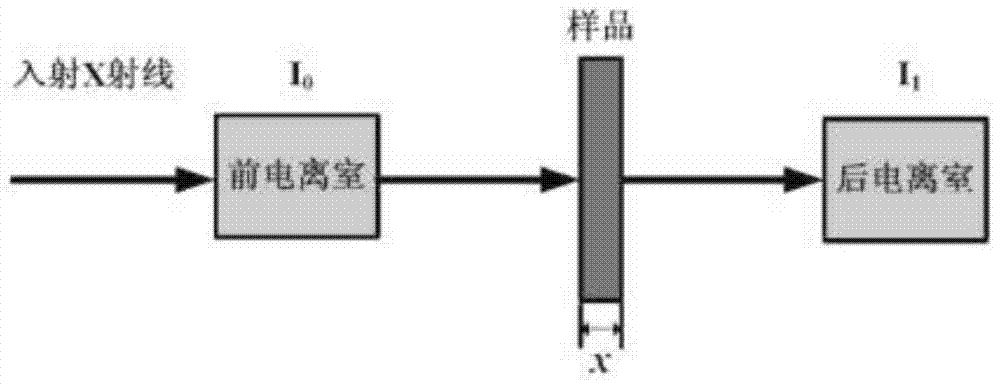
Patents
Literature
43 results about "X-ray absorption fine structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
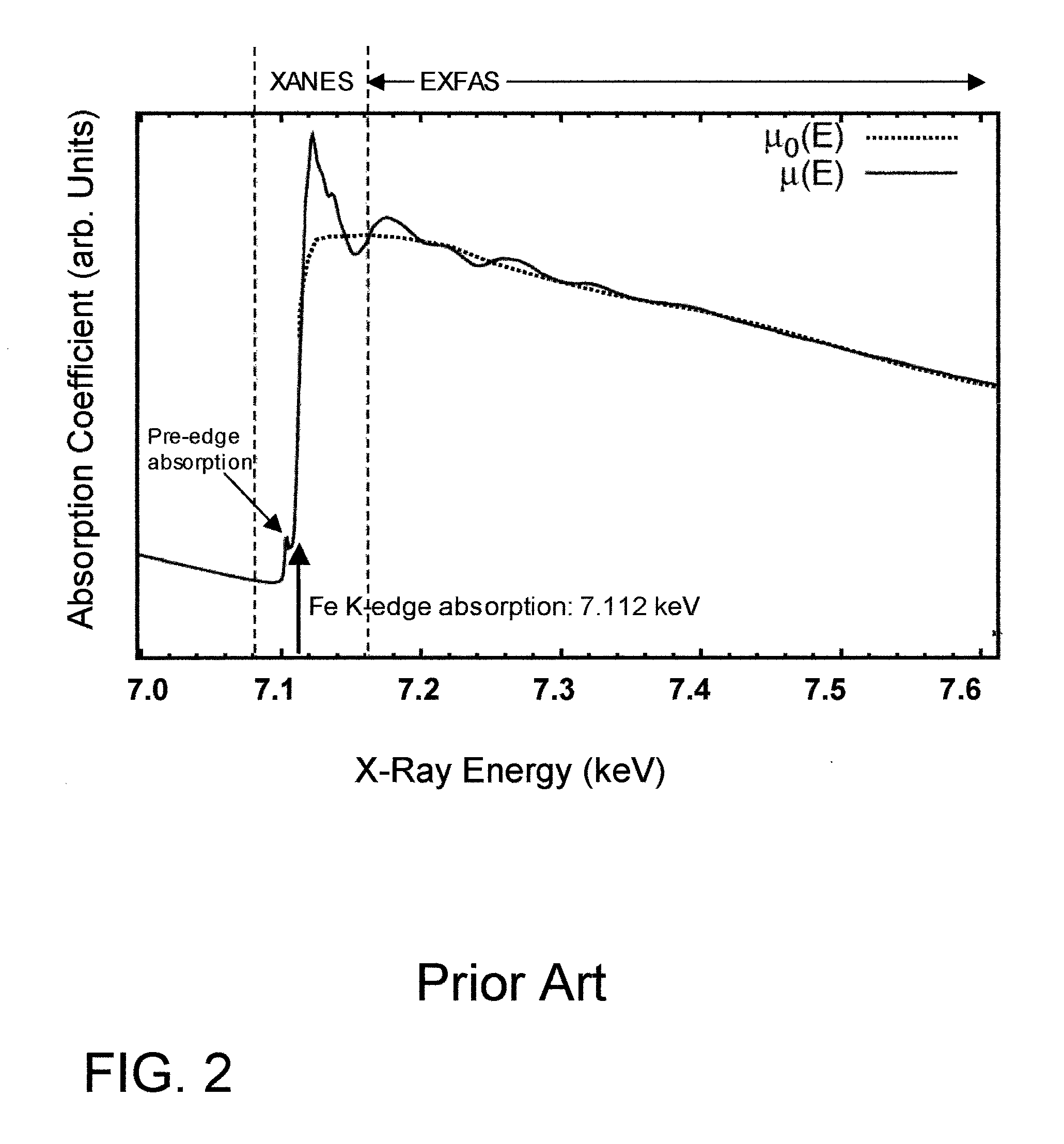
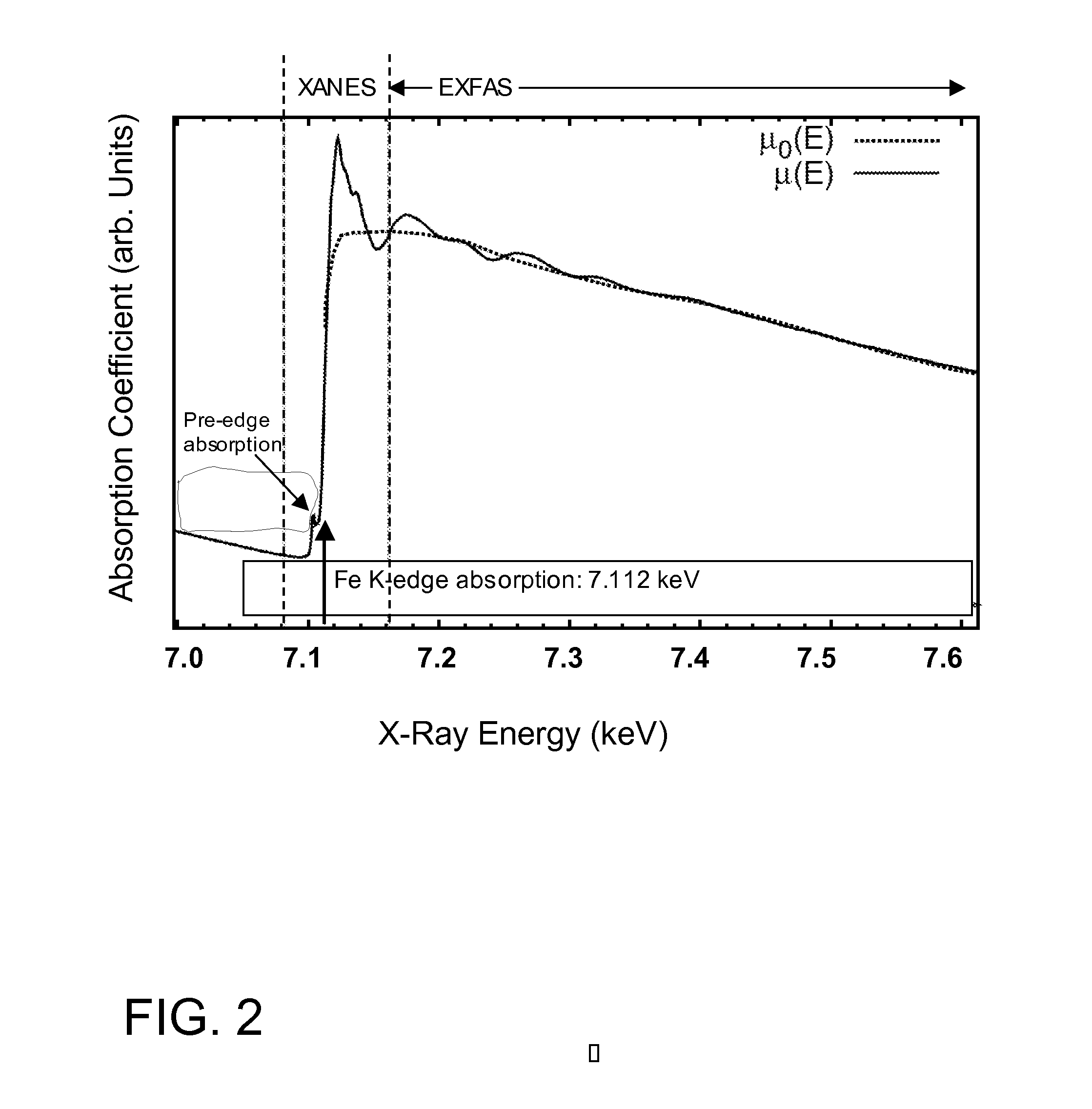
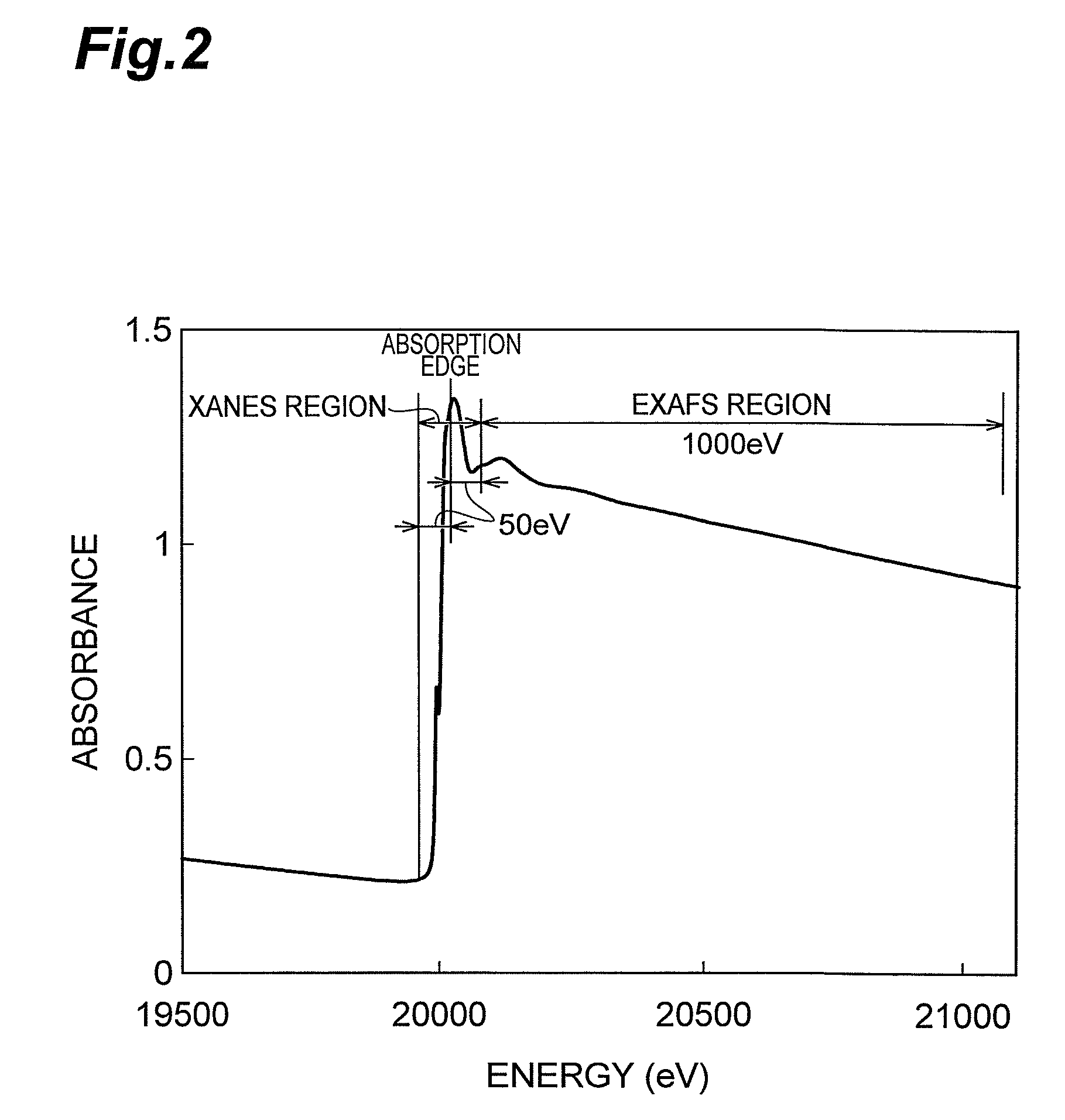
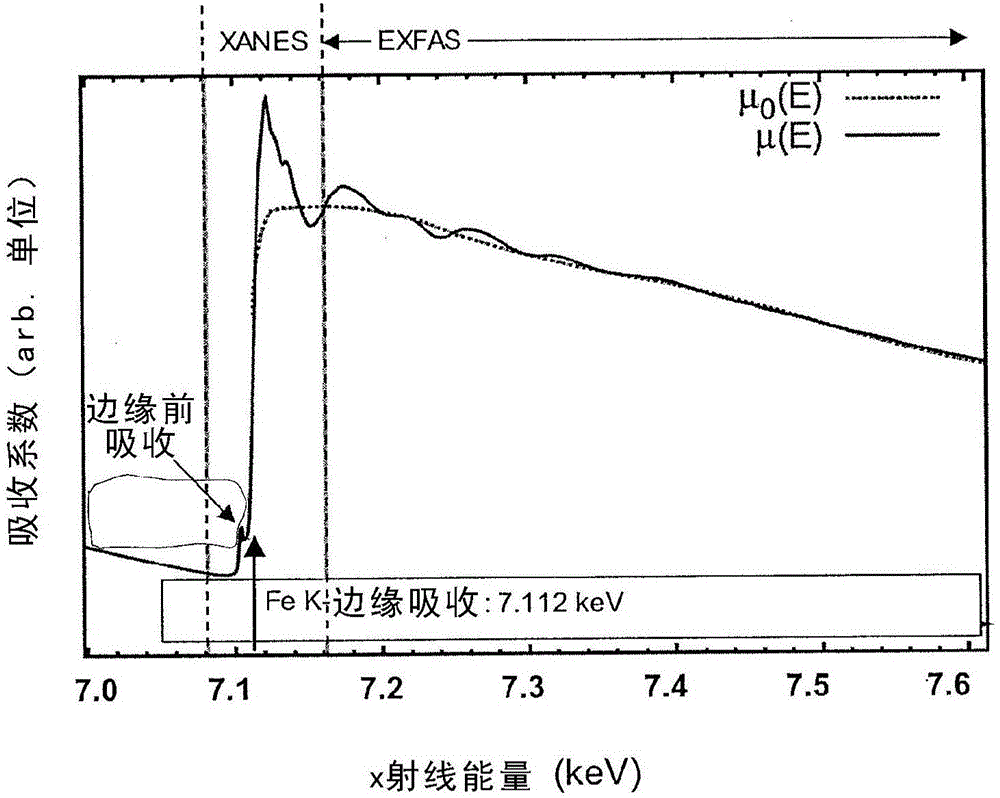
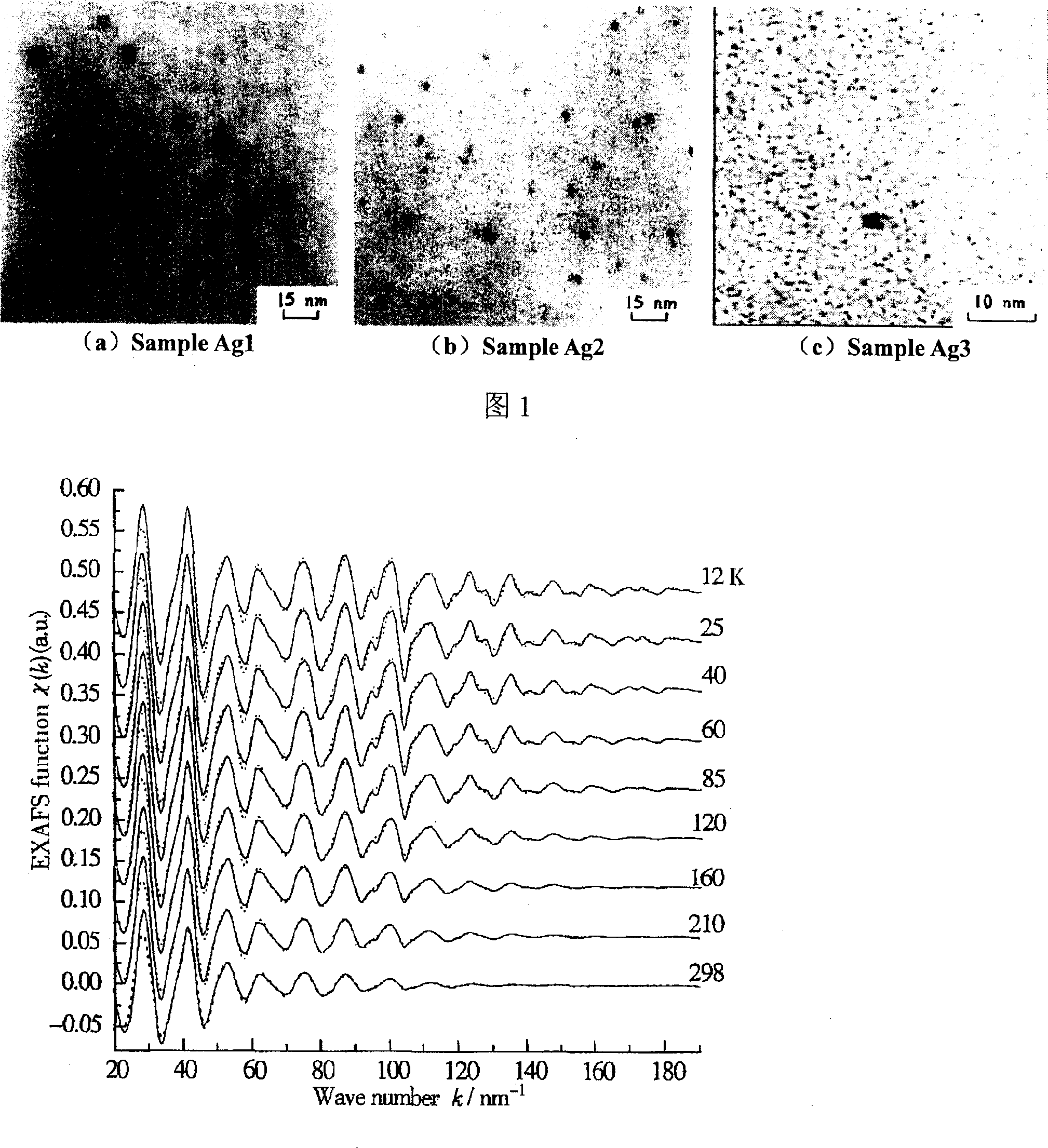
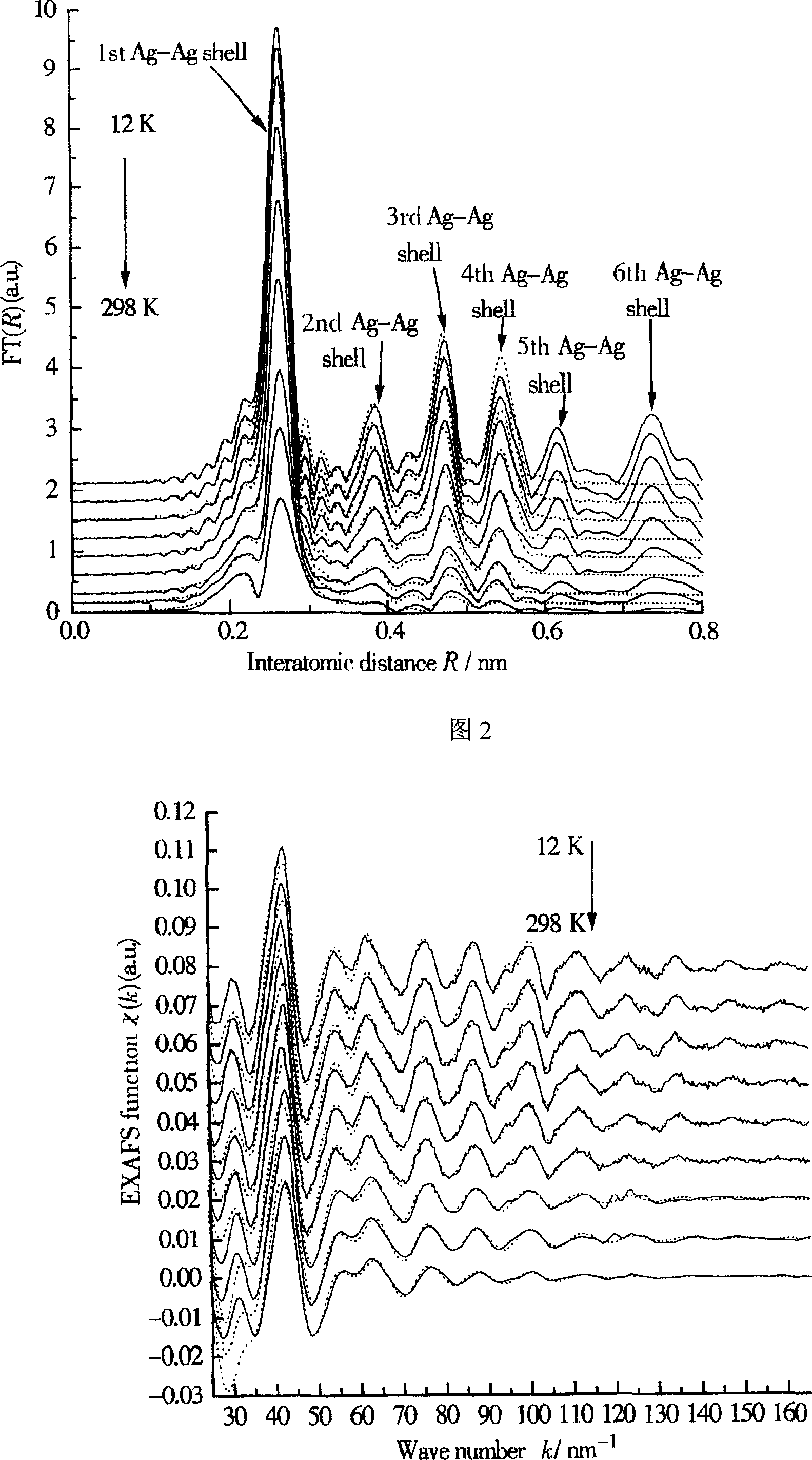
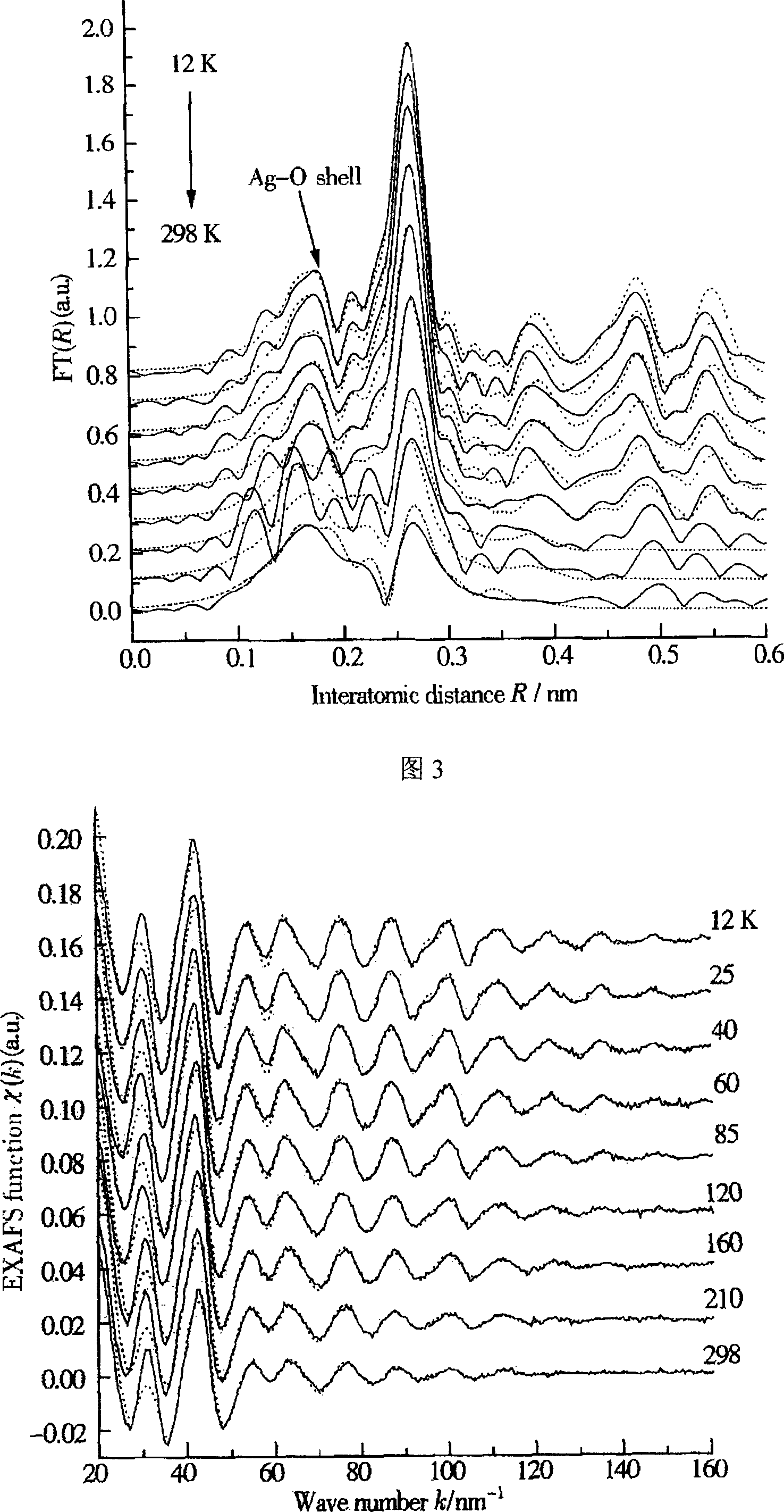
X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) is a specific structure observed in X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). By analyzing the XAFS, information can be acquired on the local structure and on the unoccupied local electronic states.
