Patents
Literature
53 results about "Phenotype correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A correlation between the nature or the location of a mutation in an individual based on observations of affected individuals and their respective genotype. GENOTYPE-PHENOTYPE CORRELATION: "The genotype-phenotype correlation are used to elucidate affects of mutation.". Related Psychology Terms.
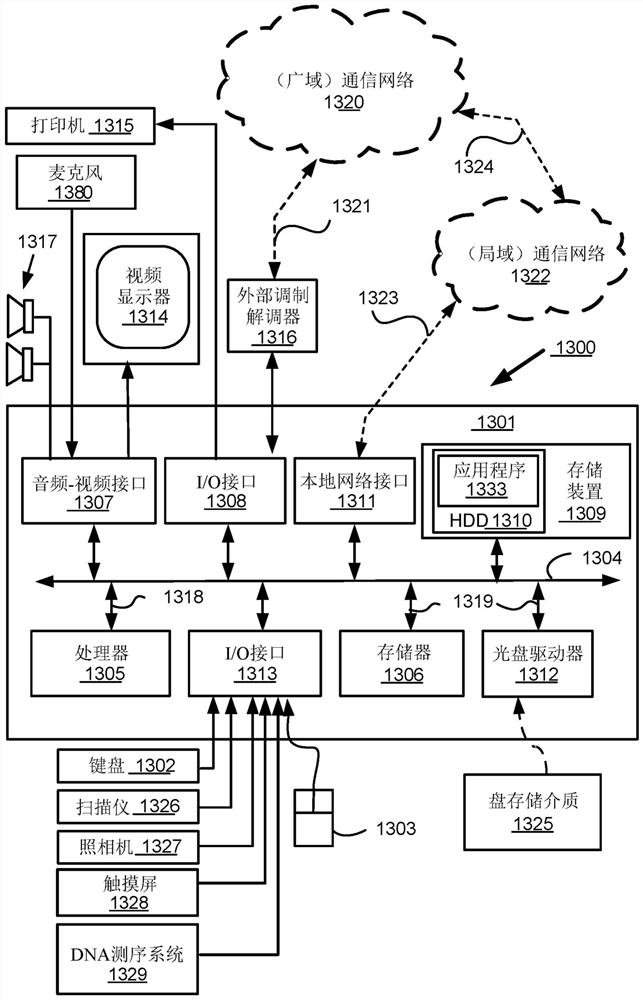
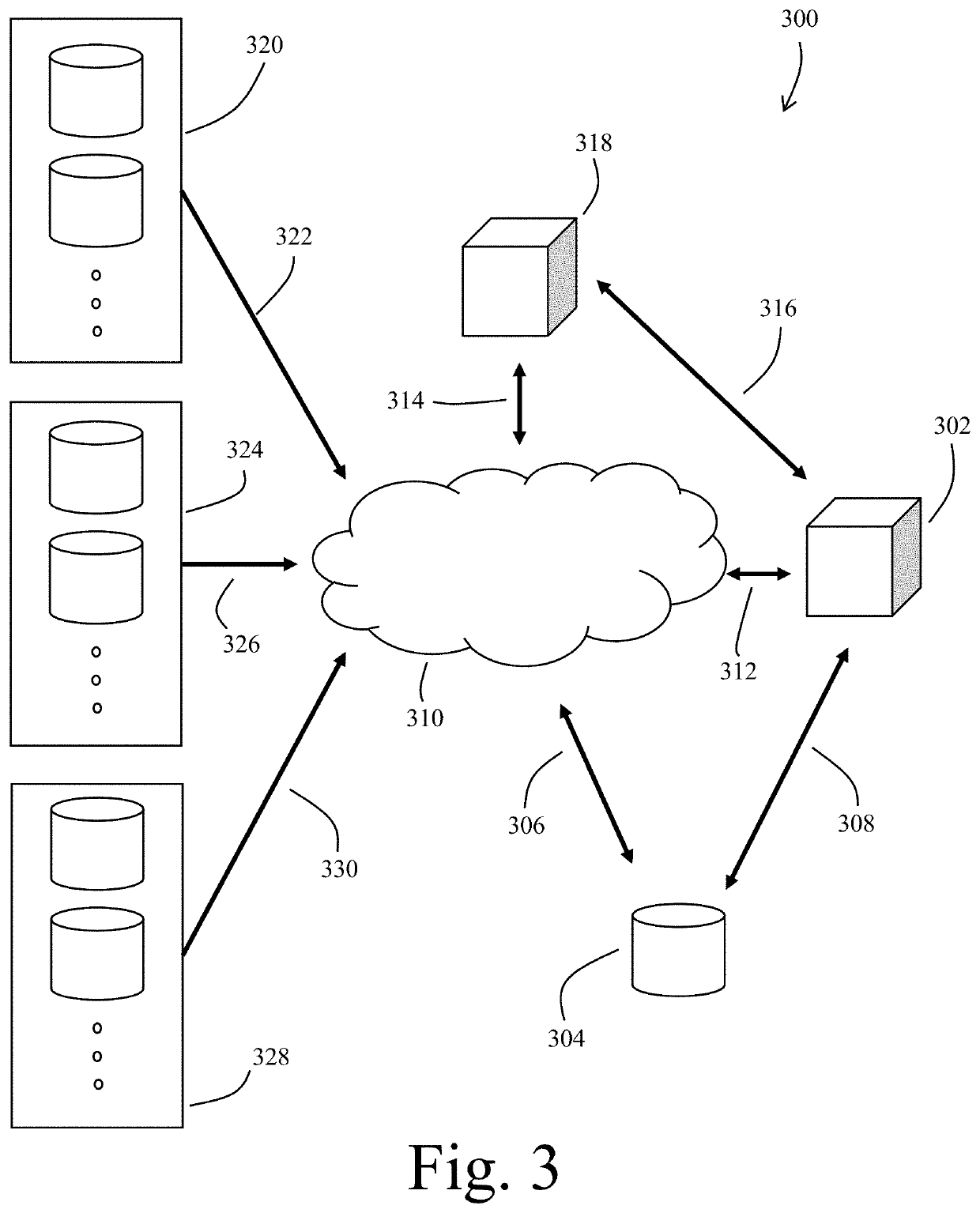
Database and data processing system for use with a network-based personal genetics services platform
Owner:23ANDME
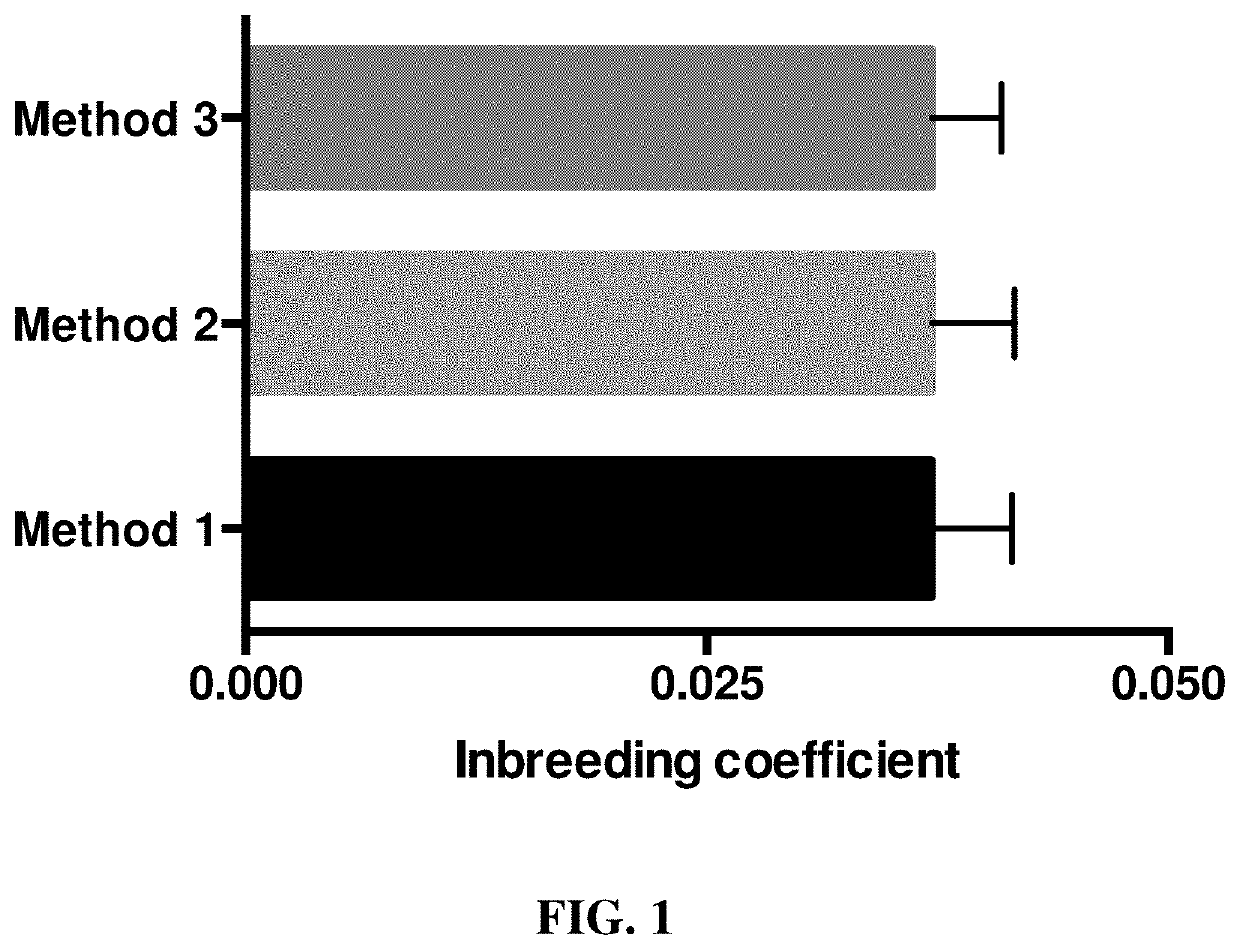
Compositions, methods, and systems for inferring canine breeds for genetic traits and verifying parentage of canine animals
InactiveUS20060008815A1Maximize healthMaximize potential performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenetic traitsHealth condition
Methods and systems are provided for managing companion animal subjects in order to maximize their individual health and potential performance and to maximize profits obtained in breeding and marketing the companion animal subjects. The methods and systems draw an inference of a phenotype for a genetic trait of a companion animal subject by determining the nucleotide occurrence of at least one companion animal SNP that is determined to be associated with the phenotype. The methods and systems described can be utilized to identify individual animals, determine or verify parentage of a single dog from any breed if the putative parent(s) are also available for testing, and are associated with, and predictive of, canine breeds. The inference is used in some aspects to diagnose a health condition or predisposition of a companion animal subject.
Owner:MMI GENOMICS
Single nucleotide polymorphisms sensitively predicting adverse drug reactions (adr) and drug efficacy
InactiveUS20070128597A1Reducing primaryReducing secondary riskGenetic material ingredientsDisease diagnosisNucleotideEfficacy
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms sensitively predicting Advserse Drug Reactions (ADR) and Drug Efficacy Abs tract. The invention provides diagnostic methods and kits including oligo and / or polynucleotides or derivatives, including as well antibodies determining whether a human subject is at risk of getting adverse drug reaction after statin therapy or whether the human subject is a high or low responder or a good a or bad metabolizer of statins. The invention provides further diagnostic methods and kits including antibodies determining whether a human subject is at risk for a cardiovascular disease. Still further the invention provides polymorphic sequences and other genes. The present invention further relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding a phenotype associated (PA) gene polypeptide useful in methods to identify therapeutic agents and useful for preparation of a medicament to treat cardiovascular disease or influence drug response, the polynucleotide is selected from the group comprising: SEQ ID 1-168 with allelic variation as indicated in the sequences section contained in a functional surrounding like full length cDNA for PA gene polypeptide and with or without the PA gene promoter sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Phenotype-based pathogenic gene quantitative measurement and calculation method and equipment
