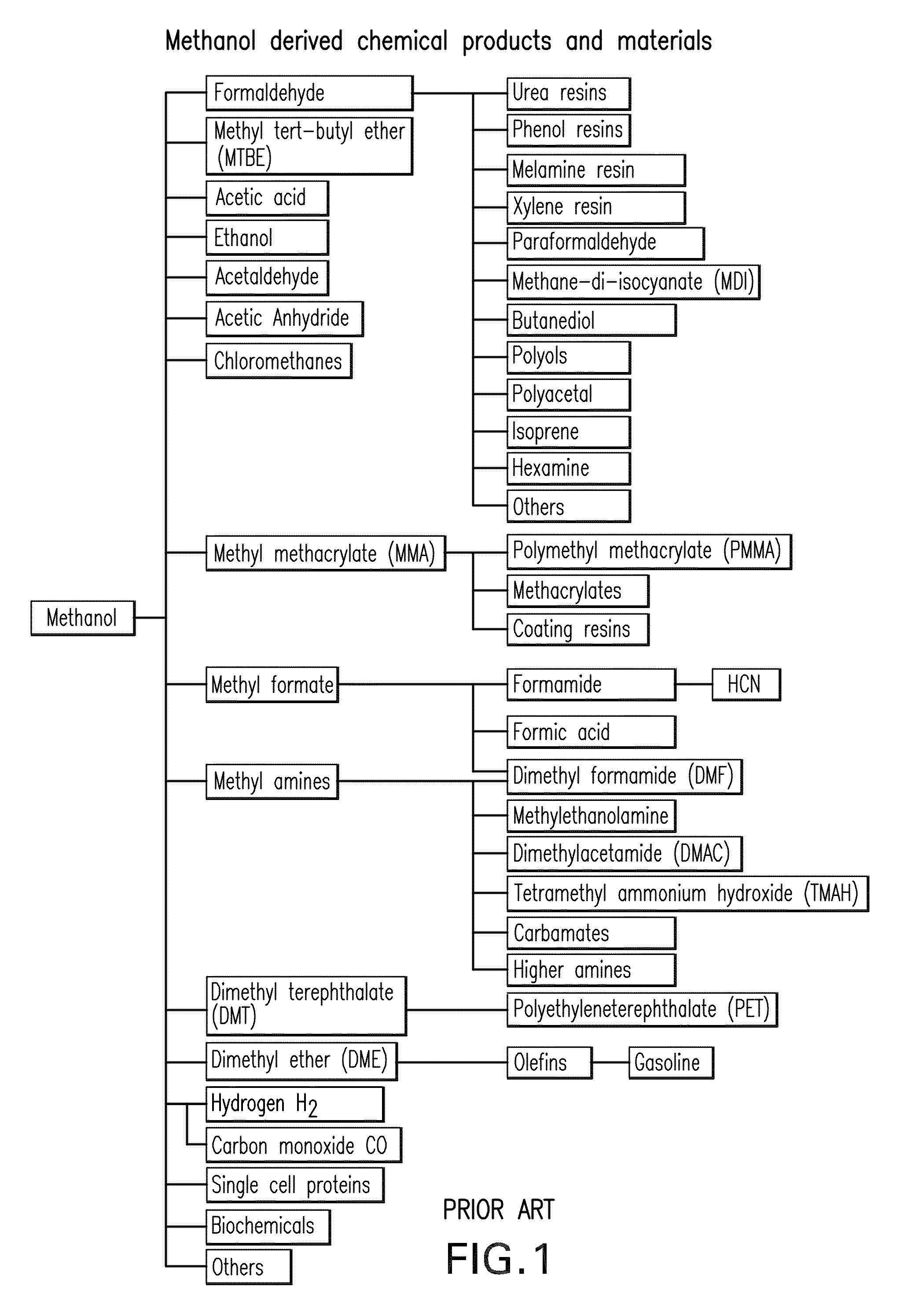
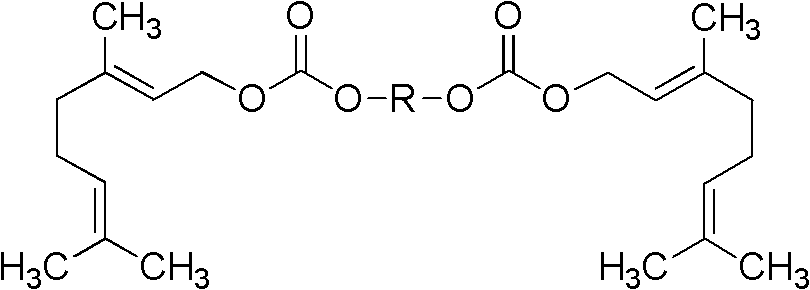
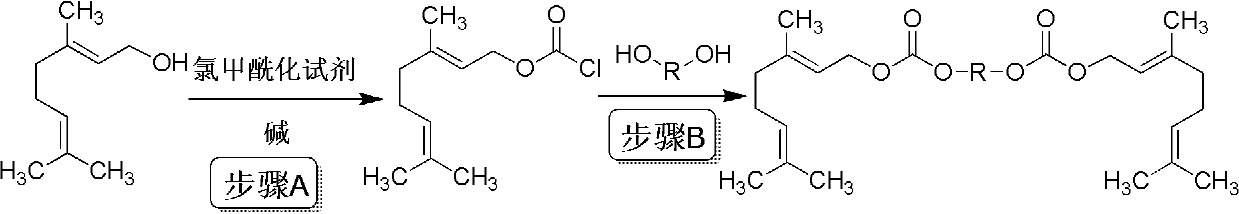
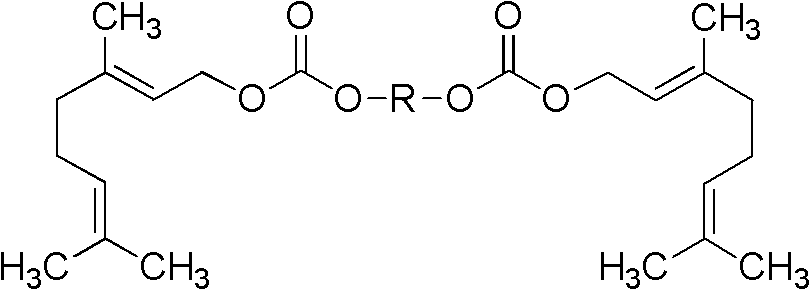
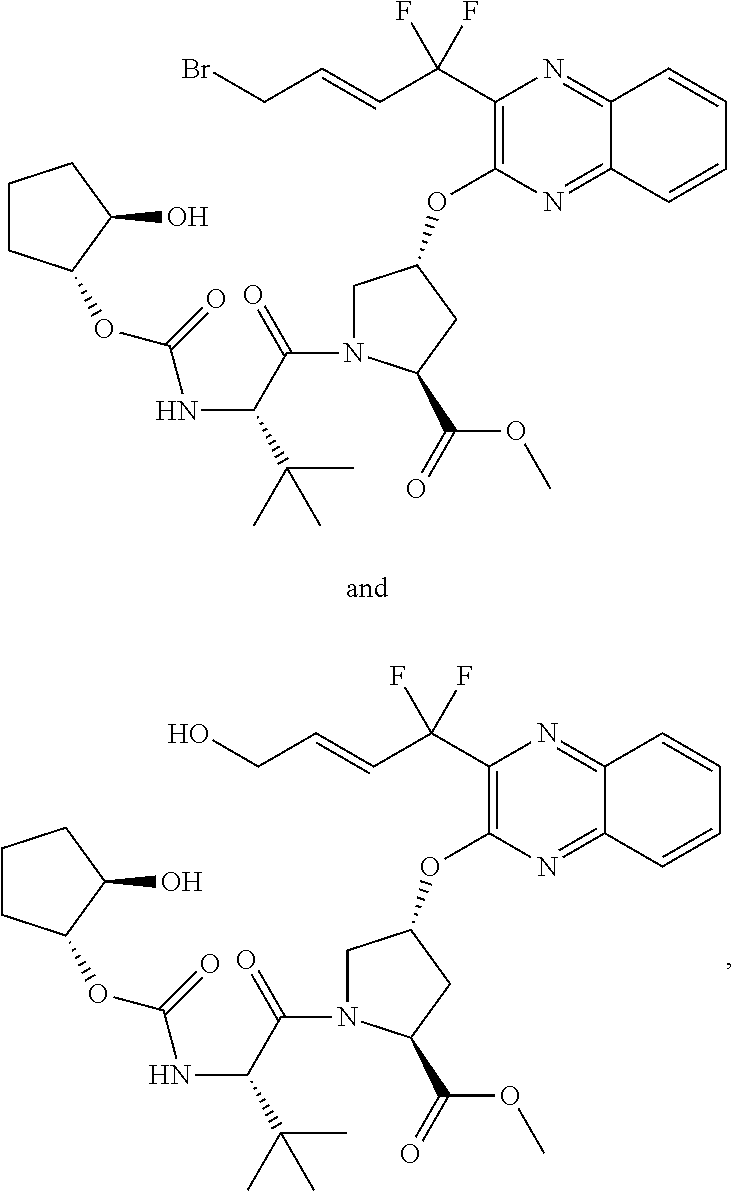
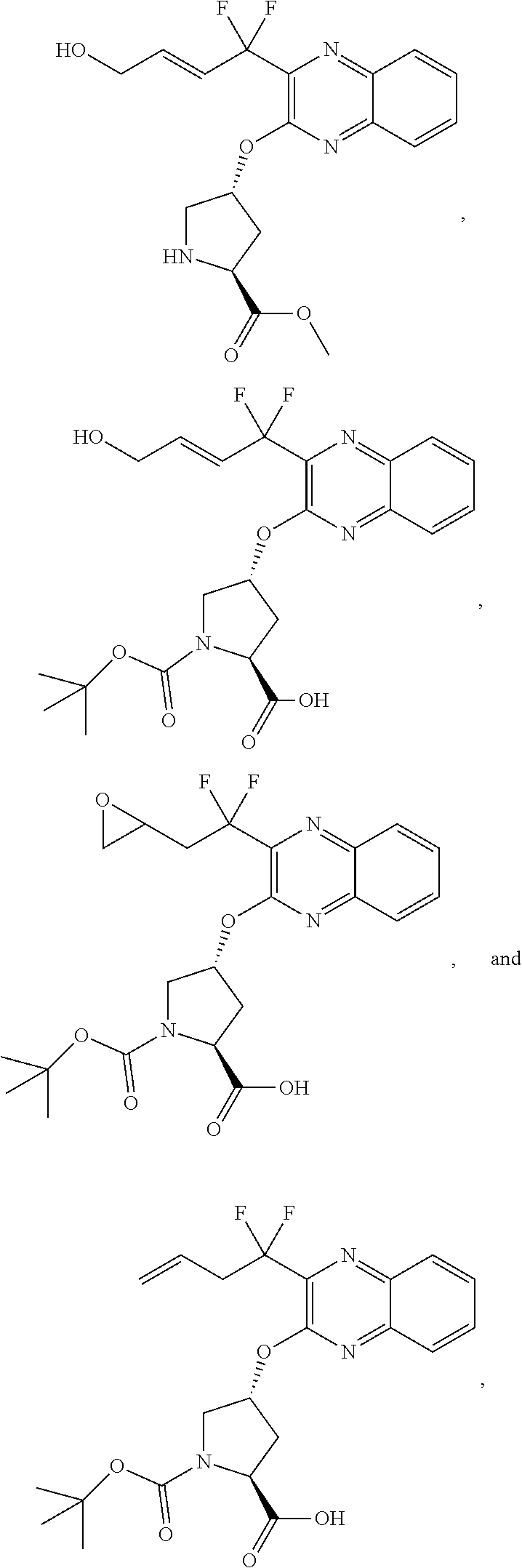
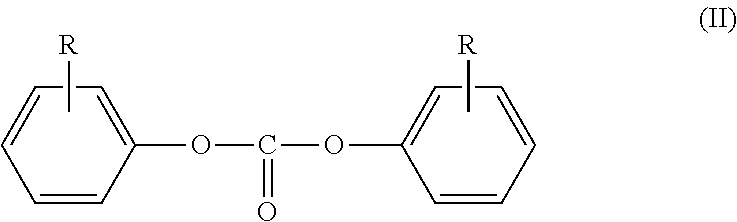
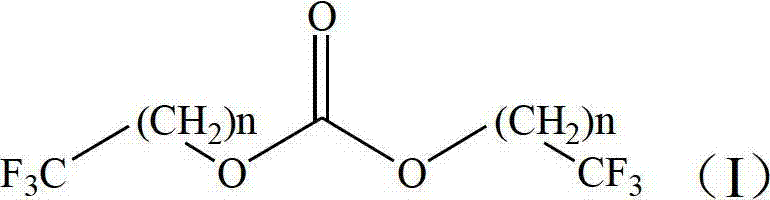
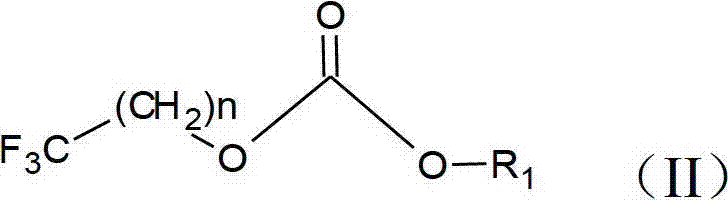
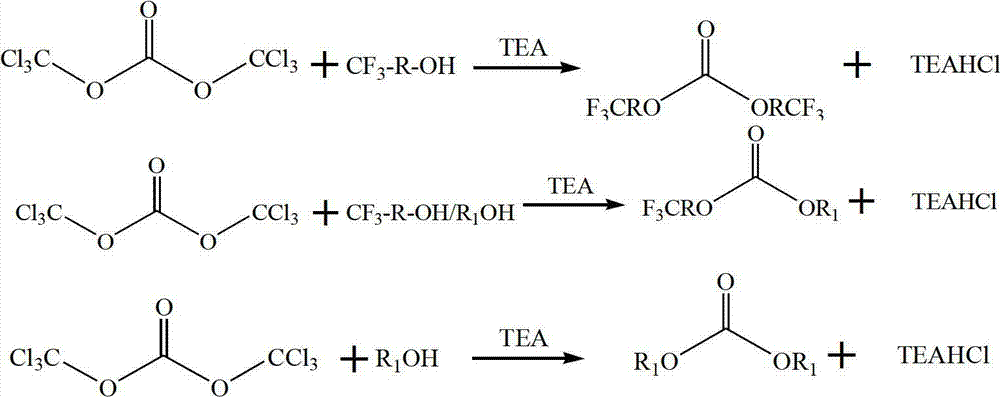
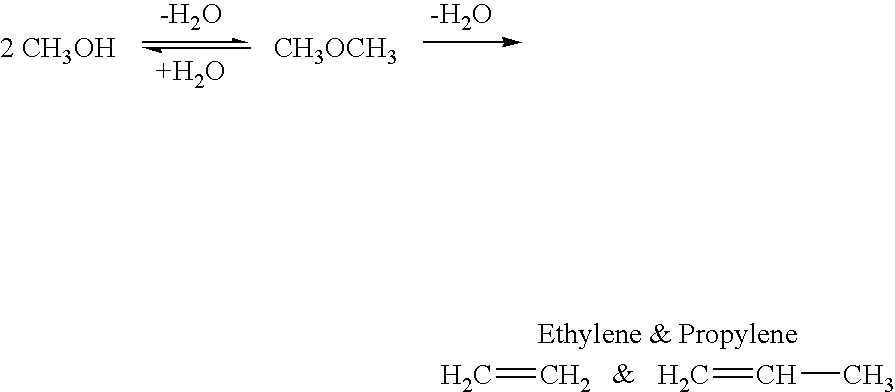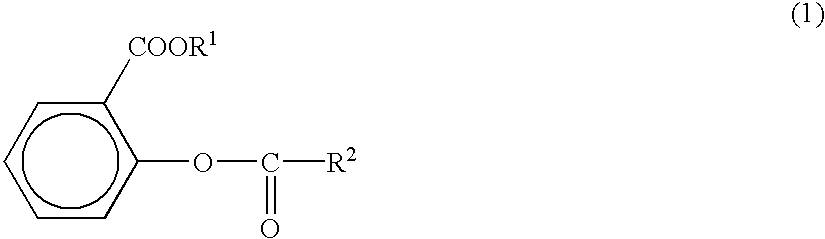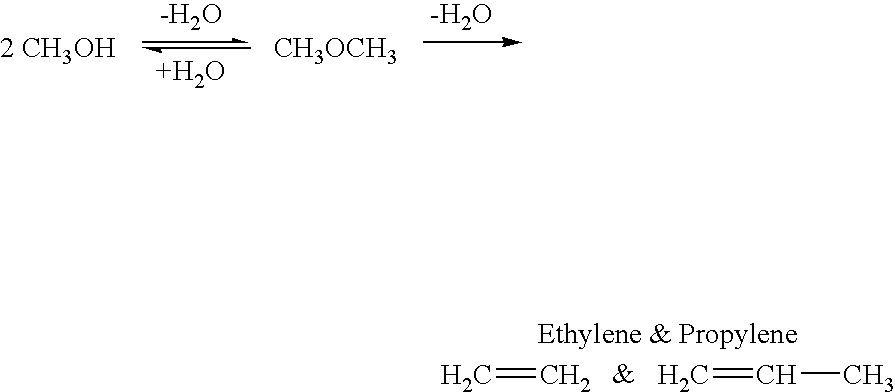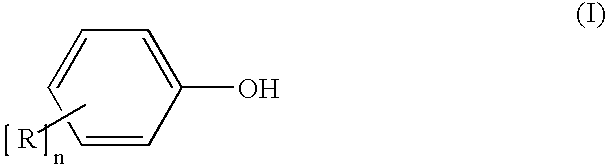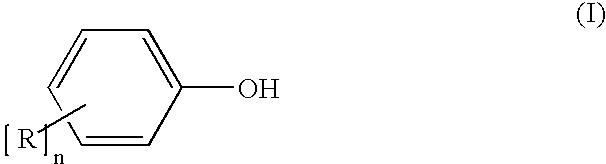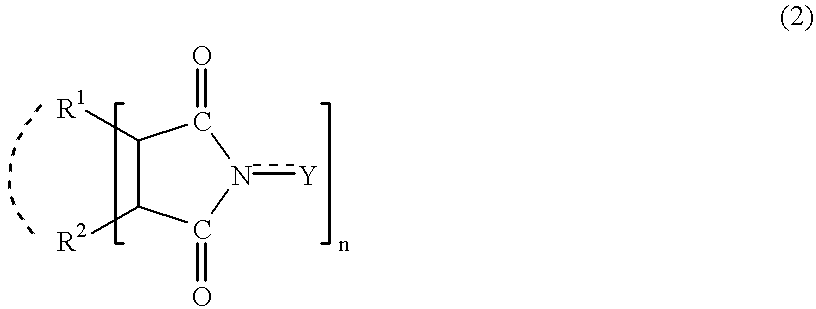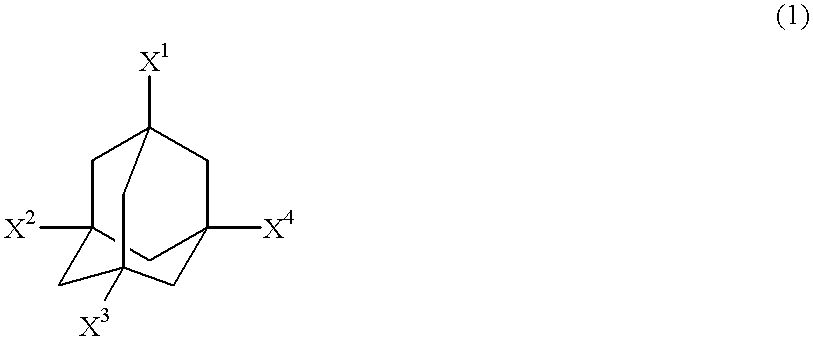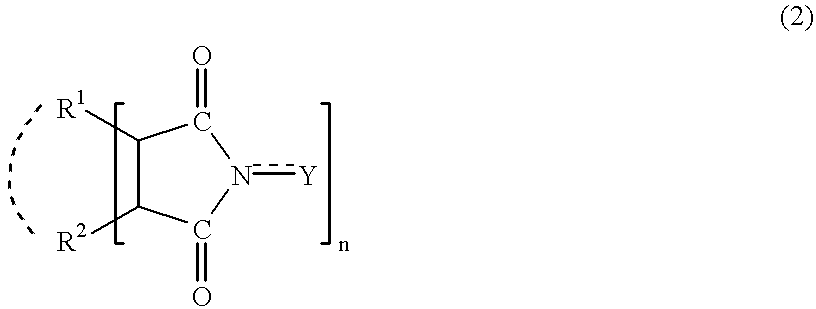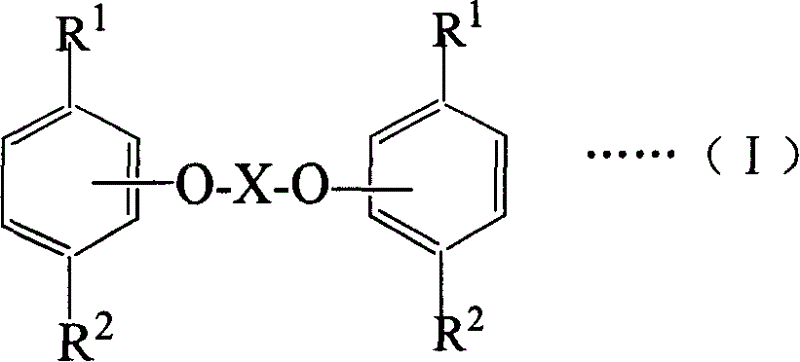Patents
Literature
206results about "Preparation from phosgene or haloformates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
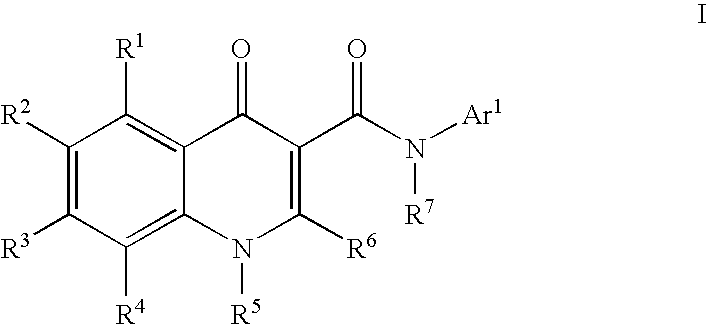
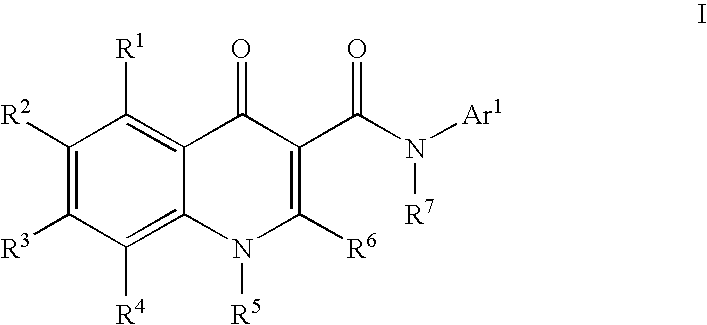
Modulators of ATP-binding cassette transporters
ActiveUS7495103B2Cosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseATP-binding cassette transporter
The present invention relates to modulators of ATP-Binding Cassette (“ABC”) transporters or fragments thereof, including Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator, compositions thereof, and methods therewith. The present invention also relates to methods of treating ABC transporter mediated diseases using such modulators.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Modulators of ATP-binding cassette transporters
ActiveUS20060074075A1Organic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsDiseaseATP-binding cassette transporter
The present invention relates to modulators of ATP-Binding Cassette (“ABC”) transporters or fragments thereof, including Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator, compositions thereof, and methods therewith. The present invention also relates to methods of treating ABC transporter mediated diseases using such modulators.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
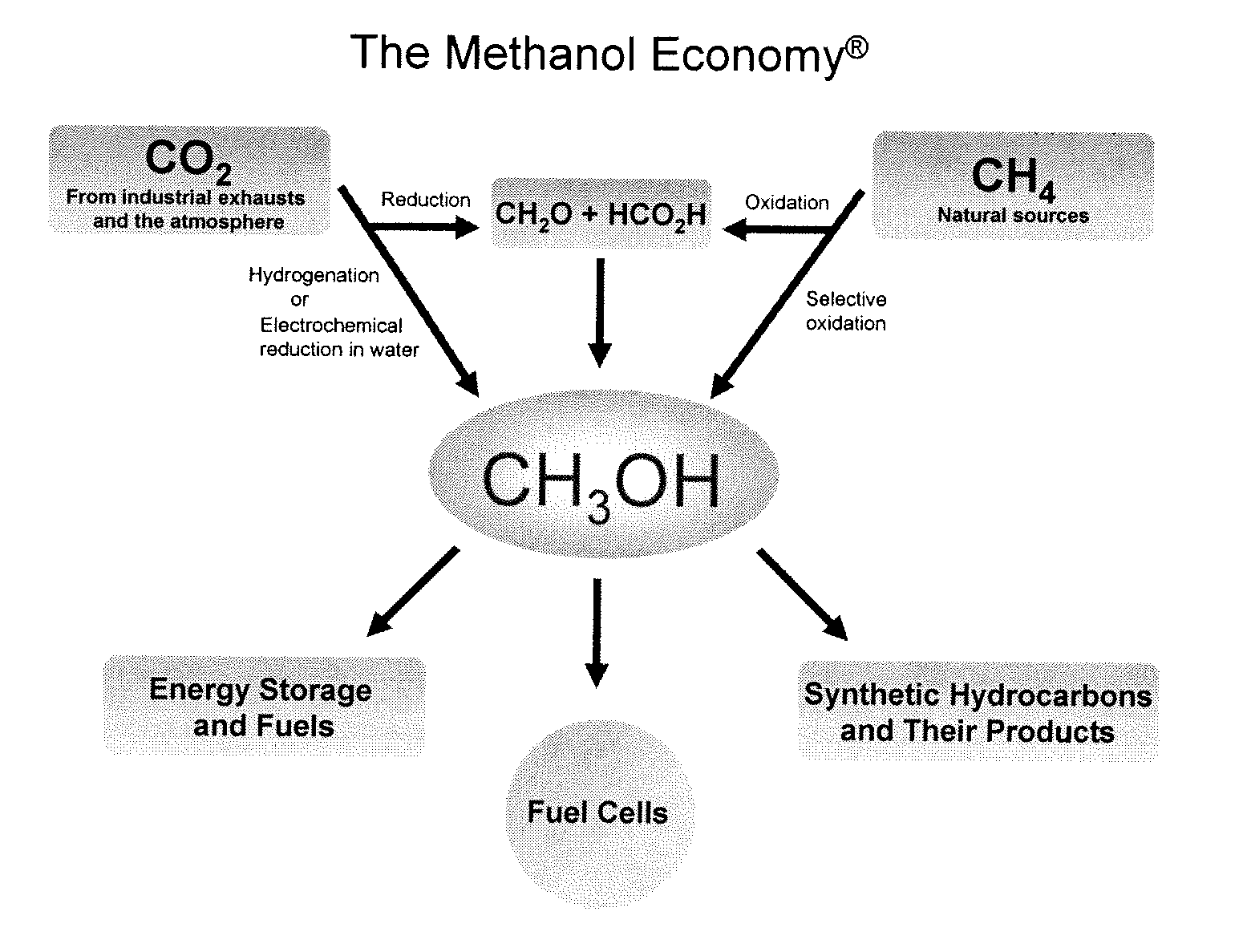
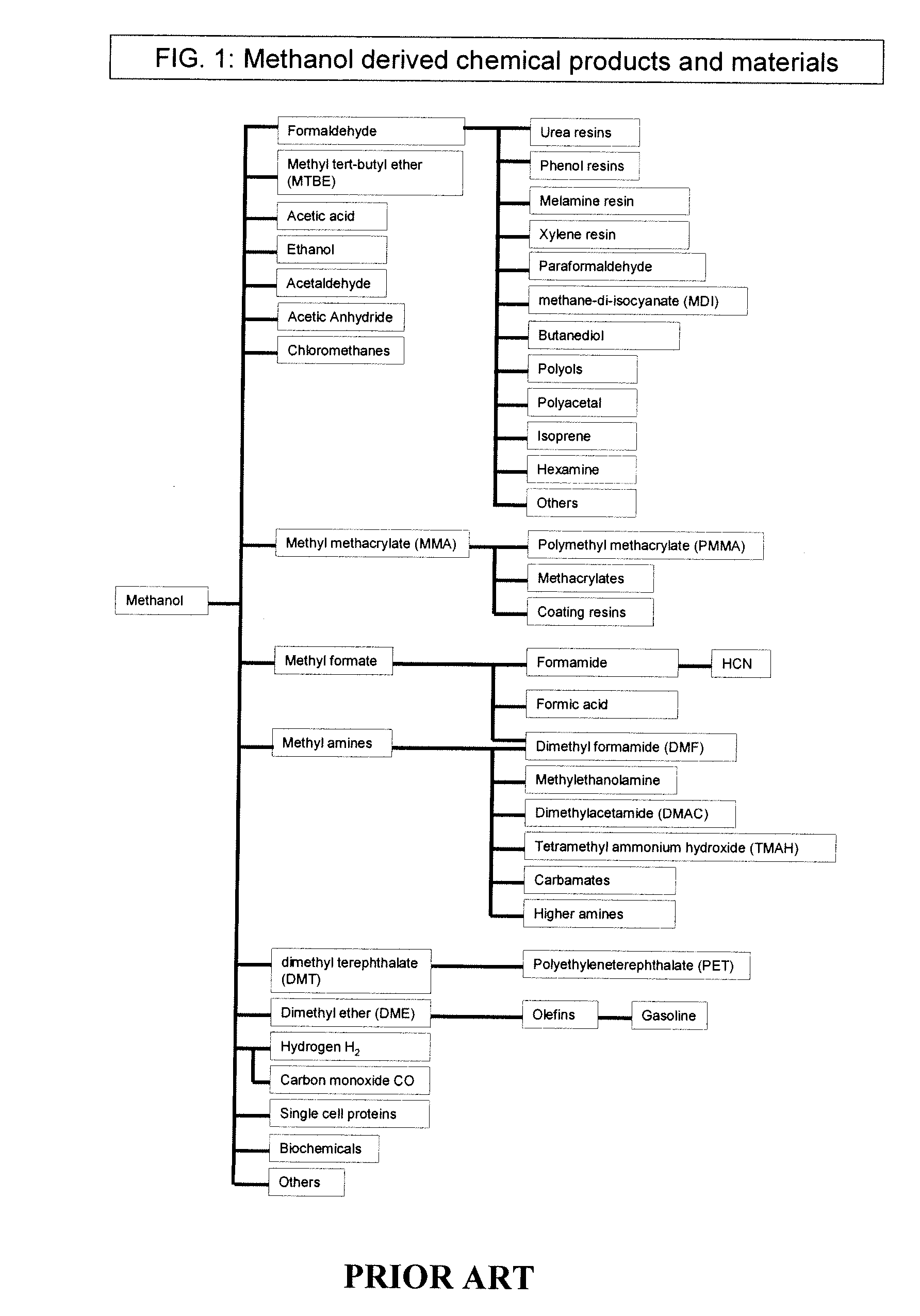
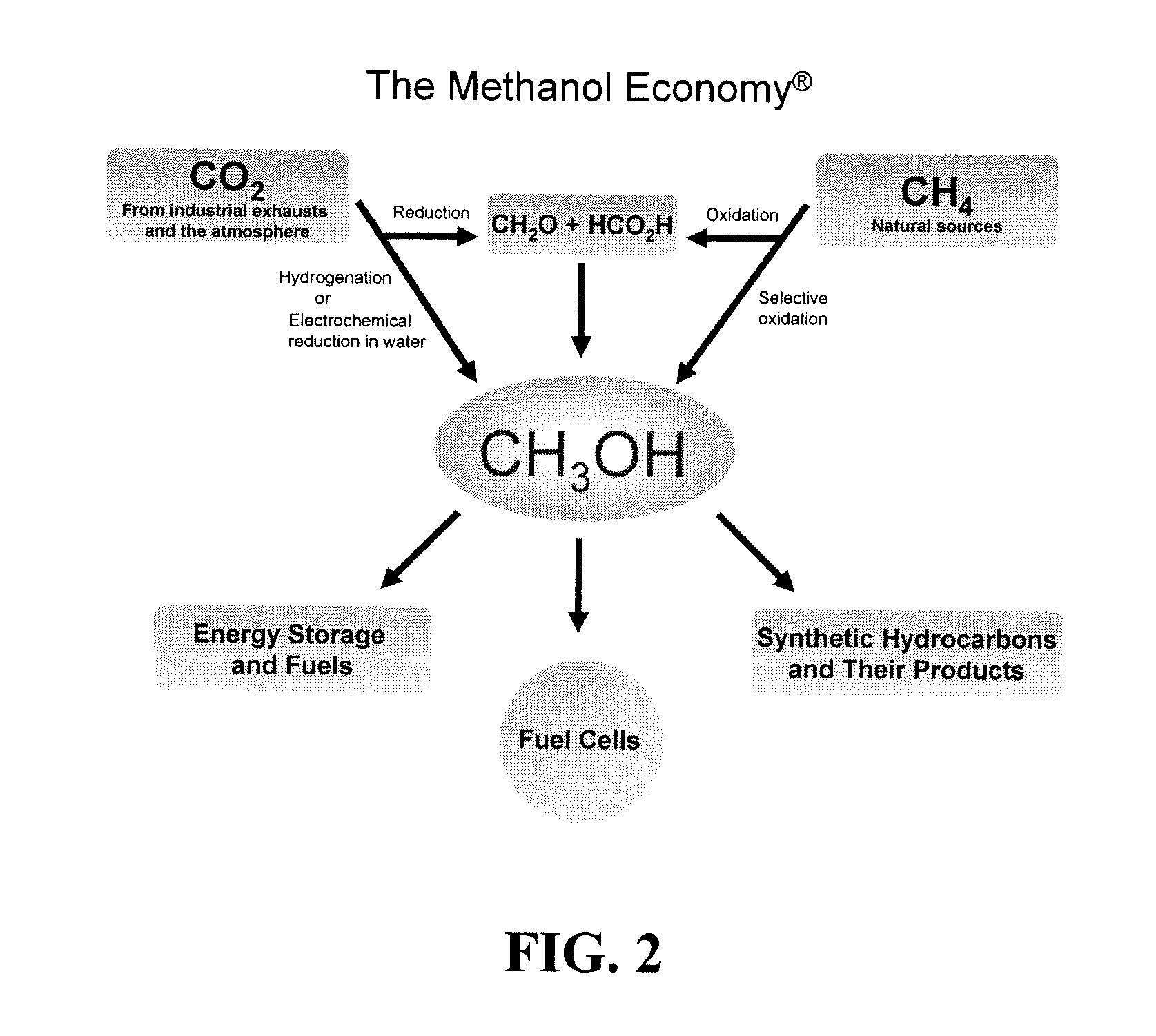
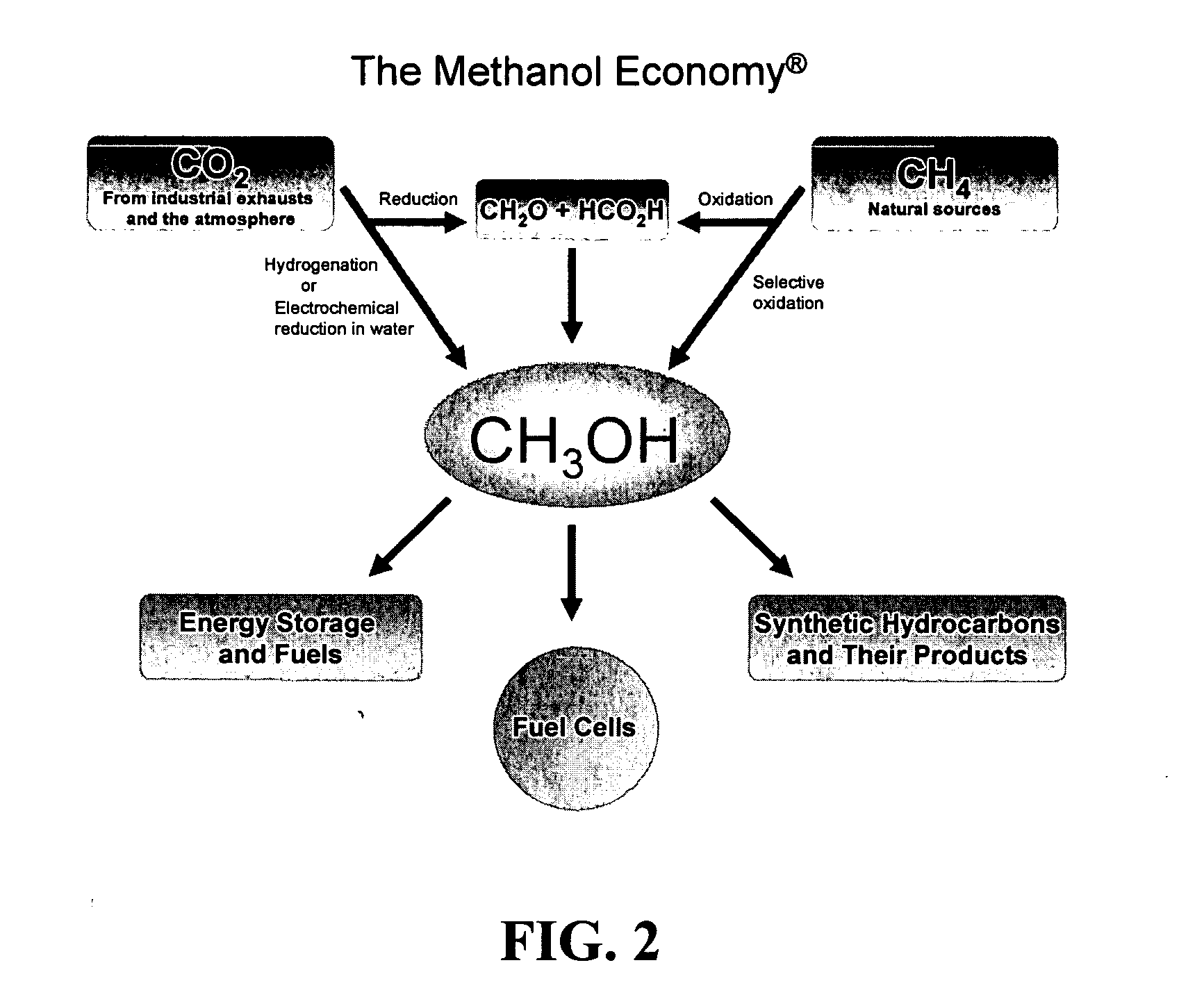
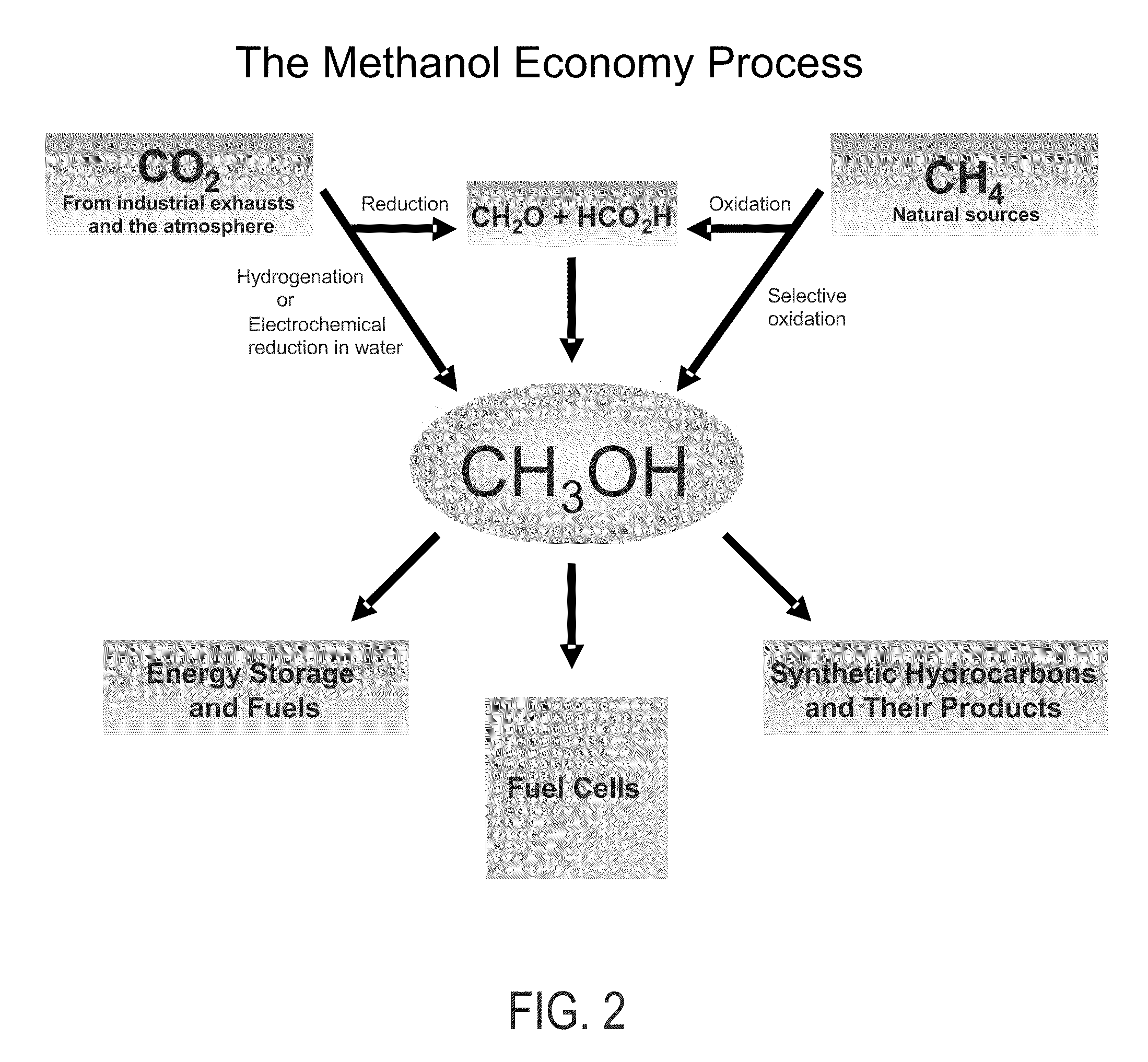
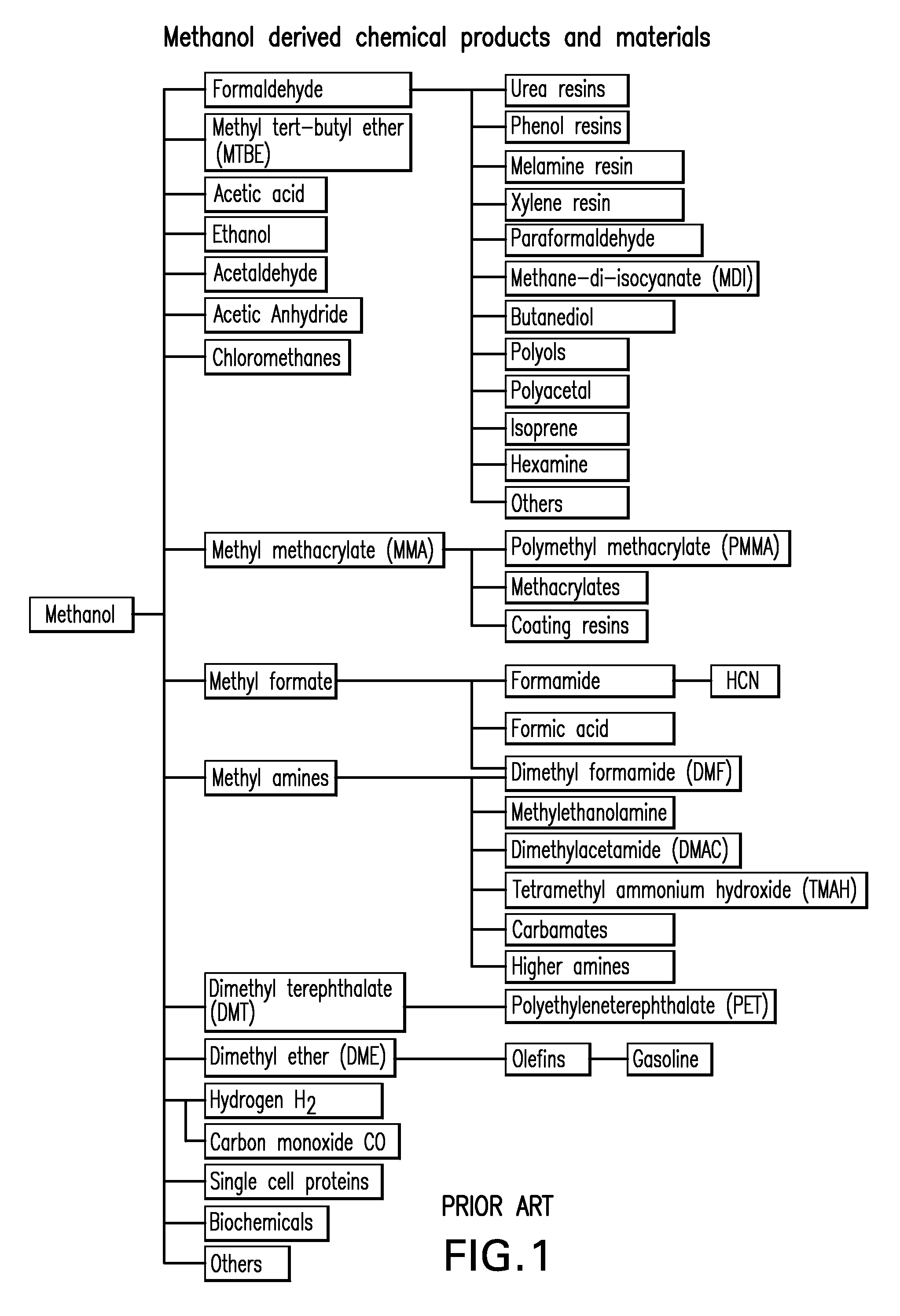
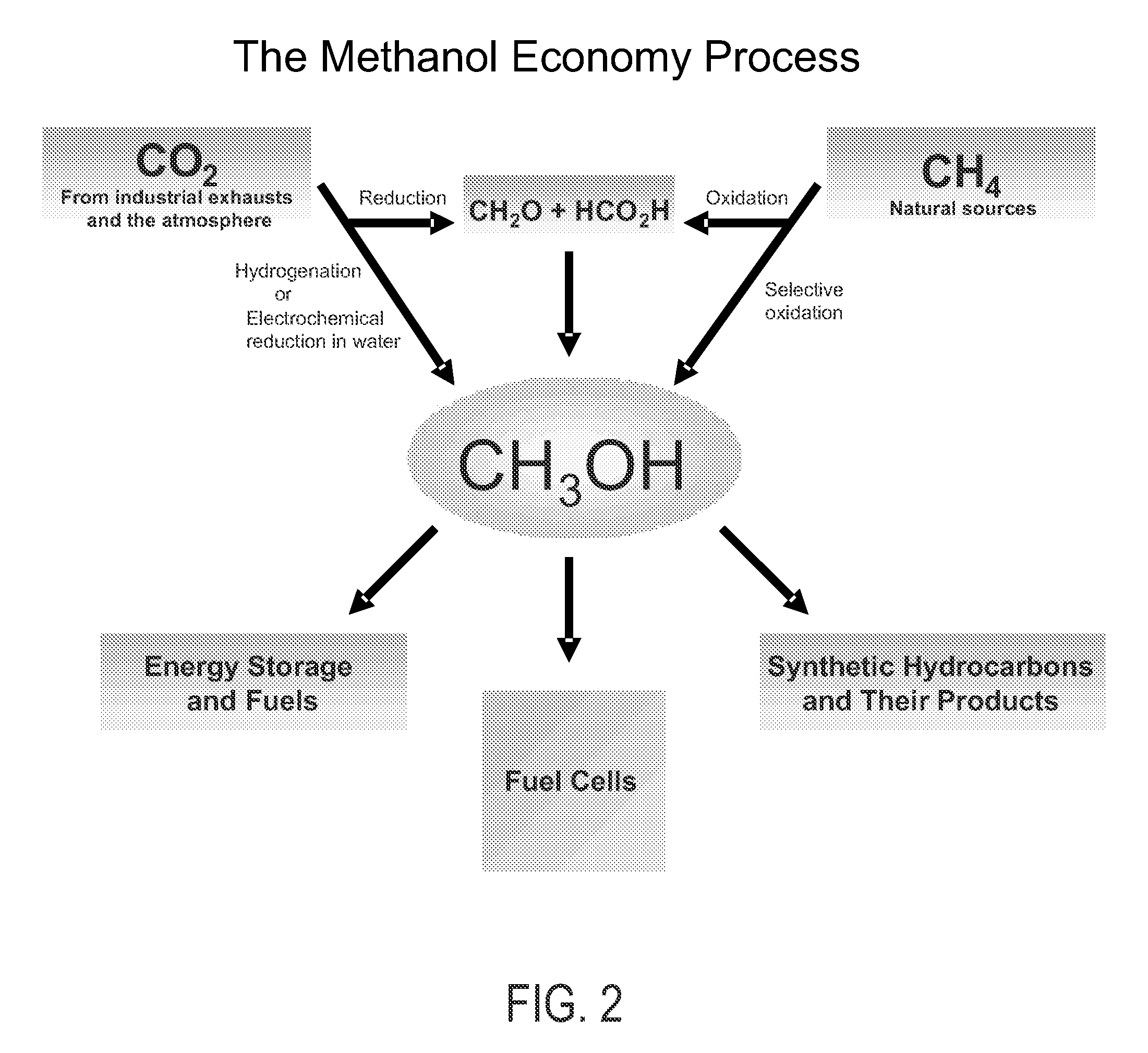
Efficient and selective chemical recycling of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20070254969A1Avoid emissionsElectrolysis componentsOxygen compounds purification/separationElectrochemistryDimethyl ether
