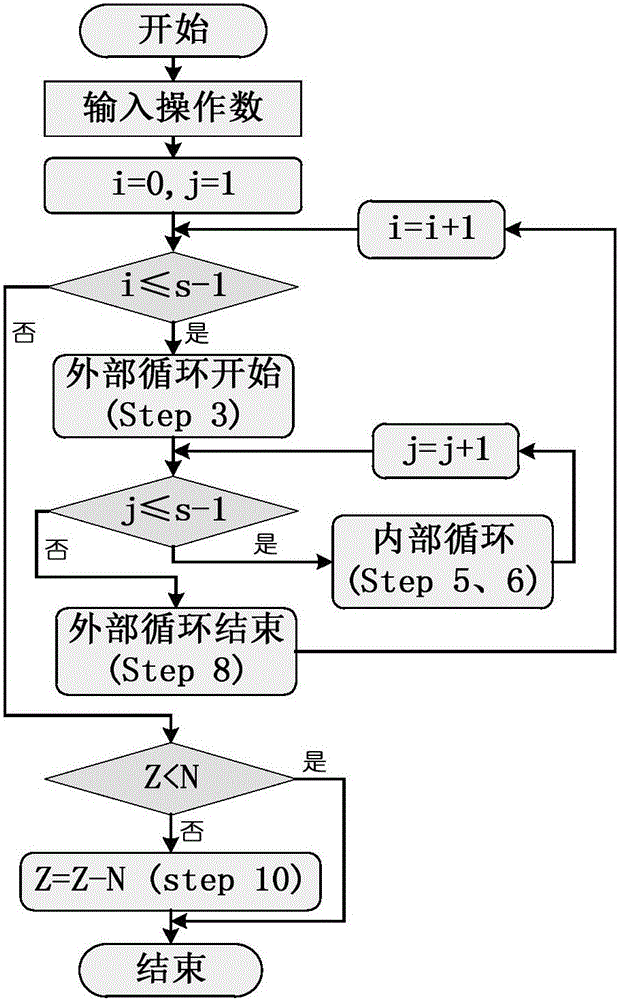
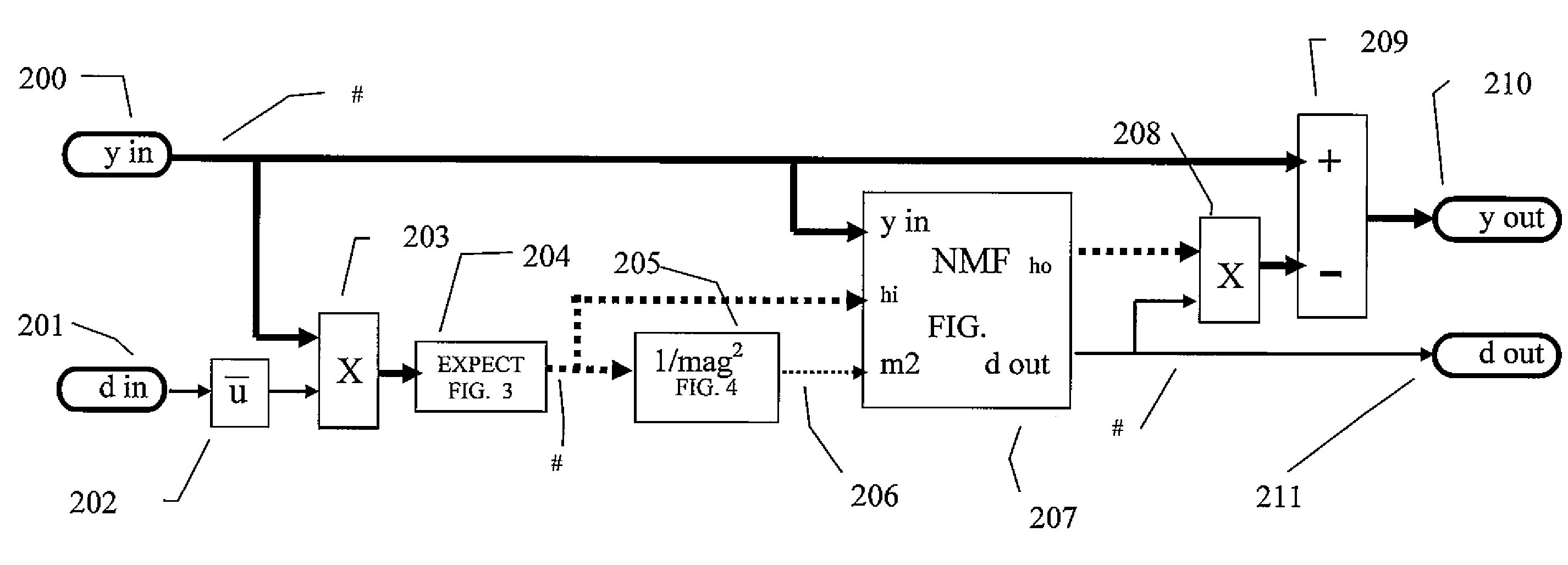
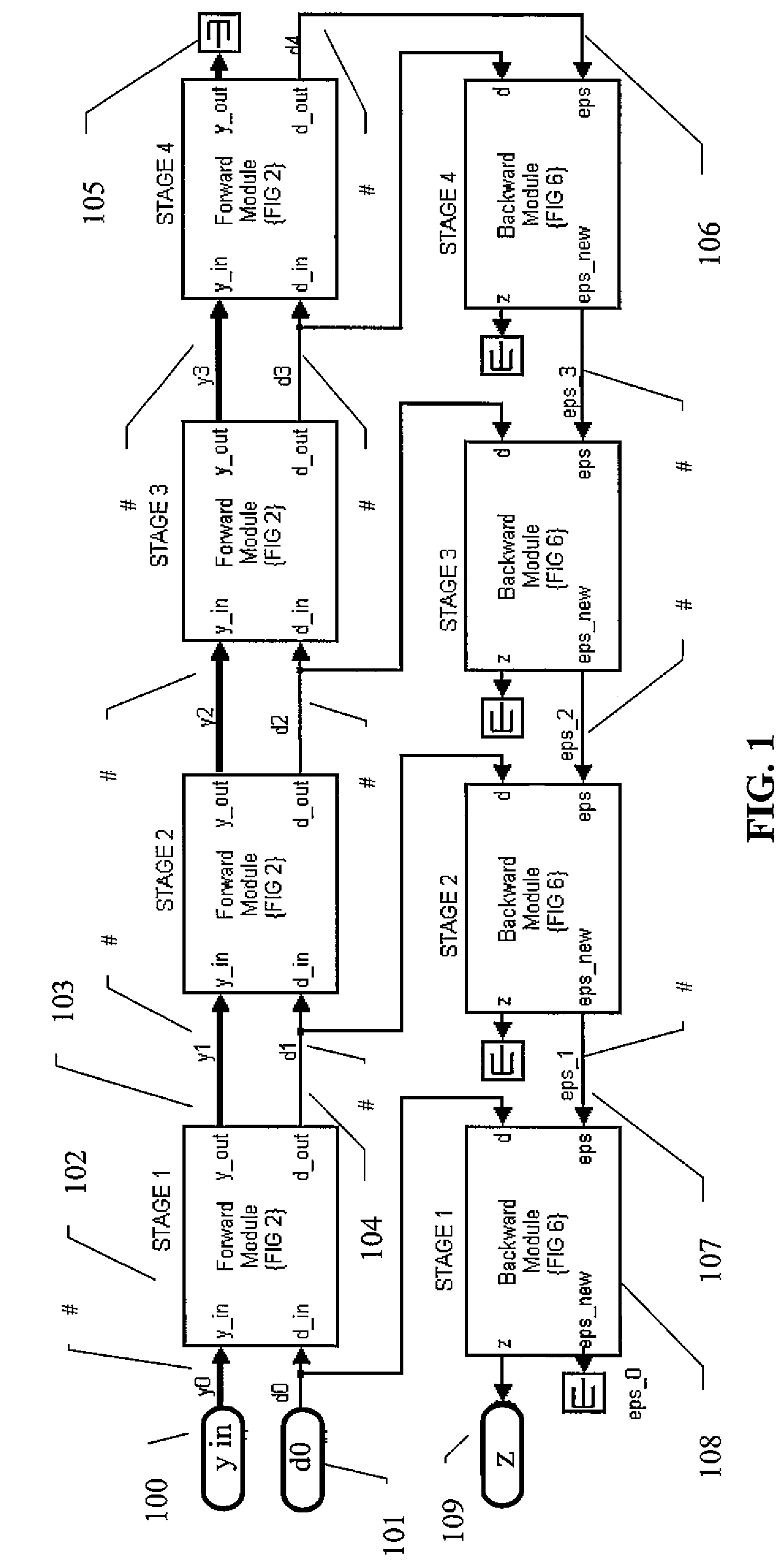
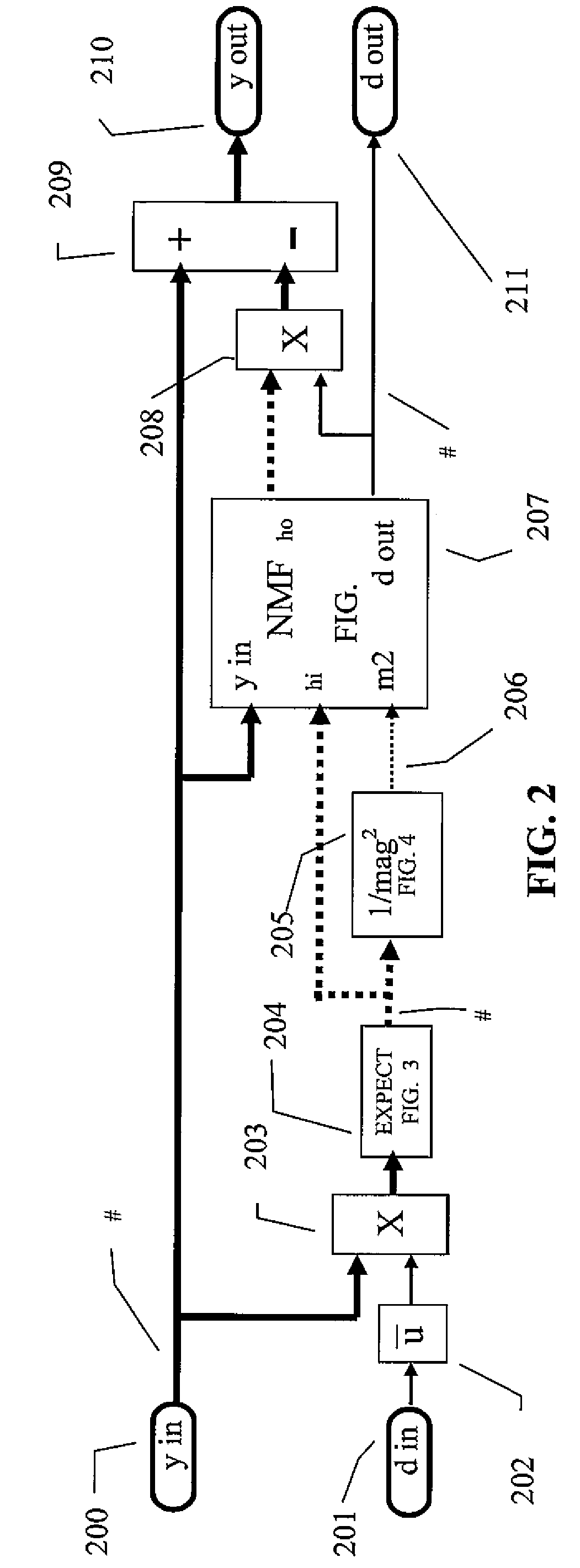
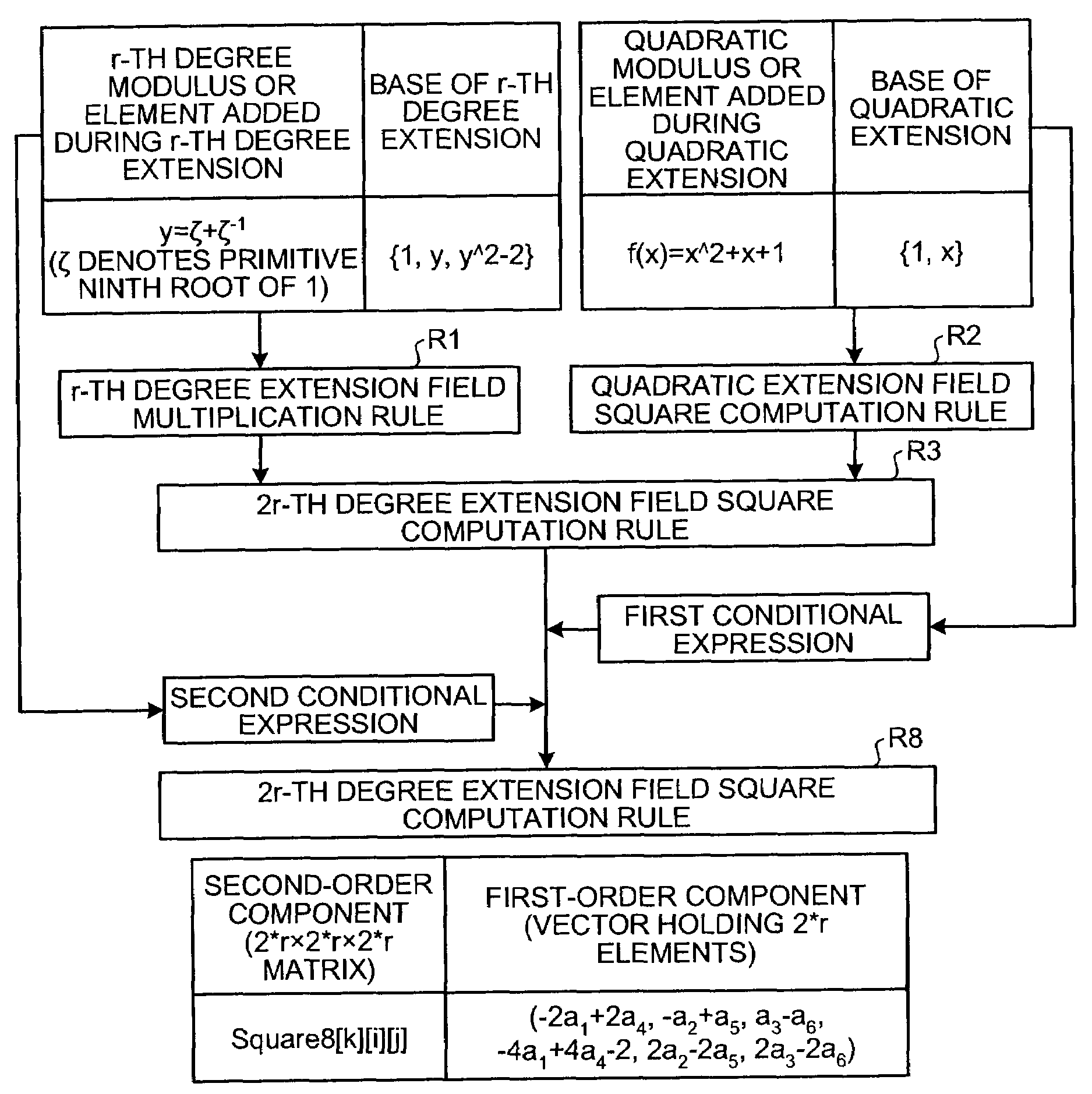
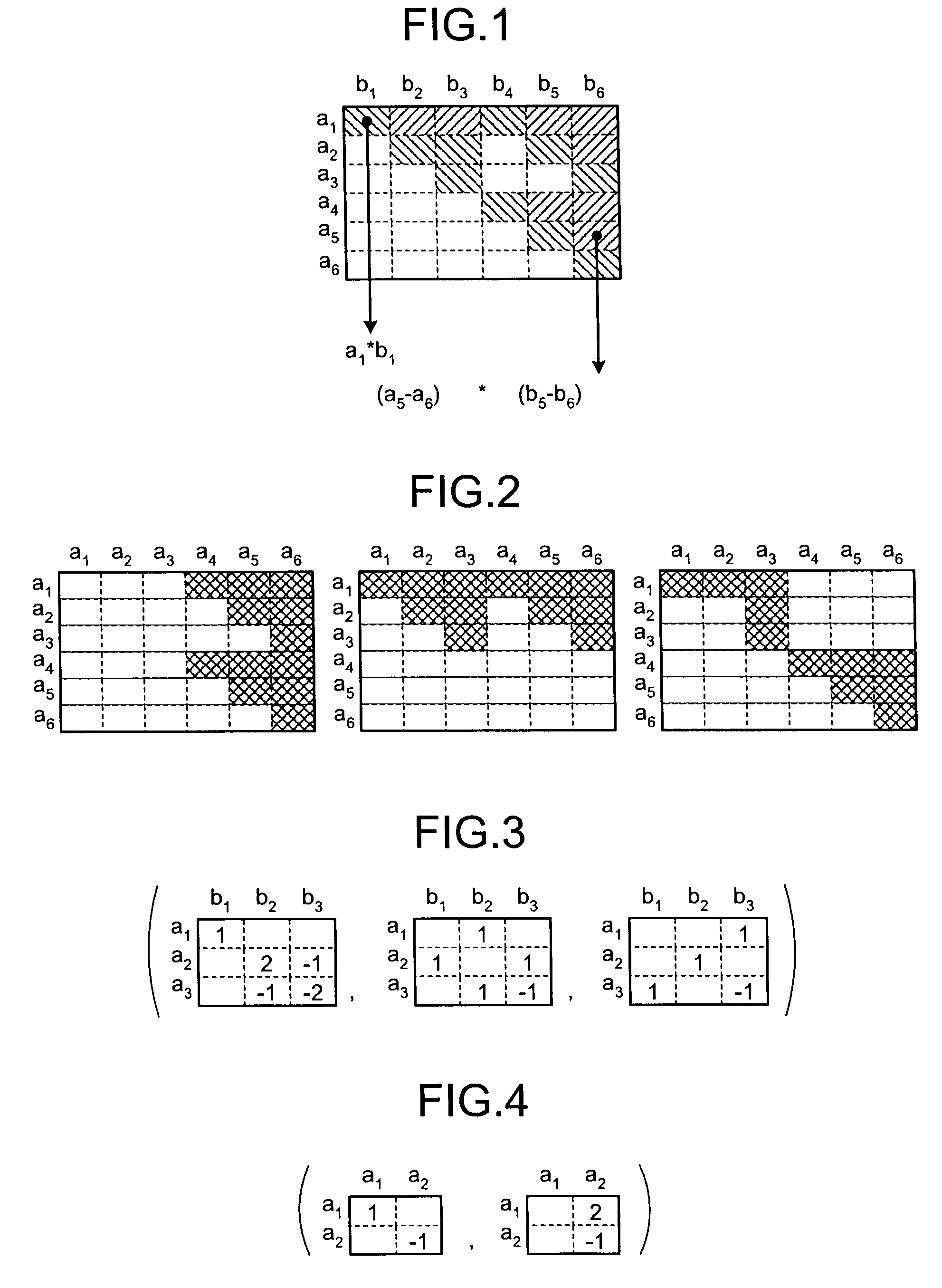
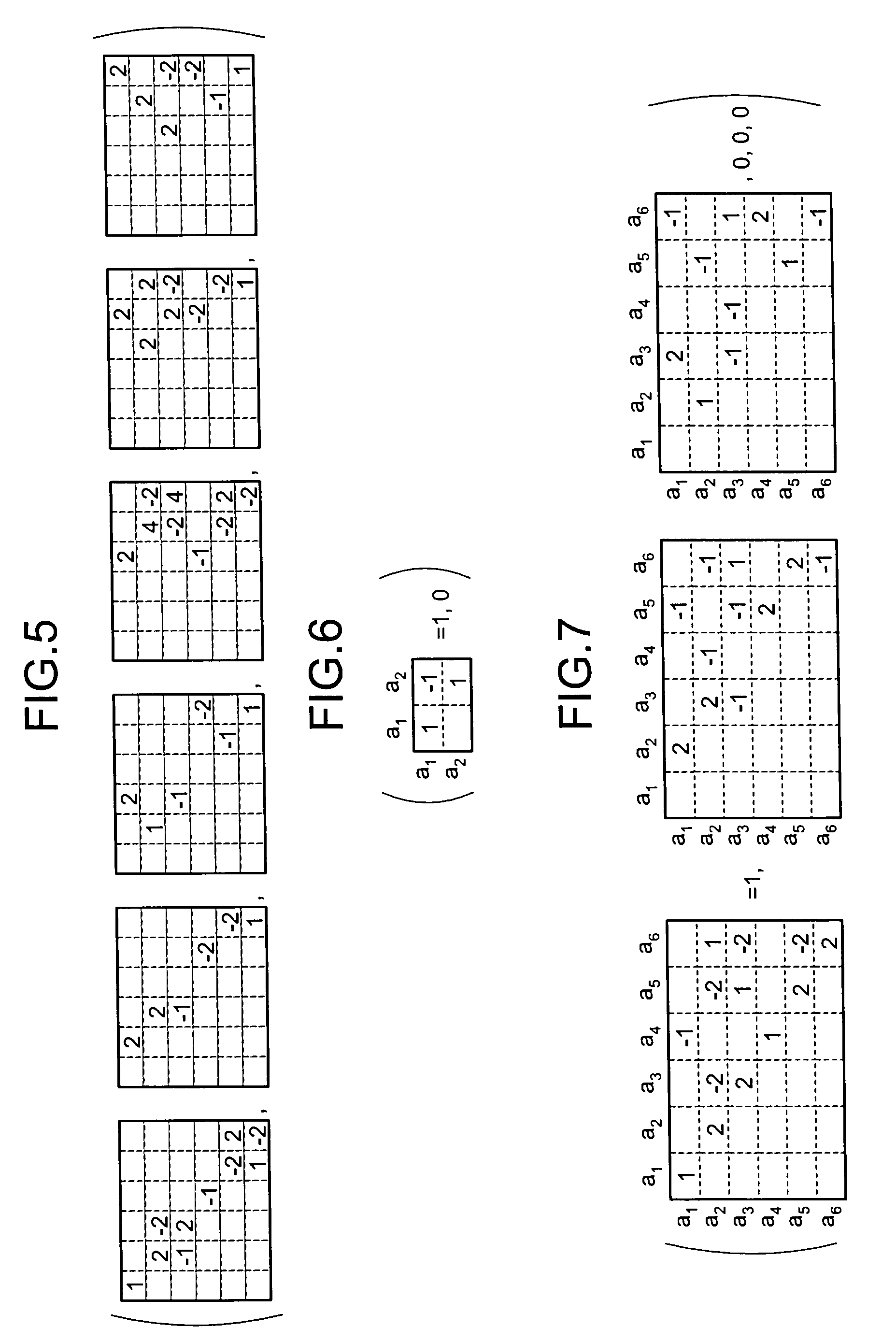
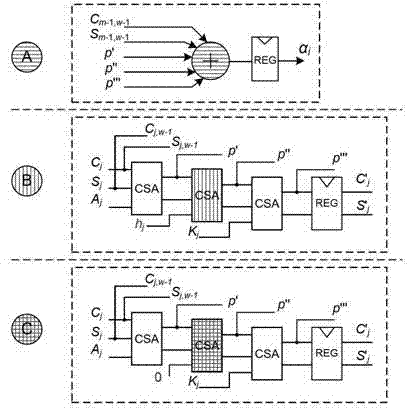
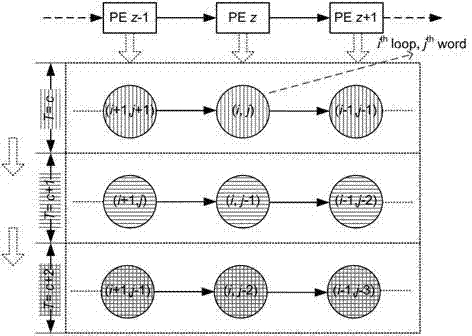
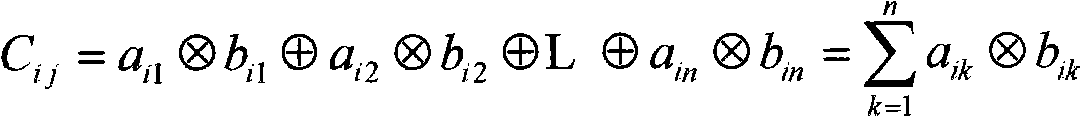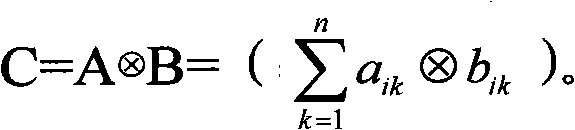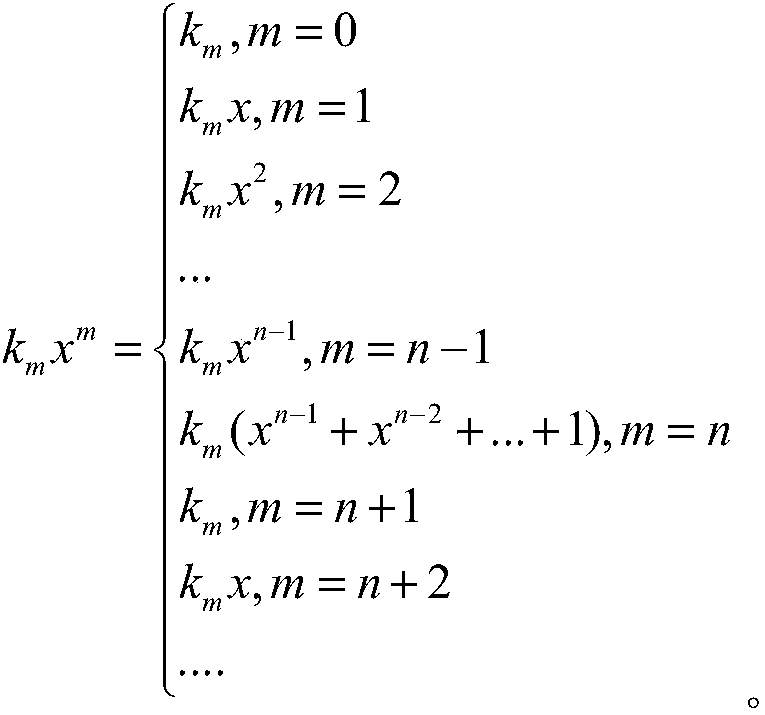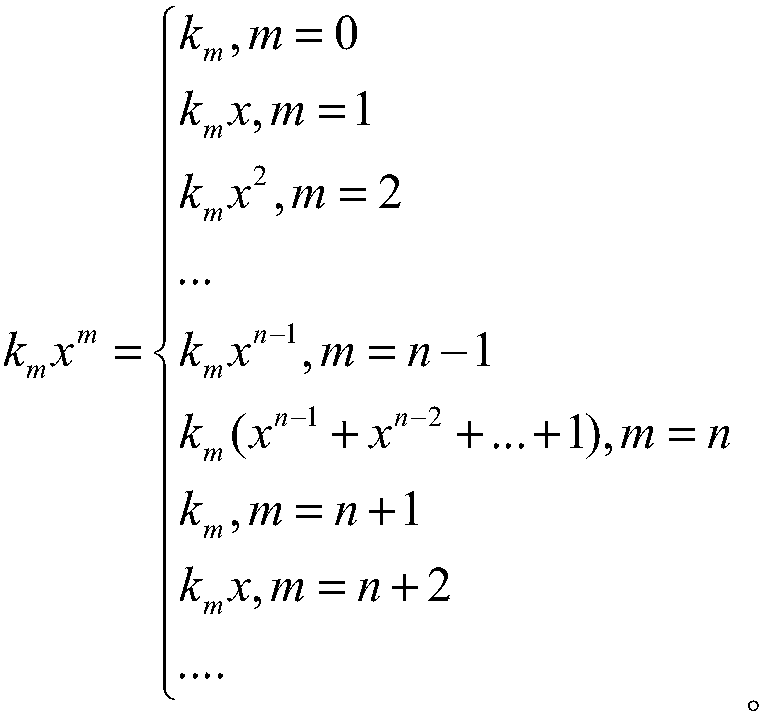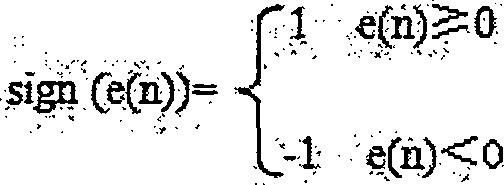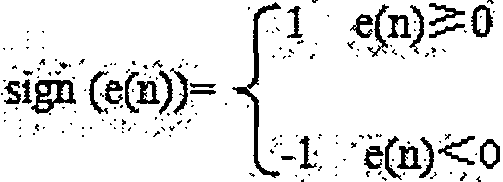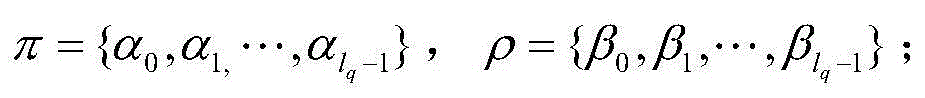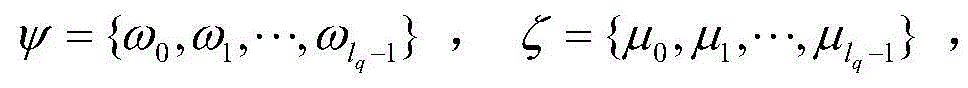Patents
Literature
44 results about "Multiplication operator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In operator theory, a multiplication operator is an operator Tf defined on some vector space of functions and whose value at a function φ is given by multiplication by a fixed function f. That is, Tfφ(x)=f(x)φ(x) for all φ in the domain of Tf, and all x in the domain of φ (which is the same as the domain of f). This type of operators is often contrasted with composition operators. Multiplication operators generalize the notion of operator given by a diagonal matrix.
