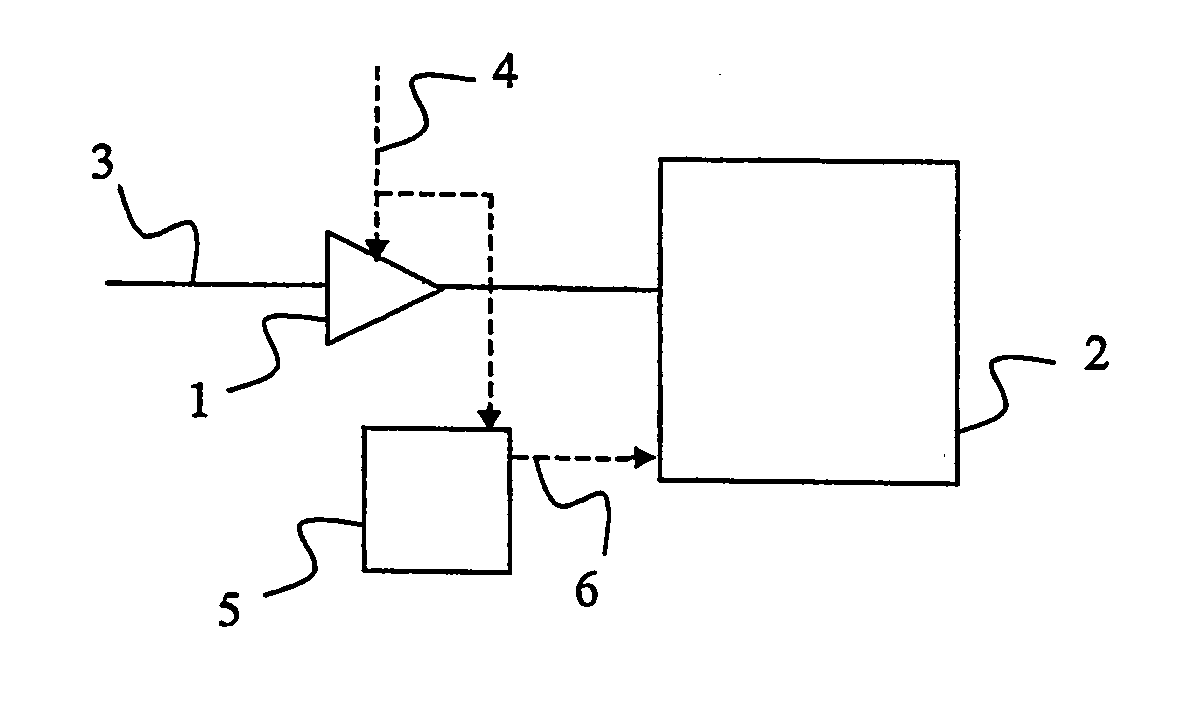
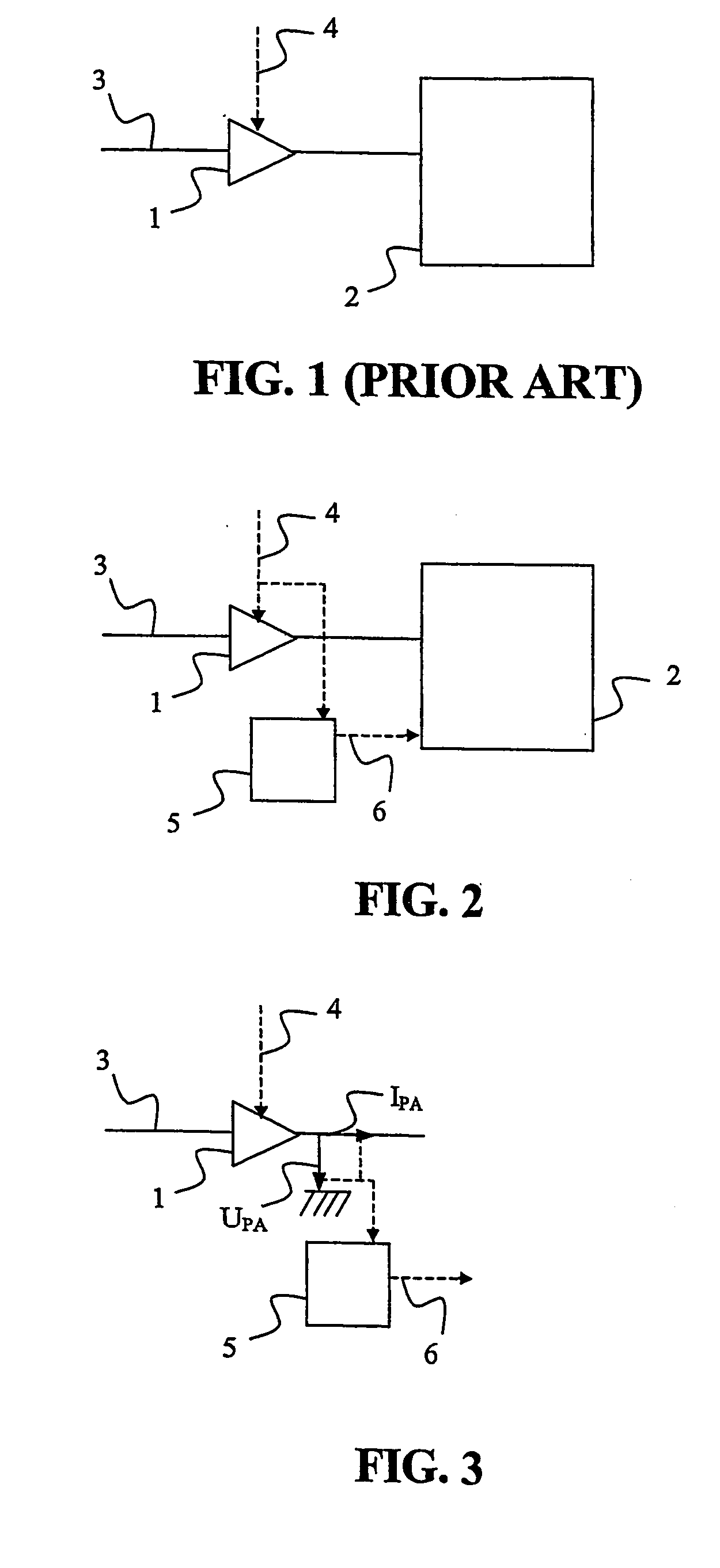
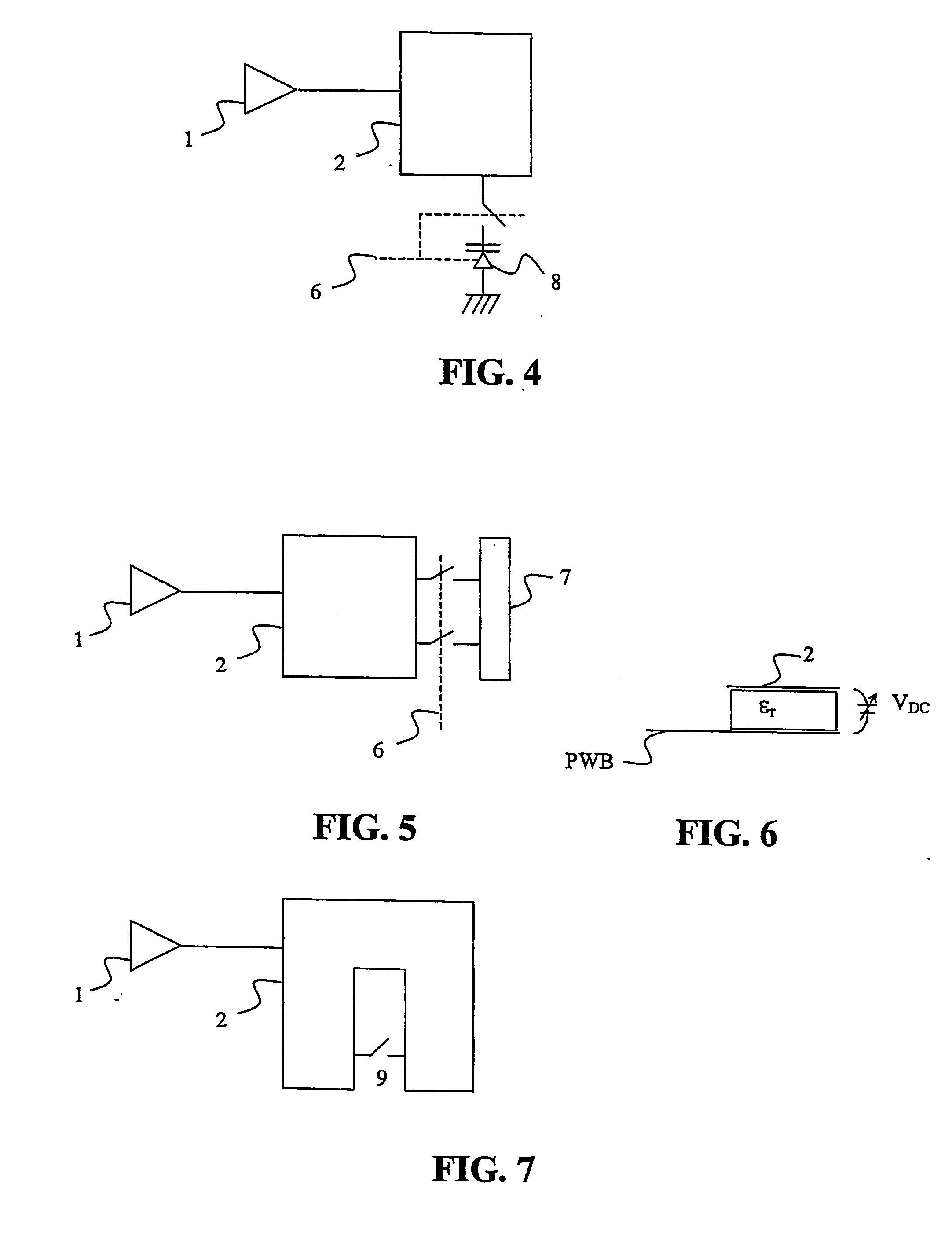
Patents
Literature
47 results about "Radiation impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In acoustics, radiation impedance is the impedance of any vibrating solid or fluid that radiates sound in the surrounding medium.
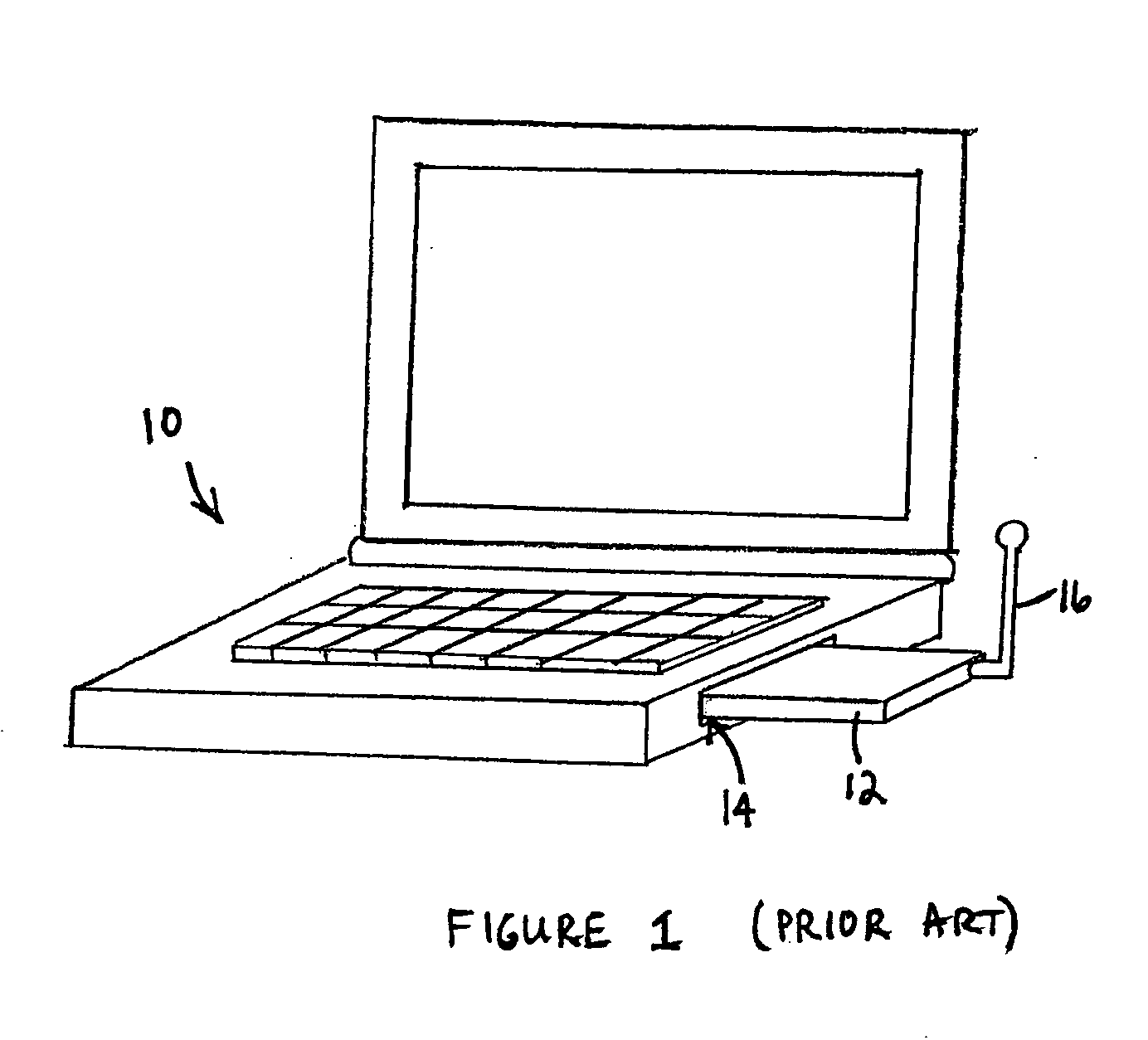
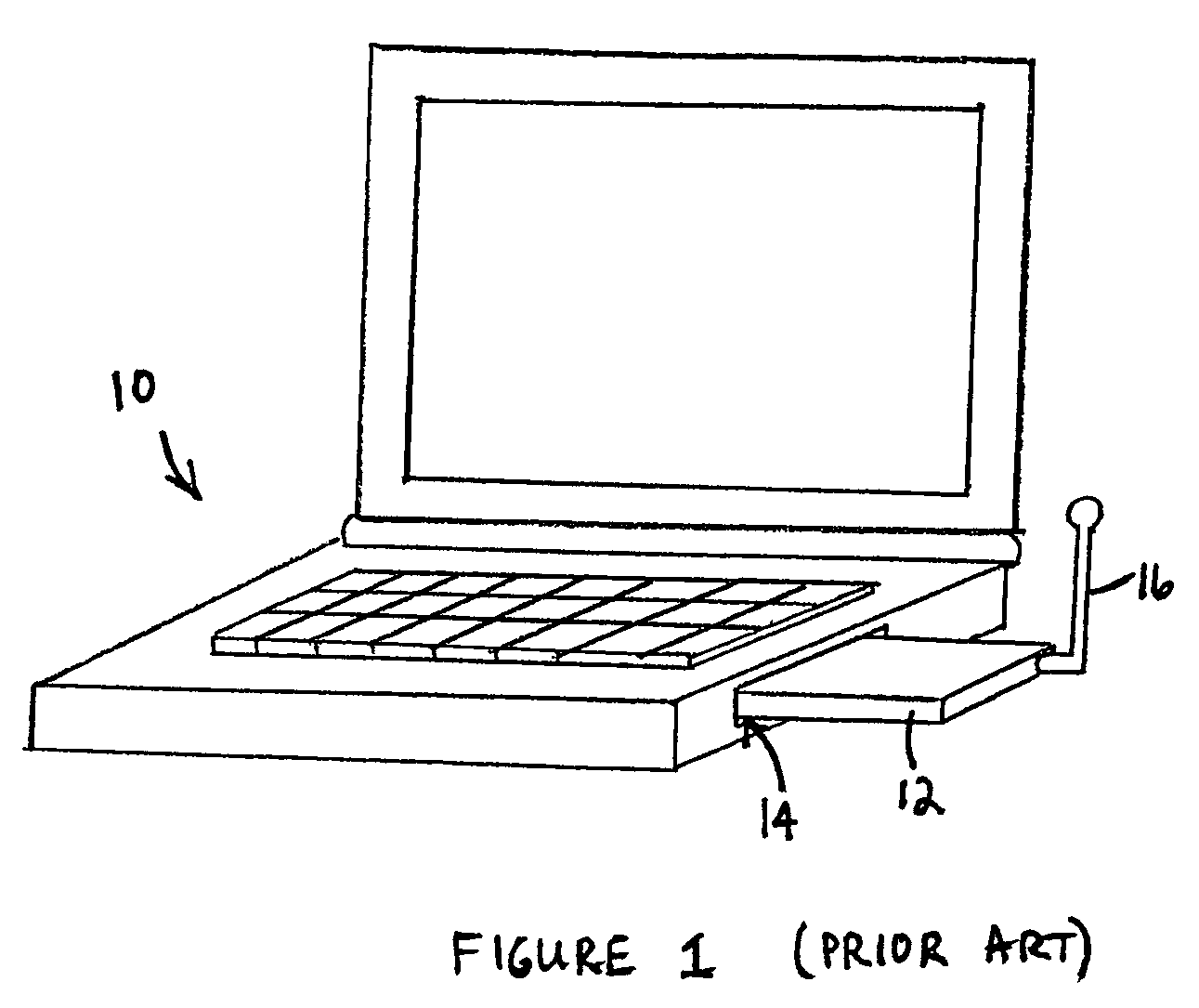
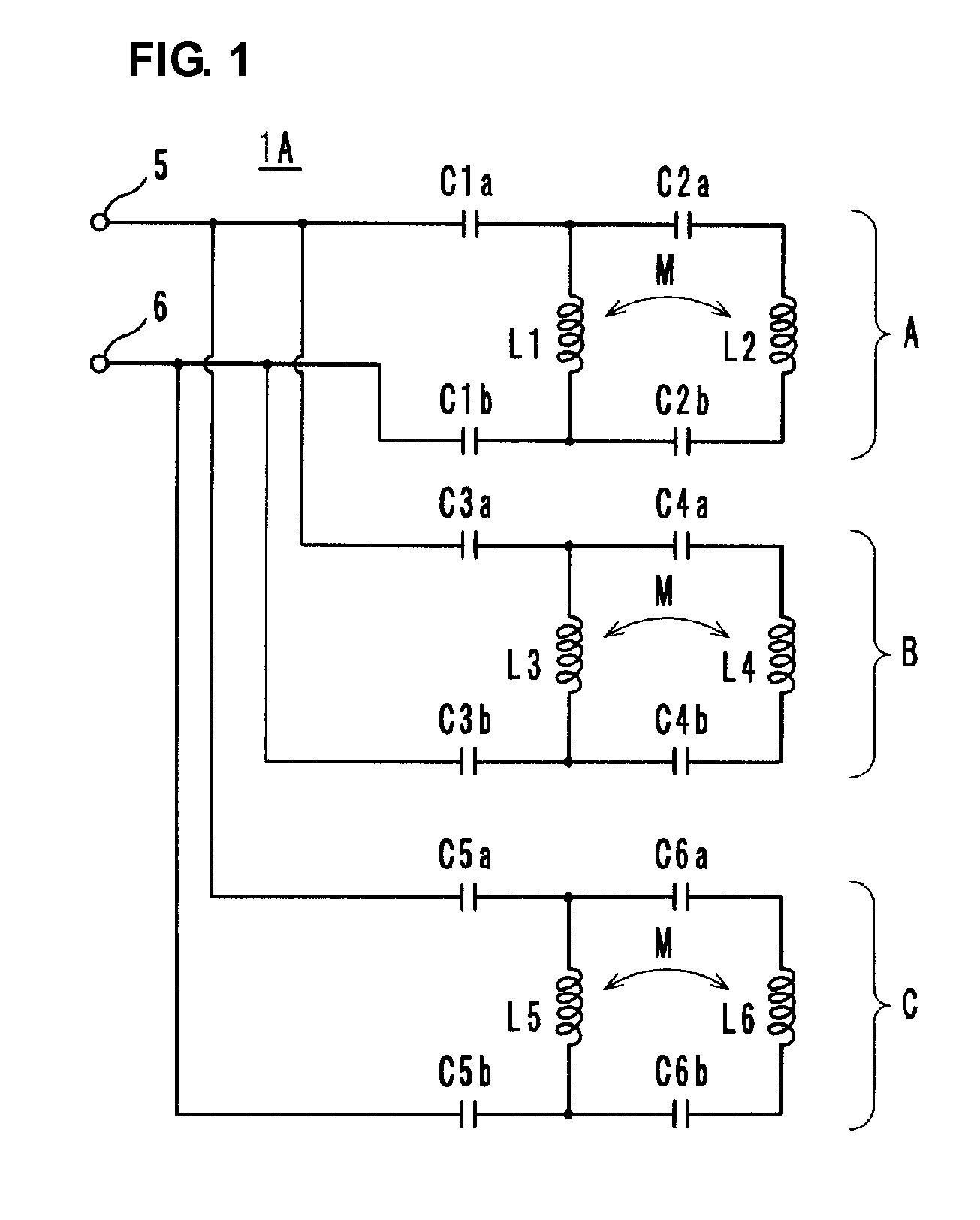
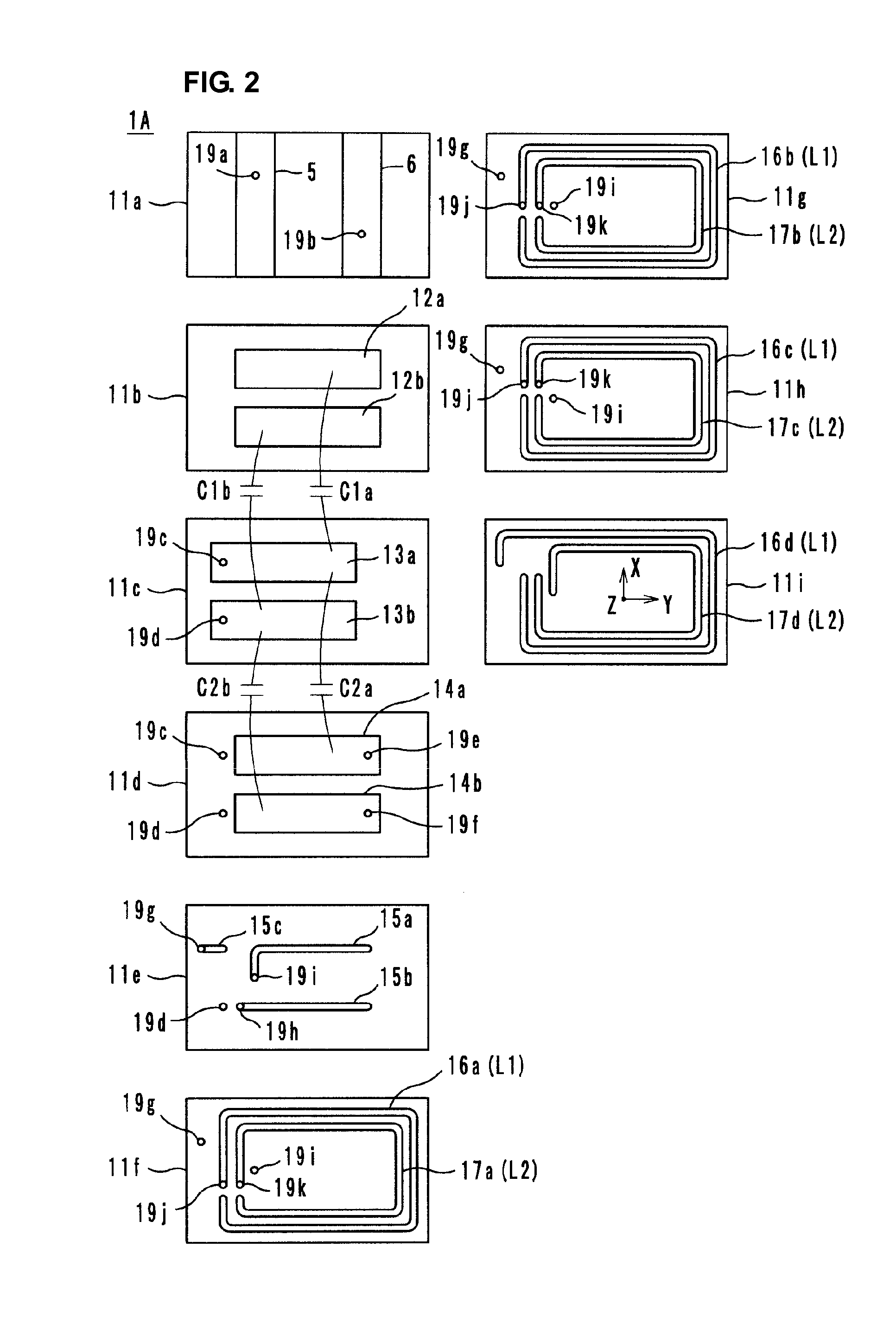
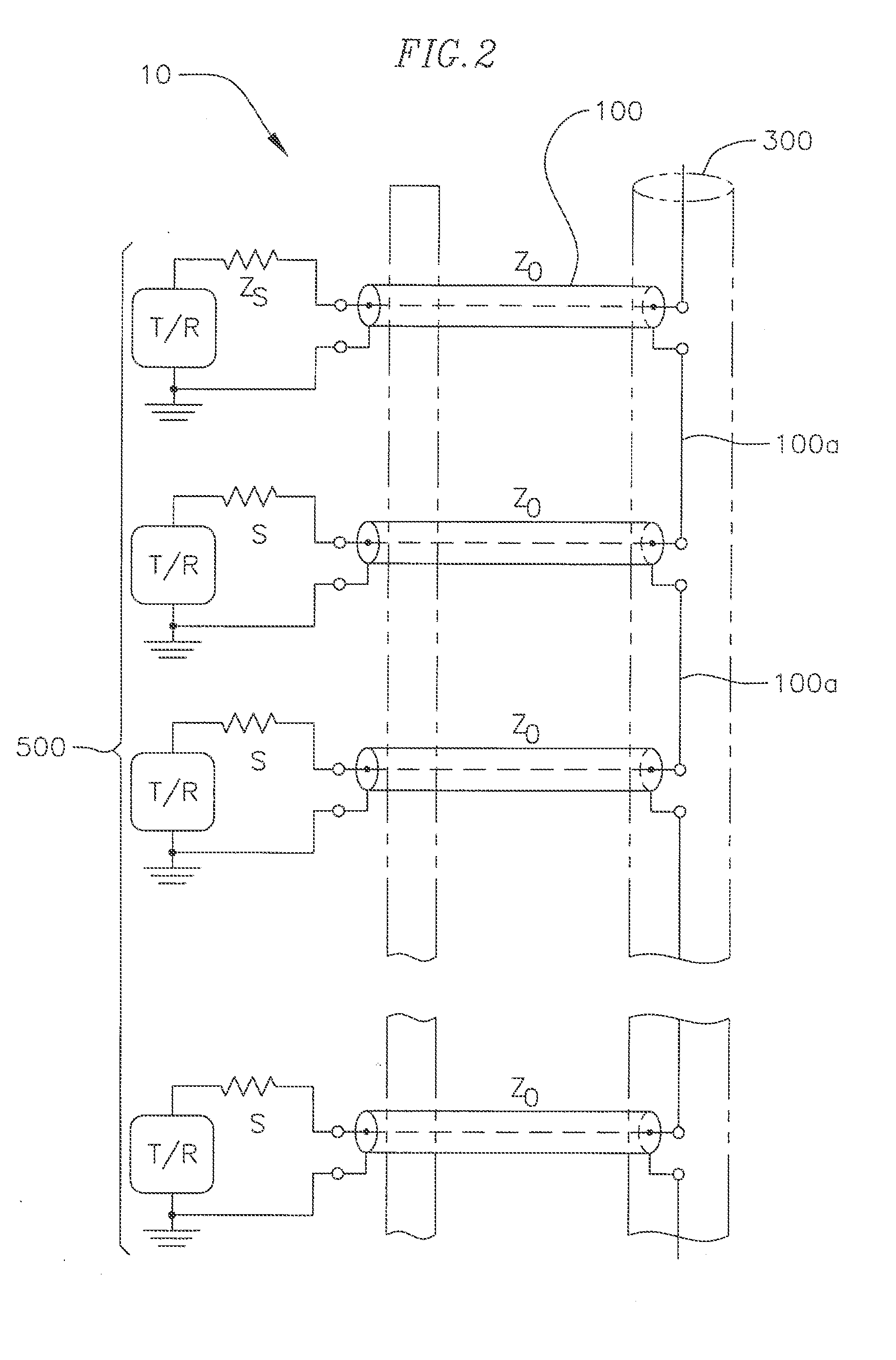
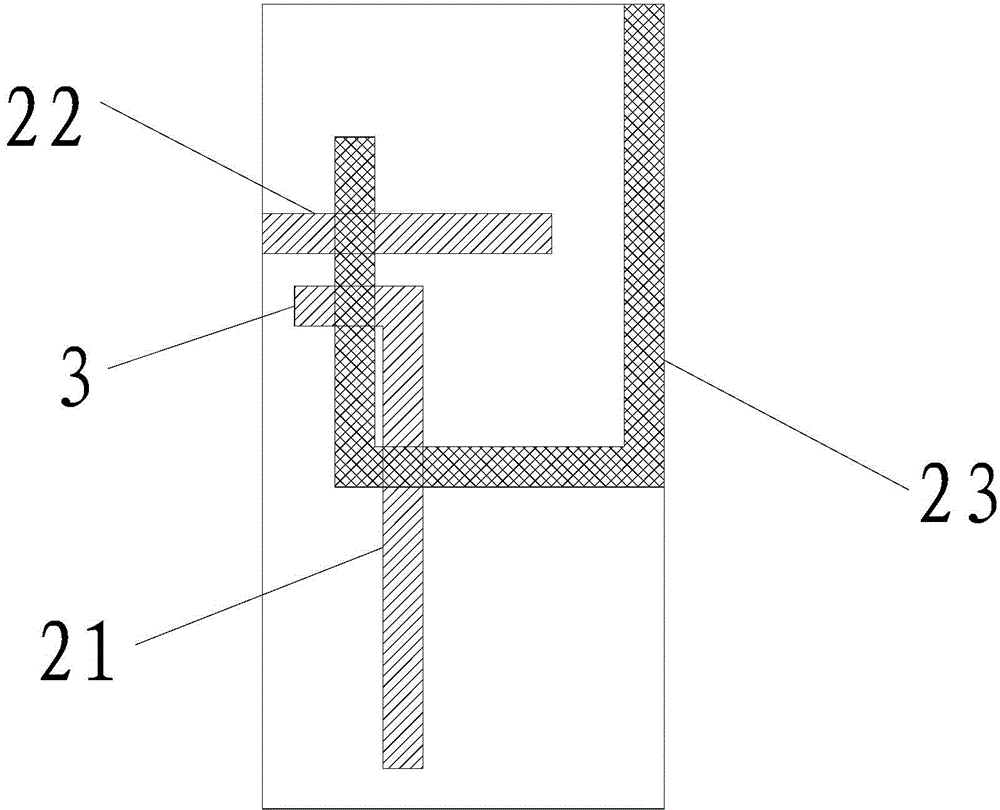
Method and system for adapting a loudspeaker to a listening position in a room
ActiveUS8144883B2Loudspeaker enclosure positioningFrequency response correctionEngineeringLoudspeaker
The invention relates to a method and a system for adapting a loudspeaker to a specific listening position relative to the loudspeaker according to which method and system the acoustic power radiated by the loudspeaker is corrected by means of a correction filter inserted in the signal path through the loudspeaker, the response of said correction filter being determined by comparison between the a quantity characterising the radiated acoustic power measured at an actual listening position and a similar quantity measured at a reference listening position. According to a specific embodiment of the invention said characterising quantities are the radiation resistances measured at the actual listening position and the reference listening position respectively.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
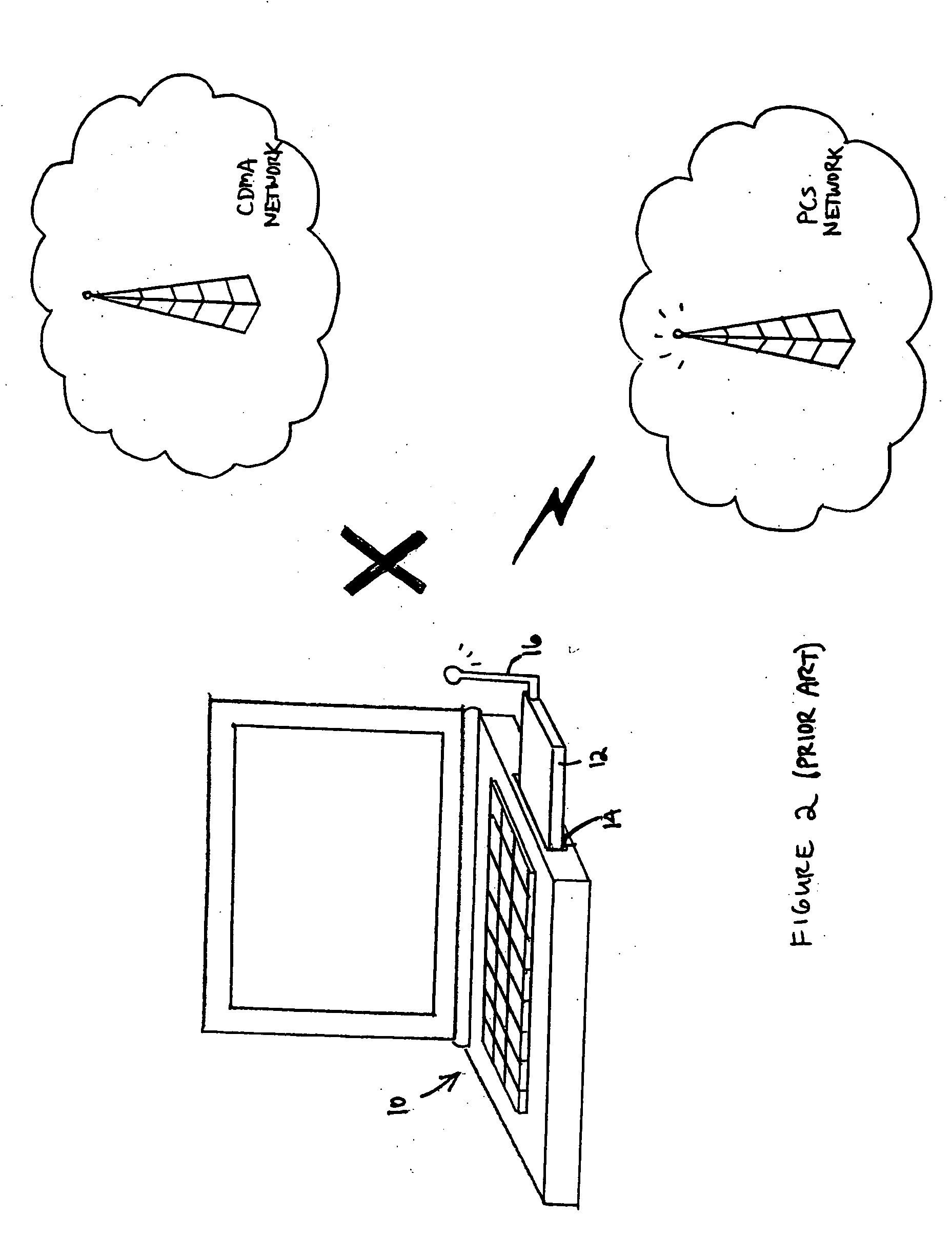
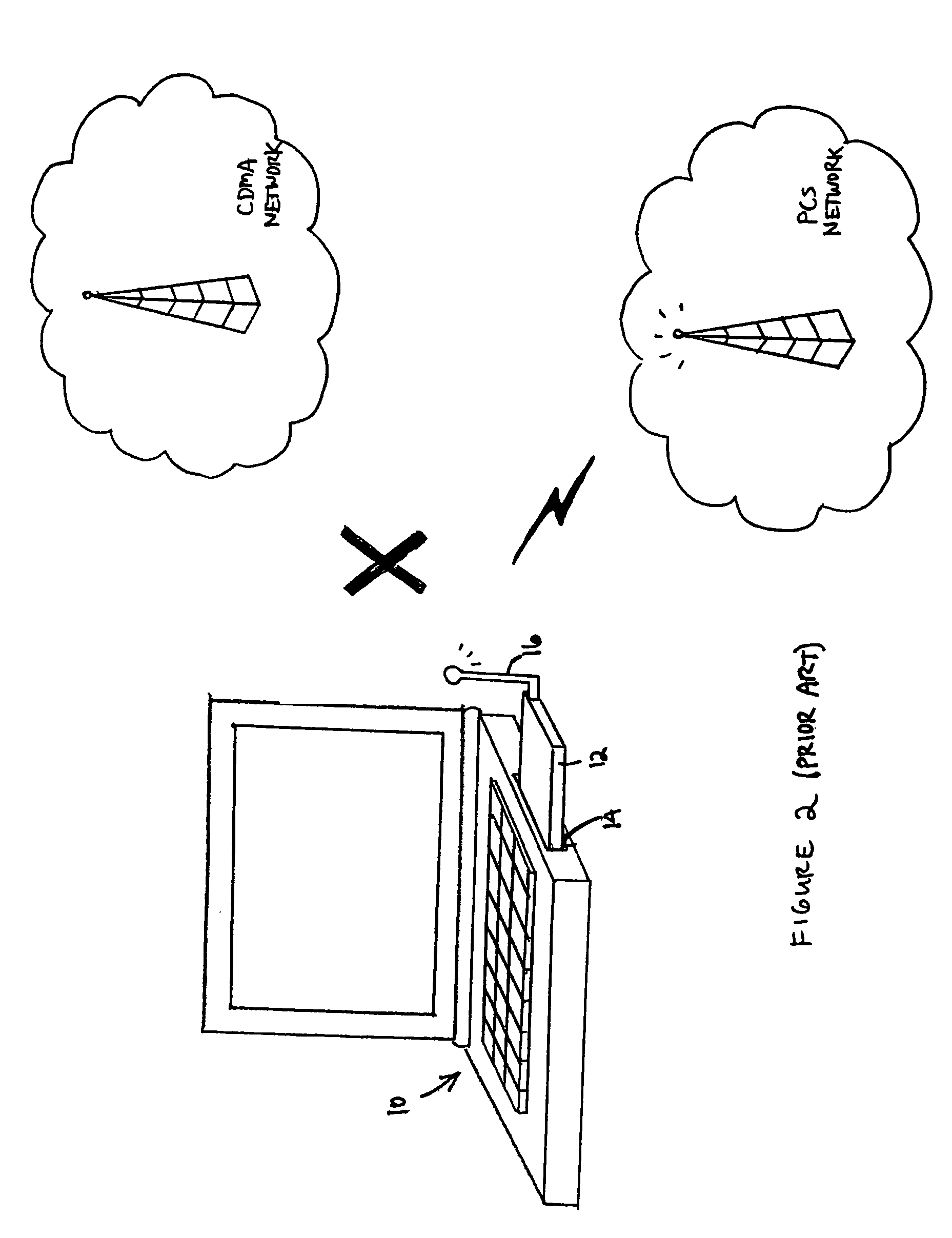
Multi-band antenna system
ActiveUS20050156796A1High impedanceSuitable lengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectrical conductor
