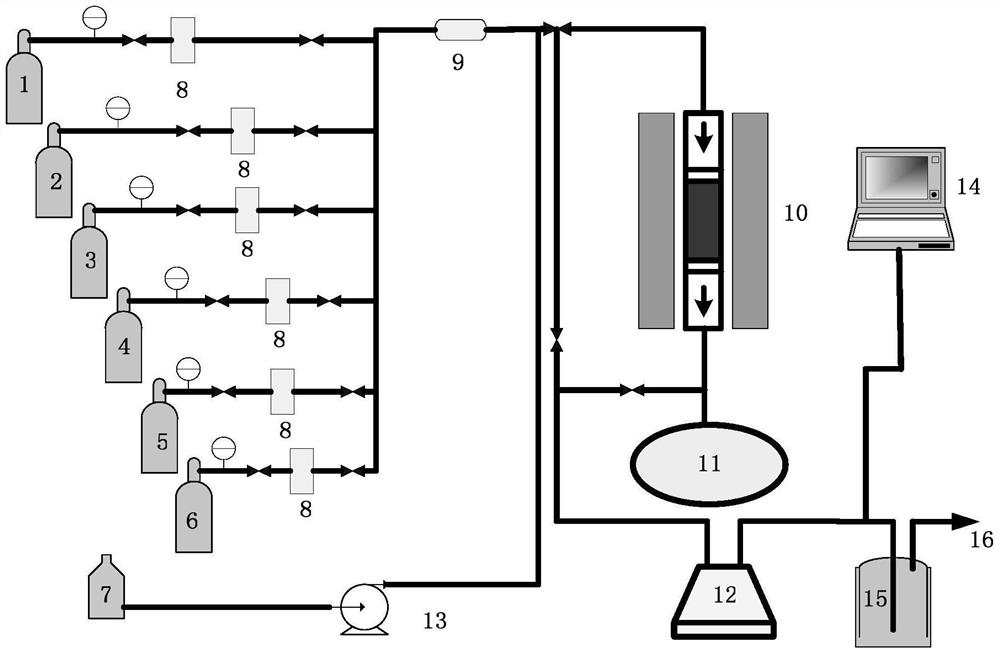
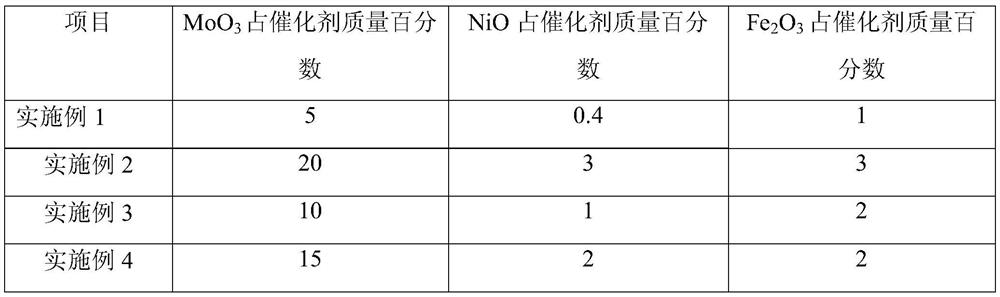
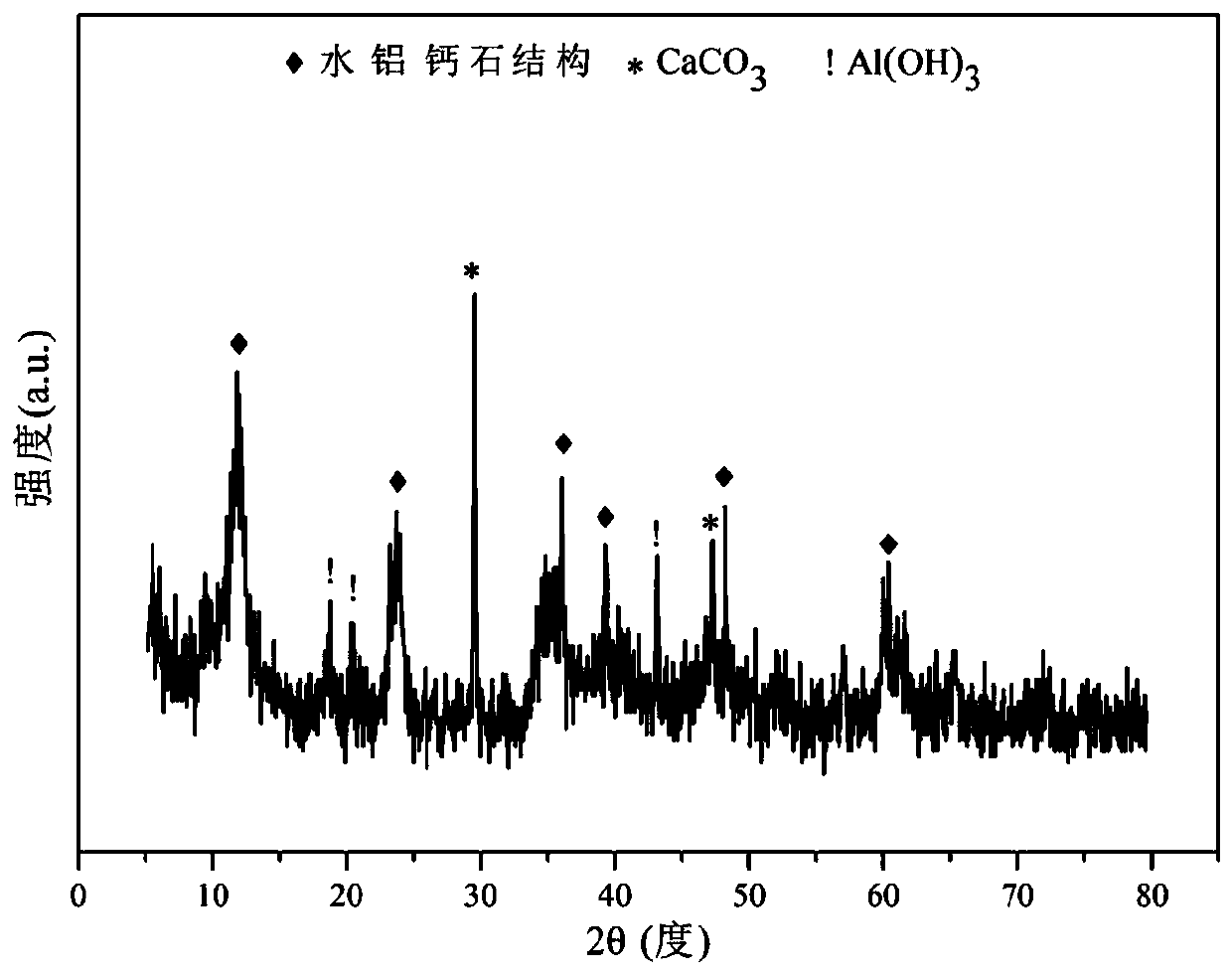
Patents
Literature
30results about How to "With anti-coke" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nickel-base catalyst used for autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101972656AEasy to introduceLarge specific surface areaHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsManganeseCarbon deposit
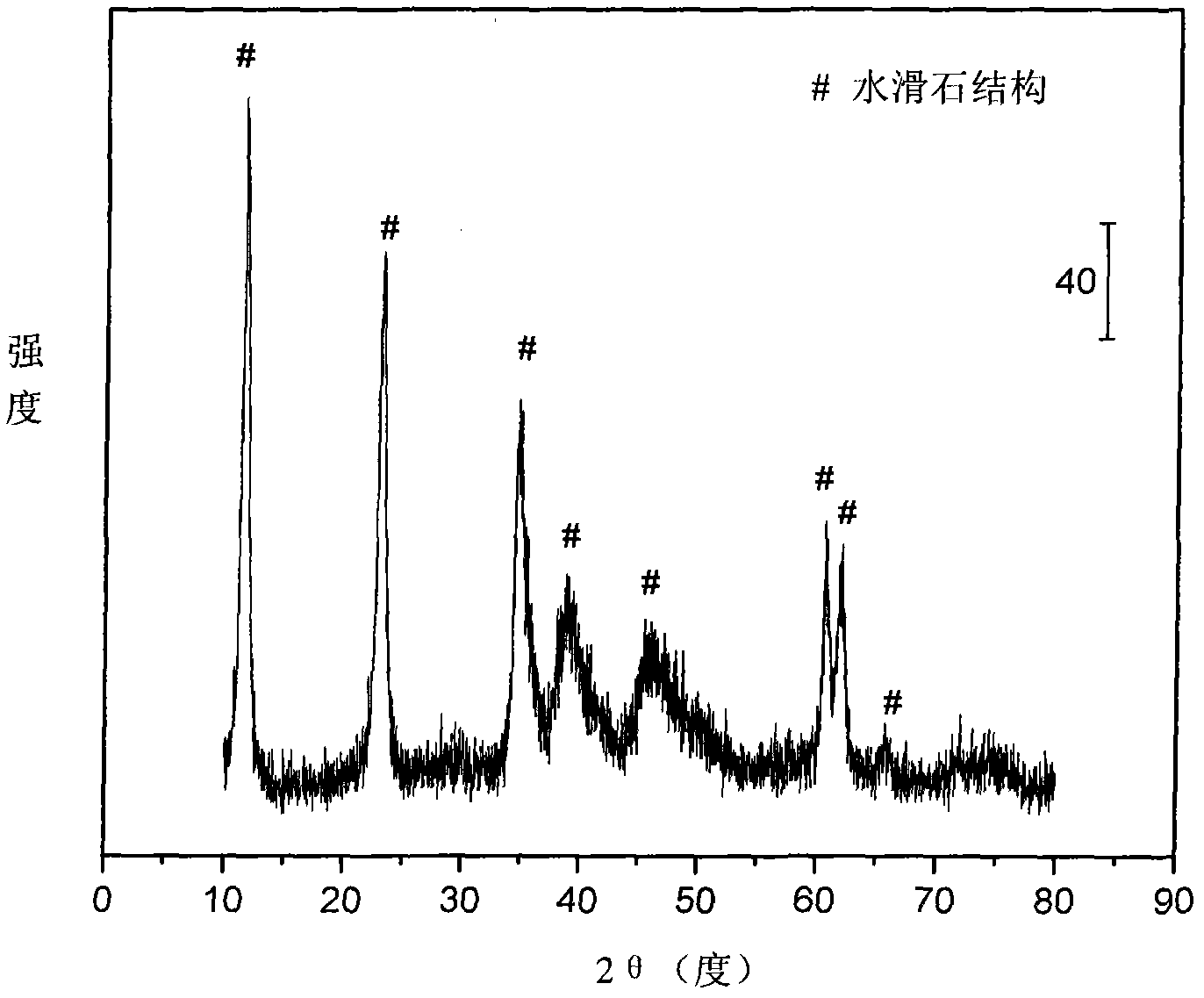
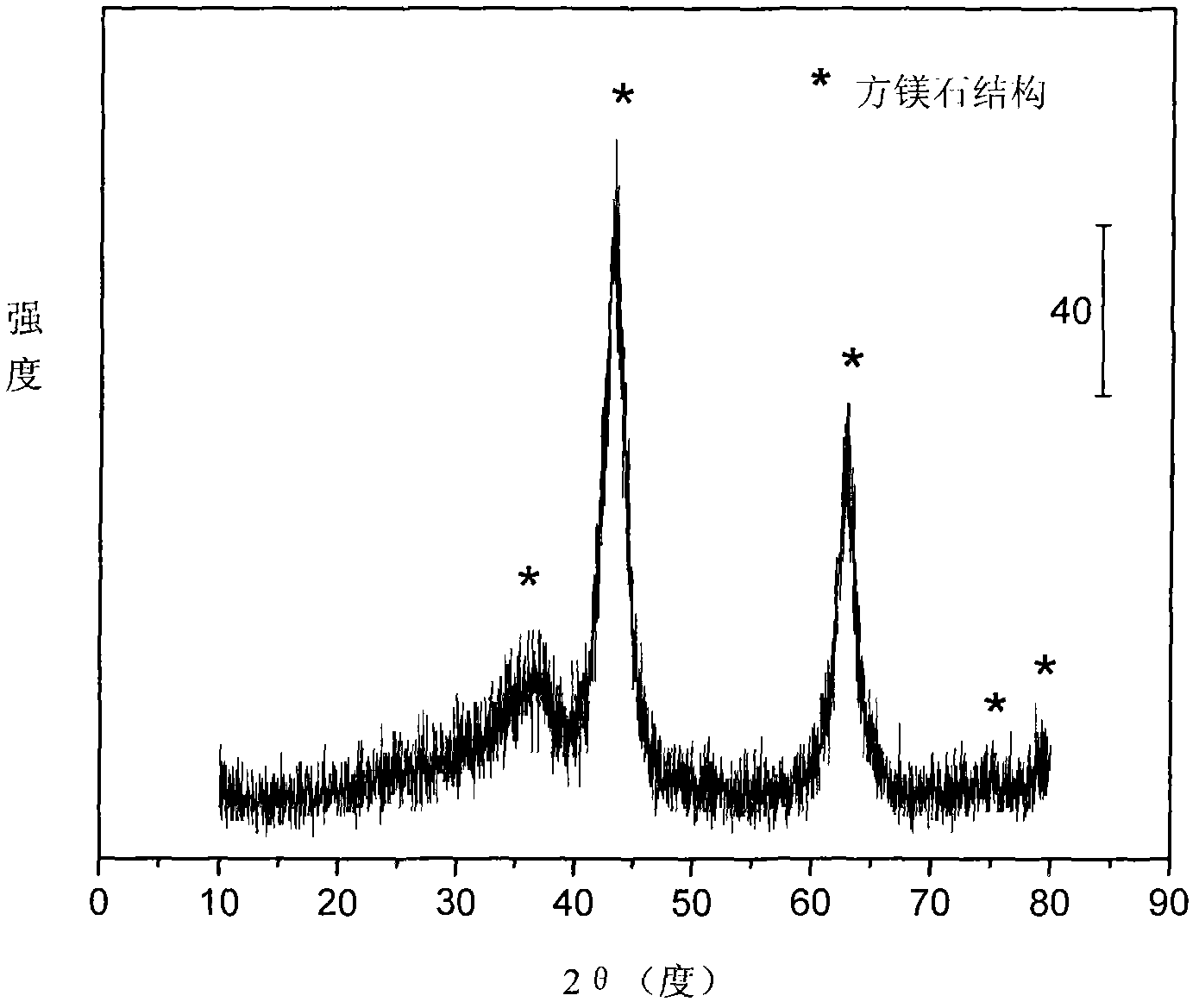
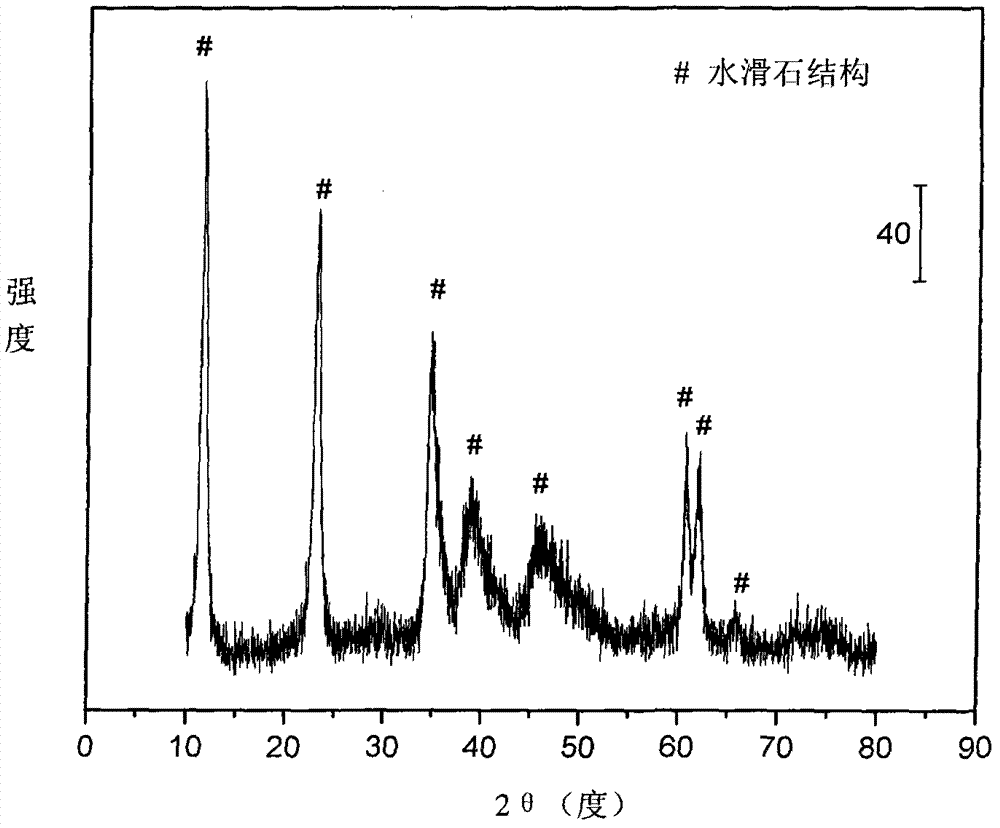
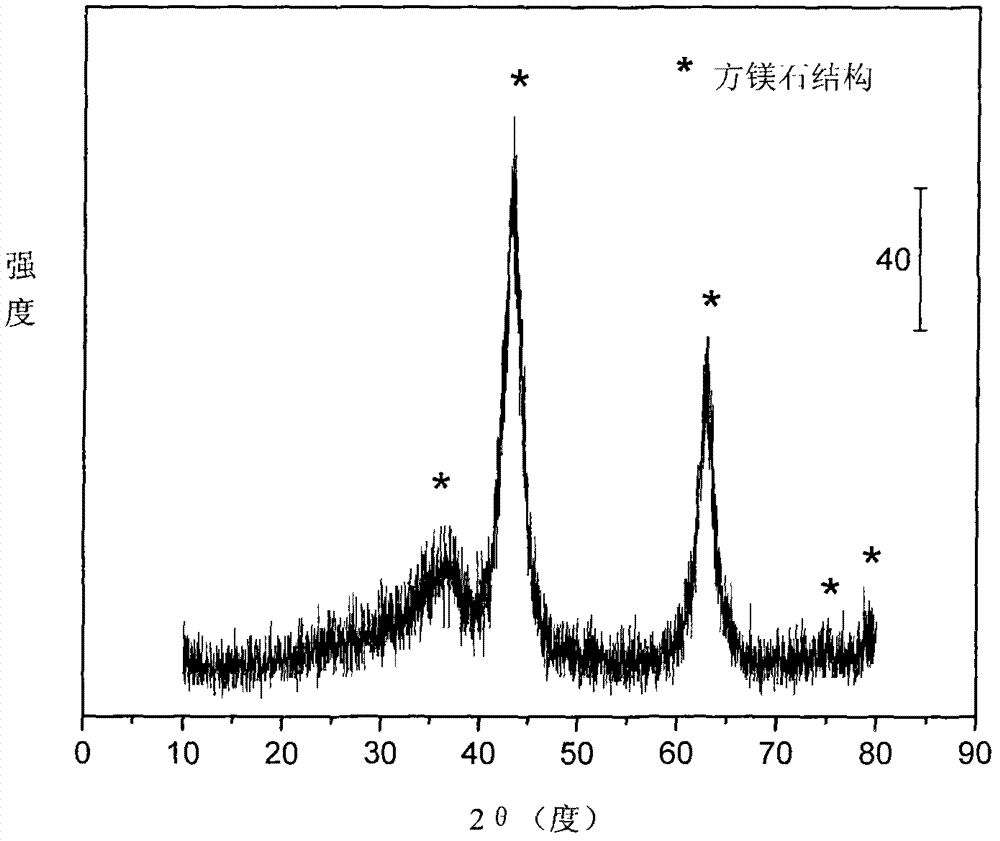
The invention relates to a nickel-based catalyst used for the autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and a preparation method thereof. Aiming at the problems of structural change, oxidation and sintering of active ingredients and deactivation of the conventional catalyst during the autothermal reforming of the ethanol, the invention provides a novel catalyst with a stable structure, sintering resistance, carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity. The chemical formula of the catalyst is NiaMgbAlcXdO4.5+ / -delta, wherein X is an auxiliary agent Fe or Mn, a is 0.25 to 0.40, b is 2.6 to 2.75, c is 0.1 to 0.8 and d is 0.2 to 0.9. A brucite-based (Mg(OH)2.mH2O) hydrotalcite structure is taken as a precursor, so that the active ingredient nickel and the auxiliary agent heteroion component are introduced into a laminated structure and a position between laminated structures; meanwhile, the auxiliary agent iron or magnesium is introduced, so the reducibility and stability of the active ingredients of the catalyst are improved, and the yield of the hydrogen is obviously improved and remains stable.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
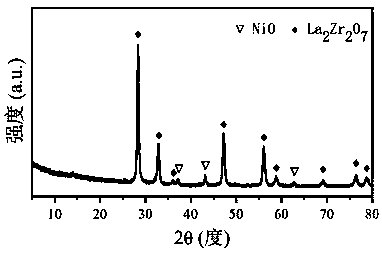
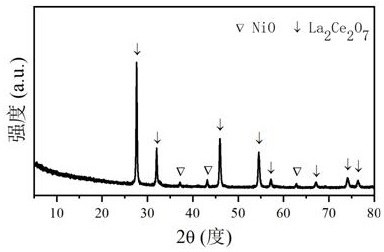
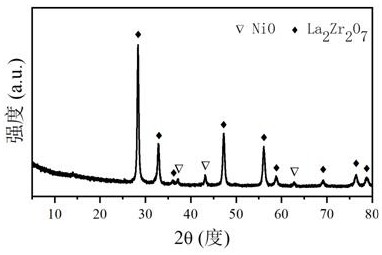
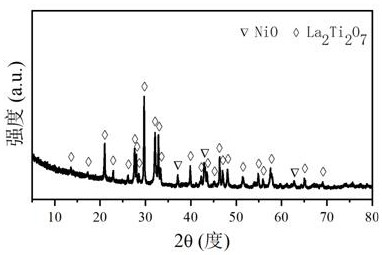
Ni/La2X2O7 catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN111111674AGood choiceHigh catalytic activityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsAcetic acidPtru catalyst
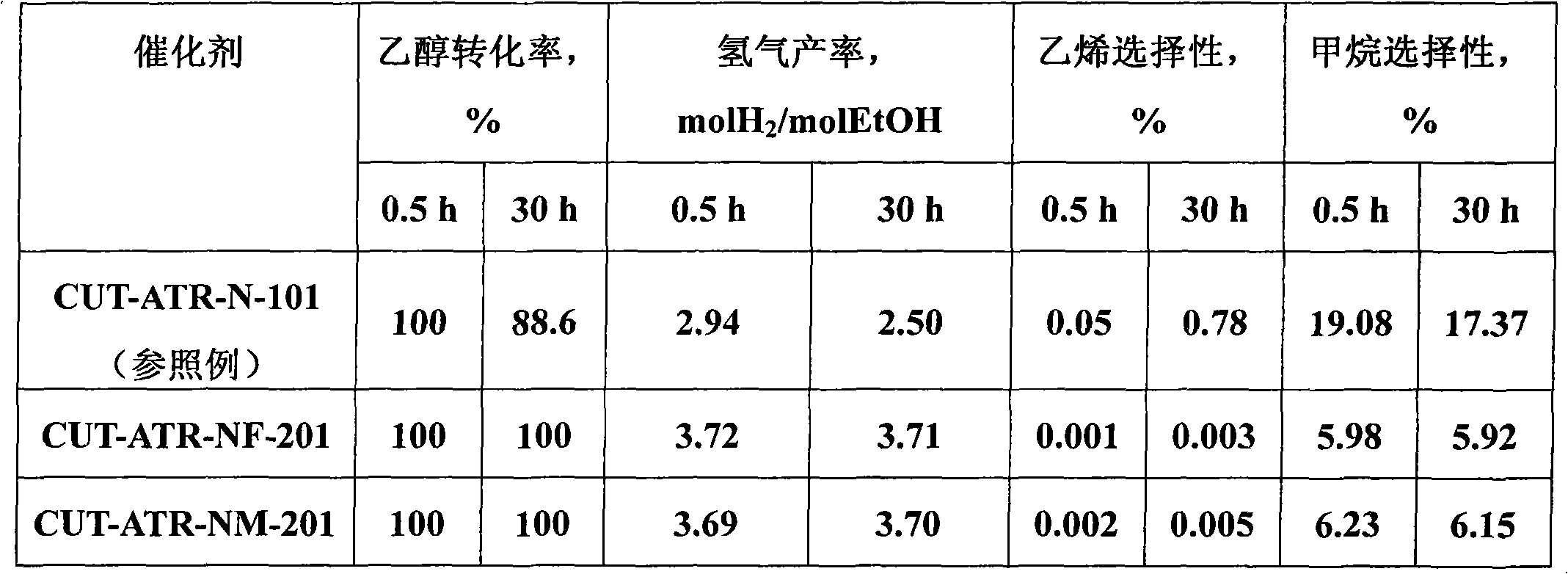
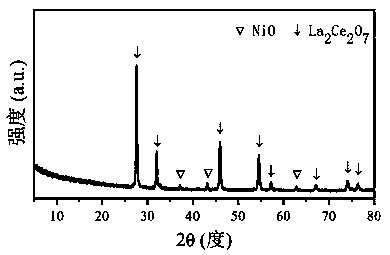
The invention relates to a Ni / La2X2O7 catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. , Aiming at the problem of inactivation of an existing catalyst in the acetic acid autothermal reforming process, the invention provides the novel catalyst which is stable in structure and high in activity. A catalyst precursor is prepared by adopting a sol-gel method, and roasted by adopting an impregnation method to obtain the Ni / La2X2O7 (X is Ce, Zr or Ti) catalyst. According to the catalyst, the stability of active components is improved, the yield of hydrogen is increased, and generation of byproducts such as methane and acetone is effectively inhibited.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Perovskite catalyst used for autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101972659AChange the adsorption and desorption propertiesEnhanced autothermal reforming activityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsManganeseOxygen
The invention relates to a perovskite catalyst used for the autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and a preparation method thereof. Aiming at the problems of structural change, oxidation and sintering of active ingredients and deactivation of the conventional catalyst during the autothermal reforming of the ethanol, the invention provides a novel catalyst with sintering resistance, carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity. The chemical formula of the catalyst is LaaSrbNicXdO3, wherein X is one of Fe, Mn and Cr, a is 0.7 to 1.0, b is 0 to 0.3, c is 0.7 to 0.95 and d is 0.05 to 0.3. The nickel-based catalyst with an ABO3 perovskite structure is prepared by a glycine complexation method, lanthanum is partially substituted by strontium at a position A and nickel is partially substituted by an auxiliary agent at a position B, so oxygen defects and lattice structure defects on the surface of the perovskite catalyst are increased; meanwhile, the auxiliary agent, namely iron, magnesium or chromium is introduced, so the acidity of the catalyst is inhibited, the reducibility and stability of the active ingredients of the catalyst are improved, and the yield of the hydrogen is obviously improved and remains stable.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
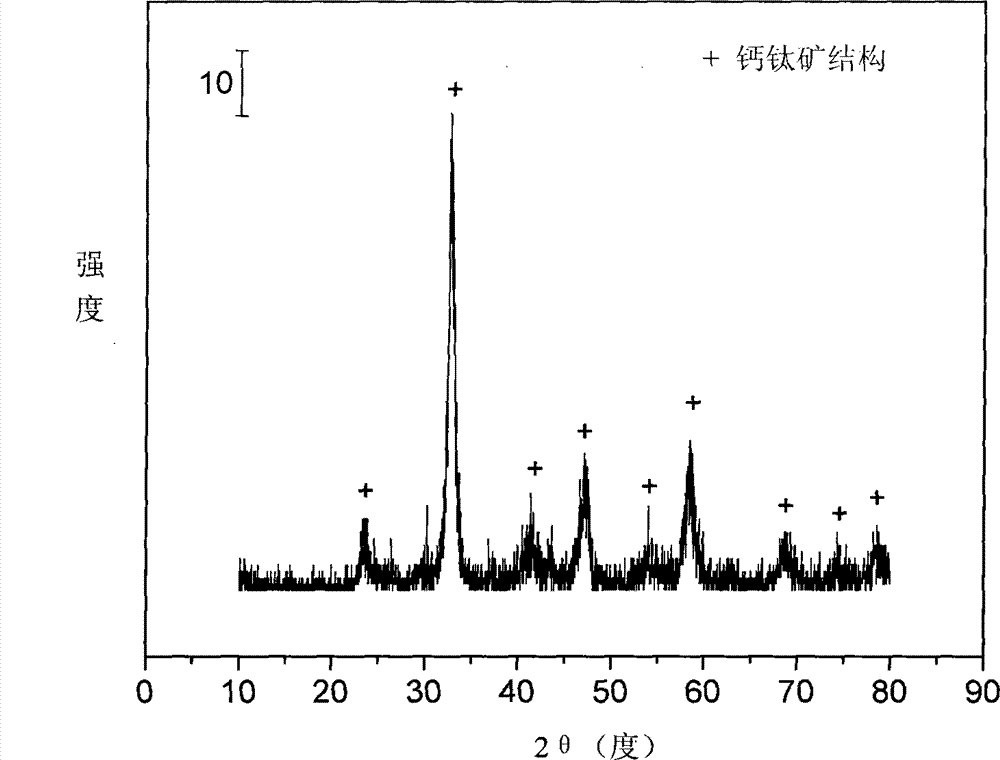
Layered perovskite catalyst for hydrogen generation from acetic acid autothermal reforming and preparation method
ActiveCN107042111AImprove stabilityAdd Surface Defect BitsHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsLanthanumHYDROSOL
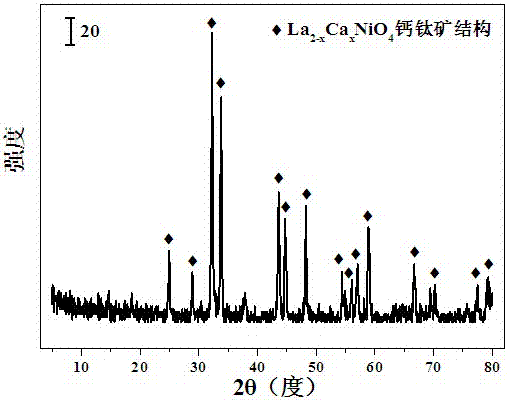
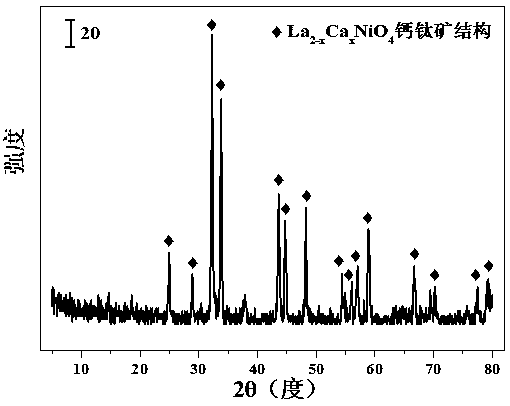