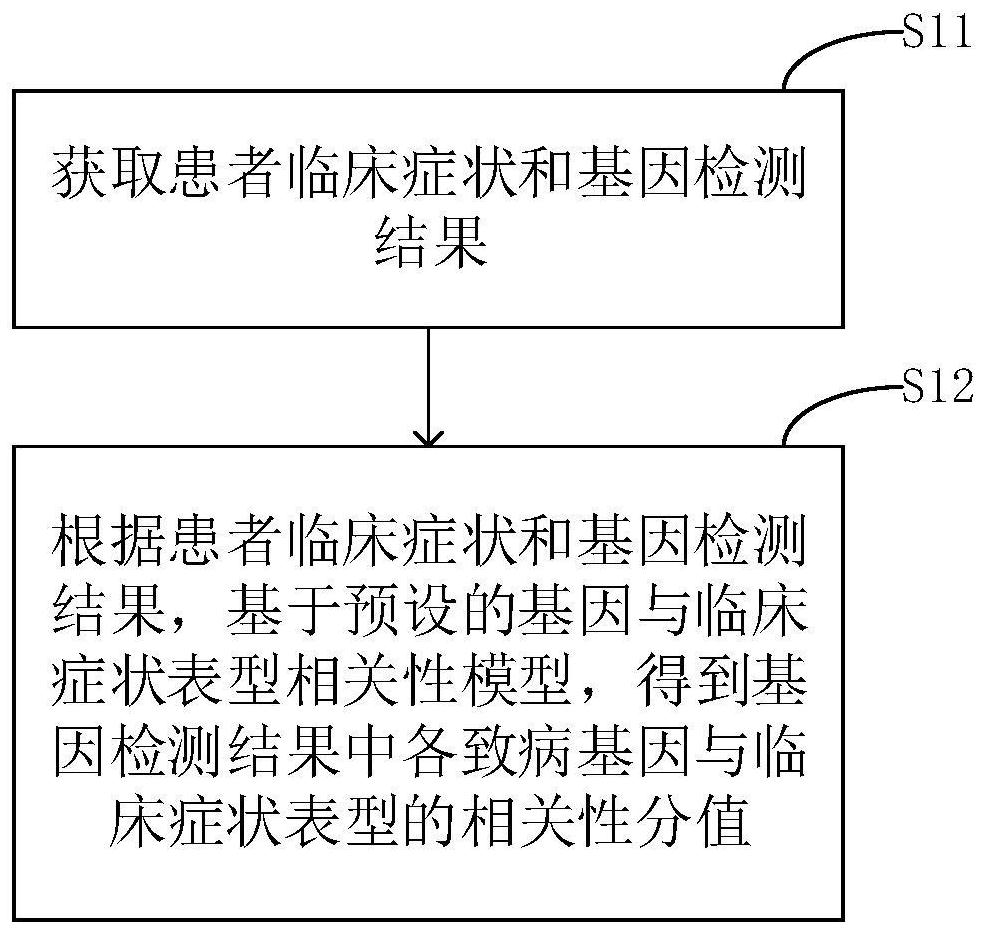
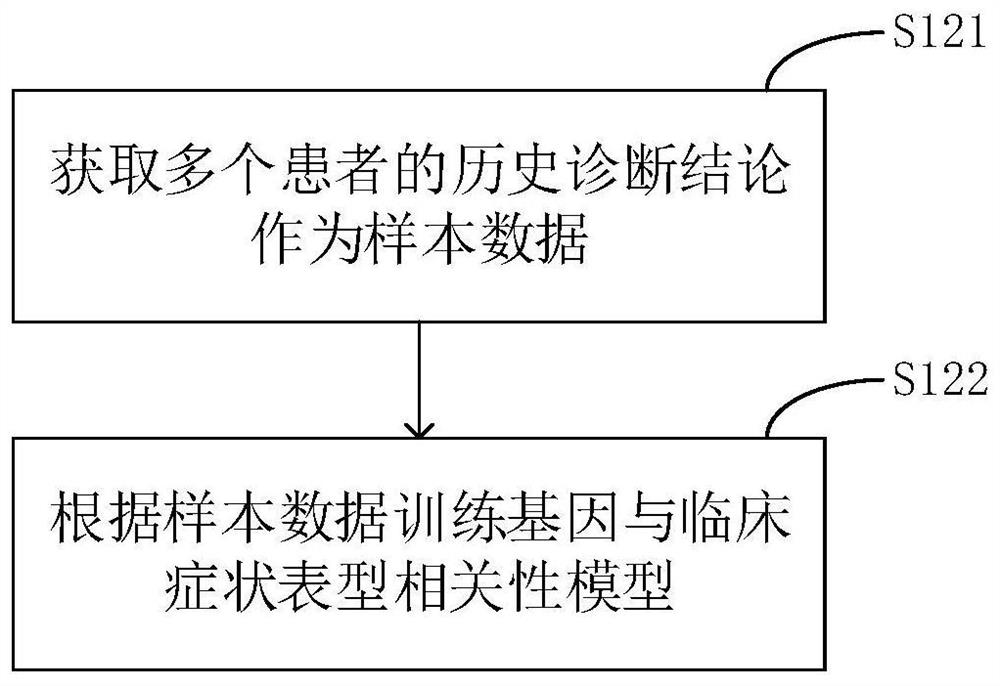
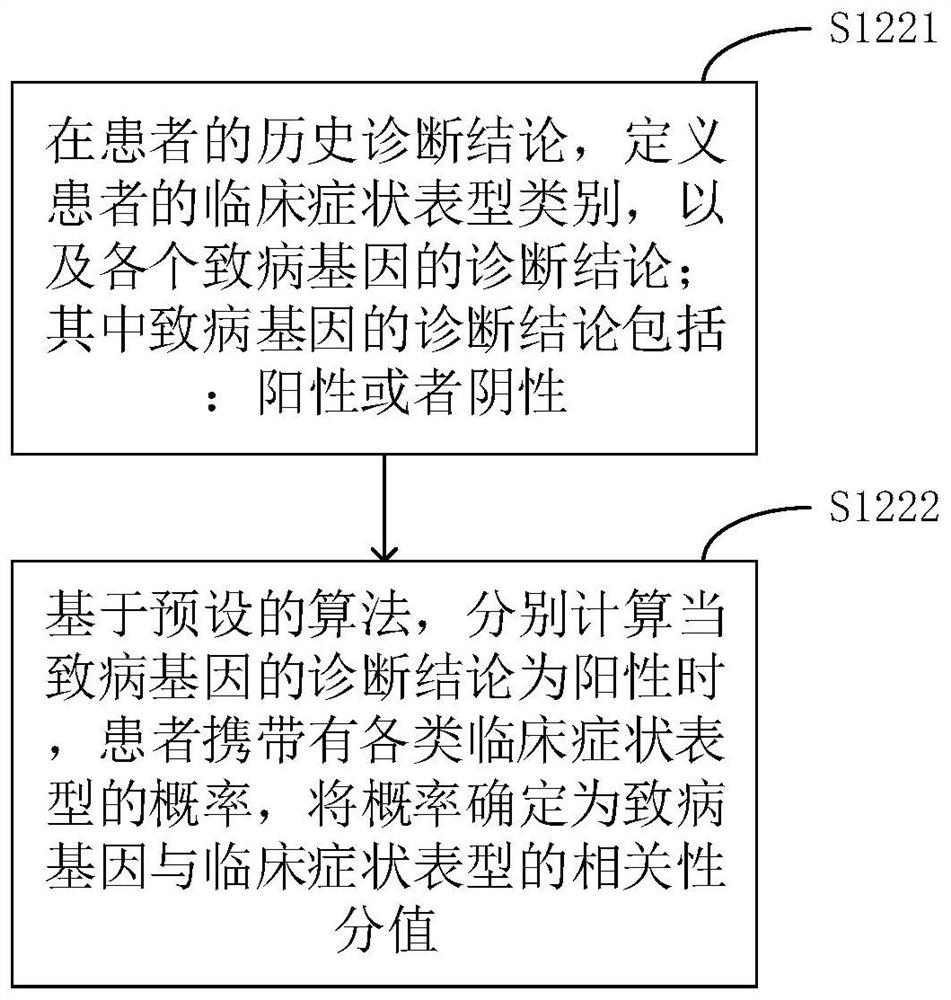
The invention relates to a phenotype-based pathogenic gene quantitative measurement and calculation method, which comprises the following steps: obtaining clinical symptoms and gene detection resultsof a patient, and obtaining correlation scores of pathogenic genes and clinical symptom phenotypes in the gene detection results based on a preset gene and clinical symptom phenotype correlation modelaccording to the clinical symptoms and the gene detection results of the patient. According to the invention, due to the fact that a gene cannot necessarily and completely cause certain clinical symptom phenotype, a quantitative index is required to describe the possibility, and according to clinical symptoms shown when a patient sees a doctor and gene detection results obtained through gene sequencing, correlation scores of all pathogenic genes in the gene detection results and clinical symptom phenotypes are calculated, and the higher the correlation scores of the pathogenic genes and a certain clinical symptom phenotype are, the more easily the clinical symptom phenotype is caused by the pathogenic genes, so that a genetic counselor can conveniently evaluate the pathogenic gene causingthe disease symptoms of the patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
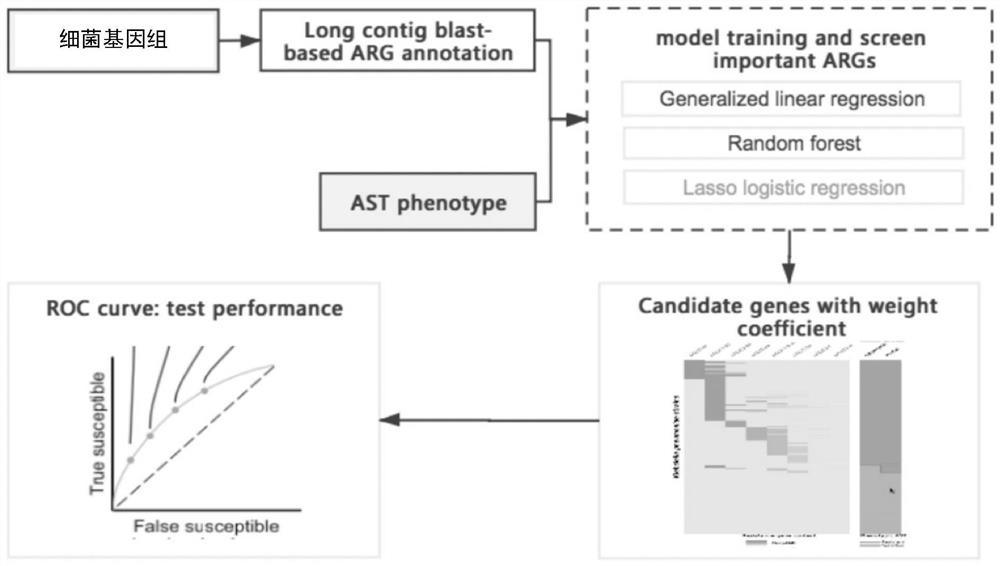
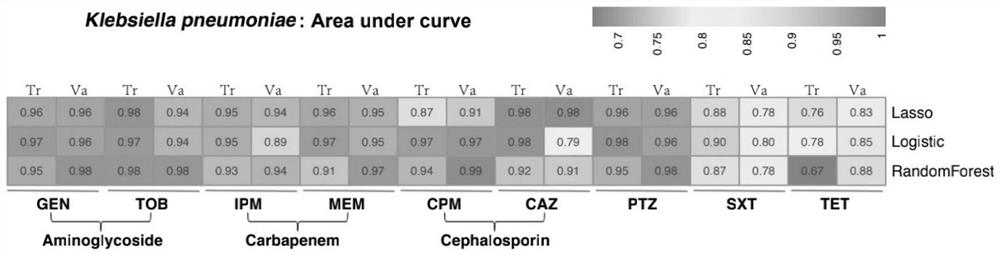
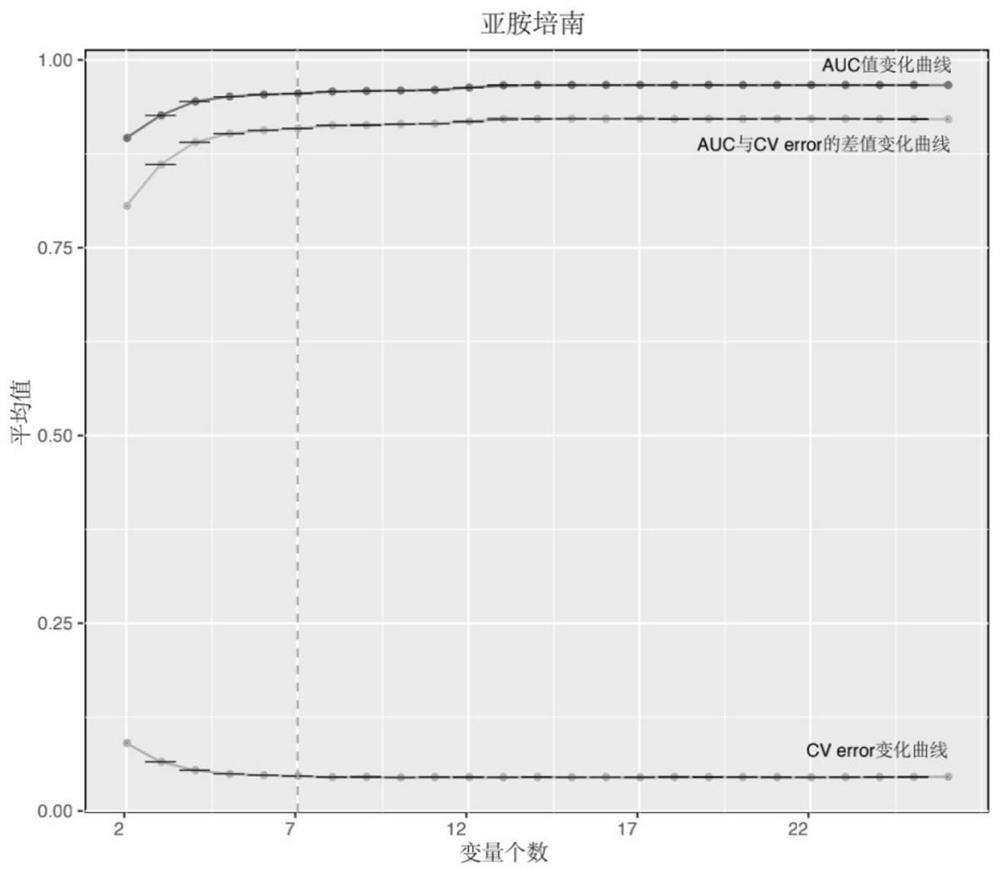
Method for screening important characteristic genes related to drug resistance phenotype of bacteria based on machine learning
ActiveCN114067912AFacilitate translational applied researchExpand Screening MiningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAntibiotic resistanceCorrelation analysis
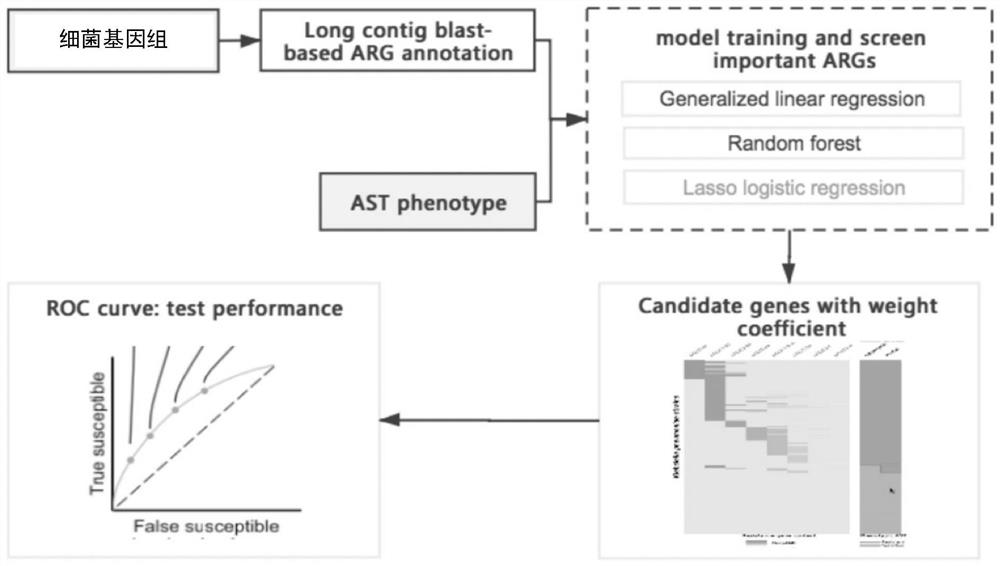
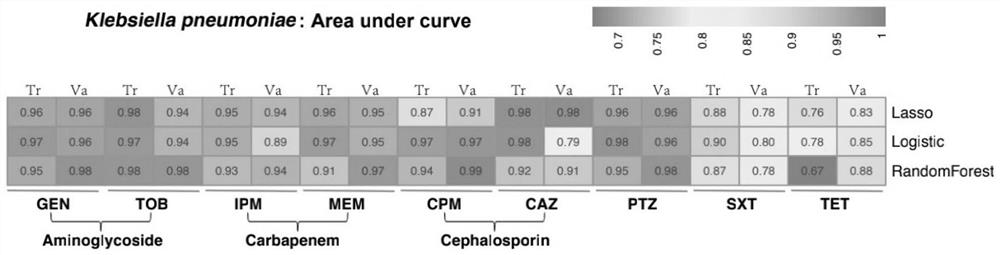
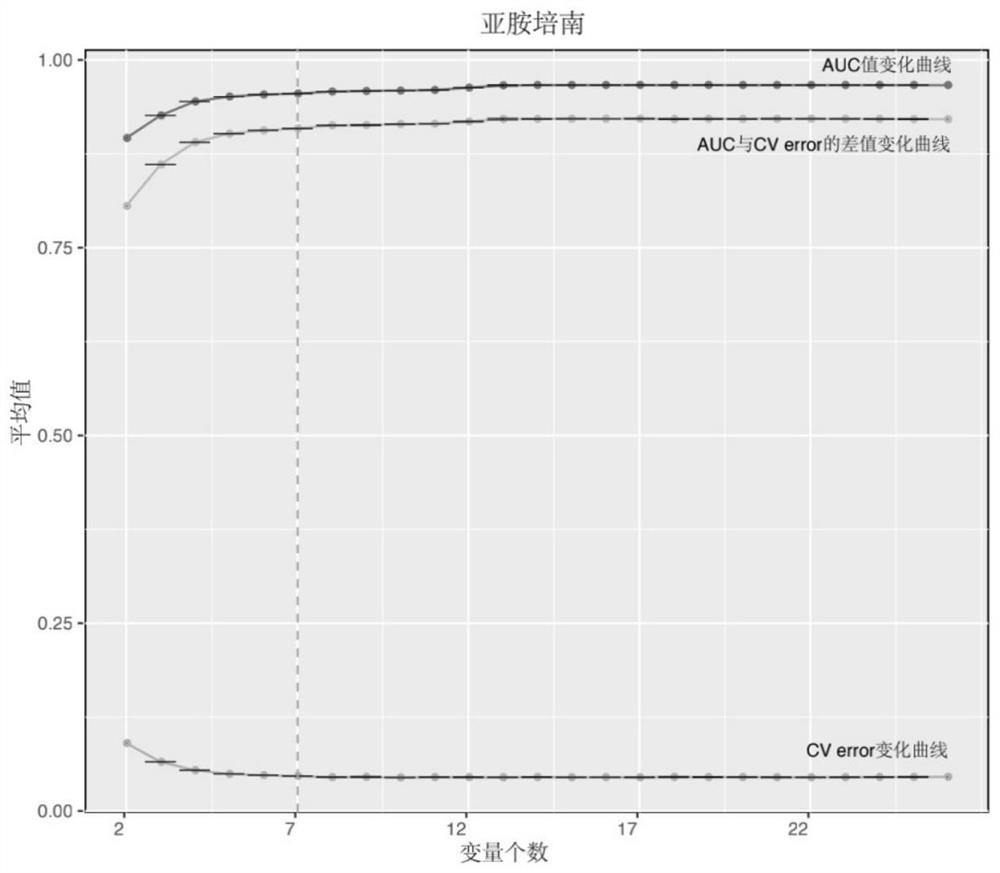
The invention relates to a method for screening important characteristic genes related to the drug resistance phenotype of bacterial based on a machine learning technology. According to the method, for the antibiotic resistance of the bacterial, on the basis of the BGWAS thought, target bacterial genomes on a public platform or large-sample-size bacterial strain genome data obtained after current collection, sequencing and assembly, and corresponding antibiotic drug susceptibility test results are collected, and correlation analysis between genotypes and drug resistance phenotypes is carried out by using the machine learning method, so that important characteristic genes (non-core drug-resistant genes) related to the drug resistance phenotypes are screened out, weight coefficients of the important characteristic genes are obtained;and finally the reliability of the drug-resistant genes related to drugs is determined by using ROC analysis.
