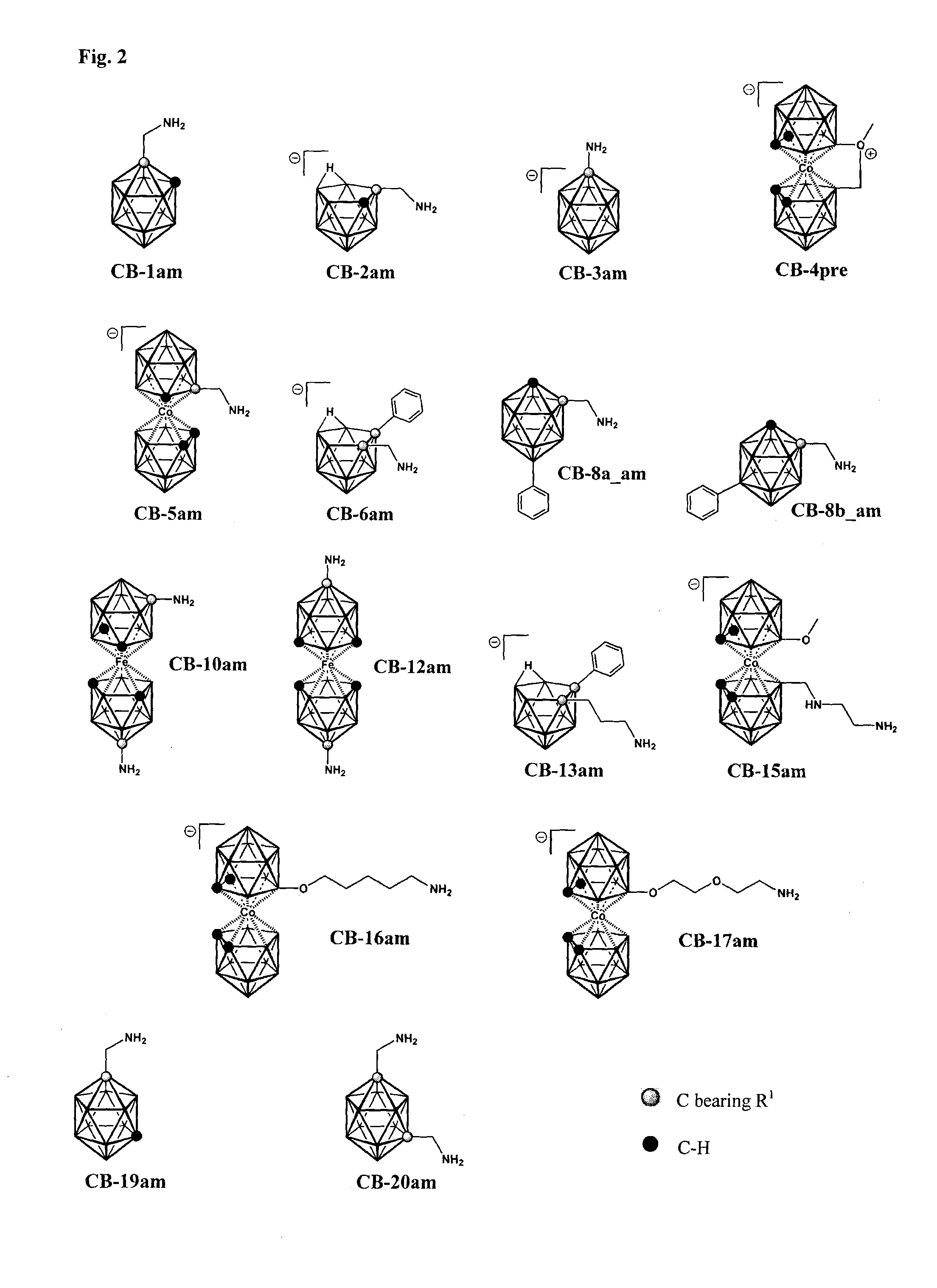
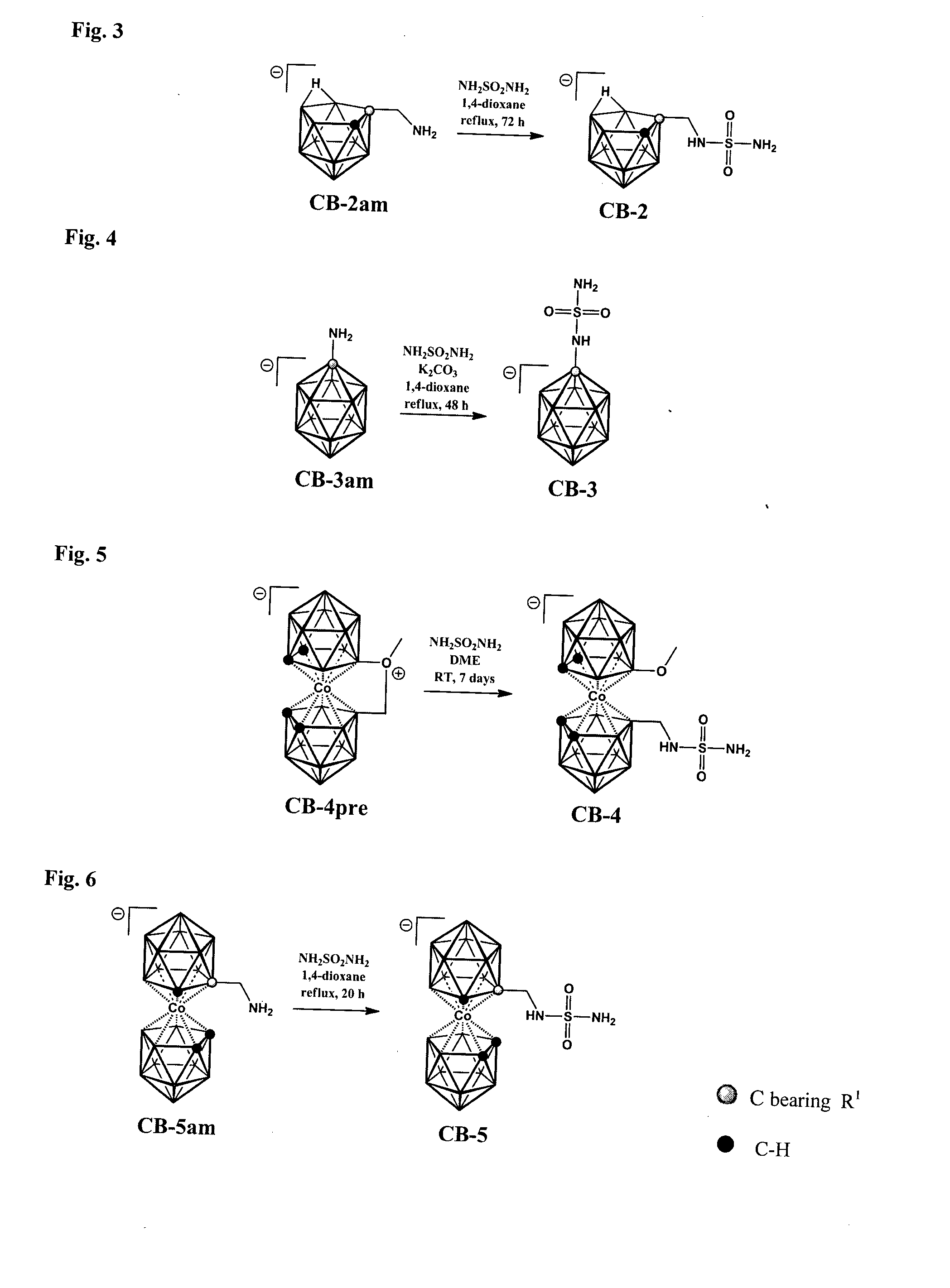
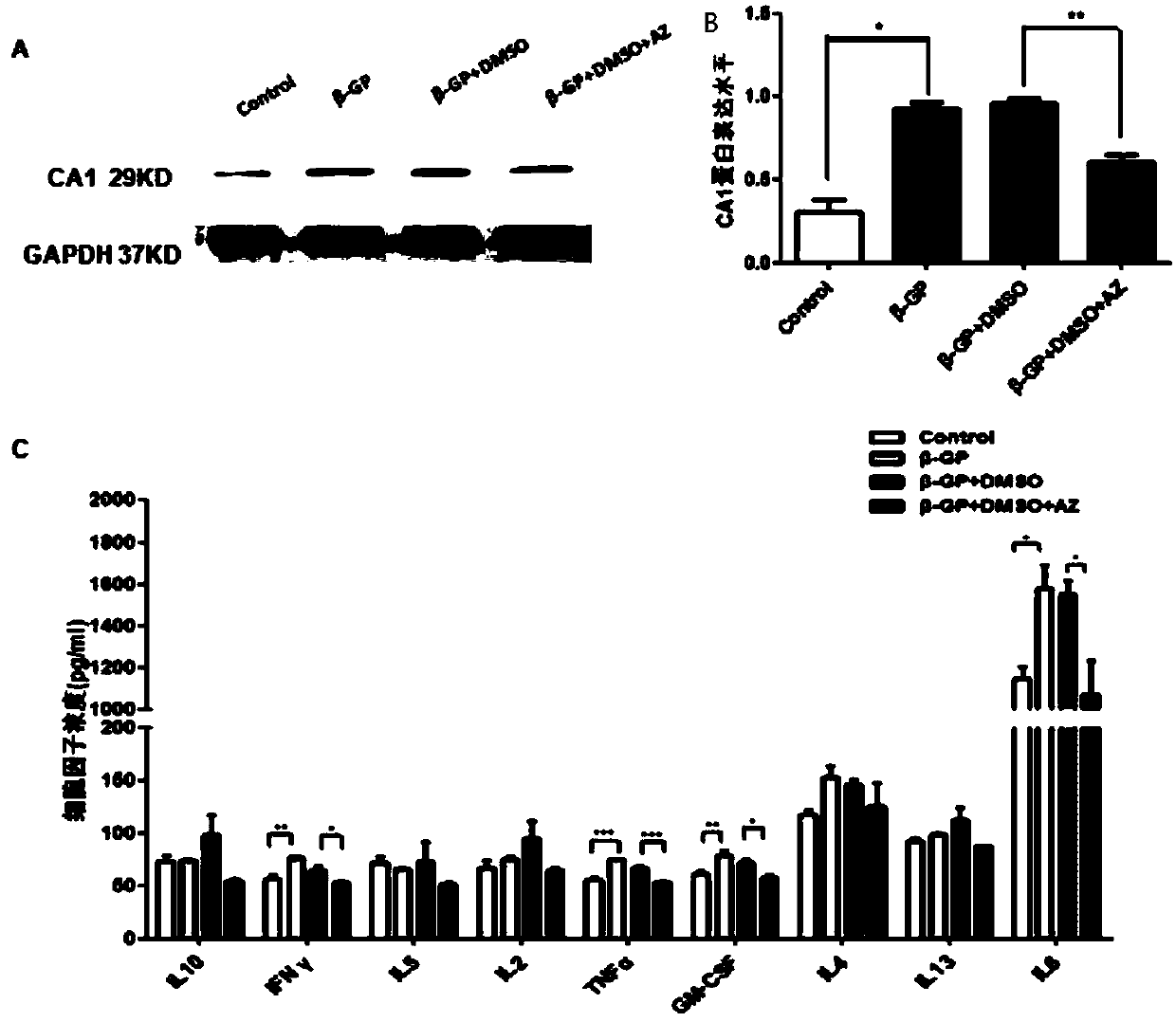
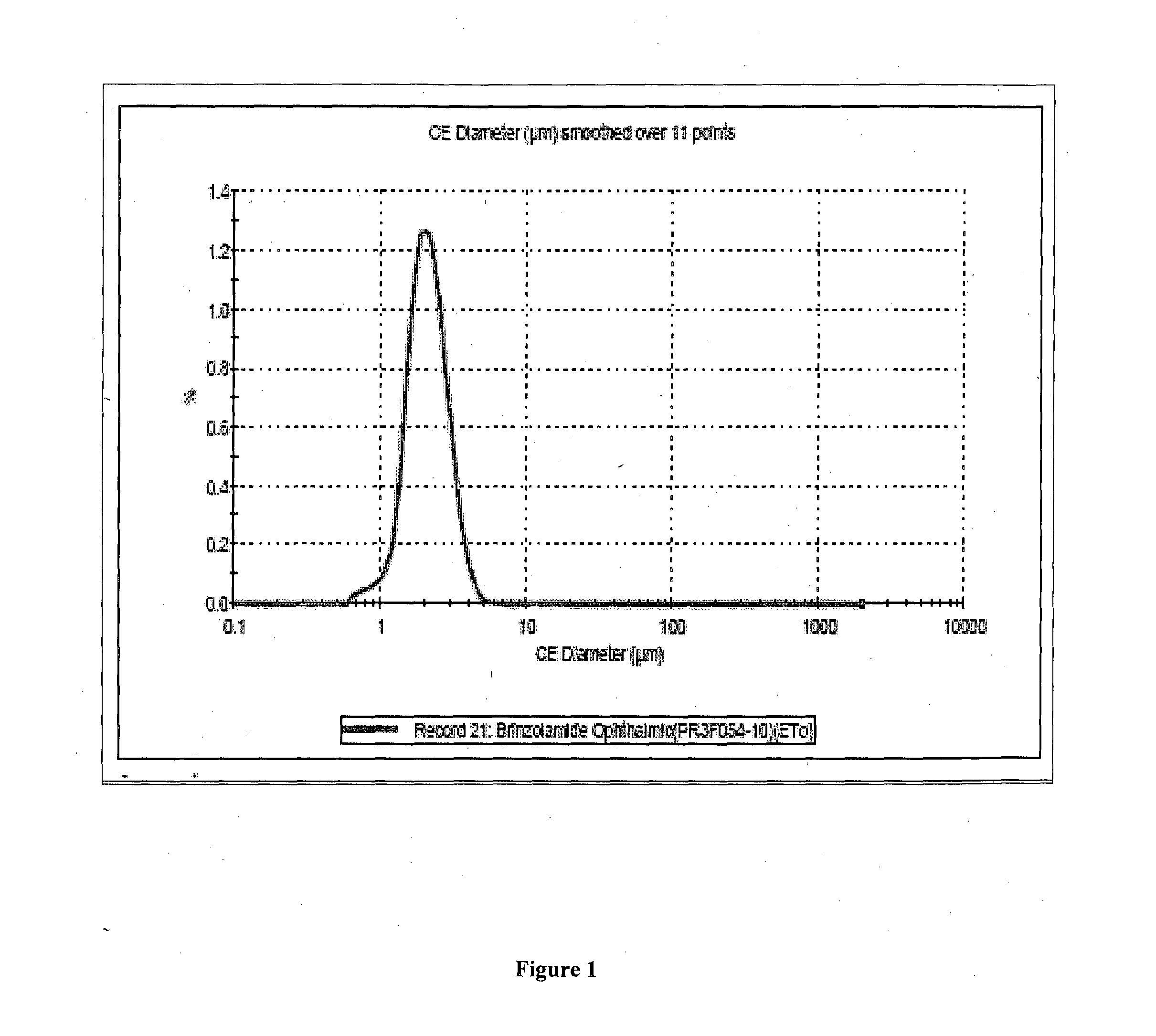
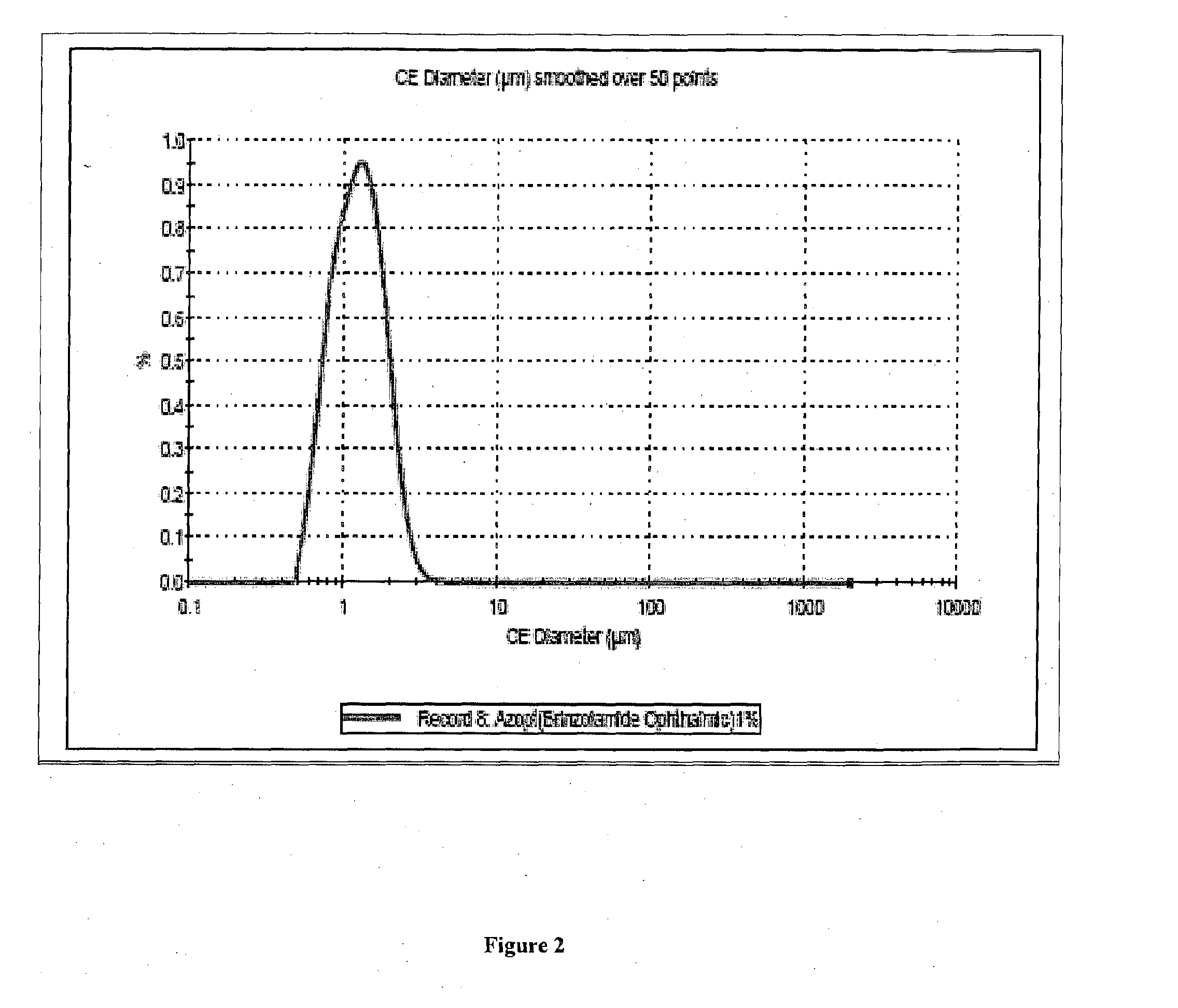
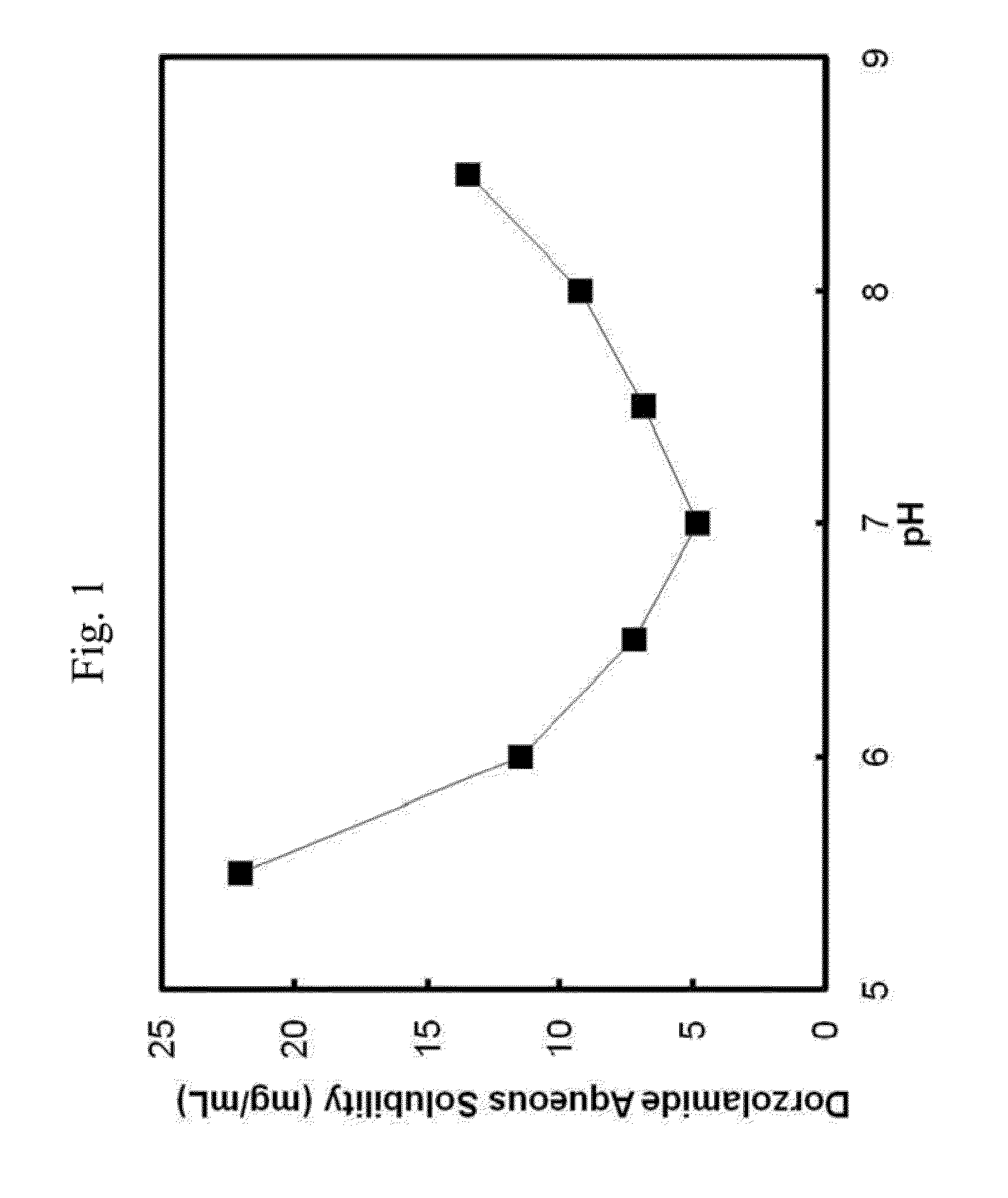
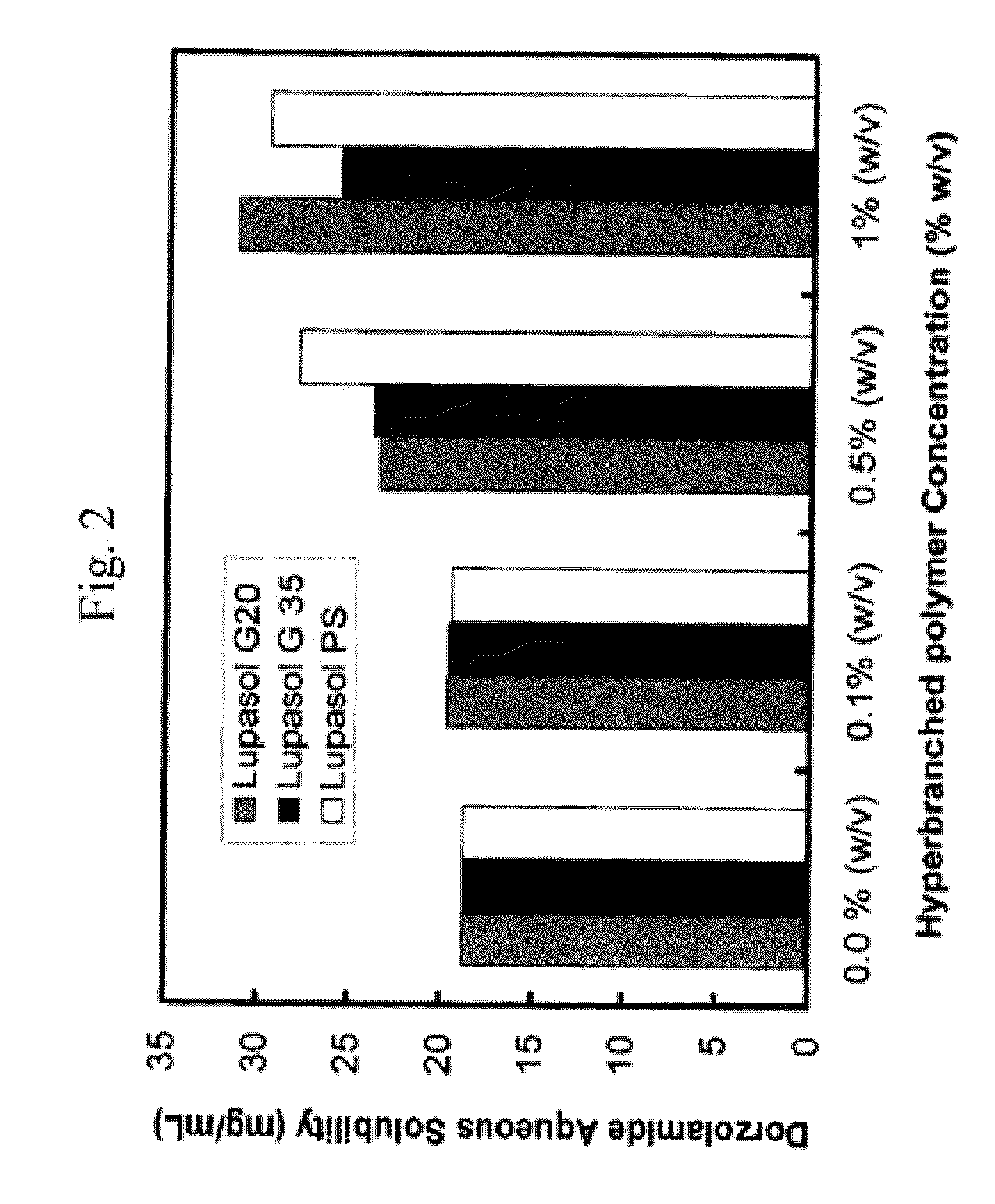
Patents
Literature
77 results about "Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, neurological disorders, or osteoporosis.
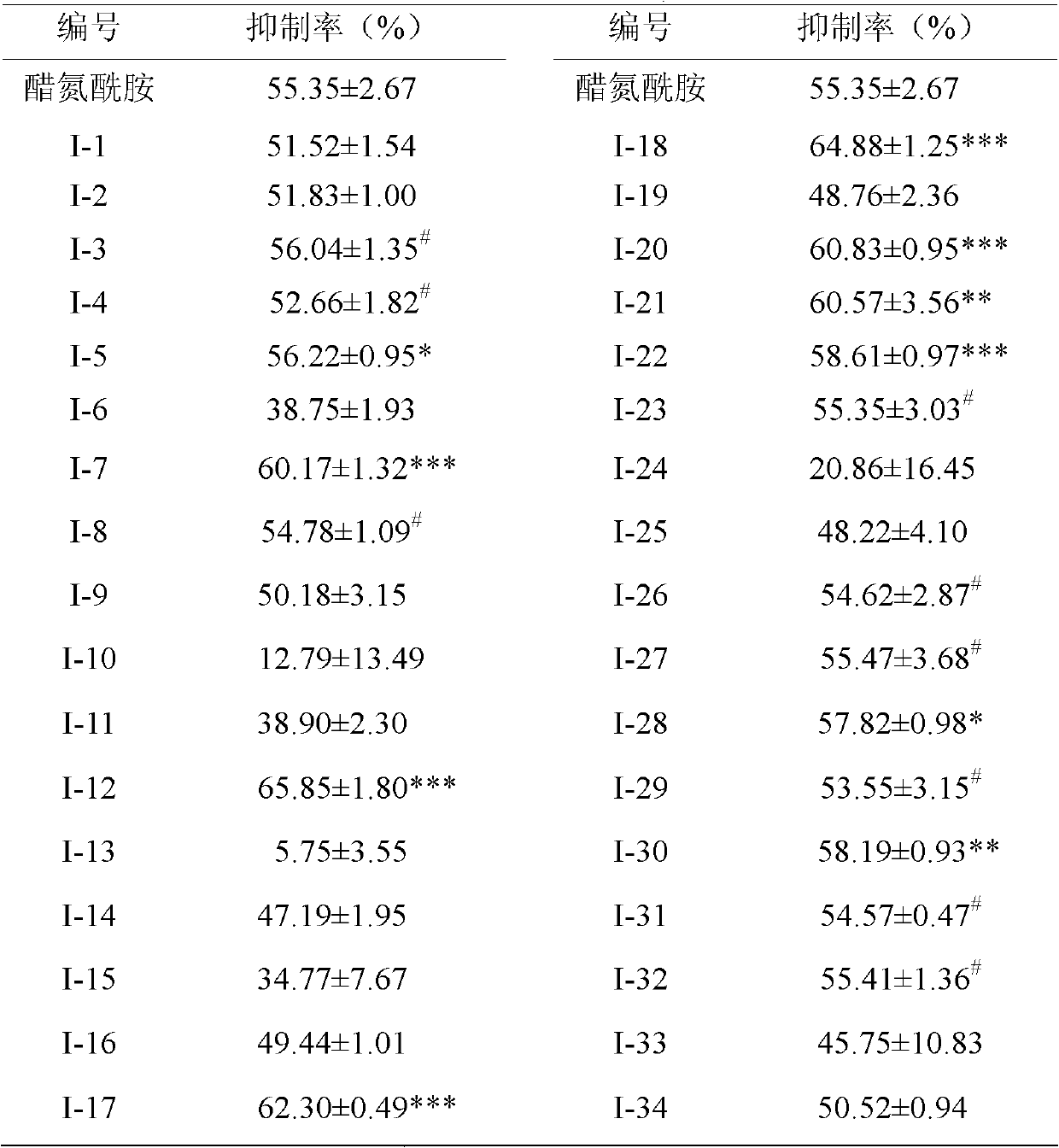
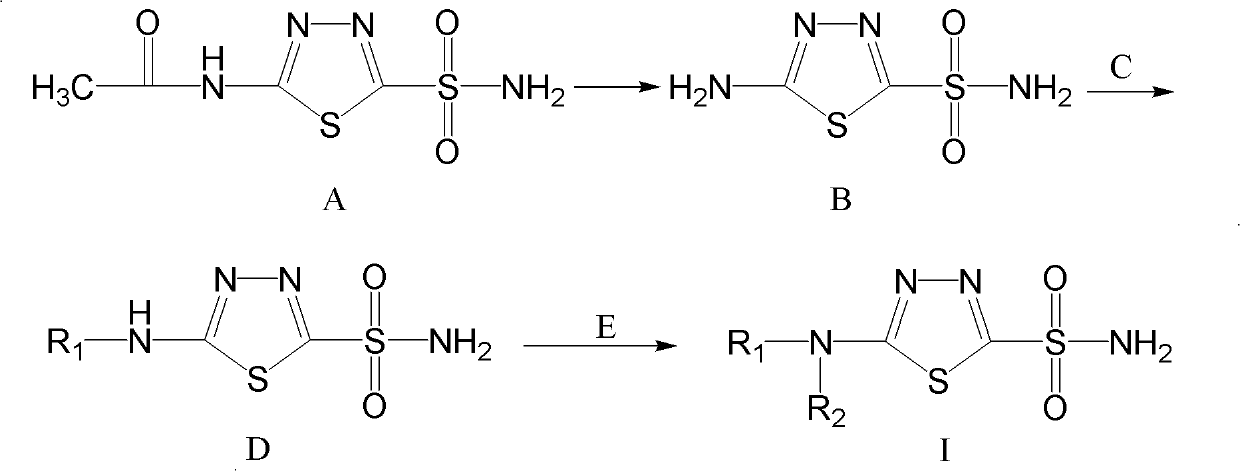
Sulfonamides compound for inhibiting carbonic anhydrase II and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN101921245AHigh resource utilizationThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsCarbonic anhydrase II
The invention relates to a sulfonamides compound for inhibiting carbonic anhydrase II and a synthesis method and an application thereof. The compound has the structure as shown in the specification. The invention features economical and reasonable synthetic route and high utilization of resources. The synthesis method is simple and easy to carry out and is more suitable for large-scale industrialized production. With human carbonic anhydrase II (Human Carbonic Anhydrase II, hCA II) expressed by procaryotic cell as an enzyme source, the invention establishes an in-vitro carbonic anhydrase inhibitor screening model. In addition, the compound of the invention has inhibitive effect on activity of the human carbonic anhydrase II.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL +1
Synergistic enhancement of cognitive ability
The present invention relates to the combination of a methylxanthine and a carbonic anhydrase activator to provide synergistic effects. The invention further relates to the improved / enhanced cognitive ability of individuals, particularly those suffering from various disorders, such as Alzheimer's Disease, stroke, hypoxia, general dementia, ADHD, mental retardation, and "sun down" syndrome.
Owner:WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
Method of treating glaucoma and intraocular hypertension
InactiveUS20110294730A1Senses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin-like growth factorProstaglandin analog
A safe and effective treatment for glaucoma for mammalian species comprises the steps of applying insulin and / or insulin like growth factors (IGF-1) to an eye. In addition to the insulin, another therapeutic agent may be applied to enhance the activity of the insulin. The therapeutic agent may be a pharmaceutical agent or a biochemical pharmaceutical agent. The therapeutic agents include prostaglandin analogs, topical beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists-β blockers, Alpha2-adrenergic agonists hair growth therapeutic agents, beta2-agonist action agents, parasympathomimetic miotic agents, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and Physostigmine. In another embodiment, a combination of at least two agents are applied to the eye. To enhance the effect of the insulin, uptake facilitators may be used. Additionally, an antibacterial agent may be applied to control bacterial infection.