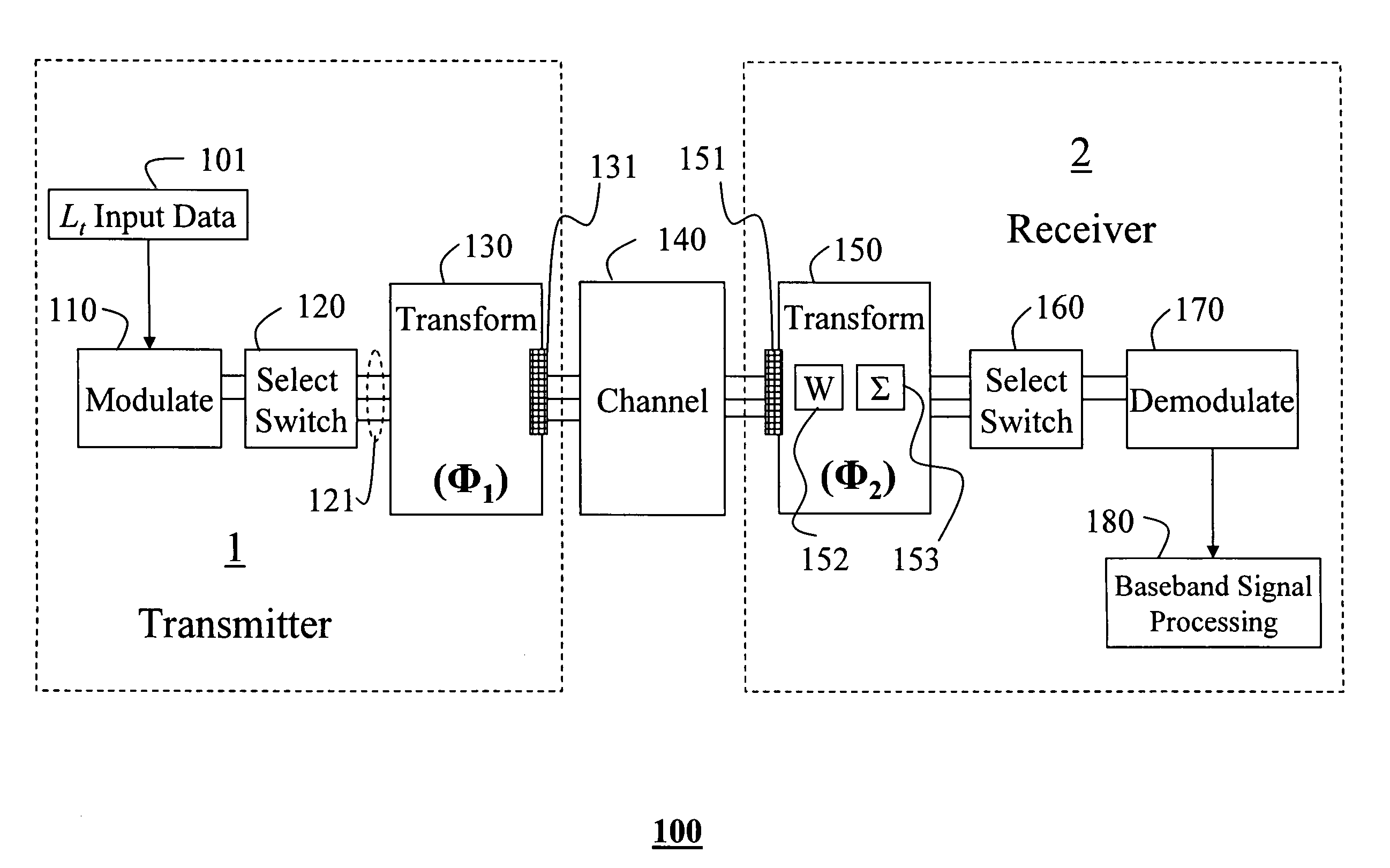
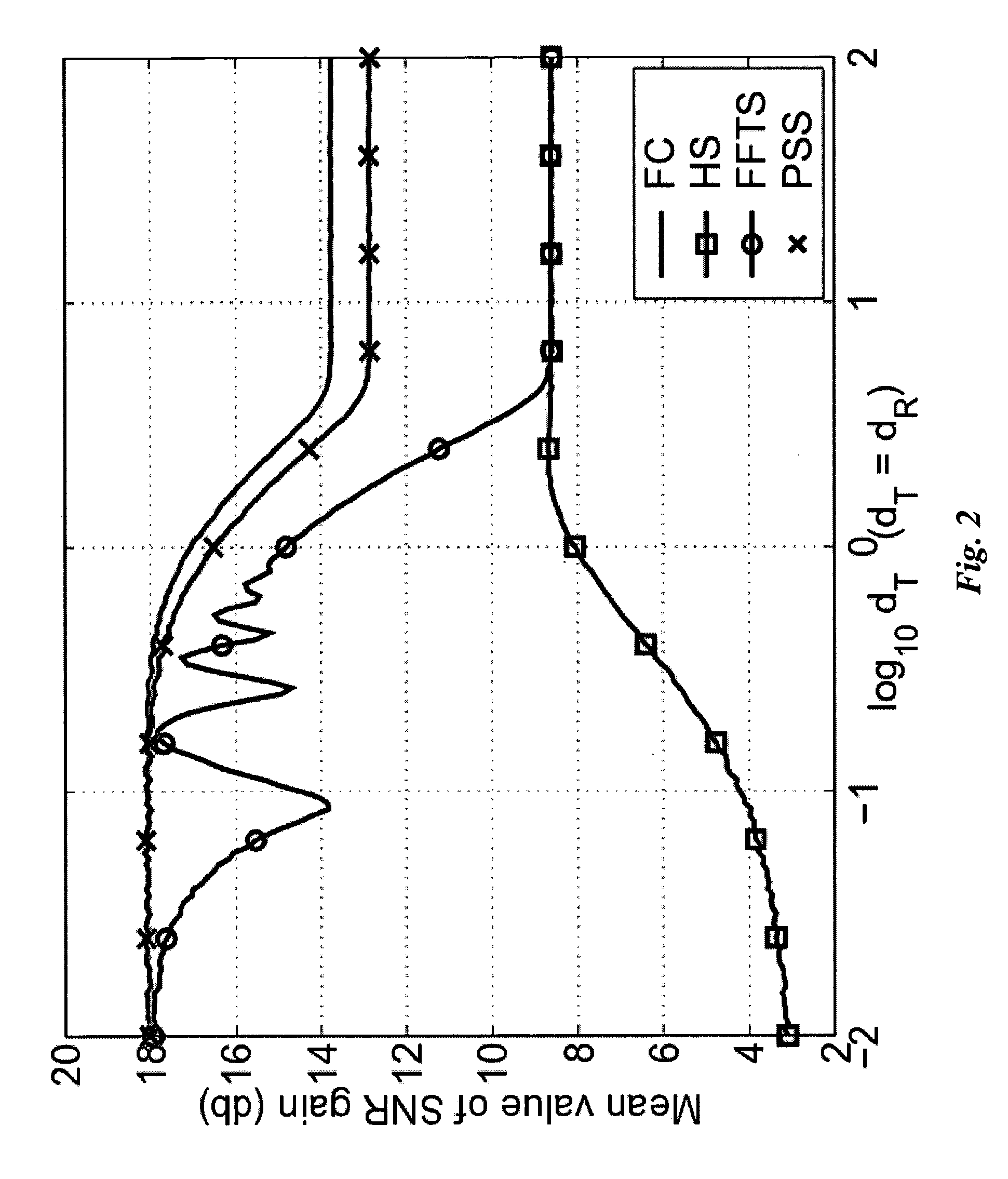
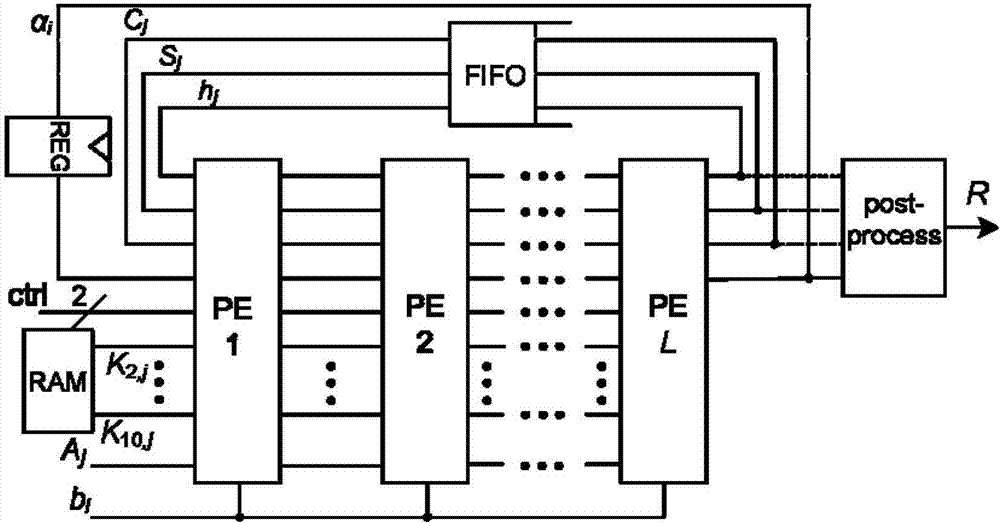
RF signal processing in multi-antenna systems
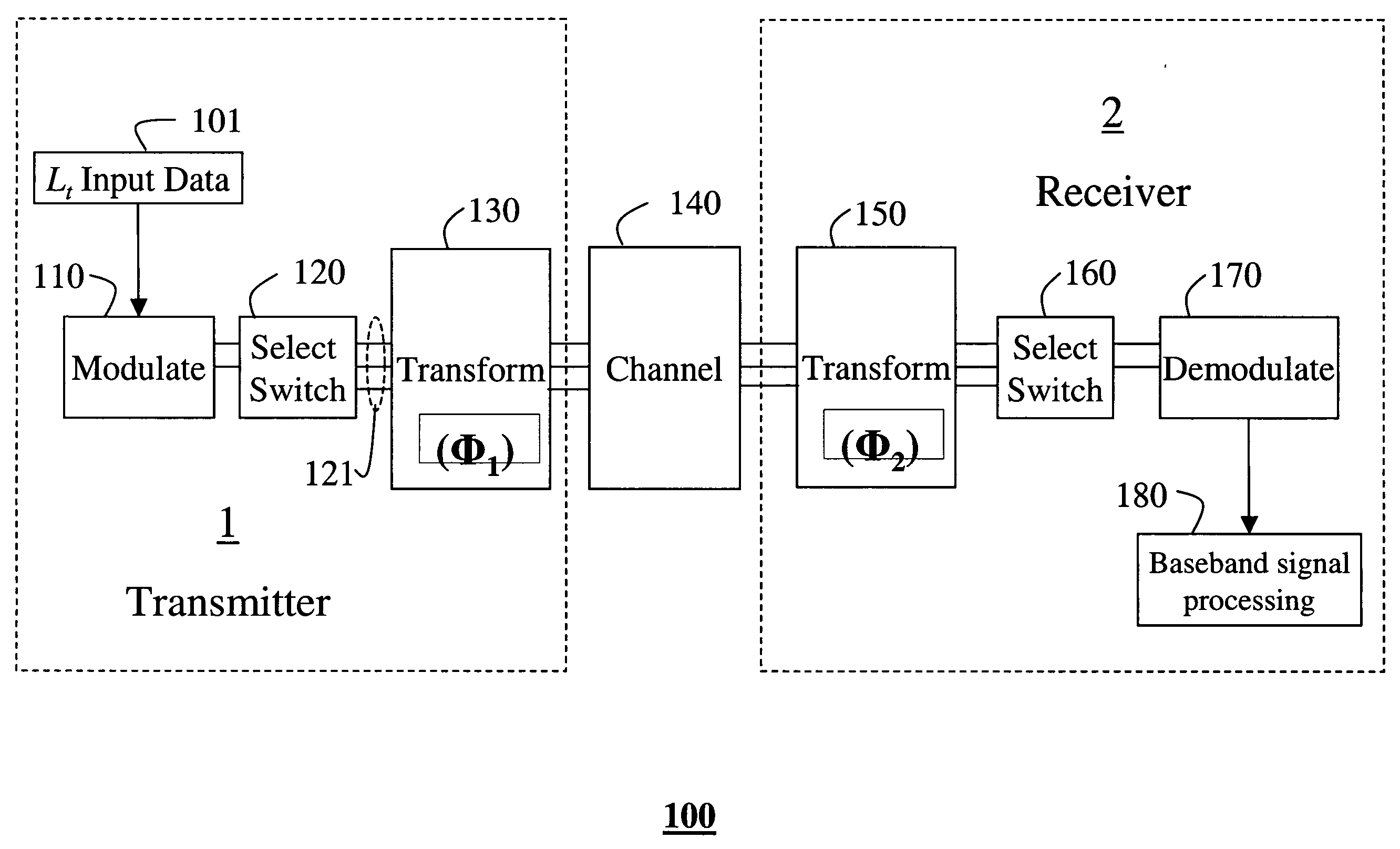
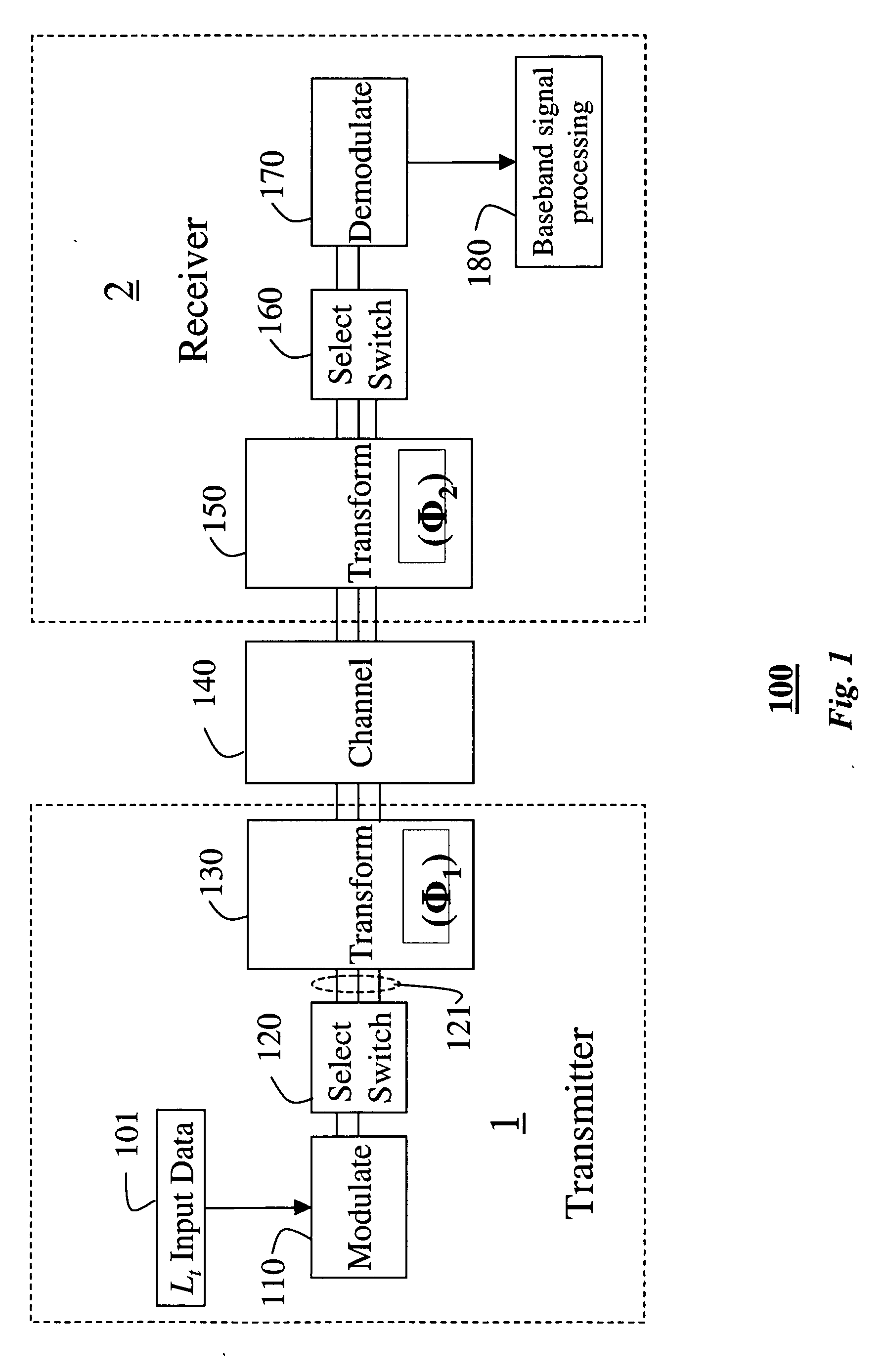
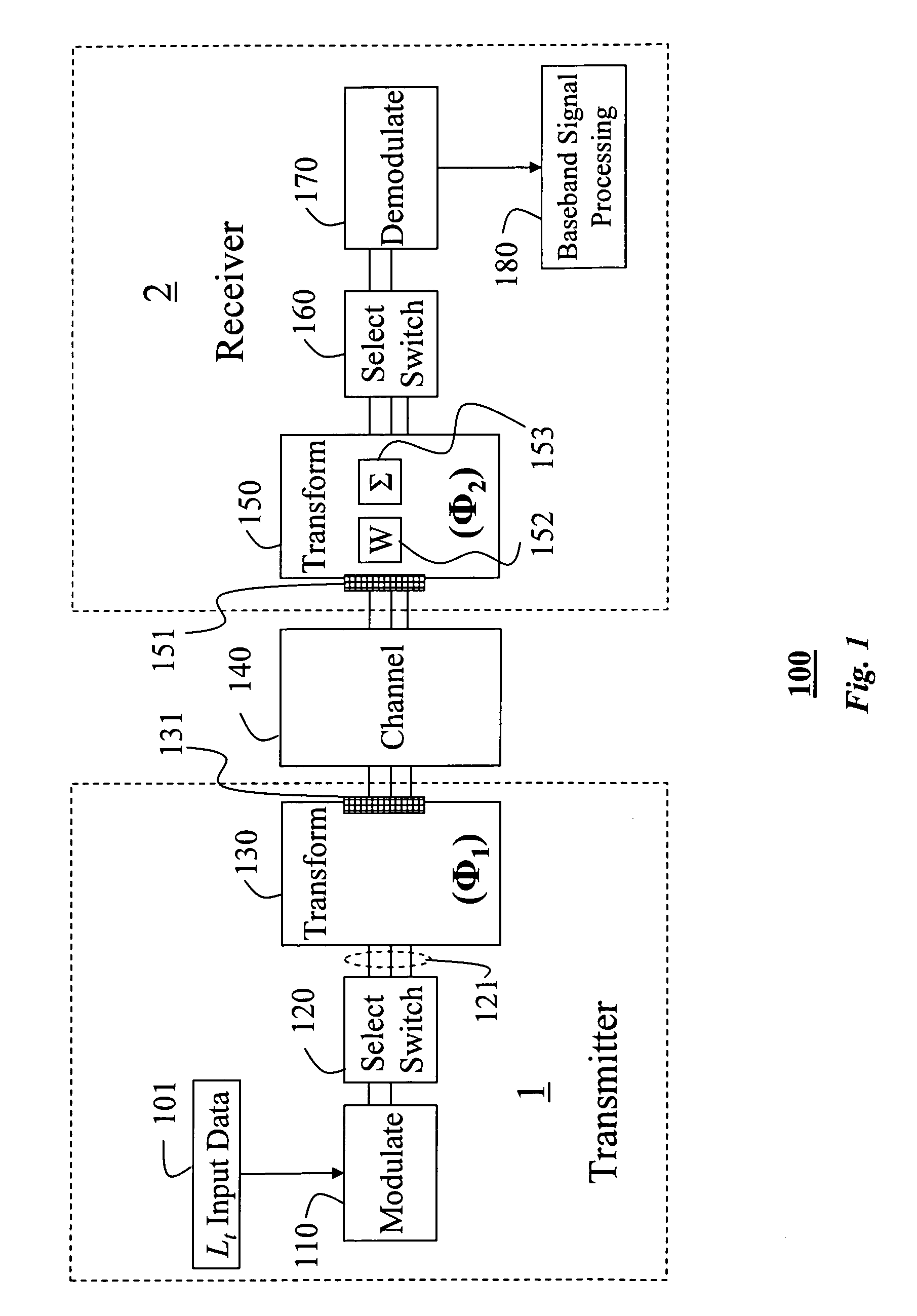
A method for antenna subset selection by joint processing in RF and baseband in a multi-antenna systems. Lt input data streams are generated in a transmitter for either diversity transmission or multiplexing transmission. These streams are modulated to RF signals. These signals are switched to the t branches associated with the t transmit antennas, and a phase-shift transformation is applied to the RF signals by a t×t matrix multiplication operator Φ1, whose output are t≧Lt RF signals. These signals are transmitted over a channel by t antennas. The transmitted signals are received by r antennas in a receiver. A phase-shift transformation is applied to the r RF signals by a r×r matrix multiplication operator Φ2. Lr branches of these phase shifted streams are demodulated and further processed in baseband to recover the input data streams.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION
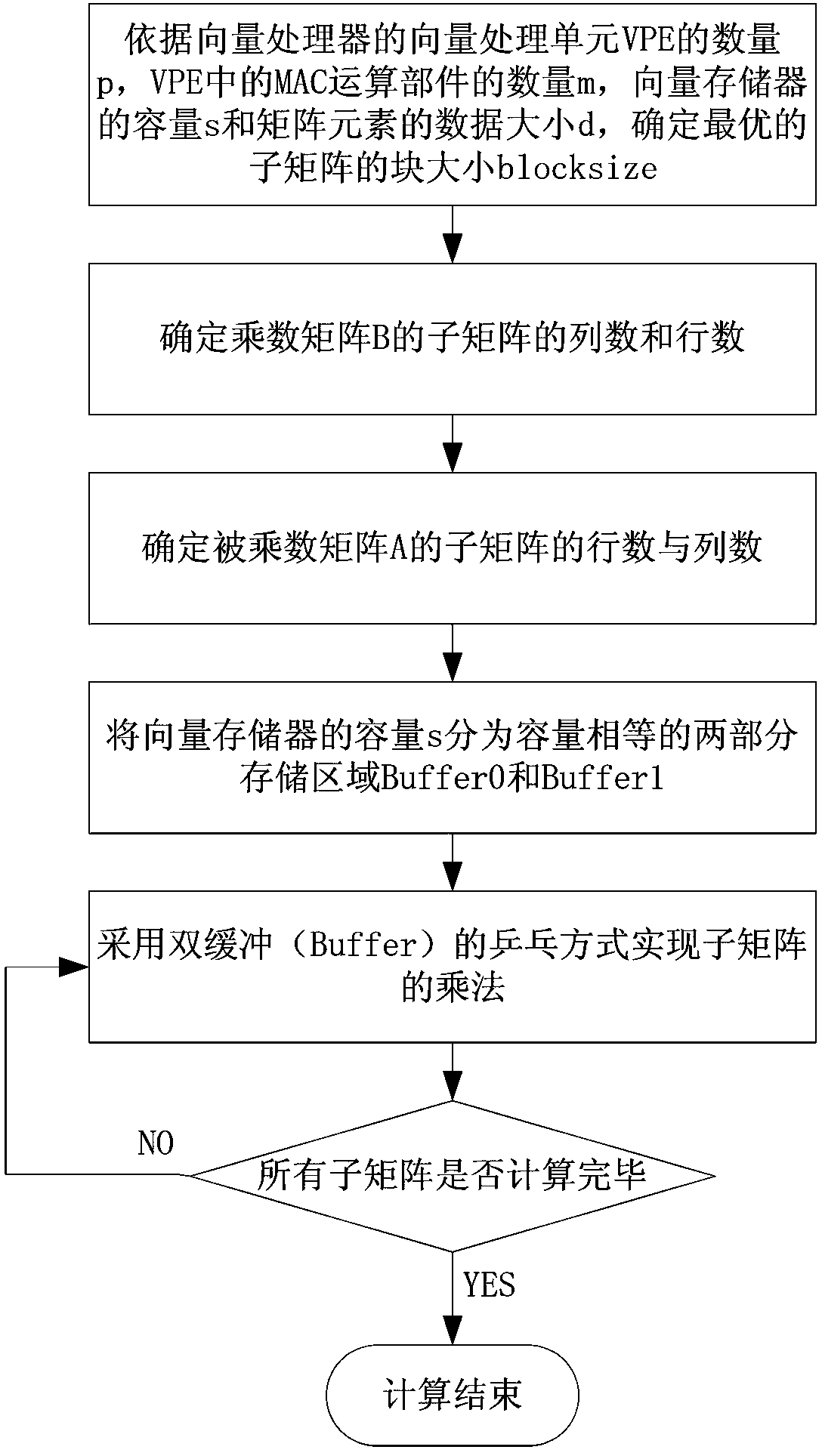
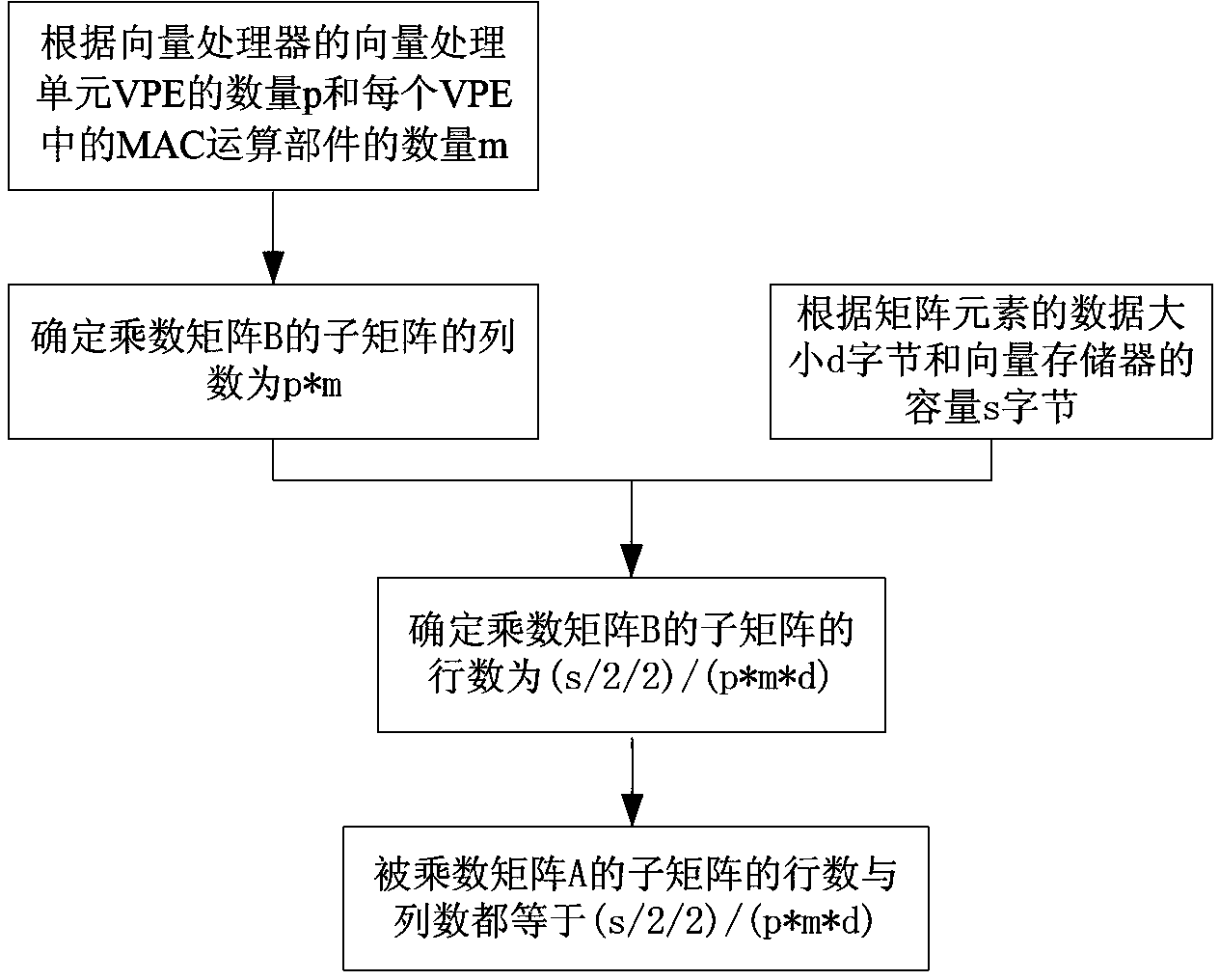
Block matrix multiplication vectorization method supporting vector processor with multiple MAC (multiply accumulate) operational units
ActiveCN103294648AImprove the computing memory access ratioImprove computing efficiencyComplex mathematical operationsProcessing elementMultiplication operator
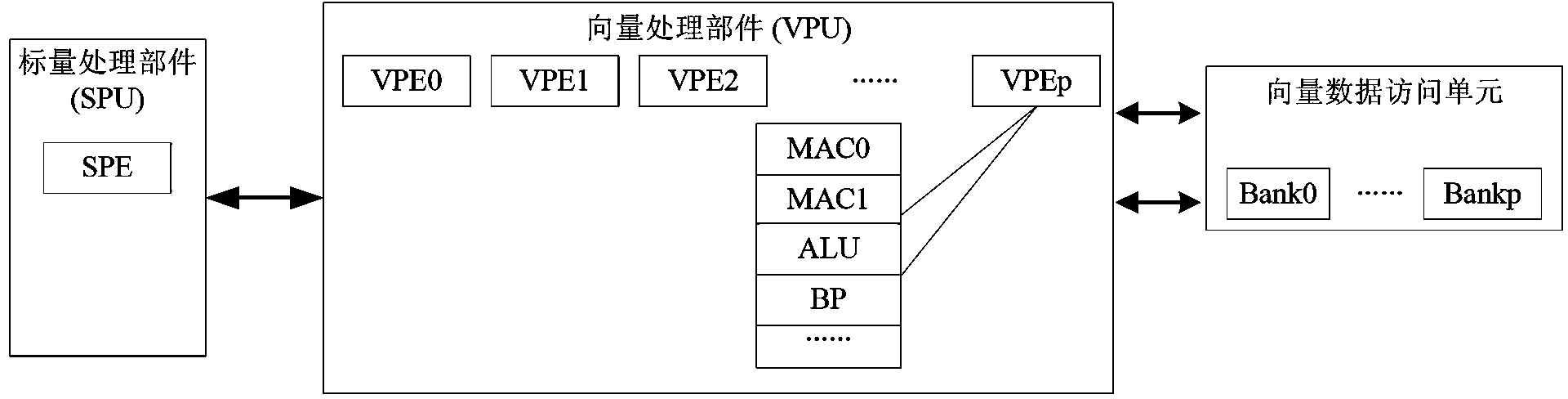
A block matrix multiplication vectorization method supporting a vector processor with multiple MAC (multiply accumulate) operational units includes the steps of (1), determining the optimum block size of submatrix, the quantity of lines and rows of the submatrix of a multiplier matrix B and the quantity of lines and rows of the submatrix of a multiplier matrix A according to the quantity p of vector processing elements (VPE) of the vector processor, the quantity m of the MAC operational units in the VPE, the capacity s of a vector memory and data size d of matrix elements, (2) equally dividing the capacity s of the vector memory into two storage areas of Buffer 0 and Buffer 1, and realizing multiplication of the submatrix in the Buffer 0 and the Buffer 1 in a Pingpong mode until completing the multiplication operation of the whole matrix. The block matrix multiplication vectorization method has the advantages of easiness in implementing, convenience in operation, capabilities of improving parallelism of the vector processor and increasing operation efficiency thereof, and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
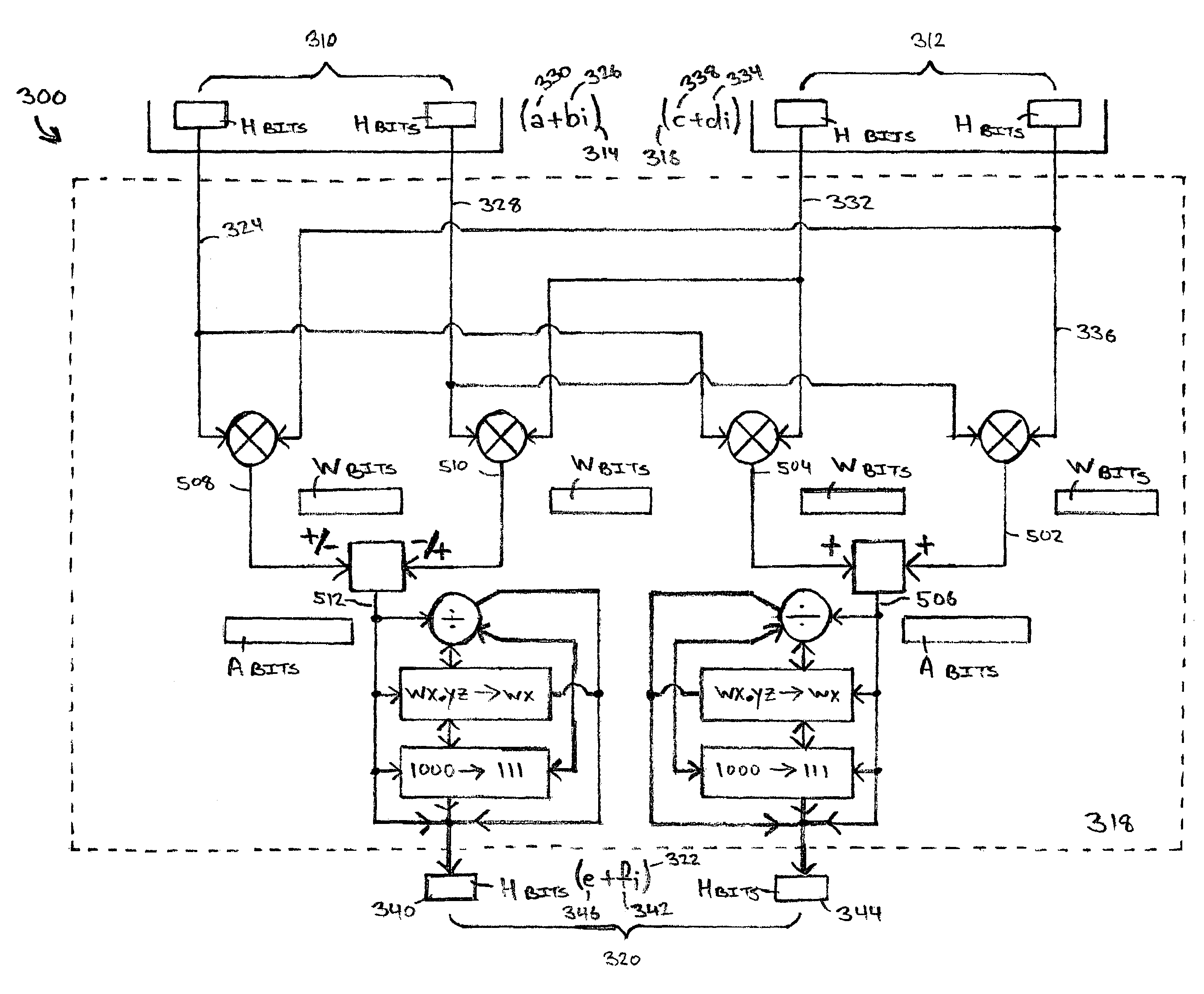
Systems for performing multiplication operations on operands representing complex numbers
InactiveUS7546329B2Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsExecution unitOperand
A method for multiplying, at an execution unit of a processor, two complex numbers in which all four scalar multiplications, concomitant to multiplying two complex numbers, can be performed in parallel. A real part of a first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by a real part of a second complex number to produce a first part of a real part of a third complex number. An imaginary part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by an imaginary part of the second complex number to produce a second part of the real part of the third complex number. A first arithmetic function is performed at the execution unit between the first part of the real part of the third complex number and the second part of the real part of the third complex number. The imaginary part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by the real part of the second complex number to produce a first part of an imaginary part of the third complex number. The real part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by the imaginary part of the second complex number to produce a second part of the imaginary part of the third complex number. A second arithmetic function is performed at the execution unit between the first part of the imaginary part of the third complex number and the second part of the imaginary part of the third complex number.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Fusion processing device and method for floating-point number multiplication-addition device
ActiveCN102339217ASimplify operation stepsSave resourcesDigital data processing detailsComputer moduleParallel computing
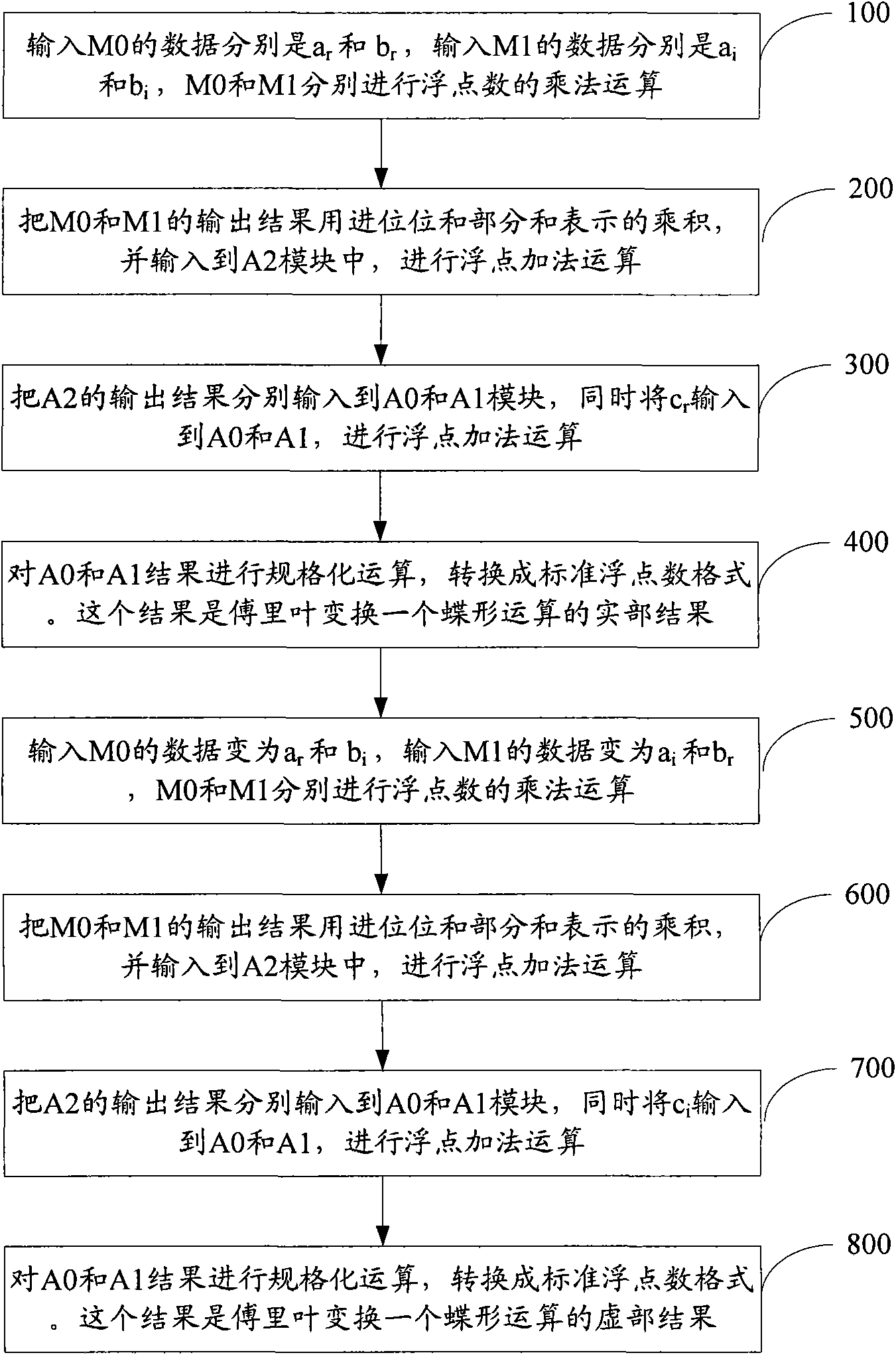
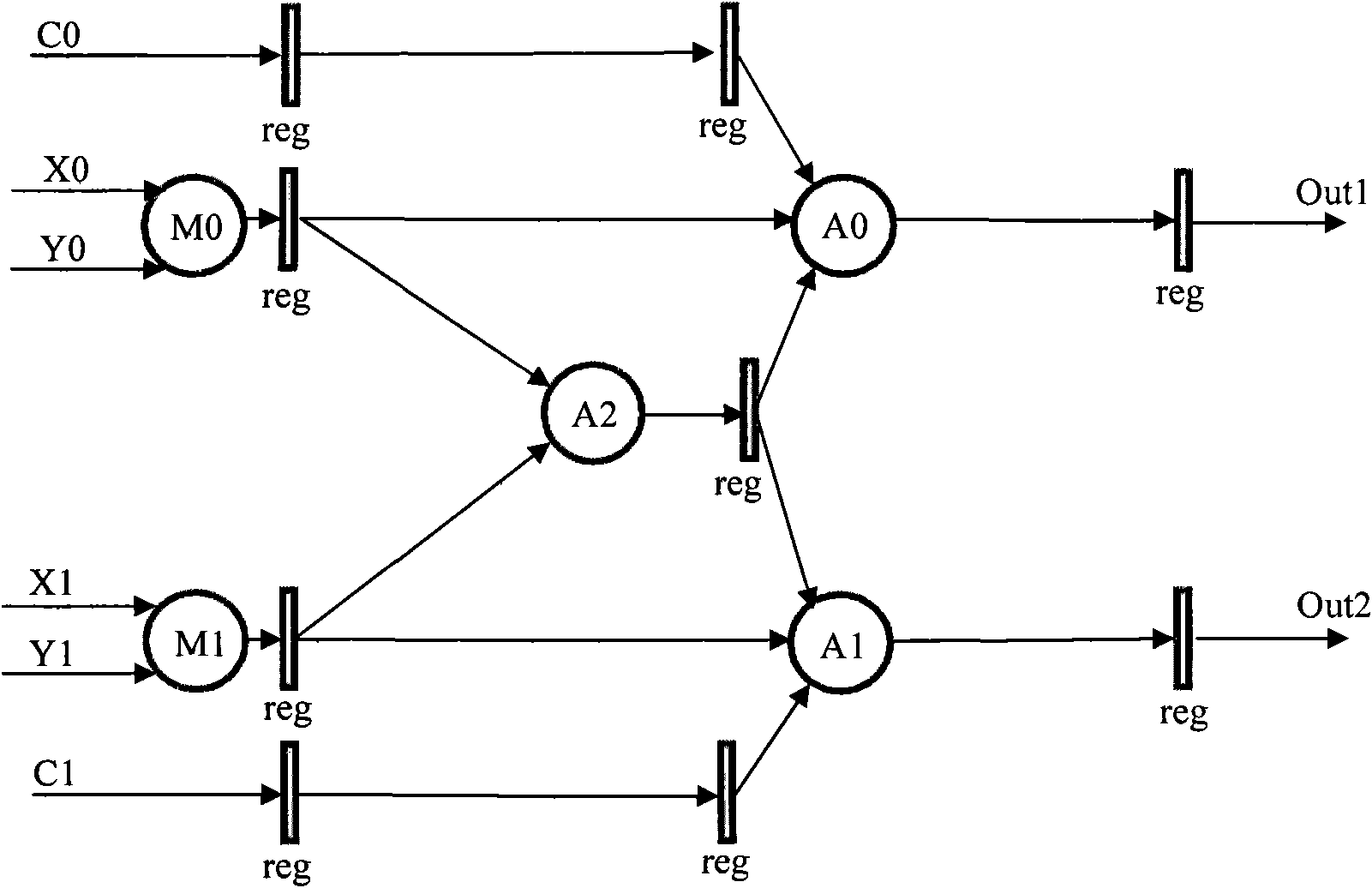
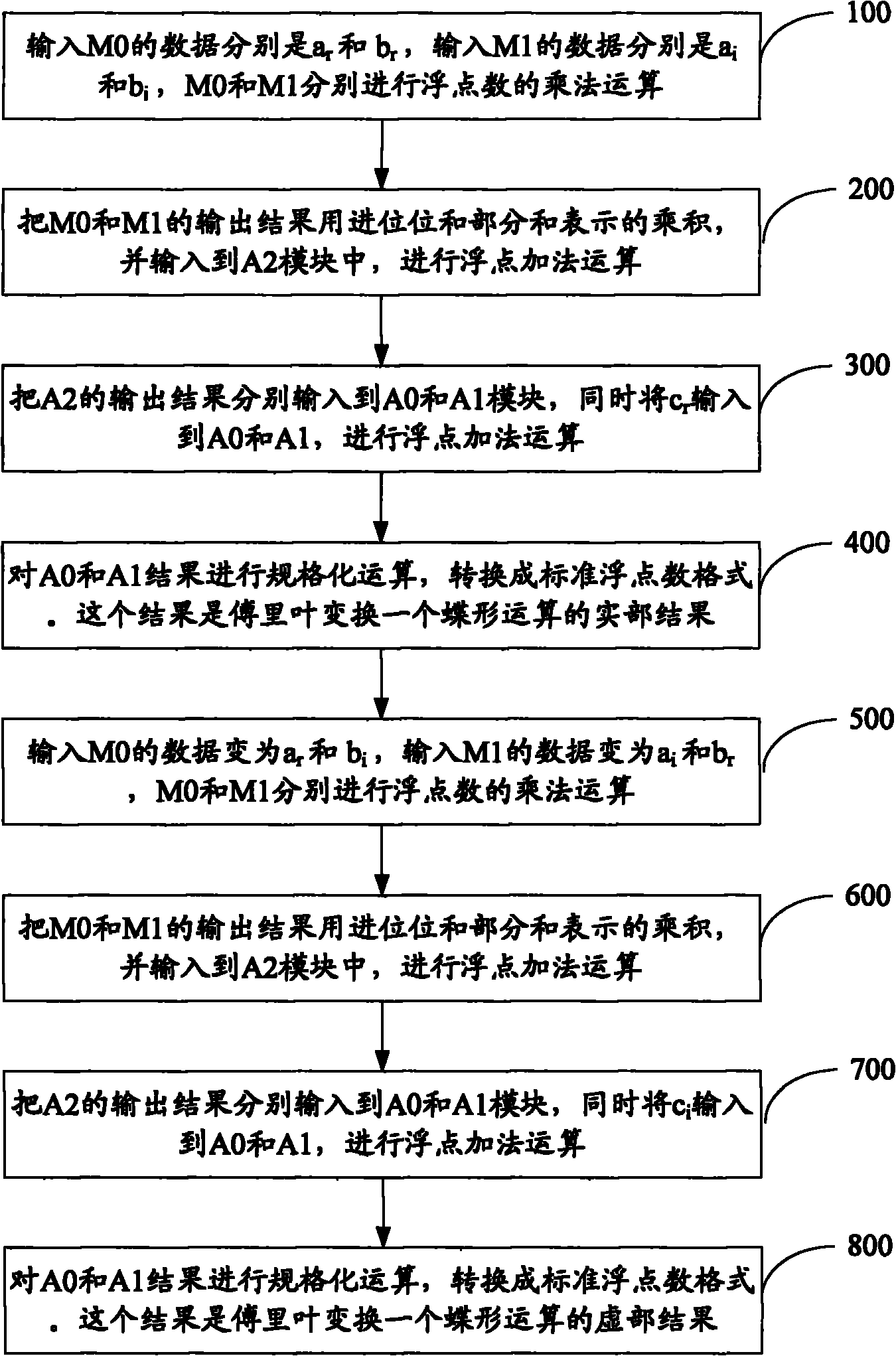
