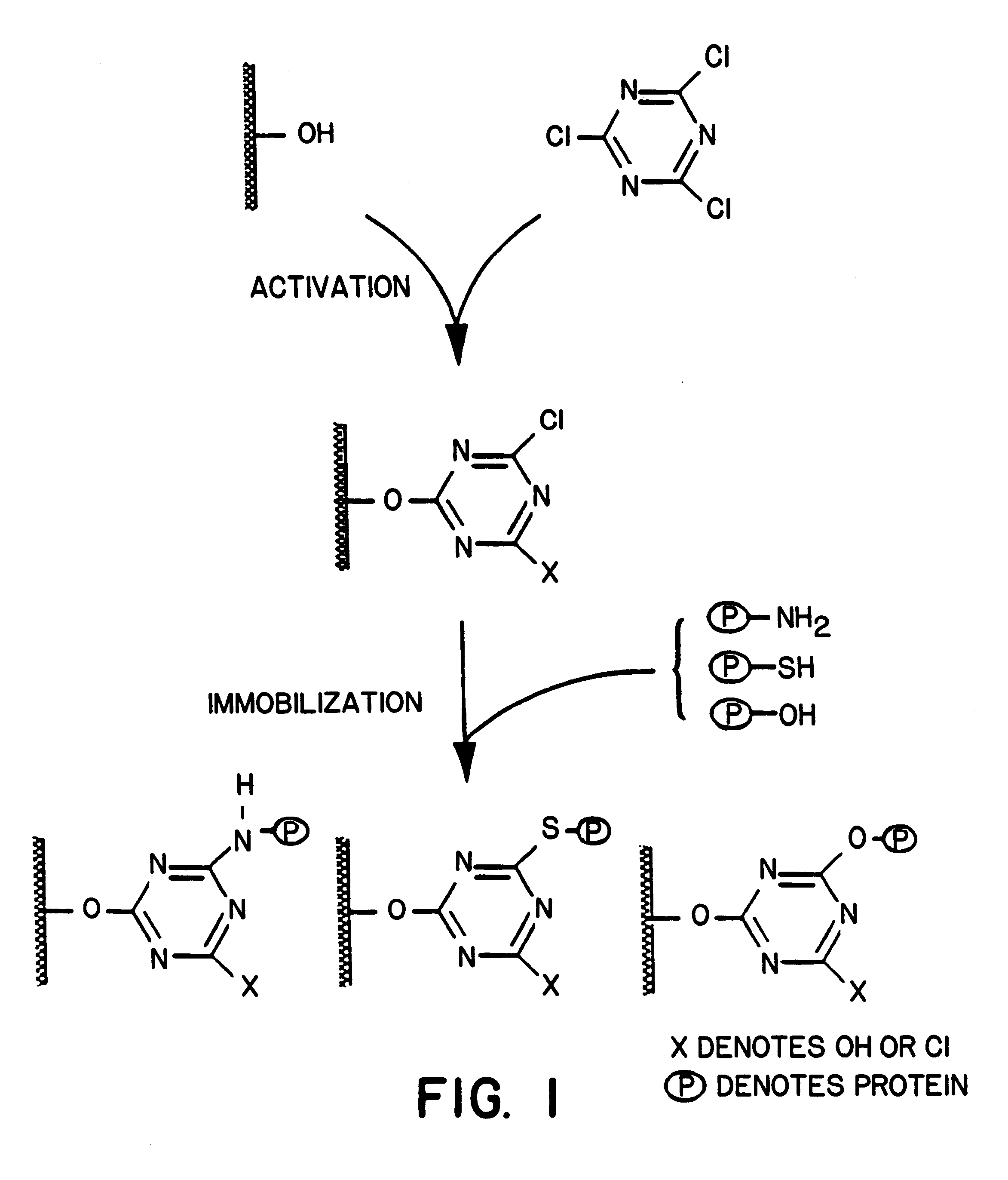
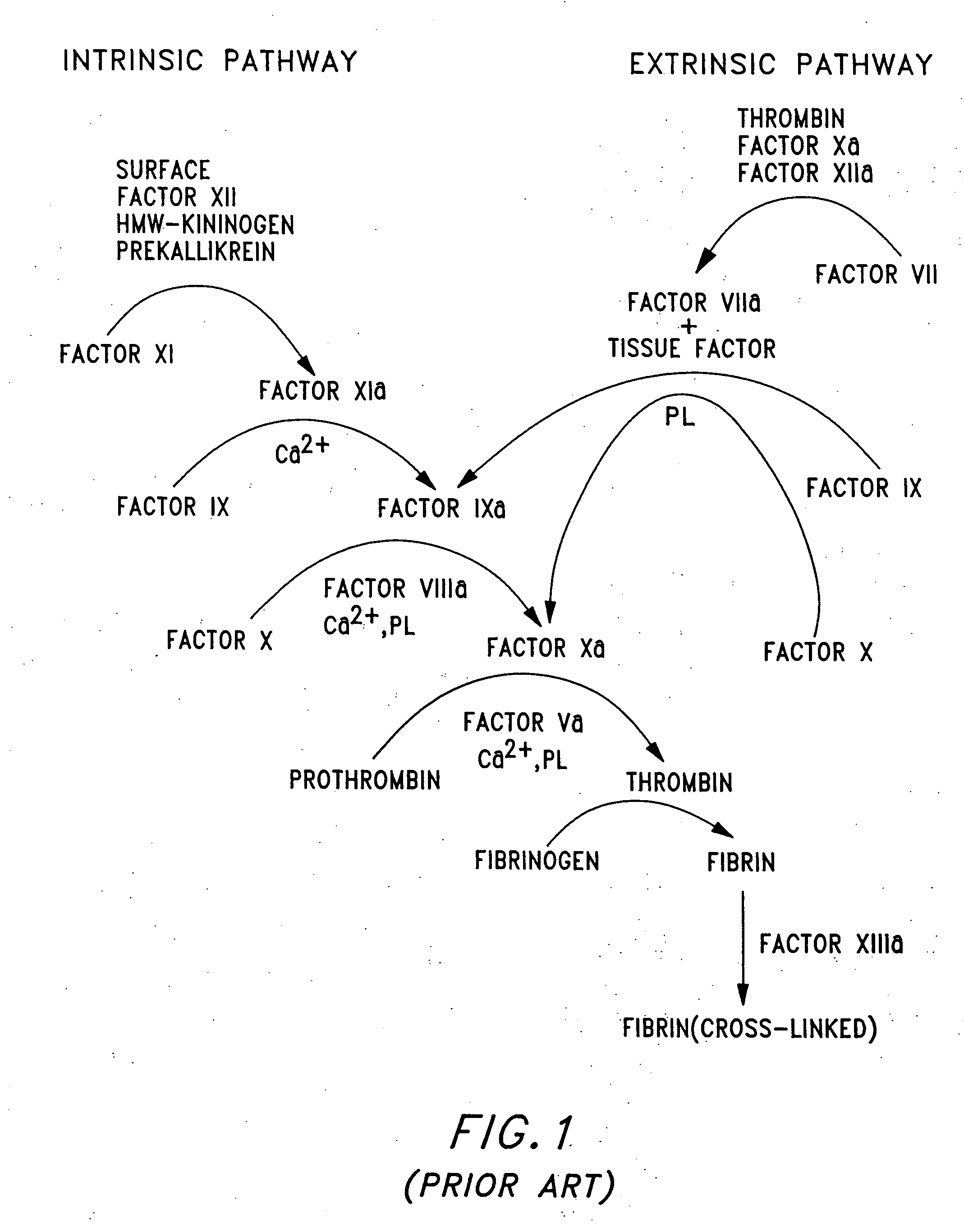
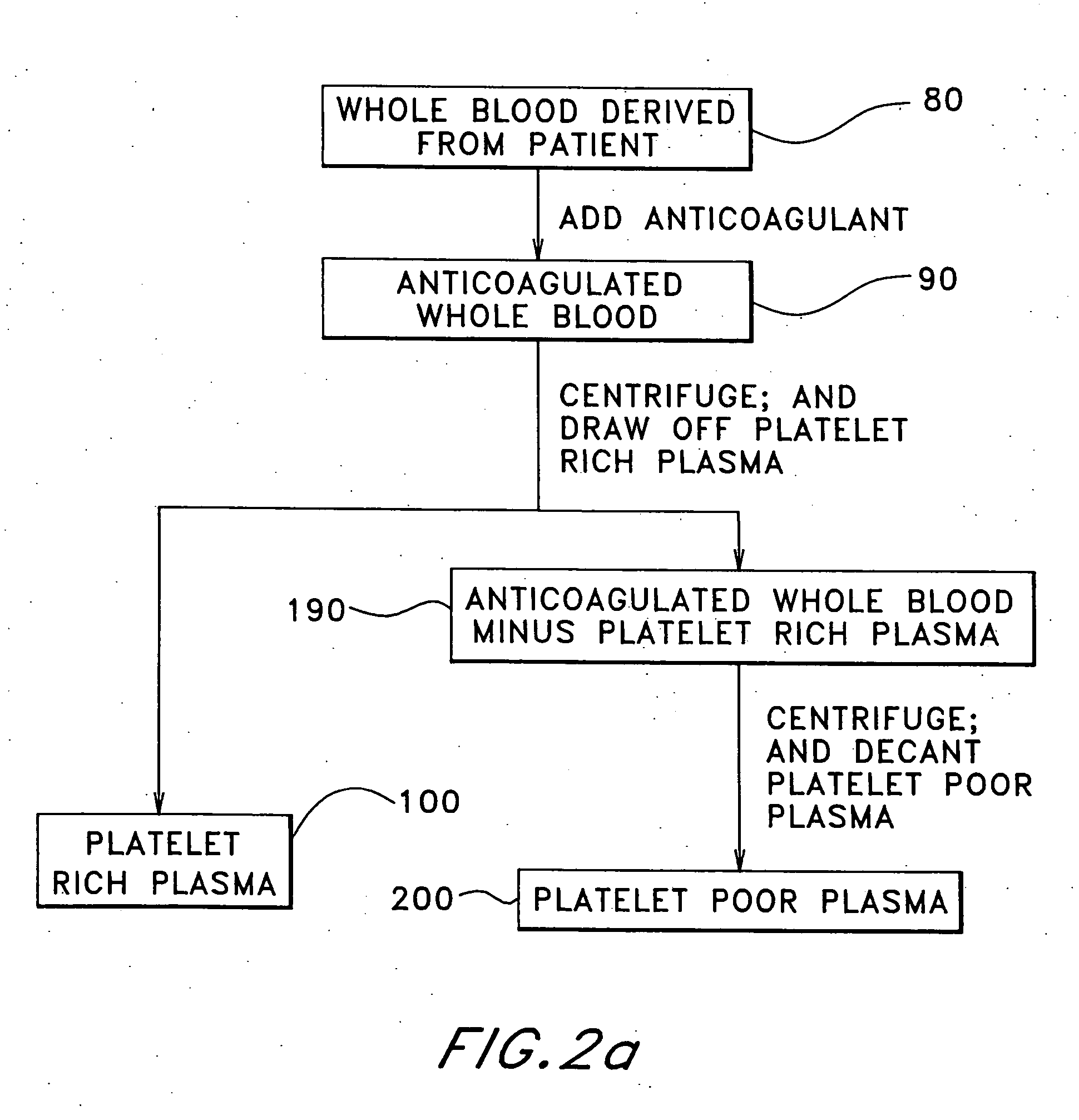
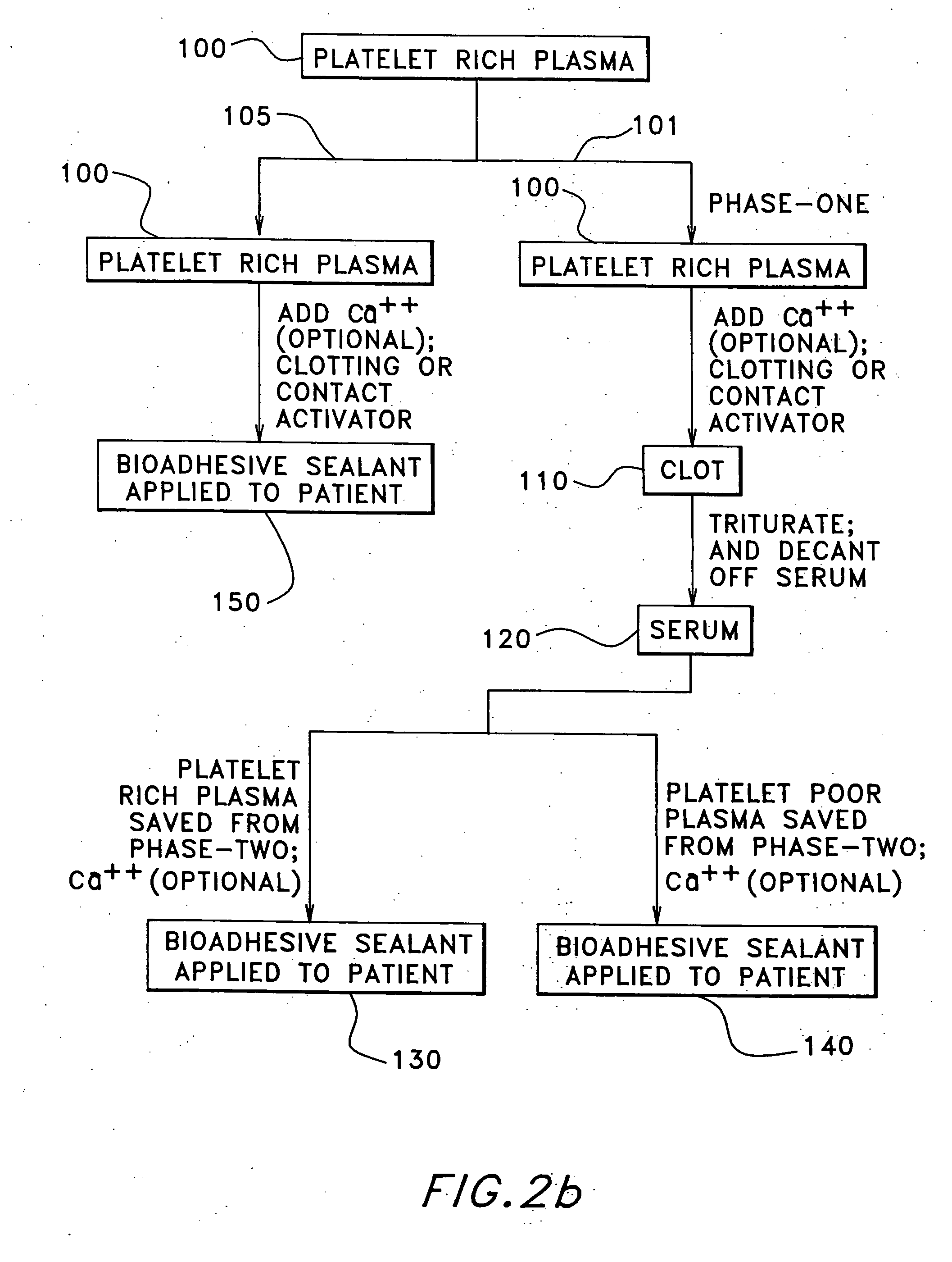
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Fibrin sealants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
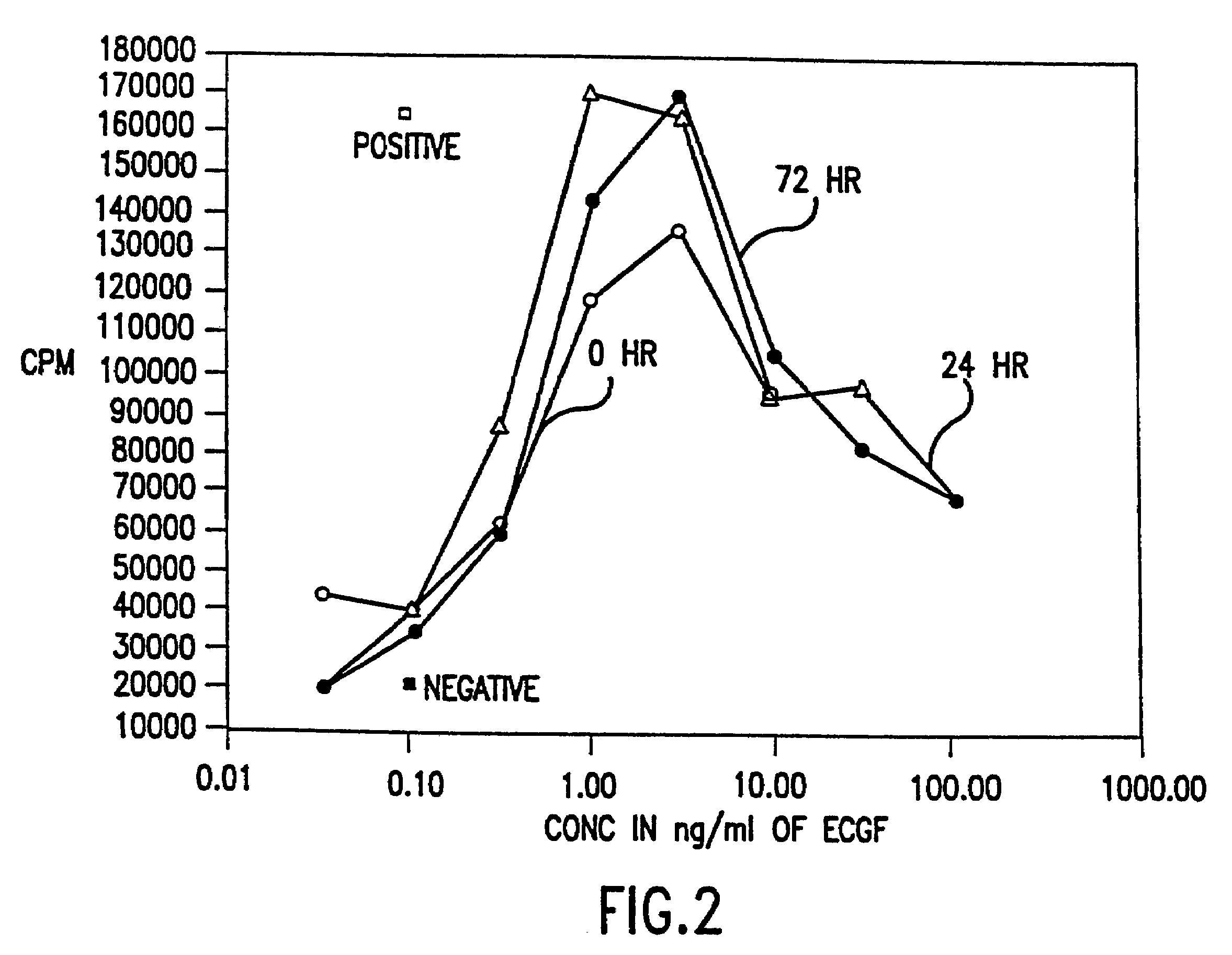
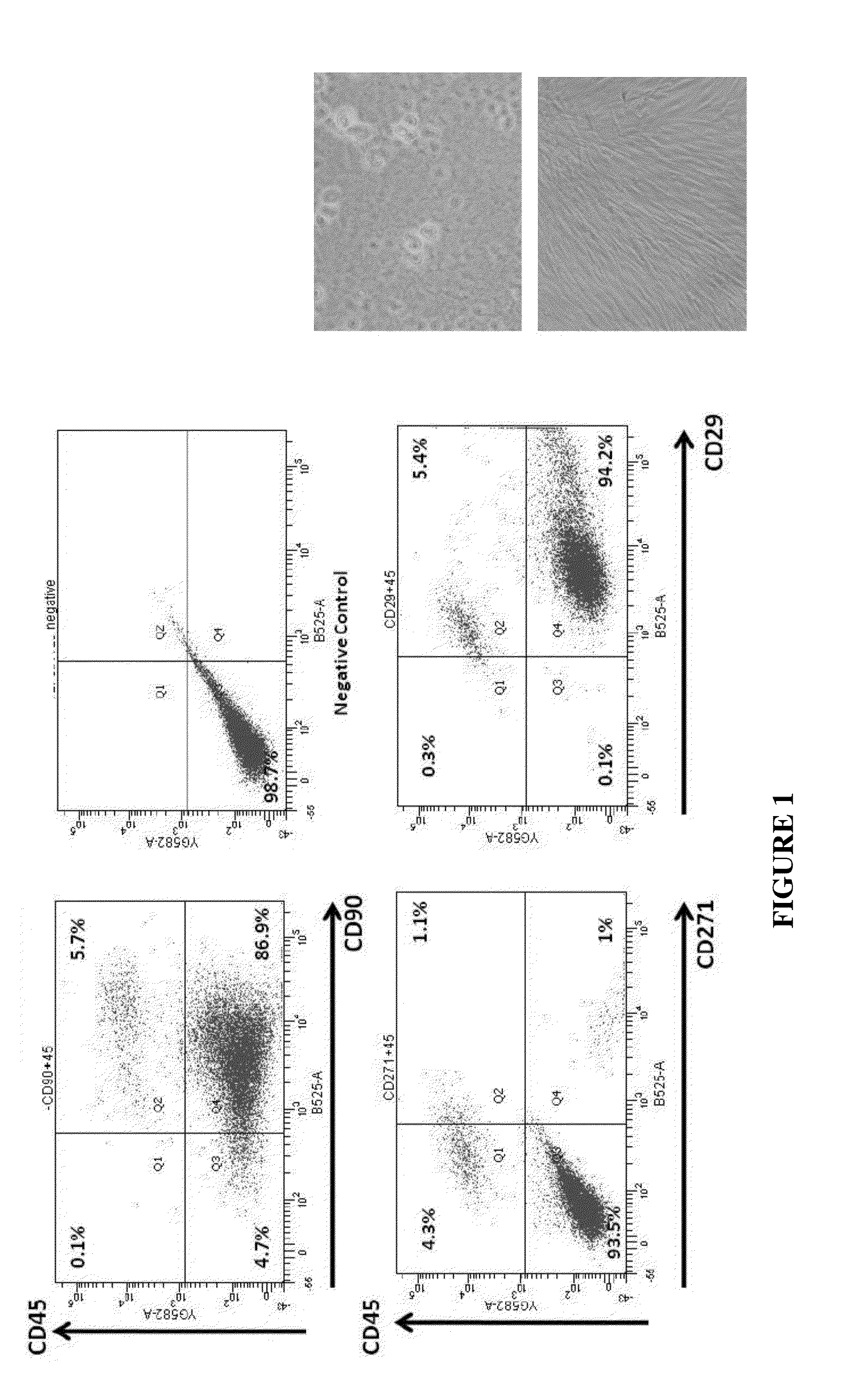
Fibrin sealants are a type of surgical tissue adhesive derived from human and animal blood products. The ingredients in these sealants interact during application to form a stable clot composed of a blood protein called fibrin. Fibrin sealants are also called fibrin glues.
