Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Suppression of surface waves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microstrip antenna array with periodic filters for enhanced performance
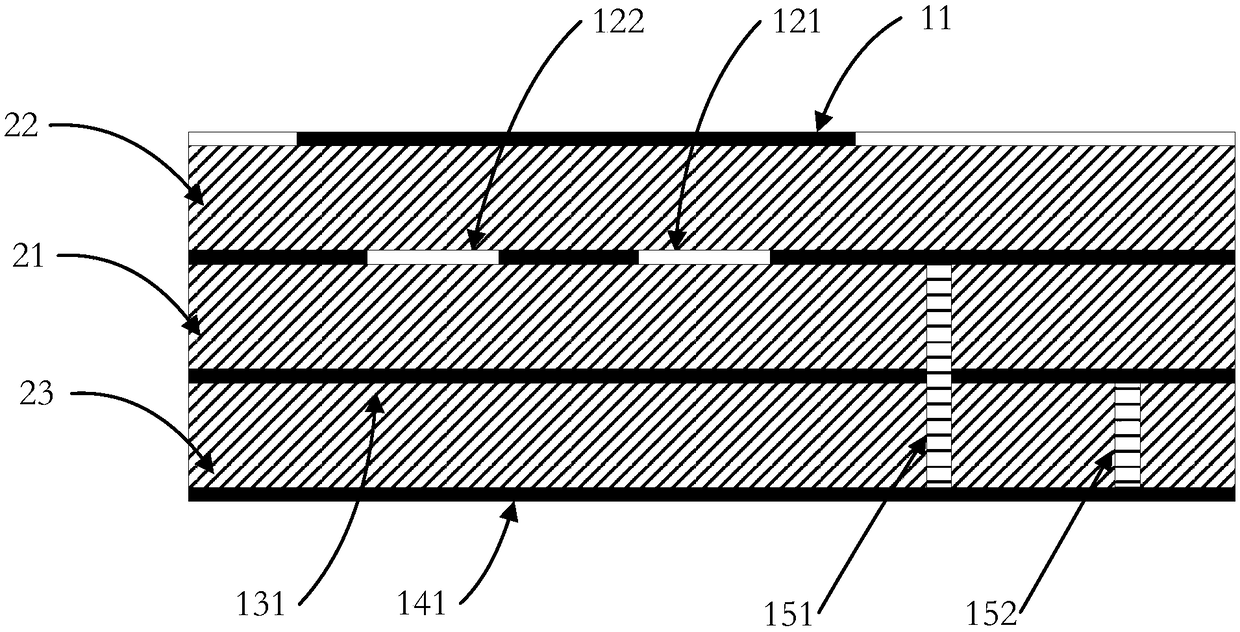
InactiveUS6954177B2Improve isolationComponent is expensiveSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip antenna arrayGround plane
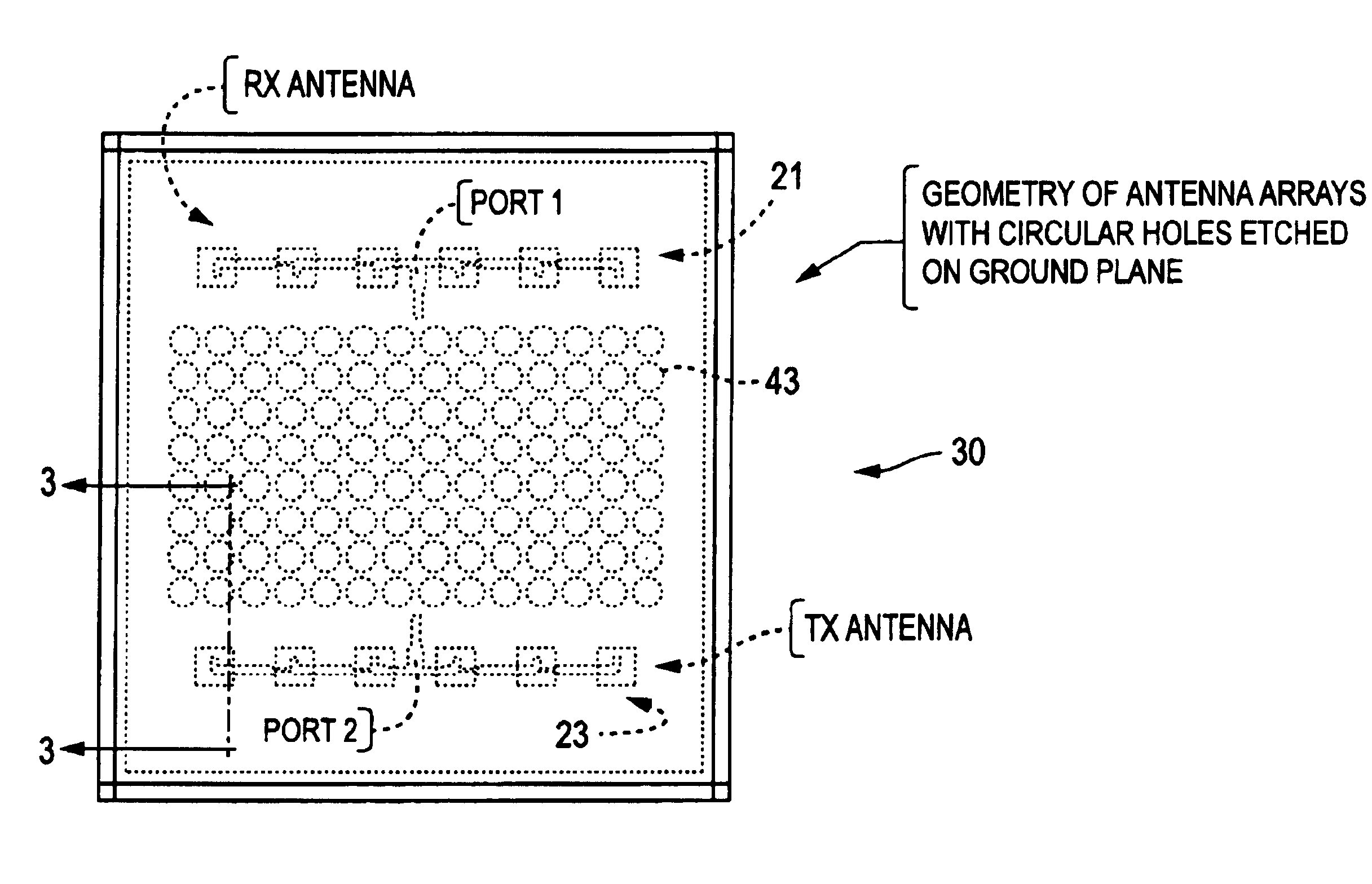
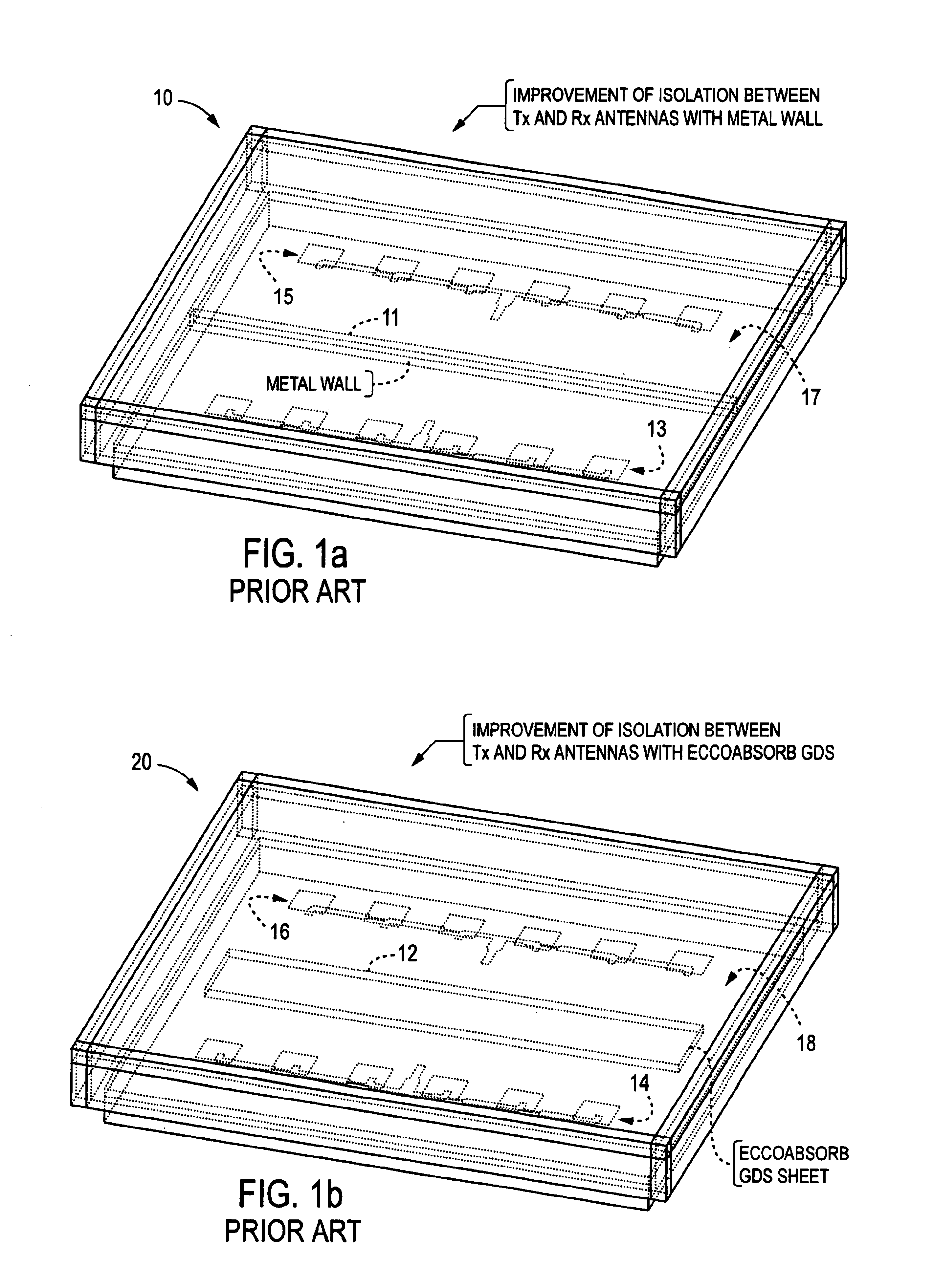
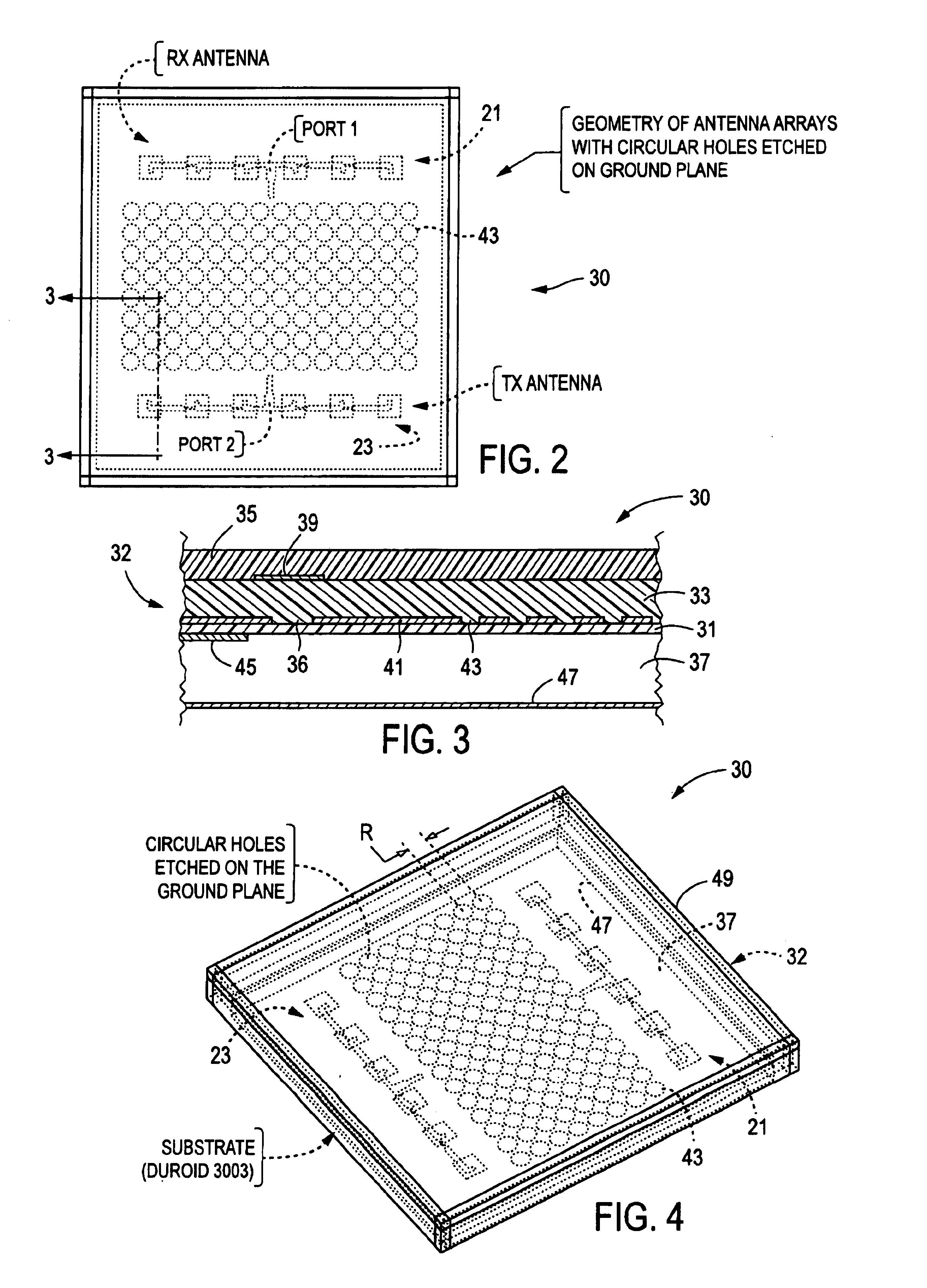
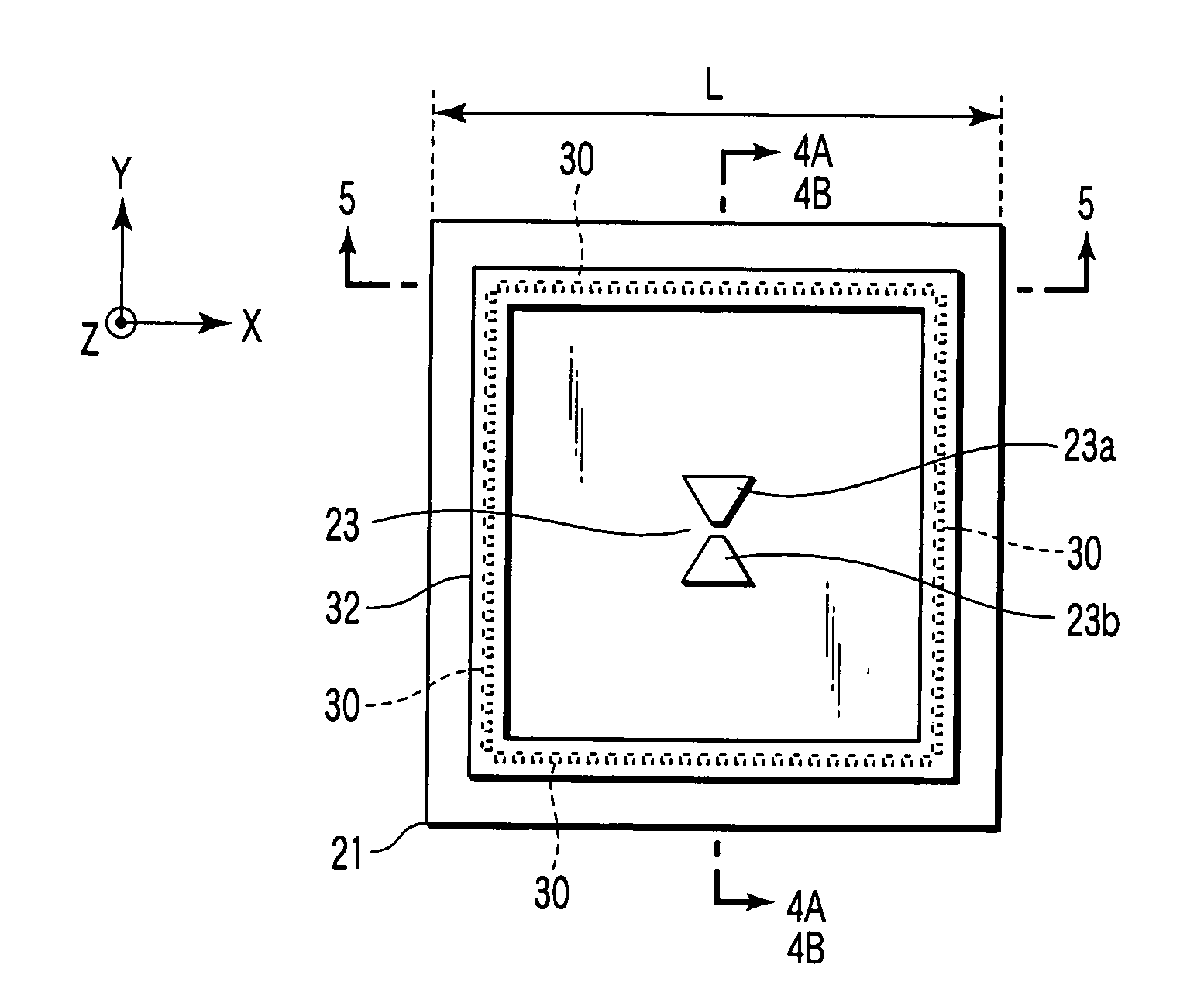
An antenna unit formed in the shape of a hollow box comprising (a) a substrate forming the front side of the antenna unit, (b) a first microstrip antenna array formed on the substrate, (c) a second microstrip antenna array formed on the substrate, (d) a ground plane forming the rear side of the antenna unit, and (e) a plurality of periodic filters formed on the ground plane. The periodic filters are formed by etching a series of circular patterns, or holes, through the ground plane. The periodic stop band filters provide for improved isolation between the microstrip antenna arrays, without the need for adding additional costly or space consuming components.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
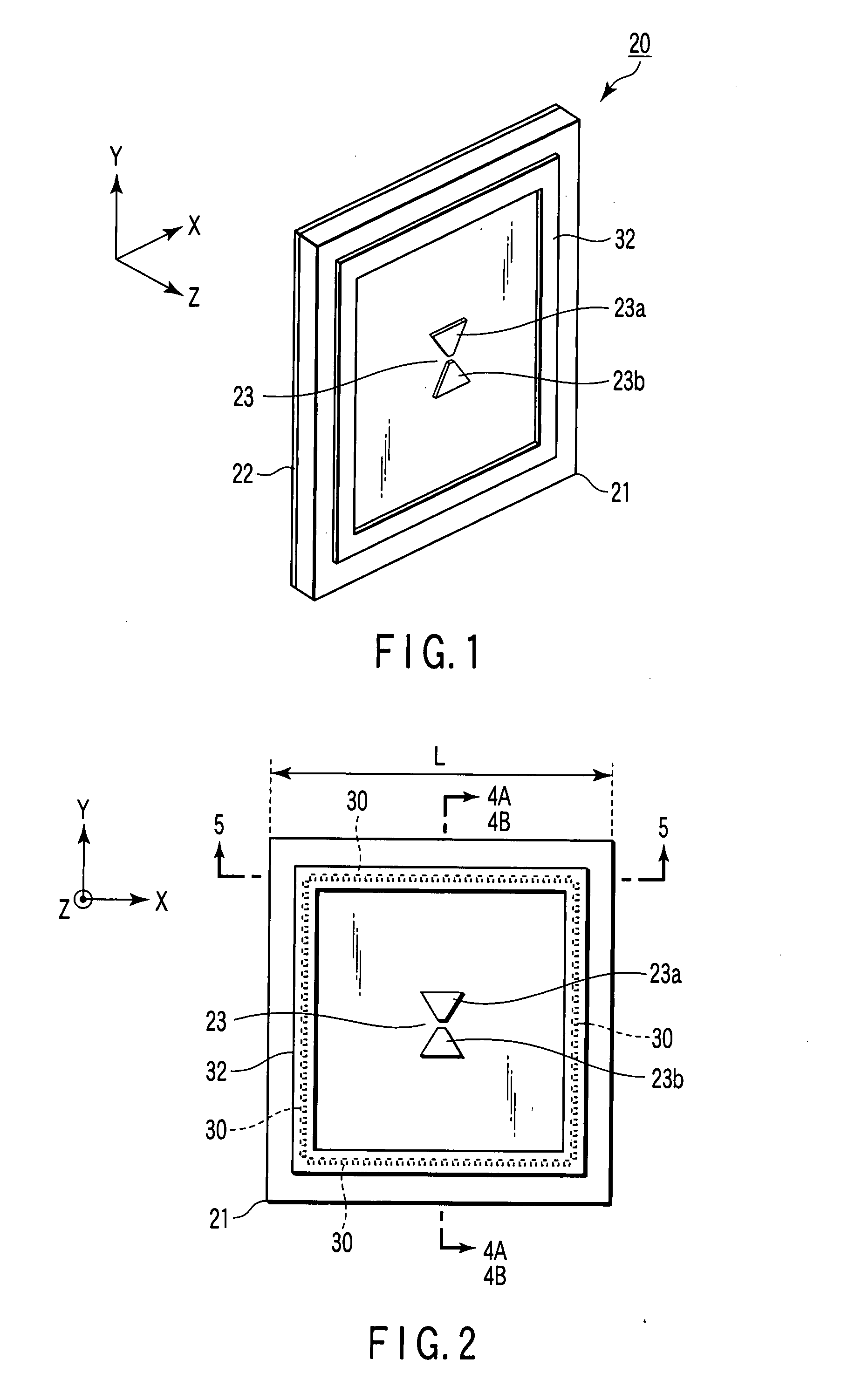
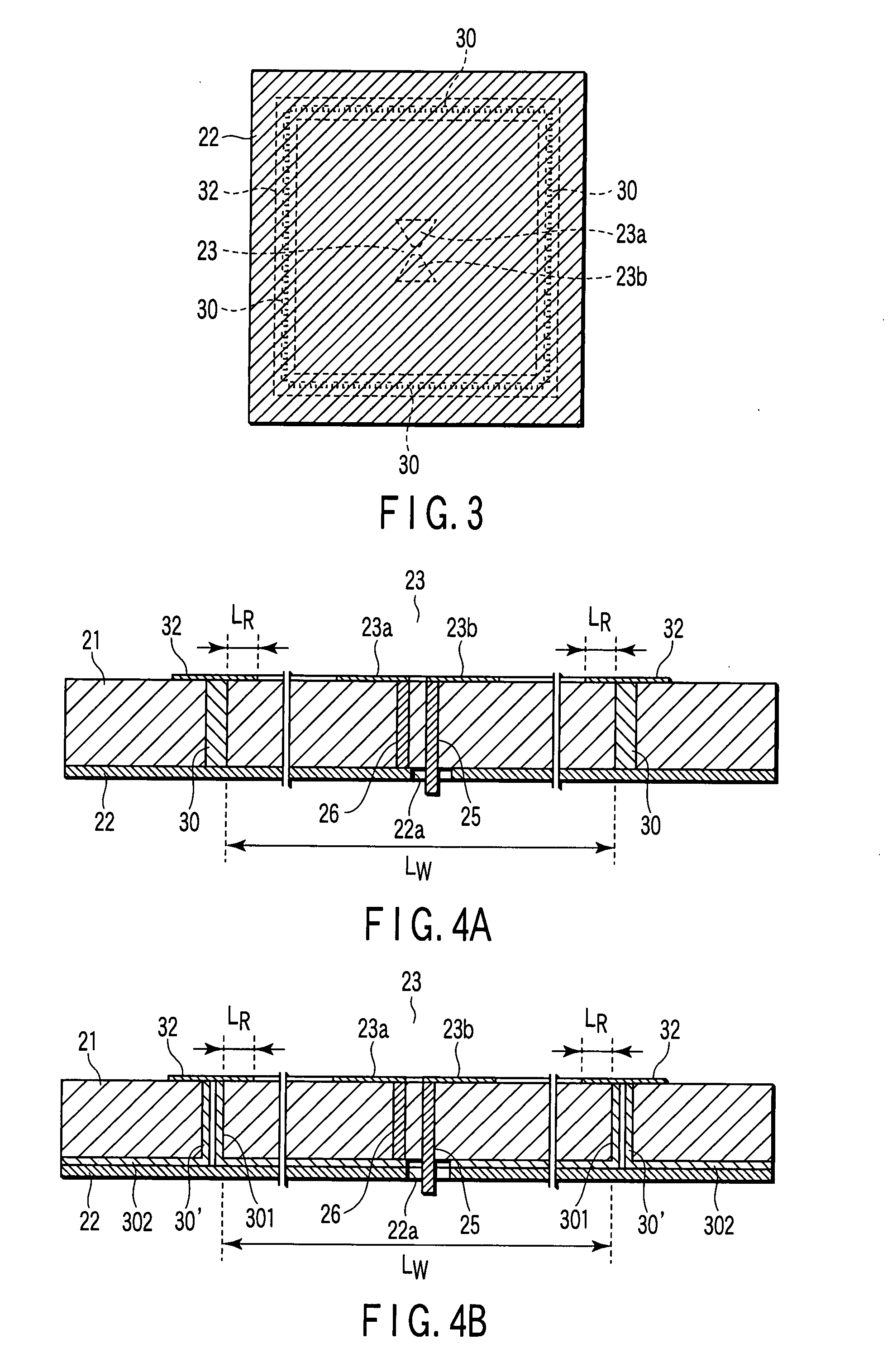
Linearly Polarized Antenna and Radar Apparatus Using the Same
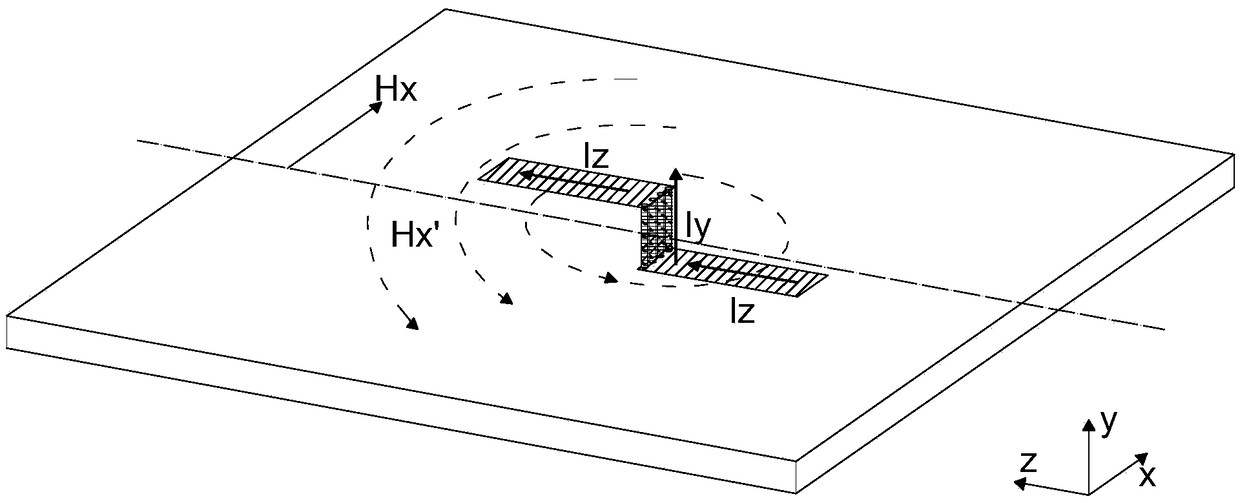
InactiveUS20070290939A1Suppression of surface wavesSuppress generationAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsPhysicsLinear polarization
A linearly polarized antenna includes a dielectric substrate, a ground conductor which is overlapped on one surface of the dielectric substrate, an antenna element made of linearly polarized, which is formed on an opposite surface of the dielectric substrate, a plurality of metal posts in which one end side of each of the plurality of metal posts is connected to the ground conductor, the plurality of metal posts piercing through the dielectric substrate along a thickness direction thereof, another end side of each of the plurality of metal posts being extended to the opposite surface of the dielectric substrate, the plurality of metal posts being provided at predetermined intervals to form a cavity so as to surround the antenna element, and a conducting rim which short-circuits the other end side of each of the plurality of metal posts along a line direction of the plurality of metal posts on the opposite surface side of the dielectric substrate, the conducting rim being provided while extended by a predetermined distance toward a direction of the antenna element, the conducting rim having, e.g., a triangular portion. In the linearly polarized antenna, generation of a surface wave is suppressed by the cavity and the conducting rim, and the antenna can be set to the desired radiation characteristic. Additionally, a frequency characteristic of an antenna gain can have a steep decline (notch) in an RR radio-wave emission prohibited band by utilizing a resonance phenomenon of the cavity. Therefore, the linearly polarized antenna is effective in decreasing radio wave interference with EESS or radio astronomy service.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
A low profile LTCC millimeter wave dual polarization antenna
InactiveCN109066065ASuppression of surface wavesImprove radiation efficiencyRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationHigh isolationWaveguide
The invention discloses a low-profile LTCC millimeter wave dual-polarization antenna, comprising: a first slot and a second slot crossing each other are arranged on the lower surface of a substrate integrated cavity; The lower surface of the upper waveguide is provided with a third slot; A low surface of that transition structure is provided with a fourth gap; The electromagnetic wave input from the first port is transmitted in the upper substrate integrated waveguide, coupled into the substrate integrated cavity through the first slot, and polarized in the first direction. The electromagneticwave input from the second port is transmitted through the lower waveguide, coupled into the upper waveguide through the fourth and third slots, coupled into the substrate integrated cavity through the second slot, and polarized in the second direction. When the antenna receives the electromagnetic wave in the first direction, the electromagnetic energy enters the upper waveguide through the first slot. As that antenna receive the electromagnetic wave in the second direction, the electromagnetic energy enters the upper substrate integrate waveguide through the second slot and is coupled intothe lower waveguide through the third and fourth slots. The invention realizes high gain, wide frequency band and high isolation of the bipolar antenna.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Circular-polarized back-cavity waveguide slot array antenna realized near-field coupling polarizer
