Patents
Literature
61results about How to "Smoother profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
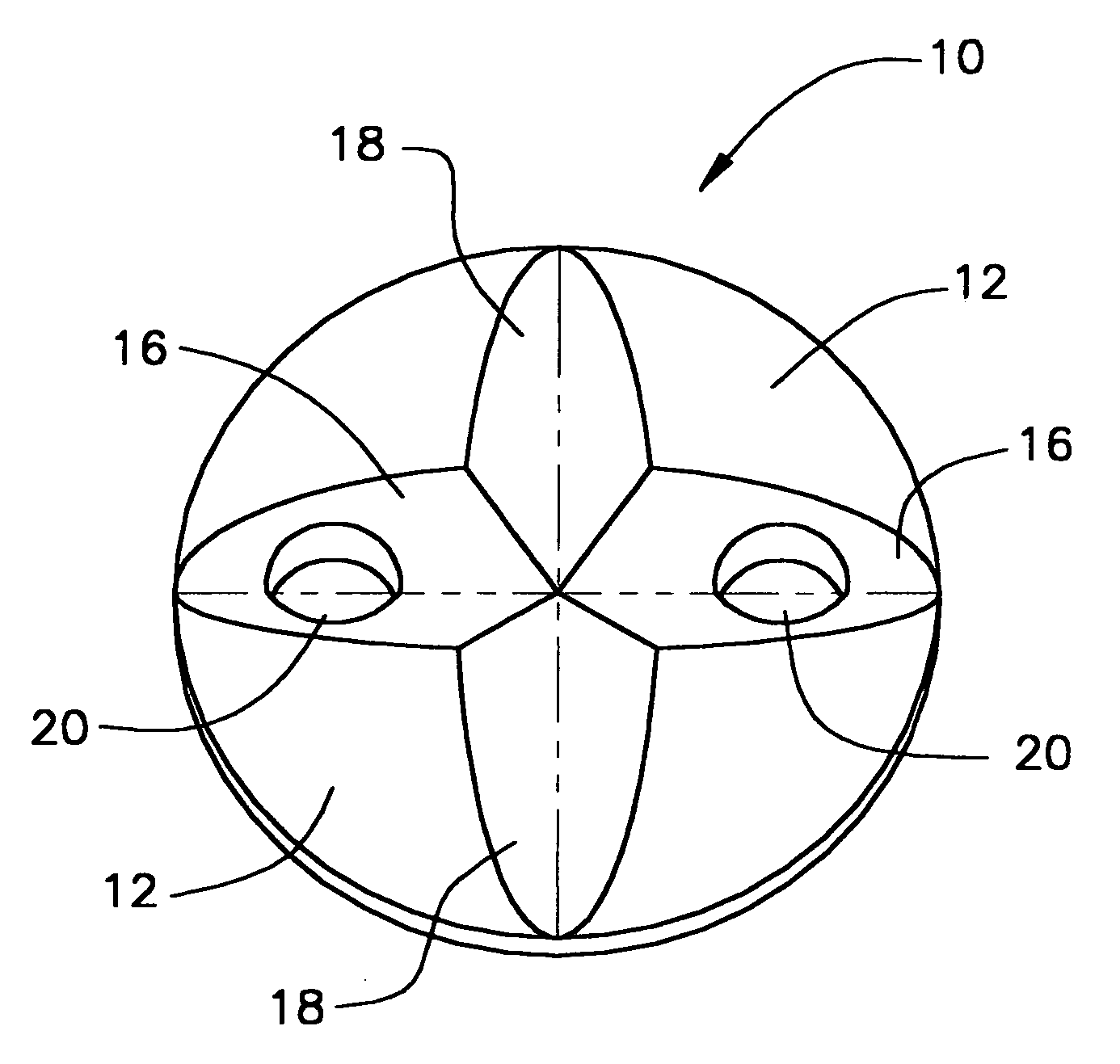
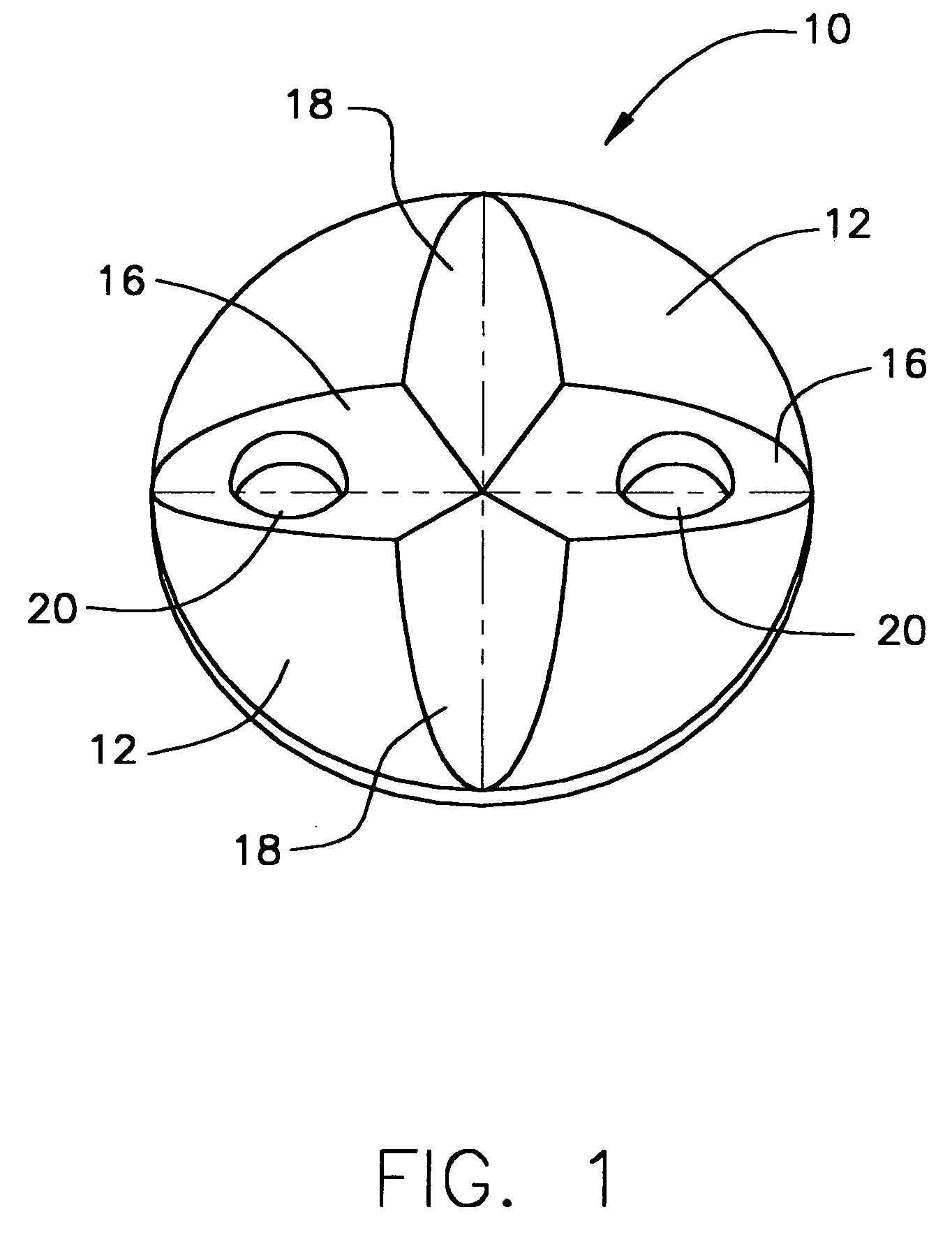
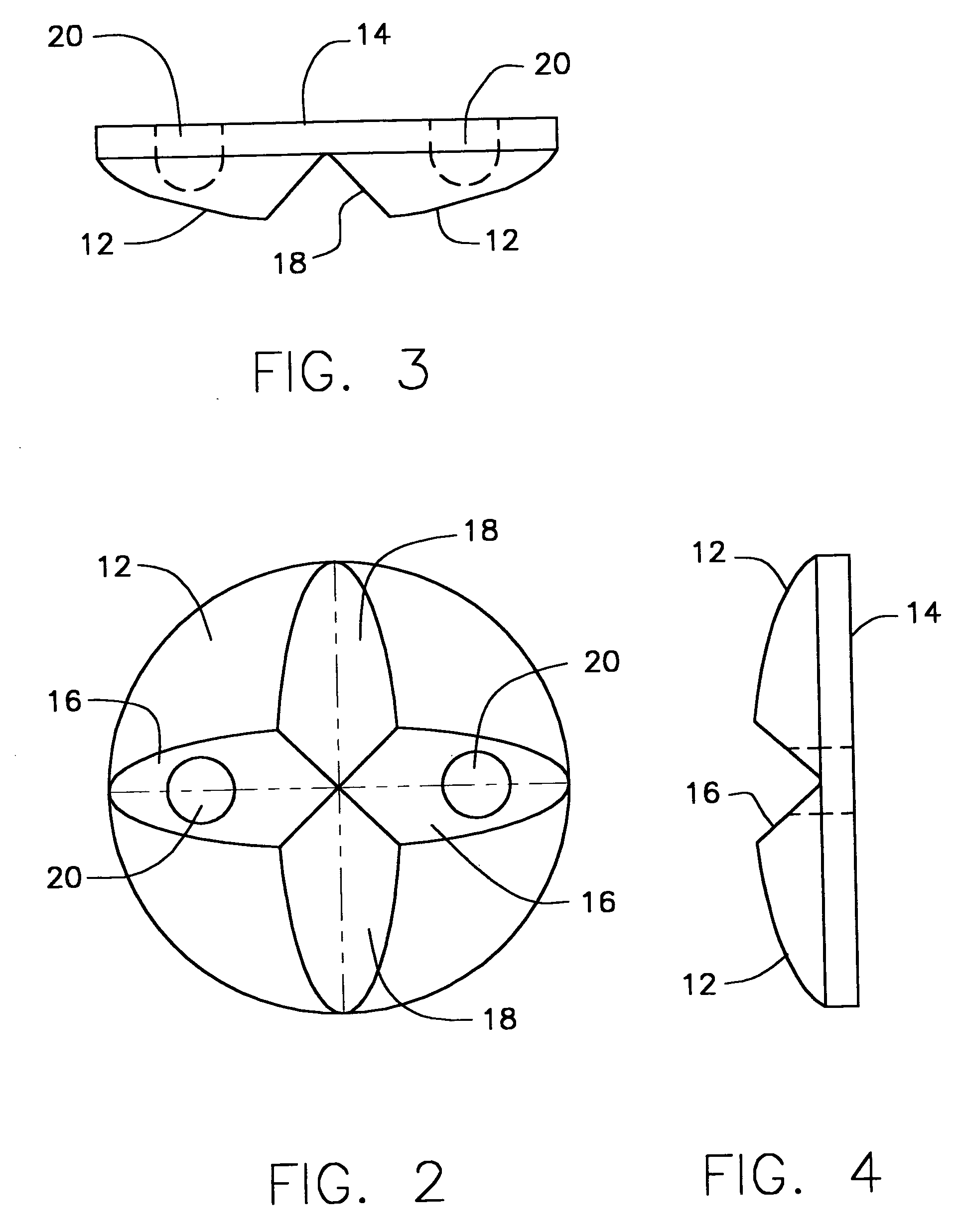
Subcutaneously implanted cannula and method for arterial access
InactiveUS6398764B1Avoid blood lossReduce exerciseMedical devicesCatheterDifferential pressureSubcutaneous implantation
A catheter with valve for implantation in a vascular structure of a living being. The catheter is in the general shape of a "T" with the top of the "T" implanted within the lumen of a vascular structure, and the leg of the "T" extending out of the vascular structure through an incision in the vascular structure. The lumen of the implanted portion of the catheter completely occupies the lumen of the vascular structure, causing all blood flow through the vascular structure to be directed through the implanted portion of the catheter. A valve is placed in the wall of the implanted portion of the catheter which opens into the lumen of the leg of the "T" of the catheter upon application of sufficient differential pressure between the lumens of the two portions of the catheter. The leg of the "T" is connected to the side wall of the implant portion of the catheter at an angle, such that the axis of the lumen of the leg of the "T" intersects the axis of the lumen of the implanted portion of the catheter at approximately a 45 degree angle.
Owner:VASCA
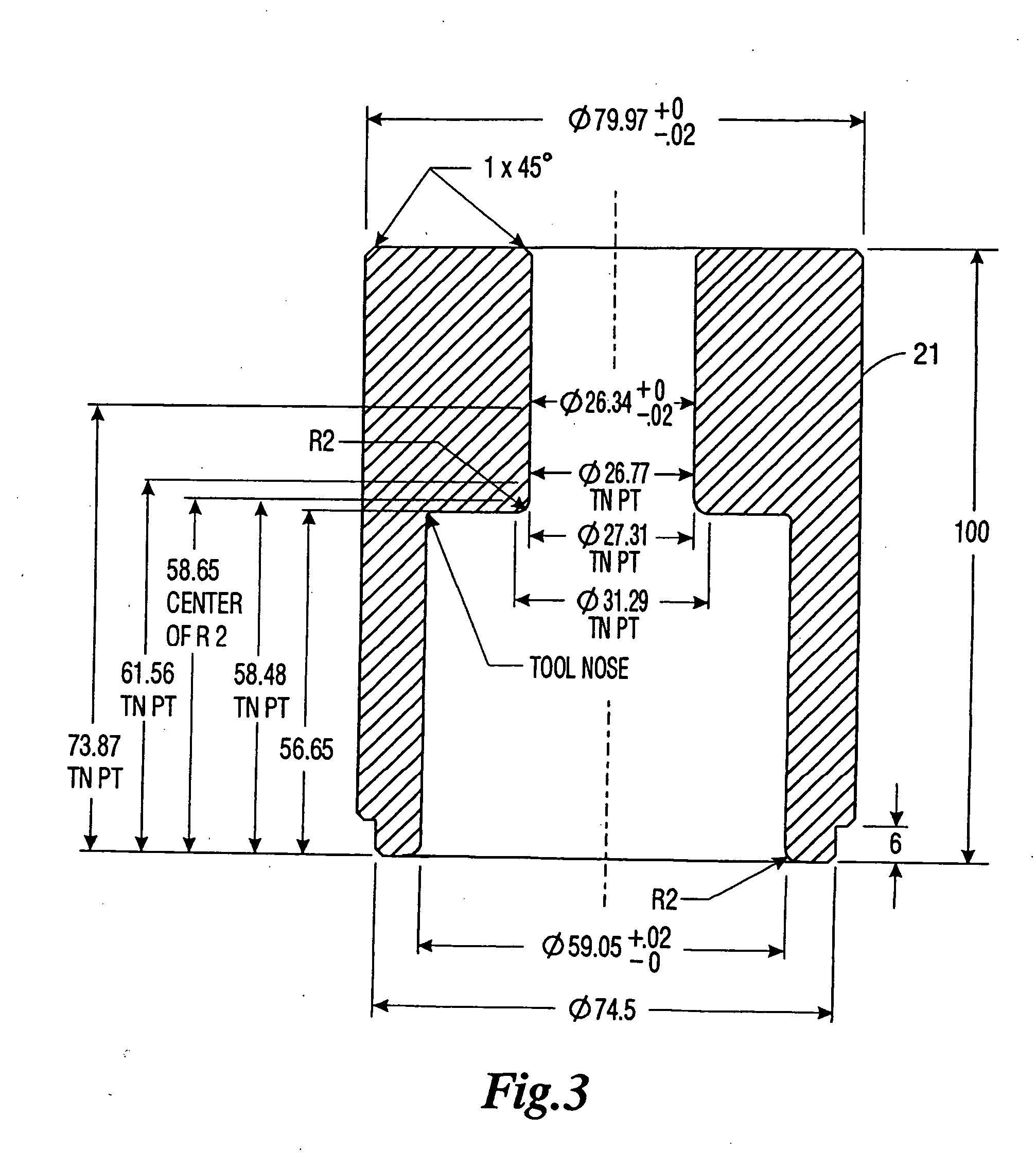
Method of manufacturing an aluminum receptacle with threaded outsert
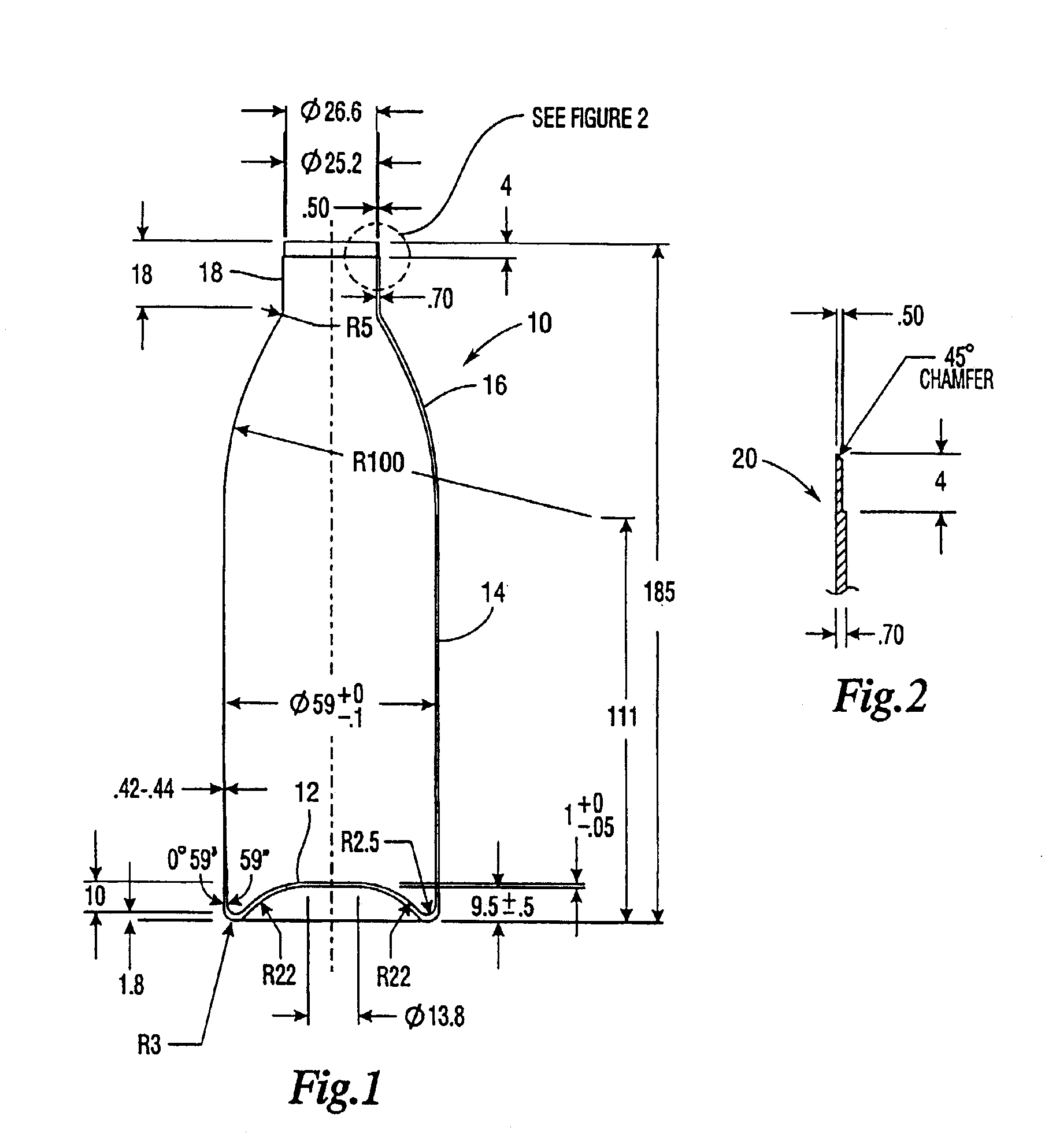
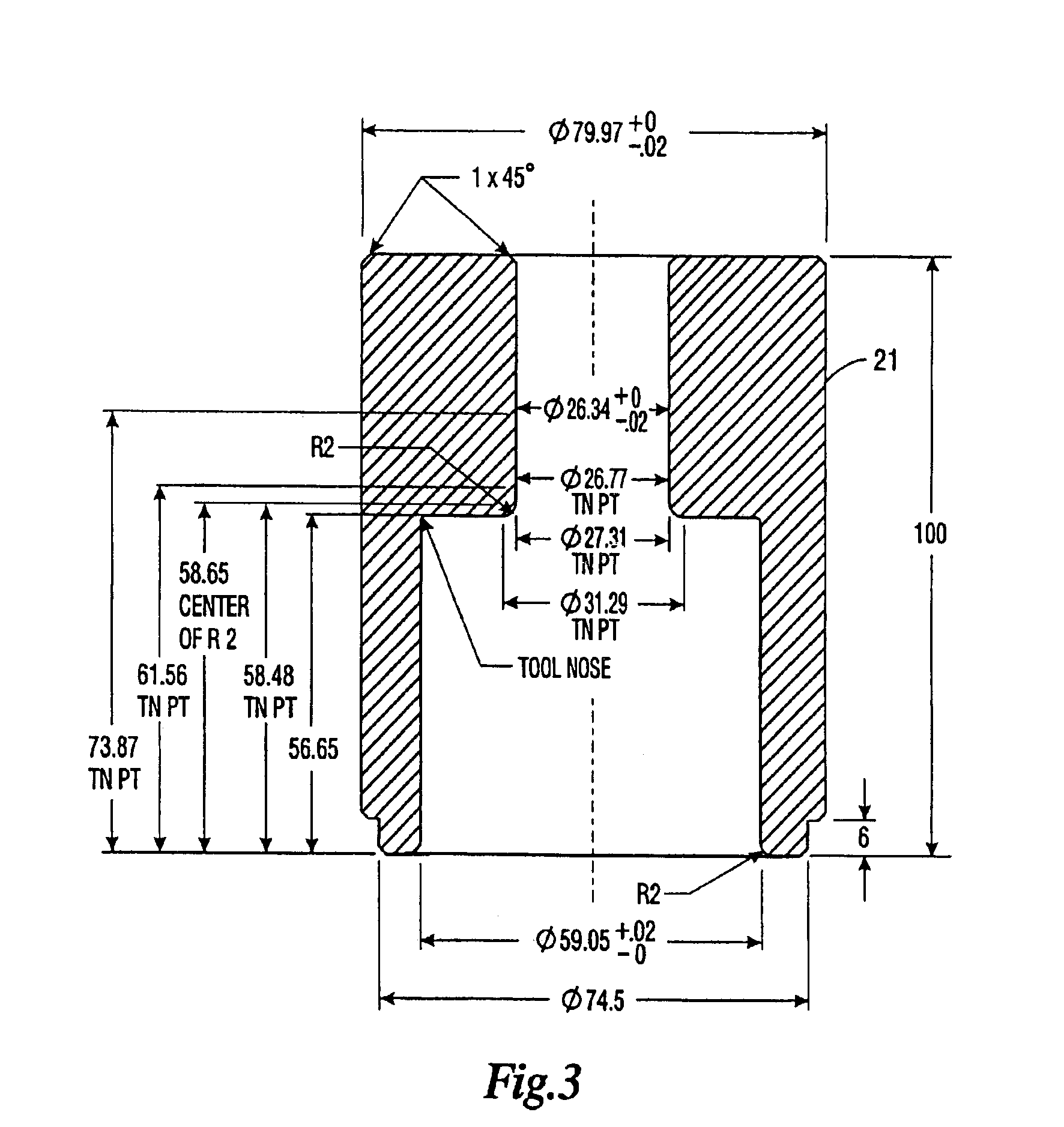
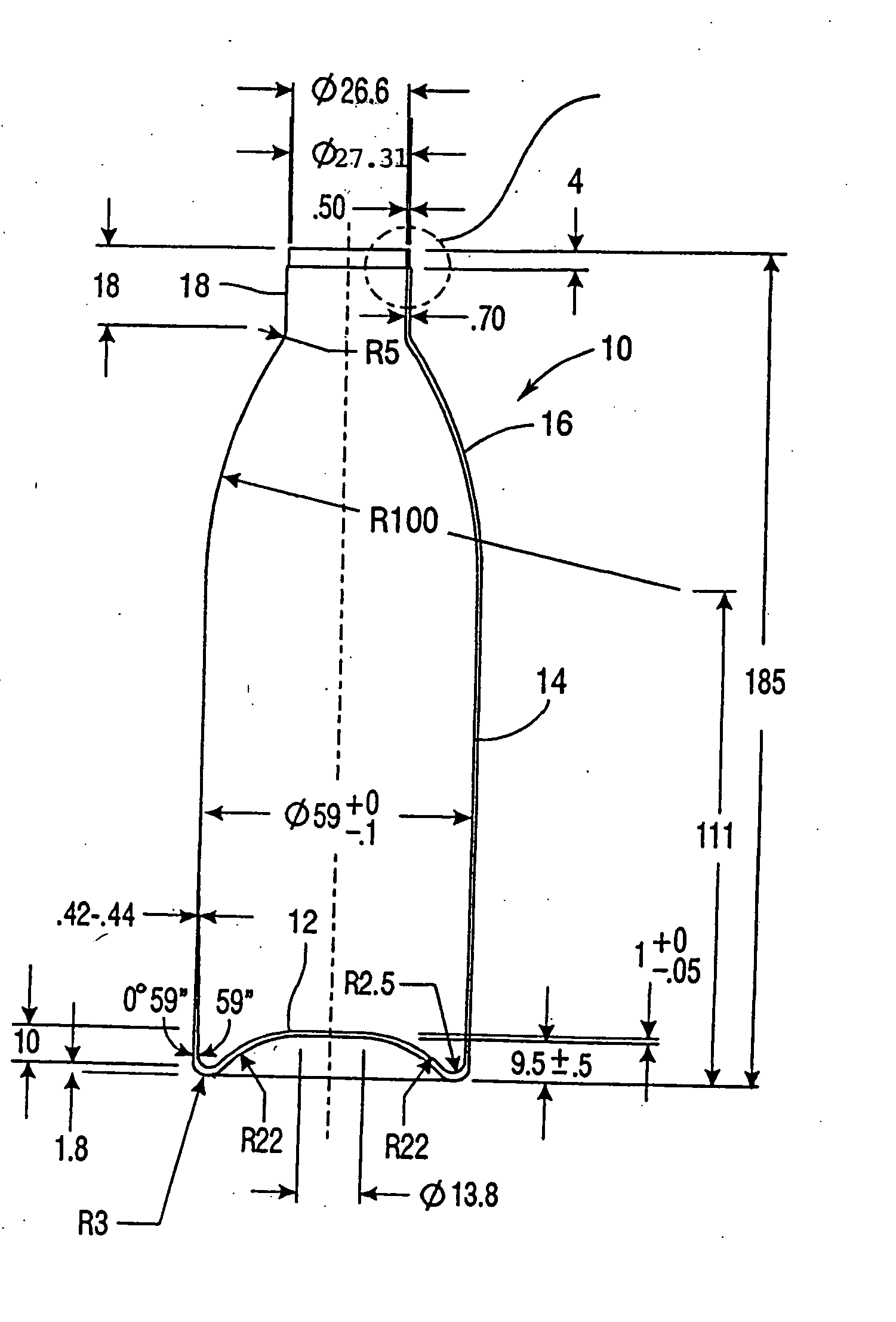
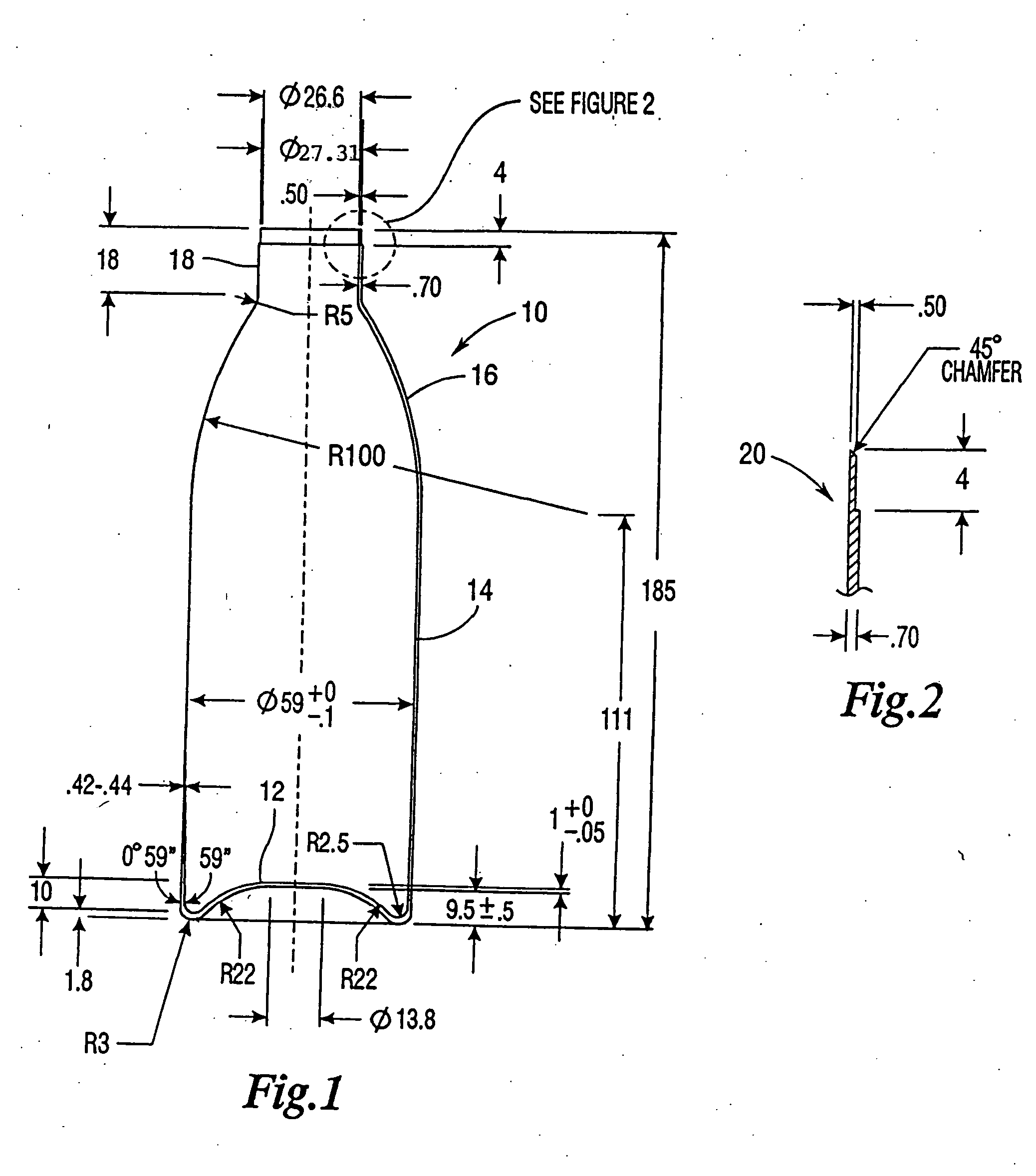