Owner:天津金匙医学科技有限公司 +2
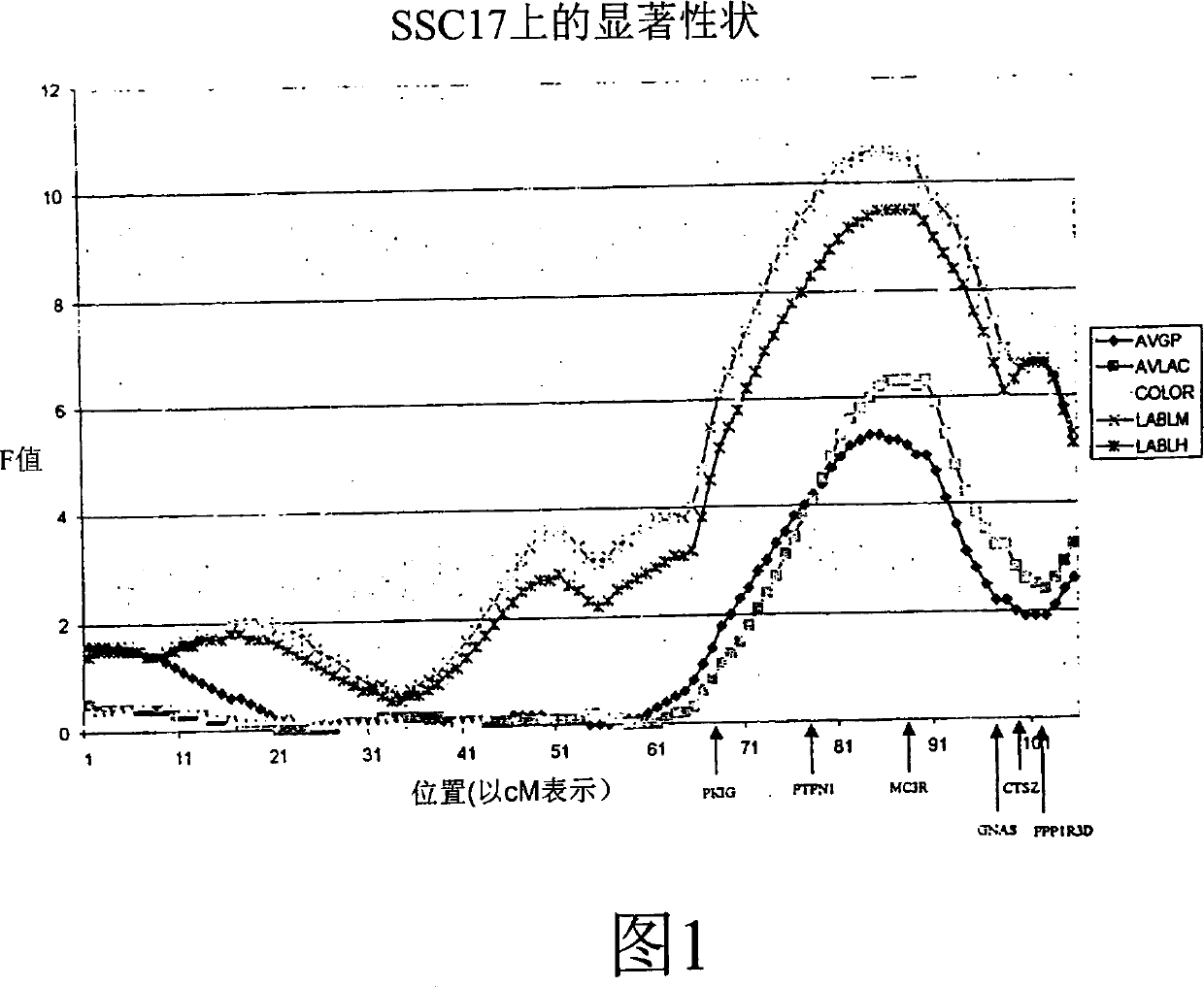
Fine mapping of chromosome 17 quantitative trait loci and use of same for marker assisted selection
InactiveCN1809644AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
Disclosed herein is fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus on Chromosome 17 which is associated with meat traits, growth and fatness. The quantitative trait locus correlates with several major effect genes which have phenotypic correlations with animal growth and meat quality which may be used for marker assisted breeding. Specific polymorphic alleles of these genes are disclosed for tests to screen animals to determine those more likely to produce desired traits.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
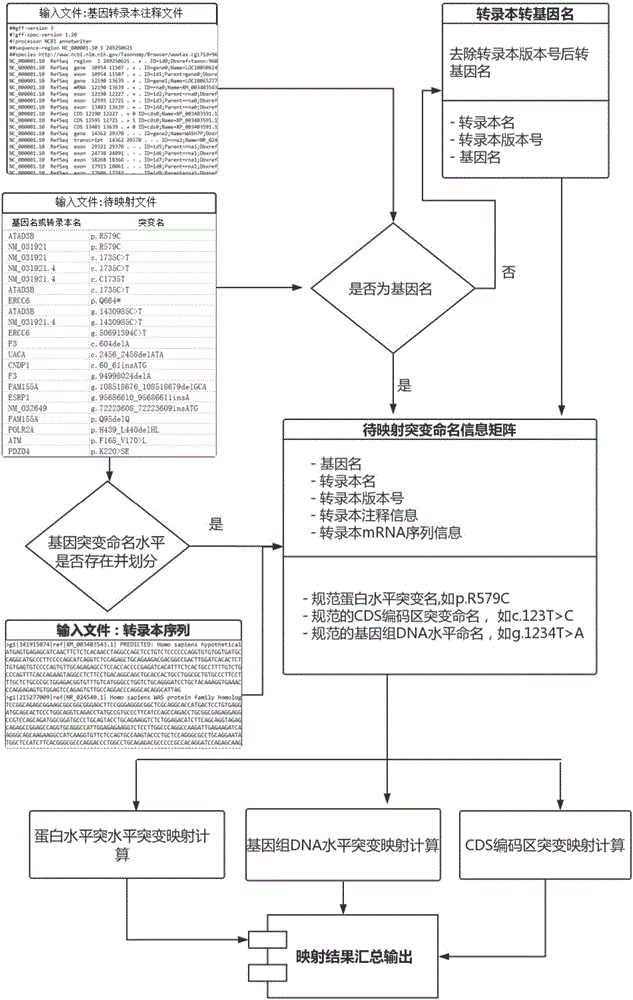
DNA and protein level mutation analysis method
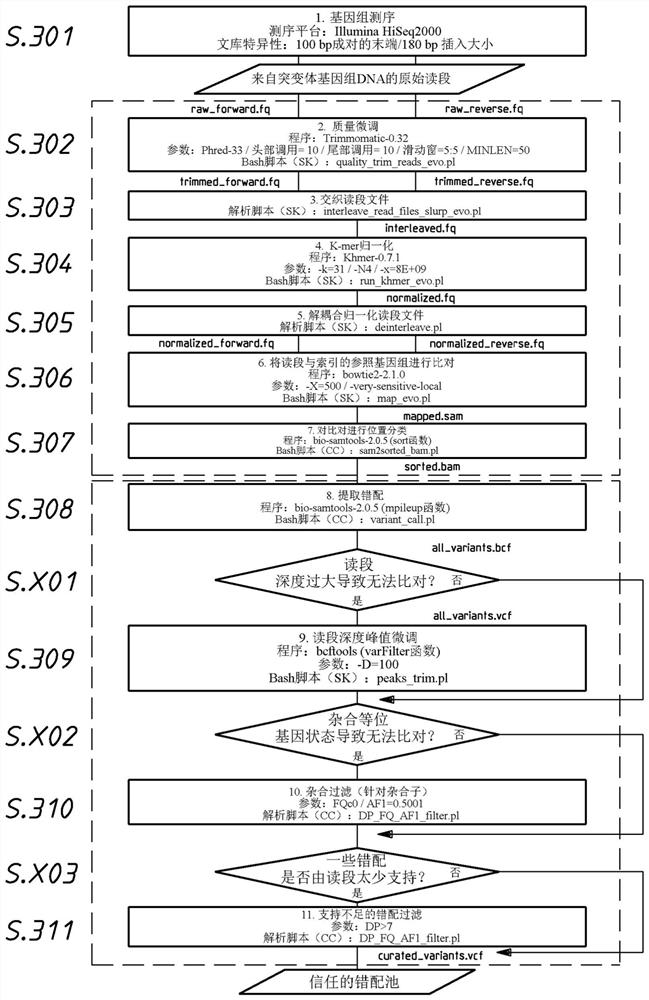
The invention discloses a DNA and protein level mutation analysis method. The method comprises the steps of 1, reading a gene mutation file, and formatting the file into a standard name; 2, indexing a transcript sequence, gene information and gene transcript annotation information, thereby forming an amino acid codon corresponding relationship table; judging a mutation level and a mutation mode, and judging whether a mutation name is protein level mutation, genome DNA level mutation or CDS code area mutation; and 4, entering different level mutation mapping processes according to a judging result of the step 3, thereby obtaining mapping relationships of three mutation names. According to the method, the mapping relationships of various mutation names are output by carrying on phenotypic correlation gene mutation and polymorphic sites mined from literatures, thereby finishing annotating correspondence between pathogenic variation mined from the literatures, and gene mutation and polymorphic sites identified by sequencing.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
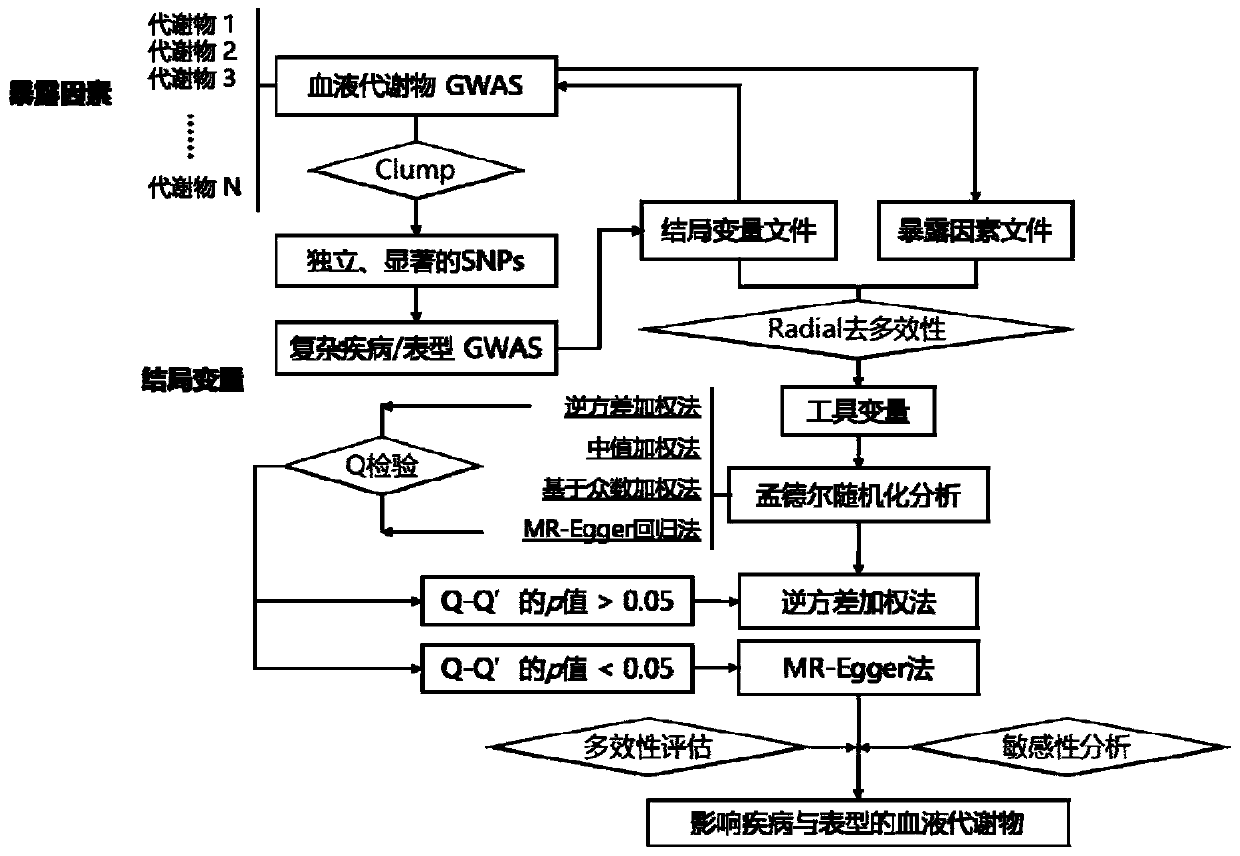
Method for predicting complex diseases and phenotypic related metabolites based on Mendel randomization
PendingCN111341448ARich in biological functionsImprove statistical powerHealth-index calculationProteomicsMetaboliteNutrition
The invention discloses a method for predicting complex diseases and phenotypic related metabolites based on Mendel randomization analysis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting andsorting blood metabolite whole genome association research data; (2) screening tool variables and removing multiple effects; and (3) performing double-sample Mendel randomization analysis according to the screened tool variables, and obtaining metabolites related to diseases or phenotypes by integrating judgment of effect values and sensitivity analysis of multiple analysis methods. According tothe method, the influence of 363 blood metabolites on complex diseases and phenotypes is predicted through double-sample Mendel randomization analysis in combination with screening and discriminationof multiple methods, and an important foundation is laid for subsequent searching of drug targets for the blood metabolites and nutrition intervention.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
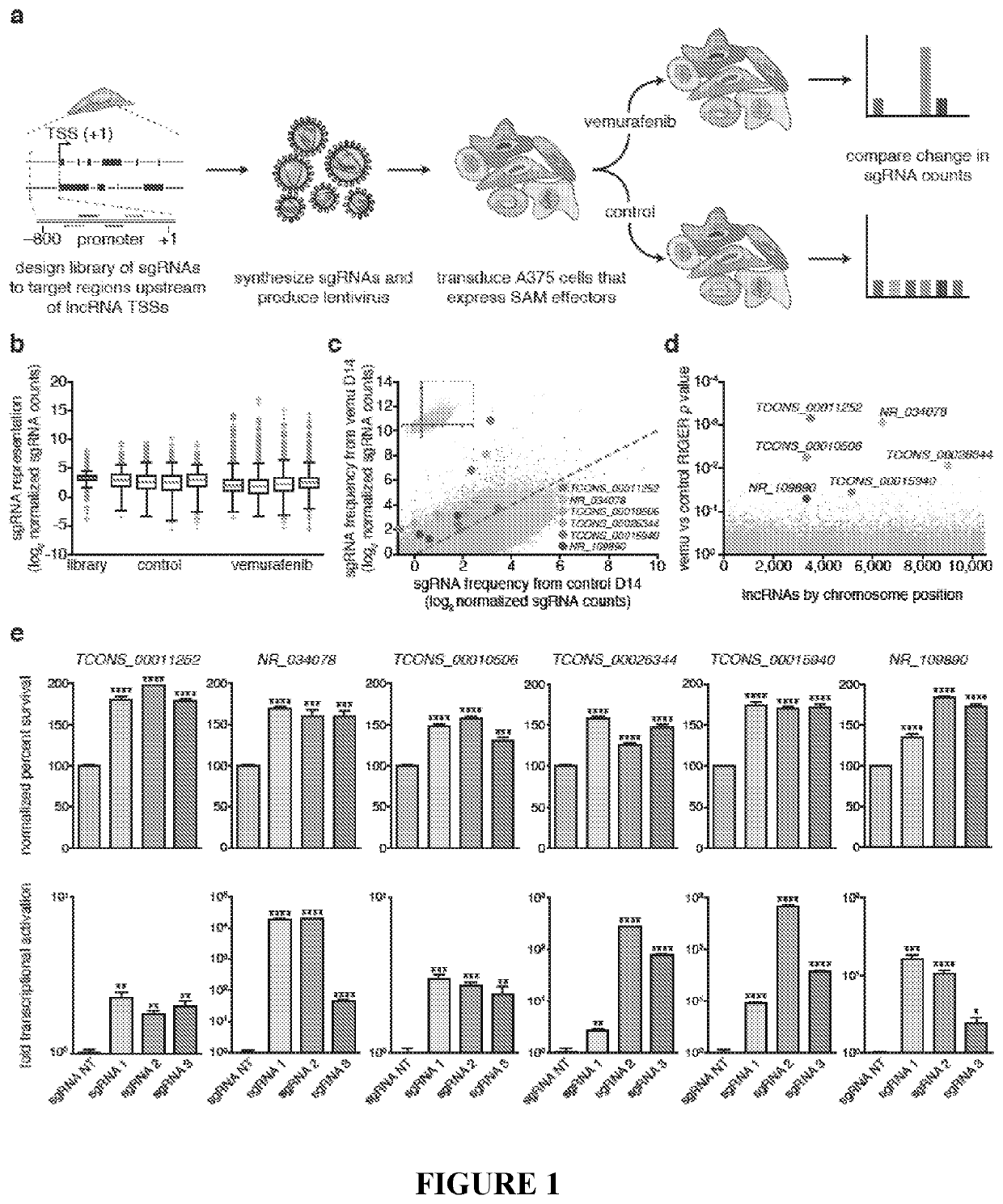
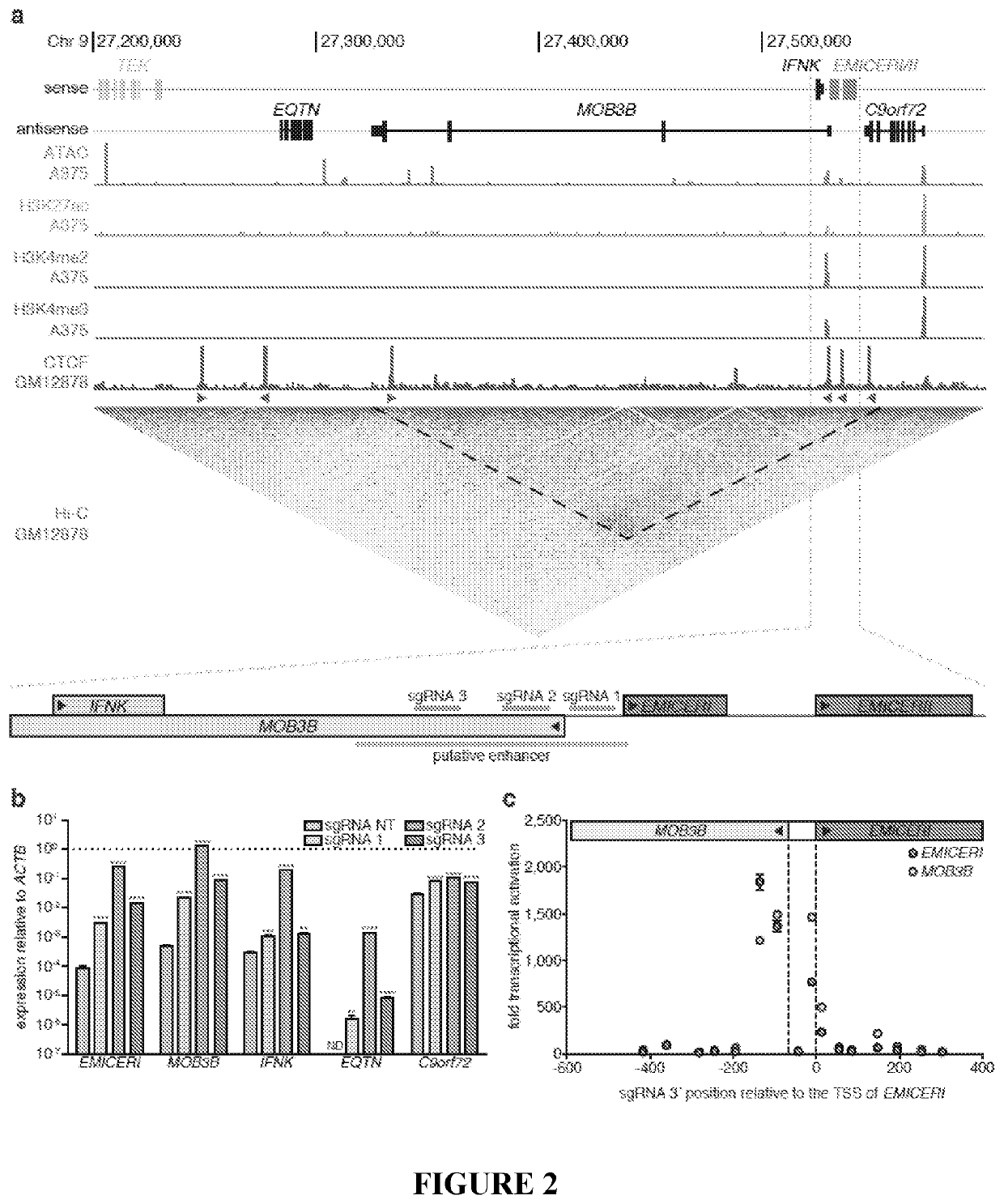
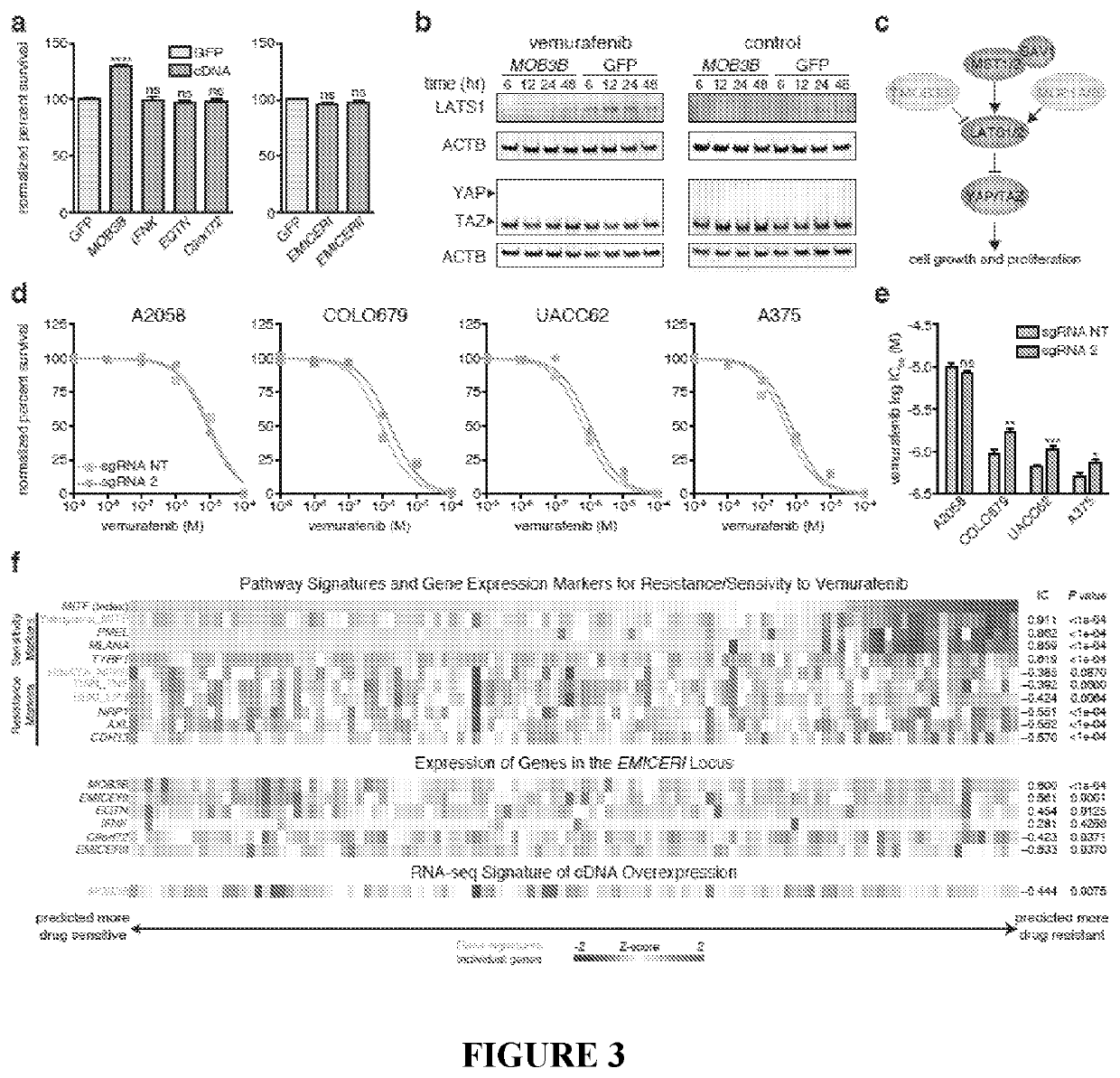
Methods for identification and modification of lncrna associated with target genotypes and phenotypes
ActiveUS20200248184A1Increase productionIncreased abiotic stress toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMelanomaDrug resistance
The application relates to methods for compositions for identifying IncRNA loci associated with target genotypes or phenotypes, including desirable plant genotypes or phenotype. The application also relates to regulatory regions and genes associated with drug resistance, such as resistance to BRAF-inhibitors. Such regulatory regions and genes form the basis for methods for identifying resistance to BRAF-inhibitors, which is useful for improving disease prognosis, treatment, and likely outcomes. The regulatory regions and genes are also suitable targets for therapy in melanoma that is resistant to BRAF-inhibitors.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
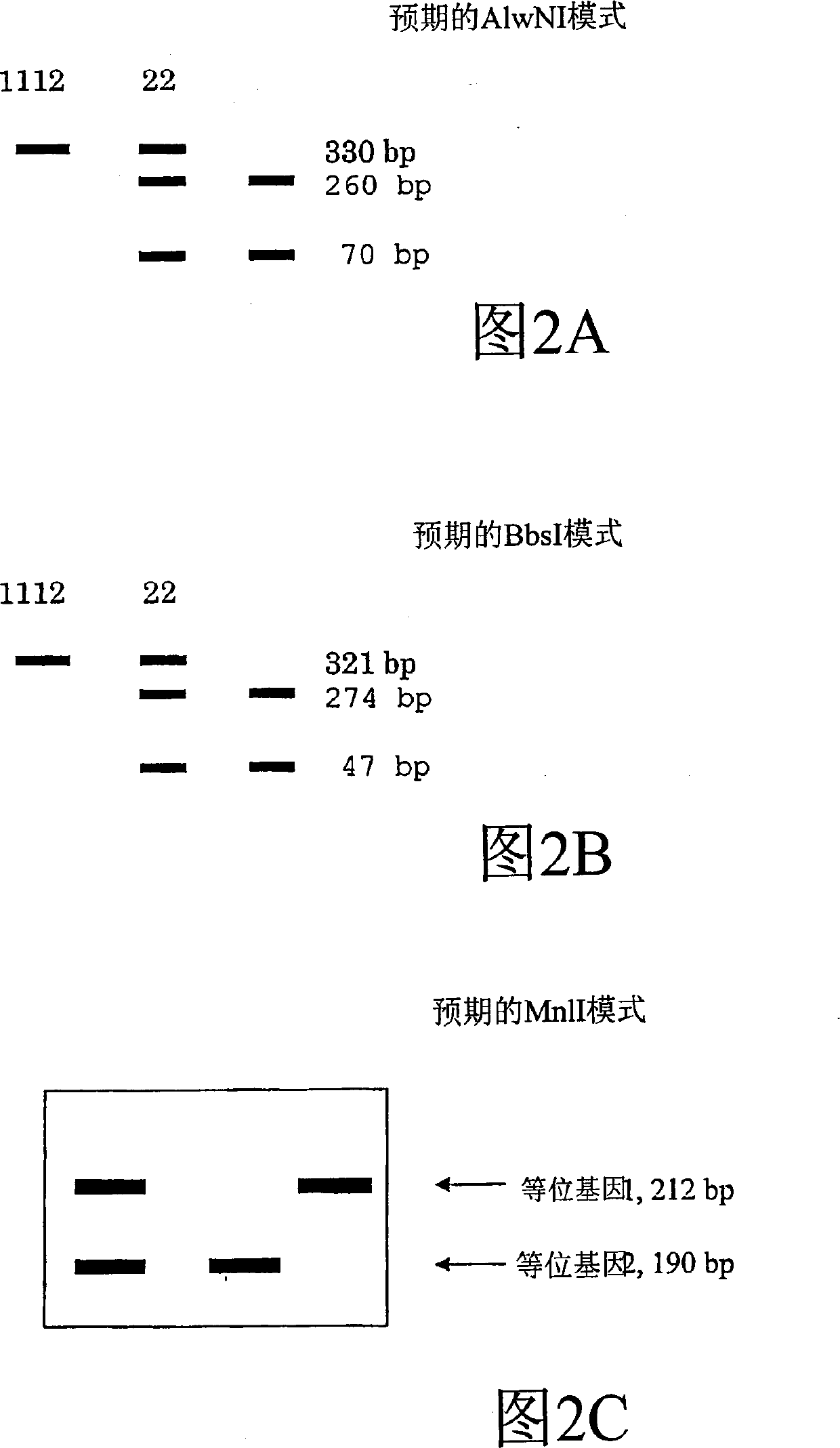
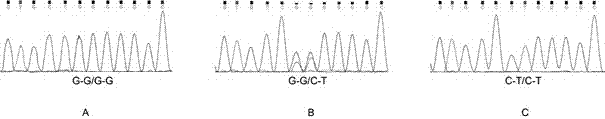
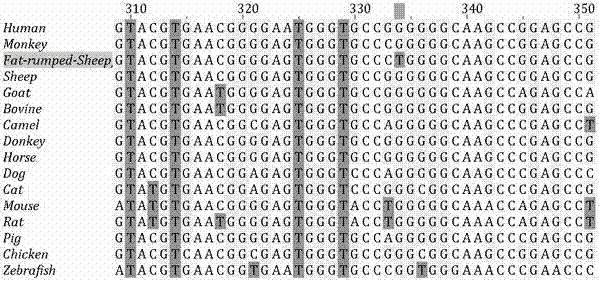
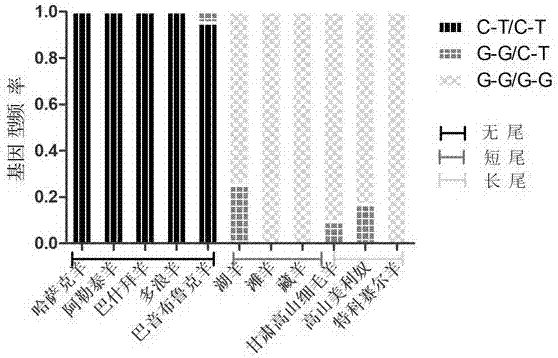
Molecular marker correlated with tailless phenotype of fat-rumped sheep in China and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN107988397ADetection of local sheep breeds in China
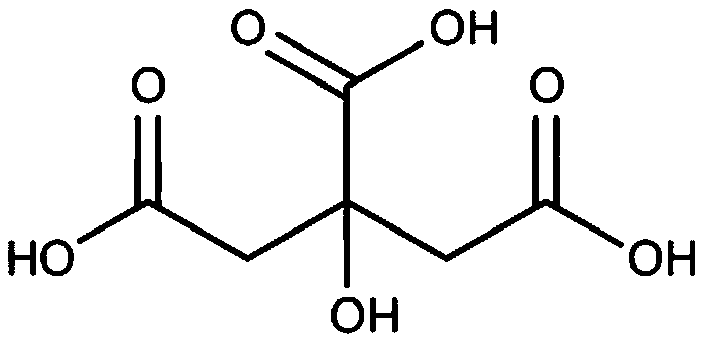
<i>T</i>
Accurate and reliable method for gene single nucleotide polymorphismSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTailComplete linkage
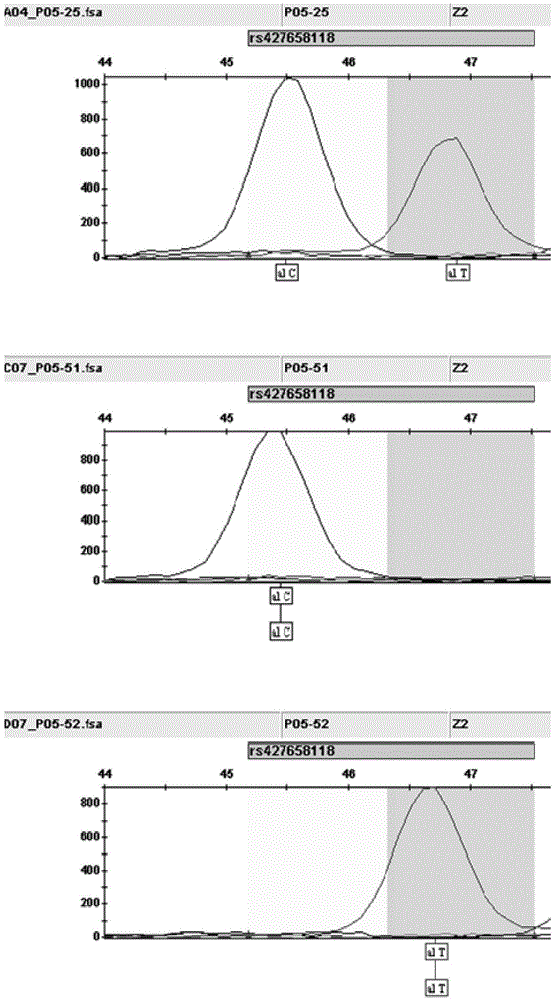
