Patents
Literature
81 results about "Frozen vegetables" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frozen vegetables are vegetables that have had their temperature reduced and maintained to below their freezing point for the purpose of storage and transportation (often for far longer than their natural shelf life would permit) until they are ready to be eaten. They may be commercially packaged or frozen at home. A wide range of frozen vegetables are sold in supermarkets.
Method for production of frozen vegetables or fruits
InactiveUS20040096559A1Improve featuresLess leachingMilk preservationWort preparationFrozen vegetablesChemistry
The present invention relates to a method for producing frozen and dehydro-frozen vegetables and fruits, wherein the method includes the method of cryogenically freezing the fruits or vegetables.
Owner:CONAGRA FOODS +2
Air-exhausting flexible packaging bag for frozen vegetables and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an air-exhausting flexible packaging bag for frozen vegetables, belonging to the technical field of flexible packages. A packaging bag body is provided with micron-scale breather holes punctured by laser, wherein the diameters of the breathing holes are 60-300 mu m, the distance between every two breathing holes is 4-500mm, and the breathing holes are in 1-16 rows. A preparation method of the air-exhausting flexible packaging bag comprises the step of: arranging a film on a material feeding device; setting the parameter of the breathing holes on a central controller and sending the parameters to a high-pulse laser source; synchronizing the material feeding speed with the speed of a rotary prism lens so as to ensure that a distribution laser beam can