Patents
Literature
160 results about "Quasi periodic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quasi-periodic function. A function such that for some continuous function of variables that is periodic with respect to with periods , respectively. All the are required to be strictly positive and their reciprocals have to be rationally linearly independent.
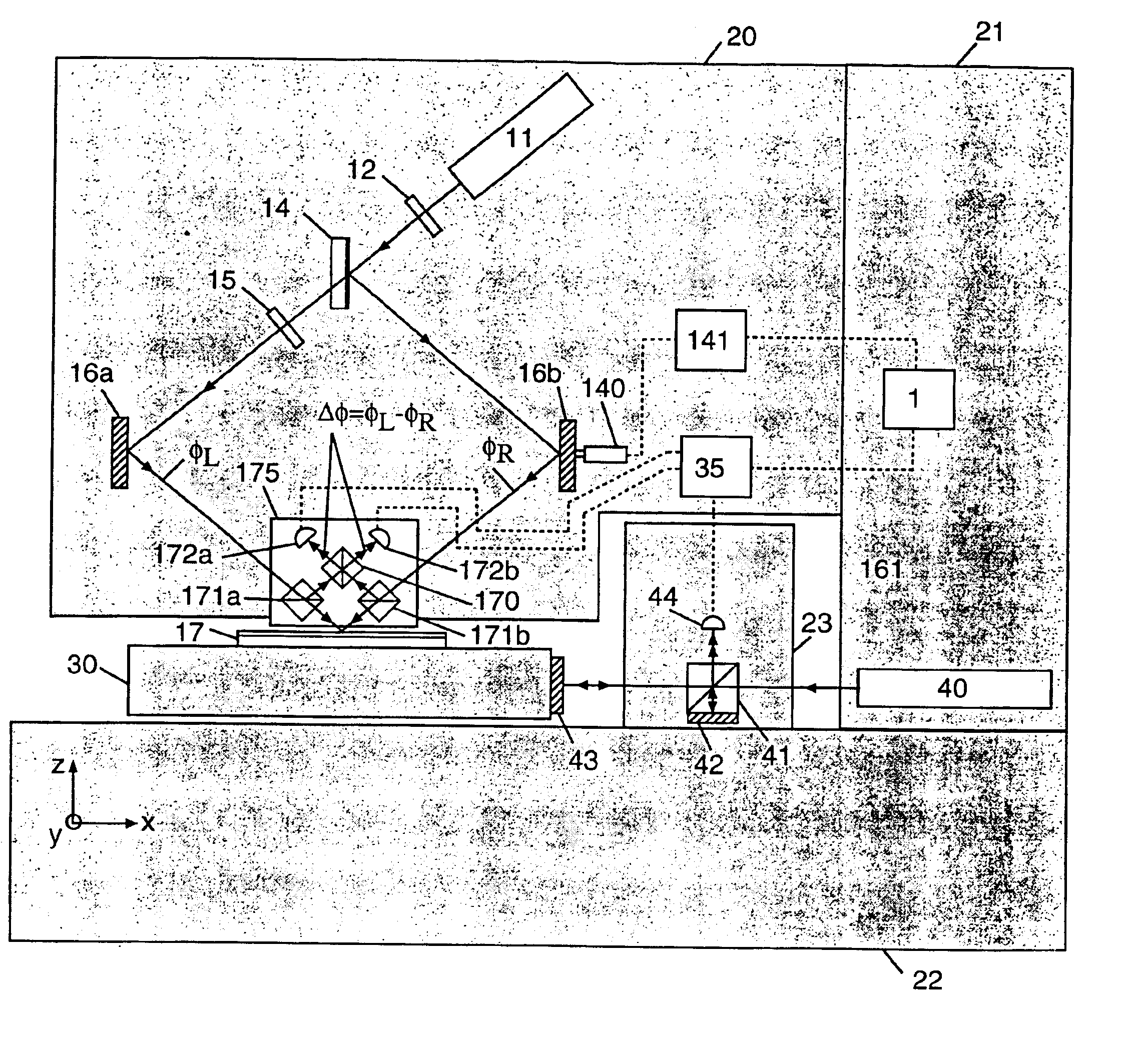
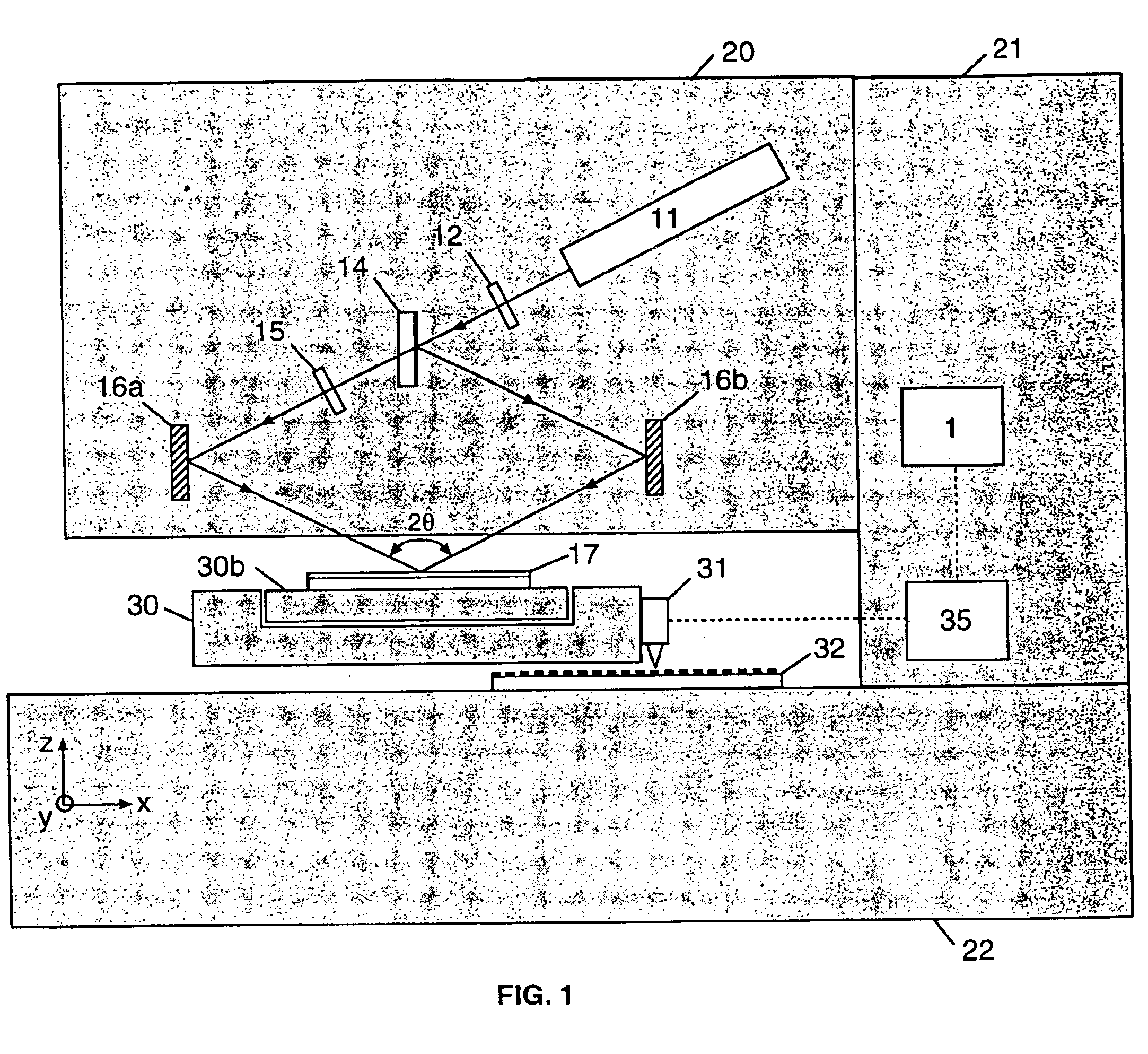
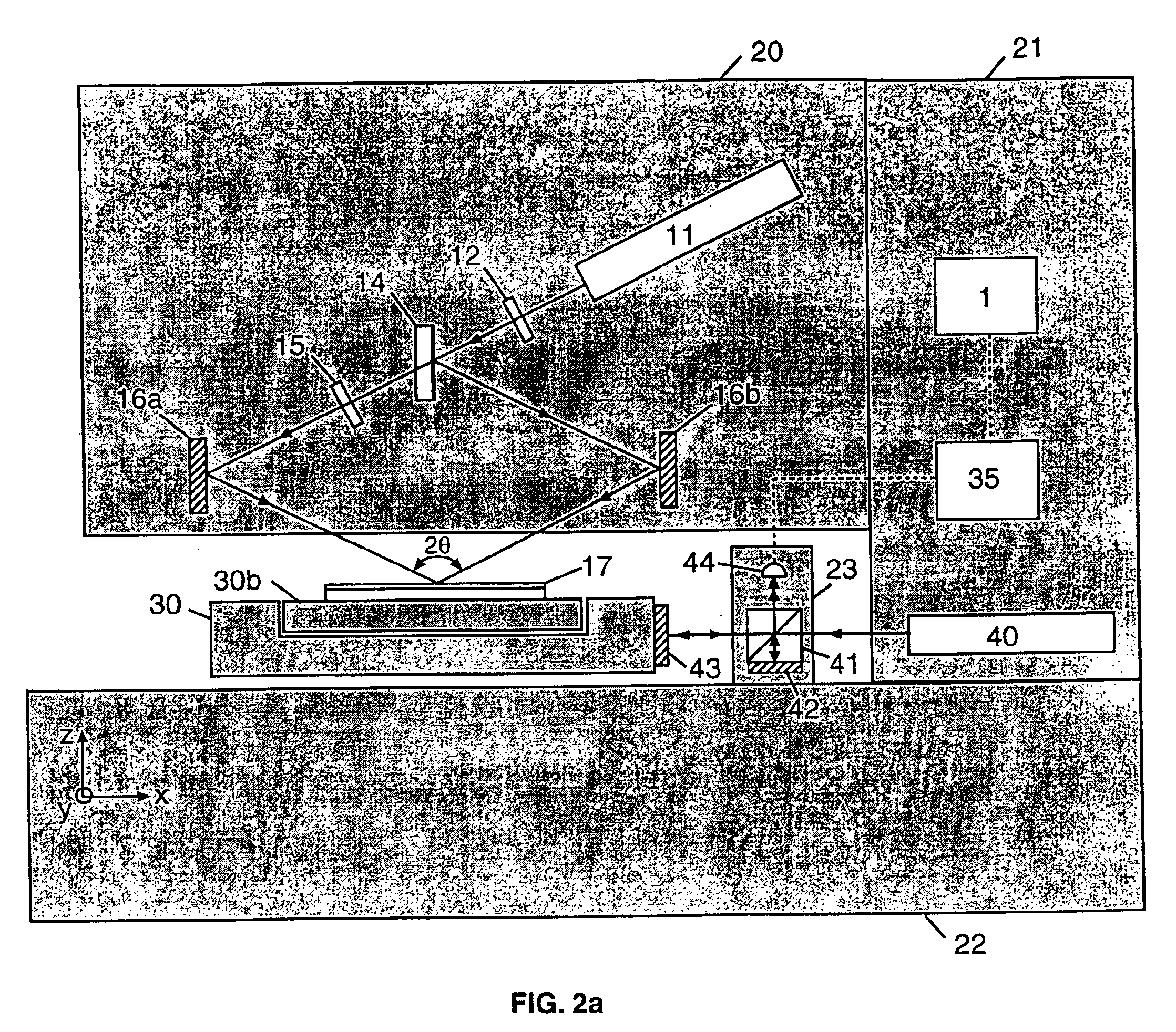
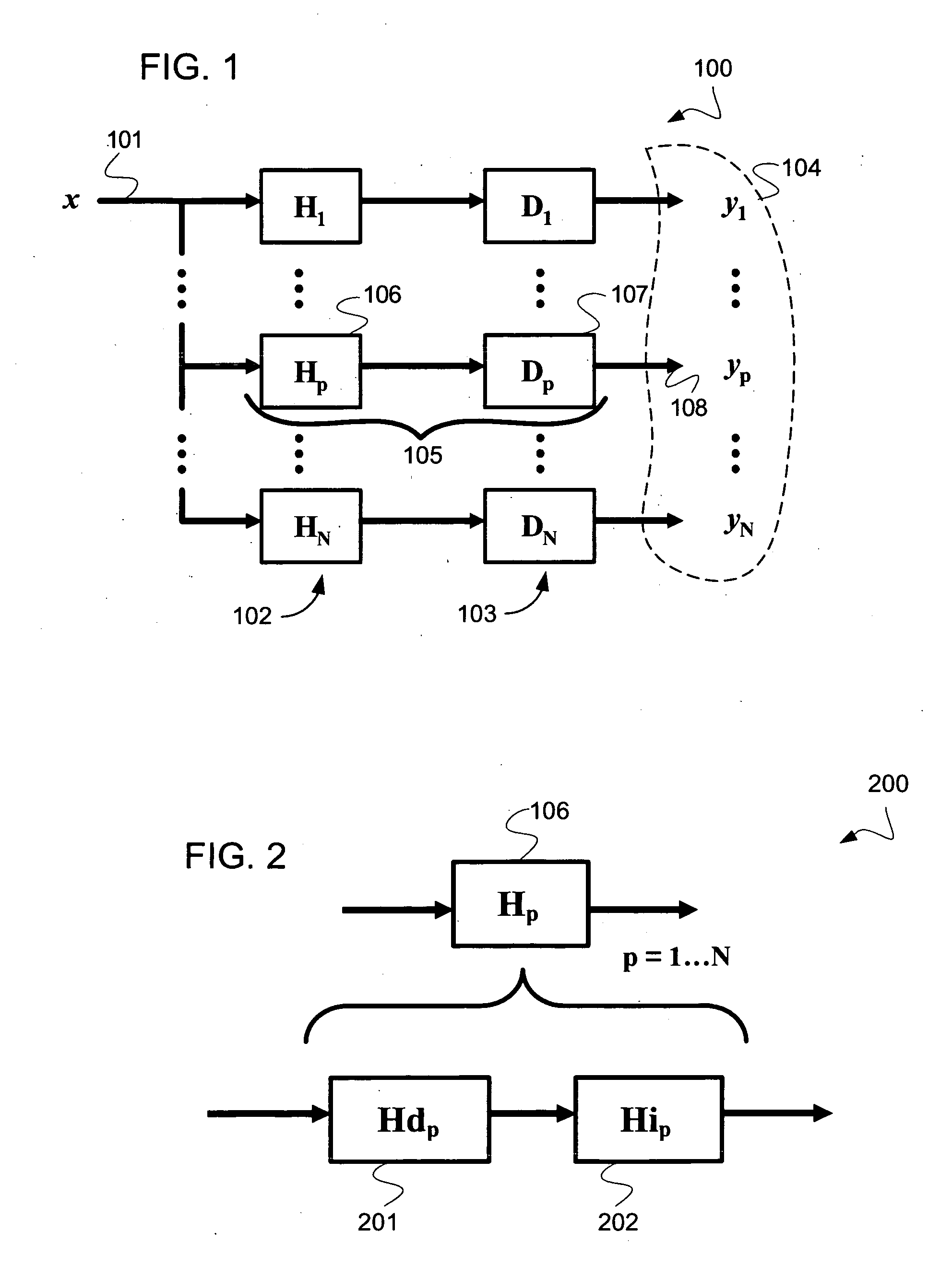
