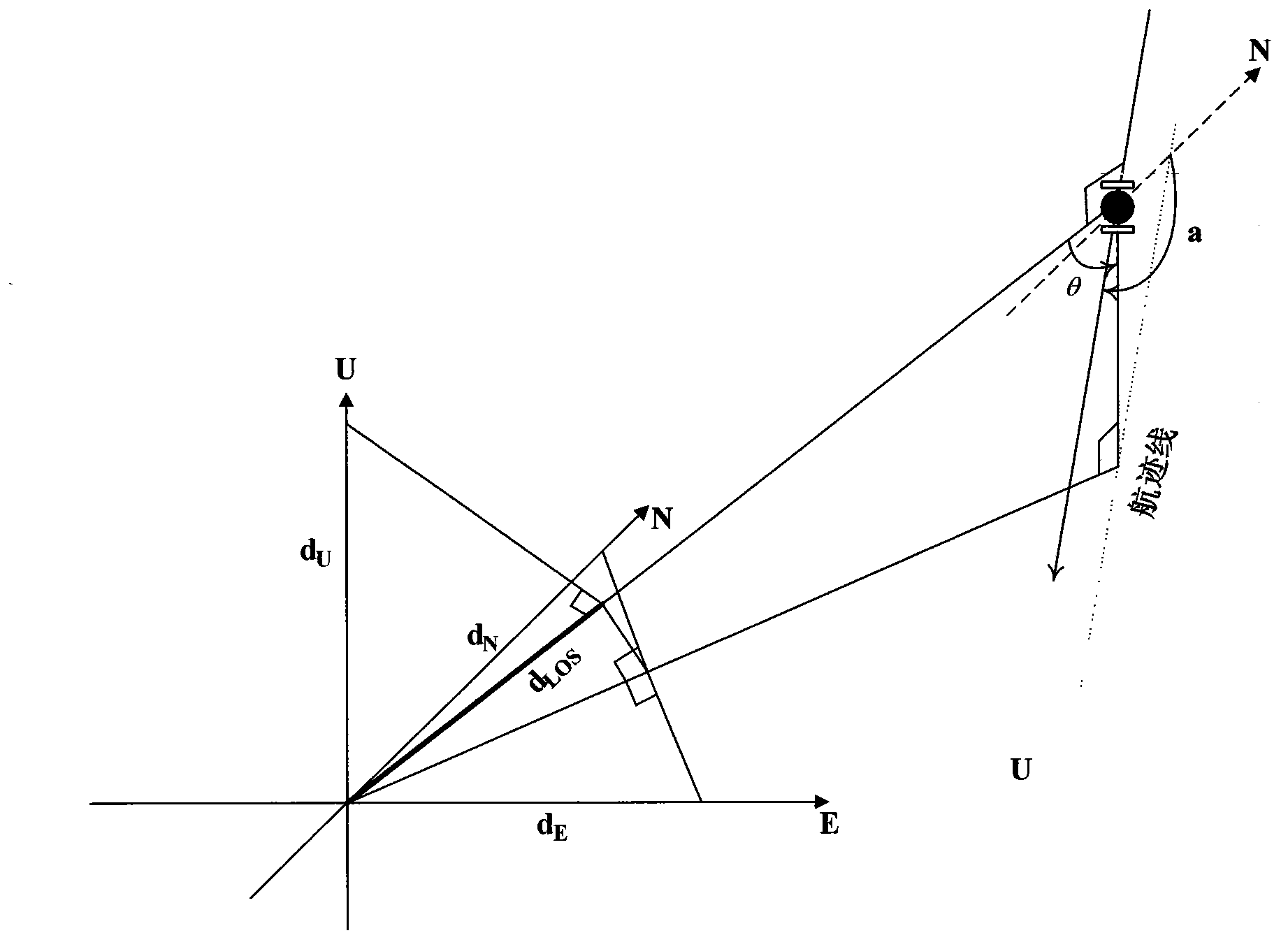
Patents
Literature
58 results about "Atmospheric effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
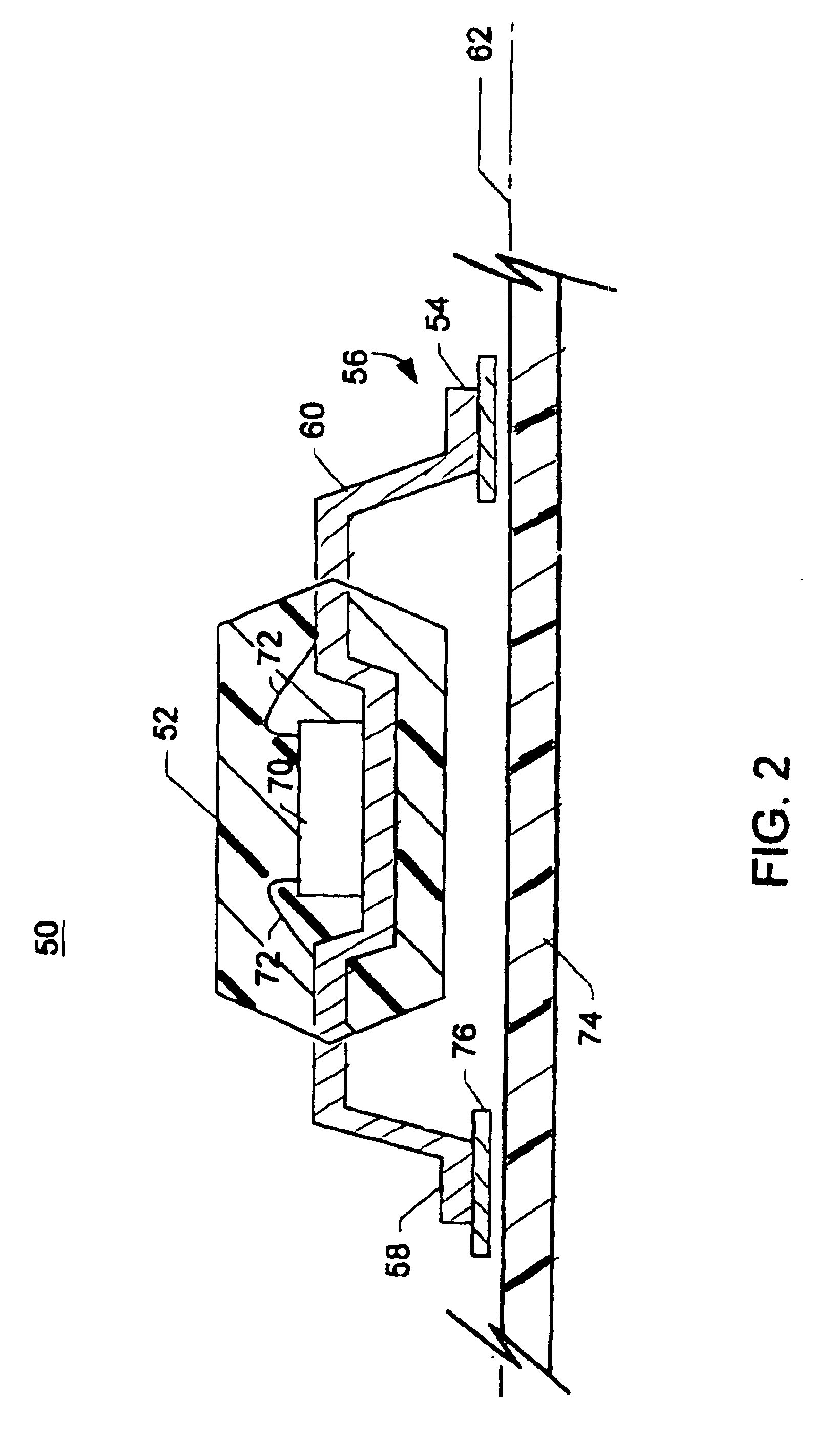
System and method for generating and playback of three-dimensional movies
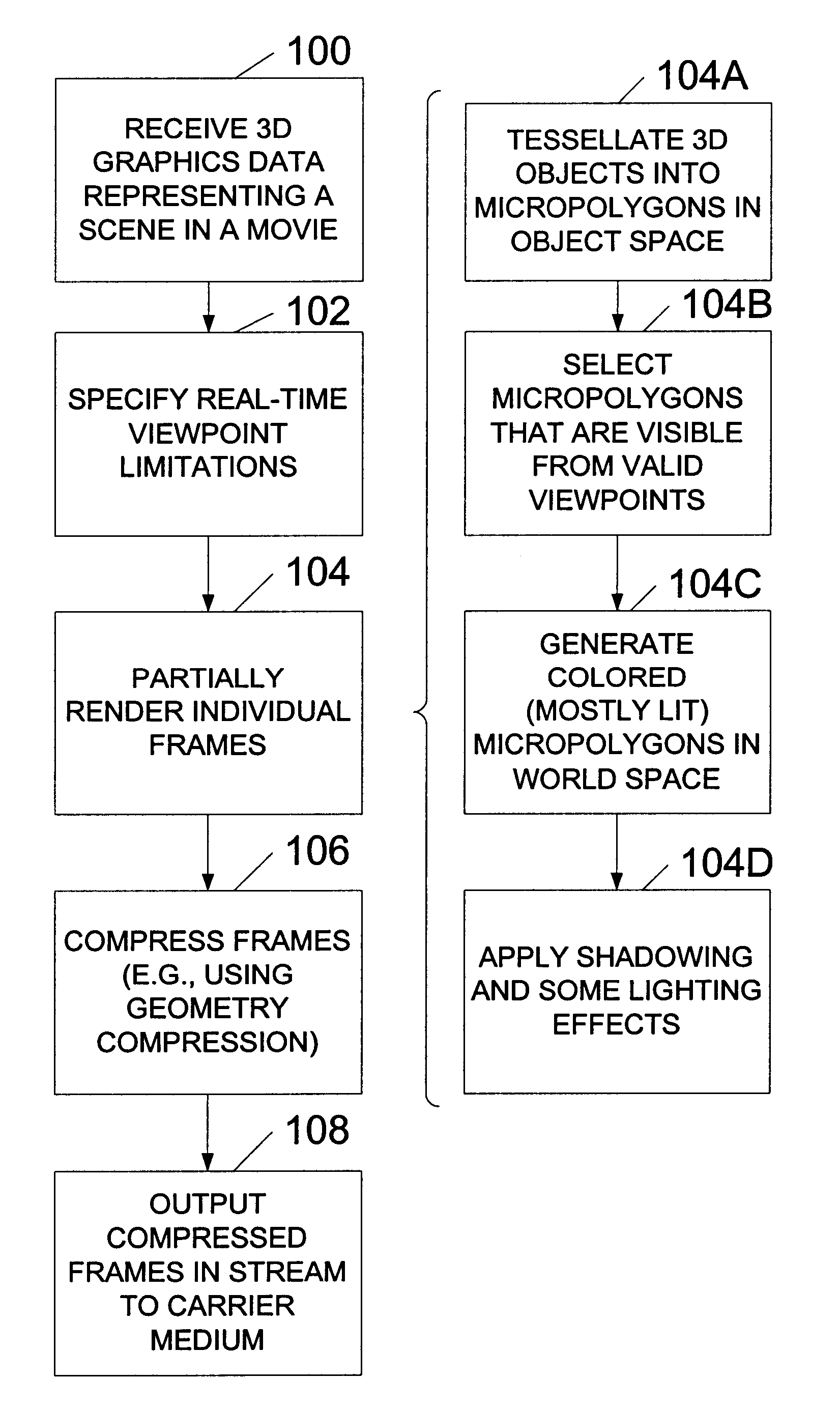
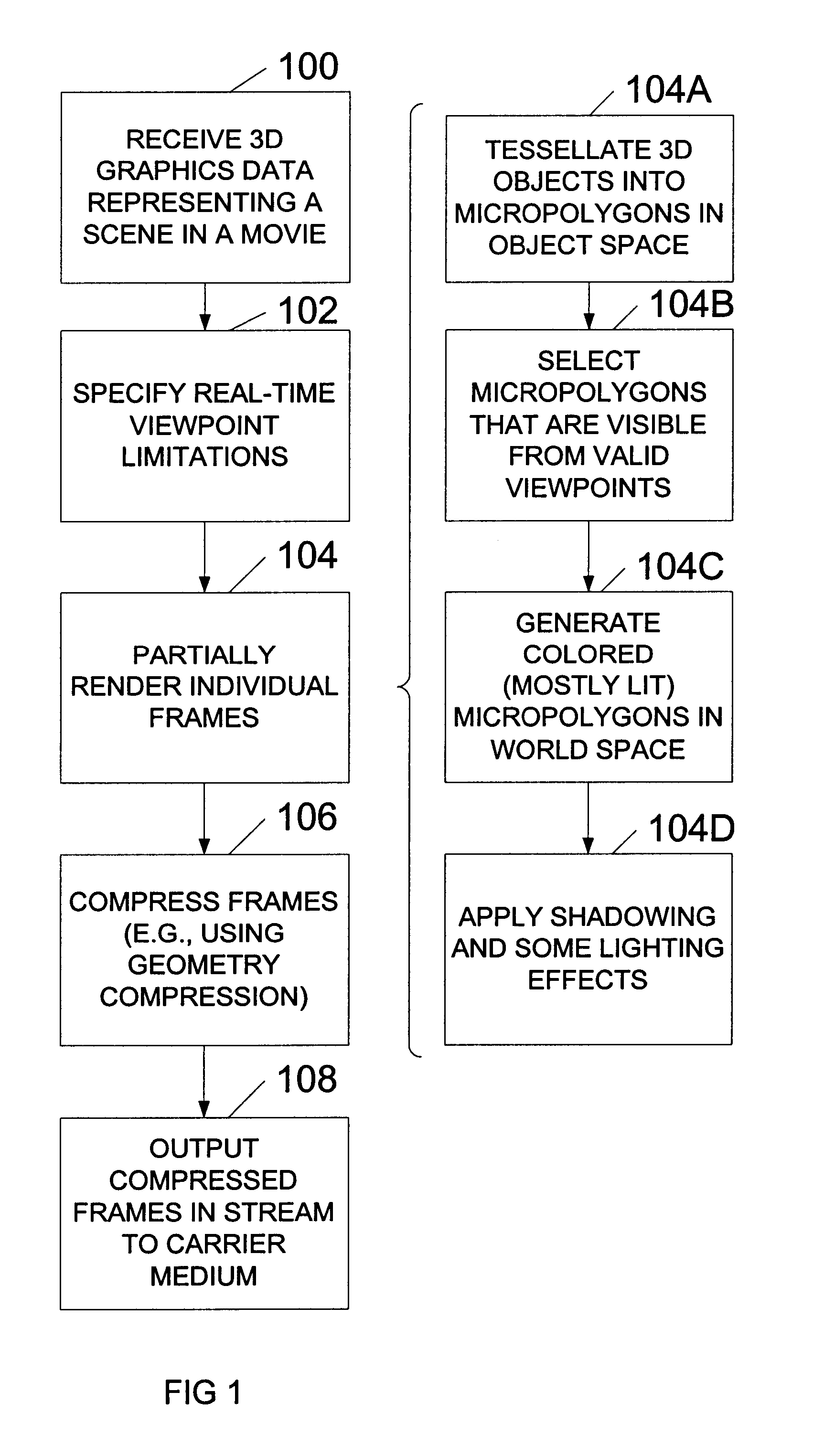
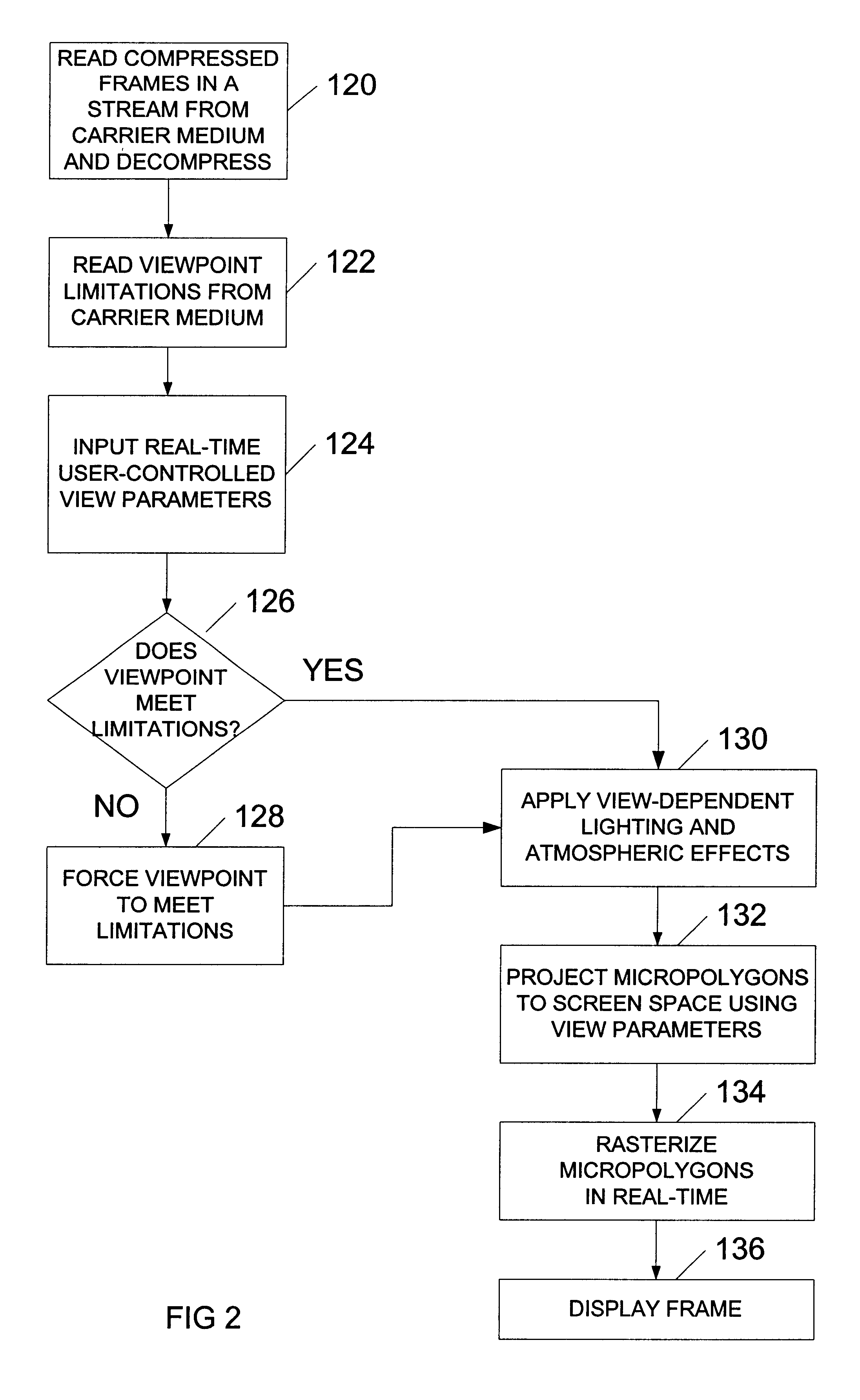
A system and method for generating and playing back three-dimensional (3D) movies are disclosed. The system is capable of partially rendering frames without relying upon exact viewpoint information. The partially rendered frames may be rendered to the extent possible without performing viewpoint-dependent processes, and then compressed and stored to a carrier medium. To reduce the amount of data to be stored, the viewer's possible viewpoints may be restricted (e.g., by defining a viewpoint-limiting volume or region). The resulting partially-rendered geometry data may be compressed using geometry compression. During playback, the compressed frames are read as a stream, and decompressed. Any final viewpoint-dependent rendering operations may then be performed (e.g., some lighting calculations and atmospheric effects, some fogging, specular highlighting, and reflections). A sensor such as a head-tracker may provide real-time viewpoint information that may be used by the playback system. After rendering, the frames are rasterized and then displayed in stereo.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
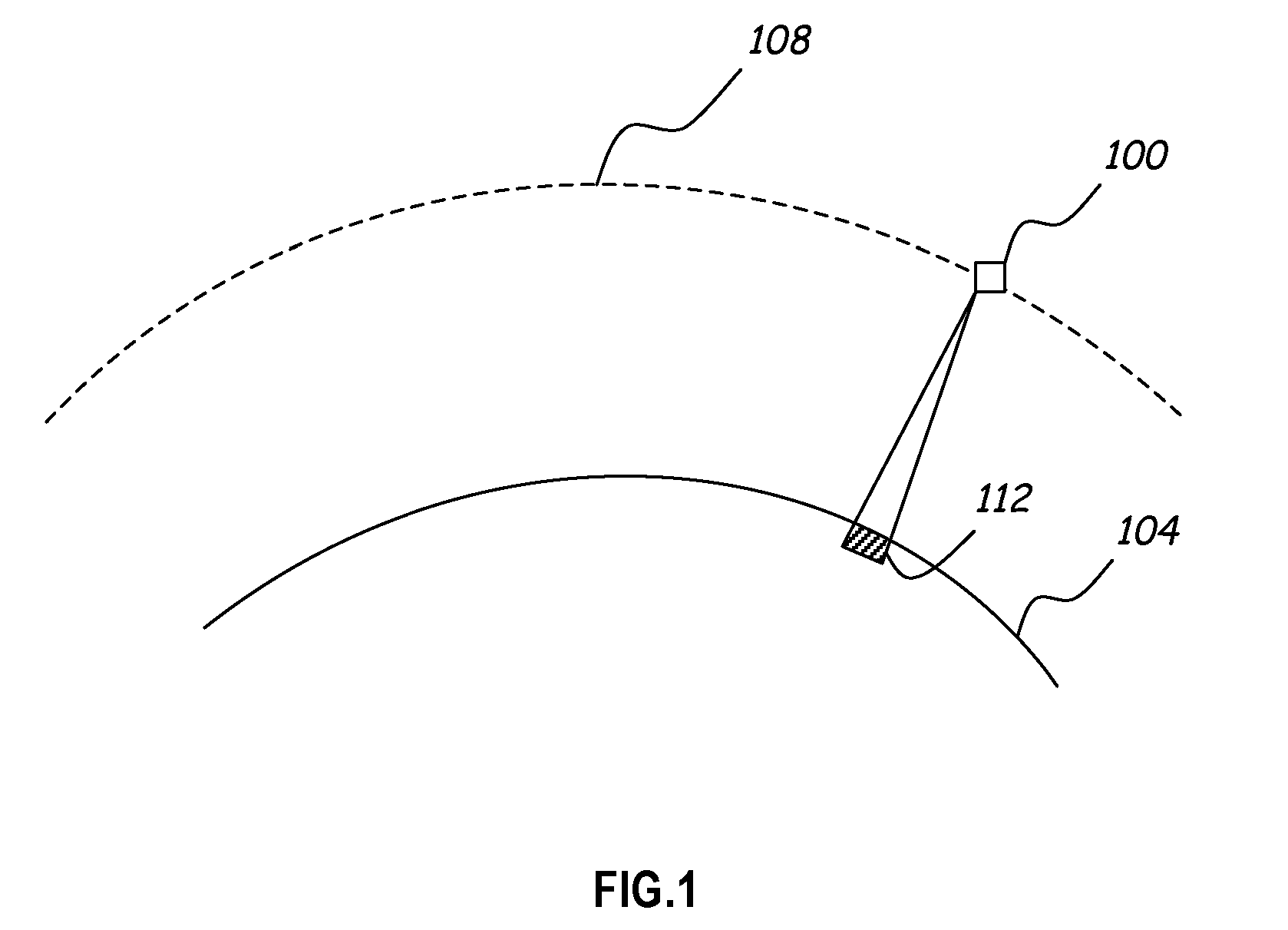
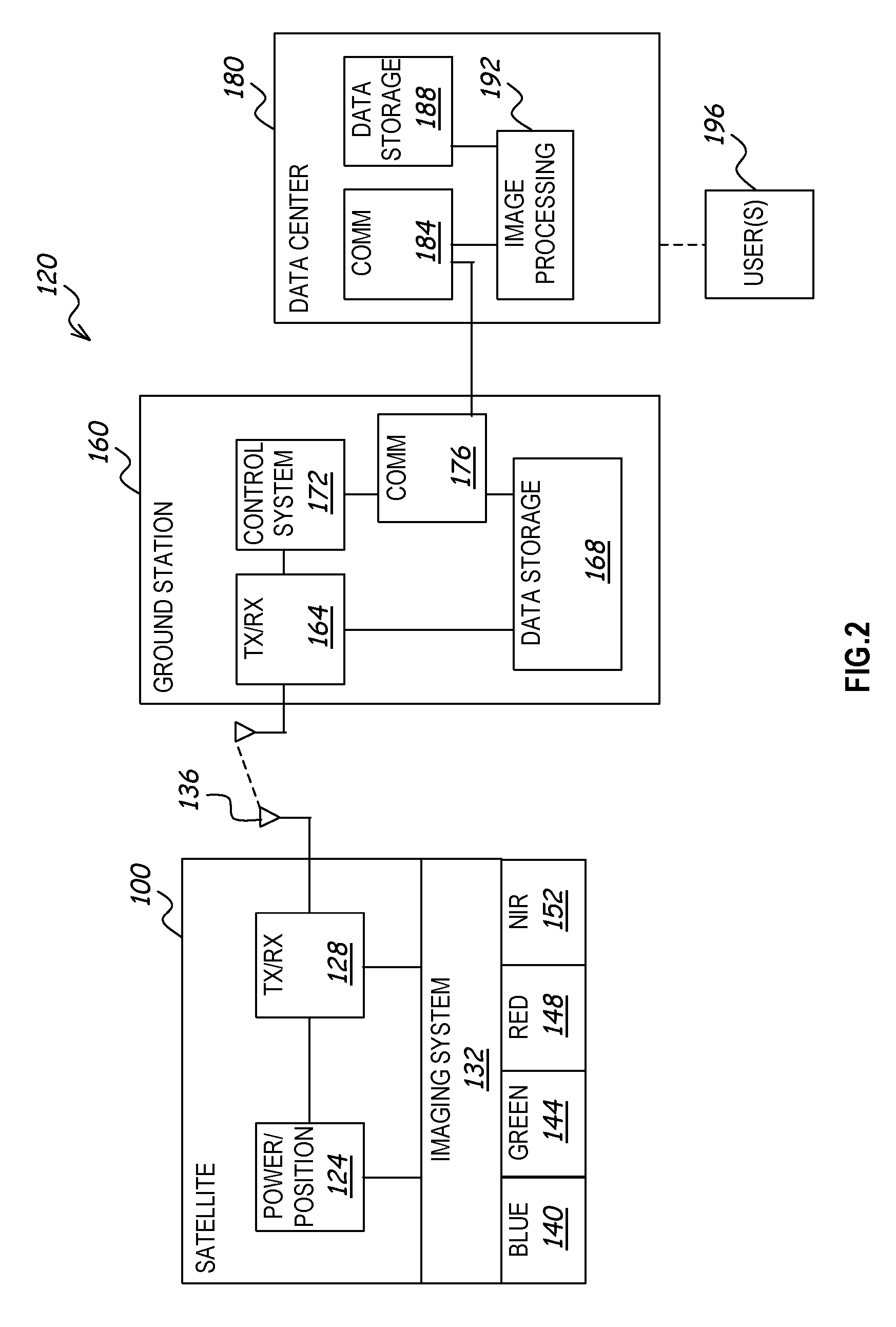
Method and apparatus for enhancing a digital image
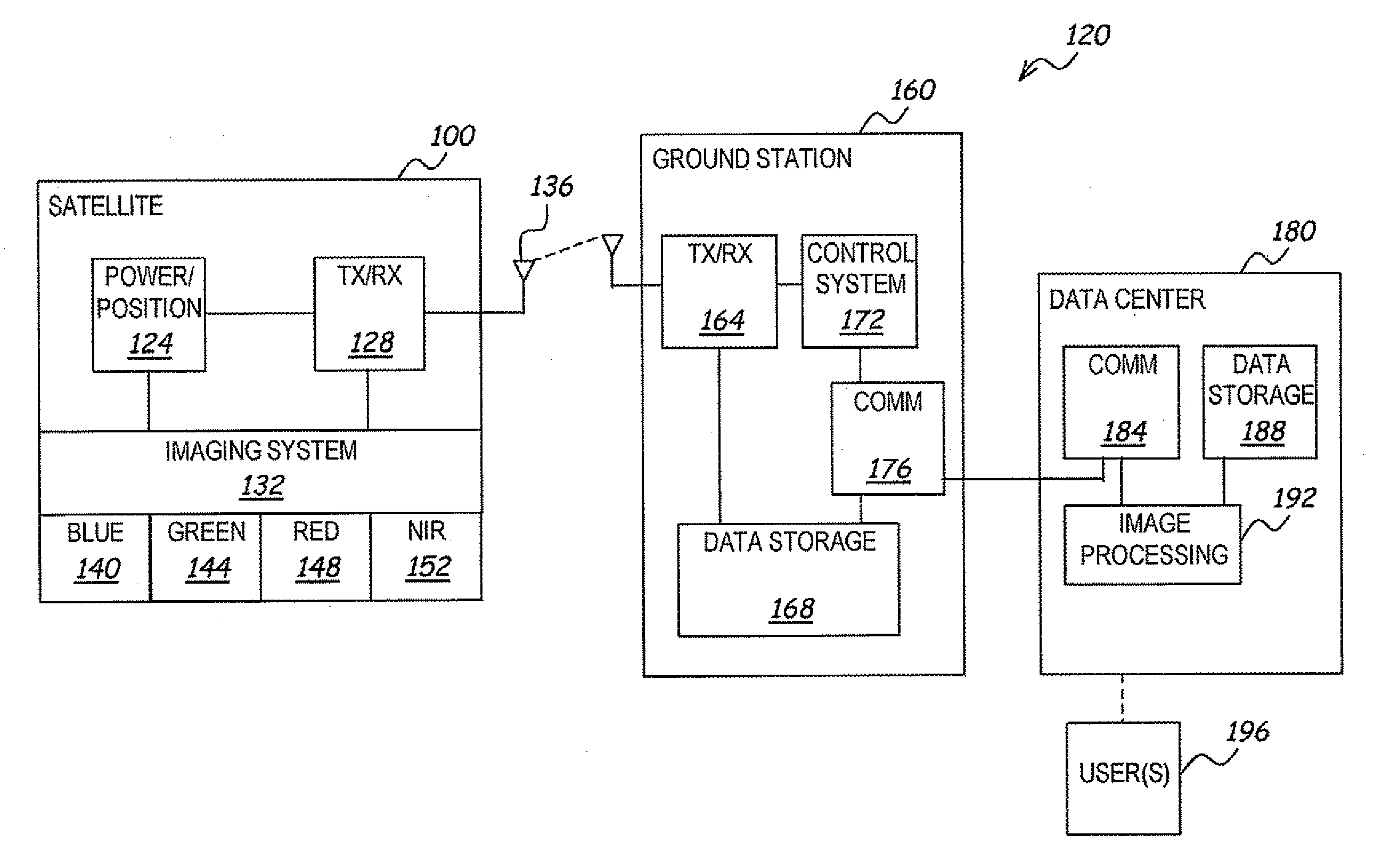
InactiveUS20060126959A1Easy visual interpretationEnhanced digital imageImage enhancementImage analysisAtmospheric effectColor correction
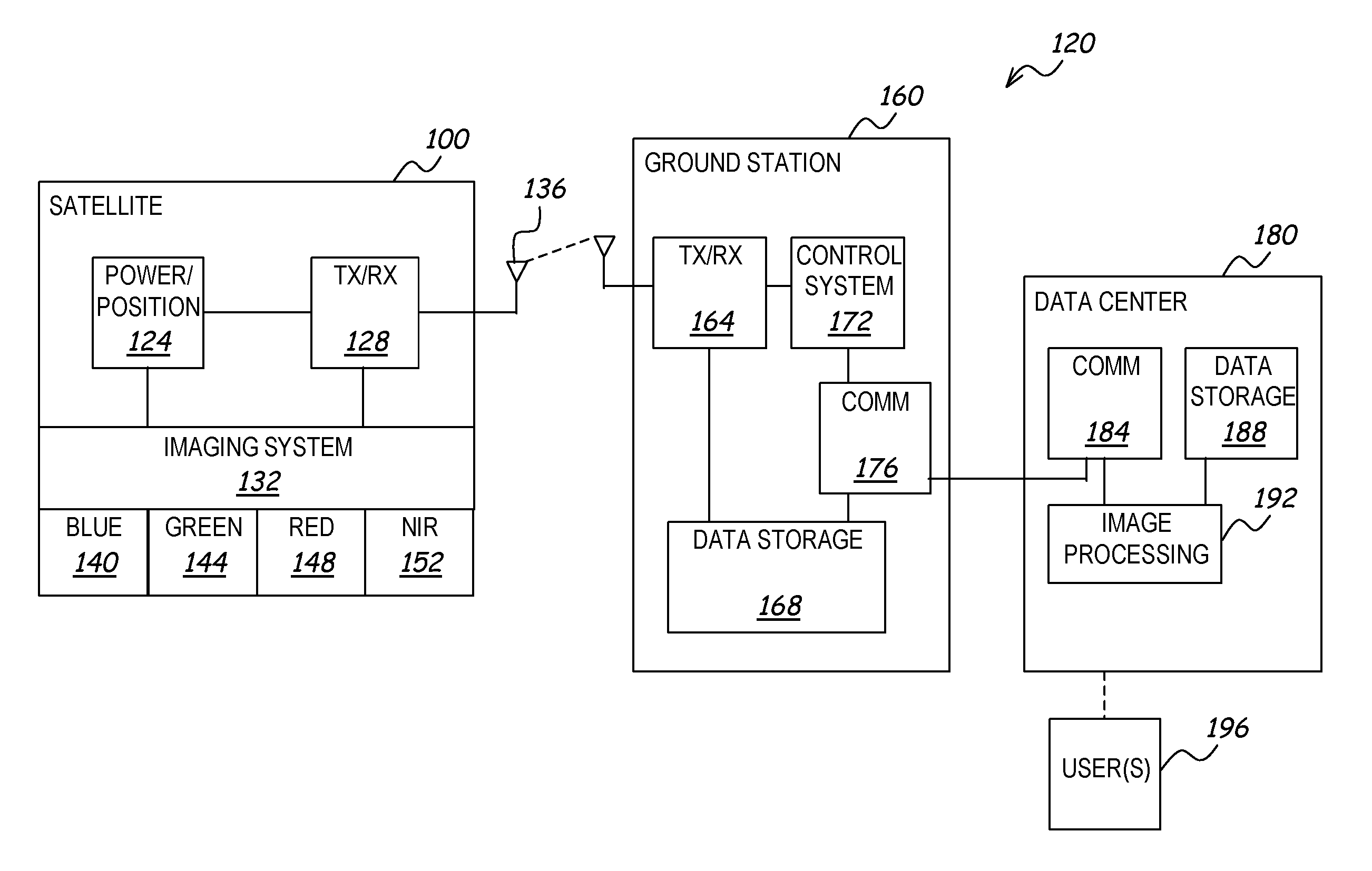
A system and method processes original digital numbers (DNs) provided by a satellite imaging system to produce a set of spectral balanced and contrast enhanced multispectral images. Spectral balancing is achieved based on physical characteristics of sensors of the imaging system as well as compensation for atmospheric effects. The DNs in the multispectral bands may be processed using a relatively small amount of processing resources otherwise required to produce such images. Such images may be processed completely automatically and provide relatively easy visual interpretation. Each image pixel may be, for example, in an 8-bit or 16-bit format, and the image may be displayed and / or printed without applying any additional color correction and / or contrast stretches.