puncture regular and ordered breathing holes on a composite film; and finally, slitting the film punctured with the breathing holes and processing into bags. The packaging bag is made of a PE (Poly Ethylene) composite membrane or a PE multilayer co-extrusion composite membrane, is suitable for flexible packages of frozen vegetables at -18 DEG C, modified-atmosphere vegetables at 0-4 DEG C, and frozen vegetables for microwave oven heating. When being heated, the packaging bag exhausts air automatically so that explosion cannot occur. In addition, because the breathing holes are of micron-scale, the air-exhausting flexible packaging bag has good pollution resistance and causes no potential food safety hazard.
Owner:惠州宝柏包装有限公司
Freezing vegetables
InactiveUS20040065094A1Limit softeningQuality improvementLighting and heating apparatusCooling fluid circulationCore temperatureFrozen vegetables
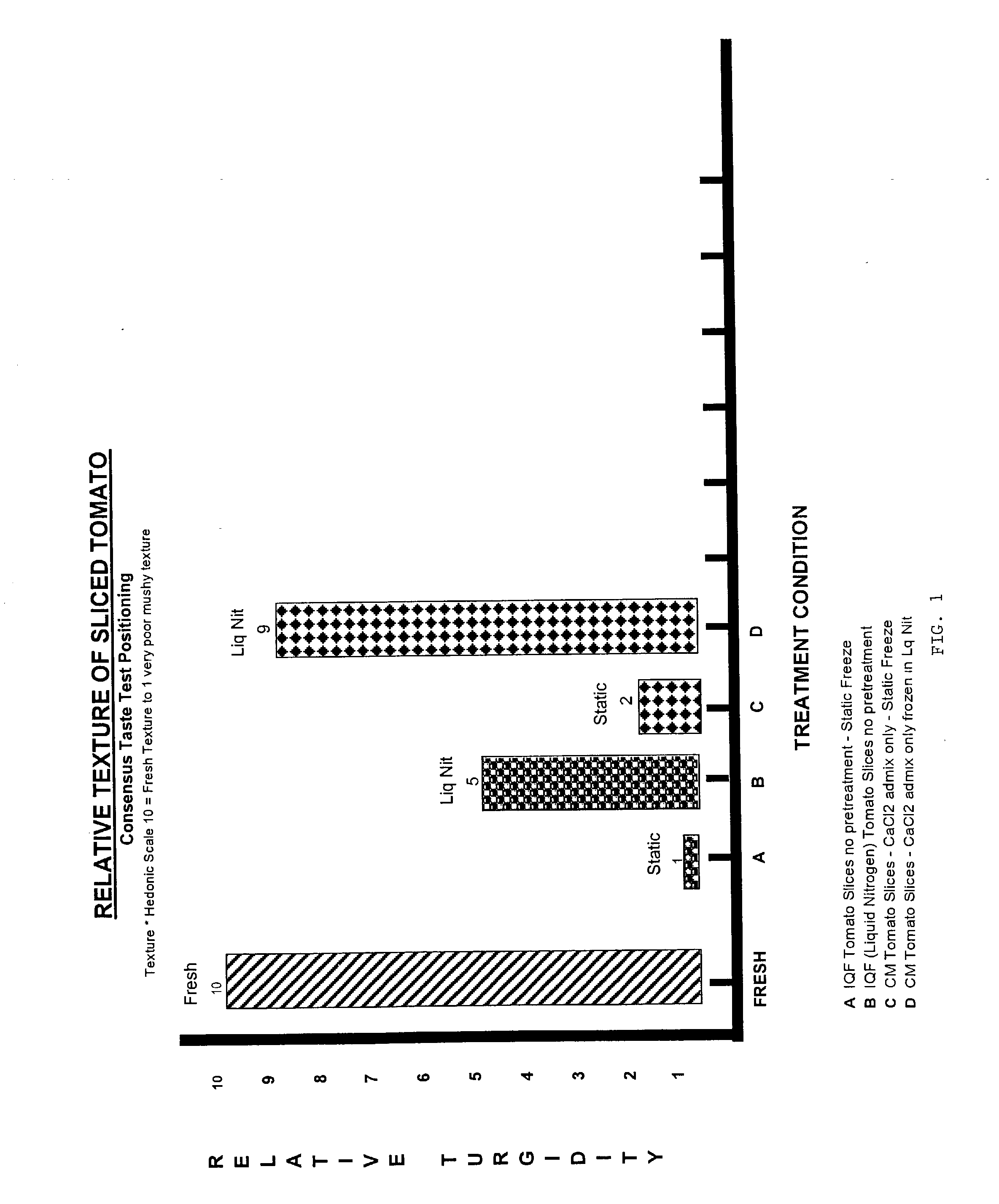
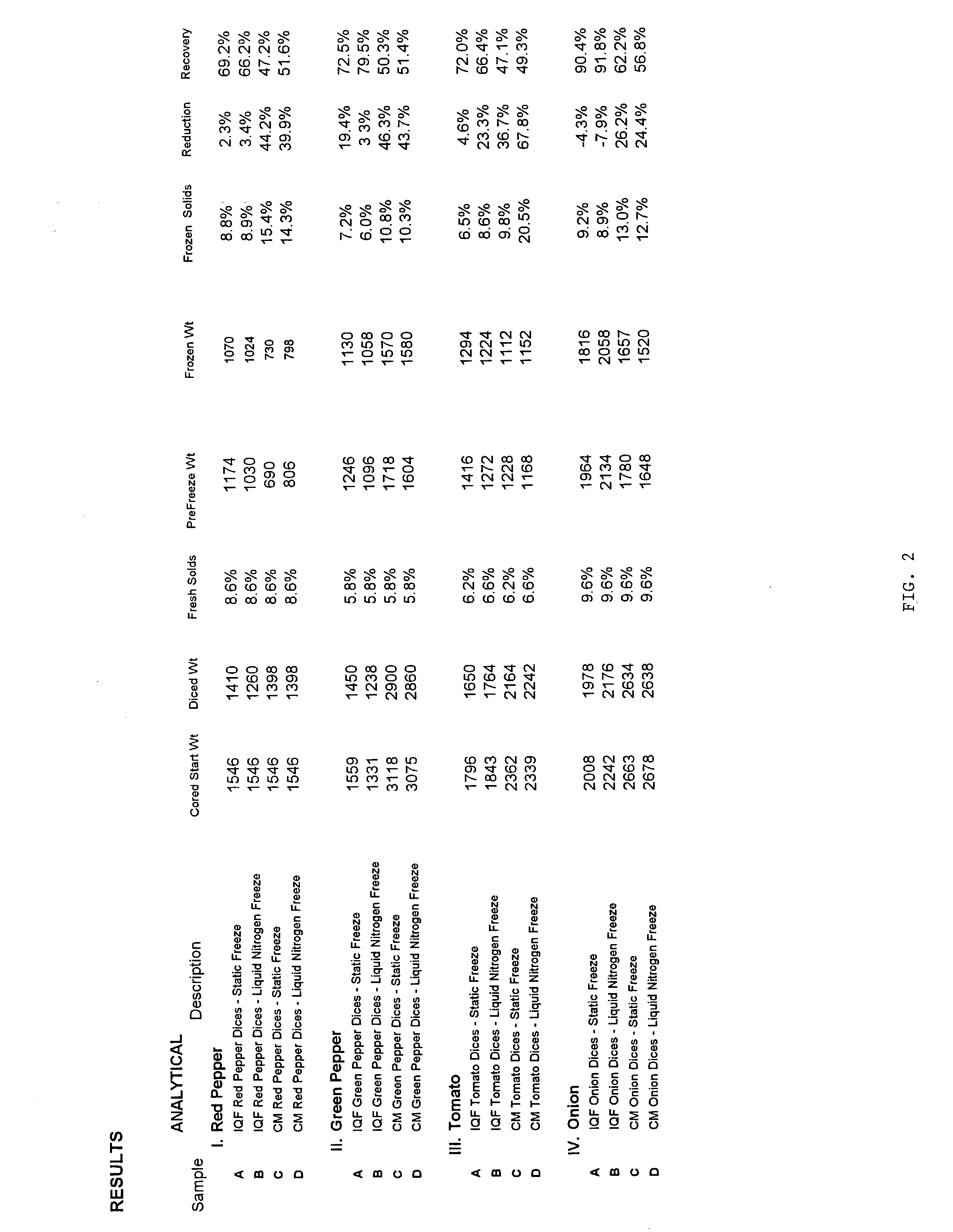
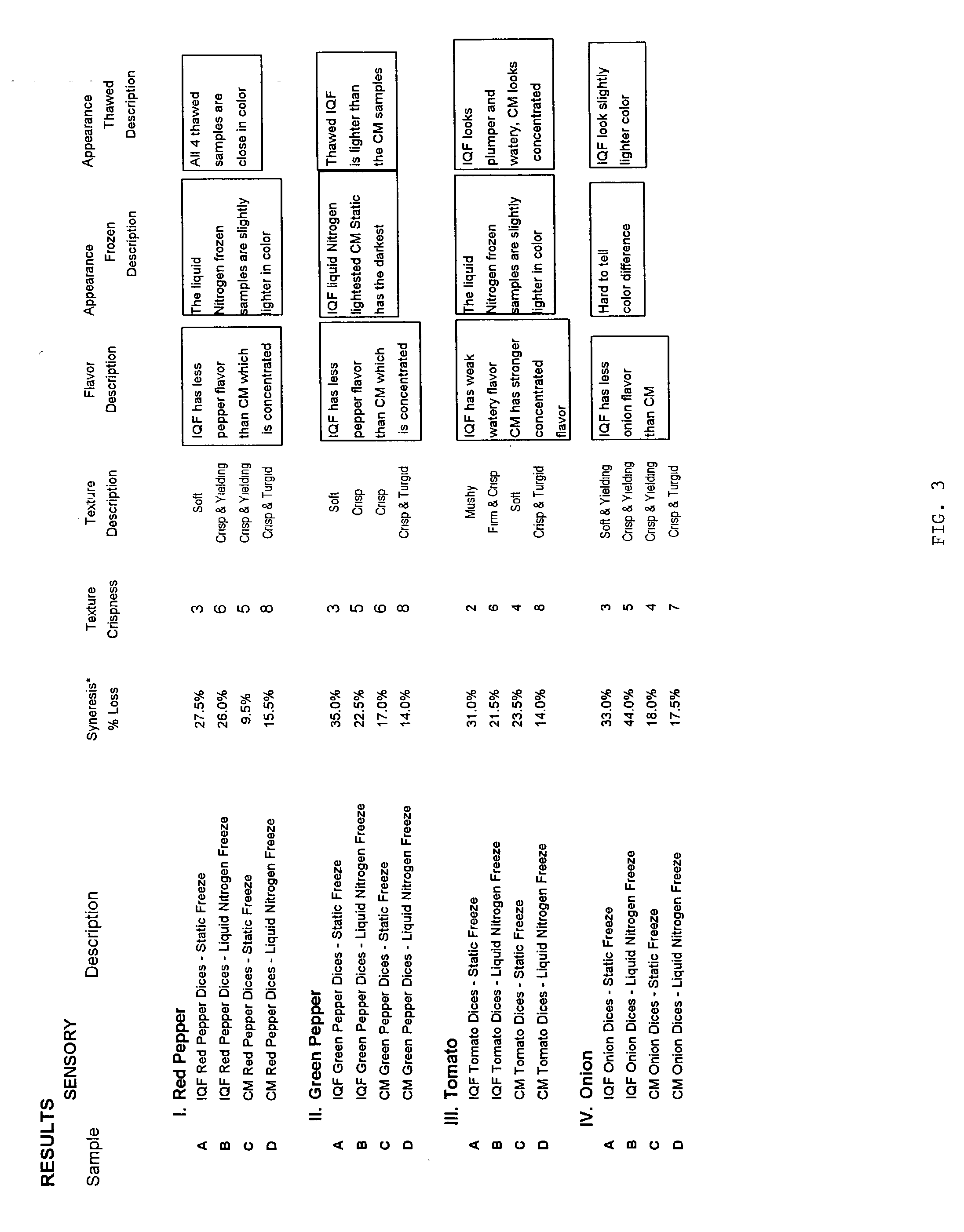
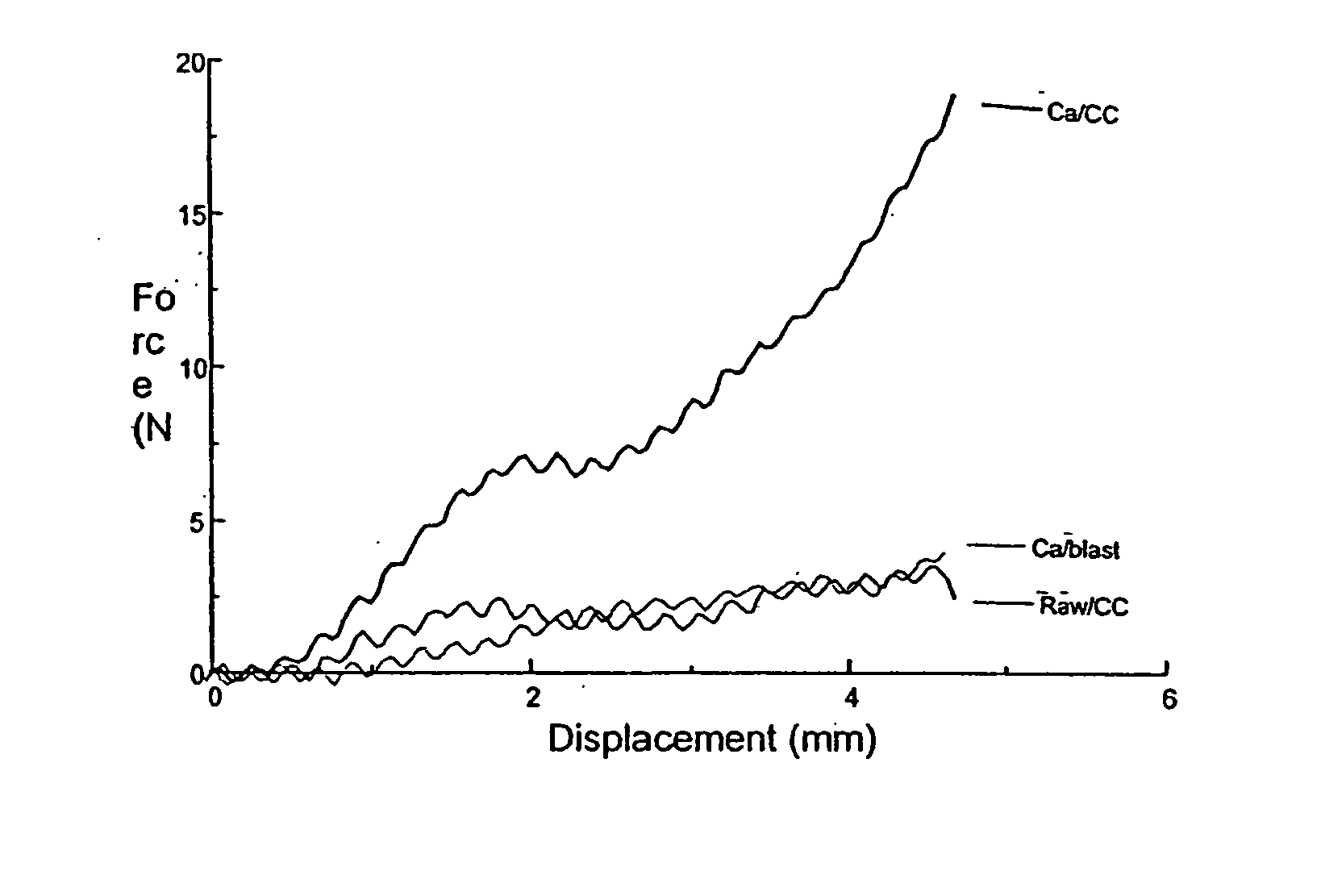
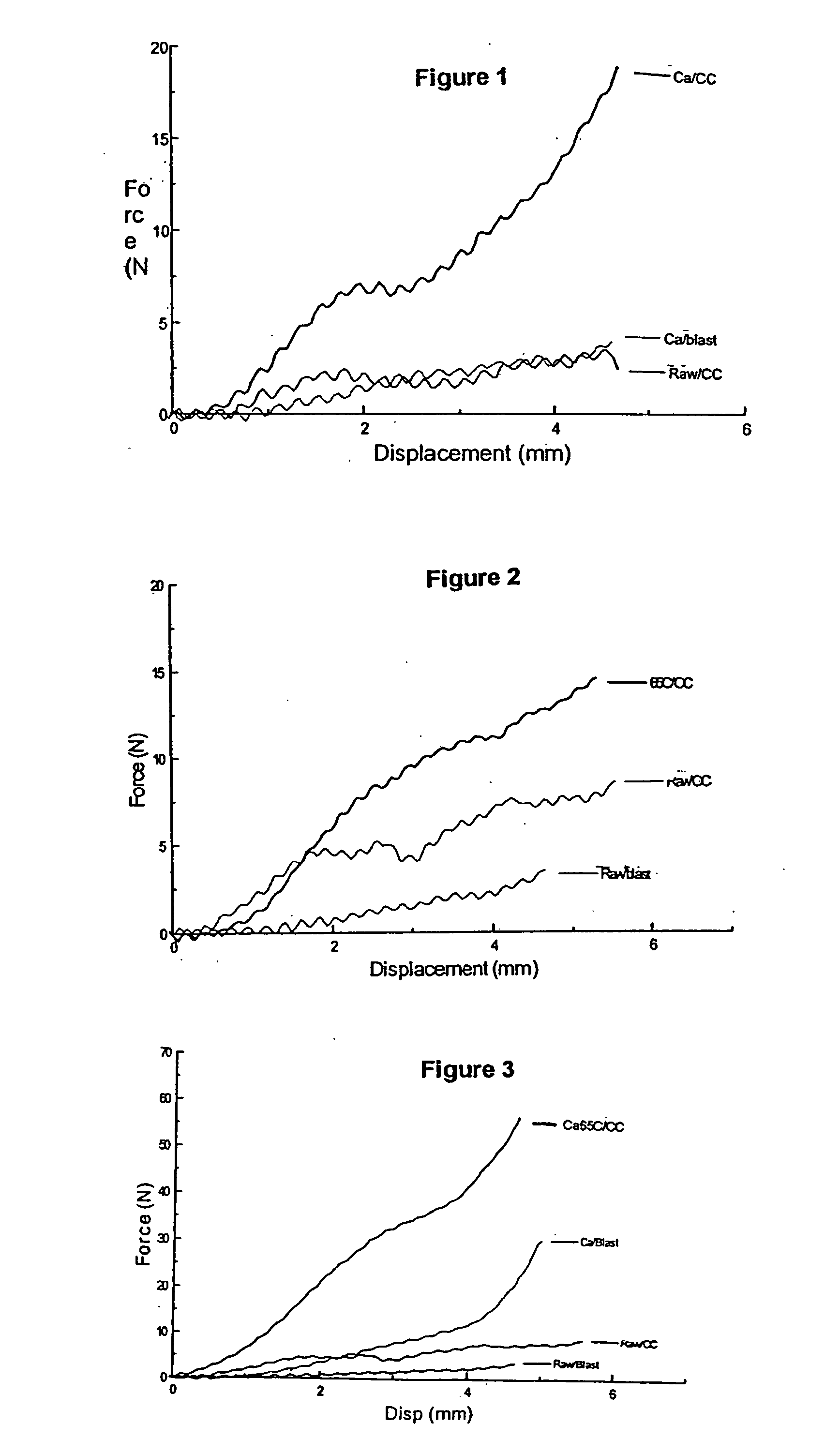
A process for the production of a frozen vegetable or part thereof, wherein said process comprises the steps: (i) subjecting a vegetable or part thereof to a firming treatment selected from: a) immersing the vegetable or part thereof in a solution of a calcium salt. b) heating the vegetable or part thereof to a temperature in the range 50 to 70° C., and c) a combination of a) and b); (ii) under-cooling to a core temperature of less than or equal to -5° C.; (iii) reducing the temperature to less than or equal to -18° C. The frozen vegetables, when thawed, possess a texture and appearance which closely resembles that of fresh vegetables.