A multi-band antenna system for a portable communications device (e.g. a PC Card wireless modem) is disclosed. The multi-band antenna system comprises a dipole antenna, a reactive circuit, and transmission means coupled between the reactive circuit and the dipole antenna. For signals having frequencies within a first frequency band (e.g. the CDMA 0.86 GHz band), the reactive circuit operates as a trap, i.e. as a substantially high impedance, which enables a radiation impedance of a monopole formed by the presence of the trap to be coupled directly into the feed system (e.g. a diplexer) of the antenna system. The dipole antenna is configured and dimensioned to receive signals within a second frequency band (e.g. the PCS 1.92 GHz band). Second frequency band signals received by the dipole antenna are conducted through the signal conductor of the transmission means to the feed system substantially unimpeded by the reactive circuit. The multi-band antenna system may further include a diversity antenna, which may be configured so that it is polarized orthogonal the to dipole antenna.
Owner:NETGEAR INC
Multi-band antenna system
A multi-band antenna system for a portable communications device (e.g. a PC Card wireless modem) is disclosed. The multi-band antenna system comprises a dipole antenna, a reactive circuit, and transmission means coupled between the reactive circuit and the dipole antenna. For signals having frequencies within a first frequency band (e.g. the CDMA 0.86 GHz band), the reactive circuit operates as a trap, i.e. as a substantially high impedance, which enables a radiation impedance of a monopole formed by the presence of the trap to be coupled directly into the feed system (e.g. a diplexer) of the antenna system. The dipole antenna is configured and dimensioned to receive signals within a second frequency band (e.g. the PCS 1.92 GHz band). Second frequency band signals received by the dipole antenna are conducted through the signal conductor of the transmission means to the feed system substantially unimpeded by the reactive circuit. The multi-band antenna system may further include a diversity antenna, which may be configured so that it is polarized orthogonal the to dipole antenna.