The invention discloses an SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker correlated with detection of tail type characters of sheep and an application of the SNP marker. The SNP marker correlated with detection of the tail type characters of the sheep in China is characterized by being located in two loci, namely, 87804590 / 87804589 of chromosome 8 of the sheep; the two loci of the SNP molecular marker are linked completely; polymorphisms are G-G and C-T; the genotypes comprise G-G / G-G, G-G / C-T and C-T / C-T, the genotype C-T / C-T is only detected in fat-rumped sheep in China, and statistical testsprove that the genotype C-T / C-T is significantly correlated with the tailless phenotype of the sheep. The SNP marker can be applied to early breeding for the tail type characters of local sheep breedsin China, accurate screening can be even performed on sheep in embryonic period or at birth, and a method has the advantages of being accurate, reliable and simple and convenient to operate when usedfor identifying local purebred fat-rumped sheep breeds in China.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
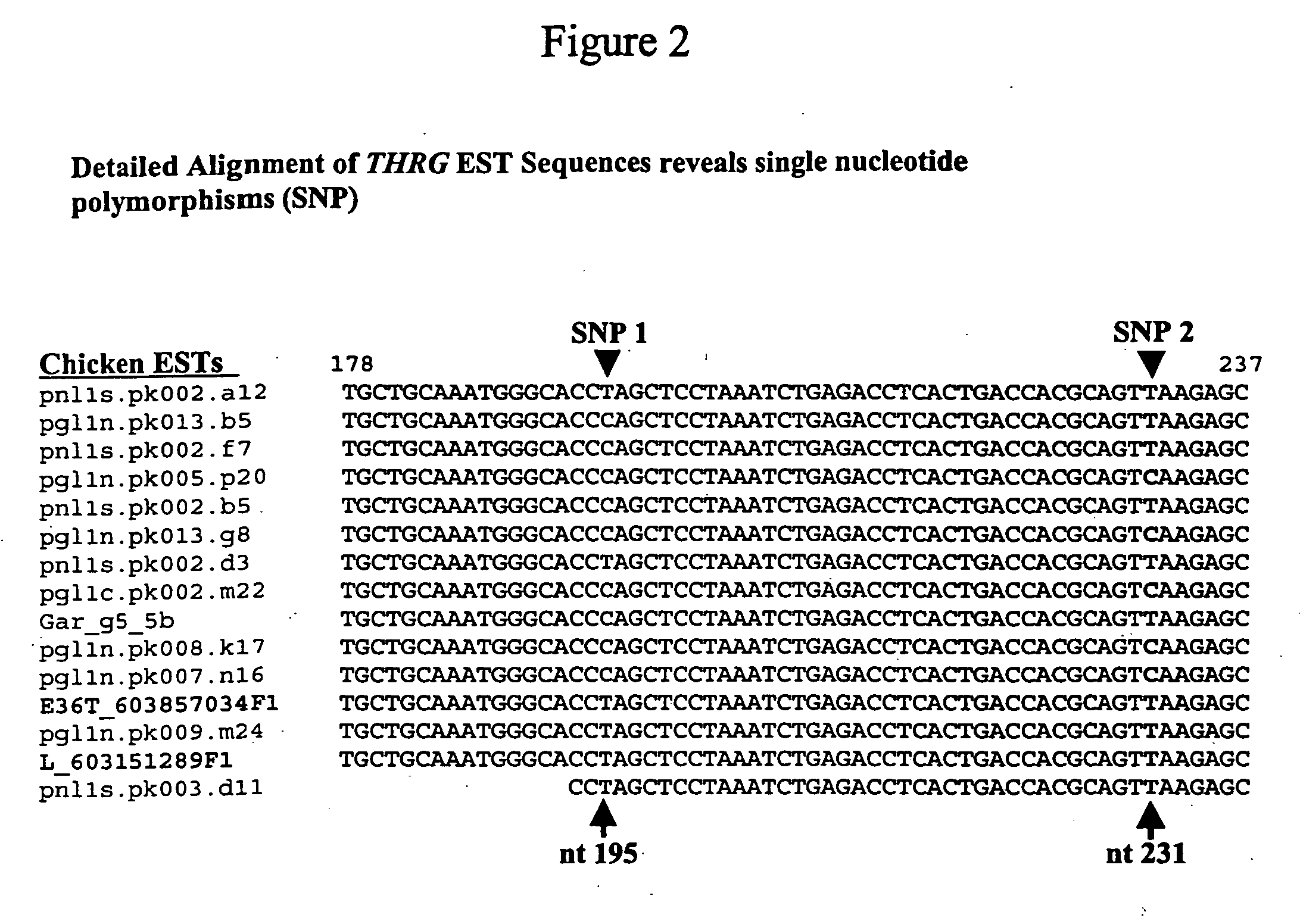
Molecular markers for identification of fat and lean phenotypes in chickens
InactiveUS20070092909A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLean meatThyroid hormones
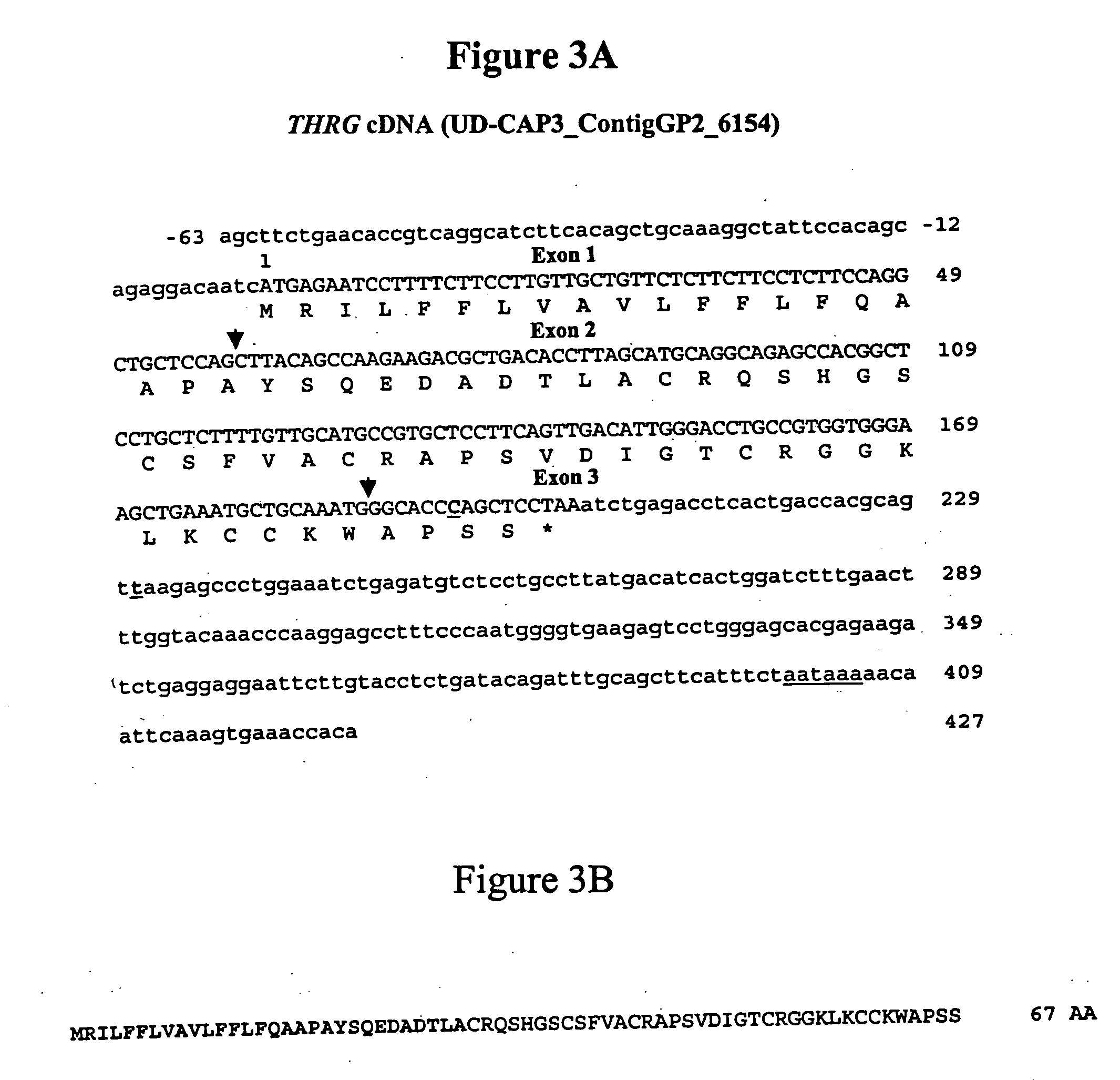
The invention provides molecular methods of screening chickens to determine those more likely to have a lean or fat phenotype by identifying the presence of at least one polymorphism in genetic material of a chicken in the thyroid hormone repressible gene (THRG) or its 3′ untranslated region (SEQ ID NO: 1) that is associated with a fat phenotype or a lean phenotype. The invention also provides methods of screening chickens to identify a polymorphism associated with a fat or lean phenotype. The invention further provides oligonucleotide probes and primers useful for detecting the polymorphisms associated with a fat or lean phenotype.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
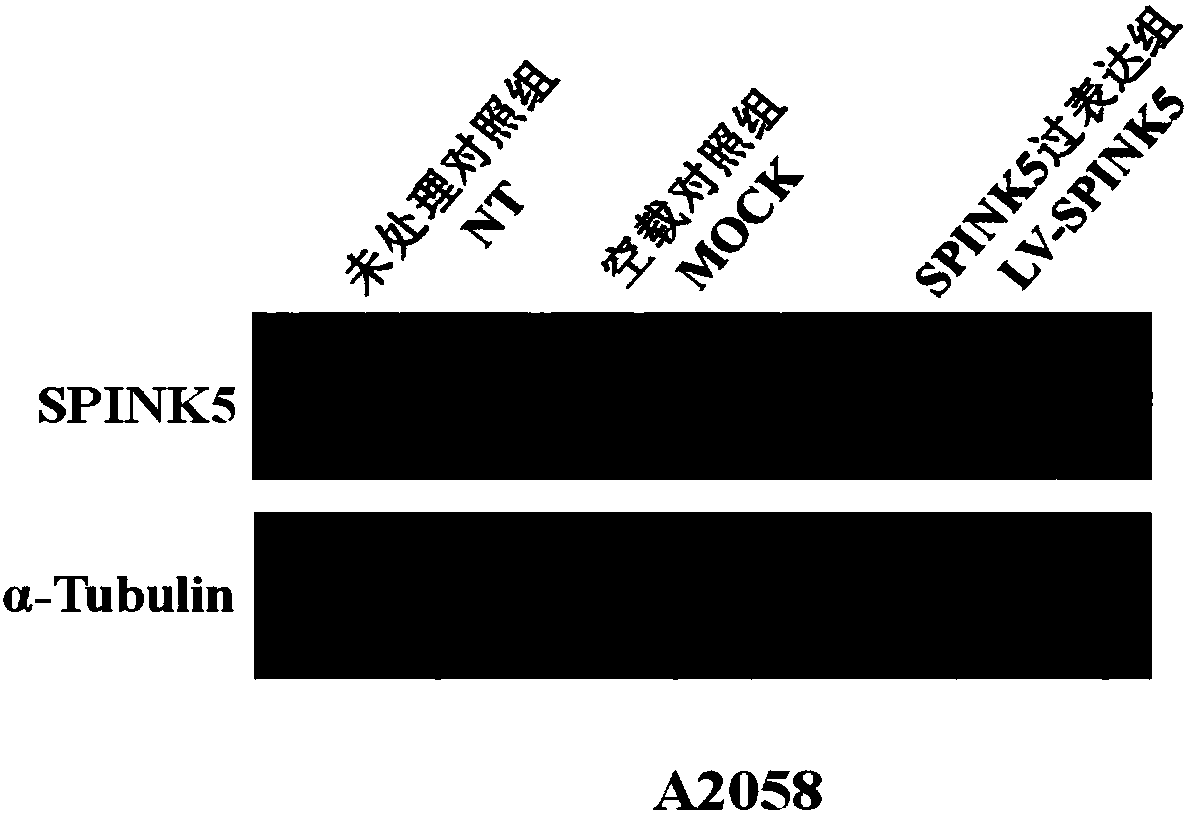
Method for constructing plasmids of recombinant human SPINK5 genes and application of plasmids
PendingCN108374022AHigh expressionRegulation of proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid vectorSerine peptidaseMelanoma
The invention discloses a method for constructing plasmids of recombinant human SPINK5 genes and application of the plasmids. The method and the application have the advantages that the pathogenesis of melanoma with a high fatality rate is deeply explored, further research and development on novel therapeutic targets for inhibiting malignant behavior such as melanoma cell proliferation and invasion are carried out, and accordingly sufficient laboratory bases can be provided to clinical treatment for the melanoma; interference segments of coding genes SPINK5 of a Lympho-Epithelial Kazal-type related inhibitor (LETKI) are constructed and are applied to the aspects of melanoma cell proliferation and invasion, and accordingly novel experimental evidence can be provided to fundamental researchon the melanoma and research and development on clinical therapeutic targets. The full name of the SPINK5 is Serine Peptidase Inhibitor Kazal Type 5.
Owner:信雅生物科技(苏州)有限公司
Method for screening disease phenotype related mutation sites and application thereof
PendingCN112735594ASmall sample sizeAvoid allele frequency effectsMedical data miningProteomicsDisease phenotypeDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformatics, in particular to a method for screening disease phenotype related mutation sites and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sequencing data of a plurality of disease samples and normal samples, and carrying out variation detection; performing association rule mining by taking the phenotype of the samples and the mutation type of the detected mutation site as a total project set to obtain a mutation site having a strong association relationship with the phenotype of the disease samples; and performing modeling analysis on the mutation sites obtained through association rule mining and screening to obtain mutation sites related to disease phenotypes. Alleles are converted into classification variables for association rule mining, and then modeling analysis is carried out on sites strongly associated with disease phenotypes, so that the total quantity of analyzed samples can be effectively reduced, and the influence of allele frequency on an analysis result is avoided; and screening and analysis of disease phenotype related sites can be completed only by obtaining mutation genotype information.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Accurate prediction method for pathogenic genetic variation
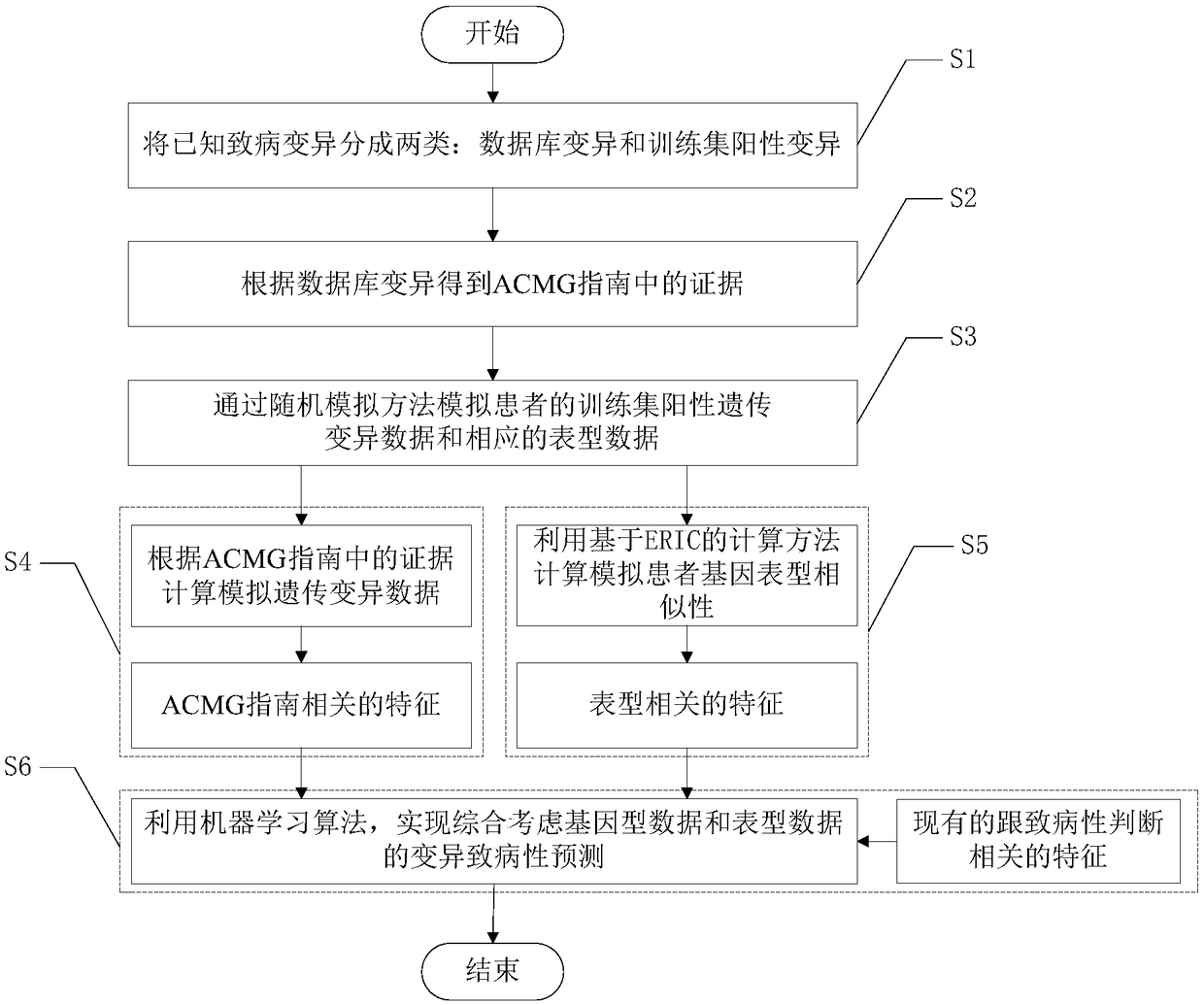
ActiveCN108363902AImprove interpretabilityImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmClinical phenotype
The invention discloses an accurate prediction method for pathogenic genetic variation. Known pathogenic variations are classified into two types: database variation and training set positive variation; partial evidences in an ACMG guide are obtained through the database variation; training set positive genetic variation data and corresponding phenotypic data of a patient are simulated through a random extraction method; guide related features are calculated; phenotype related features are calculated by utilizing an ERIC-based calculation method; and in combination with existing pathogenicityjudgment related features, and by utilizing a machine learning algorithm, variation pathogenicity prediction performed by comprehensively considering genotype data and phenotype data is realized. Themethod solves the problem that accurate prediction of variation pathogenicity cannot be performed due to incomplete clinical phenotype data, noises and inaccurate description in an actual scene.