Owner:UNILEVER BESTFOODS NORTH AMERICA DIV OF CONOPCO
Production method of frozen conditioning dish
The invention discloses a production method of frozen conditioning dish, which comprises the following steps of stirring minced fillet or mashed potato in a stirrer, then sequentially adding a seasoning mixture, vegetable, seafood or meat materials, stirring, then adding starch, and stirring to obtain stuffing; pressing and forming the stuffing to obtain vegetable cake, treating the vegetable cake by flour wrapping, pulp wrapping, flour coating and bran wrapping, freezing and packaging to obtain frozen vegetable cake; mixing flavoring, starch and water, heating, cooling, bagging, and then freezing to obtain conditioning sauce bag; and placing the frozen vegetable cake and the conditioning sauce bag in a packaging bag, and sealing to obtain the frozen conditioning dish. The production method of the frozen conditioning dish disclosed by the invention breaks through the traditional production method of Chinese style dish, and realizes Western-style eating method of the Chinese style dish.
Owner:SANQUAN FOOD
Microwavable frozen garden salad entrees
The present invention relates to frozen entrées comprising vegetables and a dressing that when combined together deliver the consistency and flavor expected. Moreover the entrées of the present invention include a stabilizer such as a matrix of gums and starch that allow for the creation of a dressing to utilize the moisture and vapor created when microwaving frozen vegetables and other toppings.
Owner:BELLISIO FOODS
Method for quality-guaranteed and uniform unfreezing of quick-frozen vegetables
InactiveCN103564036AImprove defrosting qualityDefrost quality shortenedFruit and vegetables preservationVegetable materialFrozen vegetables
The invention discloses a method for quality-guaranteed and uniform unfreezing of quick-frozen vegetables. The method comprises the following steps: selecting suitable vegetables for cutting, that is fresh vegetable raw materials are selected, cleaned and cut, and different kinds of vegetables are cut into different sizes, and the cutting surface area rate is distinguished according to tuber vegetables, wherein lump vegetables are 1.5 to 2.0 in weight, and leaf vegetables are 1.2 to 1.8 in weight. The method for quality-guaranteed and uniform unfreezing of quick-frozen vegetables, provided by the invention, conforms to nutritional requirements of human bodies and the theory of traditional Chinese medicine, and reduces or avoids the problems of nonuniformity in unfreezing, browning, nutrition loss and the like in the unfreezing process, thereby improving the unfreezing quality of the quick-frozen vegetables.
Owner:QINGDAO BOHONG MARINE BIOTECH
Cooking salt formulations and methods
The present invention relates to cooking salt formulations and related additives and aqueous cooking compositions to be used to prepare foods. Various foods including pasta, rice, fresh and frozen vegetables and meats may be instilled with unexpectedly desirable organoleptic qualities by cooking the food in water containing effective concentrations of salt formulations according to the present invention. Methods for cooking food are another aspect of the present invention.
Owner:BLUE SKY POTIONS