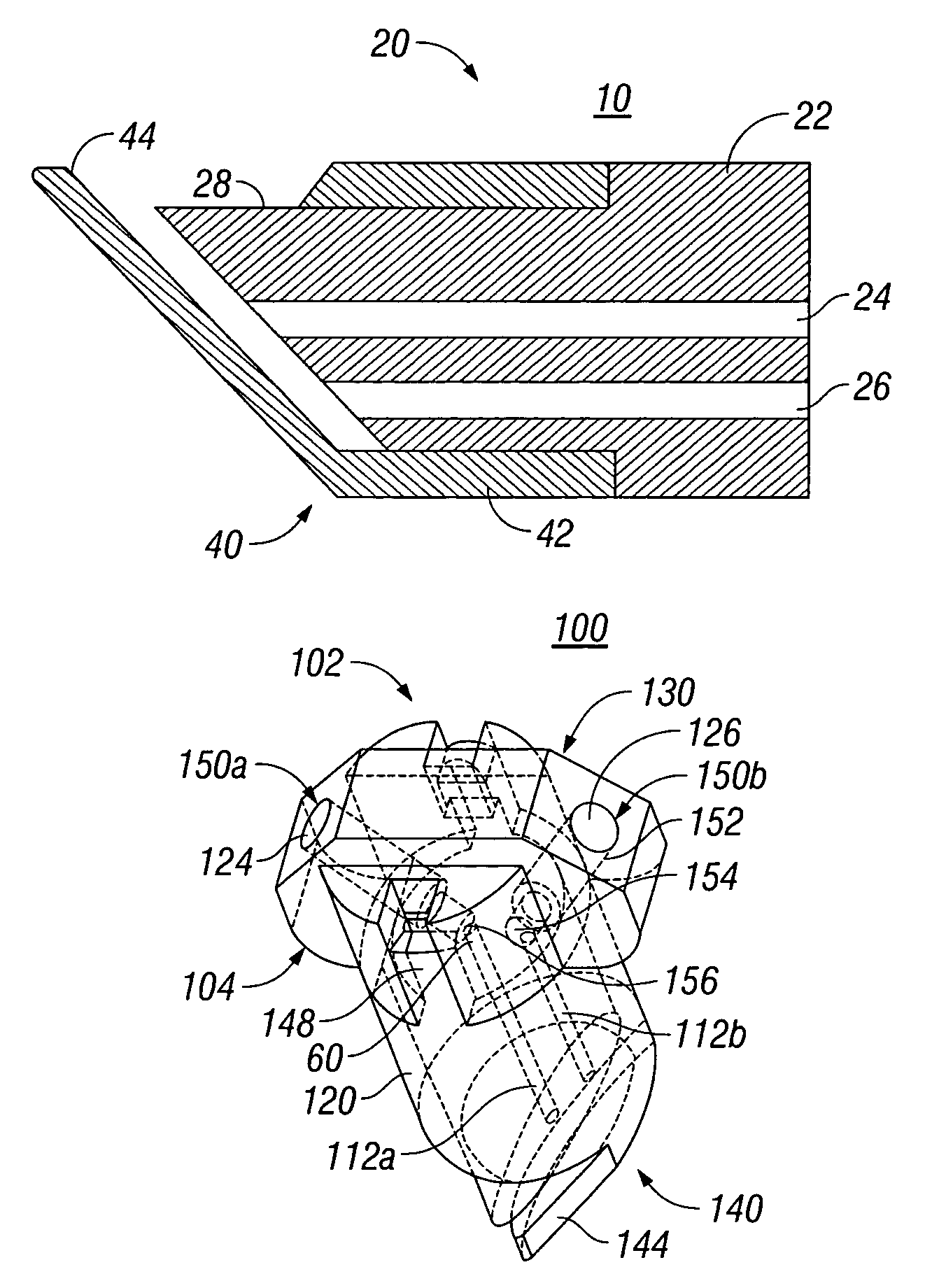
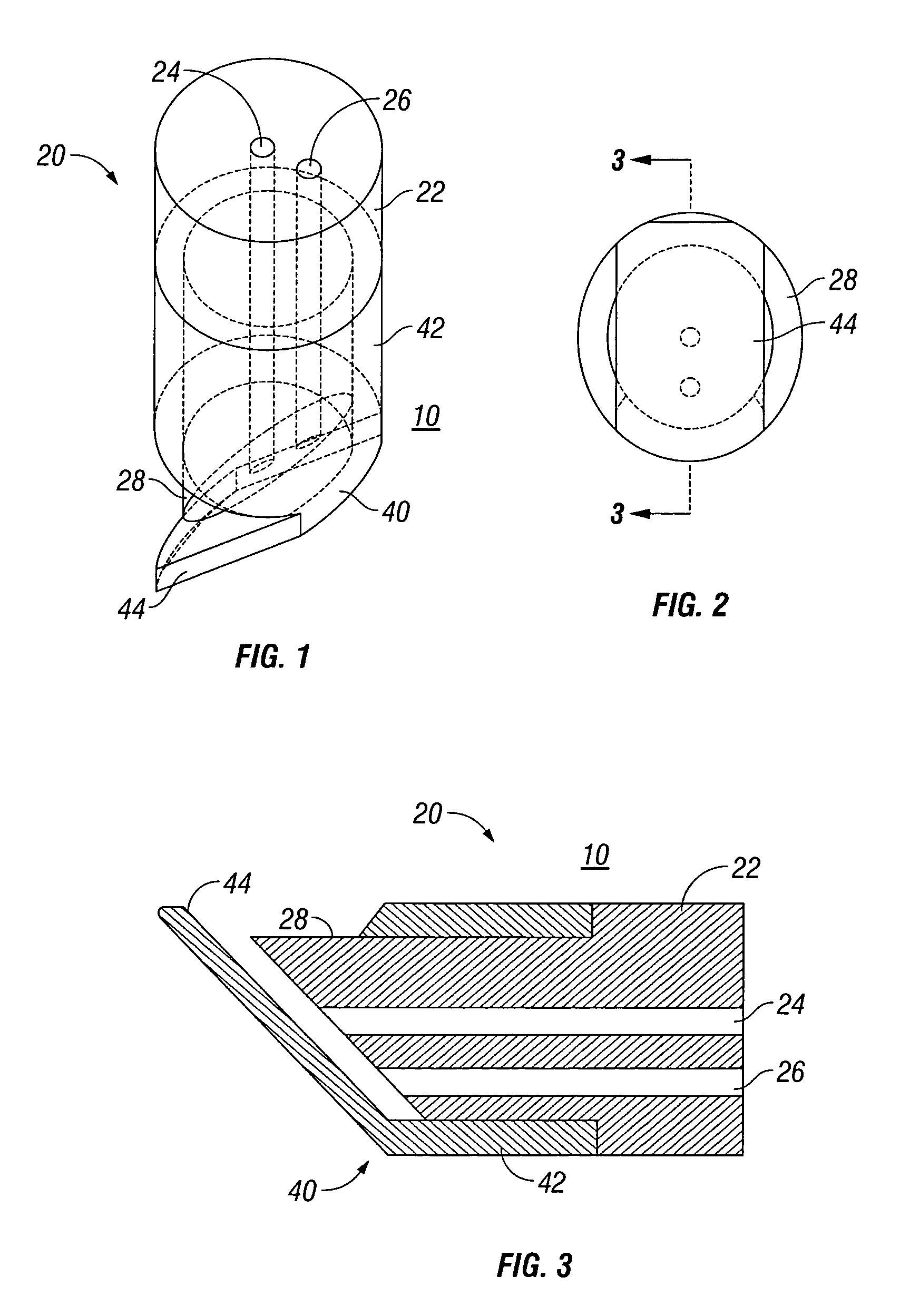
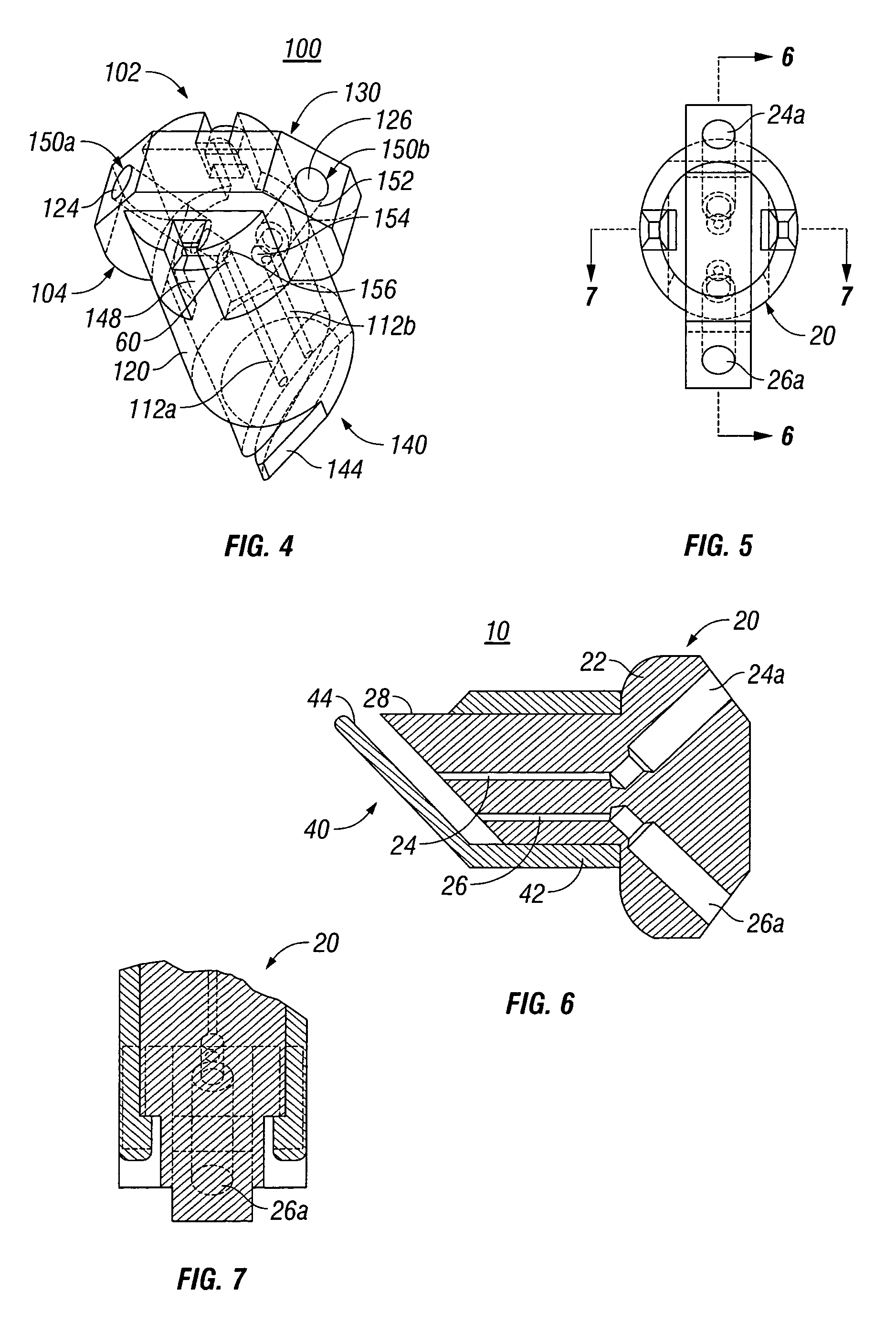
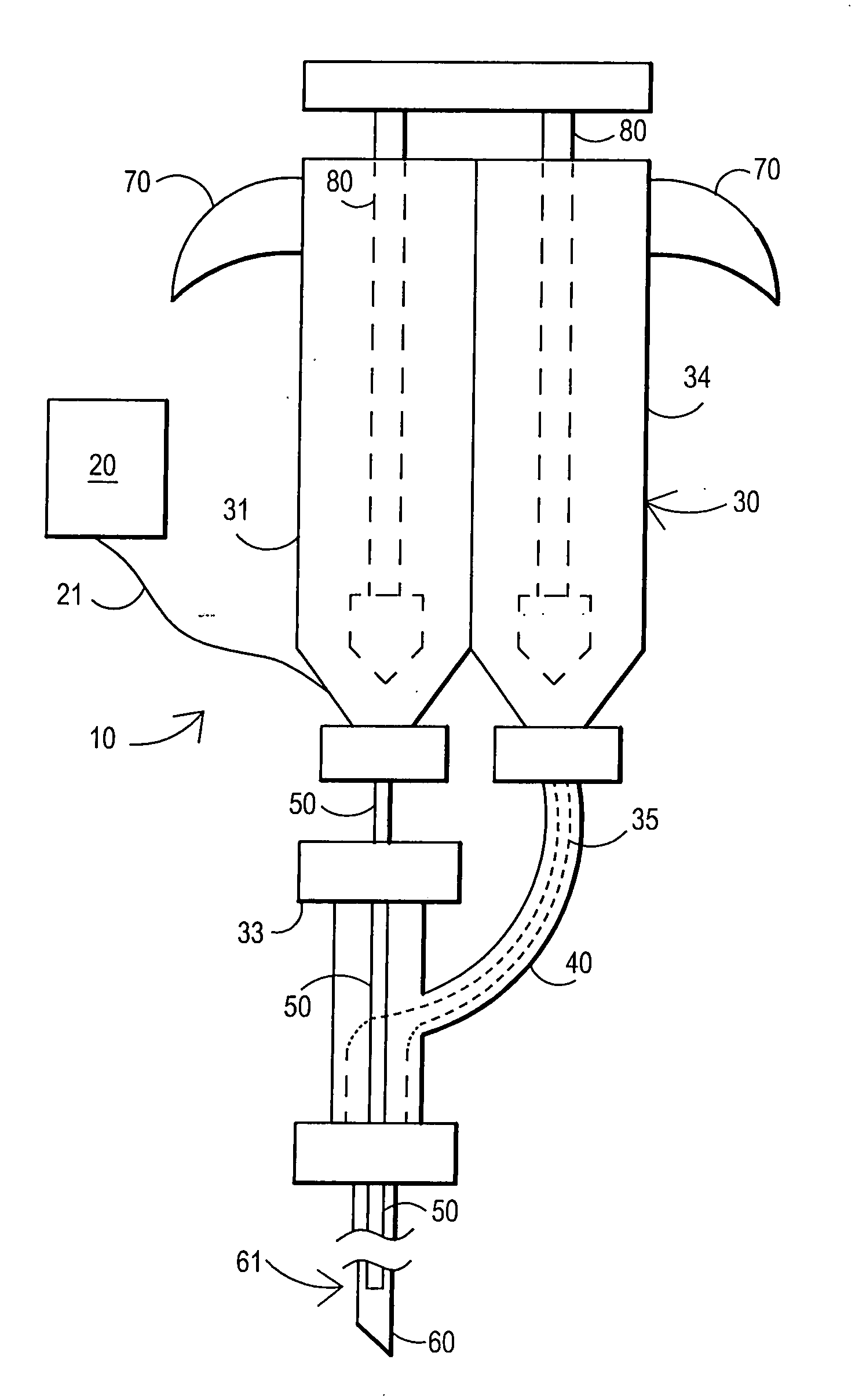
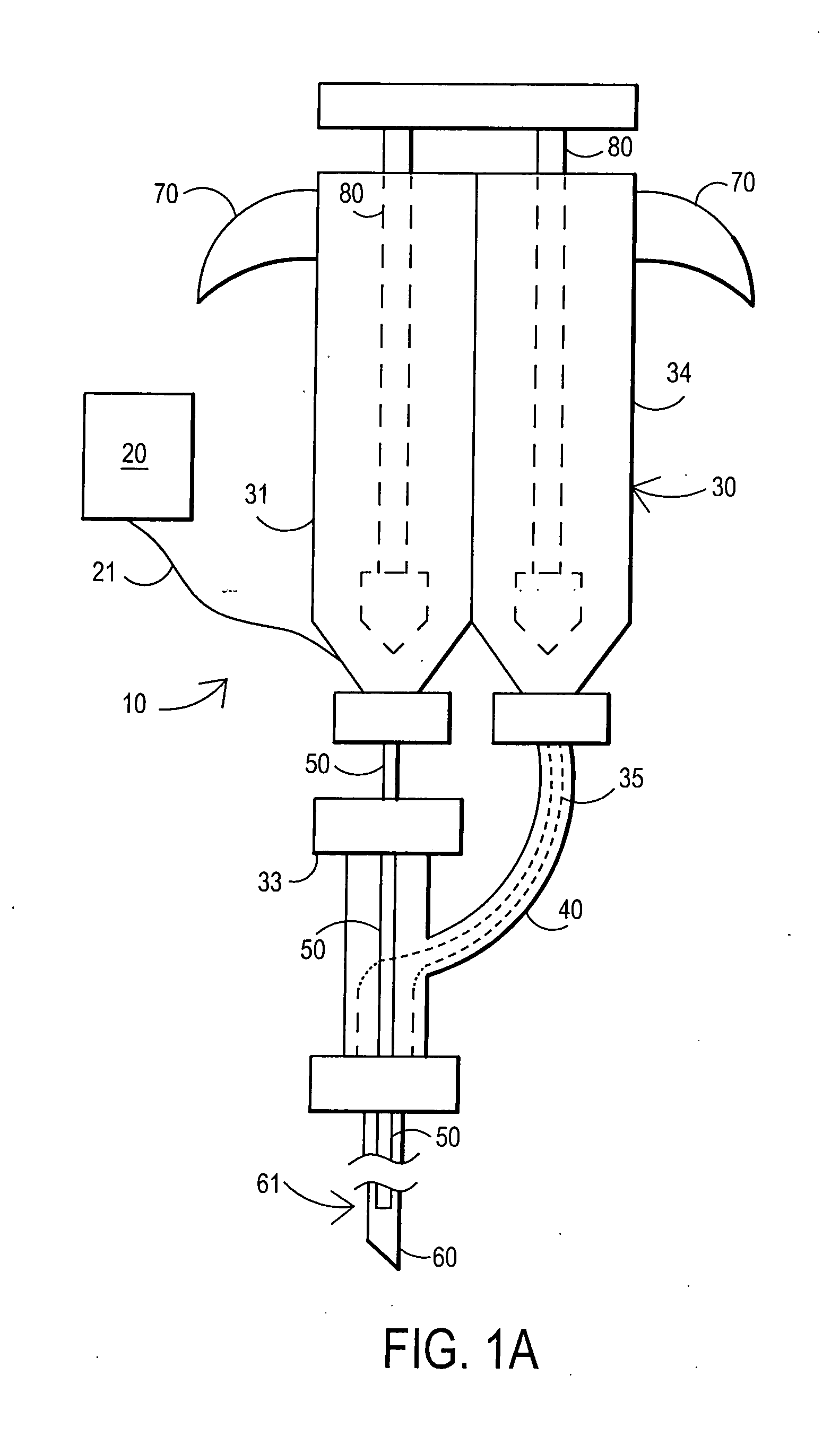
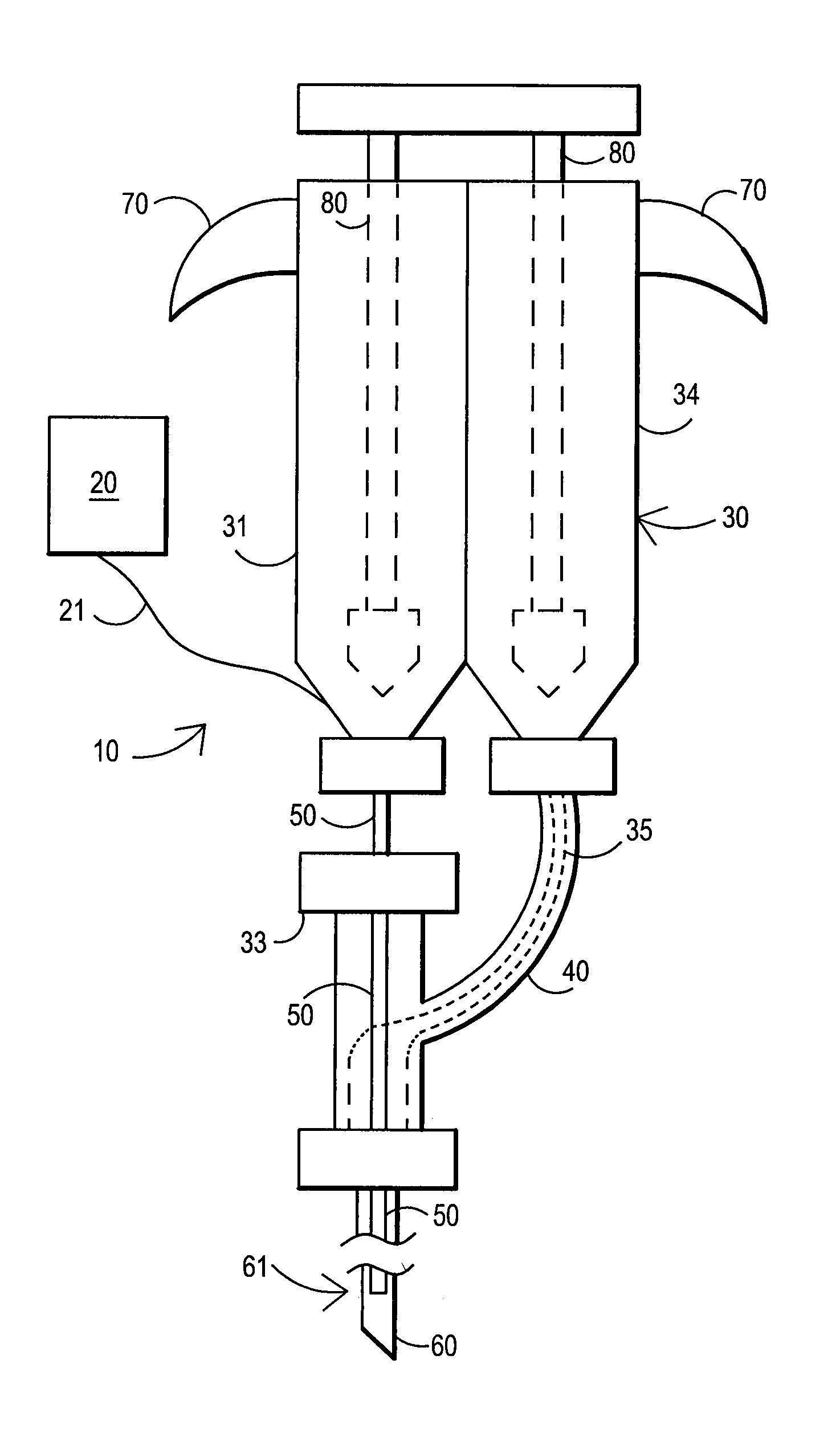
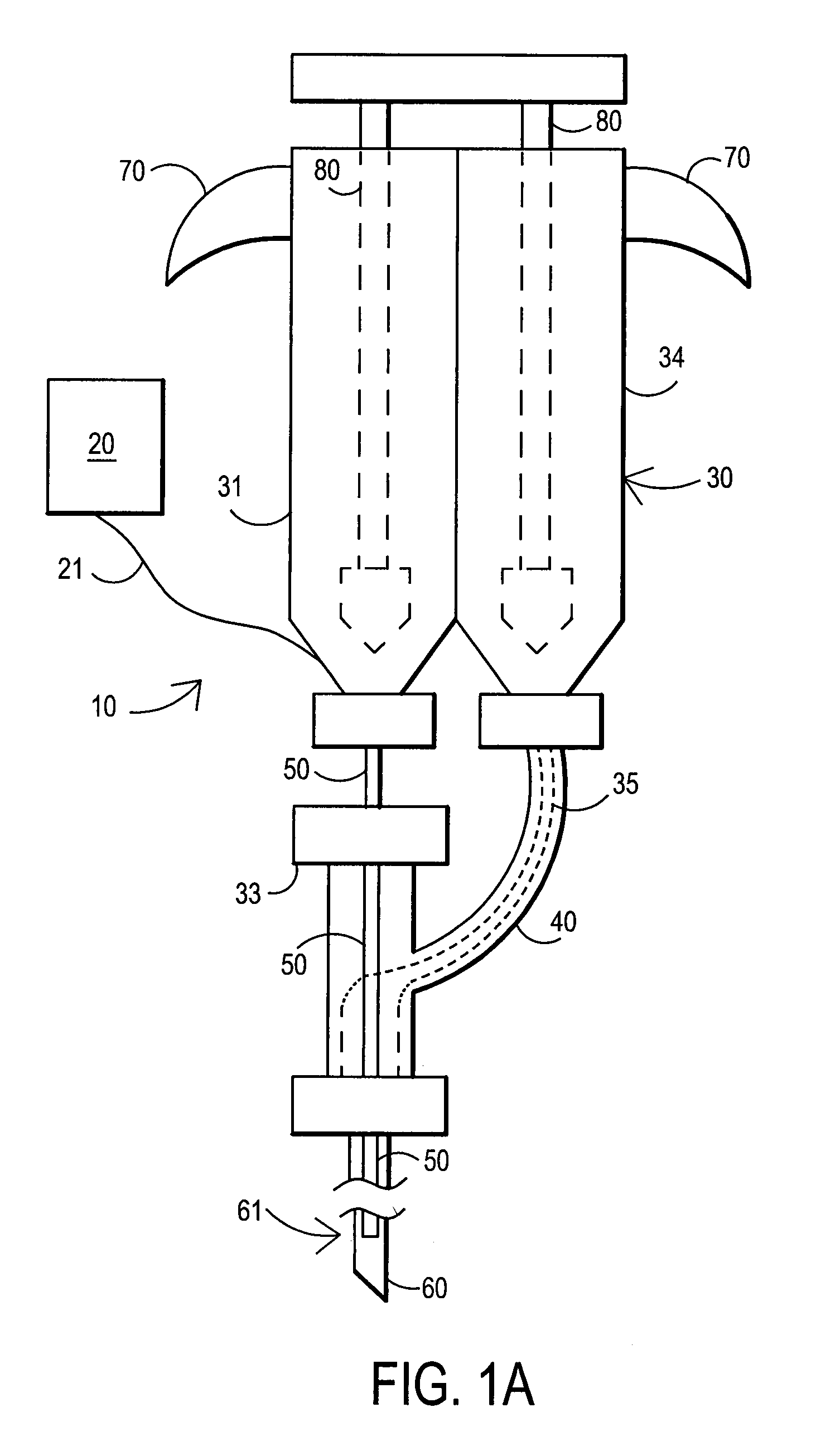
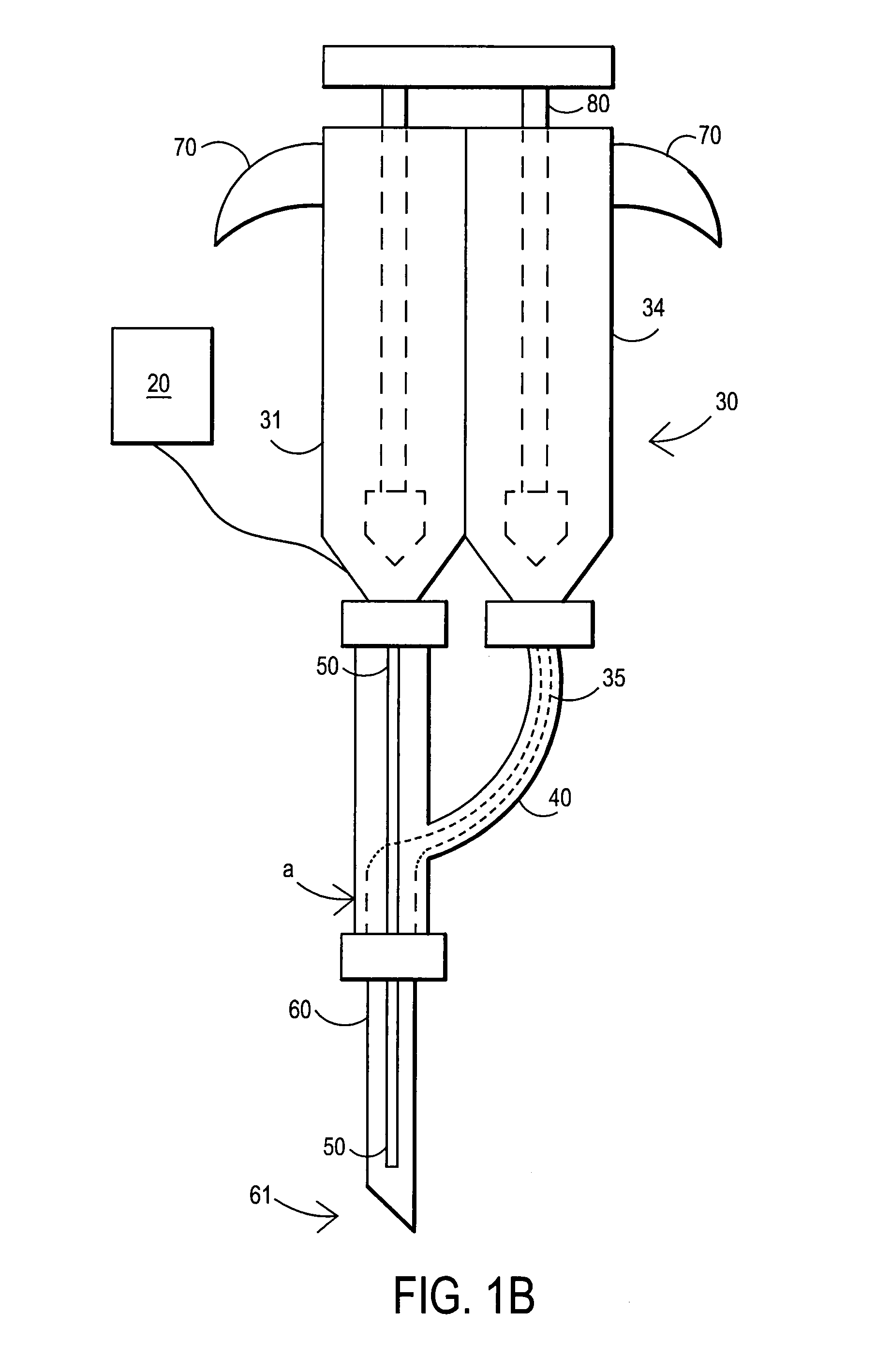
External mixer assembly
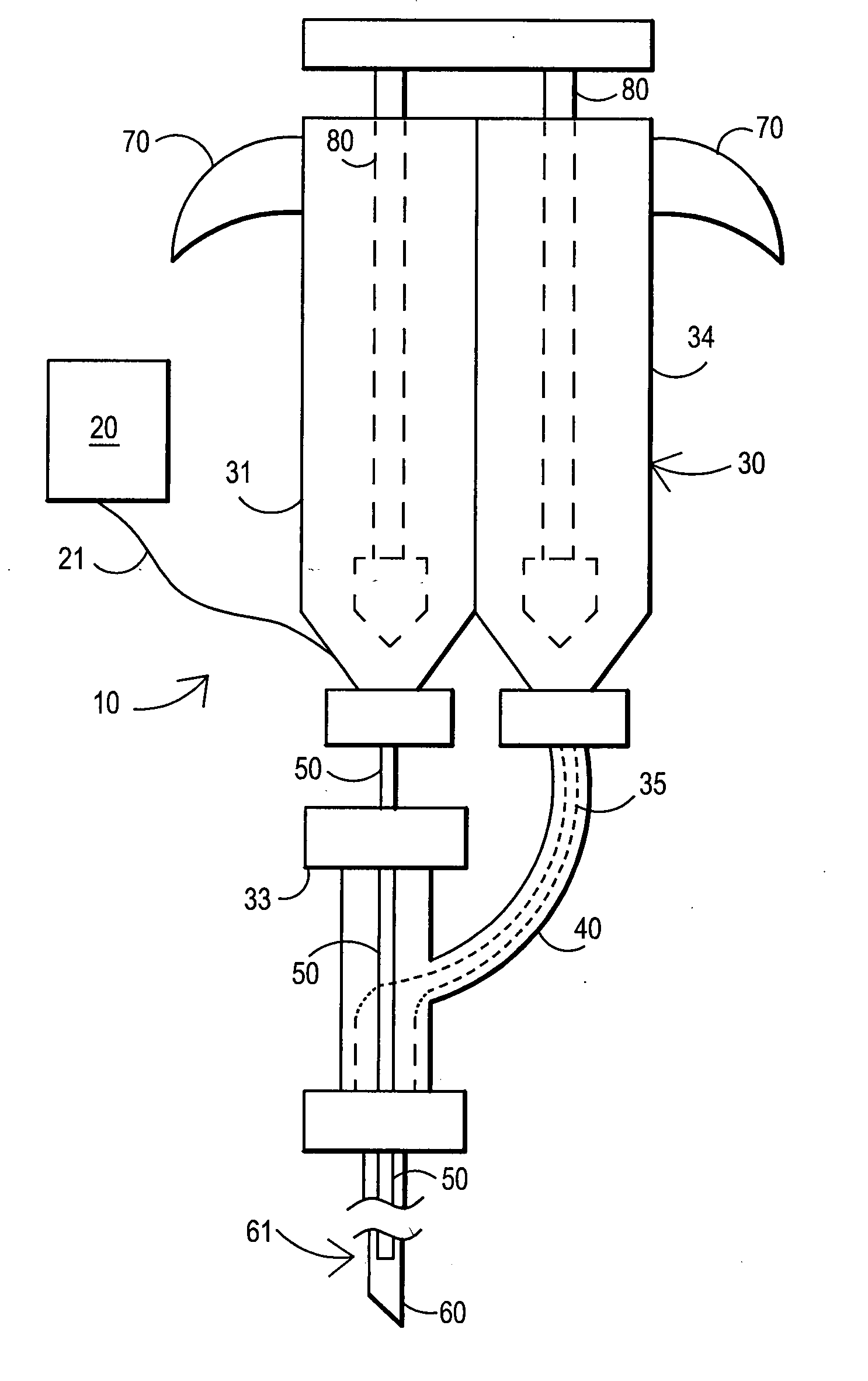
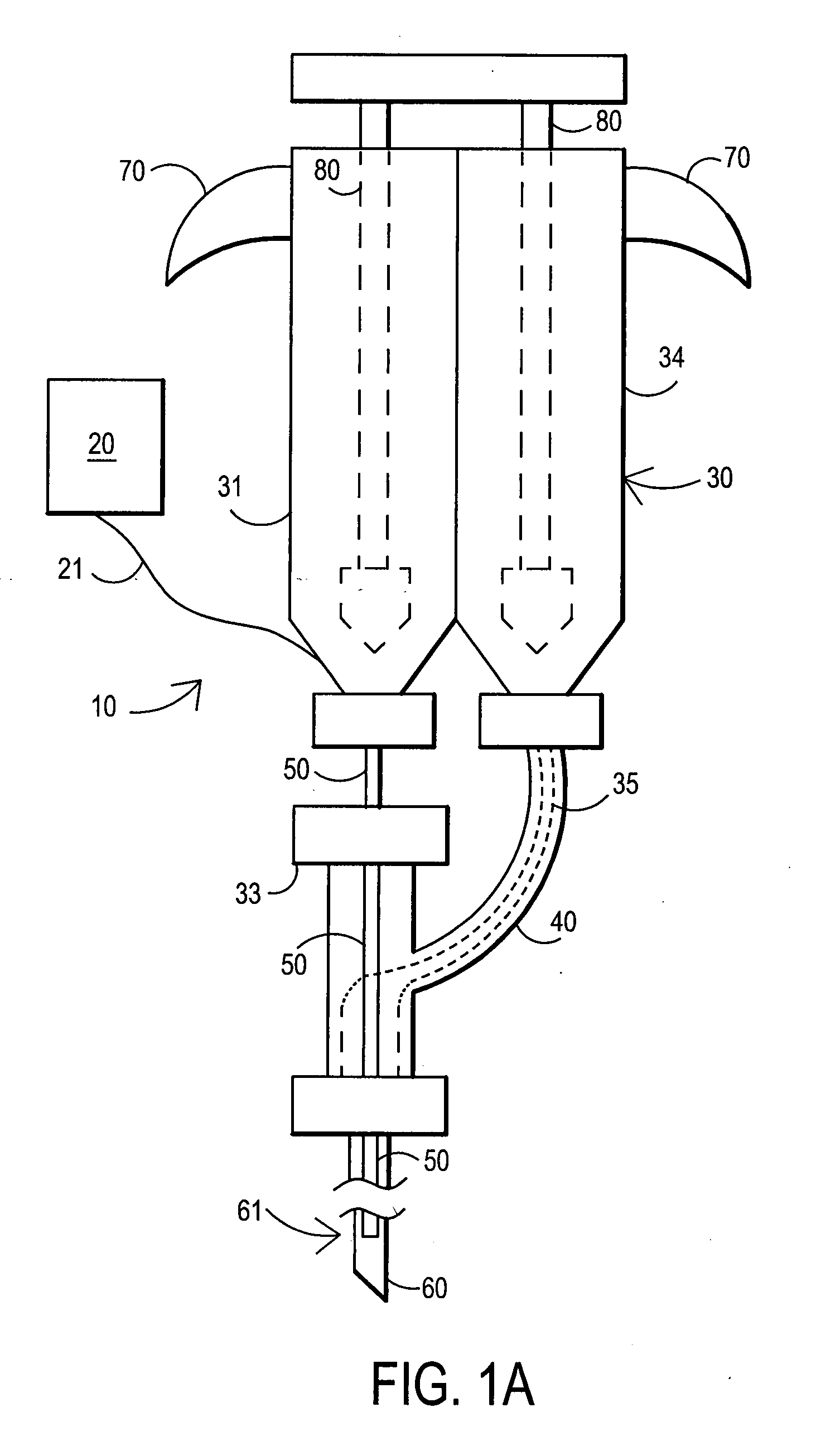
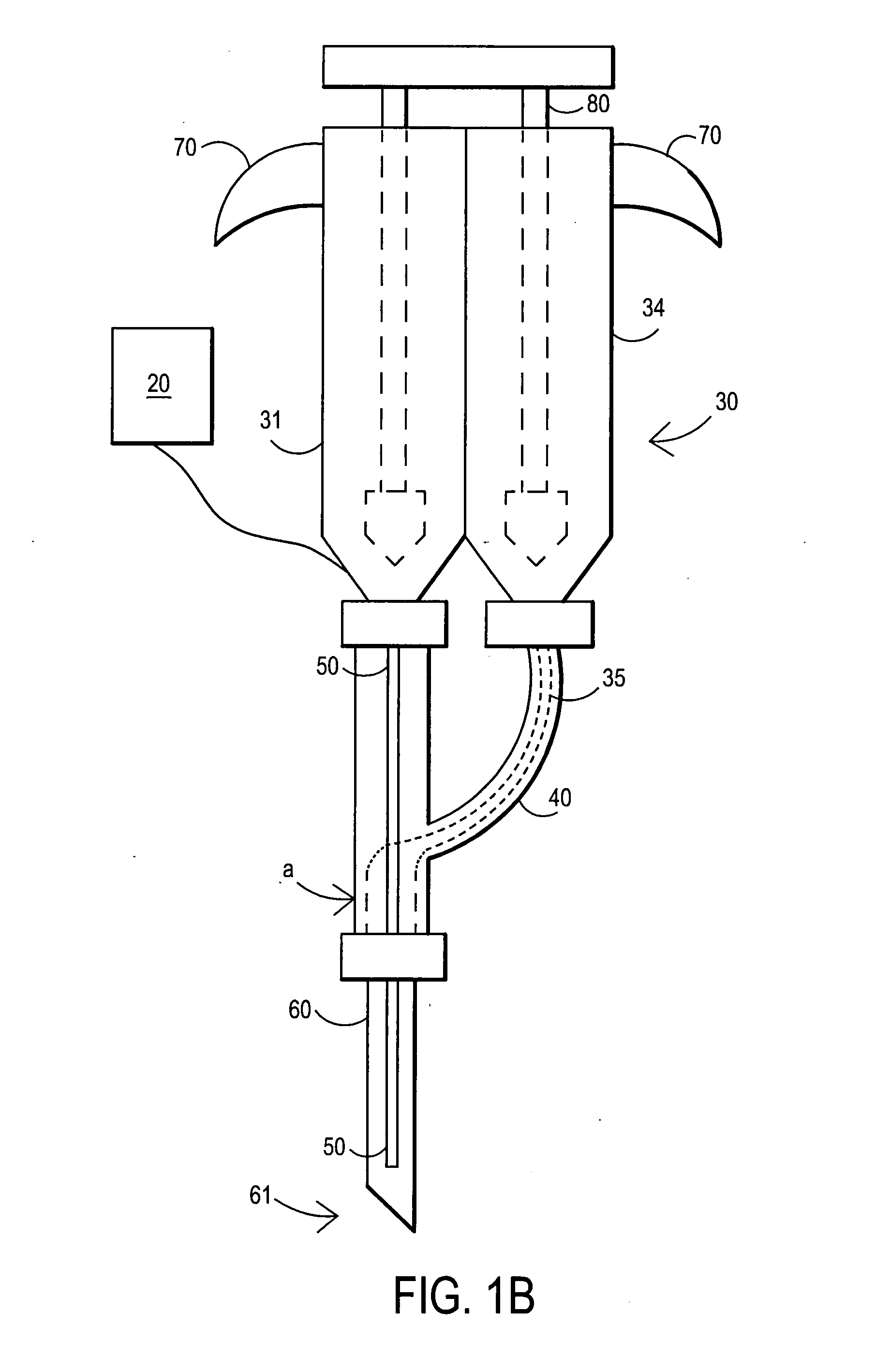
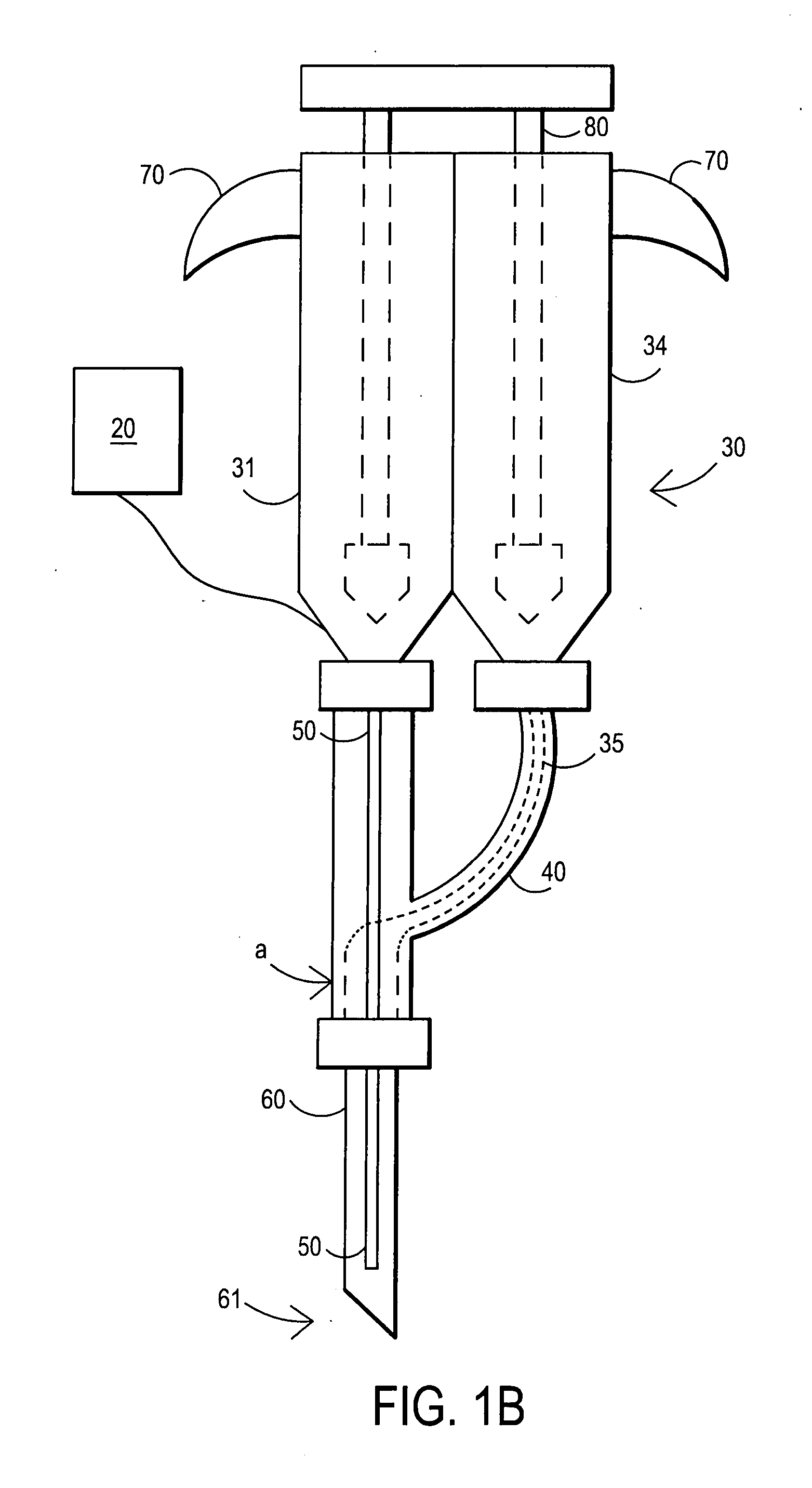
An external mixer assembly is provided which externally mixes and delivers a first and a second component of a biological adhesive to tissues or organs for sealing wounds, stopping bleeding and the like. The first and second components are mixed immediately after exiting from separate outlet ports disposed in fluid communication with component reservoirs. In on embodiment, the external mixer assembly includes a housing having a housing head for enclosing therein a first reservoir containing the first component, and a second reservoir containing the second component. The housing further includes a discharge nozzle defining a longitudinal axis for enclosing therein a conduit assembly having a first and a second conduit in communication with the first and second reservoir, respectively. A deflector assembly is connected to the discharge nozzle. The deflector assembly includes a deflector plate to provide a space for initial mixing of the first and second components. The deflector plate is oriented in generally parallel juxtaposed relation distal to the distal face of the discharge nozzle. The first and second components are preferably fibrinogen and thrombin which intermix to form a fibrin sealant.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Crosslinking agents and methods of use
Methods and compositions are provided for preparing protein concentrates from protein comprising aqueous compositions. In the subject methods, an initial protein comprising aqueous compositions, such as whole blood or a derivative thereof, is contacted with a non-protein denaturant hydrogel under conditions sufficient for a substantial amount of water present in the composition to be absorbed by the hydrogel, resulting in the production of a protein concentrate, such as a fibrinogen rich composition. Of particularl interest is the use of the subject methods to prepare fibrinogen rich compositions, where such compositions produced according to the subject invention are useful in fibrin sealants, drug delivery vehicles and in a number of other diverse applications.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