An efficient and environmentally beneficial method of recycling and producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by chemical or electrochemical reduction secondary treatment to produce essentially methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Efficient and selective conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20060235091A1Minimize or eliminate the disadvantages or dangers inherentElectrolysis componentsCarbon compoundsHydrogenFlue gas
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by electrochemical reduction produces formic acid acid and some formaldehyde and methanol mixtures. The formic acid can be used as source of carbon as well as hydrogen to produce methanol, dimethyl ether and other products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Modulators of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters
ActiveUS20080071095A1Cosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
The present invention relates to modulators of ATP-Binding Cassette (“ABC”) transporters or fragments thereof, including Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator, compositions thereof, and methods therewith. The present invention also relates to methods of treating ABC transporter mediated diseases using such modulators.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
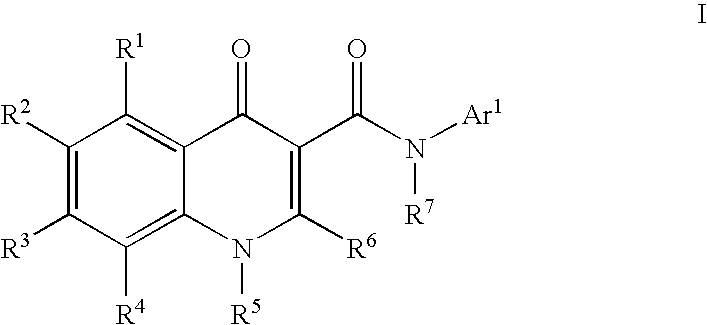
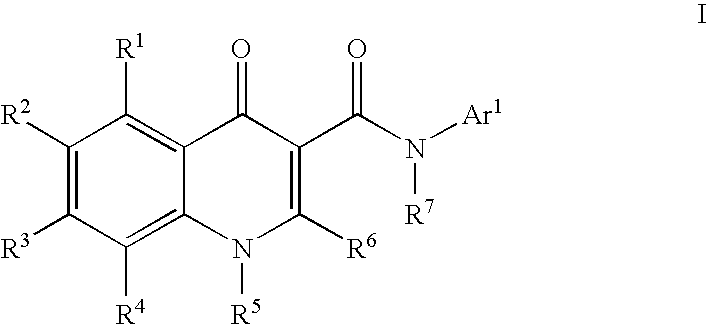
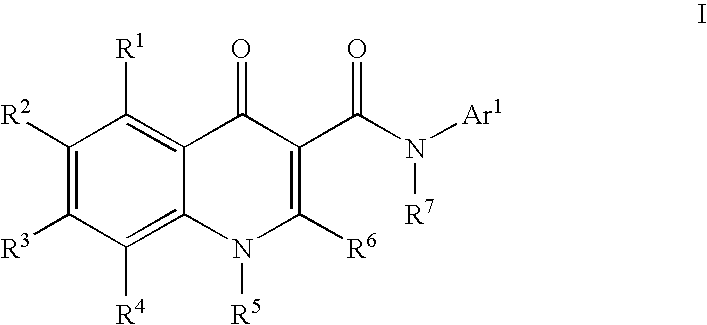
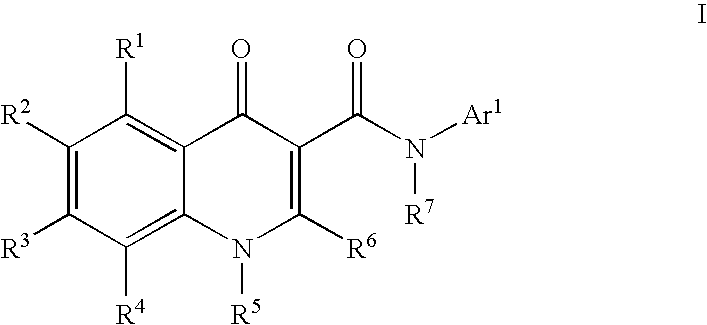
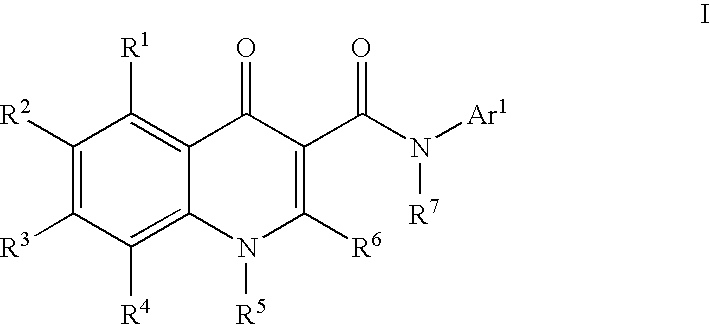
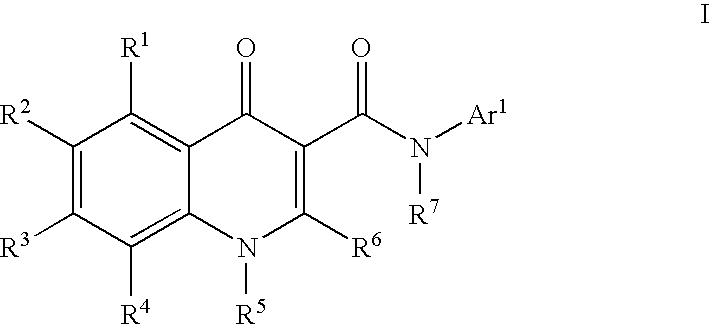
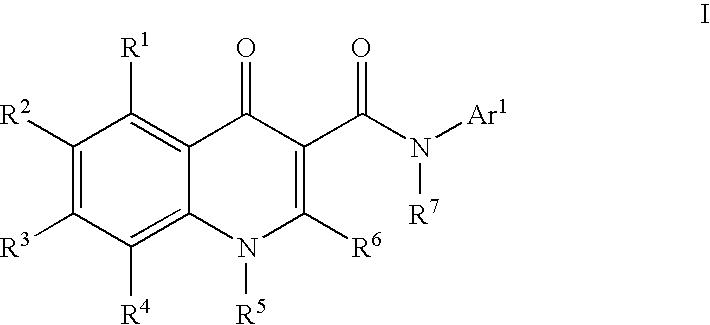
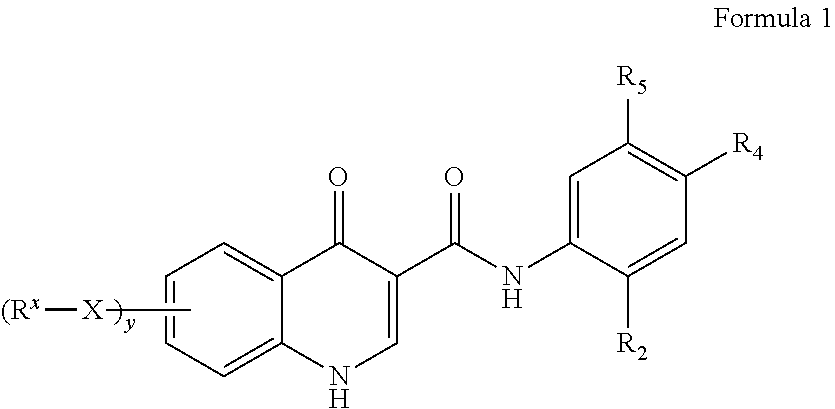
Process for making modulators of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
InactiveUS20120122921A1Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderCarboxylic acidCystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
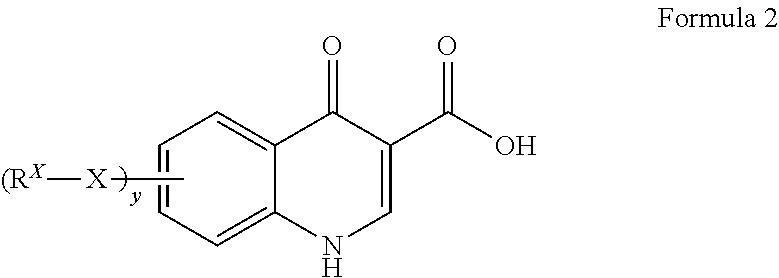
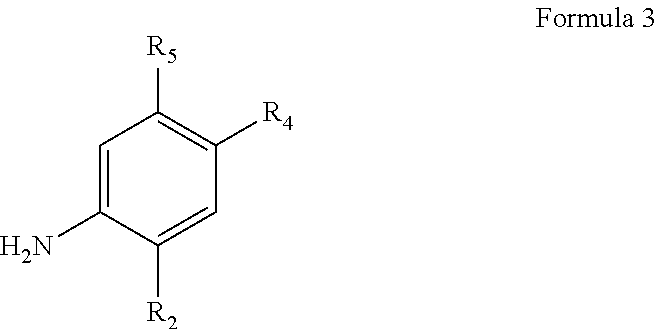
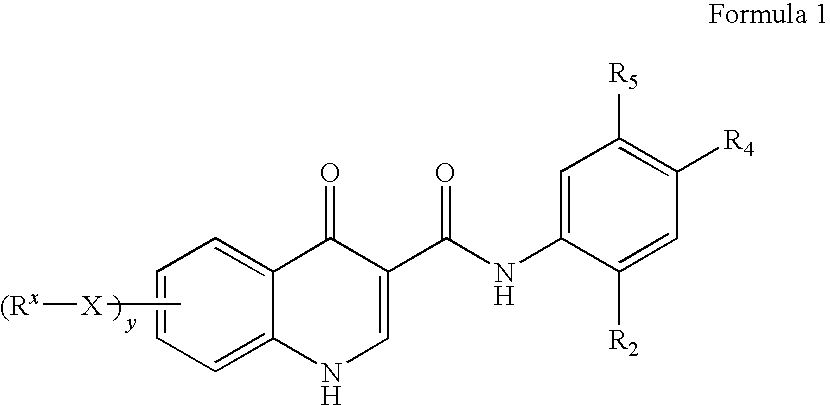
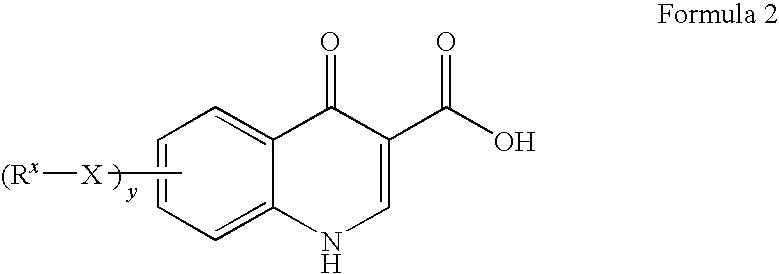
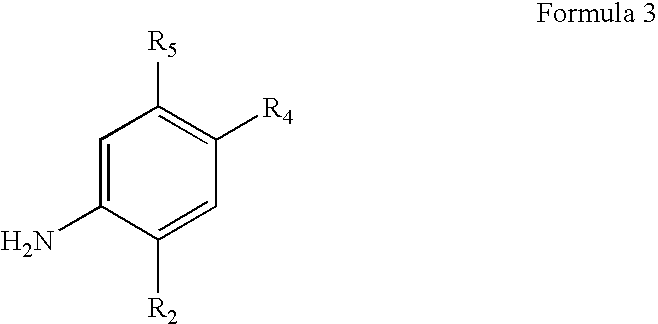
The invention provides a process for the preparation of a compound of Formula 1,comprising coupling a carboxylic acid of Formula 2with an aniline of Formula 3in the presence of a coupling agent.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Process for making modulators of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
ActiveUS20100267768A1Lower the volumeOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCarboxylic acidCystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
The invention provides a process for the preparation of a compound of Formula 1,comprising coupling a carboxylic acid of Formula 2with an aniline of Formula 3in the presence of a coupling agent.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
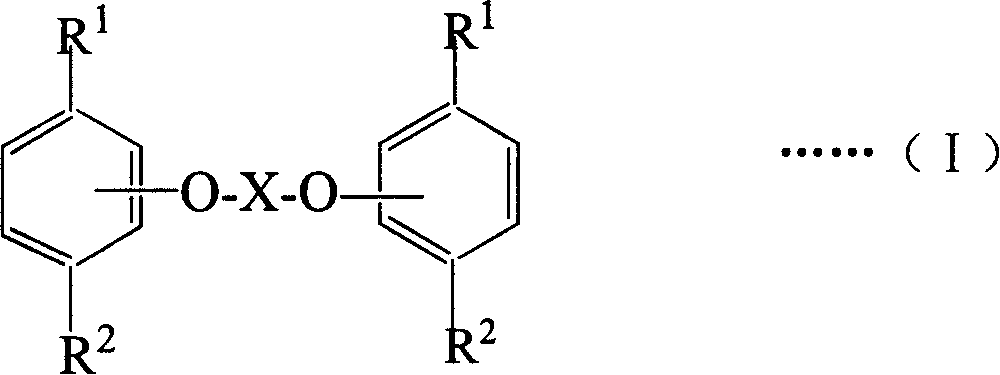
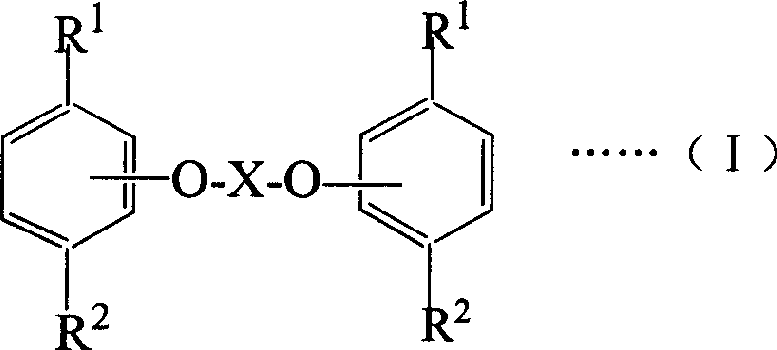
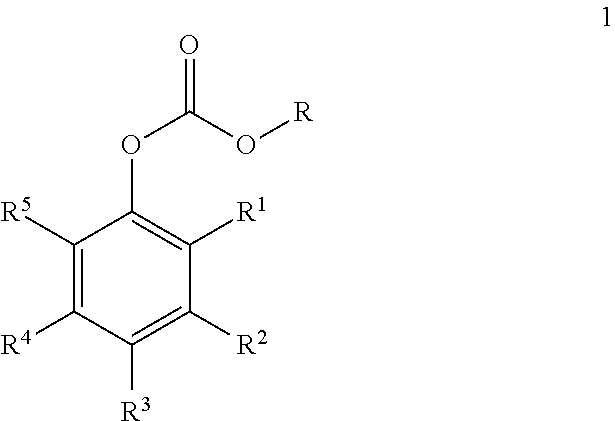
Salicylic acid ester derivative and its production