Frozen vegetable burger and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a frozen vegetable burger comprising stuffing and a wrapping material, wherein the stuffing is prepared from the following raw materials: raw material meat, vegetables, salt, white granulated sugar, tripolyphosphate, monosodium glutamate, ginger powder, chilli powder, five-spice powder, soy proteins, corn starches and ice water; and the wrapping material is a paste layer and is prepared from the following raw materials by weight ratio: wheat flour, corn flour, milk powder, glutinous rice flour, the salt, salad oil and water. The meat stuffing and the vegetables are used as main raw materials, therefore, the prepared frozen vegetable burger has more unique features compared with the general meat burger, not only has delicious taste, but also has rich nutrient components; in addition, the preparation method is simple and the movable multipurpose socket board is suitable for families and industrialized production.
Owner:天津宝迪农业科技股份有限公司
Quick-frozen fresh beans type vegetables without bad taste, and its processing method
A quickly frozen vegetable-fresh bean without freeze odor is disclosed, which includes water scalded one and oil scalded one. Its preparing process features that different kinds of fresh bean and vegetable are scaled by different Sun's scalding degrees to prevent the internal cells from being freeze-damaged, resulting in no change in color, quality and taste.
Owner:孙景文
Method for controlling harmful microbe in preparation process of quick frozen vegetables food
InactiveCN1969692AStrong seasoning bufferDoes not affect antibacterial and antibacterial abilityFruits/vegetable preservation by heatingFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingMicroorganismSodium fumarate
The invention discloses a controlling method of harmful microbe in the food manufacturing course of rapid-freezing opsonic food, which comprises the following steps: blending inhibitor in the compound of vegetable and water with the weight rate of compound and inhibitor at 100: 1-4 evenly; sterilizing vegetable at 98 deg.c; cooling in the vacuum; freezing; allocating inhibitor with 55%-67% dehydrosodium acetate, 19%-37% sodium gly acid and 3%-17% sodium fumarate.
Owner:NINGBO JIAYI FOOD
Method for mechanically producing multi-color vegetable nutritious noodles
The invention relates to a method for mechanically producing multi-color vegetable nutritious noodles and belongs to the field of deep food processing. The method comprises the following steps: selecting and rejecting bad fruits and bad leaves of multiple vegetables, washing for later use, and performing low-temperature quick-freezing at the temperature of 18-20 DEG C below zero for separating the moisture in the vegetables; respectively putting the multiple quick-frozen vegetables in a drying oven at the temperature of 35-40 DEG C under the air speed of 10-13 meters per second, and airing for later use; respectively crushing waterless vegetables made in the second step, screening through a screen with the size of 200 meshes, and manufacturing vegetable powder; mixing the vegetable powder of different colors made in the third step according to a ratio of the vegetable powder being 1 to obtain multi-color total-nutrition vegetable powder; uniformly stirring and mixing the multi-color total-nutrition vegetable powder made in the fourth step and wheat core flour according to a ratio of the vegetable powder to wheat core flour being 1:5 to form multi-color total-nutrition vegetable dough; and curing and pressing the dough made in the fifth step into cakes, wherein other processes are performed according to a common noodle production standard. The noodles made by the previous steps present multiple colors and contain multiple nutrients.