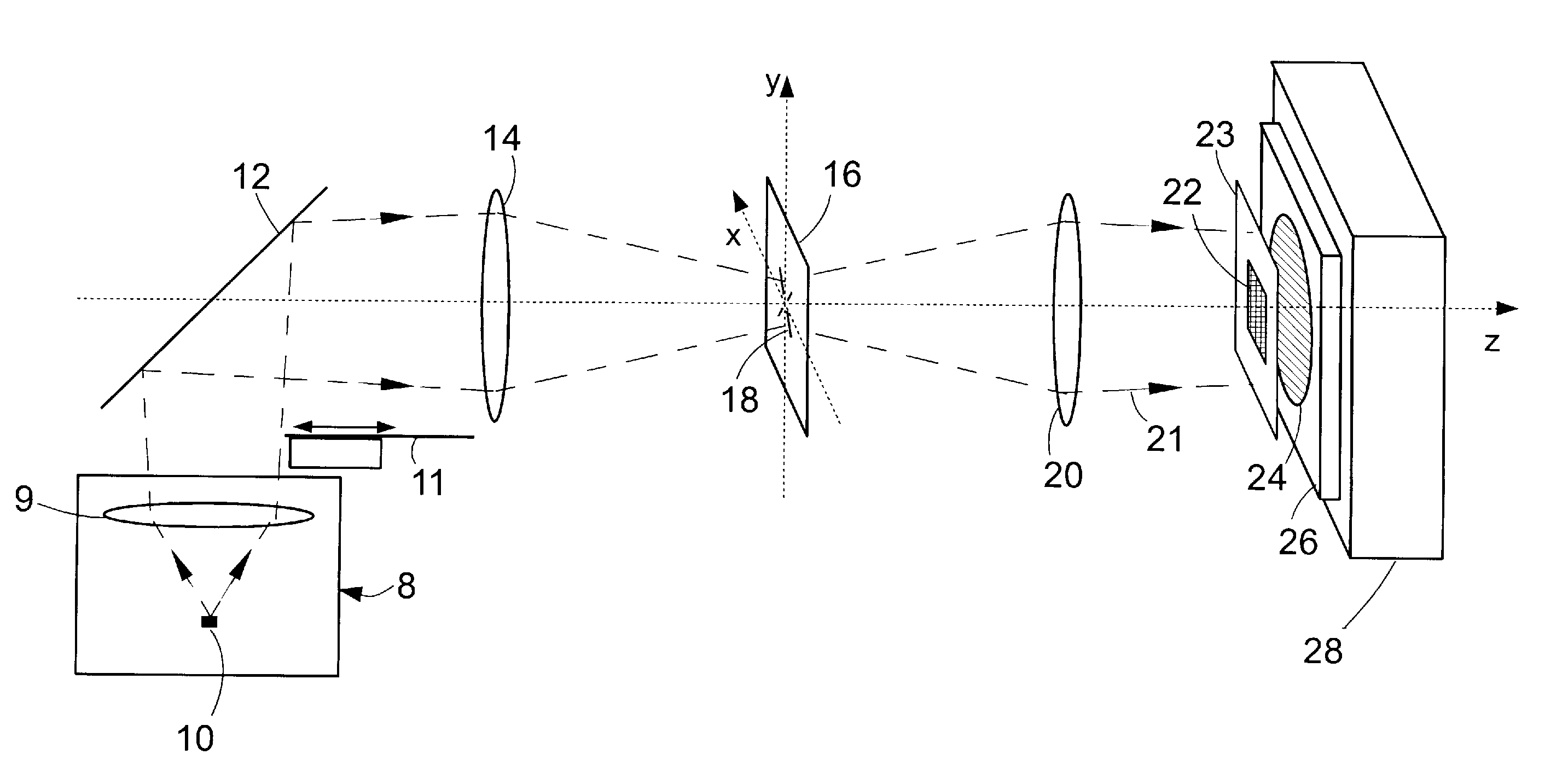
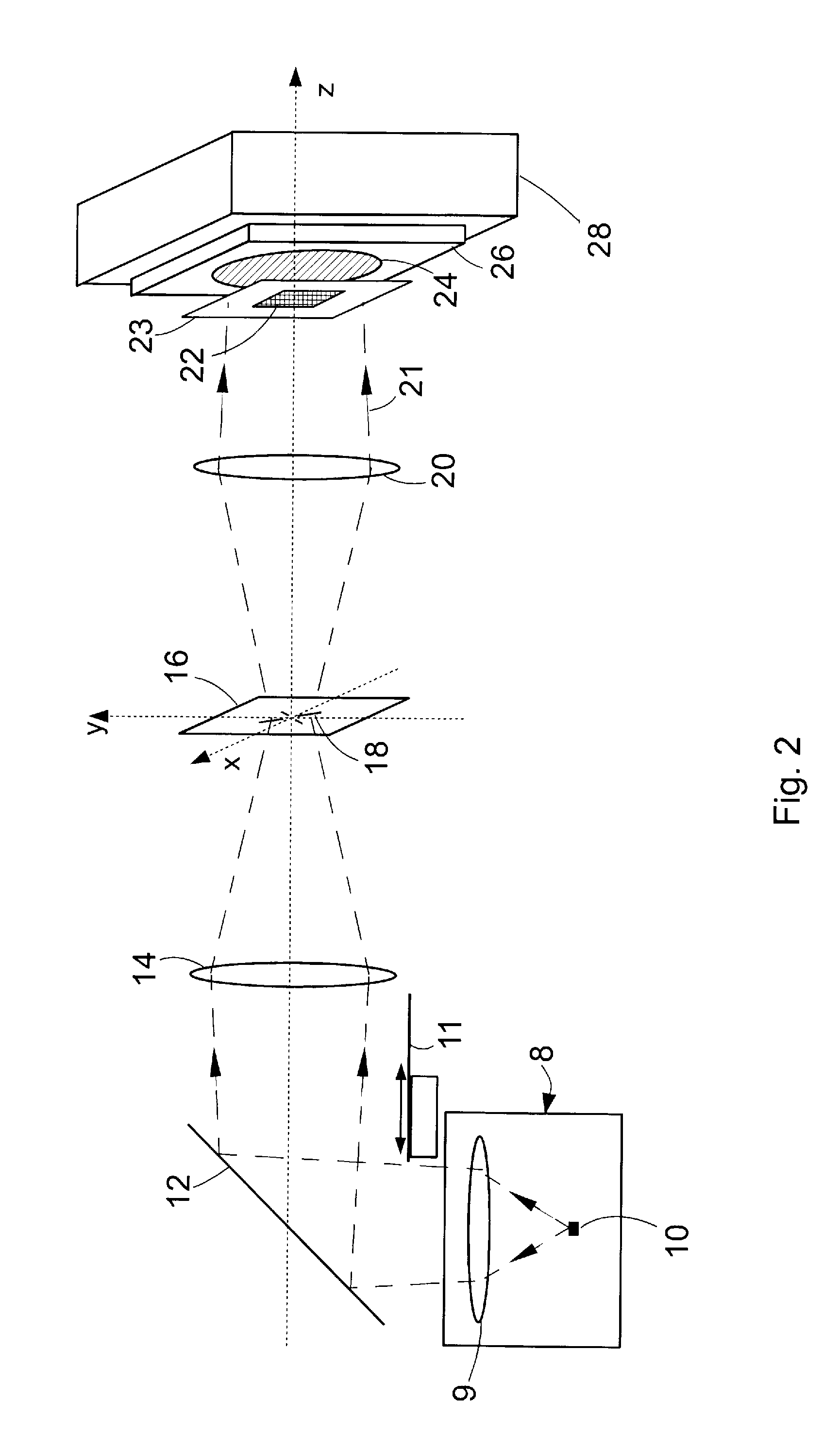
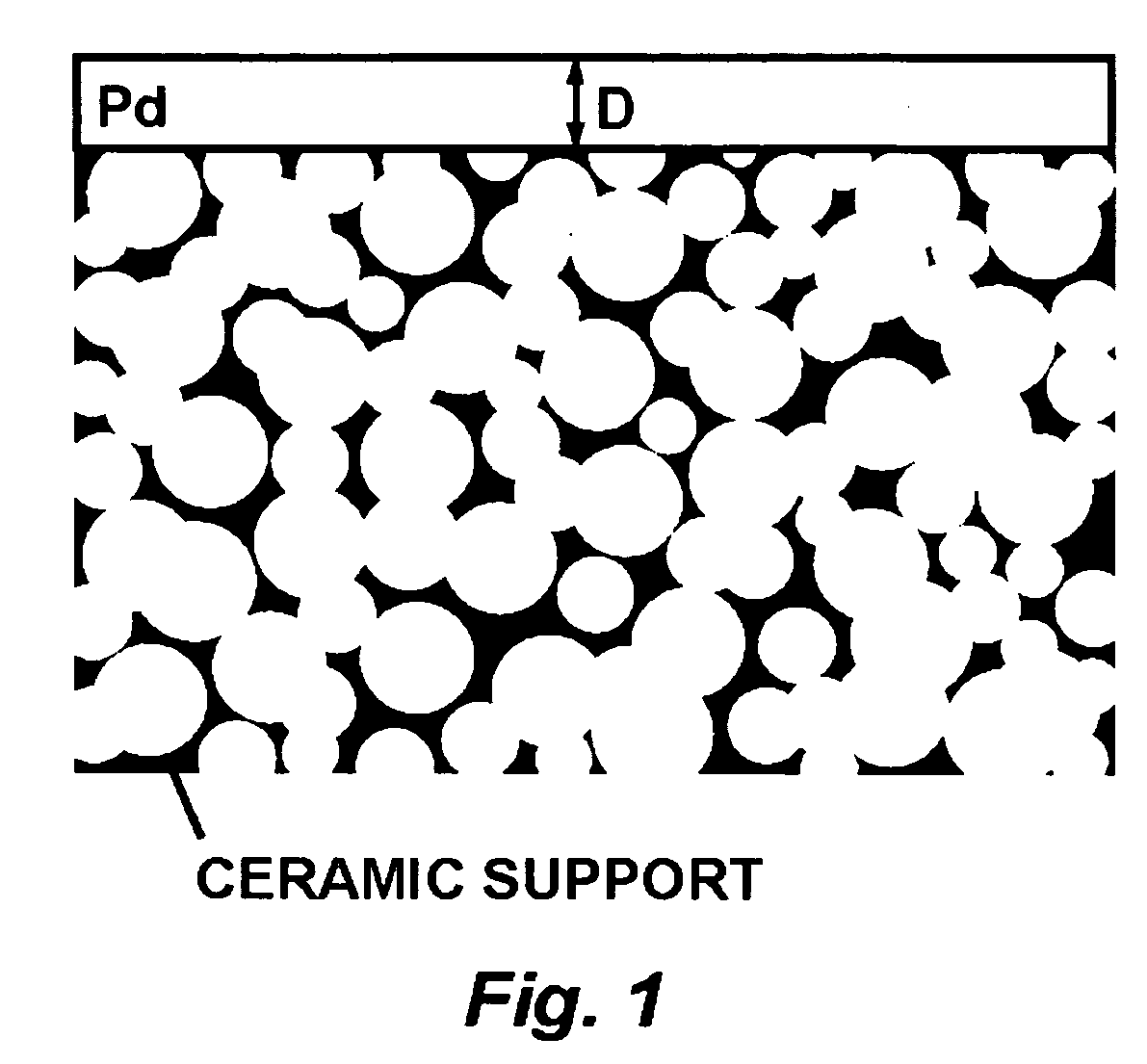
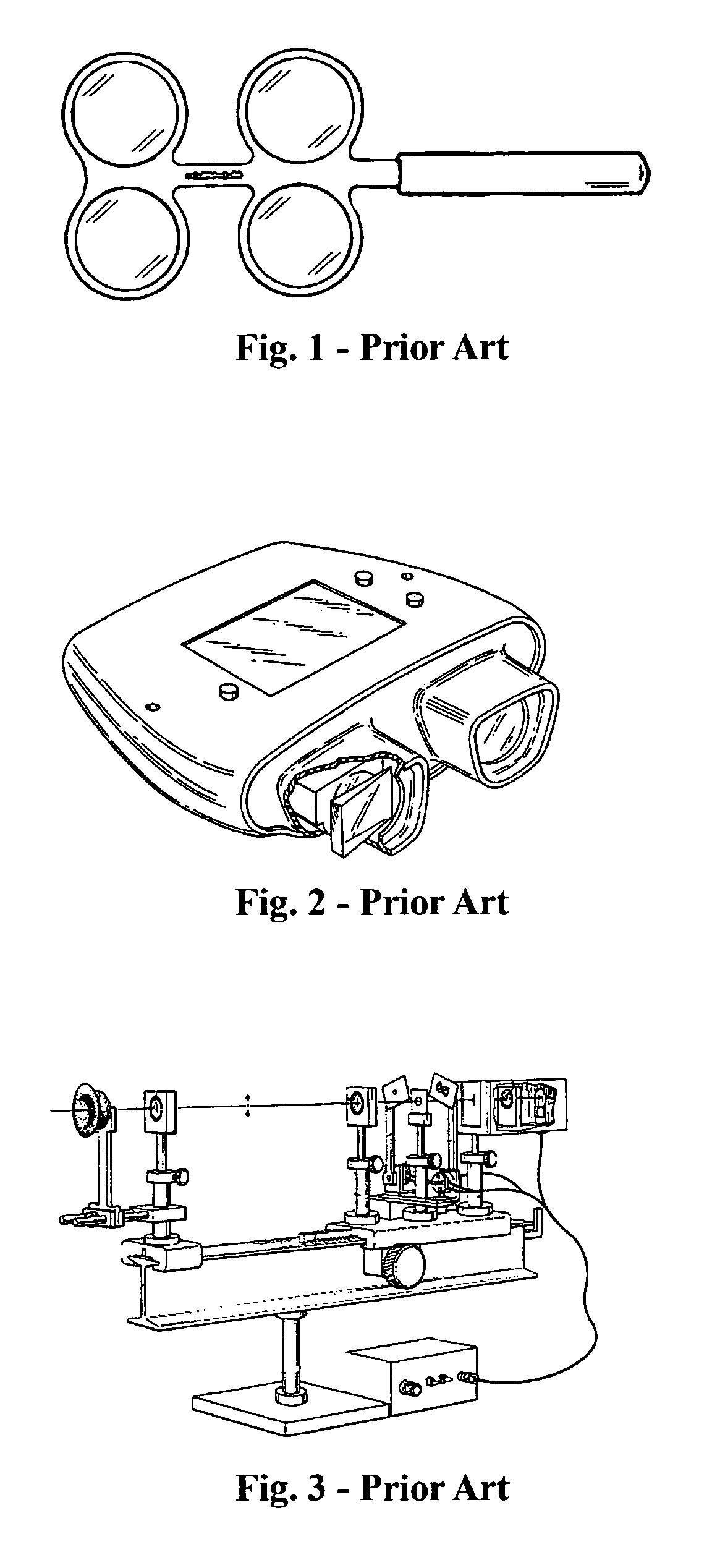
Method and system for interference lithography utilizing phase-locked scanning beams
InactiveUS6882477B1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesActive addressable light modulatorLithographic artistLight beam
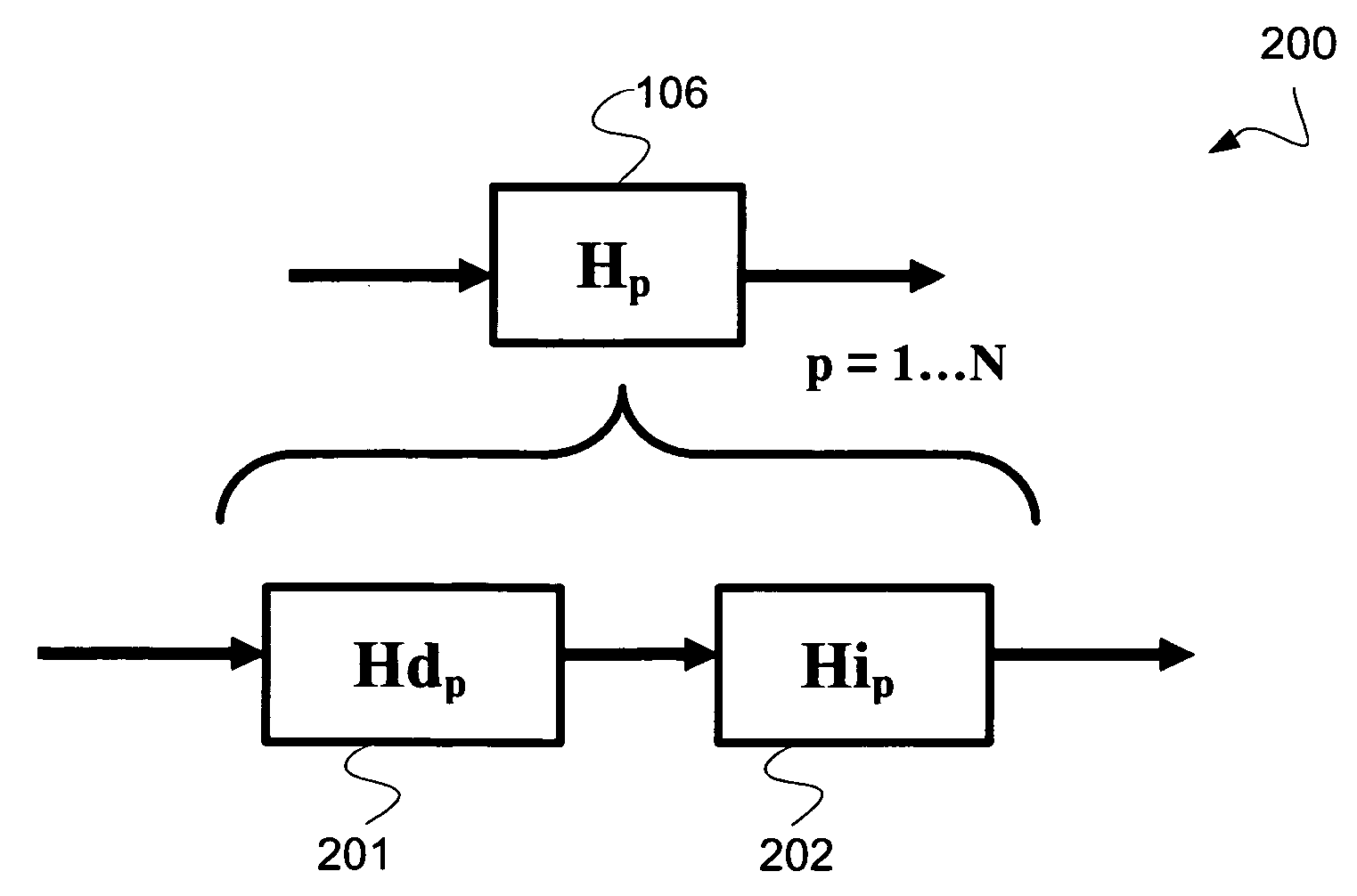
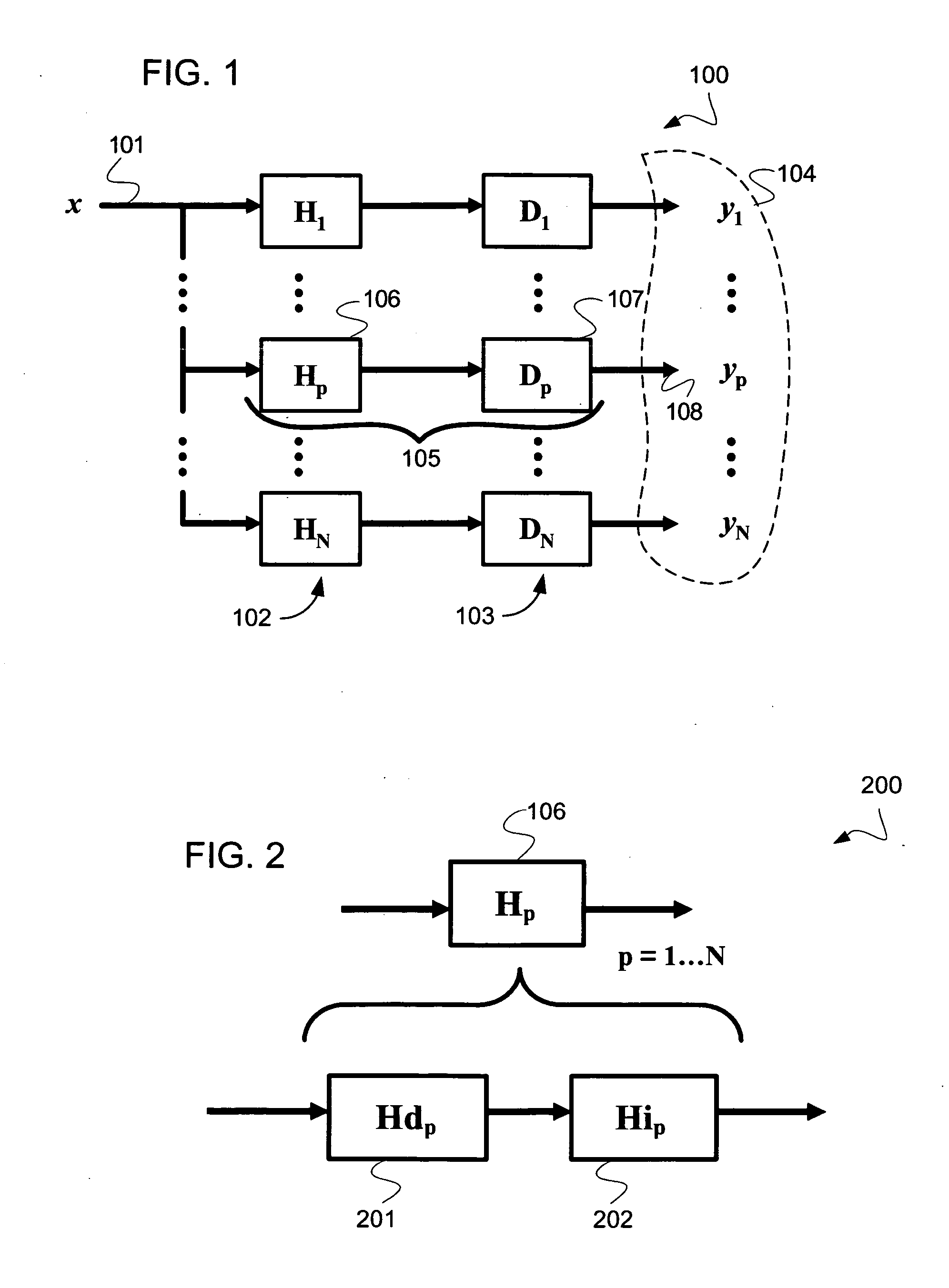
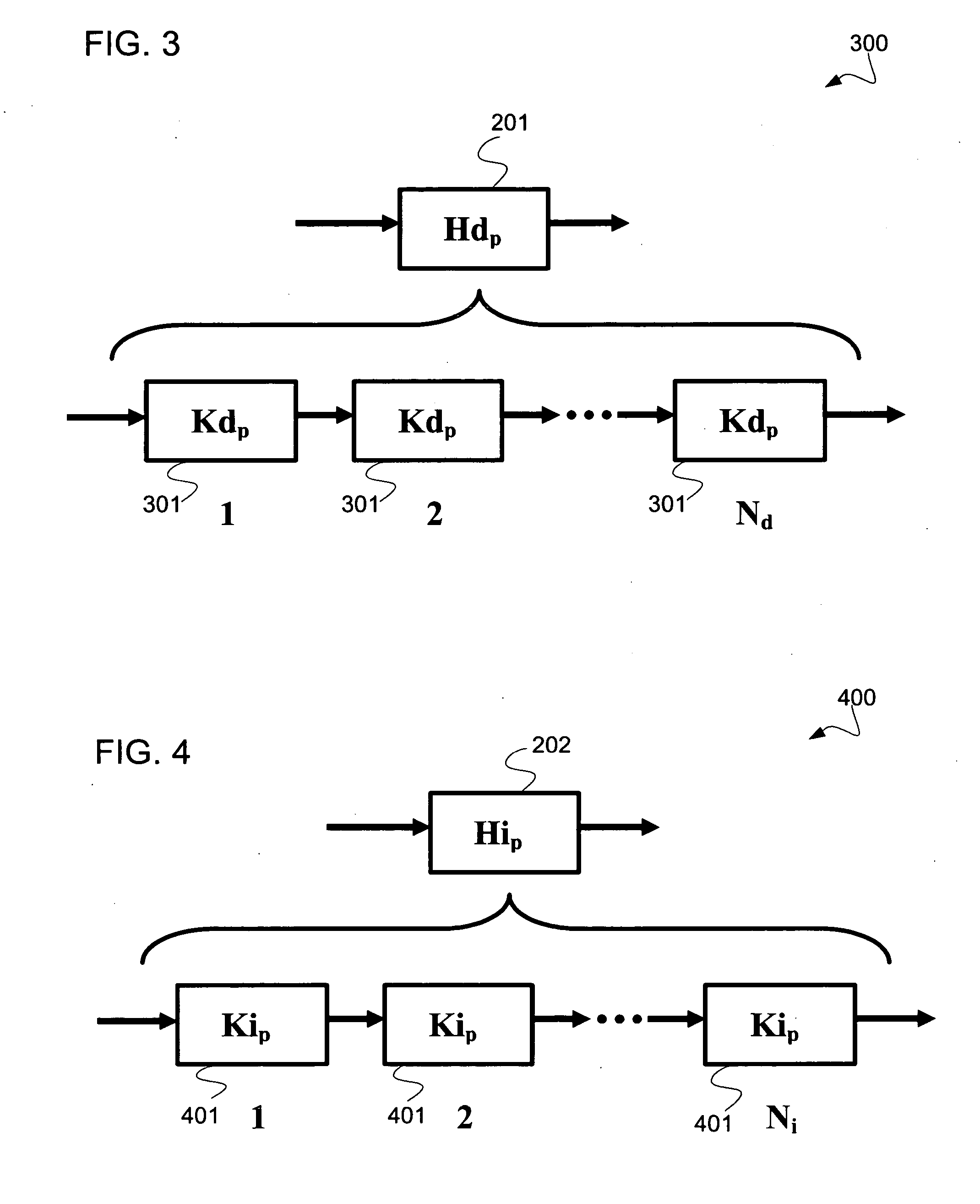
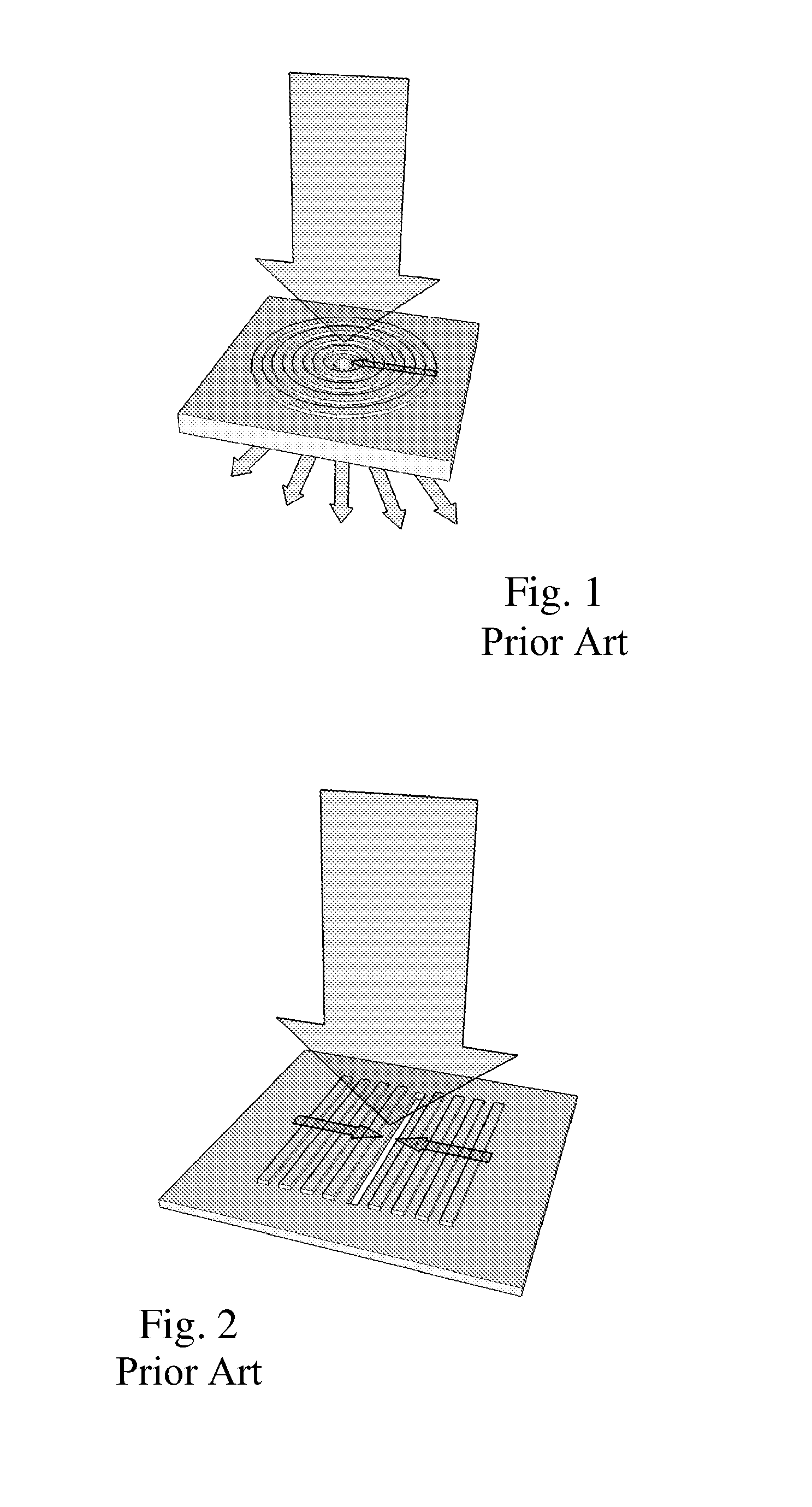
