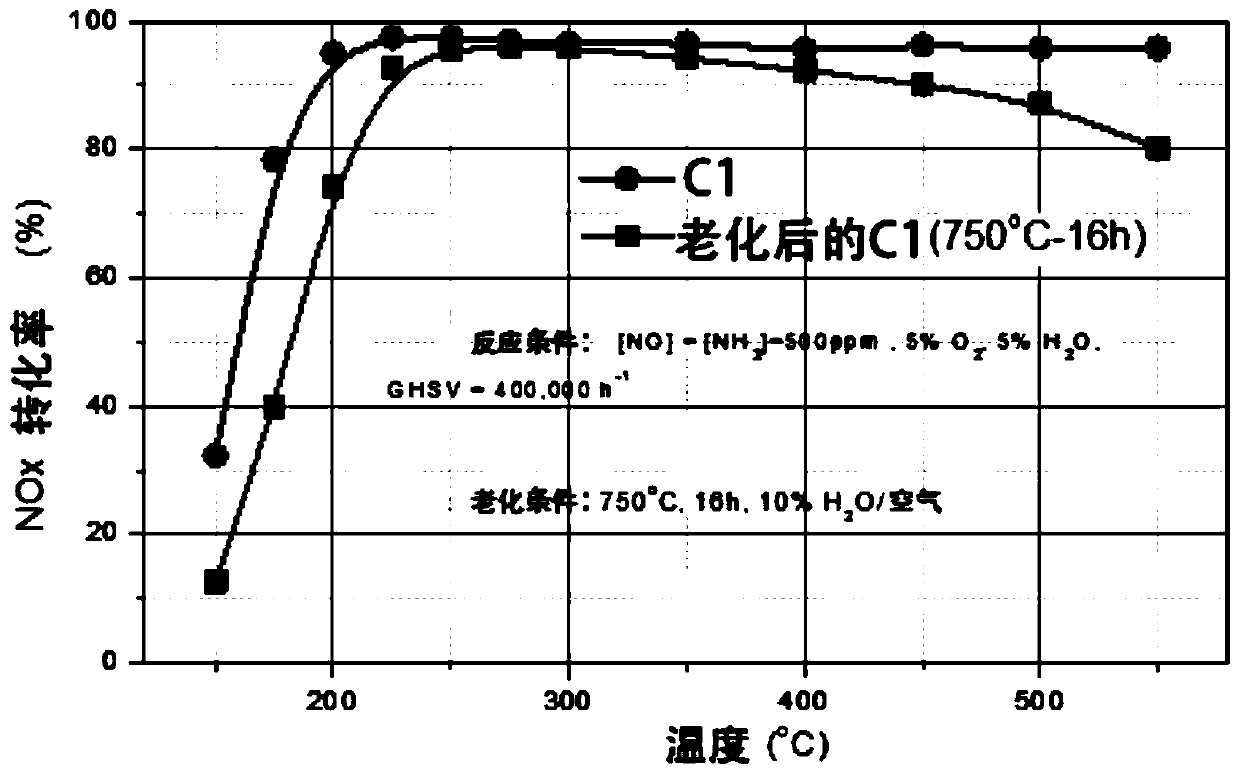
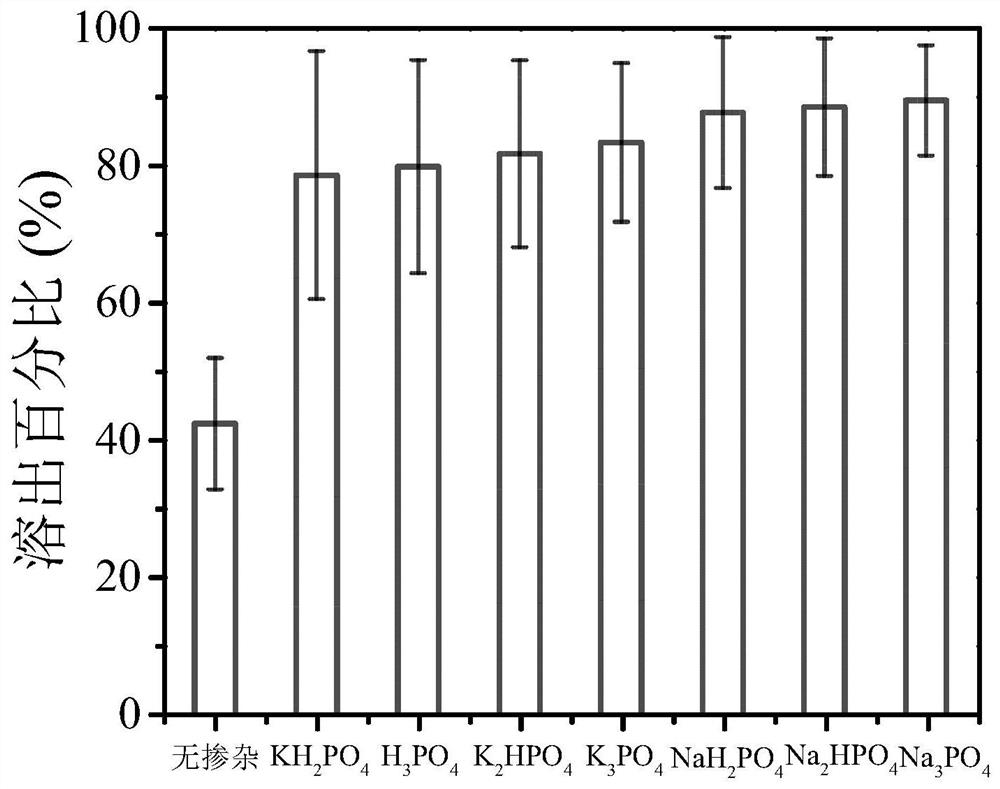
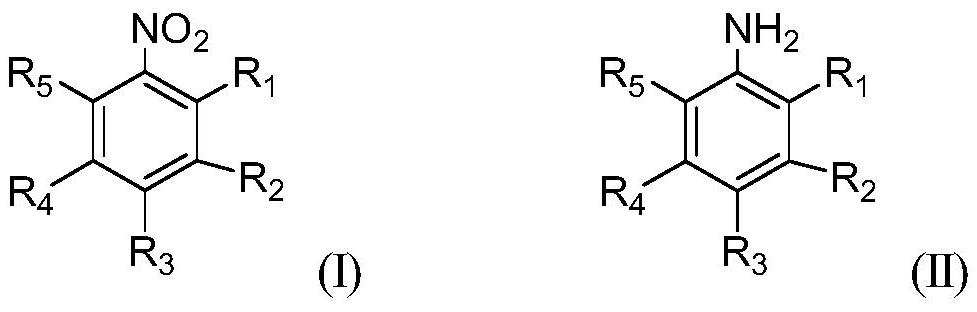Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Enhanced adsorption and activation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
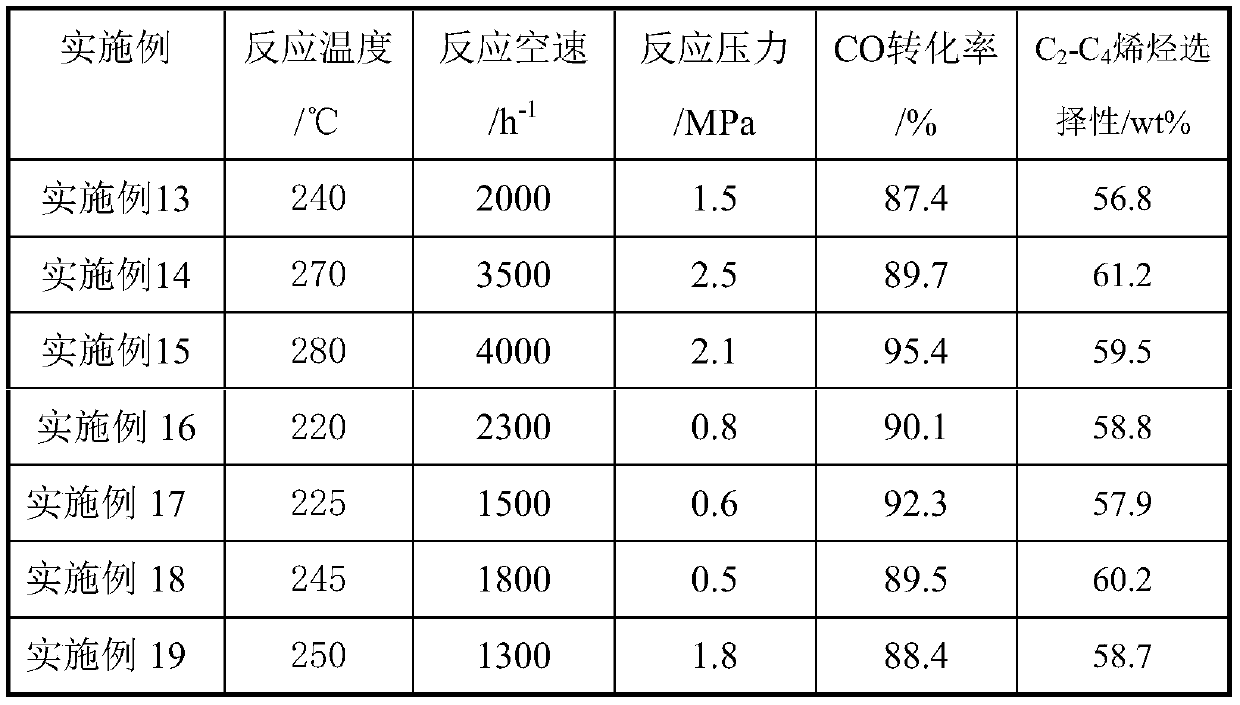
Application Year
Inventor
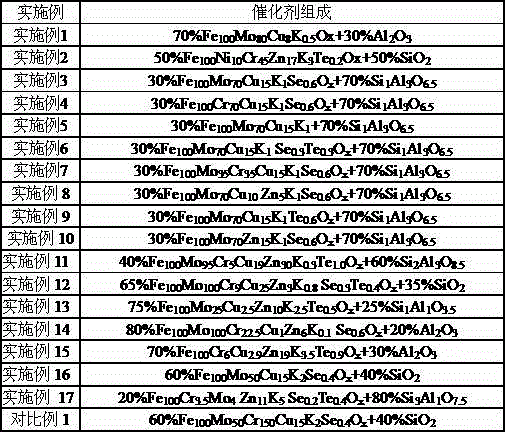
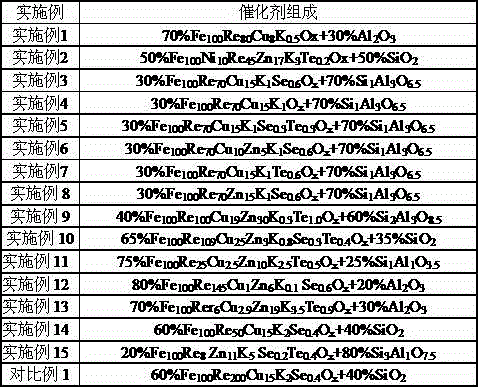
Catalyst for preparing low-carbon olefin from synthesis gas as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
ActiveCN104549343AGood choiceEnhanced adsorption and activationHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to a catalyst for preparing low-carbon olefin from synthesis gas as well as a preparation method and application of the catalyst, and aims at mainly solving the problems in a process of preparing the low-carbon olefin from the synthesis gas that the activity and the selectivity of the catalyst are low at a low temperature. The problems are solved very well by adopting the technical scheme that a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst is adopted and is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: (1) 20%-80% of an active component; (2) 20%-80% of a carrier, wherein the carrier is selected from at least one of SiO2 and Al2O3; the active component is represented by the following formula according to an atomic ratio: Fe100AaBbKcOx, wherein A is at least one of Cu and Zn; B is at least one of Cr and Mo; the value range of a is 5-50; the value range of b is 5-150; and the value range of c is 0.1-5. The catalyst can be used for industrial production of preparing the low-carbon olefin from the synthesis gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for grease to be decarbonylated into long-chain alkane under hydrogen-free condition
ActiveCN108586181AHigh efficiency decarbonylation conversionImprove decarbonylation abilityHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlkaneOil and grease
The invention relates to a method for grease to be decarbonylated into long-chain alkane under a hydrogen-free condition. One or more of long-chain fatty acid or / and fatty acid ester, animal and vegetable fats and oils, aqueous algal oil and waste cooking oil are used as raw materials, a carrier which contains Ca is loaded with Pt and used as a decarbonylation catalyst, carboxyls are removed though the decarbonylation, and thus the long-chain alkane is generated. The method is simple in process and high in operational safety, sources of the raw materials are wide, and the investment costs of devices and the raw materials are reduced. Green and reproducible grease is used as the raw material, and usage of fossil energy is avoided, so that the method accords with green and environmental-friendly concepts. A catalytic reaction is conducted under the hydrogen-free condition, and the carrier with Ca promotes adsorption and activation of grease molecules, so that the decarbonylation efficiency is greatly improved, and the aim of preparing the long-chain straight-chain alkane from the grease through the decarbonylation at a lower temperature under the hydrogen-free condition can be achieved.