PendingCN107196067AImprove performanceReserve wide bandwidthParticular array feeding systemsRadiating elements structural formsResonant cavityEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of the communication, specifically a Circular-polarized back-cavity waveguide slot array antenna realized near-field coupling polarizer. The antenna array is composed of two parts: the lower end is the linear-polarized back-cavity waveguide slot array with high gain and low section, and the upper end is a biparasitic corner-truncated patch polarizer; the corner-truncated patch polarizer is composed of two corner-truncated parasitic patches, each two patches are isolated by using a metal belt electrically connected with a metal through hole; the linear-polarized back-cavity waveguide slot array is composed of a coaxial interface, a feed waveguide network, a coupling slot, a resonant cavity, a radiation slot and a support column; a periodical metal prop integrally machined with lower end antenna is supported between the polarizer and the antenna array plane; the assembling is convenient, the structure is compact, the additional loss material is unnecessary to import, and the features of high gain and low loss of the original waveguide back-cavity antenna are maximally reserved; furthermore, the surface wave between a polarizer medium substrate and an air contact surface can be commonly inhibited, and the performance of the antenna is effectively improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Linearly polarized antenna and radar apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7623073B2Improve featuresImprove productivityAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsRadarDielectric substrate
A linearly polarized antenna includes a dielectric substrate, a ground conductor which is overlapped on one surface of the dielectric substrate, an antenna element made of linearly polarized, which is formed on an opposite surface of the dielectric substrate, a plurality of metal posts in which one end side of each of the plurality of metal posts is connected to the ground conductor, the plurality of metal posts piercing through the dielectric substrate along a thickness direction thereof, another end side of each of the plurality of metal posts being extended to the opposite surface of the dielectric substrate, the plurality of metal posts being provided at predetermined intervals to form a cavity so as to surround the antenna element, and a conducting arm which short-circuits the other end of the plurality of metal posts along a line direction of the plurality of metal posts on the opposite surface side of the dielectric substrate, the conducting arm being provided while extended by a predetermined distance toward a direction of the antenna element, the conducting arm having a triangular portion.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Dual polarized antenna array and dual polarized phased-array antenna
PendingCN108461929ASuppression of cross-polarization componentsEliminate radiationAntennas earthing switches associationPolarised antenna unit combinationsCouplingOptoelectronics
The invention provides a dual polarized antenna array and a dual polarized phased-array antenna. The dual polarized antenna array comprises a polarized feeder component, a coupling slot component, a plurality of radiation patches and a metallized via hole component, wherein the polarized feeder component comprises a first polarized feeder and a second polarized feeder, the coupling slot componentcomprises a plurality of first coupling slots and a plurality of second coupling slots perpendicular to each other, the radiation patches are positioned at the upper layer of the coupling slot component, and a plurality of metallized via holes arranged side by side are positioned between the first coupling slots and the second coupling slots. Through introducing the metallized via hole, each polarized feed network is isolated, so that the cross polarization component caused by cross coupling between the feeders can be effectively inhibited, and the cross polarization isolation of the dual polarized phased-array antenna provided by the scheme is more than 35dB.
Owner:XTR SOLUTIONS
2-3GHz band microstrip antenna with negative permeability material
InactiveCN101626108ASimple processSuitable for large-scale industrial productionAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsSMA connectorPhysics
The invention relates to a 2-3GHz band microstrip antenna with a negative permeability material, in particular to a microstrip antenna with a negative permeability material with two-sided dendritic structures. The microstrip antenna in the invention comprises a dielectric substrate, a metal radiation patch and a metal ground plate; wherein, the metal radiation patch and the metal ground plate are etched at both sides of the dielectric substrate; an SMA connector connects the metal radiation patch and the metal ground plate and serves as a feed-in interface of radio wave signals of the antenna; dendritic structure cell arrays arranged periodically are etched at both sides of the space around the metal radiation patch and the metal ground plate. When electromagnetic waves enter vertically, the negative permeability effects generated by the two-sided dendritic structures can be adopted to improve the transmitting efficiency and directionality of the microstrip antenna and increase the antenna gain.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Structure for realizing the nested connection of an antenna and a circuit