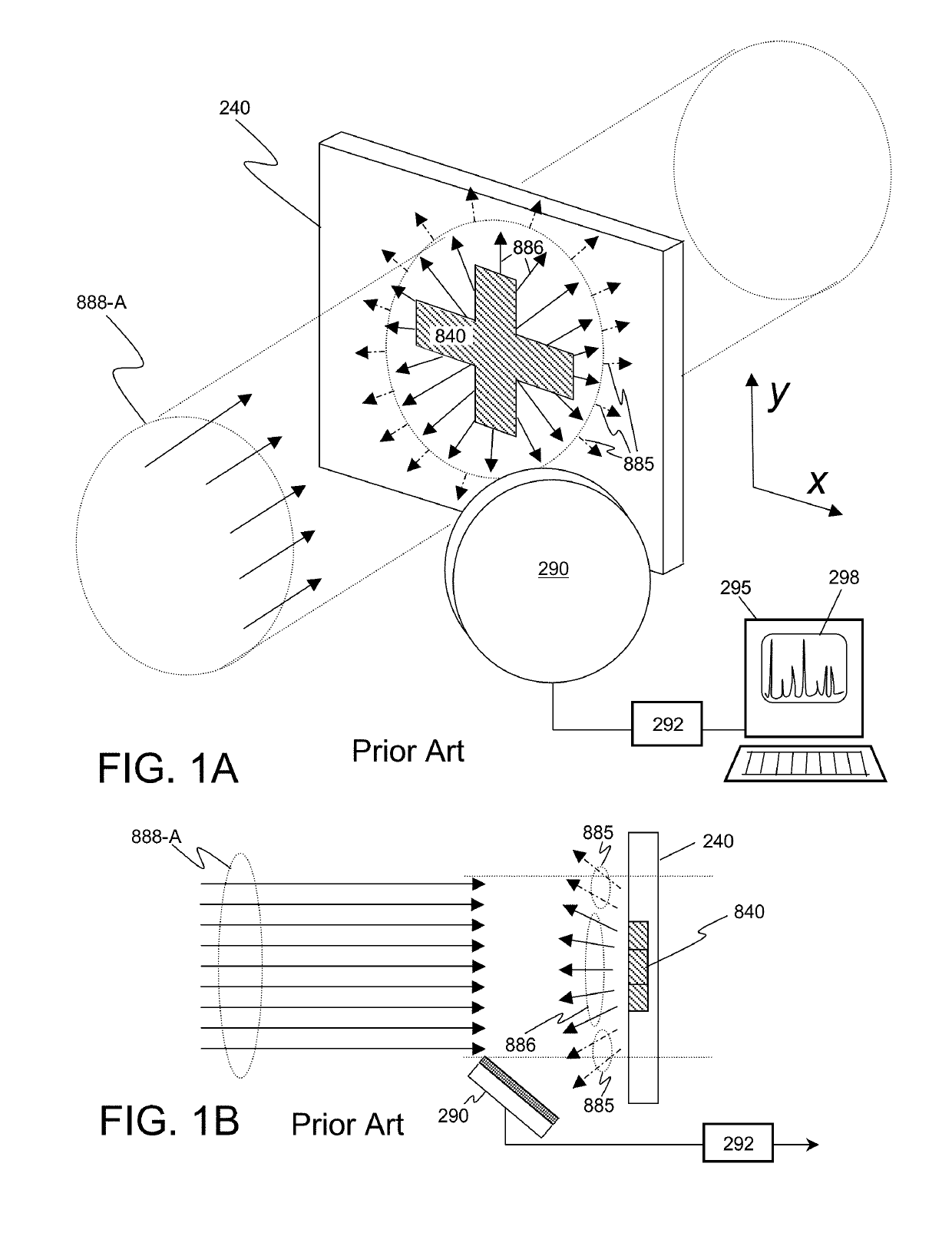
High brightness X-ray absorption spectroscopy system
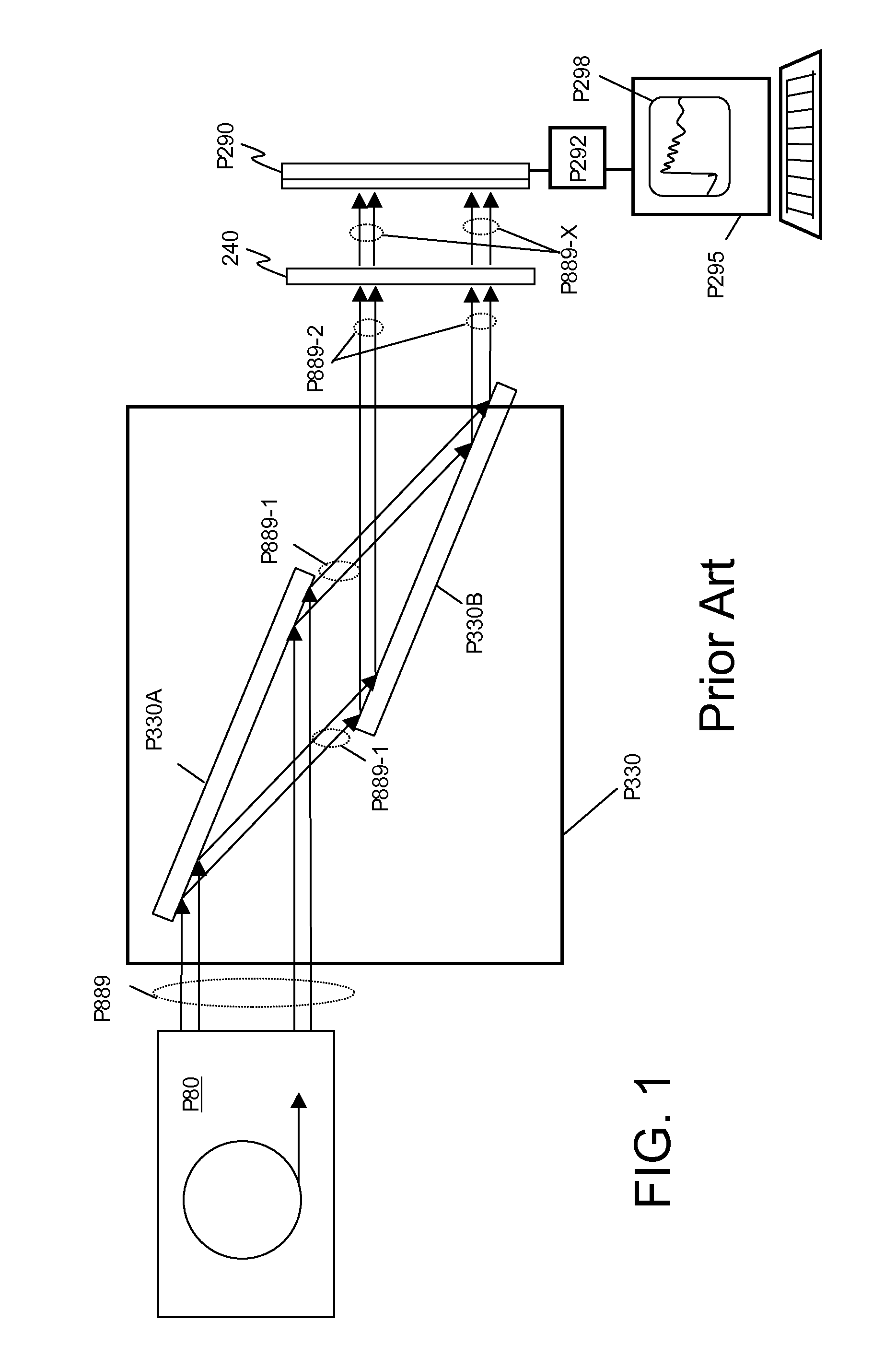
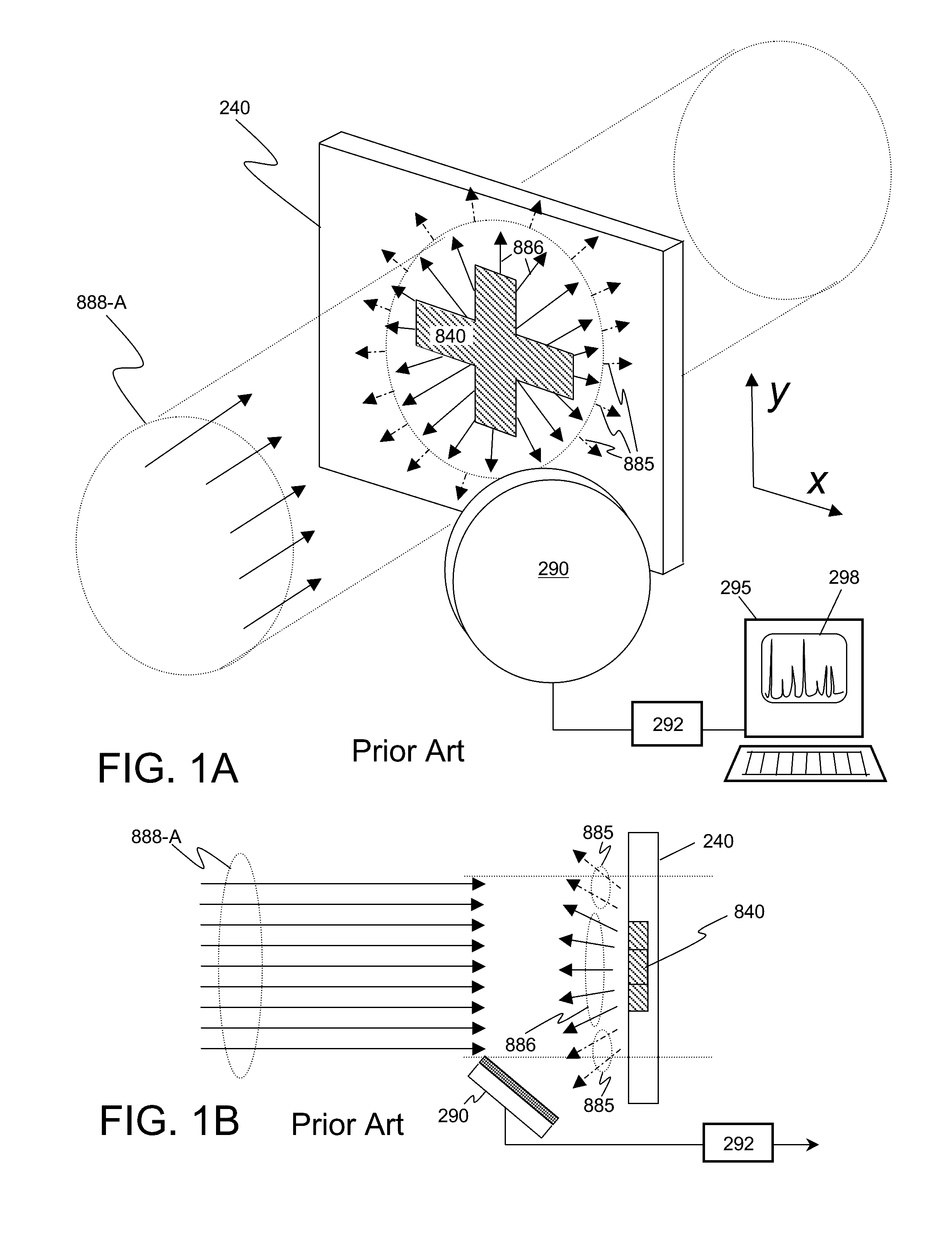
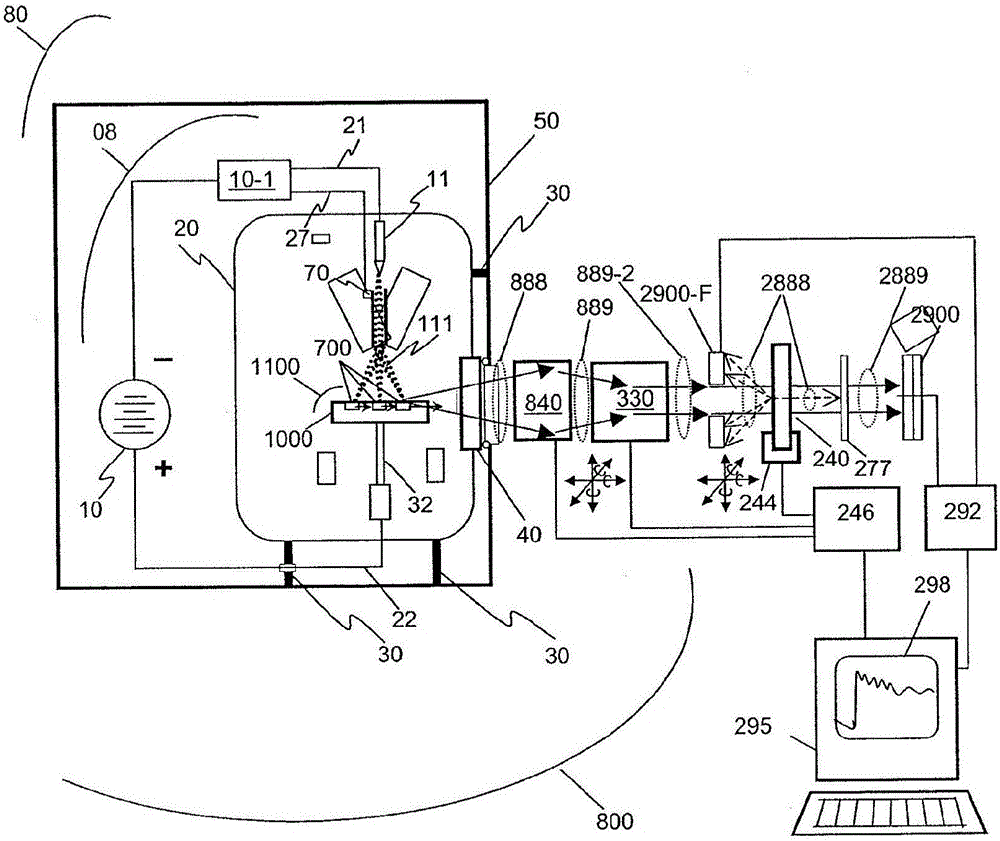
InactiveUS9448190B2Increase brightnessImprove thermal conductivityRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyDesign for X
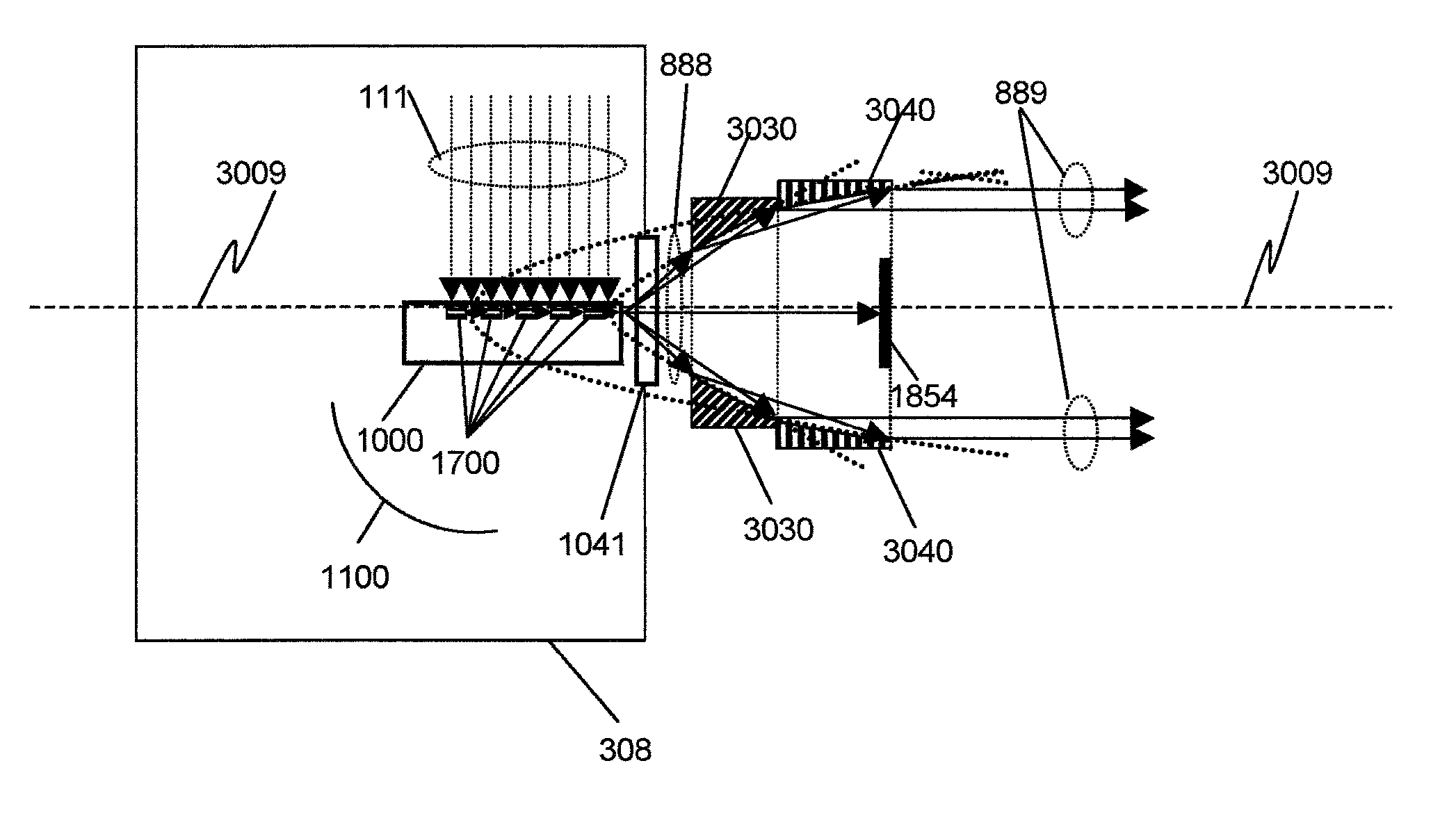
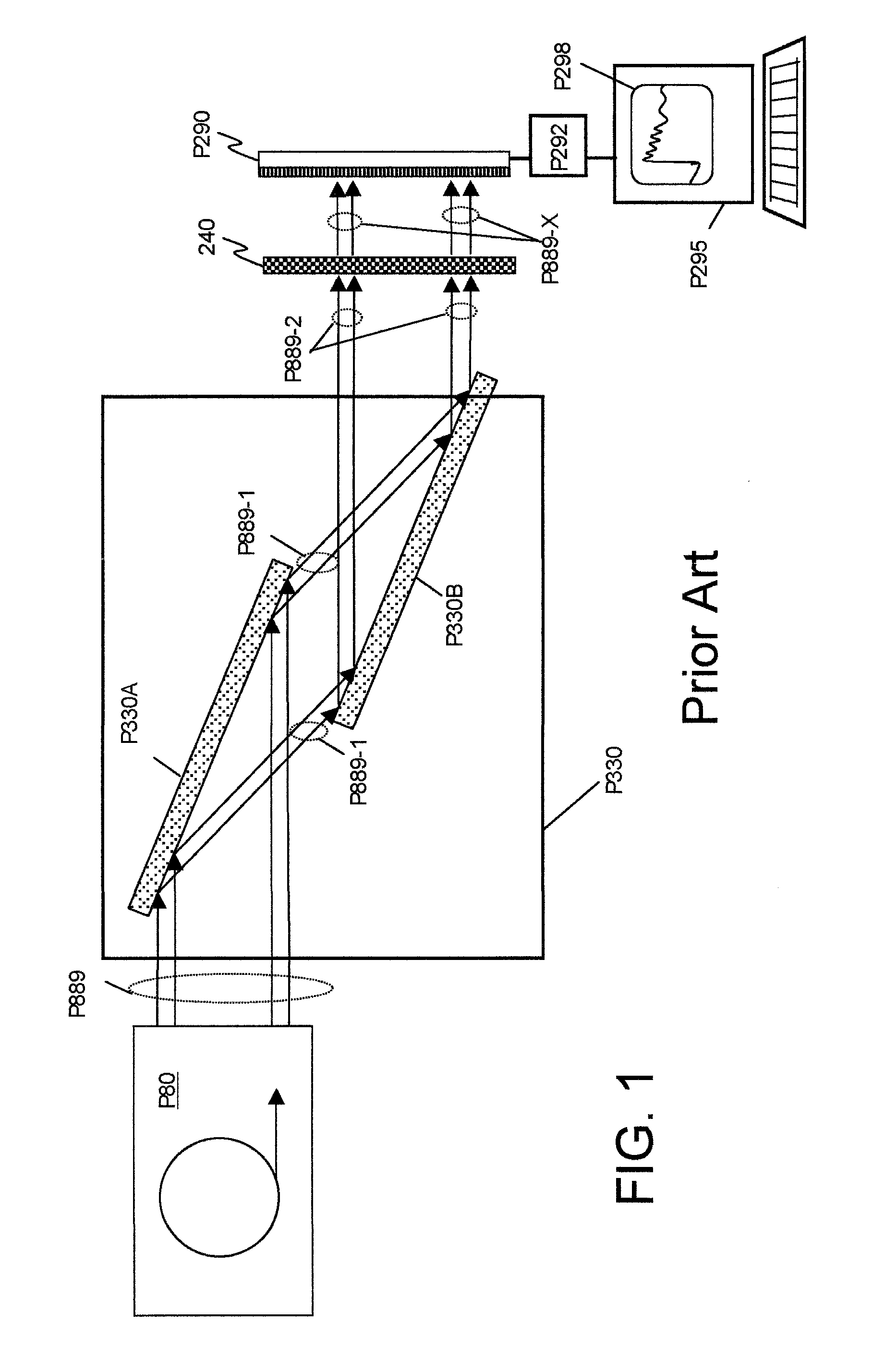
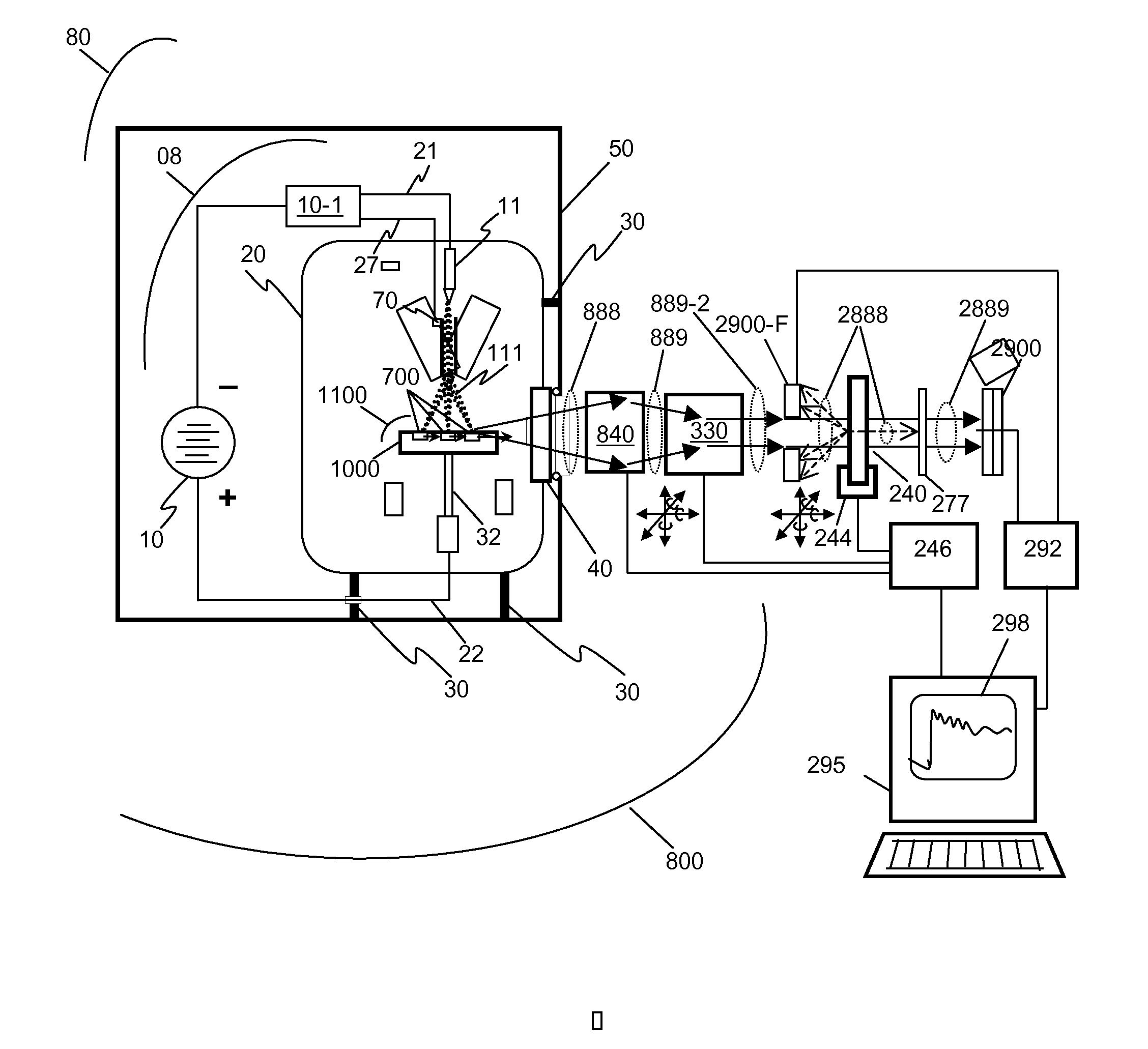
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements that have x-ray flux and flux density several orders of magnitude greater than existing compact systems. These are useful for laboratory or field applications of x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) or extended x-ray fine absorption structure (EXFAS) spectroscopy. The higher brightness is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets that comprise a number of aligned microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness and high flux. The high brightness x-ray source is then coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system to collimate the x-rays, and a monochromator, which selects the exposure energy. Absorption spectra of samples using the high flux monochromatic x-rays can be made using standard detection techniques.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
High brightness x-ray absorption spectroscopy system
InactiveUS20150357069A1Increase brightnessImprove thermal conductivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementHigh energyDesign for X
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements that have x-ray flux and flux density several orders of magnitude greater than existing compact systems. These are useful for laboratory or field applications of x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) or extended x-ray fine absorption structure (EXFAS) spectroscopy.The higher brightness is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets that comprise a number of aligned microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness and high flux.The high brightness x-ray source is then coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system to collimate the x-rays, and a monochromator, which selects the exposure energy. Absorption spectra of samples using the high flux monochromatic x-rays can be made using standard detection techniques.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
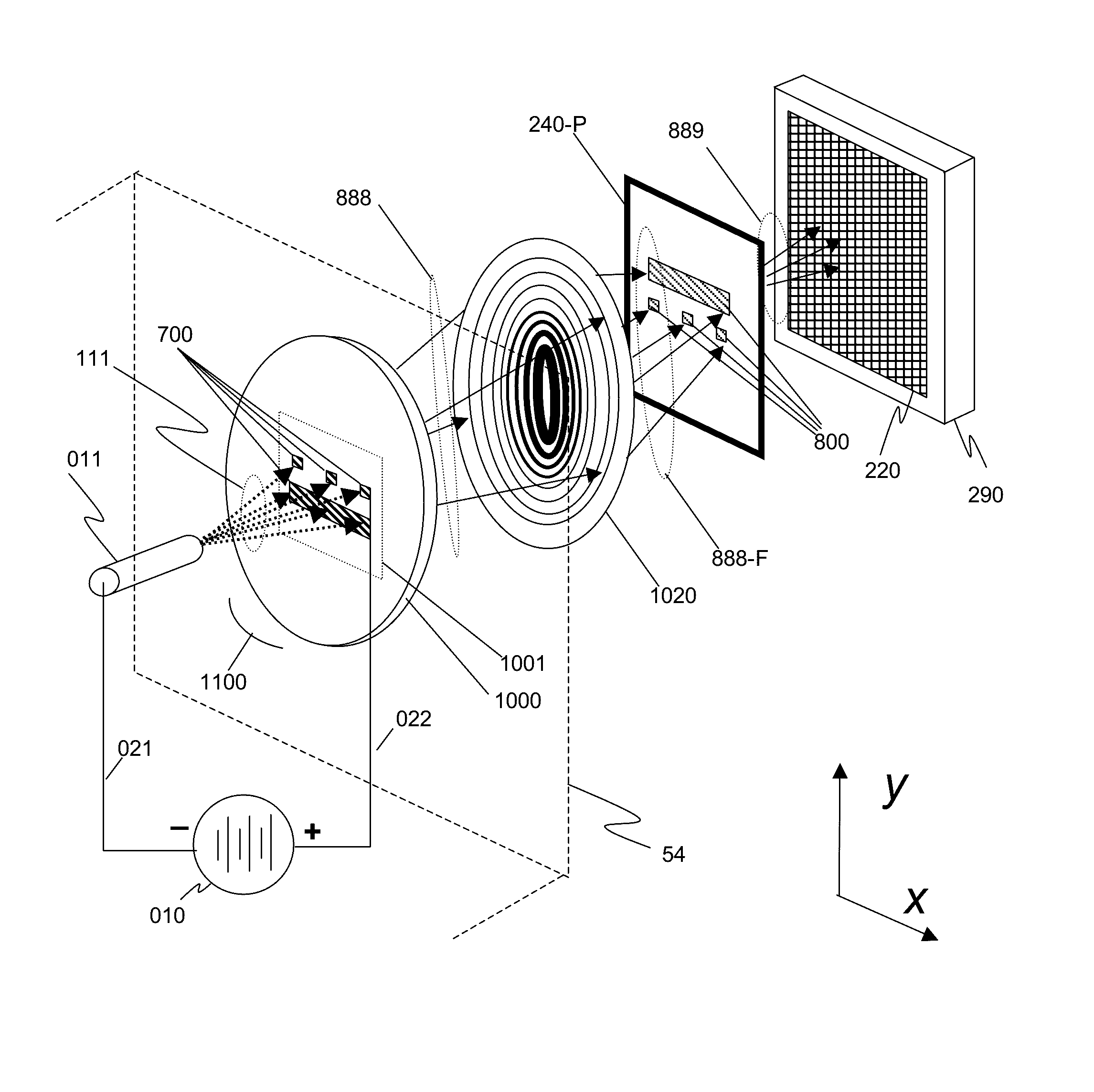
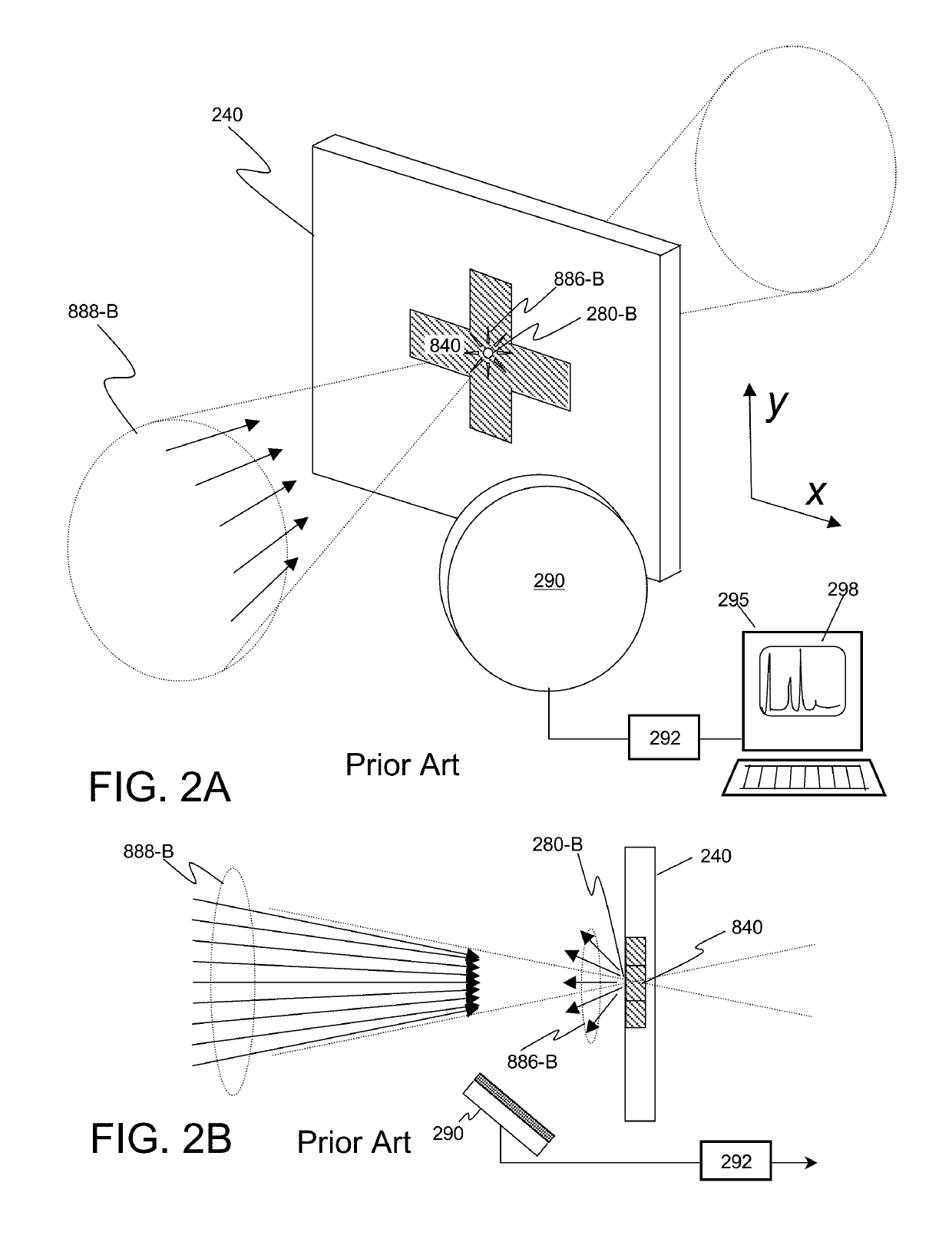
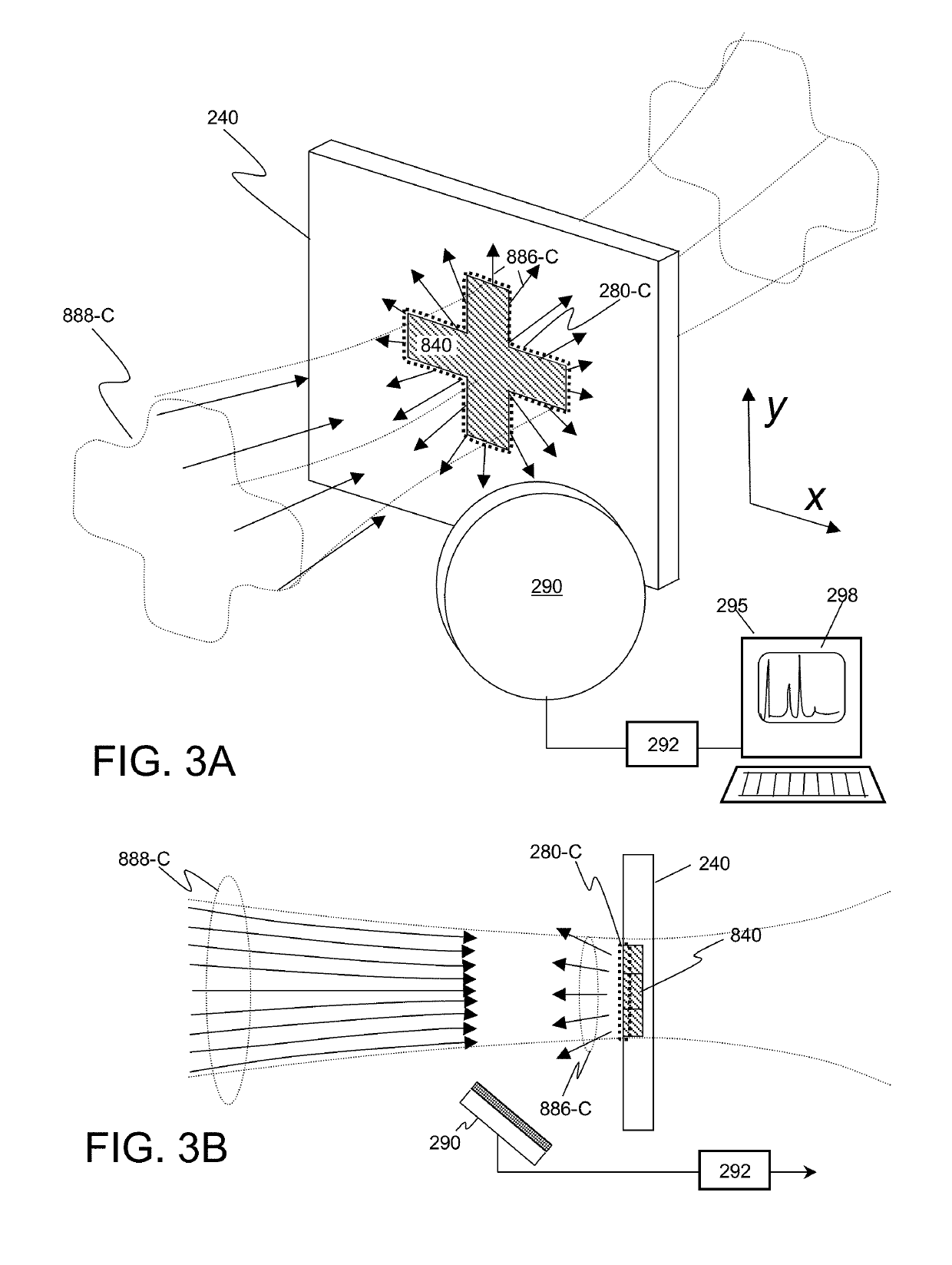
X-ray techniques using structured illumination
ActiveUS20160320320A1Great x-ray fluxEnhanced signalImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesX Ray Emission SpectroscopySmall-angle X-ray scattering
This invention discloses a method and apparatus for x-ray techniques using structured x-ray illumination for examining material properties of an object. In particular, an object with one or more regions of interest (ROIs) having a particular shape, size, and pattern may be illuminated with an x-ray beam whose cross sectional beam profile corresponds to the shape, size and pattern of the ROIs, so that the x-rays of the beam primarily interact only with the ROIs. This allows a greater x-ray flux to be used, enhancing the signal from the ROI itself, while reducing unwanted signals from regions not in the ROI, improving signal-to-noise ratios and / or measurement throughputThis may be used with a number of x-ray measurement techniques, including x-ray fluorescence (XRF), x-ray diffraction (XRD), small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS), x-ray absorption fine-structure spectroscopy (XAFS), x-ray near edge absorption spectroscopy, and x-ray emission spectroscopy.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
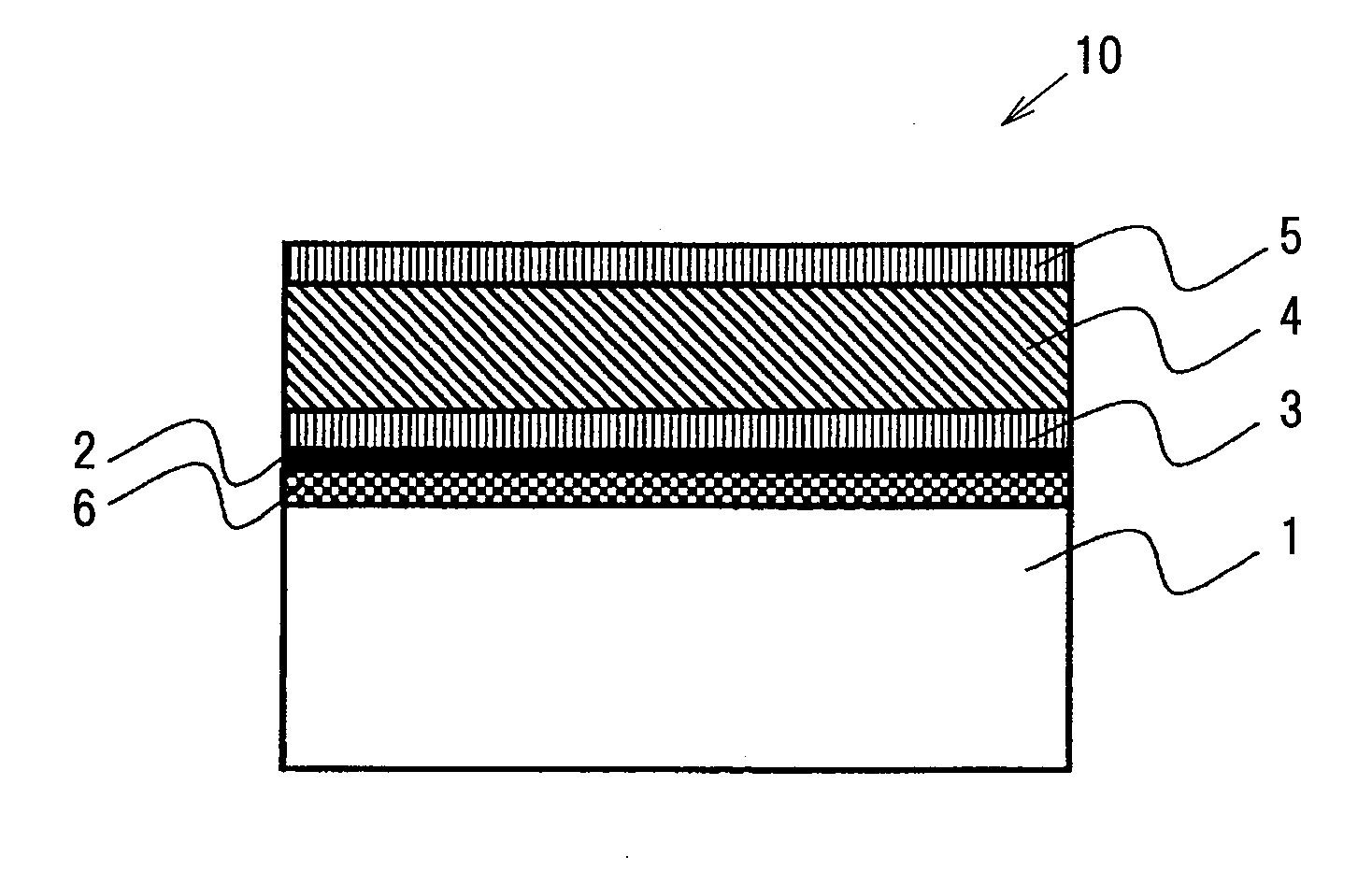
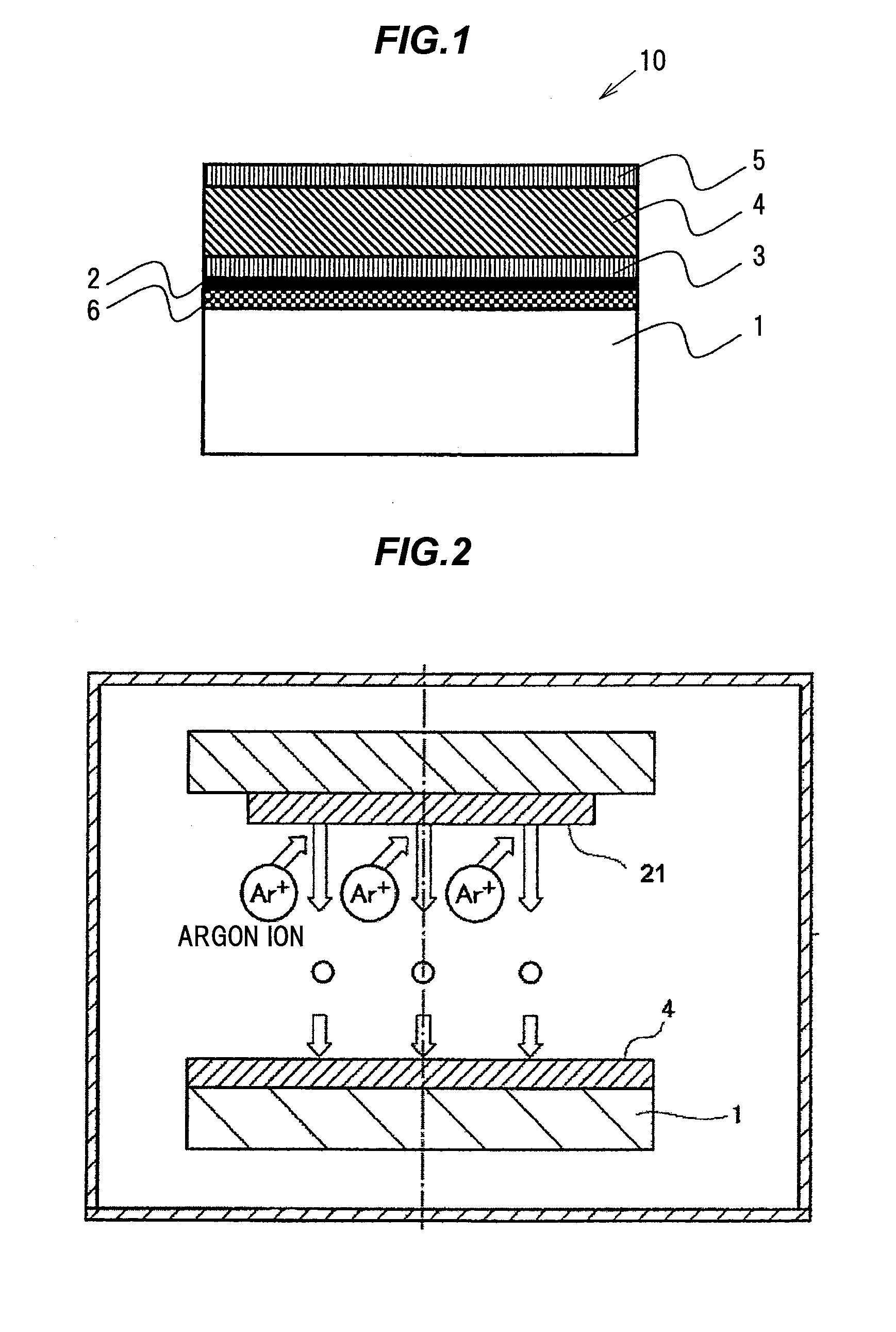
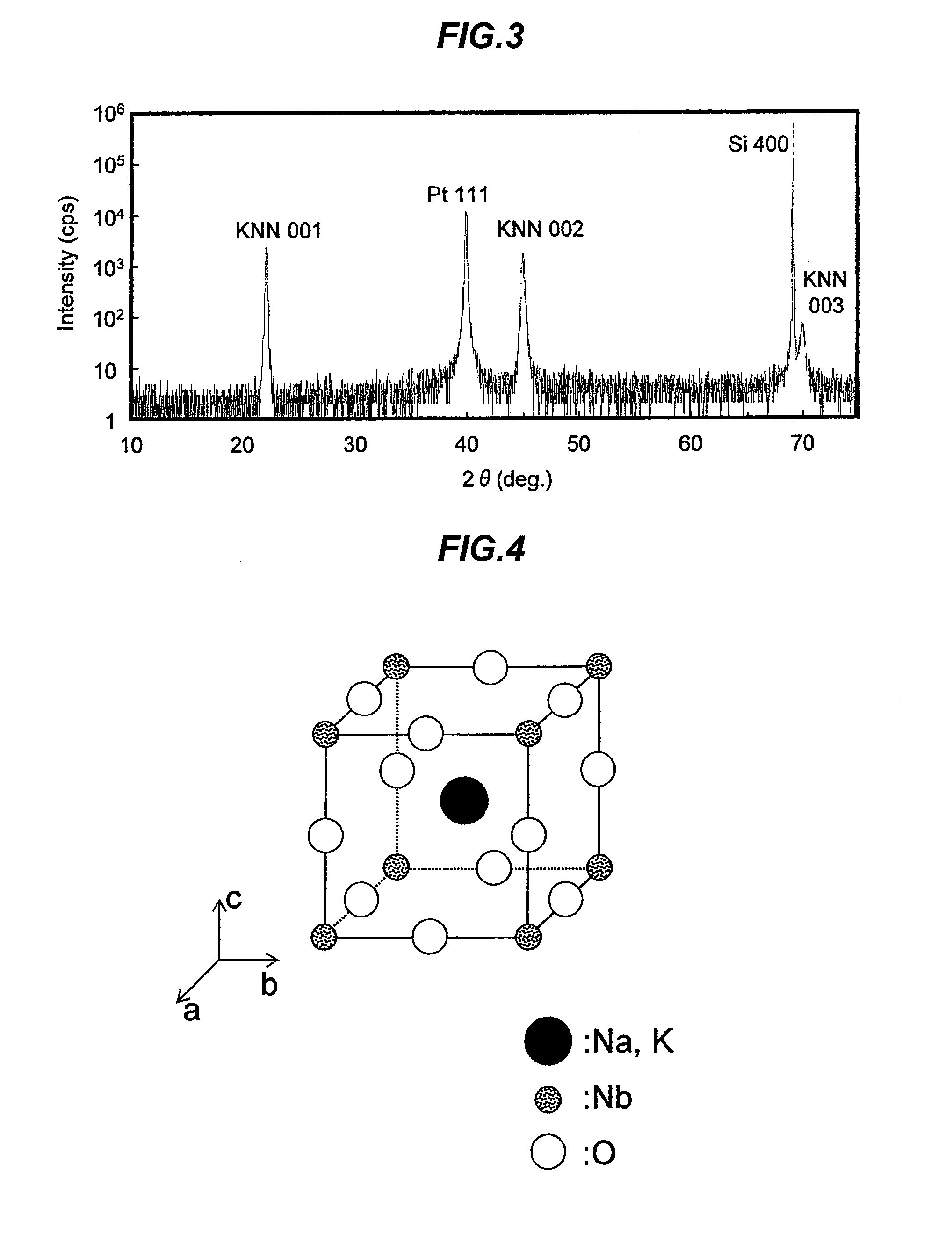
Piezoelectric element, piezoelectric device and method of manufacturing piezoelectric element
InactiveUS20140042875A1Excellent piezoelectric propertiesHigh precisionPolycrystalline material growthPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyX-ray absorption fine structureElectron energy loss spectroscopy
A piezoelectric element includes a substrate, and a lower electrode layer, a piezoelectric film represented by a general formula of (NaxKyLiz)NbO3 (0<x≦1, 0<y≦1, 0≦x≦0.2, x+y+z=1) and an upper electrode layer formed on the substrate. The piezoelectric film has a crystal structure of pseudo-cubic crystal, tetragonal crystal, orthorhombic crystal, monoclinic crystal or rhombohedral crystal, or has a state that at least two of the crystal structures coexist. A difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of an energy of Na-K absorption edge measured by an electron energy loss spectroscopy or an X-ray-absorption fine-structure spectroscopy in a direction of the film thickness of the piezoelectric film is not more than 0.8 eV.
