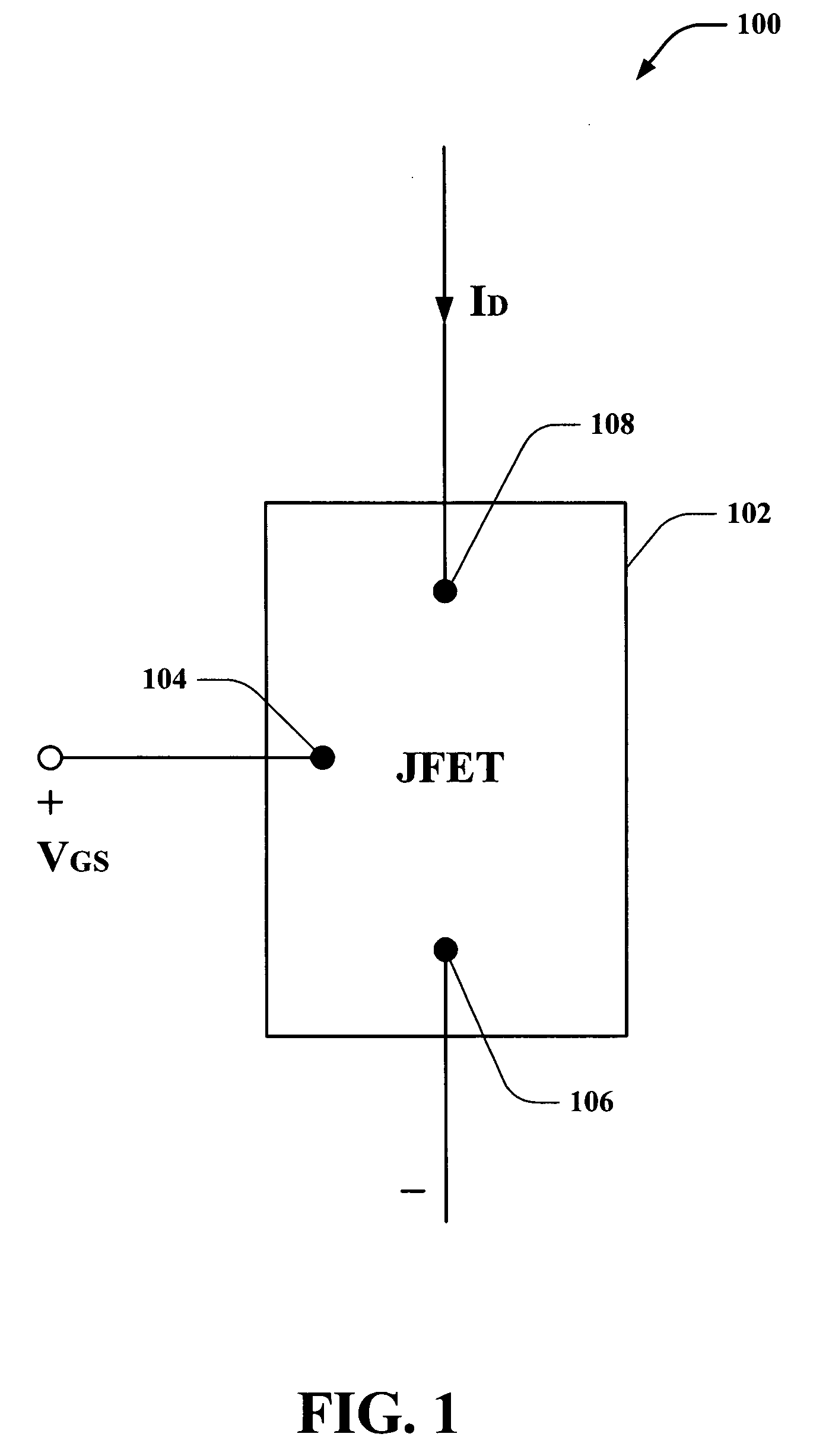
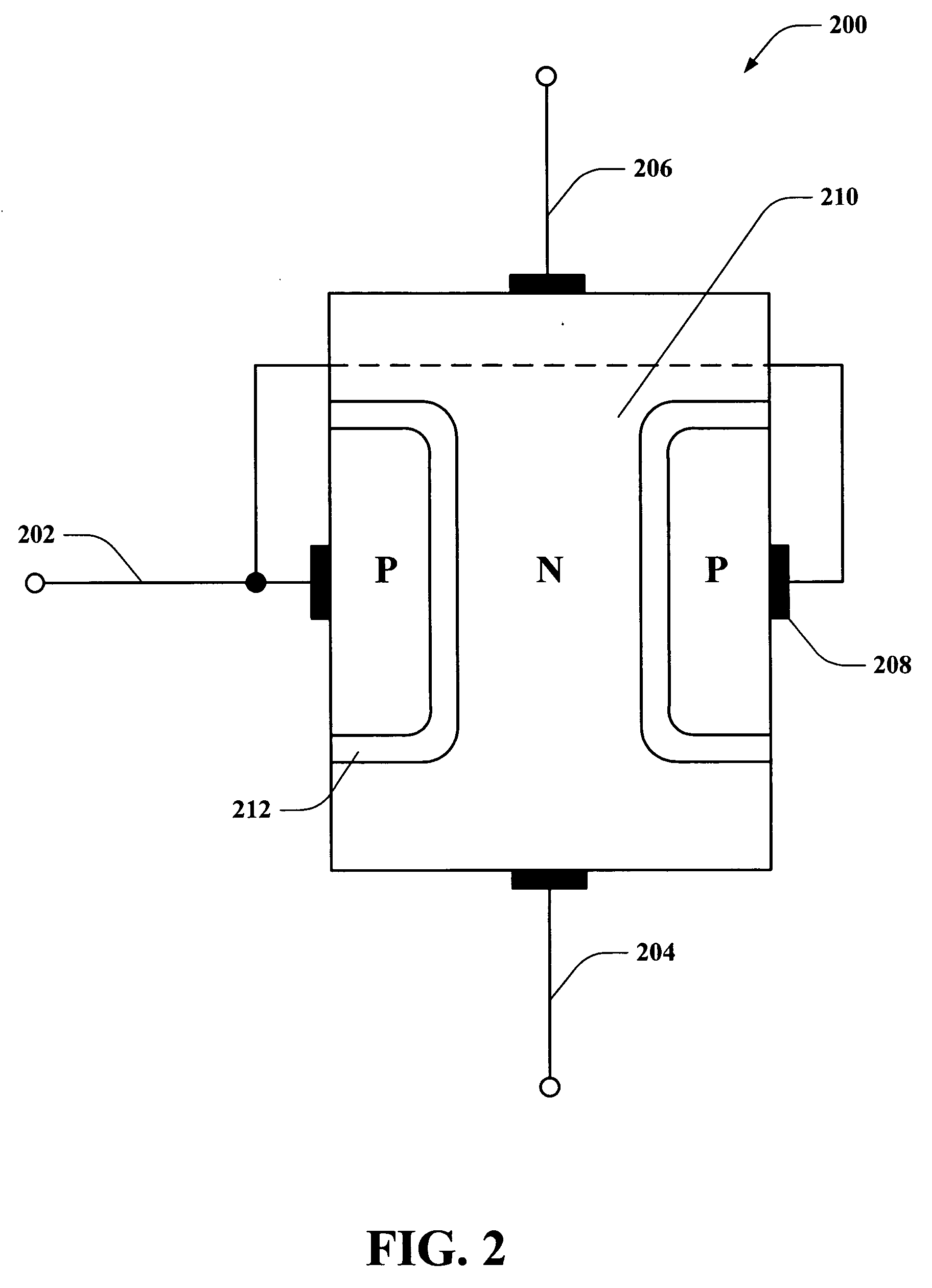
Vertical JFET as used for selective component in a memory array
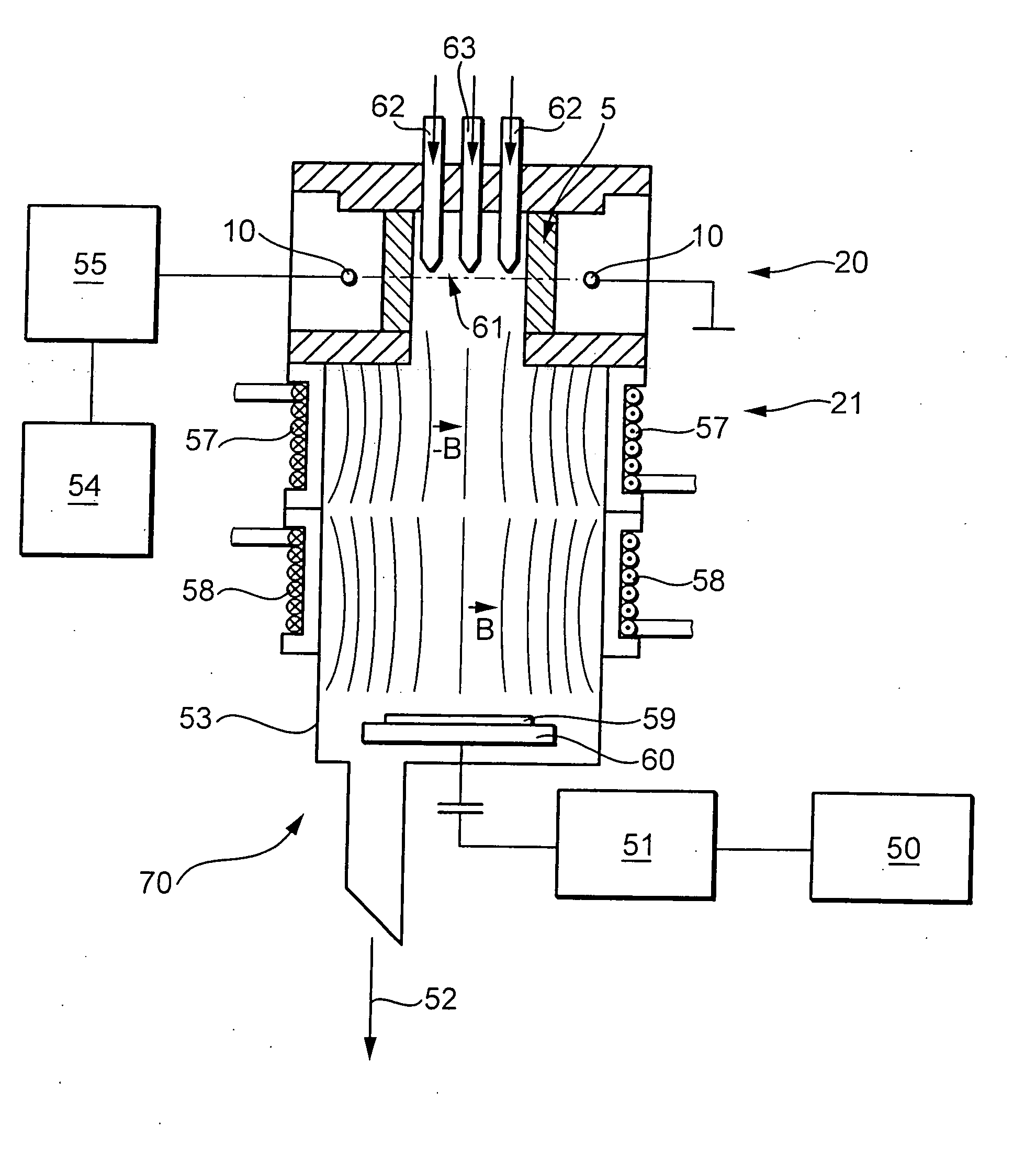
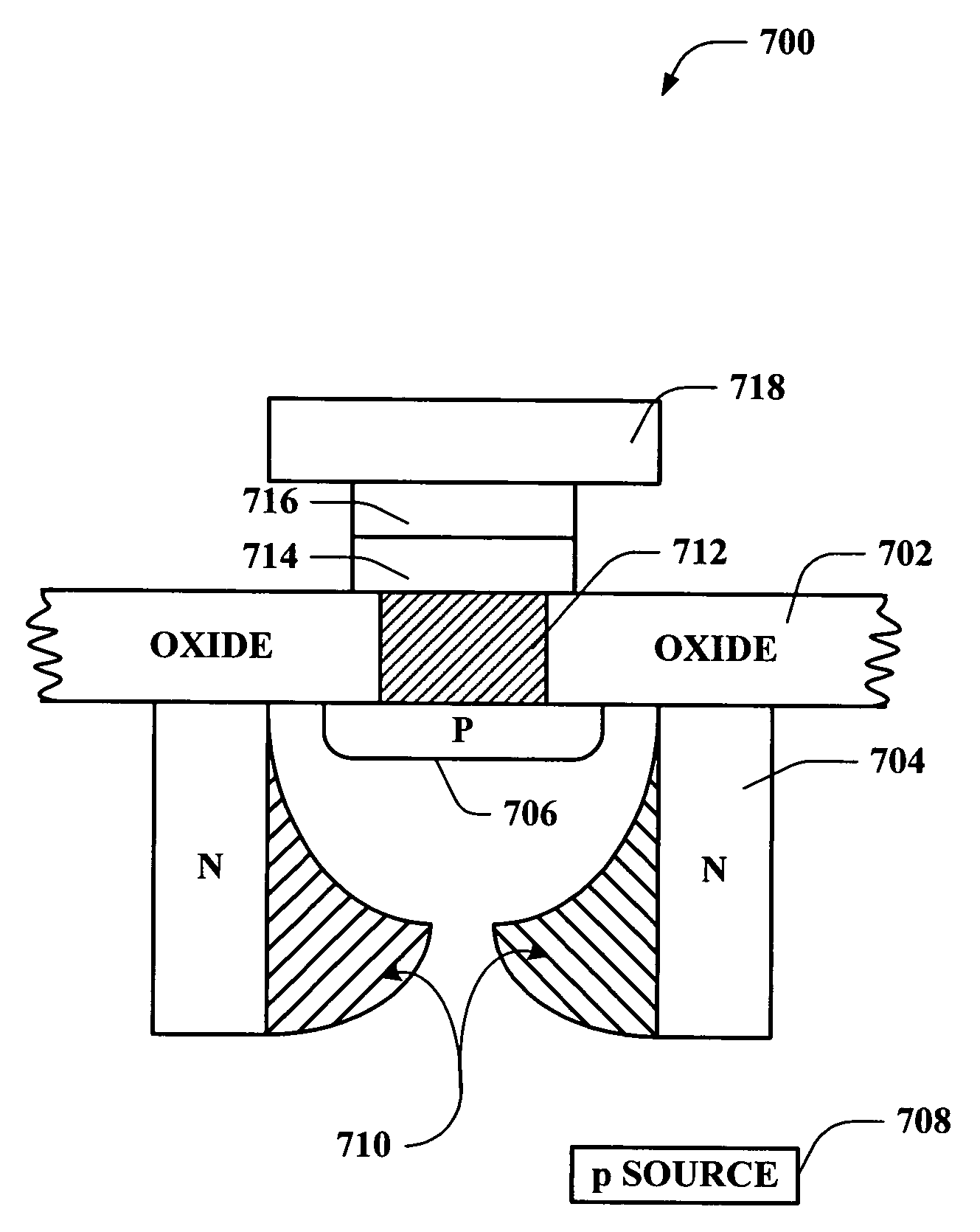
Systems and methods are disclosed that facilitate providing a selective functionality to a polymer memory cell in a memory array while increasing device density in the memory cell array. A vertical JFET is described to which voltages can be selectively applied to control internal current flow there through, which in turn can be employed to manipulate the state of a polymer memory cell coupled to the vertical JFET. By mitigating gaps between gates, or