Owner:NETGEAR INC
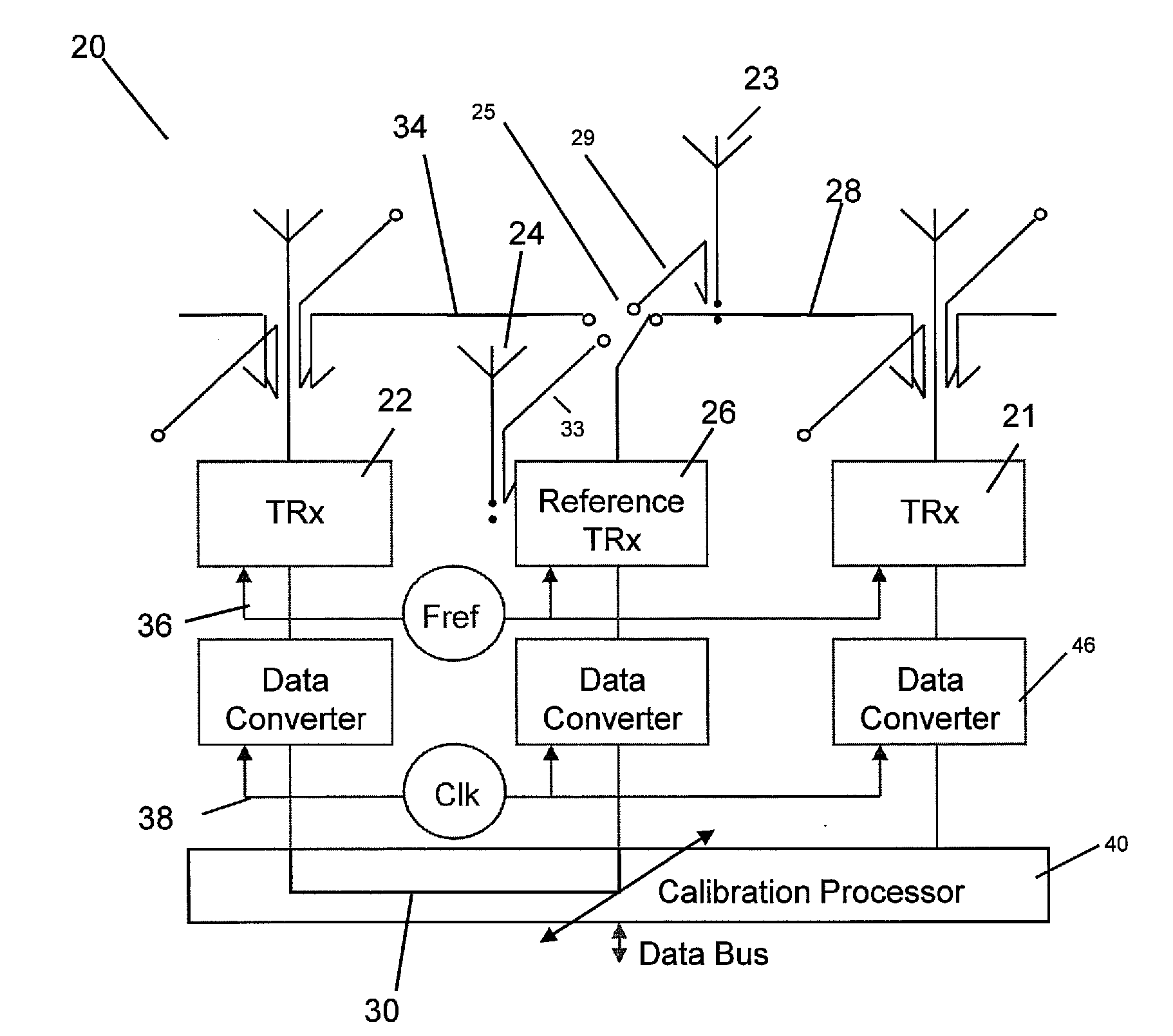
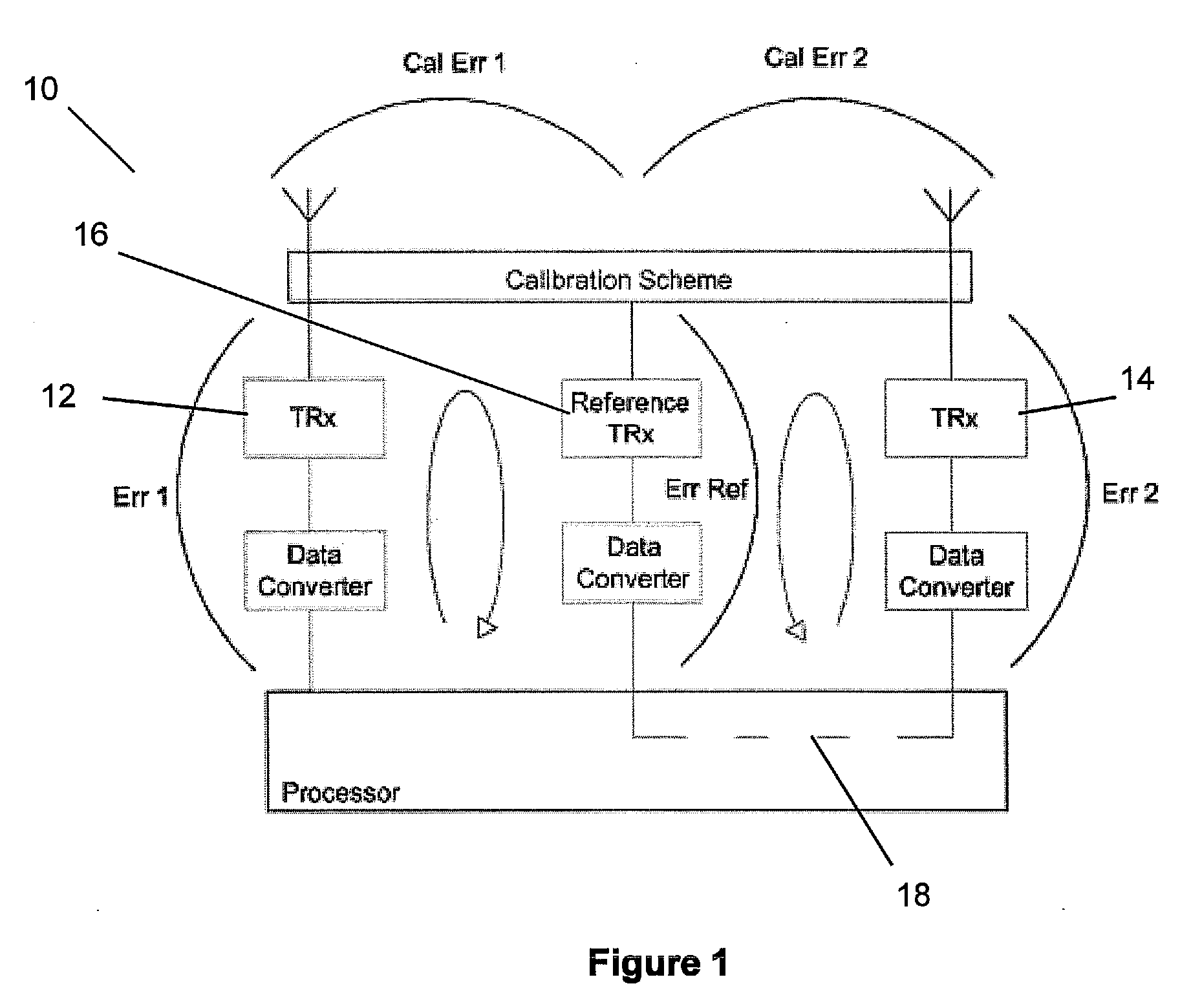
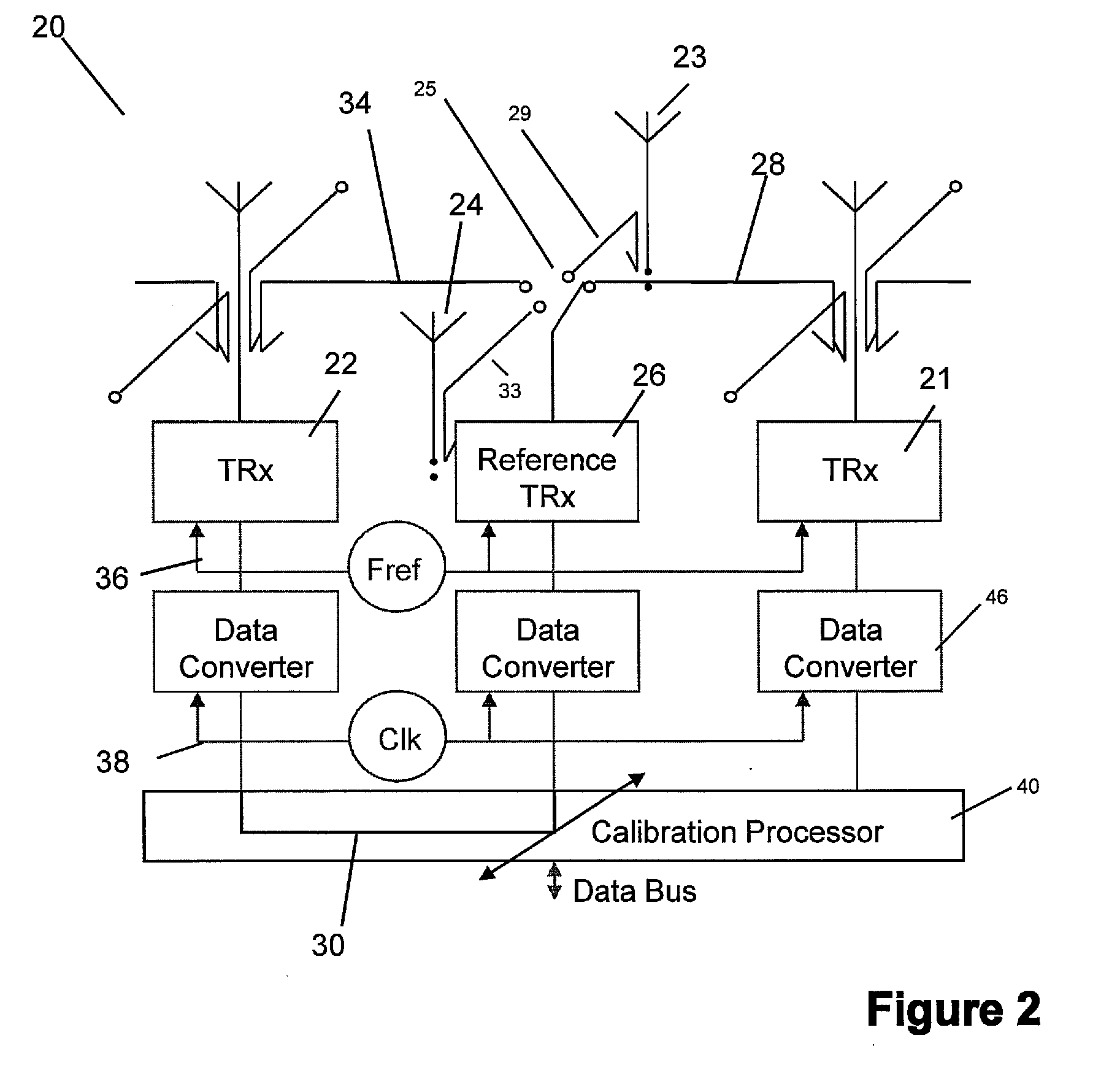
Antenna array calibration
ActiveUS20090267824A1Easy to copyAvoid complex processTransmitters monitoringWave based measurement systemsRadiative transferTransceiver
An antenna array comprises a surface comprising a replicated pattern of conductive tracks, the tracks defining a plurality of ports. A plurality of antennae are located at ports distributed about the surface. A plurality of radiative transceivers are electrically connected to a respective antenna. A plurality of reference transceivers are electrically connected to a non-radiative impedance located at a respective port so that each reference transceiver is surrounded by a group of antennae and electrically coupled to the group of antennae by the tracks. At least one antenna from at least one group of antennae belongs to one other group of antennae. Calibration circuitry includes a controller associated with each reference transceiver, each controller being arranged to transmit a calibration signal through an associated reference transceiver and to receive and store a received calibration signal from a selected transceiver for the group of antennae coupled to the reference transceiver. Each controller is further arranged to receive and store a calibration signal from the selected transceiver for the group of antennae coupled to the reference transceiver. The calibration circuitry further includes for each other transceiver for the group of antenna, circuitry for adjusting the phase and amplitude of signals transmitted and received by the radiative transceivers relative to the stored calibration signals for the selected radiative transceiver.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF IRELAND MAYNOOTH
Calculation method of external ear sound signal transfer function and application
ActiveCN105323666AFaithful replayEarpiece/earphone attachmentsRadiation impedanceOptical transfer function
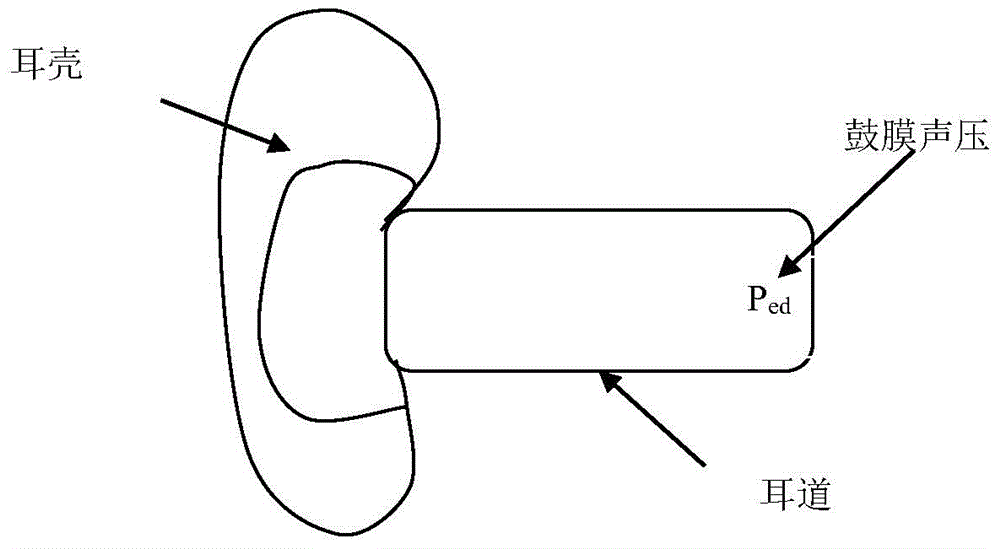
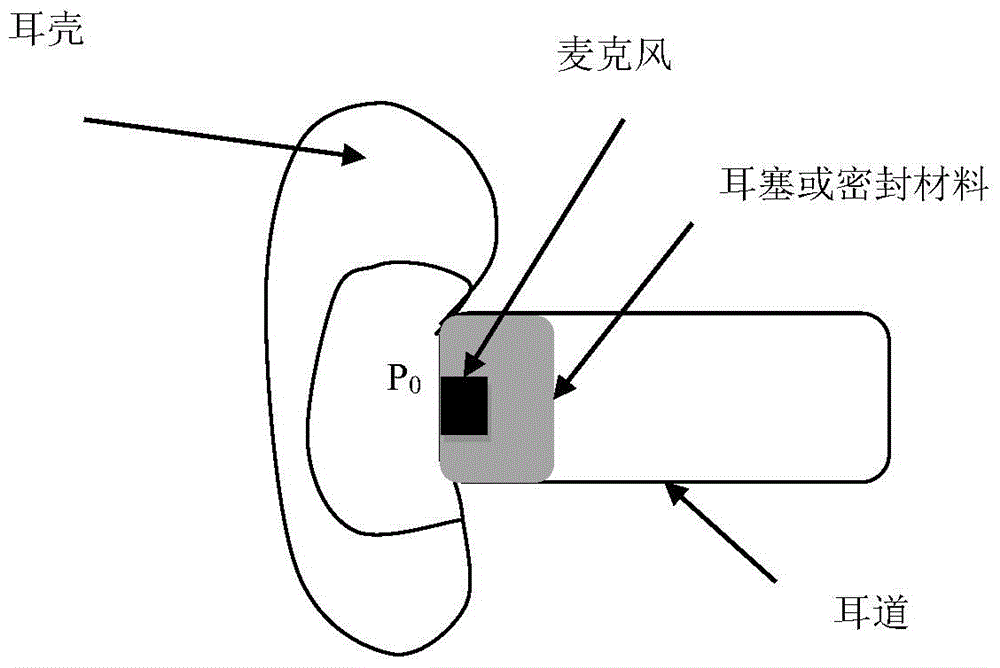
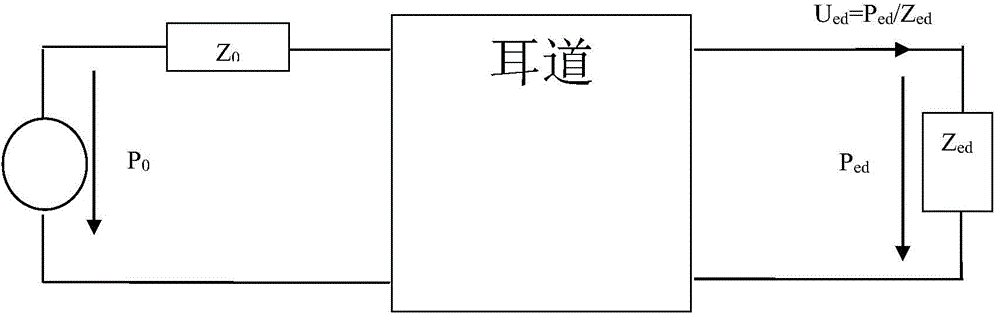
The invention relates to a calculation method of an external ear sound signal transfer function, which comprises the steps of calculating a reflection coefficient of an external earlap of a human body; simulating an external auditory canal of the human body to be a combination of a plurality of sound pipes with a certain length and a cross section function, and calculating a reflection coefficient of each sound pipe at the boundary; calculating a reflection coefficient at the tympanic membrane of the human body; acquiring a transfer function between an equivalent volume velocity source of a listener