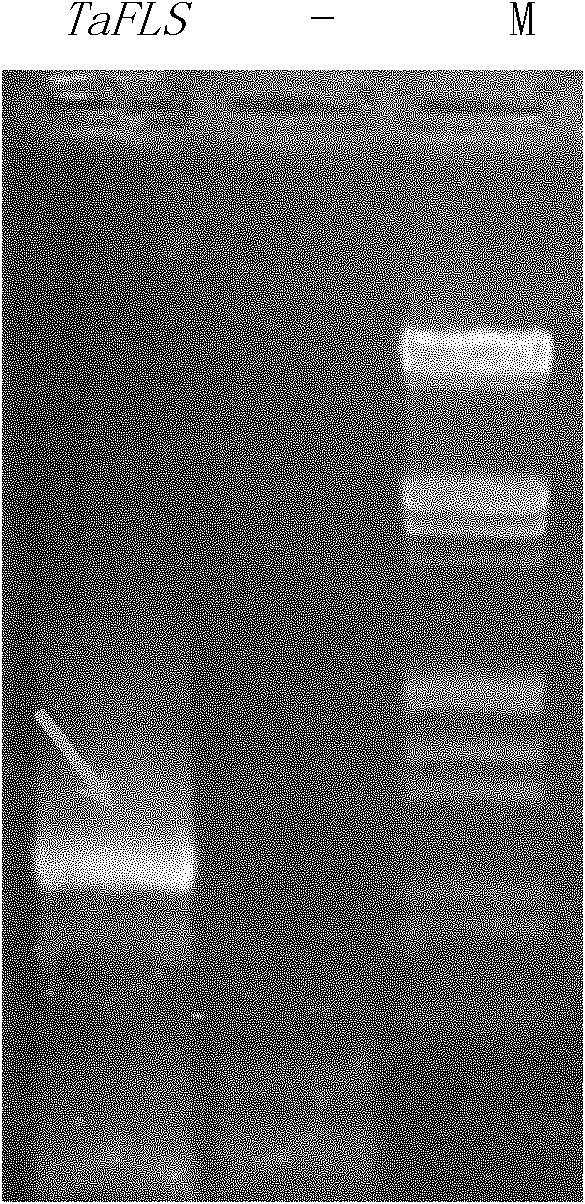Patents
Literature
31 results about "Flavonoid synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant flavonoid synthesis regulation gene and its application
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineering lactobacilli for producing plant flavonoid to synthesize related enzymes, construction and application thereof
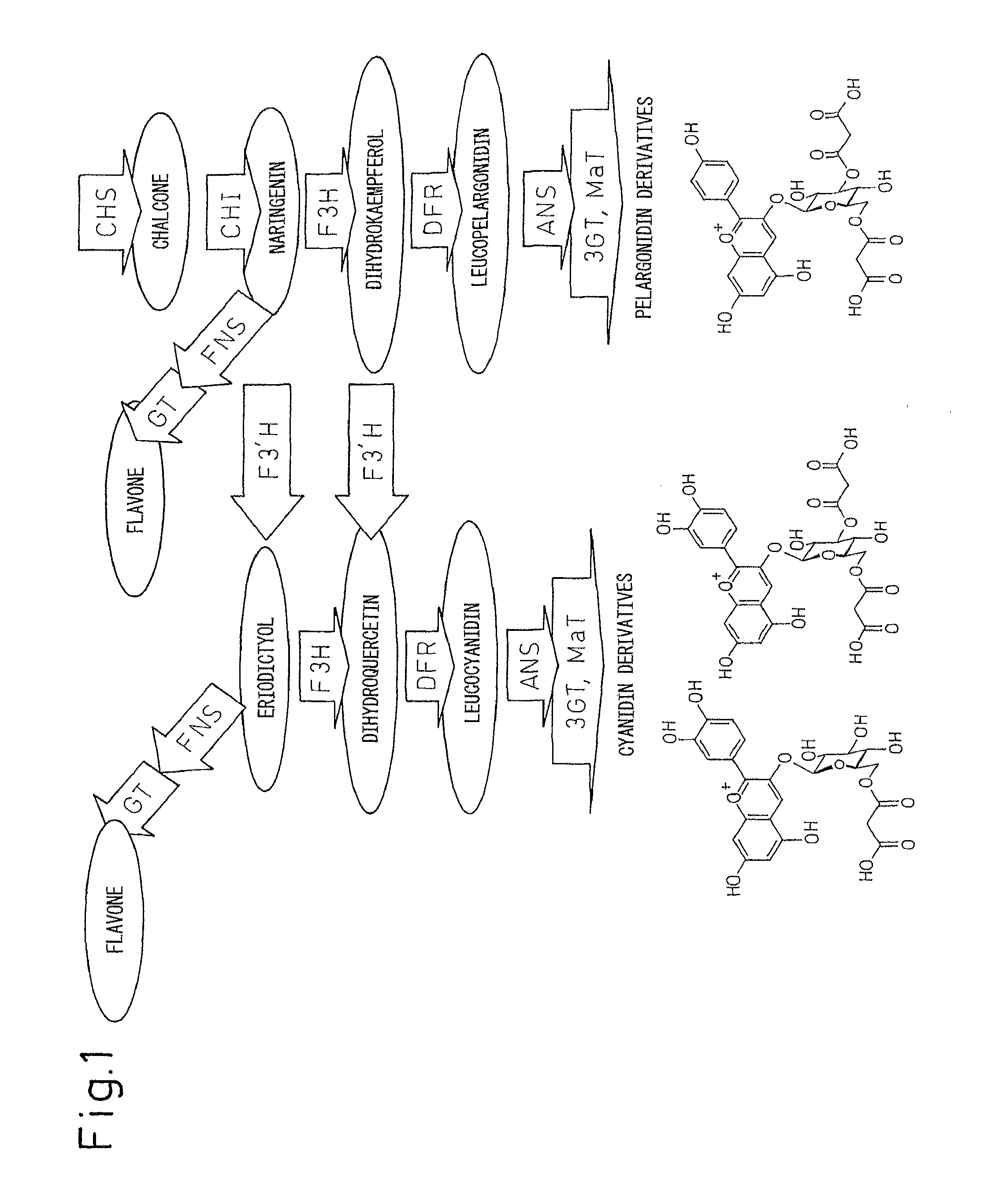
The invention discloses engineering lactobacilli for producing plant flavonoid to synthesize related enzymes, construction and application thereof, belonging to the field of lactobacillus reformation of genetic engineering. The engineering lactobacilli is produced by the steps of: synthesizing flavonoid completely from Chinese locally planted soybeans (Glycine max(L.)Merr.) into related enzyme genes PAL, 4CL, CHS and CHI which are connected into a polycistron structure PLA-4CL-CHS-CHI; then constructing the polycistron structure onto a reformed lactobacillus expression vector pMG26e to form a recombinant vector pMG26e-4GS; and then electrically shocking and converting the pMG26e-4GS into lactobacilli to obtain the engineering lactobacilli for producing plant flavonoid to synthesize related enzymes. The preservation number of the recombinant lactobacilli is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4086, and the engineering lactobacilli has more abundant physiological functions compared with original lactobacilli and can be applied to the field of food. Through fermentation, the flavonoid output of the obtained recombinant strain is in the level of mg / l, which is higher than the fermentation levels of like recombinant escherichia coli and recombinant yeast.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Peony PsMYB12 transcription factor as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a peony PsMYB12 transcription factor as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The peony PsMYB12 transcription factor is a protein of (a) or (b) which is described as follows: (a) a protein consists of an amino acid sequence shown by a sequence 1 in a sequence table; (b) proteins which are derived from (a), are associated with peony color spot formation and / or anthocyanin synthesis and are formed by replacing and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues in the amino acid sequence shown by the sequence 1 in the sequence table. By means of VIGSsilencing and heterologous excess transformation analysis, the results show that the peony PsMYB12 transcription factor can regulate the expression of key enzyme genes in an anthocyanin synthesis route. The peony PsMYB12 transcription factor is speculated to play an important role in the synthesis and accumulation of anthocyanin in peony flower spots and the formation of color spots. The specifically expressed gene is cloned for the first time and the functions of the gene are verified, so that a foundation is laid for the molecular mechanism of the formation of the color spots, and technicalbasis and thought are provided for further analysis of the synthesis and regulation of flavonoids in peony flowers.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
New application of arabidopsis At4g09820 gene in plant salt resistance aspect
ActiveCN103540607AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
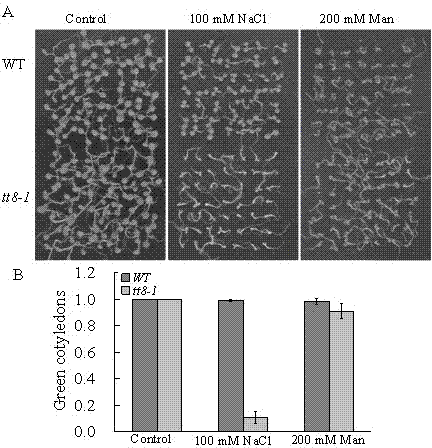
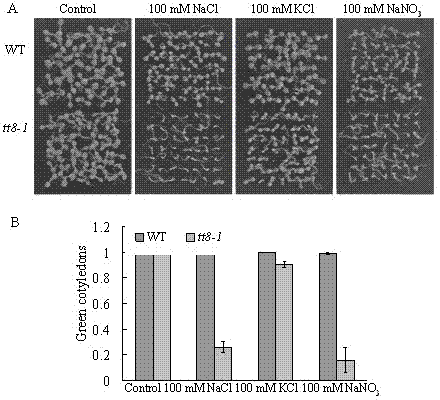
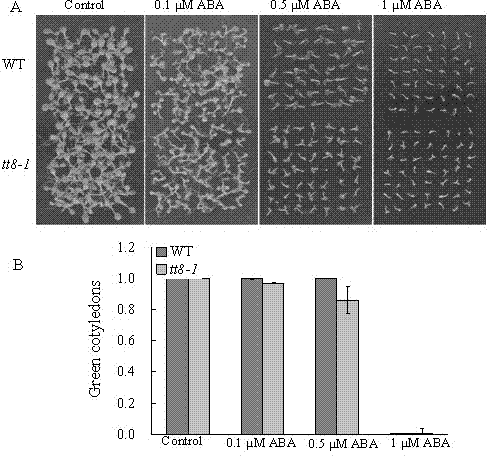
