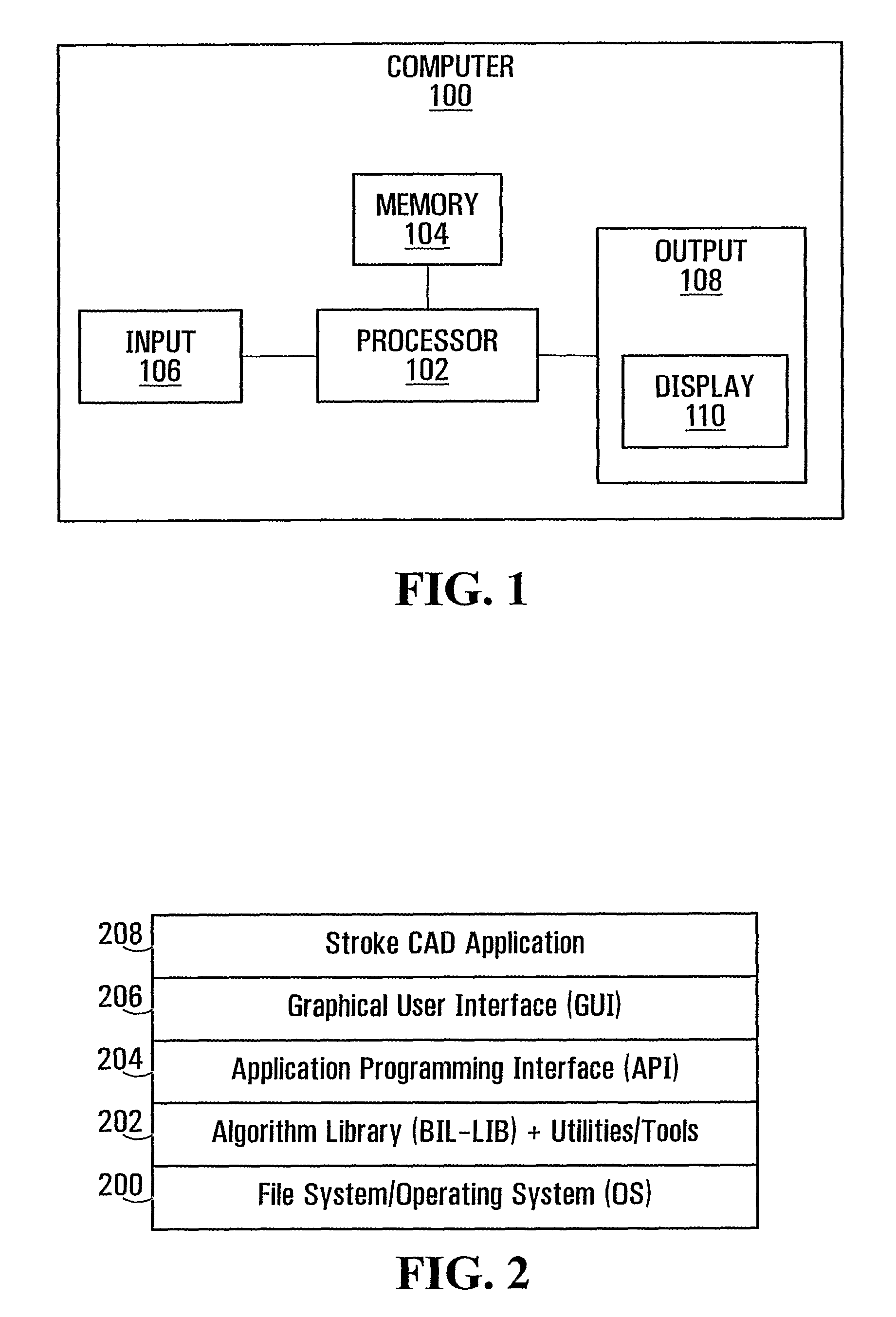
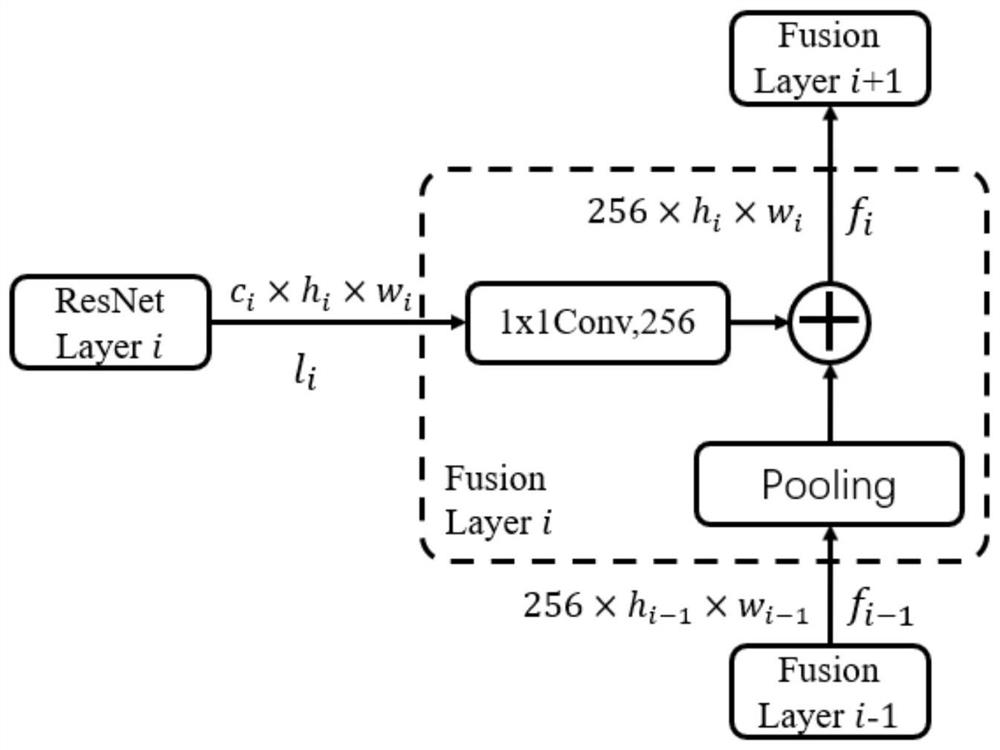
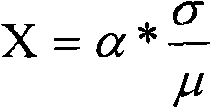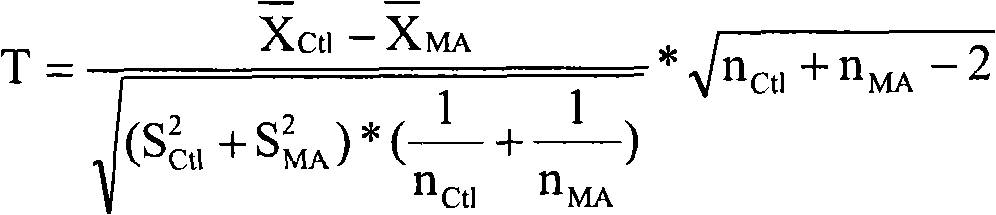Patents
Literature
112 results about "Brain imag" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
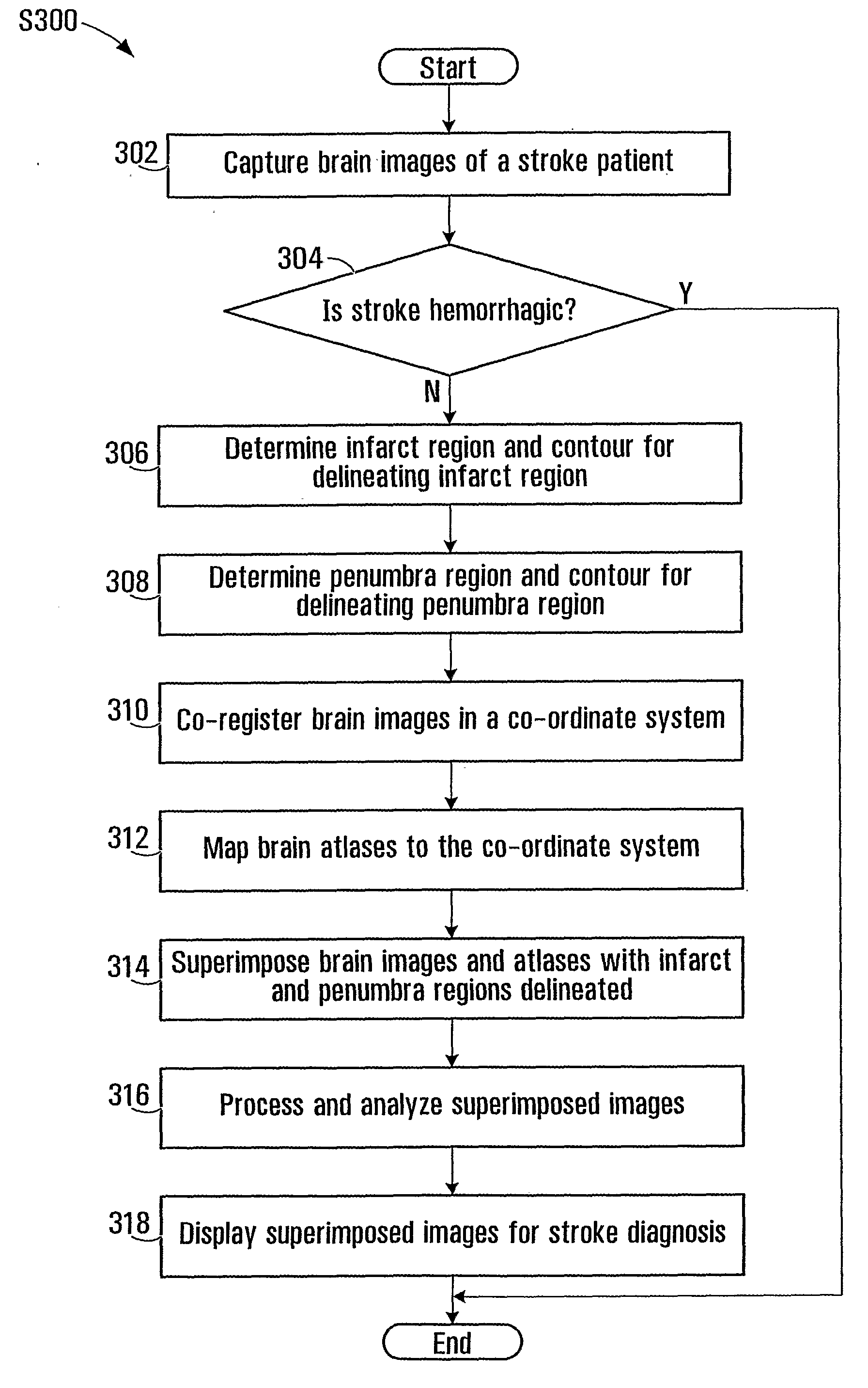
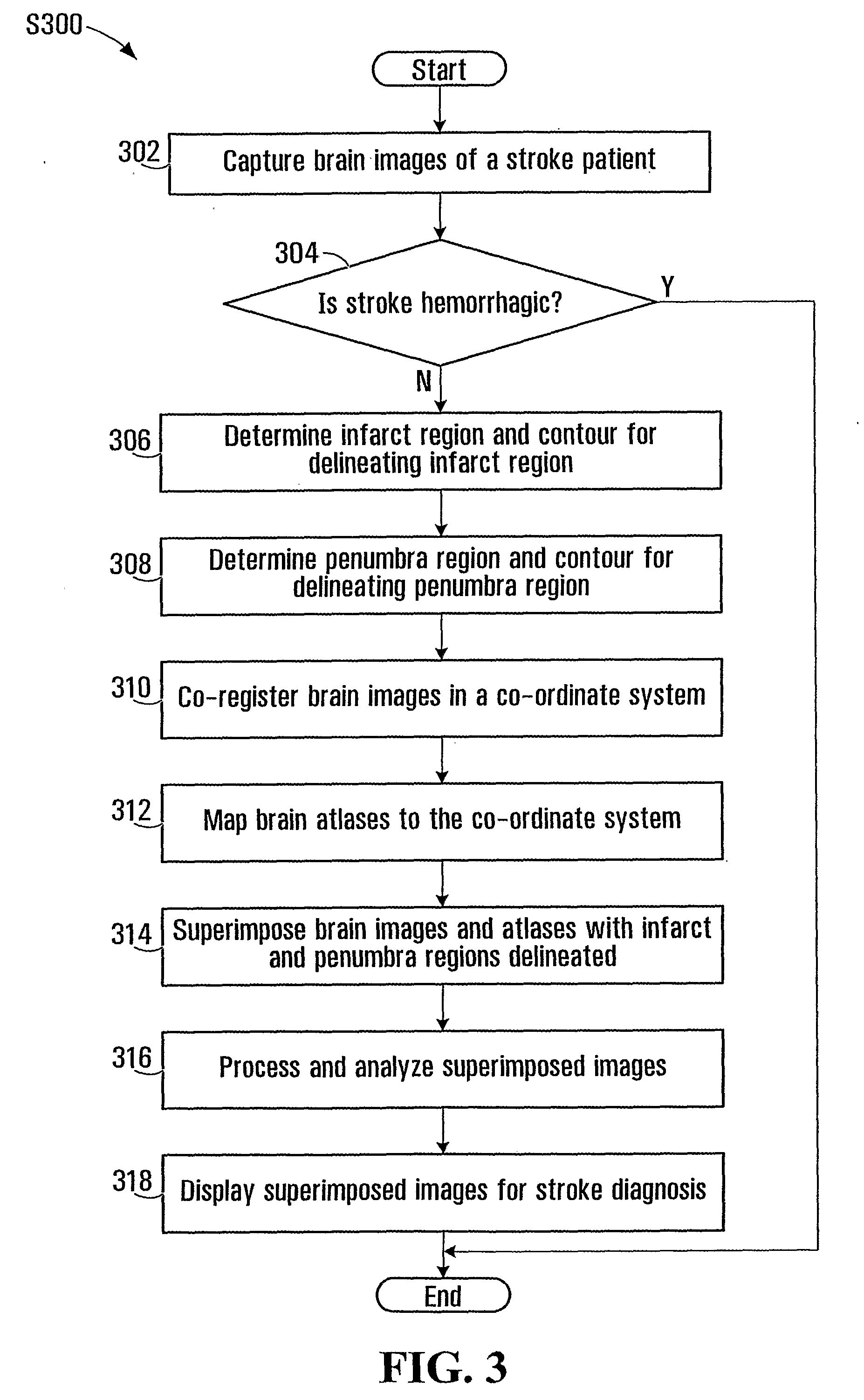
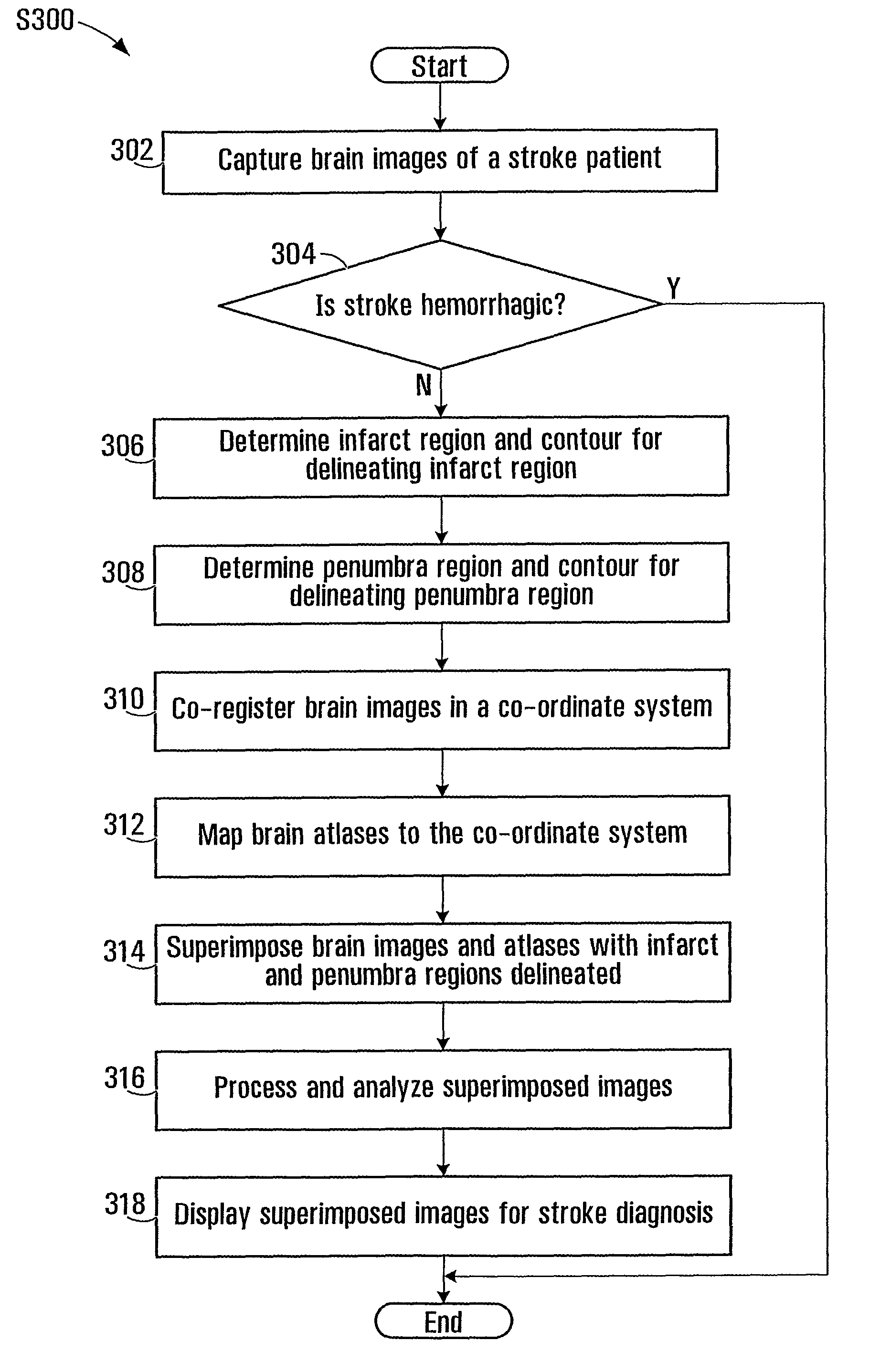
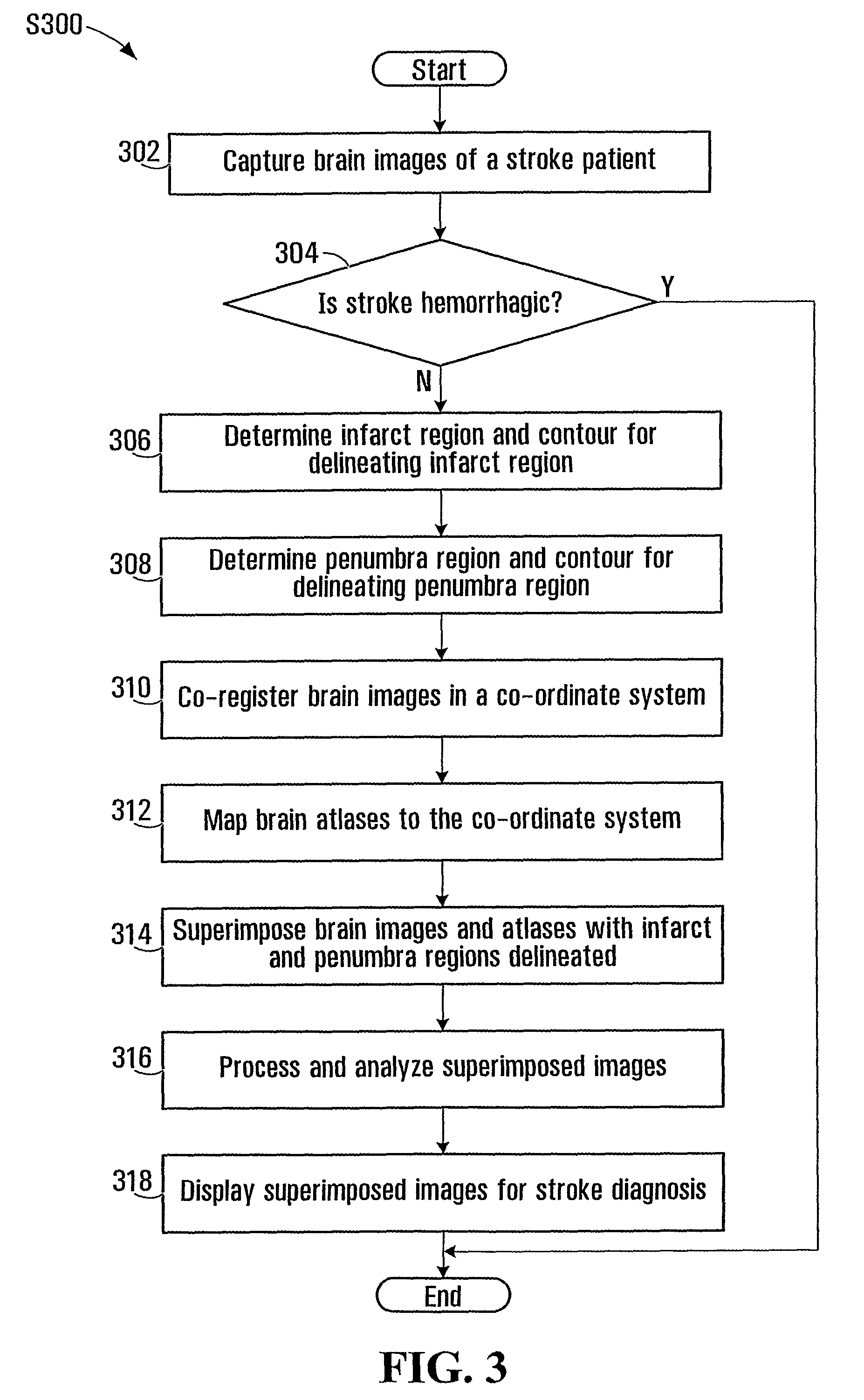
Superimposing brain atlas images and brain images with delineation of infarct and penumbra for stroke diagnosis
InactiveUS20090034812A1Conveniently identifiedConveniently visualizedImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresRisk stroke
Brain images are processed and analyzed with the aid of a computer for stroke diagnosis or therapeutic decision making, where multiple stroke-related images are superimposed. The superimposed images include brain images that have infarct and penumbra regions, and patient-specific brain atlas images. The infarct and penumbra regions are determined and delineated on the superimposed images. Each patient-specific brain atlas image may be formed by mapping a pre-existing brain atlas to a co-ordinate system in which the brain images are co-registered. A brain atlas may depict brain structures such as anatomy structures, blood supply territories (BST), or cerebral vasculature. The superimposed images may be used to determine any overlap between a particular brain structure and the infarct and penumbra regions.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
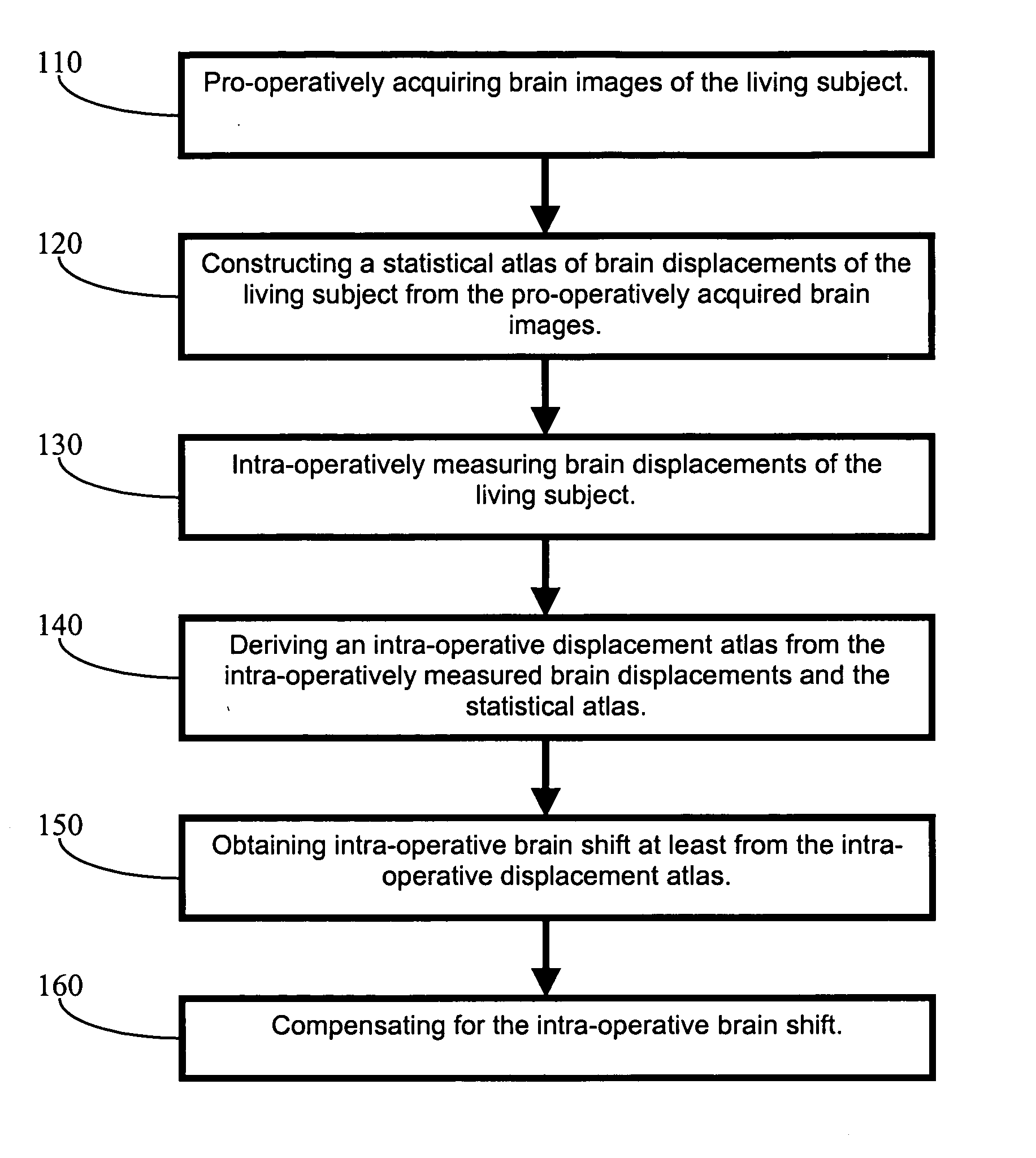
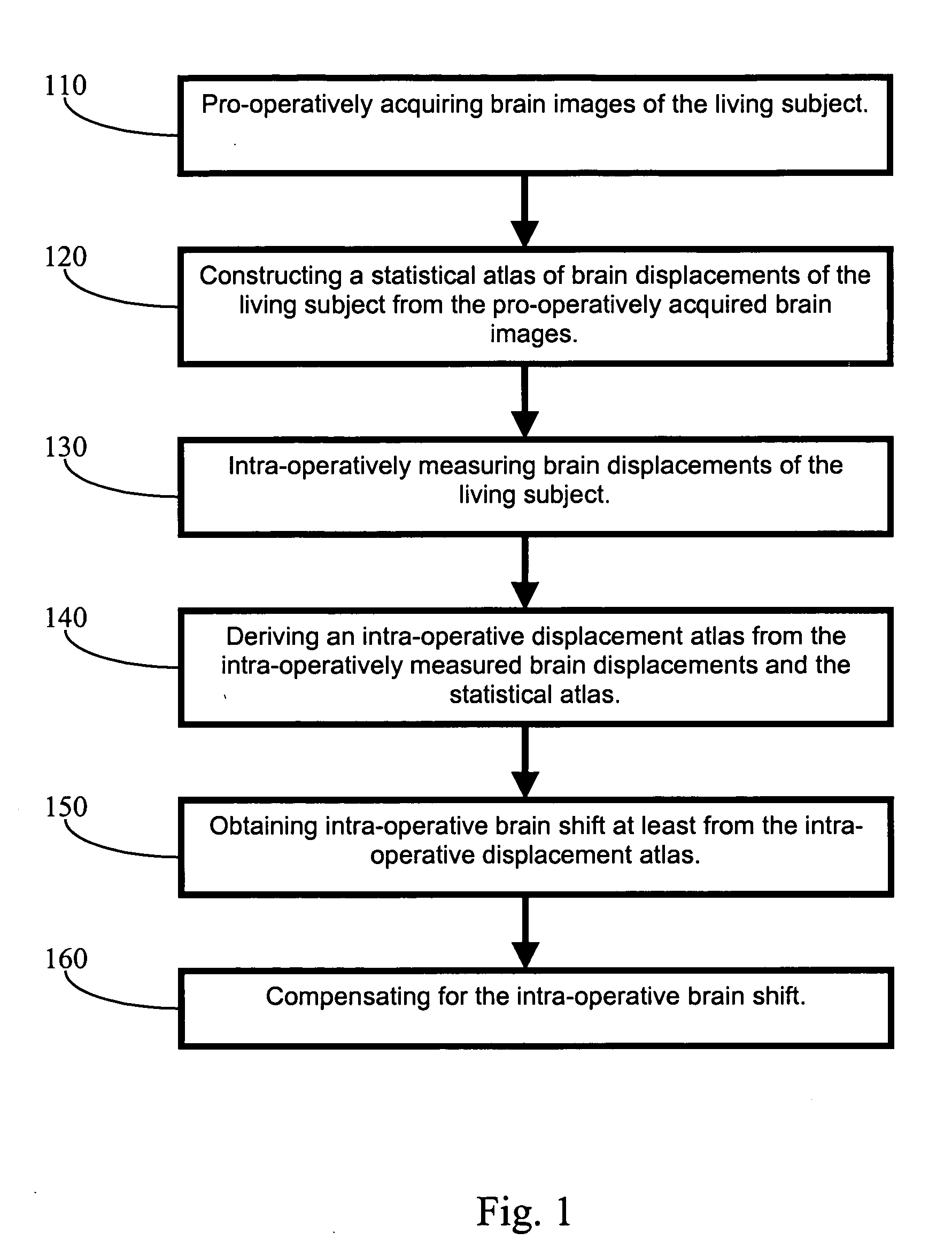
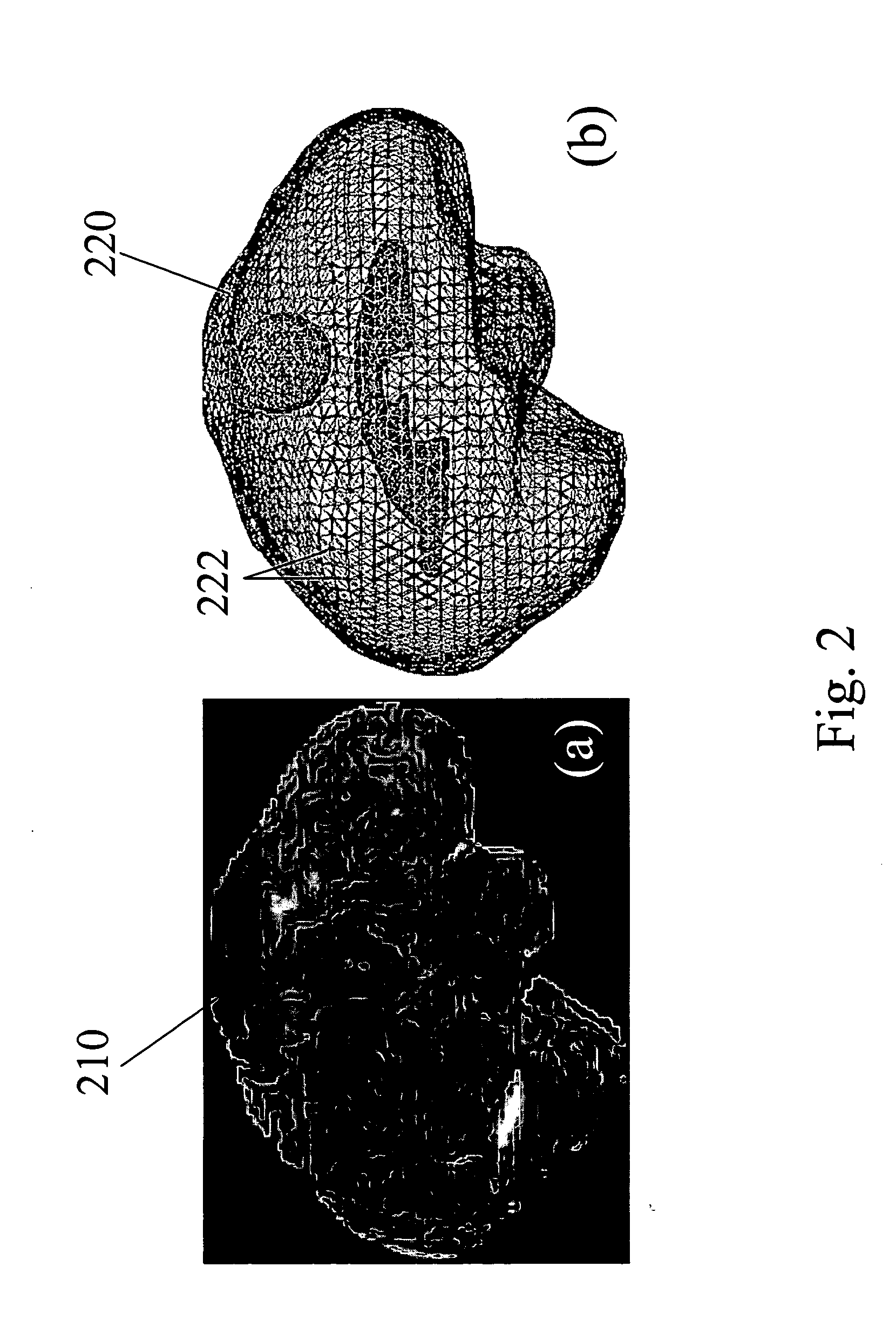
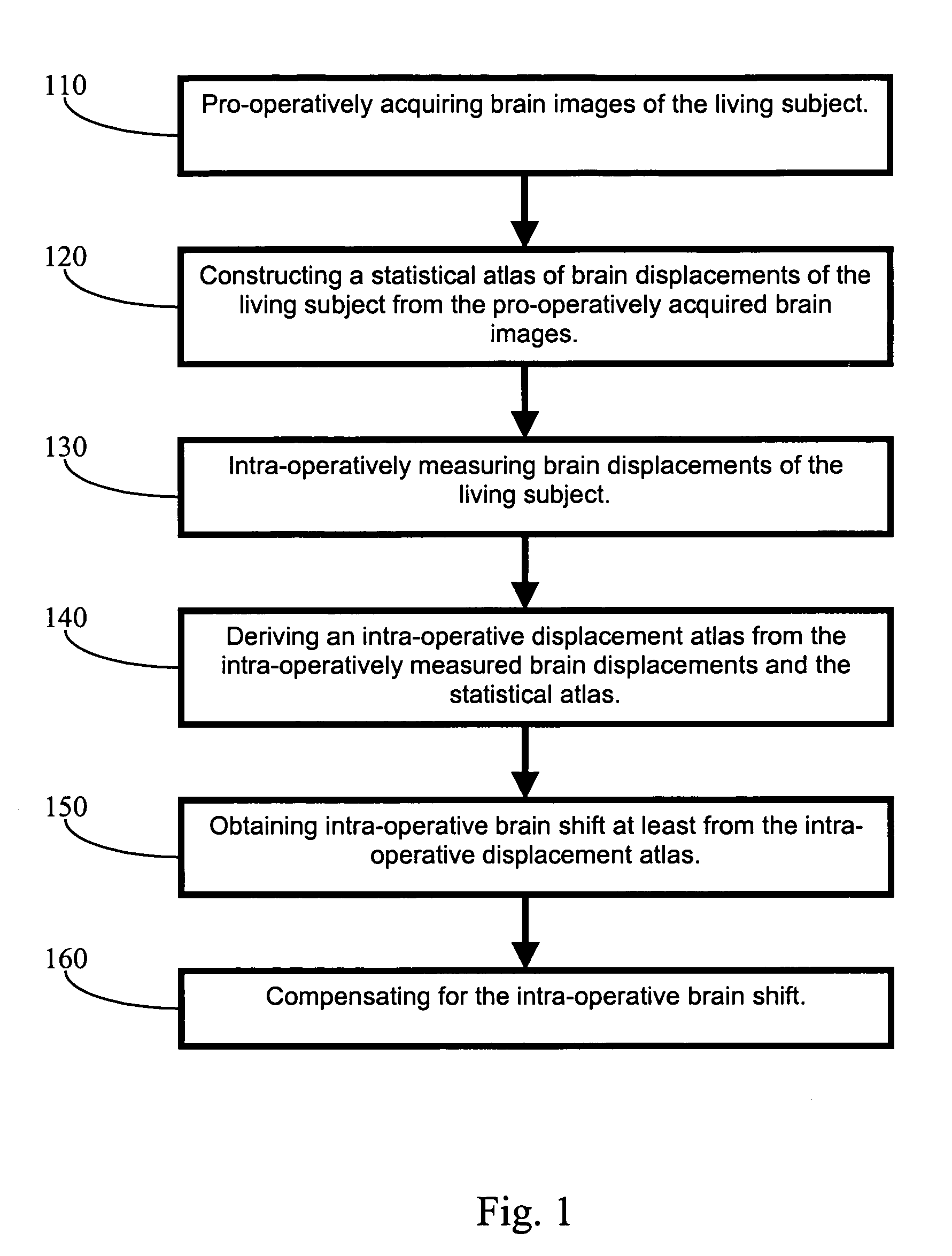
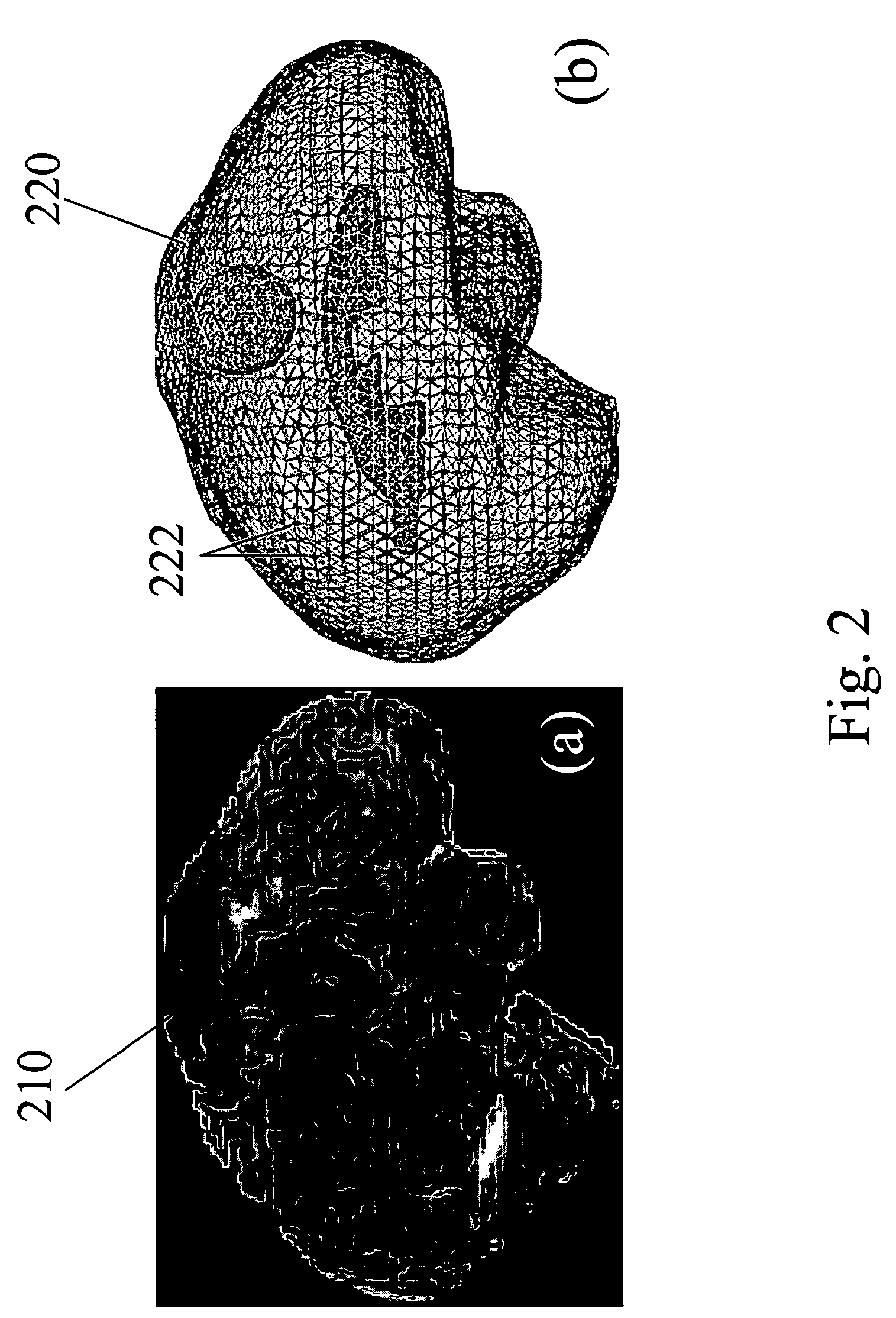
Apparatus and methods of brain shift compensation and applications of the same
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Method for assisting in diagnosis of cerebral diseases and apparatus thereof
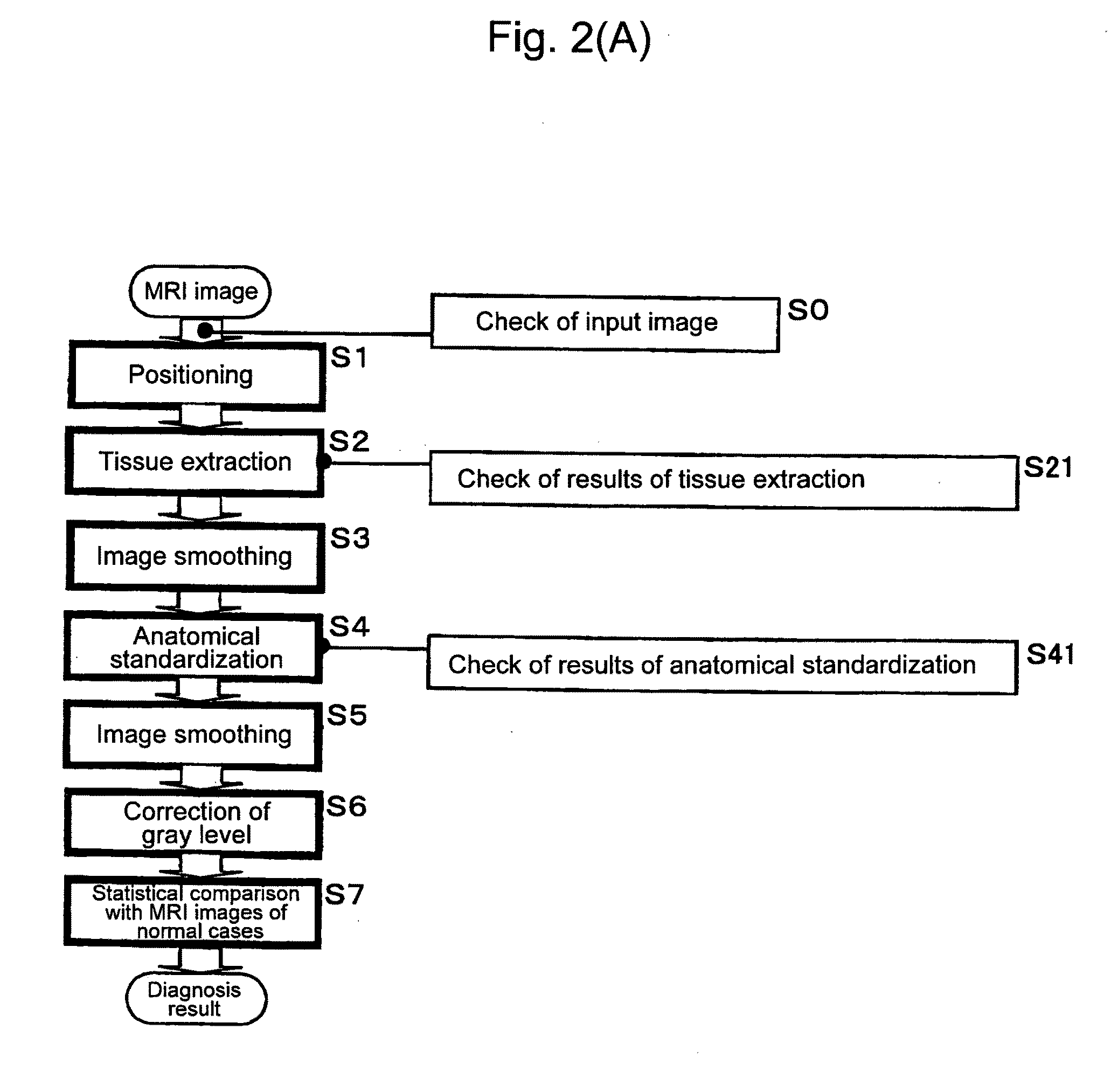
Input MRI brain images are positioned so as to correct a spatial deviation, gray matter tissues are extracted from these images to effect a first image smoothing, the thus-obtained images are subjected to anatomical standardization, a second image smoothing is effected, the gray level is corrected, brain images after correction are statistically compared with MRI brain images of normal cases, thereby providing the diagnosis result. In this instance, the brain images are automatically checked for input images regarding the resolution dot density and the like, the result of gray matter tissue extraction and the result of anatomical standardization, by which specifications of input images and the like can be confirmed objectively and automatically to make a diagnosis automatically by image processing. Further, an ROI-based analysis is made to provide the analysis result as the diagnosis result.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Apparatus and methods of brain shift compensation and applications of the same
ActiveUS7072705B2Image analysisSurgical navigation systemsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMidbrain
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Superimposing brain atlas images and brain images with delineation of infarct and penumbra for stroke diagnosis
InactiveUS8019142B2Conveniently identifiedConveniently visualizedImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresMedicine
Brain images are processed and analyzed with the aid of a computer for stroke diagnosis or therapeutic decision making, where multiple stroke-related images are superimposed. The superimposed images include brain images that have infarct and penumbra regions, and patient-specific brain atlas images. The infarct and penumbra regions are determined and delineated on the superimposed images. Each patient-specific brain atlas image may be formed by mapping a pre-existing brain atlas to a co-ordinate system in which the brain images are co-registered. A brain atlas may depict brain structures such as anatomy structures, blood supply territories (BST), or cerebral vasculature. The superimposed images may be used to determine any overlap between a particular brain structure and the infarct and penumbra regions.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Brain disease diagnosis method based on 3D convolutional neural network