The invention relates to a layered perovskite catalyst for hydrogen generation from acetic acid autothermal reforming and a preparation method. A novel catalyst which is sintering resistant, carbon deposition resistant, antioxidant and high in activity is provided for the problem of catalyst deactivation due to sintering, oxidation and carbon deposition of an existing catalyst in the acetic acid autothermal reforming process. A nickel-based catalyst with an A2BO4 layered perovskite structure is prepared by employing a sol-gel method; and the chemical component is La<2-x>Ca<x>NiO<4>, wherein x is equal to 0-1.5. An oxygen defect and a lattice structure defect of the surface of the perovskite catalyst are increased through replacing lanthanum with a calcium part, and the reducibility, the heat stability and the oxidation resistance of the active component nickel are improved, so that the activity and the stability of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
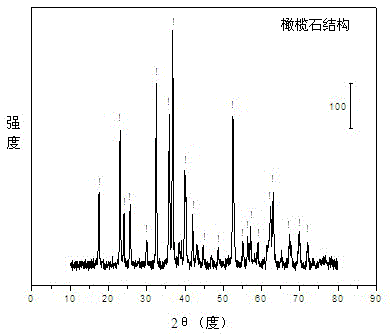
Olivine nickel-based catalyst for preparing hydrogen through autothermal reforming of acetic acid
InactiveCN103657654AIncrease lattice defectsEnhanced autothermal reforming activityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNickel catalystAcetic acid
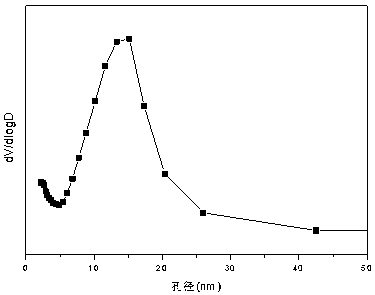
The invention relates to an olivine nickel-based catalyst for preparing hydrogen through autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Aiming to solve the problems of low hydrogen yield and oxidation / sintering inactivation of active constituents of the conventional supported nickel-based catalyst in an autothermal reforming process of acetic acid, the invention provides a novel catalyst with the effects of large specific surface area, stable structure, sintering resistance, oxidation resistance and stable activity. The catalyst provided by the invention has a chemical component of MgaFebNicSiO4, wherein a is 1.0-1.7, b is 0-0.7 and c is 0.3-0.5. The nickeliferous catalyst taking an olivine structure as a main body is prepared by a hydro-thermal synthesis method; the catalyst has rich hole structures so that the specific surface area and the dispersity of active constituents of the catalyst are effectively improved; meanwhile, the active constituents, such as nickel and iron, and additives substitute for bivalent magnesium to enter an olivine skeletal structure to effectively refrain the phenomenon of oxidation / sintering inactivation of the catalyst, so that the stability and the hydrogen yield of the catalyst in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Solid solution catalyst for acetic acid self-heating hydrogen production by reforming and preparation method
ActiveCN106391036AGood dispersionImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPolyethylene oxideEvaporation
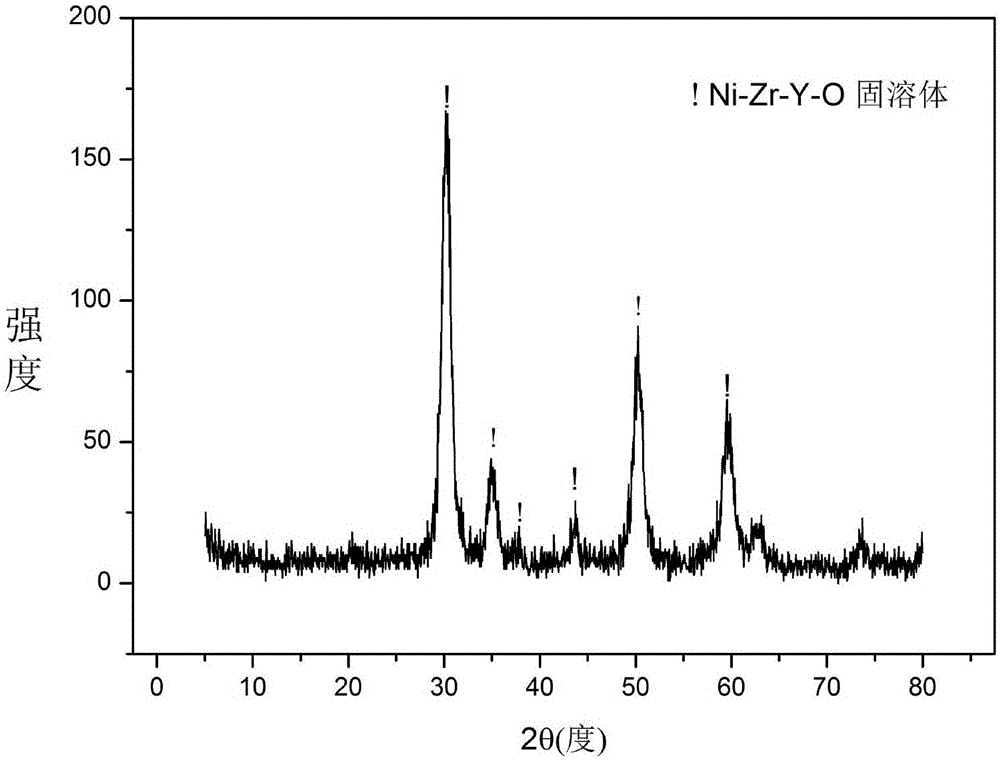
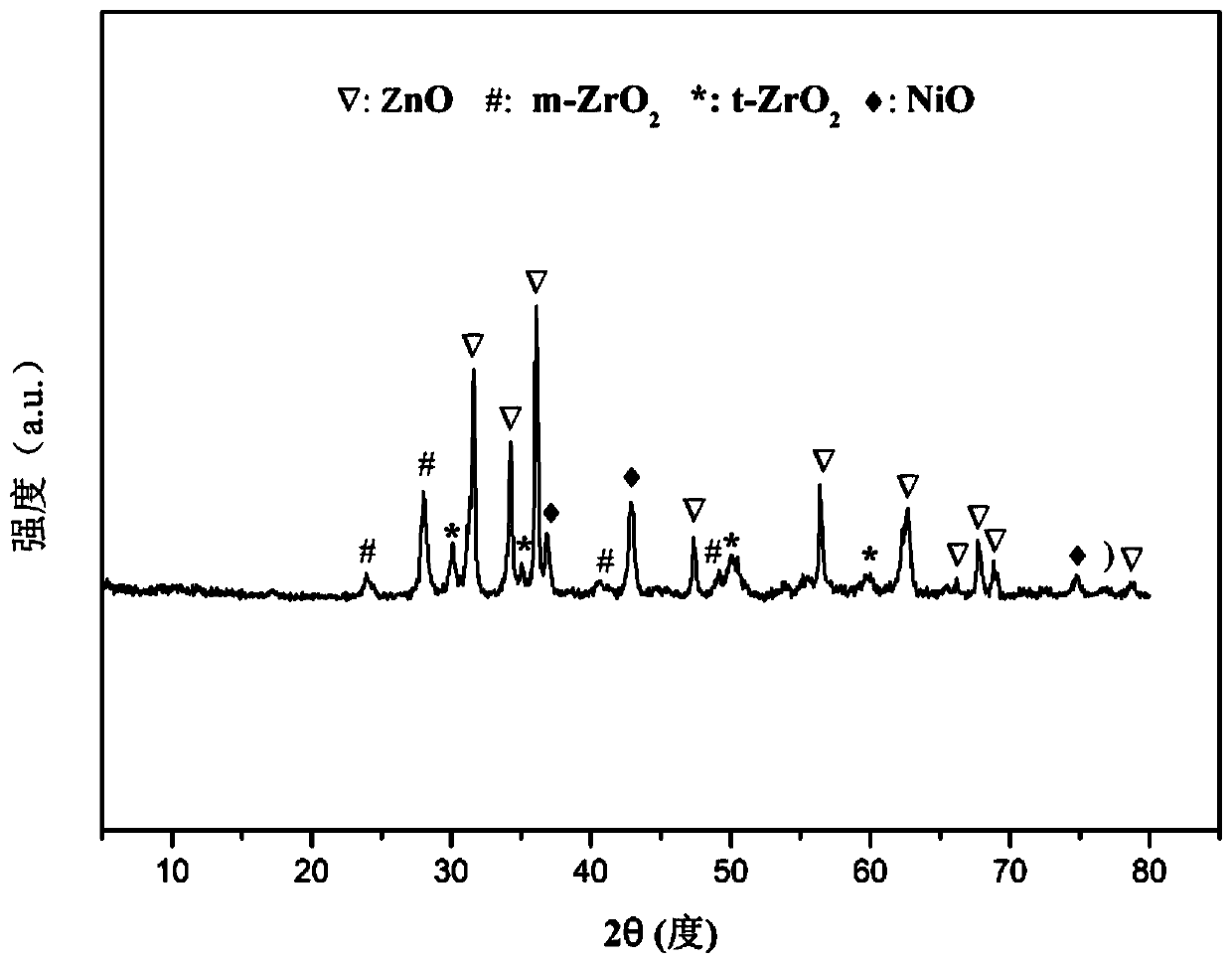
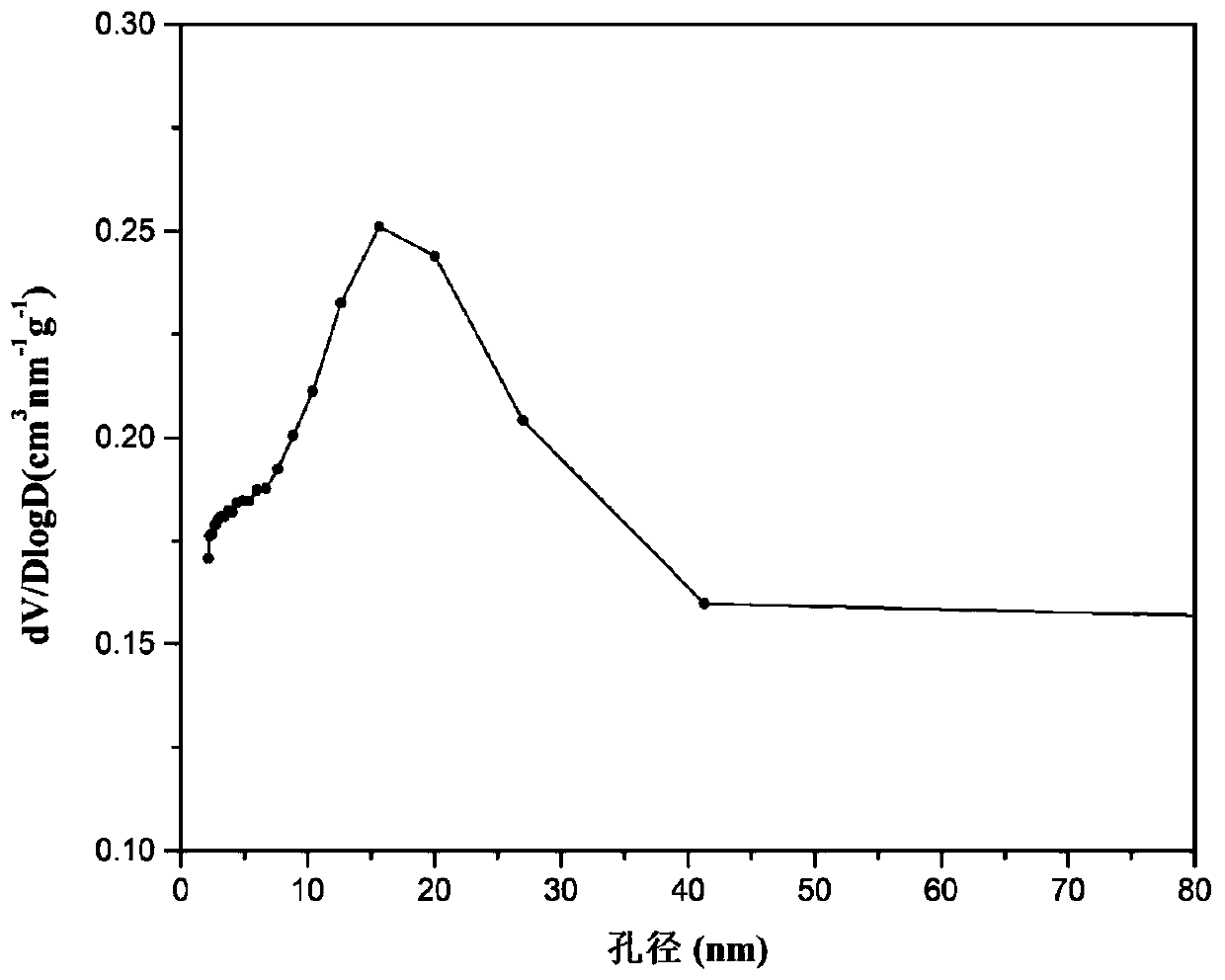
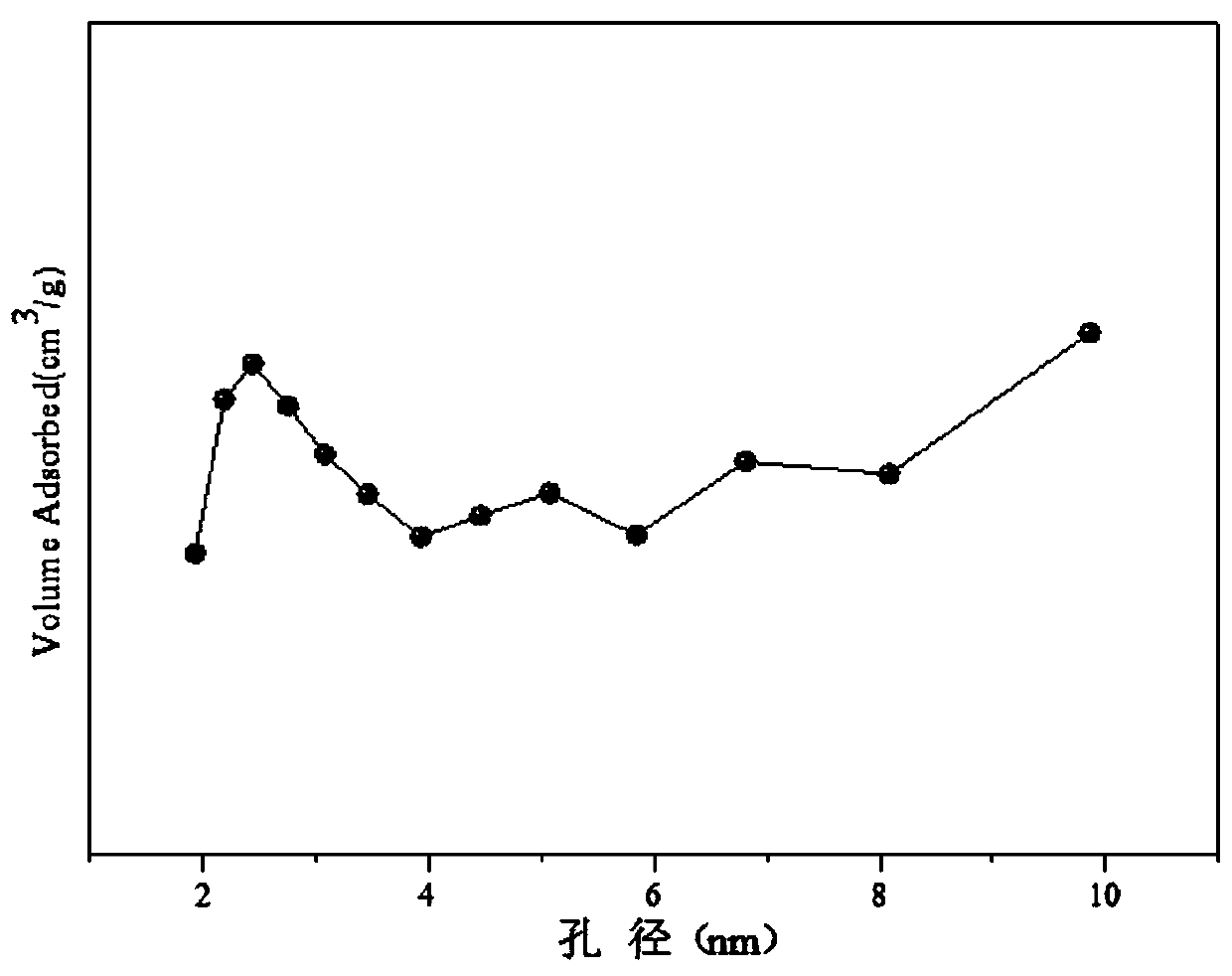
The invention relates to a solid solution catalyst for acetic acid self-heating hydrogen production by reforming. Aiming at the problem that in an acetic acid self-heating reforming reaction of an existing catalyst, by means of oxidizing, sintering, carbon depositing and other factors of the active components of the catalyst, the catalyst is inactivated, the novel catalyst is stable in structure, resistant to sintering, resistant to carbon depositing and oxidization and stable in activity, and the composition by weight of the catalyst is (NiO)a(YO1.5)b(ZrO2)c, wherein a ranges from 0.07 to 0.20, b ranges from 0.02 to 0.35, and c ranges from 0.58 to 0.91. According to the catalyst, zirconium oxide is adopted as a carrier, an aid yttrium oxide is introduced, a polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide-polyethylene oxide triblock copolymer is adopted as a template, a mesoporous structure is formed through evaporation self-assembly, and the nickel-based catalyst with the stable ZrxY1-xOy solid solution as the main structure is obtained. The hydrogen productivity, stability and carbon depositing resisting capacity of the acetic acid self-heating reforming process are effectively improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
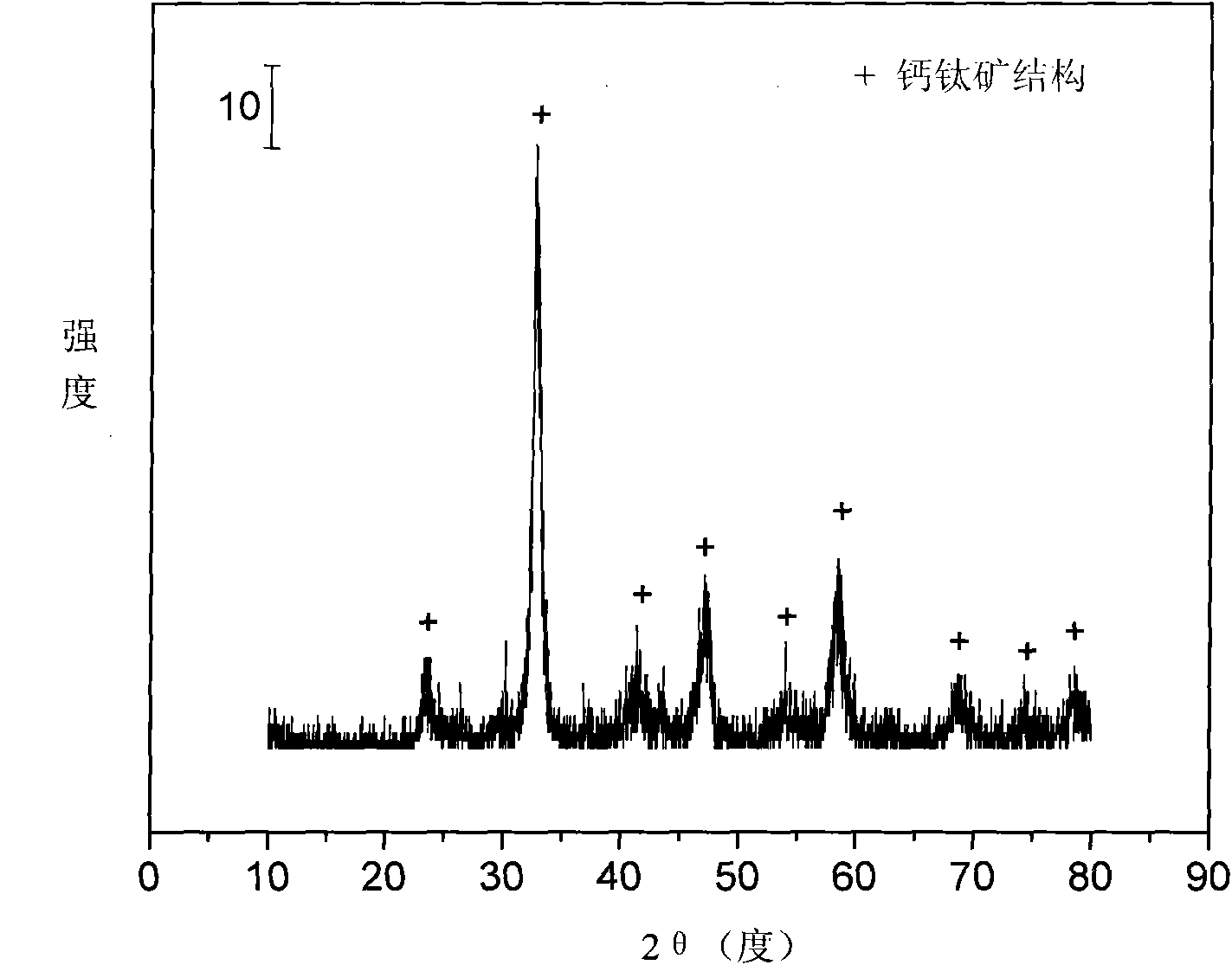
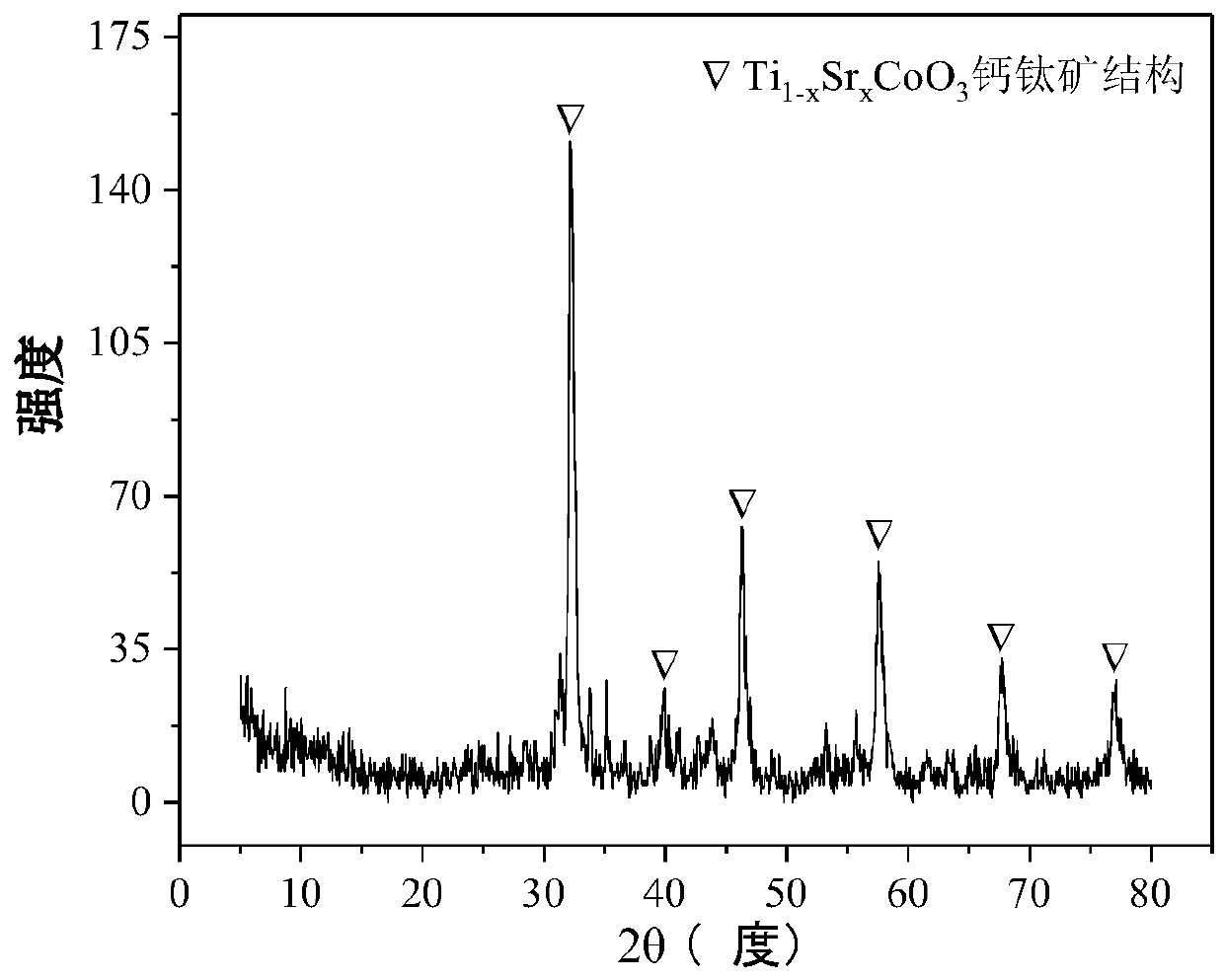
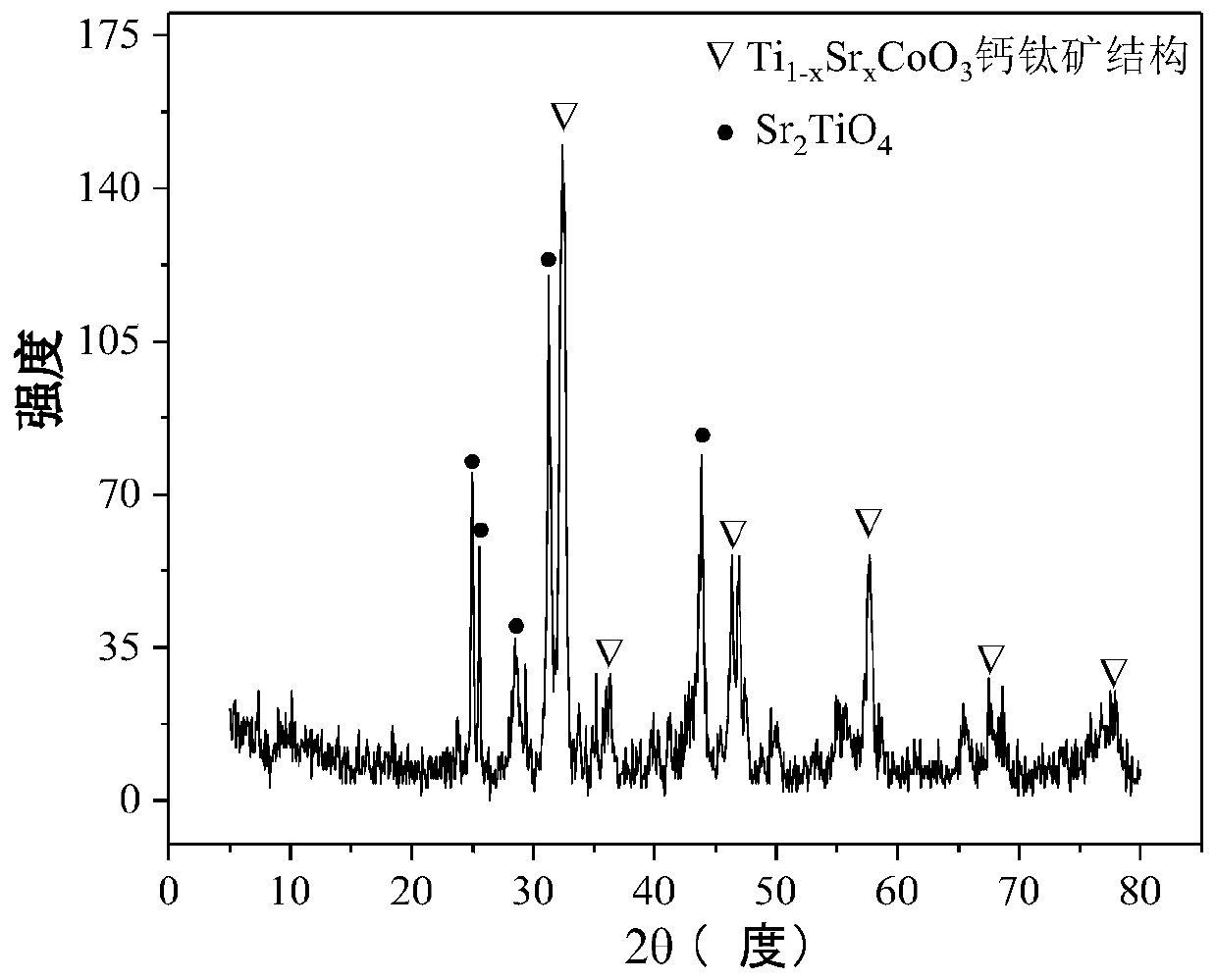
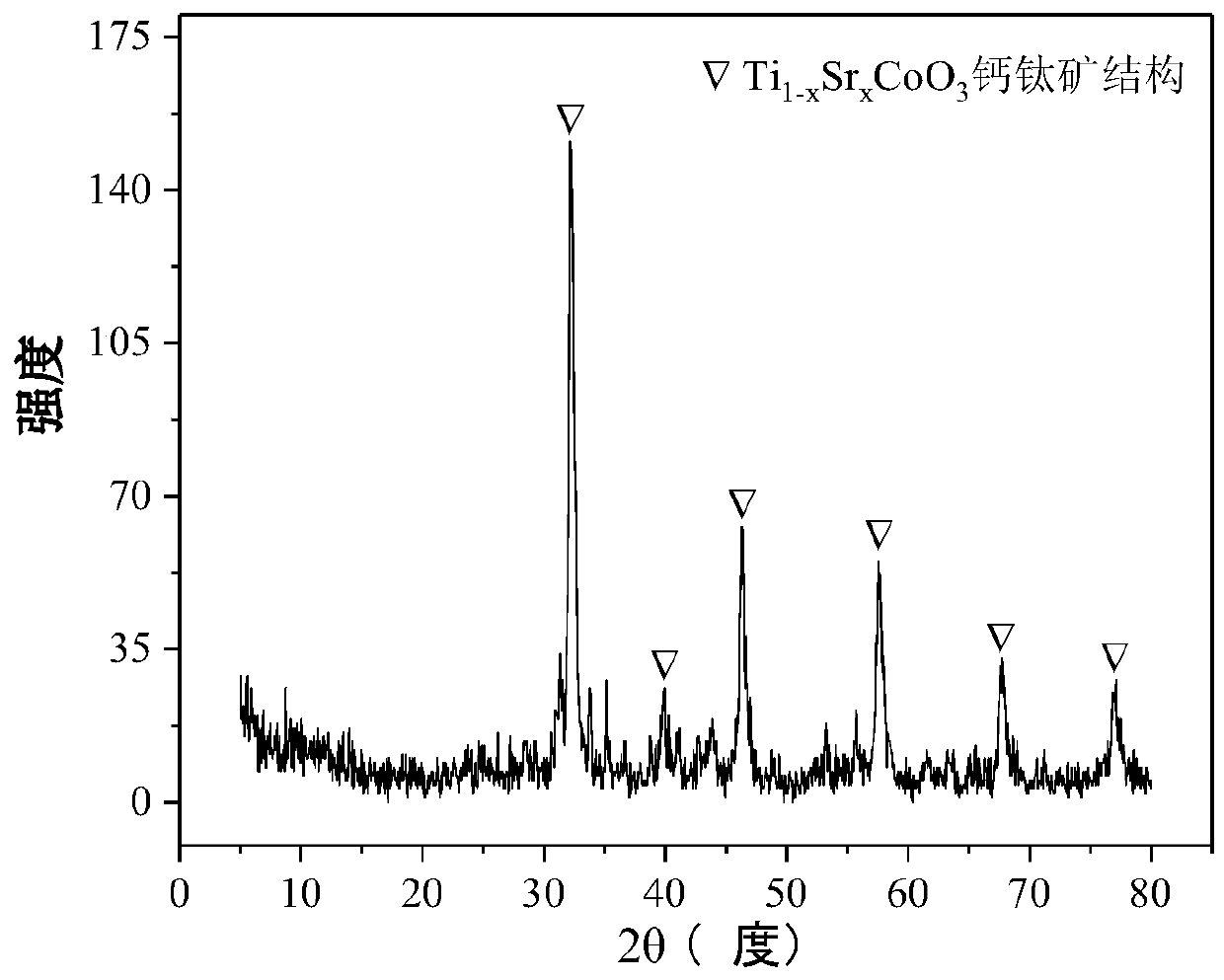
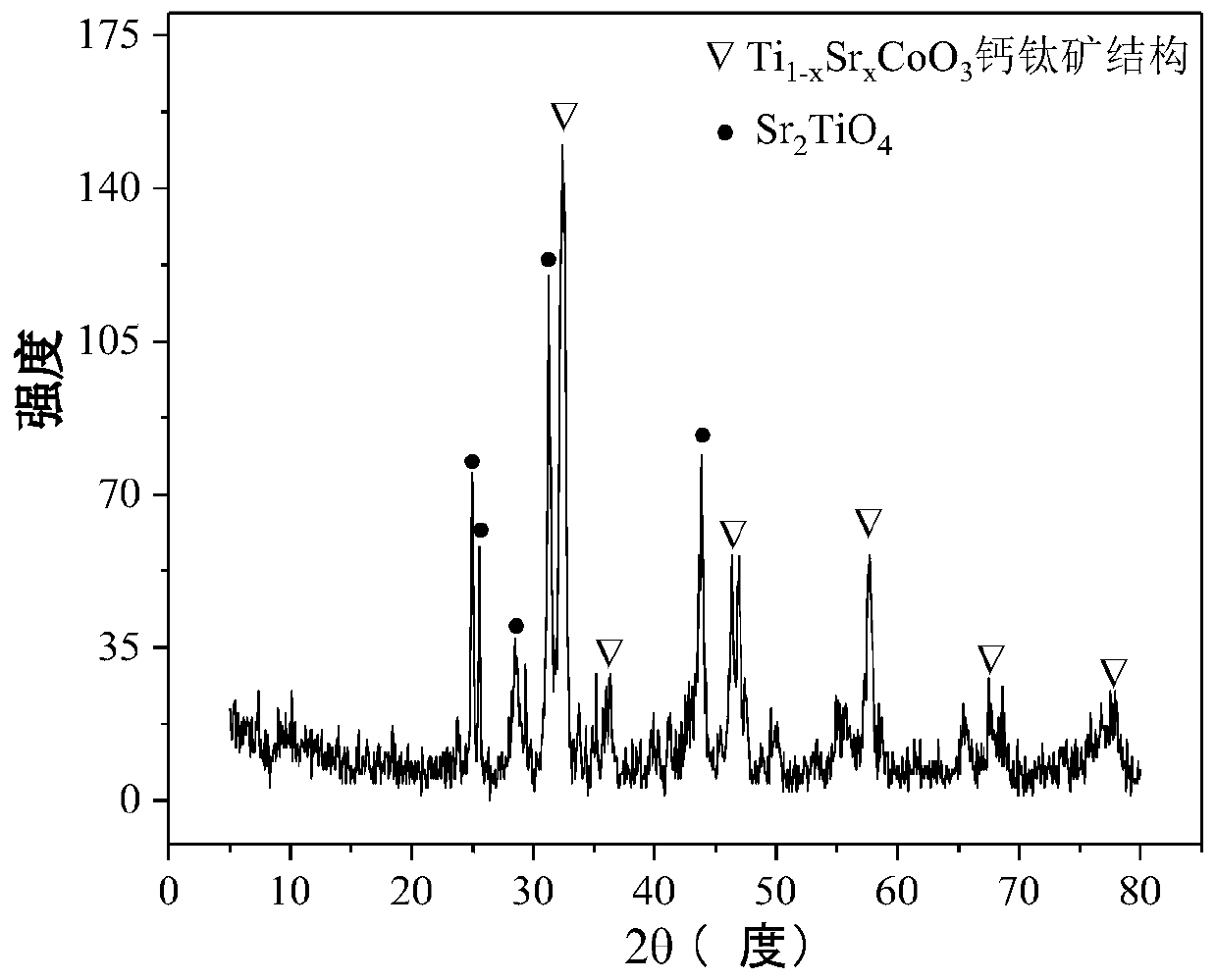
Perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN109759070ALower activation energyStable activityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsComposite oxideSol-gel
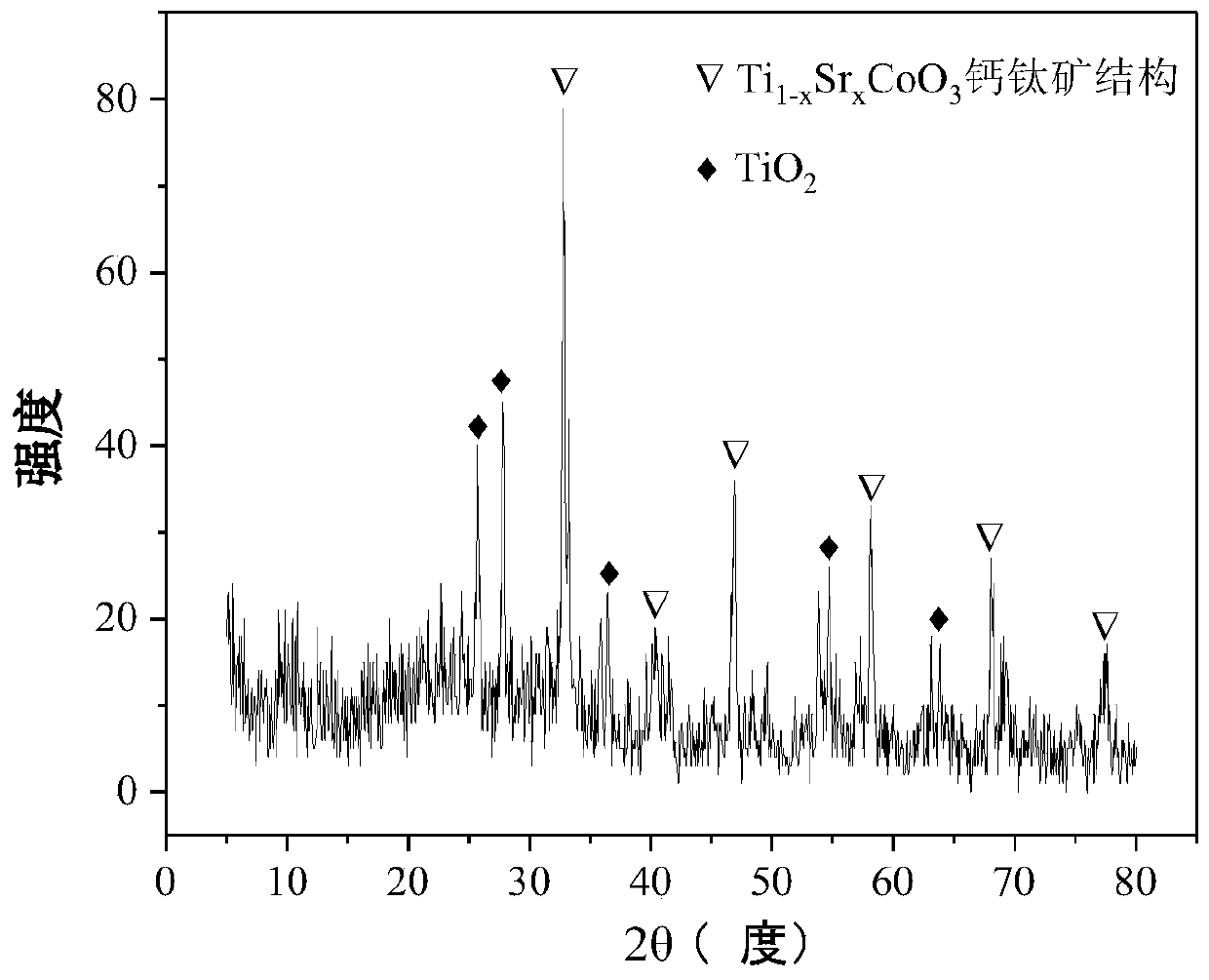
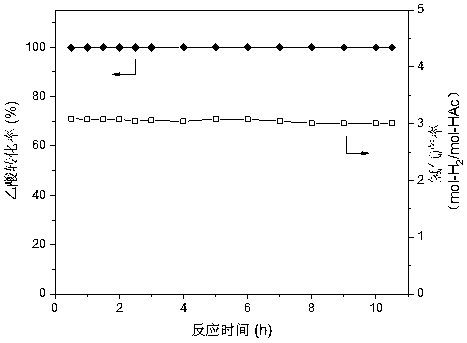
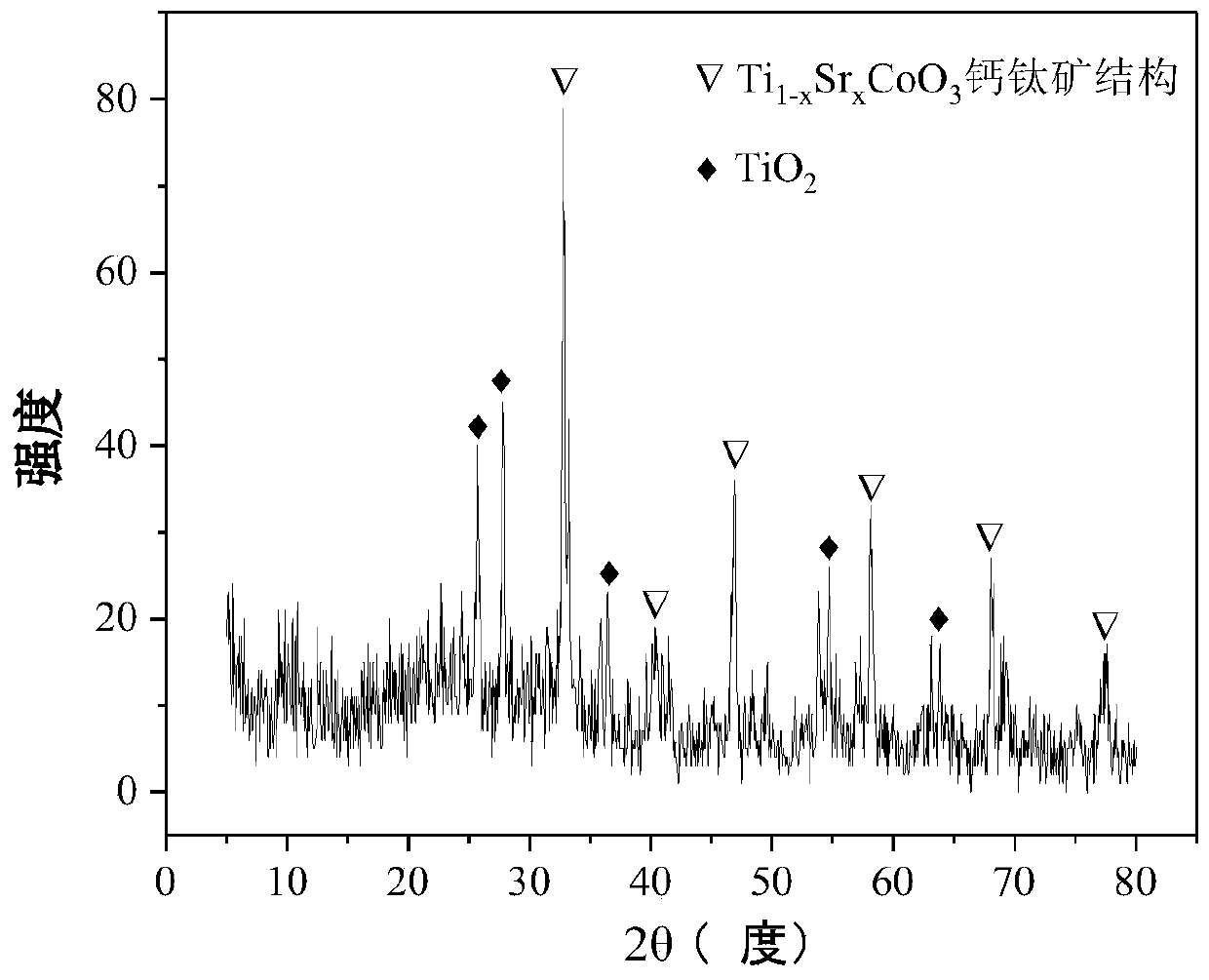
The invention relates to a perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and a preparation method. The catalyst with resistance tosintering, anti-carbon deposit, oxidation resistance and high activity is provided to aim at solving the problems that an existing catalyst has carbon deposits, sintering and oxidation of active components in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid, and deactivation of the catalyst is caused. According to the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for the hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and the preparation method, a sol-gel method is adopted to prepare the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst, and after calcination, a perovskite composite oxide catalyst Ti<1-x>Sr<x>CoO3 is obtained, wherein x=0-0.8. The perovskite structure facilitates the dispersion of an active component Co, strengthens the synergistic effect between the active component and a carrier, and inhibits the aggregation and growth of Co, thereby obtaining stable small-particle-size Co particles. In addition, Ti is partially replaced with Sr to increase the surface defect position and lattice defect structure of the perovskite-type catalyst, so that the carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and thermal stability of the active component cobalt are improved, the diffusion of acetic acid, water vapor and oxygen is further facilitated, and the catalytic activity is increased.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Hydrotalcite-like type iron-promoted nickel-based catalyst for hydrogen preparation through autothermal reforming of acetic acid and preparation method
