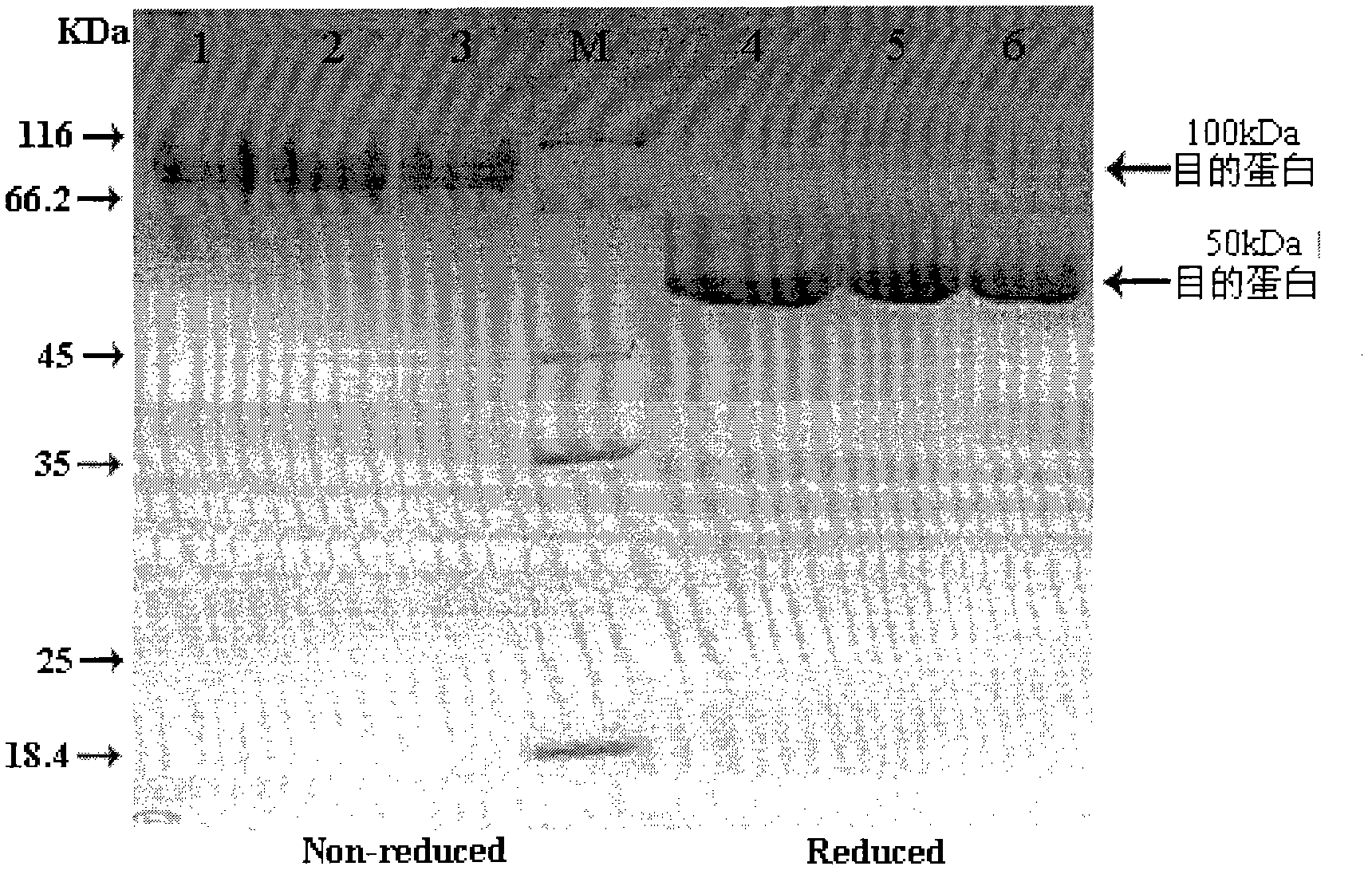
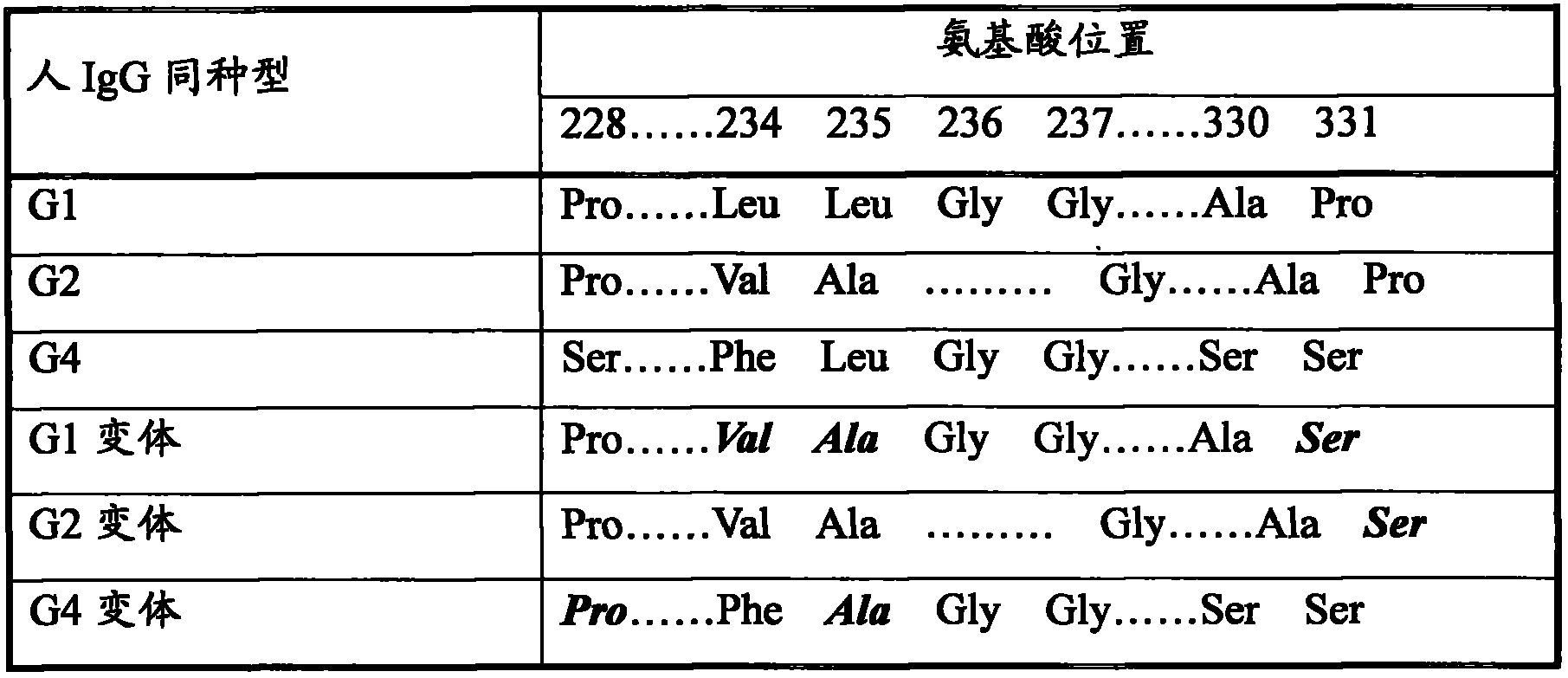
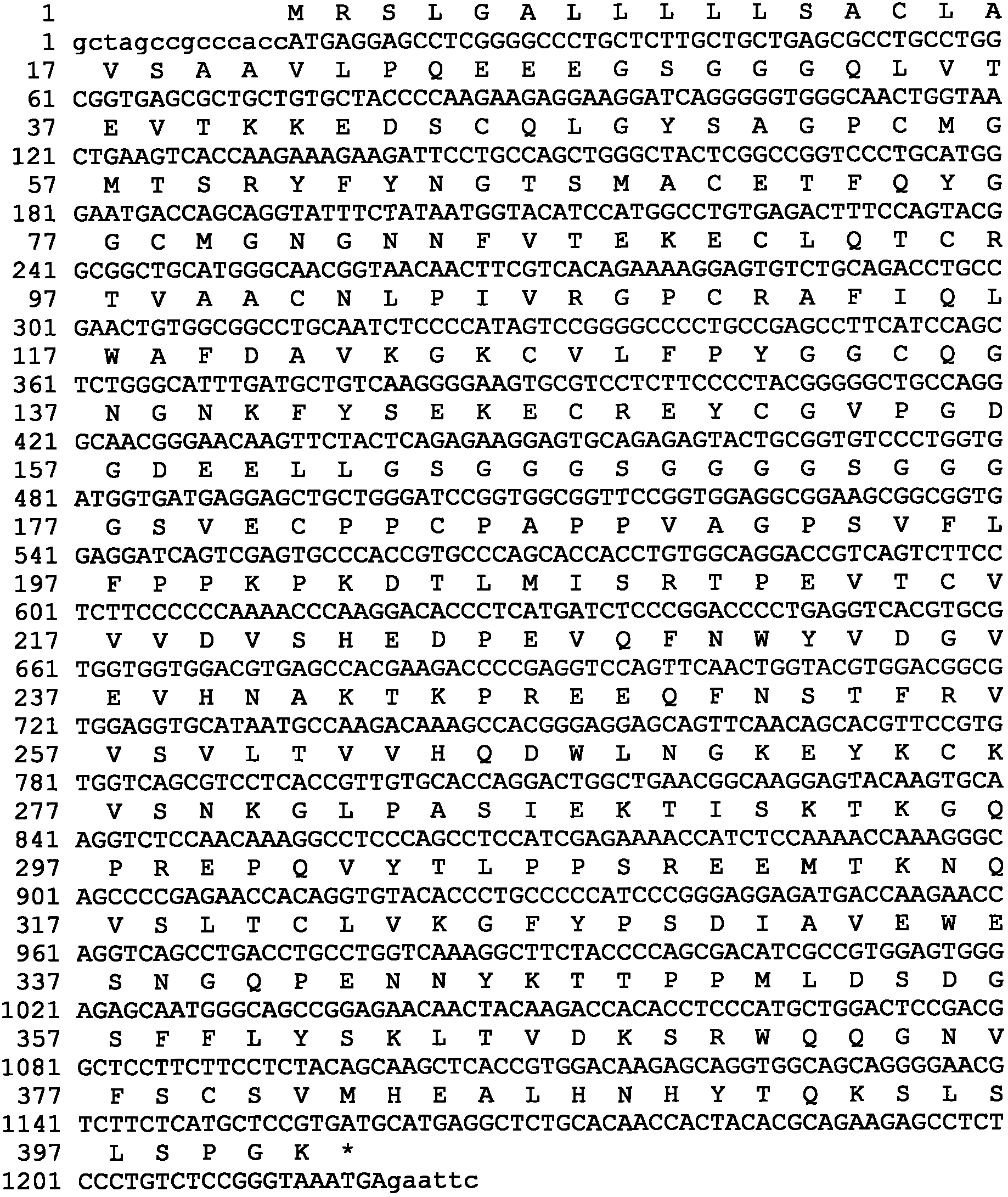
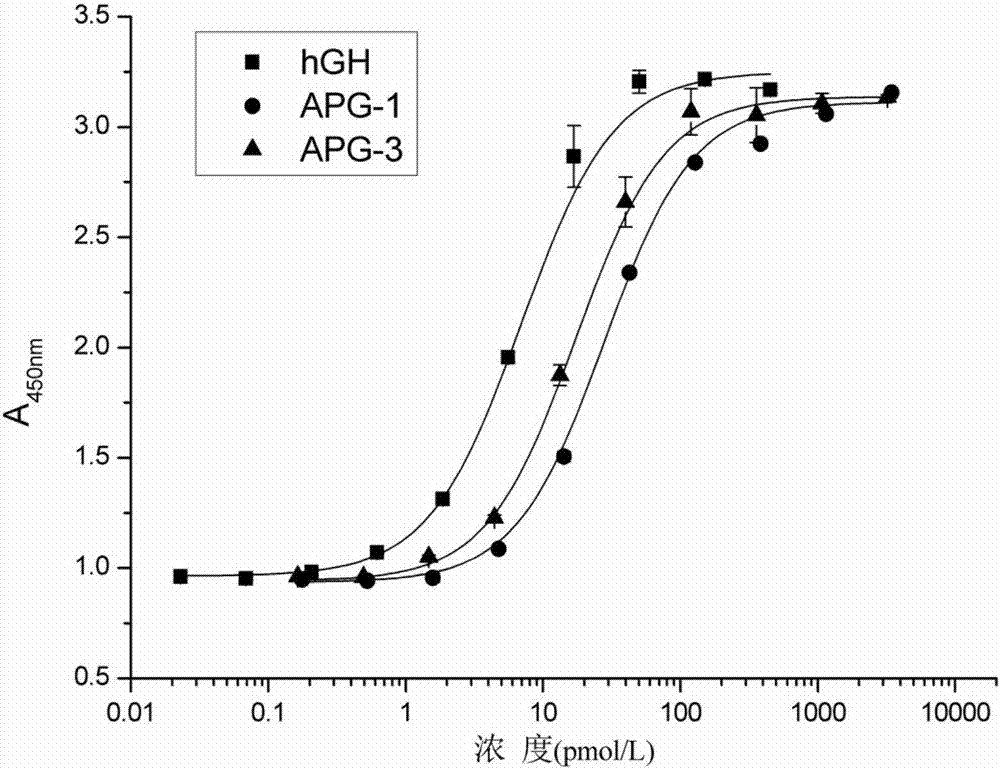
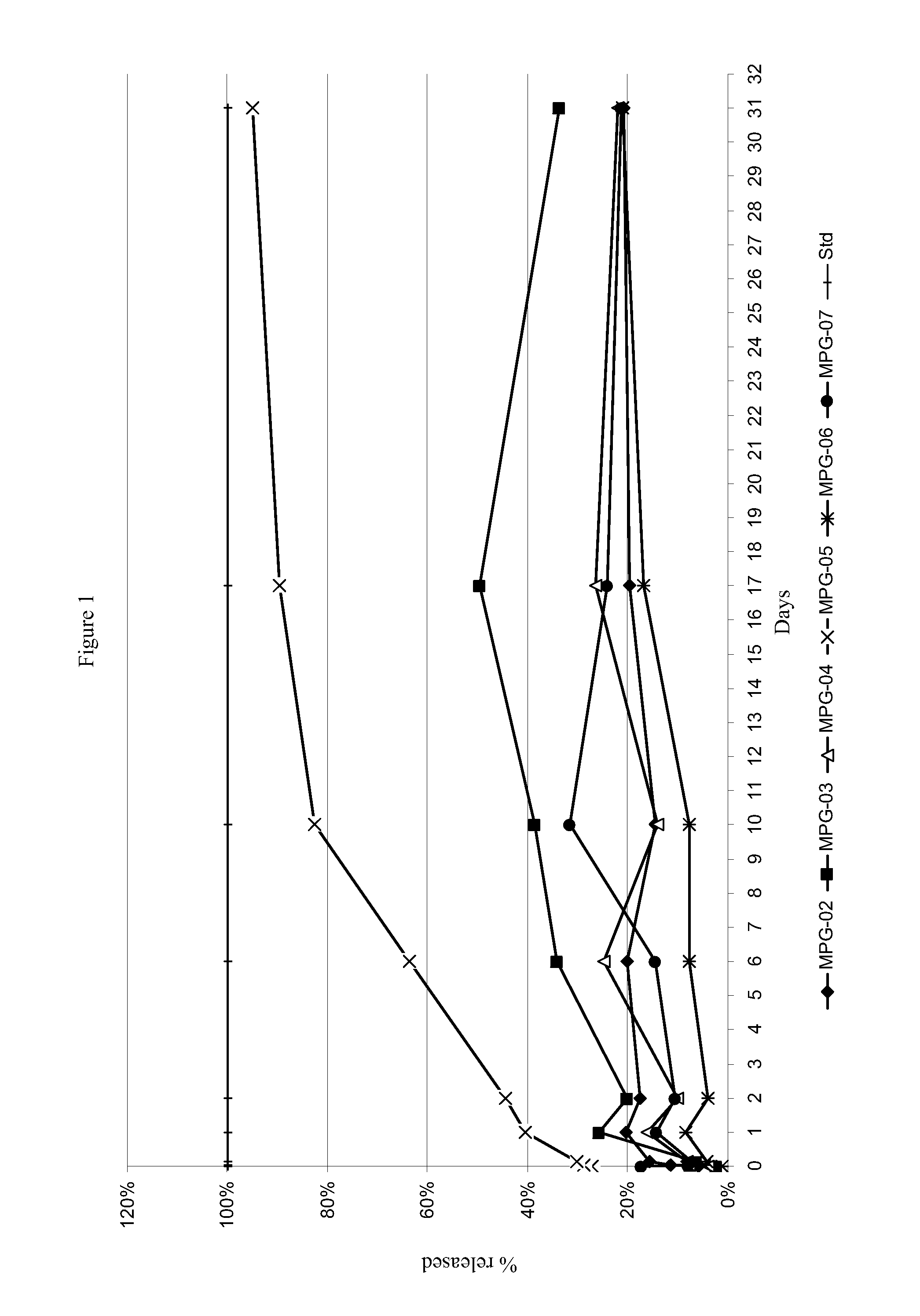
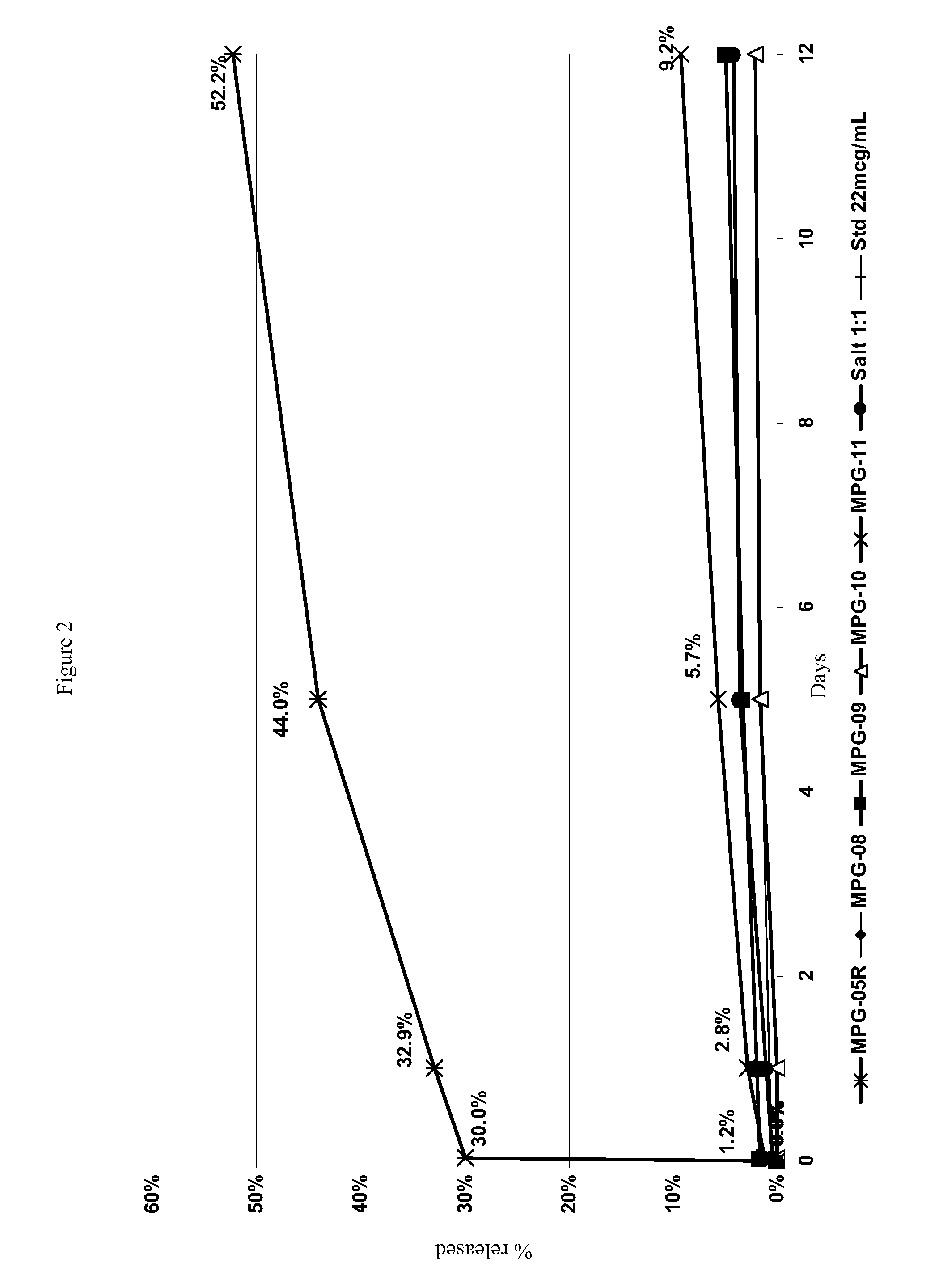
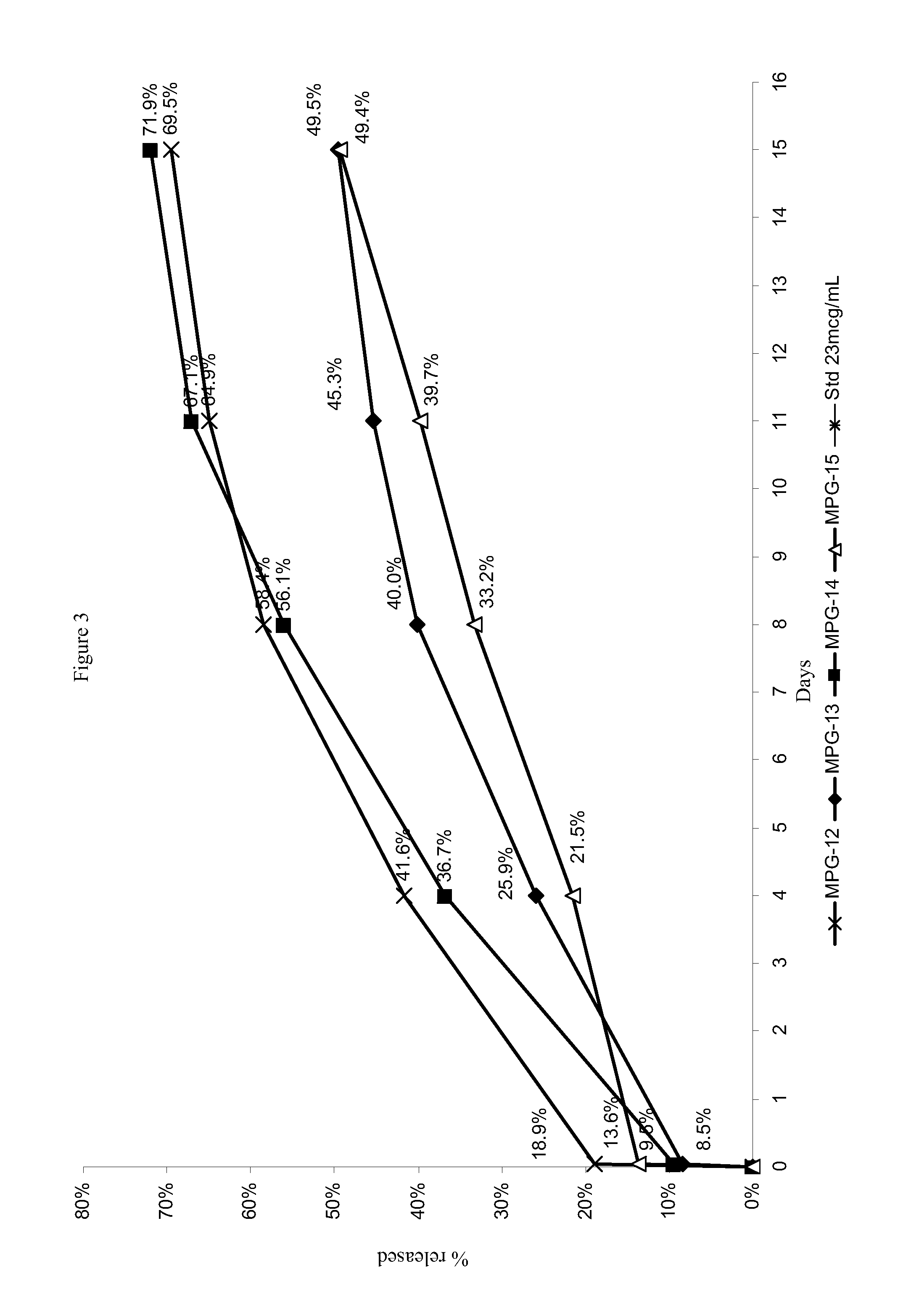
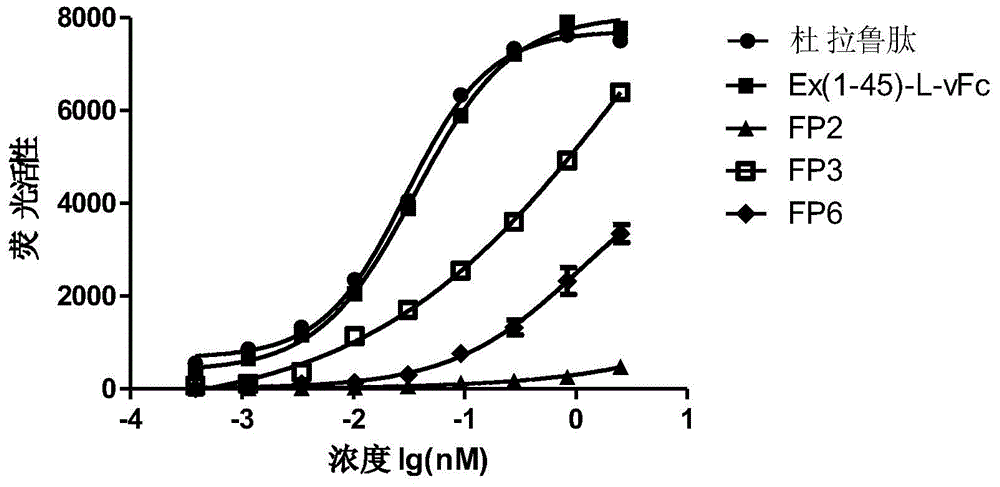
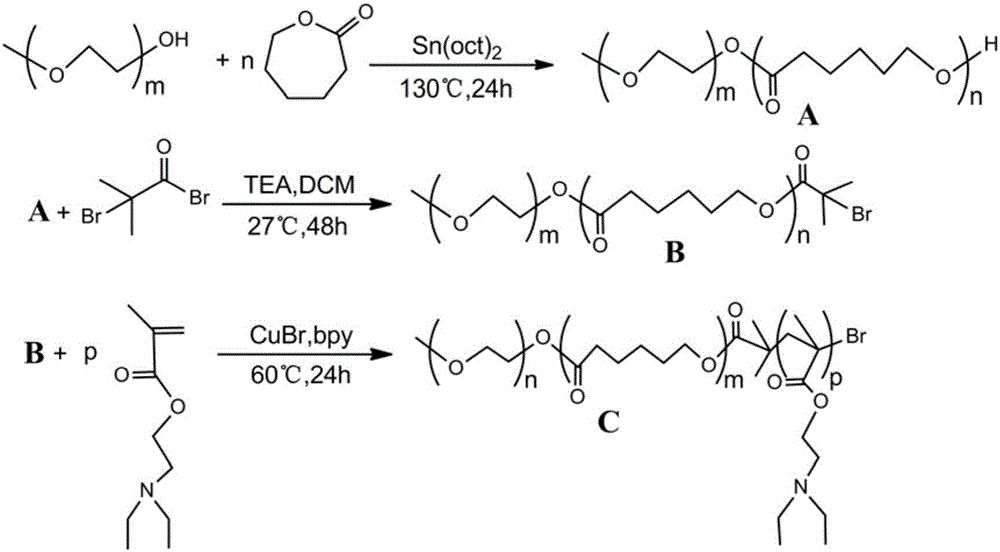
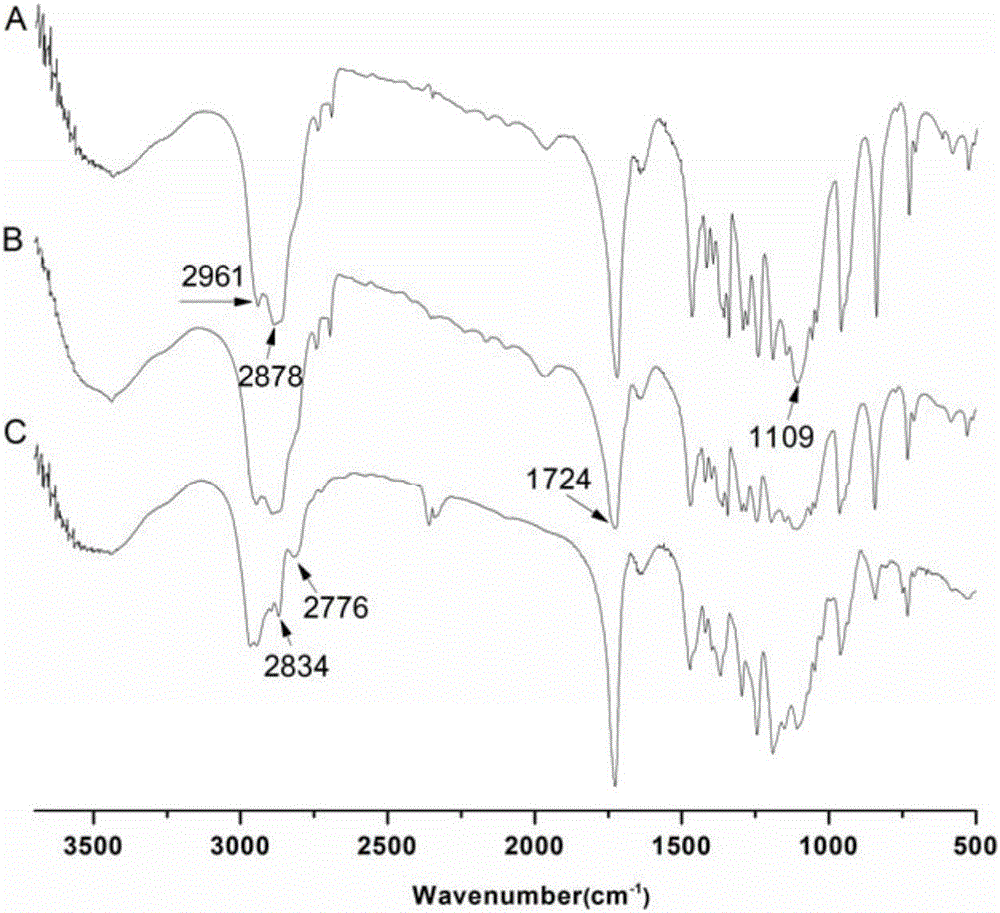
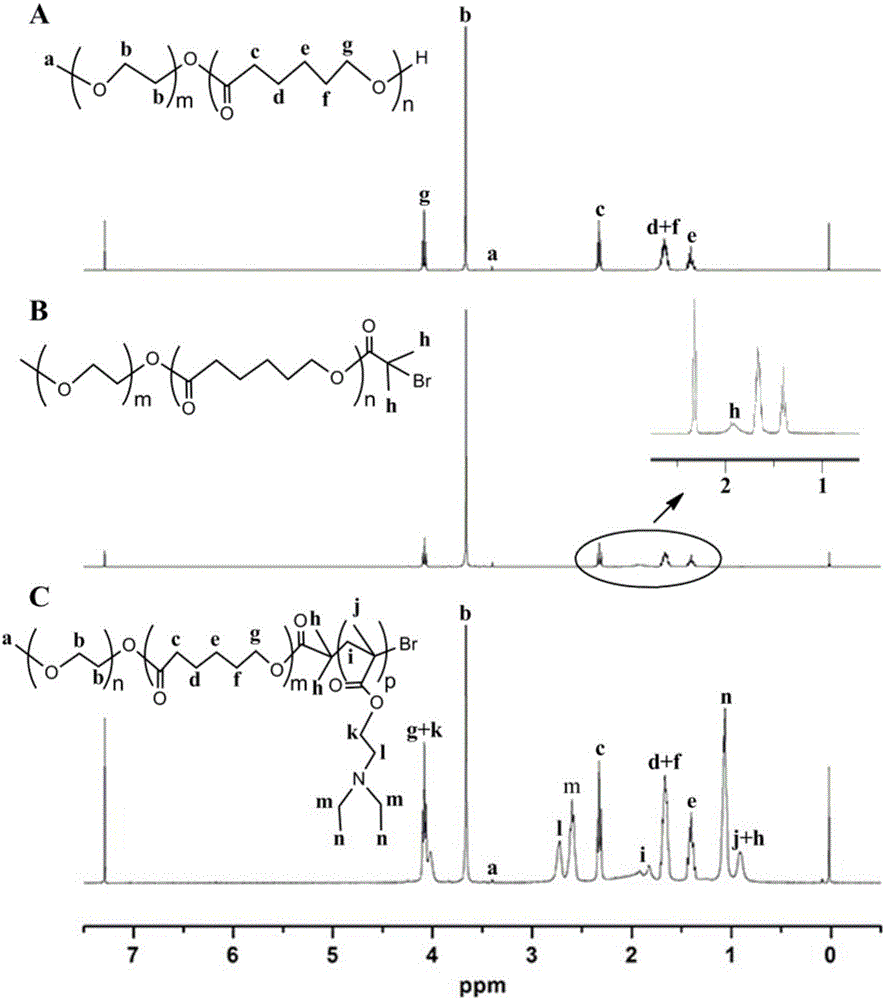
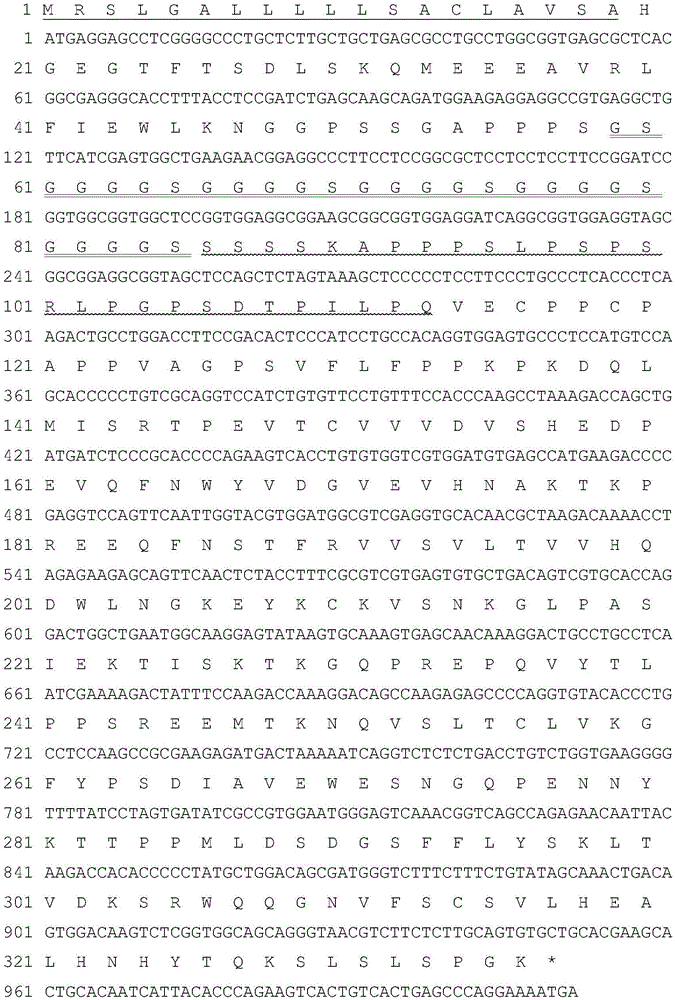
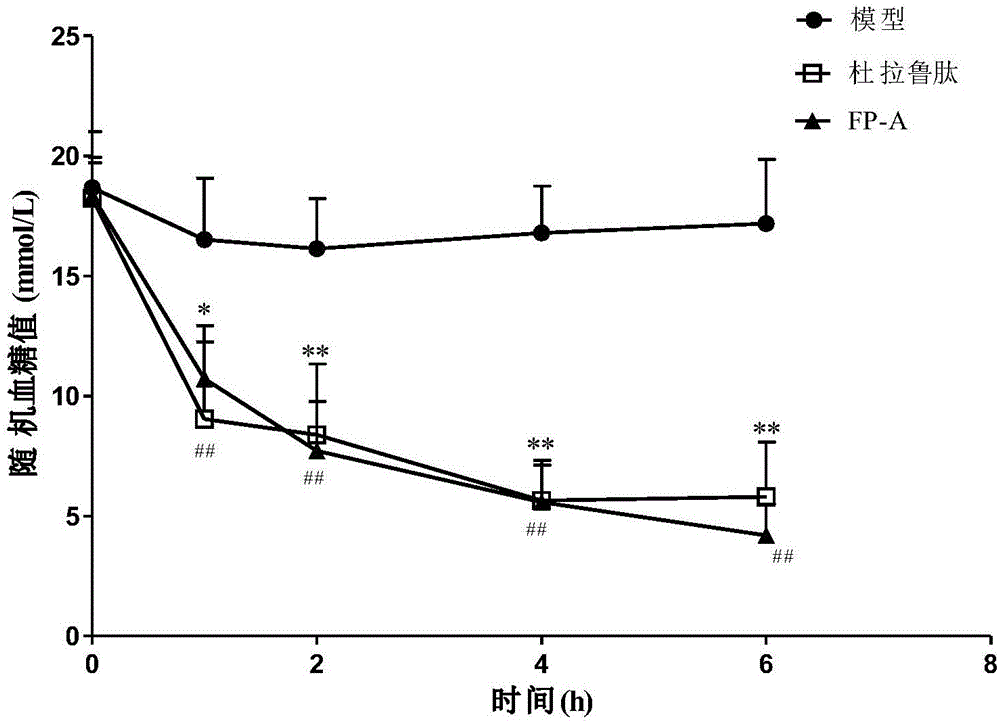
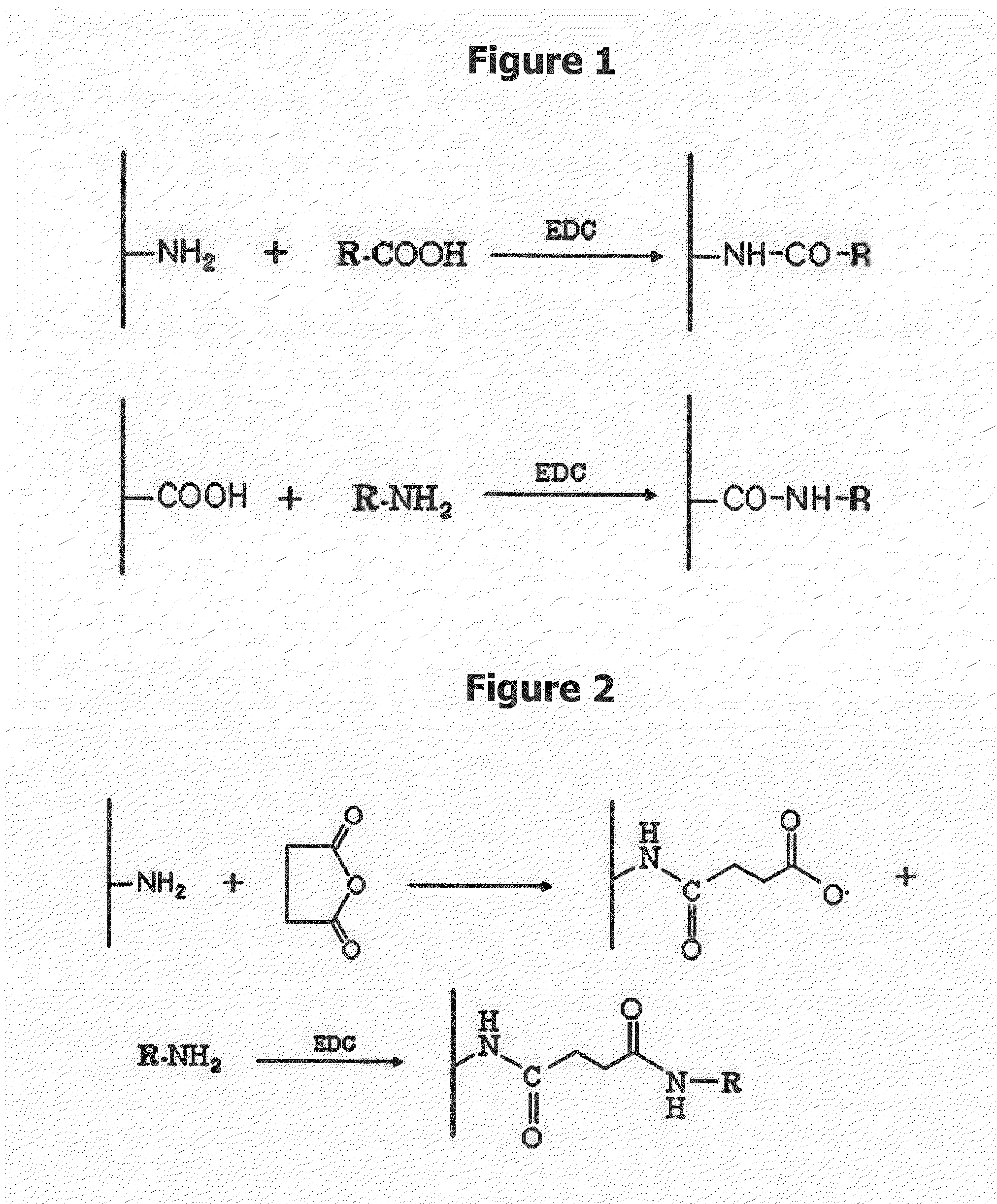
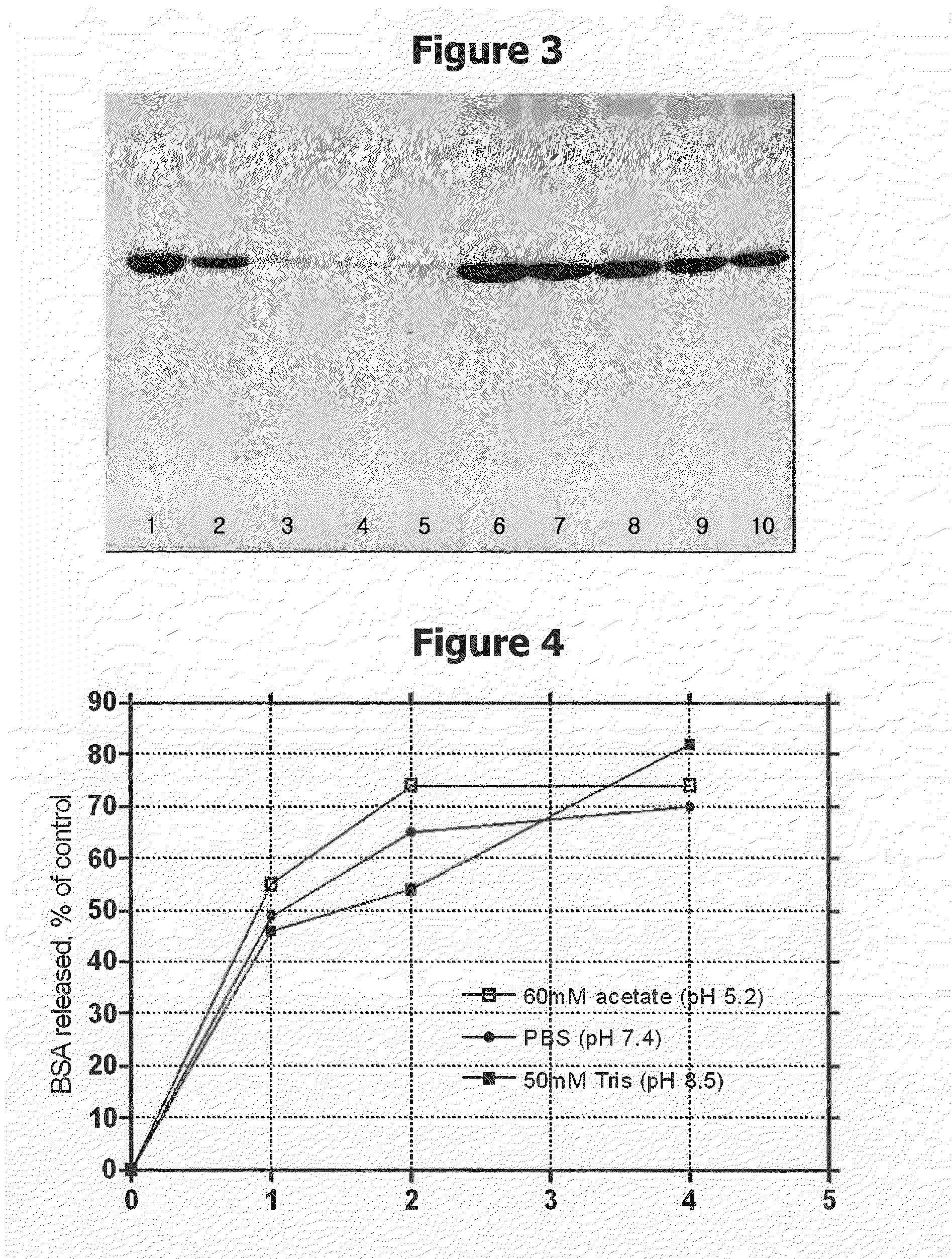
