Patents
Literature
199 results about "Premature baby" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
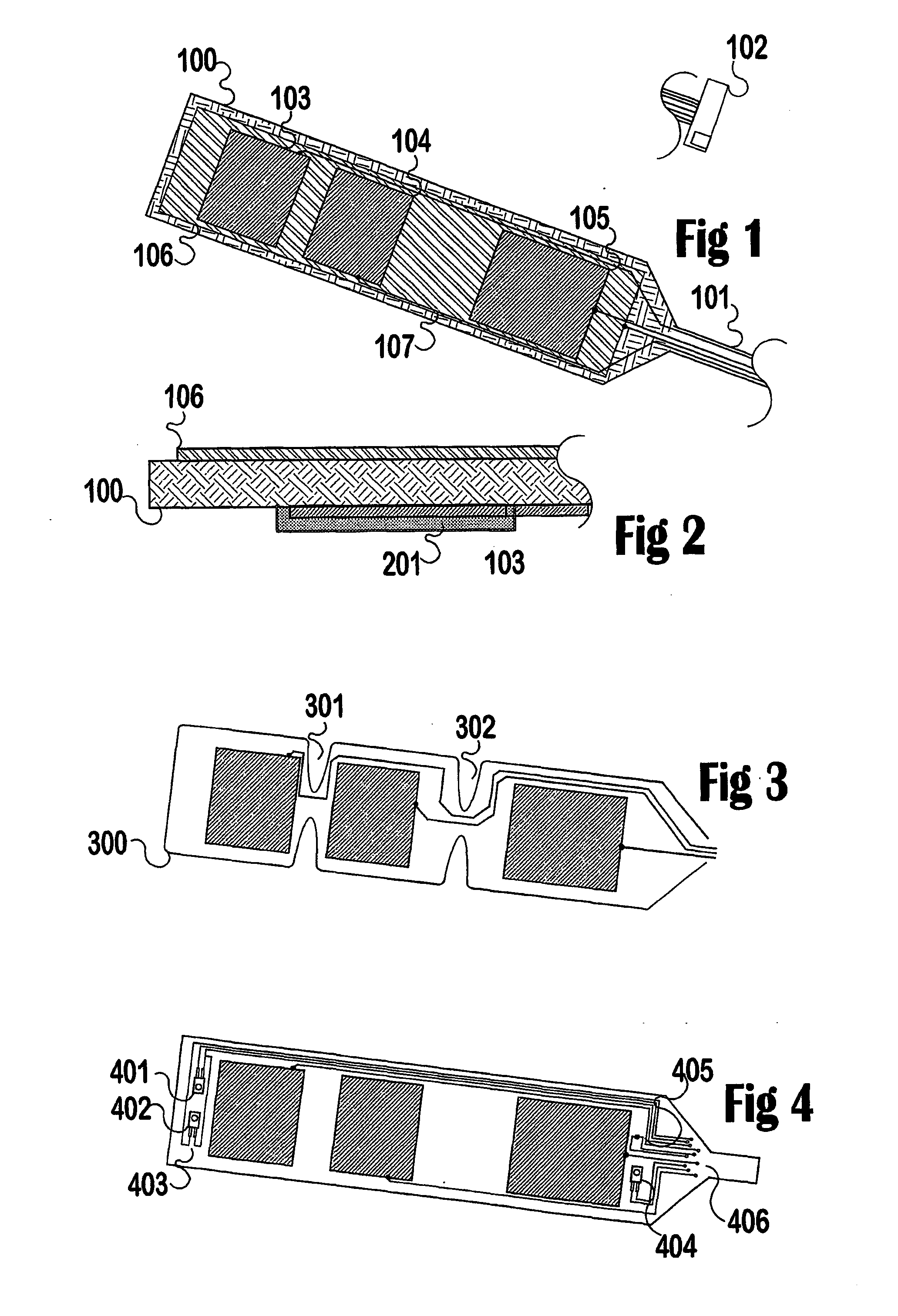
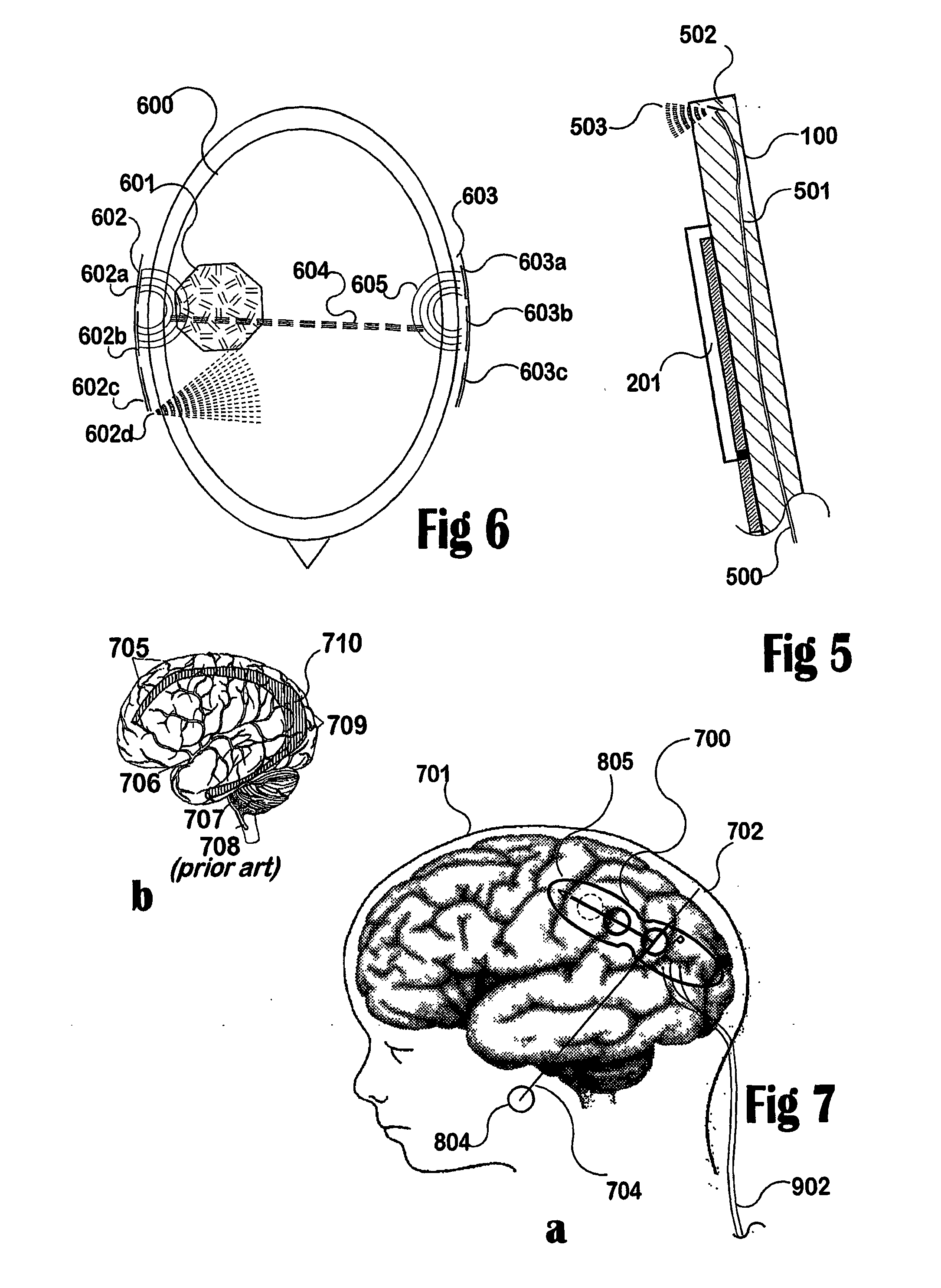
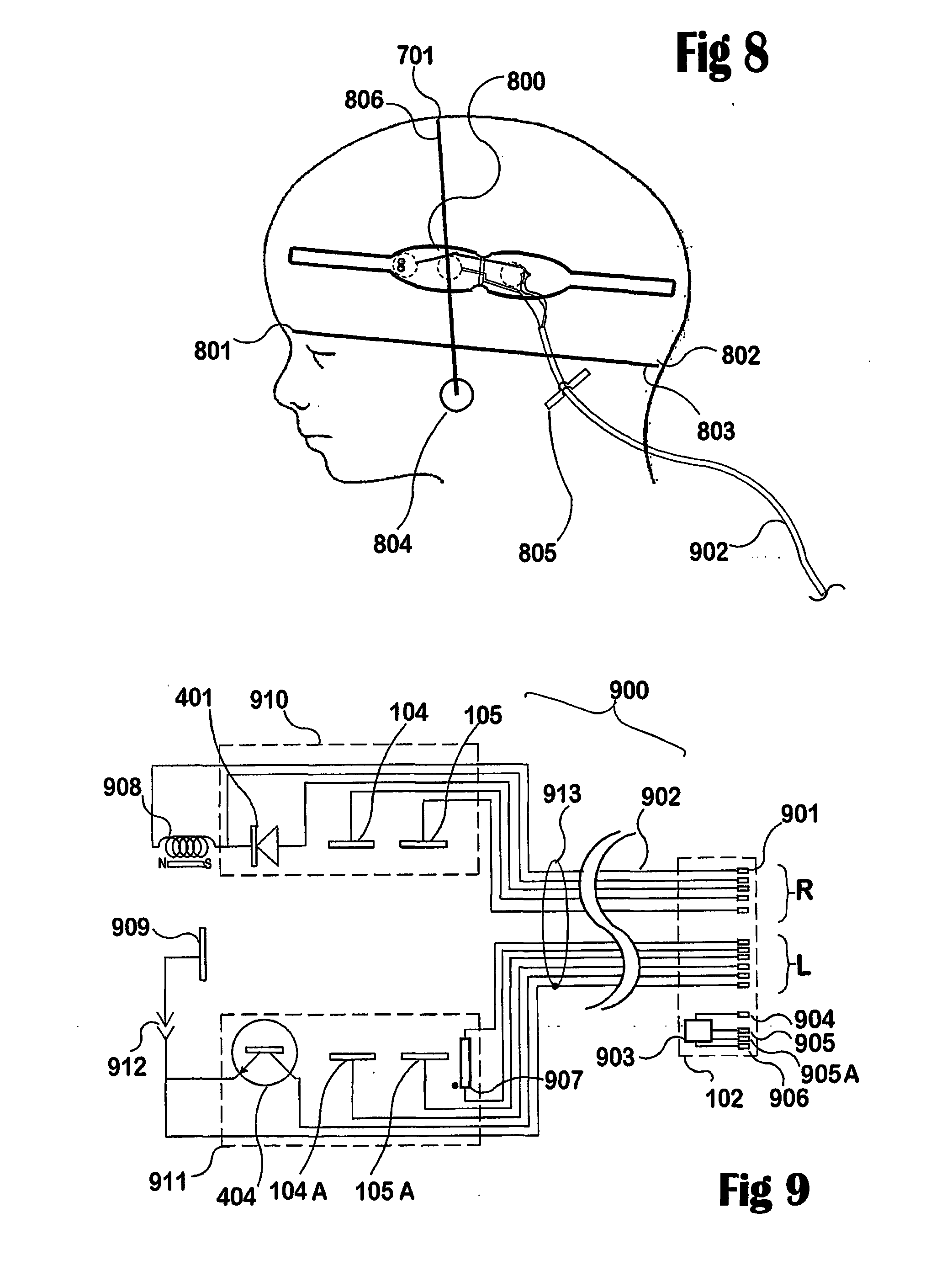
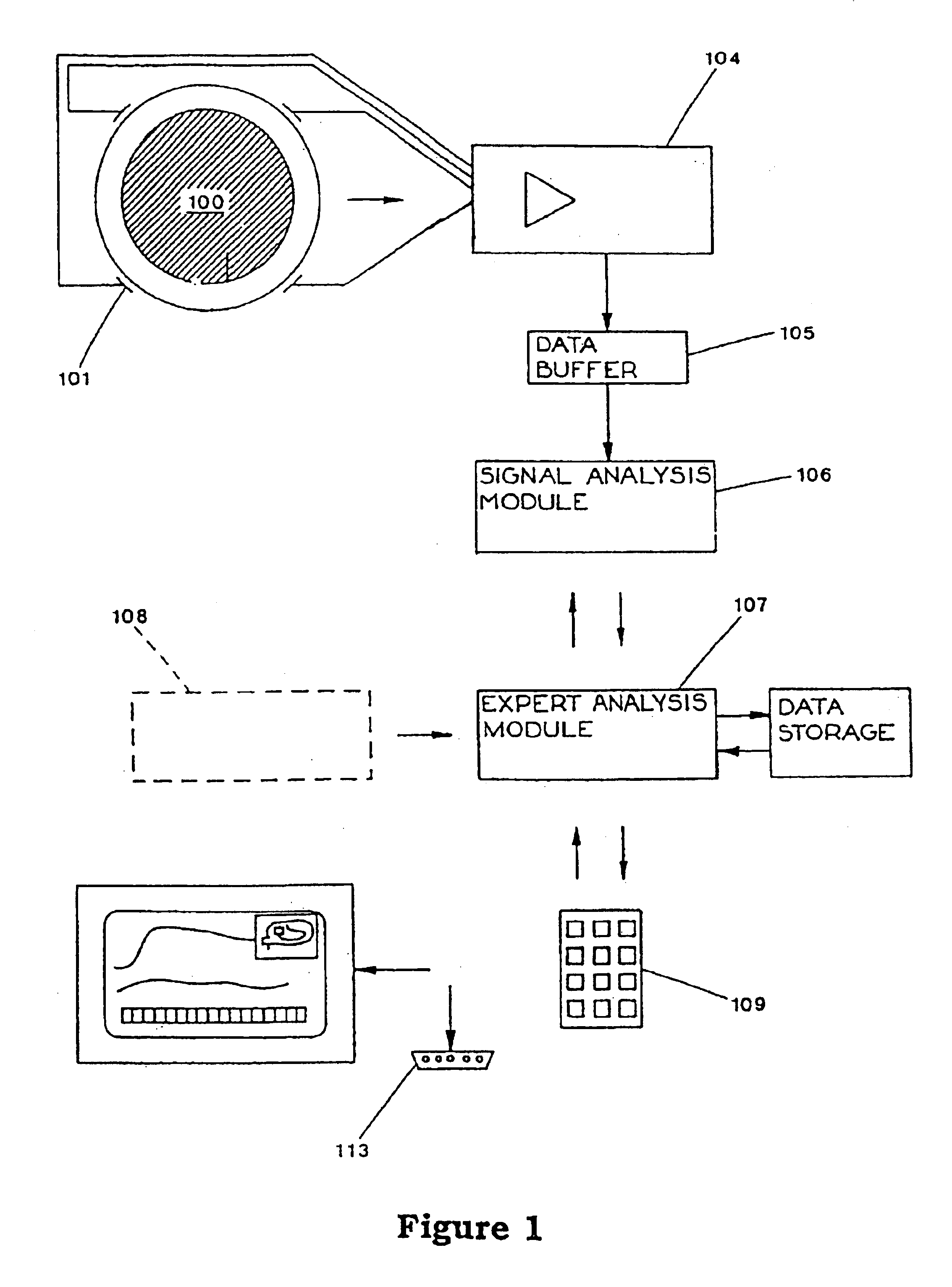
Sensor assembly for monitoring an infant brain
InactiveUS20040030258A1Risk minimizationGood flexibilityElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using lightNeuronal swellingTreatment effect
A flexible, conformable, sensor assembly is provided, including an electrode array especially adapted for stable, long-term recording of EEG signals from a pre-term or neonatal infant in intensive care. A kit or sterile pack includes guidance for placement of the electrodes over a designated area of the infant's brain, an area likely to be injured. The sensor assembly includes a left-side and a right-side flexible strip bearing at least electrodes and optional temperature, motion, and optical sensors provide for the monitoring of an extended range of parameters including aspects of cerebral perfusion and metabolism. Optional impedance measurements provide an indication of neuronal swelling. Stable performance over from three days to about a week is intended so that progress, effects of treatment, and outcome can be considered.
Owner:TRU TEST
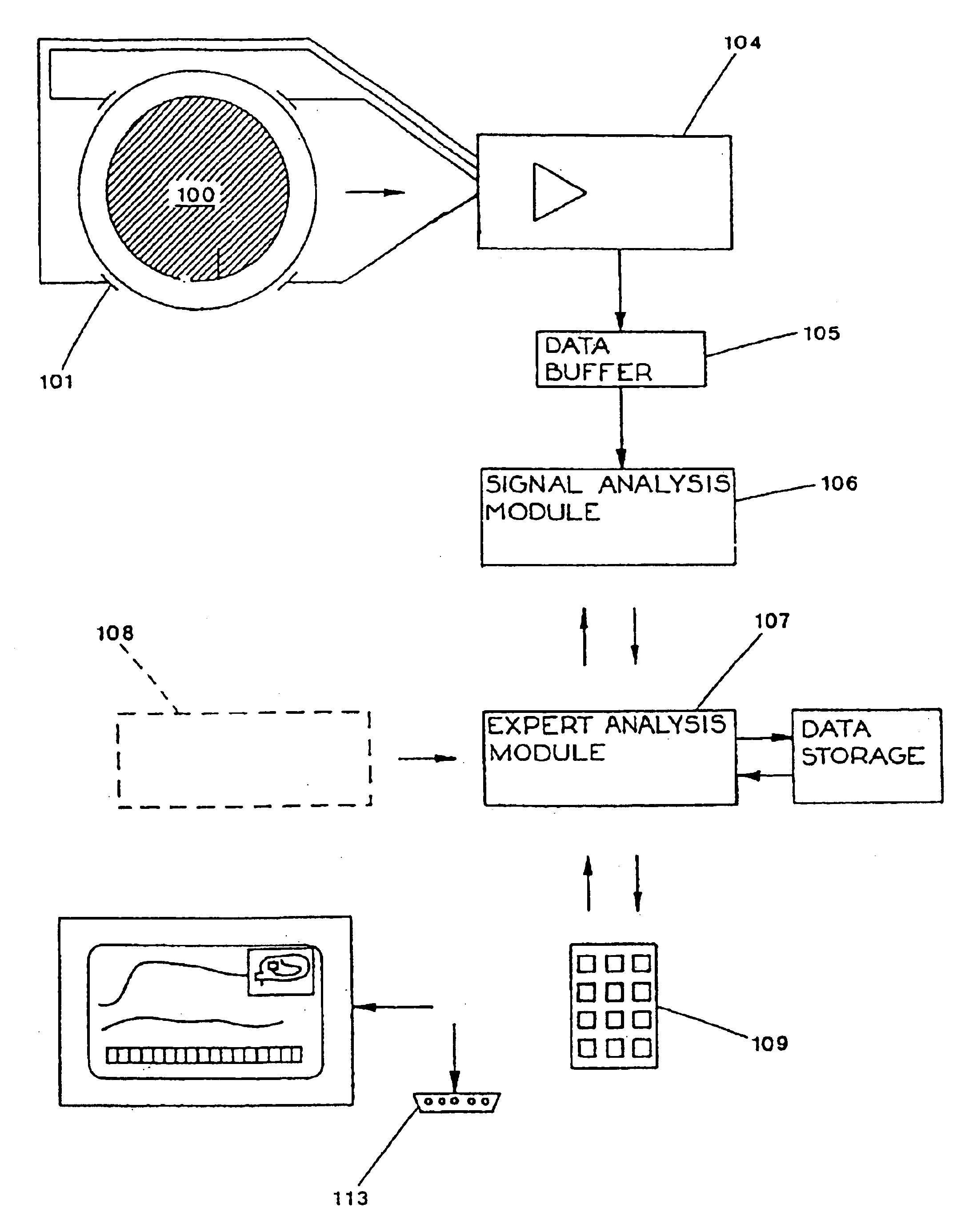
Processing EEG signals to predict brain damage
Rapid and accurate in-vivo assessment of cerebral white matter injury particularly for pre-term infants, for timely treatment and / or prediction of outcomes has been very limited. This invention exploits the discovery that reduced high-frequency EEG intensity, particularly as shown by the upper spectral edge frequency, is a good indicator of cerebral white matter neural injury and is well correlated with MRI results. With more experience of clinical cases, a