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering application, and in particular relates to an application of an arabidopsis At4g09820 gene in an aspect of breeding a new variety of salt resistant plants. The arabidopsis At4g09820 gene, which is called TT8 gene as well, is 1557bp in CDS length and capable of coding protein of 518 amino acids, belongs to a bHLH (basichelix-loop-helix) transcription factor and used for regulating biosynthesis of procyanidine and anthocyanin in a flavonoid synthetic route. The inventor, through research of the At4g09820 gene in a high-salinity adverse situation, discovers that the gene can specifically regulate and control an ion toxic reaction caused by NaCl and show an excellent salt resistance property; therefore, the At4g09820 gene has an important application in the plant salt resistance aspect, and an excellent salt resistant plant variety can be bred through further research and transformation on the gene.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method for producing yellow flower by controlling flavonoid synthetic pathway
InactiveUS7750209B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHost plantsFlavonoid synthesis
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for producing chrysanthemum plant having petals containing modified anthocyanin
InactiveUS20120073017A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotidePetal
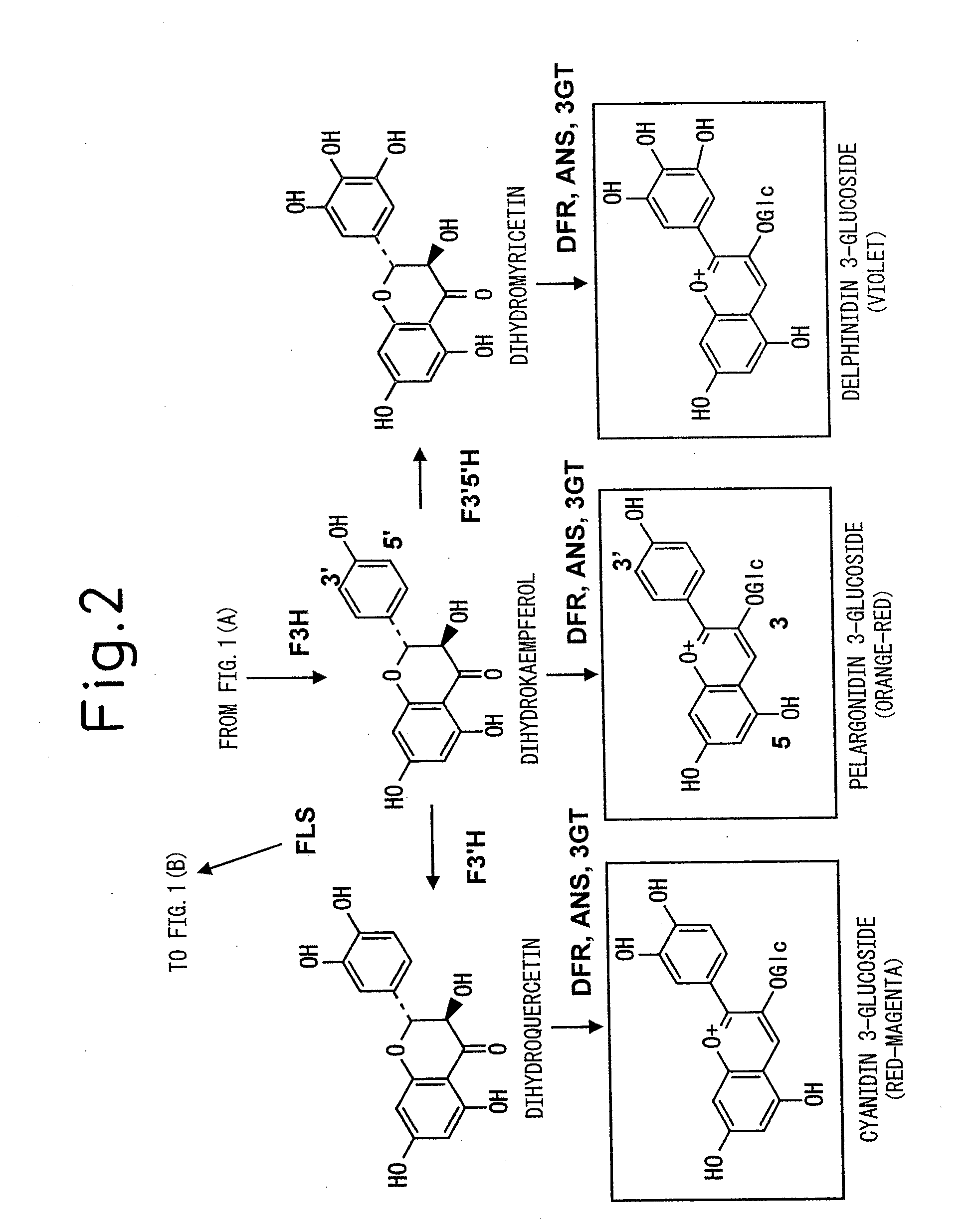
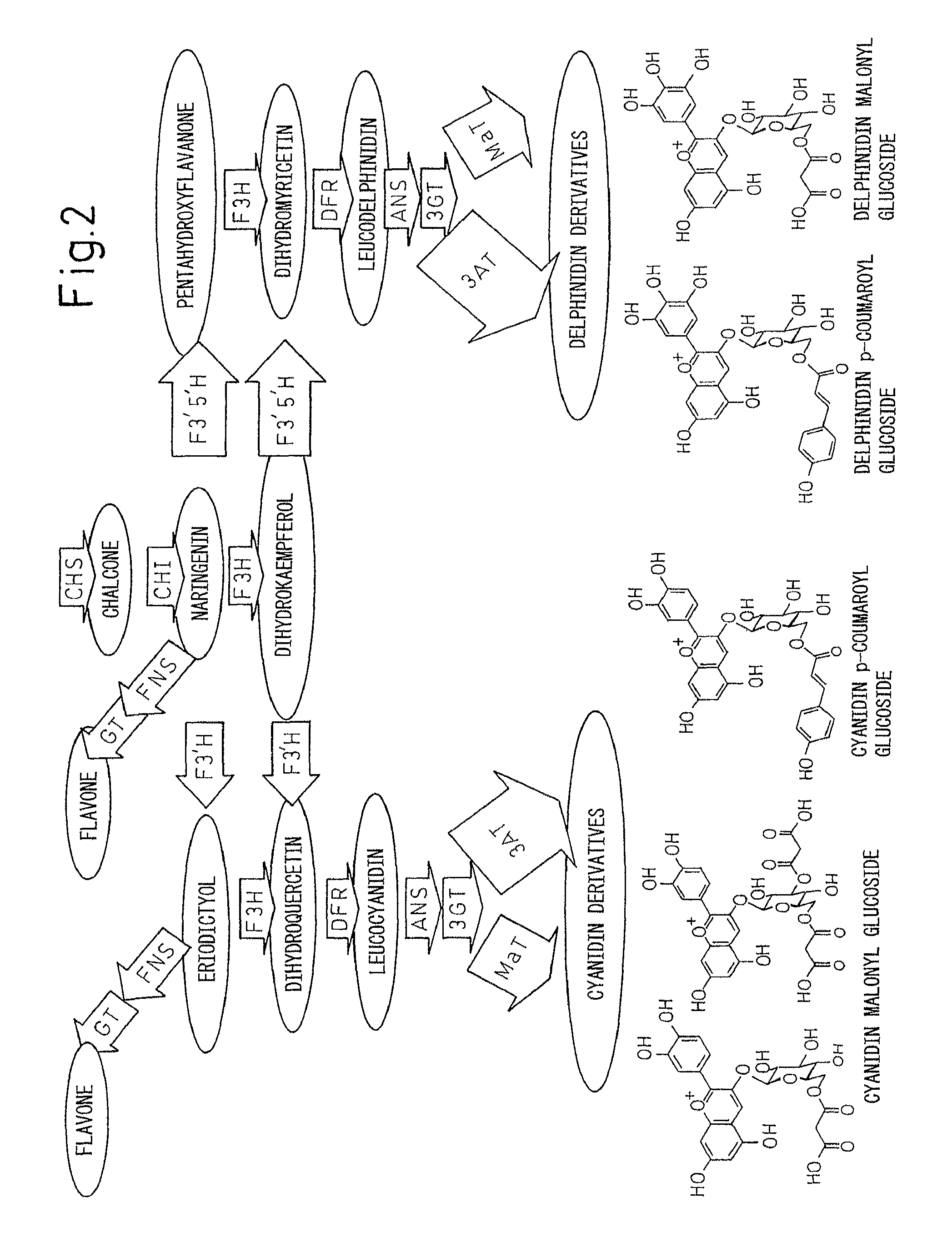
Disclosed are a method for controlling flavonoid synthesis in a chrysanthemum plant or non-chrysanthemum plant by genetic recombination technology using a transcriptional regulatory region useful for altering flower color, a method for modifying anthocyanins, a method for producing a chrysanthemum plant or non-chrysanthemum plant containing modified anthocyanins in the petals thereof, and a chrysanthemum plant or non-chrysanthemum plant, progeny thereof, or vegetatively propagated products, part or tissue thereof transformed with the regulatory region. In the method according to the present invention, an expression vector or expression cassette containing a transcriptional regulatory region of perilla anthocyanin 3-acyltransferase gene, such as a nucleic acid containing the nucleotide sequence indicated in SEQ ID NO. 1, or a transcriptional regulatory region of pansy F3′5′H gene, such as the nucleotide sequence indicated in SEQ ID NO. 15, is used.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
MYB transcription factor separated from purple white clove and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an MYB transcription factor separated from a purple white clove and a coding gene and application thereof. The purple V-marking white clove serves as the material, by means ofan RNA-Seq technology, the transcription factor TrMYB308 related to flavonoid synthesis is screened out, on the basis, a TrMYB308 gene is cloned, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The TrMYB308 gene is induced by JA and expressed in all tissues of the purple white clove. It is found from the results obtained when the TrMYB308 gene is subjected to heterologous expression in hairy roots of tartartary buckwheat that the expression quantity of part of key enzyme genes of a flavonoid metabolism pathway in transgenic roots is obviously increased, the total flavonoid content of the transgenic roots is obviously higher than that of a control group, and it is indicated that the TrMYB308 gene participates in biosynthesis regulation of secondary metabolism of flavonoid in plants. Accordingly, the theoretical basis and application basis are provided for buckwheat flavonoid synthetic molecular mechanism exploration, buckwheat quality improvement and the like.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