InactiveCN110739070AEliminate differencesHigh precisionMedical automated diagnosisNeural architecturesMedicineDiagnosis methods
The invention relates to a brain disease diagnosis method based on a 3D convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring MRI brain image data samples of normal states and diseases; 2) performing sample pretreatment: brain tissue extraction and sample standardization; 3) designing a 3D convolutional neural network for brain disease diagnosis; 4) taking the MRI brain image as the input of the 3D convolutional neural network, performing network training, extracting features, and establishing a classification diagnosis model; 5) preprocessing the MRI brain imageof the to-be-detected person, sending the preprocessed MRI brain image as input to the 3D convolutional neural network diagnosis model to obtain an output label, and judging whether the to-be-detected person is sick or not. The method has the advantages that 1) the brain disease diagnosis model is established by using the 3D convolutional neural network, and features are automatically learned from MRI brain images; a multi-hidden-layer deep learning model is constructed, accurate and effective features are automatically obtained by a computer, and finally the precision and generalization ability of the diagnosis model are improved; 2) the method is suitable for diagnosis of various different types of brain diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, depression, children hyperactivity and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Brain region effect connection analysis system based on functional magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN103800011APerfect topologyEasy to explainDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNuclear physicsBrain imag
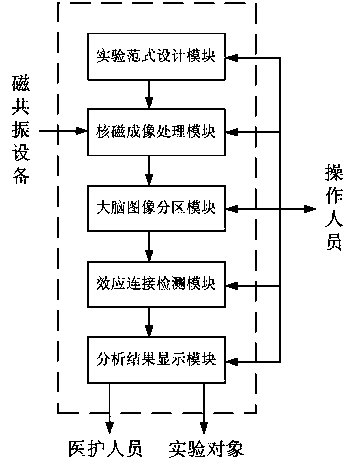
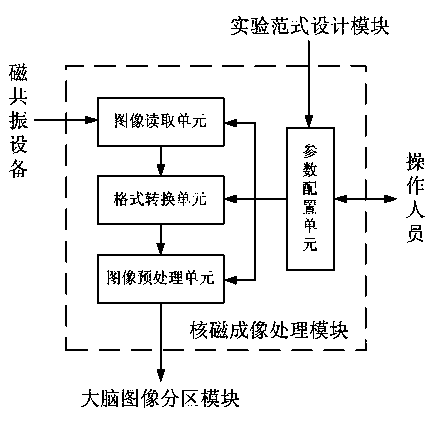
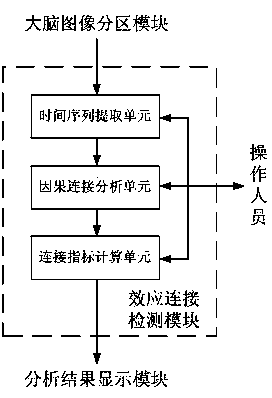
The invention discloses a brain region effect connection analysis system based on functional magnetic resonance imaging. The brain region effect connection analysis system comprises an experimental paradigm design module, a nuclear magnetism imaging processing module, a brain image partition module, an effect connection detection module and an analysis result display module. The experimental paradigm design module designs the content and the flow of an experiment in which experiment objects participate. The nuclear magnetic imaging module preprocesses and stores images acquired by magnetic resonance equipment through a parameter configuration unit. The brain image partition module loads and stores brain partition templates and conducts region division on nuclear magnetic imaging. The effect connection detection module conducts directional linear causal relationship analysis and calculates effect connection values and connection indexes. The analysis result display module feeds back the effect connection analysis result and relevant brain function indexes to medical staff and tested staff. The brain region effect connection analysis system has important application value in the fields of function magnetic resonance imaging quality evaluation, brain function diagnosis and adjustment, cognitive function research, metal disease treatment and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
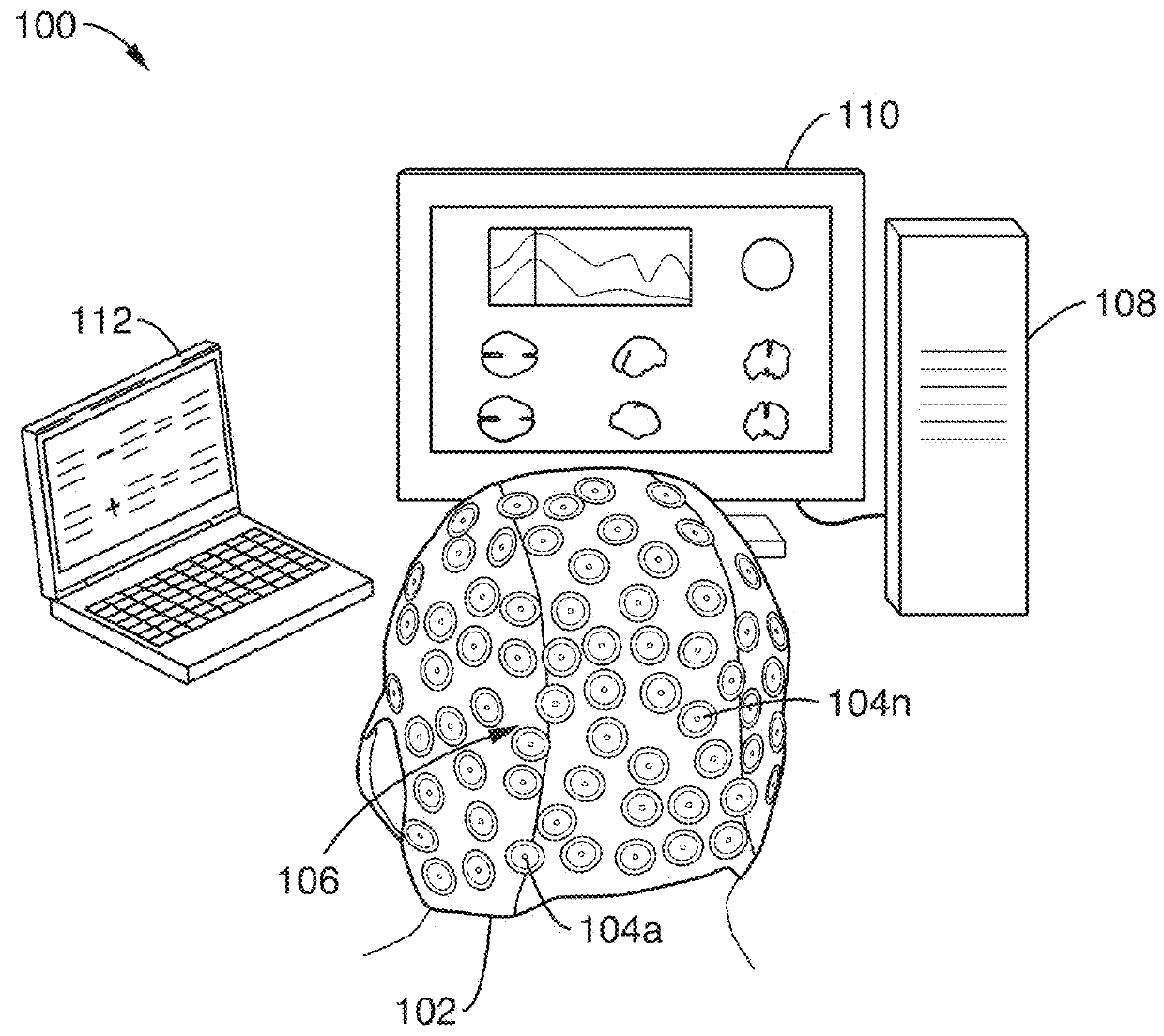
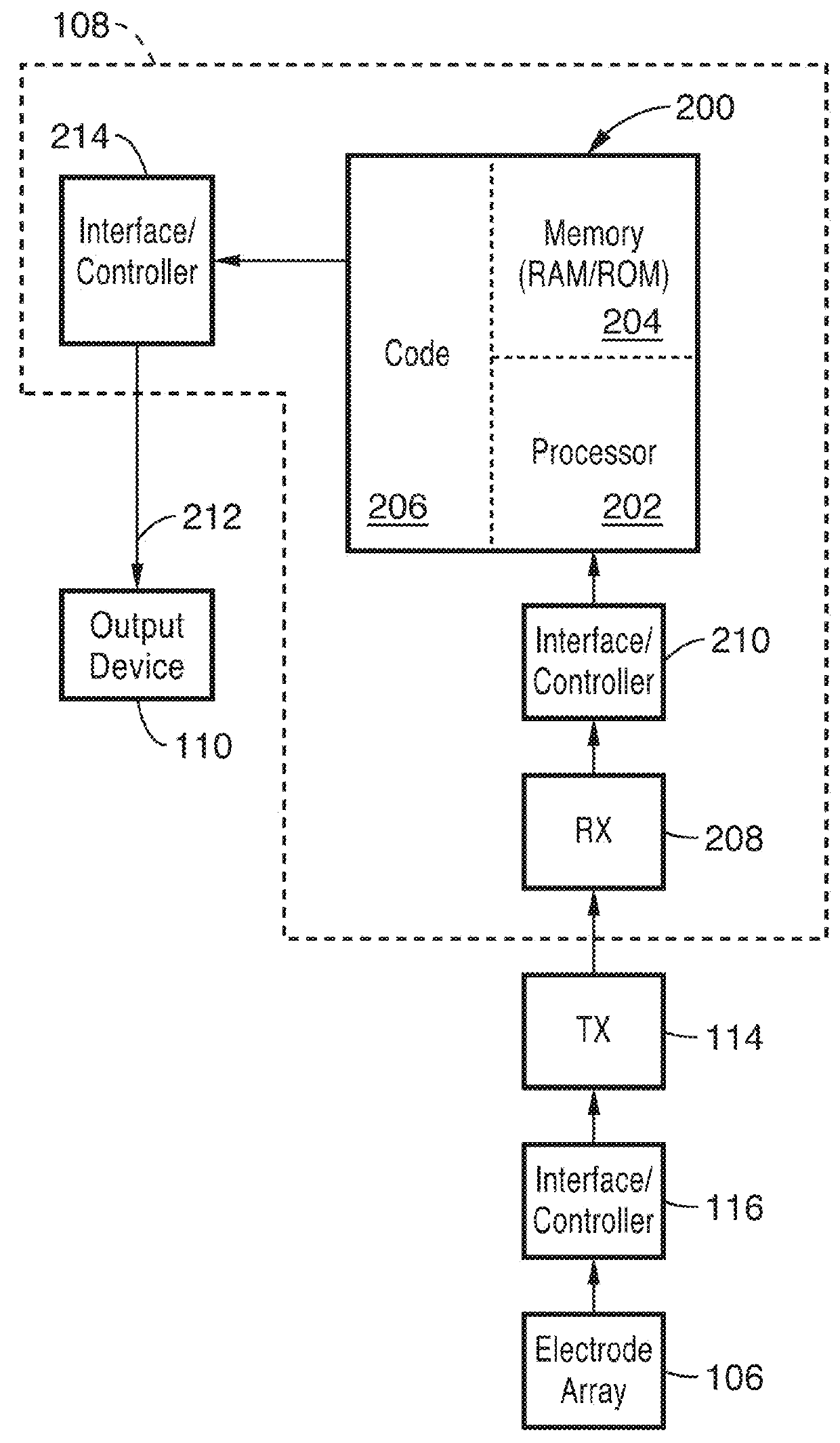
Ultra-dense electrode-based brain imaging system
ActiveUS20180276822A1Fully captureImprove accuracyElectroencephalographyImage enhancementTemporal resolutionImage resolution
