Patents
Literature
271results about "Conductive materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrophoretic medium and process for the production thereof
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Color effect compositions
A coating composition comprising a resinous binder and a color effect colorant in particulate form. The colorant includes an ordered periodic array of particles held in a polymer wherein a difference in refractive index between the polymer and the particles is at least about 0.01. The colorant reflects visible light according to Bragg's law to yield a goniochromatic effect to the coating composition.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Organic species that facilitate charge transfer to or from nanostructures
InactiveUS6949206B2Facilitates injection and extractionMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureOligomerNanocrystal
The present invention provides compositions (small molecules, oligomers and polymers) that can be used to modify charge transport across a nanocrystal surface or within a nanocrystal-containing matrix, as well as methods for making and using the novel compositions.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
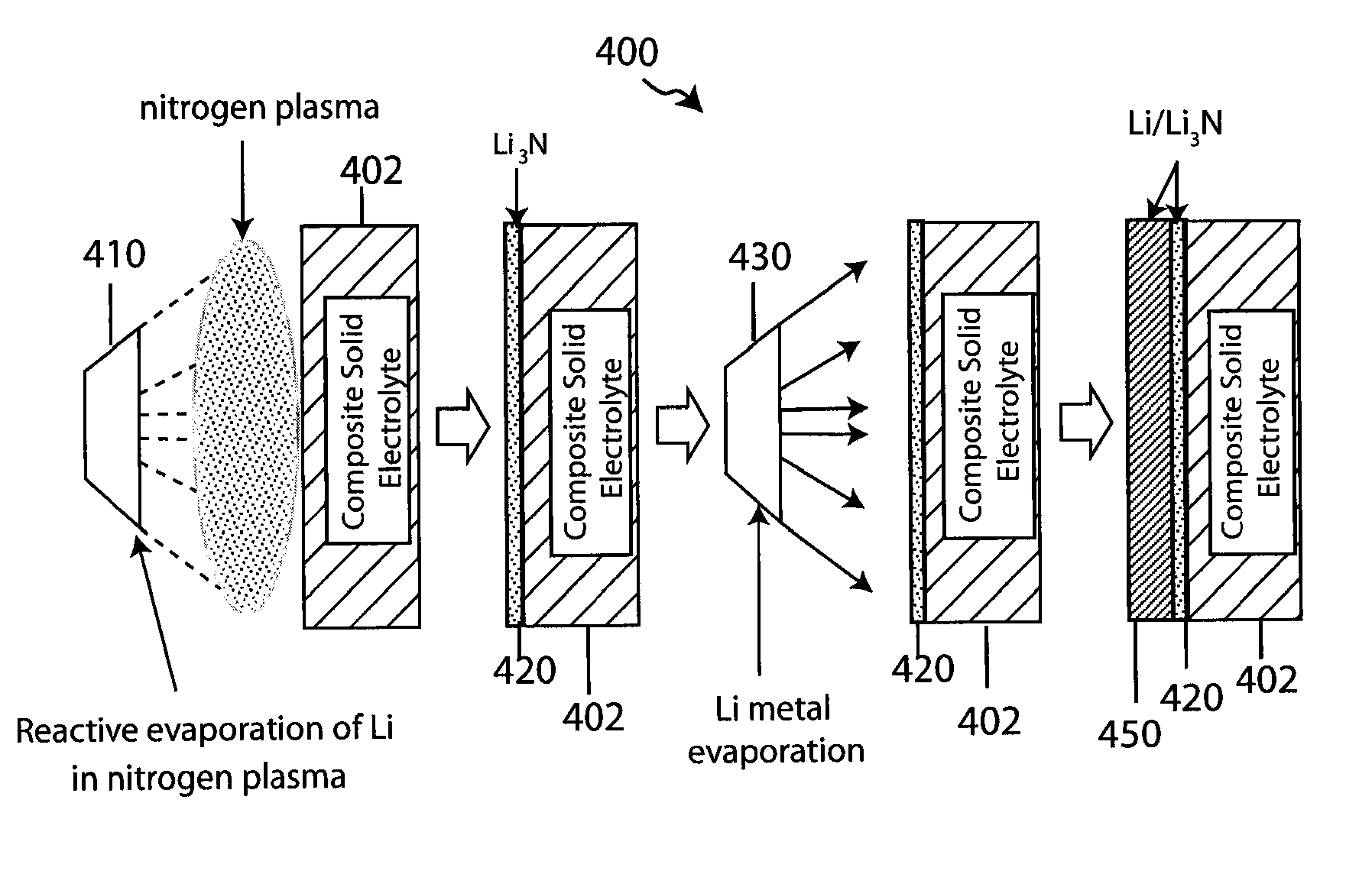
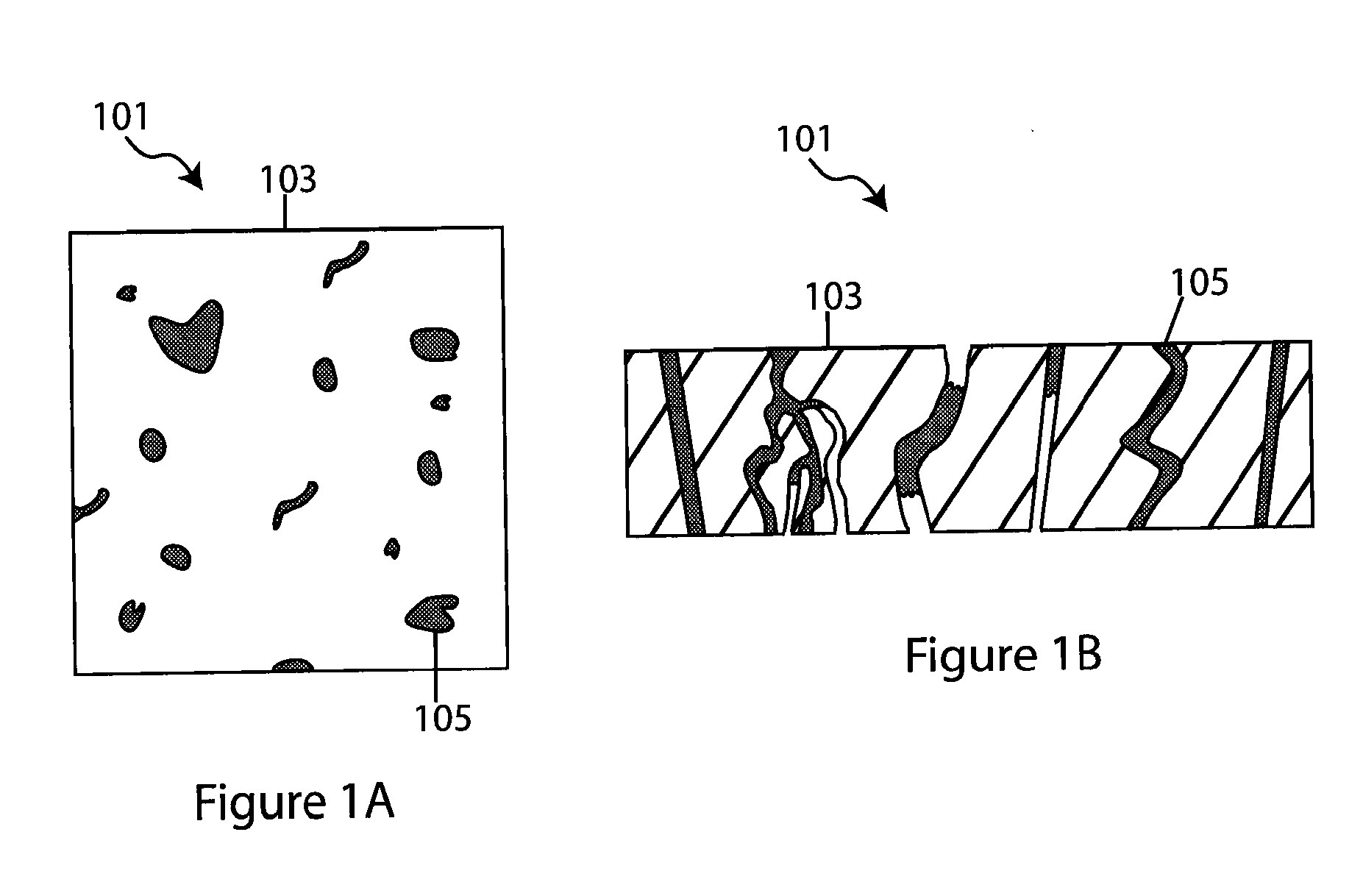
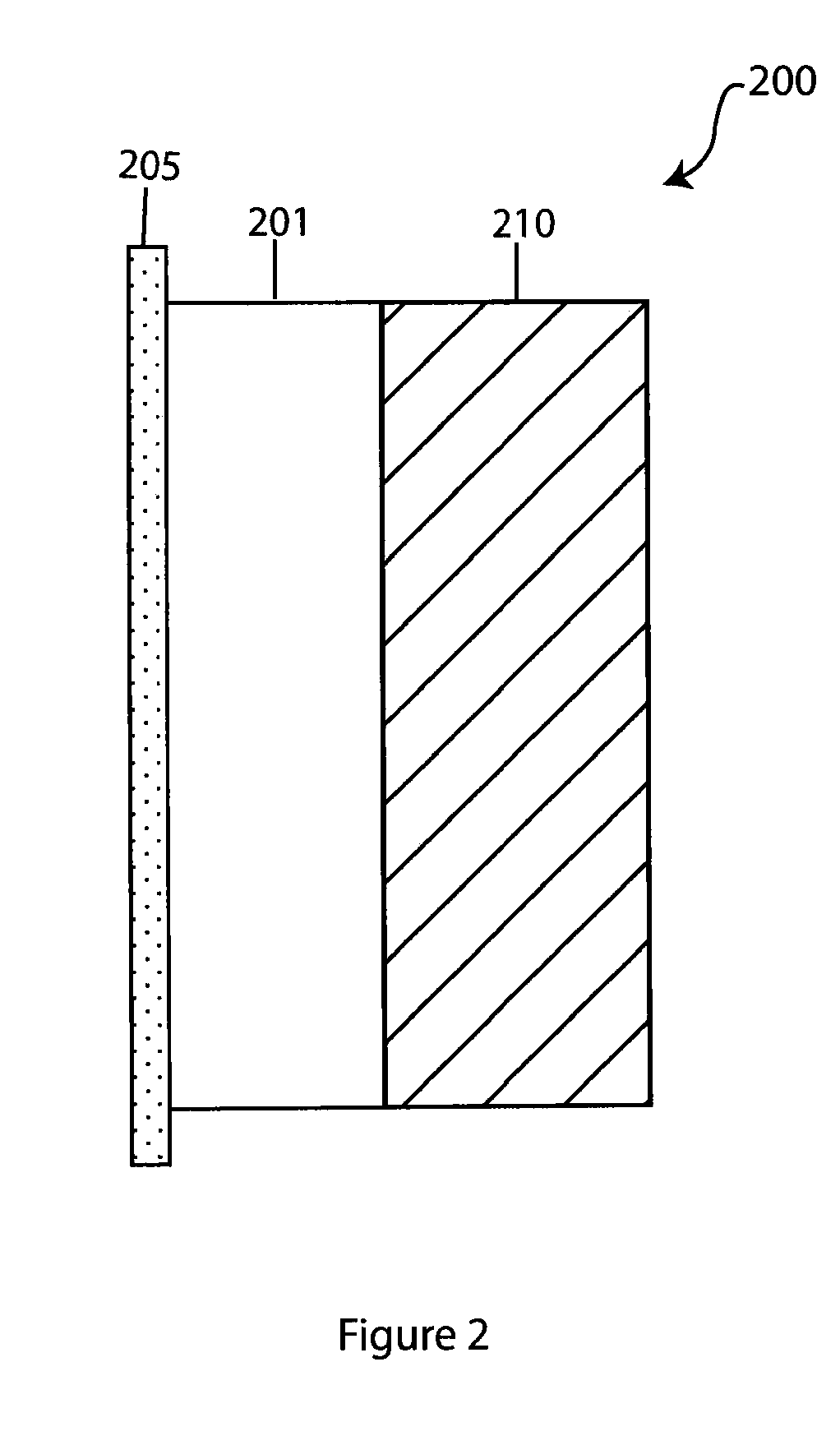
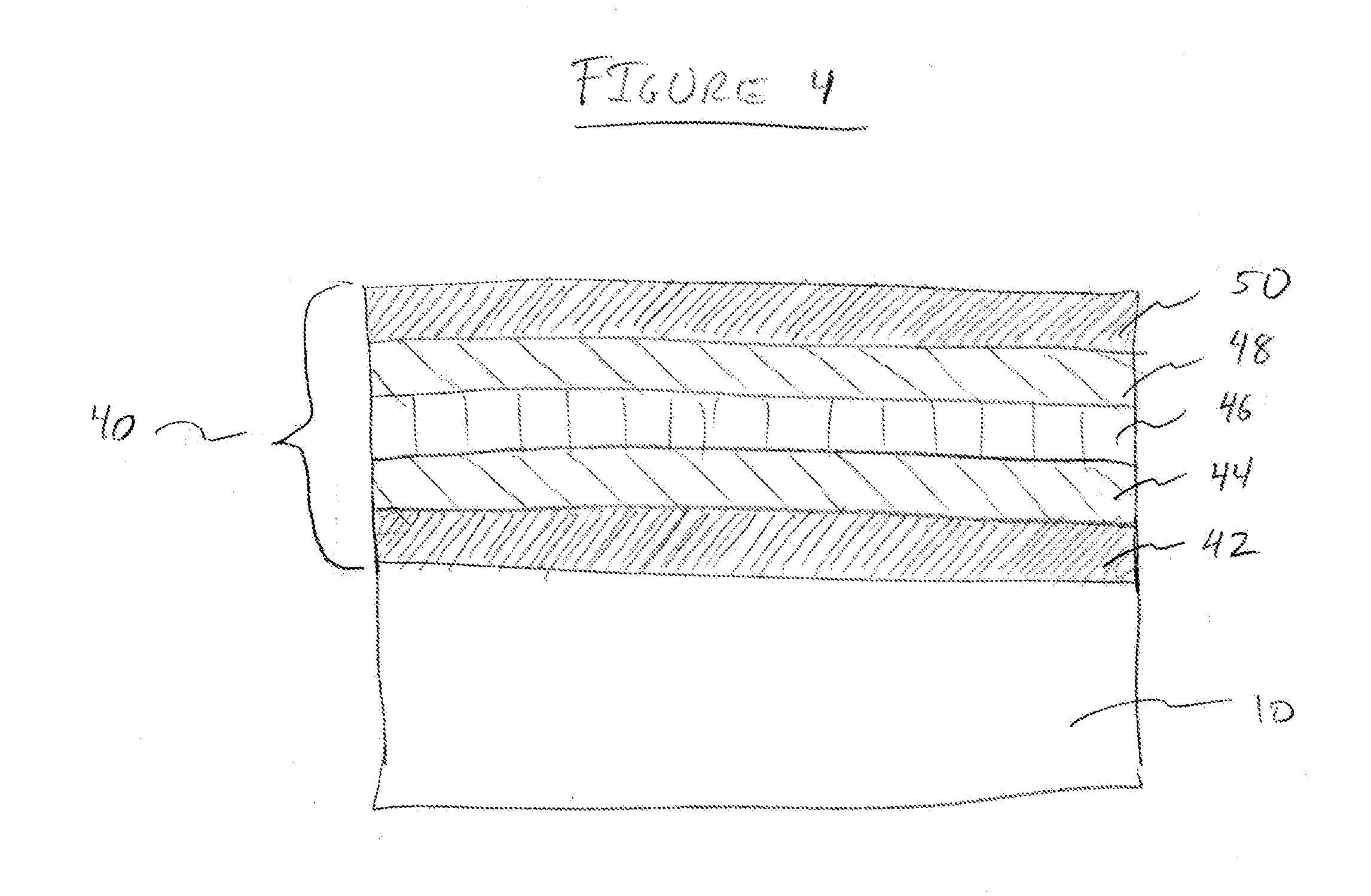
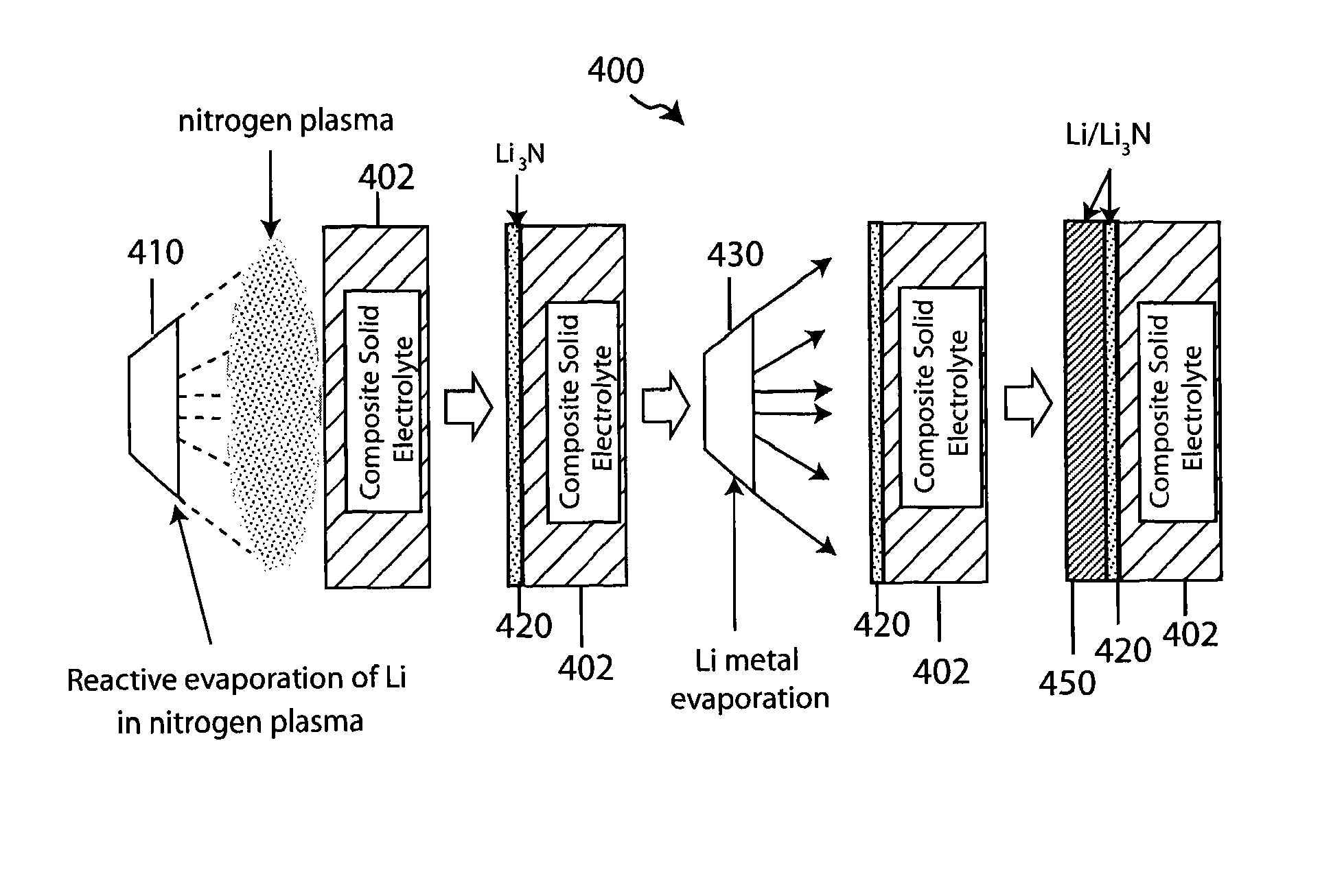
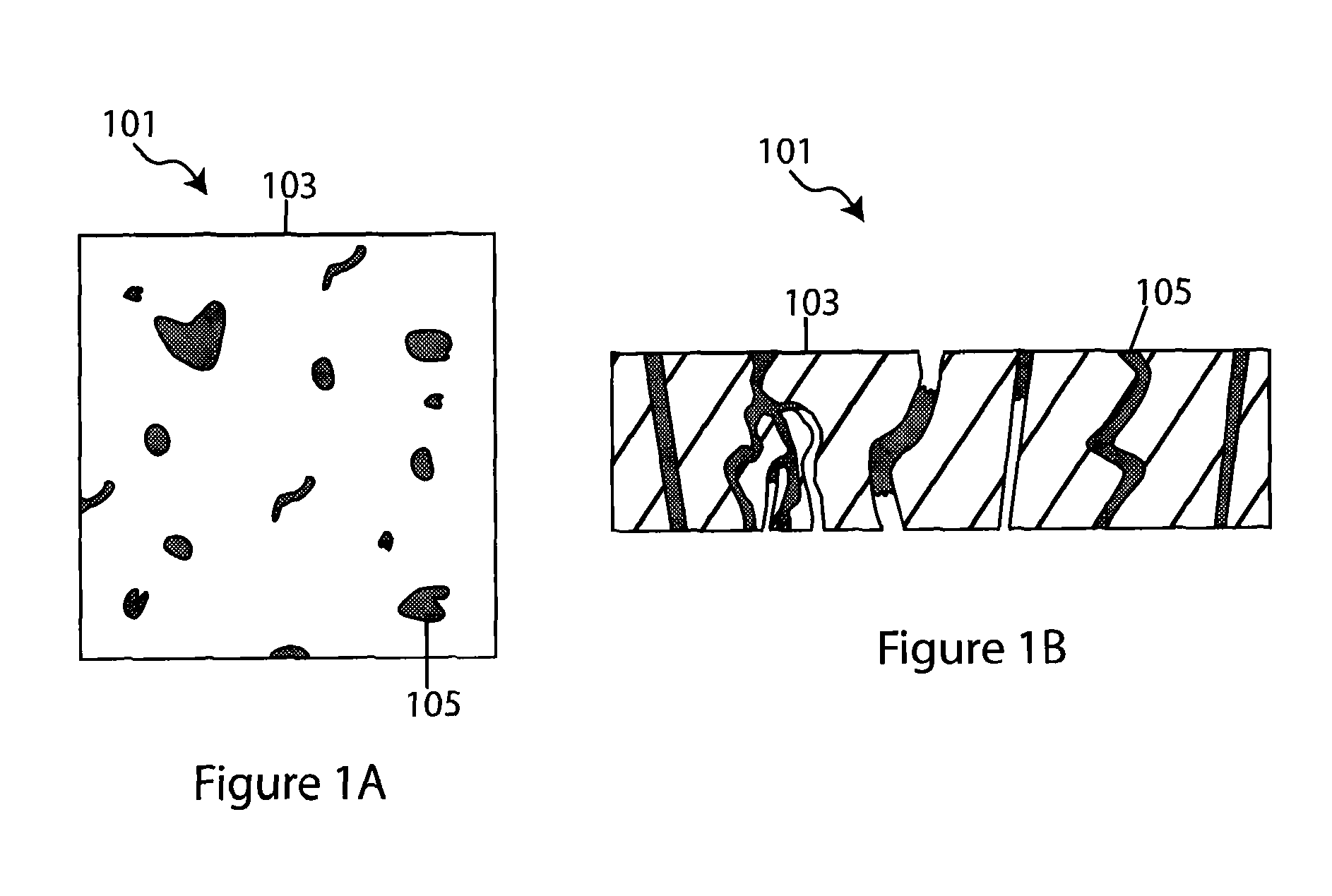
Composite solid electrolyte for protection of active metal anodes
ActiveUS20070172739A1Eliminate through-porosityHigh metal ion conductivityCell electrodesPrimary cellsPorosityTectorial membrane
A composite solid electrolyte include a monolithic solid electrolyte base component that is a continuous matrix of an inorganic active metal ion conductor and a filler component used to eliminate through porosity in the solid electrolyte. In this way a solid electrolyte produced by any process that yields residual through porosity can be modified by the incorporation of a filler to form a substantially impervious composite solid electrolyte and eliminate through porosity in the base component. Methods of making the composites is also