The invention provides a fusion processing device and a fusion processing method for a floating-point number multiplication-addition device. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting real parts and imaginary parts of a multiplier and a multiplicand of a floating point complex number into floating-point multiplication modules M0 and M1, and performing floating-point multiplication operation, wherein output results present products by using a carry bit and a partial sum; inputting the products into a floating-point addition module A2, and performing floating-point addition operation, wherein the output results present addition operation by using the carry bit and the partial sum; inputting the output results which present the addition operation into floating-point addition modules A0 and A1 simultaneously; inputting addends input from the outside into the floating-point addition modules A0 and A1, and performing floating-point addition operation; and outputting operation results. The device and the method can be better applied to butterfly computation of Fourier transform; and by the device and the method, operation steps can be simplified, hardware resources are easy to save, and the multiplication-addition operation of the floating point complex number is realized by less resources.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
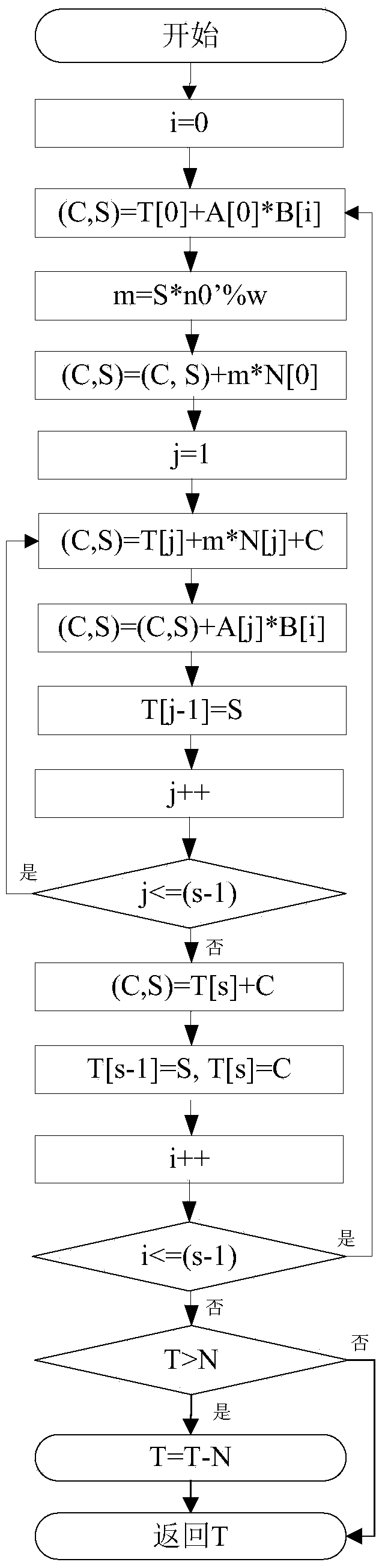
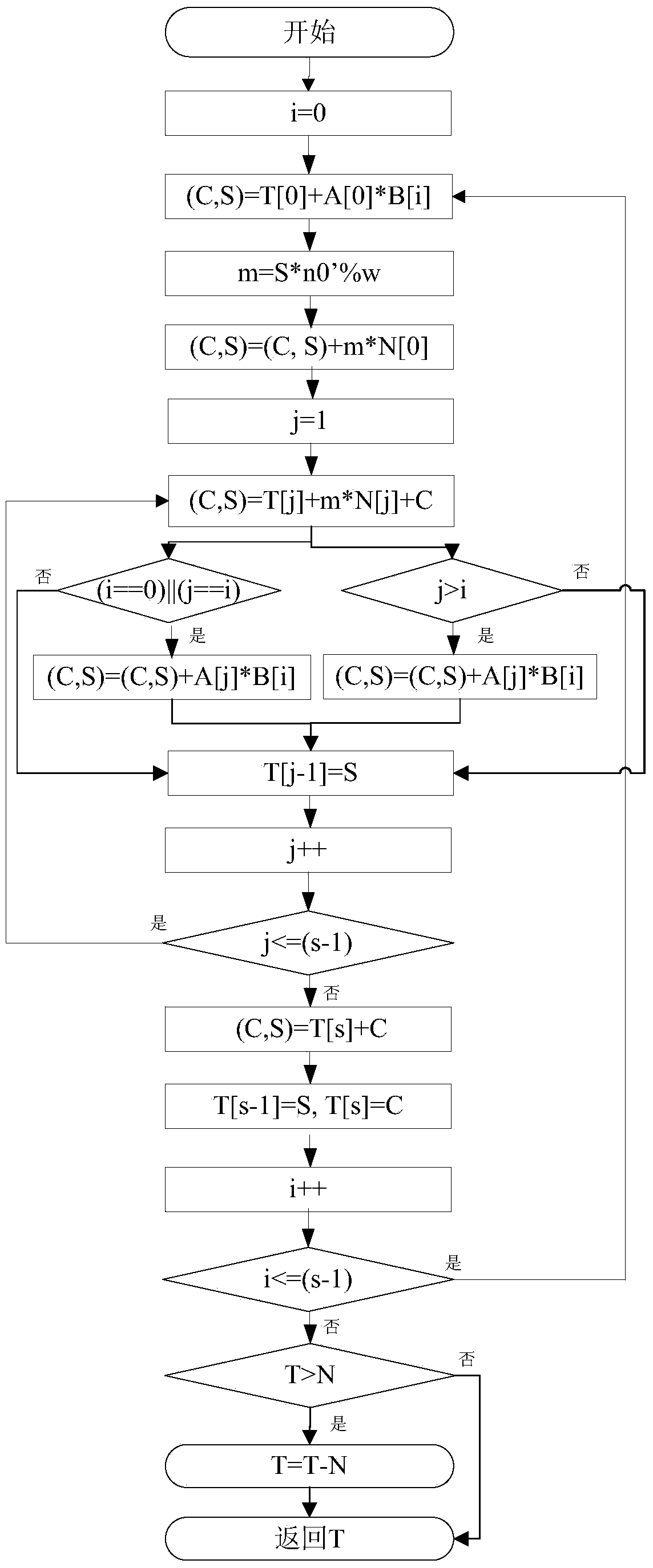
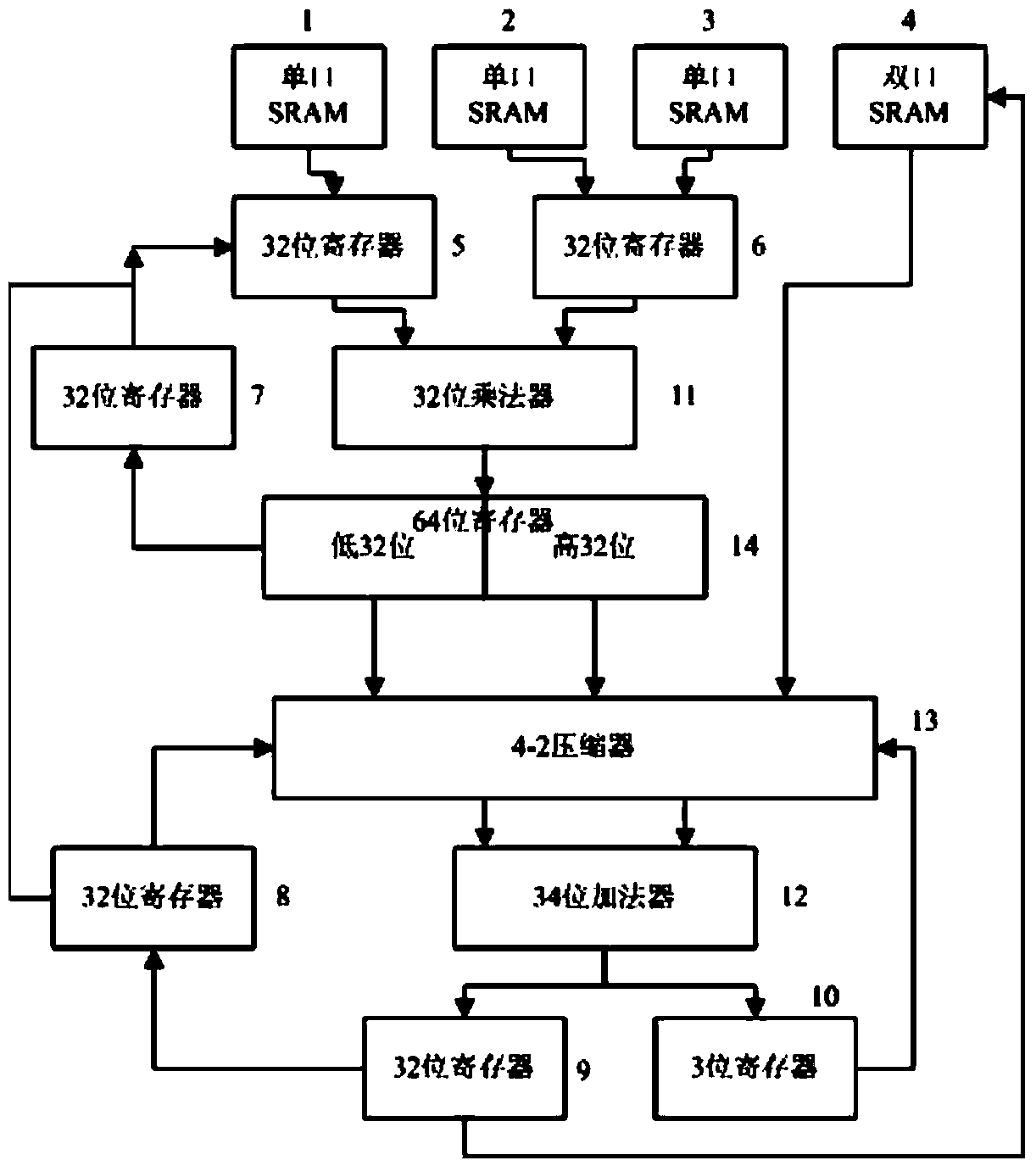
Optimized Montgomery modular multiplication method, optimized modular square method and optimized modular multiplication hardware
InactiveCN103761068AImprove computing powerReduce areaComputations using residue arithmeticBinary multiplierProcessor register
The invention discloses an optimized Montgomery modular multiplication method, an optimized modular square method and optimized modular multiplication hardware. The optimization is carried out based on an original FIOS (Finely integrated operand scanning) algorithm. The optimized modular multiplication hardware mainly comprises three single-port SRAMs, a double-port SRAM, a 32-bit multiplier, a 34-bit adder, a 4-2 compressor, a 64-bit register and six 32-bit registers. According to the optimized Montgomery modular multiplication method, the optimized modular square method and the optimized modular multiplication hardware, a high-radix modular multiplier of a two-stage parallel assembly line is adopted, the AB operation is completed through a first-stage 32-bit multiplier, the T+AB+C operation is completed through a second-stage adder, the 32-2048-bit modular multiplication operation is achieved, the area of a chip is reduced, and the modular multiplication operation performance is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
RF signal processing in multi-antenna systems
A method for antenna subset selection by joint processing in RF and baseband in a multi-antenna systems. Lt input data streams are generated in a transmitter for either diversity transmission or multiplexing transmission. These streams are modulated to RF signals. These signals are switched to the t branches associated with the t transmit antennas, and a phase-shift transformation is applied to the RF signals by a t×t matrix multiplication operator Φ1, whose output are t≧Lt RF signals. These signals are transmitted over a channel by t antennas. The transmitted signals are received by r antennas in a receiver. A phase-shift transformation is applied to the r RF signals by a r×r matrix multiplication operator Φ2. Lr branches of these phase shifted streams are demodulated and further processed in baseband to recover the input data streams.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION
Matrix operation-based parallel computing method
InactiveCN101980182AReduce difficultyParallelism no longer needs to be discovered and minedComplex mathematical operationsParallel algorithmMultiplication operator
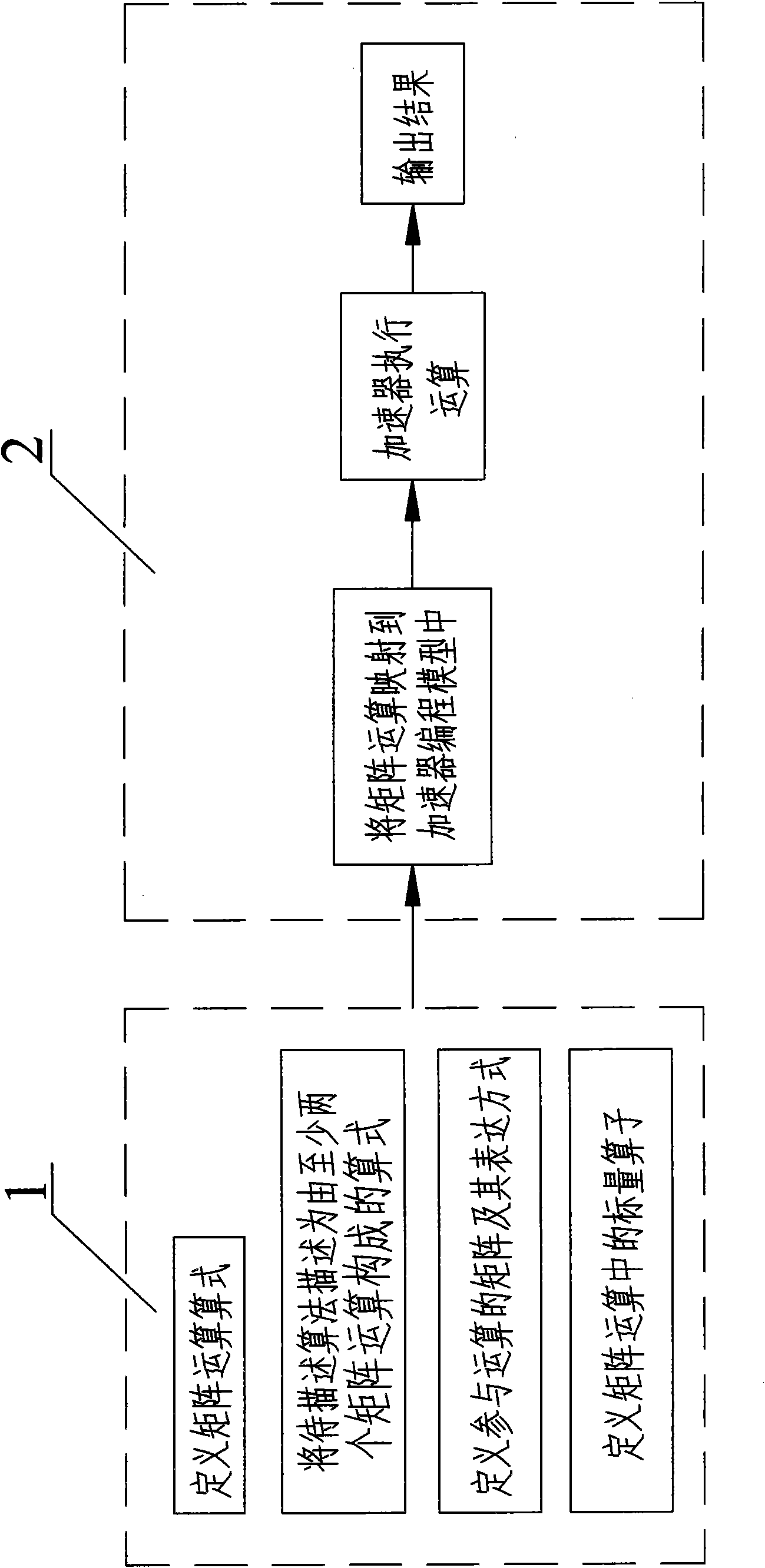
The invention discloses a matrix operation-based parallel computing method, which is mainly designed for simplifying a parallel acceleration program and reducing the realizing difficulty of a parallel algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of: describing an algorithm to be described as a matrix operation formula; abstracting a computing task as an abstracted multiplication operator and / or an abstracted addition operator among all matrixes with certain element types; mapping the matrix operation into an accelerator programming model; and executing the operation and outputting a result by using an accelerator. The method describes the parallelism of the algorithm by using a matrix operation rule so as to reduce the difficulty in describing the parallel algorithm. Meanwhile, the parallel algorithm is realized on the base of the generalized matrix operation, the characteristics of a specific algorithm can be eliminated as many as possible, the mapping of more general parallel algorithm to the accelerator is realized, and scheduling software can be designed according to the common matrix operation, so that the software can be more generally suitable for various algorithms, repetitive work for developing accelerator scheduling codes is reduced and a development process is simplified.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Key anti-power attack method