ActiveUS7189410B1Low antigenicityDecreasing thrombogenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides a fibrin sealant bandage, wherein said fibrin sealant may be supplemented with at least one composition selected from, for example, one or more regulatory compounds, antibody, antimicrobial compositions, analgesics, anticoagulants, antiproliferatives, anti-inflammatory compounds, cytokines, cytotoxins, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, demineralized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and / or using the unsupplemented or supplemented fibrin sealant bandage.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
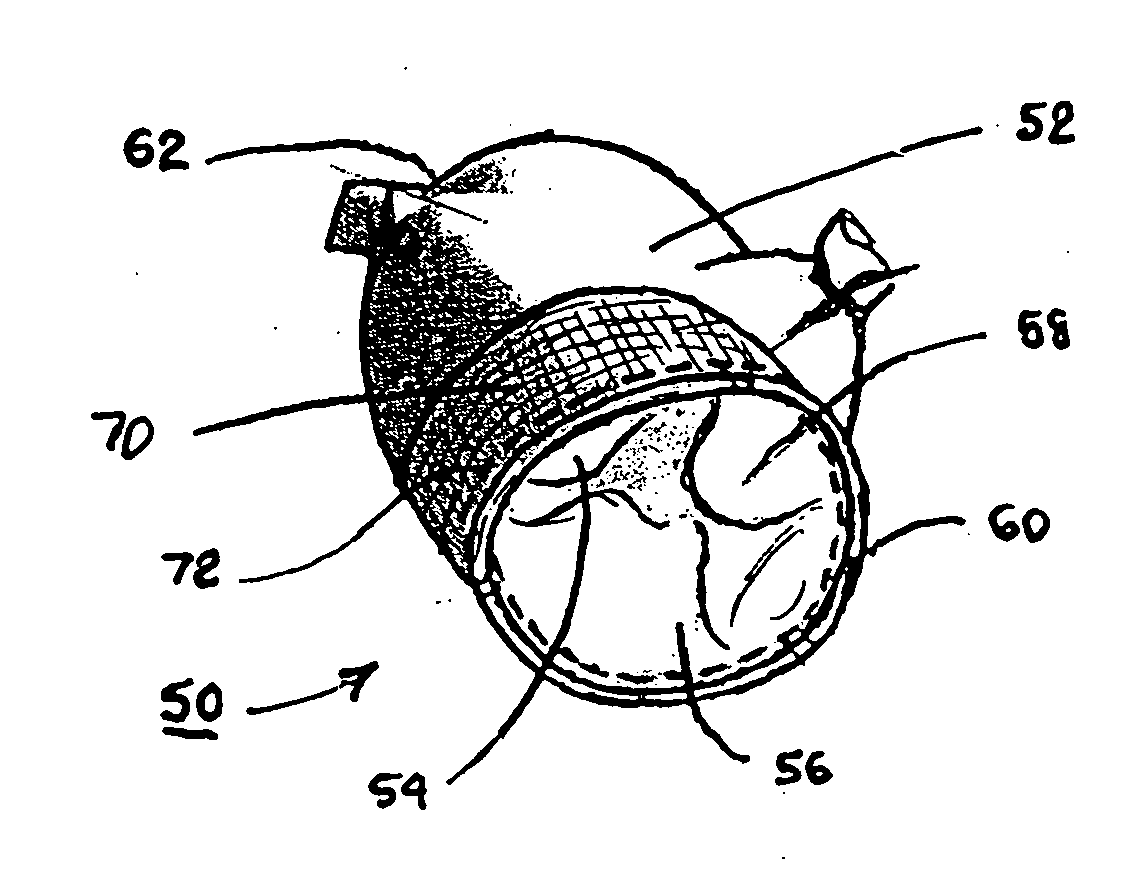
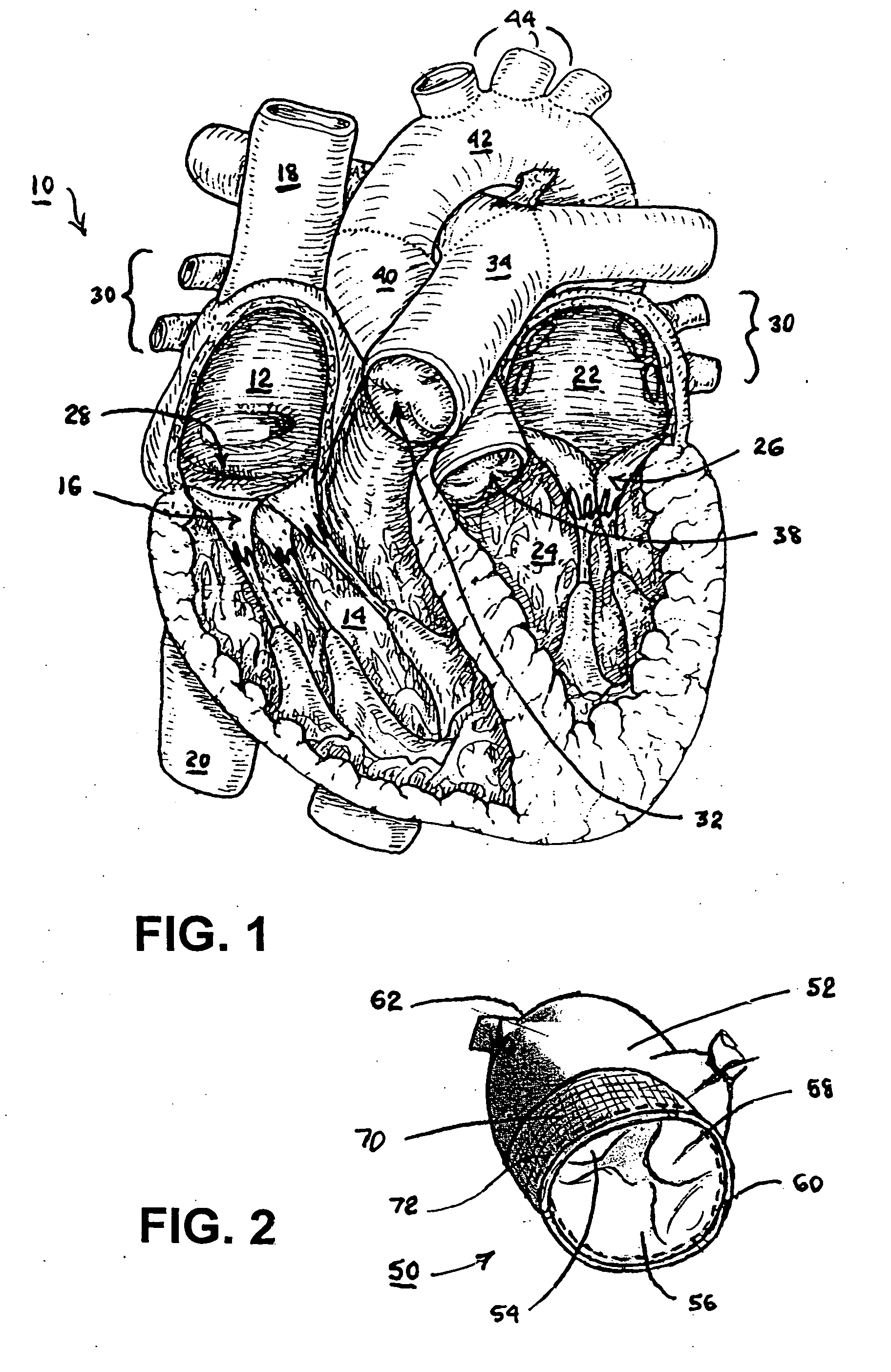
Apparatus and method for injection of fibrin sealant in spinal applications
ActiveUS20070191781A1Reduce the amount requiredGood pain reliefJet injection syringesMulti-lumen catheterMedicineBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for percutaneous delivery of a sealant comprising: at least two fluid reservoirs, an introducer needle having a distal tip that is in fluid communication with at least one reservoir, a fluid delivery tube that is in fluid communication with a second reservoir, wherein the fluid delivery tube has a tip and wherein the fluid delivery tube is configured so that the tip of the fluid delivery tube does not extend past the distal tip of the introducer needle during use.
Owner:PAUZA KEVIN
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
InactiveUSRE39321E1Decreasing thrombogenicityLow antigenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides a fibrin sealant dressing, wherein said fibrin sealant may be supplemented with at least one composition selected from, for example, one or more regulatory compounds, antibody, antimicrobial compositions, analgesics, anticoagulants, antiproliferatives, antiinflammatory compounds, cytokines, cytotoxins, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, demineralized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and / or using the unsupplemented or supplemented fibrin sealant dressing.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
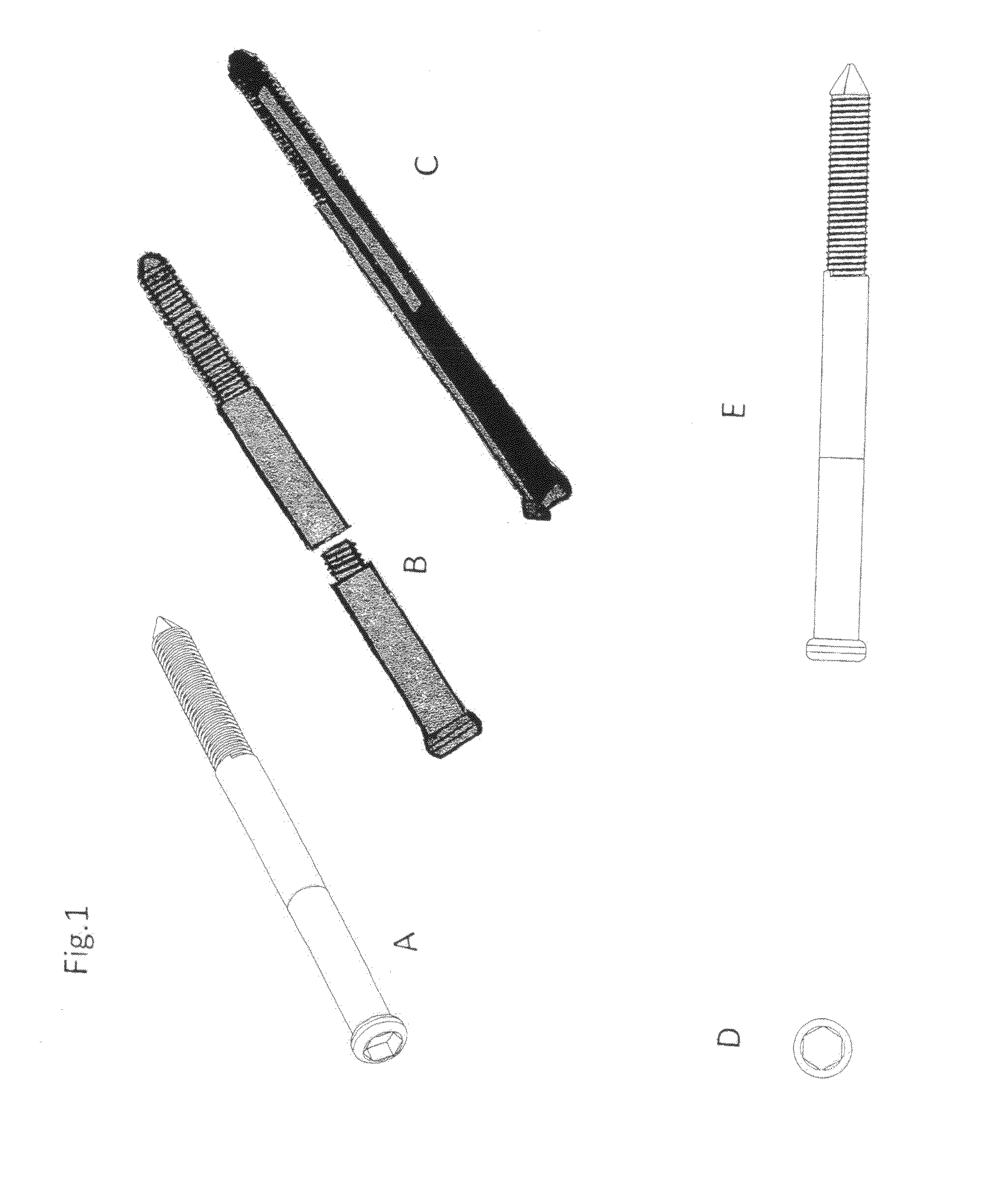
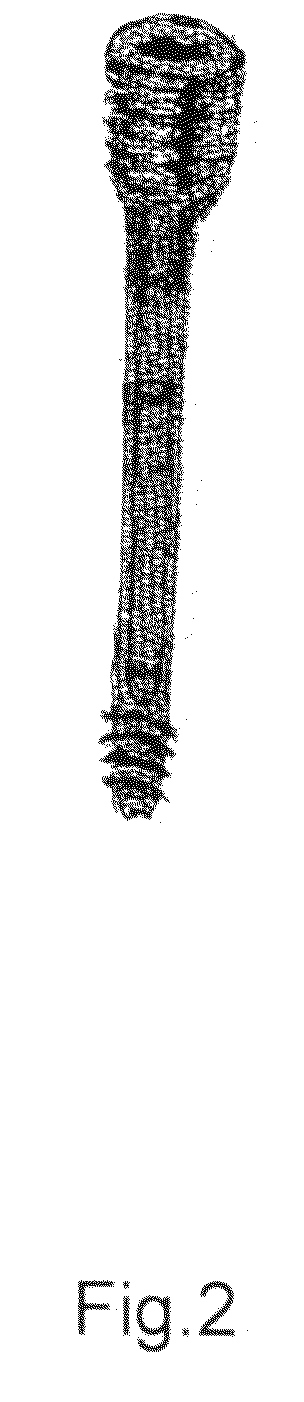
