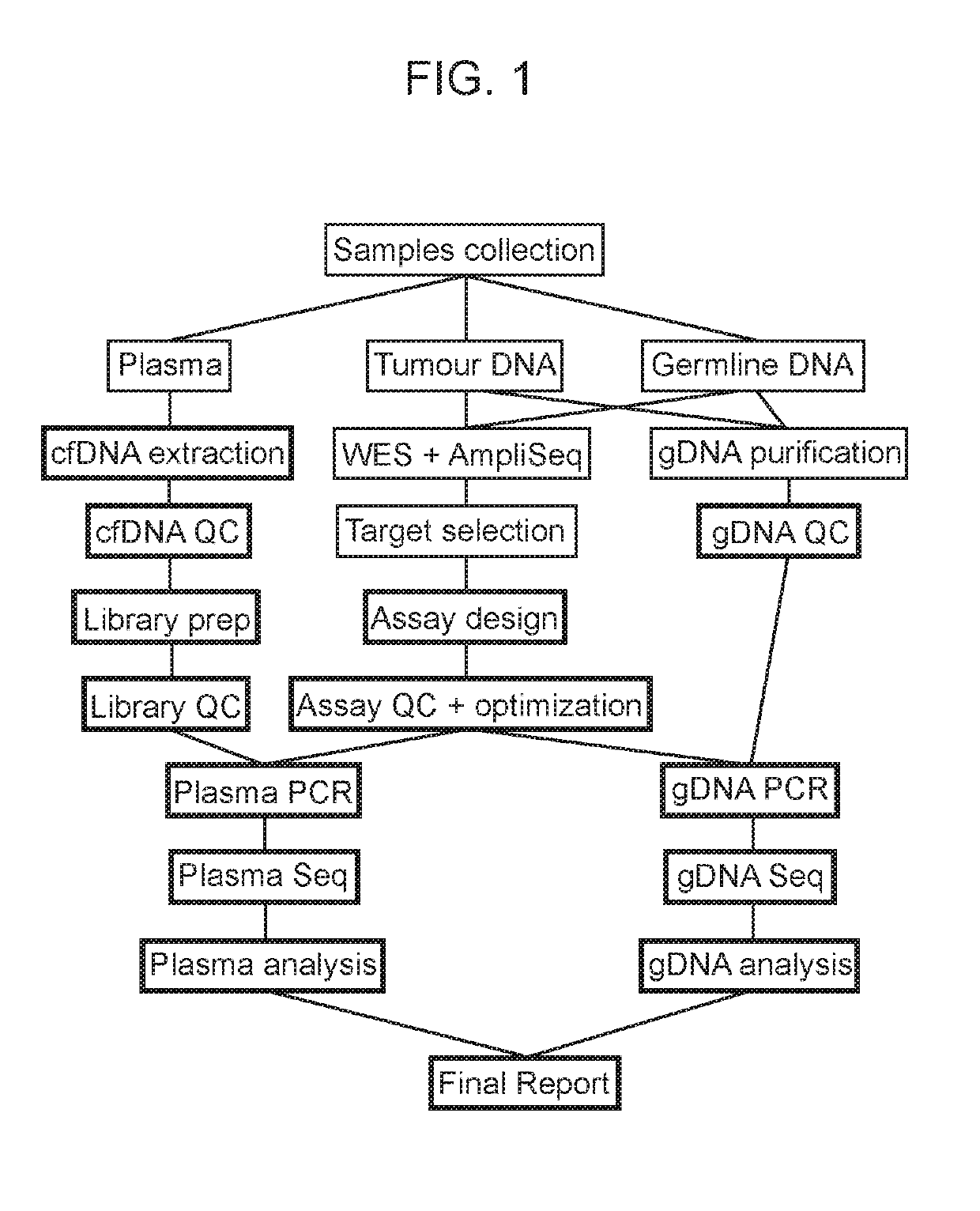
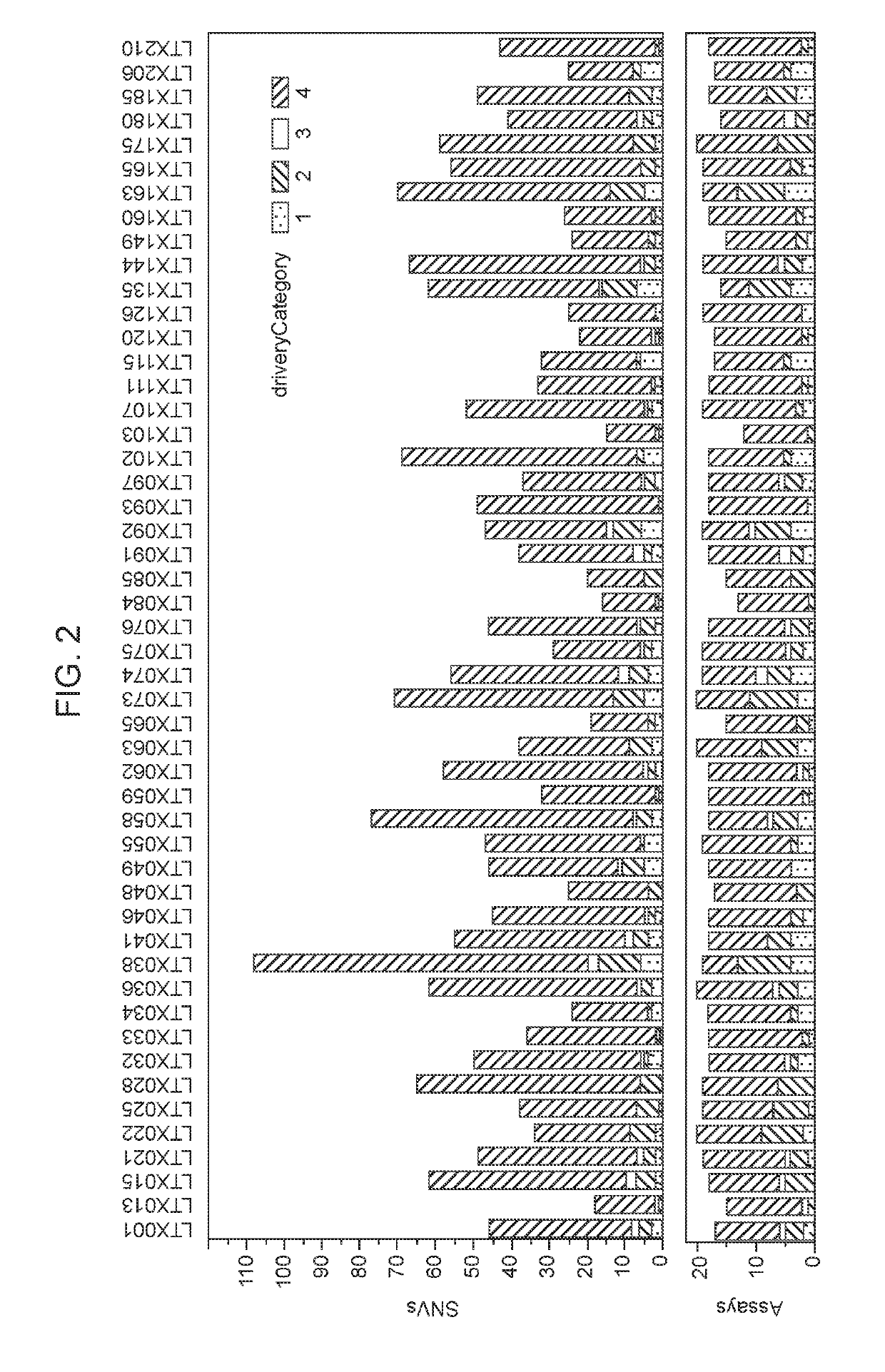
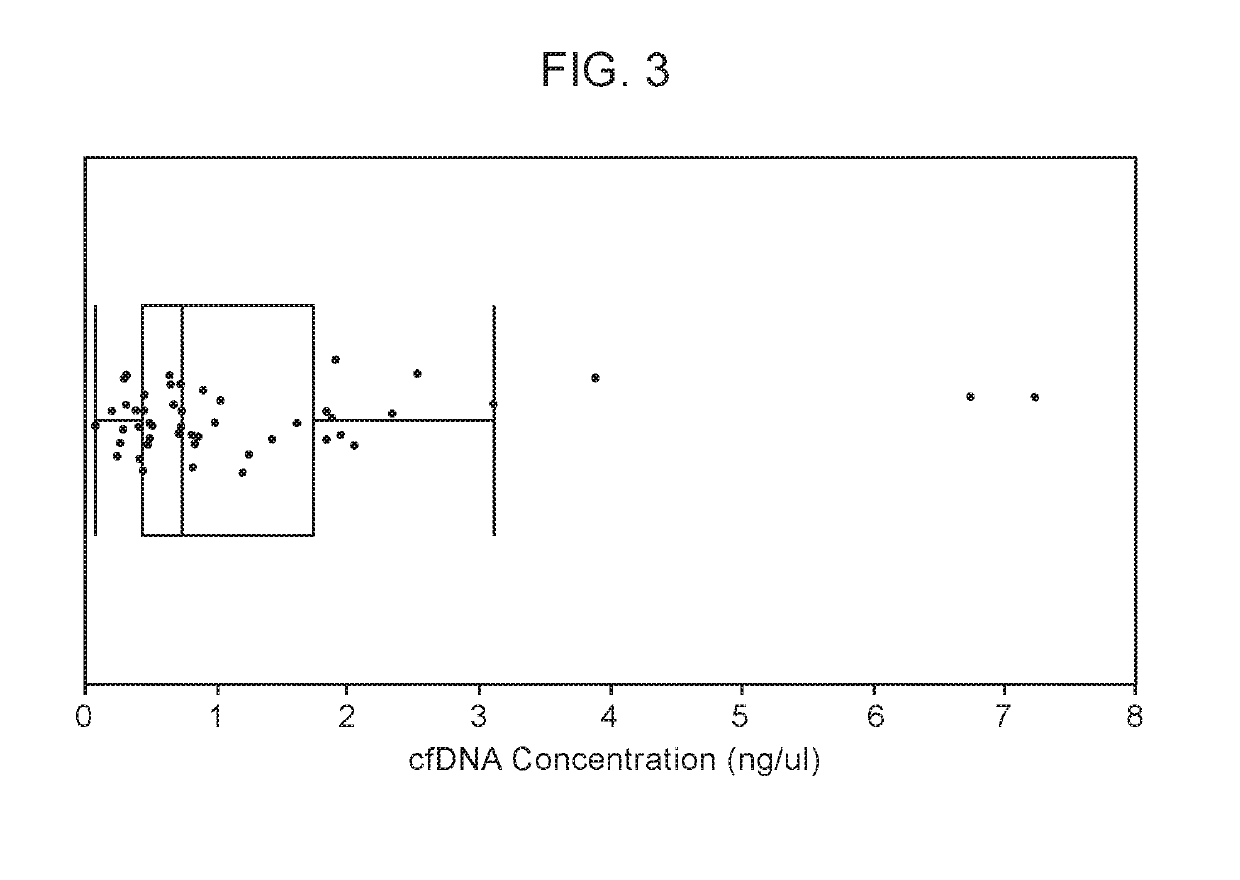
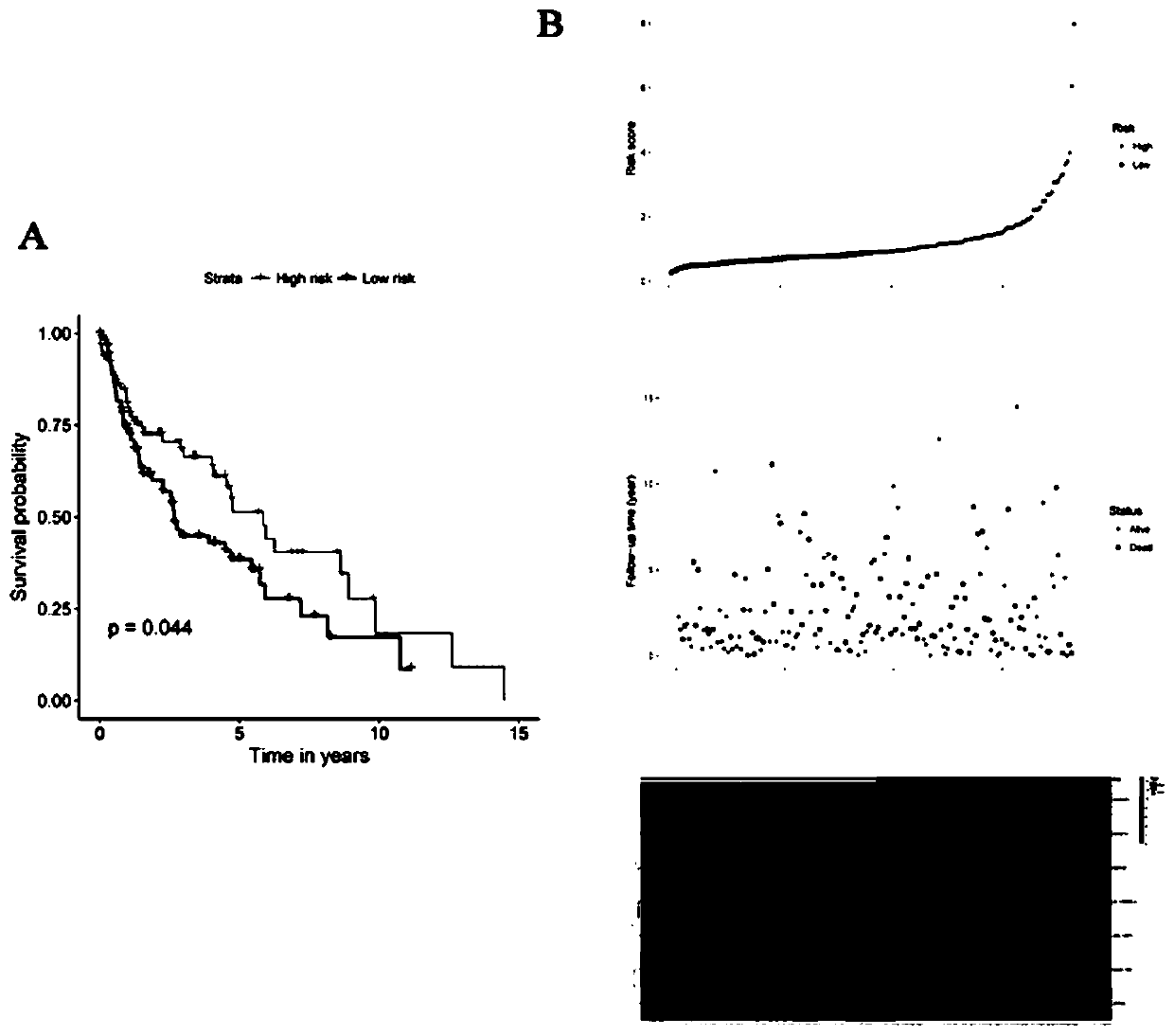
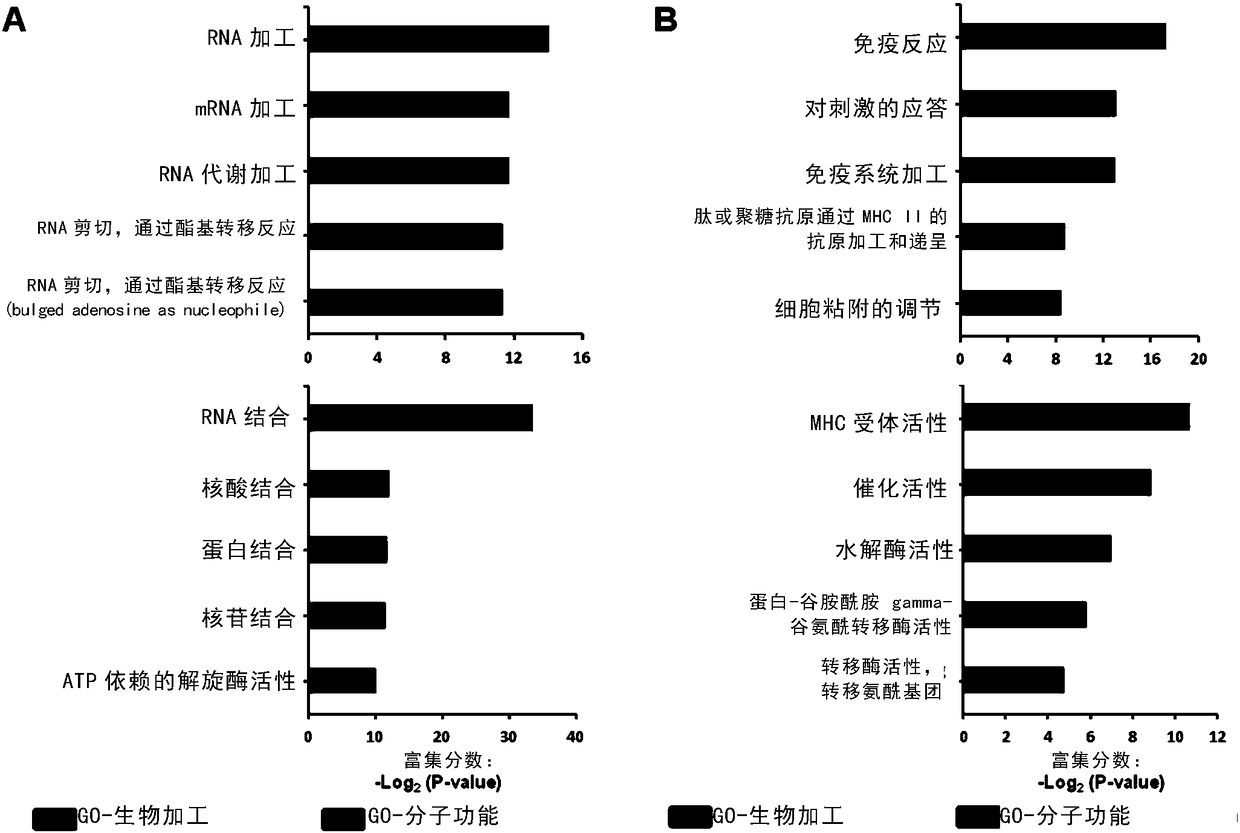
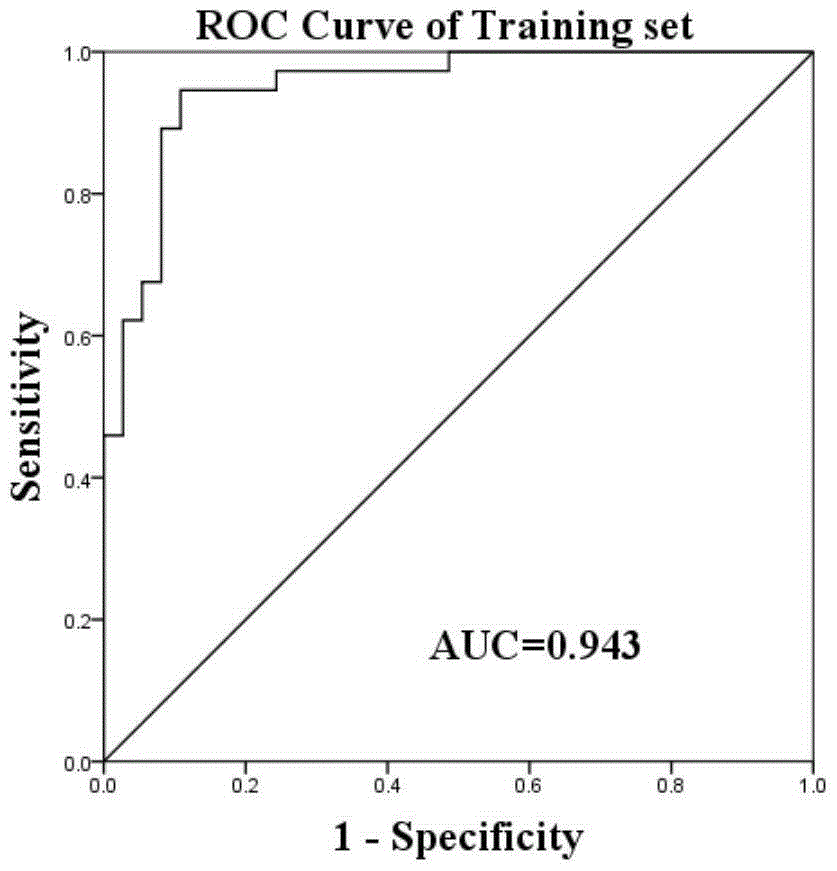
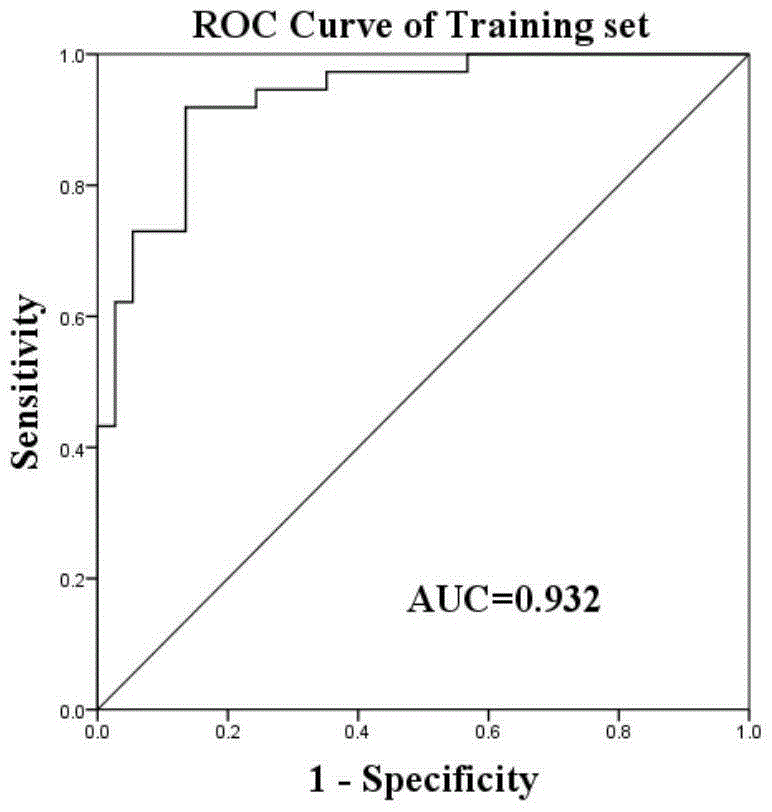
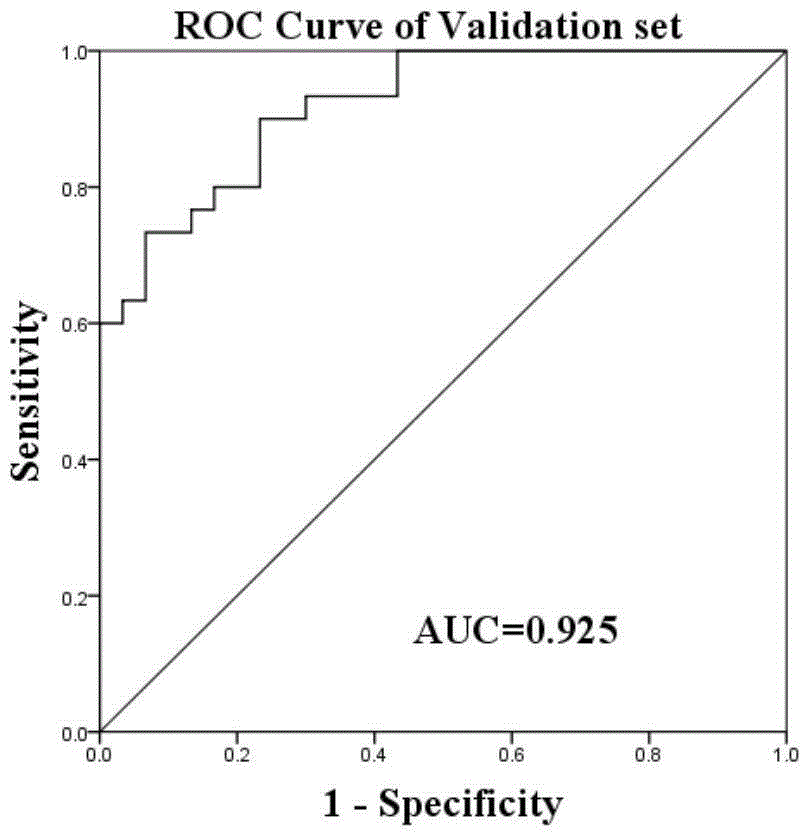
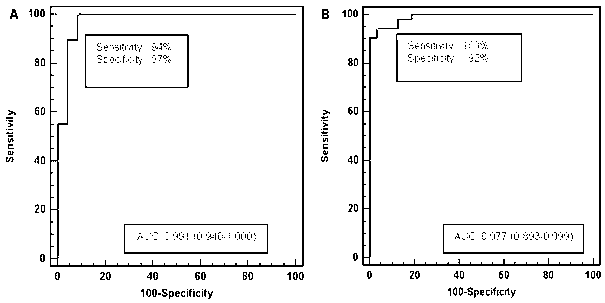
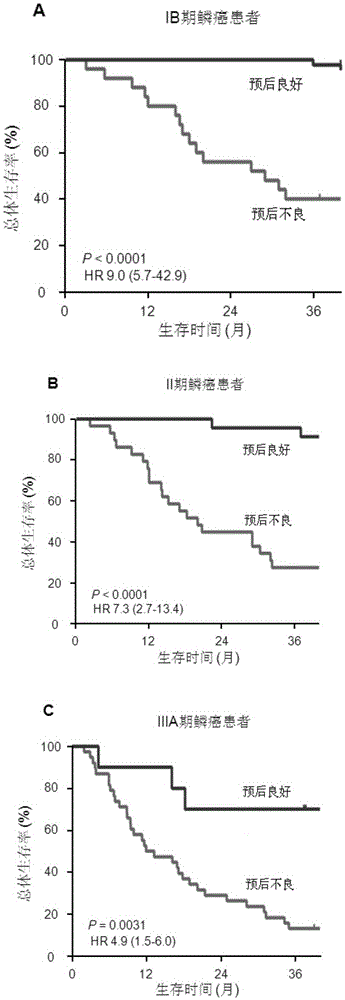
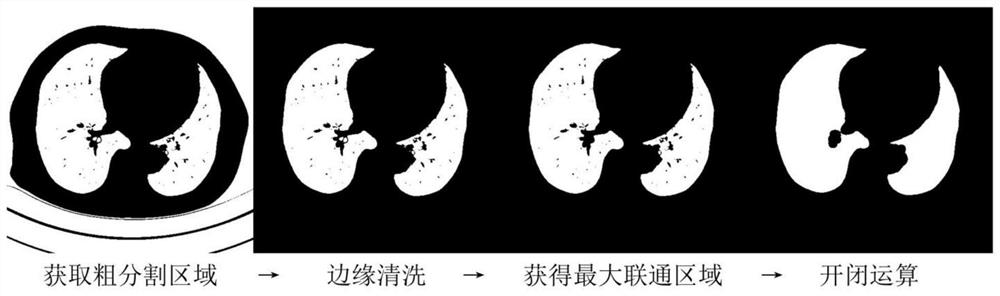
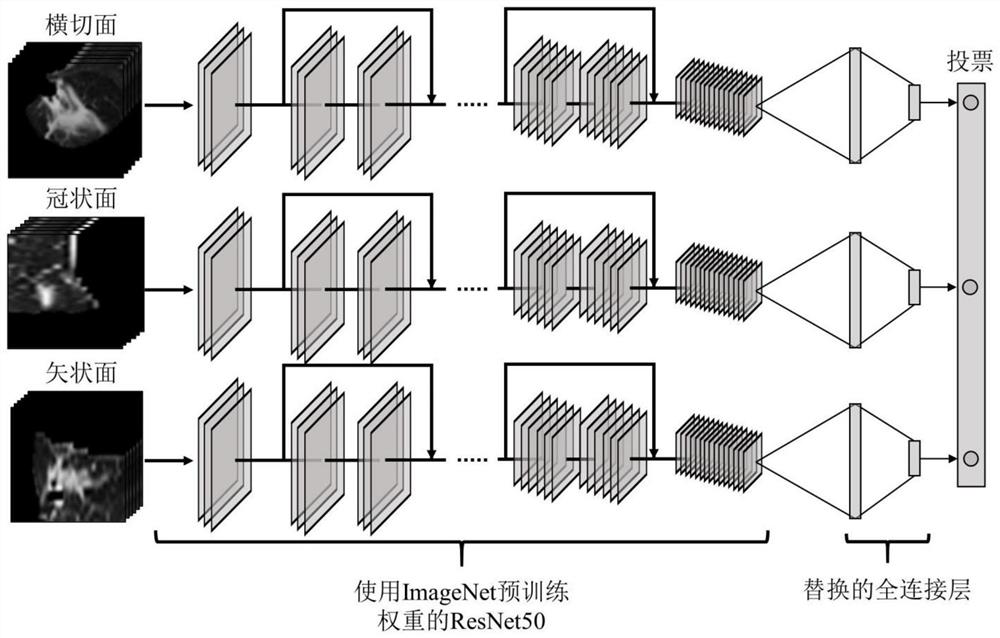
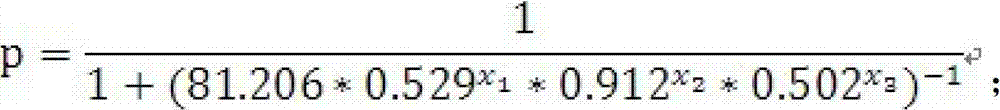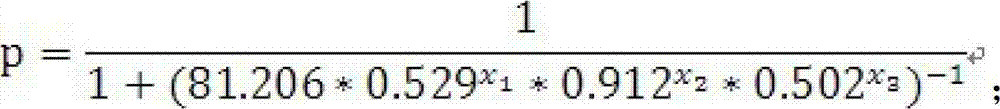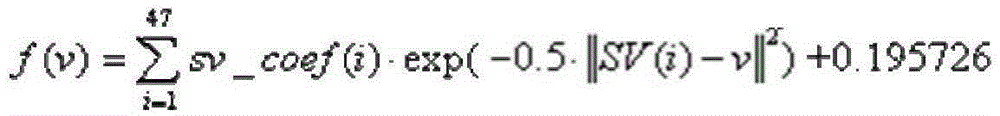Patents
Literature
114 results about "Lung squamous cell carcinoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for lung cancer detection
PendingUS20190106751A1Microbiological testing/measurementLung squamous cell carcinomaNucleic acid cloning
The invention provides methods for detecting single nucleotide variants in lung cancer, especially stage 3a lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. Additional methods and compositions, such as reaction mixtures and solid supports comprising clonal populations of nucleic acids, are provided.