ear canal and the volume velocity at the tympanic membrane by the reflection coefficient of the external earlap of the human body, the reflection coefficient at the boundary of each simulated sound pipe and the reflection coefficient at the tympanic membrane of the human body; and deducing a transfer function between a sound pressure signal of the closed ear canal and a sound pressure signal received by the tympanic membrane of the listener at an original sound field according to impedance of the tympanic membrane and radiation impedance of the earlap and the transfer function between the equivalent volume velocity source of the listener ear canal and the volume velocity at the tympanic membrane.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antenna
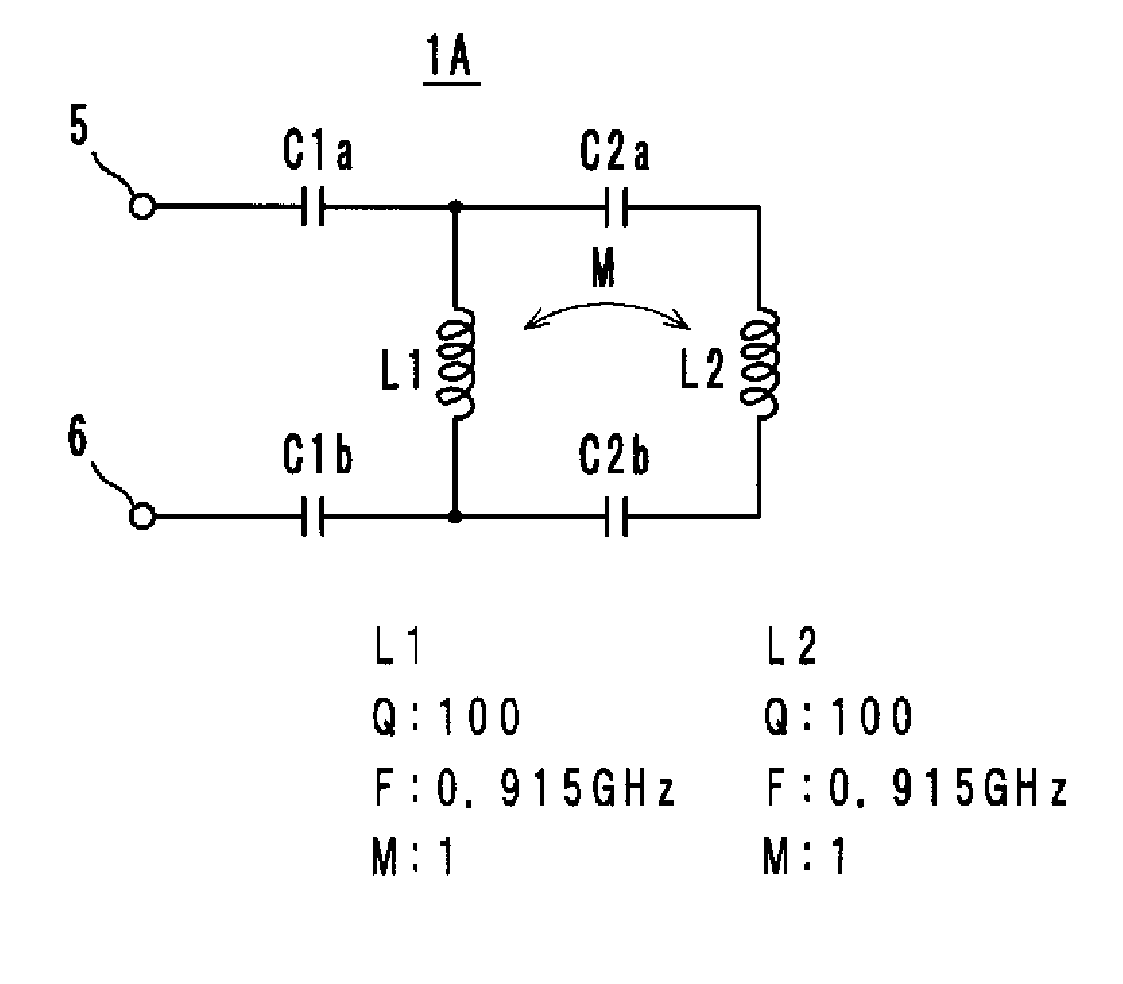
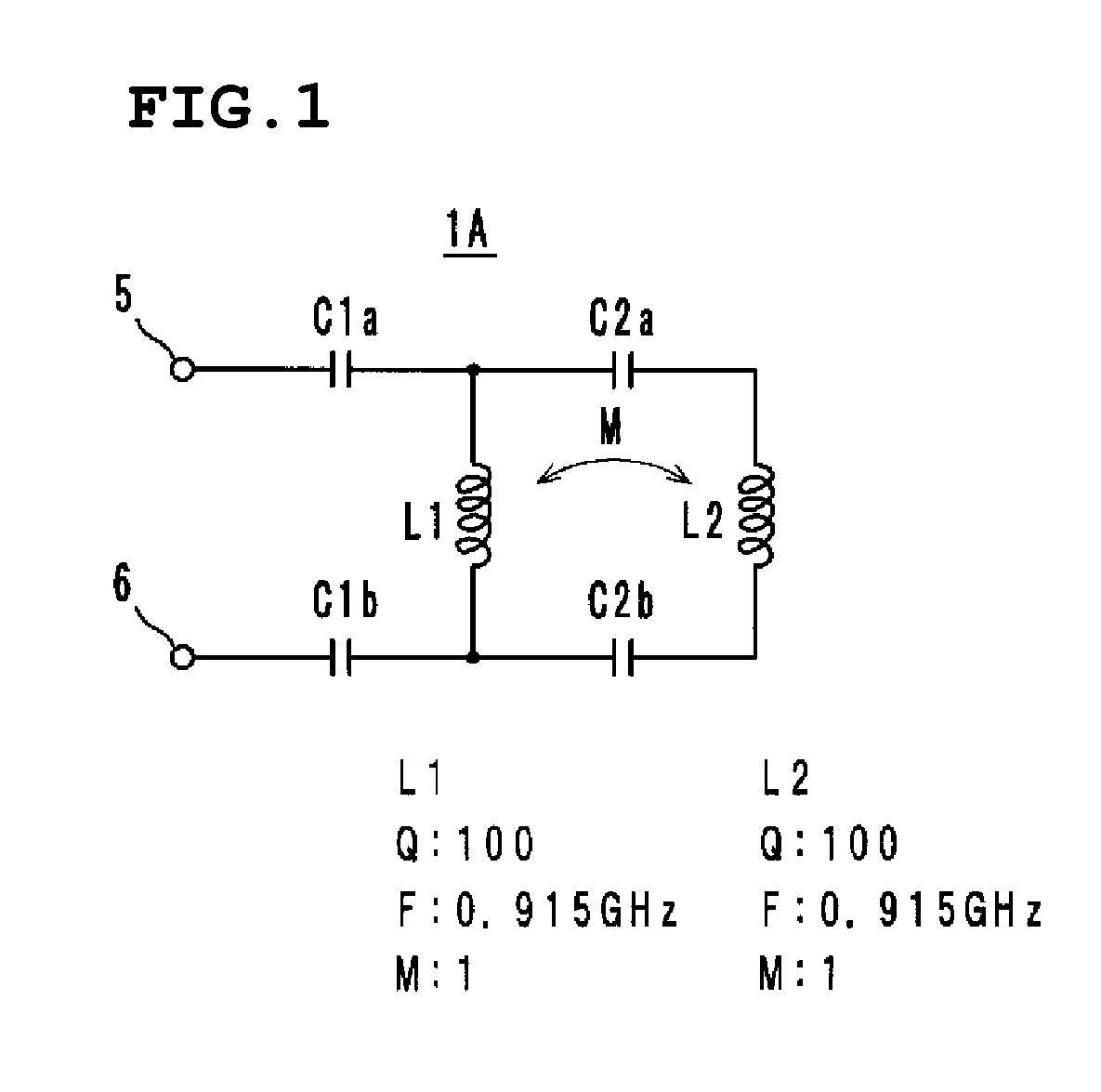
ActiveUS20080122724A1Wide bandReduction in size is not inhibitedAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceInductor
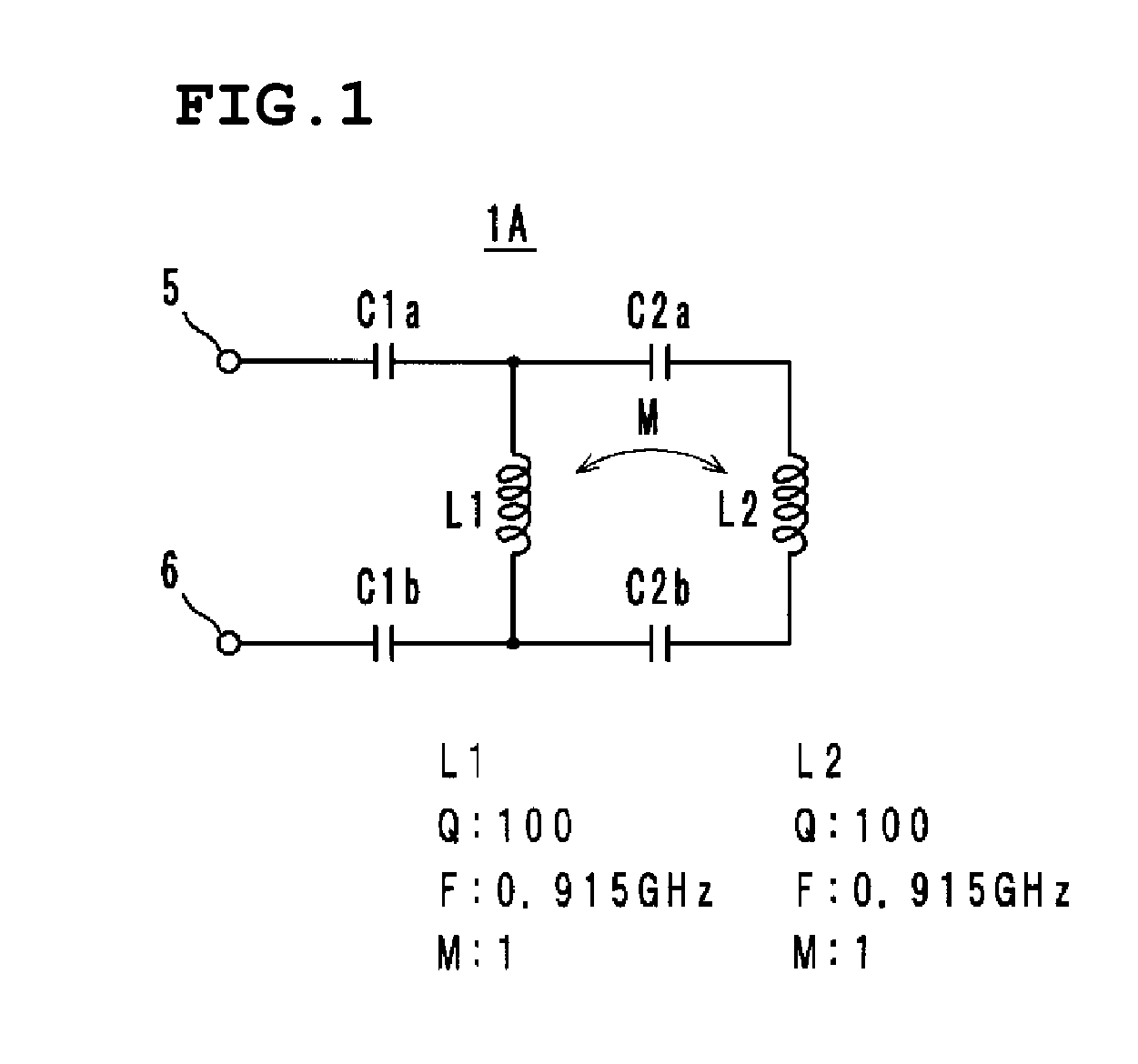
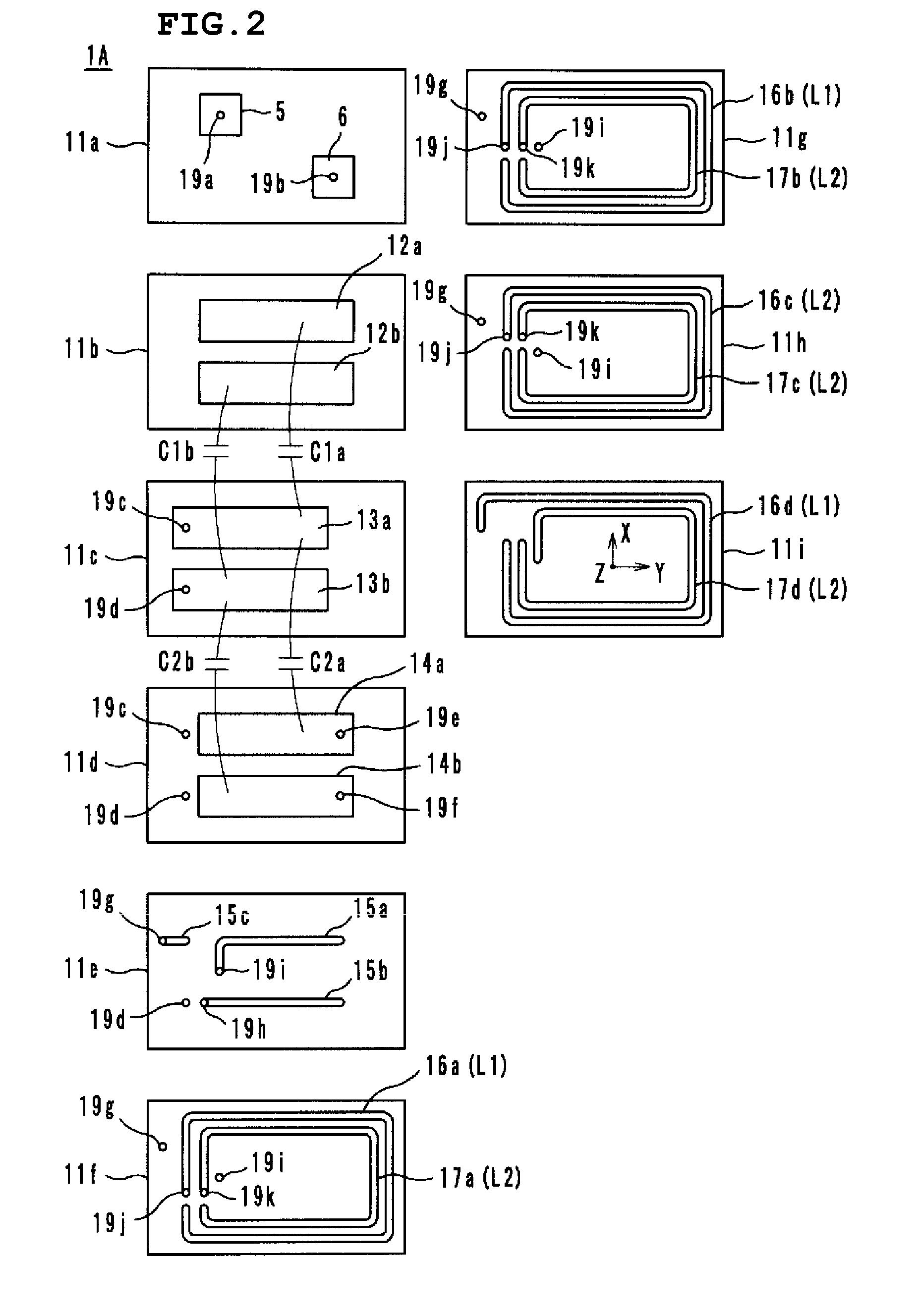
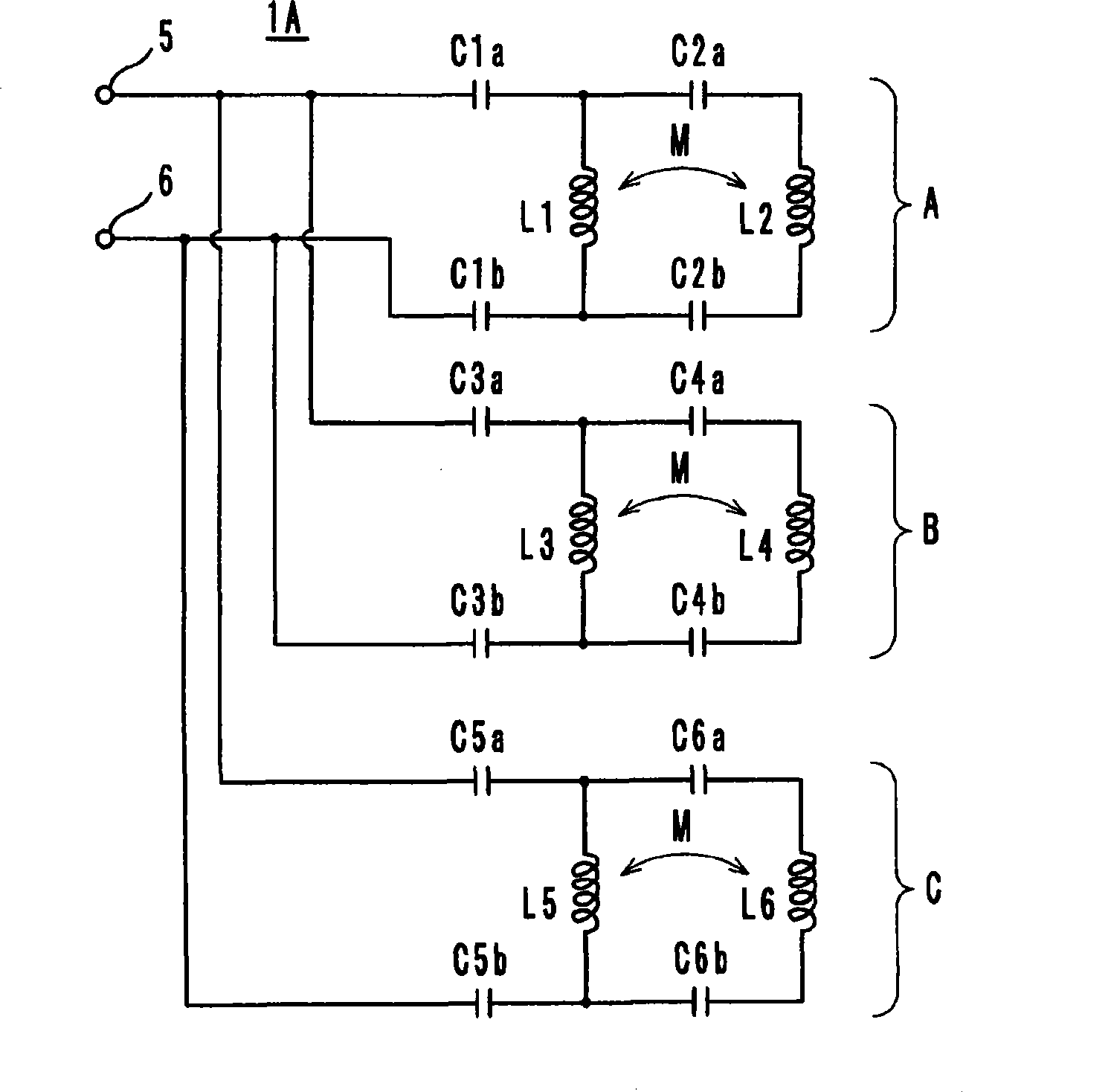
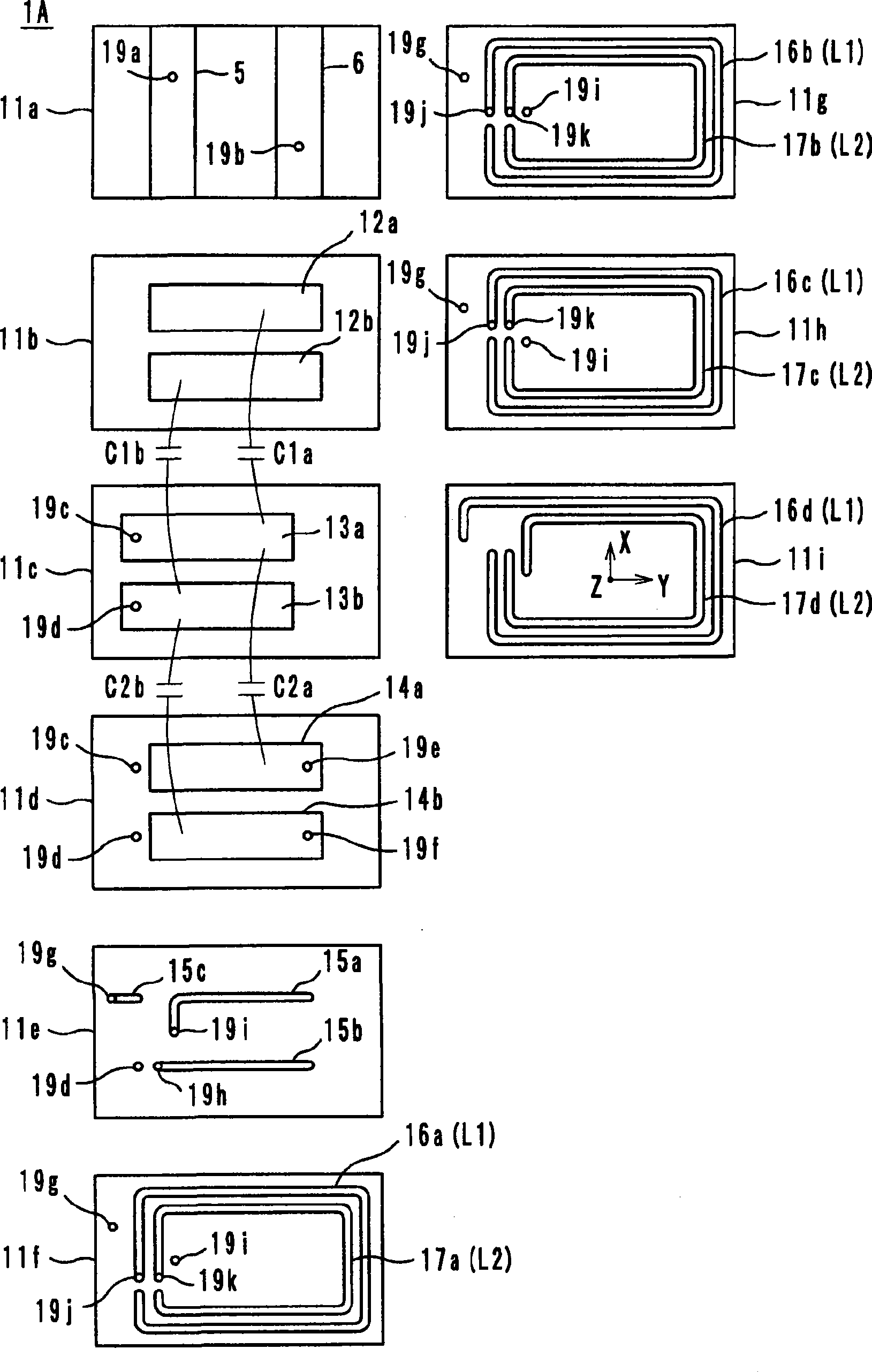
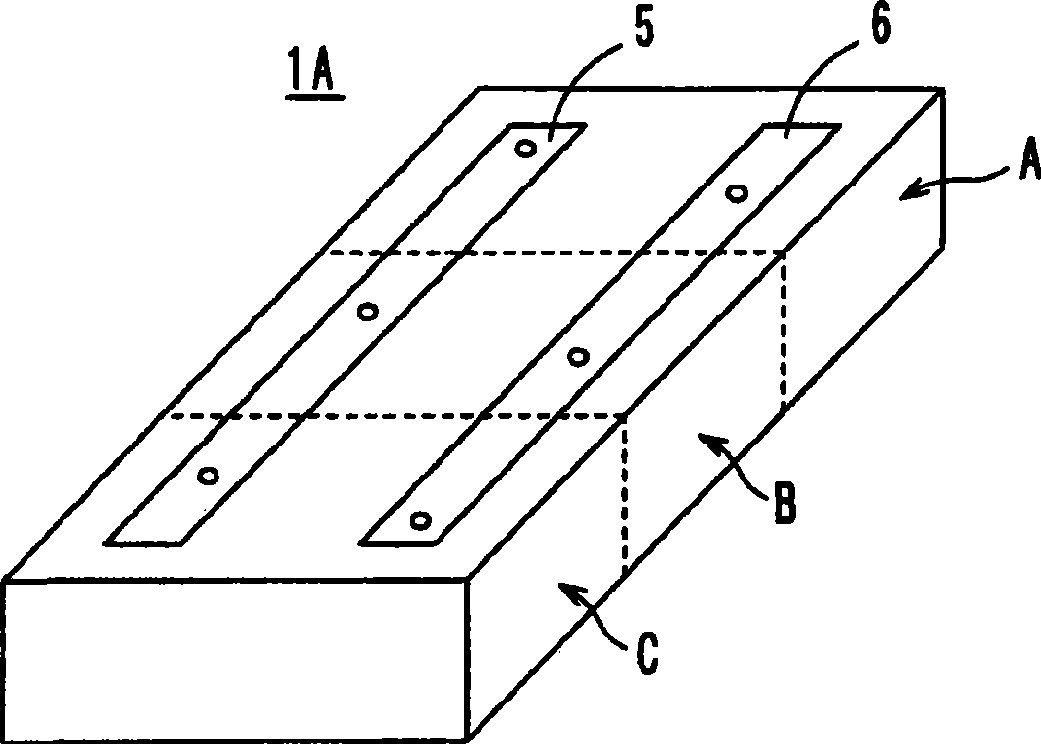
An antenna includes inductance elements that are magnetically coupled together, an LC series resonant circuit that includes one of the inductance elements and capacitance elements, and an LC series resonant circuit that includes another of the inductance elements and capacitance elements. The plurality of LC series resonant circuits are used to radiate radio waves and are used as inductances of a matching circuit that matches an impedance when a power supply side is viewed from power supply terminals and a radiation impedance of free space.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
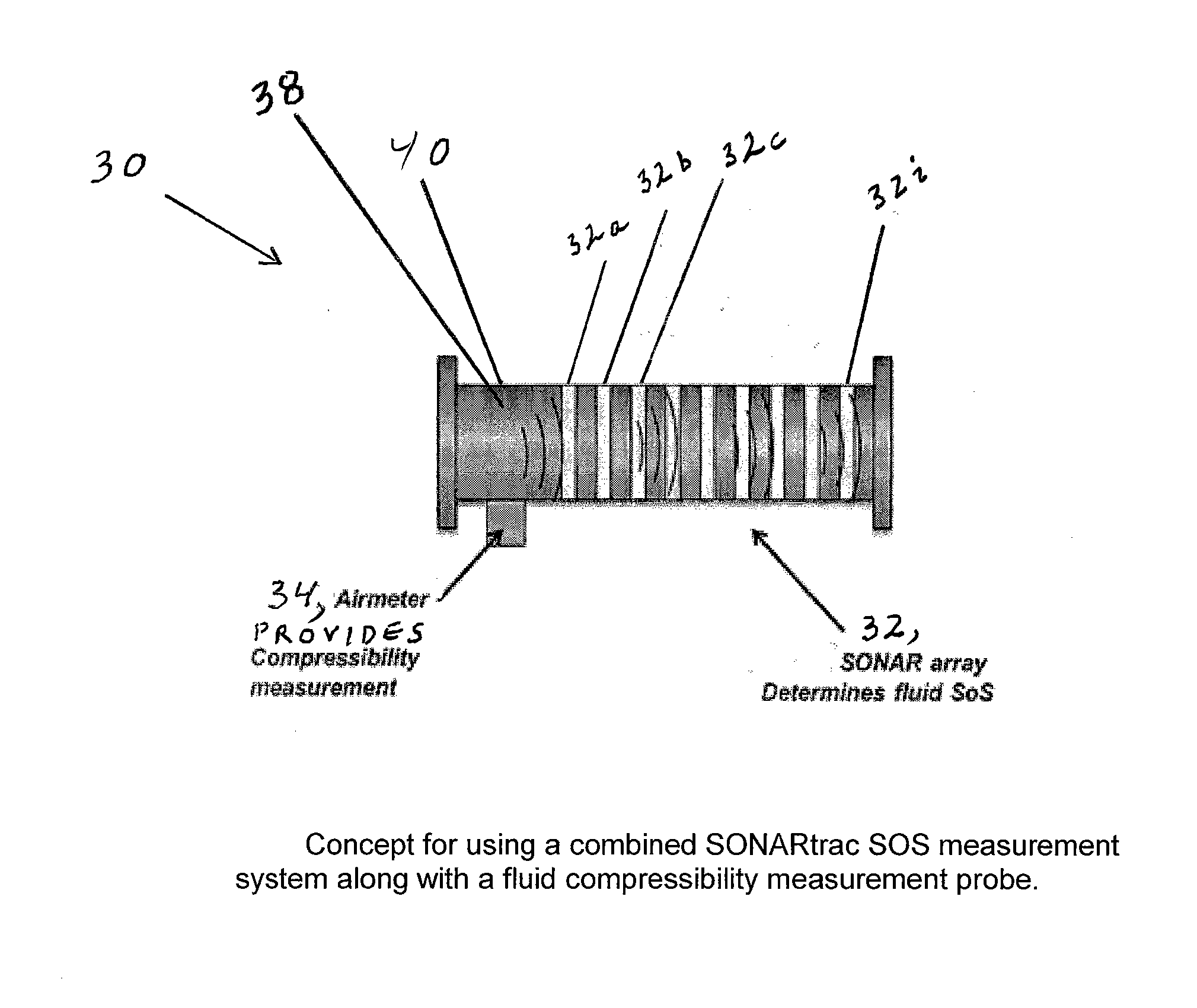
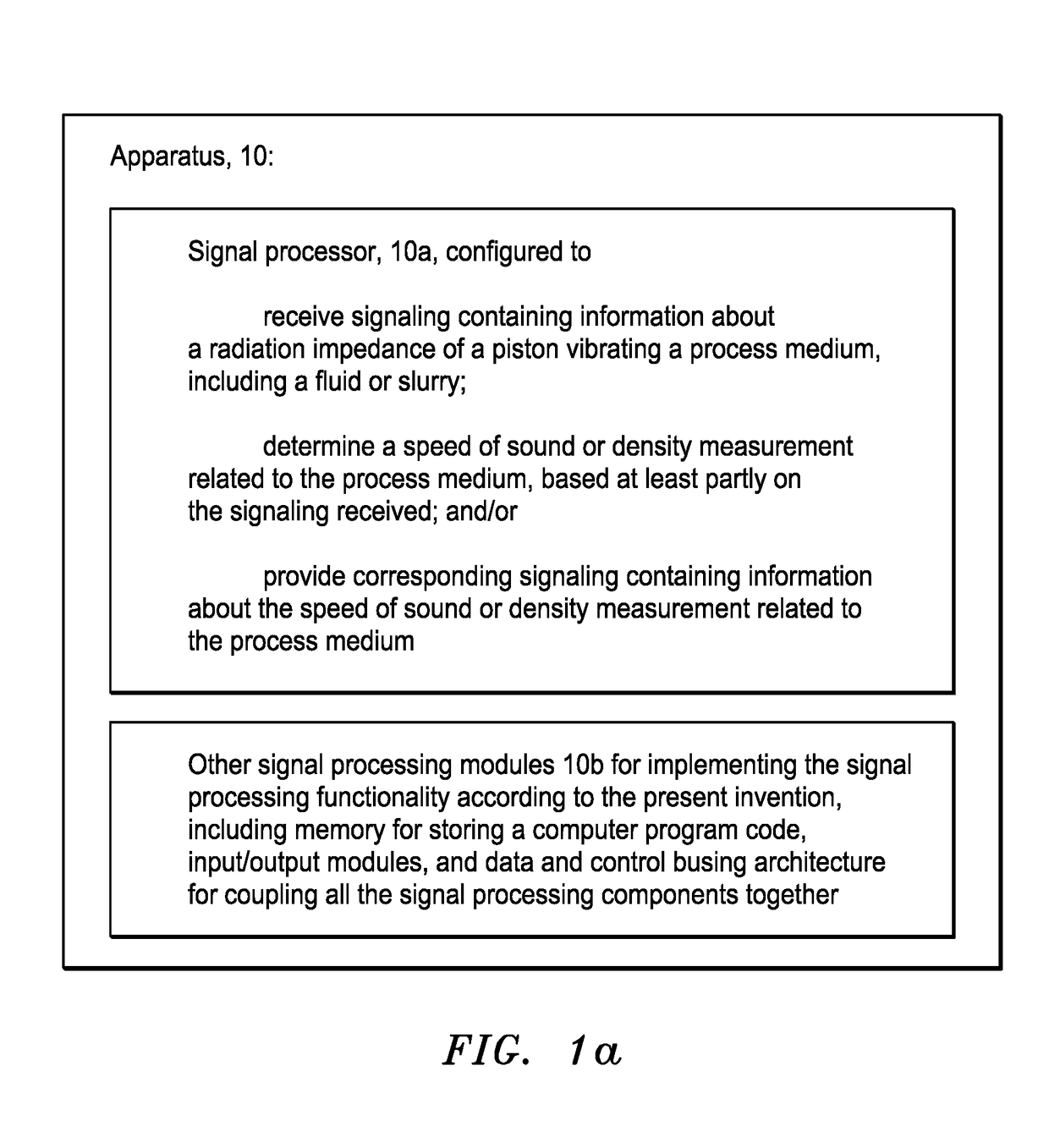
Speed of sound and/or density measurement using acoustic impedance
ActiveUS20150082862A1Useful measurementAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringSlurry
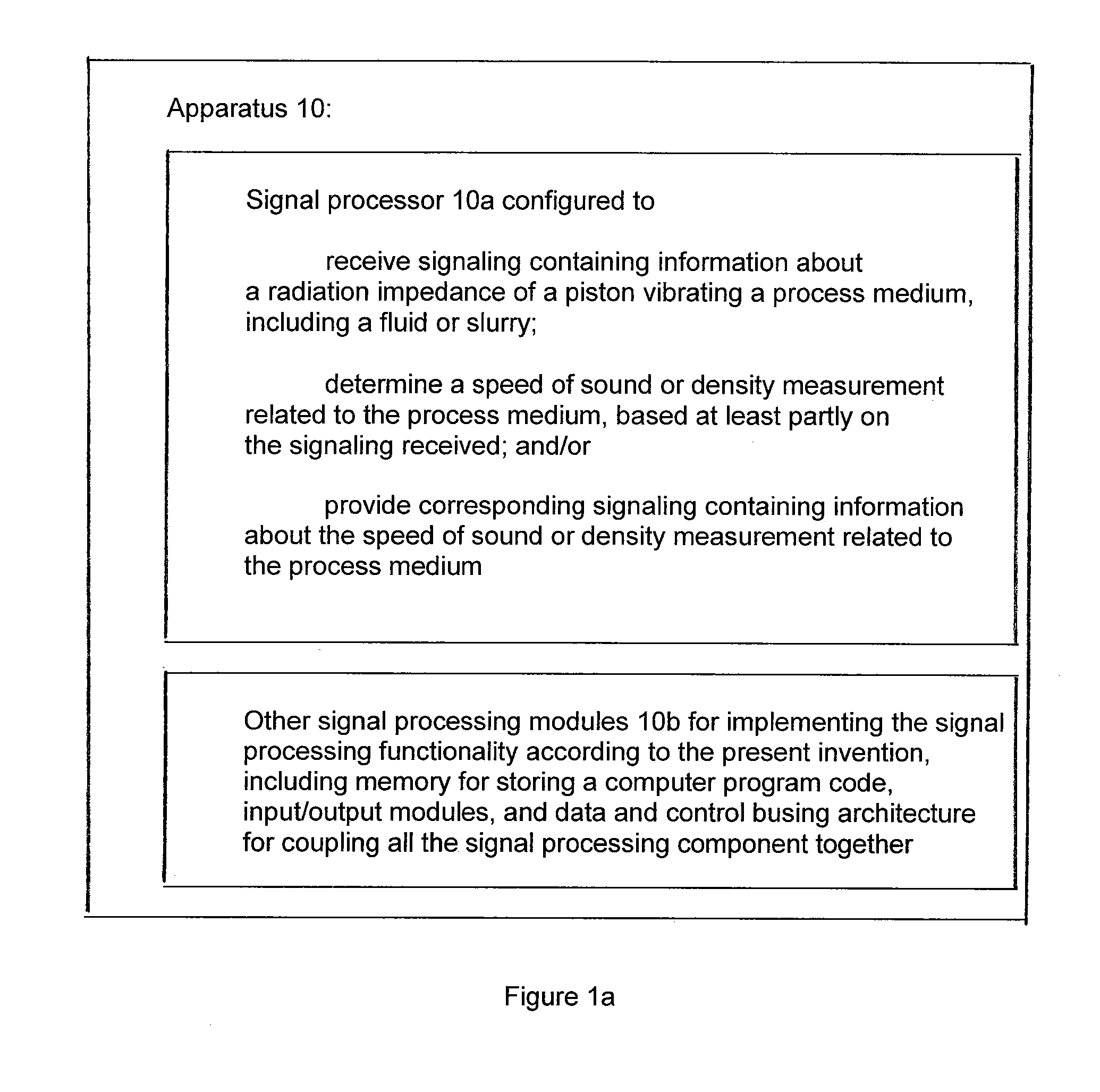
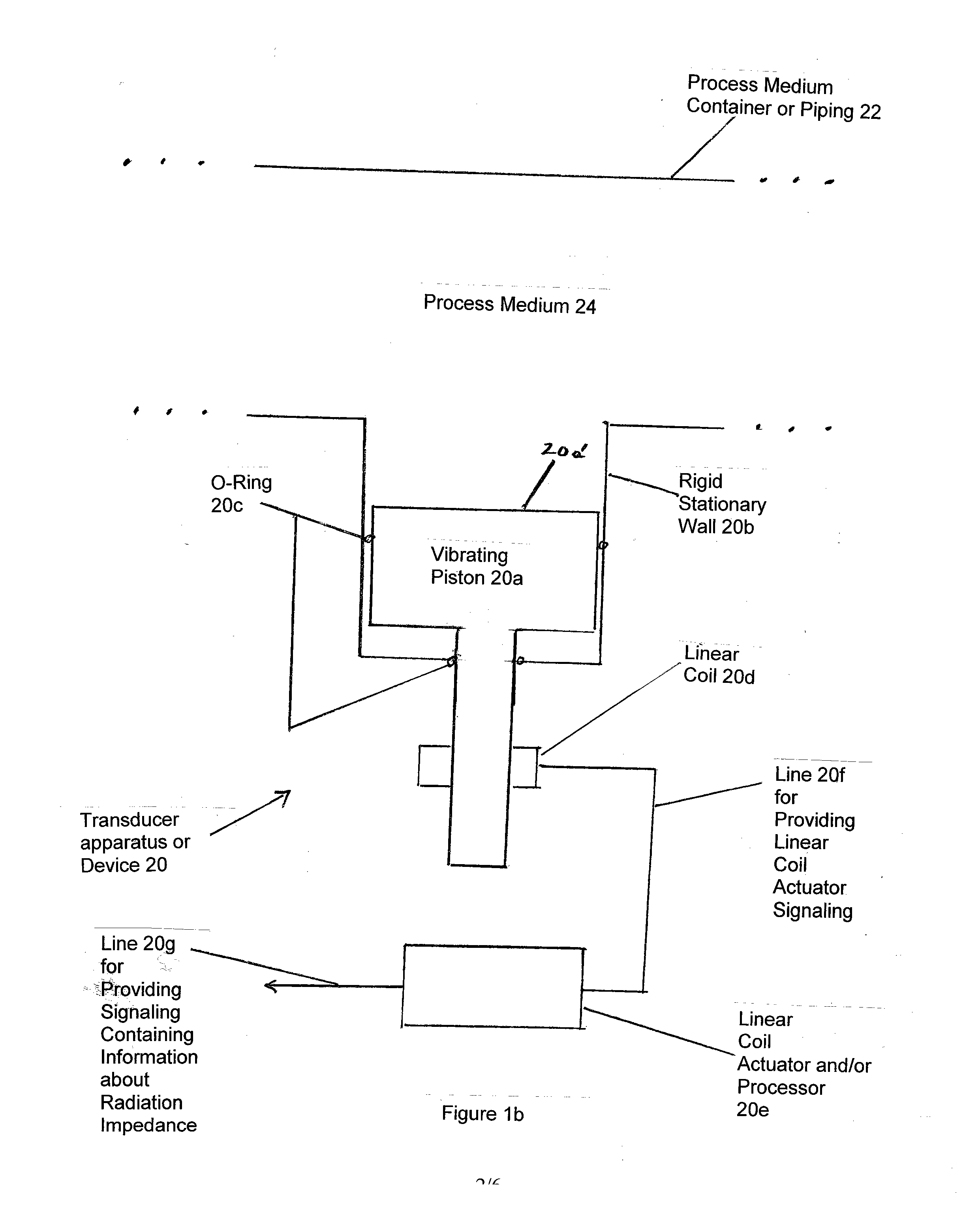
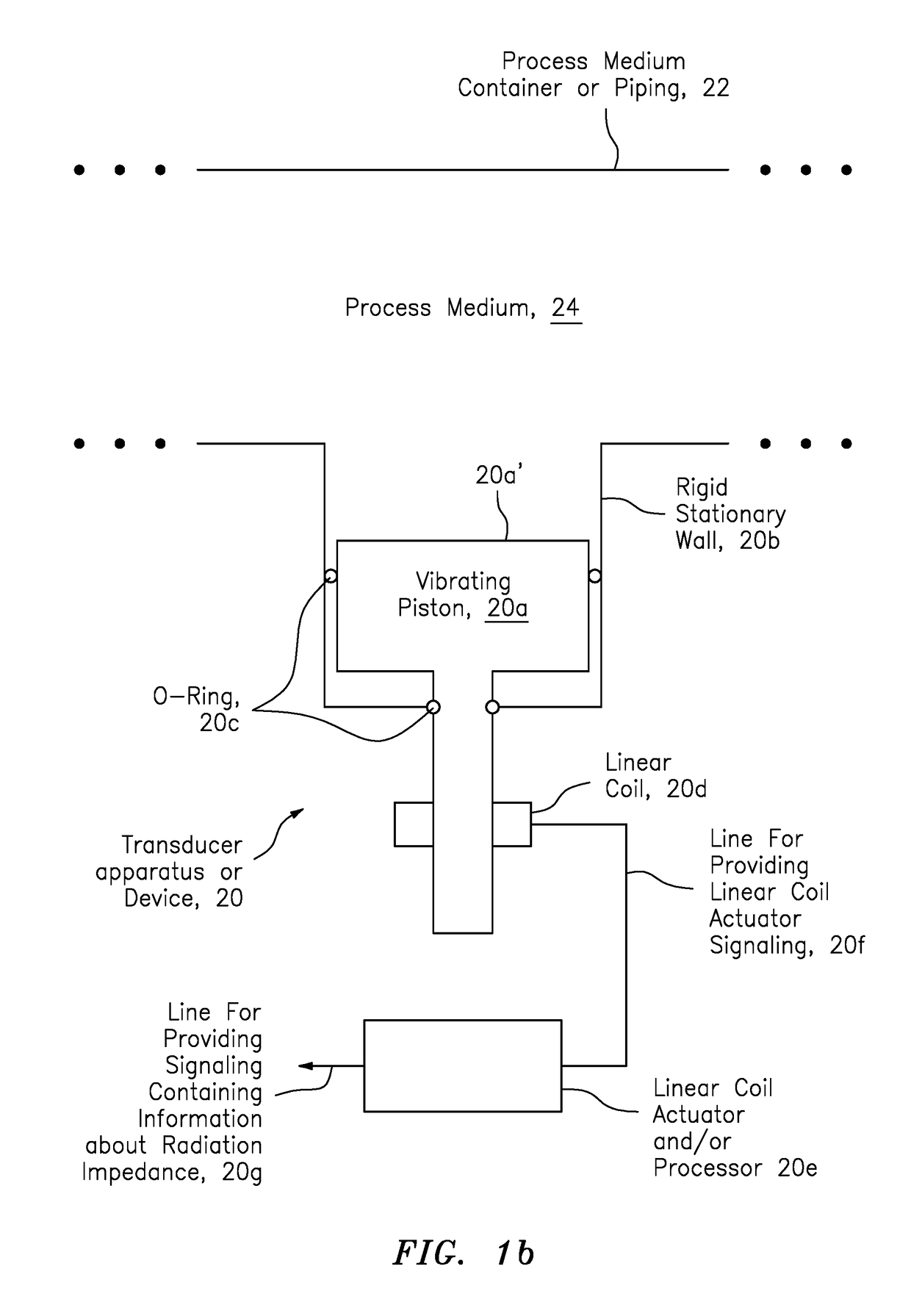
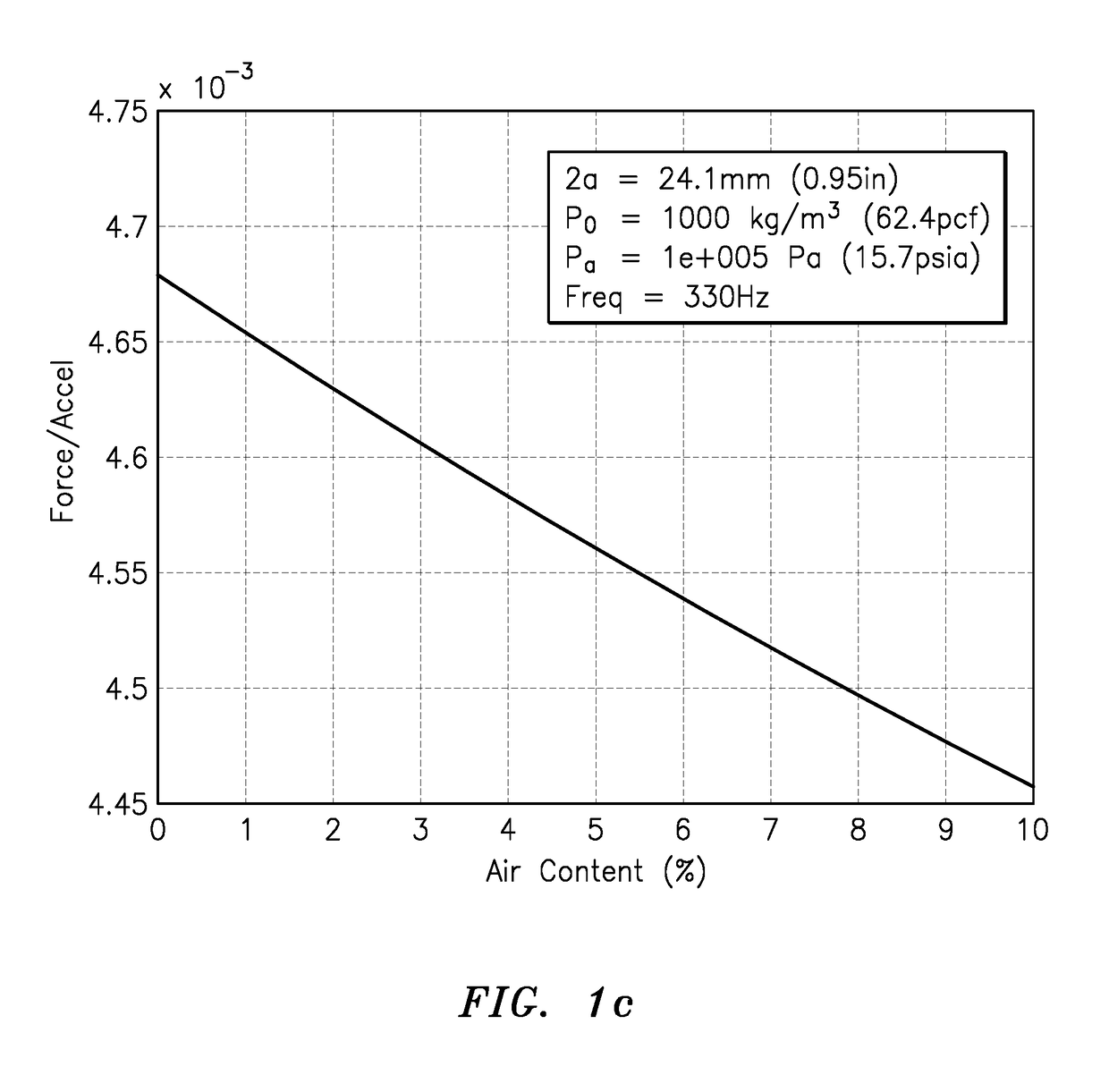
Apparatus is provided featuring a signal processor or signal processing module configured at least to: receive signaling containing information about a radiation impedance of a piston vibrating a process medium, including a fluid or slurry; and determine a speed of sound or density measurement related to the process medium, based at least partly on the signaling received. The signal processor or signal processing module may determine a speed of sound measurement related to the process medium, based on at least partly on the density of the process