Owner:SHANTHA TOTADA R +2
Ophthalmic composition
InactiveUS20130053374A1Good water solubilitySafely employedBiocideSenses disorderCarteololBeta blocker
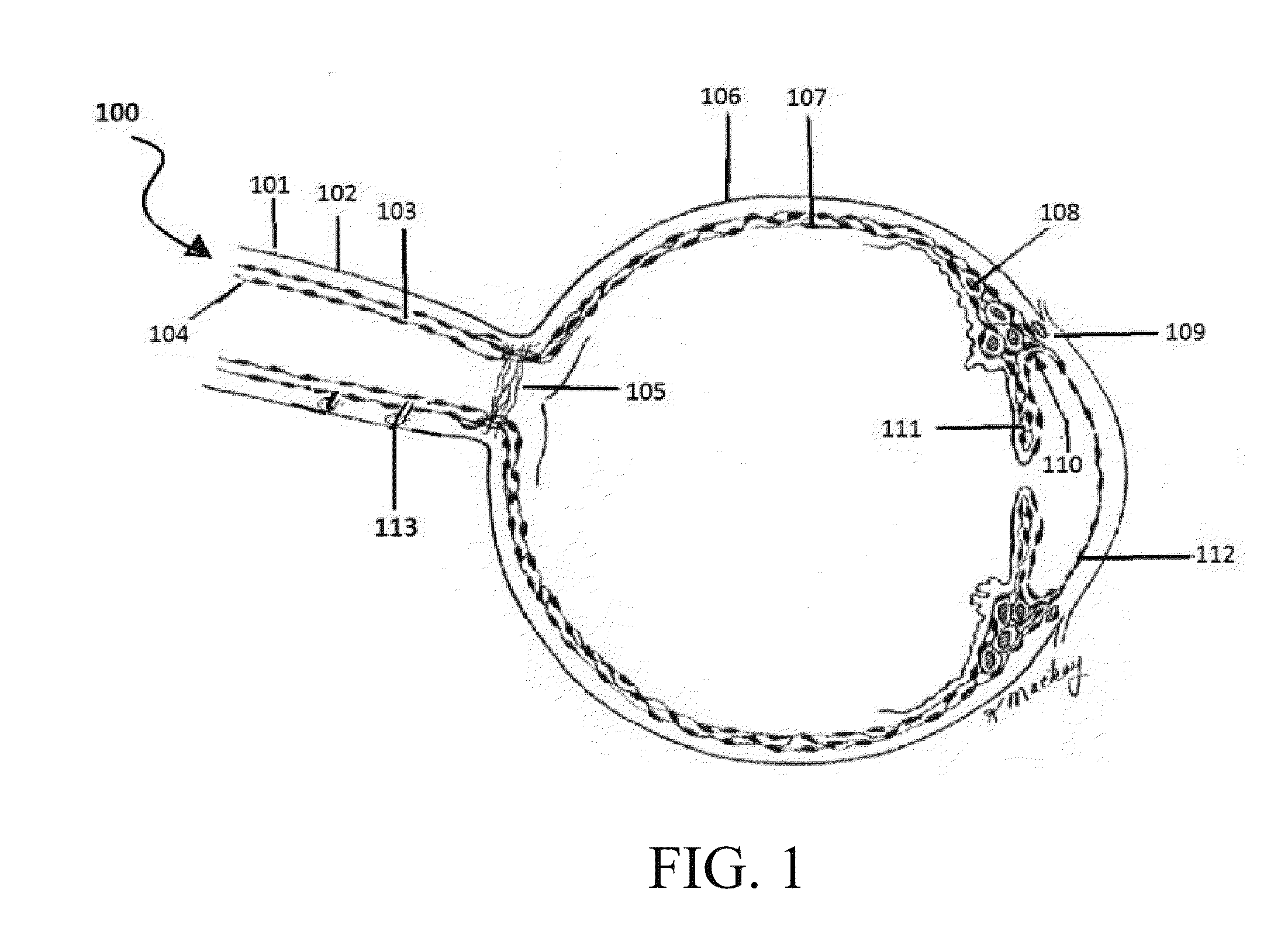
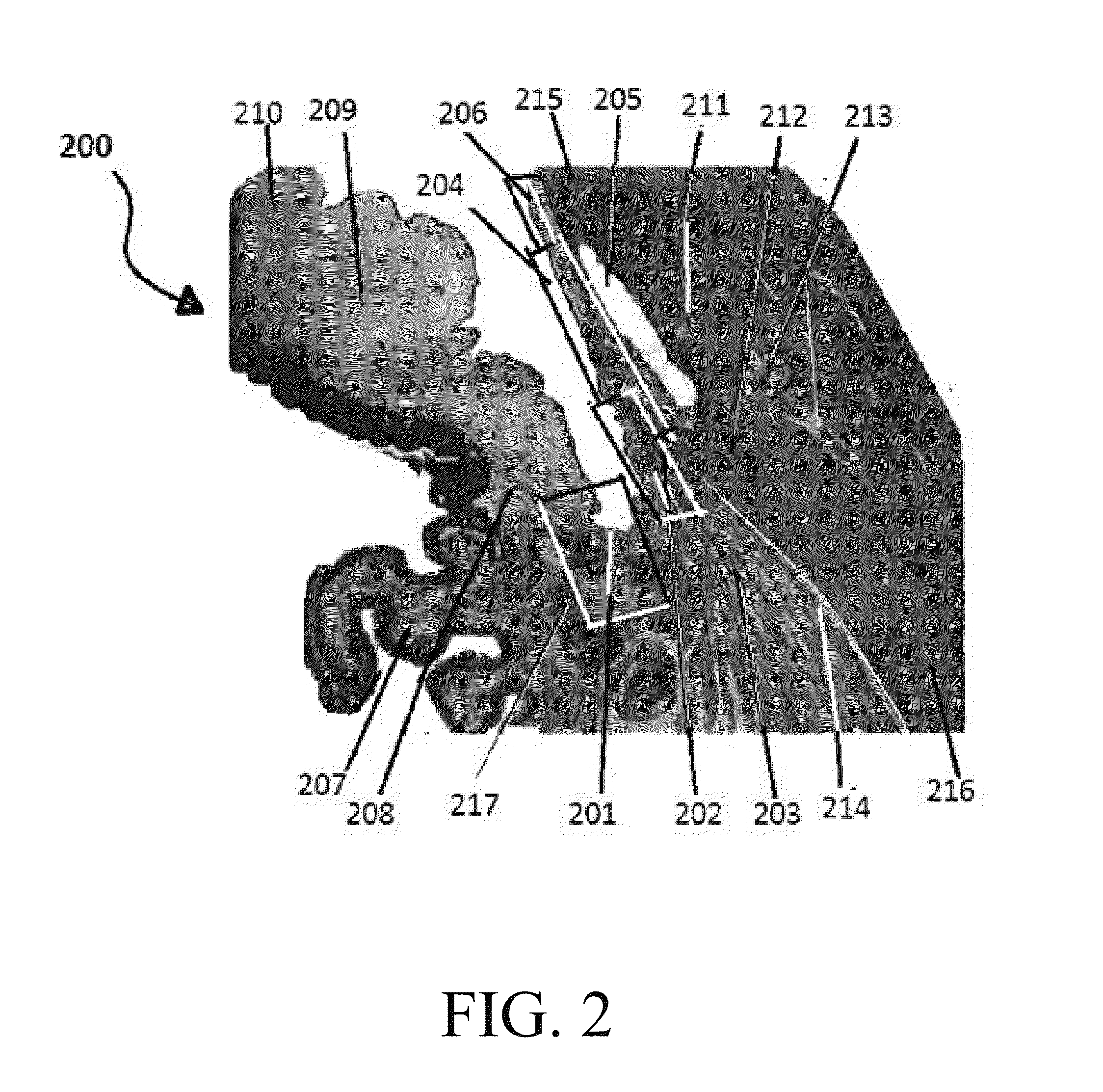
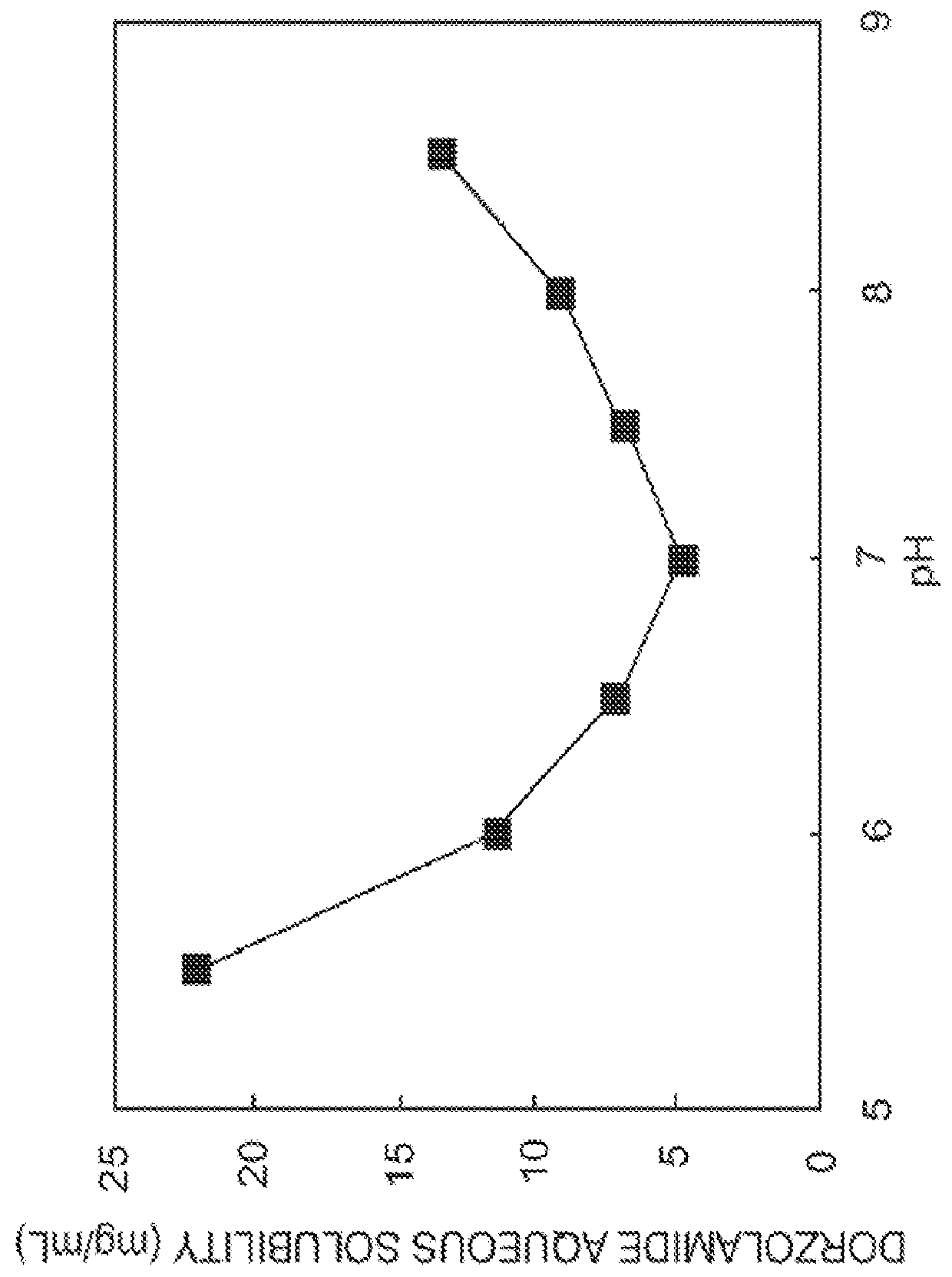
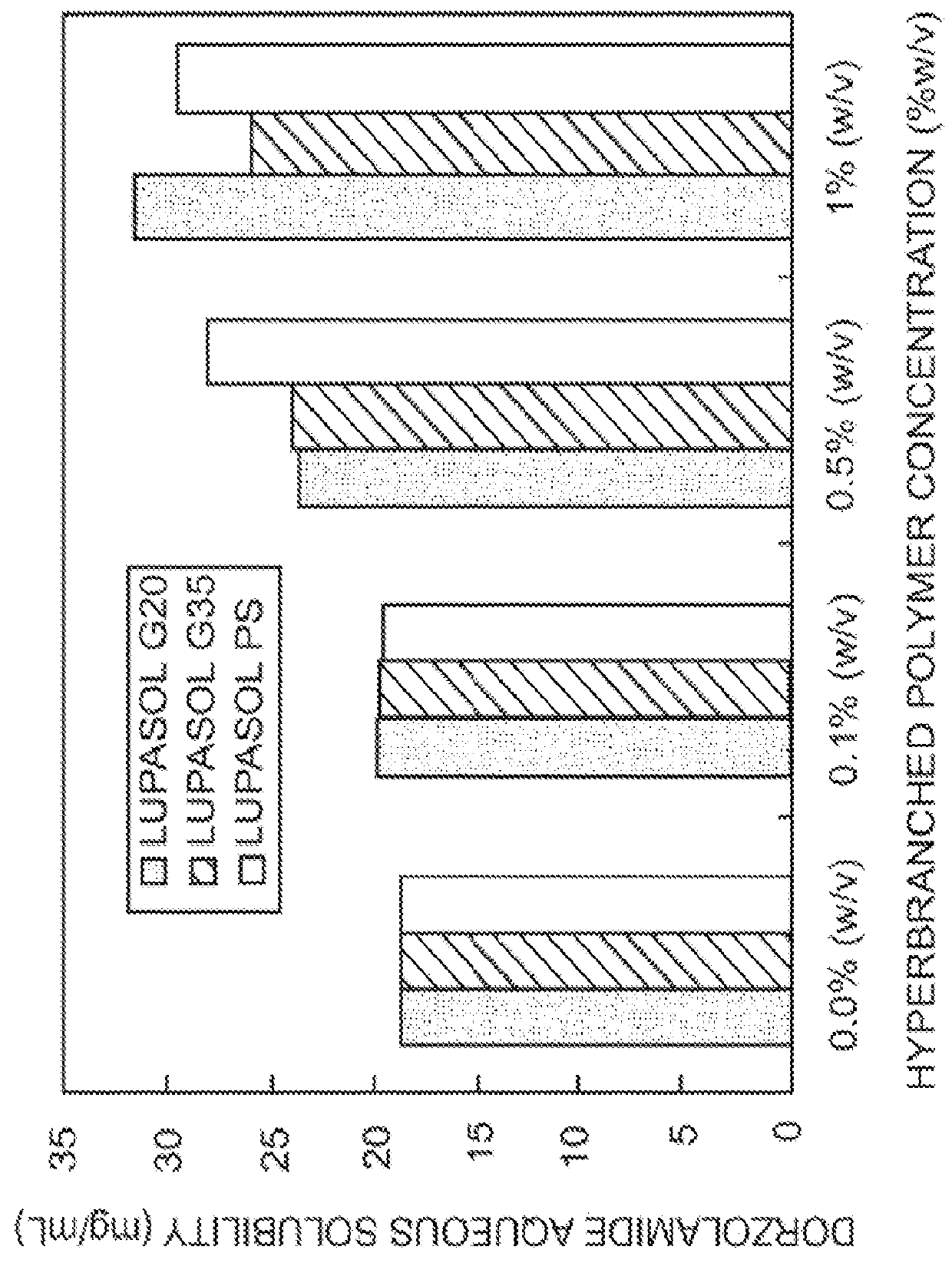
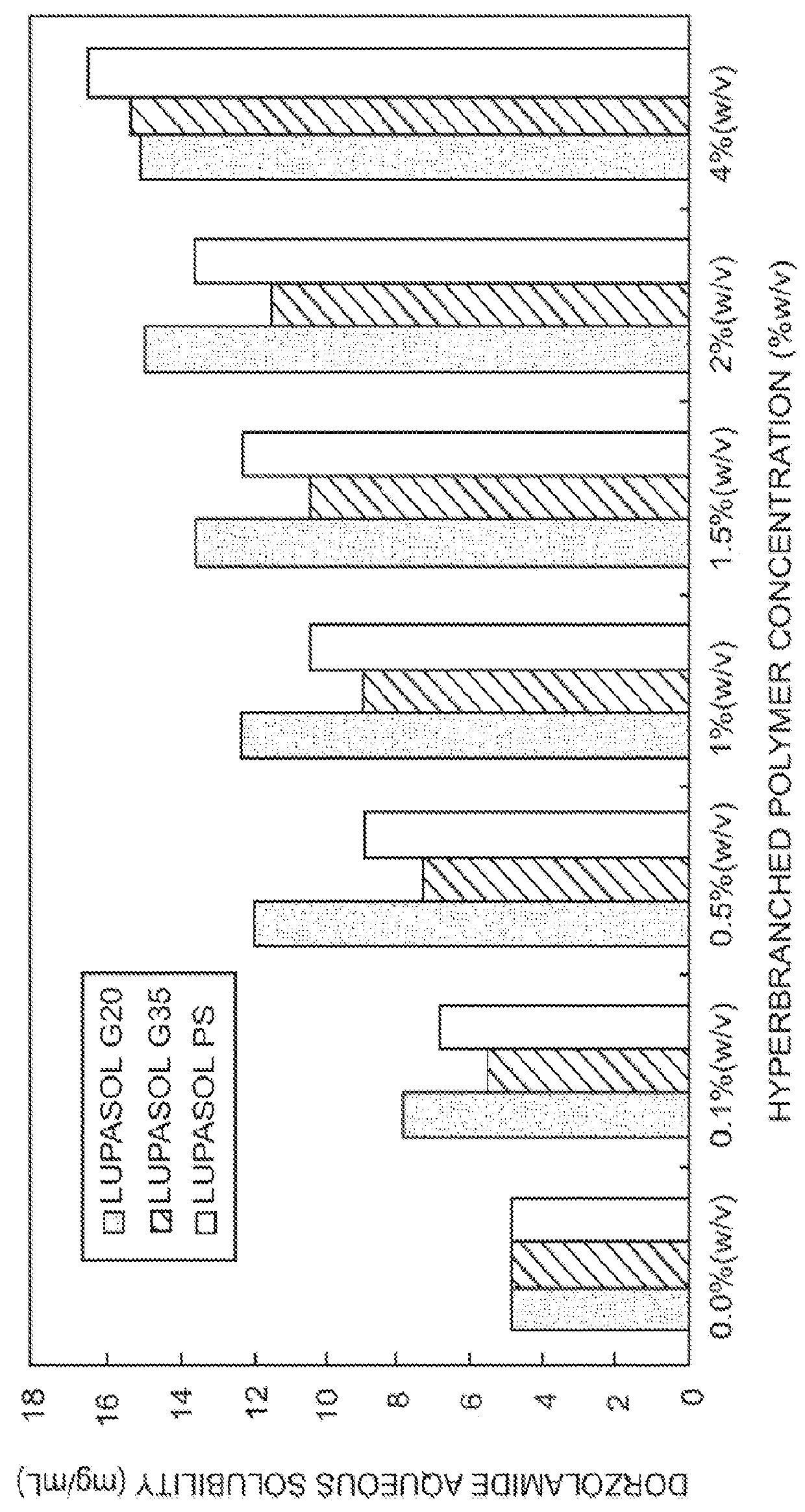
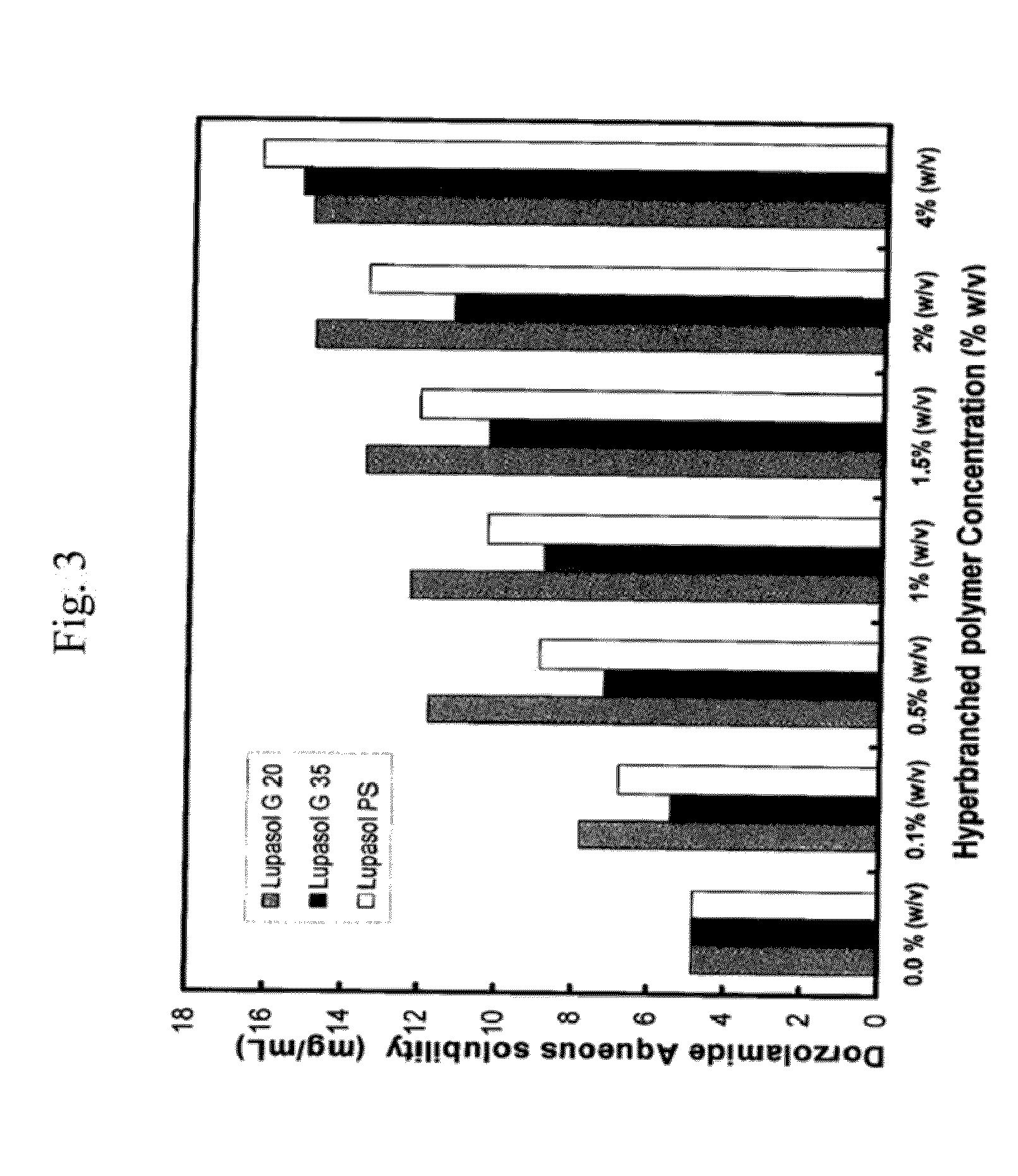
The present invention provides an ophthalmic composition comprising a hyperbranched polyester. The ophthalmic compositions may also comprise carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, wherein the hyperbranched polyester increases the aqueous solubility of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, and increases corneal permeation of the active agent. The ophthalmic compositions may also comprise non-ionic surfactants, such as PEG, Polysorbate, HPMC or HEC, and beta-blockers, such as Carteolol, Levobunolol, Betaxolol, Metipranolol, Timolol or Propranolol. The concentration of the hyperbranched polyester in the ophthalmic formulation should be less than or equal to 4% (w / v) in order to avoid any cytotoxic effects on human corneal cells and thus the eye irritation.