A method of affixing a sleeve to the neck of an aluminum container of the type having a tapered neck and wherein said sleeve has a complementary taper. The method comprises positioning said sleeve onto said neck wherein a portion of the neck extends beyond said sleeve and wherein said positioning causes said complementary taper of the sleeve and said taper of the neck to form a friction fit, said friction fit preventing rotation of said sleeve relative to said neck, wherein said friction fit is formed without expansion or deformation of said neck, and curling the portion of the neck extending beyond the sleeve so that the curl covers at least a portion of the upper end of said sleeve. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:EXAL
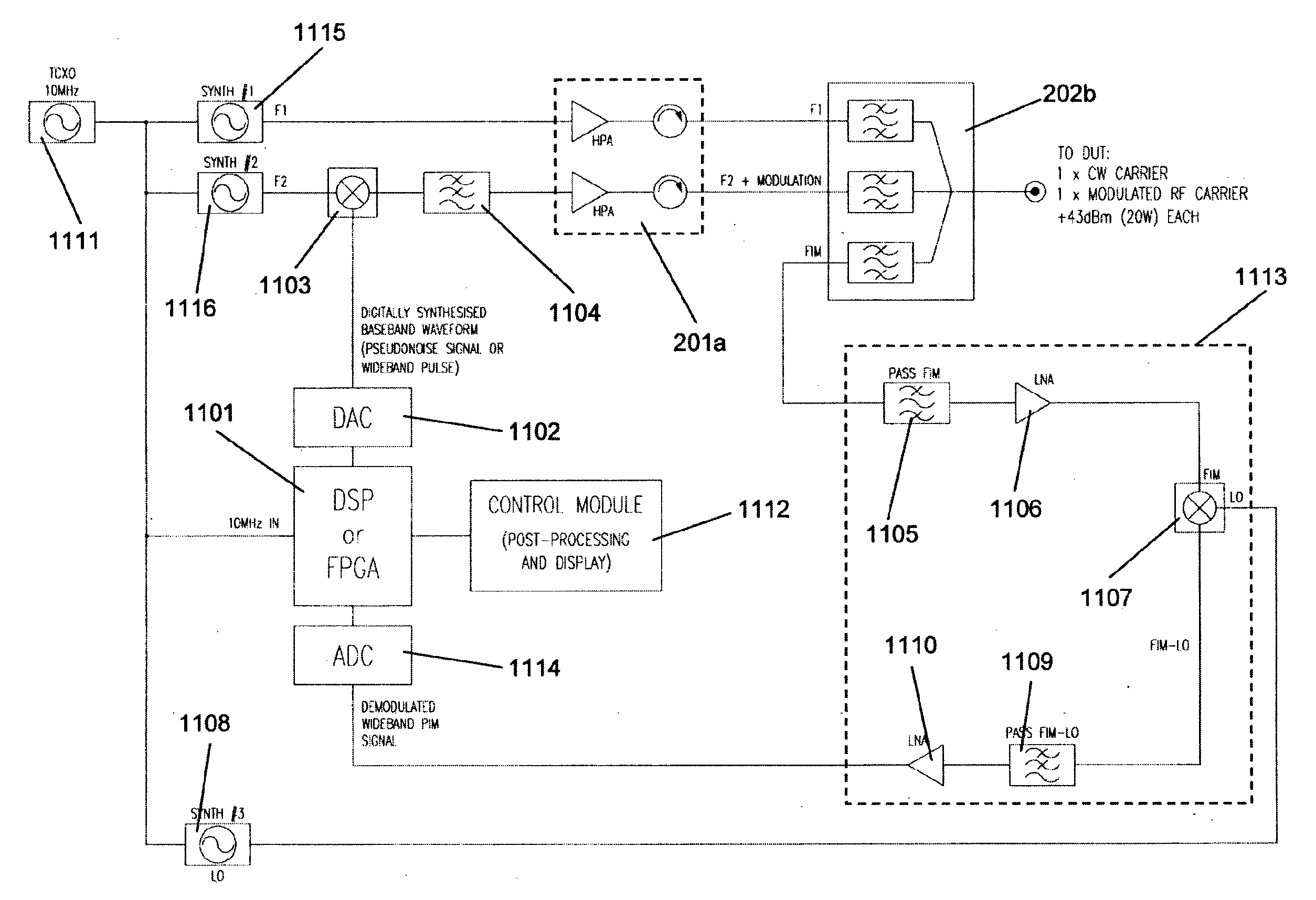
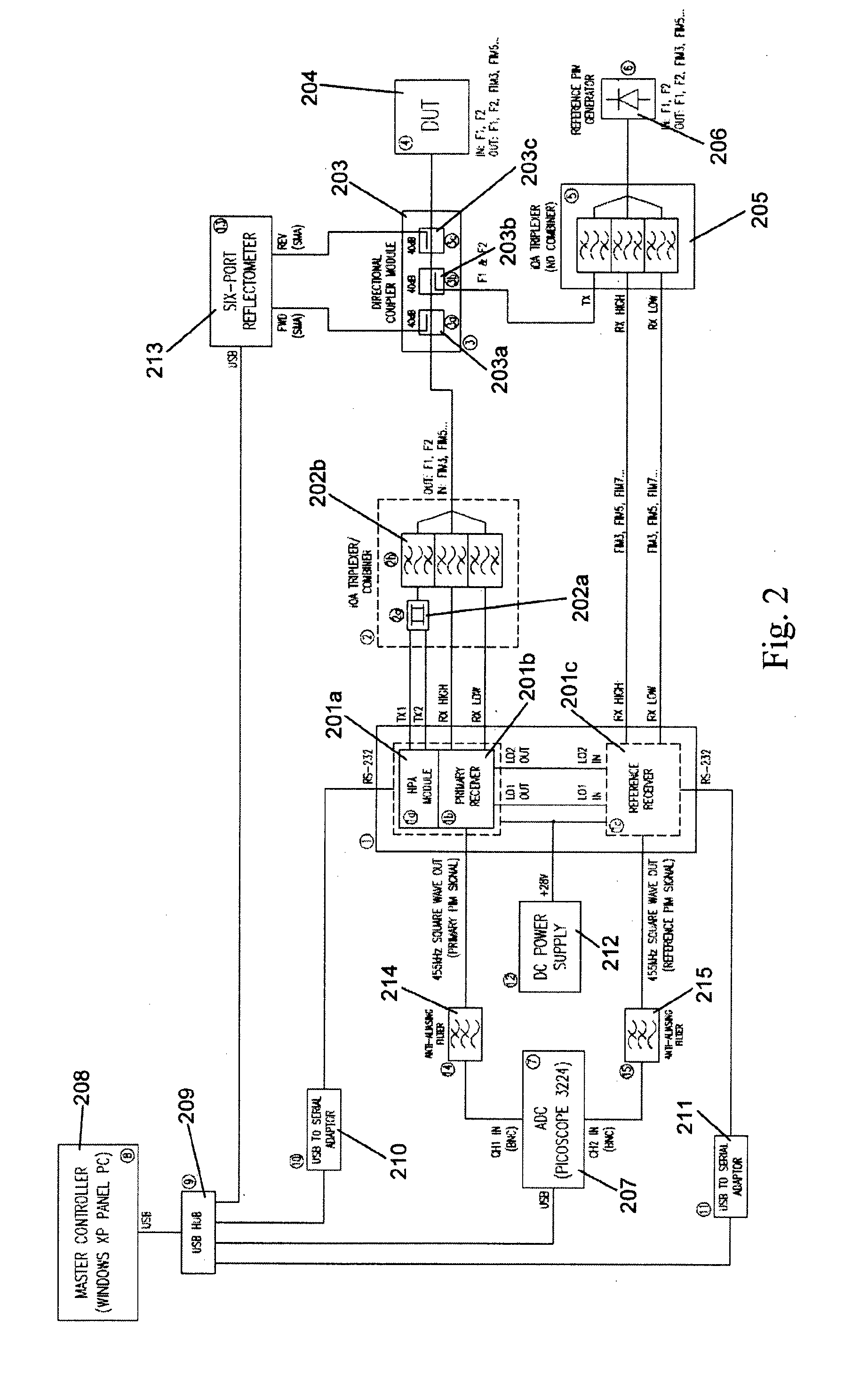
Method and apparatus for locating faults in communications networks
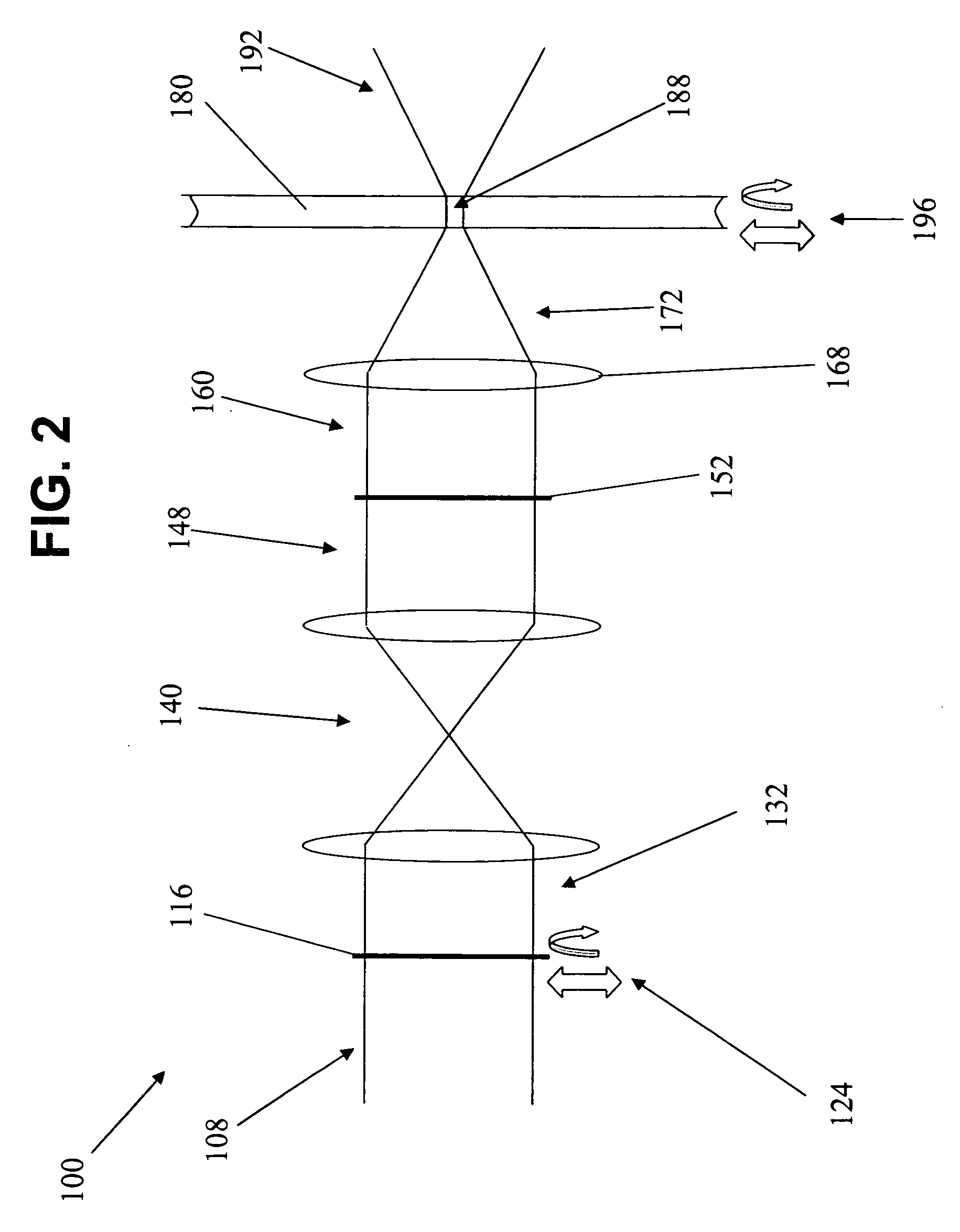
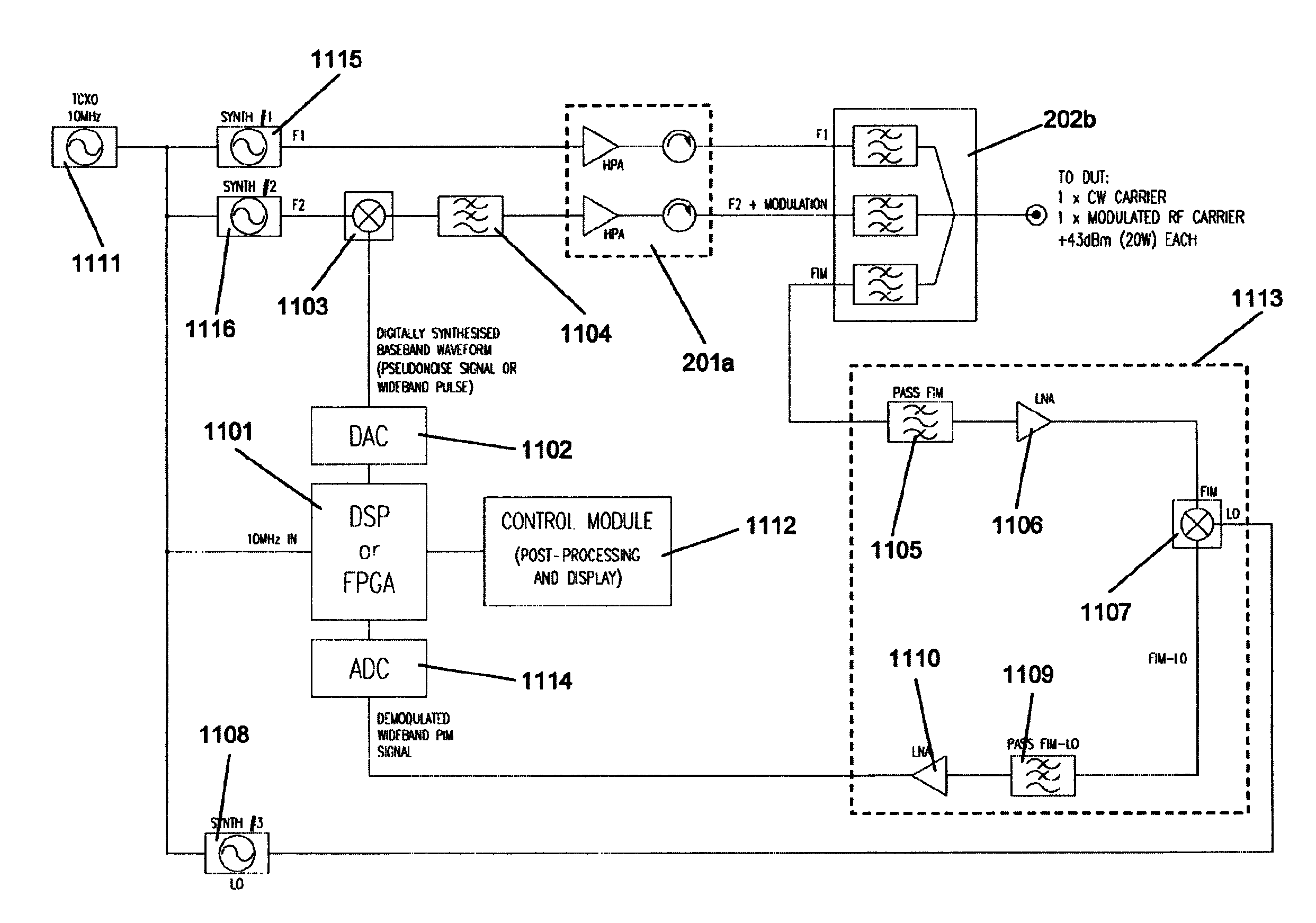
ActiveUS20130182753A1Smoother range profileEasy to identifySpectral/fourier analysisTransmitters monitoringCoaxial cableEngineering
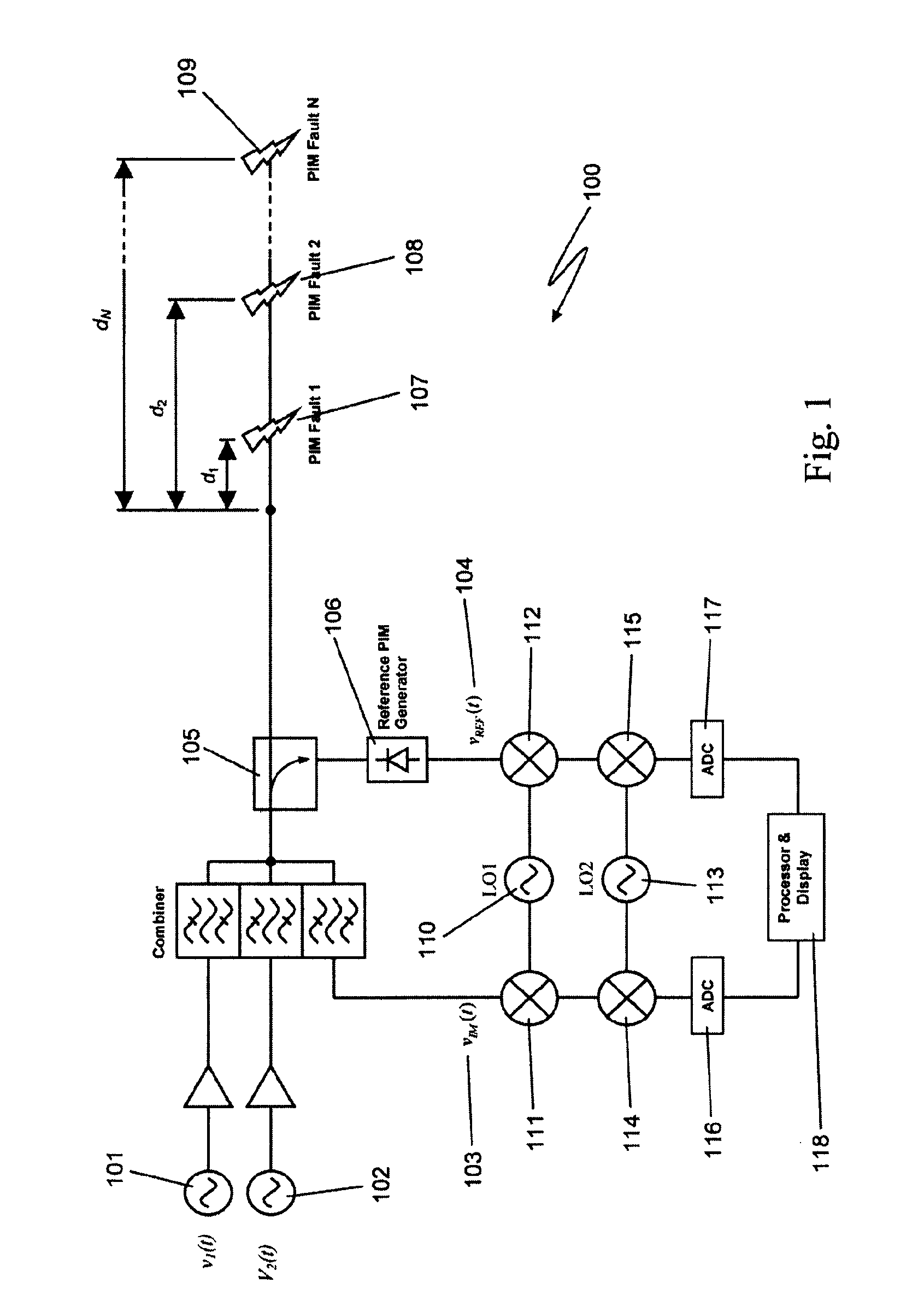
The present invention relates to a device for the location of passive intermodulation faults in a coaxial cable network. The test apparatus (100) according to one embodiment of the present invention utilises a pair of high-power, frequency-synthesised, unmodulated RF carriers v1(t) (101) and v2(t) (102) are generated inside the HPA module of the apparatus. The power and frequency of v1(t) (101) and v2(t) (102) can be independently set to a range of values, v1(t), v2(t) are combined inside the instrument and then applied to the input of the device under test (DUT). The PIM signals (107,108,109) generated in the DUT are combined to produce the primary PIM signal vIM(t) (103). The apparatus also includes two receivers (110,111,112,113,114,115) for the detection of vIM(t) 103 and vREF(t) (104). These signals are downconverted to 455 kHz. The two 455 kHz waveforms are digitised with a dual- channel A / D converter (116,117) and the amplitude ratio and phase offset between the digitised waveforms are calculated and stored.