Owner:上海科密思新能源科技有限公司
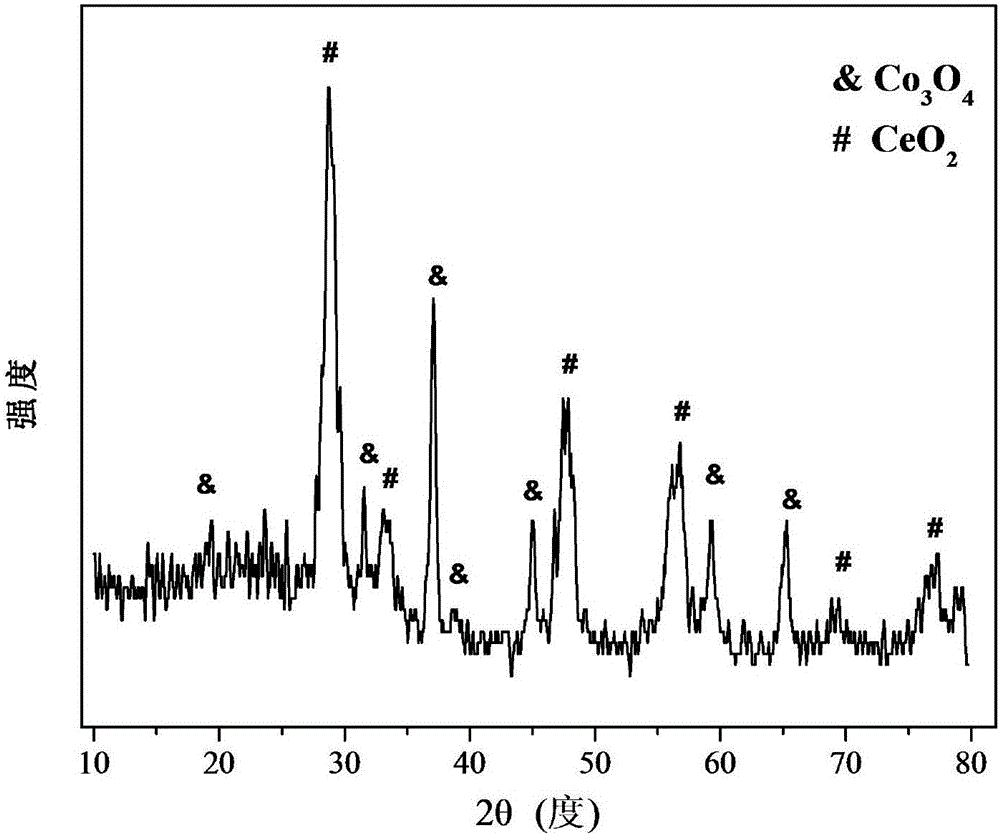
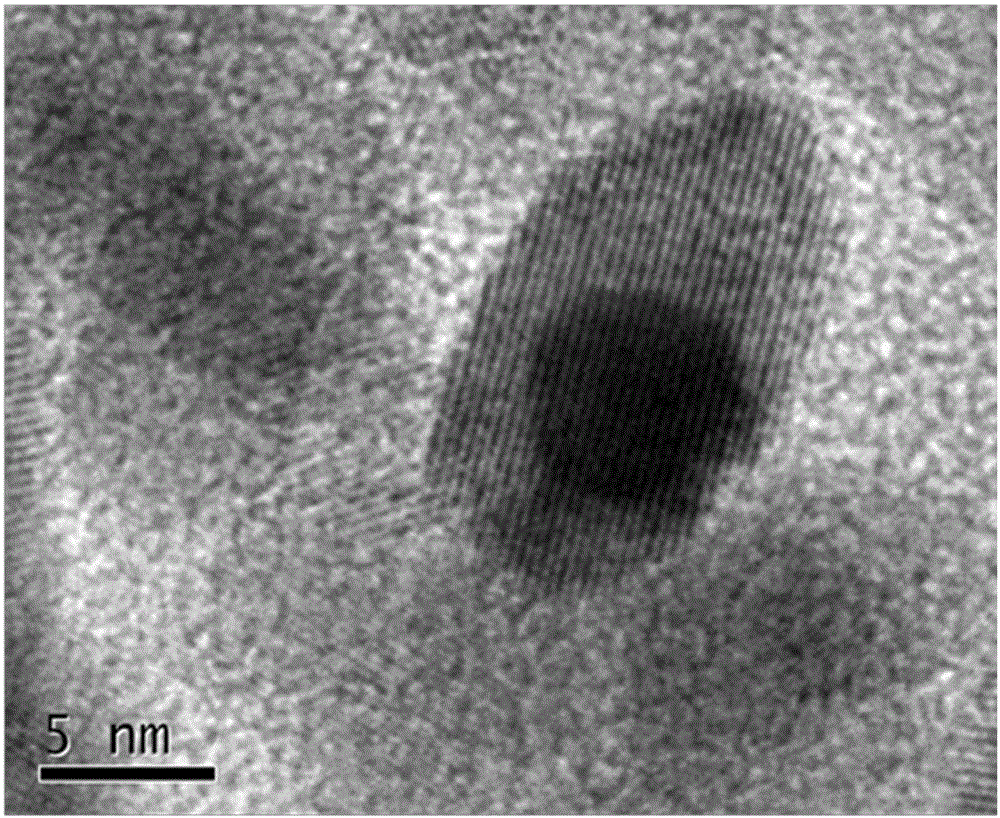
Modified Co-Ce core-shell structure catalyst for carbon monoxide (CO) low-temperature oxidation
InactiveCN105148930AIncrease the areaSimple structureDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPorosityDiffusion resistance
The invention relates to a modified Co-Ce core-shell structure catalyst for carbon monoxide (CO) low-temperature oxidation, and aims to solve the problems that when the conventional core-shell structure Co3O4-CeO2 catalyst is utilized for a CO low-temperature oxidation reaction, the porosity rate of a Co3O4 core material is relatively low, an adverse effect is caused on CO and O2 mass transfer diffusion to a reactant, and the mass transfer diffusion resistance of the conventional core-shell structure is relatively high. The modified Co-Ce core-shell structure catalyst being large in specific surface area, high in porosity rate and large in contact interface is obtained by preparing a core-shell structure material Co3O4-CeO2 through self-assembly and carrying out modification through formic acid treatment; through adoption of the modified Co-Ce core-shell structure catalyst, the capabilities of mass transfer diffusion to the reactant and adsorption-activation are effectively improved; through utilization of the oxygen storage and transfer capabilities of CeO2, the activity of the CO low-temperature oxidation reaction is effectively improved. The modified Co-Ce core-shell structure catalyst comprises 35-55wt% of Co3O4 and 45-65wt% of CeO2.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Catalyst for producing low-carbon olefin as well as preparation method and using method of catalyst
ActiveCN104549359AEnhanced adsorption and activationPromote reductionHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLow activityBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a catalyst for producing low-carbon olefin and a preparation method of the catalyst, and mainly aims to solve the problems of low activity and low selectivity of the catalyst at low temperature in synthesis gas prepared olefin. The problems can be well solved by adopting the technical scheme that the catalyst is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 20-80 percent of an active ingredient (1) and 20-80 percent of carrier (2) which is at least one of SiO2 and Al2O3, wherein the active ingredient is as shown in the general formula Fe100AaBbKcOx in an atomic ratio, A is at least one of Ag and Au, and B is at least one of Mn and V; the value range of a is 5-50, the value range of b is 5-150, and the value range of c is 0.1-5. The catalyst can be applied to industrial production of low-carbon olefin from synthesis gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
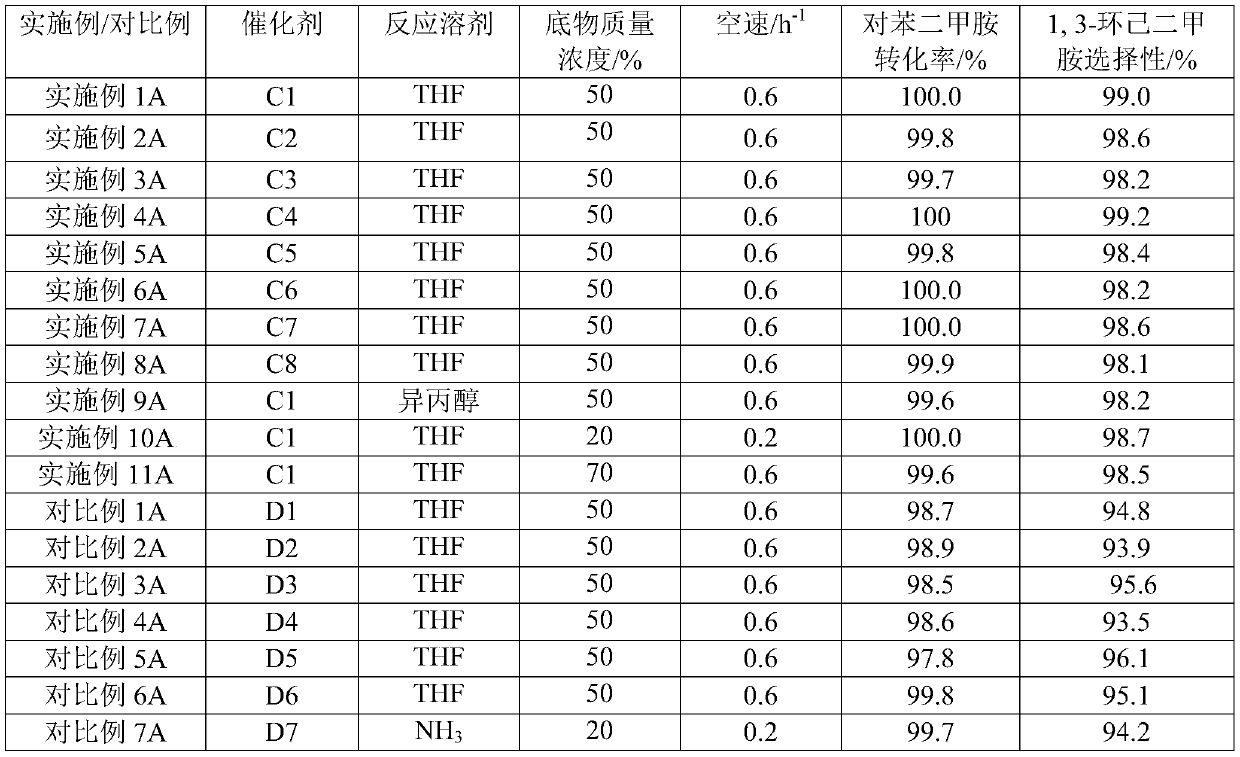
M-xylylenediamine hydrogenation catalyst, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111330629AHigh activityImprove the ability of adsorption and activationMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationMolecular sieveHydrogen synthesis
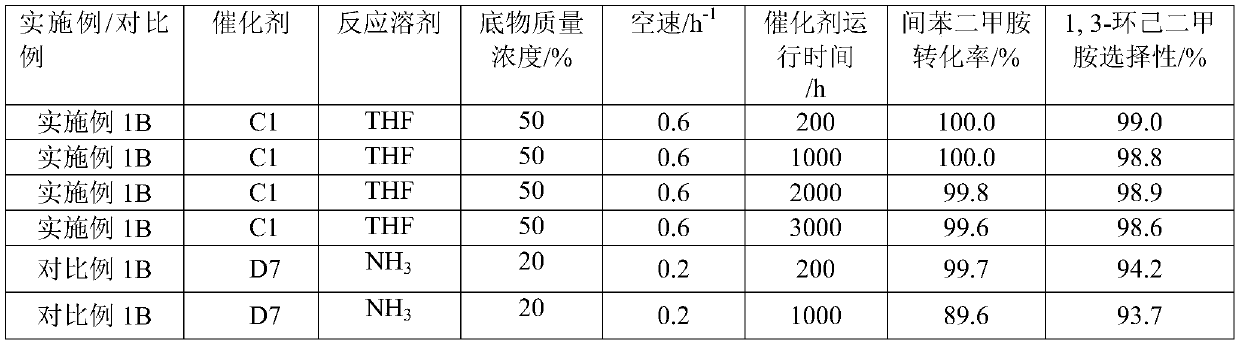
The invention provides a catalyst for synthesizing 1, 3-cyclohexanedimethylamine by hydrogenation of m-xylylenediamine and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is composed of a carrier, and an active component and an auxiliary agent which are attached to the carrier; wherein the active component is composed of one or more of metals Rh, Pt, Pd, Ir, Au, Ag, Ni and Re and noble metal Ru; the auxiliary agent is composed of an auxiliary agent I and an auxiliary agent II, the auxiliary agent I is composed of metals Eu and Yb, the auxiliary agent II is selected from one or more of metals Li, Na, k, Cu, Co, Fe, Zn, Mn, La and Ce, and the carrier is a metal compound modified molecular sieve. Compared with the prior art, the catalyst can acquire a high raw material conversion rate and 1, 3-cyclohexanedimethylamine selectivity under low reaction temperature and pressure and high substrate concentration and reaction space velocity, is stable in performance and long in service life, can obviously improve the production efficiency and reduce the production cost, and is beneficial to industrial application.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN109759070ALower activation energyStable activityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsComposite oxideSol-gel
