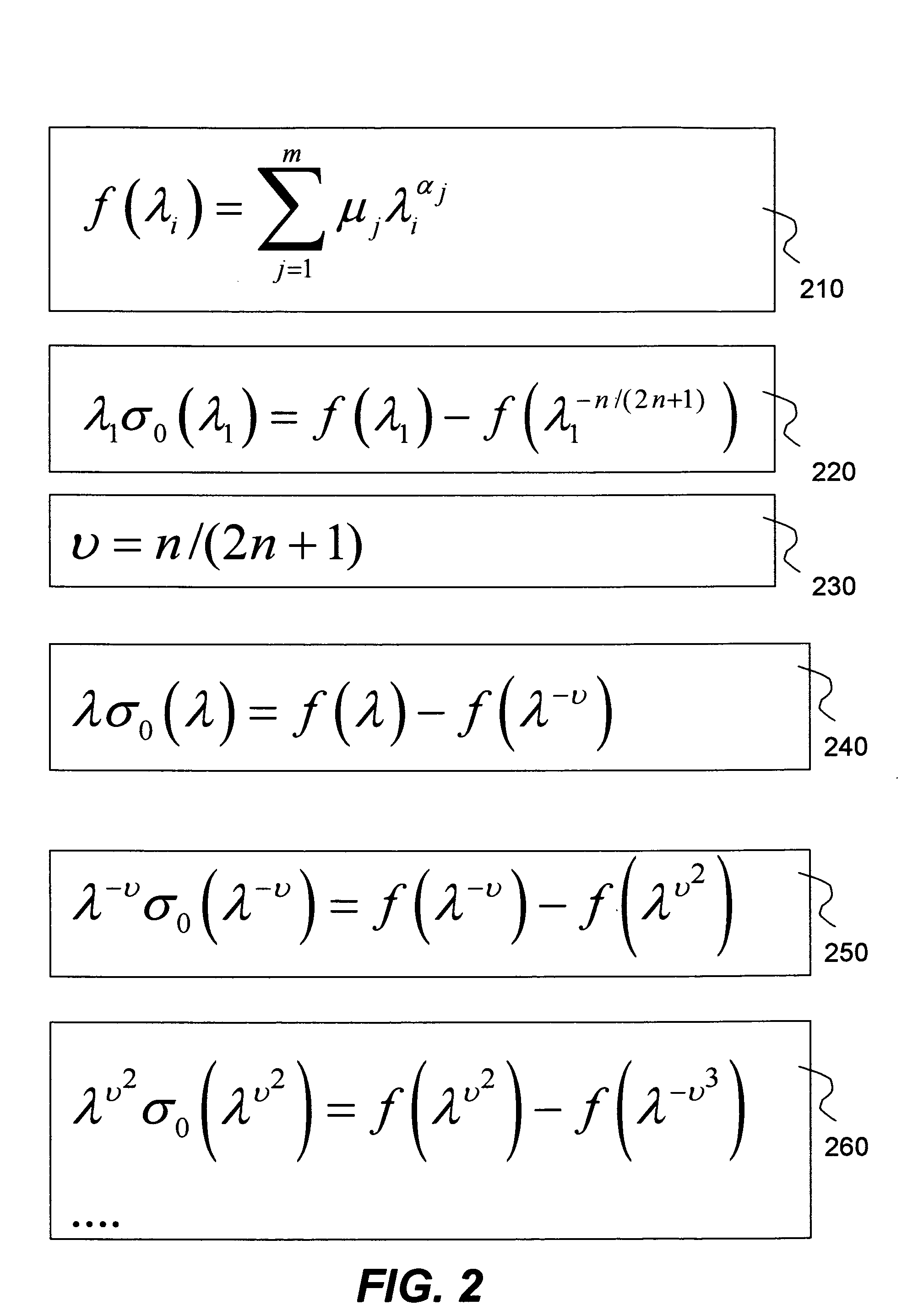Patents
Literature
215 results about "Finite element limit analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A finite element limit analysis (FELA) uses optimisation techniques to directly compute the upper or lower bound plastic collapse load (or limit load) for a mechanical system rather than time stepping to a collapse load, as might be undertaken with conventional non-linear finite element techniques. The problem may be formulated in either a kinematic or equilibrium form.
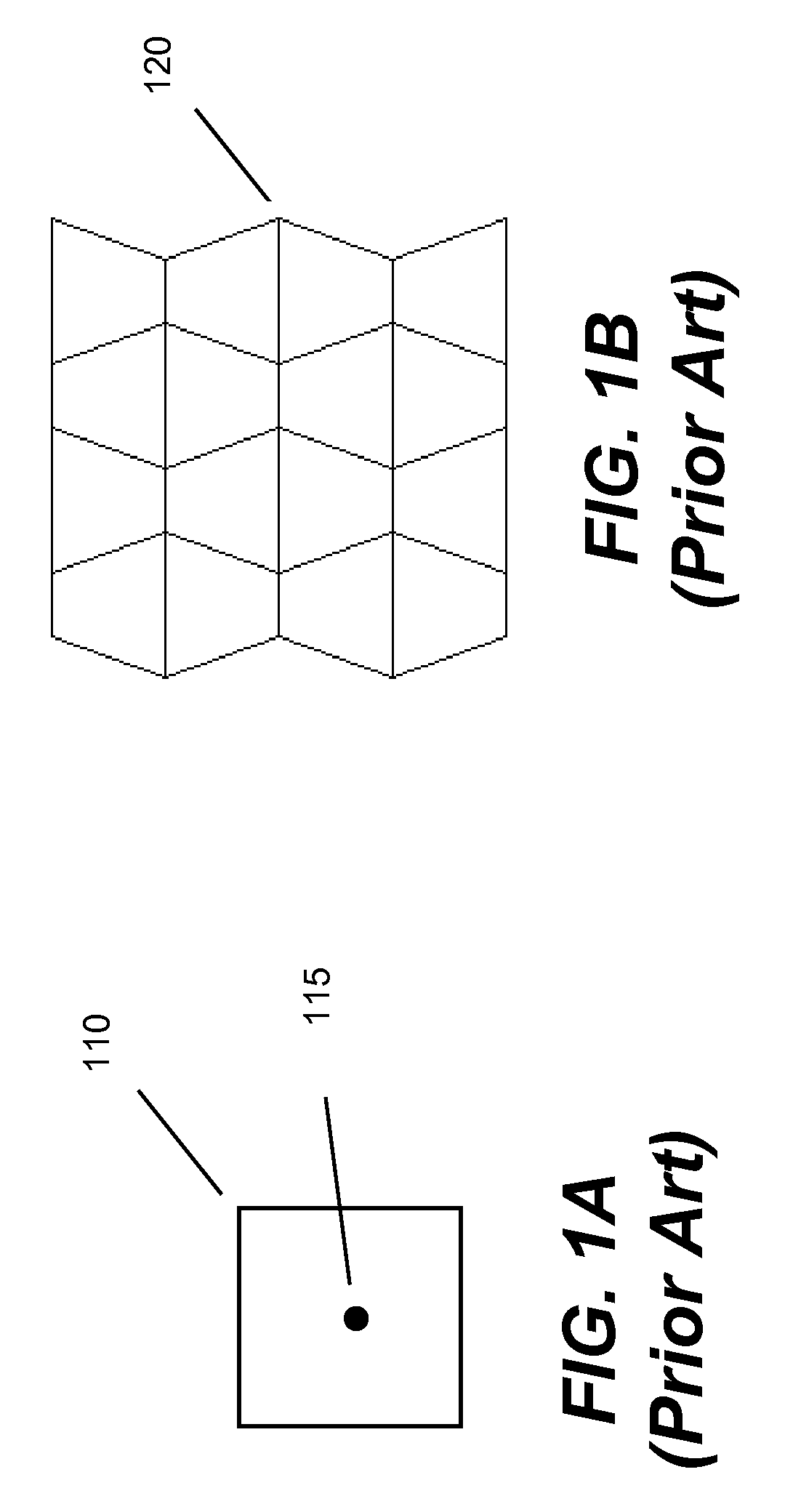
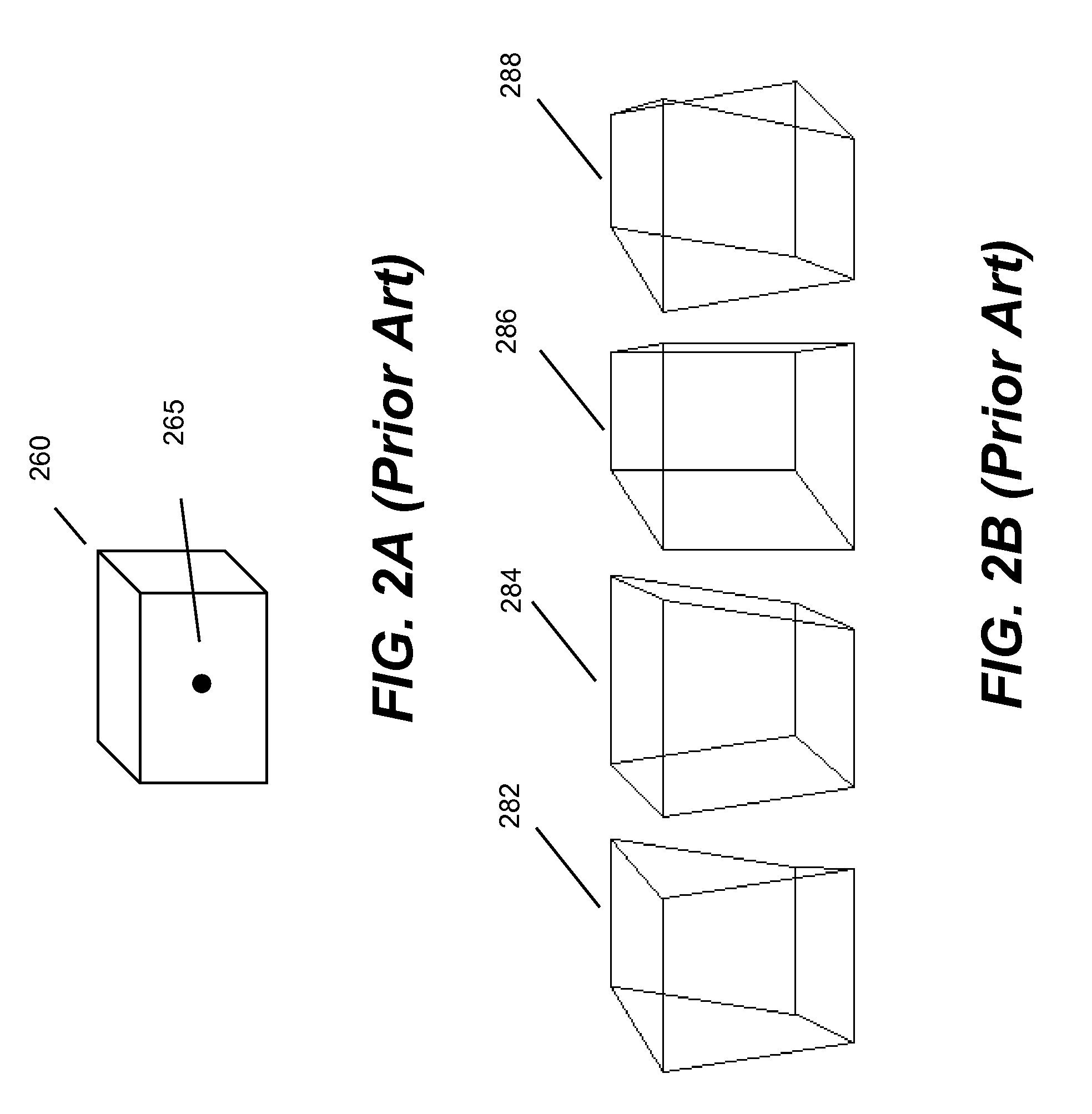
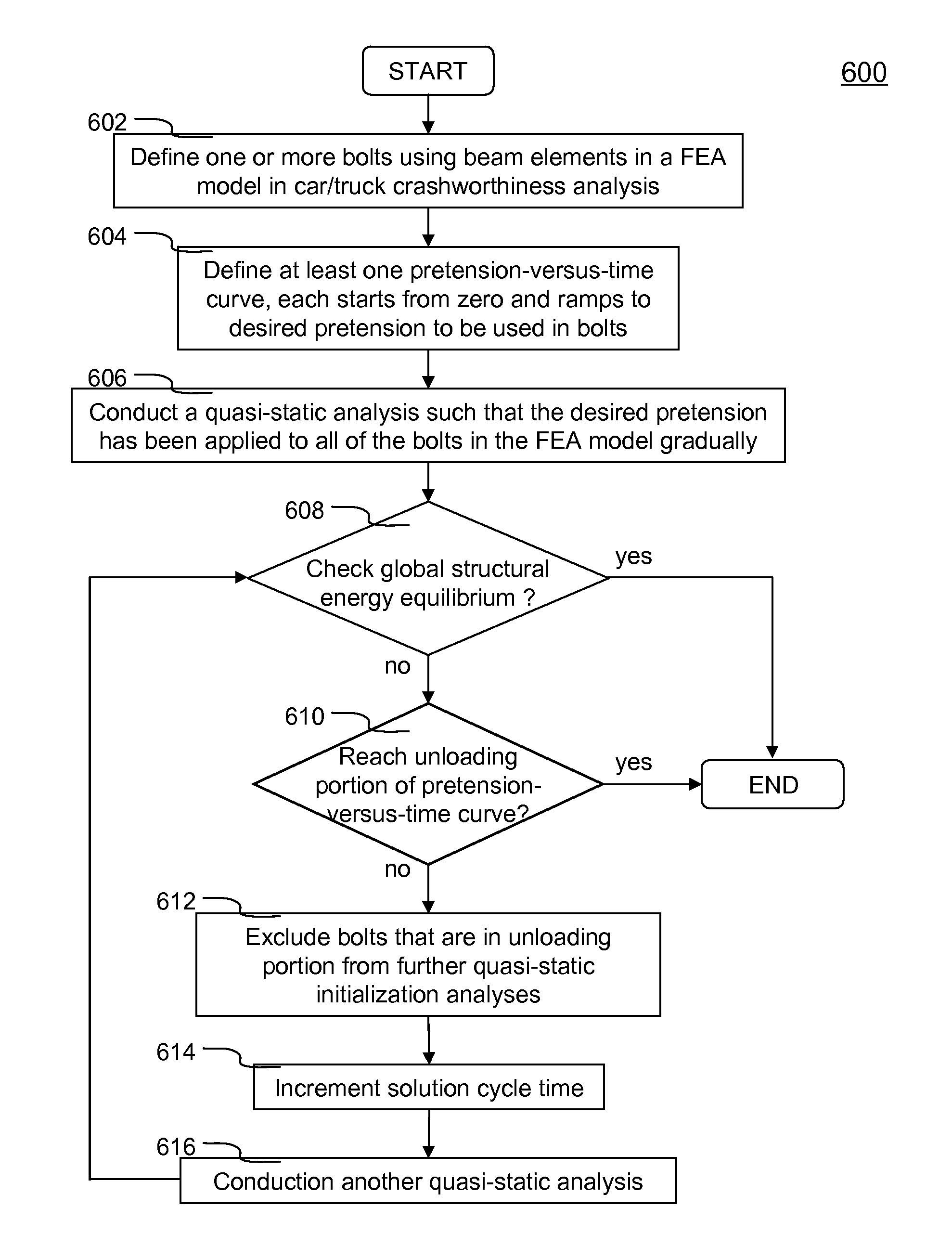
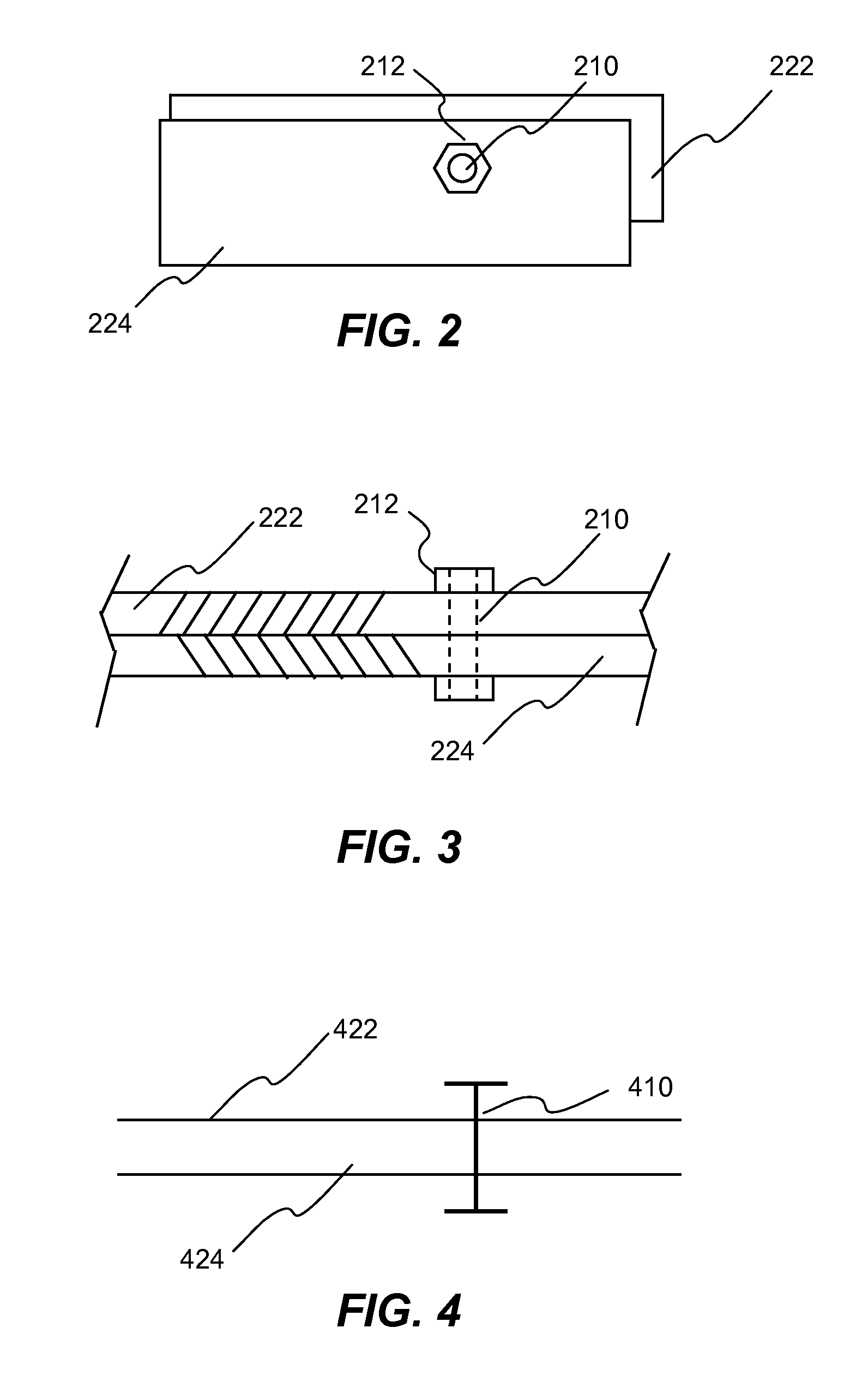
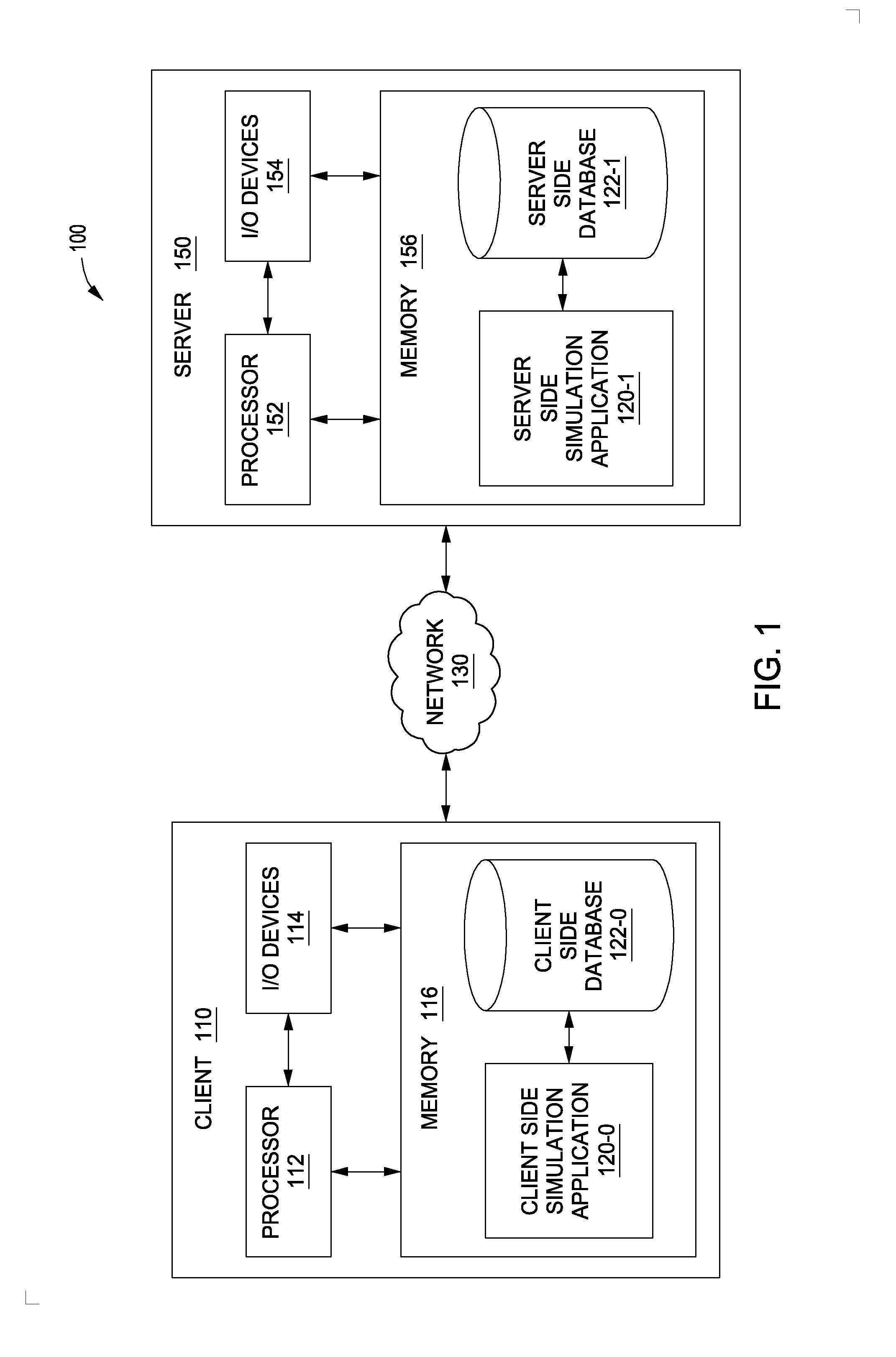
Method of initializing bolt pretension in a finite element analysis
ActiveUS8069017B2Small incrementAvoid the needDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisEngineering
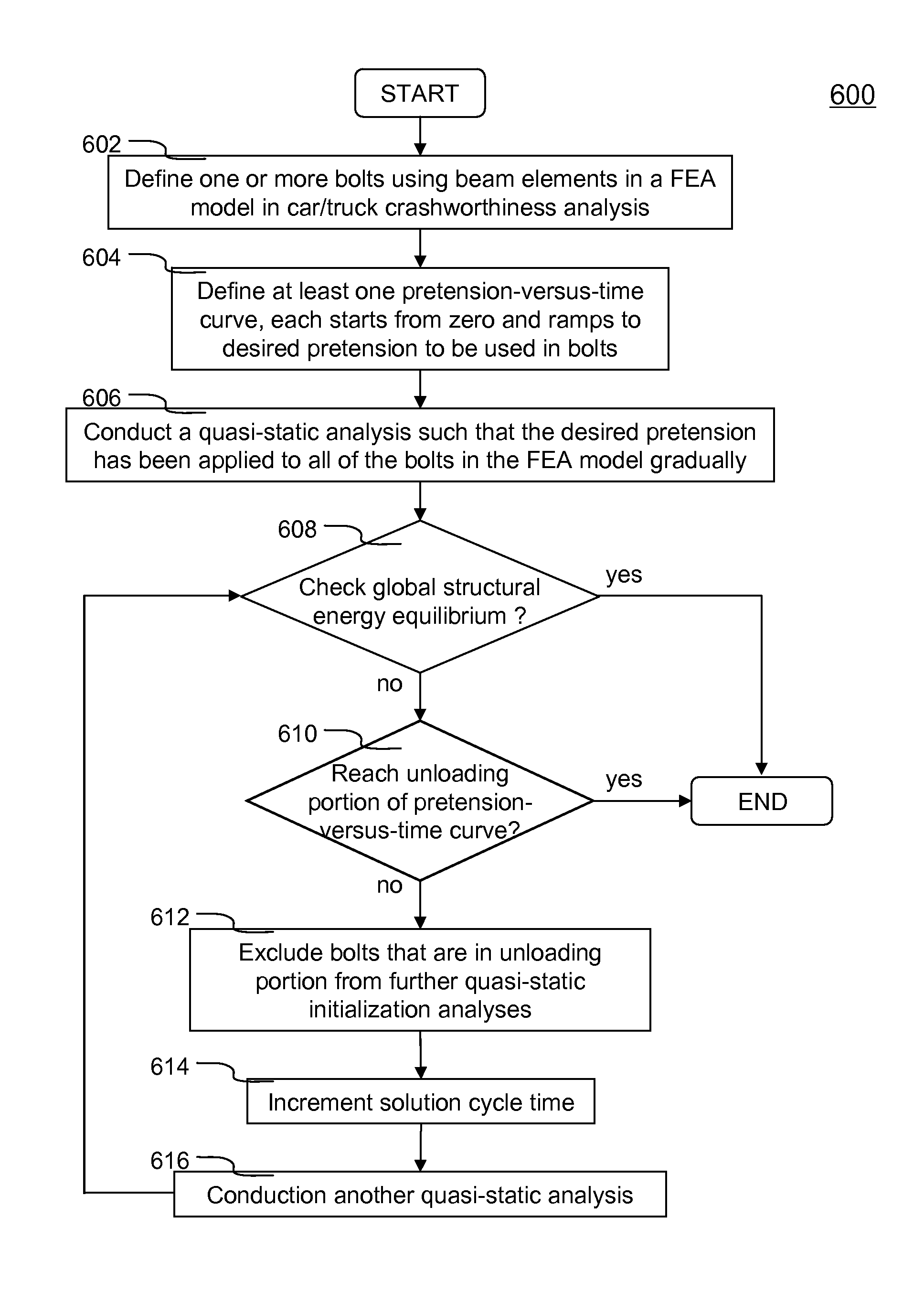
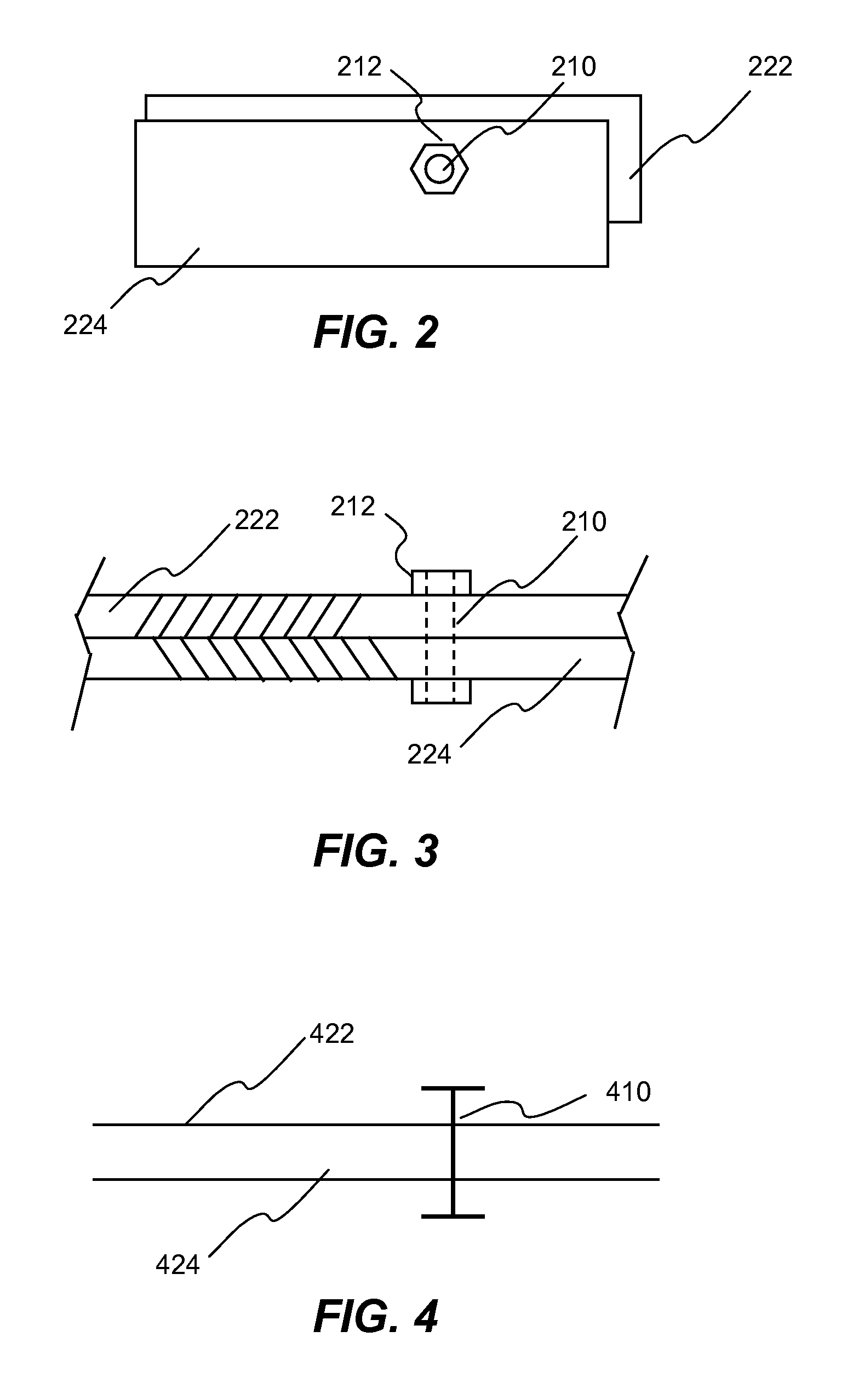
In one aspect of the invention, each bolt is modeled using a beam element in a FEA model. To apply desired pretension to one or more bolts, at least one pretension-versus-time curve is specified. Each pretension-versus-time curve includes ramp portion, desired pretension portion and optional unloading portion. Duration of the pretension-versus-time curve generally covers first 0.5-1% of total simulation time of a car crashworthiness analysis. Ramp portion starts from zero to desired pretension in a substantially linear manner, and hence being configured for applying desired pretension to a bolt gradually with smaller increments. Desired pretension portion is configured for ensuring the desired pretension can actually be applied to the beam element during an initialization process—a series of quasi-static analyses. Since the method is independent of the deformation of the beam, the method completely avoids the need to iteratively determine an axial strain or displacement that gives the desired pretension.