InactiveCN109273837AMiniaturizationSuppression of surface wavesAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsCoplanar waveguideGround plane
The invention discloses a structure for realizing the nesting connection of an antenna and a circuit, which comprises a suppression surface wave antenna, a chip circuit and a coplanar waveguide pad. The suppression surface wave antenna comprises a feeding probe and a silicon substrate, a metal floor, a dielectric layer and a radiation patch layered from bottom to top. A short-circuit concentric ring is arranged on the radiation patch, and the short-circuit concentric ring is concentrically arranged with the radiation patch, and the radiation patch is connected with the metal floor through theshort-circuit concentric ring; The radiation patch part located inside the short-circuit concentric ring is provided with a slot for placing the chip circuit. One end of the feeding probe is connectedwith a radiation patch; The coplanar waveguide pad includes a ground plane disposed on a metal ground plane and a signal line connected to the other end of the feed probe.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Filtering antenna device
InactiveCN109921177AReduce surface wave lossSuppress interferenceRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationResonant cavityCoplanar waveguide
The invention provides a filtering antenna device. The filtering antenna device comprises an SIW filtering structure and an SIW radiation structure which is cascaded with the SIW filtering structure;the SIW filtering structure comprises a first resonant cavity and a second resonant cavity which are stacked in an up-down mode and communicate with each other; the SIW radiation structure comprises aback cavity and a metal patch; the back cavity is arranged side by side together with the first resonant cavity and the second resonant cavity, and communicates with the first resonant cavity and thesecond resonant cavity; the metal patch is contained in the back cavity; the filtering antenna device further comprises a feed port and a first coplanar waveguide which are arranged on one side, faraway from the back cavity, of the first resonant cavity, a second coplanar waveguide arranged on one side, close to the back cavity, of the second resonant cavity, a transmission line arranged in theback cavity and connected with one end of the second coplanar waveguide, and a probe connected with the transmission line and the metal patch; and one end of the first coplanar waveguide is connectedwith the feed port, and the other end of the first coplanar waveguide is opposite to the end part, far away from the transmission line, of the second coplanar waveguide. Compared with the prior art, the filtering antenna device provided by the invention can inhibit the interference of out-of-band stray signals to effectively reduce the surface wave loss.
Owner:AAC TECH NANJING
Microstrip antenna unit and microstrip antenna
ActiveCN109103575AImprove broadband characteristicsImprove radiation efficiencyRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysPhysicsSurface wave
The invention belongs to the technical field of active phased array radar and antennas. In order to solve the problems that the existing blind spot suppression techniques cannot suppress the scanningblind spots in a wide frequency range and the design difficulty increases due to the introduction of additional structures, the present invention provides a microstrip antenna unit comprising a dielectric plate and a feeding structure arranged on the dielectric plate, the feeding structure being used for suppressing scanning blind spots of the microstrip antenna array. By vertically arranging thesecond feeding structure in the dielectric plate, the surface wave of the microstrip antenna element can be effectively suppressed, thereby eliminating the scanning blind spots of the microstrip antenna array in a wide scanning range.
Owner:LEIHUA ELECTRONICS TECH RES INST AVIATION IND OF CHINA
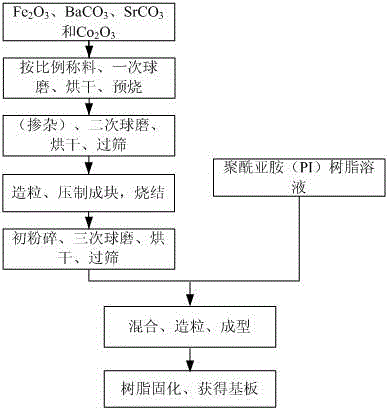
Ferrite-base composite magnetic dielectric antenna substrate material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a ferrite-based composite magnetic dielectric antenna substrate material and a preparation method thereof, which is composed of a main phase material with a mass ratio of 85% to 90% and an auxiliary phase material with a mass ratio of 15% to 10%; The main phase material is Co2Z type hexagonal ferrite, and its molecular formula is Ba3-xSrxCo2Fe24-yO41, wherein the value range of x is 0~1.5, and the value range of y is 0~4. The auxiliary phase material is polyimide resin. The magnetic-dielectric composite substrate material provided by the present invention has lower magnetic permeability and higher dielectric constant in the frequency range of 300 MHz to 3 GHz, higher miniaturization factor, and lower magnetic loss and dielectric loss at the same time ; Better resistance to mechanical shock than conventional ceramic substrate materials. It not only helps to reduce the weight and volume of the antenna, but also improves the bandwidth of the microstrip antenna and suppresses the generation of surface waves.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