Owner:NATERA
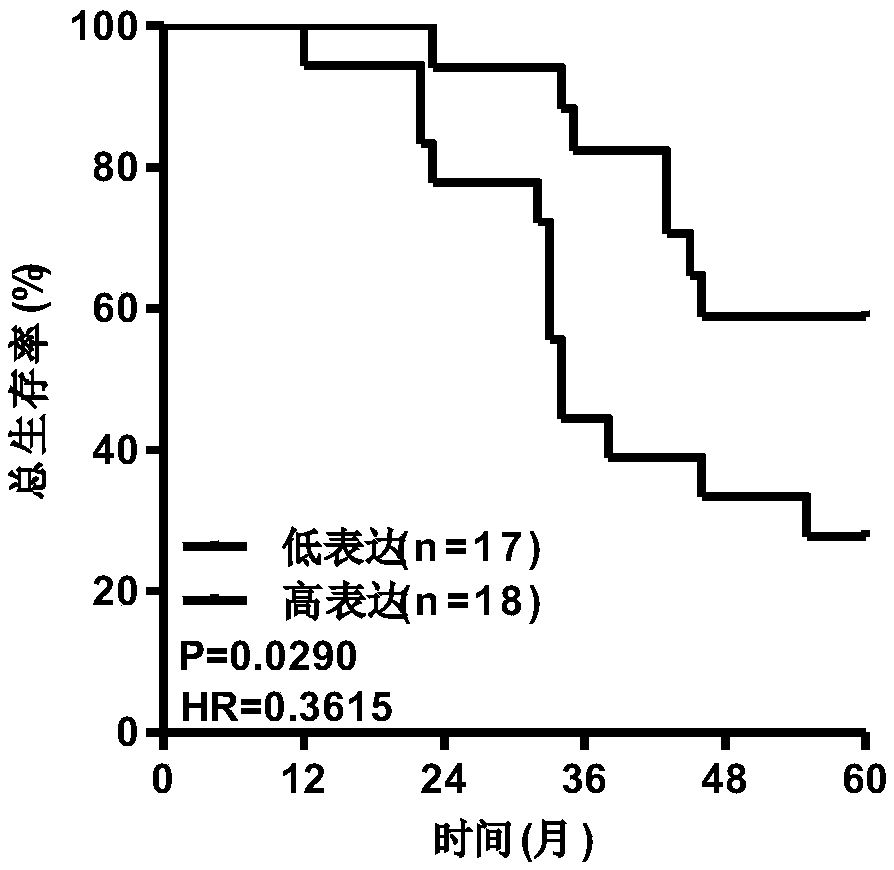
Model for predicting prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma with seven genes as biomarkers, and establishing method thereof
PendingCN109859801AVerify feasibilityBiostatisticsHybridisationOvarian Squamous Cell CarcinomaLung squamous cell carcinoma
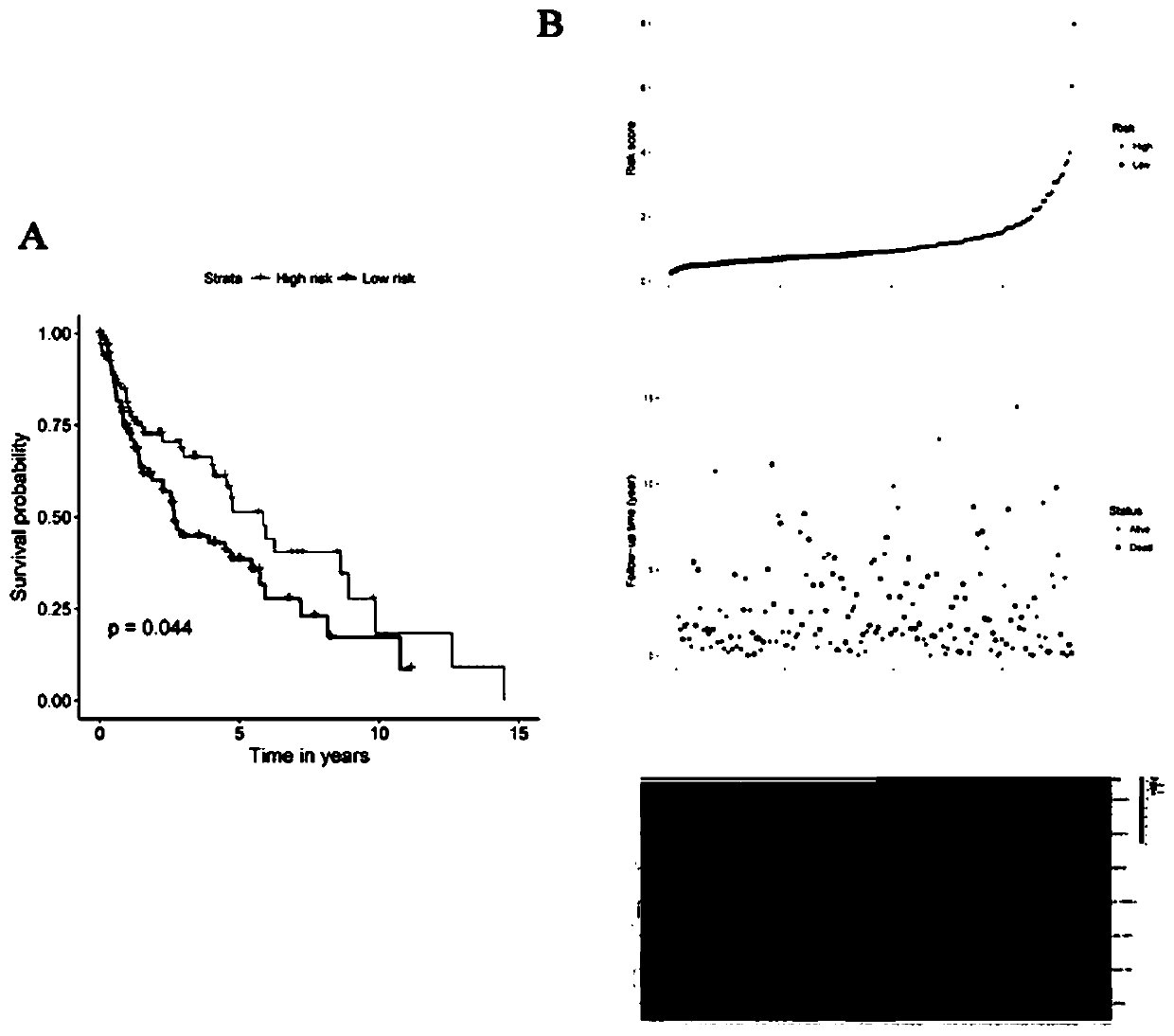
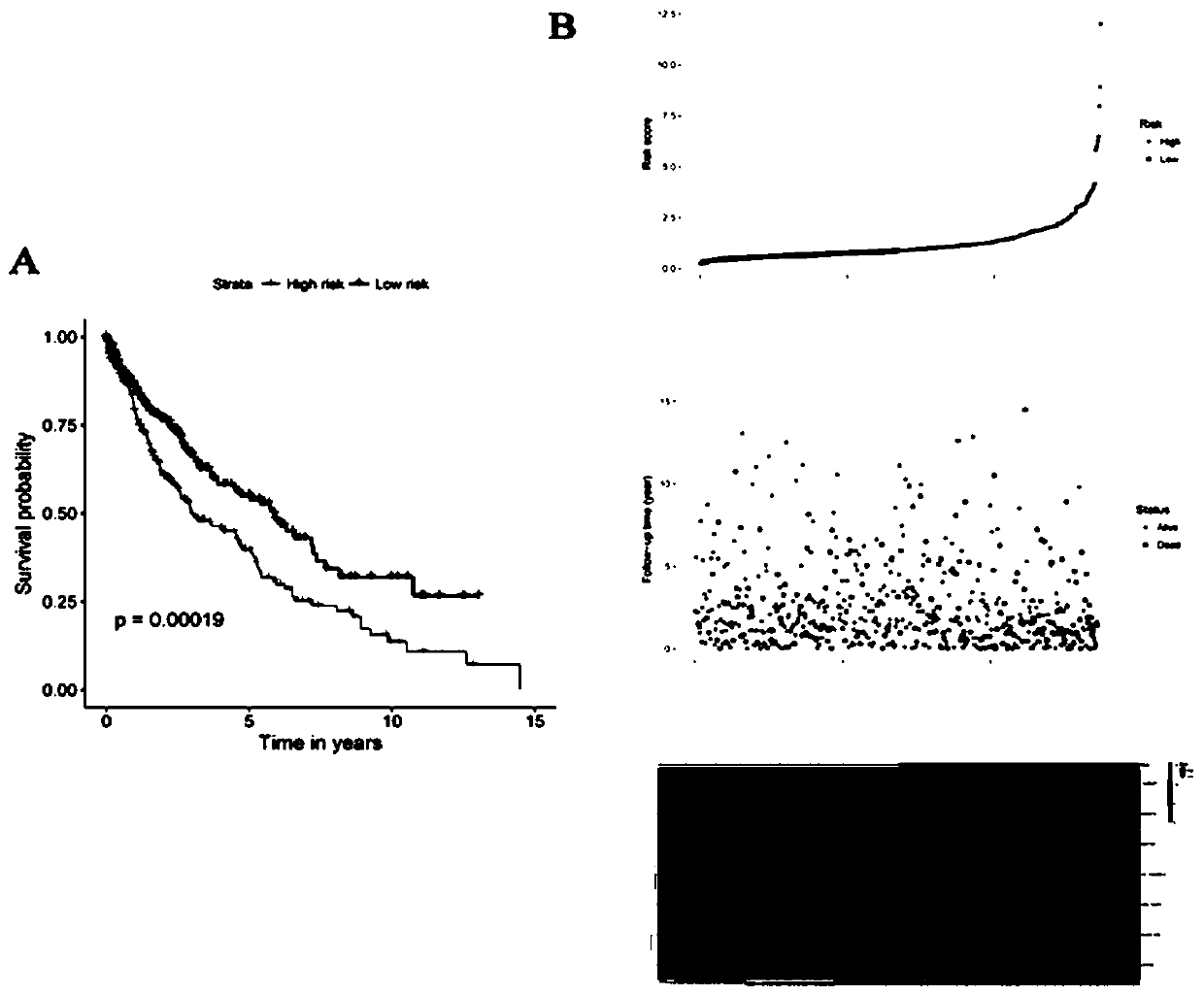
The invention relates to a the field of biomedicine, and specifically relates to a model for predicting prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma with seven genes as biomarkers, and an establishing method thereof. The model for predicting prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma includes seven genes related to prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma: CSRNP1, CLEC18B, MIR27A, AC130456.4, DEFA6,ARL14EPL and ZFP42, wherein expressions of CSRNP1 and CLEC18B are positively correlated with a survival rate while expressions of MIR27A, AC130456.4, DEFA6, ARL14EPL and ZFP42 are negatively correlated with the survival rate. The model for predicting prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma provides a plurality of genes as biomarkers, and improves the prognosis sensitivity and accuracy for predicting lung squamous cell carcinoma, thereby reducing mortality and local recurrence rate in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma, and improving the prognosis of patients through the risk prediction model.
Owner:辽宁省肿瘤医院
Method for distinguishing between head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveUS20070264644A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLung squamous cell carcinomaCXCL13
The present invention is a method distinguishing between head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. In particular, a 10-gene classifier has been identified which can be used to distinguish between primary squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. These genes include CXCL13, COL6A2, SFTPB, KRT14, TSPYL5, TMP3, KLK10, MMP1, GAS1, and MYH2. A panel of one or more of these genes, or proteins encoded thereby, can be used for early diagnosis and selection of an appropriate therapeutic treatment.
Owner:WISTAR INST THE A CORP OF PA +1
Markers and diagnostic reagents for the diagnosis or prognosis of lung cancer
The present invention relates to markers and diagnostic reagents for the diagnosis or prognosis of lung cancer. The present invention discloses for the first time that DDX56 is significantly increasedin patients with early disease progression (= 12 months) after treatment of two major subtypes of small cell lung cancer (lung squamous cell carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma), and that the increased expression of DDX56 significantly affects the overall survival of the patients. Therefore, DDX56 can be used as a diagnostic marker for early recurrence of lung squamous cell carcinoma or lung adenocarcinoma.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
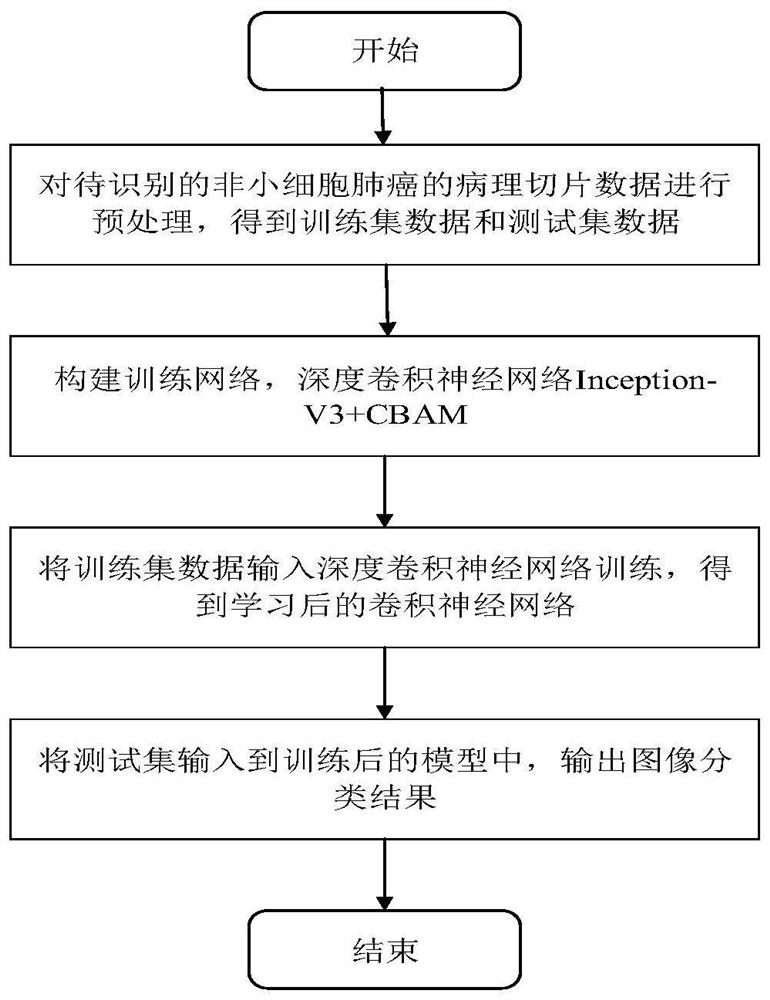
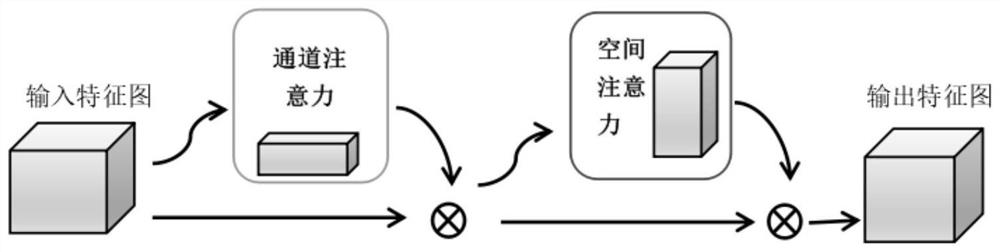
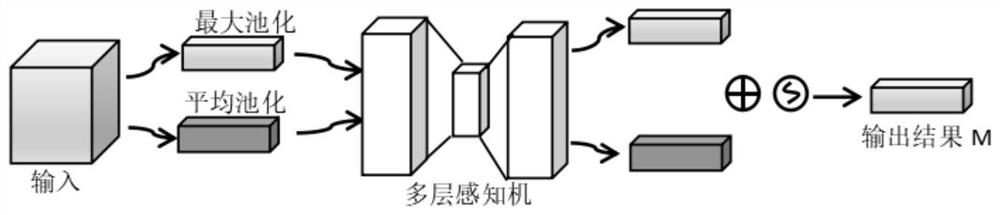
Non-small cell lung cancer pathological section identification method based on deep convolutional neural network
PendingCN112270666AImplement classificationEffective classificationImage enhancementImage analysisData setNon-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
The invention discloses a non-small cell lung cancer pathological section identification method based on a deep convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring pathological sections of non-small cell lung cancer in a public data set from TCGA; constructing a deep learning model for training; inputting the training data set into a convolutional neural network for training to obtain a learned convolutional neural network model; and inputting the training data set into a convolutional neural network for training to obtain a learned convolutional neural network model. According to the method, the Inception-v3 model and the CBAM attention mechanism are fused together, so that the classification of the non-small cell lung cancer is realized, and the network precision is improved through the attention mechanism; meanwhile, a deep convolutional neural network Inception-v3 experimental result shows that the non-small cell lung cancer pathological section identification method based on deep learning provided by the invention can effectively classify lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma, reduces the burden of doctors to a certain extent, and realizes very good performance in the field of medical image identification.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Group of LncRNA biological markers for diagnosing human lung squamous carcinoma
ActiveCN105219770ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementLung squamous cell carcinomaTrue positive rate
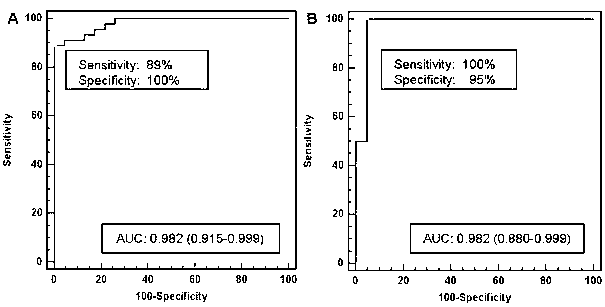
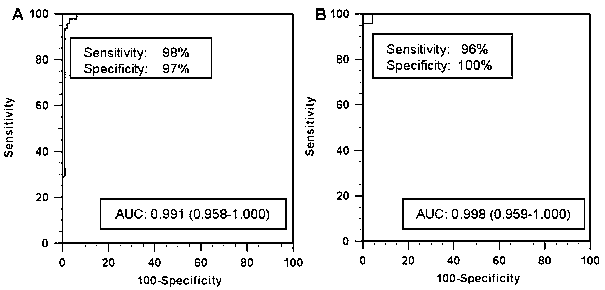
The invention relates to the field of biotechnologies, and in particular relates to a group of LncRNA biological markers for diagnosing human lung squamous carcinoma, a related kit and applications thereof. The group of LncRNA biological markers for diagnosing the human lung squamous carcinoma, provided by the invention, comprises ENST00000453324, ENST00000441841, uc011cly.2, NR_028500 and NR_046326. The LncRNA biological markers for diagnosing the human lung squamous carcinoma can be used for distinguishing human early lung squamous carcinoma, the AUC value of the LncRNA biological markers for distinguishing the early lung squamous carcinoma and pairing normal lung tissues can reach 0.932, and the sensitivity and the specificity can be 92% and 87% respectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
MicroRNA marker for identifying subtypes of lung cancer and application of microRNA marker
InactiveCN102839179ARapid differential diagnosisAccurate Targeted TherapyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTargeted therapyNon-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
The invention provides microRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) for identification of subtypes of a lung cancer. The miroRNA is chosen from the following sequence: a) a sequence shown as SEQ ID No. n (sequence identification number), or b) microRNA complementary to the sequence shown as SEQ ID No. n, wherein the n is 2, 3, 4 or 7. The invention further provides an application of the microRNA and a reagent kit based on the microRNA. The invention further provides a set formed by the microRNA, an application of the set and a reagent kit based on the set. The miroRNA has the advantages that the microRNA can form two combinations, namely SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.7, as well as SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No.4, which can be used to differentially diagnose the small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma lung cancer and squamous cell lung cancer respectively; the diagnosis is high in speed, low in cost and accurate and reliable in result; and a significant basis is provided for performing precise targeted therapy on a patient with the lung cancer.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