disclosed. The composites are generally useful in electrochemical cell structures such as battery cells and in particular protected active metal anodes, particularly lithium anodes, that are protected with a protective membrane architecture incorporating the composite solid electrolyte. The protective architecture prevents the active metal of the anode from deleterious reaction with the environment on the other (cathode) side of the architecture, which may include aqueous, air and organic liquid electrolytes and / or electrochemically active materials.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
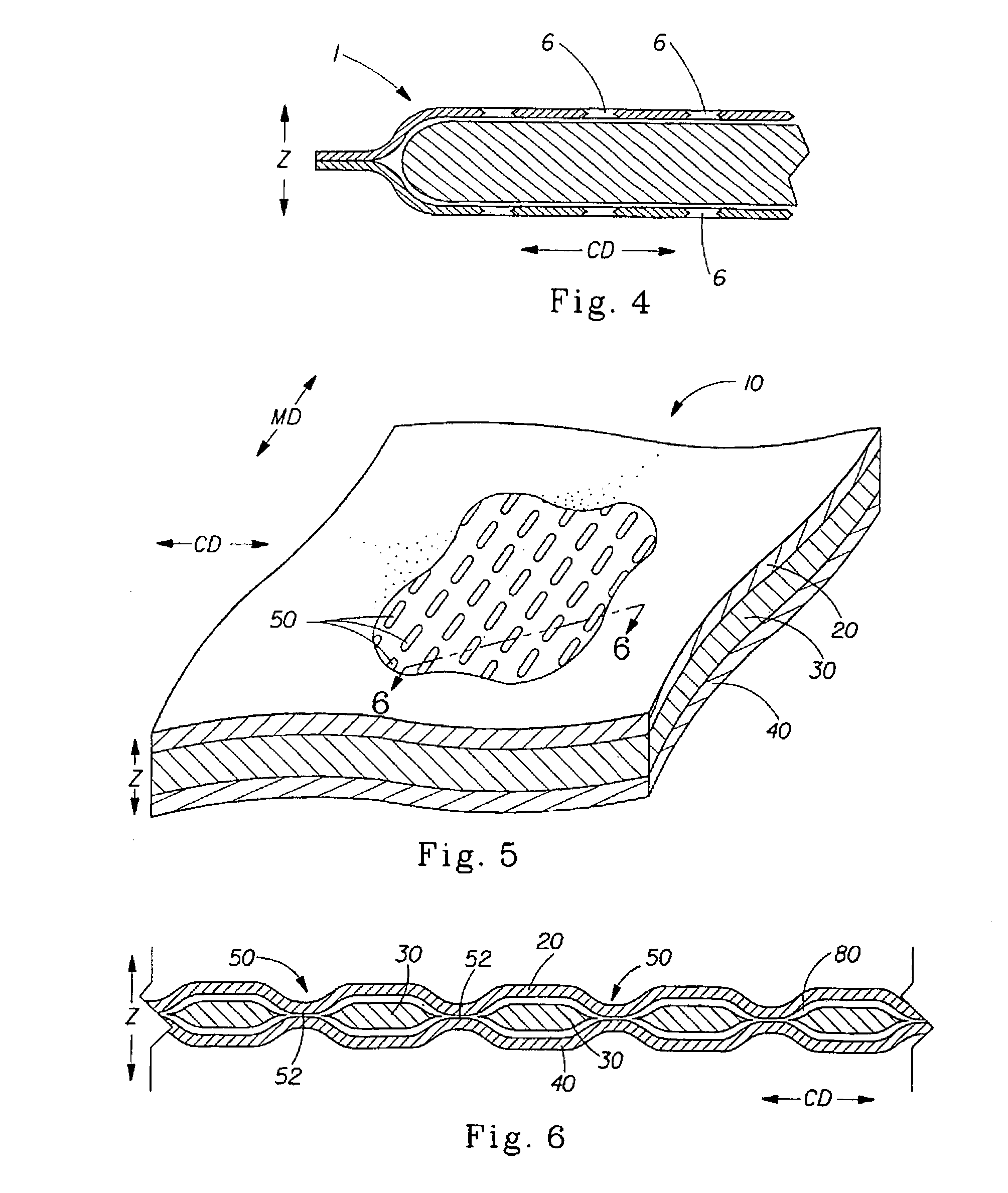
Laminate web comprising an apertured layer and method for manufacturing thereof
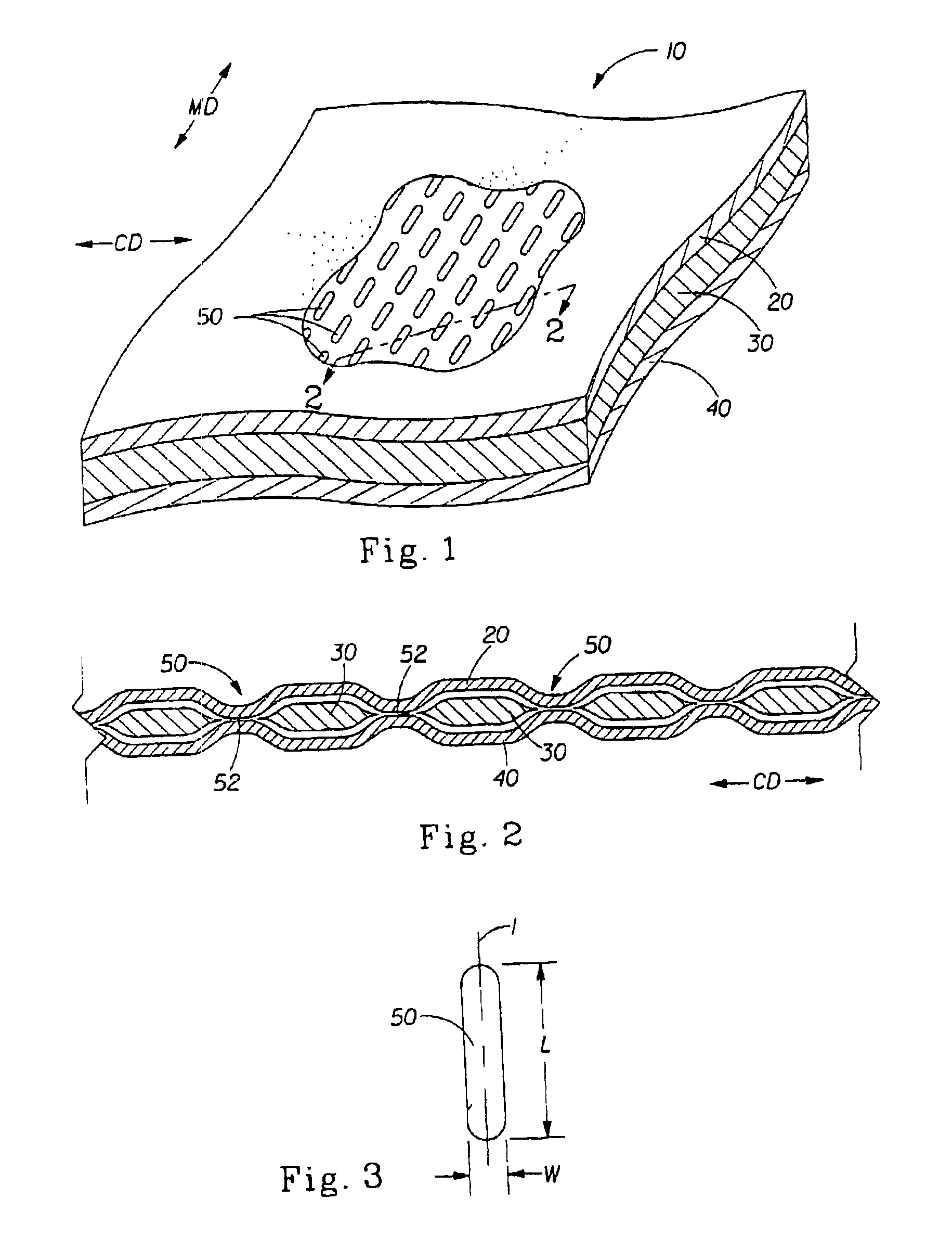
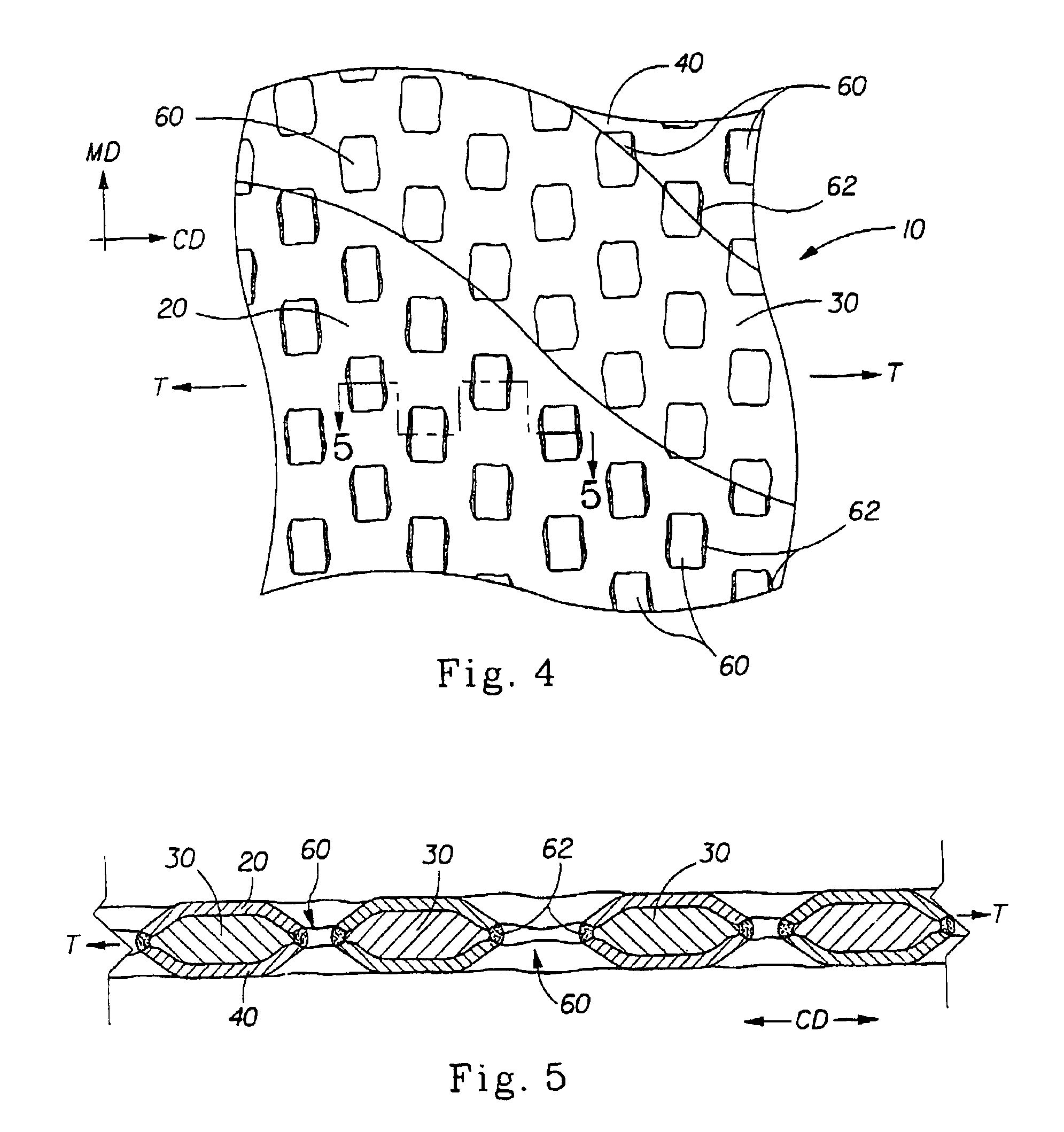
A laminate web comprising a first web, a second web joined to the first web at a plurality of discrete bond sites; and a third material disposed between at least a portion of the first and second nonwovens. The third material is apertured in regions adjacent the bond sites, such that the first and second nonwoven webs are joined through the apertures. In one embodiment an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having a first extensible web having a first elongation to break, and a second extensible web joined to the first extensible web at a plurality of bond sites, the second extensible web having elongation to break. A third web material is disposed between the first and second nonwovens, the third web material having a third elongation to break which is less than both of the first or second elongations to break. In a further embodiment, an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having first and second extensible webs being joined at a plurality of discrete bond sites and a third material disposed between the first and second nonwoven webs. The first and second nonwoven webs are in fluid communication via the apertures and have distinct regions being differentiated by at least one property selected from the group consisting of basis weight, fiber orientation, thickness, and density.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