Owner:ANSYS
On-line prediction method for high-temperature pipe damage and longevity
InactiveCN101509855AGuaranteed real-time monitoringExtend your lifeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisPredictive methods
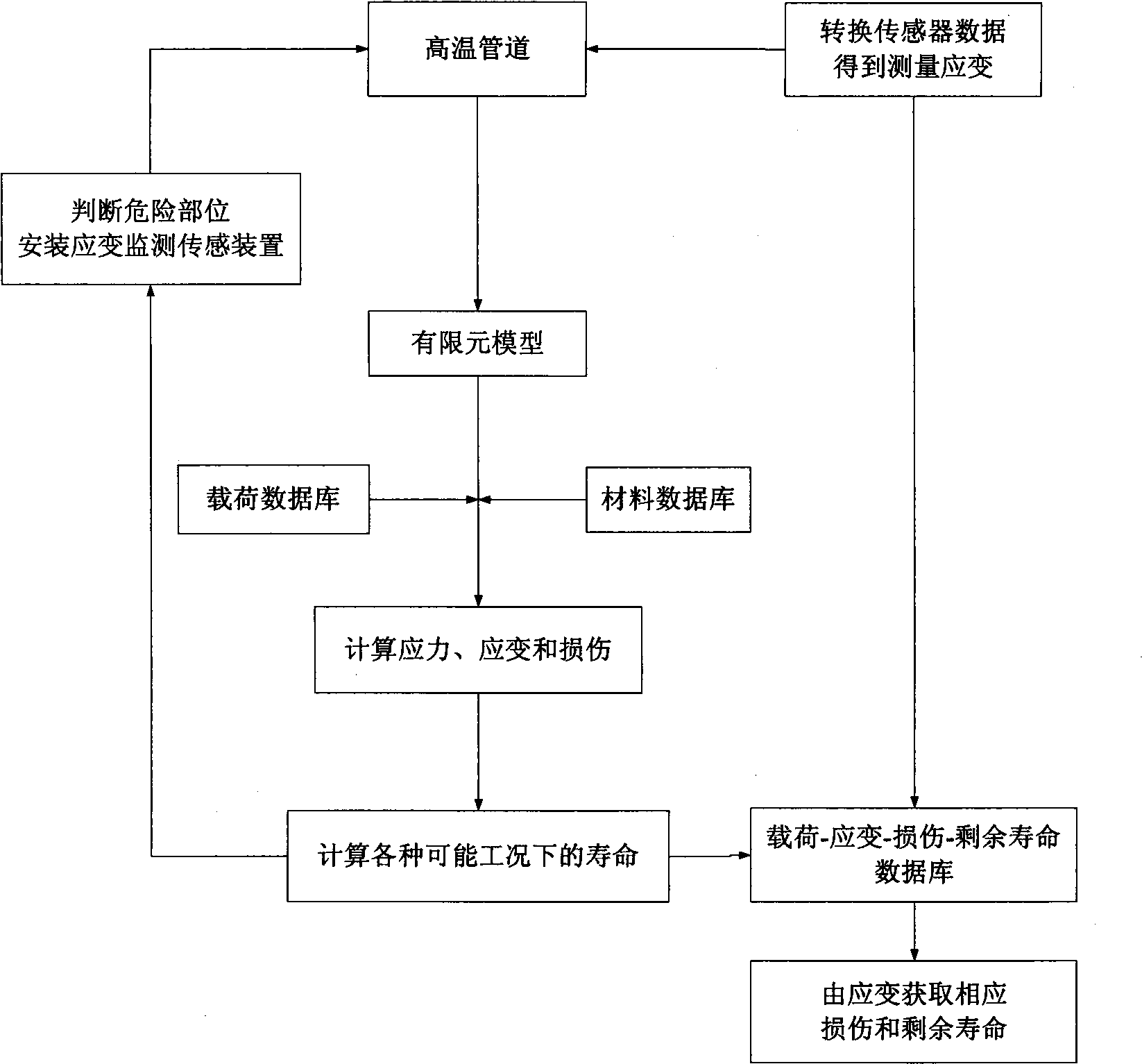
The invention relates to an online predicting method of damage and service life of a high temperature pipeline. The method comprises the following implementing steps of: (1) carrying out finite element simulation analysis of damage and coupling to the high temperature pipeline; (2) finding out important monitoring parts according to the analysis results, arranging a sensor and monitoring the strain of the sensor; (3) carrying out finite element analysis (including analytical subprogram of a constitutive equation) for different working conditions and establishing database with damage, strain and residual life and strain; and (4) carrying out online inquiry and comparison to strain values detected online and the value of the load working condition and the data in the database so as to obtain the assessment value of corresponding damage and residual life. The online predicting method has the advantages of being capable of carrying out real-time monitoring to the high temperature pipeline in operation while production is carried out normally, reflecting the deformation and damage of the important parts and key parts in time, making correct estimation to the use life and residual life of the pipeline, being beneficial to guaranteeing safe production, adjusting the production load, planning maintenance reasonably and effectively prolonging the service life of production equipment.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
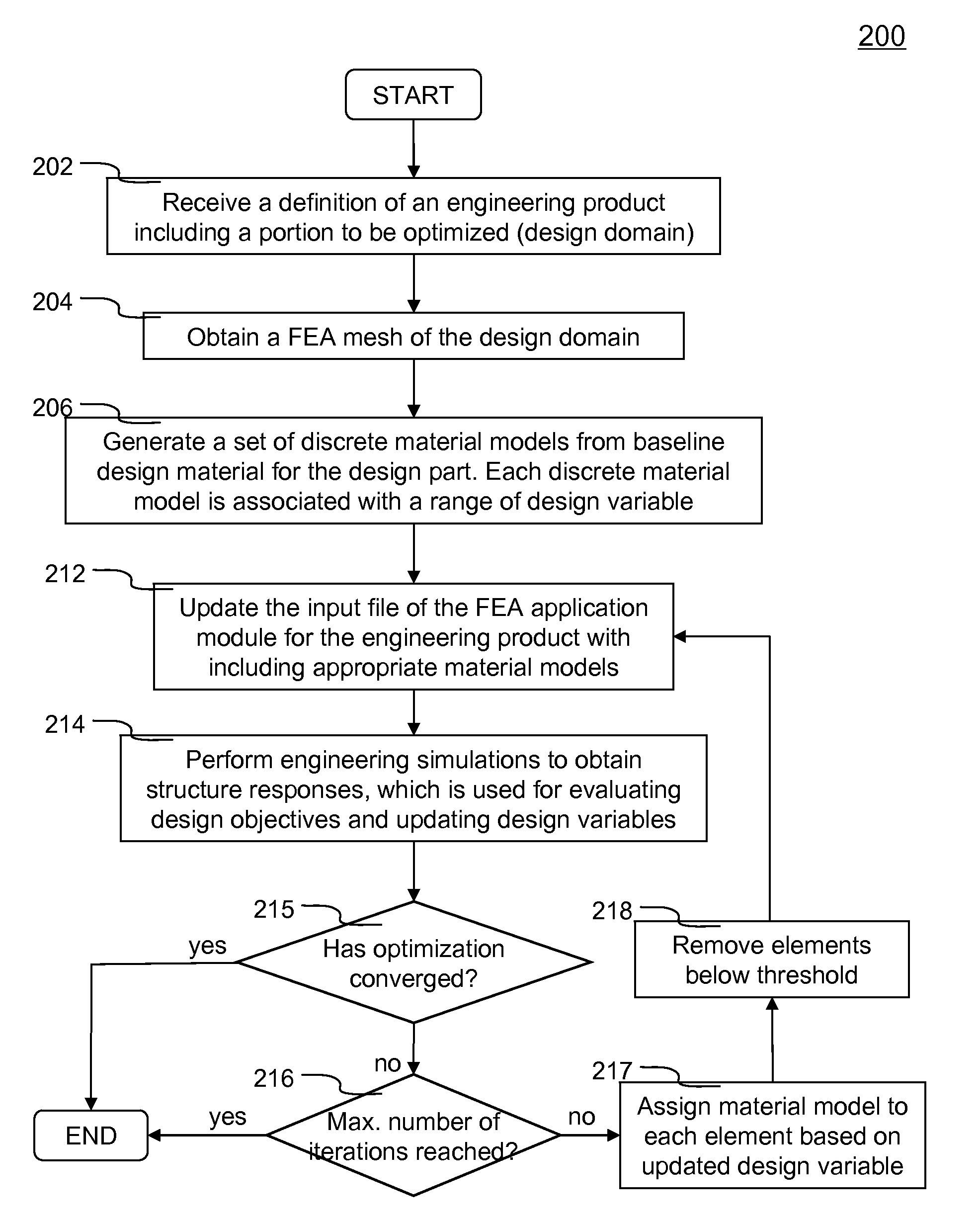
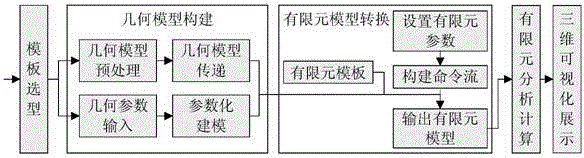
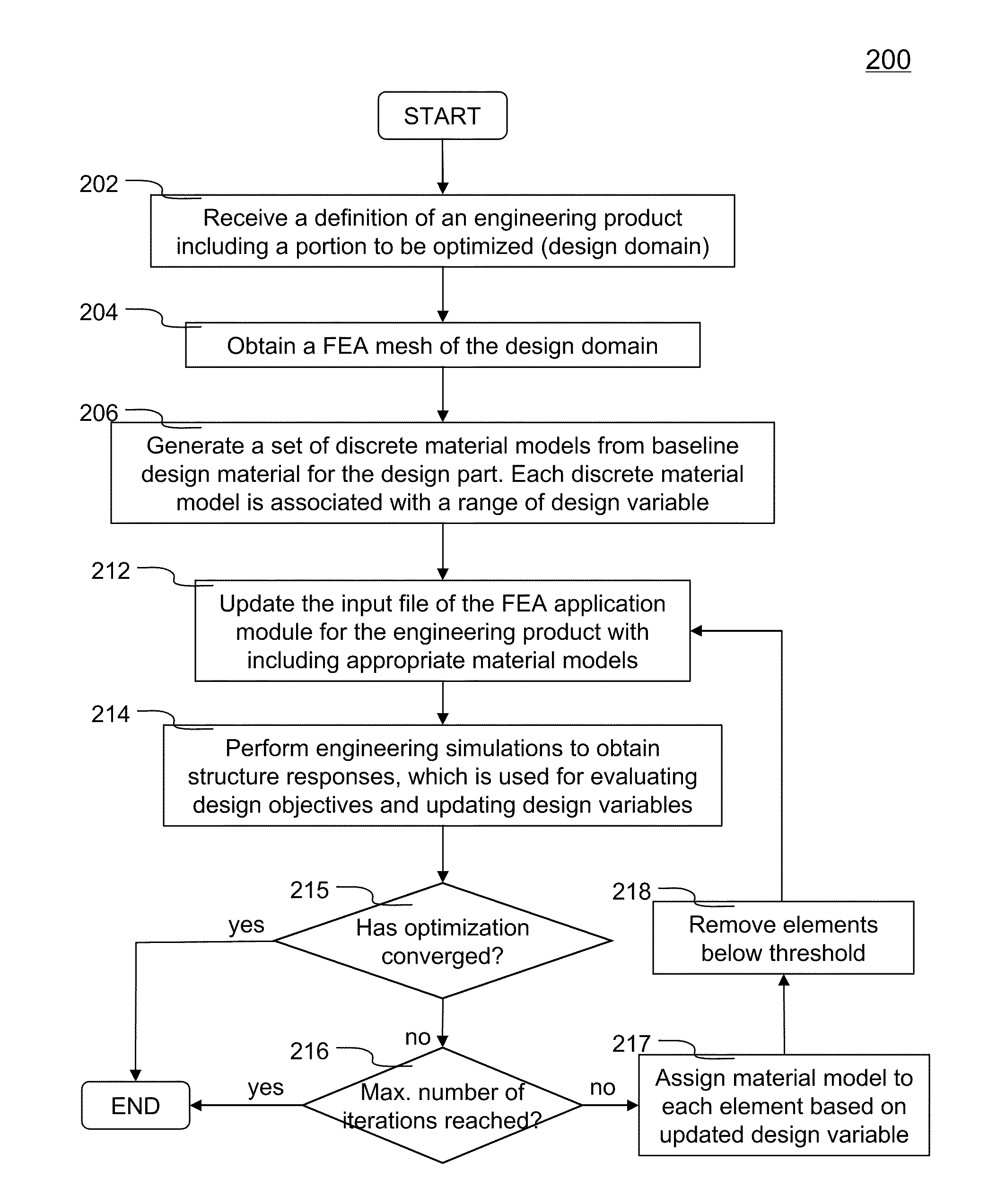
Topology optimization for designing engineering product
ActiveUS20100262406A1Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationElement analysisDesign objective
Improved topology optimization for engineering product design is disclosed. An engineering product including a design domain to be optimized is defined. Design domain can be a portion of or the entire engineering product. Design objective and optional constraint are also defined such that optimization goal can be achieved. Additionally, initial configuration of the design domain is represented by a finite element analysis (FEA) mesh. Each element or element group is associated with a design variable. A set of discrete material models is created from the baseline material used for the design domain. The set of discrete material models is configured to cover entire range of the design variable and each discrete material model represents a non-overlapping portion. Each element representing the design domain is associated with an appropriate discrete material model according to the design variable. Structure response of entire engineering product is obtained via FEA to evaluate design objective and update design variable.
Owner:ANSYS
Method for controlling machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN104077442AReduce machining accuracyShorten the processing cycleSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, extracting local structural features of the large integrated thin-walled part; 2, performing finite element simulative analysis on local structural features to obtain an optimized cutting technology; 3, numerically modeling a large integrated workblank, and loading an initial internal stress; 4, protocoling a tool path, namely protocoling the machining sequence of the feature structures; 5, performing simulative analysis on the integrated structure to obtain a predicted deformation result under the condition of process technology; 6, regulating and optimizing a clamp scheme to control machining deformation. The method adopts finite element simulation, can analyze and predict in advance before the actual machining of the parts, and thereby corresponding machining strategy is adjusted, machining deformation is effectively controlled, production cycle of the parts is shortened, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING CHENGUANG GRP +1
Eulerian-Lagrangian mapping for finite element analysis
ActiveUS7167816B1Overcome disadvantagesSuitable for studyingComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationEulerian lagrangianElement analysis
A computer system and method for performing a finite element analysis to determine the final dimensions of an object comprising automatically switching from an Eulerian formulation to a Lagrangian formulation during the analysis.