Owner:成都奇恩生物科技有限公司
Systematic screening and mapping of regulatory elements in non-coding genomic regions, methods, compositions, and applications thereof
PendingUS20200143907A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease phenotypeRegulator gene
The application relates to methods for identifying putative regulatory elements that regulates a gene, comprising: obtaining a measure of intrinsic activity of a plurality of genomic elements; obtaining a measure of proximity between each of the genomic elements and the gene; scoring a predicted impact of each of the genomic elements on the gene as a function of the measure of intrinsic activity and the measure of proximity, wherein a plurality of predicted impacts scored are ranked to identify at least one genomic element as a putative regulatory element that regulates the gene; and optionally, training, optimizing, and / or validating the scoring of predicted impact using experimental or computational data describing functional interactions between the genomic elements and the gene. The application also relates to methods for identification of transcriptional enhancers and repressors regulating a gene associated with an agricultural trait of interest in plants or a disease phenotype in mammalians.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Human MLR single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with dose-dependent congestive heart failure and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070190539A1Increased riskReduce riskCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides associated with the incidence of PPAR-agonist induced congestive heart failure. The invention also provides polynucleotide fragments corresponding to the genomic and / or coding regions of these polynucleotides which comprise at least one polymorphic locus per fragment. Allele-specific primers and probes which hybridize to these regions, and / or which comprise at least one polymorphic locus are also provided. The polynucleotides, primers, and probes of the present invention are useful in phenotype correlations, medicine, and genetic analysis. Also provided are vectors, host cells, antibodies, and recombinant and synthetic methods for producing said polynucleotides and / or polypeptides. The invention further relates to diagnostic and therapeutic methods for applying these novel polynucleotides and polypeptides to the diagnosis, treatment, and / or prevention of various diseases and / or disorders, particularly PPAR-agonist induced congestive heart failure or related indications.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
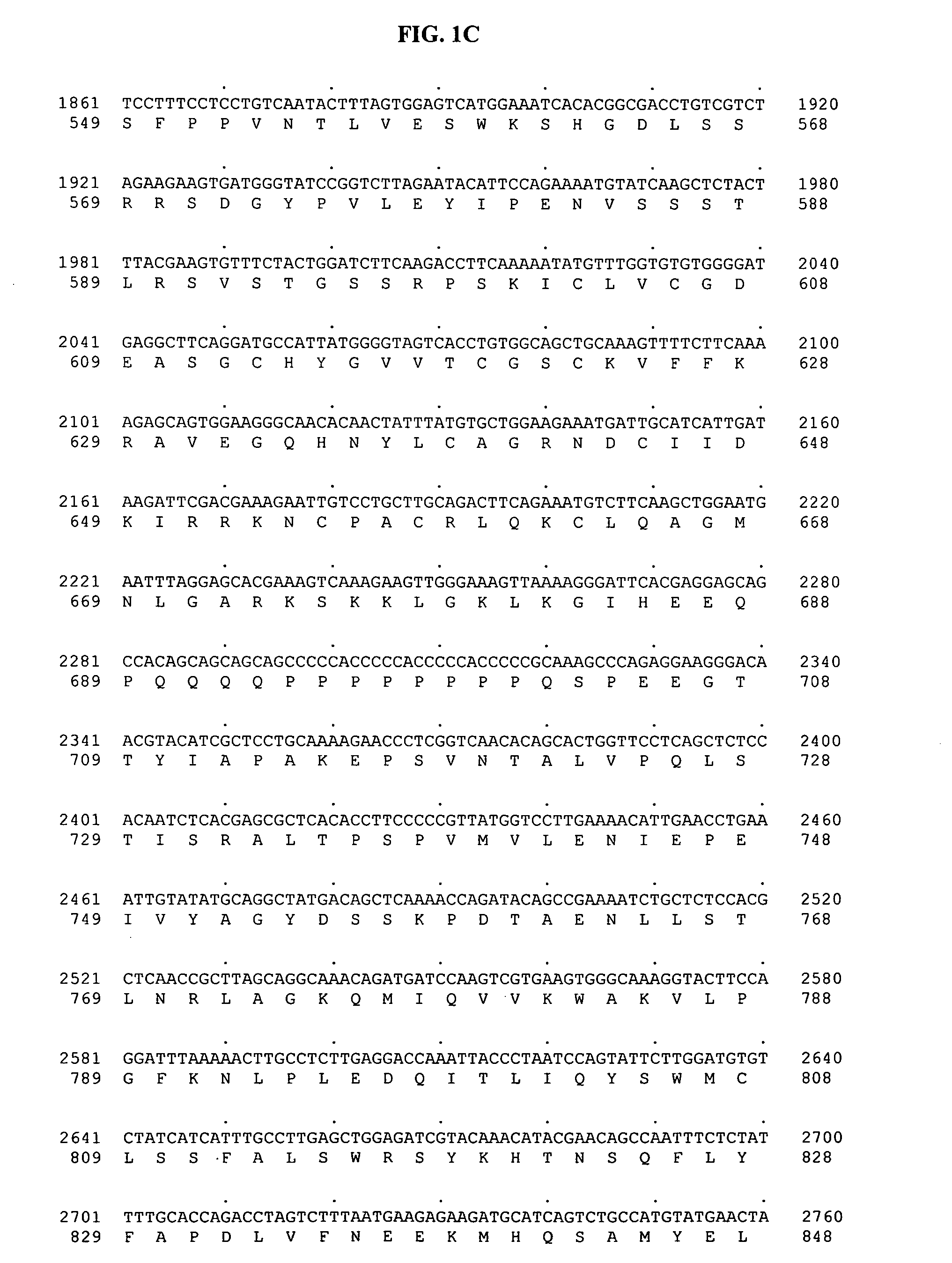
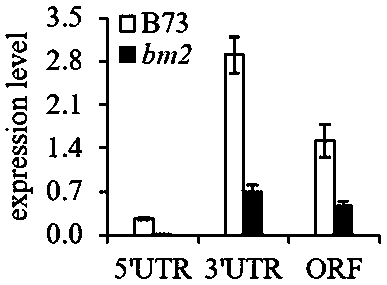
Gene related to bm2 phenotyping, variant and molecular marker thereof
ActiveCN108531482ARapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesMolecular breedingCancer research
The invention relates to a gene related to bm2 phenotyping, a variant and a molecular marker thereof, and particularly pays attention to a specific naturally-existing mutant corn MTHFR gene. A MITE transposon is inserted into a gene promoter region to promote phenotyping of lignin ingredient change in a specific corn line. The invention further provides a detection method of the MITE transposon, and a new target is provided for molecular breeding in future.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
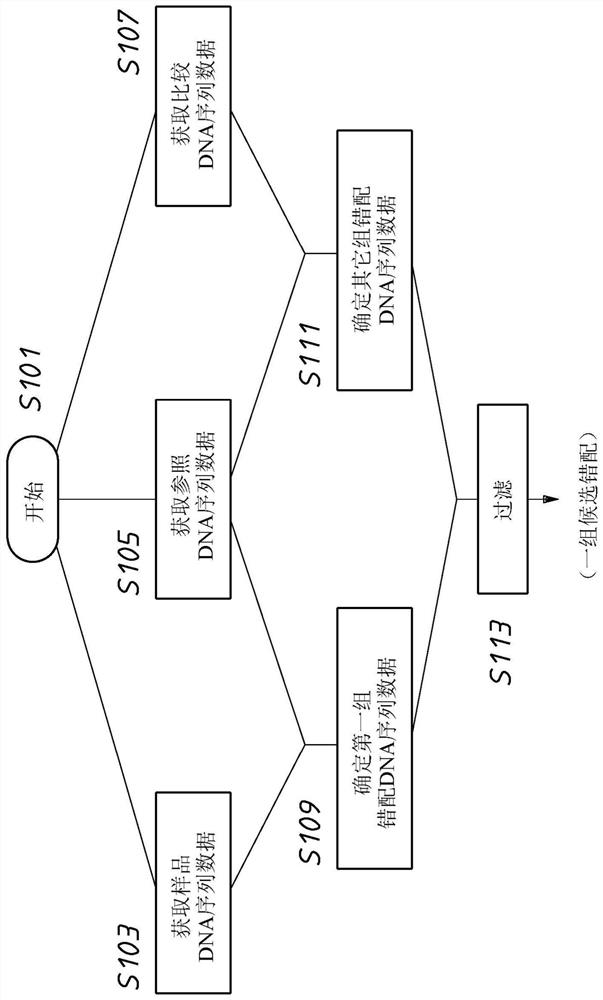
A method or system for identification of a causative mutation causing a phenotype of interest in a test sample
A method for identifying a mutation associated with a phenotype of interest in a non- vascular plant, wherein the method comprises (a) aligning the DNA sequence of a reference DNA sequence and identifying a first set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; wherein the test sample is from a mutagenized non-vascular plant; (b) aligning the DNA sequence of at least one comparison sample to the reference DNA sequence and identifying a second set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; (c) filtering the first set of mismatches with respect to the second set of mismatches to identify a subset of mismatches that are unique to the first set of mismatches, wherein the subset of mismatches are candidate mutations for the causative mutation; wherein the test sample is from a non-vascular plant exhibiting the phenotype of interest and wherein the at least one comparison sample is from an independent non- vascular plant of the same genus that does not exhibit the phenotype of interest; and wherein the reference DNA sequence is a known reference sequence for a non-vascular plant of the genus. In addition, a method for identifying a mutation associated with a phenotype of interest in a non-vascular plant, wherein the method comprises a) aligning the DNA sequence of a reference DNA sequence and identifying a first set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; wherein the test sample is from a mutagenized non-vascular plant; (b) aligning the DNA sequence of at least one comparison sample to the reference DNA sequence and identifying a second set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; (c) filtering the first set of mismatches with respect to the second set of sequence mismatches to identify a subset of mismatches that are common to the first and second sets of sequence mismatches wherein the test sample and the comparison sample(s) are from independent non-vascular plants exhibiting the phenotype of interest and wherein the independent non-vascular plants are the same genus; and wherein the reference DNA sequence is a known reference sequence or a non-vascular plant of the genus or a non-vascular plant of the genus.