Owner:SENJU USA
Pharmaceutical composition comprising brinzolamide
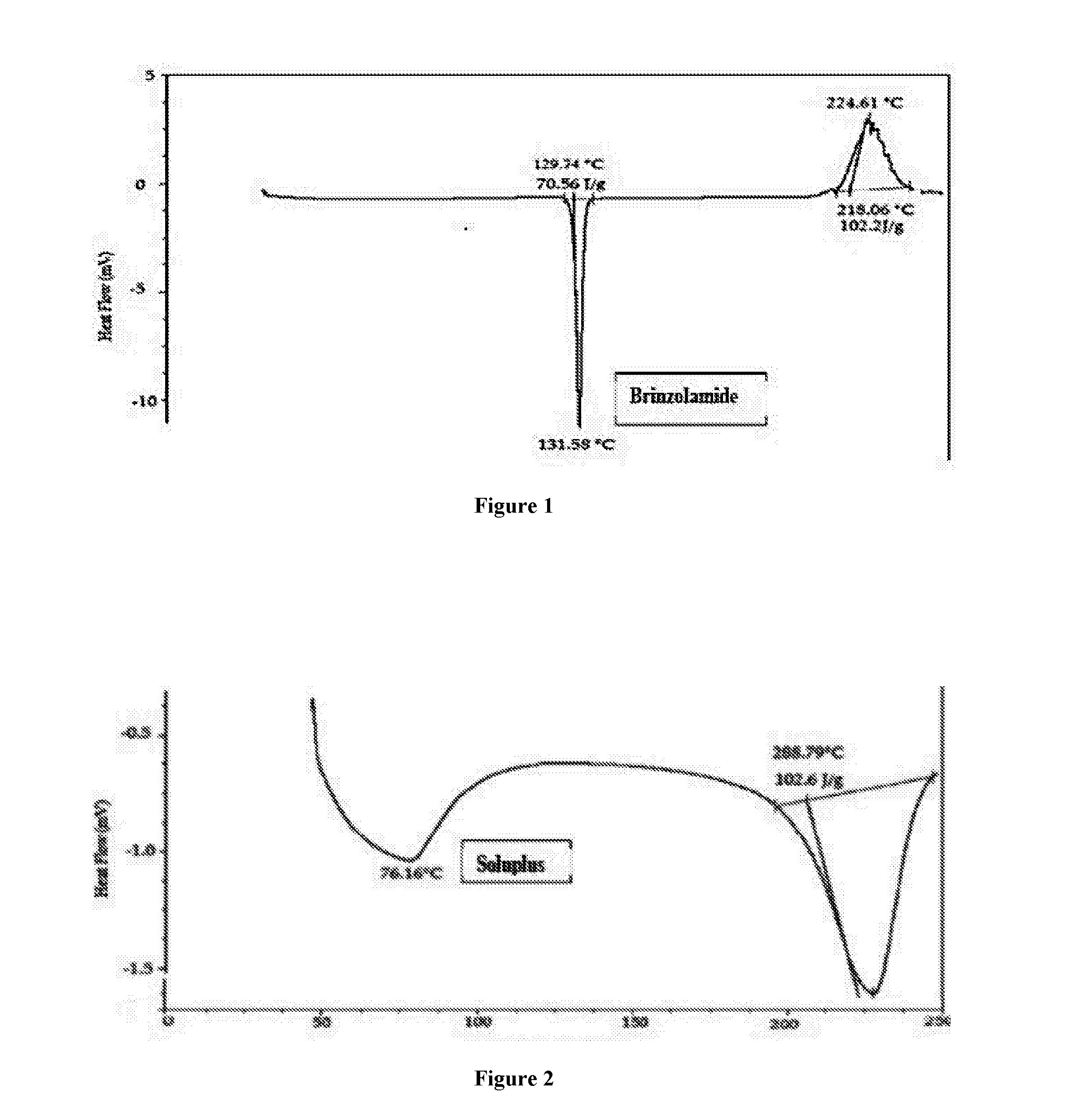
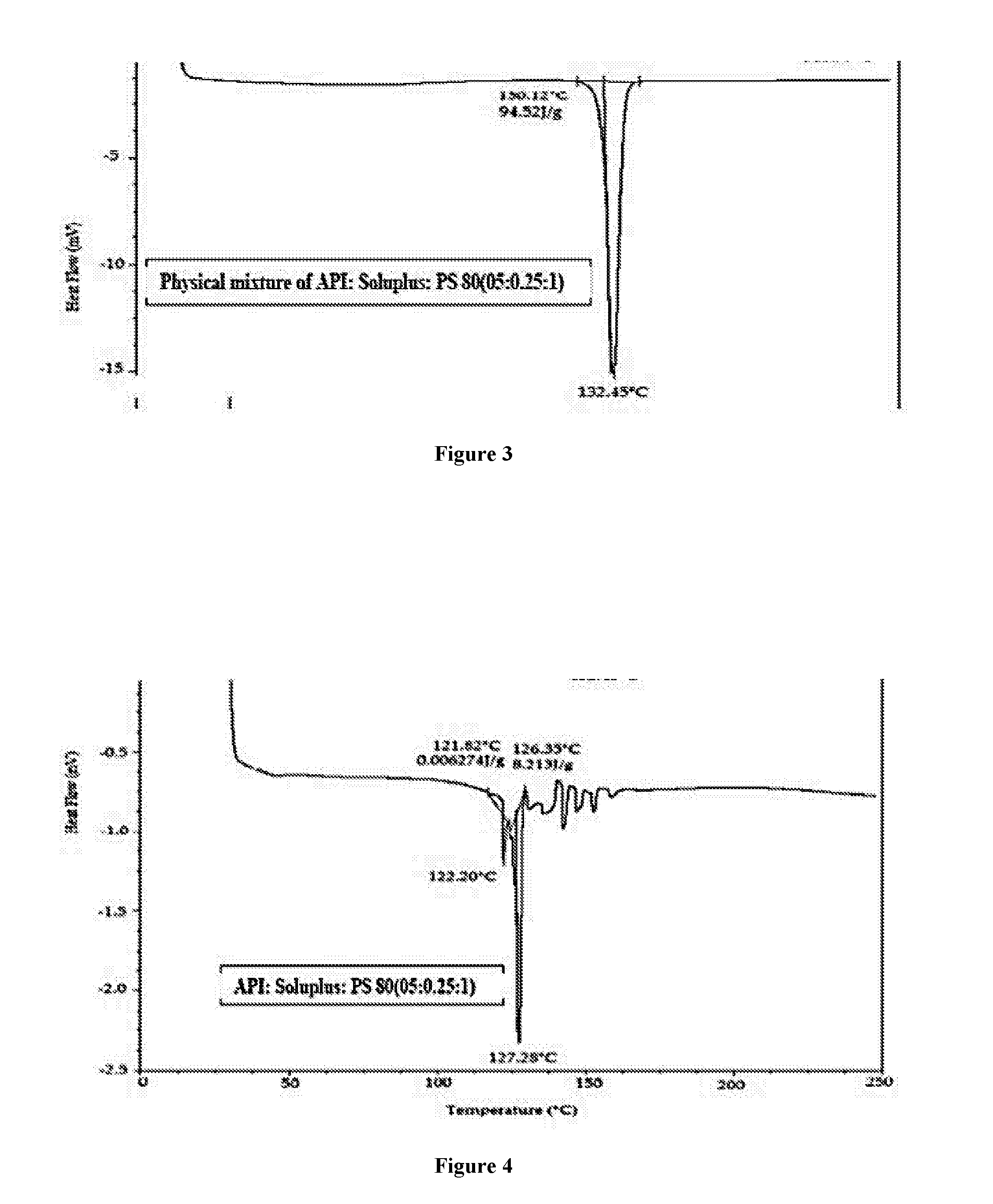
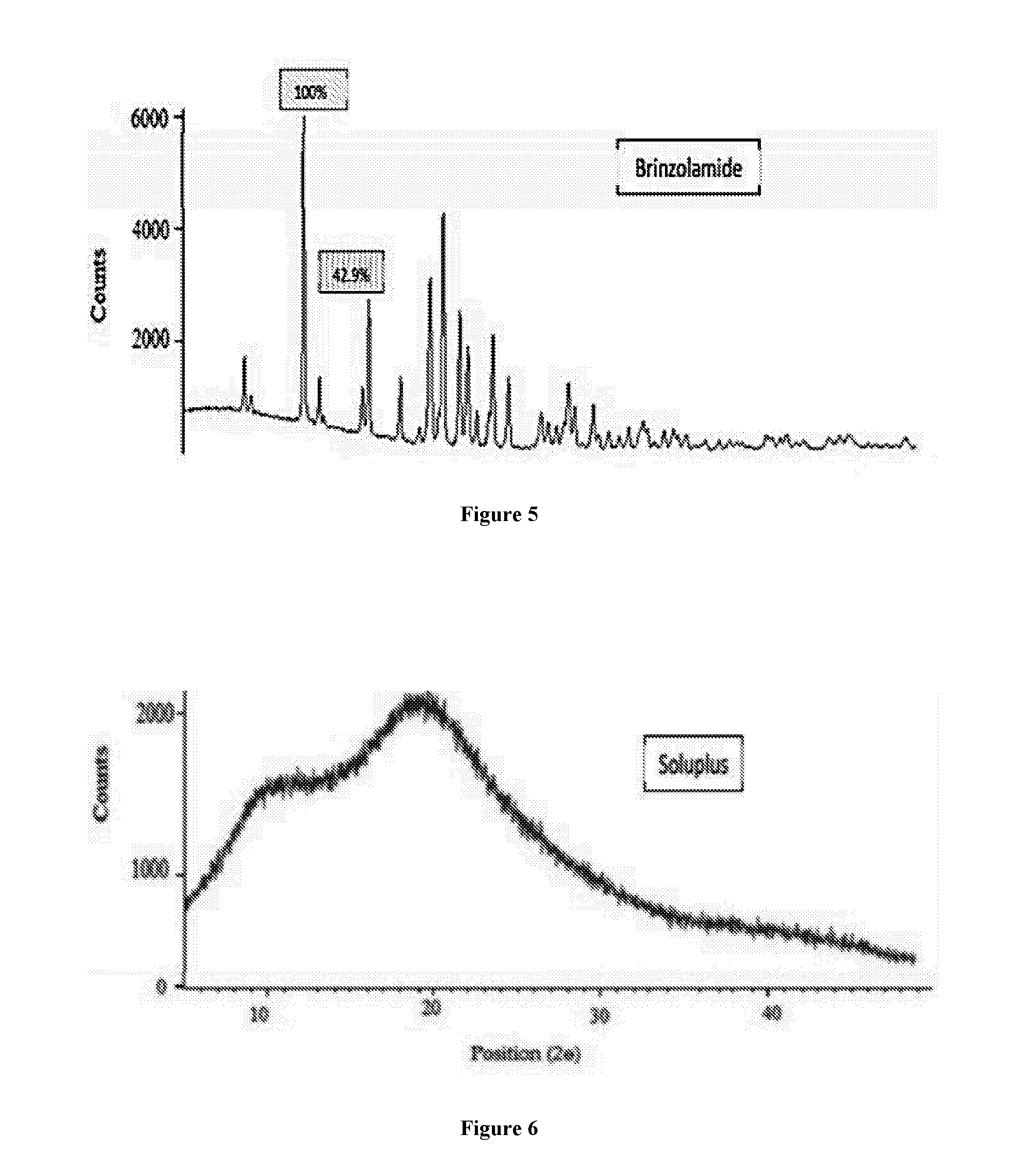
ActiveUS20160339105A1Improve bio-availabilityImprove manufacturabilityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderActive ingredientSURFACTANT BLEND
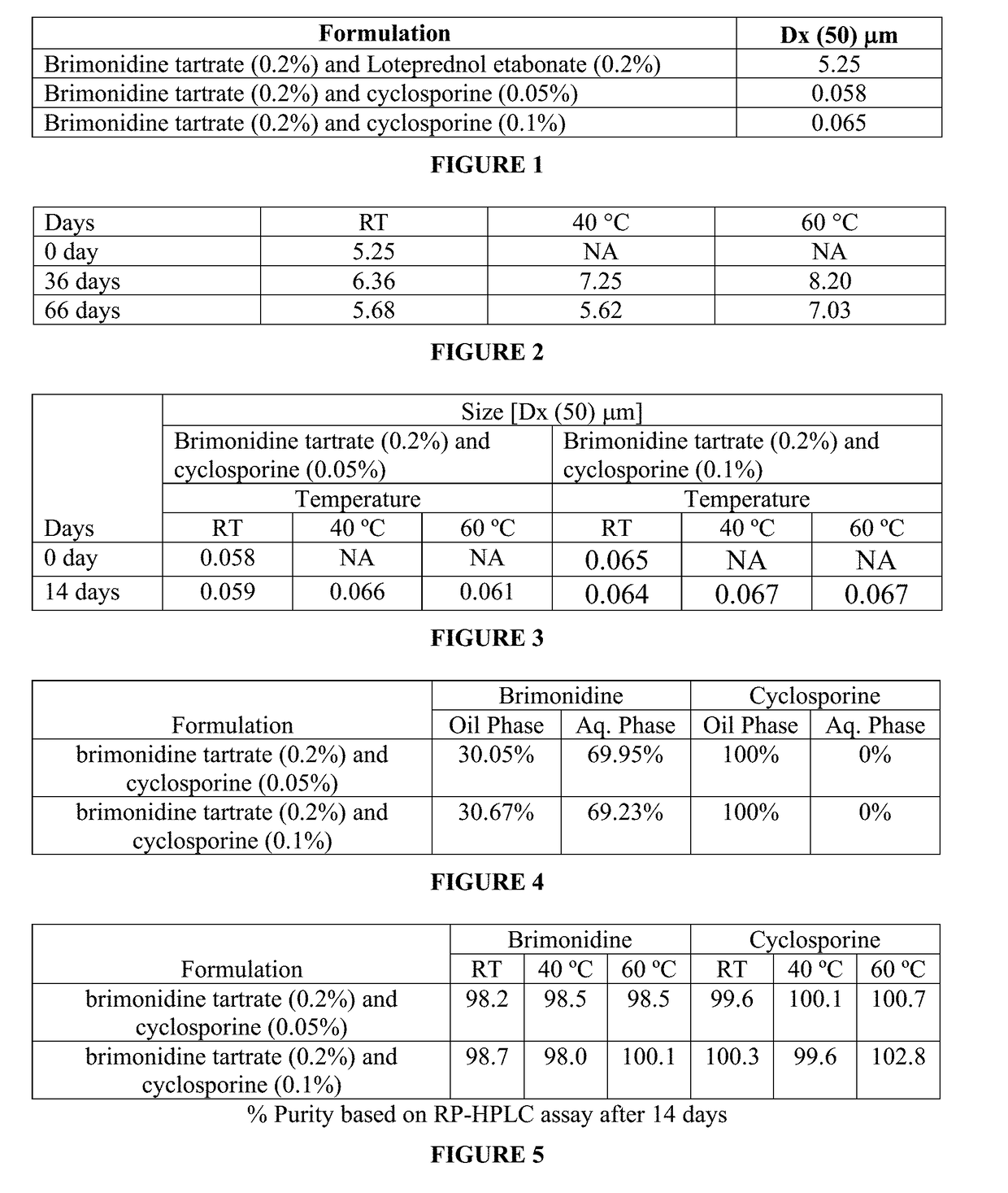
A sterile aqueous formulation of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor such as brinzolamide in combination with polymers like Soluplus® and a surfactant like polysorbate 80, as well as methods of preparation thereof, is disclosed. The formulation relates to the highly solubilized or an amorphous form of poorly insoluble drugs / active ingredient(s) to improve its bio-availability and manufacturability.
Owner:SENTISS PHARMA
Method for delivering ophthalmic drugs
This invention relates to a method of delivering ophthalmic drugs, specifically prostaglandins and prostamides. This method may also be applied to other types of intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering drugs (e.g. carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, beta blockers, alpha-adrenergic agonists, and parasympathomimetics) as well as other types of ophthalmic drugs for other indications (e.g. dry eye, inflammation, and infection).
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Treatment of sleep apnea with a combination of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and an aldosterone antagonist
InactiveUS20160045527A1Good for weight lossAlleviates sleep apneaBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismCarbonic anhydrase IIPharmaceutical formulation
This invention relates generally to methods and pharmaceutical formulations useful in treating patients suffering from sleep apnea, including obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). Treatment is effected by administering a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to the patient in combination with an aldosterone antagonist. Formulations containing a therapeutically effective amount of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and a therapeutically effective amount of an aldosterone antagonist are provided as well.