Owner:DIGITALGLOBE INC
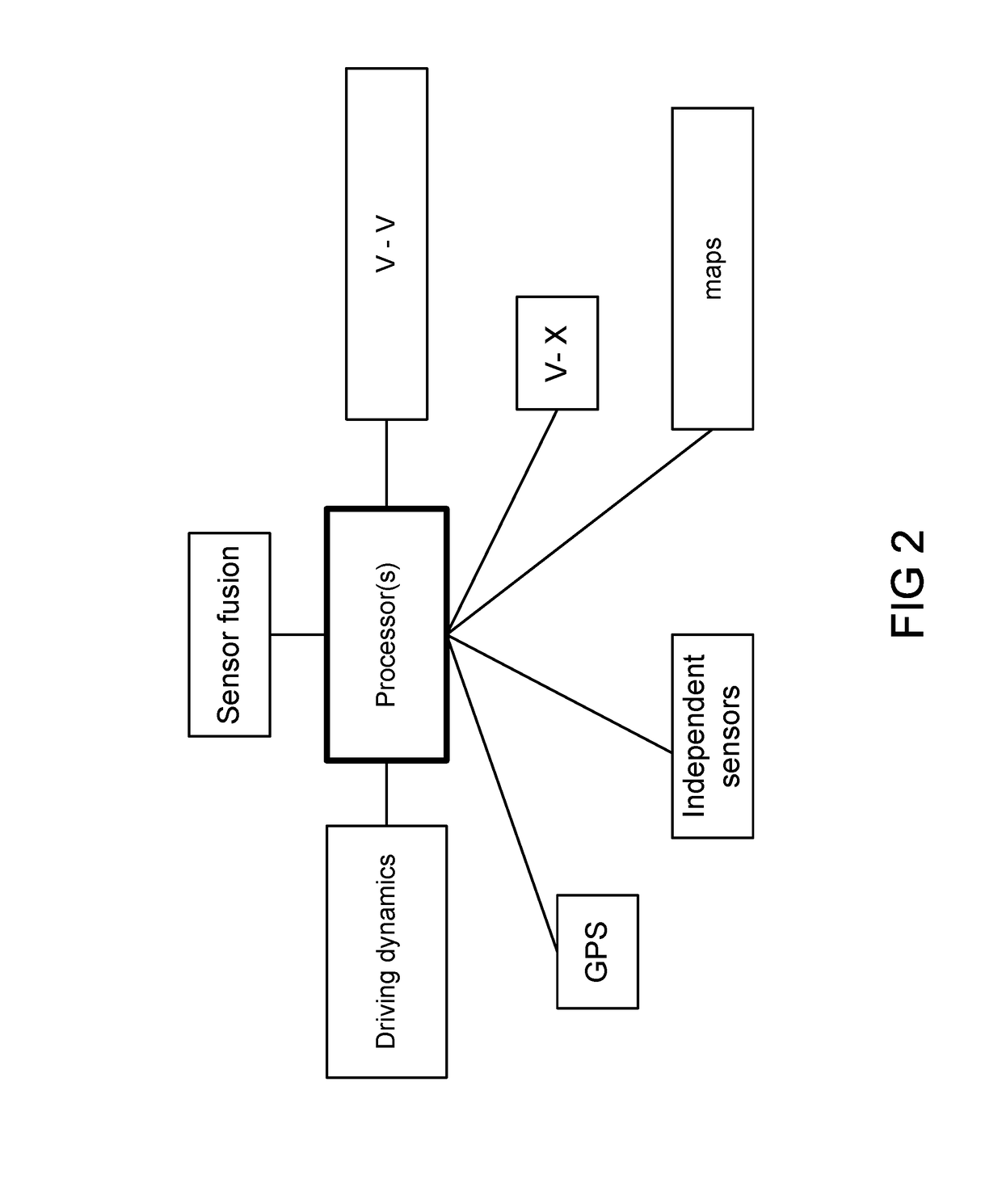
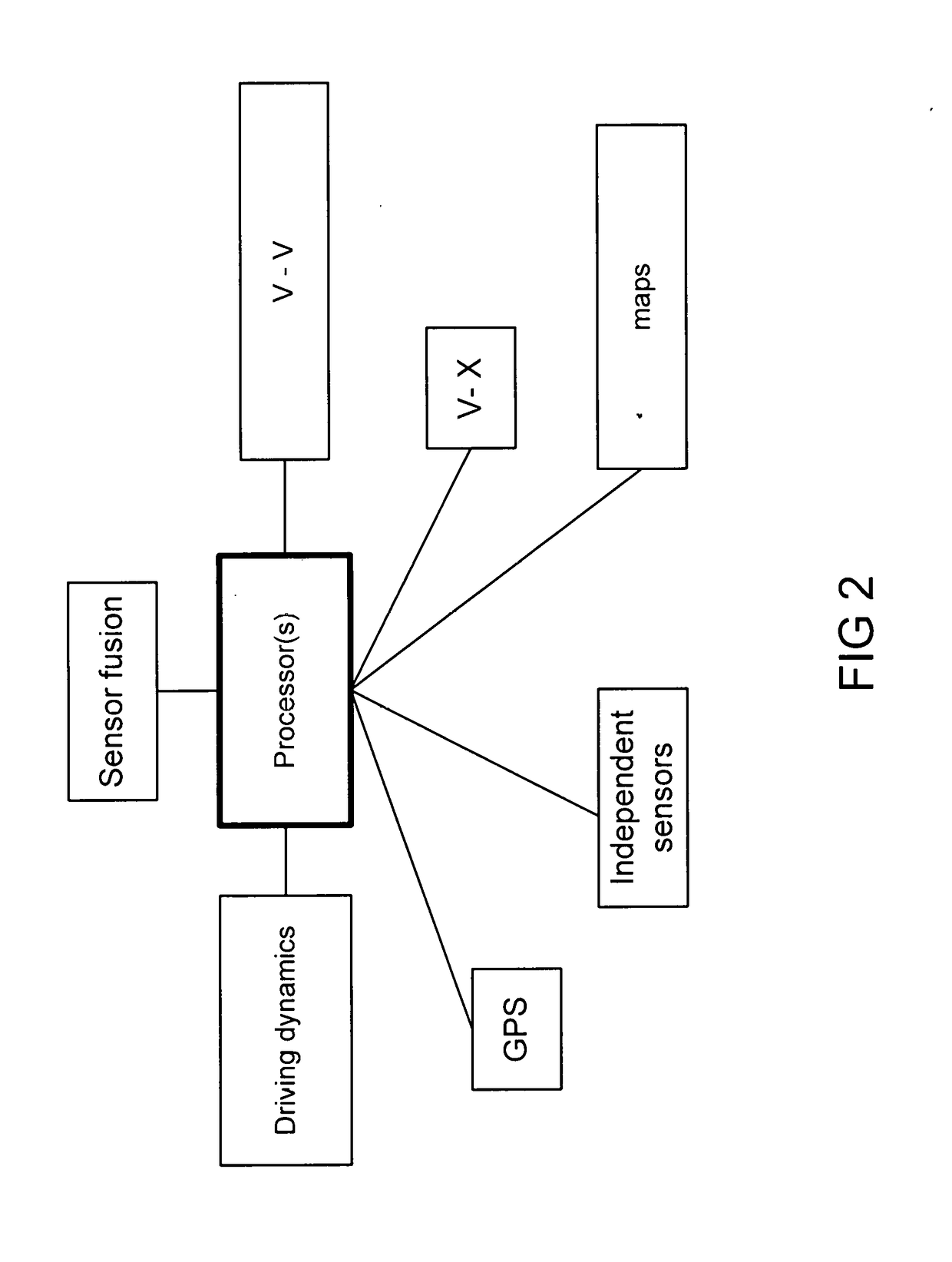
Positioning quality filter for the V2X technologies
ActiveUS20180045832A1Controlling traffic signalsNavigational calculation instrumentsTime delaysMultipath effect
This provides methods and systems for V2X applications, such as forward collision warning, electronic emergency brake light, left turn assist, work zone warning, signal phase timing, and others, mainly relying on a GNSS positioning solution transmitted via the Dedicated Short-Range Communications (DSRC) to / from the roadside units and onboard units in other V2X-enabled vehicles. However, the positioning solution from a GNSS may be deteriorated by noise and / or bias due to various error sources, e.g., time delay, atmospheric effect, ephemeris effect, and multipath effect. This offers a novel quality filter that can detect noise and the onset of drift in GNSS signals by evaluating up to four metrics that compare the qualities of kinematic variables, speed, heading angle change, curvature, and lateral displacement, obtained directly or derived from GNSS and onboard vehicle sensors. This is used for autonomous cars and vehicle safety, with various examples / variations.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Positioning System Based on Geofencing Framework
ActiveUS20180150086A1Instruments for road network navigationControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorMultipath effectAtmospheric effect
This provides methods and systems for the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) combined with the dead-reckoning (DR) technique, which is expected to provide a vehicle positioning solution, but it may contain an unacceptable amount of error due to multiple causes, e.g., atmospheric effects, clock timing, and multipath effect. Particularly, the multipath effect is a major issue in the urban canyons. This invention overcomes these and other issues in the DR solution by a geofencing framework based on road geometry information and multiple supplemental kinematic filters. It guarantees a road-level accuracy and enables certain V2X applications which does not require sub-meter accuracy, e.g., signal phase timing, intersection movement assist, curve speed warning, reduced speed zone warning, and red-light violation warning. Automated vehicle is another use case. This is used for autonomous cars and vehicle safety, shown with various examples / variations.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
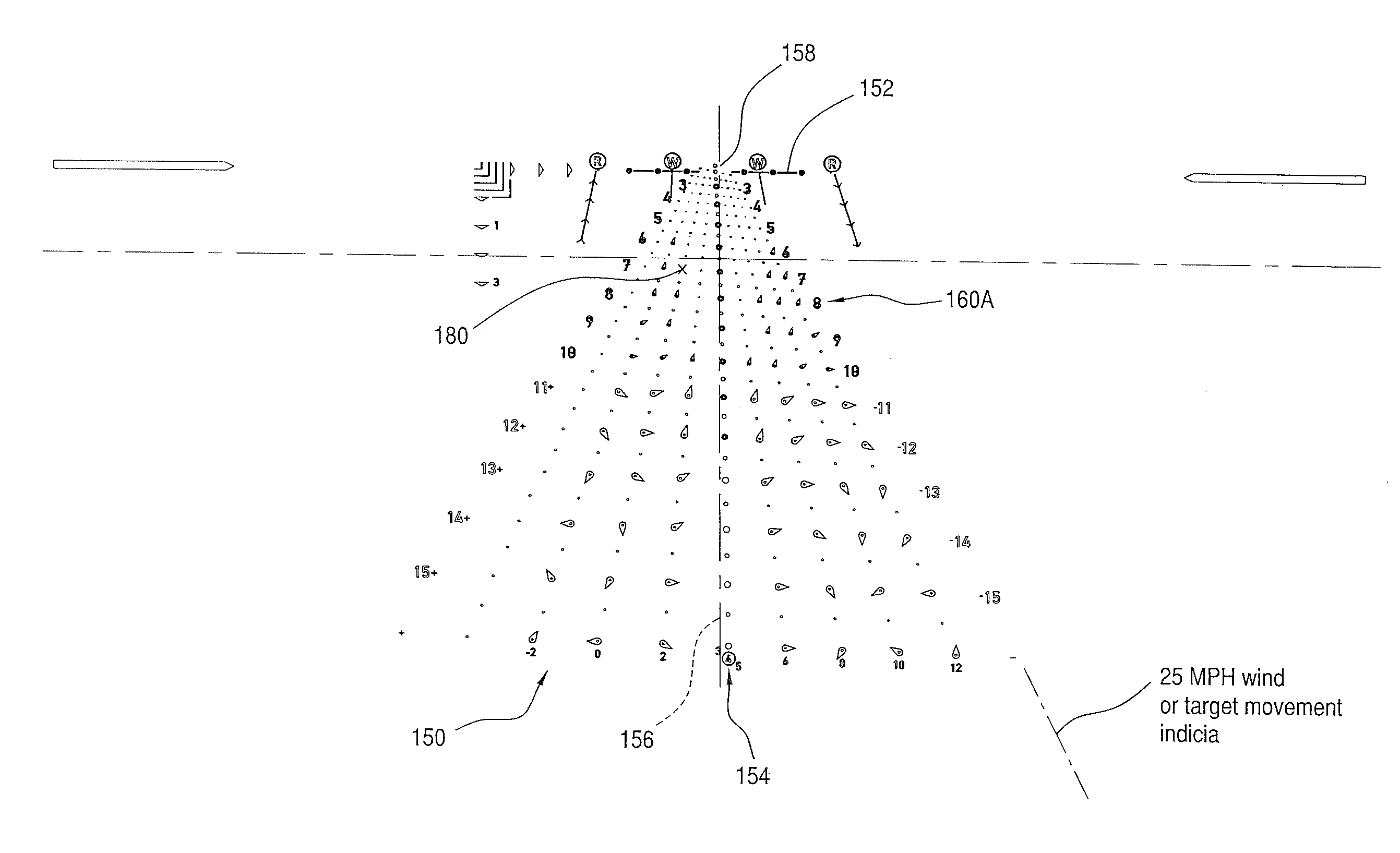
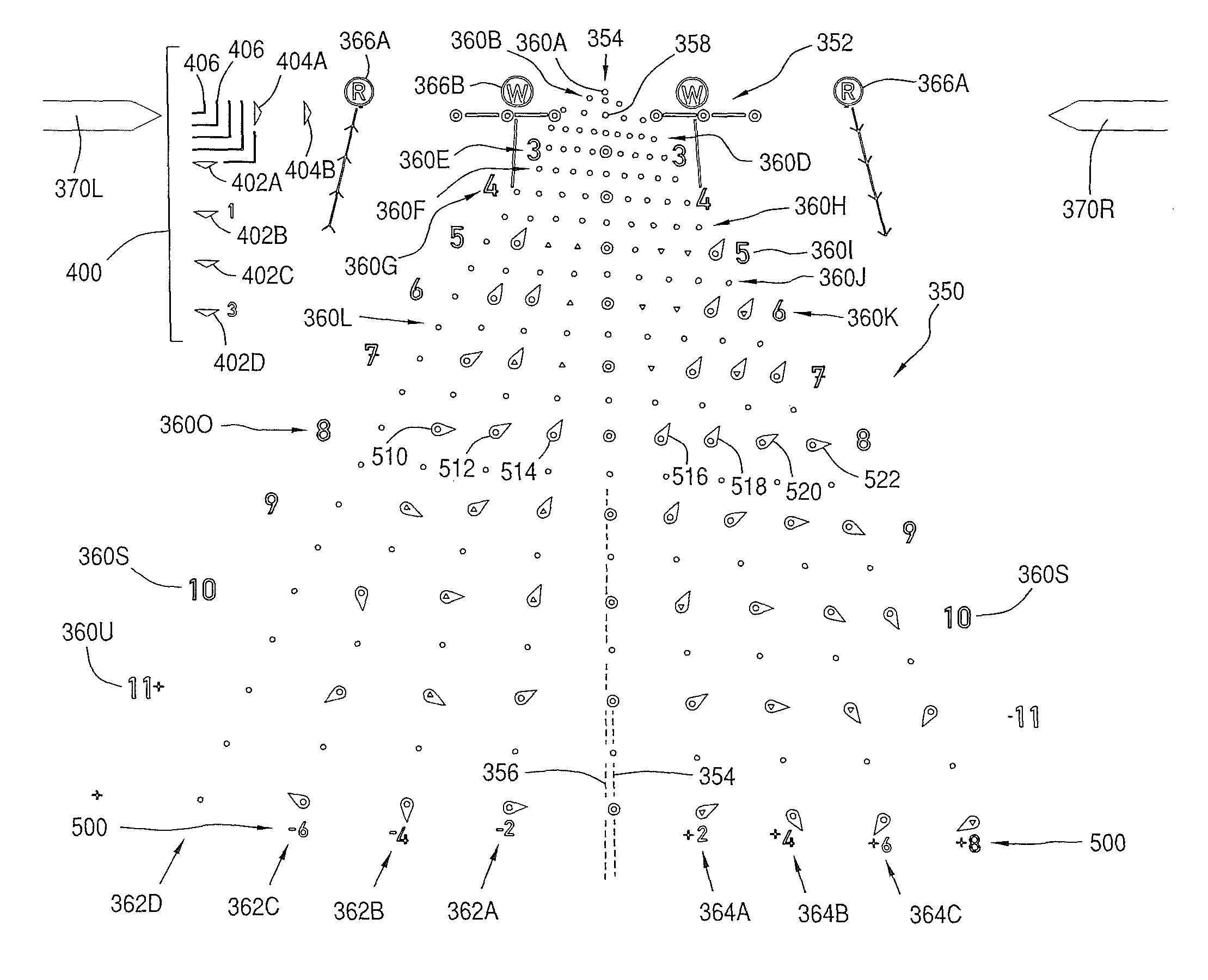
Dynamic targeting system with projectile-specific aiming indicia in a reticle and method for estimating ballistic effects of changing environment and ammunition
A dynamic ballistic effect compensating reticle and an aim compensation method for use in rifle sights or projectile weapon aiming systems includes a multiple point elevation and windage aim point field including a primary aiming mark indicating a primary aiming point adapted to be sighted-in at a first selected range (e.g., 200 yds) and a plurality secondary aiming point arrays beneath the primary aiming mark. The method for compensating for a projectile's ballistic behavior while developing a field expedient firing solution permits the shooter to express the field expedient firing solution in units of distance, (e.g., yards or meters, when describing or estimating range and nominal air density ballistic characteristics), and velocity (e.g., mph or kph, for windage hold points). The reticle aim point field permits the marksman to adjust the firing solution for momentary atmospheric effects and operational contingencies such as variations in ammunition.