User-activatible substance delivery system
InactiveUS6863960B2Facilitate exposure and deliveryCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFiberTransverse axis
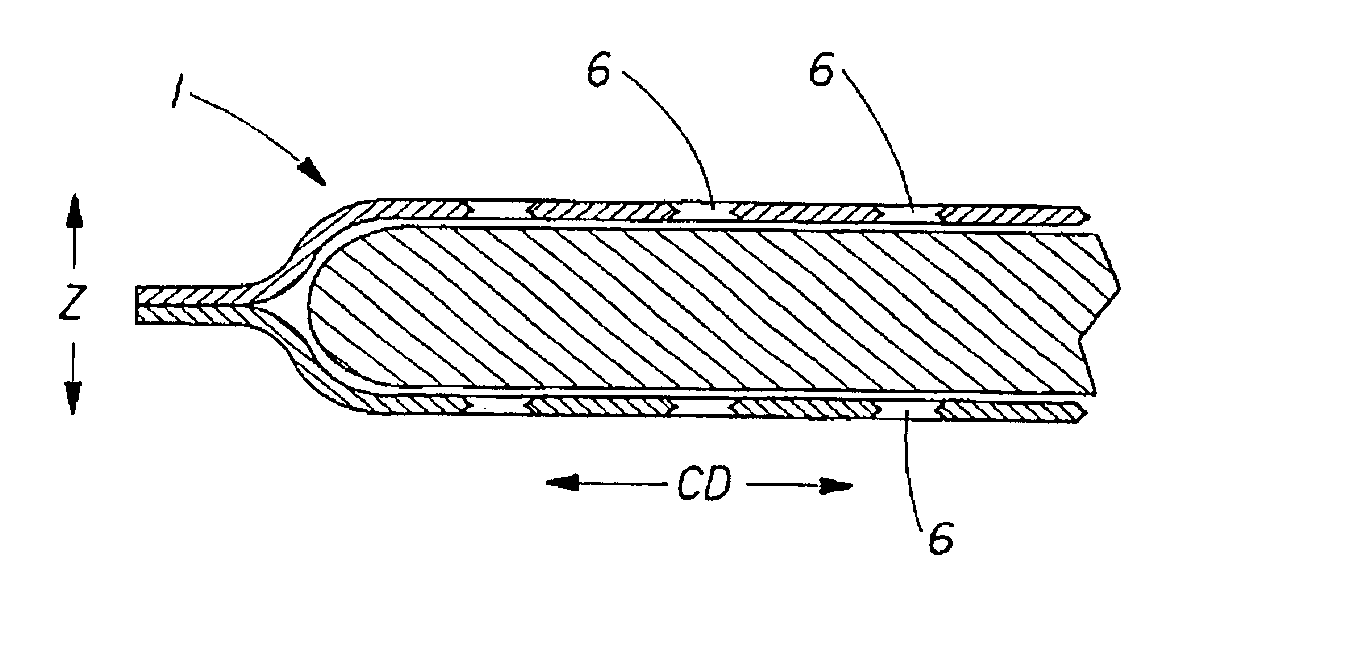
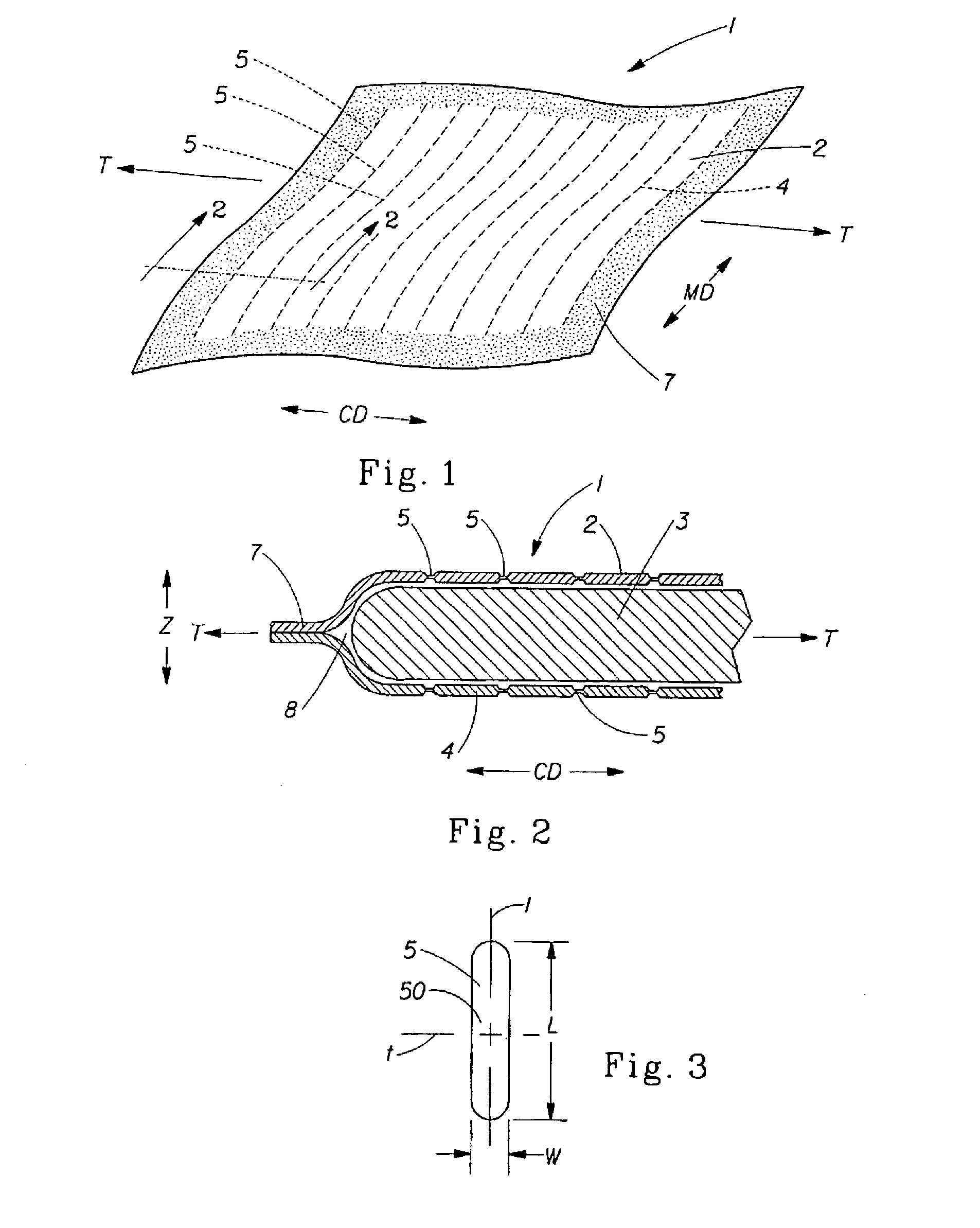
A user-activatible substance delivery system of the present invention comprises a first web and a second web, the first and second webs having a periphery and being enclosed about their respective peripheries and defining a void space therein. A substance for delivery upon user activation is disposed in the void space. At least one of the first or second webs has at least one bond site. The bond site(s) define(s) a melt weakened region such that upon application of a force having a vector component parallel to the transverse axis, the bond site(s) fracture(s) to form a corresponding aperture in the respective web. The apertures provide a fluid communication path to facilitate delivery of the substance from the void space.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
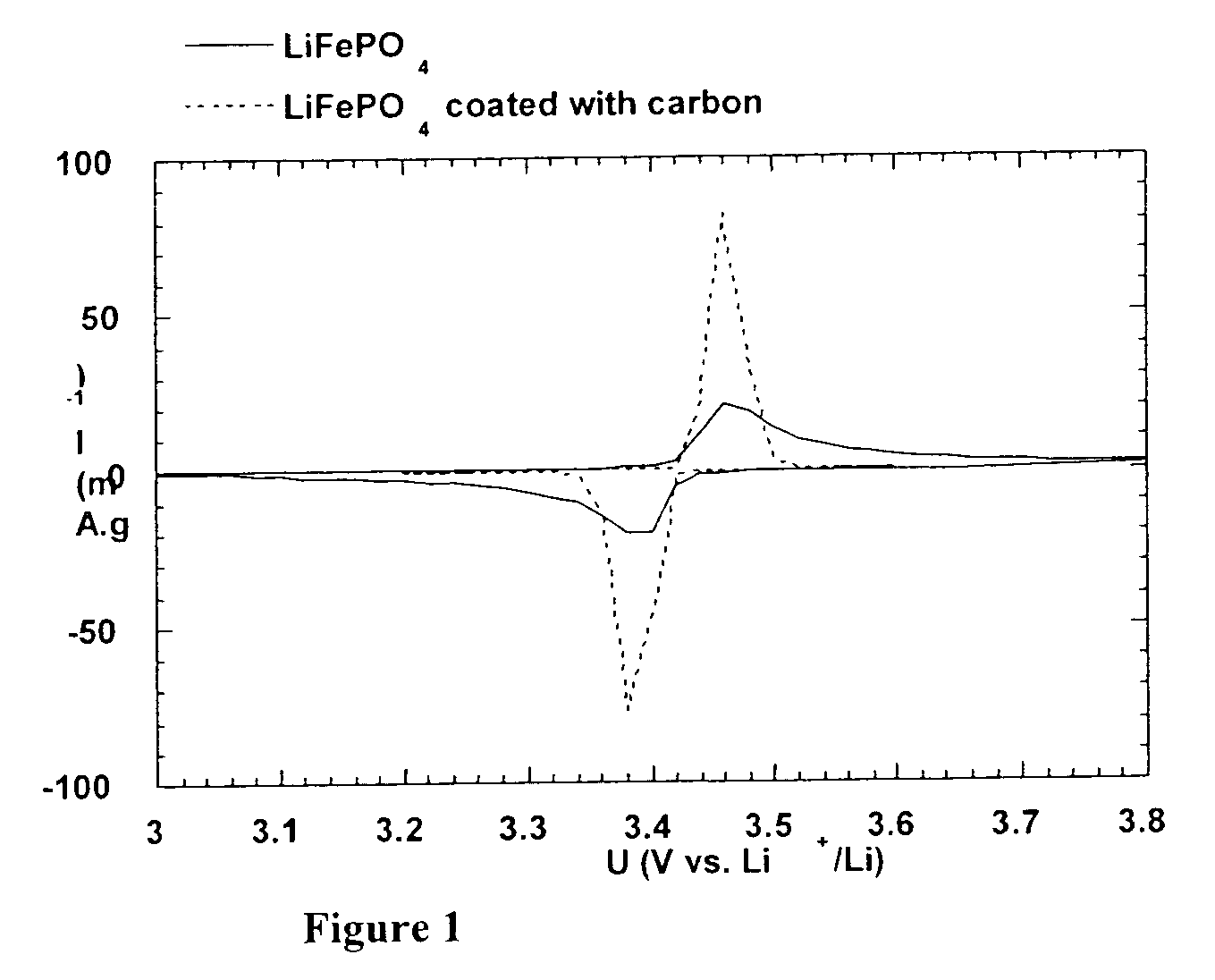
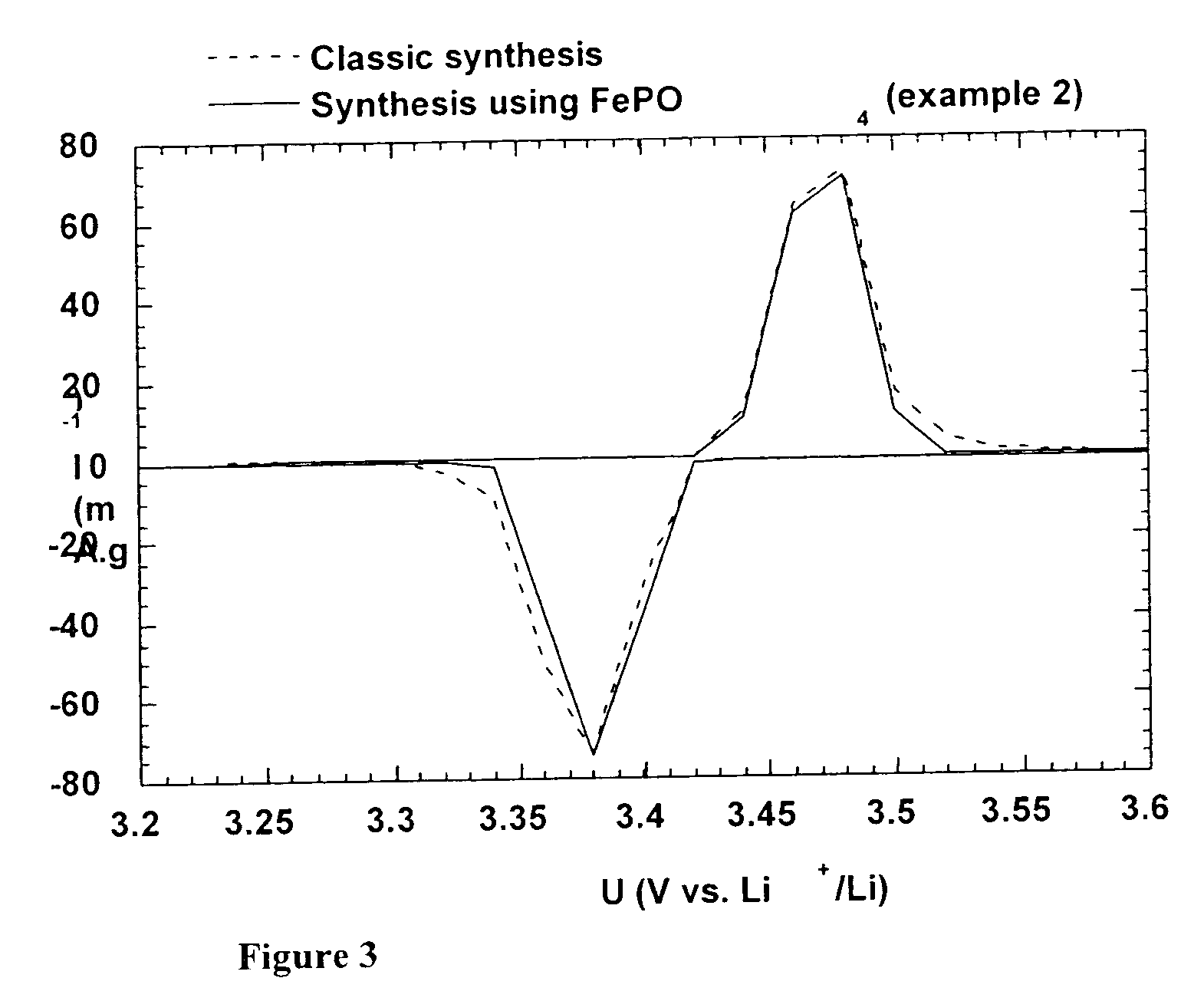
Method for synthesis of carbon-coated redox materials with controlled size
ActiveUS20040033360A1Low costReduce the numberMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitorsCross-linkRedox
A method for the synthesis of compounds of the formula C-LixM1-yM'y(XO4)n, where C represents carbon cross-linked with the compound LixM1-yM'y(XO4)n, in which x, y and n are numbers such as 0<=x<=2, 0<=y<=0.6, and 1<=n<=1.5, M is a transition metal or a mixture of transition metals from the first period of the periodic table, M' is an element with fixed valency selected among Mg<2+>, Ca<2+>, Al<3+>, Zn<2+> or a combination of these same elements and X is chosen among S, P and Si, by bringing into equilibrium, in the required proportions, the mixture of precursors, with a gaseous atmosphere, the synthesis taking place by reaction and bringing into equilibrium, in the required proportions, the mixture of the precursors, the procedure comprising at least one pyrolysis step of the carbon source compound in such a way as to obtain a compound in which the electronic conductivity measured on a sample of powder compressed at a pressure of 3750 Kg.cm<-2 >is greater than 10<-8 >S.cm<-1>. The materials obtained have excellent electrical conductivity, as well a very improved chemical activity.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