Owner:VIVUS
Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome with a combination of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and an additional active agent
InactiveUS20110224196A1Amelioration of the extent of each apneaAlleviate excessive daytime sleepinessBiocideNervous disorderZaleplonActive agent
This invention relates generally to methods and pharmaceutical formulations useful in treating patients suffering from obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). Treatment of OSAS is effected by administering a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to the patient in combination with at least one additional active agent. Examples of additional active agents include modafinil, eszopiclone, zolpidem, zaleplon, and phentermine.
Owner:VIVUS
Method for the prevention and treatment of retinopathy
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors for the prevention and treatment of diabetic retinopathy and various other retinopathies.
Owner:STEFANSSON EINAR
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension with carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
ActiveUS20080312163A1BiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsBiopharmacologyCarbonic anhydrase inhibitor
This disclosure relates generally to methods and pharmaceutical compositions useful in treating pulmonary hypertension. In one embodiment, for example, the disclosure provides a method for treating pulmonary hypertension comprising administering a therapeutically effective dose of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to a patient in need of treatment. The disclosure finds utility in the fields of medicine and pharmacology.
Owner:VIVUS LLC
Agent for prevention or treatment of glaucoma
InactiveUS8193193B2Potent effectProlong the action timeBiocideSenses disorderRho kinase inhibitorOcular hypertension
There is Provided an Agent for Prevention of glaucoma or an agent for prevention or treatment of ocular hypertension, with a potent ocular hypotensive effect and prolonged duration thereof. An agent for prevention or treatment of glaucoma comprising a Rho kinase inhibitor and a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor in combination.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
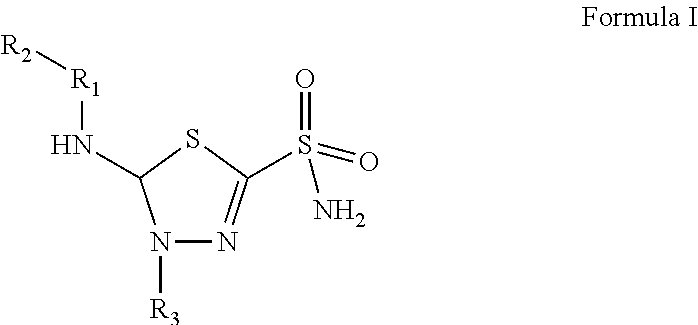
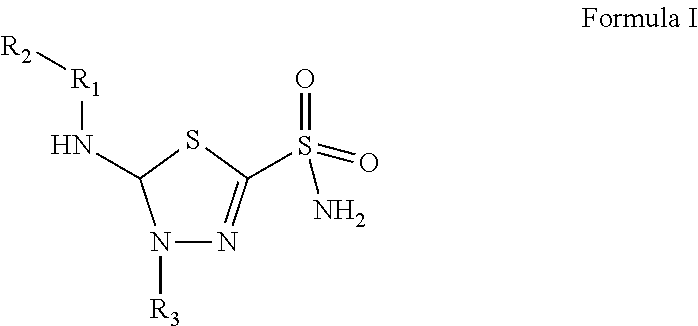
Compositions and methods for the suppression of carbonic anhydrase activity
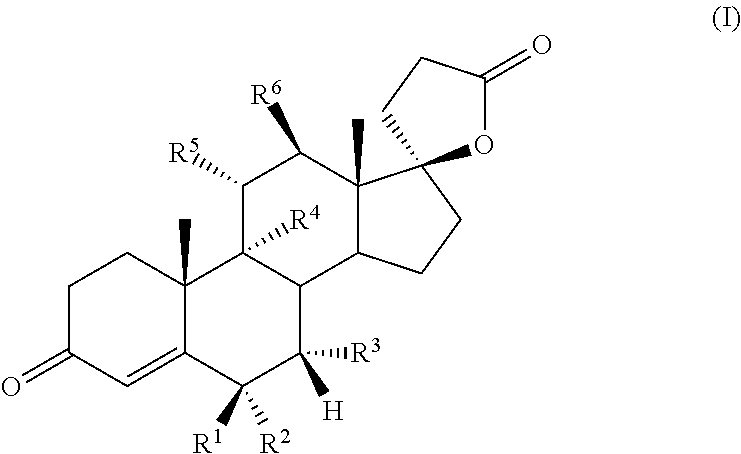
The invention relates to the compounds of formula I or its pharmaceutical acceptable salts, as well as polymorphs, solvates, enantiomers, stereoisomers and hydrates thereof. The pharmaceutical compositions comprising an effective amount of compounds of formula I, and methods for treating or preventing or modulating carbonic anhydrase activity in a disease may be formulated for oral, buccal, rectal, topical, transdermal, transmucosal, intravenous, parenteral administration, syrup, or injection. Such compositions may be used to treatment of glaucoma, epileptic seizures, Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri), altitude sickness, cystinuria, periodic paralysis and dural ectasia, congestive heart failure, drug induced edema, diuretic, intermittent claudication resulting from obstructed arteries in the limbs, and vascular dementia.
Owner:CELLIXBIO PTE LTD
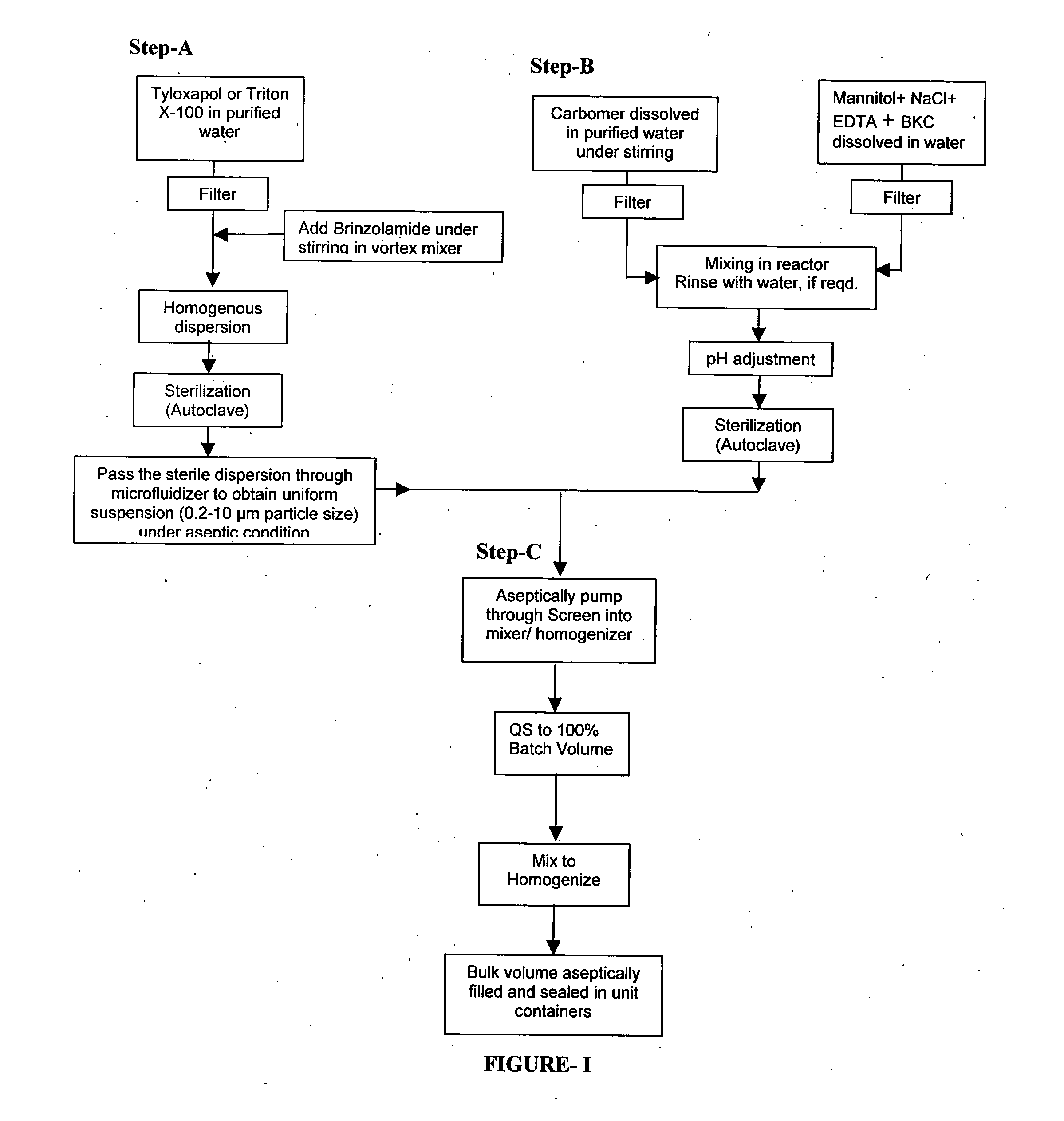
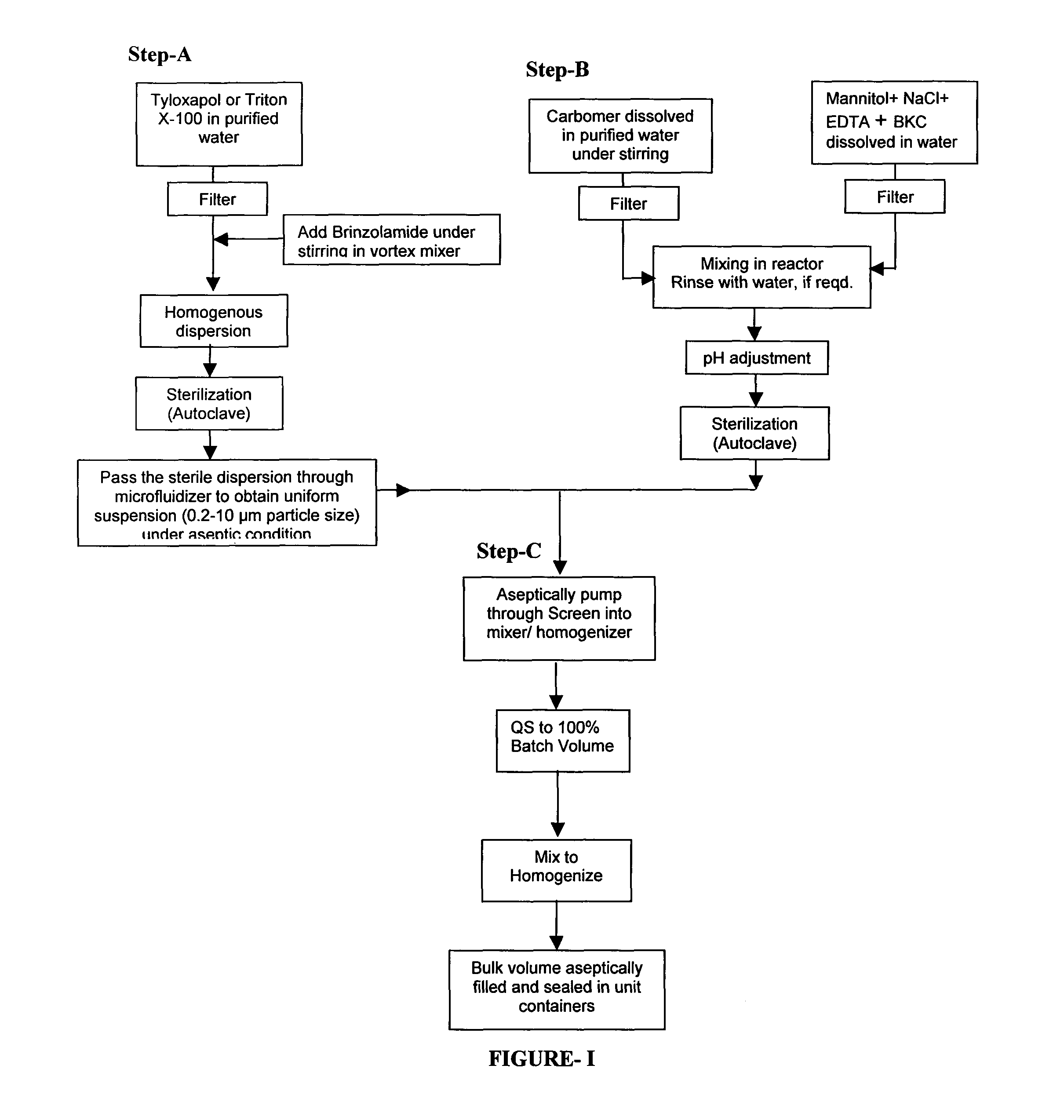
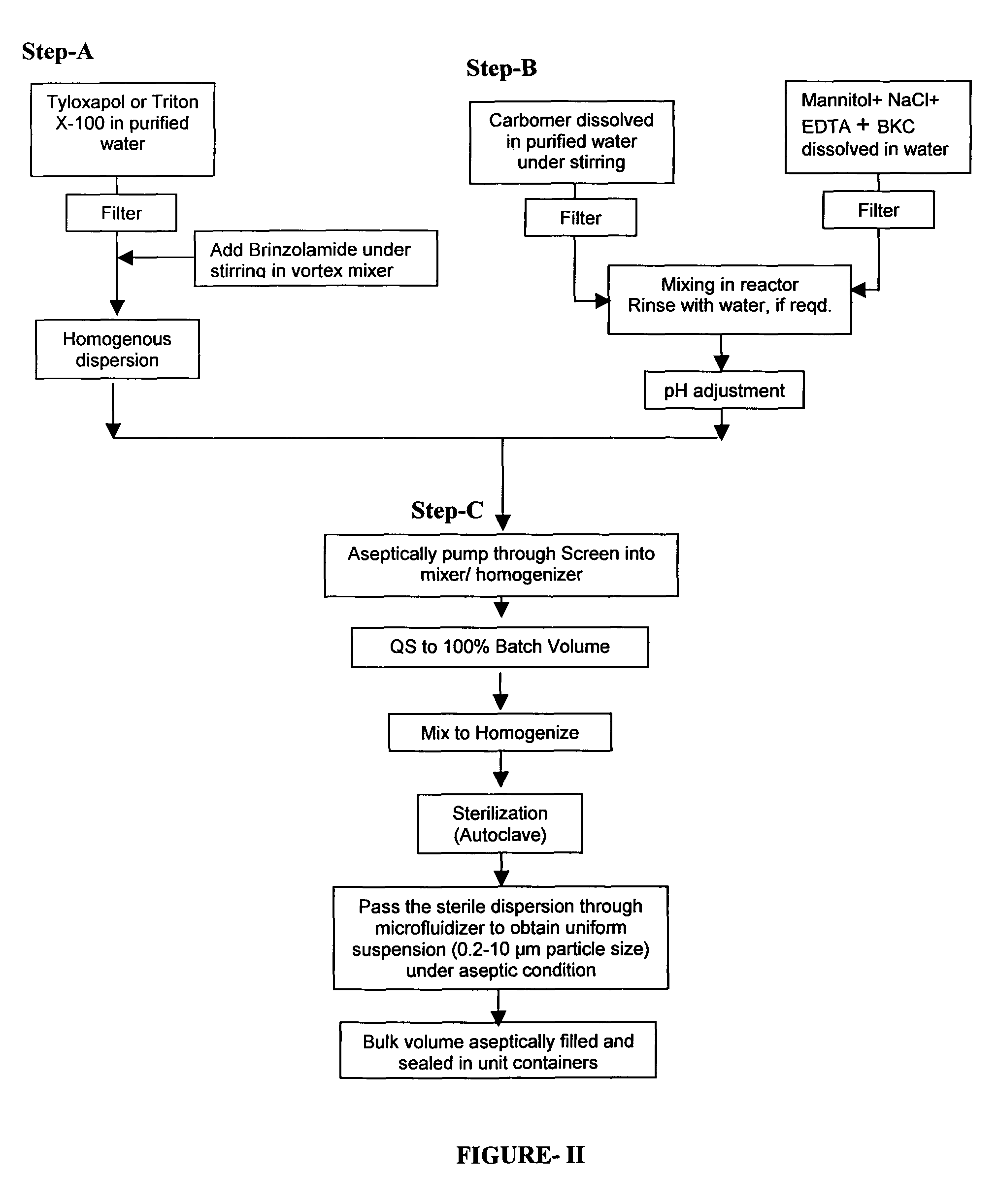
Process for preparing pharmaceutical ophthalmic compositions
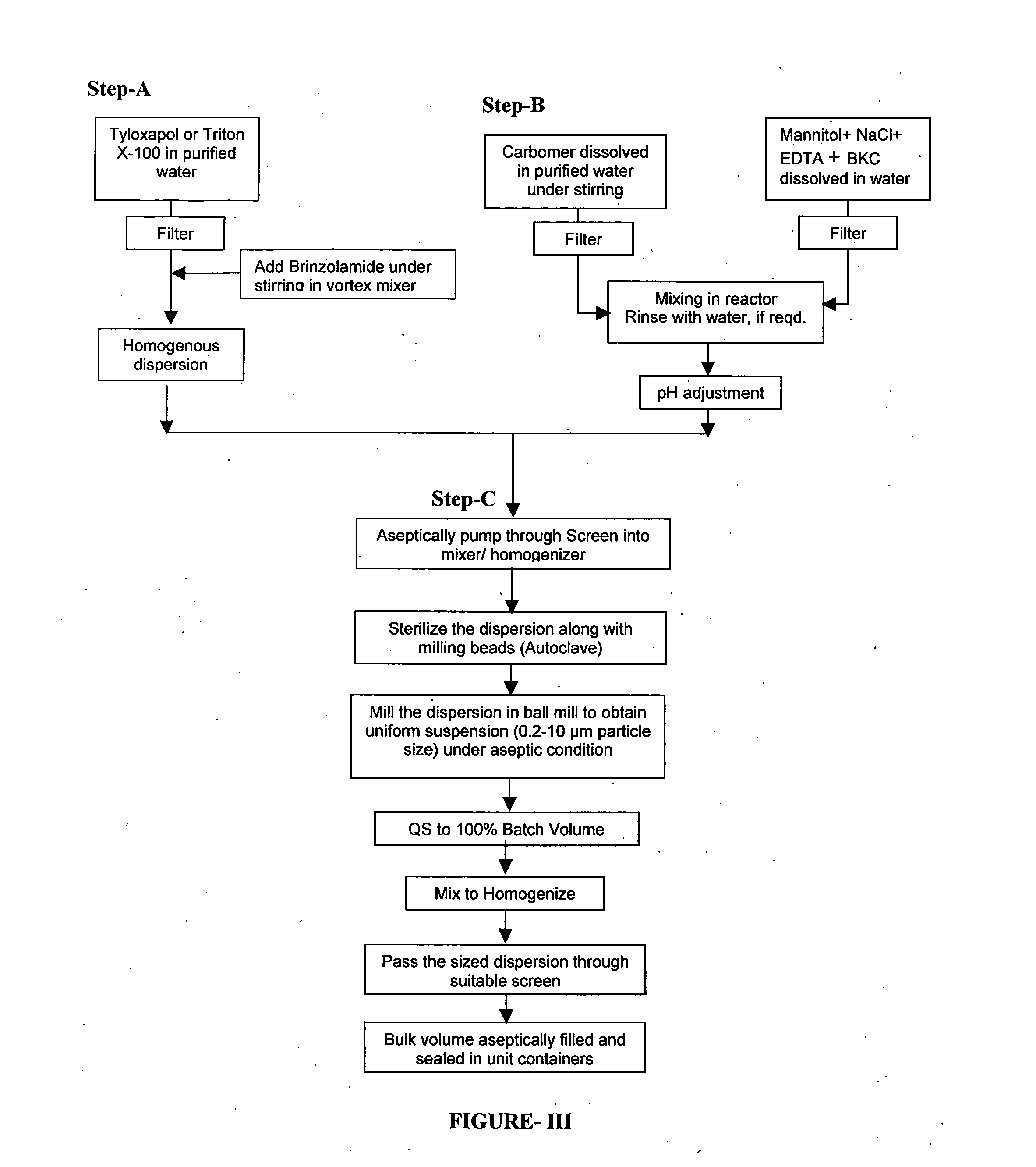
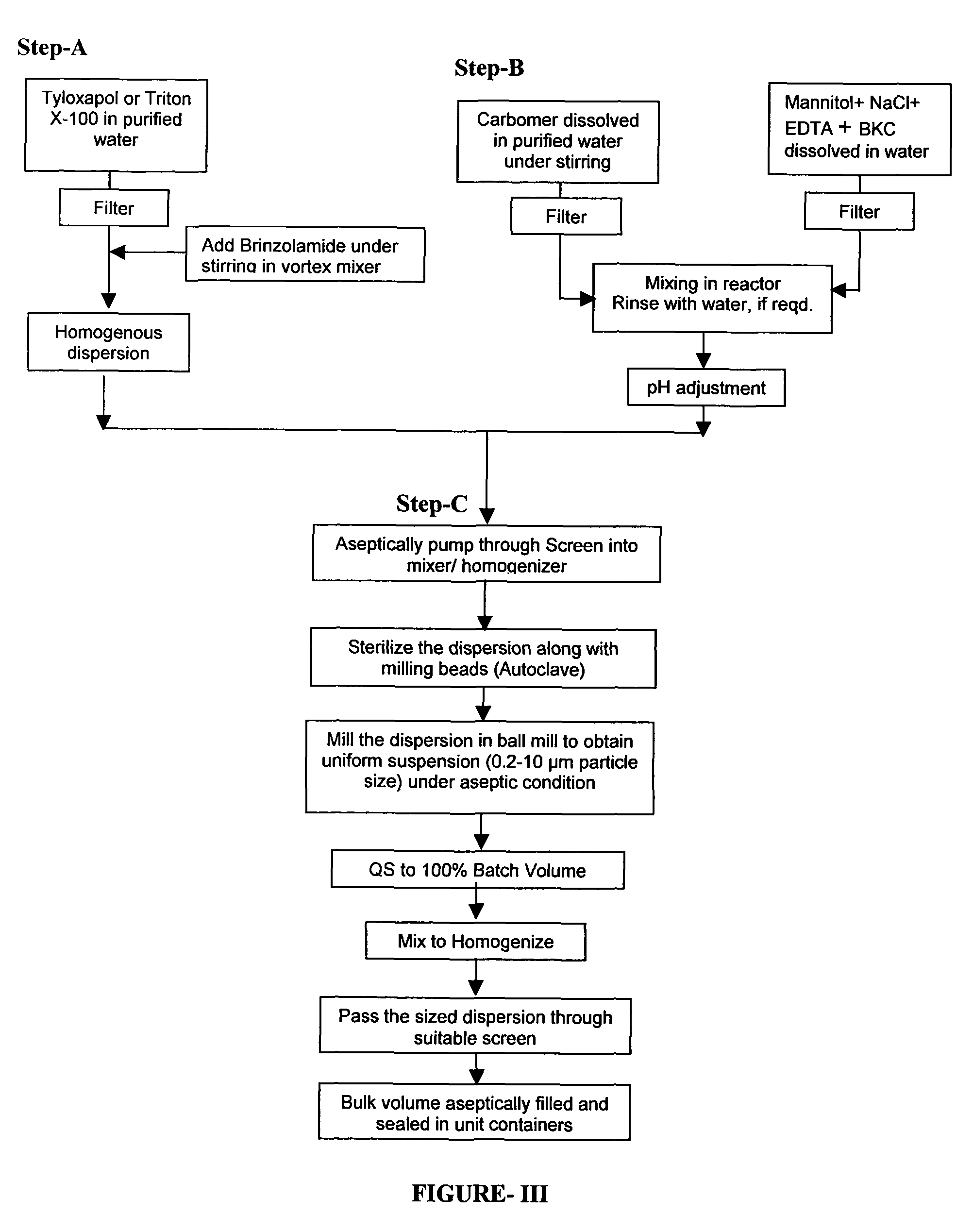
Pharmaceutical ophthalmic compositions comprising active ingredient(s) such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (CAI) or combinations and processes for making such compositions and the use of these compositions in patient populations including pediatric populations. A process for preparing an ophthalmic composition comprising a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, which comprises a) preparing a slurry comprising a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and a surfactant; b) preparing a polymer slurry comprising a polymer and water; c) preparing a solution comprising tonicity and preservative agents; d) mixing the polymer slurry of step b and the solution of step c, to form a vehicle concentrate and adjusting pH; e) adding the slurry of step a, to the vehicle concentrate of step d and mixing to homogenize; f) autoclaving the mixture of step e; g) sizing the mixture of step f, under aseptic condition.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Ophthalmic compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20190008920A1Significant comprehensive benefitsExtended releaseOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAntigenBeta blocker
The present invention relates to an ophthalmic composition comprising at least two active pharmaceutical ingredients. In particular, the active pharmaceutical ingredients are selected from the group consisting of: an alpha 2 adrenergic receptor agonist; a beta-adrenergic receptor agonist; an immunosuppressant; a lymphocyte associated antigen antagonist; an anti-inflammatory; a beta-blocker; a prostaglandin analog; a histamine receptor antagonist; a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor; and an antibiotic. In some embodiments, the composition of the invention is a nanoemulsion formulation. In one particular embodiment, the first active pharmaceutical ingredient is an alpha 2 adrenergic receptor agonist. The present invention also provides a method for treating various clinical conditions associated with an eye disorder or eye disease using the composition of the invention.