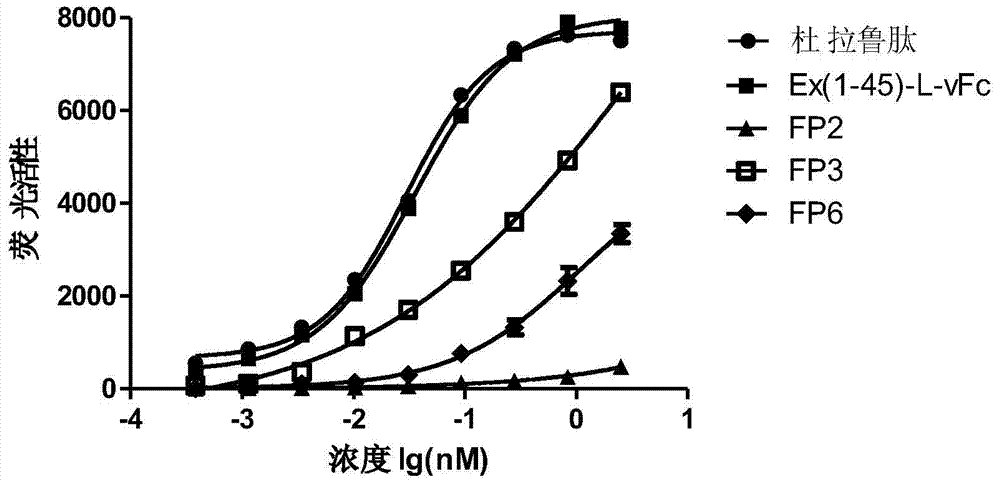
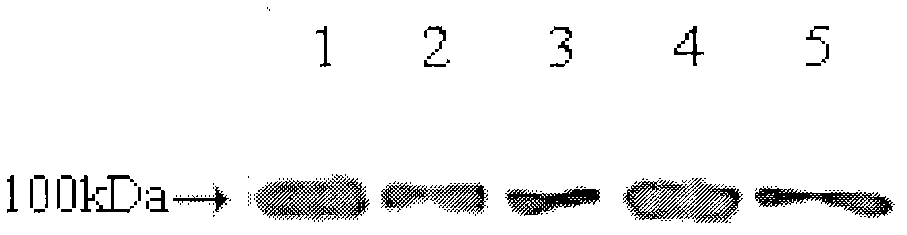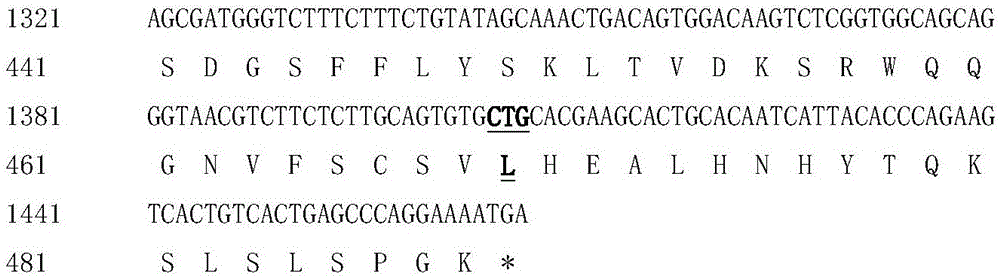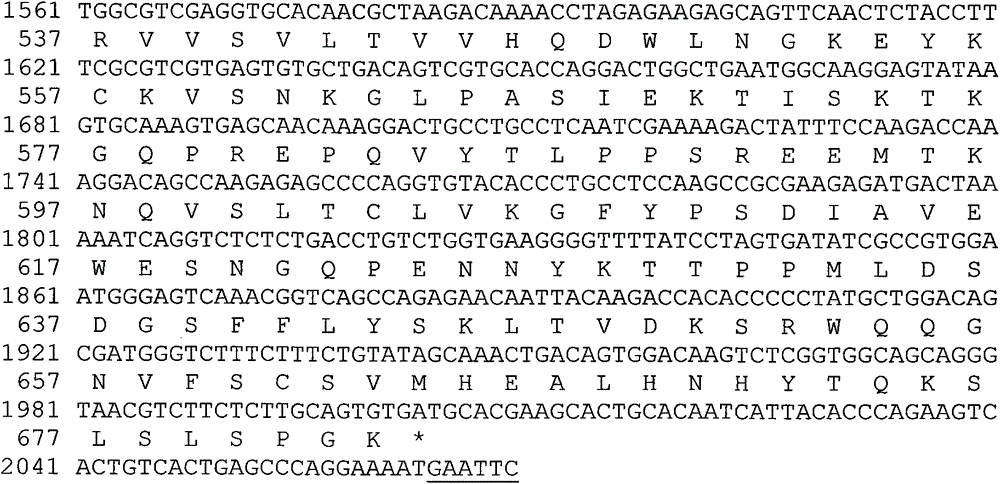Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Reduce the frequency of injections" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
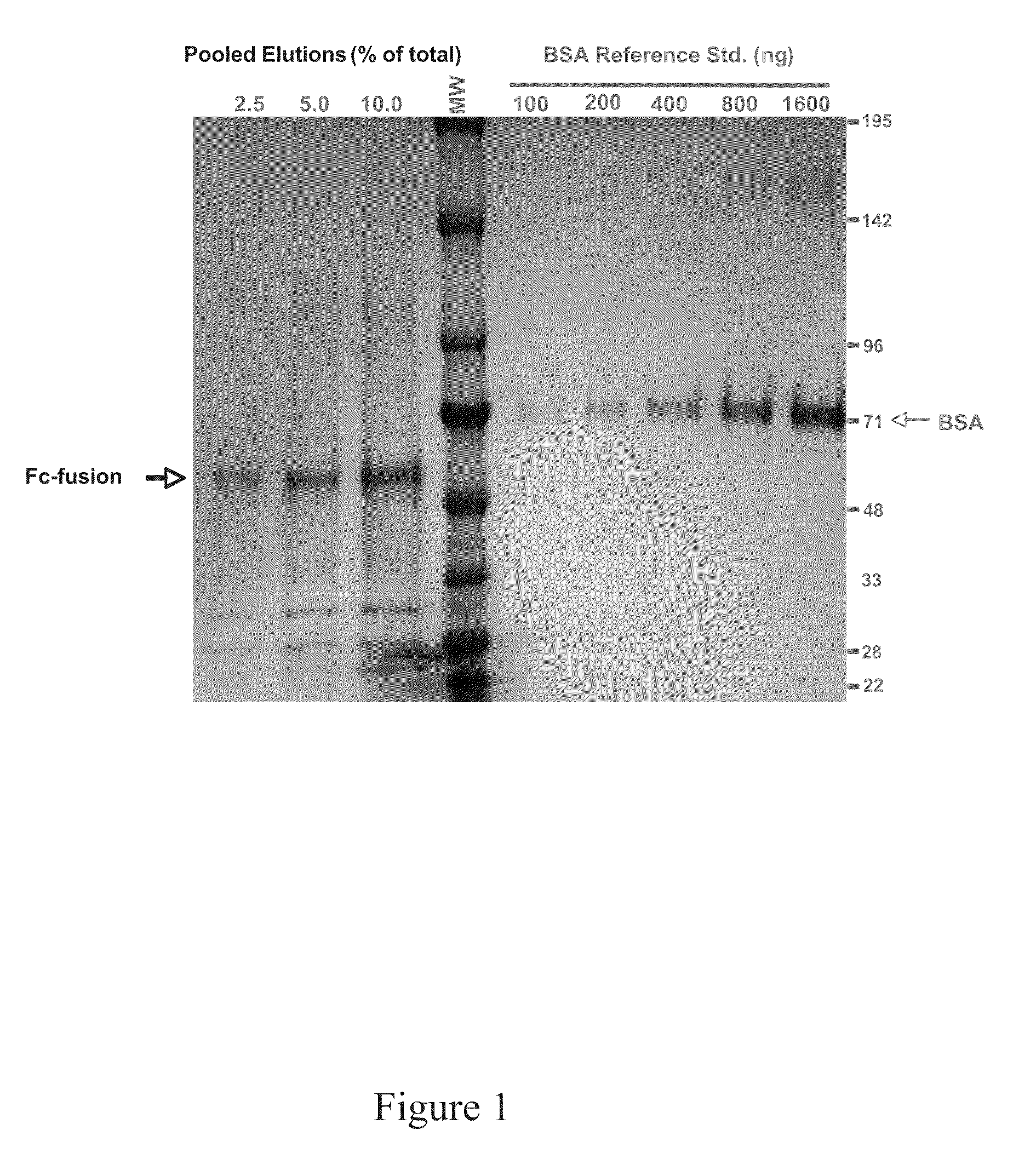
Production of fc-fusion polypeptides in eukaryotic algae
InactiveUS20110151515A1Increase serum stabilityEfficient separation and purificationUnicellular algaeVaccinesHeterologousProtein regulation
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer plastids comprising heterologous genes encoding immuno-activating domains fused to an extracellular domain (ECD) of a receptor or surface glycoprotein, a growth factor or an enzyme and produced within a subcellular organelle, such as a chloroplast. The immuno-activating domains may include those regions of a protein capable of modulating the interaction between immune effector cells via proteins containing stereoselective binding domains and specific ligands, such as the Fc regions of antibodies. The present disclosure also demonstrates the utility of plants, including green algae, for the production of complex multi-domain fusion proteins as soluble bioactive therapeutic agents.
