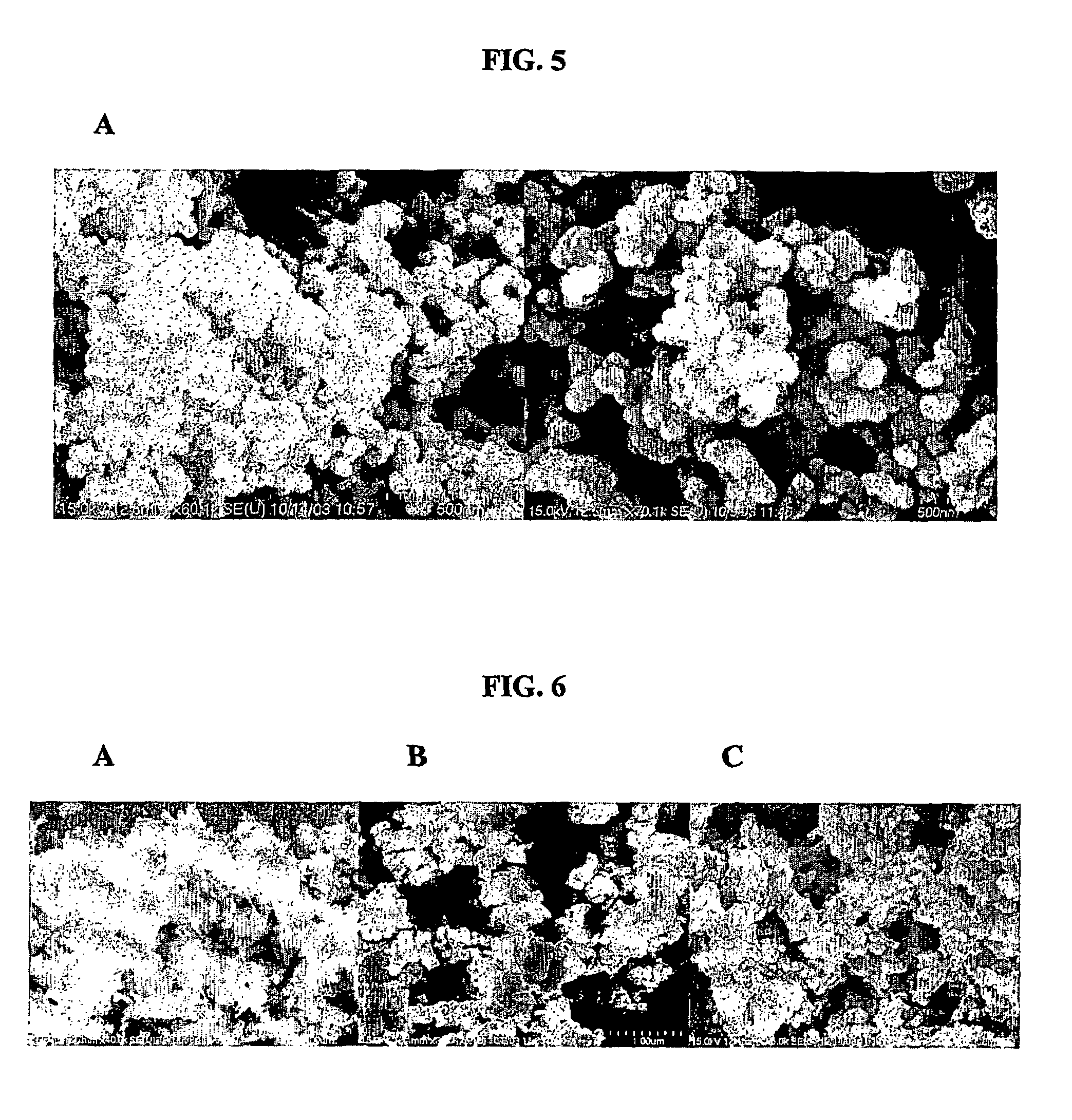
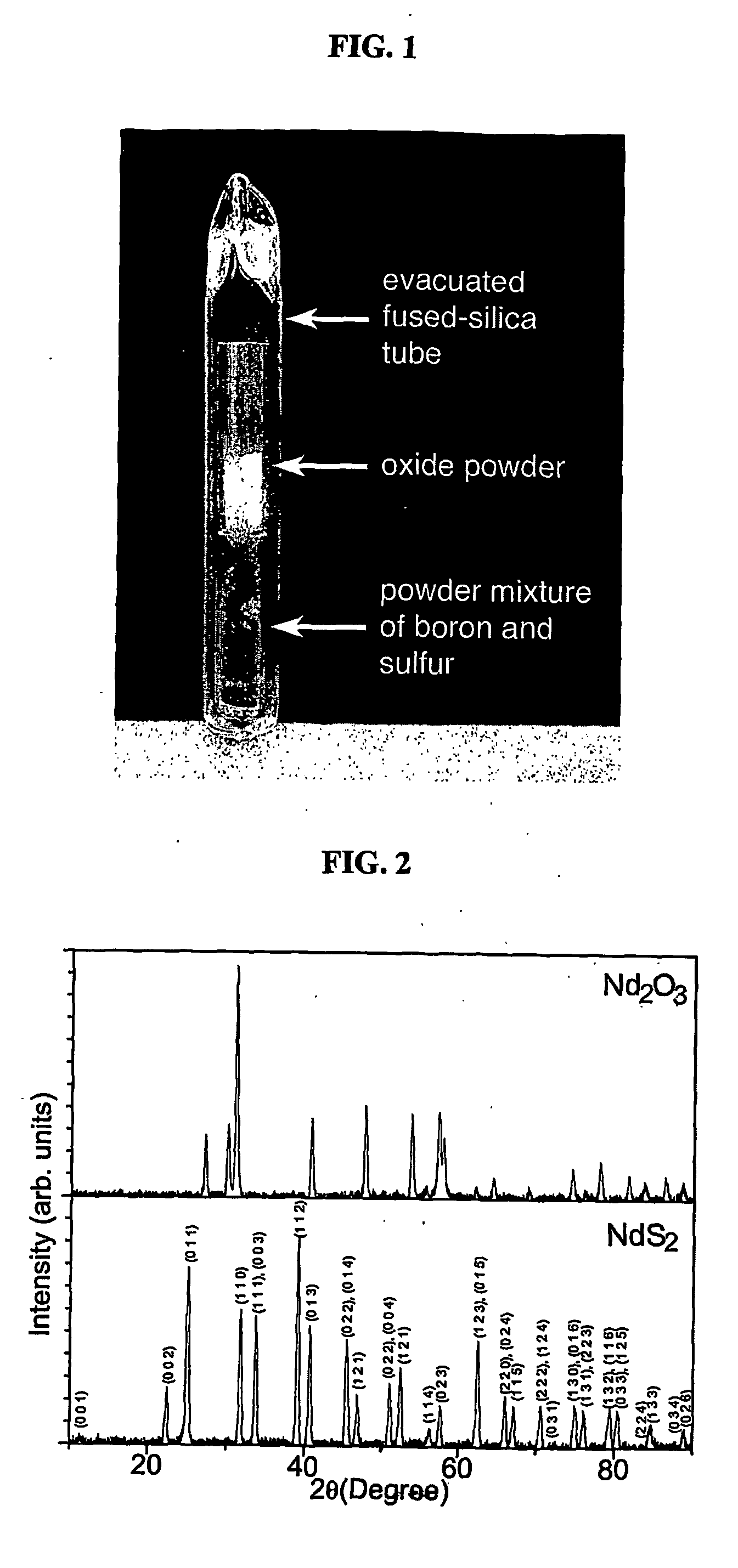
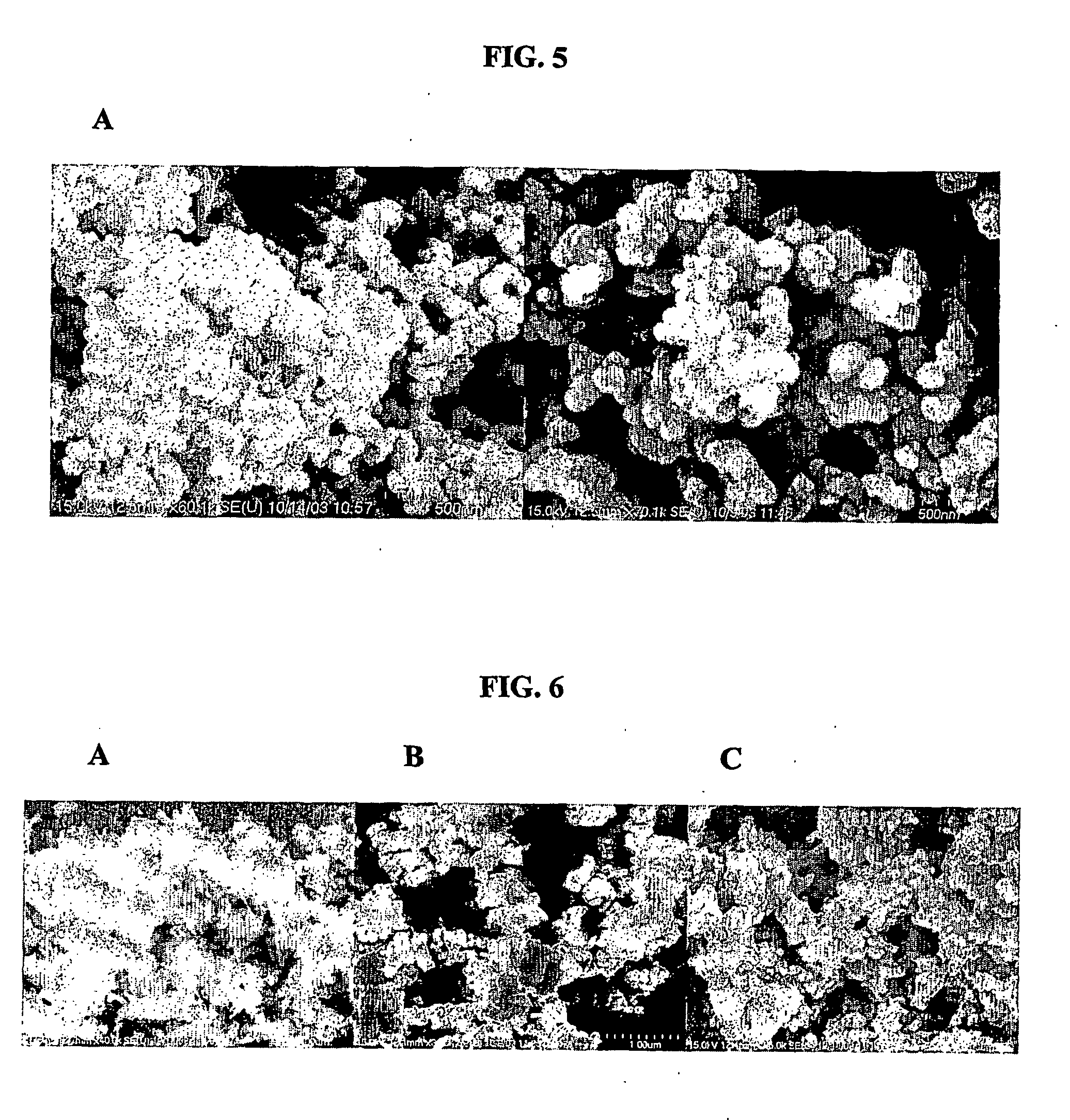
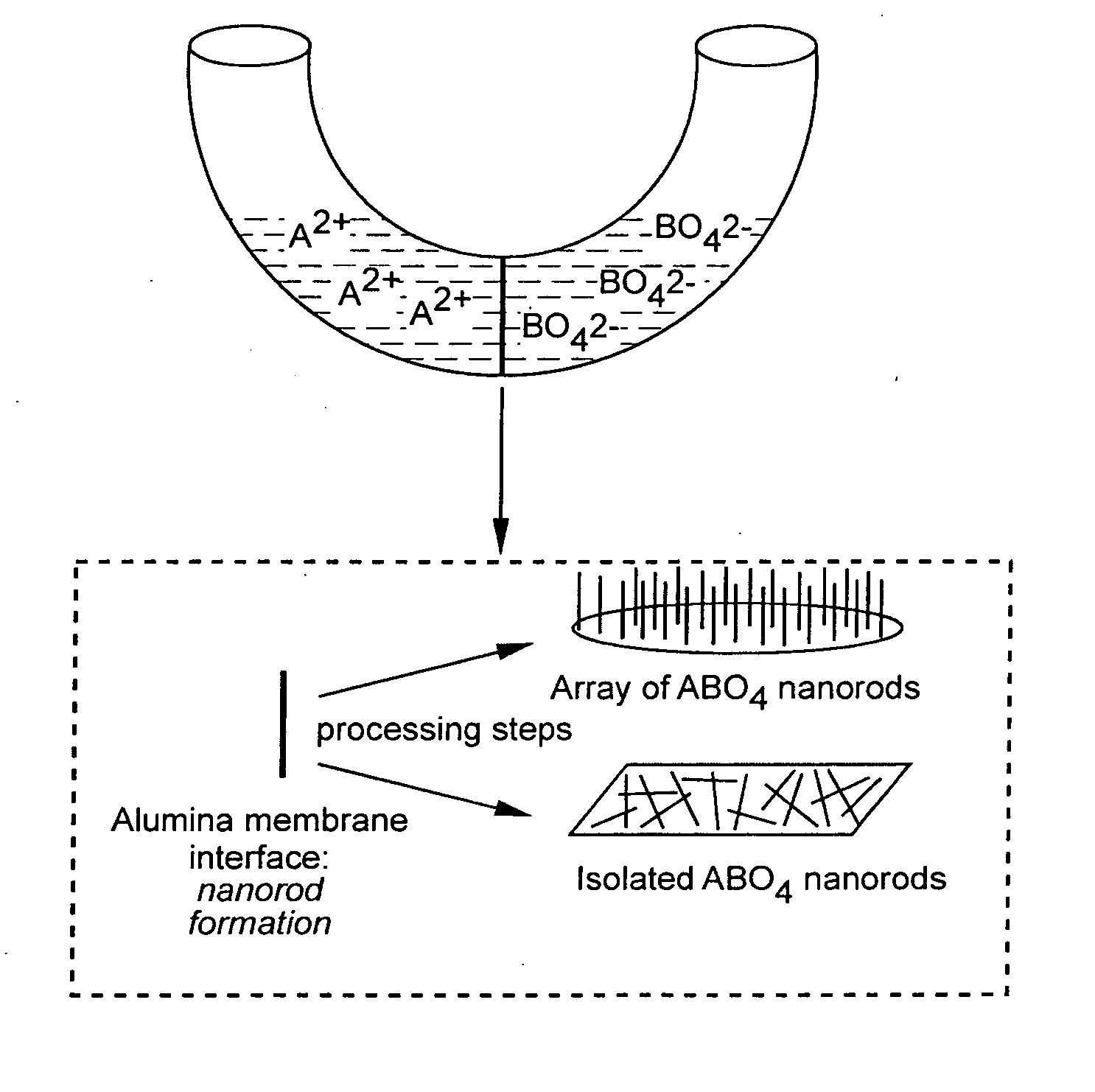
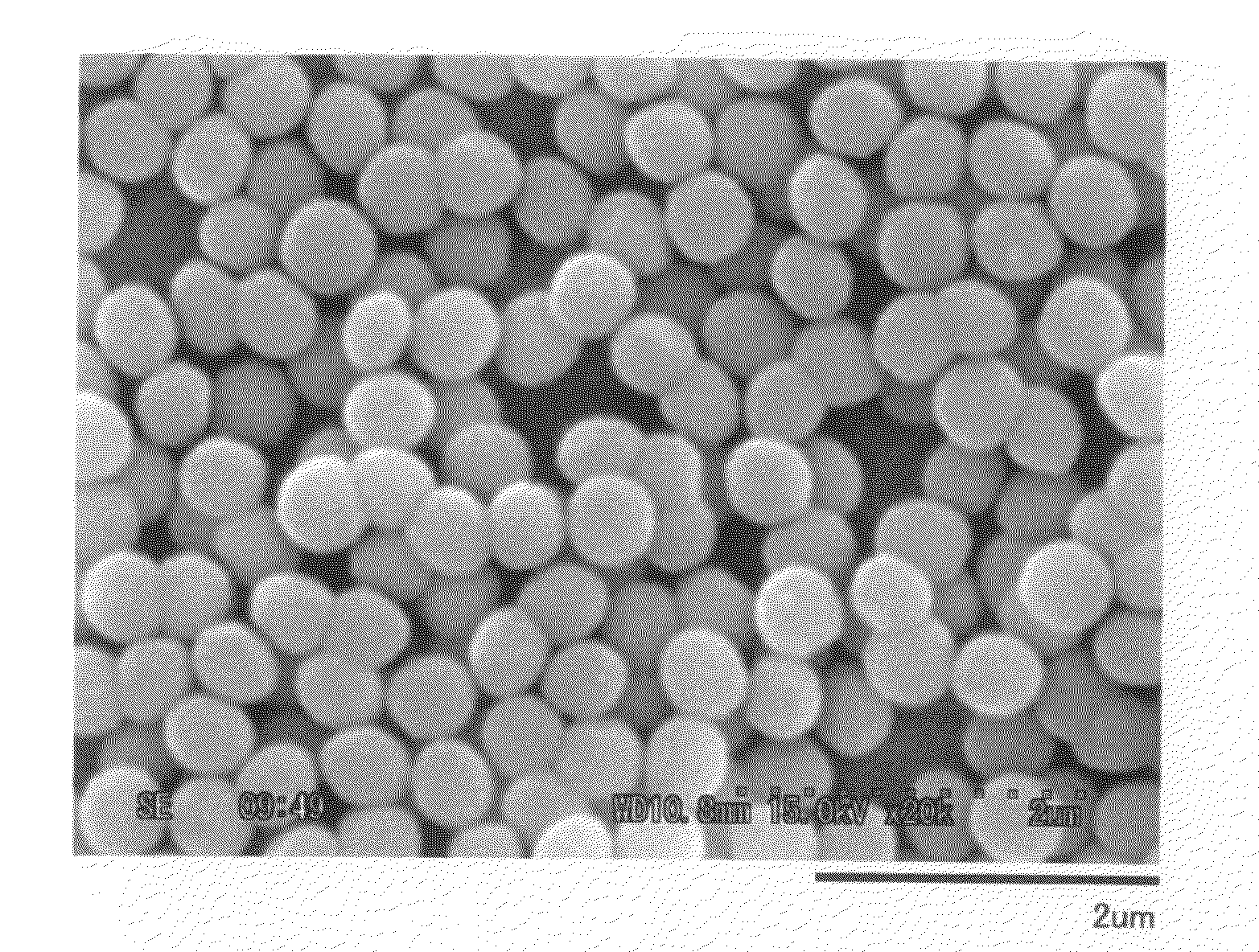
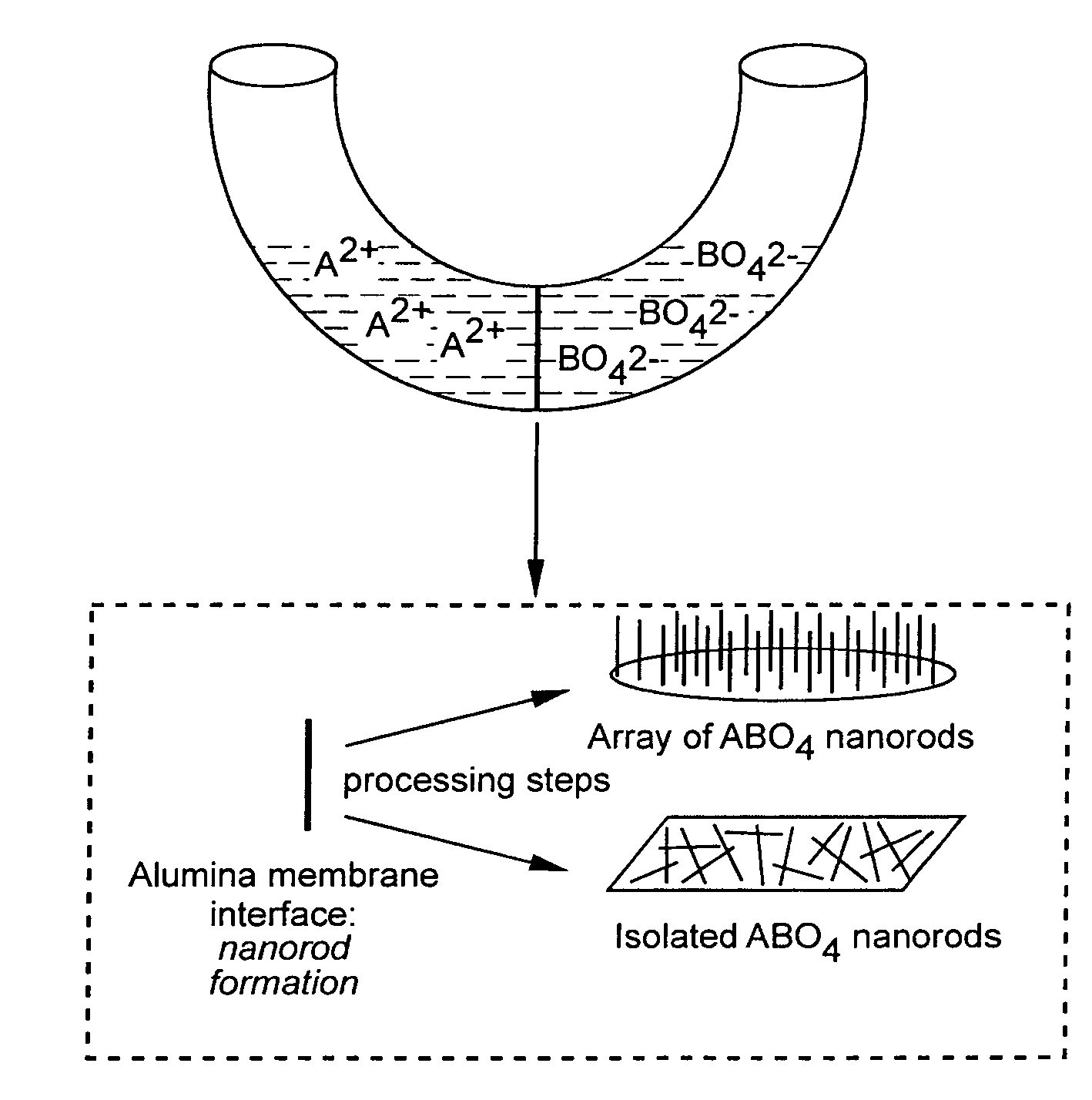
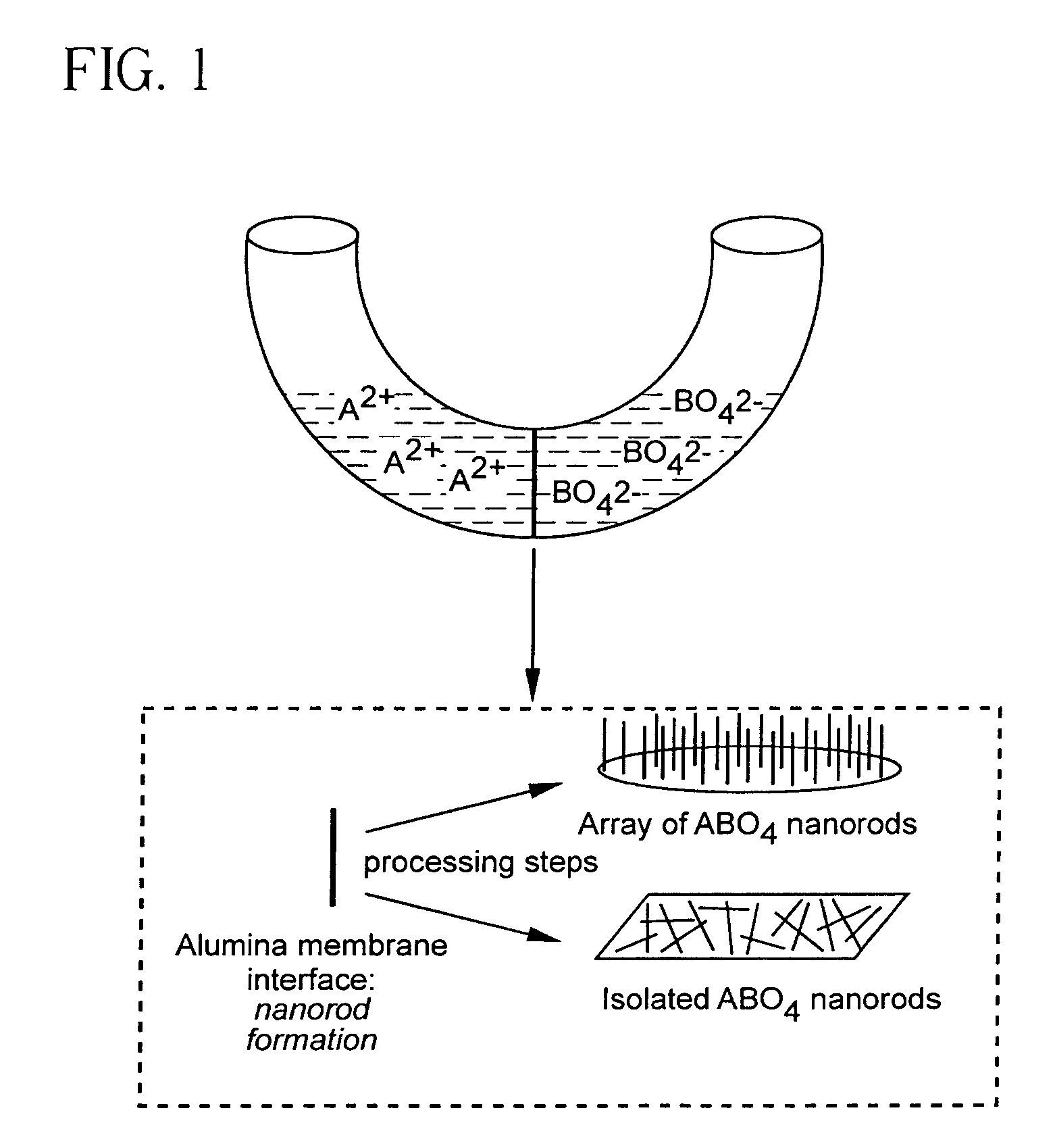
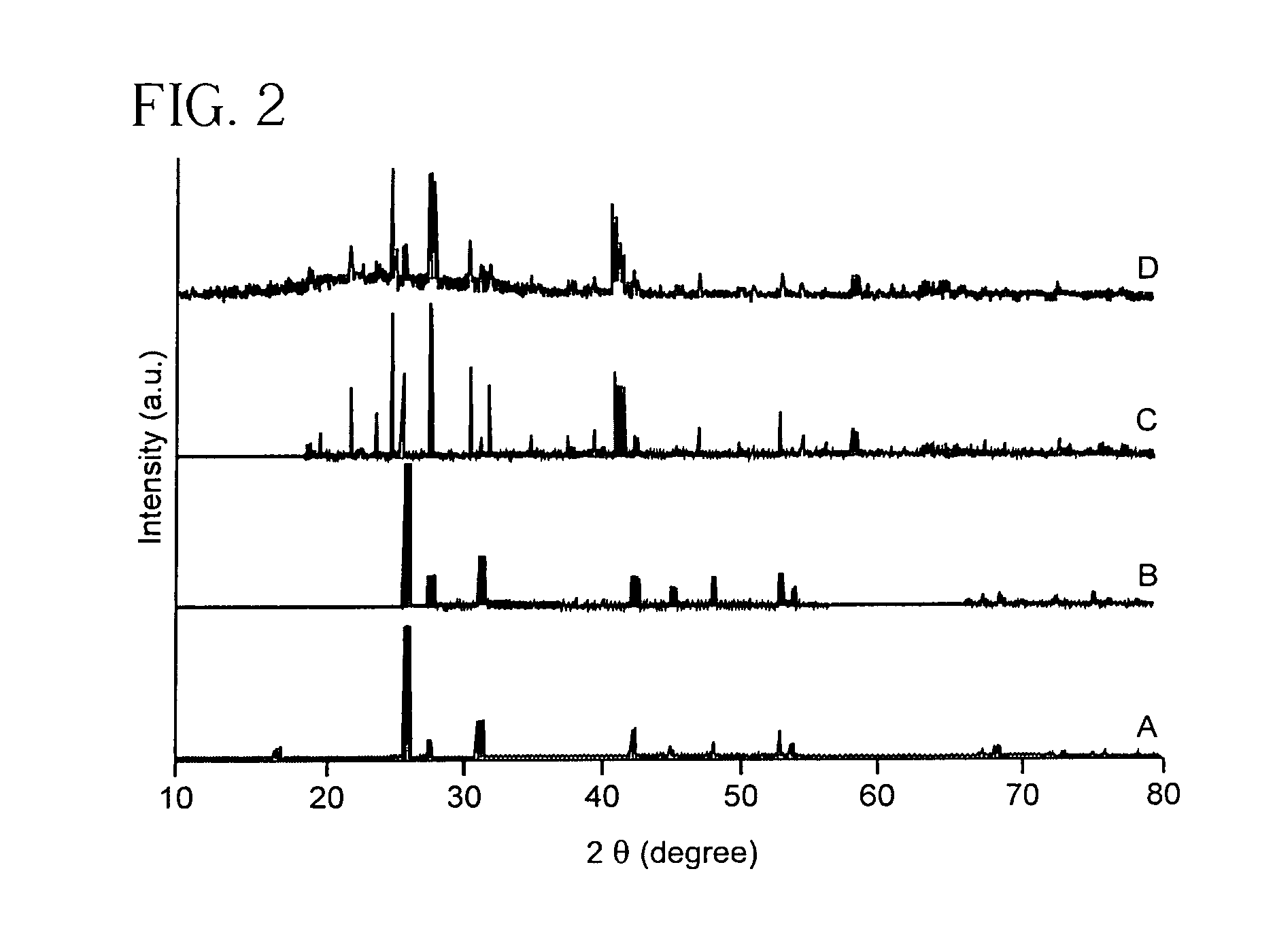
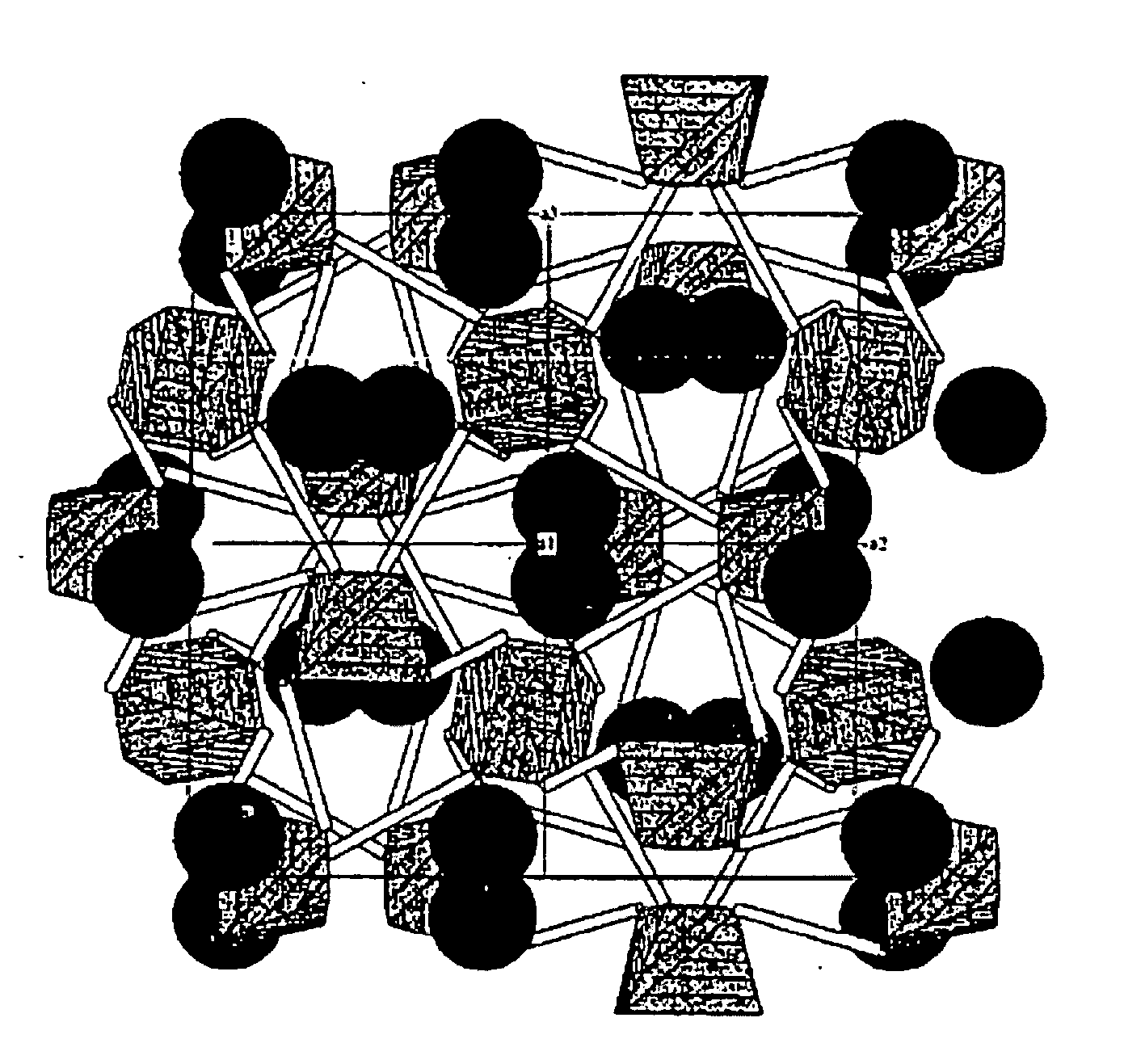
Patents
Literature
36results about "Aluminium sulfur compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
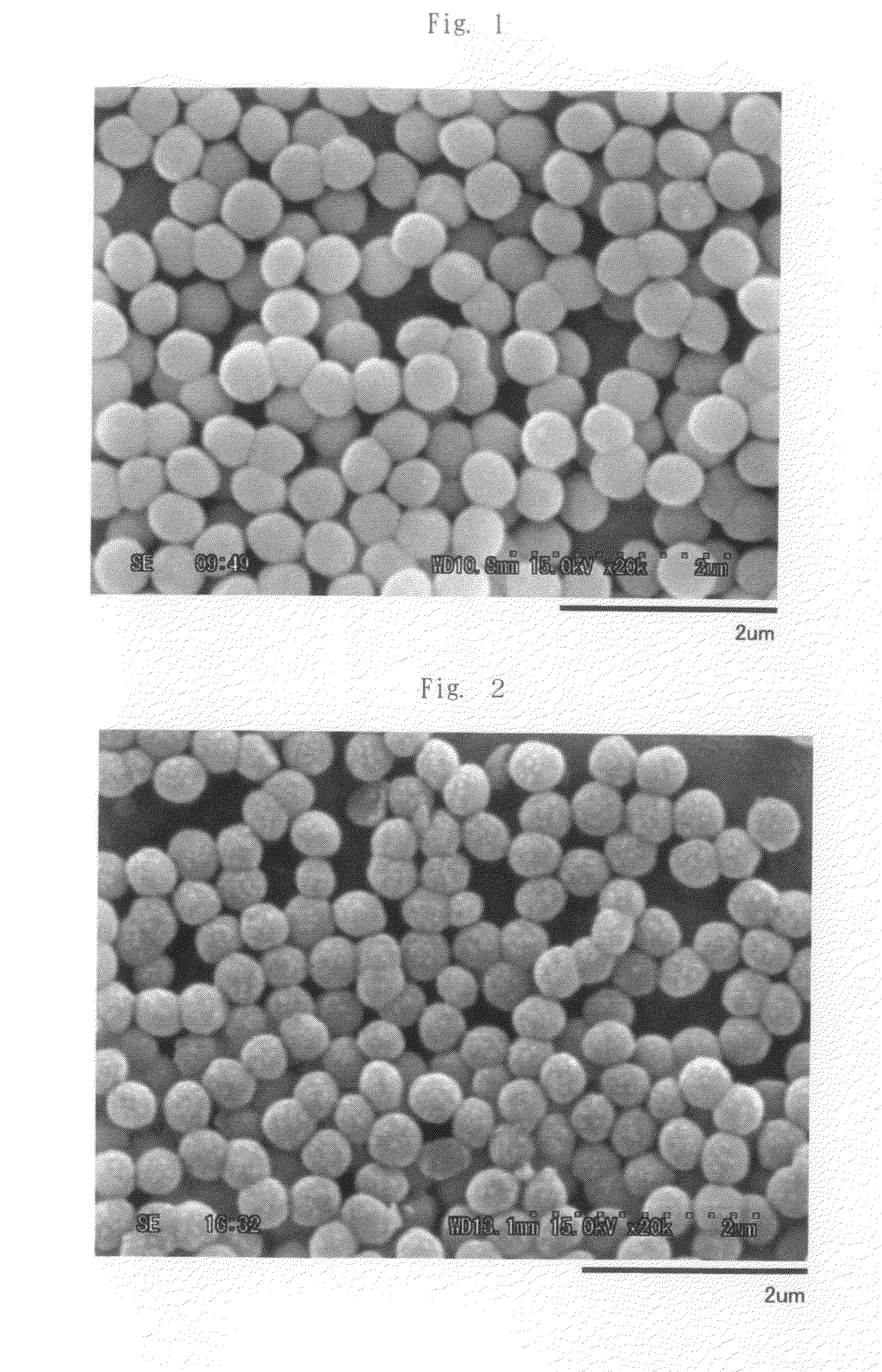
Method for synthesis of carbon-coated redox materials with controlled size
ActiveUS20040033360A1Low costReduce the numberMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitorsCross-linkRedox
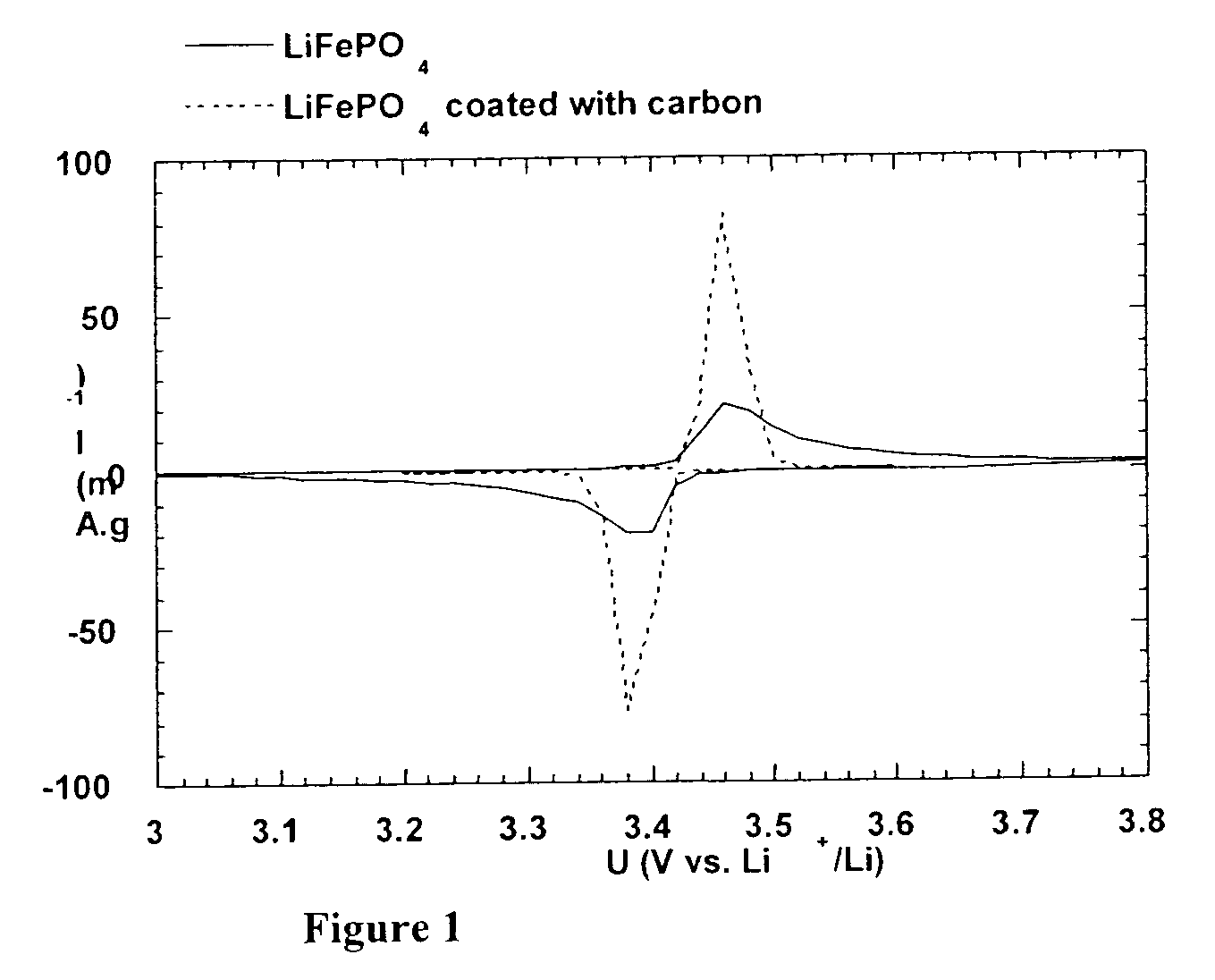
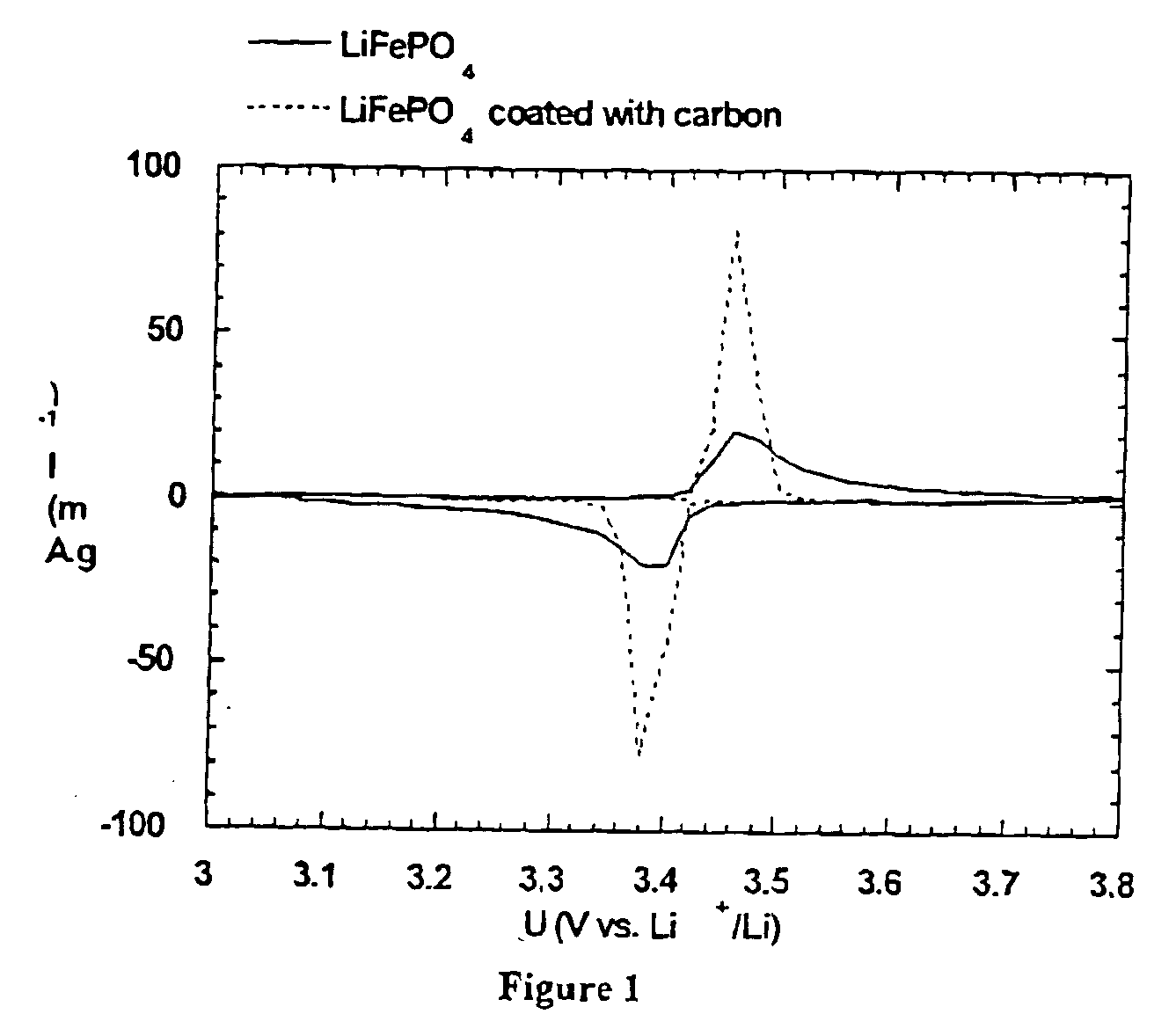
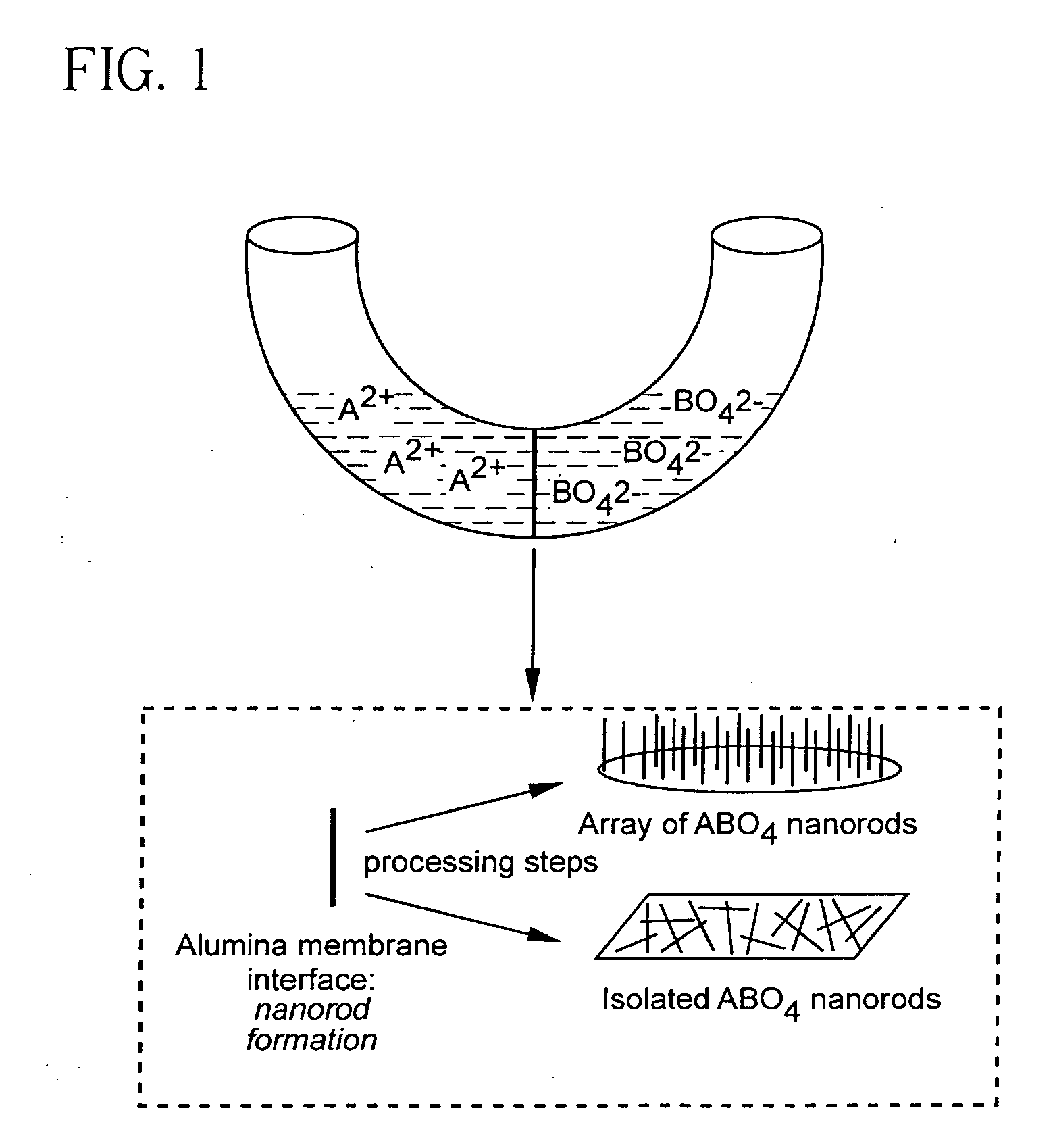
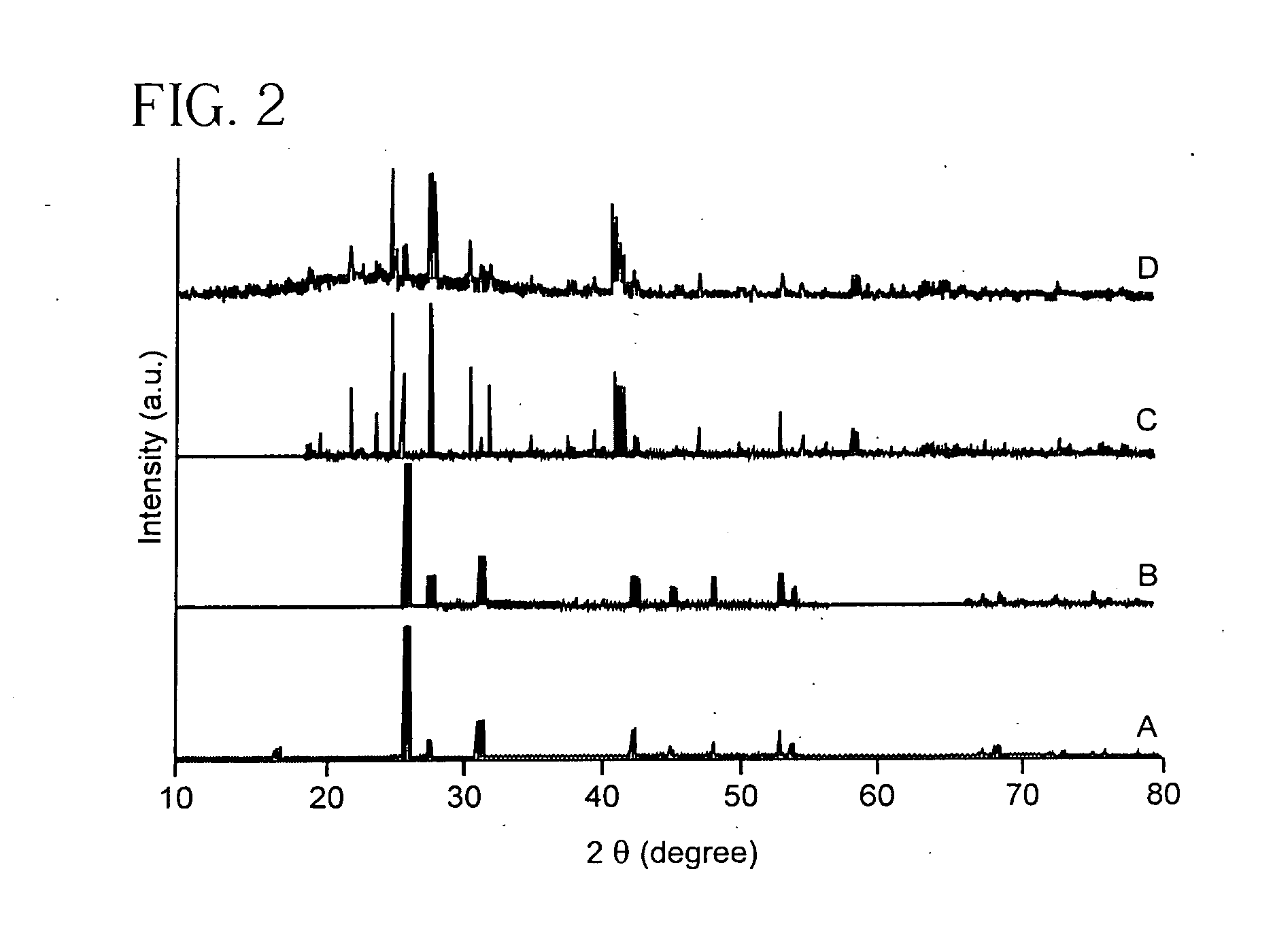
A method for the synthesis of compounds of the formula C-LixM1-yM'y(XO4)n, where C represents carbon cross-linked with the compound LixM1-yM'y(XO4)n, in which x, y and n are numbers such as 0<=x<=2, 0<=y<=0.6, and 1<=n<=1.5, M is a transition metal or a mixture of transition metals from the first period of the periodic table, M' is an element with fixed valency selected among