Owner:KAELUS
Method and Apparatus for Sensory Field Assessment
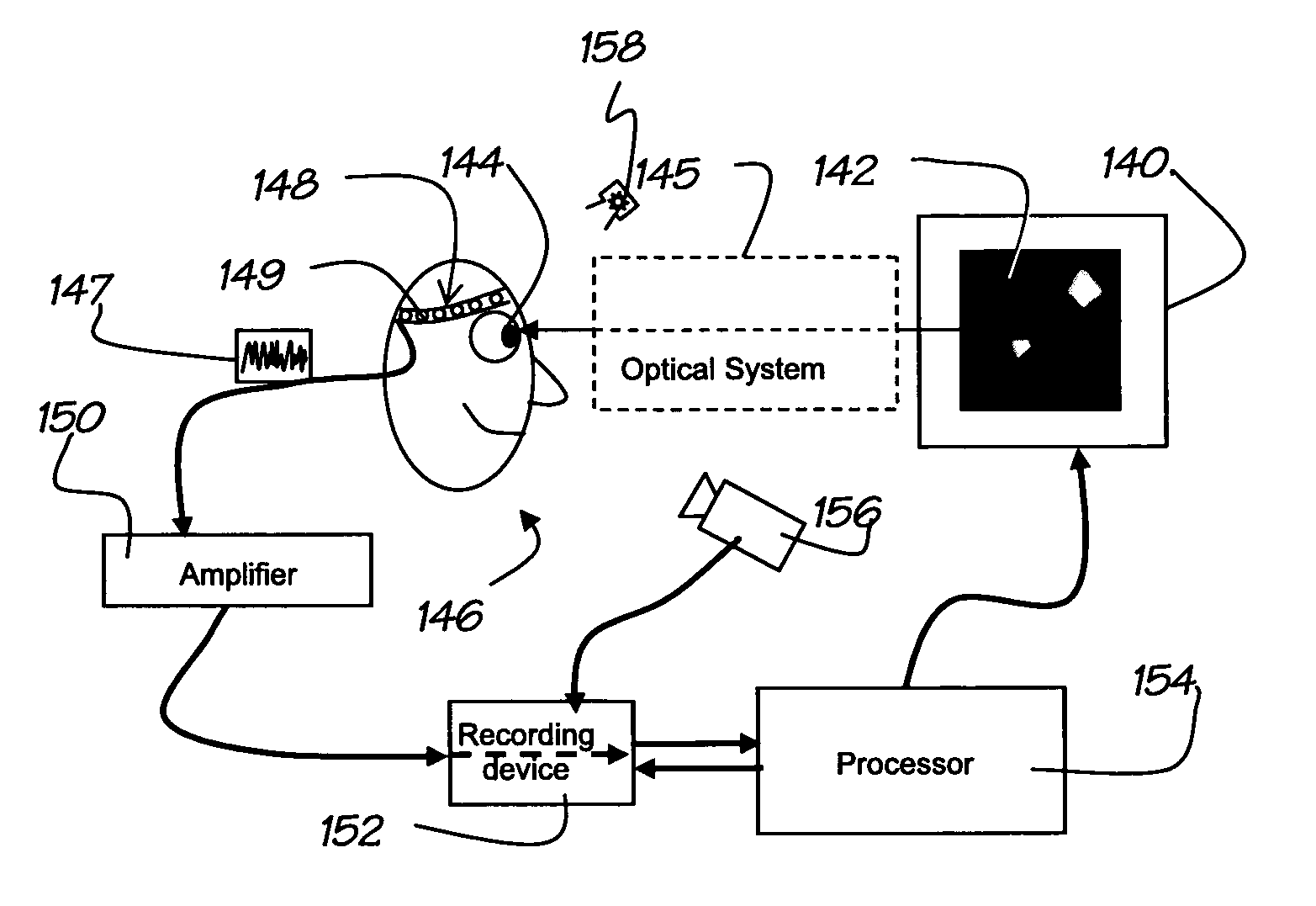
ActiveUS20100249532A1Space minimizationStable changeElectroencephalographyEye diagnosticsDisplay deviceField assessment
A method for assessing the function of at least one sensory field of a subject, and apparatus and systems for carrying out the method, the method comprising: using a display, presenting stimuli to selected locations of the sensory field, the selected locations being centred at points on a sampling grid spanning a portion of the sensory field, wherein the individual stimuli if presented simultaneously at the sampling grid points would overlap in the space defined by the sensory dimensions of the field; using a sensor, detecting responses in the subject's sensory field evoked by the stimuli; and processing the detected responses to relate them to the function of the subject's sensory field at the selected locations.
Owner:KONAN MEDICAL USA
Battery-powered vacuum cleaner
ActiveUS8549703B2Smoother profileEasily includedCleaning filter meansSuction filtersRechargeable cellEngineering
A vacuum cleaner comprising: a motor coupled to a fan for generating air flow; a body with a handle; a dirty air duct with a dirty air inlet; a battery pack housing at least one rechargeable cell for powering the motor; and a dirt separating means located in a path of the air flow generated by the fan, wherein the dirt separating means comprises: a hollow substantially cylindrical dirt container with a longitudinal central axis; and an air inlet port to the dirt container, wherein the air inlet port is in communication with the dirty air duct and wherein the battery pack has a curvilinear or annular cross-sectional profile transverse to the central axis and a curvilinear inner wall embracing the dirt container.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Surgical sutures incorporated with stem cells or other bioactive materials
InactiveUS20090318962A1Reduce concentrationReducing cell migrationSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgical siteSurgical department
Materials and Methods for immobilizing bioactive molecules, stem and other precursor cells, and other agents of therapeutic value in surgical sutures and other tissue scaffold devices are described herein. Broadly drawn to the integration and incorporation of bioactive materials into suture constructs, tissue scaffolds and medical devices, the present invention has particular utility in the development of novel systems that enable medical personnel performing surgical and other medical procedures to utilize and subsequently reintroduce bioactive materials extracted from a patient (or their allogenic equivalents) to a wound or target surgical site.
Owner:BIOACTIVE SURGICAL
Battery-powered vacuum cleaner
ActiveUS20130091657A1Separation efficiency can be improvedLess spaceCleaning filter meansSuction filtersAirflowEngineering
A vacuum cleaner comprising: a motor coupled to a fan for generating air flow; a body with a handle; a dirty air duct with a dirty air inlet; a battery pack housing at least one rechargeable cell for powering the motor; and a dirt separating means located in a path of the air flow generated by the fan, wherein the dirt separating means comprises: a hollow substantially cylindrical dirt container with a longitudinal central axis; and an air inlet port to the dirt container, wherein the air inlet port is in communication with the dirty air duct and wherein the battery pack has a curvilinear or annular cross-sectional profile transverse to the central axis and a curvilinear inner wall embracing the dirt container.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Protective device for a suture
A disc for holding a medical suture on a patient's skin is modified by providing first and second orthogonal grooves in a domed upper surface. Through openings in one of the grooves permits the suture to be tied within that groove so that the suture has a knot contained within the groove and thus below the domed upper surface. The second groove, preferably orthogonal to the first groove, permits a scalpel to be readily inserted along the second groove to traverse the first groove and cut the suture when the suture is to be removed.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
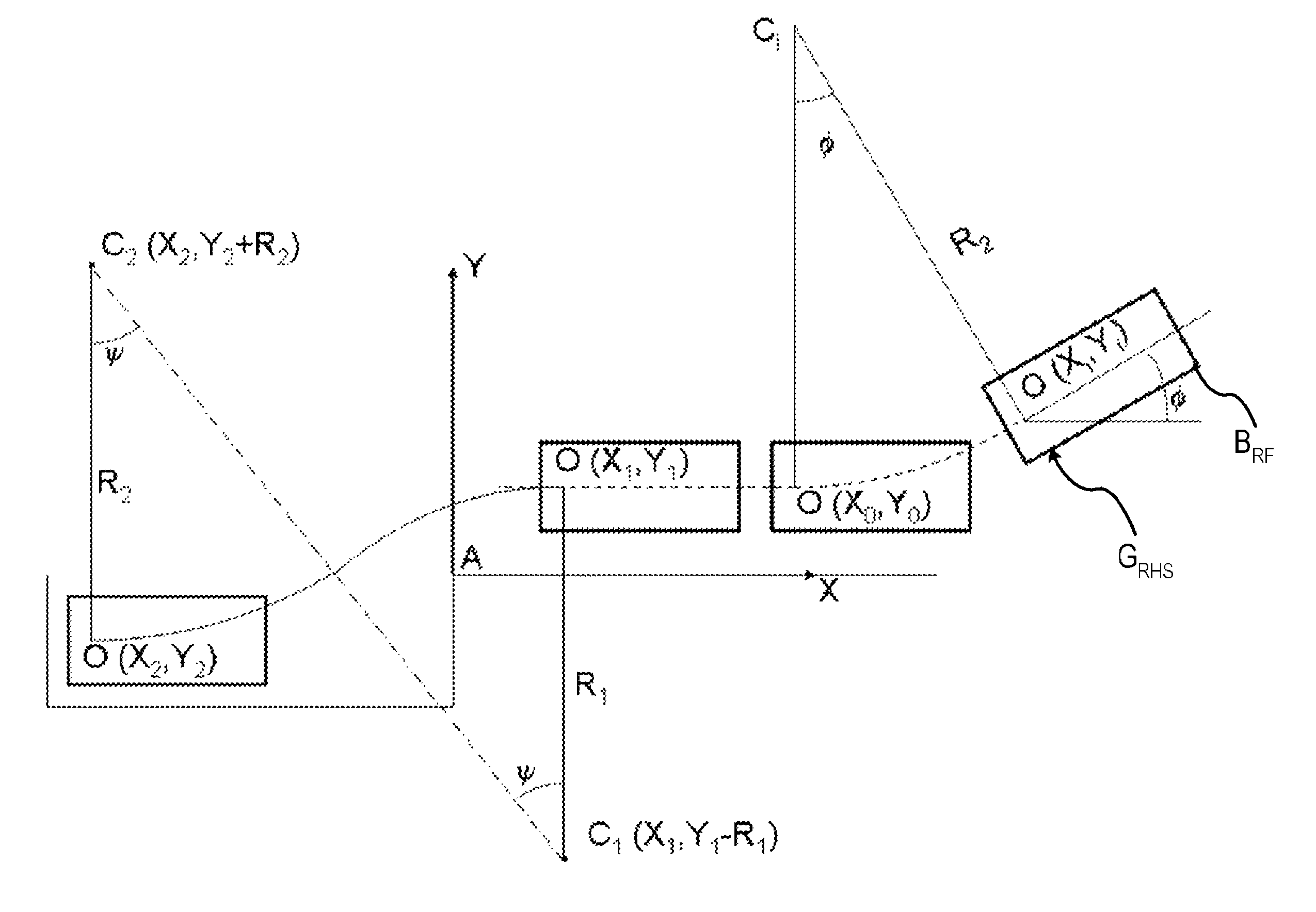
Path planning for autonomous parking
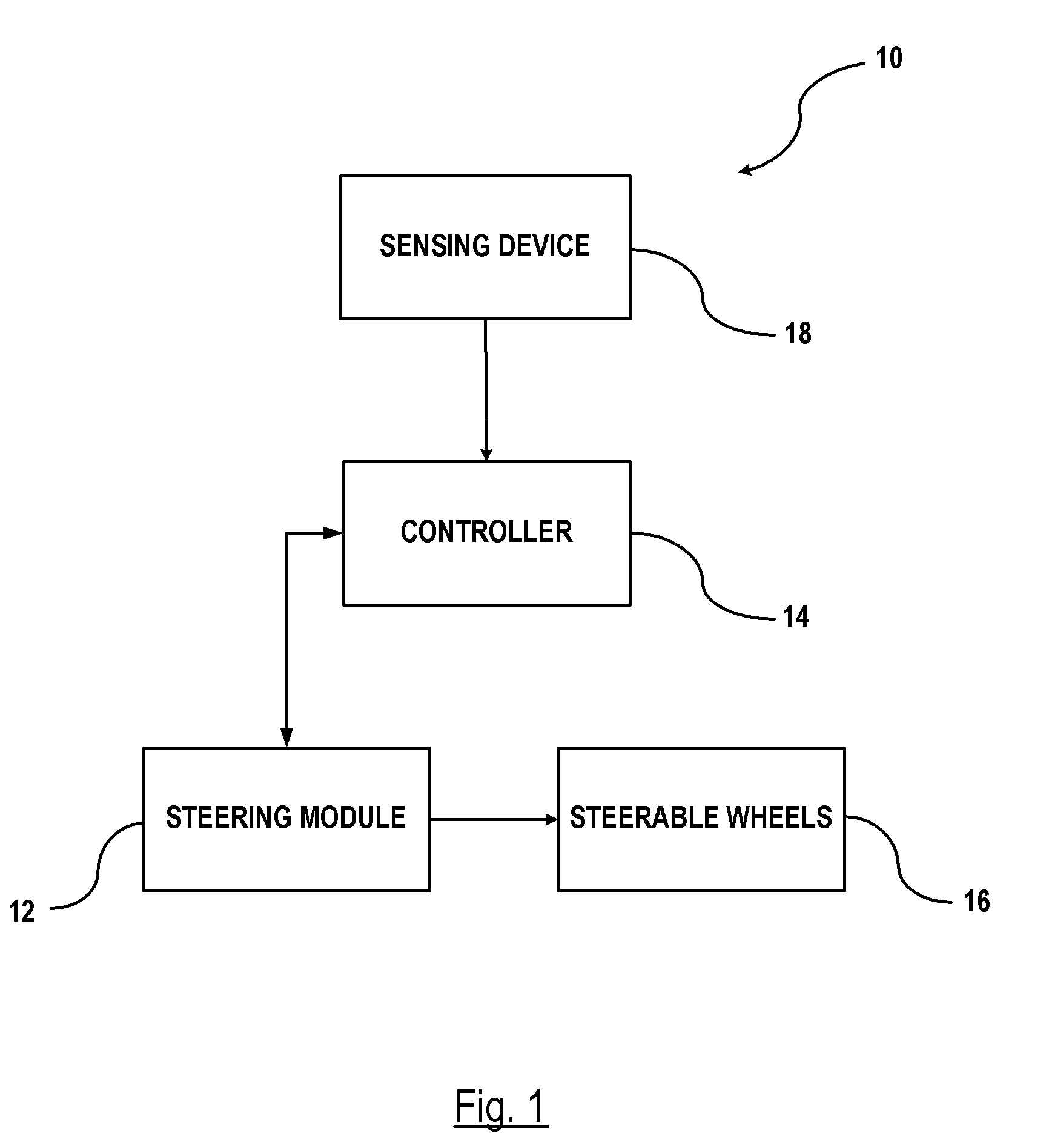
InactiveUS8099214B2Smoother profileDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsEngineeringRemote sensing
A method is provided for determining a vehicle path for autonomously parallel parking a vehicle in a space between a first object and a second object. A distance is remotely sensed between the first object and the second object. A determination is made whether the distance is sufficient to parallel park the vehicle between. A first position to initiate a parallel parking maneuver is determined. A second position within the available parking space corresponding to an end position of the vehicle path is determined. A first arc shaped trajectory of travel is determined between the first position and an intermediate position, and a second arc shaped trajectory of travel is determined between the second position and the intermediate position. The first arc shaped trajectory is complementary to the second arc shaped trajectory for forming a clothoid which provides a smoothed rearward steering maneuver between the first position to the second position.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
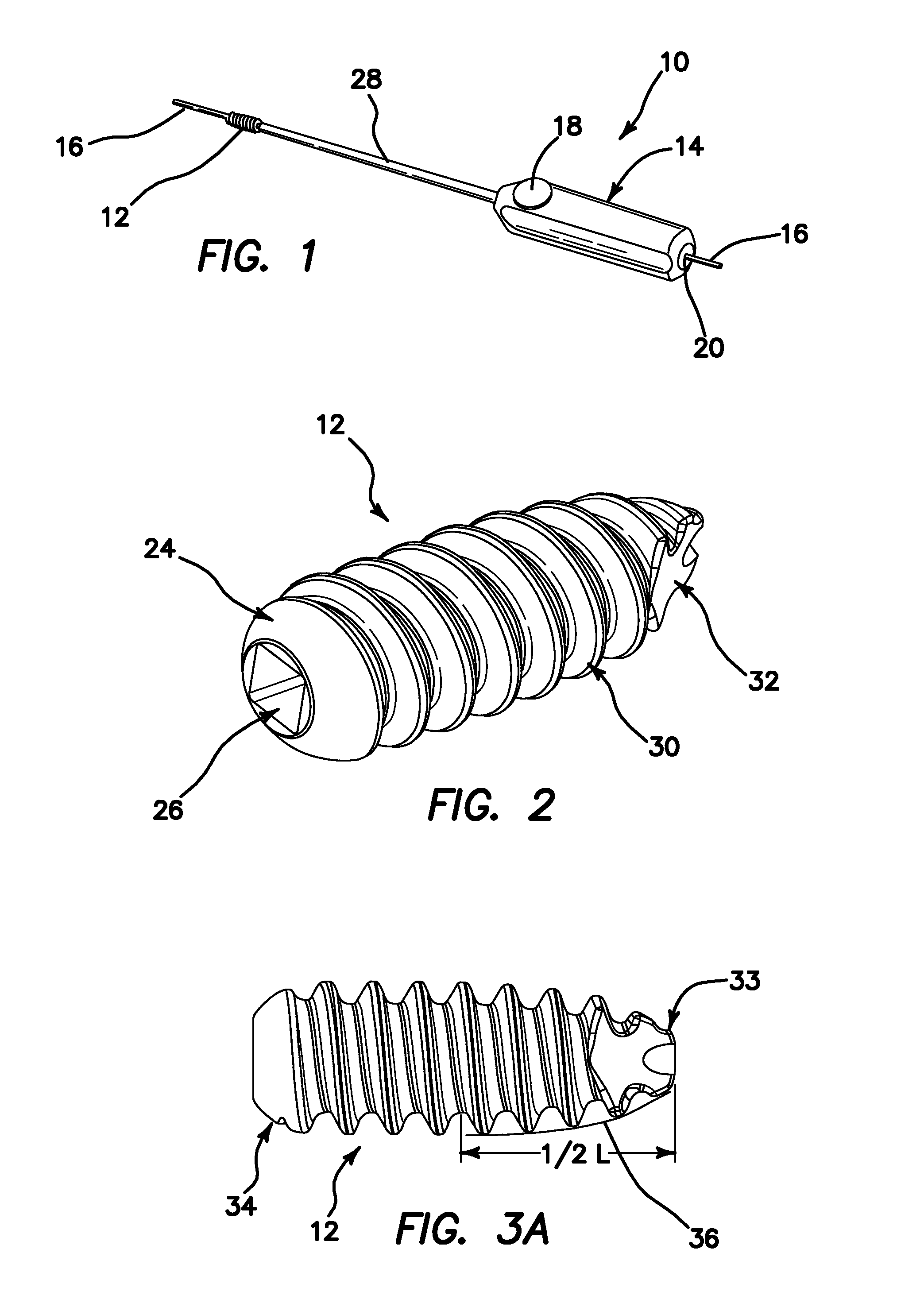
Devices with dimensions that can be reduced and increased in vivo, and methods of making and using the same
Devices are provided with an internal dimension that can be reduced and increased in vivo. In one example, an interatrial shunt for placement at an atrial septum of a patient's heart includes a body. The body includes first and second regions coupled in fluid communication by a neck region. The body includes a shape-memory material. The body defines a passageway through the neck region for blood to flow between a first atrium and a second atrium. The first and second regions are superelastic at body temperature, and the neck region is malleable at body temperature. A flow area of the passageway through the neck region may be adjusted in vivo.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Substrate support system
ActiveUS7311302B1Avoid bendingSmoother profileWork holdersPositioning apparatusSupporting systemEngineering
An improved substrate support system for clamping spring loaded pins that support substrates, such as printed circuit boards, which have even profiles, and uneven profiles due to components being installed on one side during manufacturing operations to the opposite side of the substrate. The substrate support system can utilize a cam lever, a knob, or a draw latch to move a clamping plate between an aligned position and a clamping position.