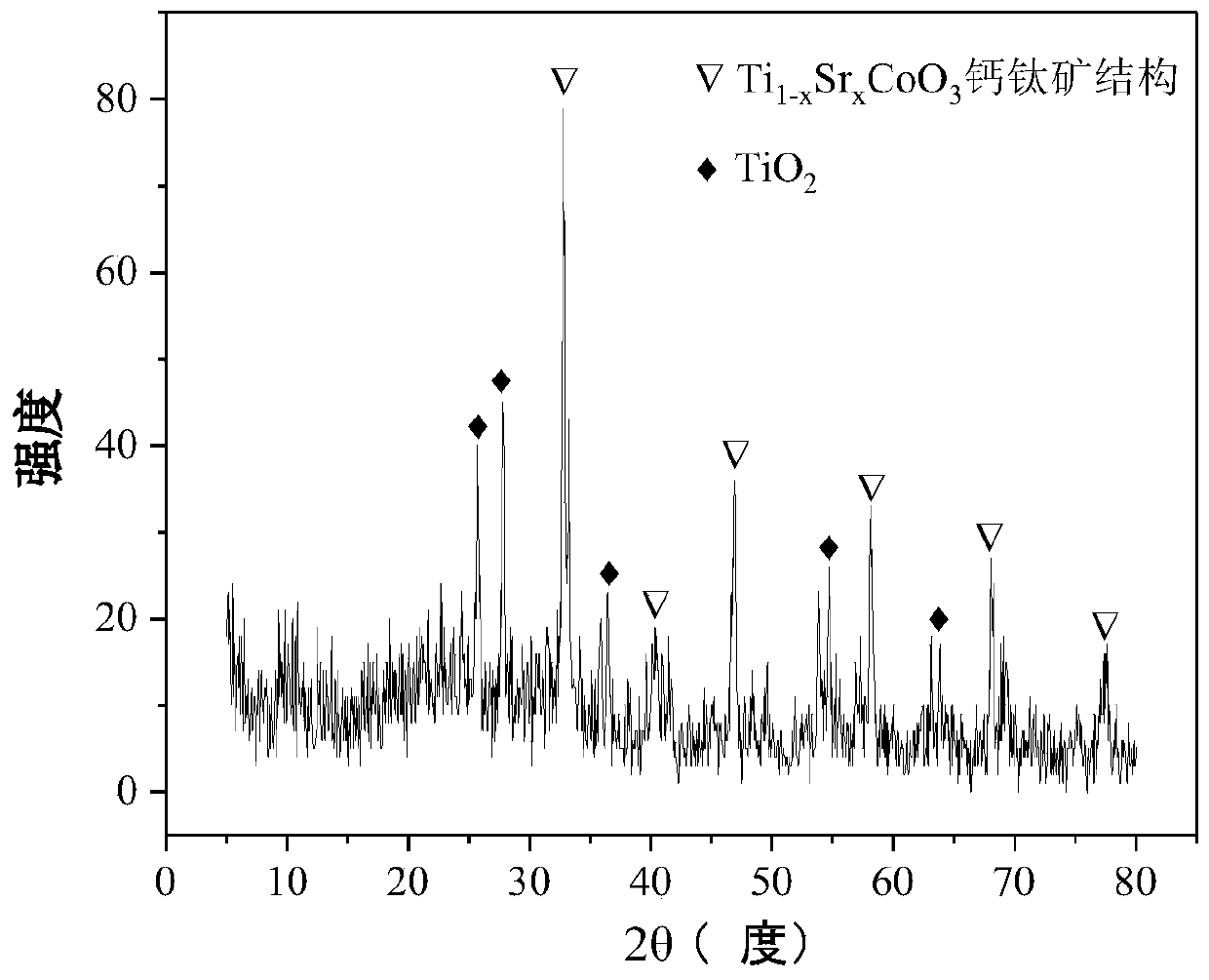
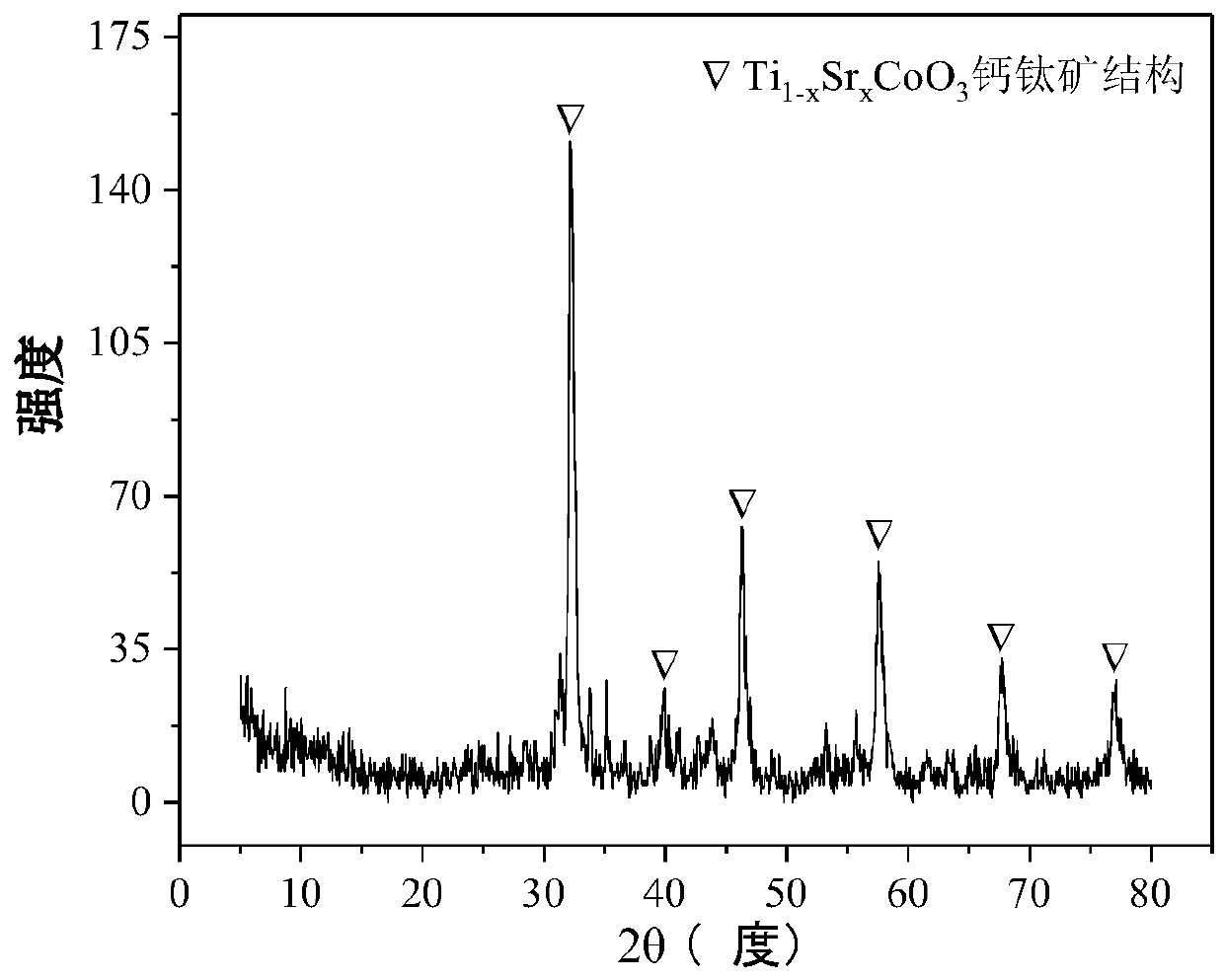
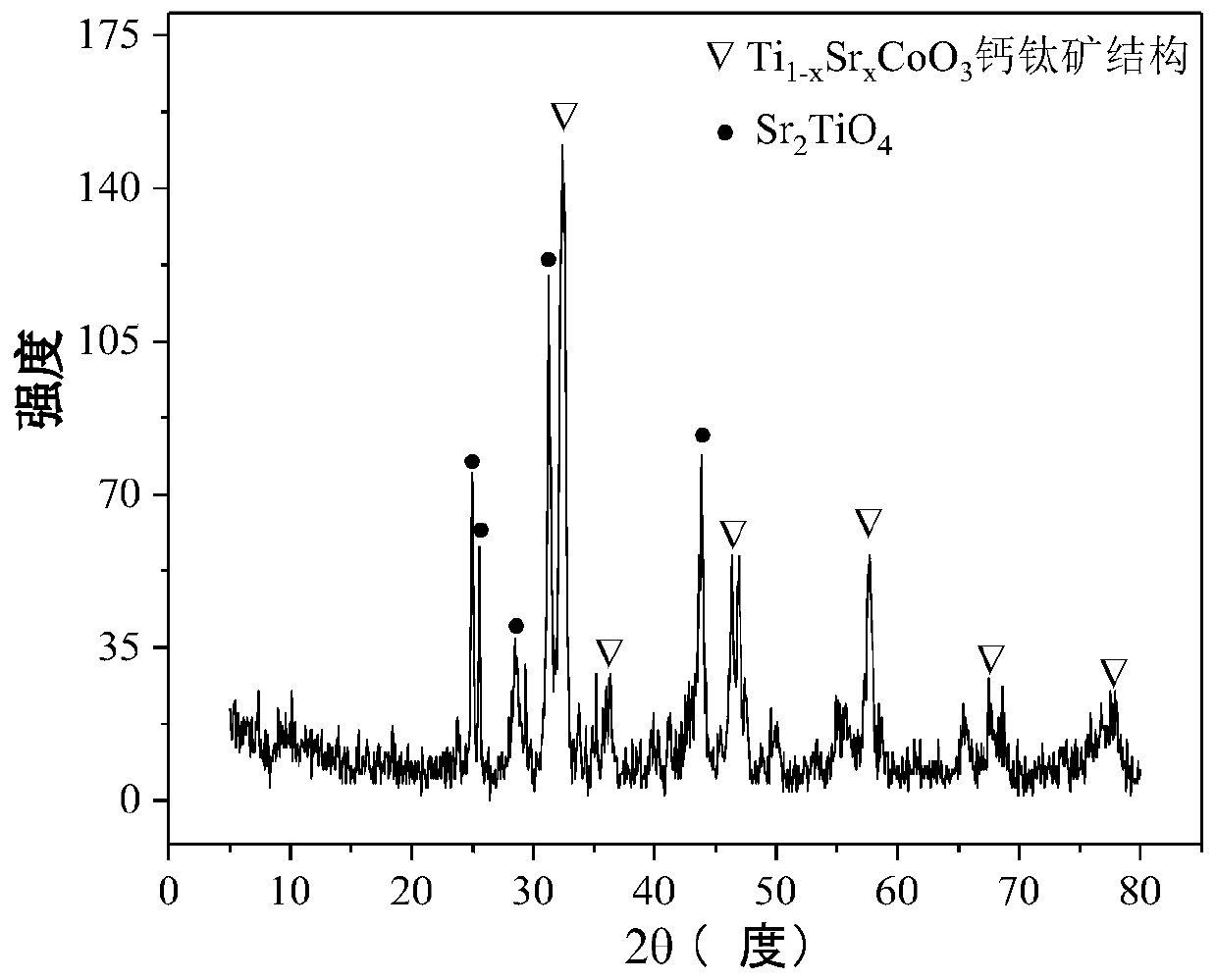
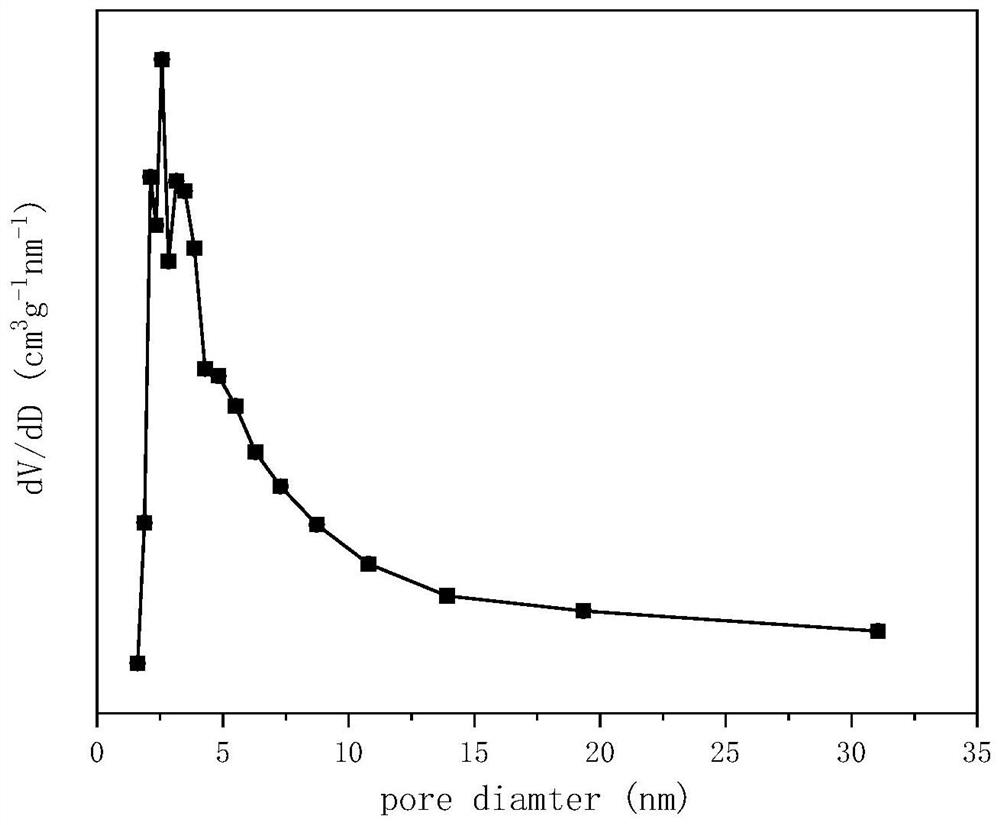
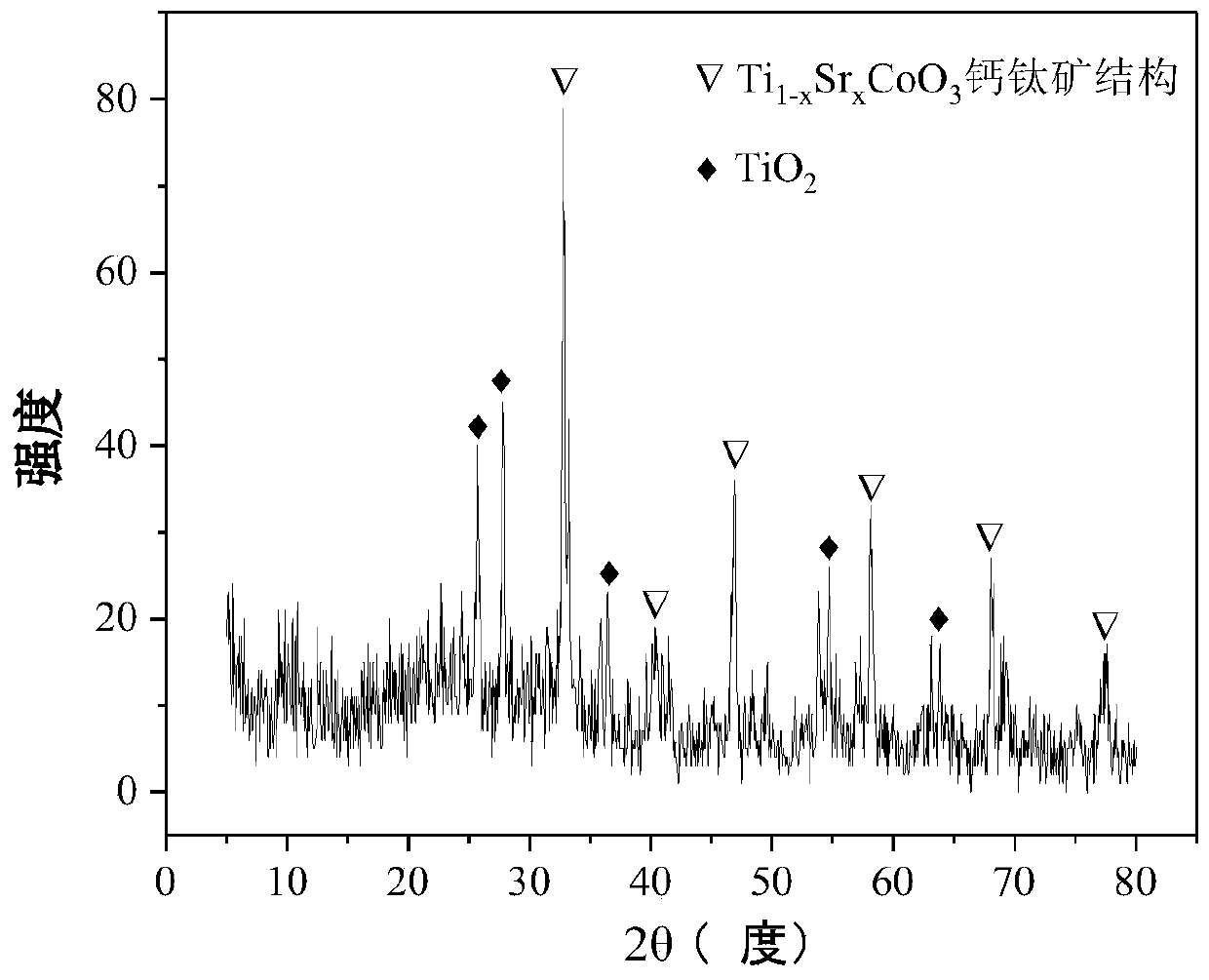
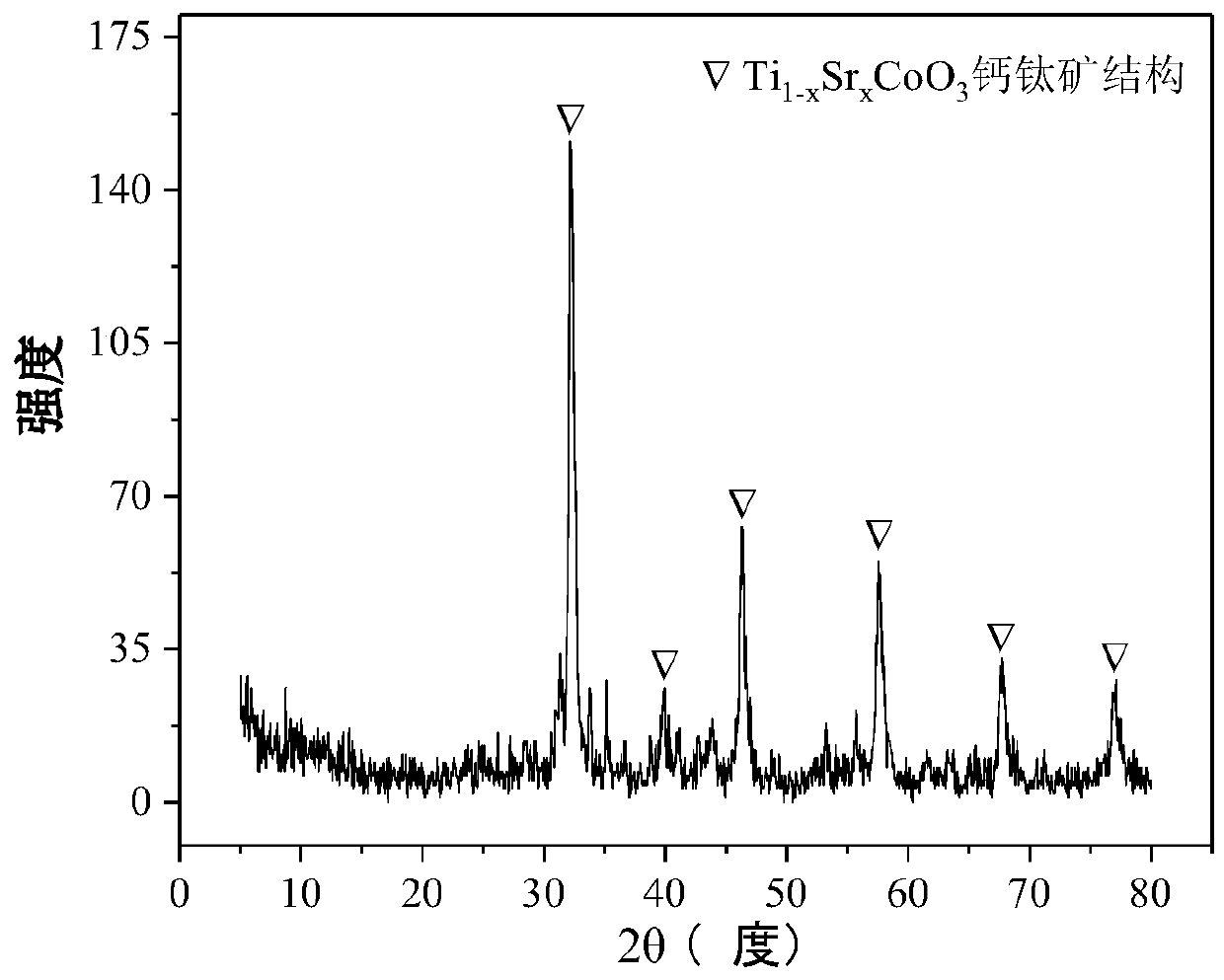
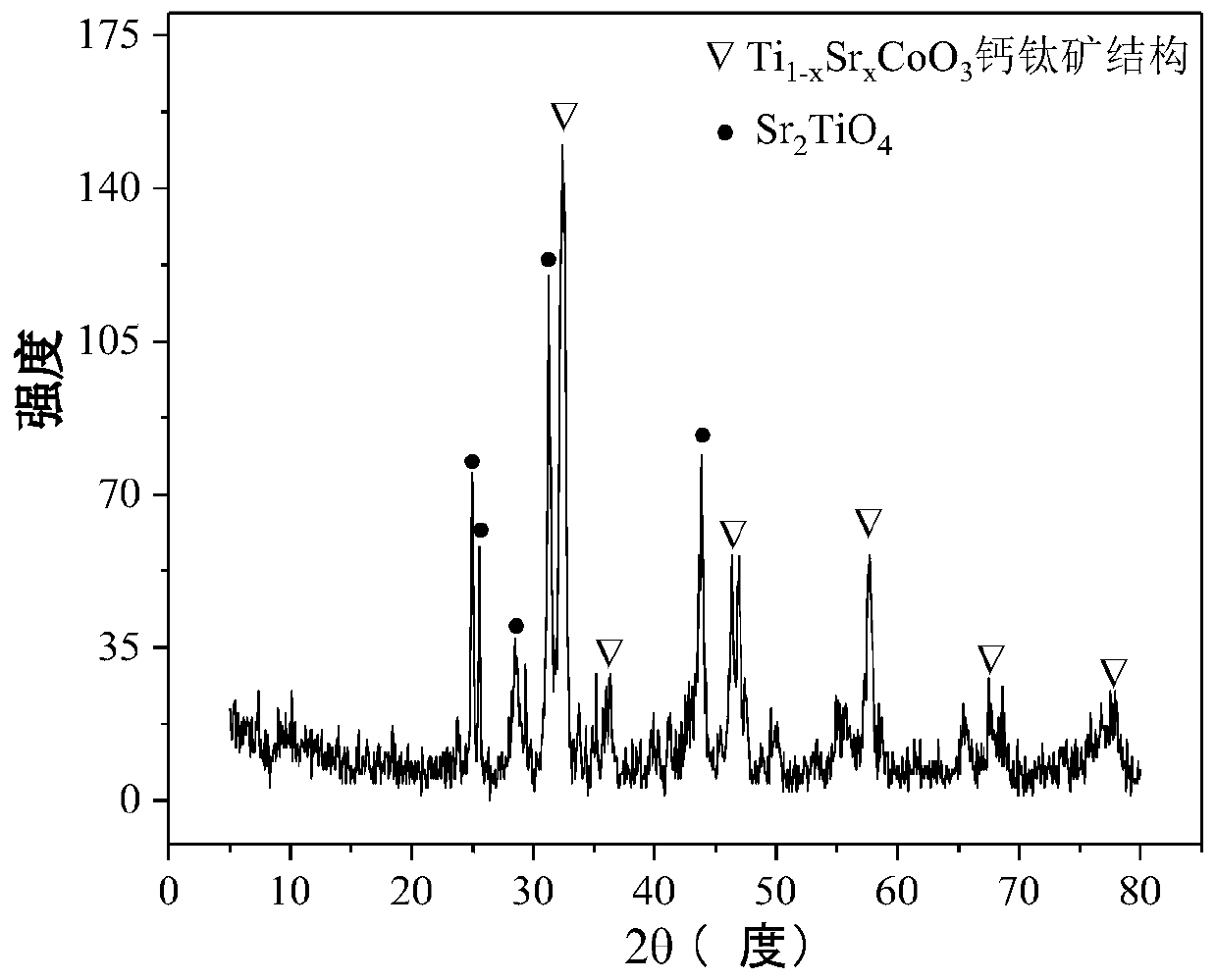
The invention relates to a perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and a preparation method. The catalyst with resistance tosintering, anti-carbon deposit, oxidation resistance and high activity is provided to aim at solving the problems that an existing catalyst has carbon deposits, sintering and oxidation of active components in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid, and deactivation of the catalyst is caused. According to the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for the hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and the preparation method, a sol-gel method is adopted to prepare the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst, and after calcination, a perovskite composite oxide catalyst Ti<1-x>Sr<x>CoO3 is obtained, wherein x=0-0.8. The perovskite structure facilitates the dispersion of an active component Co, strengthens the synergistic effect between the active component and a carrier, and inhibits the aggregation and growth of Co, thereby obtaining stable small-particle-size Co particles. In addition, Ti is partially replaced with Sr to increase the surface defect position and lattice defect structure of the perovskite-type catalyst, so that the carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and thermal stability of the active component cobalt are improved, the diffusion of acetic acid, water vapor and oxygen is further facilitated, and the catalytic activity is increased.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
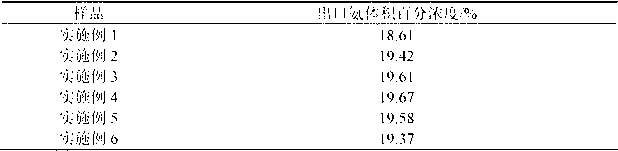
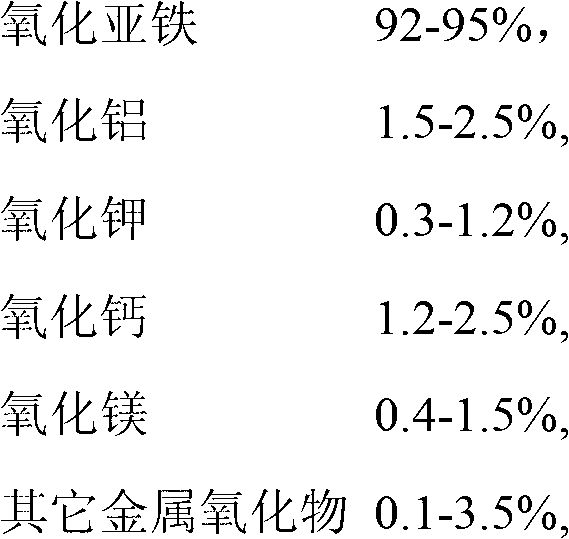
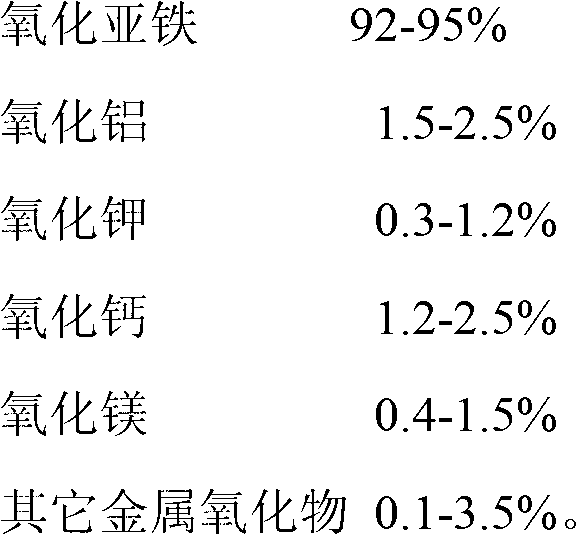
Ferrous oxide-based ammonia synthesis catalyst
ActiveCN102909030AHigh activityEnhanced adsorption and activationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBulk chemical productionHeat resistanceEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a ferrous oxide-based ammonia synthesis catalyst. The ferrous oxide is taken as a main phase component, and potassium oxide, calcium oxide, aluminum oxide, magnesium oxide and other metal oxides are used as auxiliary catalysts. The ferrous oxide-based ammonia synthesis catalyst is prepared by a melting method. The catalyst has high activity to catalyze nitrogen and hydrogenate to synthesize ammonia, easy to reduce, and great in heat resistance and antitoxic and has mechanical performances. The catalyst is suitable to be used in various sizes of ammonia synthesizing devices, and particularly suitable for a low-pressure and low-energy consumption ammonia synthesizing technique; and obvious energy saving, consumption reduction, efficiency increasing, cost saving and economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst and H-SSZ-13 molecular sieve with double aluminum centers and preparation methods and application thereof
PendingCN111514929AHigh hydrothermal stabilityHigh crystallinityGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention relates to the field of zeolite molecular sieve catalysts, and discloses a Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst and an H-SSZ-13 molecular sieve with a CHA cage having double aluminum centers and a preparation method and application thereof. The Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst includes an SSZ-13 molecular sieve and a copper element and is characterized in that the topological structure of the SSZ-13 molecular sievecomprises various ellipsoidal CHA cages including ellipsoidal CHA cages with double aluminum centers, and the content of the ellipsoidal CHA cages with the double aluminum centers is 50% or above onthe basis of the total number of the ellipsoidal CHA cages in the SSZ-13 molecular sieve. The Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst and the H-SSZ-13 molecular sieve with the CHA cage having double aluminum centers haveexcellent catalytic activity and hydrothermal resistance stability when used for catalyzing a selective reduction reaction of nitrogen oxide, and the preparation method is simple and easy to operate,good in economy and high in silicon-aluminum ratio controllability.