Mg<2+>, Ca<2+>, Al<3+>, Zn<2+> or a combination of these same elements and X is chosen among S, P and Si, by bringing into equilibrium, in the required proportions, the mixture of precursors, with a gaseous atmosphere, the synthesis taking place by reaction and bringing into equilibrium, in the required proportions, the mixture of the precursors, the procedure comprising at least one pyrolysis step of the carbon source compound in such a way as to obtain a compound in which the electronic conductivity measured on a sample of powder compressed at a pressure of 3750 Kg.cm<-2 >is greater than 10<-8 >S.cm<-1>. The materials obtained have excellent electrical conductivity, as well a very improved chemical activity.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
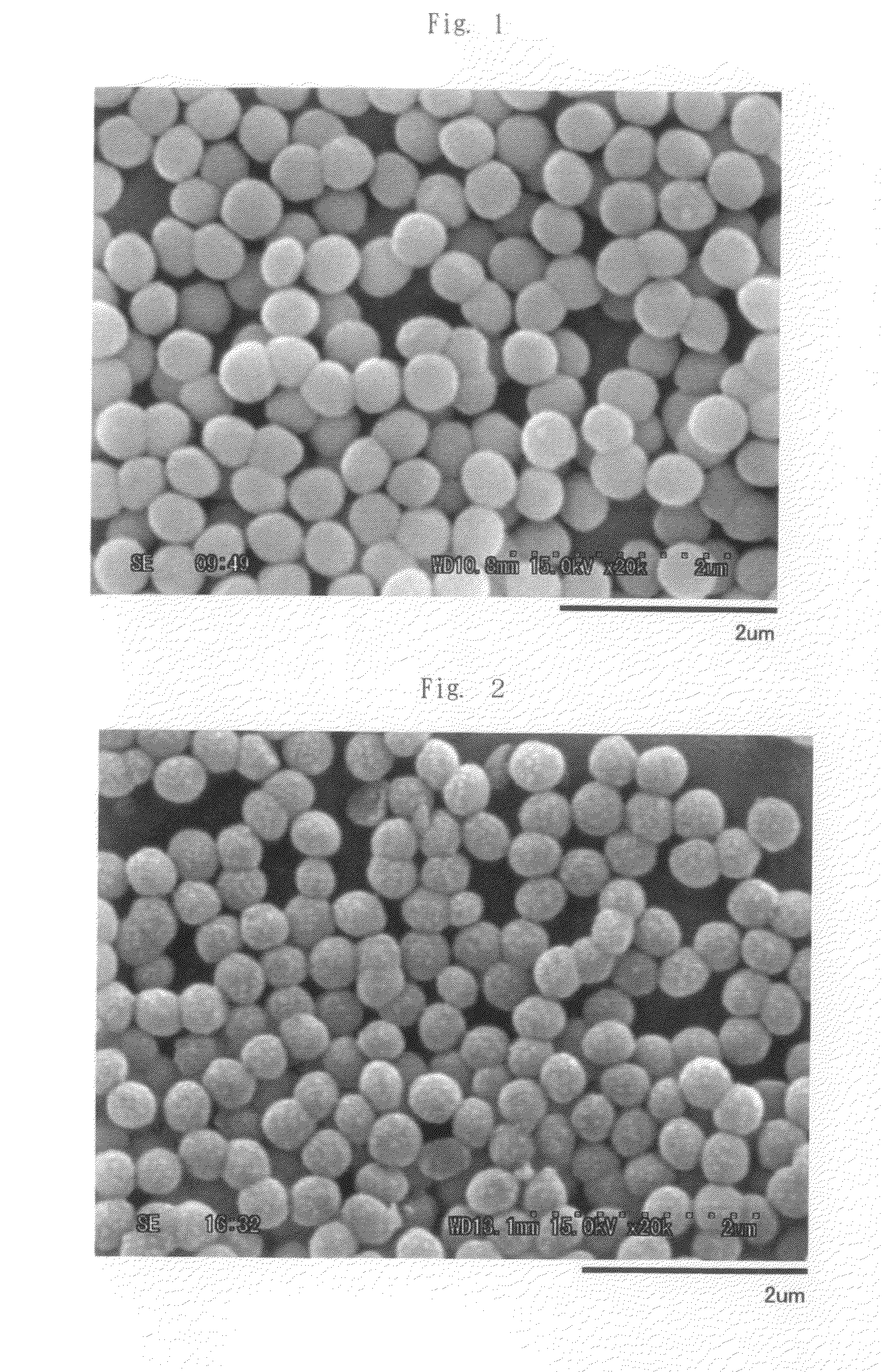
Synthesis method for carbon material based on lixm1-ym'(xo4)n
InactiveUS20040086445A1Improve performanceLow costHybrid capacitorsElectrolytic capacitorsElectrical conductorSynthesis methods
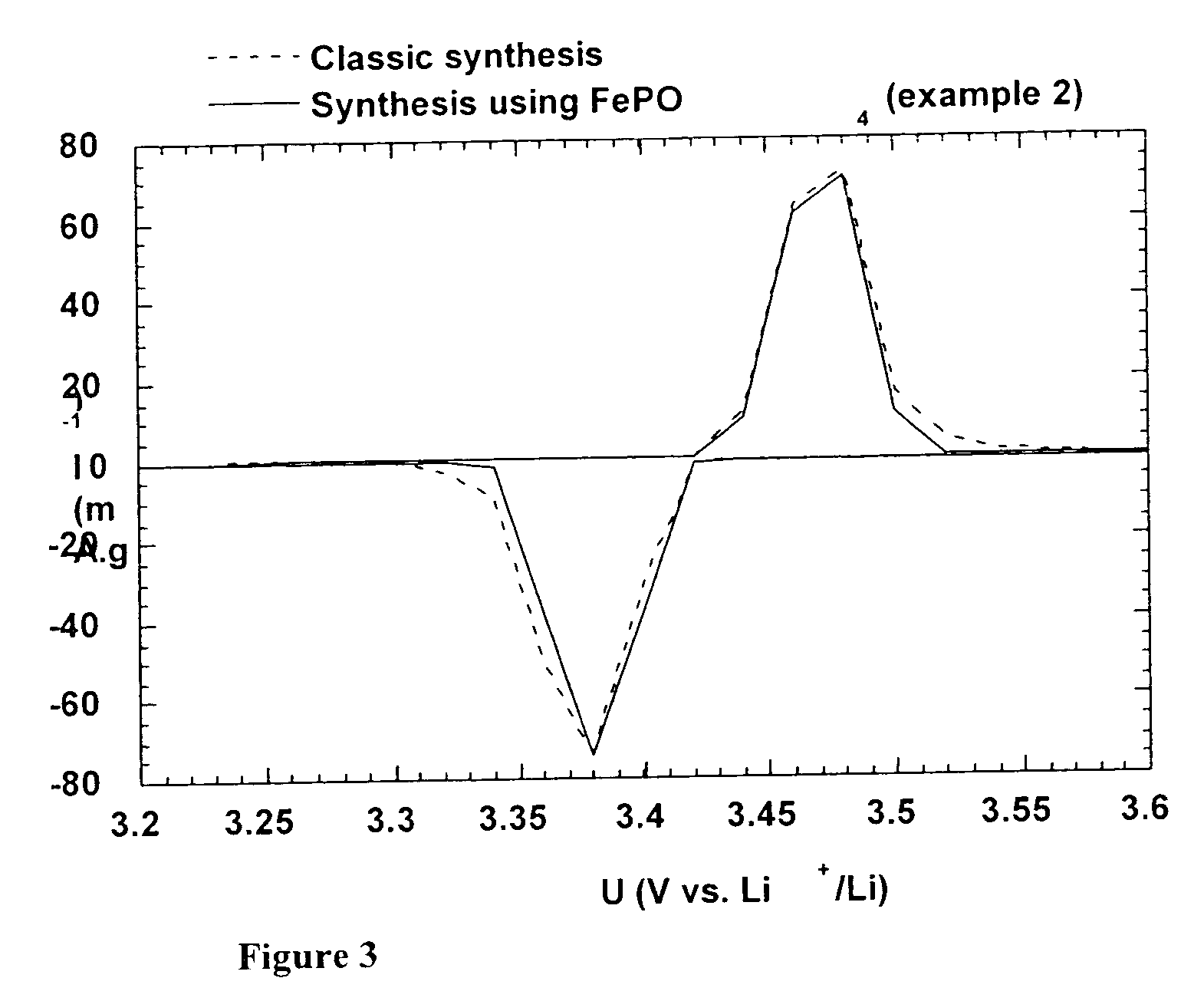
Method of synthesis for a material made of particles having a core and a coating and / or being connected to each other by carbon cross-linking, the core of these particles containing at least one compound of formula LixM1-yM'y(XO4)n, in which x,y and n are numbers such as 0<=x<=2, 0<=y<=0.6 and 1<=n<=1.5, M is a transition metal, M' is an element with fixed valency, and the synthesis is carried out by reaction and bringing into equilibrium the mixture of precursors, with a reducing gaseous atmosphere, in such a way as to bring the transition metal or metals to the desired valency level, the synthesis being carried out in the presence of a source of carbon called carbon conductor, which is subjected to pyrolysis. The materials obtained have excellent electrical conductivity as well as very improved chemical activity.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Cathode materials for secondary (rechargeable) lithium batteries
InactiveUS20050003274A1Cell electrodesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesAlkali ionsRechargeable cell
The invention relates to materials for use as electrodes in an alkali-ion secondary (rechargeable) battery, particularly a lithium-ion battery. The invention provides transition-metal compounds having the ordered-olivine, a modified olivine, or the rhombohedral NASICON structure and the polyanion (PO4)3− as at least one constituent for use as electrode material for alkali-ion rechargeable batteries.