Owner:SAPPHIRE ENERGY
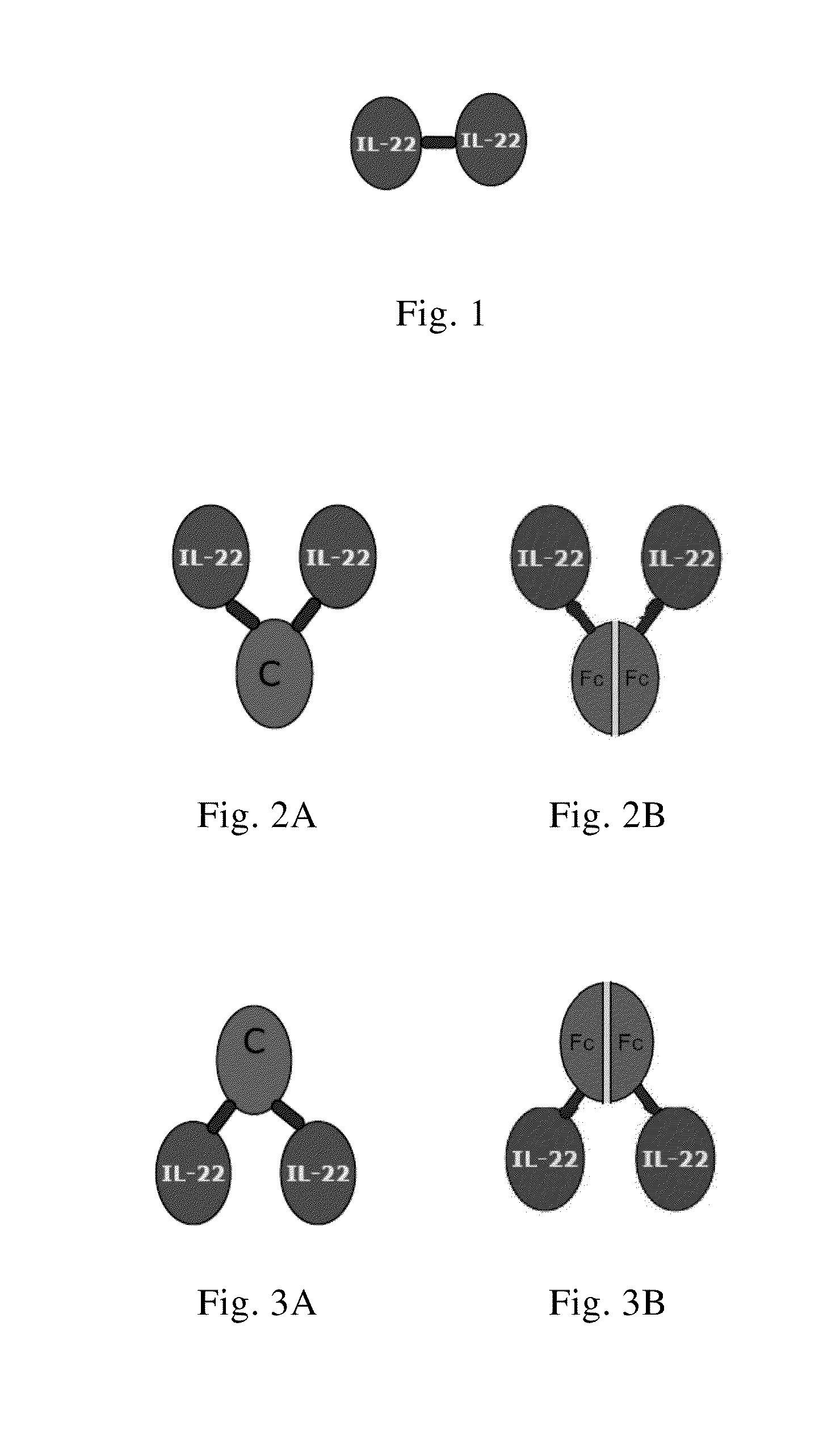
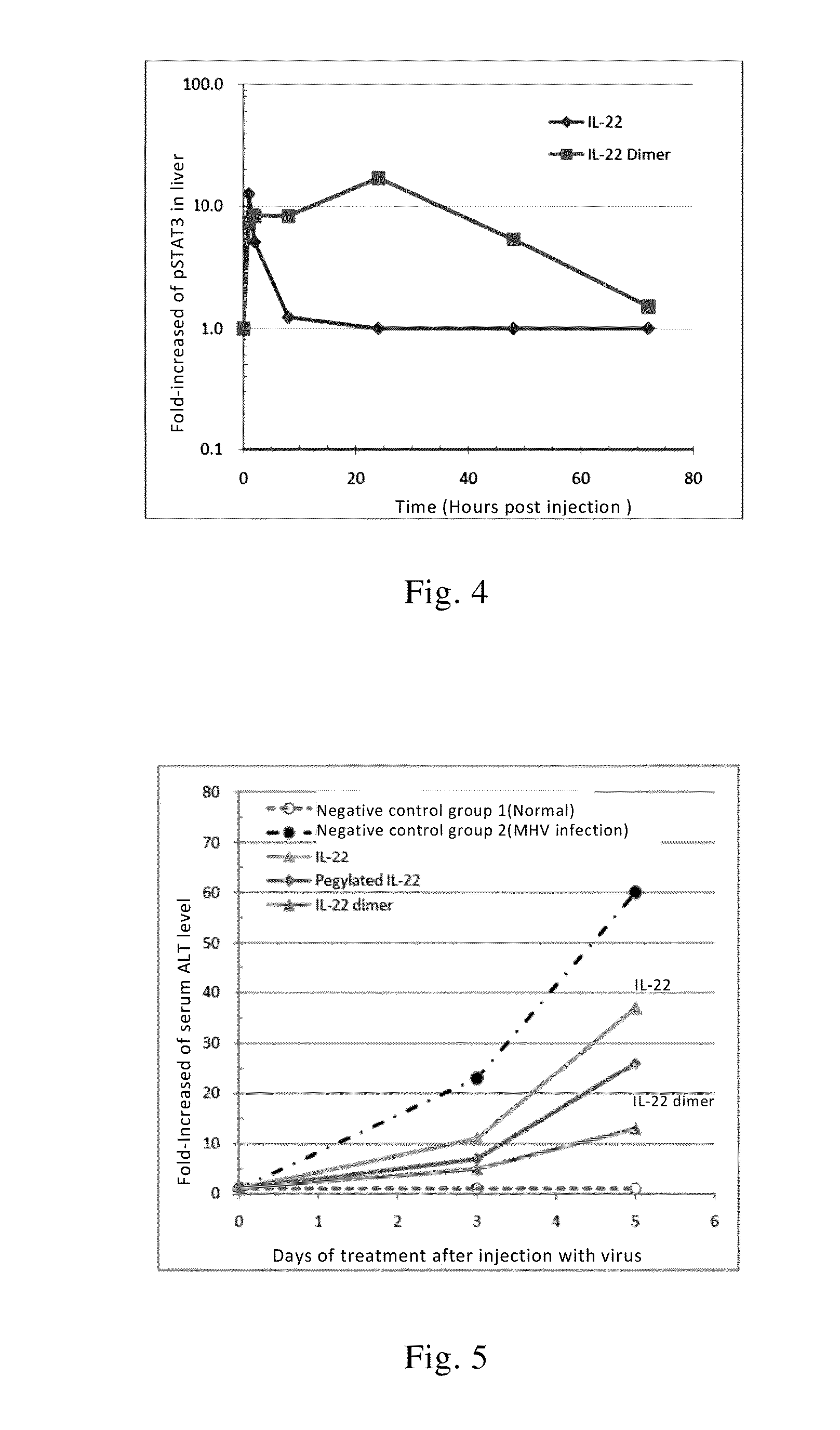
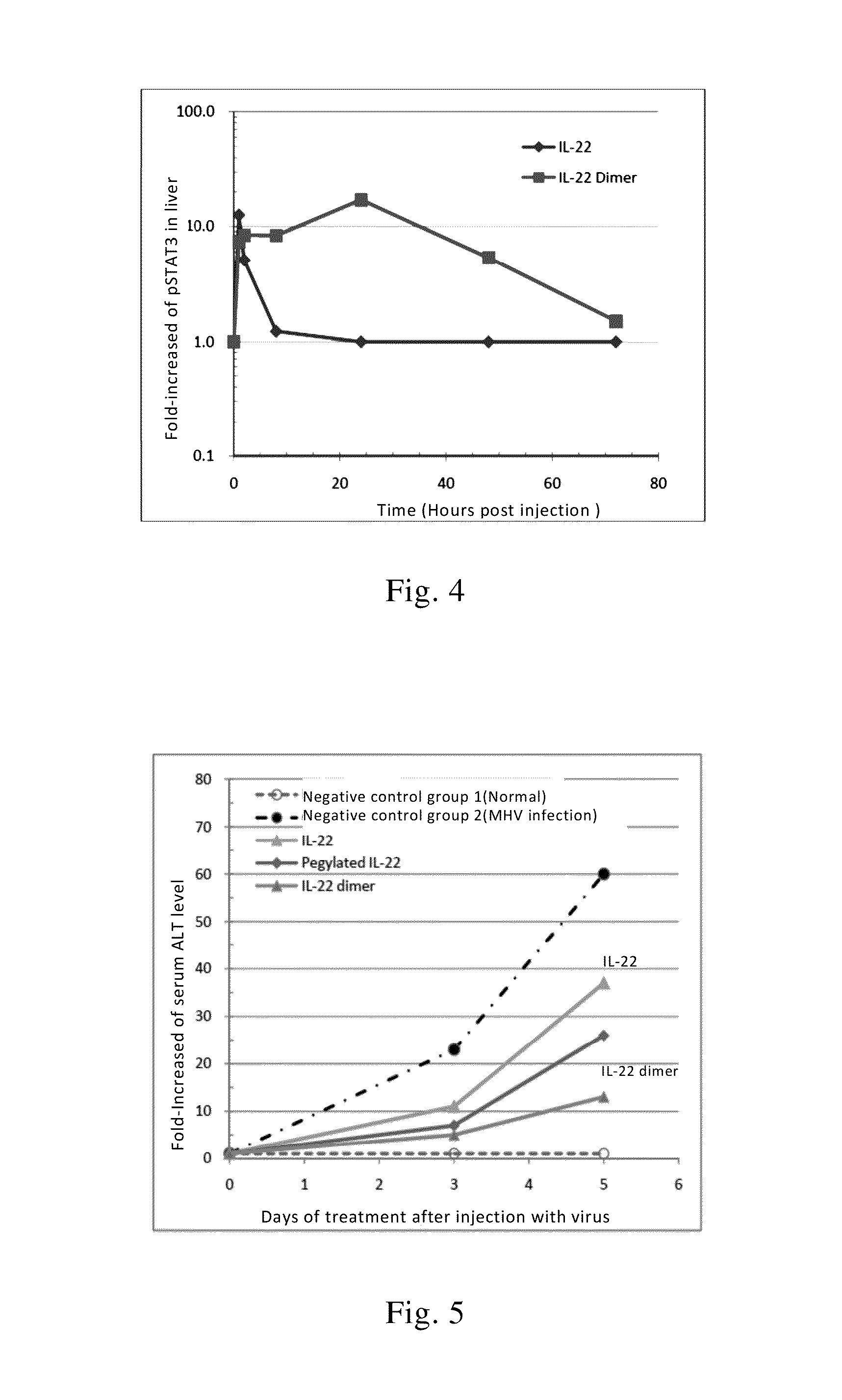
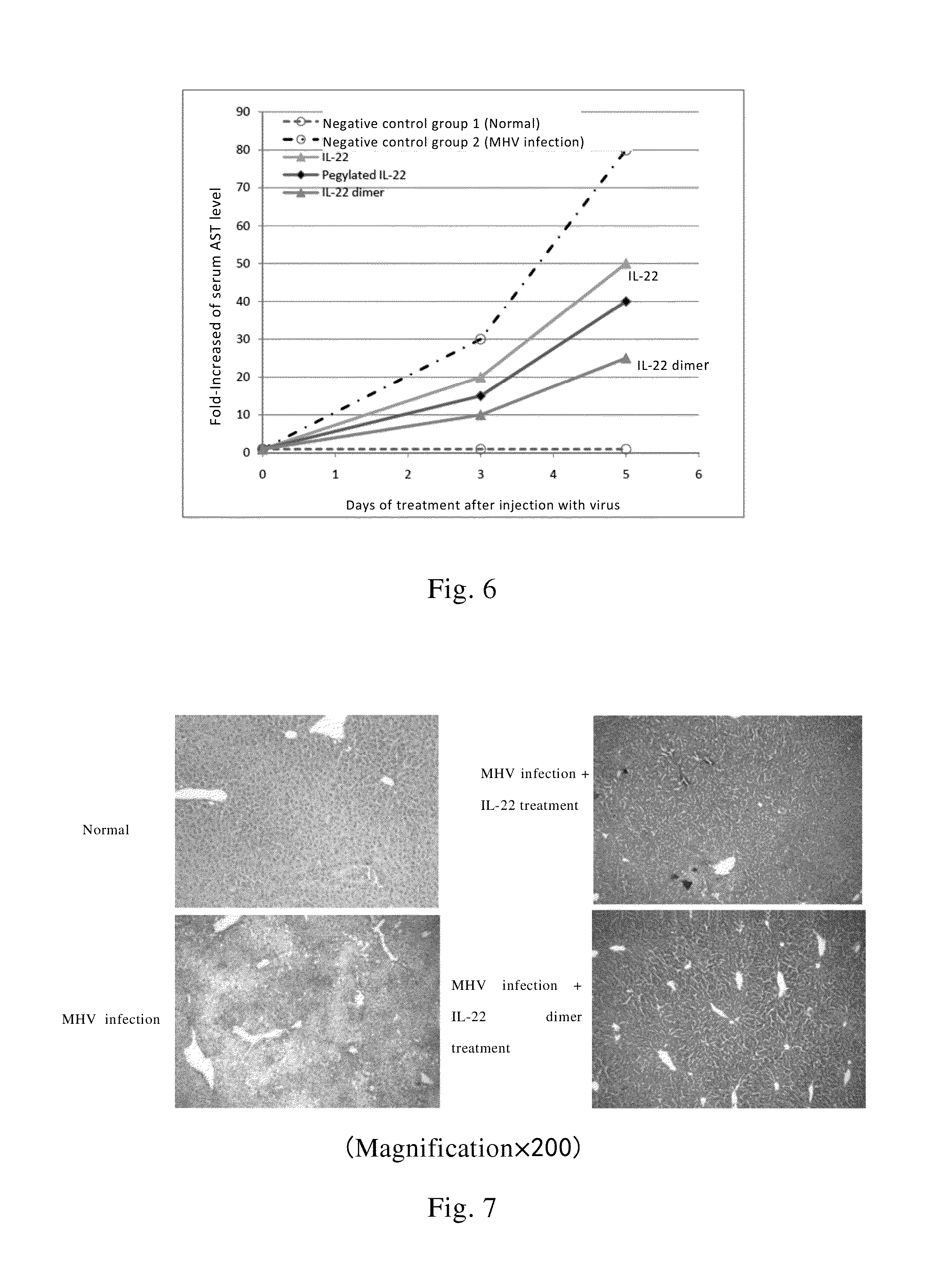
Use of interleukin-22 in treating viral hepatitis
ActiveUS20130171100A1Good curative effectEffective treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemViral hepatitis bViral hepatitis
This invention relates to a use of IL-22 in the treatment of viral hepatitis. As illustrated in the examples of this invention, IL-22 can significantly reduce liver damage caused by hepatitis virus, and can significantly reduce the increase of transaminase ALT / AST induced by hepatitis virus. In addition, the IL-22 dimer of this invention can effectively treat viral hepatitis.