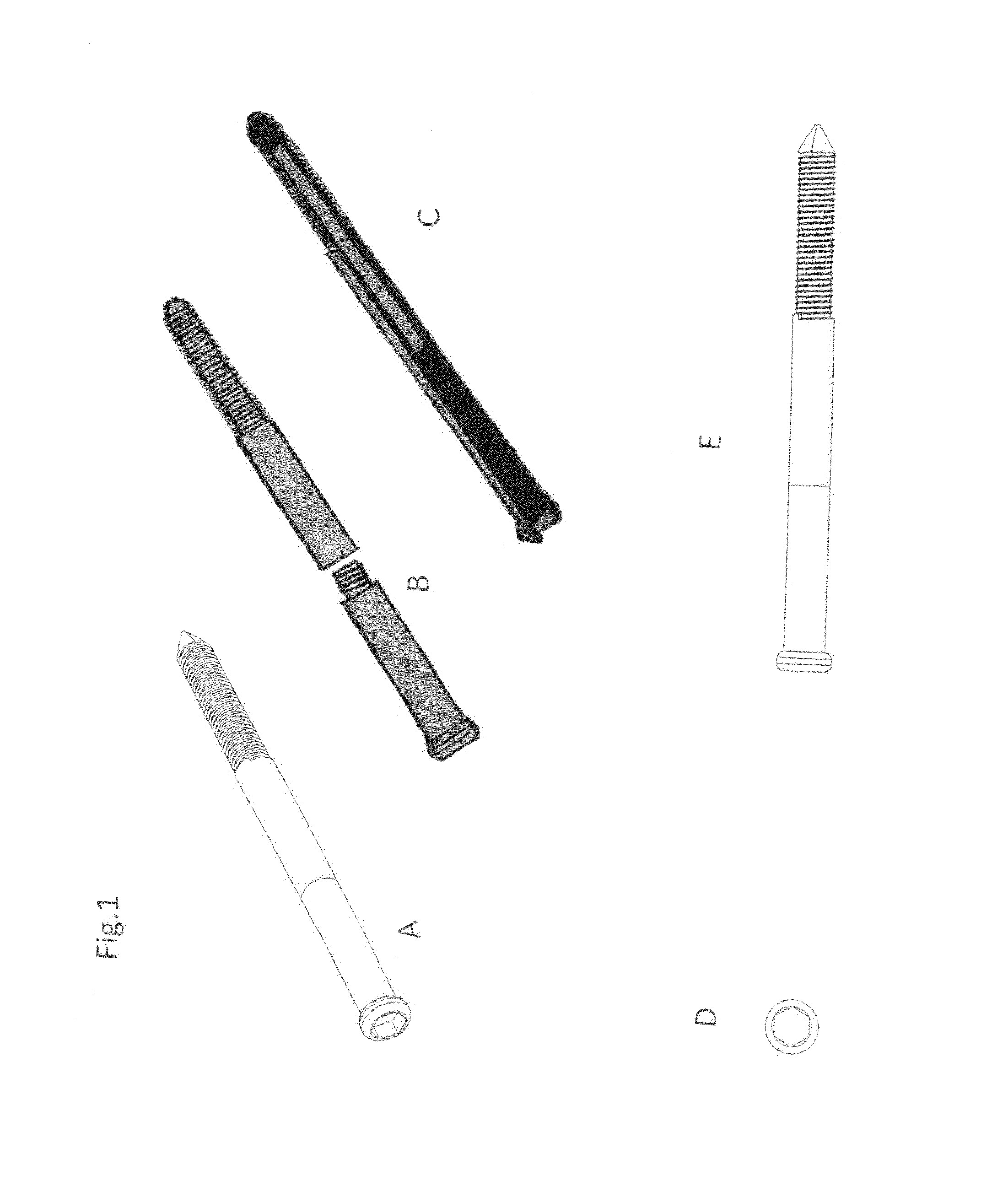
Poly-porous hollow screw for target delivery of growth factors and stem cells:the design and potential clinical application
Present invention depicts a poly-porous (micropore) hollow screws as diffusion chamber filled with core matrix for targeted delivery of growth factors and bone marrow stem cells. The screws comprise at least two parts: the distal part of the screw consists of the tip of the screw made of poly porous material and hollow inside proximally. It has threaded navel attached to the threaded nipple of the distal part of the proximal screw which has the screw head and is made of the solid material of the same kind. The screw head had hexagonal recess targeted for screw driver insertion. Assembly of screw created a chamber in the middle of the screw. The chamber is filled with core matrix consisting of gelatin nano-particles pre-impregnated with BMPs (BMP2 / BMP7 for bone or BMP12 for tendon, ligament) and fibrin sealants or Chitosan dispersed with bone marrow stem cells and / or other growth factors. Bioactive protein core material is prepared during the surgery and filled the chamber of the screw by the surgeon. Fibrin sealants or Chitosan will polymerize to form a gel to hold the growth factors and stem cell in place. The screw can be used as the lag screw or other function to provide mechanical fixation in variety of condition. Once the screw implanted in the human body, the fibrin sealant or Chitosin / gelatin nano-particles are gradually degraded and slowly release growth factors and stem cells via micropores of screw to facilitate the bone healing and regeneration. The gelatin nanoparticles and fibril sealant / or Chitosan matrix also serve as the scaffold and platform for bone in-growth to the screw or alternatively, the stem cell inside of screw can regenerate new bone, providing the biological fixation. At the mean time as the bone regenerate and / or in growth, mechanical strength of the screw increased.
Owner:WU YANGGUAN
Fibrin sealant delivery device including pressure monitoring, and method and kits thereof
InactiveUS20070213660A1Reduce the amount requiredGood pain reliefElectrotherapyMulti-lumen catheterBiomedical engineeringFibrin Seal
Apparatus for delivering biologic sealant device that includes a pressure monitor coupled to the delivery device to measure pressure within the device. A method of treating a disc using the device as well as a kit including the device is described.