AMC-based low-profile circularly-polarized cross dipole antenna and communication equipment
PendingCN112072283AReduce section heightHigh gainRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsDielectric substrateComputational physics
The invention discloses an AMC-based low-profile circularly-polarized cross dipole antenna and communication equipment. The AMC-based low-profile circularly-polarized cross dipole antenna comprises anupper dielectric substrate, a lower dielectric substrate, a main radiation unit, a parasitic unit, an AMC metasurface and a reflection floor, wherein the upper dielectric substrate and the lower dielectric substrate are arranged in parallel at a certain interval; the main radiation unit and the parasitic unit are arranged on the upper dielectric substrate; the upper surface of the lower dielectric substrate is provided with the AMC metasurface, and the lower surface of the lower dielectric substrate is provided with the reflection floor; and the main radiation unit comprises two pairs of dipoles, the two pairs of dipoles are of a cross-shaped cross structure, and a cross point is located at the center point of the upper dielectric substrate. The antenna has the characteristics of good circular polarization radiation performance, low profile and high gain, and can cover a part of C frequency bands of satellite communication.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Meta-material unit and double-layer radiation antenna device based on meta-material
ActiveCN110233353AImprove directionalityHigh gainRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsMicro structureRefractive index
The present invention discloses a meta-material unit. The meta-material unit comprises a substrate A and a micro-structure A attached to the substrate A by adopting metal. The micro-structure A comprises two triangles with an opening at the vertex angle of each triangle, and a line segment connecting the midpoints of the bases of two isosceles triangles. The present invention also discloses a double-layer radiation antenna device based on a meta-material. According to the meta-material unit, two kinds of meta-material unit structures are designed, the two kinds of meta-material unit structureshas near-zero refractive index characteristics between 13 GHz to 17 GHz, when the structures are used in the radiation antenna device, the directivity and the gain of the antenna are improved, a half-power beam contracts to half of the original size, and thus the performance of the antenna device is greatly improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Adjustable patch photonic crystal micro-stripe antenna
InactiveCN101557039ALarge dynamic range of operating frequencyHigh gainAntennasPhotonic crystalPhotonics
The invention discloses an adjustable patch photonic crystal micro-stripe antenna which comprises an RF4 substrate. The RF4 substrate is provided with a patch micro-stripe antenna in the middle; four sides of the patch micro-stripe antenna is provided with photonic crystals of a plurality of cycles; intervals of 1-2 photonic crystal cycles are provided between the photonic crystals and the patch micro-stripe antenna; scatterer units of the photonic crystals are hollow columnar scatterers; the hollow columnar scatterers are hollow columns prepared by dielectric elastic materials; inner and outer surfaces of the hollow columns are provided with compatible electrodes which are connected to an adjustable voltage source; a light flexible glue layer is provided on outer margin, thereby changing thicknesses of the hollow columnar scatterers by the adjustable voltage source to cause shifts of forbidden region frequencies of the photonic crystal, to inhibit surface waves of various frequencies; therefore, various operating frequencies of the micro-stripe antenna can be generated by coupling effect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Coplanar compact type photonic crystal GPS (Global Positioning System) receiving antenna
InactiveCN102800964AImprove performanceIncrease electromagnetic radiation powerRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsDielectric substratePhotonic crystal structure
The invention discloses a coplanar compact type photonic crystal GPS (Global Positioning System) receiving antenna which comprises a dielectric substrate, a patch antenna is arranged on the front face of the dielectric substrate, an earth plate is arranged on the back face of the dielectric substrate, a feed pin is arranged in the center of the earth plate, photonic crystal structures are periodically distributed on the earth plate, each photonic crystal structure unit comprises a square patch and an inductance wire inserted in the middle, and the adjacent photonic crystal structure units are connected via the inductance wire. In the invention, a coplanar compact type photonic crystal is introduced into the earth plate of the patch antenna, the forbidden effect of photonic crystal is utilized, surface waves propagating along a base plate medium are inhibited, the electromagnetic wave radiation power of the antenna coupled to the space is increased, the inhibition of the surface waves can increase the efficiency of the antenna, and the performance of the antenna is improved.