Owner:EVIVE BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) LTD
Long-acting recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone-Fc fusion protein (hFSH-Fc)
ActiveCN103539861AImprove biological activityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSide effectRecombinant human follicle stimulating hormone
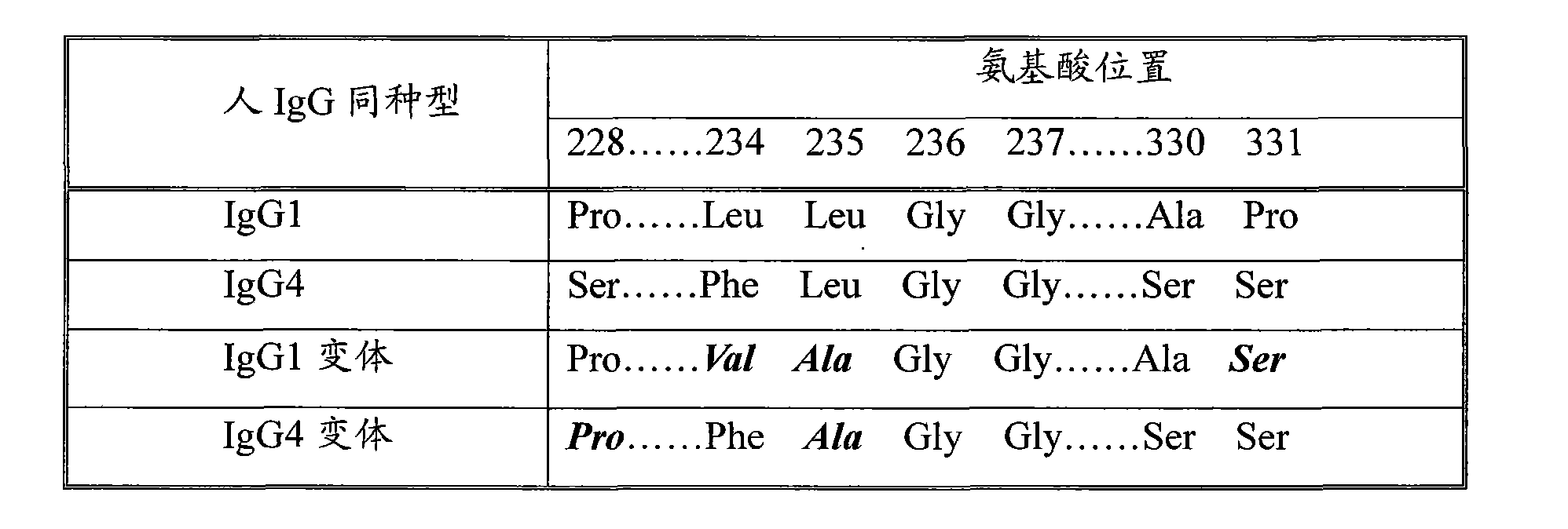
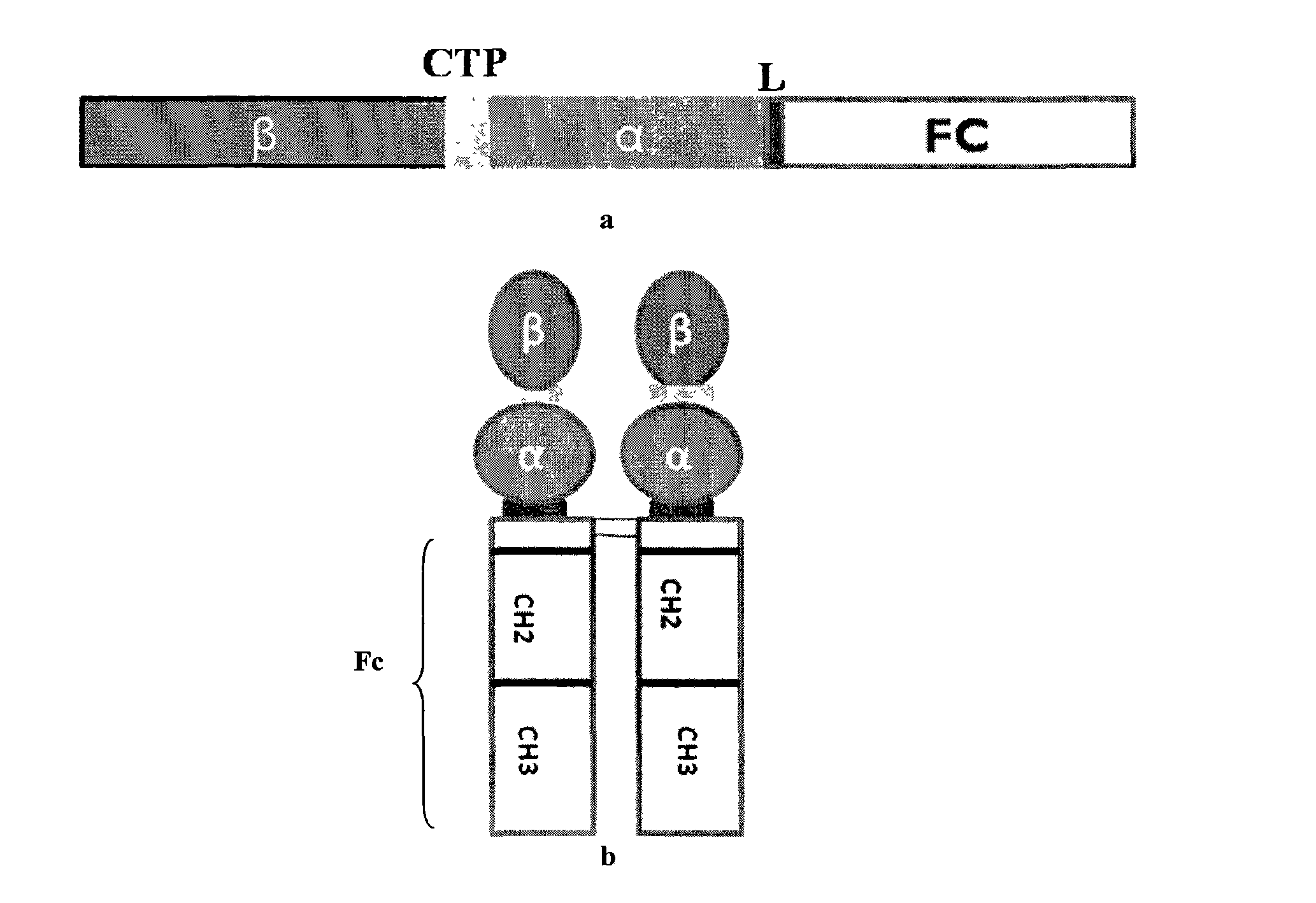
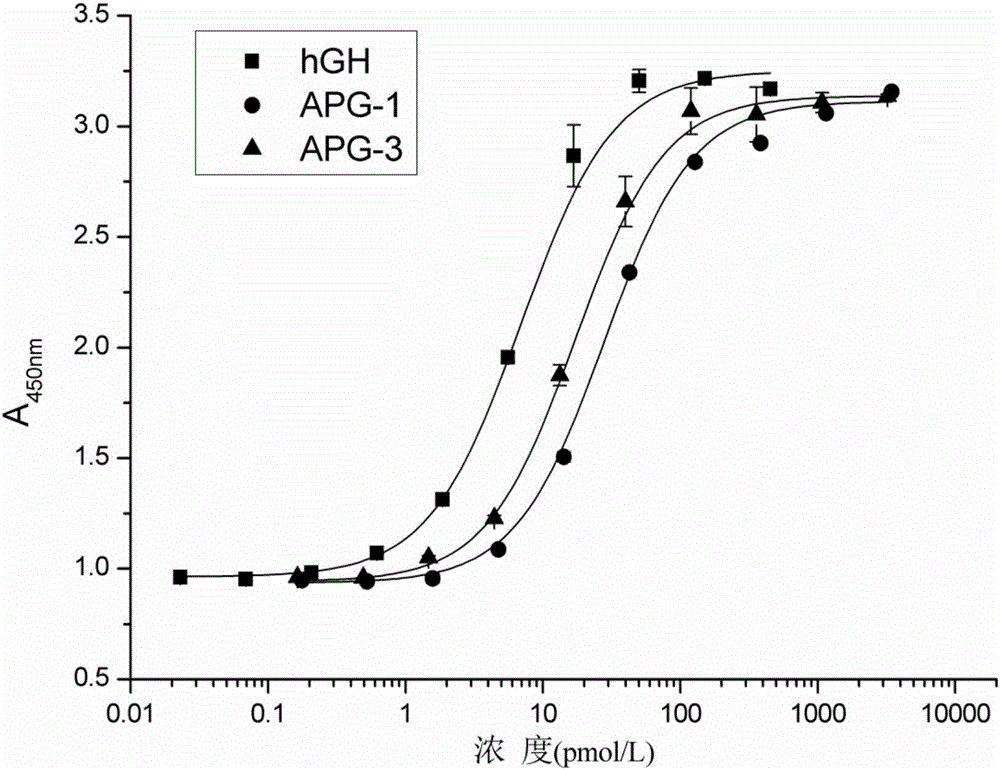
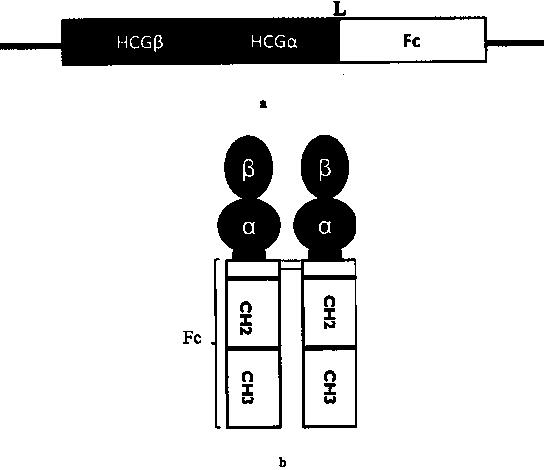
The invention discloses a long-acting recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone-Fc fusion protein (hFSH-Fc) and a preparation method thereof. The hFSH-Fc is a dimerization fusion protein. An amino acid sequence of the hFSH-Fc comprises an hFSHbeta subunit, CTP (carboxy-terminal peptide), an hFSHalpha subunit, a flexible peptide linker and a human IgG (immunoglobulin G) Fc variant from the N terminal to the C terminal in sequence. The hFSH-Fc has longer half-life in vivo and smaller side effects than existing hFSH. The invention also relates to an application of a recombinant hFSH-Fc composition to preparation of drugs for treating and / or preventing infertility.
Owner:UNICOHEALTH CO LTD
Preparation and application of human fibroblast growth factor 21 fusion protein and mutant of human fibroblast growth factor 21 fusion protein
InactiveCN102558358AGood effectStrong penetrating powerPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHalf-lifeHinge region
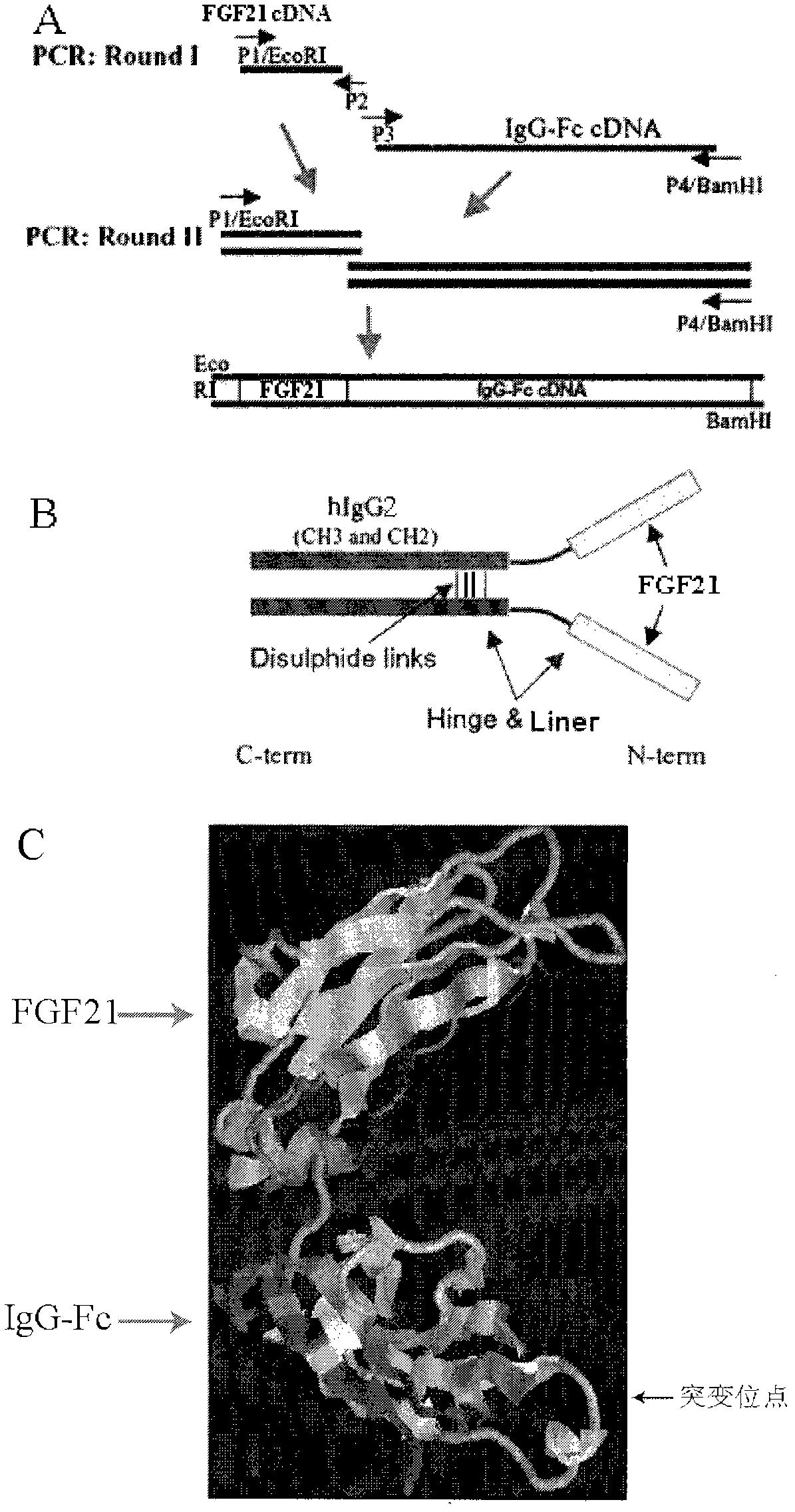
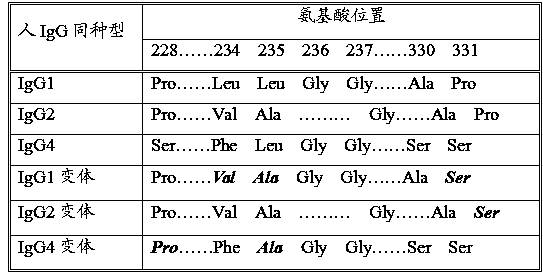
The invention provides a fusion protein used for detecting and treating human I-type diabetes mellitus and human II-type diabetes mellitus and obesity as well as a preparation and an application of the fusion protein. The fusion protein contains a human FGF21 or a mutant thereof and a human IgG2-Fc (hinge region -CH2-CH3) or a human IgG2-Fc mutant ( T250Q / M428L and T307Q / N434A), can improve the living condition of the obesity patients, reduce the blood sugar level of diabetics, effectively reduce aggregation and degradation of the FGF21 protein, and meanwhile prolong in vivo half-life period of the FGF21, and especially through the fusion of the FGF21 and the mutant and the IgG-Fc (T250Q / M428L and T307Q / N434A) mutant, the affinity with FcRn is enhanced, and in vivo half-life period of the FGF21 is further prolonged.