InactiveUS6410777B1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationArylSalicylic acid ester
The present invention provides a salicylic acid ester derivative having an impurity content lower than a specific level and expressed by the following formula (1)(in the formula, R1 is methyl group or ethyl group, R2, which may be substituted optionally, is an alkyl group having a carbon number of from 1 to 30, alkoxy group having a carbon number of from 1 to 30, aryl group having a carbon number of from 6 to 30, aryloxy group having a carbon number of from 6 to 30, aralkyl group having a carbon number of from 6 to 30 or aralkyloxy group having a carbon number of from 6 to 30). The salicylic acid ester derivative is effective as a terminal blocking agent or a polymerization. promoting agent for a polycarbonate, and gives a polycarbonate having good color tone and suitable for optical material use.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Efficient and selective conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS7605293B2Minimize or eliminate the disadvantages or dangers inherentElectrolysis componentsCarbon compoundsHydrogenFlue gas
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by electrochemical reduction produces formic acid acid and some formaldehyde and methanol mixtures. The formic acid can be used as source of carbon as well as hydrogen to produce methanol, dimethyl ether and other products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
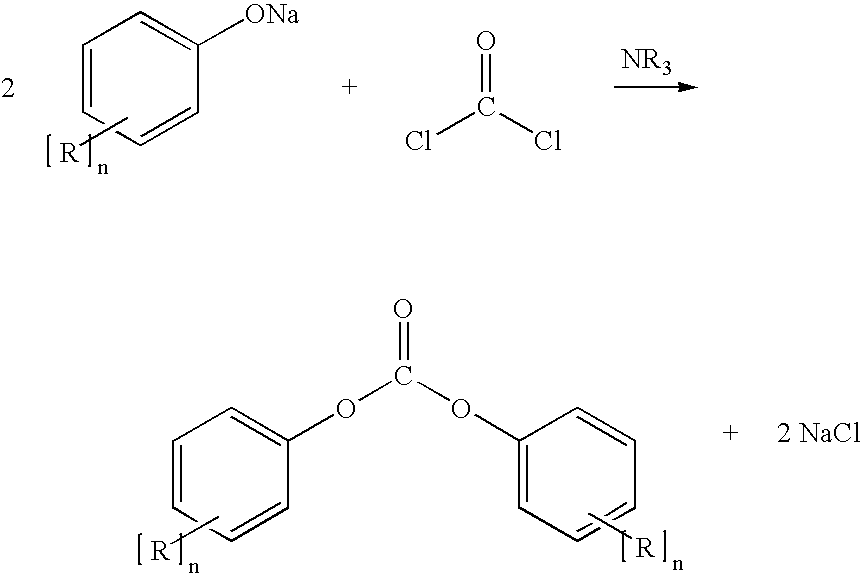
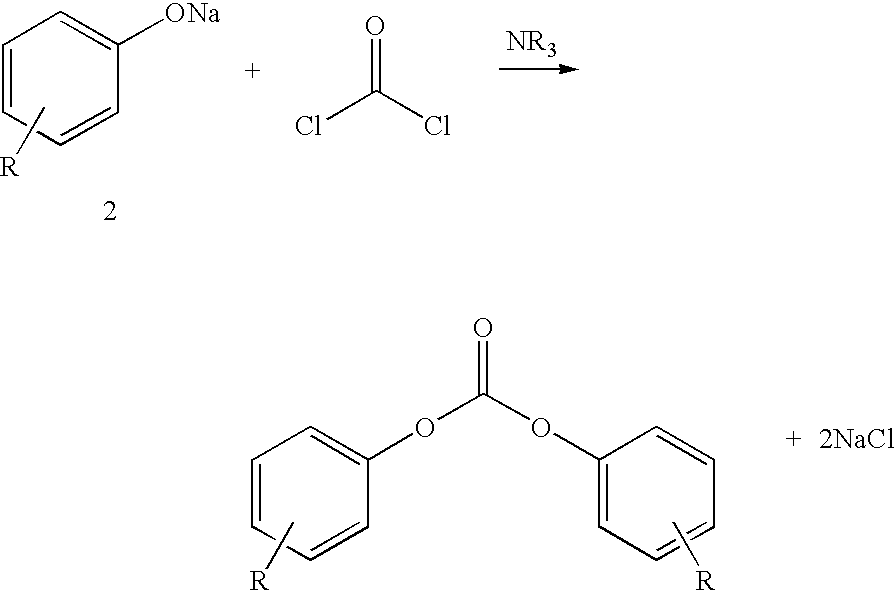
Process for the production of diaryl carbonates and treatment of alkalichloride solutions resulting therefrom
Processes comprising: (a) reacting phosgene and a monohydroxyl aryl compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst to form a diaryl carbonate and a solution comprising an alkali chloride; (b) separating the diaryl carbonate from the solution; (c) adjusting the pH of the solution to a value of less than or equal to 8 to form a pH-adjusted solution; (d) treating the pH-adjusted solution with an adsorbent to form a treated solution; (e) subjecting at least a portion of the treated solution to electrochemical oxidation to form chlorine and an alkali hydroxide solution; and (f) recycling at least a portion of one or both of the chlorine and the alkali hydroxide solution.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Adamantane derivatives and process for producing them
InactiveUS6392104B1Efficiently provideImprove isolationPreparation by oxidation reactionsOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystDouble bond