Owner:TUBB G DAVID
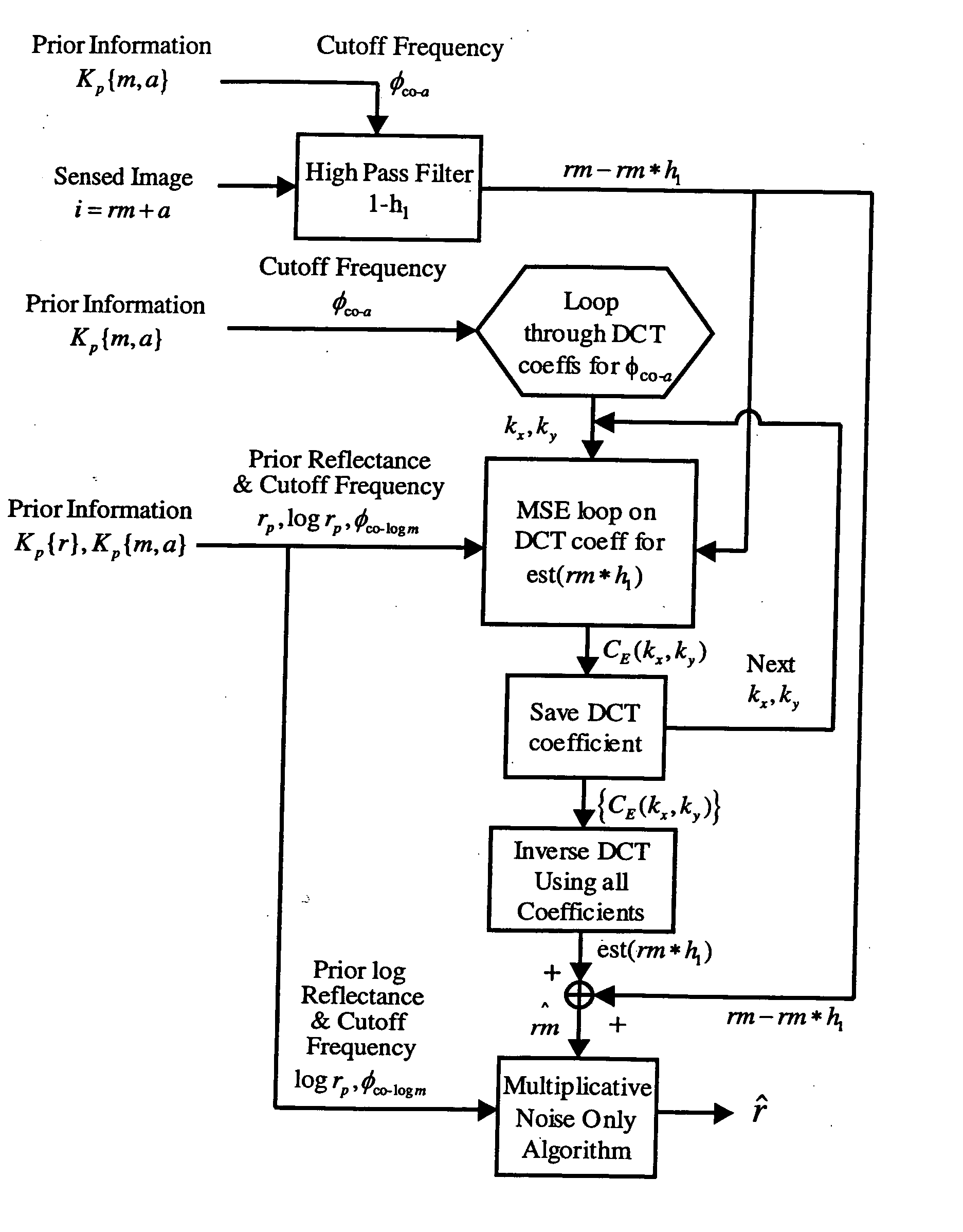
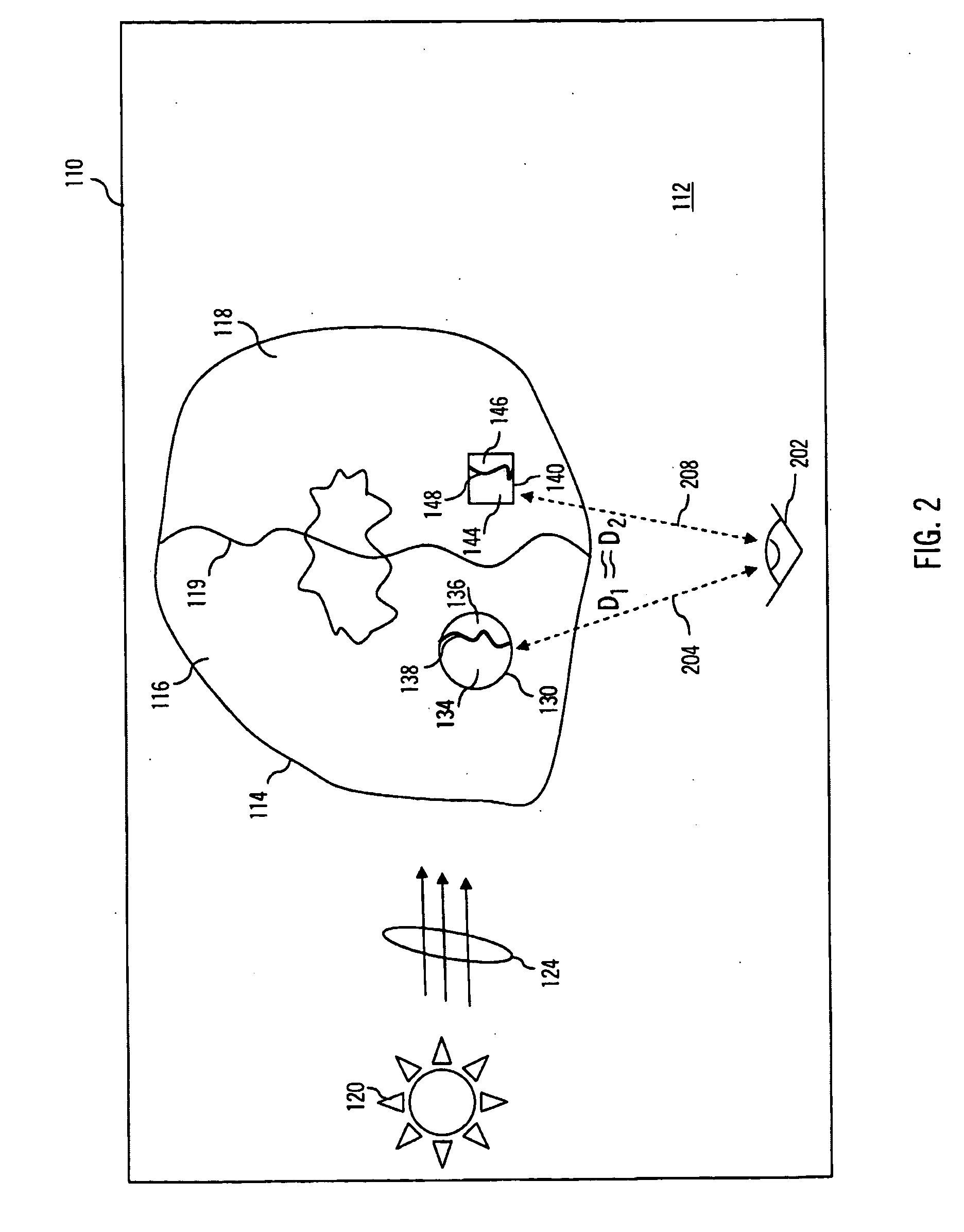
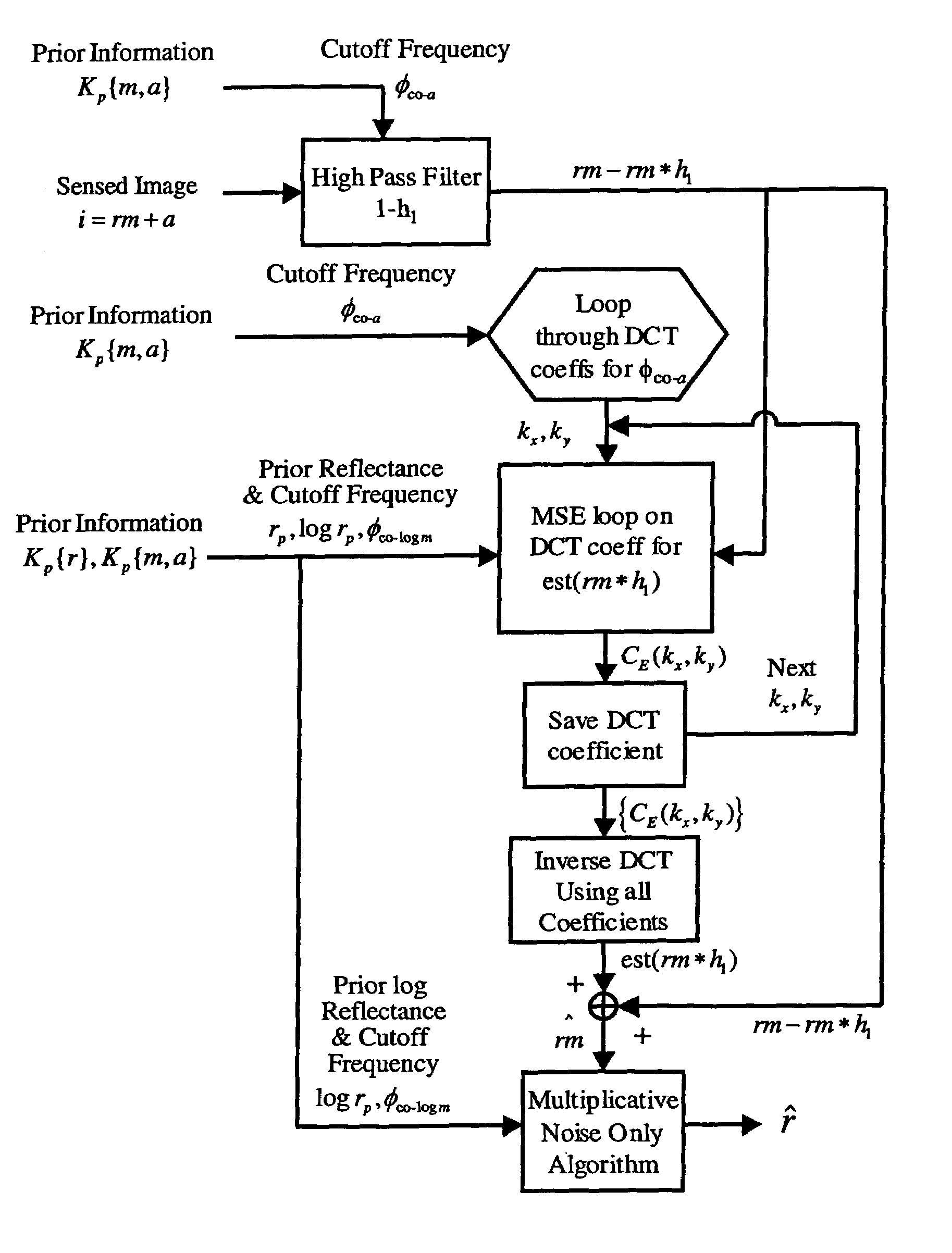
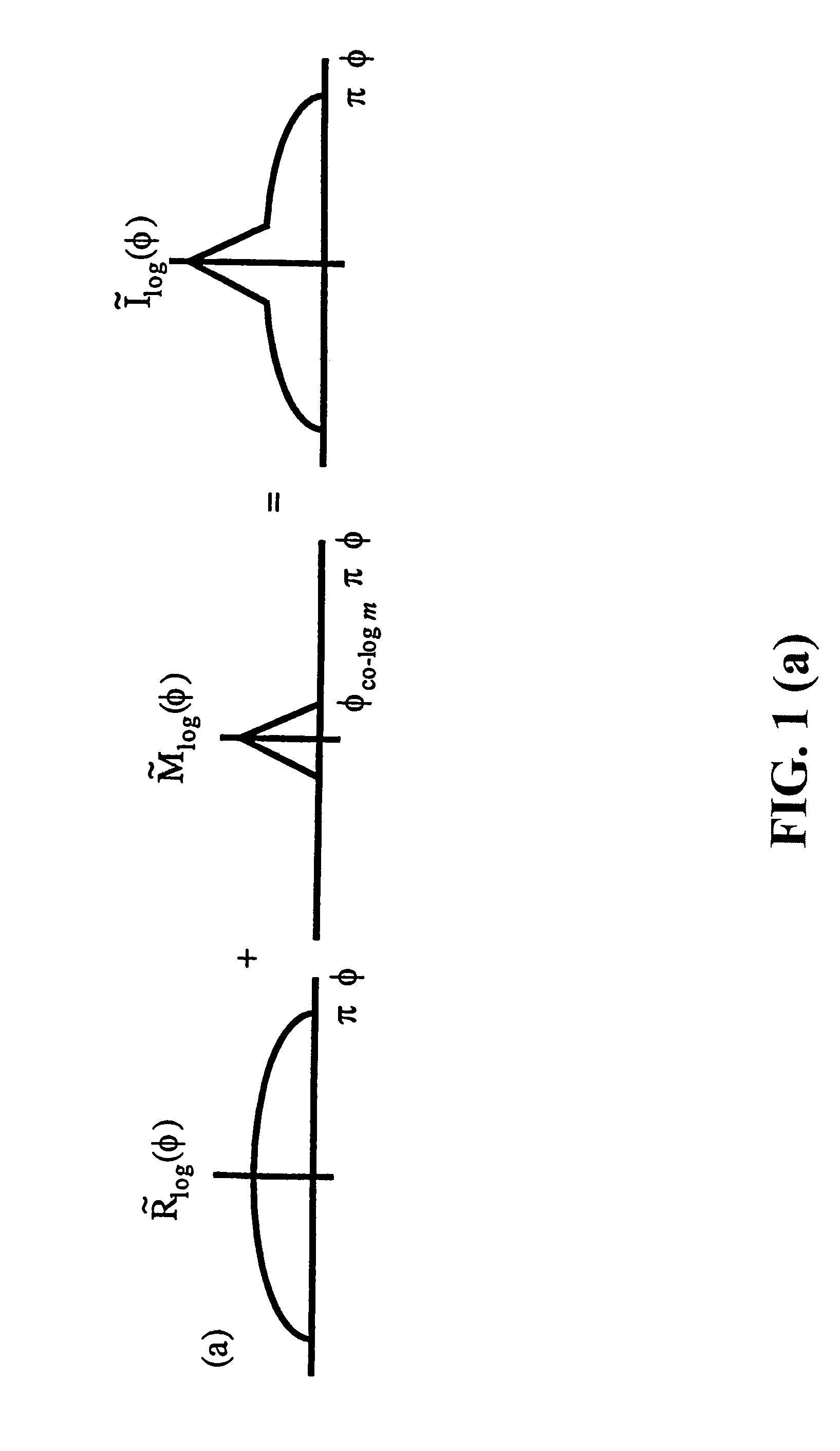
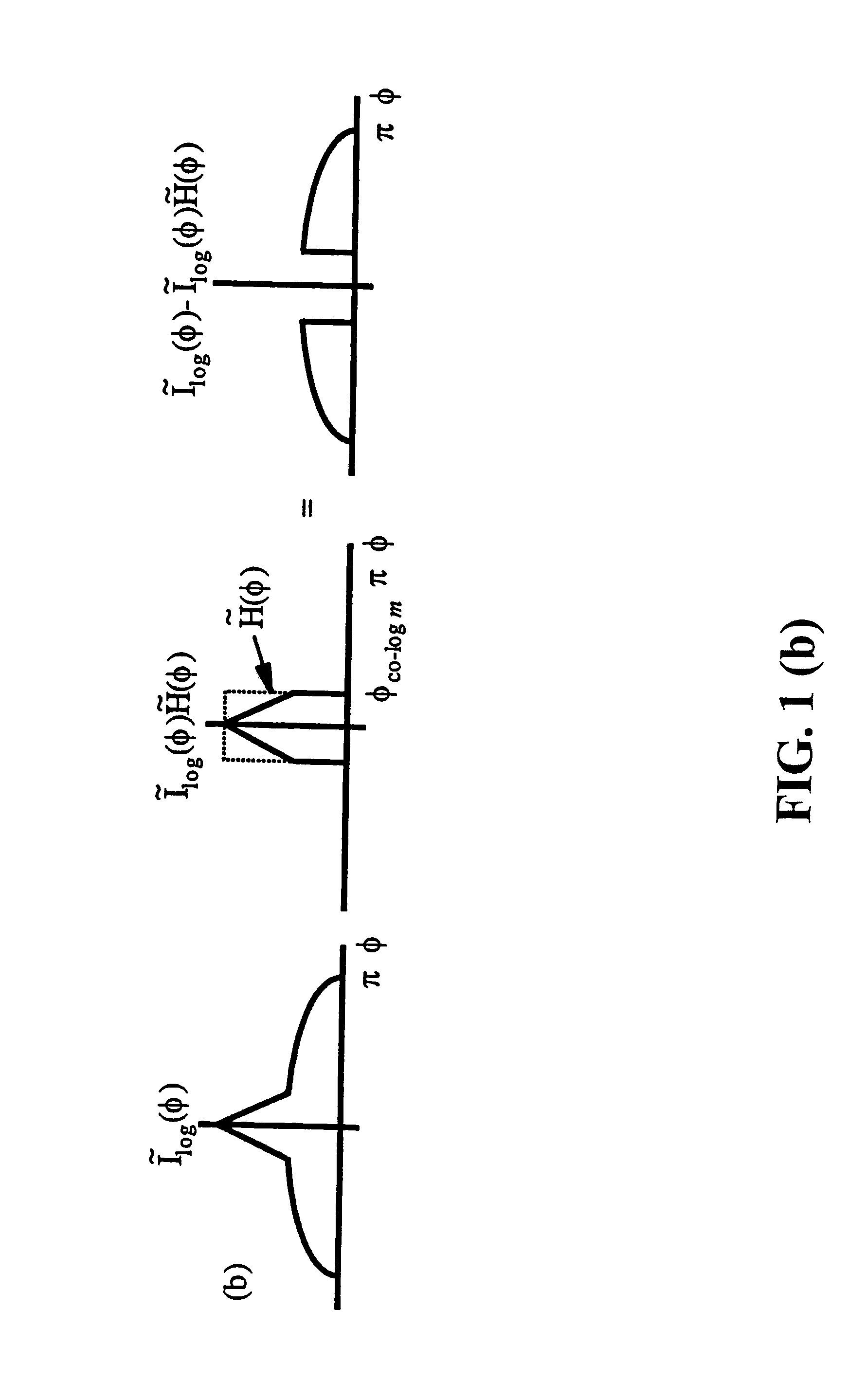
Spatial surface prior information reflectance estimation (SPIRE) algorithms
InactiveUS20050036661A1Remove additive noiseScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGround truthAtmospherics
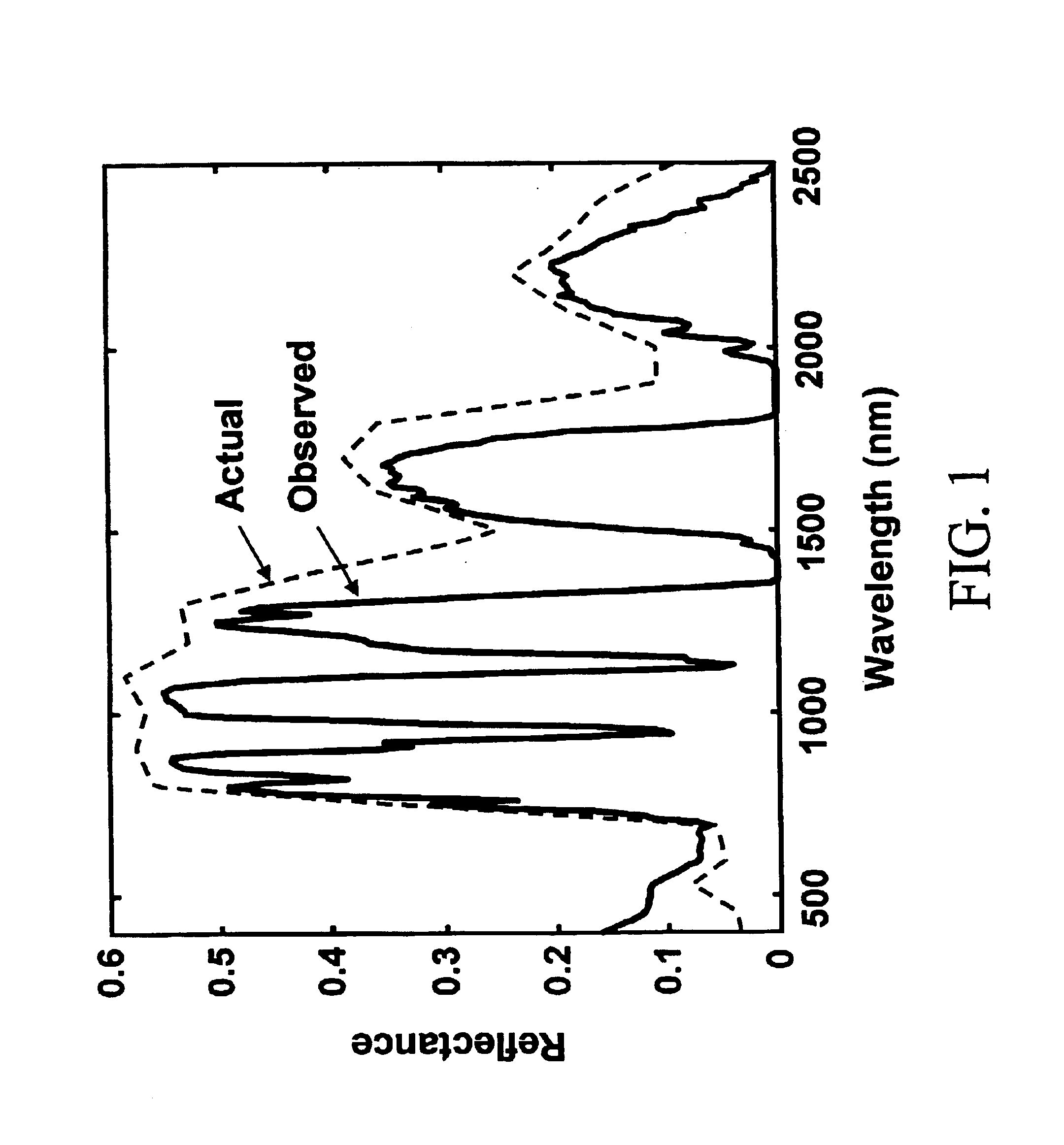
A new class of algorithms has been developed to estimate spectral reflectance in remote sensing imagery. These algorithms are called Surface Prior Information Reflectance Estimation (SPIRE) algorithms and estimate surface spectral reflectance using prior spatial and spectral information about the surface reflectance. This paper describes SPIRE algorithms that employ spatial processing of single channel data to estimate local changes in spectral reflectance under spatially and spectrally varying multiplicative and additive noise caused by variations in illumination and atmospheric effects. Rather than modeling the physics of the atmosphere and illumination (using a physics-based code such as ATREM), or using ground truth spectra at known locations to compensate for these effects (using the Empirical Line Method), prior information about the low spatial frequency content of the scene in each spectral channel is used instead. HYDICE VNIR-SWIR hyperspectral data were used to compare the performance of SPIRE, ATREM, and ELM atmospheric compensation algorithms. The Spatial SPIRE algorithm performance was found to be nearly identical to the ELM ground-truth based results, while Spatial SPIRE performed better than ATREM overall, and significantly better under high clouds and haze.
Owner:AIR FORCE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
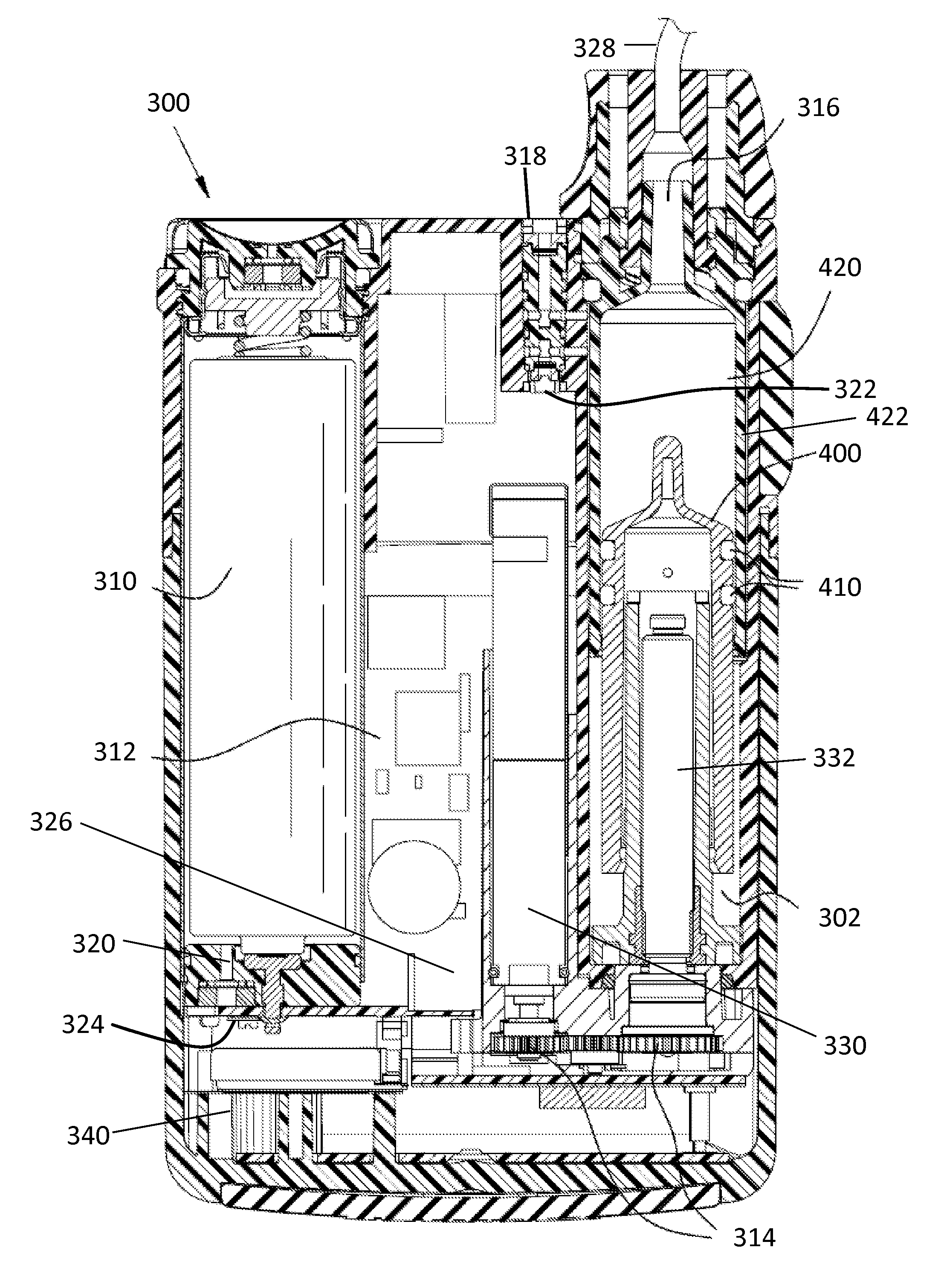
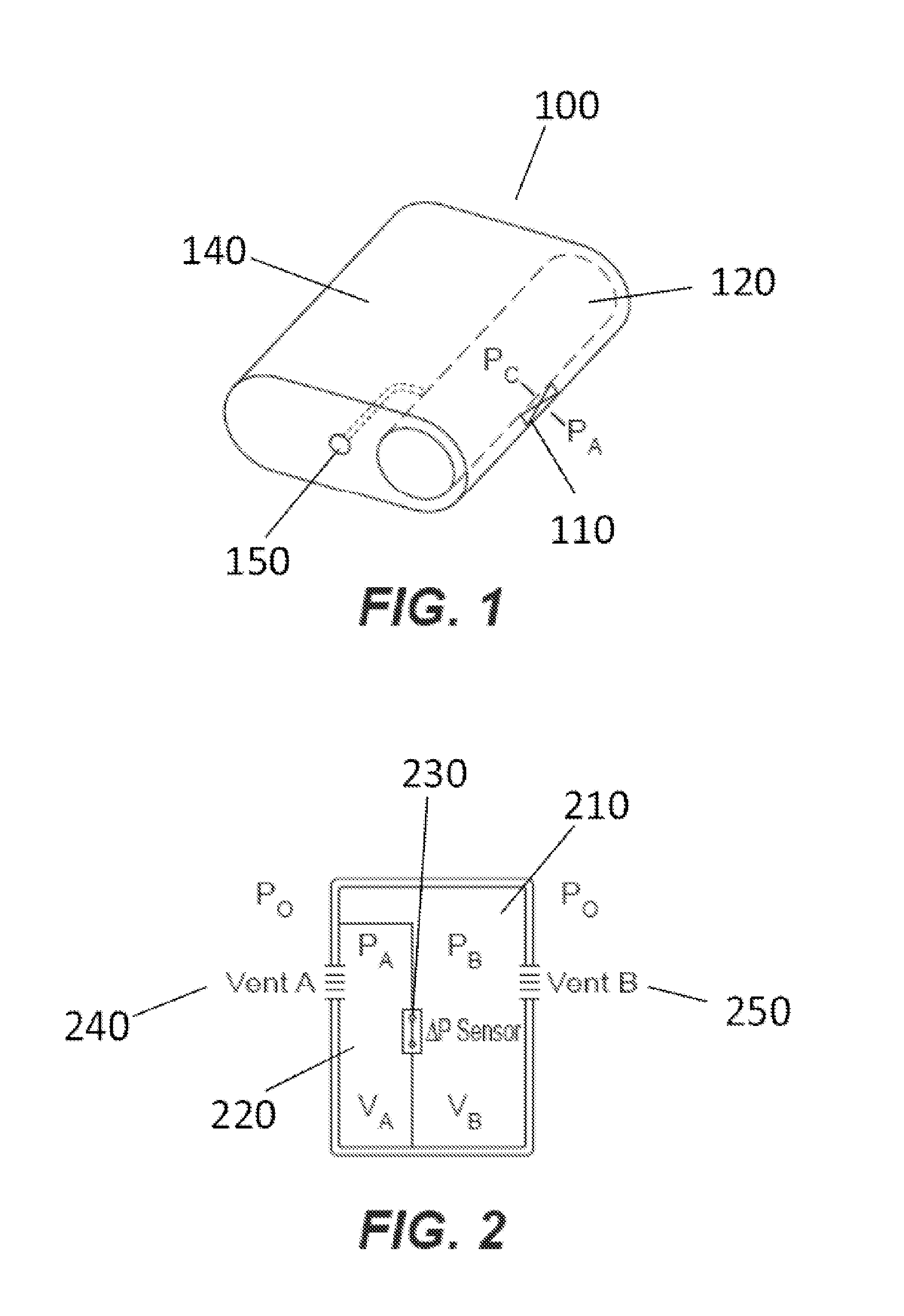
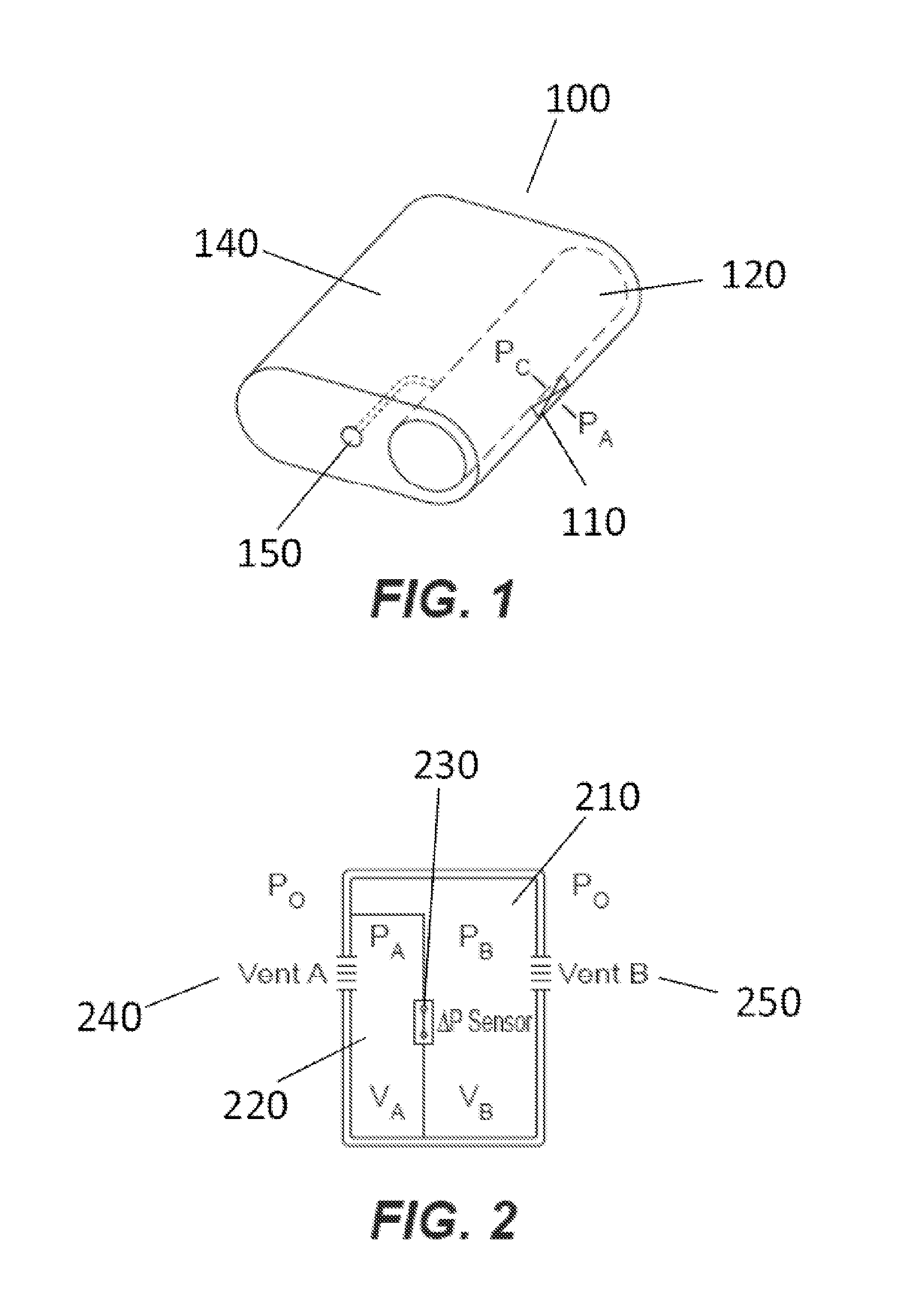
Portable infusion pump with pressure and temperature compensation
InactiveUS20130338576A1Avoid problemsMedical devicesPressure infusionDrugs infusionIntensive care medicine
Described is drug infusion device configure to maintain its intended drug delivery rate by monitoring atmospheric effects. The device may include one or more vents that permit the passage of gas between the exterior and interior of the device's housing. The device may also include one or more pressure and / or temperature sensors, the readings from which may be used to determine malfunctions in the venting of the device and / or changes in pressure that could cause the unintended over-delivery or under-delivery of medication.