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Preparation of metal chalcogenides from reactions of metal compounds and chalcogen
A method of preparing metal chalcogenides from elemental metal or metal compounds has the following steps: providing at least one elemental metal or metal compound; providing at least one element from periodic table groups 13-15; providing at least one chalcogen; and combining and heating the chalcogen, the group 13-15 element and the metal at sufficient time and temperature to form a metal chalcogenide. A method of functionalizing the surface of semiconducting nanoparticles has the following steps: providing at least one metad compound; providing one chalcogenide having a cation selected from the group 13-15 (B, Al, Ga, In, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, P, As, Sb and Bi); dissolving the chalcogenide in a first solution; dissolving the metal compound in a second solution; providing and dissolving a functional capping agent in at least one of the solutions of the metal compounds and chalcogenide; combining all solutions; and maintaining the combined solution at a proper temperature for an appropriate time.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Preparation of metal chalcogenides from reactions of metal compounds and chalcogen
InactiveUS20060239882A1Rare earth metal sulfidesSelenium/tellurium compundsSufficient timeNanoparticle
A method of preparing metal chalcogenides from elemental metal or metal compounds has the following steps: providing at least one elemental metal or metal compound; providing at least one element from periodic table groups 13-15; providing at least one chalcogen; and combining and heating the chalcogen, the group 13-15 element and the metal at sufficient time and temperature to form a metal chalcogenide. A method of functionalizing the surface of semiconducting nanoparticles has the following steps: providing at least one metad compound; providing one chalcogenide having a cation selected from the group 13-15 (B, Al, Ga, In, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, P, As, Sb and Bi); dissolving the chalcogenide in a first solution; dissolving the metal compound in a second solution; providing and dissolving a functional capping agent in at least one of the solutions of the metal compounds and chalcogenide; combining all solutions; and maintaining the combined solution at a proper temperature for an appropriate time.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Metal oxide and metal fluoride nanostructures and methods of making same
InactiveUS20070113779A1Easy to controlOvercomes shortcomingMercury oxidesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesSingle crystalNanostructure
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
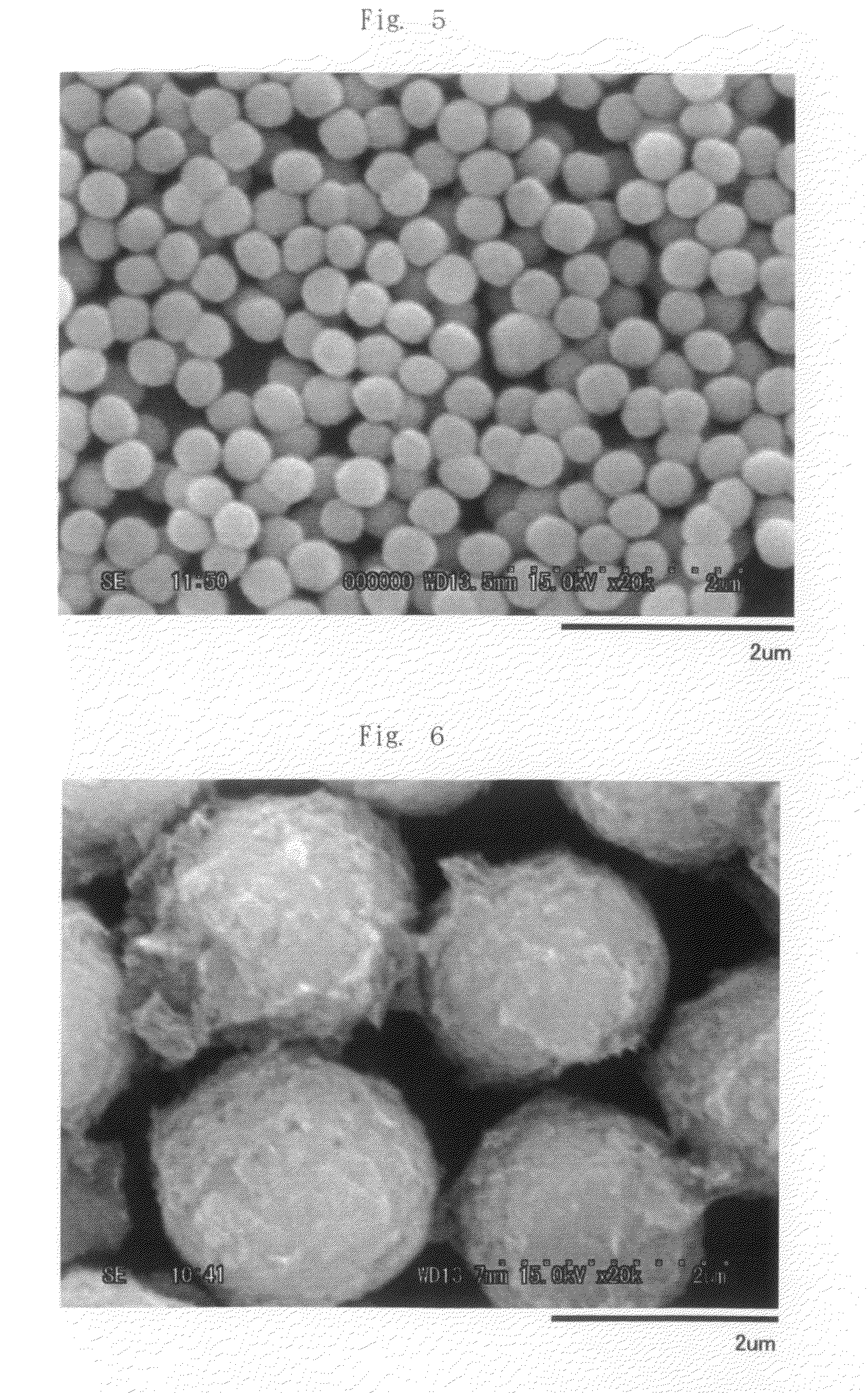
Synthesis of cathode active materials
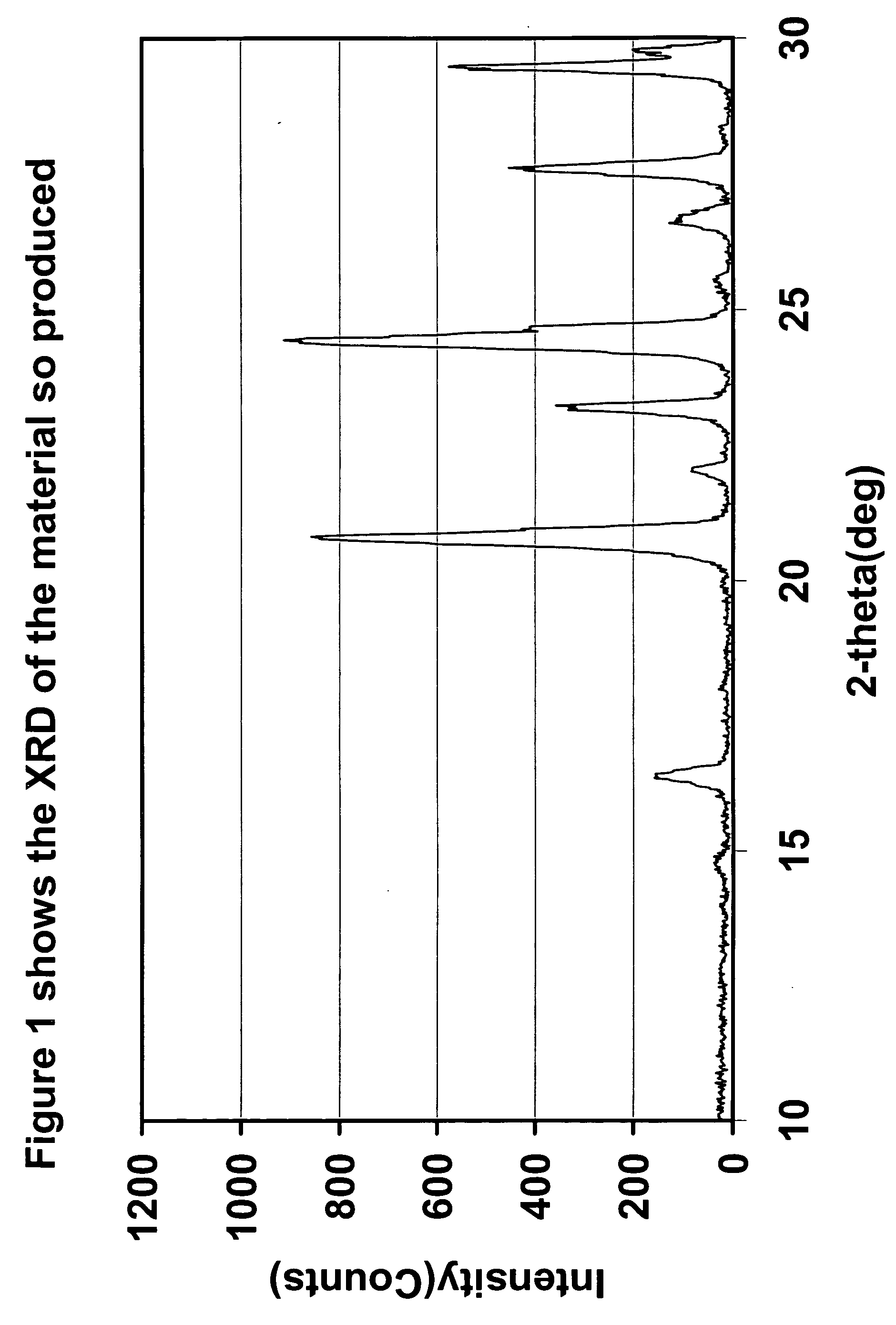
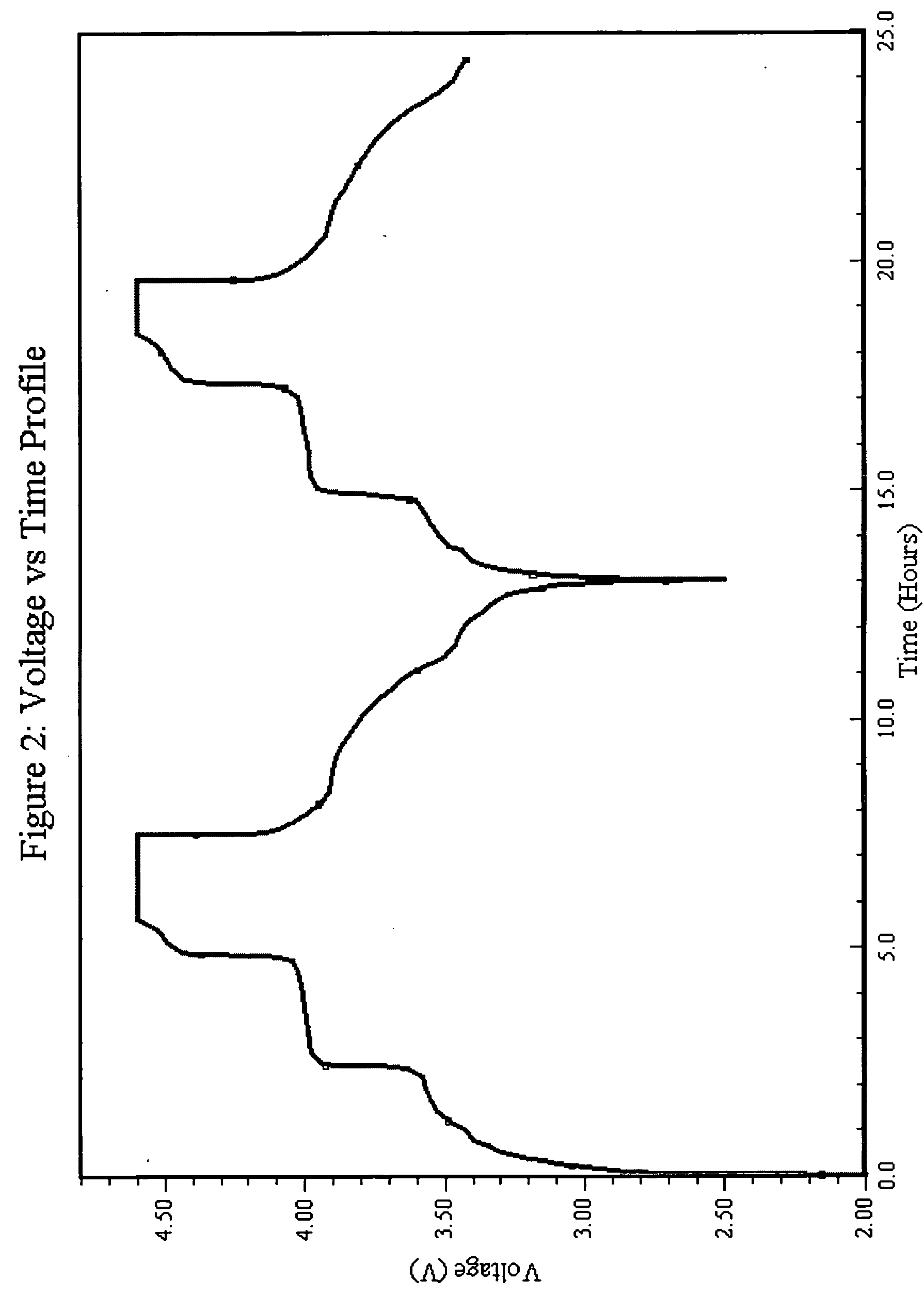
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an electroactive metal polyanion or a mixed metal polyanion comprising forming a slurry comprising a polymeric material, a solvent, a polyanion source or alkali metal polyanion source and at least one metal ion source; heating said slurry at a temperature and for a time sufficient to remove the solvent and form an essentially dried mixture; and heating said mixture at a temperature and for a time sufficient to produce an electroactive metal polyanion or electroactive mixed metal polyanion. In an alternative embodiment the present invention relates to a method for preparing a metal polyanion or a mixed metal polyanion which comprises mixing a polymeric material with a polyanion source or alternatively an alkali metal polyanion source and a source of at least one metal ion to produce a fine mixture and heating the mixture to a temperature higher than the melting point of the polymeric material, milling the resulting material and then heating the milled material. It is another object of the invention to provide electrochemically active materials produced by said methods. The electrochemically active materials so produced are useful in making electrodes and batteries.
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV +1
Synthesis of cathode active materials
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV +1
Antibacterial Agent Composed of Silver-Containing Aluminum Sulfate Hydroxide Particles and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20090047311A1Good dispersibilityHigh transparencyCosmetic preparationsInorganic active ingredientsAluminium sulfateCompound (substance)
An antibacterial agent composed of silver-containing aluminum sulfate hydroxide particles represented by the following formula (X-I) or (Y-I).(AgaBb-a)bAlcAx(SO4)y(OH)z.pH2O (X-I)[AgaBb-a]b[Ti3-cAlc](SO4)y(OH)z.pH2O (Y-I)The above antibacterial agent of the present invention provides antibacterial molded articles and further antifungal agents, cosmetics, antibacterial paper, antibacterial deodorizing sprays and agricultural chemicals when it is mixed with a resin.