In the presence of an imide compound (e.g., N-hydroxyphthalimide) shown by the formula (2):wherein R1 and R2 independently represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an alkyl group, an aryl group, a cycloalkyl group; or R1 and R2 may bond together to form a double bond or an aromatic or non-aromatic ring; Y is O or OH and n=1 to 3;or the imide compound and a co-catalyst (e.g., a transition metal compound), an adamantane derivative having a functional group such as a nitro group, an amino group, a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, a hydroxymethyl group and an isocyanato group is oxidized with oxygen. According to the above method, an adamantane derivative having a hydroxyl group together with a functional group such as a nitro group, an amino group, a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, a hydroxymethyl group and an isocyanato group is efficiently obtained.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process for production of diaryl carbonate
The invention relates to a process for production of diaryl carbonate combined with the electrolysis of the resultant alkali metal chloride-containing process wastewater. The process according to the invention makes possible, inter alia, improved utilization in electrolysis of the alkali metal chloride-containing solution obtained in the production of diaryl carbonate.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Efficient and selective chemical recycling of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS7608743B2Avoid emissionsElectrolysis componentsOxygen compounds purification/separationFlue gasExhaust fumes
An efficient and environmentally beneficial method of recycling and producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by chemical or electrochemical reduction secondary treatment to produce essentially methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
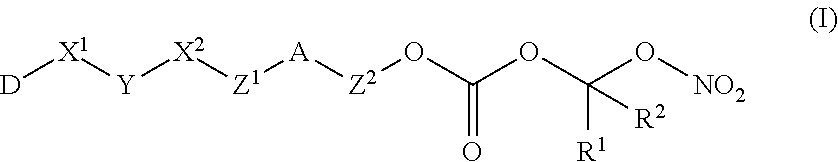
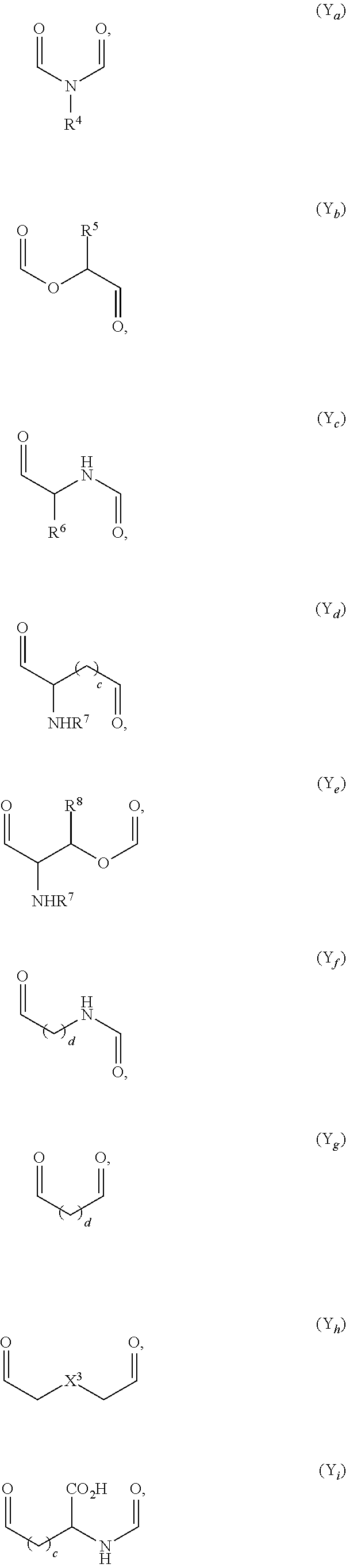
Nitric Oxide Releasing Prodrugs of Therapeutic Agents
The present invention relates to nitric oxide releasing prodrugs of known drugs or therapeutic agents which are represented herein as compounds of formula (I) wherein the drugs or therapeutic agents contain one or more functional groups independently selected from a carboxylic acid, an amino, a hydroxyl and a sulfhydryl group. The invention also relates to processes for the preparation of the nitric oxide releasing prodrugs (the compounds of formula (I)), to pharmaceutical compositions containing them and to methods of using the prodrugs.
Owner:PIRAMAL ENTERPRISES LTD +1
Method of preparing ester-substituted diaryl carbonates
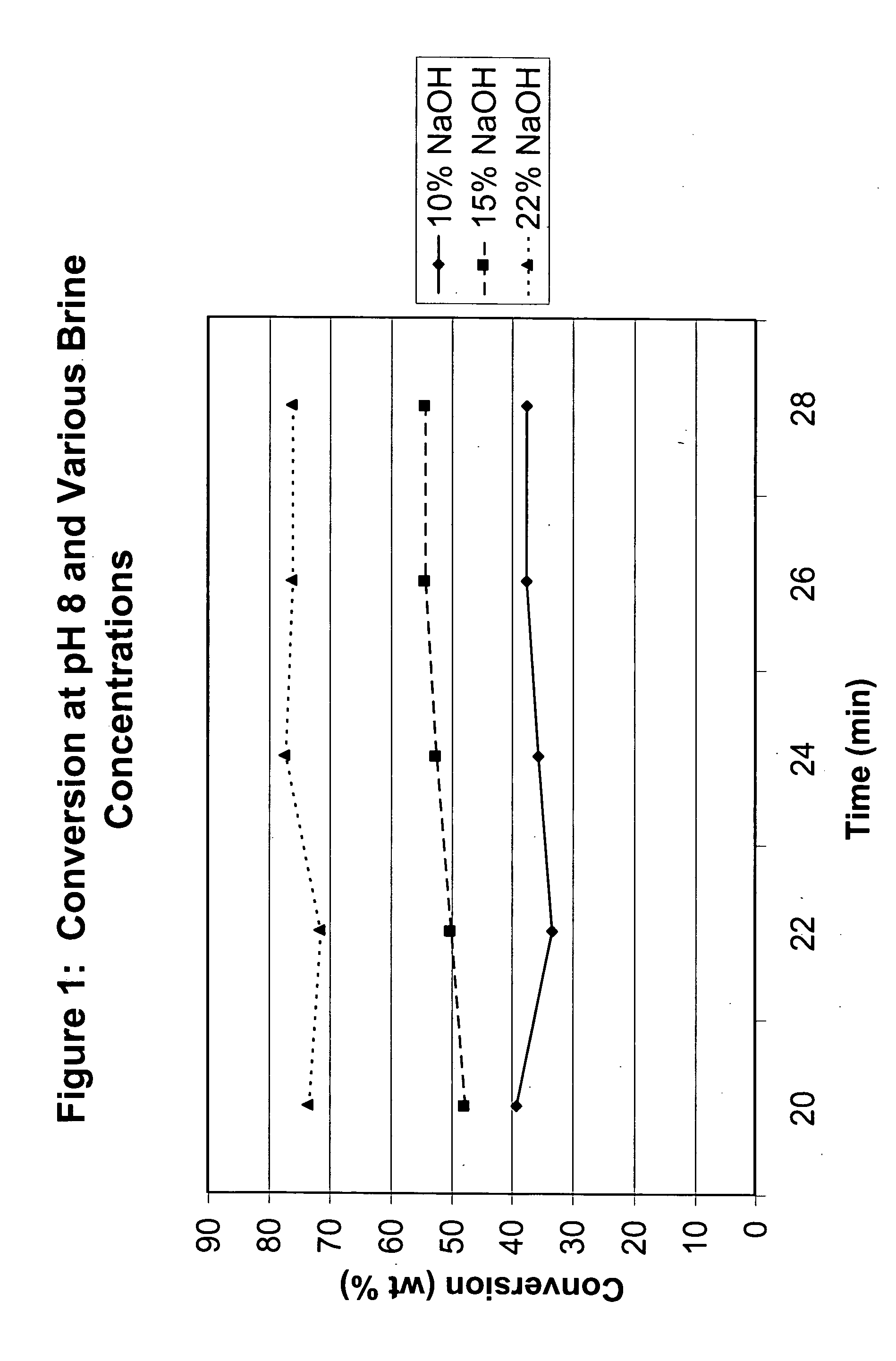
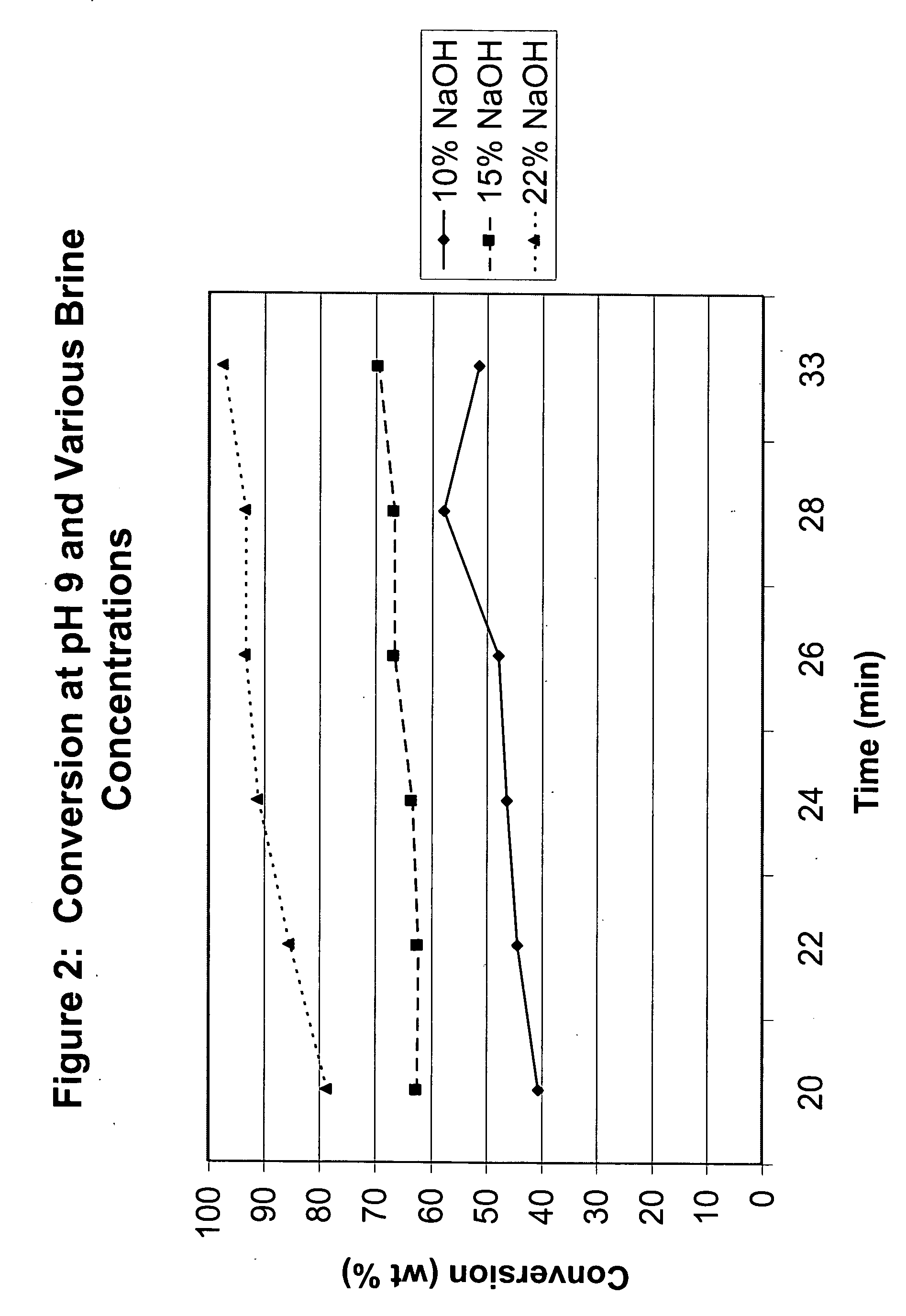
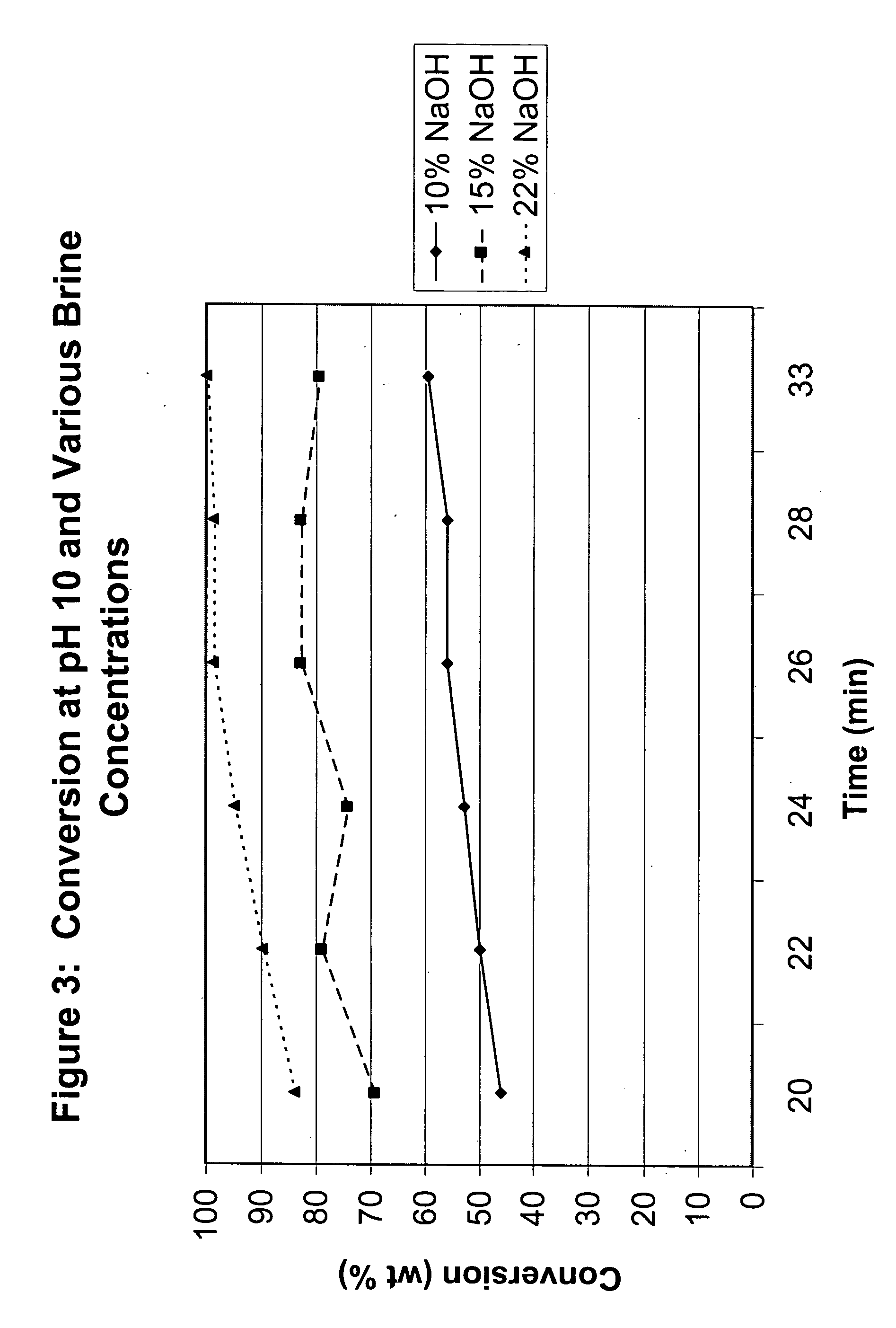
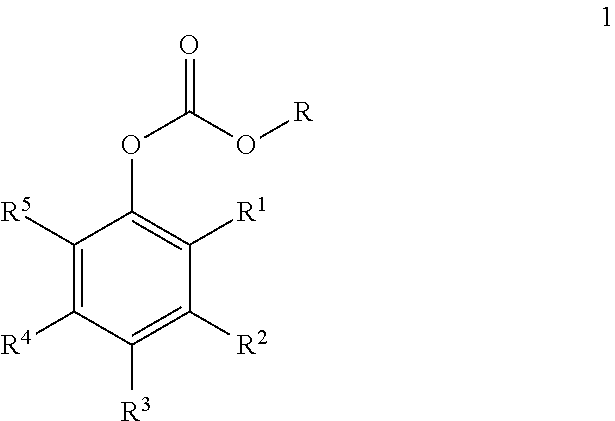
ActiveUS20060025622A1Increase conversionsHigh selectivityPreparation from phosgene or haloformatesOrganic solventPhenol