ActiveCN107282050AStable performanceEnhanced interactionHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationAluminiumHydrotalcite
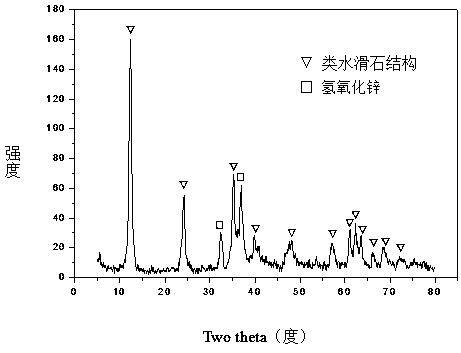
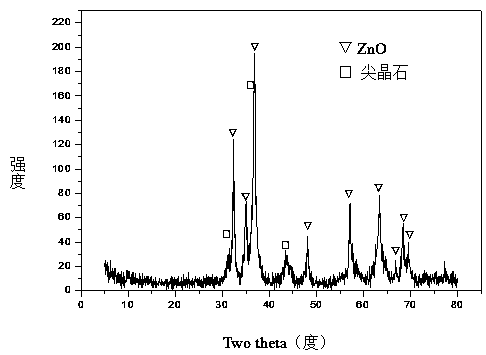
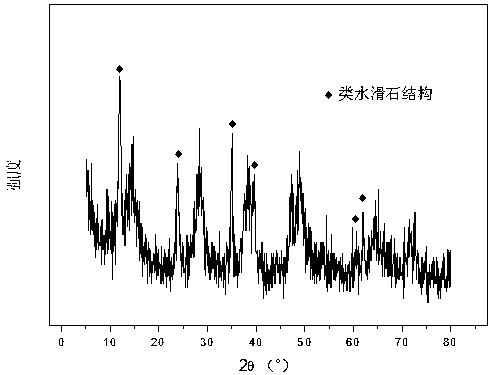
The invention relates to a hydrotalcite-like type iron-promoted nickel-based catalyst for hydrogen preparation through autothermal reforming of acetic acid and a preparation method and provides a high-activity novel catalyst resisting oxidation, sintering and carbon deposition to solve the problem that existing catalysts are inactivated due to the structure change as well as oxidation and sintering of active components of the catalysts in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid. The chemical component of the catalyst is (ZnO)a(NiO)b(AlO1.5)c(FeO1.5)d, wherein a ranges from 0.75 to 3.25, b ranges from 0.25 to 0.75, c ranges from 0 to 1.0 and d ranges from 0 to 1.0. The Zn-Al type carbonate hydrotalcite-like structure is prepared with a co-precipitation method to serve as a precursor, and an active component nickel and an auxiliary iron are introduced and enter the position of the hydrotalcite-like structure through isomorphous substitution of zinc for nickel and isomorphous substitution of aluminum for iron; a compound oxide obtained through sintering effectively inhibits possible migration, accumulation, oxidation and sintering of the active component nickel under the high-temperature reaction condition, and the activity and the stability of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
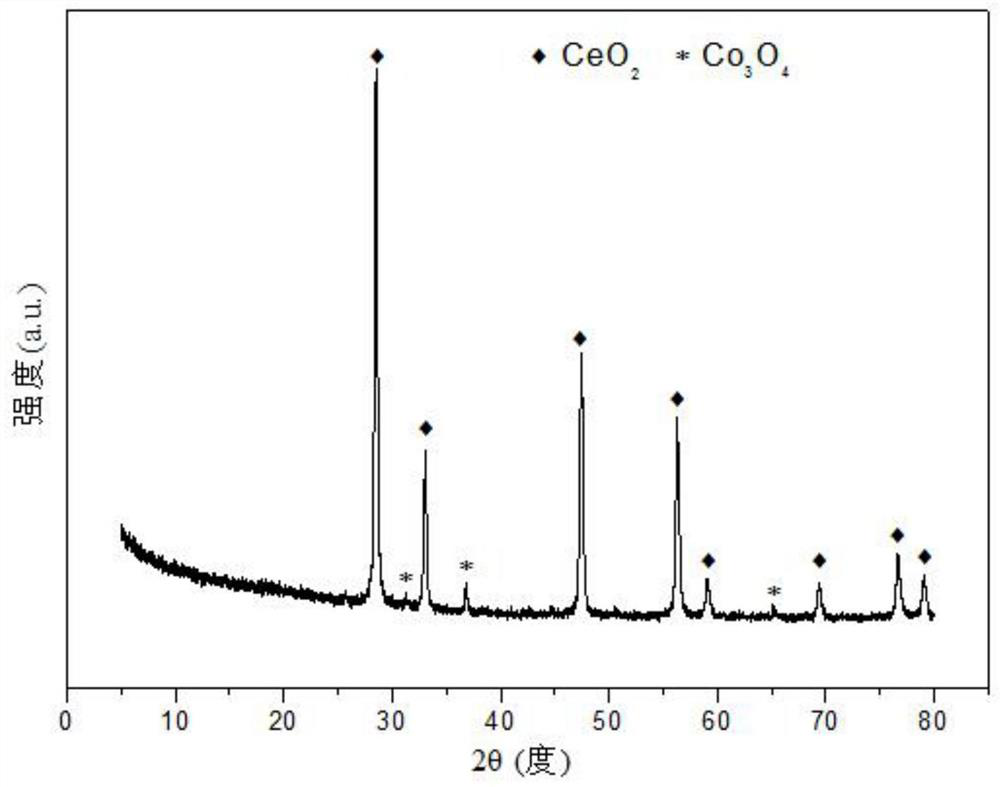
Oxygen storage solid solution loaded cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
InactiveCN109718790AGood choiceHigh catalytic activityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCarbon depositCobalt
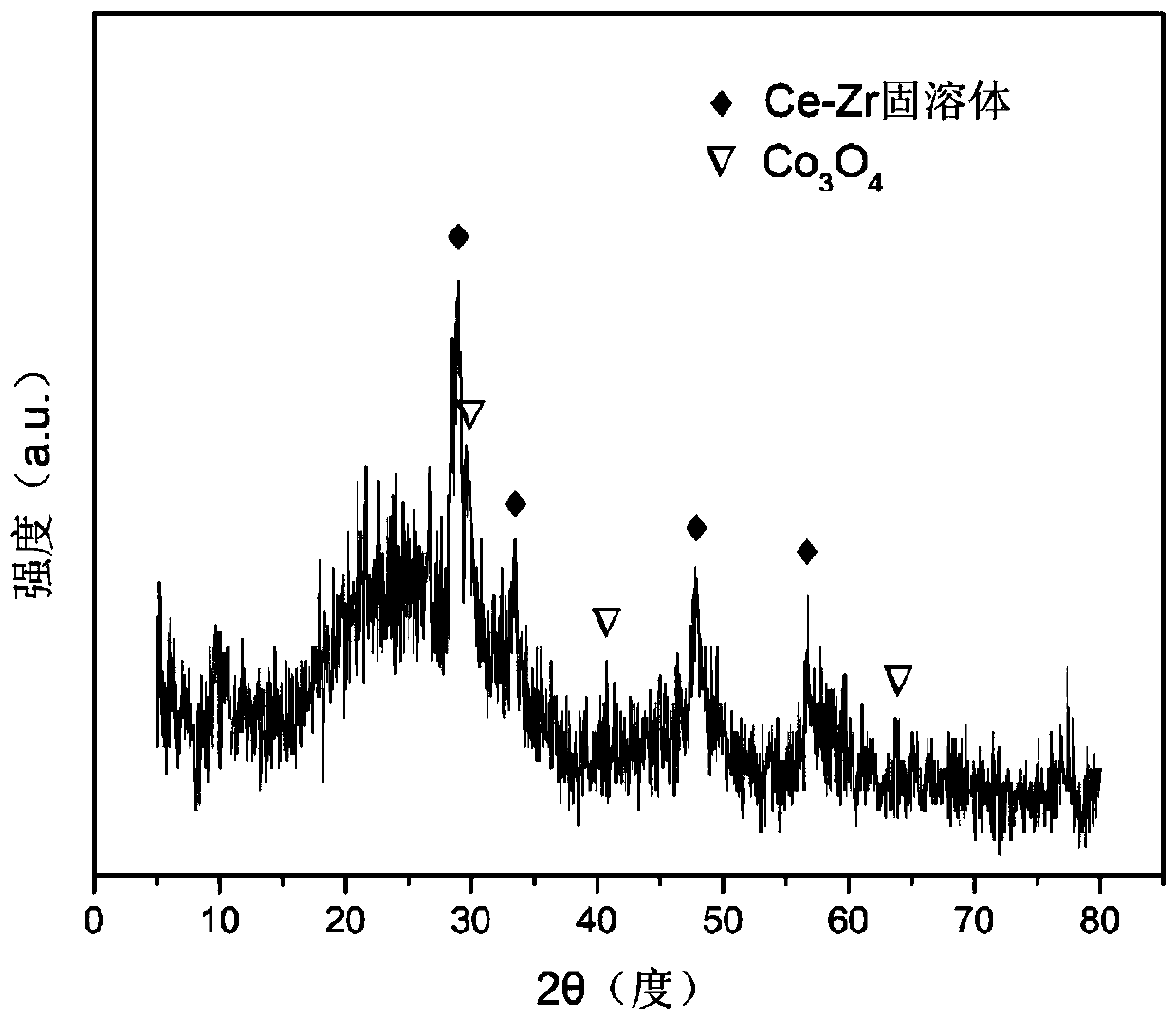
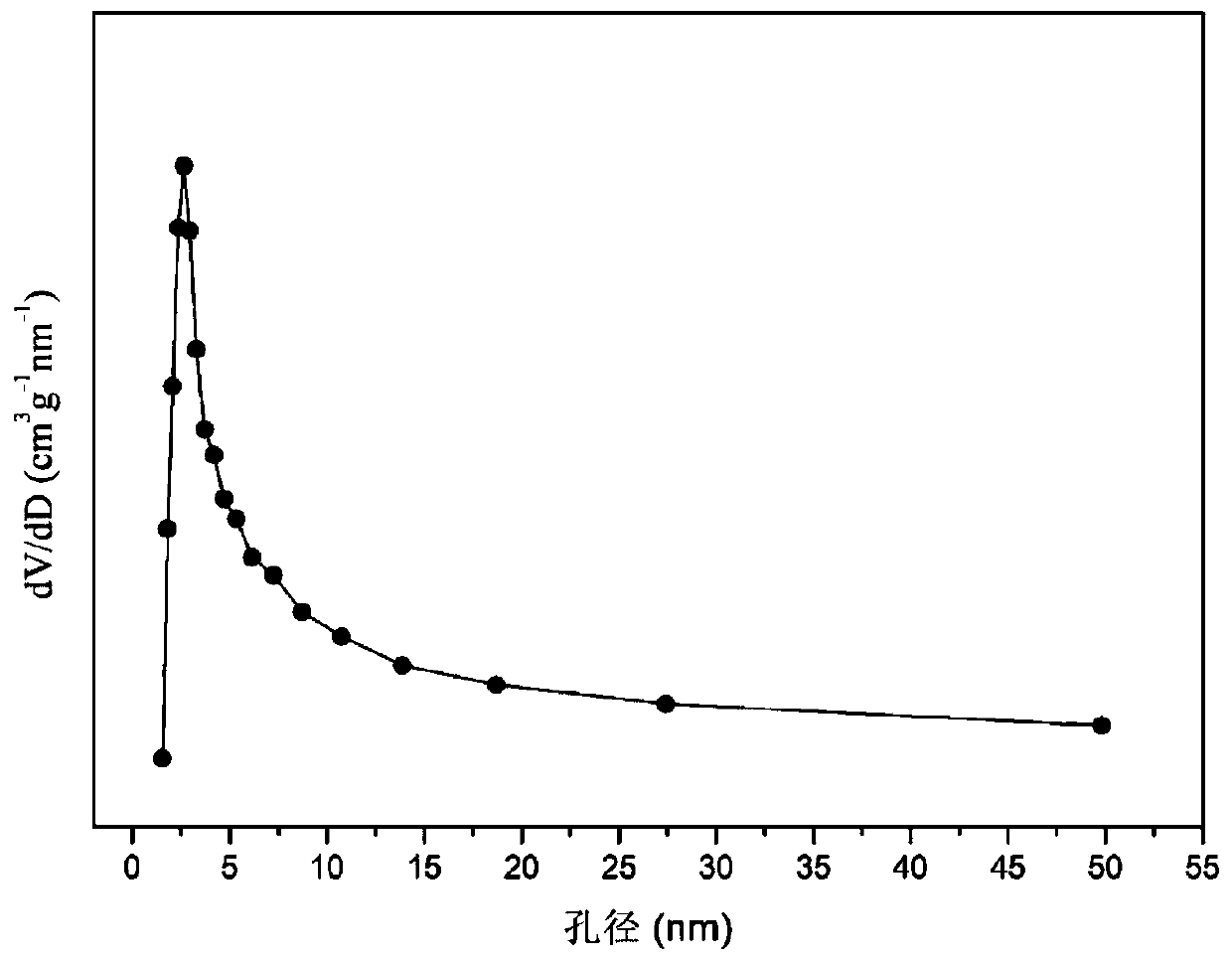
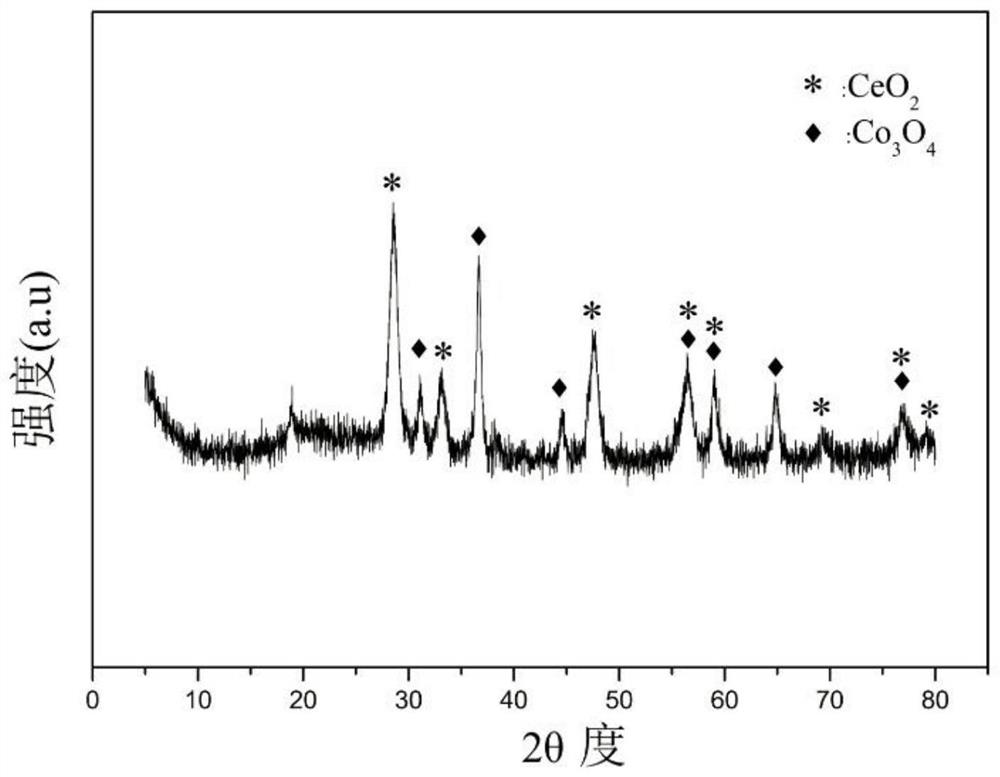
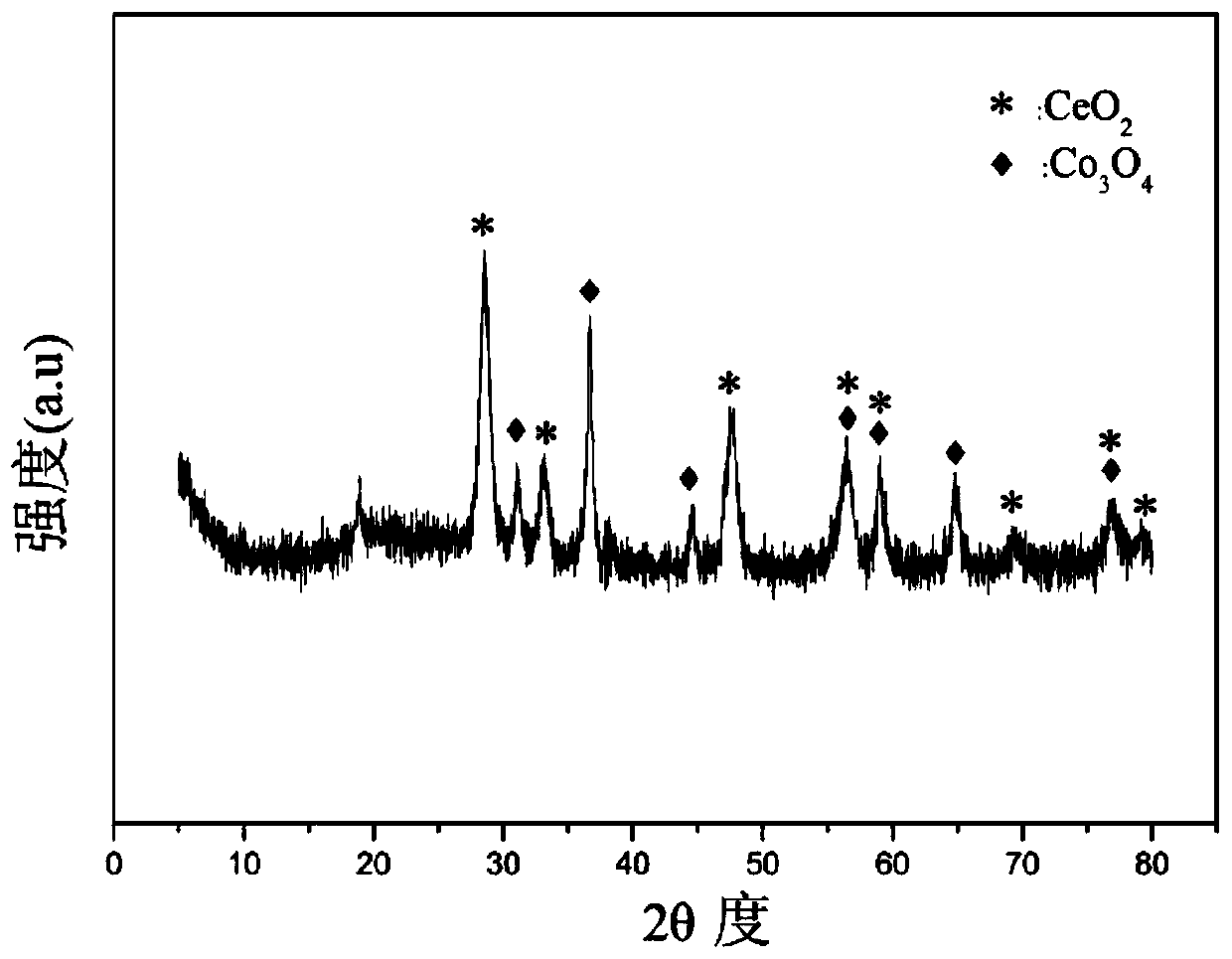
The invention relates to an oxygen storage solid solution loaded cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Directed at the problems of oxidation, sinteringand carbon deposit of existing catalysts in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid, the invention provides a new catalyst characterized by stable structure, sintering resistance, carbon deposition resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity. The molar composition of the catalyst is: (CoO4 / 3)a(CeO 2)b(ZrO2)c, wherein a is 0.68-1.46, b is 1.00-3.00, and c is 1.00-3.00. The invention adopts coprecipitation method to prepare a catalyst precursor, and then roasting is carried out to obtain the oxygen storage solid solution loaded cobalt-based catalyst containing Co3O4 and Ce-Zr-Ox. The catalyst provided by the invention effectively improves the yield of hydrogen and the stability of active components, and effectively inhibits the formation of methane, acetone and other by-products.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
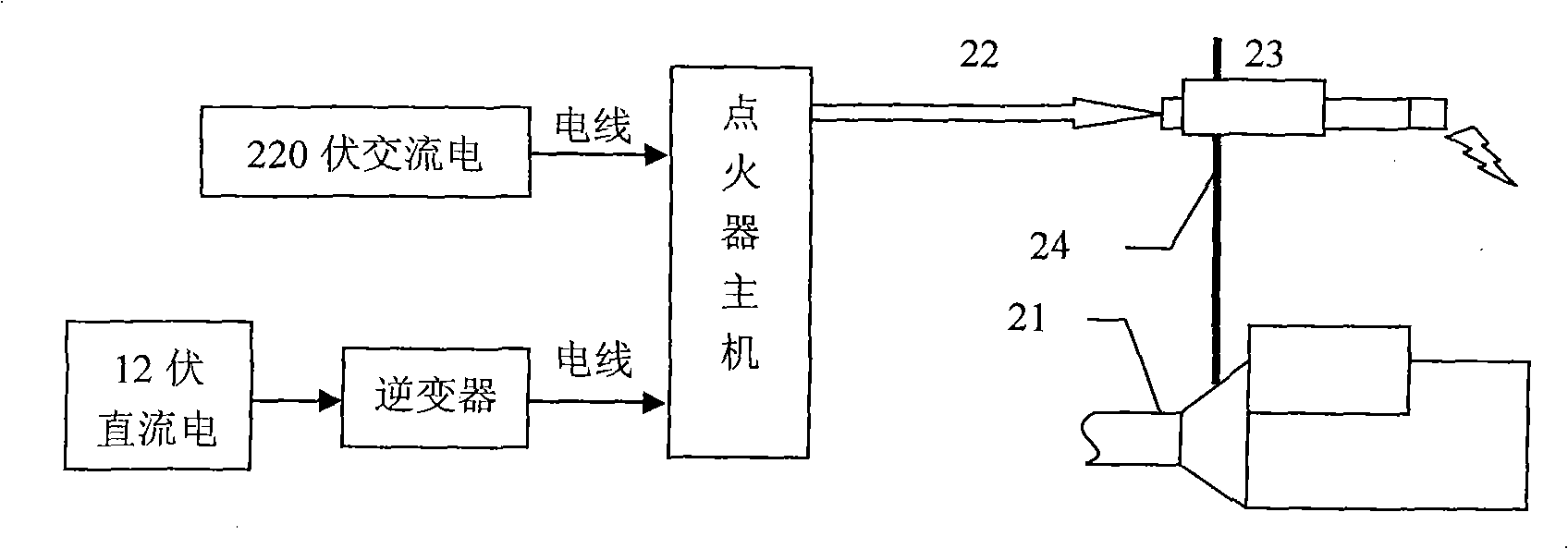
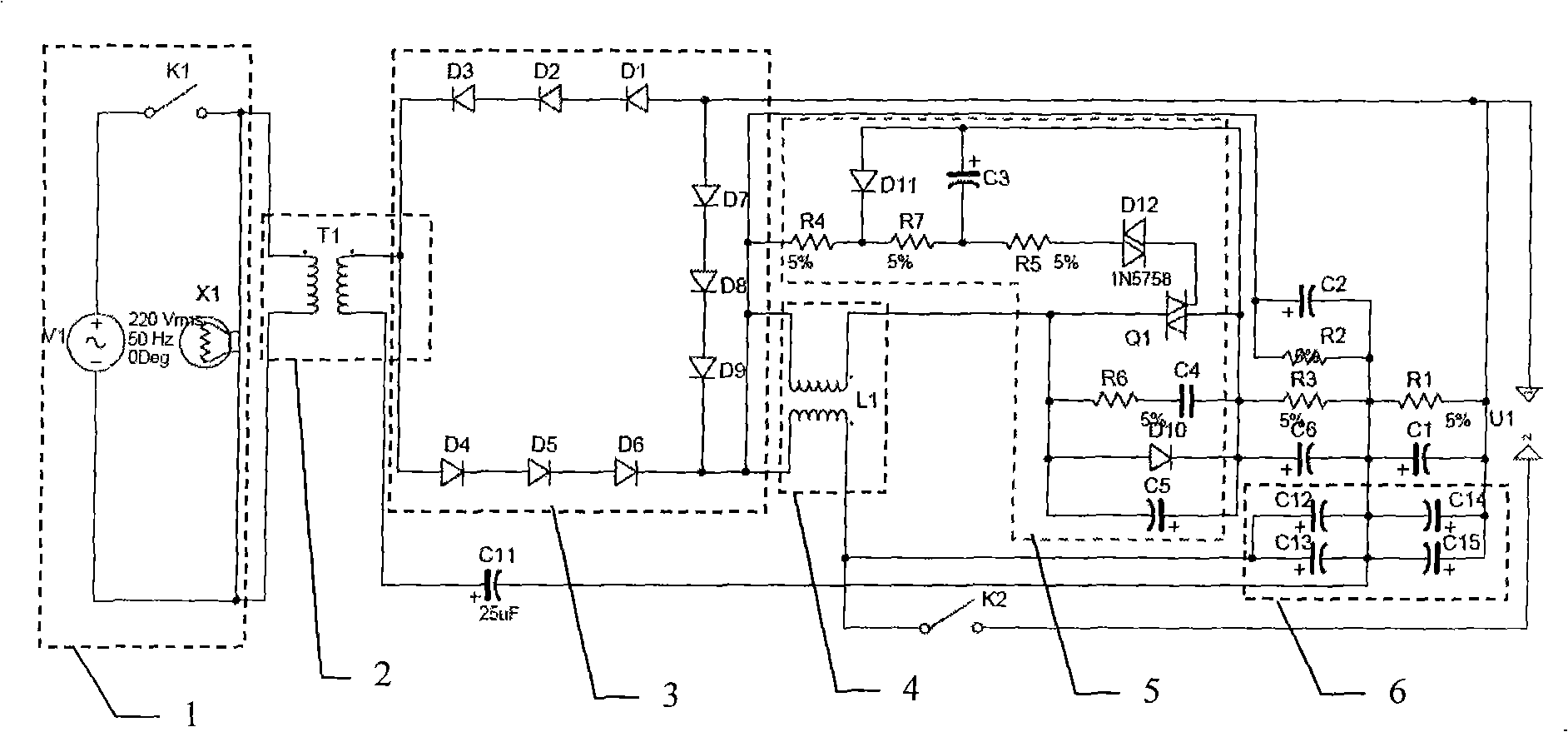
High energy electronic ignition system for high pressure gas well
ActiveCN101539087AAccurate ignition performanceHigh discharge energyInstallations with induction energy storageIgnition coilAutomotive engineering
The invention discloses a high energy electronic ignition system for a high pressure gas well, which is suitable for igniting an open flow spout in the petrochemical field, especially the open flow field of the gas well (oil well). The high energy electronic ignition system for the high pressure gas well comprises an input power supply and an open flow device, wherein the input power supply is connected with a host machine of an igniter, the host machine of the igniter is connected with an ignition rod by a flame resistant cable, and the ignition rod is fixed above the open flow device by an ignition rod bracket. The high energy electronic ignition system for the high pressure gas well can solve the problem of various ignition modes that ignited fire is easy to be extinguished by spouted water; and the high energy electronic ignition system has the advantages of high reliability, no potential safety hazard and accurate and efficient ignition performance, and the operation of ignition can still be successfully carried out under the adverse environment in the premise that the gas concentration reaches the lower limit of inflammation concentration.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +2
Hydrocalumite derived cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN109718785AImprove anti-sintering performanceImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAcetic acidActive component