An ultra-dense electrode-based brain imaging system with high spatial and temporal resolution. A Sparsity and Smoothness enhanced Method Of Optimized electrical TomograpHy (s-SMOOTH) based reconstruction technique to improve the spatial resolution and localization accuracy of reconstructed brain images is described. Also described is a graph Fractional-Order Total Variation (gFOTV) based reconstruction technique to improve the spatial resolution and localization accuracy of reconstructed brain images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
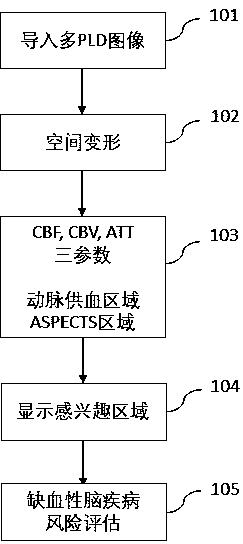
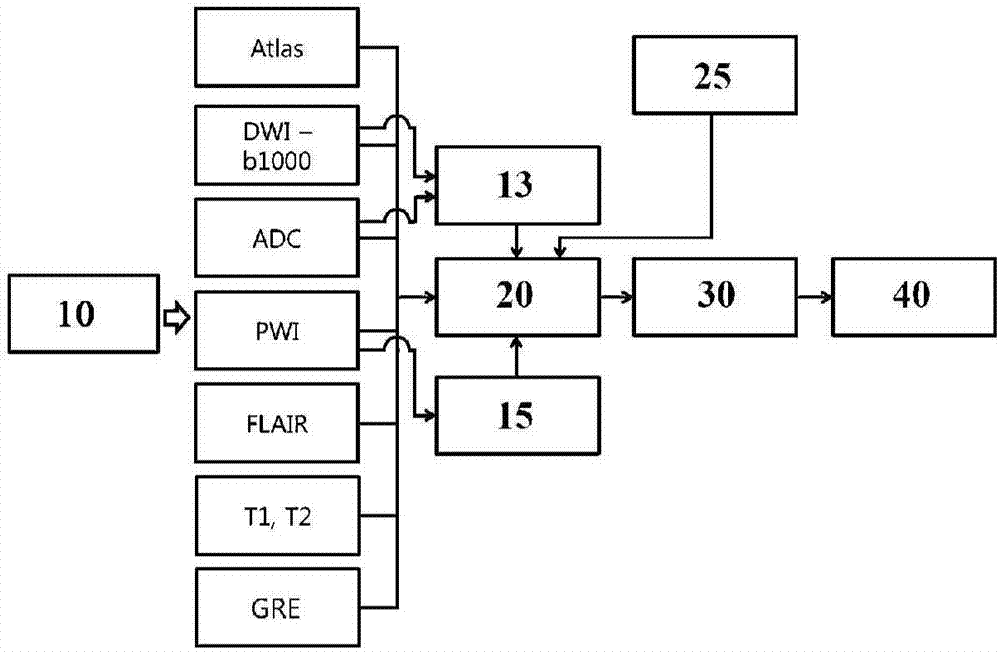
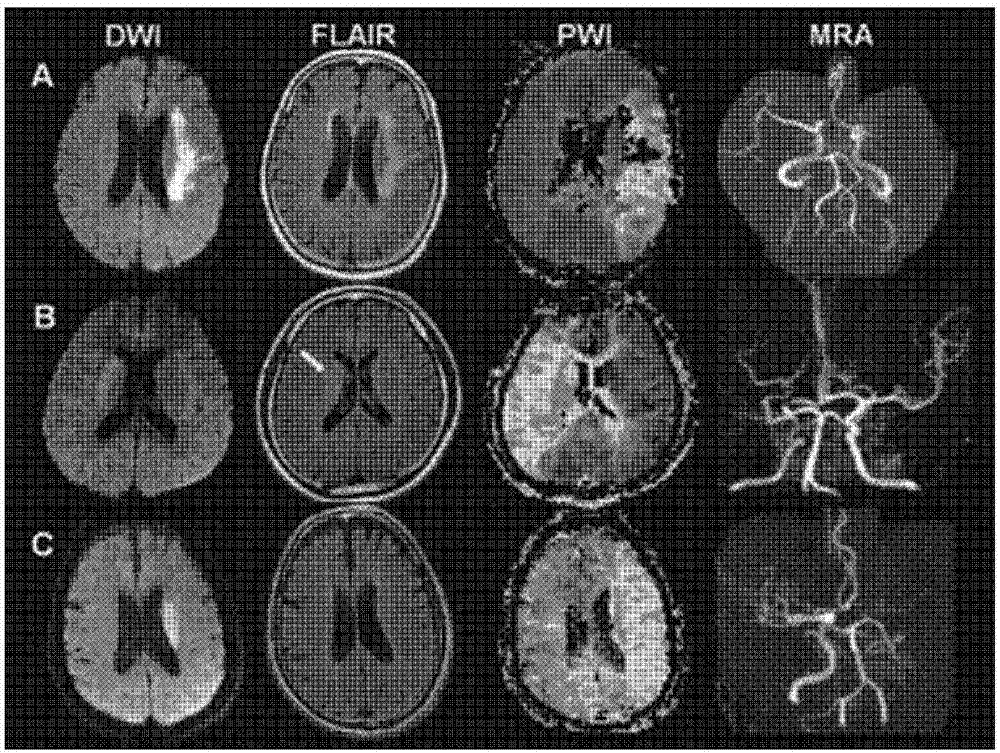
Method for auxiliary assessment of ischemic disease risk based on magnetic resonance cerebral perfusion image
InactiveCN110490871AEffective assessment methodImage enhancementImage analysisHead movementsDisease cause
The invention provides an automatic image processing and displaying method based on a magnetic resonance cerebral perfusion image, which is used for assisting in evaluating cerebral ischemia disease risks and is characterized by comprising spatial deformation, multi-parameterization, brain map coverage and a method for evaluating ischemic cerebral disease risks. The image space deformation methodcomprises the following steps: head movement correction, which is used for adjusting a space difference generated by head movement in a cerebral perfusion imaging process; and standard brain registration: taking the standard brain as a reference to realize standardization of the imported cerebral perfusion image. The multi-parameterization is used for converting the original nuclear magnetic datainto cerebral image perfusion parameters such as cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume and artery arrival time, wherein the coverage brain map is used for enabling the parameterized cerebral perfusion image data to cover standard brain maps of different templates to form different regions of interest, and calculating average parameter values of the different regions of interest.The standard cerebral map comprises a cerebral artery blood supply area and an early CT scoring area of an Albetan stroke project. The ischemic brain disease risk assessment method is used for comparing the averageparameter value of the region of interest with a reference range, displaying the differentiation degree and automatically displaying the region of interest beyond the reference range. According to the invention, multi-parameter automatic partitioning and quantitative processing from nuclear magnetic cerebral perfusion original number to ischemic cerebral disease early-stage risk assessment are realized, and an effective assessment method is provided for early-stage screening, early-stage diagnosis and early-stage treatment of cerebral ischemic diseases.
Owner:安影科技(北京)有限公司
Image processing method for automatically judging fetal hydrocephalus from ultrasonic images
InactiveCN101791231ALess subjective dependenceThe method is simple and fastImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationHistogram
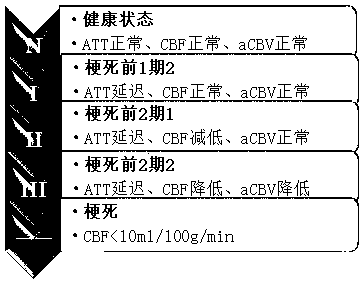
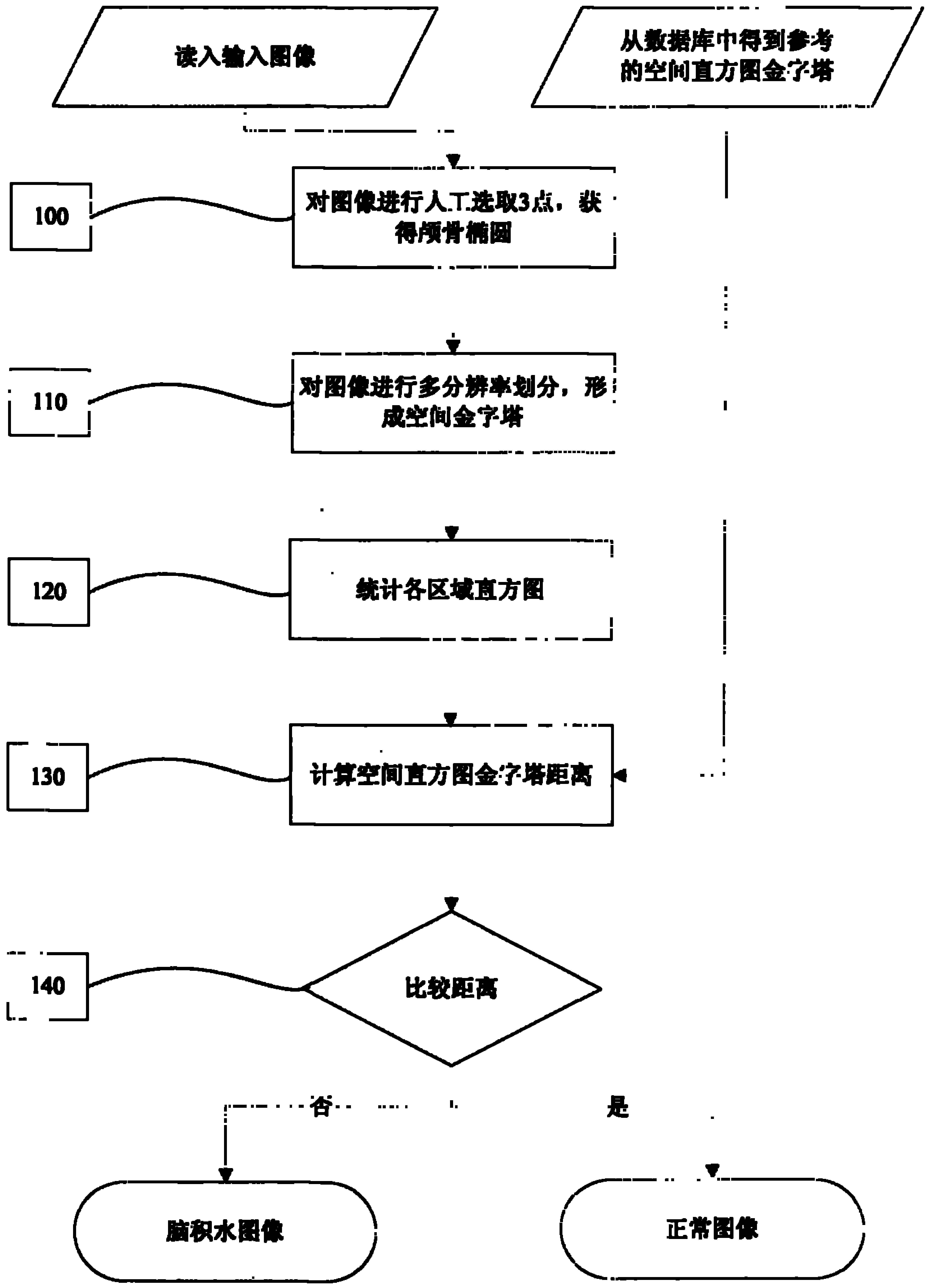
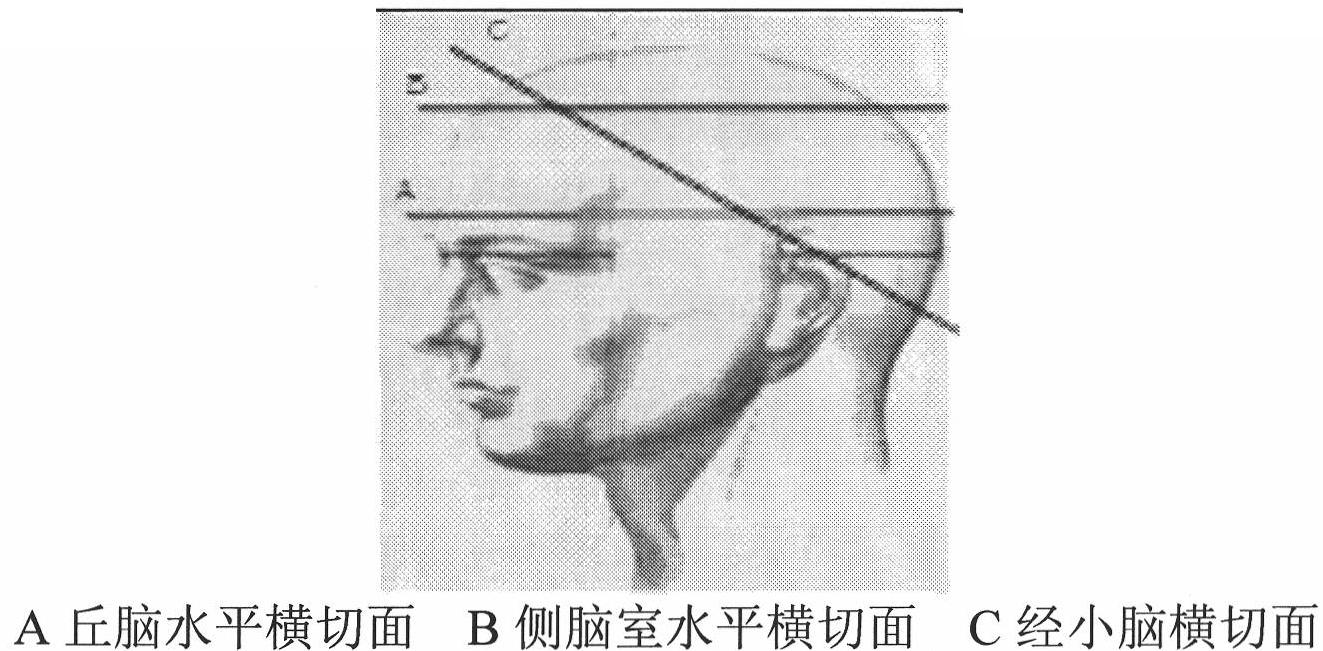
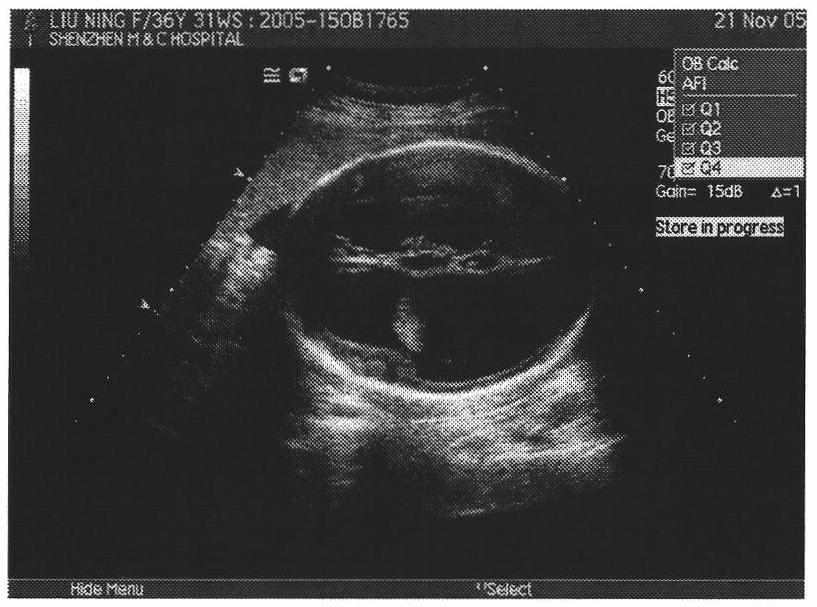
The invention provides an image processing method for automatically judging fetal hydrocephalus from ultrasonic images, comprising the following steps: firstly extracting skull ellipse of a new fetal brain image on the second plane, lateral ventricle horizontal plane; establishing a space histogram pyramid in the interior zone of the ellipse in the image; respectively calculating the distances among the space histogram pyramids of the given fetal ultrasonic image, the normal fetal brain images in the same gestational week and the image of hydrocephalus in the brain on the lateral ventricle horizontal plane in the same gestational week; and setting a threshold and giving the possibility of fetal hydrocephalus from judgment according to the relationship between the distances among the space histogram pyramids and the threshold.