Owner:吕景海
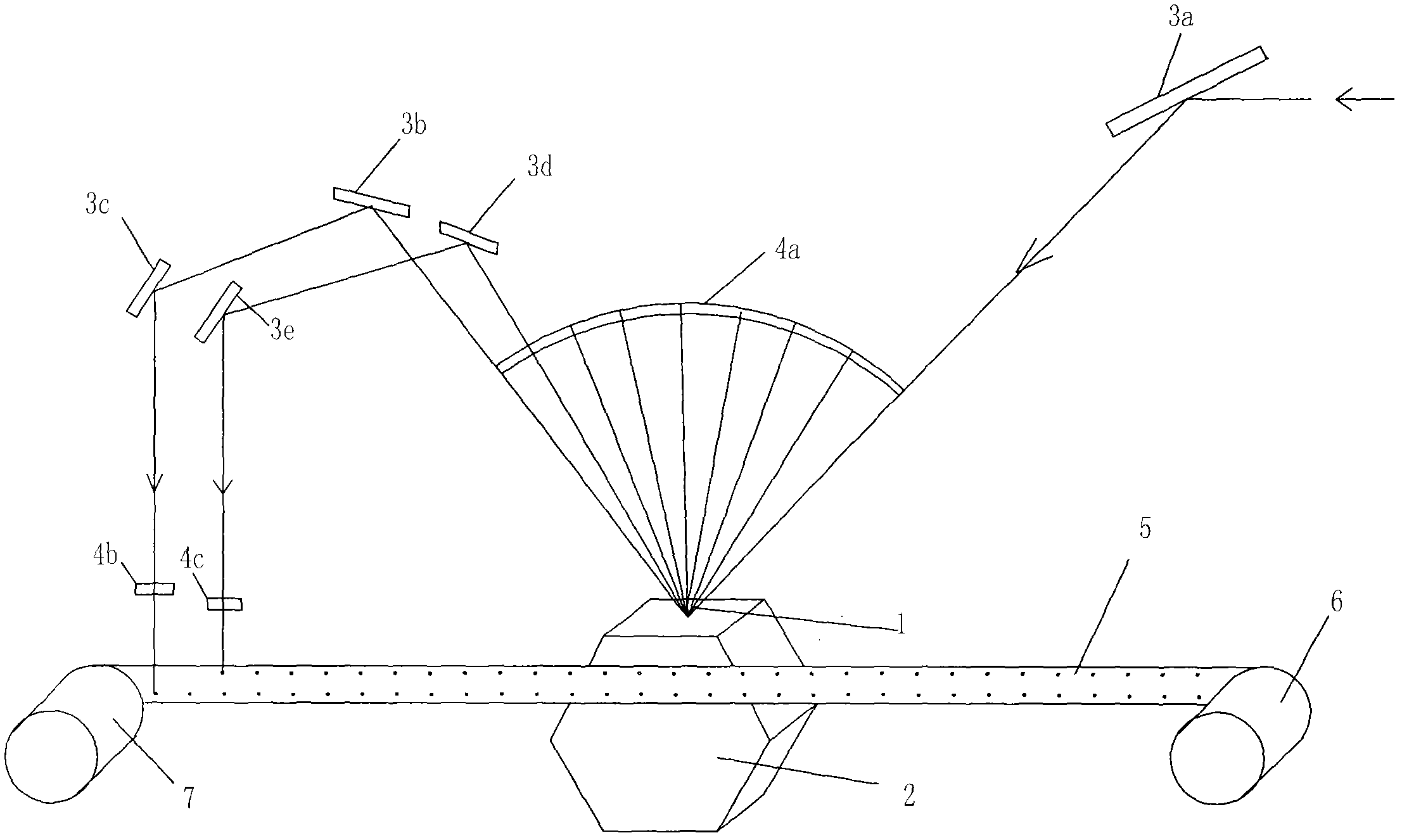
Extraction method and apparatus of juice and/or puree, in particular from partially or completely frozen vegetables
ActiveUS8367132B2Improve extraction efficiencyQuick extractionMilk preservationDough treatmentThermal energyFruit juice
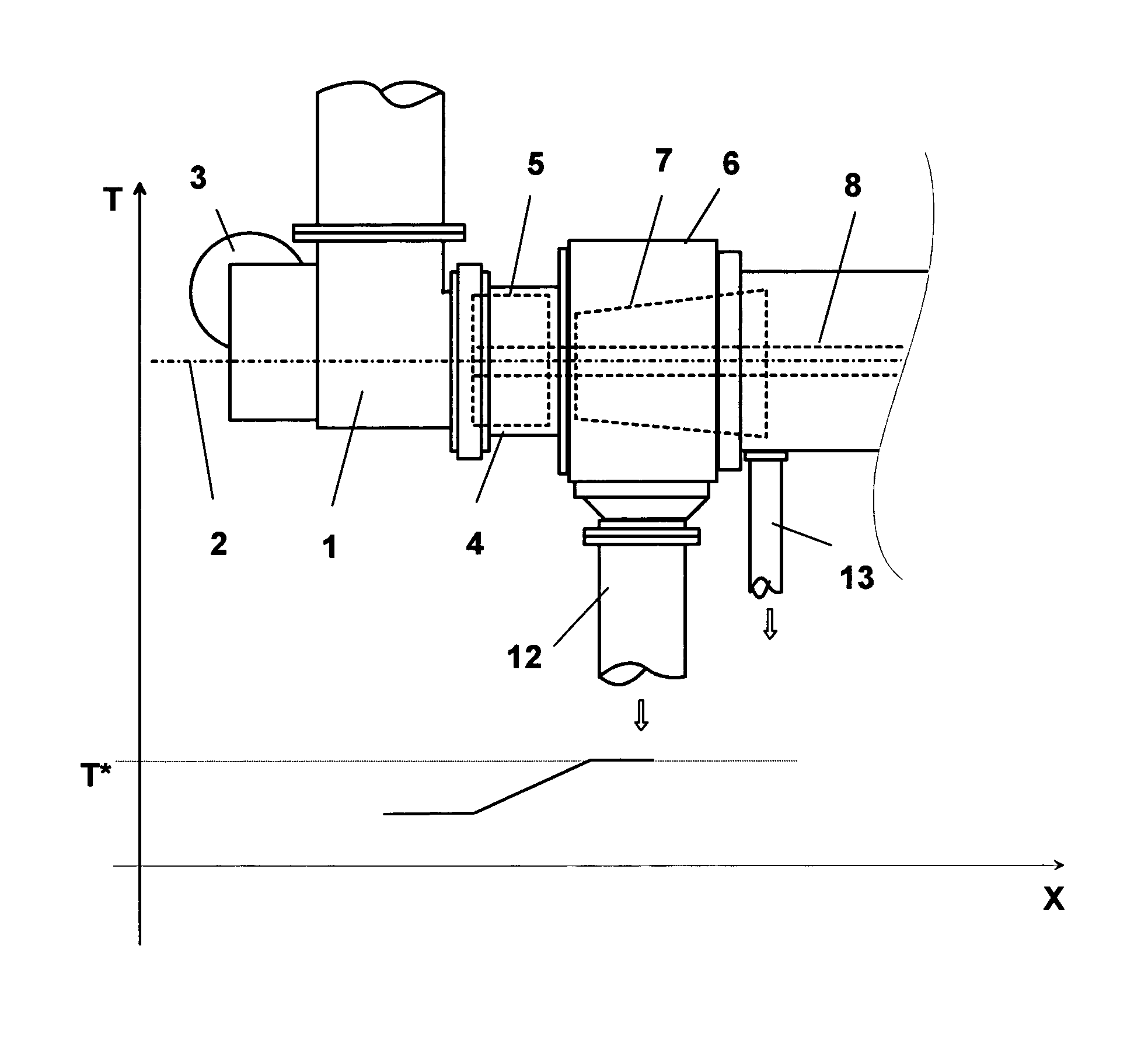
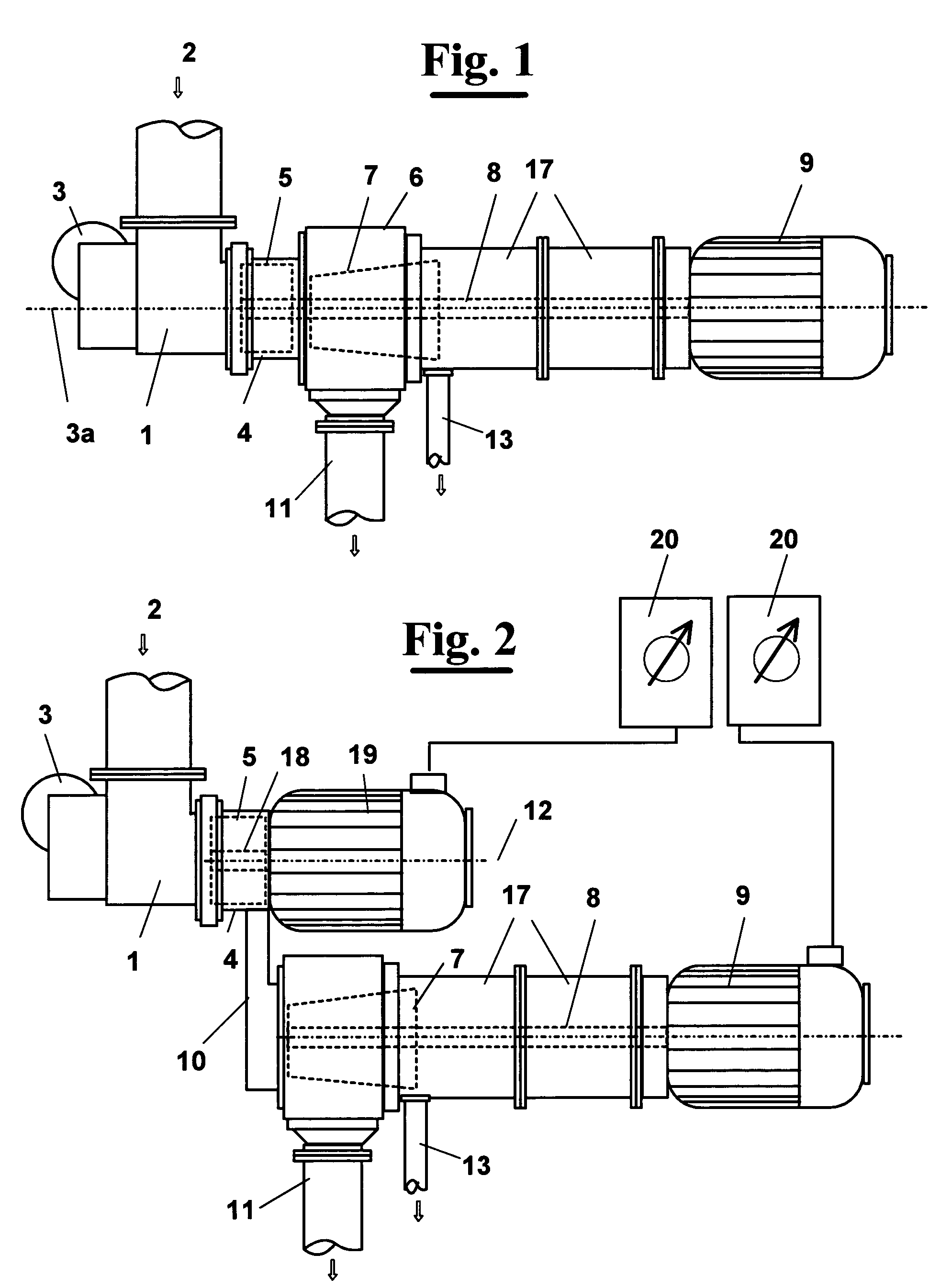
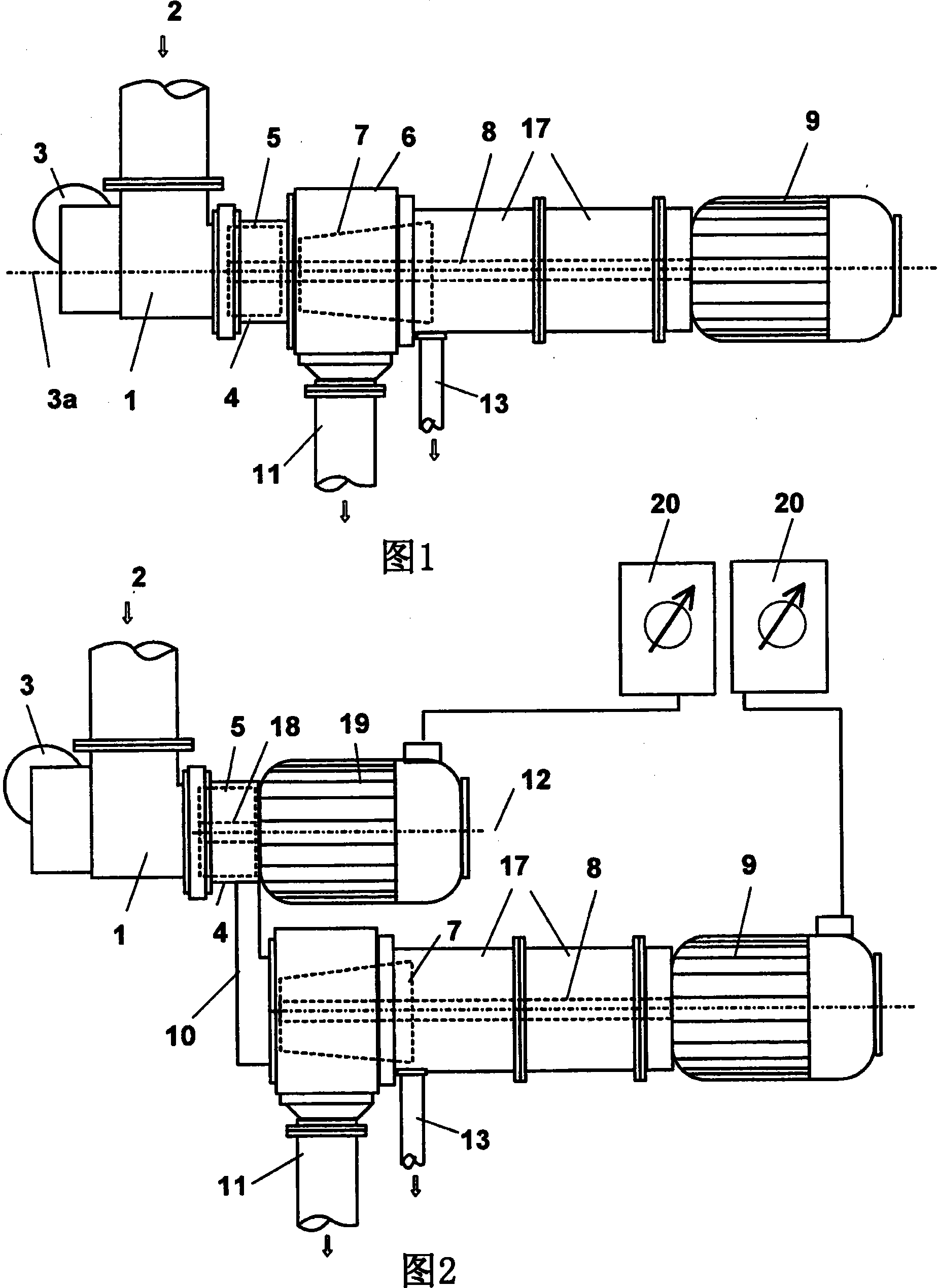
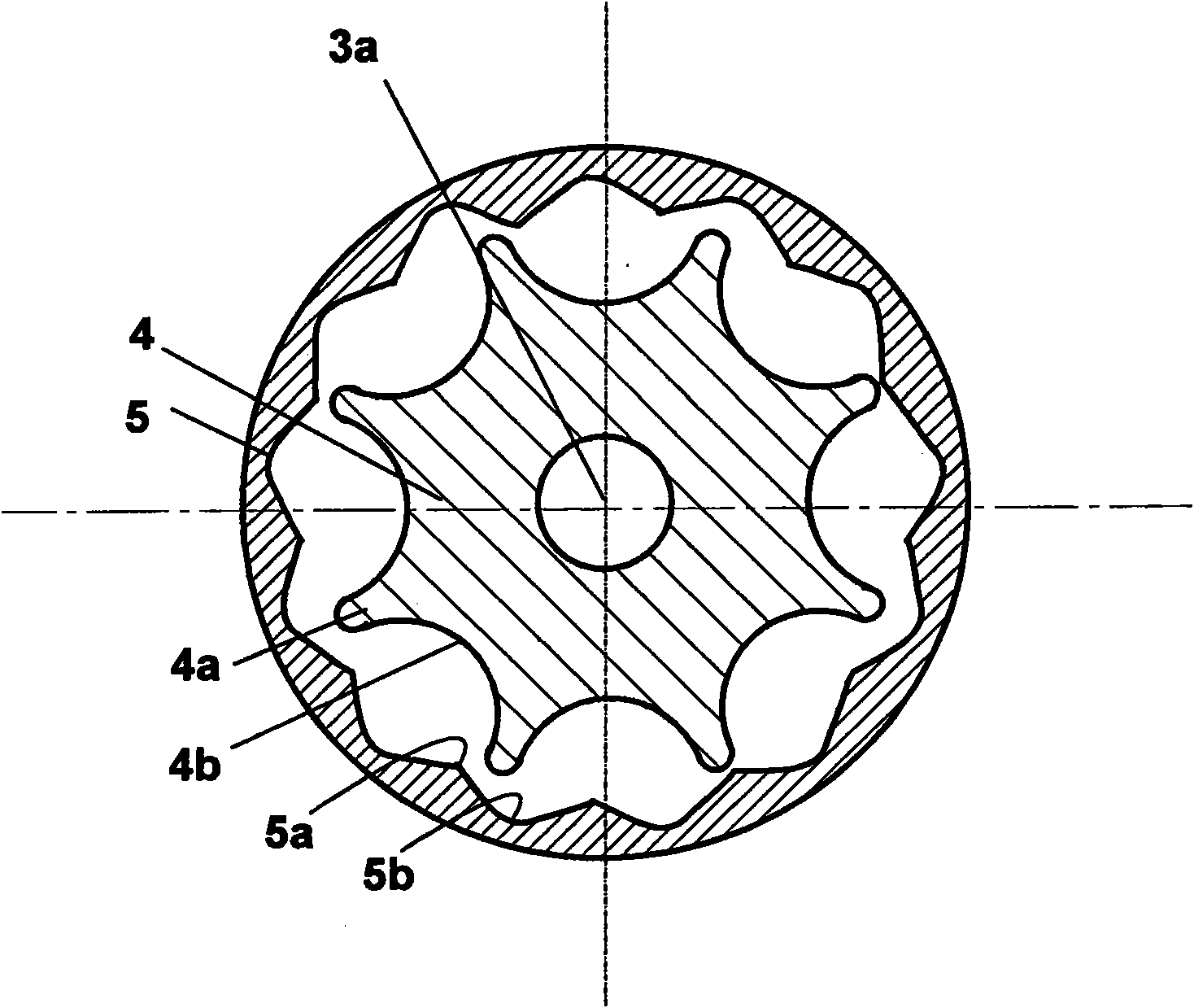
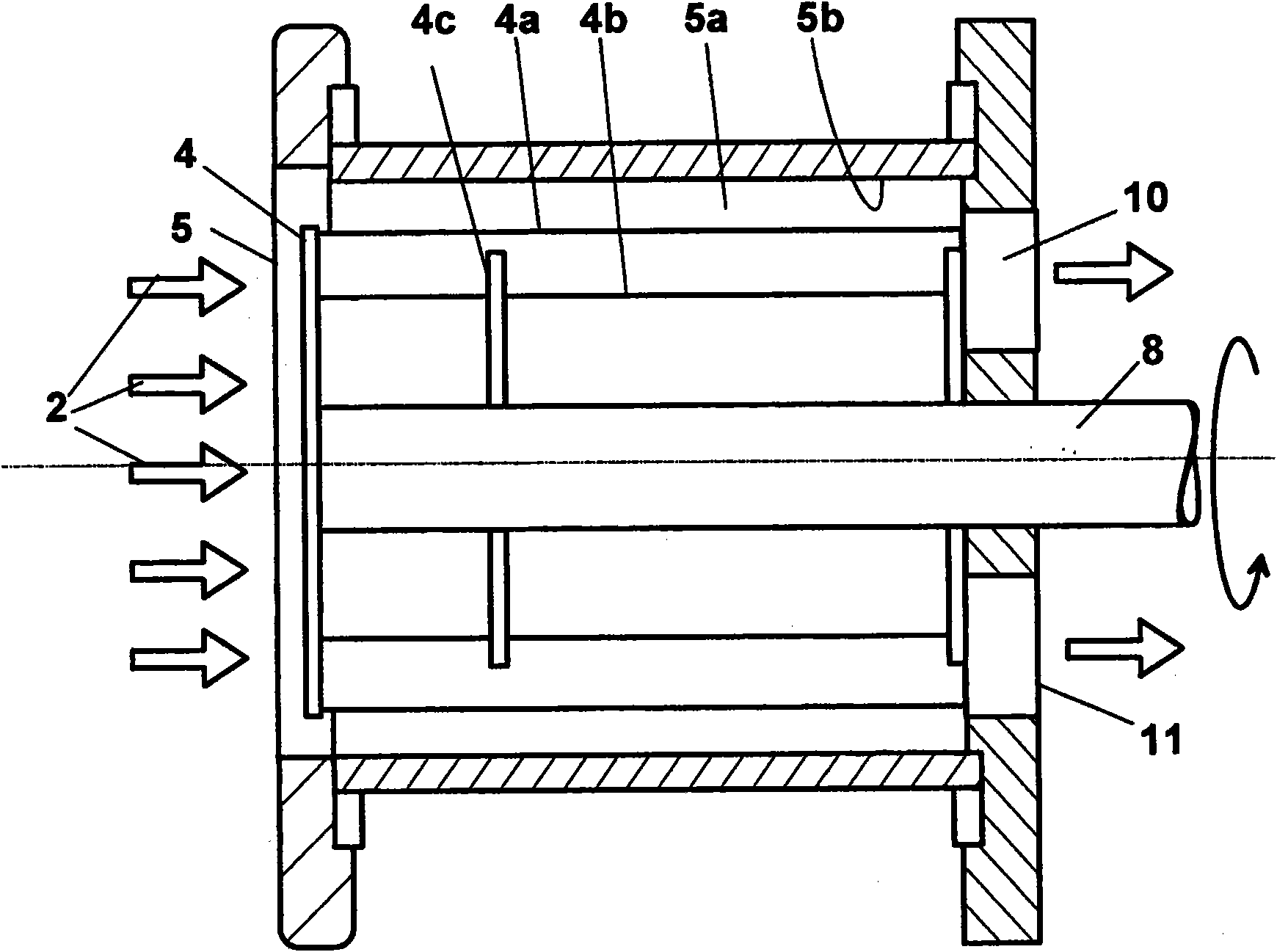
A rotating machine operated along an axis (3a) by a motor (3), for extraction of puree or juice from animal or vegetable food, comprises an inlet duct (1) where the animal or vegetable food (2) is loaded, for example fruit or vegetables, conveyed by a feeding screw conveyor not shown. The food pulps of the products (2) are loaded in frozen condition and enter then a shredding section comprising an armature (4) rotatable at a high speed in a stator (5) where the product is subjected to pressure pulses in quick succession by the movement of the frozen product (2) between the armature (4) and the stator (5). This way, there is a significant transformation of the mechanical energy into thermal energy that assists partial defrosting (at least 10%) of the product, obtaining a desired, temperature course of the product at least up to the end of the extraction with respect to the defrosting temperature (T*) of the product, which can be 0OC or even less. A fluid material is obtained that has the consistency of a puree even if it contains still small frozen parts. On the external wall of the stator (5) thermal power can be applied contemporaneously to the pressure pulses, in order to heat the inner surface of the stator (5) or the rotor (4), by applying vapor or by means of electric resistance.
Owner:BERTOCCHI ALESSANDRO
Method for producing frozen vegetable food material having soft texture
InactiveCN102176837AFood preparationFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingPectinaseFood material
Provided is a method for producing a frozen vegetable food material having a soft texture which is particularly suitable for foods for the elderly, suffers no damage in shape in the course of distribution, uniformly softens to the core and sustains the shape thereof. The above-described method comprises (1) a step of freezing a vegetable food material and thawing the same to prepare a thawed food material, (2) a step of immersing the thawed food material as described above in a liquid dispersion of pectinase or cellulase under reduced pressure, (3) a step of separating the vegetable food material having been enzymatically treated as described above from the liquid dispersion, (4) a step of cold-treating the thus separated vegetable food material having been enzymatically treated as described above at 0 to 10 DEG C for 8 to 24 hours to prepare a cold-treated vegetable food material, (5); a step of heating the cold-treated vegetable food material as described above at such a temperature for such a period of time as sufficient for the inactivation of the pectinase or cellulase as described above, and (6) a step of freezing the vegetable food material having been heated as described above. Alternatively, the thawing procedure in the above step (1) may be conducted simultaneously with the immersion procedure in the enzyme dispersion under reduced pressure of the subsequent step.