Owner:李云龙
Method for photocatalytic dissolution of metal by using phosphate radical modified photocatalyst
ActiveCN113373307AImprove efficiencyIncrease reaction ratePhysical/chemical process catalystsProcess efficiency improvementOrganic chloride compoundPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a method for photocatalytic dissolution of metal by using a phosphate radical modified photocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps that a metal-containing material to be dissolved is dispersed into a mixed solution containing a nitrile compound and an organic chloride, an inorganic phosphate radical modified photocatalyst is added, oxygen is introduced or a substance capable of generating oxygen is added, metal is dissolved under the condition of light irradiation, and after the metal is dissolved, a metal organic coordination compound is formed in the solution and has the general formula of (NH4) xMCly. Compared with the prior art, the preparation process of the photocatalyst is simple and convenient, after inorganic phosphate modification, oxygen adsorption can be improved, more superoxide free radicals are generated, visible light absorption of the catalyst can be improved so as to enhance the reaction rate of photocatalytic dissolution of metal, a feasible scheme is provided for actual production development, and the method has extremely high application value in the aspects of waste metal dissolution and recovery, photocatalytic oxidation reaction and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application method of photo catalyst for high-efficiency photo-catalytic propylene epoxidation material
InactiveCN107051580AHigh catalytic activitySimple preparation processOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsGeneration ratePhotocatalytic reaction
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application method of a photo catalyst for a high-efficiency photo-catalytic propylene epoxidation material. The preparation method comprises the following processes: preparing a titanium silicon molecular sieve TS-1 carrier by adopting a hydrothermal method and directly supporting Au and Ag bimetals on the carrier by utilizing an impregnation-reduction method to prepare a bimetallic-supported Au-Ag / TS-1 photocatalyst. The prepared photocatalyst is put in a fixed bed reactor; propylene, oxygen and diluent gas are introduced; photo-catalytic reaction is performed by taking a 100W ultraviolet mercury lamp as a light source to prepare propylene epoxide PO. The propylene can be efficiently and highly-selectively converted into the propylene epoxide, and the optimal generation rate and the selectivity of the propylene epoxide are 68.3 mu mol.g<-1>h<-1> and 52.3 percent respectively. The preparation method and the application method provided by the invention have the advantages of being simple in process condition, low in cost, good in repeatability and friendly in environment in the reaction process and can convert the propylene into an industrial product with higher value added.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mullite-loaded W-promoted Co-based catalyst for hydrogen production by auto-thermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN112742412AImprove thermal stabilityImprove anti-sintering performanceHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a Mullite carrier-loaded W-promoted Co-based catalyst for hydrogen production by auto-thermal reforming of acetic acid. The invention provides a novel catalyst which is high in activity, resistant to carbon deposition, resistant to sintering and resistant to oxidation, aiming at the problem of catalytic inactivation of an existing catalyst in the auto-thermal reforming process of acetic acid. The molar composition of the catalyst provided by the invention is (CoO)a(WO3)b(3Al2O3-2SiO2)c, a is in a range of 0.469 to 0.517, b is in a range of 0.010 to 0.054, and c is in a range of 0.449 to 0.502. According to the preparation method, Co and W components are impregnated on a Mullite carrier by adopting an impregnation method, a mesoporous composite oxide Co-W / Mullite catalyst containing spinel CoAl2O4 and a composite oxide CoWO4 is formed after calcination, and a Co-W-Al-O active center loaded on Mullite is obtained. The catalyst provided by the invention efficiently promotes the adsorption activation of acetic acid molecules and the conversion of intermediate products, inhibits the generation of by-products, and further improves the hydrogen yield and the stability of the catalyst.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Catalyst with double-alloy composite micro-mesoporous structure as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
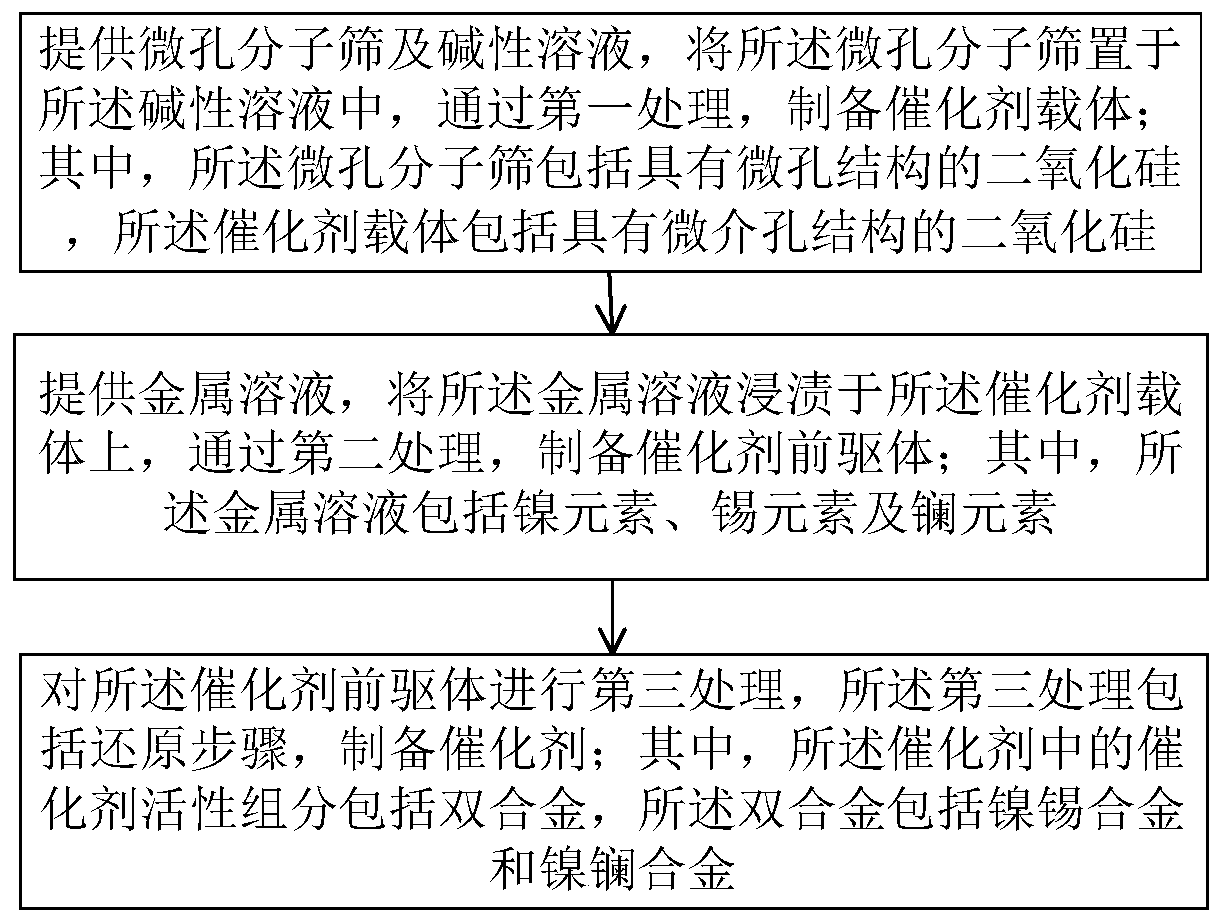
ActiveCN111001408AEnhanced adsorption and activationHigh activityHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionMetallic NickelCarbon deposition
The invention provides a catalyst with a double-alloy composite micro-mesoporous structure, a preparation method and application, the catalyst comprises a catalyst active component and a catalyst carrier, the catalyst active component comprises double alloys, the double alloys comprise a nickel-tin alloy and a nickel-lanthanum alloy, and the catalyst carrier comprises silicon dioxide with a micro-mesoporous structure; due to the existence of the double alloys, the electronic structure around active metal nickel particles can be effectively adjusted, adsorption and activation of methane and carbon dioxide are promoted, the activity of the catalyst is improved, and the carbon deposition resistance and the sintering resistance of the nickel particles are improved; through the silicon dioxidecatalyst carrier with the composite micro-mesoporous structure, the dispersity of active components of the catalyst can be improved, the sintering of nano nickel particles is inhibited, the carbon deposition phenomenon of the catalyst is reduced, and the activity and stability of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Novel center-radial nickel-carbon catalytic material as well as preparation method and application thereof