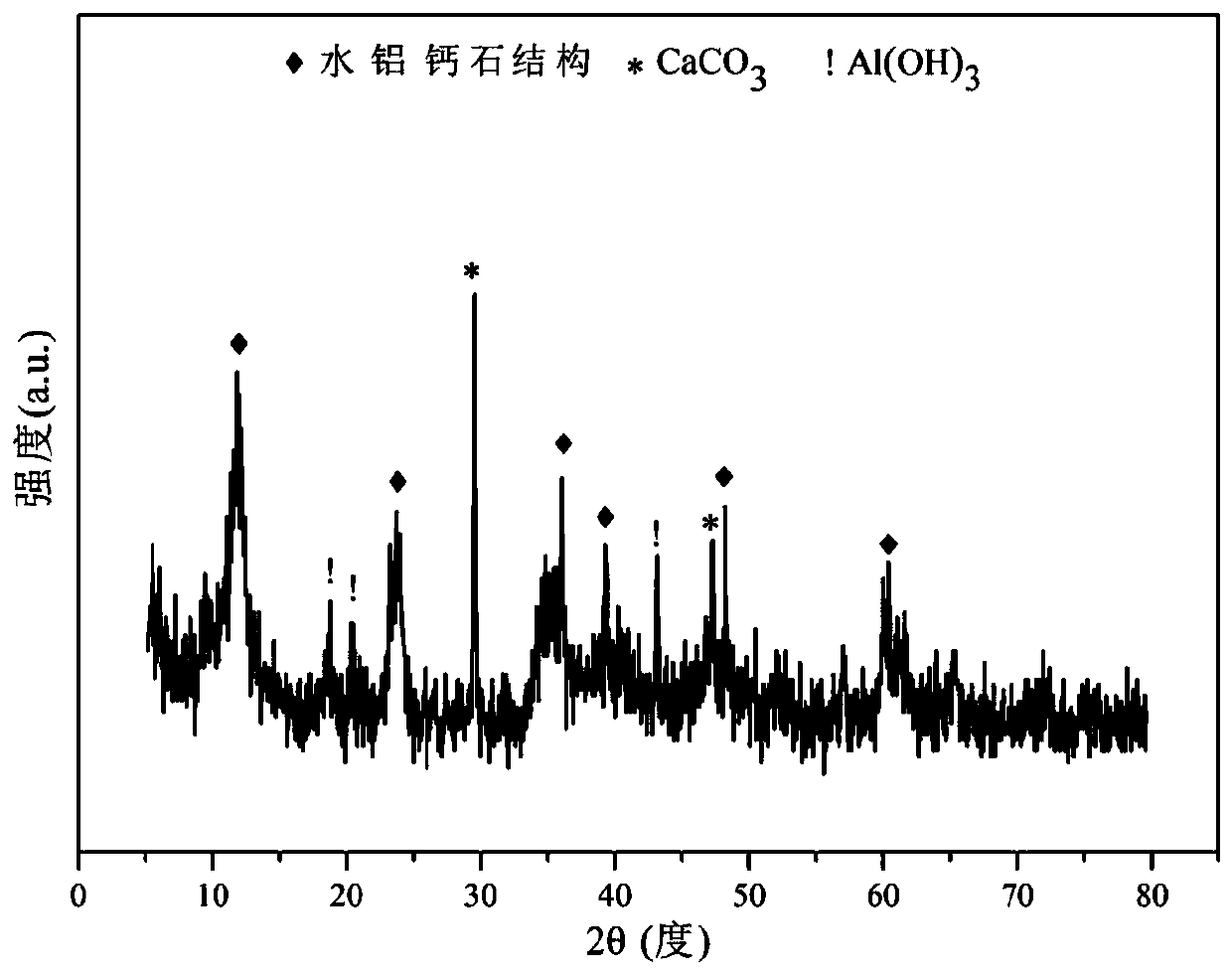
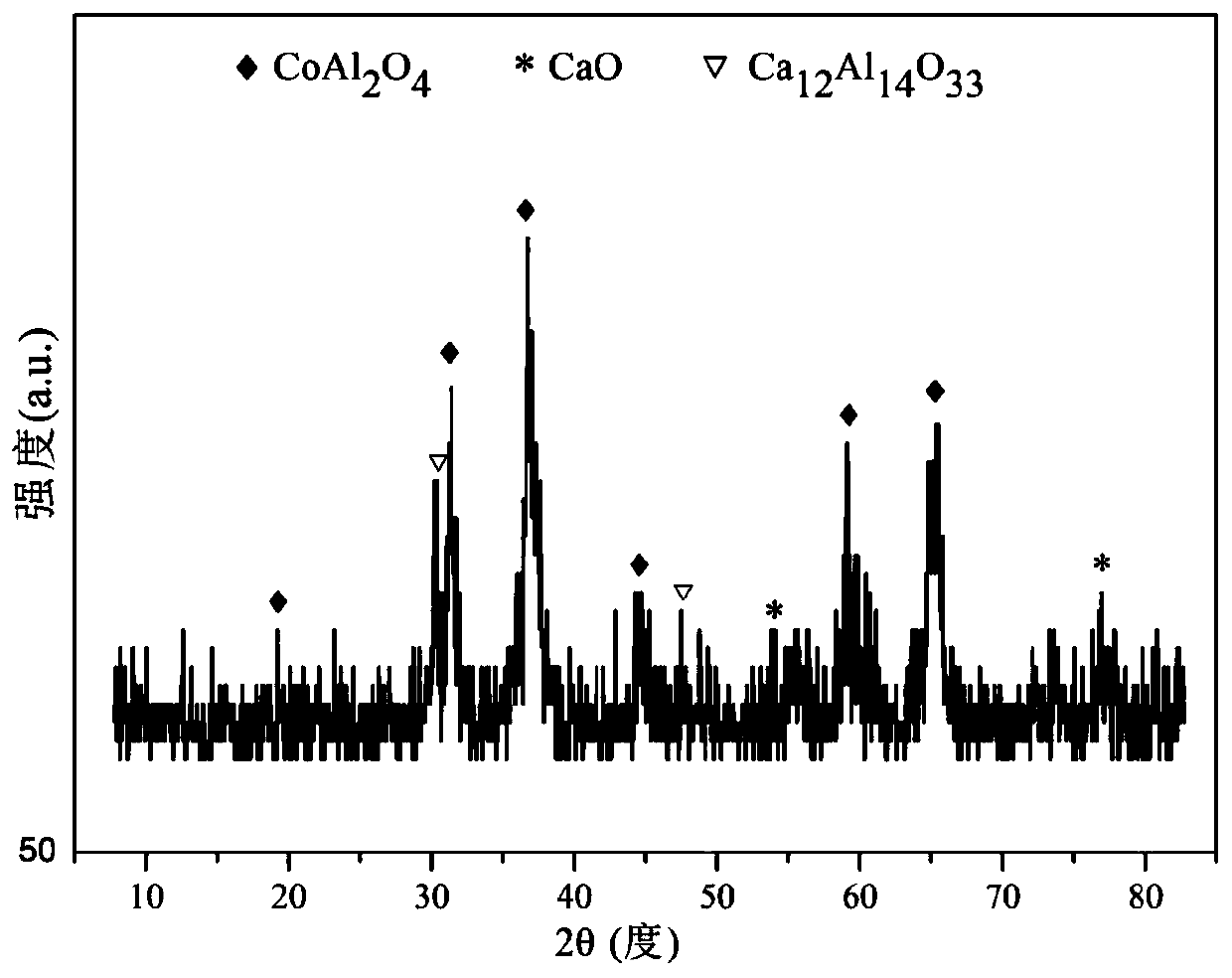
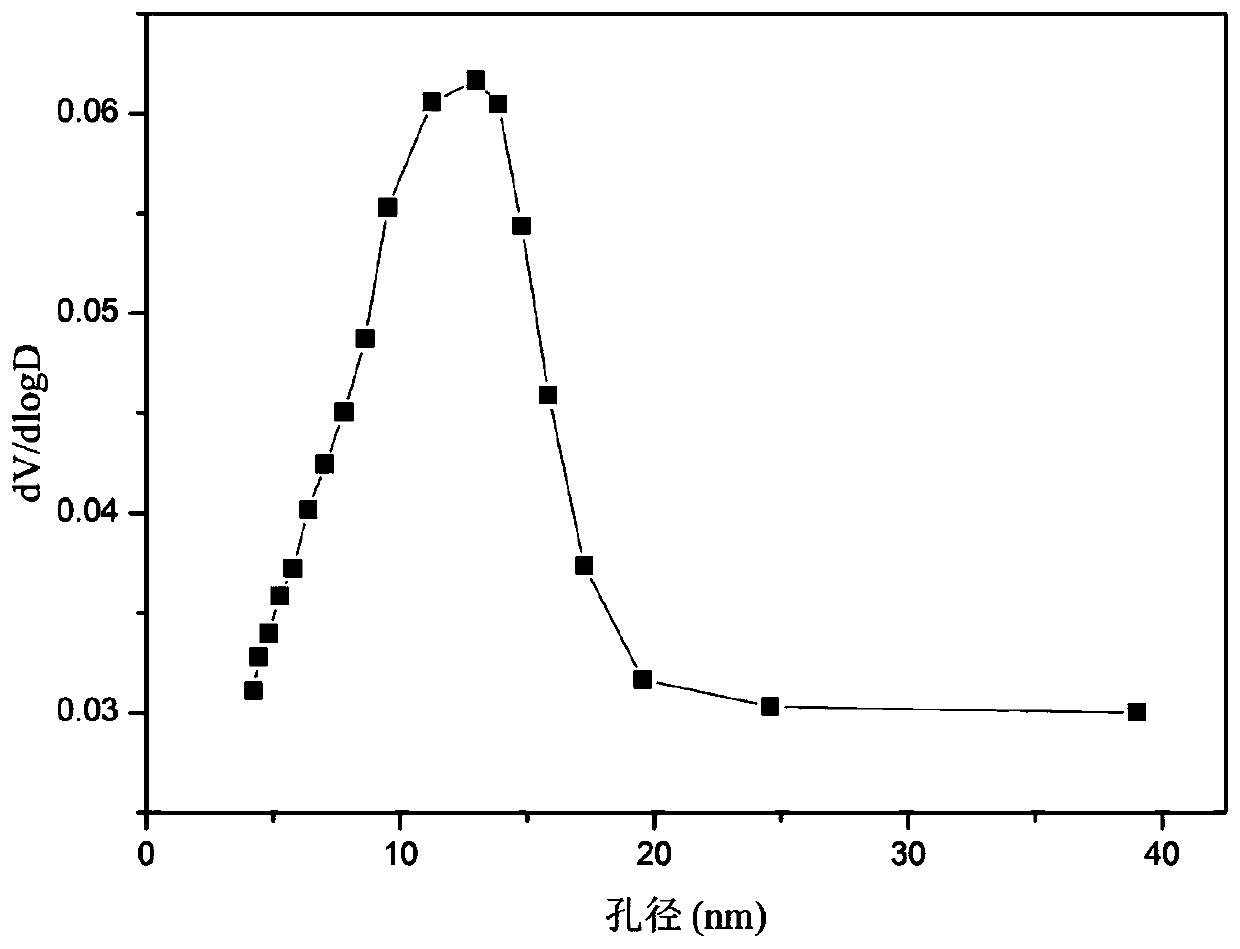
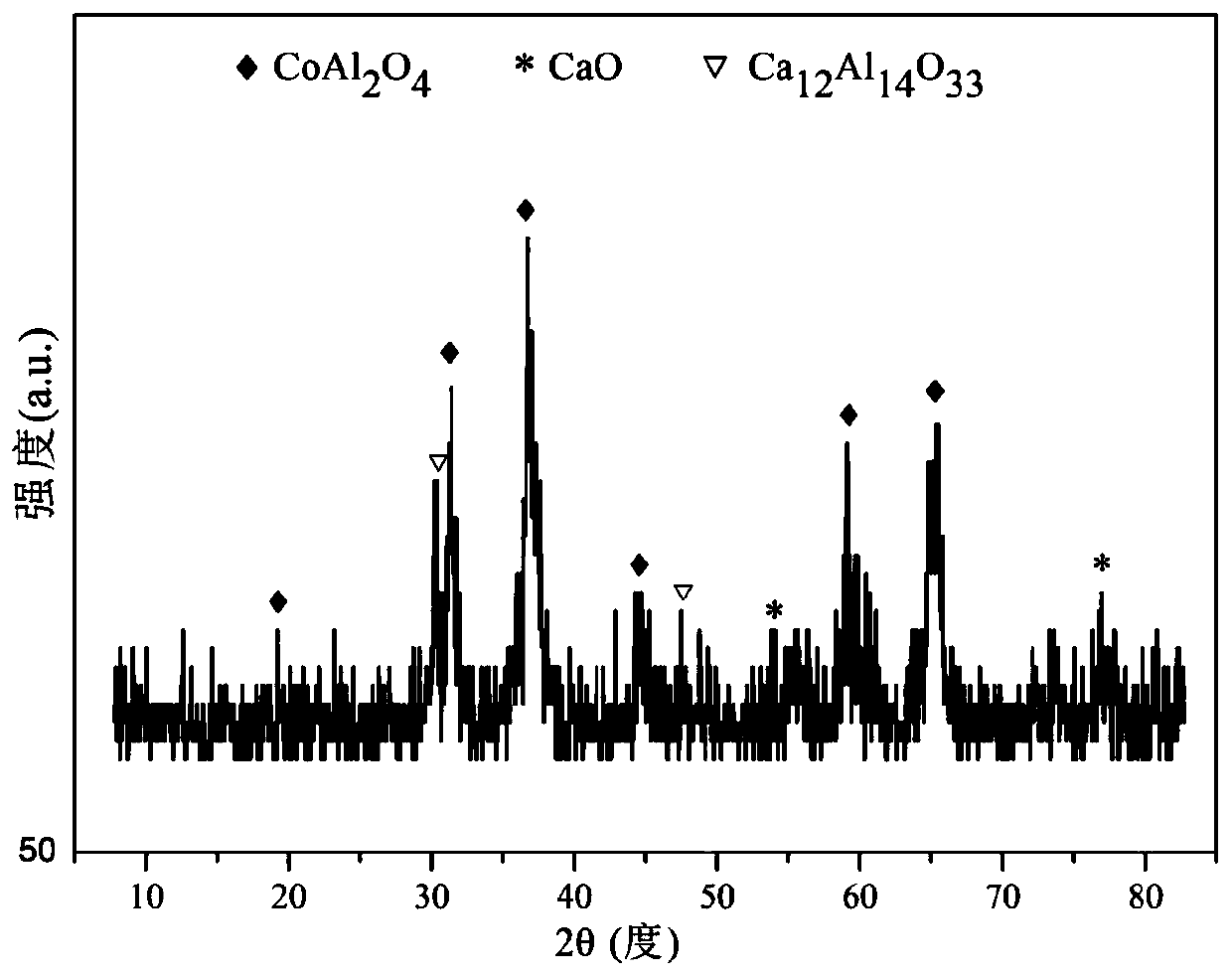
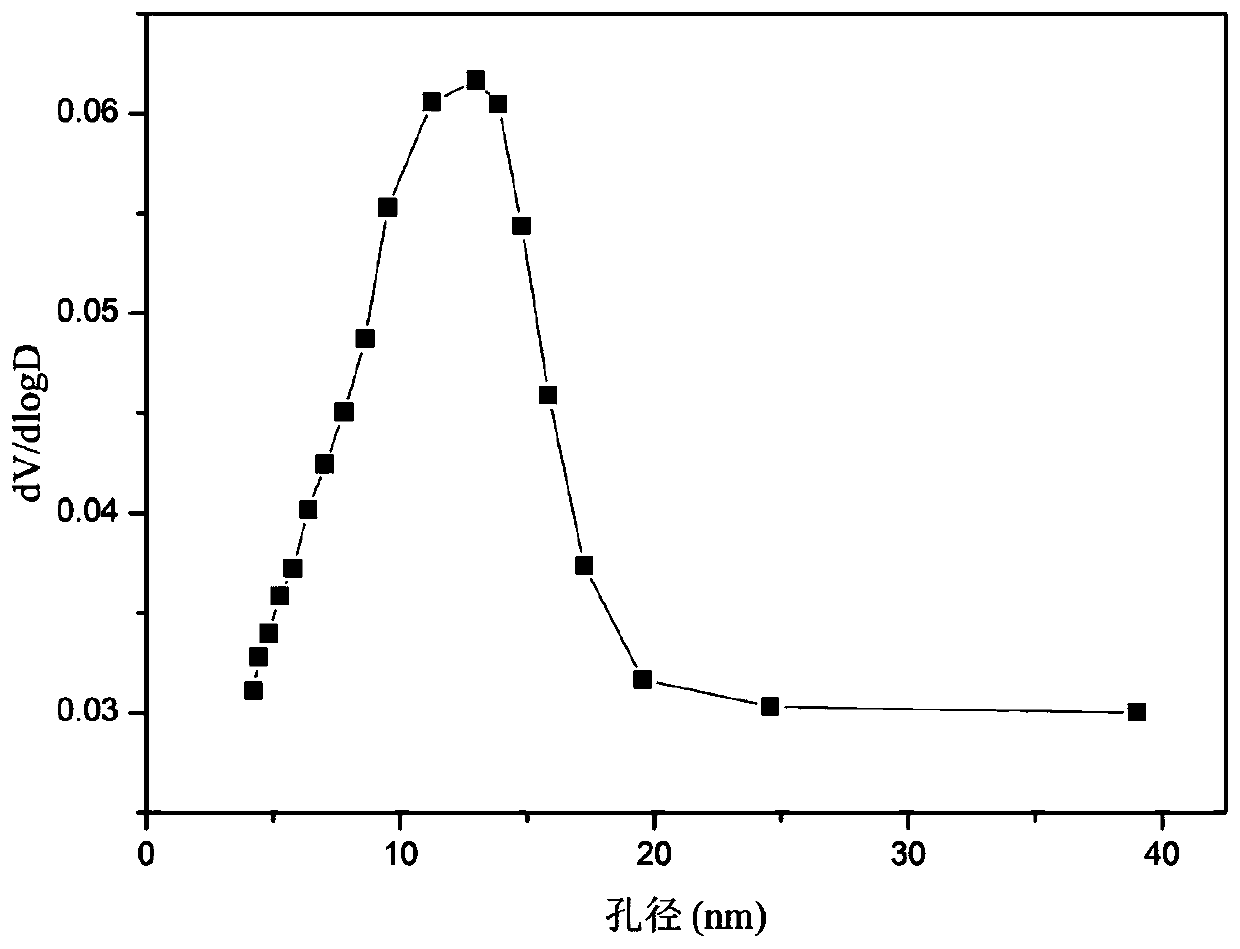
The invention relates to a hydrocalumite derived cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Directed at the problem that catalyst structure change and the oxidation and sintering of active components can cause catalyst deactivation in existing catalysts during the autothermal reforming reaction of acetic acid, the invention provides a new catalyst characterized by stable structure, sintering resistance, oxidation resistance, carbon deposition resistance, and high activity. The molar composition of the catalyst is (CaO)a(CoO)b(AlO1.5) c, wherein a is1.66-5.19, b is 0.34-0.81 and c is 1.0. The invention adopts coprecipitation method to prepare a catalyst precursor, and then roasting is carried out to obtain the Ca-Co-Al-O mesoporous composite oxide. The catalyst takes calcium oxide as the framework, contains cobalt-alumina spinel phase and a small amount of Ca12Al14O33, inhibits the acidity of the catalyst, improves the carbon deposition resistance and sintering resistance of the catalyst, and improves the activity of hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
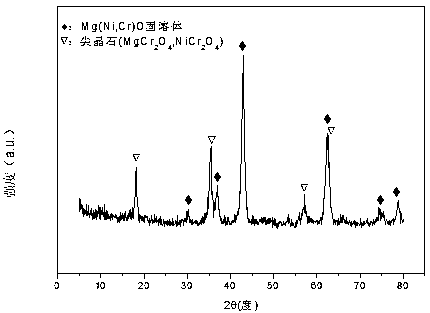
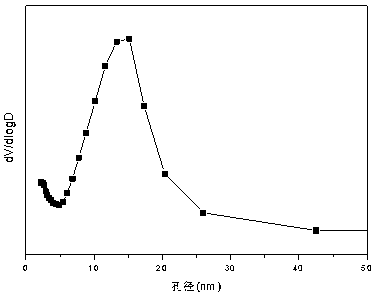
Nickel-magnesium-chromium composite oxide catalyst for auto-thermal reforming of acetic acid to produce hydrogen
ActiveCN108927164AIncrease dispersionImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsComposite oxideMagnesium
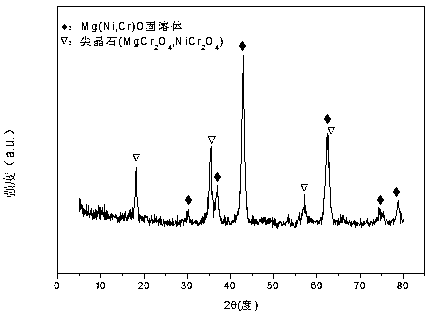
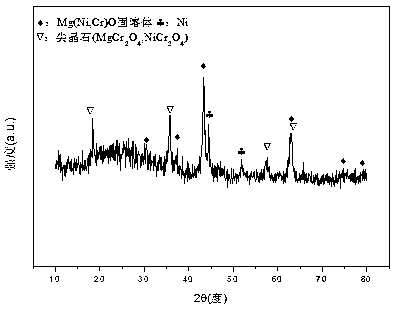
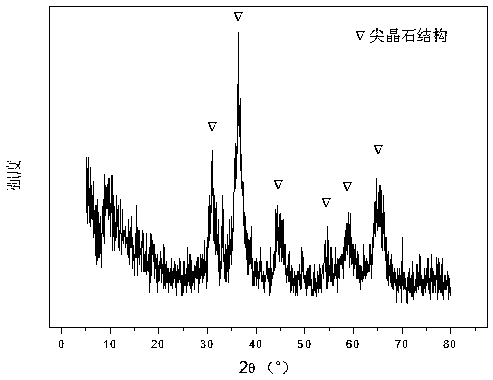
The invention relates to a nickel-magnesium-chromium mesoporous composite oxide catalyst for auto-thermal reforming of acetic acid to produce hydrogen. The invention aims to solve the problem that inthe prior art, during the acetic acid auto-thermal reforming process, the structure of a conventional catalyst changes, the active components are oxidized and sintered, and thus the catalyst is deactivated, and provides a novel catalyst having the advantages of stable structure, sintering resistance, carbon deposition resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity. The chemical formula of thecatalyst is (NiO)a(MgO)b(CrO1.5)c; wherein a is 0.08-0.12, b is 0.55-0.92, c is 0-0.33, and nickel oxide accounts for 12.0 to 20.0 wt.% of the catalyst, magnesium oxide accounts for 40.0 to 88.0 wt.%of the catalyst, and chromium oxide accounts for 0 to 40.0 wt.% of the catalyst. A catalyst precursor is prepared by a co-precipitation method, chromium is introduced into the catalyst and is taken asan auxiliary agent; after burning, a stable mesoporous composite oxide catalyst, which comprises a MgCr2O4 and NiCr2O4 spinel structure and a Mg-Ni-Cr-O solid solution, is formed; the reducing performance and stability of the active components are enhanced; at the same time, the hydrogen yield of acetic acid auto-thermal reforming, sintering resistant performance, and carbon deposition resistantperformance are all strengthened.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
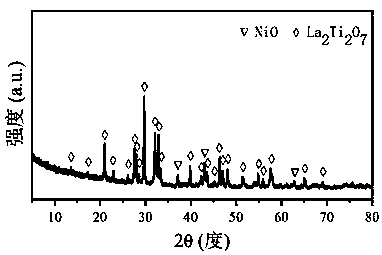
Ni/la for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid 2 x 2 o 7 catalyst
ActiveCN111111674BGood choiceHigh catalytic activityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a Ni / La2X2O7 catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. , Aiming at the problem of inactivation of an existing catalyst in the acetic acid autothermal reforming process, the invention provides the novel catalyst which is stable in structure and high in activity. A catalyst precursor is prepared by adopting a sol-gel method, and roasted by adopting an impregnation method to obtain the Ni / La2X2O7 (X is Ce, Zr or Ti) catalyst. According to the catalyst, the stability of active components is improved, the yield of hydrogen is increased, and generation of byproducts such as methane and acetone is effectively inhibited.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
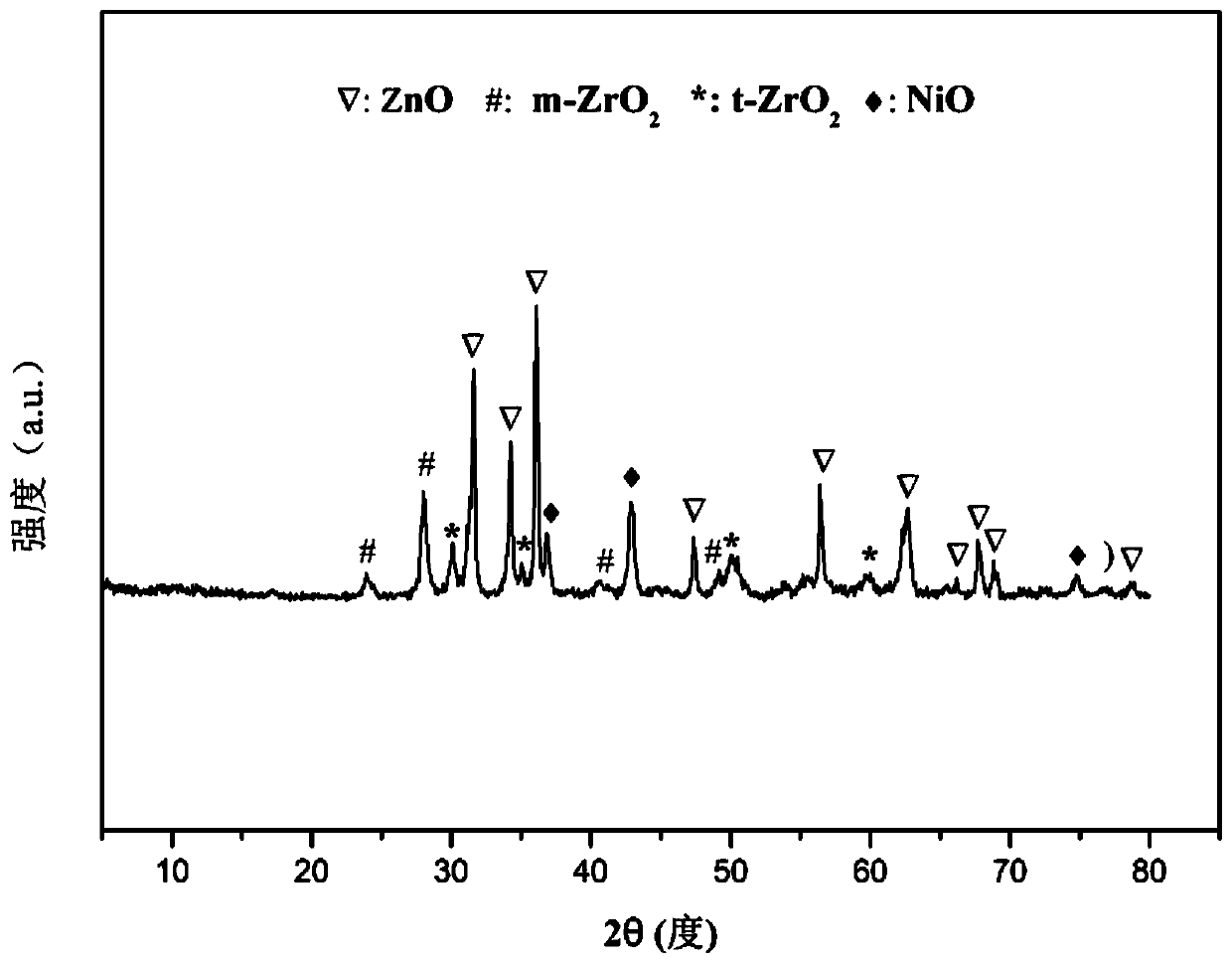
Zinc-nickel-zirconium mesoporous composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN109718784AGood dispersionImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh activityComposite oxide
The invention relates to a zinc-nickel-zirconium mesoporous composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Directed at the problem that catalyst structure change and the oxidation and sintering of active components can cause catalyst deactivation in existing catalysts during the autothermal reforming reaction of acetic acid, the invention provides a new catalyst characterized by stable structure, sintering resistance, carbon deposition resistance, oxidation resistance, and high activity. The chemical composition of the catalyst is (ZnO)a(NiO)b(ZrO2)c,wherein a is 0.60-2.25, b is 0.40-0.75 and c is 1.00. The invention adopts Ni as the active component, uses ZnO and ZrO2 as the carrier, and adopts coprecipitation method to prepare the Ni / ZnO-ZrO 2composite oxide catalyst, which effectively inhibits the formation of ketene, acetone and other by-products in the reaction process, improves the yield and selectivity of hydrogen, and improves the carbon deposition resistance, sintering resistance and oxidation resistance of the catalyst.