Owner:MISHIMA FOODS
Processing method of dehydrated vegetables
InactiveCN104222260AWon't be lostWill not oxidizeFruit and vegetables preservationAdditive ingredientSpins
The invention provides a processing method of dehydrated vegetables, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The processing method is realized by adopting the following technical scheme comprising the following steps: blanching by adopting hot water of 80-100 DEG C for multiple seconds to multiple minutes, immediately cooling after blanching; spin-drying cooled vegetables, rapidly freezing the spin-dried materials at a freezing temperature of below minus 30 DEG C; placing the frozen vegetables in a vacuum container, reducing the pressure to below a three-phase point by means of a vacuum system, and supplying heat to the materials by virtue of a heating system to ensure that water in the materials is evaporated until the materials are dried to a water end point. According to the processing method of the dehydrated vegetables, provided by the invention, the dehydrated vegetables are produced under the conditions of low-temperature freezing and vacuum oxygen deficiency, the inherent shapes of the vegetables can not contract, thermosensitive substances can not be damaged, aromatic substances can not dissipate, readily oxidizable substances can not be oxidized, and thus the shapes, colors, tastes and nutritional ingredients of the dehydrated vegetables are basically consistent with those of fresh vegetables, and the reconstitution properties are specially good.
Owner:许姗姗
Microwave frozen and recuperated vegetable and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the microwave frozen conditioning vegetable, comprising the frozen vegetable and the frozen flavouring block. The frozen flavouring block is made by mixing the flavour-develop flavouring and the modified starch with water. The making method adopts the following steps: a. freezing the fresh vegetable for reserve; b. mixing the flavour-develop flavouring and the modified starch with water, heating for 3 to 7 minute at 80 to 90 DEG C and then making the frozen flavouring block by packing and freezing sharp; c. mixing the frozen vegetable and the frozen flavouring block together in proration, then putting into a special microwave bag and at least closing to make the microwave frozen conditioning vegetable. The taste of the vegetable can not be influenced during storing process and the vegetable and the flavour-develop flavouring can join together well when microwave heating due to taking the modified starch in the frozen flavouring block as the thickening agent. The conditioning vegetable has the advantages of good taste and beautiful appearance.
Owner:NINGBO HAITONG FOOD SCI & TECH CO LTD
Quick-frozen vegetable ball
InactiveCN104381888ANot perishableConvenient for refrigerated storageFood preparationBiotechnologyBrassica
The invention relates to a quick-frozen vegetable ball, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The quick-frozen vegetable ball comprises the following materials: brassica napobrassica, shepherdspurse herb, mint, brassia, lotus root, nori, wheat meal, egg liquid and the like. The quick-frozen vegetable ball is unlikely to degrade after being fried, so that the quick-frozen vegetable ball is convenient to refrigerate and store. Furthermore, the quick-frozen vegetable ball contains multiple vegetables, so that the quick-frozen vegetable ball is rich in nutrients, safe and sanitary.
Owner:SUZHOU FULL FORTUNE FOOD CO LTD
Quick-frozen vegetable Samosa and making method thereof
ActiveCN108576607AImprove adhesionImprove ductilitySugar food ingredientsFood coatingVegetable samosaGluten
The invention discloses quick-frozen vegetable Samosa. The quick-frozen vegetable Samosa comprises wrappers and fillings, wherein the wrappers are made from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 90-110 parts of dough made with boiling water, 38-44 parts of medium-gluten flour, 0.5-0.7 part of a vegetable Samosa modifying agent, 3-5 parts of glucose, 4-6 parts of soybean oil, 0.4-0.7 partof emulsifying oil and 18-22 parts of water. According to the quick-frozen vegetable Samosa provided by the invention, the dough made with boiling water and the medium-gluten flour are added to the wrappers, and the vegetable Samosa modifying agents and the emulsifying oil are used for cooperation, so that the eating mouth feel of the wrappers is soft and slight in glutinous properties, the wrappers have good elasticity and tenacity and are stable in property and not liable to be subjected to frost crack, and the requirement of industrial production can be met. The invention further providesa making method of the quick-frozen vegetable Samosa. Mechanized operation is adopted, so that the production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:河南创新研霖食品科技有限公司
Processing technology of quick-frozen green soybeans
InactiveCN111011473APlay a moisturizing roleGood synergistic effectFruit and vegetables preservationFood ingredientsProcess engineeringFrozen vegetables
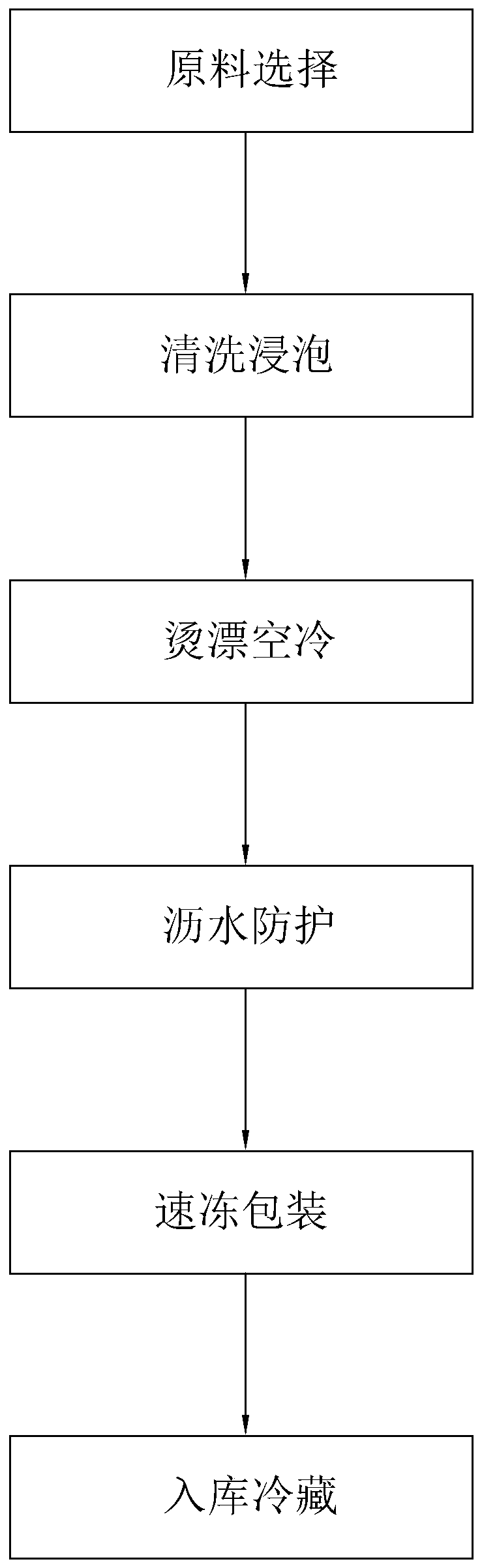
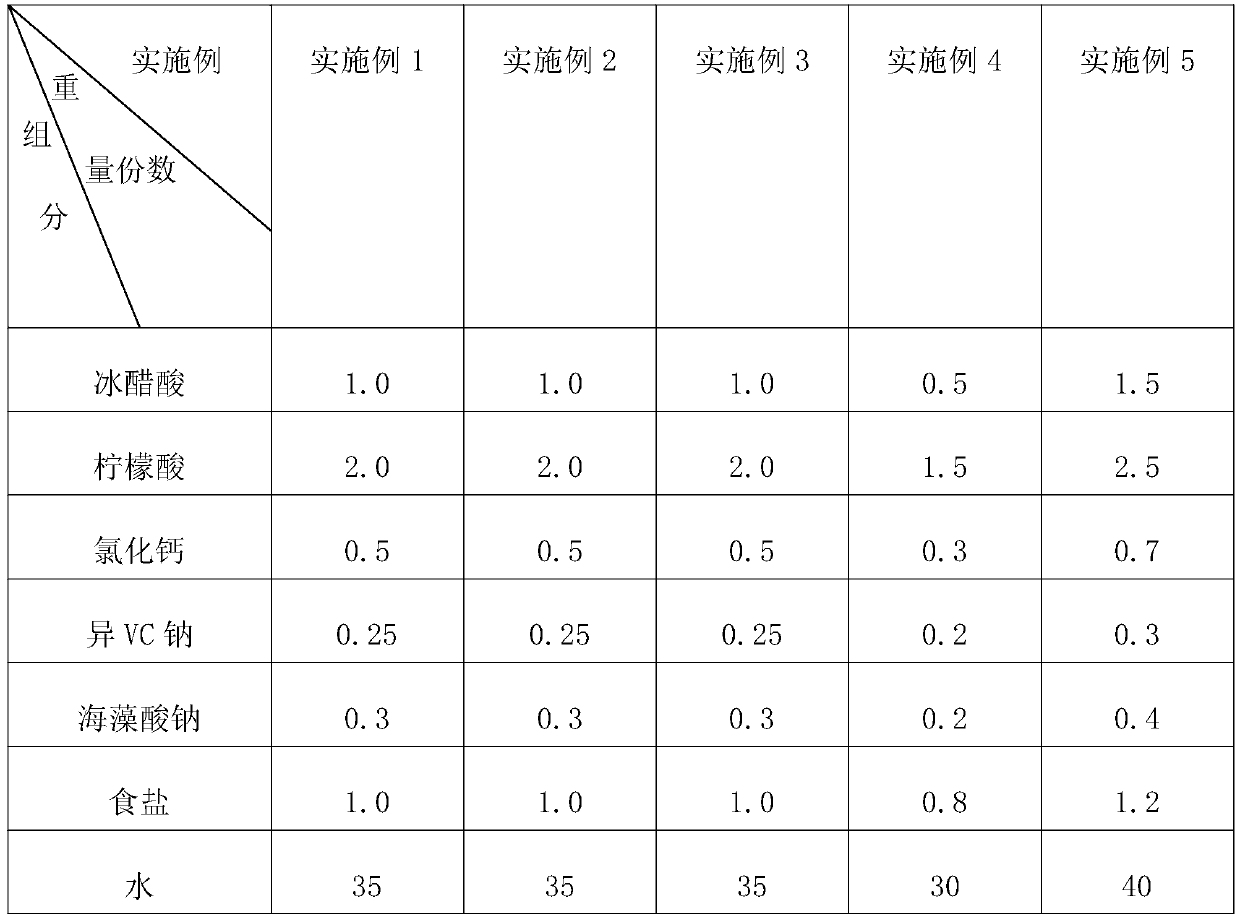
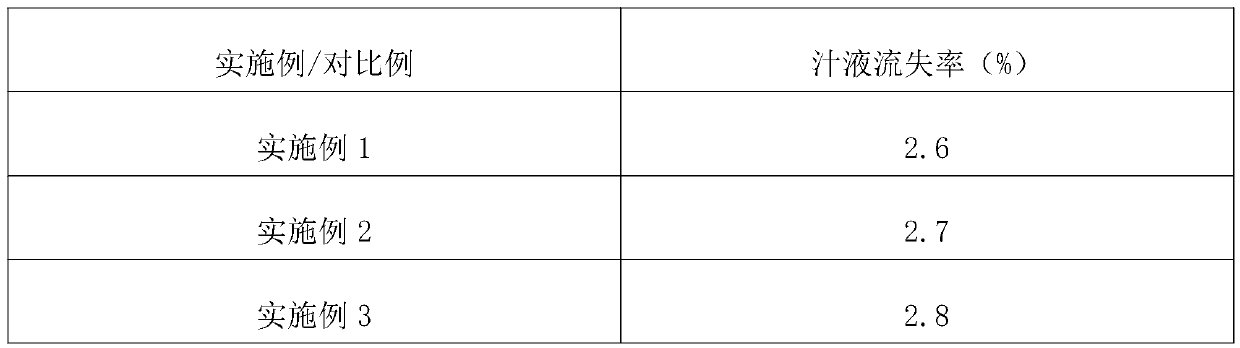
The invention discloses a processing technology of quick-frozen green soybeans, which relates to the technical field of quick-frozen vegetables, and solves the problem that the overall quality of thequick-frozen green soybeans is greatly reduced due to the fact that the juice loss rate of the conventionally processed quick-frozen green soybeans is high after the quick-frozen green soybeans are unfrozen. The processing technology of the quick-frozen green soybeans comprises the following steps of step 1, selecting raw materials; step 2, cleaning and soaking; step 3, blanching and air cooling;step 4, draining and protecting; and step 5, quick-freezing and packaging; and step 6, warehousing and refrigerating. According to the processing technology of the quick-frozen green soybeans, in theactual application process, the obtained quick-frozen green soybeans have the low juice loss rate, and the overall application effect is good.