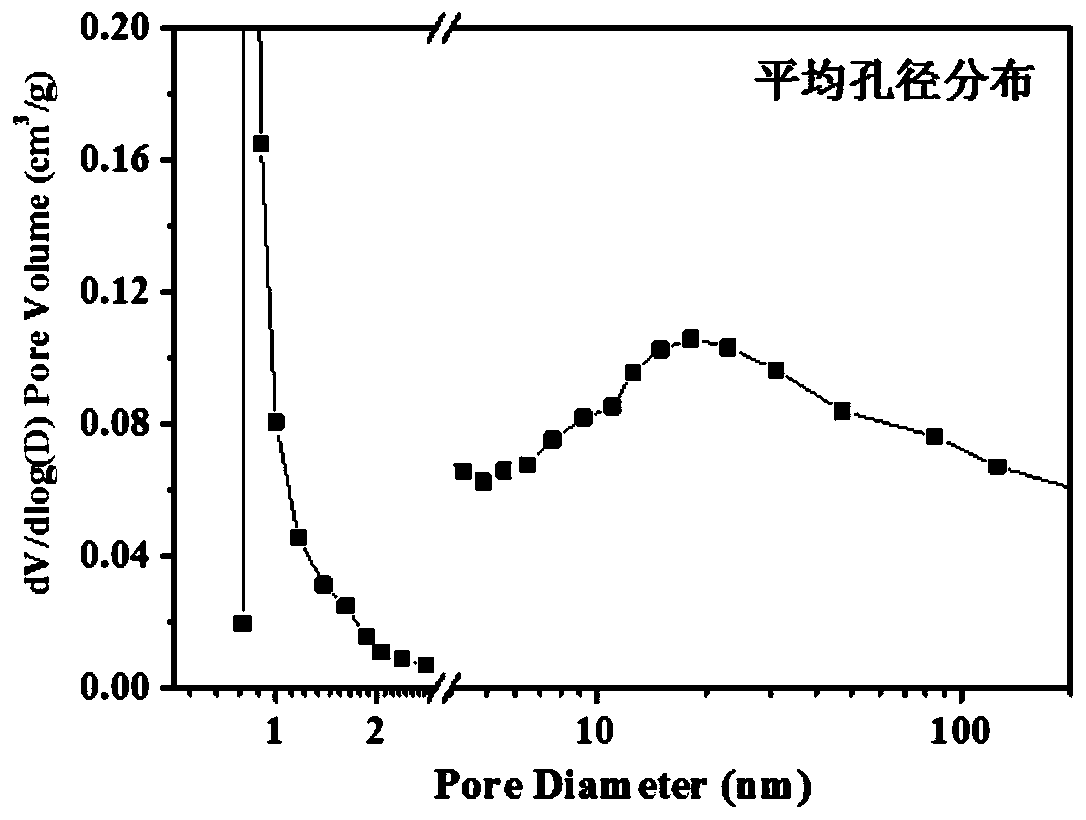
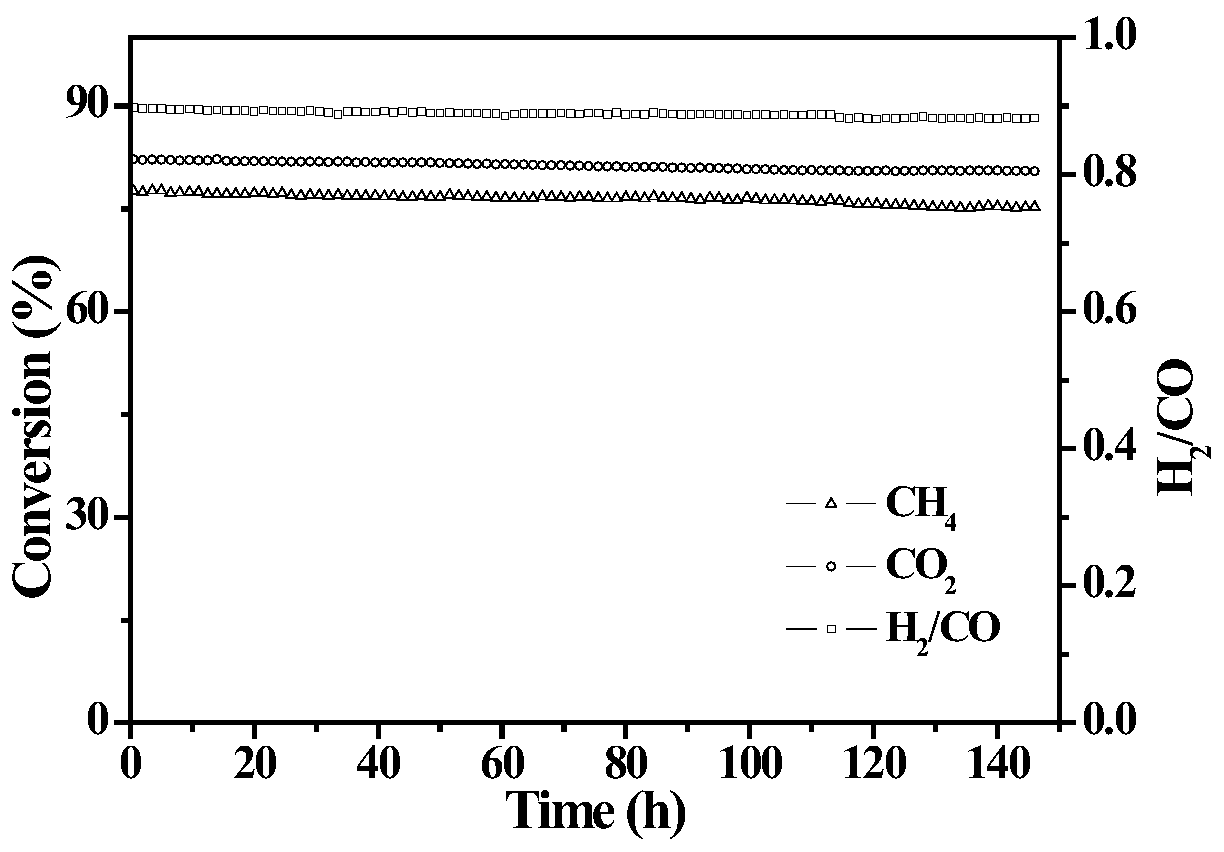
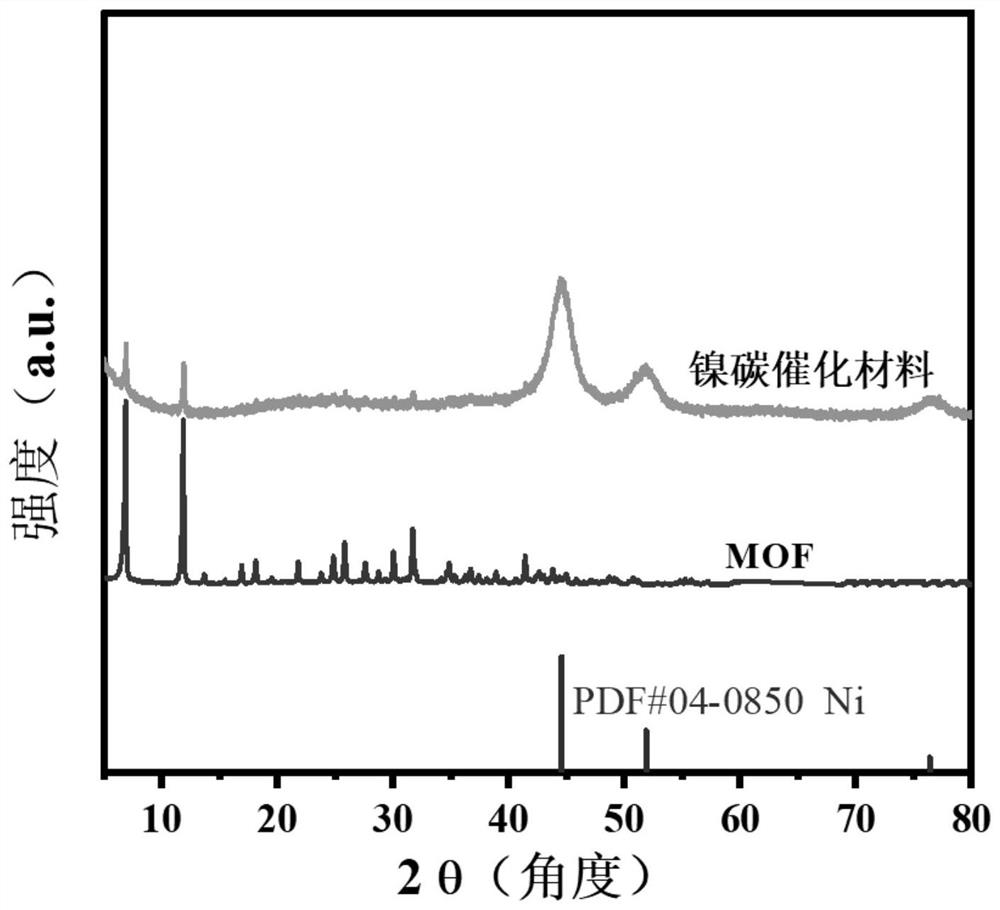
PendingCN114558578AIncrease exposureFacilitated DiffusionOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNanoparticleActive site
The invention relates to the technical field of fine chemical engineering, in particular to a center-radial novel nickel-carbon catalytic material, the nickel-carbon catalytic material is a composite material obtained by uniformly dispersing Ni nanoparticles in an incompletely carbonized MOF framework, the external morphology of the nickel-carbon catalytic material is a hexagonal rod morphology, and the interior of the nickel-carbon catalytic material is of a center-radial structure; the nickel-carbon catalytic material is of a hierarchical pore structure, the specific surface area is 250-900 m < 2 > / g, and the pore volume is 0.7-1.05 cm < 3 > / g. The nickel-carbon catalytic material is large in specific surface area, has central radial internal pore channels, can provide more catalytic active sites for reactant molecules, and can promote efficient adsorption and activation of the reactant molecules, so that the selectivity of a target product is improved under mild conditions. Meanwhile, the invention provides a preparation method and application of the compound.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Iron-cobalt-potassium-loading zirconium dioxide catalyst, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN110871075AGood selectivity to ethyleneEnhanced adsorption and activationHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalystsPtru catalystOxygen vacancy
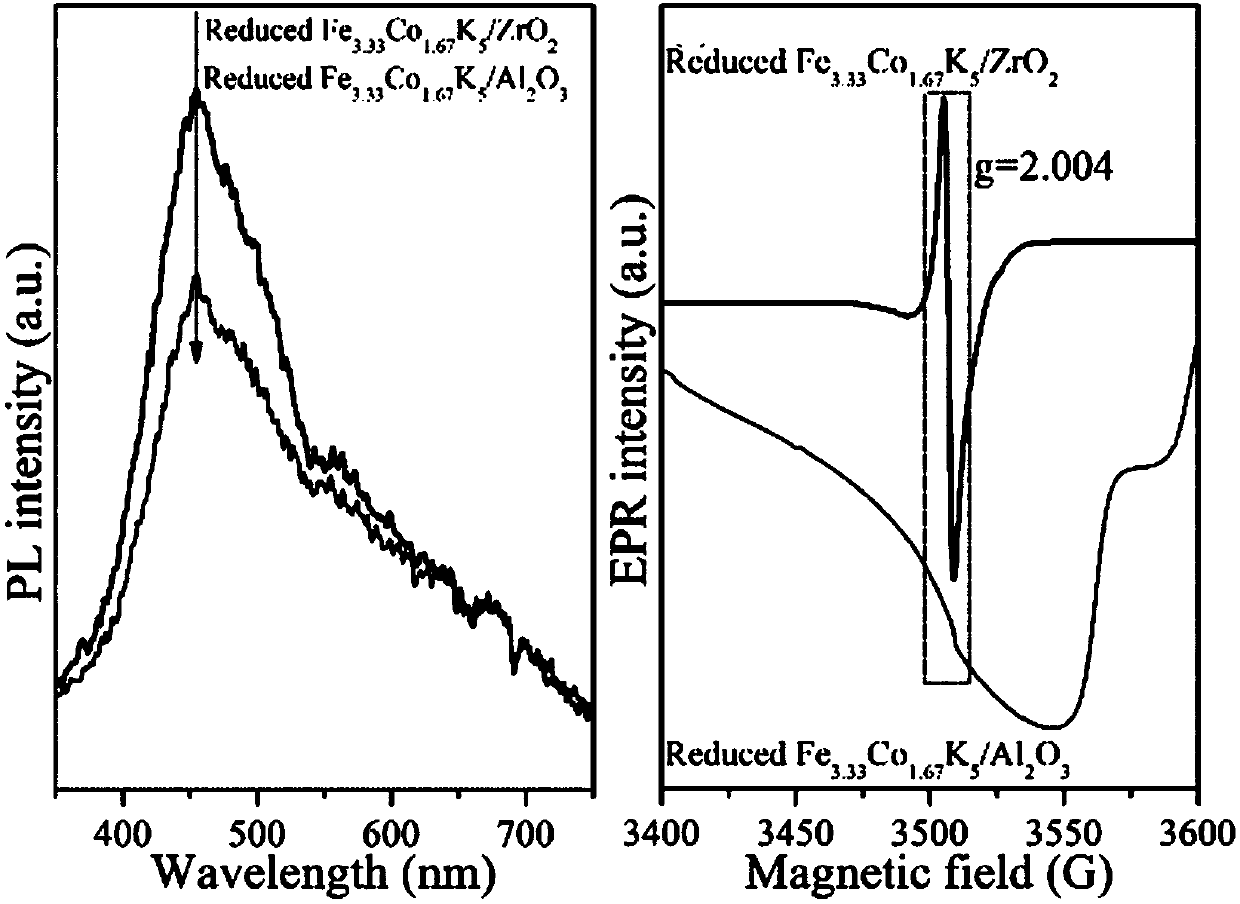
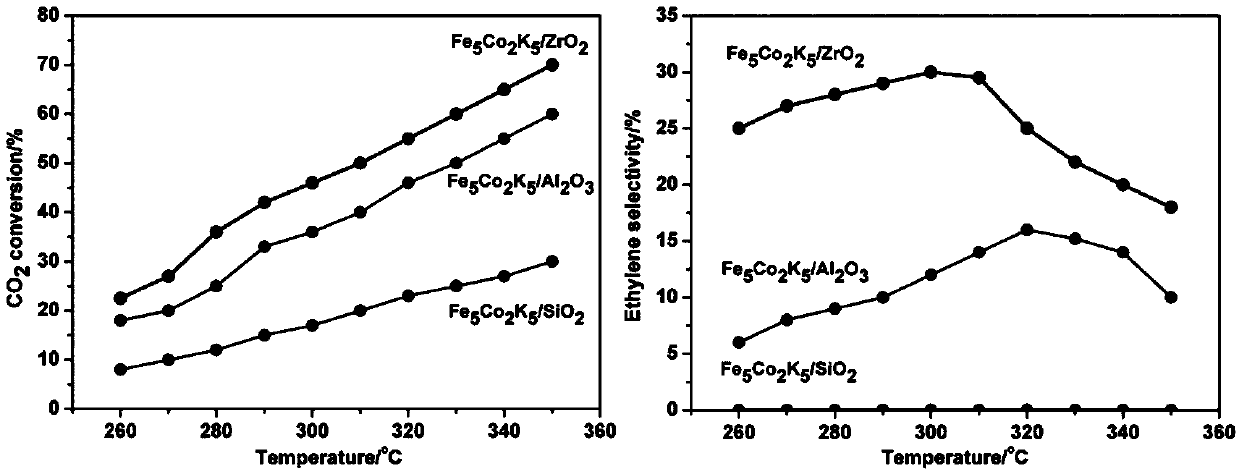
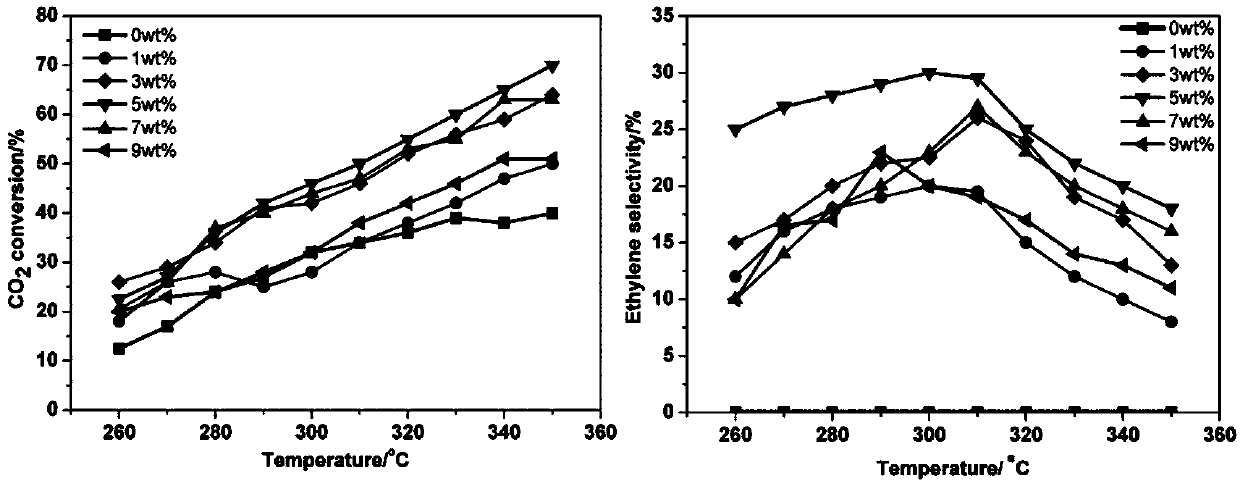
The invention discloses an iron-cobalt-potassium-loading zirconium dioxide catalyst and a preparation method thereof, and applications in preparation of ethylene through selective catalytic reductionof carbon dioxide. According to the method, a mixed solution of a Fe salt, a Co salt, a K salt and ZrO2 is subjected to a hydrothermal reaction at a temperature of 120-160 DEG C through a one-step hydrothermal method to obtain the iron-cobalt-potassium-loading zirconium dioxide catalyst. According to the iron-cobalt-potassium-loading zirconium dioxide catalyst of the invention, ZrO2 is used as a carrier so as to provide high surface oxygen vacancy, promote the conversion from CO2 to CO and increase the conversion rate of CO2; and through the synergistic promotion of iron-cobalt-potassium and zirconium dioxide, the catalyst has high catalytic activity, maintains good catalytic performance after continuous reaction is conducted for 250 h, and has high stability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
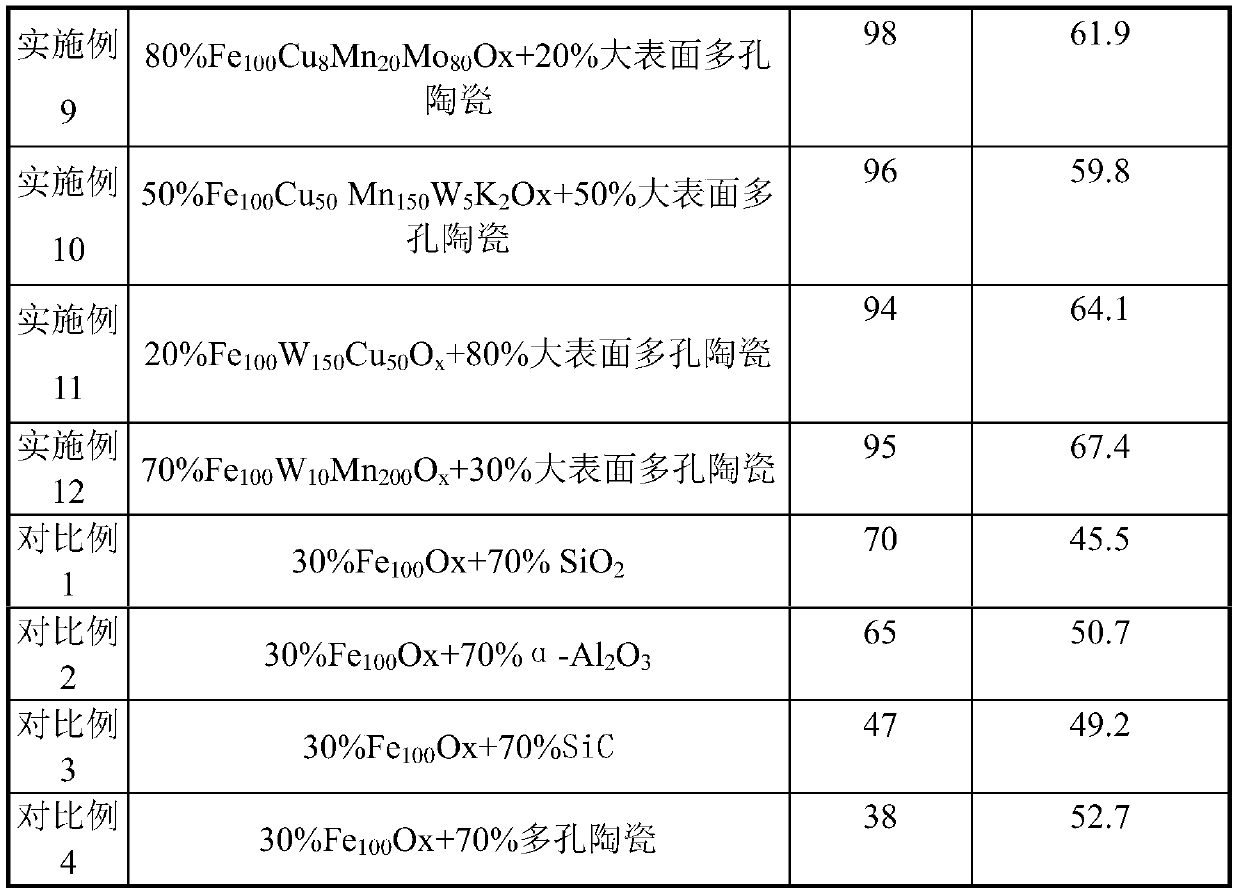
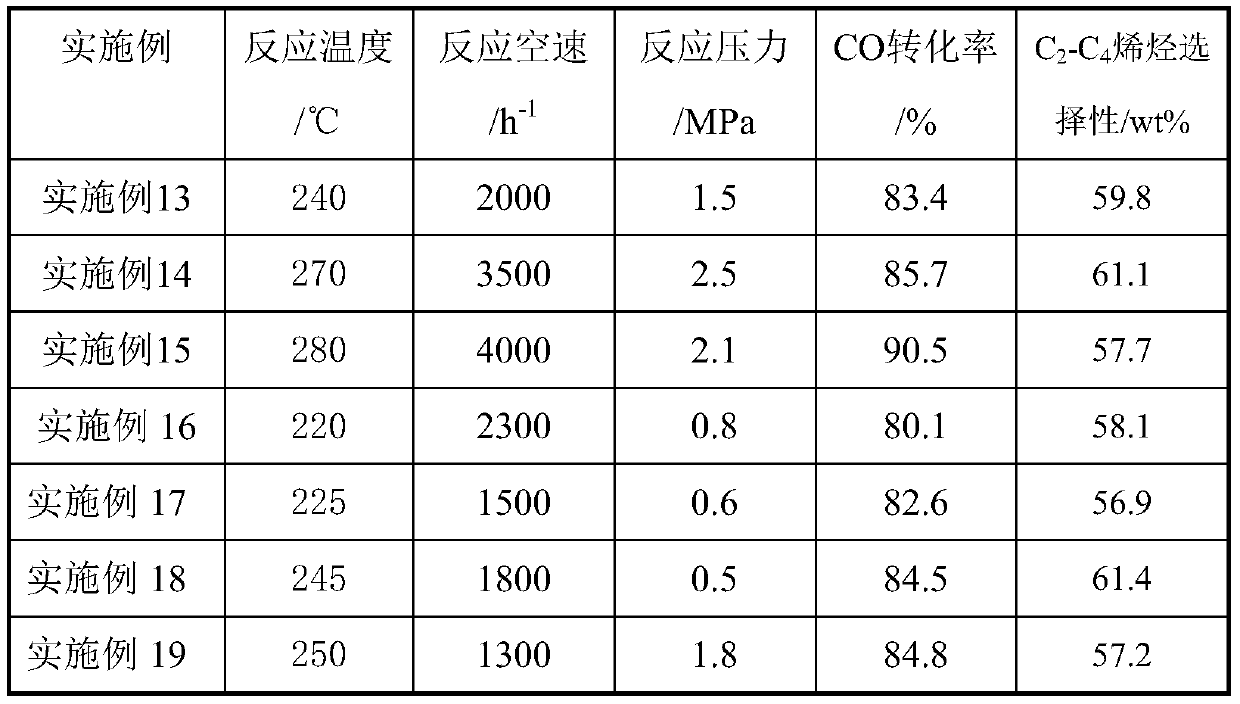
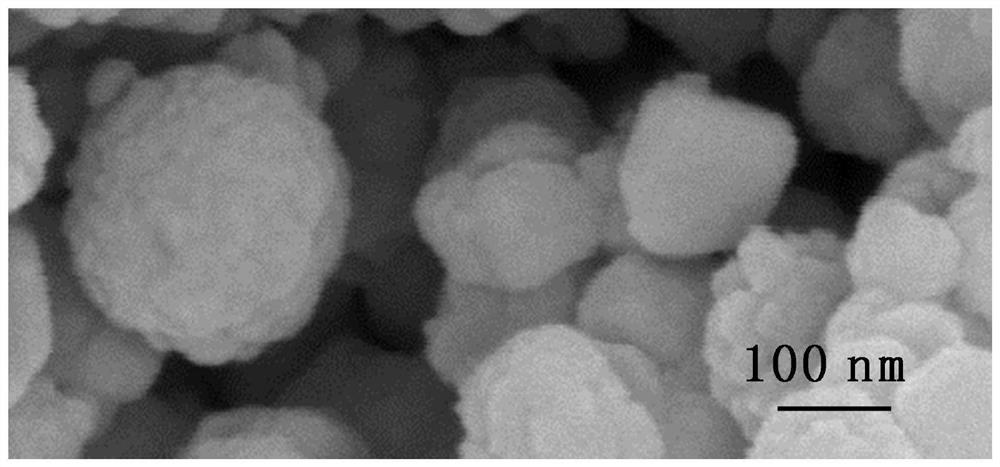
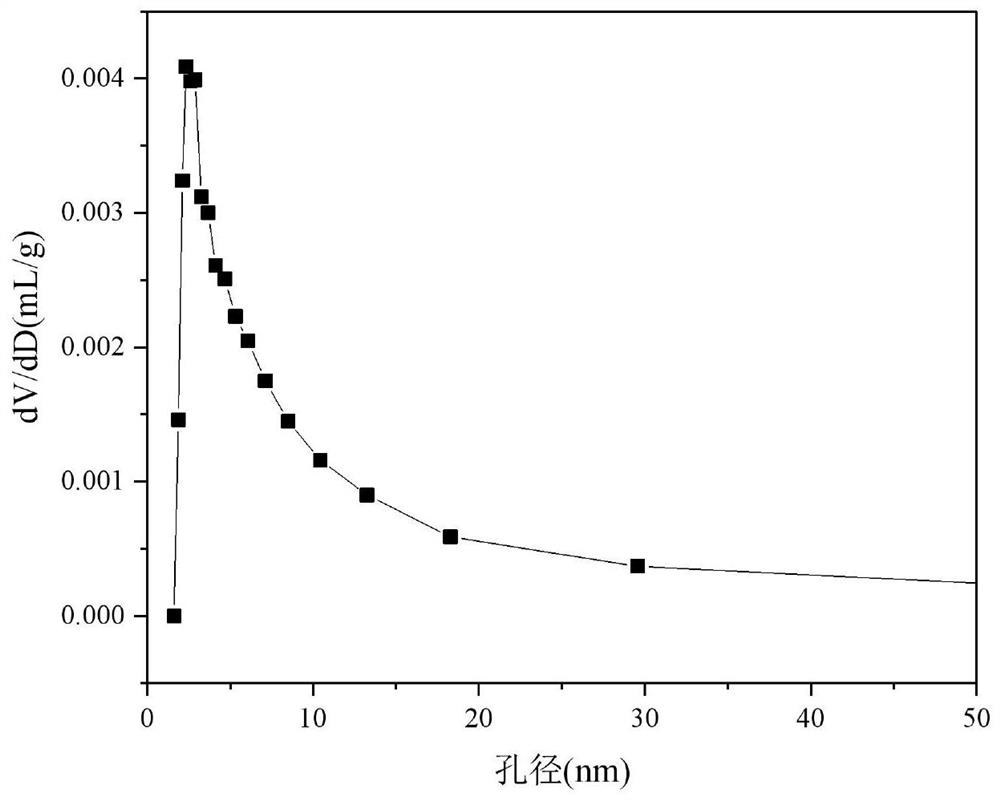
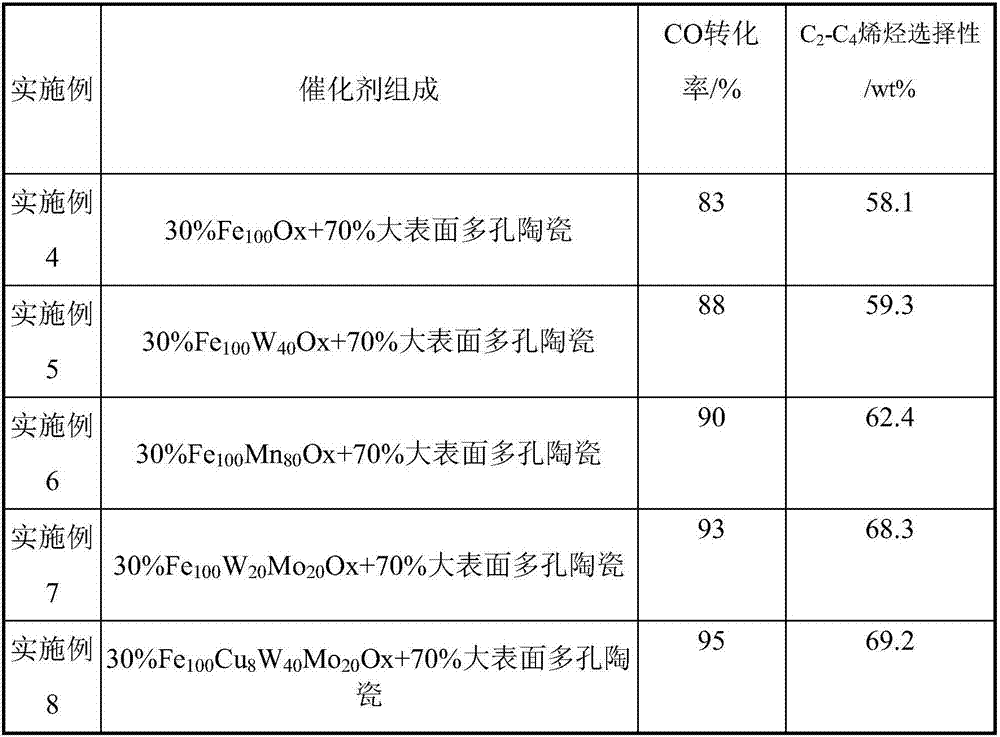
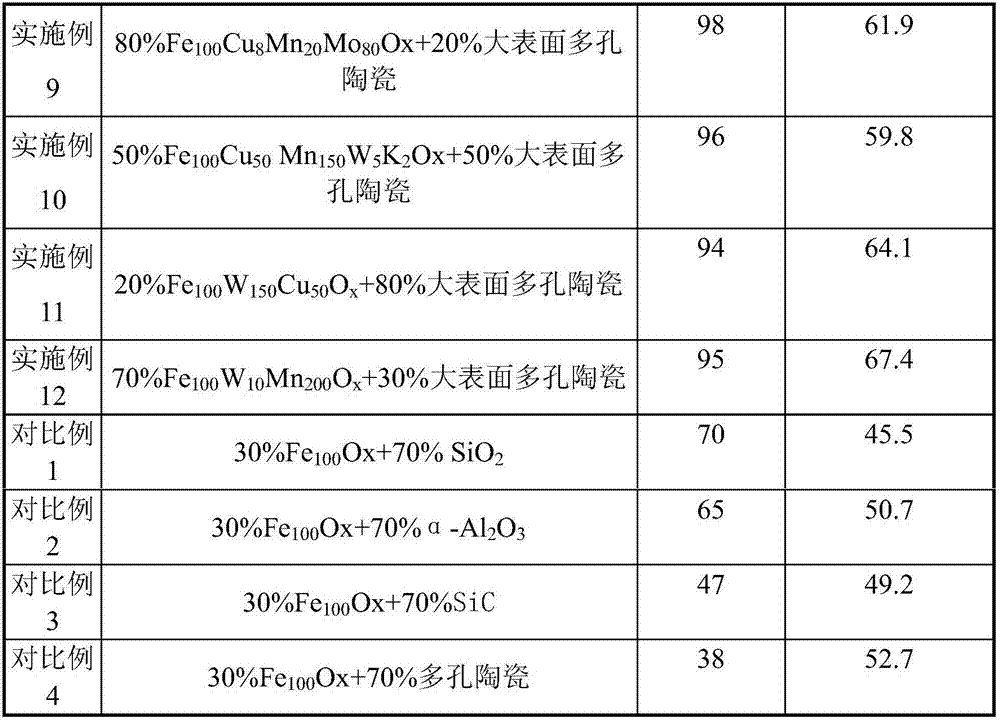
Porous ceramic supported iron-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and method of use thereof
ActiveCN107537586BReduce secondary reactionsDiffusion fastHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystAlkene
The invention relates to a porous ceramic supported iron-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst, a preparation method and a using method of the catalyst, and mainly solves the problem of low activity and selectivity of the catalysts at a low temperature for preparing olefin by using synthesis gas. In the method, a technical scheme of using a synthesis gas to prepare the low-carbon olefin catalyst is adopted to solve the problem well, wherein the catalyst comprises the following components in percentage by weight: (1) 20-80% of Fe contained active components, and (2) 20-80% of large-surface porous ceramic carriers. The catalyst can be used in industrial application of preparing low-carbon olefin by synthesis gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
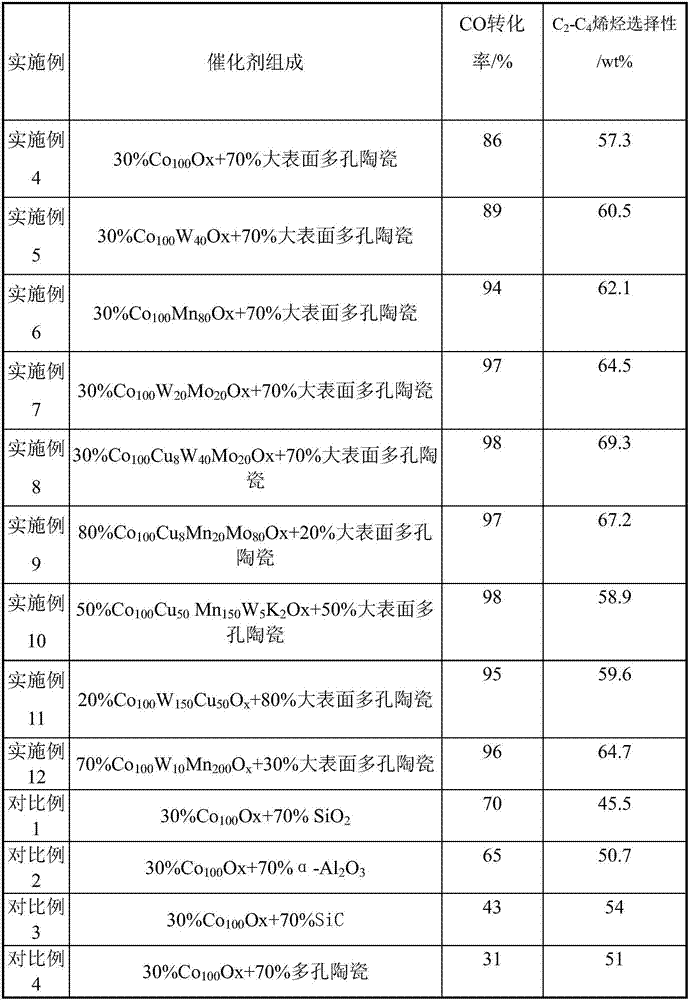
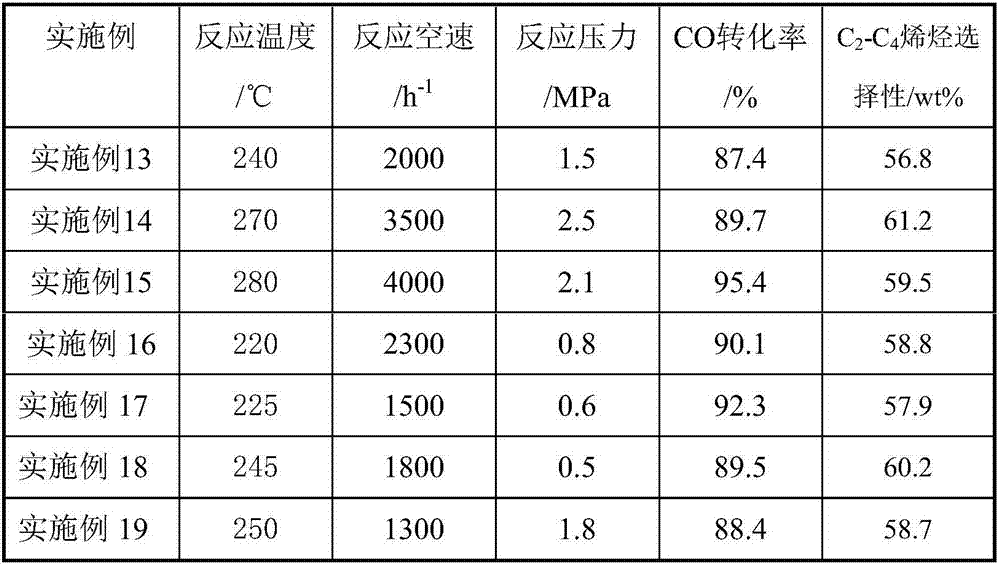
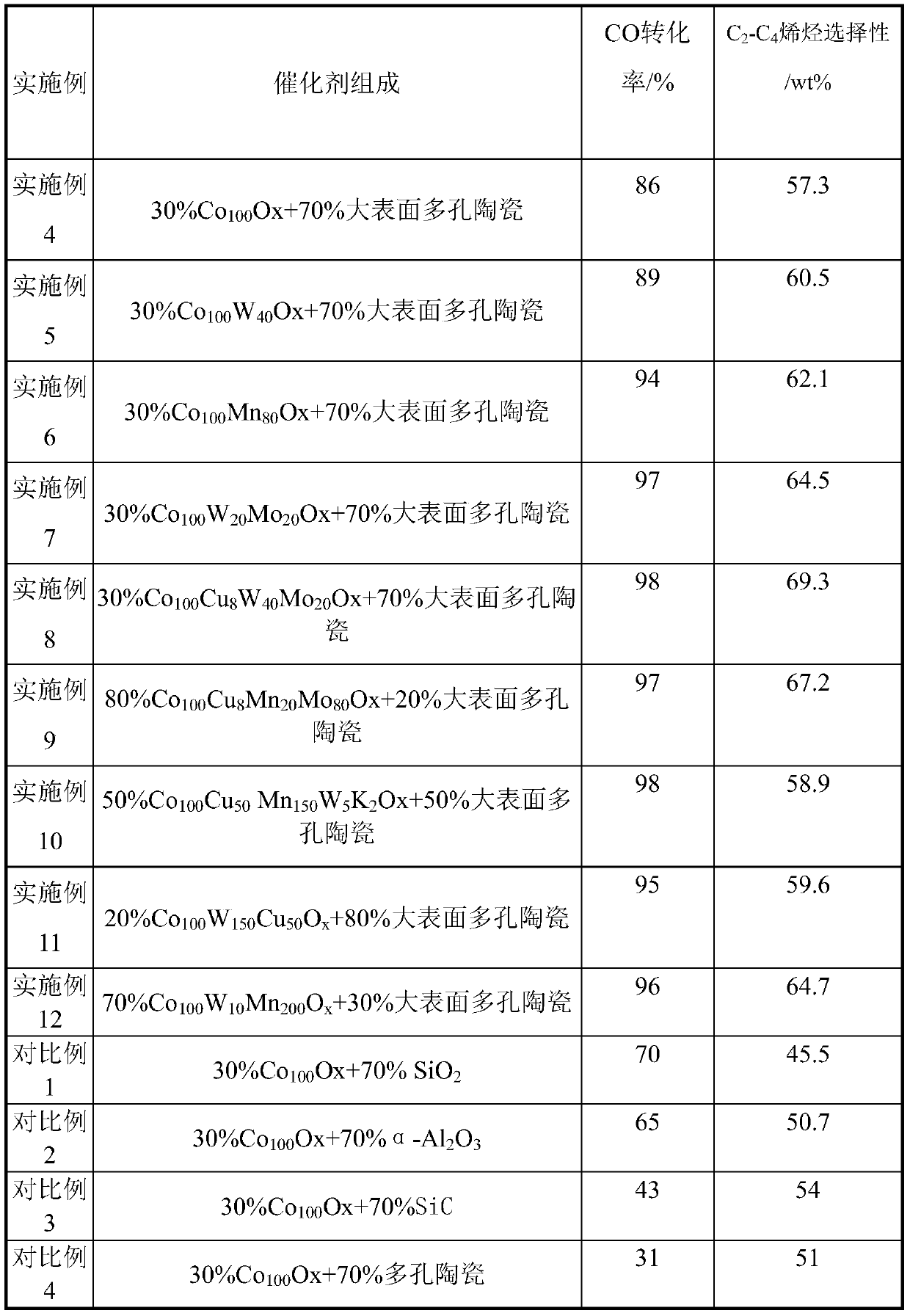
Porous ceramic supported cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and using method thereof
ActiveCN107537494AReduce secondary reactionsDiffusion fastHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCobaltPorous ceramics
The invention relates to a porous ceramic supported cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst as well as preparation and using methods thereof. The porous ceramic supported cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst mainly aims at solving the problem that the catalyst is low in activity and selectivity at lower temperature in a process of preparing olefins by using synthetic gas. The problem is better solved by the technical scheme that a catalyst for preparing light olefins by using the synthetic gas, and the catalyst comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-80% of Co-containingactive ingredients (1) and 20-80% of large-surface porous ceramic carriers (2). The porous ceramic supported cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst can realize industrial application to preparation oflight olefins by using the synthetic gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst for synthesizing light olefins, preparation method and use method thereof