Owner:PAUZA KEVIN
Recombinant fibrin chains, fibrin and fibrin-homologs
The invention is directed to fibrin materials for use in fibrin compositions and methods that avoid the need to use thrombin as an activating agent for fibrin monomer-based sealants. The invention provides for substantially pure fibrin chains, fibrin chain precursors, fibrin chains with other N-terminal extensions, fibrin monomer, fibrin-homolog and fibrin-analog. The invention further provides for variant fibrin .gamma.-chains. The variant gamma-chain contains one or more mutations and / or deletions in the C-terminal region following the coiled-coil forming region such that, when incorporated into fibrin-homolog, the homolog lacks the ability to self-polymerize but has the ability to form non-covalent bonds, and thereby form mixed polymers useful as sealants, with fibrinogen. The invention also provides nucleotide sequences encoding fibrin chains or fibrin chain variants and cells expressing fibrin chains, fibrin chain variants, fibrin monomer, fibrin precursor or fibrinogen-analog. The invention further provides a method of forming fibrin-related proteins in vitro from their component fibrin chains. The invention additionally provides a method for forming a fibrin sealant by a reacting a first fibrin-related protein that is incapable of self-polymerizing with a second fibrin-related protein that is incapable of self-polymerizing. Fibrin chains produced by methods of the present invention may be used as sources of substantially pure starting material for the production of important fibrin-derived factors that regulate angiogenesis, platelet aggregation, and other physiological processes.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Use of a regenerative biofunctional collagen biomatrix for treating visceral or parietal defects
ActiveUS20090142396A1Avoiding and inhibiting persistent tissue leakImprove lung functionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical treatmentTissue defect
Techniques for treating visceral or parietal membrane and tissue defects include the application of a collagen biomatrix to the defect to repair and regenerate a visceral or parietal membrane, for example in patients suffering tissue defects or undergoing visceral or parietal surgical treatment. Such approaches avoid persistent tissue leaks and their consequences such as fluid leaks and air leaks. The use of collagen biomatrix, optionally in conjunction with a fibrin sealant, an anti-adhesive, or both, can minimize tissue leaks or fluid leaks in injured patients suffering tissue defects or subjects undergoing surgery such as visceral or parietal resections and other operations.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
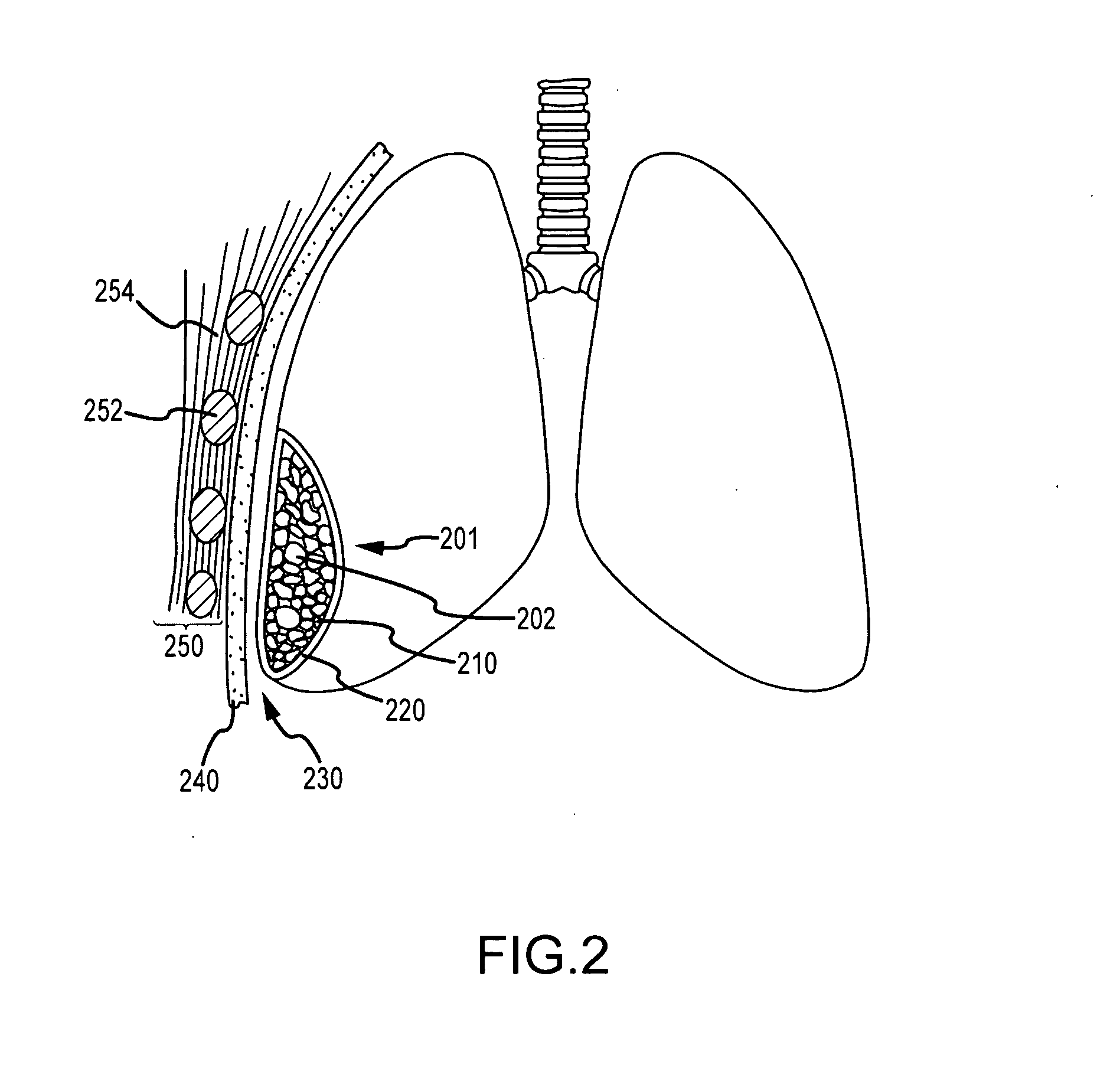
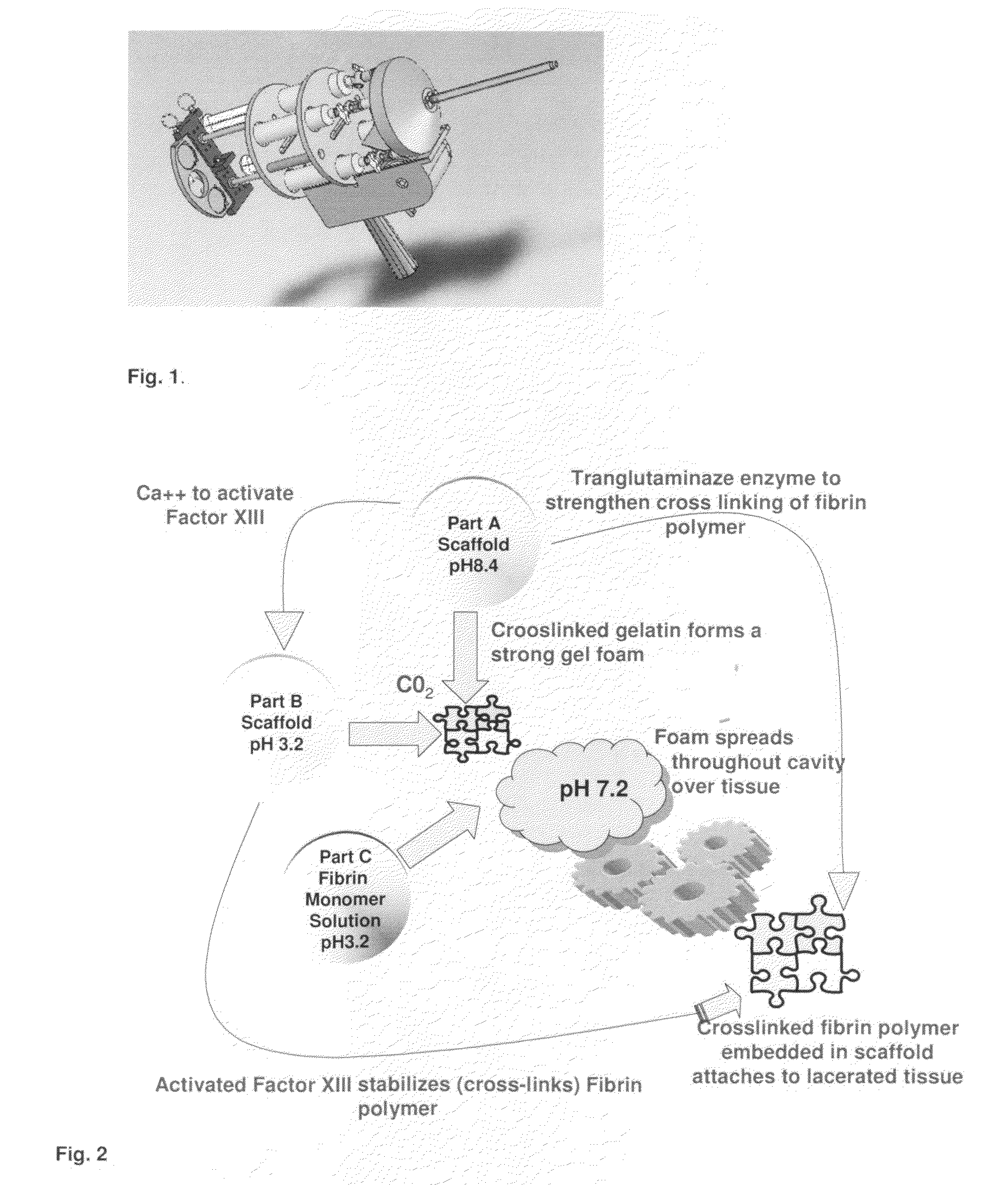
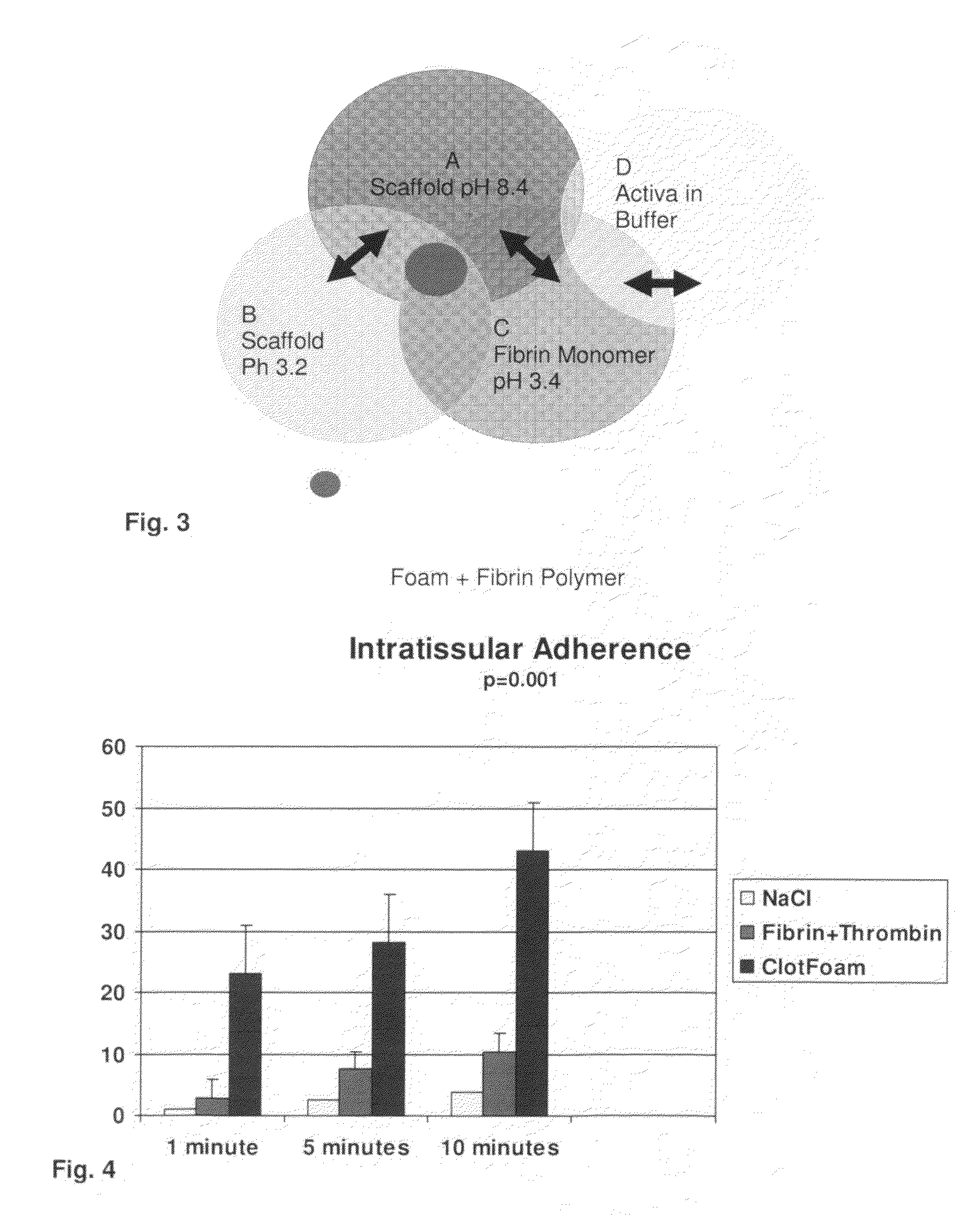
Tissue Sealant for Use in Non Compressible Hemorrhage
InactiveUS20110066182A1Excellent hemostatic agent candidateLeast riskSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryTissue sealantThoracic cavity
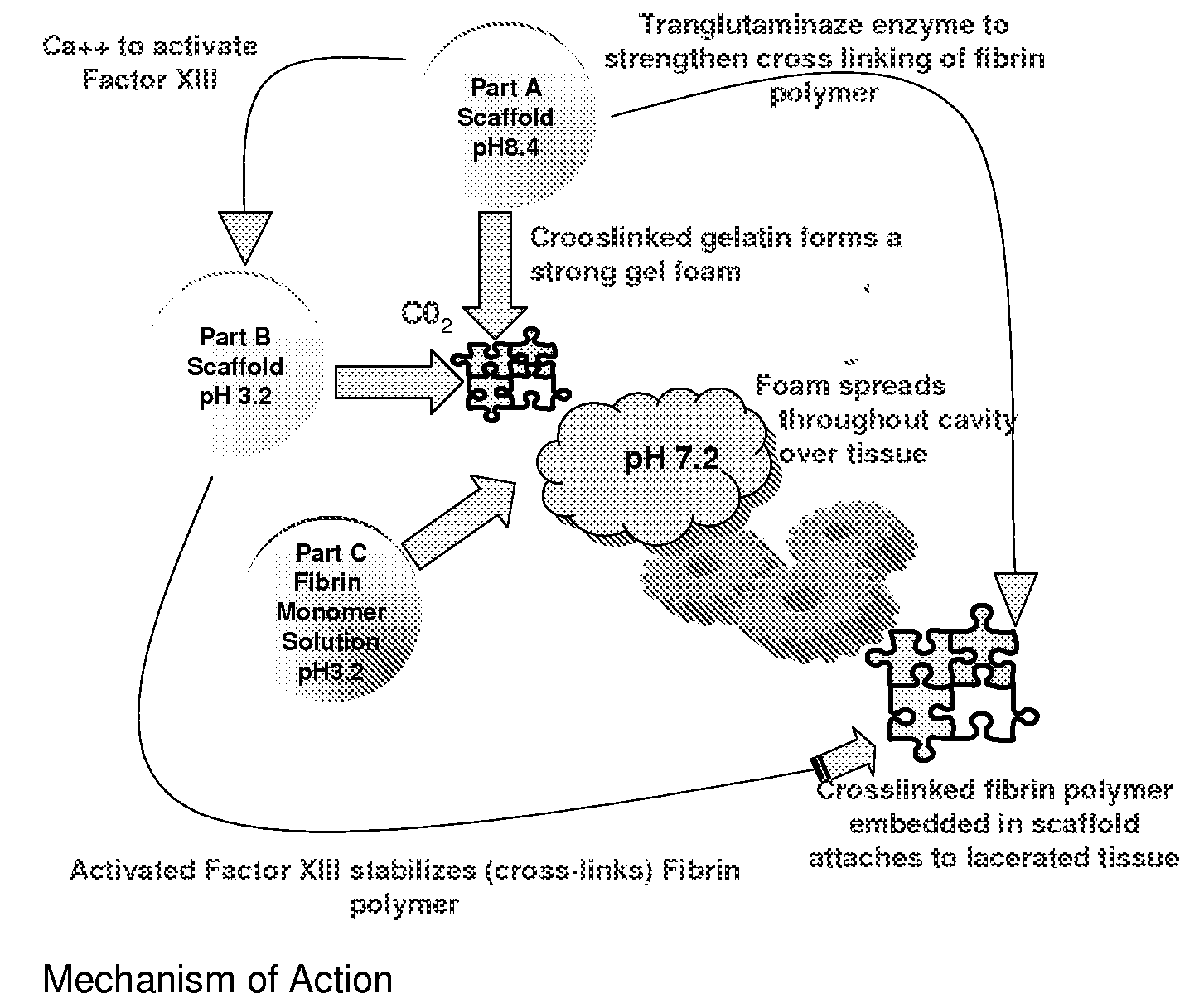
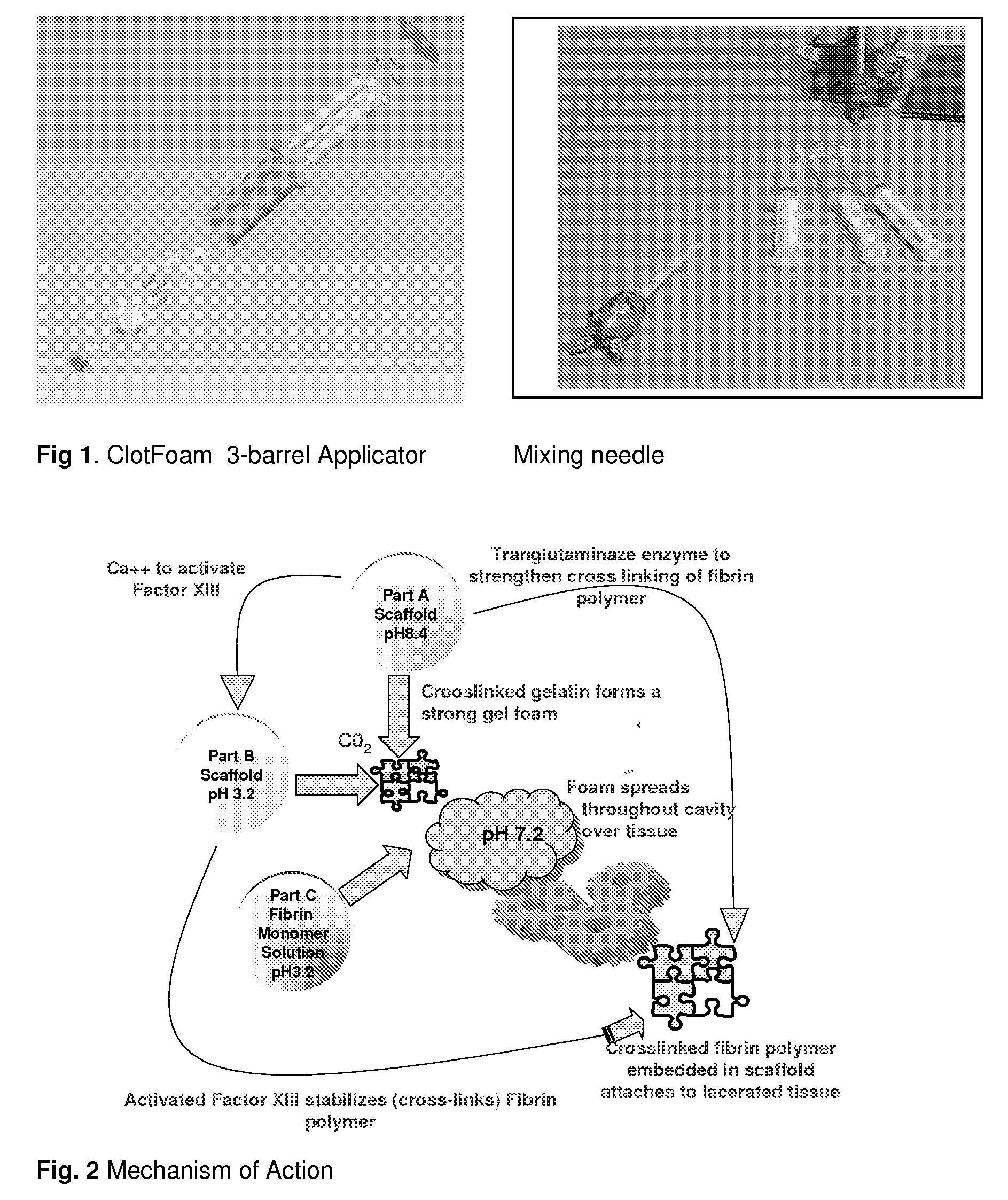
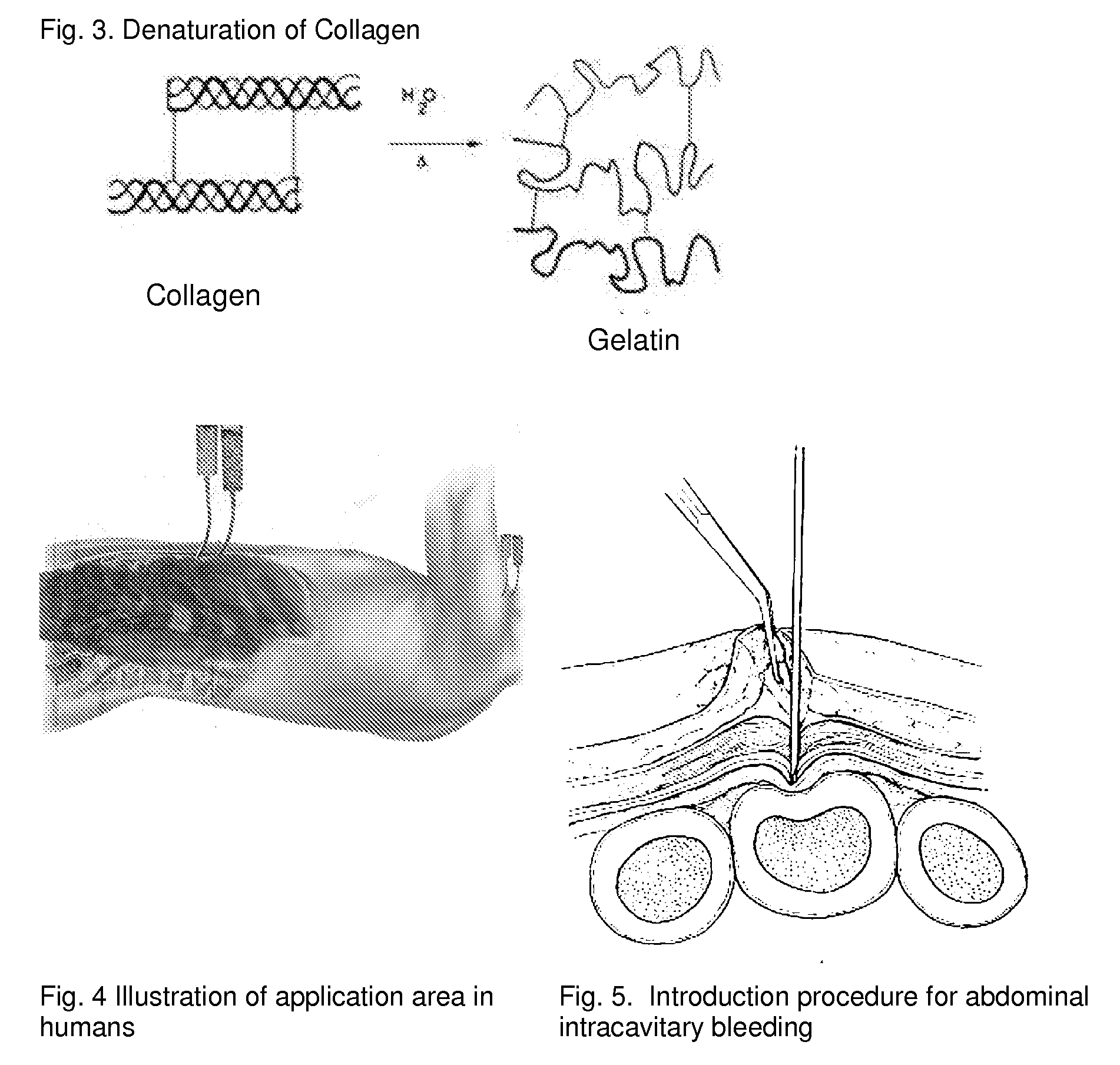
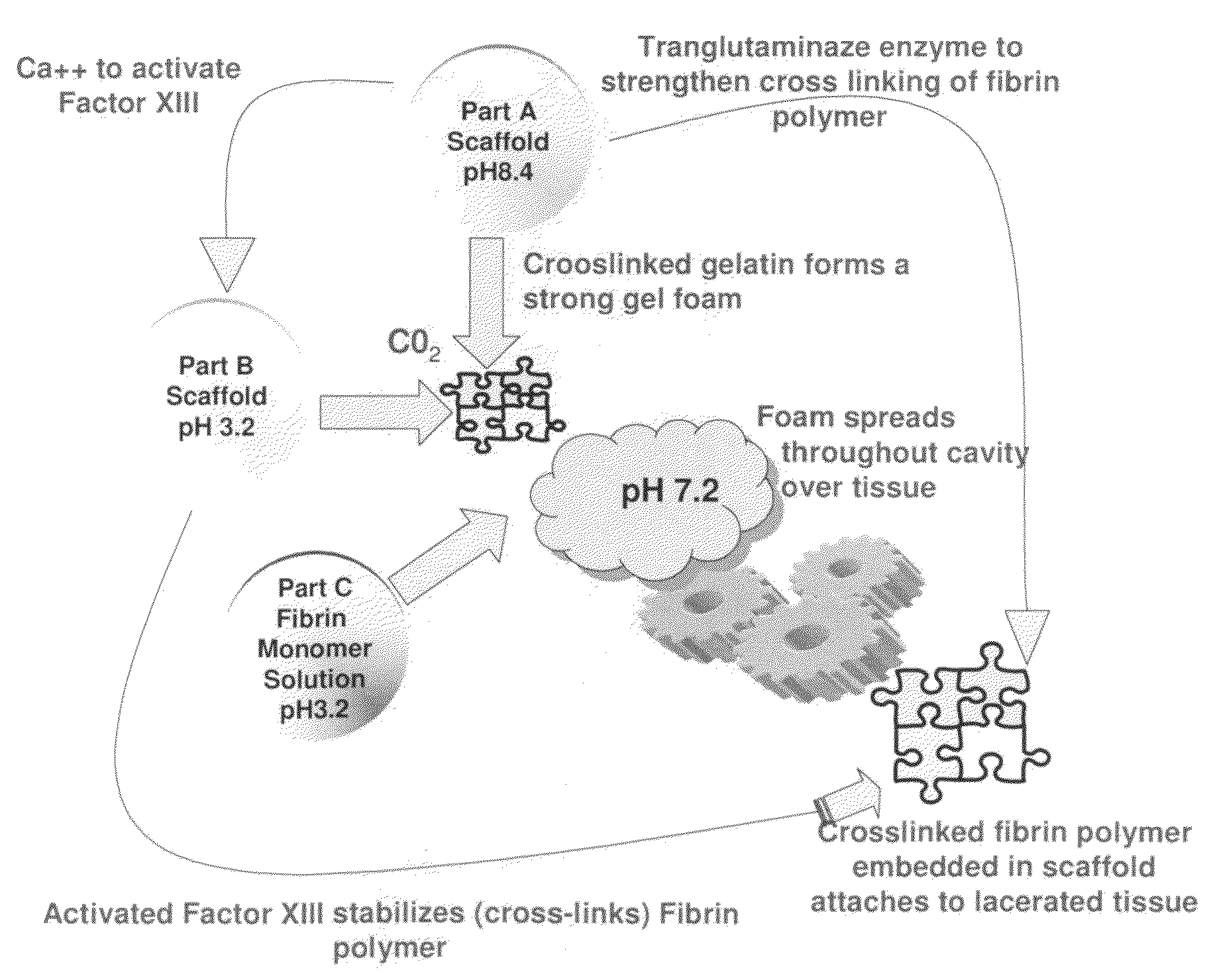
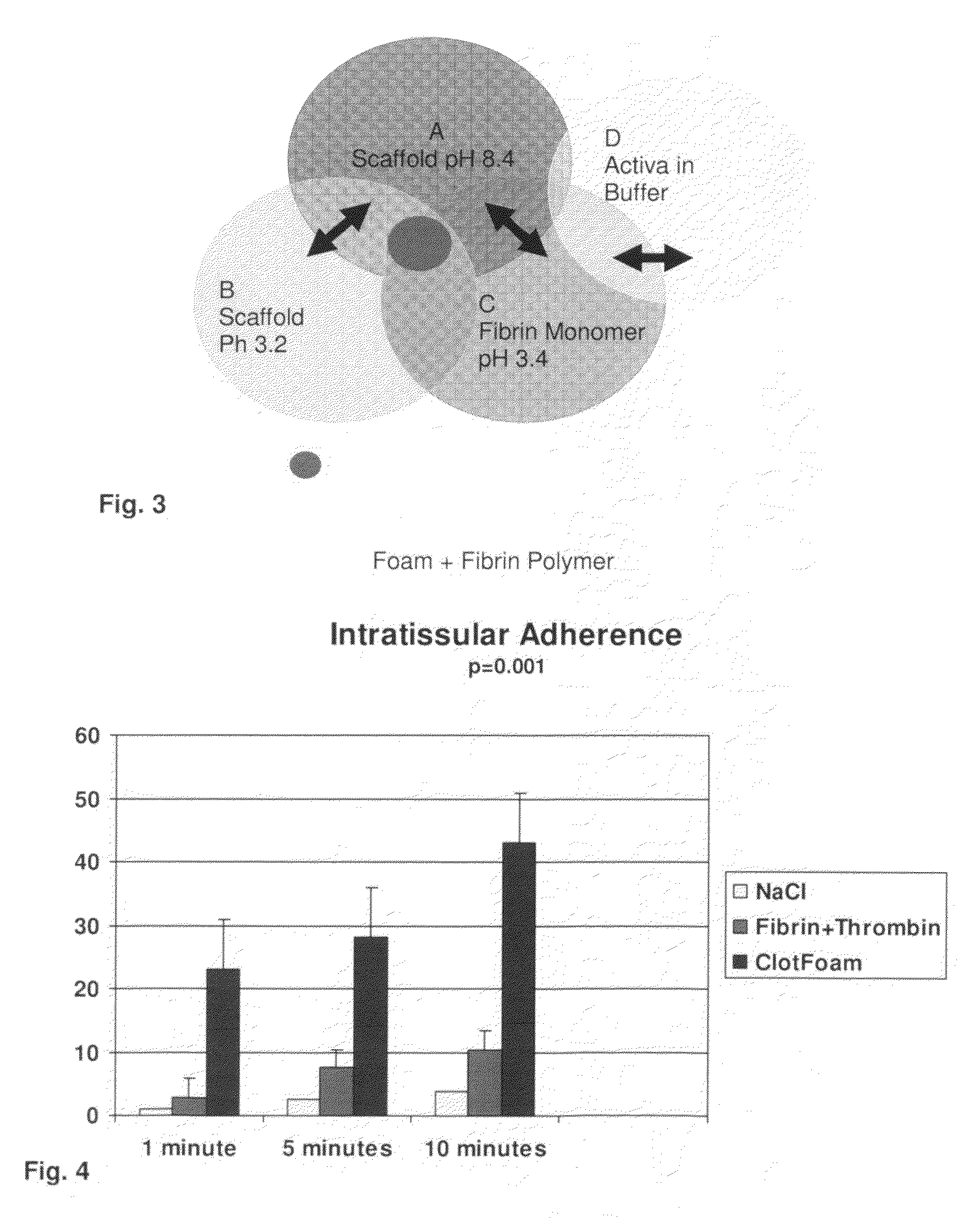
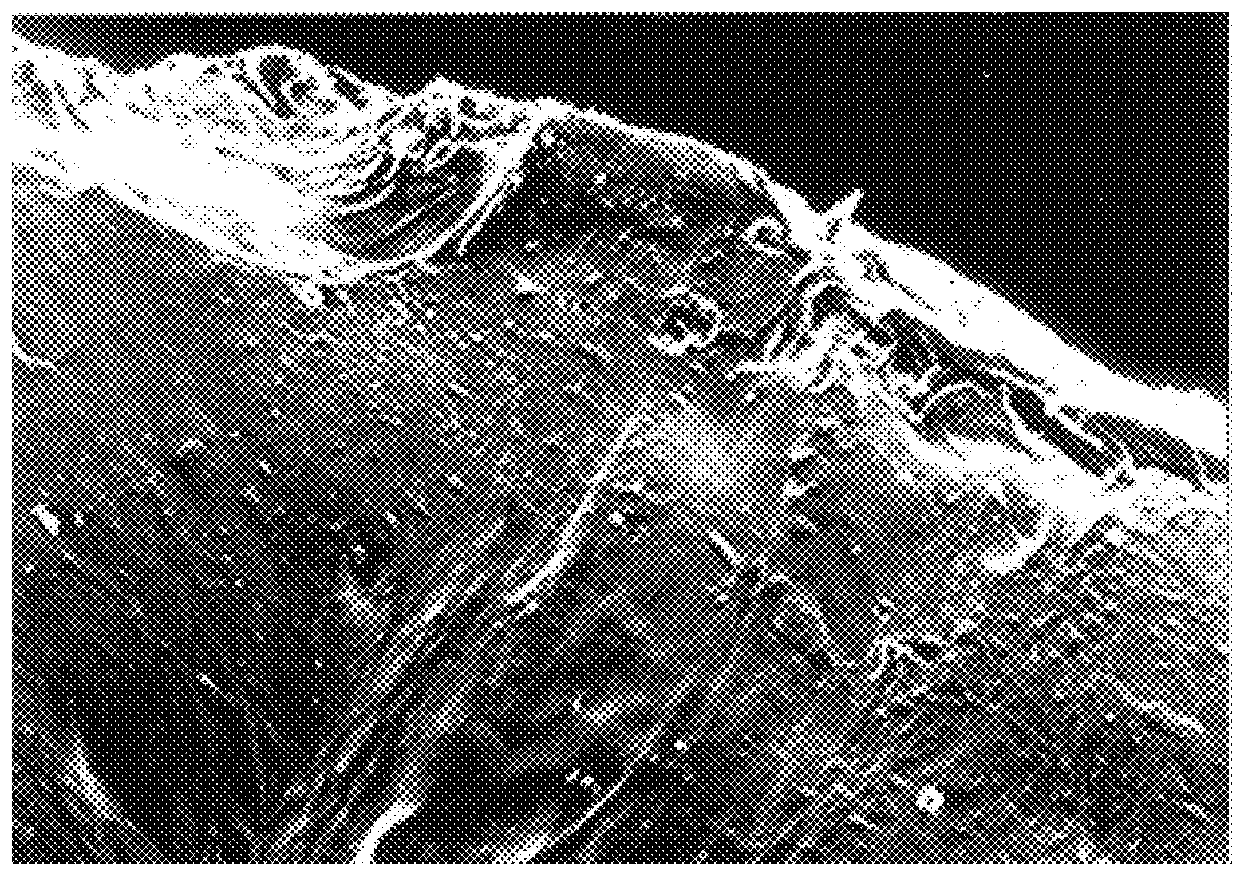
ClotFoam is a surgical sealant and hemostatic agent designed to be used in cases of non-compressible hemorrhage. It can be applied in the operating room through laparoscopic ports, or directly over lacerated tissue in laparotomy procedures or outside the operating room through a mixing needle and / or a spray injection method following abdominal, chest, extremities or other intracavitary severe trauma to promote hemostasis. Its crosslinking technology generates an adhesive three-dimensional polymeric network or scaffold that carries a fibrin sealant required for hemostasis. When mixed, Clotfoam produces a foam that spreads throughout a body cavity reaching the lacerated tissue to seal tissue and promote the coagulation cascade.The viscoelastic attachment properties of the foam as well as the rapid formation of a fibrin clot that ensure that the sealant remains at the site of application without being washed away by blood or displaced by movement of the target tissue .
Owner:FALUS GEORGE D PHD
Autologous fibrin sealant and method for making the same
InactiveUS20050152886A1Eliminate riskBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBlood plasmaPlasma rich platelet