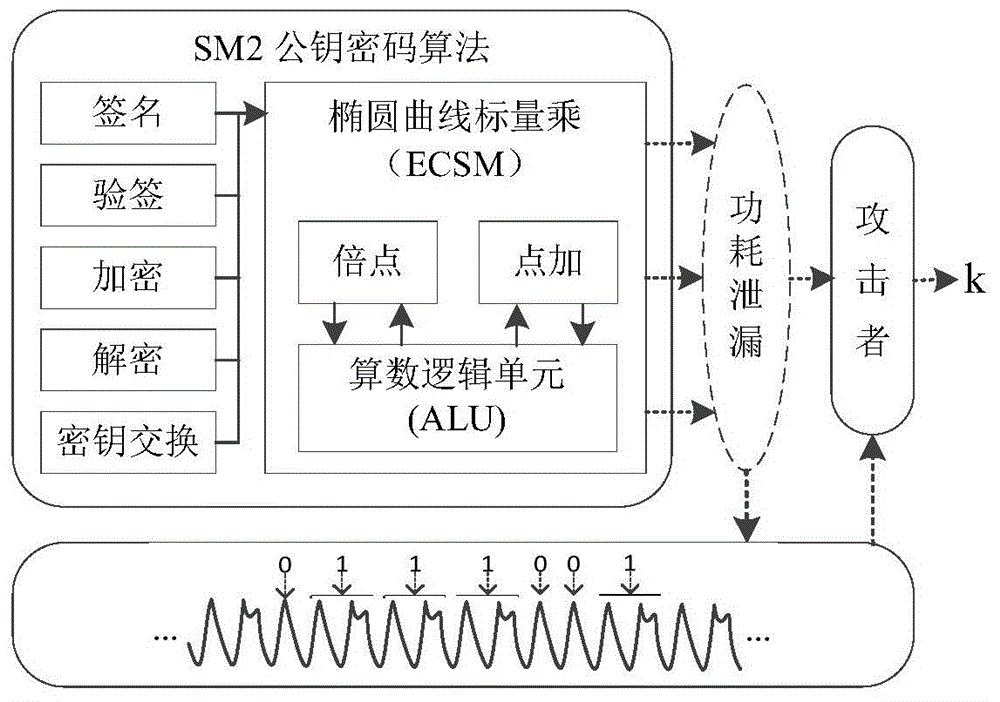
ActiveCN104917608AEasy to operateReduce computationKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareInner loop
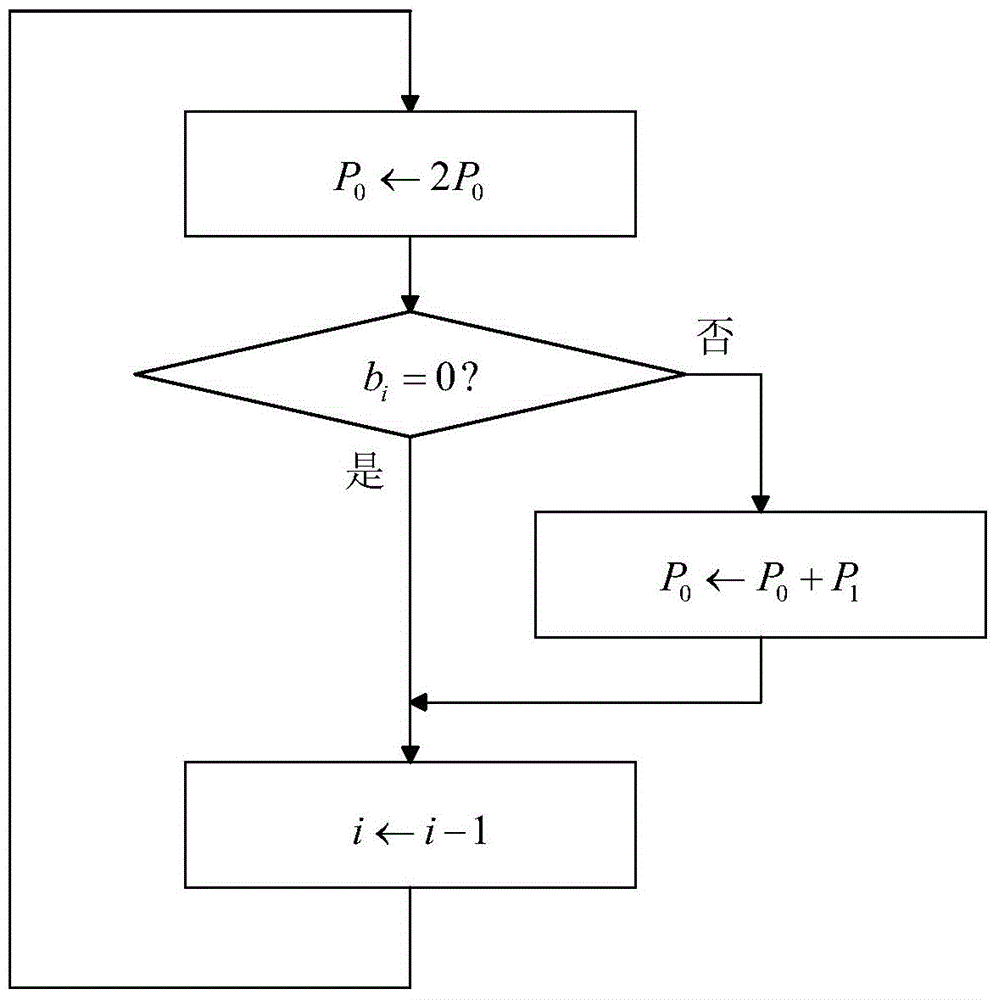
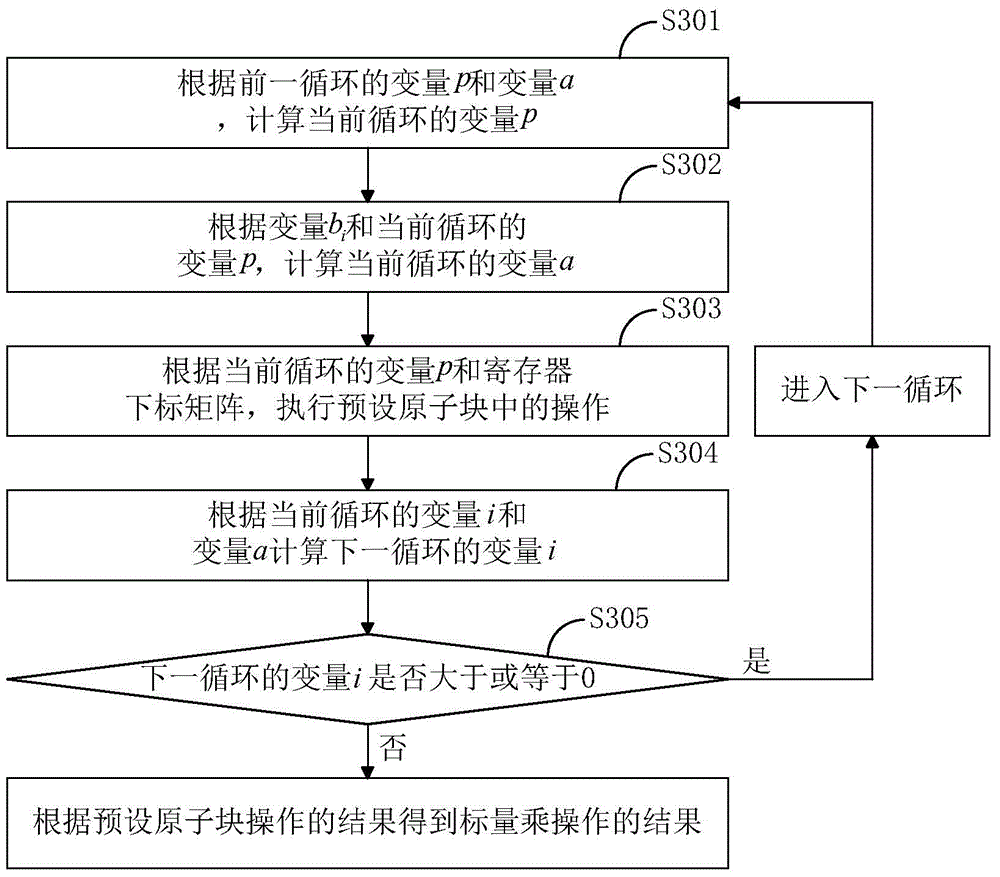
The invention discloses a key anti-power attack method. The method includes the step that a preset atomic block is utilized to perform point multiplying and / or point adding operation in scalar multiplication, wherein the preset atomic block contains modular multiplication operation, addition operation and subtraction operation. According to the method, the concept of the atomic algorithm is combined with the characteristics of a public key cryptographic algorithm, and therefore, the procedures of point adding operation and point multiplying operation can be optimized; an corresponding variables are adopted to control the internal loop of the scalar multiplication, and the scalar multiplication is converted to a modular multiplication-addition-subtraction atomic block loop. With the method of the invention adopted, computation burden required by the scalar multiplication can be greatly decreased, and the security of keys can be ensured, and the computation speed of the public key cryptographic algorithm can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
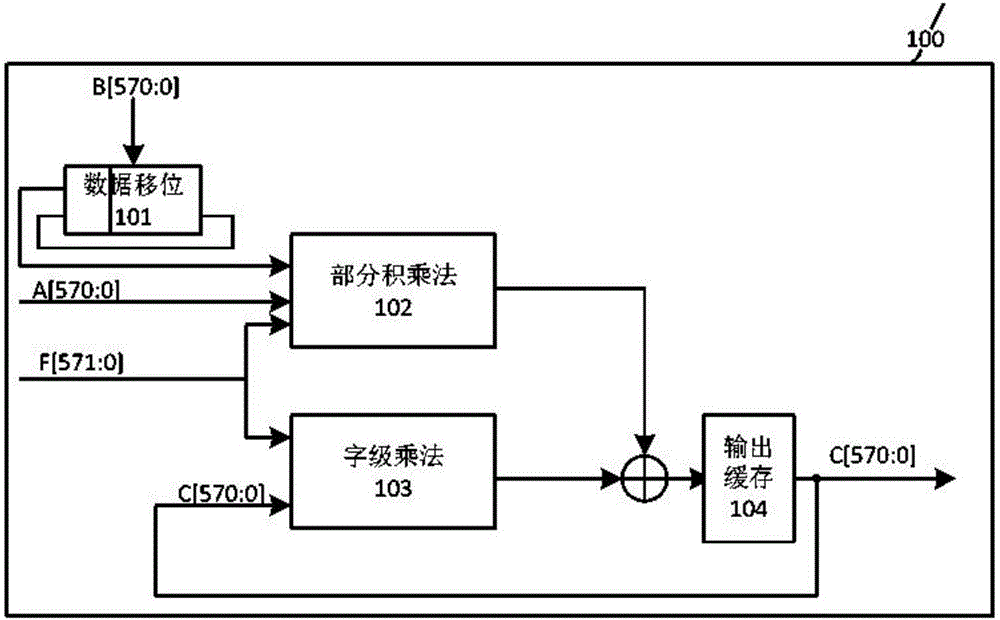
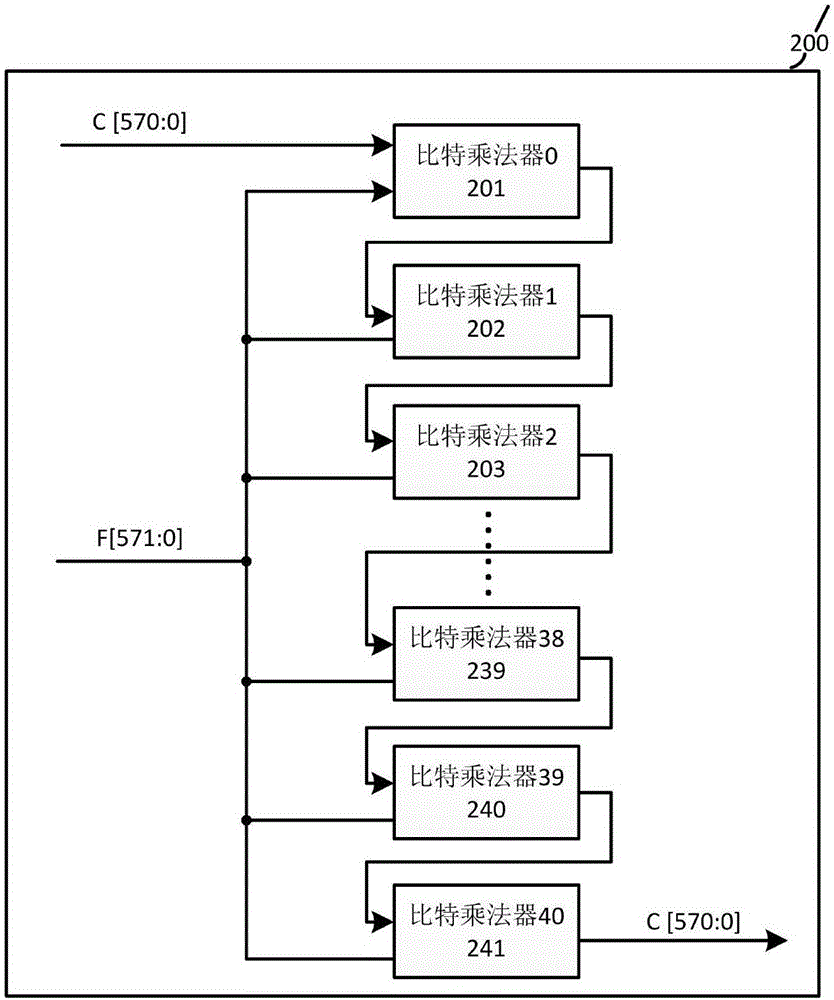
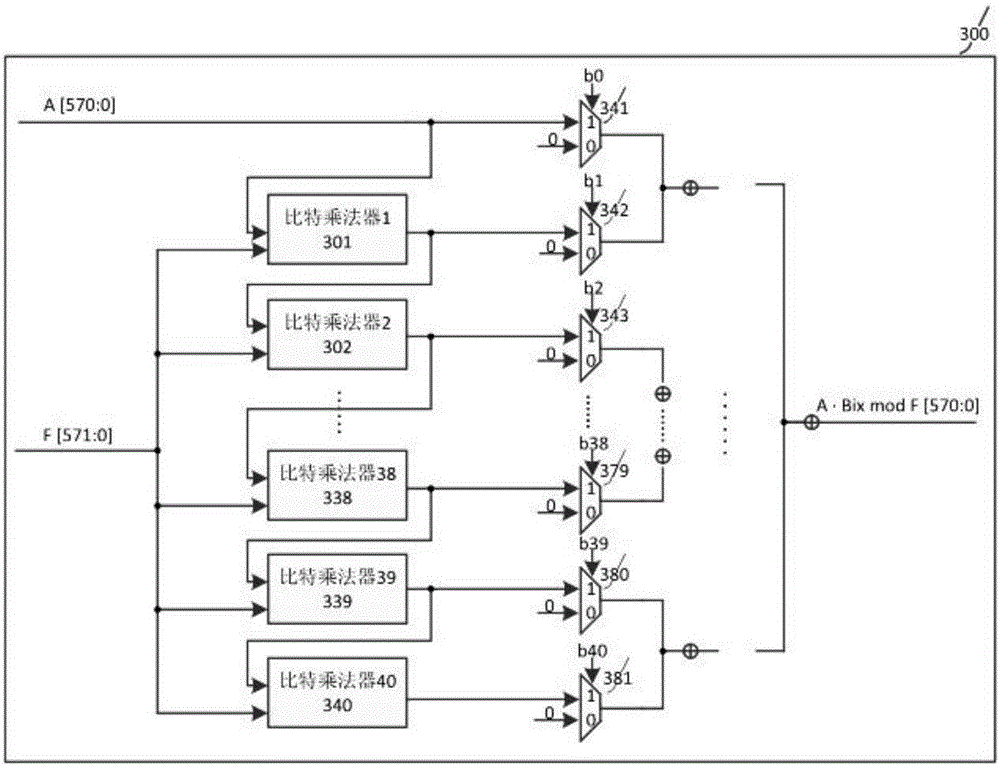
Binary field bit-width-variable modular multiplication operator
ActiveCN106484366AImprove applicabilityMeet different bit width requirementsComputations using residue arithmeticHardware structureStep number
The invention discloses a modular multiplication operator implemented by a series-parallel combination way, and belongs to the field of elliptic curve cryptography algorithms. The binary field bit-width-variable modular multiplication operator comprises a partial product multiplication unit, a word level multiplication unit, an output cache unit, a data shifting unit and a control unit. The modular multiplication operator is based on a polynomial basis under a binary field; input data are read in an MSB-first (Most Significant Bit first) way; the step number of loop computing is controlled according to computing digits by a state machine; a word multiplication operation and a partial multiplication operation are performed concurrently in the steps; and lastly, computing results in all the steps are integrated, and output in series. The operating rate is increased in the series-parallel combination way, and the computing complexity is lowered. Meanwhile, a bit multiplier capable of computing data of a plurality of bit widths is designed internally, so that reutilization of a hardware structure is realized. Compared with the prior art, the modular multiplication operator is more advantageous on the aspects of area, flexibility and the like, and a relatively high operation rate is ensured at the same time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
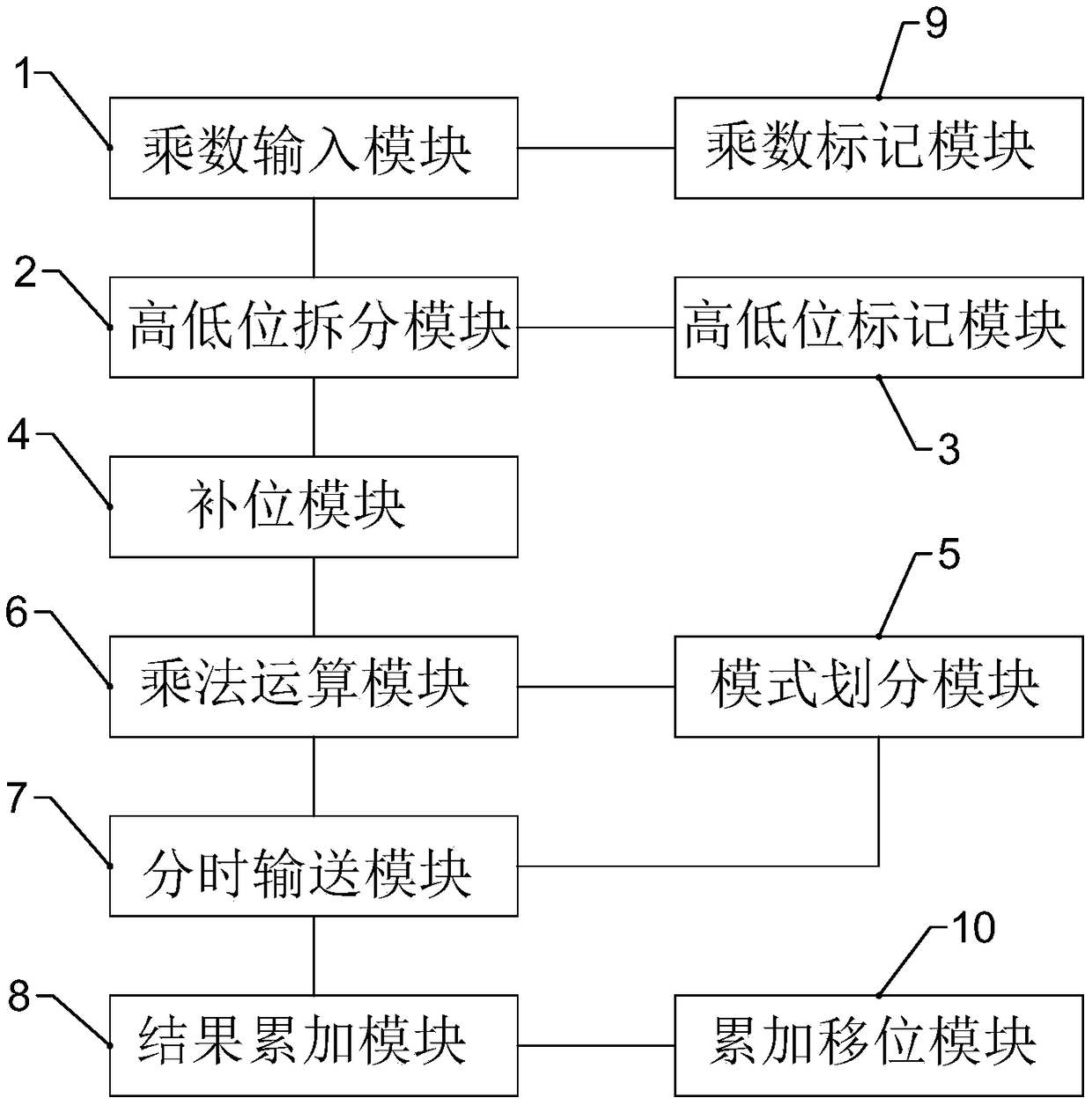
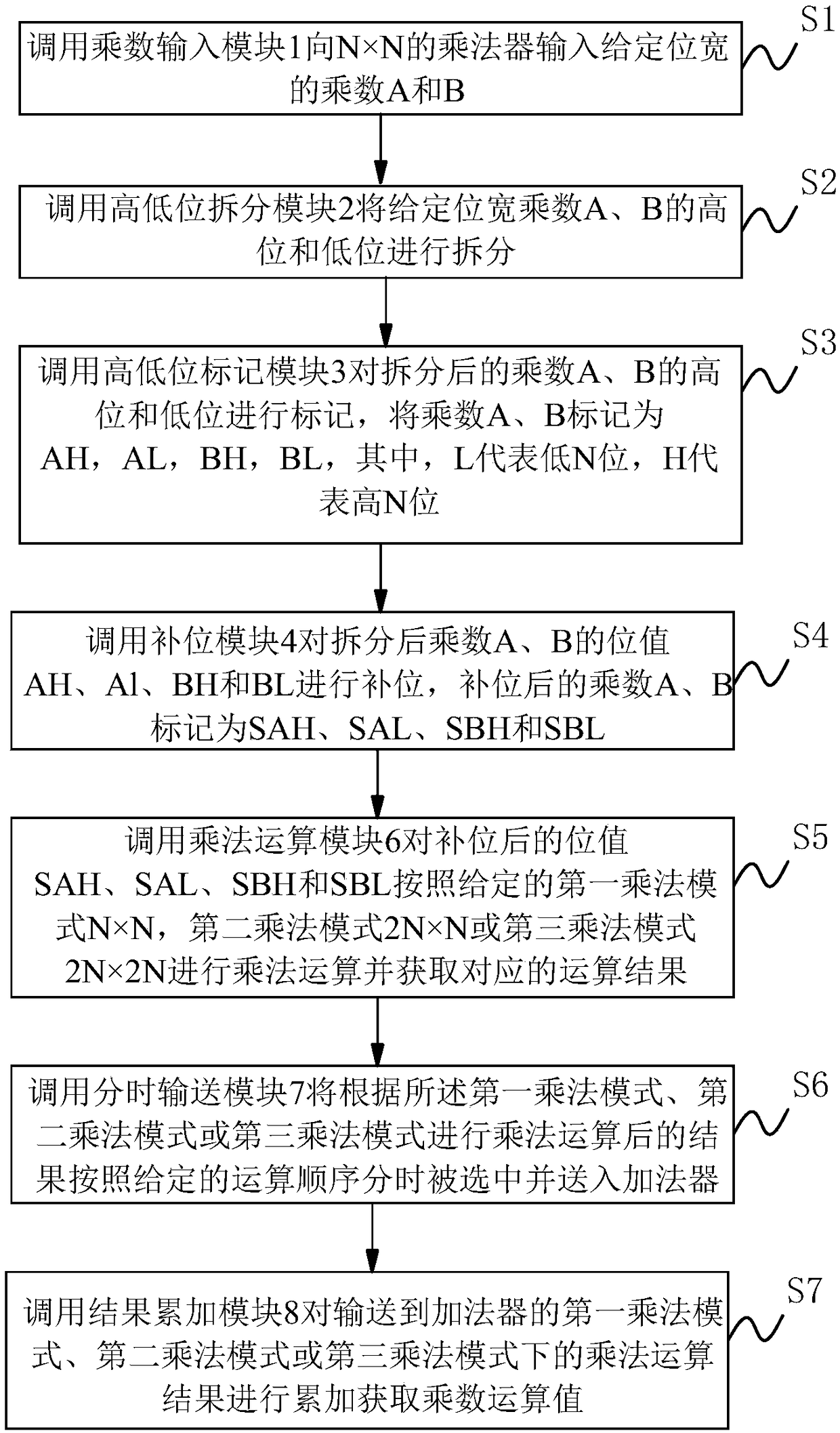
A multiplication device and method
InactiveCN109284083AImplementation supportReduce complexityDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareBinary multiplier
The invention discloses a multiplication device and a multiplication method. A multiplier input module is called to input a multiplier with wide positioning to a multiplier. A high and low bits of thepositioning wide multiplier are split by calling the high and low bits splitting module. A complement module is called to complement the bit value after splitting; a multiplication module is called to perform multiplication operation on the bit value after complementing according to the given multiplication mode, and the operation result corresponding to the multiplication mode is obtained. A time-sharing transport module selects results obtained through multiplication according to a first multiplication mode, a second multiplication mode and a third multiplication mode in a time-share manneraccording to a given sequence and sends to an adder. A result accumulating module is called to accumulate the multiplication result sent to the adder to obtain the multiplier operation value. The invention realizes the support of the low bit width multiplier to the high bit width operation through the time expansion, solves the problem of completing the multiplication operation of the large bit width multiplier through the multiplier with less bit width, and reduces the complexity of the multiplication operation.