ActiveCN104549358BEnhanced adsorption and activationPromote reductionHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLow activityActive component
The invention relates to a catalyst for synthesizing light olefins as well as a preparation method and a using method of the catalyst, aiming at solving the problems that the catalyst has low activity and low selectivity at low temperature when preparing olefins by use of synthesis gas. The catalyst for preparing light olefins by use of synthesis gas is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: (1) 20-80% of active component; and (2) 20-80% of carrier selected from at least one of SiO2 or Al2O3, wherein the general formula of the active component is as follows according to the atomic ratio: Fe100AaBbKcOx, A is selected from at least one of Ag or Au, B is selected from W, the range of a is 5-50, the range of b is 5-150, the range of c is 0.1-5, and x is the total number of the oxygen atoms required for meeting valences of other elements. The catalyst can solve the problems well and can be used for industrial production for preparing light olefins by use of synthesis gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
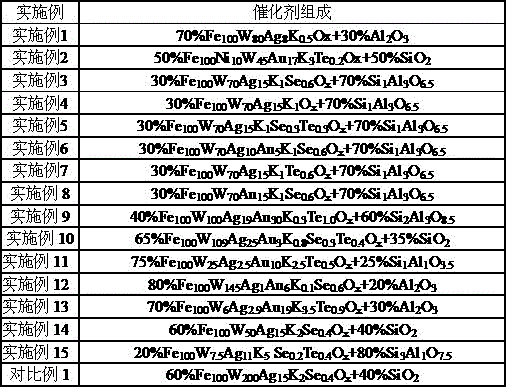
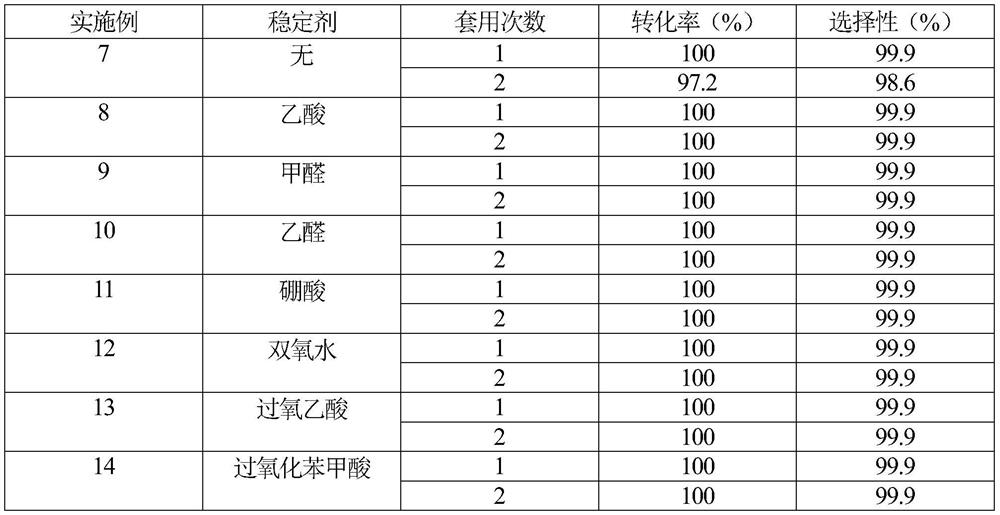
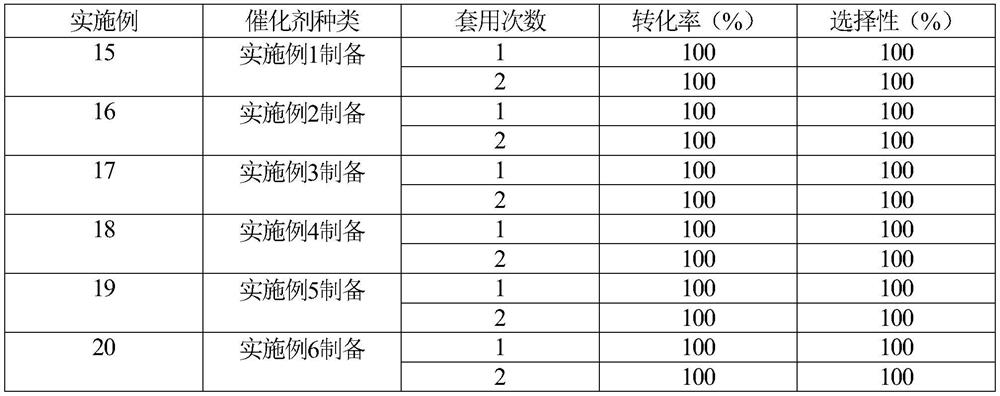
A stable and efficient catalytic hydrogenation method for the preparation of aromatic amines
ActiveCN110396046BImprove stabilizerImprove applicabilityOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationNitro compoundPtru catalyst
Owner:HEBEI JIANXIN CHEM IND CO LTD
Catalyst for preparation of low-carbon olefin from synthesis gas as well as preparation method and application method of catalyst
ActiveCN104549315AEnhanced adsorption and activationPromote reductionHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentOxygen
The invention relates to a catalyst for preparation of low-carbon olefin from synthesis gas as well as a preparation method and an application method of the catalyst and mainly aims at solving the problem that activity and selectivity of a catalyst are low at low temperature in a process of preparing the olefin from the synthesis gas. The catalyst for the preparation of the low-carbon olefin from the synthesis gas comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-80% of an active component and 20-80% of a carrier, wherein the carrier is at least one of SiO2 and Al2O3, the active component can be shown in the following general formula in an atomic ratio: Fe100AaBbKcOx, wherein A is at least one of Cu and Zn; B is Re; the value range of a is 5-50; the value range of b is 5-150; the value range of c is 0.1-5; and x is the total number of oxygen atoms required by valences of other elements. By adopting the technical scheme, the problem is relatively well solved, and the catalyst provided by the invention can be applied to the preparation of the low-carbon olefin from the synthesis gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
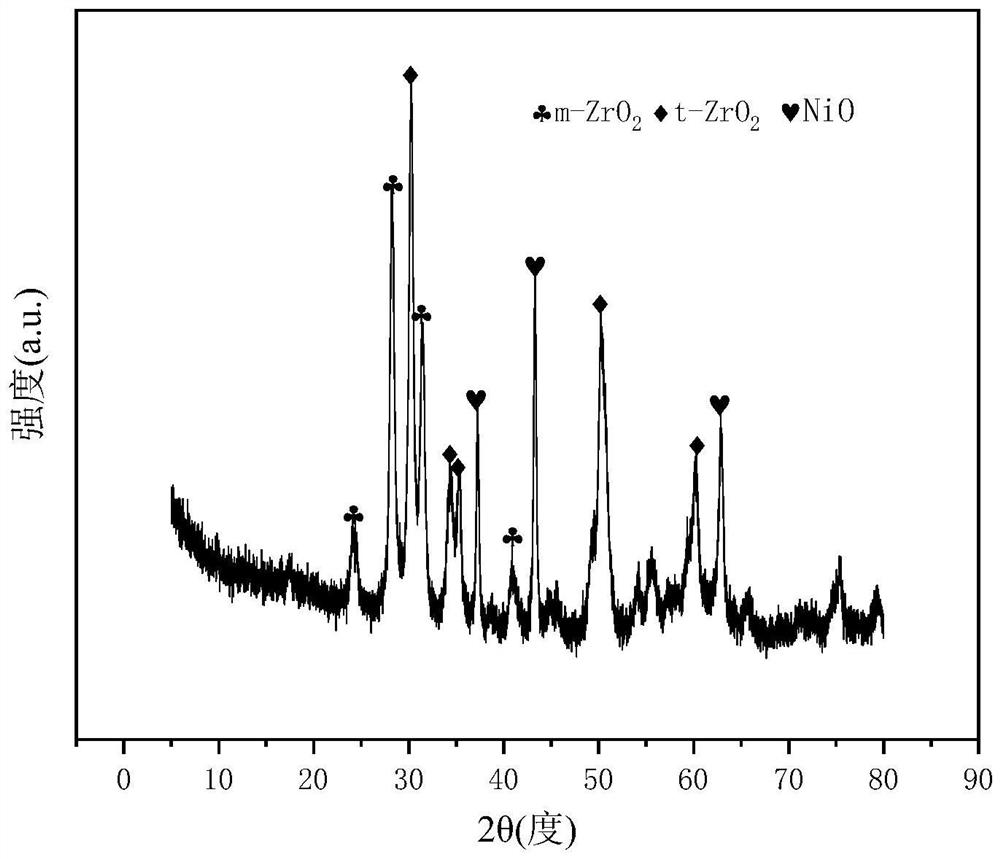
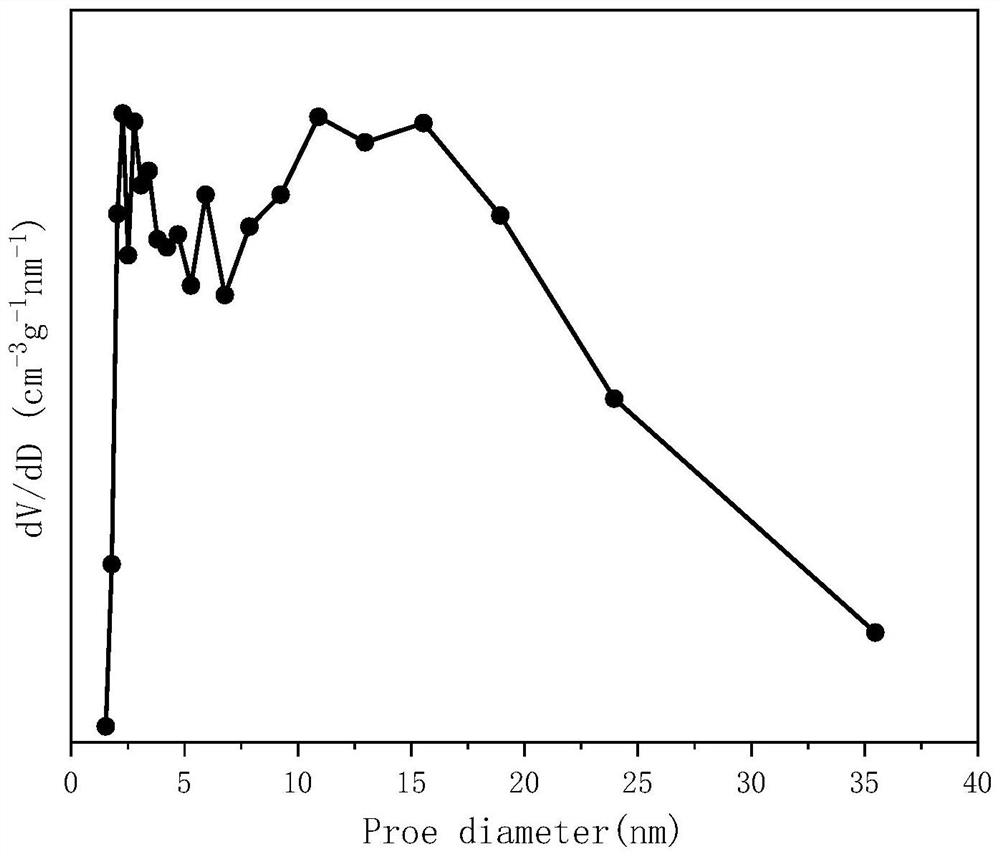
Supported Ni/W-ZrO2 catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
PendingCN114870852AImprove thermal stabilityInhibits carbon depositionHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsComposite oxideSol-gel
Aiming at the problems that an existing catalyst is poor in stability and prone to inactivation in the acetic acid autothermal reforming hydrogen production process, the Ni / W-ZrO2 catalyst is prepared through sol-gel, and the Ni / W-ZrO2 composite oxide catalyst which is loaded by a monoclinic phase and tetragonal phase composite crystal phase t-ZrO2 / m-ZrO2 and forms a Ni-W-Zr-O active center is obtained. The activity and the stability of the acetic acid autothermal reforming hydrogen production reaction are effectively improved. The molar composition of the catalyst in terms of oxide is (NiO) a (WO3) b (ZrO2) c, a is equal to 0.23-0.35, b is equal to 0-0.65 and not equal to 0, and c is equal to 0-0.77 and not equal to 0; the ceramic comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 15.0% of nickel oxide, 0-85.0% (not 0) of tungsten oxide and 0-85% (not 0) of zirconium oxide.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Porous ceramic supported cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and method of use thereof
ActiveCN107537494BReduce secondary reactionsDiffusion fastHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystAlkene
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A praseodymium-zirconium composite oxide cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN112916018BEnhanced interactionEasy to passHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a praseodymium-zirconium composite oxide cobalt-based catalyst for producing hydrogen by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Aiming at the deactivation problems such as the change of catalyst structure, sintering and carbon deposition in the existing catalyst in the autothermal reforming reaction of acetic acid, the present invention adopts the sol-gel method to prepare Co 3 o 4 and Pr-doped t‑ZrO 2 The Zr-Pr-O composite oxide cobalt-based catalyst limits the aggregation of active components and the growth of grains, and significantly improves the catalyst's anti-coking, anti-sintering ability and hydrogen production rate. Catalyst chemical composition of the present invention is (PrO 1.5 ) a (ZrO 2 ) b (CoO 1.5 ) c , where a is 0‑0.19 and not 0, b is 0.43‑0.69, and c is 0.17‑0.21.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Double-species supported catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