wordlines, and drains of the vertical JFETs, feature size can be reduced to permit increased device density. Furthermore, vertical JFETs in the array can be coupled to gates on only two opposite sides, permitting the JFETs to be arranged without gate crossbars between them, further increasing device density. In this manner, the present invention provides switching characteristics to a memory cell and overcomes problematic bulkiness associated with conventional MOS devices.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Etch pattern definition using a CVD organic layer as an anti-reflection coating and hardmask
InactiveUS20080197109A1Highly effective hard mask properties.High resolutionDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenNitrogen
A multilayer antireflective hard mask structure is disclosed. The structure comprises: (a) a CVD organic layer, wherein the CVD organic layer comprises carbon and hydrogen; and (b) a dielectric layer over the CVD organic layer. The dielectric layer is preferably a silicon oxynitride layer, while the CVD organic layer preferably comprises 70-80% carbon, 10-20% hydrogen and 5-15% nitrogen. Also disclosed are methods of forming and trimming such a multilayer antireflective hard mask structure. Further disclosed are methods of etching a substrate structure using a mask structure that contains a CVD organic layer and optionally has a dielectric layer over the CVD organic layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
De-fluoridation process
InactiveUS20080083502A1Critical dimension reductionLiquid surface applicatorsDecorative surface effectsResistCritical dimension
A feature in a layer is provided. A photoresist layer is formed over the layer. The photoresist layer is patterned to form photoresist features with photoresist sidewalls, where the photoresist features have a first critical dimension. A fluorine-containing conformal layer is deposited over the sidewalls of the photoresist features to reduce the critical dimensions of the photoresist features. Fluorine is removed from