The present invention relates to an interfacial method of preparing ester-substituted diaryl carbonates. The method includes the steps of: forming a reaction mixture comprising phosgene, an ester-substituted phenol, an organic solvent, and a catalyst selected from the group consisting of a tertiary amine catalyst and a phase transfer catalyst, said reaction mixture having an organic phase and an aqueous phase, wherein said aqueous phase has a brine strength; allowing the reaction mixture to react wherein during the reaction, (i) the aqueous phase has a pH, and the pH is adjusted, if necessary, by the addition of an alkali metal hydroxide solution in amounts such that the pH is greater than or equal to 9.0 during at least some portion of the reaction, and (ii) the brine strength of the aqueous phase is adjusted, if necessary, by varying the concentration of the alkali metal hydroxide solution being added to maintain the pH such that the brine strength is between 15% and a saturated brine solution during at least some portion of the reaction: thereby forming an ester-substituted diaryl carbonate, wherein the reaction mixture is formed with less than 15% water of formulation, and wherein the brine strength is maintained at or above 15% and the pH is maintained at or above 9 for a sufficient portion of the process that the ester-substituted diaryl carbonate is formed with a conversion of at least 90% and a selectivity of at least 98%.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
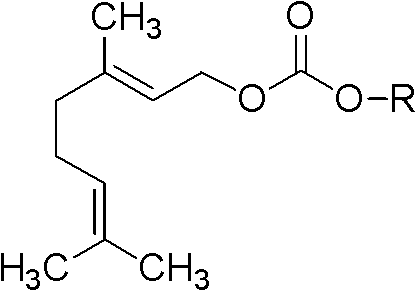
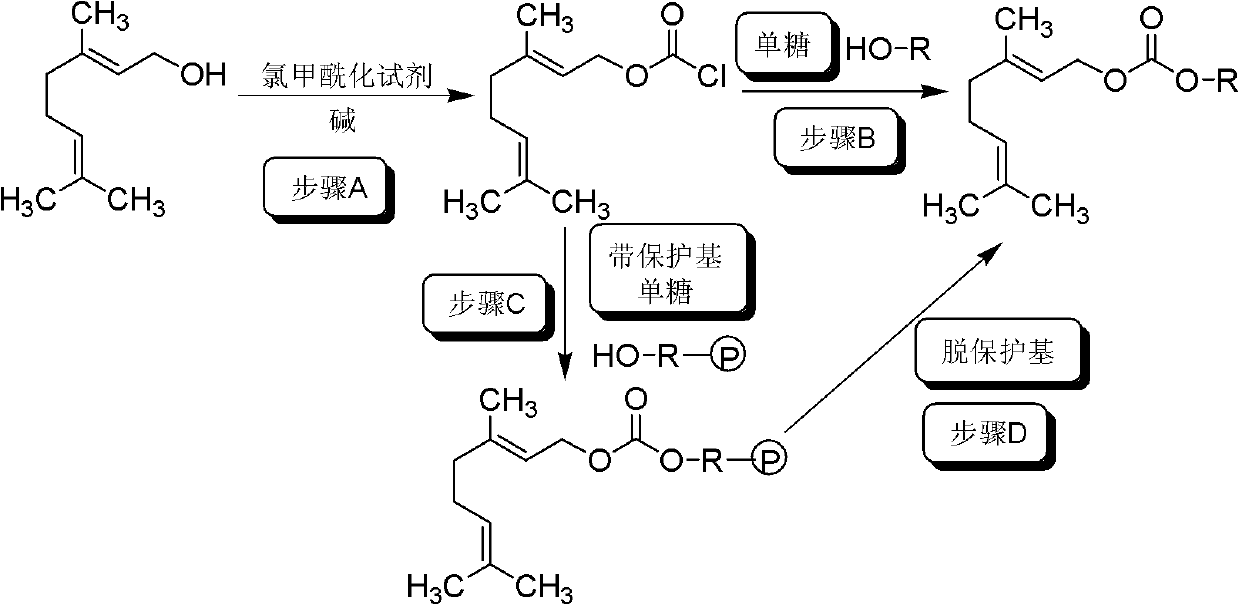
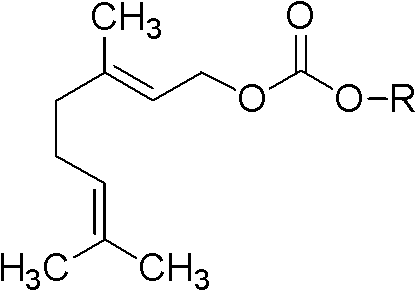
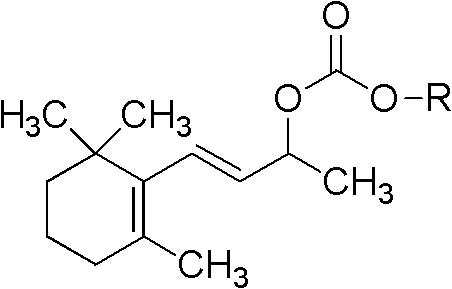
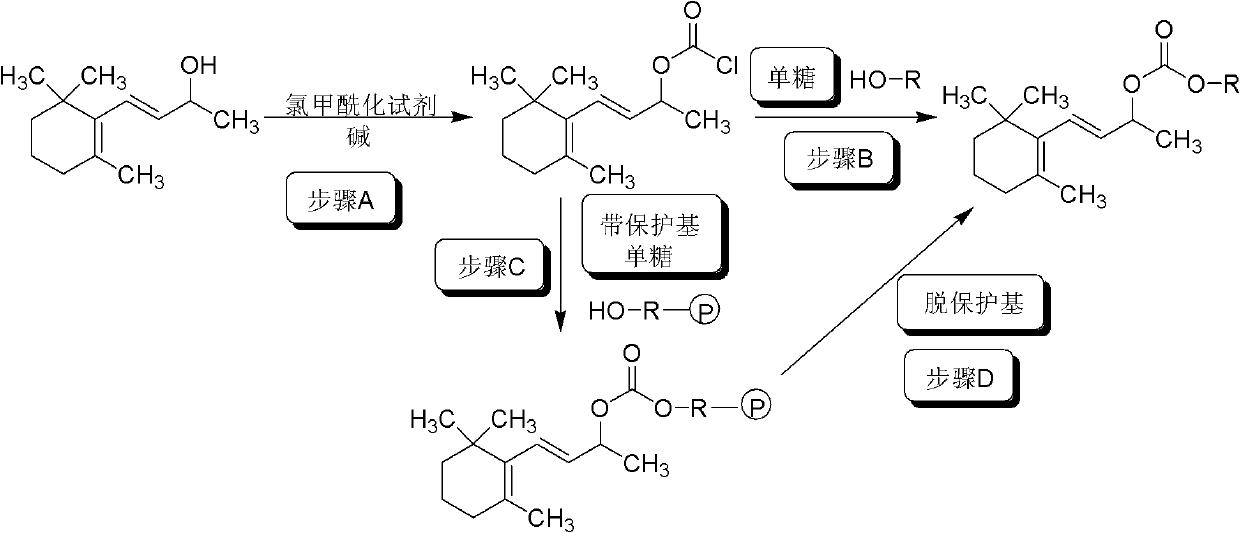
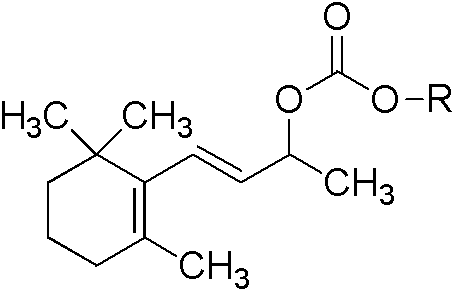
Monosaccharide geraniol carbonate monoester compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102311465ALittle changeReduce volatilityEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesGeraniolOrganoleptic
The invention relates to a cigarette humectant, discloses a monosaccharide geraniol carbonate monoester compound, also discloses a preparation method of the compound, and tests the moisture retention, damp resistance and perfume sustained release effect of the compound as a cigarette humectant. Tests demonstrate that the monosaccharide geraniol carbonate monoester compound has moisture retention performance for tobacco, and has the effect of aroma increase, uniform aroma release, and cigarette sensory quality improvement. In the formula, O-R represent residues of five-carbon monosaccharide or six-carbon monosaccharide; geraniol carbonyl is located at any possible position of the five-carbon or six-carbon monosaccharide.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO CHUANYU IND +1
Method for preparing di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