set of simple rules such as “if the spectral edge value is below 8 Hz there is a high likelihood of injury” may be validated, yet the EEG technology involved is largely invisible to the user. In the invention, EEG signals are processed by software to obtain, store, and graphically display bilaterally collected EEG spectral edge and intensity values over from hours to weeks. Rejection of corrupted signals by filtering and gating means is responsive to incoming signal characteristics, to additional inputs such as motion sensors or impedance tests, and to patient data (gestational age in particular). The invention includes the software and methods of use.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
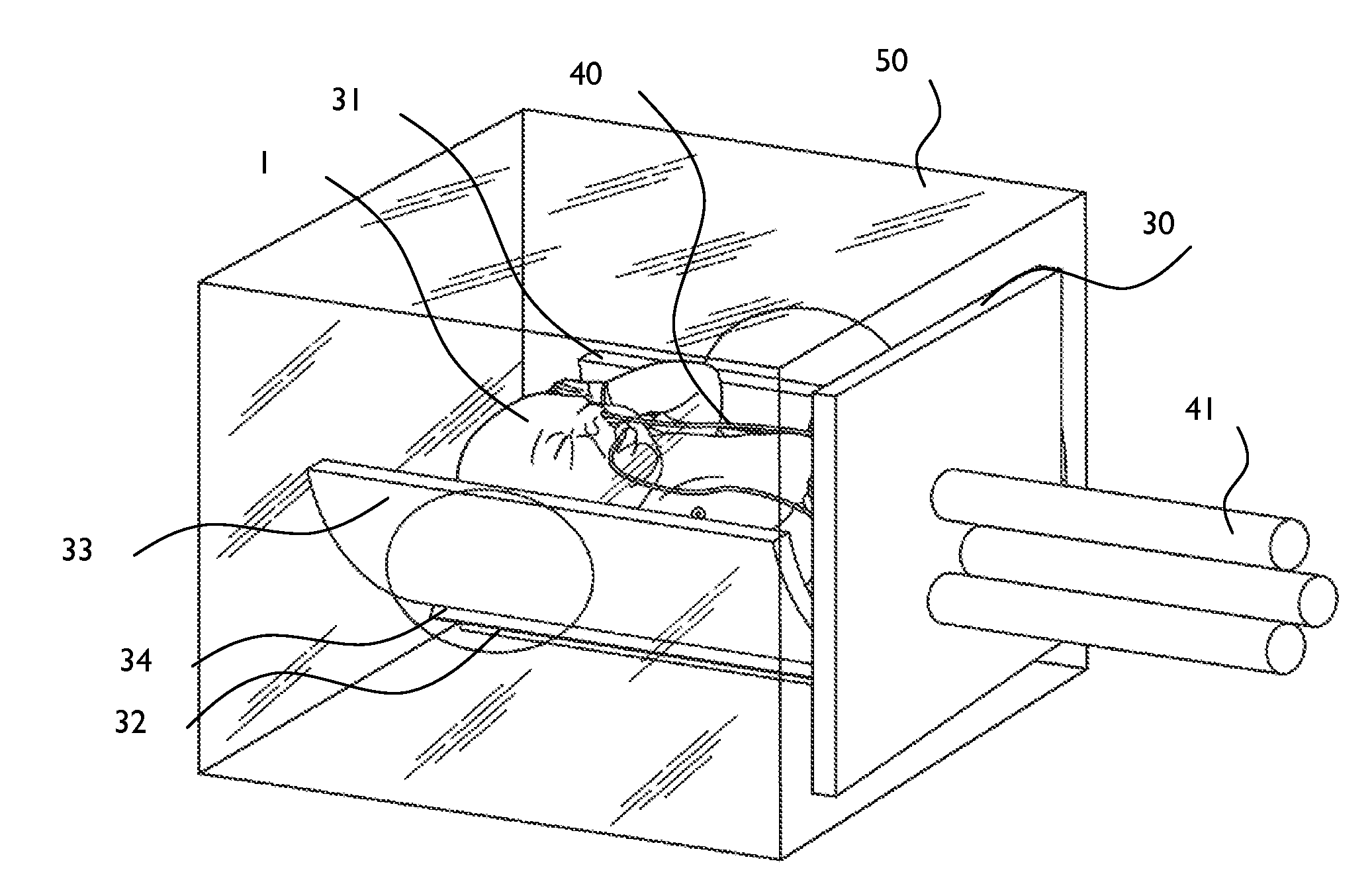
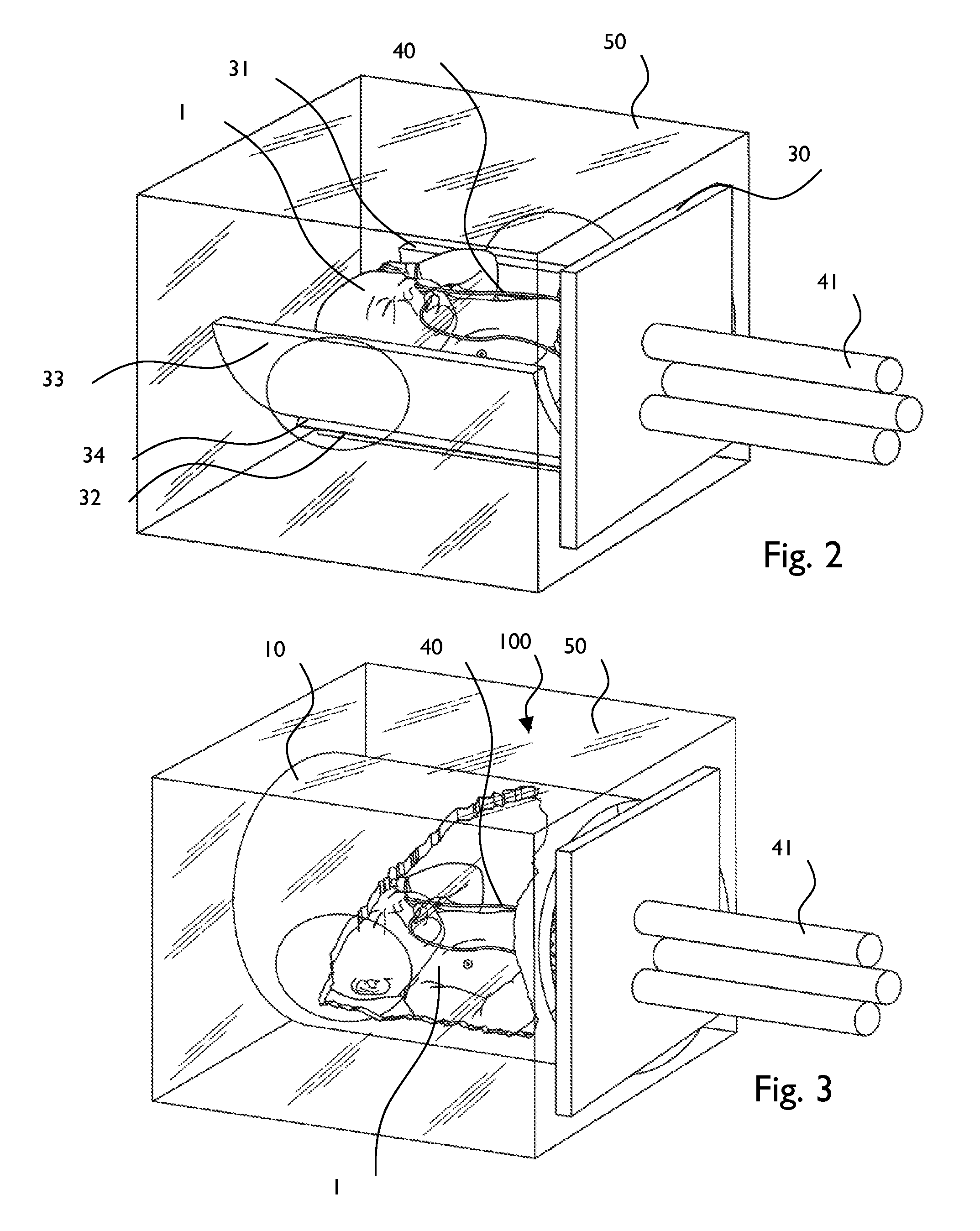
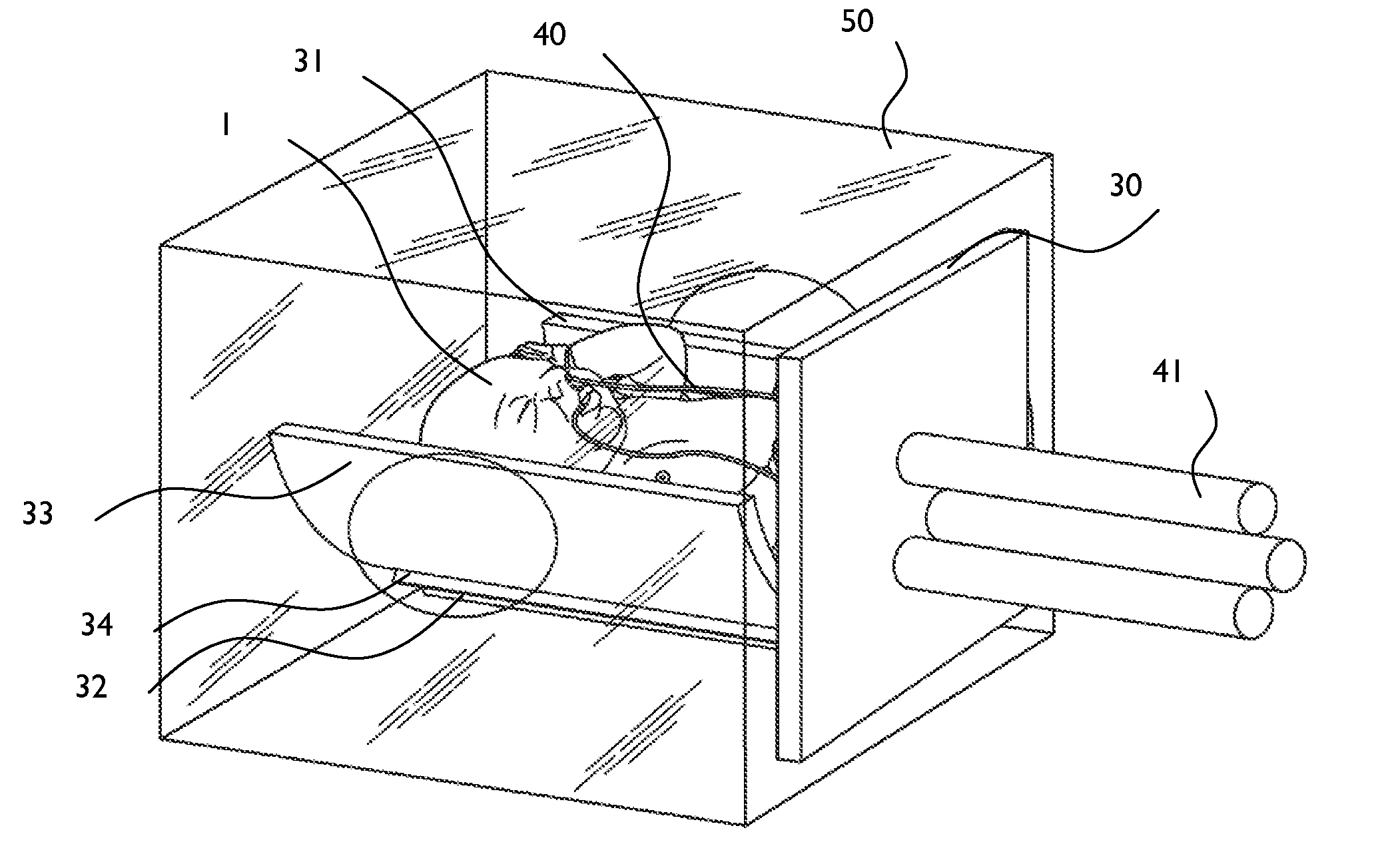
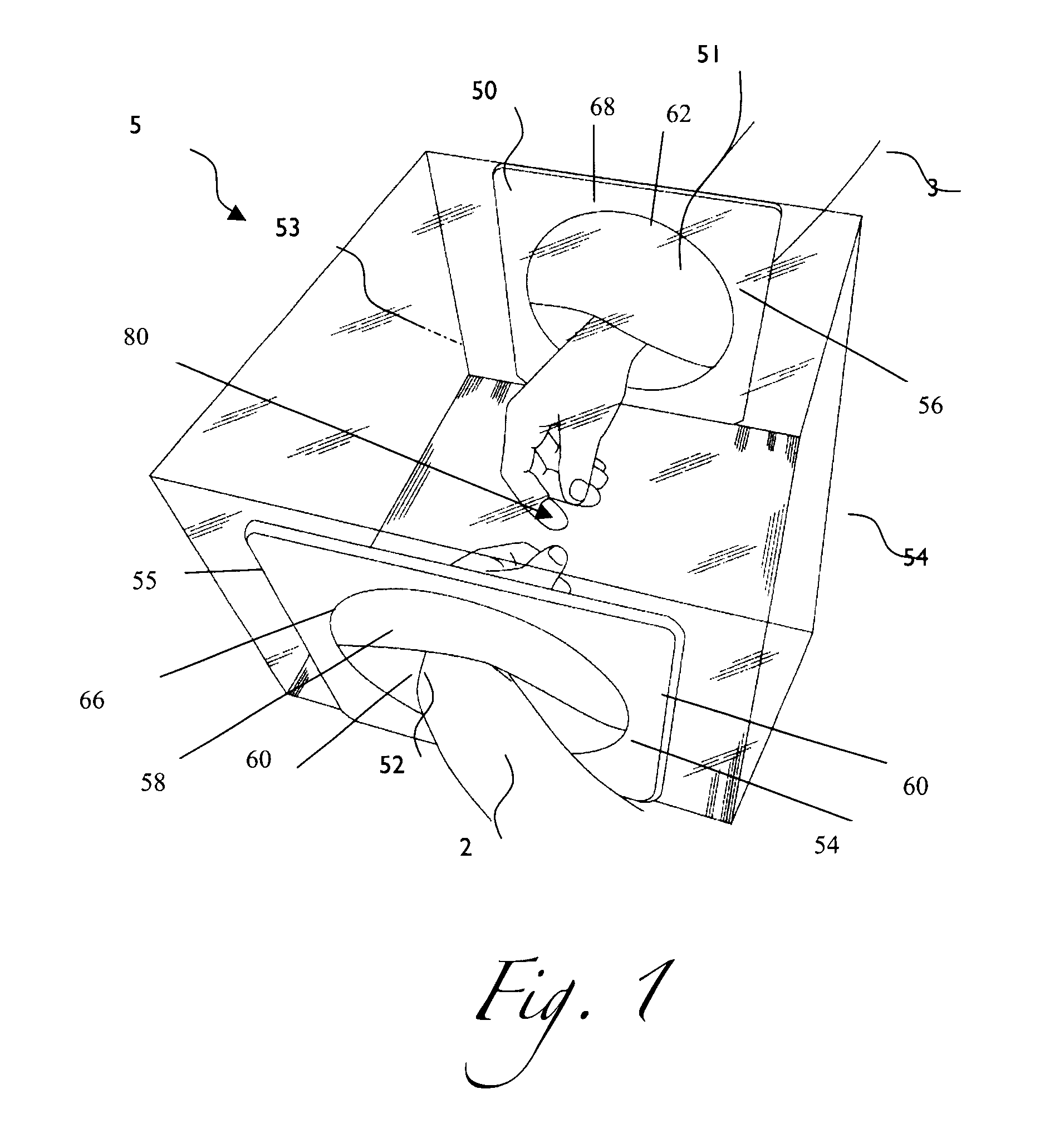
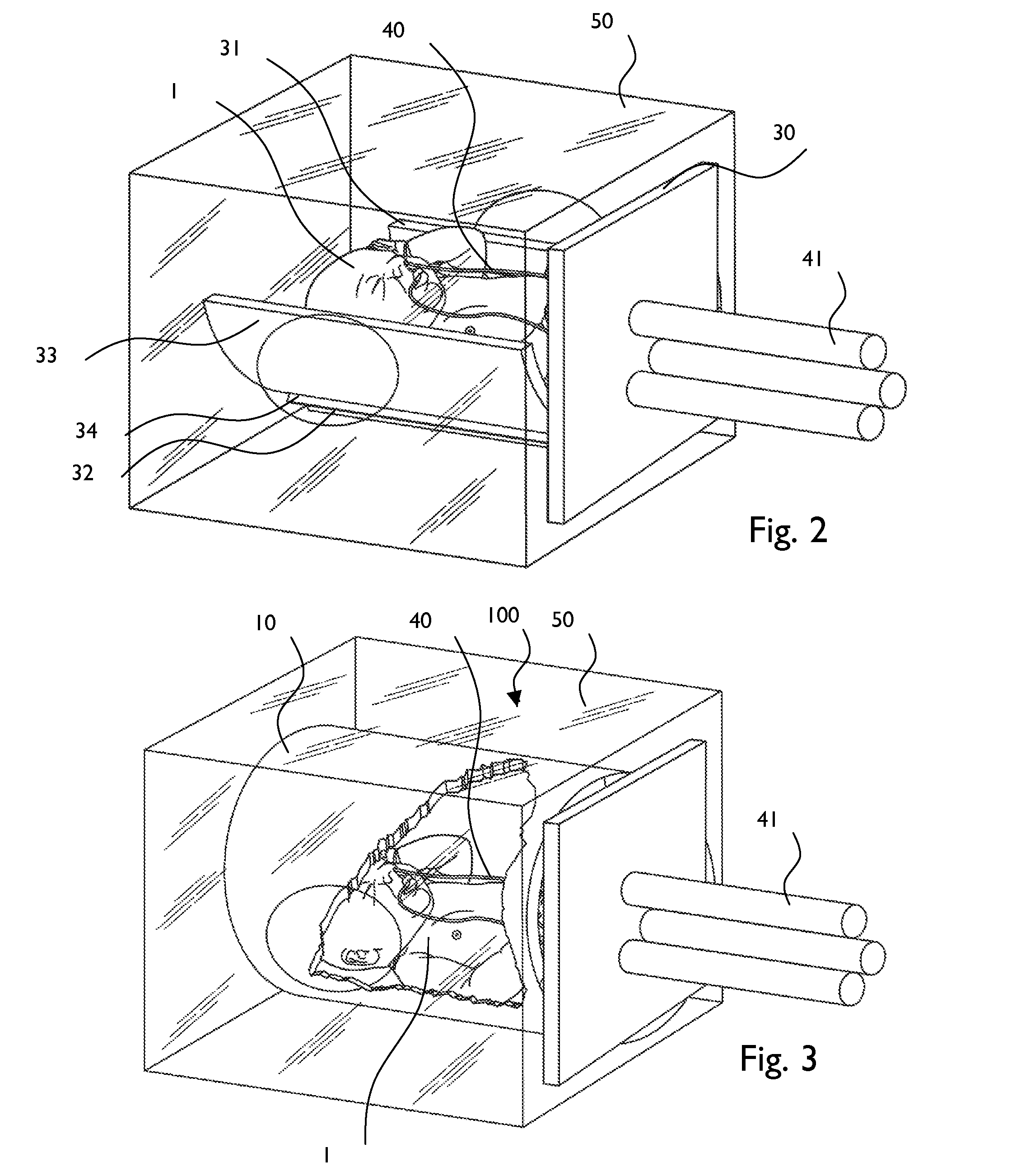
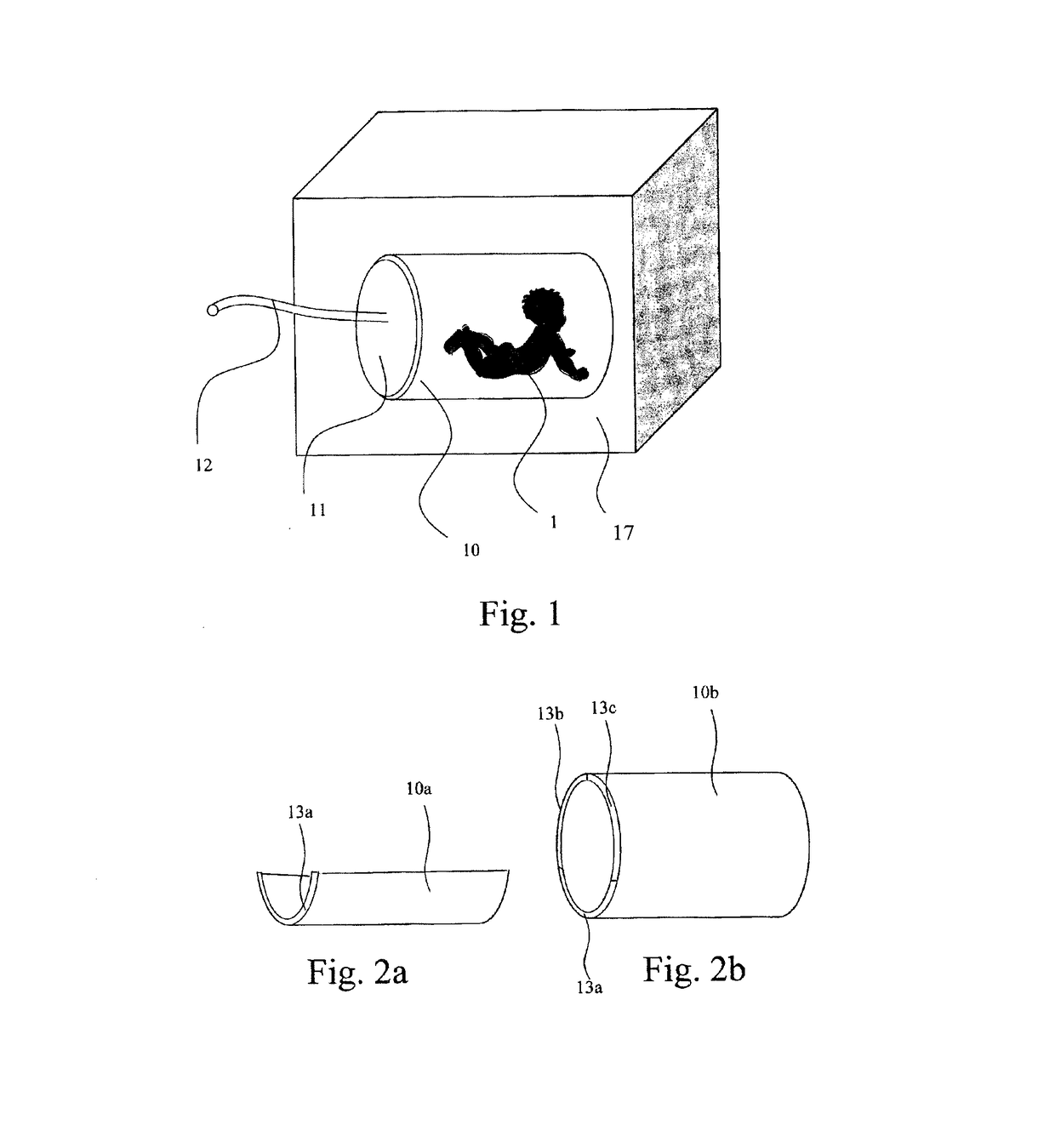
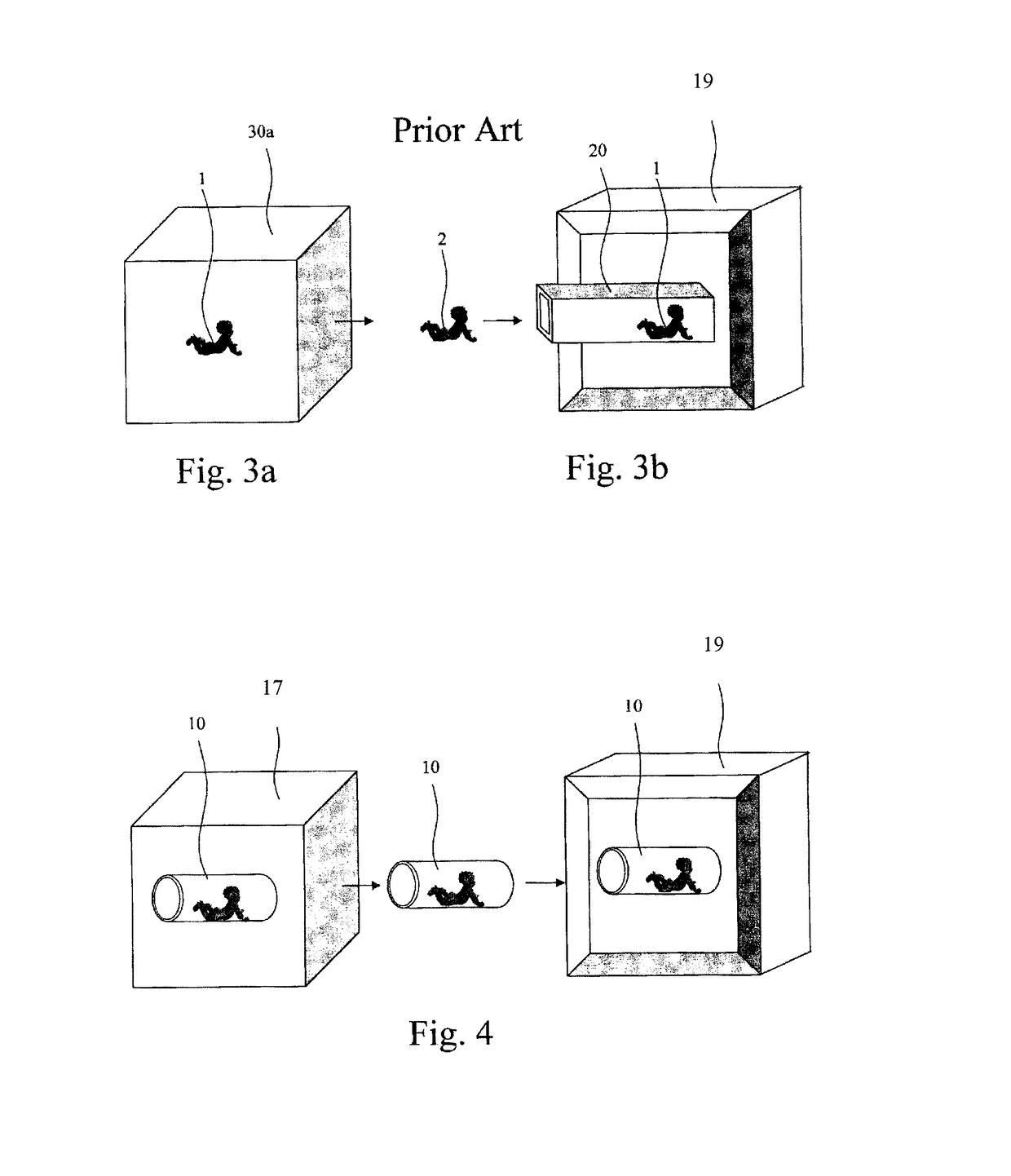
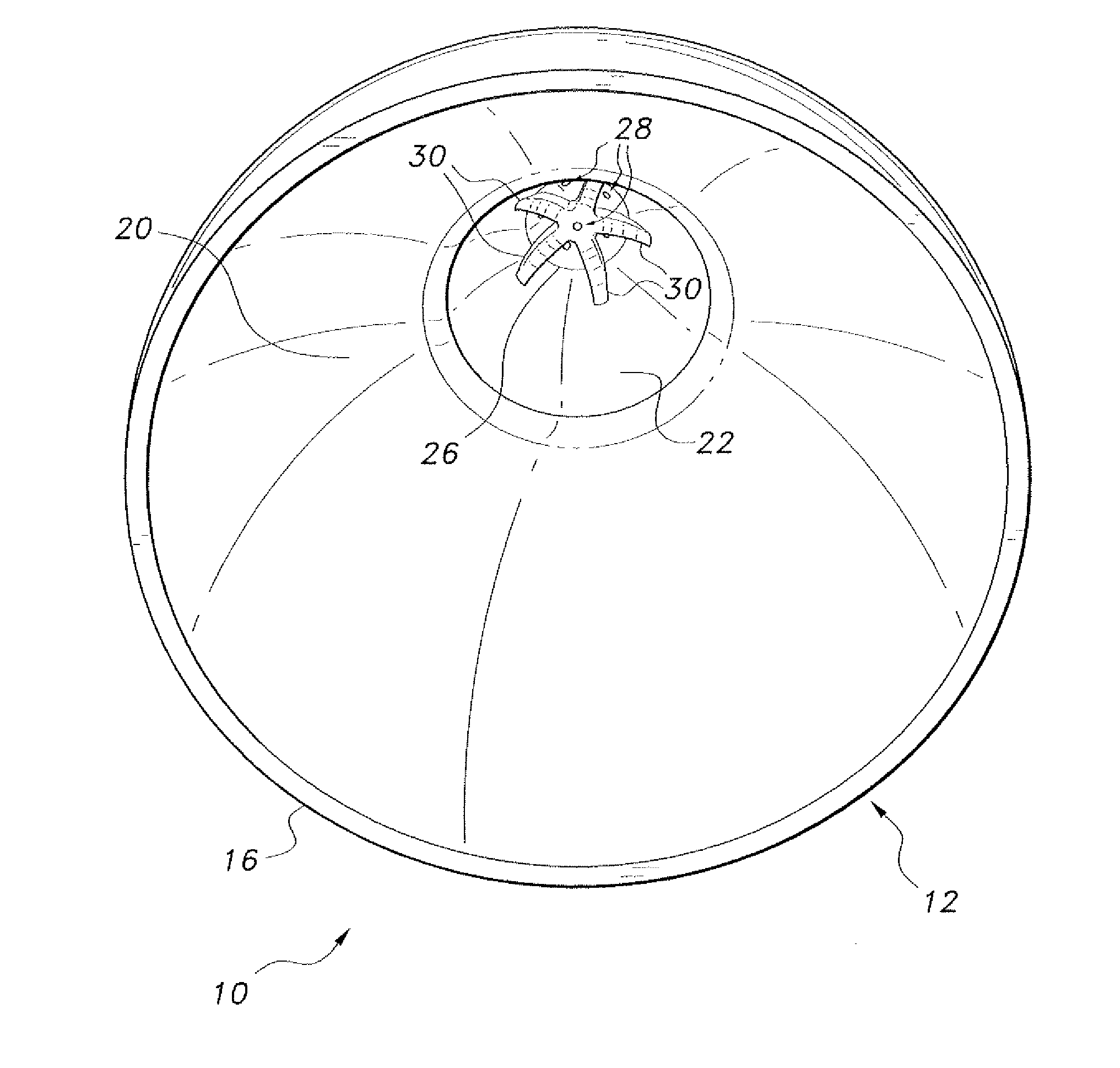
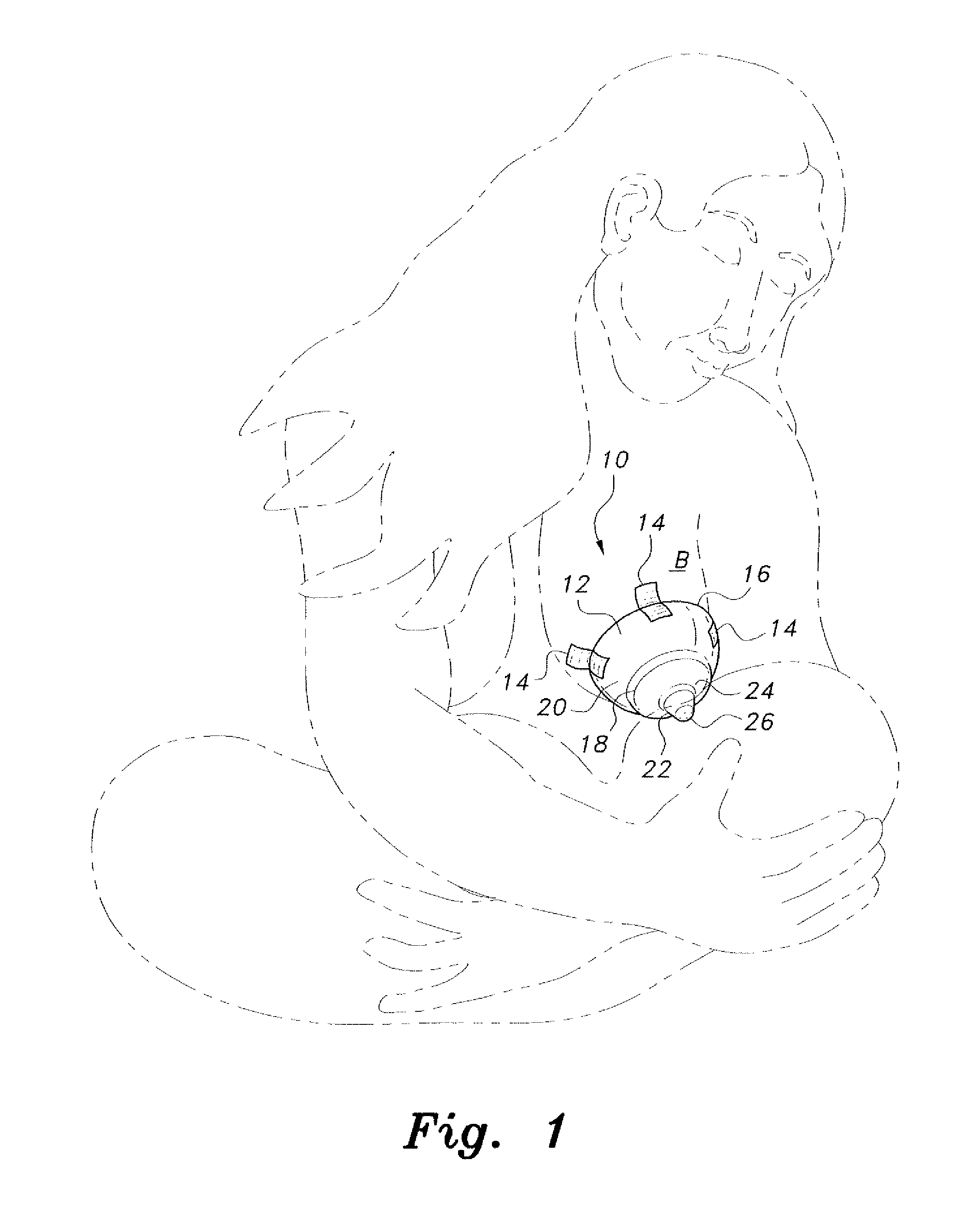
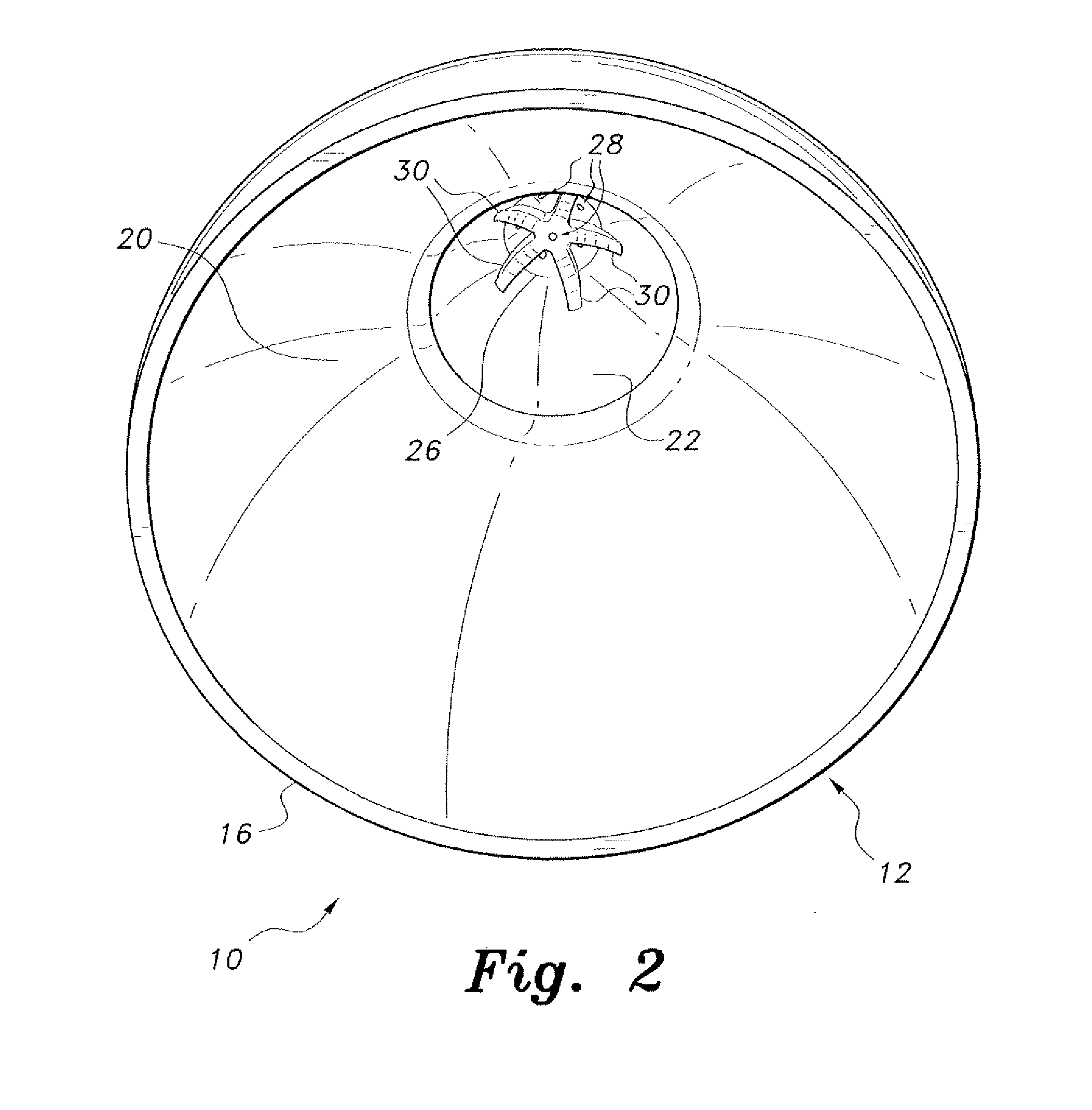
Premature neonate closed life support system
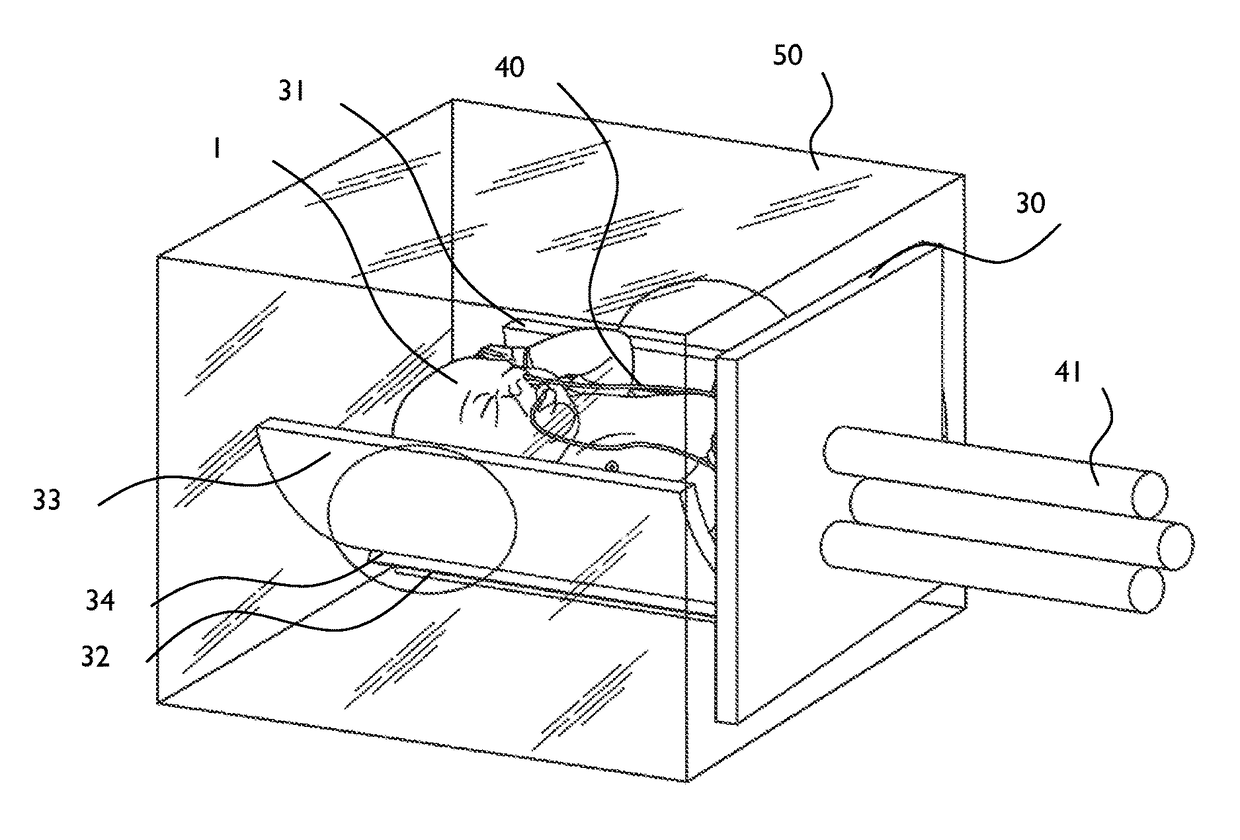
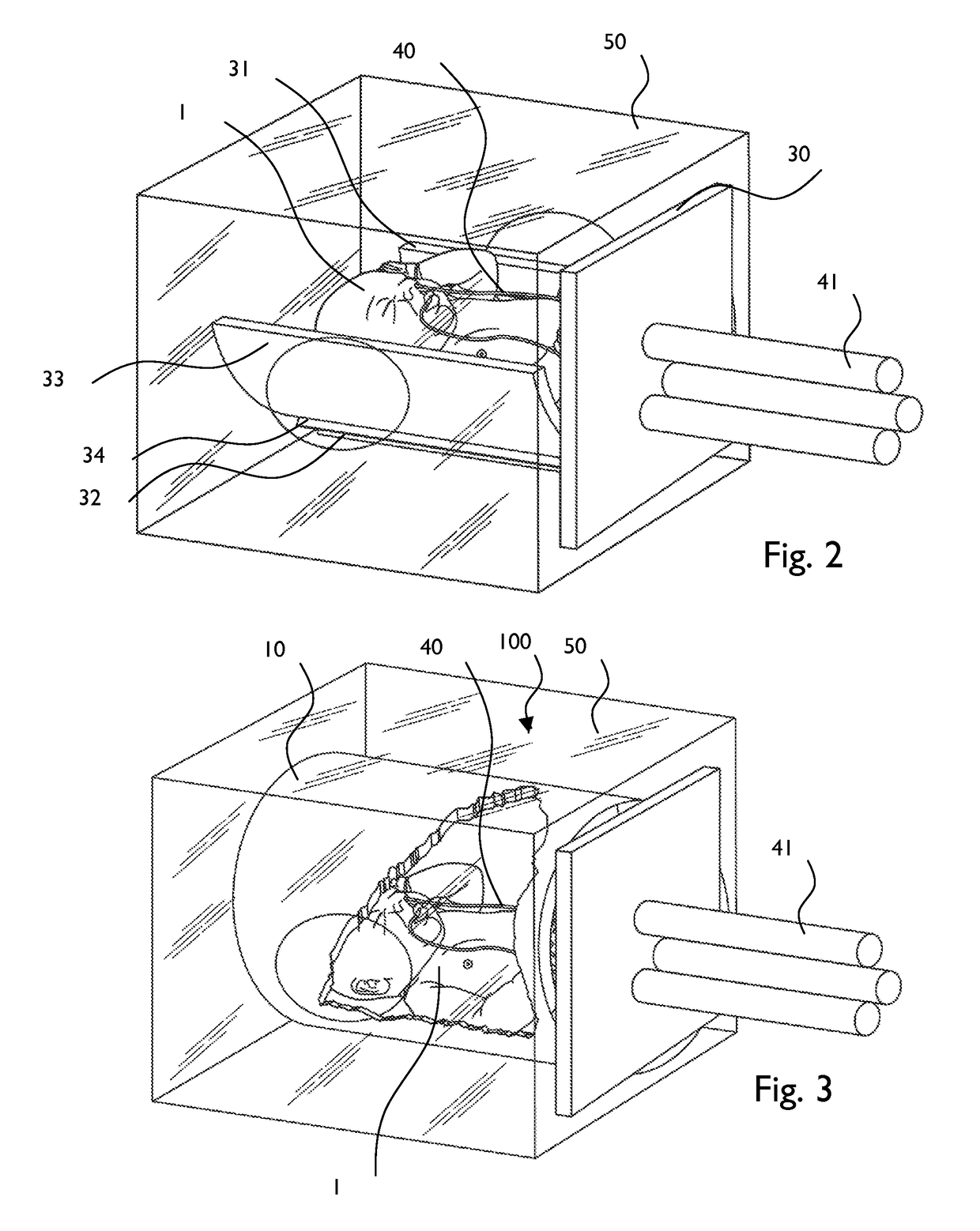
A premature neonate closed life support system (NCLSS) including: at least one chamber confining a cradle-like neonate support (CLNS) having suitable dimensions and geometric-configuration for accommodating at least one premature neonate having at least two operational configurations, said operational configurations comprising: a first operational OPEN configuration whereby said CLNS is adapted to couple said neonate to at least one life supporting system by means of at least one life supporting coupling line, prior to positioning said CLNS in a medical device; and a second operational air-tight CLOSED configuration whereby said neonate remains continuously coupled to said at least one life supporting system by means of at least one life supporting coupling line, when positioning said CLNS within said medical device. The OPEN and CLOSED configurations are reversible.