Owner:北京探境科技有限公司
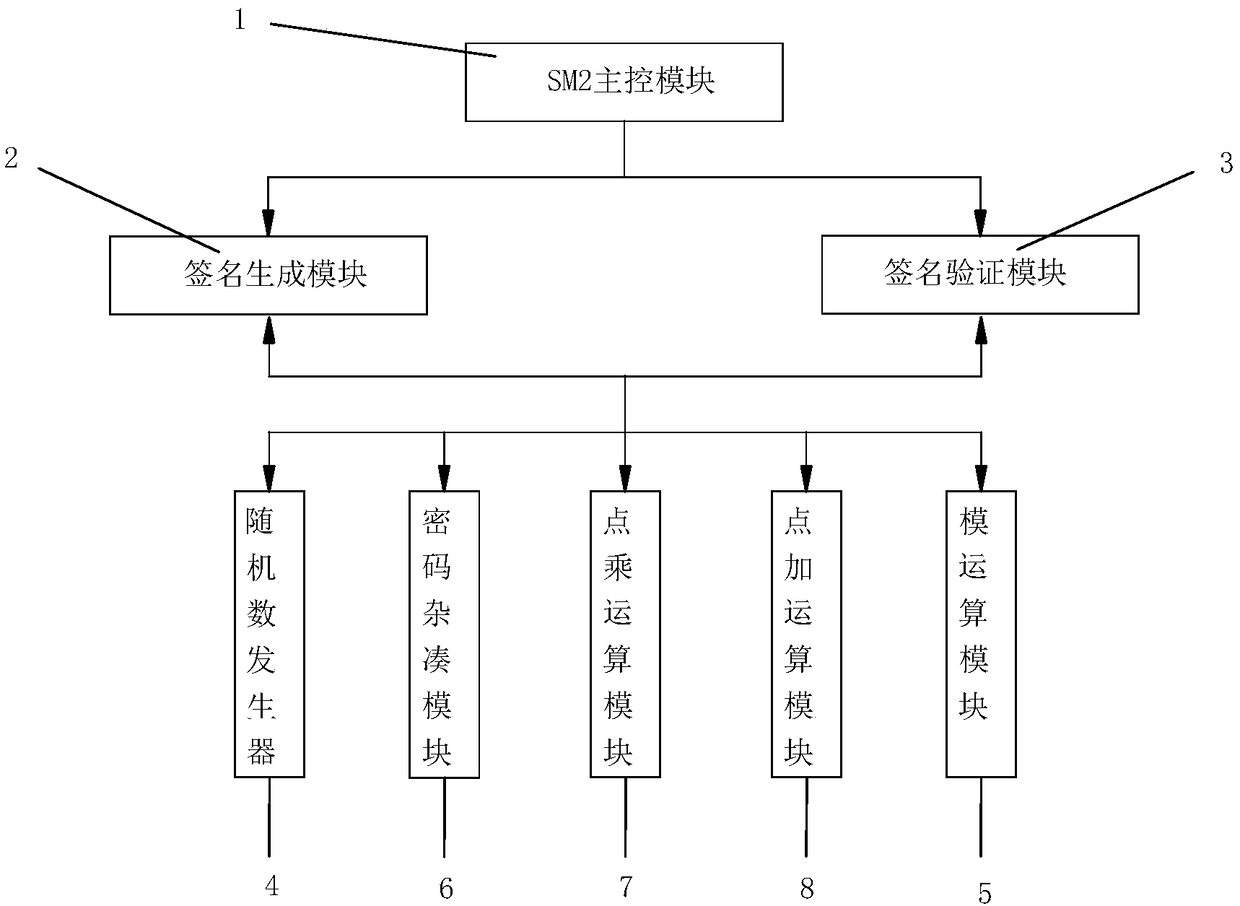
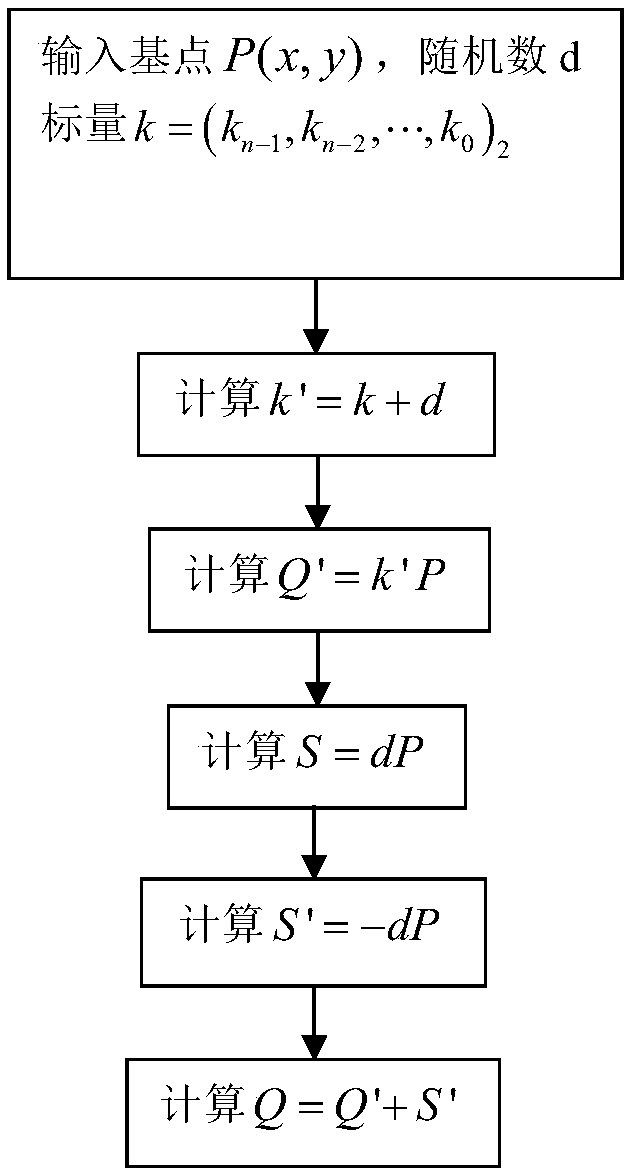
An SM2 elliptic curve signature verification hardware system and method resistant to differential power consumption attack
InactiveCN109214195AEnsure safetyGood anti-differential power attackDigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionRandomizationPower attack
The invention relates to an SM2 elliptic curve signature verification hardware system and method for resisting differential power consumption attack, the anti-differential power consumption attack method of the invention is applied to scalar multiplication, by adding the improved randomized scalar method to the point multiplication operation, the correlation between the real key information and the power curve is destroyed, which makes it difficult for the power analysis to obtain the information to resist the power analysis, and ensures the security of the differential power attack, thus playing a very good role in resisting the differential power attack. And this method is simple and easy to implement, and can be integrated into a variety of encryption chips and other hardware devices.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
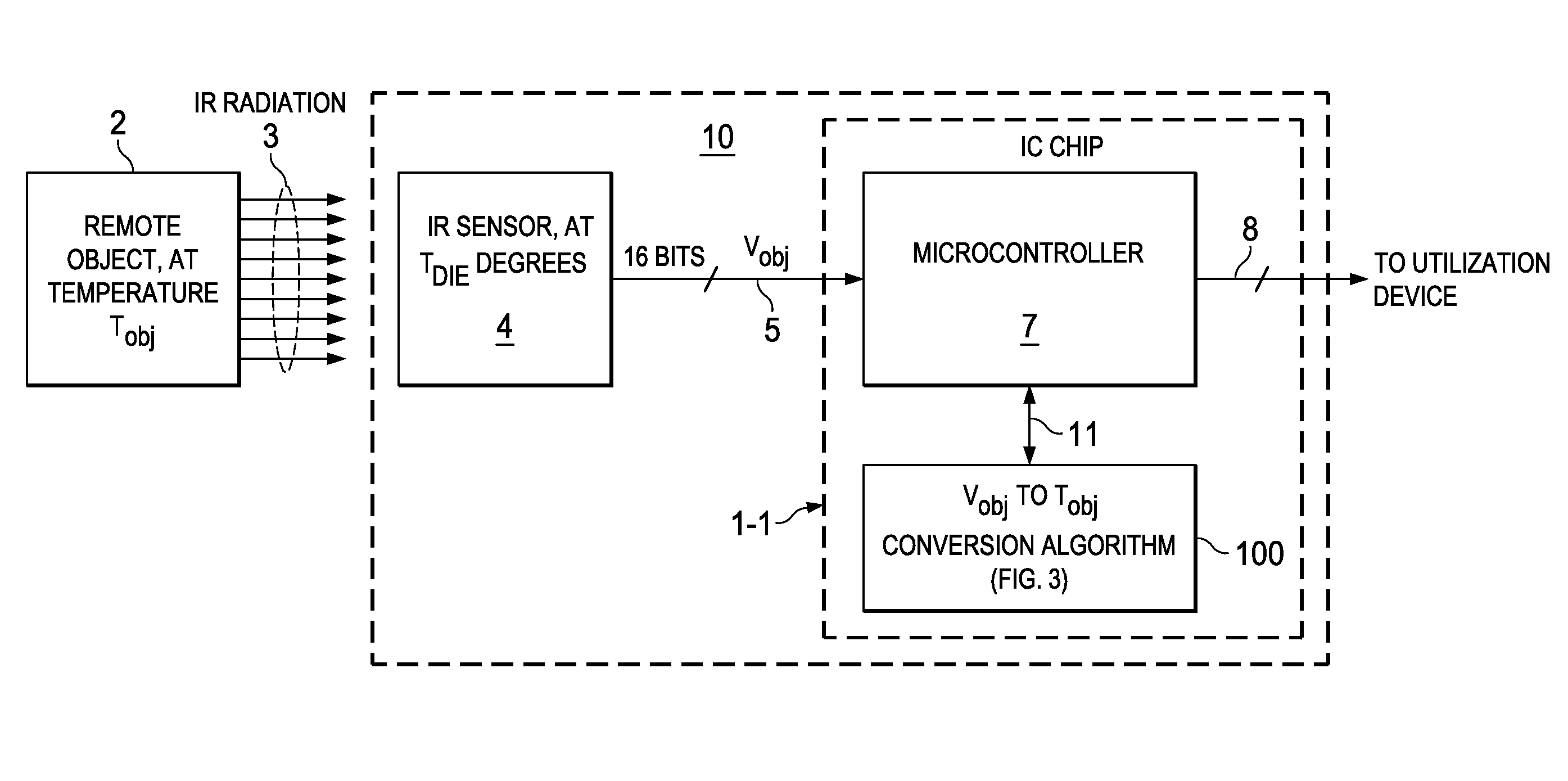
Modified Fixed-Point Algorithm For Implementing Infrared Sensor Radiation Equation
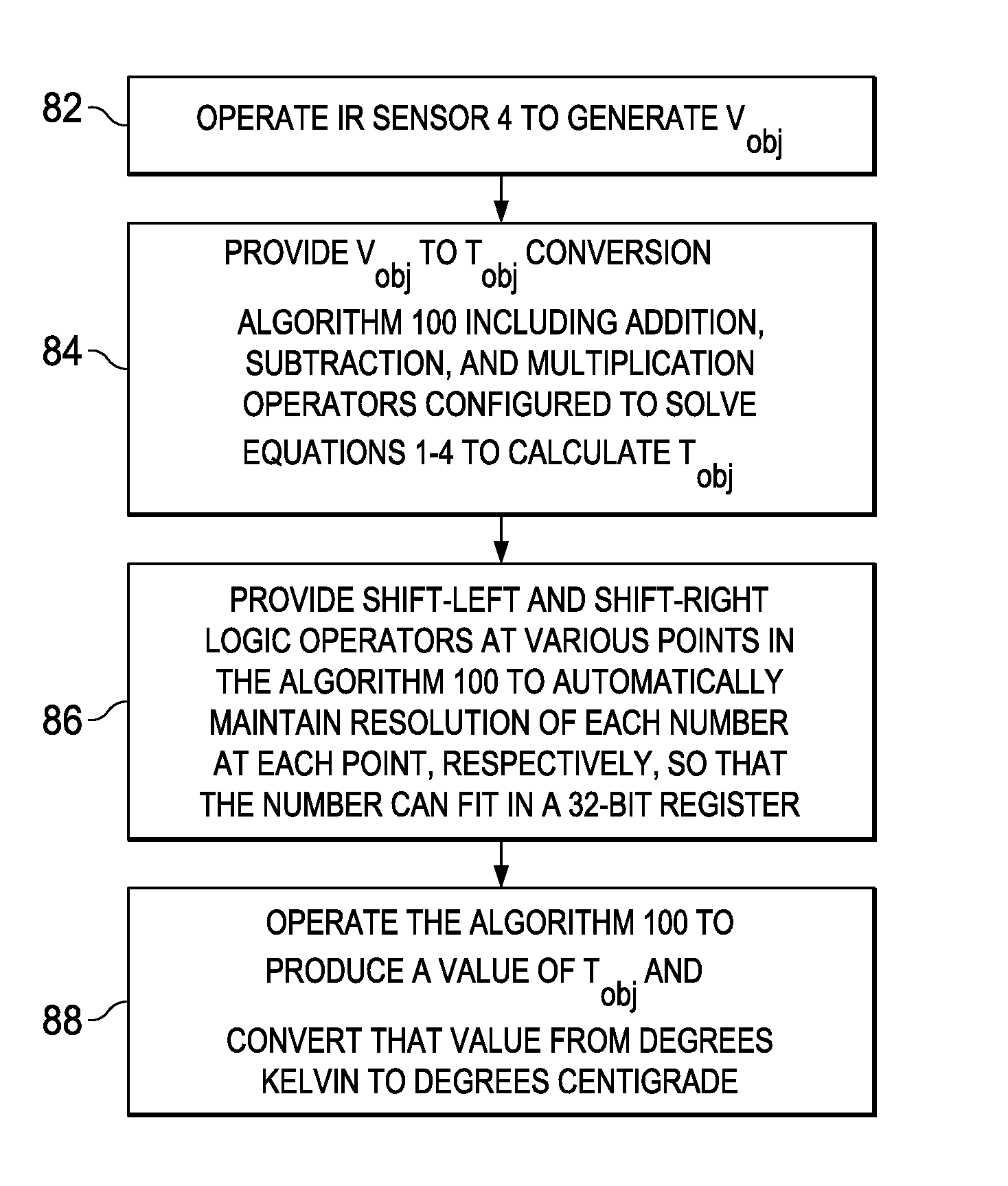
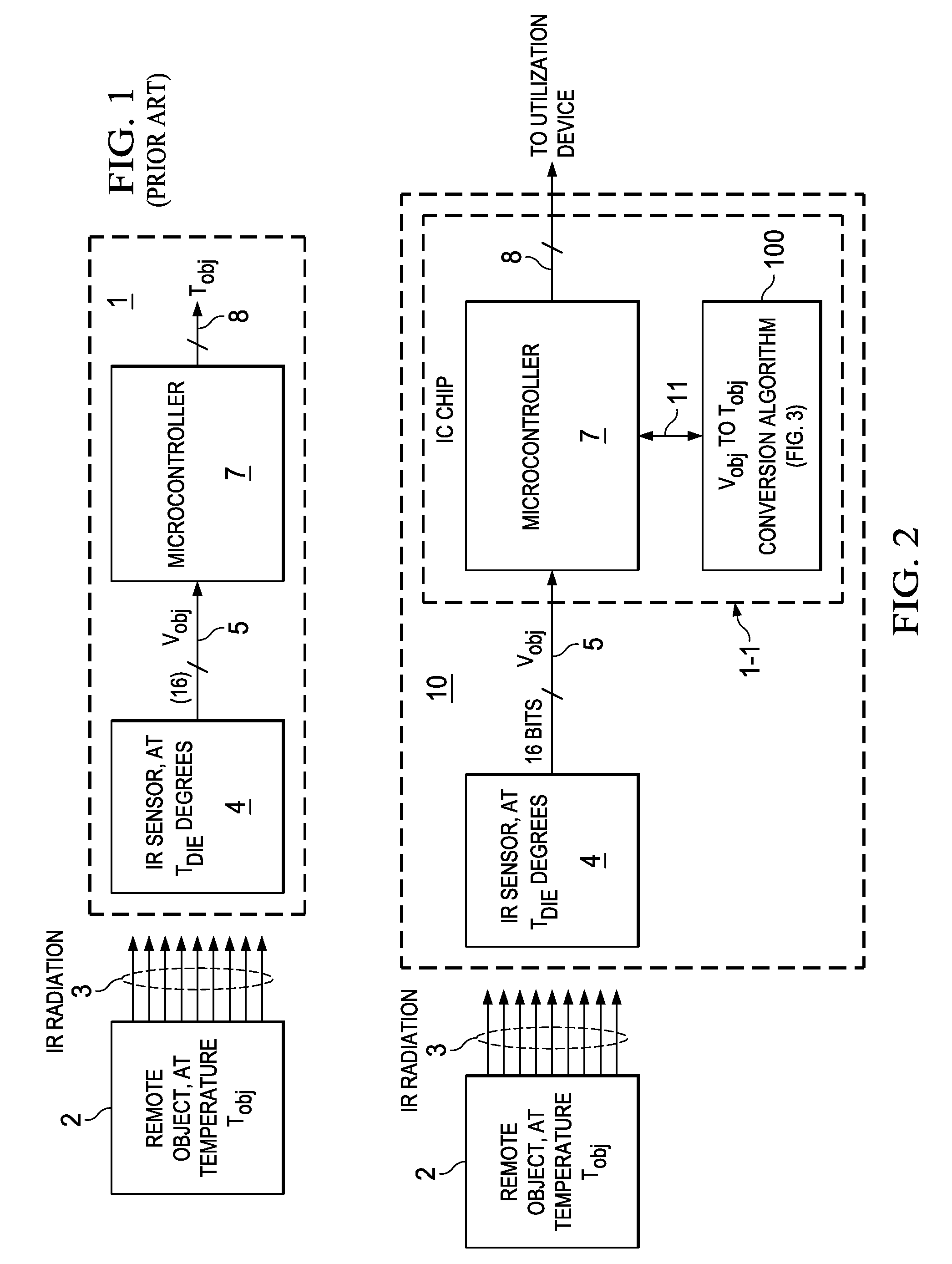
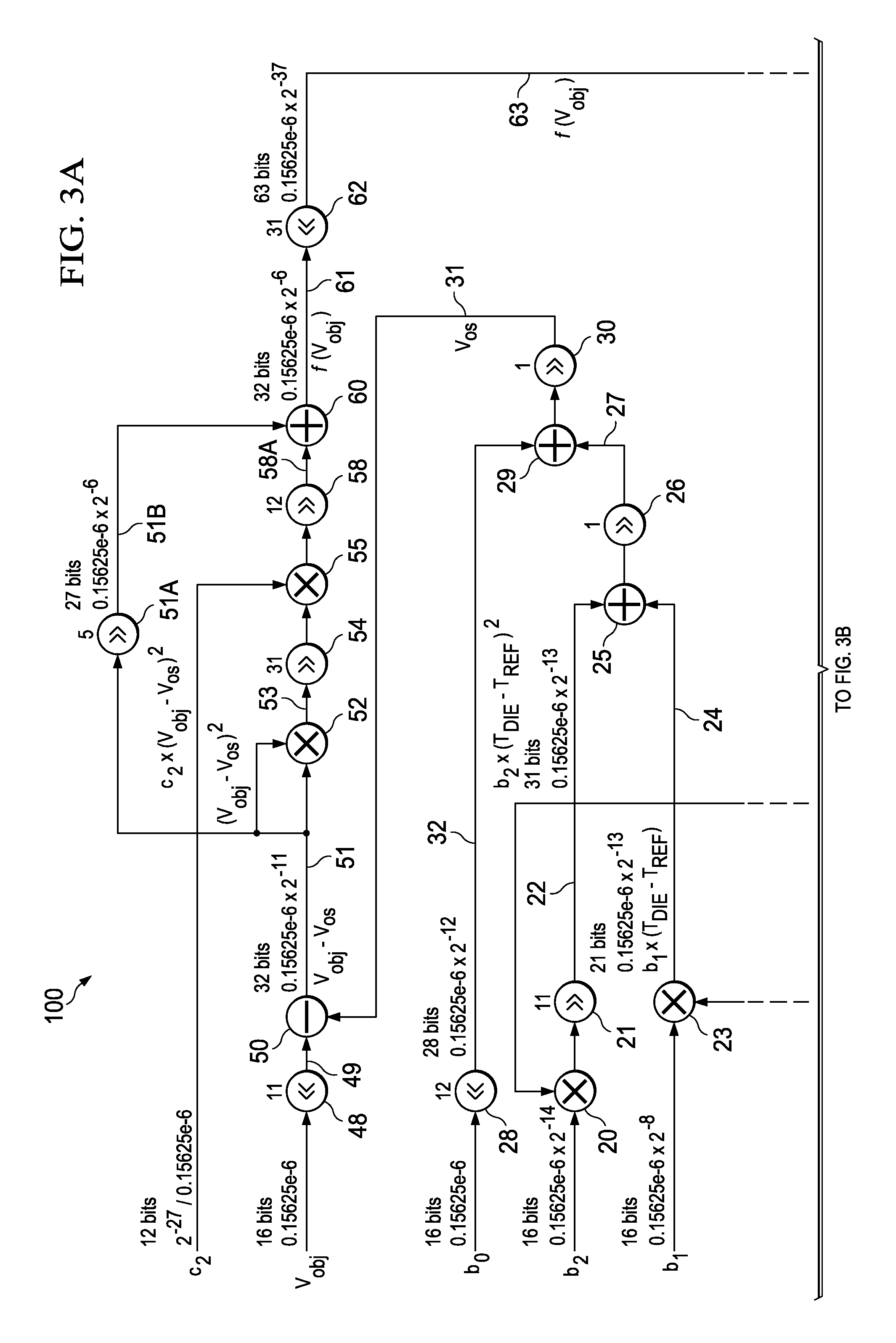
ActiveUS20140089362A1Improve accuracyFast and low-cost IR-to-objectDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsMicrocontrollerAlgorithm
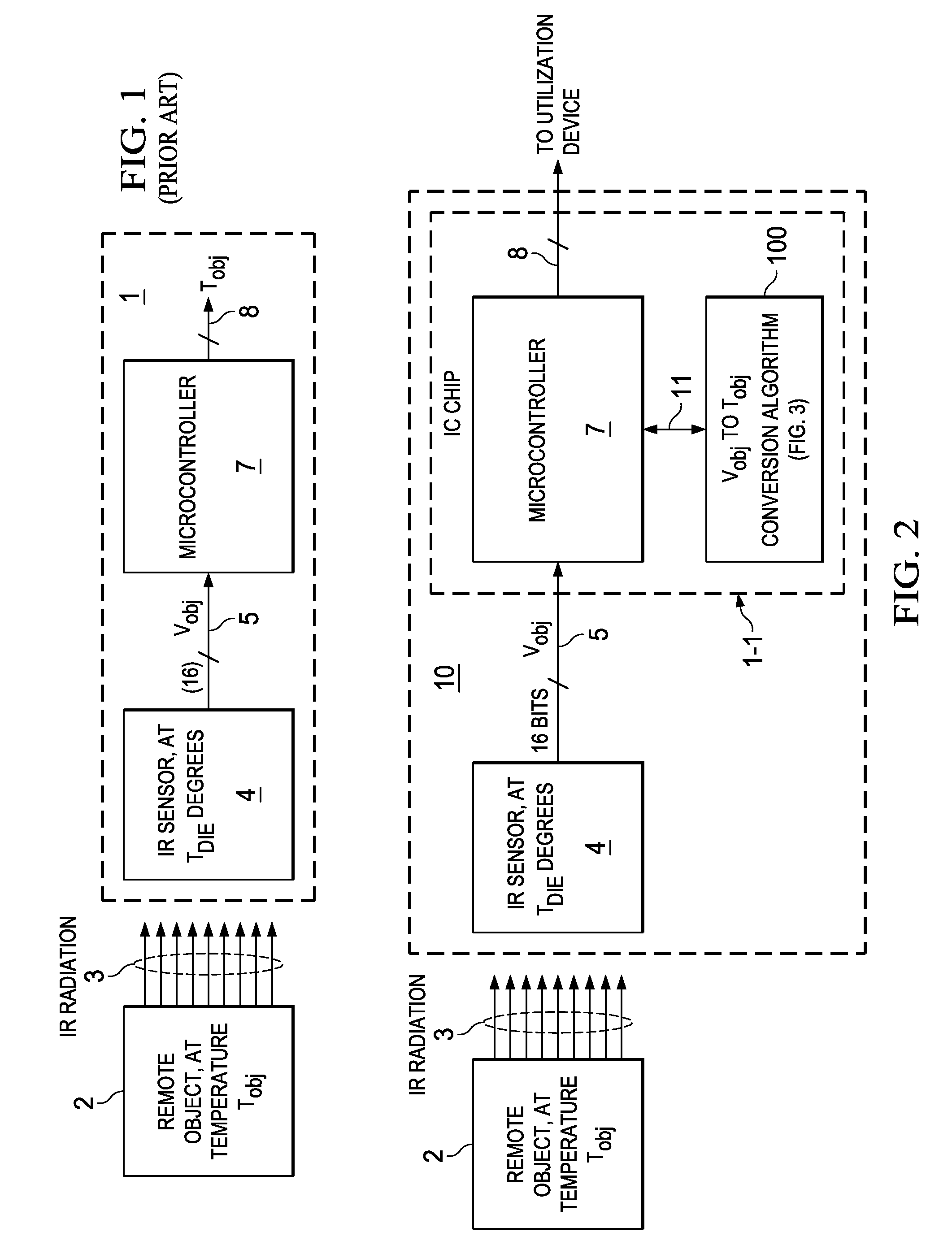
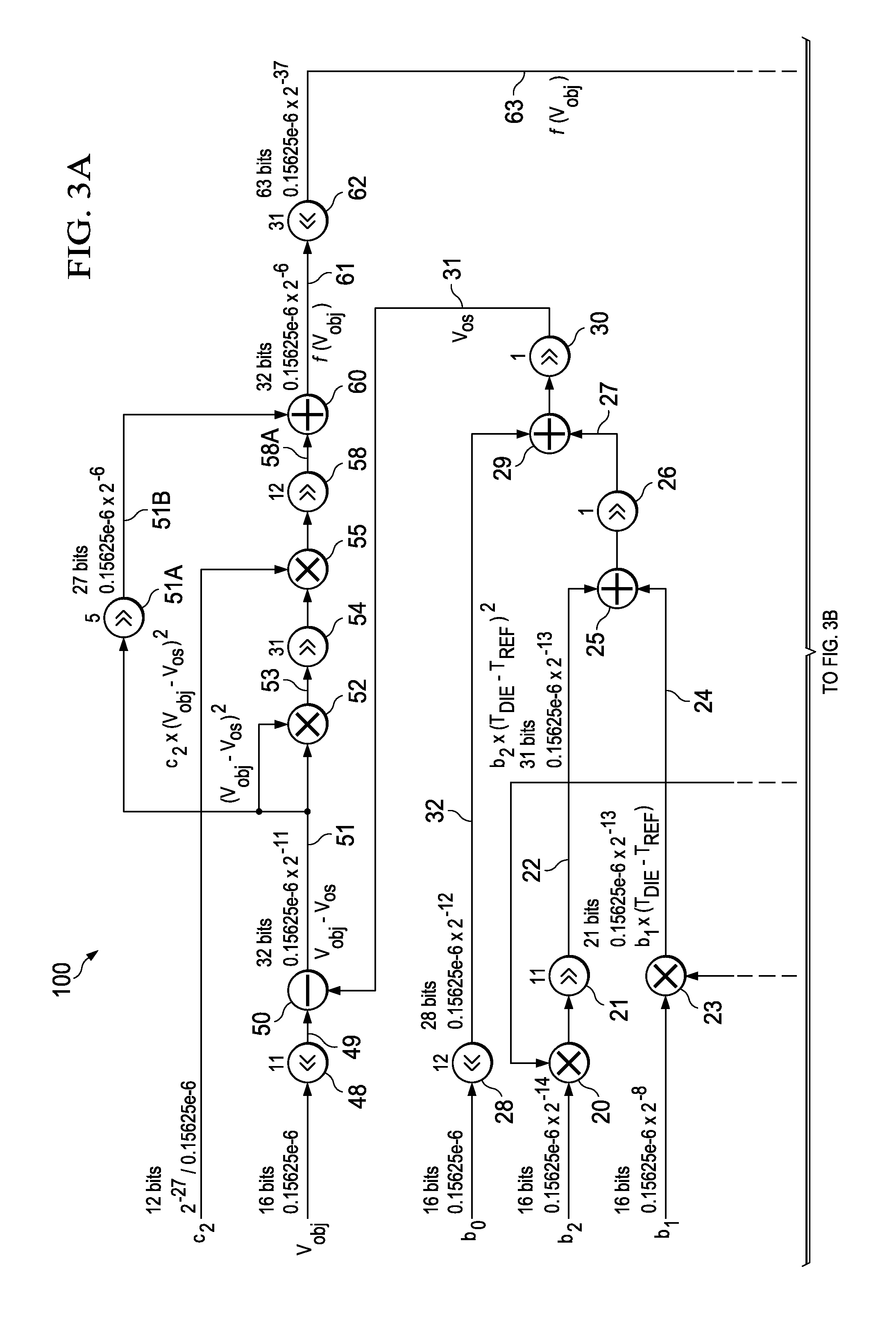
A system including an integrated circuit chip also includes a microcontroller in the chip and an algorithm for execution by the microcontroller. The algorithm includes addition, subtraction, and multiplication operators (e.g. 25,15,20) and shift-left and shift-right operators (e.g., 48,21) configured for solving particular equations (Eqns. 1-4). Input numbers are within particular ranges to allow the shift operators to shift binary bits so each number so it fits within a register of a particular width. An IR sensor (4) may convert IR radiation (3) to produce a voltage (Vobj) representing the temperature (Tobj) of an IR emitting object (2). The algorithm (100) operates in conjunction with the microcontroller (7) to convert the voltage (Vobj) into a value representing the temperature (Tobj) of the remote object (2) without keeping track of decimal points and resolution of the numbers.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Double-core parallel RSA password processing method and coprocessor
InactiveCN105871552AImprove computing efficiencyReduce areaPublic key for secure communicationCryptographic attack countermeasuresPlaintextDual core
The present invention relates to the field of information security and microprocessor design, in order to realize the conversion of modular multiplication into simple decimal addition and multiplication through FIOS modular multiplication algorithm, fully reduce the area of modular multiplication operation unit, and effectively avoid writing back a large amount of intermediate data process. From the perspective of hardware implementation, it improves the computational efficiency of the algorithm and further saves computational resources, fundamentally reduces the time and space overhead of encryption and decryption, and effectively improves the encryption and decryption performance of RSA. The technical solution adopted by the present invention is that, before encryption, a dual-core parallel RSA encryption processing method needs to rely on a certificate authority (CA) as a trusted third party to be responsible for the generation, storage, maintenance, and revocation of the user's private key and public key certificate Link, when encrypting, user B executes the operation c=m e (modN) and send the encrypted information c to user A; when decrypting, user A uses his own private key d to perform operations on the ciphertext c to recover the plaintext. The invention is mainly applied to information security processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Reduced complexity adaptive multistage wiener filter
ActiveUS8386549B1Digital technique networkDigital data processing detailsFinite impulse responseRound complexity
Multistage Wiener filters (MWF) represent a component of the MWF as an un-normalized vector of filter coefficients within a finite impulse response (FIR) filter in a manner that avoids reliance on the 2-norm operation of the un-normalized vector of coefficients. The 2-norm operation can be replaced by less expensive operations performed elsewhere in the MWF. Preferably the filter adds only a few additional addition, subtraction and multiplication operations to compensate for the elimination of the square root and the division operations used for the 2-norm operation. As a result, it is possible to eliminate all or nearly all of the square rod and arithmetic division operations of at least some implementations of the MWF.