medium, including where the density of the process medium is known, assumed or determined by the signal processor or signal processing module, or determine a density measurement related to the process medium, based on at least partly on the speed at which sound travels in the process medium, including where the speed of sound of the process medium is known, assumed or determined by the signal processor or signal processing module.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
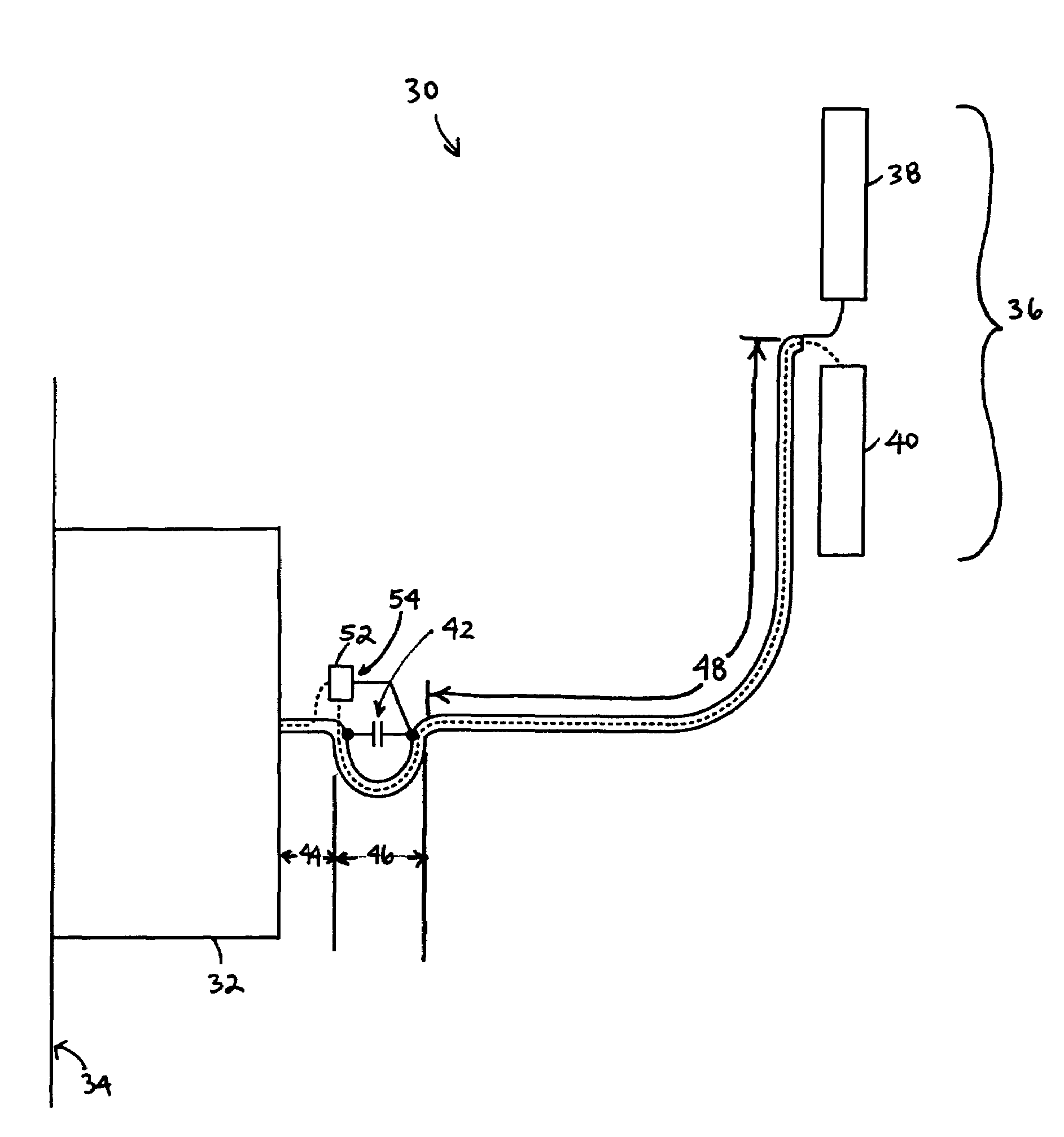
Power amplifier efficiency
ActiveUS20050239423A1Reduce power consumptionImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTResonant long antennasCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
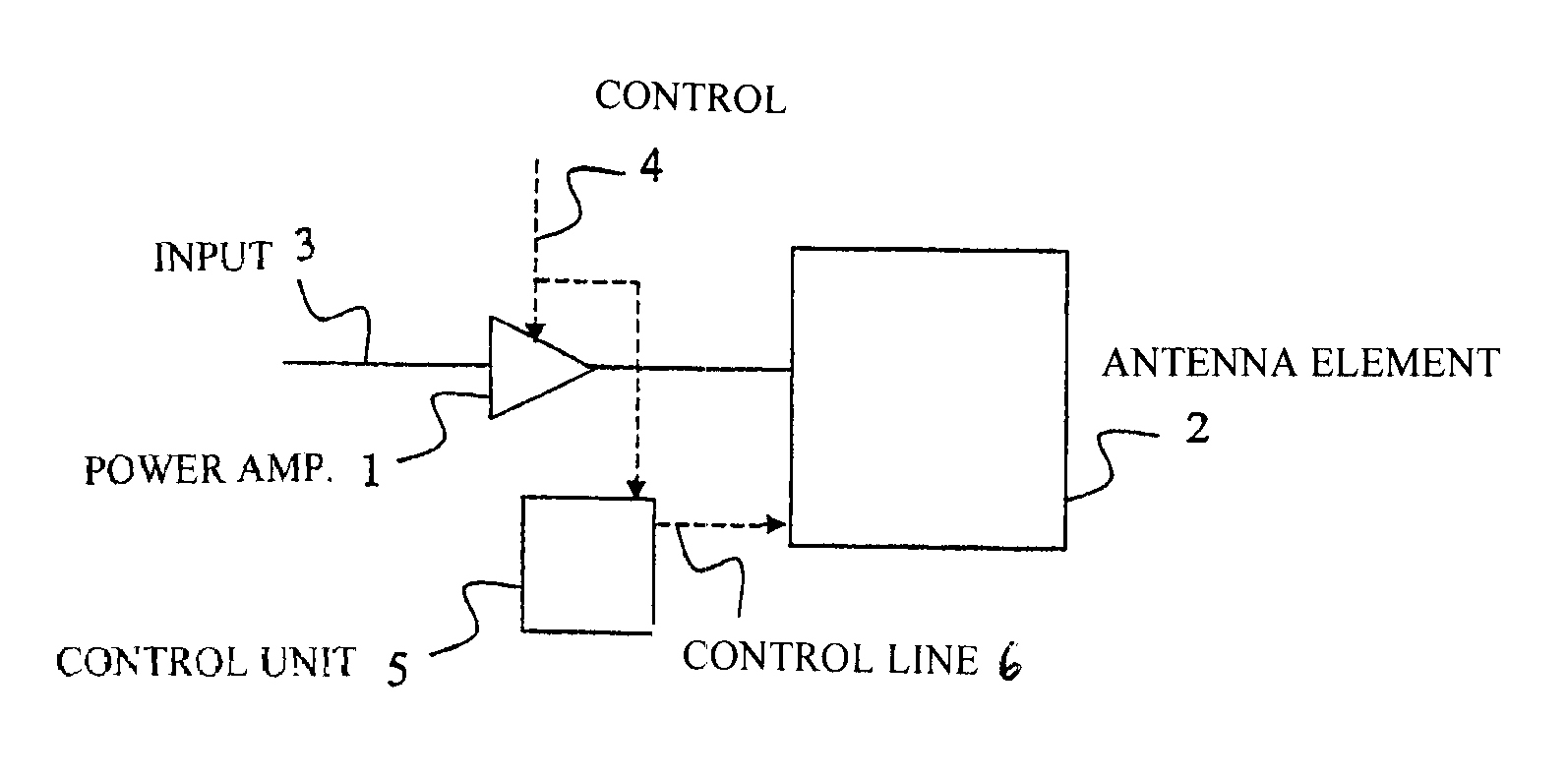
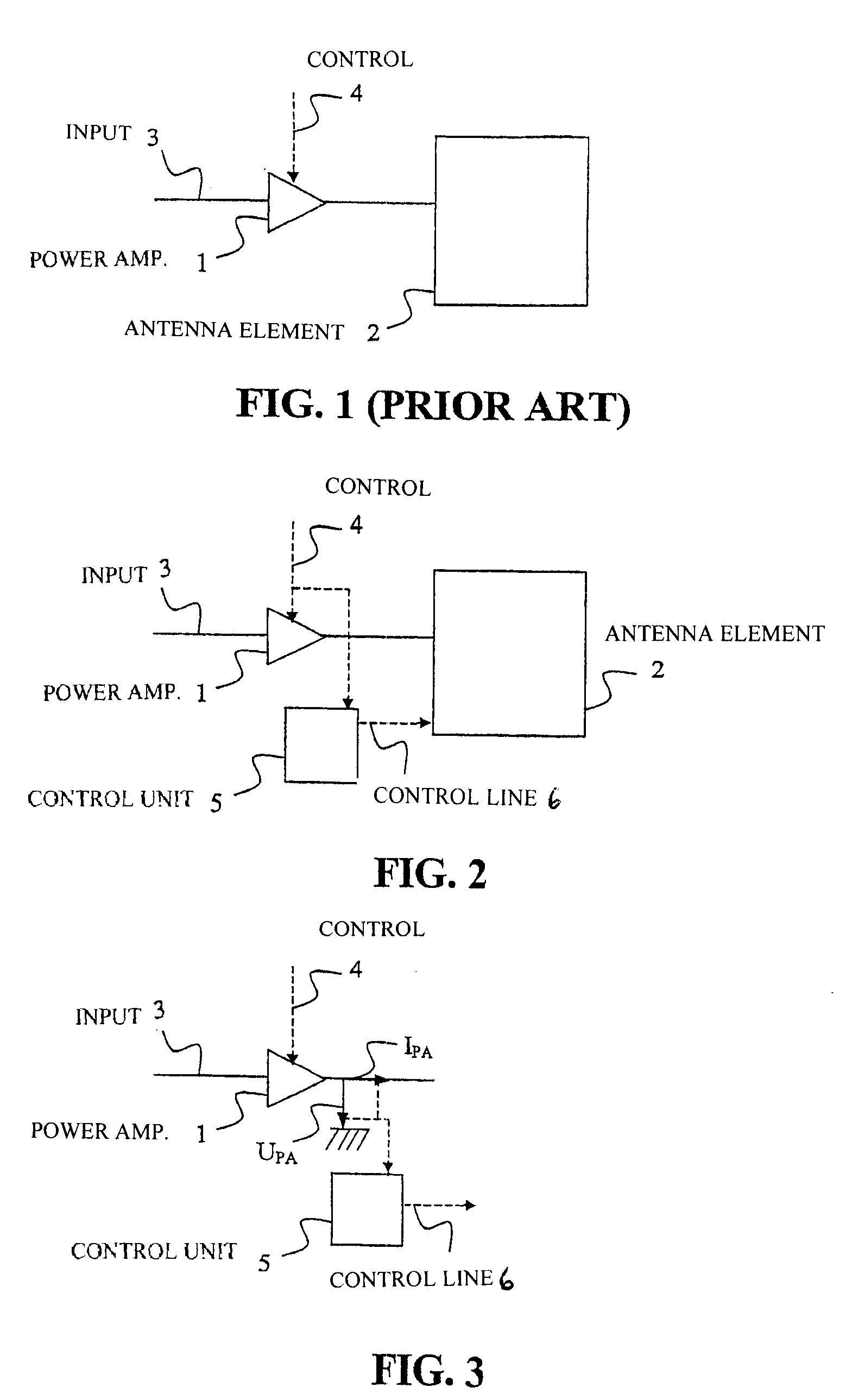
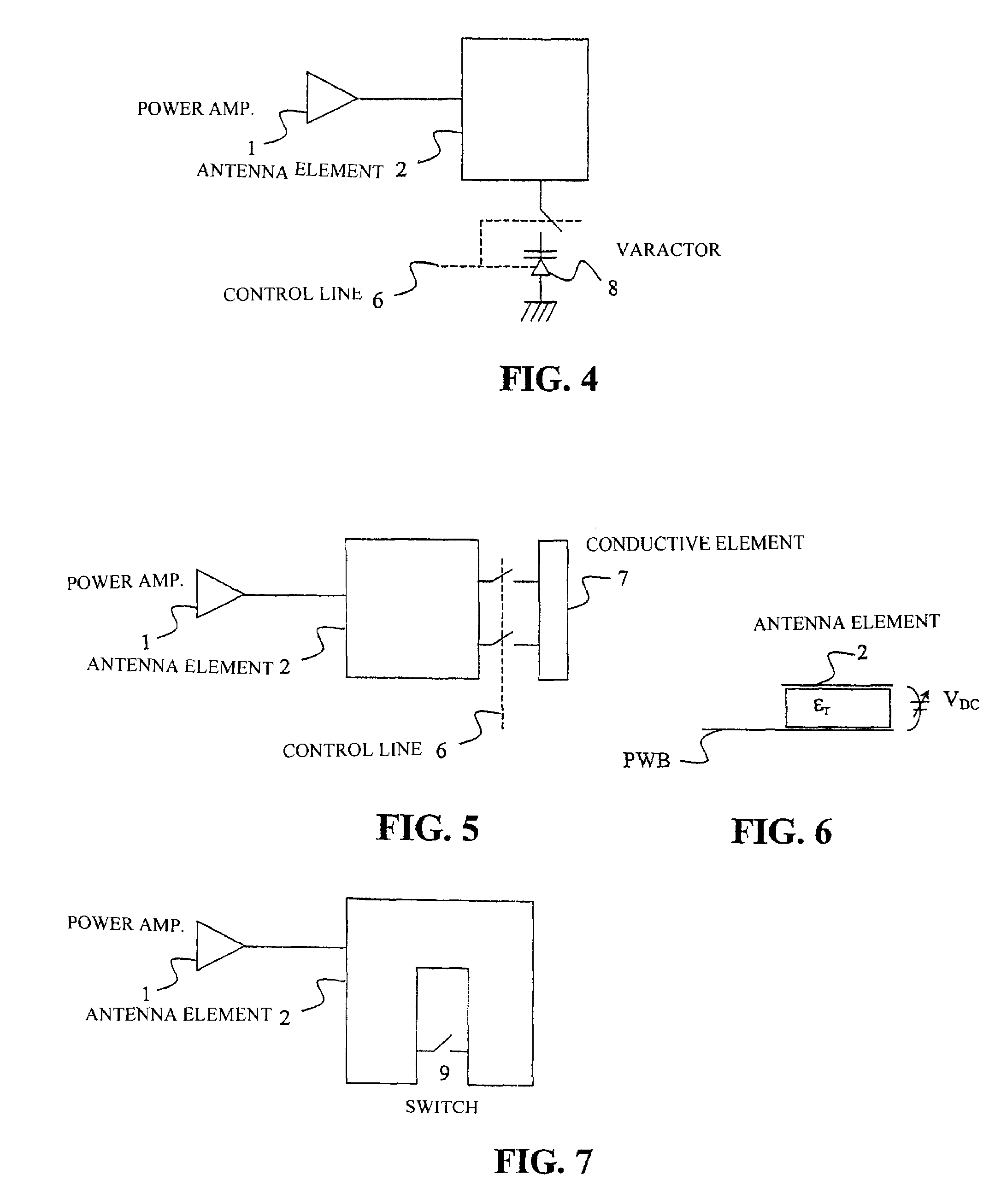
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for optimizing the efficiency of a power amplifier (1) that is utilized for transmission of radio signals in a portable radio communication device, such as a mobile phone. The impedance loading the power amplifier (1) is controlled by a controller (5) in dependence on a transmission power of the portable radio communication device, wherein the radiating impedance of an antenna element (2) loading the power amplifier is controlled in dependence of the desired load impedance. Preferably, the changing of radiating impedance is performed by changing a capacitive coupling between the antenna element and a ground element or by changing the size of the antenna element. Better efficiency and bandwidth are thereby attained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Antenna
InactiveUS20060139230A1Small sizeImprove performanceIndividually energised antenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationCoaxial cableParallel transmission lines
A transmission line includes transmission lines parallel and perpendicular, respectively, to a flat portion of a reflector, and the parallel transmission line and the flat portion form a first strip line and the perpendicular transmission line and a conductive plate similarly form a second strip line. Radiators and the transmission line have a radiation impedance and a characteristic impedance, respectively, both set at 150 Ω when the antenna's output terminal has a reference impedance of 75 Ω. If the parallel transmission line has a midpoint serving as the output terminal of the antenna this portion's receiving current is divided in two so that an impedance of half that of the strip line can be provided and a coaxial cable can directly be connected to the transmission line. A matcher or a mixer is not included in the antenna, and matching and mixing losses can be prevented.