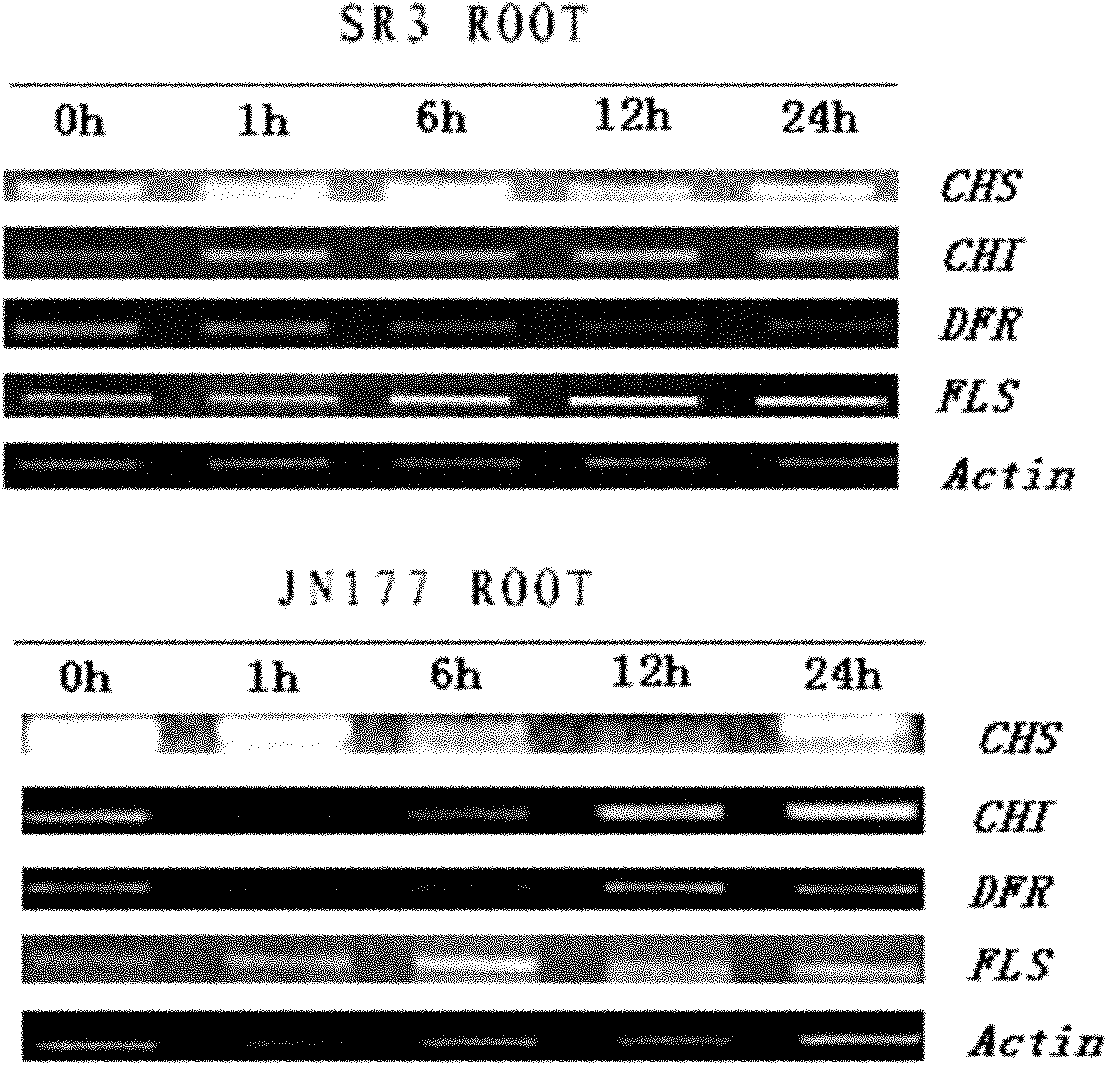
Wheat salt-resistant and oxidation-resistant gene TaFLS and application thereof
InactiveCN102234652AImprove salt toleranceImprove antioxidant capacityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologySalt resistance
The invention discloses a wheat salt-resistant gene, i.e., a wheat secondary metabolism flavone synthetic route gene TaFLS and a plant expression vector pSTART-TaFLS containing the gene TaFLS. The invention further discloses application of an expression vector of the gene to the cultivation of salt-resistant and oxidation-resistant plants. As proved by an experiment, the salt resistance and the oxidation resistance of a transgenic plant are remarkably enhanced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Key gene GbMYB6 for promoting gingko flavonoid synthesis as well as protein expressed by key gene GbMYB6, carrier and application thereof
ActiveCN112079911AIncrease contentEasy to synthesizePlant peptidesFermentationEnzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention discloses a key gene GbMYB6 for promoting synthesis of gingko flavonoids, protein expressed by the key gene GbMYB6, a carrier and application of the key gene GbMYB6, the nucleotide sequence of the key gene GbMYB6 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein expressed by the key gene GbMYB6 is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Ginkgo biloba leaves are used as materials, a GbMYB6 gene is cloned, an overexpression vector 35S:: GbMYB6 containing the gene GbMYB6 is constructed through enzyme digestion connection and transferred into ginkgo biloba calluses and arabidopsis thaliana, and the content of flavonoids in GbMYB6 transgenic ginkgo biloba calluses and transgenic arabidopsis thaliana is obviously increased, this indicates that GbMYB6 can promote the synthesis of flavonoids, the regulation and control of the expression of the GbMYB6 has important application value in the aspects of improving the medicinal quality of the ginkgo leaf tablets and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Key gene GbMYB4 for regulating synthesis of ginkgo flavonoids, protein expressed by key gene GbMYB4, vector and application
The invention discloses a key gene GbMYB4 for regulating synthesis of ginkgo flavonoids, protein expressed by the key gene GbMYB4, a vector and application. The nucleotide sequence of the key gene GbMYB4 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein expressed by the key gene GbMYB4 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. Ginkgo leaves are used as materials, the gene GbMYB4 is cloned, andan overexpression vector containing the gene GbMYB4 is constructed and transferred into ginkgo callus and arabidopsis thaliana. The content of flavonoids in the GbMYB4 transgenic ginkgo callus and thetransgenic arabidopsis thaliana is remarkably reduced, that the GbMYB4 can inhibit synthesis of the flavonoids, has a negative regulation effect on the flavonoids and can be matched with a promotinggene for flavonoid synthesis to effectively control the synthesis amount of the ginkgo flavonoids is indicated, and therefore regulation of expression of the GbMYB4 has important application value inthe aspects of improving the medicinal quality of the ginkgo leaves and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Tulip flavanone-3-hydroxylase TfF3H protein and encoding gene thereof