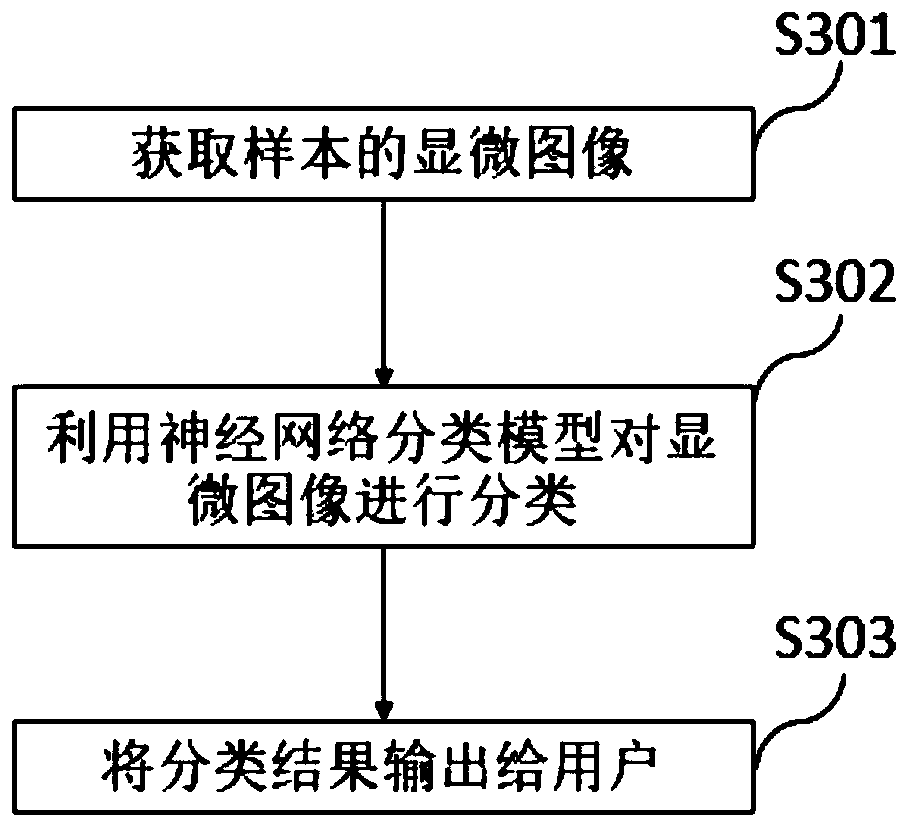
Lung cell pathology rapid on-site evaluation system and method and computer readable storage medium
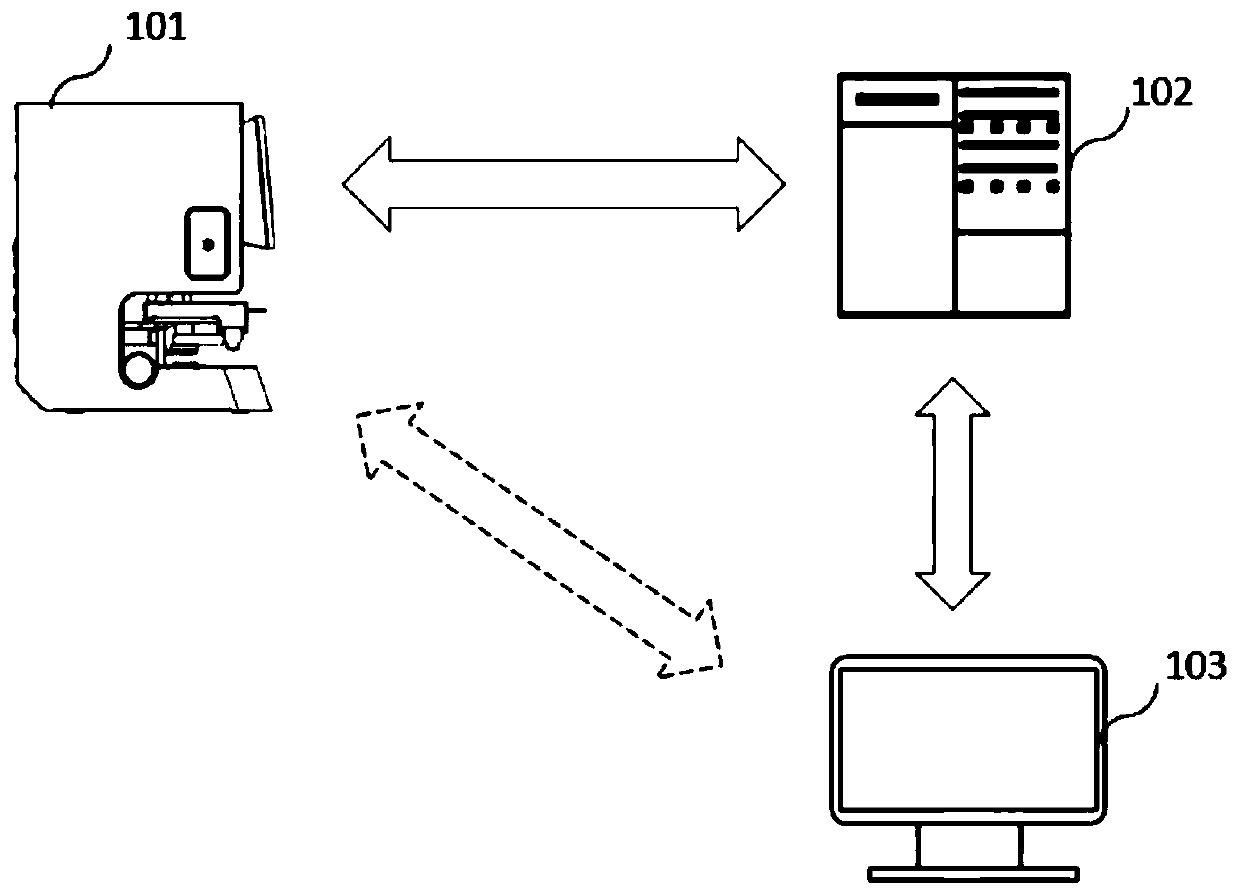
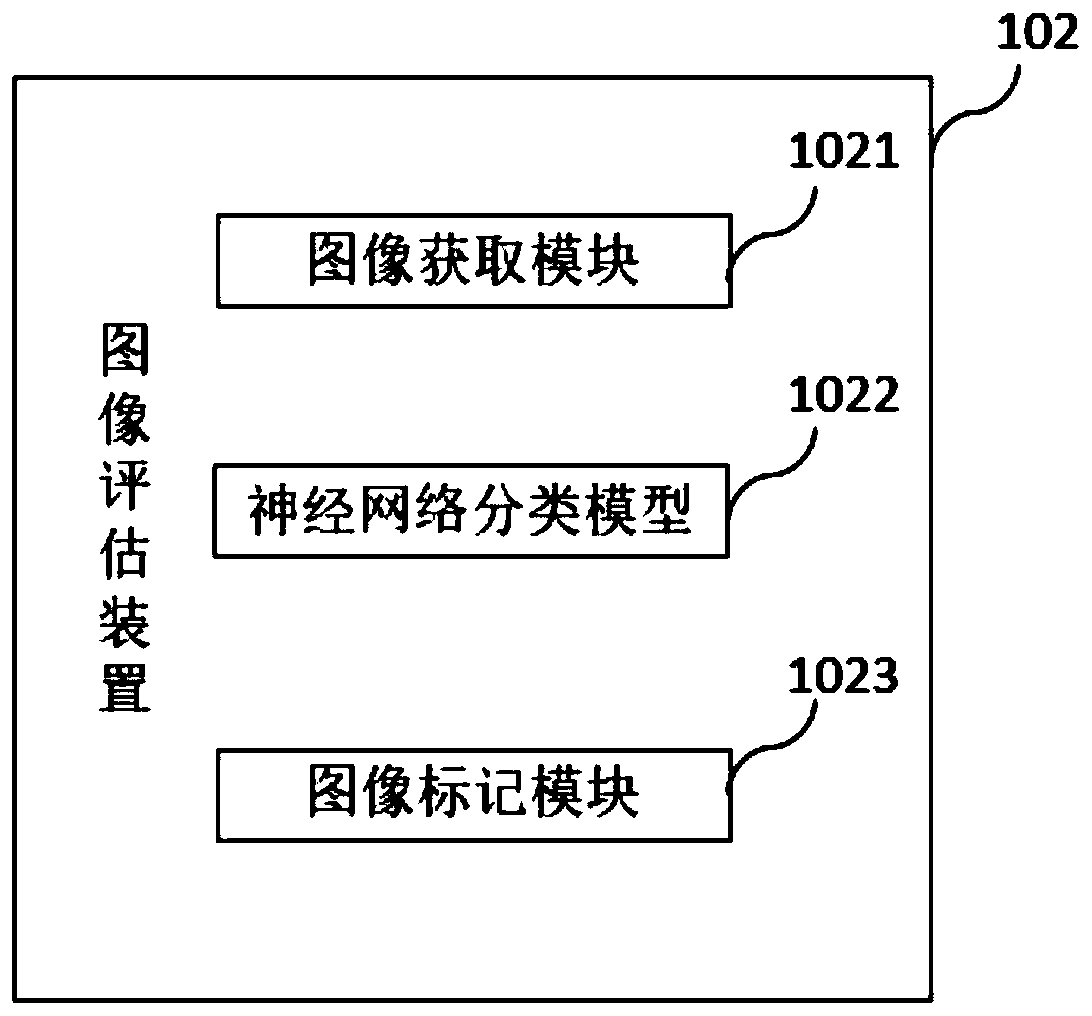
PendingCN111489833ASolve the problem that pathological diagnosis results cannot be obtained immediatelyImprove diagnostic efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMicroscopic imageCurrent cell
The invention provides a lung cell pathology rapid on-site evaluation system and method and a computer readable storage medium, which are used for rapidly evaluating a cell sample on an operation site. The lung cell pathology rapid on-site evaluation system comprises a microscopic image acquisition device which comprises an objective table used for bearing a lung cell sample and a camera used forshooting the cell sample to obtain a microscopic image of the sample; an image evaluation device with a neural network classification model used for classifying the microscopic images, wherein the obtained classification result is one of lung squamous cell carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, small cell lung cancer, unclear non-small cell lung cancer, other malignant lesions, no obvious abnormality, granuloma and inflammation; and an output device connected to the image evaluation device and used for outputting the classification result to a user. According to the invention, the neural network classification model is used for evaluating the microscopic image acquired by the microscopic image acquisition device, and an evaluation result is obtained on an operation site, so that the problems thatthe current cell pathological diagnosis is complex and time-consuming, and the pathological diagnosis result cannot be obtained immediately are solved, and the diagnosis efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGMAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
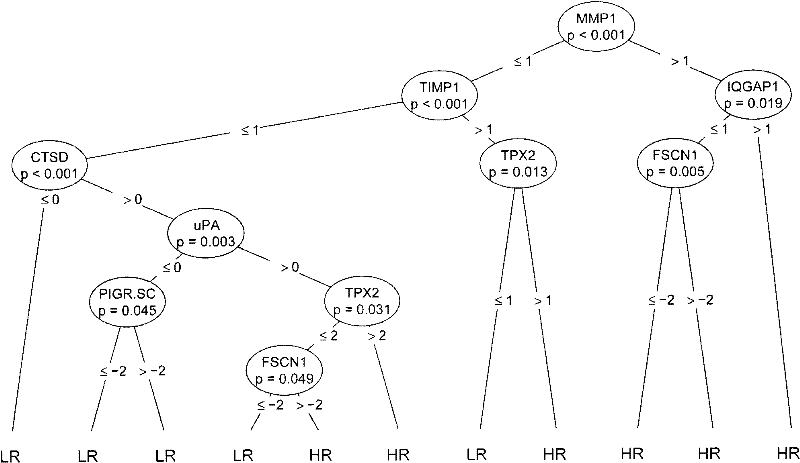
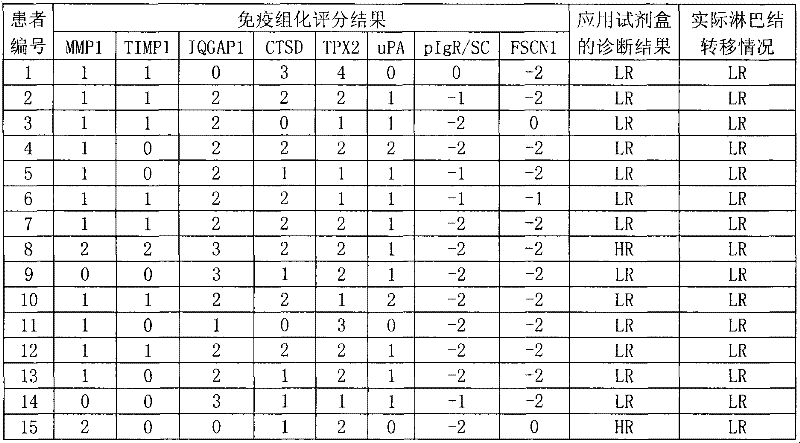
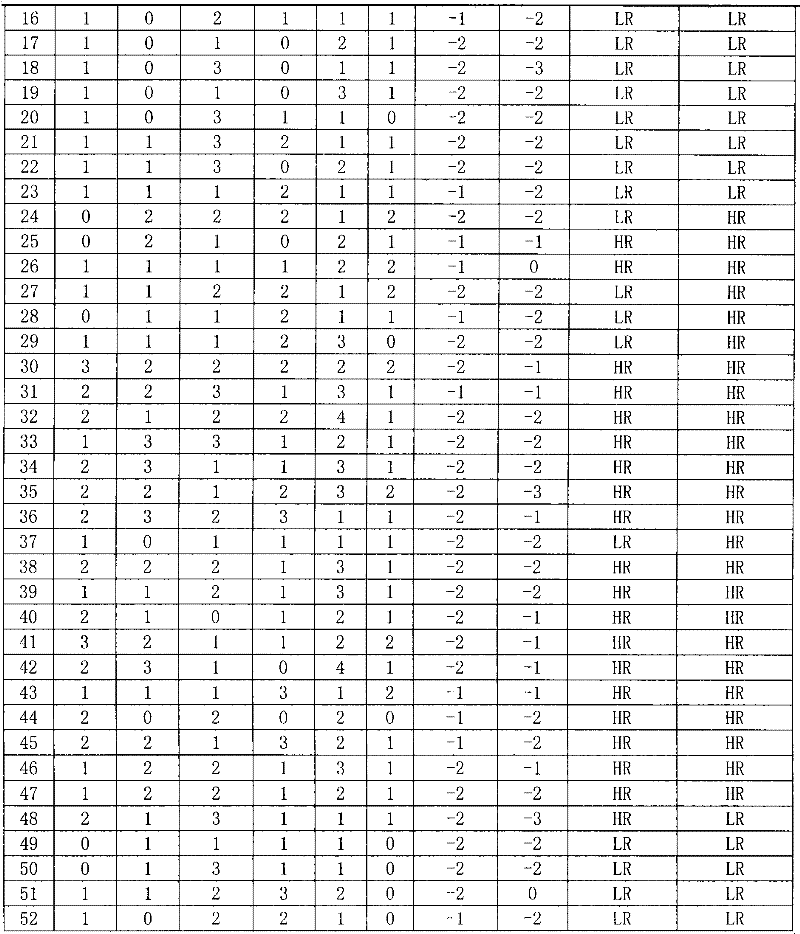
Reagent for auxiliarily diagnosing lung cancer lymph node metastasis
InactiveCN102445543AIncrease credibilityPracticalBiological testingStainingPolymeric immunoglobulin receptor
The invention discloses a reagent for auxiliarily diagnosing lung cancer lymph node metastasis, comprising 8 antibodies which are used for detecting 8 protein markers which are MMP1 (matrix metalloproteinase-1), TIMP1 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases metallopeptidase inhibitor 1), IQGAP1 (IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1), TPX2 (targeting protein for Xklp2), uPA (Urokinase-type plasminogen activator), Cathepsin-D, Fascin and pIgR / SC (polymeric immunoglobulin receptor / secretory component). By adopting the 8 antibodies and an immunohistochemical staining result, lung cancer lymph node metastasis can be auxiliarily diagnosed, and the reagent is expected to be used for the risk estimation of lung squamous cell cancer lymph node metastasis and the prognostic prediction. The reagent has high creditability, strong practicability and clinical use value based on the clinical routine immunohistochemical staining technology when the reagent is used for auxiliary diagnosis.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
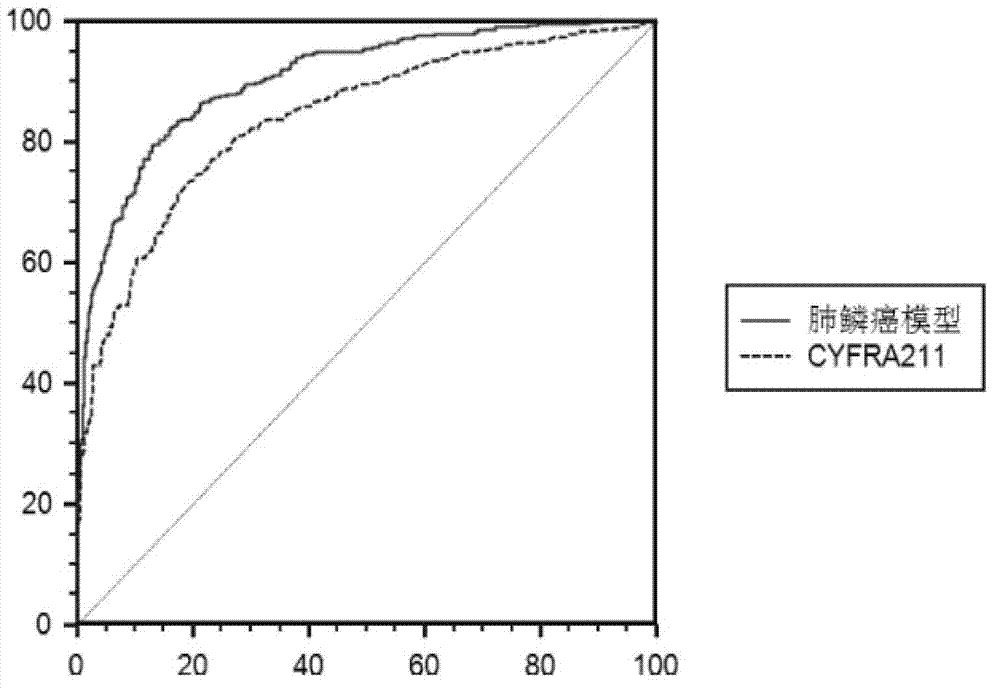
Prognosis prediction model for squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof
InactiveCN112813165ALow cost of treatmentIncreased sensitivityMedical simulationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic ImmunotherapeuticSquamous Carcinomas
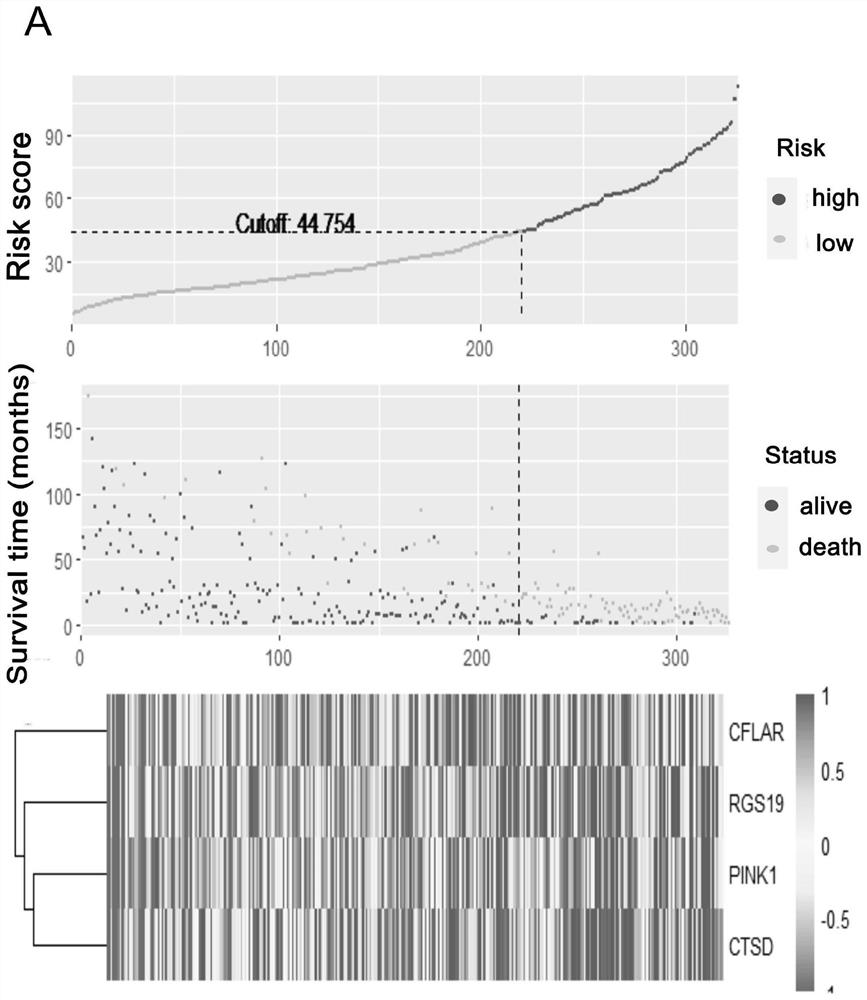
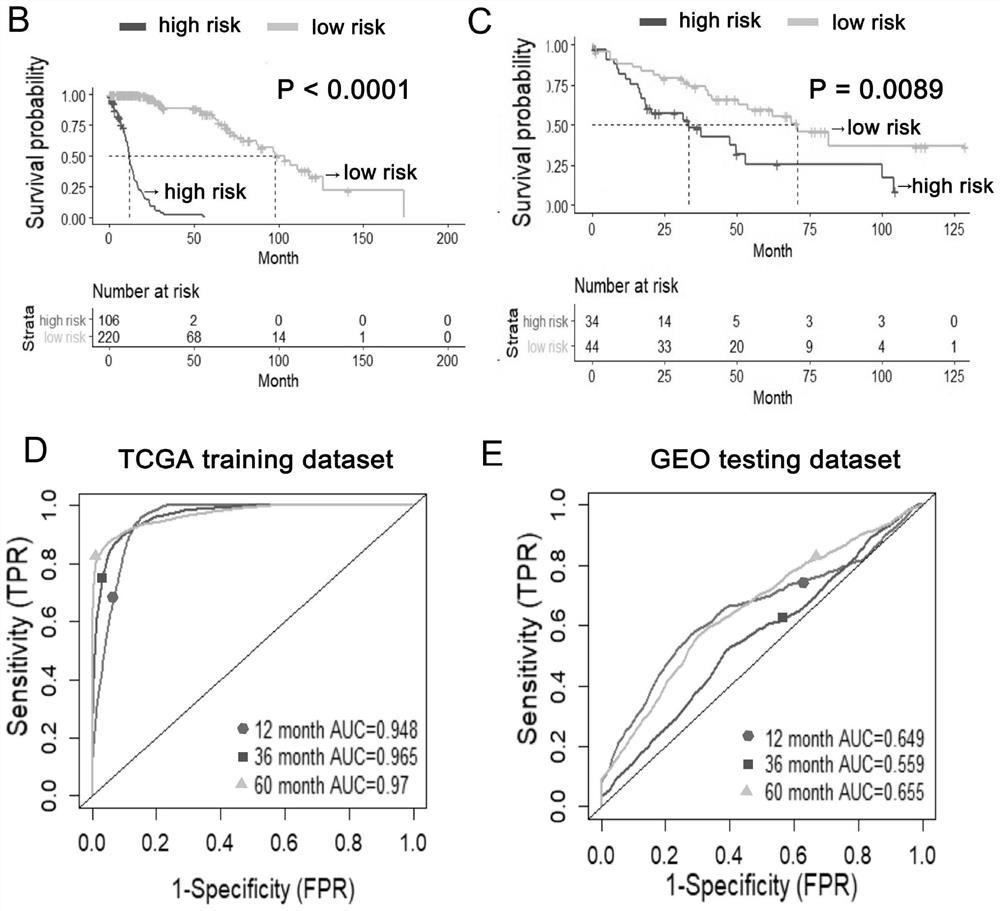
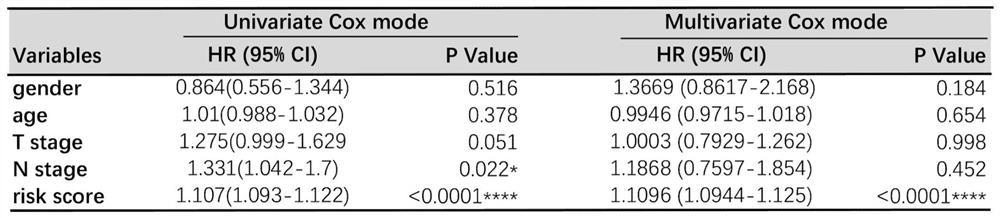
The invention relates to a prognosis prediction model for squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof. The prognosis prediction model is composed of biomarkers CFLAR, RGS19, PINK1, CTSD and related solutions. The invention also comprises application of a reagent for detecting the expression quantity of the biomarkers in preparation of a kit for evaluating the anti-tumor immunotherapy reactivity and prognosis survival of squamous cell carcinoma. According to the invention, screening and construction are carried out after whole transcriptome sequencing and machine learning of squamous cell carcinoma samples of large-sample anti-tumor immunotherapy, so that the reactivity of squamous cell carcinoma patients in anti-tumor immunotherapy can be efficiently and accurately predicted, effective guidance is provided for clinicians to make treatment decisions on squamous cell carcinoma patients, and the occurrence of invalid treatment is reduced, thereby reducing the treatment cost and discomfort experience of patients.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
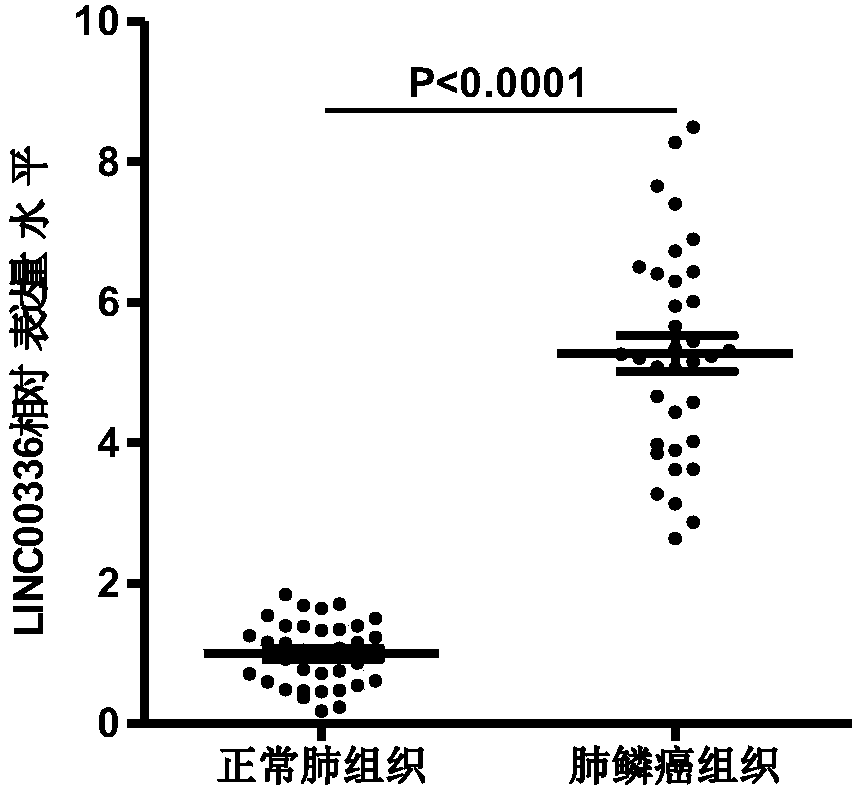
Application of long-chain non-coding RNA LINC00336 as biomarker in preparing lung squamous cell carcinoma prognosis detection preparation
ActiveCN108192976AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLung squamous cell carcinomaPrognostic prediction
The invention discloses application of long-chain non-coding RNA LINC00336 as a biomarker in preparing a lung squamous cell carcinoma prognosis detection preparation. The expression level of long-chain non-coding RNA LINC00336 in a lung squamous cell carcinoma patient can be detected, a powerful molecular biology basis is provided for prognostic prediction to the lung squamous cell carcinoma patient, and long-chain non-coding RNA LINC00336 has profound clinical significance and good popularization performance.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Kit for auxiliary diagnosis of squamous cell lung carcinoma patient
ActiveCN103175969AIncreased sensitivityHigh diagnostic confidenceBiological testingLung squamous cell carcinomaIDH1
The invention discloses a kit for auxiliary diagnosis of squamous cell lung carcinoma patient. The kit provided by the invention comprises a product for detecting a protein marker IDH1, a product for detecting a protein marker CA125, a product for detecting a protein marker CYFRA21-1 and a carrier recorded with the following functional expressions (as shown in the description): x1 stands for the concentration of the IDH1, x2 stands for the concentration of the CA125, and x3 stands for the concentration of the CYFRA21-1. The kit provided by the invention is used for the auxiliary diagnosis of squamous cell lung carcinoma patient according to the corresponding diagnosis standard, and has the characteristics of high flexibility and strong specificity, the diagnosis result reliability is far better than the diagnosis by adopting the single protein marker, and has important value and application prospect for the diagnosis and treatment of the squamous cell lung carcinoma.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
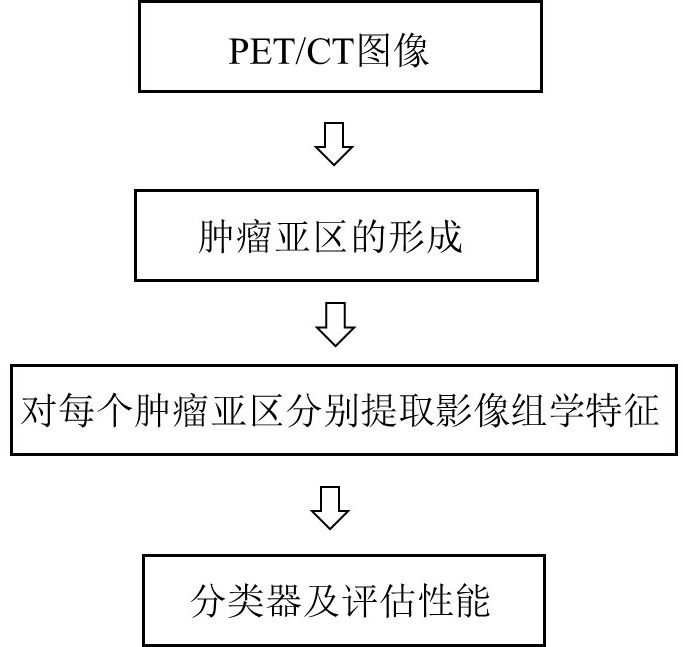
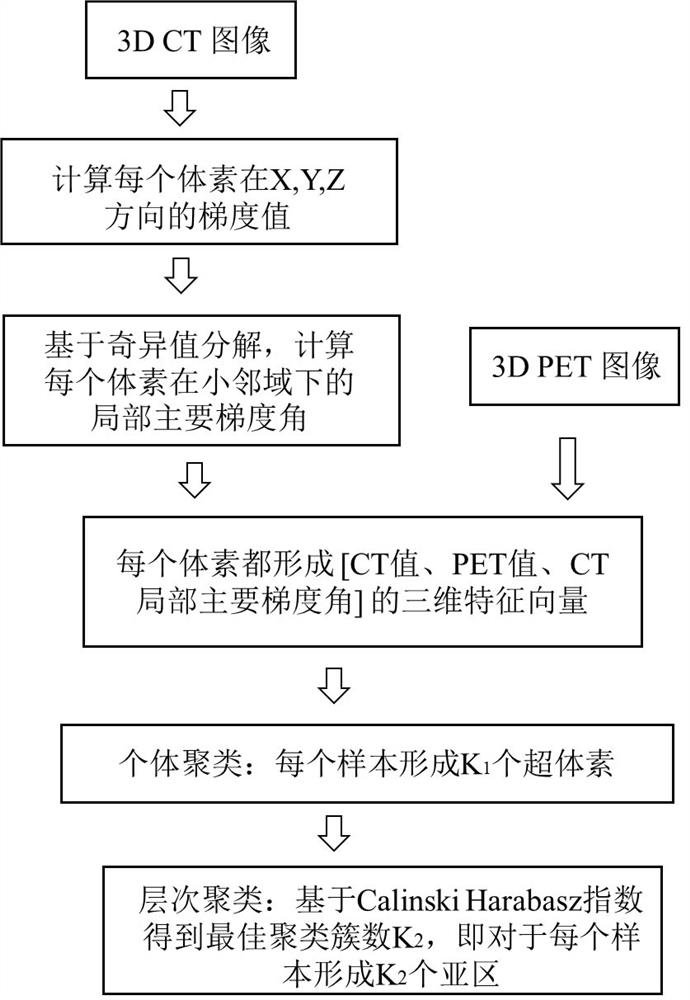