Owner:PRODN SOLUTIONS
Surgical sutures incorporated with stem cells or other bioactive materials
InactiveUS8876864B2Reduce concentrationPromote migrationSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgical sitePrecursor cell
Materials and methods for immobilizing bioactive molecules, stem and other precursor cells, and other agents of therapeutic value in surgical sutures and other tissue scaffold devices are described herein. Broadly drawn to the integration and incorporation of bioactive materials into suture constructs, tissue scaffolds and medical devices, the present invention has particular utility in the development of novel systems that enable medical personnel performing surgical and other medical procedures to utilize and subsequently reintroduce bioactive materials extracted from a patient (or their allogenic equivalents) to a wound or target surgical site.
Owner:BIOACTIVE SURGICAL
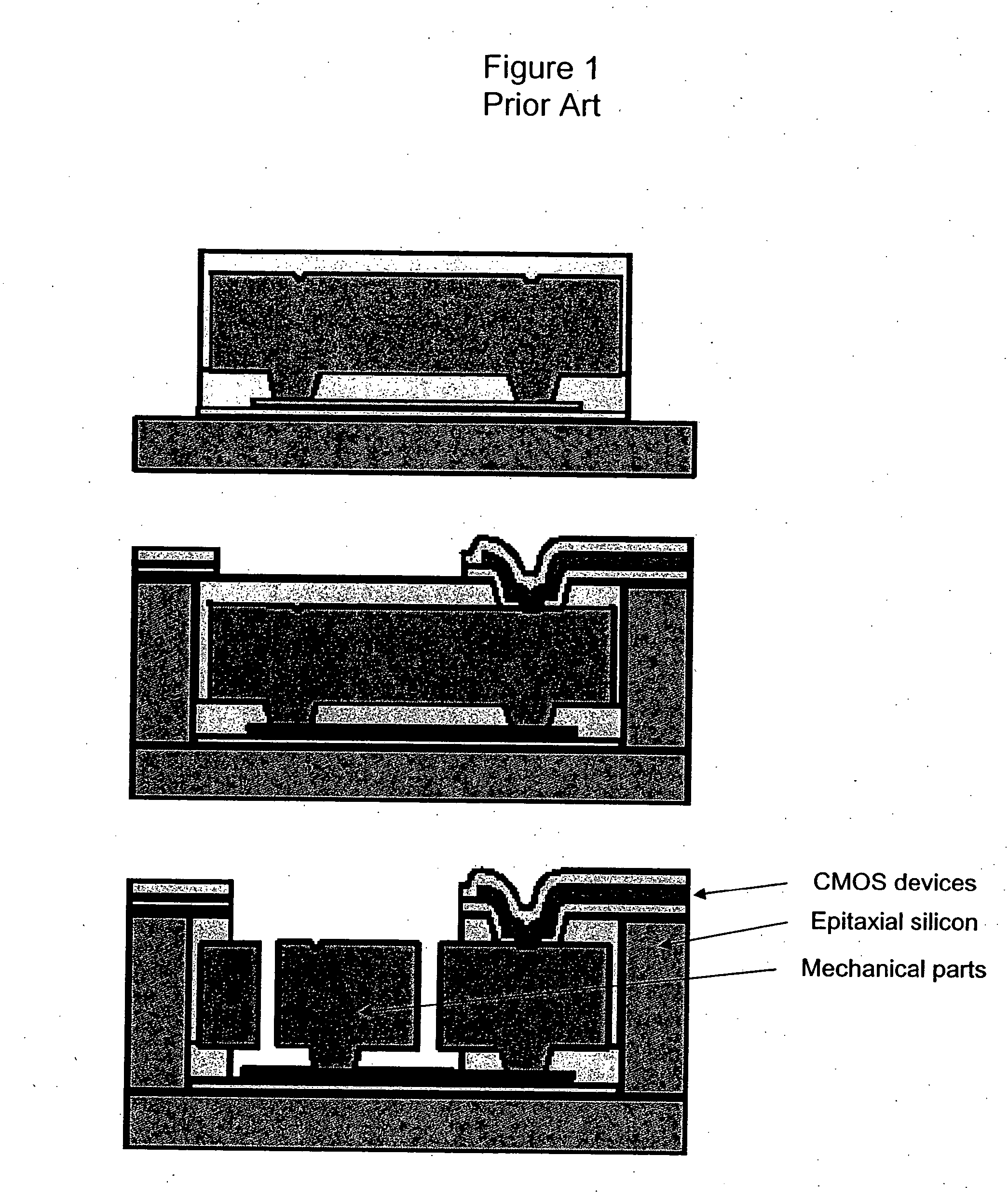
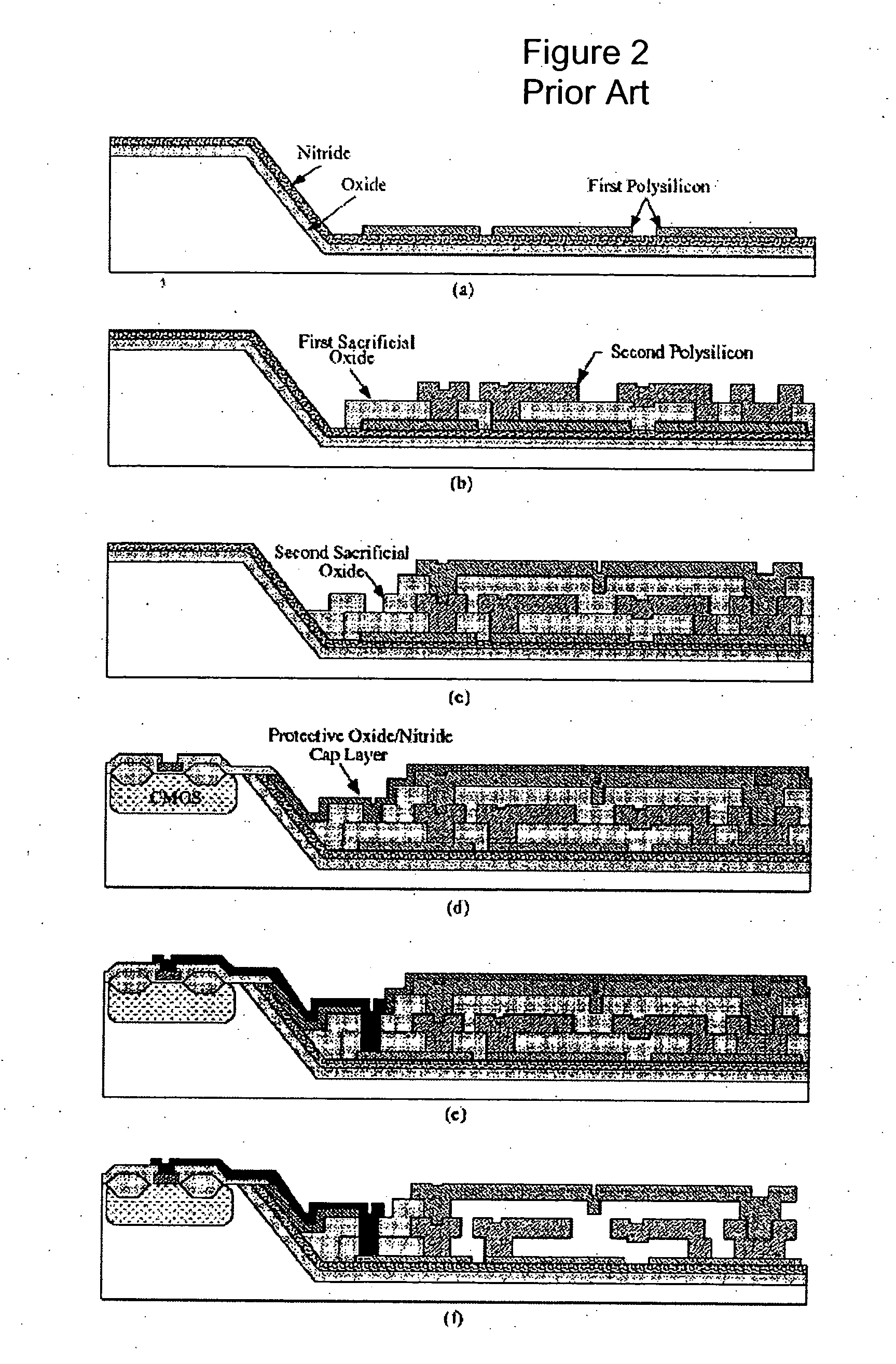
Fabrication of advanced silicon-based MEMS devices
InactiveUS20060166403A1Eliminate complex processingSmoother profileTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAmorphous siliconEngineering
A micro-electro-mechanical (MEM) device and an electronic device are fabricated on a common substrate by fabricating the electronic device comprising a plurality of electronic components on the common substrate, depositing a thermally stable interconnect layer on the electronic device, encapsulating the interconnected electronic device with a protective layer, forming a sacrificial layer over the protective layer, opening holes in the sacrificial layer and the protective layer to allow the connection of the MEM device to the electronic device, fabricating the MEM device by depositing and patterning at least one layer of amorphous silicon, and removing at least a portion of the sacrificial layer. In this way, the MEM device can be fabricated after the electronic device on the same substrate.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING INC
Method and system for increasing holographic data storage capacity using irradiance-tailoring element
InactiveUS20070091399A1Smoother profileHigh spatial frequencyHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesRecord information storageHolographic storageLight beam
The present invention provides a method and system for increasing the holographic storage capacity of a holographic recording medium using an irradiance-tailoring (e.g., optical) element by changing the irradiance profile of the modulated object beam (e.g., by imparting motion to an irradiance-tailoring element and / or the holographic recording medium and / or by reconfiguring (e.g., periodically) the phase profile of a stationary irradiance-tailoring (e.g., optical) element) to minimize the effects of fixed-pattern noise buildup from occurring in the holographic recording medium.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
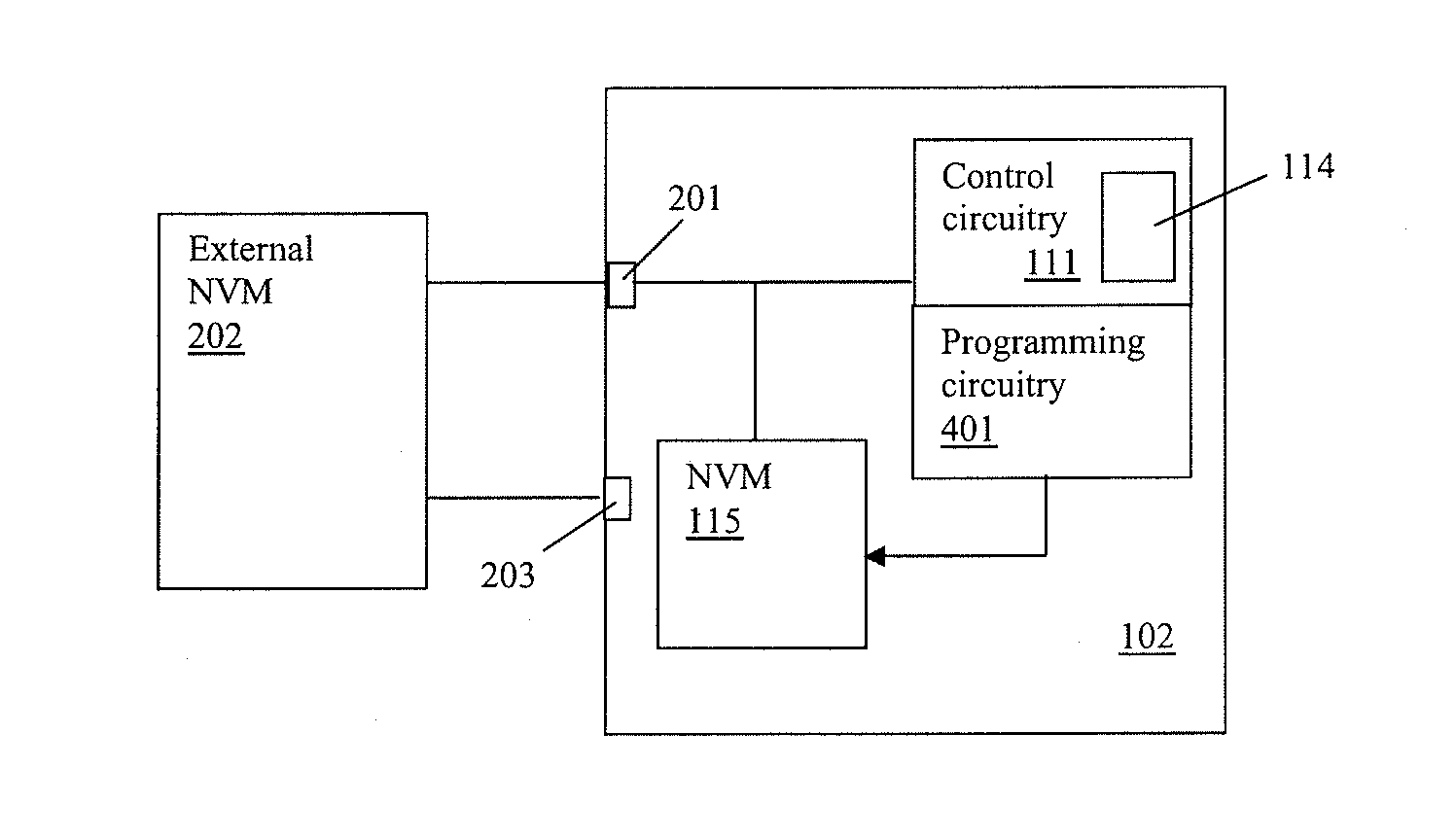
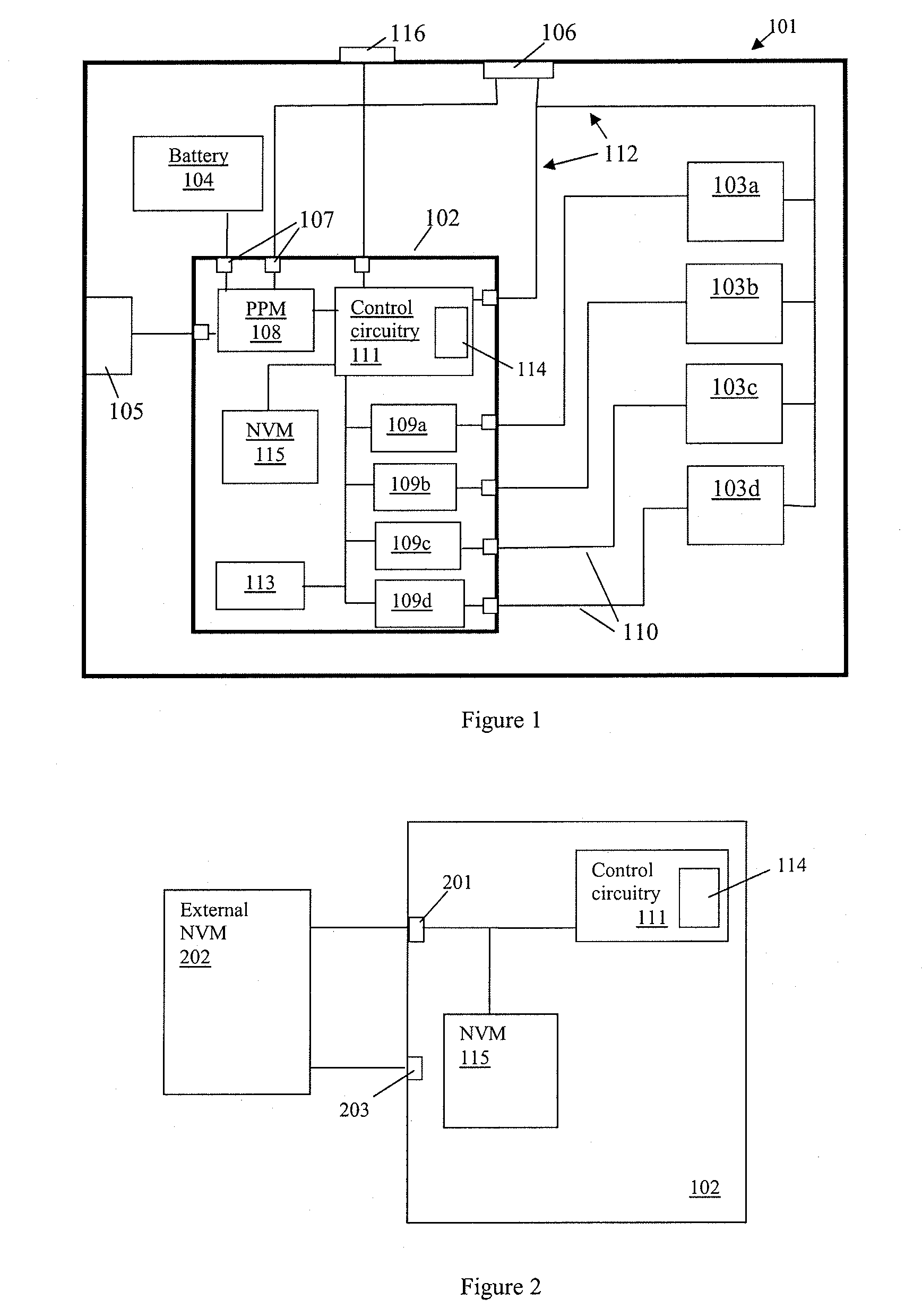
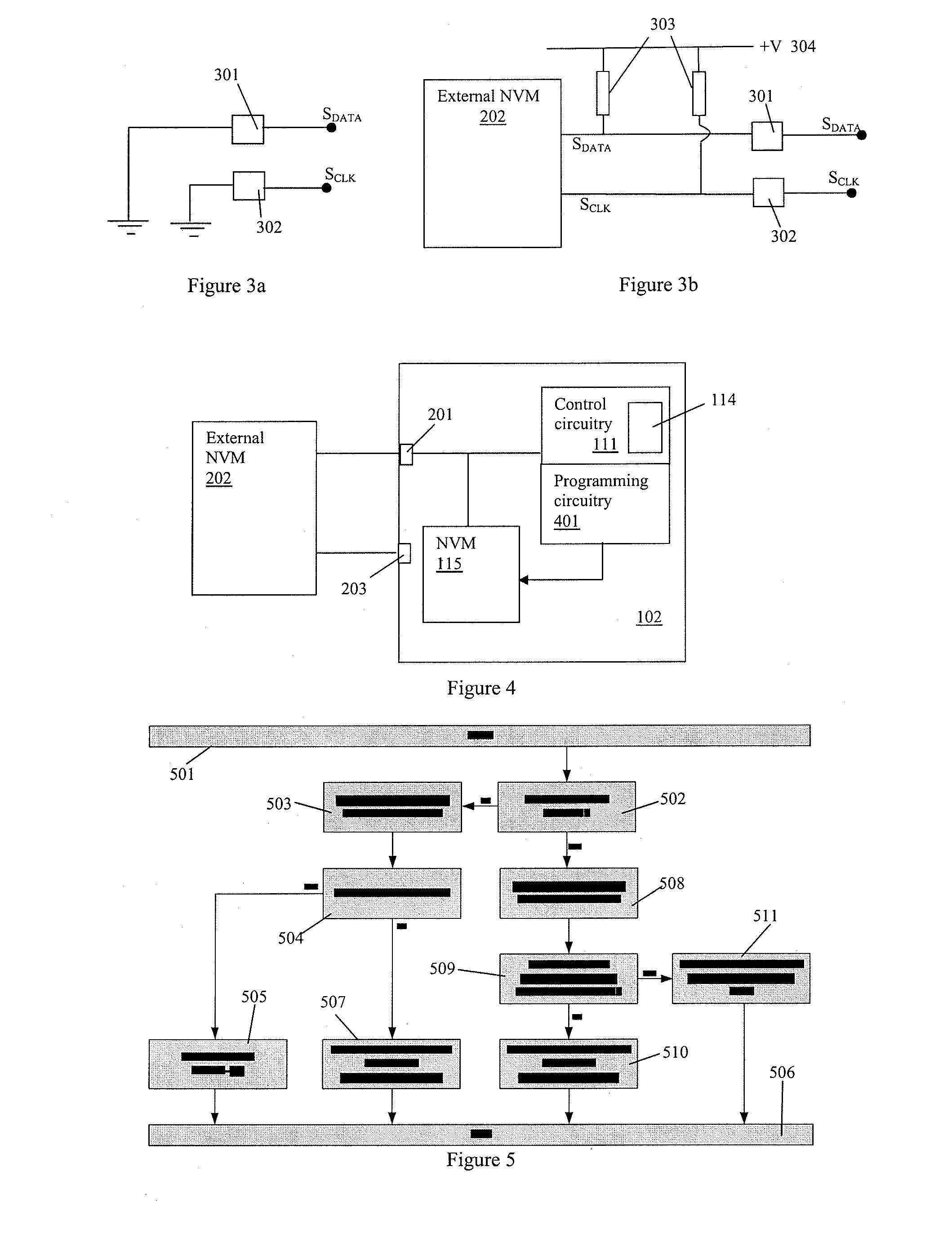
Power management apparatus and methods
ActiveUS8607036B2Low costIn-rush current can be prevented more easilyDc-dc conversionDigital computer detailsControl circuitEmbedded system
Apparatus and method for power management and especially to power management integrated circuits (PMICs). In one aspect, the invention relates to a PMIC having an internal non-volatile memory (NVM) for storing boot settings for the PMIC. The PMIC also has control circuitry for detecting whether a source of boot settings is available, such as an NVM external to the PMIC, and, if so, using any settings stored in the external source in preference to the relevant settings stored in the internal NVM. The external settings can thus override any internal settings, which is useful for fault diagnosis and / or development. In one aspect the PMIC may have programming circuitry for automatically programming boot settings from an external source into the internal NVM.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
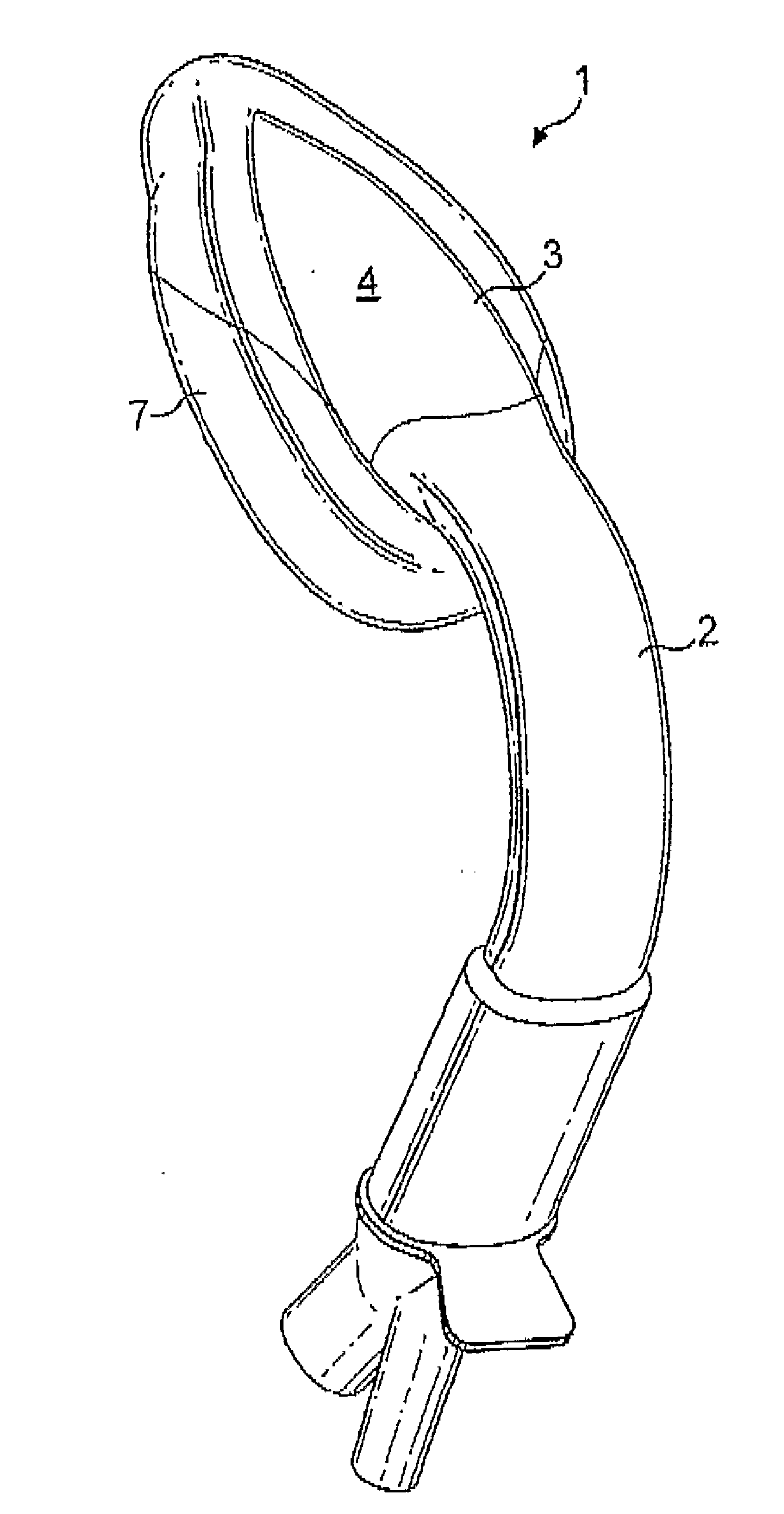
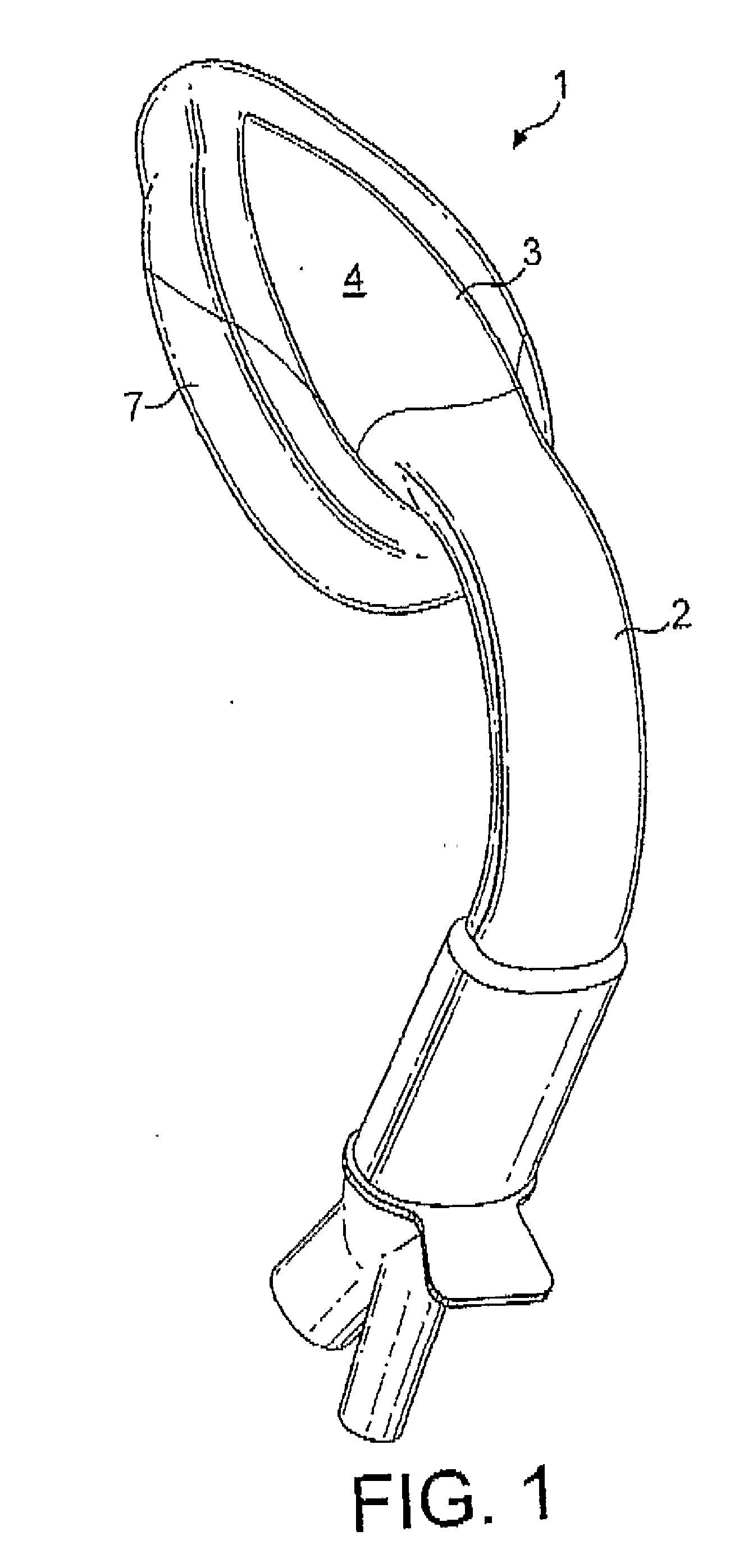
Laryngeal mask airway device