Owner:DX ANTENNA CO LTD
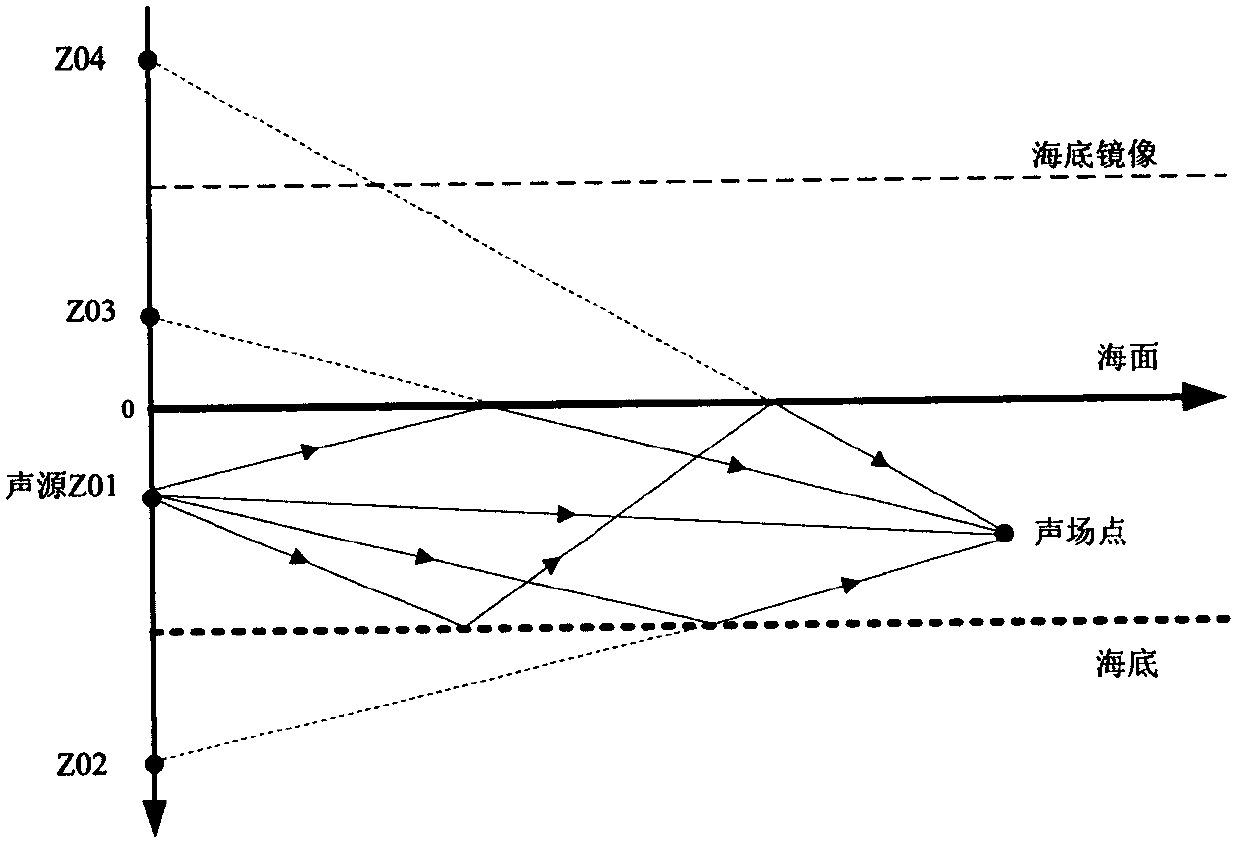
A method for calculating a complex structure radiation sound field in a marine acoustic channel
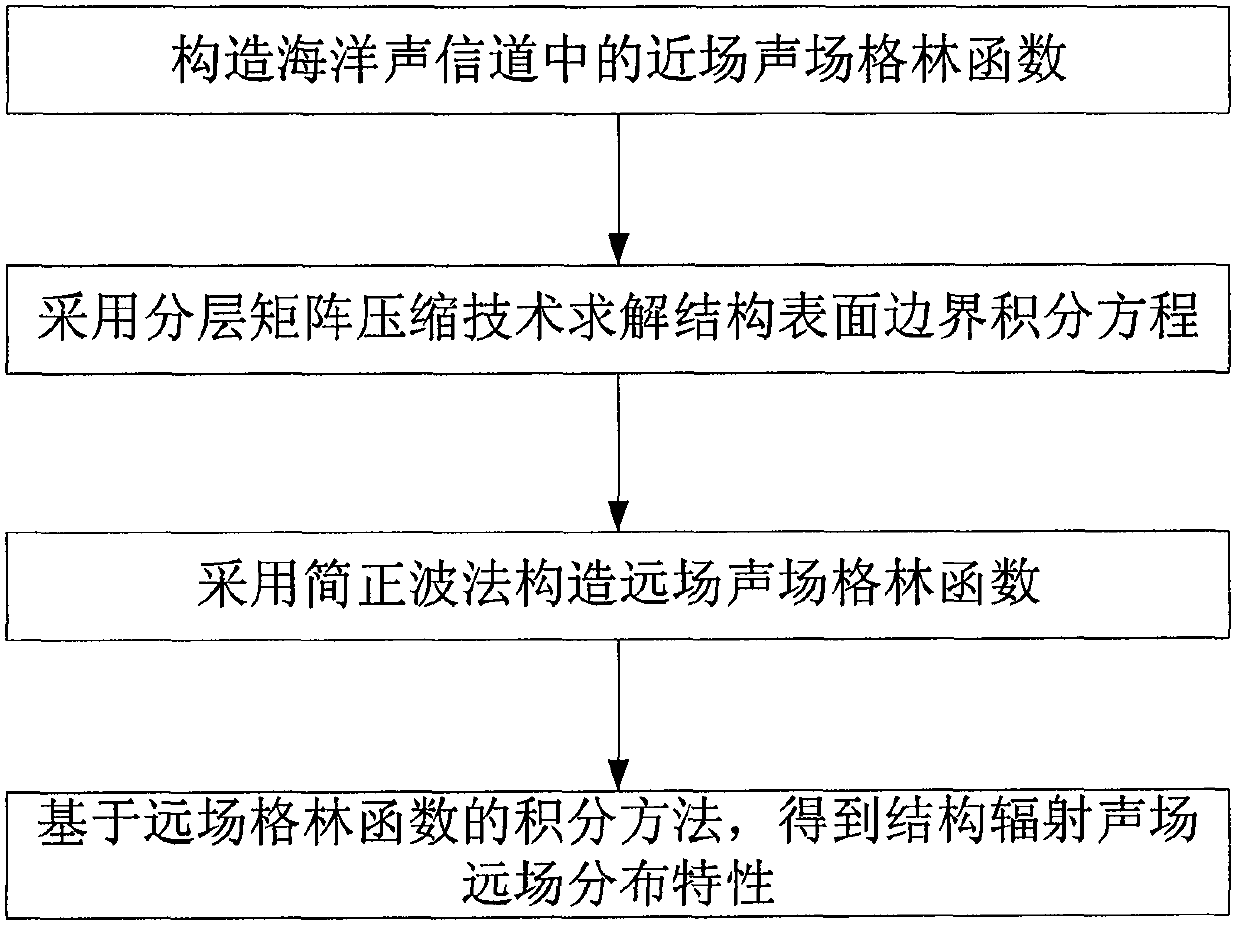
PendingCN109657257AReduce consumptionImprove adaptabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for calculating a complex structure radiation sound field in a marine acoustic channel, and belongs to the technical field of acoustic numerical calculation. The limitation that a traditional boundary element method is only suitable for free field sound field calculation is broken through, and a sound field Green function in an ocean sound channel is established. Ahierarchical matrix compression technology is adopted to divide a radiation impedance matrix into a series of hierarchical matrix blocks with different sizes, and an iteration method is further utilized to solve a matrix equation. Compared with the prior art, the method has the effects and benefits that the acoustic calculation function of the traditional boundary element method is expanded frominfinite uniform media to the bounded space of the ocean channel, and the influence of sea surface, seabed boundary and sound velocity gradient distribution can be considered. And on the other hand, the radiation impedance matrix is subjected to hierarchical compression, the consumption of a computer memory is greatly reduced by utilizing the low-rank characteristic approximate decomposition of the matrix block, the influence of the diversity of a sound field Green function under the complex marine channel condition is avoided, and the algorithm adaptability is good.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七六〇研究所
Antenna
ActiveUS20080224935A1Reduction in size is not inhibitedSmall sizeAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceInductor
An antenna includes inductance elements that are magnetically coupled together, an LC series resonant circuit that includes one of the inductance elements and capacitance elements, and an LC series resonant circuit that includes another of the inductance elements and capacitance elements. The plurality of LC series resonant circuits are used to radiate radio waves and are used as inductances of a matching circuit that matches an impedance when a power supply side is viewed from power supply terminals and a radiation impedance of free space.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
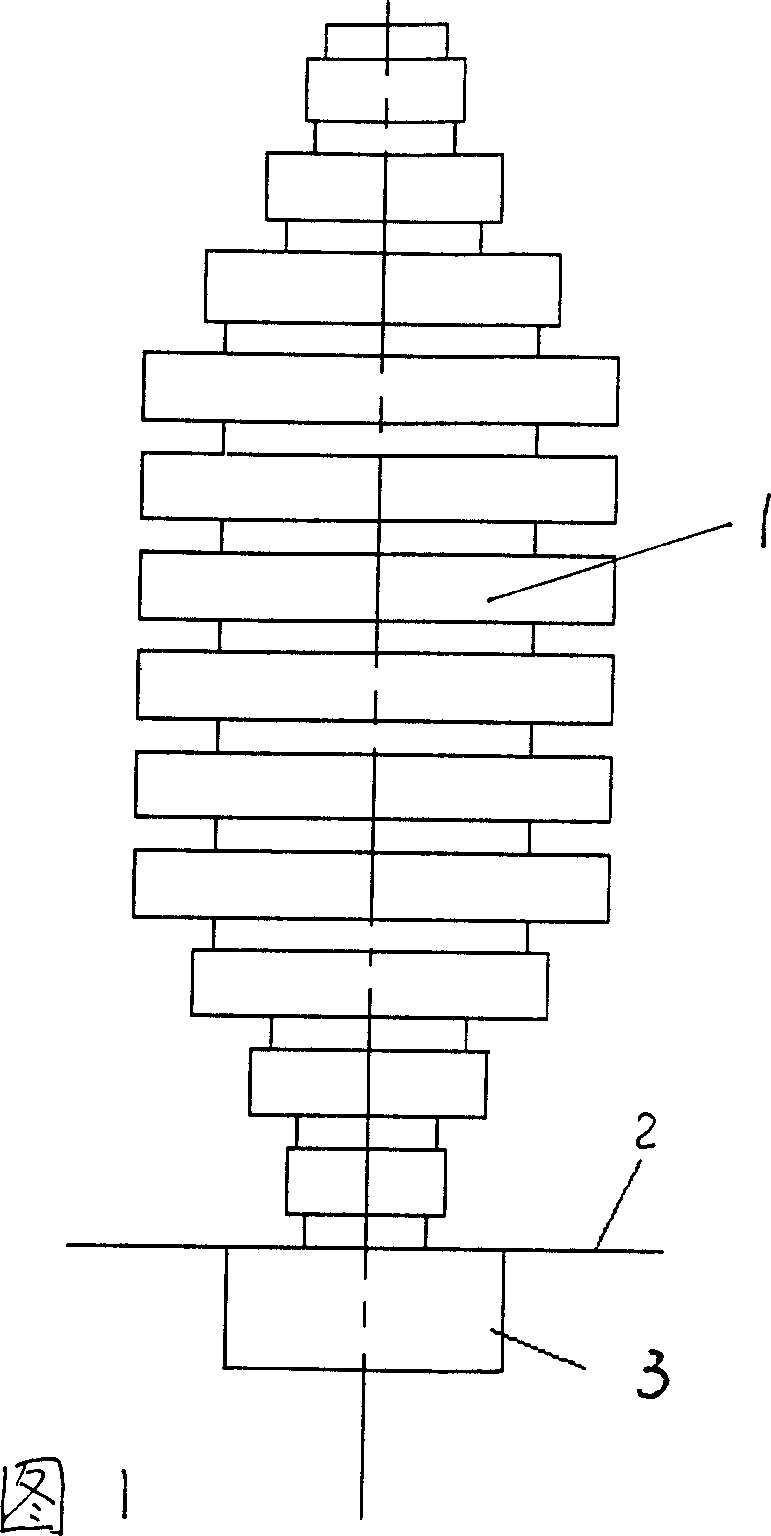
T-type superpower ultrasonic transducer
InactiveCN103212532ARadiation area is largeImprove radiation resistanceMechanical vibrations separationElectricityTransducer
The invention relates to a T-type superpower ultrasonic transducer. The T-type superpower ultrasonic transducer utilizes a longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic vibrator to generate longitudinal vibration, stimulates a metal round vibration disc directly connected with the longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic vibrator to generate the vibration of the same frequency, and radiates sound waves to media. With the help of the conversion of the vibration mode, flexural vibration is generated in the metal round vibration disc, effective conversion of the longitudinal vibration mode and the flexural vibration mode is achieved, uniformity of the radiation sound field of the transducer is greatly improved, radiation area of the transducer can be effectively increased, high-power working is realized, at the same time, radiation impedance of the transducer is improved, acoustic matching of the transducer is improved, and radiation efficiency of the transducer is improved. In addition, due to the fact that the flexural vibration disc has multiple vibration modes, the transducer can work in different vibration modes and radiate ultrasonic waves of different frequencies, and therefore an ultrasonic wave source working in multiple frequencies is formed.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Antenna
InactiveUS7205955B2Small sizeImprove performanceIndividually energised antenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationCoaxial cableBand shape
Owner:DX ANTENNA CO LTD
Wideband voltage-driven electrically-small loop antenna system and related method
An antenna system and related method are disclosed for an electrically small antenna of variable geometry capable of a harmonically pure resonant radiation pattern over a broadband coverage of frequency selection. One geometrical embodiment comprises a multiple loop antenna system is configured to radiate a switched signal via the multiple antenna elements to inhibit transmission of any of the harmonics of the signal. An additional geometrical embodiment comprises a cylindrical shell with one or more interior center conductors to overcome radiation resistance and radiate a signal pattern of desirable toroidal shape free from undesirable harmonics.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
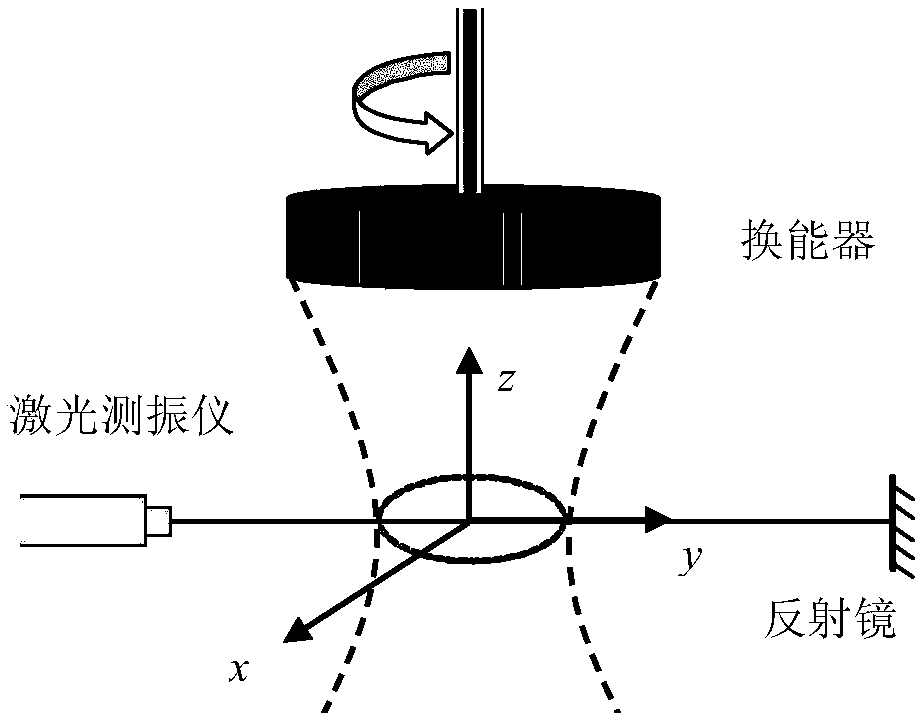
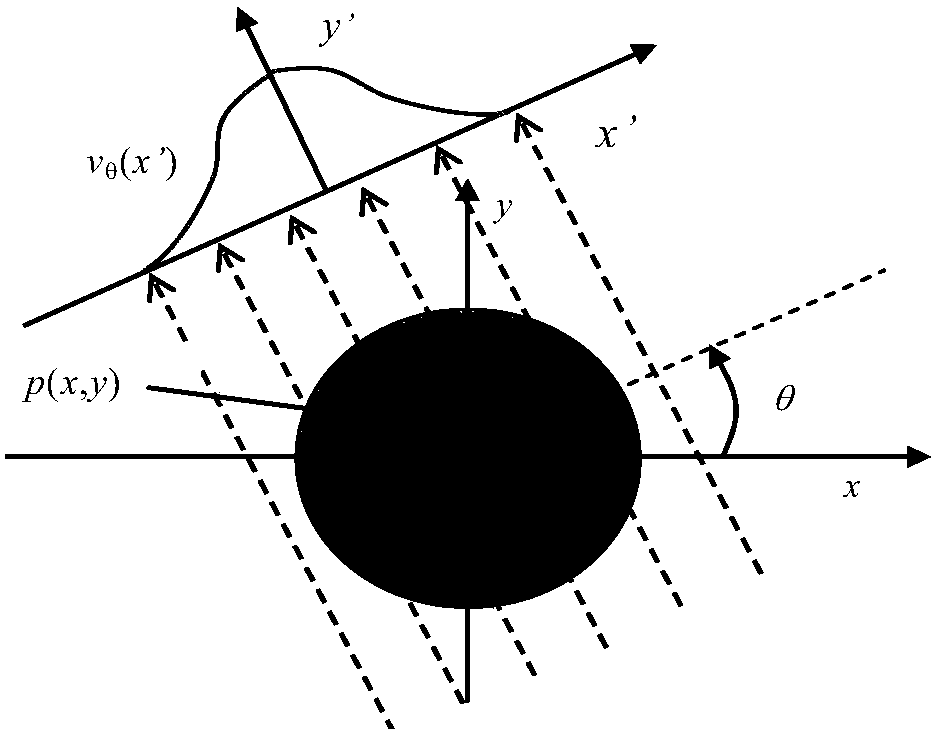
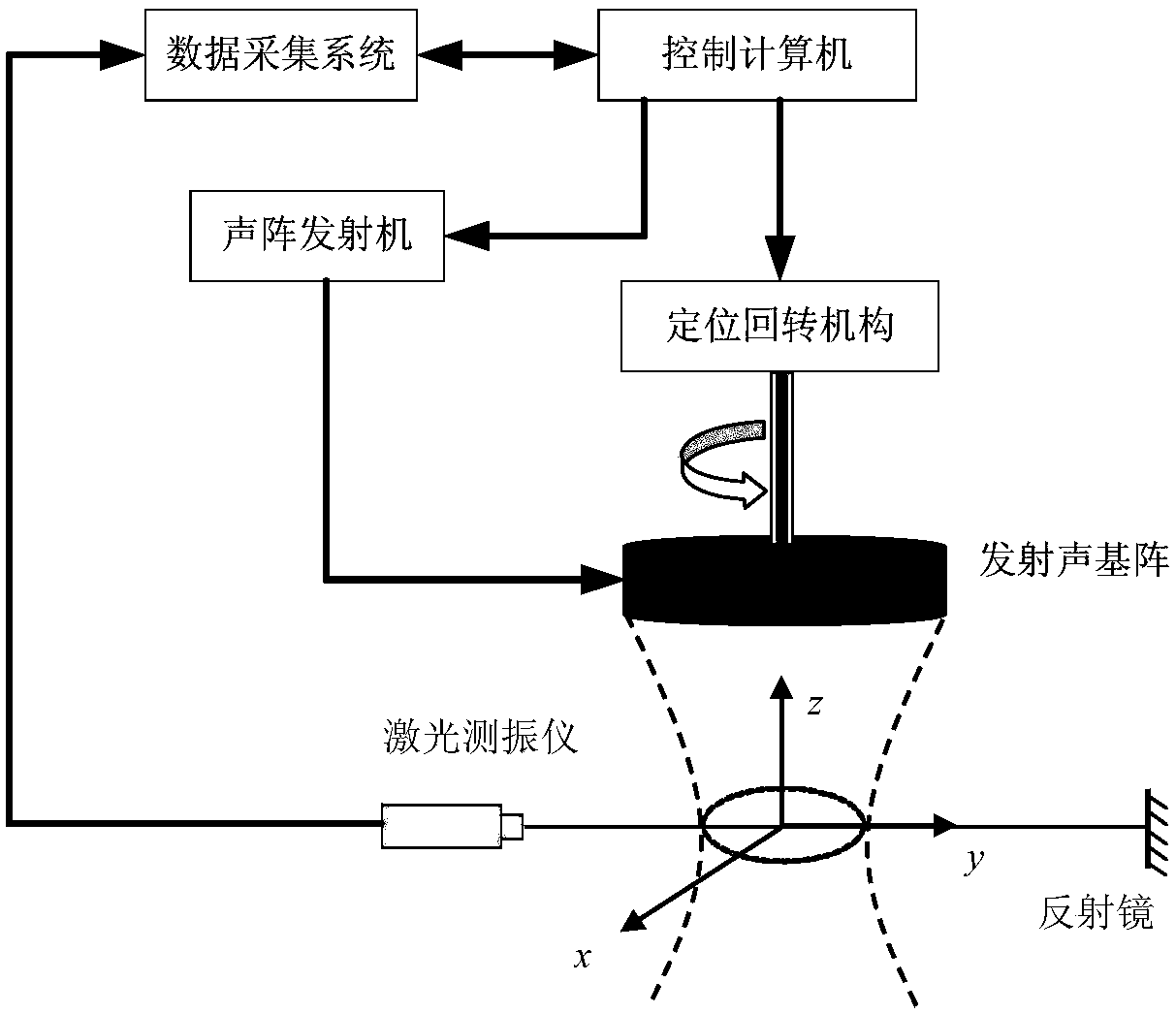
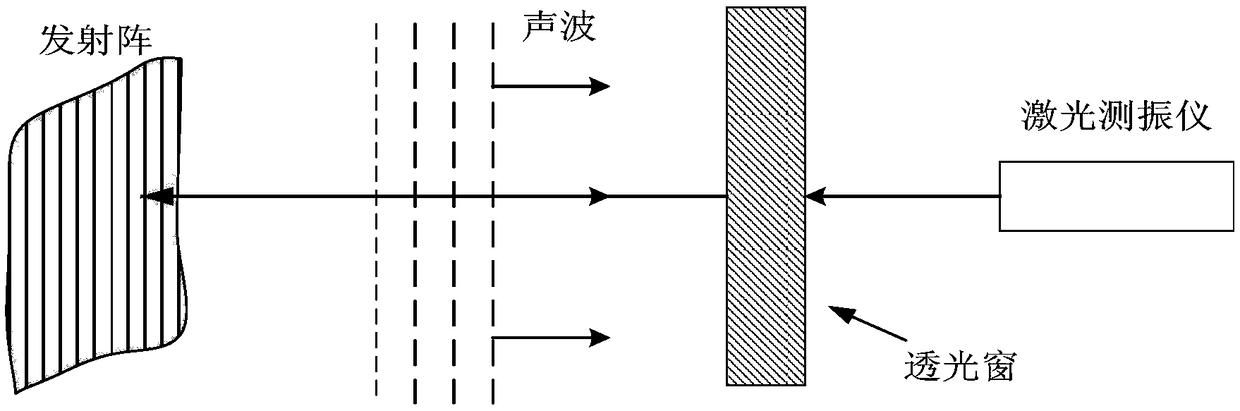
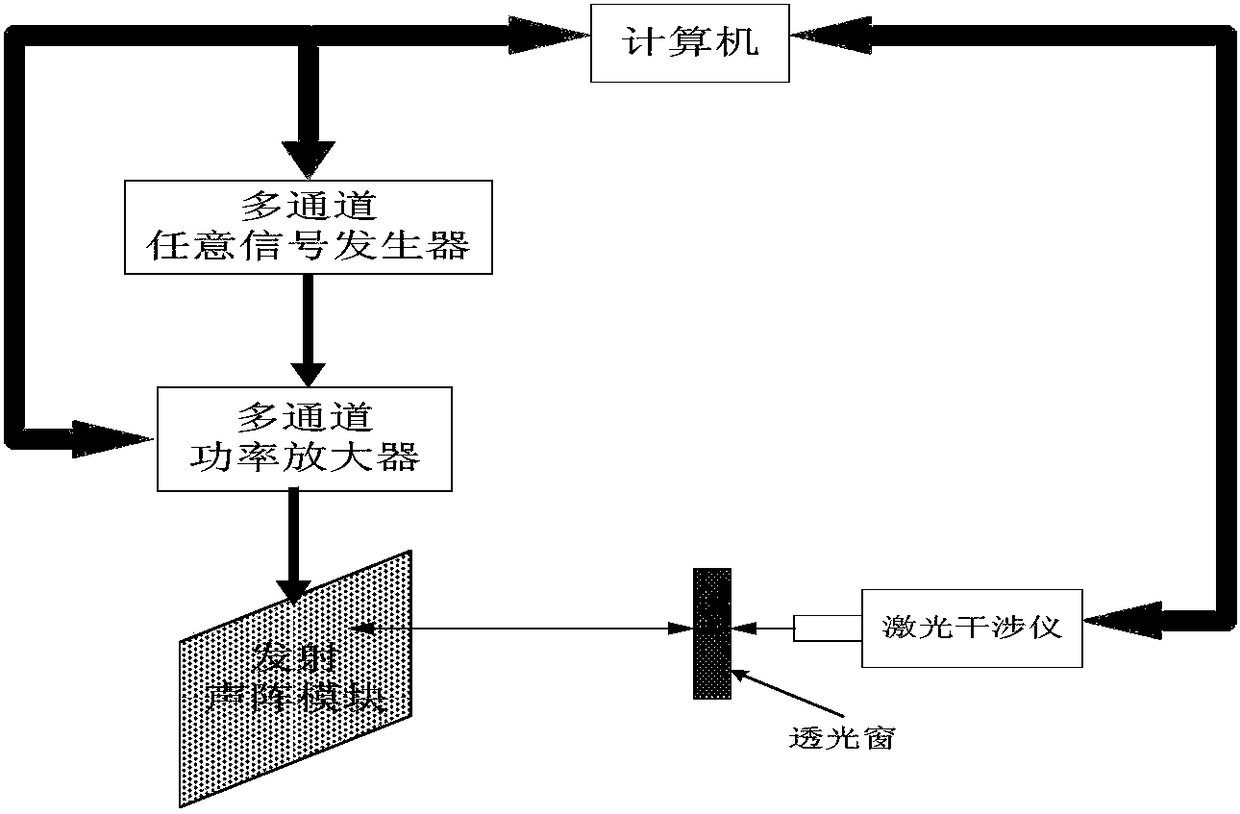
Near-field acoustic tomography test method for mutual radiation impedance of underwater acoustic array
InactiveCN108318123AImprove performanceHigh electro-acoustic efficiencySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansArray elementRadiation model
The invention belongs to the field of underwater acoustic test technology base, and mainly relates to a near-field acoustic tomography measurement method for the mutual radiation impedance of an underwater acoustic array. The method includes the following steps: obtaining near-field acoustic field information of a radiated acoustic field of an acoustic array through laser tomography measurement; processing the obtained acoustic field information by using a near-field acoustic holographic transformation technology; dividing the complex vibration velocity into blocks according to the position ofeach array element to obtain the complex vibration velocity of the source surface of each array element; calculating the complex acoustic pressure of the source surface of each array element and theradiated acoustic pressure generated by the array element in the surface positions of the other array elements; and carrying out calculation based on the classic acoustic array mutual radiation impedance theory. The beneficial effects are as follows: the shortcomings of the common intrusive acoustic array mutual radiation test method are overcome by a non-contact test method; the problem that there is no method for accurately testing the mutual radiation impedance of an underwater acoustic array at low frequency and high power is solved; a mutual radiation model is provided for the velocity control of an underwater acoustic array; and a powerful technical guarantee is provided for the design and development of a low-frequency and high-power acoustic array.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Superwide band single polar antenna
This invention relates to super wide band monopole antenna. The problem be solved is to provide one simple structure and little volume super wide band monopole antenna. The feature is that the monopole is pillar type, ring slots are distributed on outer surface of the monopole to make axial cross section circumferential as rippled wall, the central part is column, up end is cone of up large and down small, down end is cone of up large and down small. The antenna surface is rippled wall, so its radiation impedance can better match free space wave impedance in larger frequency range. The matching to input impedance is realized by morphing of the antenna diameter, so wider band and higher gain can be got. Its weight is about 70 gram and volume is small, and its manufacturing technique is good.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Information terminal device
InactiveUS20090052360A1Not deteriorate aesthetic appearanceAvoid damageRadio transmissionLoop antennasTerminal equipmentEngineering
An information terminal device includes a casing, a wireless board, and an antenna arranged to utilize a plurality of radio systems. The antenna includes a power feeding terminal and a plurality of resonant circuits. The plurality of resonant circuits are arranged to radiate radio waves. The plurality of resonant circuits further define a matching circuit that provides impedance matching between an impedance on a power feeding side as viewed from the power feeding terminal and a radiation impedance of a free space.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