Owner:SHENZHEN MATERNITY & CHILD HEALTHCARE HOSPITAL +1
Cerebral hematoma segmentation method and system based on deep learning
PendingCN111754520AReduce lossesSmall amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisBrain ctBrain hematoma
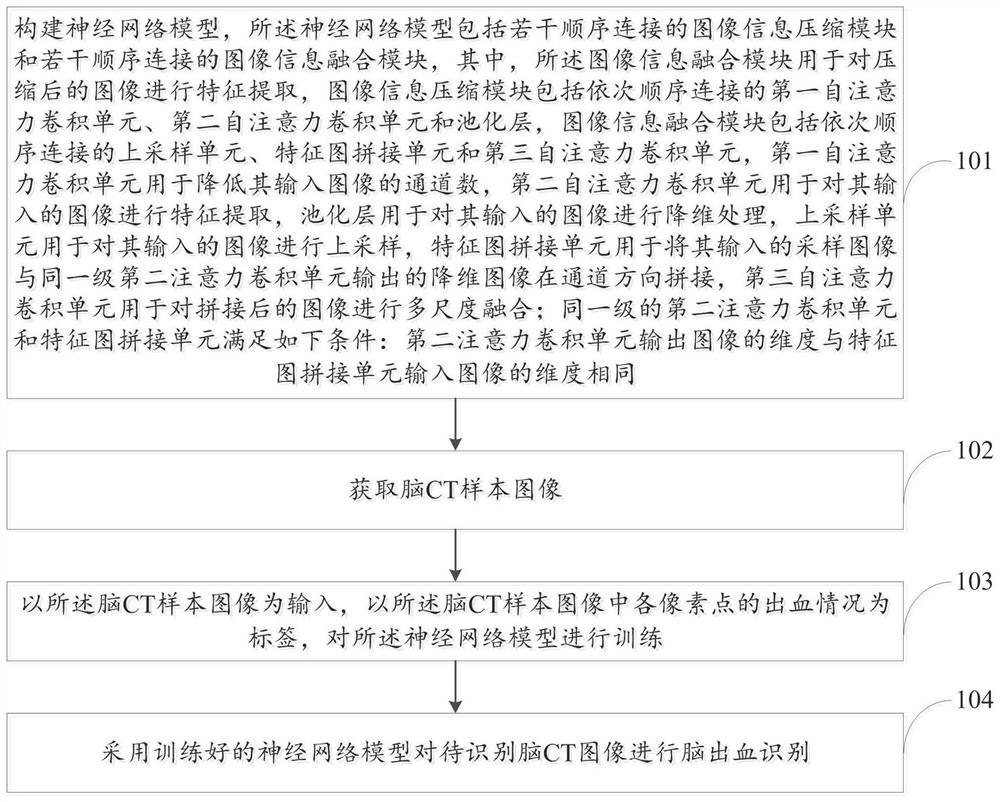
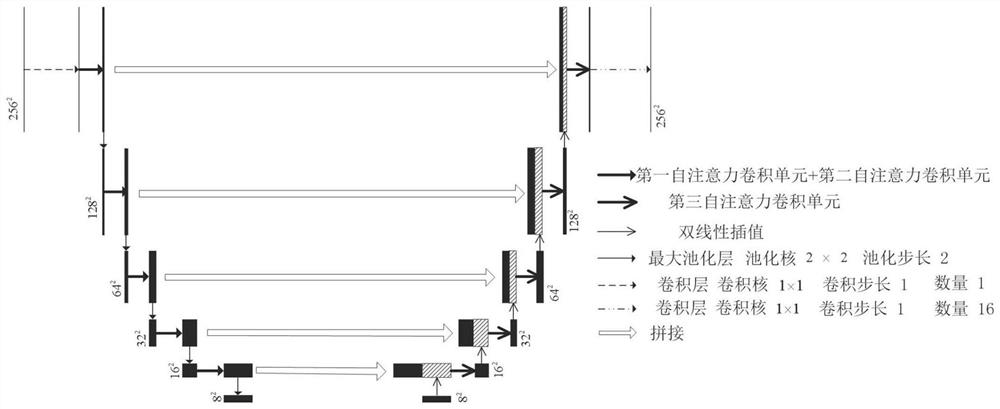
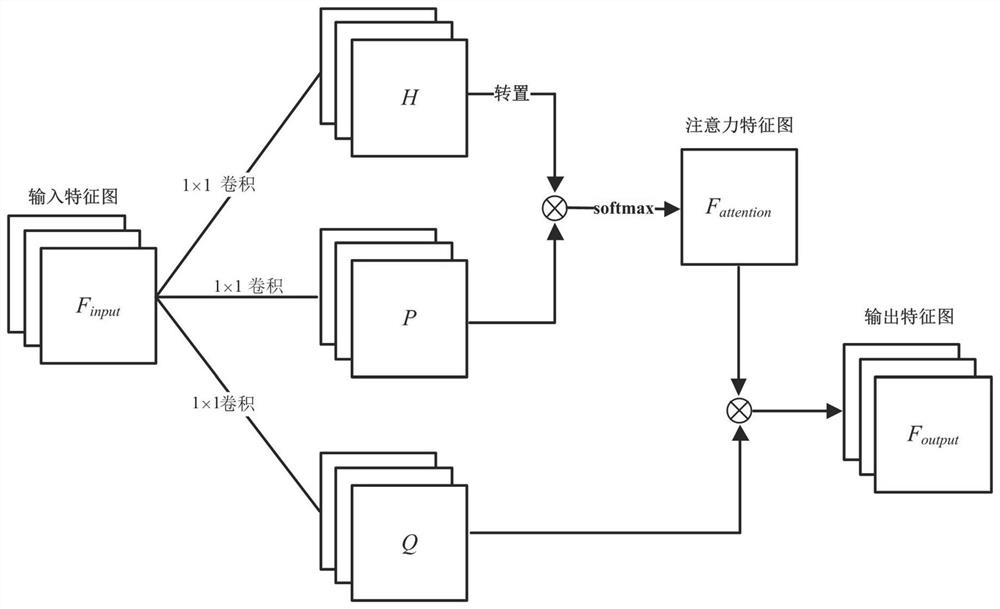
The invention discloses a cerebral hematoma segmentation method and system based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a neural network model, the neural network model comprising a plurality of image information compression modules which are connected in sequence and a plurality of image information fusion modules which are connected in sequence, wherein the image information compression module comprises a first self-attention convolution unit, a second self-attention convolution unit and a pooling layer which are connected in sequence, and the image information fusion module comprises an up-sampling unit, a feature map splicing unit and a third self-attention convolution unit which are connected in sequence; obtaining a brain CT sample image; training the neural network model by taking the brain CT sample image as input and the bleeding condition of each pixel point in the brain CT sample image as a label; and adopting the trained neural network model to perform cerebral hemorrhage identification on the to-be-segmented brain CT image. According to the method, the bleeding area in the brain CT image can be accurately and efficiently segmented.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
CT image segmentation method based on improved AU-Net network
ActiveCN112927240ABridging the Semantic GapEnhanced Feature LearningImage enhancementImage analysisBrain ctImaging processing
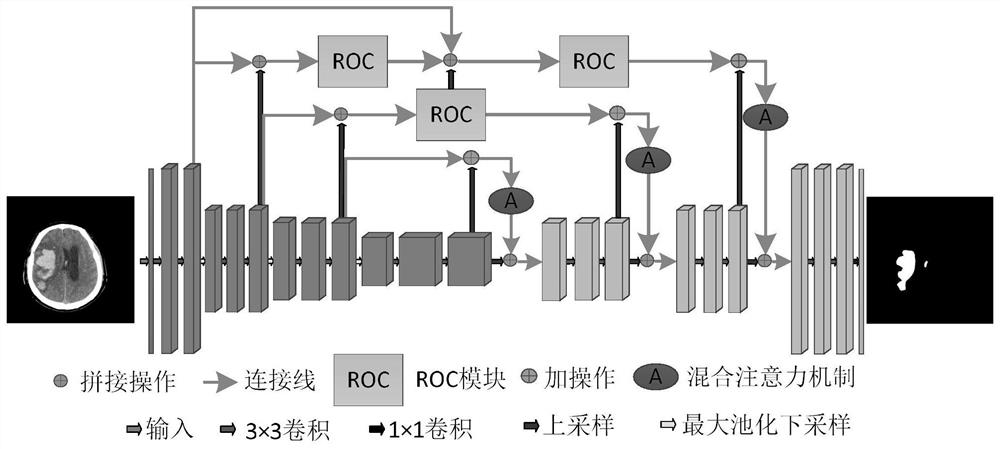
The invention belongs to the field of image processing, and particularly relates to a CT image segmentation method based on an improved AU-Net network, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-segmented brain CT image, and carrying out the preprocessing of the obtained brain CT image; inputting the processed image into the trained improved AU-Net network for image recognition and segmentation to obtain a segmented CT image; identifying a cerebral hemorrhage area according to the segmented brain CT image. The improved AU-Net network comprises an encoder, a decoder and a hopping connection part. Aiming at the problem of low segmentation precision caused by large size and shape difference of the hemorrhage part of the cerebral hemorrhage CT image, the invention provides a coding-decoding-based structure, and a residual octave convolution module is designed in the structure, so that the model can segment and identify the image more accurately.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
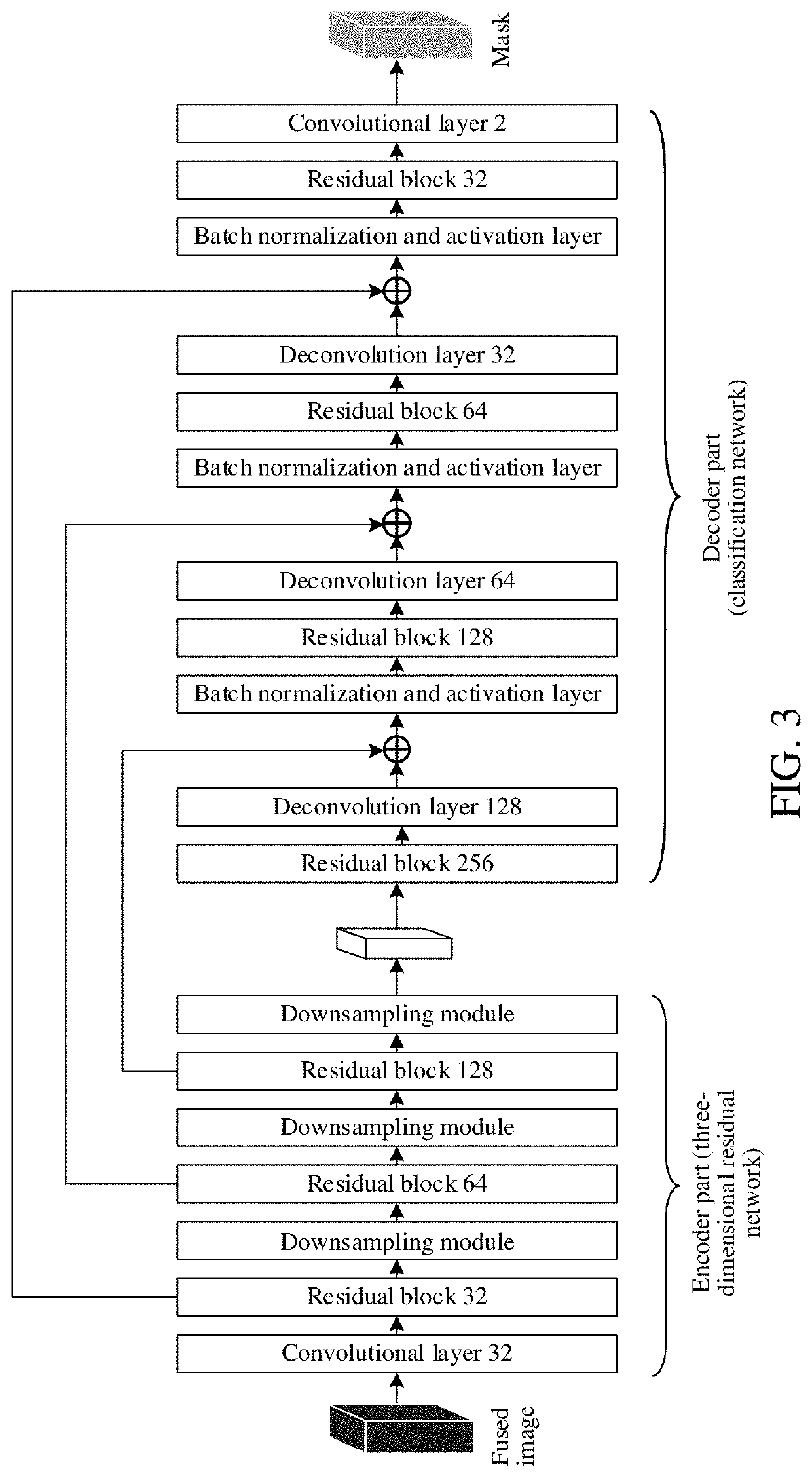
Brain image segmentation method and apparatus, network device, and storage medium
PendingUS20210248751A1High expressionImprove Segmentation AccuracyImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologySkull bone
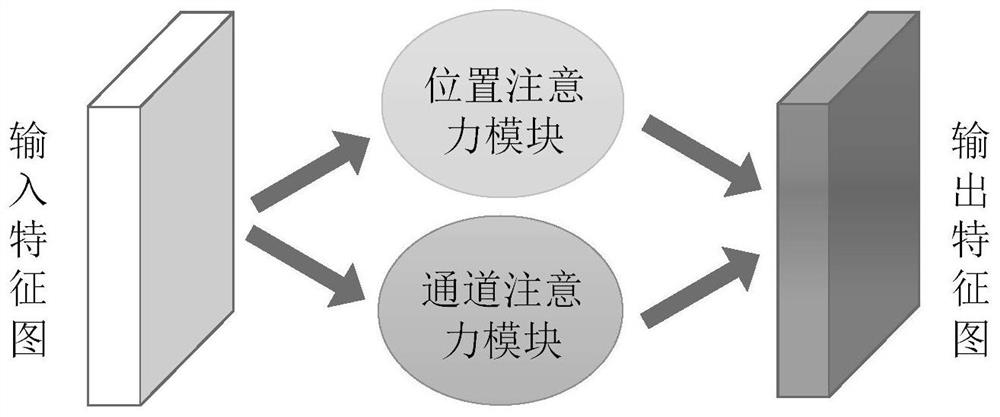
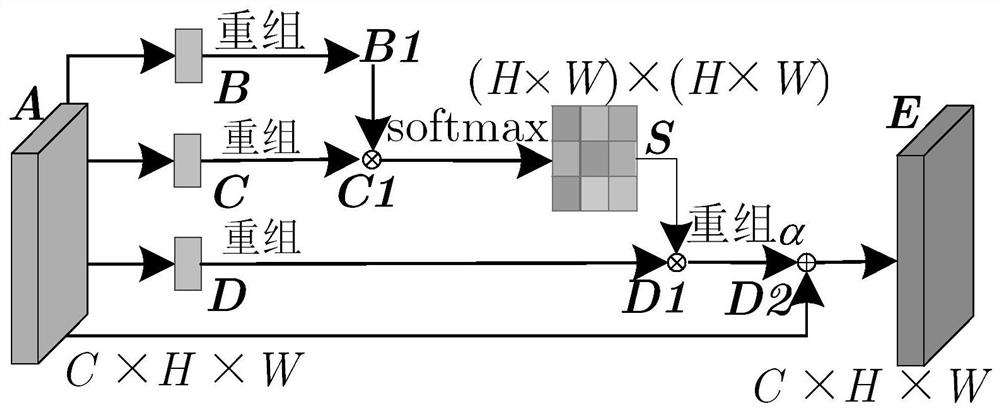
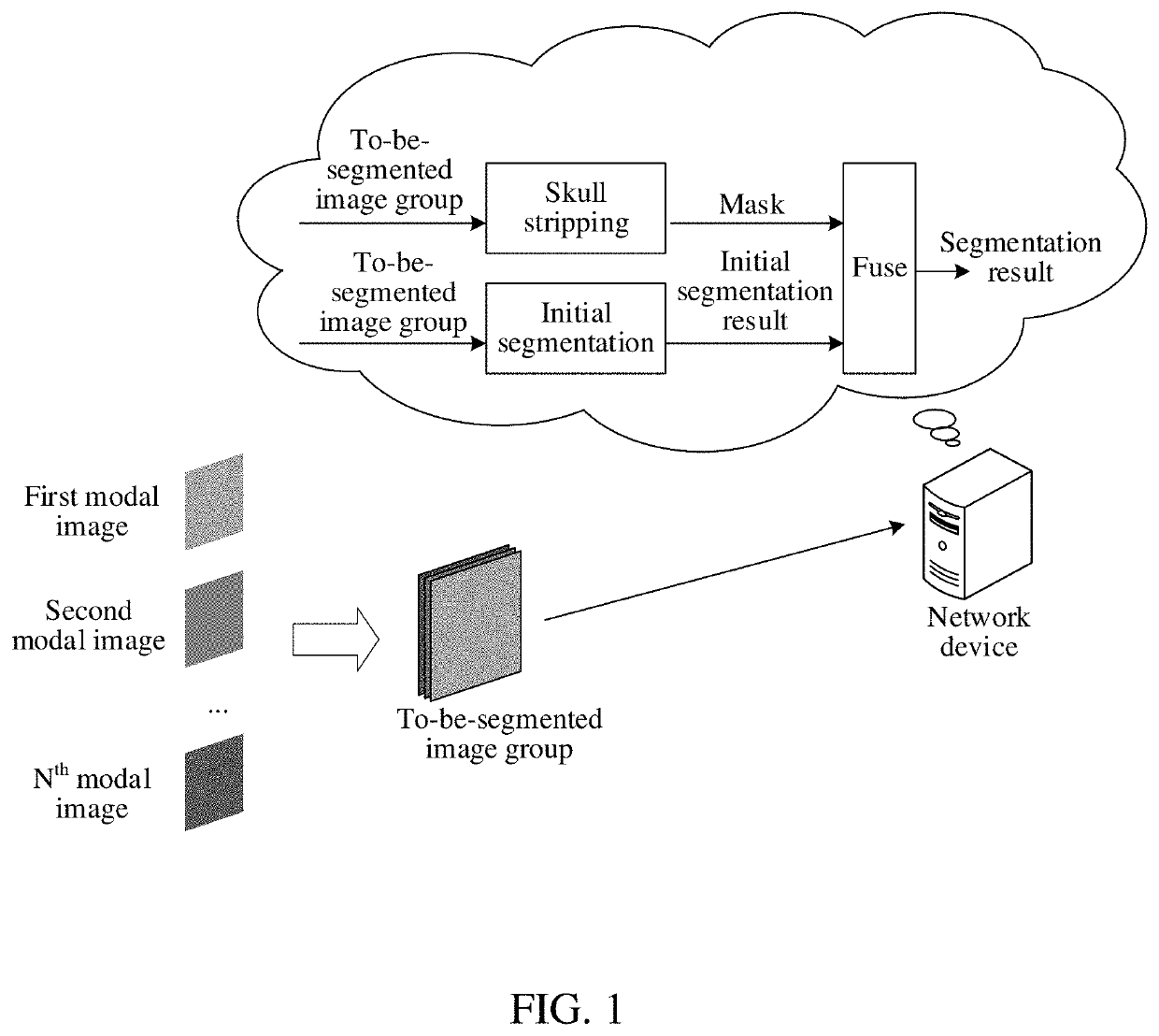
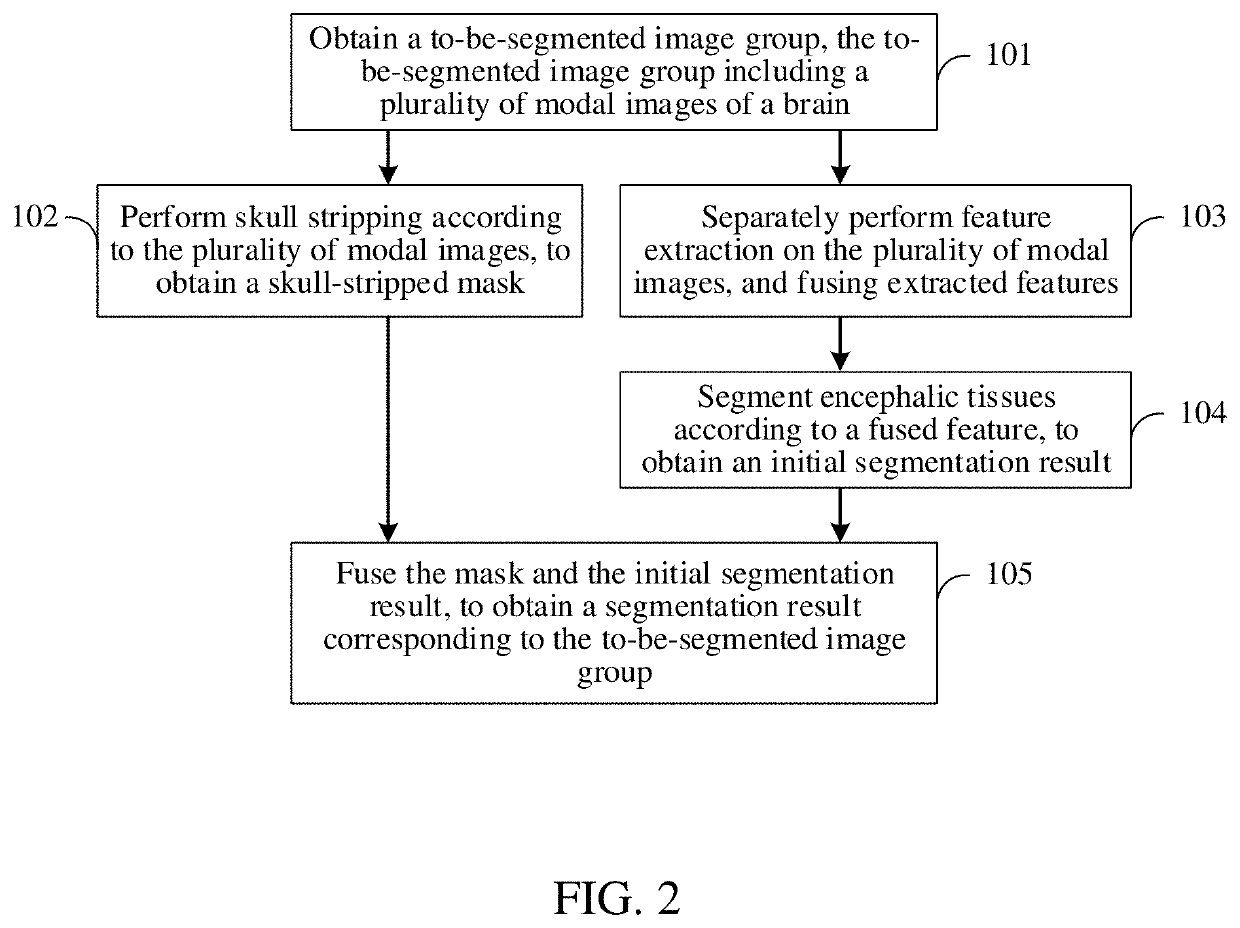
Embodiments of this application disclose a brain image segmentation method and apparatus, a network device, and a storage medium. The method includes obtaining, by a device, a to-be-segmented image group comprising a plurality of modal images of a brain. The device includes a memory storing instructions and a processor in communication with the memory. The method further includes performing, by the device, skull stripping according to the plurality of modal images to obtain a skull-stripped mask; separately performing, by the device, feature extraction on the plurality of modal images to obtain extracted features, and fusing the extracted features to obtain a fused feature; segmenting, by the device, encephalic tissues according to the fused feature to obtain an initial segmentation result; and fusing, by the device, the skull-stripped mask and the initial segmentation result to obtain a segmentation result corresponding to the to-be-segmented image group.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Image analysis of brain image data
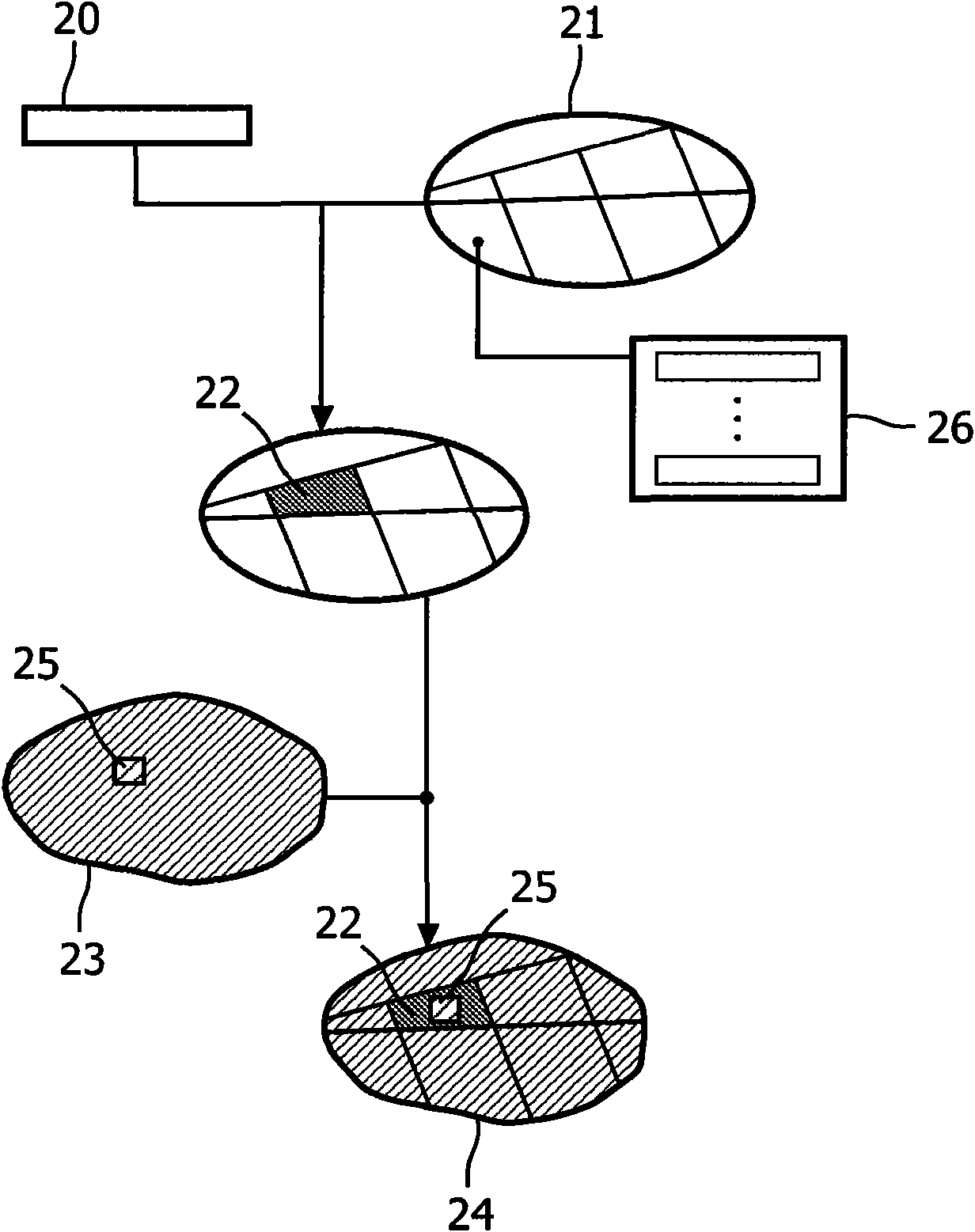
InactiveUS20100260394A1Extract information very effectivelyEfficient processingMedical simulationImage enhancementImaging analysisBrain imag
The present invention relates to analysis of image data, e.g. brain image data, where regions of interest are identified in patient specific image data based on non-image data. The brain image data is analyzed by correlating non-image data (20) in the form of data indicative of a neurological deficit and an object model (21) to identify one or more regions of interest (22) in the brain model, mapping the brain model to patient specific brain image data to obtain target image data (24), and identifying the one or more regions of interest in the target image data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for localizing implanted intracranial electrode
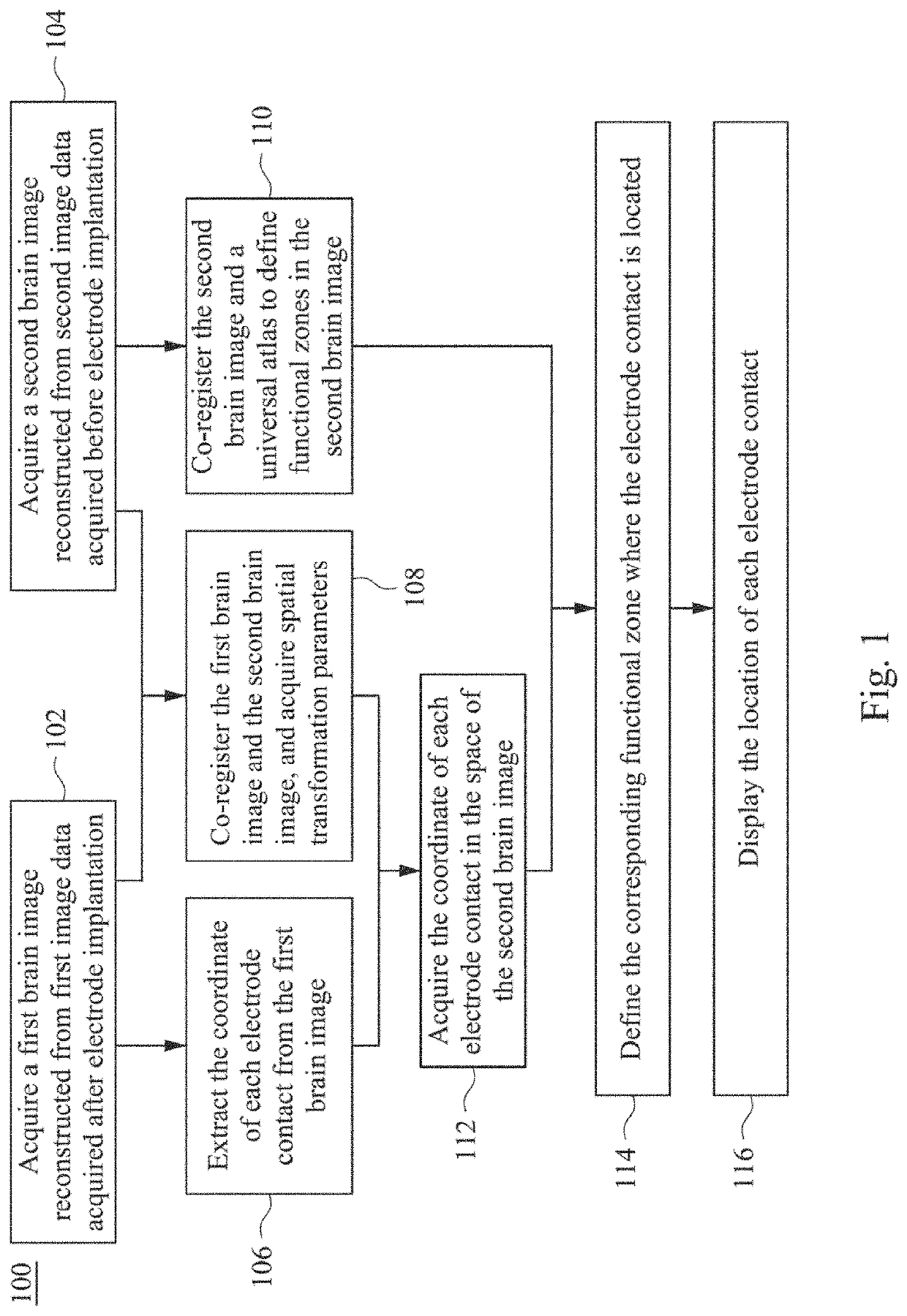
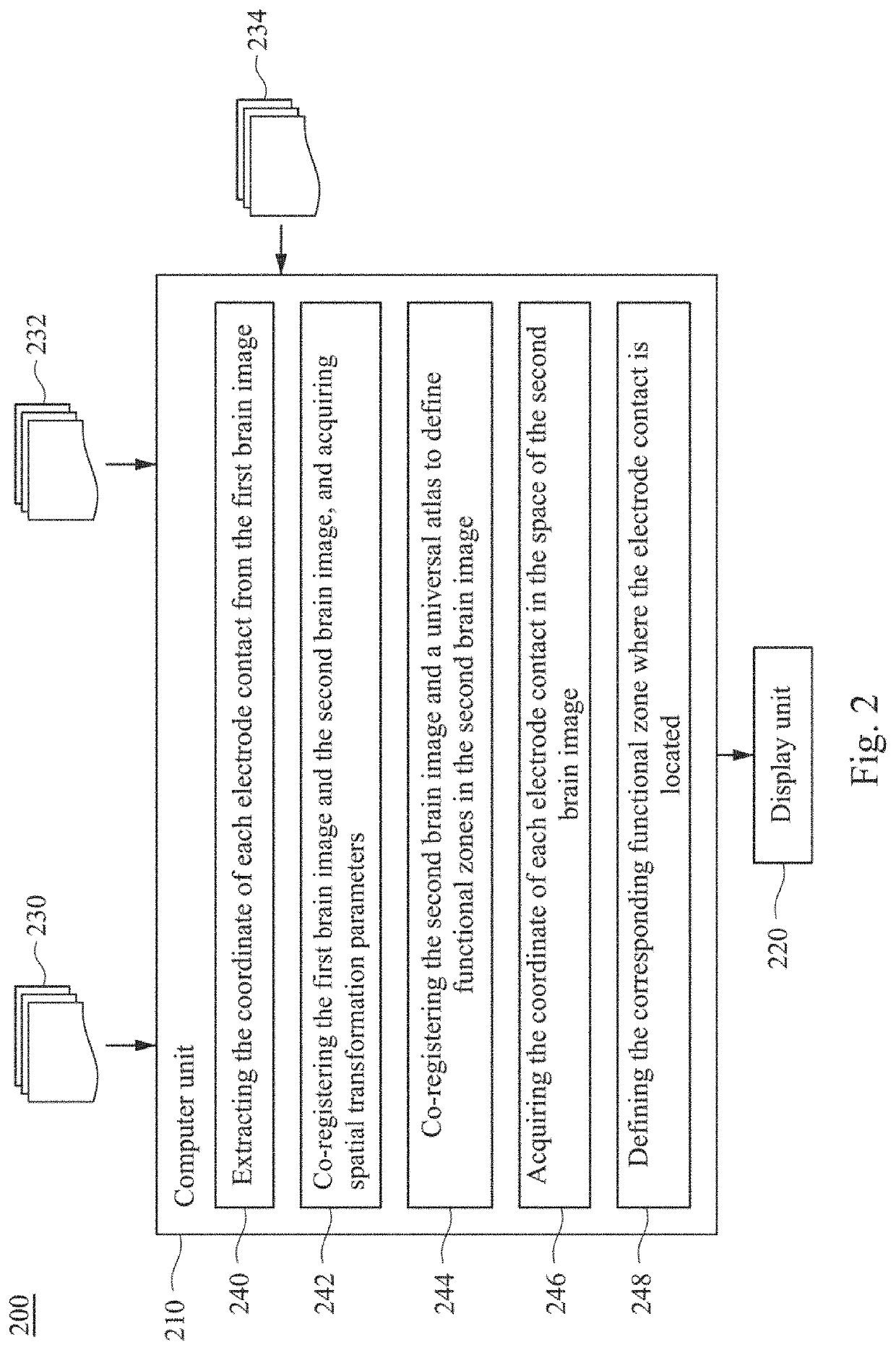
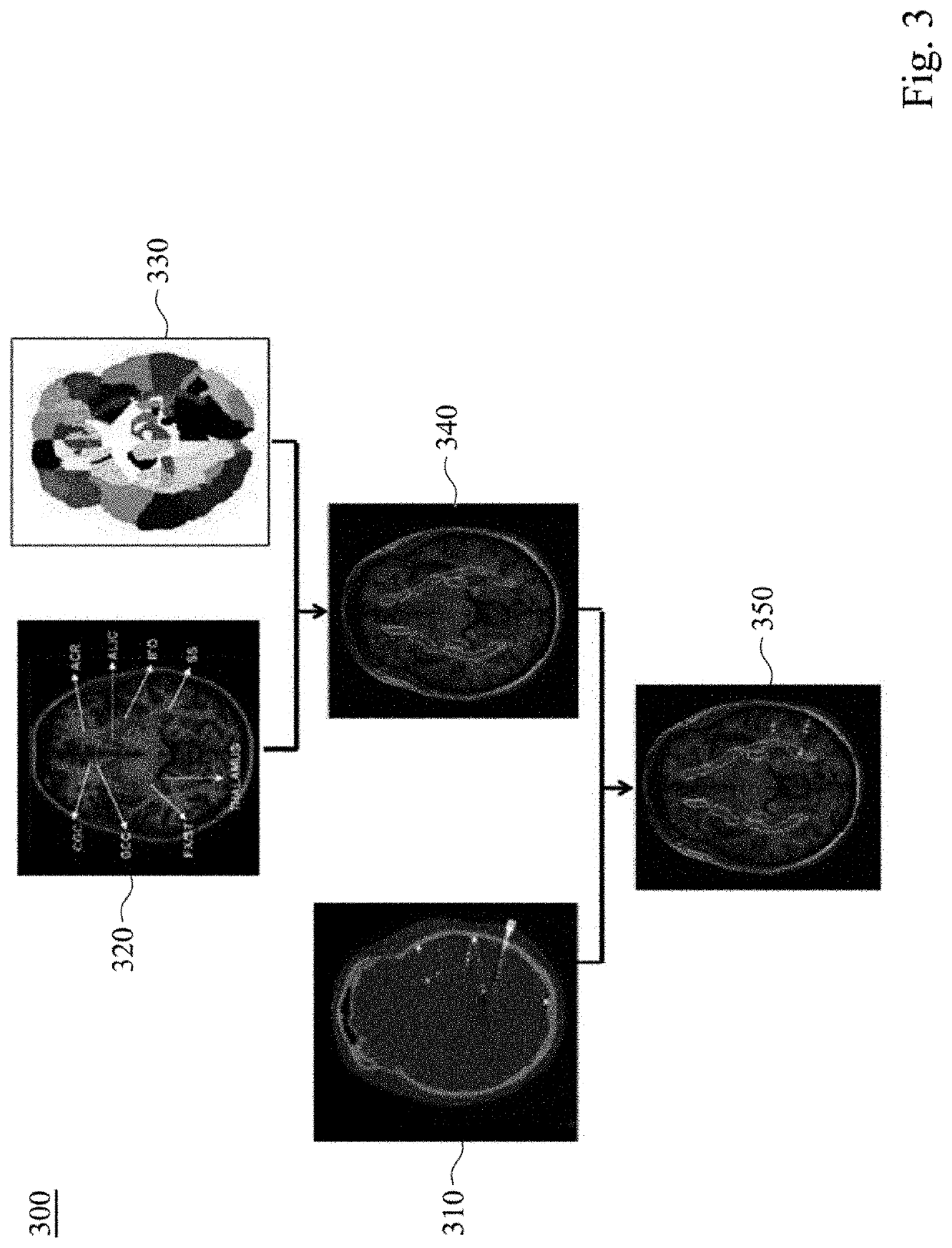