Owner:OCUGEN INC
Hypoxic tumor targeted short chain polypeptide micromolecule self-assembly nanometer material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110585441AHigh biosecurityThe production process is simpleOrganic active ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a hypoxic tumor region targeted short chain polypeptide micromolecule self-assembly nanometer material. The nanometer material is a shortchain polypeptide modified micromolecule carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, wherein an N end of short chain polypeptide is combined with a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic group. Through targeting carbonic anhydrase expressing film height of hypoxic tumor cells, tumor microenvironment in situ responsive self-assembly is realized, and specific internalization of the hypoxic tumor cells is induced,so that the hypoxic tumor cells are adjusted, controlled, killed and damaged. The material is simple in preparation technology, has higher biological safety biological safety, can effectively kill and damage the hypoxic tumor cells, can significantly improve conventional clinical chemotherapy treatment effects, can retard tumor metastasis process and can provide more thinking and means for clinical tumor treatment.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and method of their production
ActiveUS20140303390A1High yieldHeavy metal active ingredientsInorganic boron active ingredientsBoron clustersMedicinal chemistry
Derivatives of boron cluster compounds of general formula I and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and solvates, and their specific inhibition effect on the enzyme carbonic anhydrase IX, a protein overexpressed in cancer tissues. Methods of synthesis and the use of the novel derivatives. These inhibitors of human carbonic anhydrase IX can be used as active compounds of pharmaceuticals for diagnostics and / or therapy of cancer diseases.
Owner:USTAV ORGANICKE CHEM A BIOCHEM AKADE VED CR V V I +3
Targeted treatment of anerobic cancer
InactiveUS20160279084A1Easily damagedFavorably affect therapeutic resultSurgical adhesivesHydroxy compound active ingredientsBlood vessel occlusionPotassium
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical cocktail and methods of cancer treatment. In particular, one such cocktail comprises a combination of effective amounts of a lactate transporter inhibitor, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, a sodium potassium chloride cofactor (NKCC) transporter inhibitor, a member of the hydroxycinnamate class of drugs or a derivative thereof, and / or an angiogenesis inhibitor, including a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor such as bevacizumab in combination with blood vessel occlusion. As most cancers in an untreated state uses both aerobic and anaerobic / glycolytic pathways treatments contemplated herein can affect both metabolic pathways.
Owner:UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS OF CLEVELAND CLEVELAND
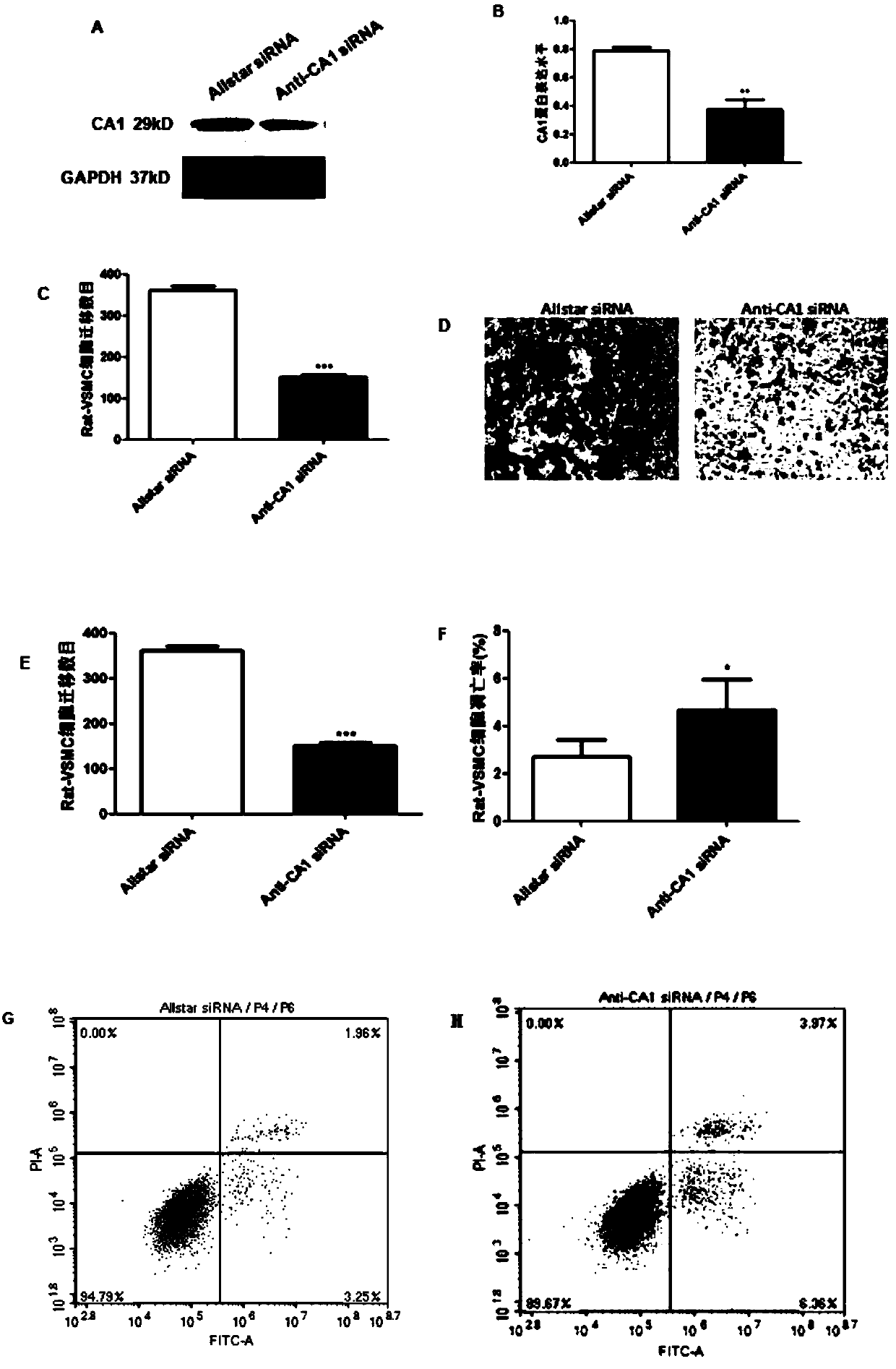
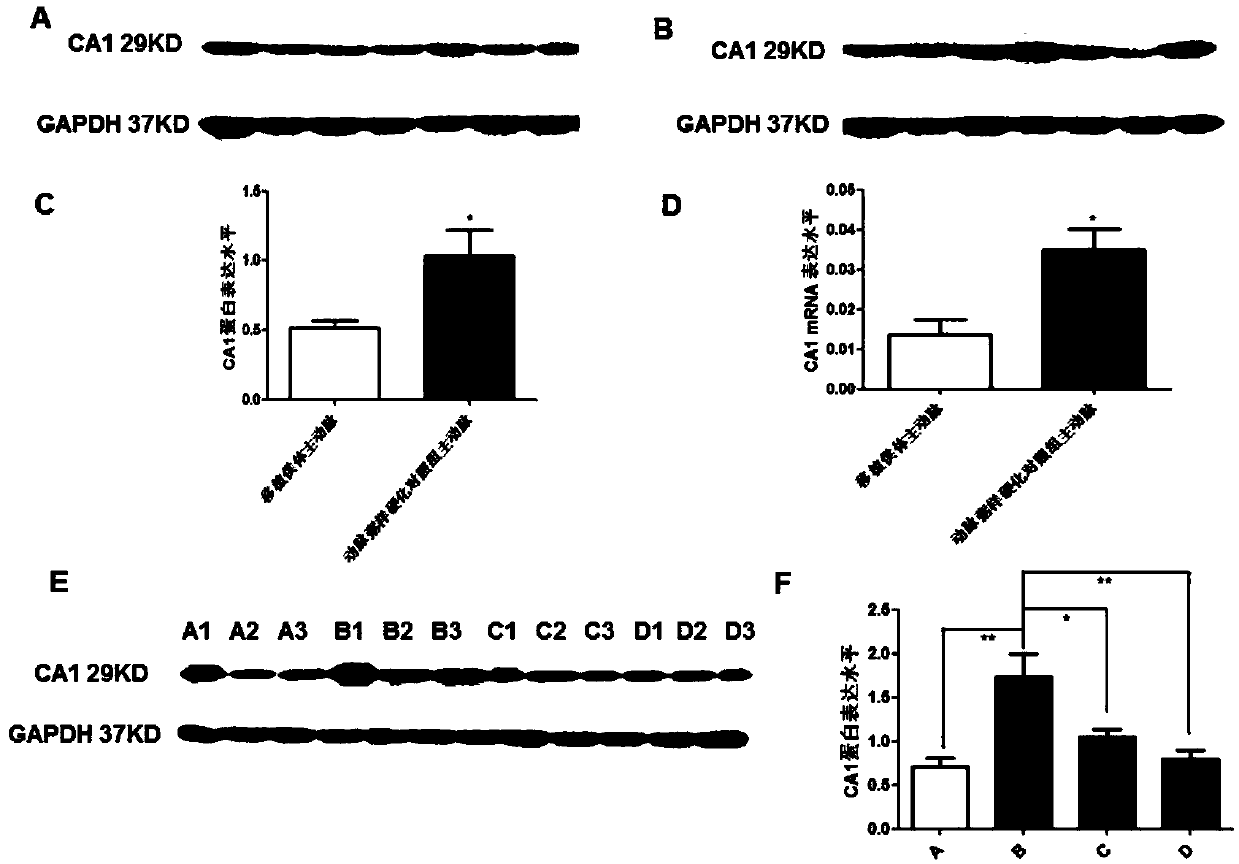
Application of carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to preparation of anti-atherosclerosis drugs
ActiveCN109568315APromote calcificationReduce calcificationOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderInflammatory factorsCarbonic anhydrase II
The invention belongs to the field of anti-arteriosclerosis drugs, and particularly relates to application of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to preparation of the anti-arteriosclerosis drugs. The study finds for the first time that carbonic anhydrase 1 (CA1) is highly expressed in arteriosclerosis calcified tissue, and CA1 is related to vascular smooth muscle calcification and affects cell proliferation and apoptosis. Methazolamide, the inhibitor of CA1, can significantly reduce the progression of atherosclerosis and inhibit atherosclerotic inflammatory factors. The results suggest that calcification plays an important role in atherosclerosis, and CA1-dominated calcification promotes the course of the atherosclerosis. Methazolamide has a potential therapeutic effect on the atherosclerosisby inhibiting expression of CA1. The findings not only further explain the close relationship between the atherosclerosis and the calcification, but also explore the calcification mechanism of the atherosclerosis, and further prove that inhibition of the calcification is a key point in the treatment of the atherosclerosis. The application of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to the preparation of the anti-arteriosclerosis drugs provides new ideas for the treatment of the atherosclerosis.
Owner:青岛汇嘉医学科技有限公司
Aqueous composition
InactiveUS20160256470A1Improve compound stabilityAvoid spreadingSenses disorderInorganic non-active ingredientsHigh temperature storageHalogen
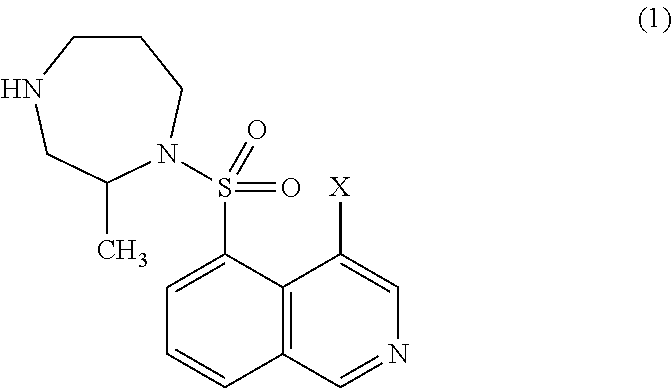
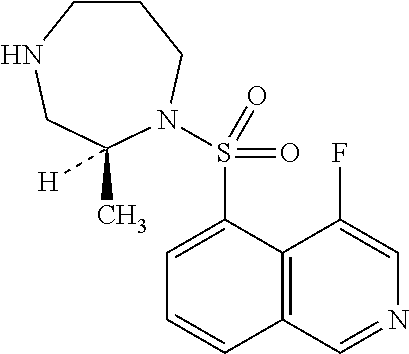
Provided is a technology for suppressing discoloration of a halo-isoquinoline derivative-containing aqueous composition during high-temperature storage. Provided is an aqueous composition containing a compound of formula (1):wherein X is a halogen atom, a salt of the compound, or a solvate of the compound or the salt; and a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Fluorinated benzenesulfonamides as inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase
Novel fluorinated benzenesulfonamides compounds of general formula (I)can be used in biomedicine as active ingredients in pharmaceutical formulations, because they inhibit enzymes which participate in disease progression.