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
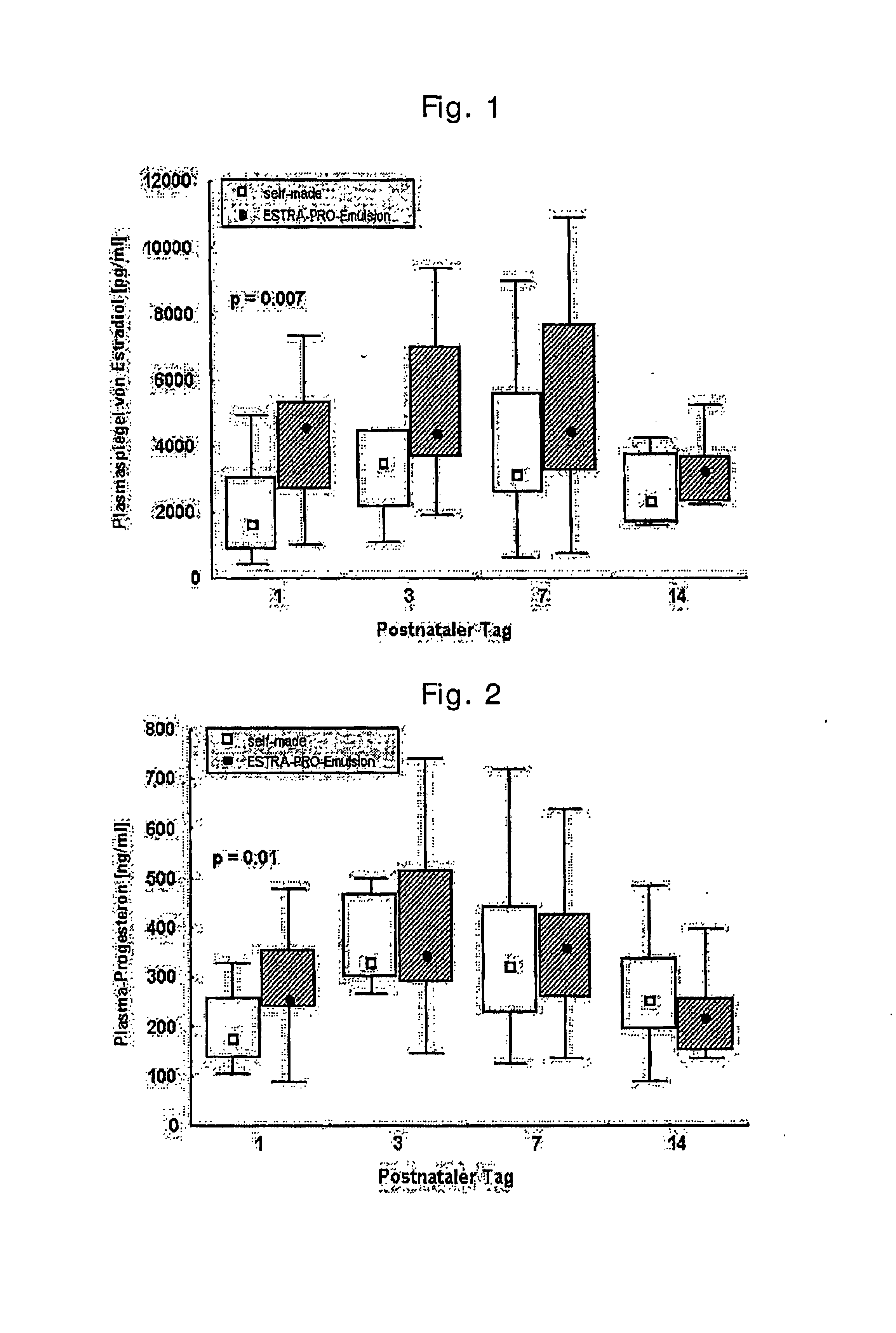
Oil emulsion for postnatal hormone substitution
InactiveUS20070071777A1High serum levelImprove usabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationVein
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of hormone-containing oil emulsions (lipid emulsions), an isotonic oil emulsion obtainable by such process, and the use of the emulsion according to the invention for the preparation of a medicament for intravenous administration, especially for postnatal hormone substitution in premature babies and for the treatment of neurological damage after strokes.
Owner:B BRAUN MELSUNGEN AG
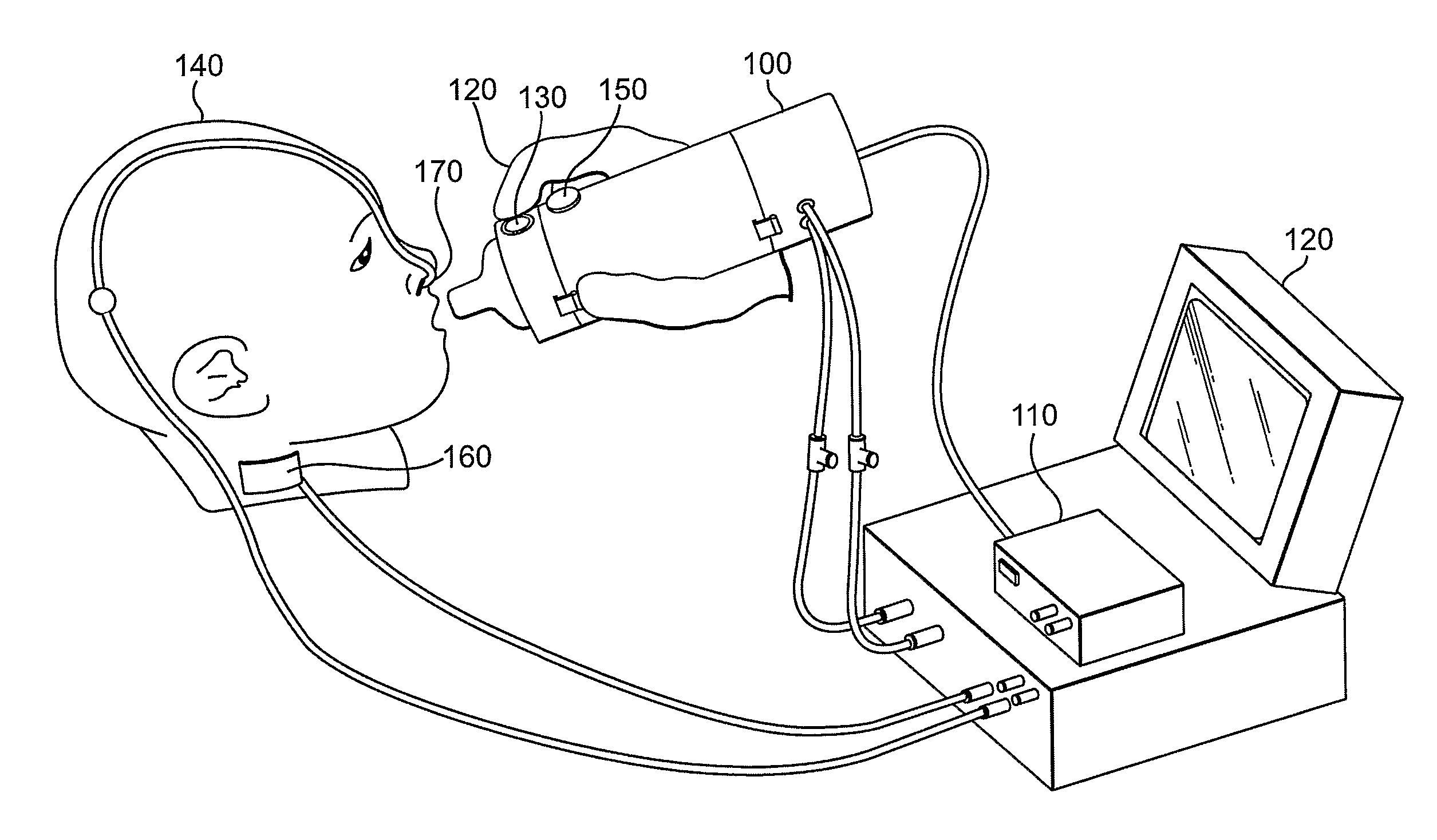
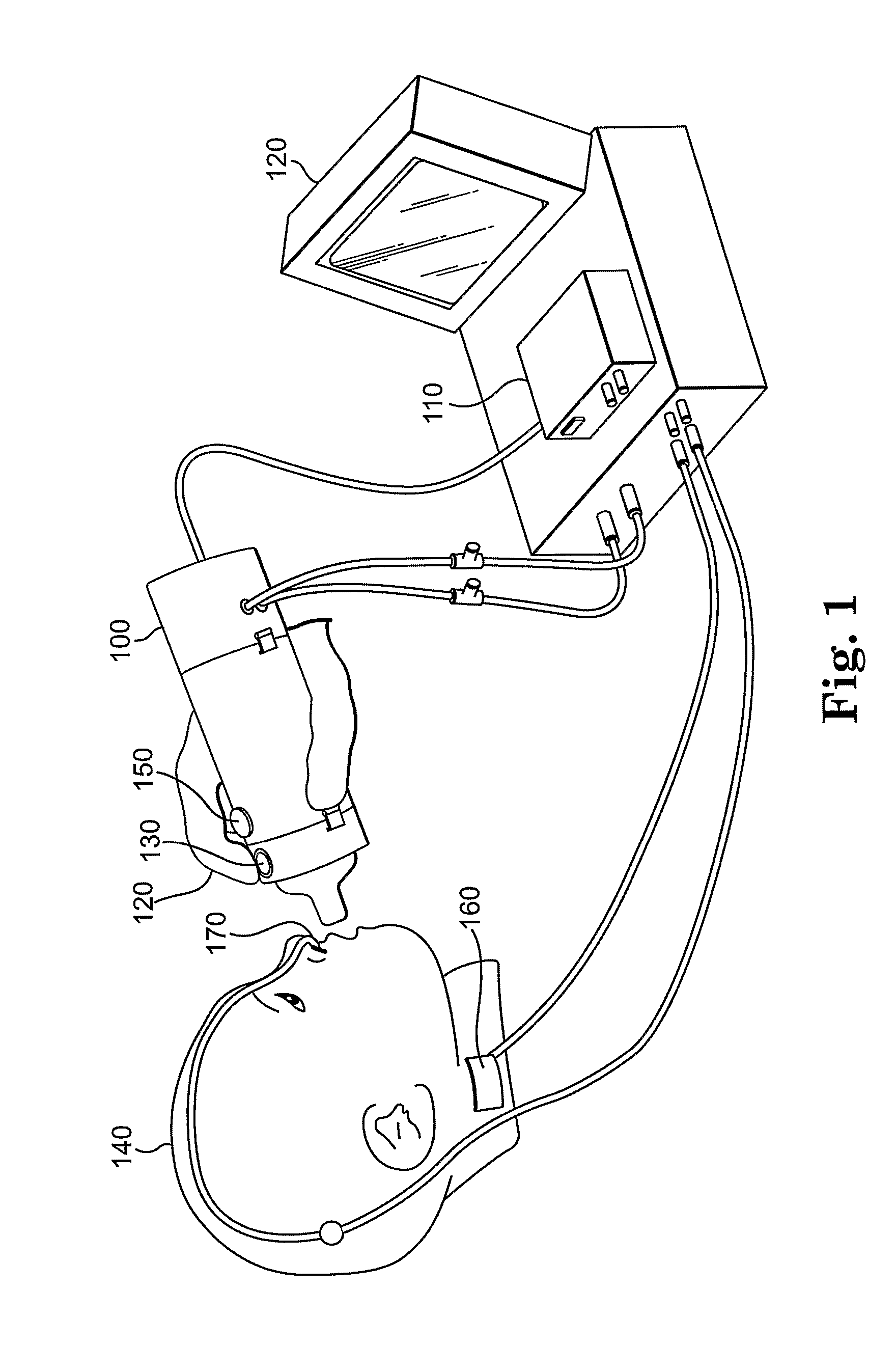
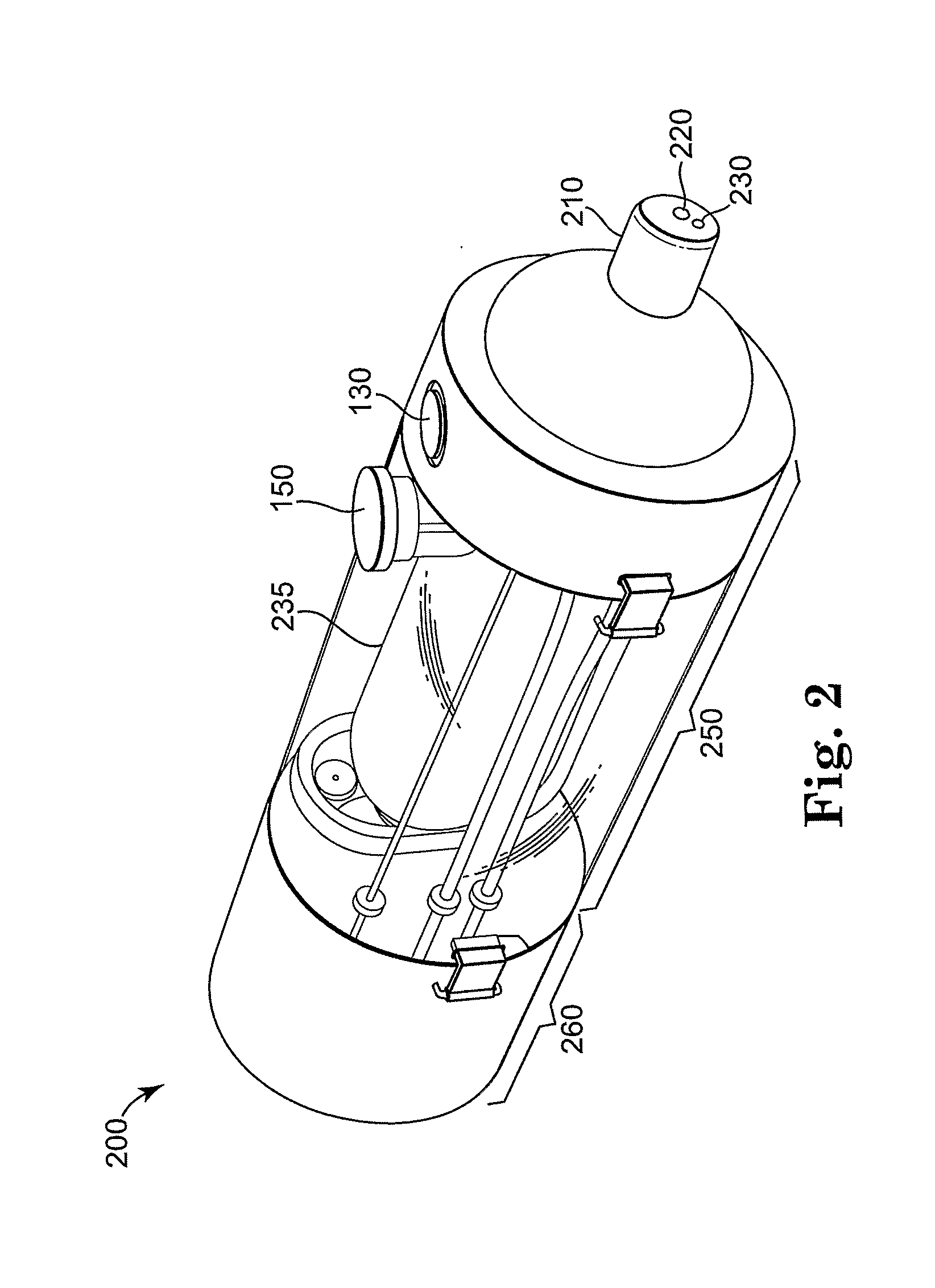
Computer Controlled Bottle for Oral Feeding of a Patient
Generally, the present invention relates to medical devices and more particularly to an computer controlled bottle system for example, for a preterm infant oral feeding. An embodiment of the invention is directed to a method for delivering nutritional fluids orally to a preterm infant comprising the steps of measuring the infant's inspired breath to breath amplitude, measuring the infant's intraoral sucking pressure, establishing threshold values for infant's inspired breath to breath amplitude and infant's intraoral sucking pressure, and delivering nutritional fluids to the infant only when the infant's inspired breath to breath amplitude and infant's intraoral sucking pressure both simultaneously satisfy their respective threshold values.