A method for localizing an intracranial electrode in a subject's brain is provided. The intracranial electrode has at least one electrode contact. The method includes: acquiring a first brain image reconstructed from first image data acquired after electrode-implantation; acquiring a second brain image reconstructed from second image data acquired before the electrode-implantation; co-registering the first brain image and the second brain image to acquire spatial transformation parameters; extracting a first coordinate of the electrode contact from the first brain image; converting the first coordinate into a second coordinate in the second brain image by using the spatial transformation parameters; co-registering the second brain image and a universal brain atlas to define functional zones in the second brain image; and defining a corresponding functional zone where the second coordinate is located. Another alternative method and a system for localizing an intracranial electrode are also provided herein.
Owner:NAT YANG MING CHIAO TUNG UNIV
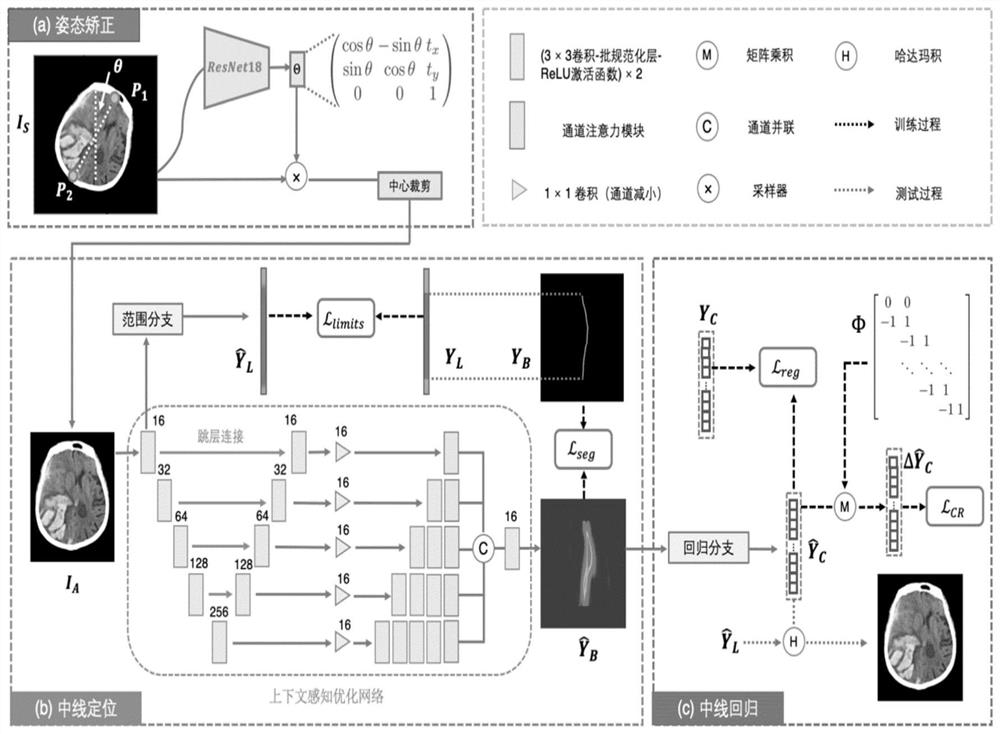
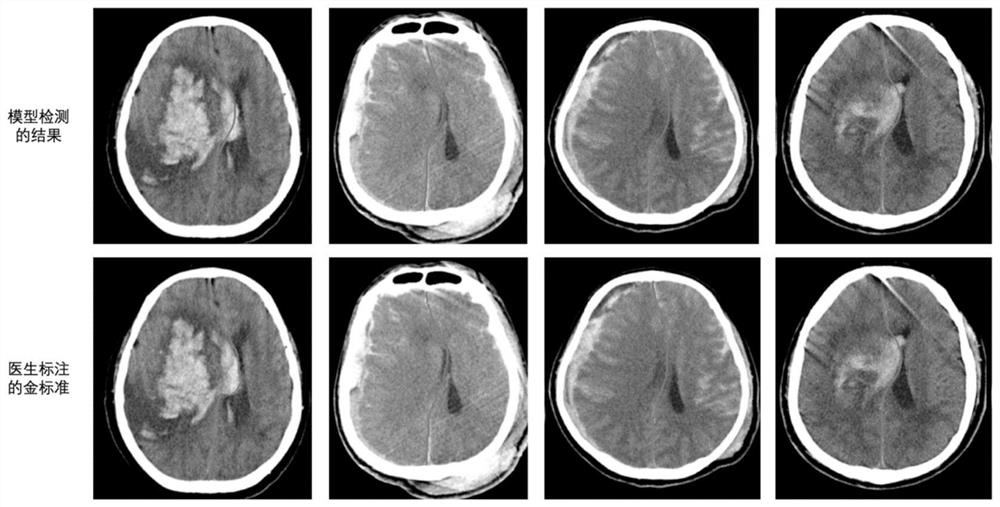
Brain centerline detection method and system, terminal and storage medium
PendingCN111861989AEfficient detectionAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisBrain ctComputer vision
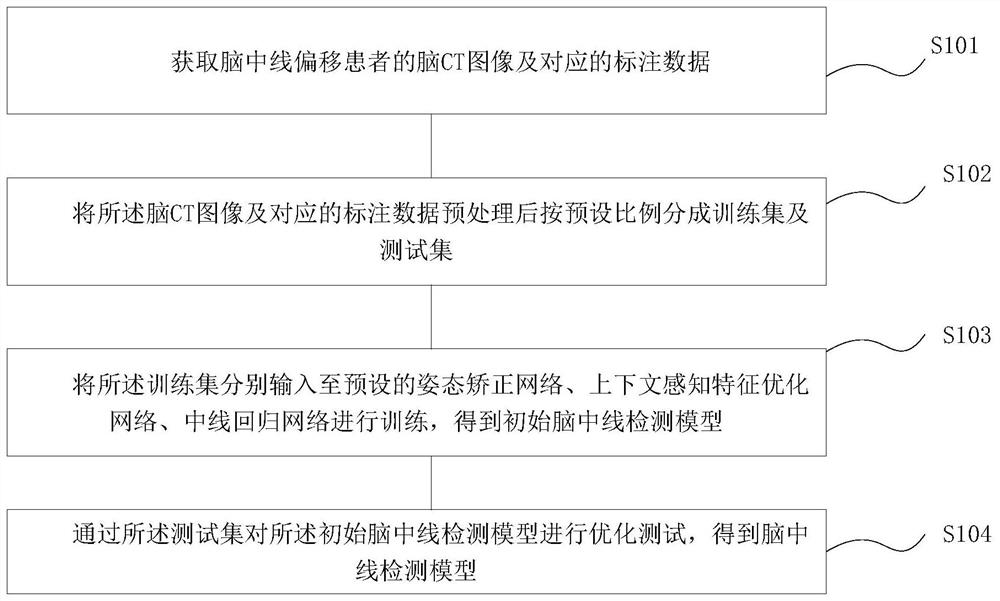
The invention provides a brain centerline detection method and system, a terminal and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a brain CT image and corresponding annotation data of a brain centerline offset patient; preprocessing the brain CT image and the corresponding annotation data, and dividing the preprocessed brain CT image and the corresponding annotation data into a training set and a test set according to a preset proportion; respectively inputting the training set into a preset attitude correction network, a context-aware feature optimization network and a neutral line regression network for training to obtain an initial brain neutral line detection model; performing optimization test on the initial brain centerline detection model through the test set to obtain a brain centerline detection model. The invention can automatically detect the brain centerlines with different offset degrees, can be used for subsequent measurement of brain centerline offset to obtain the coordinate of the offset brain centerline, and realizes efficient and accurate detection of the brain centerline.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +1
Method for analysing an image of the brain of a subject, computer program product for analysing such image and apparatus for implementing the method
InactiveCN101681508AImprove accuracyEffective classificationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage segmentation
The invention provides a method for analysing an image of the brain of a subject, comprising: collection of an image in at least three dimensions of the brain of a subject, parcellation of said imageinto regions of interest (ROIs) in a brain native reference frame characteristic of said brain, determination in an automated manner, for each ROI, of at least one discriminating value based on imagedata measured on the image, said image data being representative of an anatomical or functional feature of the brain, said discriminating value being relative with regard to the discriminating valuesof the other ROIs.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Brain image processing method and system, computer equipment and storage medium
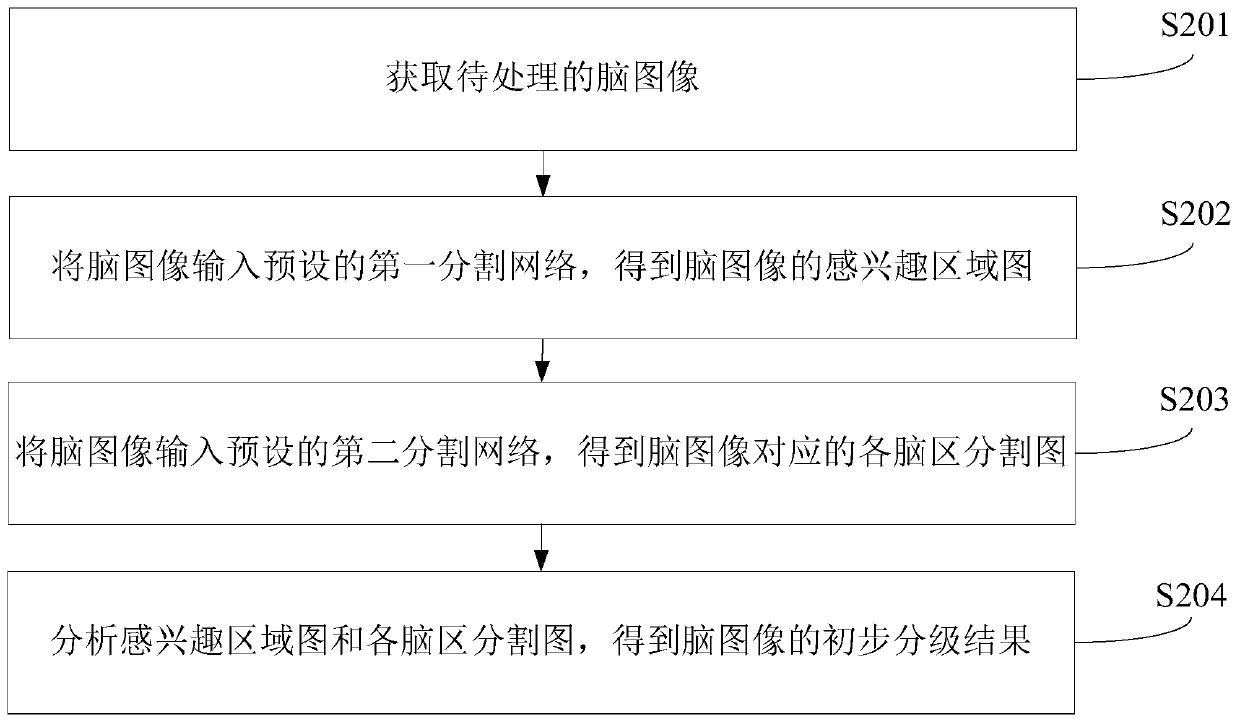
ActiveCN111445451APrioritizeRapid Preliminary Grading ResultsImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingNuclear medicine
The invention relates to a brain image processing method and system, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-processed brain image; inputting the brain image into a preset first segmentation network to obtain a region-of-interest graph of the brain image; inputting the brain image into a preset second segmentation network to obtain each brain region segmentation image corresponding to the brain image; and analyzing the region-of-interest image and the brain region segmentation images to obtain a preliminary grading result of the brain image.By adopting the method, the diagnosis efficiency of the to-be-processed brain image can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for early prediction of neurodegenerative decline
PendingUS20210228079A1Easy to useImage enhancementMedical imagingEarly predictionPredictive biomarker
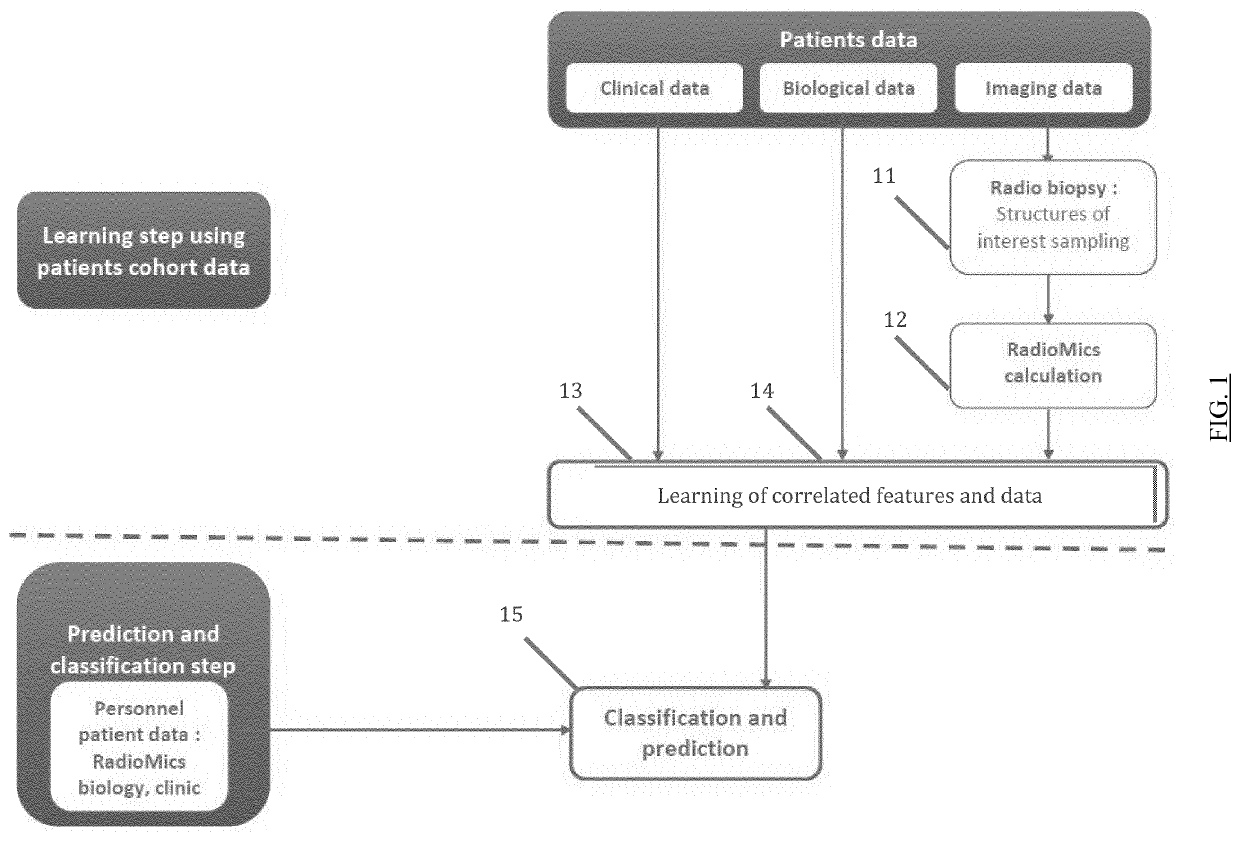
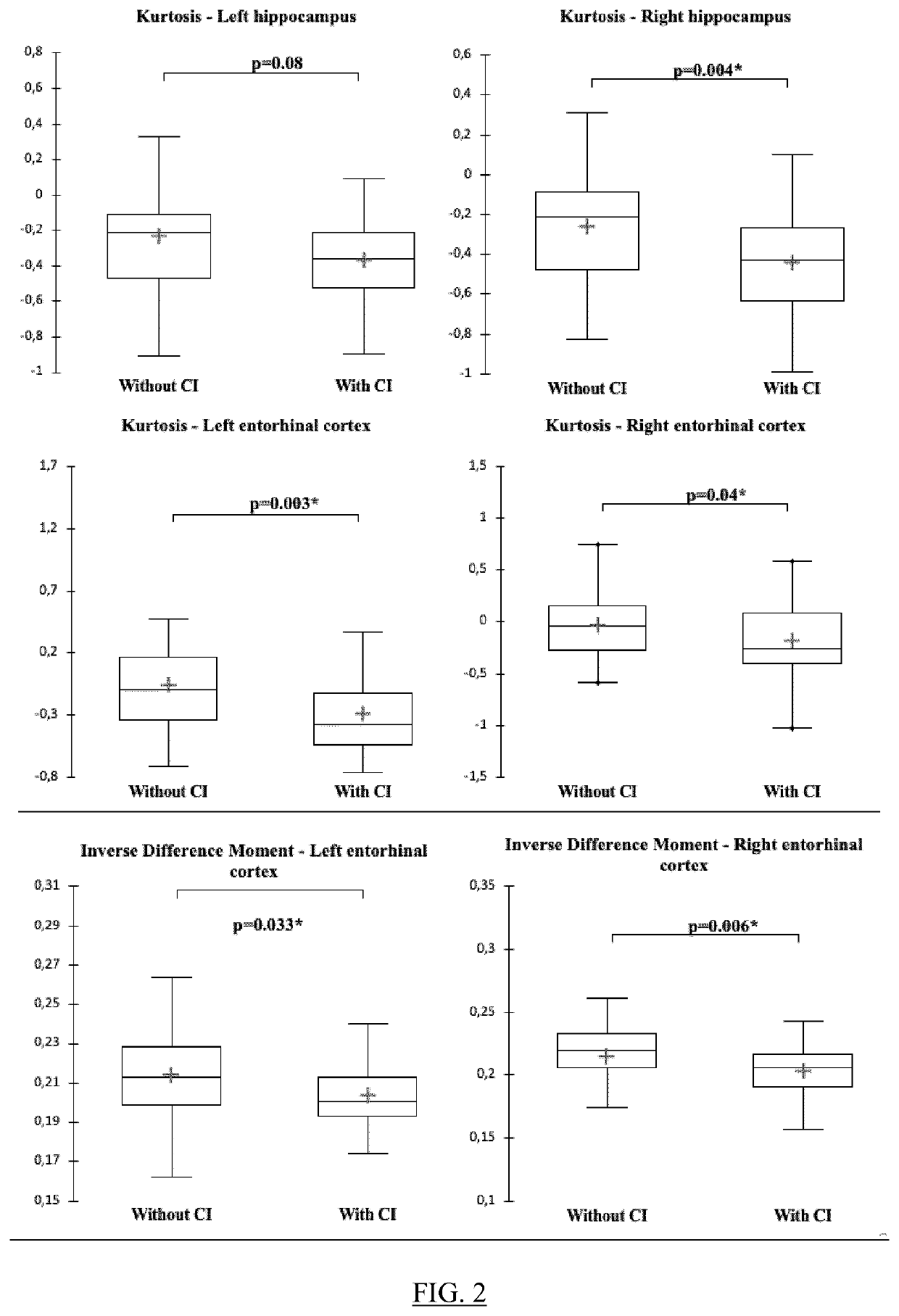
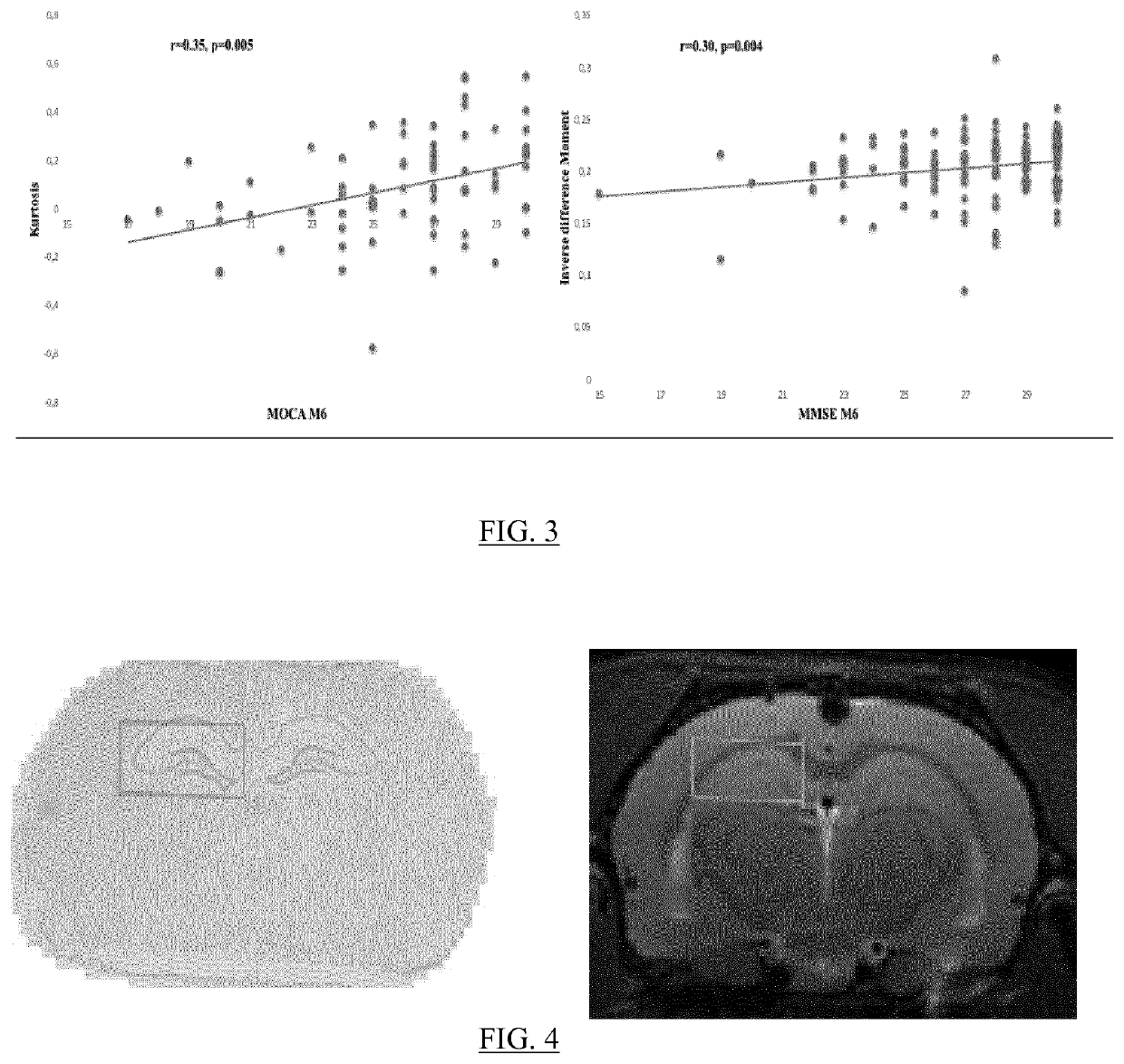