InactiveCN103614348AImprove viewing valueInhibit synthesisOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyHydroxylase gene
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Plant flavonoid synthesis regulation gene and its application
InactiveCN103131715BAffect biosynthesisPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceTotal rna
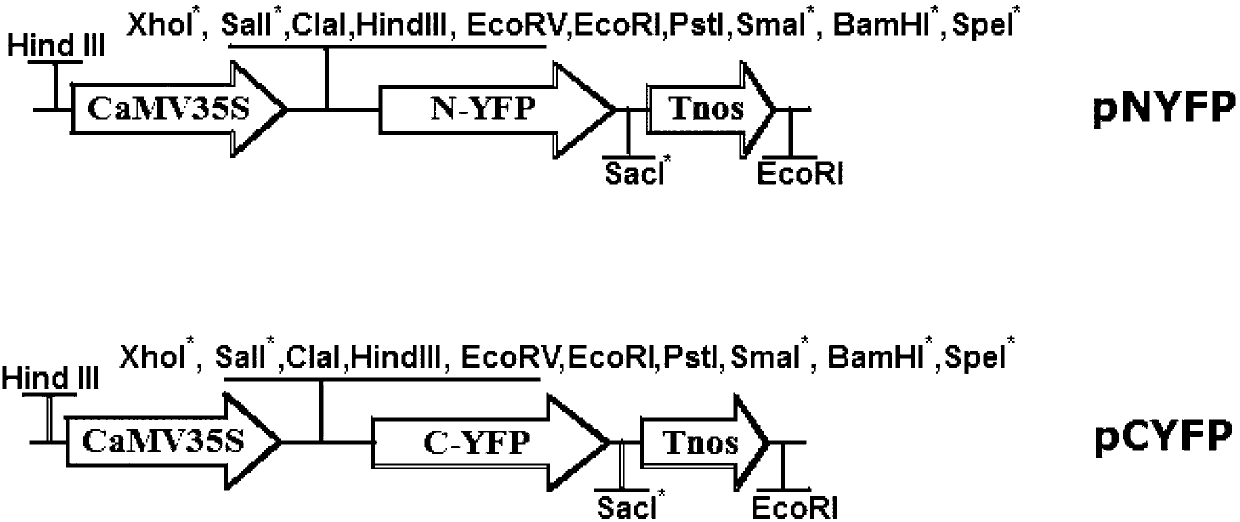
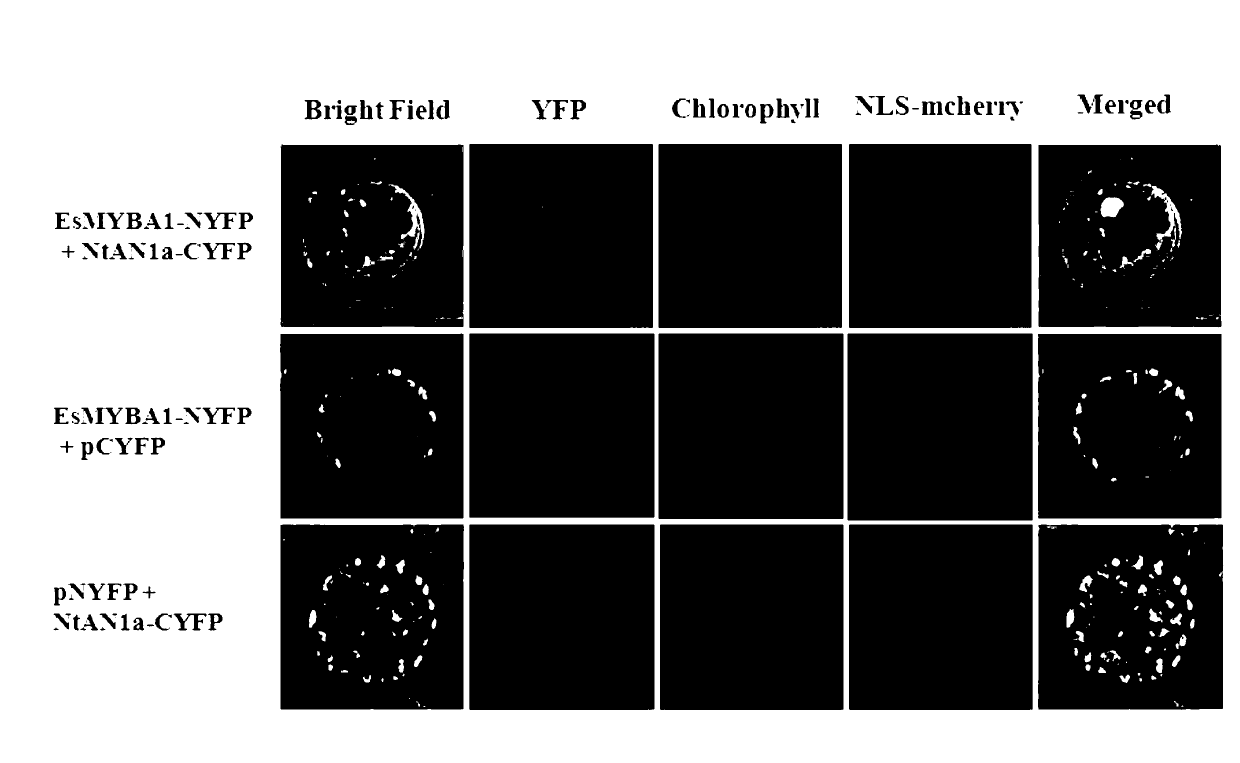
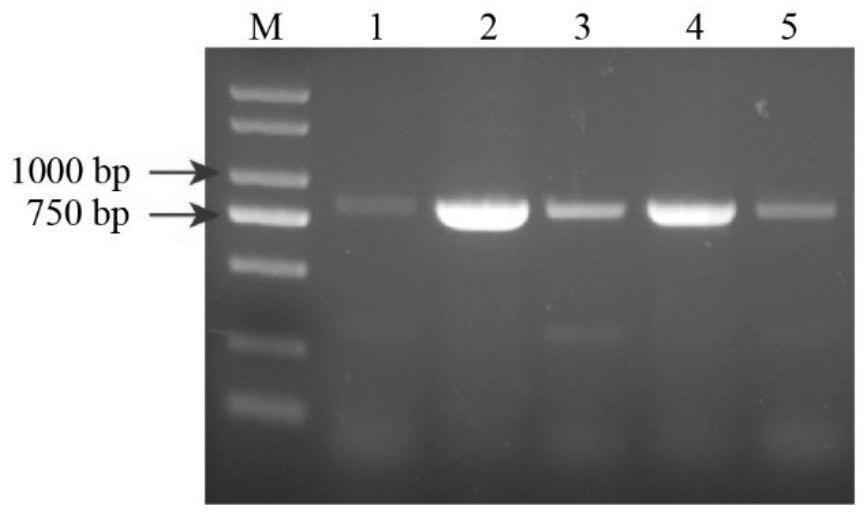
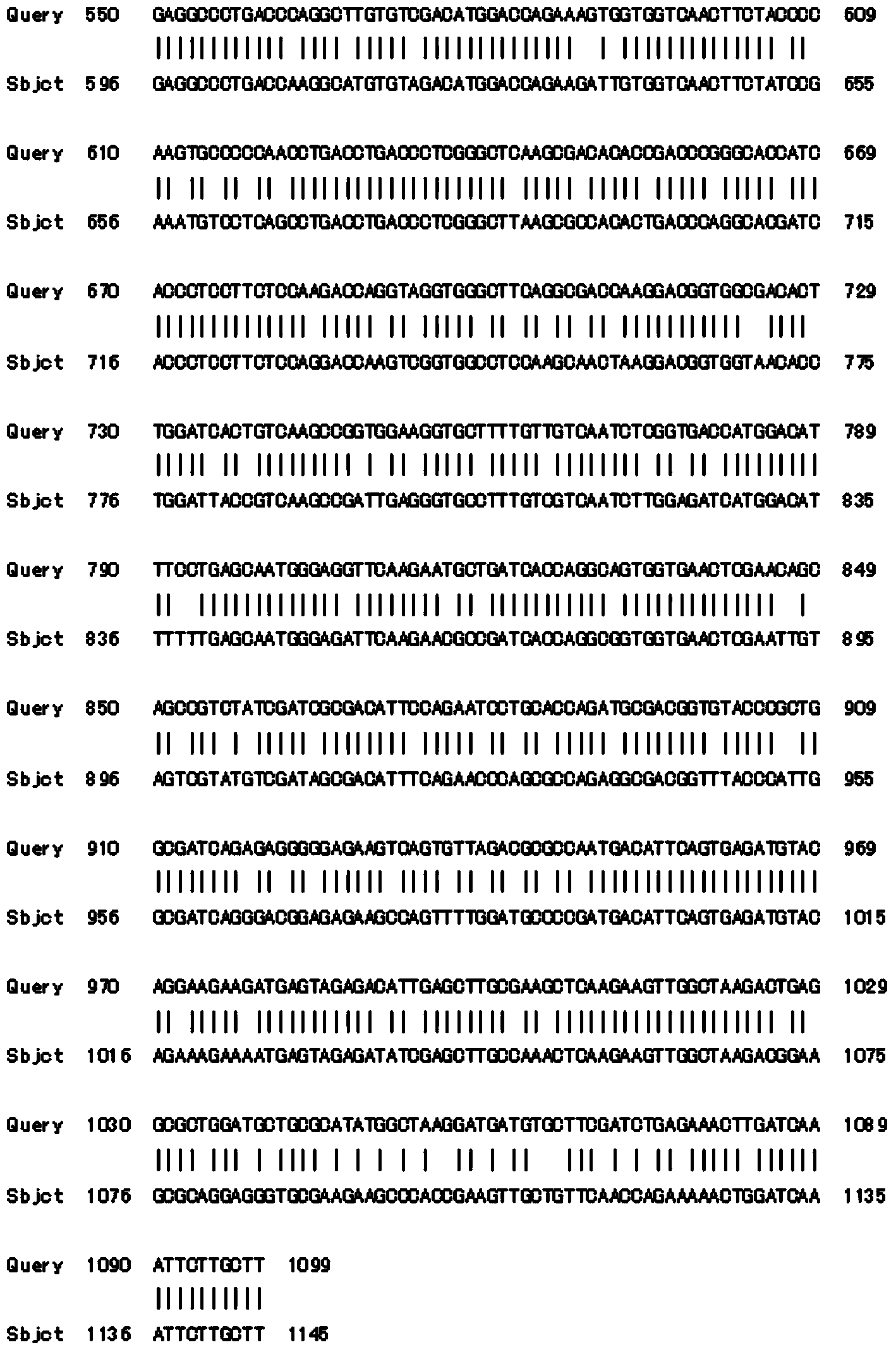
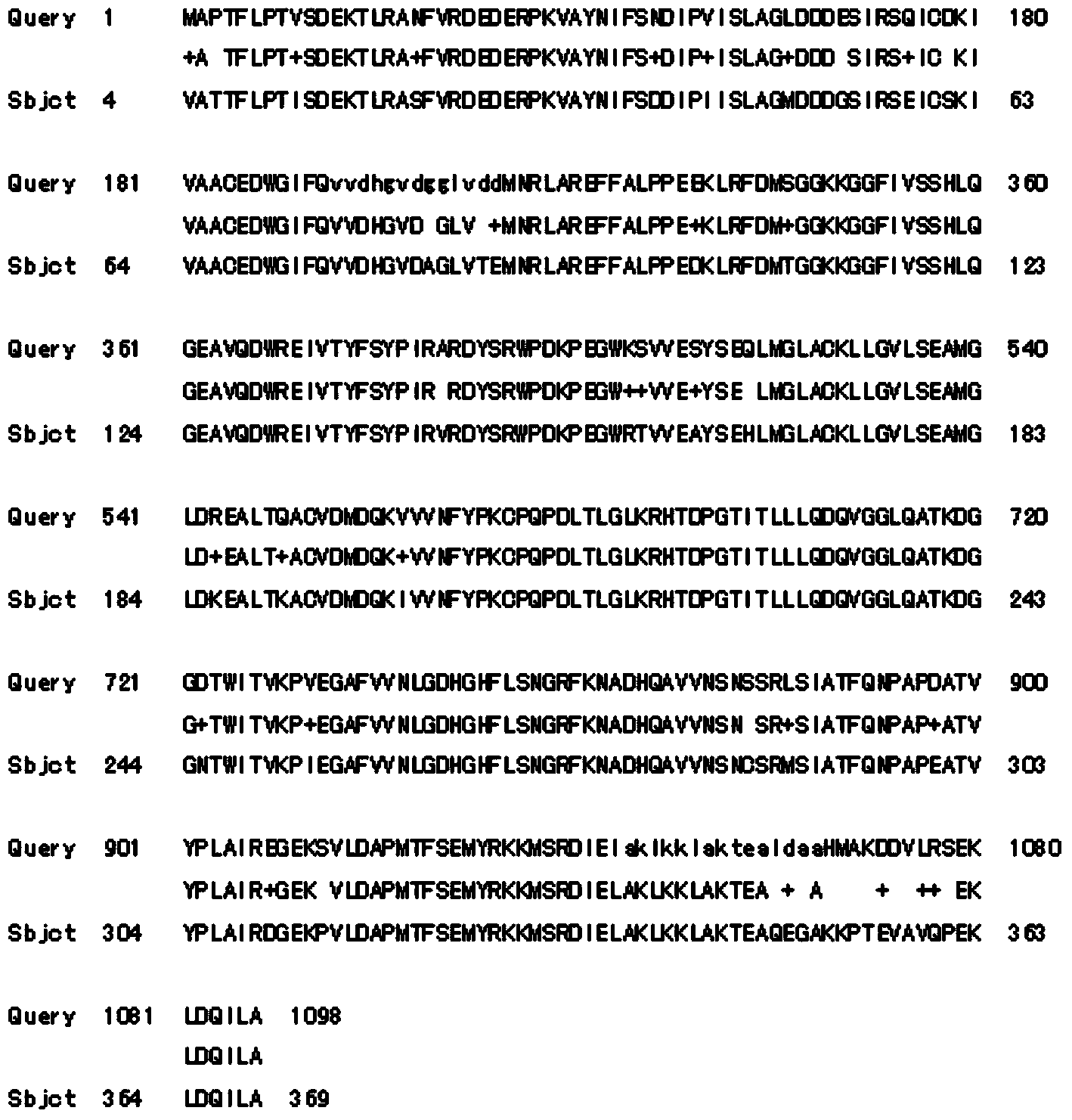
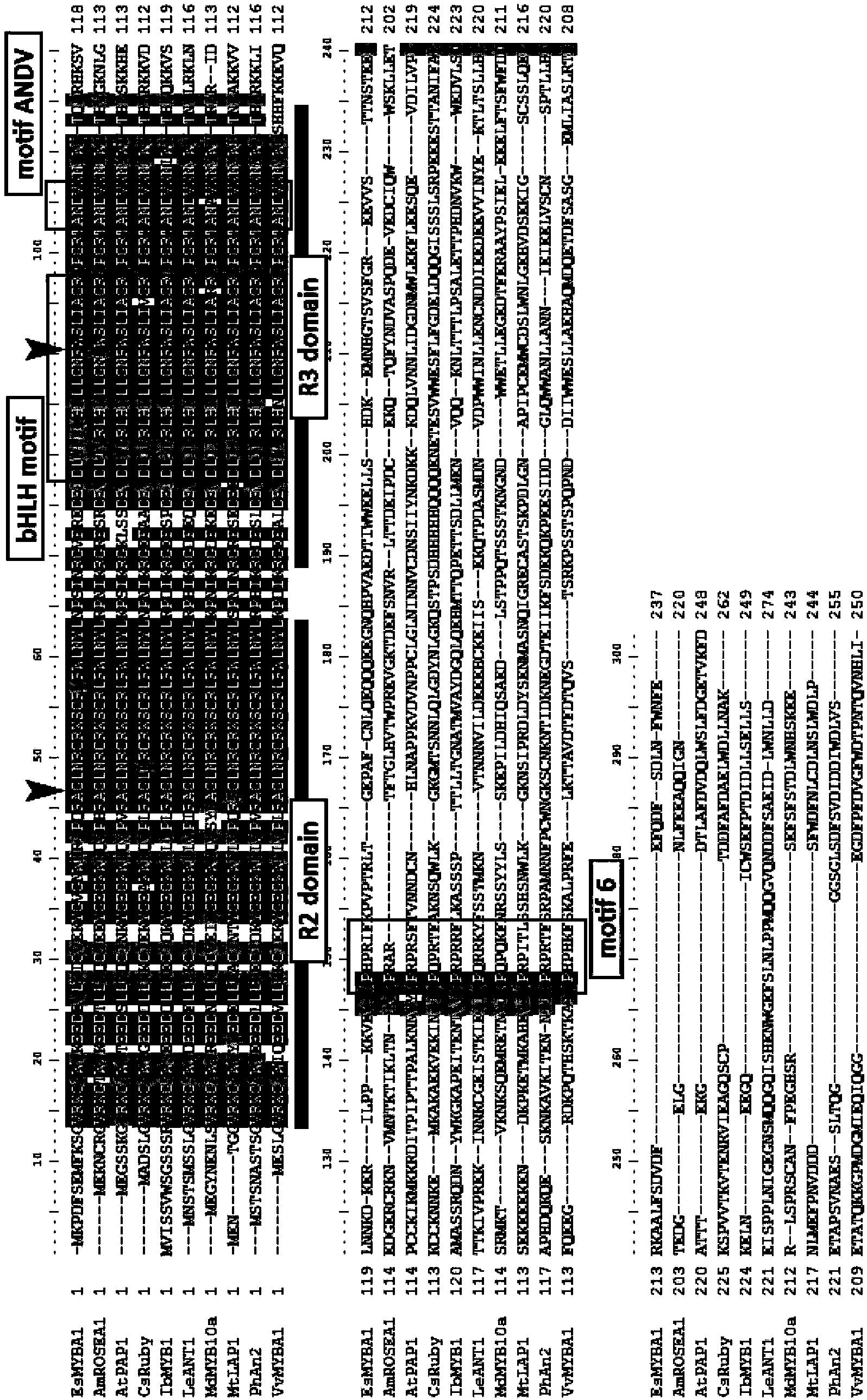
The invention discloses a plant flavonoid synthesis regulation gene and its application. CDNA obtained through the inverse transcription of the total RNA of Epimedium brevicornum Maxim blades is treated as a template and undergoes PCR to obtain a 233bp fragment, the 233bp fragment has a very high homology with flavonoid related R2R3-MYB gene, a full-length cDNA sequence is obtained through an RACE technology and is named EsMYBA1 gene, and the sequence of the EsMYBA1 gene is represented by SEQIDNO.1. The EsMYBA1 gene codes an R2R3-MYB transcription factor which has an about 50% homology with other MYB regulation genes for controlling the flavonoid synthesis approaches, and the improvement of the expression level of the EsMYBA1 gene through a genetic engineering technology promotes the synthesis and the accumulation of anthocyanidin.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing yellow flower by controlling flavonoid synthetic pathway
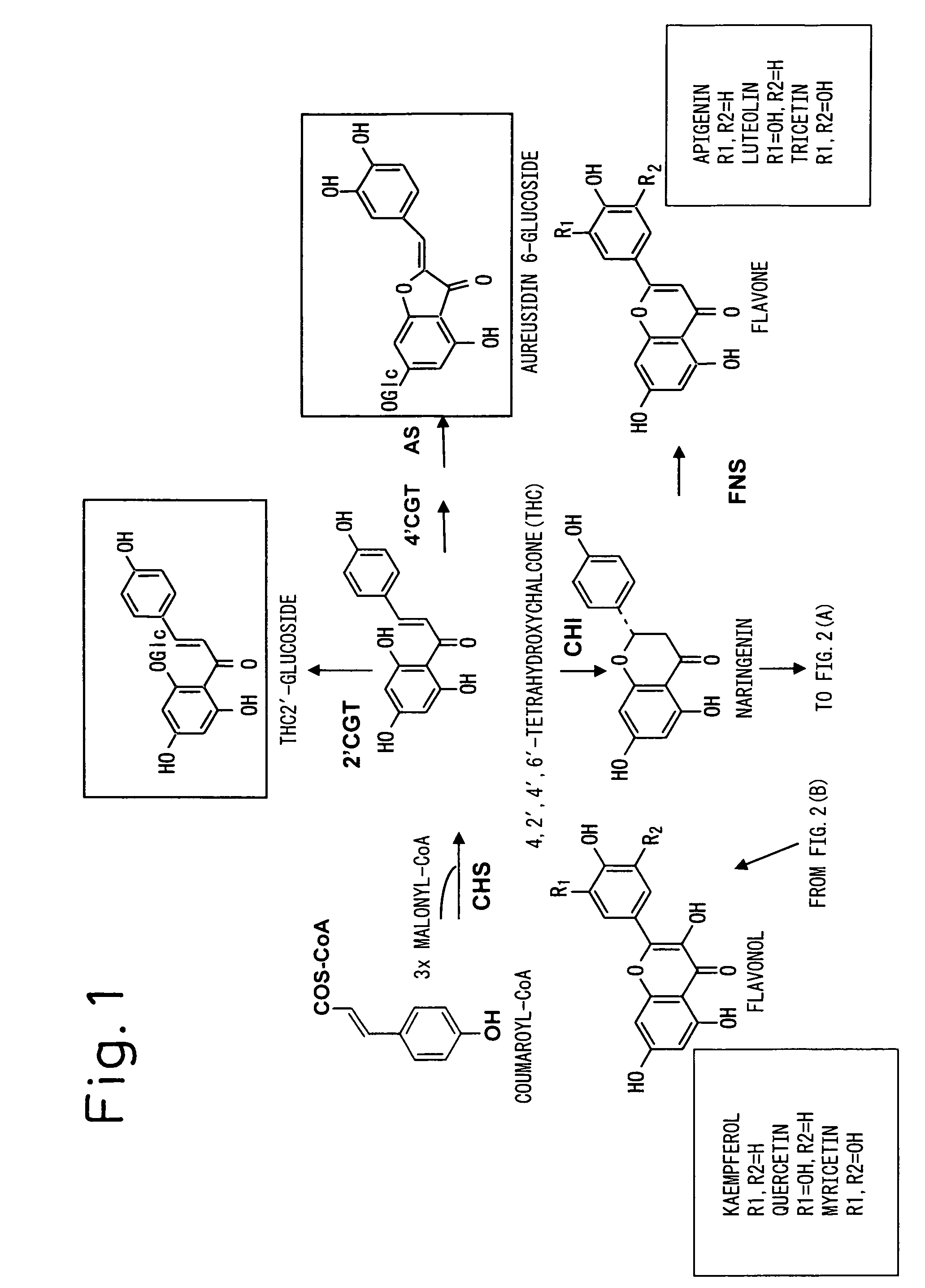
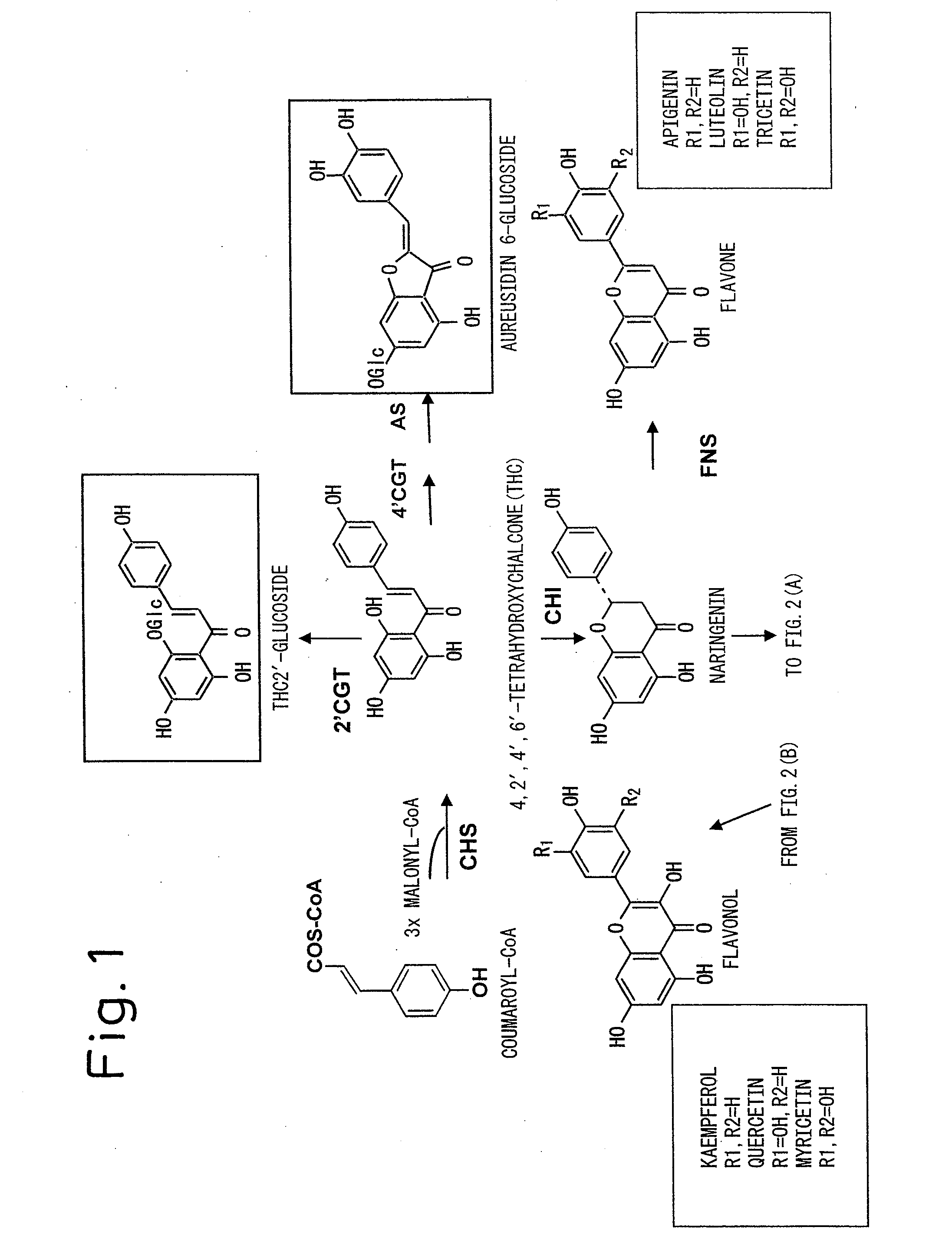
There is provided a gene coding for the amino acid sequence listed as SEQ ID NO: 2 or SEQ ID NO: 70, for example. Co-expression of the 4′CGT gene and AS gene in a plant lacking natural aurone synthesis ability is carried out to successfully accumulate aurones and alter the flower color to have a yellow tint. In addition to the expression of both genes, the flavonoid pigment synthesis pathway of the host plant itself is inhibited to obtain flowers with a more defined yellow color.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
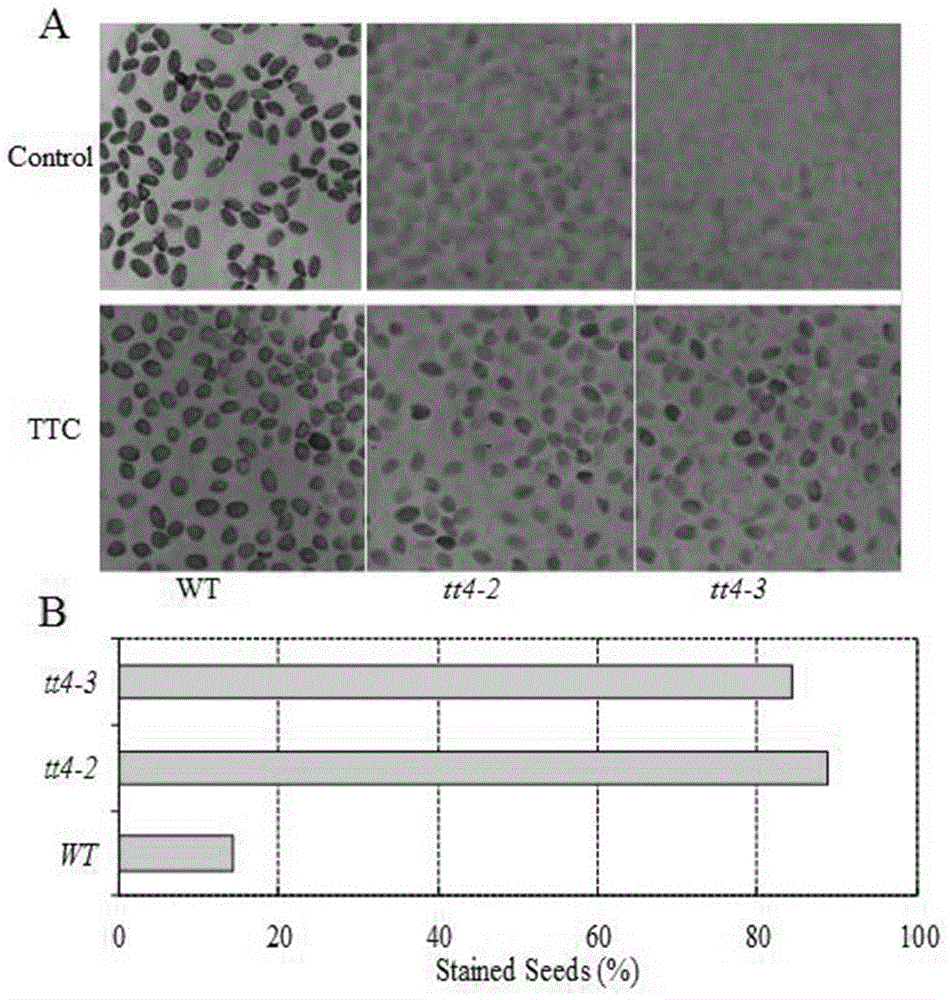
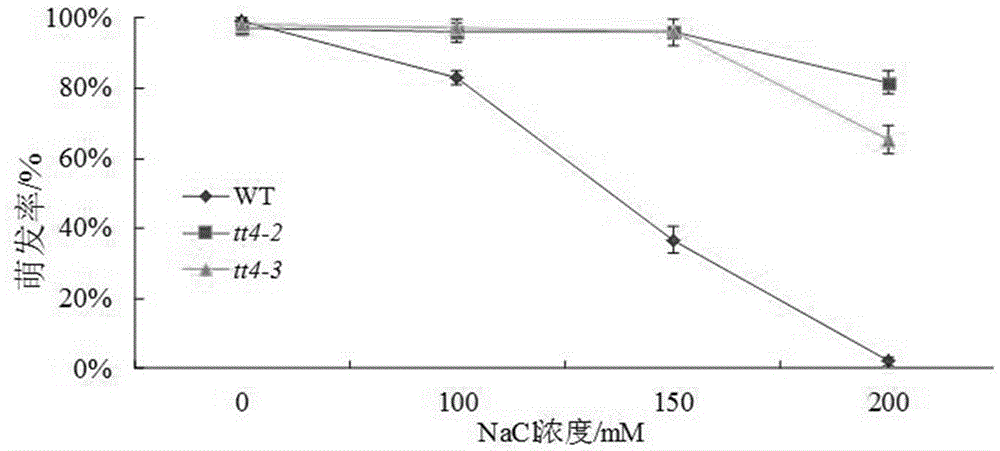
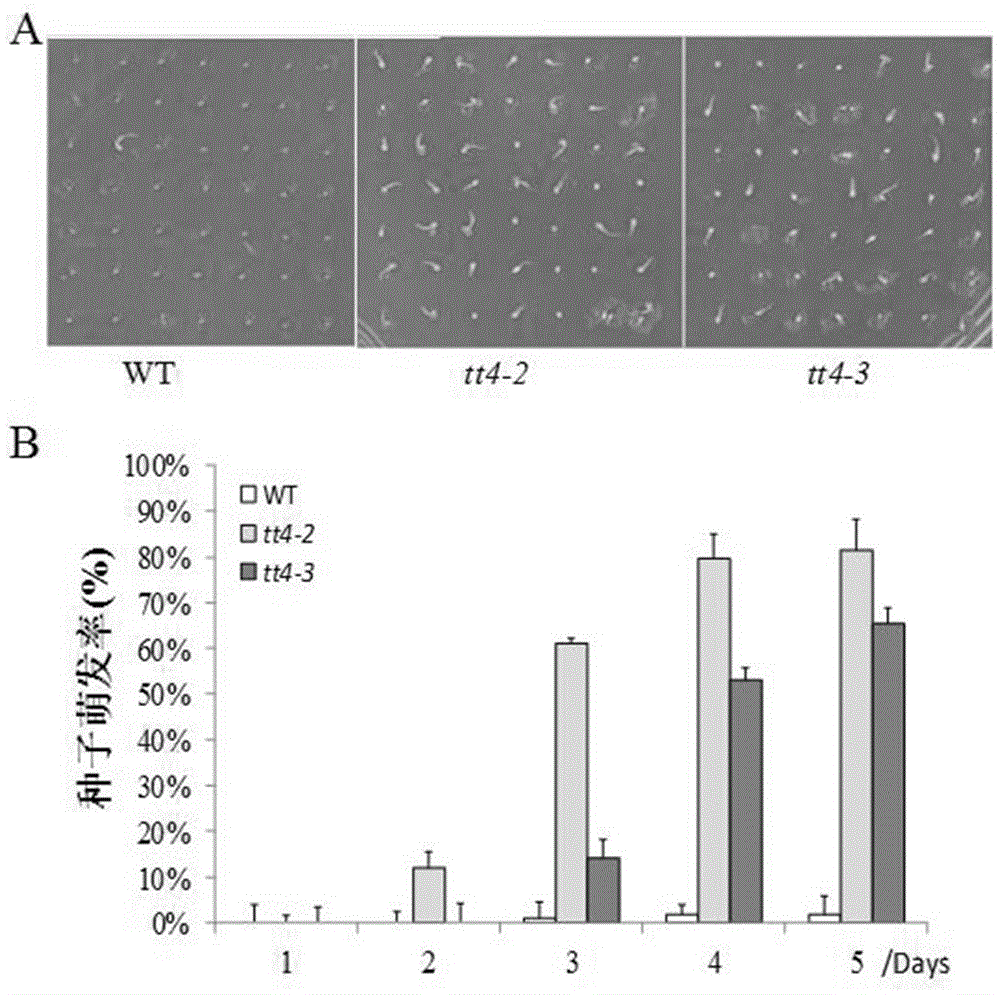
Novel application of Arabidopsis thaliana TT4 gene to salt resistance of plants
ActiveCN105647883AAcyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionGene silencingGenetic engineering
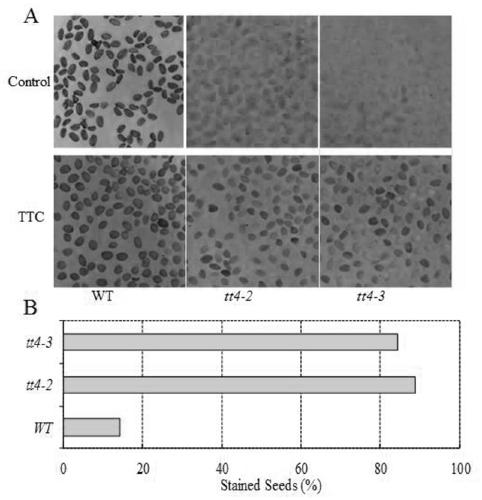
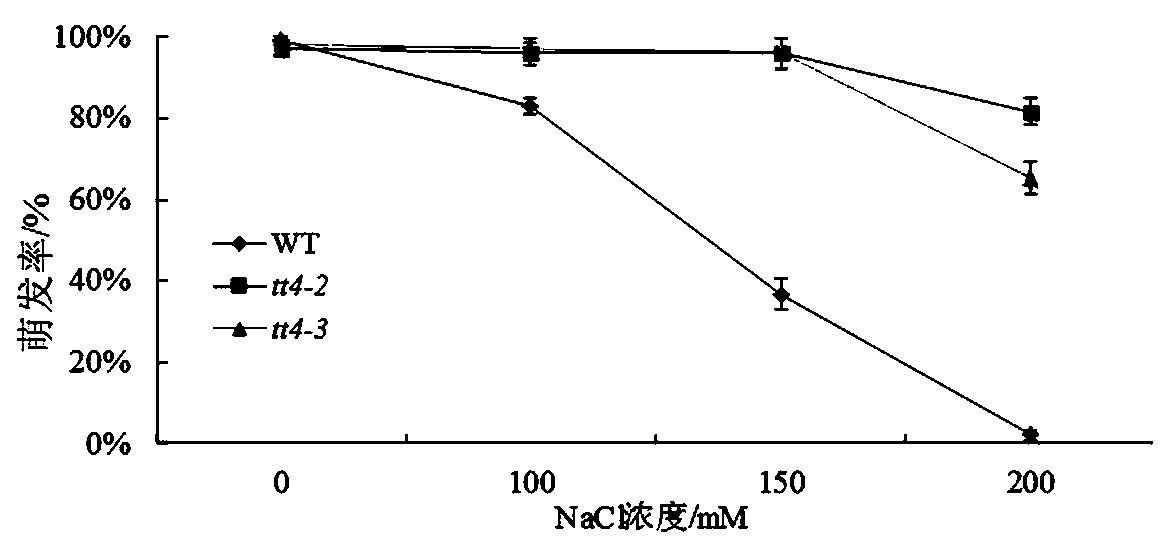
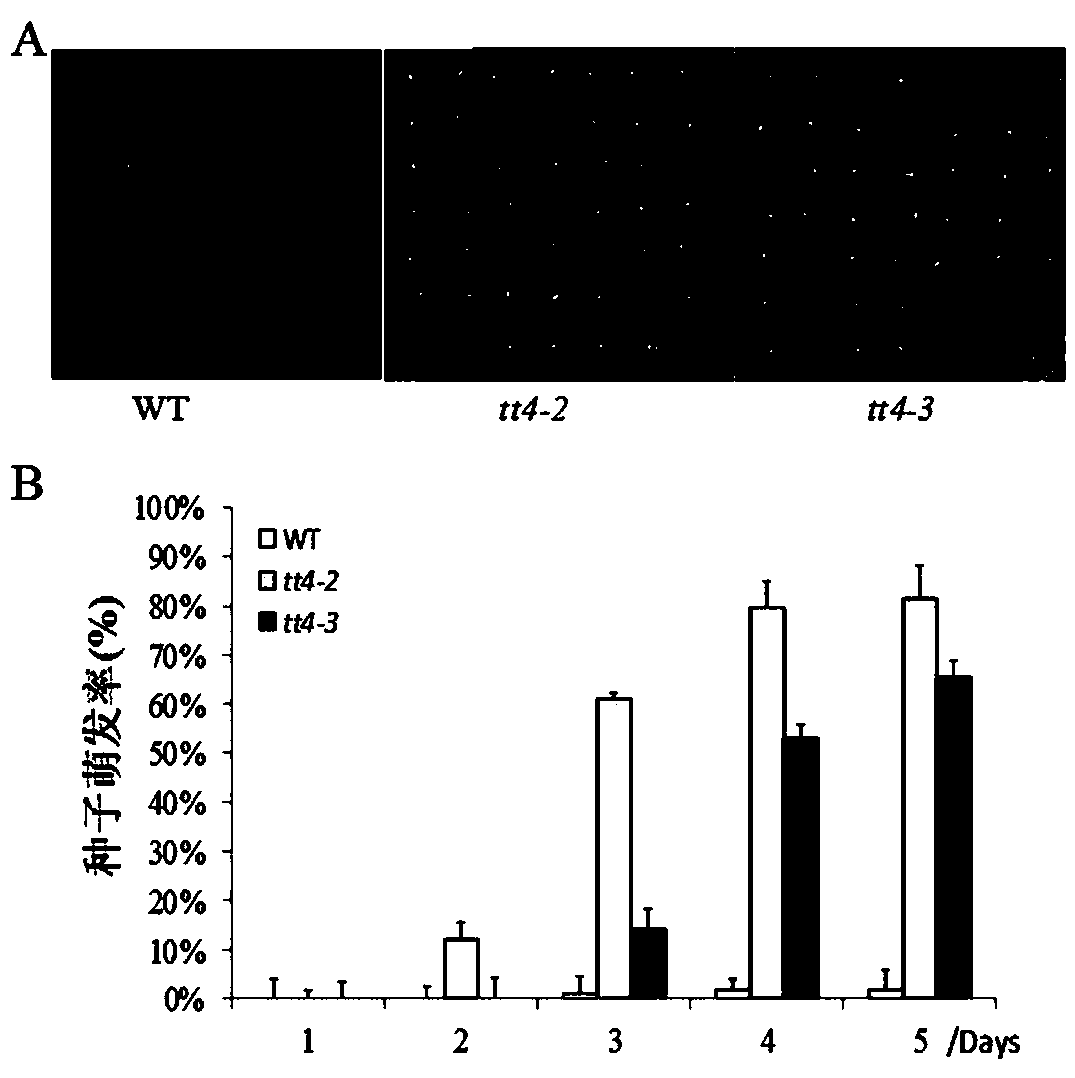
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering application and particularly relates to application of an Arabidopsis thaliana TT4 gene (Arabidopsis thaliana genome code At5g13930) to culture of new varieties of salt-resistant plants. The TT4 gene with a CDS length being 1188bp encodes proteins of 395 amino acids and is related to seed activity, and the gene enables release of Arabidopsis thaliana seed activity after genetic mutation, namely the gene is capable of enhancing seed activity to accelerate seed germination and improve seed germinability after genetic mutation. The TT4 gene mainly serves as a first specific enzyme in a flavonoid synthesis route and participates in regulation of development of seed coats and seed coat pigments of Arabidopsis thaliana. According to researches of the TT4 gene in simulated dry or high-salinity adverse situations, plants under specific regulation of the gene has an osmotic stress reaction to salts and the like, and after silencing of the gene, mutant plants show favorable salt resistance at an initial germination stage.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