The invention relates to a laryngeal mask airway device (1) for insertion into a patient to provide an airway passage to the patient's glottic opening, the device (1) comprising an airway tube (2), a mask (3) attached to the airway tube (2), the mask (3) comprising a body (4) having a distal end (5) and a proximal end (6), a peripheral inflatable cuff (7), and defining an outlet (8) for gas, the mask (3) being connected to the airway tube (2) for gaseous communication between the tube (2) and the mask, the distal end of the mask being ventrally displaced, relative to the proximal end.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI PTE LTD
High-voltage semiconductor component
InactiveUS6894329B2Improve sturdinessIncrease load capacityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh pressureP–n junction
A semiconductor component has a semiconductor body comprising blocking pn junction, a source zone of a first conductivity type connected to a first electrode and bordering on a zone forming the blocking pn junction of a second conductivity type complementary to the first conductivity type, and a drain zone of the first conductivity type connected to a second electrode. The side of the zone of the second conductivity type facing the drain zone forms a first surface, and in the region between the first surface and a second surface located between the first surface and the drain zone, comprises areas of the first and second conductivity type nested in one another. The second surface coincides with the surface of the drain zone facing the source zone, such that the regions of the first and second conductivity type nested inside each other reach the drain zone.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
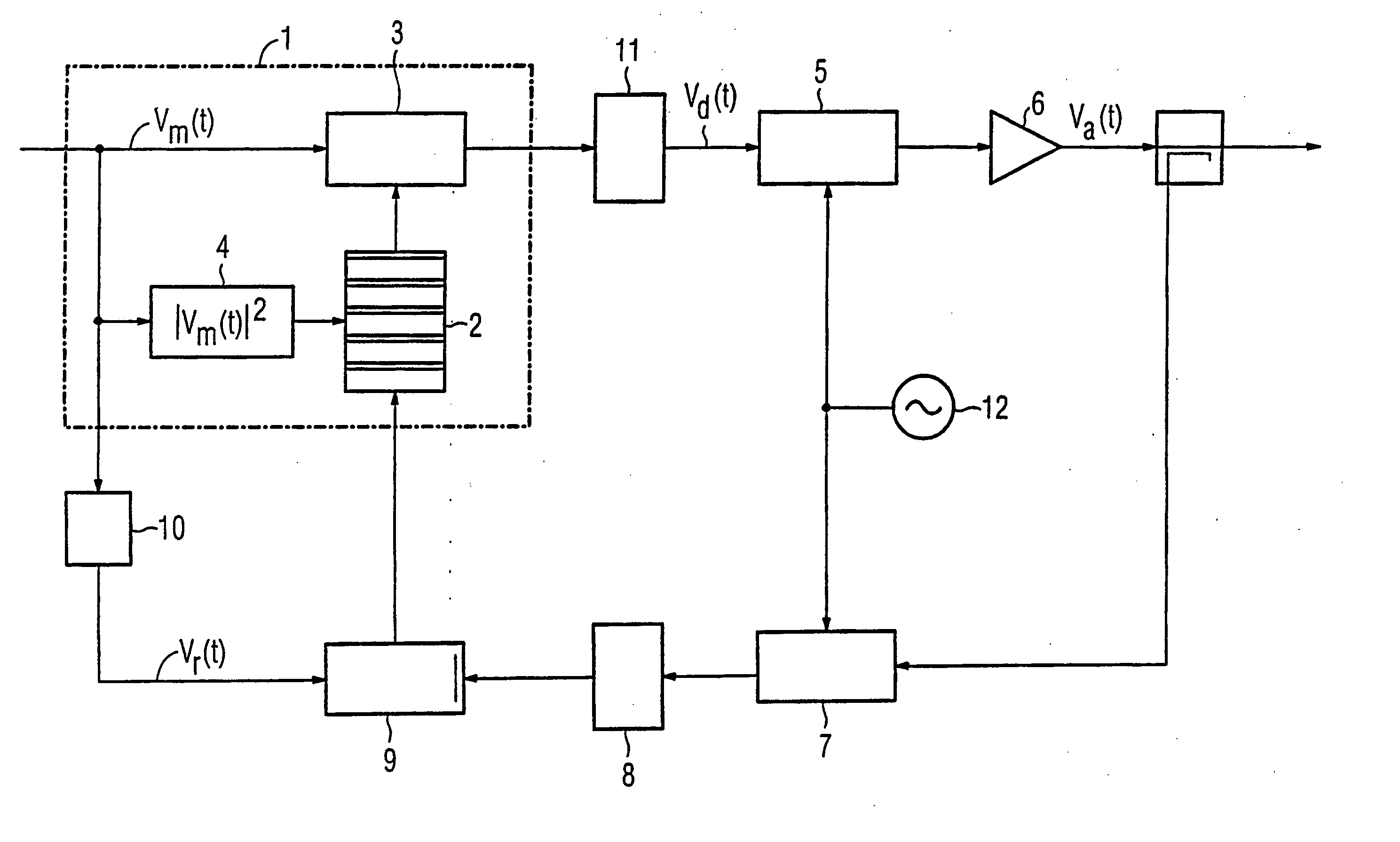
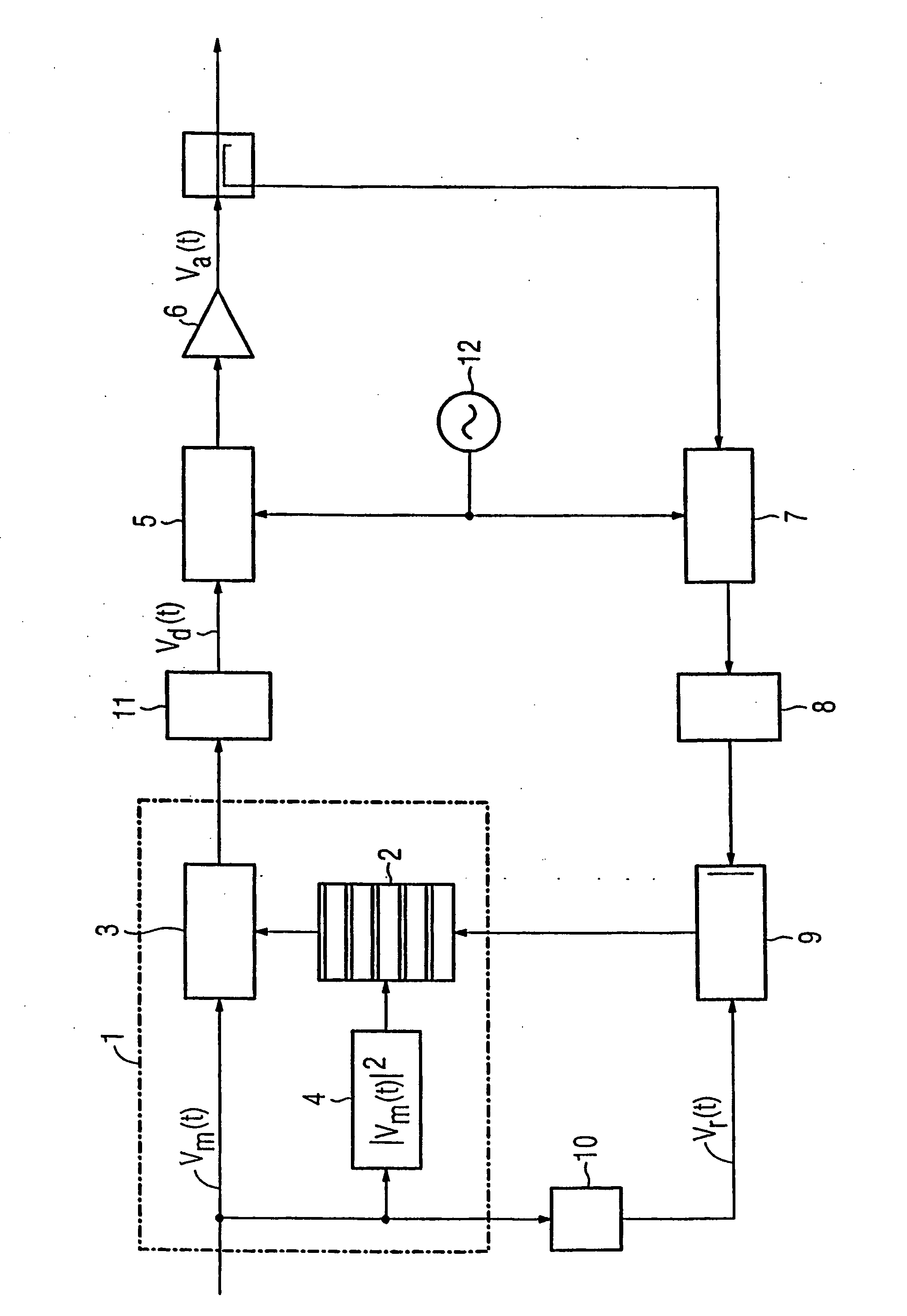
Method for the adaptive pre-distortion of digital raw data values and device for carrying out said method
InactiveUS20060008027A1Smoother profileAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method is provided for the adaptive pre-distortion of digital raw data values for a communication appliance output stage having a power amplifier, the method including the following steps: a) the raw data values (Vm) are pre-distorted by multiplying the raw data values by pre-distortion values from a lookup table (2) containing an association between amplitudes of the raw data values and pre-distortion values; b) output signal values (Vr) of the power amplifier (6) are redirected to an adaptation unit (9); d) temporally corresponding raw data values and output signal values are compared in the adaptation unit in order to assess the distortions of the power amplifier (6); and e) the lookup table (2) is adapted on the basis of results of step d). The present invention seeks to dispense with computing power required to adapt pre-distortion values. To this end, the adaptation unit (9) functions discontinuously and the pre-distortion values of the lookup table (2) are interpolated / extrapolated at least for non-occurring raw data values (Vm). A device is also provided for carrying out the inventive method.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Bicycle fork and steering tube
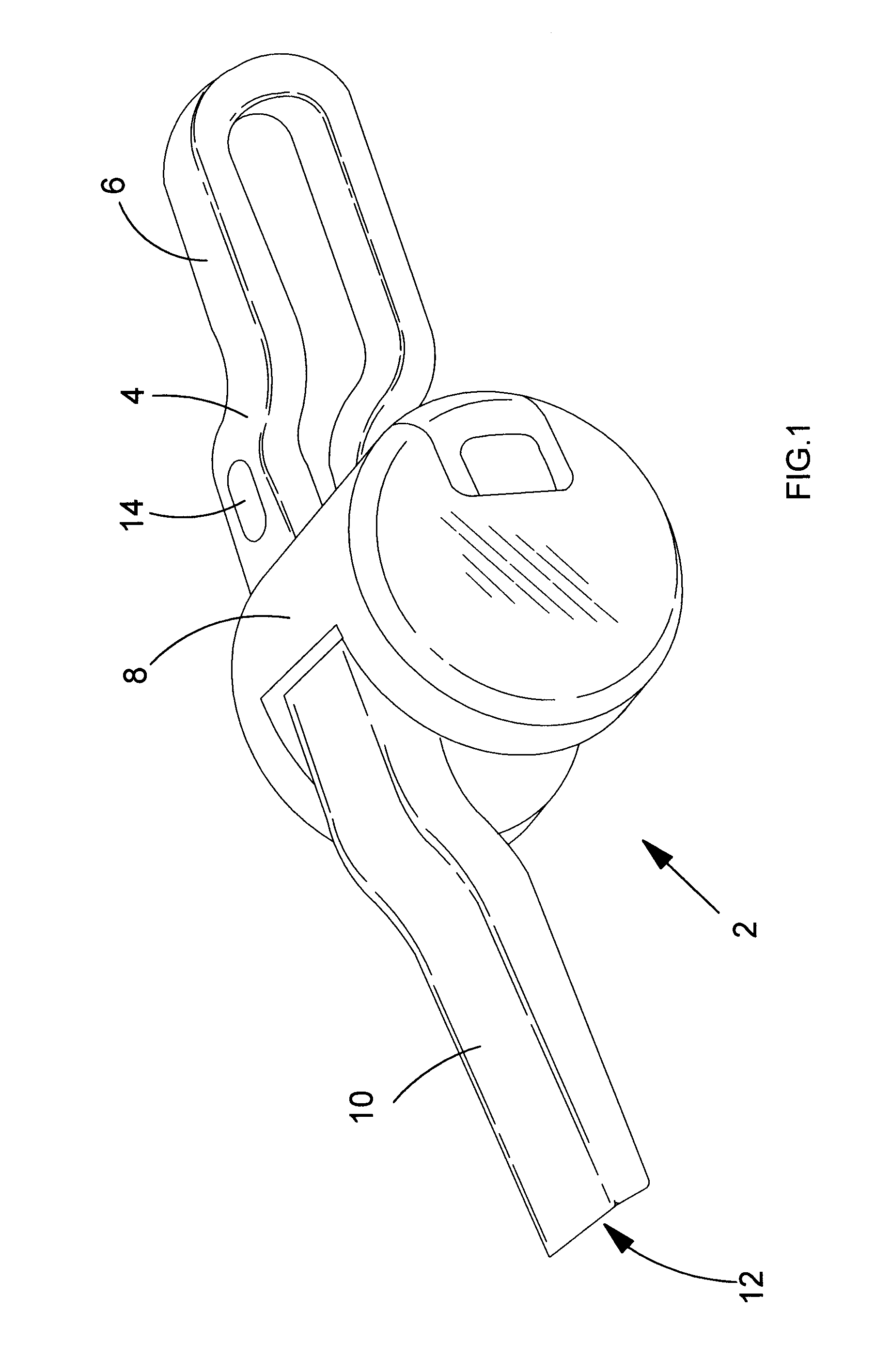
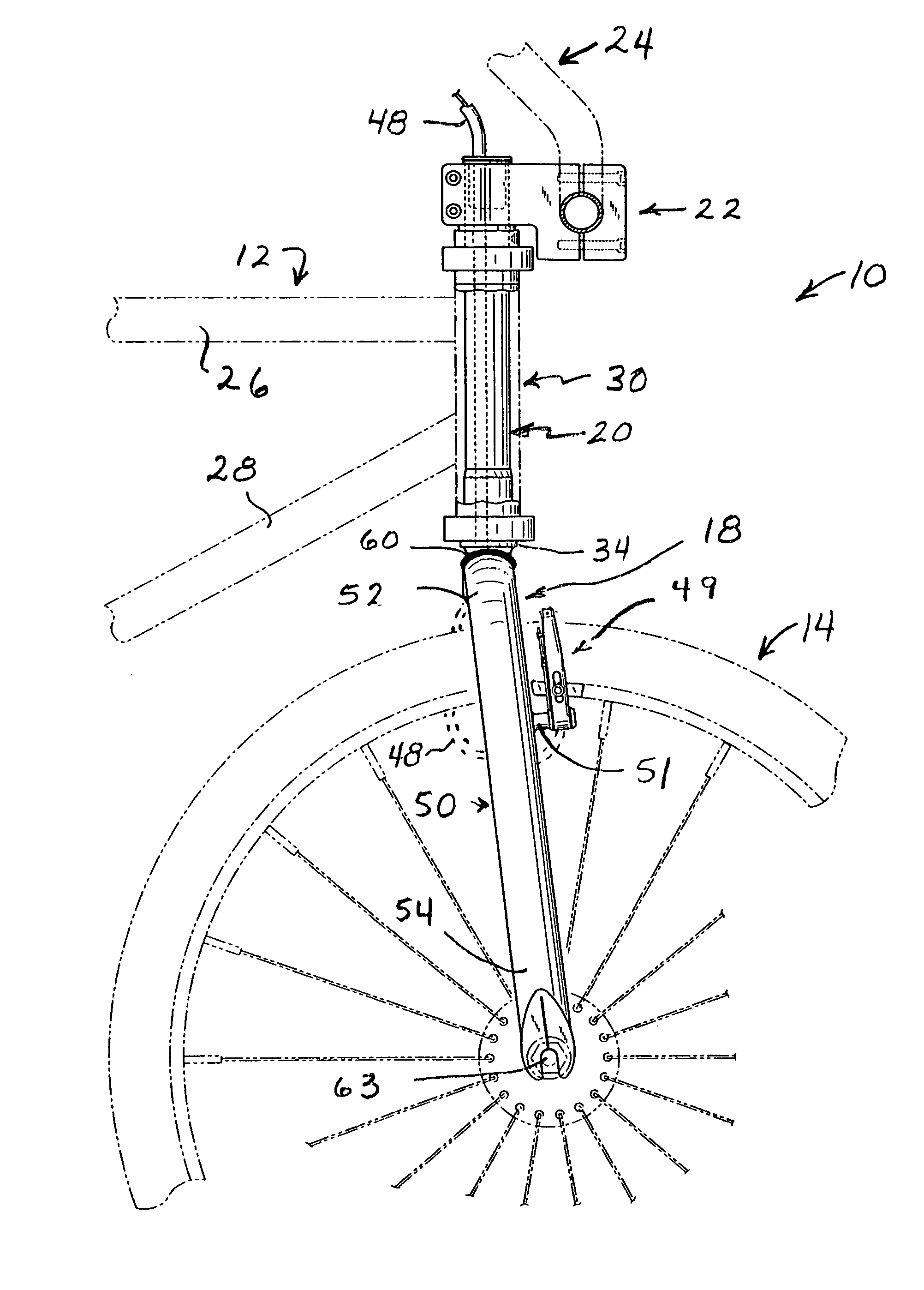
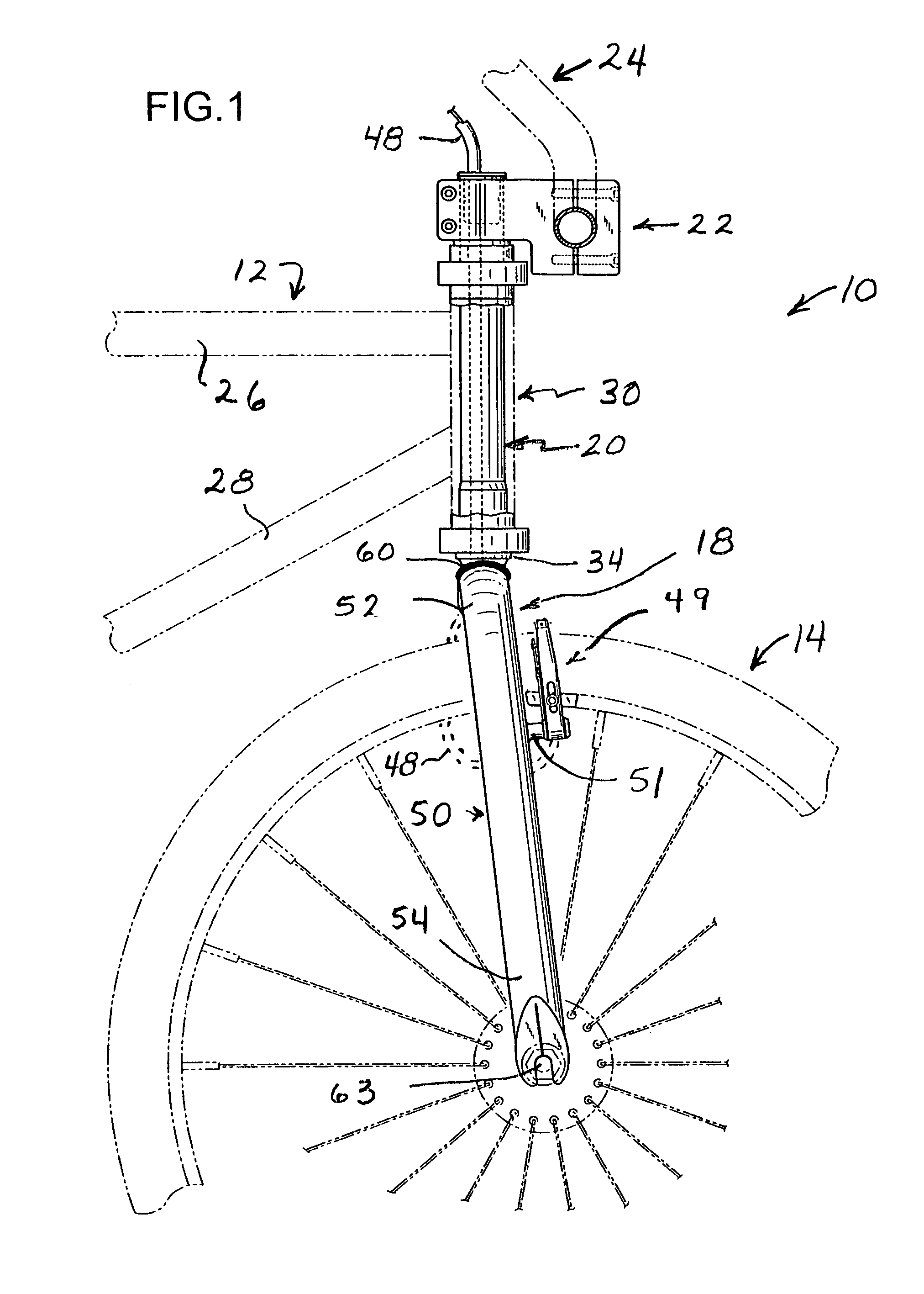
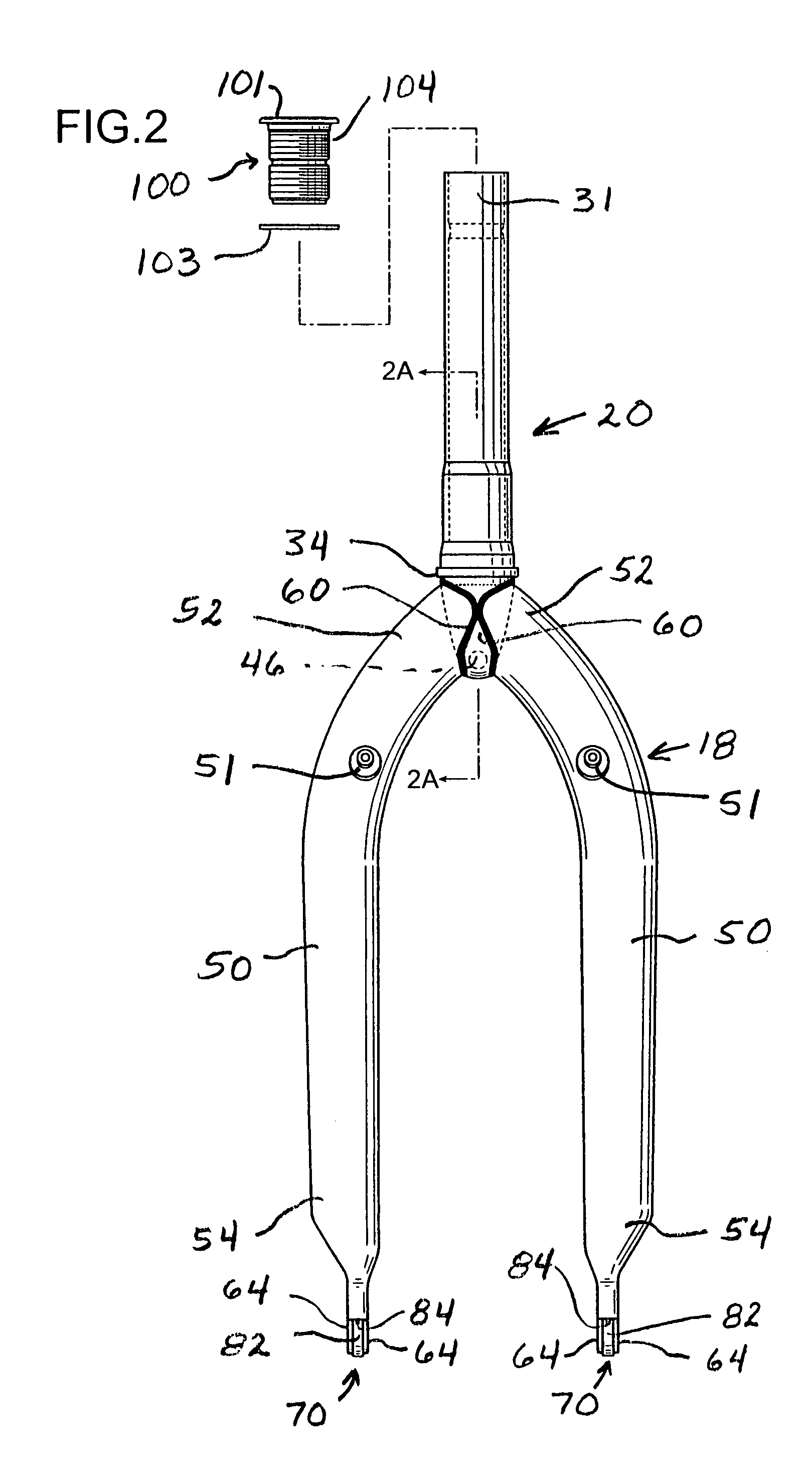
InactiveUS7591474B1Reduce weightSuperior and weight-reducing constructionPassenger cyclesWheel based transmissionWrenchAbutment
A combination bicycle fork and steering tube assembly is formed with a pair of downwardly directed, mutually converging end closure tabs that are bent over into abutment and welded together to define peripherally enclosed fork openings at the ends of the steerer tube. The upper ends of the hollow fork legs are configured to follow the surface contours of the lower end of the steerer tube and are welded to the end closure tabs about the circumferences of the enclosed fork openings at the lower end of the steering tube. The front wheel axle dropouts are formed directly in the lower ends of the fork legs, which include internal dropout support inserts. The dropout support inserts are sandwiched in between a pair of flat, mutually parallel dropout tabs defined directly in the lower ends of the fork legs. The preload bolt has an internal partition that defines a wrench socket that is radially displaced from the axial center of the preload bolt. A large cable routing passage is thereby created through the hollow preload bolt.