Owner:余姚市鸿基食品有限公司
Frozen blend of sauce and vegetables
InactiveUS20110171356A1Eliminate objectionable fat separationSoft textureMilk preparationDough treatmentAdditive ingredientCheese sauce
A frozen Queso Fundido preparation or similar product is formed in individual frozen chunks so as to be conveniently microwavable. A cheese sauce is first prepared, including heating the cheese with salts, starch and any other desired ingredients, then cooling the sauce in a sheet and freezing it. The frozen sauce is cut into cubes or other chunks and kept frozen. Separately, vegetables, meat or other ingredients are frozen in chunks and the frozen vegetable chunks are placed with the cheese sauce chunks in packaging and sealed. The consumer takes the frozen package, empties it into a bowl and microwaves the chunks together. The individual chunks will thaw and melt efficiently.
Owner:MATTSON PETER H +1
Extraction method and apparatus of juice and/or puree, in particular from partially or completely frozen vegetables
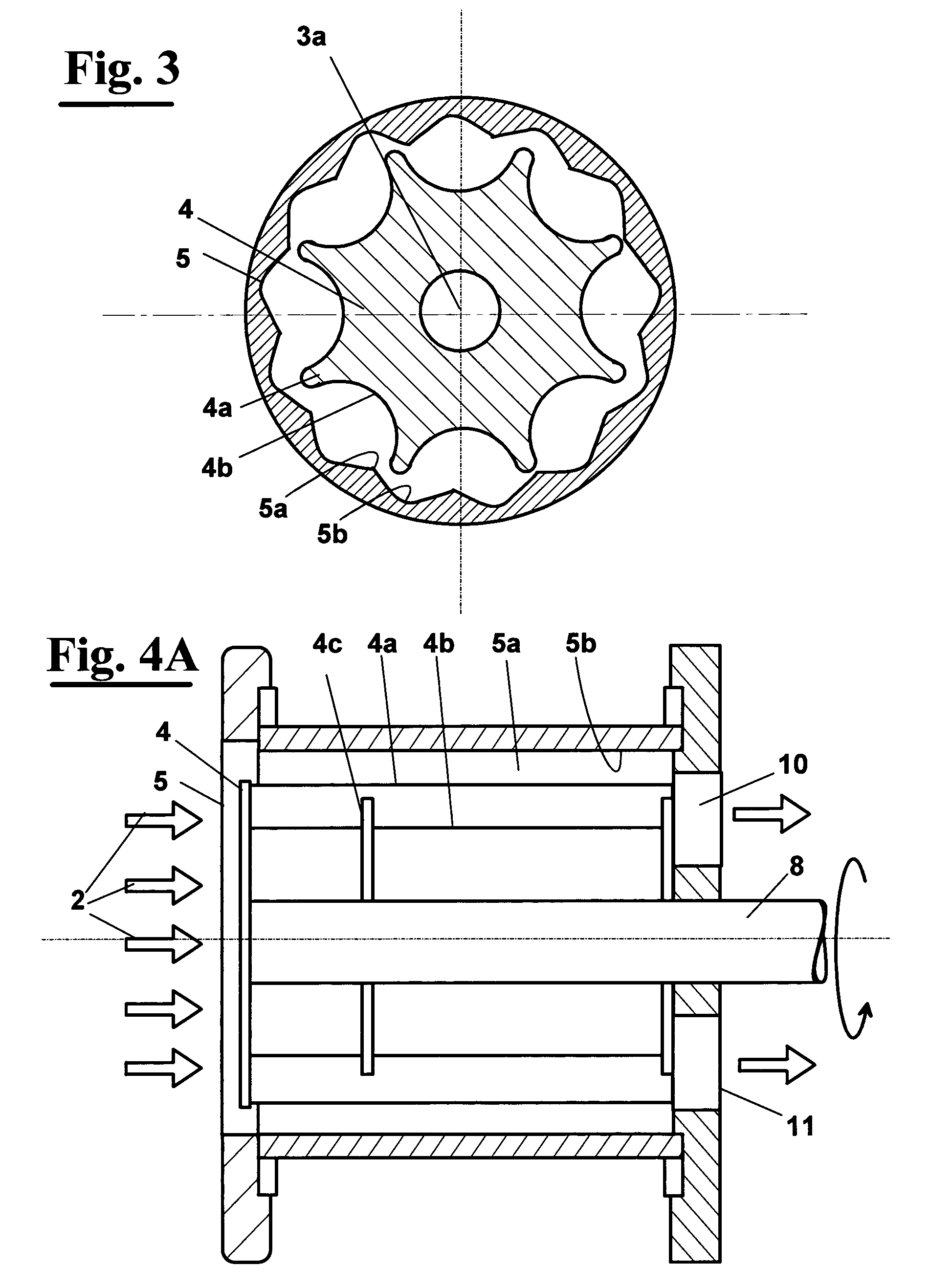
A rotating machine operated along an axis (3a) by a motor (3), for extraction at room temperature of puree or juice from animal or vegetable food, comprises an inlet duct (1) where the animal or vegetable food (2) is loaded, for example fruit or vegetables, conveyed by a feeding screw conveyor not shown. The food pulps of the products (2) are loaded in frozen condition and enter then a shredding section comprising an armature (4) rotatable at a high speed in a stator (5) where the product is subjected to pressure pulses in quick succession by the movement of the frozen product (2) between the armature (4) and the stator (5), which have inner surfaces that are facing each other and have protrusions and recesses in order to apply to frozen food pulps also a strong friction. This way, there is a significant transformation of the mechanical energy into thermal energy that assists partial defrosting (at least 10%) of the product, obtaining a desired, temperature course of the product at least up to the end of the extraction with respect to the defrosting temperature (T*) of the product, which can be 00C or even less, a fluid material is obtained that has the consistency of a puree even if it contains still small frozen parts that are sized like the holes of a sieve. On the external wall of the stator (5) thermal power can be applied contemporaneously to the pressure pulses, in order to heat the inner surface of the stator (5) or the rotor (4), by applying vapour or by means of electric resistance.
Owner:A 贝尔托基
Production and storage method of quick-frozen green soy beans
InactiveCN104365819AAvoid cloggingFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingEvaporationHigh pressure
The invention relates to a production and storage method of quick-frozen green soy beans, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The method comprises the following steps of soaking, blanching, quick-freezing and storing. According to the production and storage method of quick-frozen green soy beans, water is atomized by using a high-pressure dry fog machine to form small particles with the particle sizes of smaller than 10 microns to ensure that water mist can be evaporated within extremely short time after being sprayed out, so that the rather high humidity in a refrigeration house is maintained, furthermore, the evaporation speed of water on the surfaces of quick-frozen vegetables is reduced, and the quick-frozen vegetables can be kept fresh.
Owner:SUZHOU FULL FORTUNE FOOD CO LTD
Processing technology of quick-frozen corn
PendingCN111011487AAvoid churnGood color retentionSeed preservation by freezing/coolingFood ingredient functionsProcess engineeringFrozen vegetables
The invention discloses a processing technology of quick-frozen corn, relates to the technical field of quick-frozen vegetables, and solves the problem that the overall quality of the quick-frozen vegetables is greatly reduced due to the fact that the color of the quick-frozen corn is easy to change in the storage process. The processing technology of the quick-frozen corn comprises the followingsteps: step 1, cooling raw materials; step 2, cleaning and soaking; step 3, blanching and air cooling; step 4, draining and protecting color; and step 5, quick-freezing and packaging; and step 6, warehousing and refrigerating. According to the processing technology of the quick-frozen corn, in the actual application process, the obtained quick-frozen corn has a relatively high color preservation rate in a storage process, so that the obtained quick-frozen corn has excellent color and luster and relatively high overall quality.