Owner:SORIN CRM +1
X-ray techniques using structured illumination
ActiveUS10401309B2Enhanced signalReducing unwanted signalImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesX Ray Emission SpectroscopySmall-angle X-ray scattering
Owner:SIGRAY INC
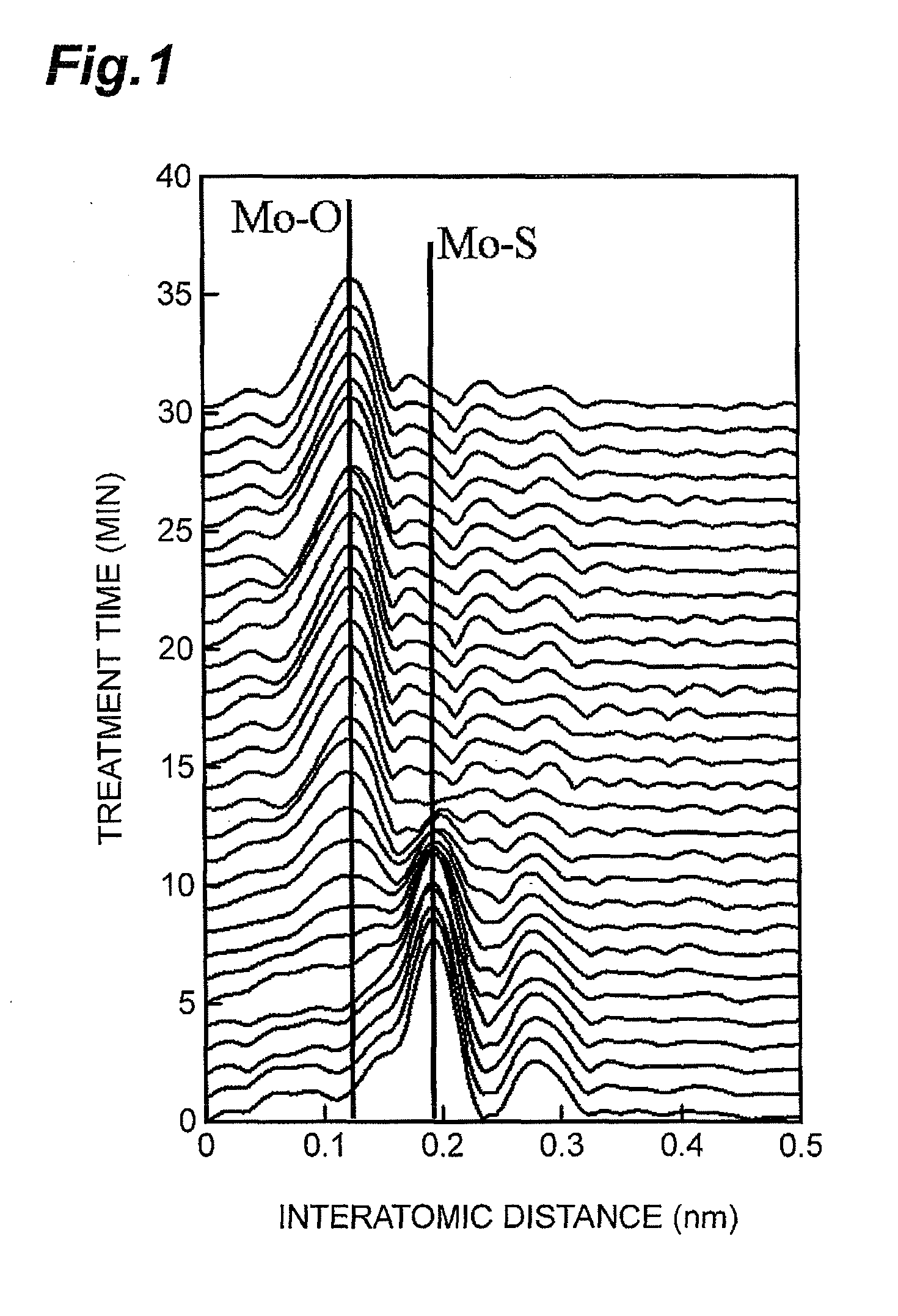
Regenerated hydrotreatment catalyst
InactiveUS8795514B2Solve the lack of activityCheap to manufactureMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesXANES SpectroscopyX-ray
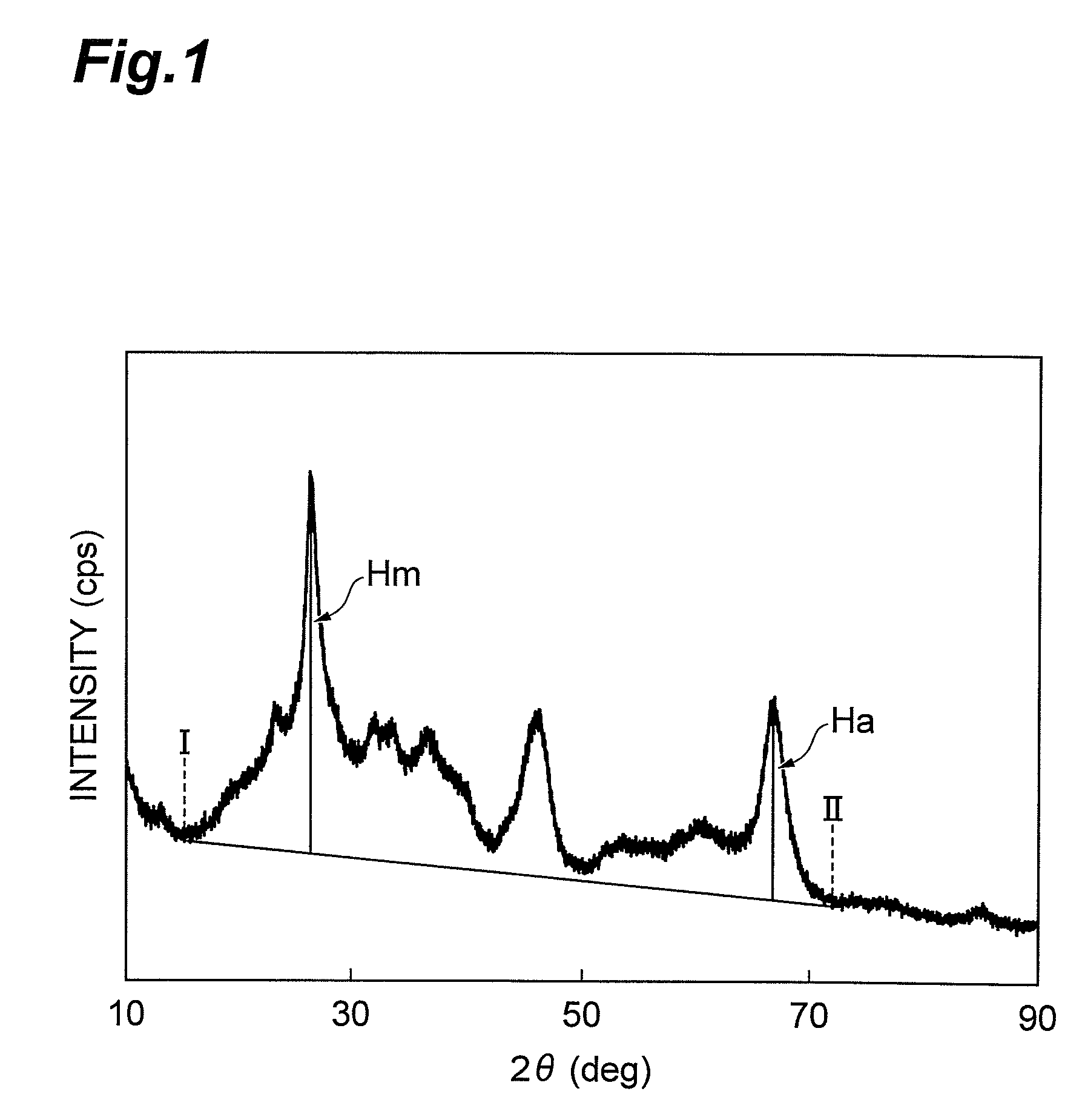
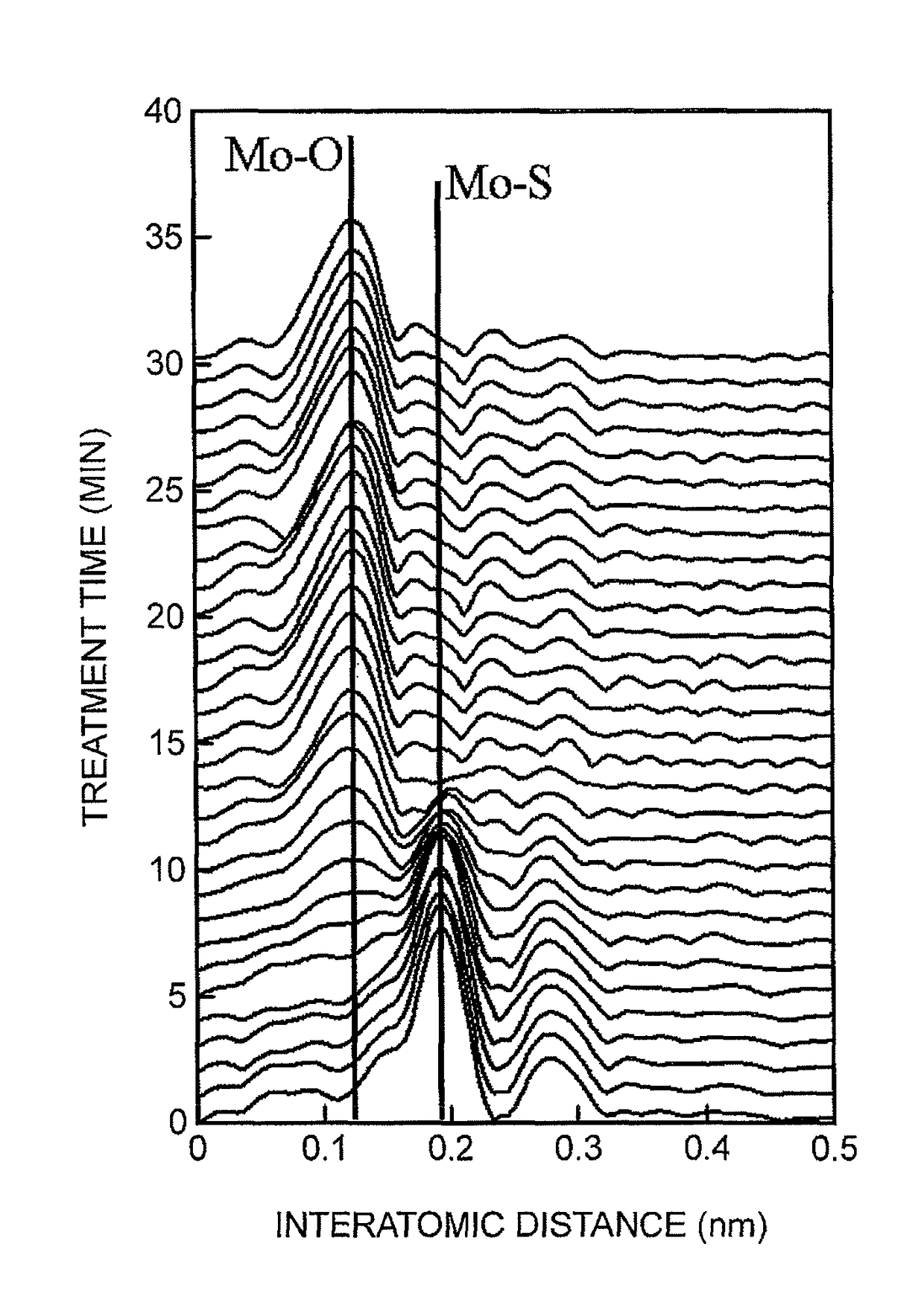
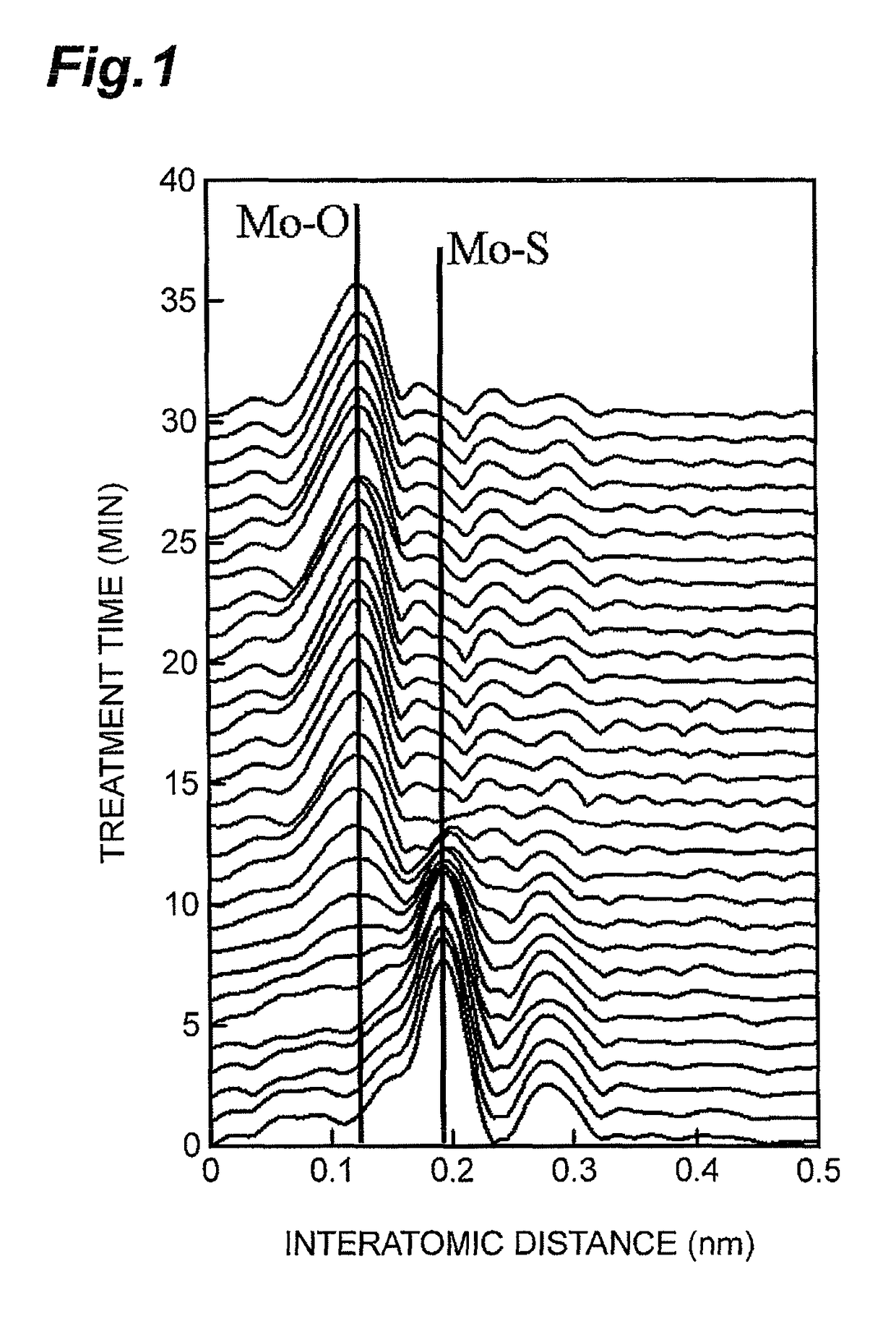
The present invention relates to a regenerated hydrotreatment catalyst regenerated from a hydrotreatment catalyst for treating a petroleum fraction, the hydrotreatment catalyst being prepared by supporting molybdenum and at least one species selected from metals of Groups 8 to 10 of the Periodic Table on an inorganic carrier containing an aluminum oxide, wherein a residual carbon content is in the range of 0.15 mass % to 3.0 mass %, a peak intensity of a molybdenum composite metal oxide with respect to an intensity of a base peak is in the range of 0.60 to 1.10 in an X-Ray diffraction spectrum, and a peak intensity of a Mo—S bond derived from a residual sulfur peak with respect to an intensity of a base peak is in the range of 0.10 to 0.60 in a radial distribution curve obtained from an extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectrum of an X-ray absorption fine structure analysis.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP +1
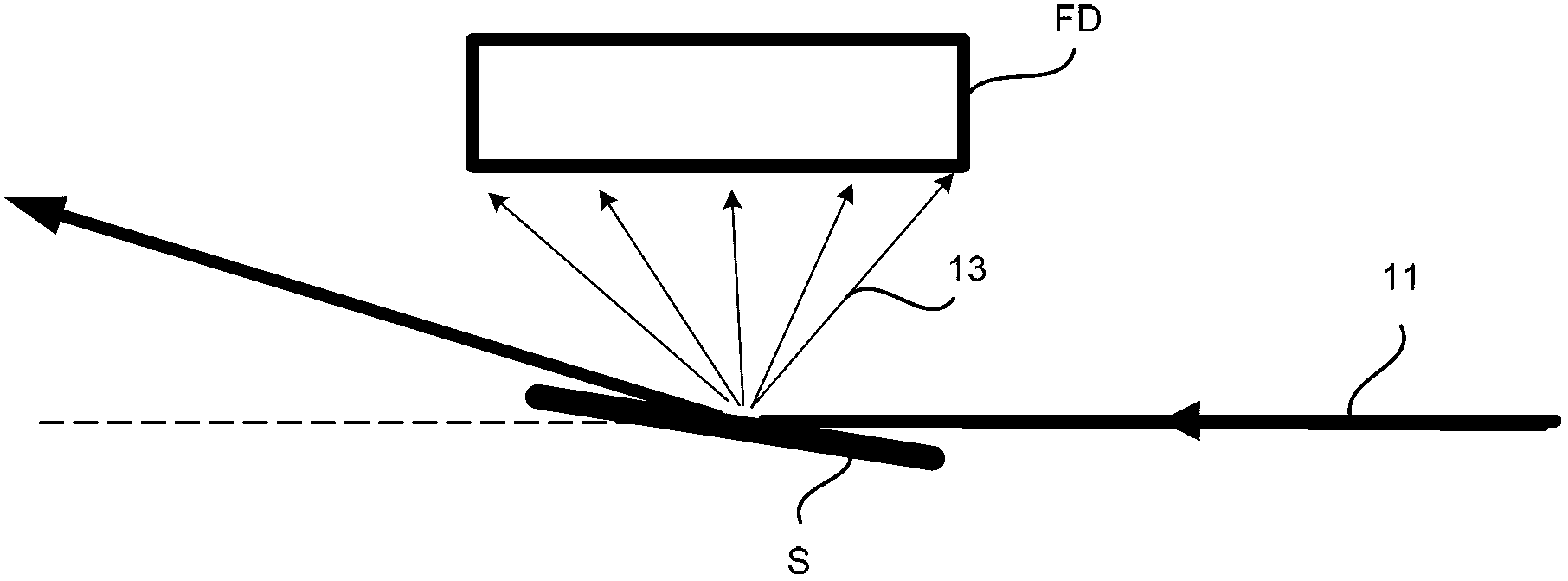
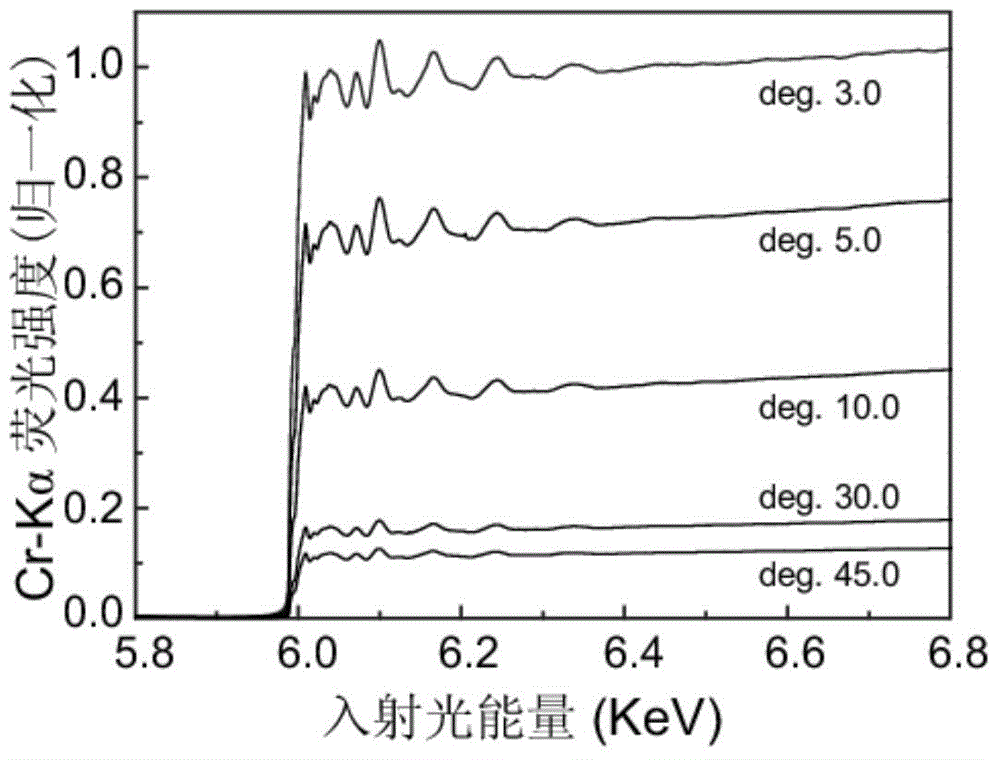
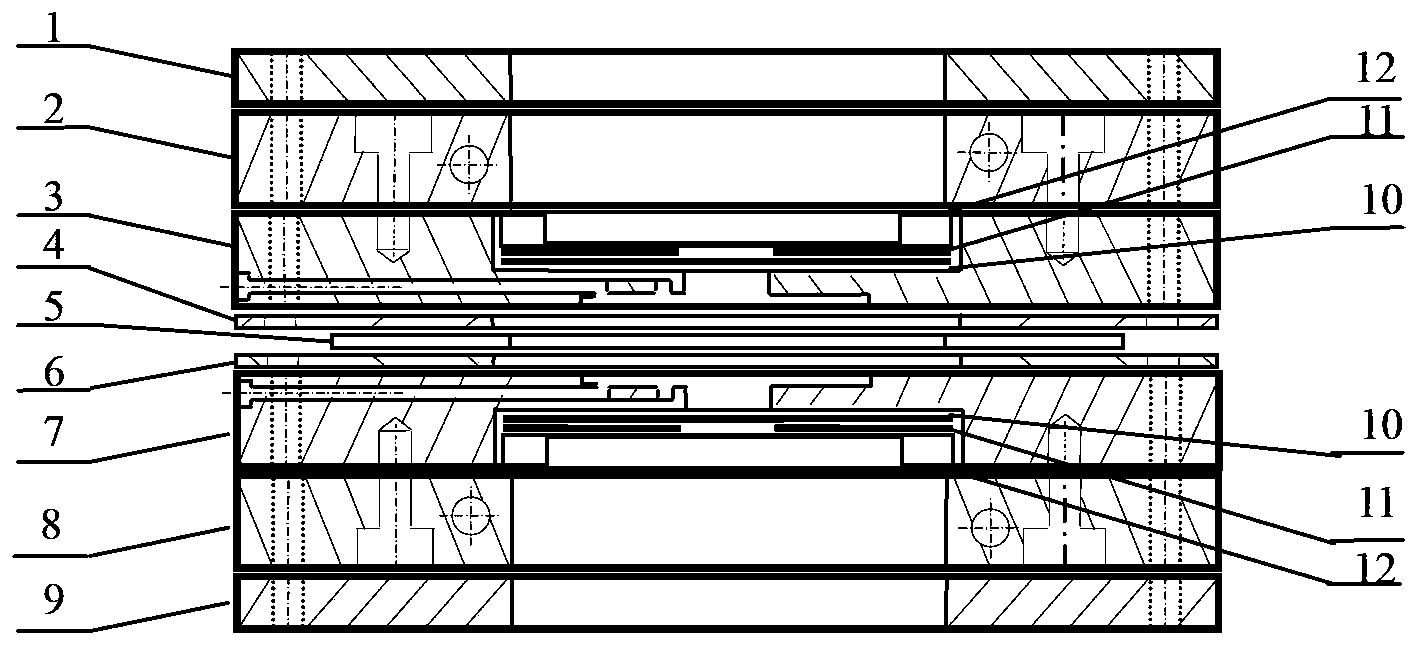
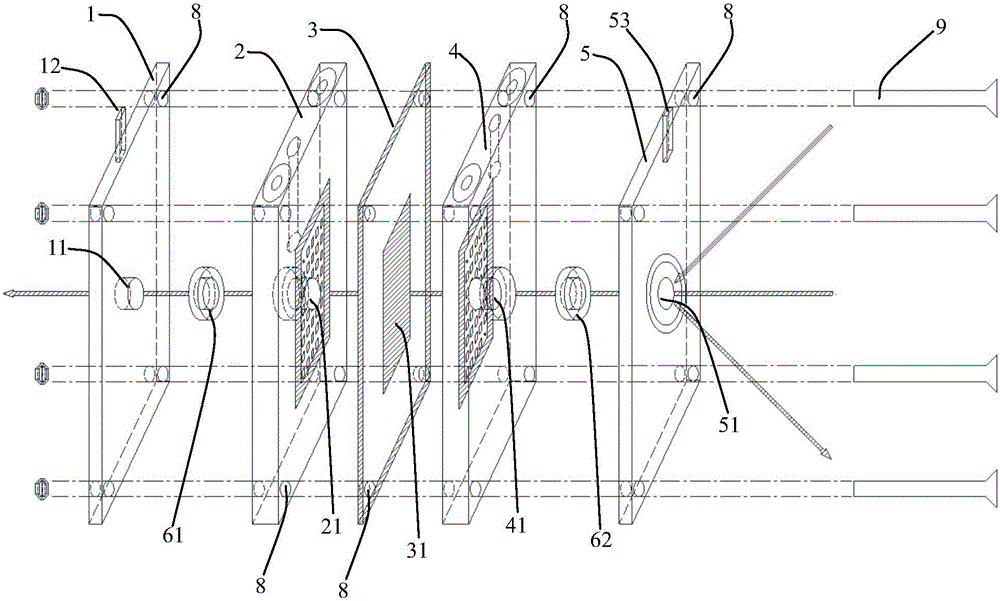
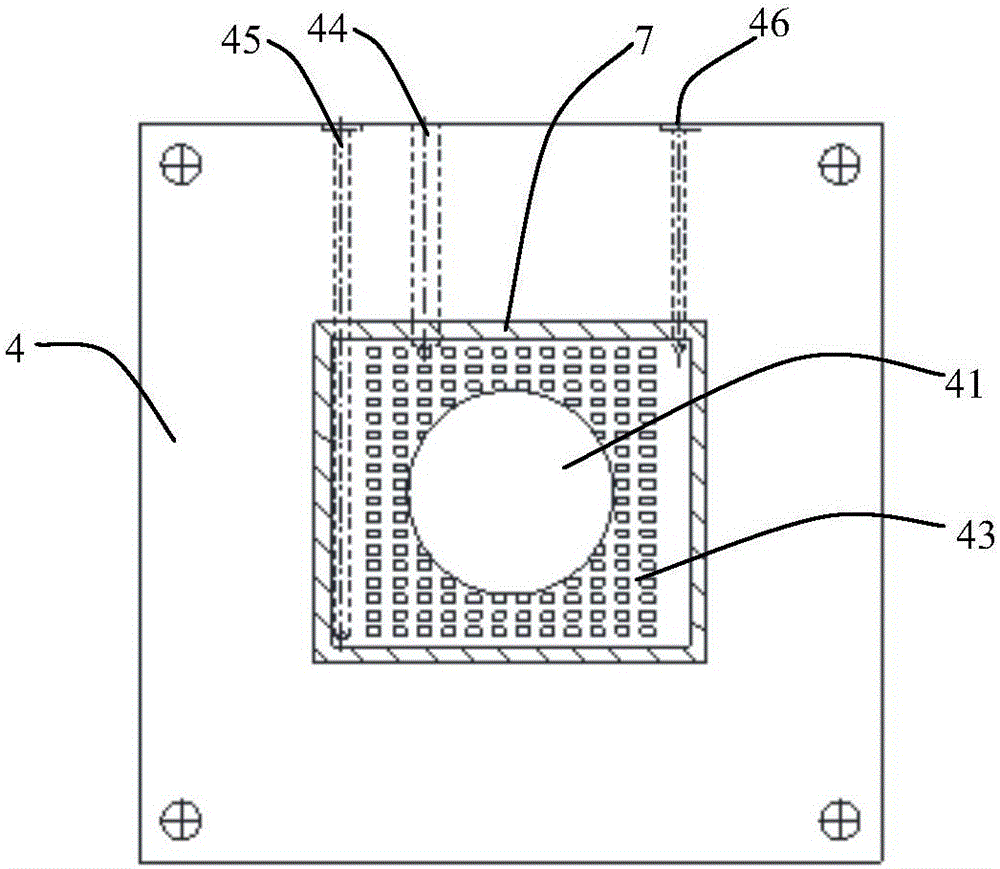
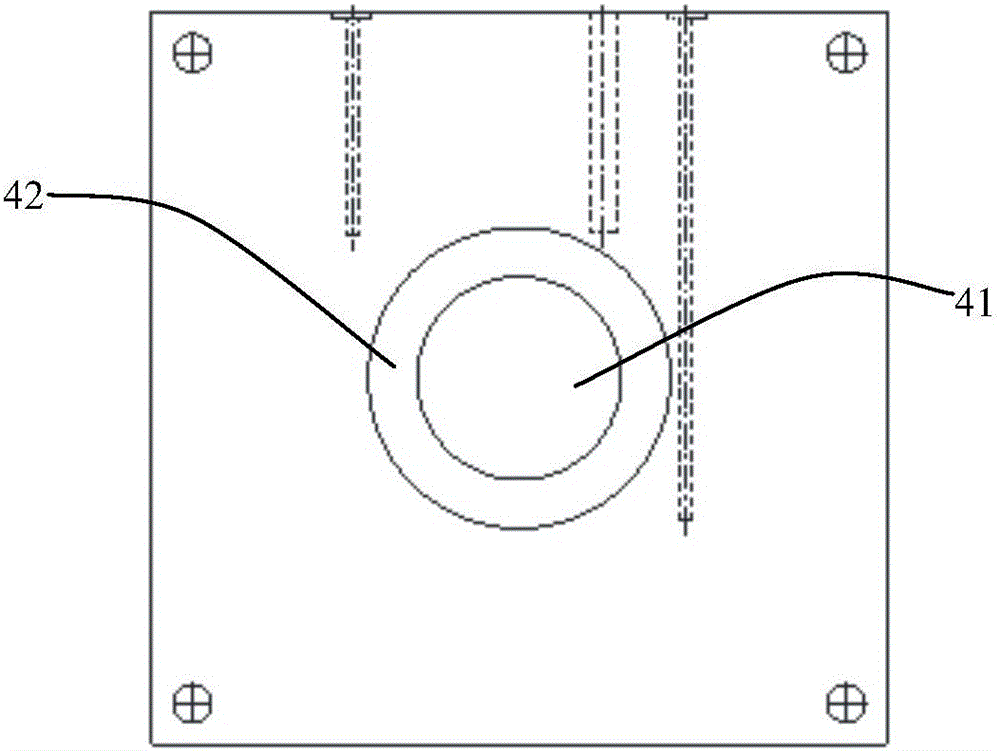
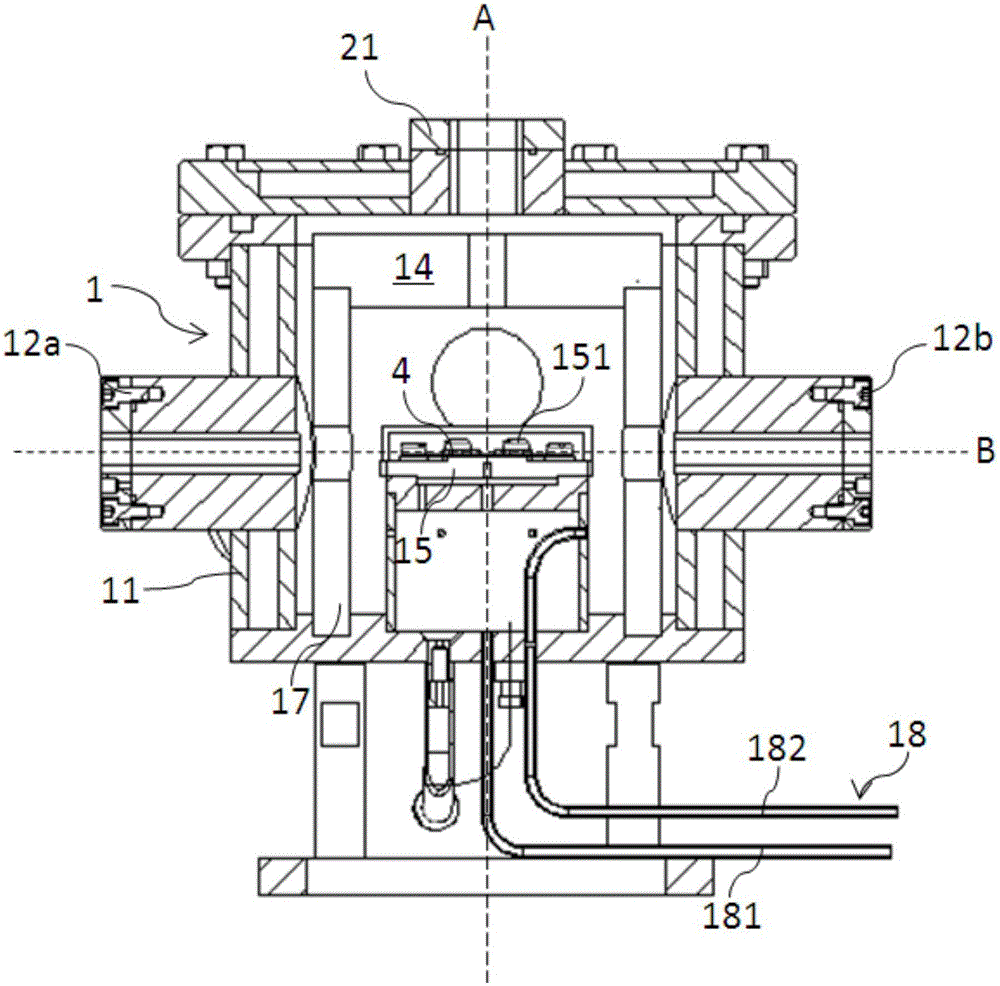
Device specially used for grazing incidence XAFS (X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) experiment and regulating method of device
ActiveCN103175857AQuality improvementAccurate settingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGrazingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
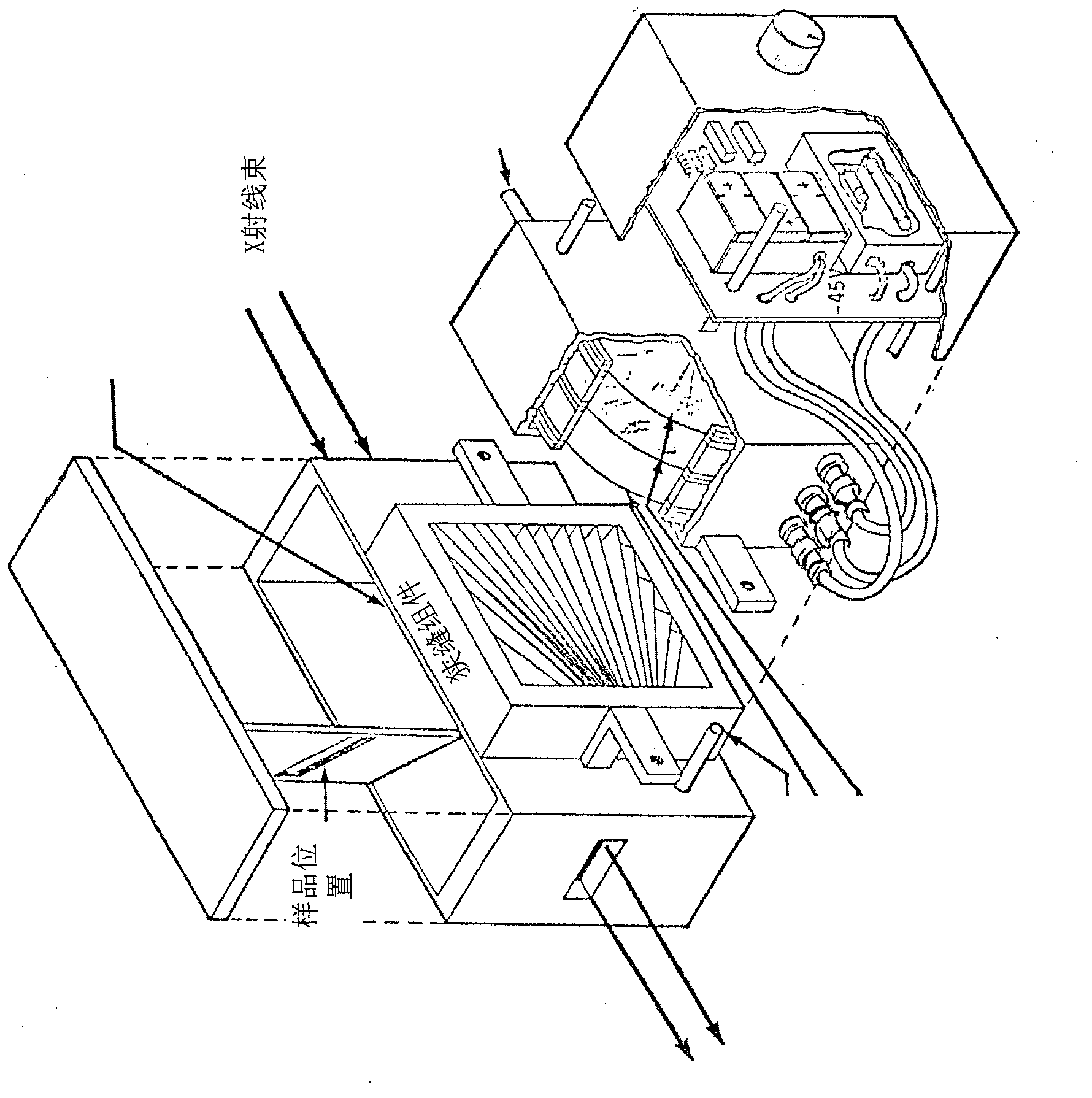
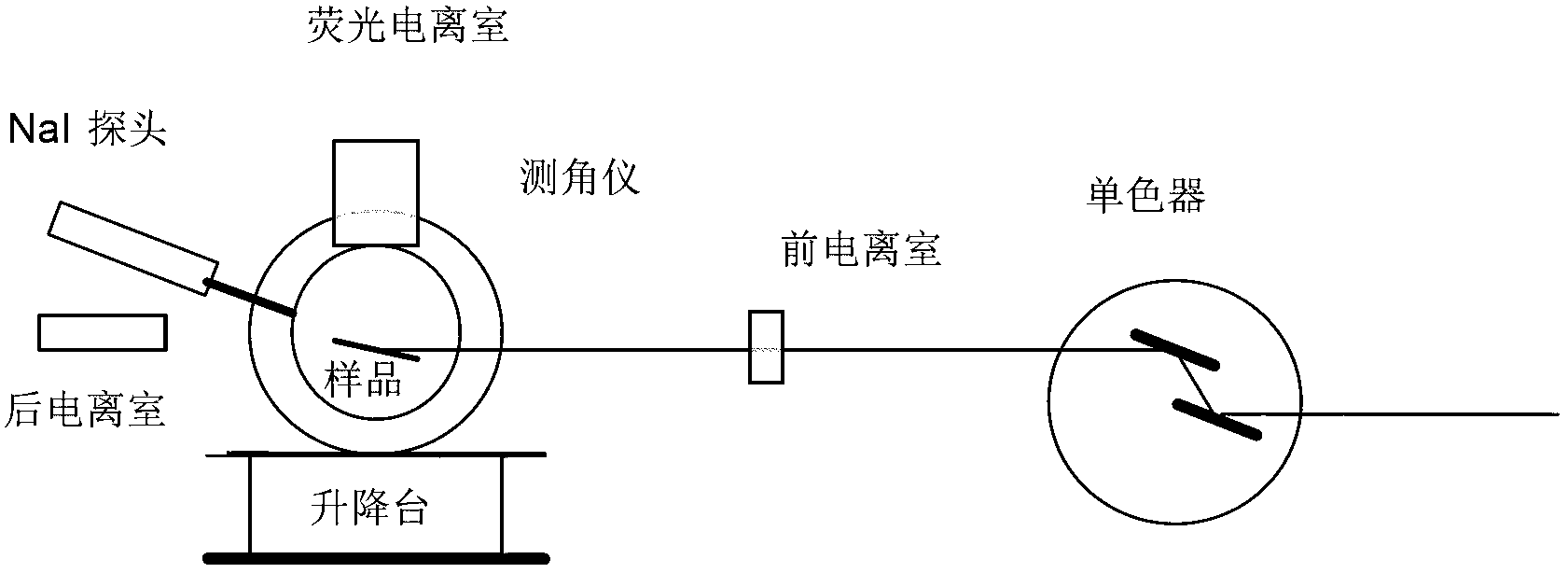
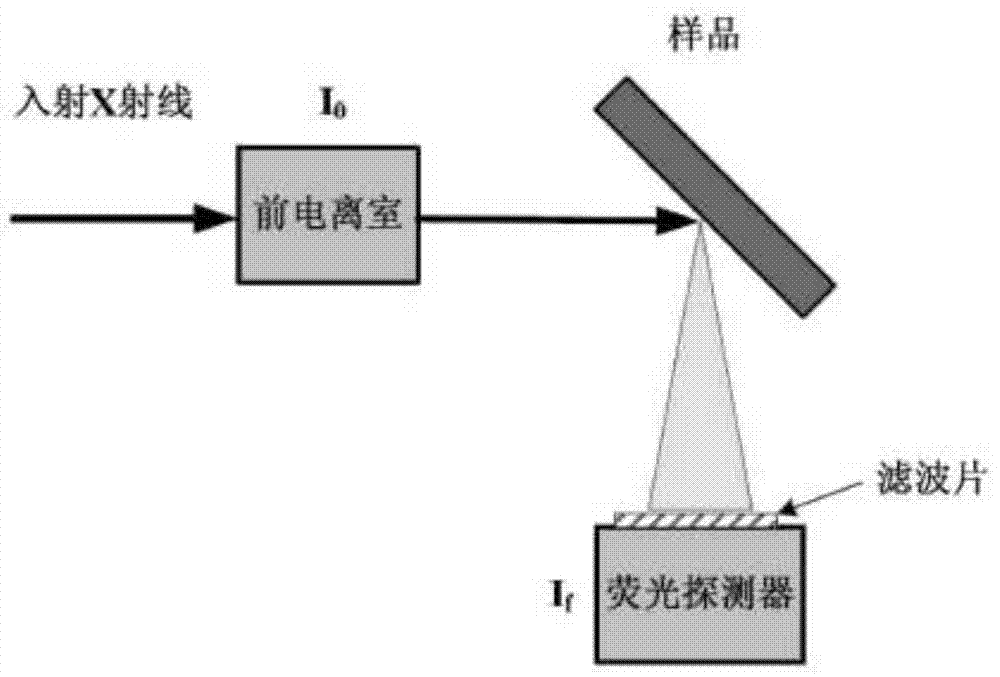
The invention discloses a device specially used for a grazing incidence XAFS (X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) experiment and a regulating method of the device. The device comprises a device for generating an X ray required by the grazing incidence XAFS experiment, a front slit for defining the size of the X ray, a first lifting platform for enabling the front slit to go up and down in the vertical direction, a sample frame for bearing a sample, a rotating platform for rotating the sample on the sample frame to obtain the required X ray grazing incidence angle, a second lifting platform for enabling the rotating platform to go up and down in the vertical direction, a rear slit for limiting the size of a total-reflection X ray, a third lifting platform for enabling the rear slit to go up and down in the vertical direction, a first detector for detecting a fluorescence signal sent by the sample, and a second detector for detecting a total-reflection X ray signal. By adopting the device and method, the initial position of the sample can be rapidly and accurately set, the sample angle can be accurately regulated, experimental detection data of the sample can be obtained at high signal to noise ratio, and a high-quality grazing incidence XAFS experiment spectrum is acquired.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
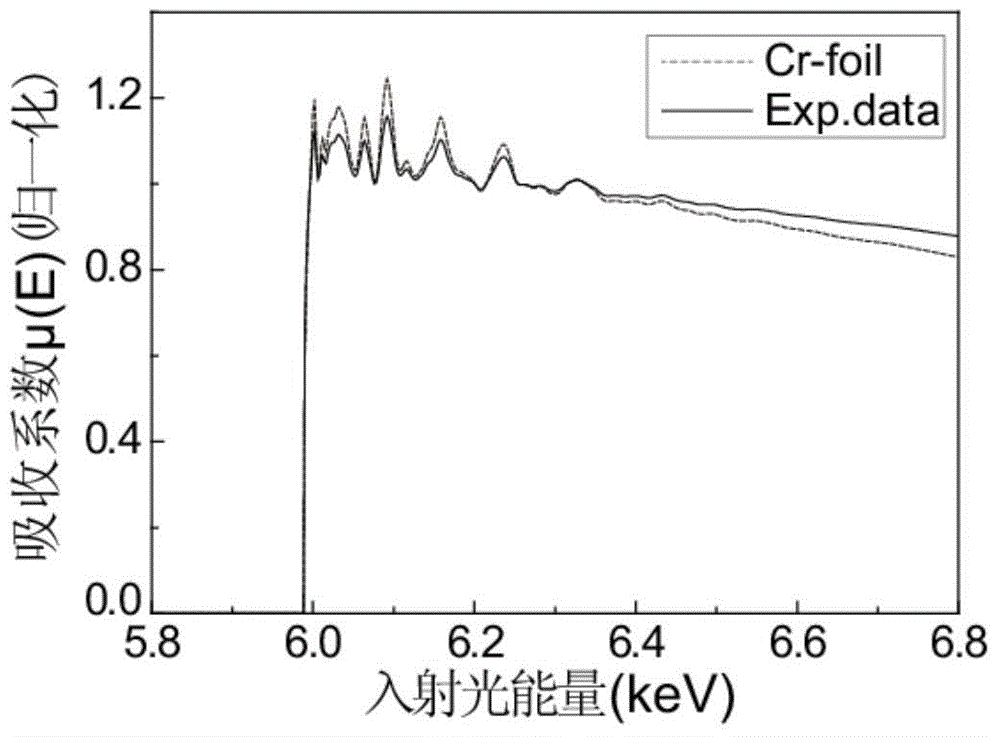
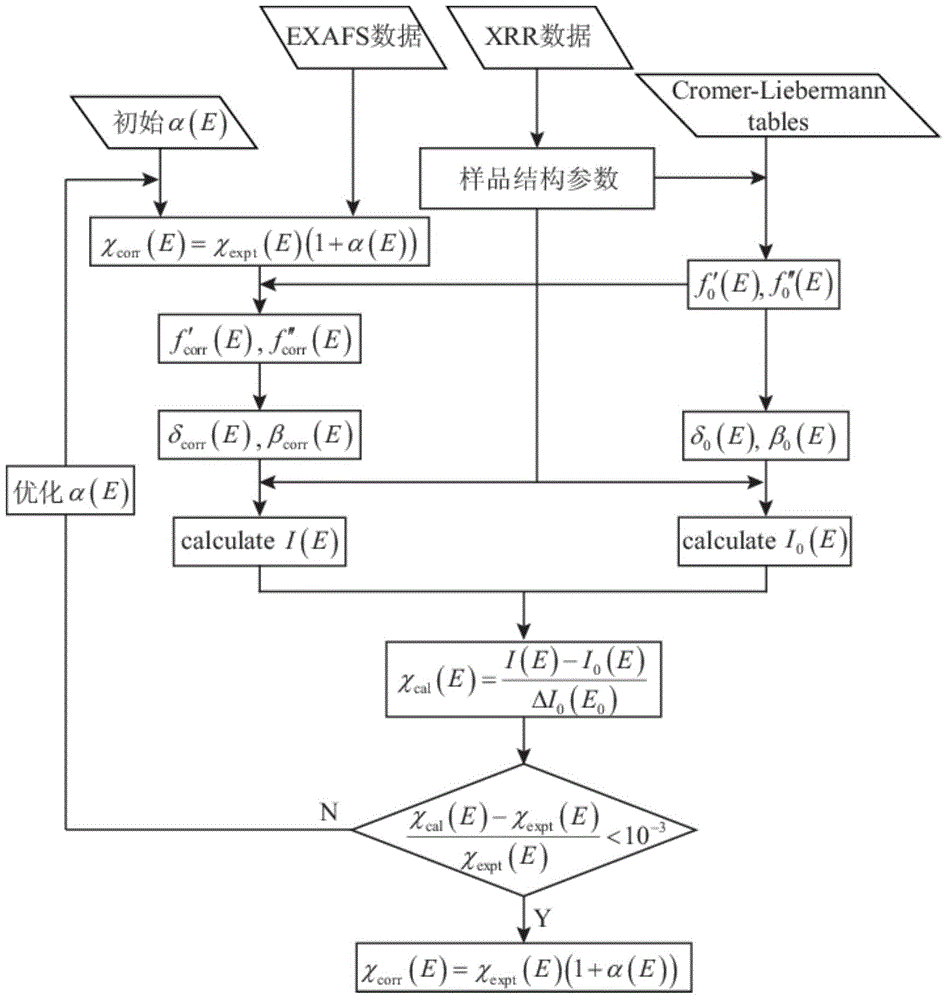
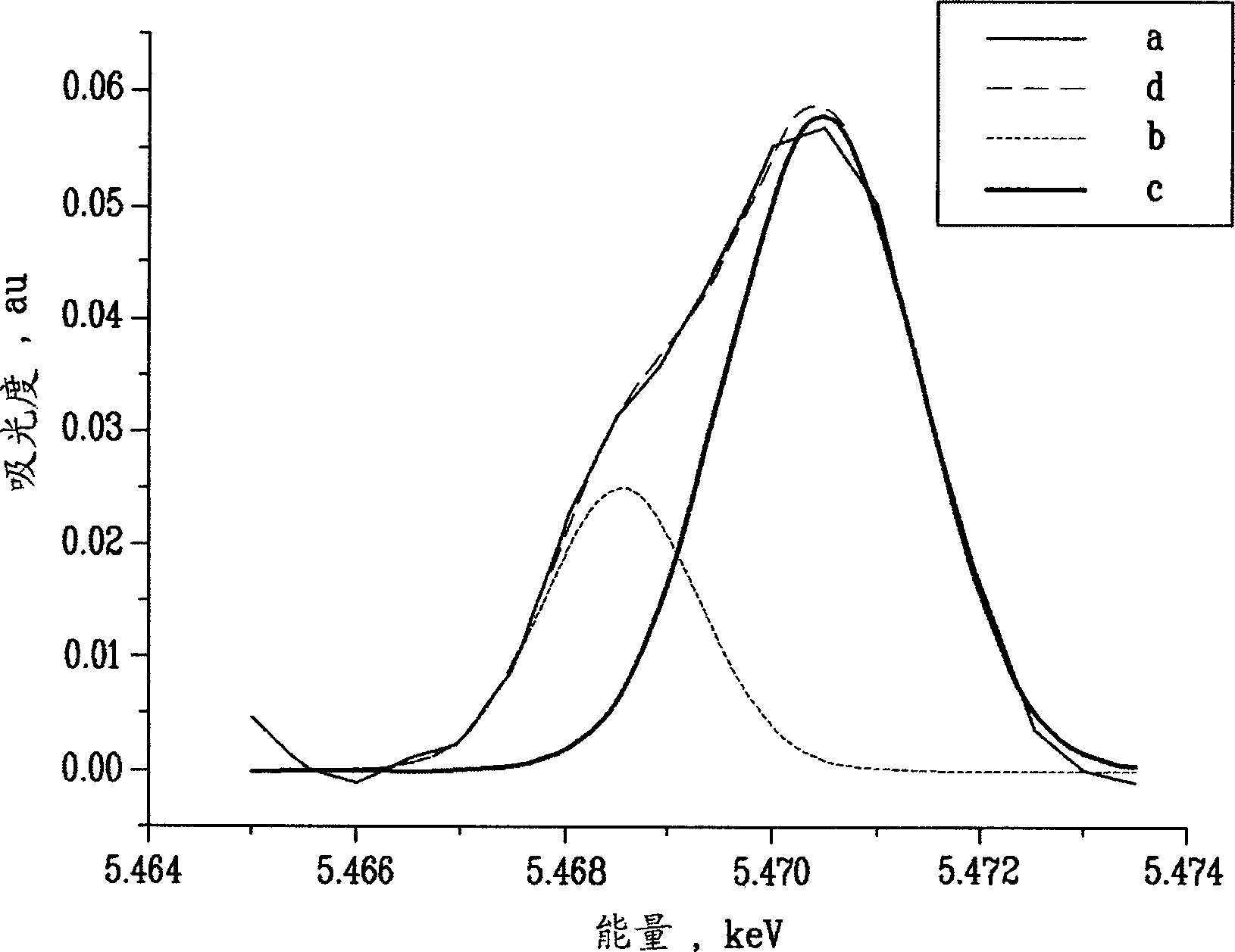
Self-absorption effect revising treatment method for fluorescence EXAFS (Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) data
InactiveCN103604818AApplicable self-absorption effectUniversalMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAbsorption factorXANES Spectroscopy