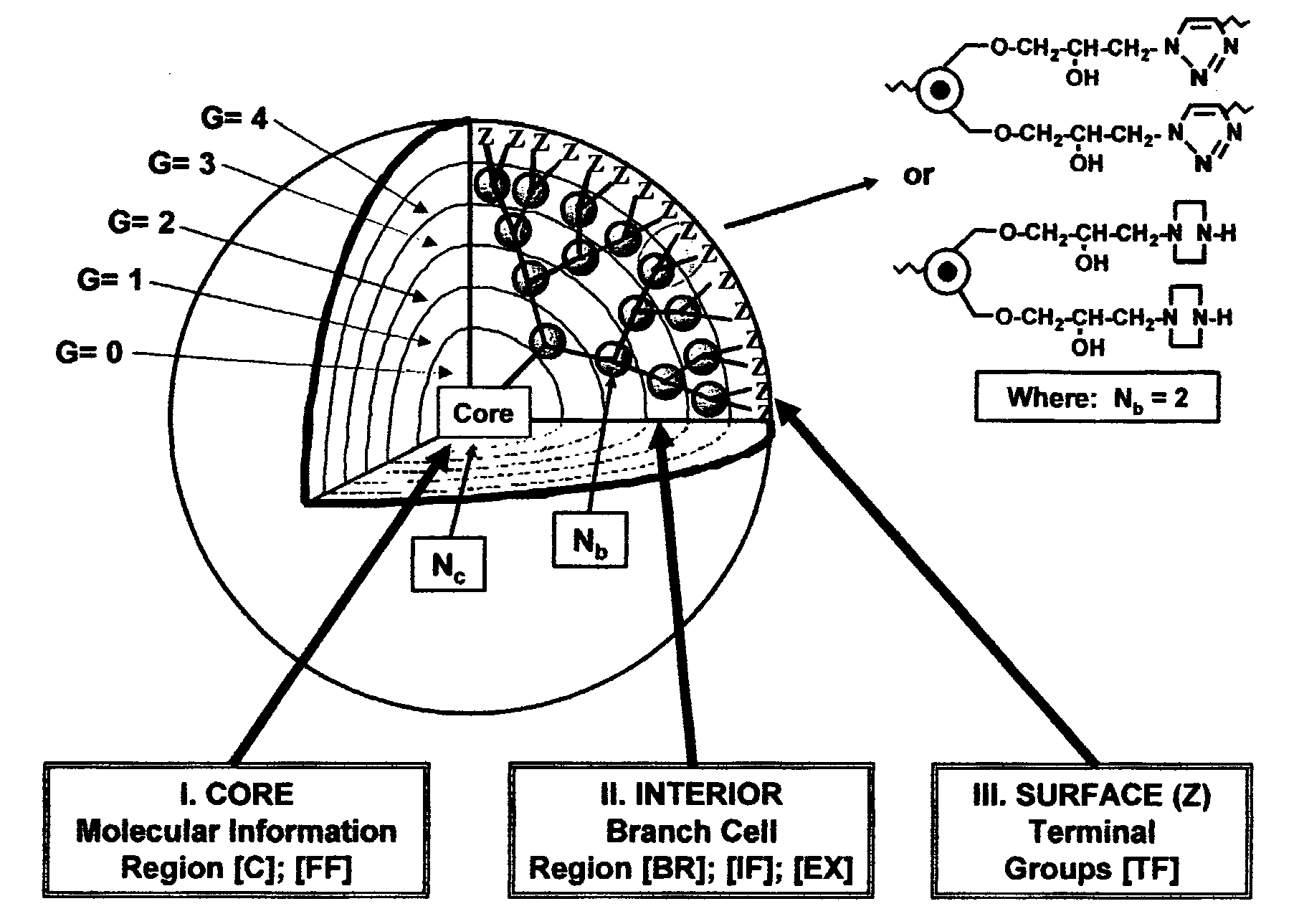
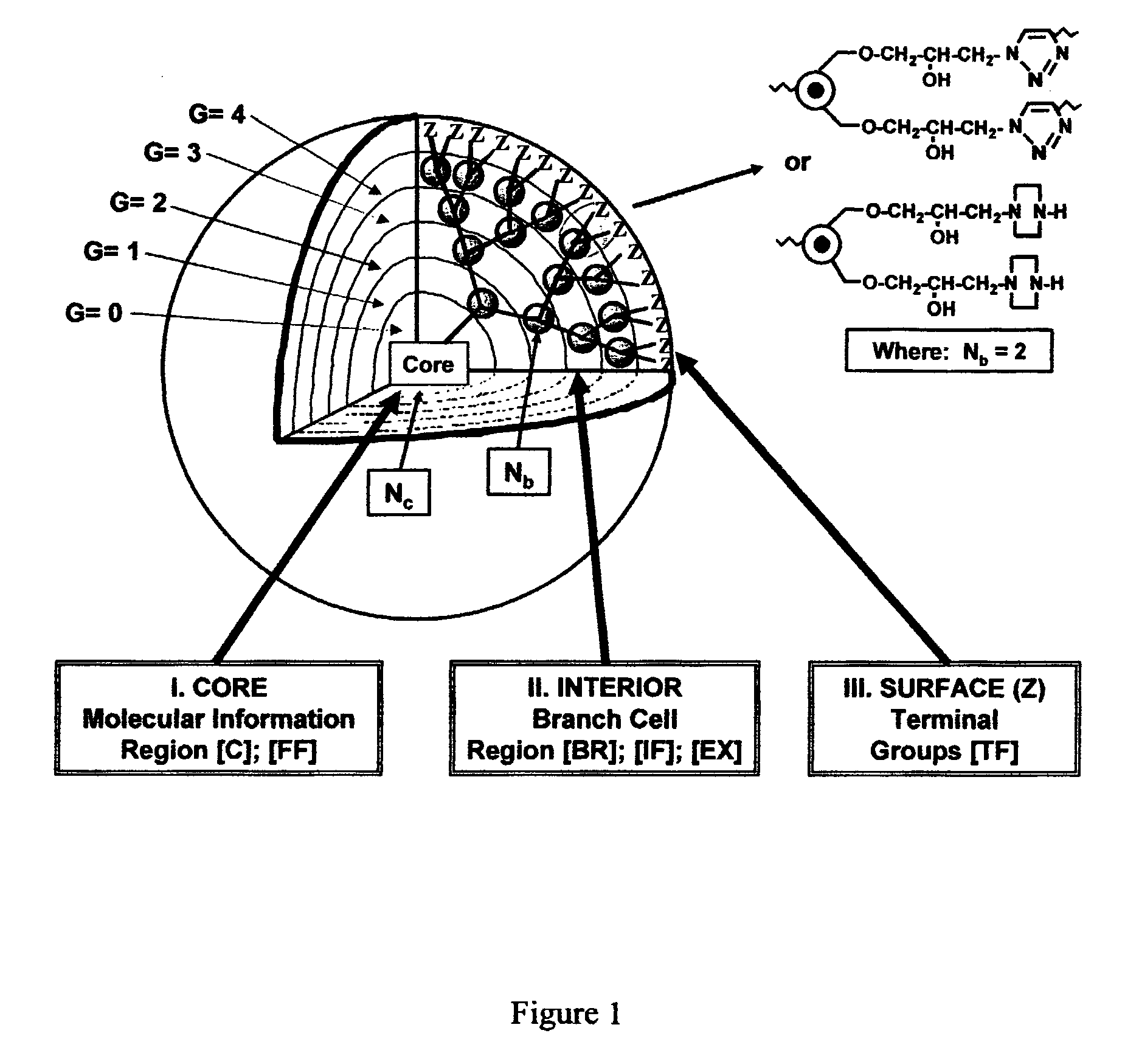
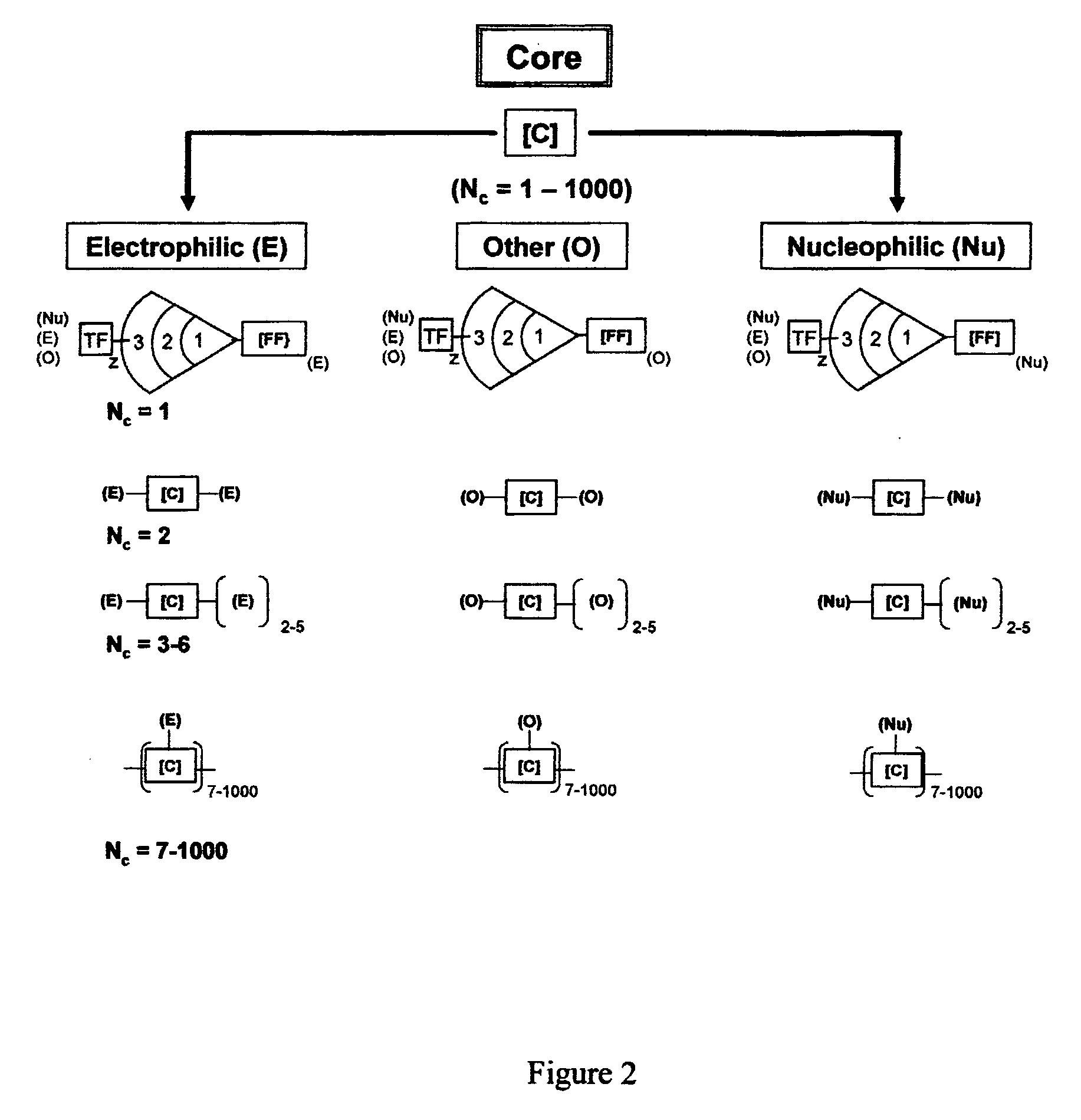
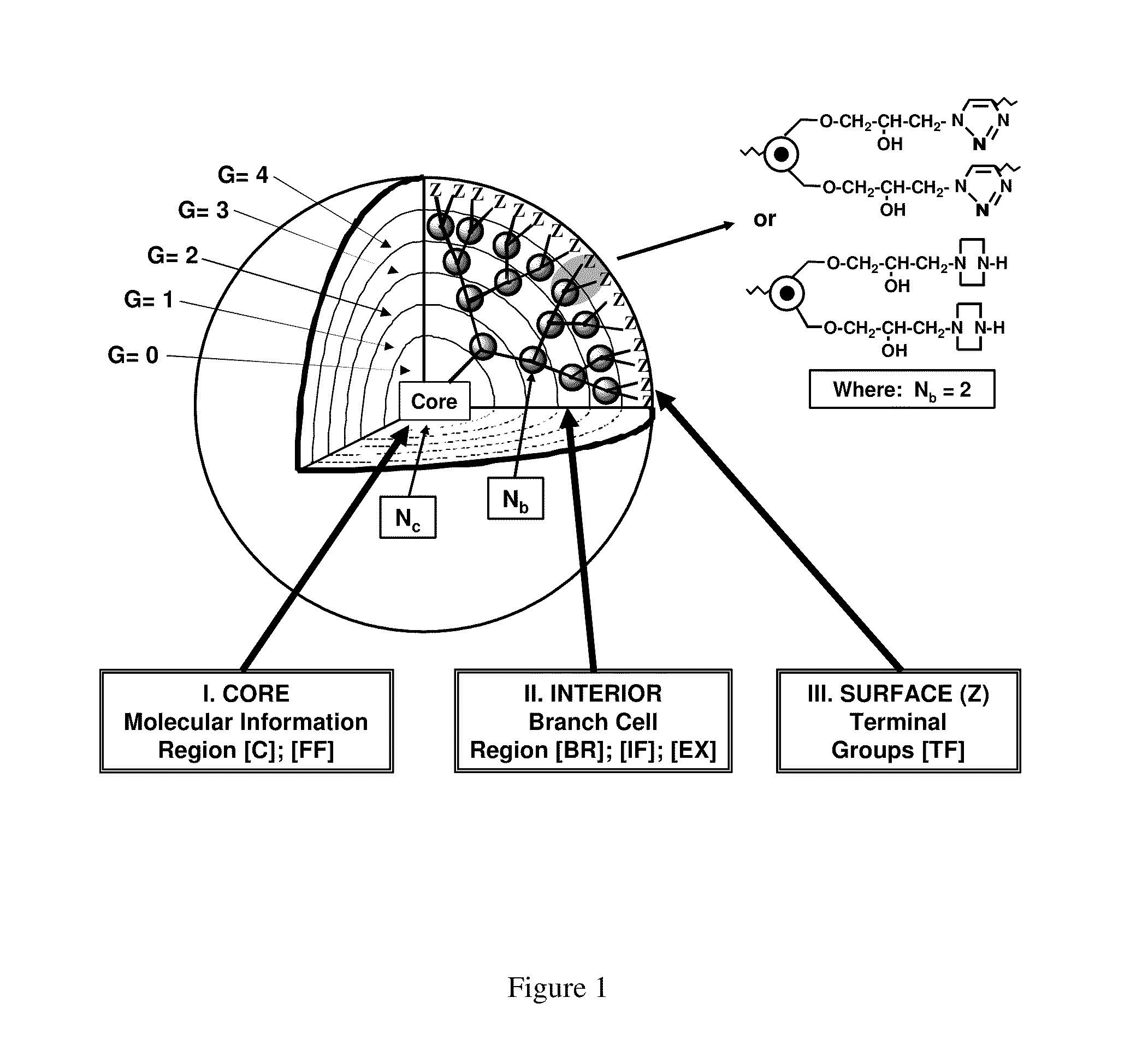
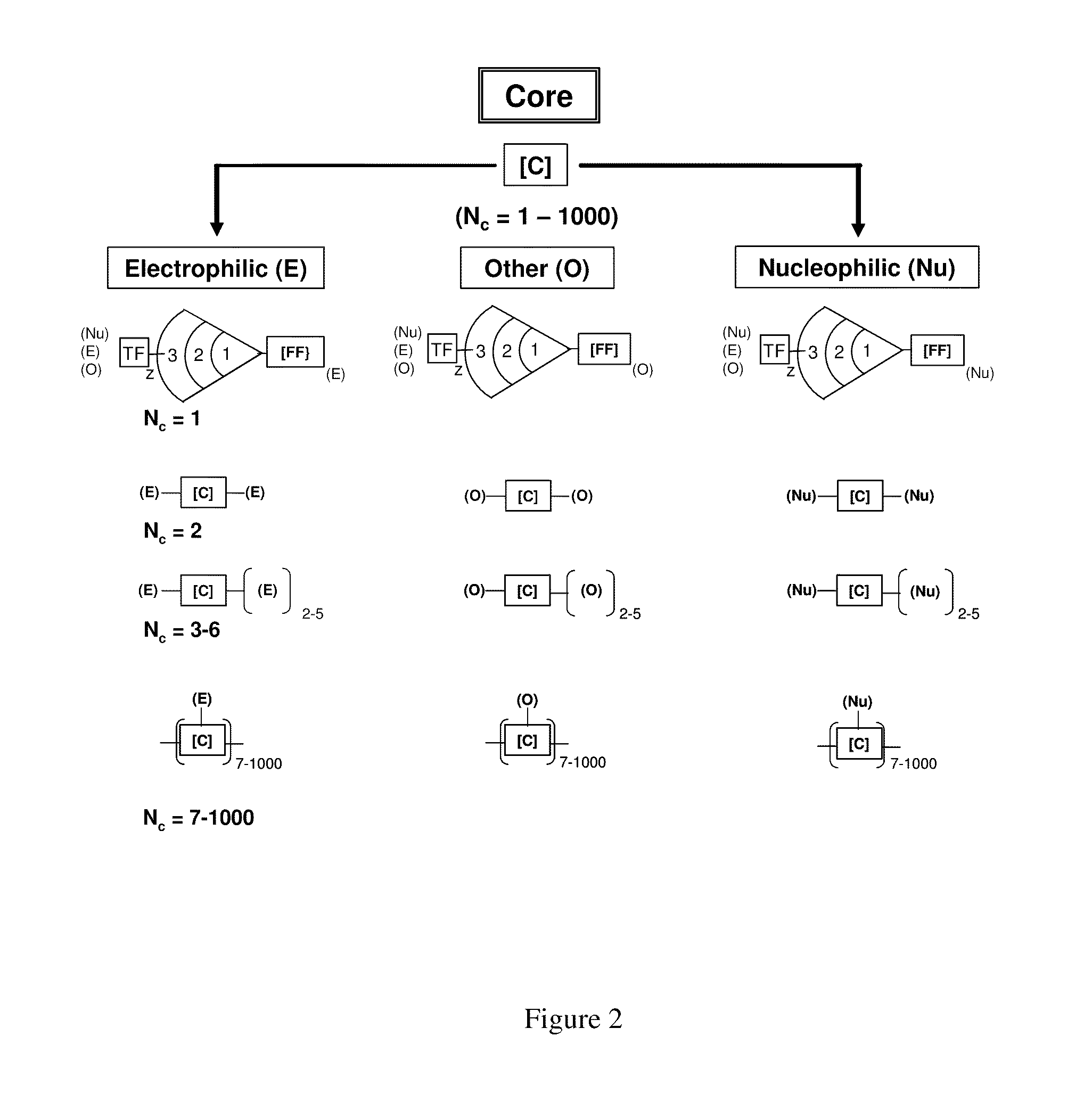
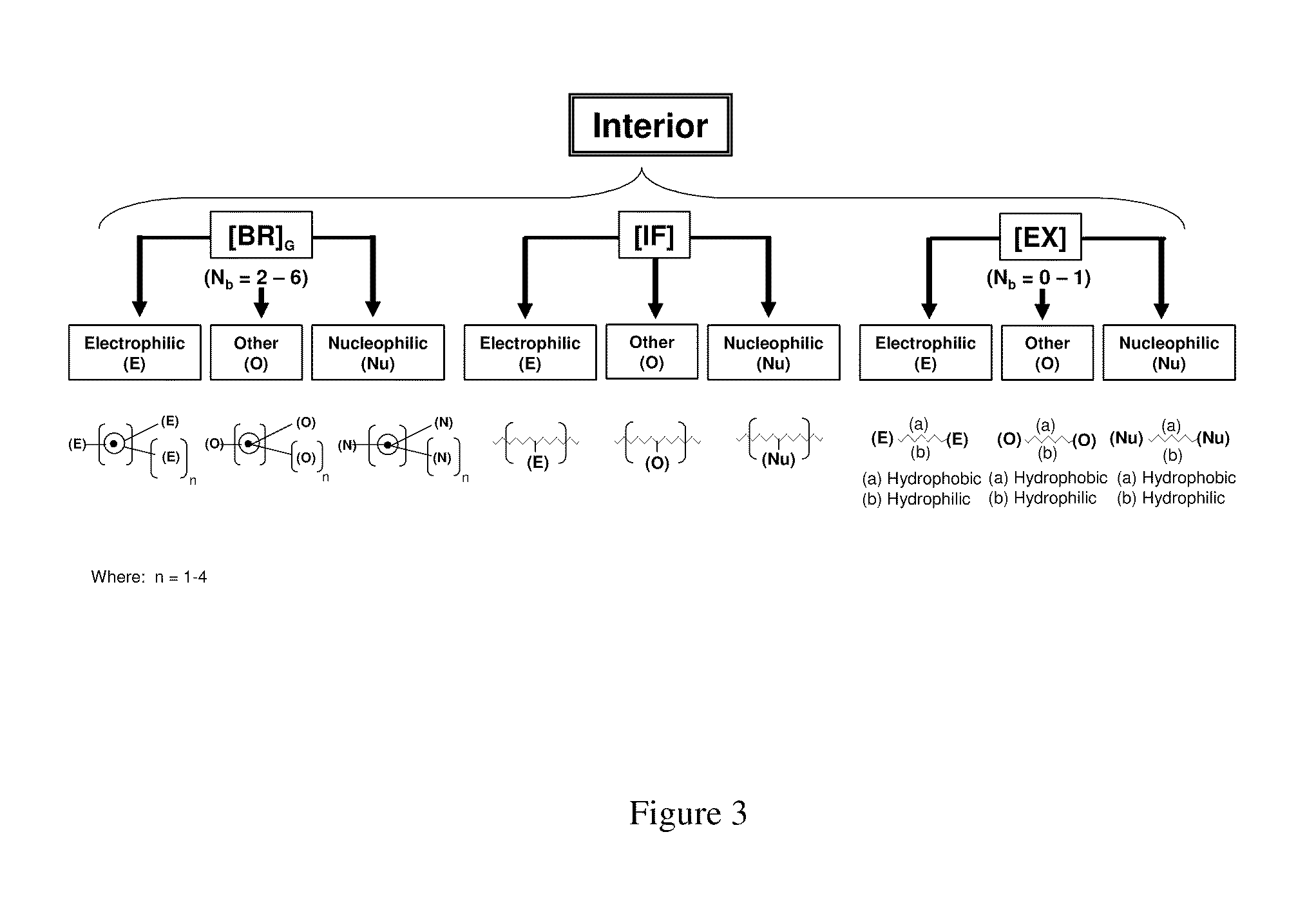
Dendritic Polymers With Enhanced Amplification and Interior Functionality
ActiveUS20070298006A1Reduced responseSizePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkScavenger
Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality are disclosed. These dendritic polymers are made by use of fast, reactive ring-opening chemistry (or other fast reactions) combined with the use of branch cell reagents in a controlled way to rapidly and precisely build dendritic structures, generation by generation, with cleaner chemistry, often single products, lower excesses of reagents, lower levels of dilution, higher capacity method, more easily scaled to commercial dimensions, new ranges of materials, and lower cost. The dendritic compositions prepared have novel internal functionality, greater stability (e.g., thermal stability and less or no reverse Michael's reaction), and reach encapsulation surface densities at lower generations. Unexpectedly, these reactions of polyfunctional branch cell reagents with polyfunctional cores do not create cross-linked materials. Such dendritic polymers are useful as demulsifiers for oil / water emulsions, wet strength agents in the manufacture of paper, proton scavengers, polymers, nanoscale monomers, calibration standards for electron microscopy, making size selective membranes, and agents for modifying viscosity in aqueous formulations such as paint. When these dendritic polymers have a carried material associated with their surface and / or interior, then these dendritic polymers have additional properties for carrying materials due to the unique characteristics of the dendritic polymer, such as for drug delivery, transfection, and diagnostics.