The present relates to an autologous bioadhesive sealant composition or fibrin glue prepared by a two-phase method, wherein all of the blood components for the bioadhesive sealant are derived from a patient to whom the bioadhesive sealant will be applied. A platelet rich plasma and a platelet poor plasma are formed by centrifuging a quantity of anticoagulated whole blood that was previously drawn from the patient. In one embodiment, the platelet rich plasma is divided into two portions. In phase one, a compound that reverses the effect of the anticoagulant is added to the first portion and a clot is allowed to form. The clot is then triturated, and the resulting serum containing autologous thrombin is collected. In phase two, the serum obtained from phase one is mixed with the second portion of the platelet rich plasma to form the bioadhesive sealant of the present invention.
Owner:ARTERIOCYTE MEDICAL SYST
Fibrin sealants and platelet concentrates applied to effect hemostasis at the interface of an implantable medical device with body tissue
InactiveUS20060190017A1Stem bleedingAdvantageously employedHeart valvesAbsorbent padsParenchymaInternal bleeding
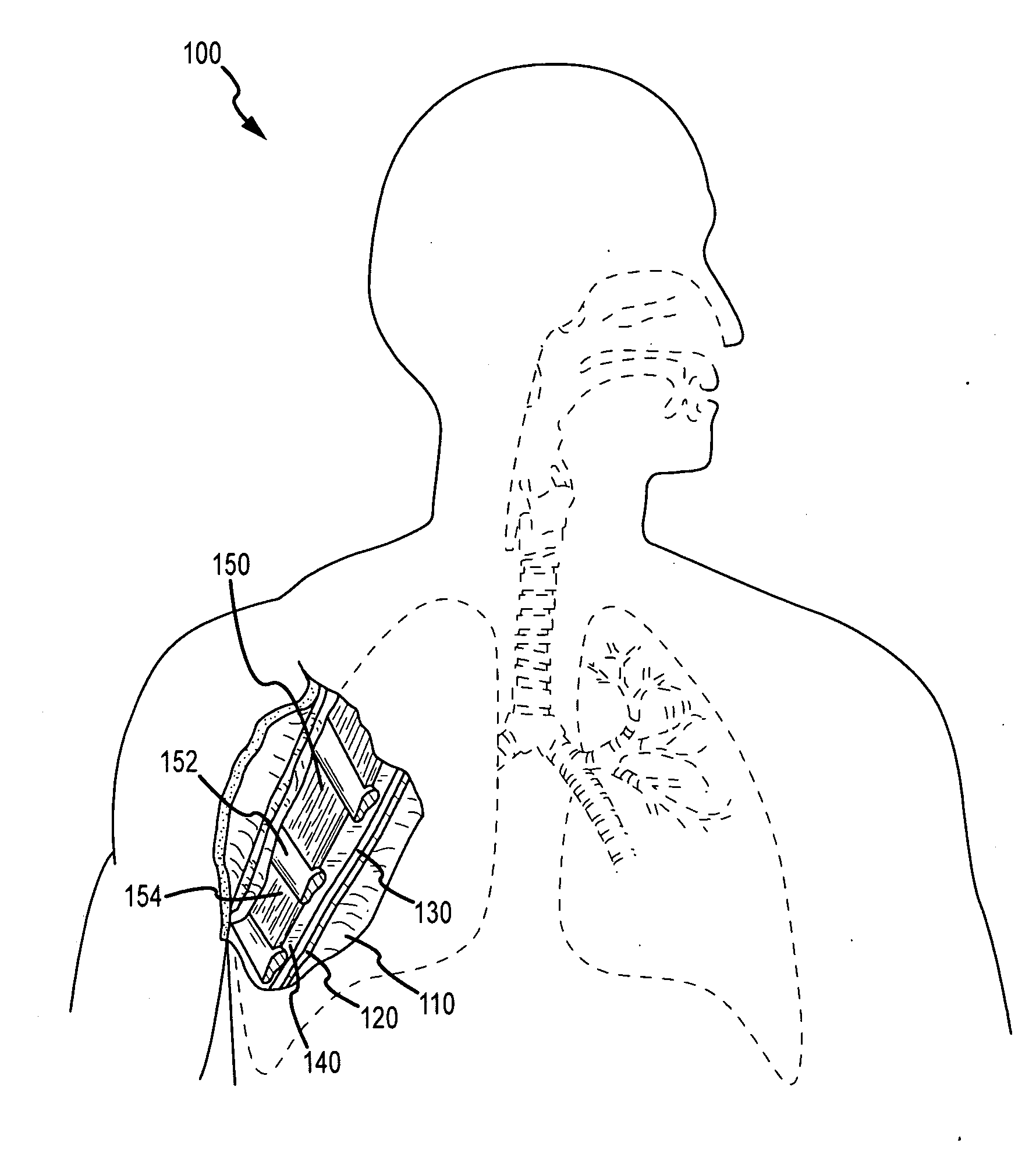
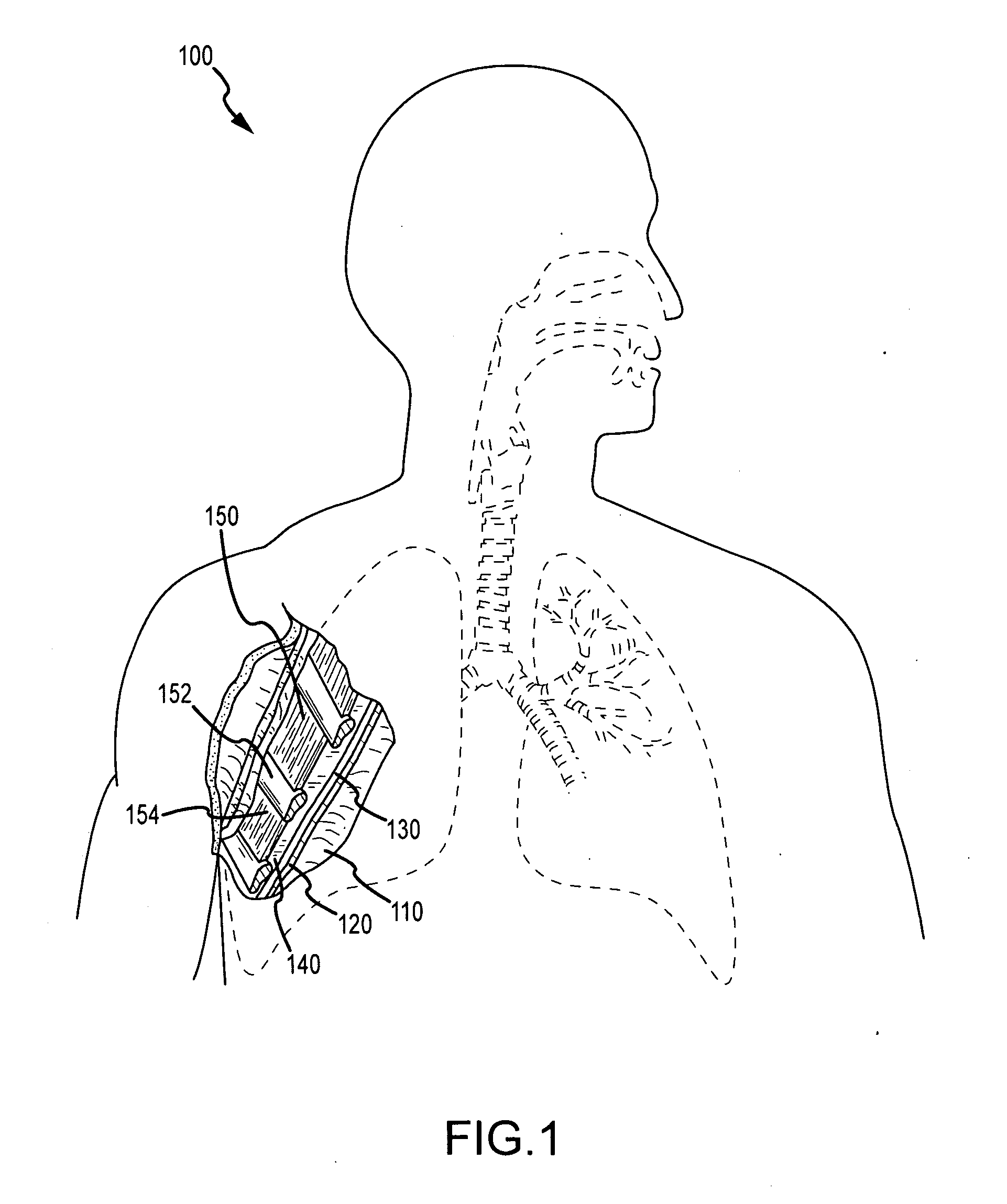
Surgical methods of and kits for applying and stabilizing a mass of fibrin sealant or platelet concentrate at the site of surgical attachment of an implantable medical device to effect hemostasis to stem internal bleeding at the site of surgical attachment are disclosed. A mass of fibrin sealant or platelet concentrate is applied onto a porous fabric, whereby the mass is supported in the interstices or pores of the fabric, and the supported mass is applied against the site of high pressure blood leakage. The supported mass achieves hemostasis as it does not wash away from the site. The present invention is particularly useful to effect hemostasis at sutures and suture holes extending through thin-walled tissue valves and grafts when such tissue valves or grafts are sutured in place, particularly at high blood pressure sites as at the valve annulus of the aortic valve or the aorta.
Owner:ARTERIOCYTE MEDICAL SYST
Dry powder fibrin sealant
ActiveUS8846105B2Increase absorbanceSpeed up the flowSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrinogenFibrin adhesive
Owner:MALLINCKRODT PHARMA IP TRADING D A C
Formulations for Wound Therapy
InactiveUS20140369991A1Enhance powder flowImprove wettabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicineWound therapy
The present invention relates to novel formulations comprising a dry powder fibrin sealant comprised a mixture of fibrinogen and / or thrombin, for use in the treatment of wounds or injuries, in particular for use as a topical hemostatic composition or for surgical intervention.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT PHARMA IP TRADING D A C
Method to produce fibrin monomer in acid media for use as tissue sealant
InactiveUS8367802B2Prevent re-bleedingReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFiberTissue sealant
A hemostatic agent designed for use in cases of non-compressible hemorrhage. It can be applied through a mixing needle and / or a spray injection method following abdominal, chest, extremities or other intracavitary severe trauma to promote hemostasis, or it can be used for laparoscopic procedures or other surgical procedures in which compression is not possible or recommended. Its crosslinking technology generates an adhesive three-dimensional polymeric network or scaffold that carries a fibrin sealant required for hemostasis. When mixed, it produces a foam that spreads throughout a body cavity reaching the lacerated tissue to seal tissue and promote the coagulation cascade. The fibrin components are produced by a novel dialysis method which does not present thrombin to the immune system and can be maintained in solution for six weeks without significant proteolytic degradation.
Owner:MEDVED LEONID PHD +1
Tissue sealant for use in noncompressible hemorrhage
InactiveUS20100256671A1Excellent hemostatic agent candidateLeast riskBiocidePowder deliveryLaparoscopyTissue sealant
ClotFoam is an hemostatic agent designed for non-compressible hemorrhage. It can be applied outside the operating room through a mixing needle and / or a spray injection method following abdominal, chest, extremities or other intracavitary severe trauma to promote hemostasis, or it can be used in the operating room for laparoscopic procedures or other surgical procedures in which compression is not possible or recommended. Its crosslinking technology generates an adhesive three-dimensional polymeric network or scaffold that carries a fibrin sealant required for hemostasis. When mixed, Clotfoam produces a foam that spreads throughout a body cavity reaching the lacerated tissue to seal tissue and promote the coagulation cascade. The viscoelastic attachment properties of the foam as well as the rapid formation of a fibrin clot that ensure that the sealant remains at the site of application without being washed away by blood or displaced by movement of the target tissue .