The invention relates to a self-absorption effect revising treatment method for fluorescence EXAFS (Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) data. The self-absorption effect revising treatment method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining structure parameters of a sample to be detected and a scattering amplitude factor and scattering amplitude of an isolated atom of a corresponding element of the sample to be detected; (2) calculating a refraction factor and an absorption factor of the isolated atom; (3) calculating refractive indexes of upper and lower films of the sample to be detected according to an X-ray waveband refractive index expression and calculating fluorescence intensity I0 (E) generated by the isolated atom by utilizing a multi-layered film fluorescence intensity calculation method; (4) initializing a revising factor alpha (E) and calculating a scattering amplitude and a scattering amplitude factor, which have fine oscillating structures and are not influenced by a self-absorption effect; (5) calculating a refraction factor and an absorption factor, which have oscillating structures; (6) utilizing the multi-layered film fluorescence intensity calculation method to calculate fluorescence intensity I (E) with an oscillating structure; (7) calculating an oscillating structure function Xcal(E) according to the I0 (E) and the I (E); and (8) judging whether the Xcal(E) meets the requirements or not. Compared with the prior art, the self-absorption effect revising treatment method for the fluorescence EXAFS data has the advantages of high reliability, wide application range and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
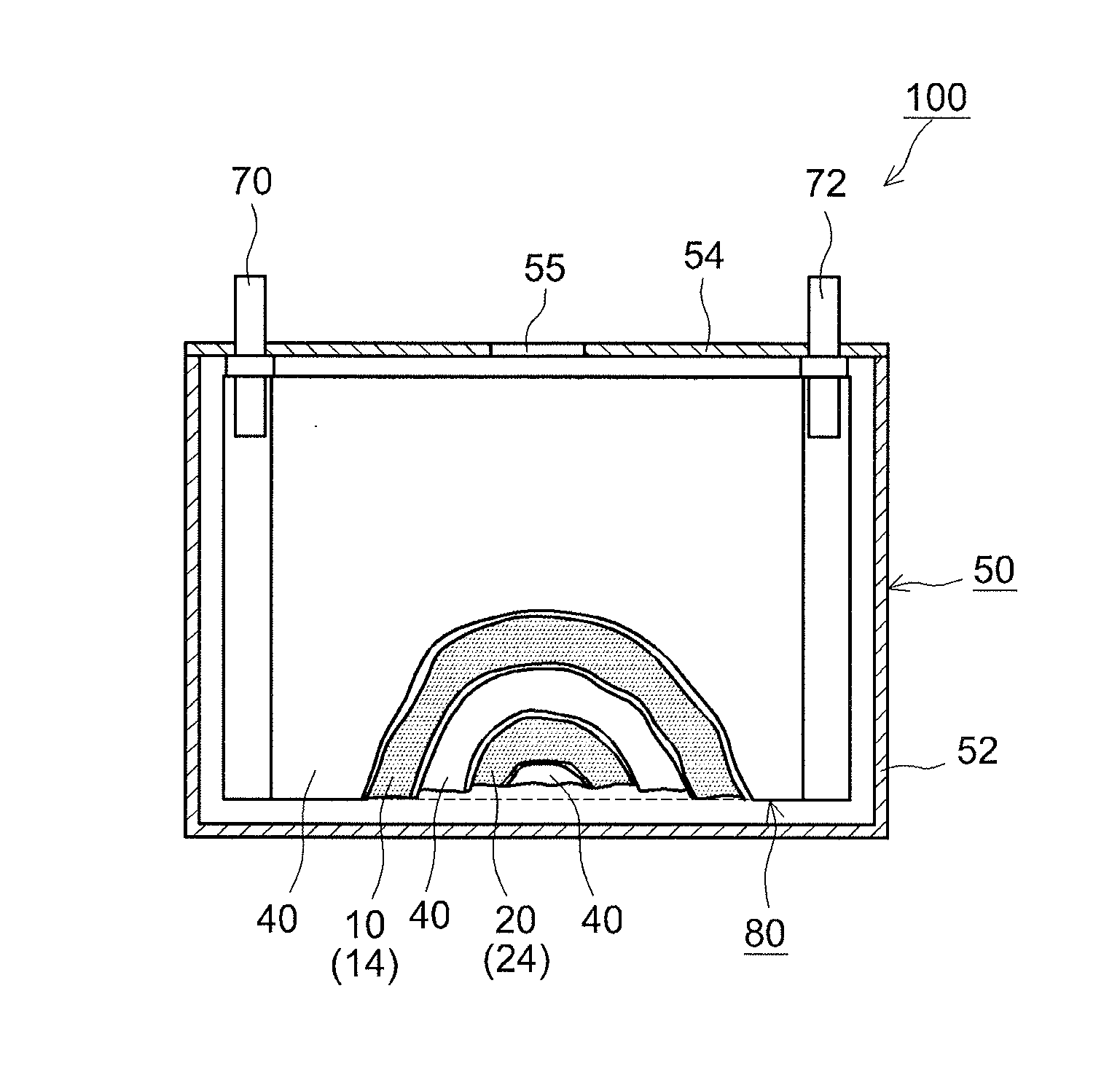
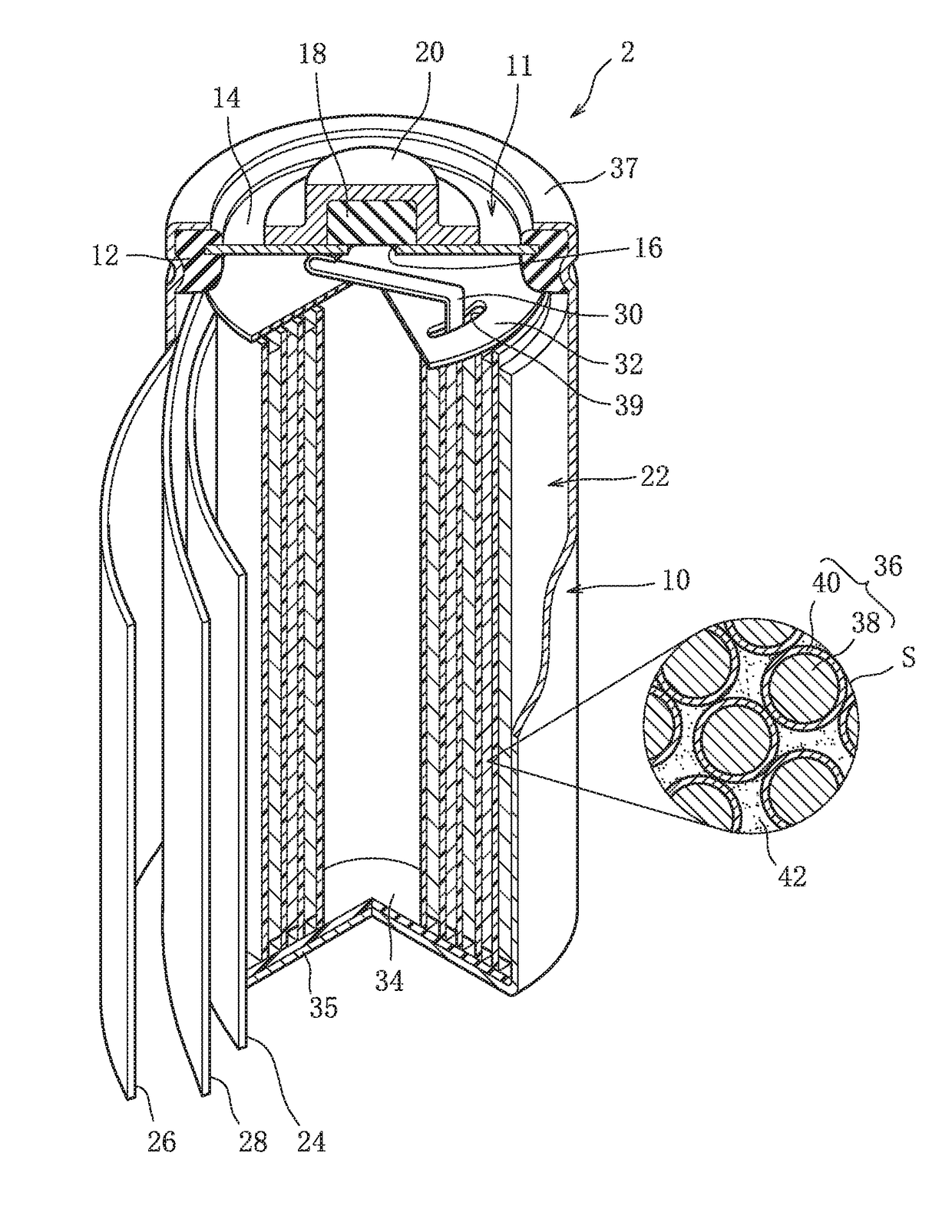
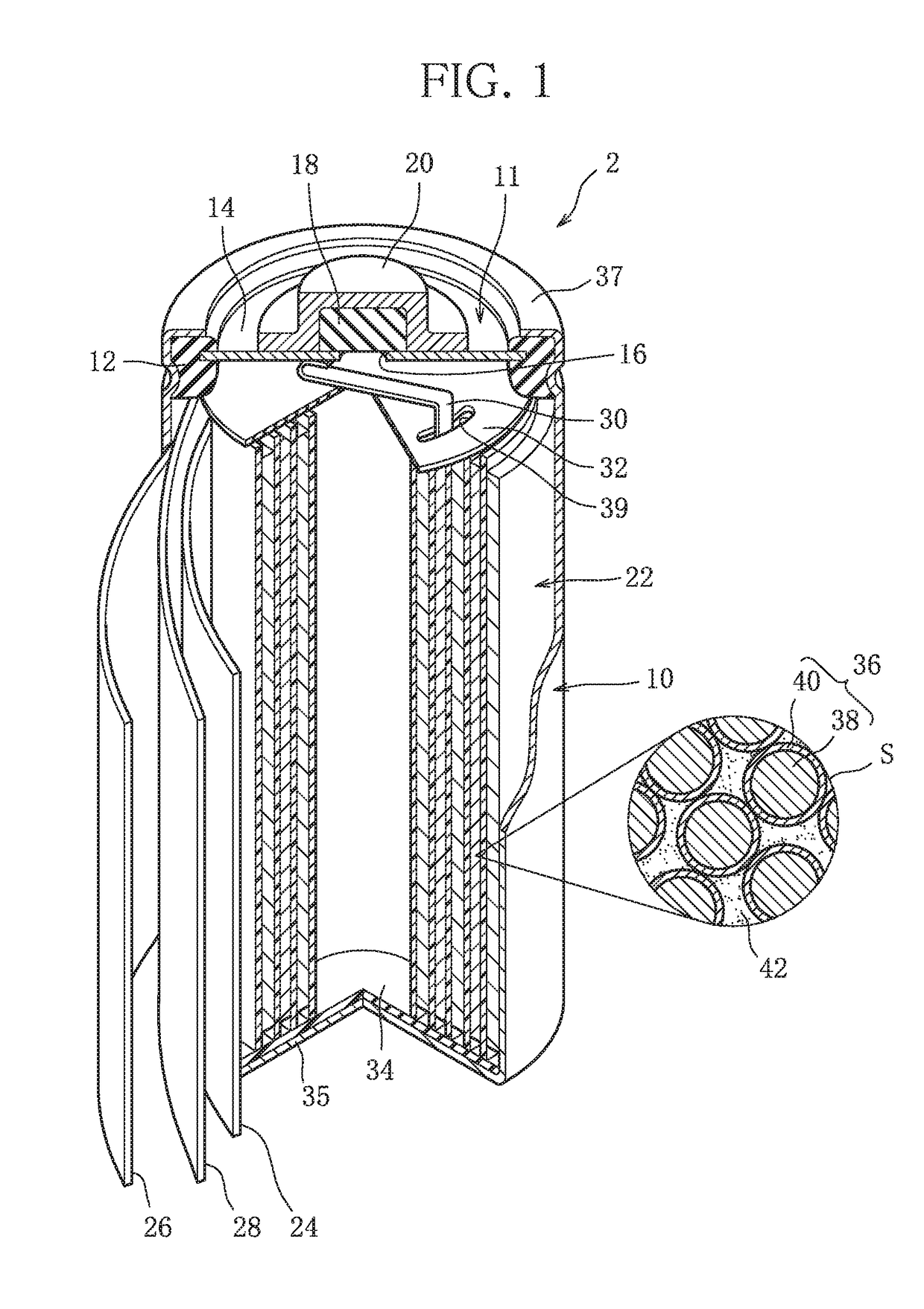
Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and production method thereof
InactiveUS20150303519A1Improve output characteristicsResistance discharge can be suppressedFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithiumX-ray absorption fine structure
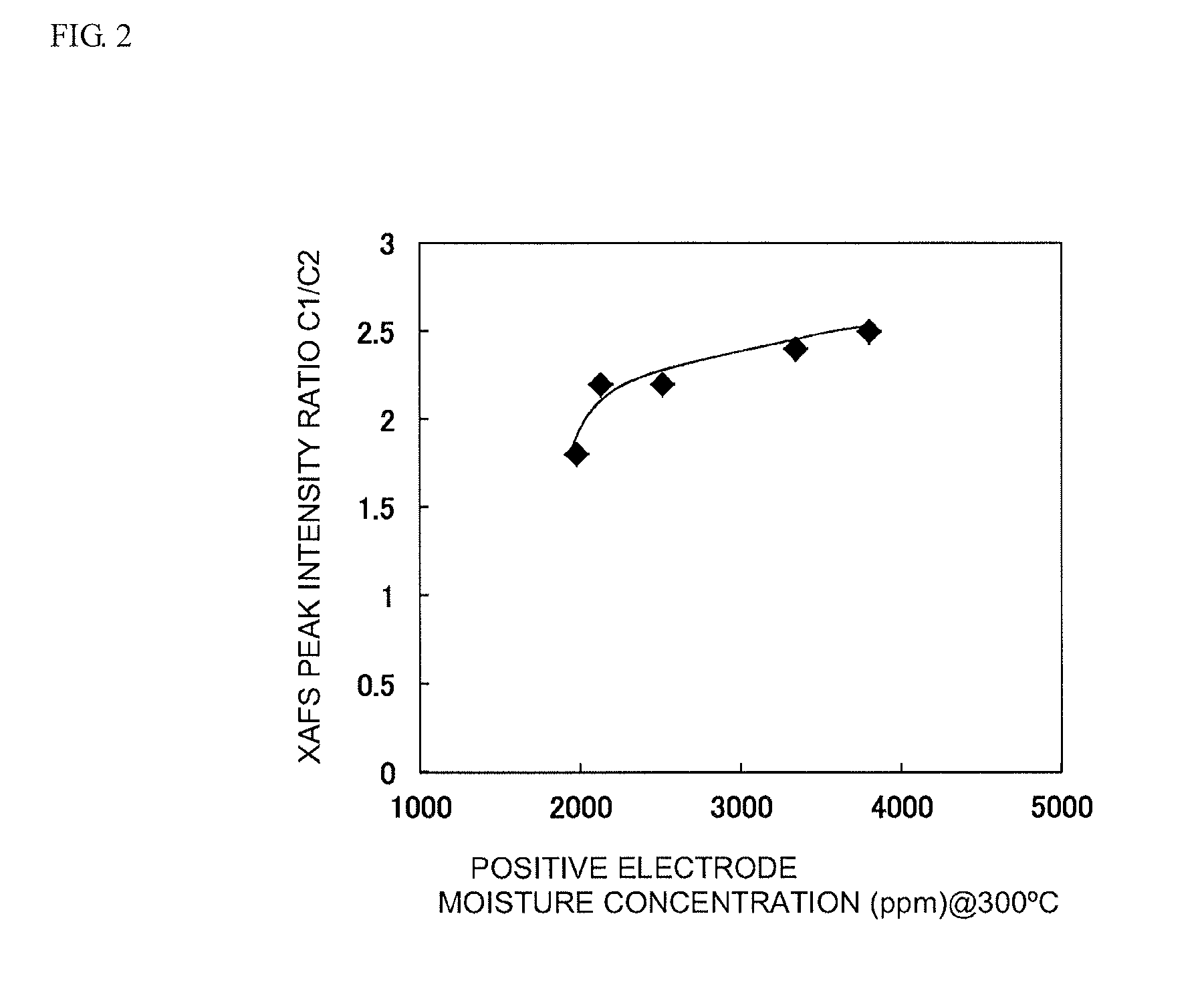
Provided is a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery having both superior output characteristics and durability. The positive electrode and the negative electrode of this battery are respectively provided with a film containing lithium ions and fluoride ions. The film of the positive electrode is such that a ratio (C1 / C2) of a first peak intensity C1 of 58 to 62 eV to a second peak intensity C2 of 68 to 72 eV, based on X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) analysis of the Li—K absorption edge, is 2.0 or more, and the fluoride ions are contained at 1.99 μg / mg to 3.13 μg / mg per unit mass of the positive electrode active material layer. In addition, the film of the negative electrode is such that a ratio (A1 / A2) of a first peak intensity A1 of 58 to 62 eV to a second peak intensity A2 of 68 to 72 eV, based on X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) analysis of the Li—K absorption edge, is 2.0 or less.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
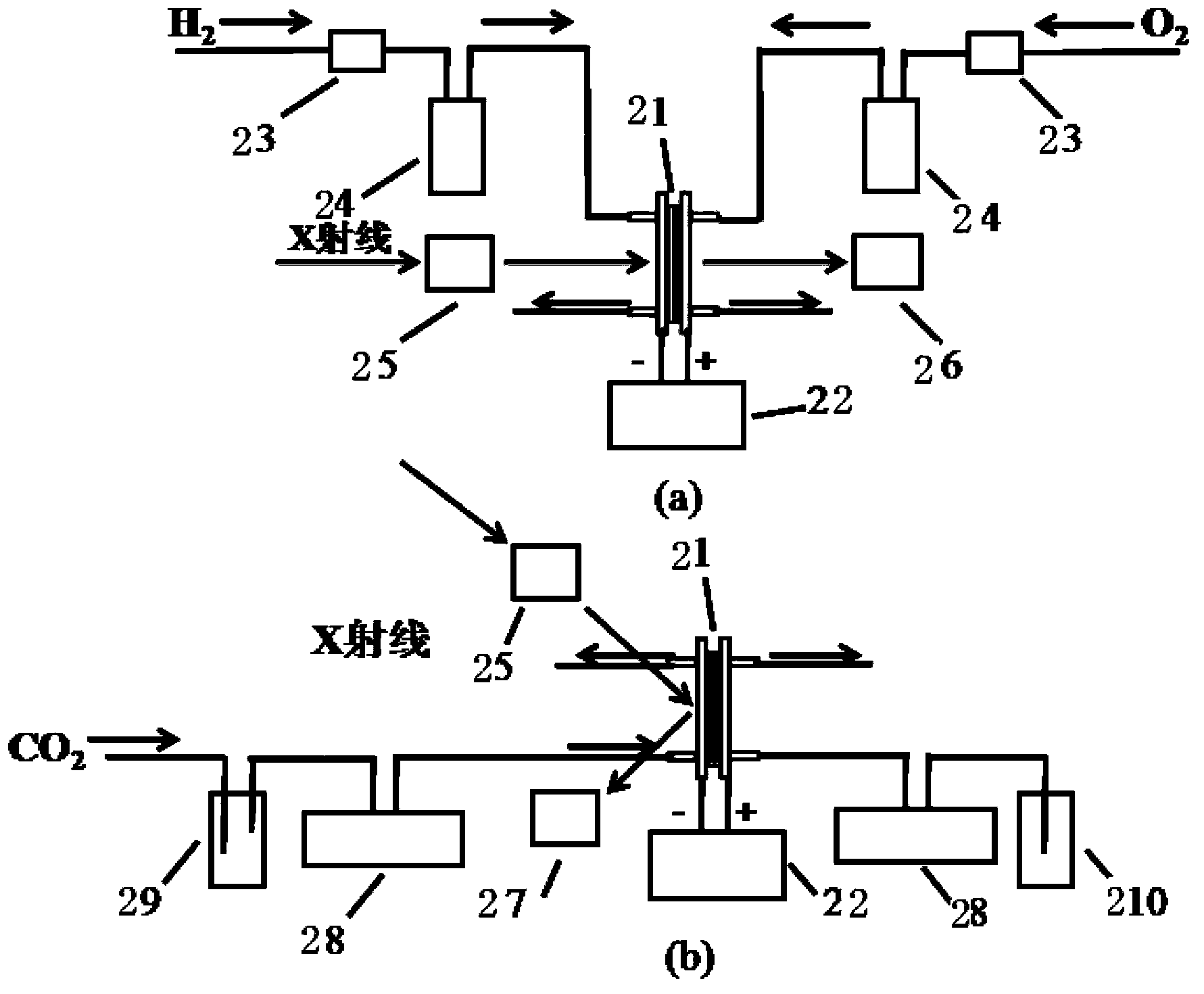
Synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device used for electrocatalysis reaction
ActiveCN103884728AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSoft x rayElectricity
The invention discloses a synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device used for electrocatalysis reaction. The synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device comprises a synchrotron radiation X ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) line station front ionization chamber, a synchrotron radiation XAFS line station back ionization chamber (or a fluorescence detector) and an in-situ pool. A membrane electrode for electrocatalysis reaction is arranged in the in-situ pool, and in the condition that detection windows of components of the in-situ pool are in the same center line, X-ray irradiates onto the membrane electrode, and then reaches, in a transmission or reflection way, to the synchrotron radiation XAFS line station back ionization chamber or the fluorescence detector so as to achieve in-situ detection of the catalyst structure in the electrocatalysis reaction process; the detection windows of the in-situ pool are in the center of a flow field plate, the dead volume is less, the accuracy and reliability of experimental data can be improved, a heating plate and the flow field plate in the in-situ pool are fixed together by bolts, the detection windows on the flow field plate are sealed, and the assembly and replacement of the membrane electrode are facilitated. The synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device is a set of detection device suitable for the study of the electrocatalytic reaction process and mechanism.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Negative active material for non-aqueous electrolyte battery,method of preparing same and non-aqueous electrolyte battery
InactiveCN1783551AElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsFine structureX-ray absorption fine structure
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS20150147630A1Low degradation potentialInhibition is effectivePrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureX-ray absorption fine structureEngineering