Lung gland squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis device based on PET/CT image sub-region imaging omics characteristics
ActiveCN112465824AImprove accuracyConsider heterogeneityImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelSquamous Carcinomas
The invention discloses a lung glandular squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis device based on PET / CT image subarea imaging omics characteristics, and belongs to the field of medical images. The diagnosisdevice comprises: a voxel three-dimensional feature extraction module, which is used for extracting a CT local main gradient angle feature value of each voxel of a lung tumor in a neighborhood in a PET / CT image, a CT value of the voxel and a PET value, and forming a three-dimensional feature vector of the voxel; a feature clustering module used for clustering the obtained three-dimensional feature vector of each voxel to obtain a tumor sub-region partition; a radios image omics feature extraction module used for extracting radios image omics features of each tumor sub-region in a partitioningmanner; and a classification module used for distinguishing whether the tumor is lung squamous cell carcinoma or lung adenocarcinoma according to the extracted radiomics characteristics of the radiomics. According to the diagnosis device, the heterogeneity in the tumor is better considered, and the accuracy of tumor diagnosis is effectively improved by extracting more effective imaging omics characteristics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
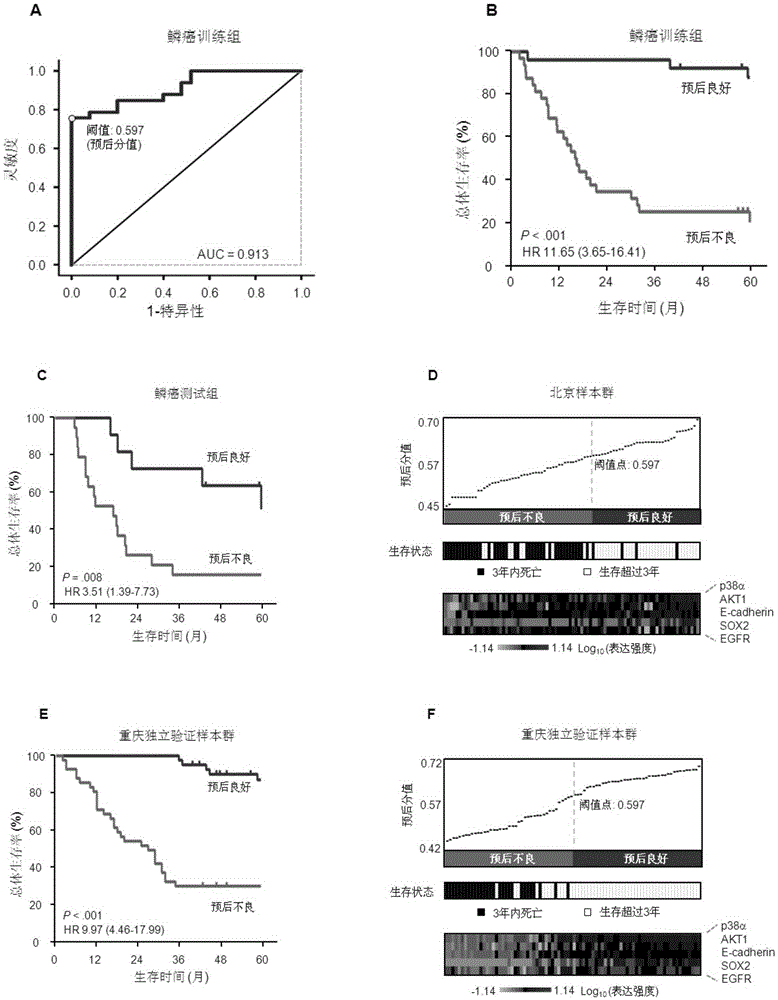
System for predicting prognosis of patient with lung squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN106442990AAccurately predict clinical prognosisImproving the level of prognosis predictionBiological material analysisSquamous CarcinomasSOX2
The invention discloses a system for predicting the prognosis of a patient with lung squamous cell carcinoma. The system includes a subsystem for detecting the expression quantity of such five proteins as EGFR, p38alpha, AKT1, SOX2 and E-cadherin and a protein expression quantity data processing system. The subsystem for detecting the expression quantity of the five proteins is allowed to measure the expression quantity of the proteins through an immunohistochemistry staining method; the protein expression quantity data processing system is allowed to convert the expression quantity of the five proteins from the squamous cell carcinoma tissues separated from the patient with the lung squamous cell carcinoma to a prognostic score; based on the prognostic score, the prognosis of a patient with the lung squamous cell carcinoma is predicted.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL ANALYSIS CENT OF ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Non-small cell lung cancer subtype classification system based on multi-view deep learning
PendingCN113850328AImprove classification accuracyEfficient calculation speedImage enhancementImage analysisOncologyBiology
The invention discloses a non-small cell lung cancer subtype classification system based on multi-view deep learning, which realizes classification of lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous carcinoma based on a CT image, generates and displays image data of an examined part based on volume data generated by performing lung CT on an examined body, and obtains non-small cell lung cancer subtype classification result of the examined body. The non-small cell lung cancer pathological subtype classification system comprises an information acquisition module, a network module and a training module. According to the system, automatic lung field segmentation can be realized, interlayer information and three-dimensional information carried by a CT image are fully utilized by a multi-view model, an obtained classification model can be used as a tool for assisting a doctor through automatic feature extraction and classification training, and the system has the characteristics of high automation and high practicability.
Owner:北京志沅医疗科技有限公司
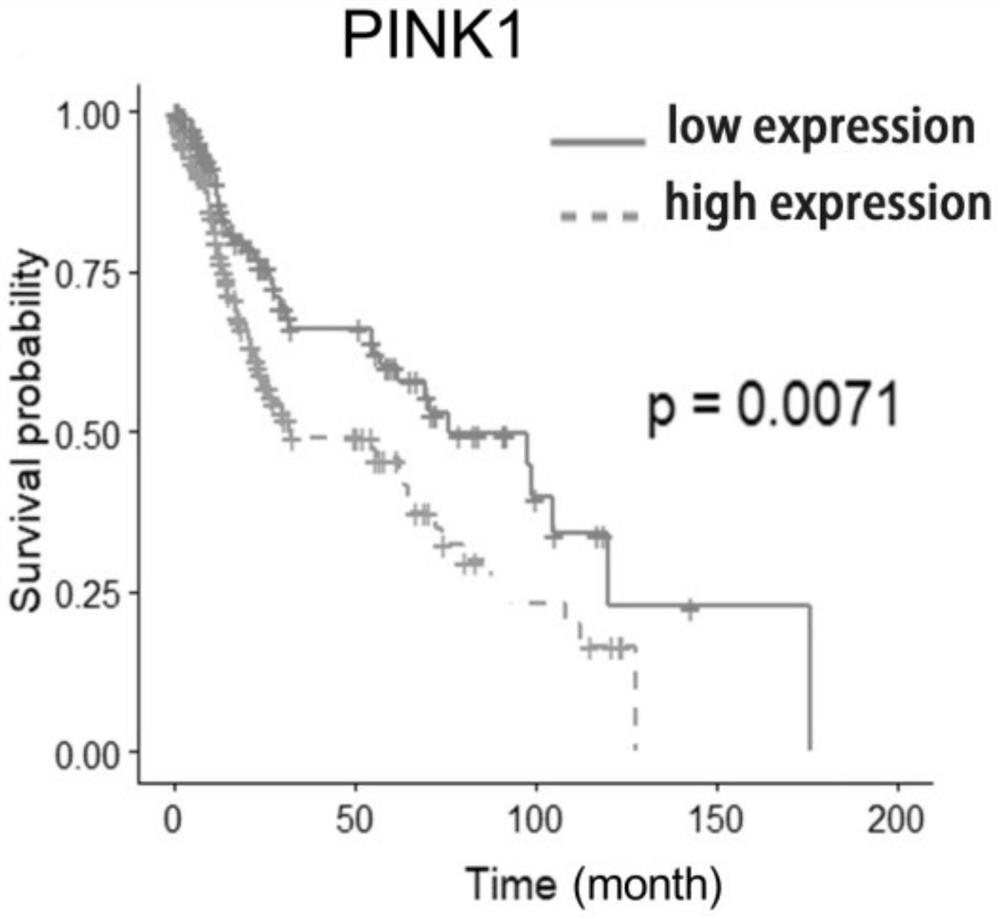
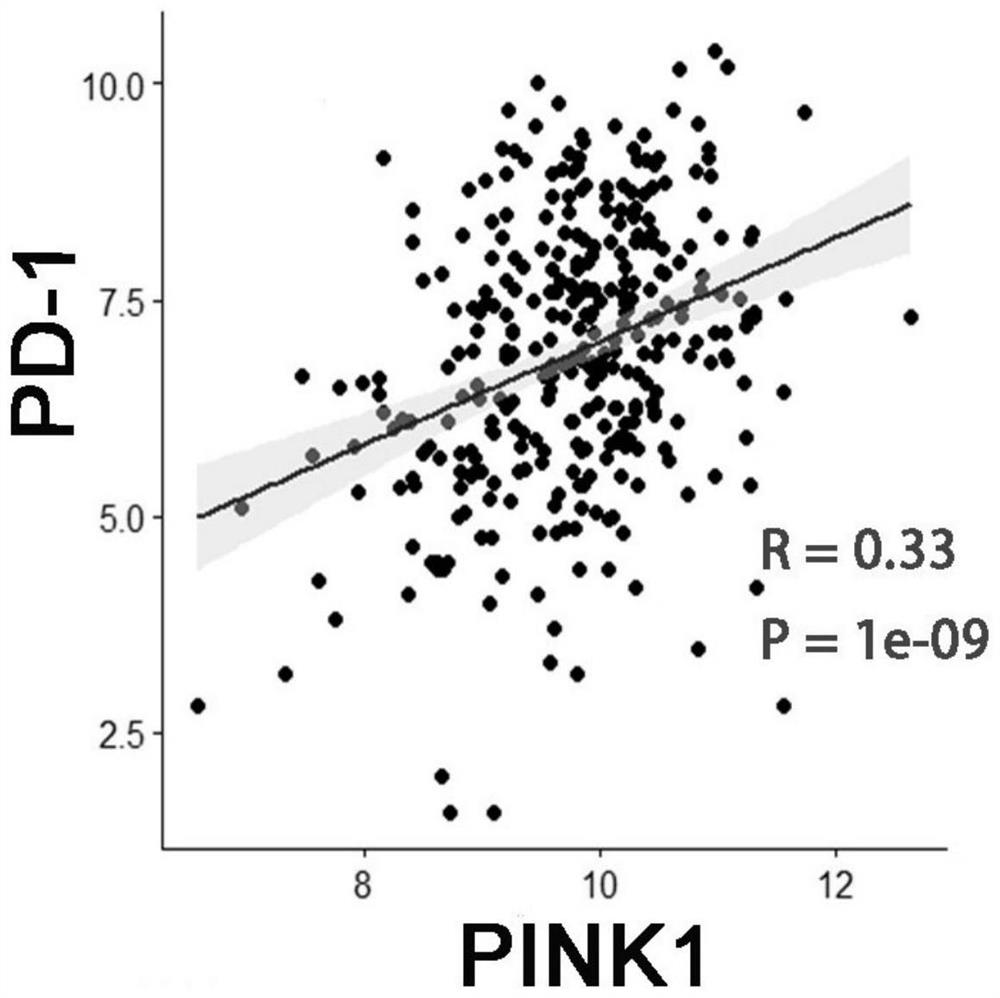
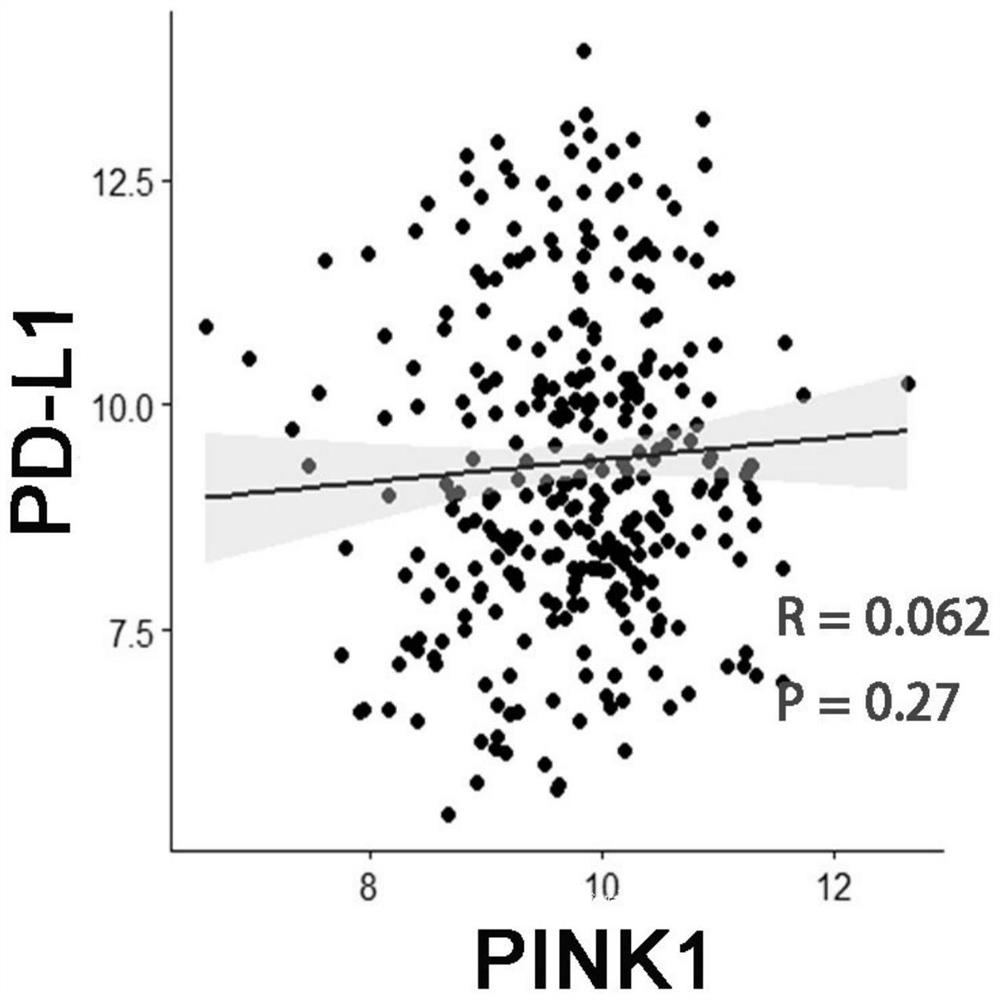
Application of PINK1 as diagnostic marker in construction of lung squamous cell carcinoma prognosis prediction model
PendingCN112908406AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMolecular designHealth-index calculationBiomarker (medicine)Biology
The invention relates to the technical field of bio-medicine, in particular to application of PINK1 serving as a diagnostic marker in construction of a lung squamous cell carcinoma prognosis prediction model. The biomarker PINK1 and other clinical indexes are used in a combined mode, and lung squamous cell carcinoma prognosis detection can be assisted. According to the invention, screening and construction are carried out after full transcriptome sequencing and machine learning of a lung squamous cell carcinoma specimen based on large-sample anti-tumor immuno-therapy, so that the prognosis condition of a lung squamous cell carcinoma patient can be efficiently and accurately predicted; and meanwhile, according to the correlation between the risk and different immune cell infiltration levels, immune-related pathways, key immune checkpoint inhibitor expression levels and the like, comprehensive evaluation of the tumor immune micro-environment is achieved, effective guidance is provided for clinicians to make a treatment decision on lung squamous cell carcinoma patients, invalid treatment is reduced, and therefore, the treatment cost and discomfort experience of the patients are reduced.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
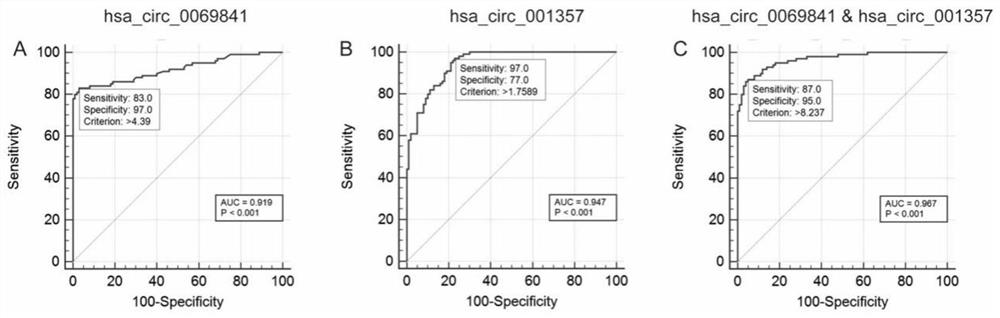
CircRNA composition marker for identifying non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) subtypes and application of circRNA composition marker
ActiveCN112375826AAids in differential diagnosisFast diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOncologyTargeted therapy
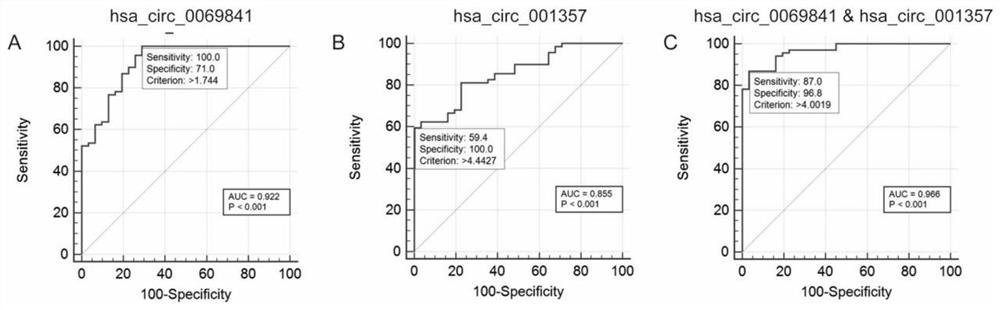
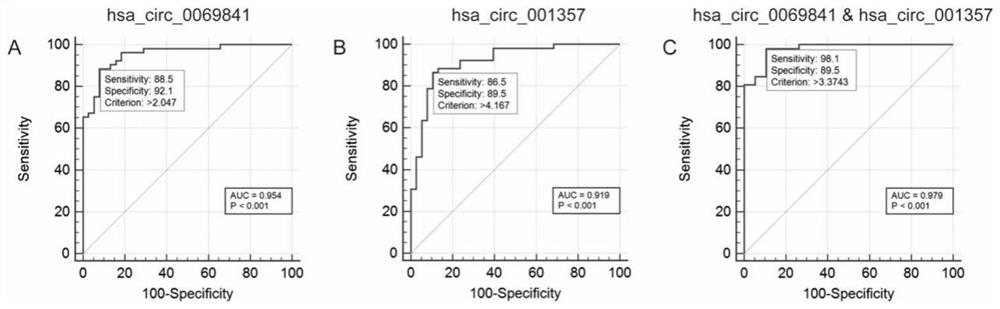
The invention discloses a circRNA composition marker for diagnosing and identifying non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) subtypes and application of the circRNA composition marker, including applicationof hsa_circ_0069841, hsa_circ_001357 and a combination of hsa_circ_001357 and hsa_circ_0069841 in identifying the NSCLC subtypes, and further provides a kit and gene chip prepared from a reagent fordetecting the hsa_circ_0069841, the hsa_circ_001357 and the combination of the hsa_circ_001357 and the hsa_circ_0069841. It is found that the hsa_circ_0069841 and the hsa_circ_001357 can have remarkable specificity and sensitivity to identification of lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma in the NSCLC independently or in a combined mode, the diagnosis speed is high, the cost is low,the result is accurate and reliable, rapid and accurate identification of lung cancer subtypes is facilitated through the prepared kit and gene chip, and a reliable basis is provided for targeted therapy of NSCLC patients.