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with dietary weight loss
InactiveUS20110159489A1Improve targetingIncrease success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyPhenotype
The present invention relates to genetic polymorphisms associated with obesity and obesity-related phenotypes and their use in predicting if an individual successfully completes a dietary weight loss intervention program.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
RXDP2 gene SNP marking composition related to sheep horn phenotype and application thereof
ActiveCN105483125AHigh research valueHorn shape is stableMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiologyAnimal production
The invention relates to an SNP marking composition related to a sheep horn phenotype. The SNP marking composition is located on a sheep RXDP2 gene and comprises RXDP2-SNP1 and RXDP2-SNP2; according to the annotation (XM_015097982) of a database latest version RXDP2 of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), C->T mutation at the chr10: 29439053 (1999) locus serves as the RXDP2-SNP1, and C->T mutation at the chr10: 29439007 (1957) locus serves as the RXDP2-SNP2. By means of the SNP marking composition, the phenotypic characteristics of sheep horns can be identified, and therefore animal production and local variety protection can be guided; particularly, pure line Tibetan sheep can be identified by means of the SNP marking composition. Meanwhile, the loci have the greater scientific research value, and some genetic evolutionary laws can be researched through the obvious horn phenotype model.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
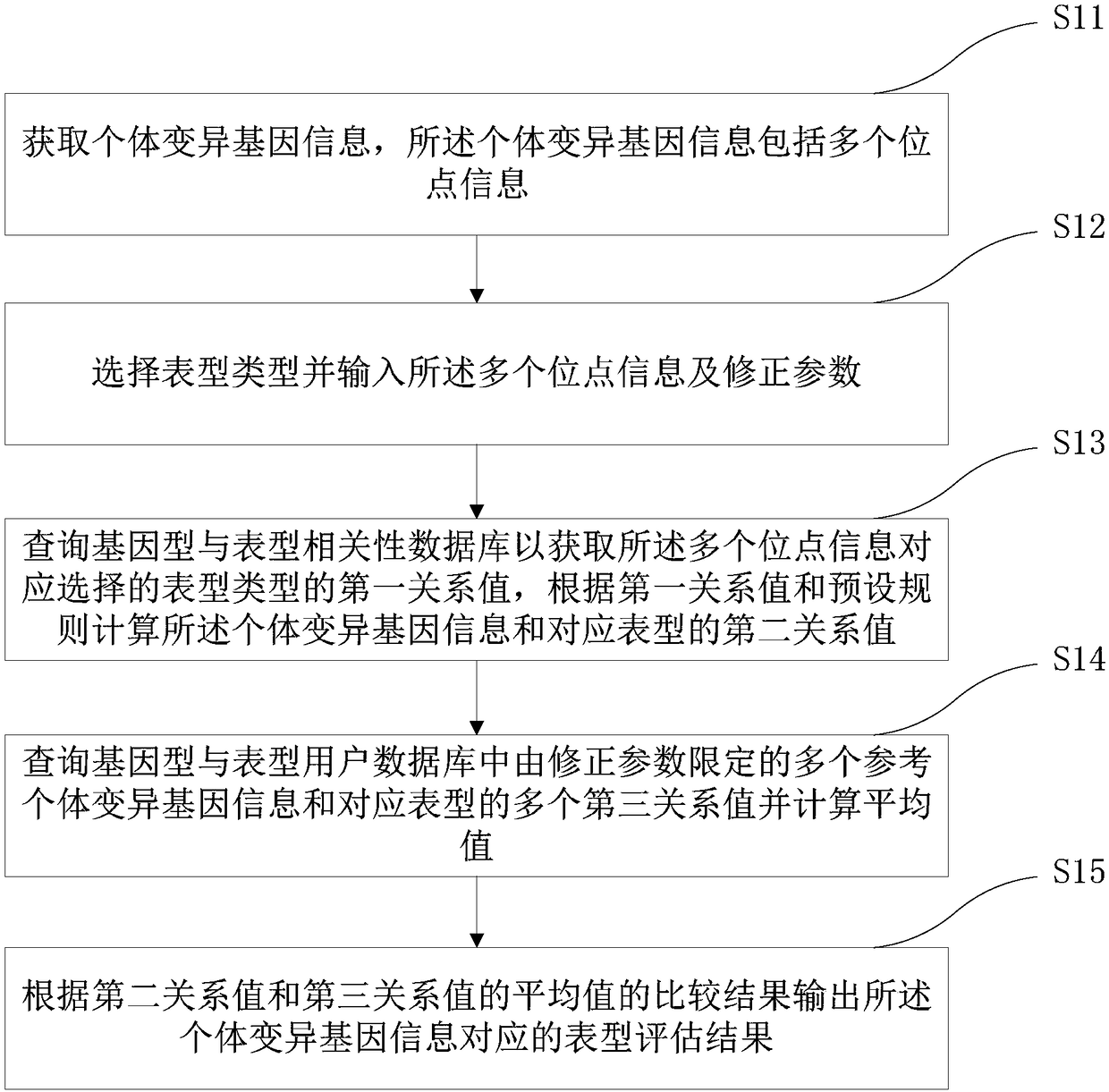
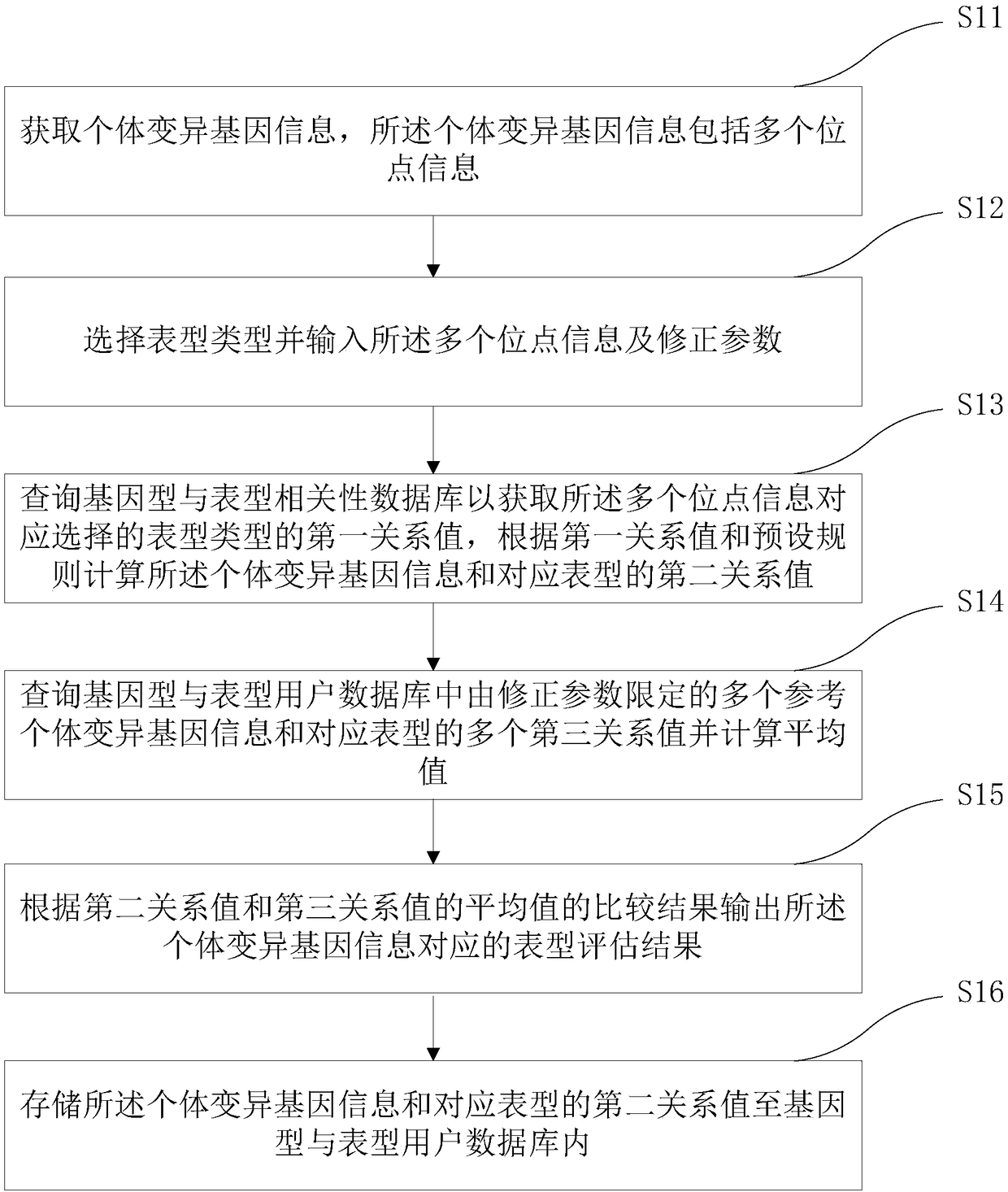
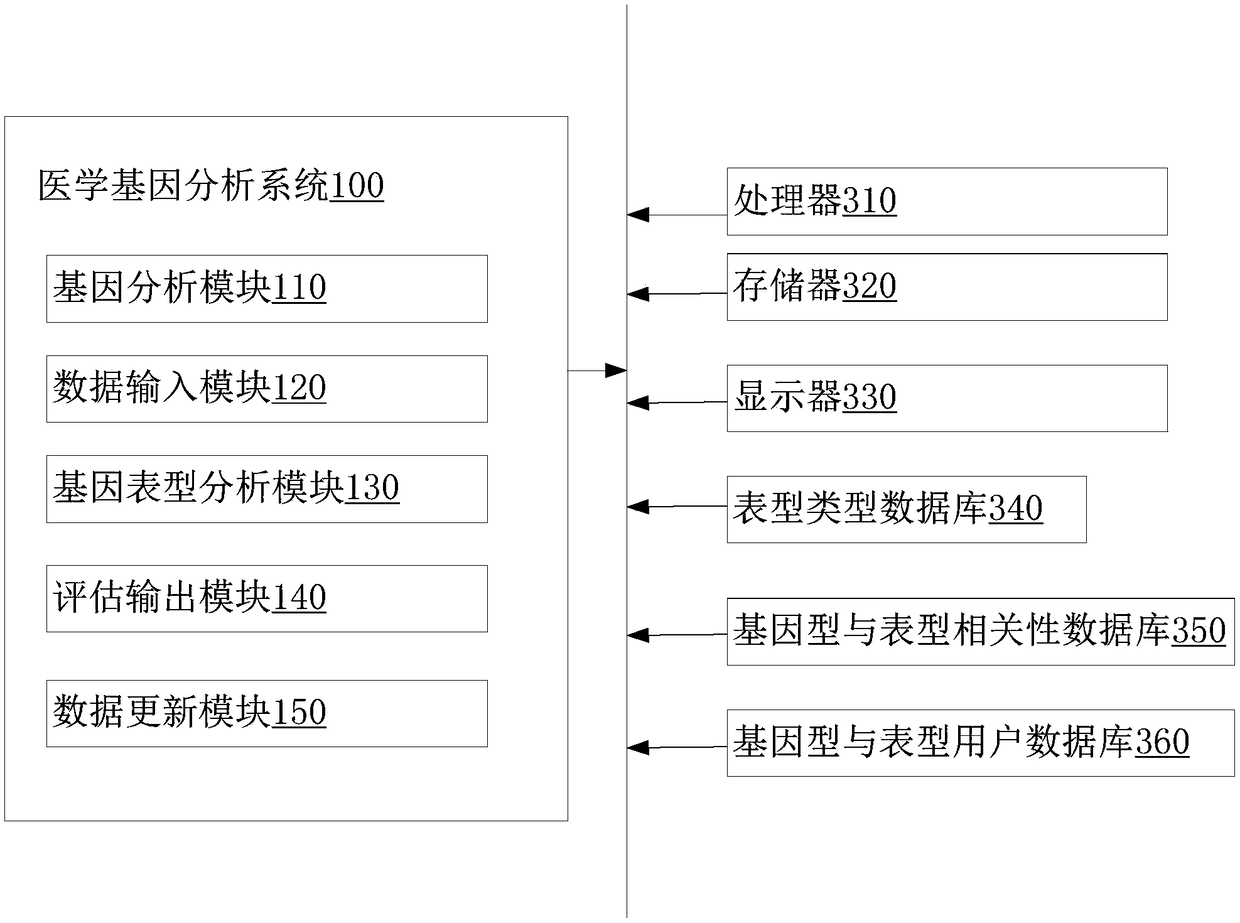
Medical gene analysis method and system
InactiveCN108629153AMeeting forecast needsImprove accuracyHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsMulti siteAnalysis method
The invention relates to a medical gene analysis method. The method comprises the steps of obtaining individual variation gene information, wherein the individual variation gene information comprisesmulti-site information; selecting a phenotype and inputting the multi-site information and a correction parameter; querying a genotype and phenotype correlation database to obtain a first relationshipvalue of the phenotype correspondingly selected by the multi-site information, and according to the first relationship value and a preset rule, calculating a second relationship value of the individual variation gene information and the corresponding phenotype; querying multiple third relationship values of multi-reference individual variation gene information limited by the correction parameterand the corresponding phenotype in a genotype and phenotype user database, and calculating an average value; and according to a comparison result of the second relationship value and the average valueof the third relationship values, outputting a phenotype assessment result corresponding to the individual variation gene information. The invention furthermore provides a medical gene analysis system. The medical gene analysis method and system can meet the prediction demand of a user on own gene and phenotype relationships.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGXINRUI GENE HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Chromosomal Blocks as Markers for Traits
InactiveUS20090246774A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenetic linkage disequilibrium
The present invention provided a method for predicting a phenotype in a bovine animal, the method comprising analysing a nucleic acid sample from said animal for the presence of at least one genetic marker known to reside in an Linkage Disequilibrium (LD) block in any one of bovine chromosomes BTA-I to BTA-29, wherein said LD block is associated with said phenotype. The phenotype can be Australia profit ranking (APR), Australian selection index (ASR), protein yield (PROT), protein percent (PROT %), milk volume (MILK), fat yield (FAT), fat percent (FAT %), breeding value overall type (Overall Type), somatic cell count (SCC), and / or breeding value cow fertility (Cow Fertility). Also provided is a linkage disequilibrium unit (LDU) map of any one or more of bovine chromosomes BTA-I to BTA-29, the map comprising a plurality of chromosomal regions, and the regions defined by their co-inheritance across generations substantially as entire linkage disequilibrium (LD) blocks.