Owner:VILNIUS UNIV
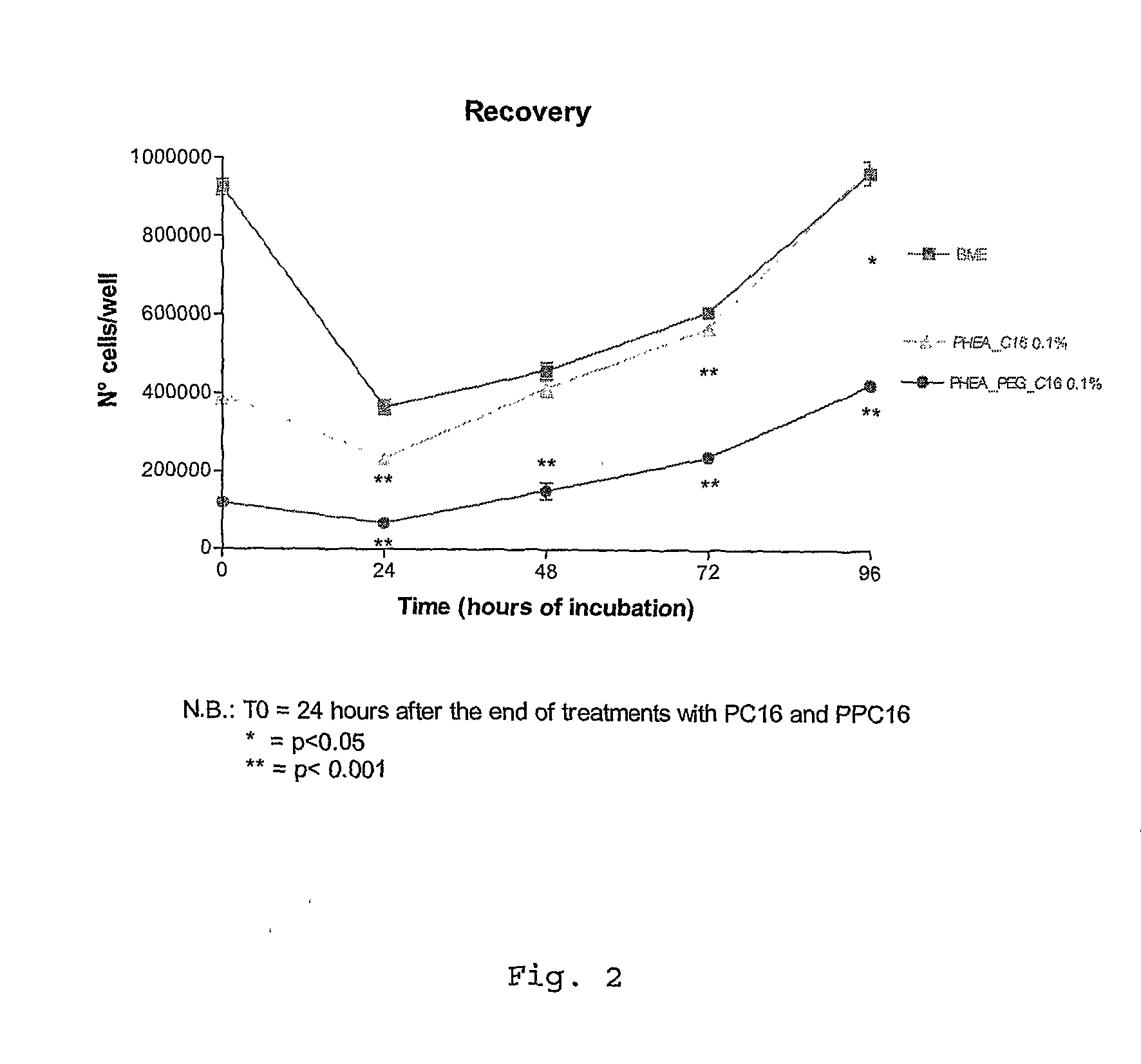
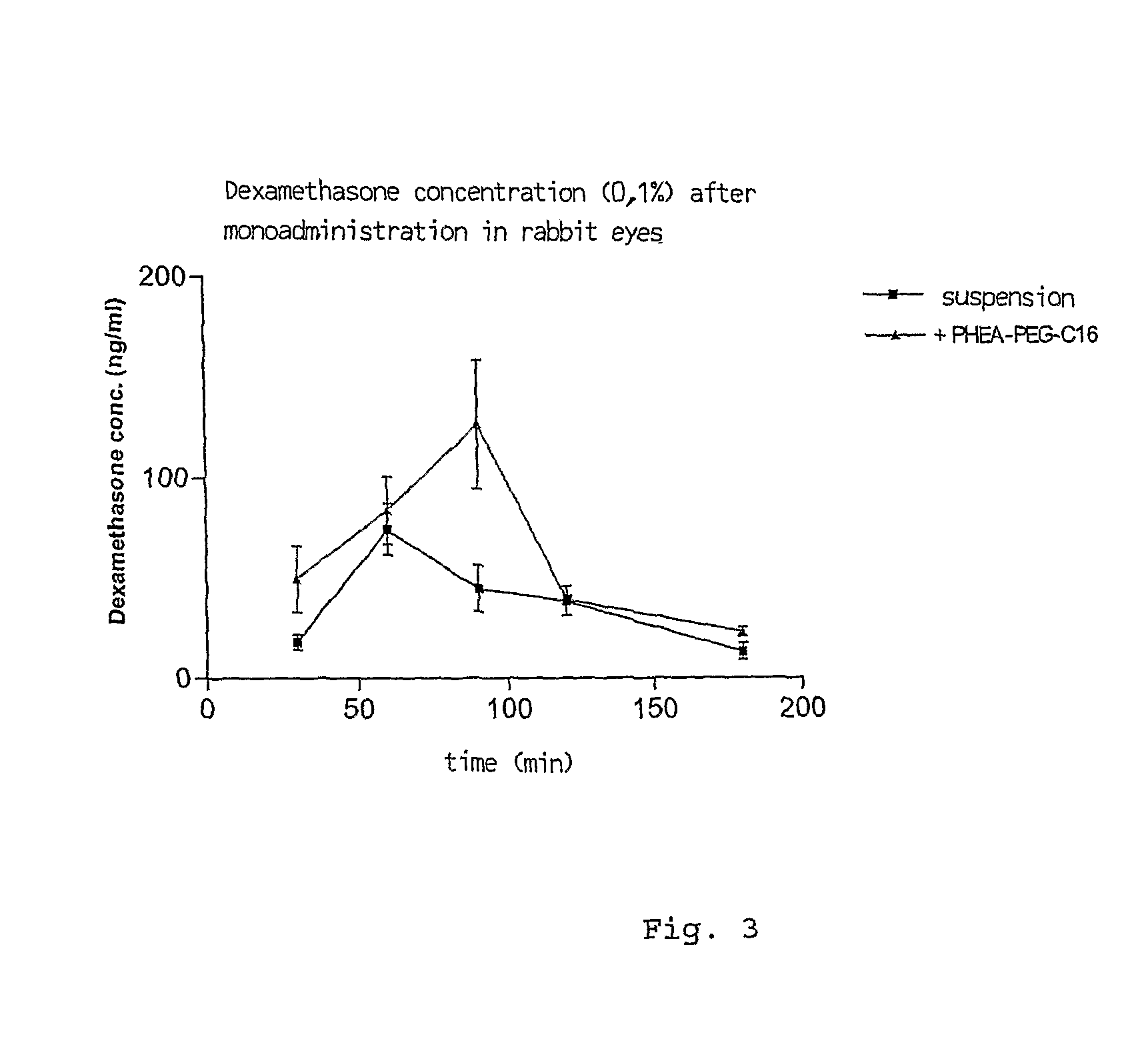
Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Composition Containing Amphiphilic Polyaspartamide Copolymers
InactiveUS20090221545A1Increase the number ofLess non-productive absorptionBiocideAnimal repellantsPenicillinBeta blocker
The present invention relates in general to the use of amphiphilic graft-type copolymers of polyaspartamide for the ophthalmic administration of drugs, such as for example steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antimicrobial agents such as aminoglycosides, macrolides, cephalosporin, tetracycline, quinolones, penicillin, beta-lactams, anti-glaucoma agents such as prostaglandins, alpha- and beta-blockers, inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase, cannabinoids, antiviral agents, diagnostic agents, anti-angiogenic agents, antioxidants.
Owner:S I F I SPA
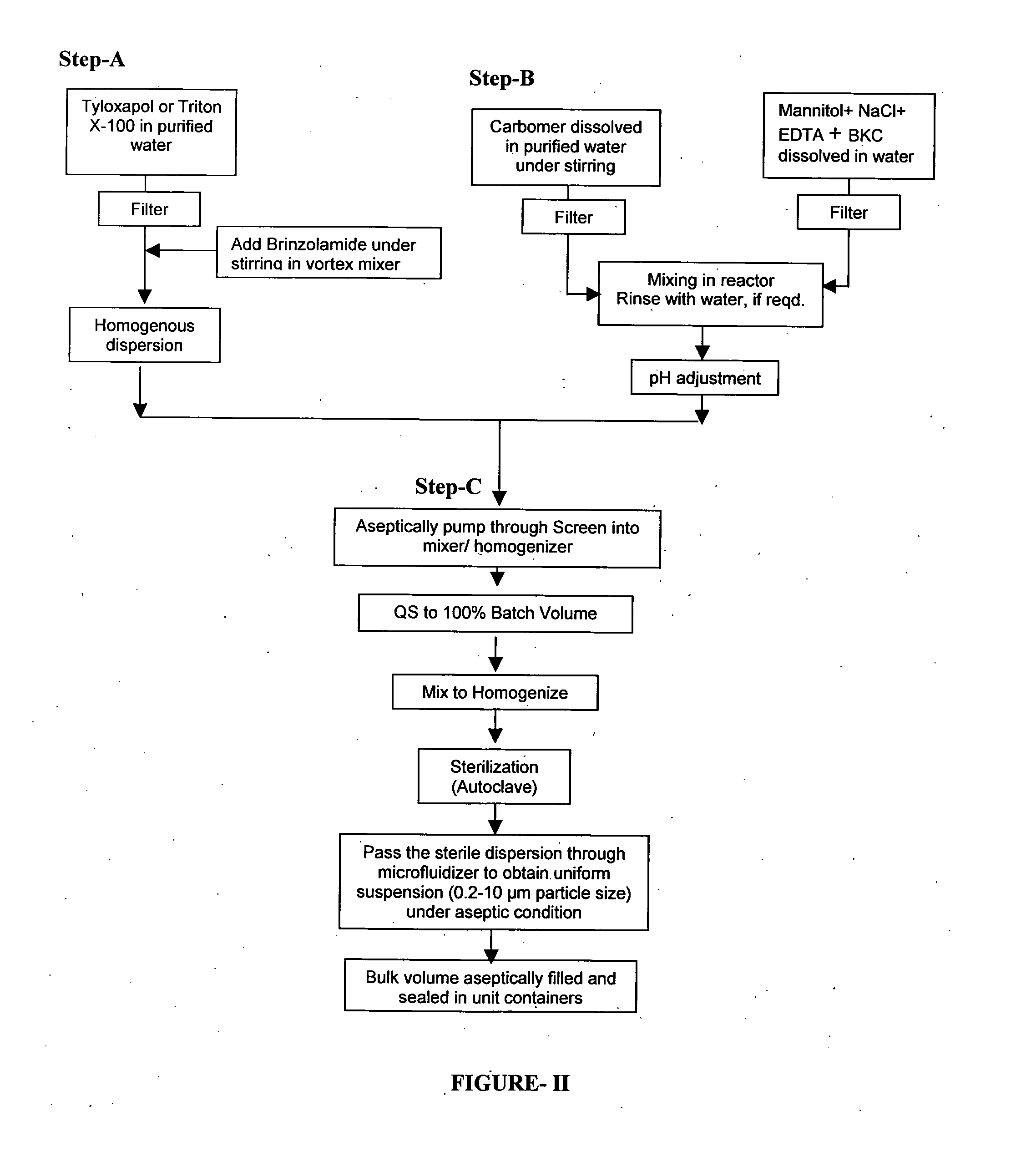
Process for preparing pharmaceutical ophthalmic compositions
Pharmaceutical ophthalmic compositions comprising active ingredient(s) such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (CAI) or combinations and processes for making such compositions and the use of these compositions in patient populations including pediatric populations. A process for preparing an ophthalmic composition comprising a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, which comprises a) preparing a slurry comprising a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and a surfactant; b) preparing a polymer slurry comprising a polymer and water; c) preparing a solution comprising tonicity and preservative agents; d) mixing the polymer slurry of step b and the solution of step c, to form a vehicle concentrate and adjusting pH; e) adding the slurry of step a, to the vehicle concentrate of step d and mixing to homogenize; f) autoclaving the mixture of step e; g) sizing the mixture of step f, under aseptic condition.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
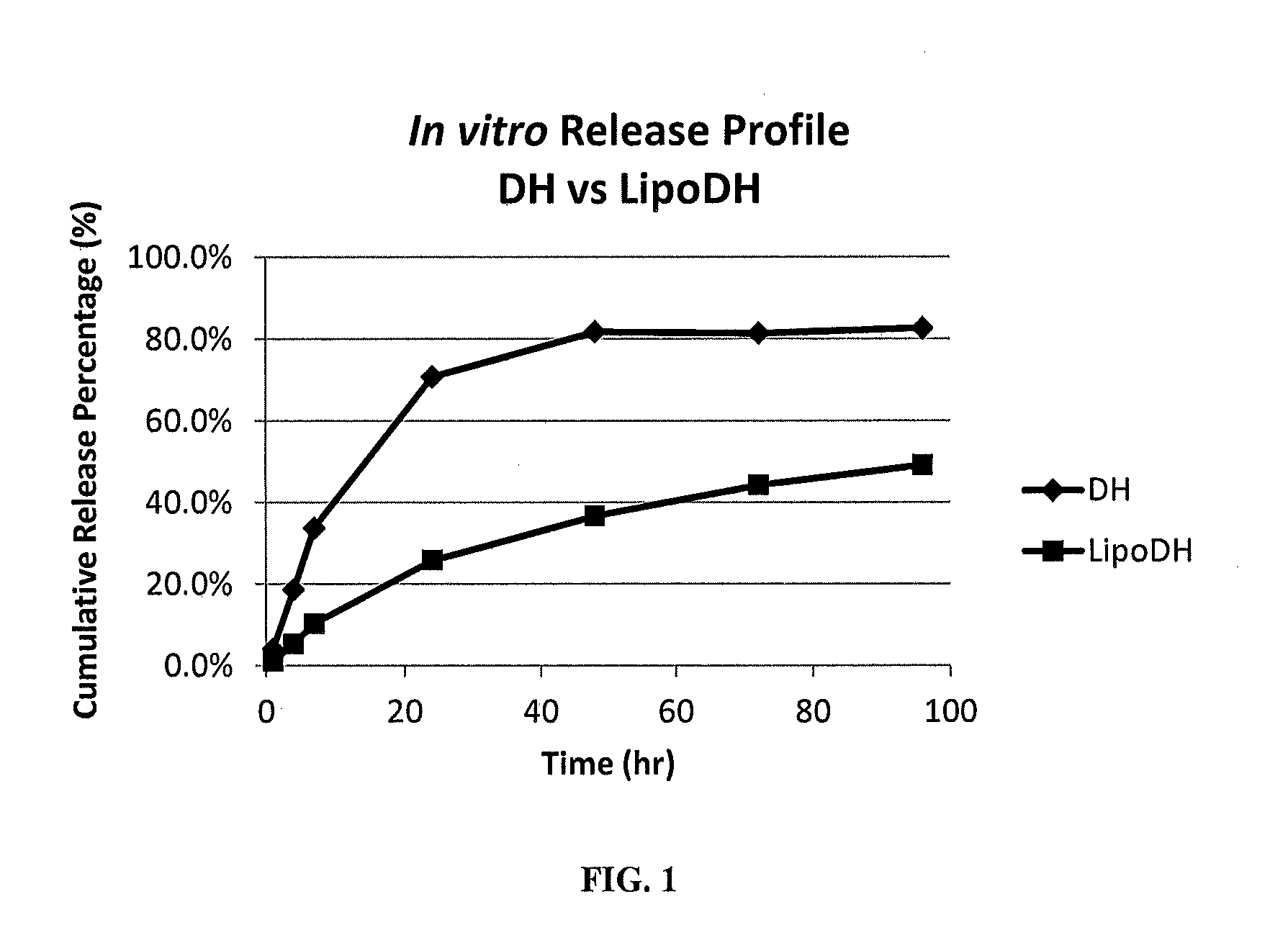
Stable liposomal formulations of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors for ocular drug delivery
InactiveUS20170042809A1Reduce deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLiposomal deliveryOphthalmologyLipid bilayer
A stable liposomal formulation for ocular delivery of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. The formulation contains (i) a liposome that includes a lipid bilayer formed of a phosphatidylcholine, and (ii) a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor encapsulated in the liposome. Also provided is a method for treating an ocular disorder with the formulation.