Owner:YUANJIAN BIOTECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Method for detecting lung cancer typing
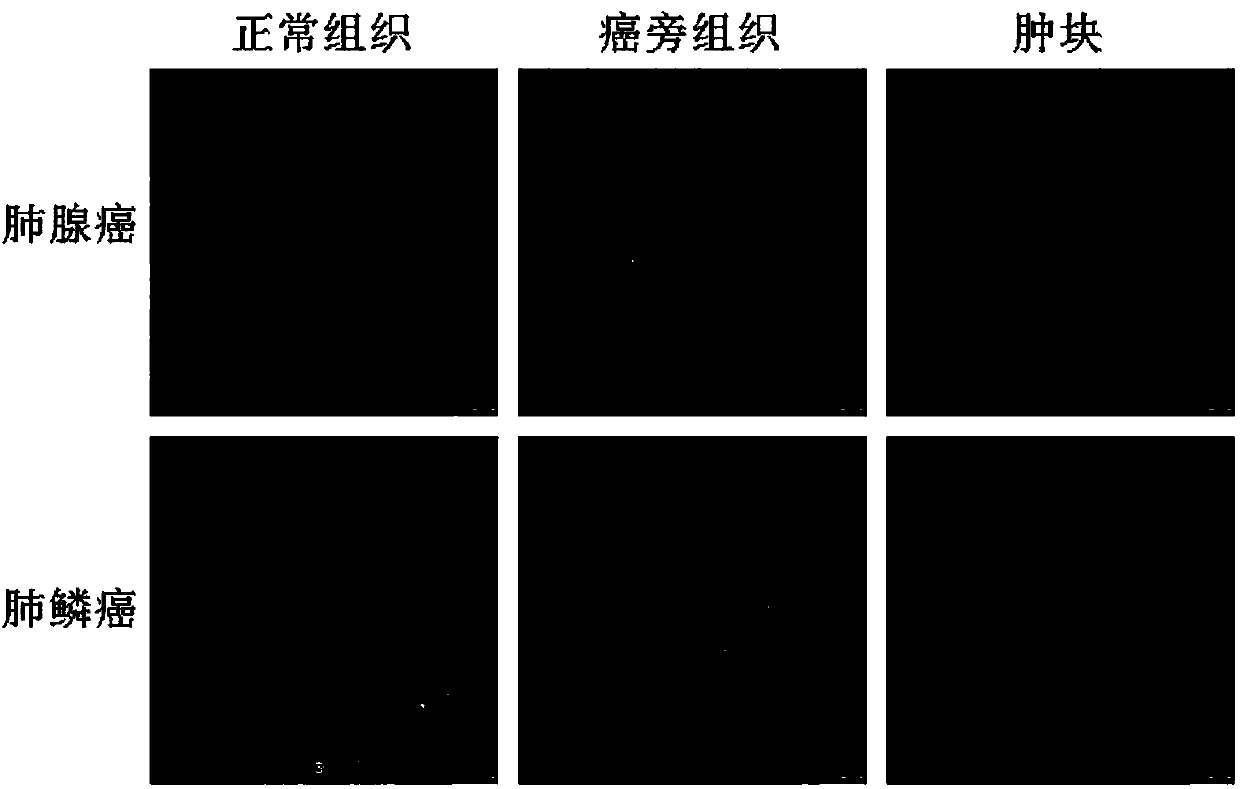
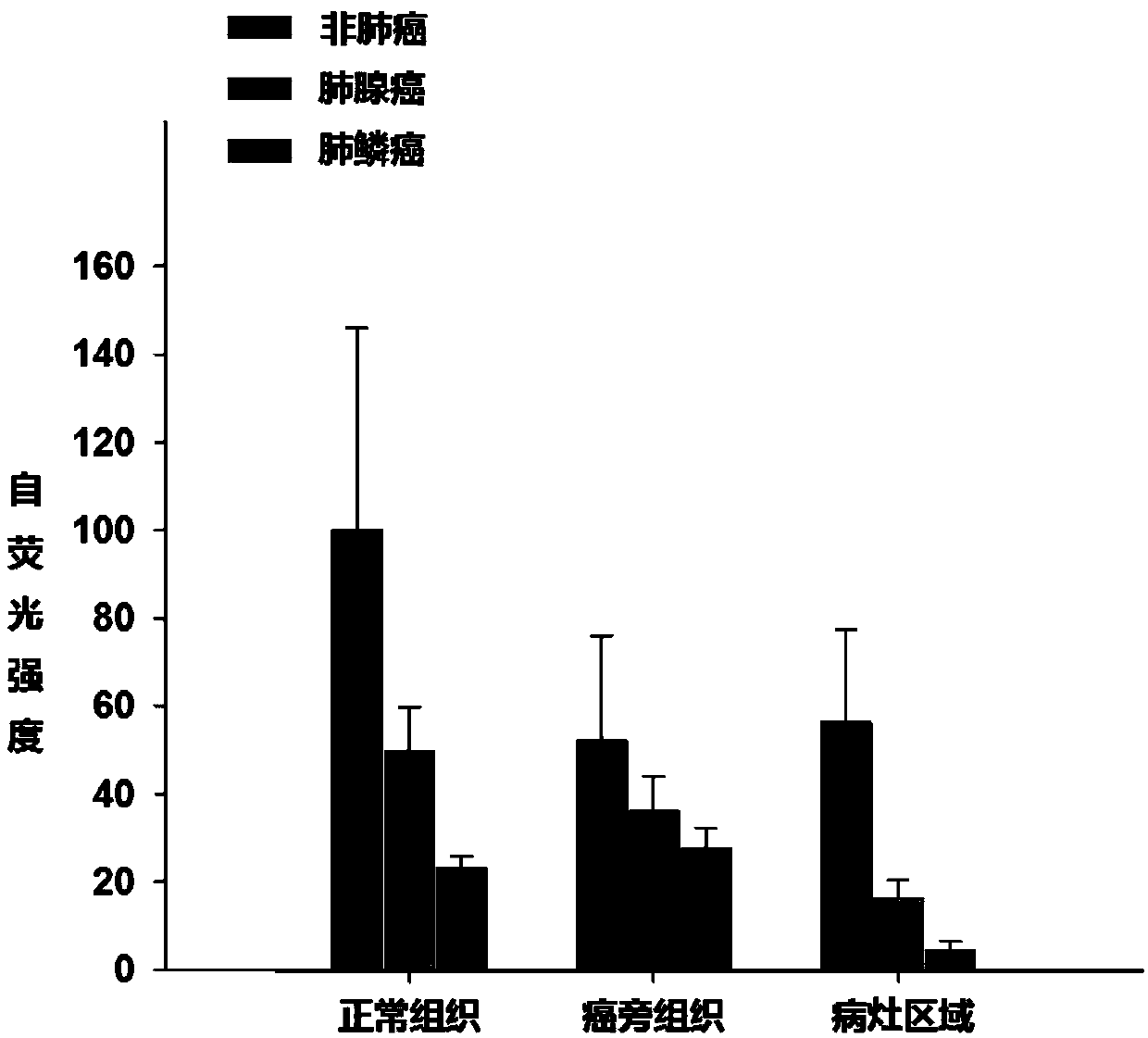
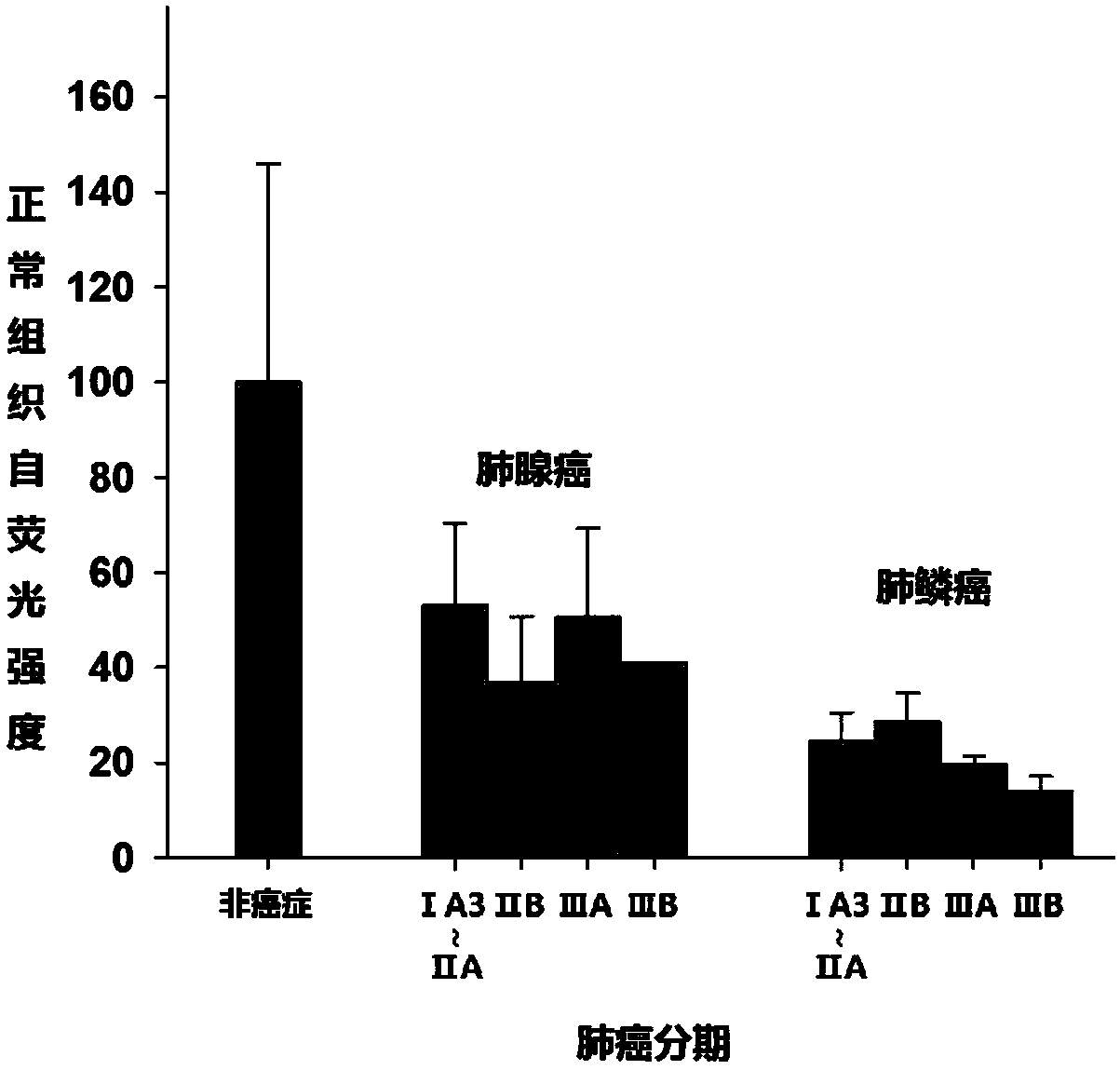
InactiveCN109954148ADianostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsFluorescenceAdenocarcinoma of the lung
The invention provides a method for diagnosing and predicting lung cancer typing, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (1) exciting normal tissues, paracancerous tissues or cancer lesiontissues of a patient lung by exciting light with the wave length of 440-700 nm; (2) receiving spontaneous fluorescent light with the wave length of 460-800 nm; and (3) analyzing the intensity and / or fluorescence distribution pattern chart of spontaneous fluorescent light, and identifying adenocarcinoma or adenosquamous carcinoma of lung.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods for subtyping of lung squamous cell carcinoma
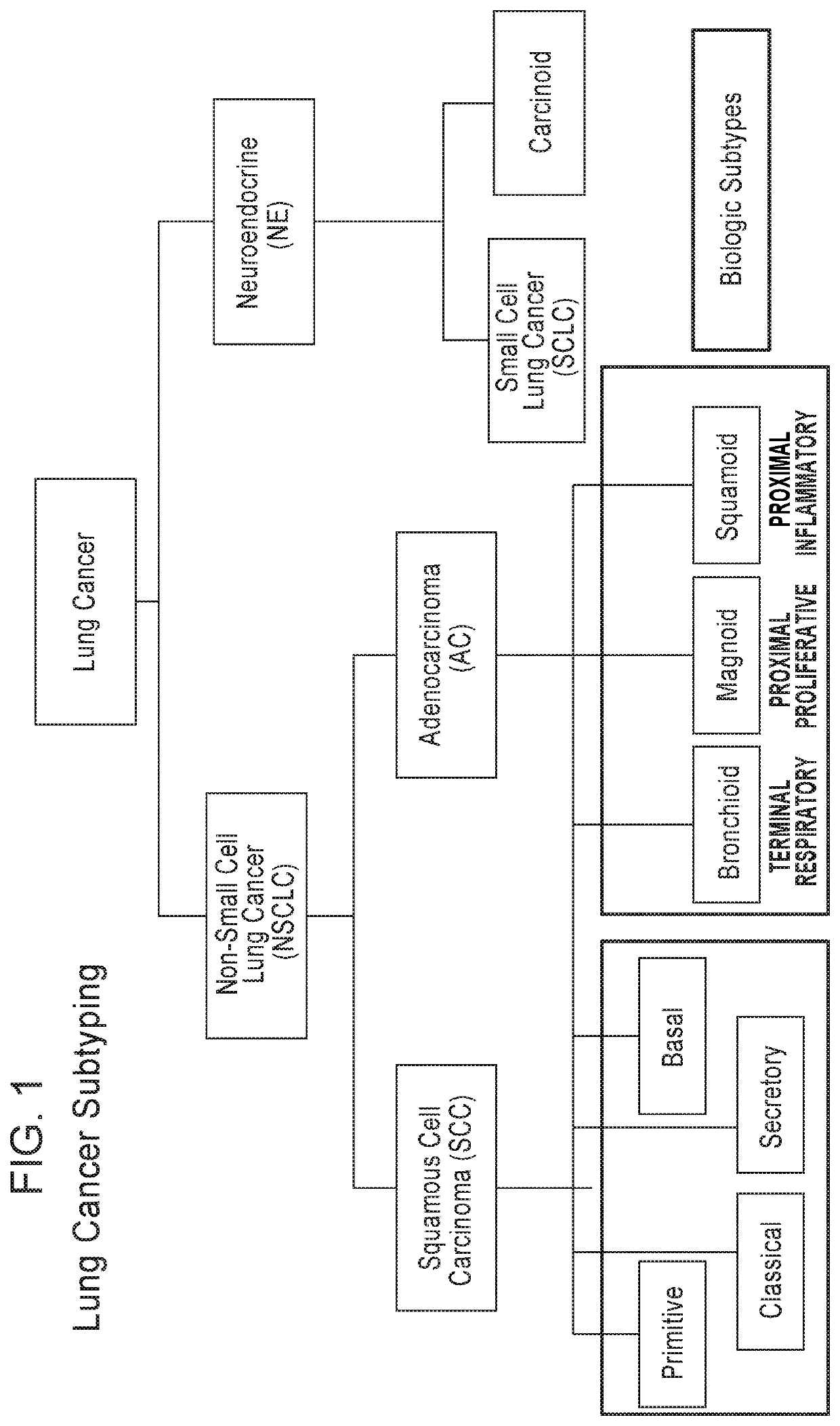
ActiveUS20190338366A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHealth-index calculationLung squamous cell carcinomaSquamous Carcinomas
Methods and compositions are provided for determining a subtype of lung squamous cell carcinoma (SQ) of an individual by detecting the expression level of at least one classifier biomarker selected from a group of gene signatures for lung squamous cell carcinoma. Also provided herein are methods and compositions for determining the response of an individual with a squamous cell carcinoma subtype to a therapy such as immunotherapy.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
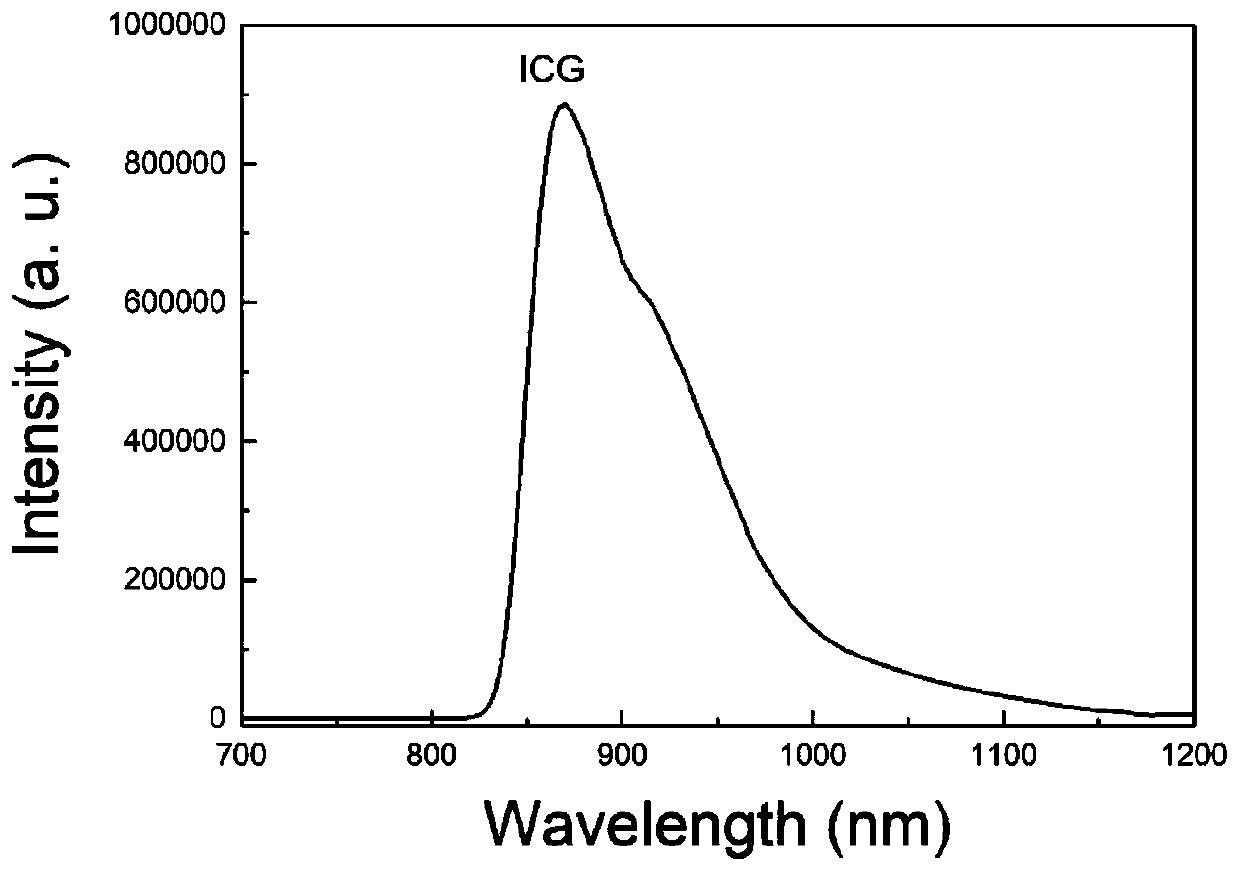
Fluorescence imaging probe, preparation method and applications thereof
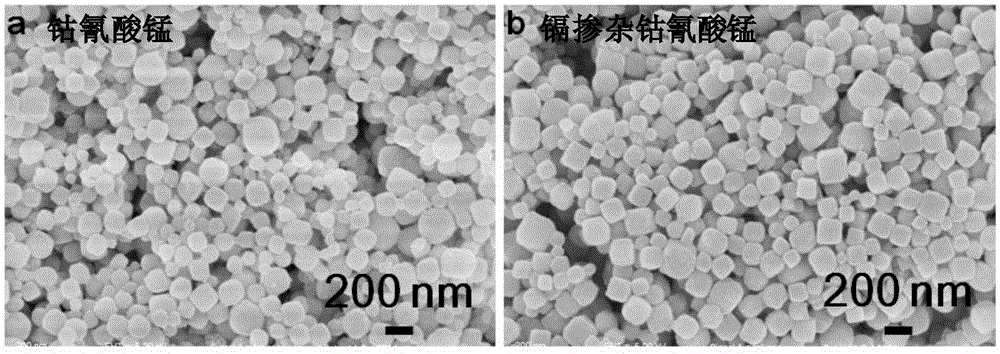
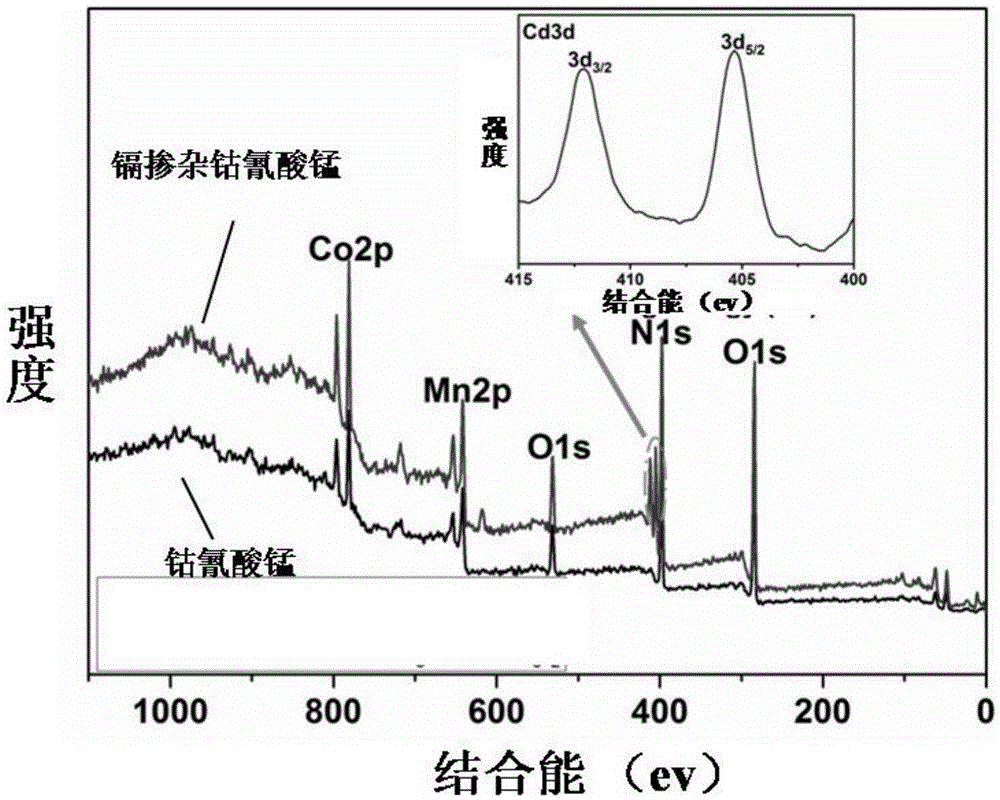
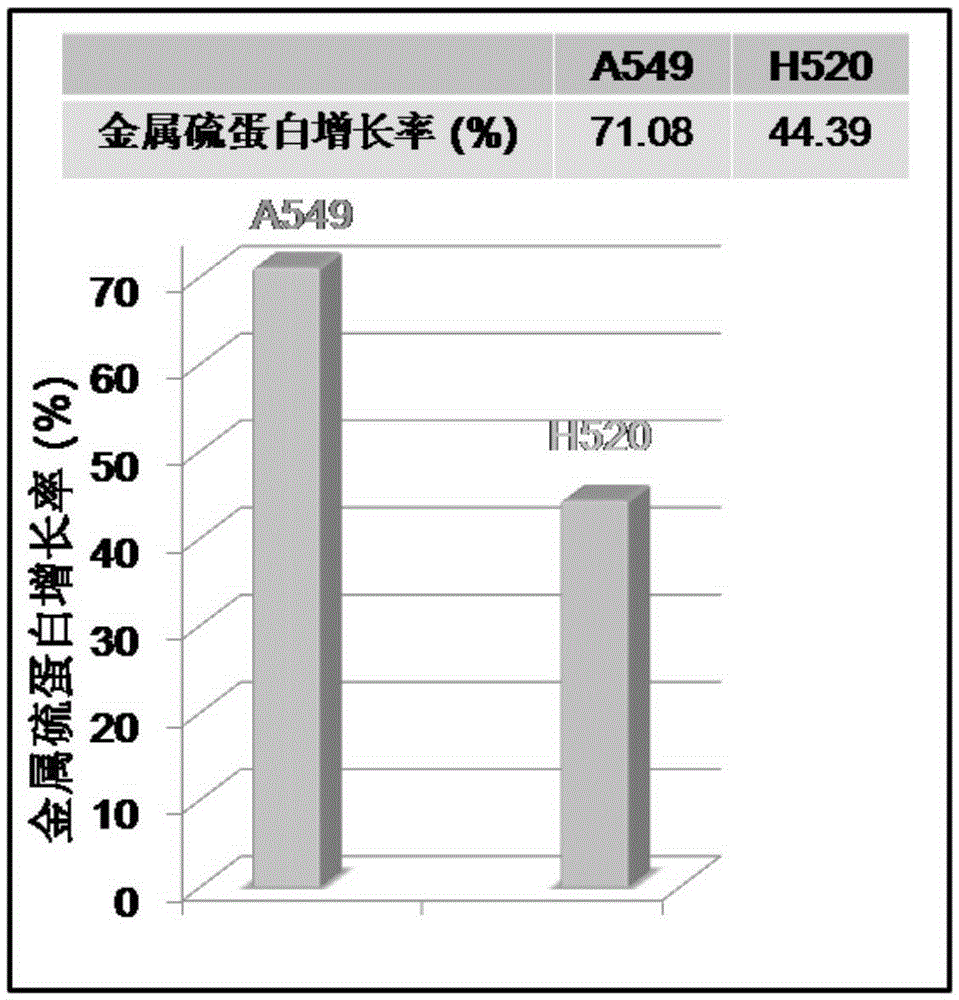
ActiveCN105388136ASeparate accuratelyFluorescence/phosphorescenceLung squamous cell carcinomaFluorescent imaging
The invention relates to the field of nano medicine, and especially relates to a fluorescence imaging probe, a preparation method and applications thereof. The nano fluorescence imaging probe comprises a material having a metal-organic skeleton structure and heavy metal ions. The probe can enter lung cancer cells through endocytosis. The nano fluorescence imaging probe can stimulate different lung cancer cells to generate different contents of metallothionein, then the probe can combine with metallothionein, then the probe and metallothionein are discharged from the cells, and the amount of residual nano fluorescence imaging probe in cells will determine the intensity of cell fluorescence images, so according to the difference of intensity of cell fluorescence images, the lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma can be precisely differentiated.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
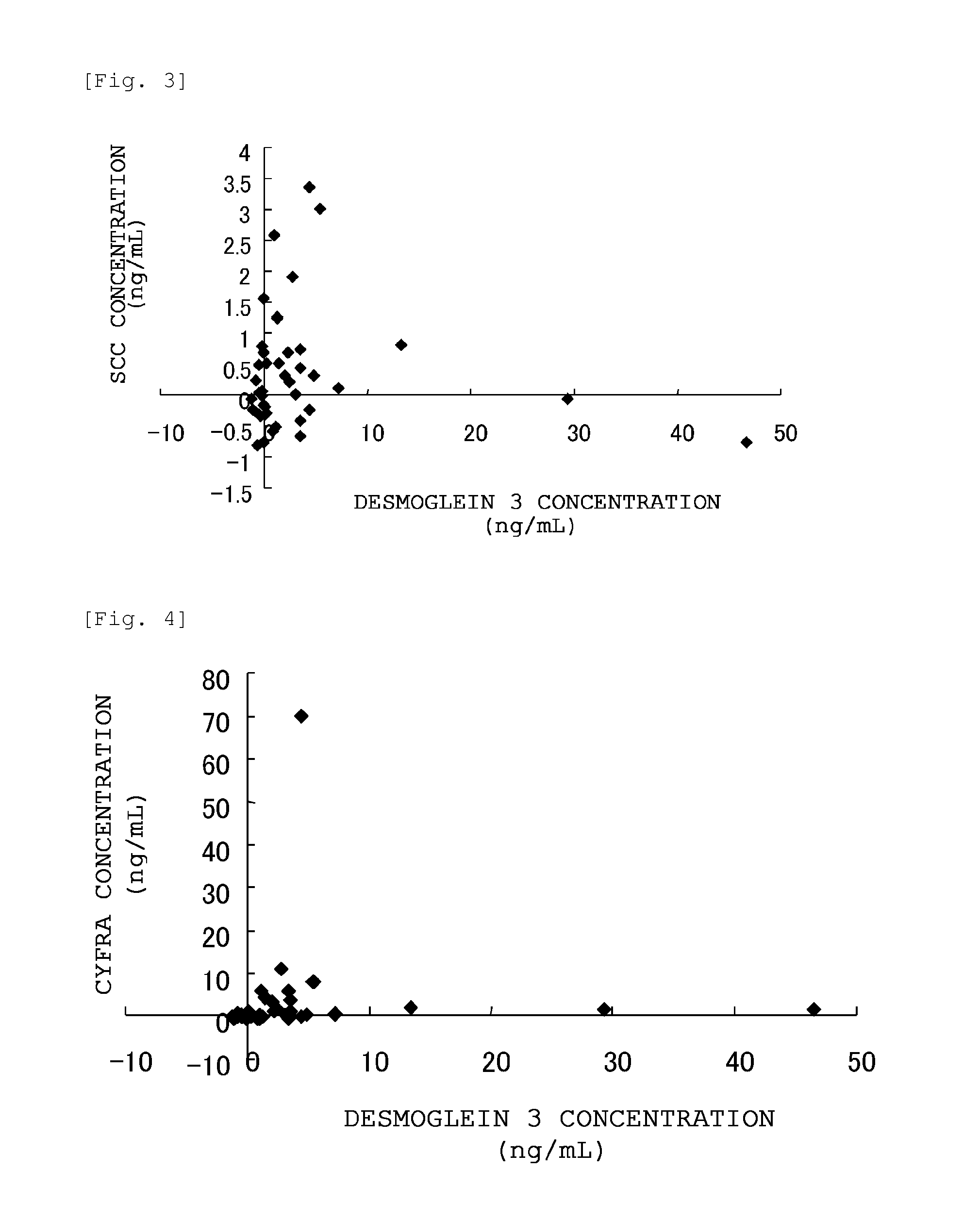