The present invention relates to a method for predicting neurodegenerative decline and / or its severity for a patient, especially of cognitive impairment (CI). Strokes and Parkinson's disease are frequently associated with occurrence of long-term cognitive impairment or dementia with still incompletely resolved mechanisms. The discovery of diagnostic and predictive biomarkers thus remains a major challenge. The method of the invention uses radiomics corresponding to texture features extracted from a plurality of previously-acquired medical brain images and correlated with previously-acquired clinical and / or biological data. A classifier is trained beforehand for learning these radiomics, and then operated on radiomics computed from at least one brain image of a patient to generate a score representative of its risks of neurodegenerative decline. By applying this method on a cohort of 160 MCI and non-MCI patients, the inventors show that MCI patients could be early predicted with a mean accuracy of 88%. In the same way, the method was able to discriminate very early stages of cognitive decline in a Parkinson's disease population of 100 patients.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Brain image processing method, computer equipment and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110720906AAccurate analysisQuick analysisMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringPattern recognitionSample graph
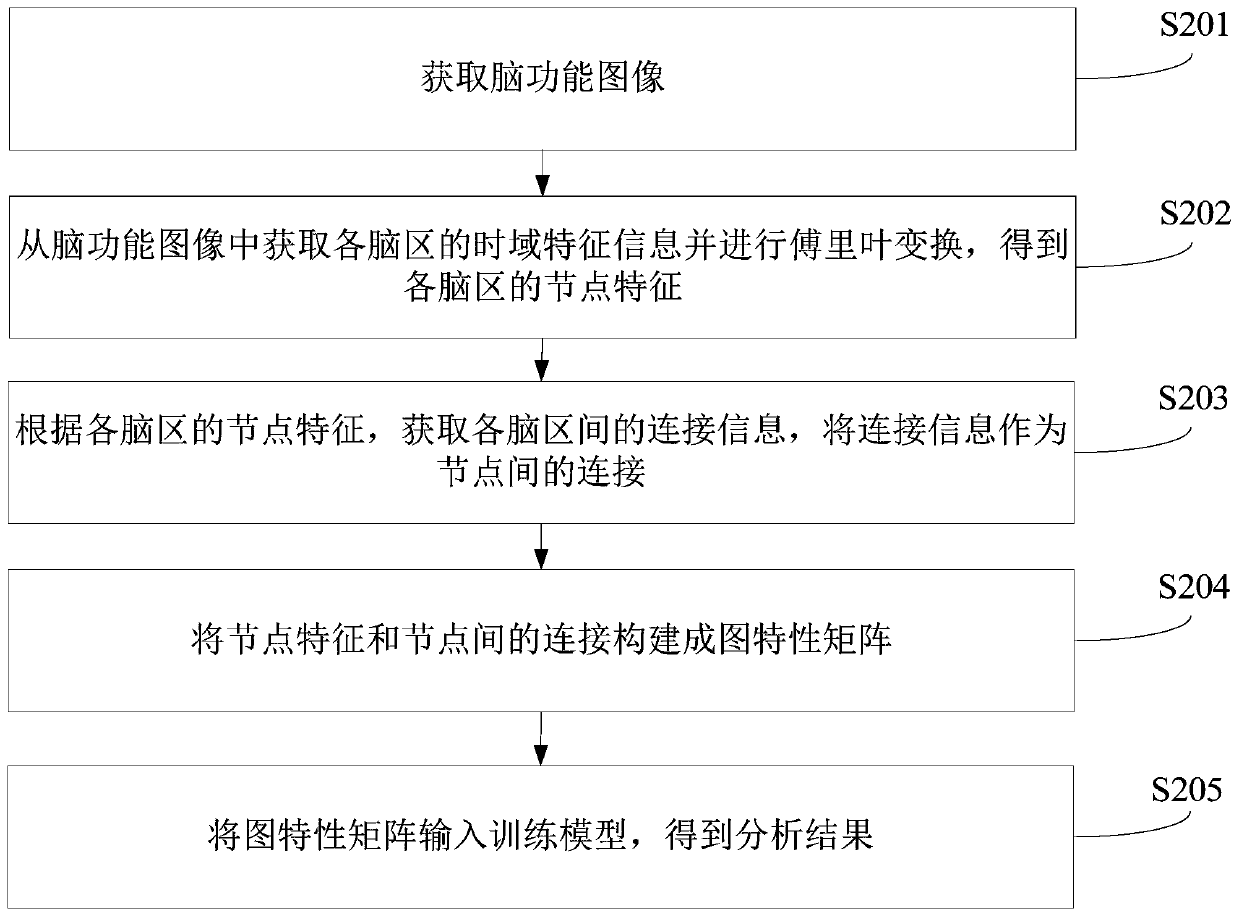
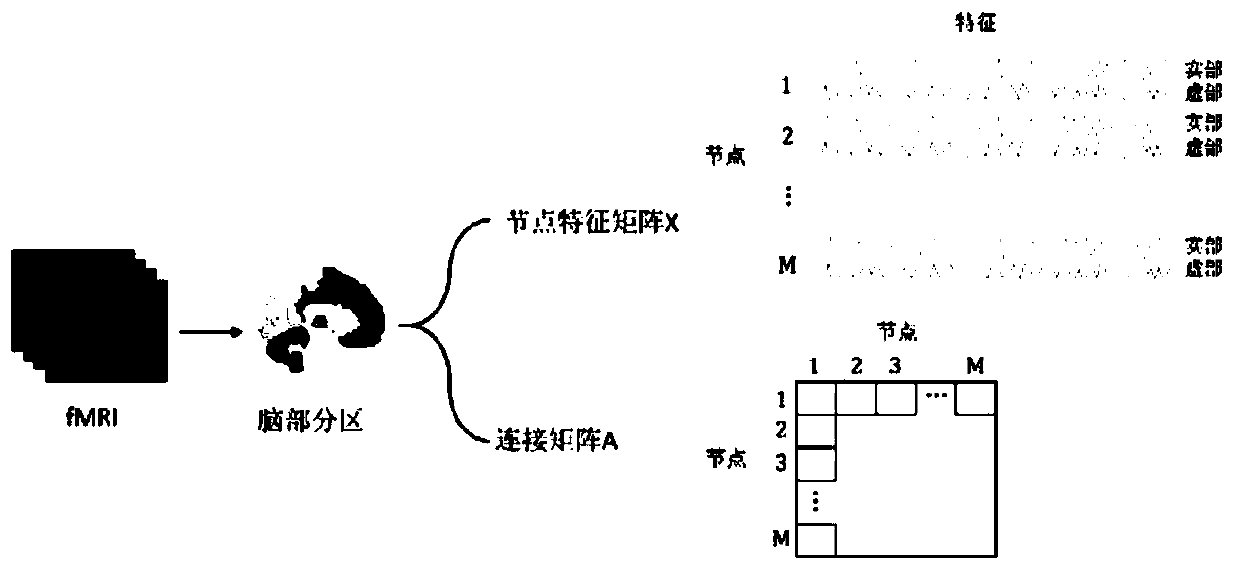
The invention relates to a brain image processing method, computer equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a brain function image; obtaining time domain feature information of each brain region from the brain function image and performing Fourier transform to obtain node features of each brain region, wherein the node characteristics comprise frequency domain real part features and frequency domain imaginary part features; according to the node characteristics of each brain region, obtaining connection information of each brain region, and taking the connection information as connection between the nodes; constructing a graph characteristic matrix by the node characteristics and the connection among the nodes; and inputting the graph characteristic matrix into a training model to obtain an analysis result, wherein the training model is the model obtained by inputting the sample graph characteristic matrix constructed by the sample brain function image into a graph network for training. According to the method, the frequency domain features obtained by performing Fourier transform on the time domain feature information of each brain region are used as the node characteristics of each brain region, so that the noise in the brain function image can be better distinguished, and the accuracy of the obtained analysis result is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Visual representation learning for brain tumor classification
Independent subspace analysis (ISA) is used to learn (42) filter kernels for CLE images in brain tumor classification. Convolution (46) and stacking are used for unsupervised learning (44, 48) with ISA to derive the filter kernels. A classifier is trained (56) to classify CLE brain images based on features extracted using the filter kernels. The resulting filter kernels and trained classifier areused (60, 64) to assist in diagnosis of occurrence of brain tumors during or as part of neurosurgical resection. The classification may assist a physician in detecting whether CLE examined brain tissue is healthy or not and / or a type of tumor.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Image analysis of brain image data
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
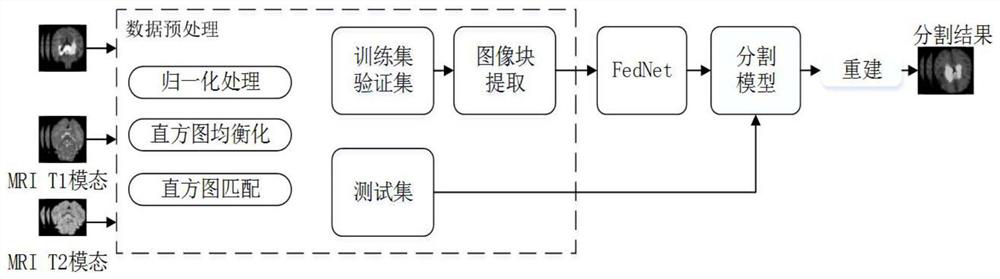
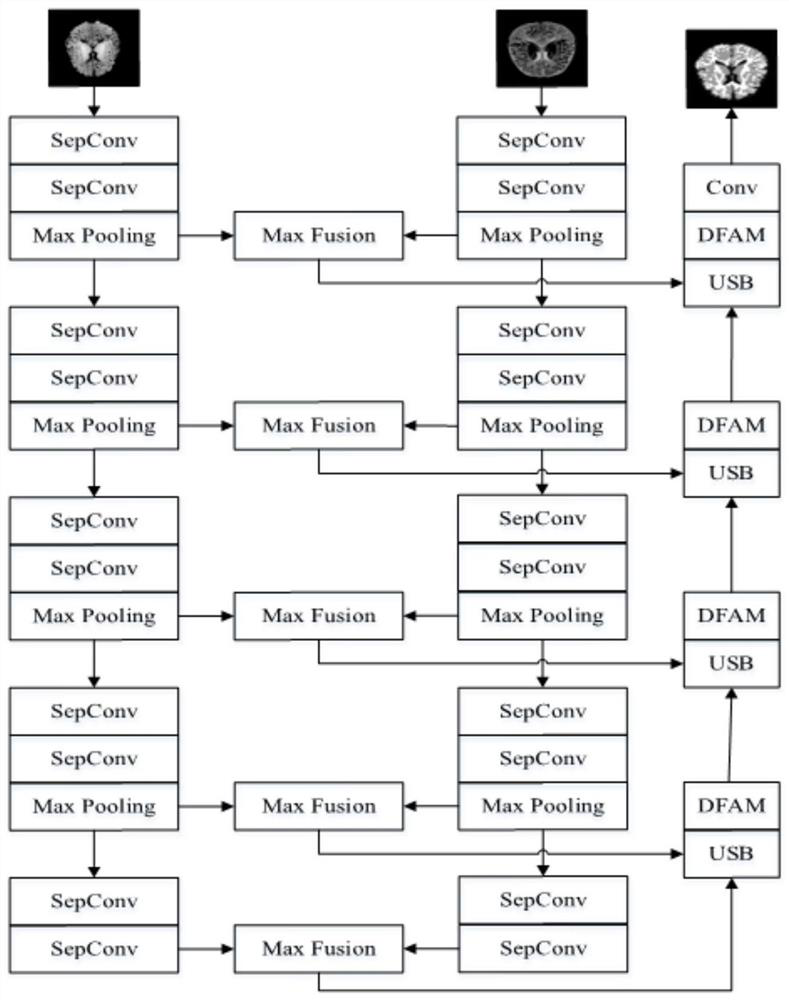
Newborn brain image segmentation method and model construction method based on deep learning
PendingCN112950644AFully combine diversityHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
The invention provides a newborn brain image segmentation method and model construction method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing a data set including a bimodal magnetic resonance image and a reference image; pre-constructing a feature enhancement bimodal segmentation network model FedNet, wherein the processed data set is used for training the feature enhancement bimodal segmentation network model FedNet, the processed data set is input into the trained feature enhancement bimodal segmentation network model FedNet, and a segmented two-dimensional image is output; reconstructing the segmented two-dimensional image, and outputting a segmented newborn brain magnetic resonance image with the same size as the pre-processed image. According to the invention, the down-sampling module is enhanced by adopting the dual-channel features, convolution and maximum pooling processing are respectively carried out through different modes, the diversity of the feature information output by the dual channels is fully combined, the up-sampling module is noticed in the invention, so that the segmentation network can have noticed features, and the accuracy of network segmentation is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Method for estimating time of occurrence of infarct region on basis of brain image
The disclosure relates to a method for estimating the time of occurrence of an infarct region based on basis of a brain image, including: a step of obtaining a brain image; a step of extracting a fixed value set that changes according to an onset time of the infarcted region in the brain image; and a step of using corresponding relation prepared such that the fixed value set corresponds to the onset time of the infarct region, so that the fixed value set corresponds to the onset time of the infarction region.