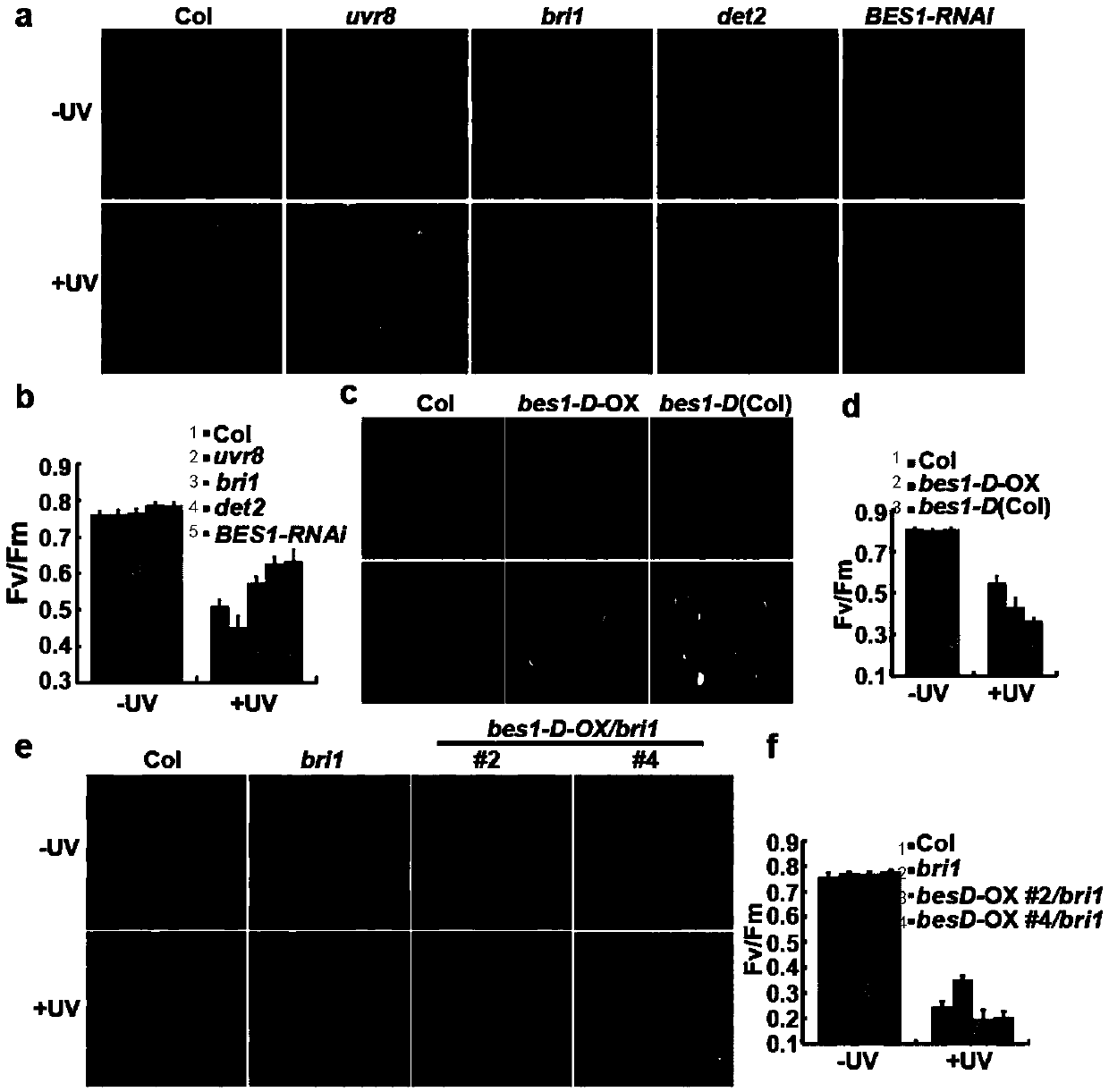
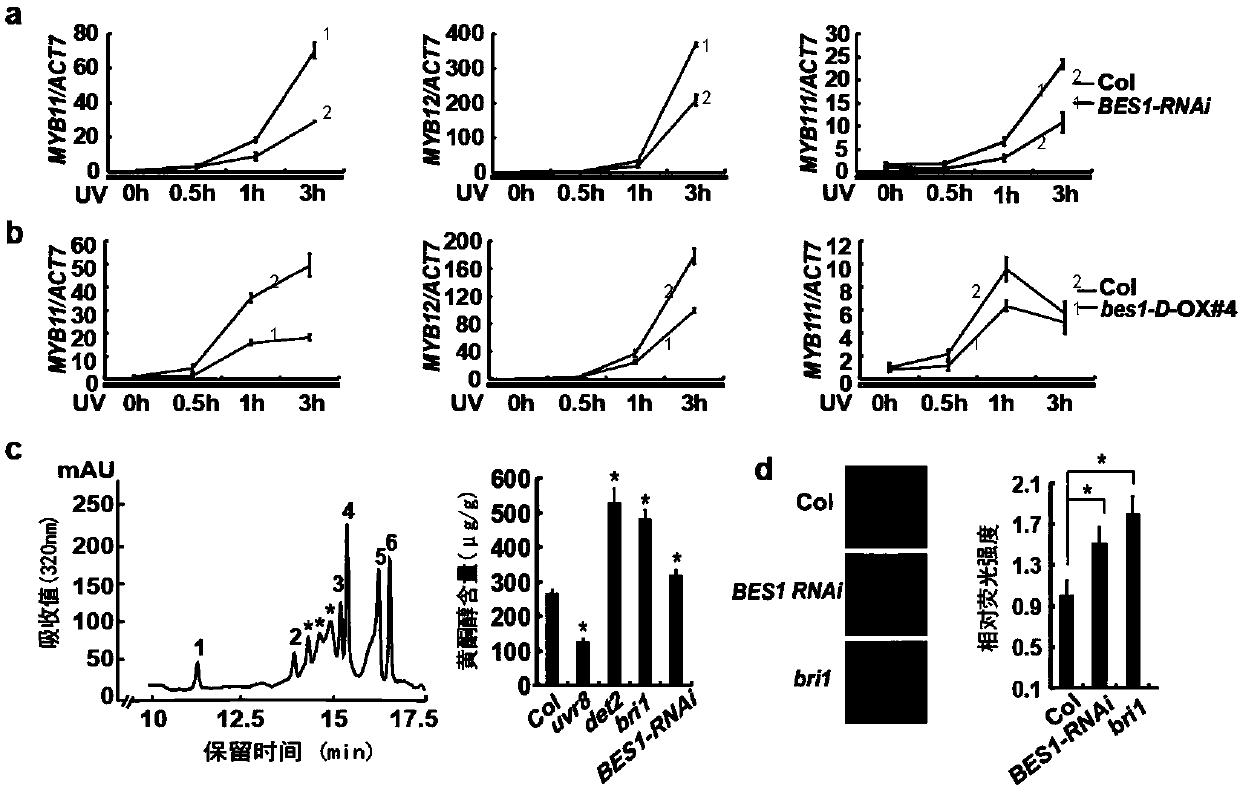
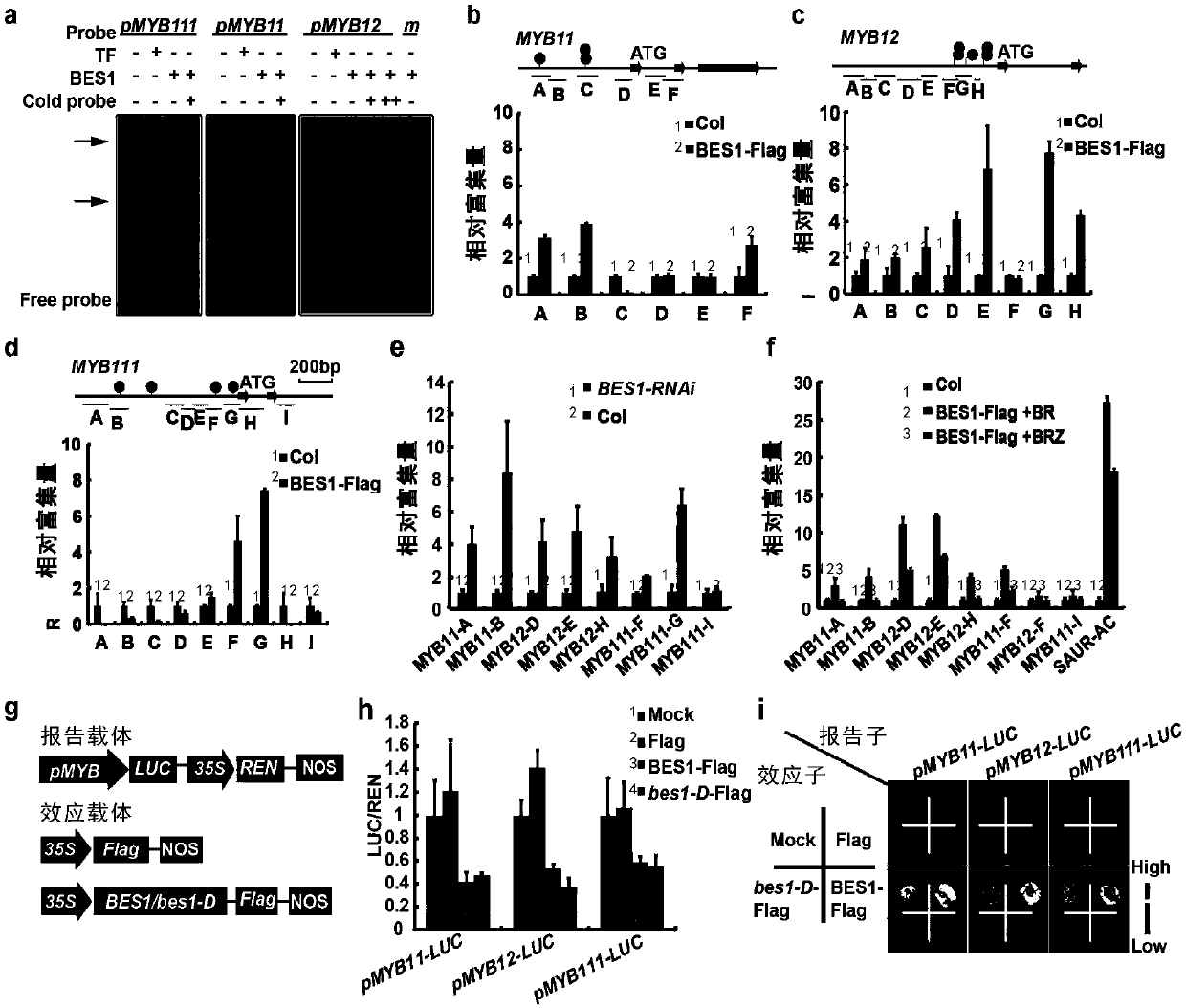
Gene for regulating flavonoid synthesis and ultraviolet resistance of plants and application of gene
ActiveCN110894506AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionSignalling pathwaysMYB
The invention relates to a gene for regulating flavonoid synthesis and ultraviolet resistance of plants and application of the gene. Effects and molecular mechanisms of brassinosteroid signaling pathway on the flavonoid synthesis in plants and resistance of plants to ultraviolet rays are studied and revealed for the first time. The brassinosteroid signaling pathway, particularly transcription factor BES1 in the brassinosteroid signaling pathway, can negatively regulate MYB transcription factor, regulate the flavonoid synthesis in plants on the basis, and further regulate the resistance of plants to ultraviolet rays.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
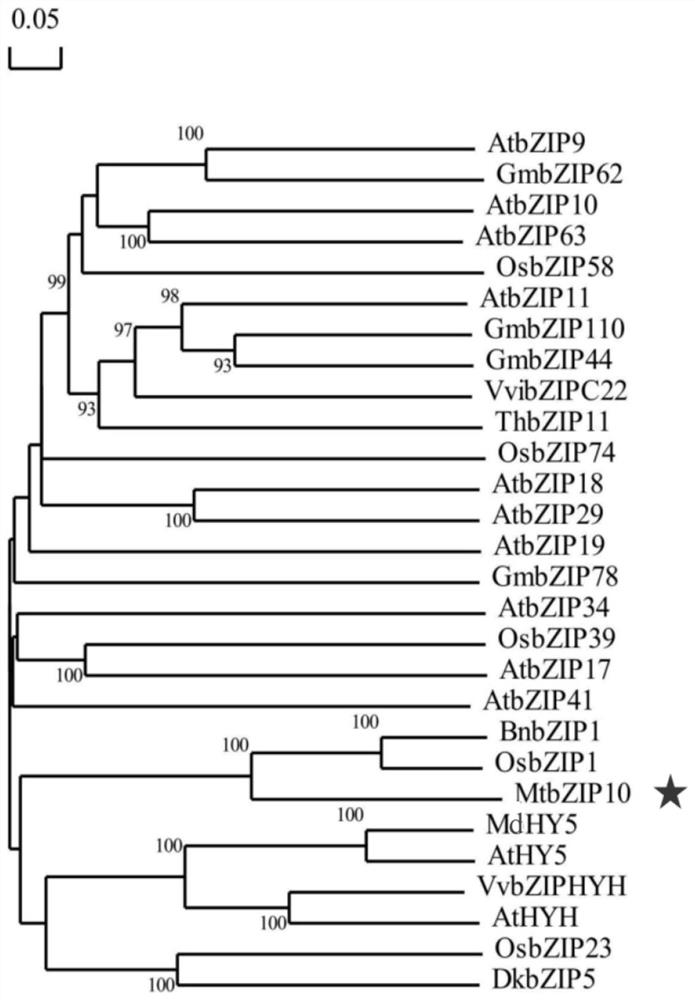
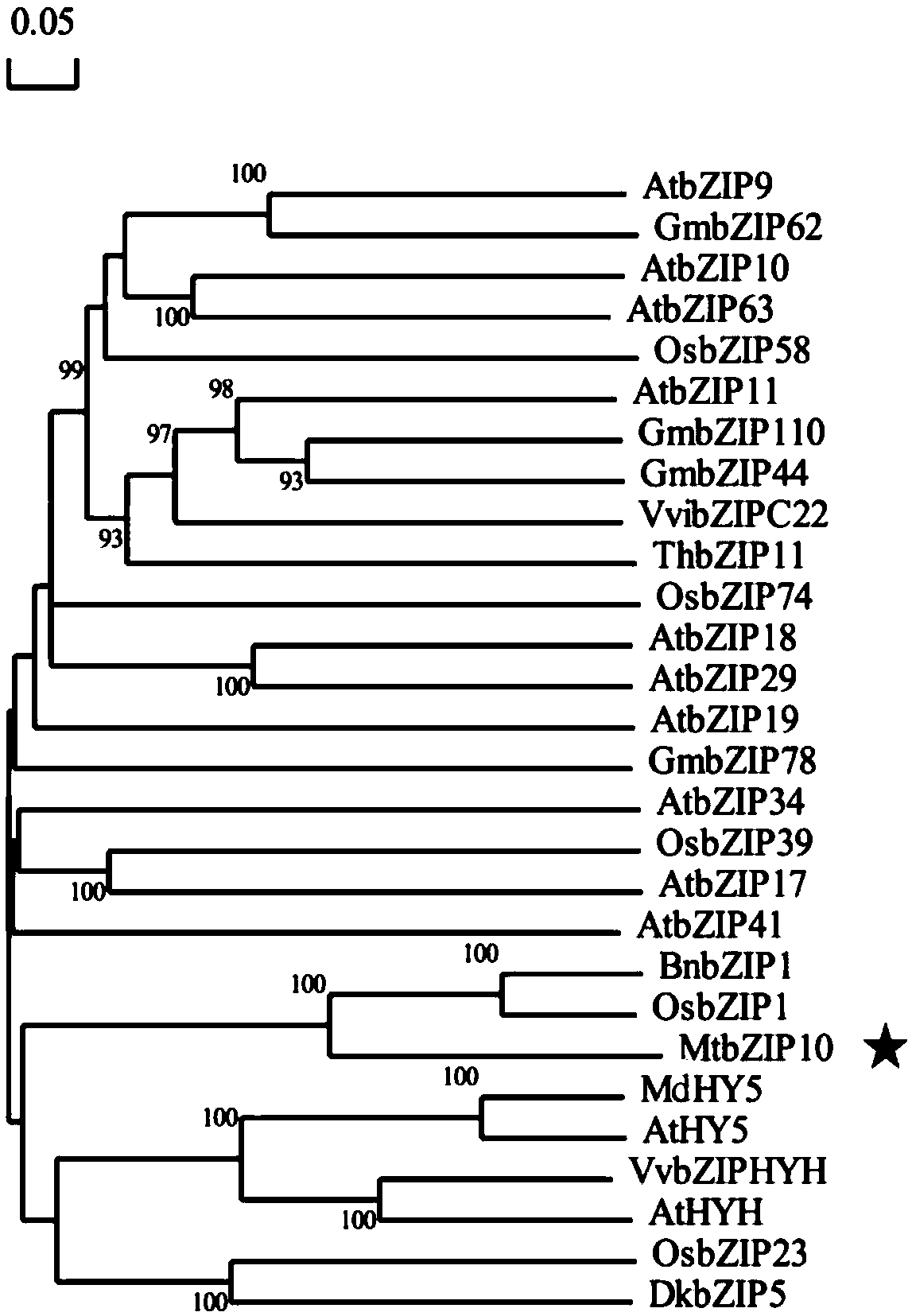
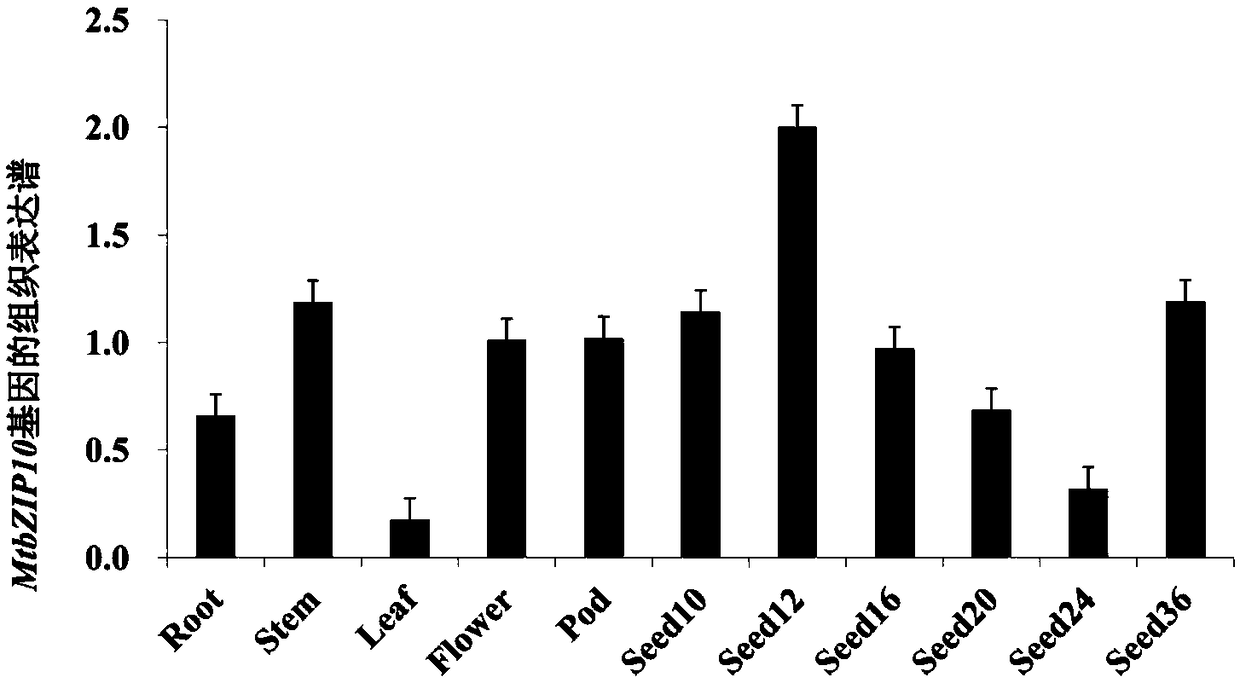
Transcription factor gene for regulating and controlling synthesis of plant flavonoid and use thereof
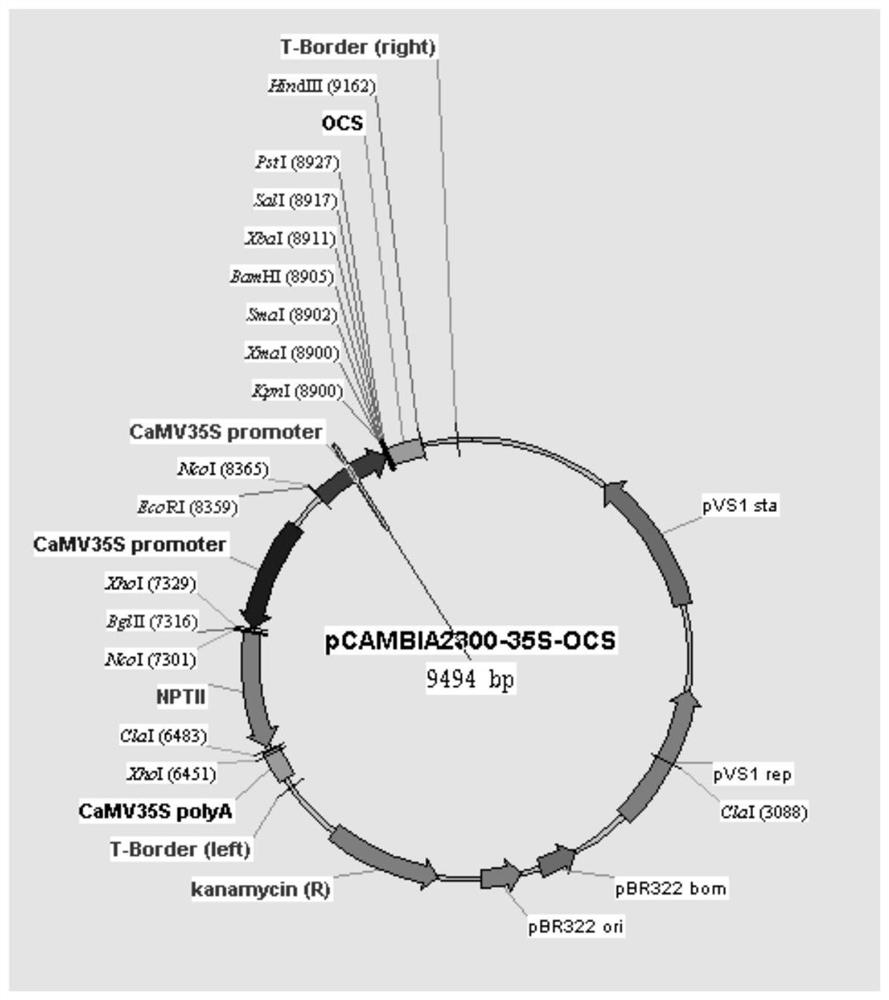
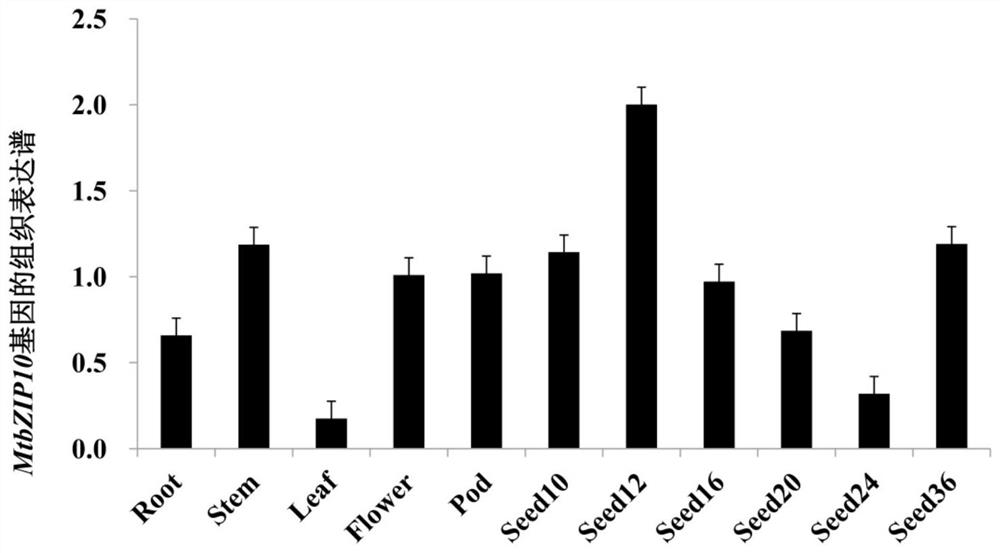
The invention discloses a transcription factor gene for regulating and controlling synthesis of plant flavonoid. The transcription factor gene is an MtbZIP10 gene authenticated from a leguminous plant, namely medicago truncatula, and the gene sequence of the transcription factor gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. Furthermore, the invention discloses functions and application of the transcriptionfactor gene. The transcription factor gene has the advantages that the transcription factor gene capable of positively regulating and controlling the synthesis of flavonoid compounds is cloned from the leguminous plant, namely medicago truncatula, the system identification of the functions of the transcription factor gene is carried out, and the system identification result shows that the gene iscapable of activating multiple genes in the biosynthetic pathway of flavonoid and the content of the flavonoid compounds is increased.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Transcription factor of tree peony psmyb12 and its coding gene and application
The invention discloses a peony PsMYB12 transcription factor as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The peony PsMYB12 transcription factor is a protein of (a) or (b) which is described as follows: (a) a protein consists of an amino acid sequence shown by a sequence 1 in a sequence table; (b) proteins which are derived from (a), are associated with peony color spot formation and / or anthocyanin synthesis and are formed by replacing and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues in the amino acid sequence shown by the sequence 1 in the sequence table. By means of VIGSsilencing and heterologous excess transformation analysis, the results show that the peony PsMYB12 transcription factor can