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Sulfur tail gas hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109382109BImprove oxygen resistanceWith anti-cokeHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsSulfur preparation/purificationAntioxidant capacityPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of sulfur recovery, and in particular relates to a sulfur tail gas hydrogenation catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The raw materials of the carrier include pseudo-boehmite, modified diatomite and antioxidant additives, and the active components are molybdenum, nickel and iron; the modified diatomite is as follows: diatomite is treated with phosphoric acid, filtered, Roasting after drying to obtain modified diatomite; the specific surface area of diatomite is greater than 50m 2 / g. The invention further increases the oxygen resistance by adding low-temperature catalytic active components and anti-oxidation additives, and has the characteristics of strong anti-oxidation ability, high low-temperature activity, anti-coke and adaptability to high water vapor content, and can be used to induce liquid sulfur removal The gas enters the hydrogenation reactor for treatment, which meets the new national environmental protection standards to be implemented, and has significant economic and social benefits; it can be widely used in various sulfur recovery tail gas treatment devices.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Hydrocalumite-derived cobalt-based catalysts for autothermal reforming of acetic acid to produce hydrogen
ActiveCN109718785BImprove anti-sintering performanceImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh activityCobalt
The invention relates to a hydrocalumite derived cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Directed at the problem that catalyst structure change and the oxidation and sintering of active components can cause catalyst deactivation in existing catalysts during the autothermal reforming reaction of acetic acid, the invention provides a new catalyst characterized by stable structure, sintering resistance, oxidation resistance, carbon deposition resistance, and high activity. The molar composition of the catalyst is (CaO)a(CoO)b(AlO1.5) c, wherein a is1.66-5.19, b is 0.34-0.81 and c is 1.0. The invention adopts coprecipitation method to prepare a catalyst precursor, and then roasting is carried out to obtain the Ca-Co-Al-O mesoporous composite oxide. The catalyst takes calcium oxide as the framework, contains cobalt-alumina spinel phase and a small amount of Ca12Al14O33, inhibits the acidity of the catalyst, improves the carbon deposition resistance and sintering resistance of the catalyst, and improves the activity of hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A nickel-chromium-manganese mesoporous composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN109225250BGood dispersionImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsManganeseReduced properties
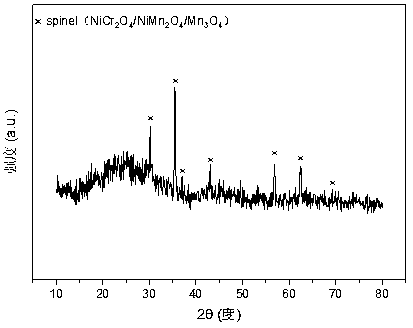
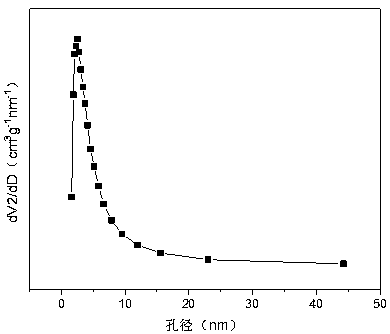
The invention relates to a nickel, chromium and manganese mesoporous compound oxide catalyst for acetic acid self-heating hydrogen production by reforming. In order to solve the problems that existingcatalysts are oxidized, sintered and deposited in carbon in the process of acetic acid self-heating by reforming, the invention provides a novel catalyst which is stable in structure, sintering-resistant, carbon deposition-resistant and oxidiation-resistant. The catalyst is as shown in a formula by mole: (NiO)a(MnO)b(CrO1.5)c, wherein a is 0.12-0.18, b is 0.7-0.33 and c is 0.14-0.5. The catalystis prepared by means of a coprecipitation method, and the Ni-Cr-Mn-O mesoporous compound oxide catalyst which is stable and contains spinels such as NiMn2O4, NiCr2O4 and Mn3O4 is obtained after sintering. The reducing property of active components and the stability of the catalyst are improved. In the process of acetic acid self-heating by reforming, generation of byproducts such as methane and acetone is inhibited, and the hydrogen yield is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A cobalt-cerium-manganese composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN111450840BHigh selectivityReduce generationHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a cobalt-cerium-manganese composite oxide solid solution catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Aiming at the problem of catalyst deactivation of an existing catalyst in an acetic acid autothermal reforming reaction, the invention provides an efficient and stable new catalyst. The chemical component of the catalyst provided by the invention is (CoO1.5) a (CeO2) b (MnOx) c, wherein a is 0.15 to 0.19, b is 0.41 to 0.72, and c is 0.09 to 0.44. Co is used as an active component, Ce and Mn are introduced by adopting a coprecipitation method to form the Co / Ce-Mn-Ox composite oxide solid solution catalyst, generation of byproducts such as acetaldehyde and acetone in the reaction process is effectively inhibited, and the yield of hydrogenand the carbon deposition resistance, sintering resistance and oxidation resistance of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
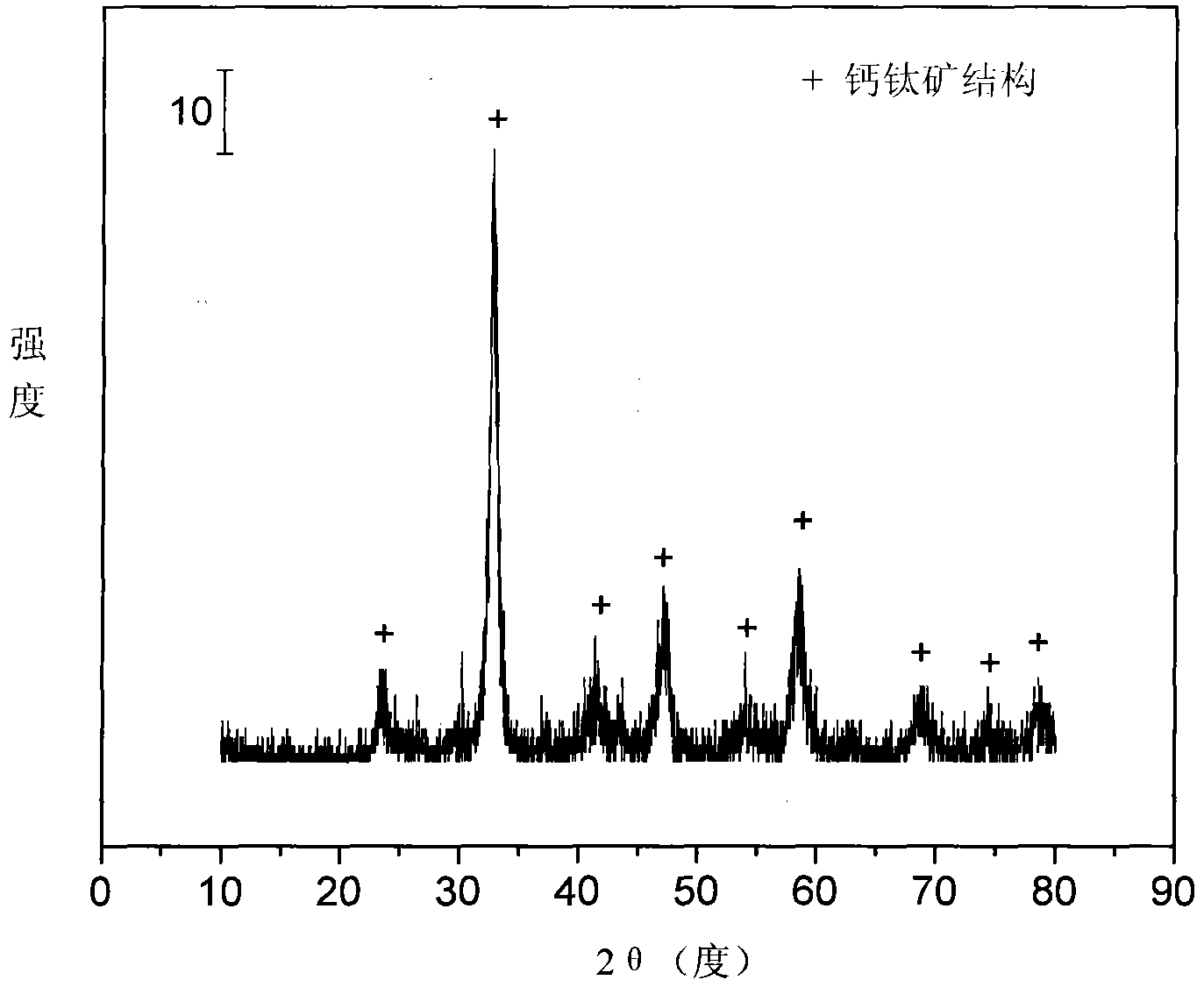