Owner:BEARCORP
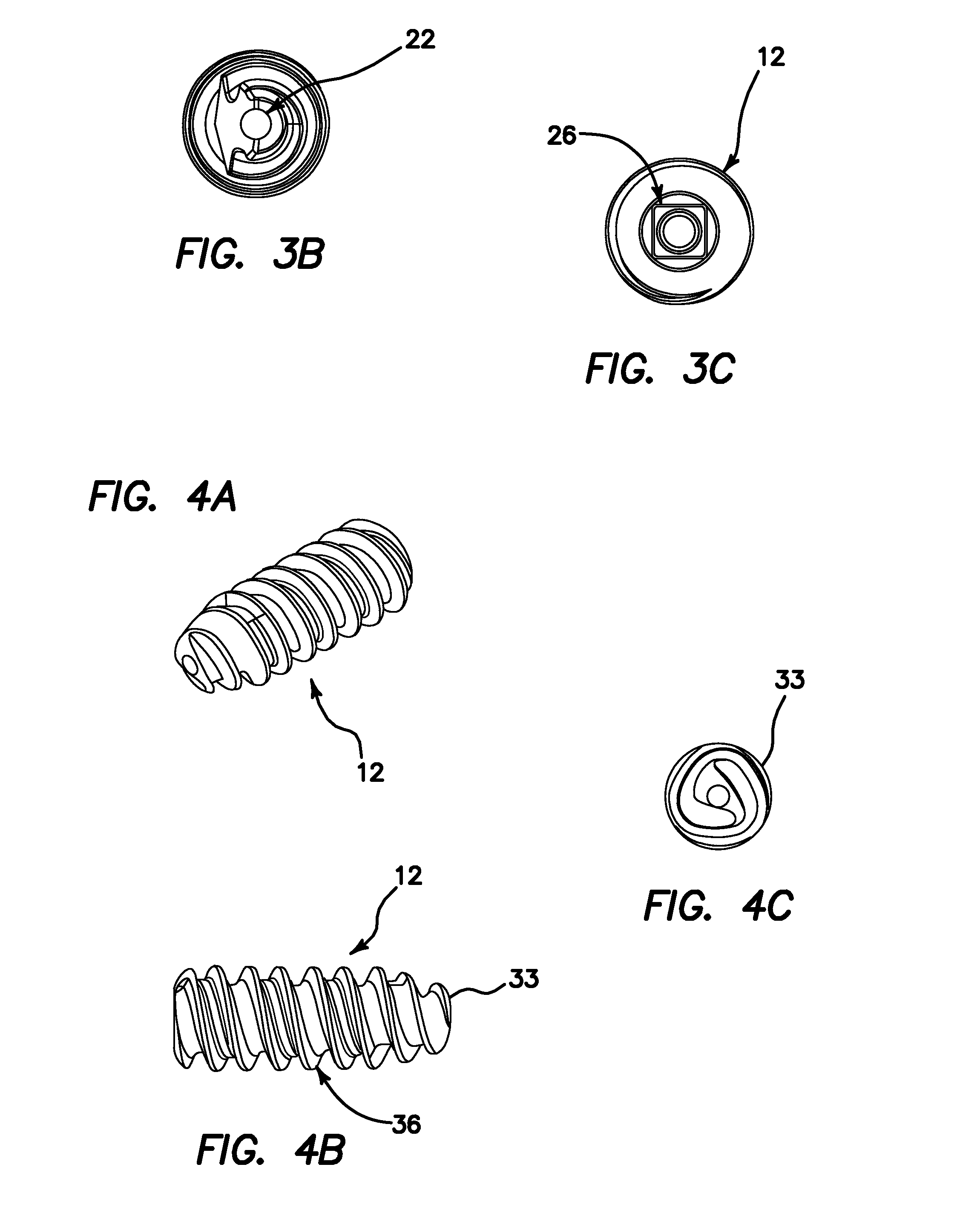
Self-tapping biocompatible interference bone screw
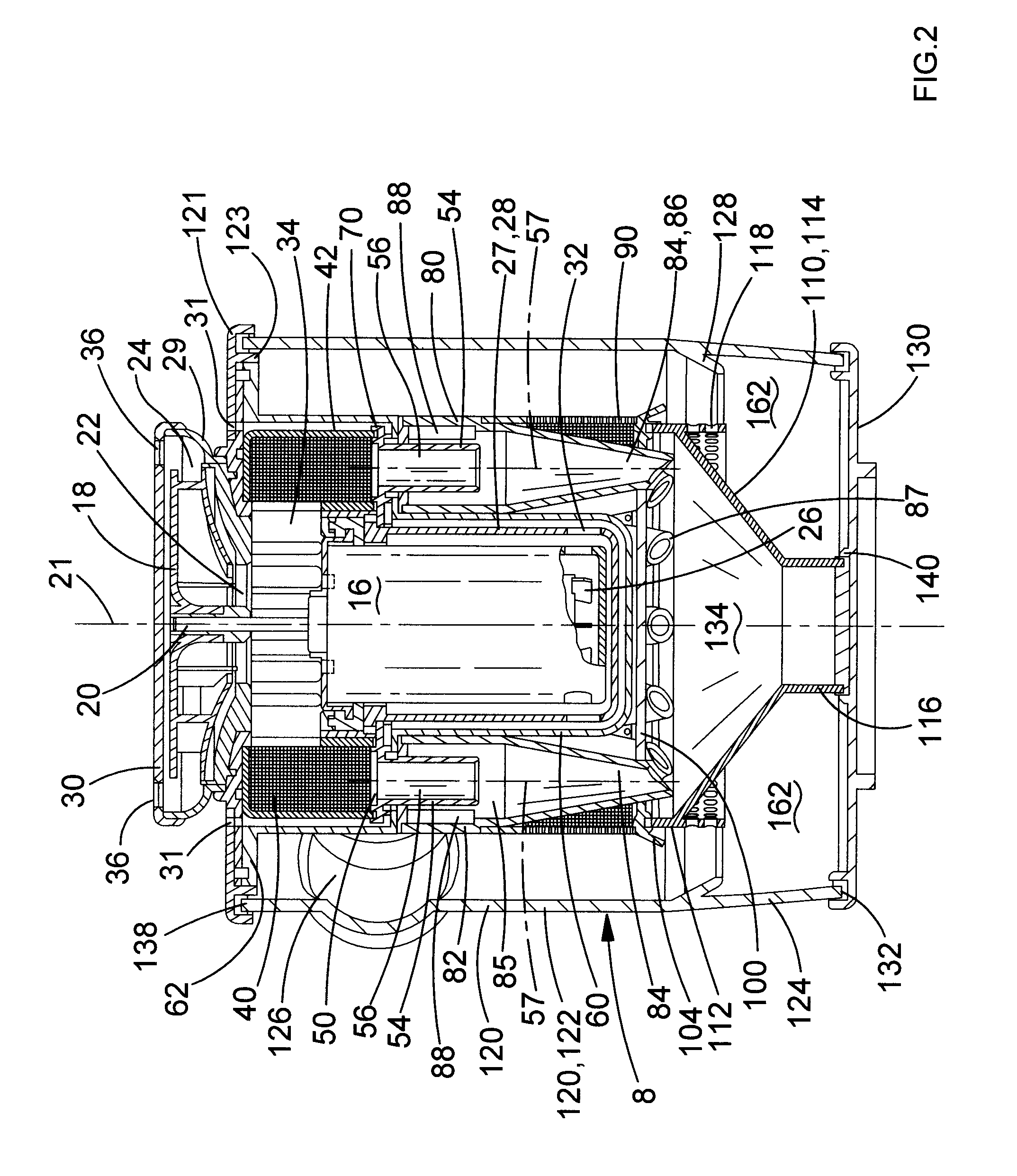
InactiveUS20130204309A1Limited amountPotential confusionSuture equipmentsLigamentsEngineeringKeyhole
A biocompatible interference screw for soft tissue or bone-to-bone fixation comprises a screw body extending from a screw head to a distal tip of the screw. The screw body has an outer surface, and comprises polyether-ether-ketone (PEEK) material. Advantageously, the body outer surface has a textured surface finish for substantially improving pull-out strength of the interference screw. The textured surface finish is textured, in preferred embodiments, with a minimum of approximately 16 micro inches of surface roughness. The screw head comprises a tapered square keyhole for receiving a distal end of a driver instrument. The screw comprises a series of threads, which have a relatively smooth profile, in order to prevent graft tissue laceration as the screw is being inserted. The distal tip of the screw body comprises a narrow tip, and a distal end of the screw body is angled inwardly toward the narrow distal tip.
Owner:CAYENNE MEDICAL INC
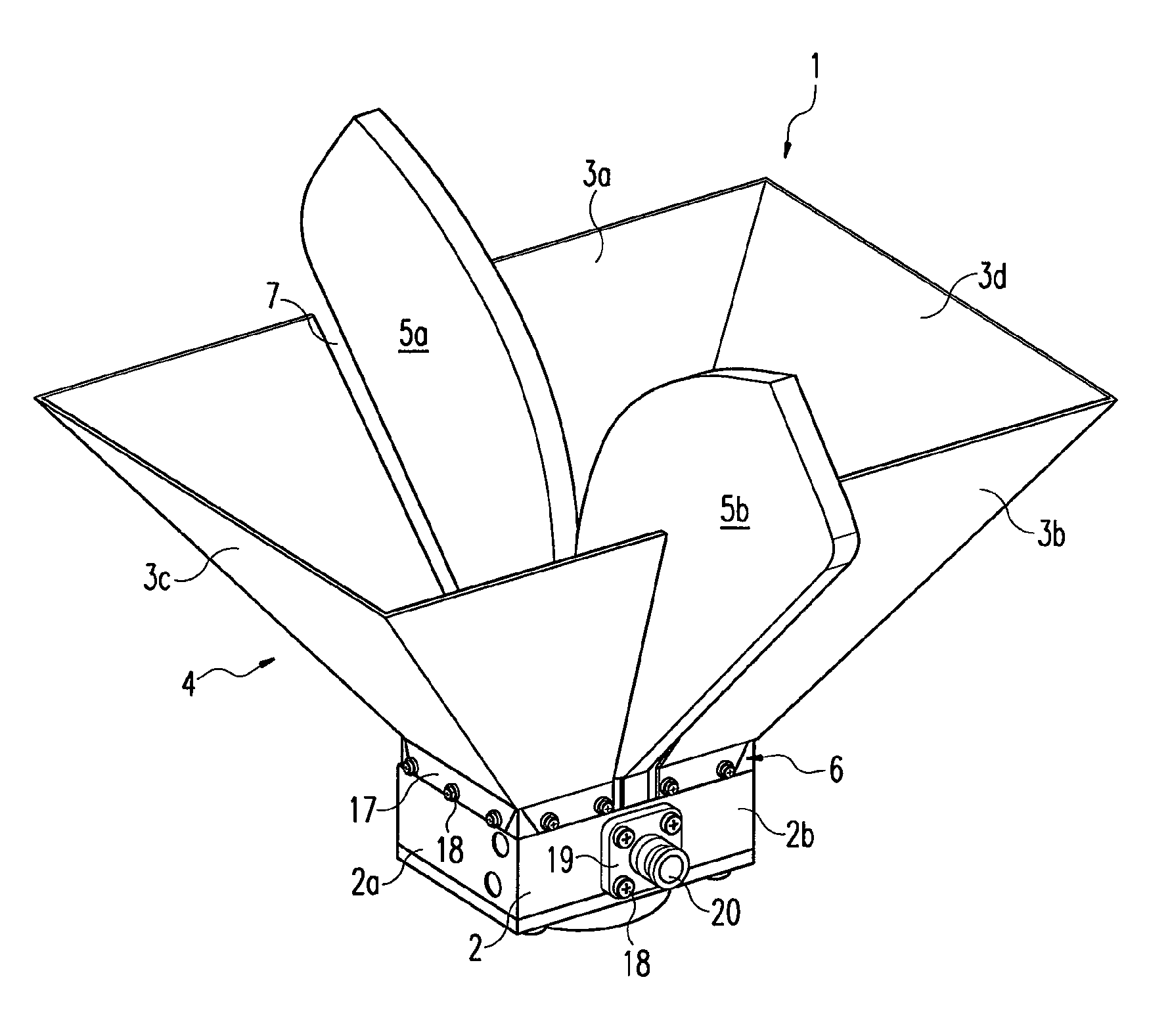
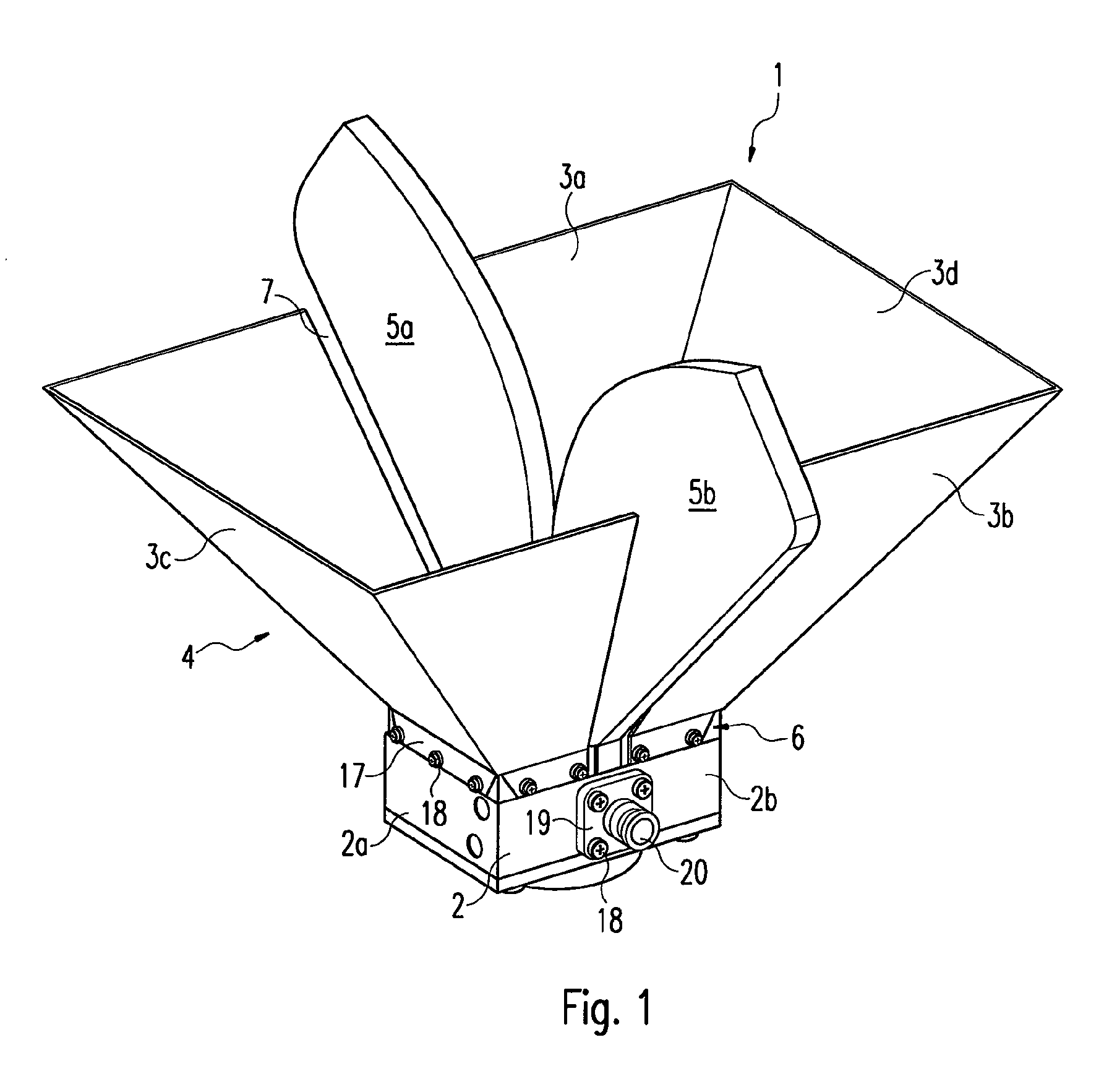
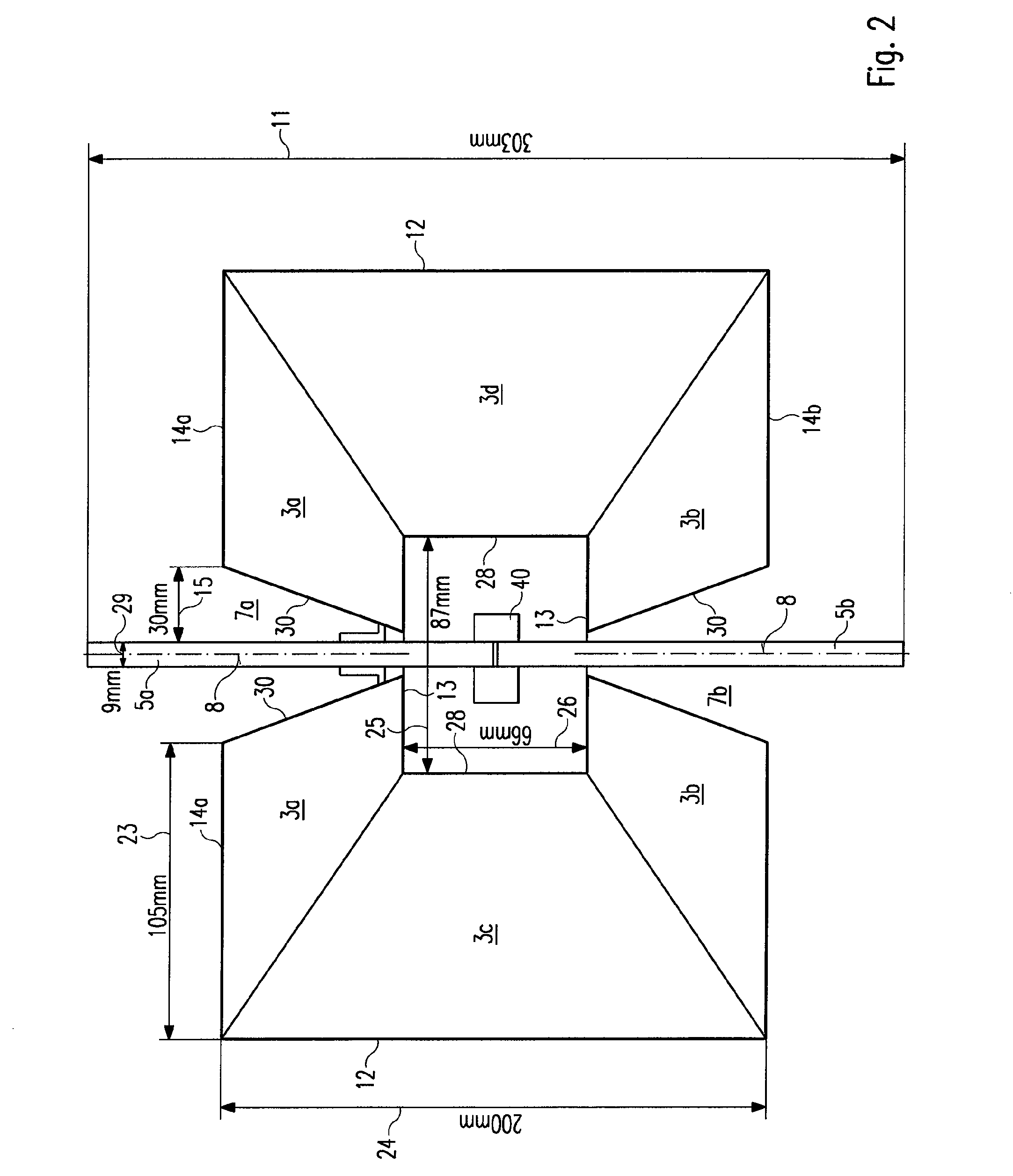
Horn antenna
The invention relates to an antenna (1) for a transmitting operation and / or a receiving operation with a decoupling apparatus (2a) and / or a coupling apparatus (2b) for electromagnetic waves. The antenna (1) according to the invention comprises a horn funnel (4) which is composed of at least two side walls (3a, 3b, 3c, 3d), and also comprises at least two fins (5a, 5b) which extend into the interior of said horn funnel (4). The at least two side walls (3a, 3b, 3c, 3d) have a cutout (7a, 7b) in each case.