regulate the expression of key enzyme genes in an anthocyanin synthesis route. The peony PsMYB12 transcription factor is speculated to play an important role in the synthesis and accumulation of anthocyanin in peony flower spots and the formation of color spots. The specifically expressed gene is cloned for the first time and the functions of the gene are verified, so that a foundation is laid for the molecular mechanism of the formation of the color spots, and technicalbasis and thought are provided for further analysis of the synthesis and regulation of flavonoids in peony flowers.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wheat salt-resistant and oxidation-resistant gene TaFLS and application thereof
The invention discloses a wheat salt-resistant gene, i.e., a wheat secondary metabolism flavone synthetic route gene TaFLS and a plant expression vector pSTART-TaFLS containing the gene TaFLS. The invention further discloses application of an expression vector of the gene to the cultivation of salt-resistant and oxidation-resistant plants. As proved by an experiment, the salt resistance and the oxidation resistance of a transgenic plant are remarkably enhanced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A gene regulating flavonoid synthesis and its encoded protein and application
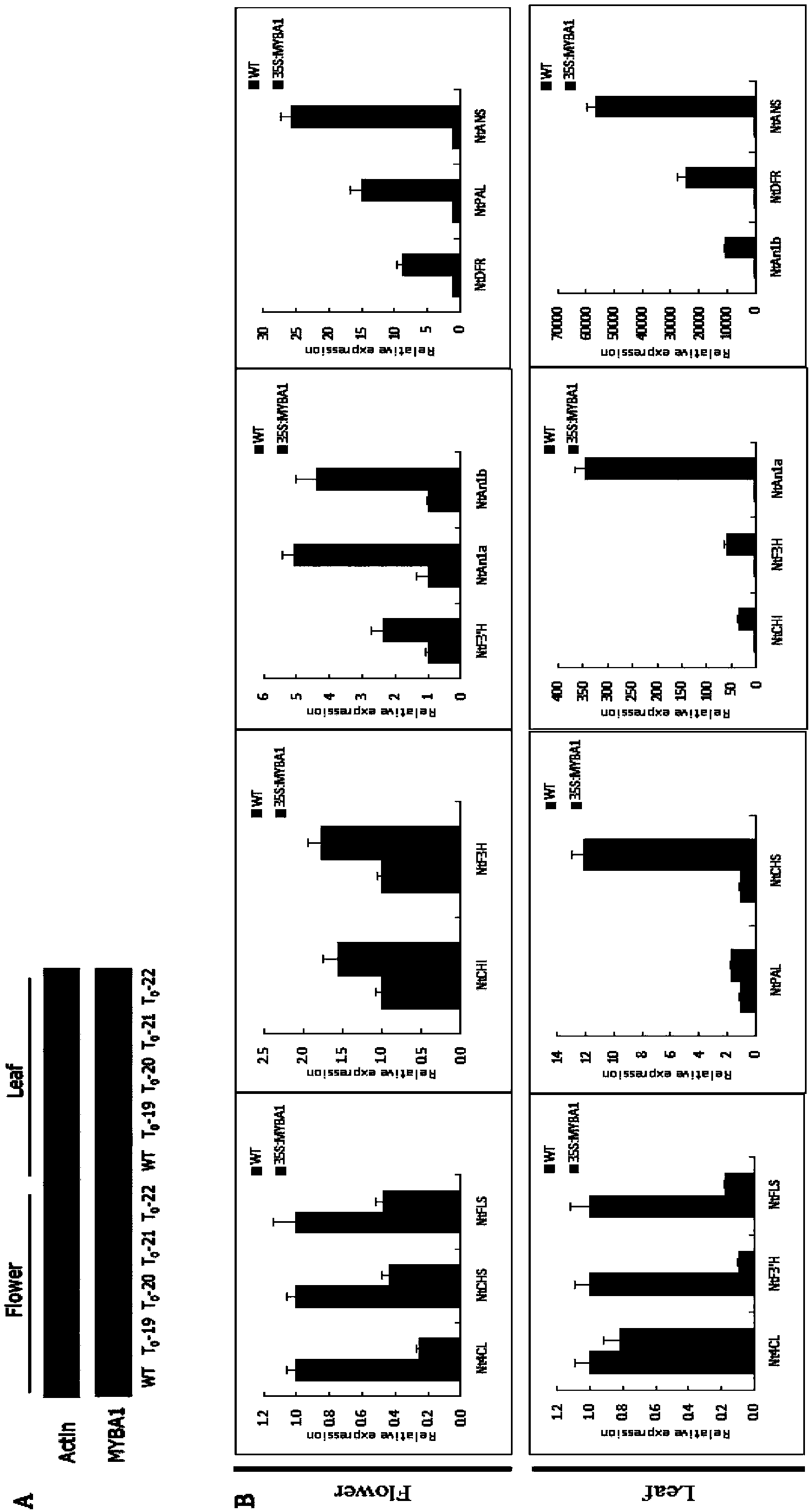
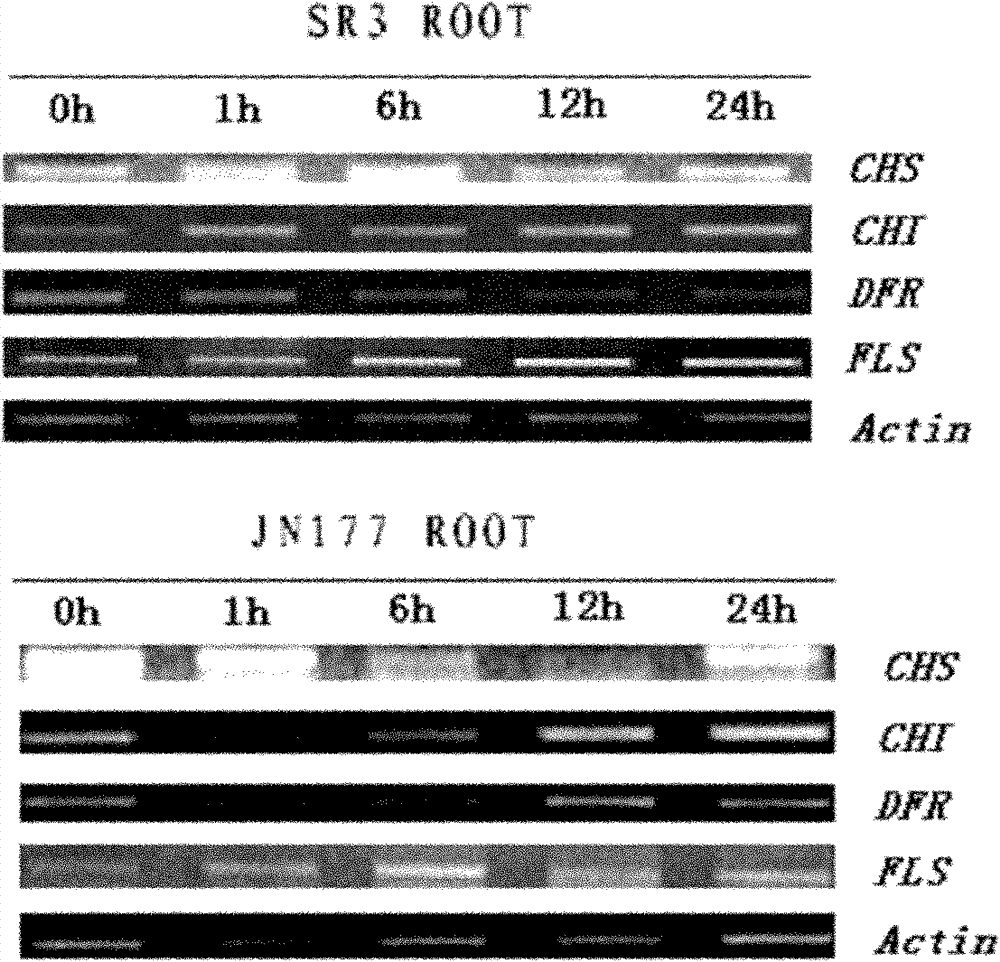
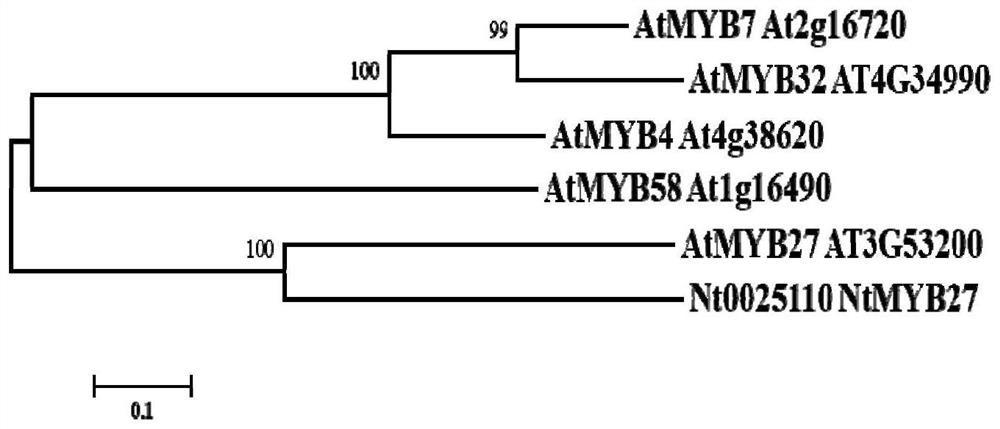
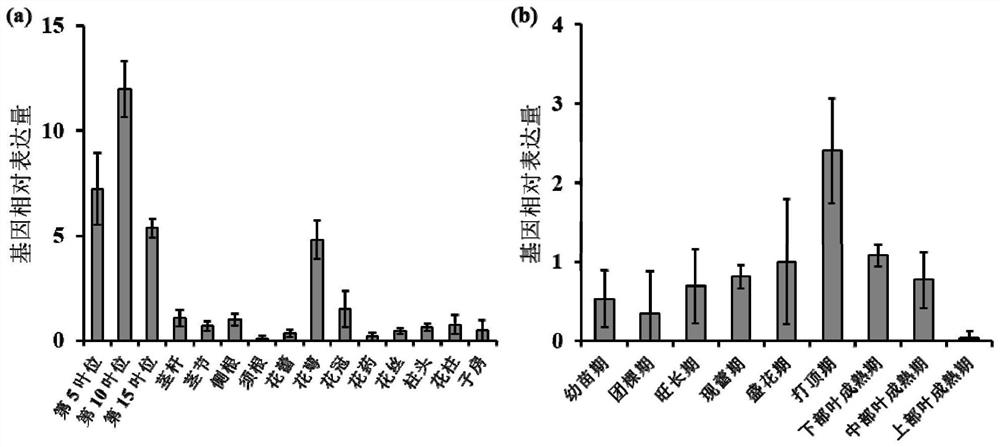
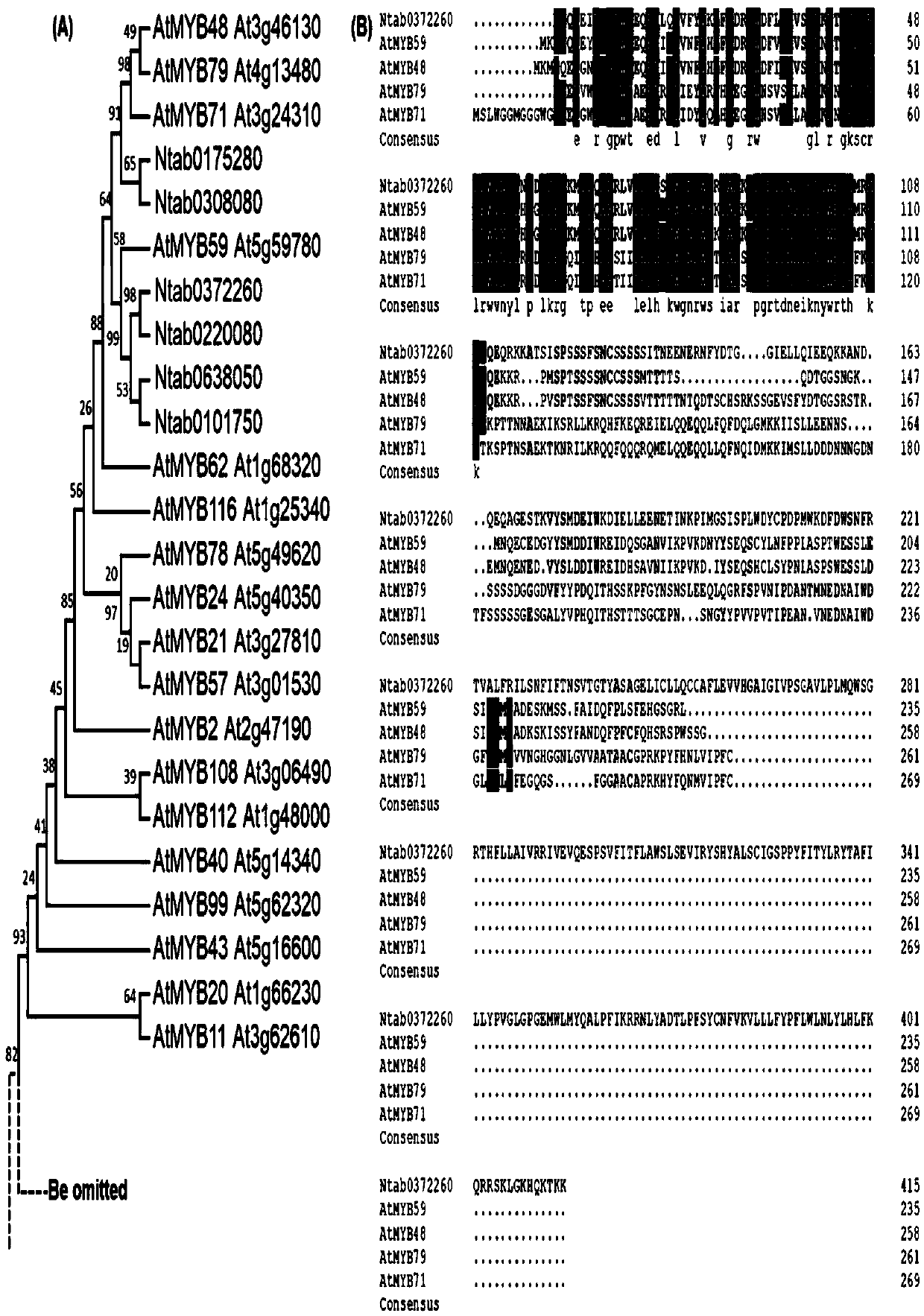
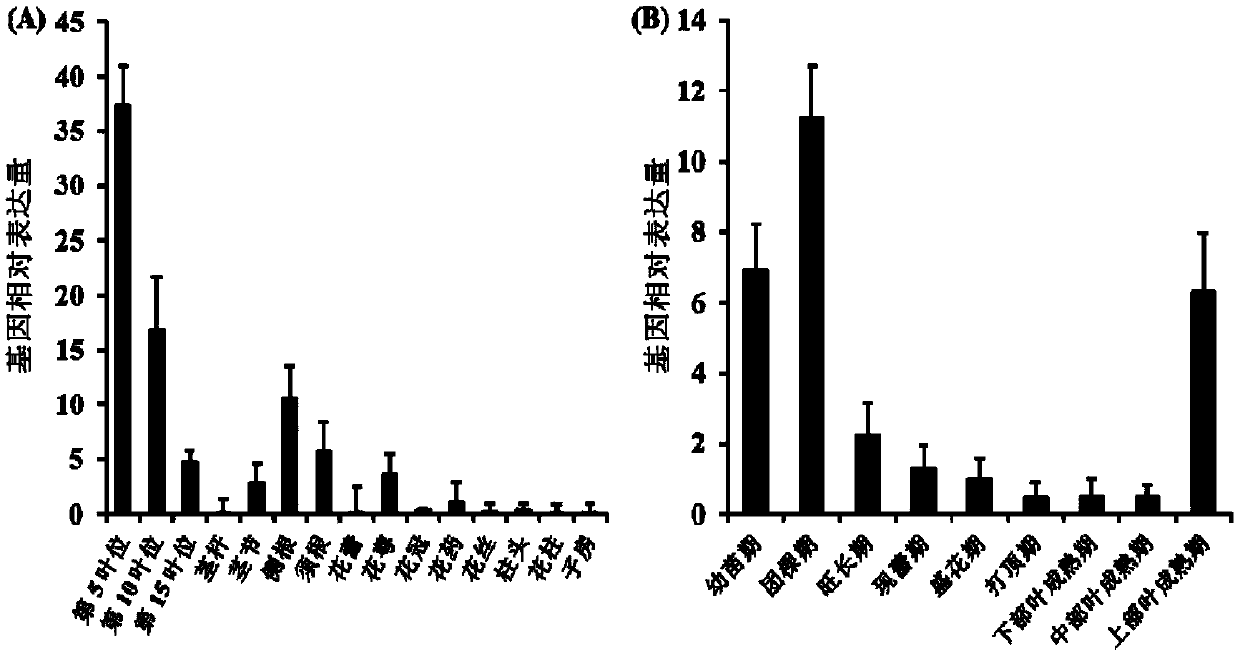
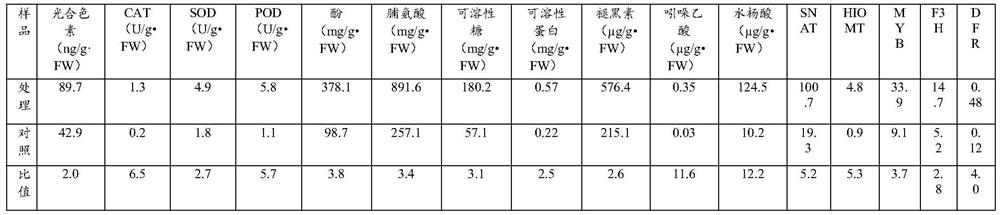
ActiveCN110777151BInhibit synthesisIncrease contentPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a gene for regulating the synthesis of flavonoids, its coded protein and its application, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The gene regulating flavonoid synthesis, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, which is derived from common tobacco, named NtMYB27, the NtMYB27 gene is 1240bp in length, contains 3 introns and 4 exons, and its coding region is complete 597 bp long. The present invention finds that the NtMYB27 transcription factor can inhibit the synthesis of flavonols in leaves through cloning analysis of gene sequences, construction of expression vectors, and gene expression detection, and this inhibition is achieved by inhibiting the expression of NtFLS and NtCHS genes of. Therefore, the present invention confirms that NtMYB27 is a negative regulator of plant flavonol synthesis. When the expression of this gene is inhibited or its function is lost, it can significantly increase the content of flavonols in plant leaves, providing a basis for the subsequent use of gene editing technology to enhance plant flavonols. Assays provide clear target genes.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
A key gene gbmyb6 that promotes the synthesis of ginkgo flavonoids and its expressed protein, vector and application
ActiveCN112079911BIncrease contentEasy to synthesizePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a key gene GbMYB6 for promoting the synthesis of ginkgo flavonoids and its expressed protein, carrier and application. The nucleotide sequence of the key gene GbMYB6 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid of the expressed protein is The sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The present invention uses Ginkgo biloba leaves as materials, clones the GbMYB6 gene, constructs an overexpression vector 35S::GbMYB6 containing the gene GbMYB6 by enzyme cleavage, and transfers it into Ginkgo callus and Arabidopsis thaliana, GbMYB6 transgenic Ginkgo callus and transgene The content of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana was significantly increased, which indicated that GbMYB6 can promote the synthesis of flavonoids. Therefore, regulating the expression of GbMYB6 has important application value in improving the medicinal quality of Ginkgo biloba leaves.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