Owner:INNOVATIVE DAIRY PRODS TRUSTEE FOR THE PARTICIPANTS OF THE COOP RES CENT FOR INNOVATIVE DAIRY PRODS
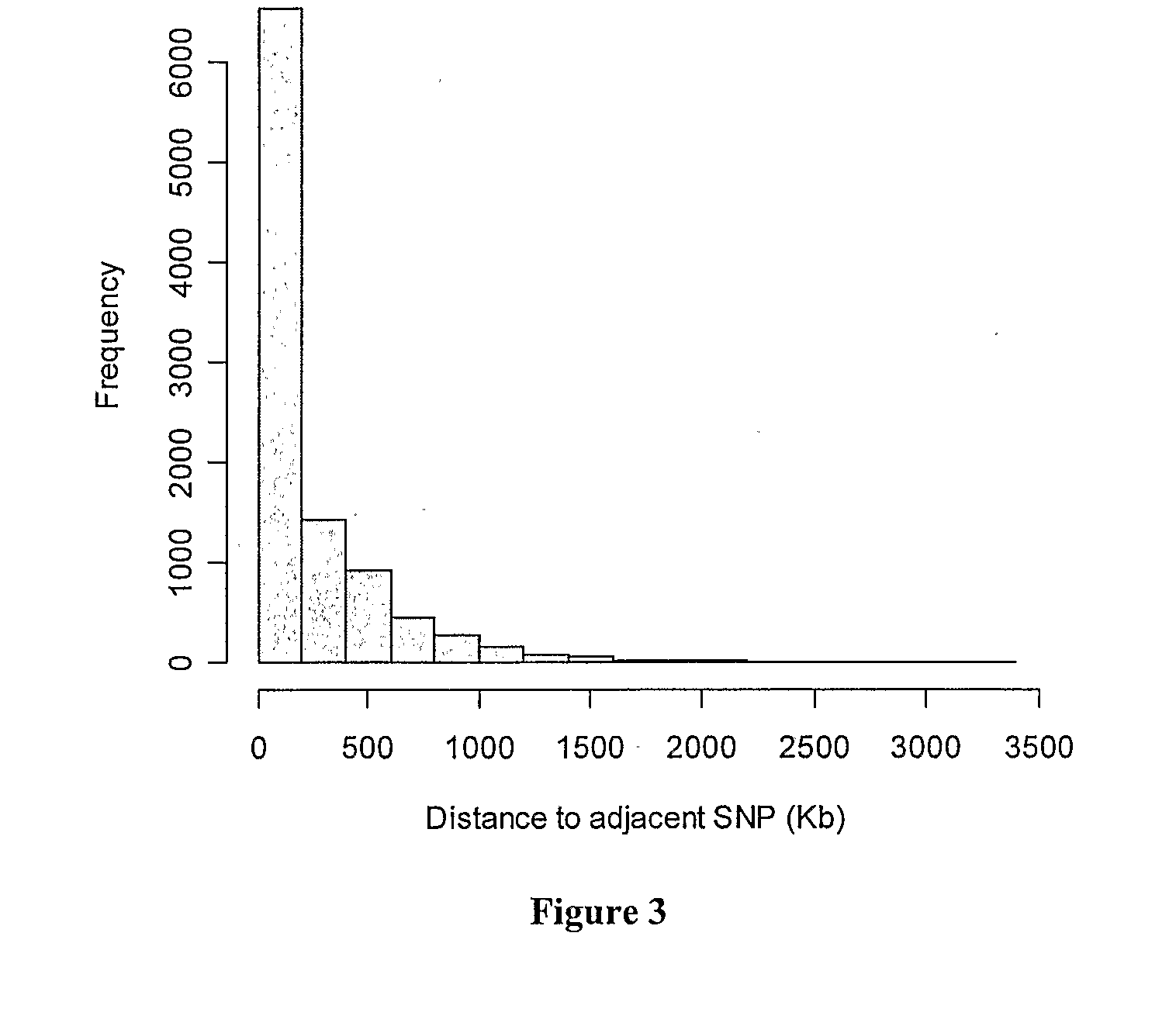
STAT6 effects on livestock animal growth
InactiveUS7972790B2Increase profitabilityLow costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The present invention provides for selection of livestock animals, including bovines, whose genotypes based in the STAT6 gene are correlated with phenotypes reflecting desirable carcass and feedlot traits. These phenotypes include back fat (BFAT), calculated yield grade (CALCYG), cutability (CUT), hot carcass weight (HCW), dry matter intake (DMI), days on feed (DOF), back fat rate (BFAT RATE) and average daily gain (ADG), based on the knowledge of the STAT6 genotypes. The predictive value is based in part on the discovery that certain single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the STAT6 gene are linked to phenotypes of economically these important carcass and feedlot traits. Also provided are SNPs within the STAT6 gene useful in reliably distinguishing between a Bos taurus and a Bos indicus bovine. The invention provides methods and compositions for determining STAT6 genotypes and for screening livestock animals to predict which animals will have desirable carcass traits and feedlot traits, allowing producers to selectively breed and manage animals based on desired characteristics, thereby maximizing productivity and profitability in commercial meat production operations.
Owner:IGENITY +1
Identification method of sex-linkage Luhua chicken genotype of Chinese native chickens
ActiveCN110016508AEasy to operateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTranscription initiation siteGallus gallus gallus
The invention discloses an interlocking SNP site combination related to the sex-linkage Luhua phenotype of Chinese native chickens. The SNP sites comprise SNP1, SNP2 and SNP3, wherein the SNP1 is a position of 267 bp of a CDKN2A gene promoter region and transcription initiation site upstream, the SNP2 is a position of 380 bp of CDKN2A gene intron 1, and the SNP3 is a position of 170 bp of CDKN2A gene exon 1. The invention finds the three SNP sites related to the sex-linkage Luhua chicken phenotype of Chinese native chickens for the first time, and establishes a method for detecting the phenotype and the genotype of sex-linkage Luhua chickens by the SNP sites. The method has the advantages of simple operation, high accuracy, good repeatability and time saving, is available to mutual detection, realizes 100% accuracy, can be used for cultivating auto-sexing commercial strains, performs auto-sexing by using feather colors, is high in accuracy and simple and convenient to operate, saves time and cost, has good application value, and is worthy of great popularization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
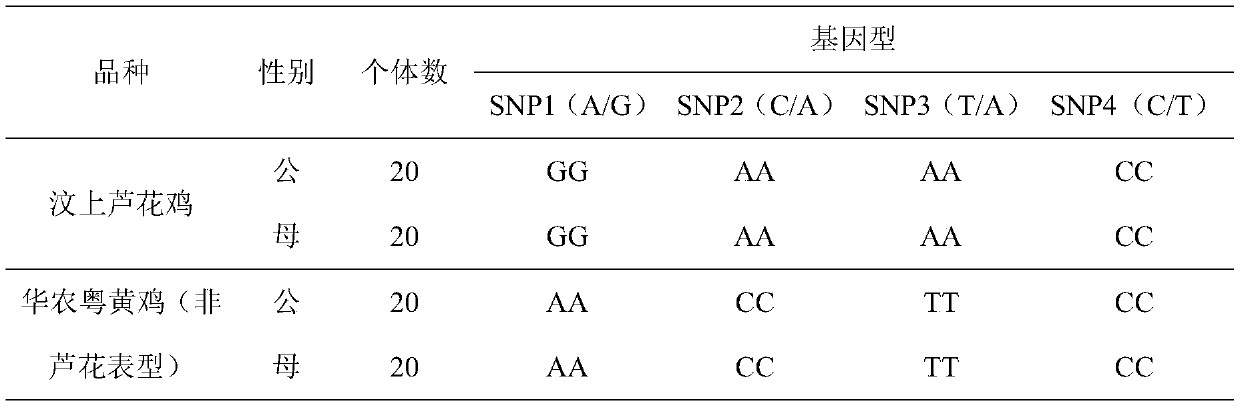
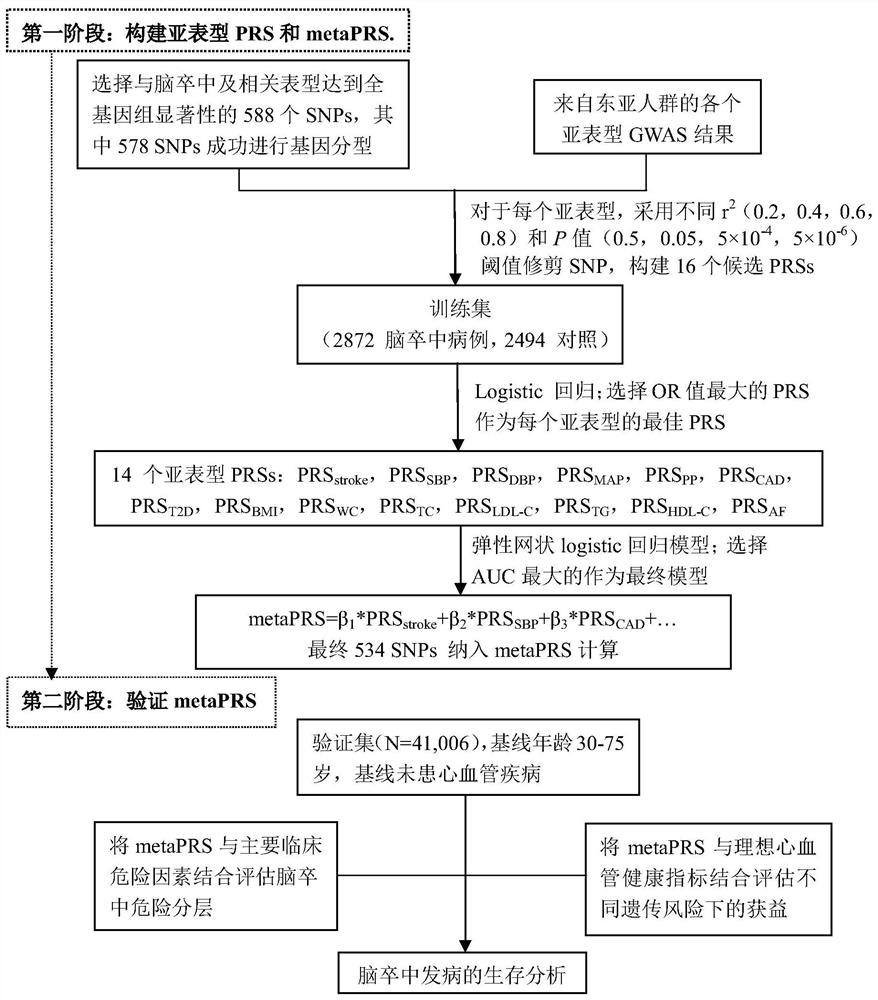
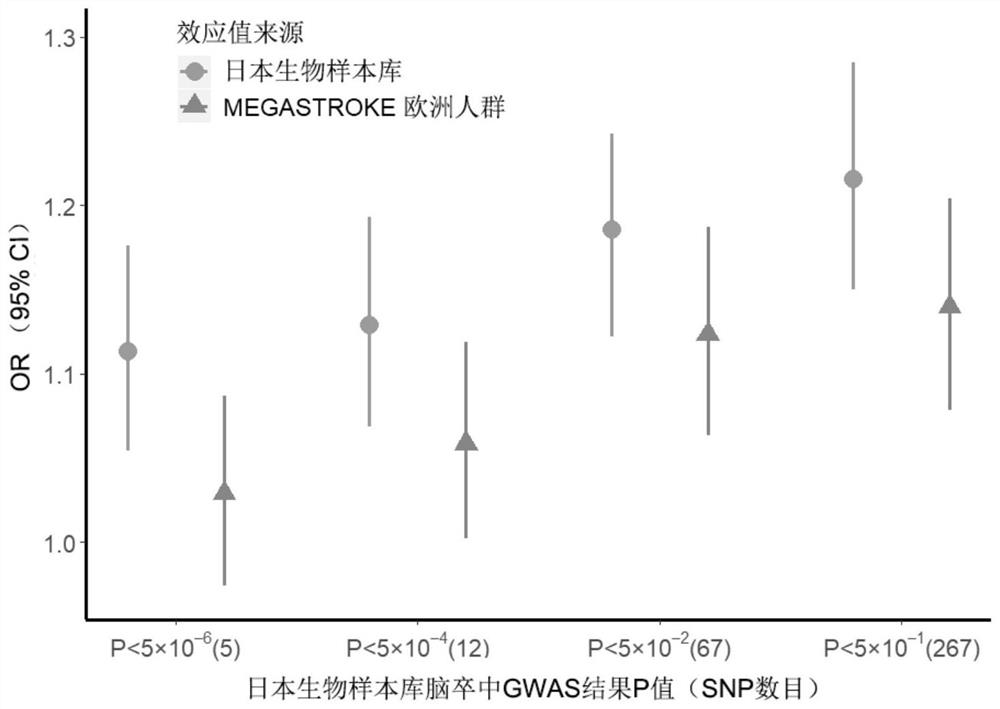
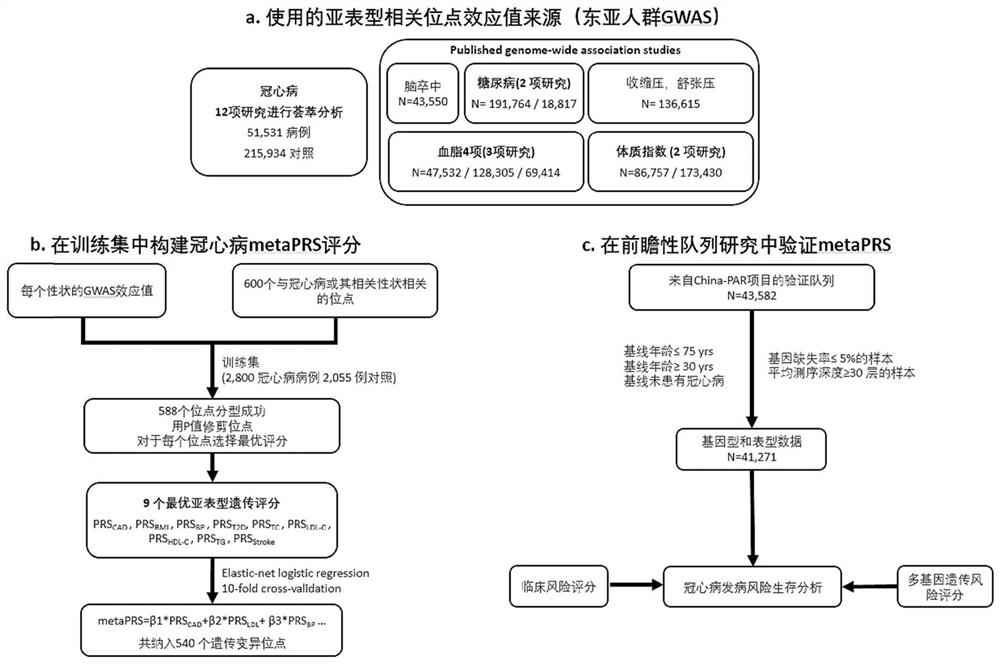
Construction method and device for cerebral apoplexy multi-gene genetic risk comprehensive score (metaPRS) and application
The invention provides a construction method and device for a cerebral apoplexy multi-gene genetic risk comprehensive score (metaPRS) and the application thereof. The construction method of the cerebral apoplexy multi-gene genetic risk comprehensive score (metaPRS) comprises the following steps: screening a set of SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) related to cerebral apoplexy or cerebral apoplexy related phenotypes; detecting the genotype of the to-be-detected SNP of the individual; respectively extracting dangerous alleles, effect values and P values of the detected SNP corresponding to a plurality of sub-phenotypes from a whole genome correlation research result, constructing a plurality of candidate sub-phenotype PRSs, and screening an optimal sub-phenotype PRS; determining the weight of each sub-phenotype PRS; the weight of the subphenotype PRS is converted into the weight of the SNP level; constructing a comprehensive score metaPRS of the multi-gene genetic risk of the cerebral apoplexy; and evaluating the effect of metaPRS on cerebral apoplexy risk prediction and layering. The method is of great significance to assessment of cerebral apoplexy onset risk.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
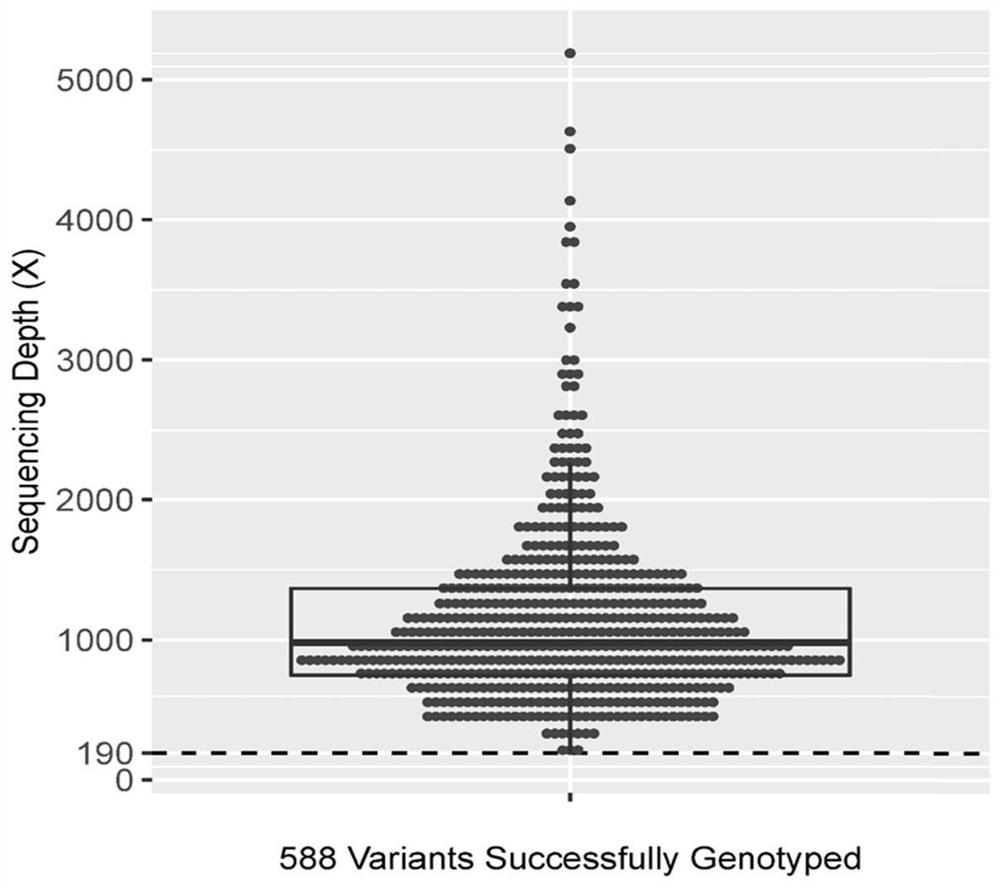
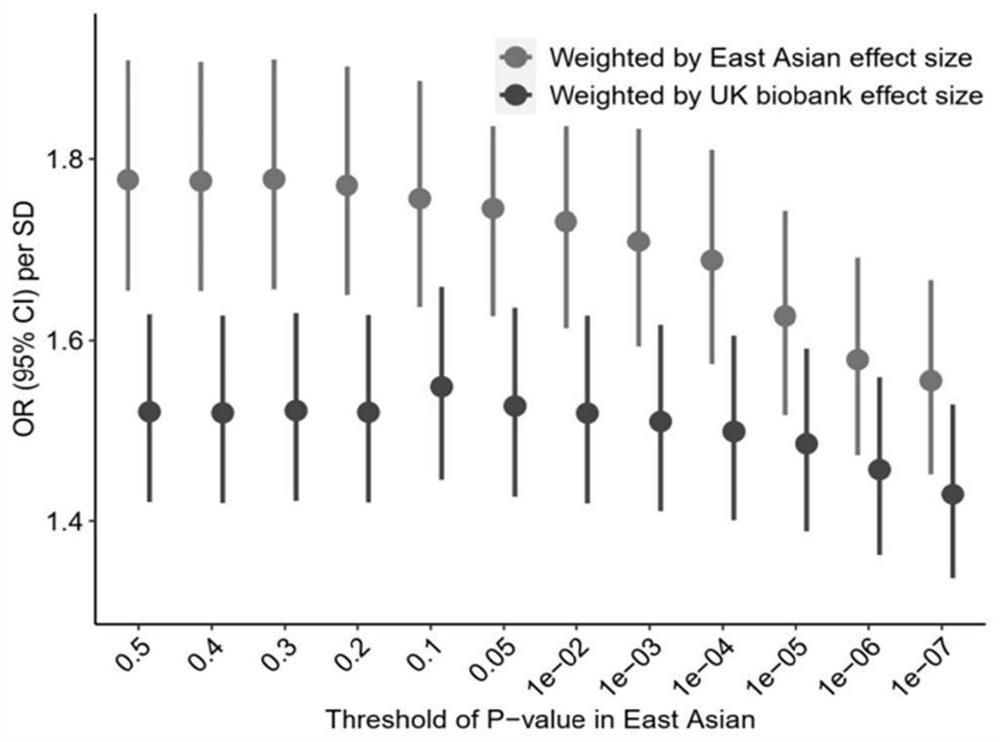
Method and device for constructing polygene genetic risk comprehensive score of coronary heart disease and application