Owner:KYOWA CHEM IND
Powder material, electrode structure, production processes thereof, and secondary lithium battery
InactiveUS6932955B2Increase capacityImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesSulfurOxygen
Owner:CANON KK
Continuous preparation of calcined chemically-treated solid oxides
The present invention discloses a continuous calcination vessel which can be used to prepare calcined chemically-treated solid oxides from solid oxides and chemically-treated solid oxides. A process for the continuous preparation of calcined chemically-treated solid oxides is also provided. Calcined chemically-treated solid oxides disclosed herein can be used in catalyst compositions for the polymerization of olefins.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Metal composite oxide with novel crystal structure and their use as ionic conductors
ActiveUS20060051278A1Predict ionic conductivityEasy to moveCell electrodesSulfur compoundsElectrical conductorCrystal structure
Disclosed is metal composite oxides having the new crystal structure. Also disclosed are ionic conductors including the metal composite oxides and electrochemical devices comprising the ionic conductors. The metal composite oxides have an ion channel formed for easy movement of ions due to crystallographic specificity resulting from the ordering of metal ion sites and metal ion defects within the unit cell. Therefore, the metal composite oxides according to the present invention are useful in an electrochemical device requiring an ionic conductor or ionic conductivity.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
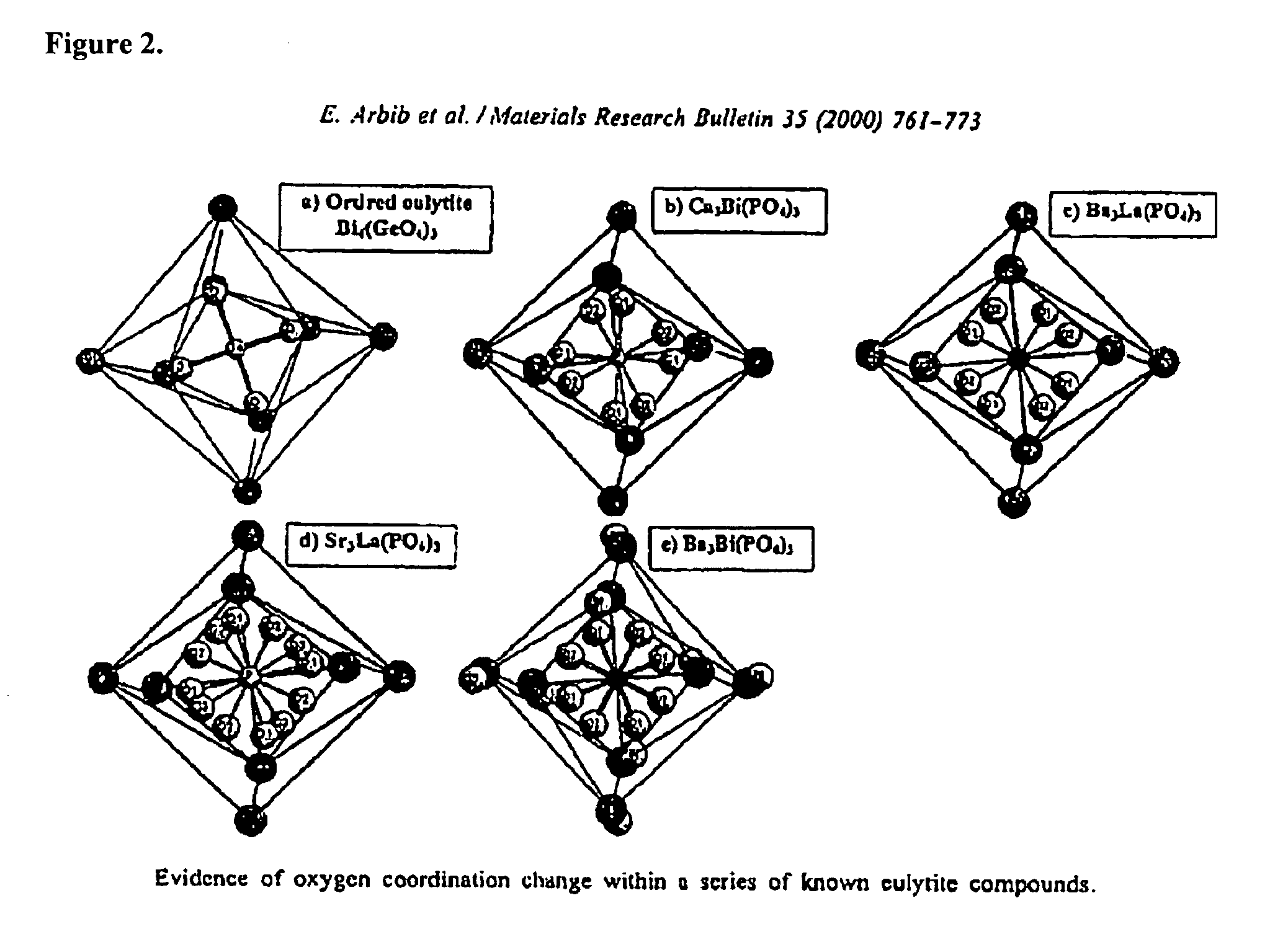
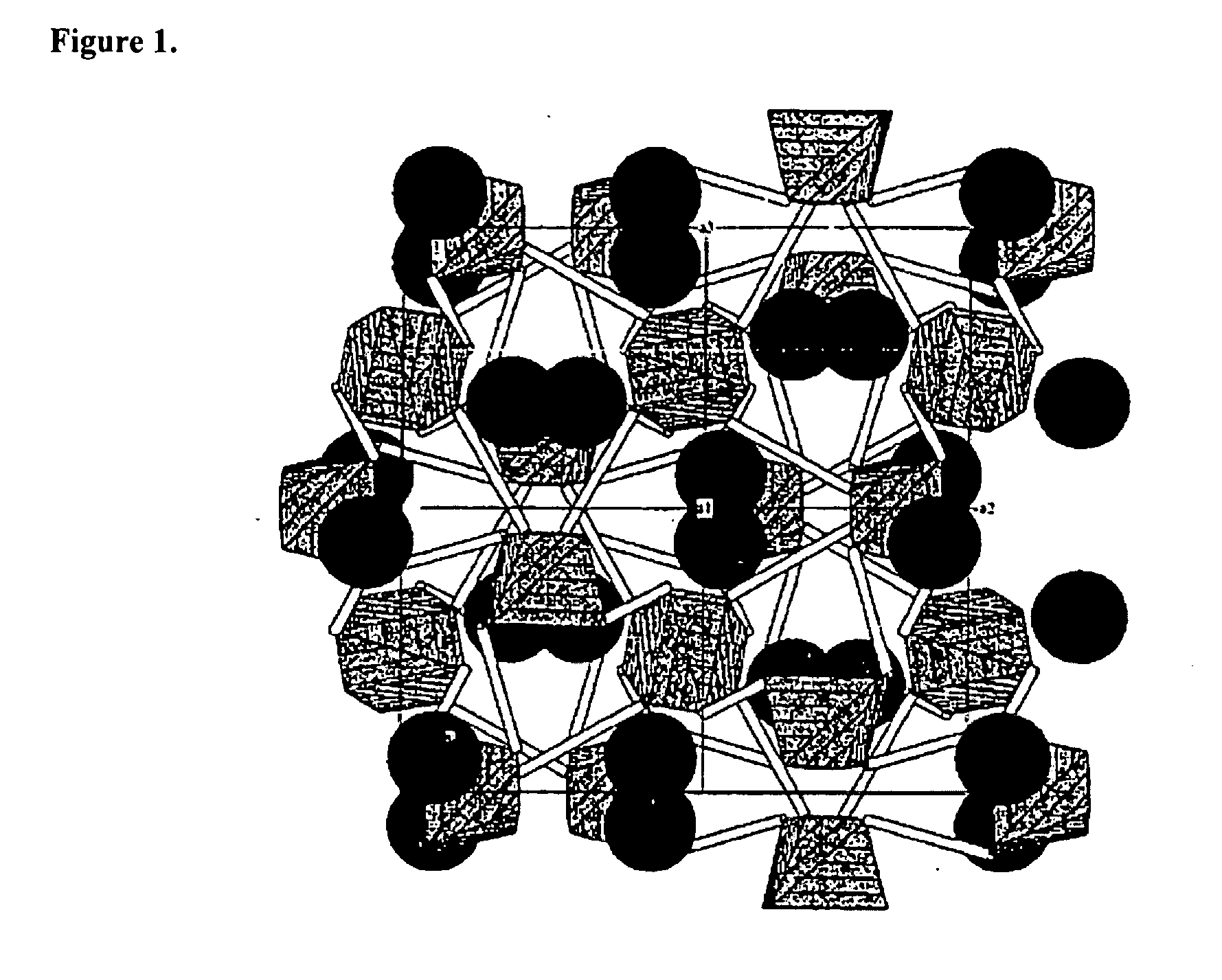
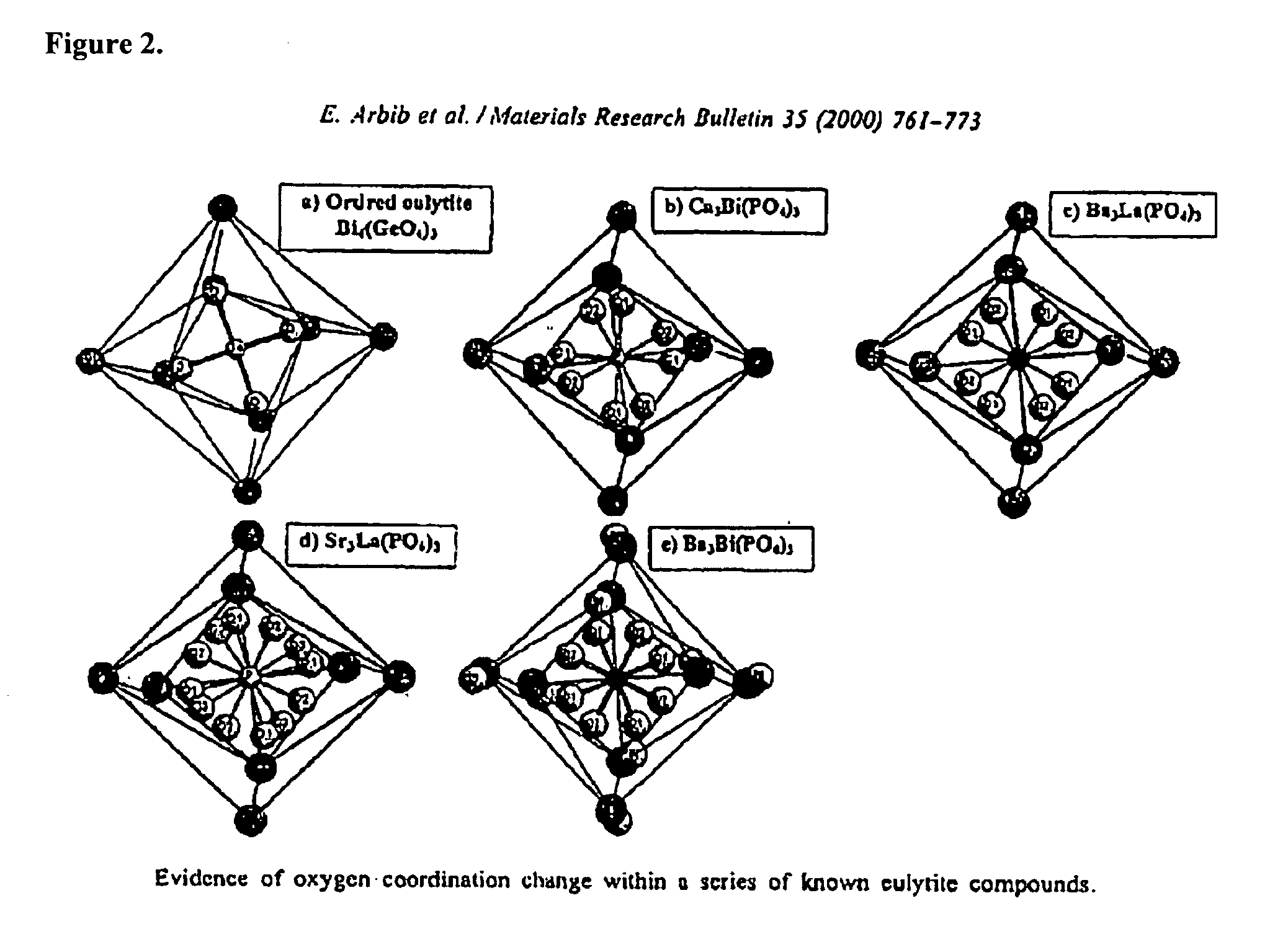
Eulytite solid acid electrolytes for electrochemical devices
Improved solid acid electrolyte materials, methods of synthesizing such materials, and electrochemical devices incorporating such materials are provided. The stable electrolyte material comprises a solid acid in a eulytine structure capable of undergoing rotational disorder of oxyanion groups and capable of extended operation at elevated temperatures, that is, solid acids having hydrogen bonded anion groups; a superprotonic disordered phase; and capable of operating at temperatures of ˜100° C. and higher.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Antibacterial agent composed of silver-containing aluminum sulfate hydroxide particles and use thereof
ActiveUS8394392B2Good dispersibilityHigh transparencyCosmetic preparationsInorganic active ingredientsAluminium sulfateCompound (substance)
An antibacterial agent composed of silver-containing aluminum sulfate hydroxide particles represented by the following formula (X-I) or (Y-I).(AgaBb-a)bAlcAx(SO4)y(OH)z.pH2O (X-I)[AgaBb-a]b[Ti3-cAlc](SO4)y(OH)z.pH2O (Y-I)The above antibacterial agent of the present invention provides antibacterial molded articles and further antifungal agents, cosmetics, antibacterial paper, antibacterial deodorizing sprays and agricultural chemicals when it is mixed with a resin.
Owner:KYOWA CHEM IND
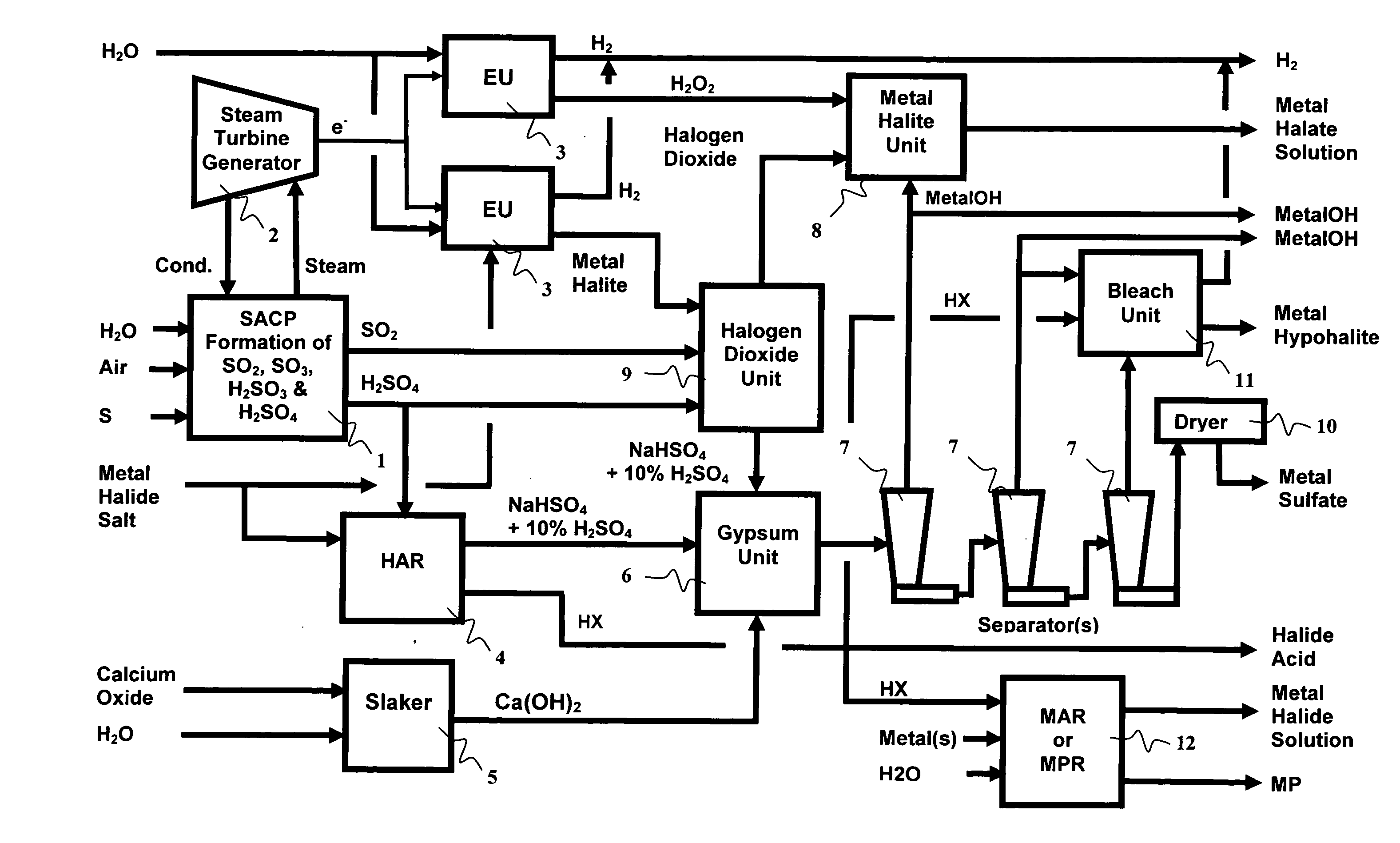
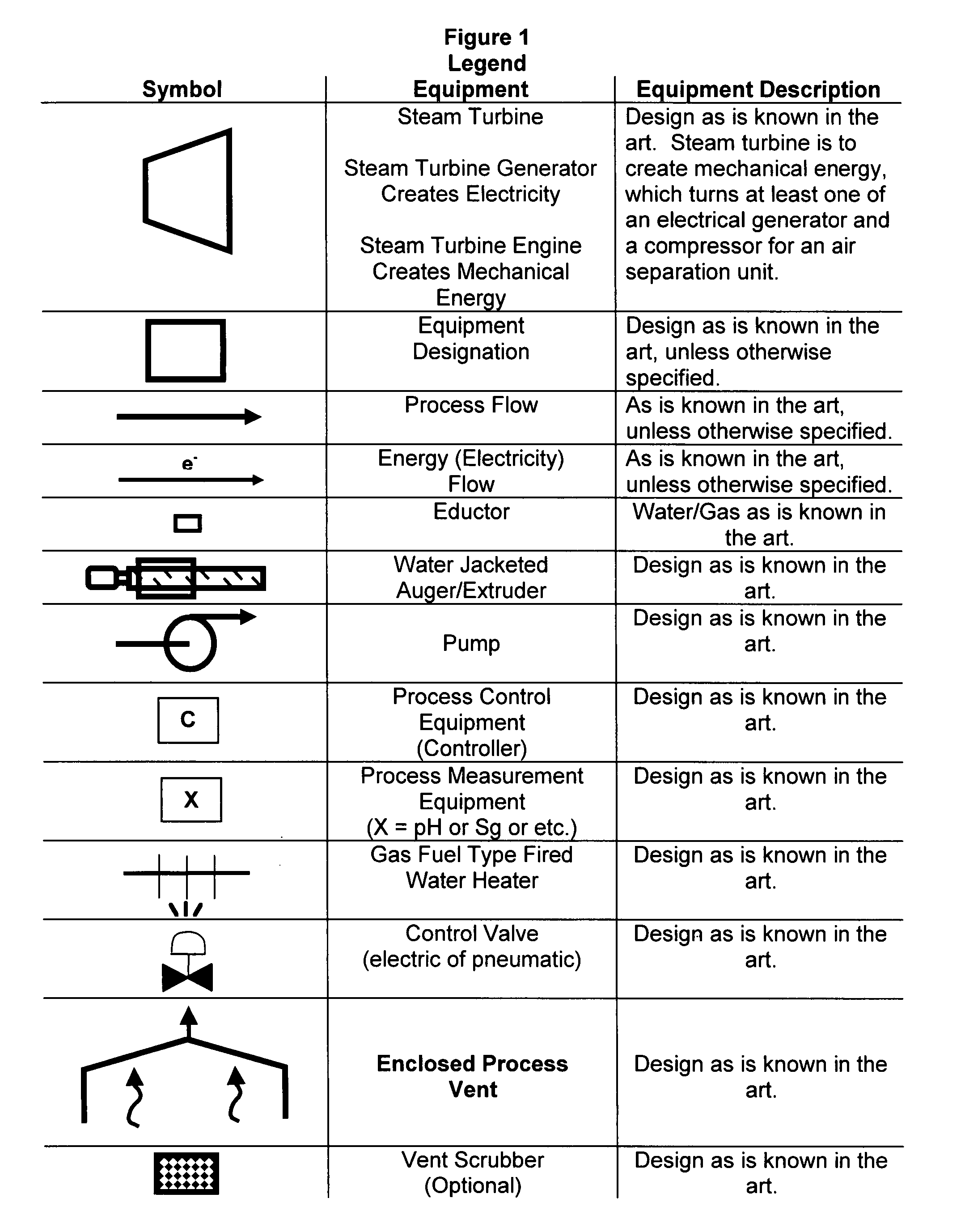
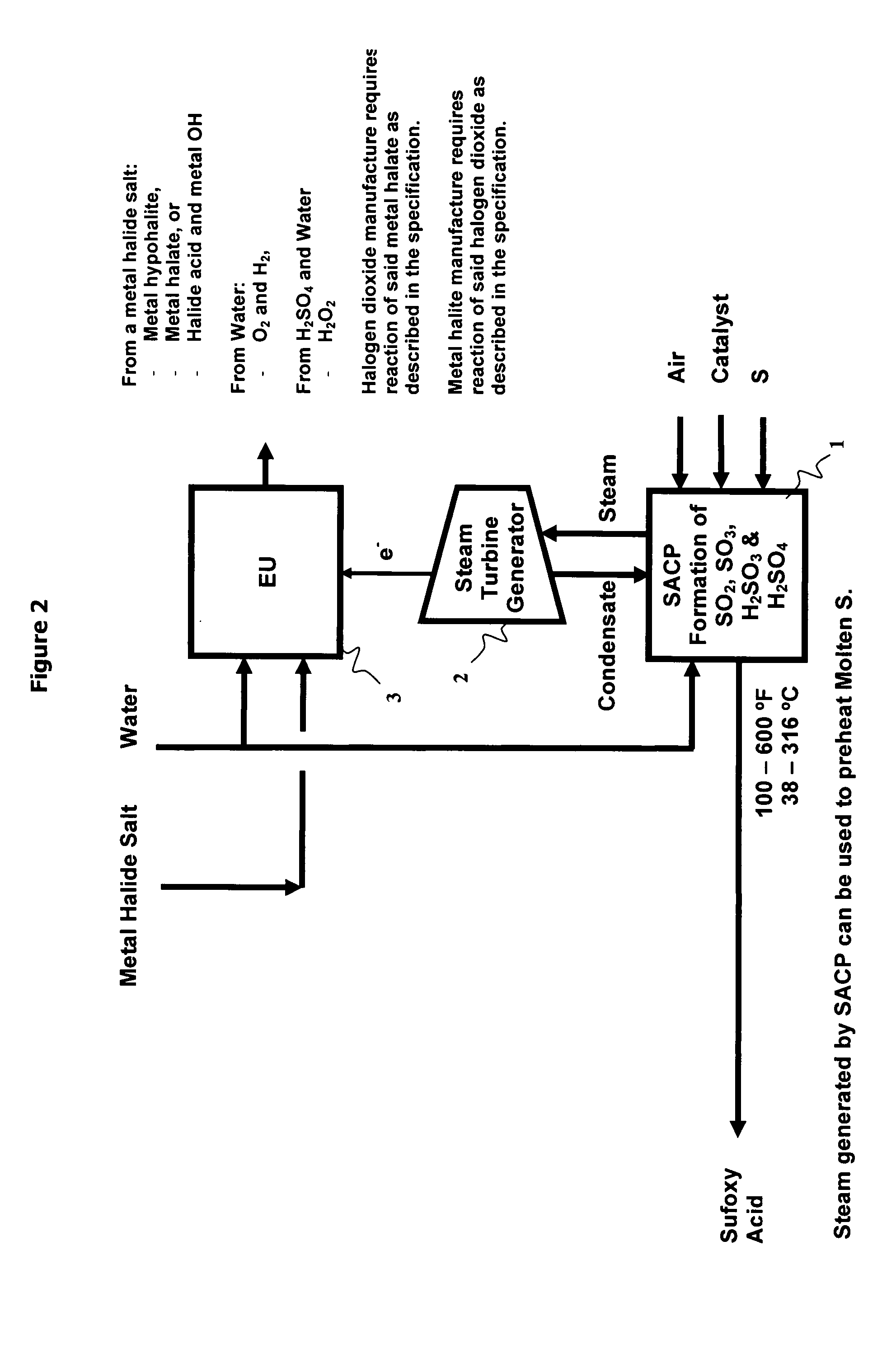
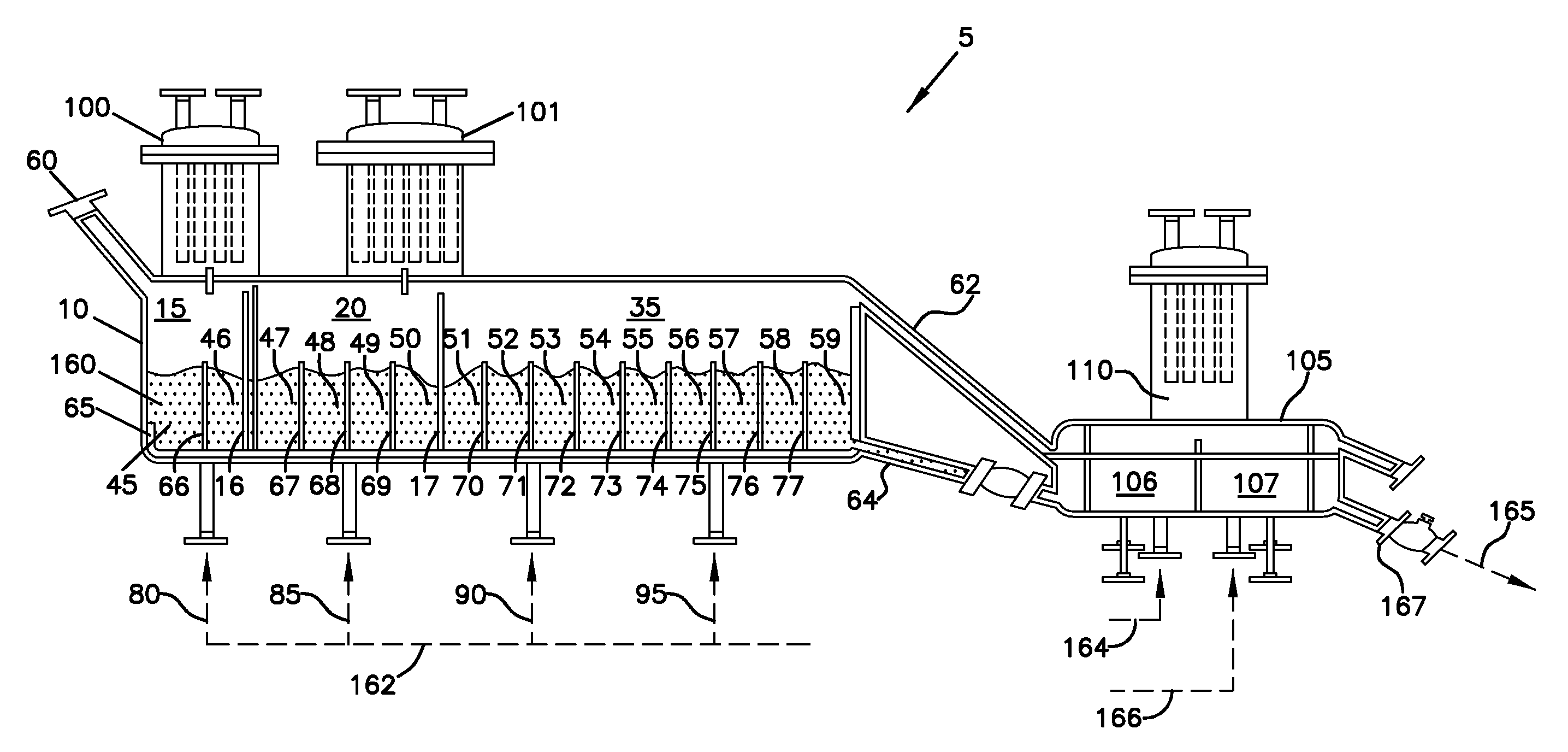
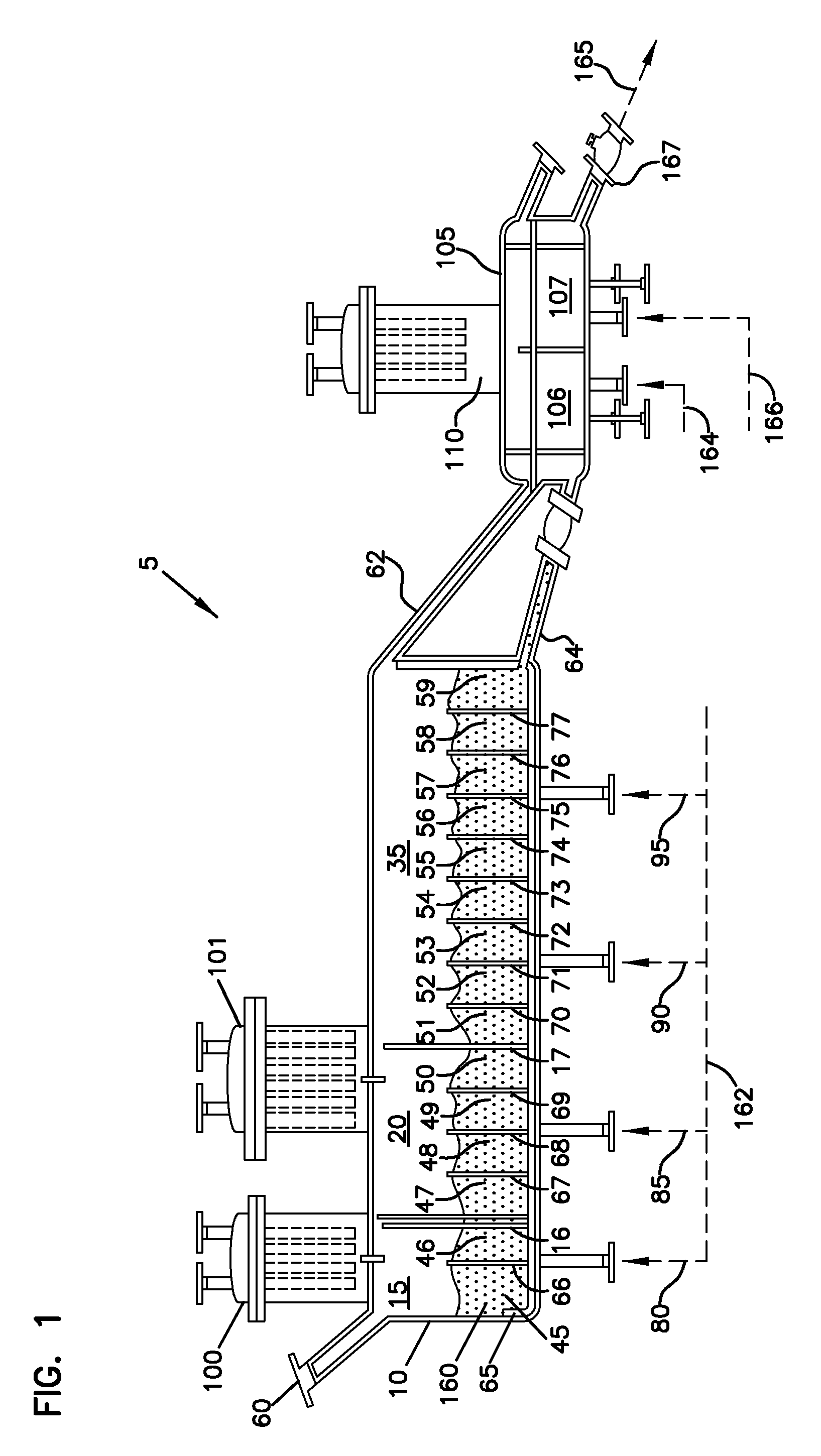
Manufacture of water chemistries
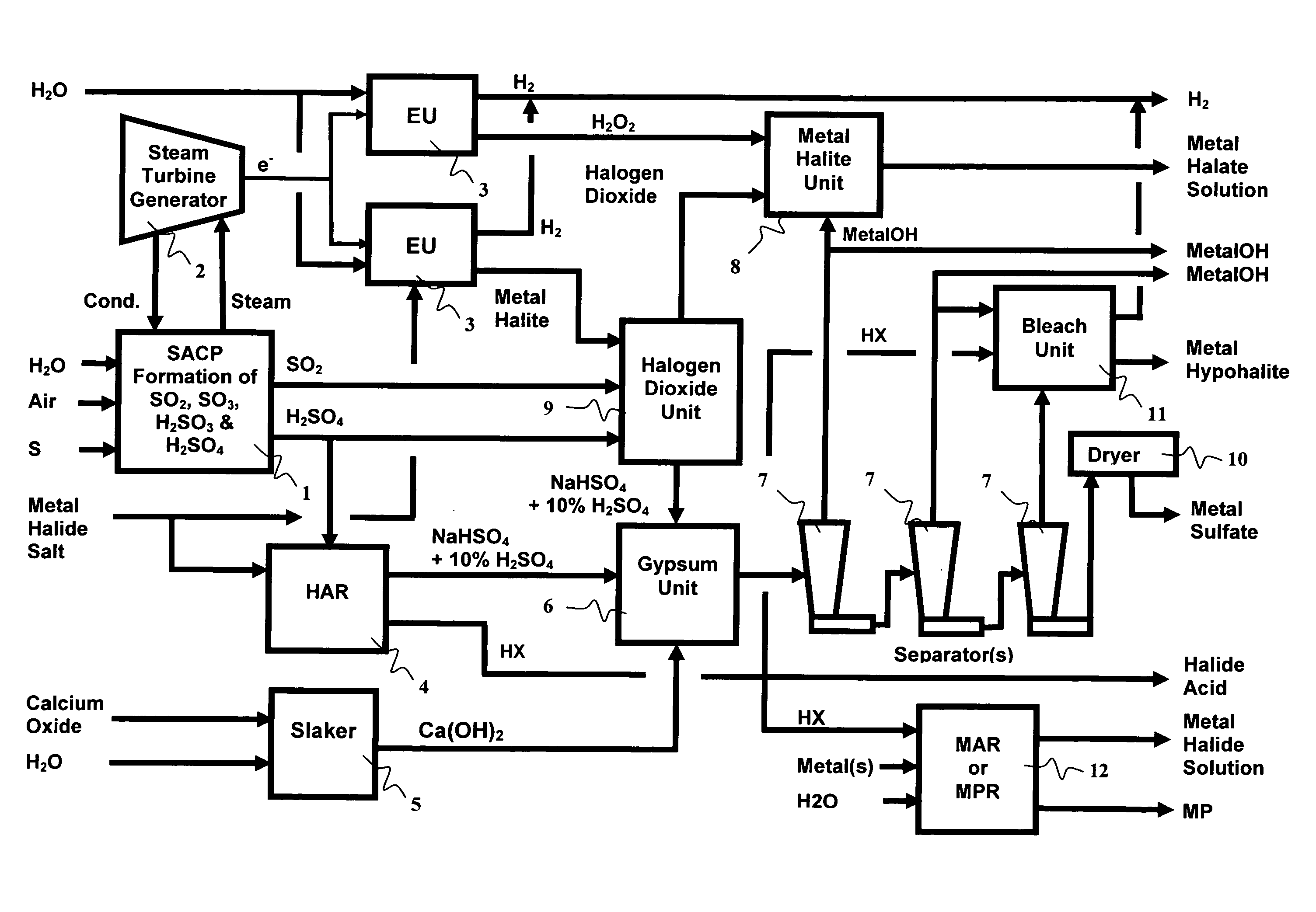
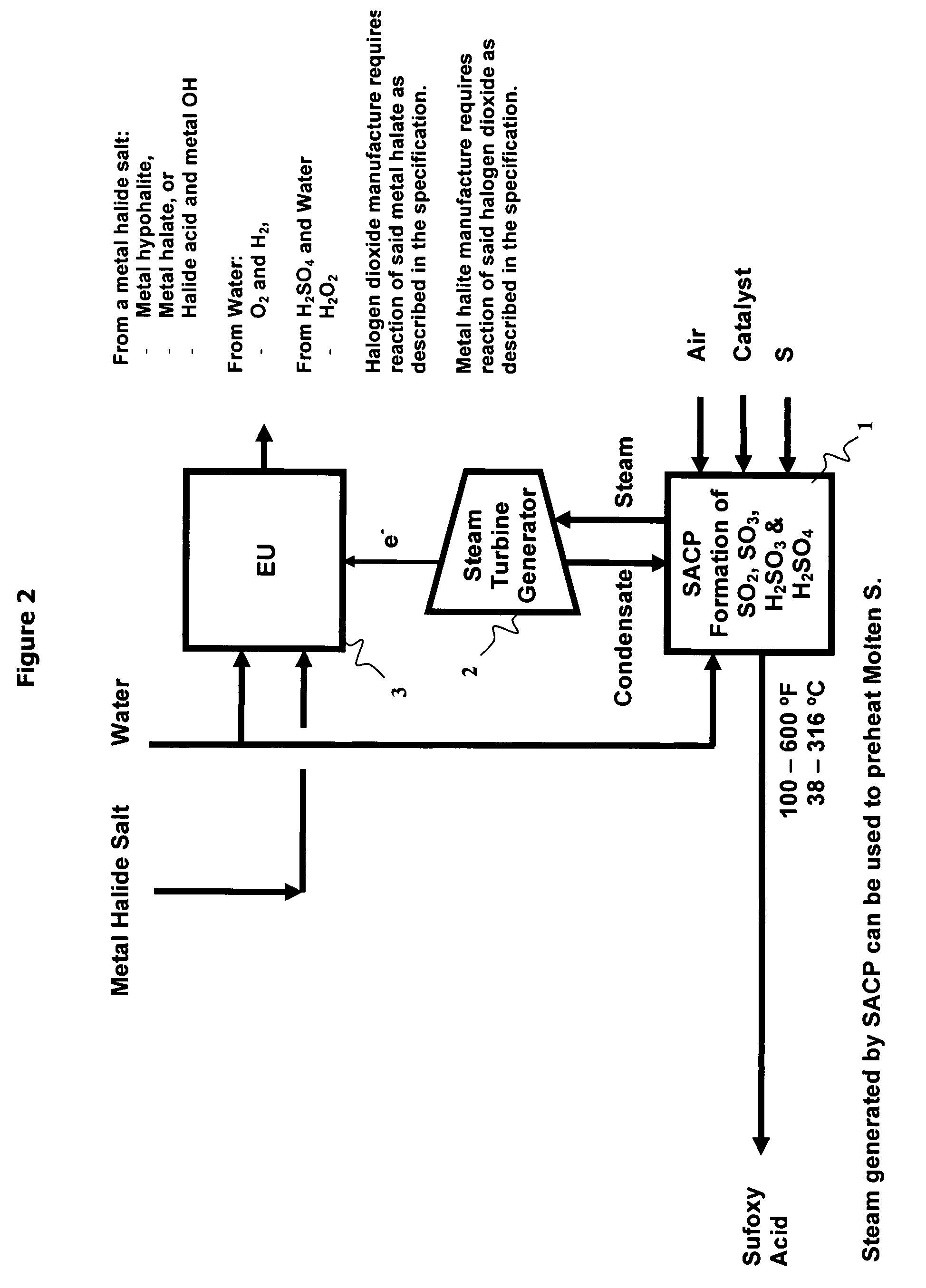
InactiveUS20080053104A1Effective and efficient and economically feasible processEfficient and effective processNitrogen compoundsElectrostatic separationPresent methodDisinfectant