A transcription factor gene regulating plant flavonoid synthesis and its application
The invention discloses a transcription factor gene that regulates the synthesis of plant flavonoids. The transcription factor gene is the MtbZIP10 gene identified from the leguminous plant Medicago truncatula, and its gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Moreover, the present invention discloses the function of the gene and its application. The advantage of the present invention is that the transcription factor gene that can positively regulate the synthesis of flavonoid compounds is cloned from the leguminous plant Medicago truncatula, and its function is systematically identified, and it is found that the gene can activate the biosynthesis pathway of flavonoids Multiple genes that increase the content of flavonoid compounds.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for producing chrysanthemum plant having petals containing modified anthocyanin
Disclosed are a method for controlling flavonoid synthesis in a chrysanthemum plant or non-chrysanthemum plant by genetic recombination technology using a transcriptional regulatory region useful for altering flower color, a method for modifying anthocyanins, a method for producing a chrysanthemum plant or non-chrysanthemum plant containing modified anthocyanins in the petals thereof, and a chrysanthemum plant or non-chrysanthemum plant, progeny thereof, or vegetatively propagated products, part or tissue thereof transformed with the regulatory region. In the method according to the present invention, an expression vector or expression cassette containing a transcriptional regulatory region of perilla anthocyanin 3-acyltransferase gene, such as a nucleic acid containing the nucleotide sequence indicated in SEQ ID NO. 1, or a transcriptional regulatory region of pansy F3′5′H gene, such as the nucleotide sequence indicated in SEQ ID NO. 15, is used.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Asparagus Chalcone Isomerase Gene, Its Encoded Protein and Its Application
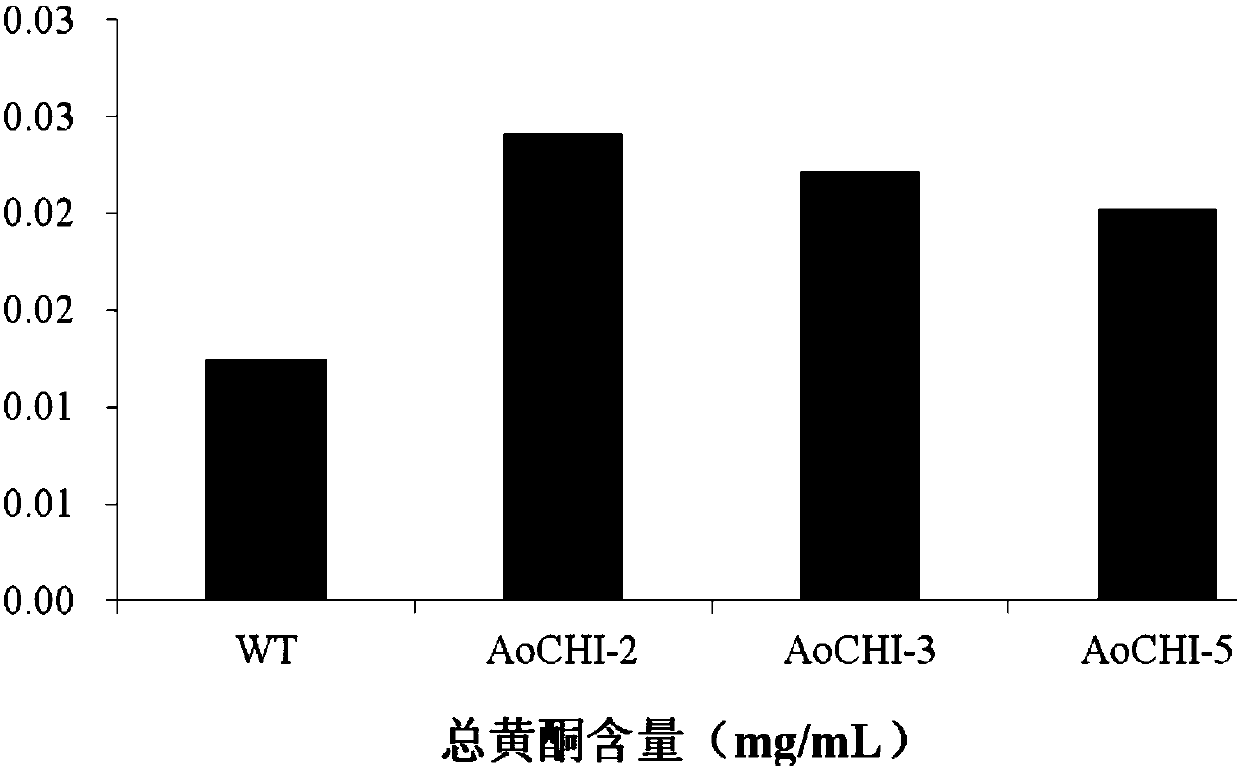
The invention provides a chalcone isomerase gene of asparaguses, a protein encoded by the chalcone isomerase gene and application of the chalcone isomerase gene. The CDS sequence of the chalcone isomerase gene AoCHI1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO: 2. The chalcone isomerase gene AoCHI1 is cloned from the asparagus for the first time, and is one of key genes for synthesizing plant flavonoids; by the adoption of a method of gene engineering, the gene AoCHI1 is transferred into a target plant, so that the total flavonoids content of a transgenic plant can be increased, to improve the plant quality by using a gene engineering technology in the future; furthermore, an important theoretical basis is provided for obtaining medicines or food with high oxidization resistance, and the chalcone isomerase gene has a wide application prospect and high economic value.