Owner:北京康明百奥科技有限公司
Human urinary trypsin inhibitor (hUTI) of reorganization-dimerization and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103044554AIncrease productionEfficient and convenient purificationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticURINARY TRYPSIN INHIBITORHalf-life
The invention discloses a human urinary trypsin inhibitor (hUTI) of reorganization-dimerization and preparation method and application thereof, wherein the hUTI protein of reorganization-dimerization successively comprises amino acid residue sequence of human UTI, a peptide linker and a human IgGFc variant from N-terminal to C-terminal. The hUTI protein of reorganization-dimerization has the in-vitro biological activity similar with that of the human urinary trypsin inhibitor, higher biological activity in vivo and an extended half-life period in vivo.
Owner:PHARMAB
Recombined long-acting glucagons peptide analogue and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101525387ABiologically activeImprove expression efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesHalf-lifeCurative effect
The invention relates to a recombined fusion protein, in particular discloses a recombined long-acting glucagons peptide analogue and a preparation method thereof. The long-acting glucagons peptide analogue is polypeptide by directly connecting duodenin analogue exendin-4 and human serum albumin, and no connecting peptide exists between the exendin-4 and the human serum albumin. The long-acting glucagons peptide analogue greatly prolongs the half-life of the exendin-4 and is clinically used to reduce the frequency of injection administration, lighten the suffering of patients, improve the curative effect and decrease the hospitalization cost.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Hyperglycosylated Extendin-4, fusion protein of analogue thereof, and preparation method and application of fusion protein
ActiveCN106117370AReduce fluctuations in drug concentrationReduce generation riskPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseHuman Chorionic Gonadotropin Beta Subunit
The invention discloses hyperglycosylated Extendin-4, fusion protein of analogue thereof, and a preparation method and the application of fusion protein. The fusion protein comprises Extendin-4, the analogue of the Extendin-4, a flexible peptide joint, at least one human chorionic gonadotropin beta carboxyl terminal peptide rigid unit and a human immunoglobulin Fc fragment. The invention also discloses the preparation method and the application of the fusion protein. The fusion protein has optimal biological activity, obviously prolonged circulation half-time, lowered immunogenicity and improved bioavailability. The fusion protein can be used for treating diabetes, obesity and other diseases benefited by lowering fasting plasma glucose, inhibiting stomach and / or bowel movement and inhibiting and / or bowel evacuation or inhibiting food intake.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
Modified exendins and uses thereof
ActiveUS8716221B2Long retention timeProlonged actionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineAgonist
The present invention discloses a modified exendin or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein the modified exendin comprises an amino acid sequence having at least 90% sequence identity to SEQ ID No. 17 and the amino acid sequence has a higher stability than the non-modified exendin of SEQ ID No. 4. These compounds are useful in treating type 2 diabetes as GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Owner:JIANGSU HANSOH PHARMA CO LTD
Modified exendins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120196802A1Improve actionInduce secretion of insulinPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAgonistAmino acid
The present invention discloses a modified exendin or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein the modified exendin comprises an amino acid sequence having at least 90% sequence identity to SEQ ID No. 17 and the amino acid sequence has a higher stability than the non-modified exendin of SEQ ID No. 4. These compounds are useful in treating type 2 diabetes as GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Owner:JIANGSU HANSOH PHARMA CO LTD
Hyperglycosylated human growth hormone fusion protein and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106256835AImprove stabilityLow immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
The invention discloses hyperglycosylated human growth hormone fusion protein. The human growth hormone fusion protein sequentially contains a human growth hormone (hGH), a flexible peptide joint (L), human chorionic gonadotropin beta-carboxyl terminal rigid peptide (CTP) and a human immunoglobulin Fc fragment from the N terminal to the C terminal. The invention further discloses a method for efficiently preparing the fusion protein. Compared with a recombinant hGH, the built fusion protein has more excellent in-vivo drug efficacy, the in-vivo circulation half-life period is prolonged, the administration frequency is greatly decreased, and the bioavailability is improved; meanwhile, the production process is simpler and more efficient.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
Long-acting recombinant human chorionic gonadotrophin-Fc fusion protein
ActiveCN103897064AImprove biological activityProlong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsProtein compositionHalf-life
The invention discloses a recombinant human chorionic gonadotrophin-Fc fusion protein (HCG-Fc for short) and a preparation method thereof. The HCG-Fc protein is a dimerized fusion protein, and the amino acid sequence of the fusion protein sequentially comprises an HCG beta subunit, an HCG alpha subunit, a flexible peptide joint and a human IgG Fc mutant from an N end to a C end. Compared with the existing chorionic gonadotrophin, the fusion protein has longer in-vivo half life, higher bioavailability and lower side effect. The invention also relates to an application of a recombinant HCG-Fc fusion protein composition in preparation of medicaments for treating and / or preventing infertility.
Owner:UNICOHEALTH CO LTD
Use of interleukin-22 in treating viral hepatitis
ActiveUS8945528B2Effective treatmentProlong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsWhite blood cellViral hepatitis b
This invention relates to a use of IL-22 in the treatment of viral hepatitis. As illustrated in the examples of this invention, IL-22 can significantly reduce liver damage caused by hepatitis virus, and can significantly reduce the increase of transaminase ALT / AST induced by hepatitis virus. In addition, the IL-22 dimer of this invention can effectively treat viral hepatitis.
Owner:EVIVE BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) LTD
High-glycosylation human growth hormone fusion protein and preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN107286248AReduced effector functionImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman Chorionic Gonadotropin Beta SubunitHalf-life
The invention discloses high-glycosylation human growth hormone fusion protein. The human growth hormone fusion protein provided by the invention is characterized in that human growth hormone (hGH), flexible peptide joint (L), at least one human chorionic gonadotropin beta-subunit carboxyl terminated rigid peptide (CTP) and human immunoglobulin Fc fragments are sequentially contained from the end N to the end C. The invention also discloses a method for effectively preparing the fusion protein. The built fusion protein has more excellent in vivo medicine effect than recombination hGH; the in vivo circulation half-life period is prolonged; the medication administration frequency is greatly reduced; in addition, the bioavailability is improved; meanwhile, the production process is more simple and efficient.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
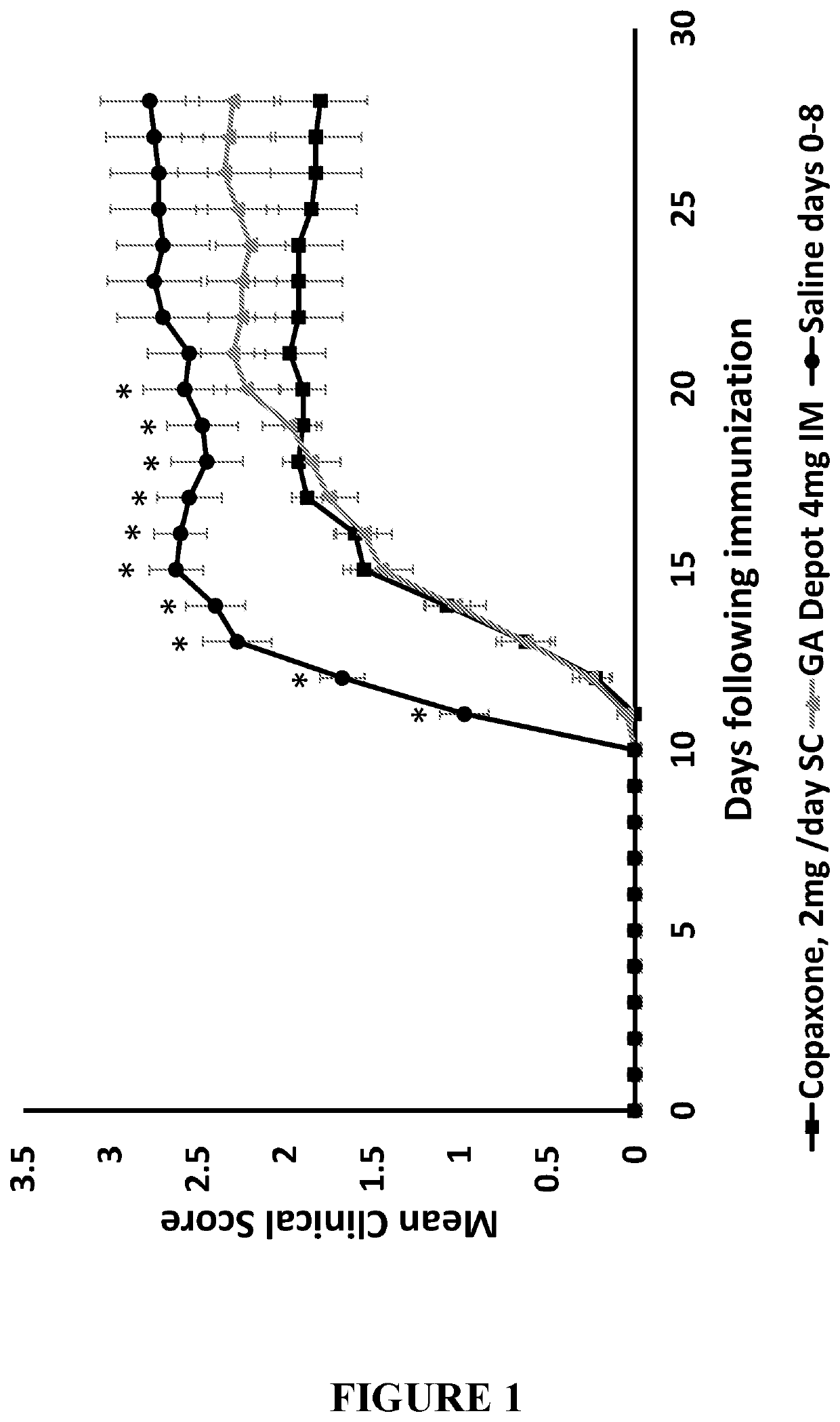
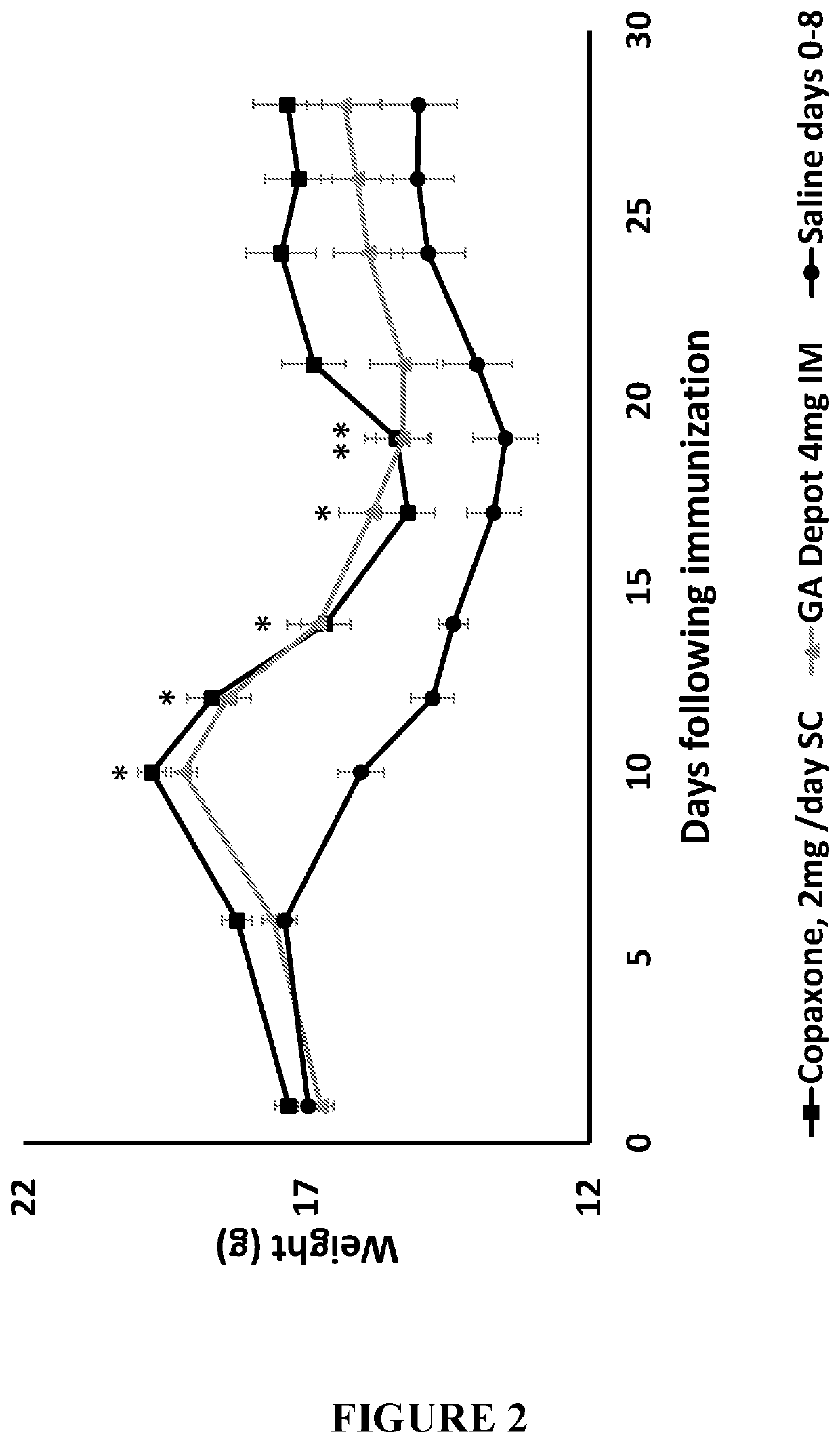
Depot systems comprising glatiramer or pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof
ActiveUS20120164229A1Low levelReduce in quantityPowder deliveryNervous disorderGlatiramer acetateLong acting
The present invention provides long acting parenteral pharmaceutical compositions comprising a therapeutically effective amount of glatiramer. In particular, the present invention provides a long acting pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of glatiramer acetate in depot form suitable for administering at a medically acceptable location in a subject in need thereof. The depot form is suitable for subcutaneous or intramuscular implantation or injection.
Owner:MAPI PHARMA
Aqueous solution of recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101954067AReduced clearance rateProlong biological half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineInterferon alpha
The invention relates to stable aqueous solution of a recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and belongs to the technical field of biological preparations. The aqueous solution of the recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein is prepared by dissolving the recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and pharmaceutically acceptable stable auxiliary material in pharmaceutically acceptable buffer solution, and is characterized in that the pharmaceutically acceptable stable auxiliary material is arginine at a concentration of 5 to 30 g / L. The aqueous solution of therecombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein can prevent the aggregation, degradation, oxidation, denaturation and the like of the recombinant fusion protein effectively so as to retain bioactivity and is suitable to be used in clinic.
Owner:QILU PHARMA
Exendin-4 analogue fusion protein and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106279430AReduce fluctuations in drug concentrationImprove the quality of lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseHalf-life
The invention discloses an Exendin-4 analogue fused with a human IgG2 Fc variation and a preparation method of the Exendin-4 analogue. The circulating half-life period of the fusion protein is remarkably prolonged, and the biological availability is greatly improved. The fusion protein can be used for treating diabetes, obesity and other diseases that are benefited by lowering plasma glucose, inhibiting gastric and / or intestinal motion and inhibiting gastric and / or intestinal emptying or inhibiting food intake.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
Long-acting recombinant human growth hormone fusion protein and engineering cell thereof
ActiveCN110256575ADecreased ADCC activityExtended half-lifeAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGrowth hormonesHalf-lifeIn vivo
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, in particular to the technical field of gene recombination long-acting human growth hormone. The invention particularly relates to a long-acting recombinant human growth hormone fusion protein and an engineering cell thereof. By the long-acting recombinant human growth hormone fusion protein rhGH-Fc, the serum half-life can be prolonged, the biological activity of the protein in vivo is improved, the immunogenicity of the protein is reduced, therefore, the drug effect is improved, the required injection administration frequency in the treatment time is greatly reduced, the compliance of patients is improved, and convenience of doctors and patients is improved; and the engineering cell for expressing rhGH-Fc constructed by the invention has the characteristics of high protein expression amount and good biological activity, and is particularly suitable for industrial large-scale preparation of gene recombinant long-acting human growth hormone.