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
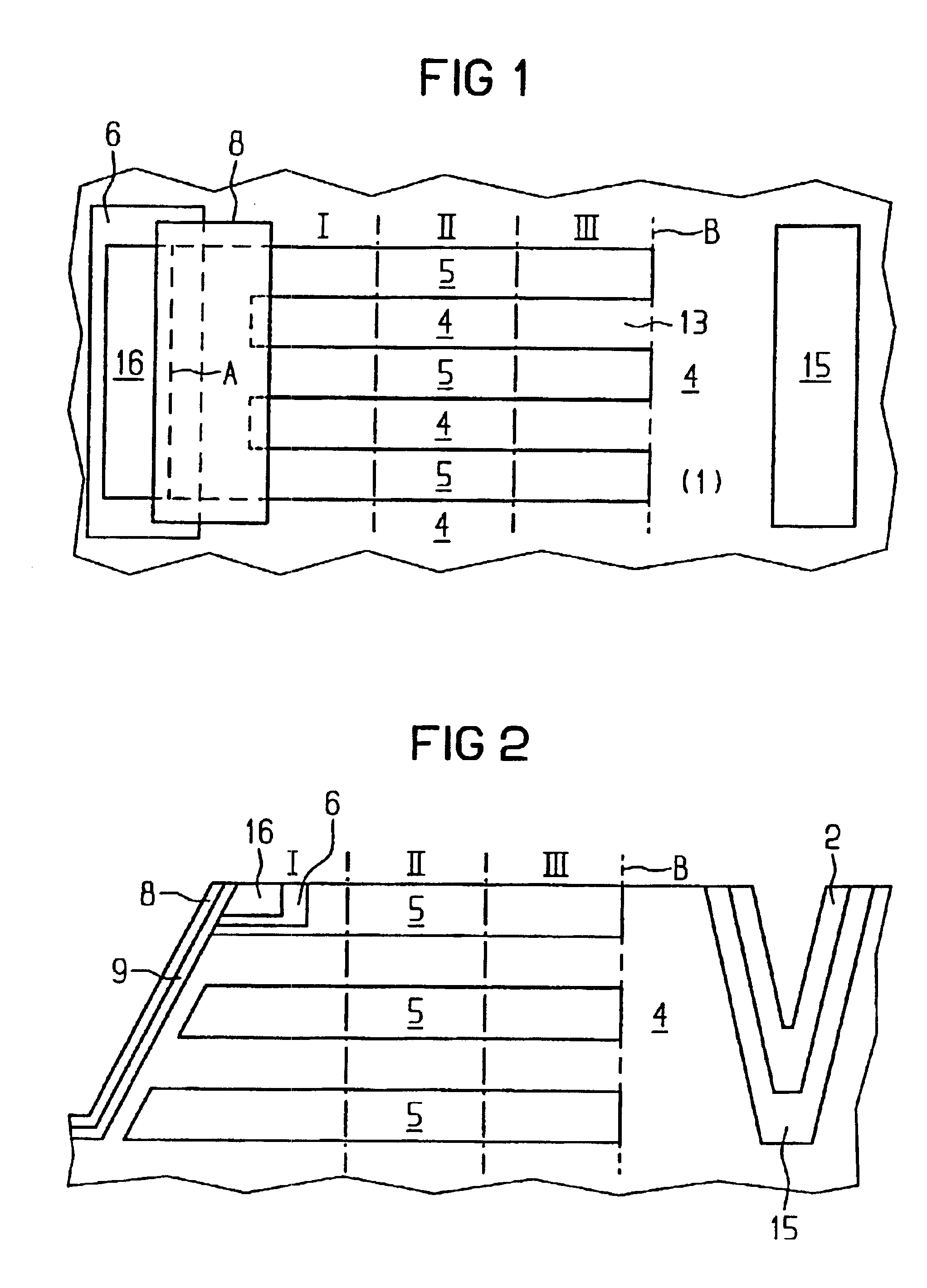
Method for eliminating standing waves in a photoresist profile
InactiveUS20030235998A1Smoother profileSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingStanding wavePhotoresist
A semiconductor manufacturing method that includes defining a substrate, depositing a layer of first material over the substrate, providing a layer of photoresist over the layer of first material, patterning and defining the photoresist layer to form at least one photoresist structure having at least one substantially vertical sidewall and one substantially horizontal surface, wherein a surface of the at least one substantially vertical sidewall is in the shape of a standing wave, and depositing a layer of polymer over the patterned and defined photoresist layer, wherein the polymer layer is substantially conformal and covers the at least one substantially vertical sidewall and one substantially horizontal surface, and wherein the polymer layer covers the standing wave on the surface of the at least one substantially vertical sidewall to form a substantially smooth profile.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
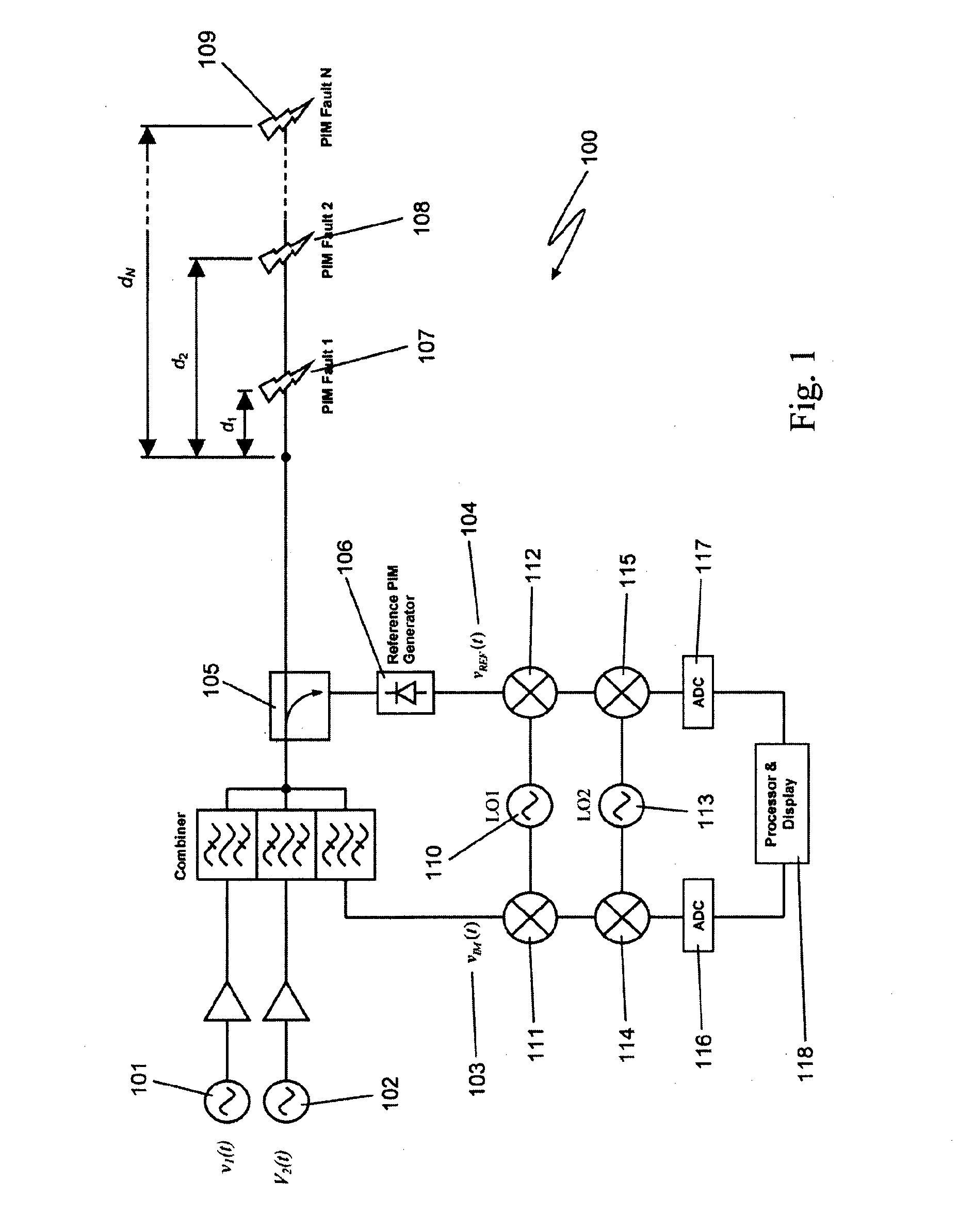
Method and apparatus for locating faults in communications networks
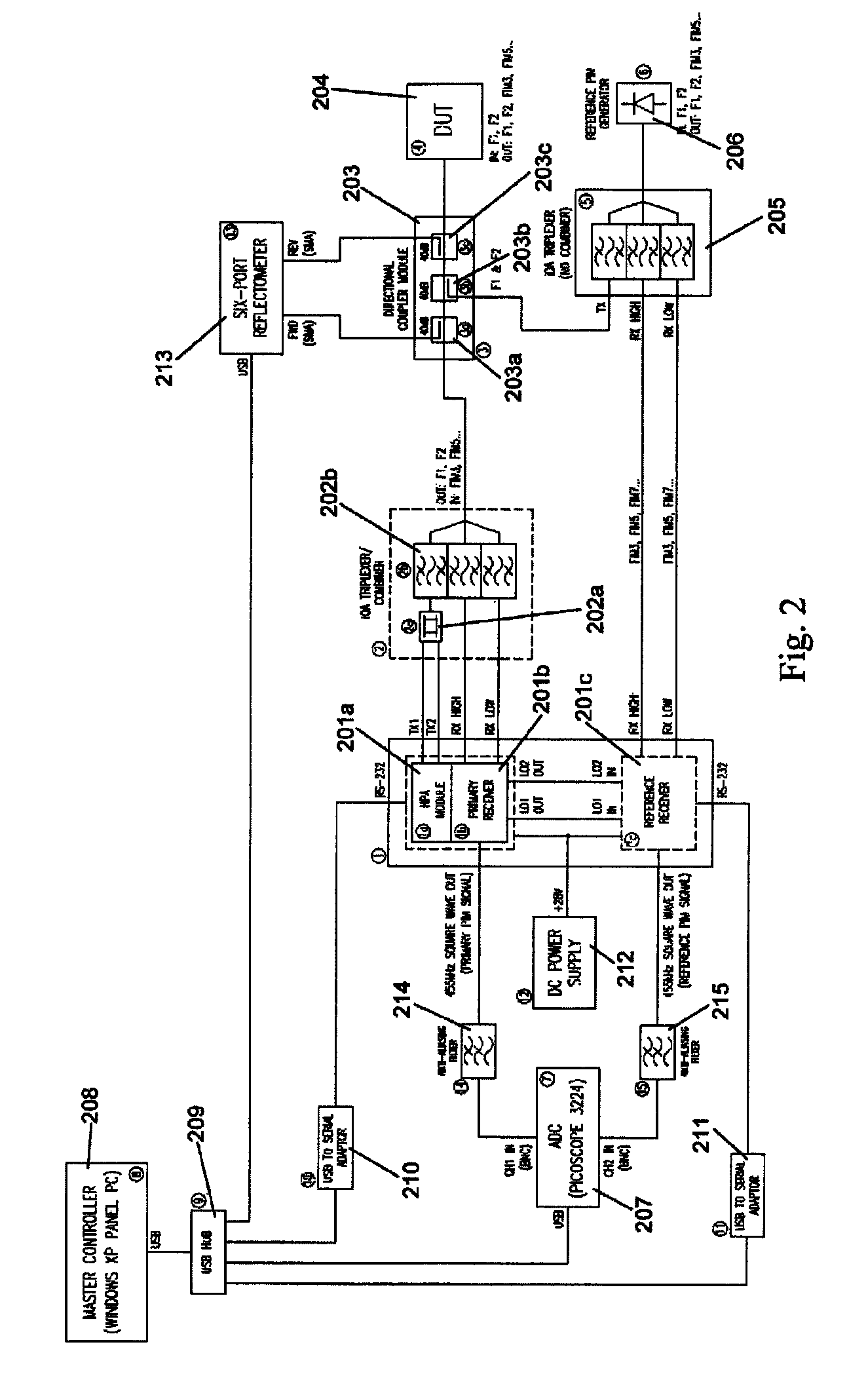
ActiveUS8995517B2Wide bandwidthEasy to identifySpectral/fourier analysisTransmitters monitoringCoaxial cableComputer module
The present invention relates to a device for the location of passive intermodulation faults in a coaxial cable network. The test apparatus (100) according to one embodiment of the present invention utilizes a pair of high-power, frequency-synthesized, unmodulated RF carriers v1(t) (101) and v2(t) (102) are generated inside the HPA module of the apparatus. The power and frequency of v1(t) (101) and v2(t) (102) can be independently set to a range of values, v1(t), v2(t) are combined inside the instrument and then applied to the input of the device under test (DUT). The PIM signals (107,108,109) generated in the DUT are combined to produce the primary PIM signal vIM(t) (103). The apparatus also includes two receivers (110,111, 112,113,114,115) for the detection of vIM(t) 103 and vREF(t) (104). These signals are downconverted to 455 kHz. The two 455 kHz waveforms are digitized with a dual- channel A / D converter (116,117) and the amplitude ratio and phase offset between the digitized waveforms are calculated and stored.
Owner:KAELUS
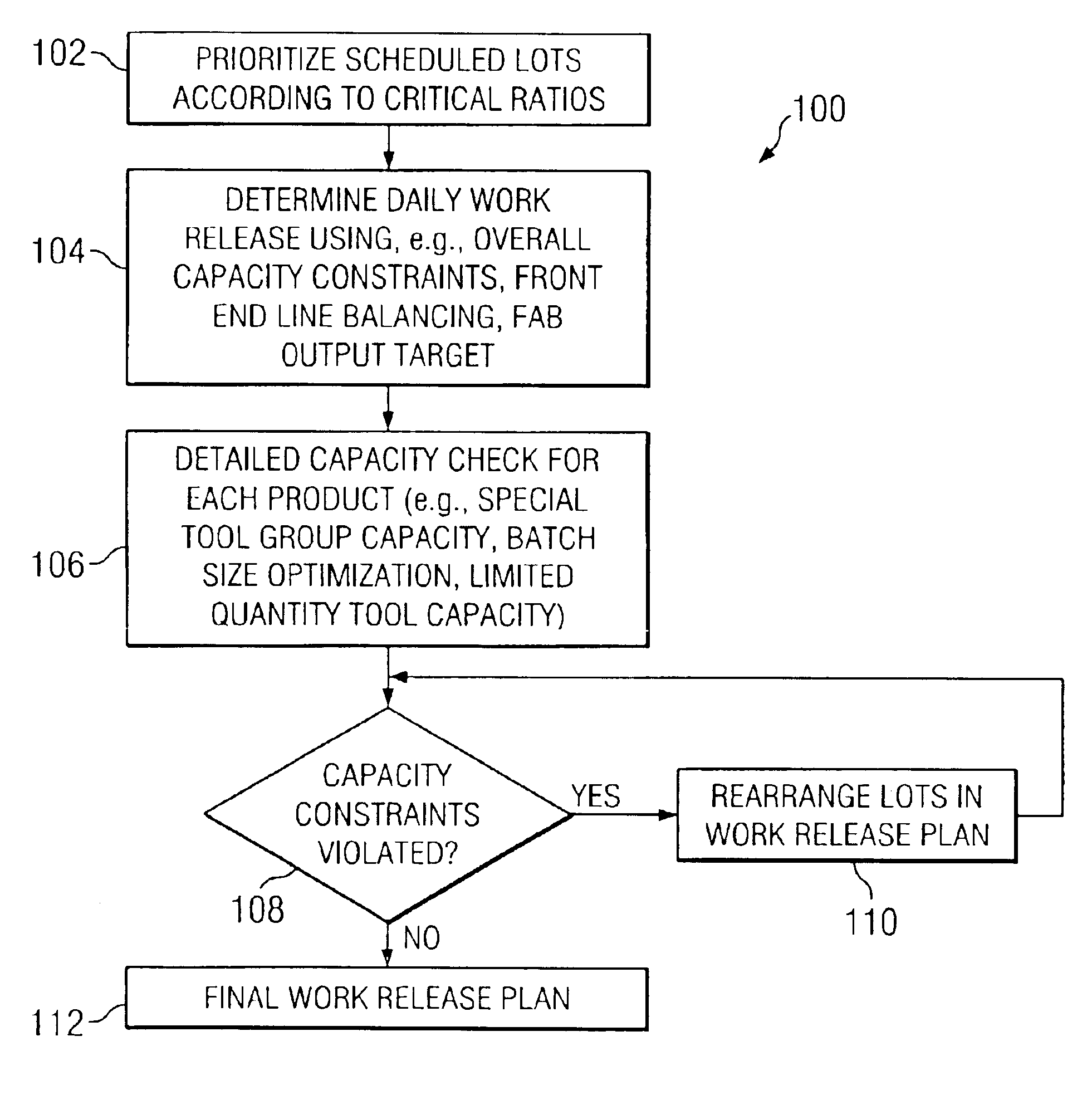
Method and apparatus for robust shape filter generation
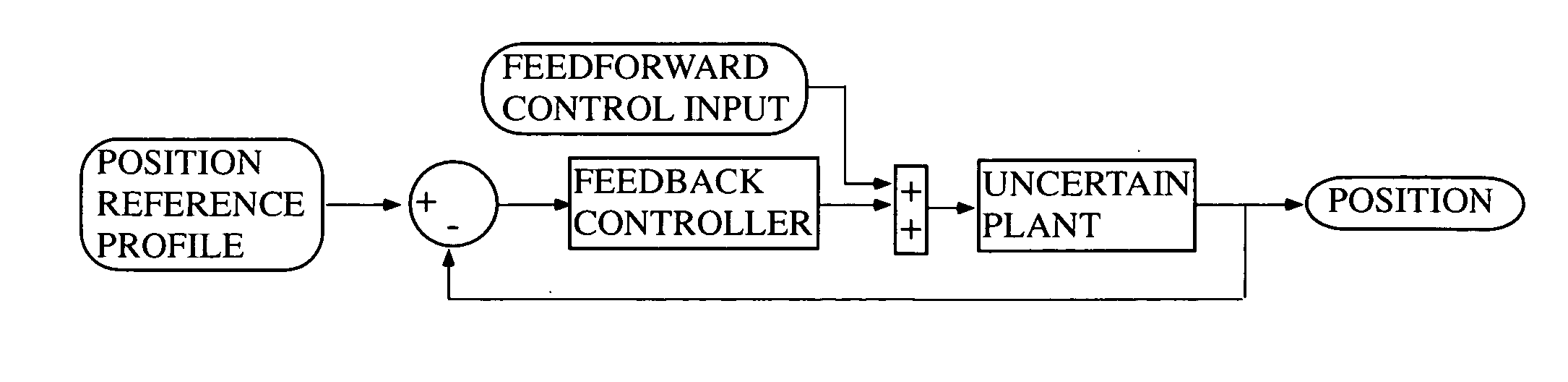
InactiveUS20070067049A1Improve control robustnessSmoother profileAnti-hunting elementsAdaptive controlResidual vibrationClosed loop
According to a preferred aspect of the instant invention, there is provided a system and method of robust control profile generation which suppresses one or some resonant modes in a flexible dynamic system. This robust control profile is a smooth function which can be used as a velocity profile, or as a shape filter to an arbitrary control command. The robustness can be arbitrarily improved. The robustness brings about a smoother profile. The technique can be applied to both open-loop and closed-loop systems. As a consequence of the use of the instant invention, the movement of a flexible arm that is performed according to this sort of function will be one that has minimal or reduced residual vibration after it has reached its destination.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
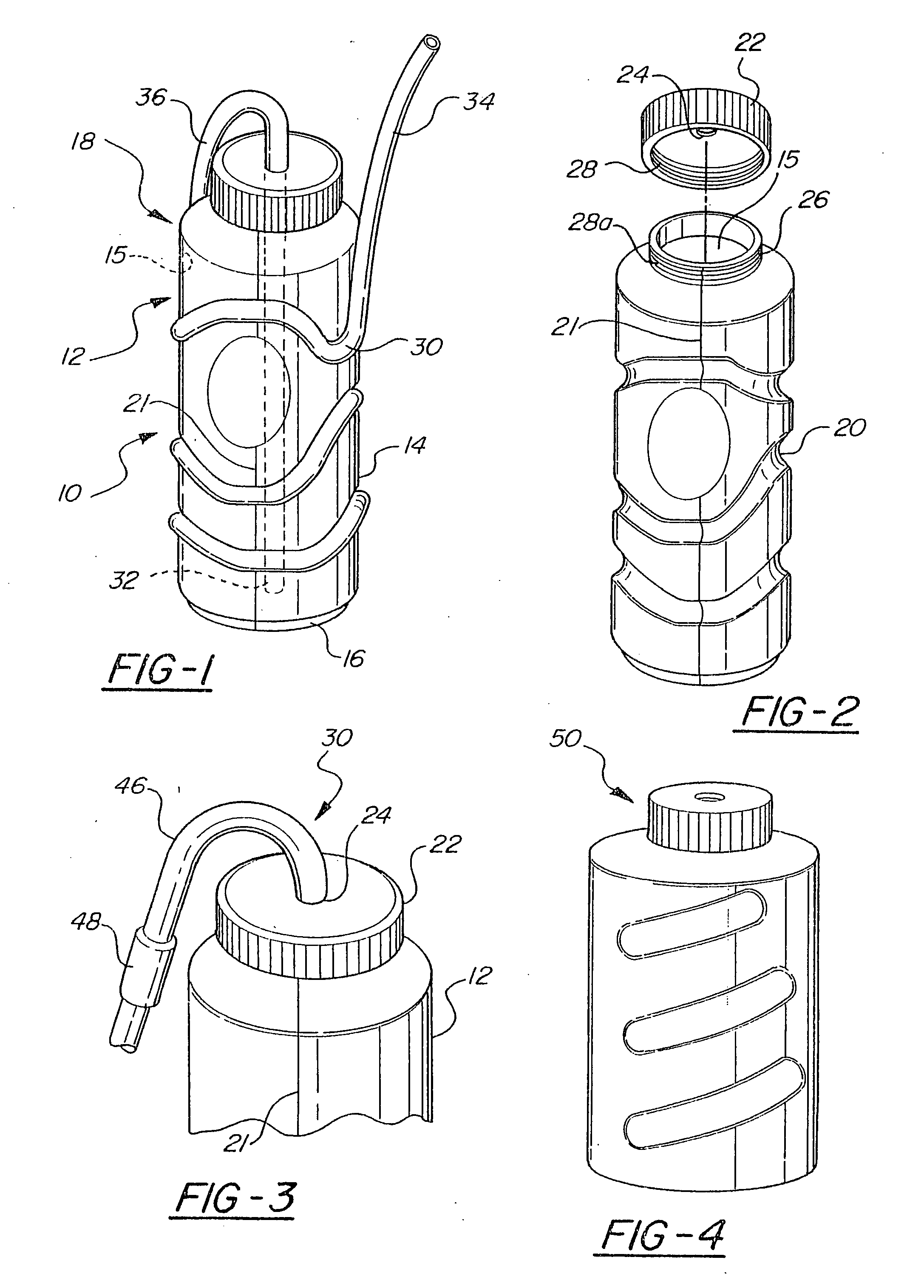
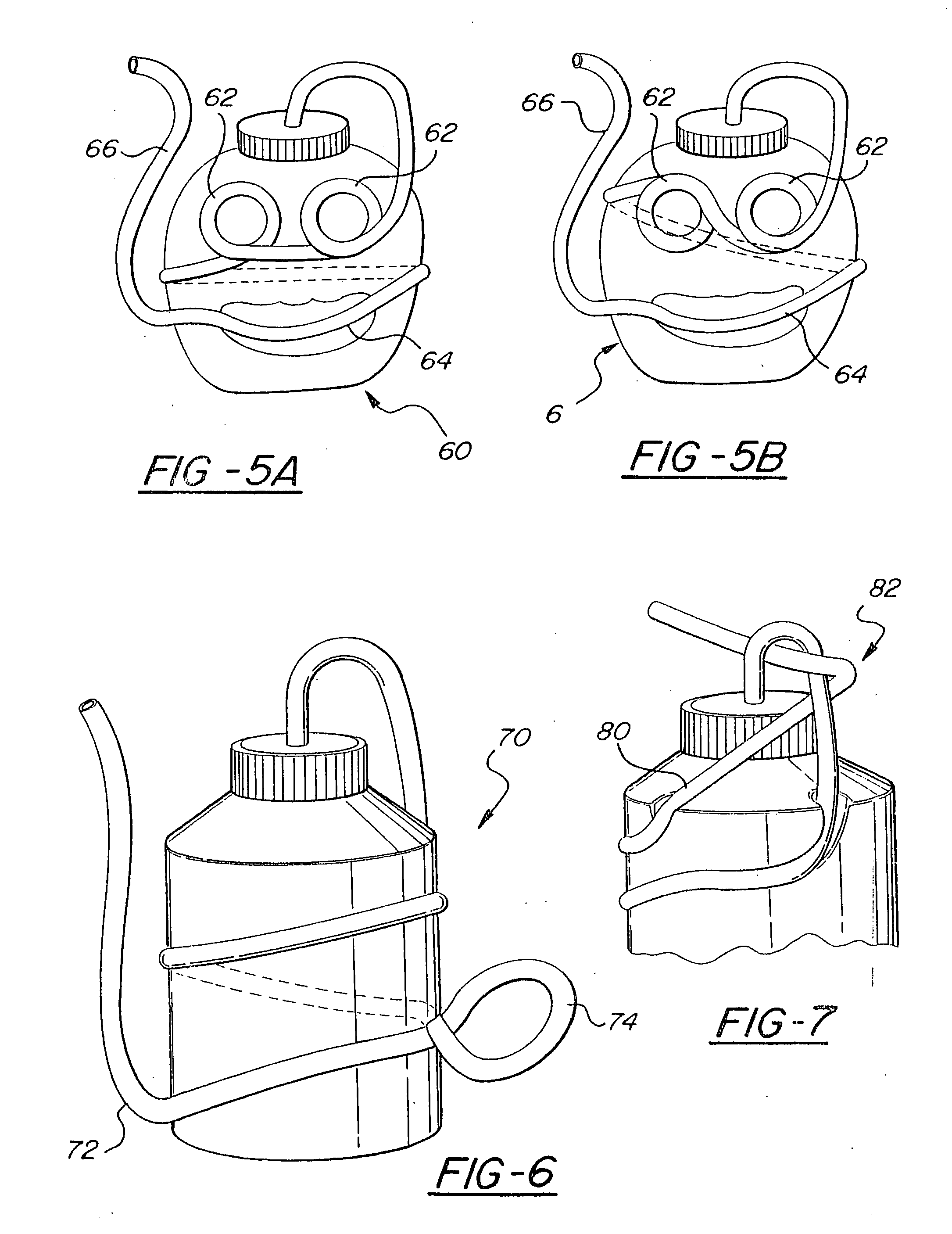
Drink container with molded straw and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7021490B2Easy to disassembleEasy to carryDispensing apparatusDrinking vesselsEngineeringDrinking straw
A combination drinking container and straw and method of manufacture. The container has at least one straw retaining member molded into either the outer or inner surface of the container wall, or a portion of the wall may be shaped to include a constricted stem. A malleable straw is fitted onto each such retaining member so that at least a portion of the pathway of the straw is defined by the retaining members. A first end of the straw extends into the container and a second end extends upwardly so that beverage may be sipped therefrom. A lid may close the container, the lid optionally including an aperture to permit passage of the straw, the straw passing through the aperture. Also disclosed is a lidded container wherein the lid is provided with an aperture. A first portion of a drinking straw extends from inside the container, through the hole and to the container's outside to form a hinge for the lid. A second portion of the straw is attached to the container. In this way, the lid remains attached to the straw and container even when removed from the container.