Owner:DENDRITIC NANO TECH INC
Conformal coatings comprising carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS7118693B2Material nanotechnologyMagnetic/electric field screeningModified carbonElectromagnetic interference
Owner:EIKOS
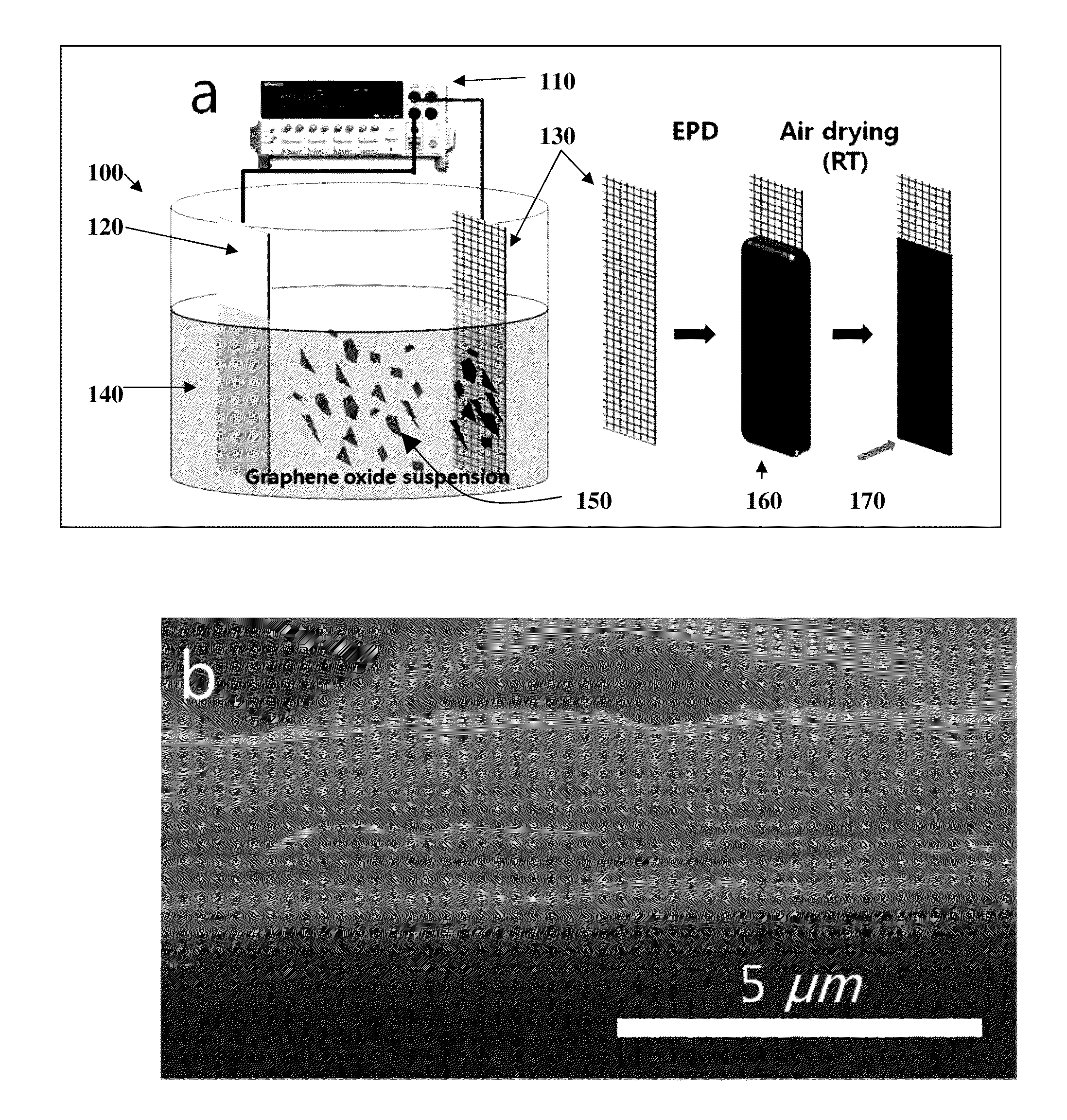
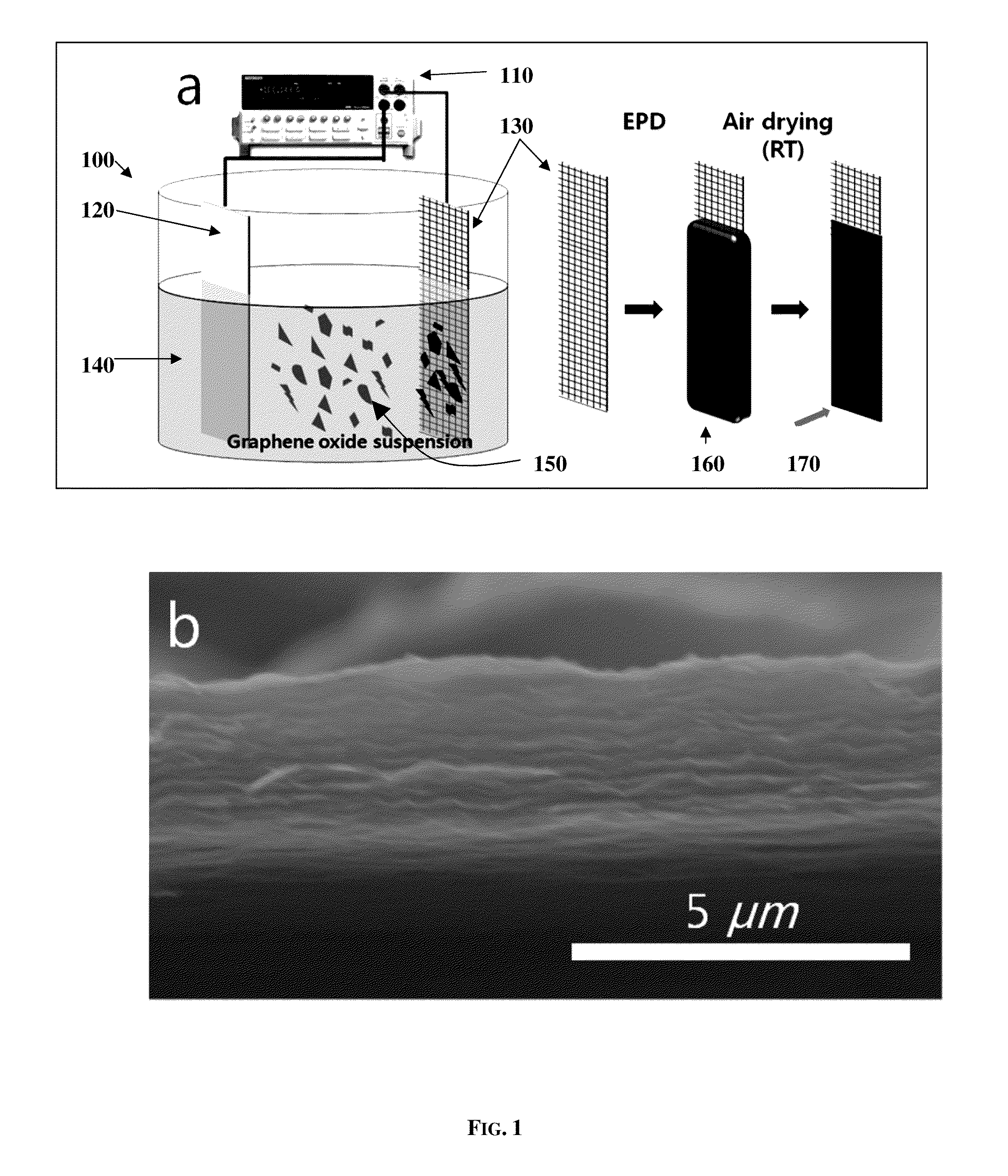
Electrophoretic deposition and reduction of graphene oxide to make graphene film coatings and electrode structures
Owner:RUOFF RODNEY S +4
Liquid Composite Compositions Using Non-Volatile Liquids and Nanoparticles and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080209876A1Reduce CTEImprove performanceElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesOrganic solventNanoparticle
A solvent composition comprising an organic solvent; dispersed nanoparticles; and a non-volatile electrolyte.
Owner:ESIONIC
Antimicrobial compositions containing colloids of oligodynamic metals
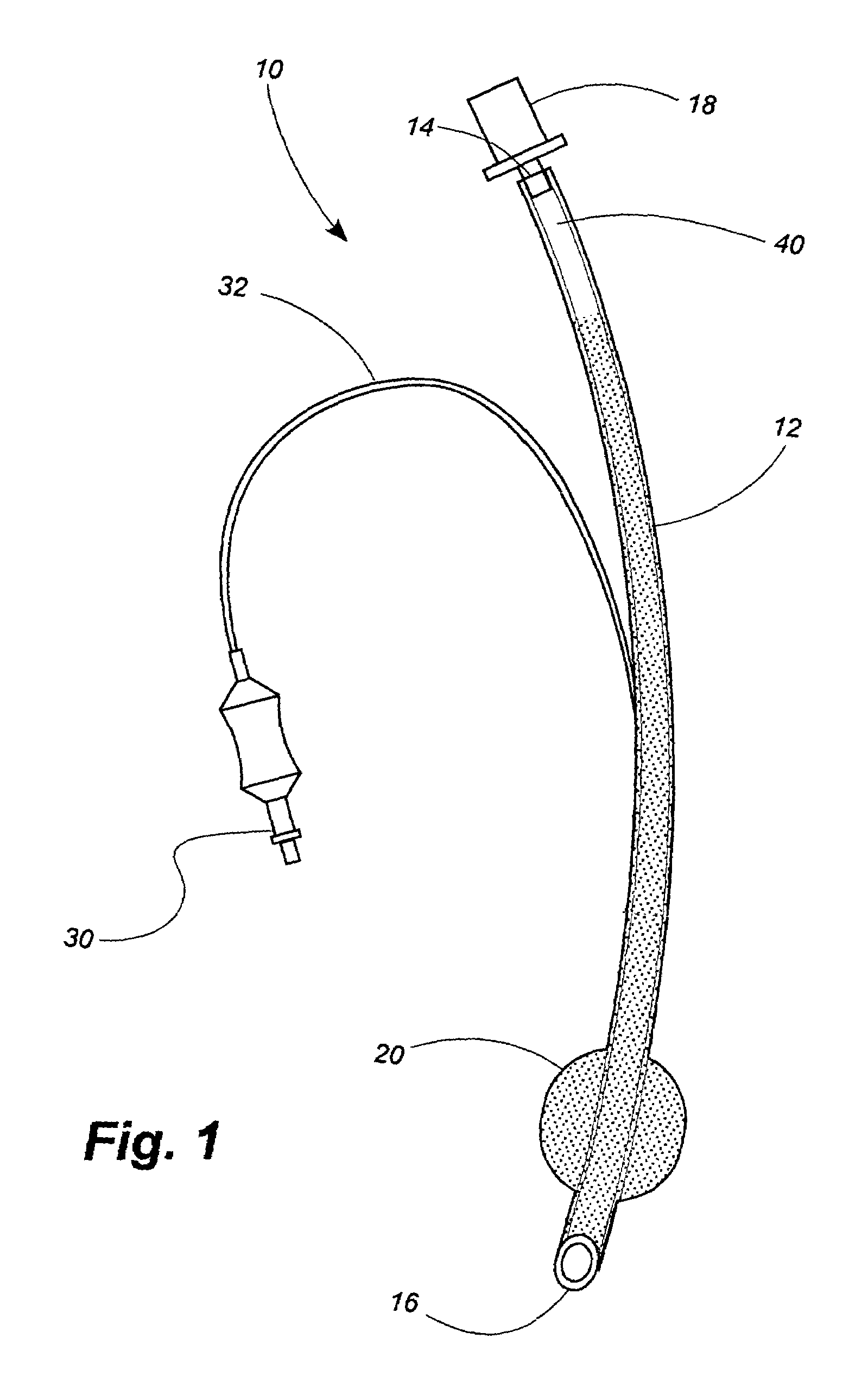
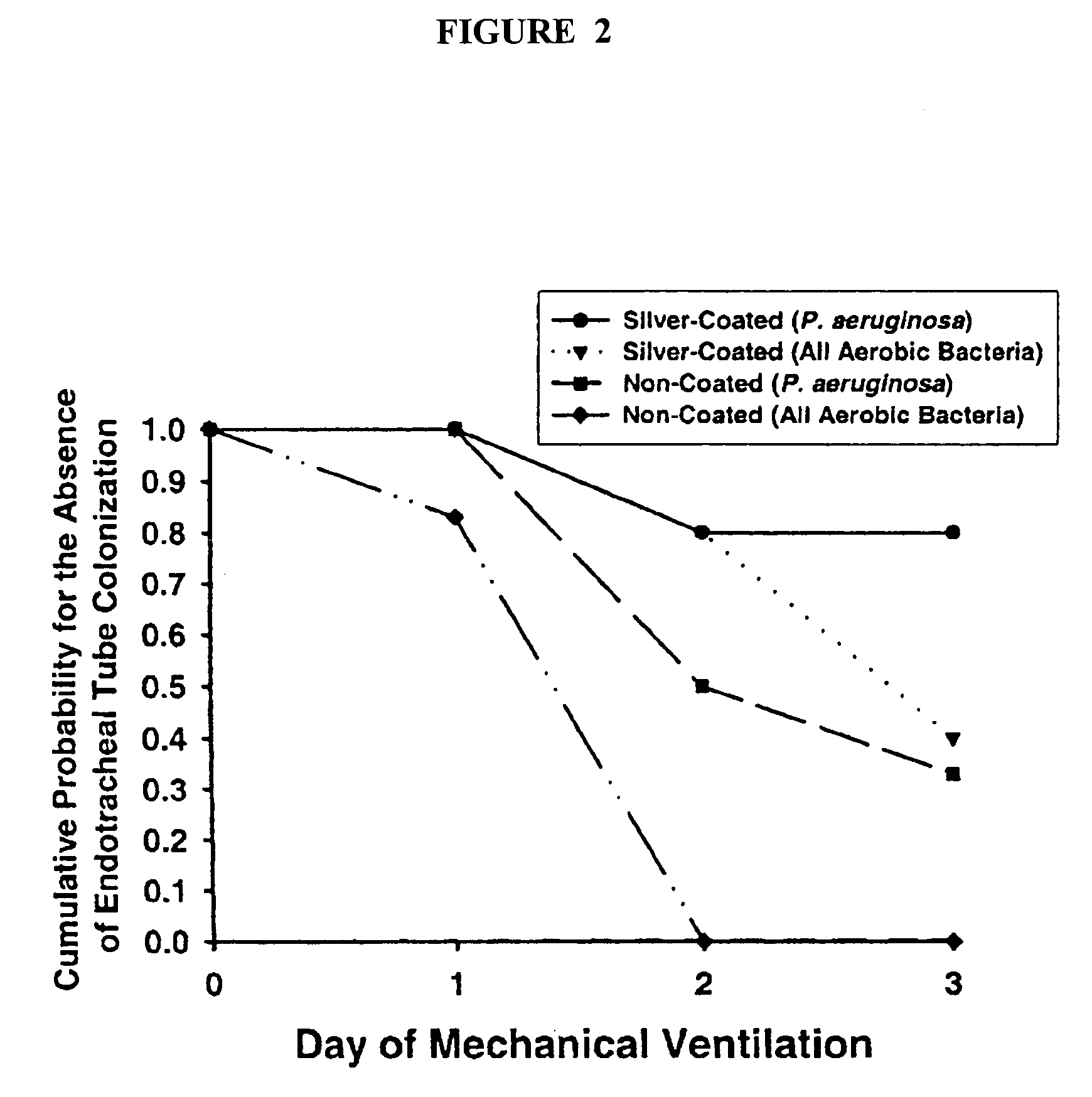
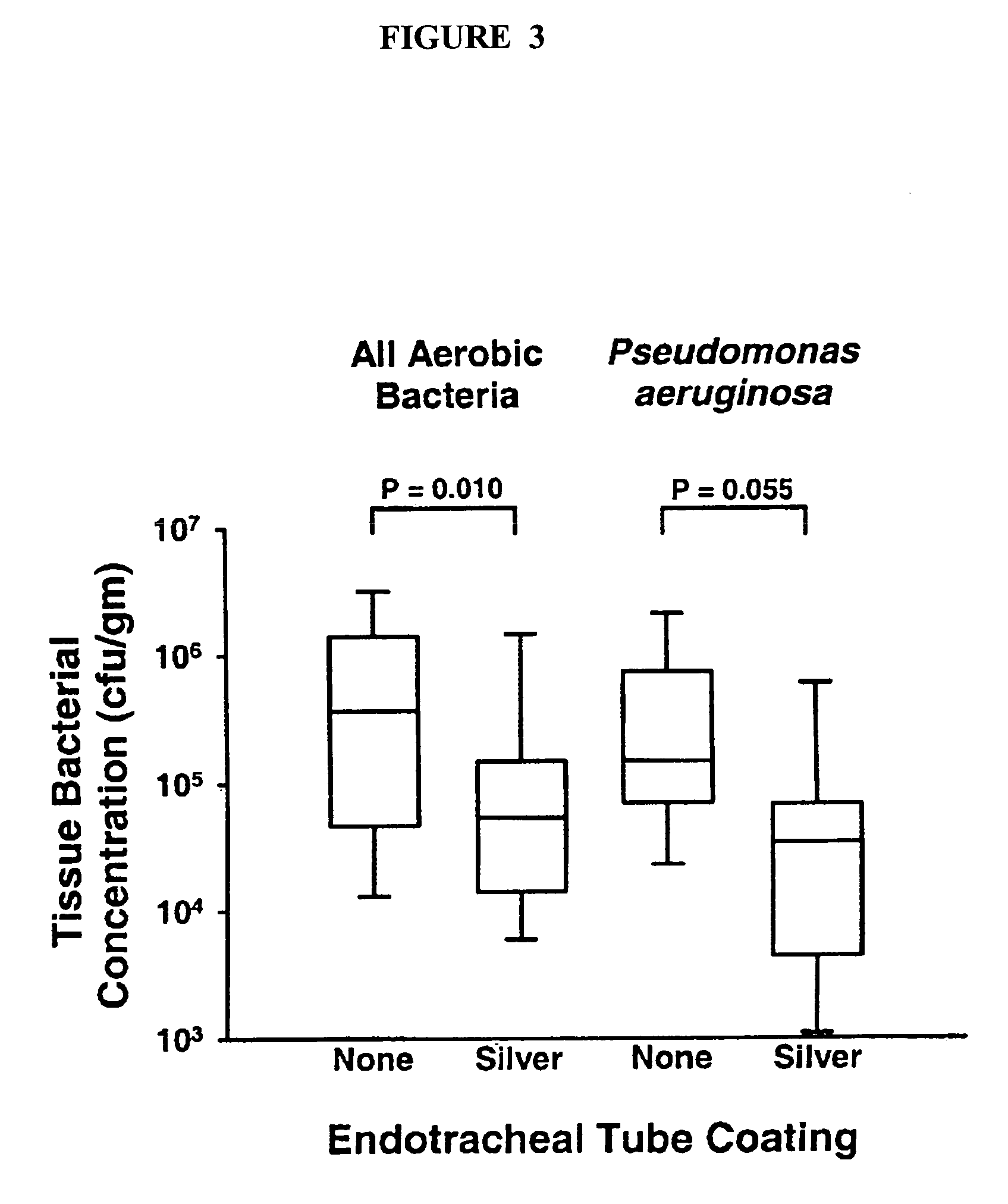
InactiveUS7179849B2Reduced settlingReduce agglomerationOrganic active ingredientsPretreated surfacesSolubilityCatheter
Owner:CR BARD INC
Polymeric material
ActiveUS20120100217A1Improve mechanical propertiesEasy to usePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsConductive polymerPolymer chemistry
Disclosed herein is a polymeric material comprising a conductive polymer substantially homogeneously distributed within a hydrogel. Also disclosed are methods for making the polymeric material and uses for the polymeric material.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Use of metalnanoshells to impede the photo-oxidation of conjugated polymer
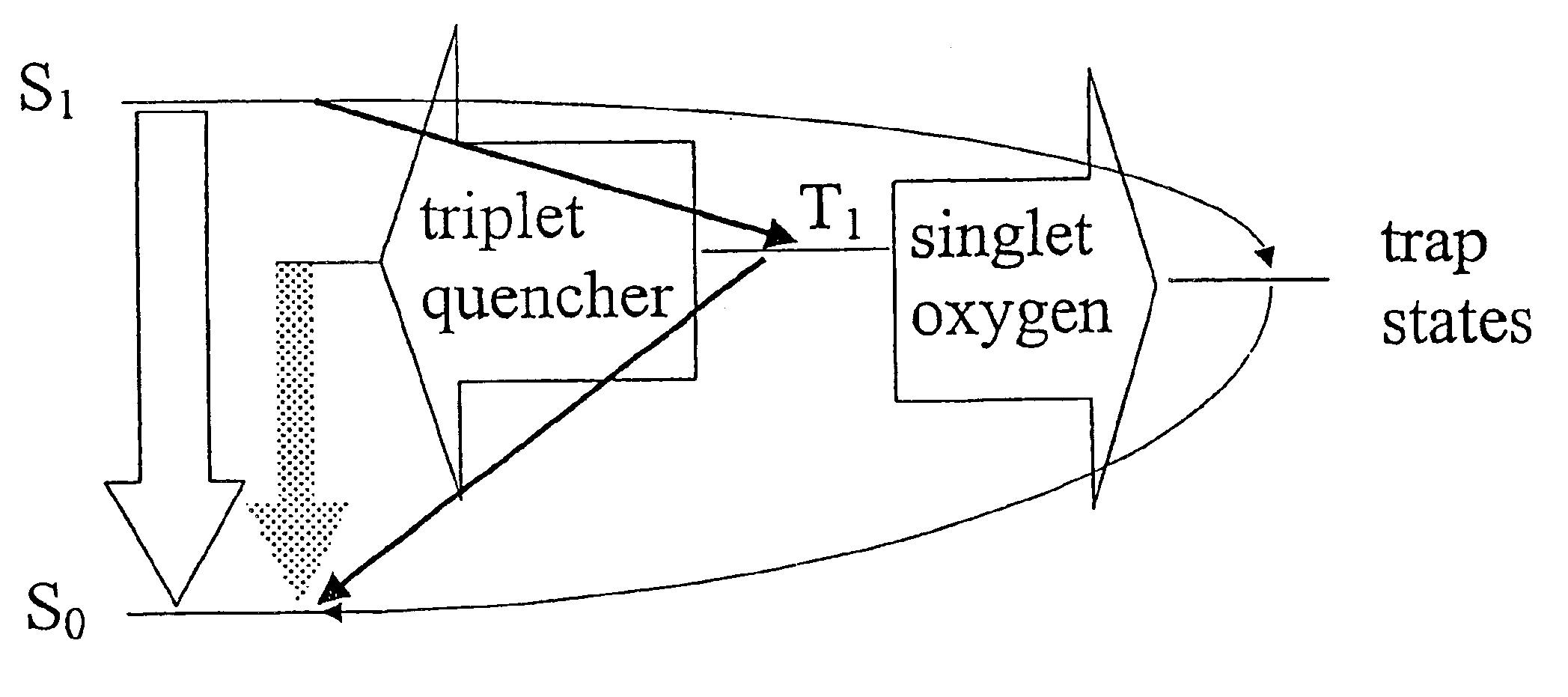
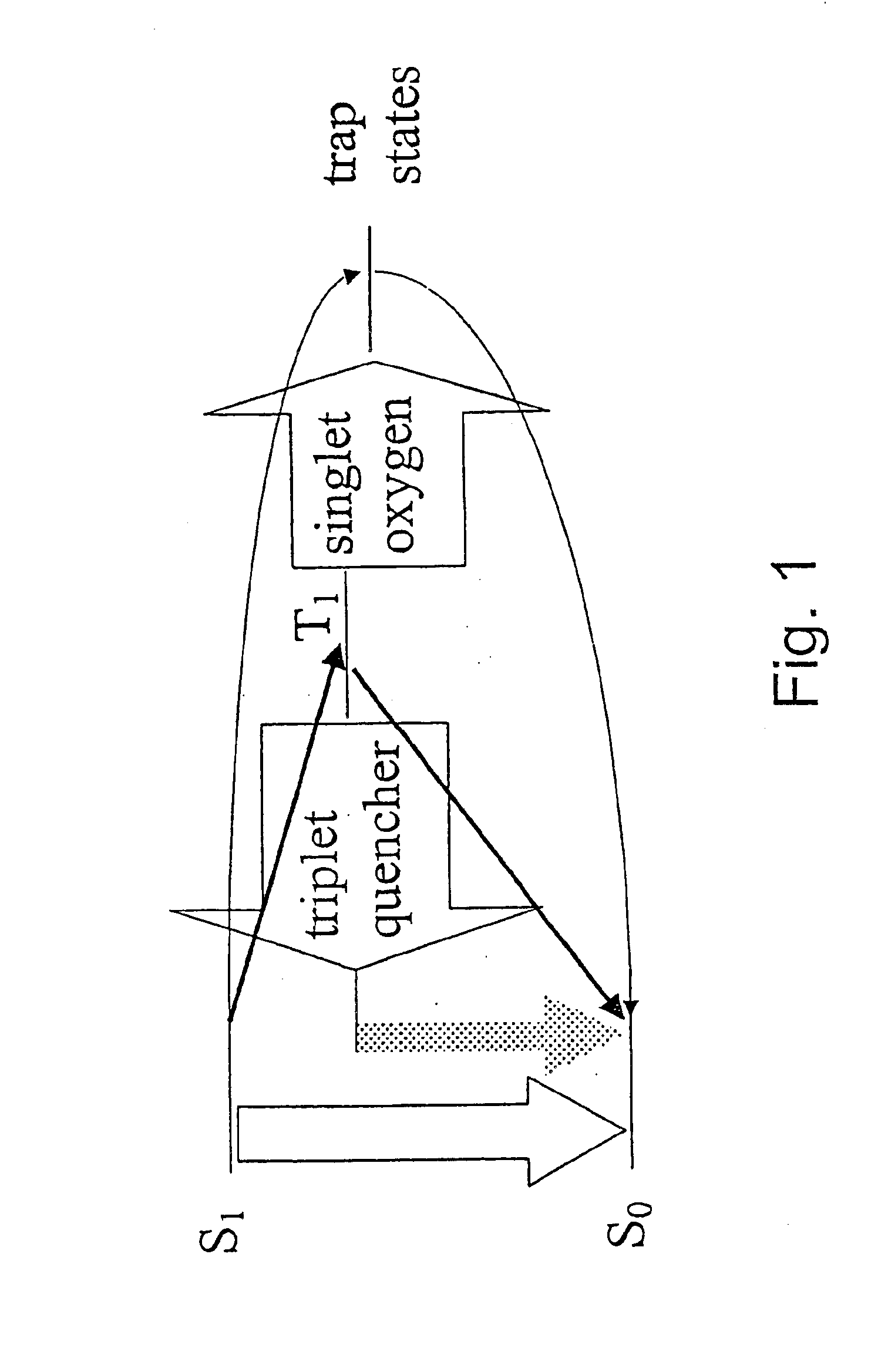
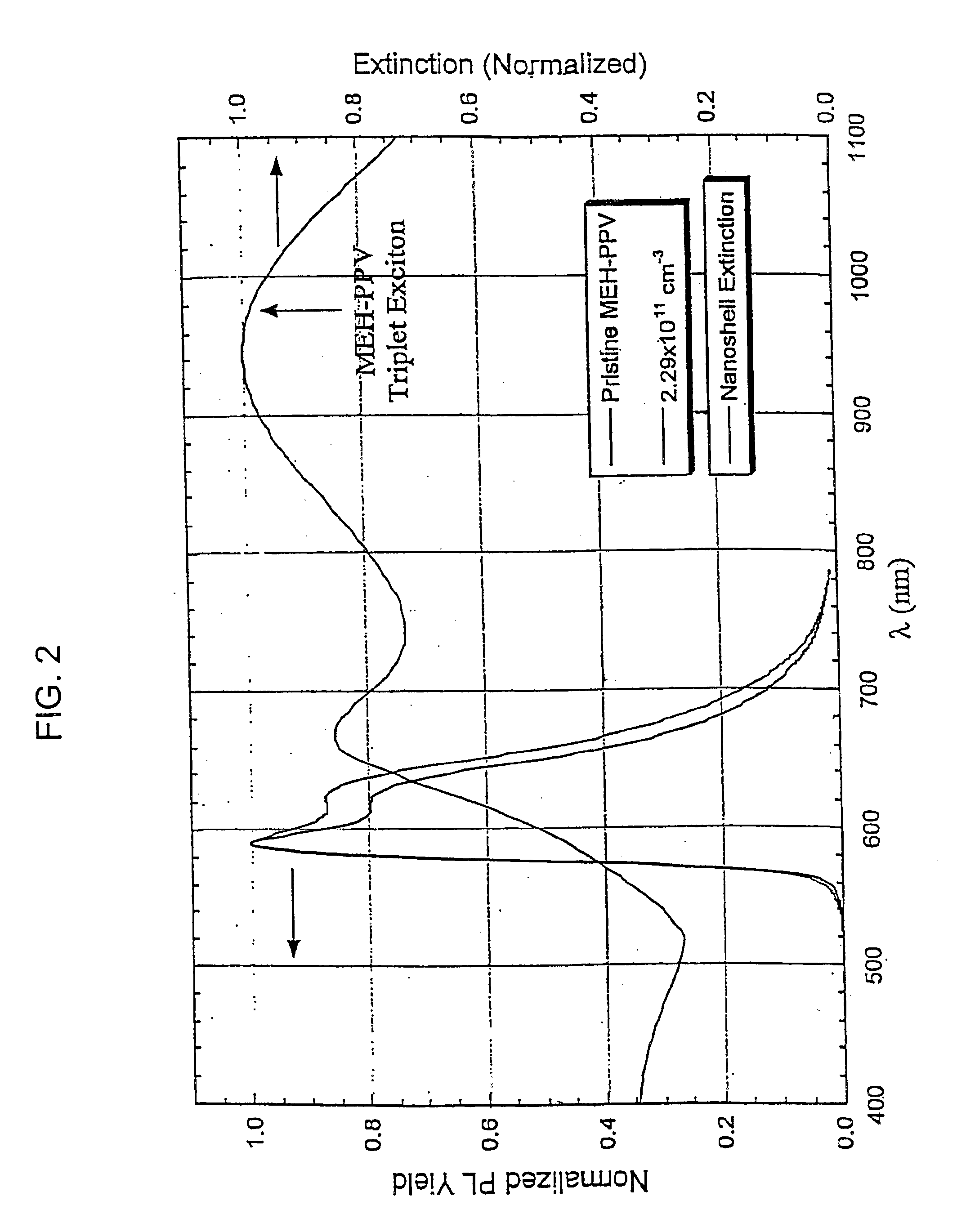
InactiveUS6852252B2Impede photo-oxidation processReduce degradationMaterial nanotechnologyDiffusing elementsPhoto-oxidation of polymersVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to incorporating metal nanoshells specifically designed to interact with triplet excitons in polymers. By interacting with triplet excitons, the rate of photo-oxidation can be slowed and the density of luminescence-quenching traps can be reduced.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Composite solid electrolyte for protection of active metal anodes
ActiveUS8182943B2Eliminate through-porosityImprove ionic conductivityCell electrodesPrimary cellsPorosityLithium
A composite solid electrolyte include a monolithic solid electrolyte base component that is a continuous matrix of an inorganic active metal ion conductor and a filler component used to eliminate through porosity in the solid electrolyte. In this way a solid electrolyte produced by any process that yields residual through porosity can be modified by the incorporation of a filler to form a substantially impervious composite solid electrolyte and eliminate through porosity in the base component. Methods of making the composites is also disclosed. The composites are generally useful in electrochemical cell structures such as battery cells and in particular protected active metal anodes, particularly lithium anodes, that are protected with a protective membrane architecture incorporating the composite solid electrolyte. The protective architecture prevents the active metal of the anode from deleterious reaction with the environment on the other (cathode) side of the architecture, which may include aqueous, air and organic liquid electrolytes and / or electrochemically active materials.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Solid ion conductor which has a garnet-like crystal structure and has the stoichiometric composition L7+XAXG3-XZr2O12
ActiveUS8658317B2Easily employedImprove ionic conductivityFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectrical conductorCrystal structure
The invention is directed to a solid ion conductor which has a garnet-like crystal structure and has the stoichiometric composition L7+xAxG3−xZr2O12, whereinL is in each case independently a monovalent cation,A is in each case independently a divalent cation,G is in each case independently a trivalent cation,0≦x≦3 andO can be partly or completely replaced by divalent or trivalent anion.