Owner:长春生物制品研究所有限责任公司
PH response insulin slow release nanoparticle, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106581647AConcentration fluctuates greatlyModerate particle sizePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderControlled releaseNanocapsules
The invention relates to a pH response insulin slow release nanoparticle, and a preparation method and an application thereof, and concretely discloses a triblock copolymer. The triblock copolymer is an A-B-C block copolymer, wherein the A block is biodegradable polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether, and the molecular weight is 4000-6000; the B block is polycaprolactone, and the molecular weight is 8000-15000; and the C block is N,N-diethylaminoethyl polybasic polymethacrylate, and the molecular weight is 8000-12000. The pH response insulin slow release nanoparticle is formed by a nanocapsule formed by self-assembling the triblock polymer and insulin loaded on the nanocapsule. The nanoparticle can accurately deliver drugs according to different pH values, and can simultaneously reach sustained and controlled release effects.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Highly glycosylated exendin-4 and its analogue fusion protein, its preparation method and use
ActiveCN106117370BReduce fluctuations in drug concentrationReduce generation riskPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseBlood plasma
The invention discloses hyperglycosylated Extendin-4, fusion protein of analogue thereof, and a preparation method and the application of fusion protein. The fusion protein comprises Extendin-4, the analogue of the Extendin-4, a flexible peptide joint, at least one human chorionic gonadotropin beta carboxyl terminal peptide rigid unit and a human immunoglobulin Fc fragment. The invention also discloses the preparation method and the application of the fusion protein. The fusion protein has optimal biological activity, obviously prolonged circulation half-time, lowered immunogenicity and improved bioavailability. The fusion protein can be used for treating diabetes, obesity and other diseases benefited by lowering fasting plasma glucose, inhibiting stomach and / or bowel movement and inhibiting and / or bowel evacuation or inhibiting food intake.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
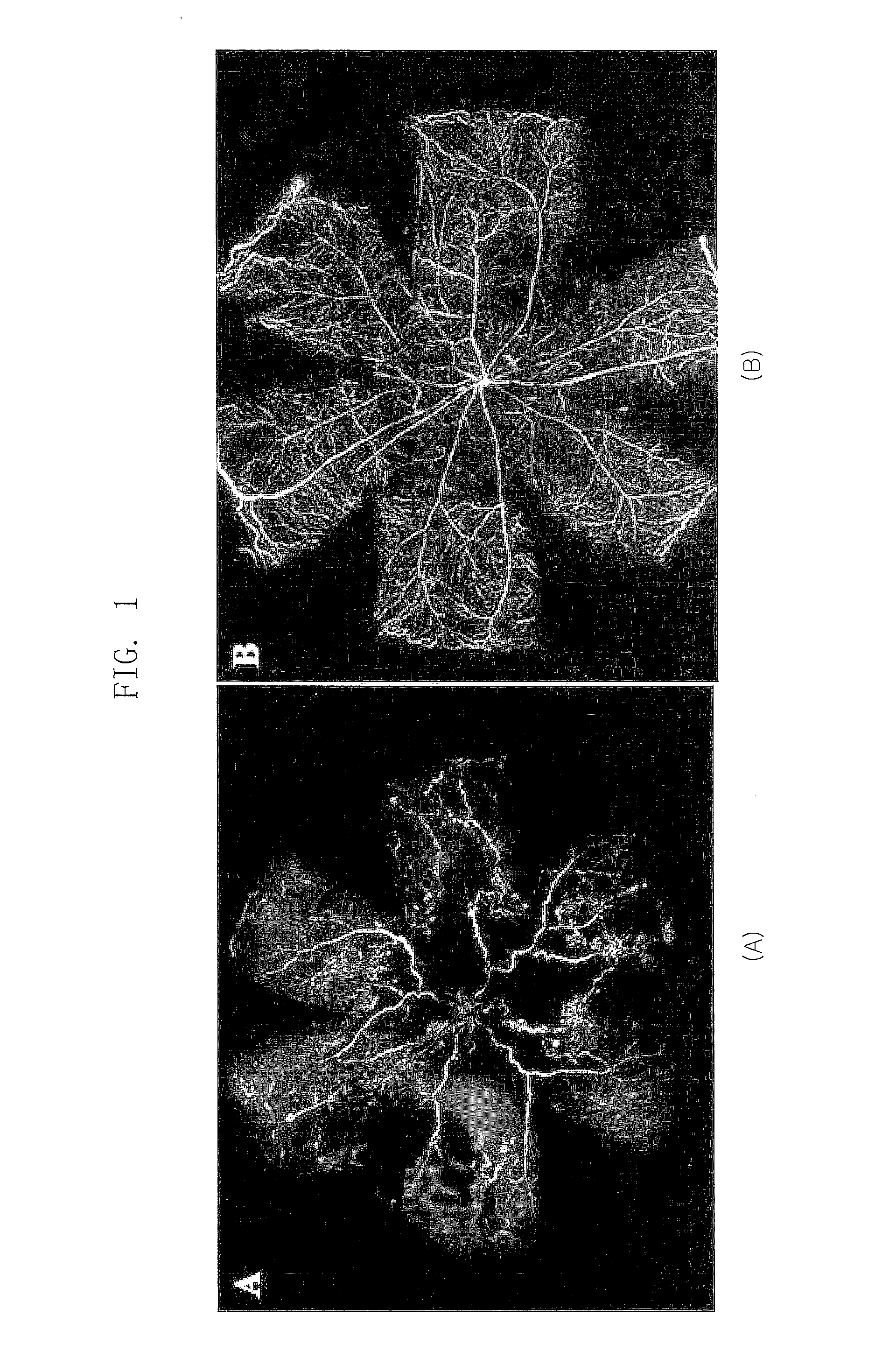
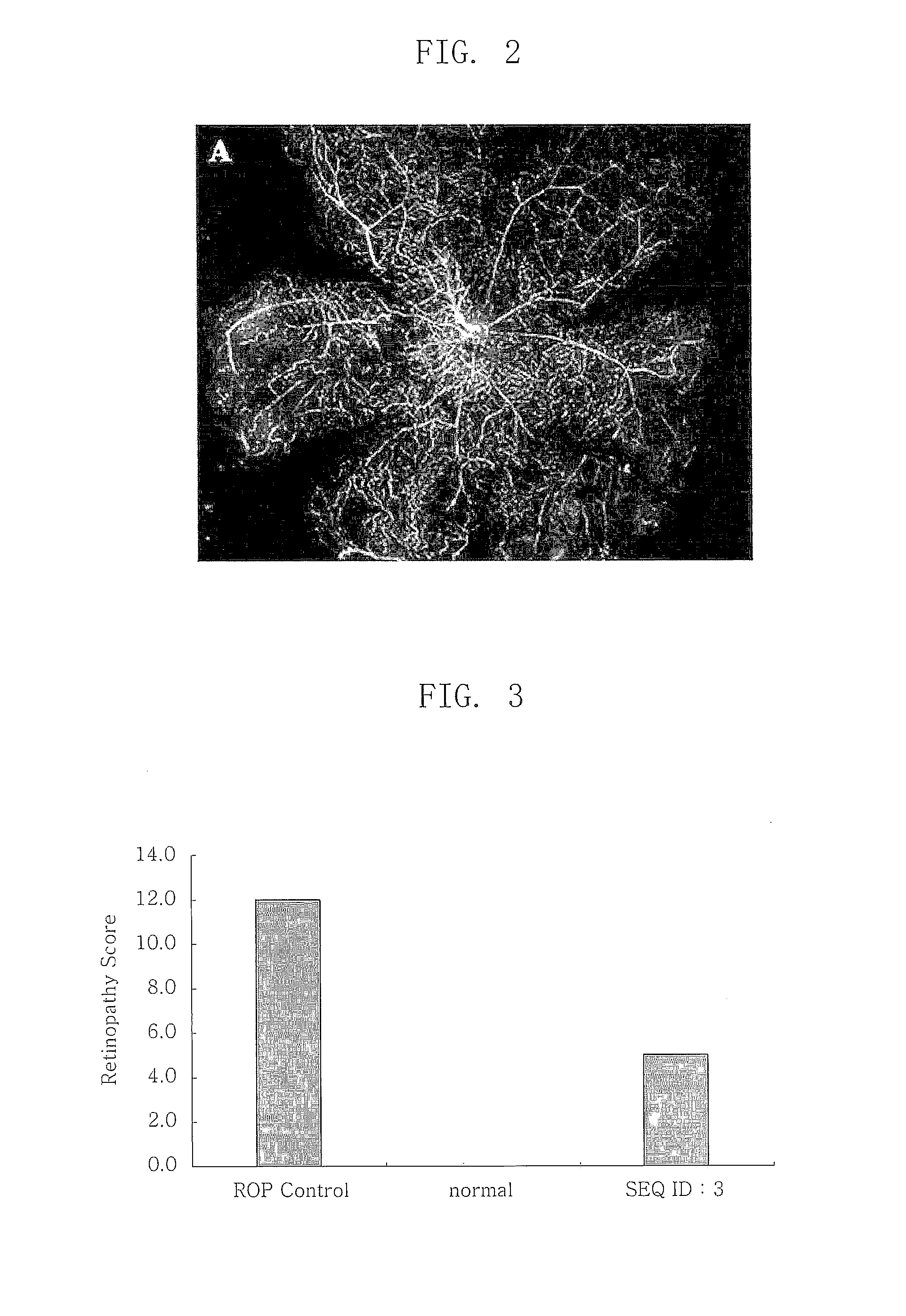
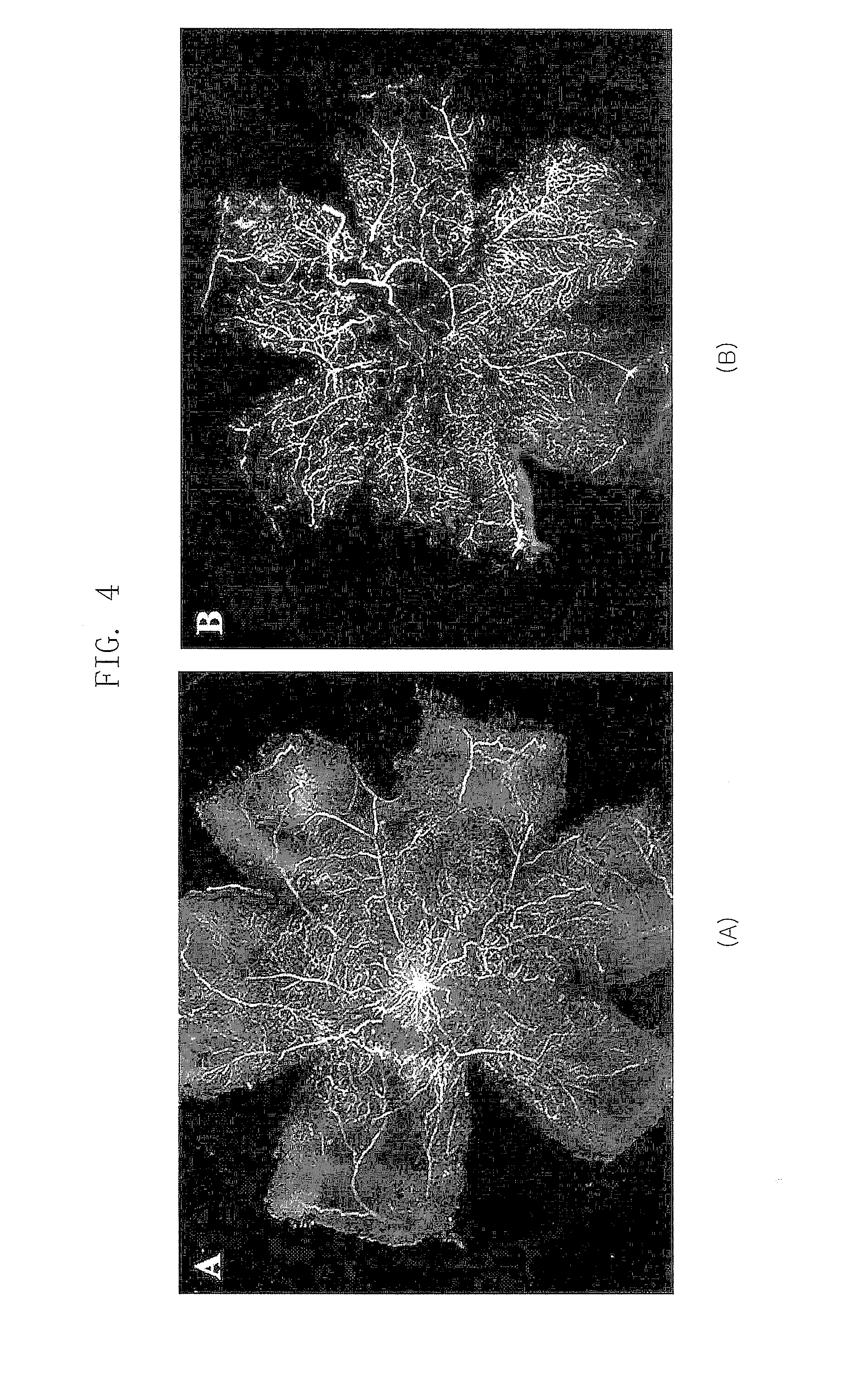
Composition for Treating Retinopathy or Glaucoma Comprising Thrombin Derived Peptides
ActiveUS20100297100A1Reduce the frequency of injectionsReduce formationSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGlaucomaThrombin activity
Disclosed is a composition for treating retinopathy comprising thrombin derived peptide as an effective component.
Owner:EYEGENE INC
Drug Delivery Carrier
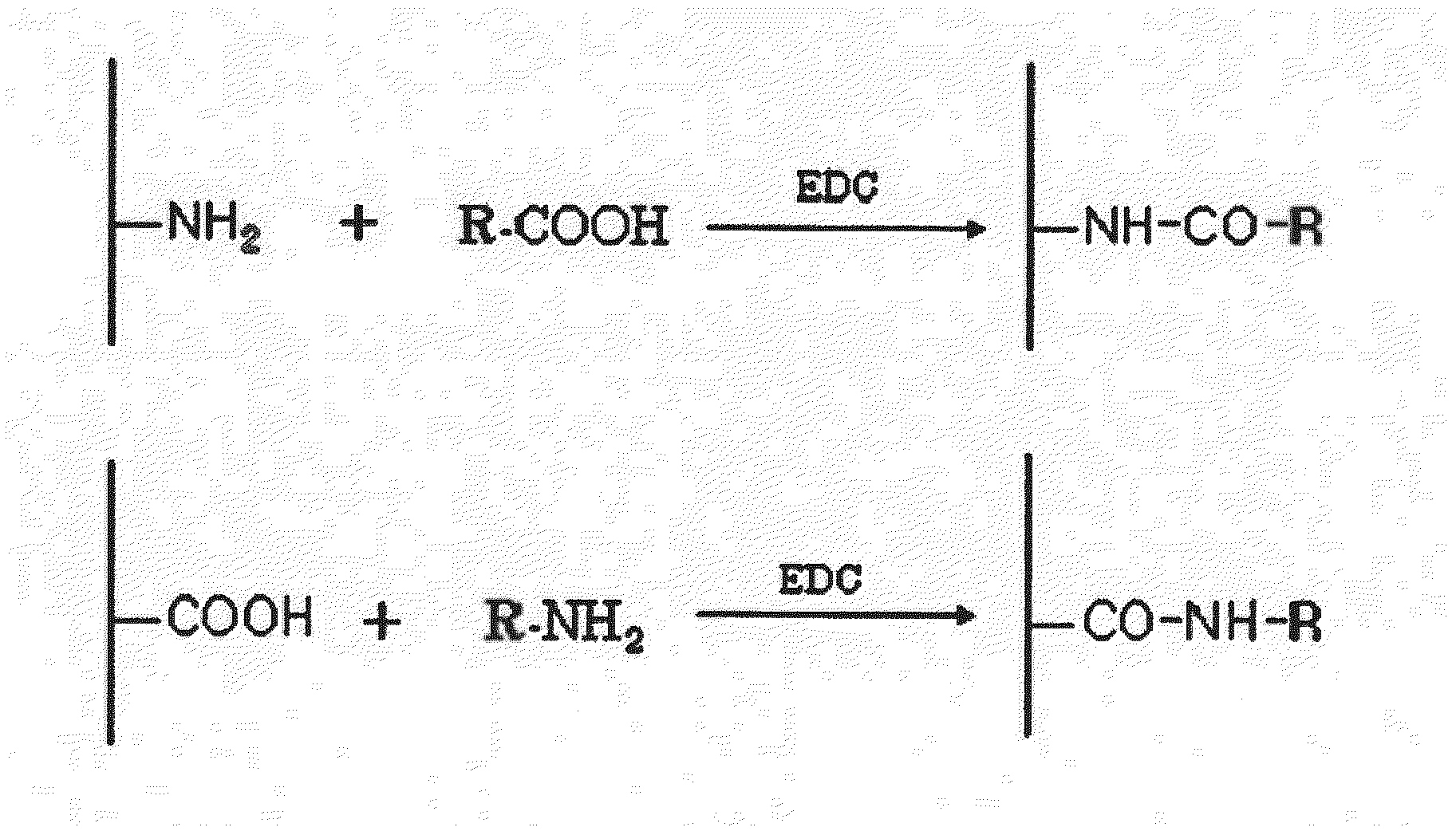
InactiveUS20110136722A1Improve bioavailabilityLow water solubilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug adsorptionPharmaceutical Substances
The present disclosure relates to a method for the sustained release of a drug, comprising the steps of: (a) preparing a biocompatible polymer having a hydrophobic group conjugated to the biocompatible polymer; and (b) contacting the biocompatible polymer to the drug for adsorbing the drug to the hydrophobic group of the biocompatible polymer, thereby obtaining a drug delivery carrier for the sustained release of the drug; wherein the drug is a protein, a peptide or a non-hydrophilic chemical drug; wherein when the drug adsorbed to the hydrophobic group of the biocompatible polymer is administered to a mammal, it shows a sustained release profile in the mammal. The drug delivery carrier according to the present disclosure having the hydrophobic group conjugated to the biocompatible polymer may be useful for adsorption of synthetic drugs having very low solubility in water. Further, it may regulate discharge rate of adsorbed drugs by regulating a portion of hydrophobic groups conjugated to the polymeric material. Thus, the present disclosure provides a broad-spectrum platform technology applicable to new hydrophobic synthetic drugs to be developed in the future as well as those that have been developed already but face difficulties due to low bioavailability.