Owner:ANIMAS CORP
Method for performing automated in-scene based atmospheric compensation for multi-and hyperspectral imaging sensors in the solar reflective spectral region
InactiveUS6909815B2Optimize calculation speedSuitable for applicationSpectrum investigationScene recognitionFrequency spectrumOptical depth
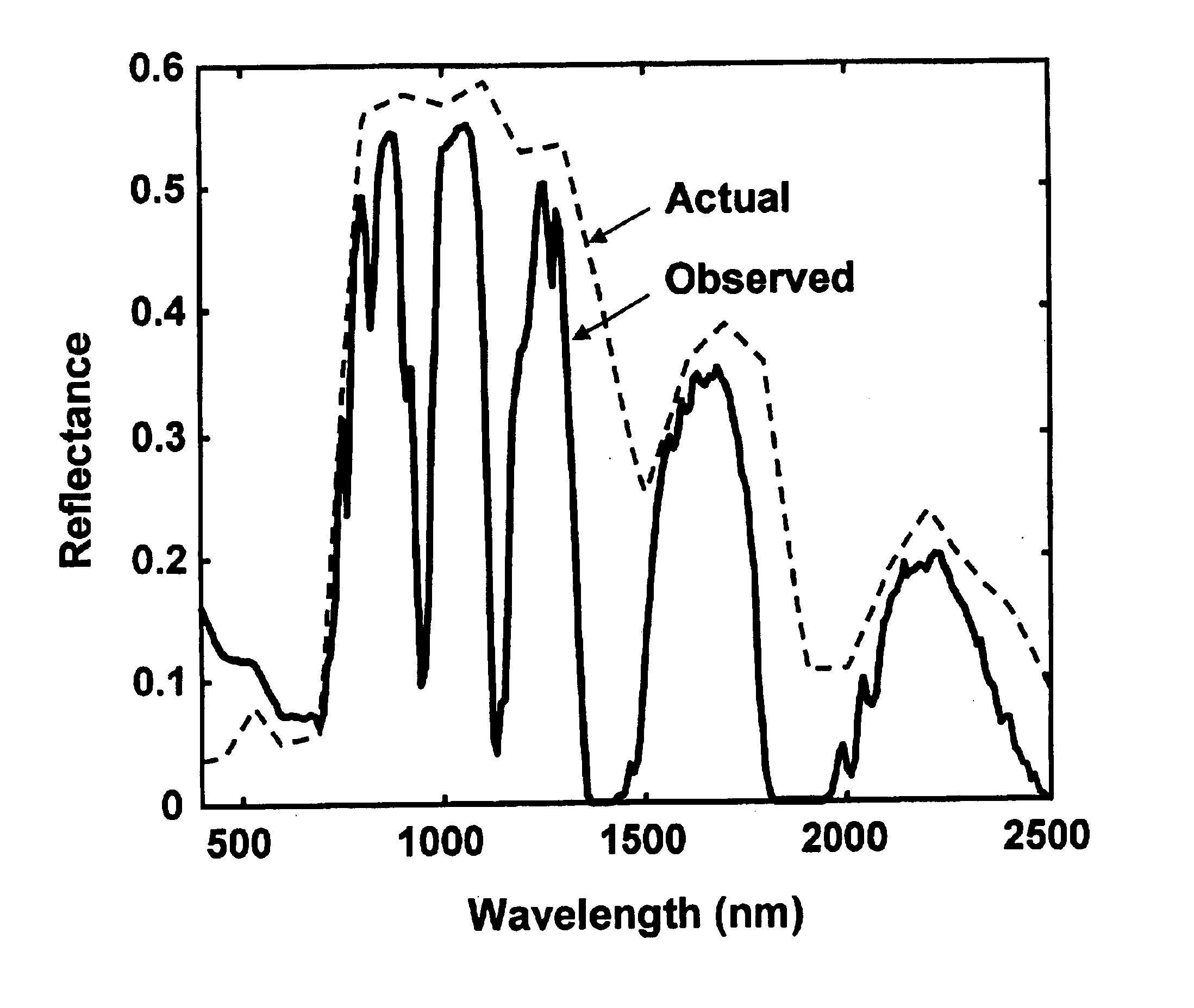
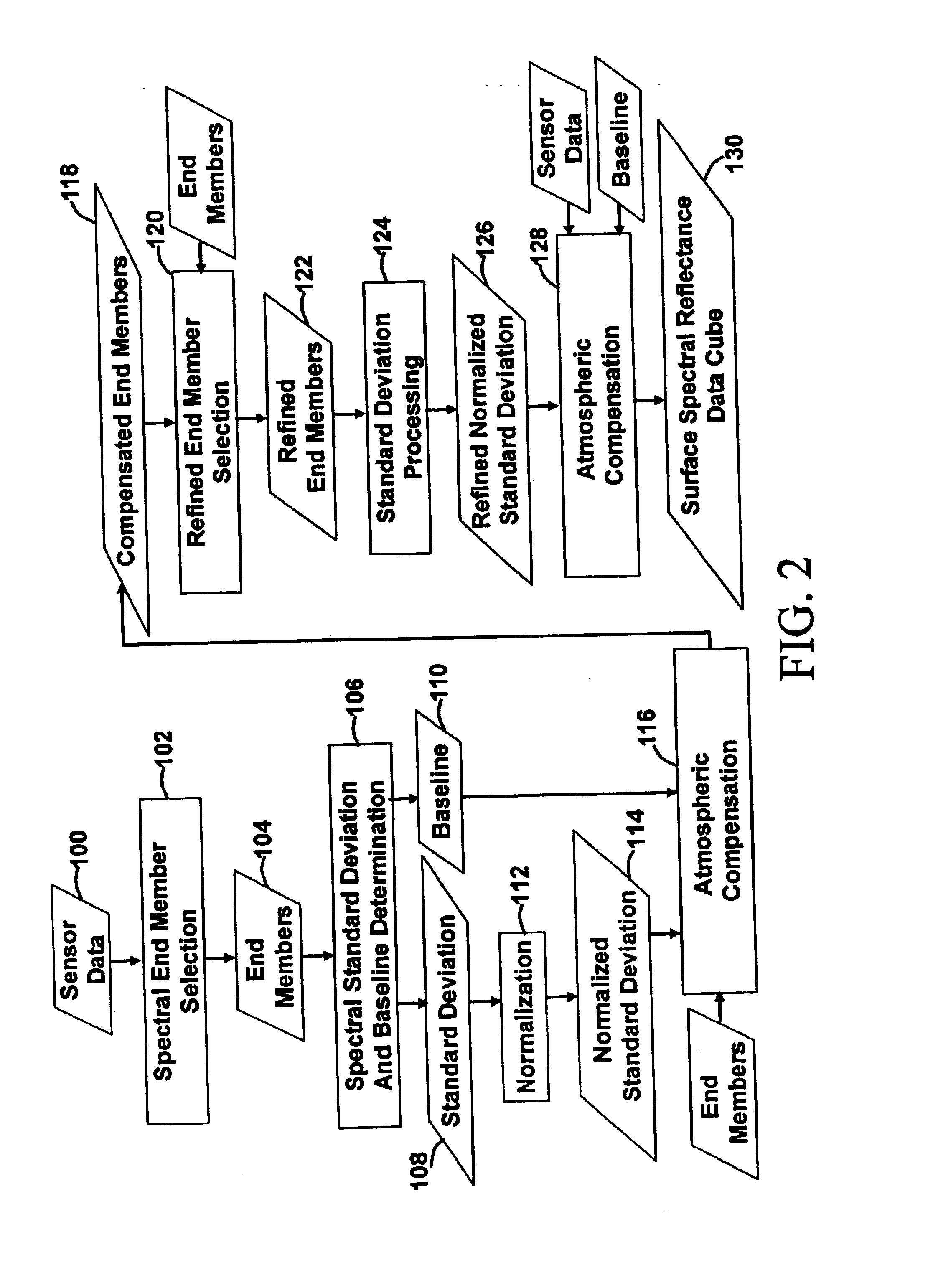
A method of automatically compensating a multi- or hyper-spectral, multi-pixel image for atmospheric effects, comprising resolving a plurality of spectrally-diverse pixels from the image, determining a spectral baseline from the spectrally-diverse pixels, determining a statistical spectral deviation of the spectrally-diverse pixels, normalizing the statistical spectral deviation by applying a scale factor, and compensating image pixels with both the spectral baseline and the normalized spectral deviation. Another embodiment features a method of automatically determining a measure of atmospheric aerosol optical properties using a multi- or hyper-spectral, multi-pixel image, comprising resolving a plurality of spectrally-diverse pixels from the image, determining a statistical spectral deviation of the spectrally-diverse pixels, correcting the statistical spectral deviation for non-aerosol transmittance losses, and deriving from the statistical spectral deviation one or more wavelength-dependent aerosol optical depths. A final embodiment features a method of automatically determining a measure of atmospheric gaseous optical properties using a multi- or hyper-spectral, multi-pixel image, comprising resolving a plurality of spectrally-diverse pixels from the image, determining a statistical spectral deviation of the spectrally-diverse pixels, and deriving from the statistical spectral deviation wavelength-dependent gaseous optical depths.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
Dynamic targeting system with projectile-specific aiming indicia in a reticle and method for estimating ballistic effects of changing environment and ammunition
A dynamic ballistic effect compensating reticle and an aim compensation method for use in rifle sights or projectile weapon aiming systems includes a multiple point elevation and windage aim point field including a primary aiming mark indicating a primary aiming point adapted to be sighted-in at a first selected range (e.g., 200 yds) and a plurality secondary aiming point arrays beneath the primary aiming mark. The method for compensating for a projectile's ballistic behavior while developing a field expedient firing solution permits the shooter to express the field expedient firing solution in units of distance, (e.g., yards or meters, when describing or estimating range and nominal air density ballistic characteristics), and velocity (e.g., mph or kph, for windage hold points). The reticle aim point field permits the marksman to adjust the firing solution for momentary atmospheric effects and operational contingencies such as variations in ammunition.
Owner:TUBB G DAVID
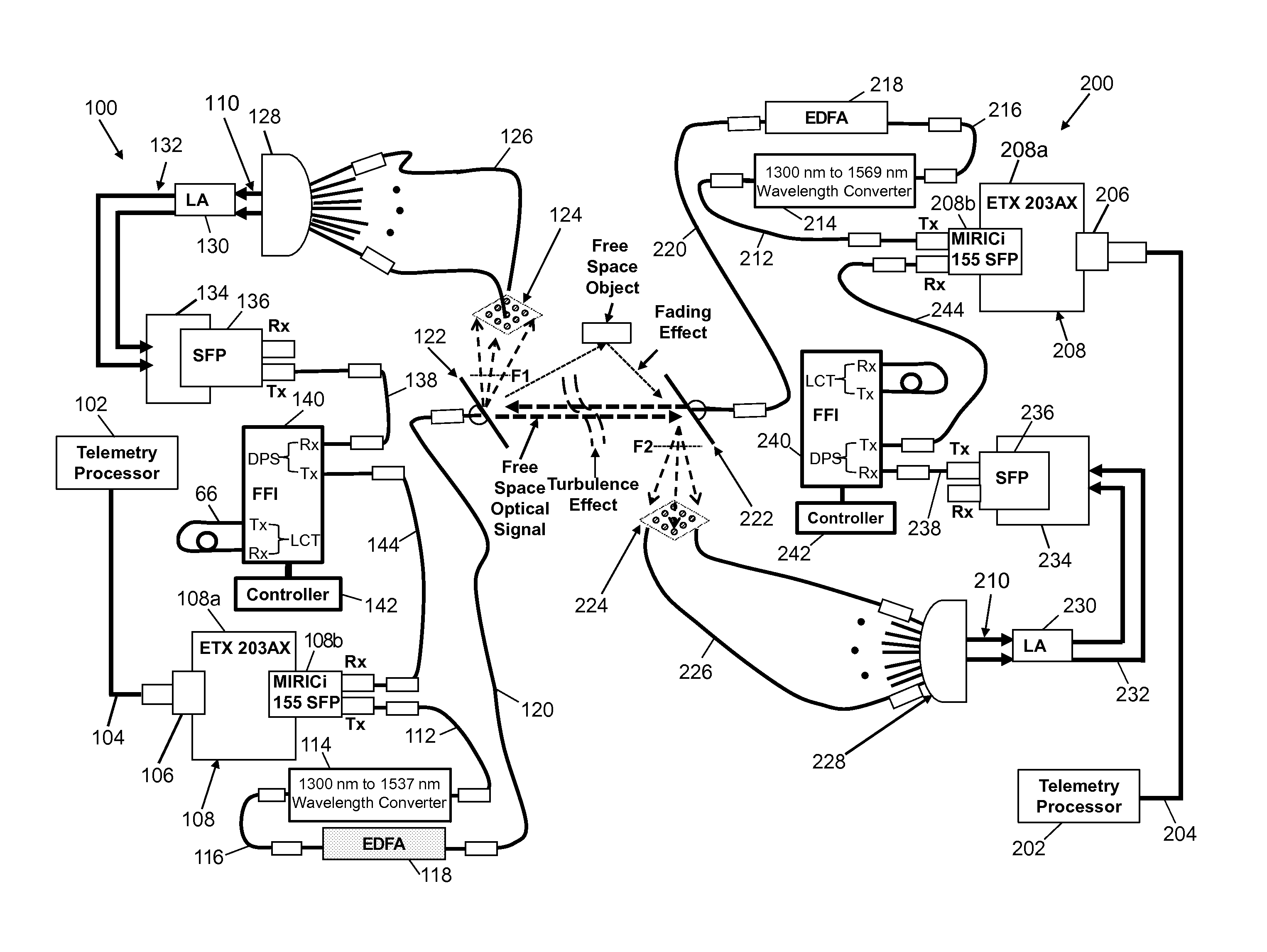
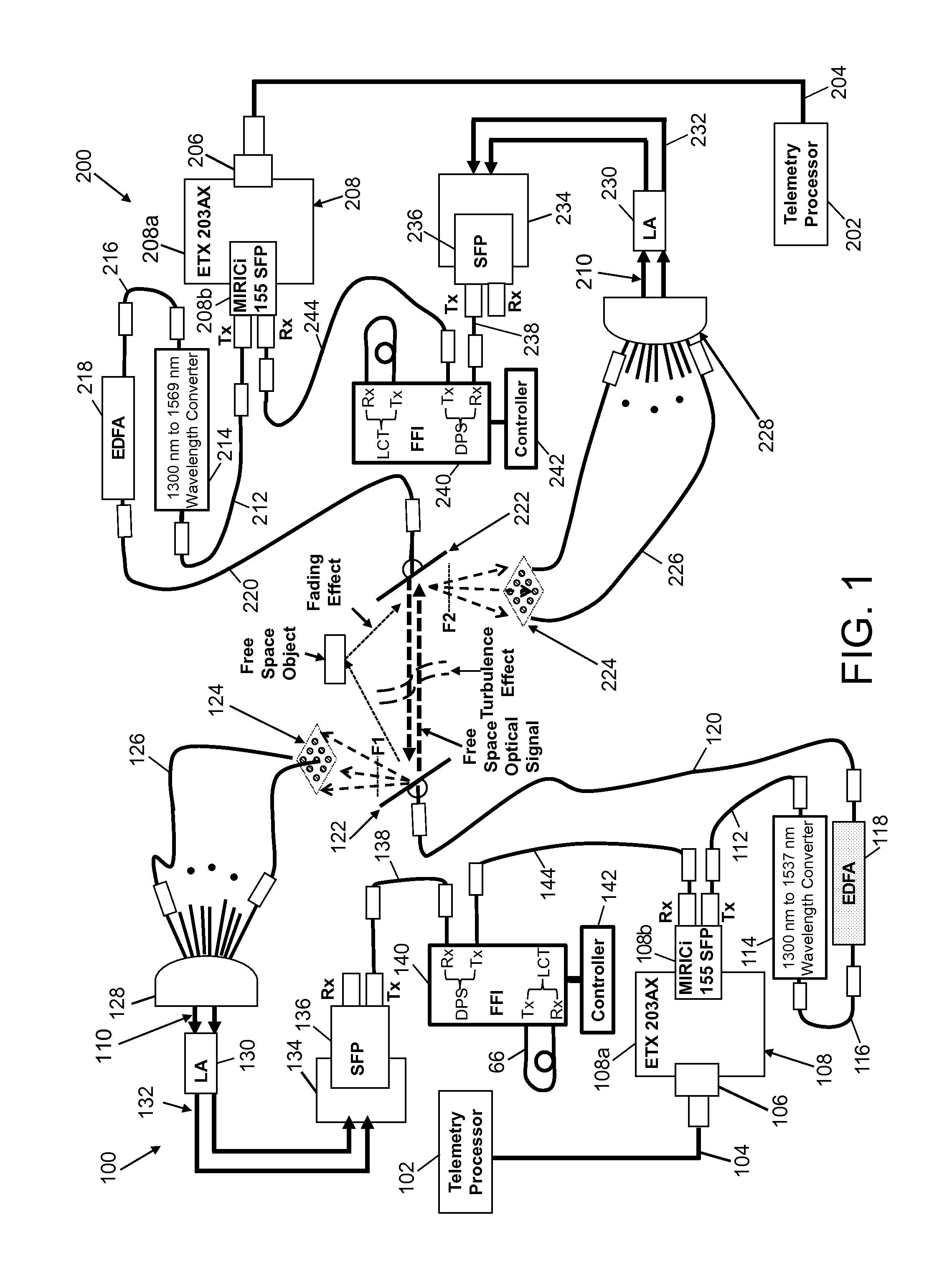
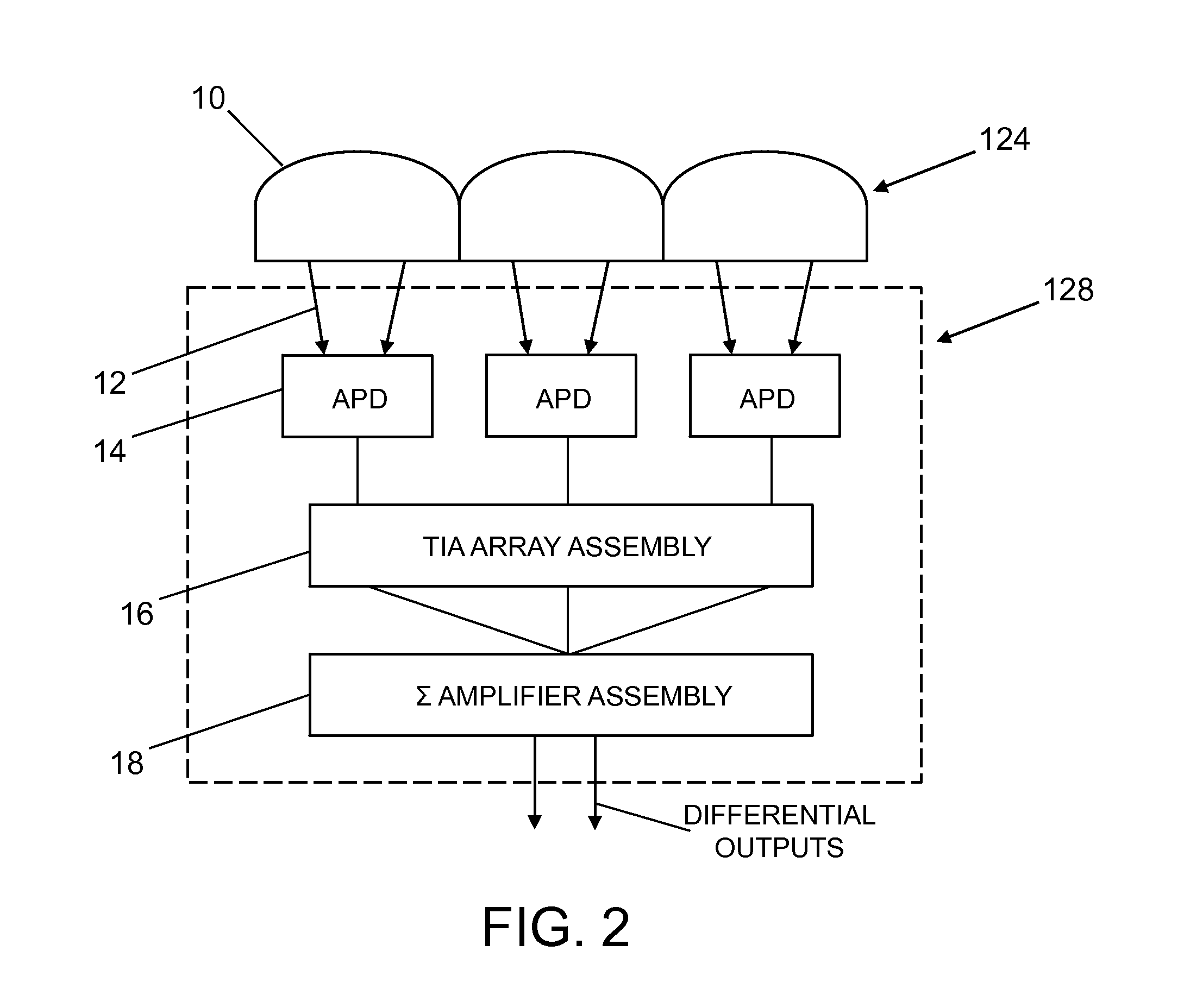
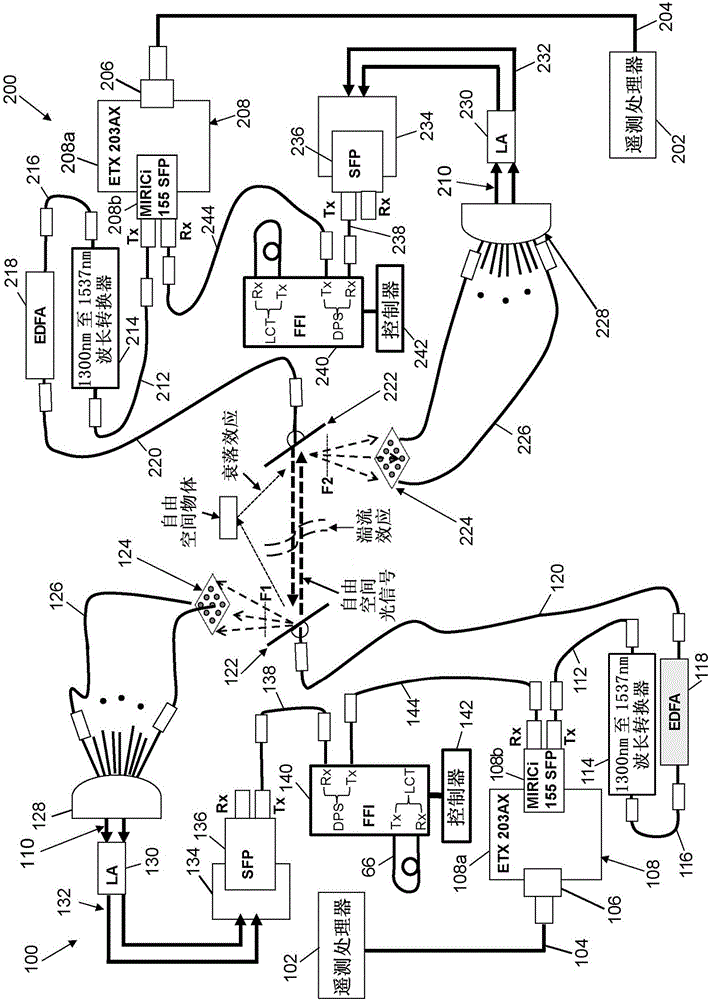
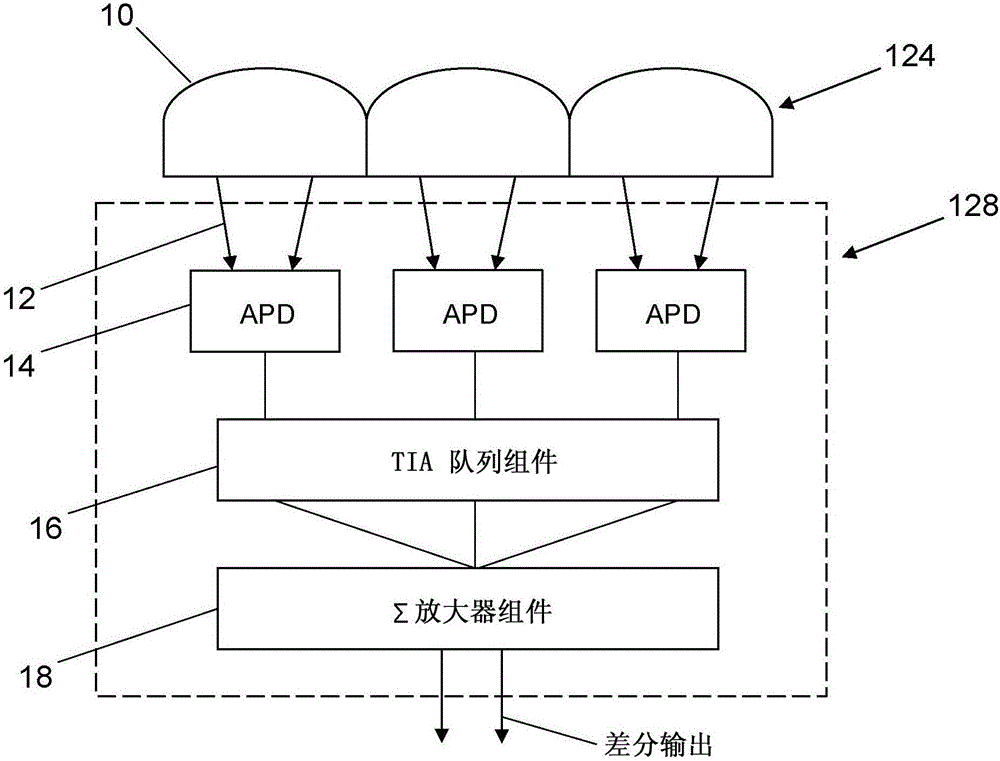
System for bidirectional free-space laser communication of gigabit Ethernet telemetry data
ActiveUS9438338B1Reduce the impactLow costTime-division multiplexLine-of-sight transmissionCorrection algorithmTelecommunications link
A free-space laser communication system for bidirectional transmission of telemetry data in Gigabit Ethernet (GBE) protocol using a dual atmospheric effect mitigation approach. This free-space bidirectional GBE laser communication system utilizes an Optical Combining Receiver Array and a Framer / Forward Error Correction / Interleaver (FFI) device to mitigate the combined effects of atmospheric turbulence and channel fading. Since the FFI device is designed for Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) protocol, an intelligent (or smart) media converter is used to convert GBE telemetry data to SONET frames, which enables the FFI device to perform an error correction algorithm and provide a seamless error-free GBE laser communication link for distance over a kilometer. This bidirectional laser communication system can be implemented with low-cost commercially available components.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
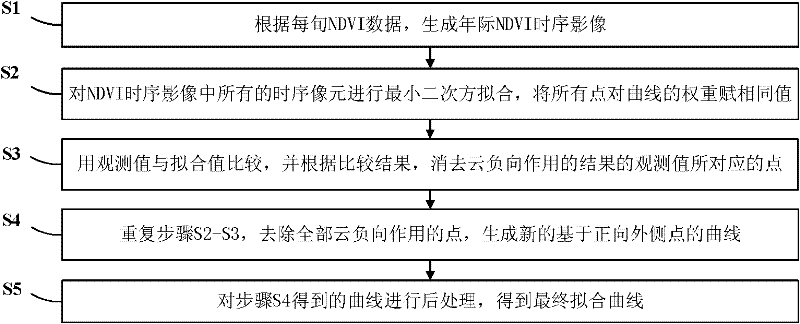
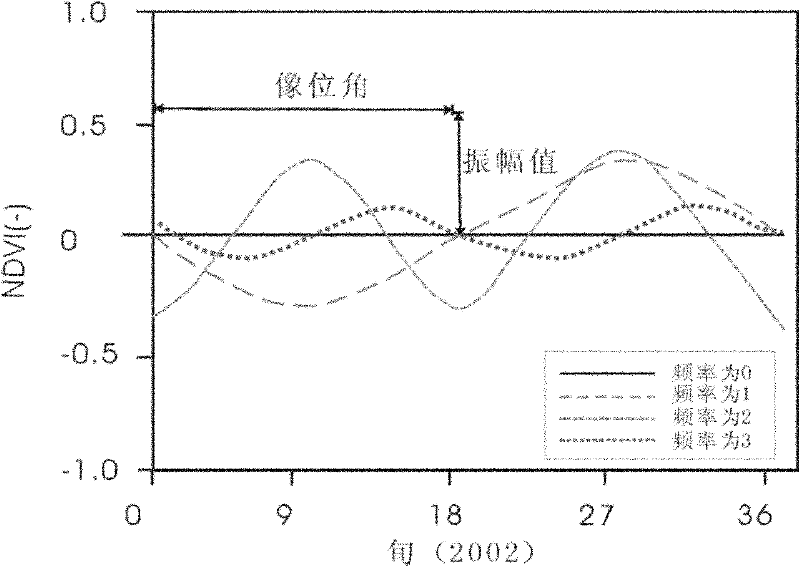
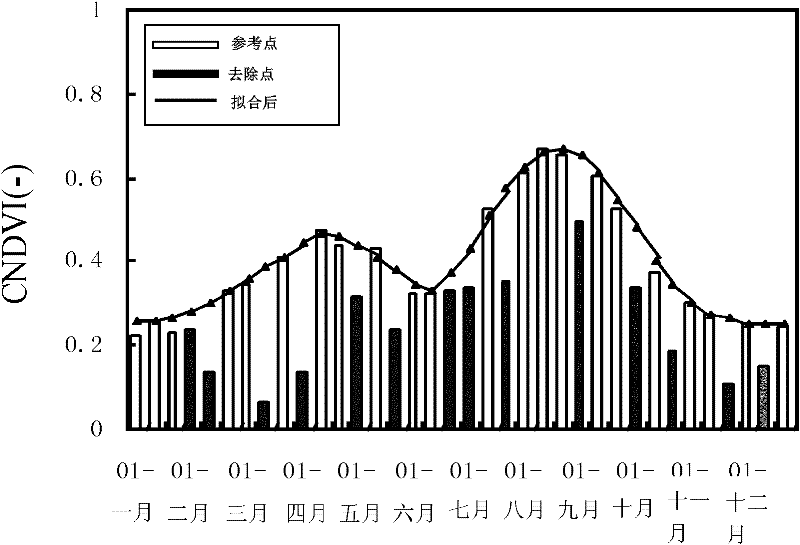
Method for removing cloud noise effects in normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time sequence image
InactiveCN102176242AEfficiently remove shadowsEffectively removes atmospheric effectsImage enhancementData acquisitionComputer vision
The invention discloses a method for removing cloud noise effects in a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time sequence image. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, generating an annual NDVI time sequence image according to NDVI data of every ten days; S2, carrying out least square fitting on all time sequence pixels in the NDVI time sequence image, and assigning same values to weights of all points relative to a curve; S3, comparing an observed value with a fitted value, and eliminating points under negative cloud action; S4, repeating the steps S2 and S3, eliminating all the points under the negative cloud action, and generating a new curve; and S5, post-processing the curve obtained in the S4 to obtain a finally fitted curve. In the method disclosed by the invention, by utilizing an NDVI time sequence file and a harmonic function analysis method based on the least square fitting, cloud shielding and atmospheric effects on a sensor in a data acquisition process are effectively removed, the time sequence image with cloud contamination removed can be generated, the obtained curve has the advantages of obvious trend, strong relative property among years and high precision, and the method has a wide applicable range.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
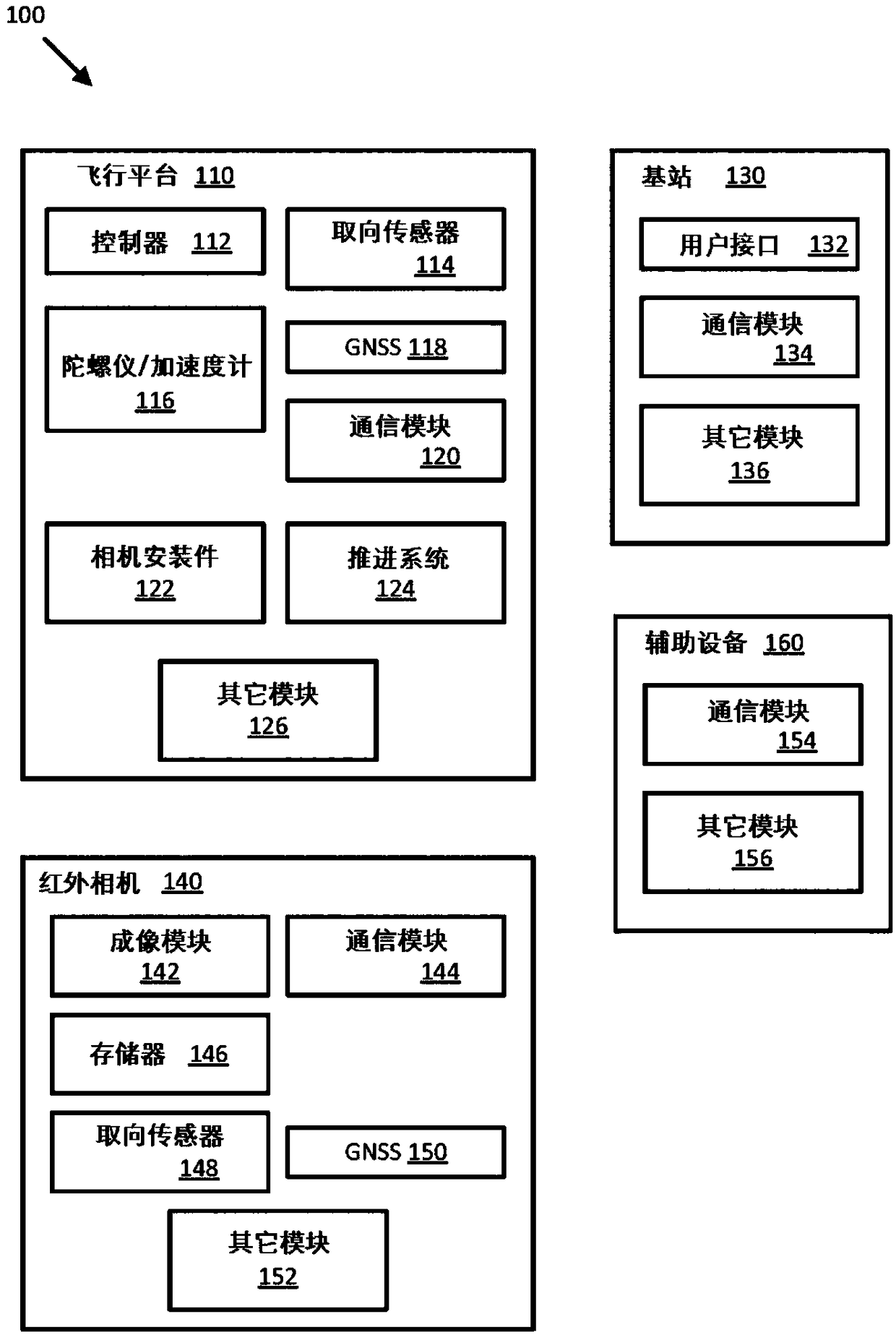
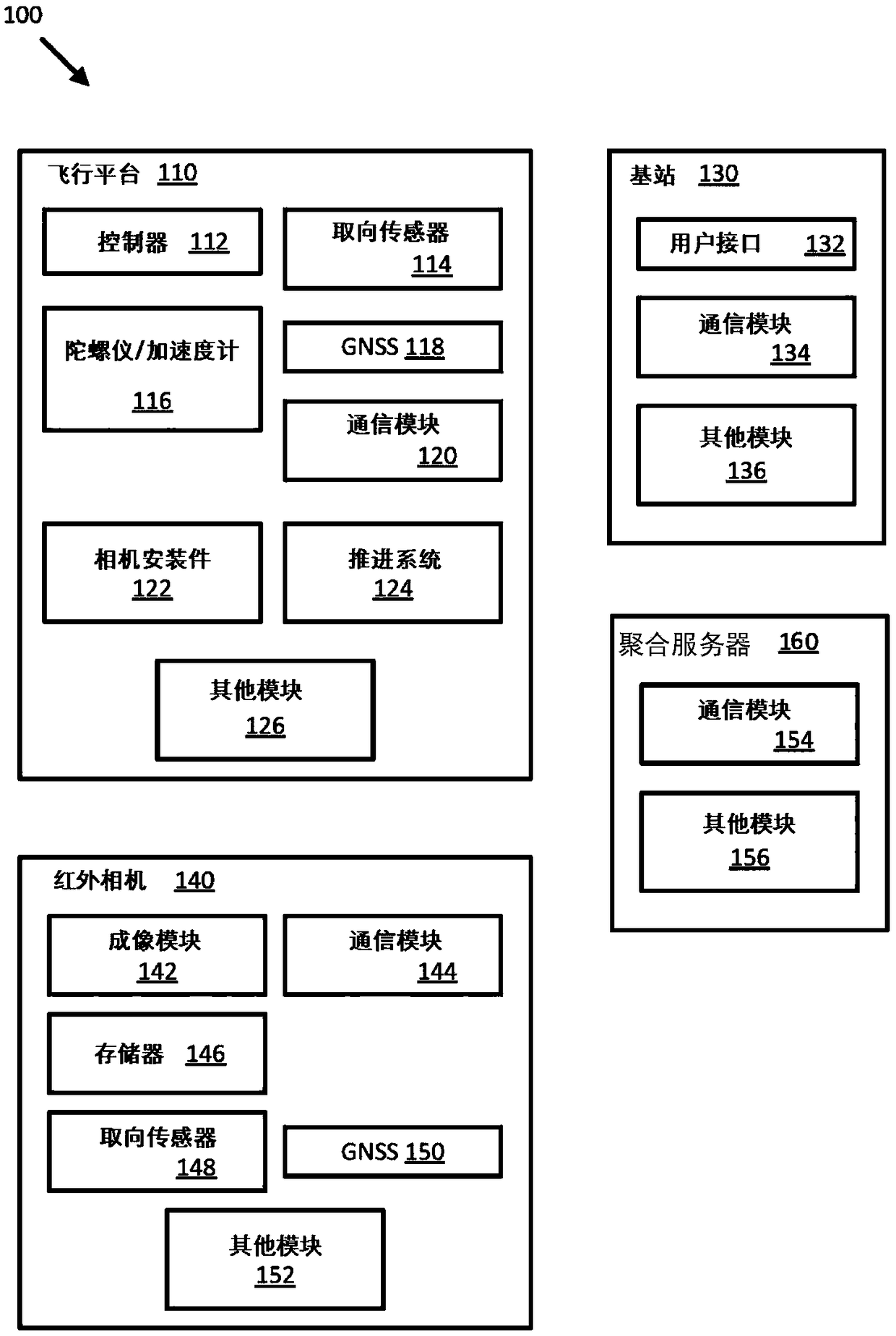
Unmanned aerial system based thermal imaging systems and methods
ActiveCN108603790ATelevision system detailsPhotovoltaic monitoringEnvironmental effectMonitoring system