Owner:ACORN TECH INC
Computing device, method, and computer program product
ActiveUS20100063986A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsParallel computingMultiplication operator
Owner:TOSHIBA DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
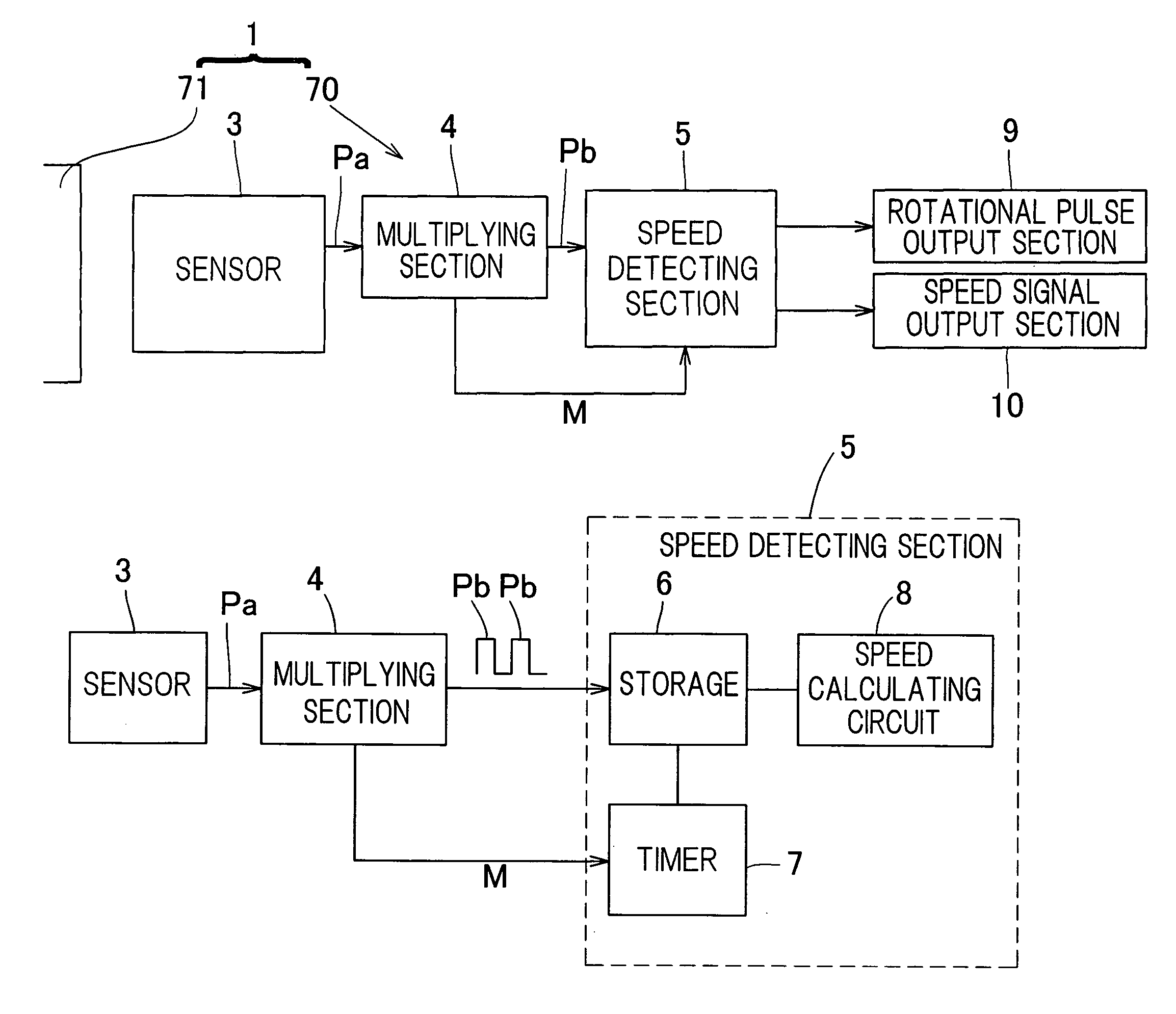
Rotation detection device and bearing having rotation detection device
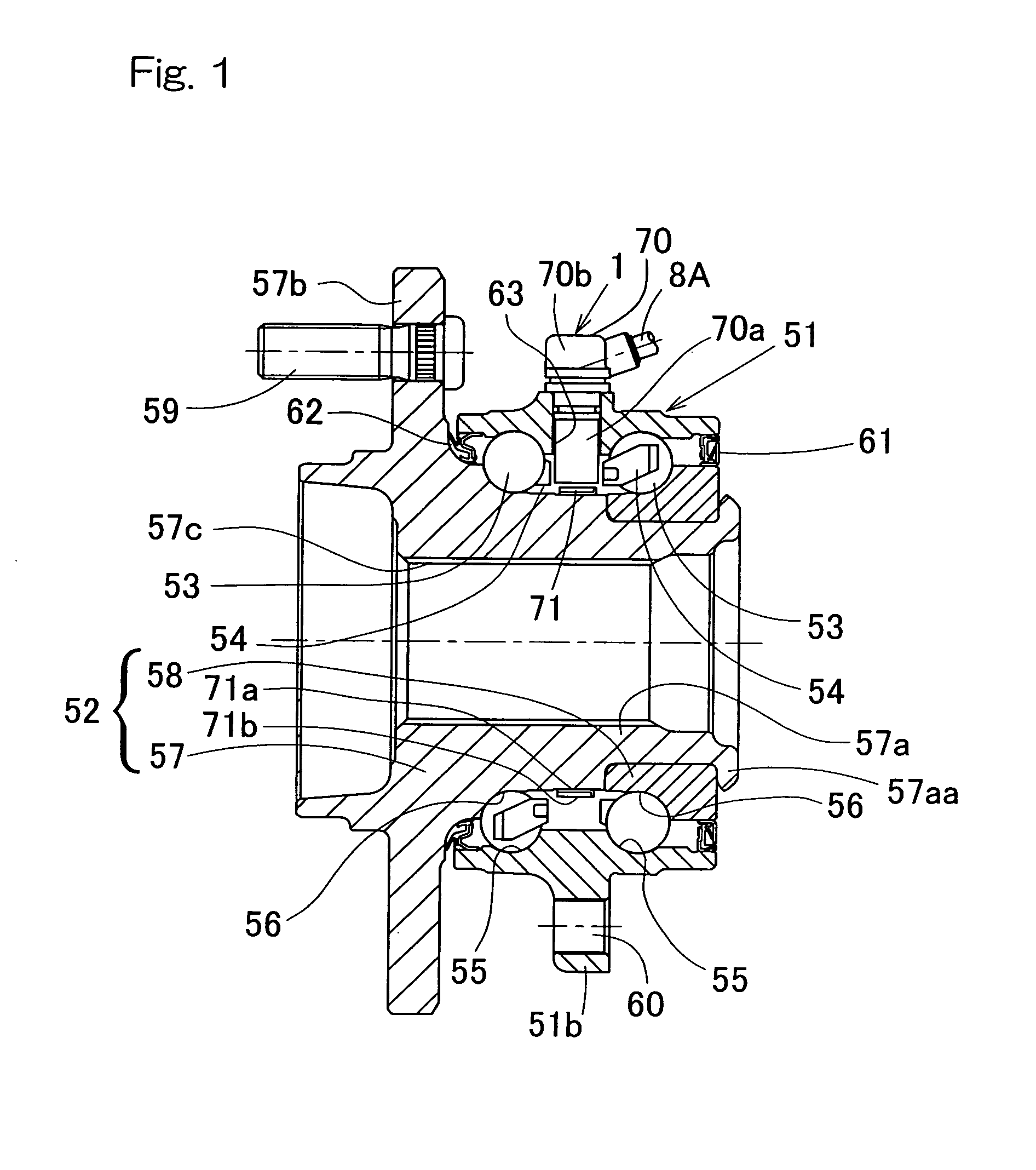
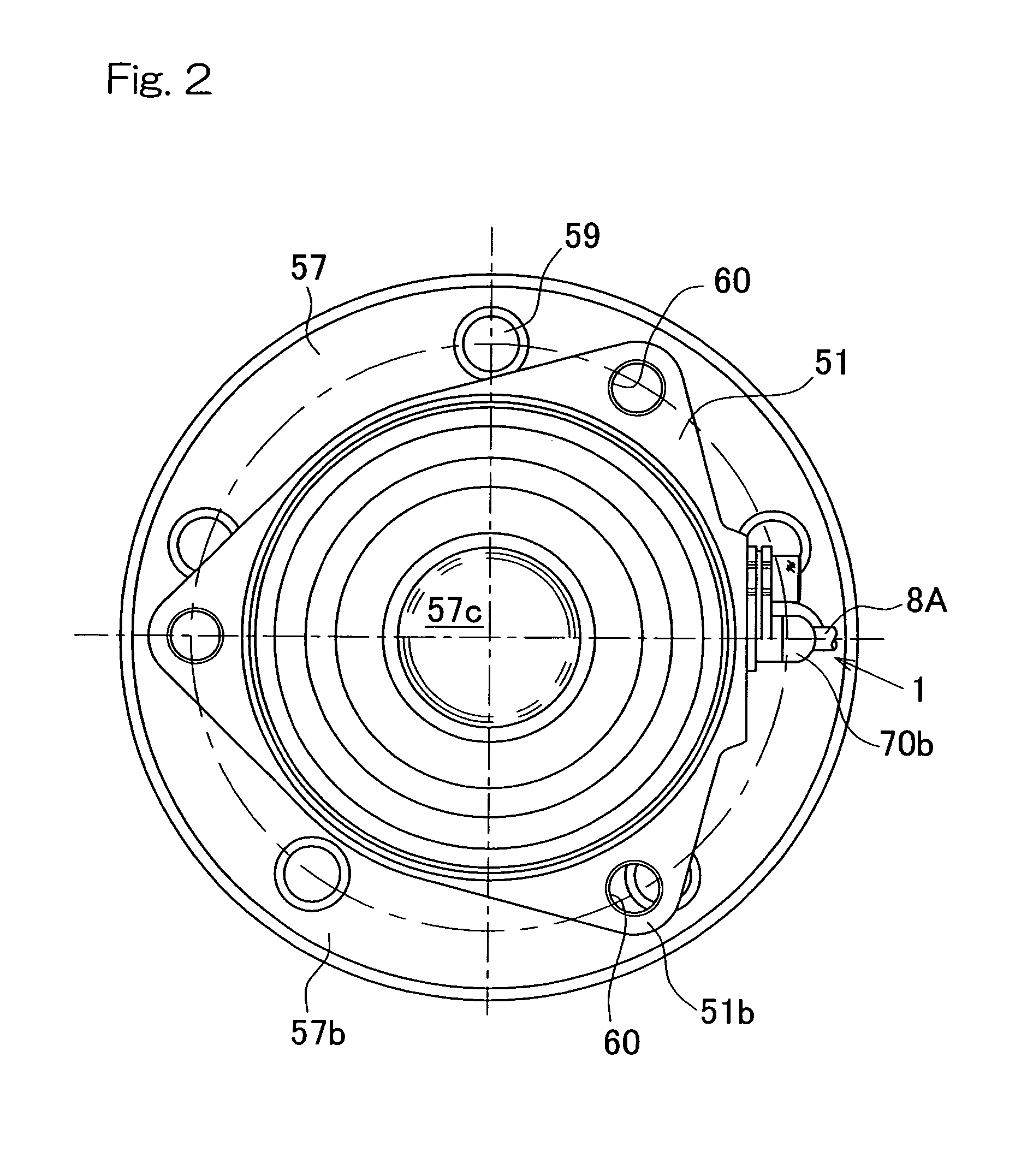
ActiveUS7825653B2Improve detection resolutionVariation in rotational speedBearing assemblyHubsImage resolutionEngineering
To provide a rotation detecting system of a type having a high detecting resolution, in which the rotational position can be detected accurately, in which a sufficient gap can be secured between the sensor and the rotating body and which is effective to simplify assemblage and processing to thereby reduce the manufacturing cost, the rotation detecting system is provided with a multiplying section 4 for multiplying the pulses, generated by the sensor 3, by a multiplication factor to form multiplied pulses Pb and a speed detecting section 5 for detecting an period average speed of the encoder 71 during the interval, in which the latest N pieces of the multiplied pulses Pb have been generated where N represents the multiplication factors by which the multiplied pulses Pb have been multiplied.
Owner:NTN CORP
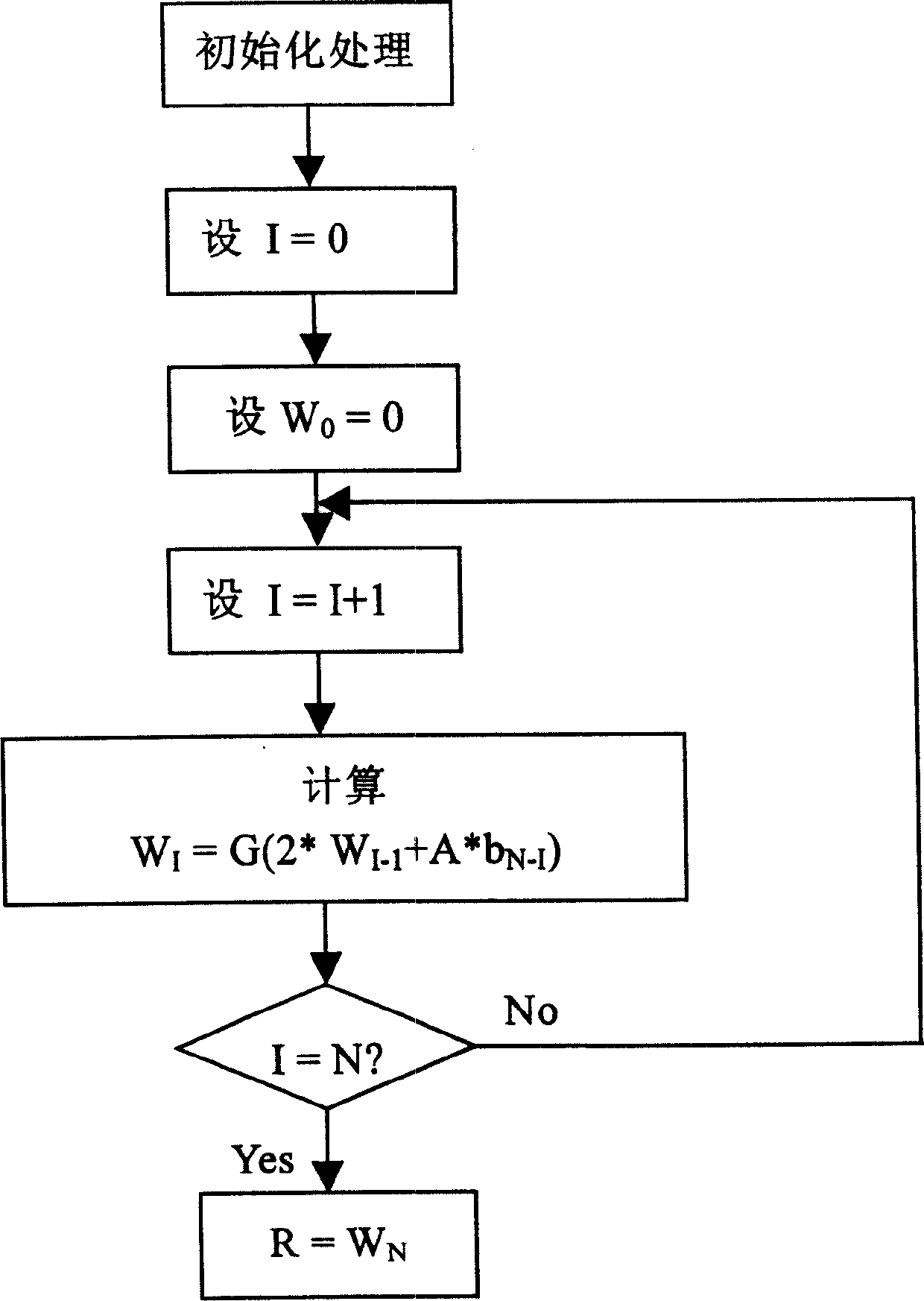
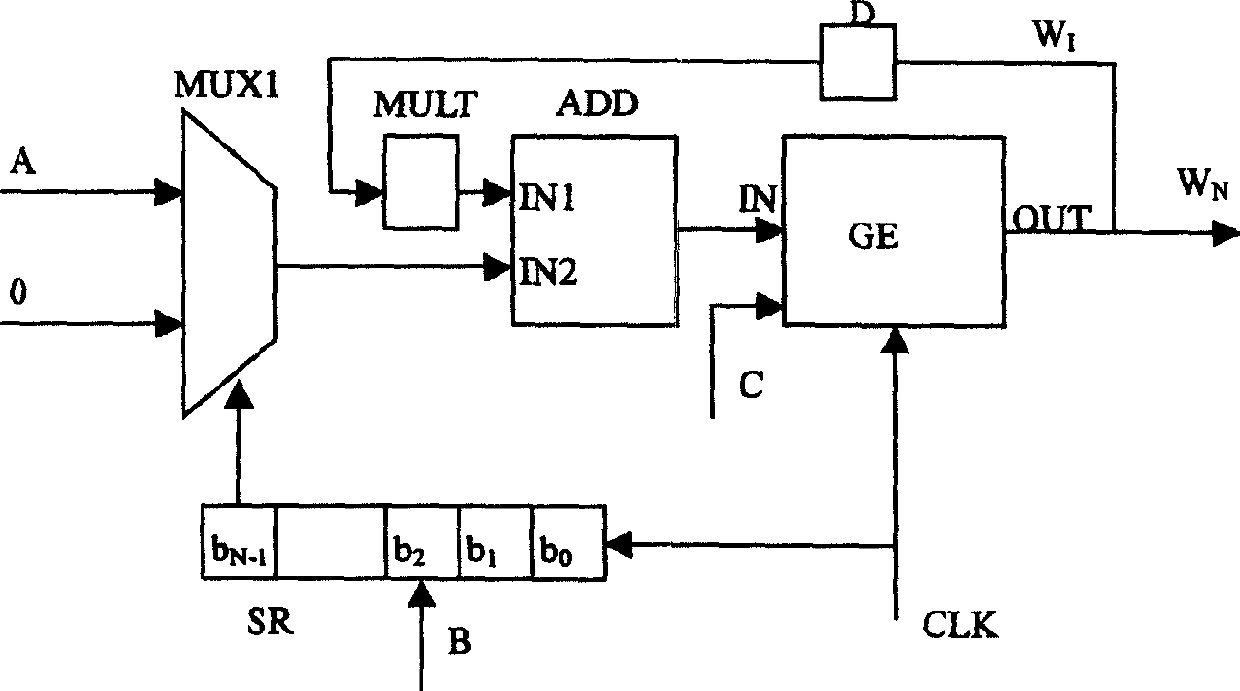
A method of module multiplication operation and apparatus and use thereof
InactiveCN1691580AReduce complexitySimplify Design ComplexitySecuring communicationRound complexityCommunications system
The invention relates to an apparatus and method for modular multiplying arithmetic and its usage. The inventive modular multiplying arithmetic method comprises the steps of: breaking up the modular multiplying operating formula to realize it by using the recursive solution which repeated applying a fixing algorithm (or function) on the result of the prior algorithm; get the wanted remainder. The invention provides a method for realizing the lower algorithm complexity of the Montgomery modular multiplying and a quick and low power consuming apparatus for the algorithm. It can be used in RSA encryption processing system and the interlace mode generation of the internal interlace device of the Bode coder-decoder in the third generation communication system.