Owner:PRONEXX
GLP-1 analogue-Fc fusion protein and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110172103AIncreases the half-life of circulation in the bodyProlonged circulating half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDrug injectionHalf-life
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and specifically relates to GLP-1 analogue-Fc fusion protein and a preparation method and application thereof. The GLP-1 analogue-Fc fusion protein structurally comprises a GLP-1 analogue and an antibody Fc fragment. The GLP-1 analogue-Fc fusion protein involved in the invention effectively increases an in vivo circulation half-life period of the GLP-1 analogue, enhances in vivo and in vitro activity and stability of the GLP-1 analogue, improves affinity with FcRn, enhances penetrability and transcellular action of an in vivo tissue system of the GLP-1 analogue, improves drug effects, reduces drug injection frequency, relieves pain of patients and reduces treating cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEMO WANBANG BIOPHARMA
Exendin-4 analog fusion protein and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN106279430BReduce fluctuations in drug concentrationImprove the quality of lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseIntestinal structure
The invention discloses an Exendin-4 analogue fused with a human IgG2 Fc variation and a preparation method of the Exendin-4 analogue. The circulating half-life period of the fusion protein is remarkably prolonged, and the biological availability is greatly improved. The fusion protein can be used for treating diabetes, obesity and other diseases that are benefited by lowering plasma glucose, inhibiting gastric and / or intestinal motion and inhibiting gastric and / or intestinal emptying or inhibiting food intake.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
Recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103432569AReduced clearance rateProlong biological half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAdjuvantArginine
The invention relates to a stable recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution, belonging to the technical field of biological agents. The stable recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution is prepared by dissolving a recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable stability adjuvant in a pharmaceutically acceptable buffer solution. The invention is characterized in that the pharmaceutically acceptable stability adjuvant is arginine, and the concentration is 5-30 g / L. The recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution provided by the invention can sufficiently prevent the recombinant fusion protein from aggregation, degradation, oxidation, denaturization or the like, thereby keeping the biological activity of the recombinant fusion protein; and the recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution is suitable for clinical application.
Owner:QILU PHARMA CO LTD
Depot systems comprising glatiramer acetate
PendingUS20210283209A1Reduce in quantityReduce frequencyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMS multiple sclerosisPharmacology
The present invention provides compositions and methods of use thereof for treating or ameliorating multiple sclerosis (MS) by administering a depot formulation comprising 40 mg glatiramer acetate intramuscularly to the MS patient.
Owner:MAPI PHARMA
Fusion protein for serum albumin and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist and uses thereof
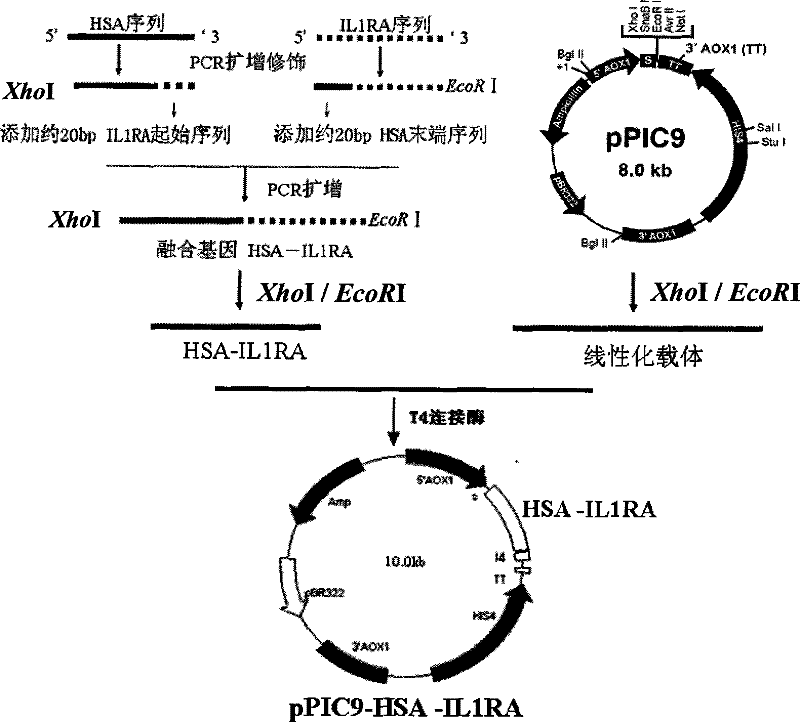
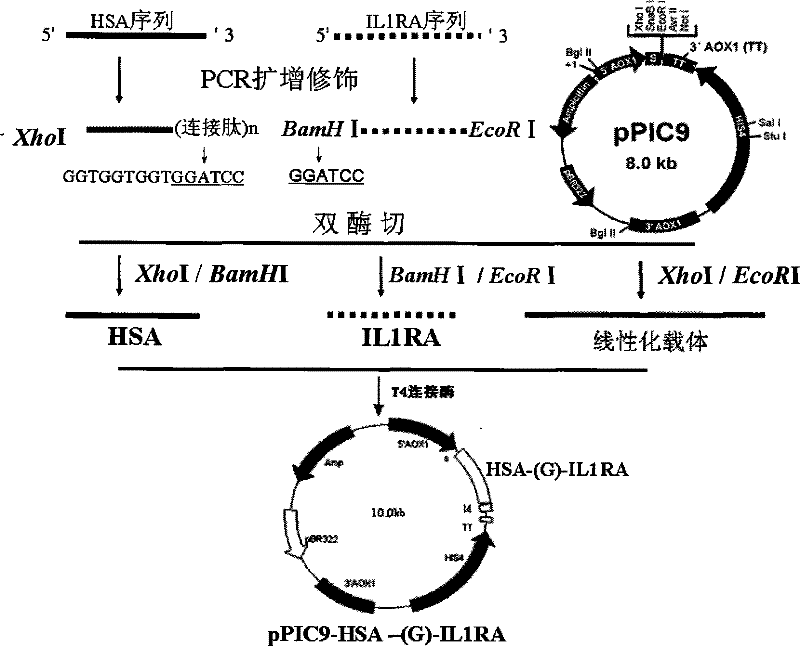
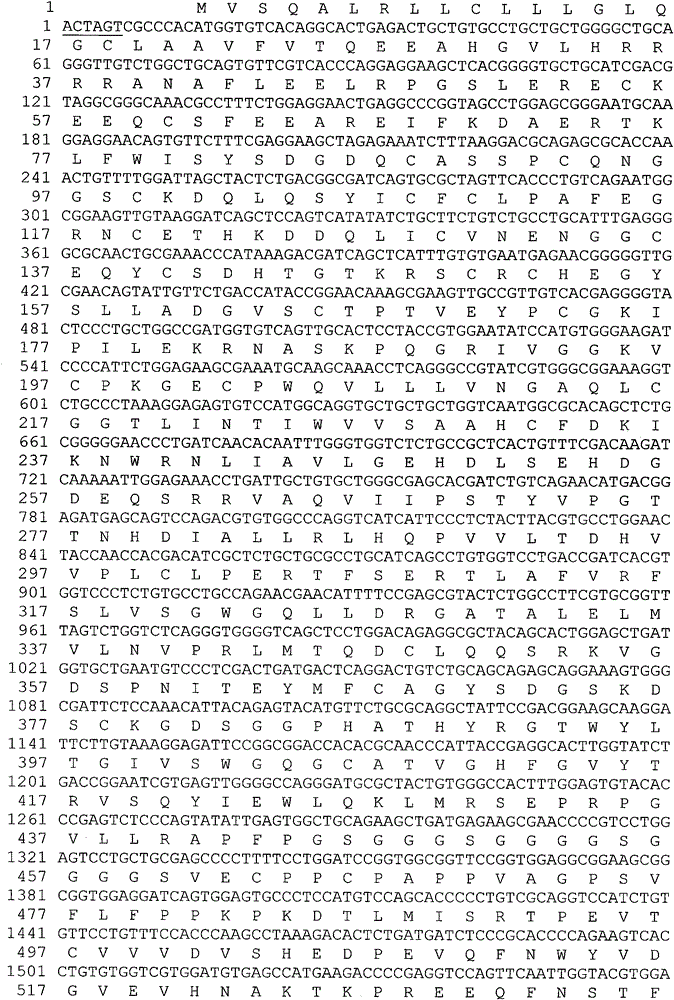
ActiveCN101255197BReduce clearanceExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticSide effectHalf-life
The invention provides a amalgamation albumen of serum albumin and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, comprising human serum albumin HAS, peptide joint and human interleukin1 receptor antagonist IL1ra, wherein the peptide joint is 0-20 aminophenol long and exists between human HSA and human IL1ra, the construct is [GlyGlyGlyGlyser]<n>, n represents an integer from 0 to 4. The amalgamation albumen is obtained by constructing recombination pichia cell line, inducing expression of recombination amalgamation albumen in a growth culture medium and purifying. The amalgamation albumen, on the basis of original vivo and vitro biology function, reduces the clearance of IL1ra in vivo, prolongs the half-life of IL1ra in vivo, decreases dose and ejection frequency, make the maximum treat action, reduces the potential side effect of IL1ra or toxicity, improves safety and tolerance, is substantial an aid to treat moderate and bad rheumatoid arthritis, and can be used in the preparation of interleukin receptor antagonist.
Owner:HISUN BIORAY PHARMA CO LTD +1
Pharmaceutical composition containing modified type human coagulation factor FVII-Fc fusion protein
InactiveCN103599527AIncrease productionEfficient and convenient purificationPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesSide effectLysis
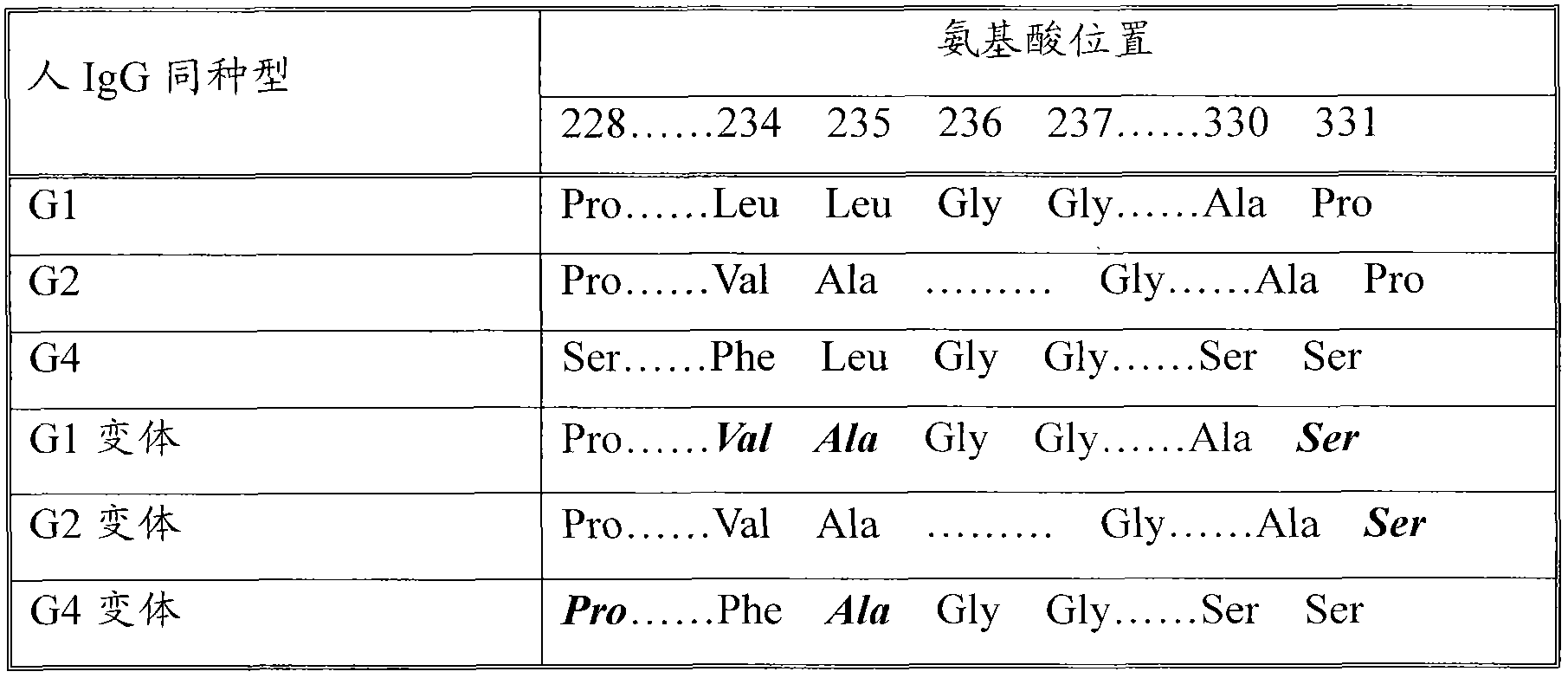
The invention discloses a recombined human coagulation factor FVII-Fc fusion protein, a preparation method thereof and applications thereof. The fusion protein successively comprises, from the N end to the C end, human FVII, a flexible peptide joint and an IgG2Fc mutant. The Fc mutant has no lysis property and exhibits very low bad Fc-mediated side effect. The fusion protein has similar or higher bioactivity than the human FVII, and prolonged the serum half time, thus improving pharmacokinetics and efficacy.
Owner:PHARMAB
Human urinary trypsin inhibitor (hUTI) of reorganization-dimerization and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103044554BIncrease productionEfficient and convenient purificationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticURINARY TRYPSIN INHIBITORHalf-life
The invention discloses a human urinary trypsin inhibitor (hUTI) of reorganization-dimerization and preparation method and application thereof, wherein the hUTI protein of reorganization-dimerization successively comprises amino acid residue sequence of human UTI, a peptide linker and a human IgGFc variant from N-terminal to C-terminal. The hUTI protein of reorganization-dimerization has the in-vitro biological activity similar with that of the human urinary trypsin inhibitor, higher biological activity in vivo and an extended half-life period in vivo.
Owner:PHARMAB
Recombined long-acting glucagons peptide analogue and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101525387BBiologically activeImprove expression efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisDrug biological activity
The invention relates to recombinant proteins and discloses a preparation method of a long-acting glucagon peptide analog, including the following steps: inoculating gene engineering Pichia pastoris strain in a fermentation tank; performing fermentation culture in the fermentation tank; centrifuging fermentation liquor and collecting the supernatant; separating and purifying the long-acting human glucagon peptide analog in the supernatant of the fermentation liquor so as to finally obtain a product with a purity degree of greater than 95%. The preparation method of the long-acting glucagon peptide analog has easy control for technologic conditions, thereby being capable of obtaining the long-acting glucagon peptide analog with biological activity, and having high protein expression efficiency and high product purification yield.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103432573AReduced clearance rateProlong biological half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAdjuvantArginine
The invention relates to a stable recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution, belonging to the technical field of biological agents. The stable recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution is prepared by dissolving a recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable stability adjuvant in a pharmaceutically acceptable buffer solution. The invention is characterized in that the pharmaceutically acceptable stability adjuvant is arginine, and the concentration is 5-30 g / L. The recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution provided by the invention can sufficiently prevent the recombinant fusion protein from aggregation, degradation, oxidation, denaturization or the like, thereby keeping the biological activity of the recombinant fusion protein; and the recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution is suitable for clinical application.
Owner:QILU PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com