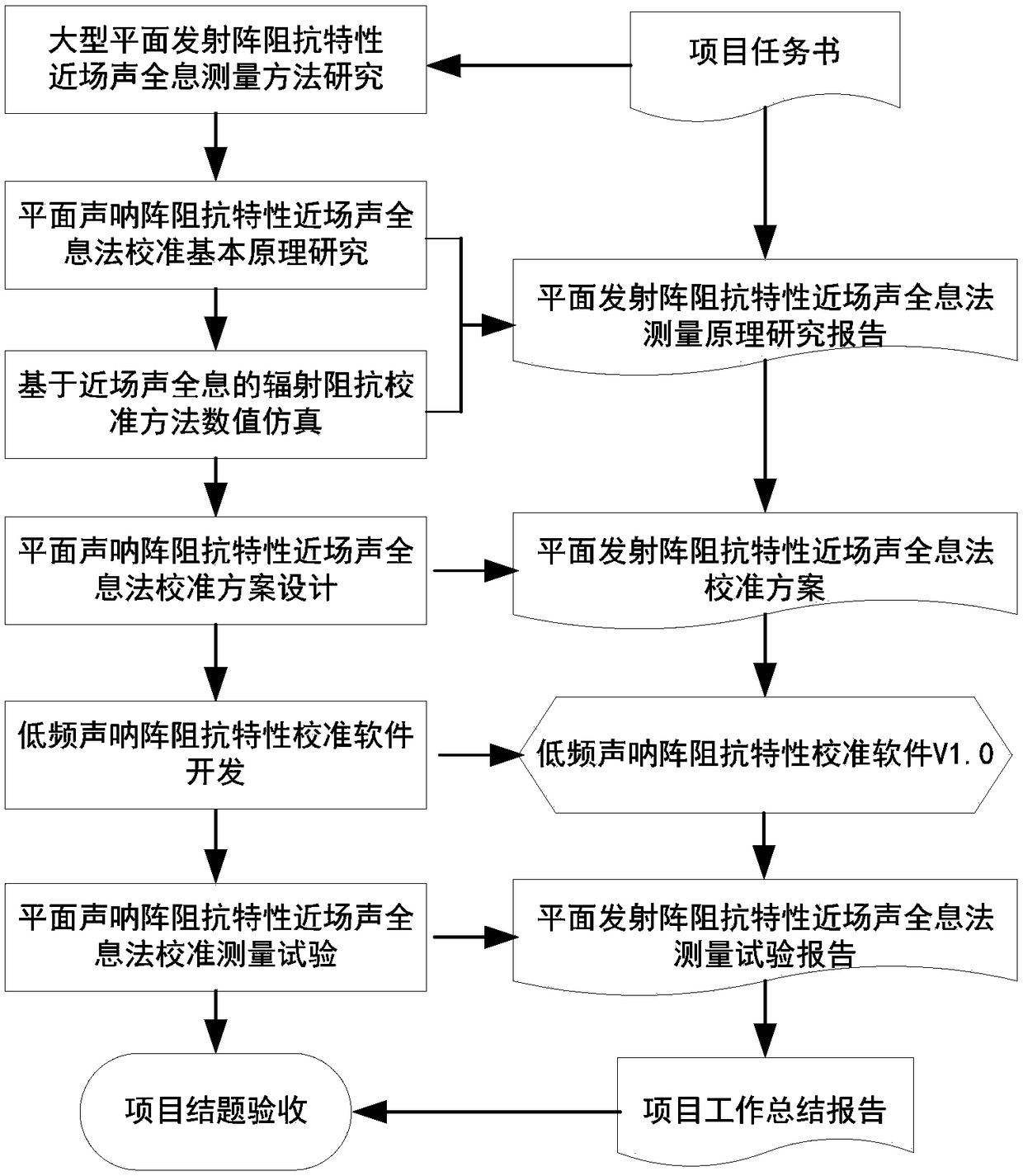
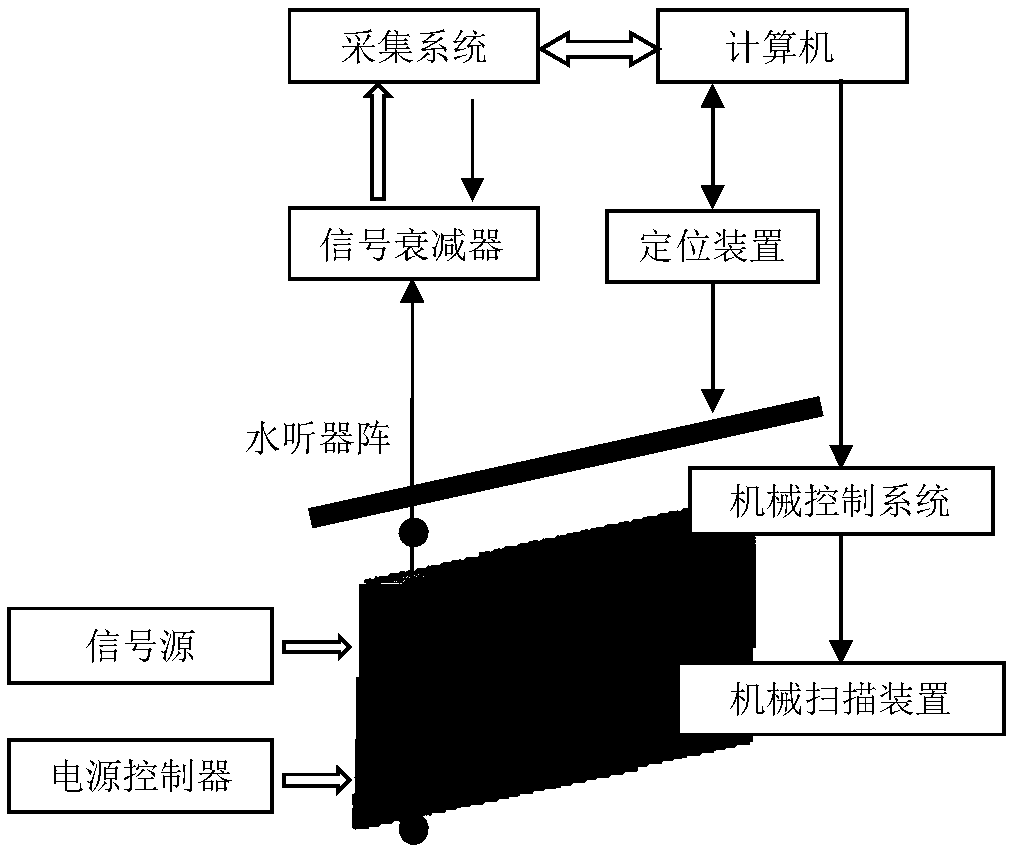
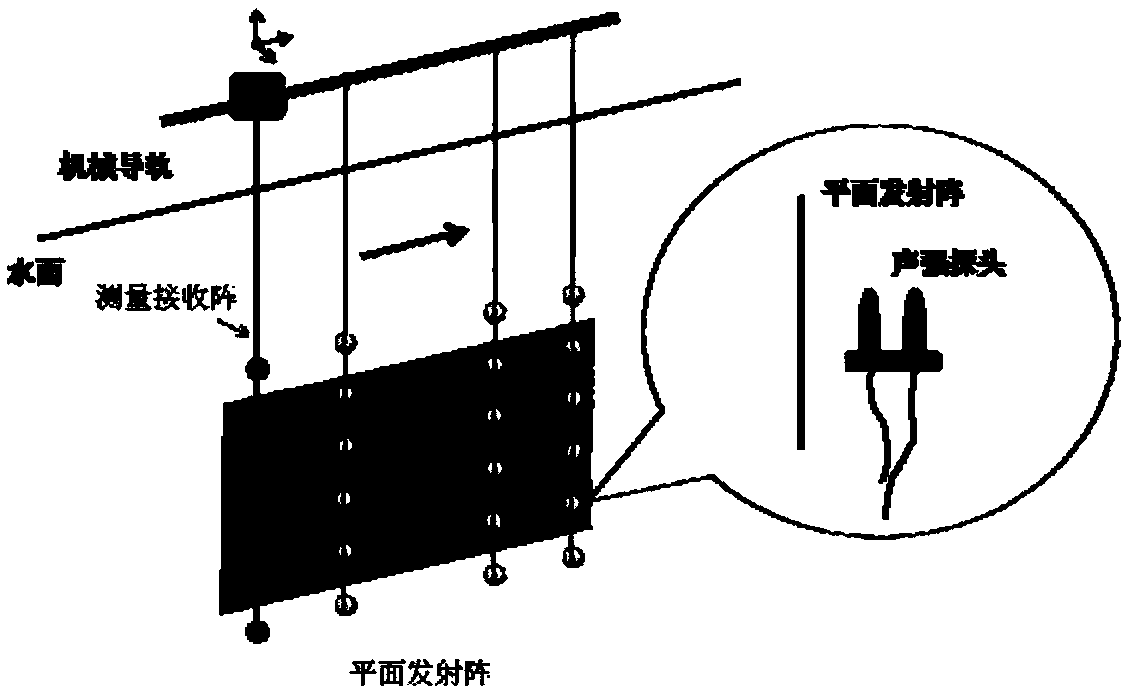
Near-field acoustic holographic calibration and measurement method for impedance characteristic of planar sonar array
ActiveCN109444861ASolve evaluation problemsEasy CalibrationWave based measurement systemsWater resource assessmentSonarTheory testing
A near-field acoustic holographic calibration and measurement method for an impedance characteristic of a planar sonar array belongs to the technical field of research on the near-field acoustic holographic measurement method for the impedance characteristic of large planar emission arrays. The method is characterized by including an impedance characteristic calculation method of the planar emission array; a radiation impedance calibration method based on near-field acoustic holography; a BAHIM method based near-field acoustic holographic transformation method and algorithm; value simulation via a radiation impedance calibration method based on near-field acoustic holography; and establishment of a near-field acoustic holographic theoretical test model for the impedance characteristic of alow-frequency planar sonar array. Acoustic characteristic calibration demands of an active sonar device can be monitored according to water sound, research on basic principles of near-field acousticholographic calibration for the impedance characteristic of the planar sonar array, design of a near-field acoustic holographic calibration scheme, development of impedance calibration software of thelow-frequency sonar array, and near-field acoustic holographic calibration and measurement test can be implemented in a targeted way, and thus, the calibration capability of a low-frequency emissionenergy transducer calibration system can be improved, and problems in evaluating the impedance characteristic of the low frequency sonar are solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
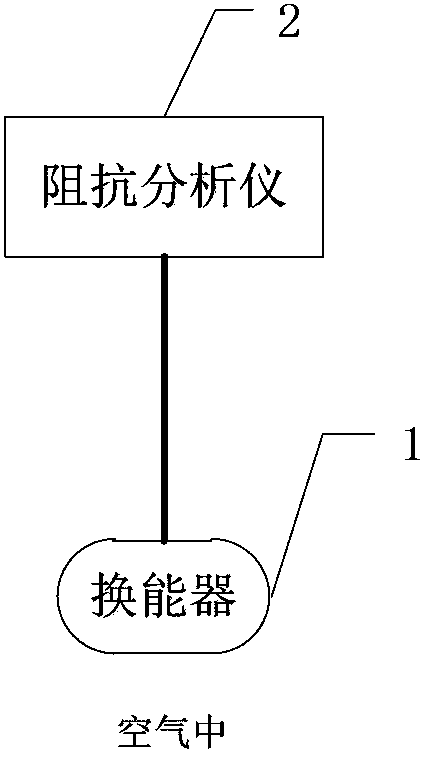
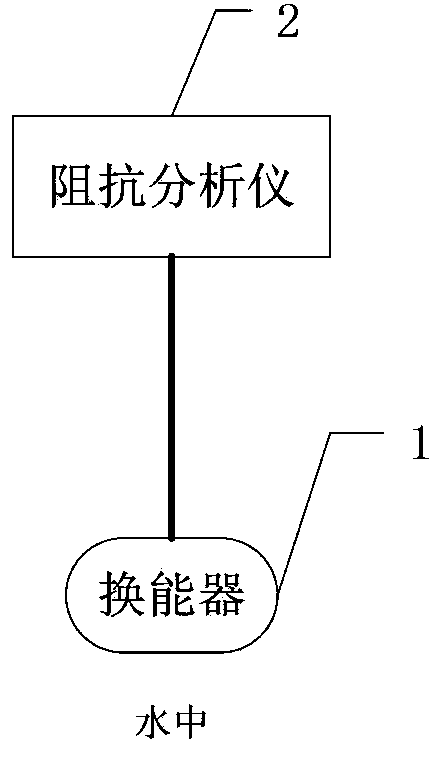
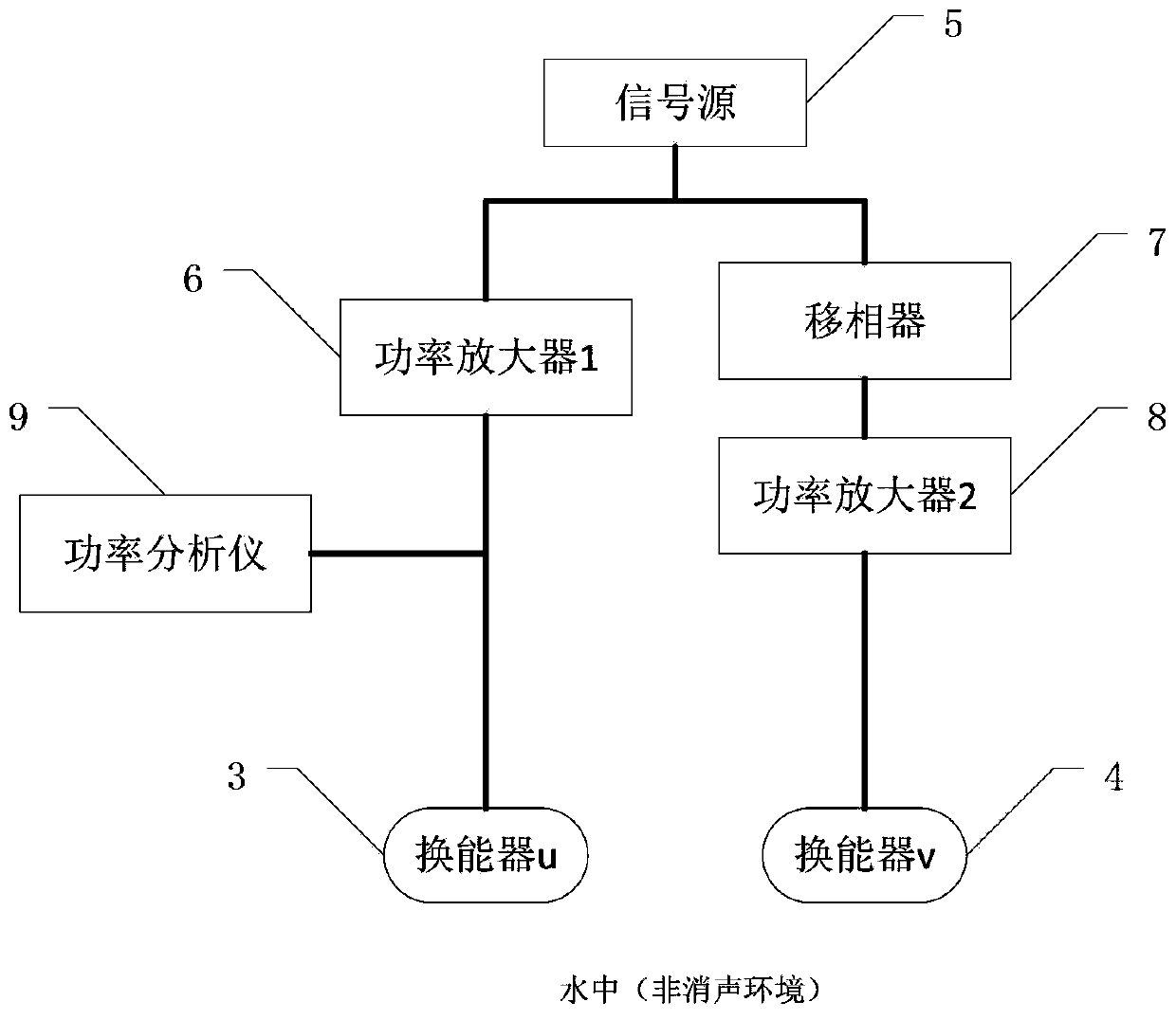
Method for measuring mutual radiation impedance of transducer array in non-anechoic tank and system thereof
ActiveCN103869163ALow costResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The invention provides a method for measuring mutual radiation impedance of a transducer array in a non-anechoic tank and a system thereof. the method comprises the following steps: Step 101, resonant frequency of each transducer in the air and resonant frequency of each transducer in water are measured; Step 102, Q distribution points are selected in the non-anechoic tank and are used for distributing a transducer pair to be measured; Step 103, the transducer pair to be measured is distributed on some point in the distribution points, resistance and reactance of a first transducer under various working conditions are obtained when the first transducer and a second transducer operate at same-phase resonant frequency of the first transducer in the air and in water and at reversed-phase frequencies of the first transducer in the air and in water; Step 104, the above Step 103 is repeated until resistance and reactance measurement of the above transducer pair to be measured at all Q distribution points are completed; and Step 105, mutual radiation resistance and mutual radiation impedance of the transducers to be measured at each point are obtained so as to obtain Q mutual radiation resistances and mutual radiation impedances, and mean value of the Q mutual radiation resistances or mutual radiation impedances is calculated to be respectively used as mutual radiation resistance and mutual radiation impedance of the final measurement.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel broadband PCB antenna suitable for Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
PendingCN107946748AEffective radiationHigh bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsBranch traceEngineering
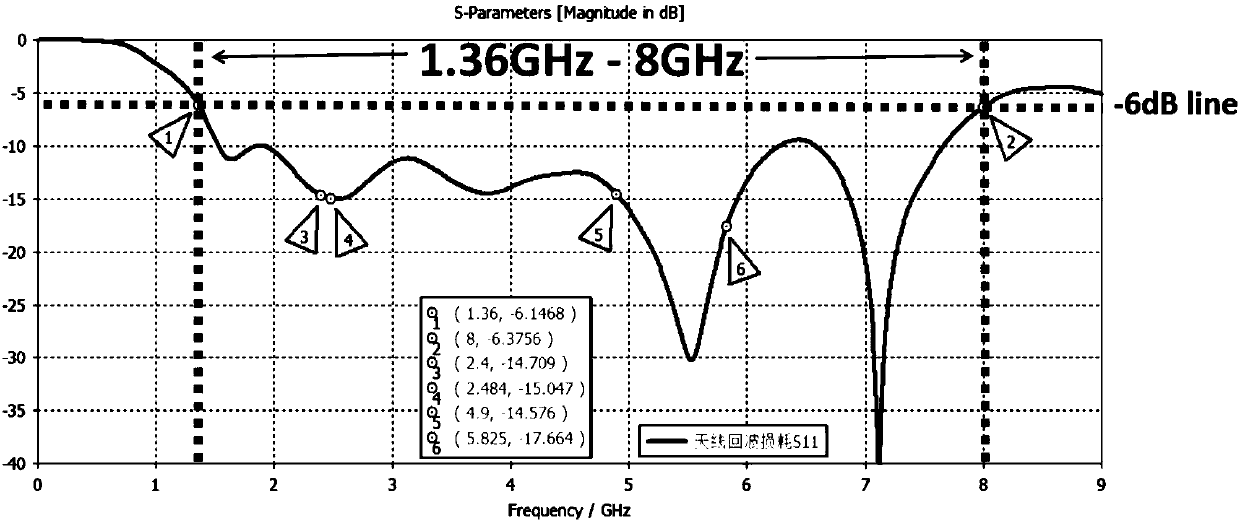
The invention relates to a novel broadband PCB antenna suitable for a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). The novel broadband PCB antenna includes a printed circuit board and an antenna radiation unit, the antenna radiation unit is located on the printed circuit board, the antenna radiation unit and the printed circuit board serve as antenna system, a grounding wire is located on an edge of the antenna radiation unit and the printed circuit board, a first radiating body is arranged beside the grounding wire, and a second radiating body, the grounding wire and a third radiating body form a broadband loop antenna; the third radiating body is coupled to a lower side metal floor plate; a fourth radiating body serves as a branch line of an antenna radiating body and is located at an included angle position of two side faces of the metal floor plate. Three principles of forming the loop antenna, antenna branch line and antenna ground coupling are utilized to realize broadband radiation impedance, thereby realizing antenna effective radiation in an ultra-wide range of 1.36GHz to 8GHz, covering a WLAN 2.4GHz frequency band and a 5GHz frequency band, and having very high robustness to surrounding environment of the antenna.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIATE COMM ELECTRONICS
Continuous current rod antenna
ActiveUS20130038504A1Stabilizes radiation impedanceLow profile packagingProtective material radiating elementsRadiating element housingsComputer moduleRadiation impedance
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Low-frequency broadband efficient array forming structure based on bent disc transducer
InactiveCN111935594ALower resonant frequencyWorking bandwidthTransducers for subaqueous useSound producing devicesBroadbandingWavelength
The invention discloses a low-frequency broadband efficient array forming structure based on a bent disc transducer, which mainly comprises a transmitting array. The transmitting array comprises a plurality of groups of transducer units, the transmitting array is formed by arranging a plurality of groups of same transducer units at equal intervals in the horizontal direction, and the postures of the transducer units in the transmitting array are consistent; the acoustic center distance between the transducer units is not greater than the half wavelength of the transducer units at a resonant frequency point, and therefore the near-field mutual radiation influence on each group of transducer units is kept consistent; each transducer unit is formed by arranging one or more bent disc transducers in the axial direction. Radiation impedance of the bent disc transducers can be changed by arraying the bent disc transducers according to a specific arraying mode, and therefore resonant frequencyof a transmitting array is reduced; working bandwidth is expanded, electro-acoustic efficiency is improved; the transmitting array is enabled to meet development requirements of a future maneuveringdetection system.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
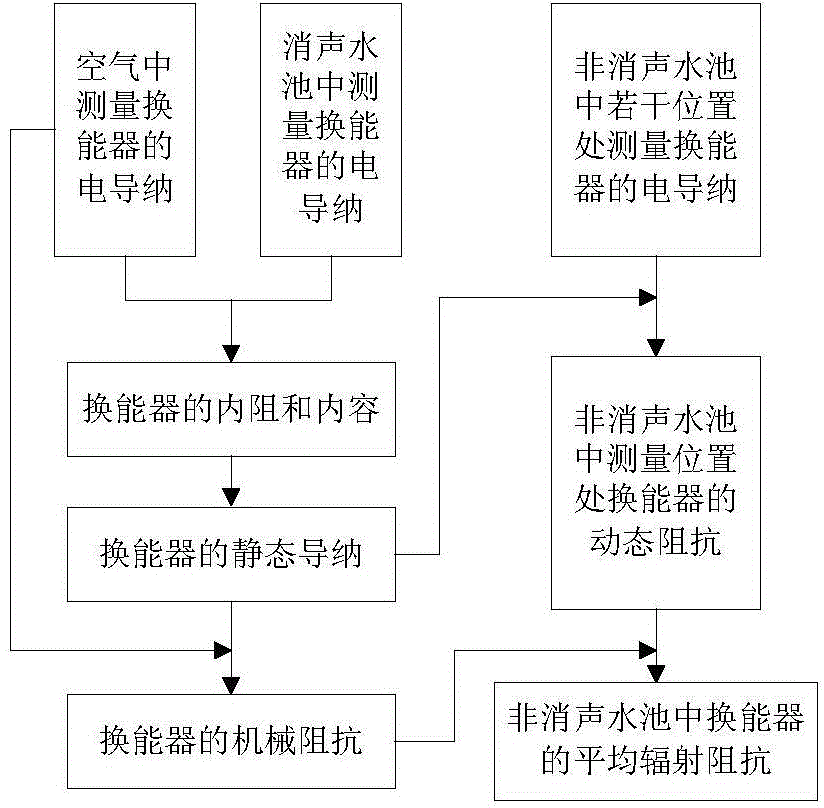
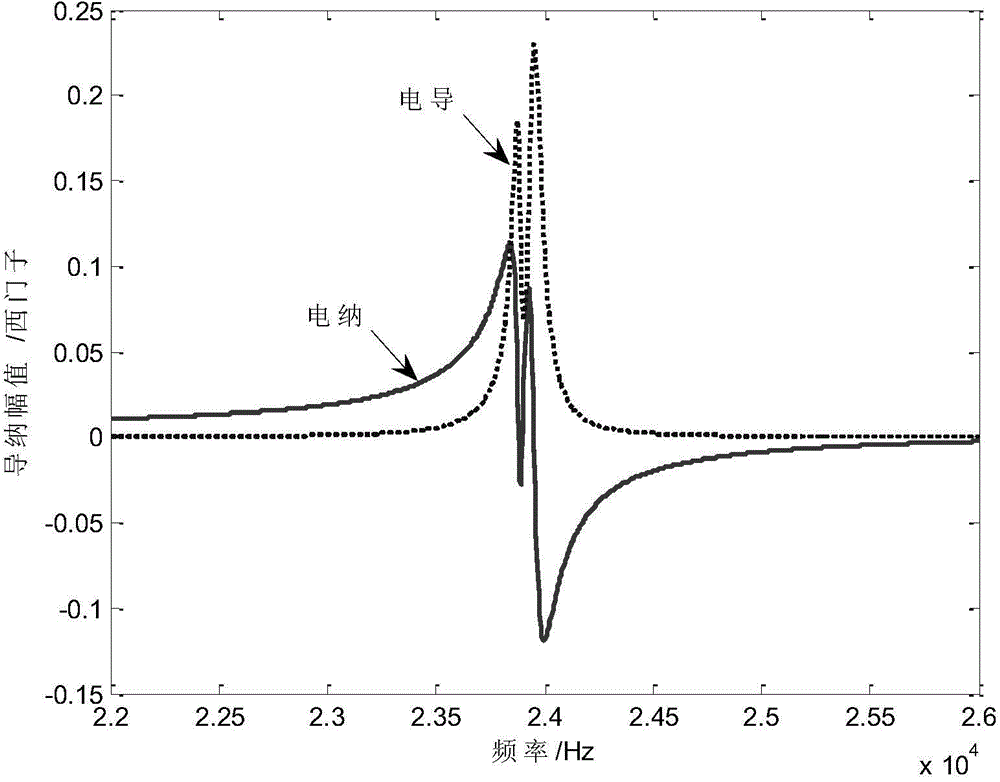
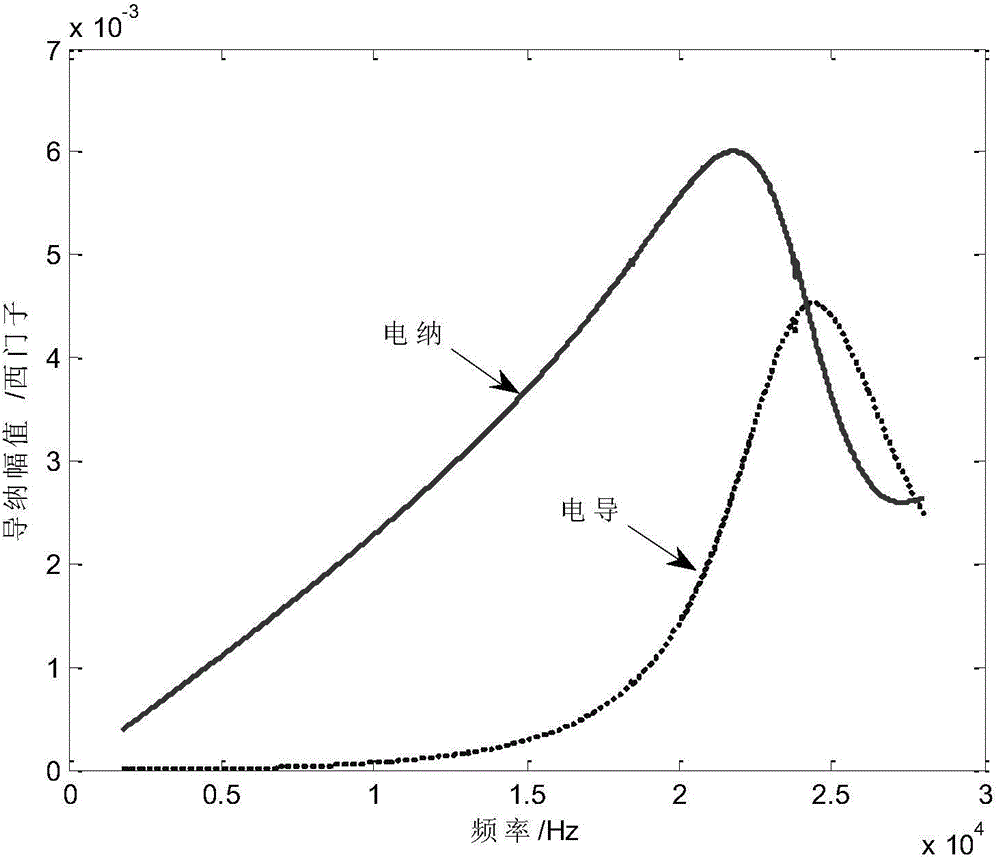
Method for measuring average radiation impedance of underwater sound piezoelectric transducers in non-silencing pools
ActiveCN104793056AThe method is efficient and fastThe test conditions are easy to meetResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceElectricity
The invention discloses a method for measuring the average radiation impedance of underwater sound piezoelectric transducers in non-silencing pools. The method includes measuring electric admittance of the underwater sound piezoelectric transducers in the air, electric admittance of the underwater sound piezoelectric transducers in silencing pools and electric admittance of the underwater sound piezoelectric transducers at N measurement positions in non-silencing pools; determining internal resistance, internal capacitance and static admittance of the underwater sound piezoelectric transducers; determining mechanical impedance of the transducers; determining dynamic impedance of the transducers at N measurement positions of the to-be-measured non-silencing pools; determining the average radiation impedance of the transducers in the to-be-measured non-silencing pools. The method has the advantages that the electric admittance of the underwater sound piezoelectric transducers is measured, so that the average radiation impedance of the underwater sound piezoelectric transducers in the non-silencing pools can be indirectly measured, only impedance analyzers which are measurement devices are required, and the method is simple and speedy, is low in test cost and has great practical value.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Speed of sound and/or density measurement using acoustic impedance