As population density increases, the transportation of hazardous chemicals, including acids and disinfectants, lead to an increased incidence of spills while the consequences of spills become more serious. While solutions of halide acids, hypohalites and halites are safer disinfectants for transportation, handling, storage and use than traditional gaseous chlorine, the manufacturing cost of these disinfectants has here-to-fore limited their use. Economical processes are presented for the manufacture of O2, halogen oxides, halide acids, hypohalites, and halates; as well as polynucleate metal compounds, metal hydroxides and calcium sulfate hydrate (gypsum). The instant invention presents methods and processes that incorporate the use of sulfur. This is while environmental regulators, such as the US EPA, require an increased removal of sulfur from hydrocarbon fuels, thereby creating an abundance of sulfur, such that the refining industry is in need of a way to dispose of said abundance of sulfur.
Owner:CLEARVALUE TECH
Metal oxide and metal fluoride nanostructures and methods of making same
InactiveUS7575735B2Easy to controlOvercomes shortcomingMercury oxidesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesSingle crystalFluoride
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Eulytite solid acid electrolytes for electrochemical devices
Improved solid acid electrolyte materials, methods of synthesizing such materials, and electrochemical devices incorporating such materials are provided. The stable electrolyte material comprises a solid acid in a eulytine structure capable of undergoing rotational disorder of oxyanion groups and capable of extended operation at elevated temperatures, that is, solid acids having hydrogen bonded anion groups; a superprotonic disordered phase; and capable of operating at temperatures of ˜100° C. and higher.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Preparation method of layered functional material calcium sulphoaluminate
ActiveCN109455749ASimple preparation processEasy to operateChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAluminium sulfur compoundsAluminium hydroxideSulfate
The invention relates to a preparation method of layered functional material calcium sulphoaluminate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing a certain proportion of calcium sulfate, aluminum hydroxide and calcium oxide in a full backmixing explosive nucleation reactor, and adding water more than the materials to mix; and (2) synthesizing calcium sulphoaluminate gel under the conditions that the revolving speed of a rotor is 4,000-6,000 rpm, the voltage is 220-330 V and the nucleating time is 8-16 min by adopting the full backmixing explosive nucleation reactor, then enabling the calcium sulphoaluminate gel to be crystallized for 12-16 h at 90-150 DEG C, cooling to 30-50 DEG C, stirring for 12-16 h, then heating to 90-150 DEG C, and circulating 3-5 times to prepare the layered functional material calcium sulphoaluminate. The preparation method of the layered functional material calcium sulphoaluminate has the advantages that the calcium sulfate, the aluminumhydroxide and the calcium oxide can nucleate and grow in the full backmixing explosive nucleation reactor through a 'one-pot method', the preparation process of the calcium sulphoaluminate is effectively simplified, the preparation time is shortened, the reaction operation is simplified, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU LONGCHANG CHEM
Method for preparing aluminum hydroxide sulfate
The invention relates to a method for preparing aluminum hydroxide sulfate. The method comprises the steps of preparing a sodium aluminate solution, and obtaining aluminum hydroxide through a method of adding seed crystals or introducing carbon dioxide; dissolving aluminum sulfate, so that an aluminum sulfate solution is obtained, adding aluminum hydroxide to the aluminum sulfate solution, placing the mixture into a reaction kettle, heating the mixed materials to 90-250 DEG C under the stirring condition, and conducting a reaction for 5-10 minutes, so that the aluminum hydroxide sulfate is obtained. The technological process of preparing the aluminum hydroxide sulfate is simple, and by changing the amount of added aluminum hydroxide, the aluminum hydroxide sulfate different in basicity can be obtained.