Owner:BIOMEDICA MANAGEMENT
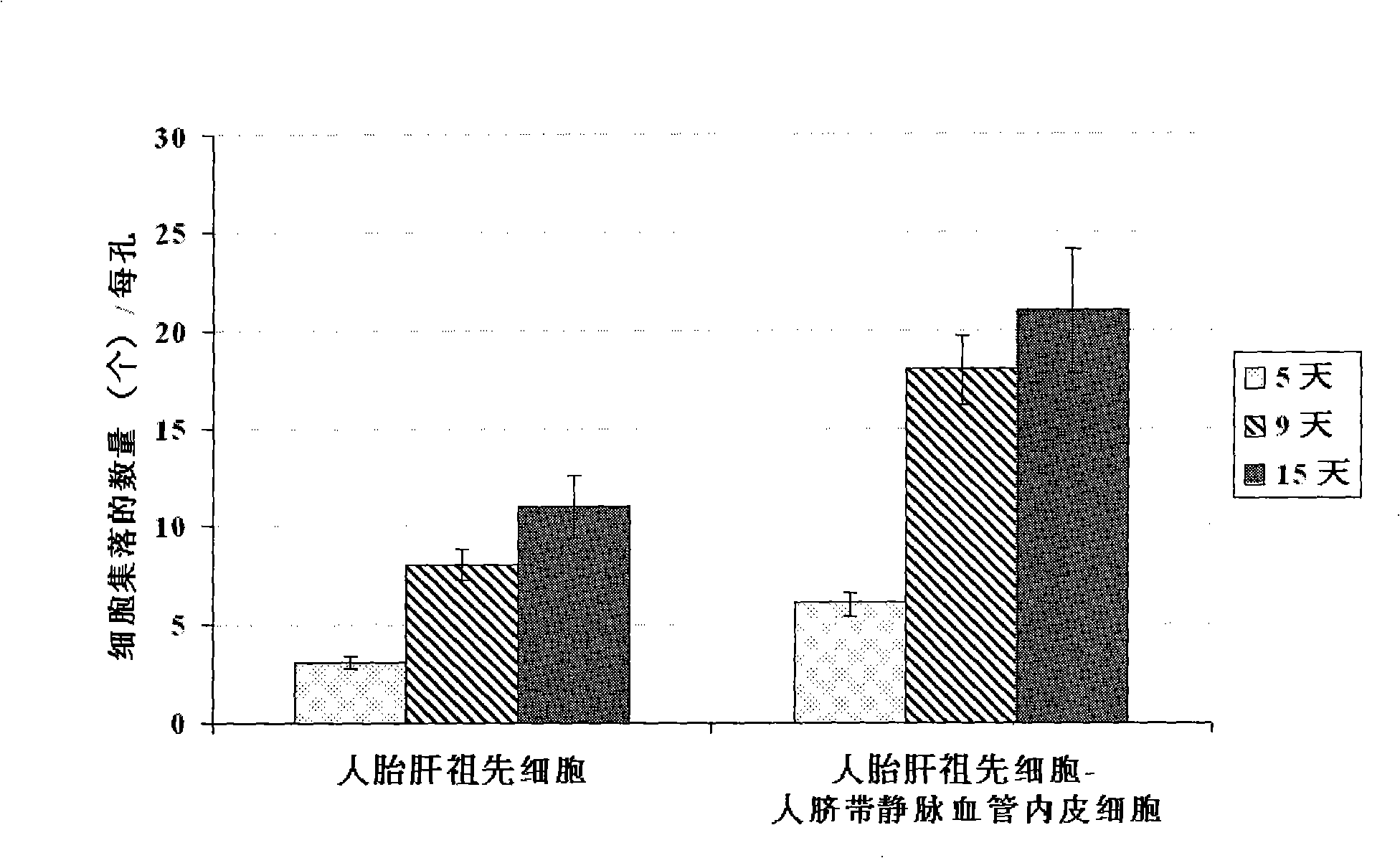
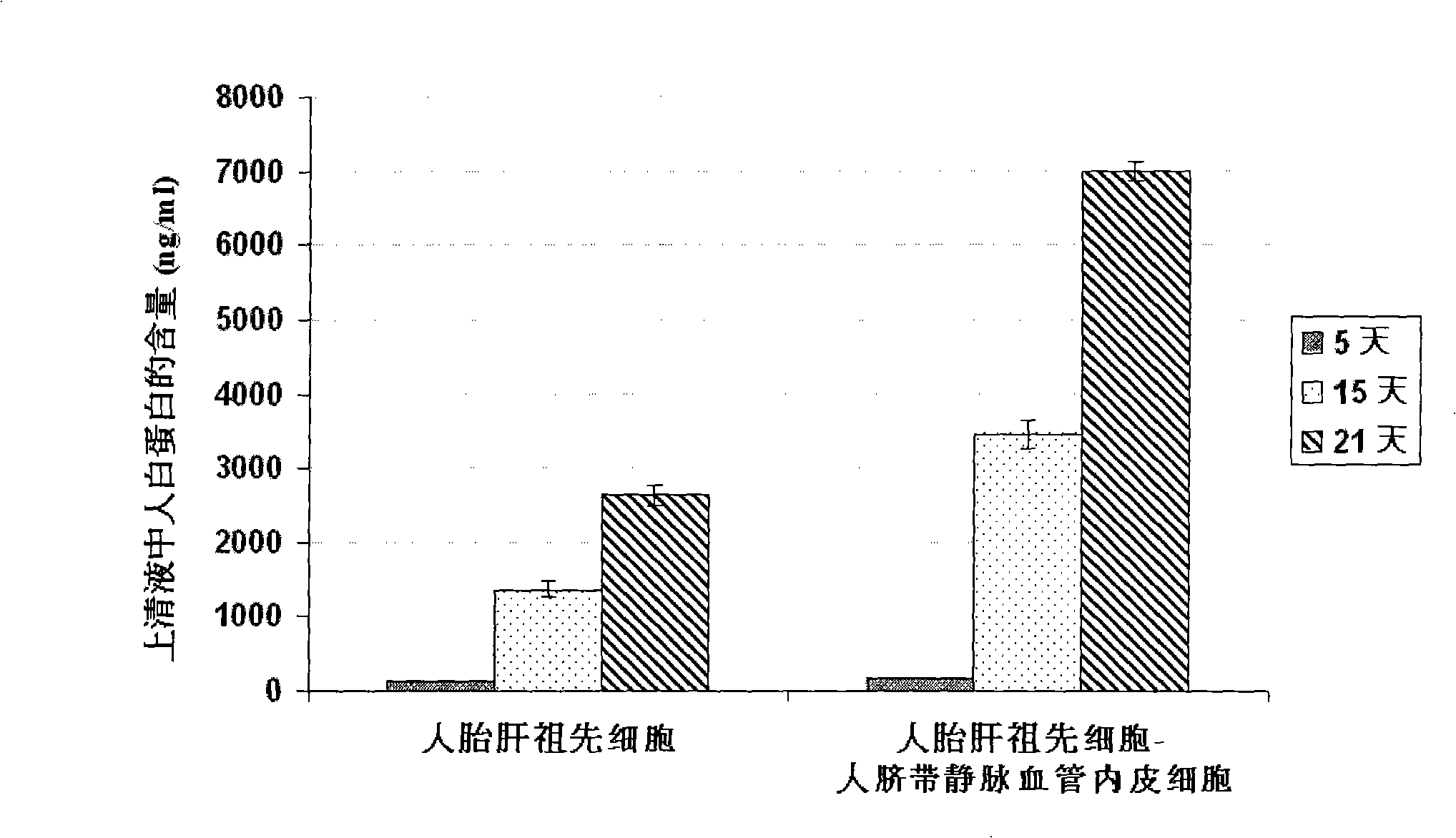
In vitro culture-amplified human liver progenitor cell and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101275121AAccelerate self-renewalConvenient sourceArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The present invention provides a preparing method of a human hepatic progenitor cell which is amplified and cultivated in vitro, including: a. separating the human hepatic progenitor cell; b. co-cultivating a feeder cell and the human hepatic progenitor cell separated from the step a by a medium having no serum on an extracellular matrix containing human fibrin sealant or other analogues, obtaining a human hepatic progenitor cell colony by amplification. The human hepatic progenitor cell colony is easy to separate from the surface of human fibrin sealant by the simple gelatinolytic band process, purified or / and subcultured by further single cell preparation technology process such as enzymatic degradation etc. The human hepatic progenitor cell prepared by the method is hepatic progenitor cell treatment, including a cell transplantation and a bioartificial liver support system, providing excellent human hepatocyte source for cytotoxicity test platform in the drug screening, virus infection and drug screening platform etc.
Owner:芦银雪
Formulations for wound therapy
InactiveUS9717821B2Increase absorbanceSpeed up the flowPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsWound therapyFibrinogen
The present invention relates to novel formulations comprising a dry powder fibrin sealant comprised of a mixture of fibrinogen and / or thrombin, for use in the treatment of wounds or injuries, in particular for use as a topical hemostatic composition or for surgical intervention.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT PHARMA IP TRADING D A C
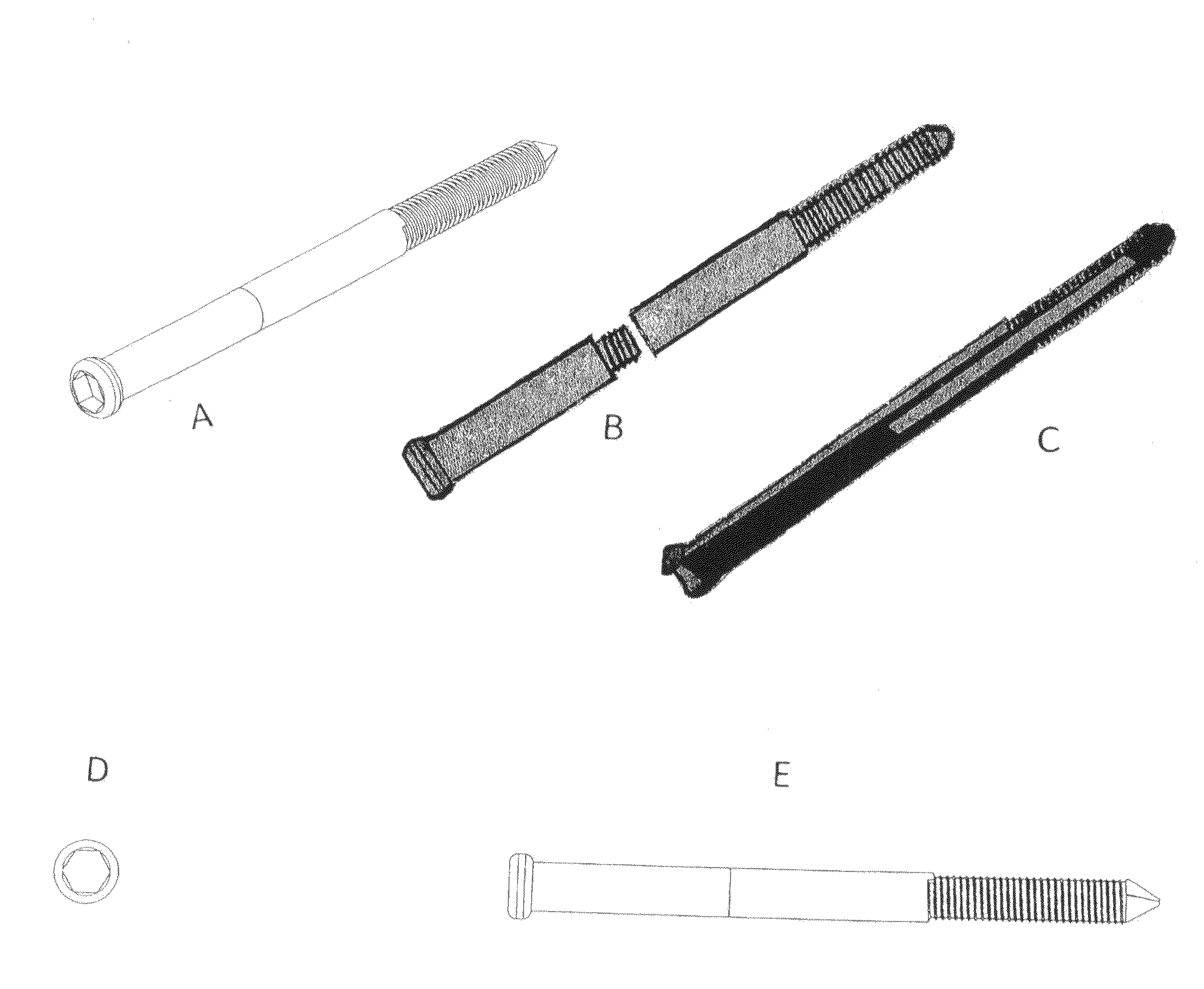
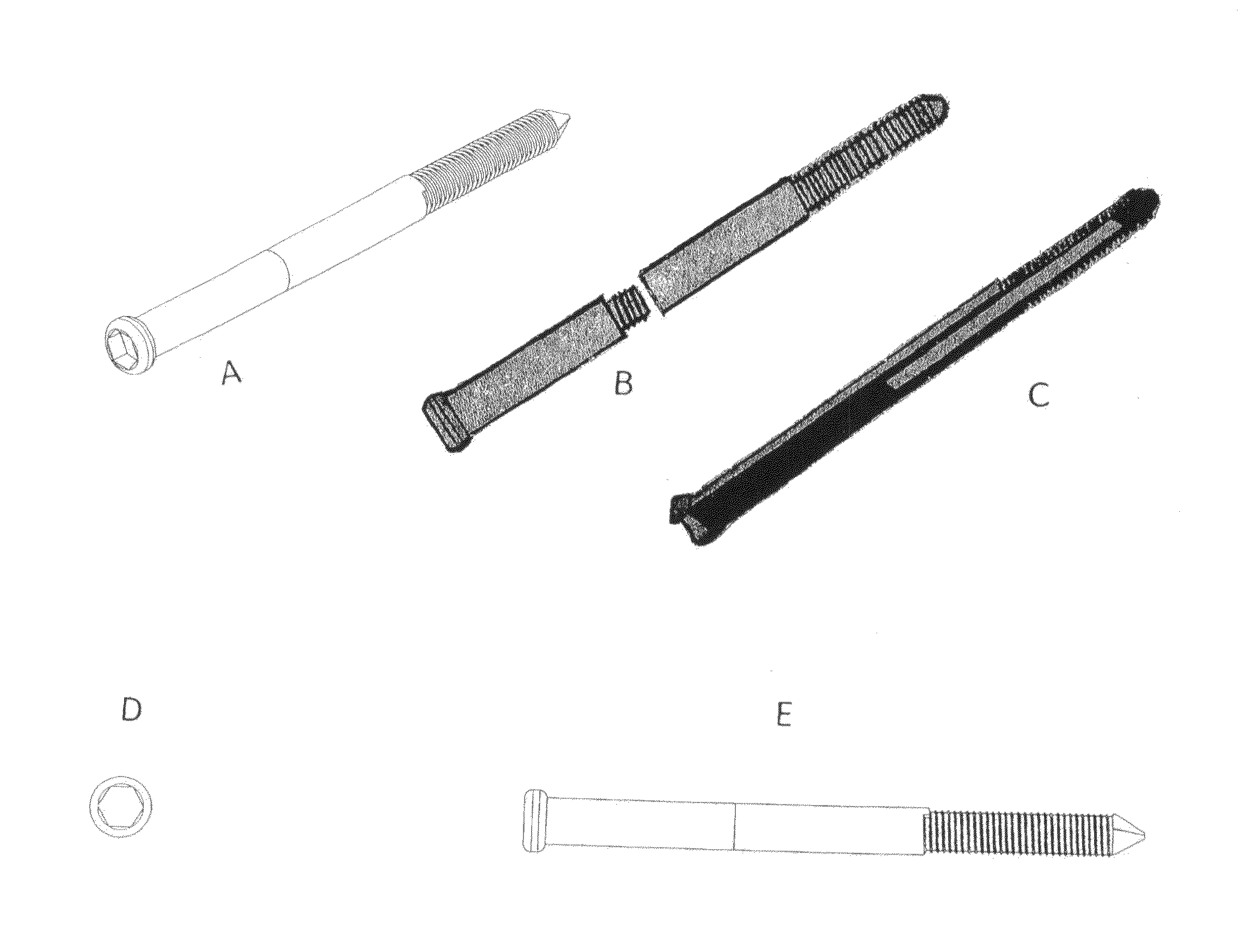
Polyporous hollow bone screw
Present invention depicts a poly-porous (micropore) hollow screws as diffusion chamber filled with core matrix for targeted delivery of growth factors and bone marrow stem cells. The screws comprise at least two parts: the distal part of the screw consists of the tip of the screw made of poly porous material and hollow inside proximally. It has threaded navel attached to the threaded nipple of the distal part of the proximal screw which has the screw head and is made of the solid material of the same kind. The screw head had hexagonal recess targeted for screw driver insertion. Assembly of screw created a chamber in the middle of the screw. The chamber is filled with core matrix consisting of gelatin nano-particles pre-impregnated with BMPs (BMP2 / BMP7 for bone or BMP12 for tendon, ligament) and fibrin sealants or Chitosan dispersed with bone marrow stem cells and / or other growth factors. Bioactive protein core material is prepared during the surgery and filled the chamber of the screw by the surgeon. Fibrin sealants or Chitosan will polymerize to form a gel to hold the growth factors and stem cell in place. The screw can be used as the lag screw or other function to provide mechanical fixation in variety of condition. Once the screw implanted in the human body, the fibrin sealant or Chitosin / gelatin nano-particles are gradually degraded and slowly release growth factors and stem cells via micropores of screw to facilitate the bone healing and regeneration. The gelatin nanoparticles and fibril sealant / or Chitosan matrix also serve as the scaffold and platform for bone in-growth to the screw or alternatively, the stem cell inside of screw can regenerate new bone, providing the biological fixation. At the mean time as the bone regenerate and / or in growth, mechanical strength of the screw increased.
Owner:WU YANGGUAN
Dry Powder Fibrin Sealant
ActiveUS20120315305A1Enhance powder flowImprove wettabilitySurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsTopical hemostatic agentThrombin activity
The present invention relates to a dry powder fibrin sealant which comprises a mixture of fibrinogen and thrombin for use in surgery, trauma and other wounds or injuries. It further relates to novel formulations comprising said dry powder fibrin sealant for use in the treatment of wounds or for surgical intervention or as a topical hemostat.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT PHARMA IP TRADING D A C
Apparatus and method for injection of fibrin sealant in spinal applications
ActiveUS8419722B2Reduce the amount requiredGood pain reliefJet injection syringesMulti-lumen catheterBiomedical engineeringFibrin sealants
An apparatus for percutaneous delivery of a sealant comprising: at least two fluid reservoirs, an introducer needle having a distal tip that is in fluid communication with at least one reservoir, a fluid delivery tube that is in fluid communication with a second reservoir, wherein the fluid delivery tube has a tip and wherein the fluid delivery tube is configured so that the tip of the fluid delivery tube does not extend past the distal tip of the introducer needle during use.
Owner:PAUZA KEVIN
Tissue sealant for use in non compressible hemorrhage
InactiveUS8314211B2Excellent hemostatic agent candidateLeast riskSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryTissue sealantLaparoscopes
Owner:FALUS GEORGE D PHD
Subversion of bacterial resistance by low solubility antibiotics
A site-specific antibiotic delivery system and related method comprising a fibrin sealant and an antibiotic releasably bound to the fibrin sealant, wherein the antibiotic is delivered in situ and wherein the dose of antibiotic delivered to the organism is sufficient to kill substantially all antibiotic-resistant bacteria present in an infectious focus.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
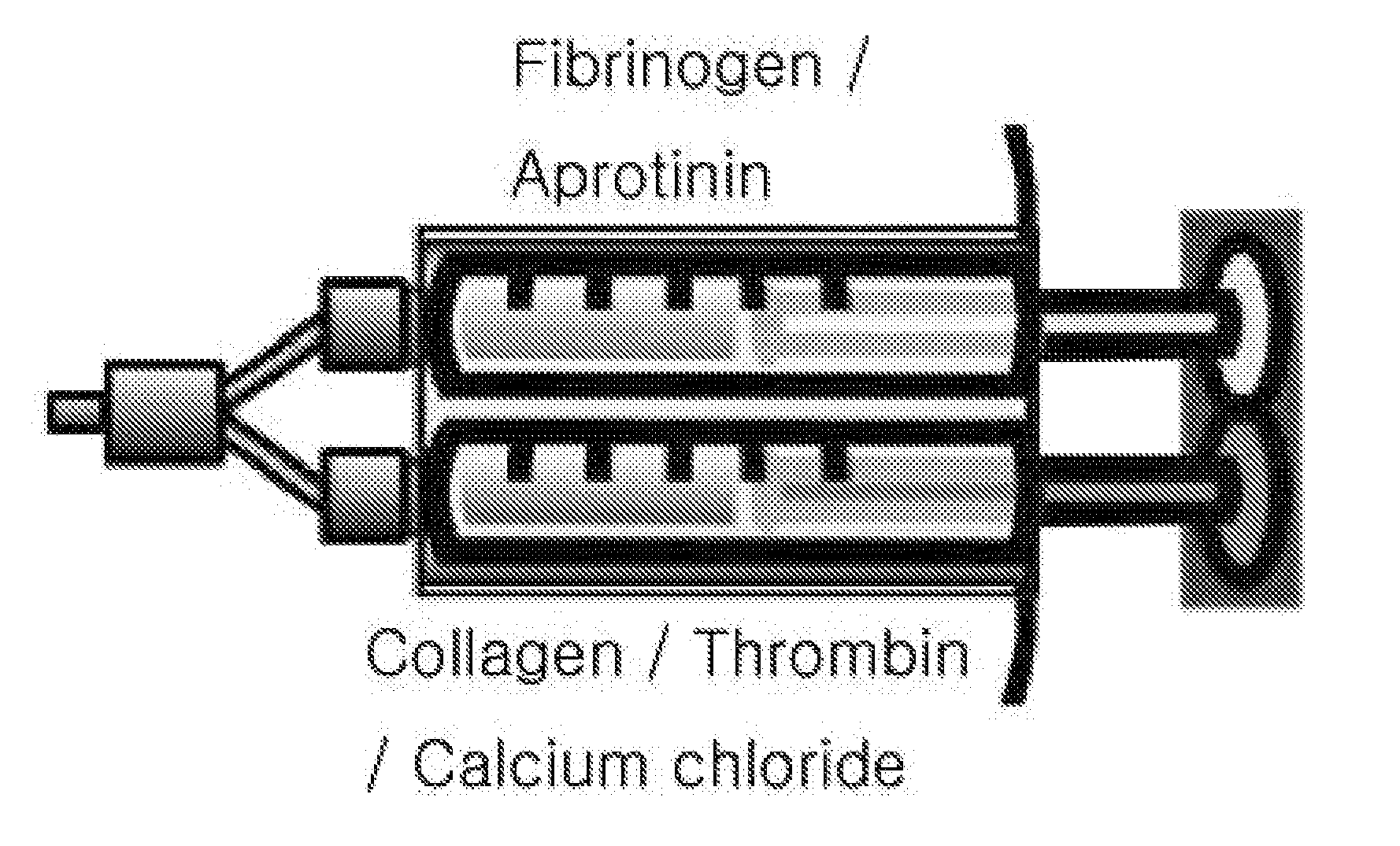
Tissue sealant in which collagen and fibrin are mixed, and method for preparing same
InactiveUS20150320904A1High strengthReduce degradationPeptide/protein ingredientsInfusion syringesTissue sealantWeakness
The present invention relates to a tissue sealant in which collagen and fibrin are mixed and to a method for preparing same. To this end, the method of the present invention comprises the steps of: mixing a first material using fibrinogen and aprotinin; mixing a second material using thrombin, calcium chloride, and collagen; and preparing a third material by mixing the first material and the second material. The tissue sealant prepared by the method may supplement weaknesses, i.e. strength and degradability, of the fibrin sealant which is currently available in the commercial marketplace. Further, the tissue sealant of the present invention is cytophilic and activates blood platelets contained in blood so as to induce tissue regeneration. Thus, quality and reliability of products can be significantly improved so as to satisfy various needs of consumers who are users, thereby presenting good image.
Owner:SEWON CELLONTECH CO LTD
Treatment of Urinary Incontinence with Regenerative Glue
InactiveUS20140227233A1Many symptomSufficient effectBiocideSurgical adhesivesUrethraLigament structure
Owner:UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS OF CLEVELAND CLEVELAND
A safe and efficient freeze-dried fibrin sealant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102258770AEnsure activityNon-lipid enveloped virusSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrin glueFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a safe and efficient freeze-dried fibrin sealant and a preparation method thereof. The freeze-dried fibrin sealant is composed of independent components in the following parts by weight: 12-15 parts of freeze-dried fibrinogen powder , 3 to 5 parts of freeze-dried thrombin powder. The invention provides a freeze-dried fibrin sealing agent that can be treated by a heat-resistant method by adopting an effective fibrinogen and thrombin stabilizer and a reasonable formula. The heat treatment of the preparation can not only ensure the inactivation of lipid-enveloped and non-lipid-enveloped viruses, but also allow the preparation to be quickly reconstituted at room temperature, which greatly facilitates clinical use, especially for fibrin glue used in first aid. significance.