Owner:PEREGRINE OPHTHALMIC PTE LTD
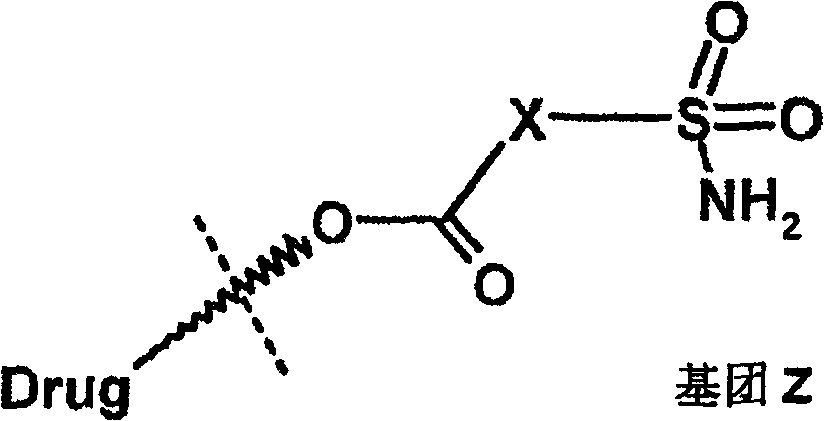
Ophthalmic composition of heteroaryl sulfamoyl carboxylic ester carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
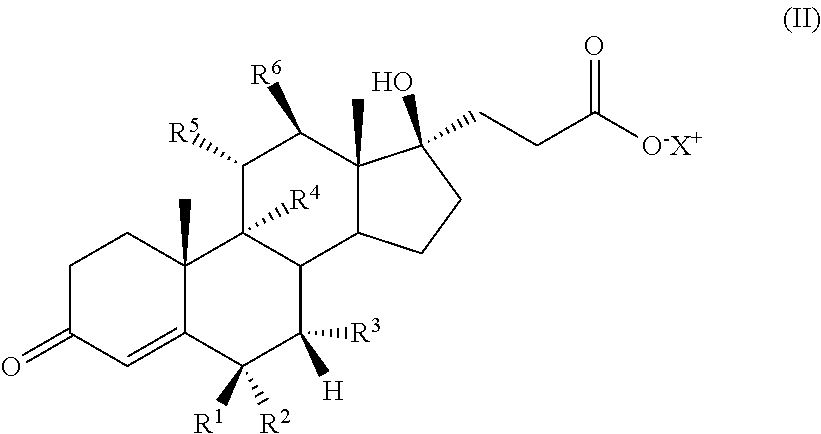
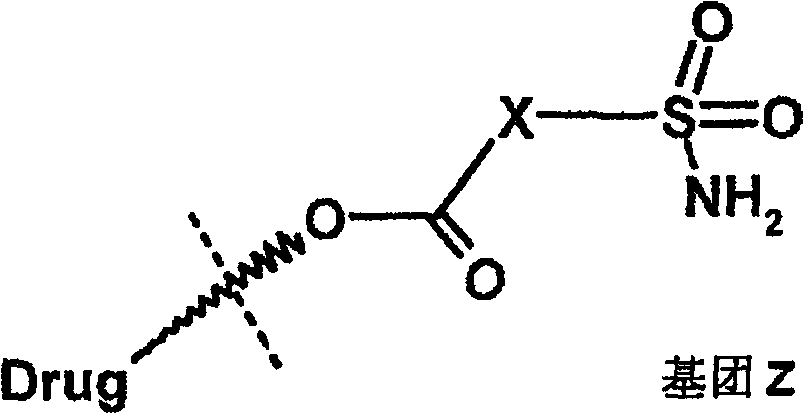
The invention relates to an ophthalmic composition of a heteroaryl sulfamoyl carboxylic ester carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, and discloses a compound in formula (II), wherein X is non-substituted or substituted heteroaryl or alkyl heteroaryl, Drug is a steroid which can form the carboxylic ester through OH group, and the X and the Drug can be selectively substituted.
Owner:TIANJIN JINYAO GRP
Use of carbonic anhydrase ii for producing a drug
InactiveUS20130101565A1Enhances nephrotoxic effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCARBONIC ANHYDRASE VACisplatin
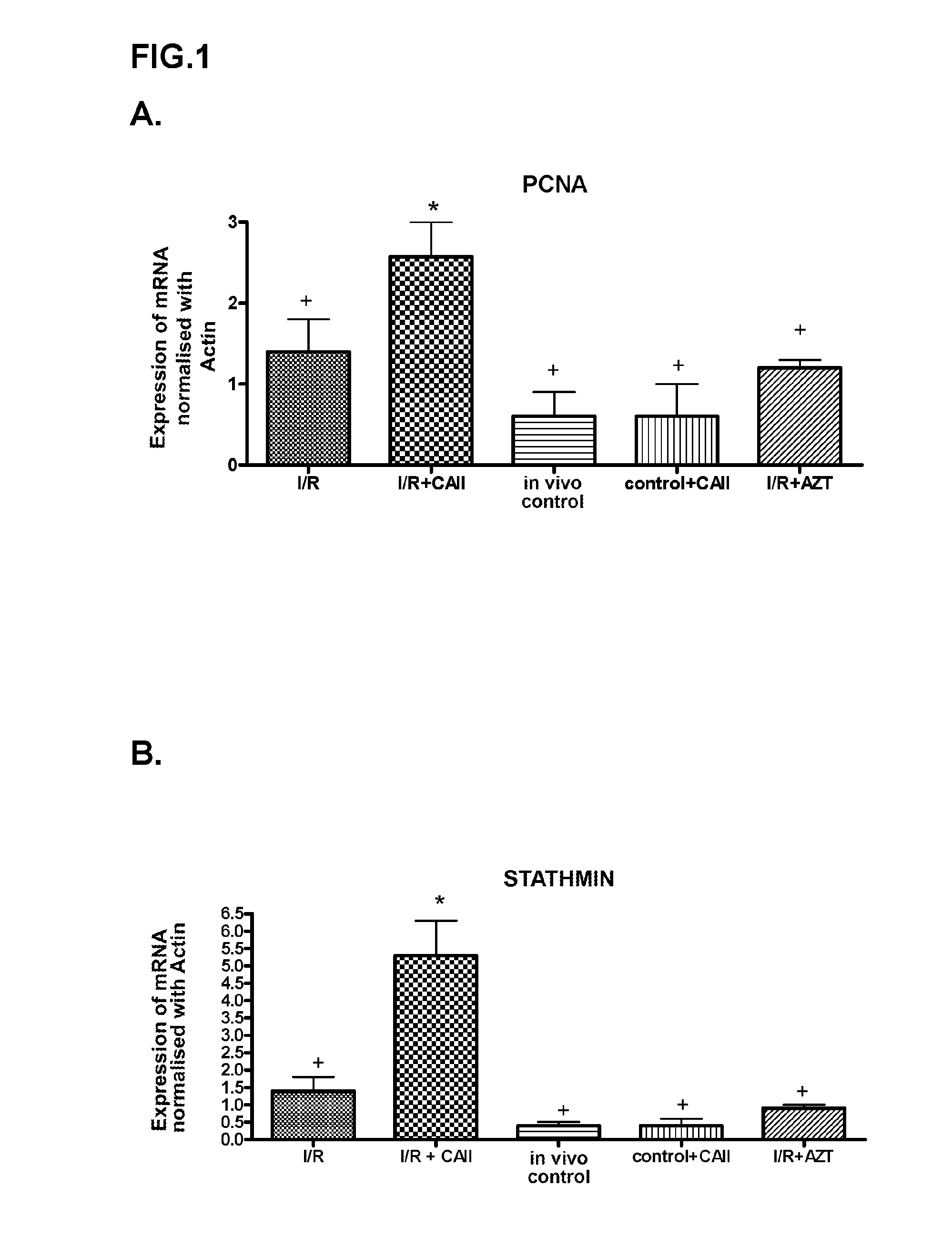
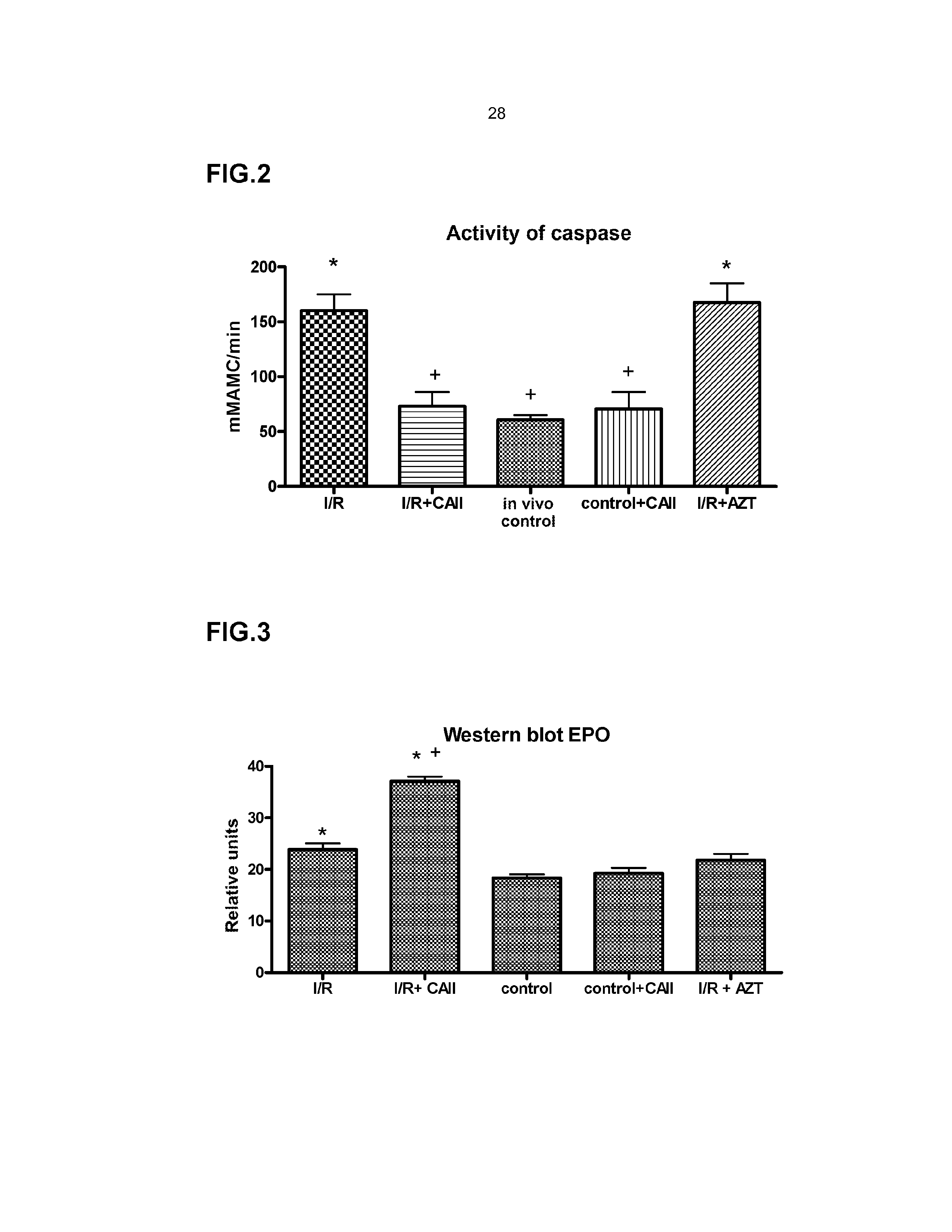
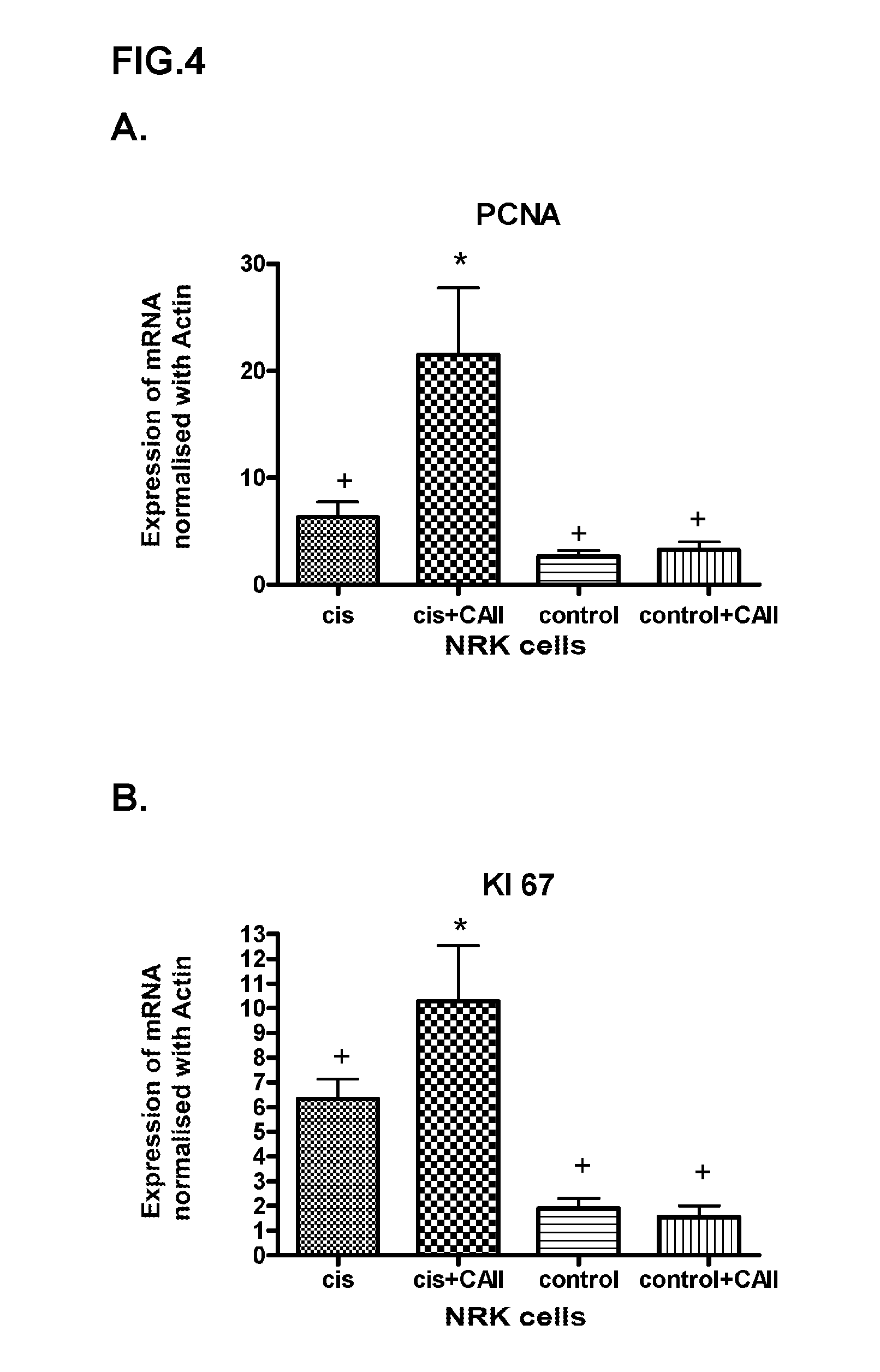
The present invention falls within the field of biomedicine. Specifically, the present invention relates to the use of carbonic anhydrase II for the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention and / or treatment of the damage caused by ischemia, ischemia followed by reperfusion or toxins, acute failure or rejection of a transplanted organ, preferably the kidney. In a preferred embodiment, the toxin is cisplatin.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Methods for the therapeutic use of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor for reducing spinal cord edema
This invention relates to methods of treating mammals at risk or affected by spinal cord edema by administering a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that crosses the blood-spinal cord barrier. Among the conditions treated are, but not limited to, spinal cord injury, spinal cord tumors and vascular malformations, spinal infections, transverse myelitis, multiple sclerosis, syringomyelia and the pre-syrinx state.
Owner:RADOJICIC MILAN
An improved process for manufacturing sterile ophthalmic pharmaceutical suspensions
ActiveUS20160279139A1Simple and efficient processSpeed up the processOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsEngineeringBottle
The present invention provides a process of manufacturing a sterile, ophthalmic pharmaceutical suspension comprising sterile active ingredient(s) such as sterile carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) wherein the process does not involve the use of any special equipment's such as ball mill, milling bottle and / or jet mill The present process is simple, cost effective and efficient.
Owner:SENTISS PHARMA
Ophthalmic composition
InactiveUS20110275617A1Simple compositionImproved aqueous solubilityBiocideSenses disorderCarteololBeta blocker
The present invention provides an ophthalmic composition comprising a hyperbranched polymer. The ophthalmic compositions may also comprise carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, wherein the hyperbranched polymer increases the aqueous solubility of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, and increases corneal permeation of the active agent. The ophthalmic compositions may also comprise non-ionic surfactants, such as polysorbate, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose or hydroxyethyl cellulose, and beta-blockers, such as carteolol, levobunolol, betaxolol, metipranolol, timolol or propranolol.
Owner:SENJU USA
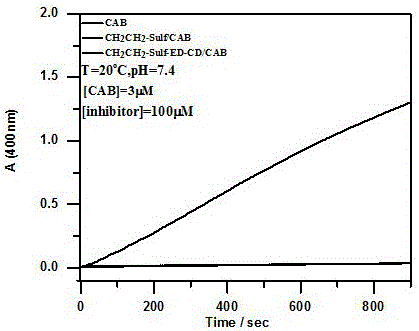
Thermosensitive cyclodextrin-based carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106822174ALow toxicityGood test characteristicsOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderTemperature responseCyclodextrin
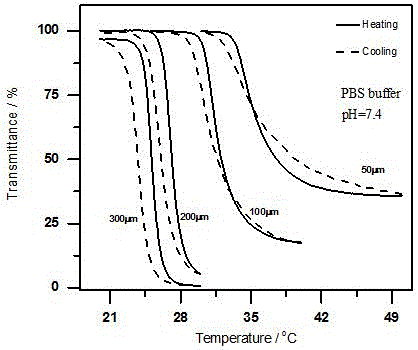
The invention discloses a thermosensitive cyclodextrin-based carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. In the inhibitor, a natural small-molecule inhibitor with a sulfonamide group is modified onto thermosensitive cyclodextrin with temperature response, an inhibitory effect on carbonic anhydrase is achieved through the sulfonamide group, and the reversible regulation of the activity of carbonic anhydrase is achieved through the thermosensitive effect of an alkoxy ether chain. When temperature is below a phase-transition temperature, the alkoxy ether chain stretches, the sulfonamide group can have good supramolecular interaction with carbonic anhydrase, and thereby the activity of carbonic anhydrase is inhibited. When temperature is above the phase-transition temperature, because the alkoxy ether chain is dehydrated to collapse to generate powerful steric resistance, destroying the supramolecular interaction between the sulfonamide group and carbonic anhydrase, and thereby the activity of the enzyme recovers again. Moreover, compared with other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, the thermosensitive cyclodextrin-based carbonic anhydrase inhibitor is lower in toxicity and wider in resource, thus having high application value in the field of biomedical materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension with carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
ActiveUS8071557B2BiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsCarbonic anhydrase IICarbonic anhydrase inhibitor
This disclosure relates generally to methods and pharmaceutical compositions useful in treating pulmonary hypertension. In one embodiment, for example, the disclosure provides a method for treating pulmonary hypertension comprising administering a therapeutically effective dose of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to a patient in need of treatment. The disclosure finds utility in the fields of medicine and pharmacology.
Owner:VIVUS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com