Owner:北京世纪地和控股有限公司
Continuous preparation of calcined chemically-treated solid oxides
The present invention discloses a continuous calcination vessel which can be used to prepare calcined chemically-treated solid oxides from solid oxides and chemically-treated solid oxides. A process for the continuous preparation of calcined chemically-treated solid oxides is also provided. Calcined chemically-treated solid oxides disclosed herein can be used in catalyst compositions for the polymerization of olefins.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Preparation method of high polymeric polyalumnium sulfa coagulant for strengthening coagulation of drinking water
InactiveCN101767809AImprove stabilitySimple processAluminium sulfur compoundsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationWater qualityTurbidity
The invention provides a preparation method of high polymeric polyalumnium sulfa coagulant, belonging to the water purification drug technical field; the preparation steps are as follows: Na2SO4 solid is added in AlCl3 solution according to 0.05-0.10 of mole ratio of SO42- / Al3+, the mixture is stirred and is dissolved completely; and then the mixture is rapidly mixed with Na2CO3 solution at normal temperature and normal pressure under strong mixing condition, the mole ratio of OH- / Al3+ is controlled to be 1.2-2.2, the total aluminum concentration is 0.2-0.4mol / L, so as to obtain the stable and transparent homogeneous phase polyalumnium sulfa solution; the homogeneous phase polyalumnium sulfa solution is heated at constant temperature from 95 to 105 DEG C, stirred and back-flows for 6-8h, and then cooling and aging are carried out to obtain the high polymeric polyalumnium sulfa coagulant. The high polymeric polyalumnium sulfa has high polymerization degree and strong stability and can remove turbidity and organic matters in the drinking water by strengthening coagulation, the water yielding quality is odiously improved and the invention has high application value.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Multi-component resource utilization method for iron tailings
PendingCN112794352AImprove resource extraction rateReduce acid consumptionAluminium chloridesSilicon compoundsBrickSILICONE DIOXIDE
The invention discloses a multi-component resource utilization method of iron tailings, which aims to solve the problems of low product compactness and low strength in the process of making building materials such as bricks, cement and the like in a common utilization method of the iron tailings. The method comprises the following steps of: screening raw materials with high content of aluminum and silicon by adopting an iron tailings grading and sorting technology, performing wet leaching on the raw materials, adjusting the leachate through a salt base to obtain a polymeric aluminum diacid product, performing wet leaching treatment on leaching residues, and washing and drying to obtain a white carbon black product. According to the technology, the aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide contents of the obtained raw materials are increased through iron tailing grading and sorting. The raw materials are subjected to acid leaching and alkali washing leaching by adopting a wet leaching process to respectively obtain the products polymeric aluminum diacid and white carbon black, so that the extraction rate of aluminum and silicon is improved, and the acid consumption is reduced. The method has the advantages of being flexible in system, wide in application range, good in economical efficiency and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
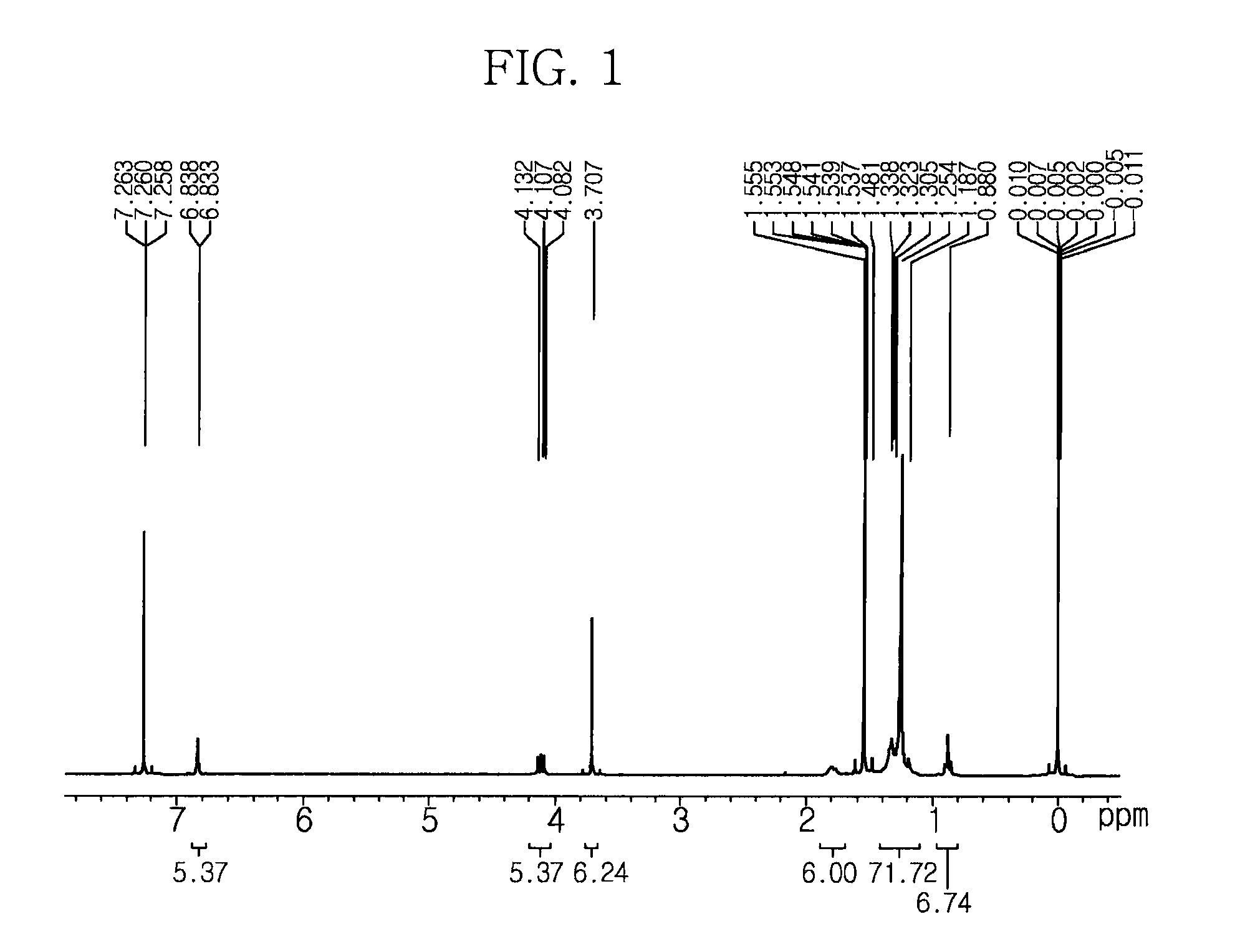
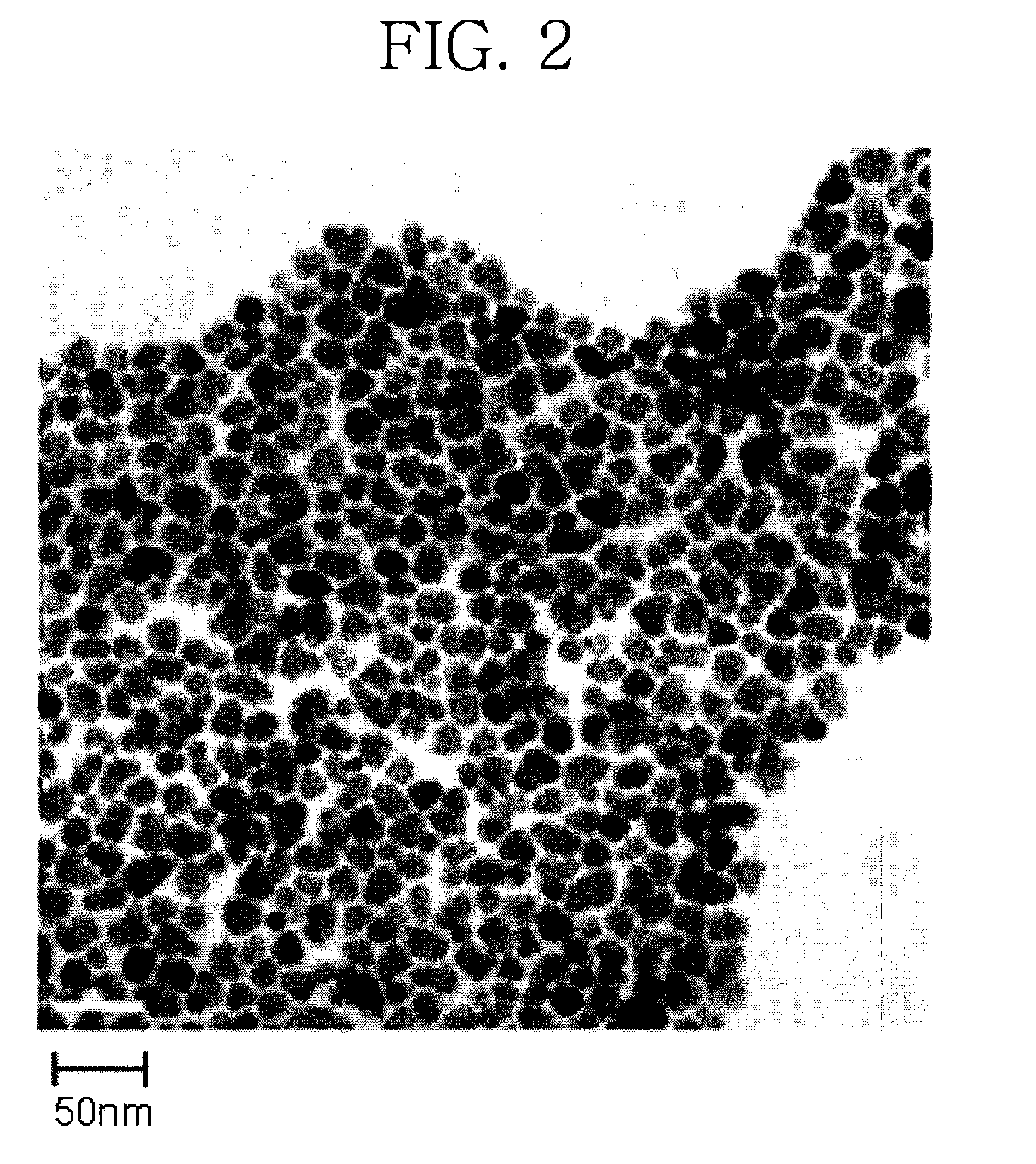
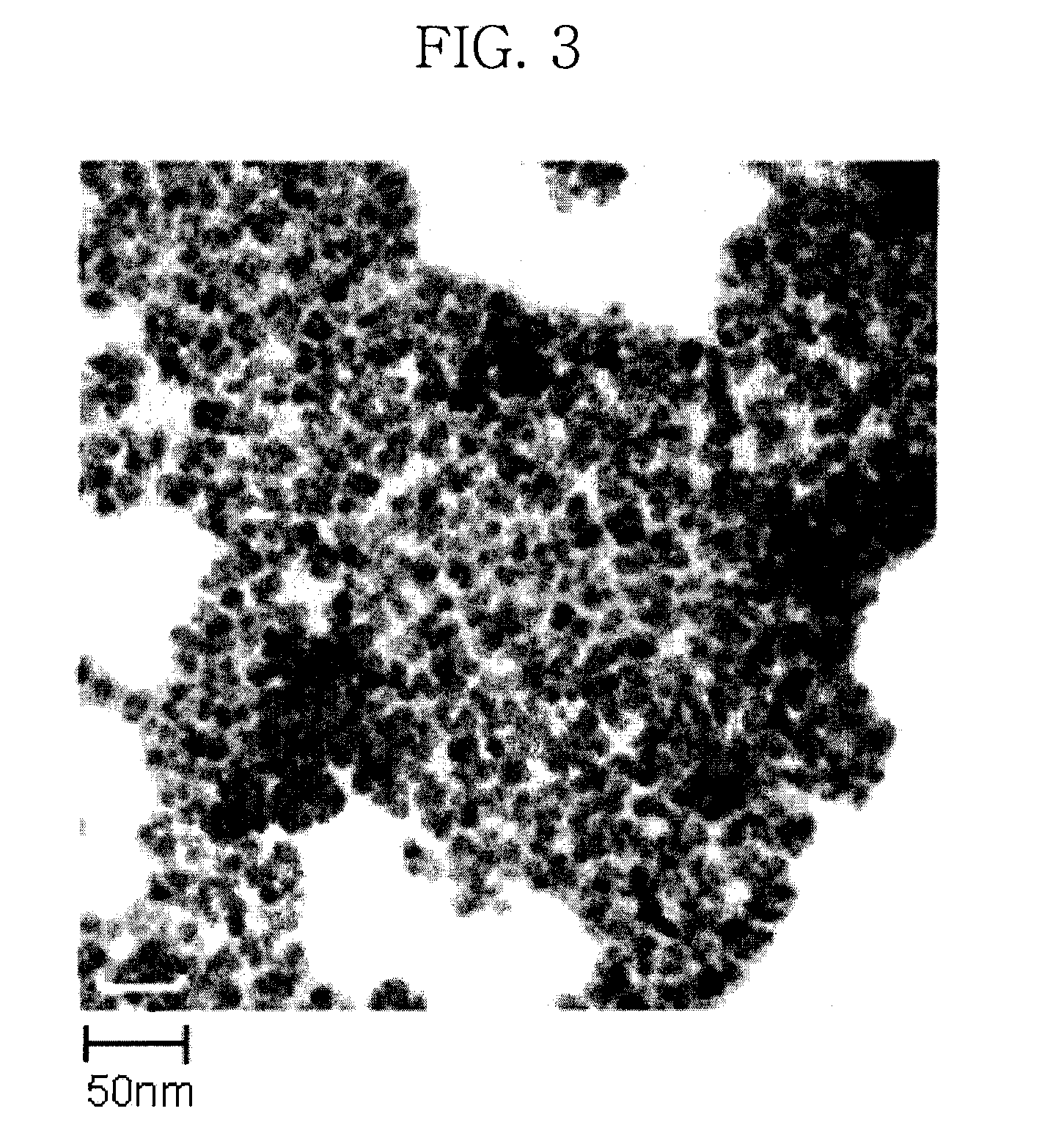
Method for preparing nanoparticles using carbene derivatives
ActiveUS8057780B2Control shapeControl sizeNanostructure manufactureSelenium/tellurium compundsOrganic solventNanoparticle
Disclosed herein is a method for synthesizing a nanoparticle using a carbene derivative. More specifically, provided is a method for synthesizing a nanoparticle by adding one or more precursors to an organic solvent to grow a crystal, wherein a specific carbene derivative is used as the precursor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic chemical absorbent, production process for the same and recycling method for the same, as well as waste-liquid treating method
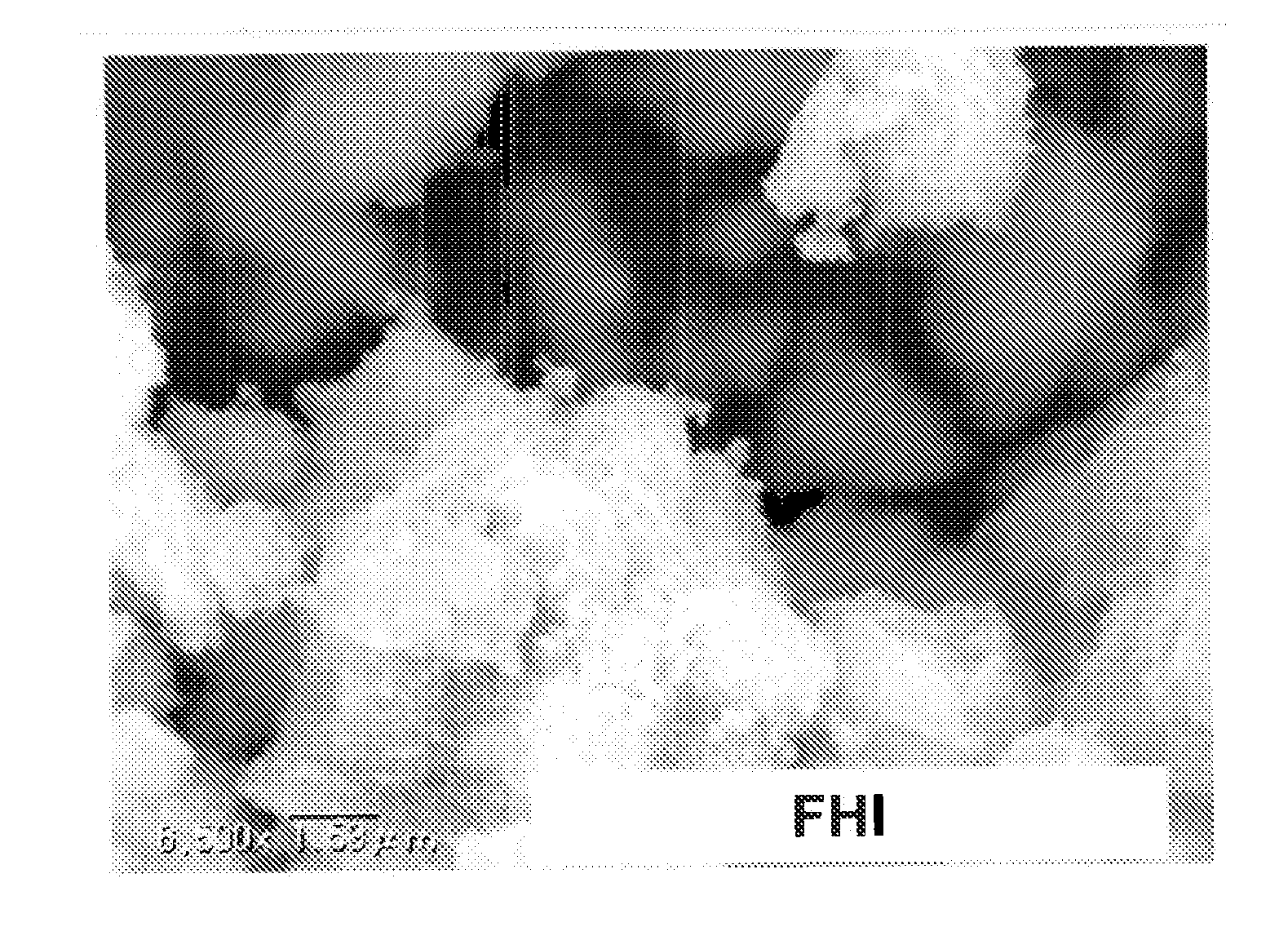
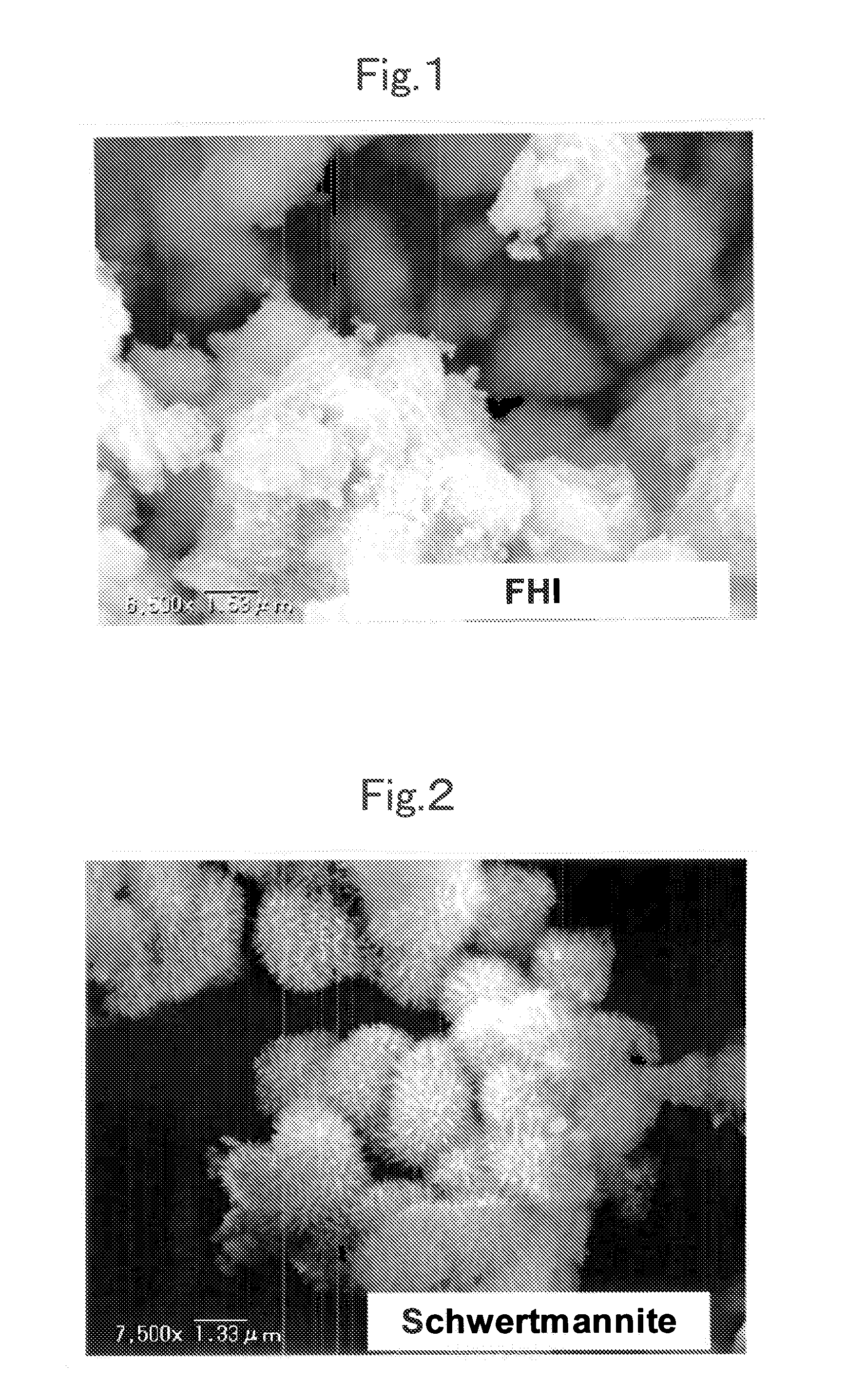
InactiveUS20090324467A1Promote absorptionLow costSolvent extractionIon-exchanger regenerationMagnetiteHydrolysis
A magnetic chemical absorbent according to the present invention is provided with a composite, which is constituted of a core substance comprising magnetite fine particles and schwertmannite being precipitated around the core substance to chemically bond therewith. This magnetic chemical absorbent can be produced in a hydrolysis reaction step, in which crystal of schwertmannite is precipitated by means of hydrolysis reaction by heating a solution of ferric salt and thereafter adding a reactive substance thereto, by means of adding magnetite fine particles into the solution after the solution is heated and before the precipitation of the crystal begins.This magnetic chemical absorbent is novel and good one whose absorption capability for harmful ion is upgraded more. In accordance with a waste-liquid treating method using this magnetic chemical substance, it is possible to intend the reduction of burdens in view of environmental and economic aspects. Moreover, this magnetic chemical absorbent is recyclable.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
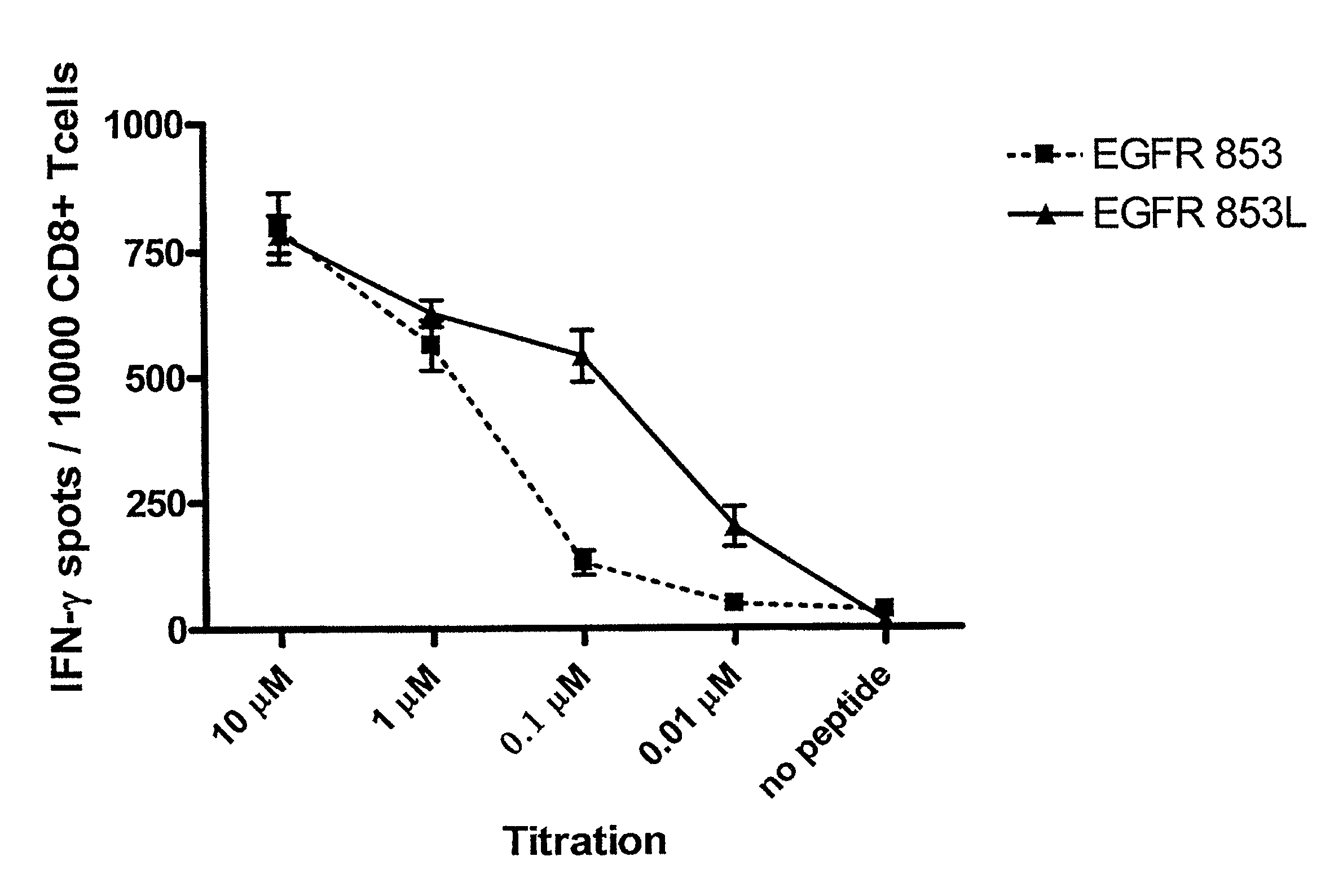
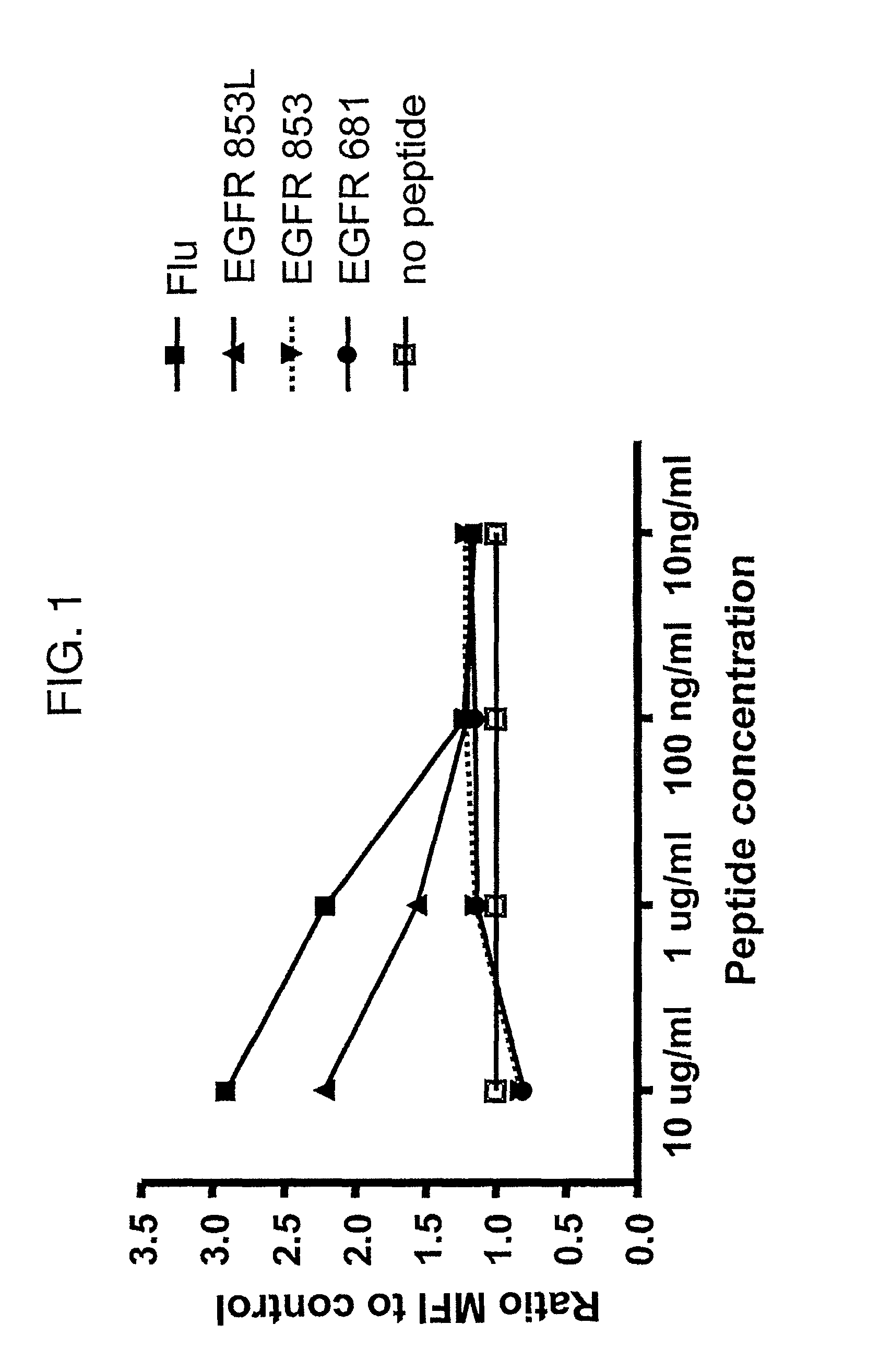
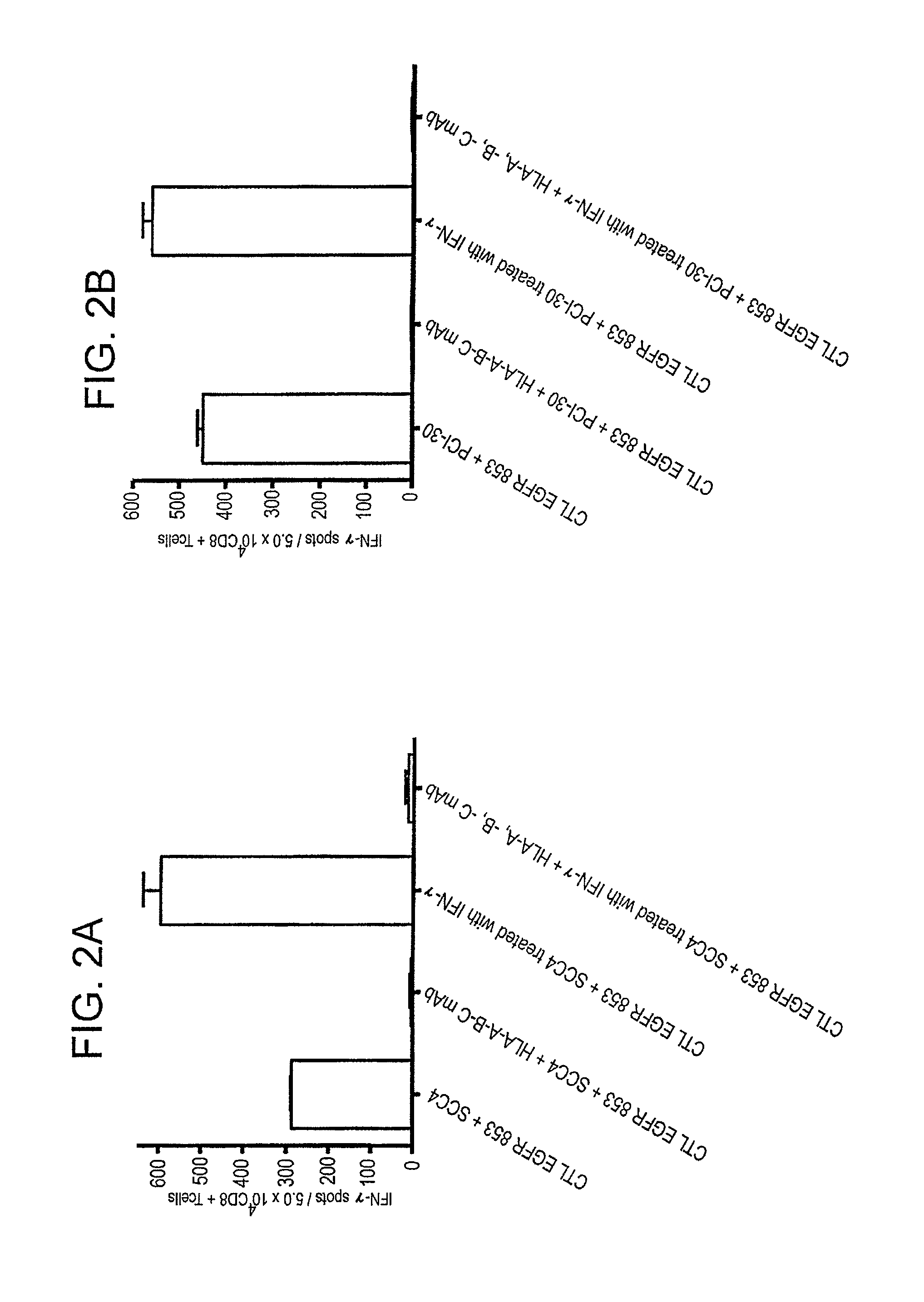
Cytotoxic T cell defined EGFR peptide and an optimized derivative peptide