the conformal layer, while the remaining conformal layer is left in place. Features are etched into the layer, wherein the layer features have a second critical dimension, which is less than the first critical dimension.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Etch process for CD reduction of arc material
InactiveUS20060223305A1Critical dimension reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingHydrogen
A method of reducing critical dimensions of a feature in a anti-reflective coating layer structure can utilize a polymerizing agent. The anti-reflective coating structure can be utilized to form various integrated circuit structures. The anti-reflective coating can be utilized to form gate stacks comprised of polysilicon and a dielectric layer, conductive lines, or other IC structure. The polymerizing agent can include carbon, hydrogen and fluorine.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
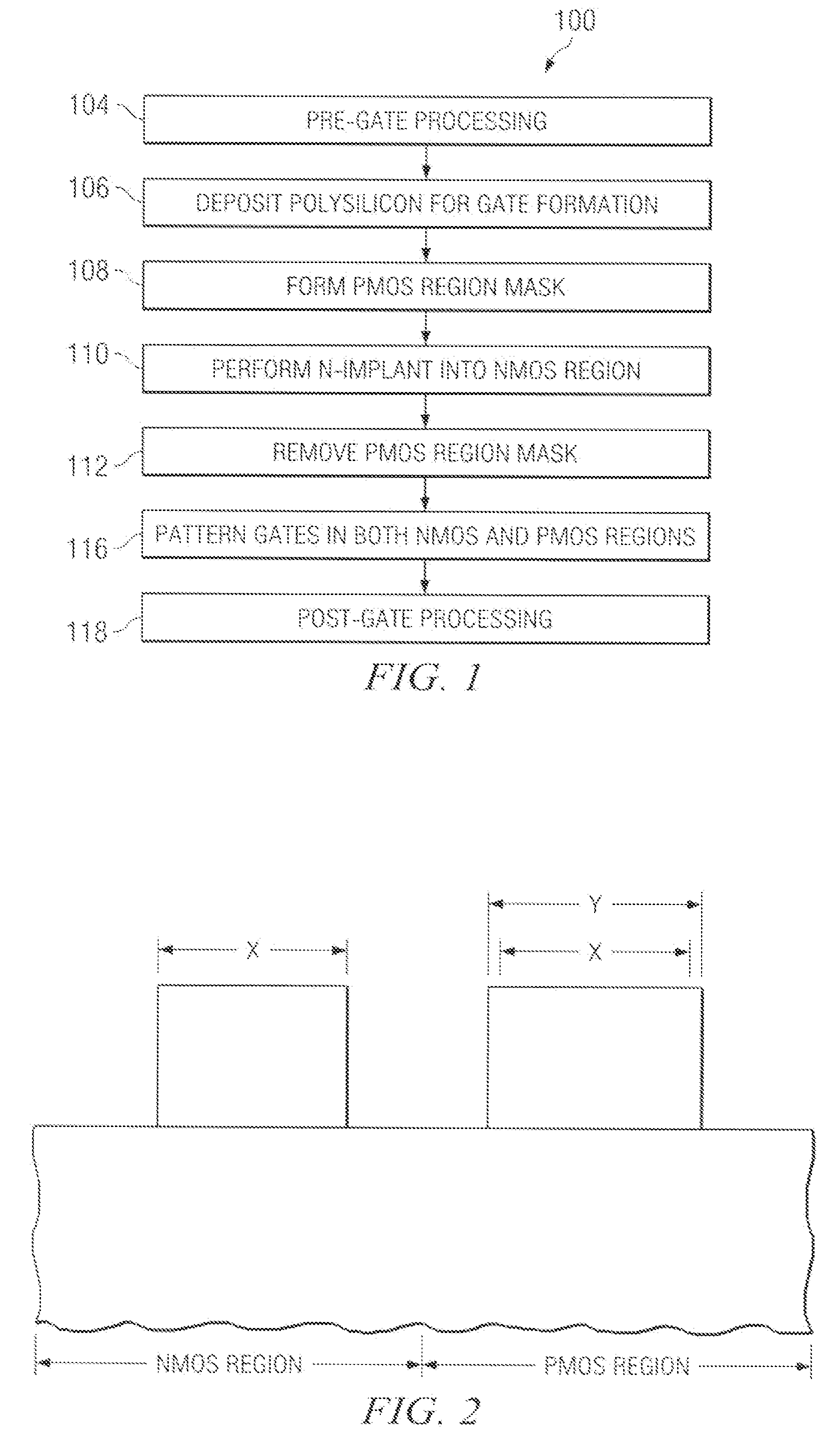
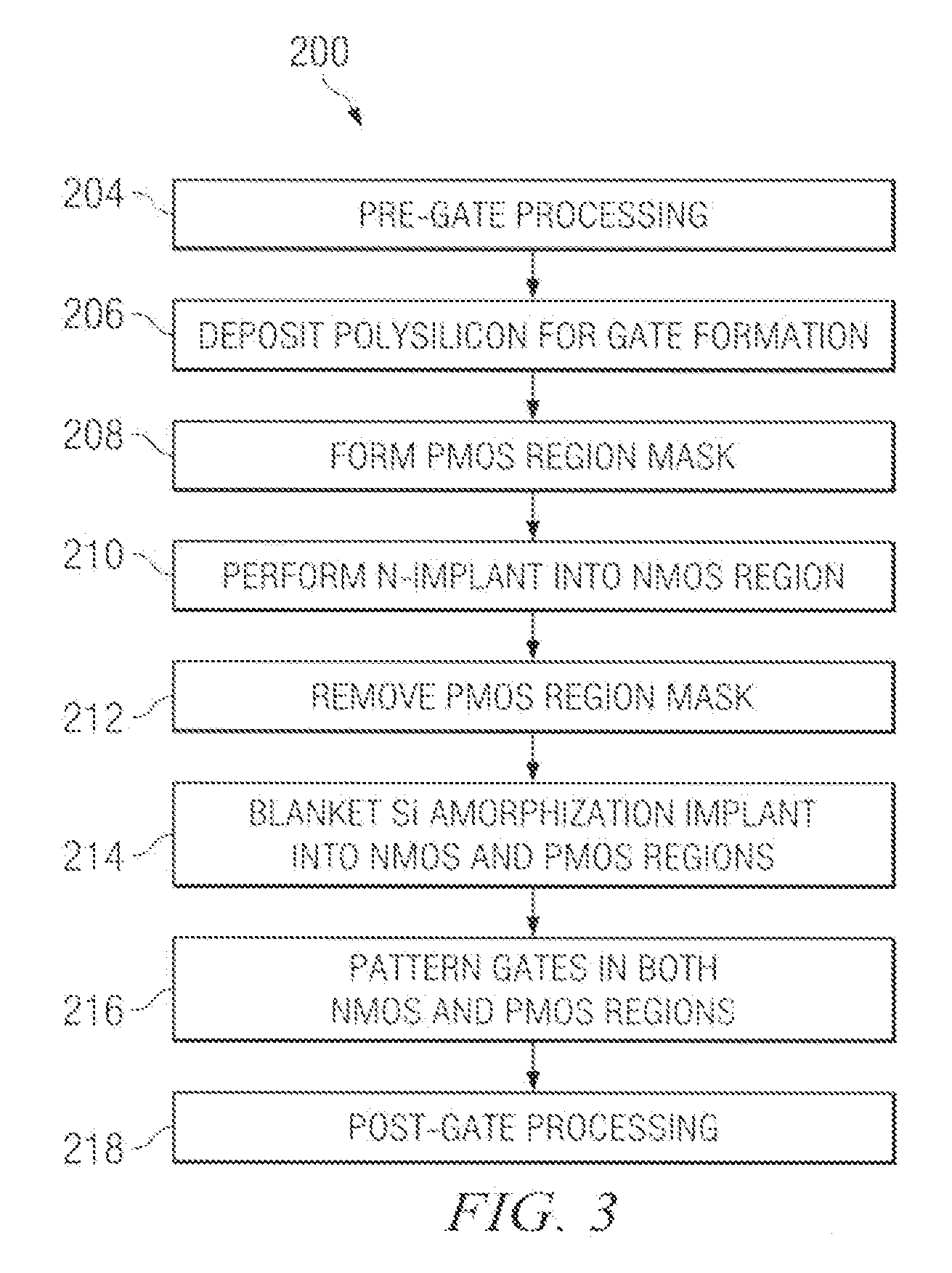
Reducing gate CD bias in CMOS processing
ActiveUS20090166629A1Critical dimension reductionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSAmorphous silicon
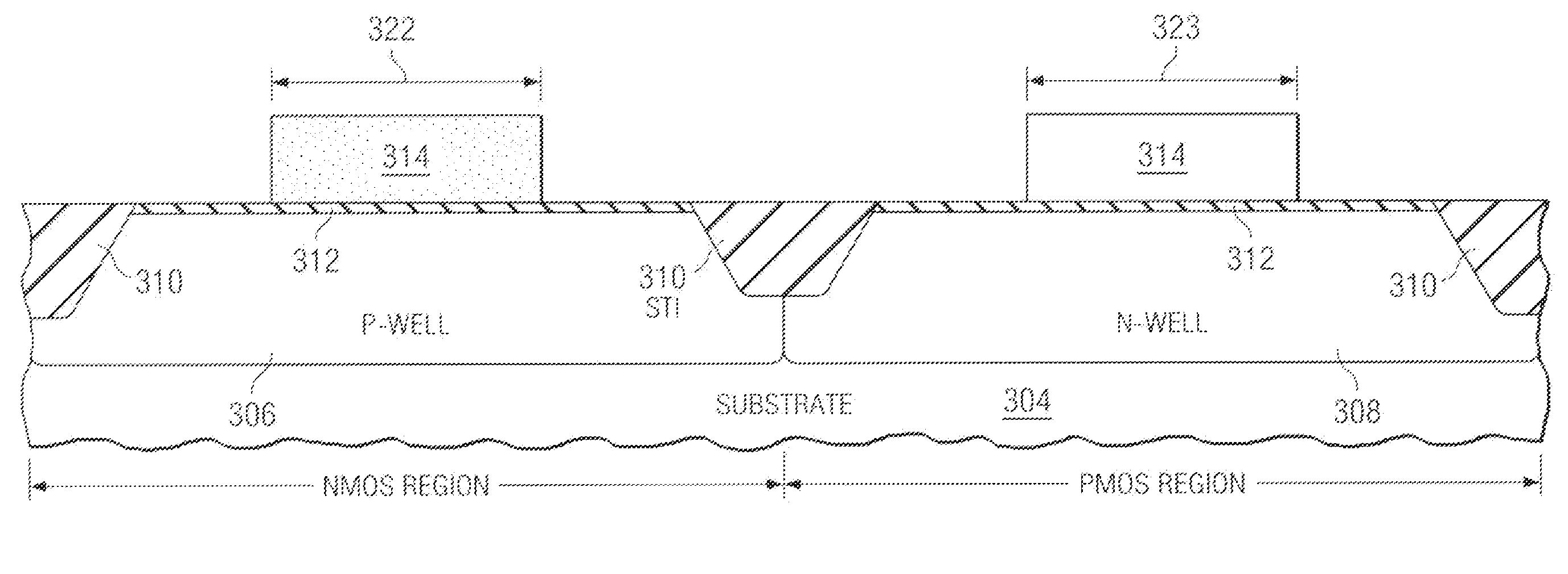
A method of forming an integrated circuit having an NMOS transistor and a PMOS transistor is disclosed. The method includes performing pre-gate processing in a NMOS region and a PMOS region over and / or in a semiconductor body, and depositing a polysilicon layer over the semiconductor body in both the NMOS and PMOS regions. The method further includes performing a first type implant into the polysilicon layer in one of the NMOS region and PMOS region, and performing an amorphizing implant into the polysilicon layer in both the NMOS and PMOS regions, thereby converting the polysilicon layer into an amorphous silicon layer. The method further includes patterning the amorphous silicon layer to form gate electrodes, wherein a gate electrode resides in both the NMOS and PMOS regions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com