Owner:INFOSCITEX +2
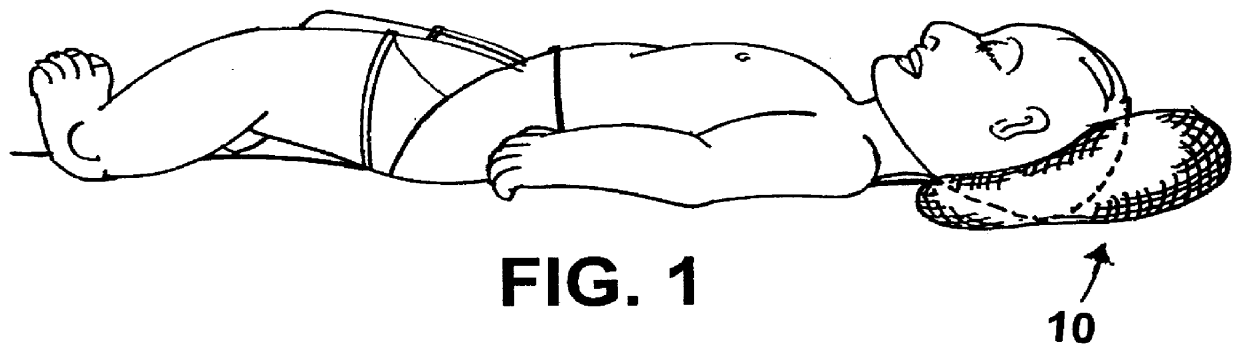
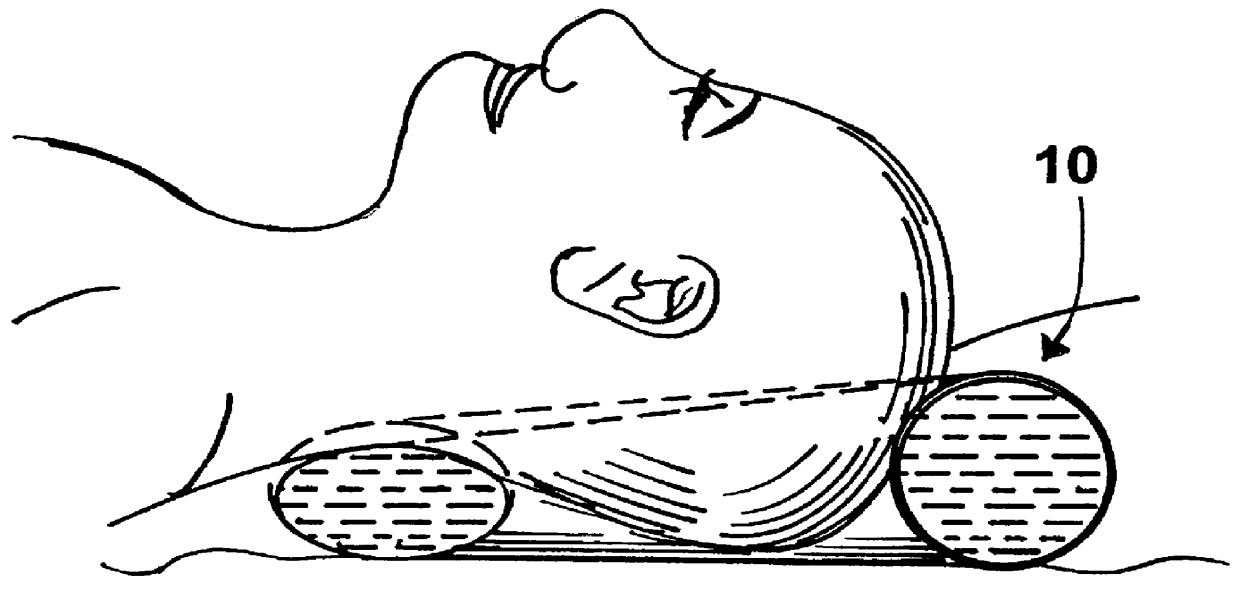
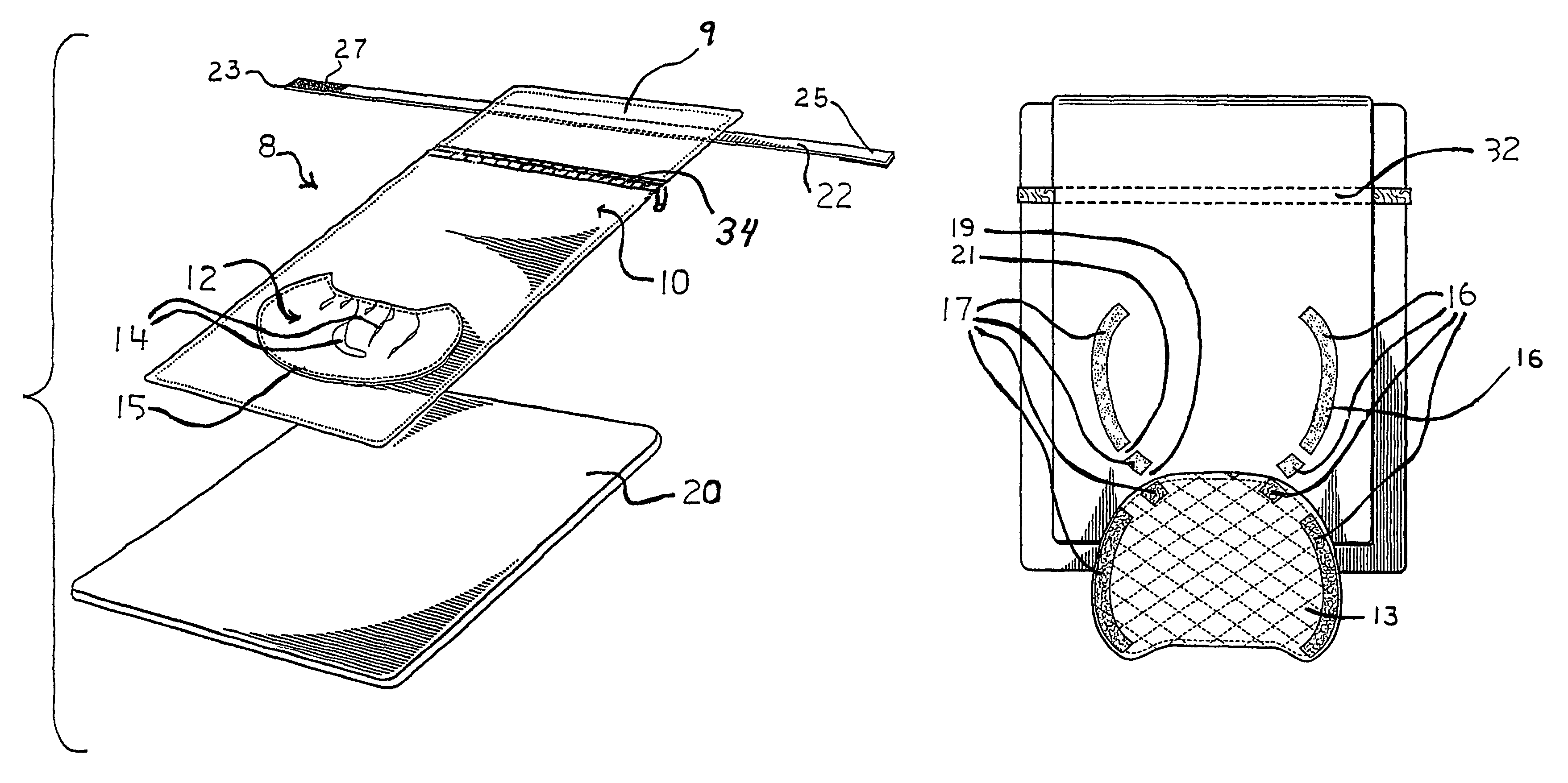
Head support device for infants
A suitable support device for newborns including premature babies comprises a doughnut-shaped structure having a gel-filled GORE-TEX casing of about five to six inches outer diameter with a central aperture of about two to three inches in diameter. The structure provides an annular tube having about a 1 to 2 inch diameter. The tube is preferably circular in cross-section at the rear or head region and preferably flattened to provide a generally oval cross-section at the front or neck region. The case is filled with a cohesive gel mass such as silicone gel or silicone elastomers with sufficiently cross-linked polysiloxane networks to substantially retain a selected shape despite the force of a limited incident weight.
Owner:LIONHEARTED IND
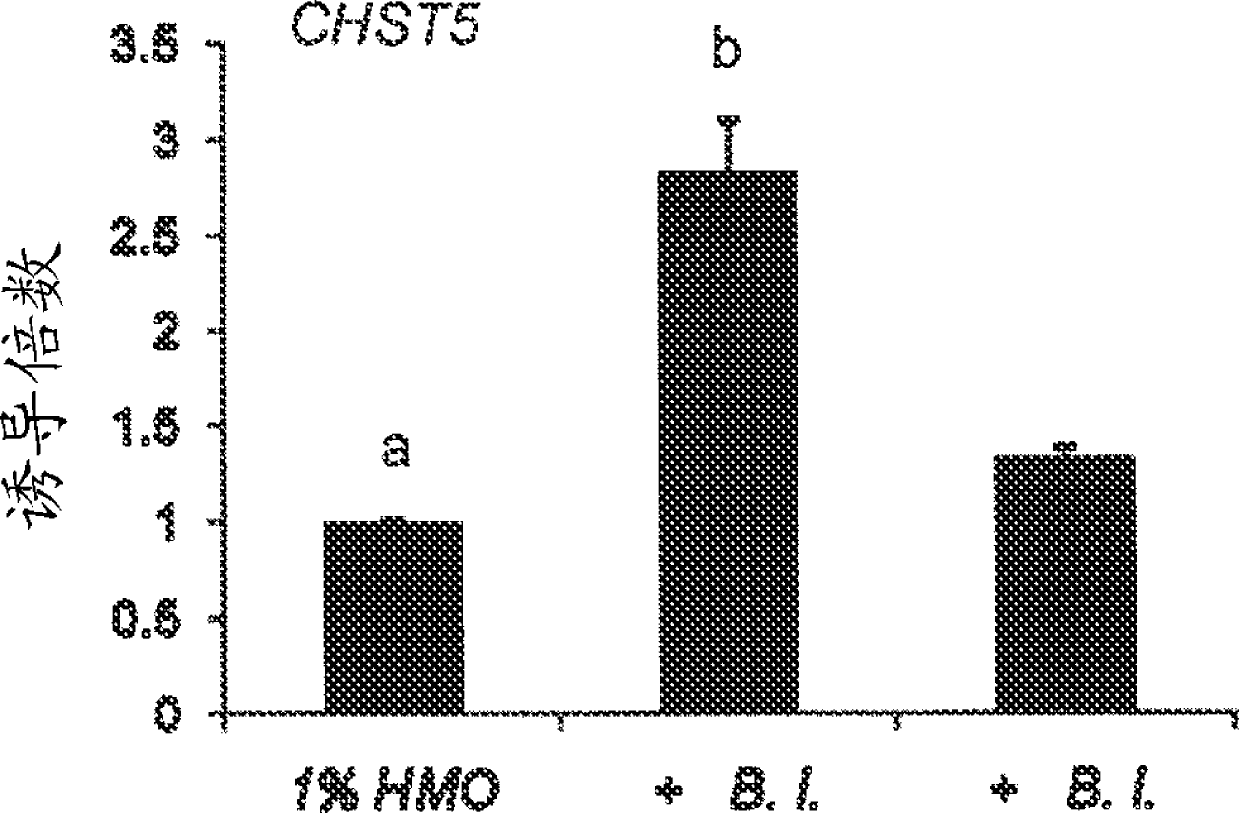
Human milk oligosaccharides for modulating inflammation
ActiveUS20120172330A1Avoid developmentReduce oxidative stressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseTerm Infant
Disclosed are nutritional compositions including human milk oligosaccharides that can be administered to preterm infants, term infants, toddlers, and children for reducing inflammation and the incidence of inflammatory diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Stable amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and particularly relates to an amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound and a preparation method thereof. The amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound has high purity and stability, does not have obvious moisture absorption and weight increase even under the condition of high humidity, ensures that relative substances do not grow, and has higher dissolution rate than crystalline ambroxol hydrochloride. The invention also relates to an application of the amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound in preparation of medicine for the treatment of acute and chronic pulmonary diseases with the symptom of ropy sputum and difficult expectoration, phlegm eliminating treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, asthmatic bronchitis and bronchial asthma, prophylactic treatment of lung complication after an operation, and treatment of infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS) of premature infants and neonates.
Owner:天津梅花生物医药科技有限公司
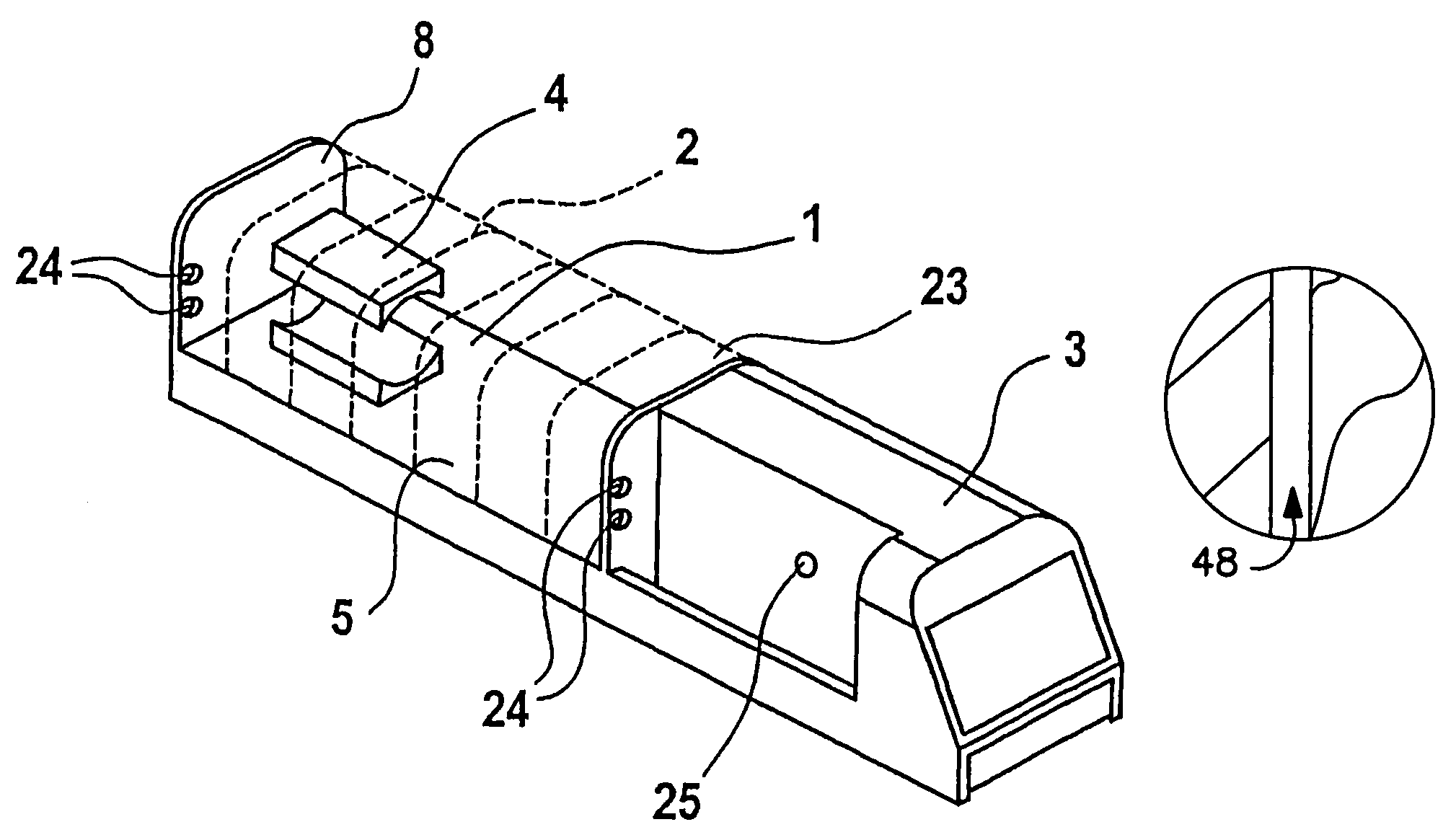
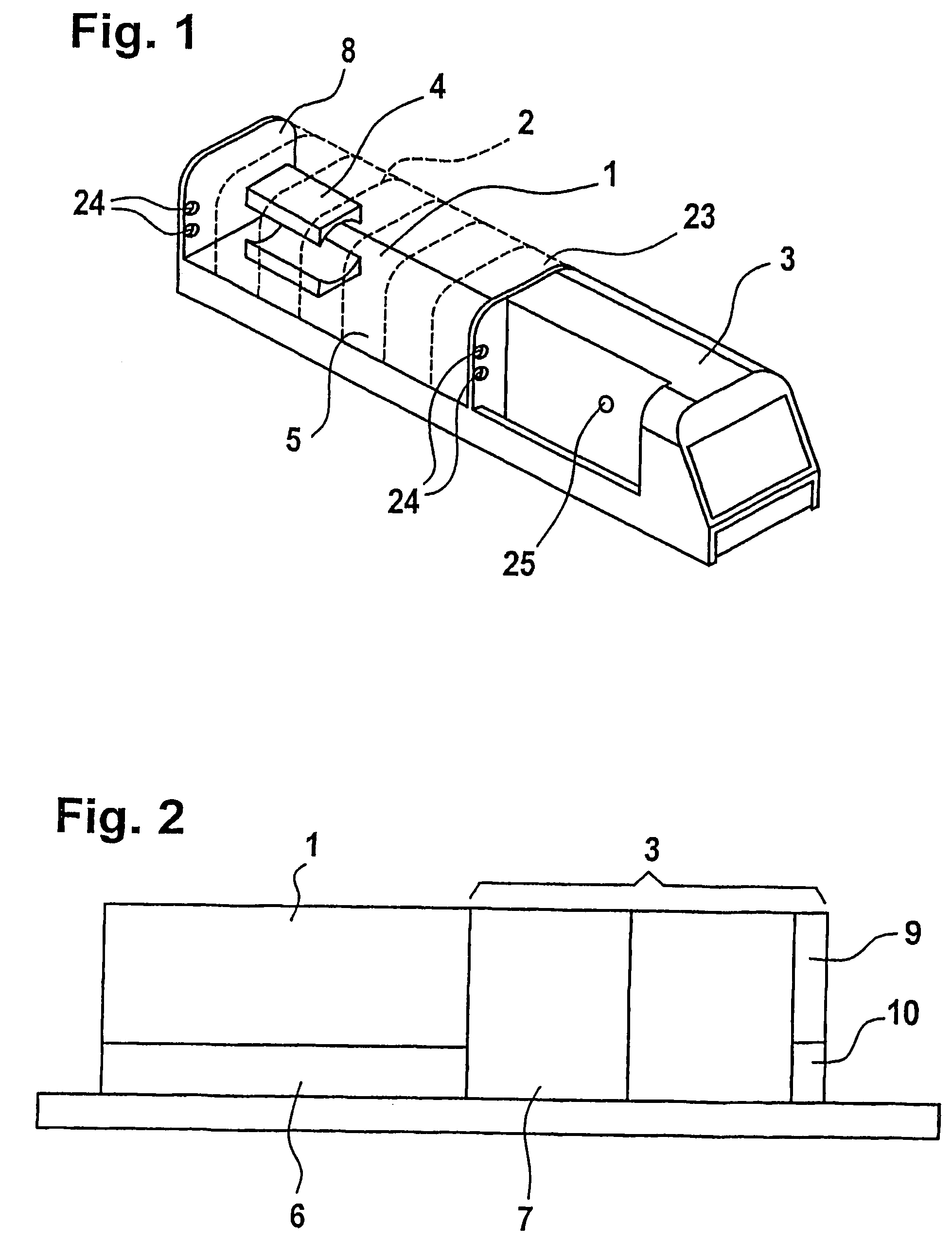
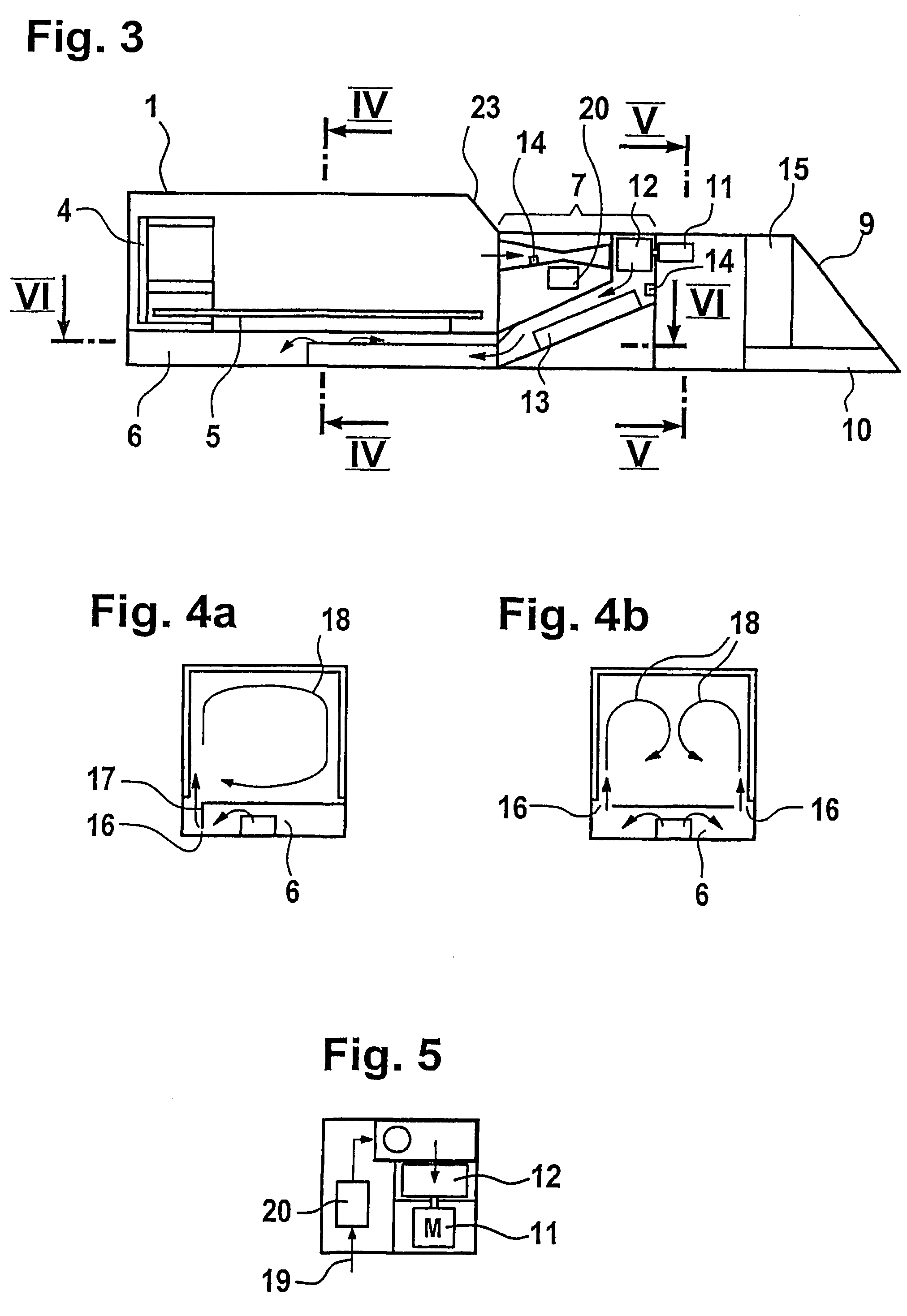
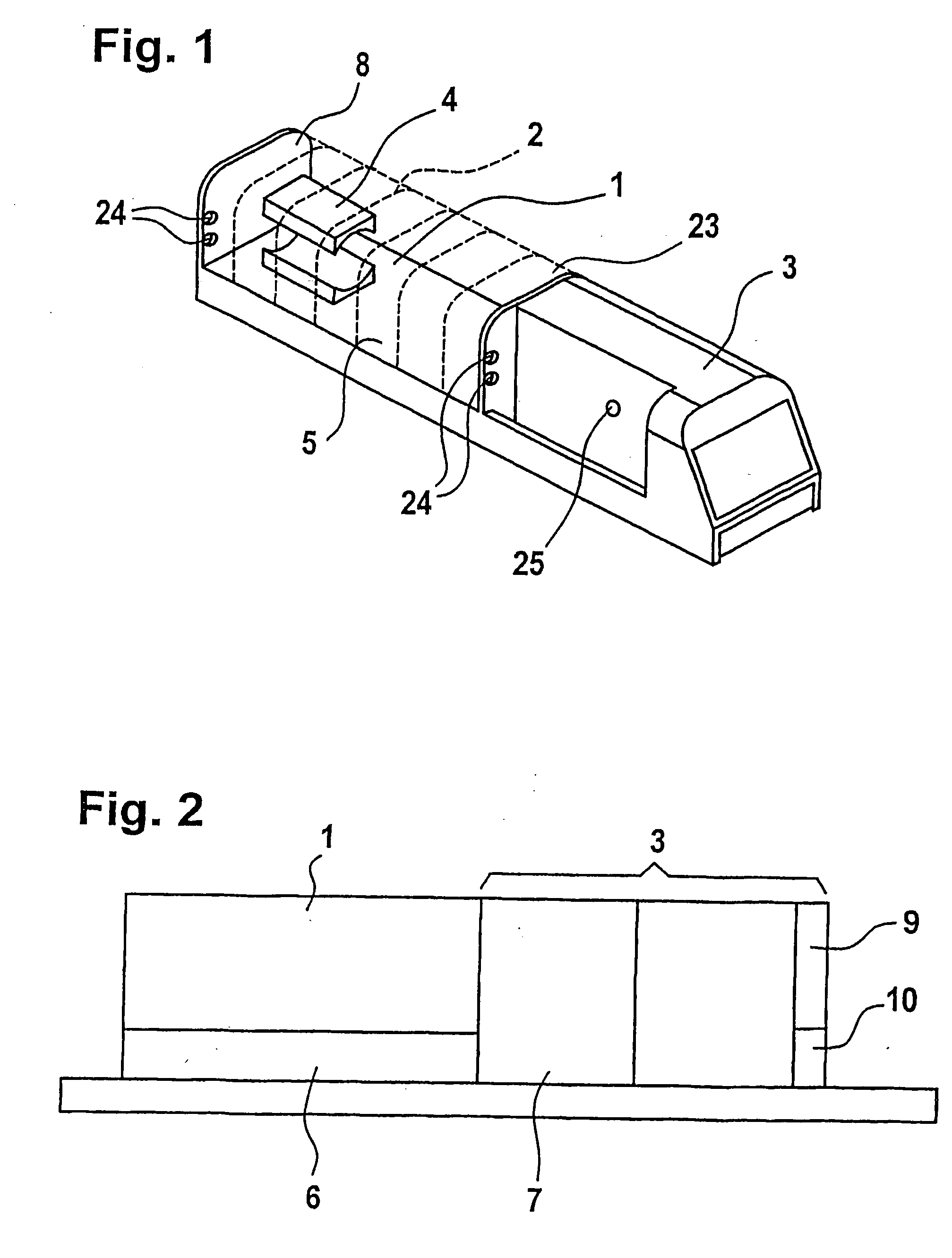
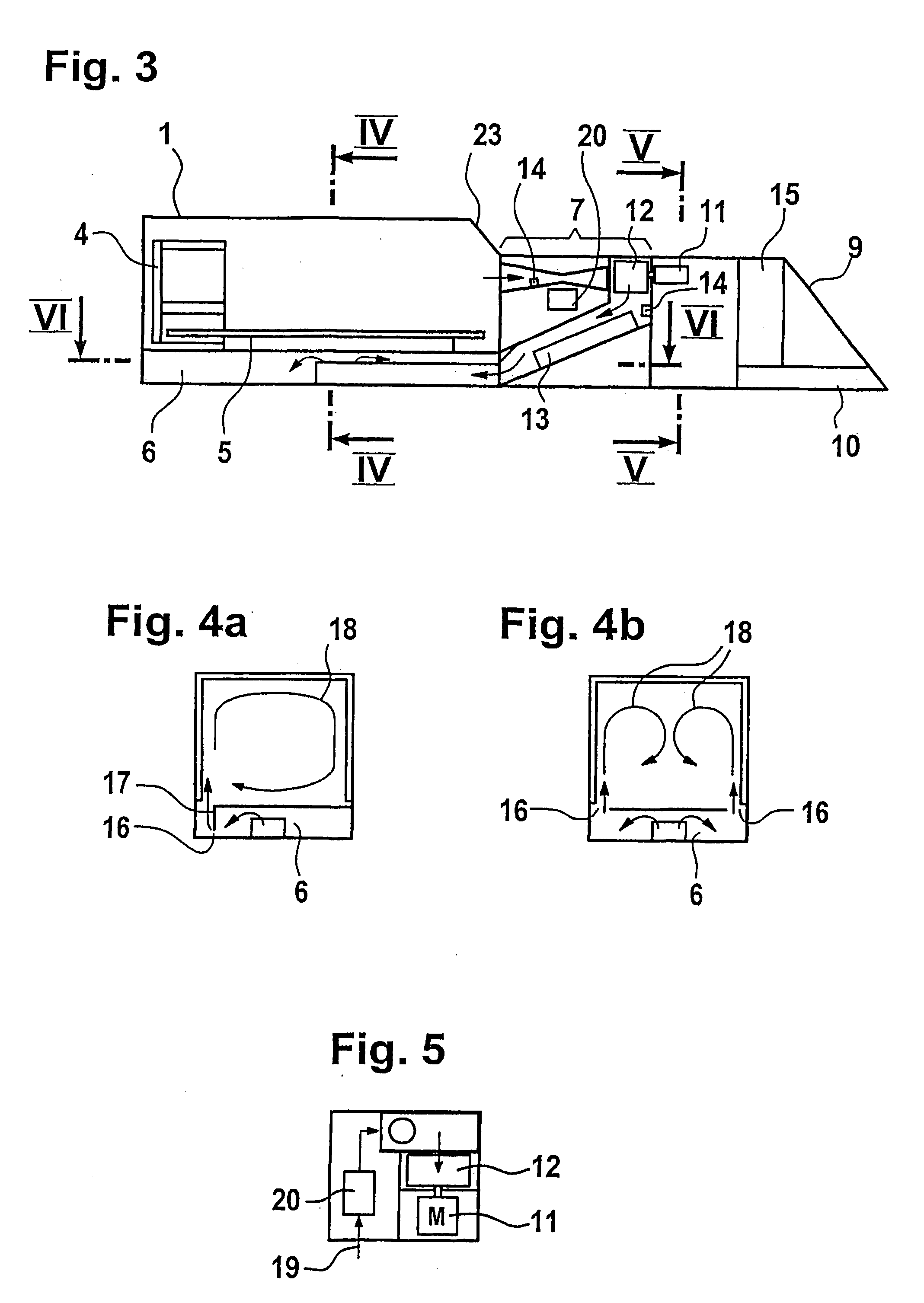
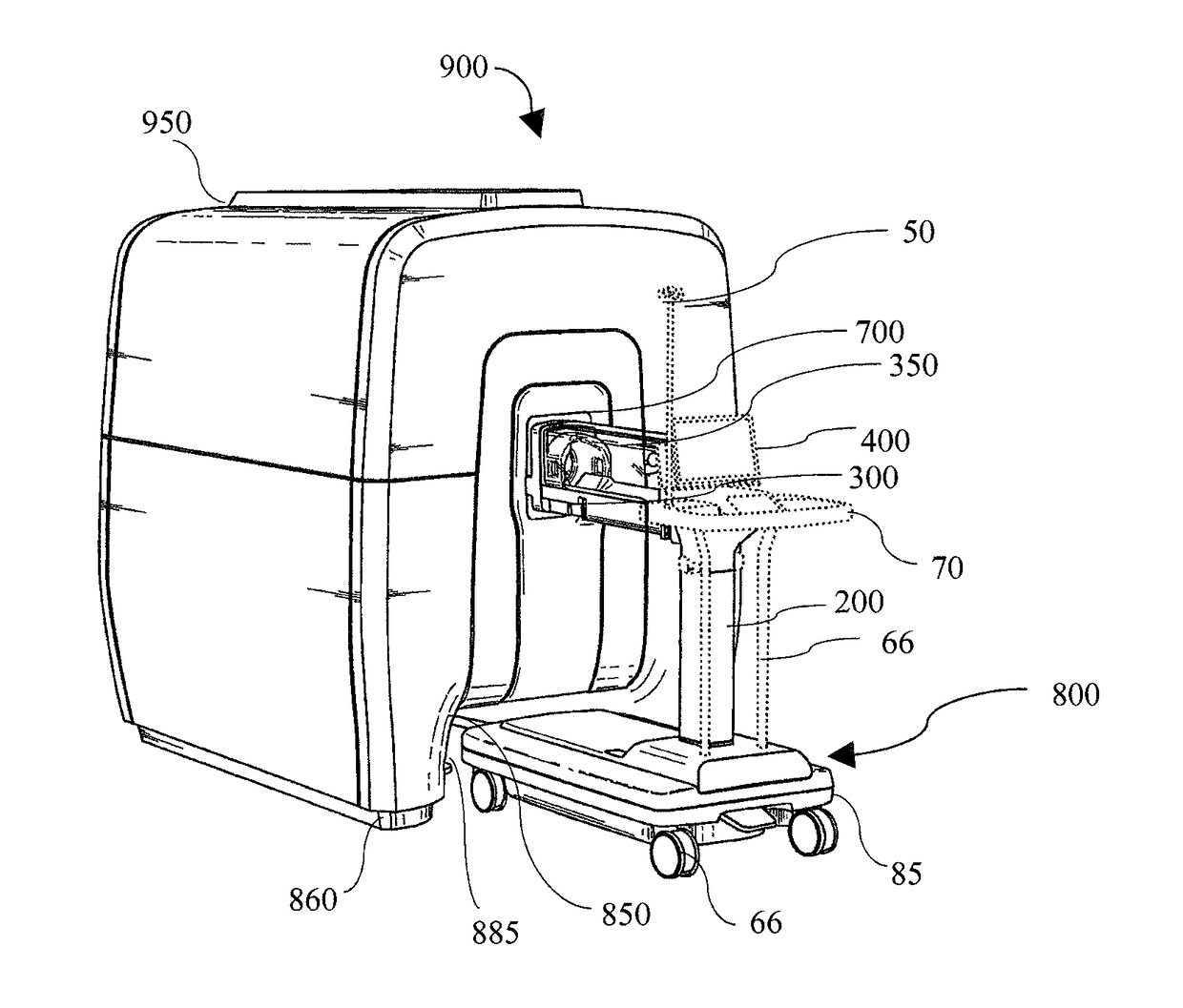
Incubator for newborn and premature patients
InactiveUS7278962B2Easy to transportEffective and gentle maintenanceBaby-incubatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringImaging equipmentAir temperature