Owner:SHANGHAI LIKANGRUI BIOLOGICAL ENG
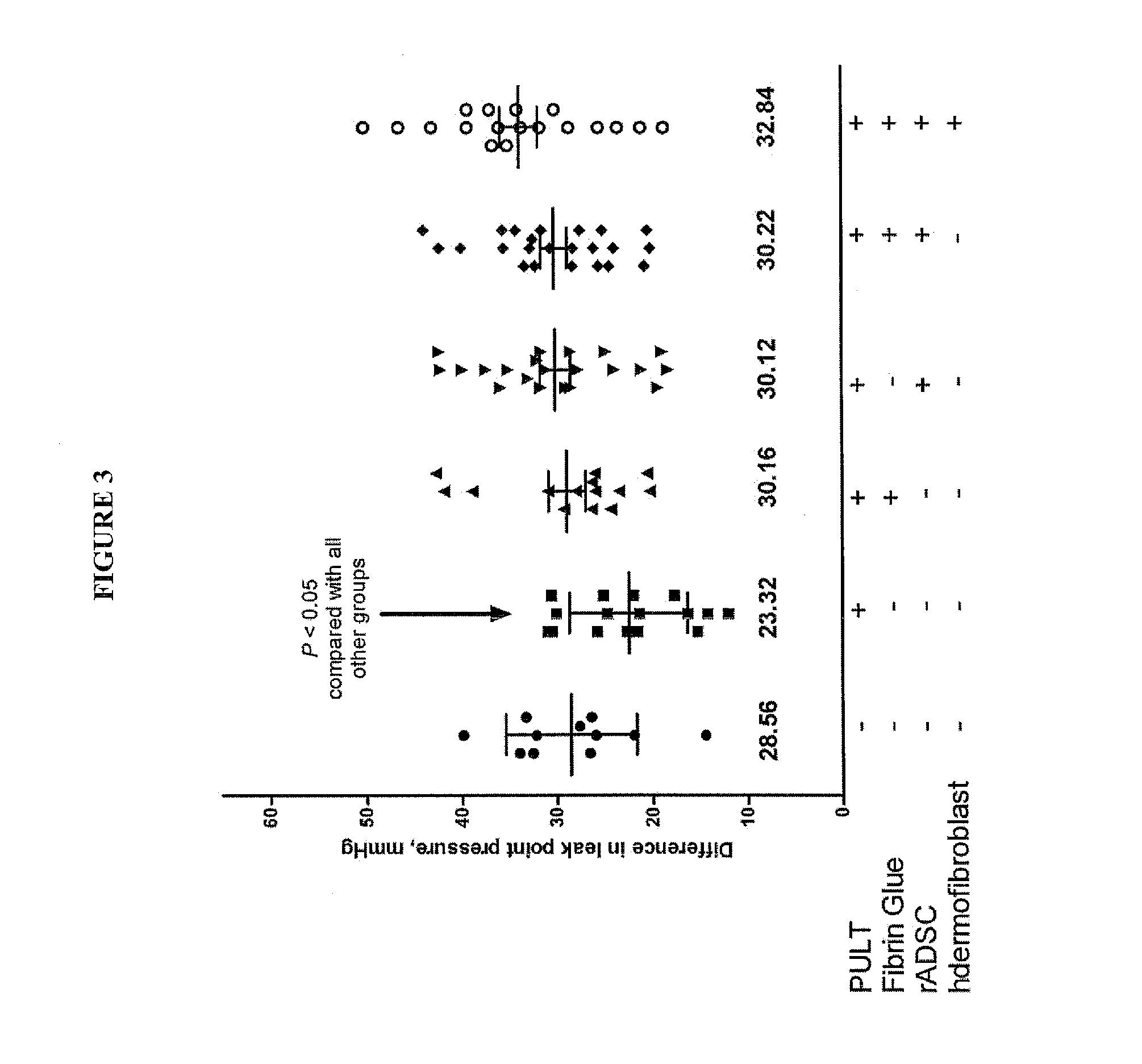
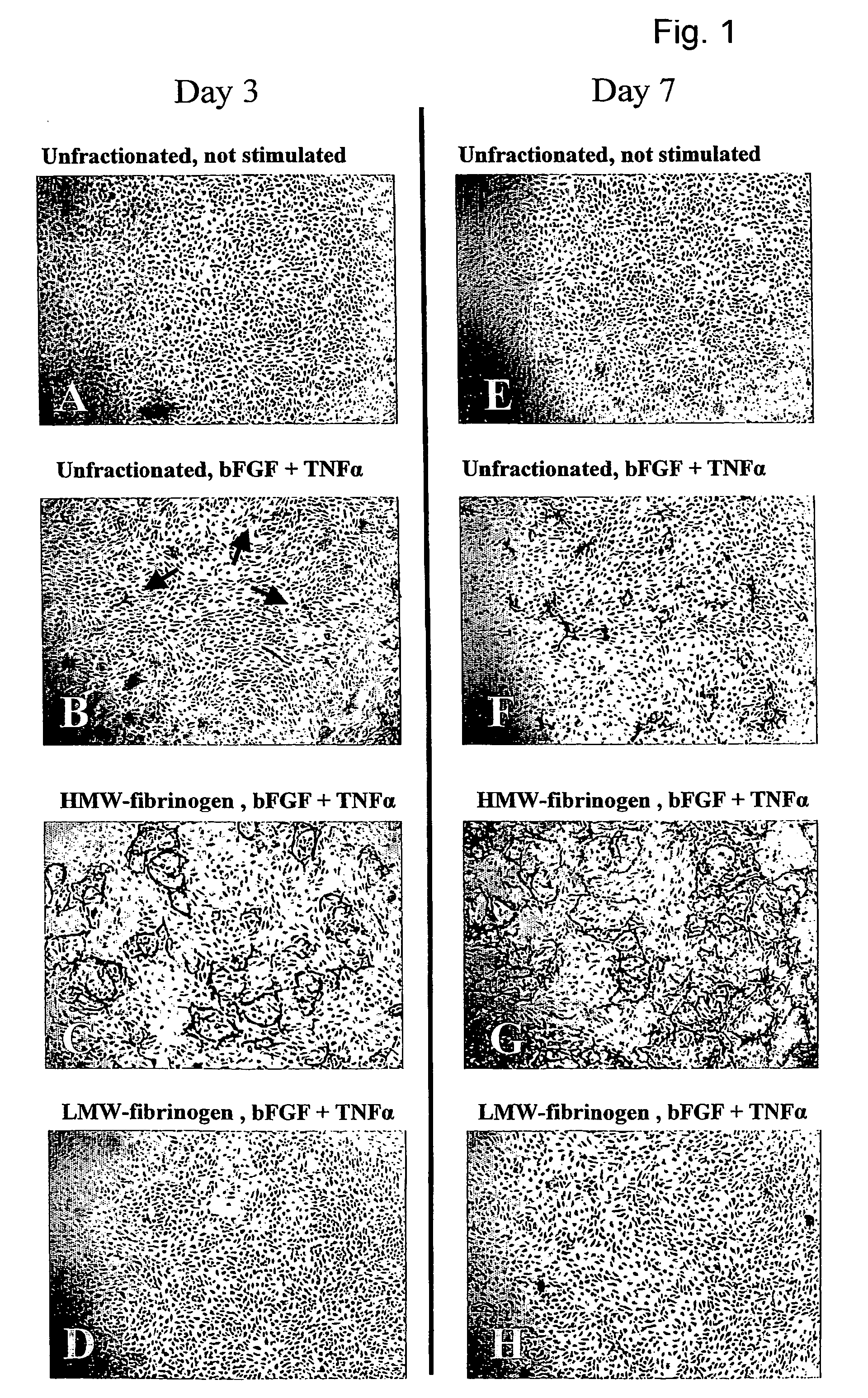
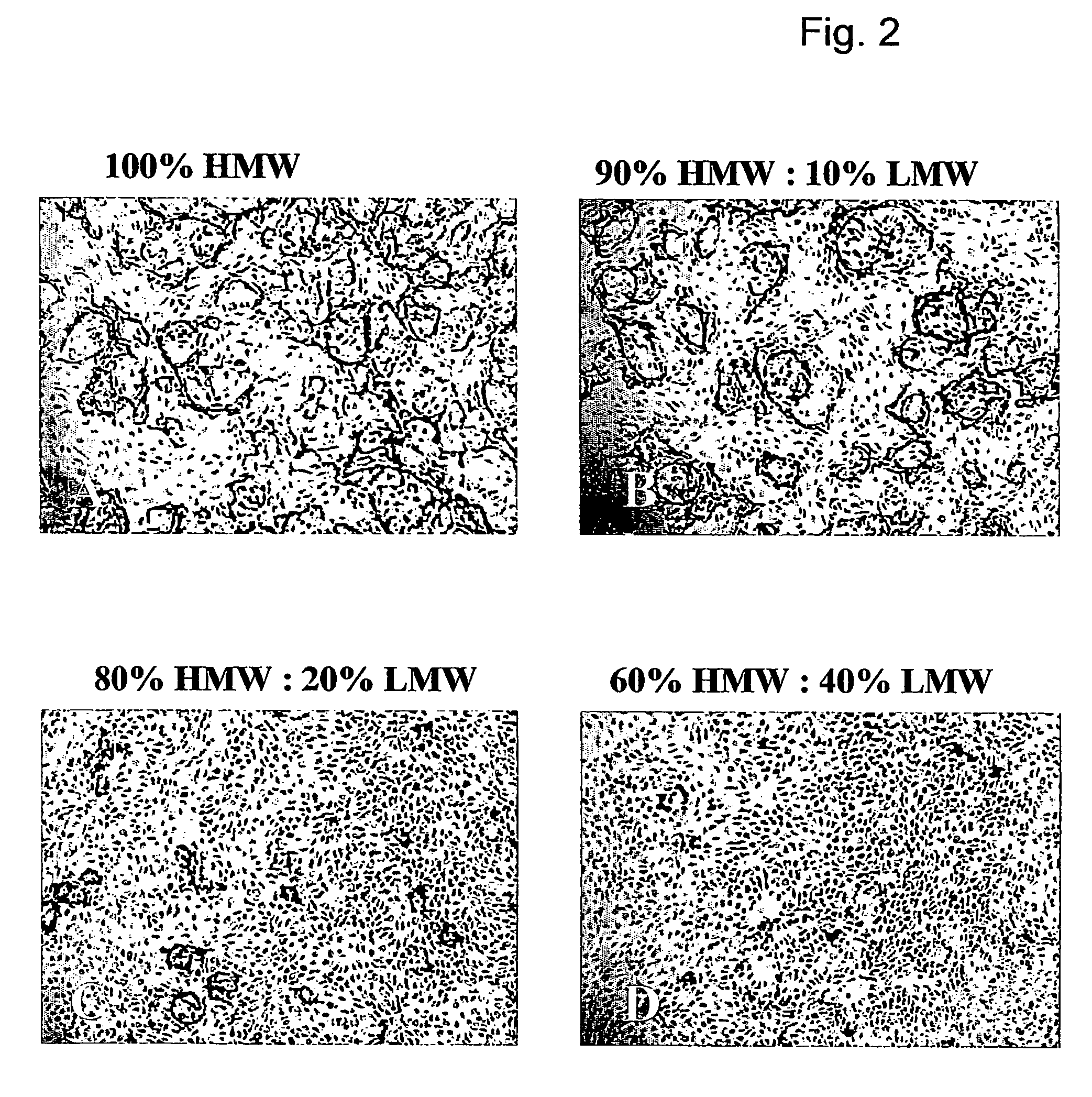
Method for the acceleration or deceleration of angiogenesis using fibrin matrix formed from increased or decreased HMW/LMW fibrinogen ratio
ActiveUS7867519B2Reduced cell and vessel ingrowthIncreased cell and vessel ingrowthFibrinogenSurgical adhesivesFiberScar tissue
A method for modifying the properties of a fibrin matrix relative to growth and ingrowth of cells, wherein for forming the fibrin matrix a fibrinogen is used consisting of a selected fibrinogen variant or a fibrinogen enriched or depleted in a selected fibrinogen variant. In particular, the use of high-molecular weight (HMW) fibrinogen leads to a fibrin having accelerated angiogenesis properties, while the use of low-molecular weight (LMW and / or LMW′) fibrinogen leads to fibrin having decelerated angiogenesis properties. The use of HMW fibrinogen when setting up angiogenesis tests results in that the tests require less time. Fibrin sealants on the basis of HMW fibrinogen can be used for burns, to promote wound healing or to inhibit scar tissue. Fibrin sealants on the basis of LMW or LMW′ fibrinogen are useful to inhibit adhesions and tumor growth, for instance after surgical operations.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK TNO
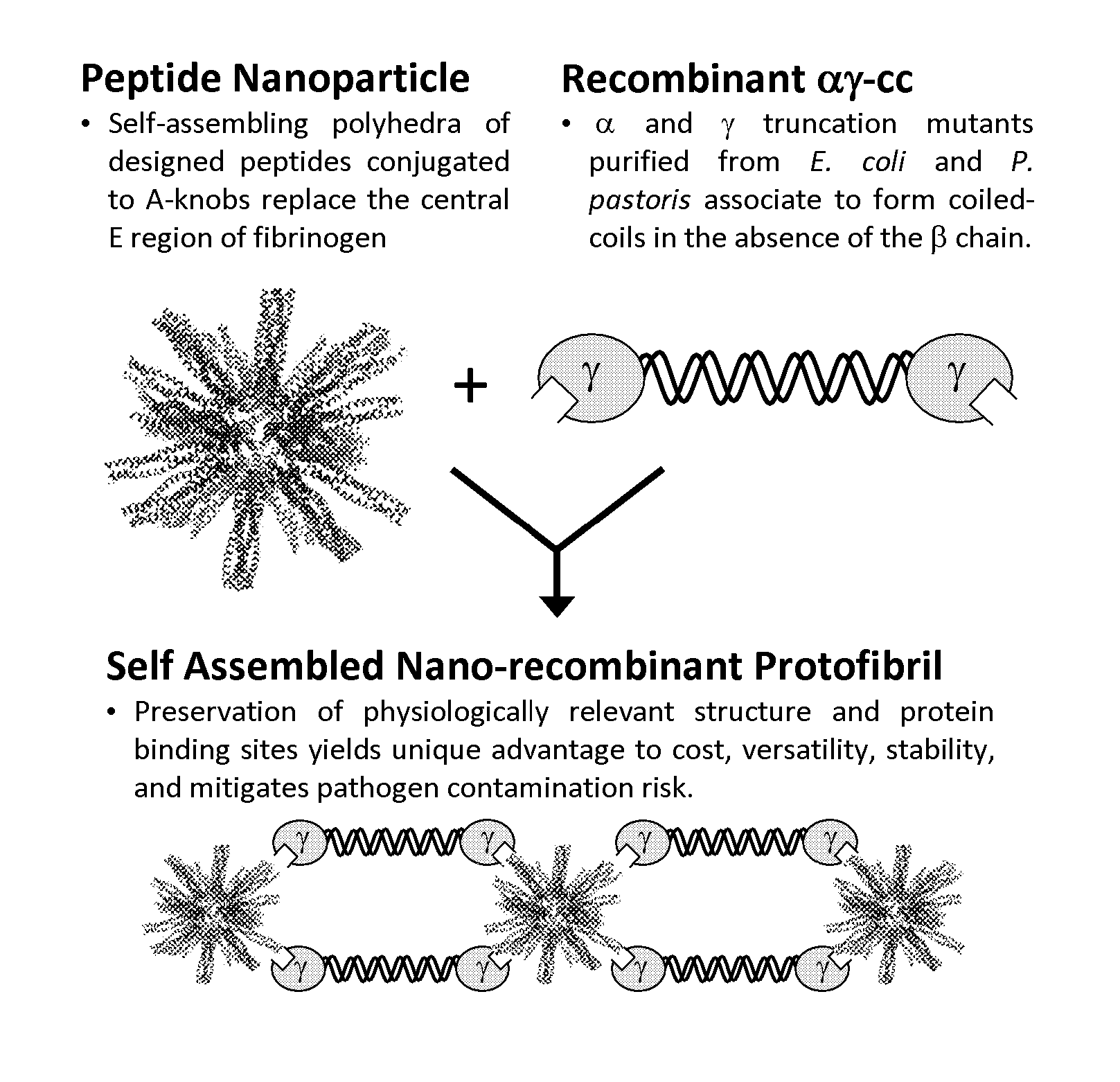
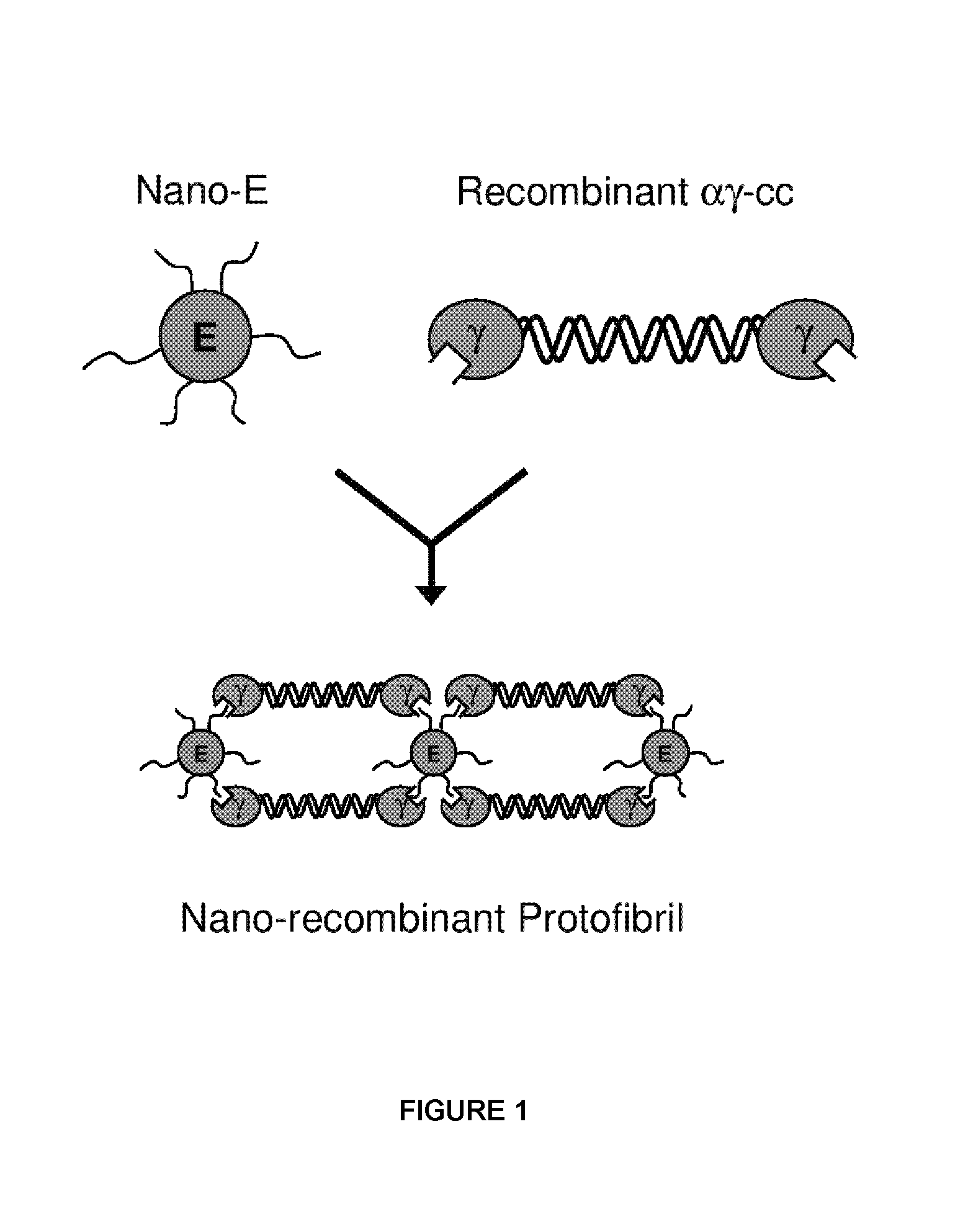
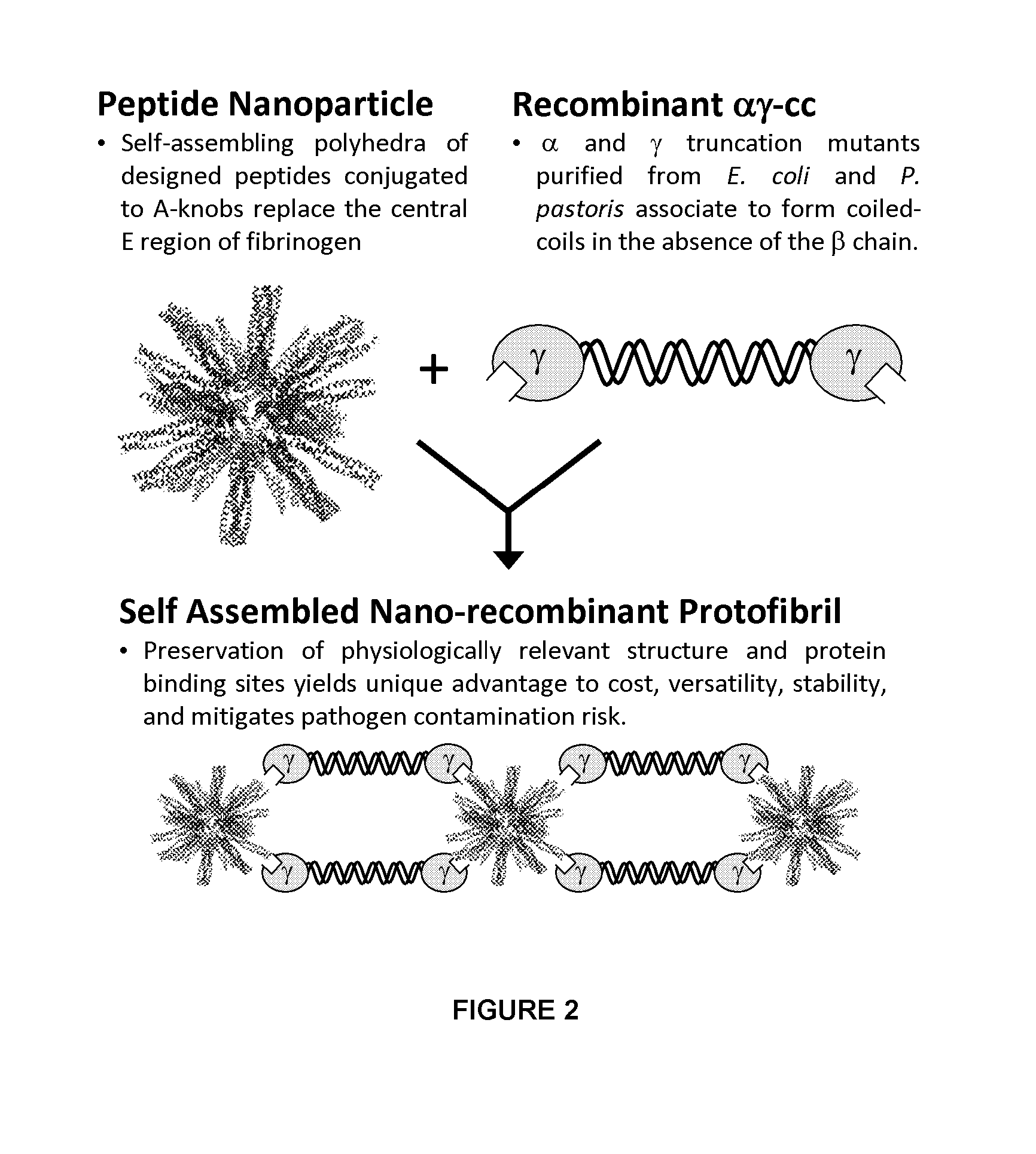
Nano-recombinant fibrinogen for fibrin sealants
A fibrin-based hemostatic agent suitable for both civilian and military use is disclosed. The hemostatic agent comprises (i) nanoparticles to which a plurality of Knob-A recognition sequences are attached, and (ii) coiled-coils of recombinantly-produced human fibrinogen α and chains and the γ chain globular domain. A delivery system for the hemostatic agent also is disclosed, which additionally comprises means for delivering (i) and (ii) to a wound site. The delivery means may be a CO2 canister or a shaker jet.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Fibrin sealant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101797377ALess disturbedFew interference factorsPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFIBRINOGEN/THROMBINPolymer
The invention provides a fibrin sealant which comprises a fibrin polymer and a thrombin-like enzyme, wherein a ratio of the thrombin-like enzyme to the fibrin polymer is 0.01 to 100 IU:1 mg. The fibrin sealant can be used on the aspects of hemostasis, healing promotion, defect enclosing, bonding prevention, tendon suture fixation tendon injury, molding repair of bony defect, regeneration of skin tissue, carrier slow release and the like.
Owner:BEIJING SAISHENG PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com