Owner:上海明波通信技术股份有限公司
Feature extracting method for power load dynamic features
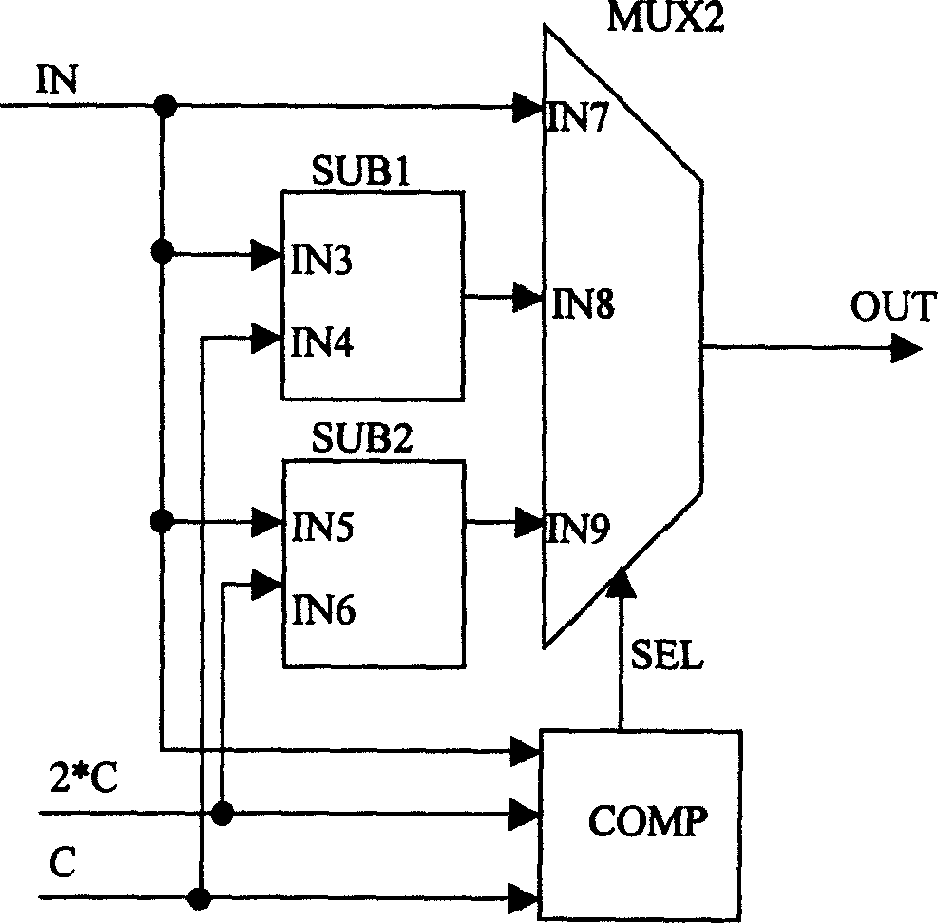
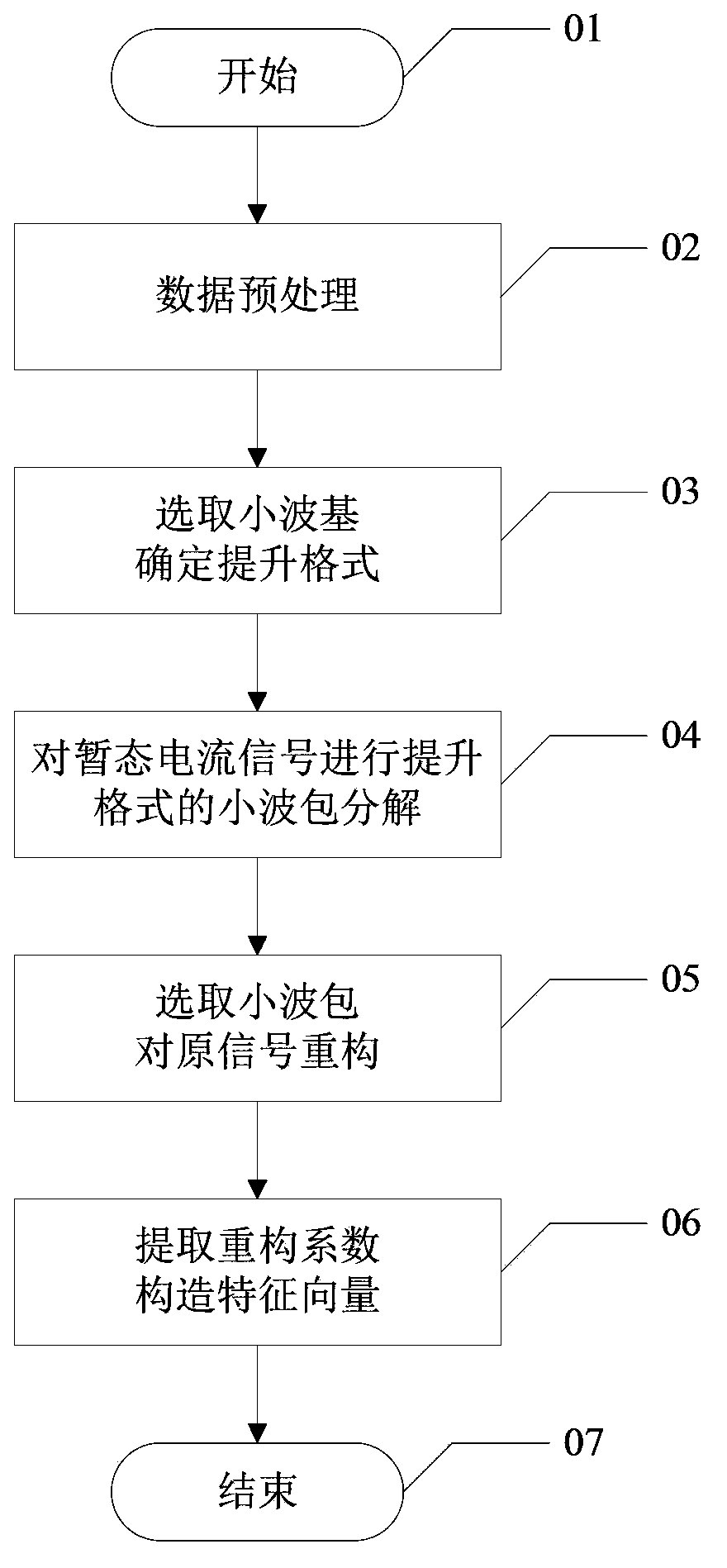
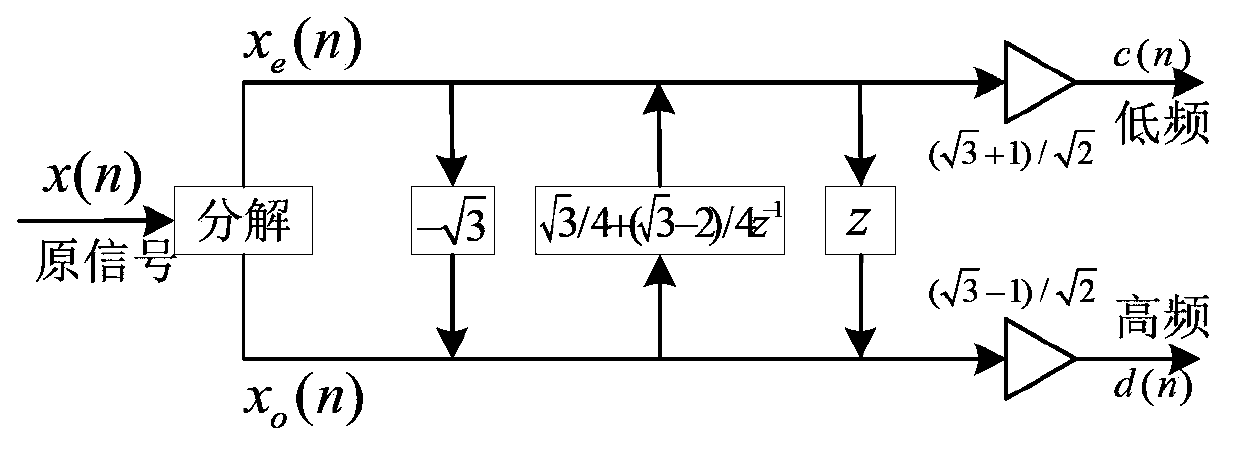
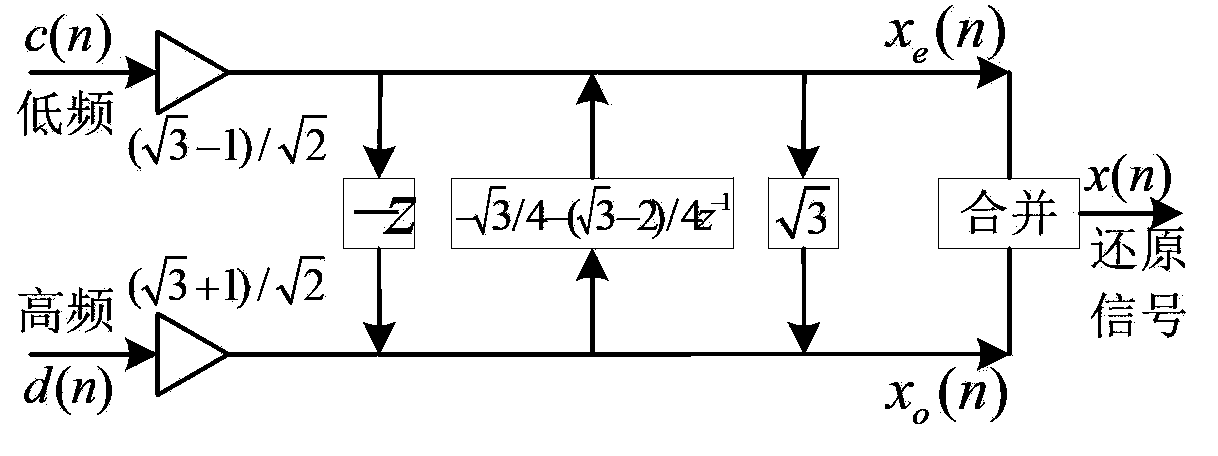
ActiveCN103390117AReduce operandsFast conversionSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmMultiplication operator
The invention discloses a feature extracting method for power load dynamic features. The method comprises the steps of S1, preprocessing the three-phase transient state current data reflecting the power load dynamic features, and selecting the sampling data in one cycle before a fault and in two cycles after the fault as samples; S2, selecting a wavelet basis, and determining the lifting scheme of the wavelet basis; S3, selecting a resolving layer number m and performing m-layer resolving on the three-phase transient state current data of each sample by utilizing the wavelet packet conversion with the lifting scheme; S4, selecting the wavelet packet to reconstruct original signals, wherein the signal number in the wavelet packet is marked as r; and S5, extracting a corresponding reconstruction coefficient and calculating an energy value Mij(k) as the sample number, wherein j is equal to 1, 2 and 3 respectively representing the three phases of currents, k is equal to 1, 2, 3, ellipsis and r represents a frequency band. The multiplication operation number of the wavelet packet conversion based on the lifting scheme is reduced by about a half, so a faster conversion speed is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Modified fixed-point algorithm for implementing infrared sensor radiation equation
ActiveUS9223545B2Improve accuracyFast and low-cost IR-to-objectDigital data processing detailsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsMicrocontrollerAlgorithm
A system including an integrated circuit chip also includes a microcontroller in the chip and an algorithm for execution by the microcontroller. The algorithm includes addition, subtraction, and multiplication operators (e.g. 25,15,20) and shift-left and shift-right operators (e.g., 48,21) configured for solving particular equations (Eqns. 1-4). Input numbers are within particular ranges to allow the shift operators to shift binary bits so each number so it fits within a register of a particular width. An IR sensor (4) may convert IR radiation (3) to produce a voltage (Vobj) representing the temperature (Tobj) of an IR emitting object (2). The algorithm (100) operates in conjunction with the microcontroller (7) to convert the voltage (Vobj) into a value representing the temperature (Tobj) of the remote object (2) without keeping track of decimal points and resolution of the numbers.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
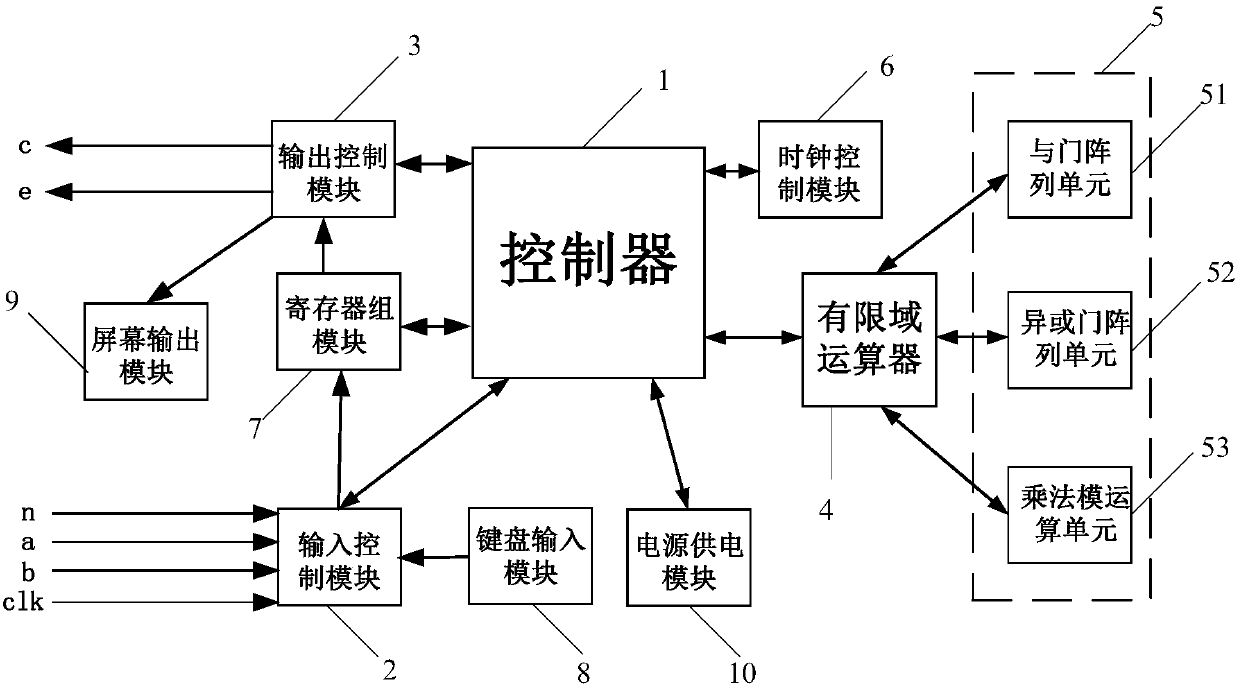
All-in-one irreducible polynomial based finite field multiplier
The invention relates to an all-in-one irreducible polynomial based finite field multiplier which comprises a controller, an input control module, an output control module, a finite field multiplier and an operation module, wherein the controller is used for controlling and scheduling data transmission among the input control module, the output control module and the finite field multiplier; the input control module is used for inputting a multiplication operation number a(x) and a multiplication operation number b(x) when detecting that a finite field GF(2n) has an all-in-one irreducible polynomial; the finite field multiplier is used for calling the operation module to carry out finite field multiplication operation on the multiplication operation number a(x) and the multiplication operation number b(x) to obtain a multiplication operation result c(x); the operation module is used for implementing and logical operation, exclusive or logic operation and modular operation; the output control module is used for outing the multiplication operation result c(x). By adopting the multiplier, the operation efficiency of finite field multiplication is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
A multiplier based on memristor RRAM
PendingCN109445747AReduce the number of unitsPromote productionComputation using non-contact making devicesWallace treeBinary multiplier
The invention provides a multiplier based on a memristor RRAM. The multiplier of the voter logic is given based on the original adder, the structure of the Wallace tree is adopted for operation, the multiplication operation is converted into the corresponding addition operation, and by utilizing the Wallace tree structure, a plurality of n-Bit numbers are added up to 2n-Bit numbers, and each fulladdition operation can be performed simultaneously by using voter logic. The multiplier of the invention improves the overall running speed and reduces the area of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
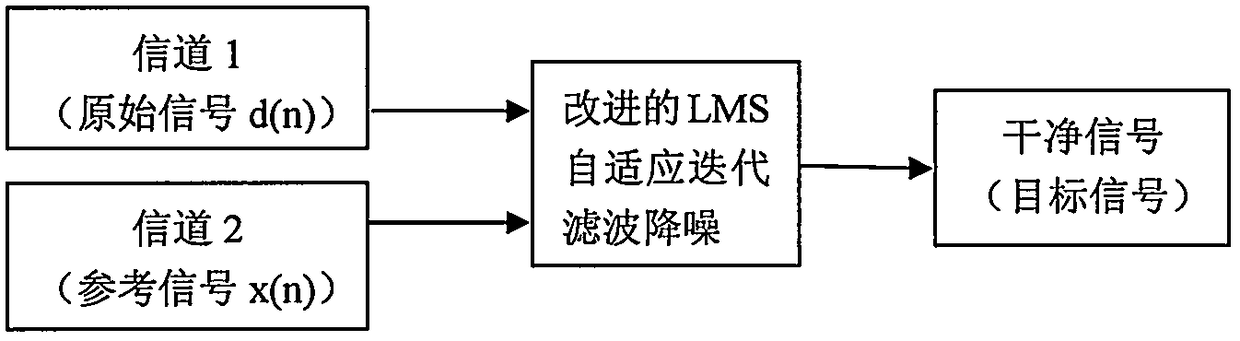
Fast iteration adaptive filtering method
The invention discloses a fast iteration adaptive filtering method. The method is implemented by adopting the steps of 1, performing data collection on dual-channel digital signals; 2, performing filtering and noise reduction processing on the collected data by adopting improved LMS (Least Mean Square) adaptive iteration filtering; and 3, adjusting a step length factor until optimal target digitalsignals are obtained. The fast iteration adaptive filtering method eliminates an operation of using a residual scalar e(n) in a weight factor iteration formula to serve as a multiplication factor, and controls the adjustment direction by a symbol of the residual scalar e(n), thereby enabling the convergence speed to be greatly improved, and simplifying the computational complexity. The fast iteration adaptive filtering method is applicable to any LMS operating environment and algorithm, and particularly applicable to operating in real time on various 16-bit MCUs.
Owner:上海闻通信息科技有限公司
Feature extraction method and system applied to deep learning
ActiveCN108805030AReduce computing timeComputing modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainFeature extraction
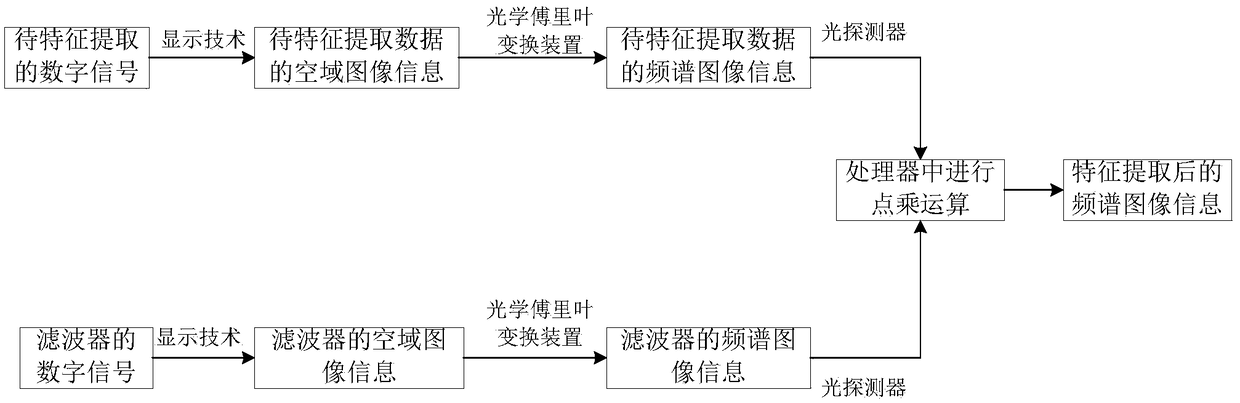
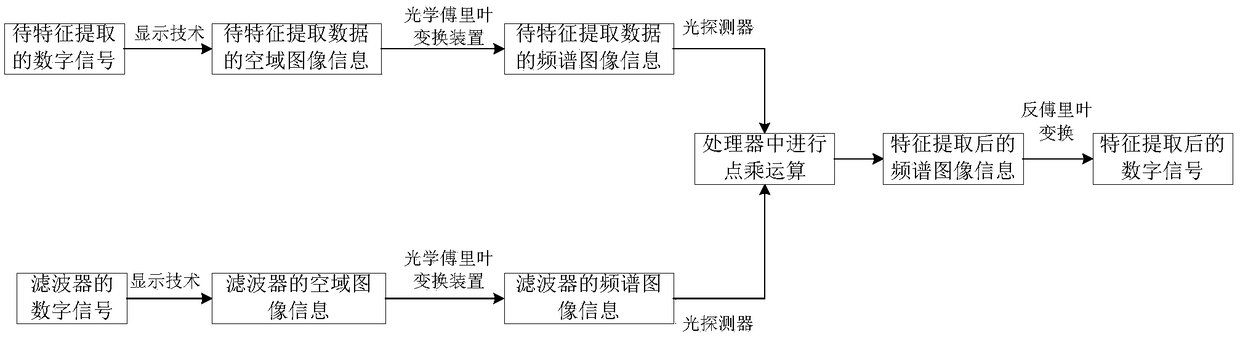
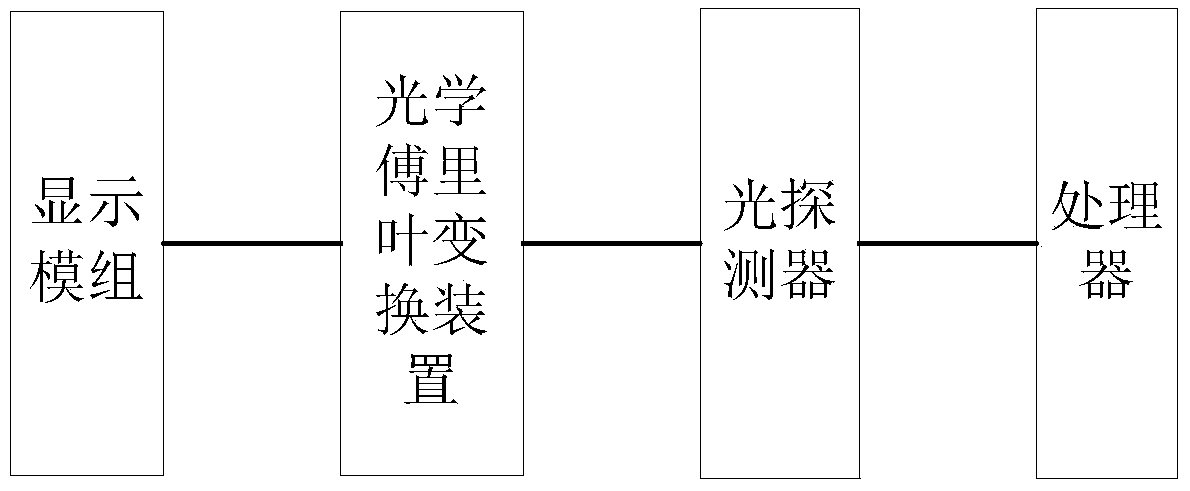
The invention discloses a feature extraction method and system applied to deep learning. An existing deep learning calculation mode is improved; in the prior art, for feature extraction in the deep learning, a group of digital signals to be subjected to feature extraction and digital signals of a filter need to be subjected to convolution; the two types of the digital signals are converted into optical signals; at the moment, the optical signals can be simply converted into a frequency domain; the convolution on a time domain is equivalent to the point multiplication on the corresponding frequency domain; the convolution on the time domain is very complex; and the point multiplication operation on the frequency domain can be much simpler. The calculation amount in the deep learning can beeffectively reduced; and after part of the operation is converted into optical calculation, the calculation speed of the part is changed to the optical calculation speed, so that the calculation timeis greatly shortened.
Owner:CHENGDU IDEALSEE TECH
Anonymous untraceable RFID mutual authentication method
InactiveCN104363096AFast operationSave storage spaceUser identity/authority verificationData setTime complexity
The invention provides an anonymous untraceable RFID mutual authentication method. Based on the problem that the safety of a Schnorr signature algorithm and the safety of a lightweight class symmetric encryption algorithm rely on discrete logarithms and are difficult to achieve, the anonymous untraceable RFID mutual authentication method has the advantages of being high in operating rate, small in storage space and the like. The phenomena that the tag cost is low and the computing power is limited are taken into consideration, a middle result which is possibly needed in the authentication process of tags is stored in the tags in a precomputation data set mode, the tags can be authenticated simply by generating random numbers through basic code operation such as Hash operation and addition and multiplication operation, and exponent operation with large operand is not needed. The anonymous untraceable RFID mutual authentication method reduces the time complexity of a system while information safety and user privacy are protected.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Modular multiplication method used for calculating classic modular multiplication and extensible modular multiplier