An incubator for newborn and premature patients includes an air delivery unit with an electric motor and heating and humidifying devices, a control unit including sensing devices to measure air temperature and humidity and a control panel integrally mounted to the incubator. Sensitive electrical components, such as the electric motor and control unit, are shielded from the magnetic field of the imaging equipment so that the incubator, with its patient, can be placed inside the imaging equipment and remain fully functional. Shielding for the electric motor is constructed of soft magnetic material and arranged to leave a dielectric gap between the shield and the motor.
Owner:LMT MEDICAL SYST
Apparatus for feeding preterm infants
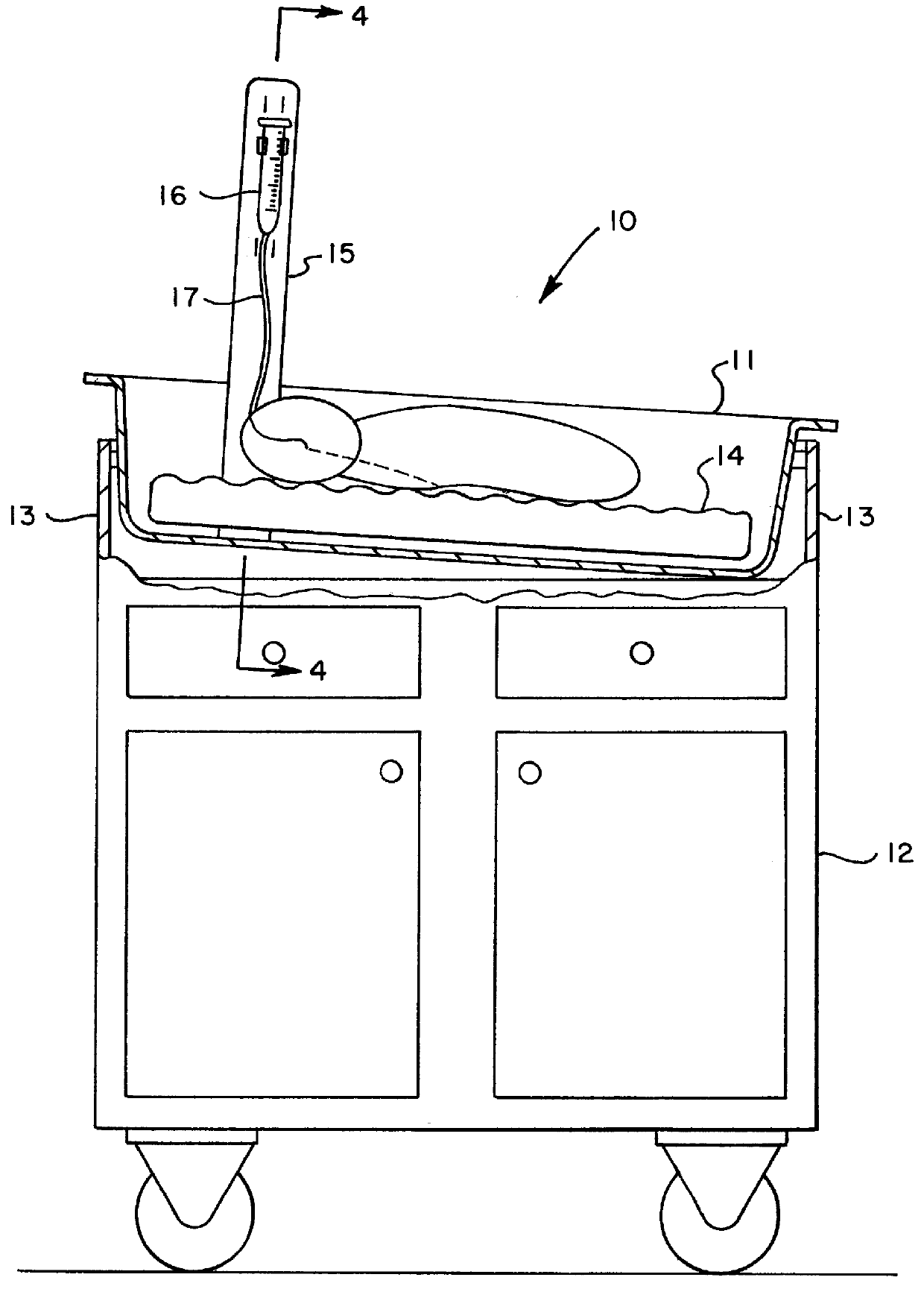
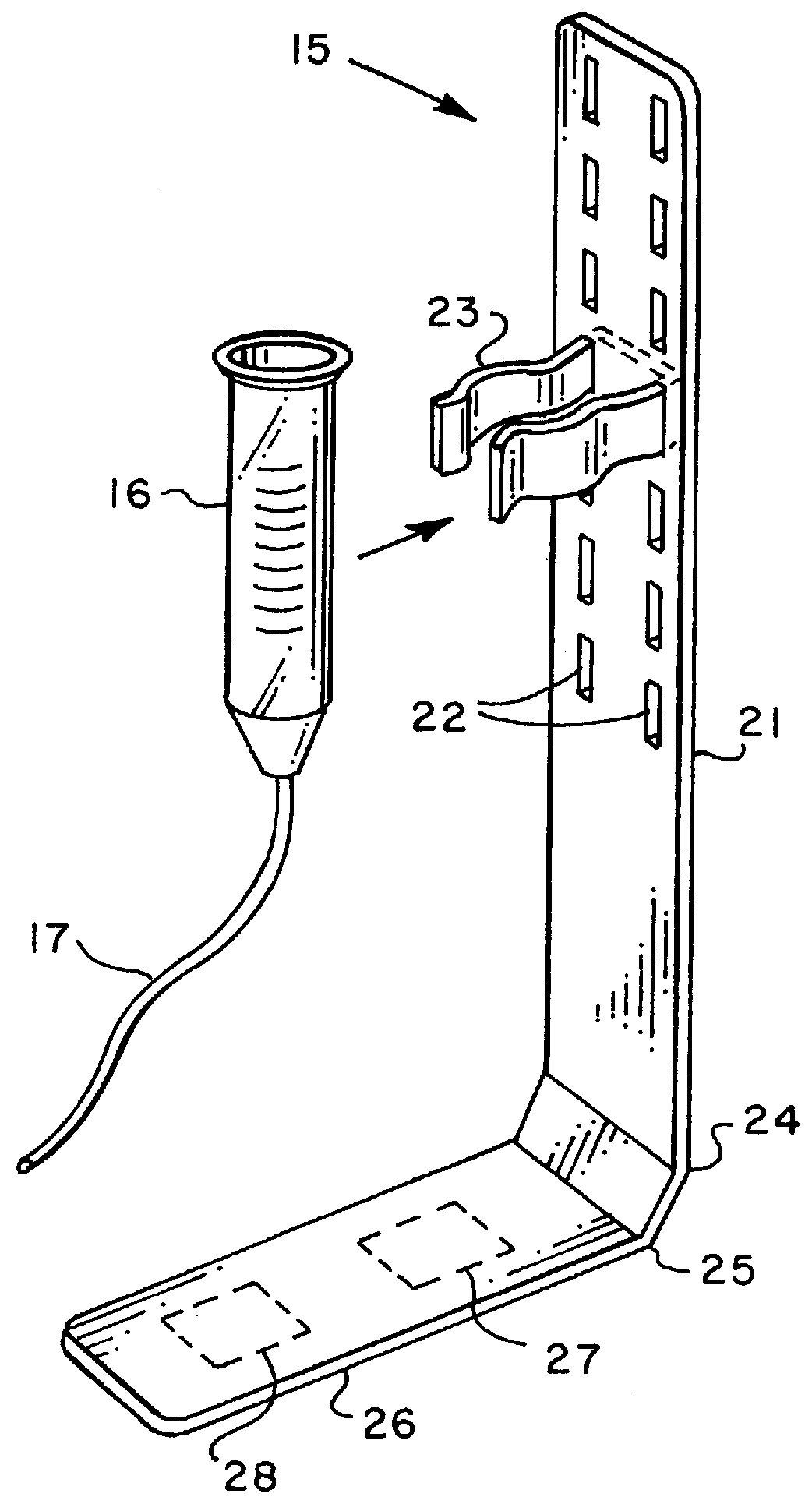
An apparatus for holding and feeding a preterm infant comprising a neonatal bassinet that holds the infant in a position for feeding, a gavage syringe for holding and dispensing nutritional liquid through a catheter, and a Gavage Syringe Restraining Device (GSRD) attached to the bassinet. The GSRD is an L-shaped bracket which holds the gavage syringe in an elevated position above the infant. The GSRD comprises a vertical arm which holds the gavage syringe and a horizontal arm which is mounted to the inside bottom surface of the bassinet under a removable mattress. The vertical arm includes a plurality of vertical slits arranged in pairs. An adjustable strap is positioned through a selected pair of slits and is wrapped around the gavage syringe to hold the syringe in a selected position. The bassinet may be mounted on a mobile cart and moved without interrupting the feeding of the infant, and without having to remove the syringe from a fixed mounting location.
Owner:GROUNDZERO CORP
Thermal and humidity barrier for extremely premature infants
A thermal and moisture barrier device for use with a specialized heating and humidifying apparatus in the care of extremely premature neonatal infants. The thermal and moisture barrier comprises a collapsible and substantially flexible cover which defines an enclosed volume, large enough to accommodate an extremely premature neonatal infant. At least one flexible opening is located on a portion of the cover which communicates with the enclosed volume. A diaphragm provides closure of the flexible openings. The diaphragm is a resiliently flexible sheet extending across the opening and has slits.
Owner:ROGONE MARY SHARON +1
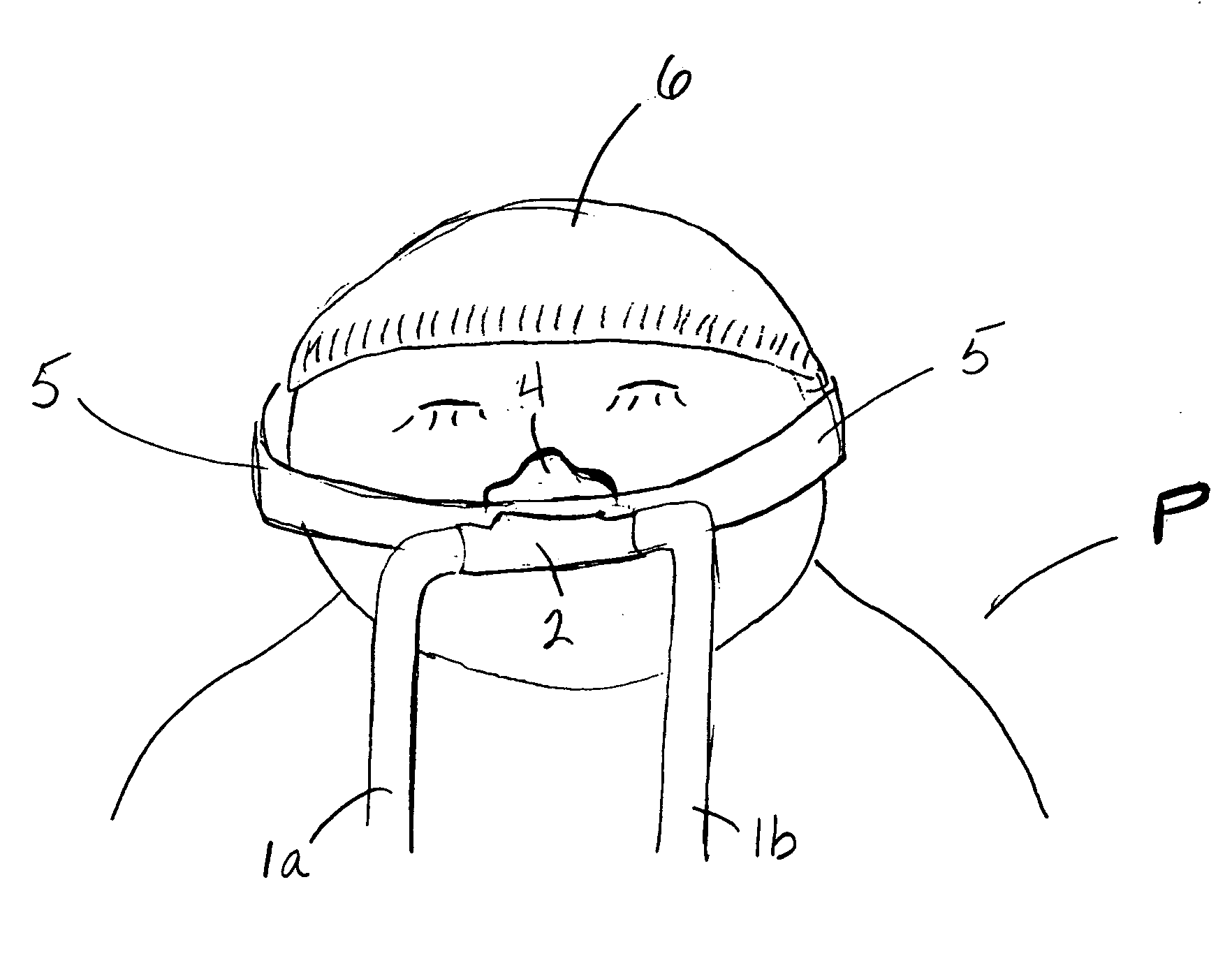
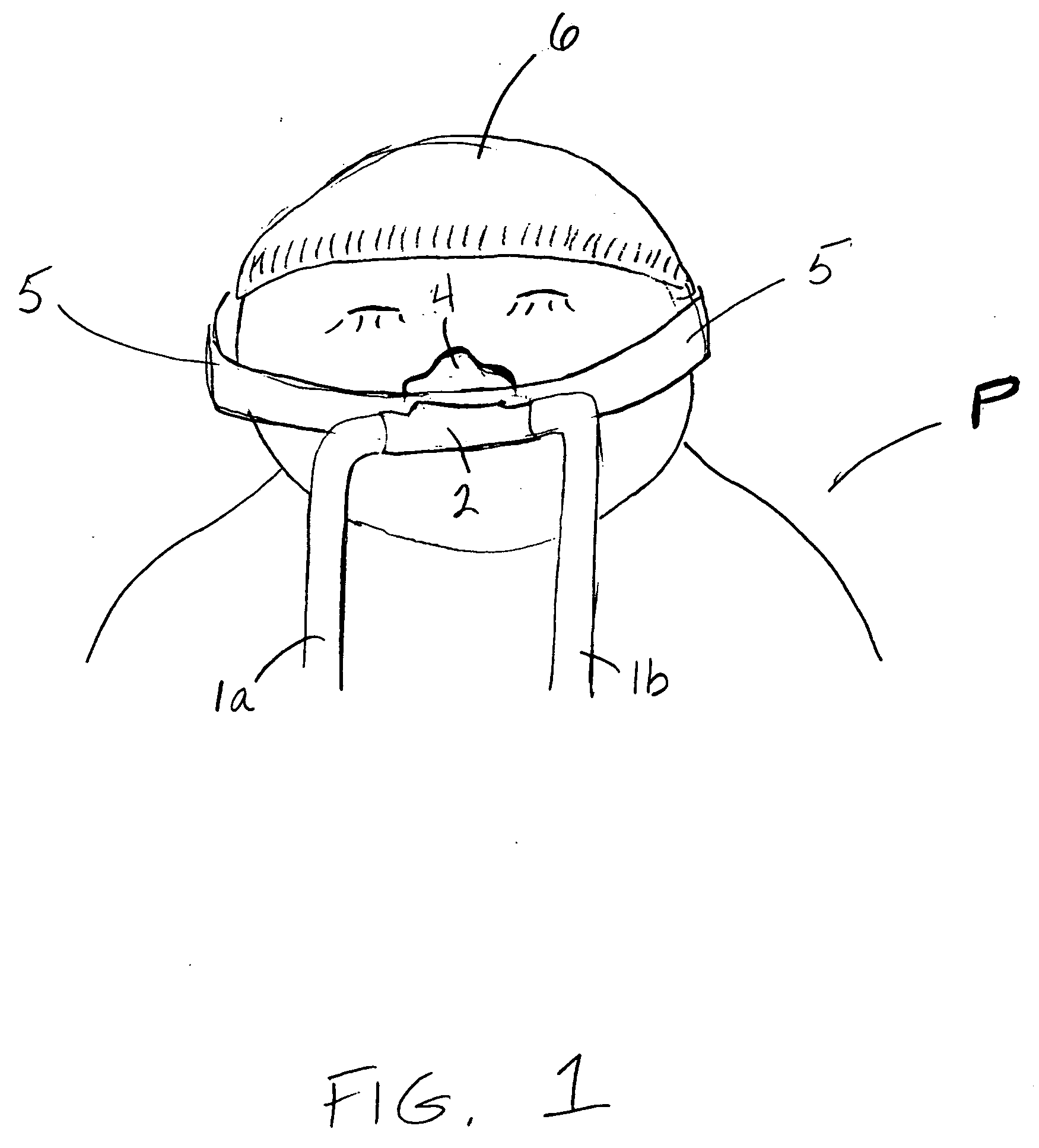
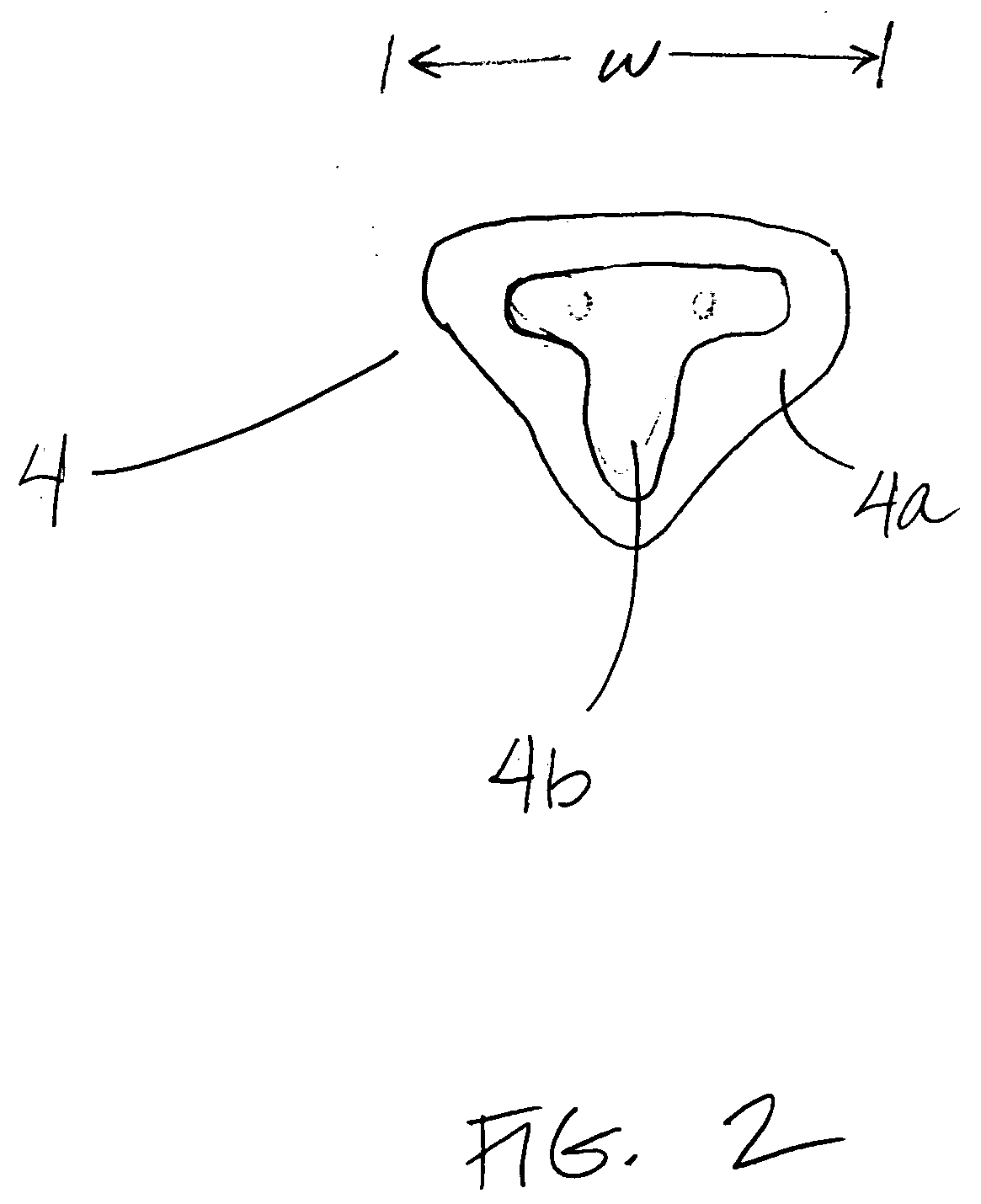
Pediatric mask, especially suited for premature infants
The inventive masks and medical gas-delivery systems make possible delivery of medical gases (such as oxygen) to pediatric patients with faces too small to be comfortably served by conventional masks and systems sized for adults. The inventive masks minimize the surface area of the baby's face being covered and also balance tubing and related parts contacting the baby. In addition, it allows efficient delivery of required pressure, while minimizing any leak of delivered oxygen or gas outside the breathing system.