Owner:CHINA ZHENHUA GRP YUNKE ELECTRONICS
High-isolation dual-band polarized reconfigurable antenna based on SIW technology
PendingCN113745817ADual bandImprove isolationRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsReconfigurable antennaSilver paste
The invention provides a high-isolation dual-band polarized reconfigurable antenna based on an SIW (substrate integrated waveguide) technology, which comprises a feed layer structure, a radiation layer structure and a fan-shaped branch direct-current bias structure, and is characterized in that the radiation layer structure is bonded above the feed layer structure in an aligned manner through silver paste; the fan-shaped branch direct-current bias structure for realizing antenna direct-current bias is arranged on the feed layer structure, and the feed layer structure comprises a substrate integrated waveguide feed layer metal cavity which is composed of a plurality of first metal through holes, an upper metal floor and a lower metal floor, wherein the upper metal floor and the lower metal floor are located at the upper end and the lower end of the feed layer structure respectively. The upper metal floor is provided with a polarization reconfigurable slot, and the radiation layer structure comprises a substrate integrated waveguide radiation layer metal cavity formed by a plurality of second metal through holes penetrating through the radiation layer structure; the antenna provided by the invention has the advantages of double frequency bands, high isolation, directional radiation and reconfigurable polarization.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Spiral resonant ring ultra-wideband simultaneous switching noise suppression power distribution network
InactiveCN105515564AImprove practicalitySimple structureVoltage/current interference eliminationUltra-widebandRealizability
The invention discloses a spiral resonant ring ultra-wideband simultaneous switching noise suppression power distribution network, and aims to provide a power distribution network having the advantages of simple structure, high engineering realizability, no need of slotting a power supply plane, no need of any periodical electromagnetic band gap structure and large simultaneous switching noise suppression depth. The technical scheme for realizing the power distribution network is characterized in that a printed circuit board (PCB) structure is adopted for the power distribution network; local isolating structures are positioned in areas where a noise source input circuit and a noise sensitive circuit on a power supply plane structure are positioned respectively, and etched with spiral resonant rings; the spiral resonant rings are etched on the power supply plane according to a power supply plane distribution structure in order to isolate simultaneous switching noise between a power supply and a ground plane; and an attenuation band is formed in a band frequency band through the resonant effects of the spiral resonant rings in conjunction with coupling resonance among the power supply plane, a ground plane metal layer and a dielectric layer, so that a transmission path of the simultaneous switching noise is blocked; surface waves are suppressed; and the simultaneous switching noise is suppressed.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Two-frequency wideband electromagnetic band gap structure and making method
InactiveCN100440616CSmall geometrySuppression of surface wavesRadiating elements structural formsWaveguide type devicesLine widthEngineering
This invention provides a double frequency wide band electromagnetic band gap (EBG) structure and its manufacturing method characterizing that the provided structure is a mixed one combining a punch structure and a high resistant surface structure, the medium substrate in the EBG structure is square with the punch and high resistant structure adhered closely on its surface, the central frequencies of the stop-bands are 1.6GHZ and 2.4GHz. The punch and high resistant structures are composed of a periodical metal plate unit, punch narrow gaps and metallic post on the plate. According to a known work frequency, the medium thickness and its dielectric constant, the micro-band line width, the sizes of the substrate, the quadrant metallic plate and high resistant surface gap are computed preliminarily then to determine its final sizes by optimizing and emulating utilizing the emulation software of HFSS8.0 edition.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Orthohexagonal EBG structure used for antenna and manufacturing technology thereof
ActiveCN109411889AMeet the requirements of structure miniaturizationGood bandgap performanceAntenna couplingsWhiteboardManufacturing technology