PendingUS20190072524A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial testing goodsSlurryEngineering
Apparatus is provided featuring a signal processor or signal processing module configured at least to: receive signaling containing information about a radiation impedance of a piston vibrating a process medium, including a fluid or slurry; and determine a speed of sound or density measurement related to the process medium, based at least partly on the signaling received. The signal processor or signal processing module may determine a speed of sound measurement related to the process medium, based on at least partly on the density of the process medium, including where the density of the process medium is known, assumed or determined by the signal processor or signal processing module, or determine a density measurement related to the process medium, based on at least partly on the speed at which sound travels in the process medium, including where the speed of sound of the process medium is known, assumed or determined by the signal processor or signal processing module.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
Power amplifier efficiency
ActiveUS7292829B2Reduce power consumptionImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTResonant long antennasCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for optimizing the efficiency of a power amplifier (1) that is utilized for transmission of radio signals in a portable radio communication device, such as a mobile phone. The impedance loading the power amplifier (1) is controlled by a controller (5) in dependence on a transmission power of the portable radio communication device, wherein the radiating impedance of an antenna element (2) loading the power amplifier is controlled in dependence of the desired load impedance. Preferably, the changing of radiating impedance is performed by changing a capacitive coupling between the antenna element and a ground element or by changing the size of the antenna element. Better efficiency and bandwidth are thereby attained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ventilated type vehicle-mounted woofer speaker system and design method thereof
ActiveCN106528907AIncreased Design FreedomThere are many parameters to adjust and controlSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a ventilated type vehicle-mounted woofer speaker system and a design method thereof. The design method is designed based on a waveguide tube, can adjust and control many parameters and is high in freedom degree. The design method of the ventilated type vehicle-mounted woofer speaker system comprises the following steps of: S1, calculating a radiation impedance of a current waveguide tube of a speaker system; S2, establishing a mathematical model of the speaker system according to the radiation impedance of the waveguide tube obtained in step S1; S3, calculating a radiation sound field of the speaker system according to the mathematical model established in step S2; and S4, comparing the radiation sound field obtained in step S3 with an expected radiation sound field, and adjusting a structure of the waveguide tube if the expected radiation sound field is not satisfied.
Optical testing method for mutual radiation impedance of underwater acoustic array
InactiveCN108344497AAdditional mass effects overcomeAvoid quality impactImpedenceUsing wave/particle radiation meansAcoustic arrayOptical test
The invention belongs to the basic field of underwater acoustic testing technologies, and mainly relates to an optical testing method for the mutual radiation impedance of an underwater acoustic array. The optical testing method comprises the steps of obtaining vibration velocity information of a radiation surface of the acoustic array and a mass point of a radiating acoustic field by adopting a laser vibrometer, and then calculating by using the classical acoustic array mutual radiation impedance theory. The invention has the beneficial effects that the shortcomings of a commonly used intrusive acoustic array mutual radiation impedance testing method are overcome by using a non-contact testing method, problems of a method required for underwater acoustic array mutual radiation impedance testing and accurate testing under low frequency and high power are solved, a mutual radiation model is provided for underwater acoustic array velocity control, and a powerful technical guarantee is provided for the development of a low-frequency high-power acoustic array.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Novel Bluetooth/WLAN antenna and intelligent equipment
ActiveCN104409834ASmall headroomImprove radiation resistanceAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsResonanceEngineering
The invention discloses a novel Bluetooth / WLAN antenna and intelligent equipment. The novel Bluetooth / WLAN antenna comprises a PCB and an antenna component, wherein an antenna clearance area is arranged on the PCB; the antenna clearance area comprises a first clearance area arranged on the upper surface of the PCB and a second clearance area arranged on the lower surface of the PCB; the antenna component comprises a first radiator, a second radiator and a third radiator; the first radiator and the second radiator are arranged inside the first clearance area; a feed part is arranged on the first radiator; the third radiator is arranged inside the second clearance area; the second radiator and the first radiator are coupled to form a first resonance branch; the second radiator and the third radiator are coupled to form a second resonance branch. The antenna disclosed by the invention is small in occupied area, high in design flexibility, high in radiation impedance and good in omni-directivity.
Owner:SUNWAY COMM JIANGSU CO LTD
Information terminal
InactiveCN101454989AEasy to addFix damageRadiating elements structural formsLoop antennasElectricityTerminal equipment
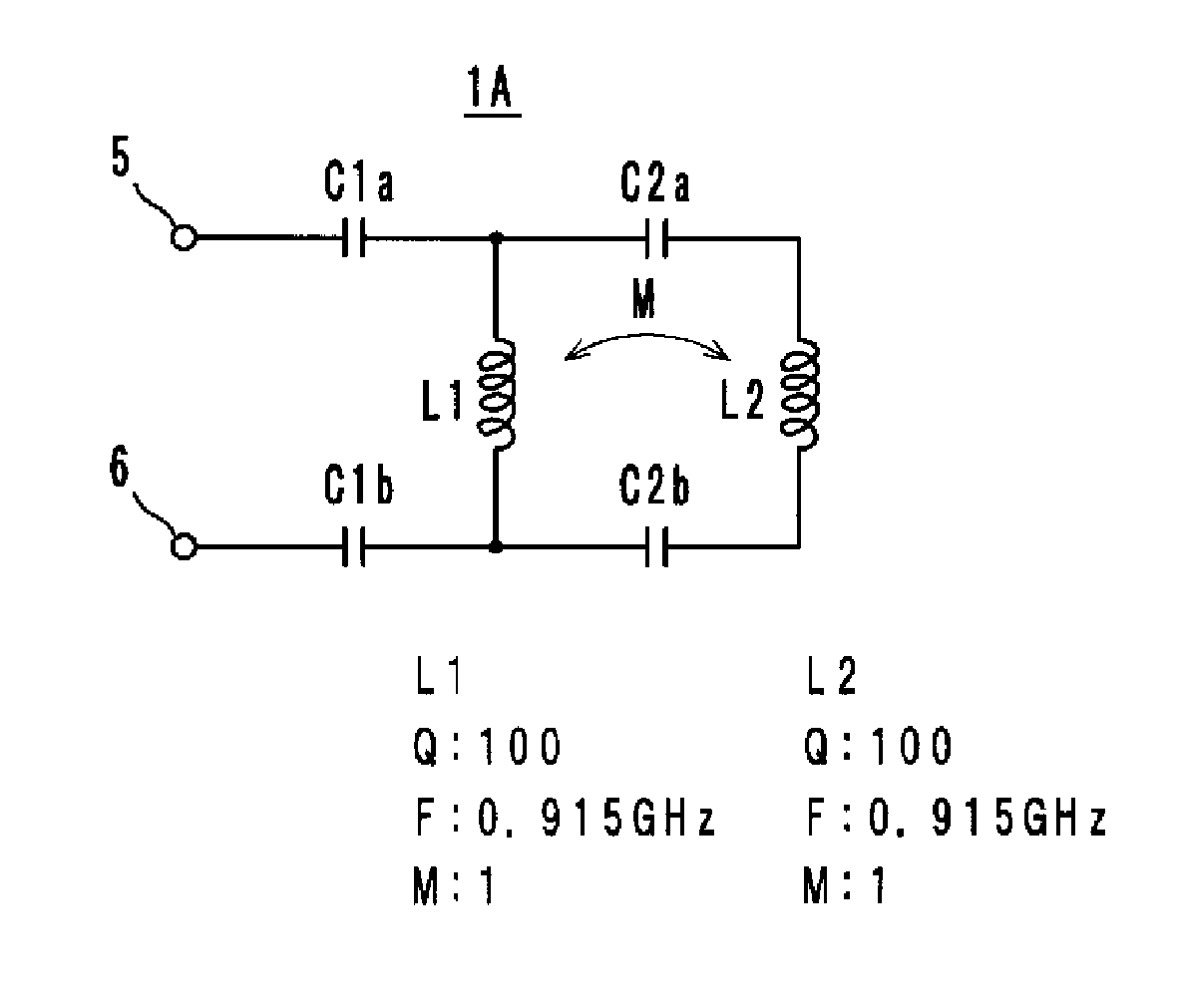
An information terminal device that can support almost all of the frequency bands of a plurality of radio systems is provided. The information terminal device includes a casing, a wireless board (110A), and one of an antenna (1A) and an antenna (1B) so as to employ a plurality of radio systems. One of the antenna (1A) and the antenna (1B) includes a power feeding terminal and a plurality of resonant circuits. The plurality of resonant circuits are used for radiating radio waves. The plurality of resonant circuits are further used for a matching circuit that provides impedance matching between an impedance on a power feeding side as viewed from the power feeding terminal (50 CR ) and a radiation impedance of a free space (377 CR ).
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
T type high power ultrasonic transducer
InactiveCN103212532BRadiation area is largeImprove radiation resistanceMechanical vibrations separationElectricityTransducer
The invention relates to a T-type superpower ultrasonic transducer. The T-type superpower ultrasonic transducer utilizes a longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic vibrator to generate longitudinal vibration, stimulates a metal round vibration disc directly connected with the longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic vibrator to generate the vibration of the same frequency, and radiates sound waves to media. With the help of the conversion of the vibration mode, flexural vibration is generated in the metal round vibration disc, effective conversion of the longitudinal vibration mode and the flexural vibration mode is achieved, uniformity of the radiation sound field of the transducer is greatly improved, radiation area of the transducer can be effectively increased, high-power working is realized, at the same time, radiation impedance of the transducer is improved, acoustic matching of the transducer is improved, and radiation efficiency of the transducer is improved. In addition, due to the fact that the flexural vibration disc has multiple vibration modes, the transducer can work in different vibration modes and radiate ultrasonic waves of different frequencies, and therefore an ultrasonic wave source working in multiple frequencies is formed.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com