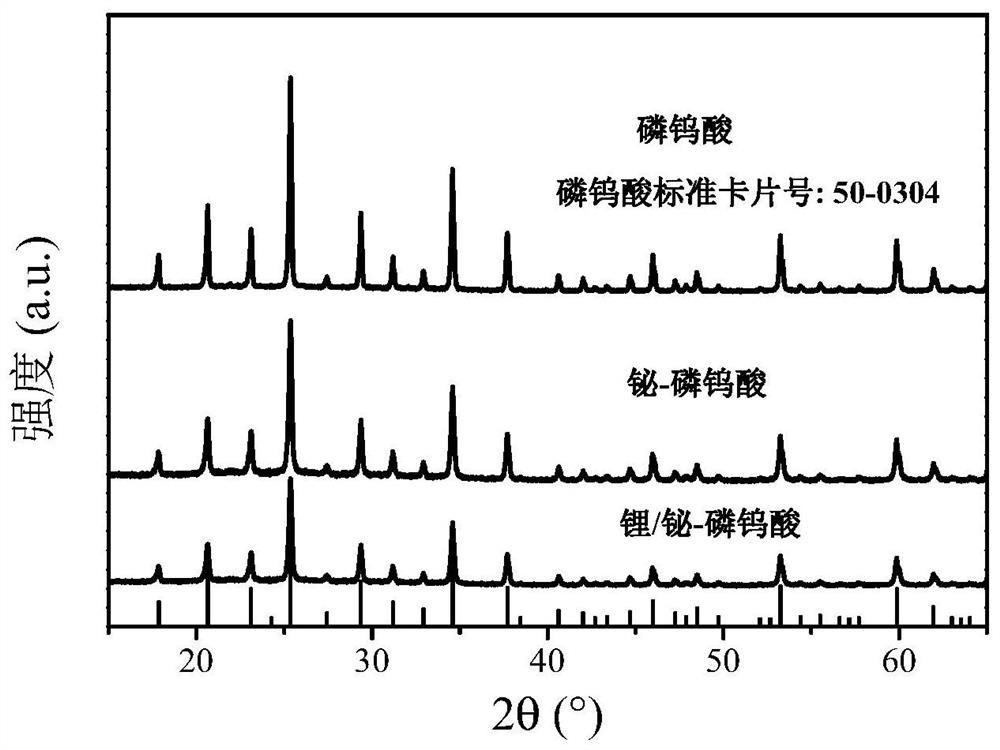
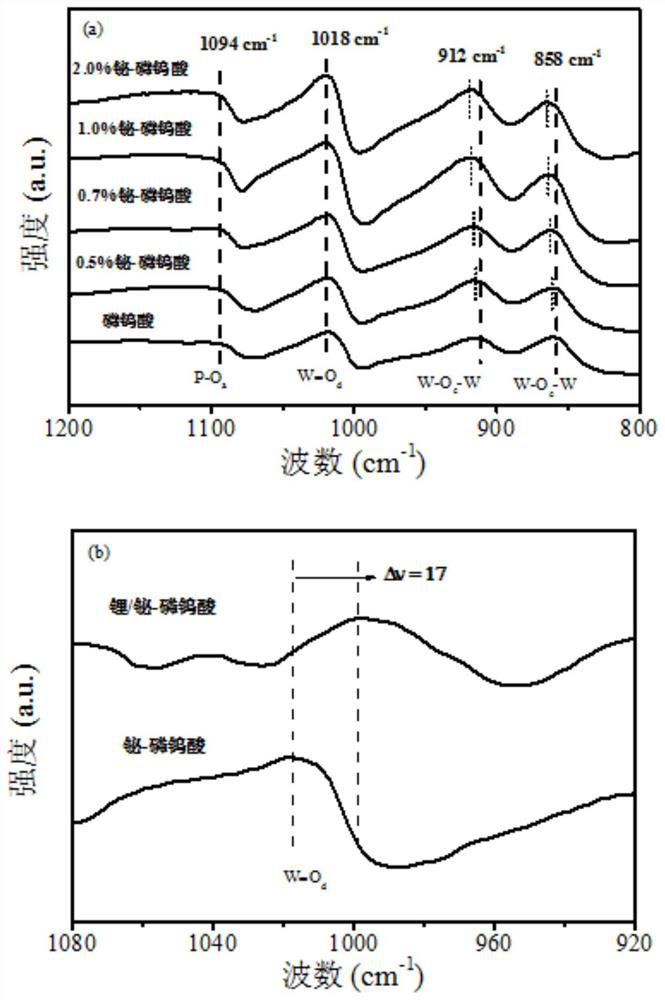
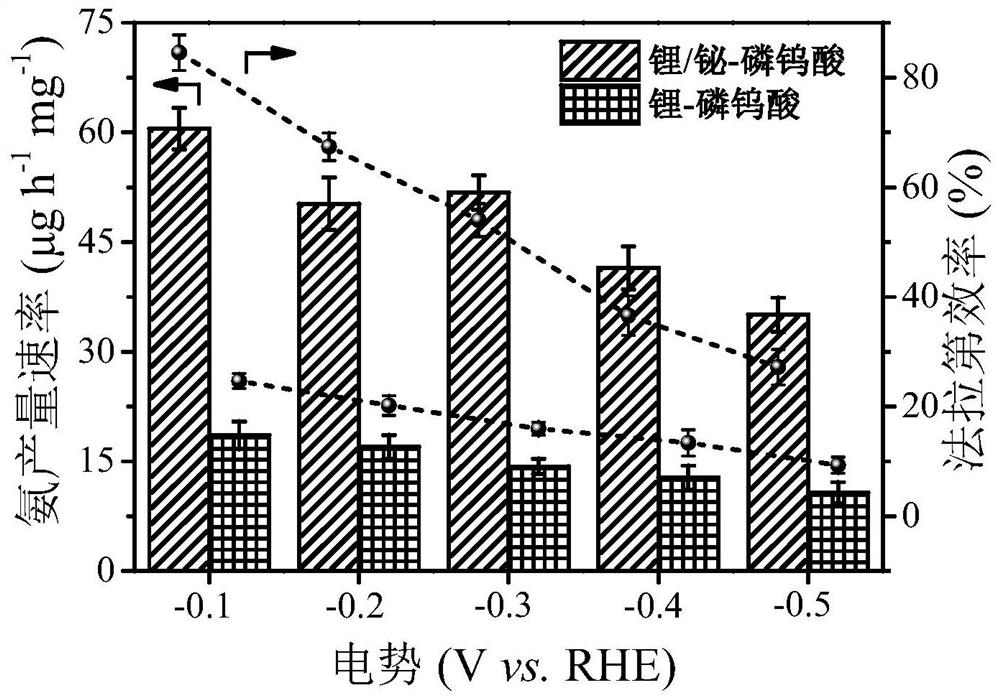
The invention discloses a double-species supported catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of material preparation, electro-catalysis and fine chemical engineering. The high-performance bismuth-lithium double-species supported phosphotungstic acid electrocatalyst for electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation is developed for the first time by taking phosphotungstic acid, a bismuth salt and lithium sulfate as raw materials, feeding in batches, heating and stirring under mild conditions, utilizing phosphotungstic acid with rich oxygen coordination sites as a carrier, and taking bismuth salt and lithium sulfate as double-species-modified precursors. The prepared electrocatalyst has good stability, excellent dinitrogen molecule adsorbing and activation capability, outstanding hydrogen evolution competitive reaction inhibition capability and good electrocatalytic performance, and the catalyst is simple in preparation process, low in cost, green and environment-friendly in production process and high in application potential.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Samarium manganese mullite type nickel-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN114308056AEnhanced adsorption and activationStable transformationHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAcetic acidPtru catalyst
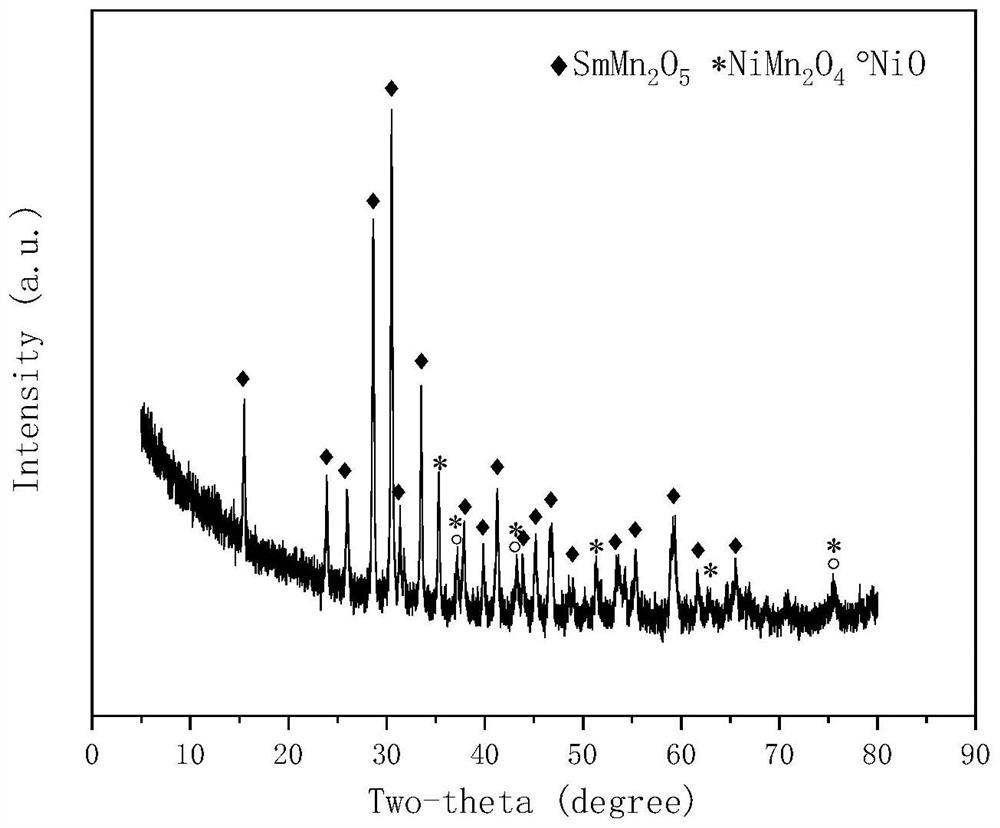
The invention relates to a samarium manganese mullite type nickel-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. The invention provides a novel catalyst which is high in activity, resistant to carbon deposition and resistant to oxidation aiming at the inactivation problem of an existing catalyst in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid. The chemical component of the catalyst is (NiO) a (SmMn2O5) b, a ranges from 0.107 to 0.281, and b ranges from 0.232 to 0.270. According to the preparation method, Ni species are loaded on a SmMn2O5 carrier by adopting an impregnation-precipitation method, and a novel catalyst which contains a stable NiMn2O4 spinel structure and has a Ni-Mn-Sm-O active center is formed through roasting. The catalyst provided by the invention effectively promotes the conversion of acetic acid, inhibits the generation of by-products such as acetone, and improves the yield and reaction stability of hydrogen.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Perovskite TiSrCo Catalyst for Hydrogen Production by Autothermal Reforming of Acetic Acid
ActiveCN109759070BEnhanced adsorption and activationSimple structureMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLattice defectsWater vapor
The invention relates to a perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and a preparation method. The catalyst with resistance tosintering, anti-carbon deposit, oxidation resistance and high activity is provided to aim at solving the problems that an existing catalyst has carbon deposits, sintering and oxidation of active components in the autothermal reforming process of acetic acid, and deactivation of the catalyst is caused. According to the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst for the hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid and the preparation method, a sol-gel method is adopted to prepare the perovskite-type titanium-strontium-cobalt catalyst, and after calcination, a perovskite composite oxide catalyst Ti<1-x>Sr<x>CoO3 is obtained, wherein x=0-0.8. The perovskite structure facilitates the dispersion of an active component Co, strengthens the synergistic effect between the active component and a carrier, and inhibits the aggregation and growth of Co, thereby obtaining stable small-particle-size Co particles. In addition, Ti is partially replaced with Sr to increase the surface defect position and lattice defect structure of the perovskite-type catalyst, so that the carbon deposit resistance, oxidation resistance and thermal stability of the active component cobalt are improved, the diffusion of acetic acid, water vapor and oxygen is further facilitated, and the catalytic activity is increased.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Nickel-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and method of use thereof
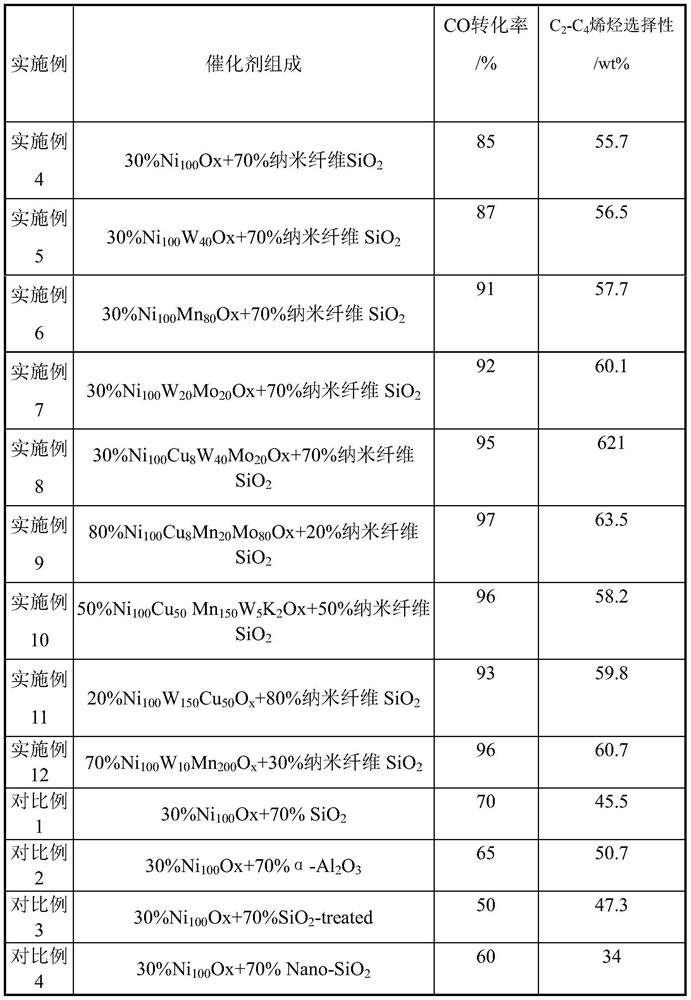
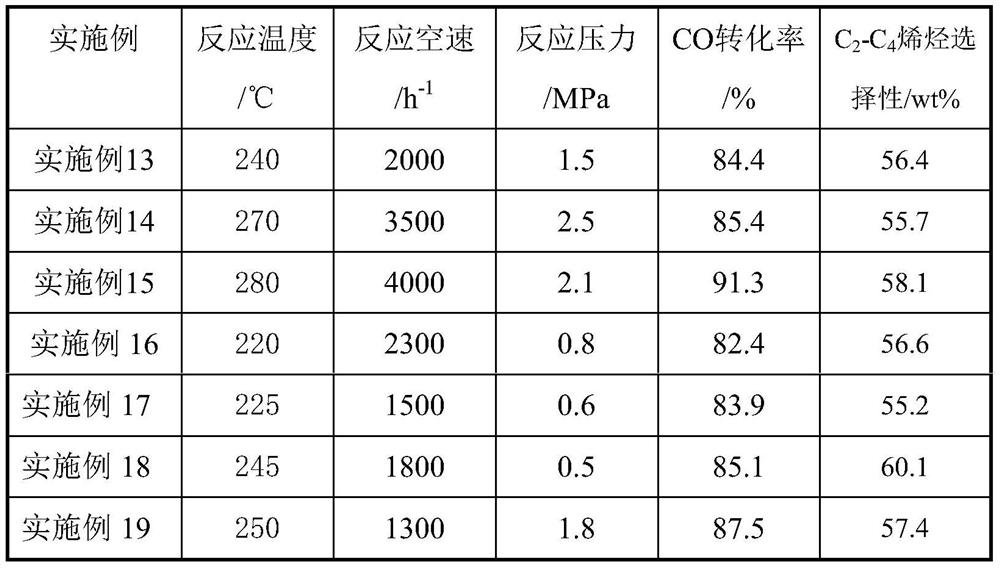
ActiveCN107537500BPromote reductionReduce secondary reactionsHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystNanofiber
The invention relates to a nickel-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and a preparation method and application method thereof, and mainly solves the problem that a catalyst for preparation of alkene from synthetic gases has low activity and selectivity at a low temperature. According to the invention, a technical scheme is adopted, wherein a catalyst is adopted for preparation of low-carbon alkene fromthe synthesis gases, and the catalyst comprises the following components of: by weight, (1) 20-80% of Ni-containing active components and (2) 20-80% of nanometer fiber SiO2 carrier; through the technical scheme, the problem is solved well, and the Ni-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and the preparation method and application method thereof can be applied to industrial application for preparation ofthe low-carbon alkene from the synthesis gases.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