Owner:ANSYS
Finite element analysis-based variable-element permanent magnet synchronous motor modeling method
ActiveCN103853891AAchieve real-time controlImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsHysteresisElement analysis
The invention relates to a finite element analysis-based variable-element permanent magnet synchronous motor modeling method which comprises the following steps of constructing a three-dimensional finite element electromagnetic field simulation model of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and performing transient field road coupling analysis on the three-dimensional finite element electromagnetic field simulation model to obtain a large quantity of characteristic parameters; creating an improved permanent magnet synchronous motor voltage equation and a torque equation; constructing a simulation model of the permanent magnet synchronous motor according to an improved permanent magnet synchronous motor math model; leading all the obtained characteristic parameters into corresponding ports of the simulation model to construct a finite element analysis-based variable-element permanent magnet synchronous motor dynamic simulation model. The permanent magnet synchronous motor model modeled by the method disclosed by the invention comprehensively considers the magnetic field saturation effect, the d-q axis cross coupling effect, the eddy current effect, the hysteresis effect and the like; the instantaneity is considered, and the accuracy of the permanent magnet synchronous motor model is improved; the permanent magnet synchronous motor model is particularly suitable for the research on the dynamic processes such as power failure-bepelt and three-phase sudden short circuit of the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
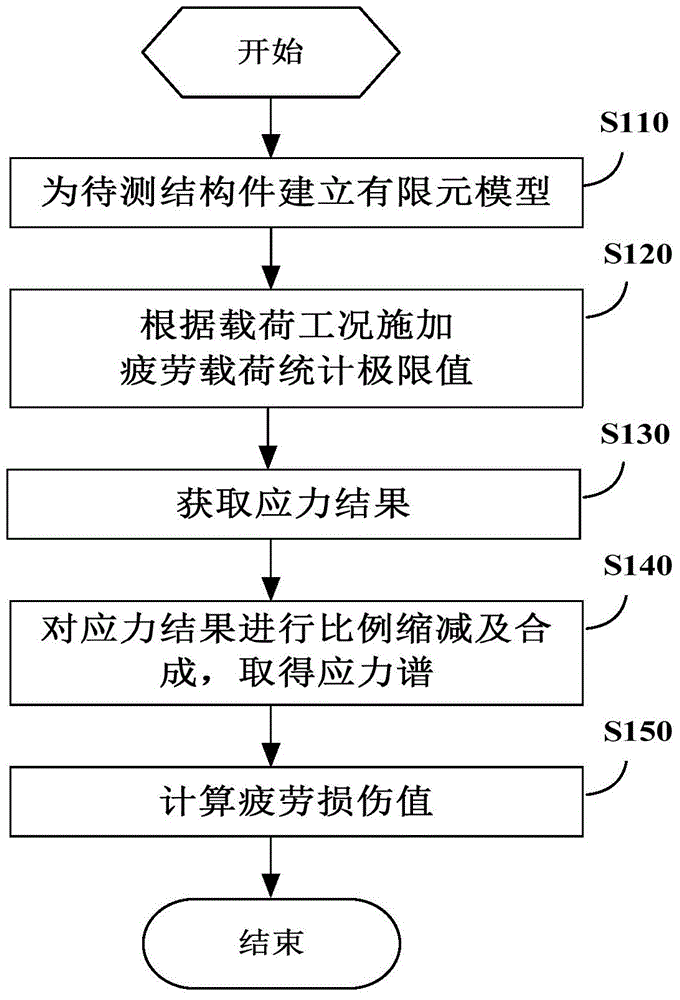
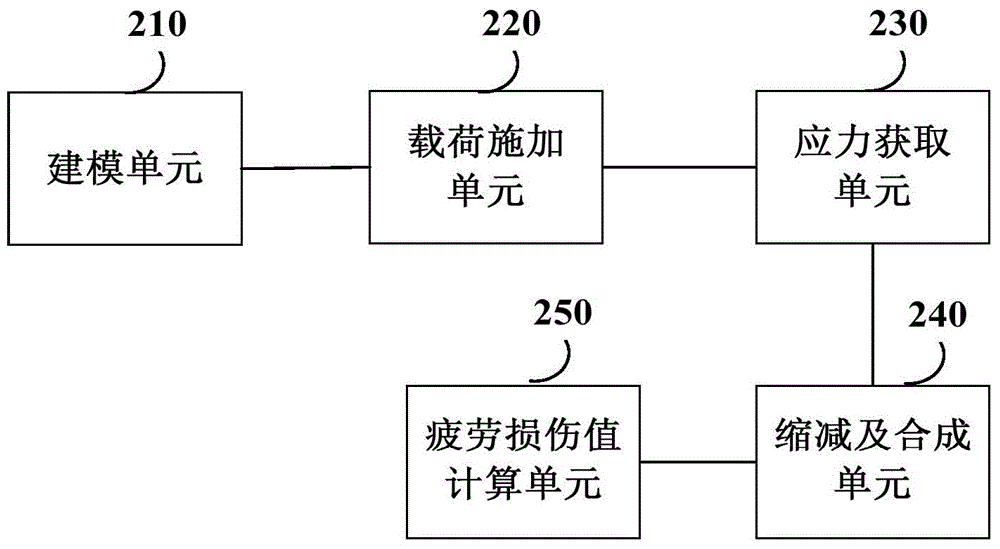
Fatigue analysis method and fatigue analysis device of structural member in wind generating set
ActiveCN104573172AStress calculation results are accurateReflect changes in stress stateSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageElement model
The invention provides a fatigue analysis method and a fatigue analysis device of a structural member in a wind generating set. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a finite element model for a to-be-measured structural member involving bearing connection and related structural members thereof; applying load to the finite element model according to various preset load working conditions respectively; acquiring each node stress result of the to-be-measured structural member under each load working condition through finite element analysis; scaling down the acquired stress results by taking a fatigue load sequence which is pretreated through regularization as a coefficient; synthesizing the stress results under the different load components after scaling down to obtain a stress spectrum of each node of the finite element model of the to-be-measured structural member; calculating a fatigue damage value of the to-be-measured structural member according to the stress spectrum of each node and the stress-life curve of the to-be-measured structural member. By applying the method and the device, the fatigue analysis result of the structural member in the wind generating set is more accurate.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
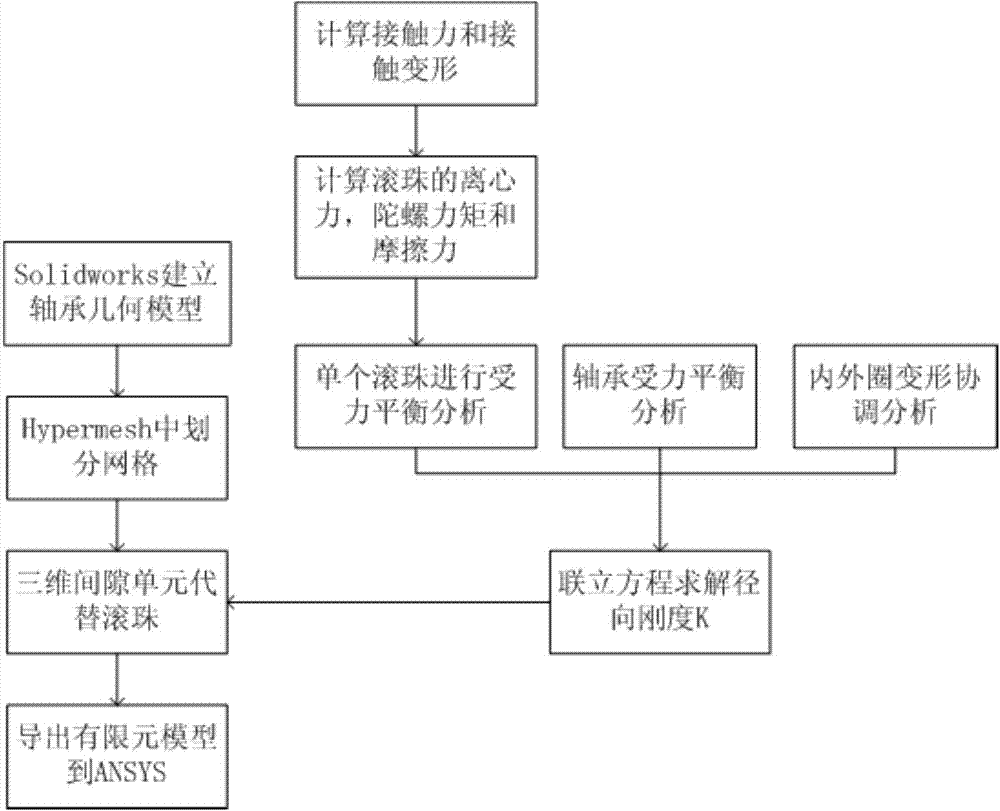
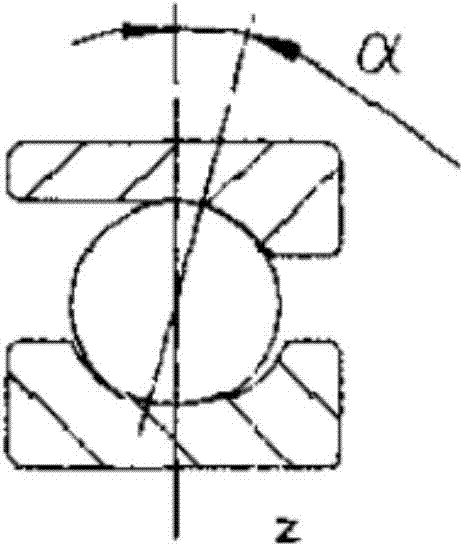
Bearing simplifying method in finite element simulation analysis
InactiveCN104239654AThe result is close to the realSimple calculationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a bearing simplifying method in finite element simulation analysis. According to the method, a three-dimensional gap unit is used for simplifying finite element analysis of an angular contact bearing, and a three-dimensional model of the bearing is drawn in three-dimensional mapping software solidworks. The bearing model is imported into finite element pre-processing software Hypermesh. An outer ring and an inner ring of the bearing are divided into hexahedral meshes. The outer ring and the inner ring of the bearing are connected through the three-dimensional gap unit. The spring stiffness K in the gap unit is worked out through a bearing radial stiffness calculation program. The finite element model is exported from the Hypermesh, then the finite element model is imported into engineering simulation software ANSYS, and mechanical calculation is conducted. According to the method, the calculation amount of finite element analysis can be simplified, the efficiency can be increased, and the calculation accuracy cannot be damaged.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
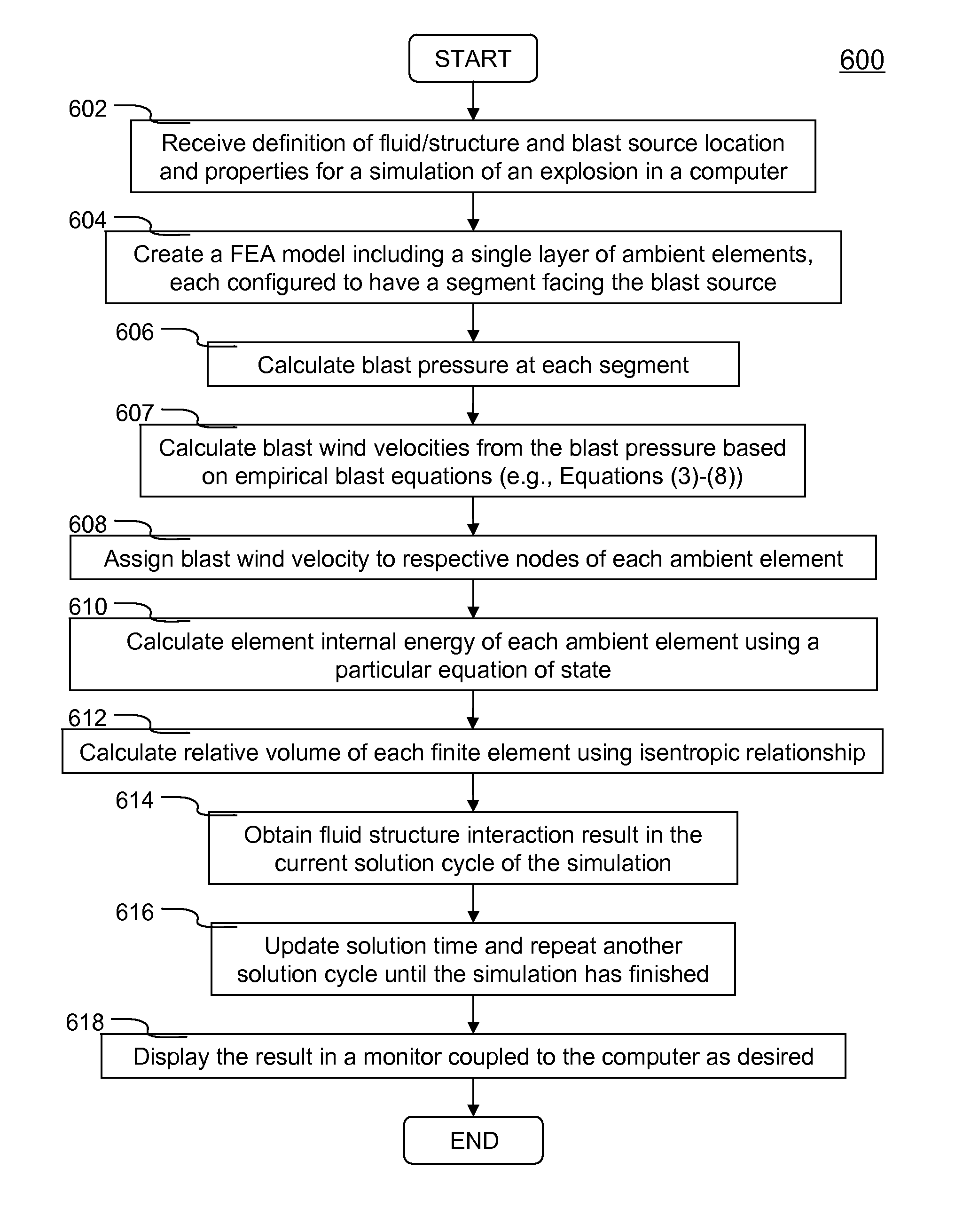
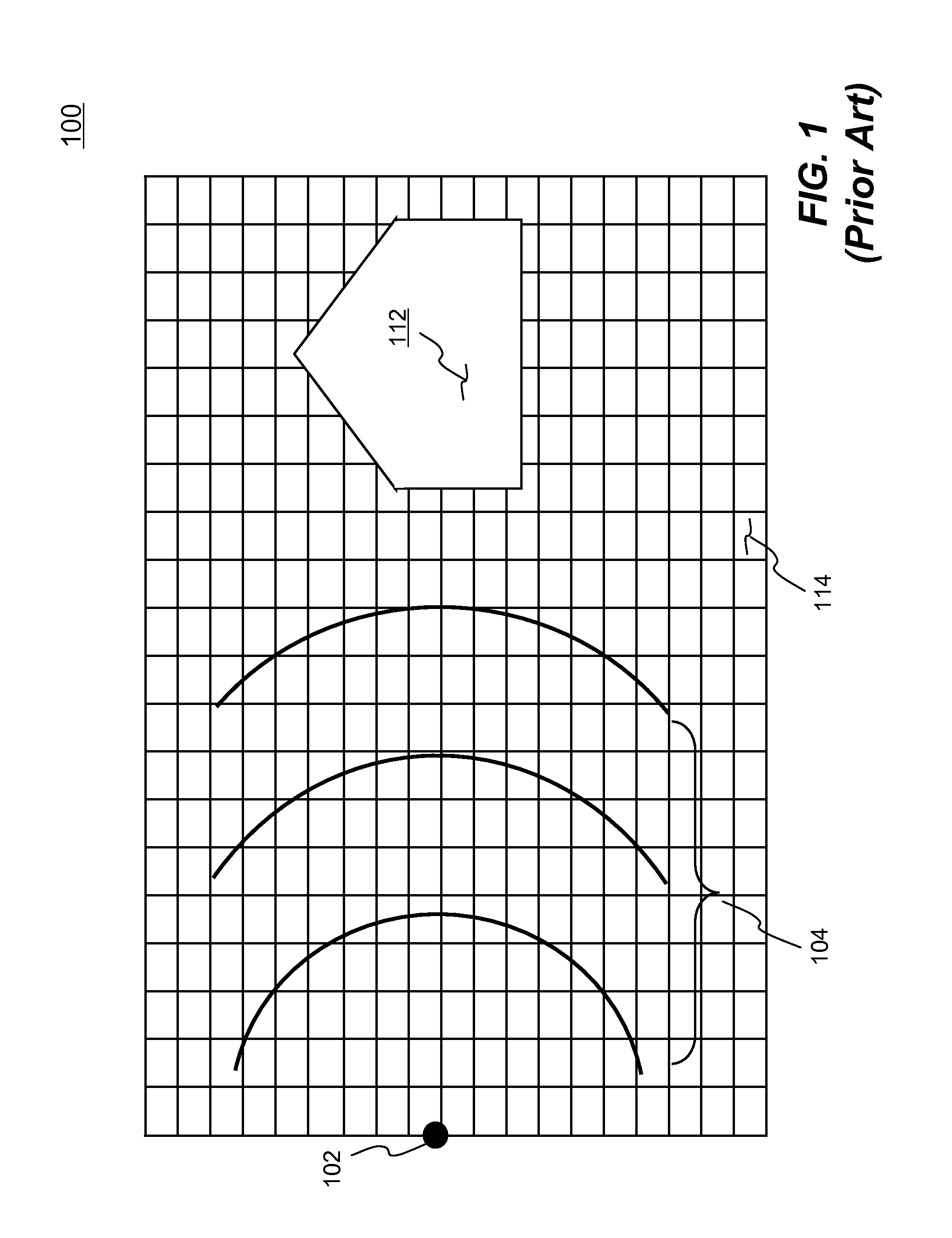
Explosion Simulation in Finite Element Analysis
ActiveUS20100256957A1Reduce computing timeImprove userComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationProduction rateElement analysis
Systems and methods of simulating an explosion in time-marching finite element analysis are disclosed in the present invention. According to one aspect, a method is configured for increasing user (e.g., engineer or scientist) productivity by reducing computation time of simulating fluid-structure interaction due to an explosion. The method comprises a creation of a finite element analysis model that includes structure, surrounding fluid, a blast source of the explosion and a single layer of ambient elements each having a segment representing a boundary of the fluid facing the blast source. Each ambient element is associated with a particular finite element representing the fluid at the boundary. The ambient elements are configured to be situated between the blast source and the structure such that the simulation can be carried on a set of boundary conditions specified thereon. The boundary conditions comprise a set of nodal velocities that are determined from the empirical formula (e.g., Friedlander equation).