InactiveCN103176768ASmall amount of calculationImprove performanceComputations using residue arithmeticParallel computingModular multiplier
The invention relates to the information security technical field, in particular to a modular multiplication method and an extensible modular multiplier, namely an extensible method used for calculating classic modular multiplication A B mod M and a corresponding extensible modular multiplier based on the Jeong - Burleson algorithm. According to the modular multiplication method and the extensible modular multiplier, due to the fact that tasks are distributed to each processing unit and operated word by word in each processing unit, on one hand, modular multiplication operation in any length or with length alterable can be calculated by utilizing limited logical resources and enough memorizers, and calculated amount is small in the situation that multiplicators or multiplicands change constantly; on the other hand, an approach for selecting design parameters and optimizing performance is provided; and meanwhile, a novel precomputation value and a low latency structure enable operation efficiency to be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
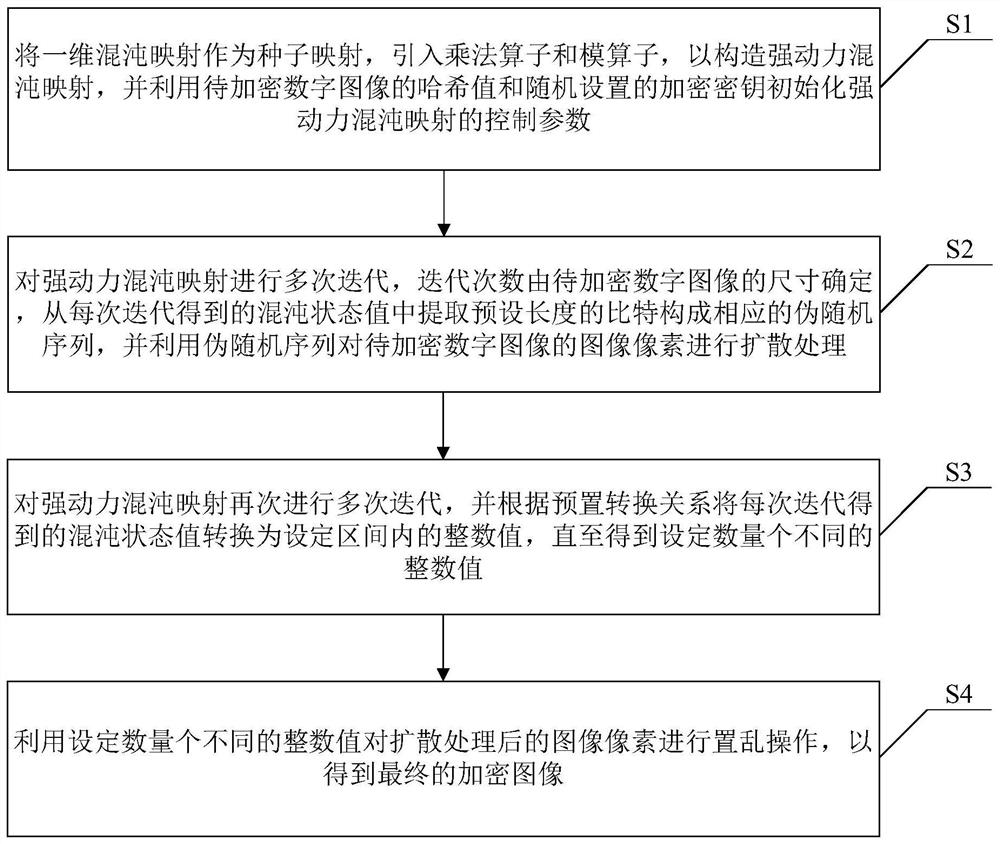
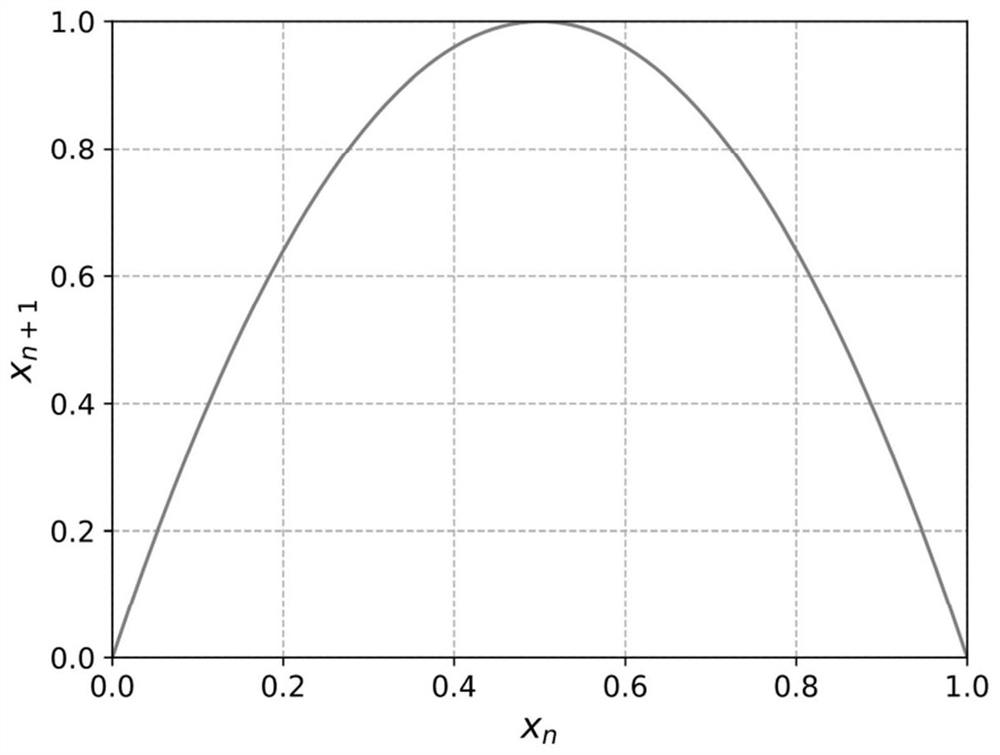
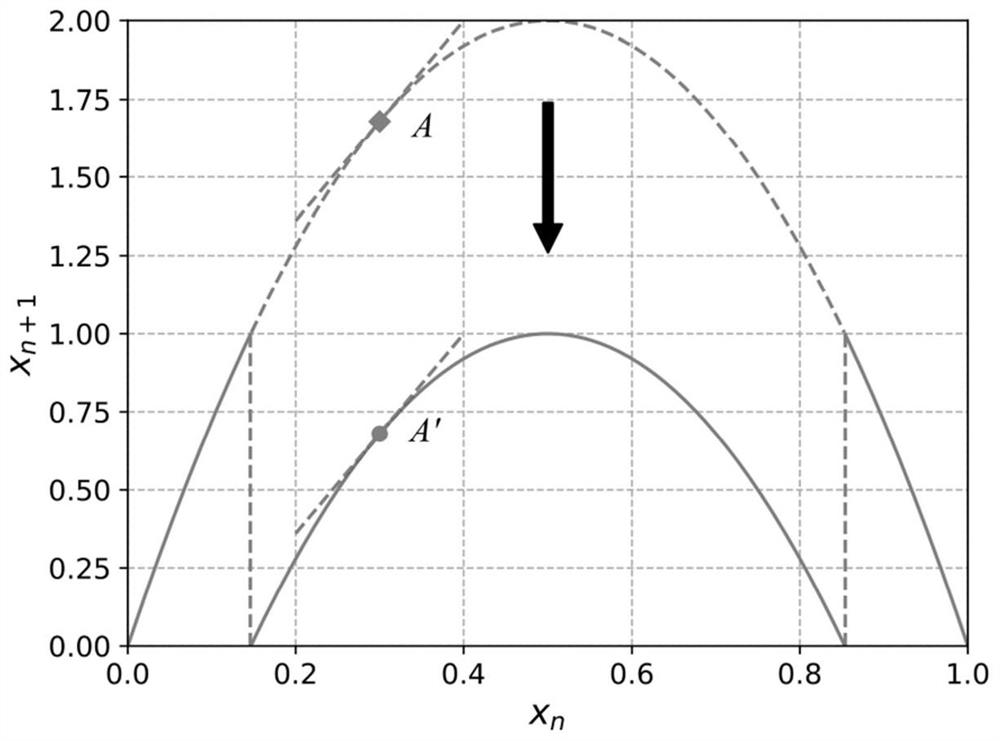
Digital image encryption method, decryption method and system based on chaotic system
PendingCN114157408ALarge dynamic propertiesStrong dynamic propertiesSecuring communication by chaotic signalsChaotic systemsDigital image
The invention discloses a digital image encryption method, decryption method and system based on a chaotic system, and belongs to the field of chaotic image encryption, and the encryption method comprises the steps: taking a one-dimensional chaotic mapping as a seed mapping, introducing a multiplication operator and a modular operator, constructing a strong dynamic chaotic mapping, initializing a control parameter of strong dynamic chaotic mapping by using the hash value of the digital image to be encrypted and the encryption key; iterating the strong dynamic chaotic mapping for multiple times, extracting bits with a preset length from a chaotic state value obtained by each iteration to form a corresponding pseudo-random sequence, and diffusing image pixels of the digital image to be encrypted by using the pseudo-random sequence; and performing multiple iterations on the strong dynamic chaotic mapping again, converting a chaotic state value obtained by each iteration into an integer value in a set interval until a set number of different integer values are obtained, and performing scrambling operation on image pixels after diffusion processing to obtain a final encrypted image. And the digital image is encrypted safely and effectively.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Floating-point division alternative techniques
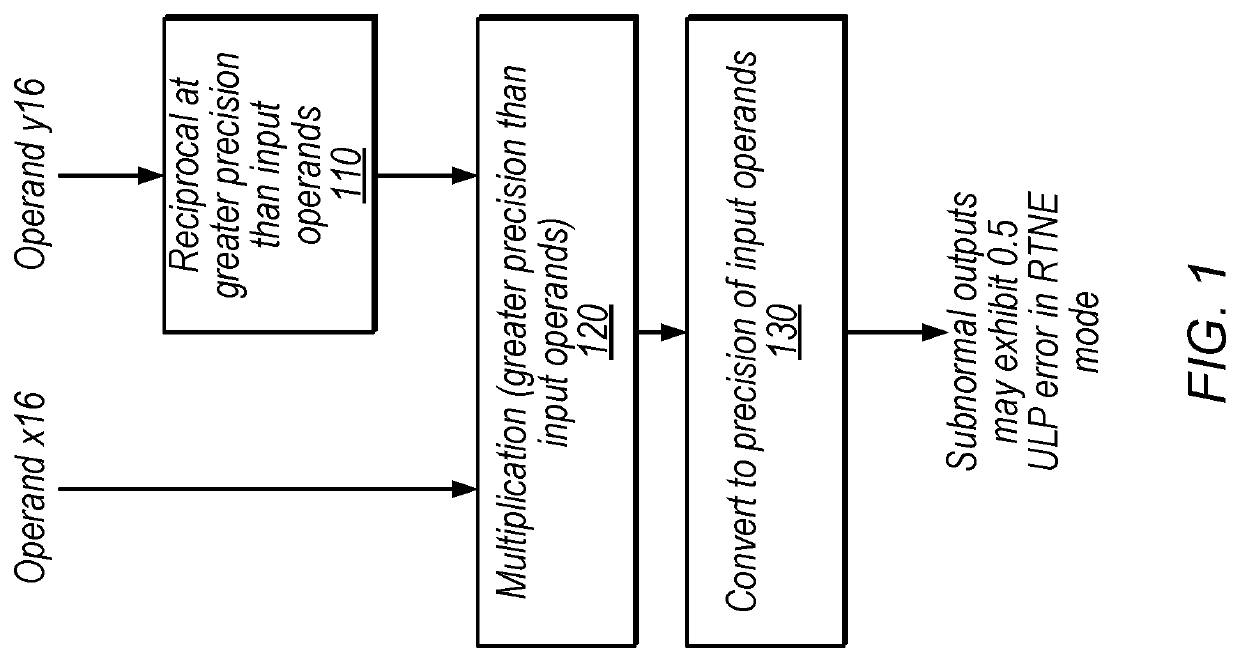
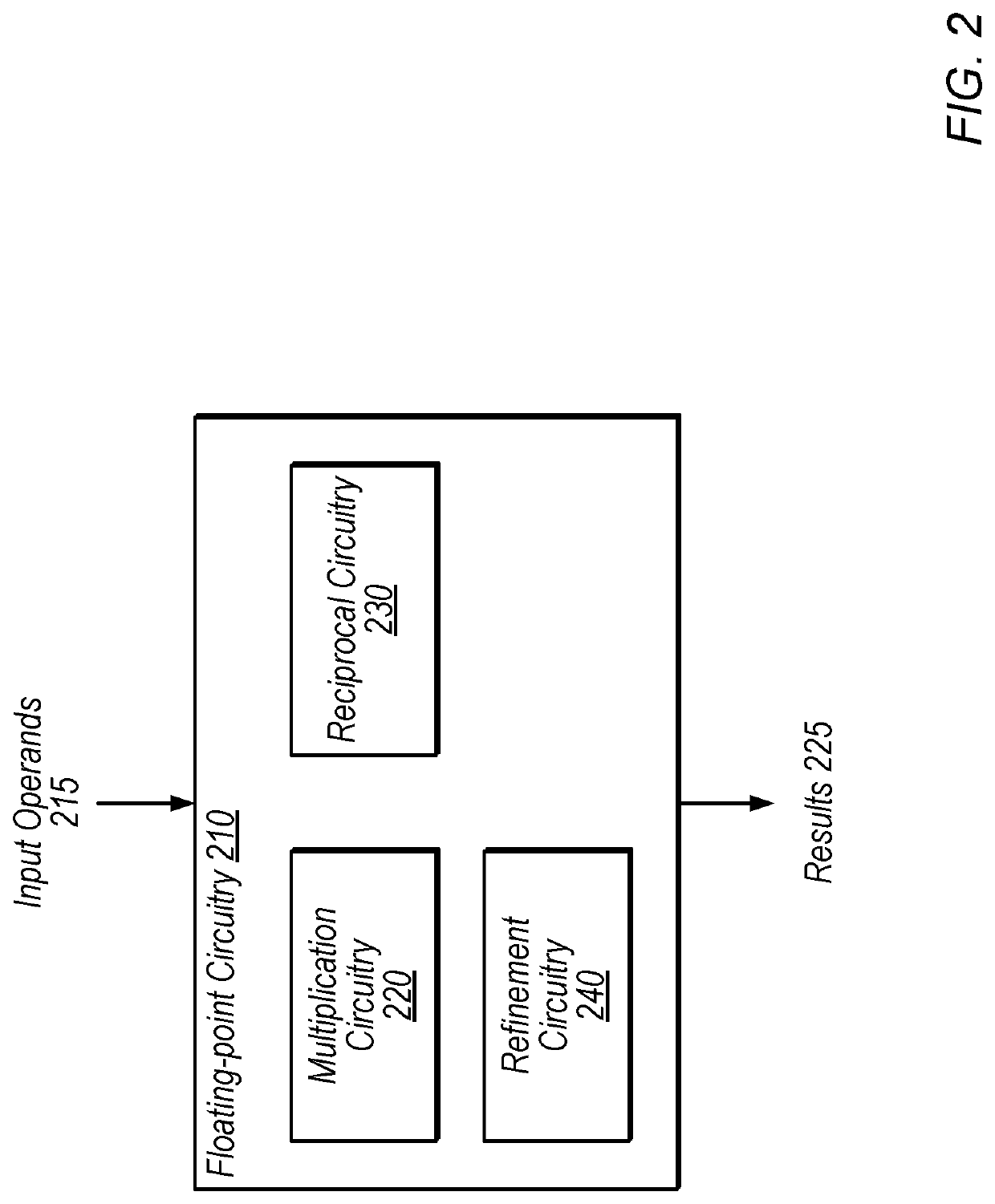
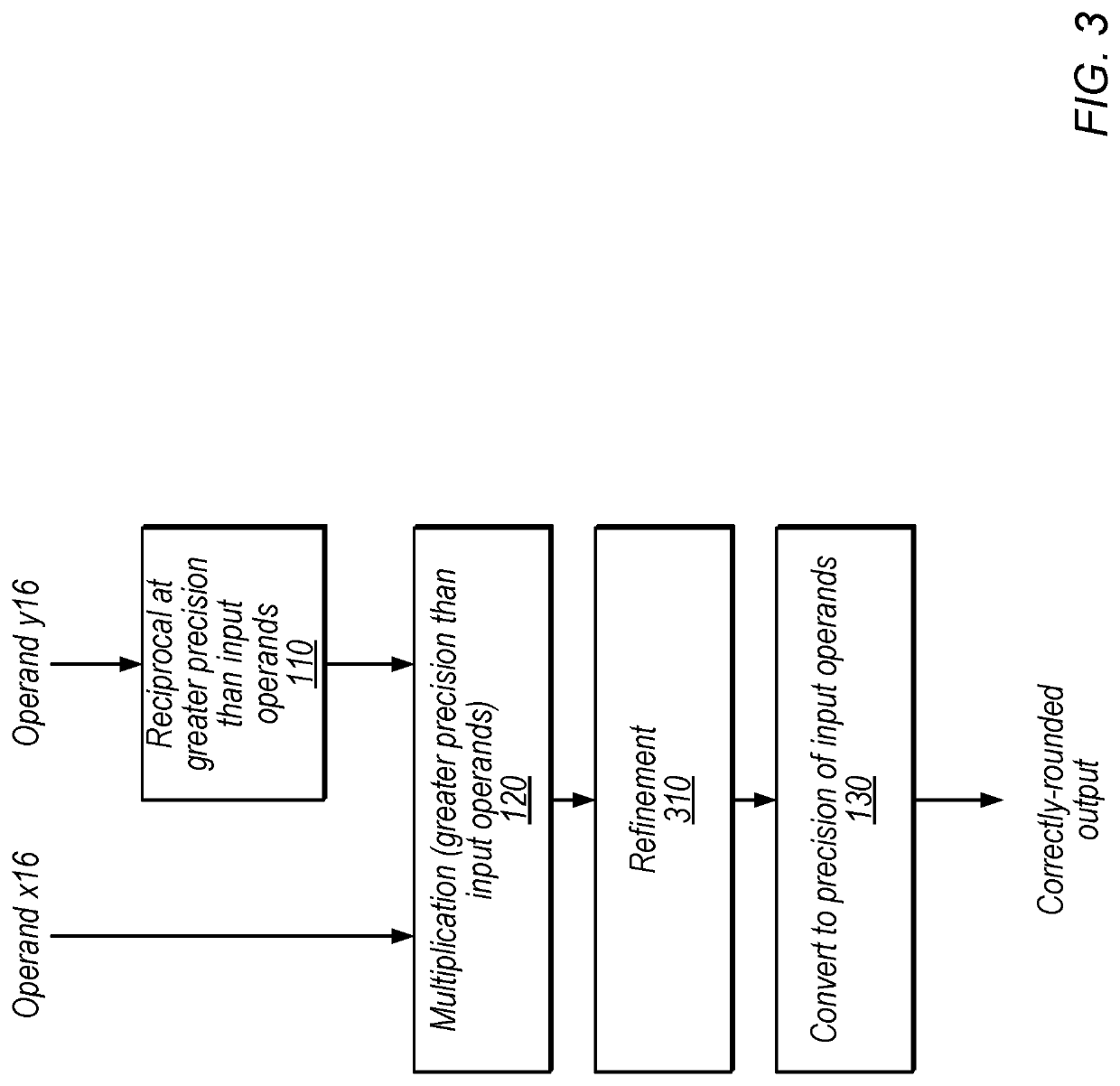
ActiveUS10503473B1Digital data processing detailsMachine execution arrangementsLeast significant bitFloating point
Techniques are disclosed relating to circuitry configured to perform reciprocal-based floating-point division. In some embodiments, floating-point circuitry includes reciprocal circuitry configured to generate a reciprocal of a divisor, multiplication circuitry configured to multiply the reciprocal results with a dividend, and circuitry configured to clear a least significant bit of an integer representation of the multiplication output to generate a modified multiplication output. The floating-point circuitry may be configured to convert the modified multiplication output to a representation using the first precision to generate a division output. In some embodiments, the refinement using the integer representation may provide correctly-rounded subnormal division results. The disclosed techniques may improve accuracy, reduce processing time, and / or reduce instructions needed for floating-point division, with little to no increase in chip area.
Owner:APPLE INC
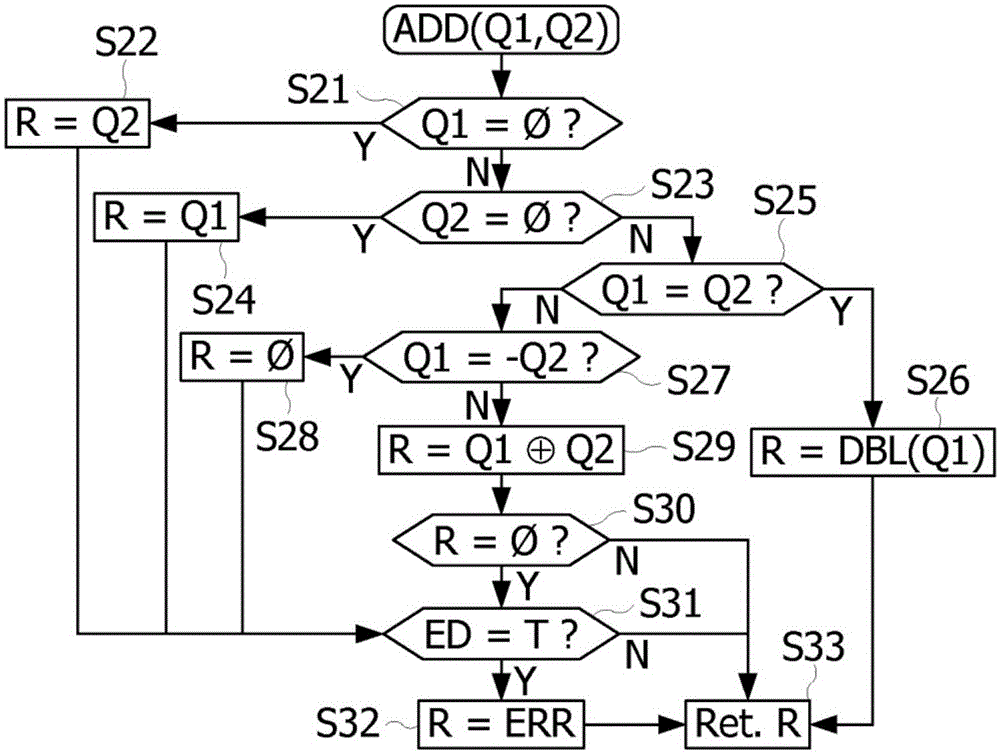
Elliptic curve encryption method comprising error detection
ActiveCN105337734ADigital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareMultiplication operator
A method in an elliptic curve cryptographic system, the method being executed by an electronic device and including a multiplication operation of multiplying a point of an elliptic curve by a scalar number, the point having affine coordinates belonging to a Galois field, the multiplication operation including steps of detecting the appearance of a point at infinity during intermediate calculations of the multiplication operation, and of activating an error signal if the point at infinity is detected and if the number of bits of the scalar number processed by the multiplication operation is lower than the rank of the most significant bit of an order of a base point of the cryptographic system.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
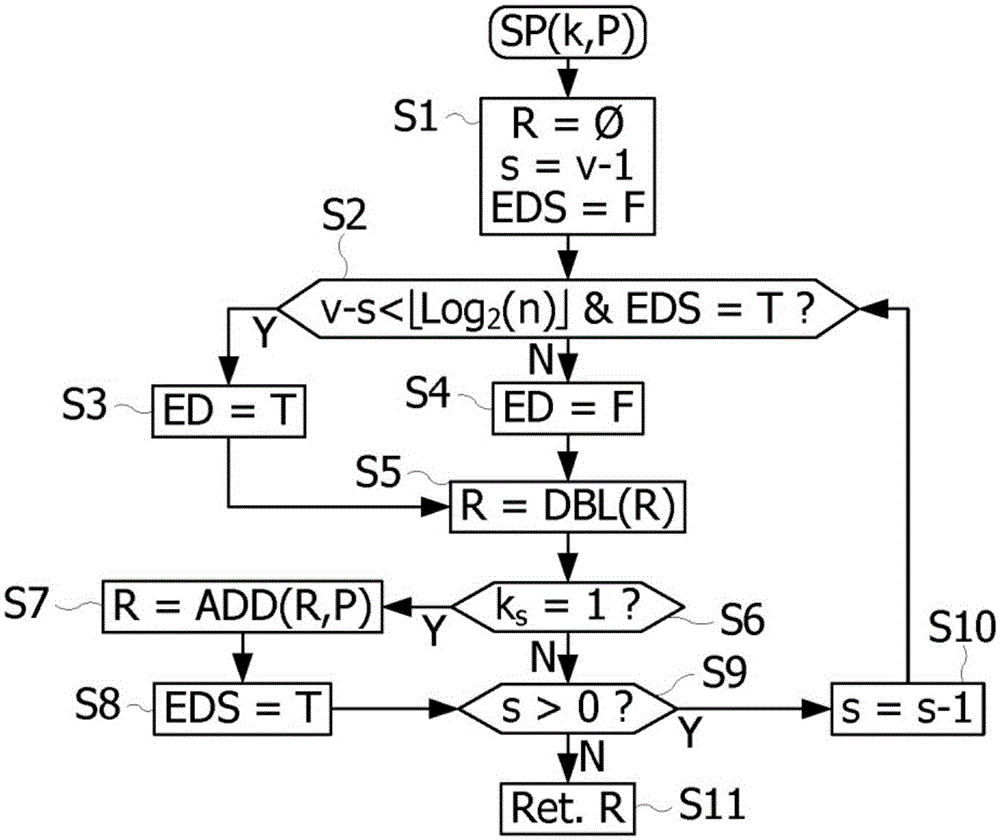
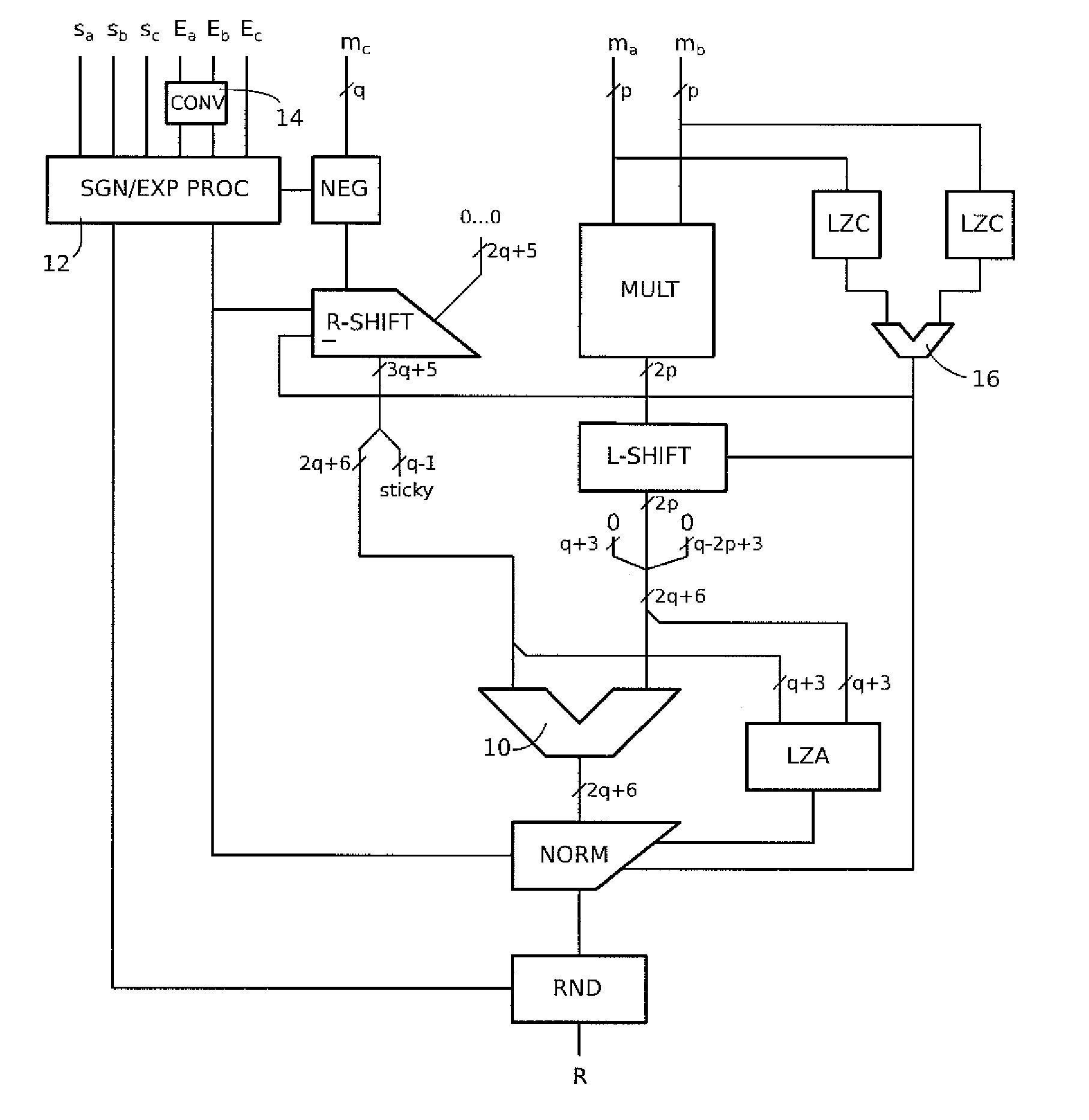
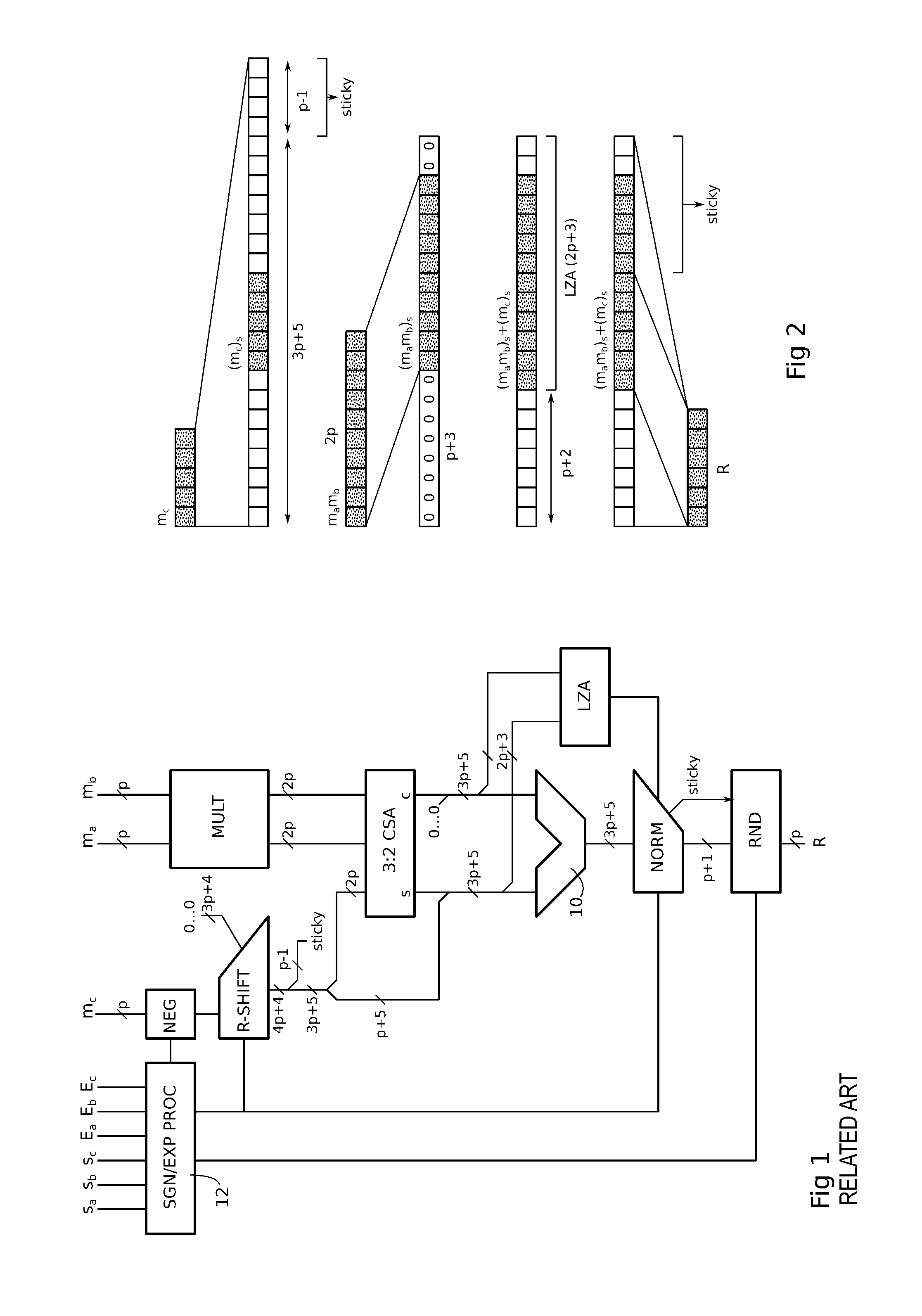
Mixed precision fused multiply-add operator
ActiveUS9367287B2Less complexComputation using denominational number representationBinary multiplierFloating point
A circuit for calculating the fused sum of an addend and product of two multiplication operands, the addend and multiplication operands being binary floating-point numbers represented in a standardized format as a mantissa and an exponent is provided. The multiplication operands are in a lower precision format than the addend, with q>2p, where p and q are the mantissa size of the multiplication operand and addend precision formats. The circuit includes a p-bit multiplier receiving the mantissas of the multiplication operands; a shift circuit aligning the mantissa of the addend with the product output by the multiplier based on the exponent values of the addend and multiplication operands; and an adder processing q-bit mantissas, receiving the aligned mantissa of the addend and the product, the input lines of the adder corresponding to the product being completed to the right by lines at 0 to form a q-bit mantissa.
Owner:KALRAY
Method for defining parallel dual butterfly computation fast Fourier transform processor structure
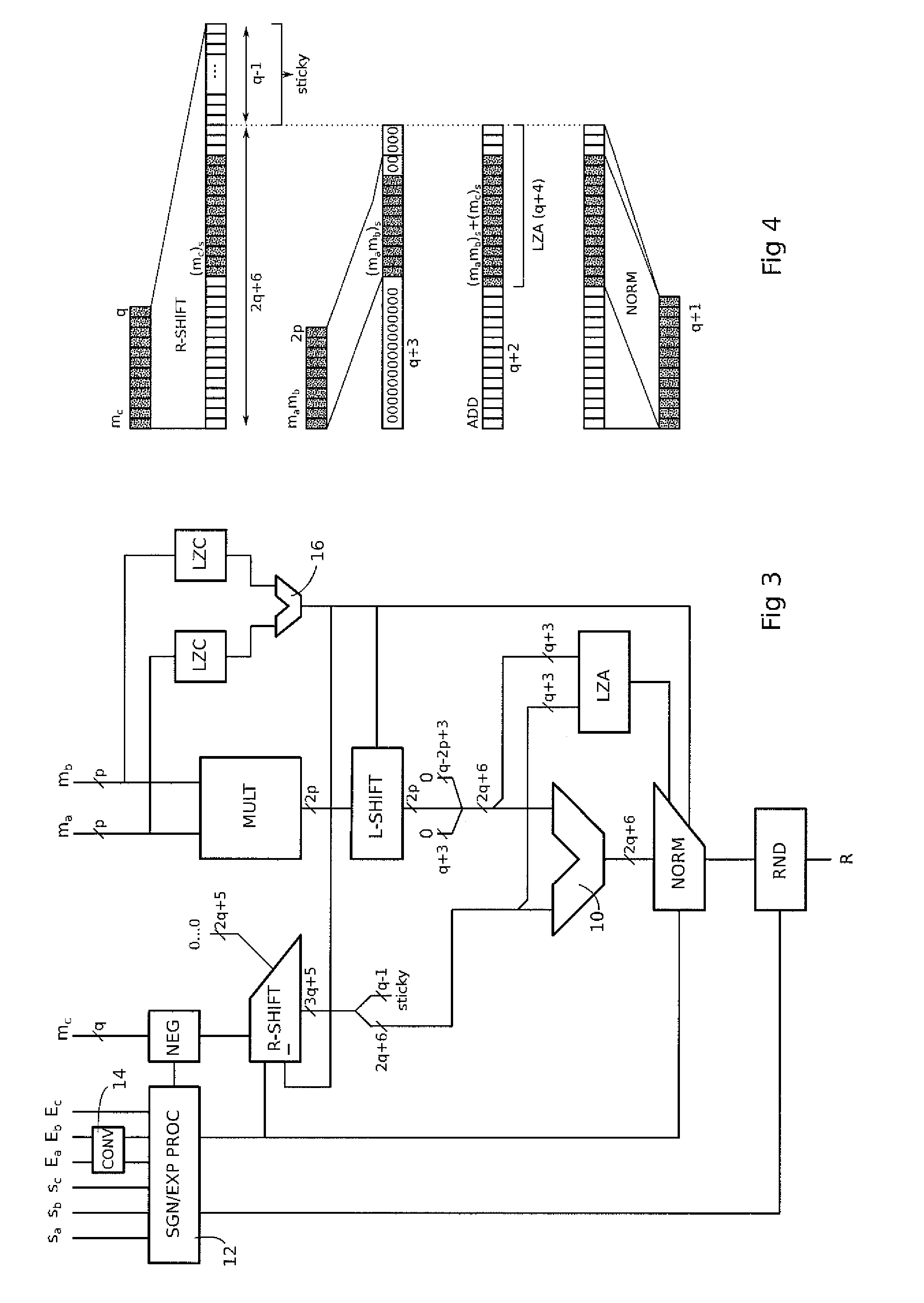
InactiveCN1259782CFast operationOrthogonal multiplexMultiple carrier systemsRotation factorFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to a method for determining the structure of a parallel double-butterfly fast Fourier transform processor, which belongs to the field of information technology. The present invention improves the core unit in the fast Fourier transform processor - the butterfly calculation unit, and obtains a parallel double butterfly calculation processing method. The processor and the adder are processed in parallel to obtain a parallel butterfly calculation structure, and then perform double butterfly calculation processing, that is, the input of the butterfly calculation unit is grouped according to the corresponding rotation factor, and then the input data is divided according to whether the butterfly calculation process contains multiplication The processor is divided into two butterfly calculation processing units for processing, and a parallel double butterfly calculation fast Fourier transform processor structure is obtained. The present invention effectively improves the operation speed of the fast Fourier transform processor, occupies less hardware resources, especially multiplier resources, thereby better solving the problem between the operation speed and hardware consumption in the fast Fourier transform processor. contradiction.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com