Perovskite TiSrCo Catalyst for Hydrogen Production by Autothermal Reforming of Acetic Acid
ActiveCN109759070BEnhanced adsorption and activationSimple structureMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLattice defectsWater vapor
The invention relates to a perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and a preparation method. The catalyst with resistance tosintering, anti-carbon deposit, oxidation resistance and high activity is provided to aim at solving the problems that an existing catalyst has carbon deposits, sintering and oxidation of active components in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid, and deactivation of the catalyst is caused. According to the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for the hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and the preparation method, a sol-gel method is adopted to prepare the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst, and after calcination, a perovskite composite oxide catalyst Ti<1-x>Sr<x>CoO3 is obtained, wherein x=0-0.8. The perovskite structure facilitates the dispersion of an active component Co, strengthens the synergistic effect between the active component and a carrier, and inhibits the aggregation and growth of Co, thereby obtaining stable small-particle-size Co particles. In addition, Ti is partially replaced with Sr to increase the surface defect position and lattice defect structure of the perovskite-type catalyst, so that the carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and thermal stability of the active component cobalt are improved, the diffusion of acetic acid, water vapor and oxygen is further facilitated, and the catalytic activity is increased.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Perovskite catalyst used for autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101972659BChange the adsorption and desorption propertiesEnhanced autothermal reforming activityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsManganeseOxygen
The invention relates to a perovskite catalyst used for the autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and a preparation method thereof. Aiming at the problems of structural change, oxidation and sintering of active ingredients and deactivation of the conventional catalyst during the autothermal reforming of the ethanol, the invention provides a novel catalyst with sintering resistance, carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity. The chemical formula of the catalyst is LaaSrbNicXdO3, wherein X is one of Fe, Mn and Cr, a is 0.7 to 1.0, b is 0 to 0.3, c is 0.7 to 0.95 and d is 0.05 to 0.3. The nickel-based catalyst with an ABO3 perovskite structure is prepared by a glycine complexation method, lanthanum is partially substituted by strontium at a position A and nickel is partially substituted by an auxiliary agent at a position B, so oxygen defects and lattice structure defects on the surface of the perovskite catalyst are increased; meanwhile, the auxiliary agent, namely iron, magnesium or chromium is introduced, so the acidity of the catalyst is inhibited, the reducibility and stability of the active ingredients of the catalyst are improved, and the yield of the hydrogen is obviously improved and remains stable.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Strontium-promoted cobalt-based composite oxide catalysts for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN111450833BEvenly dispersedIncrease contact areaHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a cerium dioxide-loaded strontium-promoted cobalt-based composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. The invention provides a novel catalyst which is stable in structure and high in activity in order to solve the problem that an existing catalyst is inactivated in an acetic acid autothermal reforming reaction. The molar composition of the catalyst is (SrO) a (CoO1.5) b (CeO2) c, wherein a ranges from 0.75 to 1.75, b ranges from 1.05 to 1.15, and c ranges from 1.50 to 2.50. According to the invention, Co is used as an activecomponent; the cerium dioxide-loaded strontium-promoted cobalt-based composite oxide is prepared by adopting a hydrothermal synthesis method; according to the catalyst, cerium dioxide is used as a skeleton, the catalyst contains a small amount of cobaltosic oxide spinel phase, and the Sr-Co-Ce-O mesoporous composite oxide solid solution catalyst is formed; possible migration, aggregation and sintering of an active component cobalt under a high-temperature condition are effectively inhibited, and the hydrogen yield, sintering resistance and carbon deposition resistance in the acetic acid autothermal reforming process are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
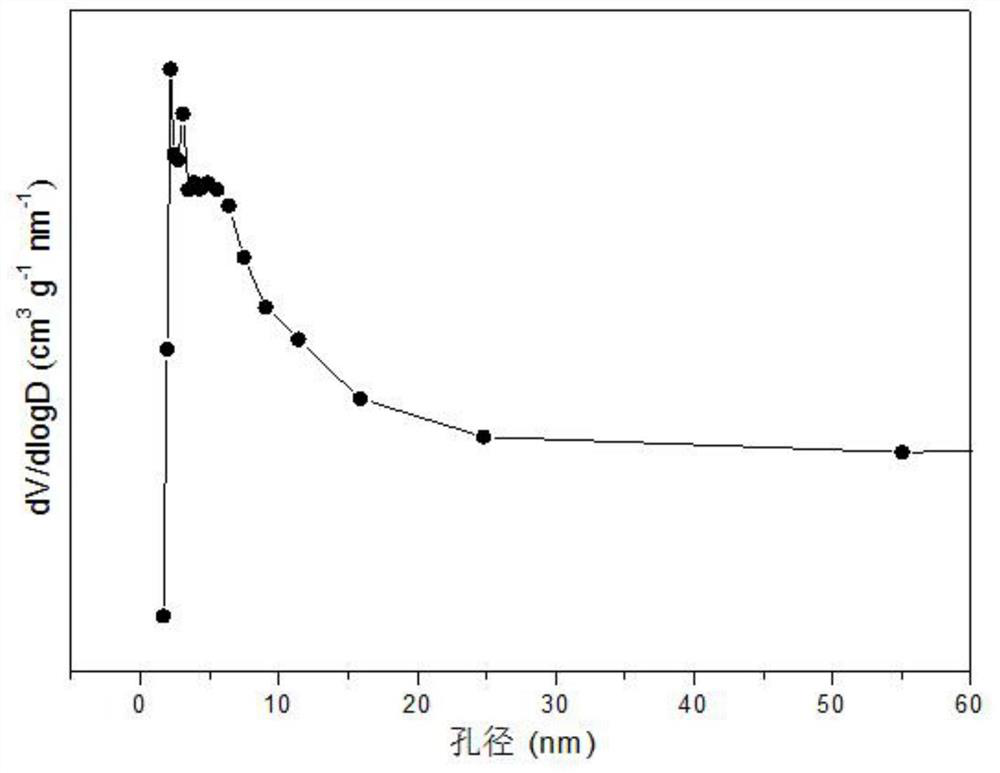
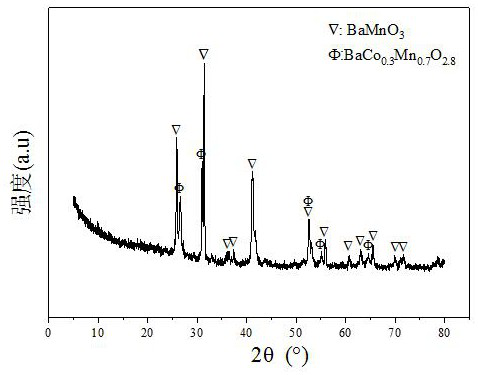
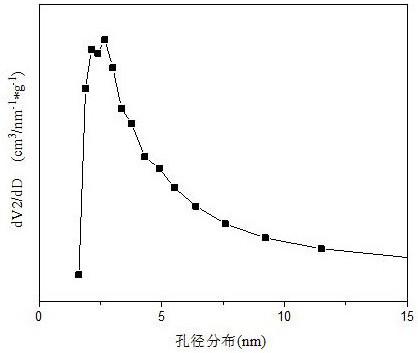
Ba-Mn perovskite-type cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN111111686BGood for adsorption and activationGood structural adjustabilityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPtru catalystPerovskite (structure)