Flight based infrared imaging systems and related techniques, and in particular UAS based thermal imaging systems, are provided to improve the monitoring capabilities of such systems over conventionalinfrared monitoring systems. An infrared imaging system is configured to compensate for various environmental effects (e.g., position and / or strength of the sun, atmospheric effects) to provide highresolution and accuracy radiometric measurements of targets imaged by the infrared imaging system. An infrared imaging system is alternatively configured to monitor and determine environmental conditions, modify data received from infrared imaging systems and other systems, modify flight paths and other commands, and / or create a representation of the environment.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
Method of compensating for atmospheric effects while using near horizon radar utilizing a Doppler signal
InactiveUS6853331B1Reduces refraction errorReduce errorsProjector film strip handlingCamera film strip handlingHorizonRadar
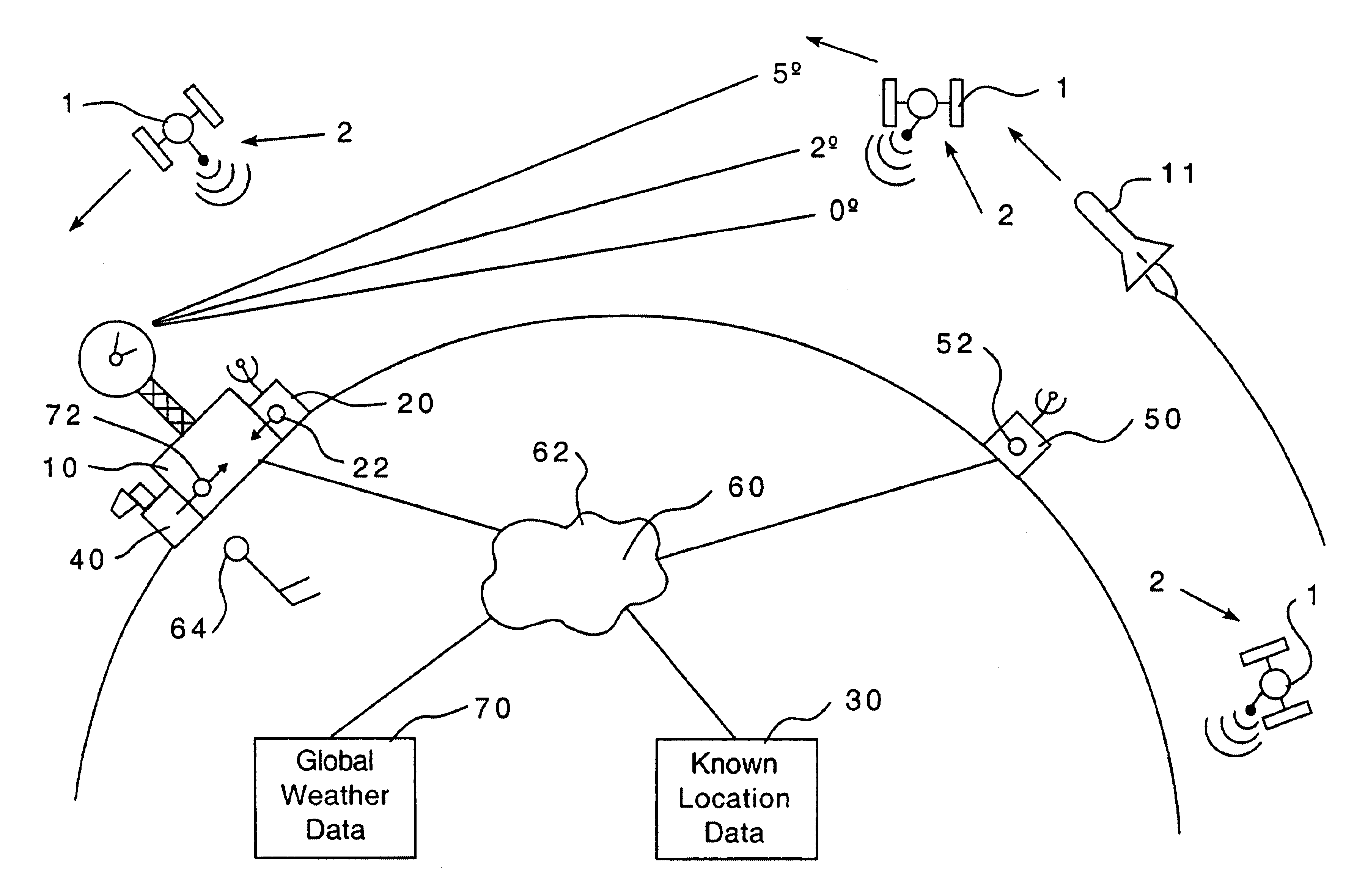
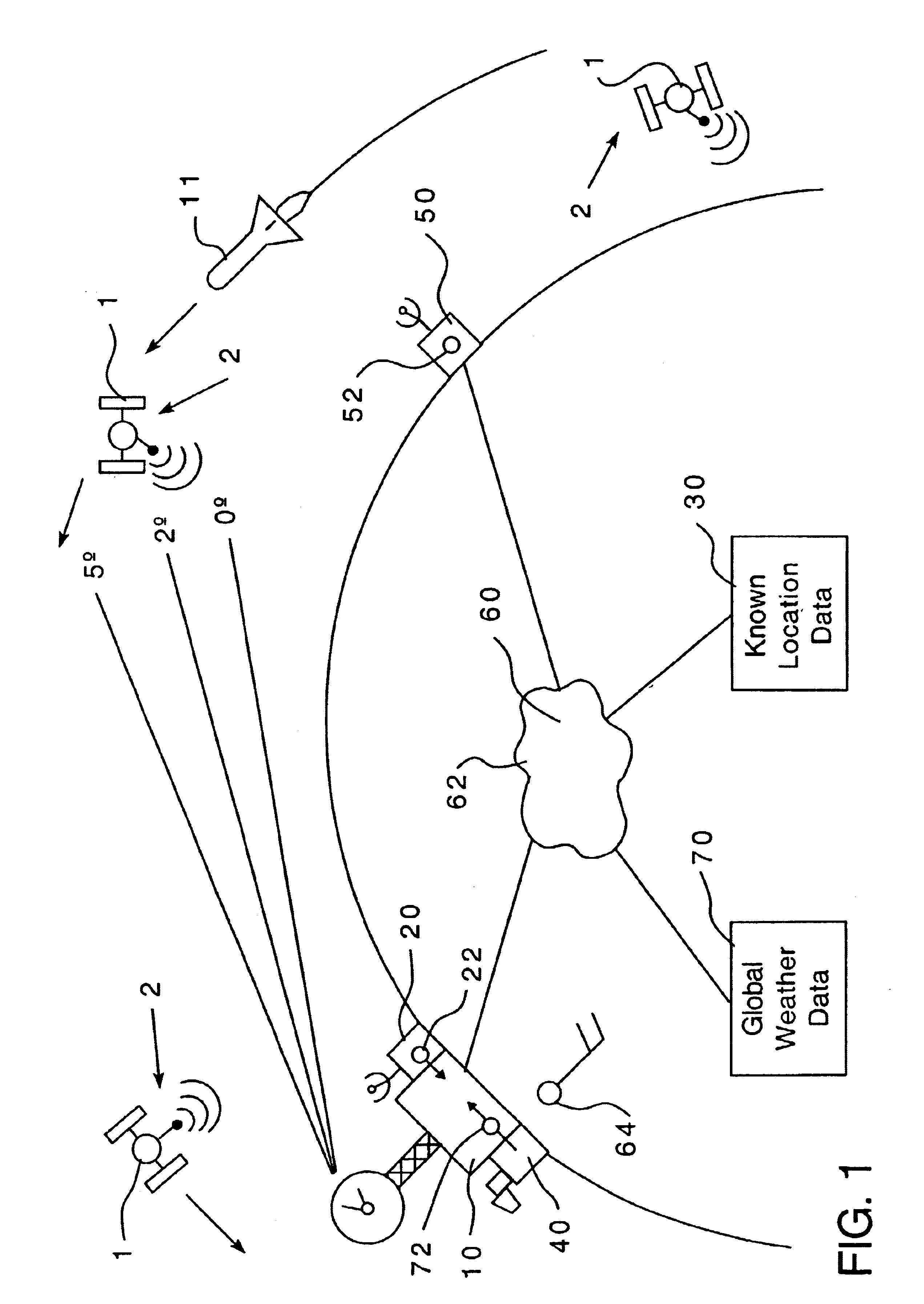
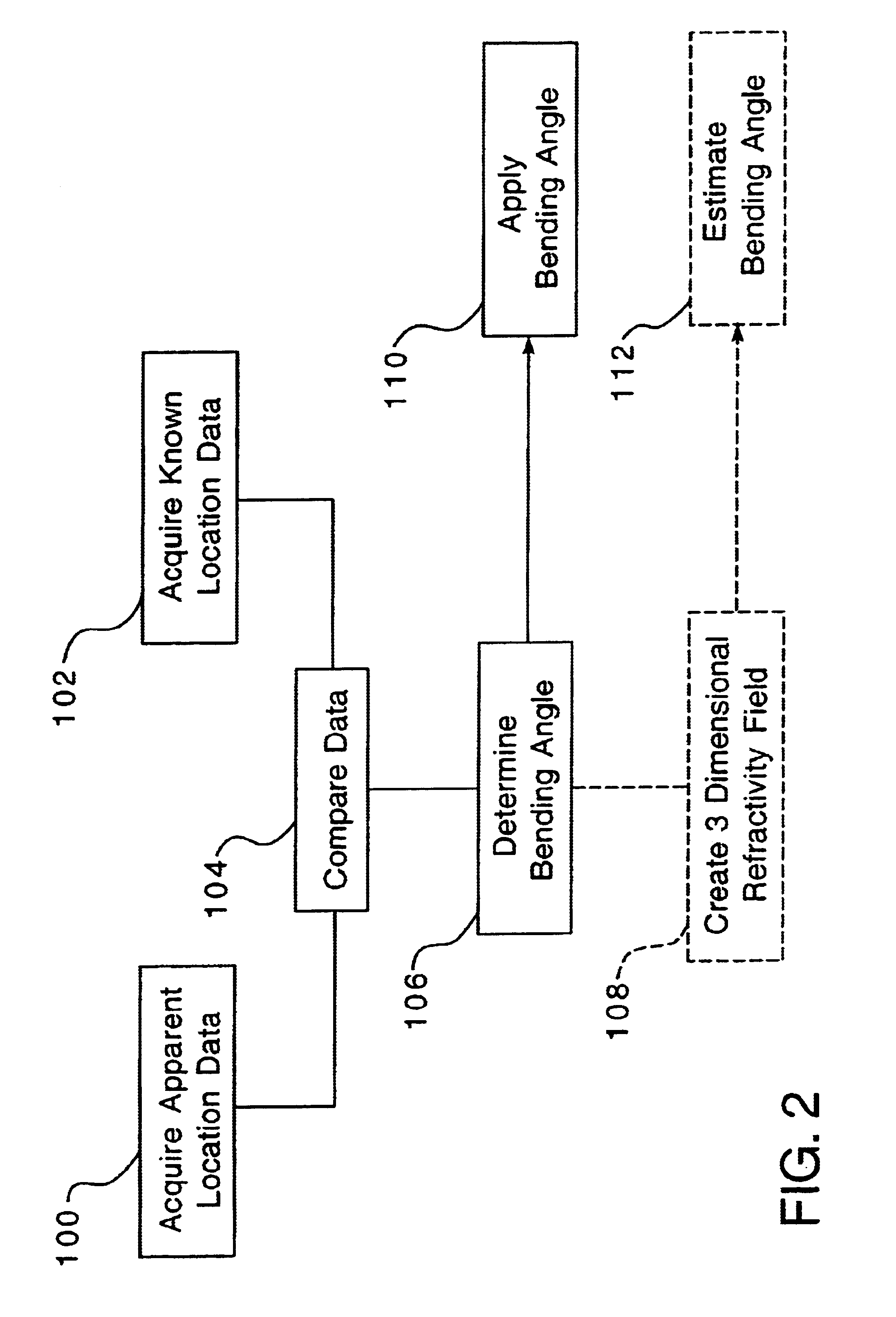
A method of compensating for atmospheric effects to detect the actual location of low elevation objects using near horizon radar to detect an object which utilizes a preexisting satellite structured to send a signal indicating the position and velocity of said satellite, wherein the location of the satellite is known. The method includes a step of providing a radar site, a first receiver structured to receive a signal from the satellite indicating an apparent location of the satellite, and a second receiver, located at a distance from the radar site, structured to receive the satellite signal and which indicates the observed location of the satellite. The first receiver is utilized to receive a signal from the satellite when the satellite is at a low elevation. This signal indicates the apparent location and velocity of the satellite. The bending angle can then be determined by comparing the apparent location data of the satellite as determined by the first receiver to the observed location data of the satellite. The satellite signal is used to determine the Doppler shift of the signal at the radar site as compared to the signal from the observed location. The Doppler shift data is used to determine the bending angle. Once the bending angle of the atmosphere is determined, the radar is used to detect the apparent location data of a low elevation object. The location of the low elevation object can then be determined by applying the bending angle to the apparent location data of the object.
Owner:GEORIGA TECH RES CORP +1
Pressure independent delivery method for portable infusion pump
InactiveUS20130338635A1Avoid problemsMedical devicesPressure infusionIntensive care medicineAtmospheric effect
Described is method for maintaining proper drug delivery rate by monitoring atmospheric effects on a drug infusion device. The device may include one or more vents that permit the passage of gas between the exterior and interior of the device's housing. The device may also include one or more pressure and / or temperature sensors, the readings from which may be used to determine malfunctions in the venting of the device and / or changes in pressure that could cause the unintended over-delivery or under-delivery of medication.
Owner:ANIMAS CORP
Computer graphics method for creating differing fog effects in lighted and shadowed areas
ActiveUS20110018890A1Accurately introduce depthCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnimationComputer animationGraphics
A method for providing fog or fading due to atmospheric effects during computer animation of an image. The method includes determining a lighting value for a scene's or an image's pixels based on the positions of the pixels relative to a light source. The method includes, for each of the pixels, setting a fade in start distance for each pixel measured from a camera location so as to define when fog is added, e.g., when to fade a pixel's color by blending this color with a fog color. The fade in start distances are set based on each pixel's lighting value, whereby pixels with smaller lighting values or shadowed pixels begin to fade first while highlighted pixels fade with greater distances. The method includes adding fog to the image starting at the fade in start distances for each of the pixels and then rendering the image.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Spatial surface prior information reflectance estimation (SPIRE) algorithms
InactiveUS7260242B2Scattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGround truthFrequency spectrum
A new class of algorithms has been developed to estimate spectral reflectance in remote sensing imagery. These algorithms are called Surface Prior Information Reflectance Estimation (SPIRE) algorithms and estimate surface spectral reflectance using prior spatial and spectral information about the surface reflectance. This paper describes SPIRE algorithms that employ spatial processing of single channel data to estimate local changes in spectral reflectance under spatially and spectrally varying multiplicative and additive noise caused by variations in illumination and atmospheric effects. Rather than modeling the physics of the atmosphere and illumination (using a physics-based code such as ATREM), or using ground truth spectra at known locations to compensate for these effects (using the Empirical Line Method), prior information about the low spatial frequency content of the scene in each spectral channel is used instead. HYDICE VNIR-SWIR hyperspectral data were used to compare the performance of SPIRE, ATREM, and ELM atmospheric compensation algorithms. The Spatial SPIRE algorithm performance was found to be nearly identical to the ELM ground-truth based results, while Spatial SPIRE performed better than ATREM overall, and significantly better under high clouds and haze.
Owner:AIR FORCE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
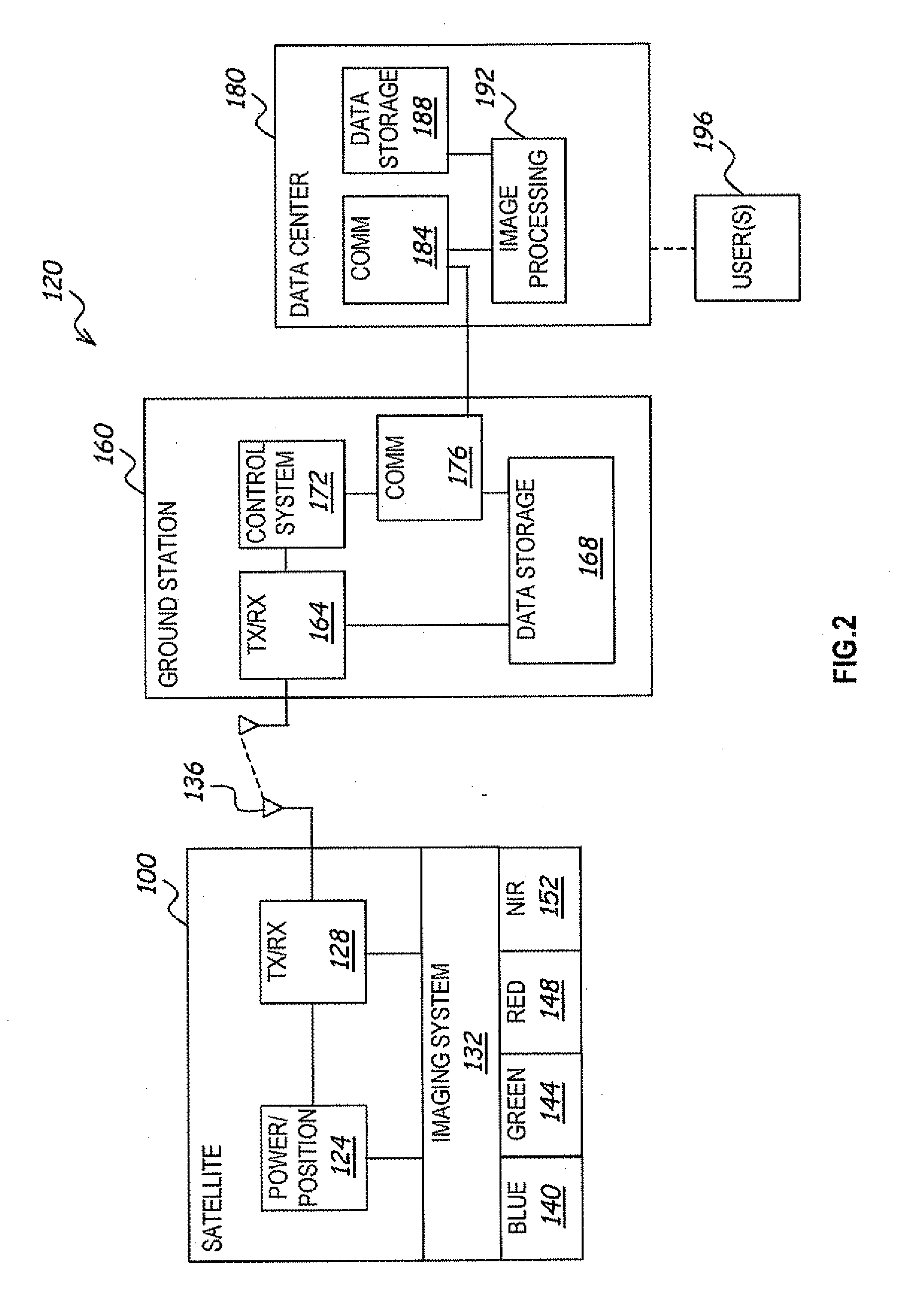
Method and apparatus for enhancing a digital image
ActiveUS20090219407A1Easy visual interpretationEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementSpectral bandsDigital number
A system and method processes original digital numbers (DNs) provided by a satellite imaging system to produce a set of spectral balanced and contrast enhanced multispectral images. Spectral balancing is achieved based on physical characteristics of sensors of the imaging system as well as compensation for atmospheric effects. The DNs in the multispectral bands may be processed using a relatively small amount of processing resources otherwise required to produce such images. Such images may be processed completely automatically and provide relatively easy visual interpretation. Each image pixel may be, for example, in an 8-bit or 16-bit format, and the image may be displayed and / or printed without applying any additional color correction and / or contrast stretches.