Method for detecting lung squamous cell carcinoma
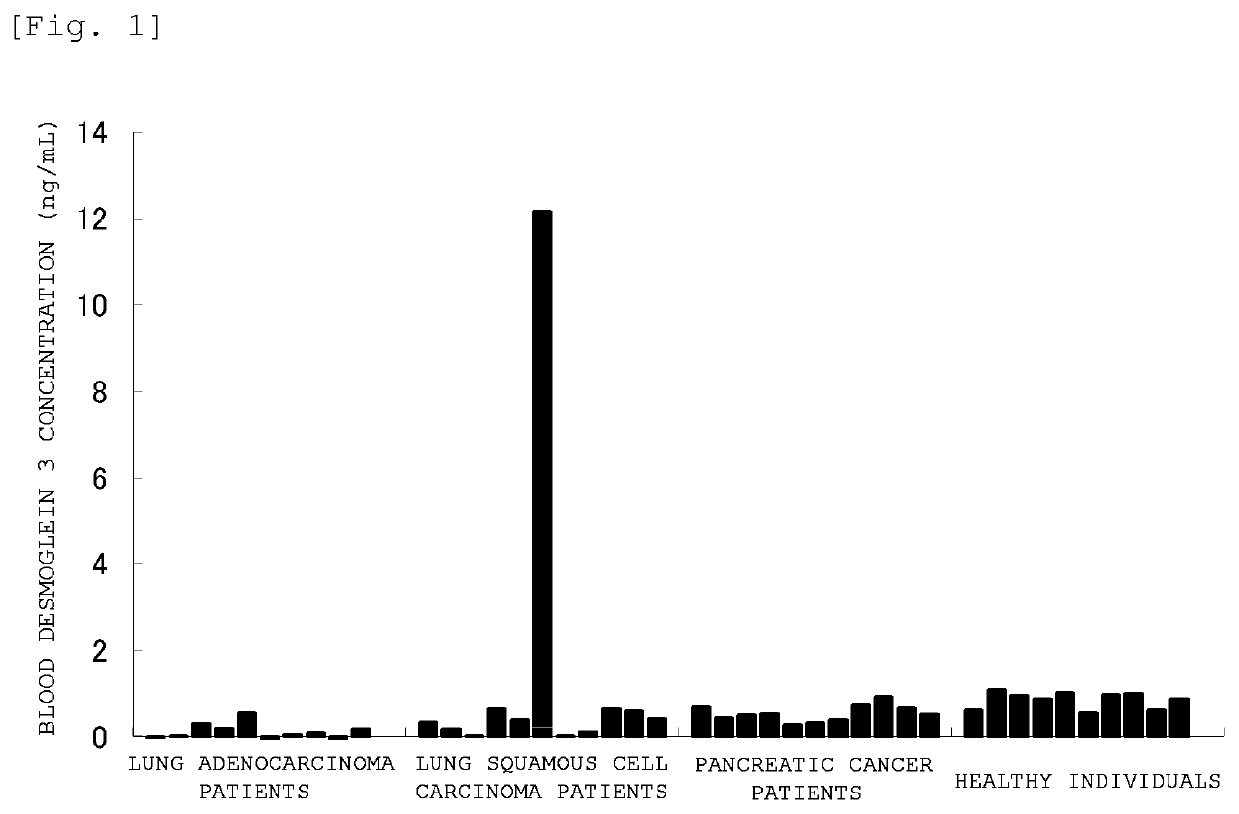
ActiveUS10502743B2The method is simple and fastHigh sensitivityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological material analysisLung squamous cell carcinomaGlycoprotein
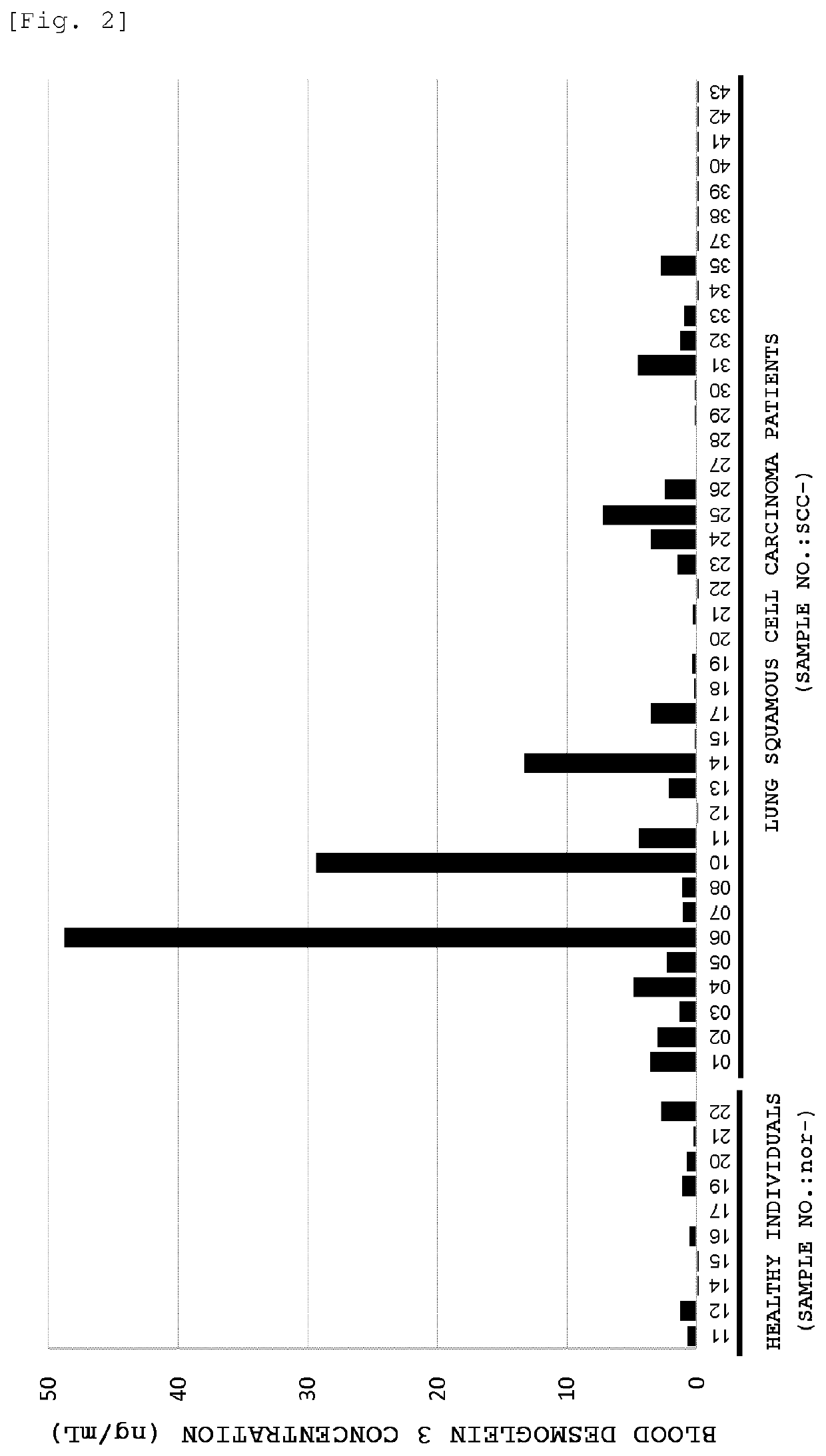
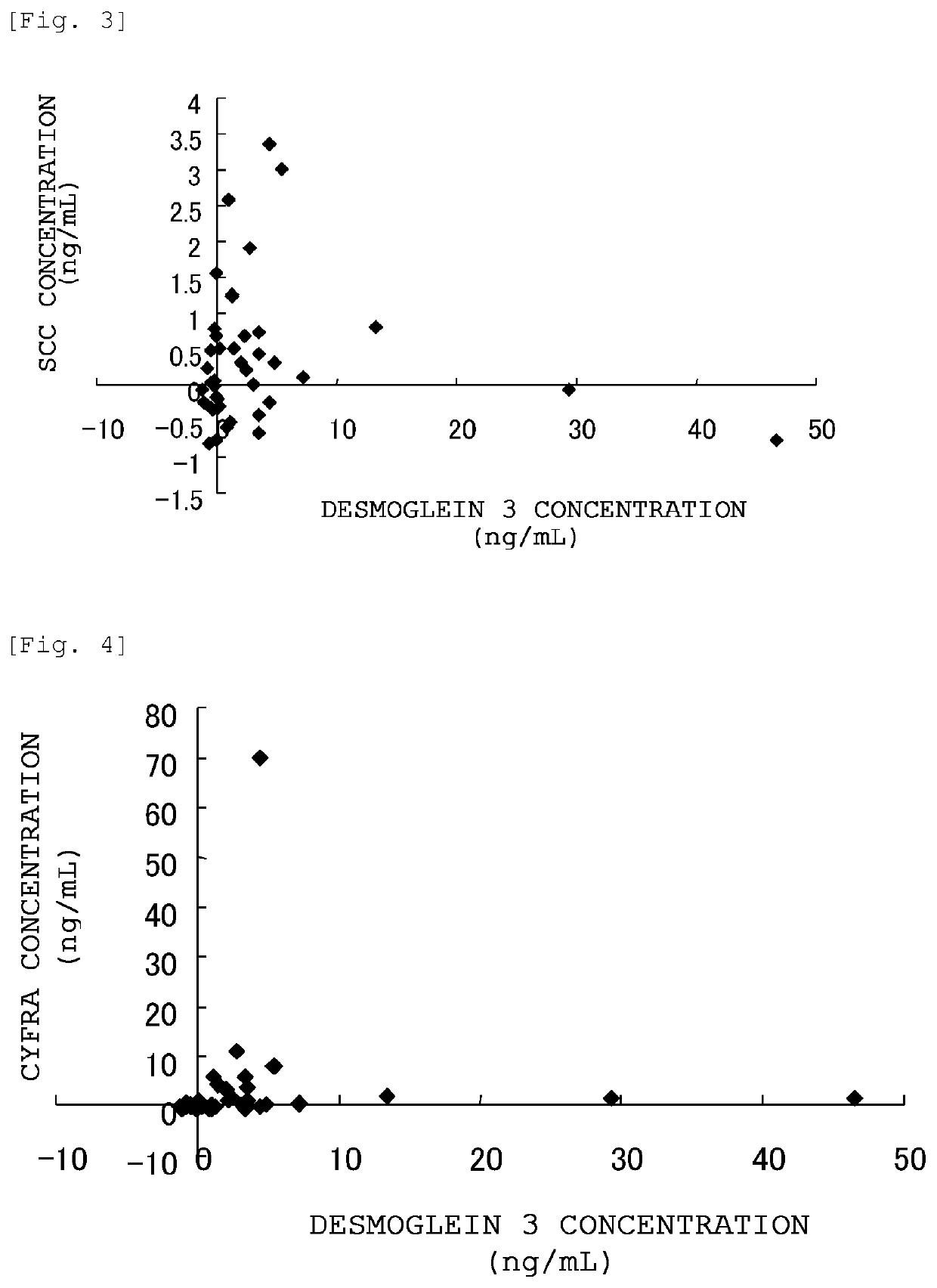
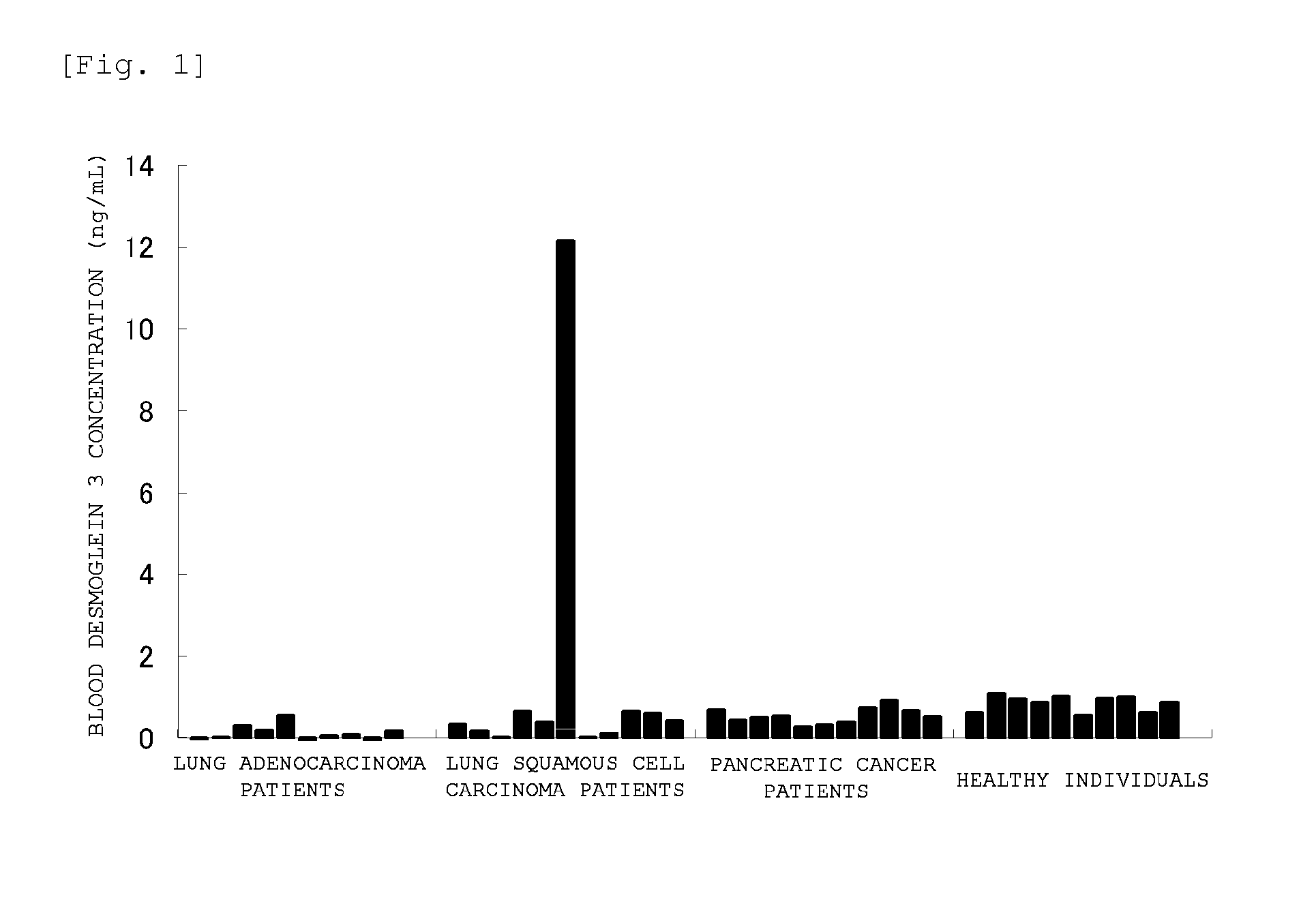
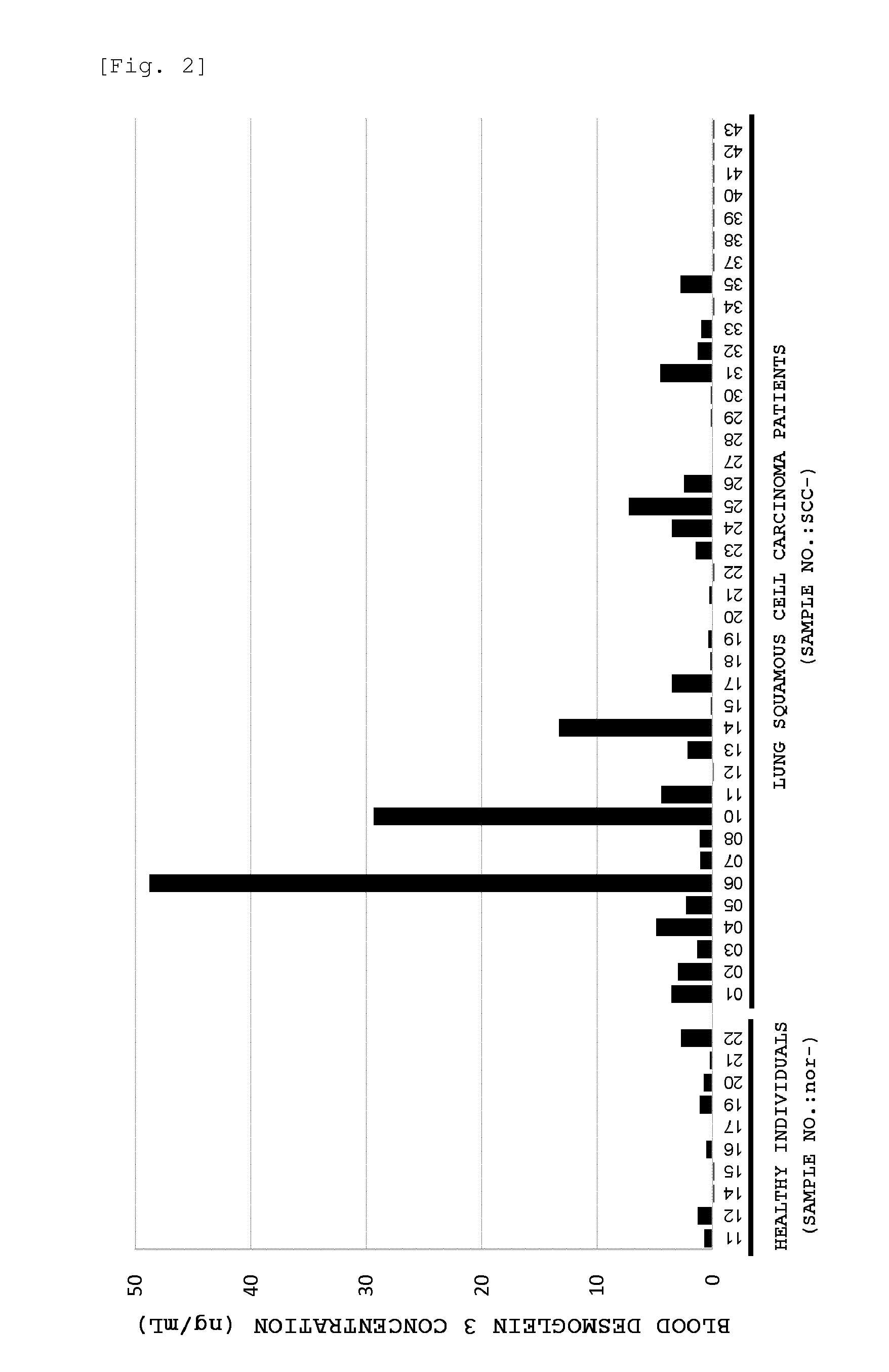
The present invention provides a method by which lung squamous cell carcinoma can be detected in a simple and prompt manner with high detection performance; and the like. The method according to the present invention detects lung squamous cell carcinoma by an assessment including the steps of: (1) performing measurement of the desmoglein 3 content in a blood sample collected from a subject; and (2) comparing the desmoglein 3 content determined by the measurement with the desmoglein 3 content in a blood sample collected from a healthy individual so as to estimate the presence of lung squamous cell carcinoma in the subject when the desmoglein 3 content is higher in the blood sample collected from the subject.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Method for detecting lung squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveUS20150276749A1The method is simple and fastHigh sensitivityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological material analysisLung squamous cell carcinomaGlycophorin
The present invention provides a method by which lung squamous cell carcinoma can be detected in a simple and prompt manner with high detection performance; and the like. The method according to the present invention detects lung squamous cell carcinoma by an assessment including the steps of: (1) performing measurement of the desmoglein 3 content in a blood sample collected from a subject; and (2) comparing the desmoglein 3 content determined by the measurement with the desmoglein 3 content in a blood sample collected from a healthy individual so as to estimate the presence of lung squamous cell carcinoma in the subject when the desmoglein 3 content is higher in the blood sample collected from the subject.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
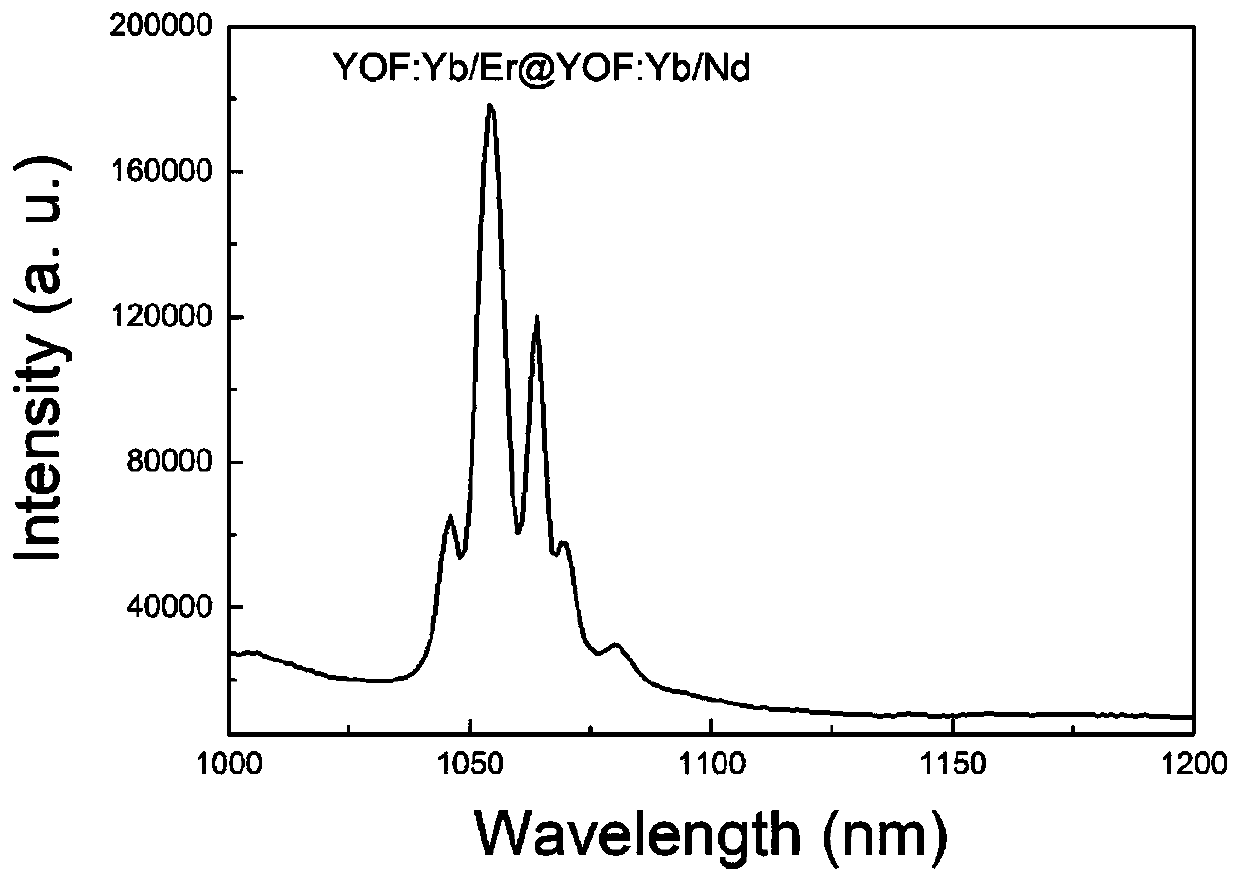
Rare earth probe capable of carrying out target recognition of lung squamous cell carcinoma, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110804434AGood up-conversion luminescence performanceGood fluorescent performance in the second near-infrared regionPowder deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsLung squamous cell carcinomaUpconversion luminescence