Provided is a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery in which the following are housed in a battery case: a nonaqueous electrolyte, a boron atom-containing oxalato complex compound, and an electrode assembly in which a positive electrode having a positive electrode active material and a negative electrode having a negative electrode active material are disposed facing each other. Here, a coat containing boron atoms originating from the oxalato complex compound is formed on the surface of the negative electrode active material, and the amount BM (μg / cm2) of the boron atom as measured based on inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopic analysis and the intensity BA for a tricoordinate boron atom as measured based on x-ray absorption fine structure analysis satisfy 0.5≦BA / BM≦1.0.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
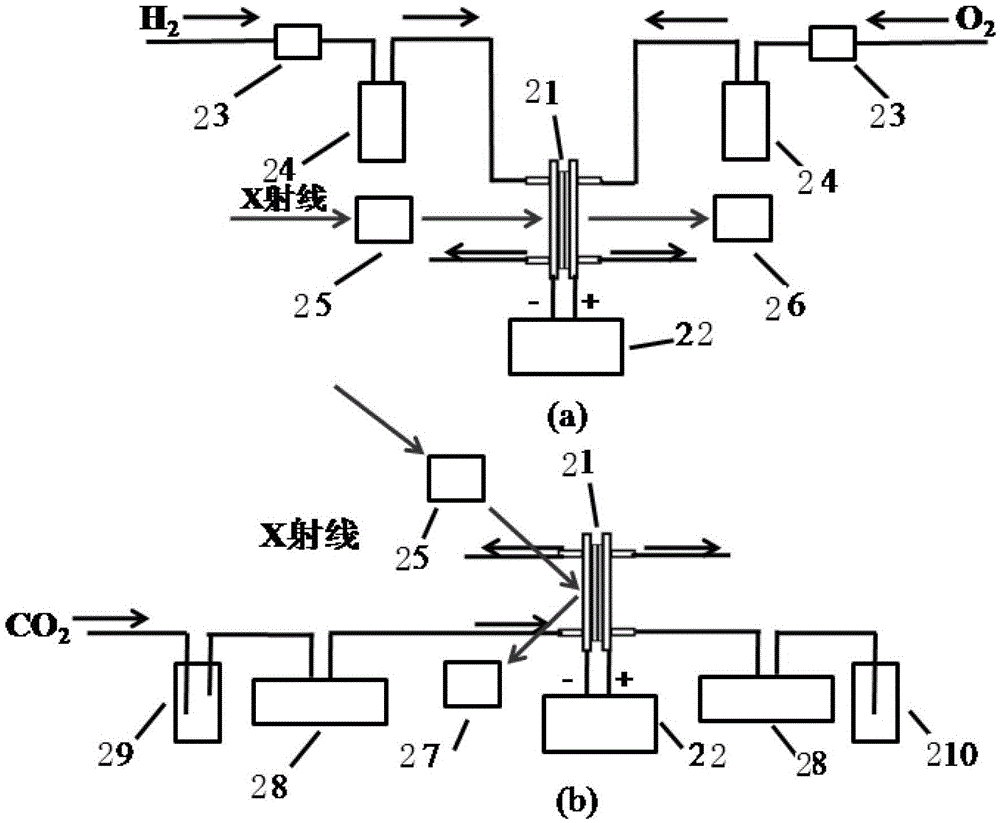
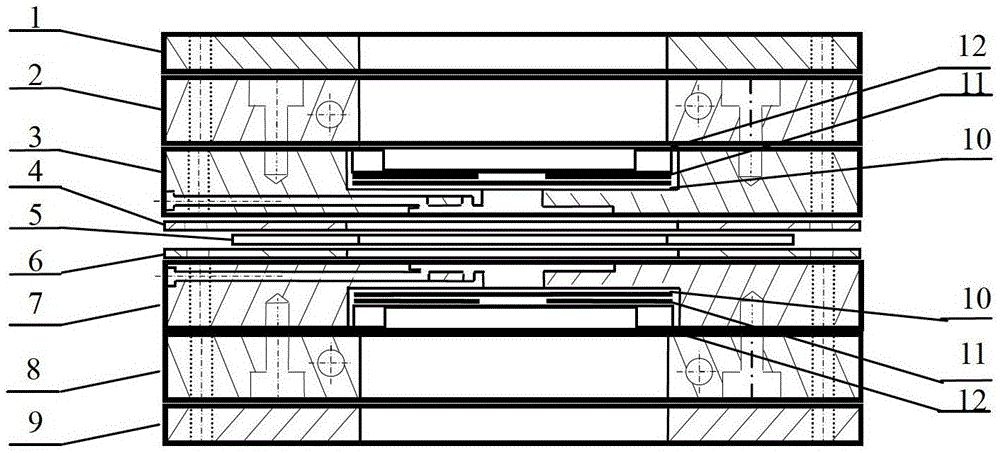
In-situ XAFS (X-ray absorption fine structure) fuel cell, system and method for catalyst experiments
InactiveCN105973920AAchieving air tightness requirementsPlay a sealing roleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCell electrodesSoft x rayFuel cells
The invention provides an in-situ XAFS (X-ray absorption fine structure) fuel cell, a system and a method for catalyst experiments. The in-situ XAFS fuel cell for the catalyst experiments comprises a support plate, a film electrode assembly, a top cover plate, an anode flow field plate and a cathode flow field plate. A first through hole is formed in the middle of the support plate, a second through hole is formed in the middle of the top cover plate, a third through hole is formed in the middle of the anode flow field plate, and a first film is fixed to the periphery of the third through hole and covers the third through hole; a fourth through hole is formed in the middle of the cathode flow field plate, and a second film is fixed to the periphery of the fourth through hole and covers the fourth through hole; the first film and the second film are made of materials which do not absorb X-rays. The in-situ XAFS fuel cell, the system and the method for the catalyst experiments have the advantages that experimental data can be acquired in perspective modes and fluorescent modes, the working temperatures of the in-situ XAFS fuel cell can be adjusted, the in-situ XAFS fuel cell, the system and the method are low in cost, the signal-noise ratios of acquired spectra can be greatly increased, and the in-situ XAFS fuel cell and the system are good in sealing performance and water resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
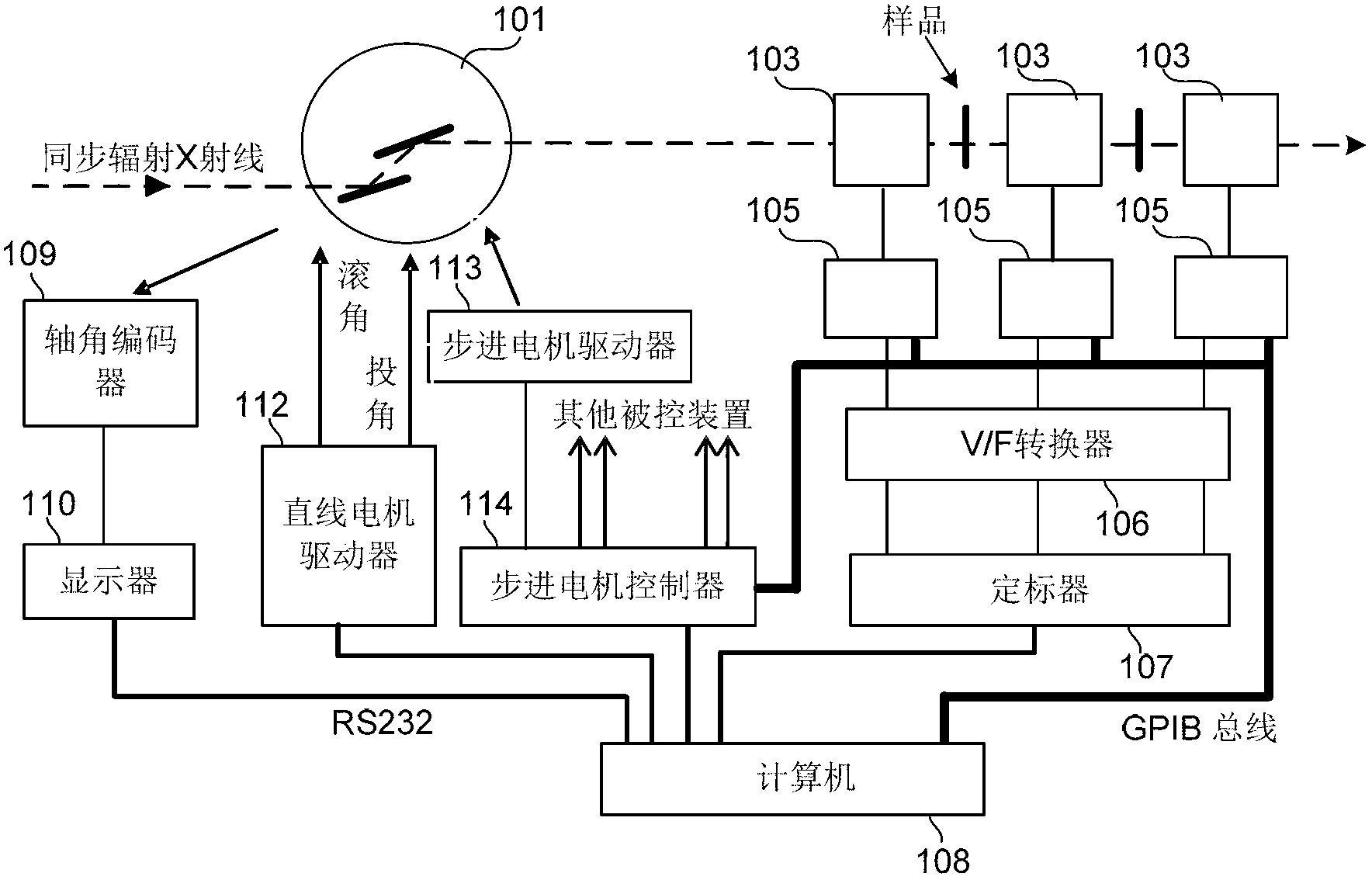
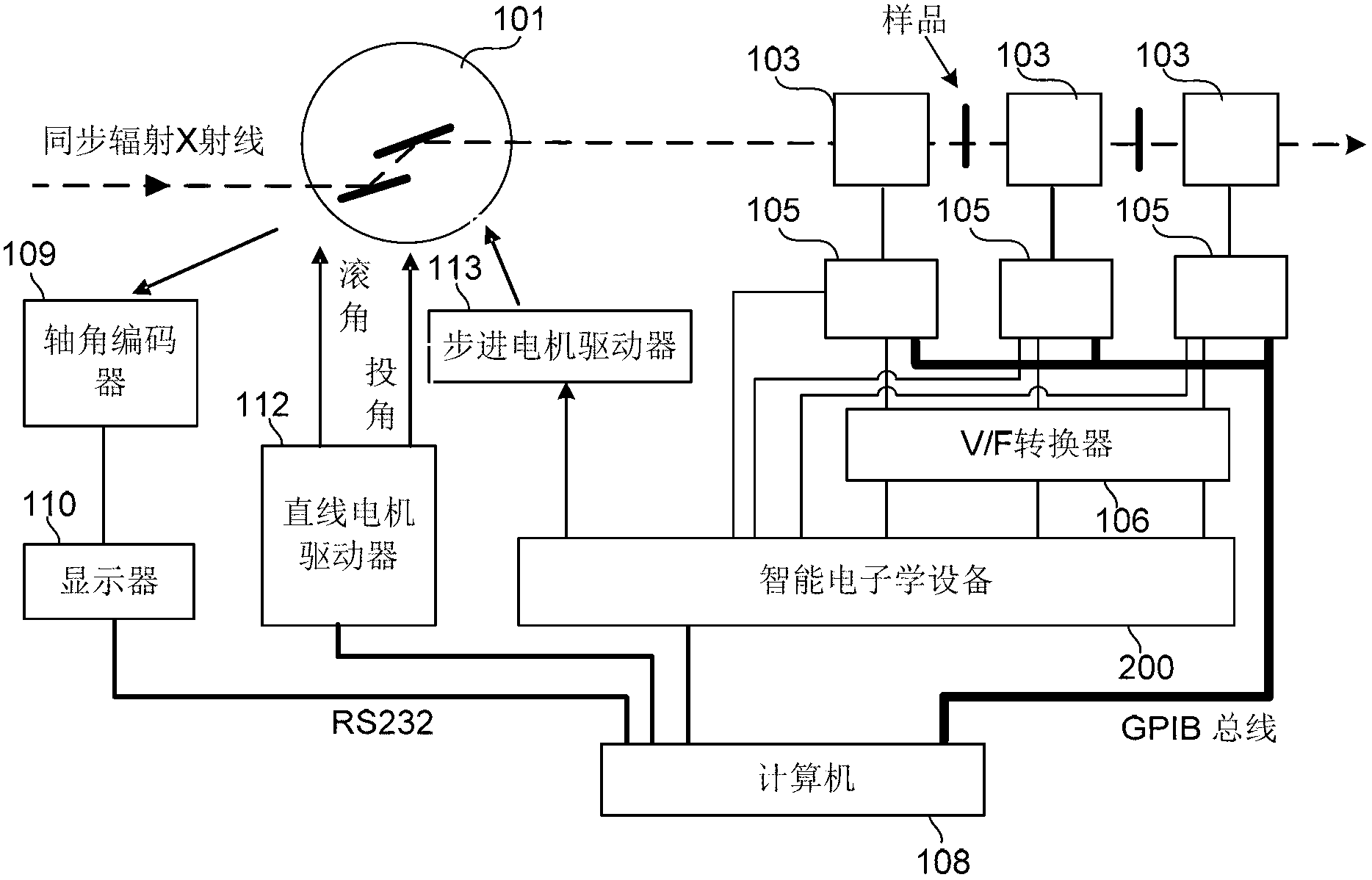
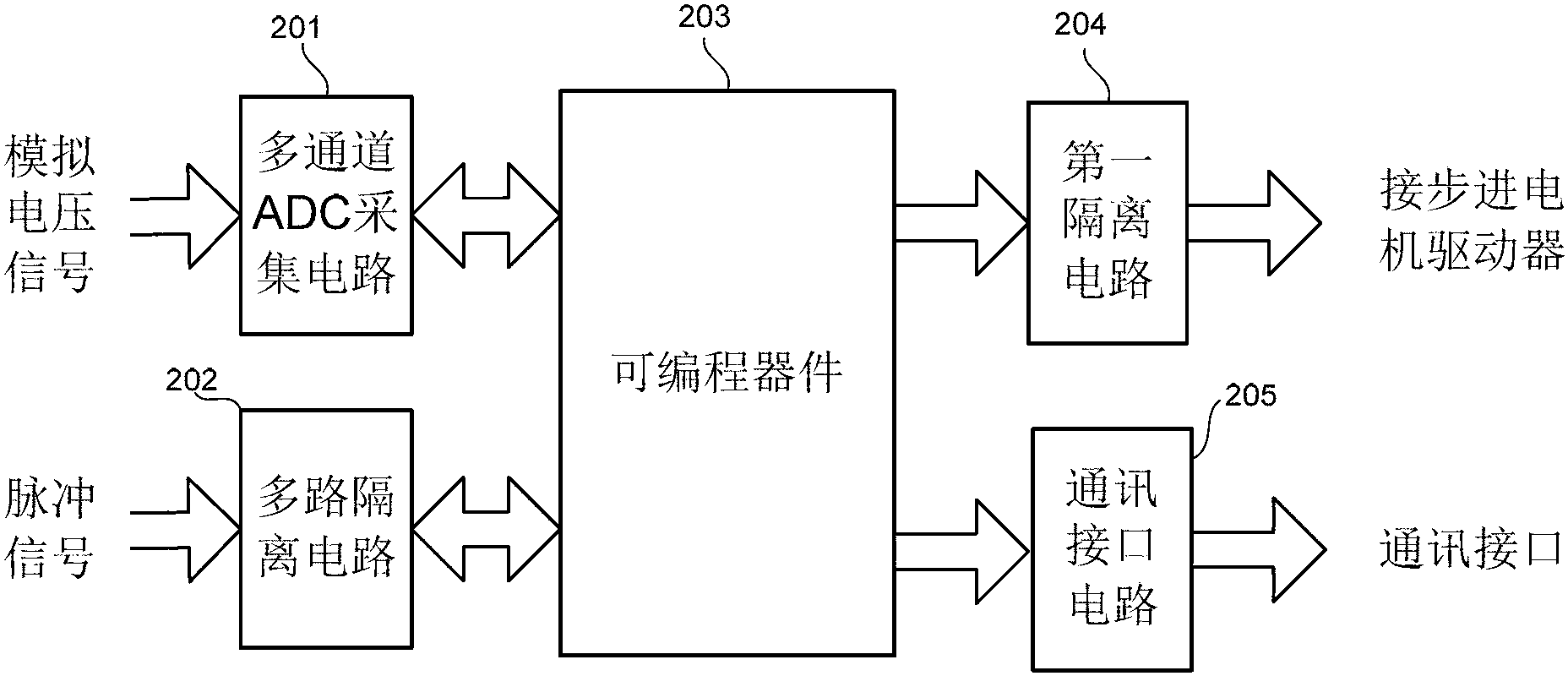
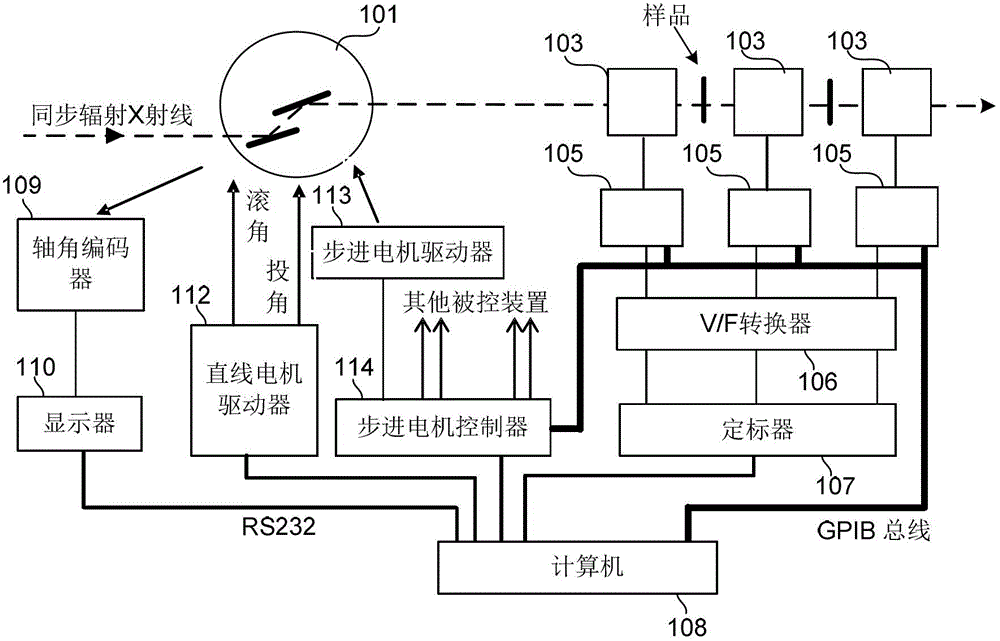
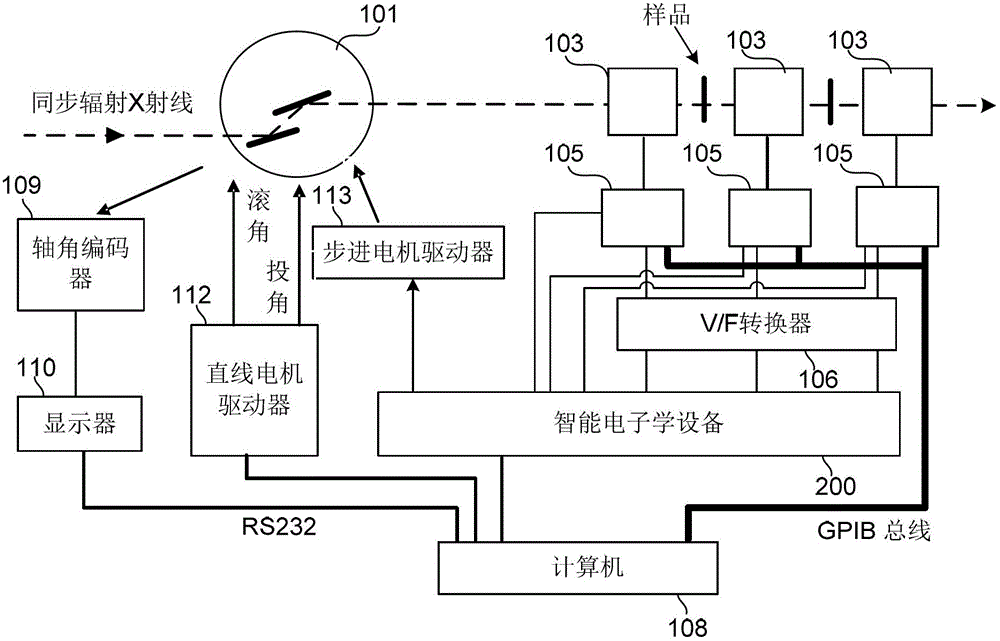
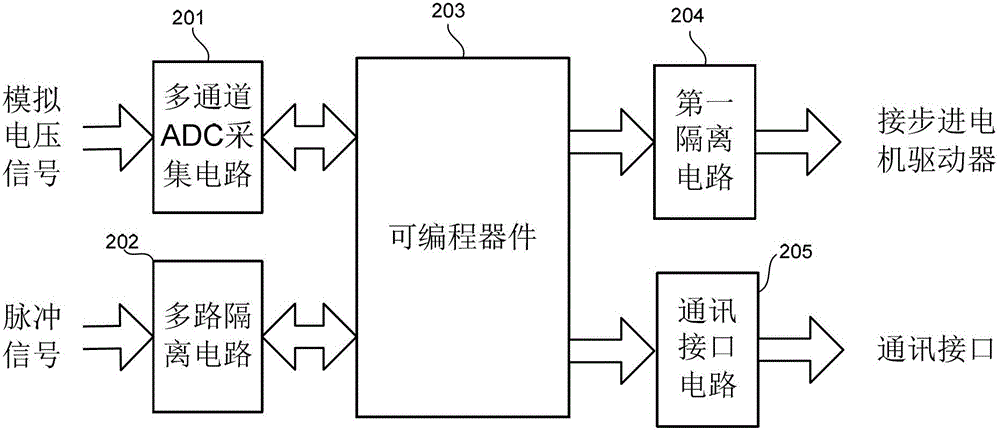
An intelligent electronic device, a QXAFS (quick X-ray absorption fine structure) system and a data acquisition and motor control method
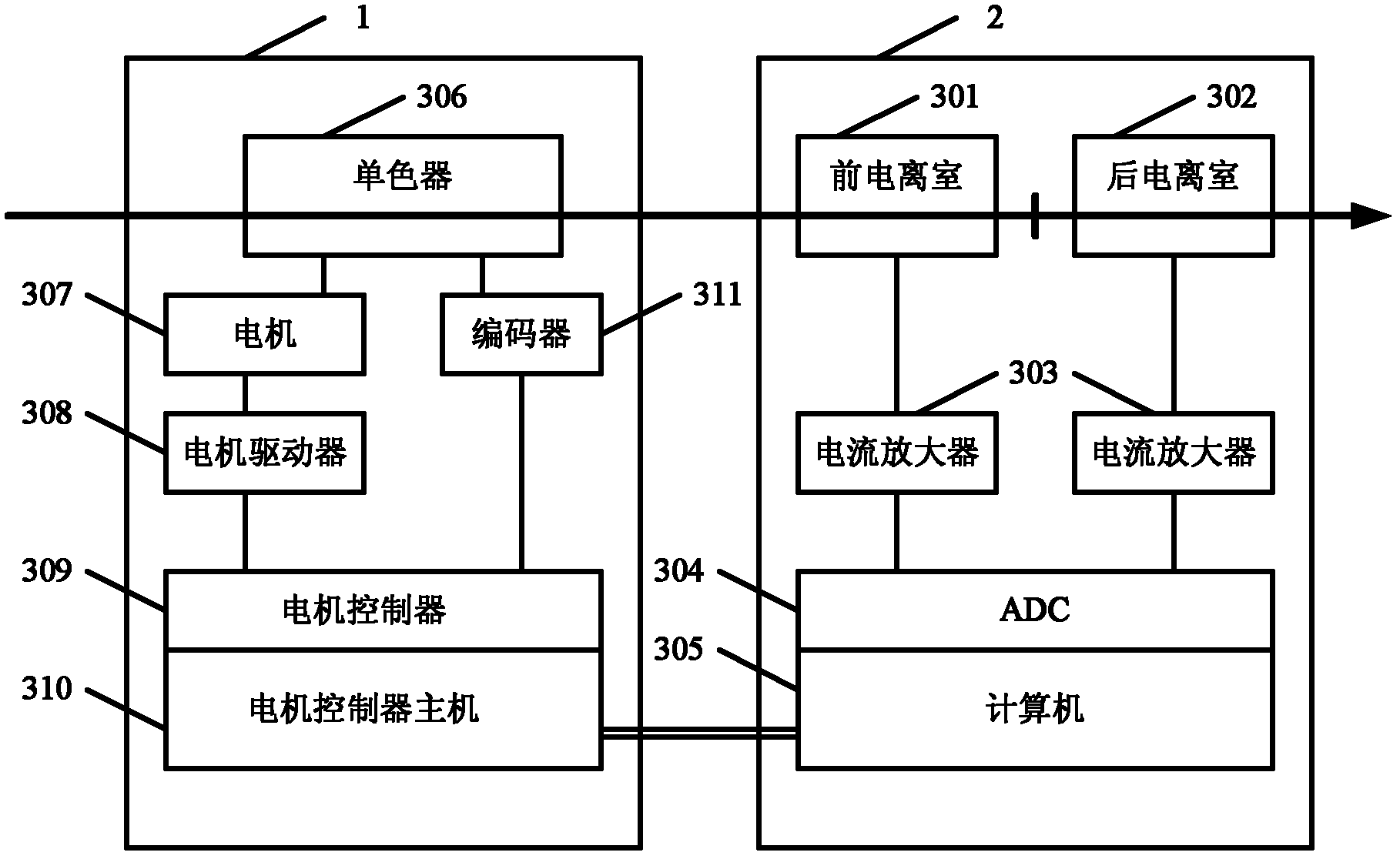
ActiveCN103234986AOvercoming the problem of limited acquisition speedDynamo-electric converter controlMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCore componentData acquisition
The application discloses an intelligent electronic device, a QXAFS (quick X-ray absorption fine structure) system and a data acquisition and motor control method. The intelligent electronic device replaces a stepper motor controller and a scaler in a conventional XAFS (X-ray absorption fine structure) experimental system; and by employing a programmable device as a core component, the electronic device realizes analog acquisition via a multi-channel ADC acquisition circuit combining with a current amplifier in the quick XAFS system, or realizes integral form data acquisition by using the counting function of a programmable device combining a V / F converter on the quick XAFS system. The programmable device controls the stepper motor through reading a control curve configured in a RAM, while performs data acquisition in a control segment allowing the data acquisition, thus achieving a high-speed synchronization of the stepper motor and the data acquisition, and through sampling data in the stationary or slow control segment of the control curve, preventing energy movement in the process of data acquisition, and obtaining a best solution in the contradiction between a spectrum sweep speed and the energy movement.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
X-ray absorption measurement system
ActiveCN106605140AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingXANES SpectroscopyDesign for X
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements that have x-ray flux and flux density several orders of magnitude greater than existing compact systems; for applications of x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) or extended x-ray fine absorption structure (EXFAS) spectroscopy. The higher brightness is achieved using designs for x-ray targets that comprise aligned microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness and high flux. The high brightness x-ray source is coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system to collimate the x-rays, and a monochromator, which selects the exposure energy. Absorption spectra of samples using the high flux monochromatic x-rays can be made using standard detection techniques.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Data collection method based on monochromator quick-scanning control system
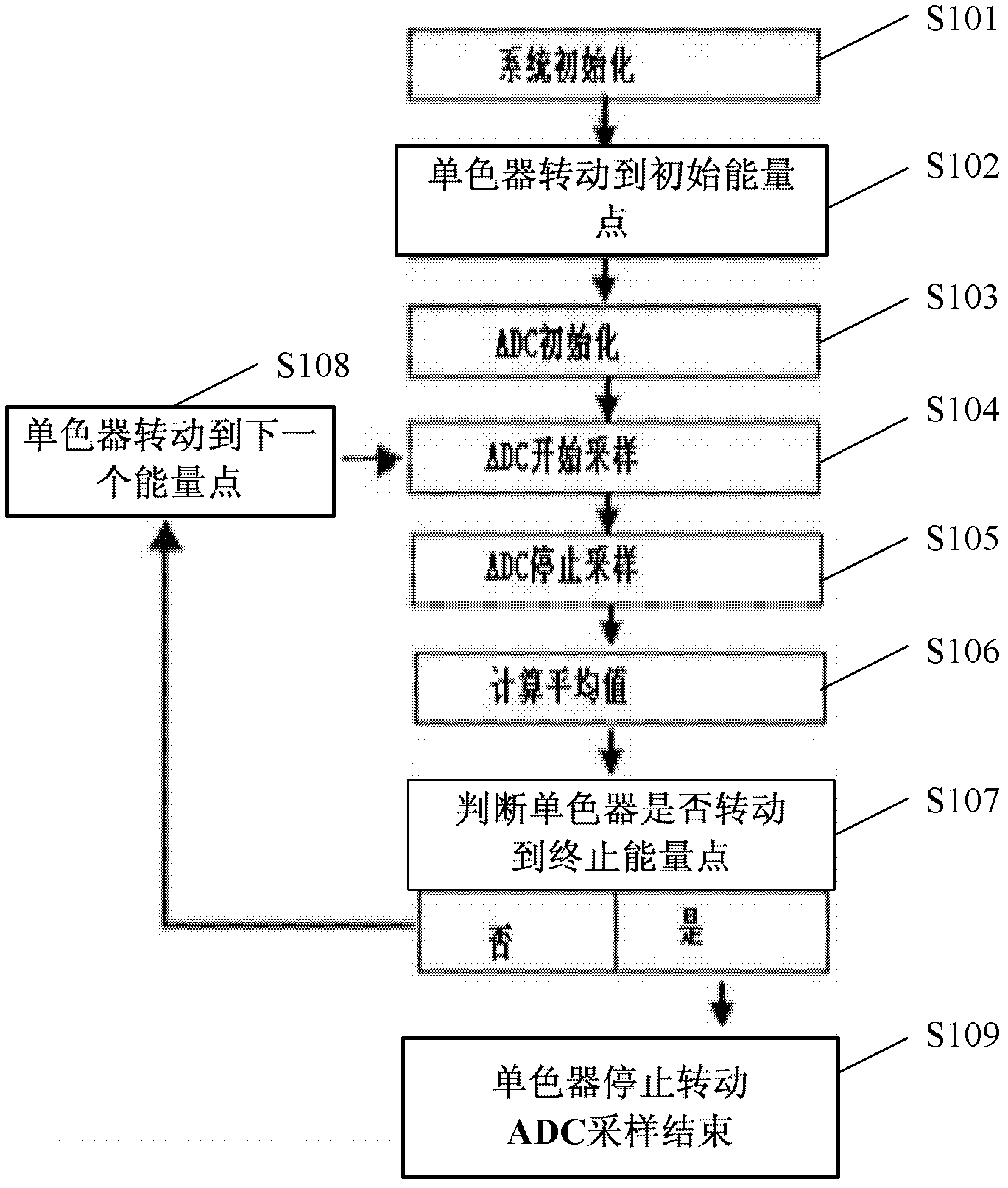
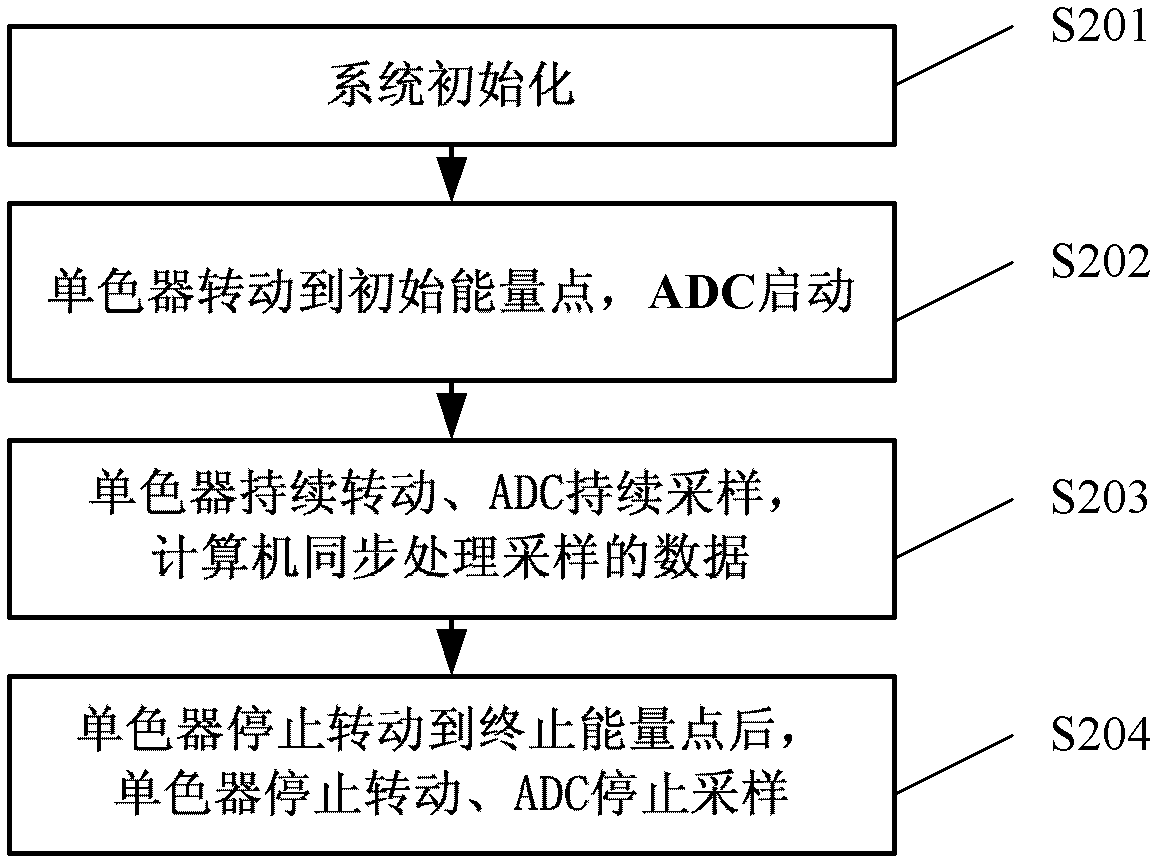
InactiveCN102621165AQuick collectionReduced sampling timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray absorption fine structureControl system
The invention provides a data collection method based on a monochromator quick-scanning control system, which is used for quickly obtaining an XAFS (X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) spectrum. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, initiating the monochromator quick-scanning control system, wherein the step of setting the rotation speed w of a monochromator is performed; 2, rotating the monochromator to an initial energy point, and starting an ADC (Analog To Digital Converter); 3, making the monochromator rotate at the constant rotation speed w continuously and the ADC carry out continuous sampling at a constant speed, carrying out synchronous processing on the data collected by the ADC to obtain the XAFS spectrum, and synchronously outputting the XAFS spectrum; and 4, stopping the rotation of the monochromator after the monochromator rotates to a final energy point, and stopping the sampling of the ADC. According to the data collection method based on the monochromator quick-scanning control system, provided by the invention, the XAFS spectrum is obtained by the continuous rotation of the monochromator and the continuous sampling of the ADC, the sampling time is greatly saved, the measuring efficiency is increased, and more importantly, a time-resolved XAFS test can be carried out.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
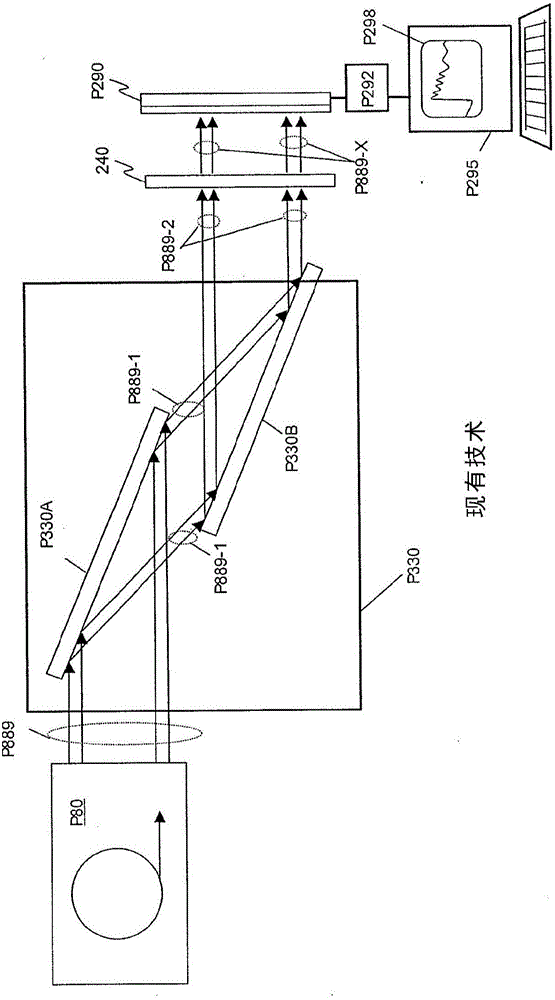
Higher-order harmonic suppression device for X-rays in low energy section
InactiveCN102591092AHigh Purity SpectrumMountingsNon-linear opticsX-ray absorption fine structurePoint of entry
The invention provides a higher-order harmonic suppression device for X-rays in low energy sections. The higher-order harmonic suppression device comprises a vacuum mirror box, at least one reflector, a clamping mechanism and an adjusting mechanism, the vacuum mirror box is provided with an X-ray inlet and an X-ray outlet, the reflectors are disposed between the X-ray inlet and the X-ray outlet, the surface of each reflector is provided with at least one reflecting area used for receiving and reflecting the X-rays, the clamping mechanism is used for clamping the reflectors, and the adjusting mechanism is connected to the lower side of the clamping mechanism. The higher-order harmonic suppression device for the X-rays in the low energy section has the advantages that positions and angles of the reflectors in the vacuum mirror box are adjusted by the aid of the adjusting mechanism, the X-rays are reflected by the reflecting areas of the surfaces of the reflectors for at least once, accordingly, higher-order harmonics of the X-rays in the low energy section are removed after the X-rays pass through a monochromator, and high-purity spectrum is provided for an XAFS (X-ray absorption fine structure) beam line station.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Measurement method of X-ray micro-zone absorption fine structure with spatial resolving capability
ActiveCN104122279ARealize functionNo need to focusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayFine structure
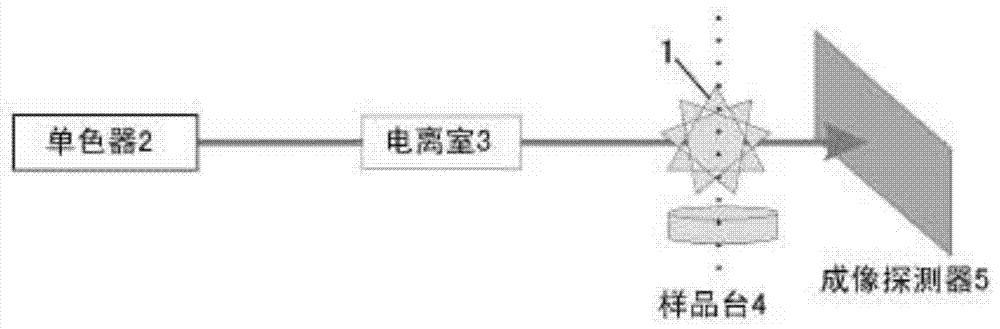
The invention provides a measurement method of an X-ray micro-zone absorption fine structure with spatial resolving capability. The measurement method is characterized by comprising the following steps: generating X-ray monochromatic light with preset energy; recording intensity information of the X-ray monochromatic light; and collecting the X-ray monochromatic light by an imaging detector with multiple pixel cells after the X-ray monochromatic light passes through a sample, thereby obtaining information of the absorption fine structure of the sample under the preset energy. According to the method, the X-ray imaging detector is utilized to collect two-dimension projection data of the sample within a certain range of X-ray energy, and the information of the X-ray absorption fine structure of a sample zone represented by each pixel dot can be obtained respectively.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Carbon black and production method therefor, and electricity storage device and conductive resin composition