Owner:MAXAR INTELLIGENCE INC
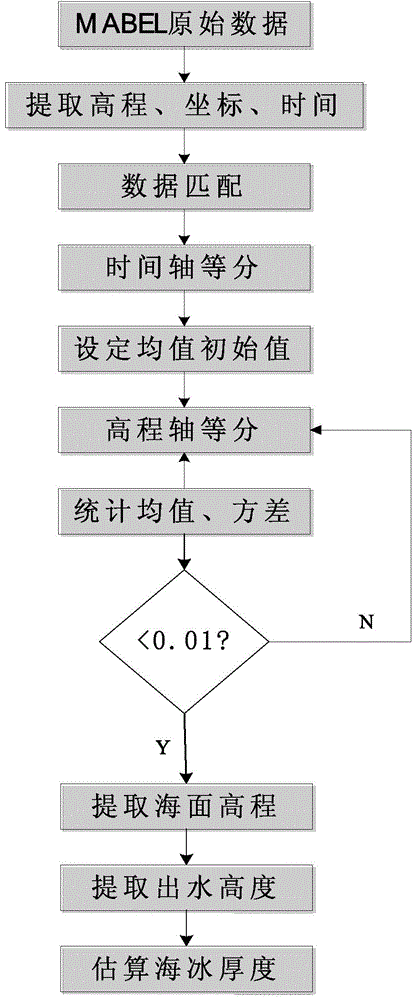
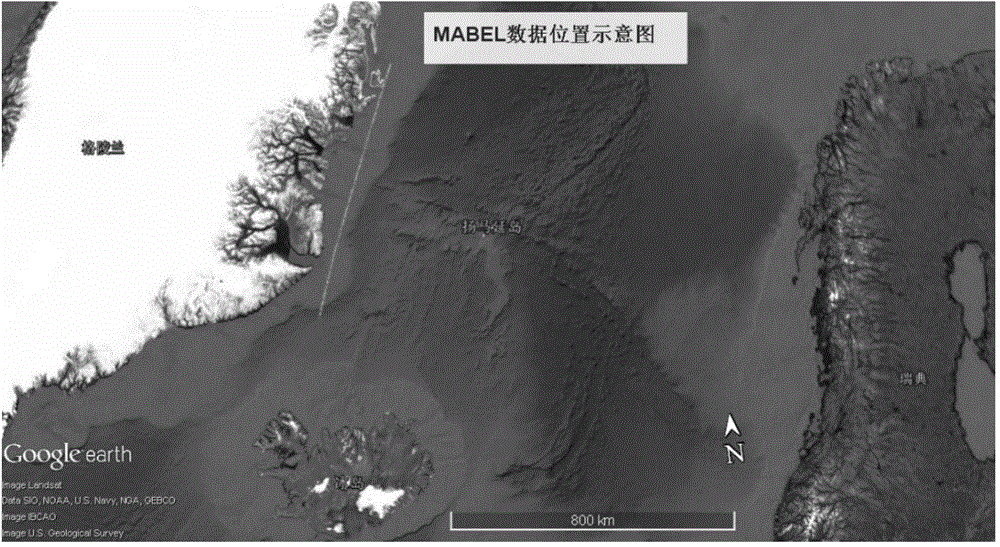
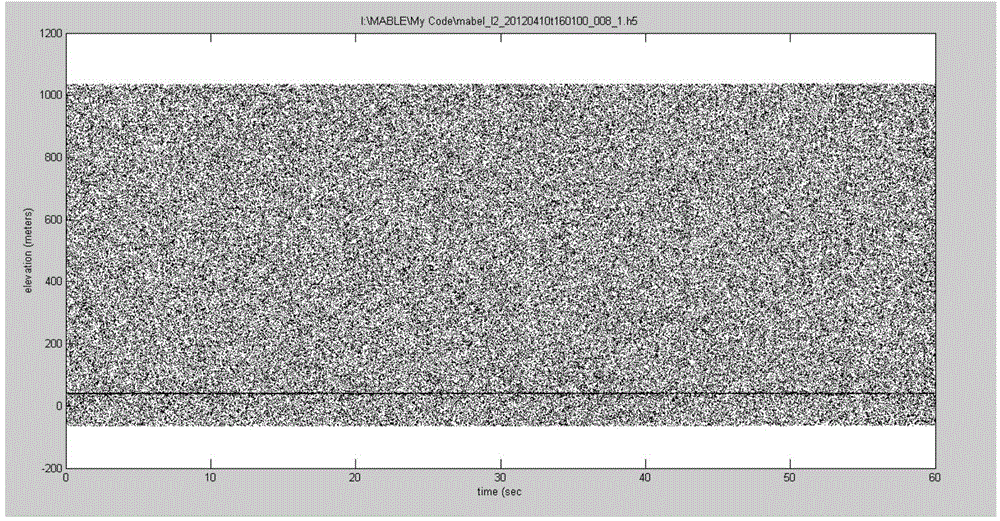
Sea ice thickness estimation method based on experimental data of multi-beam altimeter (MABEL)
The invention relates to a sea ice thickness estimation method based on experimental data of a multi-beam altimeter (MABEL). The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing MABEL data, extracting altitude and coordinate information for matching, and removing an atmospheric effect; then performing time shaft equal division and altitude division, constructing a two-dimensional grid, and extracting an interval with the largest number of photons; performing treatment of calculating mean variance and the like to further eliminate invalid photons to acquire a sea surface contour line; and finally, estimating the sea ice thickness by combining a hydrostatics equilibrium formula according to the sea ice height out of water. Compared with the traditional method, the MABEL data is introduced into the method provided by the invention to estimate the sea ice thickness, so that the precision is higher.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
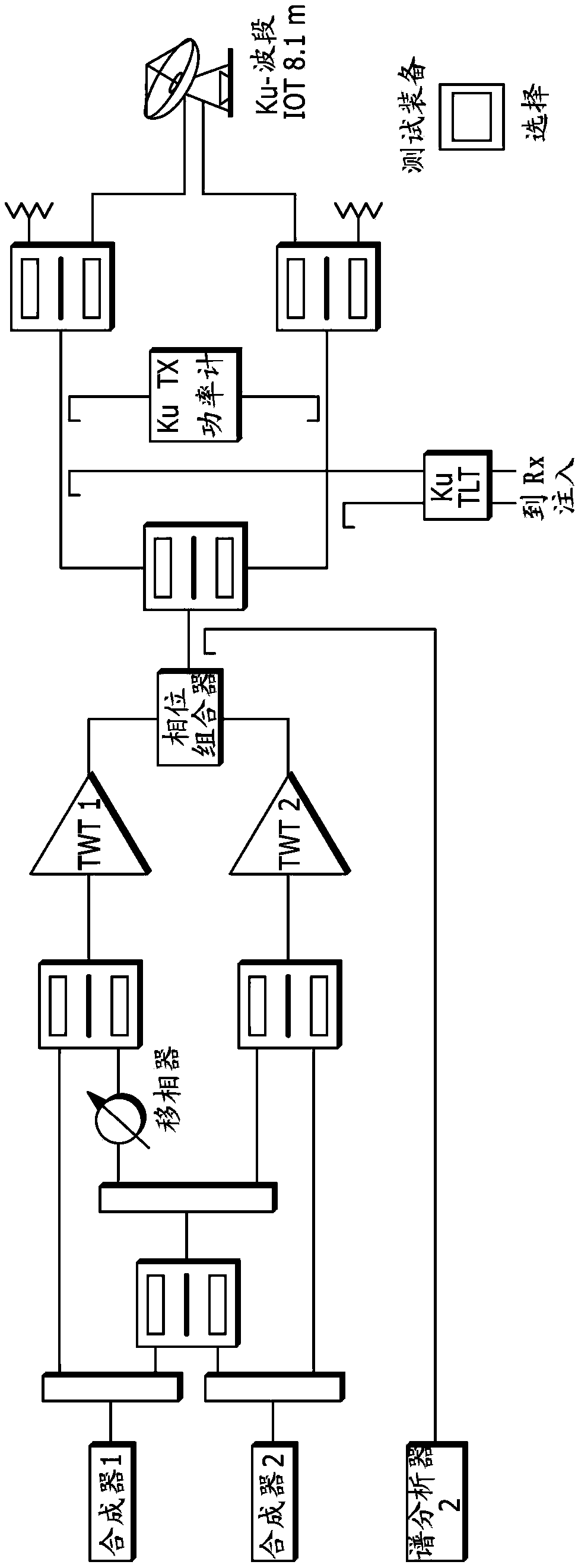
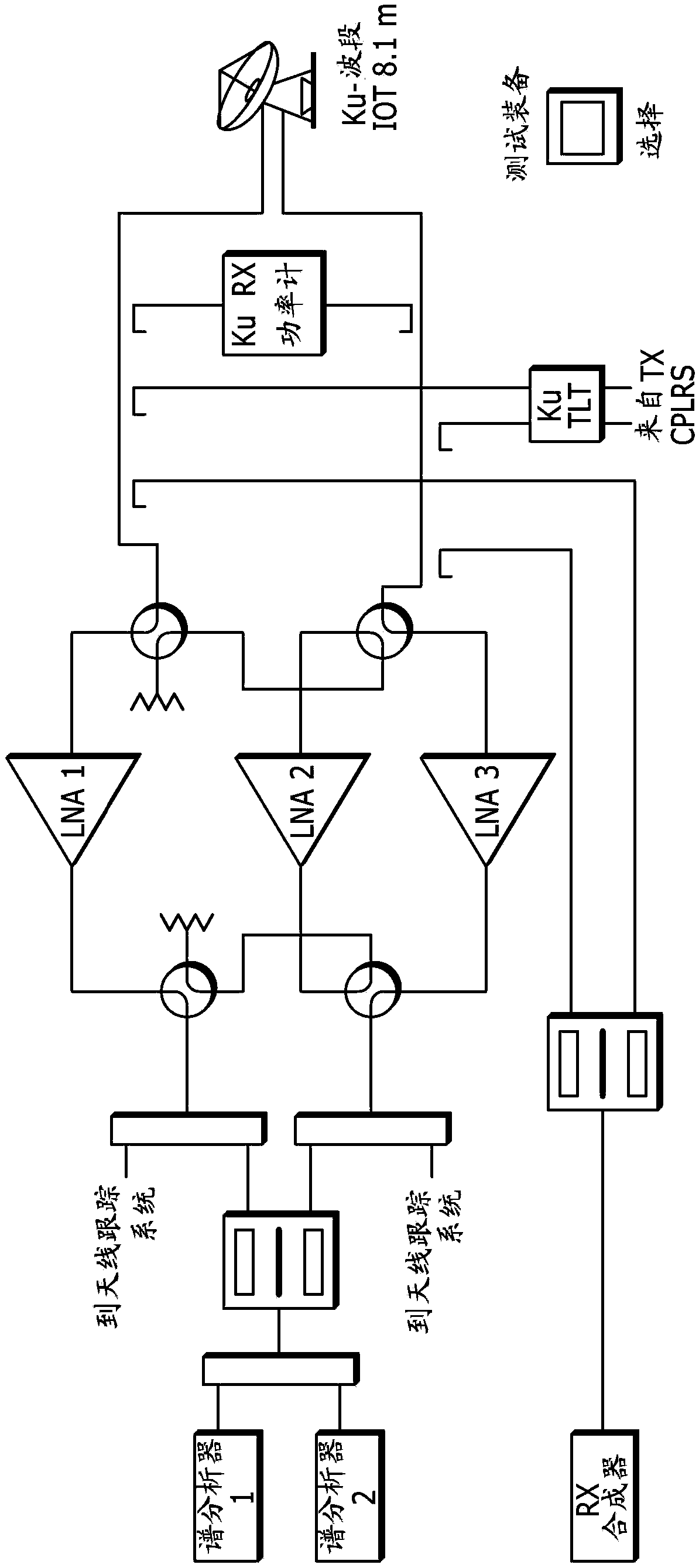
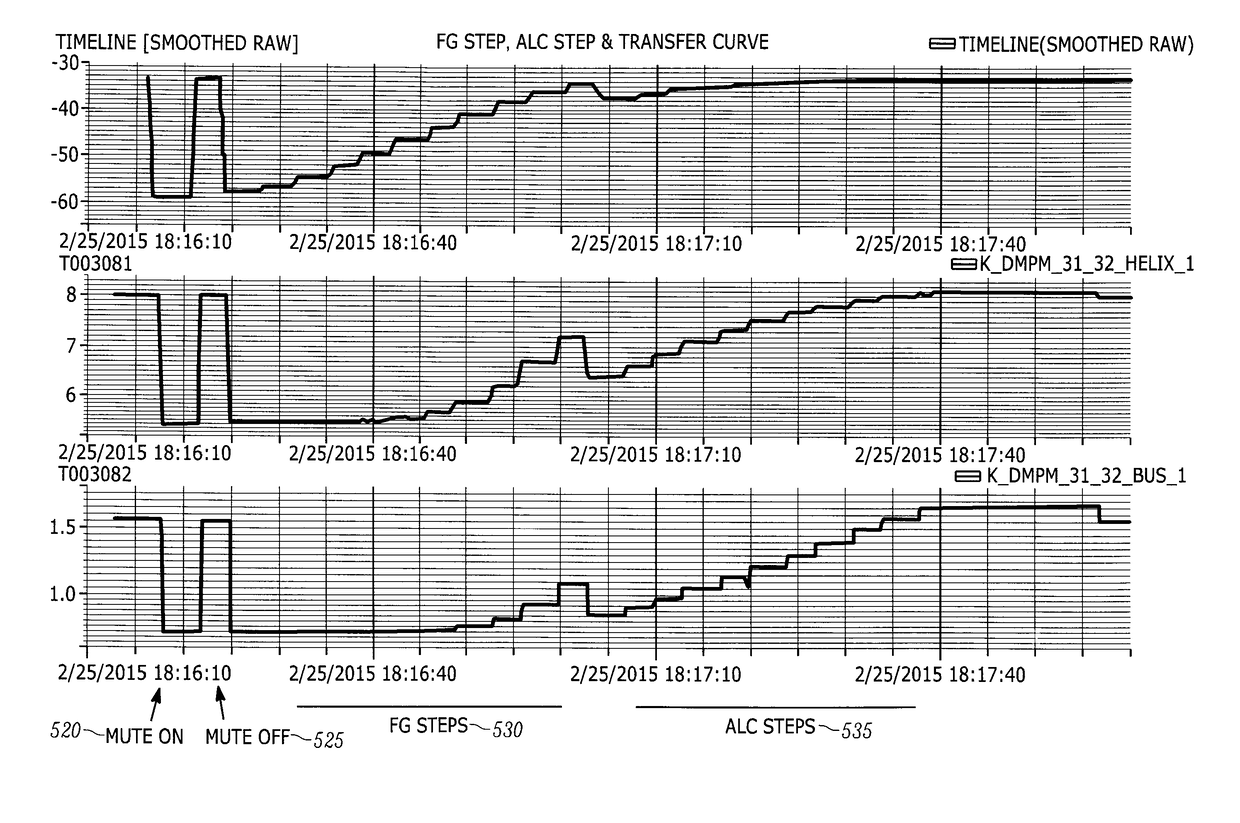
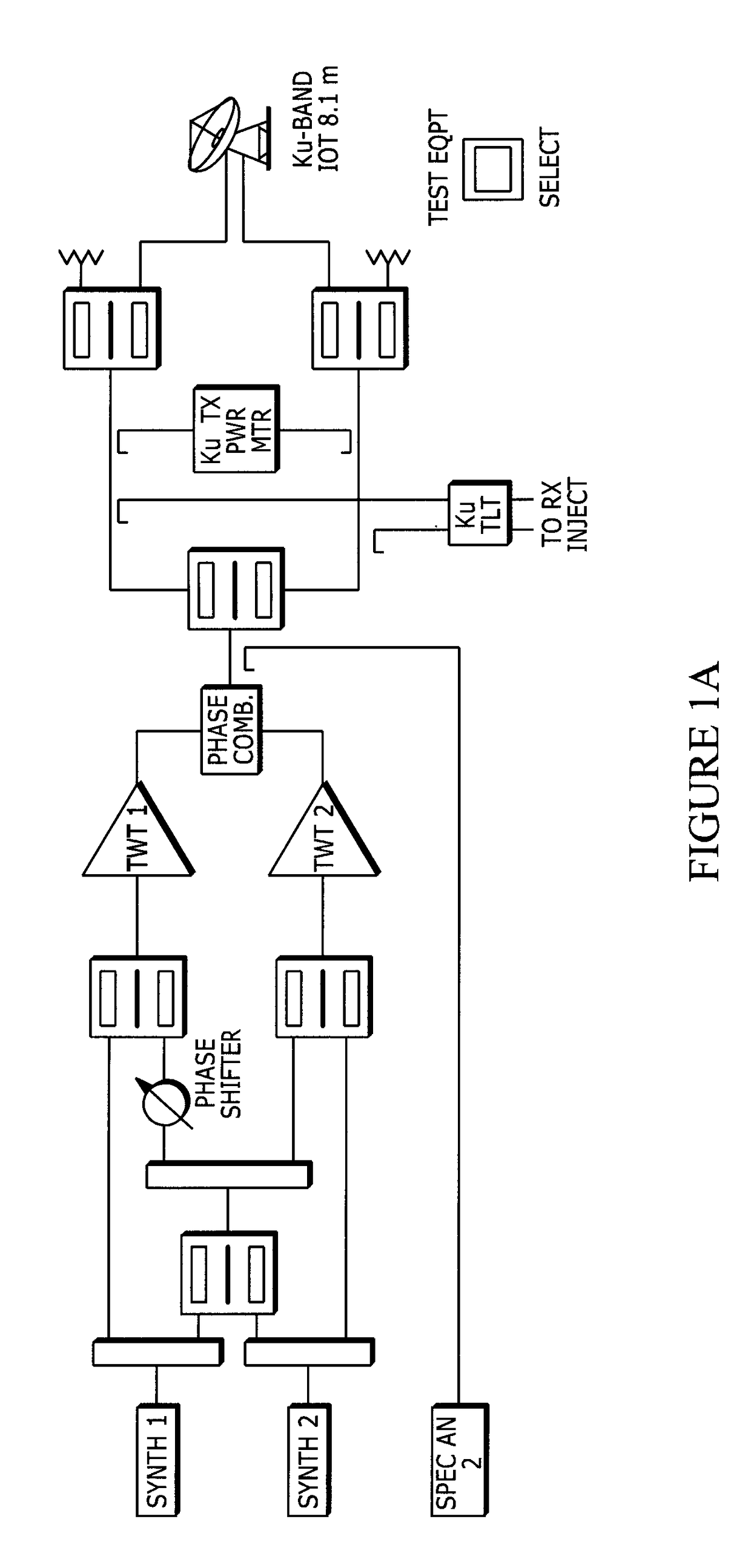
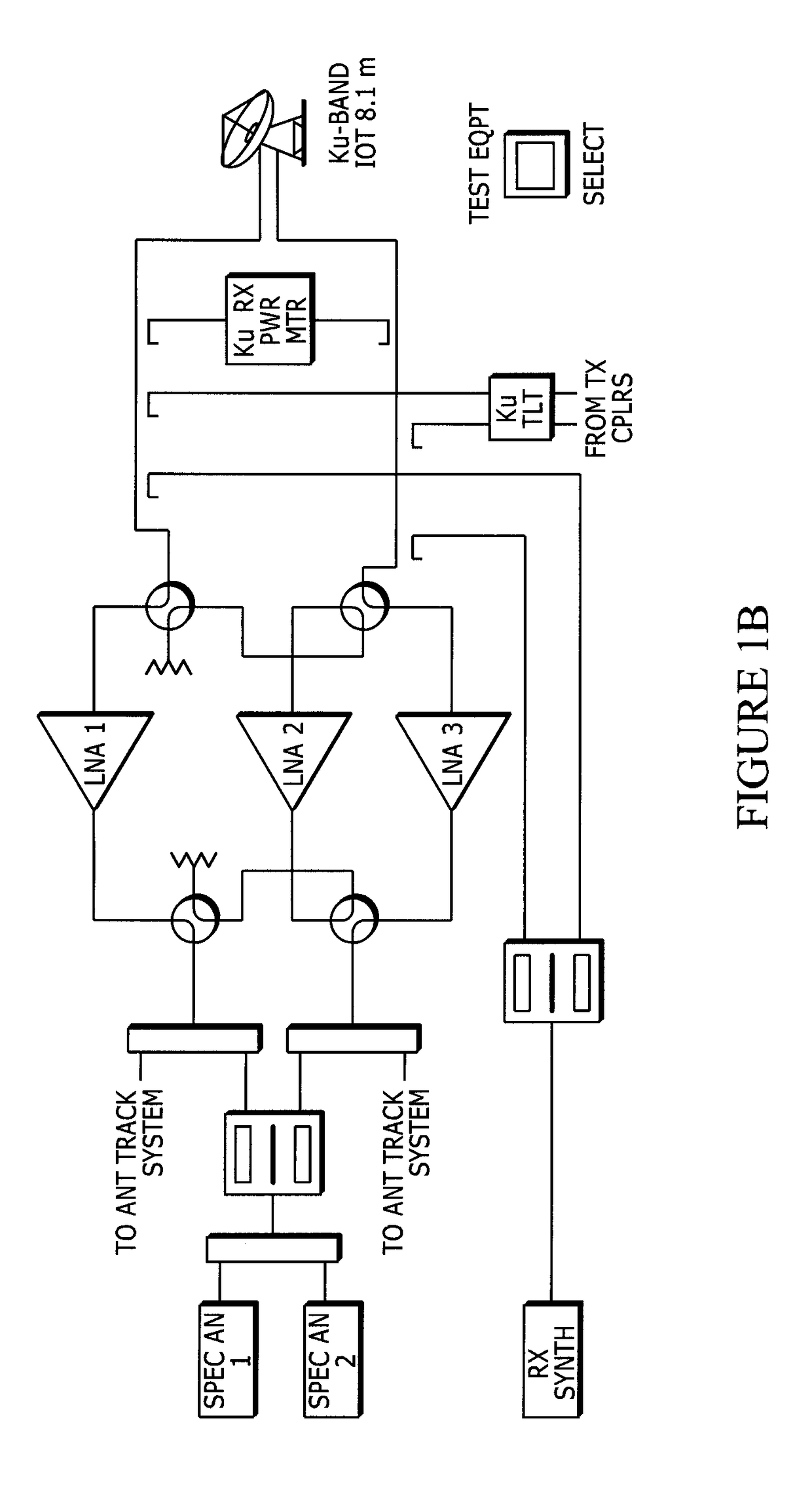
Satellite communications subsystem in-orbit verification system and methodologies
ActiveCN108886415ARemove weather effectsEliminate lossesTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringSpectrum analyzerSatellite system
The present invention relates to satellite systems and more particularly, to the provision of novel systems and methods for verifying the in-orbit performance and operation of satellite communicationssubsystems. In contrast to traditional Payload IOT (in-orbit test), the invention operates without an uplink signal, by generating hardware-specific signatures using isolated, internally generated, thermal noise. It has been found that this noise provides a very stable, repeatable signal for testing. Prior to launch, a repeater command sequence is executed to generate a hardware-specific signature based on the internally-generated noise. The same repealer command sequence is then executed in-orbit to determine whether the hardware-specific signature has changed. The two signatures may be recorded and compared using a simple tool such as a spectrum analyzer. The methods also include novel use of the sun as a test signal source to calibrate equipment, to quantify atmospheric effects and tobe used as an intermediate reference power level during measurements.
Owner:TELSAT CANADA
Free space continuous variable quantum key distribution method and system
ActiveCN110113163AImprove distribution performanceImprove performanceKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationCouplingLocal oscillator
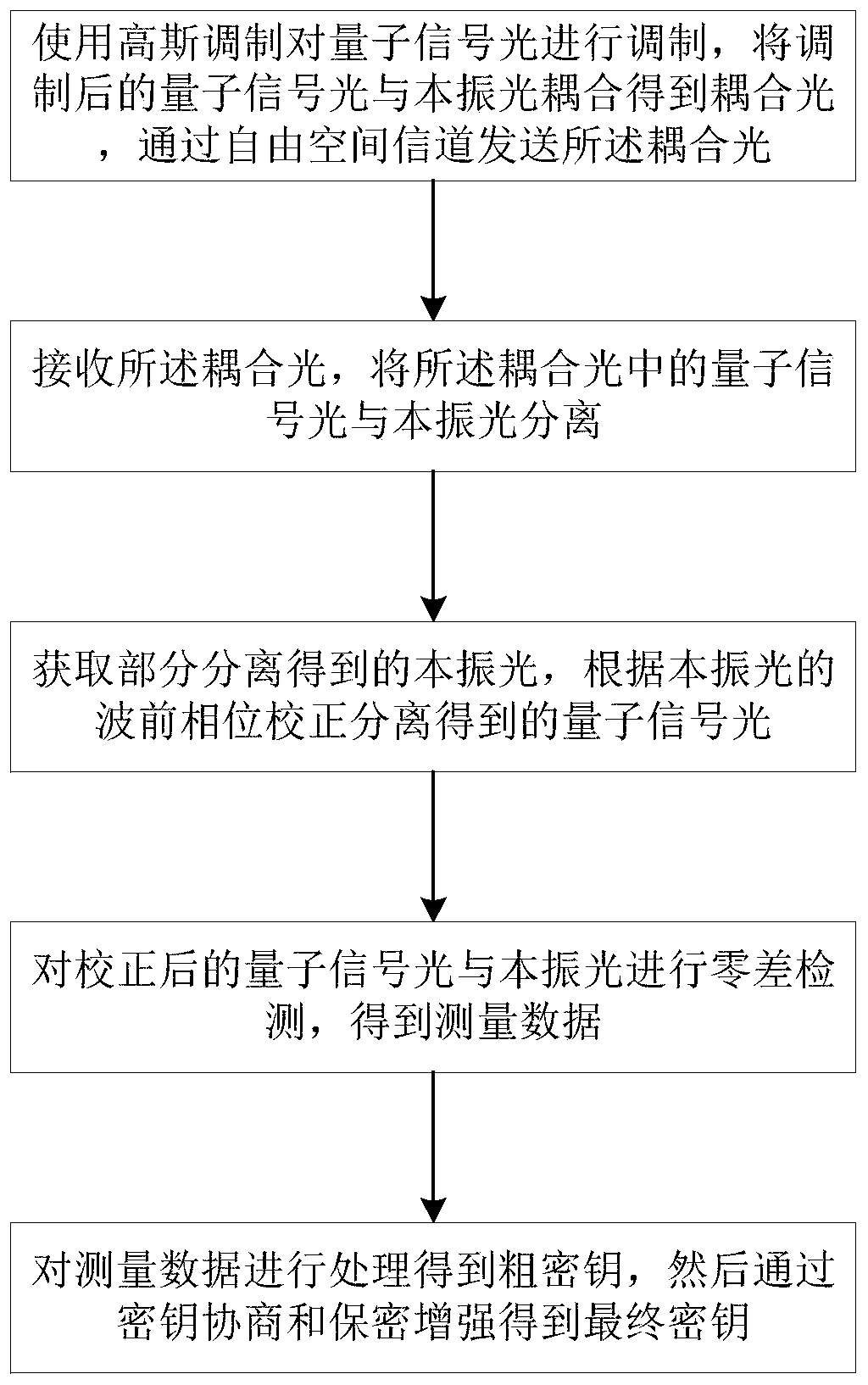
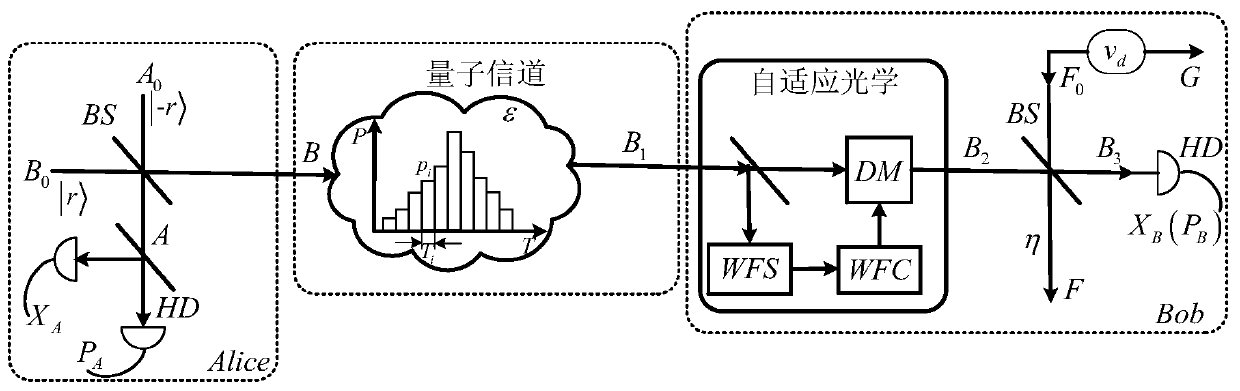
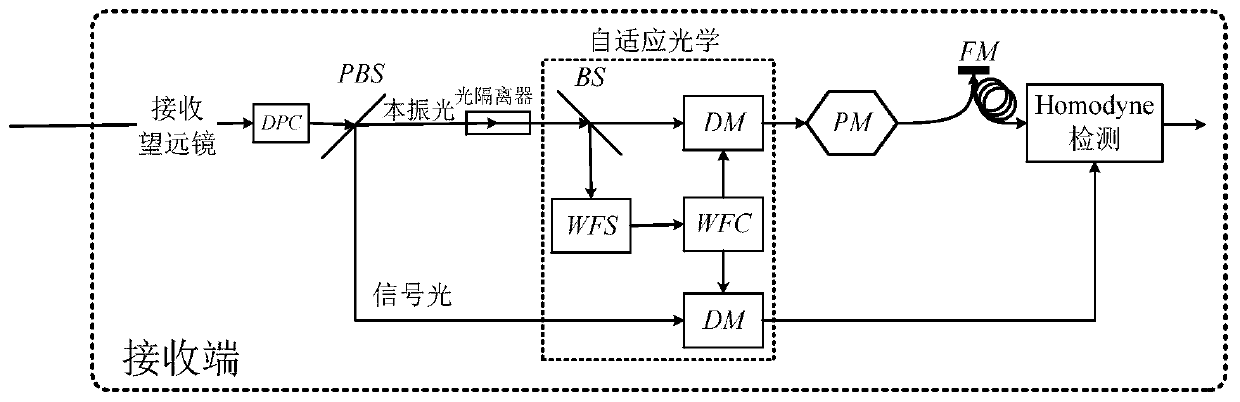
The invention provides a free space continuous variable quantum key distribution method and system, and the method comprises the steps of modulating the quantum signal light through Gaussian modulation, coupling the modulated quantum signal light with the local oscillator light to obtain the coupling light, and sending the coupling light through a free space channel; receiving the coupling light,and separating the quantum signal light in the coupling light from the local oscillation light; and obtaining part of the separated local oscillation light, and correcting the separated quantum signallight according to the wavefront phase of the local oscillation light. According to the present invention, the influence of the atmospheric effects can be weakened, and the continuous variable quantum key distribution performance is improved.