Owner:THE ASAN FOUND
Intelligent medical system
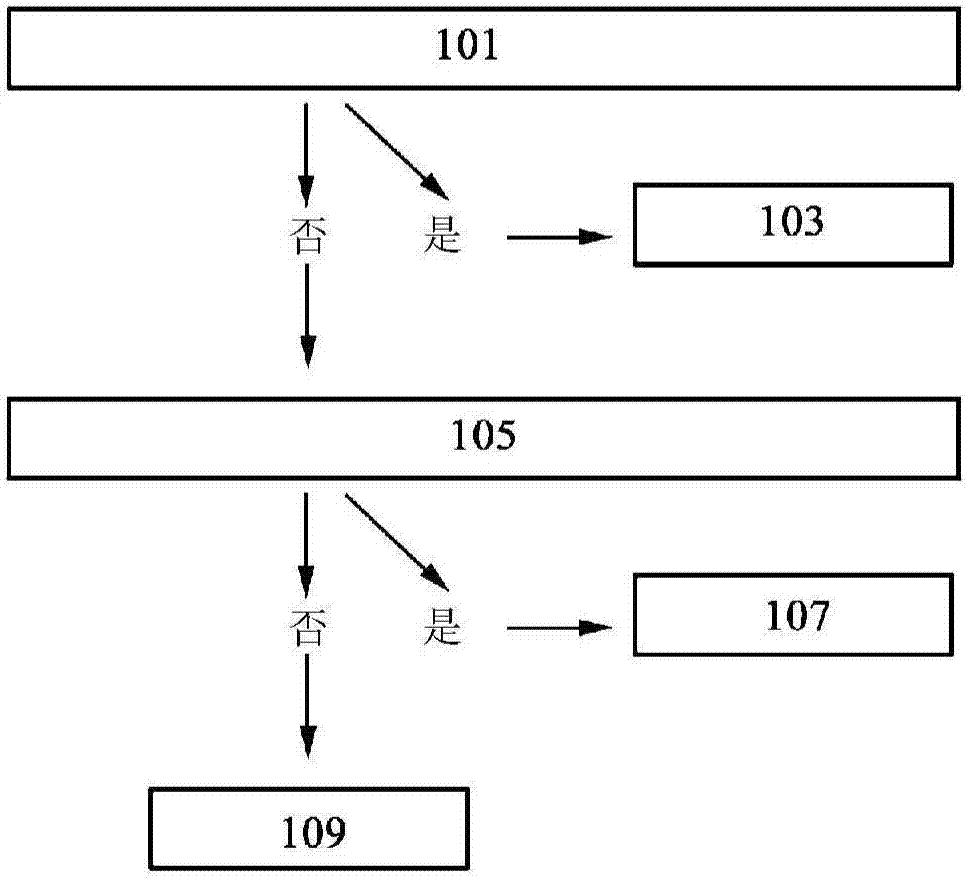
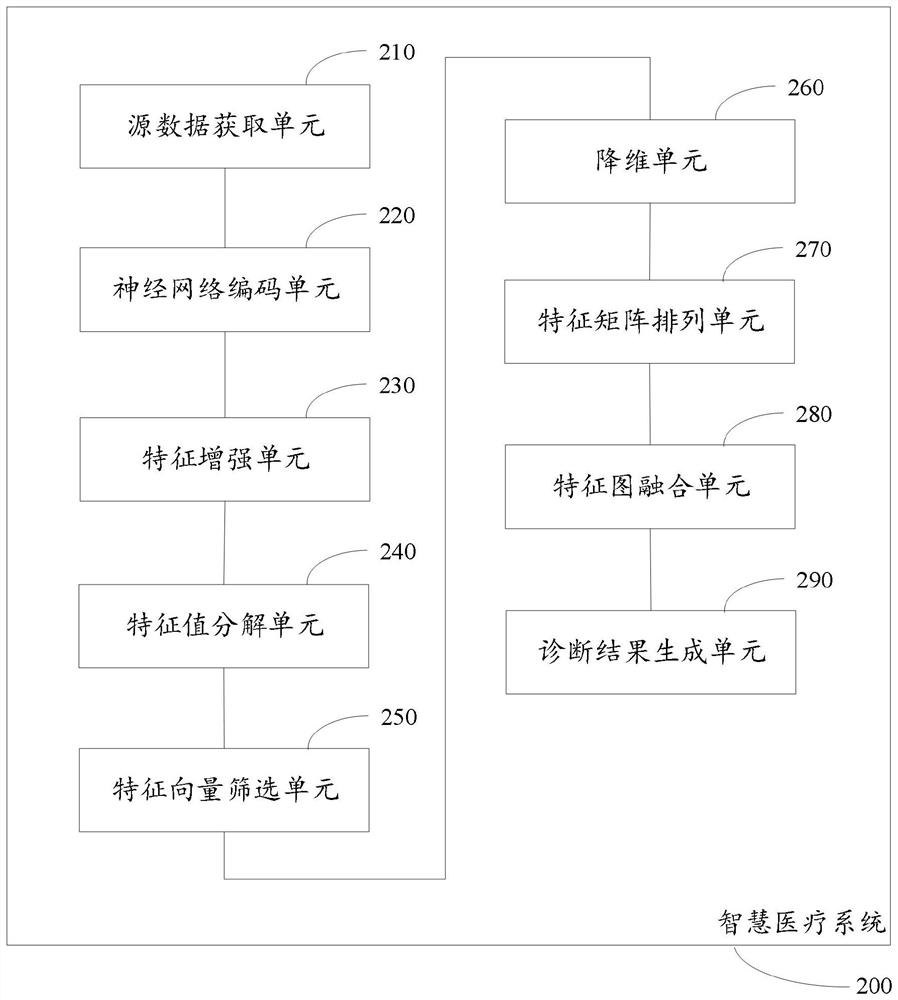
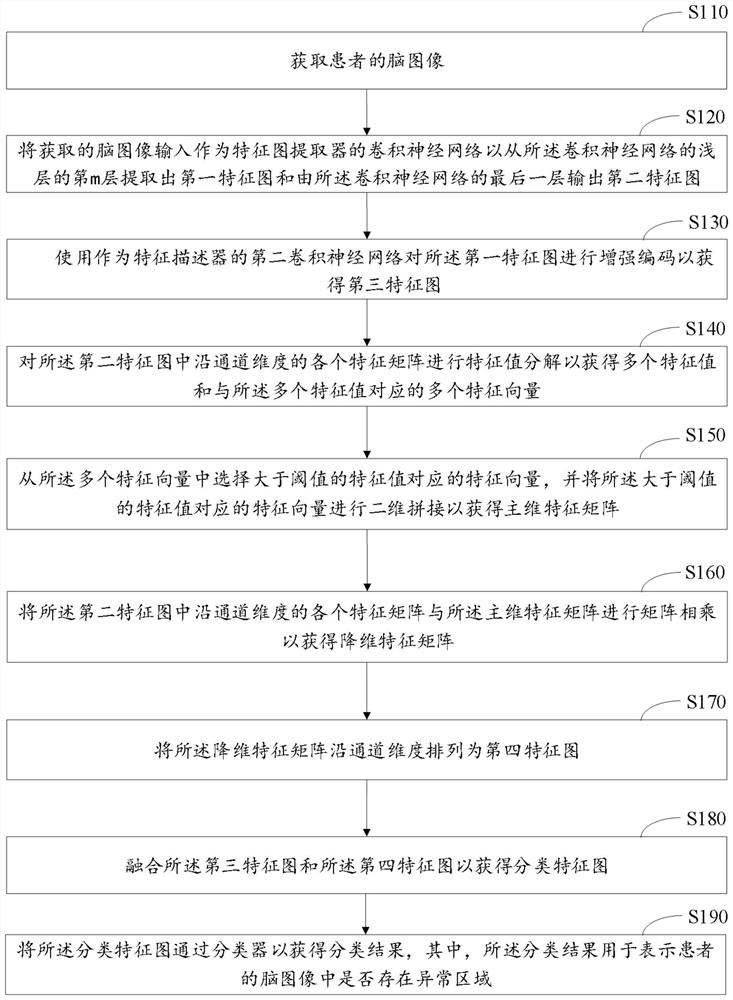
InactiveCN114648496AKeep healthyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisDimensionality reductionRadiology
The invention relates to the field of smart medical treatment, and particularly discloses a smart medical system which extracts local features of a brain image of a patient through the mth layer and the last layer of a shallow layer of a convolutional neural network serving as a feature map extractor, thereby obtaining a first feature map and a second feature map, and further using a convolutional neural network as a feature descriptor to enhance the expression of the shallow features of the first feature map, and performing singular value decomposition-based dimensionality reduction on the second feature map to pay attention to the dimensionality difference between the two feature maps, thereby improving the classification accuracy. Therefore, the abnormal region in the brain image of the patient can be accurately detected and judged, so that the health of the patient is ensured.
Owner:上海梦栀海文化传媒有限公司
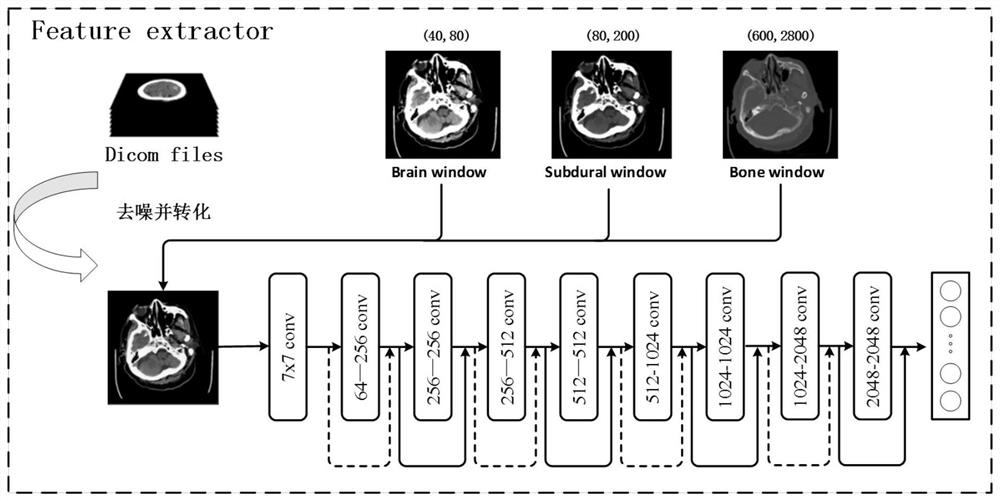
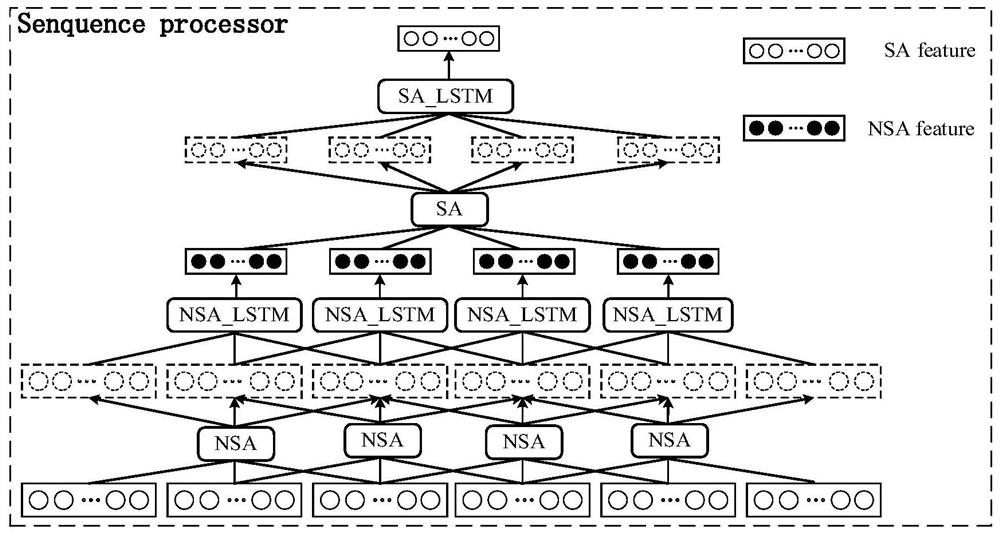
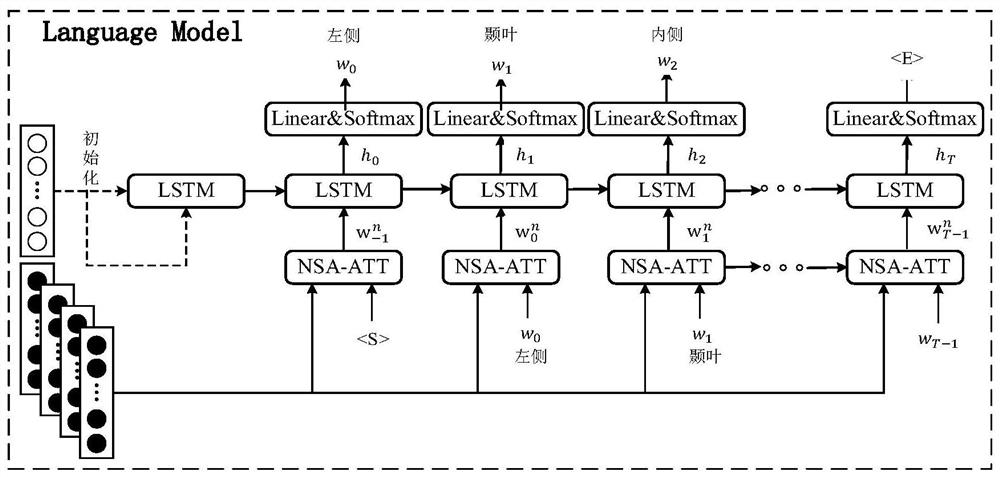
Brain CT medical report generation method based on hierarchical self-attention sequence coding
The invention discloses a medical report generation method based on hierarchical self-attention sequence coding. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a brain CT image and corresponding medical report data, and preprocessing the brain CT image and the corresponding medical report data; (2) constructing a feature extractor; (3) constructing a sequence processor, and obtaining an image feature code VNSA containing information of each adjacent fault block and a three-dimensional brain CT image feature code VSA based on the whole case after the sequence processor passes through the sequence processor; (4) constructing a decoder; and (5) performing model training. The application and development of deep learning in intelligent medical treatment are rapid, and the automatic generation technology of the medical report for the lung is mature, but the research and invention for the automatic generation of the medical report for the brain CT are vacant; therefore, according to the method the model realizes the coding of the three-dimensional brain CT data, and combines the coding with a language model in the field of image description to realize the automatic generation of the medical report of the CT image.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
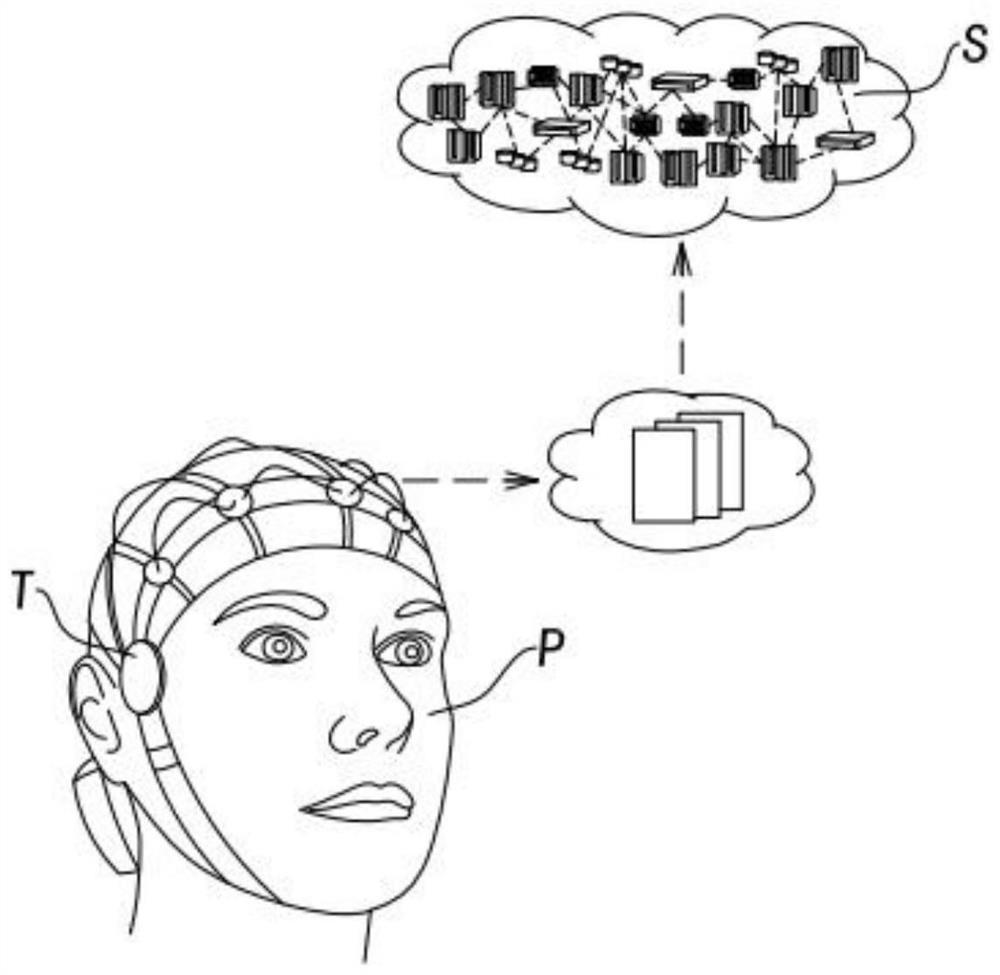
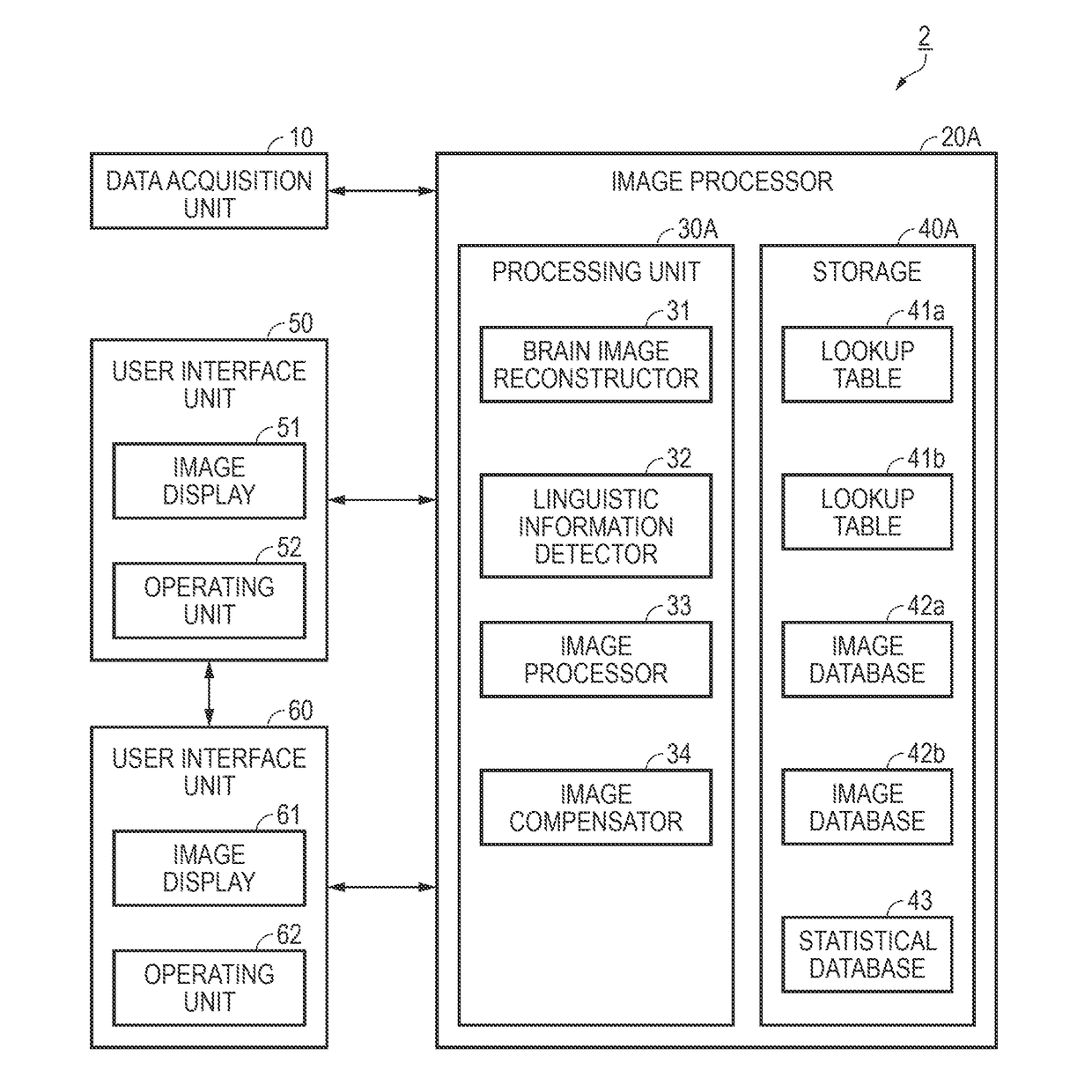
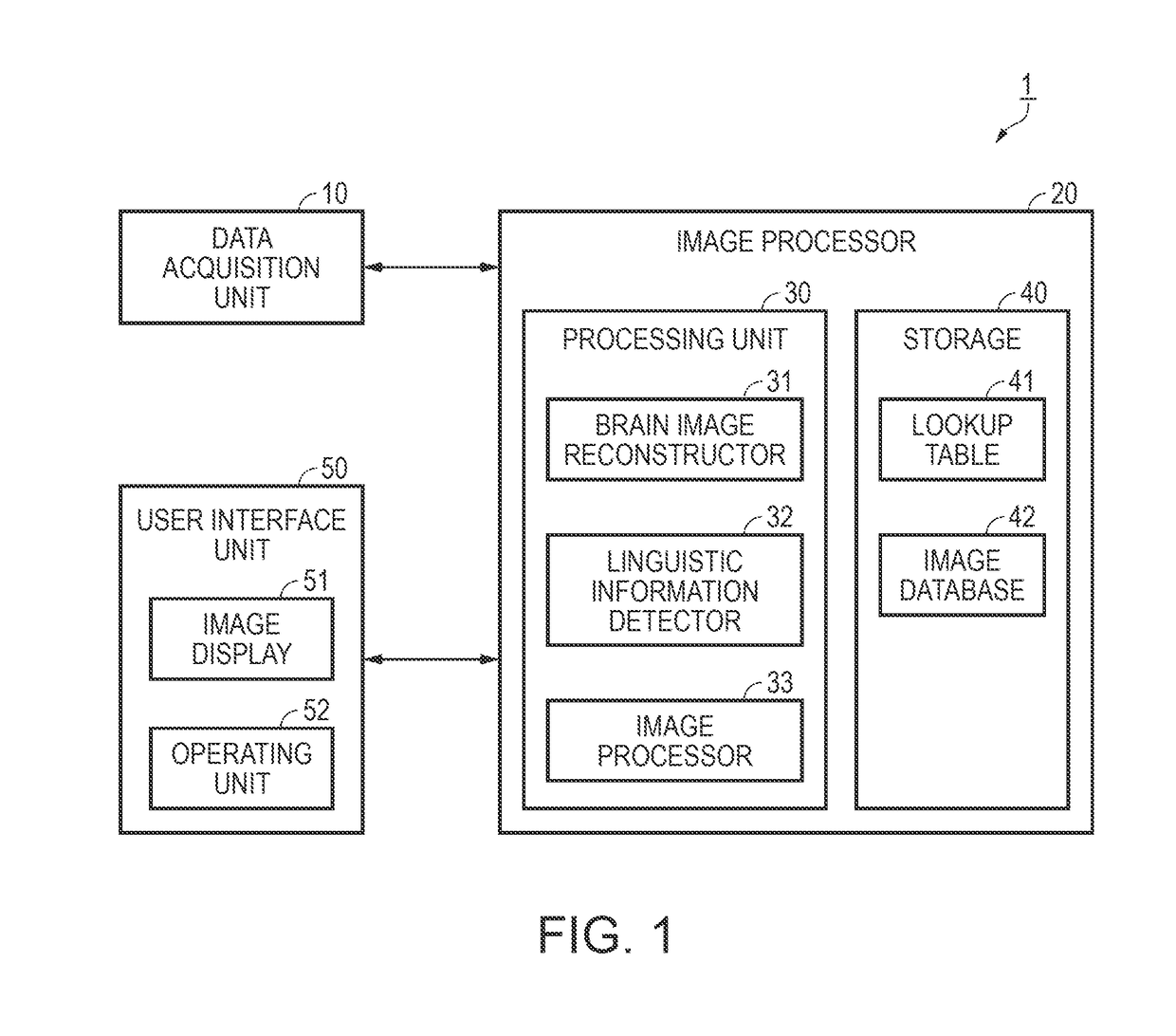
Brain image reconstruction apparatus
ActiveUS20180168452A1Easy to identifyMore accurate or frequently occurring selection optionsInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementBrain sectionSample image
A brain image reconstruction apparatus can reconstruct a brain image as a sharper image. A brain image reconstruction apparatus has a data acquisition unit that acquires brain activity data of a user; a brain image reconstructor that detects image information from the brain activity data and constructs a brain image; a linguistic information detector that detects linguistic information from the brain activity data; an image database that stores sample images corresponding to the linguistic information; and an image processor that superimposes the sample image with the brain image, and constructs a process image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
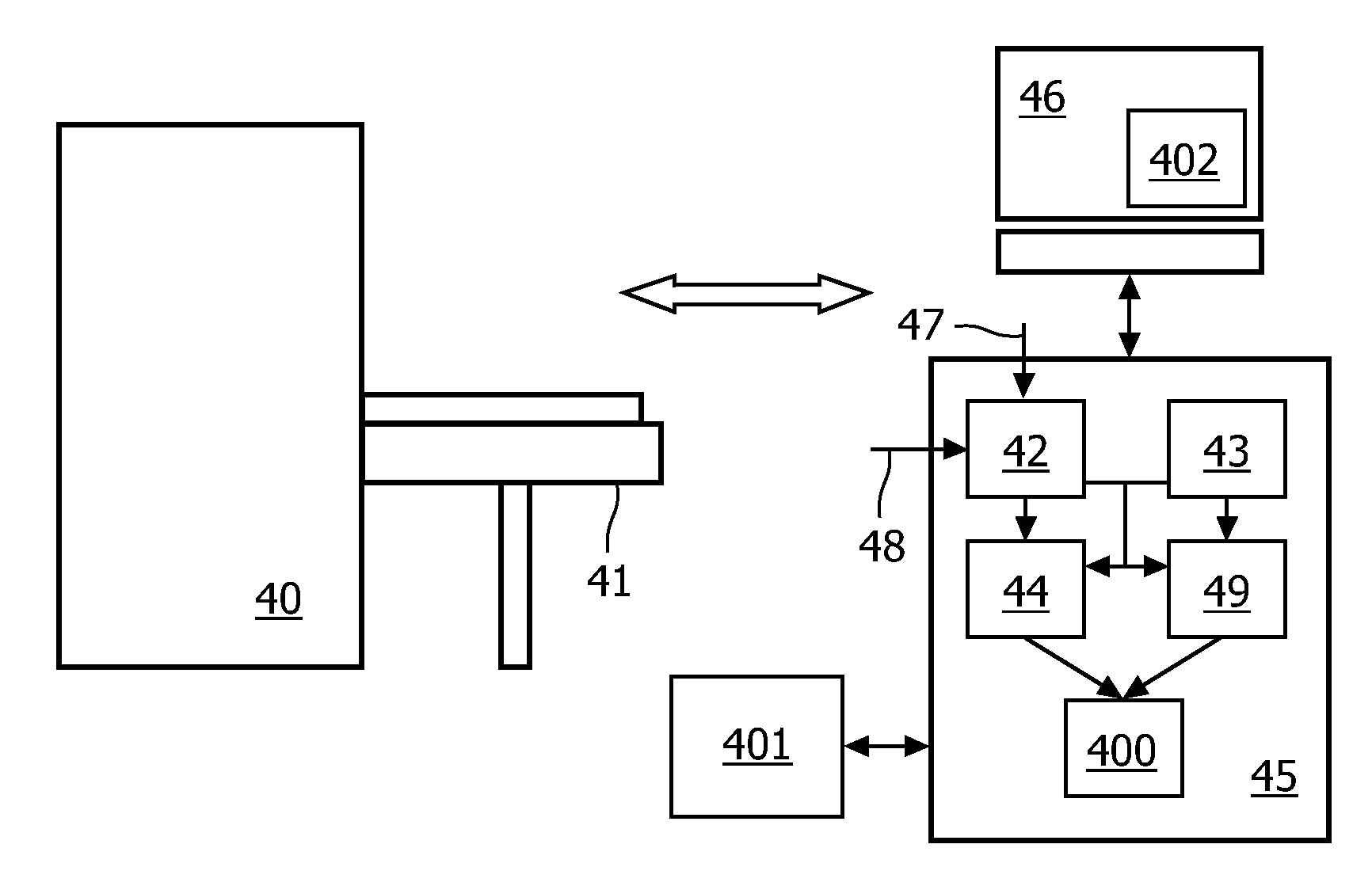
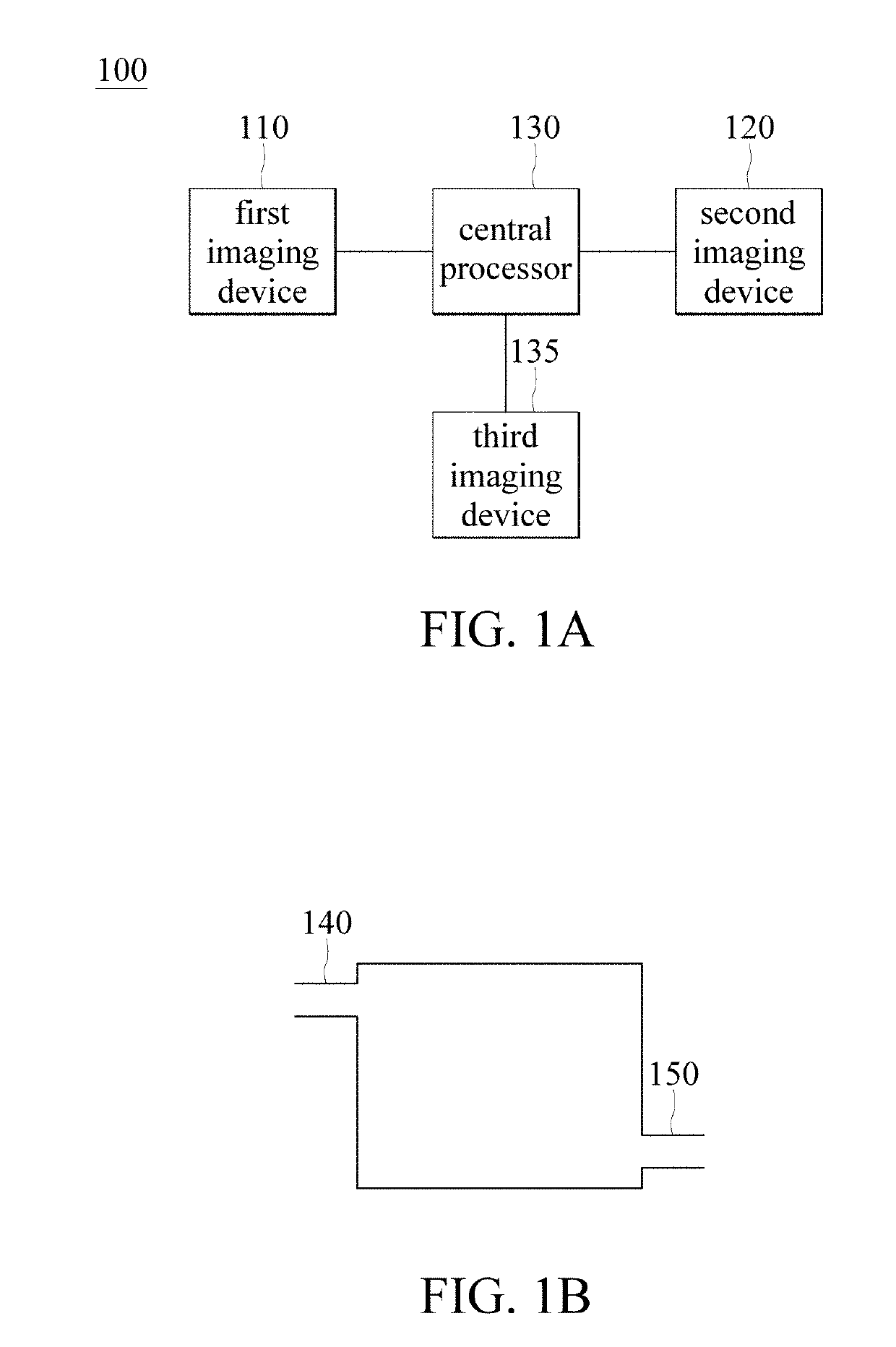
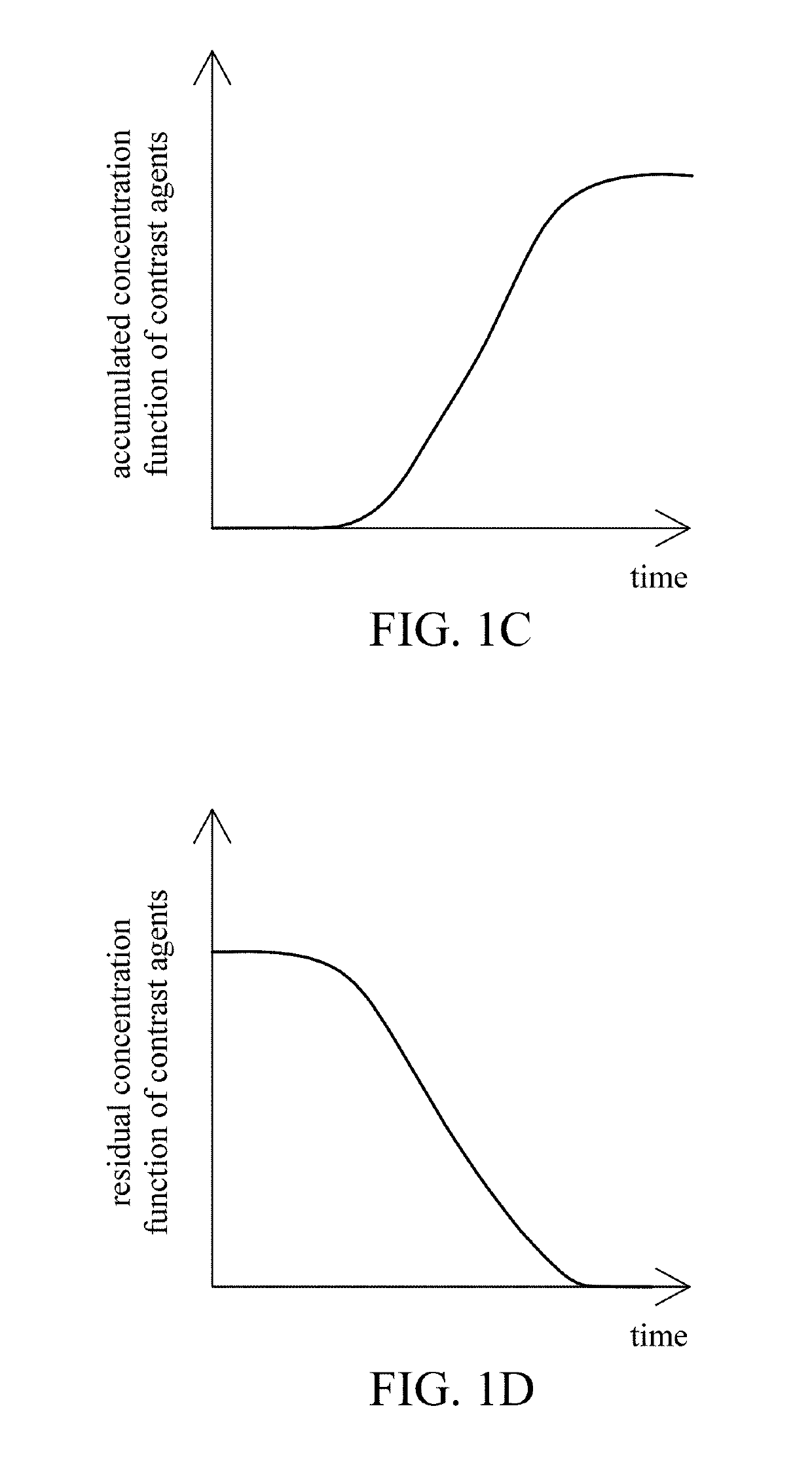
Brain imaging system and method