Owner:FUN TIME INT
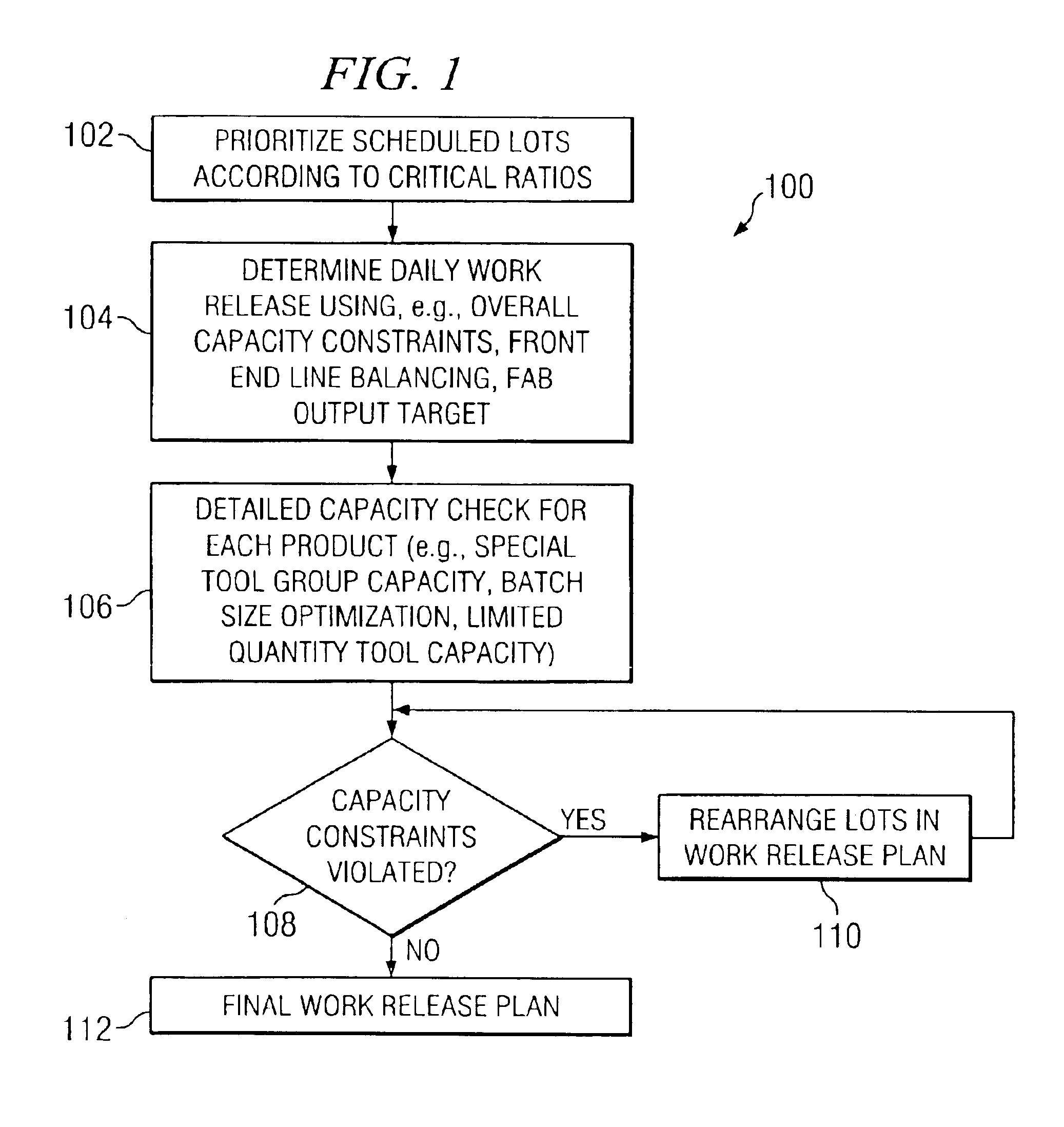
Balancing work release based on both demand and supply variables
InactiveUS6892106B2High customer satisfactionLower manufacturing requirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLogisticsProgram planningManufacturing systems
A systematic approach for generating a work release plan that considers both demand and supply variables. The approach comprises prioritizing scheduled lots in order of their critical ratios, estimating an initial daily release quota for the scheduled lots based on both pull and push requirements, and determining detailed capacity constraints for the manufacturing system. The approach further comprises testing whether the initial daily release quota complies with the detailed capacity constraints, and, if the detailed capacity constraints are violated, rearranging the lots in the initial daily release quota so that the detailed capacity constraints are met.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Drink container with molded straw and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20060157490A1Easy to carrySmoother profileDrinking vesselsTablewaresEngineeringDrinking straw
A combination drinking container and straw and method of manufacture. The container has at least one straw retaining member molded into either the outer or inner surface of the container wall, or a portion of the wall may be shaped to include a constricted stem. A malleable straw is fitted onto each such retaining member so that at least a portion of the pathway of the straw is defined by the retaining members. A first end of the straw extends into the container and a second end extends upwardly so that beverage may be sipped therefrom. A lid may close the container, the lid optionally including an aperture to permit passage of the straw, the straw passing through the aperture. Also disclosed is a lidded container wherein the lid is provided with an aperture. A first portion of a drinking straw extends from inside the container, through the hole and to the container's outside to form a hinge for the lid. A second portion of the straw is attached to the container. In this way, the lid remains attached to the straw and container even when removed from the container.
Owner:LIPSON ERIK
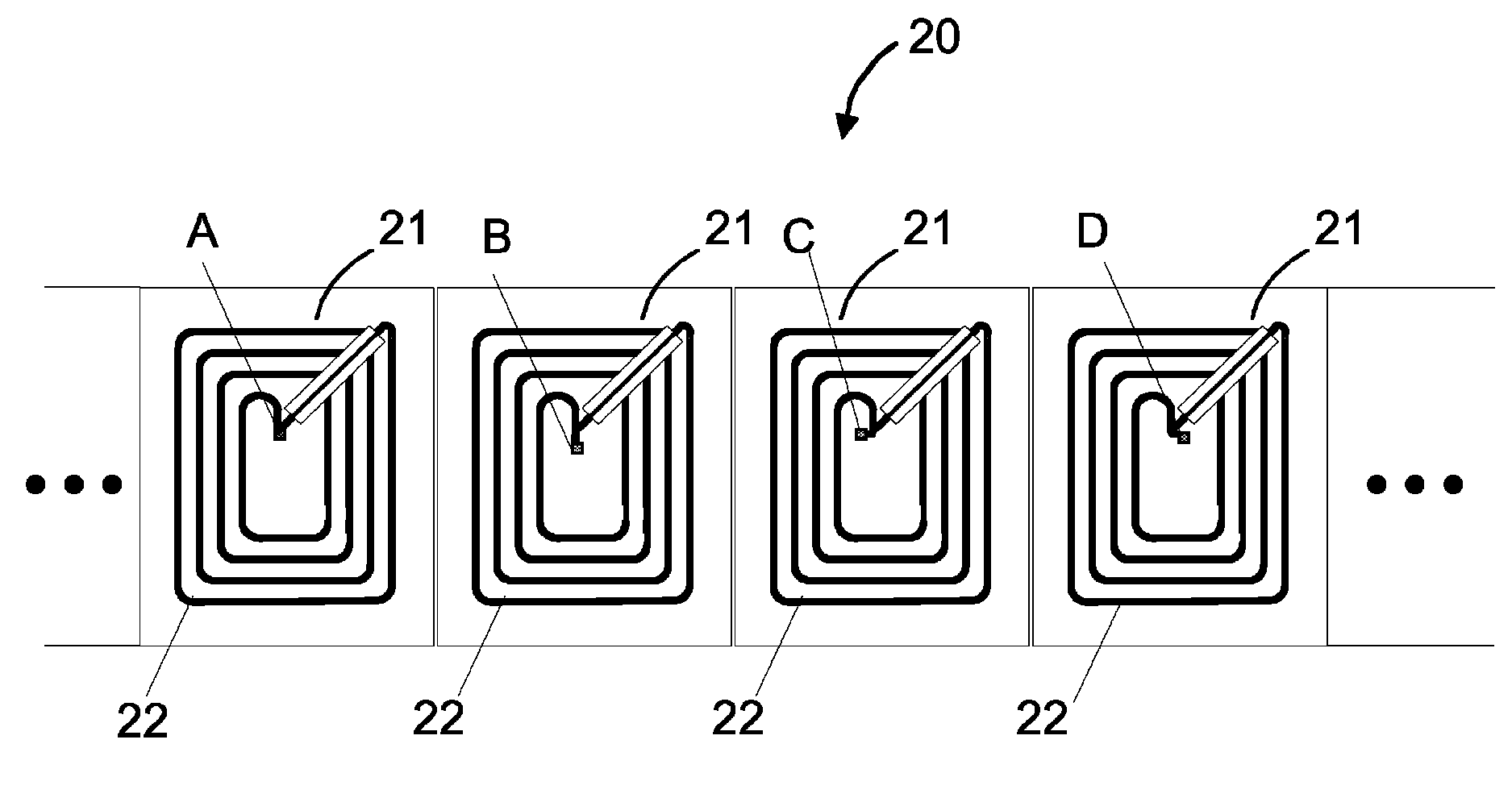
Method for producing a rollable web and a rollable web
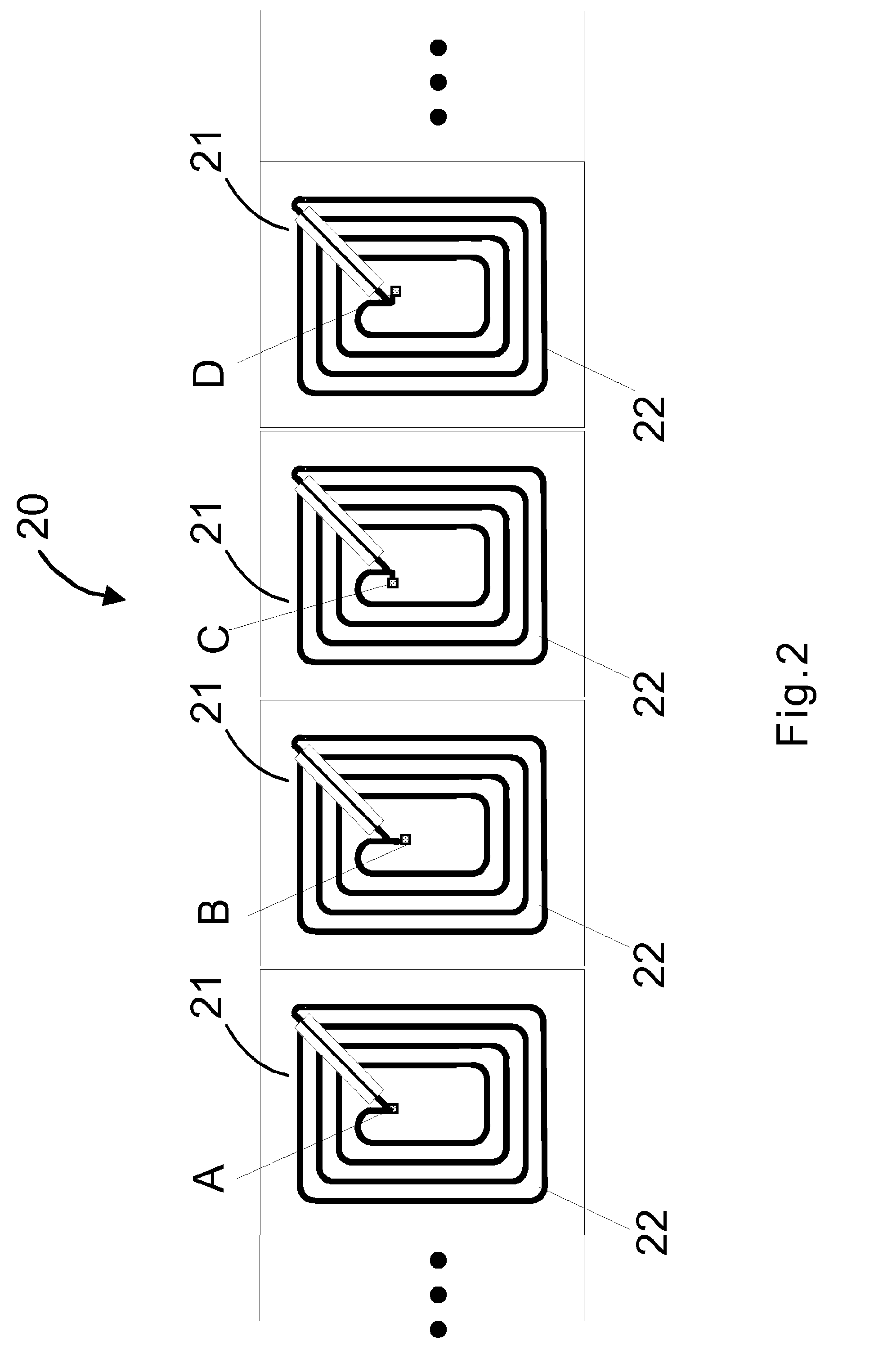
InactiveUS8467192B2Eliminate the effects ofReduce stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic chip
A method for producing a rollable web with successive antennas, where an electronic chip is attached to an antenna in a predetermined position. The position of an electronic chip changes with respect to the antenna when compared to at least some of the chips within individual and successive antennas. A rollable web includes successive antennas, where electronic chips are attached to antennas in a predetermined position. In the rollable web, the position of a chip changes with respect to the antenna compared to at least some of the chips within individual and successive antennas.
Owner:SMARTRAC INVESTMENT BV
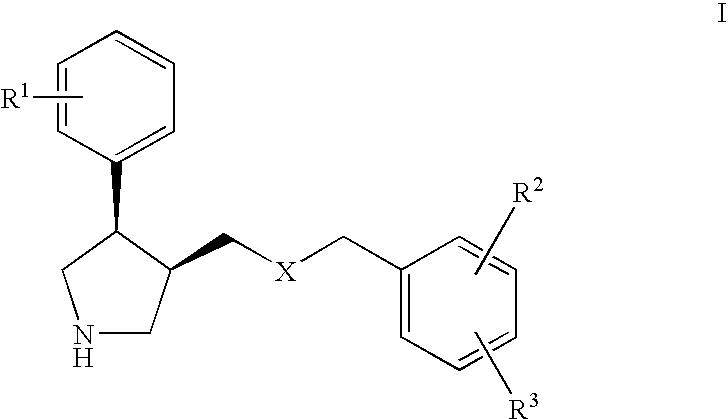
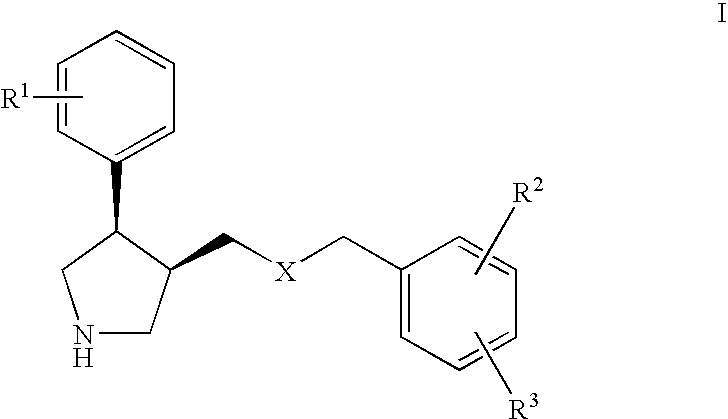
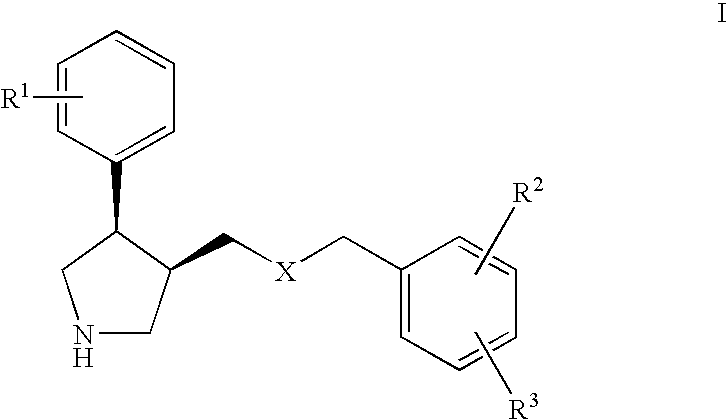
Serotonin transporter (SERT) inhibitors for the treatment of depression and anxiety
InactiveUS20070129419A1Reduce riskKeep it workingBiocideNervous disorderSerotonin transporterANXIETY COMPLEX
The present invention relates to cis-derivatives of formula wherein R1, R2, and R3 are as defined herein and to pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts thereof. The compounds of formula I are good inhibitors of the serotonin transporter (SERT inhibitors). By virtue of their efficacy as SERT inhibitors, the compounds of the present invention are particularly useful for the treatment of CNS disorders and psychotic disorders, in particular in the treatment or prevention of depressive states and / or in the treatment of anxiety.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com