The invention relates to a Ba-Mn perovskite type cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Aiming at the problem that an existing catalyst is inactivated in the acetic acid autothermal reforming process, the invention provides a novel catalyst with a stable structure and high activity. The molar composition of the catalyst is (BaO)a(MnO1.5)b(CoO1.5)c interms of oxides, wherein a is 0.177-0.430, b is 0.430-0.709, and c is 0.113-0.140; the catalyst is composed of the components in percentage by weight based on oxides: 30.4 to 60.4 percent of barium oxide, 29.5 to 59.6 percent of manganese oxide and 8.0 to 11.0 percent of cobalt oxide. A sol-gel method is adopted for preparation; cobalt is used as an active component, manganese and barium are introduced, and a stable BaMn0.7Co0.3O2.8 and BaMnO3 perovskite structure composite oxide structure is formed after roasting, so that the oxidation resistance and dispersity of active components are improved, and meanwhile, the hydrogen yield, sintering resistance and carbon deposition resistance in the acetic acid autothermal reforming process are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Olivine nickel-based catalyst for preparing hydrogen through autothermal reforming of acetic acid
InactiveCN103657654BIncrease lattice defectsEnhanced autothermal reforming activityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNickel catalystAcetic acid
The invention relates to an olivine nickel-based catalyst for preparing hydrogen through autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Aiming to solve the problems of low hydrogen yield and oxidation / sintering inactivation of active constituents of the conventional supported nickel-based catalyst in an autothermal reforming process of acetic acid, the invention provides a novel catalyst with the effects of large specific surface area, stable structure, sintering resistance, oxidation resistance and stable activity. The catalyst provided by the invention has a chemical component of MgaFebNicSiO4, wherein a is 1.0-1.7, b is 0-0.7 and c is 0.3-0.5. The nickeliferous catalyst taking an olivine structure as a main body is prepared by a hydro-thermal synthesis method; the catalyst has rich hole structures so that the specific surface area and the dispersity of active constituents of the catalyst are effectively improved; meanwhile, the active constituents, such as nickel and iron, and additives substitute for bivalent magnesium to enter an olivine skeletal structure to effectively refrain the phenomenon of oxidation / sintering inactivation of the catalyst, so that the stability and the hydrogen yield of the catalyst in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Hydrotalcite-like iron-promoted nickel-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107282050BPrevent oxidationPrevent sinteringHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a hydrotalcite-like iron-promoted nickel-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and a preparation method. The present invention aims at the problems that the existing catalyst changes in the catalyst structure and the oxidation and sintering of active components during the autothermal reforming of acetic acid, resulting in catalyst deactivation, and provides a catalyst that is resistant to oxidation, sintering, coking, and has high activity. new catalyst. The chemical component of the catalyst of the present invention is (ZnO) a (NiO) b (AlO 1.5 ) c (FeO 1.5 ) d , where a is 0.75‑3.25, b is 0.25‑0.75, c is 0‑1.0 and d is 0‑1.0. The present invention uses a co-precipitation method to prepare a Zn-Al carbonate-type hydrotalcite-like structure as a precursor, and introduces the active component nickel and the additive iron. Through the isomorphous substitution of nickel for zinc and iron for aluminum, it enters the Hydrotalcite-like structural position; the composite oxide obtained by roasting effectively inhibits the possible migration, aggregation, oxidation and sintering of the active component nickel under high-temperature reaction conditions, thus improving the activity and stability of the catalyst.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Zinc-nickel-zirconium mesoporous composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN109718784BGood dispersionImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh activityComposite oxide
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Nickel-base catalyst used for autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101972656BEasy to introduceLarge specific surface areaHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystMetallurgy
The invention relates to a nickel-based catalyst used for the autothermal reforming of ethanol for producing hydrogen and a preparation method thereof. Aiming at the problems of structural change, oxidation and sintering of active ingredients and deactivation of the conventional catalyst during the autothermal reforming of the ethanol, the invention provides a novel catalyst with a stable structure, sintering resistance, carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity. The chemical formula of the catalyst is NiaMgbAlcXdO4.5+ / -delta, wherein X is an auxiliary agent Fe or Mn, a is 0.25 to 0.40, b is 2.6 to 2.75, c is 0.1 to 0.8 and d is 0.2 to 0.9. A brucite-based (Mg(OH)2.mH2O) hydrotalcite structure is taken as a precursor, so that the active ingredient nickel and the auxiliary agent heteroion component are introduced into a laminated structure and a position between laminated structures; meanwhile, the auxiliary agent iron or magnesium is introduced, so the reducibility and stability of the active ingredients of the catalyst are improved, and the yield of the hydrogen is obviously improved and remains stable.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