Owner:上海循态量子科技有限公司
Satellite communications subsystem in-orbit verification system and methodologies
ActiveUS20180309506A1Extend signal rangeImprove dynamic rangeTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringSpectrum analyzerEngineering
The present invention relates to satellite systems and more particularly, to the provision of novel systems and methods for verifying the in-orbit performance and operation of satellite communications subsystems. In contrast to traditional Payload IOT (in-orbit test), the invention operates without an uplink signal, by generating hardware-specific signatures using isolated, internally generated, thermal noise. It has been found that this noise provides a very stable, repeatable signal for testing. Prior to launch, a repeater command sequence is executed to generate a hardware-specific signature based on the internally-generated noise. The same repealer command sequence is then executed in-orbit to determine whether the hardware-specific signature has changed. The two signatures may be recorded and compared using a simple tool such as a spectrum analyzer. The methods also include novel use of the sun as a test signal source to calibrate equipment, to quantify atmospheric effects and to be used as an intermediate reference power level during measurements.
Owner:TELESAT CANADA
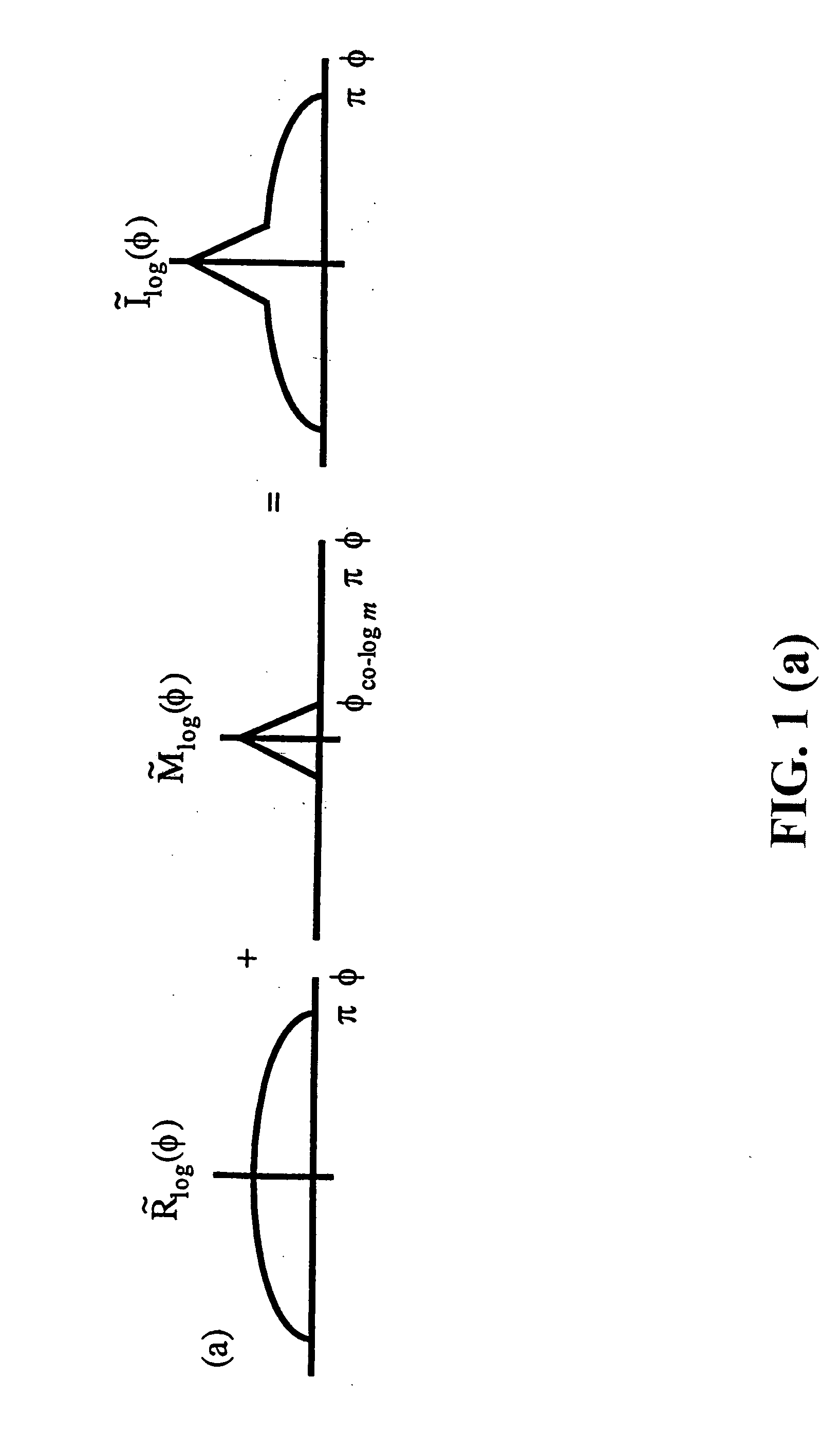
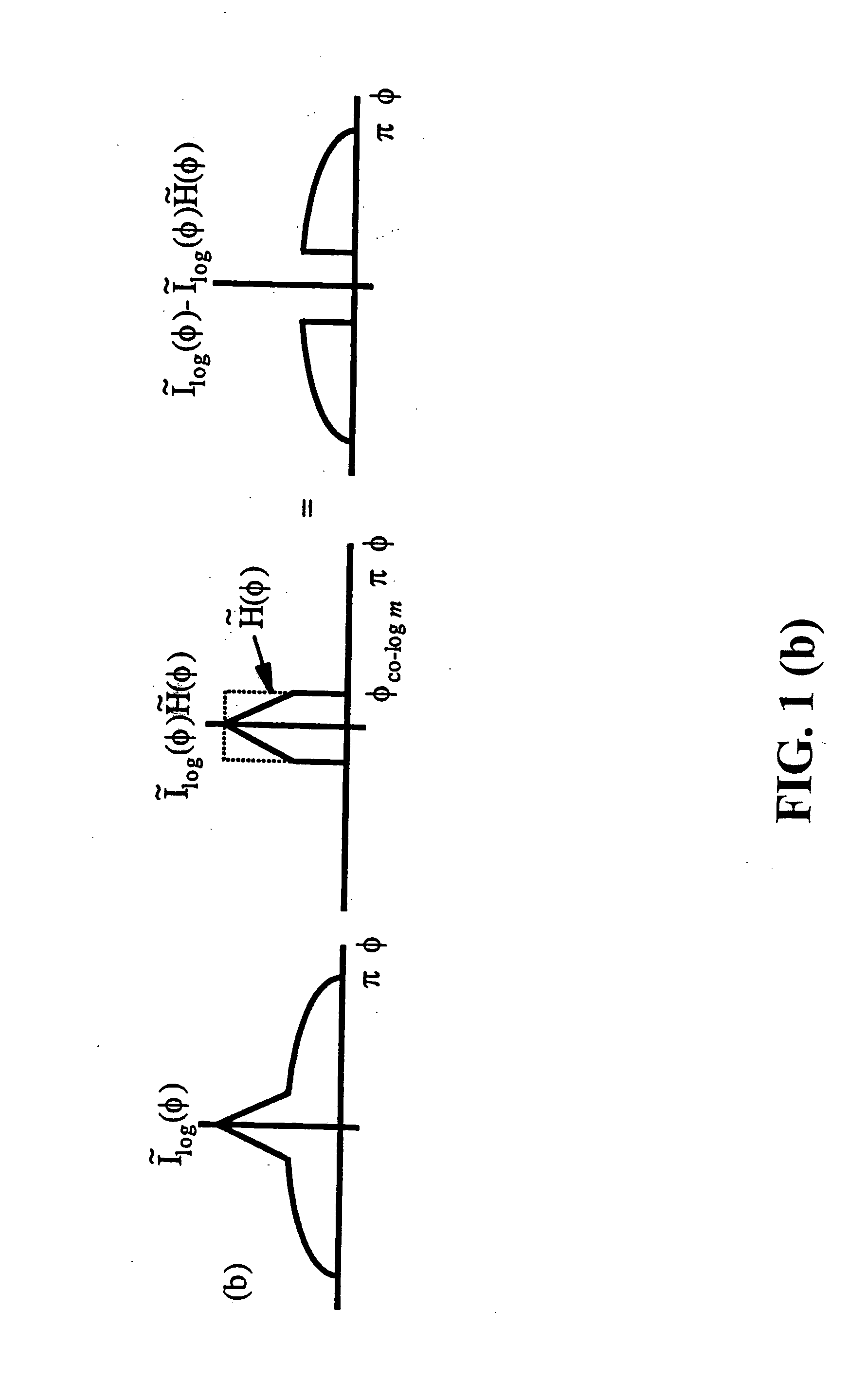
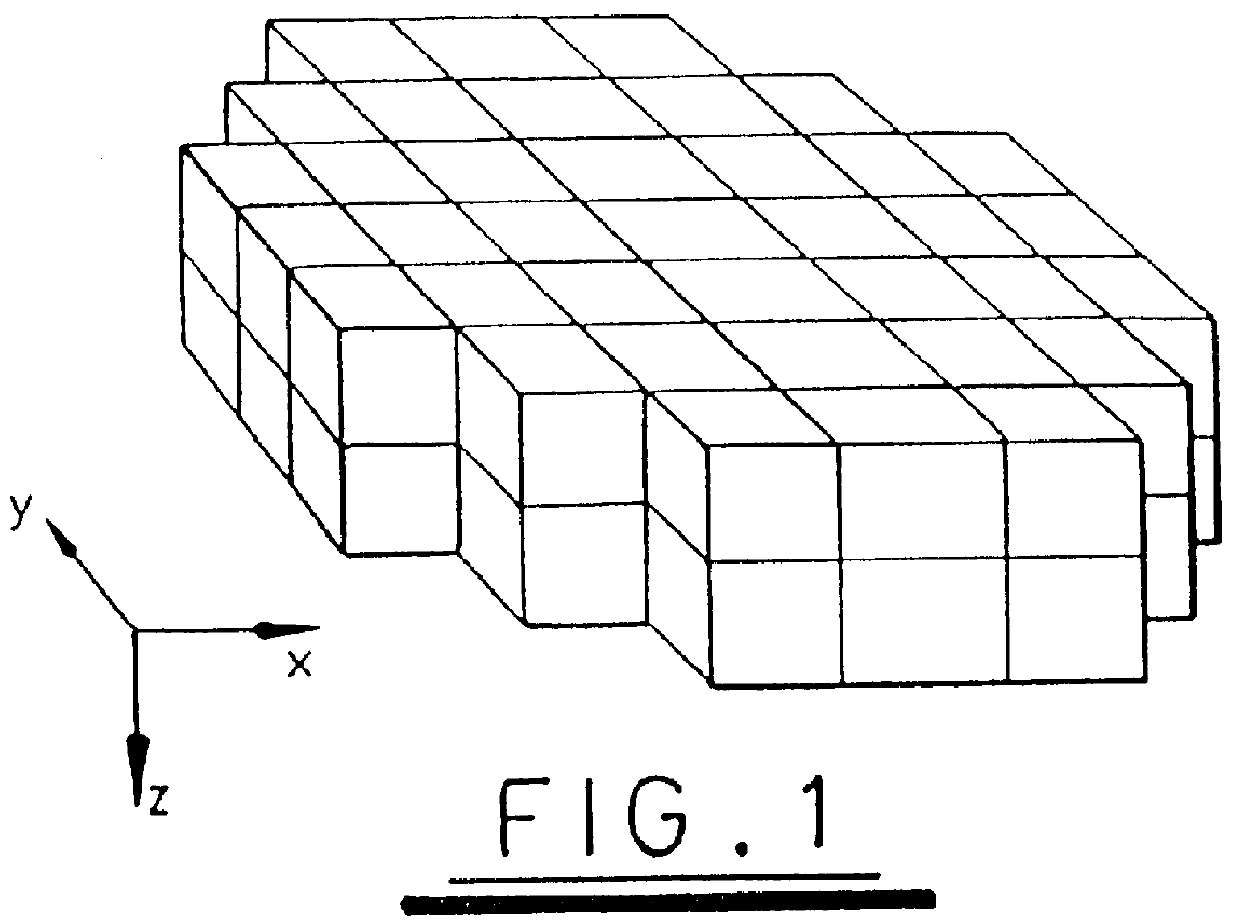
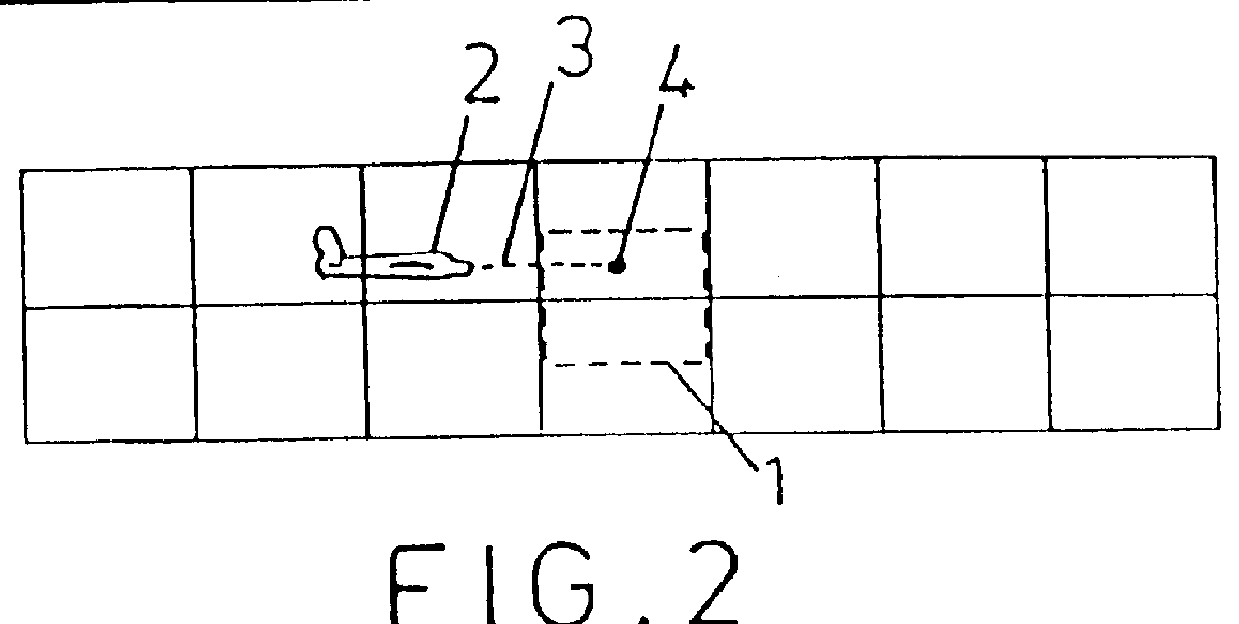
Atmospheric effects simulation
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 01484 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 13, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 13, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 03417 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 30, 1997The motion of particles such as snow is simulated in a computer generated image which represents the appearance from a predetermined viewing point of a three-dimensional worldspace through which the particles move. A three-dimensional model is defined which is made up from a regular array of abutting cubes of predetermined dimension. An object is defined which dimensions correspond to the dimensions of each cube, the object having characteristics such that it represents the motion of particles through the volume which it occupies. The three-dimensional model made up of the array of cubes is notionally positioned in worldspace such that the viewing point is located within a region of the model selected such that the field of view of particles from the viewing point is always within the model. As the viewing point travels through worldspace, it is translated in steps with the magnitude of each step corresponding to the length of any one side of the cubes. The model is moved in worldspace so as to maintain the viewing point within the selected region of the model. The image which is generated includes the model in which the object representing the moving particles occupies each of the cubes. The visibility of the cubes is faded out with distance from the viewing point so as to conceal the boundaries of the model. The model is positioned relative to the viewing point such that a notional point on a line drawn through the viewing point in a predetermined direction relative to the viewing point motion is always within a predetermined central region of the model. The distance between the notional point and the viewing point is a function of the speed of movement of the viewing point.
Owner:REDIFON SIMULATION LTD
Device and method of correcting wavefront distortion in optical retro-modulation
ActiveCN107592157AImprove transmission efficiencyImprove practicalityFree-space transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersWavefrontLiquid medium
The invention discloses a device of correcting wavefront distortion in optical retro-modulation. The device of correcting wavefront distortion in optical retro-modulation includes an active terminal and a passive terminal which are connected through an optical path. The invention also discloses a method of utilizing the above device to correct wavefront distortion in optical retro-modulation. Themethod of utilizing the above device to correct wavefront distortion in optical retro-modulation includes the steps: a convex lens at the passive terminal receives a wavefront distortion light beam, and focuses the light beam to a stimulated Brillouin scattering pool, and then a retro conjugate beam of the distortion light beam is generated after the light beam and the liquid medium in the stimulated Brillouin scattering pool interact with each other, and then a modulation signal is loaded to the light intensity of the retro conjugate beam, and during the process that the retro conjugate beamreturns along the original optical path, the phase conjugate distortion can offset with wavefront distortion to enable the wavefront phase to be restored to the initial state so as to realize compensation of wavefront distortion in optical retro-modulation. The device and method of correcting wavefront distortion in optical retro-modulation can solve the problem that wavefront distortion is generated in retro-modulation laser communication because of the influence of atmospheric effect.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Satellite navigation signal simulation method specific to terminal carrier used as high rail satellite
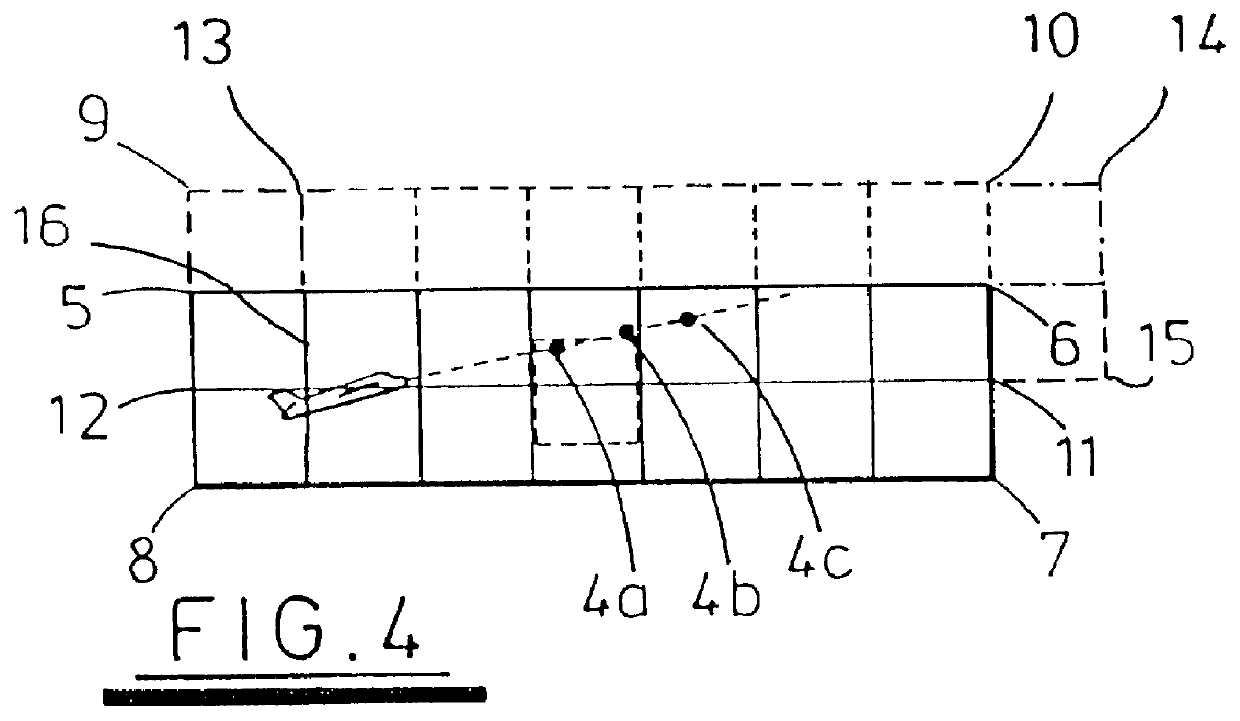
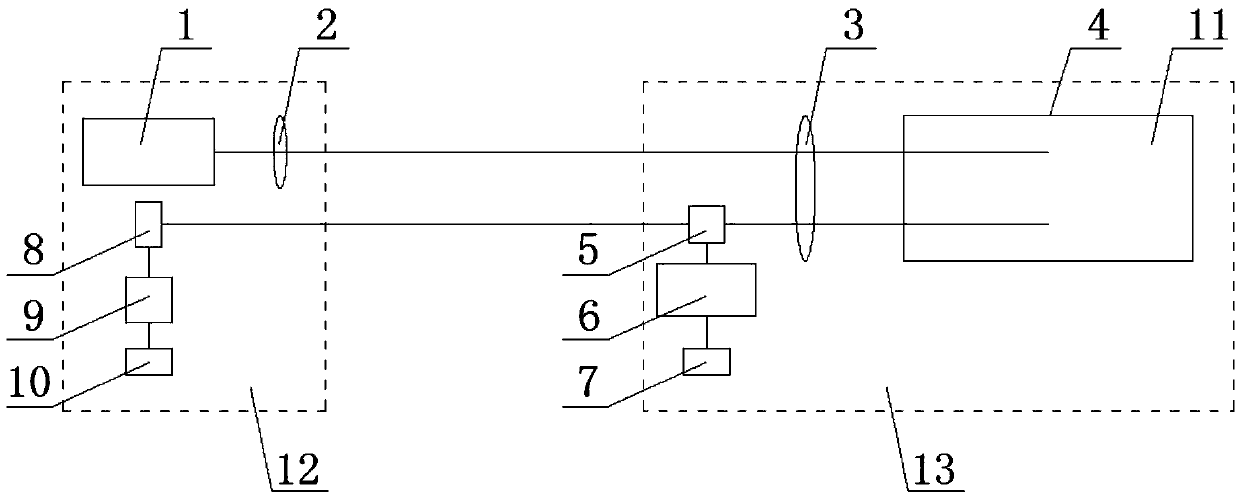
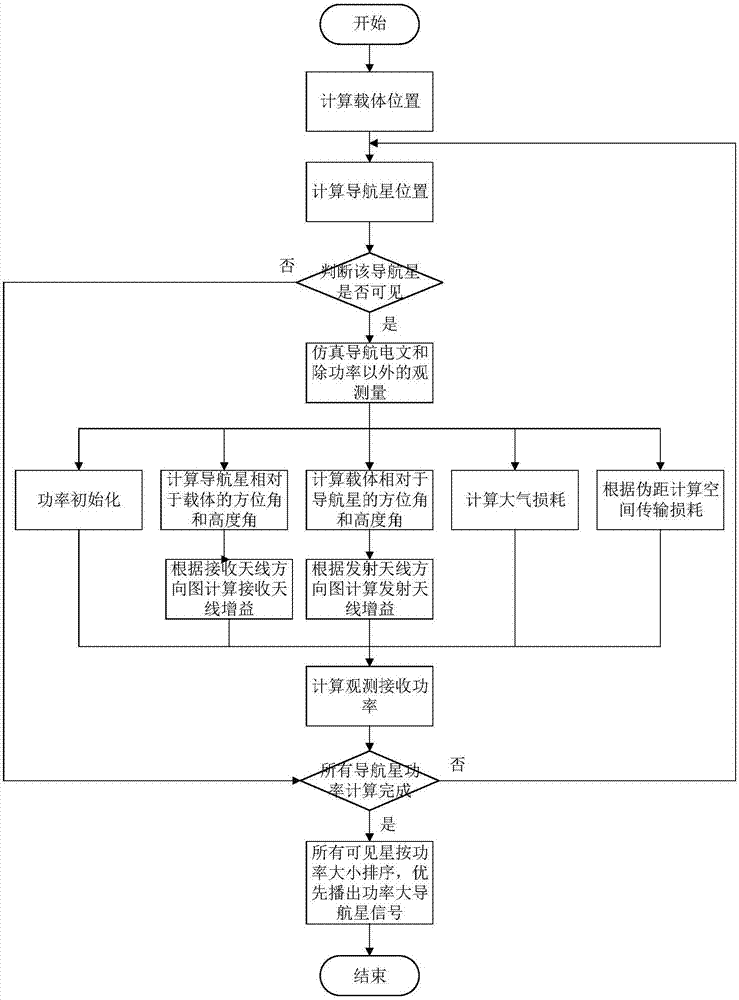
ActiveCN107991696ARealize simulationImprove the function of power simulationSatellite radio beaconingVisibilityAtmospheric layer
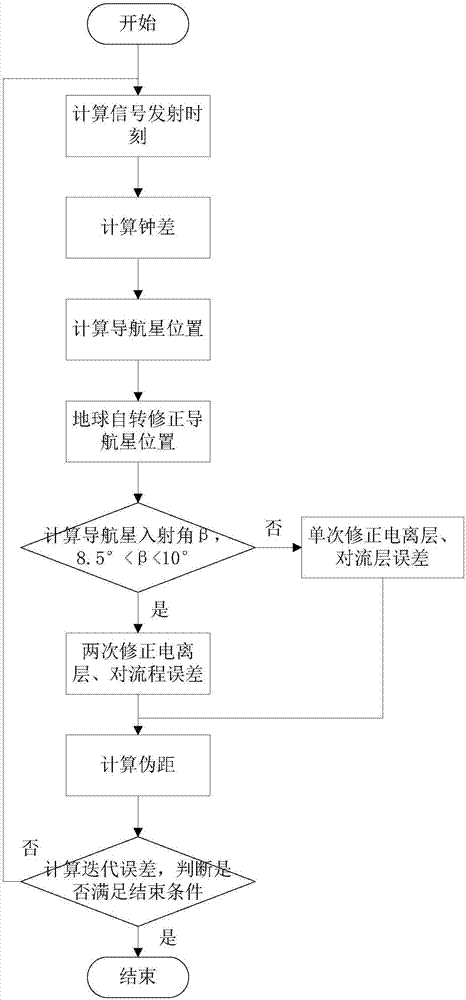
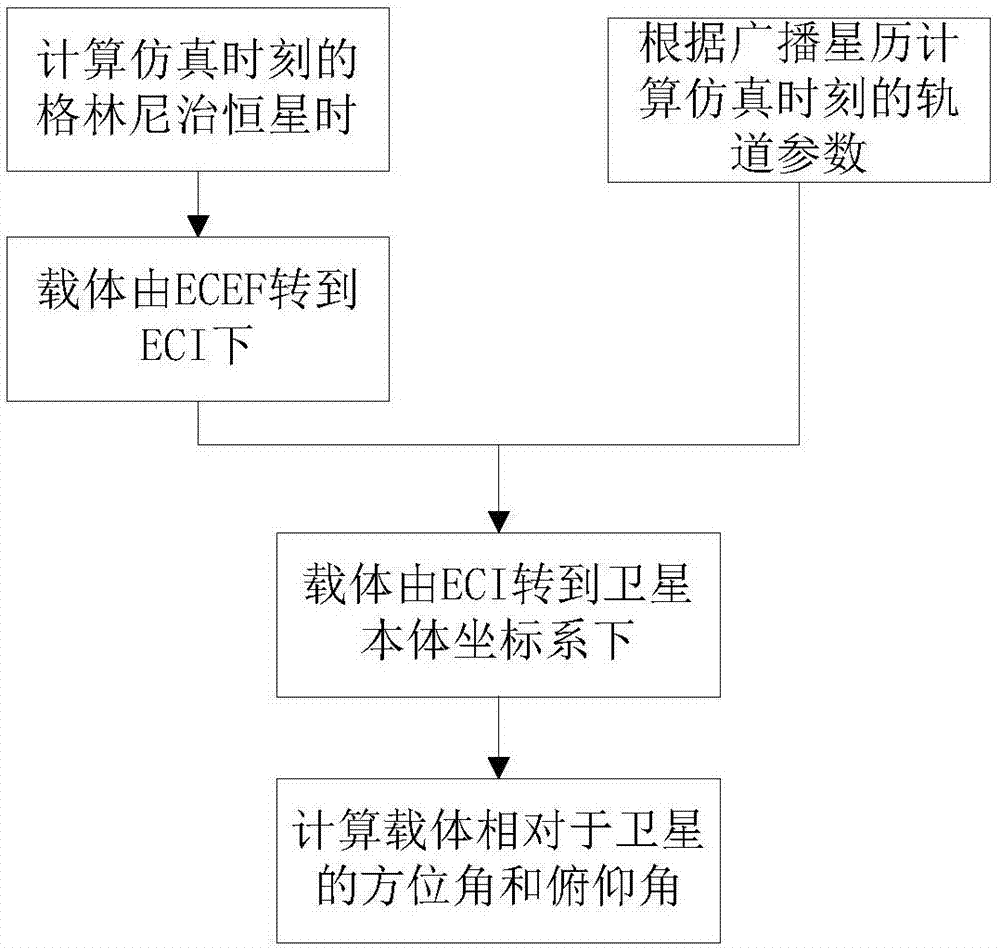
The invention provides a satellite navigation signal simulation method specific to a terminal carrier used as a high rail satellite. On the basis of the existing satellite navigation signal simulation, a navigation satellite shielding angle is calculated by adopting a way of an earth tangential line specific to the feature that the elevating angle of the navigation satellite relative to a high track GNSS receiver is less than 0 degree, so as to judge the visibility of the navigation satellite; specific to the feature of weak strength of signals received by the high track GNSS receiver, simulation of a satellite emitting antenna direction graph is added, the power simulation function is improved and the satellite is selected upon power; specific to the feature that a part of signal crossesthrough an atmospheric layer twice, the dual-atmospheric effect simulation is added. Through the method, analogue simulation of the satellite navigation signal received by the high track satellite isrealized, and the testing tool is provided for the GNSS receiver and related system loaded on the high track satellite.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE INFORMATION ENG RES INST