The invention relates to a rare earth probe capable of carrying out target recognition of lung squamous cell carcinoma, and a preparation method and application thereof. The rare earth probe is a core-shell structure formed by coating a lanthanide fluoride oxide containing an up-conversion luminous element with a lanthanide fluoride oxide containing a near-infrared second-region fluorescent imaging element, and a structure general formula is: ReOF:Ln@ReOF:Ln', wherein Re, Ln, and Ln' are all lanthanide elements. The rare earth probe has good up-conversion luminescence performance and near-infrared second-region fluorescence performance at the same time, is relatively strong in fluorescence intensity, has adjustable up-conversion fluorescence color, can realize dual-mode imaging effects, isa nano-probe with excellent fluorescence performance, and has good luminous effects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Noninvasive test kit of susceptibility gene of lung squamous carcinoma
The invention provides a noninvasive test kit of a susceptibility gene of lung squamous carcinoma. The kit comprises a specific primer of two single nucleotide polymorphism locus gene types for detecting whether Lys75Gln and GSTT1 genes on an XPD (Xeroderma Pigmentosum group D) gene are lacked or not (Present / Null), a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequencing primer, a PCR reaction assembly, a PCR product purifying assembly, a DNA sequencing reaction assembly and the like. The kit is used for estimating a risk grade for a subject suffering the lung squamous carcinoma through detecting the gene types of the two single nucleotide polymorphism loca which are relative to the lung squamous carcinoma; and the subject is guided to prevent the happening of the lung squamous carcinoma in a targeted manner from a gene level according to a gene detection result of each subject, so as to reduce the morbidity of the subject. A sampling method of the invention is as follows: an oral mucosa cell is sampled, the purposes of being painless and noninvasive and avoiding crossed infection can be realized. A sequencing detection result is accurate and reliable, a special imported instrument with expensive cost does not need to be purchased, and the method is easy to popularize and spread.
Owner:解码(上海)生物医药科技有限公司
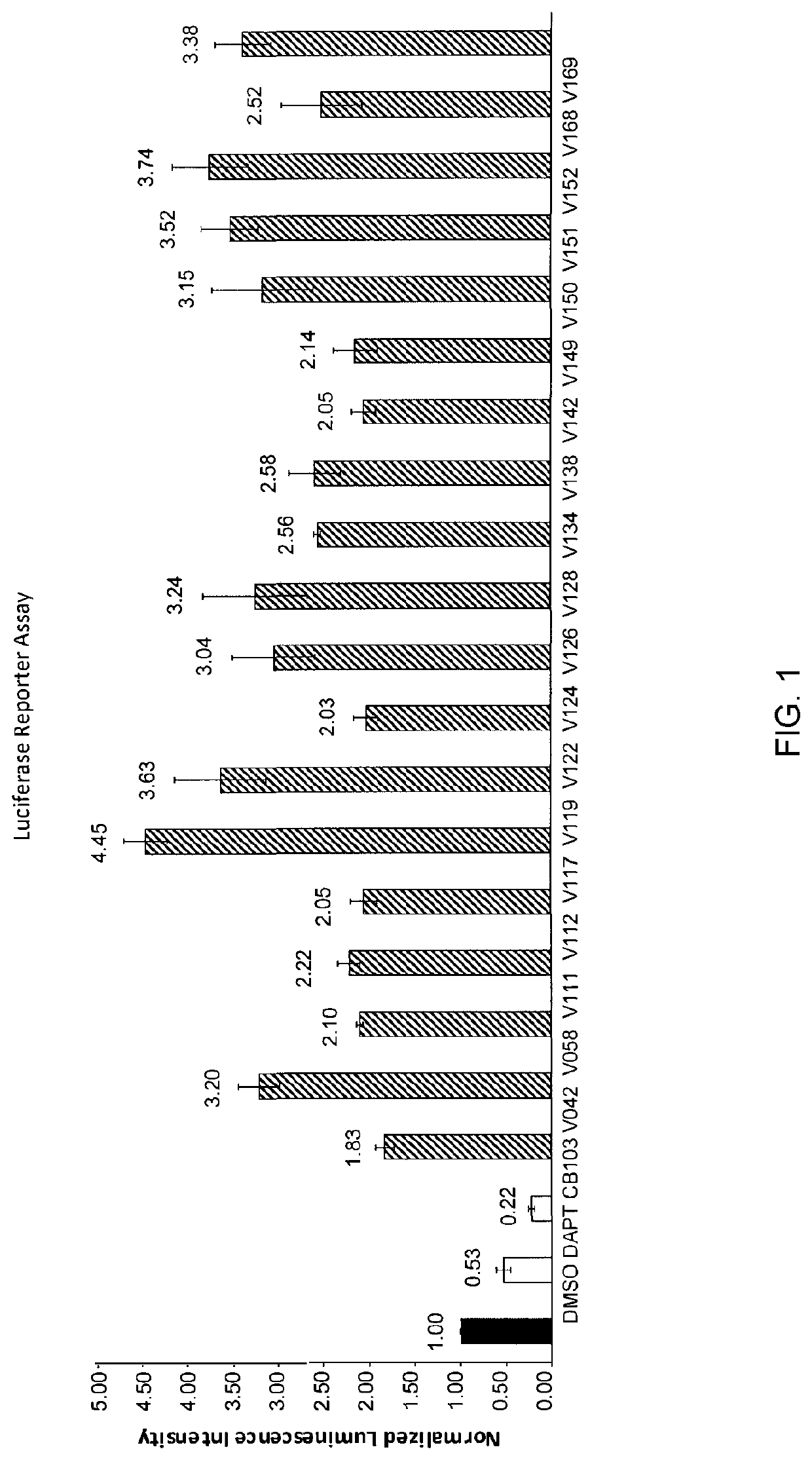
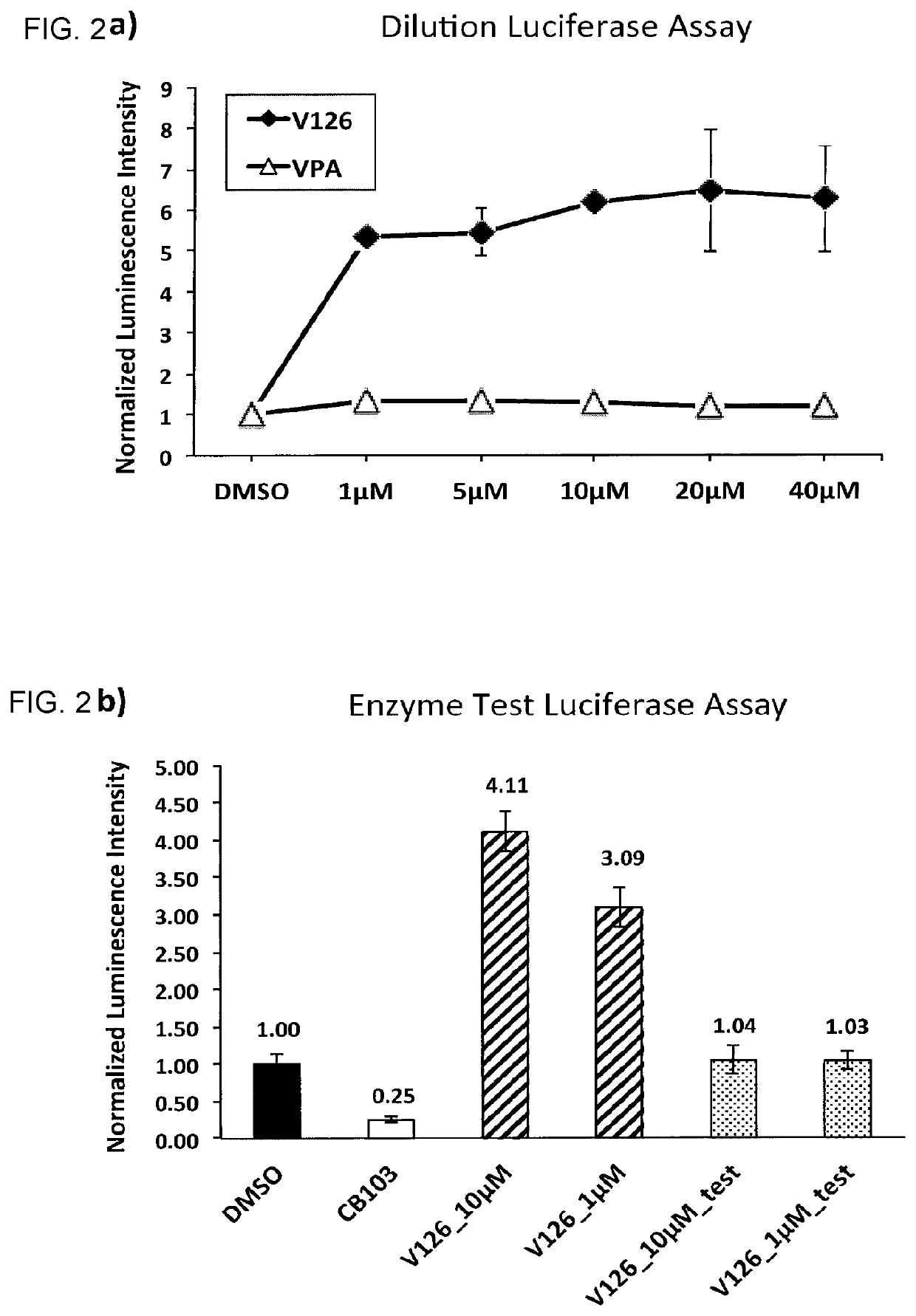
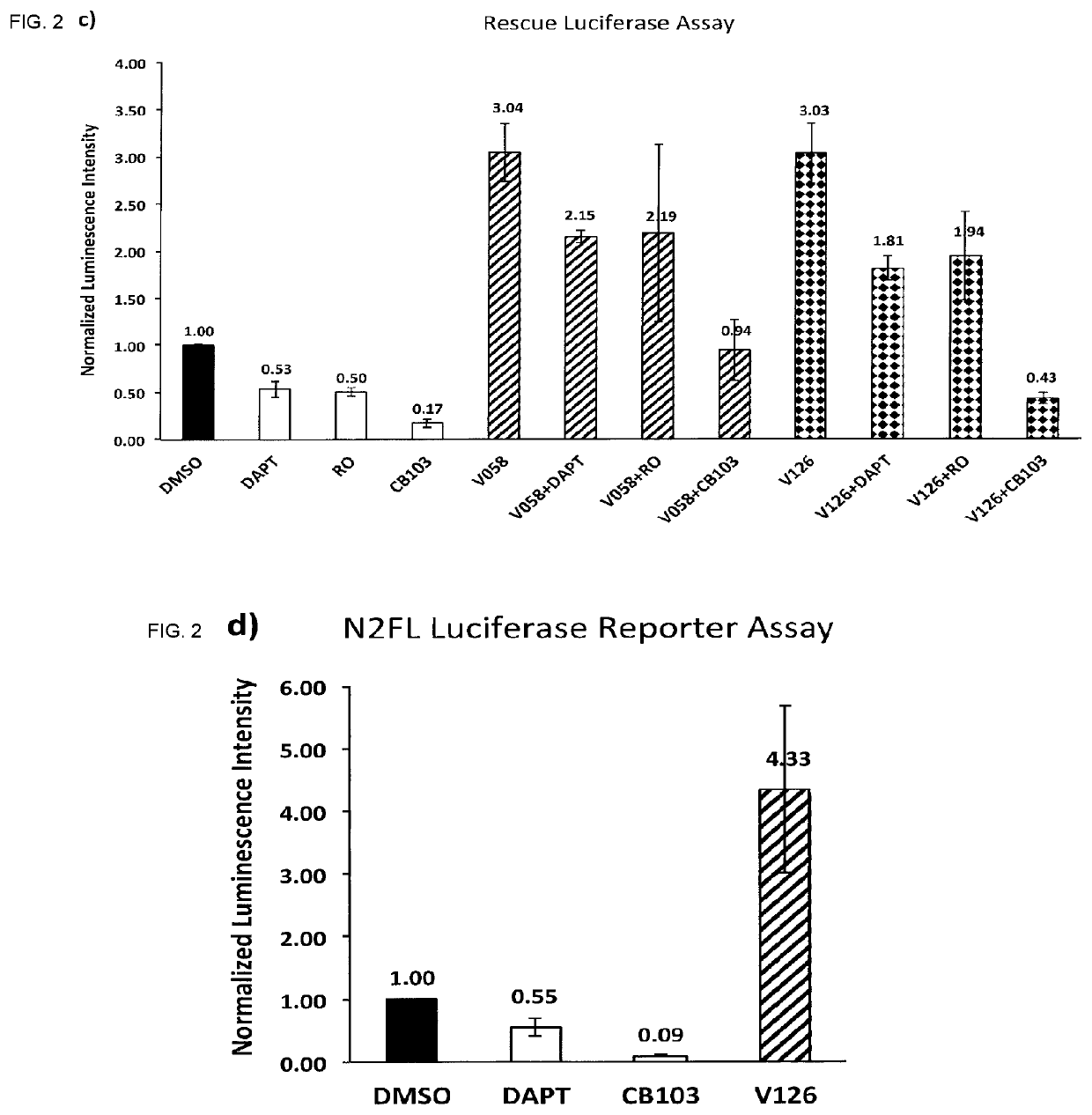
Enhancers of Notch signaling and the use thereof in the treatment of cancers and malignancies medicable by upregulation of Notch
The present invention relates to the use for enhancing Notch signaling in an individual, of a compound showing the general formula (I) and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof, for the treatment of a disease selected from the group of dermatological disorders including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, immune related disorders, cancer, squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous and lung squamous cell carcinoma, head and neck cancer, non-melanoma skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis, neuroendocrine tumors, neuroendocrine small cell carcinoma and carcinoid tumors, thyroid carcinomas, muscular disorders muscular dystrophy and impaired regeneration capacity after injury; use in immunotherapy for cancer.