Owner:BASF AG
Monolayer and/or Few-Layer Graphene On Metal or Metal-Coated Substrates
InactiveUS20100255984A1Easy to disassembleMaterial nanotechnologyParticle separator tubesHigh concentrationIn plane
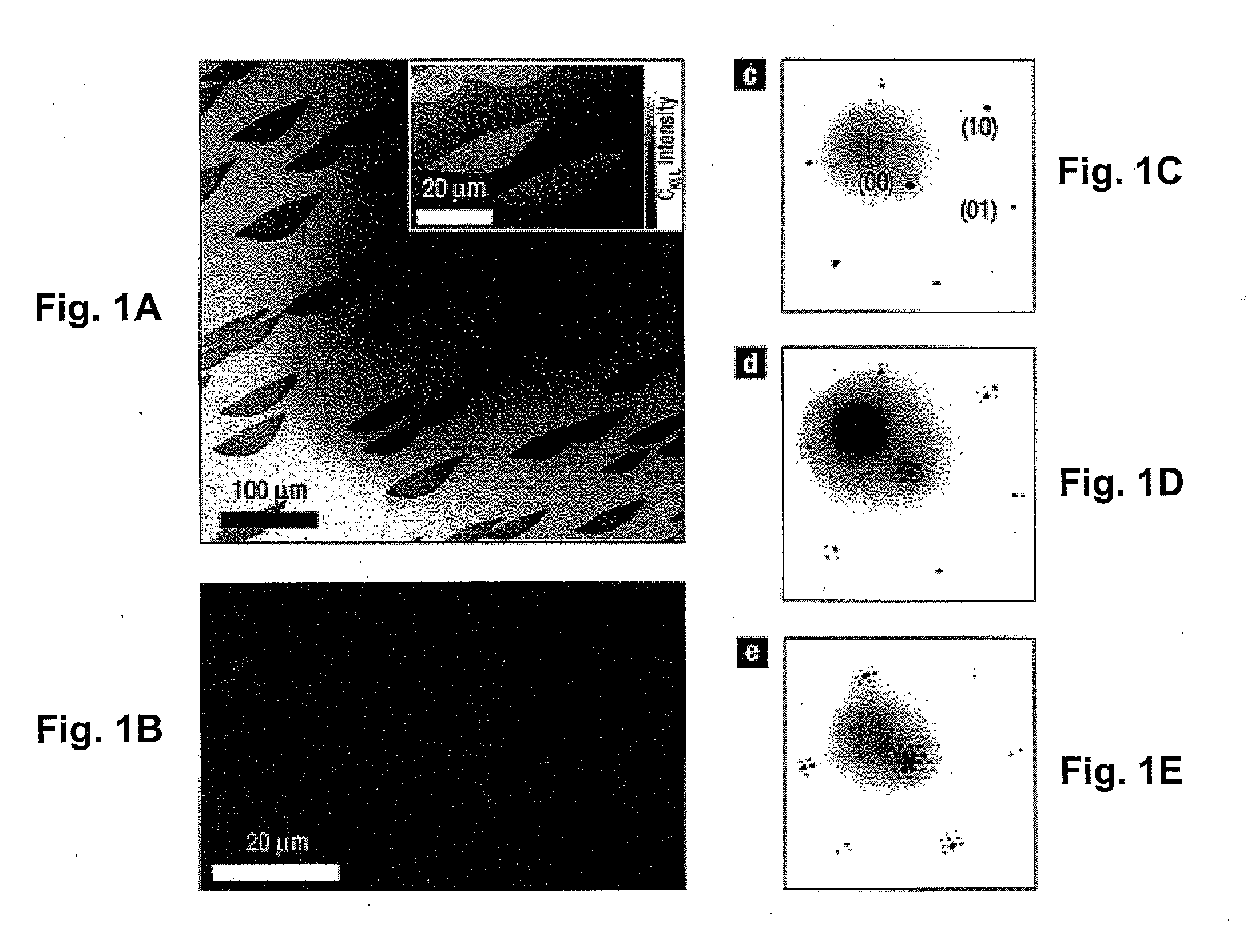
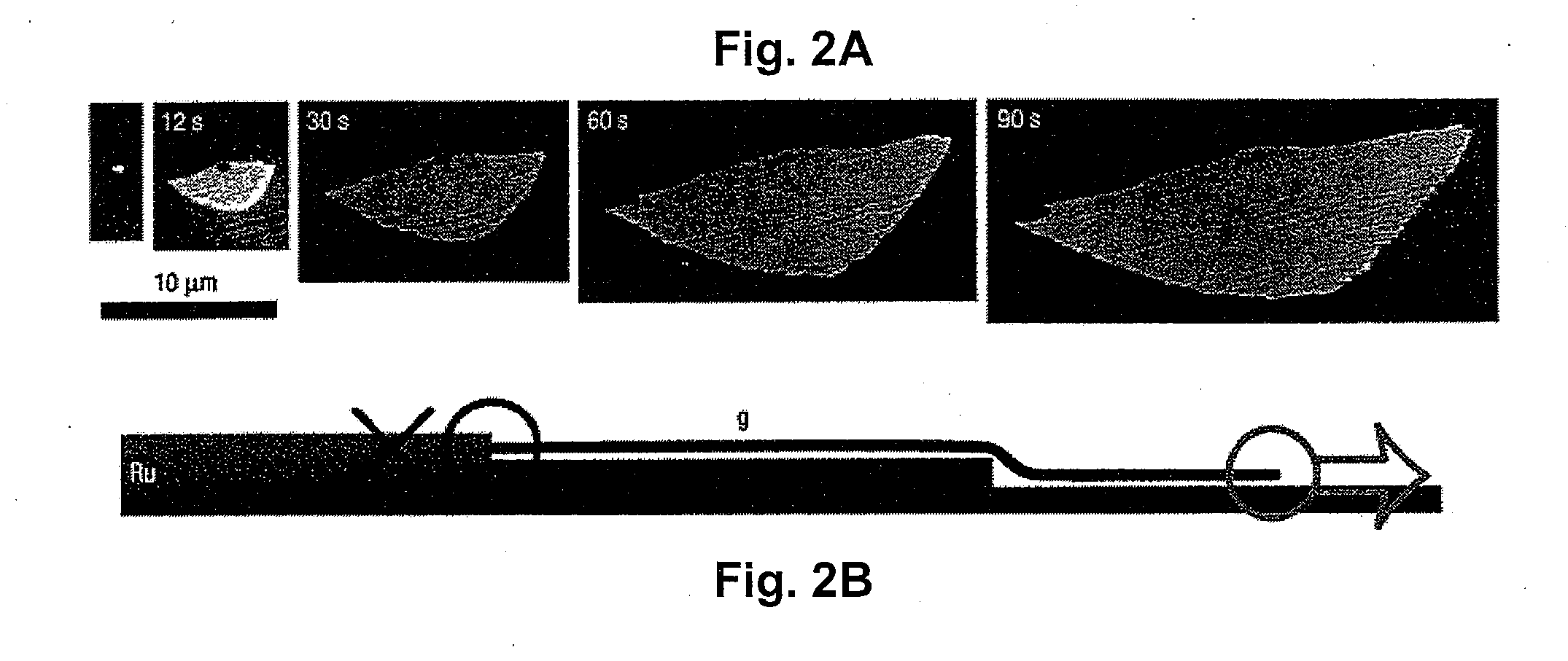
Graphene is a single atomic layer of sp2-bonded C atoms densely packed into a two-dimensional honeycomb crystal lattice. A method of forming structurally perfect and defect-free graphene films comprising individual mono crystalline domains with in-plane lateral dimensions of up to 200 μm or more is presented. This is accomplished by controlling the temperature-dependent solubility of interstitial C of a transition metal substrate having a suitable surface structure. At elevated temperatures, C is incorporated into the bulk at higher concentrations. As the substrate is cooled, a lowering of the interstitial C solubility drives a significant amount of C atoms to the surface where graphene islands nucleate and gradually increase in size with continued cooling. Ru(0001) is selected as a model system and electron microscopy is used to observe graphene growth during cooling from elevated temperatures. With controlled cooling, large arrays of macroscopic single-crystalline graphene domains covering the entire transition metal surface are produced. As the graphene domains coalesce to a complete layer, a second graphene layer is formed, etc. By controlling the interstitial C concentration and the cooling rate, graphene layers with thickness up to 10 atomic layers or more are formed in a controlled, layer-by-layer fashion.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Curing binder material for carbon nanotube electron emission cathodes
InactiveUS20070262687A1Improve adhesionReduce exhaustMaterial nanotechnologyCathode ray/electron stream lampsField emission deviceBiological activation
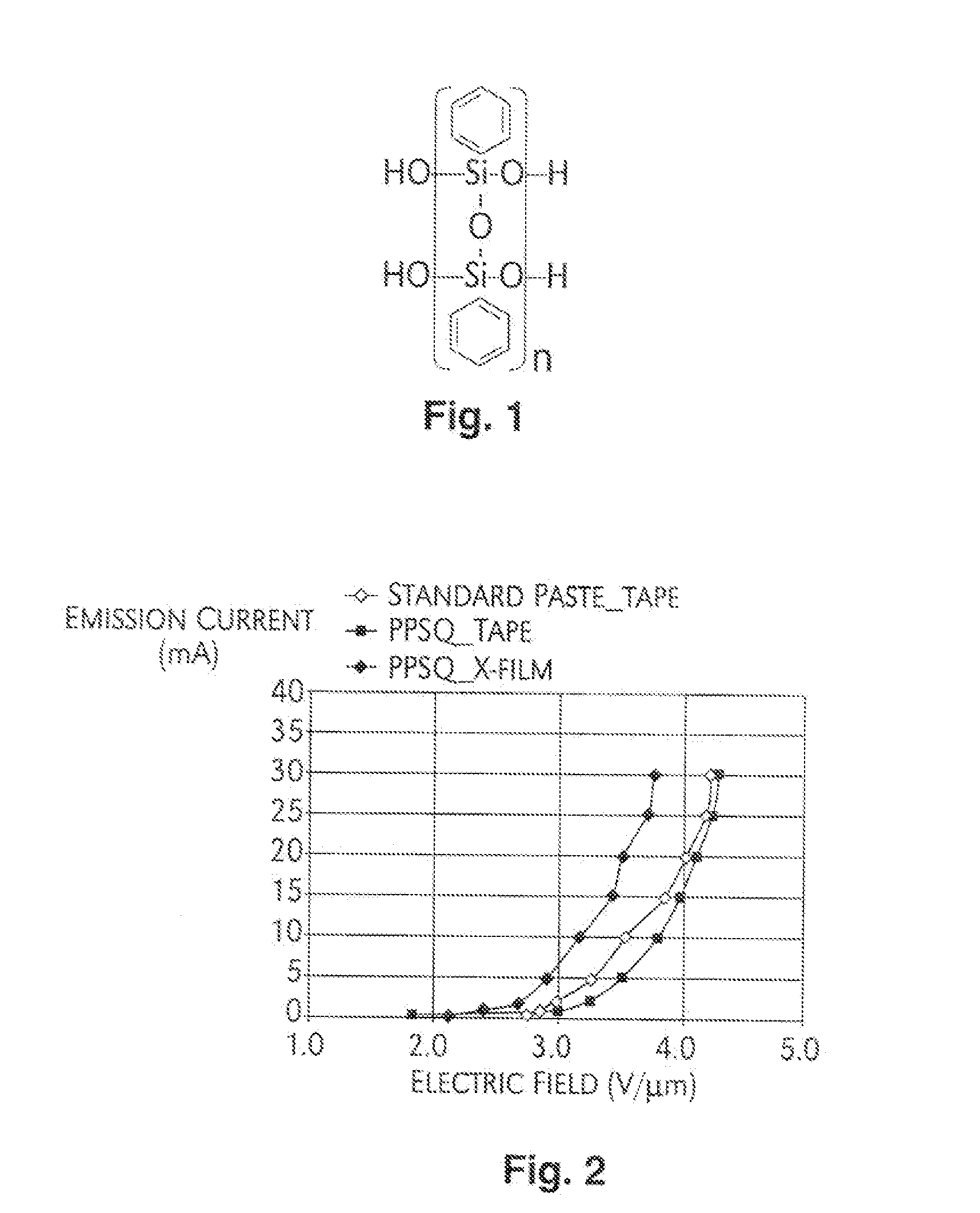
A binder material, inorganic polymer, is used to formulate carbon nanotube pastes. This material can be cured at 200° C. and has a thermal-stability up to 500° C. Low-out gassing of this binder material makes it a good candidate for long life field emission devices. Due to better adhesion with this binder material, a strong adhesive peelable polymer from liquid form can be applied on the CNT cathode to achieve a uniform activation with even contact and pressure on the surface. The peelable polymer films may be used both as an activation layer and a mask layer to fabricate high-resolution patterned carbon nanotube cathodes for field emission devices using lithographic processes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Photovoltaic fibers
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Electrode (anode and cathode) performance enhancement by composite formation with graphene oxide
ActiveUS20120100402A1Low and reduced matrix contentHigh matrix conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyBatteries circuit arrangementsFiberPerformance enhancement
Described is an electrode comprising and preferably consisting of electronically active material (EAM) in nanoparticulate form and a matrix, said matrix consisting of a pyrolization product with therein incorporated graphene flakes and optionally an ionic lithium source. Also described are methods for producing a particle based, especially a fiber based, electrode material comprising a matrix formed from pyrolized material incorporating graphene flakes and rechargeable batteries comprising such electrodes.
Owner:BELENOS CLEAN POWER HLDG
Method for preparing graphene oxide films and fibers
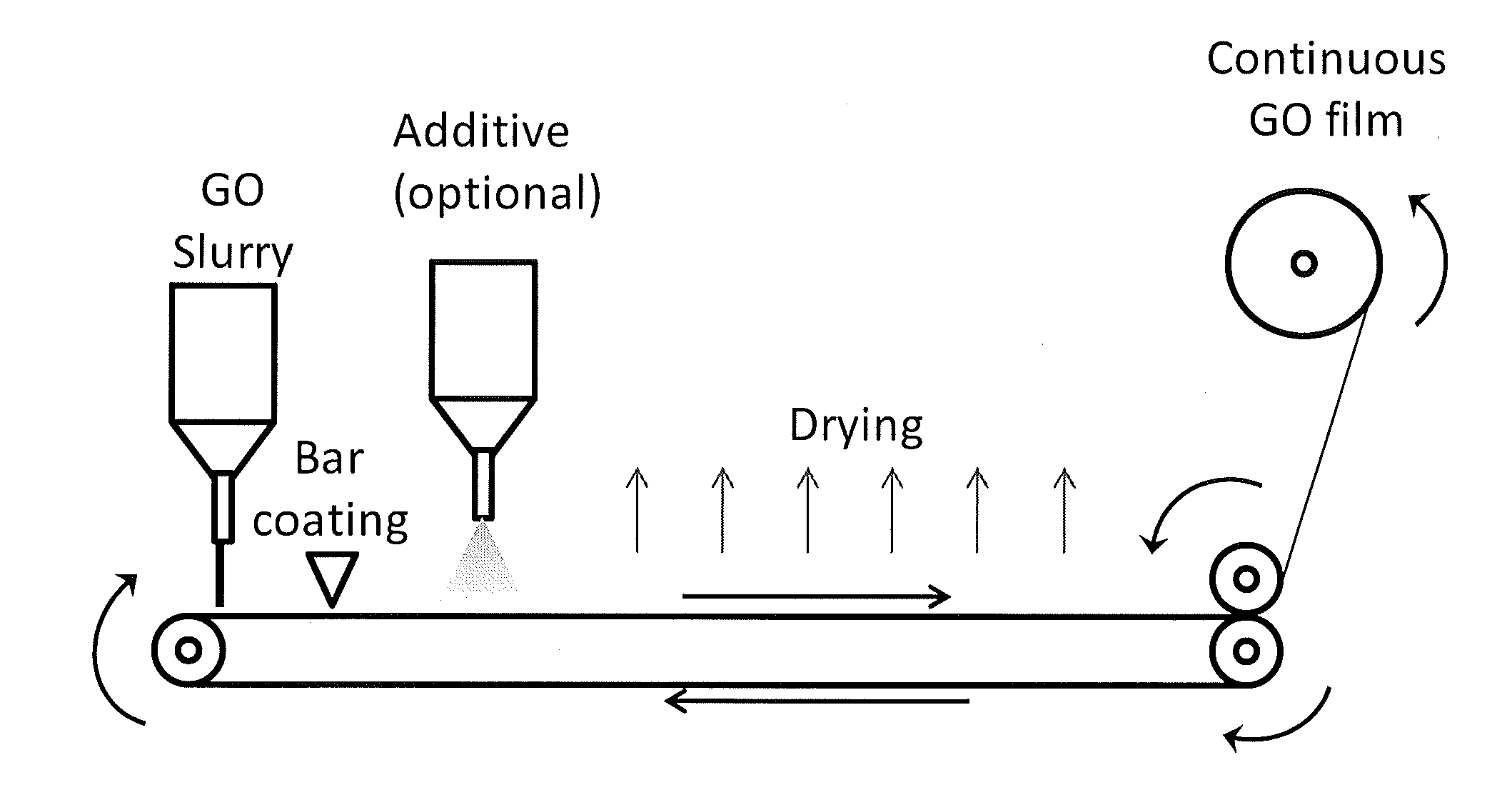
ActiveUS20150111449A1Improve conductivityHigh densityCarbon compoundsFilament/thread formingFiberSolid content