The invention discloses an orthohexagonal EBG structure used for an antenna and a manufacturing technology thereof, belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and solves the problems that a traditional EBG structure is large in structure size, difficult to meet the requirement of miniaturization and jagged in forbidden band characteristics in all directions. The orthohexagonal EBG structure used for the antenna mainly comprises a MARK layer, a first-order white board layer set, a coil layer set, a bottom electrode layer and a second-order white board layer set from top to bottomin sequence through overlapping. According to the orthohexagonal EBG structure used for the antenna, the product size is greatly reduced, and the requirement of wireless communication field on the miniaturization of the EBG structure is met; the heights of the forbidden band characteristics in all directions are the same; the technological process is reliable and practicable, the manufactured product is stable in performance, the orthohexagonal EBG structure used for the antenna is significant for improving the performance of a patch antenna, and the EBG structure can be widely applied to thetechnical field of wireless communication.
Owner:扬州市伟荣新材料有限公司
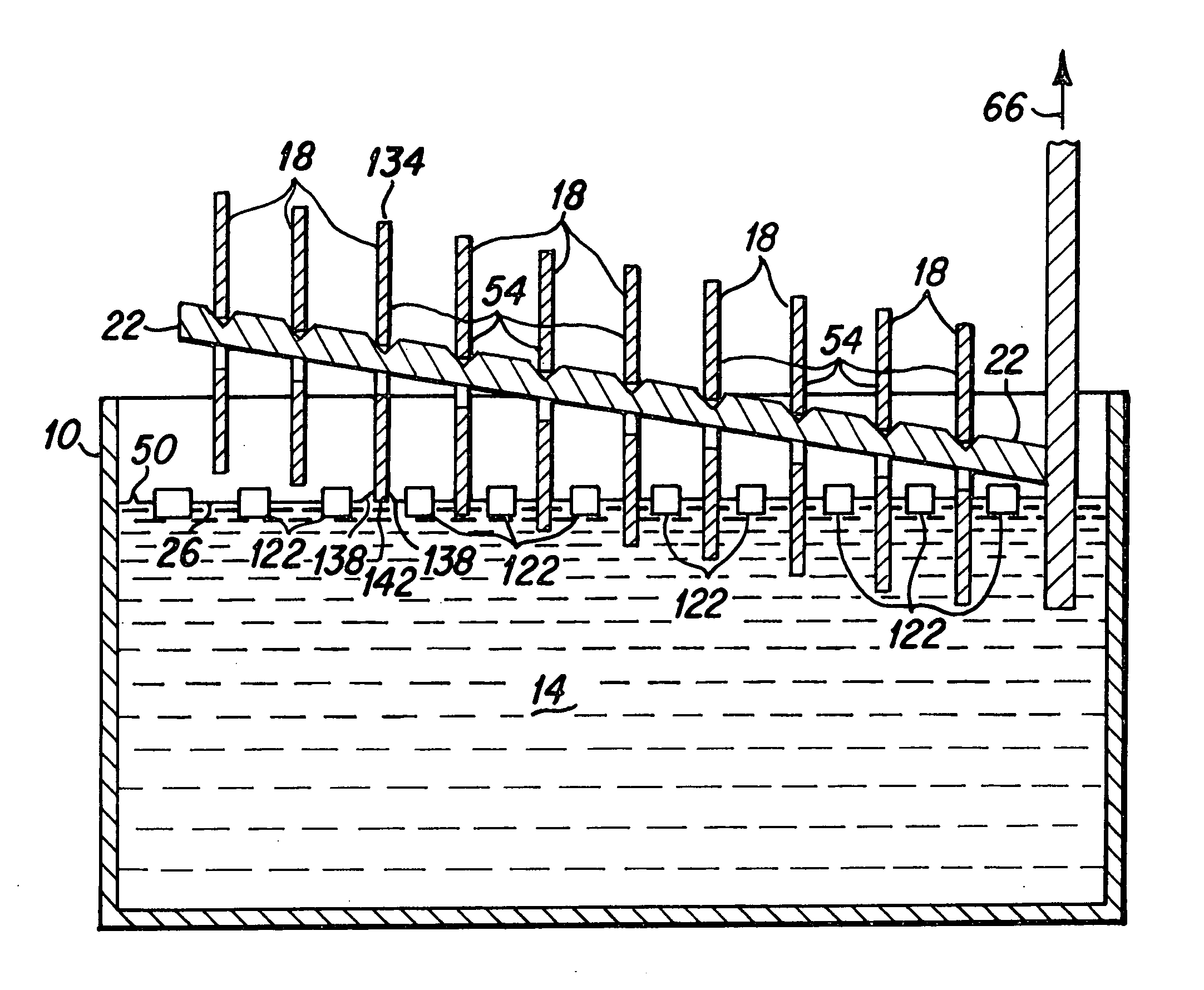
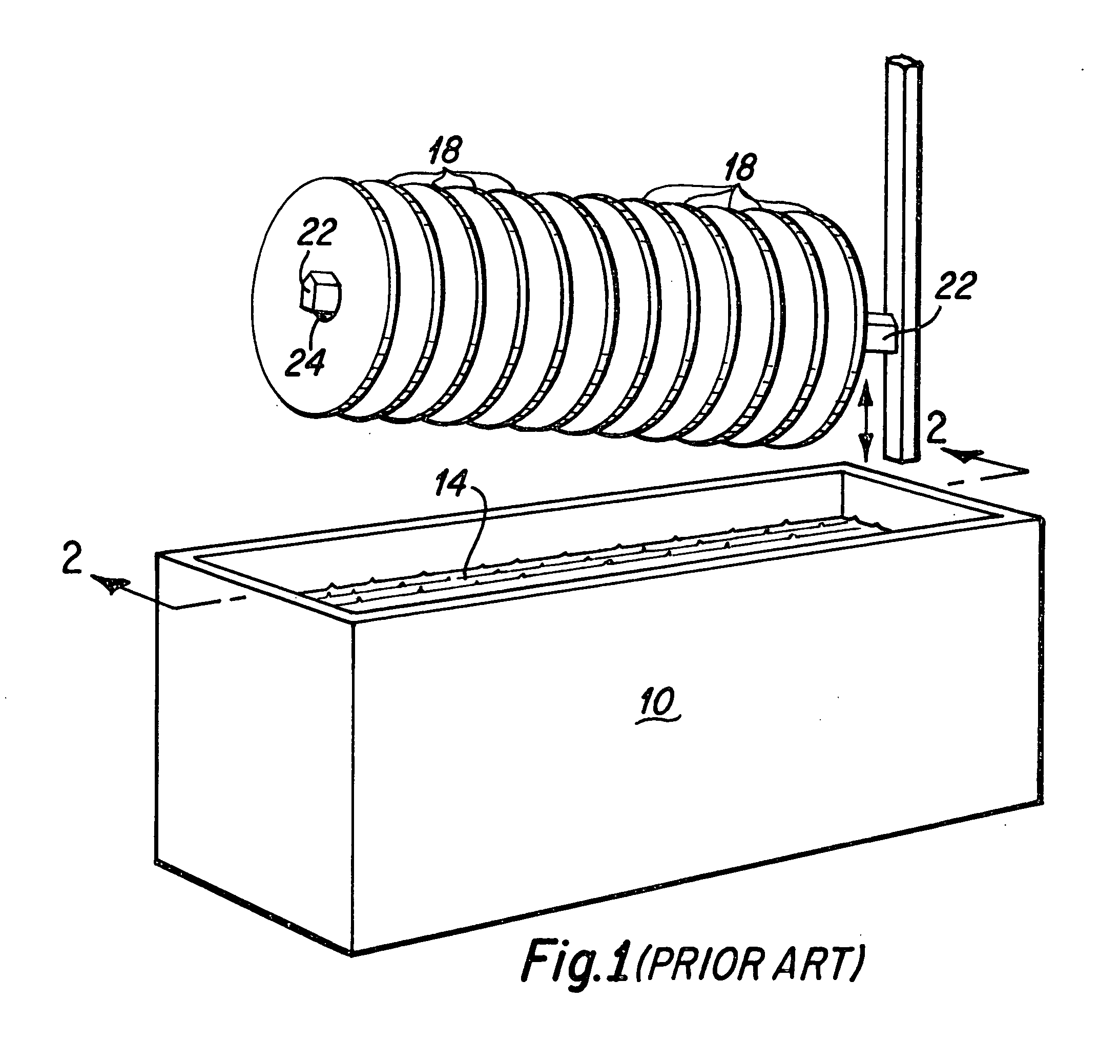
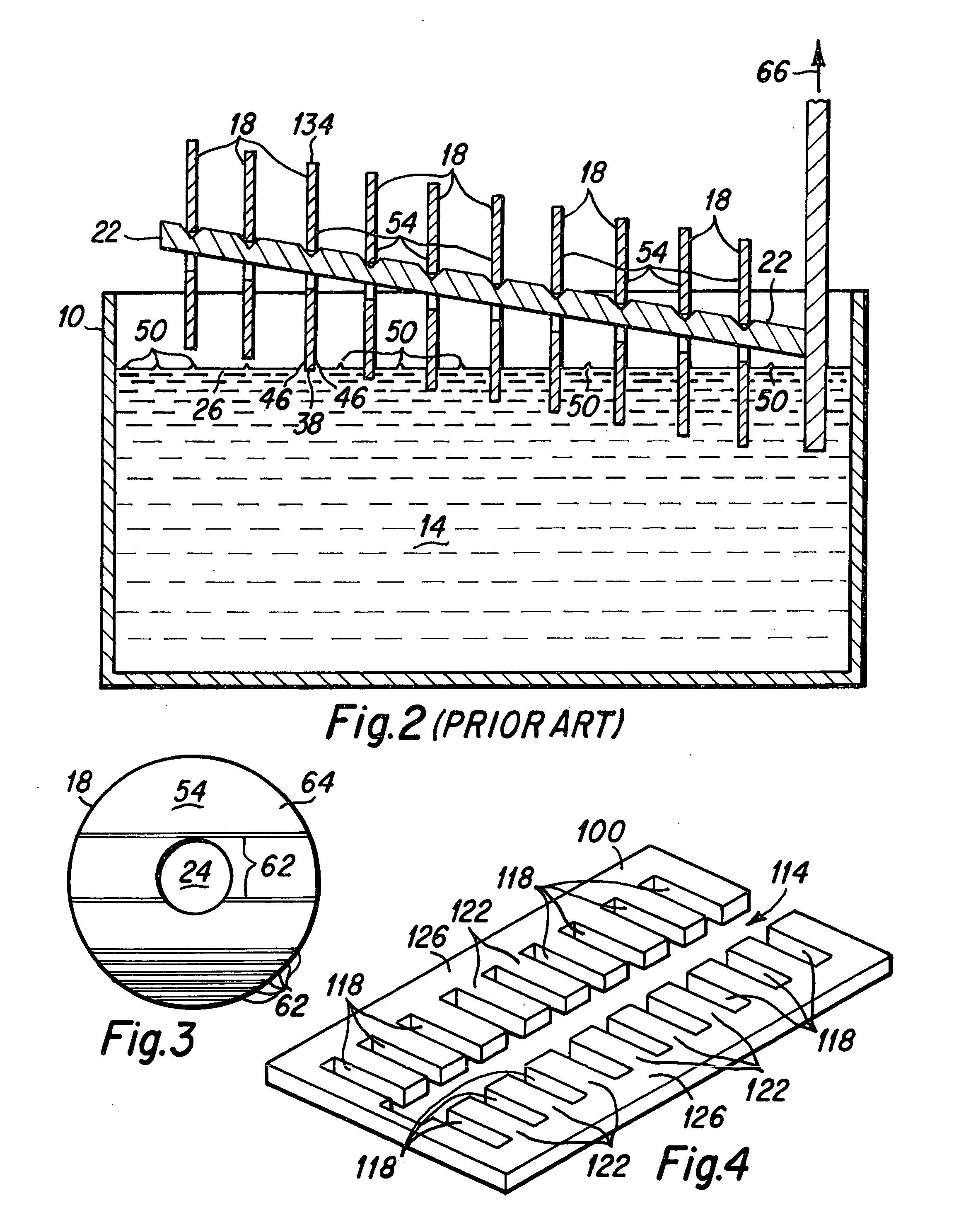
Disk lubricant tank insert to suppress lubricant surface waves
InactiveUS20060062957A1Suppression of surface wavesUniform lubricant coatingLiquid surface applicatorsLayered productsFuel tankEngineering
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
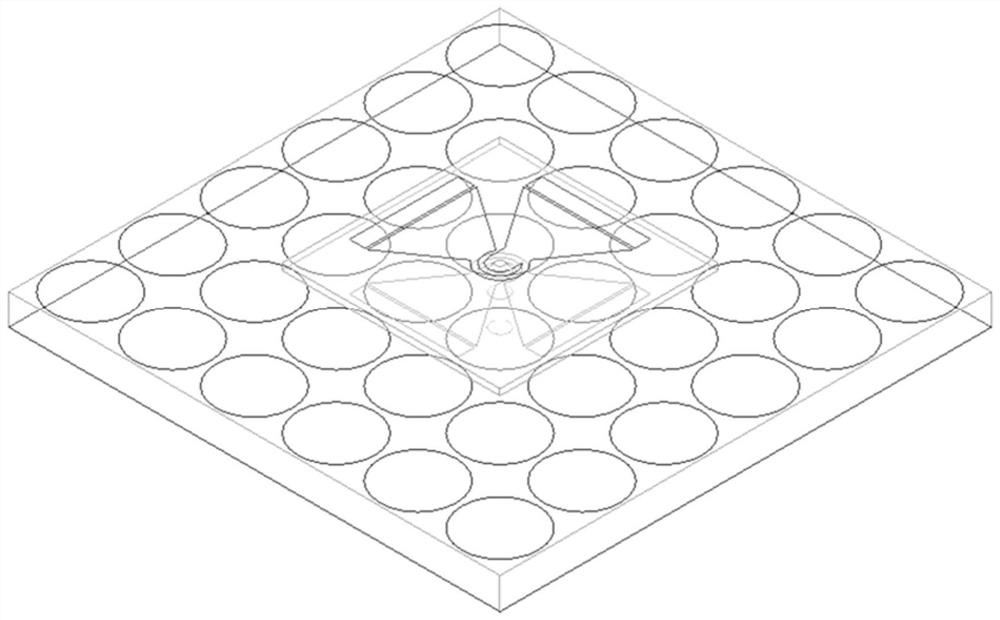
A dual-frequency ebg structure and a microstrip antenna based on the dual-frequency ebg structure
ActiveCN107134637BGood radiation characteristicsSuppression of surface wavesSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a dual-frequency EBG structure, which comprises a metal grounding plate, a dielectric substrate, a plurality of EBG metal patches arranged periodically and conductive via holes, and the EBG metal patches and metal grounding plates are respectively located on the upper and lower surfaces of the dielectric substrate , the conductive via hole is set in the center of the EBG metal patch to connect the EBG metal patch and the metal grounding plate, and the four surrounding edges of the EBG metal patch are etched with four rectangular slots symmetrically distributed about the center of the EBG metal patch and four four One-third circular groove. A microstrip antenna based on a dual-frequency EBG structure, including a microstrip patch antenna and a dual-frequency EBG structure with the above structure loaded around it, the microstrip patch antenna is located on the upper surface of a dielectric substrate and the antenna radiation patch it uses Two symmetrical rectangular slots and C-shaped bent branch slots are etched on the chip. By loading the EBG structure around the microstrip antenna, the surface wave of the antenna is suppressed, the working bandwidth of the antenna is improved, the gain of the antenna is increased, and the back radiation of the antenna is reduced.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Low-loss band-pass filter based on defected ground structure
InactiveCN101853975BImproved stop-band rejection performanceGood choiceWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceTransmission zeros
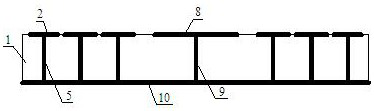
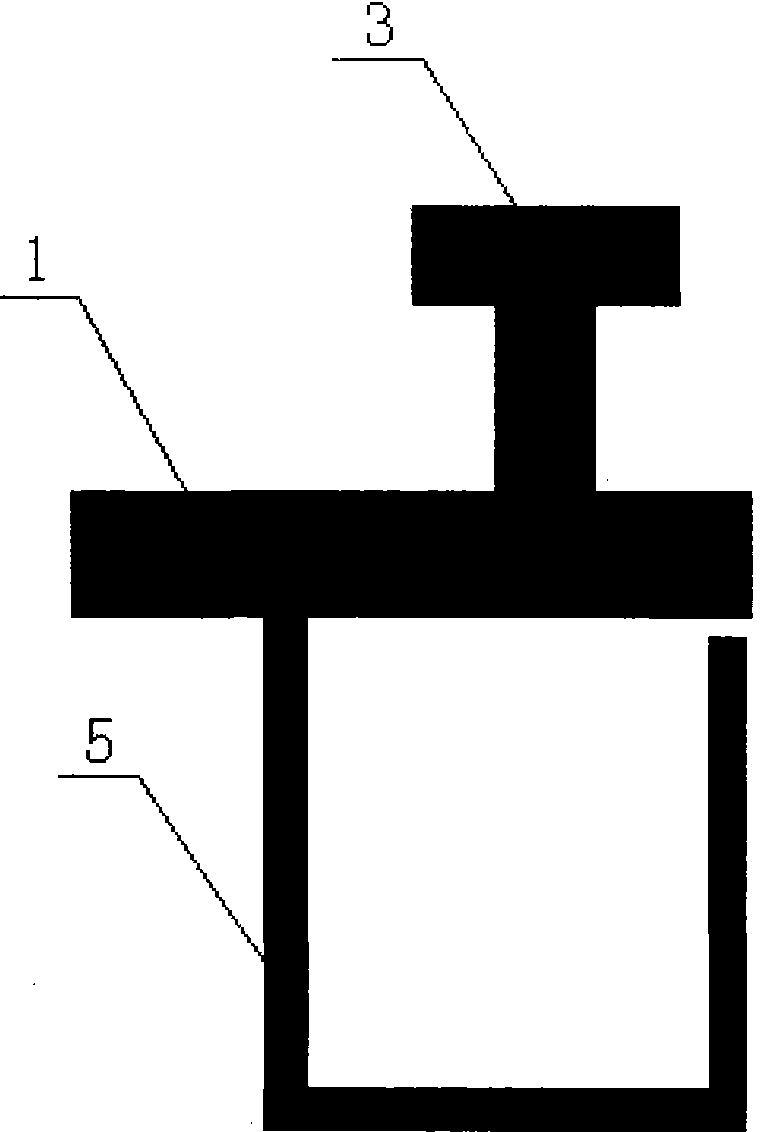
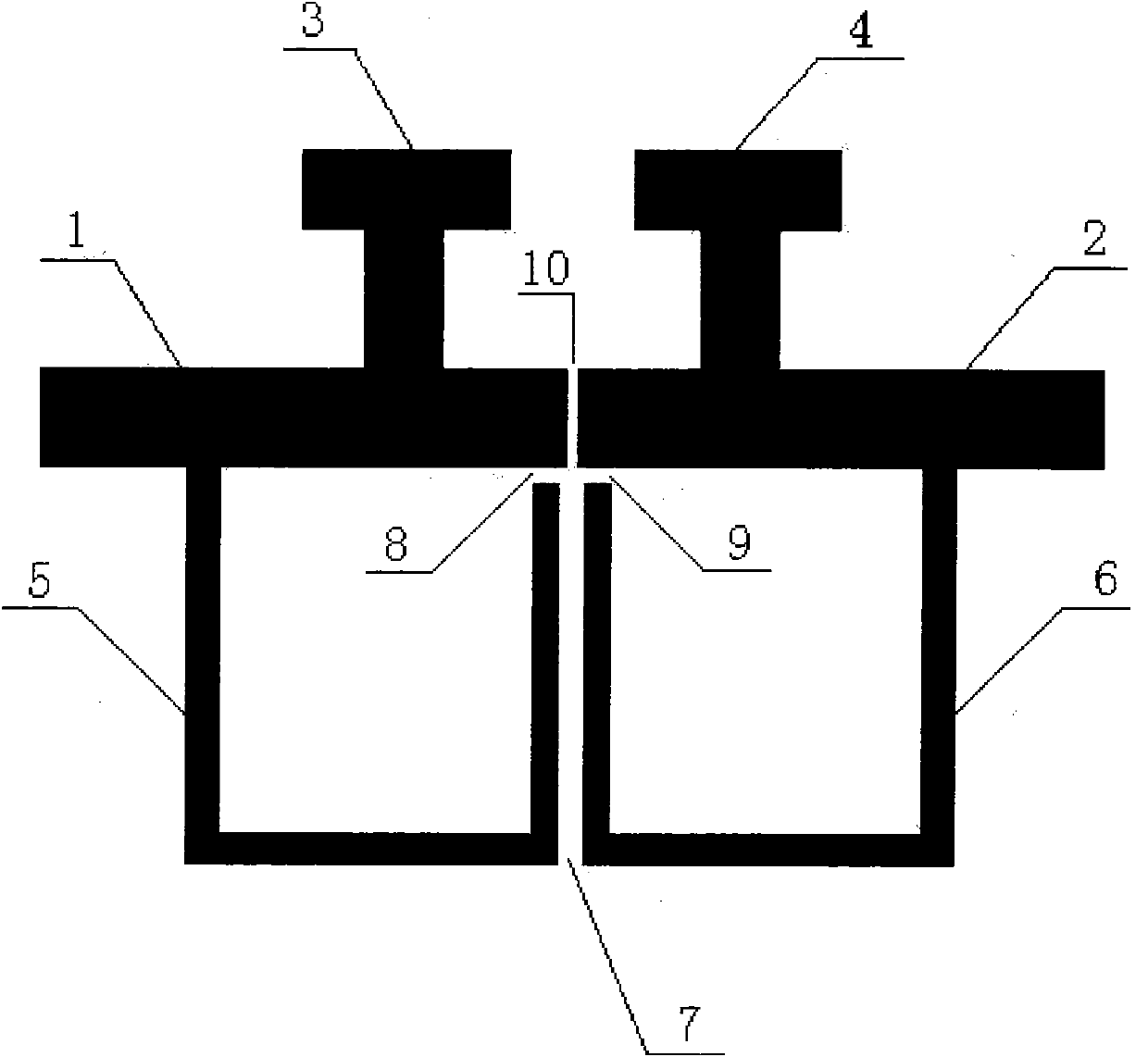
The invention discloses a low-loss band-pass filter based on a defected ground structure. A pair of folded type feeder structures (5) and (6) is adopted on micro-strip transmission lines matched at 50 ohmage impedance at the upper layer of the filter; a pair of T-type loading capacitors (3) and (4) is loaded; and a concave defected ground structure (DGS) is adopted on the horizontal plane of the filter. The folded type feeders (5) and (6) are coupled through a gap (7); and an input micro-strip transmission line (1) and an output micro-strip transmission line (2) are coupled through a gap (10). The invention adopts symmetric folded type feeder structures; the T-type loading capacitors and the concave DGS simplify the processing complexity and generate two transmission zeros around a passband; in addition, the concave DGS improves the inhibition of a filter rejection band which can inhibit the influence of surface waves and ultraharmonics, thereby obtaining better frequency selectivity. The invention has compact and tiny design, is easy to integrate, and can be used in a dense integrated circuit conveniently.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Handheld interference unit and interference unit antenna thereof
ActiveCN112635962AHigh gainWide matching bandwidthAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric plateRadome