Owner:ANSYS
Automatic data conversion method between three-dimensional modeling software and finite element analysis software
InactiveCN101763447AAutomate deliveryEasy way to implementSpecial data processing applicationsSystems designElement analysis
The invention discloses an automatic data conversion method between a three-dimensional modeling software and a finite element analysis software, which comprises the following steps of starting the finite element analysis software, loading the model and performing finite element analysis; starting the three-dimensional modeling software in the finite element analysis software; reading files and performing finite element analysis in the finite element analysis software; saving the result in format of data file by utilizing a data post-processing module and the read and write function of the finite element analysis software; and circularly running the above processes by utilizing the process control command of the finite element analysis software. The automatic data conversion method achieves seamless integration of the powerful modeling function of the three-dimensional modeling software and the finite element function of the finite element analysis software and provides a scientific, high-efficiency and reliable solution for design and analysis of a complicated mechanical system, thereby increasing the product design accuracy and design efficiency.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
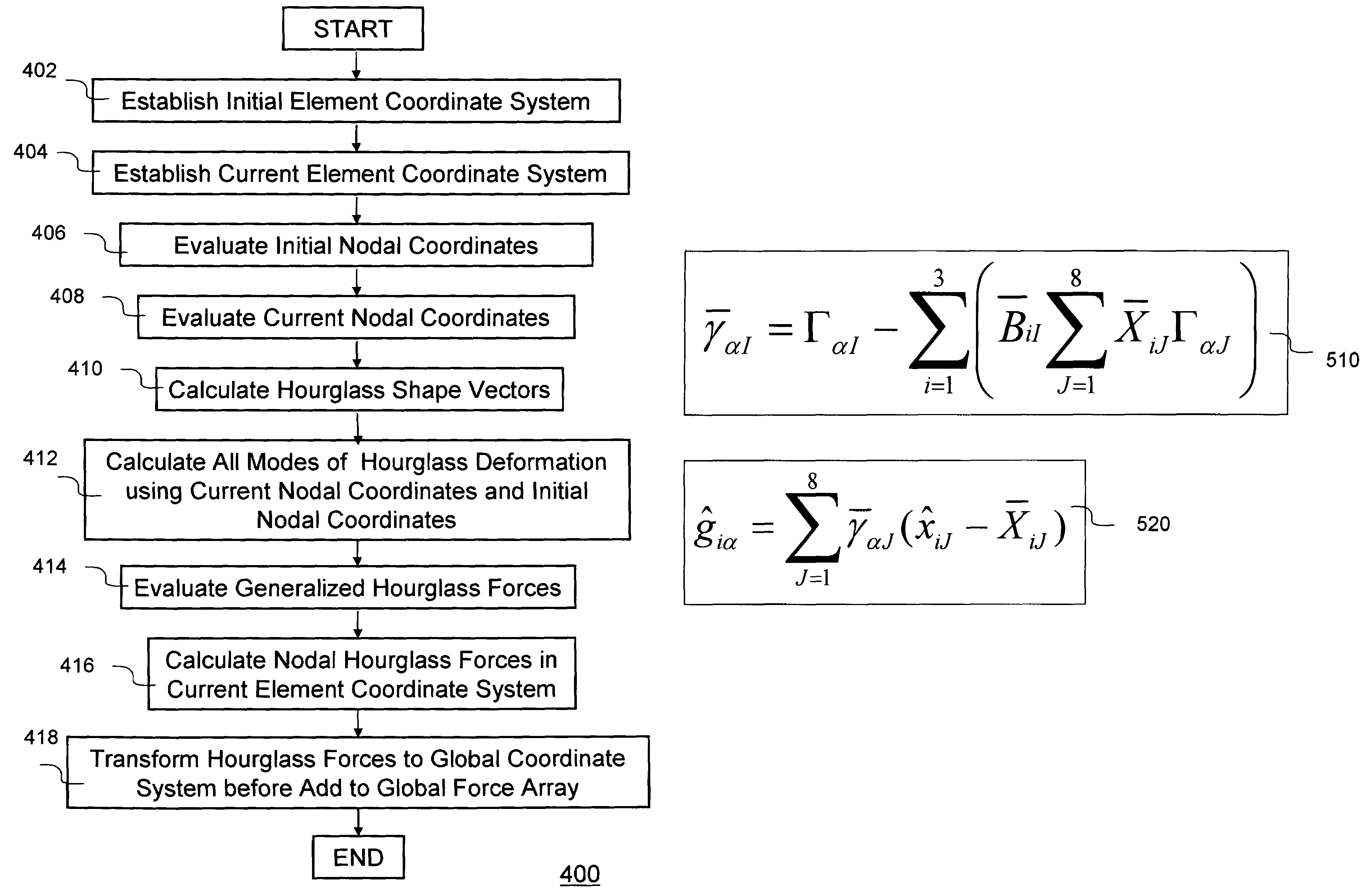
Method and system for controlling hourglass deformations of solid elements in finite element analysis
ActiveUS7392163B1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationNODALElement analysis
Hourglass deformations due to zero-energy or hourglass modes in rank-deficient solid elements must be effectively controlled, or the deformations may grow large and produce an unrealistic deformed geometry. Traditional methods of hourglass control allow error to accumulate by measuring hourglass deformation with incremental terms throughout a solution, which may produce inaccurate results due to unrealistic hourglass deformations. The present invention discloses a new method to control hourglass deformation without any incremental accumulations. Instead the nodal forces to resist hourglass deformations are calculated basing on the initial nodal coordinates and current nodal coordinates at each cycle. The present invention is implemented in a finite element software product.
Owner:ANSYS
Finite element analysis method for formula racing car frames
InactiveCN108170972ASolve problems that cannot be solved by manual calculation in experimentsImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelVehicle frame
The invention provides a finite element analysis method for formula racing car frames, belongs to the technical field of computer aided engineering, and aims at solving the problem that existing racing car frame optimization and analysis are bad in correctness and long in design period. The finite element analysis method comprises the following steps of: A, constructing a three-dimensional model and carrying out meshing to convert the three-dimensional model into a finite element model; B, applying boundary conditions according to each working condition, carrying out finite element analysis and calculation on frame bending rigidity under each working condition, and comparing the analysis result with material bending strength to carry out structure optimization; C, respectively applying forced displacement in opposite directions on two sides of the car frame, carrying out finite element analysis and calculation to obtain torsional rigidity of the car frame, and carrying out structure optimization according to the analysis result; and D, analyzing and comparing whether a fixed frequency of each order modal of the car frame is different from an external main excitation frequency or not, and carrying out structure optimization according to the result. According to the method, the correctness of optimization and analysis is improved, the expenditure is decreased and the design period is shortened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIRUN AUTOMOBILE +2
Method of initializing bolt pretension in a finite element analysis
ActiveUS20100076739A1Small incrementAvoid the needAnalogue computers for vehiclesDesign optimisation/simulationElement analysisMechanical engineering
In one aspect of the invention, each bolt is modeled using a beam element in a FEA model. To apply desired pretension to one or more bolts, at least one pretension-versus-time curve is specified. Each pretension-versus-time curve includes ramp portion, desired pretension portion and optional unloading portion. Duration_of the pretension-versus-time curve generally covers first 0.5-1% of total simulation time of a car crashworthiness analysis. Ramp portion starts from zero to desired pretension in a substantially linear manner, and hence being configured for applying desired pretension to a bolt gradually with smaller increments. Desired pretension portion is configured for ensuring the desired pretension can actually be applied to the beam element during an initialization process—a series of quasi-static analyses. Since the method is independent of the deformation of the beam, the method completely avoids the need to iteratively determine an axial strain or displacement that gives the desired pretension.
Owner:ANSYS
Methods and systems for creating a smooth contact-impact interface in finite element analysis
ActiveUS8180605B1Describe wellRealisticComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceNODAL
Improved systems and methods of creating a smooth contact-impact interface (i.e., a curve fitted surface) in finite element analysis are disclosed. According to one aspect, a smooth contact interface is created for a master segment used for simulating contacts. First, for every nodal point in the master segment, a list of elements that share at least the node is determined. Then a nodal normal vector is calculated using a weighted average of respective element normal vectors of all elements in the list. The calculated nodal normal vector is adjusted for special edge effect, which is an intersection between flat and curved geometries. A set of edge control points are created using a pair of adjacent corner nodes. A mid-element control point is further created for quadrilateral shell elements. The smooth contact interface is configured to encompass all corner nodes and all of the control points.
Owner:ANSYS
Computing method for hub ultimate strength of wind turbine generator system
InactiveCN103366049ACalculation intensityLow costSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelElement analysis