Owner:VEGETABLE & FLOWER INST JIANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
New Application of Arabidopsis tt4 Gene in Plant Salt Tolerance
ActiveCN105647883BAcyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionGene silencingGenetic engineering
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Gene for regulating flavonoid synthesis and encoded protein and application of gene
The invention relates to a gene for regulating flavonoid synthesis and an encoded protein and application of the gene, and belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering. A gene sequence ofthe gene for regulating flavonoid synthesis is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene derives from common tobacco, is named NtMYB59, the full length of the NtMYB59 gene is 9552bp, the NtMYB59 gene includes 10 introns and 11 exons, and the total length of a coding region of the NtMYB59 gene is 1251bp. According to the gene for regulating flavonoid synthesis and the encoded protein and application of the gene, through technologies of cloning and analysis of gene sequences, construction of expression vectors, gene expression detection and the like, it is found that NtMYB59 transcription factors can inhibit the synthesis of flavonoids in leaves, and the inhibition is achieved by inhibiting the expression of NtFLS and NtMYB12 genes; and by changing the expression level of NtMYB59 gene, the contentof the flavonoids in plant leaves can be significantly changed, and a theoretical basis and target genes for improving crop quality are provided.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
High-temperature-resistant coloring early selection method for early-medium-maturing apple hybrid seedlings
PendingCN113736848AReduce in quantityImprove breeding efficiencyComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMelatonin synthesis
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant coloring early selection method for early-medium-maturing apple hybrid seedlings, and belongs to the technical field of forestry planting. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting hybrid seedling fields; selecting and treating experimental materials; and screening plants with increased metabolites, increased hormone levels, melatonin synthesis related genes, MYB transcription factors and up-regulated F3 gene expression in flavonoid synthesis pathways in samples as selection objects. Early selection and pre-selection of the hybrid seedlings are carried out by utilizing the correlation between fruits and leaves, so that bad types are eliminated, the number of selected plants is reduced, and the breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF POMOLOGY
Genes regulating flavonoid synthesis and their encoded proteins and their applications
The invention relates to a gene for regulating flavonoid synthesis, its encoded protein and its application, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The gene that regulates the synthesis of flavonoids, the gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the gene is derived from common tobacco, named NtMYB59, the full length of the NtMYB59 gene is 9552bp, including 10 introns and 11 exons, which encodes The total length of the region is 1251bp. The present invention finds that the NtMYB59 transcription factor can inhibit the synthesis of flavonoids in leaves through cloning analysis of gene sequences, construction of expression vectors, and gene expression detection, and this inhibition is achieved by inhibiting the expression of NtFLS and NtMYB12 genes . The invention can significantly change the content of flavonoid substances in plant leaves by changing the expression level of NtMYB59 gene, and provides theoretical basis and target genes for improving crop quality.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
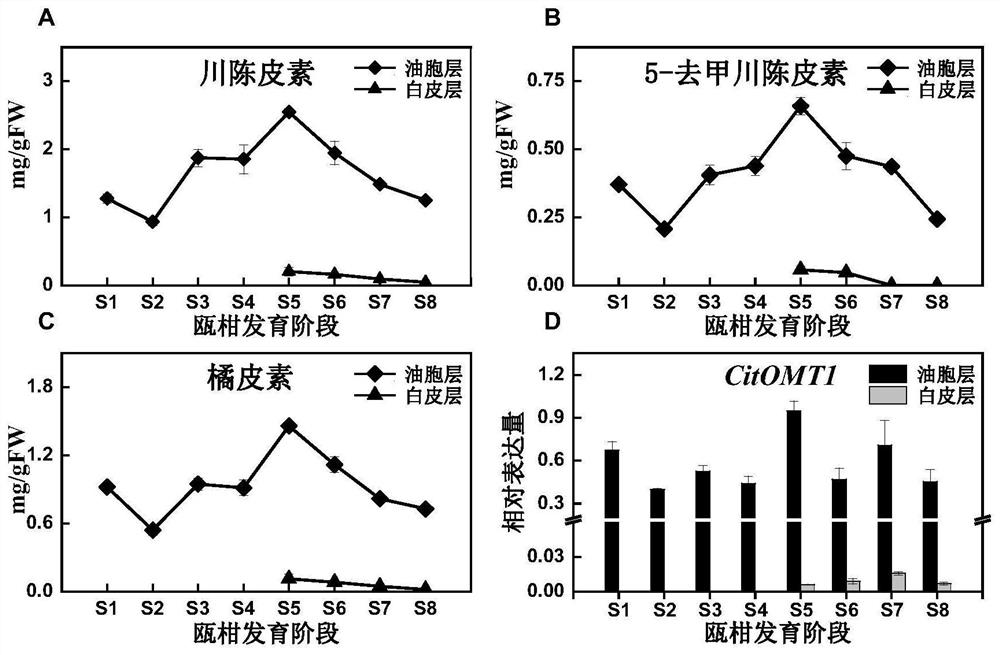
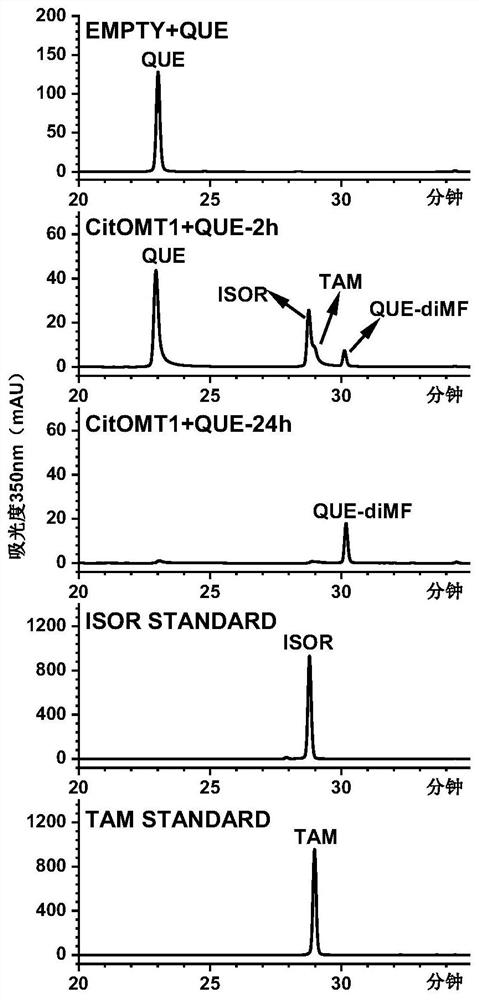
Oxymethyltransferases involved in the synthesis of flavonoids in citrus peel and their coding genes and applications
The invention provides an oxymethyltransferase involved in the synthesis of citrus peel flavonoids and its coding gene and application. The expression level of CitOMT1 is positively correlated with the accumulation of polymethoxylated flavonoids during the fruit development of Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima; The in vitro enzyme activity test shows that the oxygen methyltransferase can be used in catalyzing the specific site methylation of flavonoids, especially can catalyze quercetin to generate quercetin 3', 4' dimethyl ester; catalyze eriodiction to generate hesperetin and homo eriodictyol, catalyze baicalein to generate saflavone A; catalyze 7,8-dihydroxyflavone to generate 7-hydroxy-8-methoxyflavone . The enzyme activity reaction conditions are simple, and no additional metal ions need to be added, so it has high application value and research prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A key gene gbmyb4 that regulates the synthesis of ginkgo flavonoids and its expressed protein, vector and application
The invention discloses a key gene GbMYB4 that regulates the synthesis of ginkgo flavonoids and its expressed protein, carrier and application. The nucleotide sequence of the key gene GbMYB4 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid of the expressed protein is The sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The present invention uses Ginkgo leaves as materials, clones the GbMYB4 gene, constructs an overexpression vector containing the gene GbMYB4 and transfers it into Ginkgo callus and Arabidopsis thaliana, and the flavonoids in the GbMYB4 transgenic Ginkgo callus and transgenic Arabidopsis of the present invention The contents of the flavonoids were significantly reduced, which indicates that GbMYB4 can inhibit the synthesis of flavonoids, negatively regulate flavonoids, and cooperate with genes that promote flavonoid synthesis to effectively control the synthesis of flavonoids such as Ginkgo biloba, thus regulating the expression of GbMYB4 It has important application value in improving the medicinal quality of Ginkgo biloba leaves.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Sweet potato leaf development and flavonoid enhancement related protein IbBBX29 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN114524868AIncrease the content of flavonoidsReduced flavonoid contentPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyBiological materials
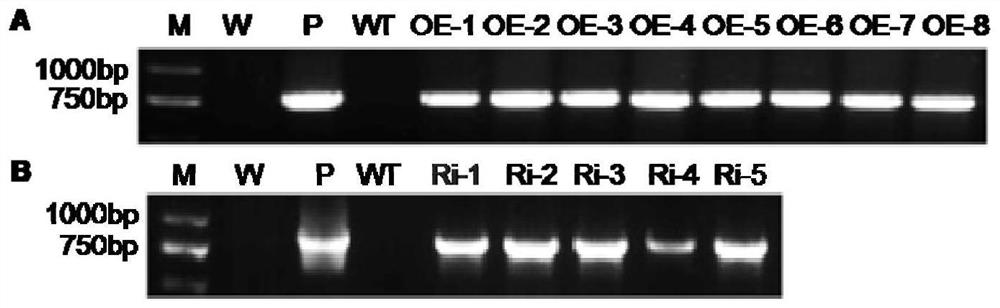
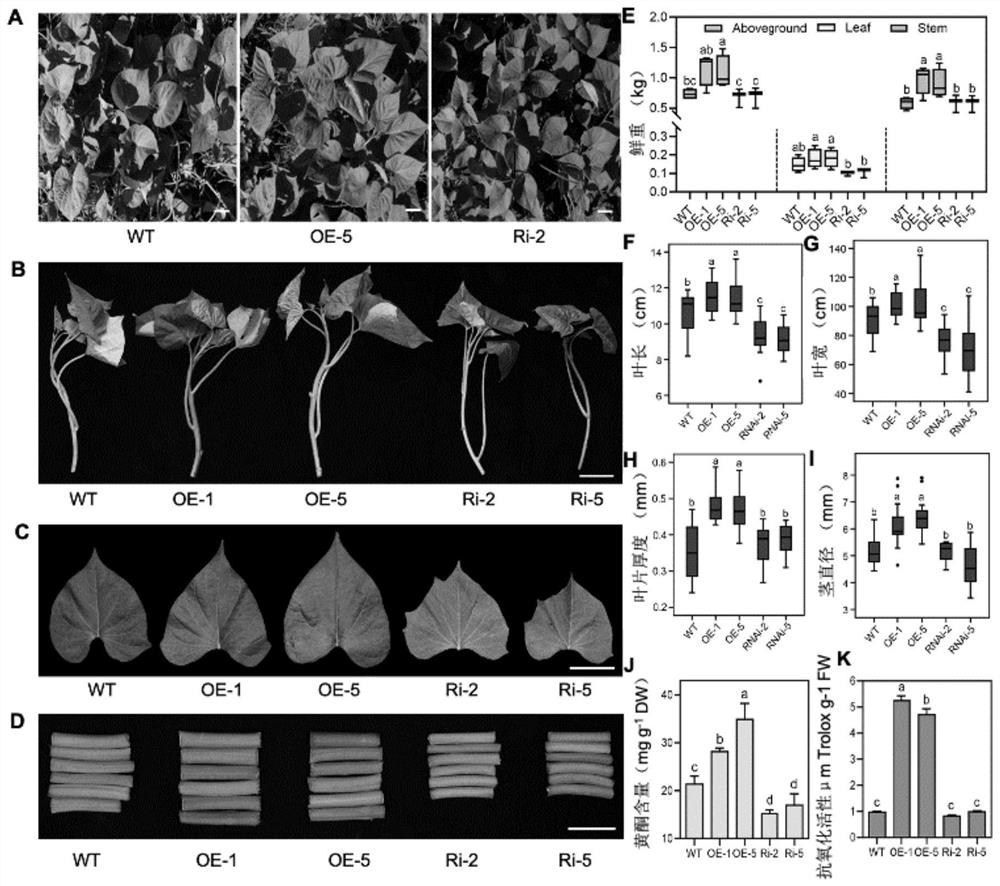
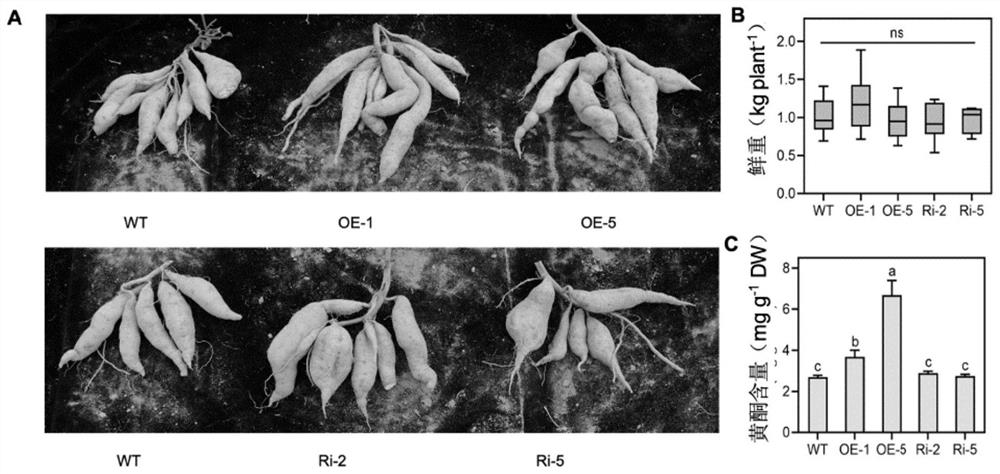
The invention discloses a sweet potato leaf development and flavonoid enhancement related protein IbBBX29 as well as a coding gene and application of the sweet potato leaf development and flavonoid enhancement related protein IbBBX29. The invention specifically discloses a protein with an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No.1, a coding gene, a related biological material and application of the protein to regulation and control of plant leaf development and / or flavonoid content in leaves. According to the invention, the IbBBX29 gene is introduced into a wild sweet potato, so that a transgenic sweet potato plant over-expressing the IbBBX29 gene is obtained, and meanwhile, an IbBBX29 gene knockout plant is constructed. Compared with a wild plant, the fresh weights of the overground part, the leaves and the stems of the overexpressed plant are obviously increased, and the flavonoid content in the leaves is also obviously increased. Experiments show that the IbBBX29 gene plays a key role in regulation and control of sweet potato leaf development and flavonoid synthesis, and important functional genes and breeding materials are provided for genetic improvement of sweet potato leaf development and / or regulation and control of the flavonoid content in leaves.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com