ActiveCN1915963AEasy to operateEase of mass productionPreparation from phosgene or haloformatesSolventCarbon dioxide
This invention discloses a method for preparing di-tert-butyl dicarbonate. The method comprises: (1) stirring sodium tert-butoxide and hexane for cooling; (2) introducing CO2, and keeping the temperature at 5-15 deg.C; (3) adding bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate or trichloro methyl chloroformate; (4) keeping the temperature, and adjusting the pH to 5-6; (5) adding water, keeping the temperature at 0-5 deg.C, stirring and wshing with water to neutrality; (6) removing the solvent under normal pressure to 80-90 deg.C, and cooling to room temperature; (7) freezing and crystallizing; (8) separating and drying by centrifuging; (9) placing the dried material in a kettle, keeping the temperature at 25-30 deg.C, stirring, evacuating to -0.095 MPa, discharging and storing at -5-10 deg.C. The method uses chloroformate as a substitute for sulfuryl chloride, thus has such advantages as easy operation, little waste, high yield and high product purity, and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:宁夏金象医药化工有限公司
Monosaccharide geraniol carbonate diester compound, preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN102304155AWater solubleFat solubleEsterified saccharide compoundsTobacco treatmentGeraniolStructural unit
The invention relates to a tobacco humectant, discloses a monosaccharide geraniol carbonate diester compound, and further discloses a preparation method for the monosaccharide geraniol carbonate diester compound. According to the present invention, the effects of humidity preserving, damp proofing, slow perfume releasing and sensory evaluation of the monosaccharide geraniol carbonate diester compound adopted as the tobacco humectant are tested. The test results show that: the monosaccharide geraniol carbonate diester compound provides the humidity preserving property for the tobacco, and has effects of aroma increasing, uniform aroma releasing and improvement of organoleptic quality of the tobacco. In the formula provided by the present invention, O-R-O represents a residue of five-carbon or six-carbon monosaccharide, the two geraniol carbonate structure units are positioned on any two possible locations of the five-carbon or six-carbon monosaccharide.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO CHUANYU IND +1
Ester compound of thymol and/or carvacrol, preparing method and its medicinal active composition
The present invention relates to the ester compound of thymol and / or carvacrol with the general expression as shown. The active medicine composition of the ester compound is new generation of farm animal medicine for treating parasitic disease and bacterial infection, including infection caused by drug resistant bacteria.