The invention provides a polypeptide having a sequence of amino acids consisting of IXDFGLAKL (SEQ ID NO: 1), as well as a nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide, vector comprising the nucleic acid, cell comprising the vector, and compositions thereof. The invention also provides a method of inducing a T-cell response in a patient with epithelial cancer, and a method inhibiting epithelial cancer, wherein the methods comprise administering the composition of the invention. The invention further provides a method of stimulating a cell with the inventive polypeptide and a cell so stimulated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Manufacture of water chemistries
InactiveUS8268269B2Efficient and effective processHigh purityNitrogen compoundsElectrostatic separationPresent methodDisinfectant
As population density increases, the transportation of hazardous chemicals, including acids and disinfectants, lead to an increased incidence of spills while the consequences of spills become more serious. While solutions of halide acids, hypohalites and halites are safer disinfectants for transportation, handling, storage and use than traditional gaseous chlorine, the manufacturing cost of these disinfectants has here-to-fore limited their use. Economical processes are presented for the manufacture of O2, halogen oxides, halide acids, hypohalites, and halates; as well as polynucleate metal compounds, metal hydroxides and calcium sulfate hydrate (gypsum). The instant invention presents methods and processes that incorporate the use of sulfur. This is while environmental regulators, such as the US EPA, require an increased removal of sulfur from hydrocarbon fuels, thereby creating an abundance of sulfur, such that the refining industry is in need of a way to dispose of said abundance of sulfur.
Owner:CLEARVALUE TECH
Metal composite oxide with novel crystal structure and their use as ionic conductors
Disclosed is metal composite oxides having the new crystal structure. Also disclosed are ionic conductors including the metal composite oxides and electrochemical devices comprising the ionic conductors. The metal composite oxides have an ion channel formed for easy movement of ions due to crystallographic specificity resulting from the ordering of metal ion sites and metal ion defects within the unit cell. Therefore, the metal composite oxides according to the present invention are useful in an electrochemical device requiring an ionic conductor or ionic conductivity.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
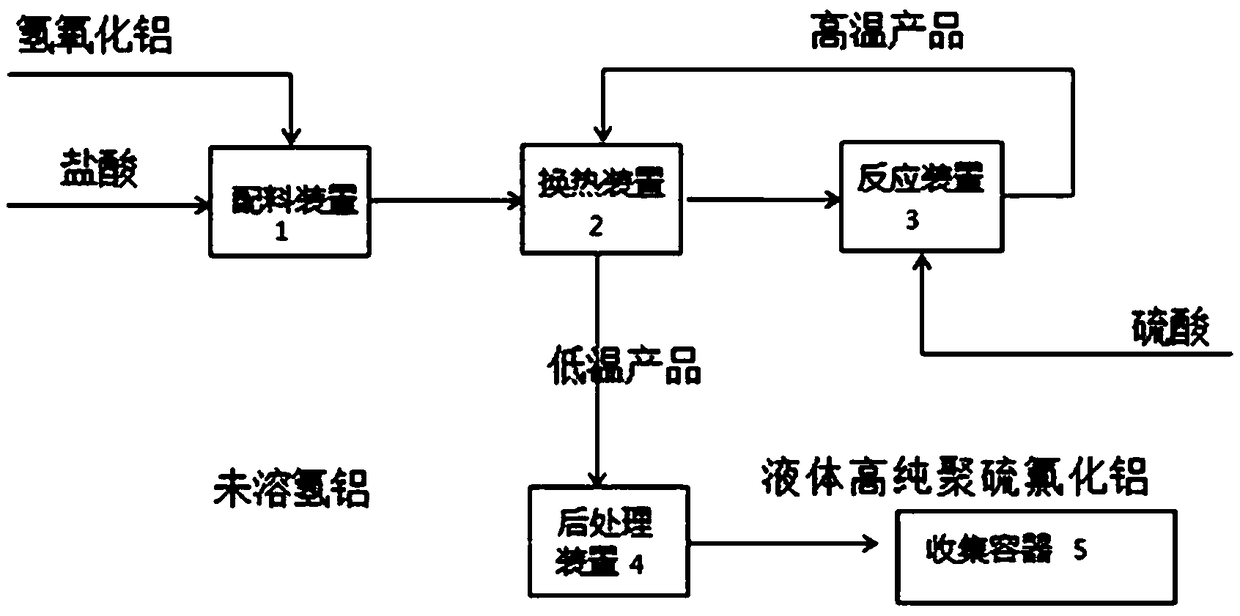
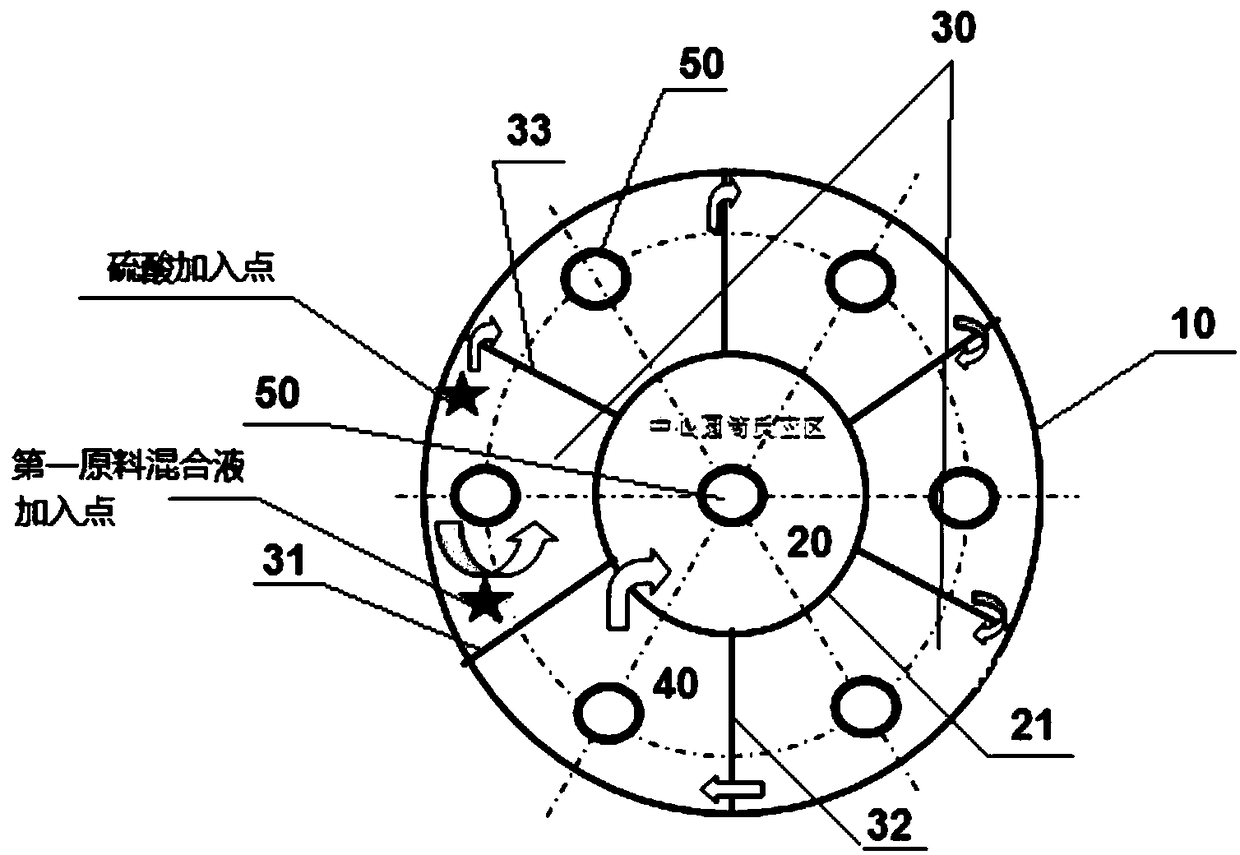
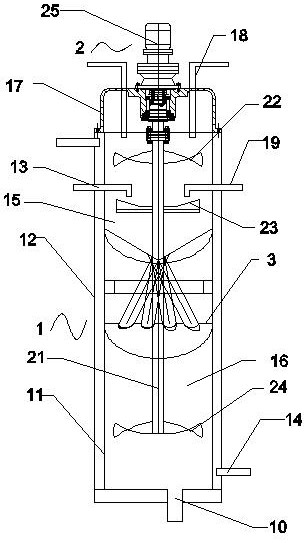
Production method and production system of high-purity polyaluminum sulfate chloride
InactiveCN108946779ASimple structureAvoid heatingChemical industryAluminium sulfur compoundsBiochemical engineeringSulfate
The invention discloses a production method and production system of high-purity polyaluminum sulfate chloride. The system comprises a preparation device, a reaction device, a post-treatment device, acollection container and a heat exchange device, wherein the heat exchange device is communicated with the outlet of the preparation device, the first inlet of the reaction device, the outlet of thereaction device and the inlet of the post-treatment device; a first raw material mixed liquid input through the outlet of the preparation device flow through the heat exchange device, and is used forexchanging heat with a reaction product input through the outlet of the reaction device; the heated first raw material mixed liquid is input into the reaction device through the first inlet of the reaction device; and the cooled reaction product is input into the post-treatment device through the inlet of the post-treatment device. The production system is simple and convenient in structure, and can be used for continuously and automatically preparing polyaluminum sulfate chloride; and the preparation method has high efficiency and low energy consumption, is energy-saving and environment-friendly since reaction heat, dilution heat and product heat are sufficiently utilized; and the prepared product has high purity and good quality, and accords with the national standard of GB15892-2009.
Owner:SHANGHAI GAOQIAO DATONG WATER PURIFICATION MATERIAL CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of layered functional material calcium sulfoaluminate
ActiveCN109455749BSimple preparation processEasy to operateChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAluminium sulfur compoundsMedicineAluminium hydroxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of calcium sulfoaluminate, a layered functional material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing a certain proportion of calcium sulfate, aluminum hydroxide and calcium oxide into a fully back-mixed explosive nucleation reactor , and add water higher than that of each material for mixing; (2) Use a fully back-mixed explosive nucleation reactor to synthesize sulfur under the conditions of a rotor speed of 4000-6000rpm, a voltage of 220-330V, and nucleation of 8-16min Calcium aluminate gel, then crystallize calcium sulfoaluminate gel at 90-150°C for 12-16h, cool down to 30-50°C, stir for 12-16h, then heat up to 90-150°C, cycle 3-5 times, can The layered functional material calcium sulfoaluminate is prepared. The advantage of the present invention is: the preparation method of the layered functional material calcium sulfoaluminate of the present invention, calcium sulfate, aluminum hydroxide and calcium oxide are nucleated and grown in a full back-mixing explosive nucleation reactor through a "one-pot method" , which effectively simplifies the preparation process of calcium sulfoaluminate, shortens the preparation time, simplifies the reaction operation, and improves the production efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU LONGCHANG CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com