Owner:XENIOPRO GMBH
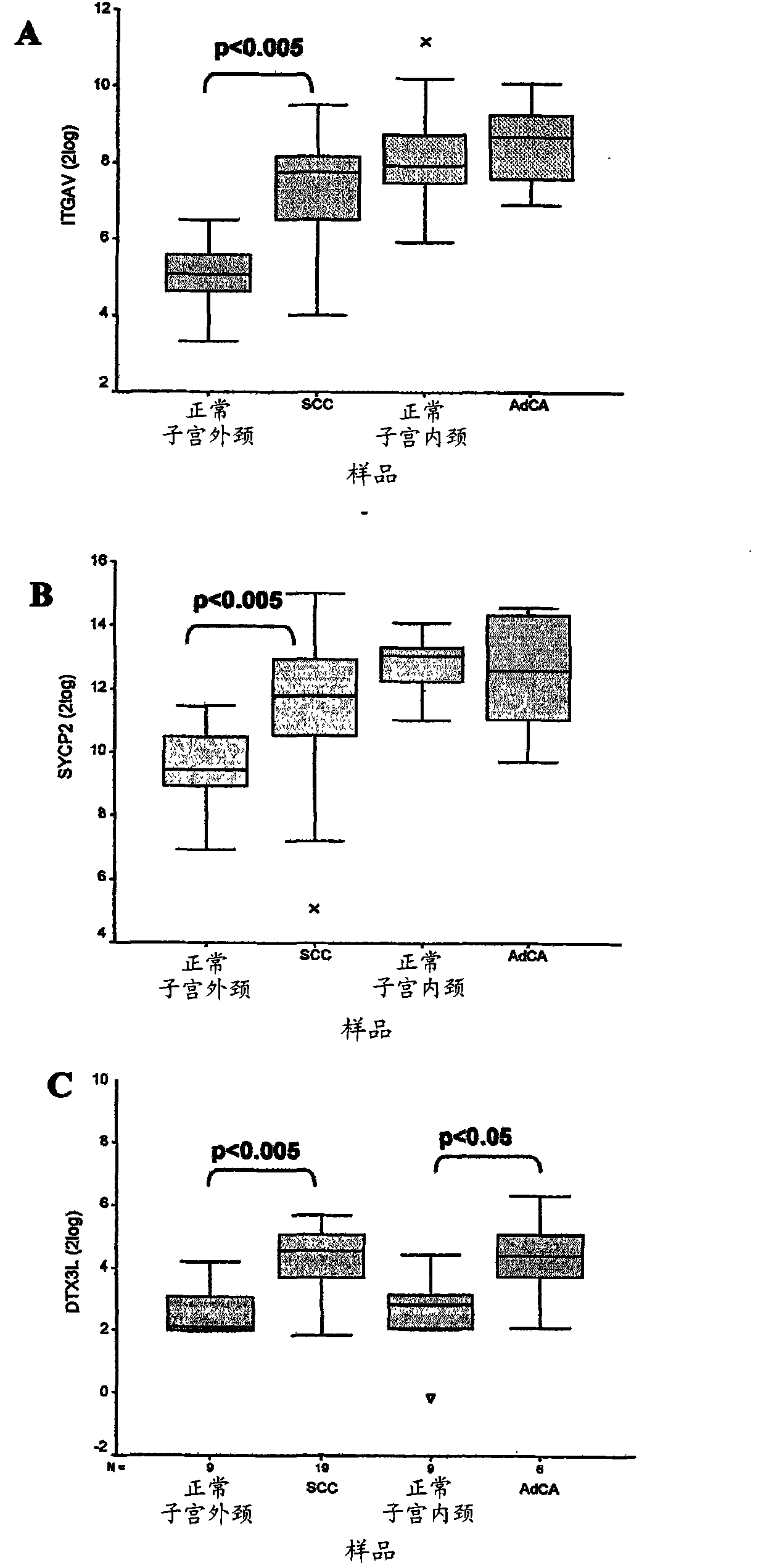
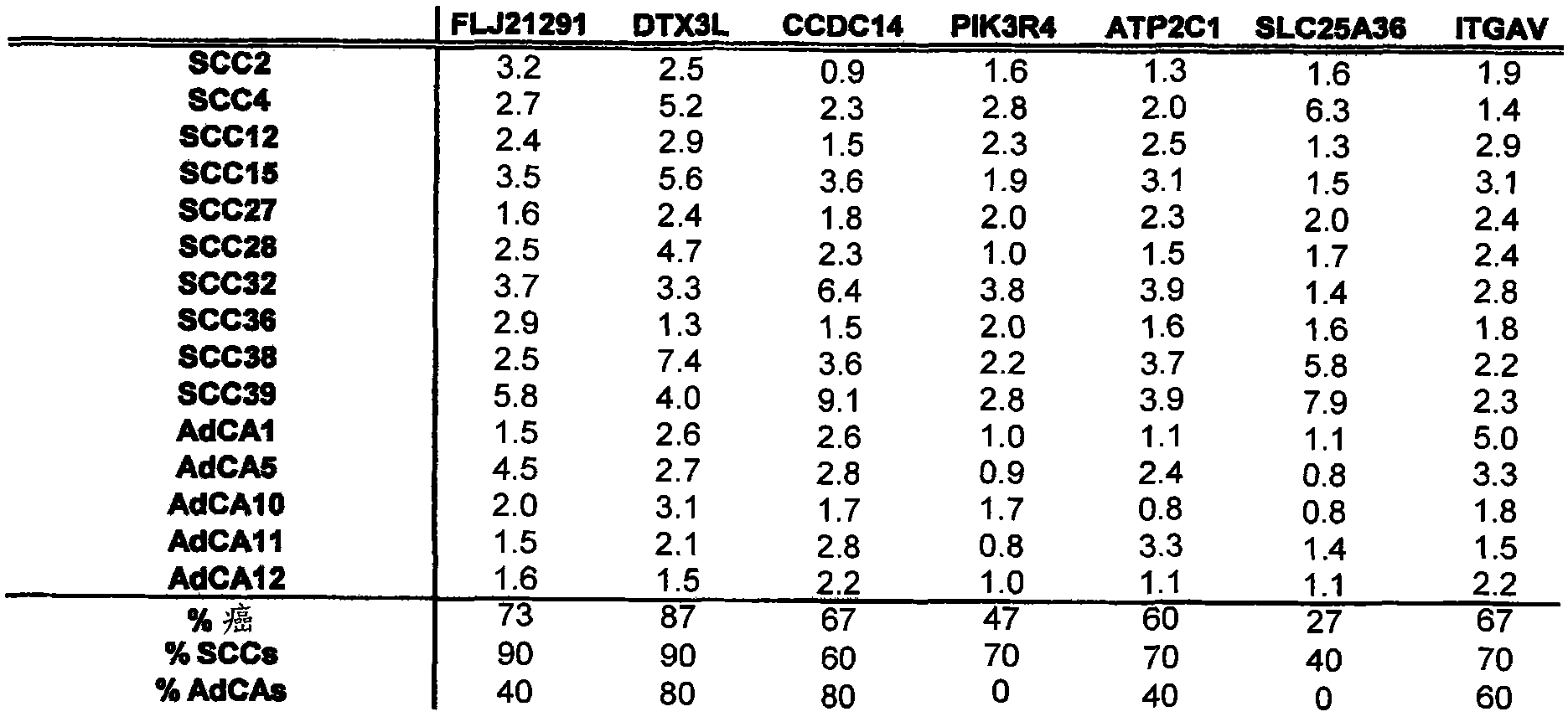
New molecular markers for detection of squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas and high-grade precursor lesions thereof
InactiveCN101827948AHas immune-inducing activityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsLung squamous cell carcinomaCancer research
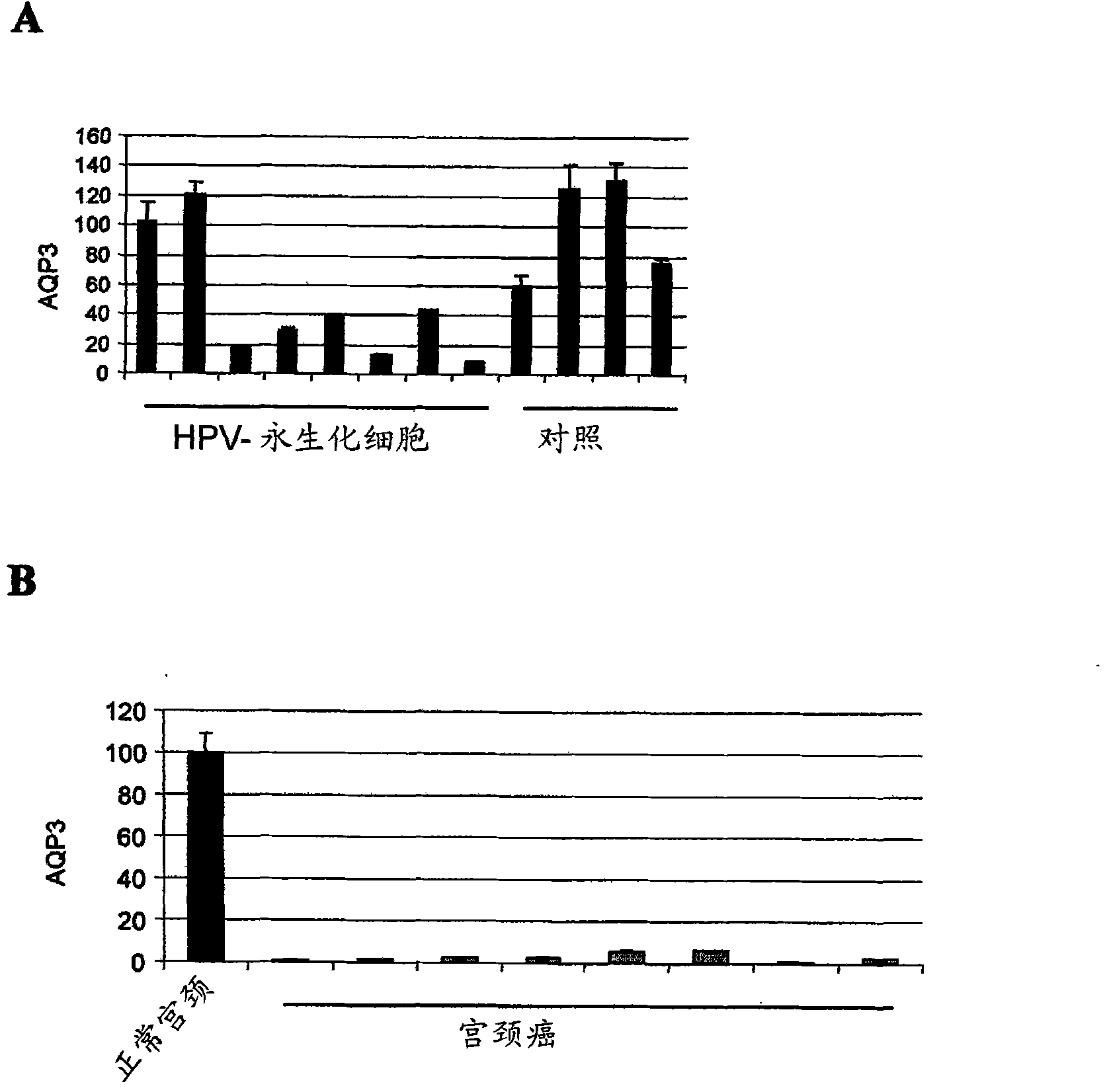
The present invention provides for new markers for the detection of HPV-induced or lung squamous cell carcinoma and / or adenocarcinoma and high-grade precursor lesions thereof, comprising the genes of the present invention. Detection can take place by detection over expression or down regulation of said genes either by nucleic acid assay or by assays for the proteins produced by said genes.
Owner:VER VOOR CHRISTELIJK HOGER ONDERWIJS WETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK & PATIENTENZORG
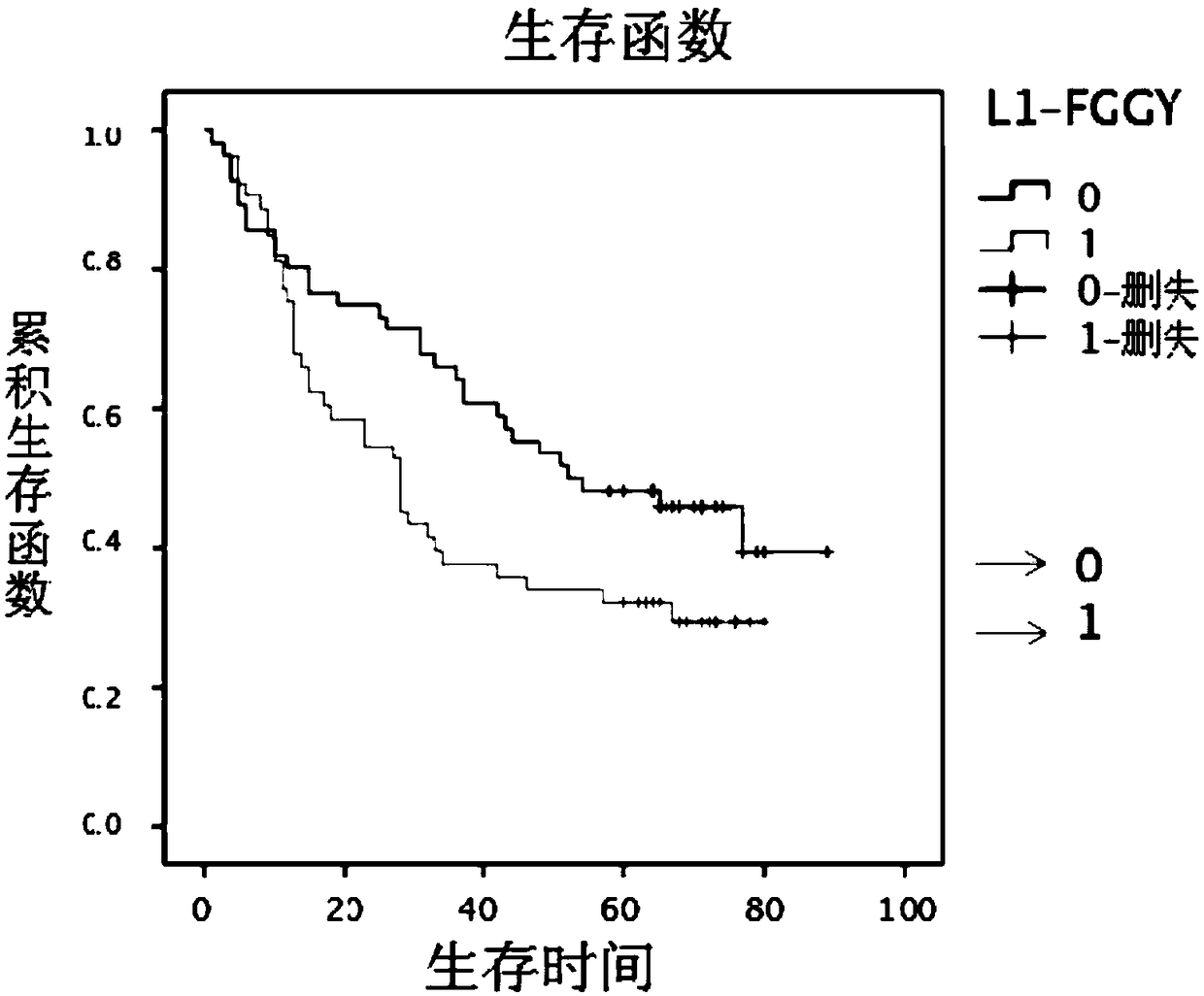
Retrotransposition gene L1-FGGY and application thereof as marker of lung squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN108796079AIncreased proliferationIncrease aggressivenessOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLung squamous cell carcinomaNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses retrotransposition gene L1-FGGY and application thereof as a marker of lung squamous cell carcinoma. The nucleic acid sequence of the retrotransposition gene L1-FGGY is SEQ IDNO. 1; the nucleic acid sequence of an upstream detection primer of the retrotransposition gene L1-FGGY is SEQ ID NO. 2; and the nucleic acid sequence of a downstream detection primer is SEQ ID NO. 3.A retrotransfer inhibitor nevirapine or efavirenz can inhibit the expression level of the retrotransposition gene L1-FGGY for treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma. The retrotransposition gene L1-FGGY disclosed can be used as a new tumor marker, and the detection of L1-FGGY can be used for early diagnosis, molecular typing and prognosis evaluation of lung squamous cell carcinoma, and L1-FGGYcan also become a potential therapeutic target for clinical treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma and has broad application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV CANCER INST & HOSPITAL
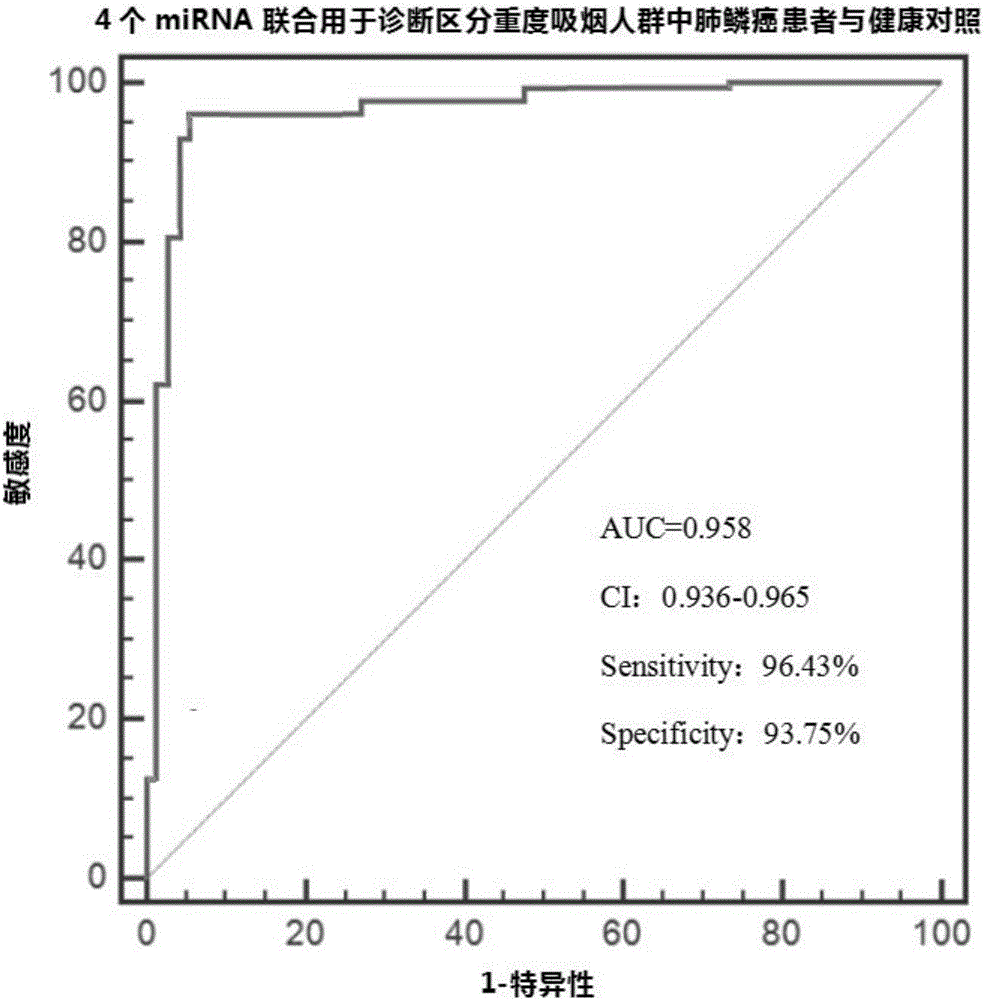
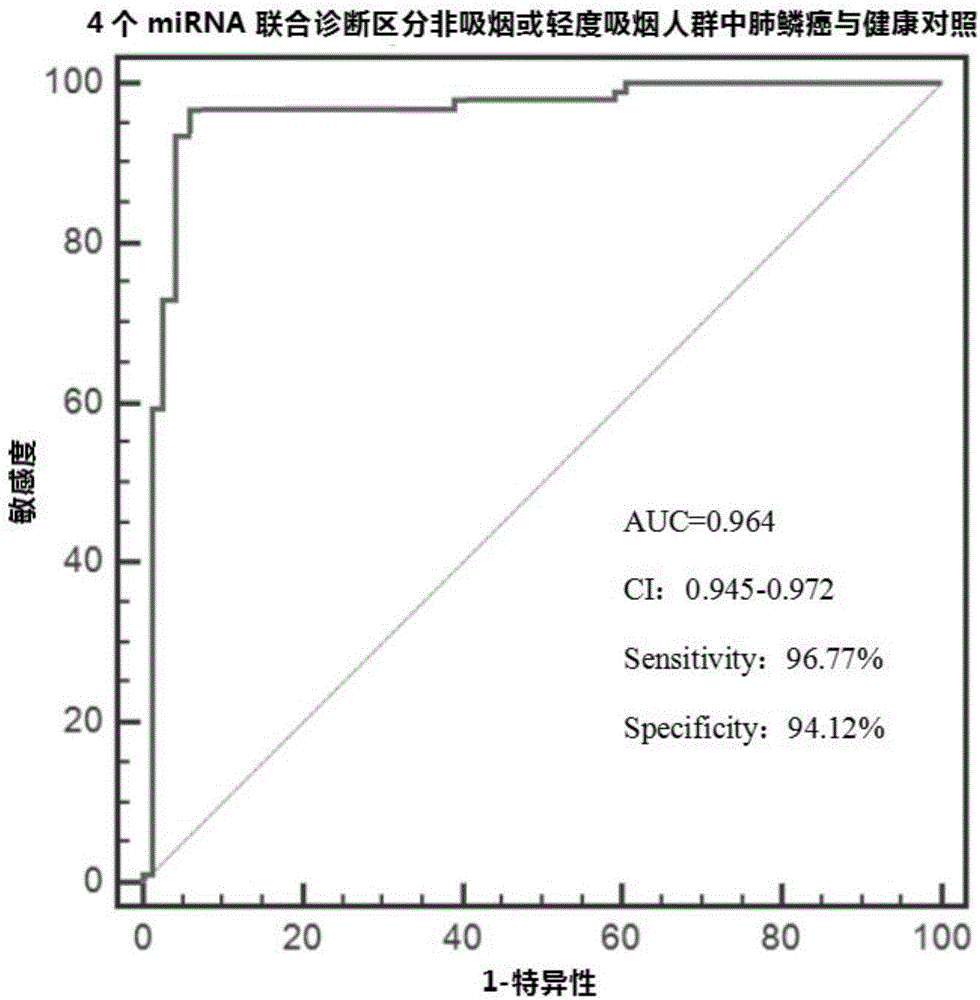
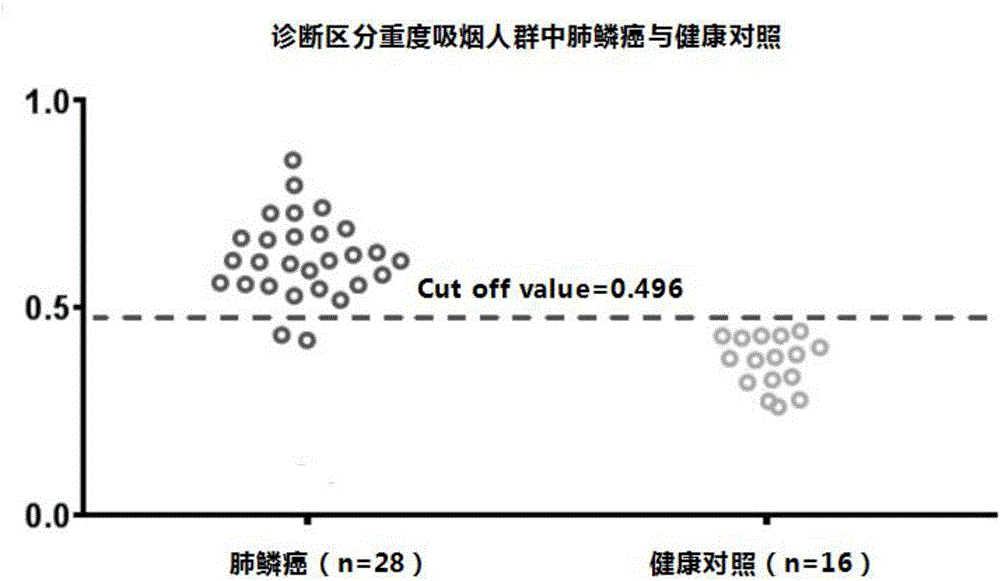
Non-invasive marker and kit for diagnosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma patients among non-smoking or mild-smoking people
ActiveCN106636450AIncreased sensitivityReduce sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLung squamous cell carcinomaMedicine
The invention discloses a non-invasive marker and a kit for diagnosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma patients among non-smoking or mild-smoking people, wherein the mild-smoking people refers to people with smoking index being lower than 200. The non-invasive marker is composed of the following microRNAs: miR-644a, miR-619-5p, miR-222-3p and miR-575, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the miR-644a is represented as the SEQ ID No.5; the nucleotide sequence of the miR-619-5p is represented as the SEQ ID No.6; the nucleotide sequence of the miR-222-3p is represented as the SEQ ID No.7; and the nucleotide sequence of the miR-575 is represented as the SEQ ID No.8. The microRNAs non-invasive marker is high in diagnosis accuracy and has high sensitivity and strong specificity.
Owner:MIRXES HANGZHOU BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
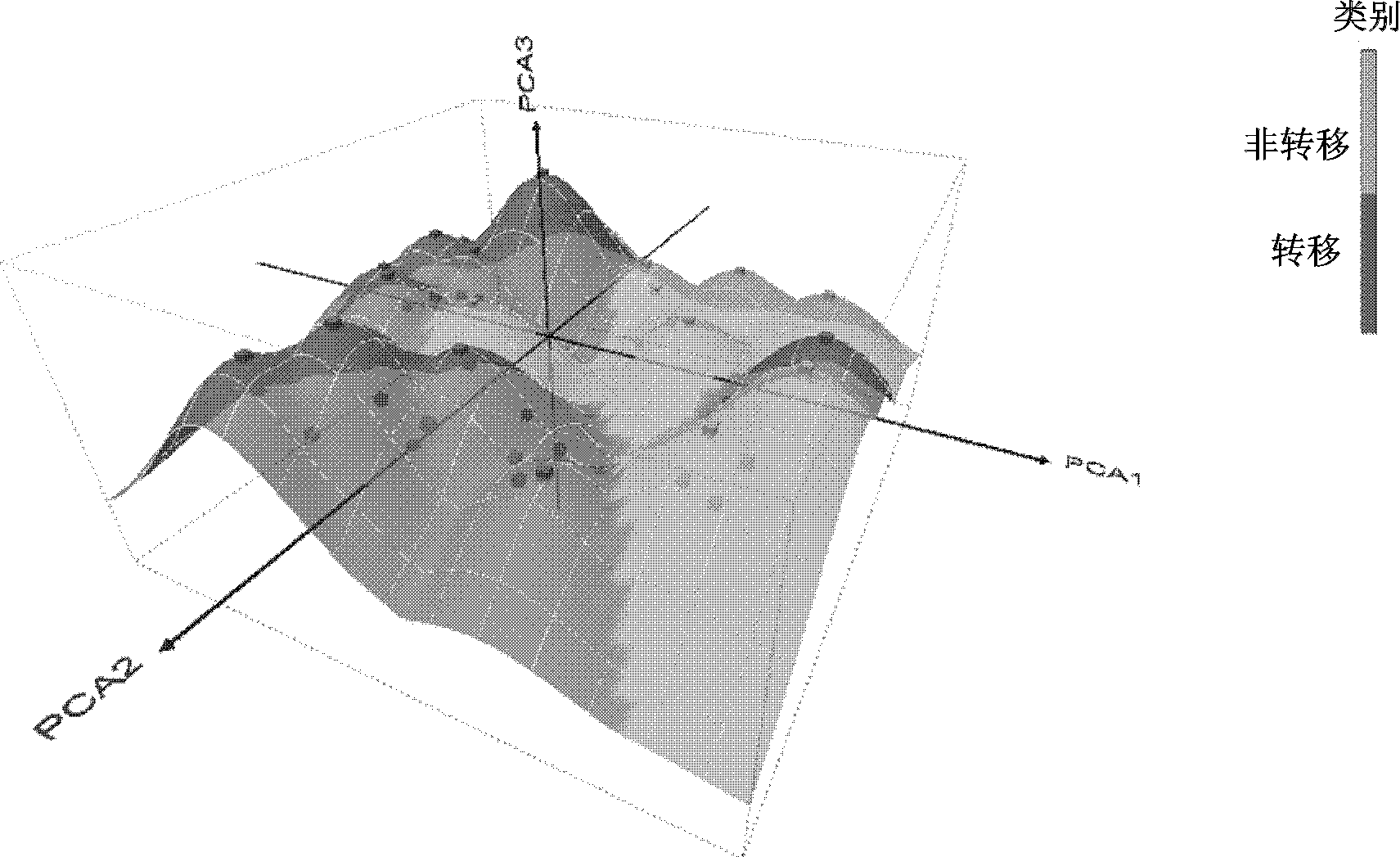
MicroRNA markers for discriminating metastatic and non-metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma
InactiveCN102851283BNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementLung squamous cell carcinomaMicroRNA
The invention relates to 21 microRNA markers for discriminating metastatic and non-metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma. More specifically, the invention relates to a class of microRNA markers for discriminating metastatic and non-metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma. It has been proved by examination that, the specific microRNA markers can effectively discriminate metastatic and non-metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma tissue. The invention also relates to a chip and a test kit for detecting the microRNA markers.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Masson pine bark extract for treating squamous cell lung carcinoma as well as preparation method and composition of masson pine bark extract
ActiveCN105456308AAvoid lostAvoid mixingAntineoplastic agentsConiferophyta medical ingredientsSide effectMedicine
The invention discloses a masson pine bark extract for treating squamous cell lung carcinoma as well as a preparation method and a composition of the masson pine bark extract. The preparation method of the extract comprises the following steps: (1) smashing masson pine bark till the size reaches 200-800 meshes, thus preparing masson pine bark powder; (2) at 4-25 DEG C, adding water into the masson pine bark powder, and soaking for 1-10 h, wherein the mass-to-volume ratio of the masson pine bark powder to the water is between 1 to 2 and 1 to 15; (3) carrying out ultrasonic extraction on the masson pine bark powder water soaking solution for 5min-2h, and filtering to prepare masson pine bark water extract solution; and (4) drying the masson pine bark water extract solution. The masson pine bark extract contains the active ingredients including polyphenol, total alkali and polysaccharide, has the effective rate reaching 95.75-99.66% in treating moderate or advanced squamous cell lung carcinoma, and has the advantages of small toxic and side effects, high safety and the like.
Owner:华创安全医疗科技(广东)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com