InactiveUS20160190594A1Good dispersionReduce componentsPigmenting treatmentNon-metal conductorsHeat treatedRaw material
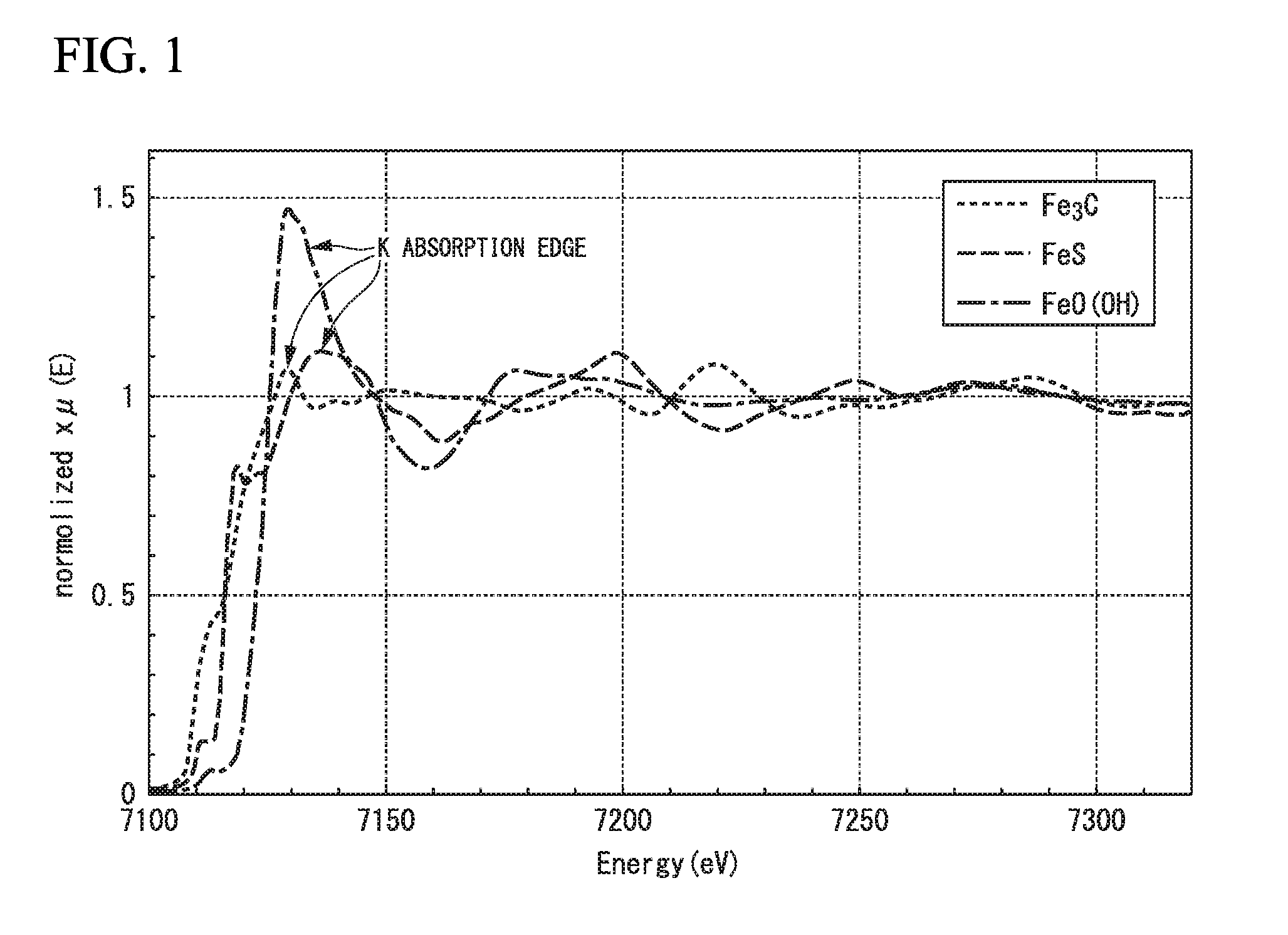
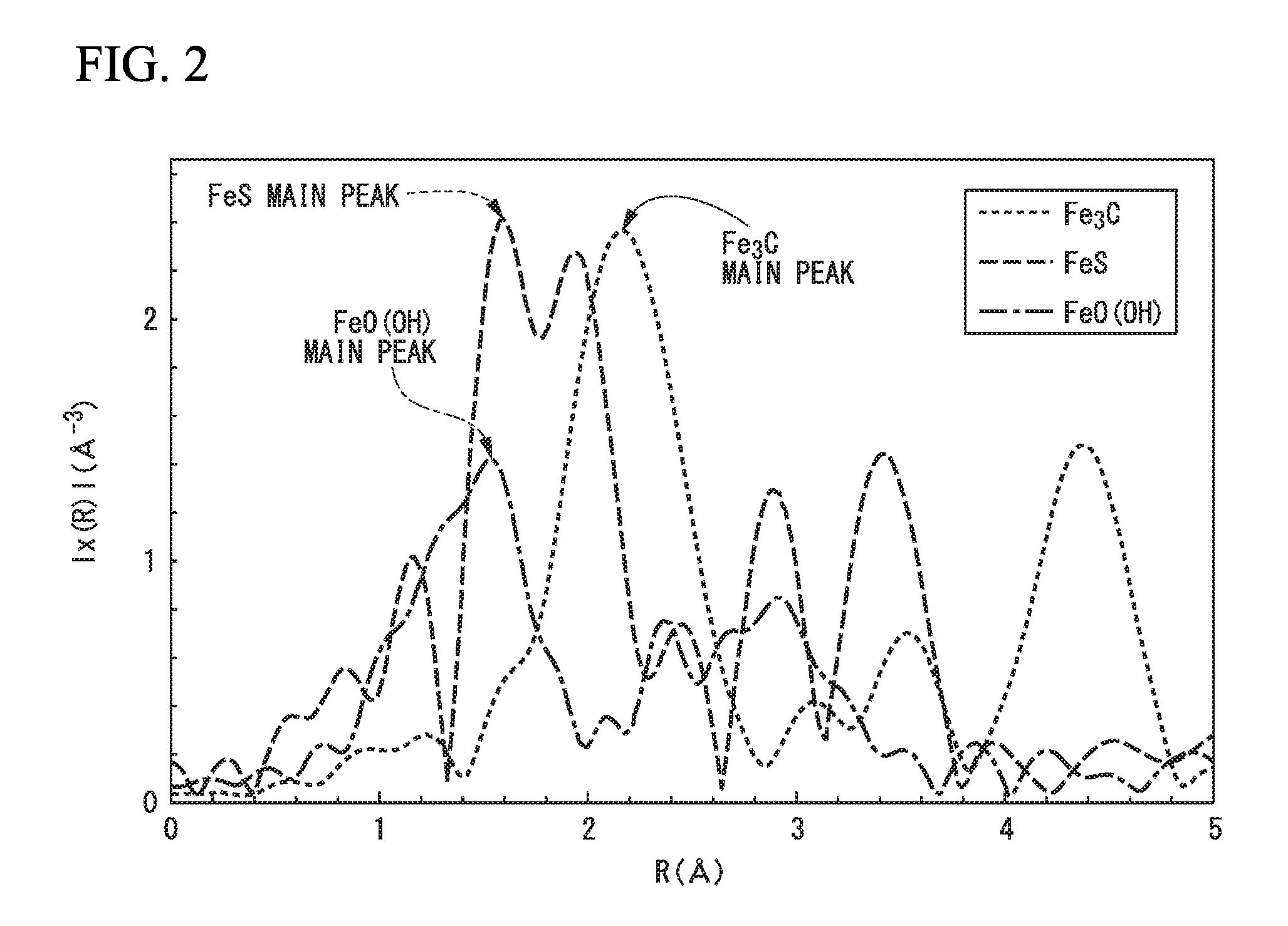
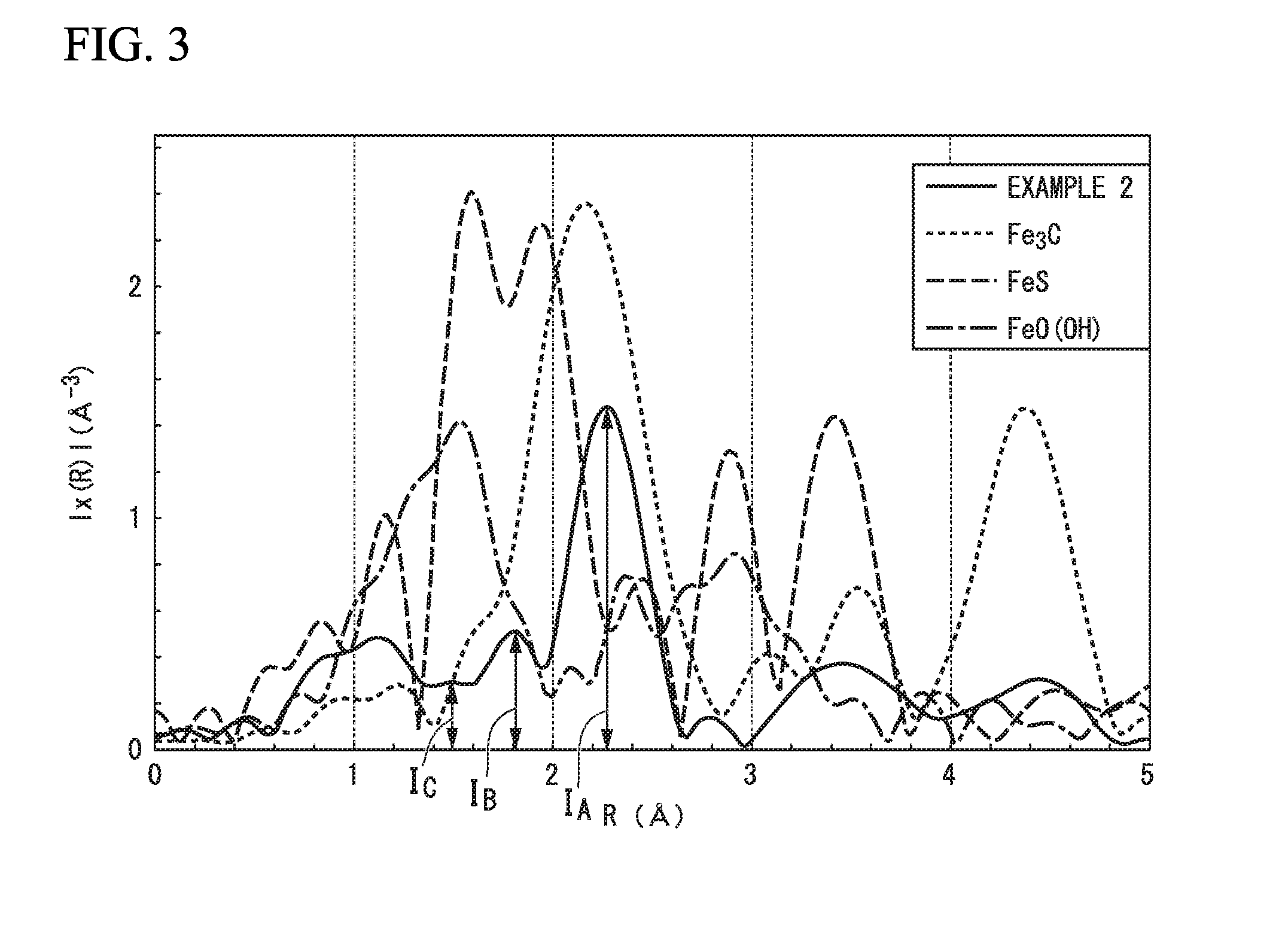
In carbon black of the present invention, peak intensity IA of a main peak derived from Fe3C, peak intensity IB of a main peak derived from FeS, and peak intensity IC of a main peak derived from FeO(OH) in a radial distribution function, which is obtained by performing Fourier transform with respect to a broadband X-ray absorption fine structure spectrum of a K absorption edge, satisfy 0.7≦IA(IB+IC)≦6.0. A production method for a carbon black of the present invention includes subjecting raw material carbon black to a heat treatment at a temperature of 900° C. to 1500° C. for a time of 5 minutes to 180 minutes under an atmosphere of a halogen element-containing gas.
Owner:LION SPECIALTY CHEM
Fuel cell anode catalyst and manufacturing method therefor
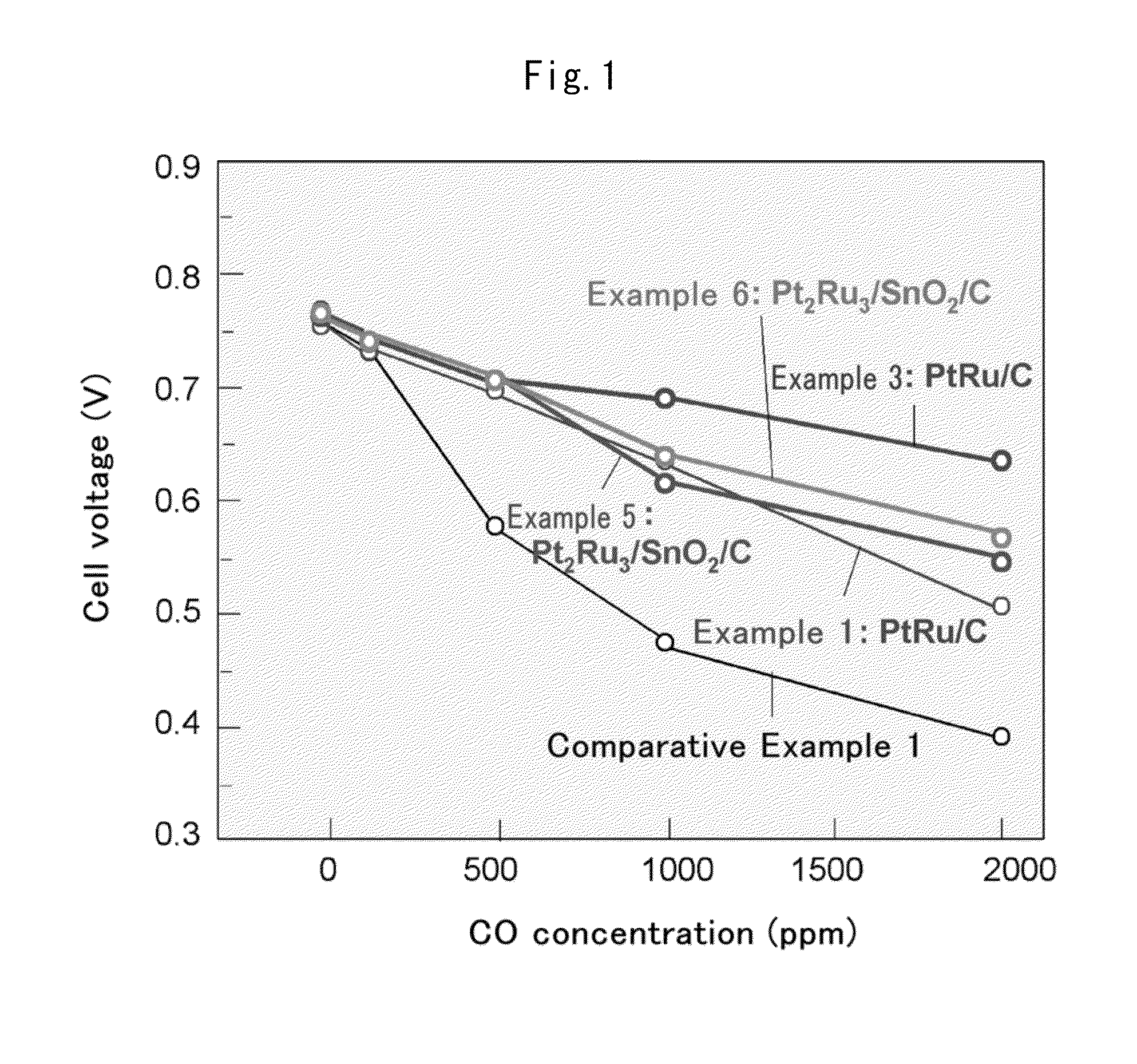
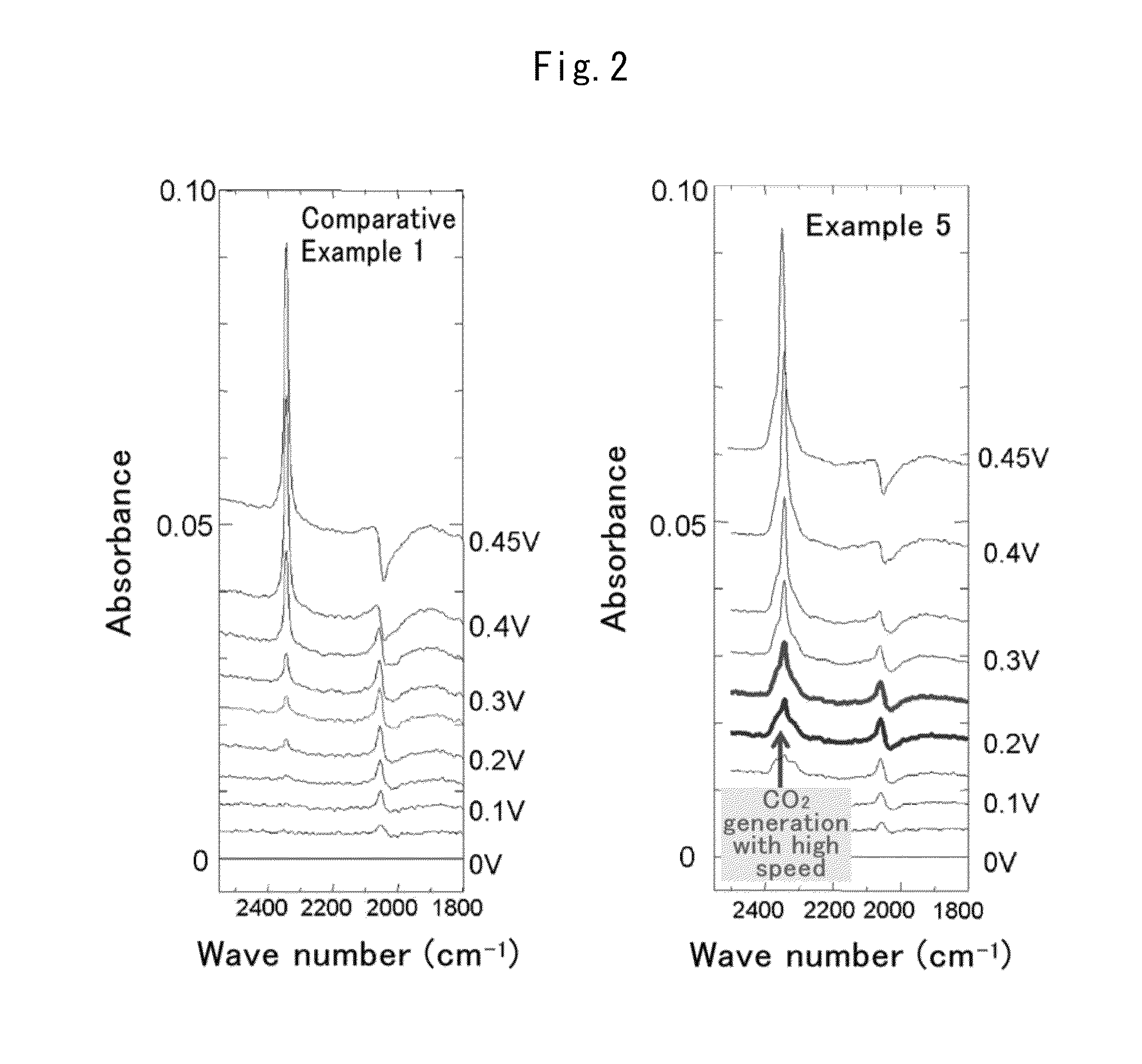
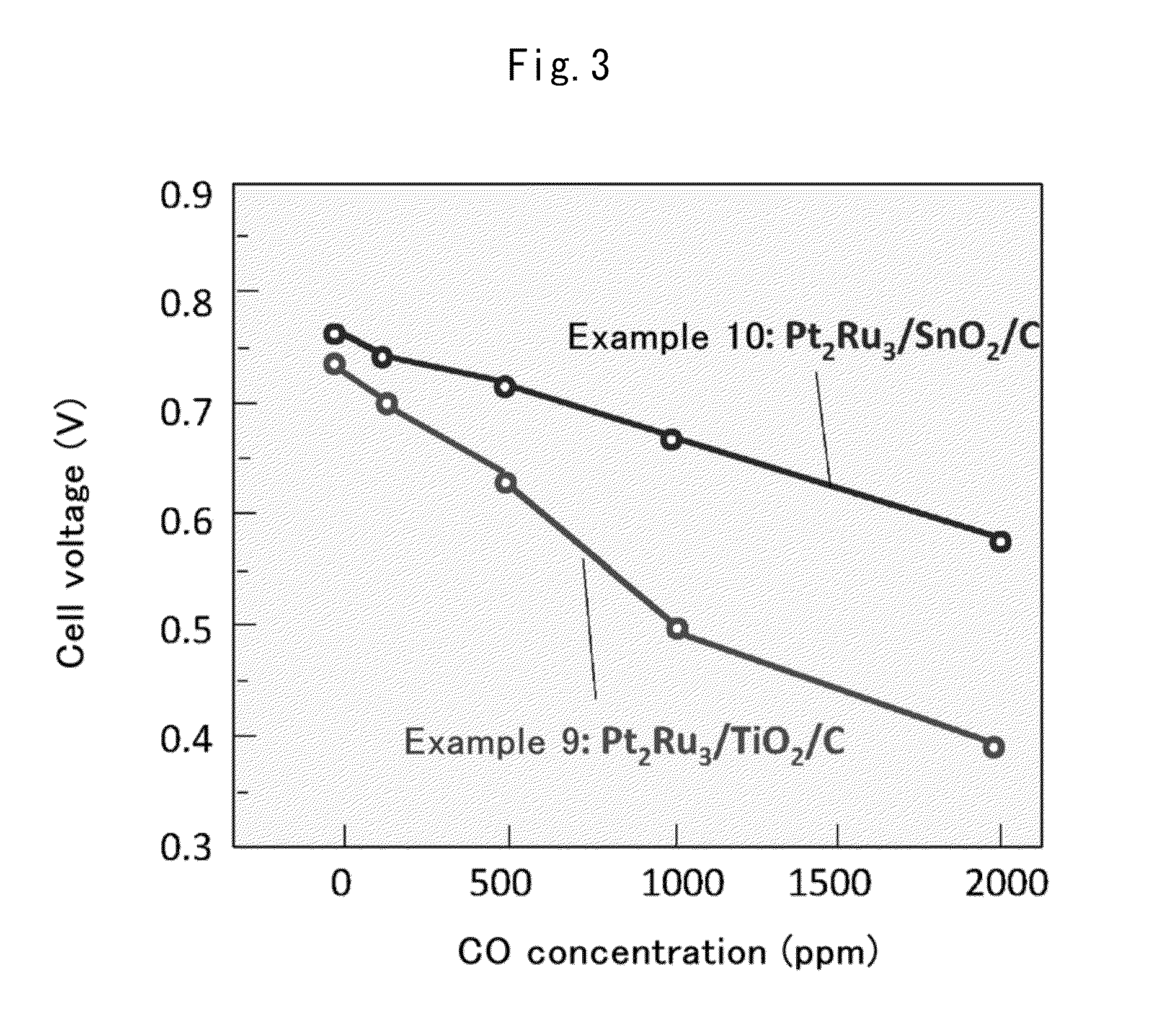
InactiveUS20140017594A1Enhanced CO toleranceImprove toleranceMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureConductive polymerX-ray
Provided is a fuel cell anode catalyst in which a platinum-ruthenium alloy is supported on a carbon material, and a manufacturing method therefor. The molar ratio (Pt:Ru) of the alloy is in the range of 1:1-5. When the coordination numbers of the Pt atom and the Ru atom of an atom site in the alloy, as measured by x-ray absorption fine structure, are expressed as N(Pt) and N(Ru) respectively, then N(Ru) / (N(Pt)+N(Ru)) in the platinum site is in the range of 0.8-1.1 times the theoretical value, and N(Pt) / (N(Ru)+N(Pt)) in the Ru site is in the range of 0.8-1.1 times the theoretical value. The average particle diameter of the alloy is in the range of 1-5 nm, and the standard deviation for the particle diameter is in the range of 2 nm or lower. Further provided is: a fuel cell anode with an anode composition layer, on a substrate surface, which contains the catalyst and a proton conductive polymer; a fuel cell membrane electrode assembly with a polymer electrolyte membrane sandwiched between the anode and a cathode; and a fuel cell containing the fuel cell membrane electrode assembly.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY
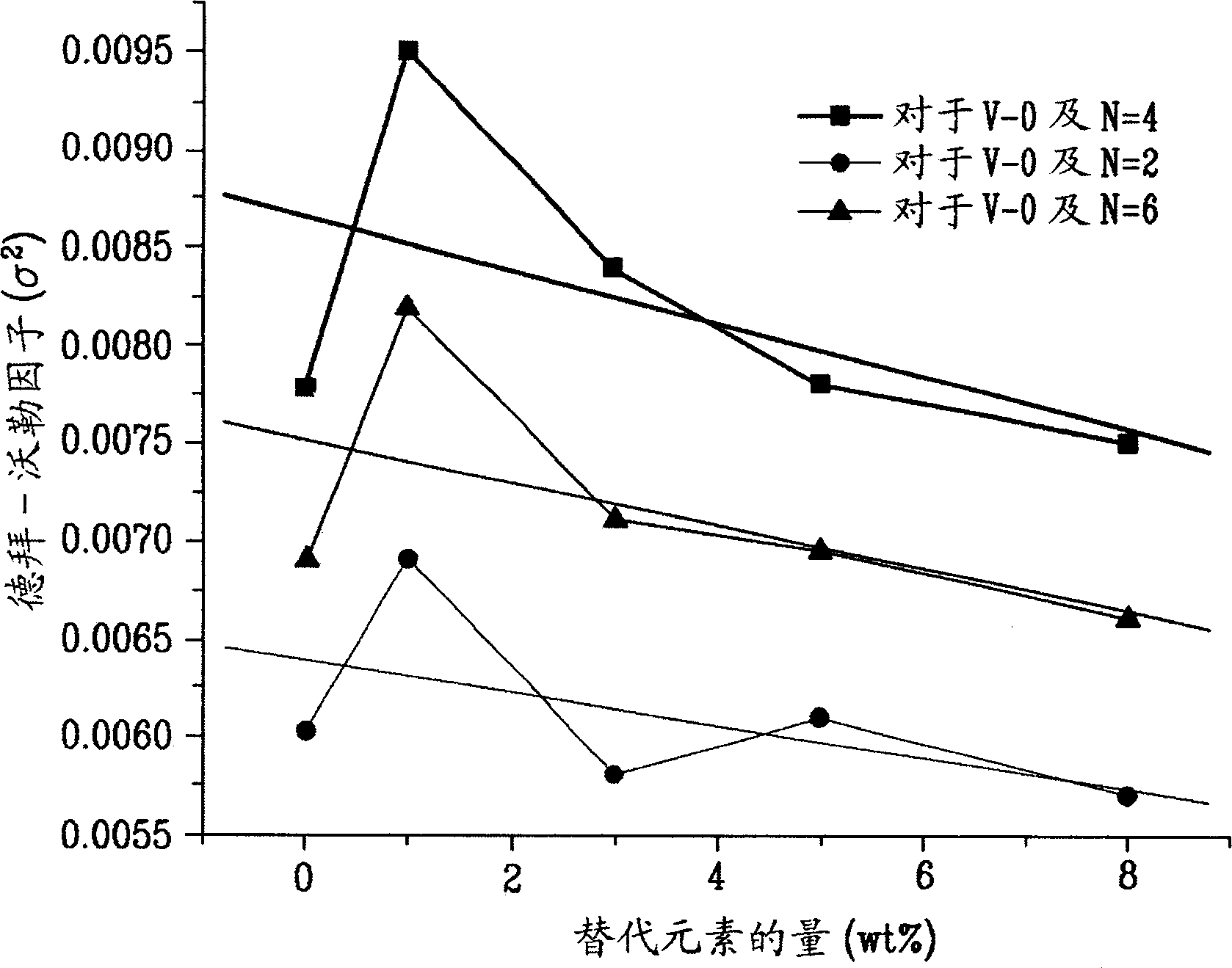
Process for nondestructively measuring nano grain stress condition
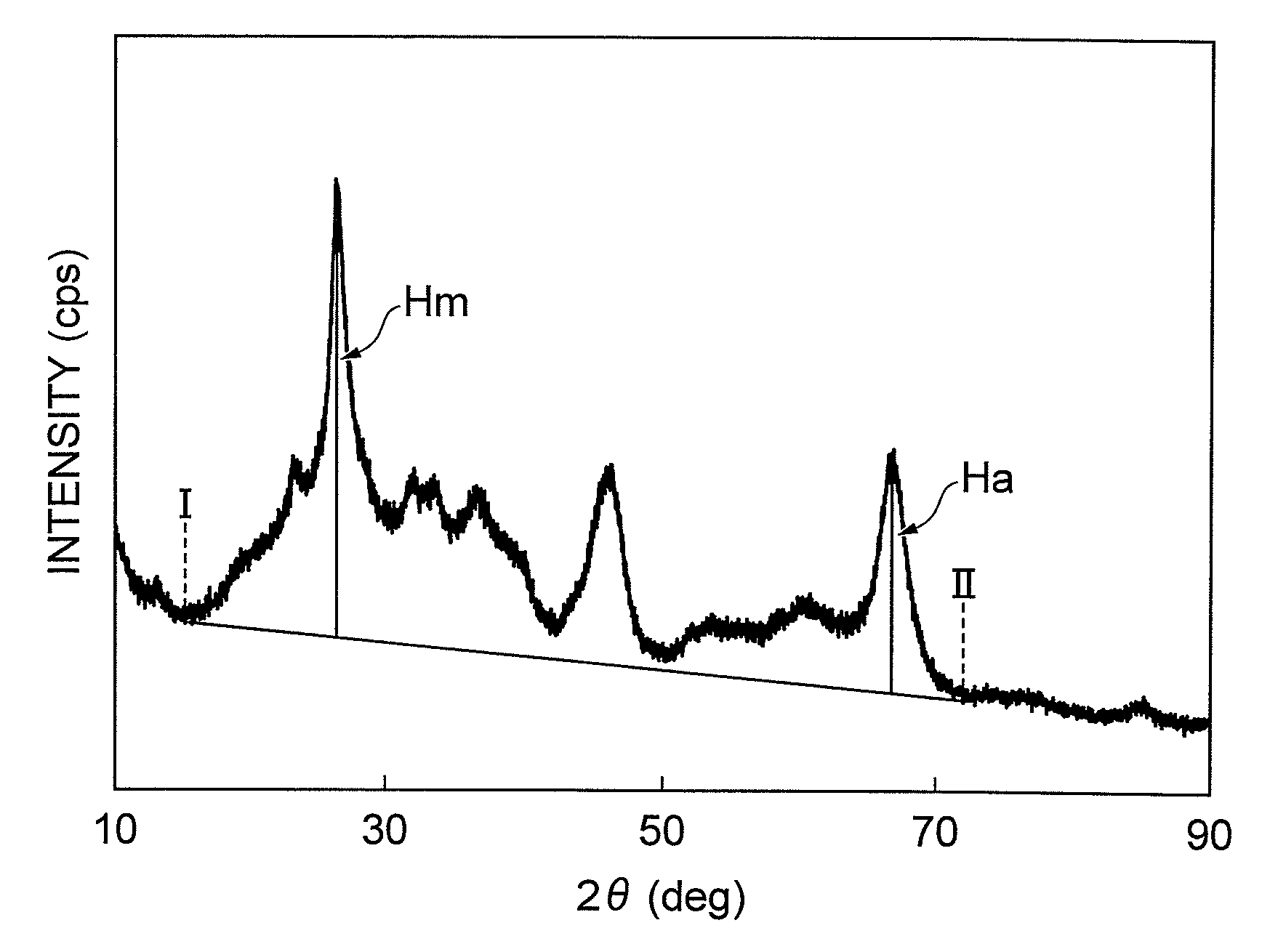
The present invention relates to a new method for nondestructively measuring nanometer particle stress state, which belongs to the X ray measuring field. An X ray absorption fine structure spectrum is used to measure the nanometer particle interatomic distance wrapped in a medium material, and through analyzing the change of the nanometer particle interatomic distance, the stress condition and the size of the nanometer particle can be calculated. The fundamental difference between the method and the existing stress measuring method is that the X ray absorption fine structure spectrum, a nondestructive measuring method is used to analyze and measure the stress of the nanometer particle. The method fundamentally fills the blank of nanometer particle stress analysis, and has obvious application value in the analysis of the nanometer particle stress state, the control of the ordered growth of the nanometer particle, and the application of a quantum device.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Cell for x-ray analysis and x-ray analysis apparatus
ActiveUS20190145915A1Easy to placePromote exchangeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayX-ray absorption fine structure
Provided are a cell for X-ray analysis and an X-ray analysis apparatus that enable simultaneous X-ray diffraction and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements of a material (sample) in the same field of view on the sample (same position on the sample). The cell for X-ray analysis of the present invention enables simultaneous X-ray diffraction and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements of a sample in the same field of view on the sample and includes a furnace including a space where the sample is held and a focused heater heating the sample, a first window provided to the furnace and through which X-rays directed at the sample is incident, a second window provided to the furnace and from which X-rays emerging from the sample exit, a third window provided to the furnace, and a holder that positions the sample in the space. The cell for X-ray analysis makes it possible to simultaneously measure X-ray diffraction of the sample at outside of the second window and X-ray absorption fine structure of the sample through the third window.