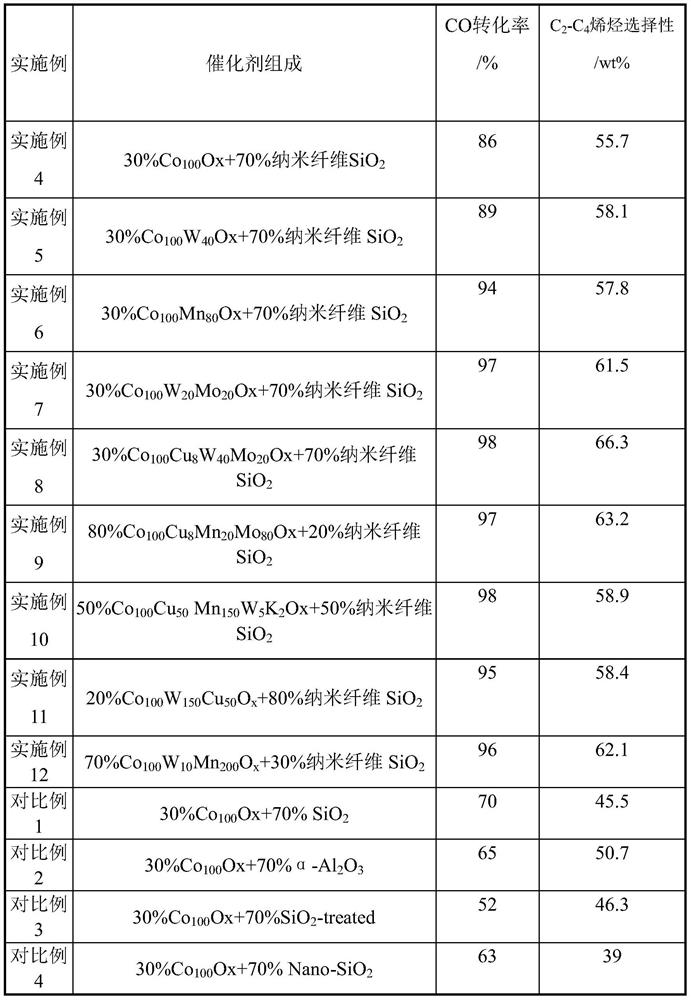
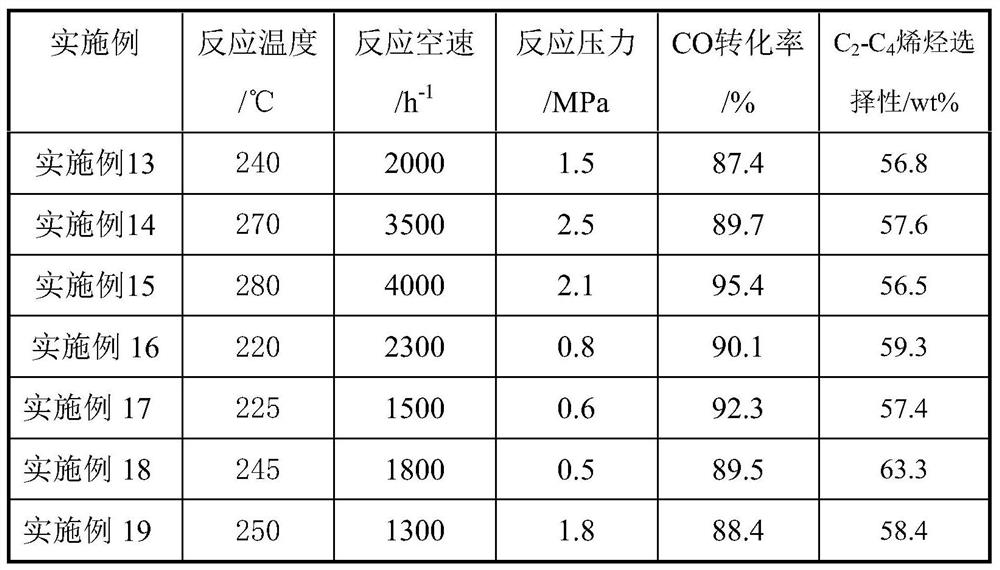
Cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and method of use thereof
ActiveCN107537493BReduce secondary reactionsSecondary response enhancementHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystNanofiber
The invention relates to a cobalt based fischer-tropsch catalyst, and a preparation method and an application method thereof. The invention is mainly to solve the problems of low activity and selectivity of a catalyst at a low temperature in preparation of olefin from synthesis gas. According to the invention, the catalyst used for preparation of light olefin from synthesis gas comprises the following components in terms of the weight percentage of the catalyst: (1) 20 to 80% of a Co containing active component; and (2) 20 to 80% of a nanofiber SiO2 carrier. Thus, the technical scheme well solves the above-mentioned problems and can be used for industrial application in preparation of light olefin from synthesis gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst with isolated dehydrogenation and oxidation double active sites and preparation and application thereof
PendingCN114797952AEnhanced adsorption and activationGenerate efficientlyMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsMolecular sievePtru catalyst
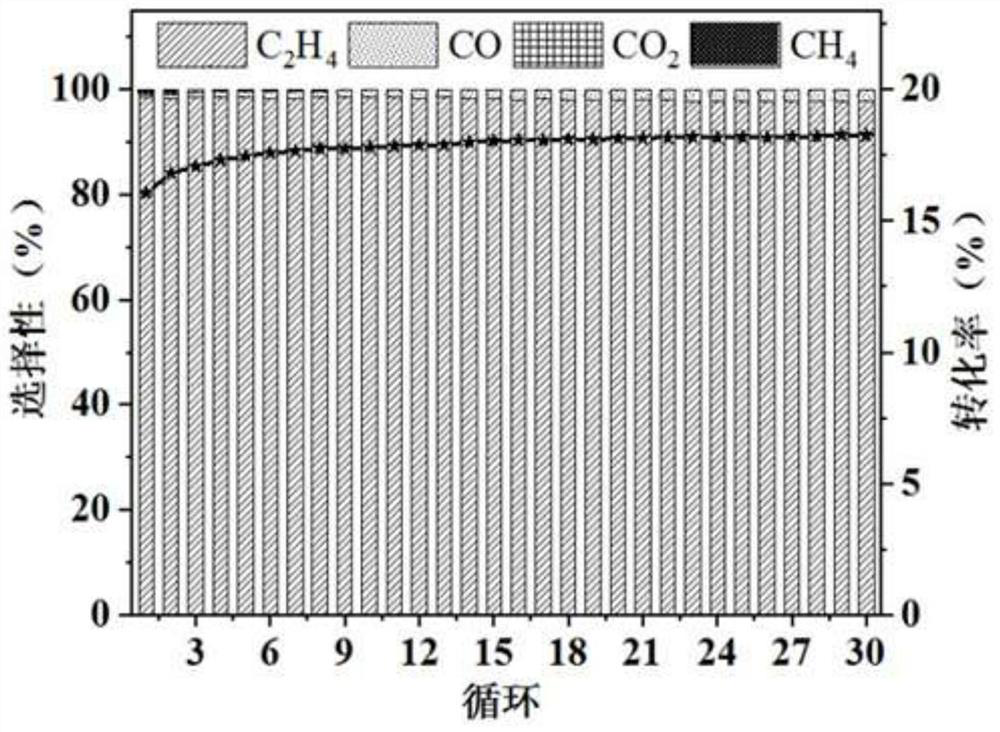
The invention relates to a catalyst with isolated dehydrogenation and oxidation double active sites as well as preparation and application of the catalyst. Double active sites of the catalyst are an active metal Lewis acid site loaded on the surface of an HY molecular sieve and a metal oxide nanocluster active site limited in a molecular sieve pore channel, the metal oxide loading amount is 1%-5% of the mass of the catalyst, and the mass ratio of the active metal Lewis acid to the metal oxide limited in the molecular sieve pore channel is 0.8-9.0. The HY molecular sieve carrier is H-type, and the SiO2 / Al2O3 ratio is 2-10. Under the reaction temperature of 500-700 DEG C, H2 generated by ethane dehydrogenation and limited range NiO selective oxidation is activated through Ni Lewis acid, ethane is converted into ethylene with high selectivity, and deep oxidation of ethane is effectively avoided. Compared with the prior art, the catalyst disclosed by the invention can be used for isolated dehydrogenation and oxidation, so that the ethylene selectivity is close to 100%, and particularly, the catalyst disclosed by the invention can also be used for catalytic decomposition of ADN-based and HAN-based single-component propellants.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ceria-Supported Cobalt-Based Catalysts for Autothermal Reforming of Acetic Acid to Hydrogen Production
ActiveCN111450834BImprove thermal stabilityModulation electronic energy levelHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAcetic acidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a catalyst taking cobalt partially substituted cerium dioxide as an active center, which is used for preparing hydrogen by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Aiming at theproblem of inactivation of an existing catalyst in an acetic acid autothermal reforming reaction, the invention provides a novel catalyst which is stable in structure, resistant to carbon deposition and resistant to oxidation. The chemical composition of the catalyst of the invention is (CoO1.5) a (CeO2) b, wherein a is 0-14.4 and does not contain 0, and b is 16.2-23.2 and does not contain 23.2. According to the invention, a two-step hydrothermal method is adopted to prepare the micro-spherical mesoporous structural material; a cobalt-partially-substituted CeO2 active center is formed after hydrogen reduction, acetic acid molecules are efficiently converted, adsorption activation on water and oxygen is improved, gasification of a carbon deposition precursor is promoted, generation of a by-product acetone is reduced, and carbon deposition resistance and oxidation resistance of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Aporous ceramic supported iron-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst and using method of the catalyst
ActiveCN107537586AReduce secondary reactionsEnhanced adsorption and activationHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLow activityLower activity
The invention relates to a porous ceramic supported iron-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst, a preparation method and a using method of the catalyst, and mainly solves the problem of low activity and selectivity of the catalysts at a low temperature for preparing olefin by using synthesis gas. In the method, a technical scheme of using a synthesis gas to prepare the low-carbon olefin catalyst is adopted to solve the problem well, wherein the catalyst comprises the following components in percentage by weight: (1) 20-80% of Fe contained active components, and (2) 20-80% of large-surface porous ceramic carriers. The catalyst can be used in industrial application of preparing low-carbon olefin by synthesis gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com