Owner:余姚市鸿基食品有限公司
Method for producing quick-frozen vegetable garden pea
InactiveCN101095429AReduce quality fission problemsImprove qualityFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingBiologyFrozen vegetables
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preserved quick-frozen vegetable powder
InactiveCN103859319AEasy to useSolve the crude fiber problemFood ingredient functionsFood preparationFood materialFrozen vegetables
The invention discloses preserved quick-frozen vegetable powder. A preparation process of the preserved quick-frozen vegetable powder comprises the following steps: selecting fresh vegetables; washing and peeling; grinding for the first time; quickly freezing; grinding for the second time; packaging to finally obtain 0.1-5-mesh fresh vegetable powder; and preserving at the temperature of -16 DEG C to -18 DEG C and the humidity of 45%-60%. The preserved quick-frozen vegetable powder is prepared by processing vegetable root and stem plants and leaf vegetables, and can be conveniently used by enterprises and families; a conventional use process is changed, the time is no longer wasted in early food material treatment, the vegetable powder is readily available and is suitable for the families, and each small packet is filled with 5g-10g of the vegetable powder.
Owner:FUNING COUNTY HENGYE VEGETABLE CO LTD
Processing technology of quick-frozen vegetables
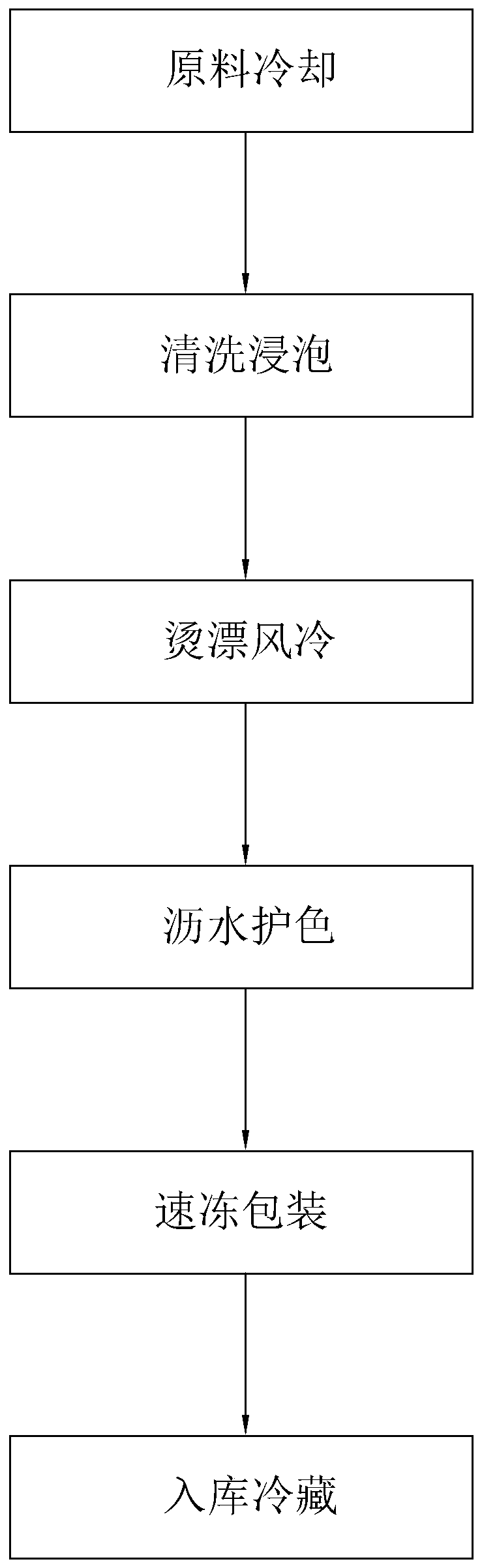
InactiveCN108936440AImprove freshnessImprove tendernessFood freezingFood ingredientsForeign matterSludge
The invention relates to the technical field of processing of vegetables, in particular to a processing technology of quick-frozen vegetables. The processing technology comprises the steps of selecting raw materials, performing cooling, performing cleaning, performing pretreatment, performing blanching, performing air cooling, performing draining, performing quick-freezing, performing packaging and performing cold storage. The processing technology disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the appearance and the freshness of general vegetable raw materials having bright colorare good, and through a color selector, the vegetables having good appearance and freshness can be selected out; in the cooling step, cooling temperature is set to be minus 5-2 DEG C, cooling time isset to be 6-12h, and the vegetable raw materials cooled under the condition can maintain the optimum freshness; in the cleaning step, through a helix cleaning machine, foreign matter of sludge and thelike on the surfaces of the quick-frozen vegetables can be eliminated to the maximum extent, the cleaning effects are better than those with a conveyor belt type cleaning machine in a conventional mode; and in the helix cleaning machine, 0.5%-1% of a calcium carbonate solution is added, so that the vegetable raw materials can maintain brittleness.
Owner:安徽荣丰食品加工有限公司
Production and storage method of quick-frozen mung beans
The invention relates to a production and storage method of quick-frozen mung beans, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The method comprises the following steps of soaking, blanching, quick-freezing and storing. According to the production and storage method of quick-frozen mung beans, water is atomized by using a high-pressure dry fog machine to form small particles with the particle sizes of smaller than 10 microns to ensure that water mist can be evaporated within extremely short time after being sprayed out, so that the rather high humidity in a refrigeration house is maintained, furthermore, the evaporation speed of water on the surfaces of quick-frozen vegetables is reduced, and the quick-frozen vegetables can be kept fresh.
Owner:SUZHOU FULL FORTUNE FOOD CO LTD
Process for preparing intermediate moisture vegetables
InactiveUS7105197B2No waste and spent infusion cocktailLow costMilk preservationAnimal feeding stuffAlcoholSugar
Methods are provided for preparing intermediate moisture vegetables. In one embodiment, this invention relates to a method for preparing intermediate moisture vegetables, said method comprising (1) predrying the vegetables to a moisture content of less than about 5 percent, (2) applying a low viscosity infusion cocktail comprising water, a polyhydric alcohol, and salt to the predried vegetables, (3) equilibrating the predried vegetables and infusion cocktail for at least about 30 minutes to provide the intermediate moisture vegetables, and (4) and packaging the intermediate moisture vegetables; wherein the infusion cocktail contains essentially no sugars or saccharides. When cooked, these intermediate moisture vegetables provide appearance, texture, and taste similar to that provided by high quality cooked individually quick frozen vegetables.
Owner:KRAFT FOODS GRP BRANDS LLC
Semi-finished quick-frozen leaf vegetables processing method
InactiveCN104336153ASmall footprintEasy to storeFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingVegetable processingSpins
The invention relates to a semi-finished quick-frozen leaf vegetables processing method, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of food. The semi-finished quick-frozen leaf vegetables processing method comprises the following steps of material selecting, rinsing, machine cutting, machine selecting, manual sorting, blanching, spin-drying, pre-packaging, quick-freezing, post-packaging and dry fog and humidity control storage. The semi-finished quick-frozen leaf vegetables processing method has the advantages that quick-frozen vegetables produced by the method cannot overlap each other; the processed leaf vegetables take a small space, the storage and transport efficiency is high, and the circulation cost is low; the method also keep the vegetables fresh; further processing is not needed in large-scale applications, so the processing time is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU FULL FORTUNE FOOD CO LTD
Processing method of half-finished quick-frozen sprouting vegetables
InactiveCN104430819ASmall footprintEasy to storeFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingSpinsBiology
The invention relates to a processing method of half-finished quick-frozen sprouting vegetables, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of foods. The processing method of the half-finished quick-frozen sprouting vegetables comprises the following steps sequentially: selecting materials, rinsing, mechanically selecting, artificially grading, blanching, spin-drying, pre-packaging, quick-freezing, post-packaging, controlling the humidity with dry fog, and storing. The quick-frozen vegetables produced by adopting the processing method of the half-finished quick-frozen sprouting vegetables, disclosed by the invention, are prevented from being overlapped, and the processed sprouting vegetables are small in occupying space, high in storage and transportation efficiency, low in circulation cost, and the fresh quality of the vegetables is kept; and in large-scale application, the further processing is not required, so that the processing time is saved.
Owner:SUZHOU FULL FORTUNE FOOD CO LTD
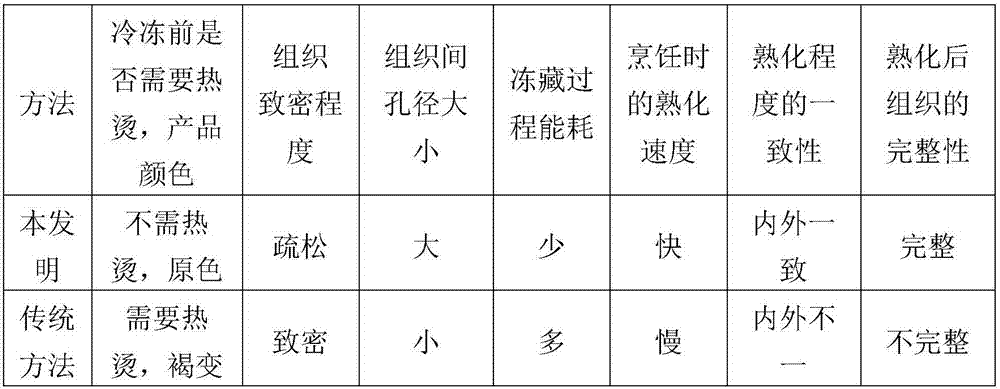
Processing and preservation method of porous tuber vegetables
InactiveCN107173429AReduce energy consumptionReduce processing timeFood freezingFood processingFood gradeSurface water
A processing and preservation method of porous tuber vegetables comprises steps as follows: the tuber vegetables are peeled and cleaned, surface water is drained, and after the tuber vegetables are not packaged or packaged with food-grade plastic bags, the tuber vegetables are stored in the environment of subzero 6 DEG C to subzero 3 DEG C for 3-5 h and can be directly used for cooking or preserved at subzero 10 DEG C to subzero 6 DEG C. The starch-rich tuber vegetables such as Chinese yams, taro and the like are treated at the temperature of subzero 6 DEG C to subzero 3 DEG C, the vegetables can be slowly frozen, water in tissue slowly forms numerous large-particle ice crystals, so that after the frozen vegetables are unfrozen, the vegetable tissue cannot completely absorb water produced during unfreezing again, part of water escapes, holes are formed in the original ice crystals, and the porous characteristic is formed. The blanching process is omitted before processing, and energy consumption is reduced; the preservation time of the tuber vegetables can be prolonged; due to formation of the porous characteristic of the vegetables, the cooking time can be shortened, insides and outsides of products are ensured to be heated uniformly, and the insides and the outsides of the tuber vegetables are cooked simultaneously.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com