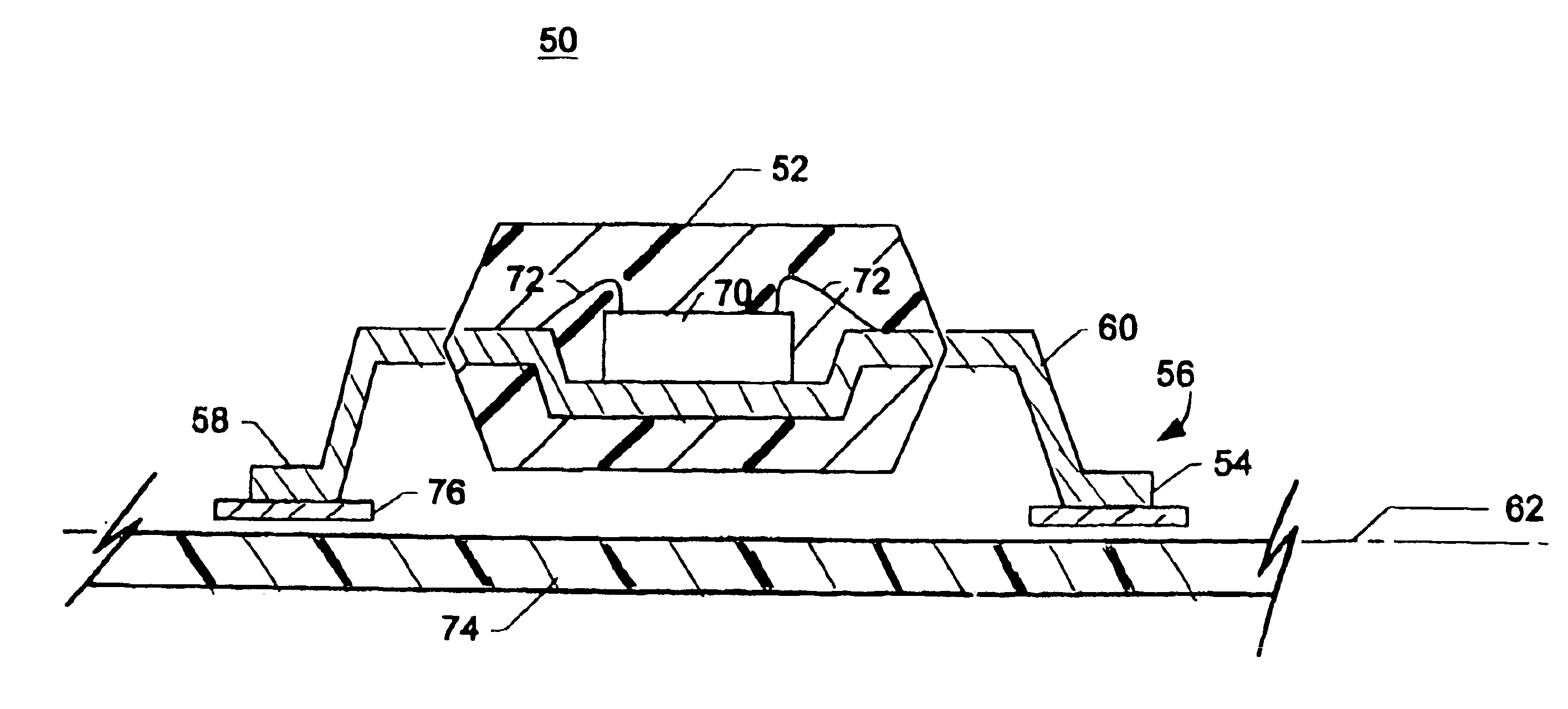
Electrical apparatus having resistance to atmospheric effects and method of manufacture therefor
InactiveUS6849806B2Reduce corrosionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted electric component incorporationAtmospheric airElectrical devices
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
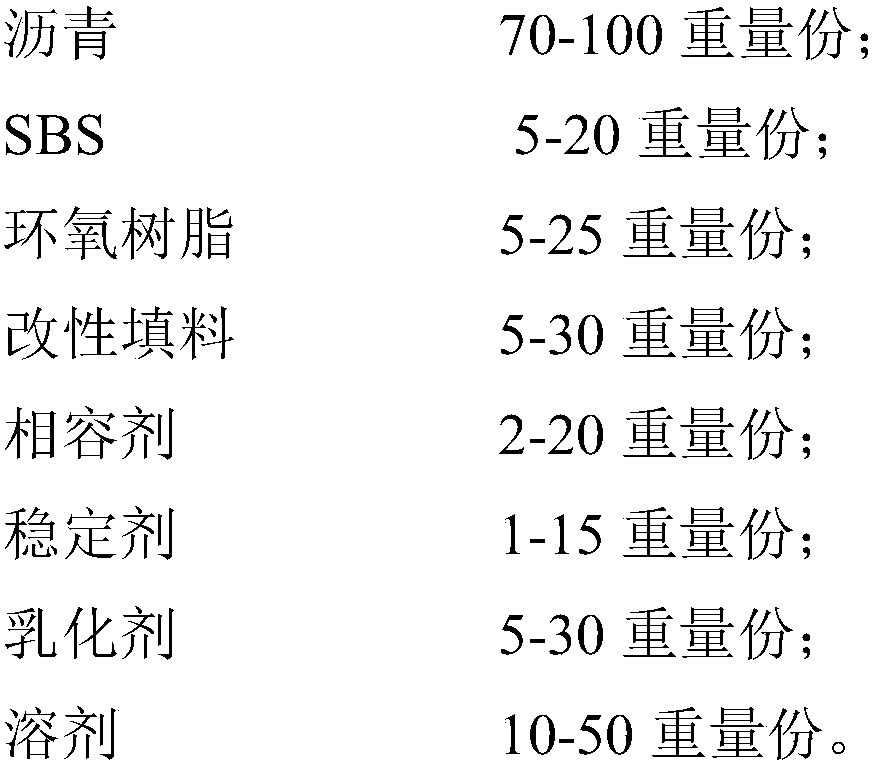
Single particle size ultra-thin anti-slip wearing layer used for road preventive maintenance and construction process thereof
InactiveCN109610262ALow paving thicknessLow costIn situ pavingsPaving detailsRoad surfaceMixed materials
The invention discloses a single particle size ultra-thin anti-slip wearing layer used for road preventive maintenance and a construction process. The single particle size ultra-thin anti-slip wearinglayer is formed by paving and rolling a single particle size asphalt mixed material on a road surface by a paver, and the asphalt mixed material includes modified emulsified asphalt and basalt aggregate. Compared with existing anti-slip performance improvement measures, the wearing layer can greatly improve the anti-sliding performance of the road surface without significantly increasing elevation of an original road surface, and has the advantages of good water resistance, seam sealing, slip resistance, noise reduction, and the like, and the modified emulsified asphalt can restore aged asphalt of an original asphalt road surface to some extent. The paving thickness of the ultra-thin anti-slip wearing layer can be low to 5 mm, so that the cost is relatively low, and the wearing layer hasan outstanding economic advantage compared with the prior art. The original asphalt road surface is directly paved with the single particle size ultra-thin anti-slip wearing layer, the influence of water and atmospheric effects on the original asphalt road surface can be alleviated, and the service life of roads is prolonged.
Owner:NANJING ROAD KEEPER TECH
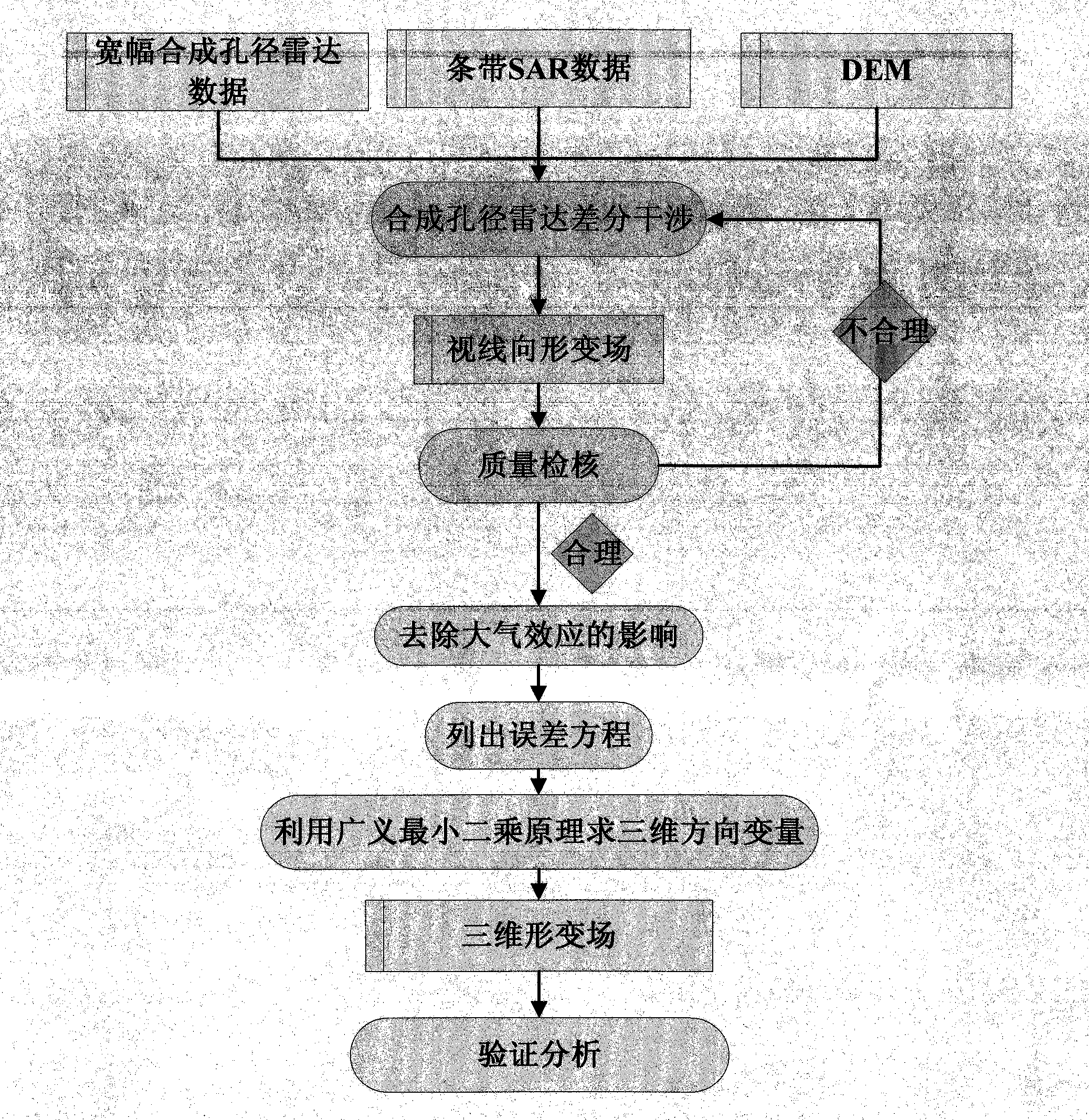
Radar three-dimensional deformation field reconstruction technology based on general least squares adjustment
InactiveCN104391296AGuaranteed continuityOvercome the shortcomings of low decomposition accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarRadar
The invention discloses a radar three-dimensional deformation field reconstruction technology based on general least squares adjustment, which is characterized in that a synthetic aperture radar satellite is used for acquiring a sight line deformation field technology; an atmospheric effect influence technology is removed; an error equation for the three-dimensional direction deformation is listed; a general least squares adjustment principle is used for solving the three-dimensional direction deformation amount; and an analysis technology is verified. The radar three-dimensional deformation field reconstruction technology based on general least squares adjustment has the following advantages that the modern advanced measurement technology and equipment are used, and a station does not need to be built in a monitoring region; the spatial domain in the case of monitoring is maintained to be continuous; three-dimensional distribution situations in the surface deformation space are acquired; and defects of low three-dimensional vector decomposition accuracy in traditional methods such as a pixel offset estimation method, a multi-aperture interference method and an external measurement assisting method can be overcome.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
System for bidirectional free-space laser communication of gigabit Ethernet telemetry data
ActiveCN106059678AMitigate the effects of atmospheric turbulenceMitigate fading effectsTime-division multiplexLine-of-sight transmissionCorrection algorithmTelecommunications link
A free-space laser communication system for bidirectional transmission of telemetry data in Gigabit Ethernet (GBE) protocol using a dual atmospheric effect mitigation approach. This free-space bidirectional GBE laser communication system utilizes an Optical Combining Receiver Array and a Framer / Forward Error Correction / Interleaver (FFI) device to mitigate the combined effects of atmospheric turbulence and channel fading. Since the FFI device is designed for Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) protocol, an intelligent (or smart) media converter is used to convert GBE telemetry data to SONET frames, which enables the FFI device to perform an error correction algorithm and provide a seamless error-free GBE laser communication link for distance over a kilometer. This bidirectional laser communication system can be implemented with low-cost commercially available components.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
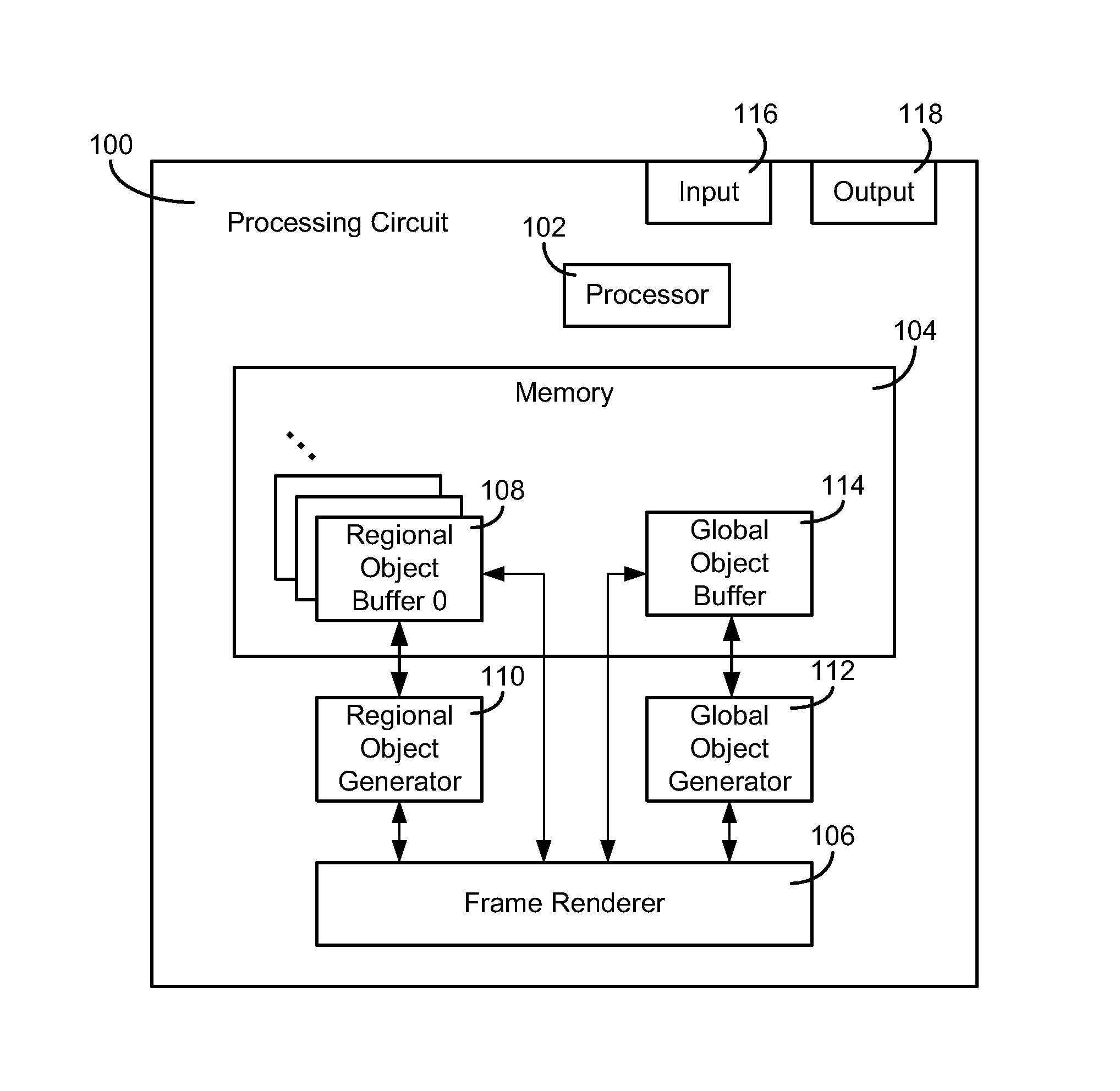
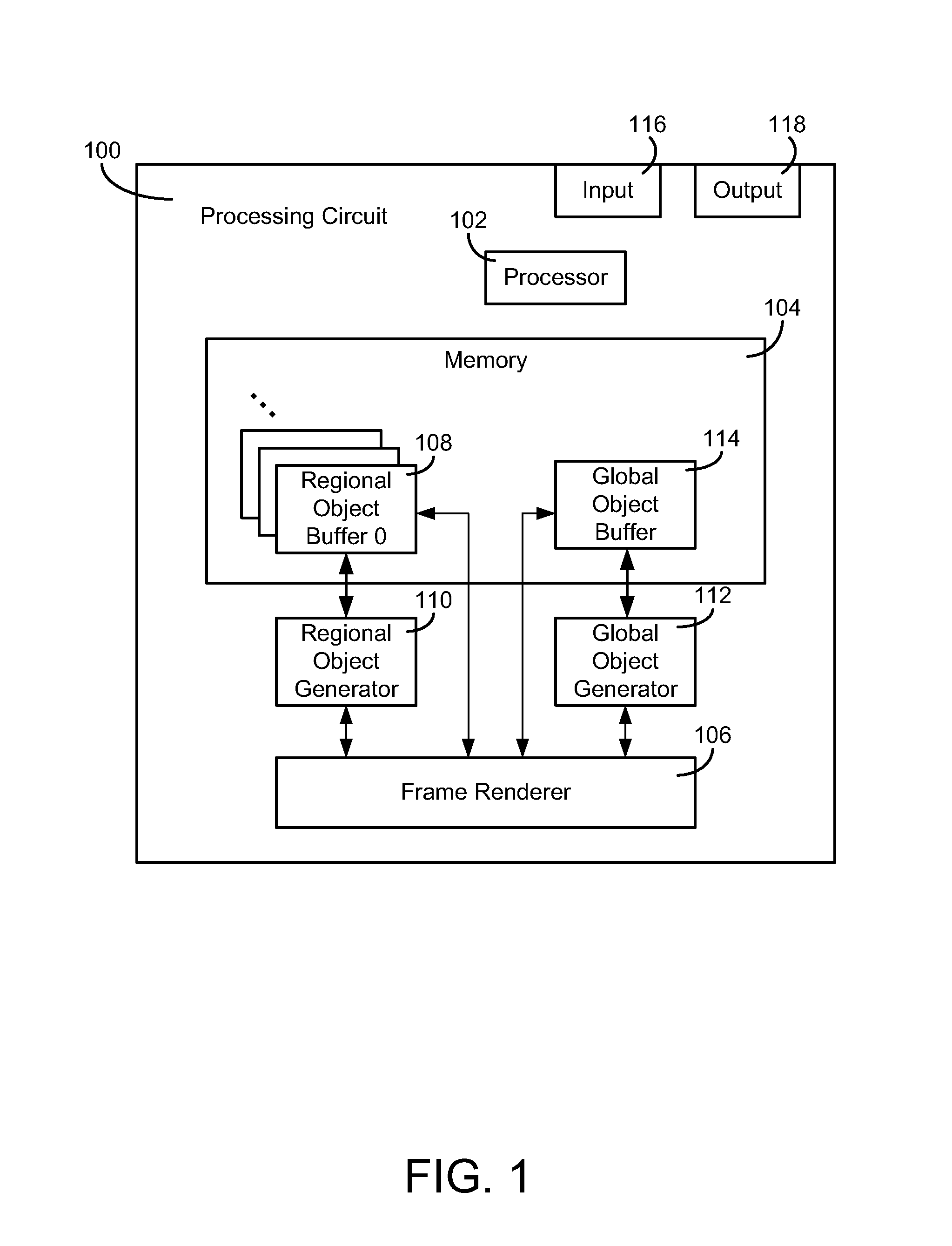
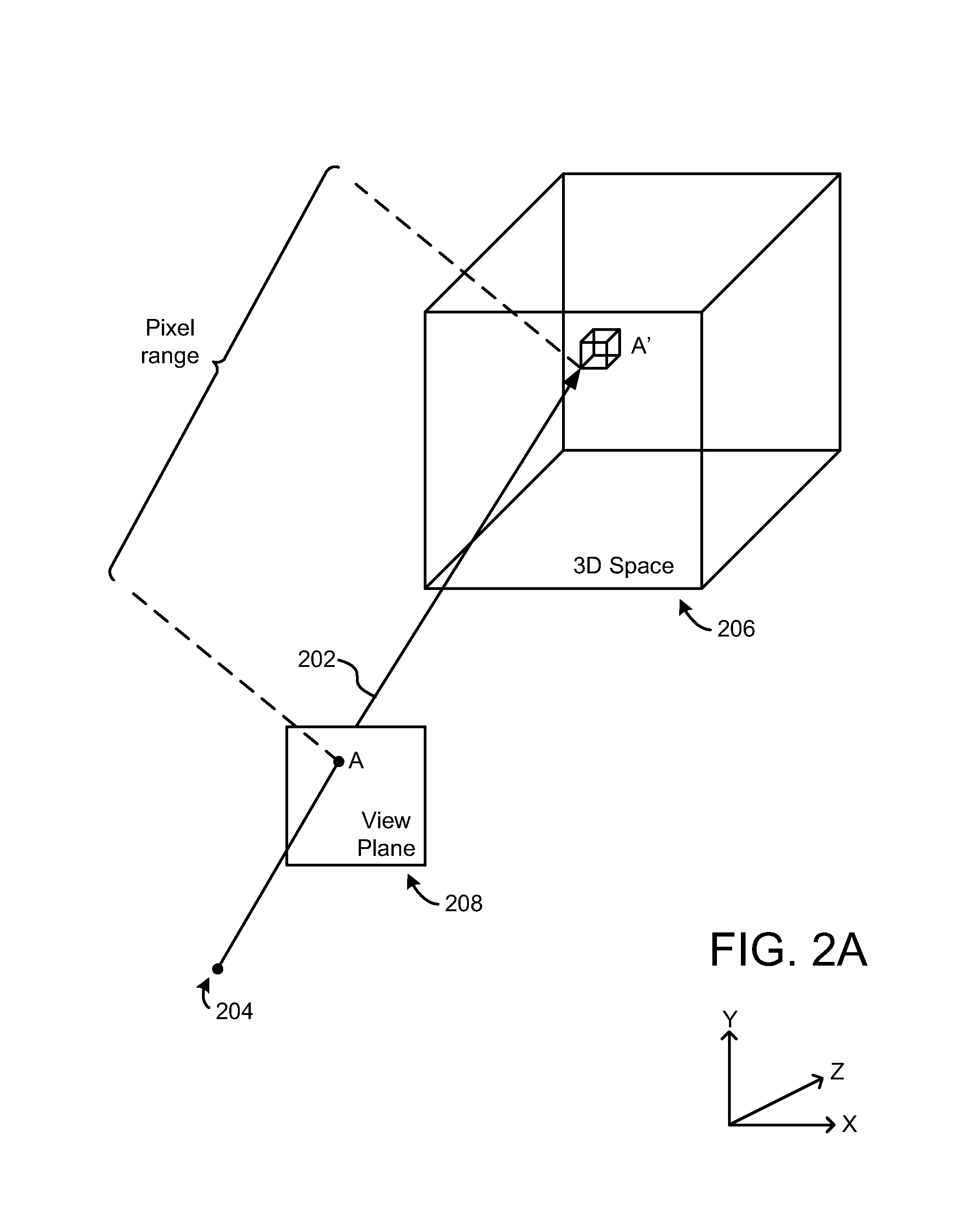
Volume rendering a graphical 3D scene containing a 3D volumetric object and atmospheric effects
A computerized method and system of rendering a graphical image containing a volumetric object on an electronic display is provided. The method includes defining, at a processing circuit, the volumetric object as a volume. The volume comprises a plurality of polygons. The method includes rendering the volume for a first plurality of pixels of the electronic display. The volume is described by volume characteristics. The method includes rendering a graphical image for a second plurality of pixels of the electronic display. The graphical image is described by global characteristics. When a view ray for at least one of the second plurality of pixels intersects at least one of the first plurality of pixels, the global characteristics and a proportion of the volume characteristics are combined when rendering the graphical image. The proportion is defined by an extent of the intersection of the view ray.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Unmanned aerial system based thermal imaging and aggregation systems and methods
Flight based infrared imaging systems and related techniques, and in particular UAS based thermal imaging systems, are provided to improve the monitoring capabilities of such systems over conventionalinfrared monitoring systems. An infrared imaging system is configured to compensate for various environmental effects (e.g., position and / or strength of the sun, atmospheric effects) to provide highresolution and accuracy radiometric measurements of targets imaged by the infrared imaging system. An infrared imaging system is alternatively configured to monitor and determine environmental conditions, modify data received from infrared imaging systems and other systems, modify flight paths and other commands, and / or create a representation of the environment.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com