Owner:INTELLIGENT ANIMAL PHARMA CHANGZHOU CITY
Synthetic route to anti-viral agents
ActiveUS9809576B1Carbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationAntiviral drugViral protease
The invention provides methods of synthesizing a viral protease inhibitor in high yield, without using expensive catalysts or challenging reaction conditions.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Process for production of diaryl carbonate
The invention relates to a process for production of diaryl carbonate combined with the electrolysis of the resultant alkali metal chloride-containing process wastewater. The process according to the invention makes possible, inter alia, improved utilization in electrolysis of the alkali metal chloride-containing solution obtained in the production of diaryl carbonate.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Preparation method of trifluoromethyl straight-chain carbonate
ActiveCN102775312AImprove stabilityImprove thermal stabilityCarbonic/haloformic acid esters purification/separationPreparation from phosgene or haloformatesAlcoholBoiling point
The invention discloses a preparation method of trifluoromethyl straight-chain carbonate, which comprises the following preparation steps: mixing trifluoromethyl saturated monohydric alcohol or a mixture of trifluoromethyl saturated monohydric alcohol and saturated straight-chain monohydric alcohol with triphosgene; regulating the temperature to 25-80 DEG C in the presence of an organic amine acid-binding agent, and reacting for 1-10 hours to obtain a trifluoromethyl straight-chain carbonate mixed solution; and filtering, separating, and performing distilling purification on the trifluoromethyl straight-chain carbonate mixed solution to obtain the trifluoromethyl straight-chain carbonate. The trifluoromethyl straight-chain carbonate prepared by the process is a high voltage type solvent for a novel power lithium battery, and can greatly enhance the heat stability, cycle performance and high voltage property of the power lithium battery. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, high yield and low cost; and meanwhile, the triphosgene is high in stability and is decomposed a little at the boiling point of 200 DEG C. Thus, the preparation process has no serious problems on safety, environmental protection and the like.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG HUASHENG CHEM CO LTD
Process for synthesizing carbonochloridic acid 9-fluorene methyl ester
InactiveCN101245001ASimple processHigh yieldPreparation from phosgene or haloformatesN dimethylformamidePhosgene
The invention provides a method for synthesizing chlorinated formic acid 9-fluoren methyl, which comprises the following steps: (1) 9-fluoren methyl and triphosgene are reacted for 0.5 to 3 hours in ice bath, under the existence of catalyst and in organic solvent; the catalyst is chosen from N with nucleophilicity, N-dimethylformamide, acetone, diisopropyl ethyl amine, diethylamine, triethylamine, ethyleendiamine, putrescine, imidazole, and the solvent is chosen from benzene, toluene, cyclohexane, hexane, heptane, cyclopentane, dichloromethane, chloroform and the compound thereof; (2) the temperature raises to 20 to 50 DEG C, and the mixture reacts for 1 to 5 hours. The method for synthesizing chlorinated formic acid 9-fluoren methyl adopts safe solid phosgene as reactant, and is simple in technique, convenient in safety, mild in condition, high in yield and easy in realization of industrialization production; the solvent can be used repeatedly after being processed simply, and the products do not need to be refined, and purity is up to more than 98 percent.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for producing carbonates
ActiveUS20170001943A1Heat exhanger conduitsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPhosgeneCarbon tetrachloride
In an embodiment, a method of producing a carbonate comprises reacting carbon monoxide and chlorine in a phosgene reactor in the presence of a catalyst to produce a first product comprising phosgene; wherein carbon tetrachloride is present in the first product in an amount of 0 to 10 ppm by volume based on the total volume of phosgene; and reacting a monohydroxy compound with the phosgene to produce the carbonate; wherein the phosgene reactor comprises a tube, a shell, and a space located between the tube and the shell; wherein the tube comprises one or more of a mini-tube section and a second tube section; a first concentric tube concentrically located in the shell; a twisted tube; an internal scaffold; and an external scaffold.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