We report a method of preparation of highly elastic graphene oxide films, and their transformation into graphene oxide fibers and electrically conductive graphene fibers by spinning. Methods typically include: 1) oxidation of graphite to graphene oxide, 2) preparation of graphene oxide slurry with high solid contents and residues of sulfuric acid impurities. 3) preparation of large area films by bar-coating or dropcasting the graphene oxide dispersion and drying at low temperature. 4) spinning the graphene oxide film into a fiber, and 5) thermal or chemical reduction of the graphene oxide fiber into an electrically conductive graphene fiber. The resulting films and fiber have excellent mechanical properties, improved morphology as compared with current graphene oxide fibers, high electrical conductivity upon thermal reduction, and improved field emission properties.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Lithium transition metal oxide with gradient of metal composition
ActiveUS20060105239A1Improve electrochemical performanceIncrease energy densityCell electrodesManganese oxides/hydroxidesManganeseMaterials science
Disclosed are primary materials, precursor materials and final materials as well as methods to prepare these materials. The final materials are mixed lithium transition metal oxides, useful as performance optimized cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. The transition metal is a solid solution mixture of manganese, nickel and cobalt, M=(Mn1-uNiu)1-u-yCoy, with 0.2
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Polymeric marker with high radiopacity for use in medical devices
ActiveUS7303798B2Overcomes shortcomingEnhance wetting and adhesive and flow propertyMedical devicesDischarge tube main electrodesPolymer resinRadiopaque agent
High radiopacity is achieved in a polymeric marker by combining a polymeric resin, a powdered radiopaque agent having uniformly shaped particles of a specific particle size distribution and a wetting agent. The method to produce the marker calls for the blending and pelletization of these materials followed by extrusion onto support beading. The resulting supported tubing is subsequently cut to length with the beading still in place. After ejection of the beading remnant the marker is slipped into place on the device to be marked and attached by melt bonding. Marking of a guidewire allows lesions to be measured while the marking of balloon catheters allow the balloon to be properly positioned relative to a lesion.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
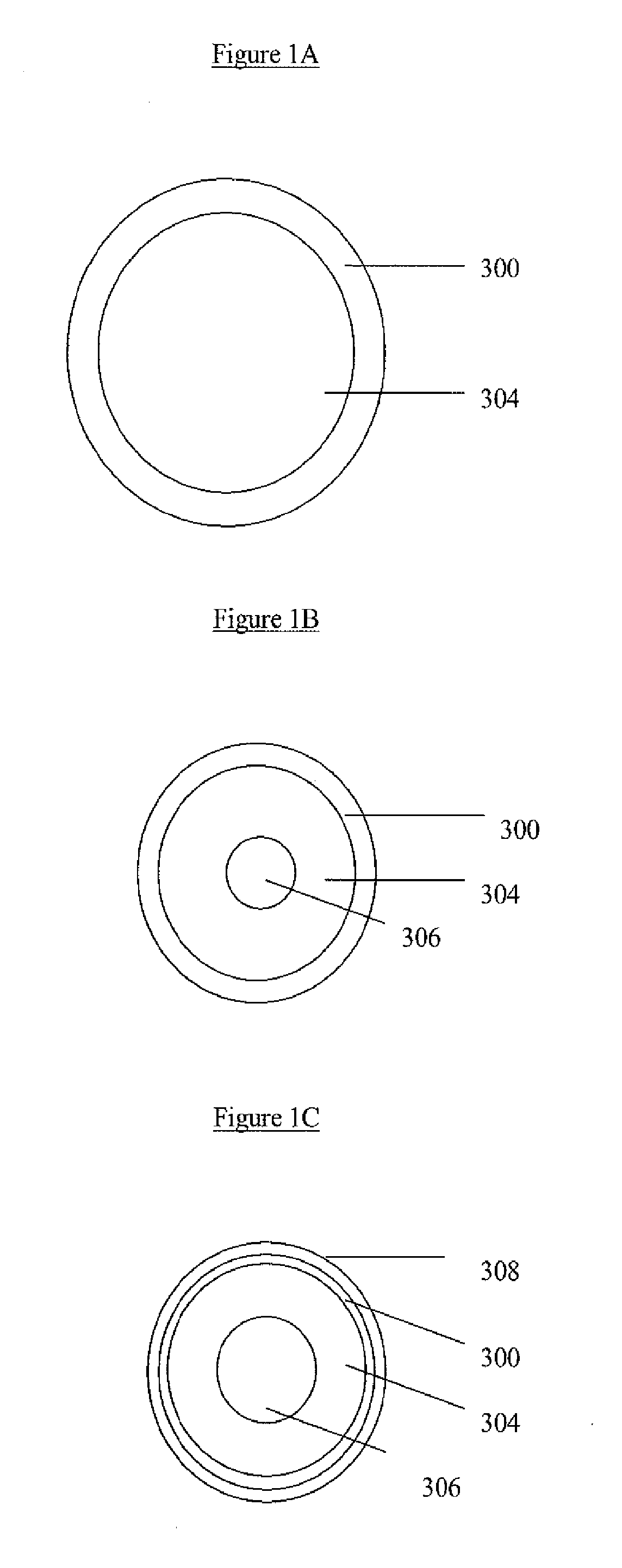
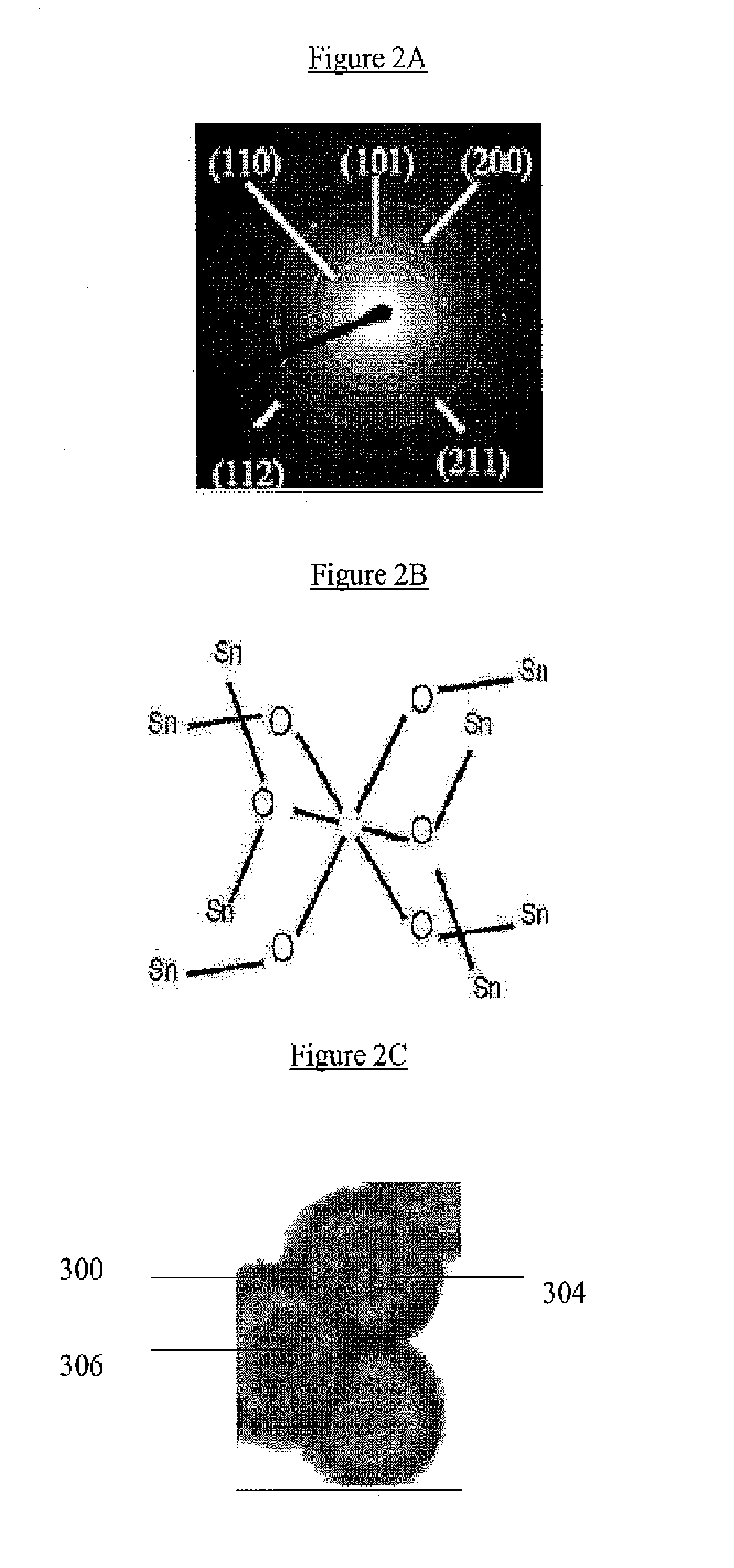
Nanostructured Metal Oxides Comprising Internal Voids and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20100258759A1Controllable sizeEasy to useMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsNanoparticleNanostructured metal
The present invention relates to nano structures of metal oxides having a nanostructured shell (or wall), and an internal space or void. Nanostructures may be nanoparticles, nanorod / belts / arrays, nanotubes, nanodisks, nanoboxes, hollow nanospheres, and mesoporous structures, among other nanostructures. The nanostructures are composed of polycrystalline metal oxides such as SnO2. The nanostructures may have concentric walls which surround the internal space of cavity. There may be two or more concentric shells or walls. The internal space may contain a core such ferric oxides or other materials which have functional properties. The invention also provides for a novel, inexpensive, high-yield method for mass production of hollow metal oxide nanostructures. The method may be template free or contain a template such as silica. The nanostructures prepared by the methods of the invention provide for improved cycling performance when tested using rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Metal oxide dispersion
ActiveUS20050069648A1Low costLess resourcesMolten spray coatingPhotosensitive materialsDispersed mediaMaterials science
The present invention relates to a metal oxide dispersion, which can form a metal thin film onto a substrate by heat treatment at a low temperature, wherein a metal oxide having a particle diameter of less than 200 nm is dispersed in the dispersion medium. By heat treating the dispersion after applying it onto a substrate, a metal thin film is formed.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Precipitated aragonite and a process for producing it
InactiveUS20030213937A1Less expensiveEfficient and less-expensiveCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsParticulatesAragonite
Disclosed is a novel form of particulate precipitated aragonite, and a novel process for producing it.