A computing method for hub ultimate strength of a wind turbine generator system belongs to the technical field of wind power generation, and comprises the following steps: modeling by adopting software of finite element analysis, performing finite element mesh generation, setting constraint conditions and computing to obtain a deformation and stress cloud chart. The modeling process is as follows: 1, drawing a 3D model for a hub, importing the 3D model into a finite element software platform, and drawing a 3D entity model for the connection part of blades and the hub and the connection part of a main shaft and the hub in the finite element software; 2, setting material attributes for the blades, the main shaft and the hub, establishing a finite element model thereof, rigidly coupling the blades, the main shaft and the hub, and determining an overall coordinate system of the hub; 3, establishing nodes at root parts of the hub and each blade, converting the nodes into a blade root coordinate system specified by Germanischer Lloyd, then rigidly coupling the nodes to the blades, so that the load can be transmitted to the hub through the blades. The computing method facilitates accurate computation of strength performance of the hub, saves the computing time and improves the computing efficiency.
Owner:CHINA CREATIVE WIND ENERGY +3
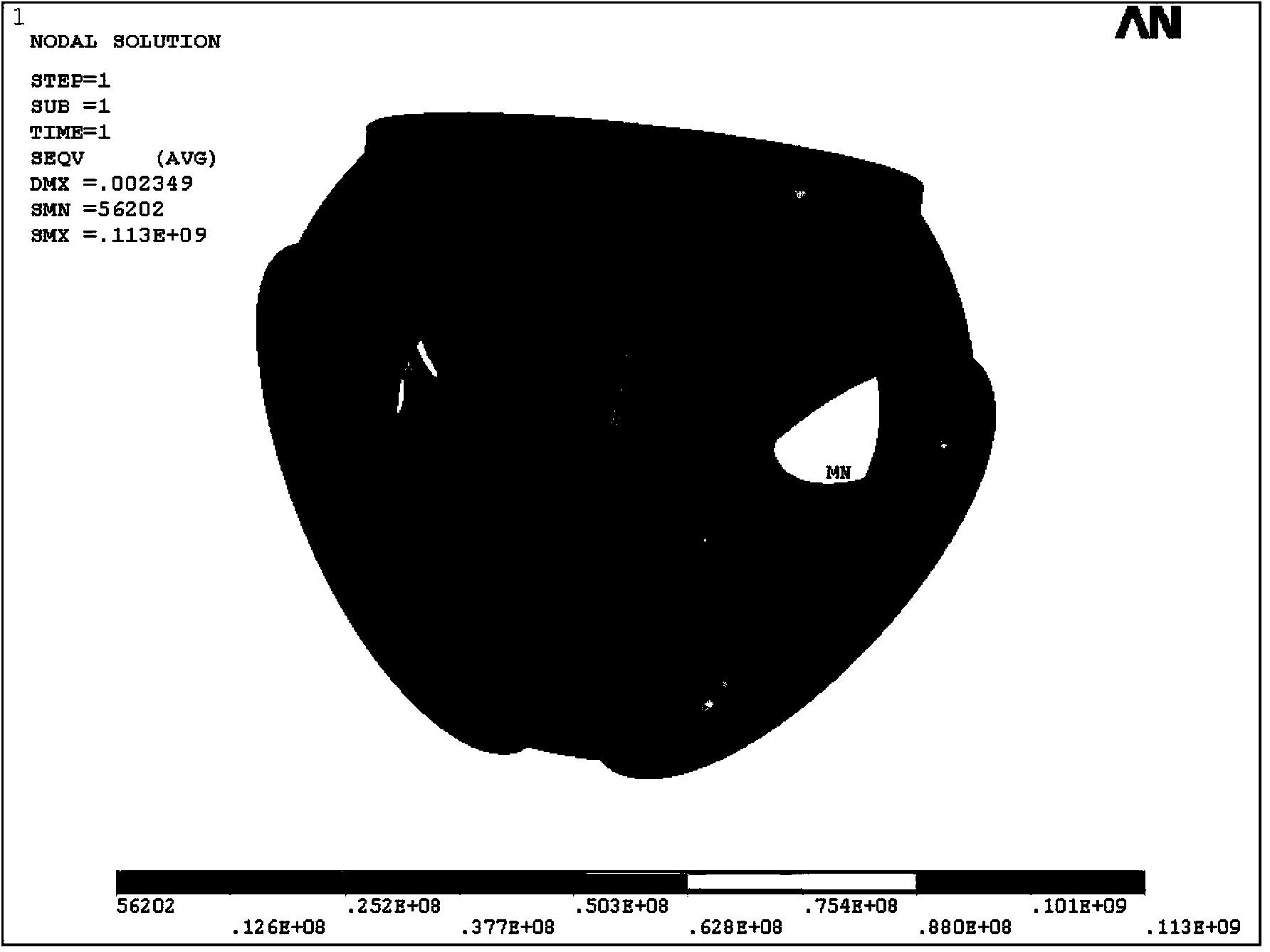
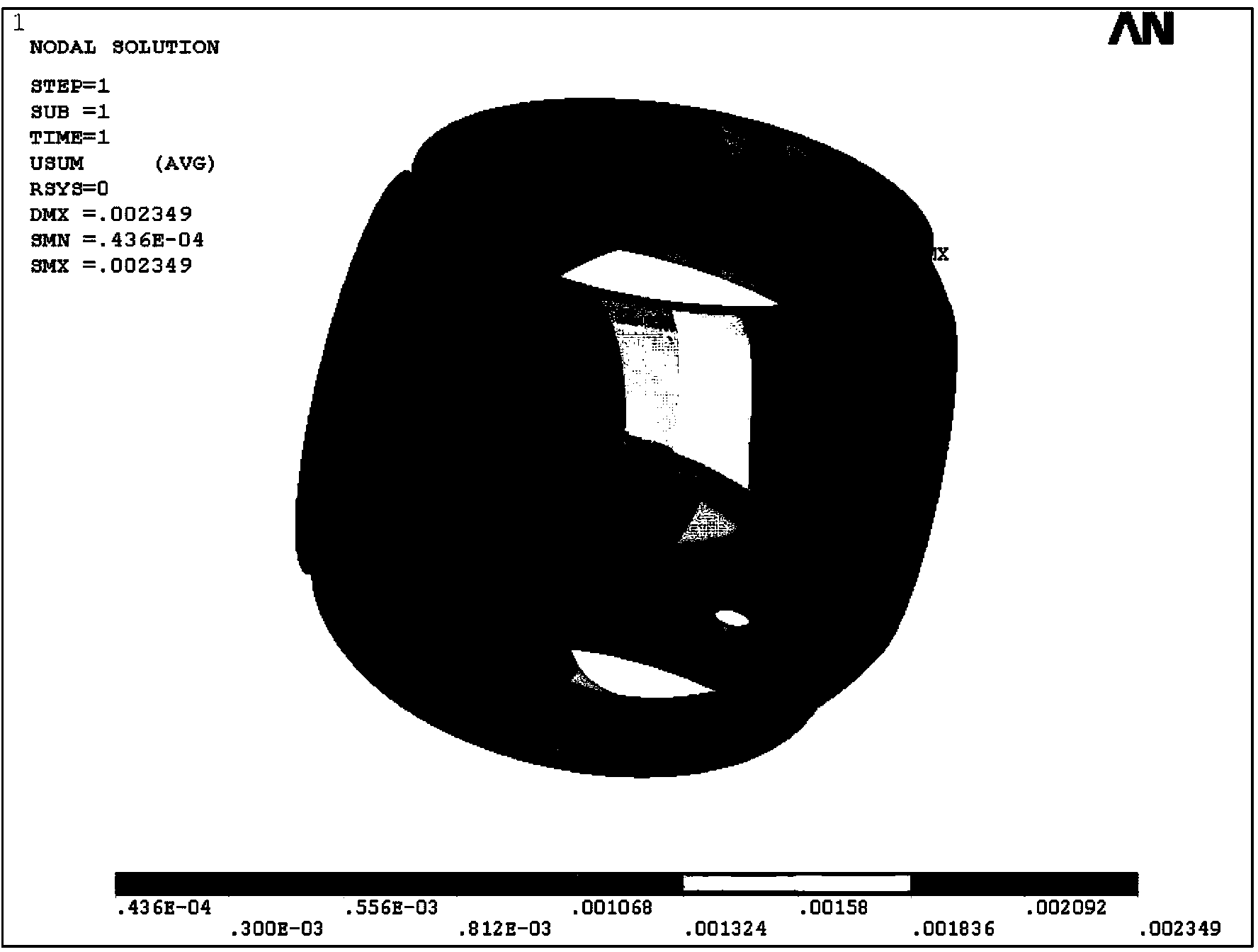
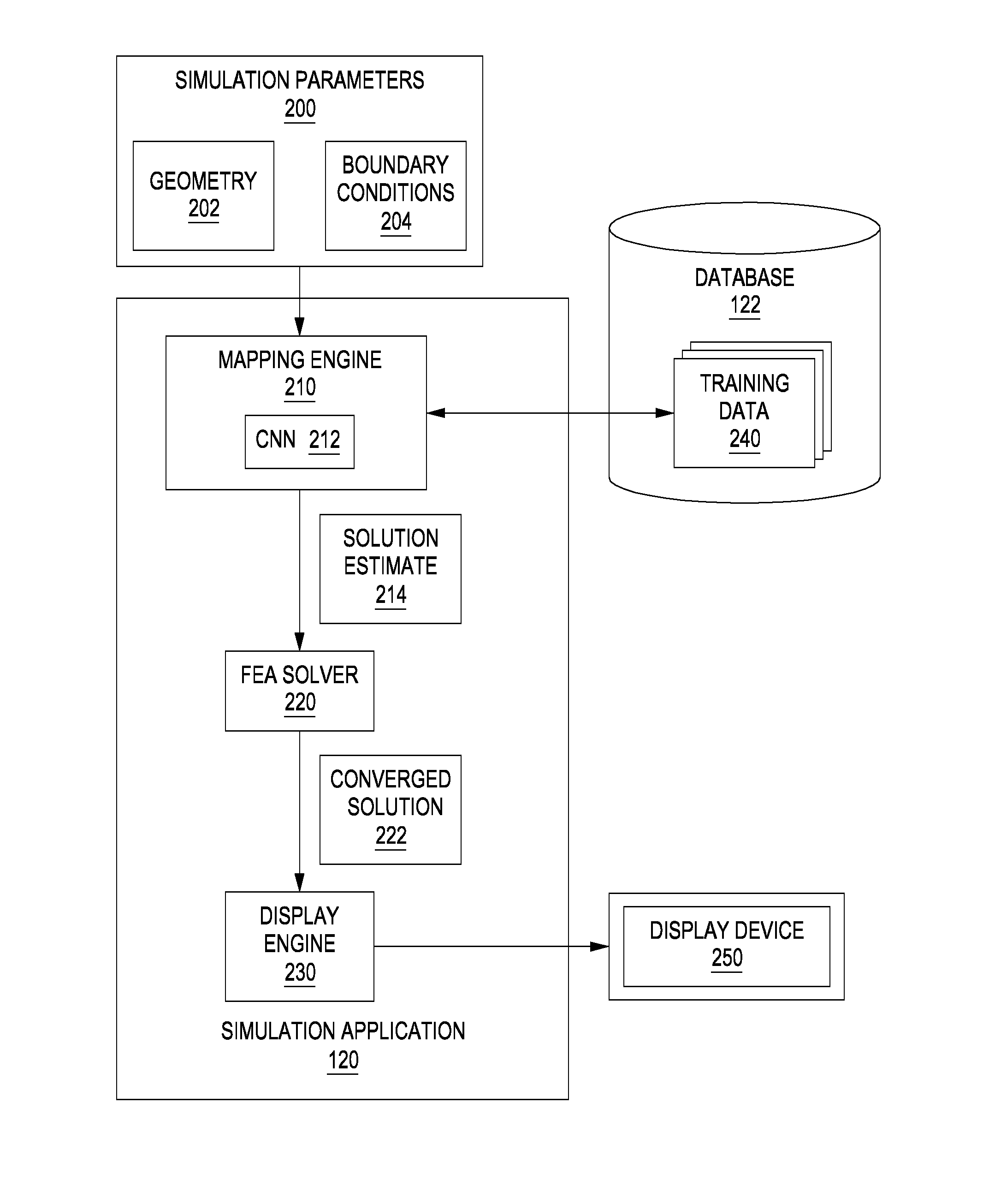
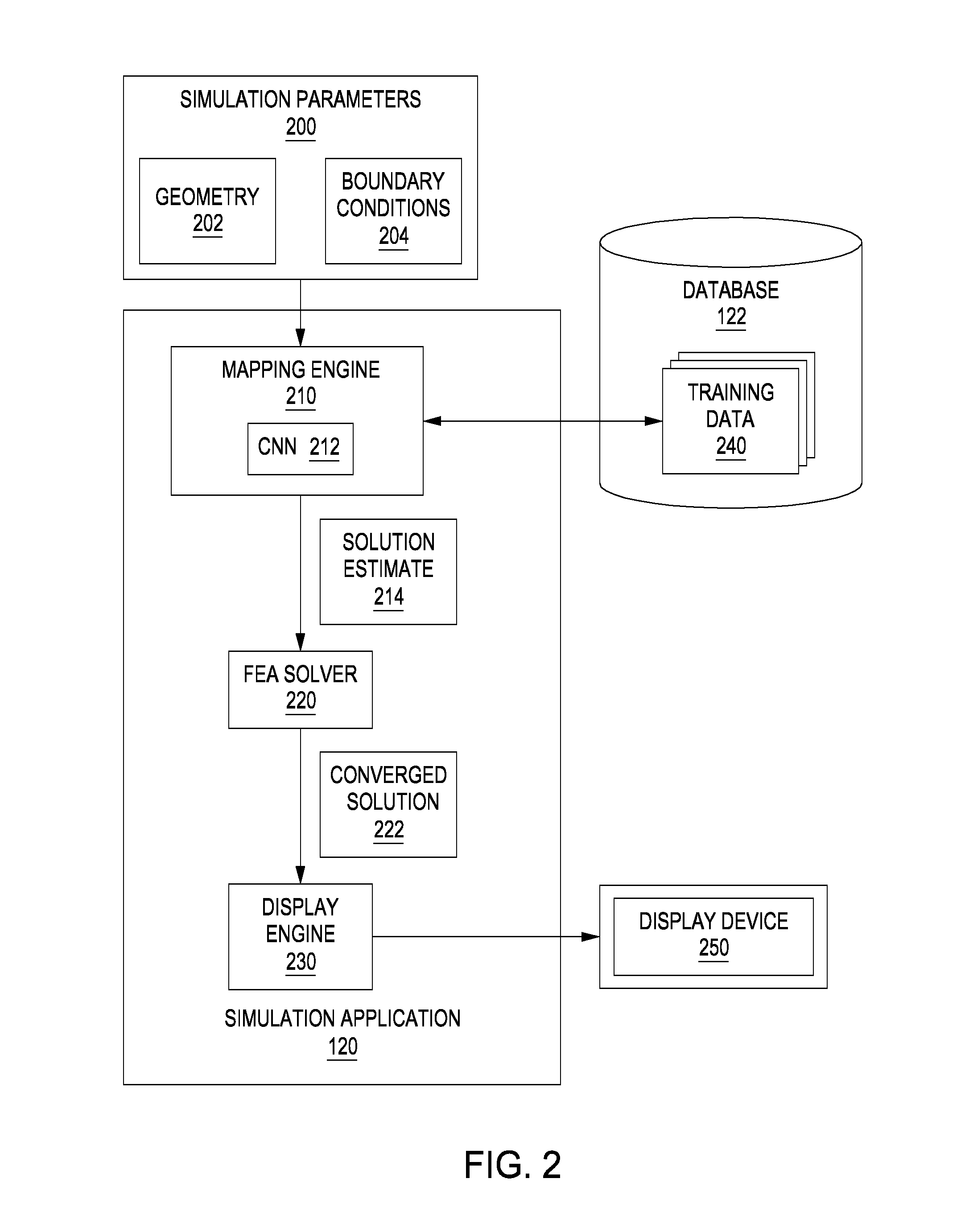
Techniques for warm starting finite element analyses with deep neural networks
ActiveUS20170032068A1Fast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationMachine learningElement analysisComputer science
A simulation application receives simulation parameters associated with a simulation to be generated. The simulation parameters include geometry associated with the simulation and corresponding boundary conditions. The simulation engine processes the simulation parameters and then, using a neural network, generates a solution estimate. Based on the estimated solution, the simulation engine then executes a finite element analysis solver using the solution estimate as a starting point. The FEA solver iterates until a converged solution is reached. The converged solution is then provided to the end-user.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Remote finite element analysis method serving for industry alliance
ActiveCN104077428ARealize interactive operationImprove the level ofSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelElement analysis
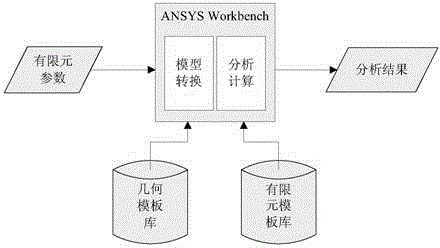
The invention provides with a remote finite element analysis method serving for an industry alliance. The remote finite element analysis method comprises the steps of (1) finite element template extraction, namely classifying and analyzing parts needing finite element analysis in the products of member enterprises in the industry alliance, and extracting finite element templates, including boundary condition types and analysis process parameters, (2) geometric model construction, namely performing geometric modeling on the structures of the needing finite element analysis in the products of the member enterprises in the industry alliance by use of a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) system mainly in a parametric modeling manner and a user-defined modeling manners, (3) boundary condition calibration, namely performing necessary calibration on pels, to which the boundary conditions are applied, in geometric models, thereby taking the geometric models as parameter input interfaces of finite element analysis, (4) finite element model conversion, namely converting the geometric models into finite element models by use of ANSYS Workbench, (5) remote finite element calculation, namely completing remote finite element analysis on the parts by controlling a collaborative simulation environment by use of a command stream, (6) finite element analysis result feedback, namely realizing three-dimensional visual feedback of the finite element analysis results by use of WebGL technology, and (7) public service platform implementation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Topology optimization for designing engineering product
ActiveUS8126684B2Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationElement analysisDesign domain
Improved topology optimization for engineering product design is disclosed. An engineering product including a design domain to be optimized is defined. Design domain can be a portion or the entire engineering product. Design objective and optional constraint are defined such that optimization goal is achieved. Additionally, initial configuration of the design domain is represented by a finite element analysis (FEA) mesh. Each element or element group is associated with a design variable. A set of discrete material models is created from the baseline material used for the design domain. The set of discrete material models is configured to cover entire range of the design variable and each discrete material model represents a non-overlapping portion. Each element representing the design domain is associated with an appropriate discrete material model according to the design variable. Structure response is obtained via FEA to evaluate design objective and update design variable.
Owner:ANSYS INC
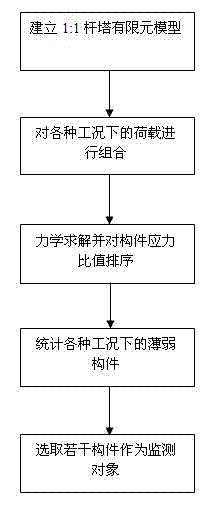
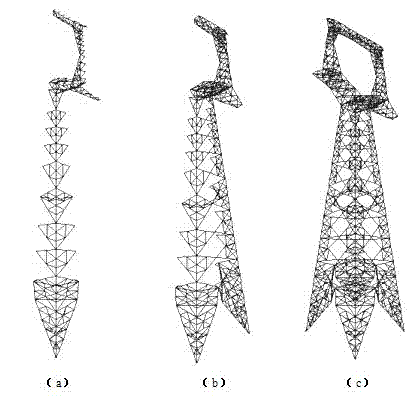
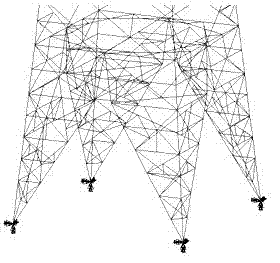
Tower weak component location method based on finite element dynamic analysis
ActiveCN102930103AAccurate locationFailure warningSpecial data processing applicationsThree dimensional simulationStress ratio
The invention discloses a tower weak component location method based on finite element dynamic analysis and belongs to the field of online monitoring of disaster prevention and reduction of a power transmission line. The method includes building a three-dimensional simulation model according to a tower structure, utilizing an orthogonal test method to select a load set, simulating all possible dynamic loads in operation of the tower, conducting finite element dynamic calculation, obtaining axial stress ratio of tower components according to simulation results under each load combination and selecting weak components according to the axial stress ratio. The tower weak components can be accurately located by means of the method. The method can be used for online monitoring of disaster prevention and reduction of the power transmission line and is capable of directly conducting effective early warning on effect failure of the tower components.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method of performing a finite element analysis of a composite structure
The invention provides a method of analyzing a building made from Expanded Poly Styrene (EPS) which is coated on the inside and outside with Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) or other strengthening coating. The building is designed in a CAD program. Then, the building is divided up into small volumes in the CAD program or in a Finite Element Analysis program using an automeshing program. Plates are added to the inner and outer surfaces of the volumes using copying and automeshing commands. Appropriate characteristics of the EPS and GFRC are assigned to the volumes and plates. A FEA analysis can then be run.