Owner:ALY HANY
Premature neonate closed life support system
A magnetically permeable neonate transport capsule (MPNTC) for transporting a premature neonate from a host infant incubator having a steady environmental condition to an MRD. The MPNTC has at least one first normally open configuration when the capsule is disposed within the incubator and a second closed configuration for removal, transportation, insertion, measurement and vice versa within an MRD device. The MPNTC includes an environmental control system thereby adapted to maintain continuous attachment of the neonate with life support connection lines. The MPNTC is further adapted to maintain environmental conditions substantially similar to the host infant incubator environmental condition when the MPNTC is transported from the incubator to the MRD device.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Incubator for newborn and premature patients
InactiveUS20050192473A1Easy to transportUniform temperature distributionBaby-incubatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringImaging equipment
An incubator for newborn and premature patients includes an air delivery unit with an electric motor and heating and humidifying devices, a control unit including sensing devices to measure air temperature and humidity and a control panel integrally mounted to the incubator. Sensitive electrical components, such as the electric motor and control unit, are shielded from the magnetic field of the imaging equipment so that the incubator, with its patient, can be placed inside the imaging equipment and remain fully functional. Shielding for the electric motor is constructed of soft magnetic material and arranged to leave a dielectric gap between the shield and the motor.
Owner:LMT MEDICAL SYST
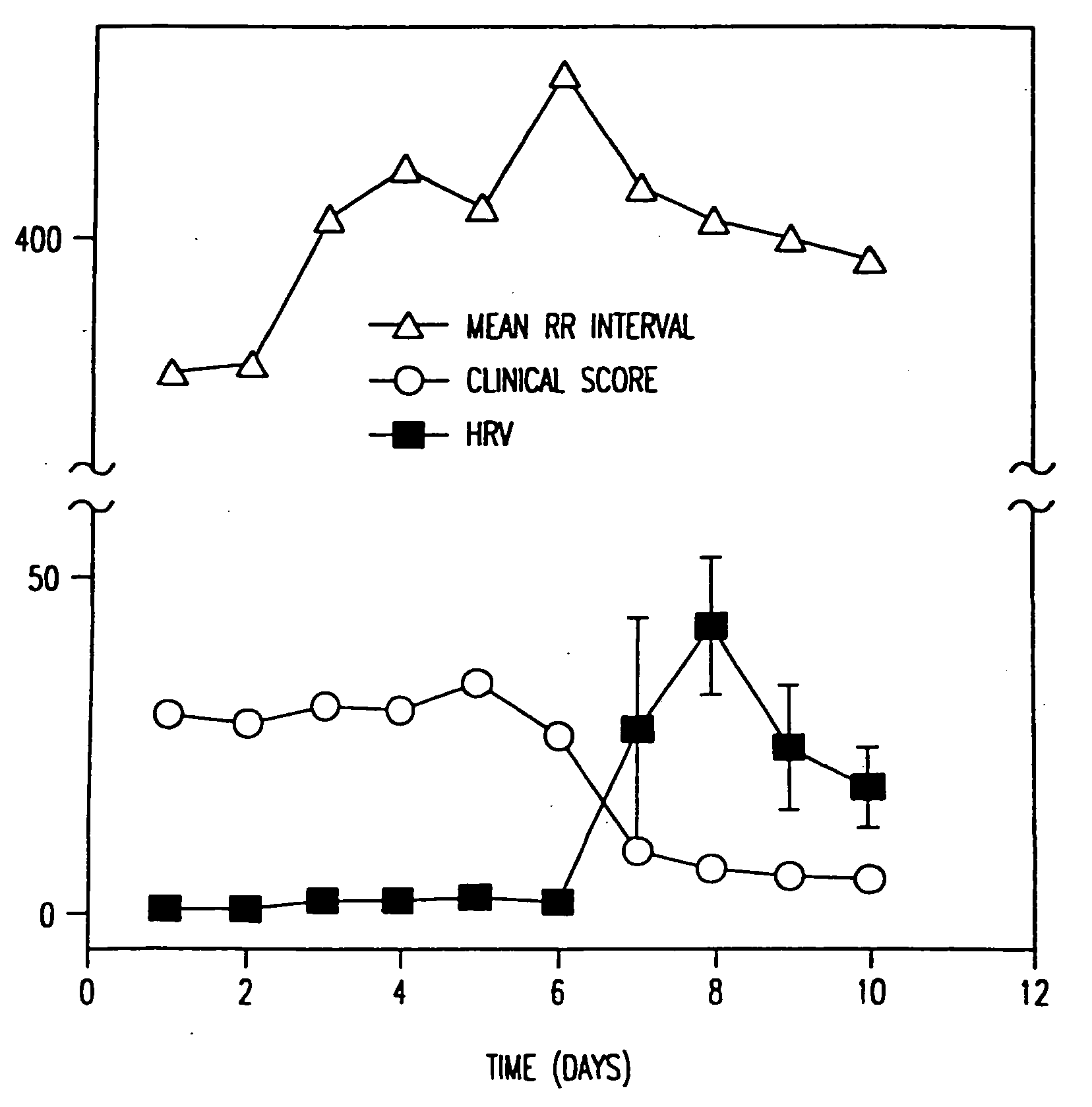
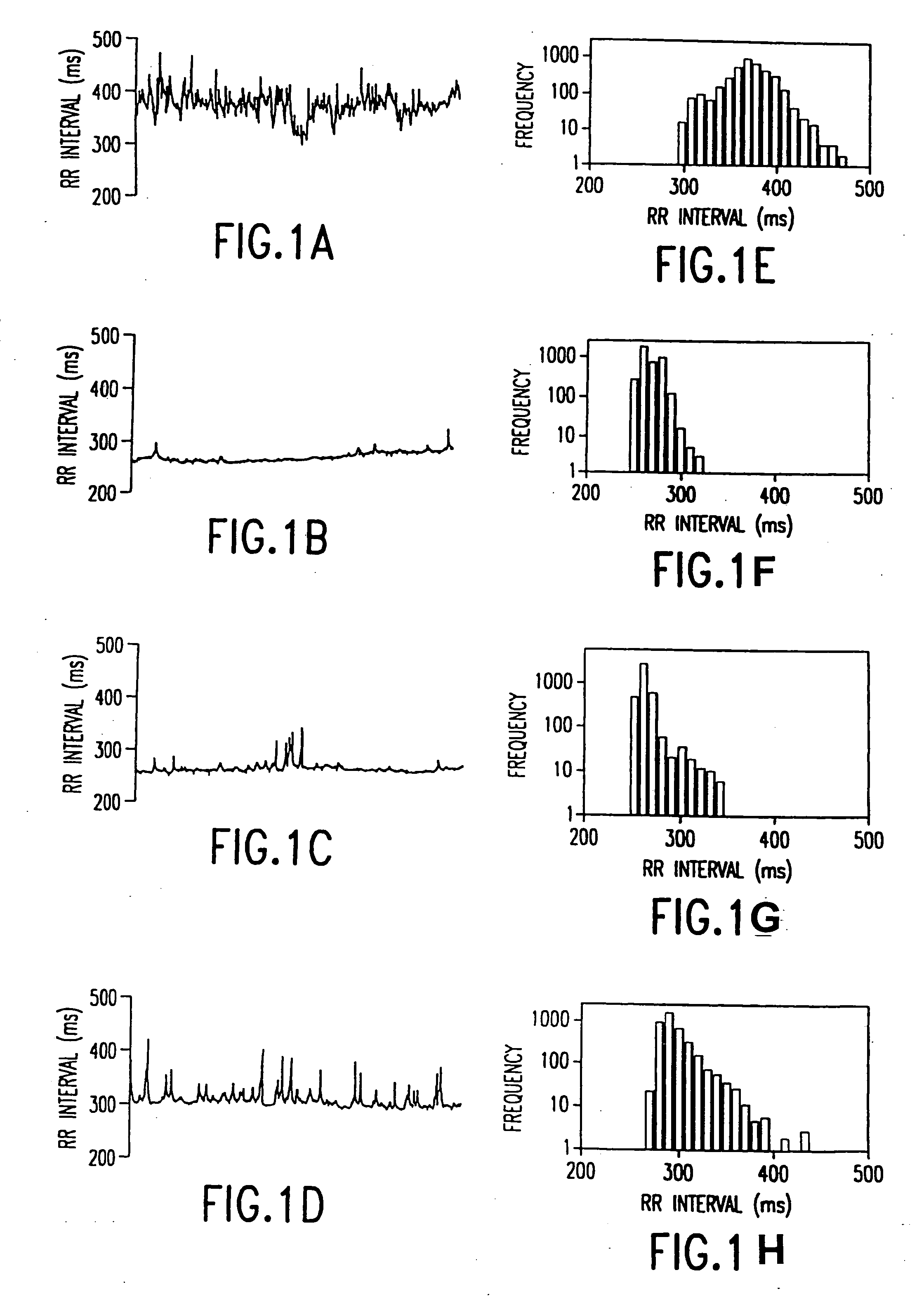
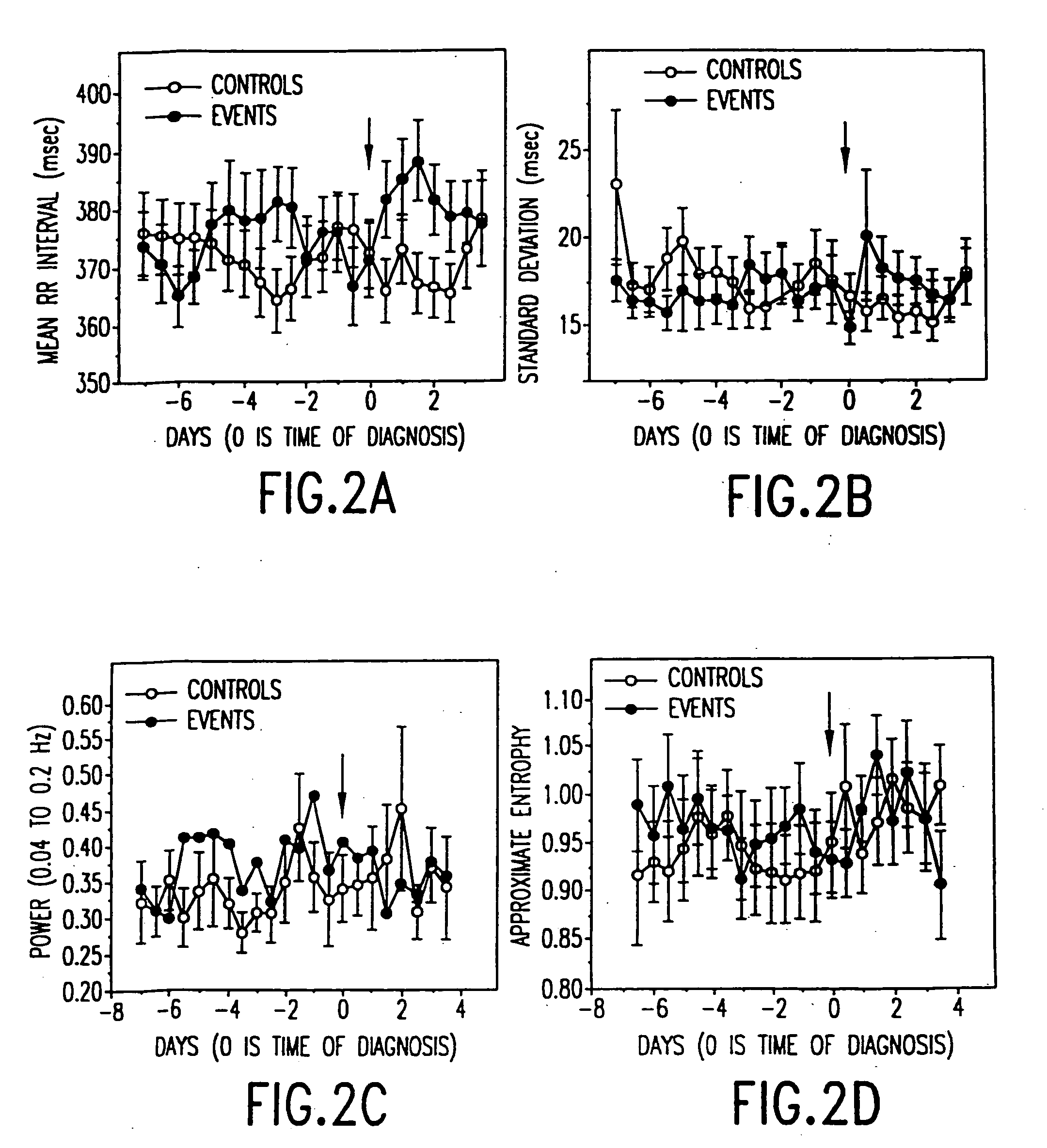
Method and apparatus for the early diagnosis of subacute, potentially catastrophic illness
In one aspect of the invention, there is provided a method and apparatus for early detection of subacute, potentially catastrophic infectious illness in a premature newborn infant. The method comprises: (a) continuously monitoring heart rate variability in the premature newborn infant; and (b) identifying at least one characteristic abnormality in the heart rate variability that is associated with the illness. This method can be use to diagnose illnesses such as, but not limited to, sepsis, necrotizing enterocolitis, pneumonia and meningitis. In another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method and apparatus for early detection of subacute, potentially catastrophic infectious illness in a patient. The method comprises: (a) continuously monitoring the patient's RR intervals; (b) generating a normalized data set of the RR intervals; (c) calculating one or more of (i) moments of the data set selected from the third and higher moments and (ii) percentile values of the data set; and (d) identifying an abnormal heart rate variability associated with the illness based on one or more of the moments and the percentile values.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Preterm formula
InactiveUS20100234286A1Improve oral toleranceExtended shipping timeBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOral tolerizationTolerability
Owner:NUTRICIA
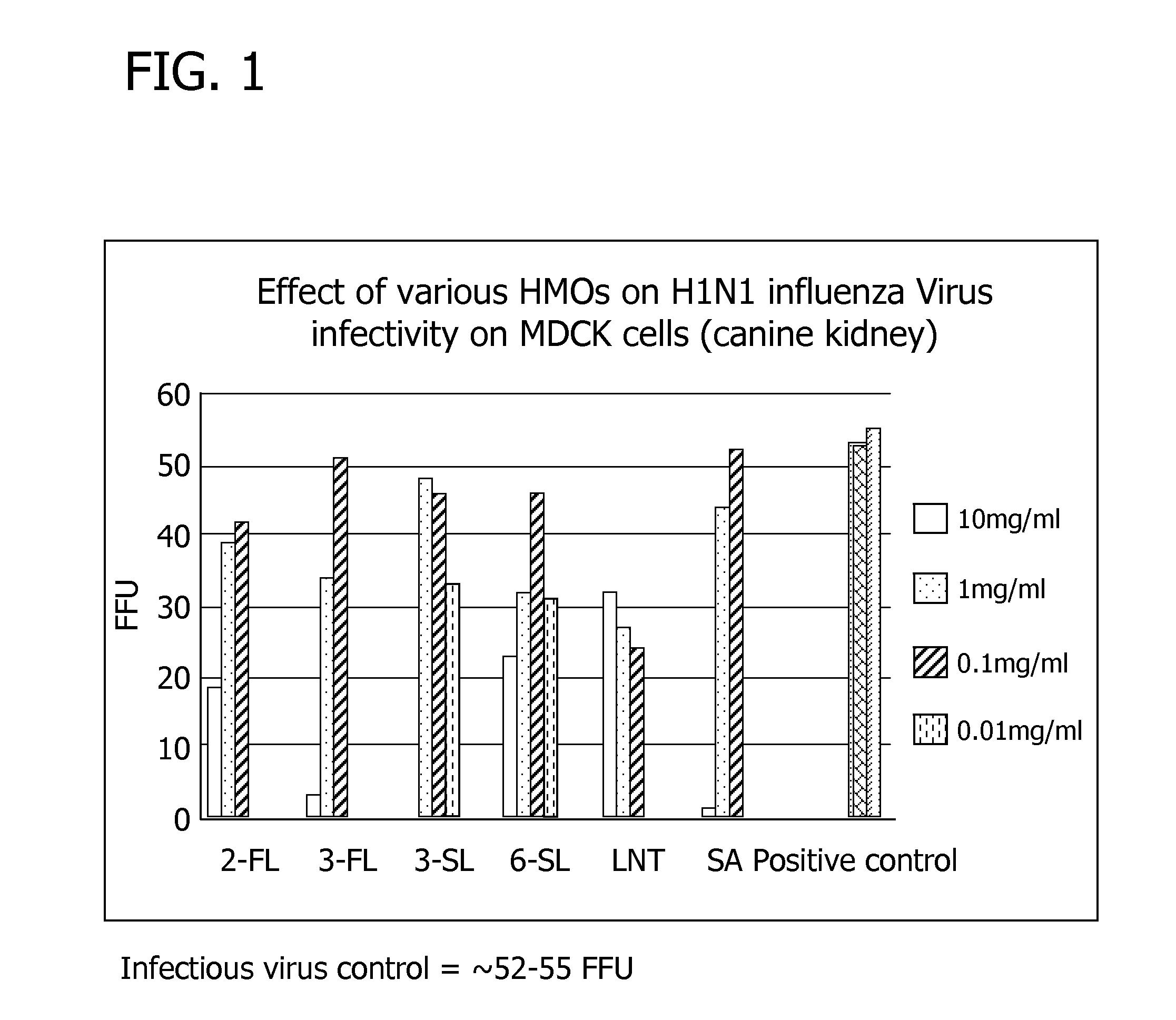
Nutritional compositions comprising human milk oligosaccharides and nucleotides and uses thereof for treating and/or preventing enteric viral infection
ActiveUS20120184503A1Decrease infectivityDecrease in replicationBiocideFood ingredient as antioxidantNutritional compositionPreterm baby
Disclosed are nutritional compositions including human milk oligosaccharides and nucleotides that can be administered to preterm infants, term infants, toddlers, and children for reducing inflammation and the incidence of inflammatory diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Generating a flow-volume loop for respiratory function assessment
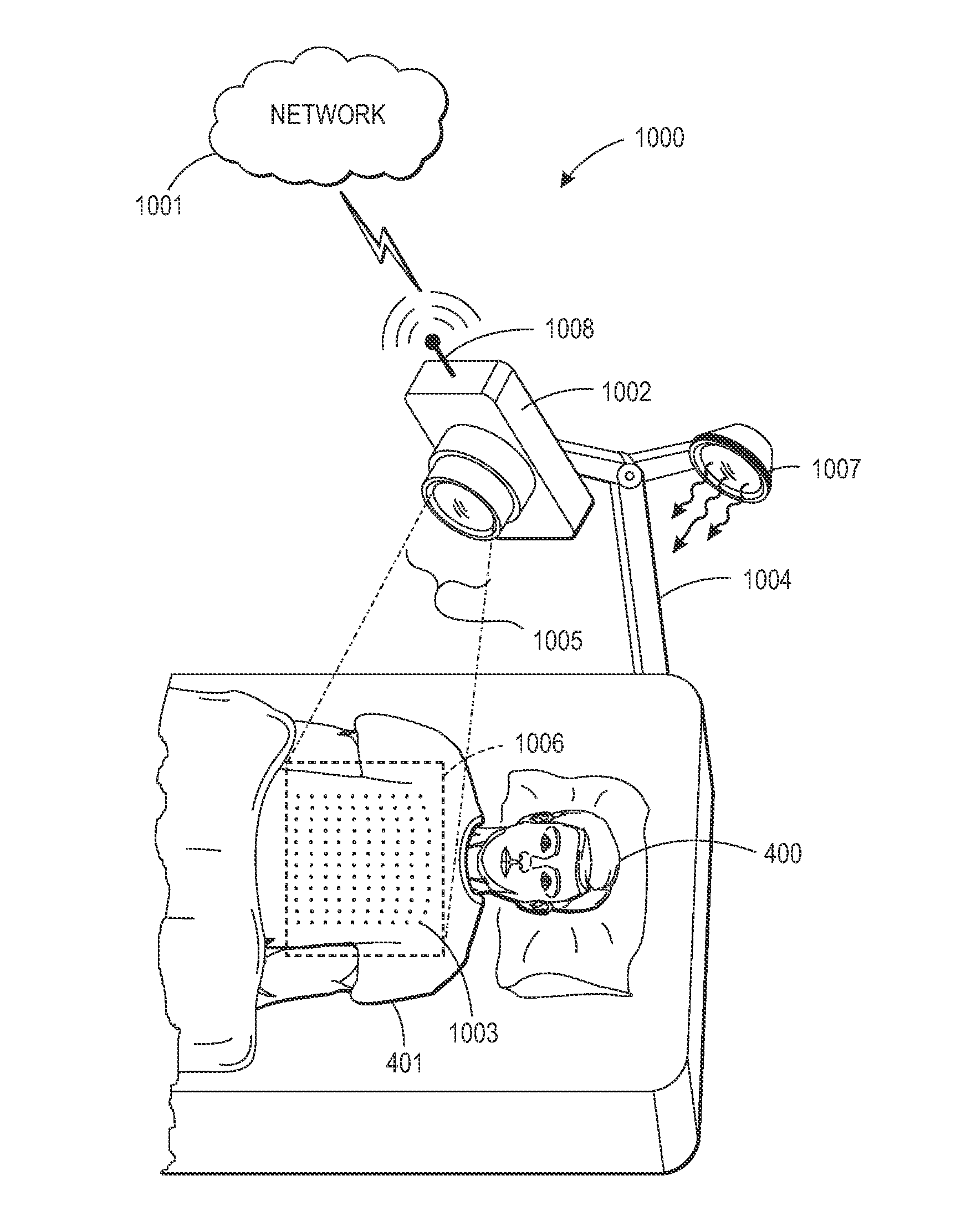
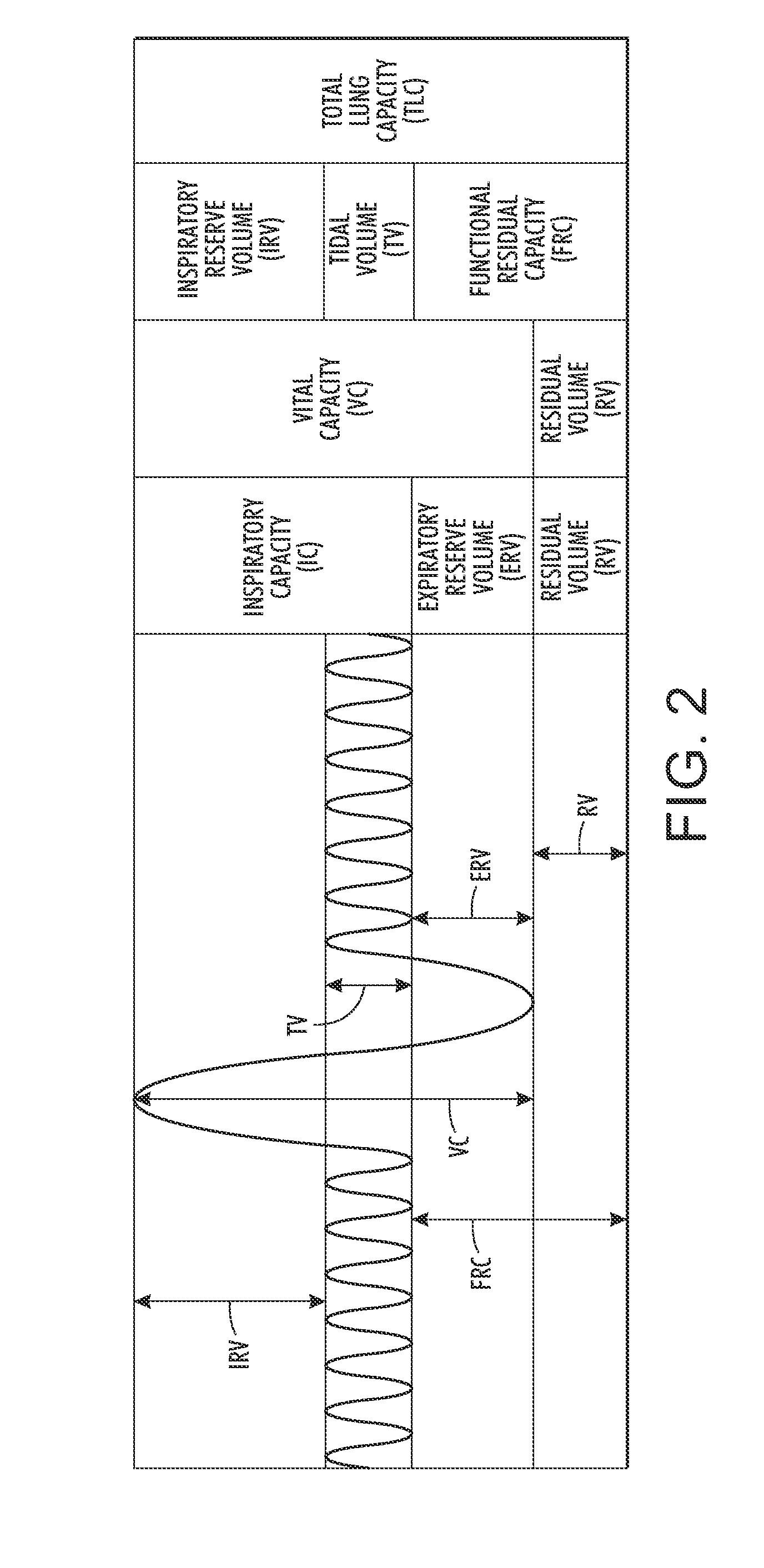
What is disclosed is a system and method for generating a flow-volume loop for respiratory function assessment of a subject of interest in a non-contact, remote sensing environment. In one embodiment, a time-varying sequence of depth maps of a target region of a subject of interest being monitored for respiratory function is received. The depth maps are of that target region over a period of inspiration and expiration. The depth maps are processed to obtain a volume signal comprising a temporal sequence of instantaneous volumes. The time-varying volume signal is processed to obtain a flow-volume loop. Changes in a contour of the flow-volume loop are used to assess the subject's respiratory function. The teachings hereof find their uses in a wide array of medical applications where it is desired to monitor respiratory function of patients such as elderly patients, chronically ill patients with respiratory diseases and premature babies.