The embodiment of the invention provides a handheld interference unit and an interference unit antenna thereof. The interference unit antenna comprises: an antenna body which comprises a first dielectric plate and a radiation patch formed on the surface of the first dielectric plate, wherein a radiation signal of the interference unit antenna is transmitted in the extension direction of the first dielectric plate, and is output from the end part of the first dielectric plate; and a metamaterial antenna housing arranged in parallel with the first dielectric plate at an interval and corresponds to the position of the radiation patch, wherein the metamaterial antenna housing covers the radiation patch in the extending direction of the first dielectric plate so as to suppress surface waves radiated from the radiation patch.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
A hand-held jammer and its jammer antenna
ActiveCN112635962BHigh gainSuppression of surface wavesAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric plateEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention provide a handheld jammer and its jammer antenna, including: an antenna body, the antenna body includes a first dielectric plate and a radiation patch formed on the surface of the first dielectric plate, the jammer antenna The radiated signal is transmitted along the extension direction of the first dielectric plate, and is output from the end of the first dielectric plate; a metamaterial radome, the metamaterial radome is arranged in parallel with the first dielectric plate, and Corresponding to the position of the radiation patch, the metamaterial radome covers the radiation patch in the extending direction of the first dielectric plate to suppress surface waves radiated from the radiation patch.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
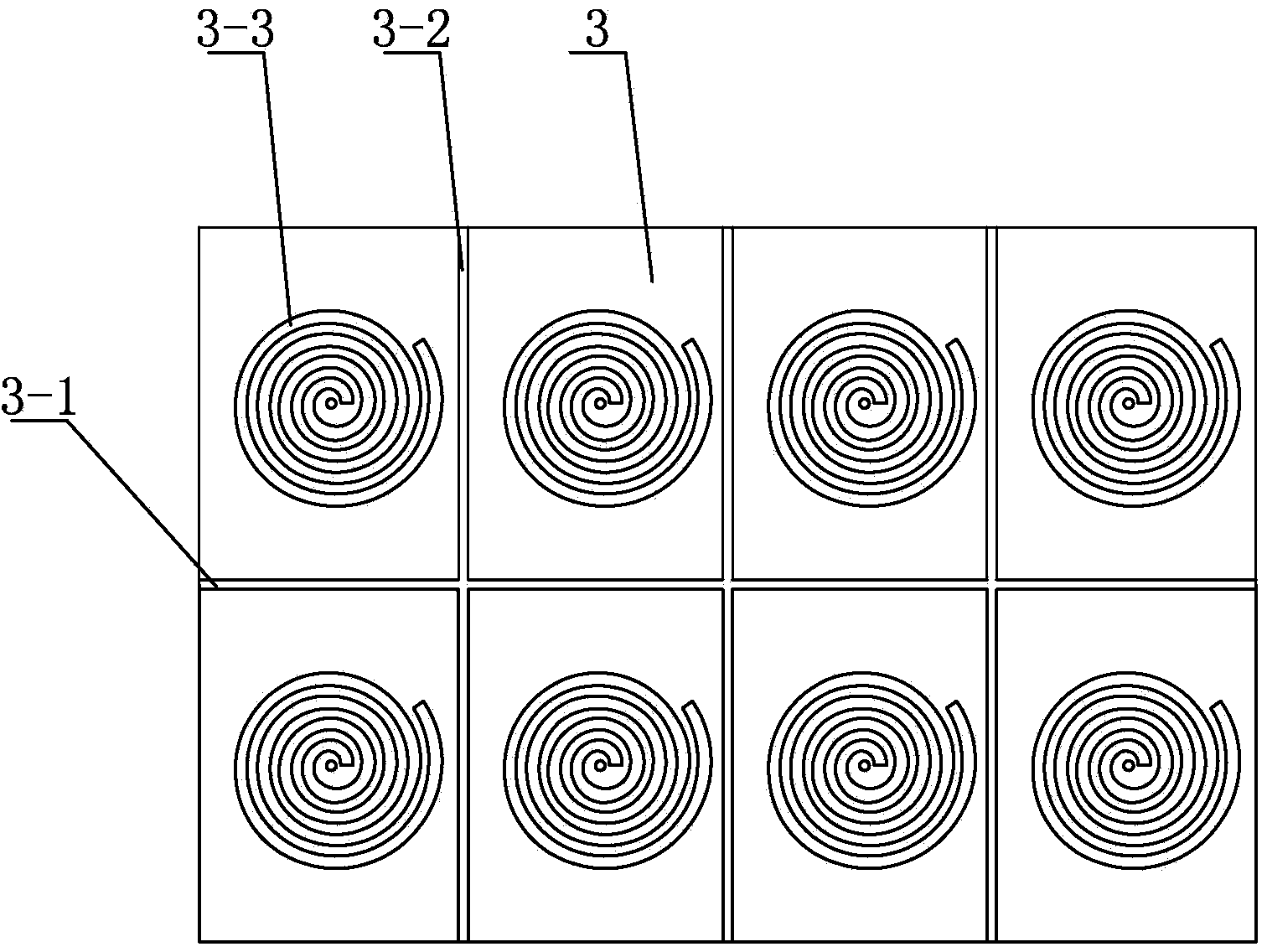
PIFA with Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as floor board
ActiveCN104241820ASuppression of surface wavesBack radiation suppressionRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention relates to a PIFA, in particular to a PIFA with an Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as a floor board. The PIFA with the Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as the floor board solves the problems that an existing PIFA is low in radiant efficiency and large in overall size. The PIFA with the Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as the floor board comprises a radiation sheet, a short circuit plate, the floor board, a coaxial inner conductor and a coaxial outer conductor; the radiation sheet and the floor board are sequentially arranged side by side in parallel from top to bottom; the tip of the left end of the radiation sheet is connected with the tip of the left end of the floor board through the short circuit plate; the coaxial outer conductor is vertically arranged below the left end of the floor board, and the upper end of the coaxial outer conductor is connected with the lower surface of the left end of the floor board; the coaxial inner conductor is vertically arranged between the radiation sheet and the floor board, and the upper end of the coaxial inner conductor is connected with the lower surface of the left end of the radiation sheet. The PIFA with the Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as the floor board is applied to the field of wireless communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A choke type gnss satellite antenna
ActiveCN110676562BHigh gainBack radiation suppressionAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsSatellite antennasInterference resistance
The invention discloses a choke-type GNSS satellite antenna, which comprises a suppressing reflection plate, a metal plate and a dielectric layer. The metal plate is arranged above the suppressing reflection plate, and there is a first distance between the lower surface of the metal plate and the upper surface of the suppressing reflection plate, and the first distance forms an air layer for communicating with air. The medium layer is arranged on the upper surface of the metal plate, and the antenna radiation piece is arranged on the medium layer. The GNSS satellite antenna provided by the present invention can realize signal superposition and cancellation in different directions of the antenna by forming an air layer between the suppressing reflector and the metal plate for communicating with the air, which not only greatly improves the gain of the antenna, Moreover, the backward radiation of the antenna is suppressed, so that the front-to-back ratio of the antenna is improved, and the invention has a good anti-interference effect. In addition, the anti-multipath signal design is achieved by adopting the anti-reflection plate and the metal plate above the anti-reflection plate, which has a simple structure, does not need to arrange multiple metal grooves, and has low cost and light weight.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GEOELECTRON
PIFA with I-shaped fractal EBG structure as floor