Owner:HIGH ENERGY ACCELERATOR RESEARCH ORGANIZATION
Grazing incidence XAFS (x-ray absorption fine structure) high-temperature in-situ furnace
The invention relates to a grazing incidence XAFS (x-ray absorption fine structure) high-temperature in-situ furnace. The furnace comprises a central longitudinal axis as well as a furnace body, a furnace cover and a furnace base which are arranged around the central longitudinal axis, wherein the furnace body is supported by the furnace base, the furnace cover is arranged above the furnace body and fixedly connected with the furnace body, the furnace body comprises a main body and a furnace chamber defined by the main body, a first window for X-ray incidence, a second window for X-ray emergence and a third window for fluorescence detection are arranged on the main body, the central axes of the first window and the second window are located in a straight line perpendicular to the central longitudinal axis, the central axis of the third window is perpendicular to a plane defined by the central longitudinal axis and the straight line, a fourth window for fluorescence detection is arranged on the furnace cover, the central axis of the fourth window overlaps with the central longitudinal axis, a sample table is arranged in the furnace chamber, and the included angle formed by the top surface of the sample table and the straight line is 0-5 degrees. The grazing incidence XAFS high-temperature in-situ furnace can perform XAFS tests on solid-liquid interfaces.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
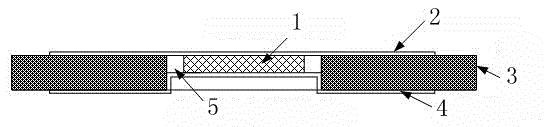
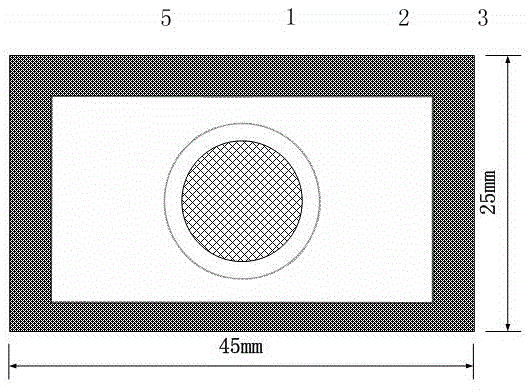
Method for preparing synchrotron-radiation X-ray absorption fine-structure test sample of hydrogen storage material
ActiveCN105651578AFor long-term storageWill not oxidizePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSteel platesX-ray absorption fine structure
The invention discloses a method for preparing a synchrotron-radiation X-ray absorption fine-structure test sample of a hydrogen storage material, and relates to the technical field of hydrogen storage materials. In the atmosphere of argon or nitrogen gas, one of LiF or BN and a to-be-tested sample are mixed and ground, and mixed powder with particle diameter ranging from 30 micrometers to 50 micrometers is obtained; a pressed sample piece is packaged in a double-mirror-surface stainless steel plate with the thickness of the stainless steel plate larger than that of the pressed sample piece, and with a through hole larger than the pressed sample piece; the pressed sample piece sealed in the double-mirror-surface stainless steel plate is then preserved in a metal container filled with argon or nitrogen gas. The method guarantees that the sample is located in the sealed argon or nitrogen gas atmosphere, and can be preserved for a long time without oxidation; moreover, the rigid stainless steel metal plate on the periphery has a good protection effect on the pressed sample piece, and the pressed sample piece cannot crack or break due to unexpected reasons, so that long-distance delivery and carrying are facilitated.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
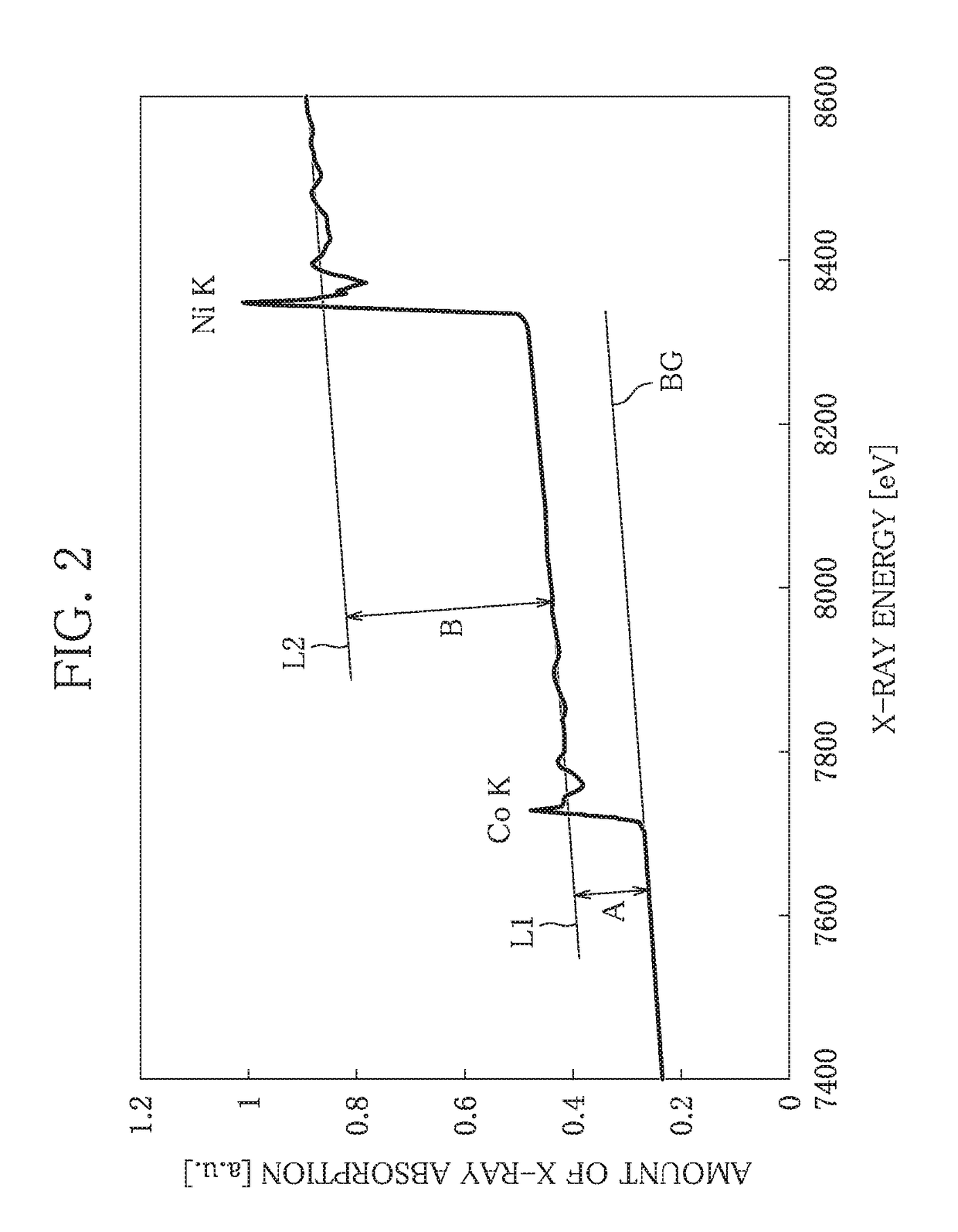
Positive electrode active material for nickel-hydrogen secondary battery, nickel-hydrogen secondary battery including the positive electrode active material, and method of evaluating positive electrode active material
ActiveUS20170141401A1Positive electrodesAlkaline accumulator electrodesHydrogenX-ray absorption fine structure
A nickel-hydrogen secondary battery includes an electrode group including a separator, a positive electrode and a negative electrode, the positive electrode includes a positive electrode active material, the positive electrode active material includes a composite particle including a compound of Co and a compound of Ni, and the ratio R represented by A / B satisfies a relationship of R≧0.3, when the amount of jumping in the X-ray absorption fine structure spectrum of the Co in 7600 to 7800 eV and the amount of jumping in the X-ray absorption fine structure spectrum of the Ni in 8300 to 8500 eV obtained by measurement according to a conversion electron yield method are defined as A and B, respectively.
Owner:FDK CORP
A kind of preparation method of synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption fine structure test sample
ActiveCN105651578BFor long-term storageWill not oxidizePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-ray absorption fine structureTest sample
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method of producing regenerated hydrotreating catalyst and method of producing petroleum products
ActiveUS9737881B2High activityMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesXANES SpectroscopyPetroleum product
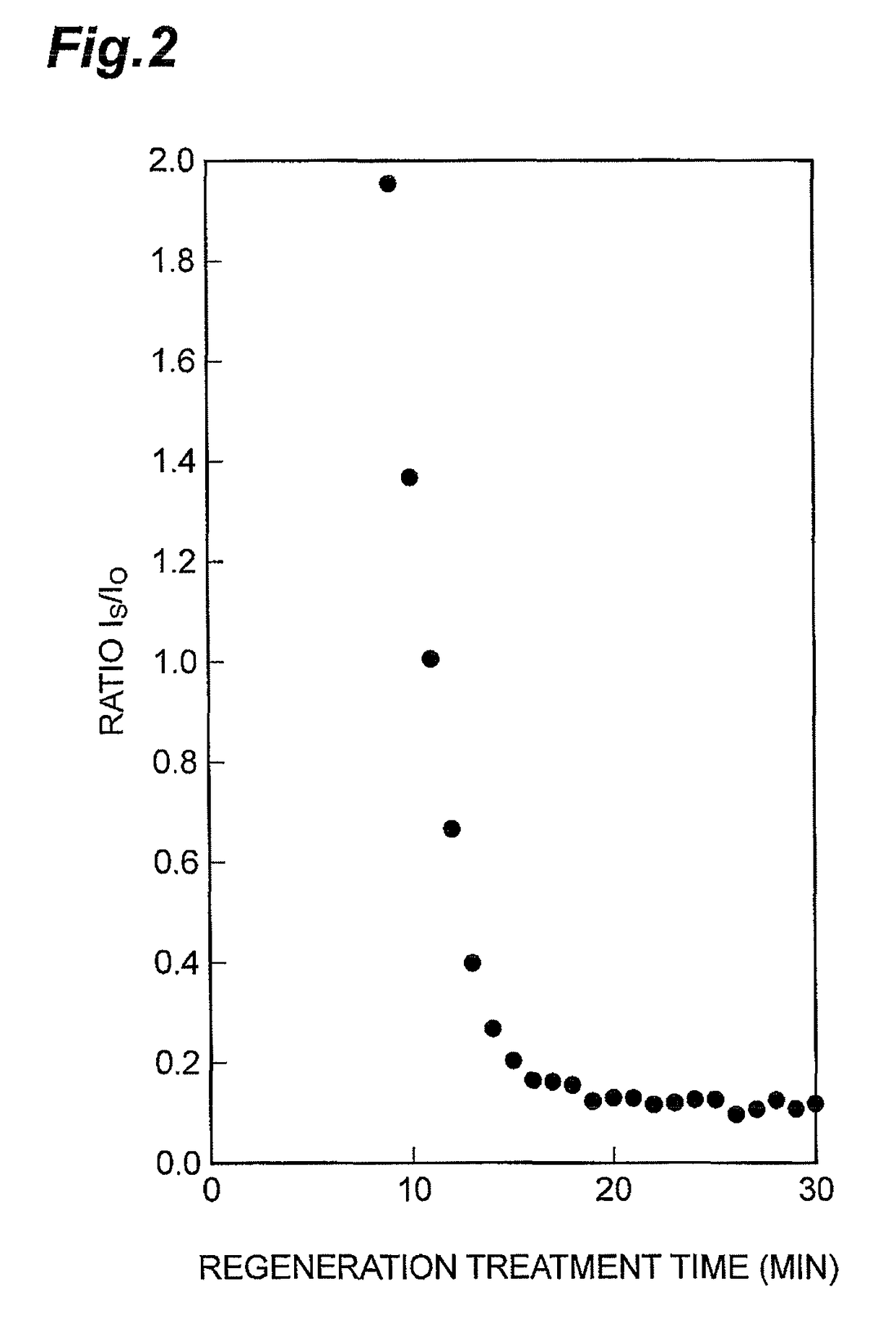
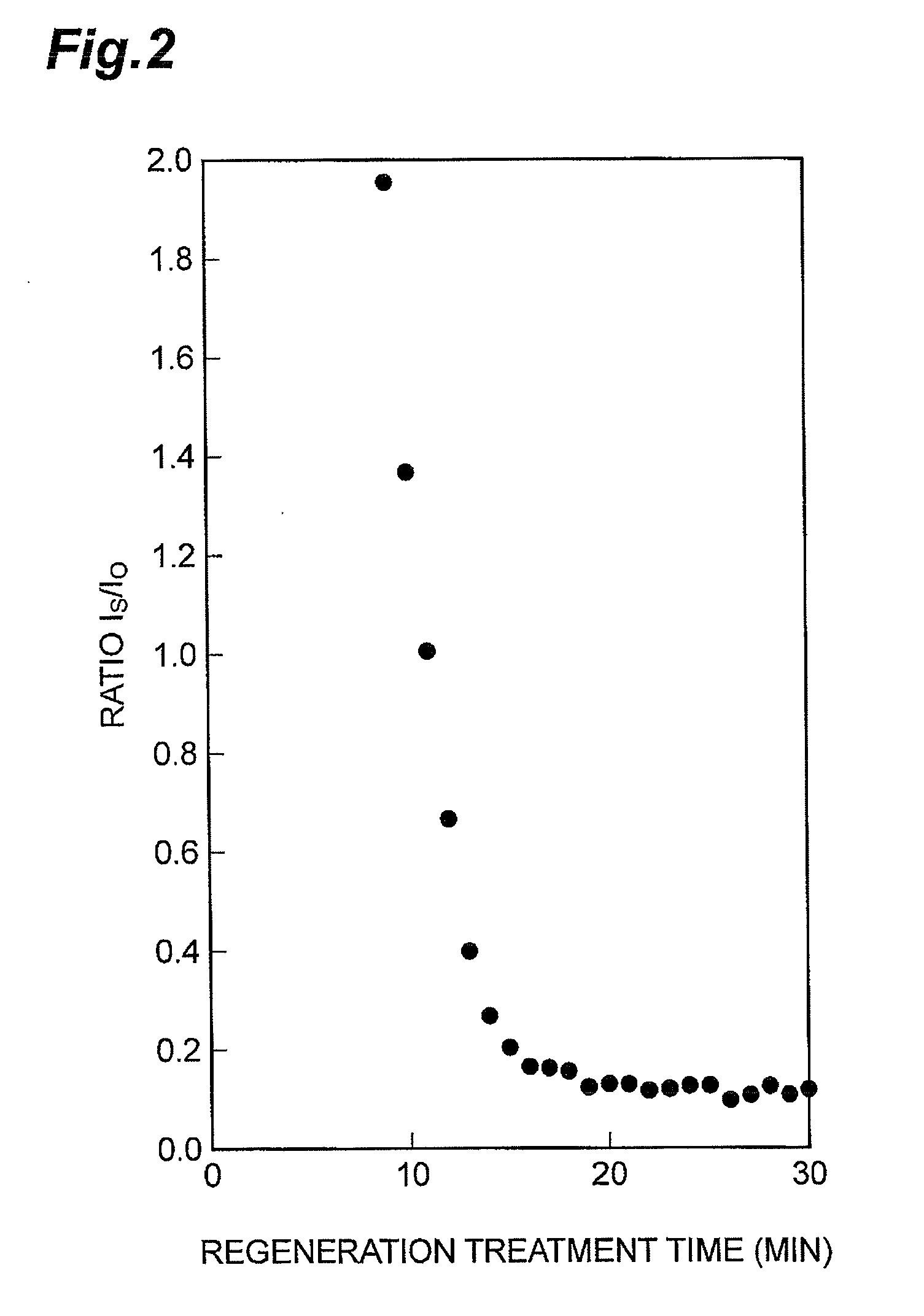
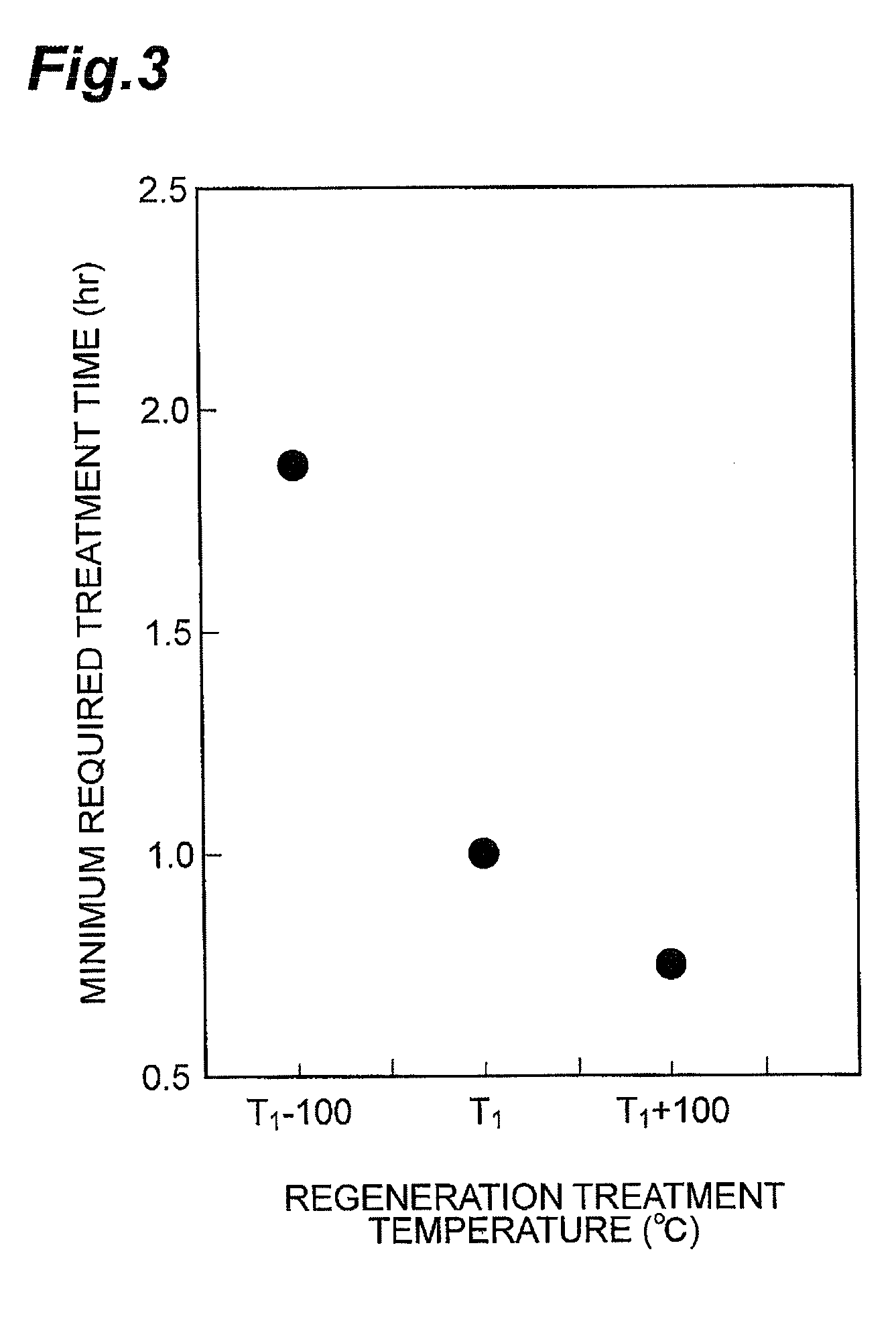
A method of producing a regenerated hydrotreating catalyst, including a first step of preparing a hydrotreating catalyst that has been used for hydrotreatment of a petroleum fraction and has a metal element selected from Group 6 elements of the periodic table; a second step of performing regeneration treatment for part of the catalyst prepared in the first step, then performing X-ray absorption fine structure analysis for the catalyst after the regeneration treatment, and obtaining regeneration treatment conditions in which a ratio IS / IO of a peak intensity IS of a peak attributed to a bond between the metal element and a sulfur atom to a peak intensity IO of a peak attributed to a bond between the metal element and an oxygen atom is in the range of 0.1 to 0.3 in a radial distribution curve obtained from an extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectrum.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
A synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device for electrocatalytic reaction
ActiveCN103884728BMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricitySoft x ray
The invention discloses a synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device for electrocatalytic reaction. It consists of a front ionization chamber, a rear ionization chamber (or a fluorescence detector) and an in situ cell of a synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (XAFS) line station. By assembling the membrane electrode for the electrocatalytic reaction in the in-situ cell, under the condition that the detection windows of each component in the in-situ cell are on the same center line, X-rays are used to irradiate the membrane electrode, and the X-rays are transmitted or reflected. After arriving at the synchrotron radiation XAFS line station, the ionization chamber or fluorescence detector realizes the in-situ detection of the catalyst structure during the electrocatalytic reaction; the detection window of the in-situ cell is in the center of the flow field plate, and the dead volume is small, which improves the accuracy of the experimental data. Accuracy and reliability; the heating plate and the flow field plate in the in-situ cell are fixed together with screws, which not only realizes the sealing of the detection window on the flow field plate, but also facilitates the assembly and replacement of membrane electrodes. It is a set of detection devices suitable for studying the process and mechanism of electrocatalytic reactions.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of producing regenerated hydrotreating catalyst and method of producing petroleum products
ActiveUS20130233769A1High activityMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesXANES SpectroscopyPetroleum product
A method of producing a regenerated hydrotreating catalyst, including a first step of preparing a hydrotreating catalyst that has been used for hydrotreatment of a petroleum fraction and has a metal element selected from Group 6 elements of the periodic table; a second step of performing regeneration treatment for part of the catalyst prepared in the first step, then performing X-ray absorption fine structure analysis for the catalyst after the regeneration treatment, and obtaining regeneration treatment conditions in which a ratio IS / IO of a peak intensity IS of a peak attributed to a bond between the metal element and a sulfur atom to a peak intensity IO of a peak attributed to a bond between the metal element and an oxygen atom is in the range of 0.1 to 0.3 in a radial distribution curve obtained from an extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectrum.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
An intelligent electronic device, a QXAFS (quick X-ray absorption fine structure) system and a data acquisition and motor control method
ActiveCN103234986BOvercoming the problem of limited acquisition speedDynamo-electric converter controlMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCore componentData acquisition
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com