Owner:SAEBI NASSER
A flexible mechanism topology optimization design method based on adaptive constraint
ActiveCN109583091AResolve connectionMeet the design requirementsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a flexible mechanism topology optimization design method based on self-adaptive constraint. The method is used for solving the problem of single hinge existing in flexible mechanism topology optimization. The method comprises the following steps that an initial design area is given, finite element grids are divided, a finite element model of a current effective structure isformed, and meanwhile a mapping relation data file of a maximum design area grid model and the finite element model of the current effective structure is generated and stored; Performing finite element analysis to obtain displacement vector data under an actual load and a unit virtual load; Establishing a function expression of adaptive constraint based on the mutual strain energy, the flexibility, the volume and the mechanism comprehensive flexibility function change rate, establishing an approximate optimization model, converting the model into an approximate quadratic mathematical programming model, and obtaining a topological variable solution; And automatically updating the structure topological variable, and reading the structure grid and the model data to form a new structure system finite element model. The above steps are repeated, and the optimal topology can be obtained when the iteration process converges.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
10-kv three-core cable finite element thermal analysis method
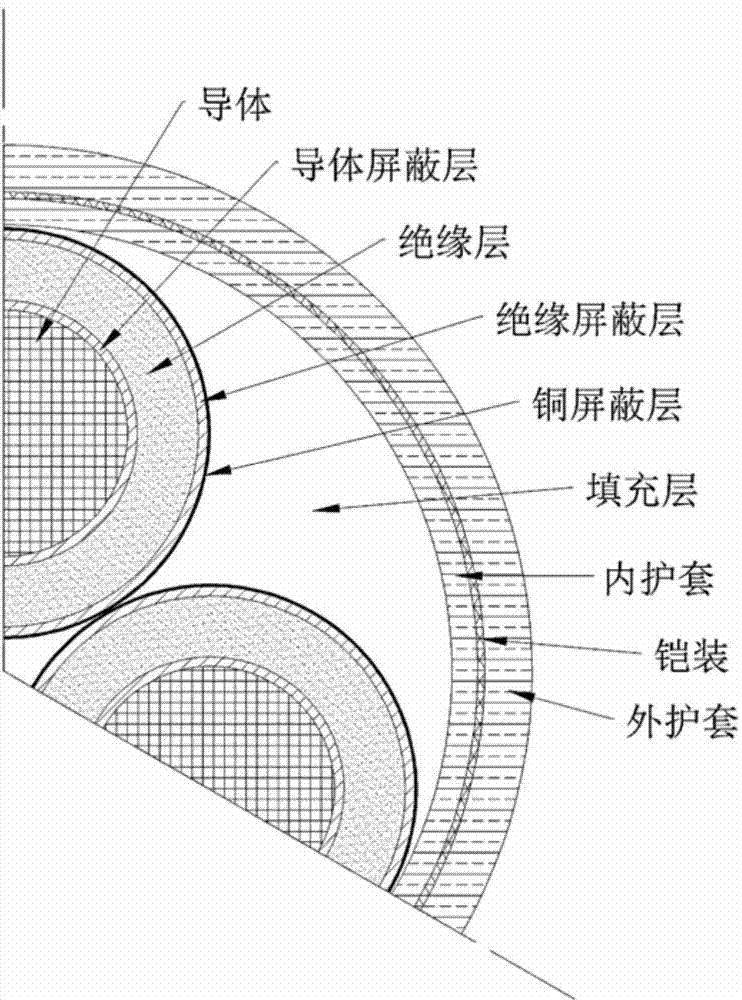
InactiveCN104731898AIntuitive understanding of heating and cooling conditionsThe modeling process is intuitive and convenientData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsProduction rateCurrent load
The invention discloses a 10-kV three-core cable finite element thermal analysis method. The method comprises the steps of 1, determining the geometric structure, size and material parameters of a 10-kV three-core cable; 2, utilizing the Solid Works for building a three-dimensional model according to the geometric structure of the 10-kV three-core cable; 3, importing the three-dimensional model built by the Solid Works into ANSYS and converting the three-dimensional model into a geometric model in the ANSYS; 4, calculating the heat production rate of a heating portion according to the current loaded by the cable and parameters of the heating portion of the cable; 5, loading material parameters of layers in the ANSYS, dividing units and applying loads to obtain the temperature field distribution result of the 10-kV three-core cable. According to the 10-kV three-core cable finite element thermal analysis method, the three-dimensional model building function of the Solid Works and the finite element analysis function of the ANSYS are combined, three-dimensional temperature field simulation of the 10-kV three-core cable is achieved, the operational process is visual and convenient, the model is precise and reliable, the operation efficiency is high, and the method can be popularized in finite element thermal analysis of complex structures like cable intermediate connectors.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Finite element analysis method of composite material
InactiveCN103455679AHigh simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelMathematical model
The invention relates to a finite element analysis method of a composite material. The method comprises the following steps: 1, building a mathematic model, i.e. building a three-dimensional model by utilizing three-dimensional software; 2, defining material attributes for the built model by utilizing finite element software, performing mesh generation, and converting the model into a finite element model, wherein the material attributes are defined according to the anisotropy of the material, i.e. the winding direction and winding thickness of each layer and the failure criterion of the material are defined; 3, loading boundary conditions on the finite element model, loading conditions on the model according to an actual stress situation, and simulating the actual situation; 4, performing finite element analysis, so as to obtain a stress distribution cloud picture and a displacement situation graph. When the finite element analysis method is used for analysis, the material attributes are defined according to the anisotropy of the material, and calculation is performed respectively according to the winding direction and winding thickness of each layer, so that the winding direction and residual pretightening force of each layer of the composite material can be well simulated.
Owner:XIANGTAN ELECTRIC MFG CORP LTD
Method and system for numerically simulating foam-like material in finite element analysis
ActiveUS7308387B1High materialEliminate requirementsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCompressible materialBi-isotropic material
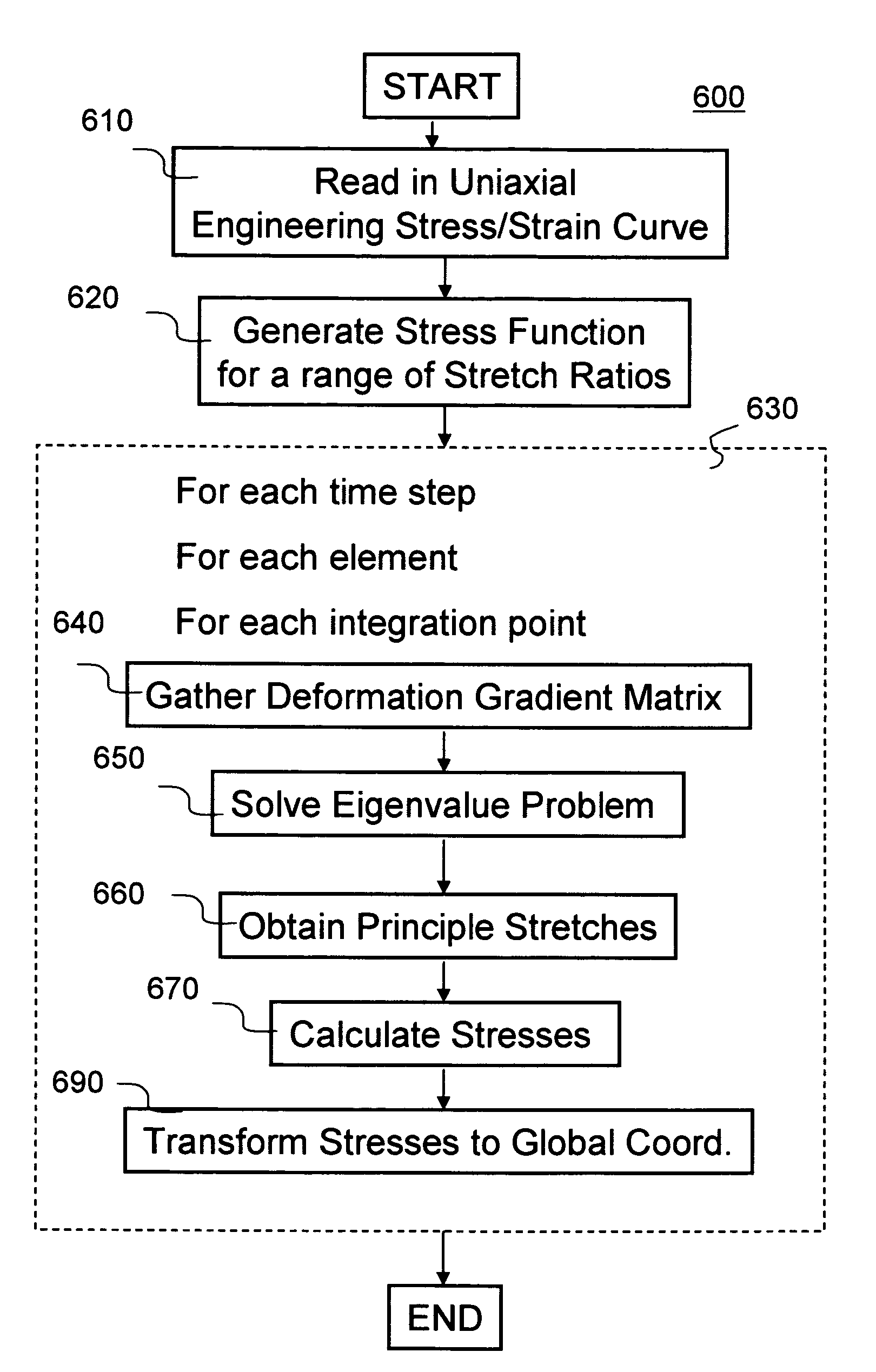
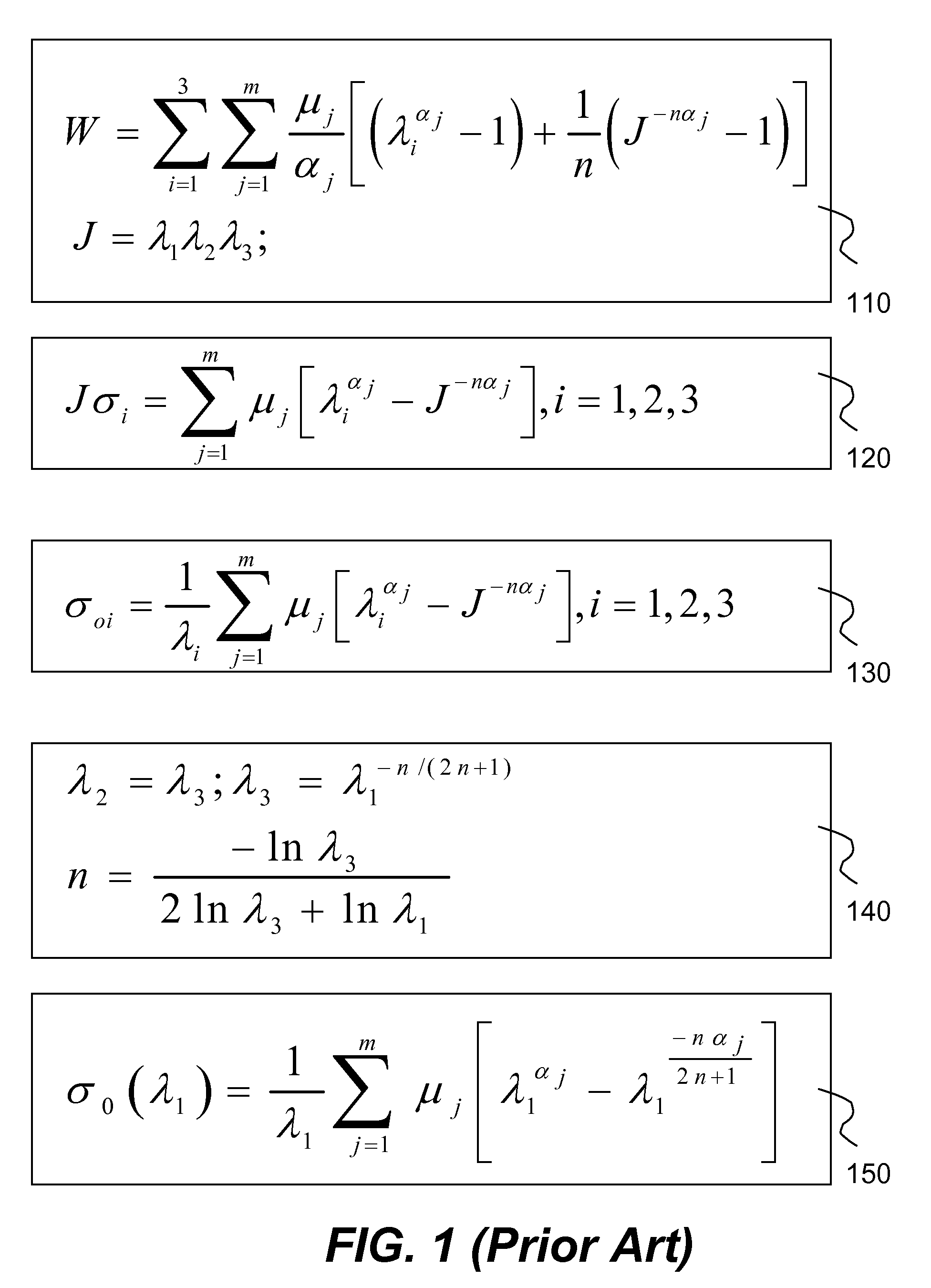
A method and system to numerically simulating structural responses of a highly compressible material such as foam in finite element analysis is disclosed. According to one aspect of the simulation, a new improved method for calculating structural responses is derived using the following assumptions: uniaxial loading and isotropic material. As a result of the new method, Ogden polynomial stress function f(λ) is replaced by a tabulated function depending upon only a set of stress-strain curves obtained via uniaxial tension and compression tests. The method is implemented in a finite element analysis software product.
Owner:ANSYS
Method for determining plastic forming limit of sheet material based on finite element calculation analysis
ActiveCN109284515AShort cycleShorten the cycle of experimentsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPost yieldEngineering
The invention provides a method for determining plastic forming limit of sheet material based on finite element calculation analysis. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining the elastic modulus, Poisson's ratio, yield strength and post-yield stress of the sheet material Strain correspondence; (2) establishing the geometrical models of punch, concave die, blank holder and sample; (3) adding the corresponding material properties and setting the corresponding friction coefficient in the material model of the finite element software; 4) determining that applied load accord to the actual downward pressure amount and downward pressure of the blank holder ring; (5) controlling the downward pressing displacement of the punch, that is, the downward pressing amount;(6) meshing the sample; (7) defining the calculation time; (8) obtaining the results of stress-strain evolution in a sample forming experiment, and outputting the stress-strain nephogram of all the units; (9) using S-G filter to perform first and second order fitting on main strain. The invention provides reliable judging basis and criterion for obtaining accurate results of sheet metal stamping forming.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Intelligent model constructuring method for analyzing cavity wall rock stability
InactiveCN1752356ASolving Modeling DifficultiesImprove actual analysis and prediction capabilitiesArtificial islandsFoundation testingElement analysisEngineering
The invented method includes the following steps: firstly, defining object problem influence factor, selecting model structure, adopting orthogonal testing design or uniform testing design method to make optimization design for influence factor, sampling range and sampling frequency, then making finite element analysis of designed value to form main sample self-group of the intelligent model, making the main sample self-group undergo the process of characterization treatment, then utilizing the value obtained after characterization treatment to construct intelligent analysis model by utilizing neural network algorithm.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Shot peening strengthening treatment process parameter determination method based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN104484538AOptimum Process ParametersSave human effortSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a shot peening strengthening treatment process parameter determination method based on finite element analysis. The shot peening strengthening treatment process parameter determination method based on the finite element analysis is characterized in that a local finite element model of a pellet and a shot-peened material is built by utilizing the material properties of the pellet and shot-peened material; the finite element analysis is carried out by setting different technological parameters, so that the maximum average stress is obtained, and an optimal regression equation is produced by utilizing a regression analysis method; the shot peening strengthening treatment process parameter is determined through the optimal regression equation. According to the shot peening strengthening treatment process parameter determination method, the change rule of the residual internal stress along with the layer depth under different parameters and the distribution situation of the residual stress is found by researching the internal relation between the shot peening strength and the shot peening process parameter, so as to scientifically and reasonably determine the shot peening process parameter according to the requirement on shot peening strength.