InactiveCN104183915AImprove radiation efficiencySuppression of antenna surface waves and back radiationRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsEngineeringRadiation
The invention relates to a PIFA, in particular to a PIFA with an I-shaped fractal EBG structure as a floor. The PIFA solves the problems that an existing PIFA is low in radiation efficiency and large in overall size. The PIFA comprises a radiation sheet, a short-circuit board, a floor, a coaxial inner conductor and a coaxial outer conductor. The radiation sheet and the floor are sequentially arranged side by side in parallel from top to bottom, the left end of the radiation sheet is connected with the left end of the floor through the short-circuit board, and the coaxial outer conductor is vertically arranged below the left end of the floor. The PIFA is applied to the field of wireless communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A metamaterial unit and a double-layer radiating antenna device based on the metamaterial
ActiveCN110233353BImprove directionalityHigh gainRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsBi layerRefractive index
The invention discloses a metamaterial unit A, comprising a substrate A, and a microstructure A attached to the substrate A by metal, the microstructure A comprising two triangles with openings at the vertices, and two isosceles triangle bases connected The line segment of the midpoint of the edge. The invention also discloses a double-layer radiation antenna device based on metamaterial. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: the present invention designs two kinds of metamaterial unit structures, and these two metamaterial unit structures have near-zero refractive index characteristics at 13GHz to 17GHz, and after being used in a radiation antenna device, the directivity and gain of the antenna are improved , the half-power beam shrinks to half of the original, greatly improving the performance of the antenna device.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Adjustable patch photonic crystal micro-stripe antenna
InactiveCN101557039BLarge dynamic range of operating frequencyHigh gainAntennasPhotonic crystalPhotonics
The invention discloses an adjustable patch photonic crystal micro-stripe antenna which comprises an RF4 substrate. The RF4 substrate is provided with a patch micro-stripe antenna in the middle; four sides of the patch micro-stripe antenna is provided with photonic crystals of a plurality of cycles; intervals of 1-2 photonic crystal cycles are provided between the photonic crystals and the patch micro-stripe antenna; scatterer units of the photonic crystals are hollow columnar scatterers; the hollow columnar scatterers are hollow columns prepared by dielectric elastic materials; inner and outer surfaces of the hollow columns are provided with compatible electrodes which are connected to an adjustable voltage source; a light flexible glue layer is provided on outer margin, thereby changingthicknesses of the hollow columnar scatterers by the adjustable voltage source to cause shifts of forbidden region frequencies of the photonic crystal, to inhibit surface waves of various frequencies;therefore, various operating frequencies of the micro-stripe antenna can be generated by coupling effect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A pifa antenna with an archimedes helix ebg structure as the floor
ActiveCN104241820BSuppression of surface wavesImprove Radiation PerformanceRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention relates to a PIFA, in particular to a PIFA with an Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as a floor board. The PIFA with the Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as the floor board solves the problems that an existing PIFA is low in radiant efficiency and large in overall size. The PIFA with the Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as the floor board comprises a radiation sheet, a short circuit plate, the floor board, a coaxial inner conductor and a coaxial outer conductor; the radiation sheet and the floor board are sequentially arranged side by side in parallel from top to bottom; the tip of the left end of the radiation sheet is connected with the tip of the left end of the floor board through the short circuit plate; the coaxial outer conductor is vertically arranged below the left end of the floor board, and the upper end of the coaxial outer conductor is connected with the lower surface of the left end of the floor board; the coaxial inner conductor is vertically arranged between the radiation sheet and the floor board, and the upper end of the coaxial inner conductor is connected with the lower surface of the left end of the radiation sheet. The PIFA with the Archimedes spiral EBG structure used as the floor board is applied to the field of wireless communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com