Owner:3P TECH
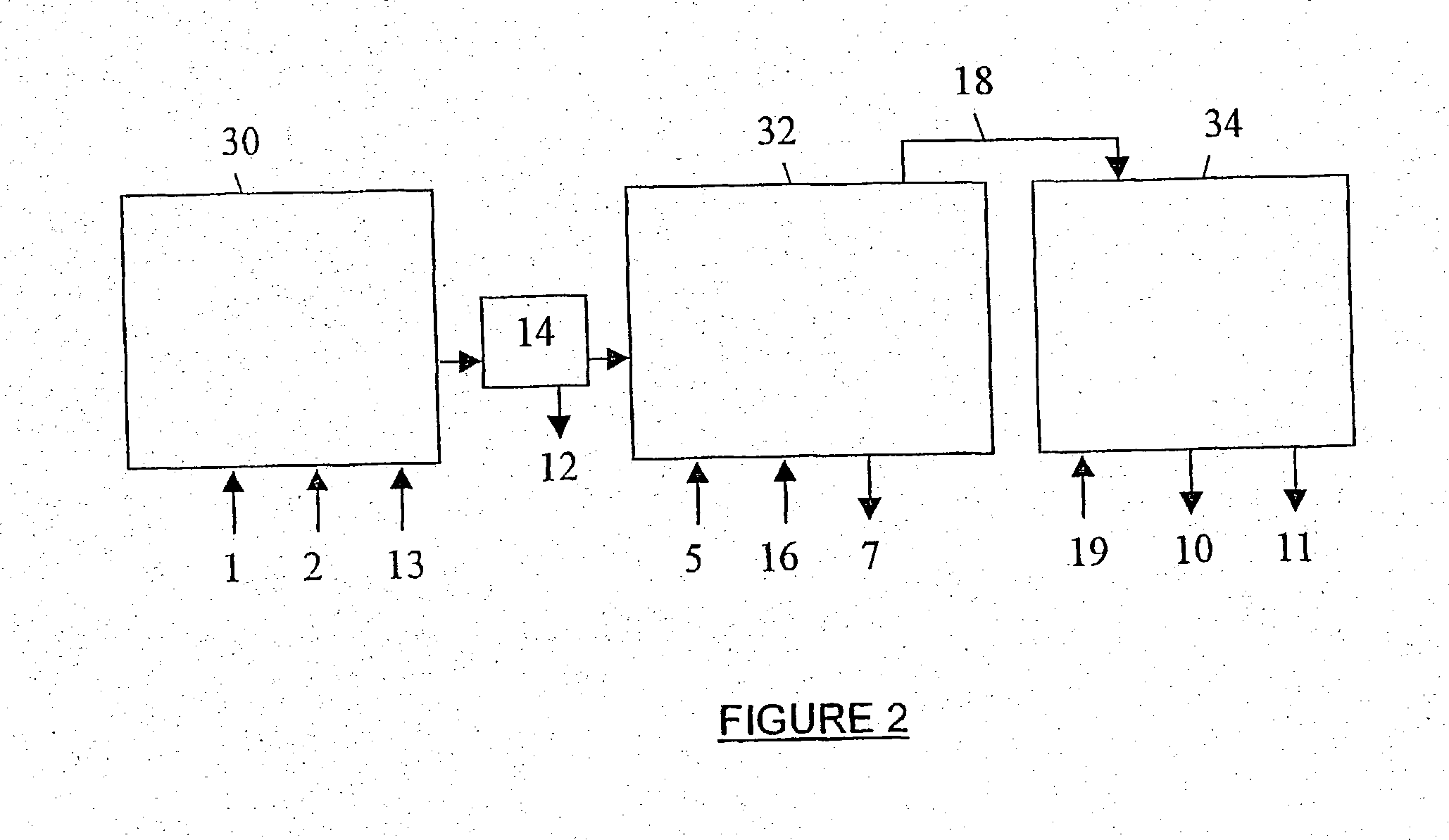
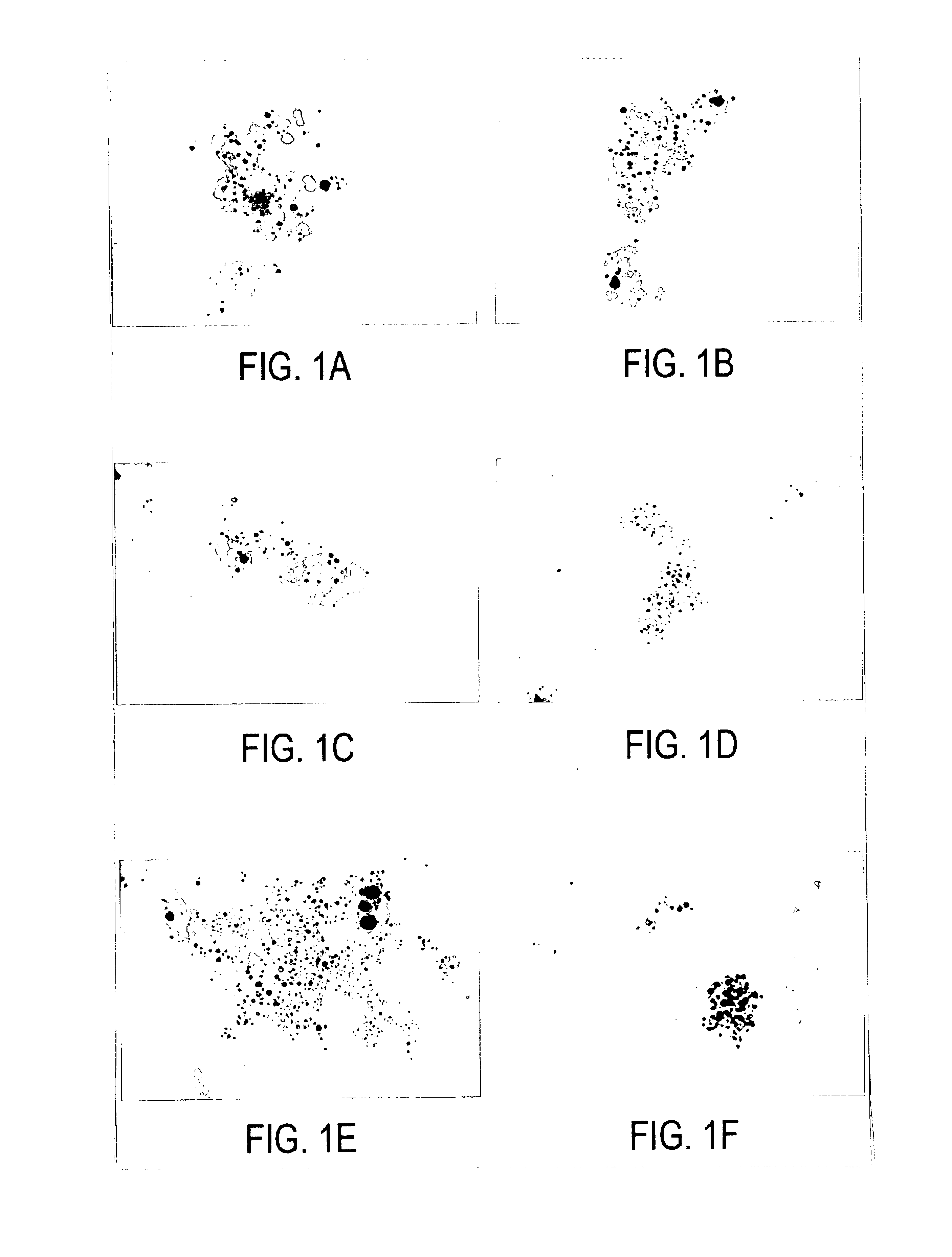
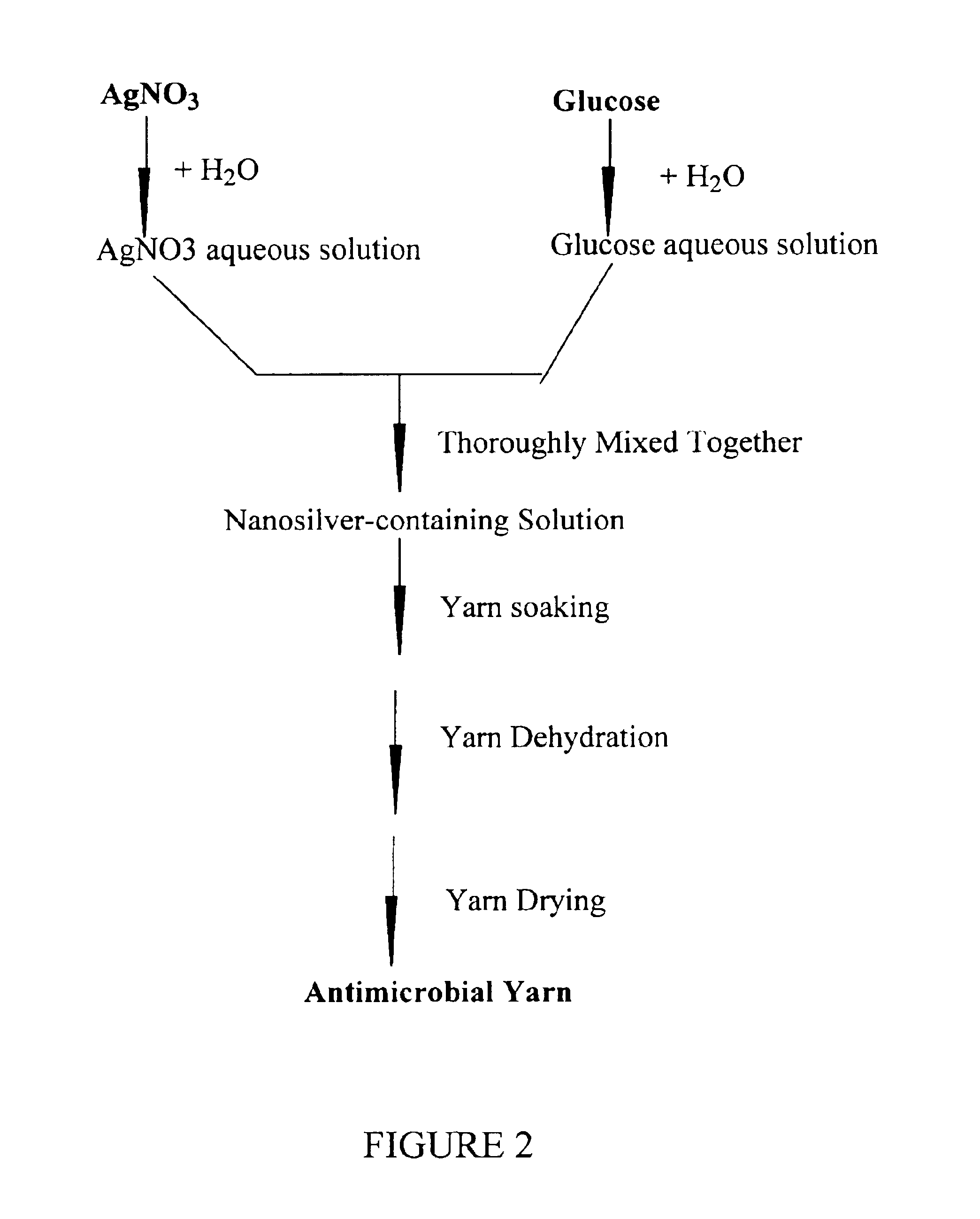
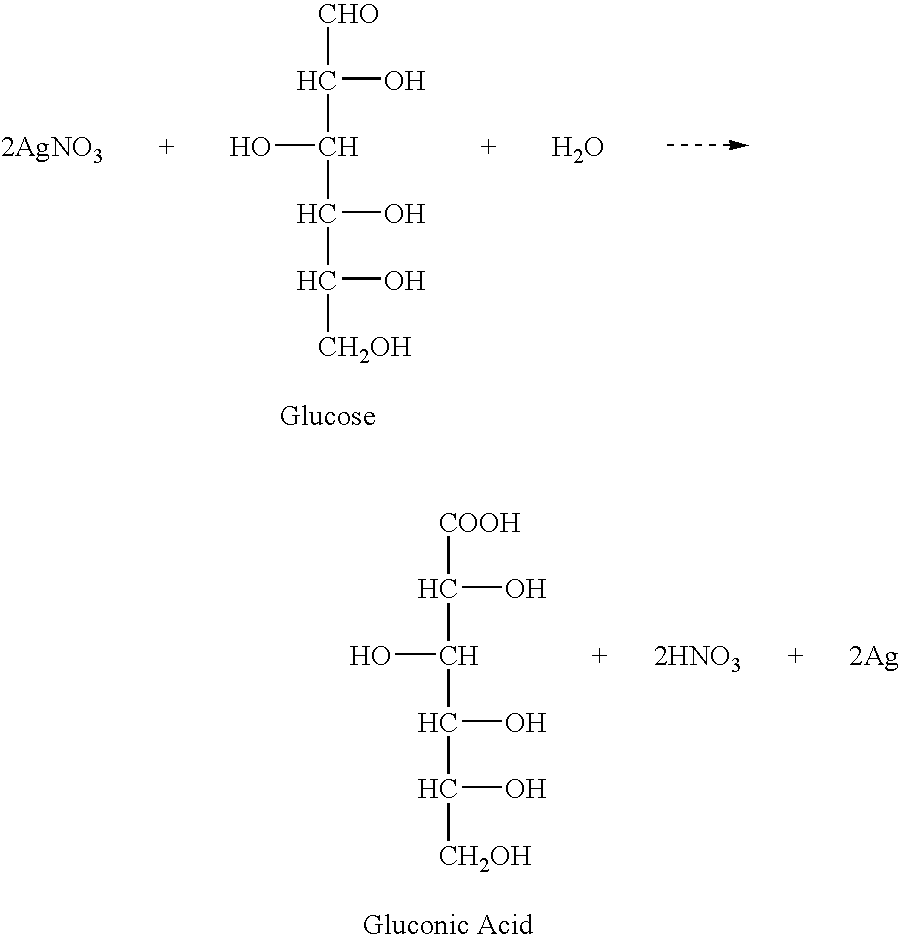
Antimicrobial yarn having nanosilver particles and methods for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6979491B2The process is simple and fastEasy to carryYarnConductive materialsYarnEngineering
The present invention provides a yarn with antimicrobial effects. The antimicrobial antifungal effect of the yarn is derived from nanosilver particles (diameter between 1 and 100 nm) which are adhered to the yarn. The yarn contains fibers which are made of cotton, linen, silk, wool, leather, blending fabric, synthetic fiber, or any combination thereof. The yarn can be used to make cloth to be used particularly for treating patients with burns or wound. The cloth made from the antimicrobial yarn can be further used to make clothes such as underwears, socks, shoe cushions, shoe linings, bed sheets, pillow cases, towels, women hygiene products, laboratory coats, and medical robes. The present invention also provides a method for making the antimicrobial yarn.
Owner:CC TECH INVESTMENT
Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality
ActiveUS7985424B2Increase productionSimple materialPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsCross-linkChemical reaction
Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality are disclosed. These dendritic polymers are made by use of fast, reactive ring-opening chemistry (or other fast reactions) combined with the use of branch cell reagents in a controlled way to rapidly and precisely build dendritic structures, generation by generation, with cleaner chemistry, often single products, lower excesses of reagents, lower levels of dilution, higher capacity method, more easily scaled to commercial dimensions, new ranges of materials, and lower cost. The dendritic compositions prepared have novel internal functionality, greater stability (e.g., thermal stability and less or no reverse Michael's reaction), and reach encapsulation surface densities at lower generations. Unexpectedly, these reactions of polyfunctional branch cell reagents with polyfunctional cores do not create cross-linked materials. Such dendritic polymers are useful as demulsifiers for oil / water emulsions, wet strength agents in the manufacture of paper, proton scavengers, polymers, nanoscale monomers, calibration standards for electron microscopy, making size selective membranes, and agents for modifying viscosity in aqueous formulations such as paint. When these dendritic polymers have a carried material associated with their surface and / or interior, then these dendritic polymers have additional properties for carrying materials due to the unique characteristics of the dendritic polymer, such as for drug delivery, transfection, and diagnostics.
Owner:DENDRITIC NANO TECH INC
Solution-based fabrication of photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20080135812A1Improve overall utilizationLow costMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleSolar cell
An ink for forming CIGS photovoltaic cell active layers is disclosed along with methods for making the ink, methods for making the active layers and a solar cell made with the active layer. The ink contains a mixture of nanoparticles of elements of groups IB, IIIA and (optionally) VIA. The particles are in a desired particle size range of between about 1 nm and about 500 nm in diameter, where a majority of the mass of the particles comprises particles ranging in size from no more than about 40% above or below an average particle size or, if the average particle size is less than about 5 nanometers, from no more than about 2 nanometers above or below the average particle size. The use of such ink avoids the need to expose the material to an H2Se gas during the construction of a photovoltaic cell and allows more uniform melting during film annealing, more uniform intermixing of nanoparticles, and allows higher quality absorber films to be formed.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com