Owner:滁州汽车与家电技术及装备研究院 +1
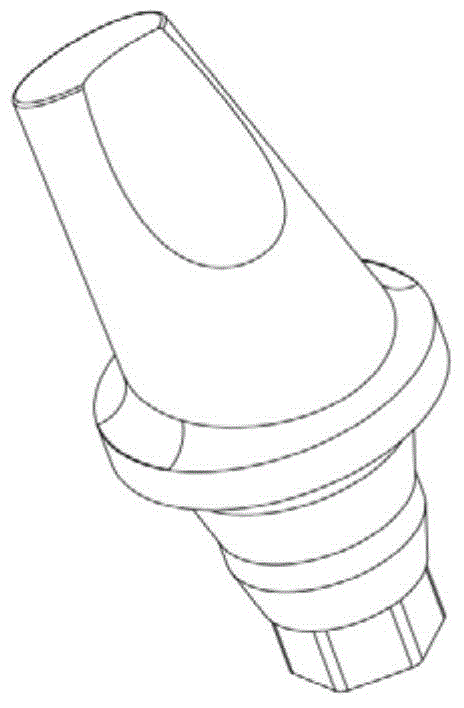
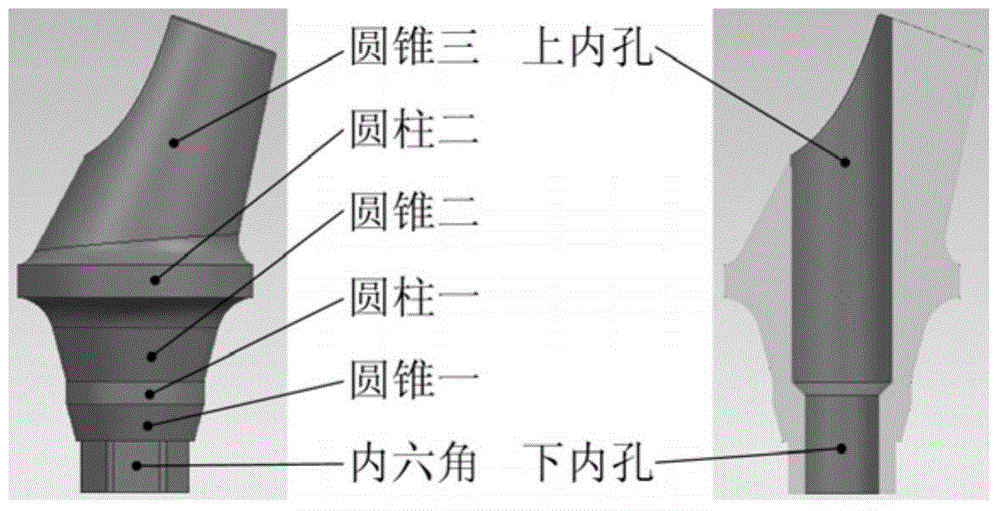
Individual abutment and manufacturing method thereof
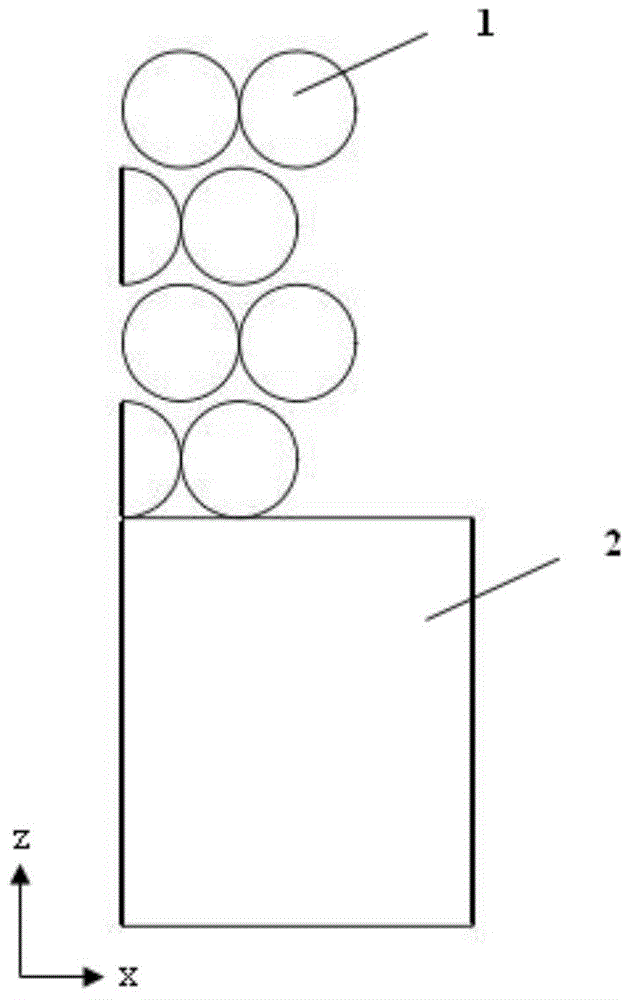
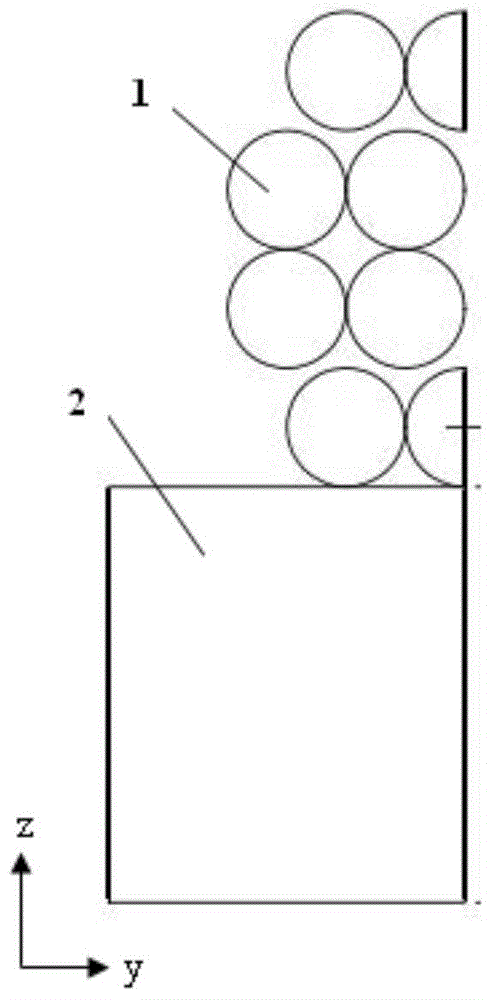
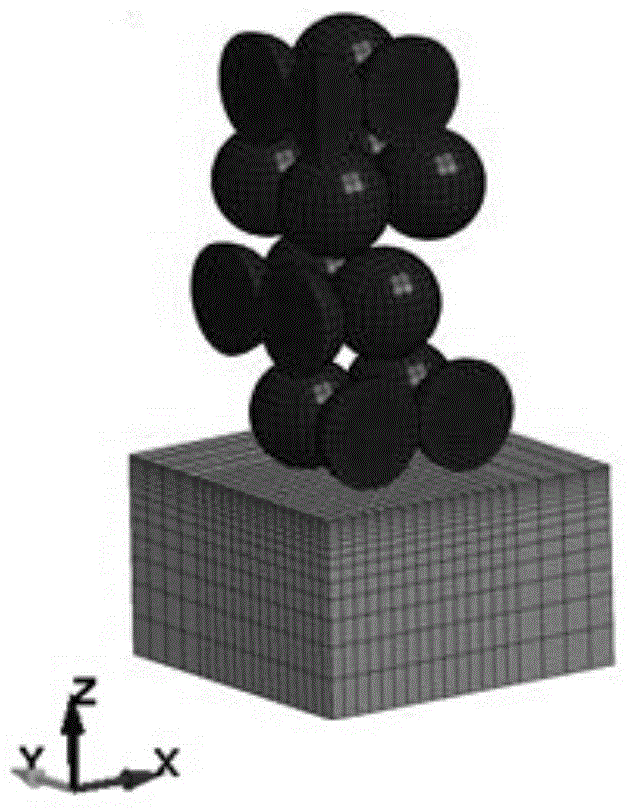
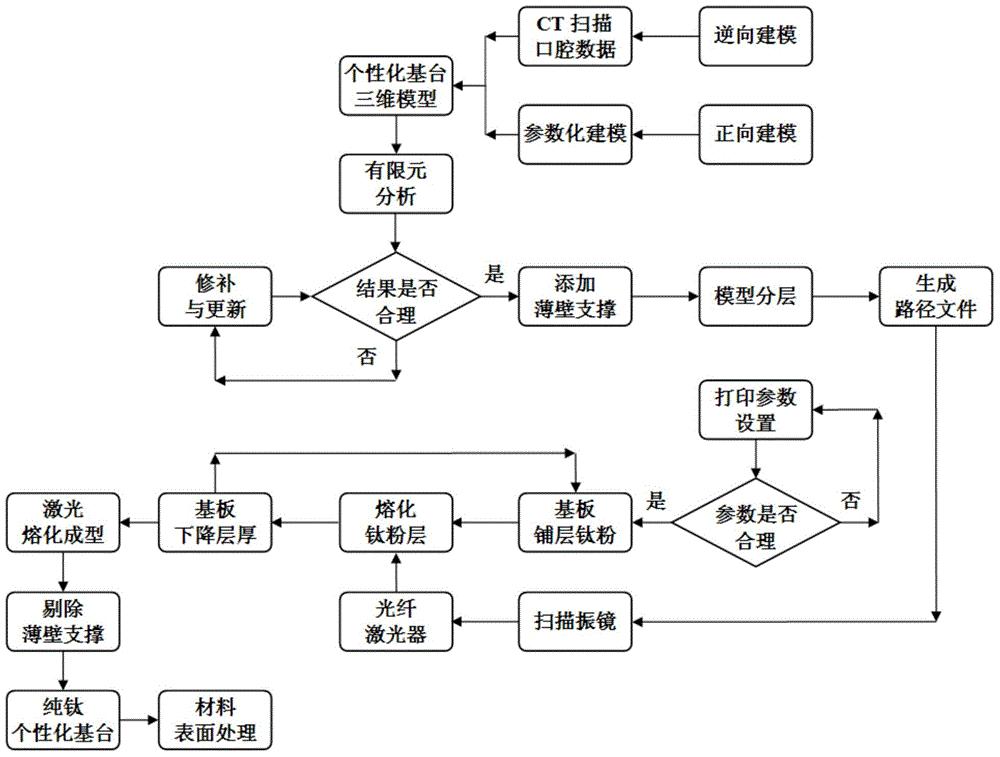
ActiveCN105055037AFit closelyImplement a parametric design processDental implantsImpression capsSelective laser meltingComputed tomography
The invention relates to an individual abutment and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out reverse modeling through CT scanning and carrying out parametrization design on a model through Unigraphics NX, implementing precise repairing on the abutment model, carrying out simulation analysis on the abutment model by virtue of a finite element analysis method, and implementing model optimization design according to a finite element stress analysis result so as to meet the attributes of an abutment material; carrying out three-dimensional hierarchical slicing treatment on the abutment model meeting the attributes of the abutment material, and promoting the generation of a corresponding path file; and according to the path file, reasonably controlling the parameters of selective laser melting equipment and molding so as to obtain the individual abutment. The manufacturing method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively guaranteeing the accuracy of stress direction and size of the abutment as well as the precision of molding, and the manufactured individual abutment can fit to jaw characteristics of a patient more precisely compared with the prior art, so that comfort in use is improved and the service life of the abutment is prolonged.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
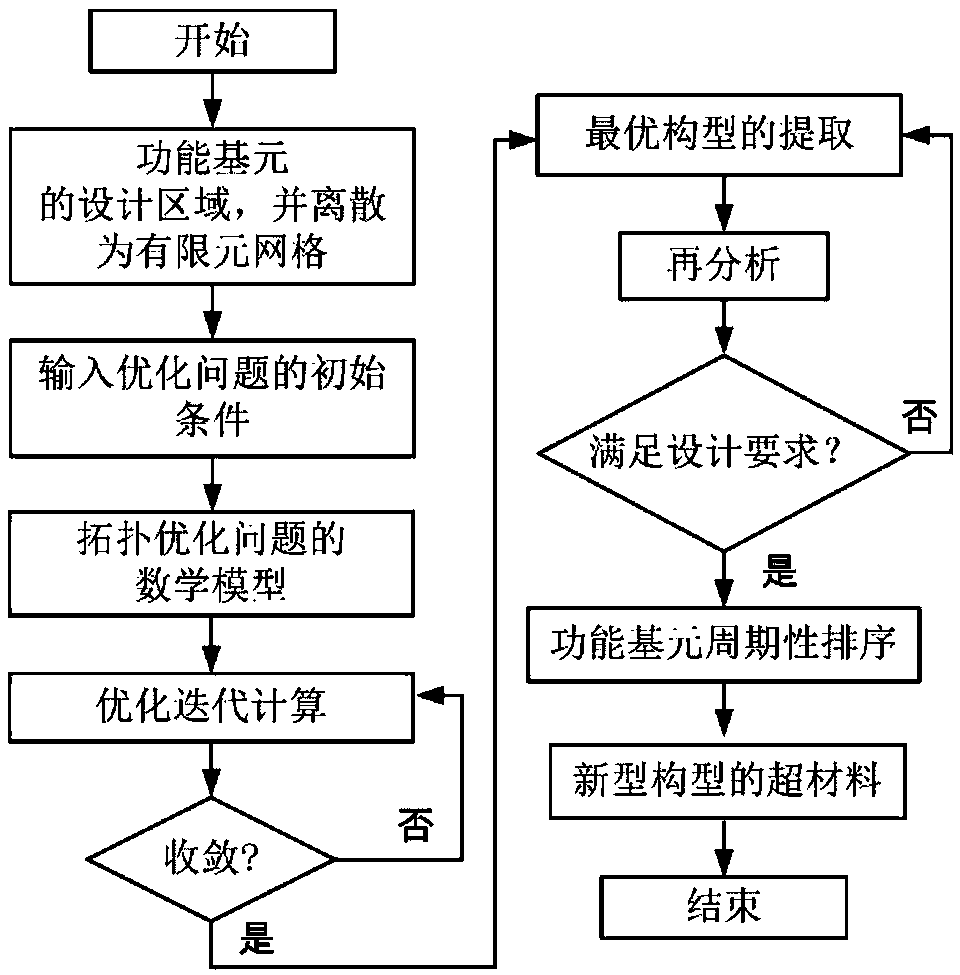
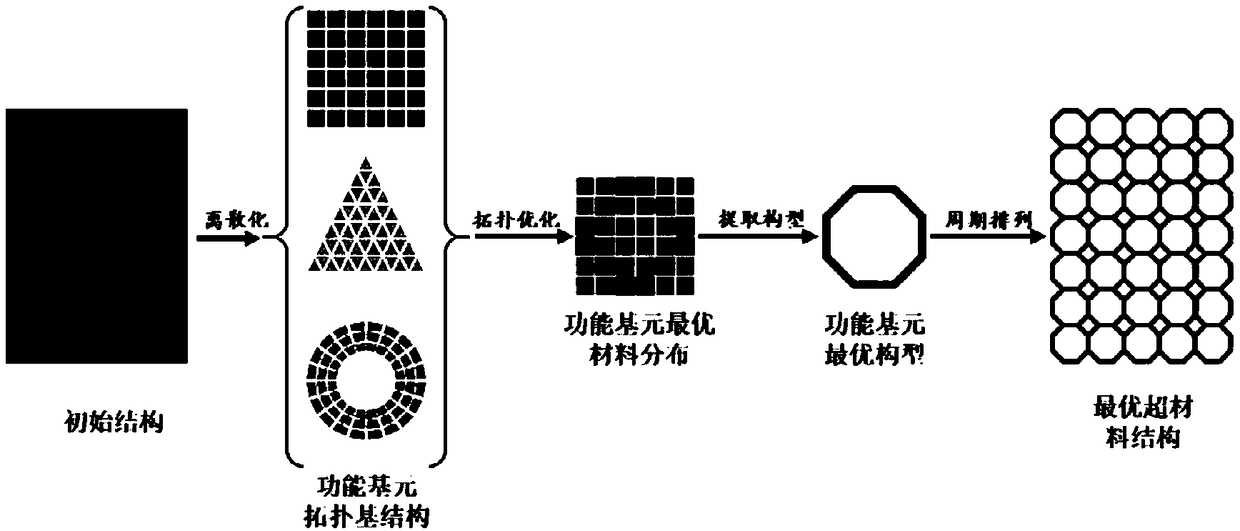
A topology optimization method for arbitrary Poisson's ratio metamaterials
InactiveCN109472056ALight weightPorousDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOptimization problemFinite element limit analysis
The invention provides a topology optimization forming method of arbitrary Poisson's ratio metamaterial, which comprises the following steps: step 1, dividing a functional unit design area in the metamaterial; 2, divide that functional basic element design region into finite element meshes and input the initial conditions of the optimization problem; 3, carry out finite element analysis and calculation on that functional design area to obtain the mechanical performance parameters of the finite element and the node; 4, establish a mathematical model of a metamaterial topology optimization design problem based on that mechanical property parameter of a finite element and a node; 5, solving a mathematical model of that topology optimization problem to obtain a topology optimization result; 6,extract that configuration of the topology optimization result for verification analysis; Step 7: Periodically repeat the ordering of the optimal configurations of the functional units to form the metamaterials. The invention can directly design a new configuration metamaterial with a specified Poisson's ratio value without specifying the geometrical topology configuration of the initial functional unit.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for carrying out finite element analysis on vehicle-mounted cabinet body
ActiveCN105183976AImprove analysis efficiencyReduce occupancySpecial data processing applicationsComputer resourcesElement analysis
The present invention relates to a method for carrying out finite element analysis on vehicle-mounted cabinet bodies. The method comprises segmenting a framework and installation elements which are connected with each other through bolts in a physical model of a vehicle-mounted cabinet body; carrying out geometry cleanup and mesh generation on the framework and the installation elements; splicing the framework and the installation elements together to be re-assembled to be the vehicle-mounted cabinet body; and configuring boundary conditions and loads so as to establish a finite element analysis model, and solving the finite element analysis model. Geometry cleanup and mesh generation are carried out on the framework and the installation elements, occupation of computer resources by the step can be greatly reduced, difficulties of technicians in mesh generation within the elements are lowered, and the finite element analysis efficiency of vehicle-mounted cabinet bodies is raised. Meanwhile, because the physical model of the vehicle-mounted cabinet body is disassembled into a plurality of parts, multiple technicians can carry out mesh generation at the same time, thereby shortening time for mesh generation.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com