Owner:XEROX CORP
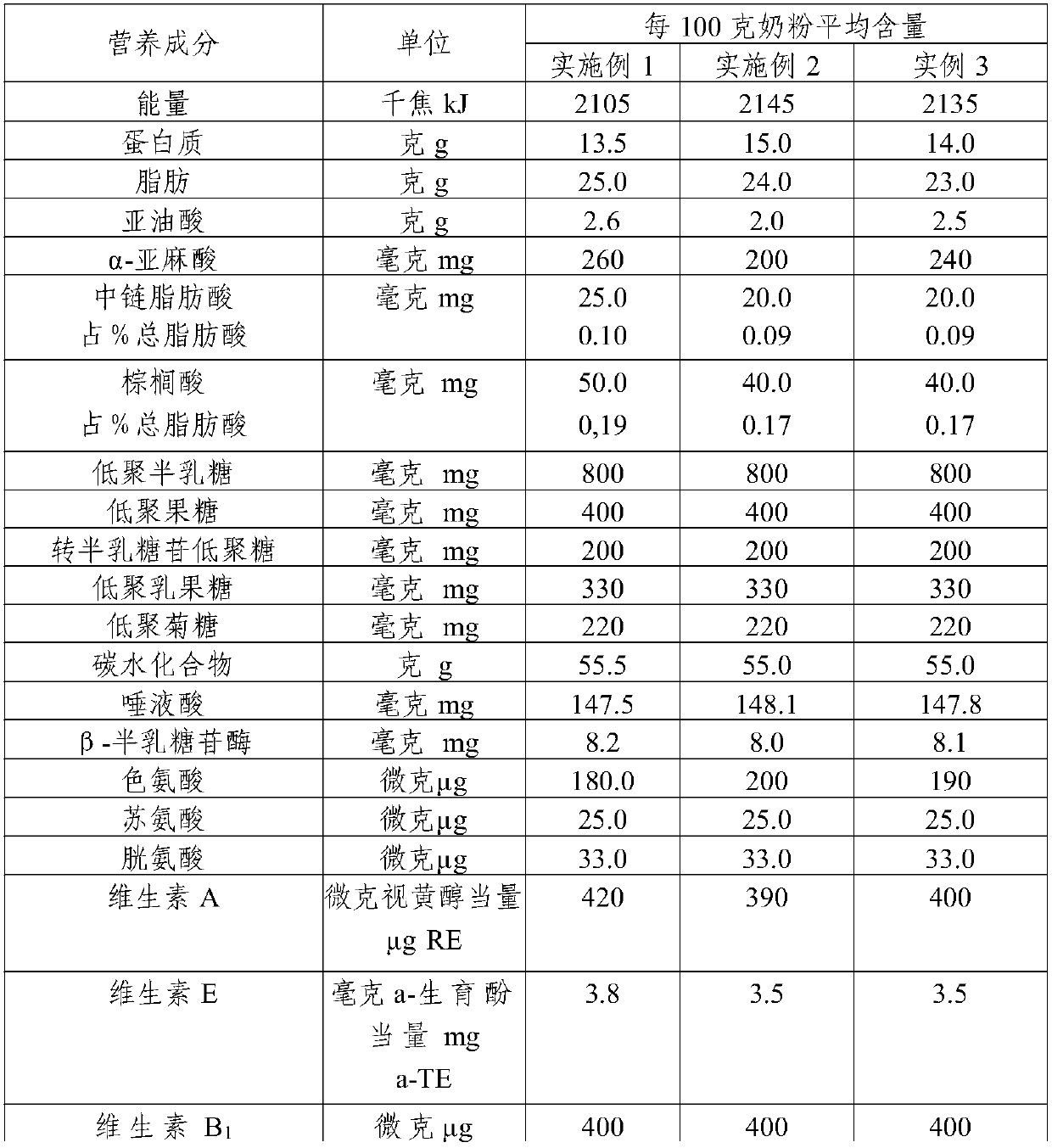
Sialic acid-added milk powder with easy digestion function for premature infants and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107712050AEnhance memoryImprove intelligenceMilk preparationVegetable oilAdditive ingredient
The invention provides sialic acid-added milk powder with an easy digestion function for premature infants and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of foods. The milk powder is prepared from the following raw materials: skim milk powder, lecithin, maltodextrin, immune globulin, refined palm olein, vitamin complex, prebiotics, minerals, alpha-whey protein, lactotransferrin, ferrous gluconate, bifidobacterium, sialic acid, edible vegetable oil mixture, beta-galactosidase, tryptophan, threonine and cystine. Compositions of the formula of the milk powder for premature infants is closer to breast milk, memory and intelligence level of premature infants can be improved by the sialic acid ingredient added into the milk powder, and nutrition essential to premature infant growth can be provided by optimizing the proportion of ingredients. The milk powder can be easily digested and absorbed, and can be used for improving the resistance of premature infants and reducing the phenomena of internal heat and iron-deficiency anemia caused by dyspepsia.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Premature neonate closed life support system
A premature neonate closed life support system (NCLSS) including: at least one chamber confining a cradle-like neonate support (CLNS) having suitable dimensions and geometric-configuration for accommodating at least one premature neonate having at least two operational configurations, said operational configurations comprising: a first operational OPEN configuration whereby said CLNS is adapted to couple said neonate to at least one life supporting system by means of at least one life supporting coupling line, prior to positioning said CLNS in a medical device; and a second operational air-tight CLOSED configuration whereby said neonate remains continuously coupled to said at least one life supporting system by means of at least one life supporting coupling line, when positioning said CLNS within said medical device. The OPEN and CLOSED configurations are reversible.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Premature neonate life support environmental chamber for use in mri/nmr devices
ActiveUS20170188879A1Limit excess handlingImprove securityBaby-incubatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceLife support
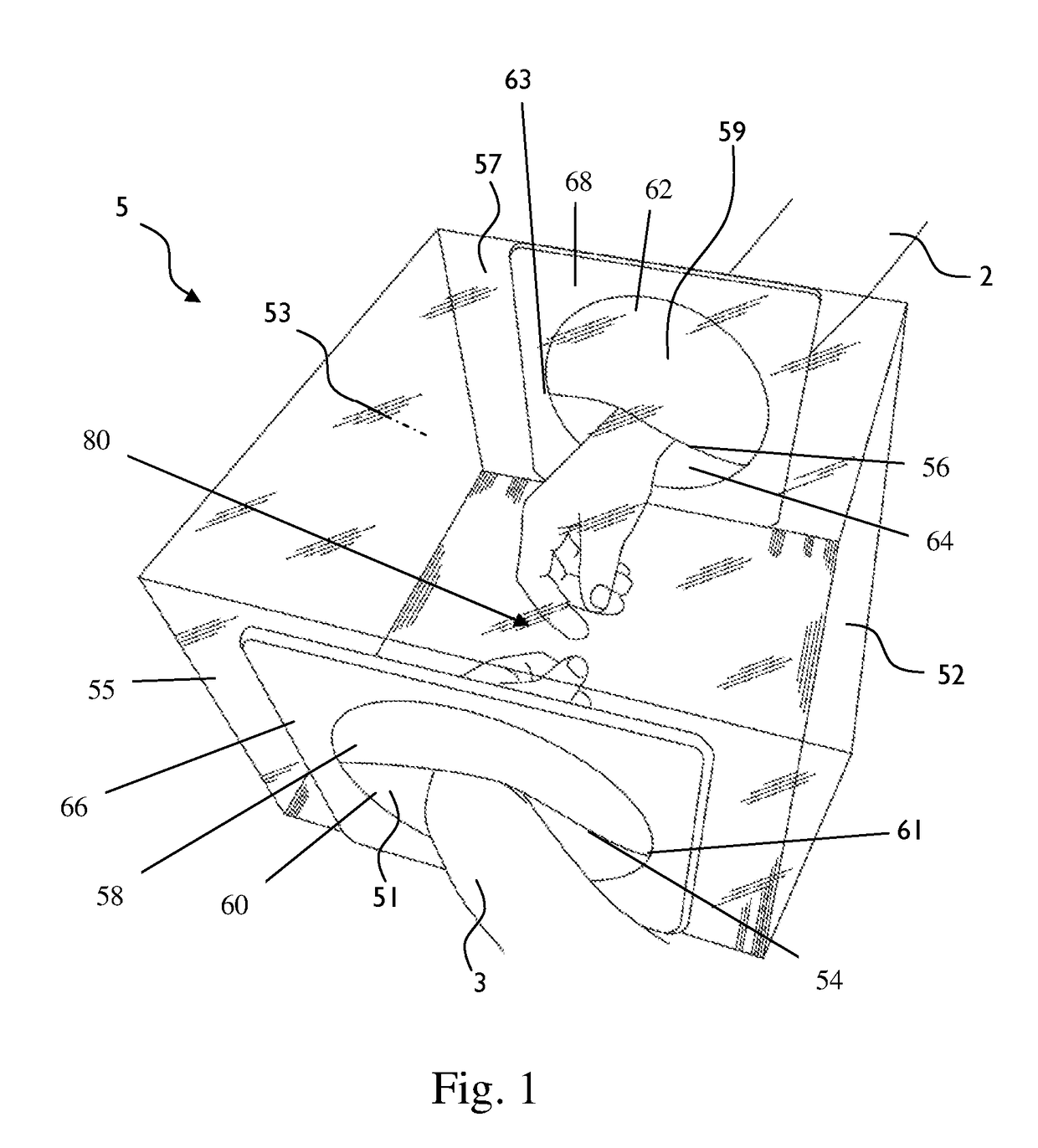
A magnetic resonance system, useful for imaging a patient, comprising: (a) a magnetic resonance device (MRD) for imaging a patient, comprising an open bore, the MRD at least partially contained in an envelope comprising in its circumference at least one recess; and, (b) an MRI-safe cart made of MRI-safe material, comprising a substantially horizontal base and at least one substantially horizontal incubator above the base, the base and the incubator are interconnected by at least one pillar. At least a portion of the cart and the MRD are configured to fit together such that at least a portion of the incubator is reversibly housed within the MRD, and further at least a portion of the base is reversibly housed within at least one recess.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Incubato/crib infant positioning blanket
InactiveUS8359687B2Easy to useInexpensive and more comfortable to the babyRestraining devicesBlanketEngineeringPremature baby
Owner:MARLOWE ELLEN T
Human Milk Oligosaccharides For Preventing Injury And/Or Promoting Healing Of The Gastrointestinal Tract
InactiveCN104023560AImprove bindingEliminate inflammationOrganic active ingredientsSugar food ingredientsNutritionGastrointestinal Injury
Disclosed are nutritional compositions including human milk oligosaccharides that can be administered to individuals including preterm infants, infants, toddlers, children, and adults for preventing injury and / or improving the healing of the gastrointestinal tract. Additional suitable methods of using the nutritional compositions including the human milk oligosaccharides are also disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Breastfeeding shield
ActiveUS20120165730A1Facilitate milk flowMilking pumpBreast-nipple shieldsFull term infantsEngineering
The breastfeeding shield is configured for comfort and to facilitate the breastfeeding of an infant. The shield is formed of a soft thermoplastic elastomeric, e.g., silicone rubber or the like, and has a major portion closely conforming to the major contours of the female human breast. The major portion is relatively thin, the portion covering the areola being relatively thick and the nipple portion having an intermediate thickness. The hollow nipple includes reinforcing and spacing ribs therein to preclude contact with the natural nipple due to suction and resulting blockage of milk flow. One embodiment is configured for use by full term infants, and another embodiment has a smaller nipple extension for use by premature infants. Different sizes may be provided to suit the nursing mother. The shield is removably secured to the breast by disposable or reusable low-stick adhesive materials.
Owner:MCCOY LATINA D
Process for the treatment of bacterial infections using 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one 1-oxide
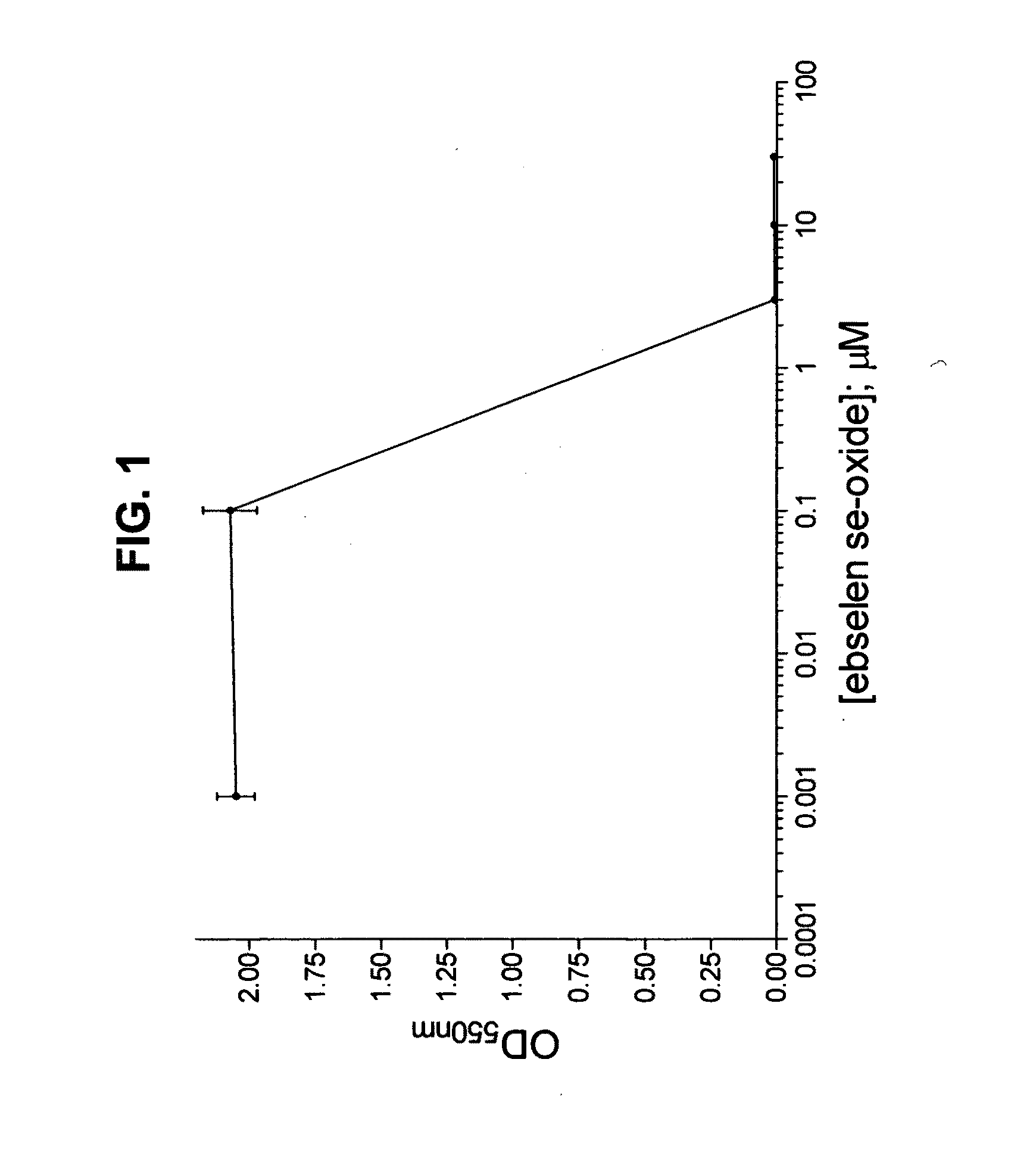
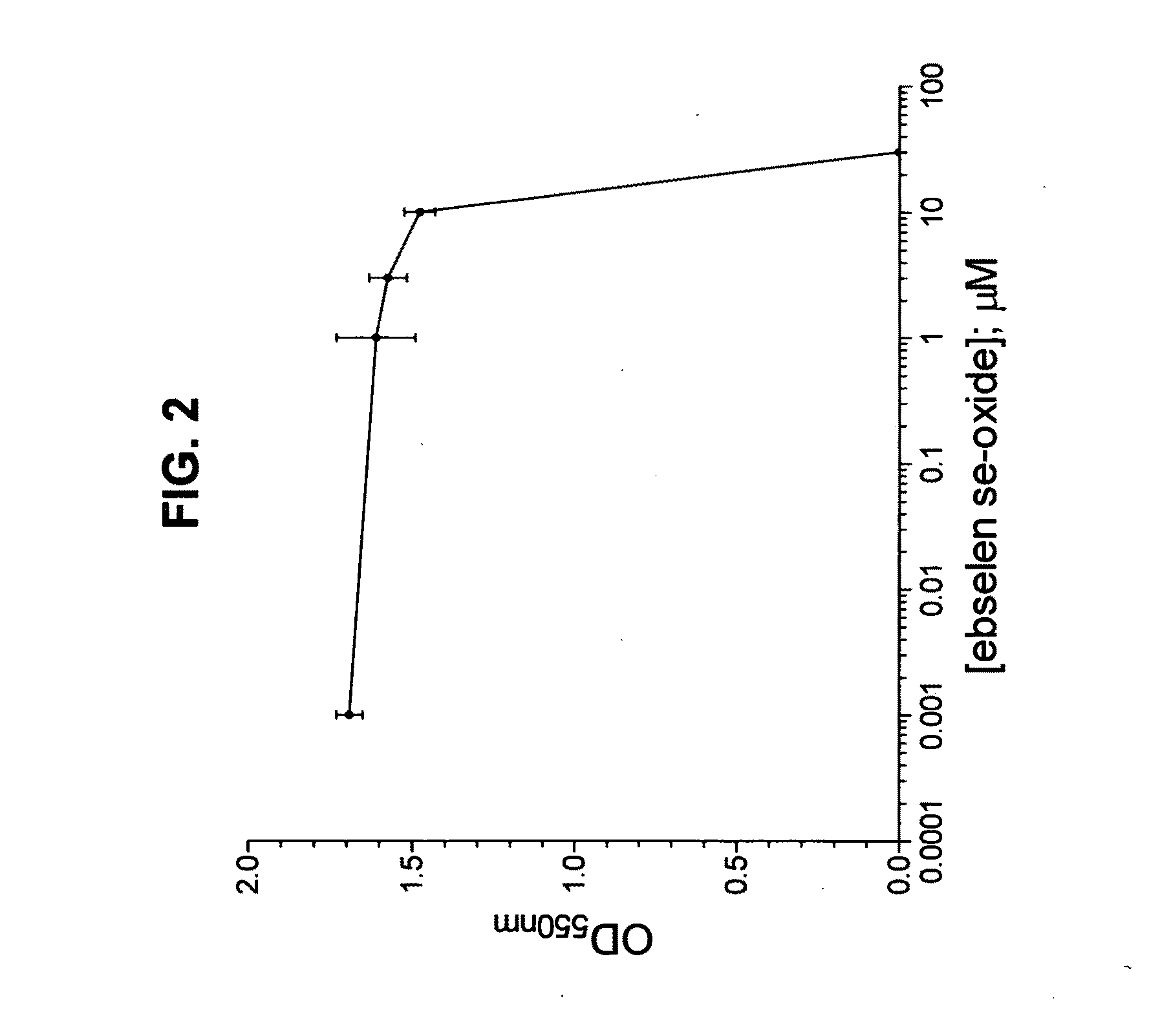
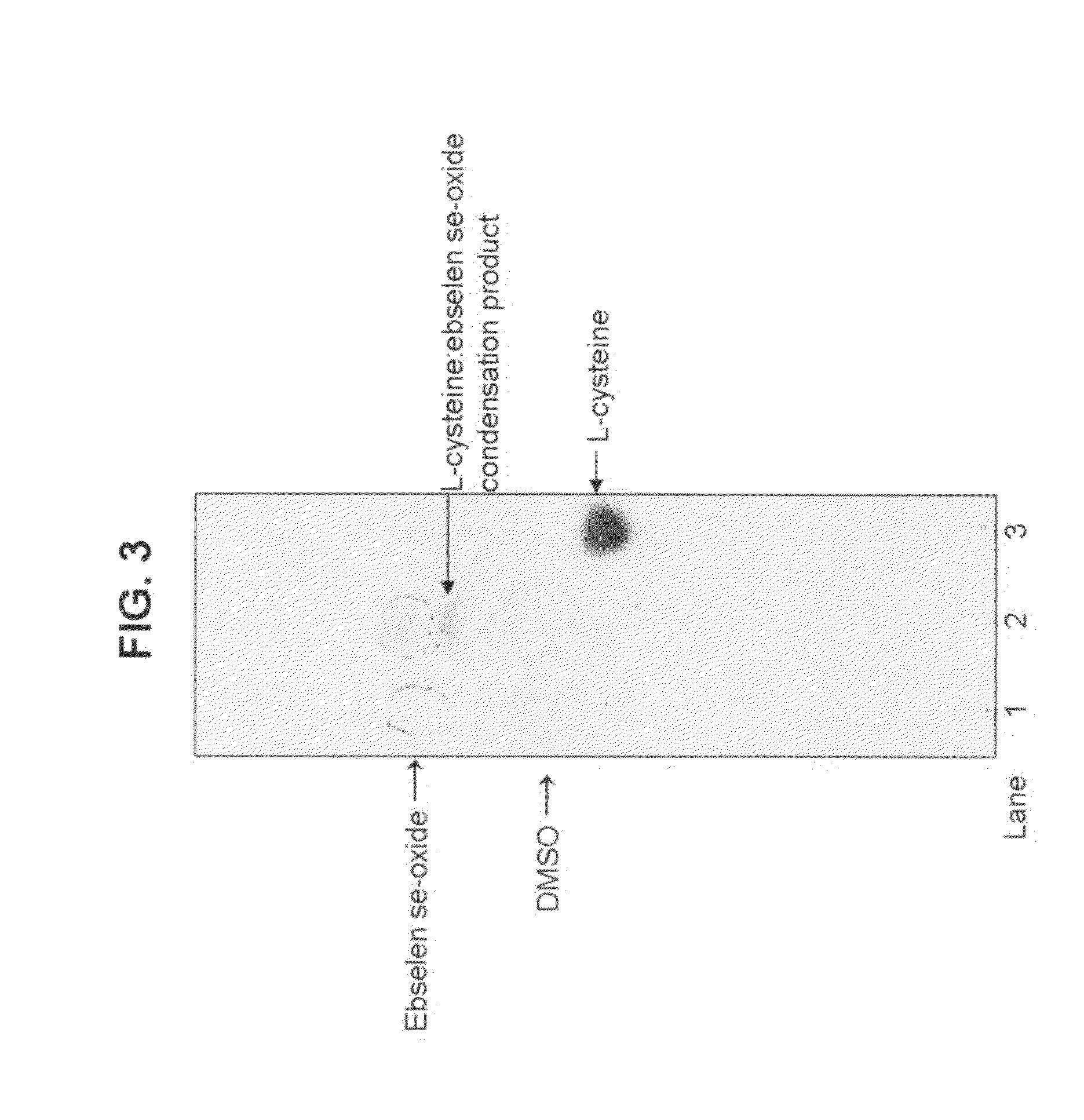
The subject invention demonstrates a novel antibacterial activity for 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one 1-oxide, commonly referred to as ebselen se-oxide, and is directed to the treatment of bacterial infections by administration of an effective amount of said compound. Bacterial infections include those infections which are either systemic or superficial in nature. The treatment is intended for a variety of animals, such as premature neonates to adult humans. Administration of ebselen se-oxide to treat superficial bacterial infections may be performed by a topical application, such as via an ointment, a spray, a cream, a mouth wash, an eye drop solution, an ear drop solution, a soap, a gel, or a lotion. In addition, an antibacterial capsule can be administered orally or intravaginally. Administration of ebselen se-oxide to treat systemic bacterial infections may be performed by an intravenous route, a rectal route, an intranasal route, an oral route, an intramuscular route, or by inhalation. Administration of said compound may also be achieved via aerosol, which can be generated by a nebulizer. Ebselen se-oxide may be administered alone, or with a carrier such as dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), an alcohol, or other suitable carrier. The effective daily amount of ebselen se-oxide is from about 1 μg / kg to 10 mg / kg of body weight.