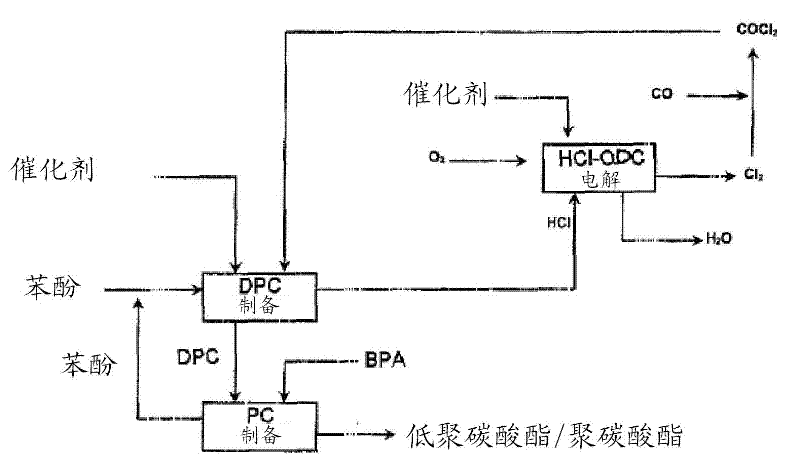
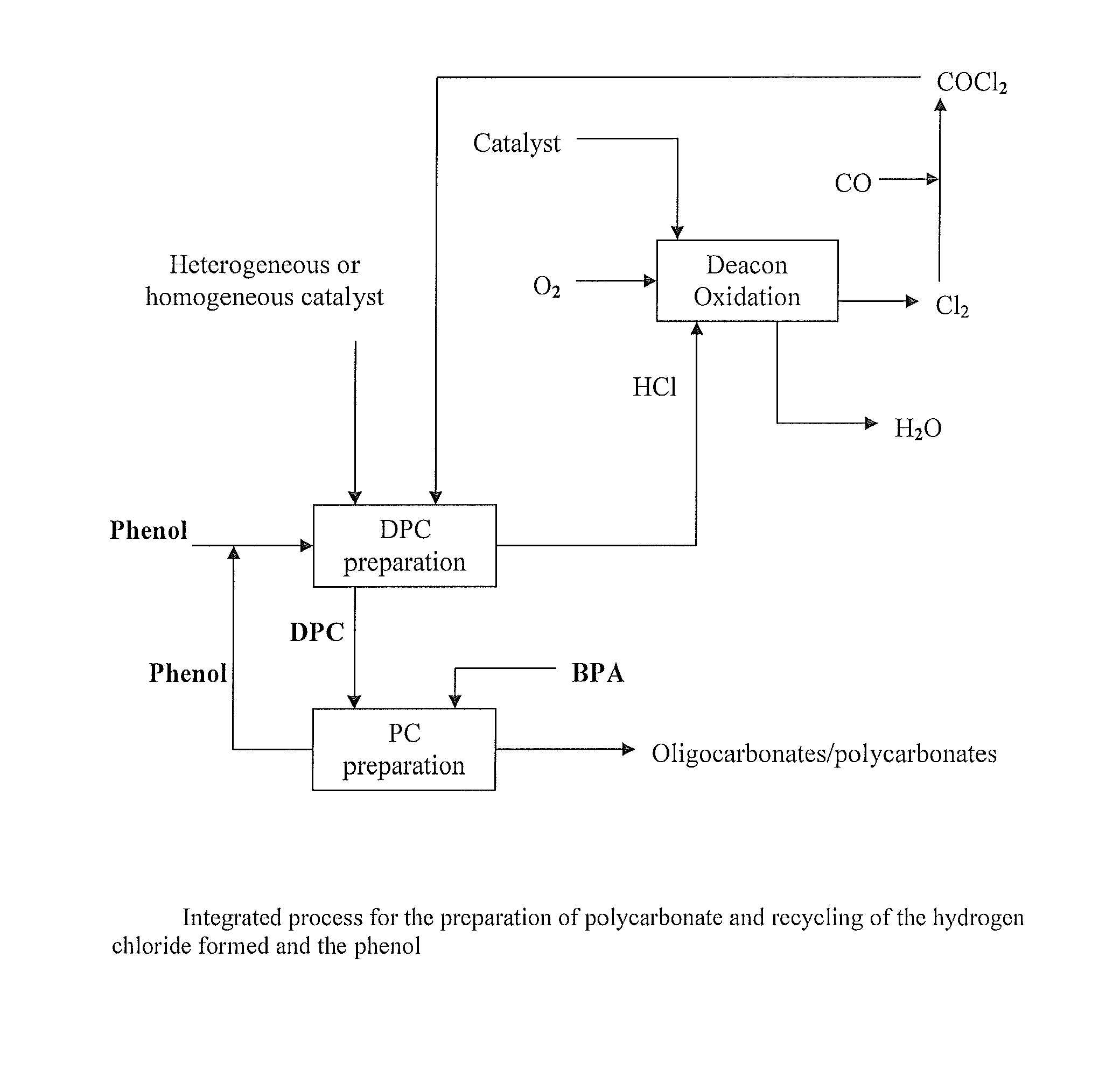
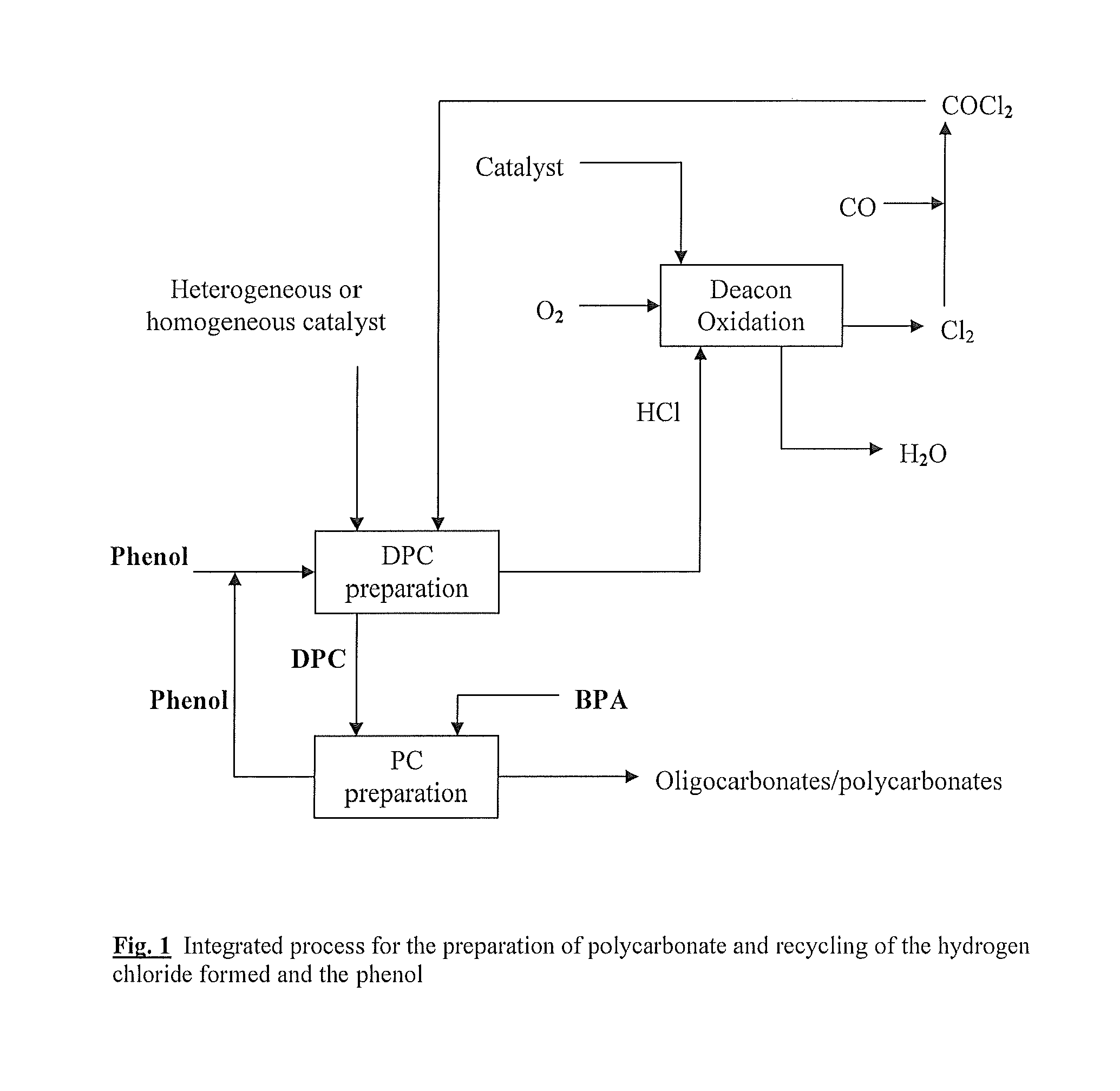
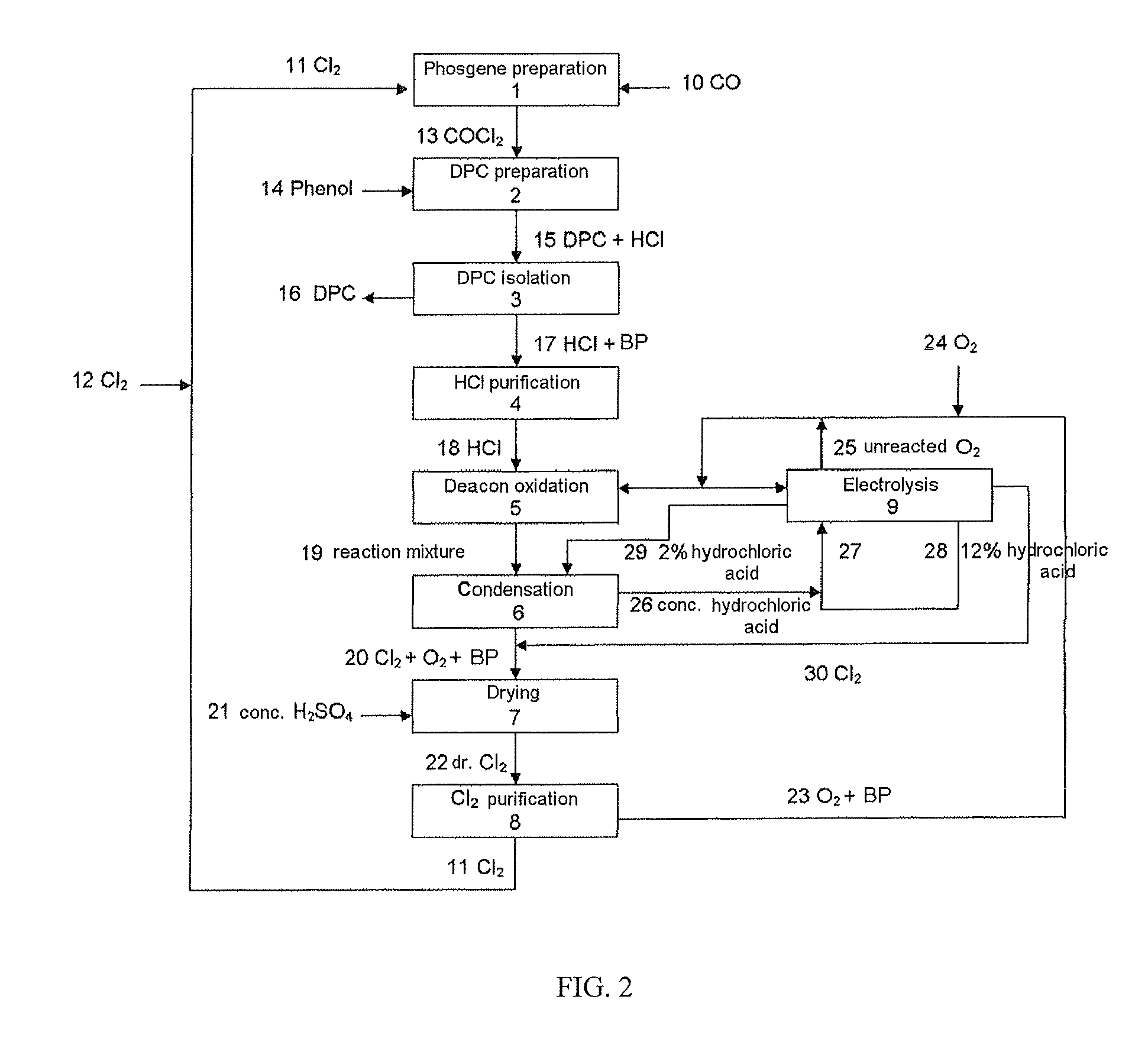
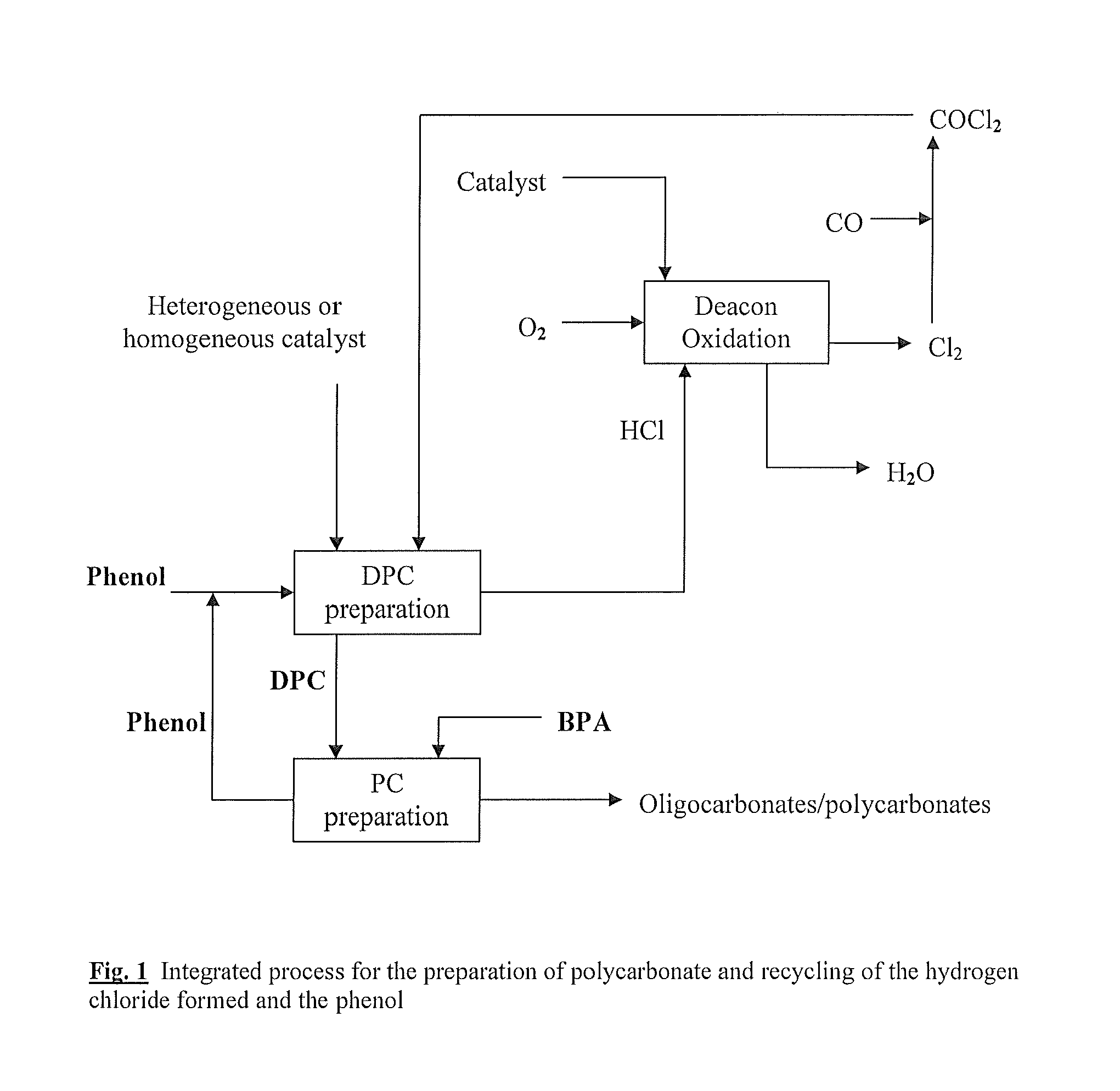
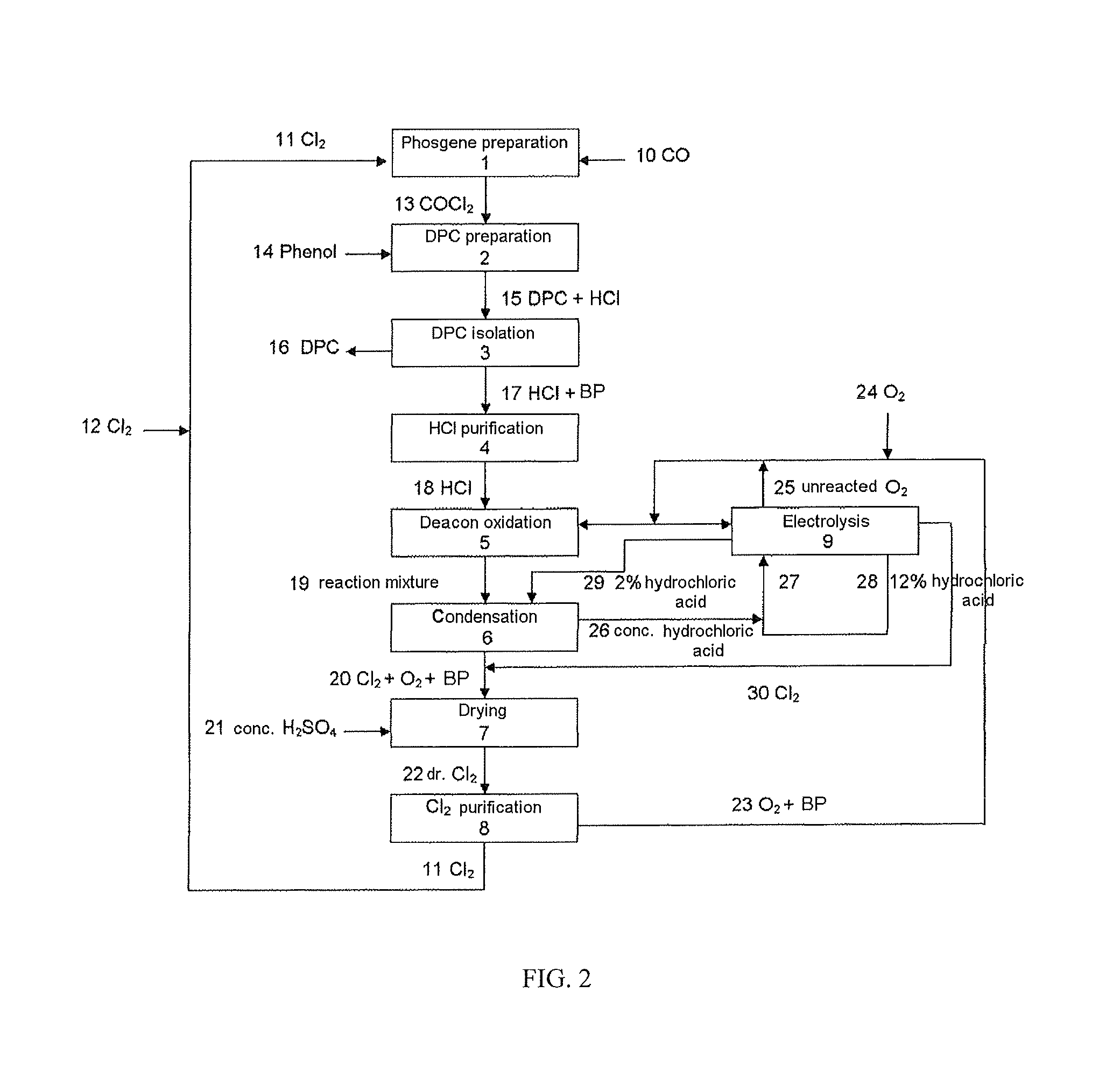
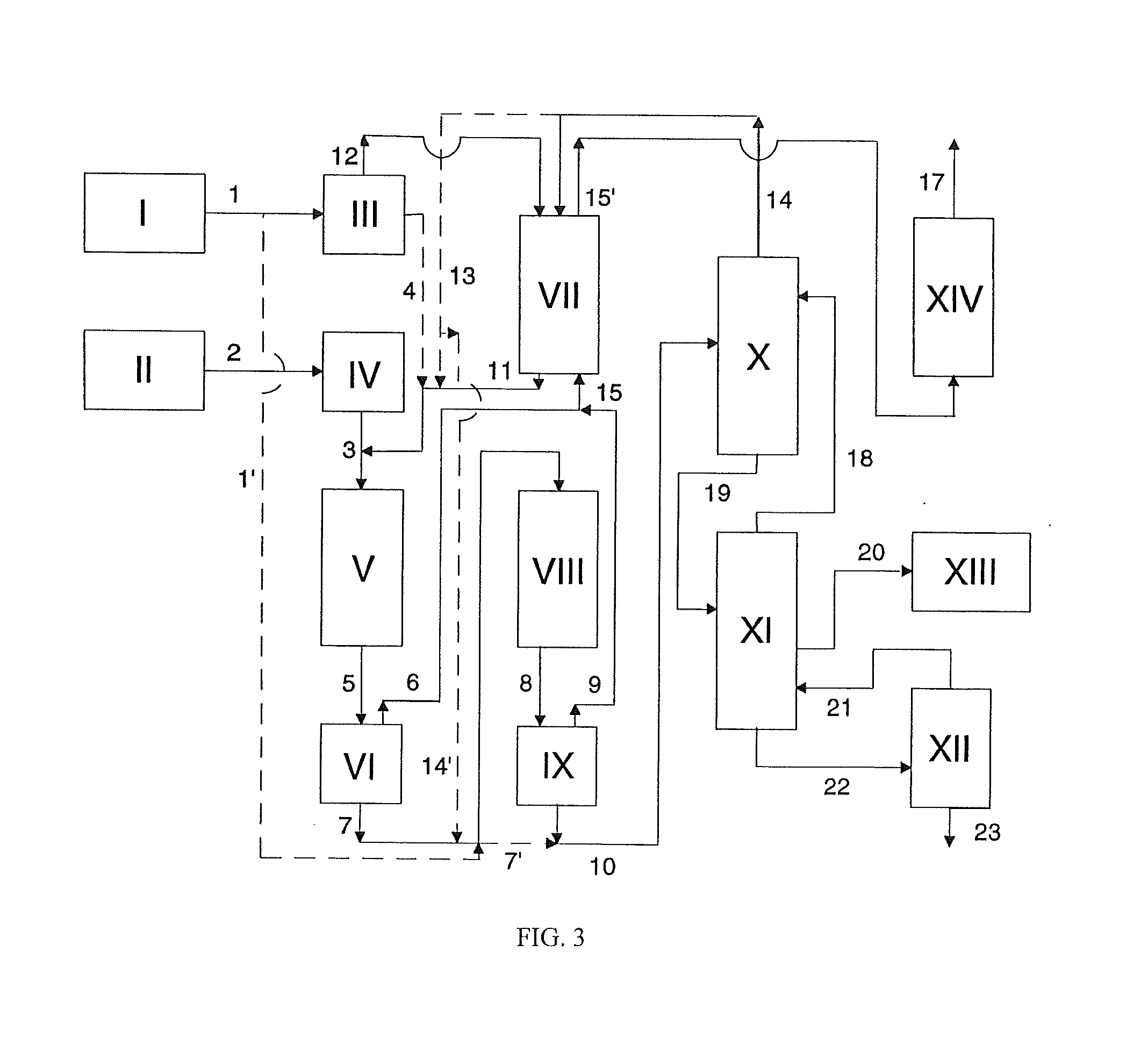
Method for preparing diaryl carbonates and polycarbonates
The invention relates to a method for preparing diaryl carbonates and polycarbonates, especially to a method for continuously preparing diaryl carbonates by using phosgene and at least one hydroxy compound (monohydric phenol) with the presence of a catalyst, and the usage thereof for preparing polycarbonates. Hydrogen chloride generated through a reaction is converted into chlorine through electrochemical oxidation, and the chlorine is then recirculated for preparation of phosgene. Especially, the method comprises a method (DPC method) of preparing diphenyl carbonate with generated hydrogen chloride.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Process for preparing diaryl carbonates and polycarbonates
ActiveUS20110245527A1High purityHigh yieldChemical industryCarbonic/haloformic acid esters purification/separationEthyl ChlorideHydrogen chloride
The present invention relates to a process for the continuous preparation of diaryl carbonates from phosgene and at least one monohydroxy compound (monophenol) in the presence of catalysts, and also the use thereof for preparing polycarbonates. The hydrogen chloride formed in the reaction is converted by thermal oxidation into chlorine, with the chlorine being recirculated to the preparation of phosgene. In particular, the process comprises utilization of the hydrogen chloride formed for the process for preparing diphenyl carbonate (DPC process).
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Process for preparing alkyl/aryl chloroformates
InactiveUS20050065361A1Reduce usageIncrease productionPreparation from phosgene or haloformatesArylAlcohol
The present invention discloses an improved method for the preparation of alky / aryl chloroformates directly from alcohols and triphosgene. This method is simple, mild and efficient avoids use of hazardous phosgene. It can be used for the preparation of various aryl as well as alkyl chloroformates in excellent yields.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Process for preparing diaryl carbonates and polycarbonates
ActiveUS9175135B2High purityHigh yieldChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationChemical industryPtru catalystCarbonate ester
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Carbonate derivatives as skin care
Carbonates of anti-aging ingredients, in particular anti-oxidants and skin illuminating phenol ingredients, have been prepared as derivatives of these ingredients with enhanced physical properties. It has been demonstrated that these carbonates will hydrolyze under enzymatic catalysis to release the parent ingredient. In contrast, esters of the phenolic groups in many cases do not hydrolyze under the same conditions.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Monosaccharide beta-ionol carbonic acid monoester compound, and preparation method and purpose
InactiveCN102336789ALittle changeReduce volatilityEsterified saccharide compoundsTobacco treatmentChemistryHumidity
The invention discloses a monosaccharide beta-ionol carbonic acid monoester compound and preparation method of the compound, which relate to a cigarette humectant. In addition, the humidity preservation, damp-proof and spice slow release effects of the compound in the application as the cigarette humectant are also tested. Tests show that the monosaccharide beta-ionol carbonic acid monoester compound has the humidity preservation performance on the cigarette and has the effects of increasing the perfume quantity, realizing the uniform perfume release and improving the cigarette sensing quality. In a formula, O-R represents residues of C5 monosaccharide or C6 monosaccharide, and beta-ionol carbonyls are positioned in any possible positions of C5 or C6 monosaccharide.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO CHUANYU IND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com