The invention provides a method and device for constructing polygene genetic risk comprehensive score (metaPRS) of coronary heart disease and application. The method for constructing polygene genetic risk comprehensive score comprises the following steps: screening a set of SNP related to coronary heart disease and / or coronary heart disease related phenotypes; detecting the genotype of the to-be-detected SNP of the individual; respectively extracting dangerous alleles, effect values and P values of the detected SNP corresponding to a plurality of sub-phenotypes from a whole genome correlation research result, constructing a plurality of candidate sub-phenotype PRSs, and screening an optimal sub-phenotype PRS; determining the weight of each sub-phenotype PRS; cnverting the weight of the subphenotype PRS into the weight of the SNP level; and constructing a coronary heart disease polygene genetic risk comprehensive score metaPRS. The method is of great significance to coronary heart disease onset risk prediction and refined layering.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
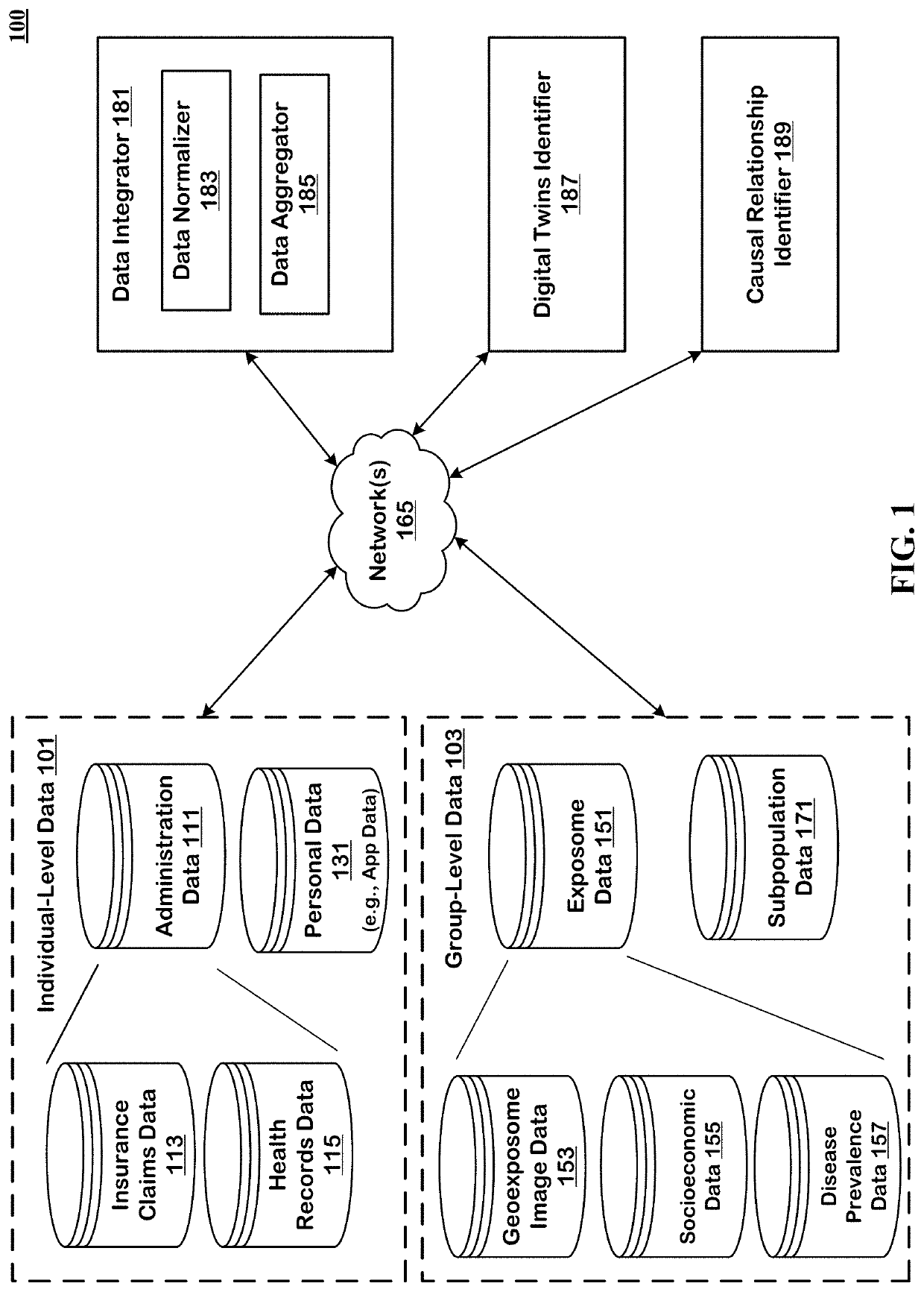
Method to Create Digital Twins and use the Same for Causal Associations
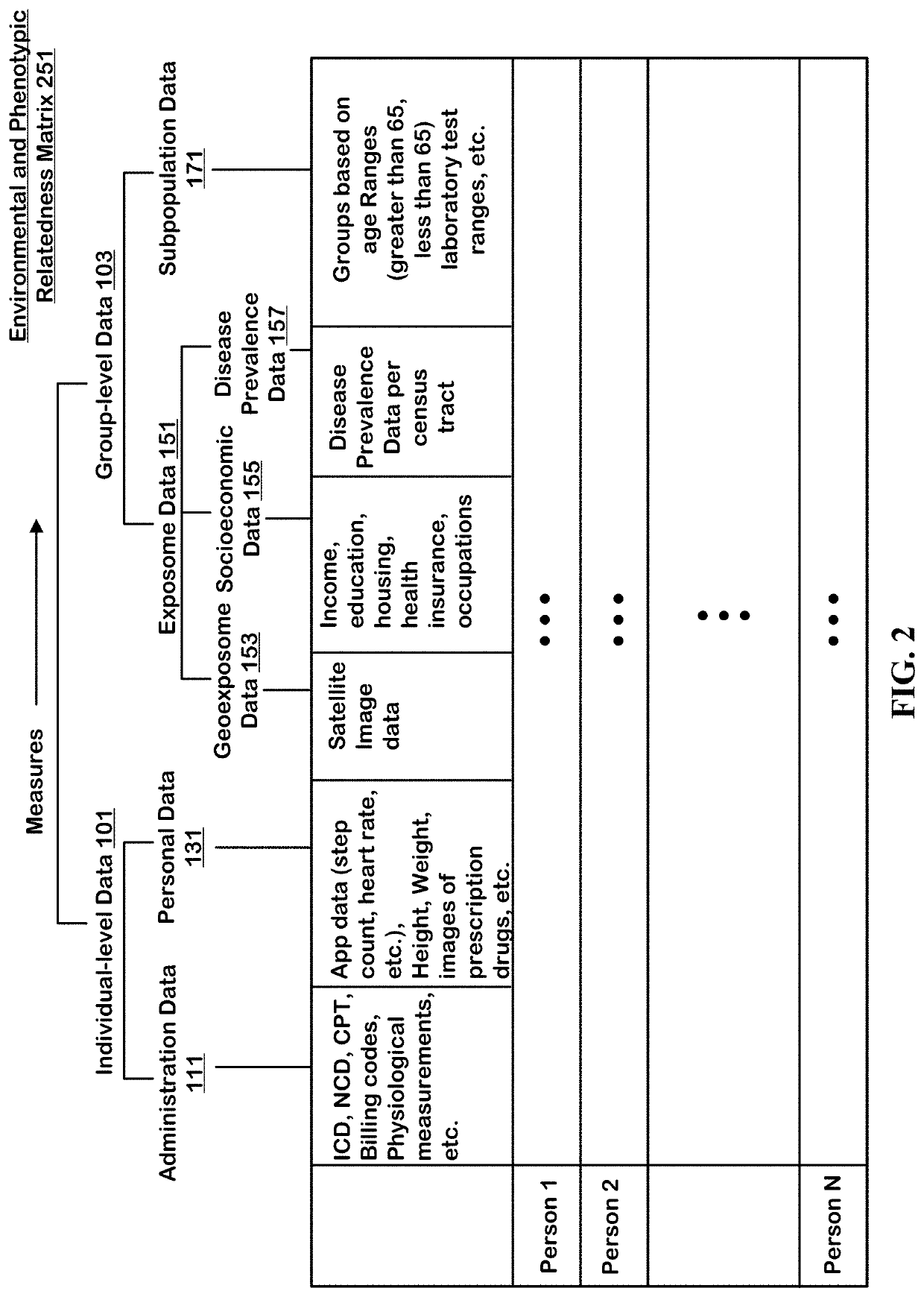
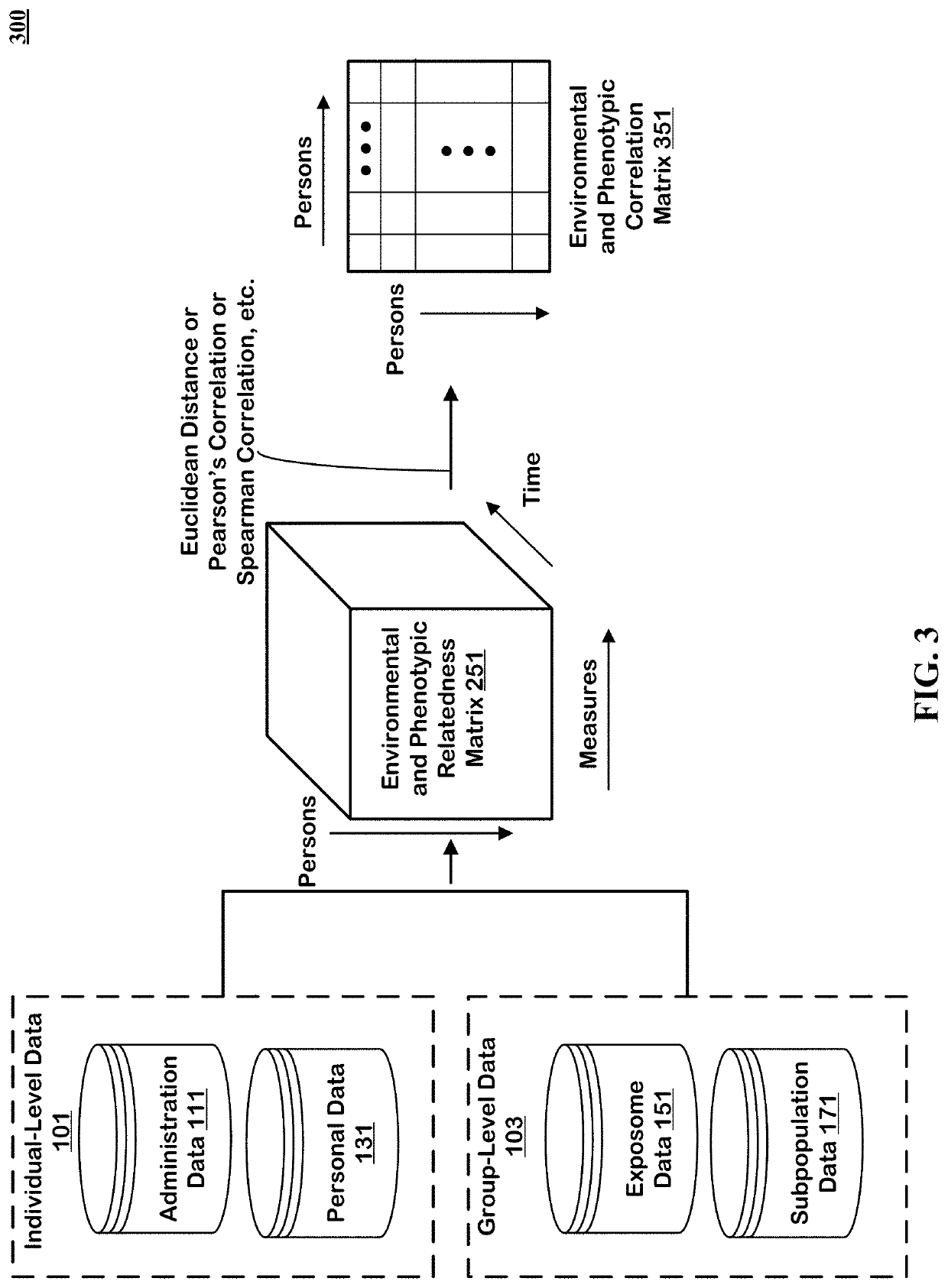
The technology disclosed relates to systems and methods for predicting digital twins. The system includes logic to use a machine learning model predict correlation between pairs of persons and save the results in an environmental and phenotypic correlation matrix. The inputs to the machine learning model can include data from individual-level and group-level datasets. The individual-level datasets include administration dataset including clinical data and person dataset including personal data. The group-level datasets include exposome dataset including environmental exposure and subpopulation dataset. The system includes logic to use the environmental and phenotypic correlation matrix as a random effect when determining associations between exposures and outcomes. The system includes a second machine learning model that can take a pair of exposure and outcome and the environmental and phenotypic correlation matrix as input to predict causal association between exposure and outcome.
Owner:CKB SOLUTIONS LTD
Phenotypic patient data derivation from economic data
The application of deep machine learning controllers to derive models of phenotypic patient data from primary economic data is disclosed herein. The use of systems and methods of employing the model are disclosed and useful in predicting treatment outcomes and compound efficacy, suggesting treatment plans and compounds, and clinical studies and phenotypical correlation studies in conjunction with medical records, economic data sets or combinations thereof.
Owner:OPENNANO PTE LTD
Method to predict heritable canine non-contact cruciate ligament rupture
PendingUS20210095346A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryCruciate ligament rupturesNucleotide
Method and kits for diagnosing propensity to non-contact cranial cruciate ligament rupture (CCLR) in a dog are described. The method includes isolating genomic DNA from a dog and then analyzing the genomic DNA from step for a single nucleotide polymorphism occurring in selected loci that have been determined to be associated with the CCLR phenotype via a genome-wide association study.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for screening important characteristic genes related to bacterial drug resistance phenotype based on machine learning
ActiveCN114067912BFacilitate translational applied researchExpand Screening MiningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsPharmaceutical drugGenomic data
This application relates to a method for screening important characteristic genes related to bacterial drug resistance phenotypes based on machine learning technology. The method is aimed at bacterial antibiotic resistance phenotypes, based on the idea of BGWAS to collect target bacterial genomes on public platforms or obtained after current collection, sequencing and assembly Genomic data of large sample strains and their corresponding antibiotic susceptibility test results, using machine learning methods to conduct correlation analysis between genotype and drug resistance phenotype, in order to screen out important characteristic genes related to drug resistance phenotype (non- Core drug resistance genes), and the weight coefficients of important characteristic genes were obtained at the same time, and finally ROC analysis was used to determine the reliability of drug-related drug resistance genes.
Owner:天津金匙医学科技有限公司 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com