A brain imaging system includes a first imaging device, a second imaging device, a third imaging device and a central processor. The first imaging device captures a first brain image, and calculates a cerebral blood flow, a cerebral blood volume, a cerebral blood mean transit time and a first contrast agent time to peak. The second imaging device captures a second brain image, and calculates the cerebral blood flow, the cerebral blood volume, the cerebral blood mean transit time and a second contrast agent time to peak. The central processor generates an image of a vessel occlusion, infarction or ischemia region respectively according to the vessel occlusion, infarction or ischemia regions in the first brain image and in the second brain image. The third imaging device obtains a brain atrophy region according to the cerebral cortex volume calculated by the third imaging device.
Owner:A MOY LTD
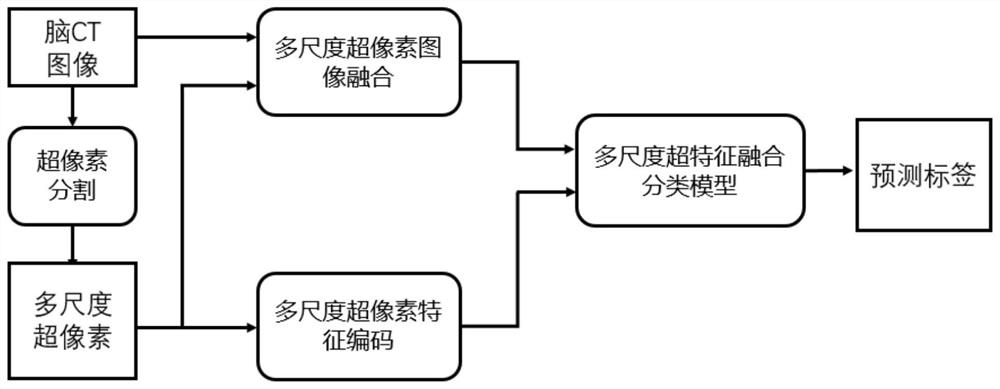
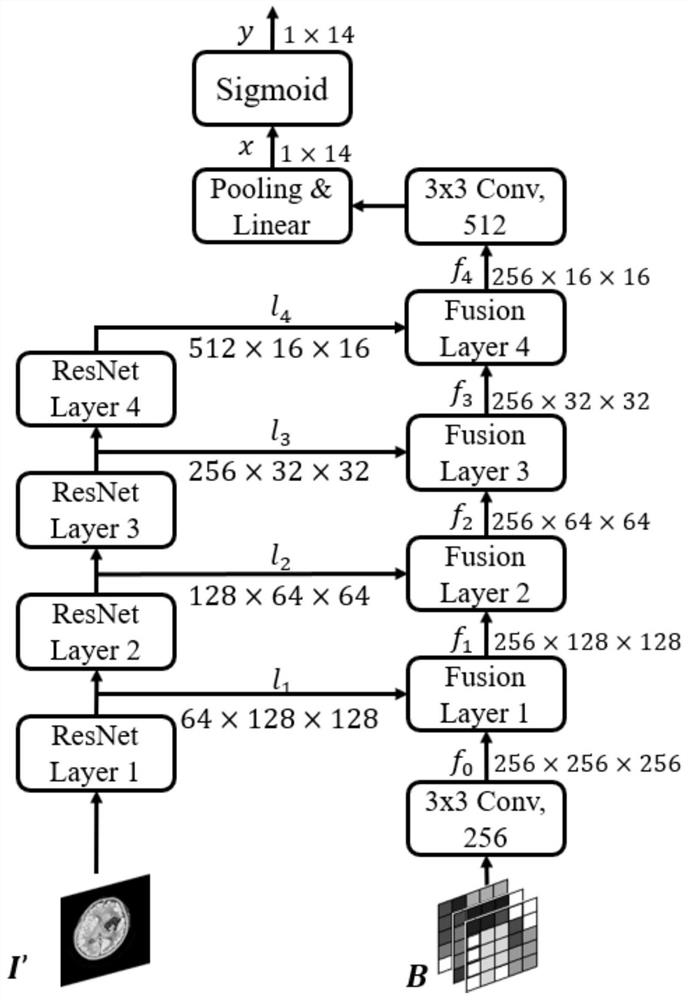
Brain CT image classification method fusing multi-scale superpixels
PendingCN112633416AImplement classificationAccurate classificationImage enhancementImage analysisBrain ctResidual neural network
The invention discloses a brain CT image classification method fusing multi-scale superpixels, and belongs to the field of medical image research. The method has the following characteristics: 1) multi-scale superpixels and a brain CT image are fused, image redundant information is removed, and the gray similarity between a focus and surrounding brain tissue pixels is reduced; 2) a multi-scale superpixel encoder based on regions and boundaries is designed, and focus low-level information contained in multi-scale superpixels is effectively extracted; 3) a fusion model fusing multi-scale super-pixel features is designed, and comprehensively utilizing of high-level features extracted by a residual neural network and low-level features of multi-scale super-pixels is carried out to realize classification of brain CT; and 4) compared with the traditional deep learning algorithm, the method provided by the invention can effectively utilize the lesion information contained in the multi-scale superpixels, thereby more accurately classifying the diseases existing in the brain CT image, and the method is reasonable and reliable, and can provide powerful help for the classification of the brain CT image.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nerve regulation and control equipment, control method, terminal and storage medium
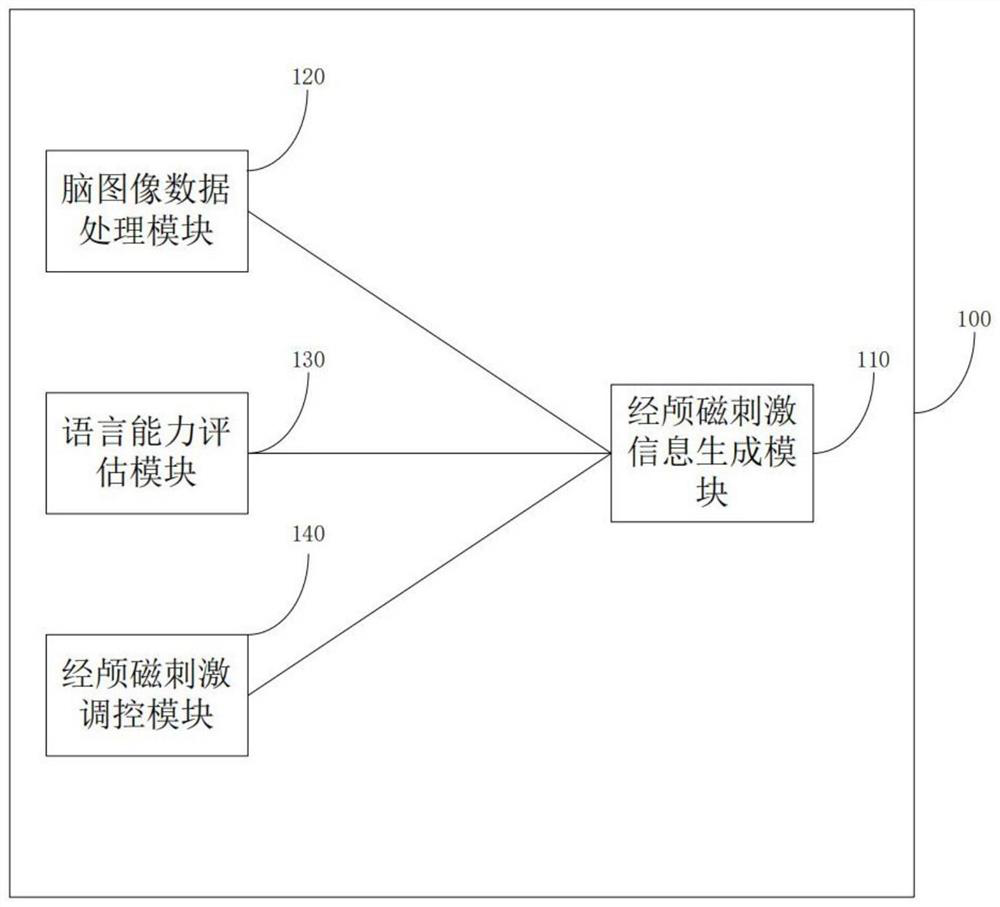
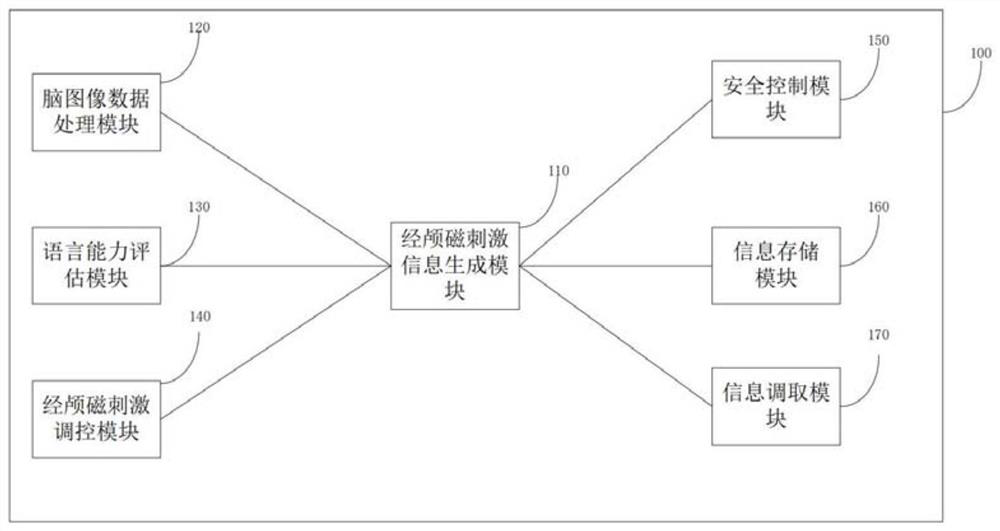
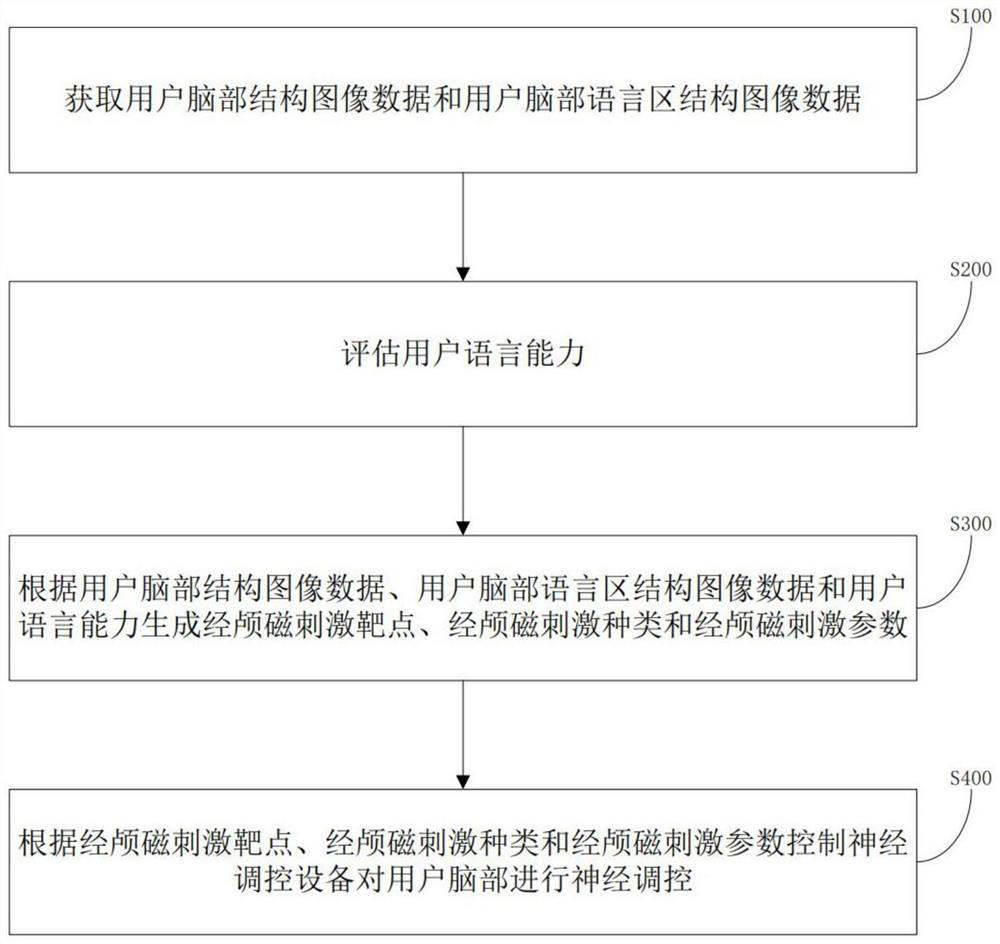
PendingCN112190836AImprove neuromodulatory efficiencyEasy to controlMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMedicineBrain section
The invention discloses nerve regulation and control equipment, a control method, a terminal and a storage medium. The equipment is applied to a Chinese language brain functional area, and is characterized by comprising a brain image data processing module which is used for obtaining user brain structure image data and user brain language area structure image data; a language ability evaluation module which is used for evaluating the language ability of the user; a transcranial magnetic stimulation information generation module which is used for generating a transcranial magnetic stimulation target point, a transcranial magnetic stimulation type and a transcranial magnetic stimulation parameter according to the user brain structure image data, the user brain language area structure image data and the user language ability; and a transcranial magnetic stimulation regulation and control module which is used for carrying out nerve regulation and control on the brain of the user accordingto the transcranial magnetic stimulation target point, the transcranial magnetic stimulation type and the transcranial magnetic stimulation parameters, can carry out nerve regulation and control on aChinese language brain functional area, obtains the brain structure, the injury area and the language ability of the user and generates accurate nerve regulation and control parameters, and can carryout nerve regulation according to the parameters.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF NEUROSCIENCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com