Owner:BILLACK BLASE CHRISTOPHER +1
Infant feed and method
InactiveUS20170172167A1Raise countReduces bacterial cell countMilk preparationFood scienceBreast feedNutrition
The present disclosure relates generally to a composition for feeding an infant. More particularly, the disclosure relates to a nutritional composition for feeding an infant comprising a stem-cell deficient first component and a second component comprising breast milk stem cells (BSCs). The second component is added to the first component, and the BSCs partially or fully replenish the stem-cell deficient first component with respect to BSCs. In some embodiments the first component is stem-cell deficient human breast milk and the second component comprises BSCs from the infant's mother's own milk. The compositions of the present disclosure have been developed primarily as a personalized, nutritional composition providing the beneficial effects of an infant's mother's own BSCs to the infant while not being able to receive the full benefits of being breastfed directly.The present disclosure also relates to a composition for feeding an infant and to processes of their production. In particular, the disclosure relates to a composition for feeding an infant comprising a first and a second component, wherein the first component provides the majority of the nutritional value to said composition, and wherein the second component comprises at least one live bacterium from human breast milk or the lactating human mammary gland. The disclosure has been developed primarily as a composition for feeding a mother's own infant, wherein the composition comprises processed human breast milk with a substantially reduced live bacterial cell count as compared to unprocessed breast milk but which at least one live bacterium, from the mother's own breast milk, is added such as to partially or fully replenish the processed human breast milk with respect to the at least one live bacterium. More particular, the composition is a personalised composition for feeding the mother's own preterm infant.The present invention also related to the combination of BSC and bacterial replenishment as described herein.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
Antiglucocorticoid Therapy for the Prevention of Neurological Damage in Premature Infants
ActiveUS20110144072A1Avoid nerve damageOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHydrocortisoneAntiglucocorticoid
This invention pertains to the discovery that agents which inhibit the binding of cortisol to its receptors can be used in methods for preventing neurological damage associated with glucocorticoid therapy in ventilator-dependent low birth weight preterm infants. Mifepristone, a potent glucocorticoid receptor antagonist, can be used in these methods.
Owner:CORCEPT THERAPEUTICS INC
Phospholipid formulations and uses thereof in lung disease detection and treatment
InactiveUS20070010429A1Deter/inhibit damagePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAir sacsSURFACTANT BLEND
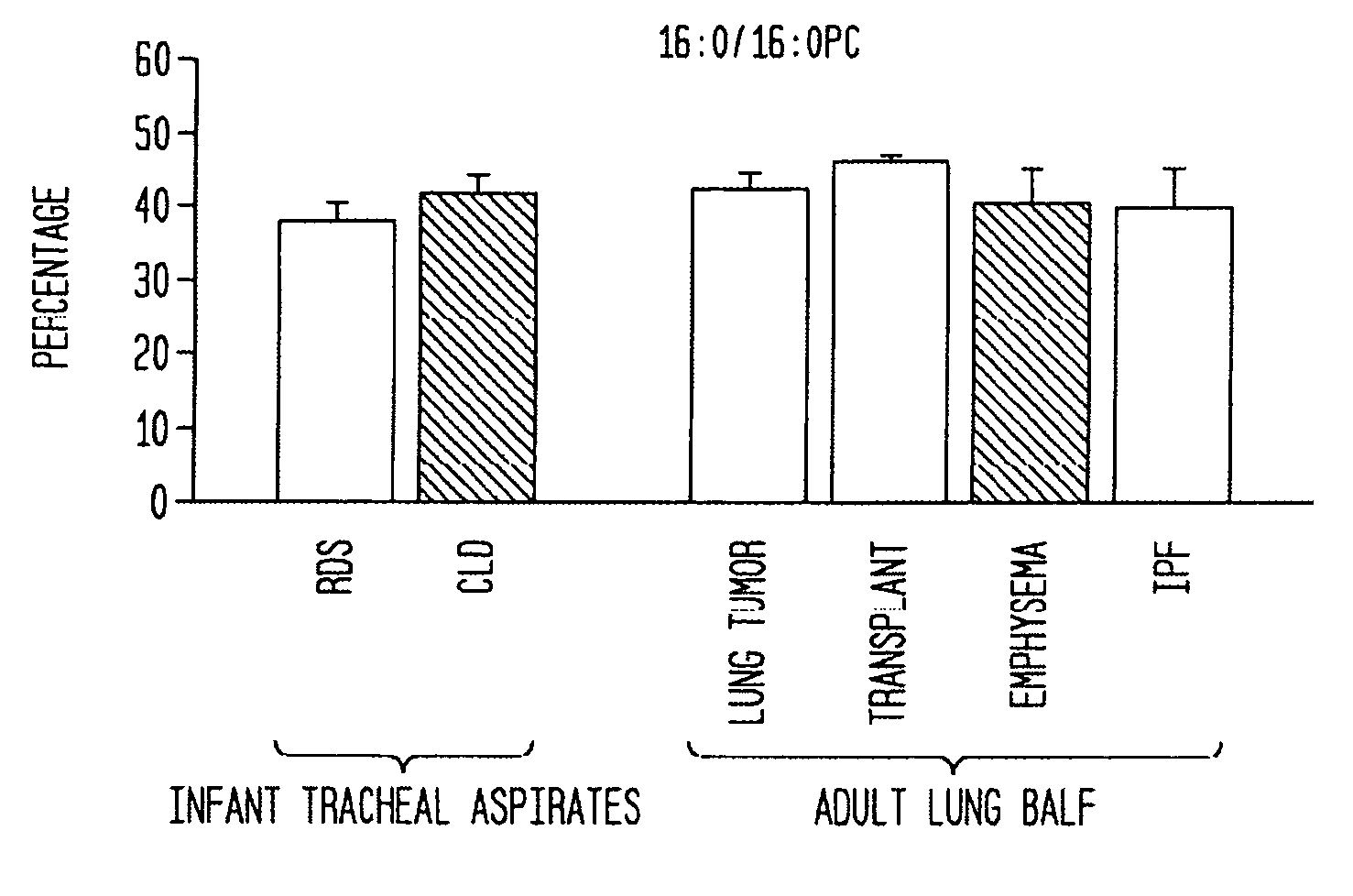
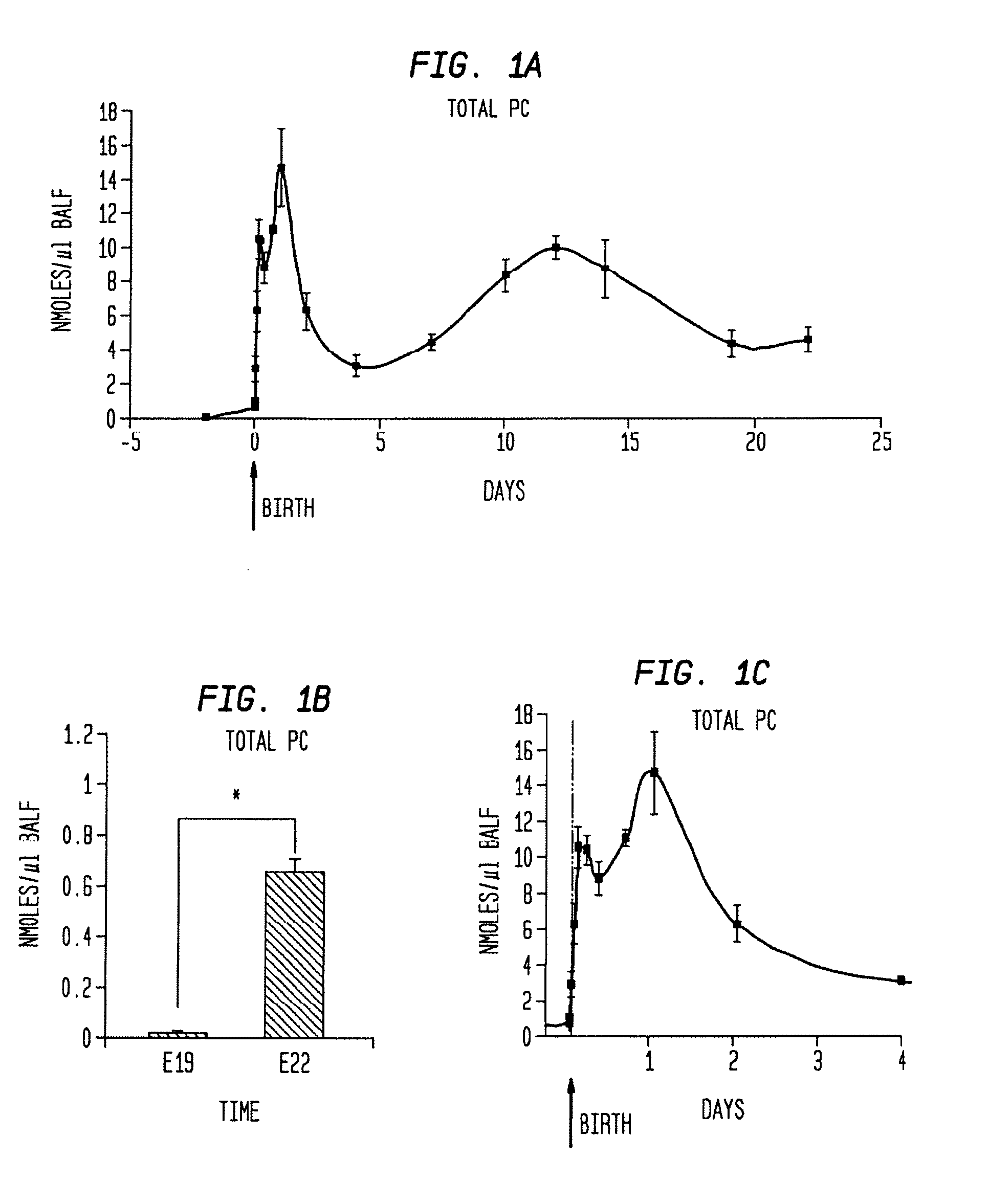
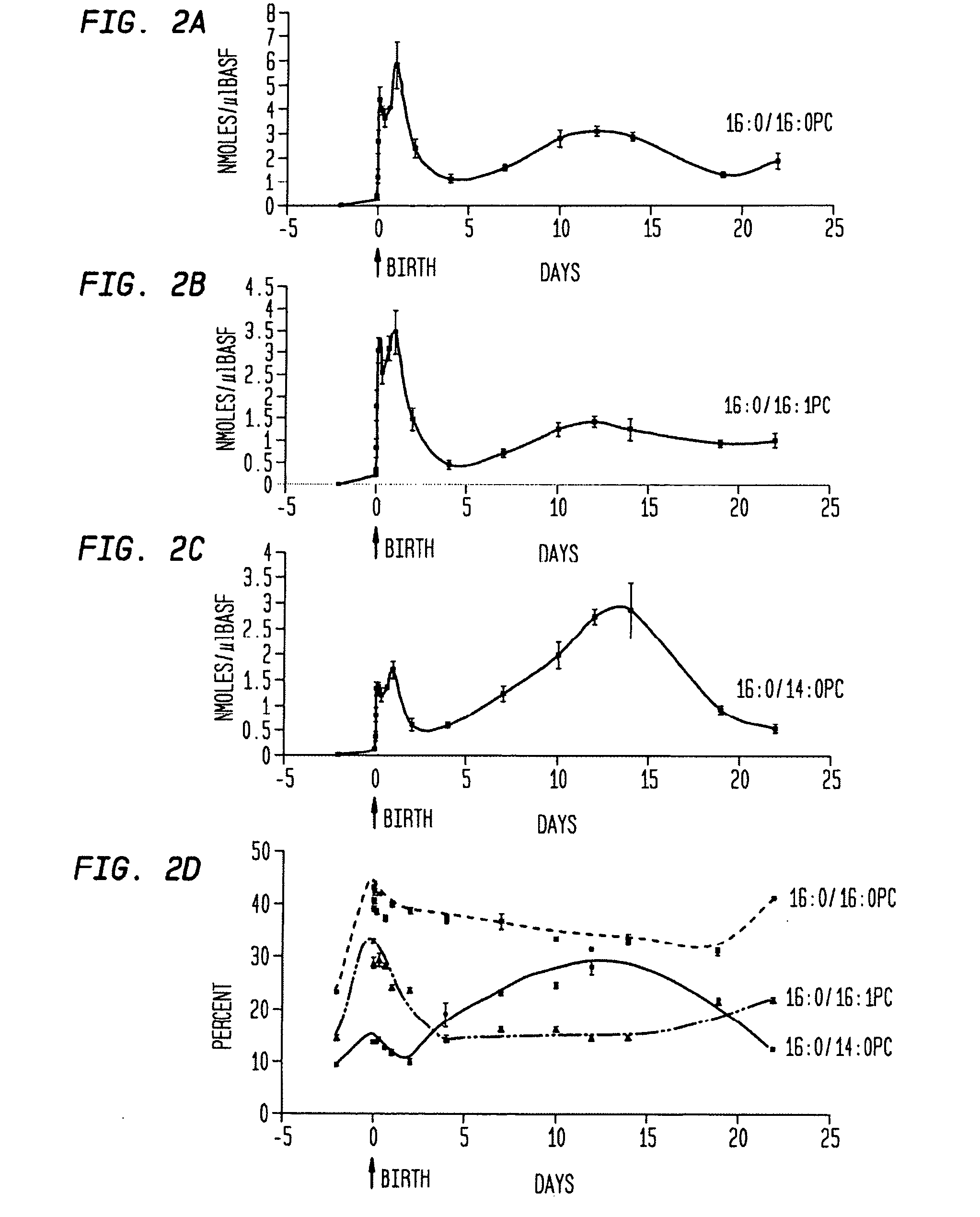
Disclosed are methods and compositions that are useful in the detection and therapy of diseases (e.g., emphysema) and damage that afflict the lungs. In some aspects, the compositions comprise a formulation enriched for a species of phosphatidylcholine, such as palmitoylmyristoyl phosphatidylcholine (16:0 / 14:0PC). The compositions may further be described as lung surfactant supplement preparations particularly useful in the treatment of pulmonary diseases and afflictions prevalent among premature infants, and in particular, Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS). A PC marker is also disclosed, 16:0 / 14:0PC, that may be used to detect pulmonary disease or reduced / compromised alveolar function in an animal. Phospholipid profiles of 16:0 / 14:0PC, 16:0 / 16:1PC and 16:0 / 16:0PC are also provided, and are correlated with particular pulmonary diseased states.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
Automatic pacing system for a baby bottle
An insert which is useable with a baby bottle, a baby bottle including an insert, and a method of feeding an infant that serves to pace the infant's feeding rhythm. Generally, these devices and methods will be of use for a preterm infant, but that is by no means limiting because full term infants could also benefit from these devices and methods. The device generally cues the infant to swallow and breathe after each 1-4 sucks by stopping the flow of the fluid from the bottle after the infant has sucked sufficiently. Once the baby breathes, the bottle resets for the next repetition.
Owner:PREEMIE PACER
Automatic breastfeeding method and automatic breastfeeding machine for premature infant
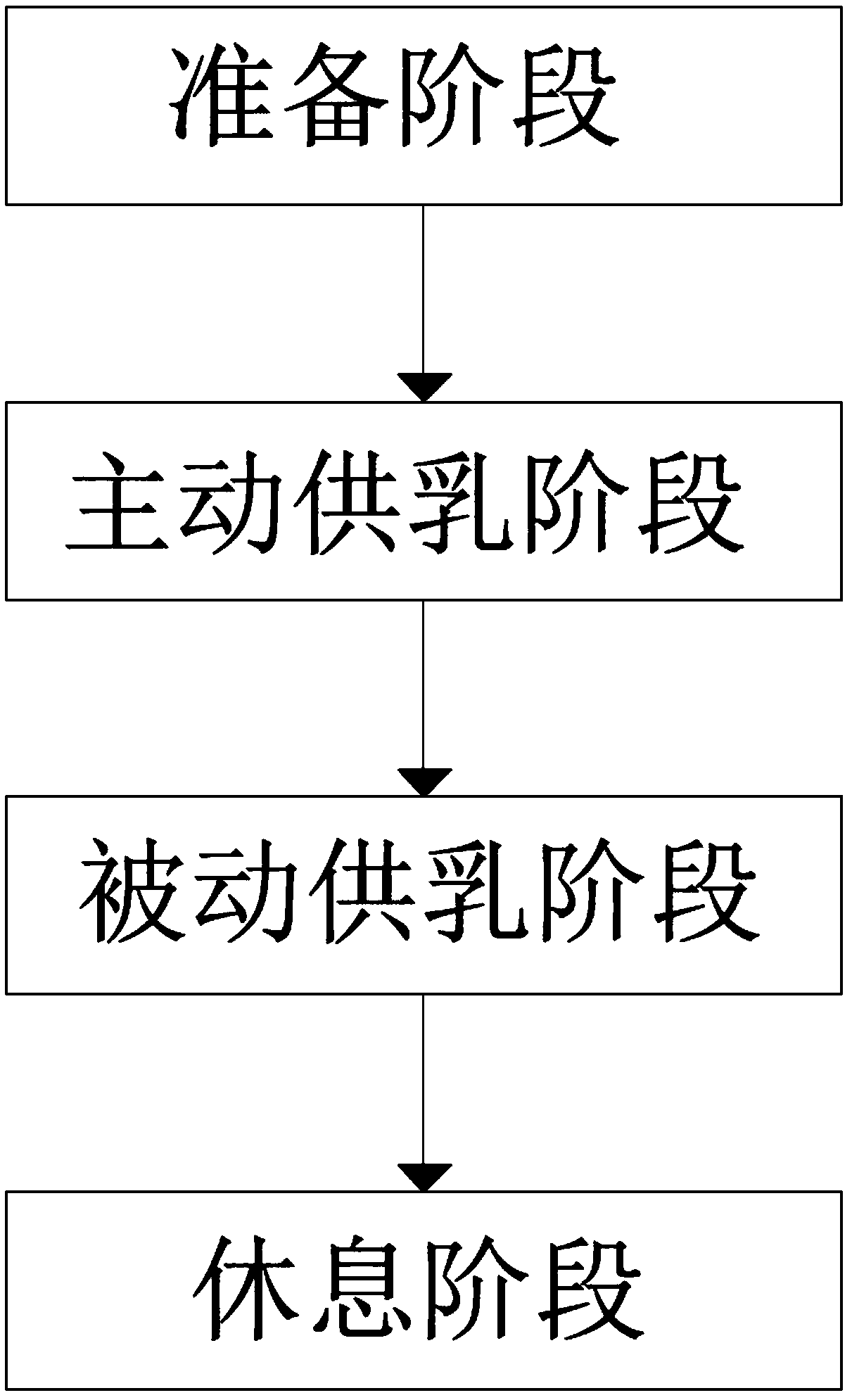
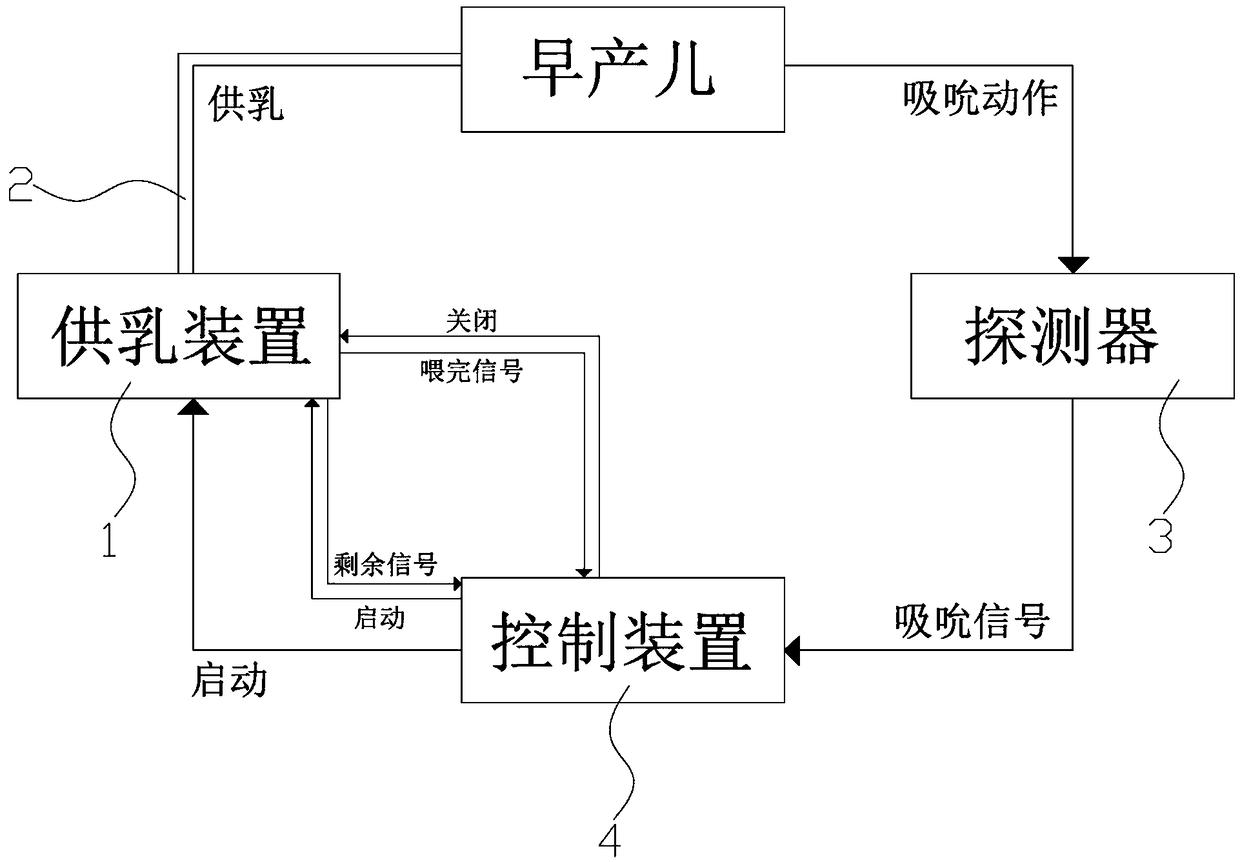
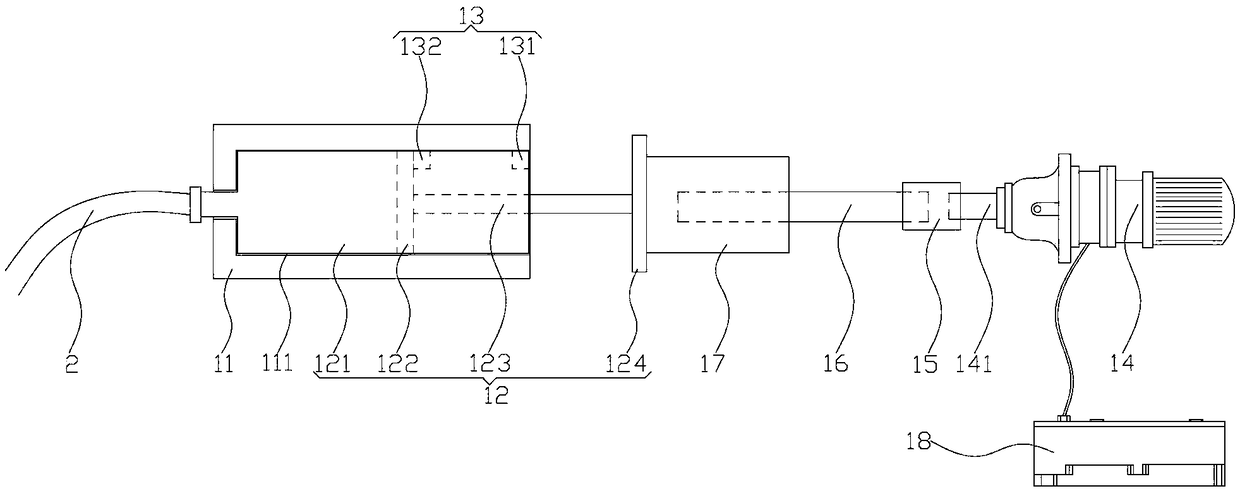
ActiveCN109106602ASelf-sucking ability trainingNo difference in dietDomestic articlesFeeding-tubesPremature thelarcheReflex
An automatic breastfeeding method of a premature infant comprises a preparation stage, an active lactation stage, a passive lactation stage and a rest stage; the invention also provides an automatic breastfeeding machine used for the automatic breastfeeding method of premature infant, comprising a stomach tube, a lactation supply device, a detector and a control device. One end of the stomach tubeis arranged in the stomach of the premature infant, and the other end is connected with the lactation supply device, the milk supply device is electrically connected with the control device, the control device is electrically connected with the detector, and the detector is arranged in the mouth of the premature infant. The self-sucking ability of the premature infant is trained, and the normal circulation of the mouth-pharyngeal-gastric-intestinal reflex of premature infants is realized, and the nutritional requirements of the premature infants are ensured taking into account the differencesof the premature infants, so that the premature infants have no difference in the care, diet, neurological development and growth and development with term infants in the future.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com