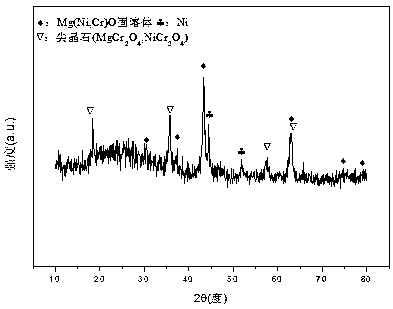
A nickel-magnesium-chromium composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN108927164BGood dispersionImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsHigh activityComposite oxide
The invention relates to a nickel-magnesium-chromium mesoporous composite oxide catalyst for auto-thermal reforming of acetic acid to produce hydrogen. The invention aims to solve the problem that inthe prior art, during the acetic acid auto-thermal reforming process, the structure of a conventional catalyst changes, the active components are oxidized and sintered, and thus the catalyst is deactivated, and provides a novel catalyst having the advantages of stable structure, sintering resistance, carbon deposition resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity. The chemical formula of thecatalyst is (NiO)a(MgO)b(CrO1.5)c; wherein a is 0.08-0.12, b is 0.55-0.92, c is 0-0.33, and nickel oxide accounts for 12.0 to 20.0 wt.% of the catalyst, magnesium oxide accounts for 40.0 to 88.0 wt.%of the catalyst, and chromium oxide accounts for 0 to 40.0 wt.% of the catalyst. A catalyst precursor is prepared by a co-precipitation method, chromium is introduced into the catalyst and is taken asan auxiliary agent; after burning, a stable mesoporous composite oxide catalyst, which comprises a MgCr2O4 and NiCr2O4 spinel structure and a Mg-Ni-Cr-O solid solution, is formed; the reducing performance and stability of the active components are enhanced; at the same time, the hydrogen yield of acetic acid auto-thermal reforming, sintering resistant performance, and carbon deposition resistantperformance are all strengthened.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A layered perovskite catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107042111BHigh activityIncrease lattice structure defectsHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a layered perovskite catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and a preparation method. The present invention aims at the problems of sintering, oxidation, and carbon deposition of existing catalysts during the autothermal reforming of acetic acid, resulting in catalyst deactivation, and provides a new catalyst that is resistant to sintering, carbon deposition, oxidation resistance, and high activity. The present invention prepares A by sol-gel method 2 BO 4 Nickel-based catalyst with layered perovskite structure, chemical composition is La 2‑x Ca x NiO 4 , where Improved catalyst activity and stability.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Cobalt-cerium-manganese composite oxide catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN111450840AHigh selectivityReduce generationHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a cobalt-cerium-manganese composite oxide solid solution catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Aiming at the problem of catalyst deactivation of an existing catalyst in an acetic acid autothermal reforming reaction, the invention provides an efficient and stable new catalyst. The chemical component of the catalyst provided by the invention is (CoO1.5) a (CeO2) b (MnOx) c, wherein a is 0.15 to 0.19, b is 0.41 to 0.72, and c is 0.09 to 0.44. Co is used as an active component, Ce and Mn are introduced by adopting a coprecipitation method to form the Co / Ce-Mn-Ox composite oxide solid solution catalyst, generation of byproducts such as acetaldehyde and acetone in the reaction process is effectively inhibited, and the yield of hydrogenand the carbon deposition resistance, sintering resistance and oxidation resistance of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A hydrotalcite-derived cobalt-based catalyst is promoted by an auxiliary for autothermal reforming of acetic acid for hydrogen production
InactiveCN108043406BFacilitates conversion and gasificationHigh catalytic activityHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsLayered structureHydrotalcite
The invention relates to an iron-promoted cobalt-based catalyst used for hydrogen preparation through auto-thermal reforming of acetic acid and derived from carbonated LDHs (layered double hydroxides)structures. In order to solve the problem about inactivation of existing catalysts due to change of catalyst structures as well as oxidation and calcination of active components in the auto-thermal reforming process of acetic acid, the catalyst with sintering resistance, carbon deposition resistance, oxidation resistance and high activity is provided. The chemical ingredient of the catalyst is (Fe2O3)a(Co3O4)b(Al2O3)1.5, wherein a ranges from 0 to 0.21 and b ranges from 0.12 to 0.16. The Co-Fe-Al LDHs structure is taken as a precursor, and accordingly, active component, namely, cobalt, can beconveniently introduced into the layered structure; meanwhile, an auxiliary, namely, iron, inhibits the acidity of a catalyst carrier, the reducibility and the stability of the active ingredient of the catalyst are improved, and the hydrogen yield is notably increased and kept stable.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com