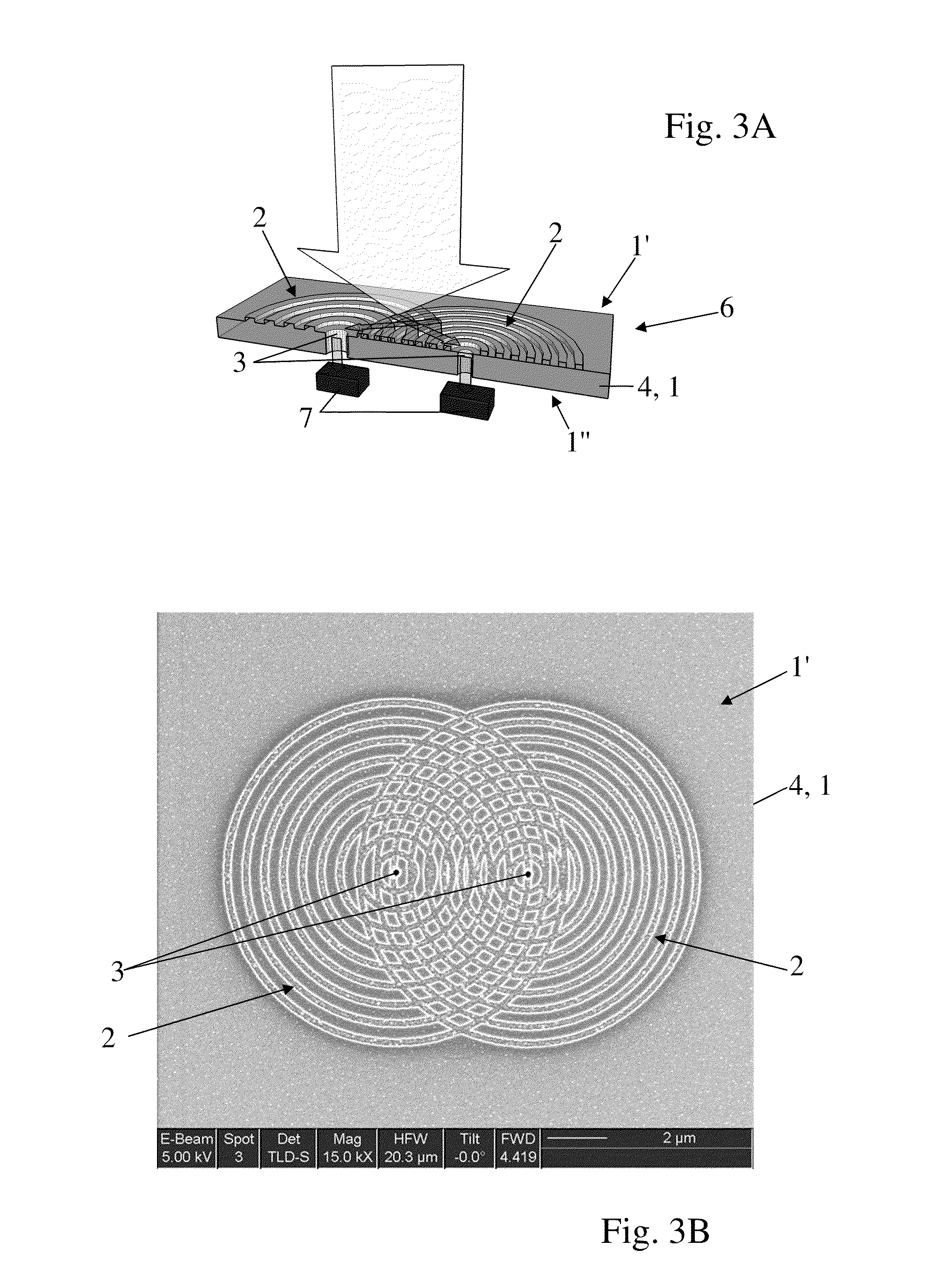
A method and system of interference lithography (also known as interferometric lithography or holographic lithography) which utilizes phase-locked, scanning beams (so-called scanning beam interference lithography, or SBIL). The invention utilizes a high-precision stage that moves a substrate under overlapped and interfering pairs of coherent beams. The overlapped beams interfere, generating fringes, which form a pattern “brush” for subsequent writing of periodic and quasi-periodic patterns on the substrate. The phase of the fringes in the overlapped region is phase-locked to the motion of the precision stage. The invention includes methods for forming, overlapping, and phase-locking interfering pairs of beams on a variety of substrates; methods for measuring and controlling the period, phase, and angular orientation of fringes generated by the overlapping beams; and methods for measuring and controlling the effects of stage mechanical and thermal drift and other disturbances during the writing process.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
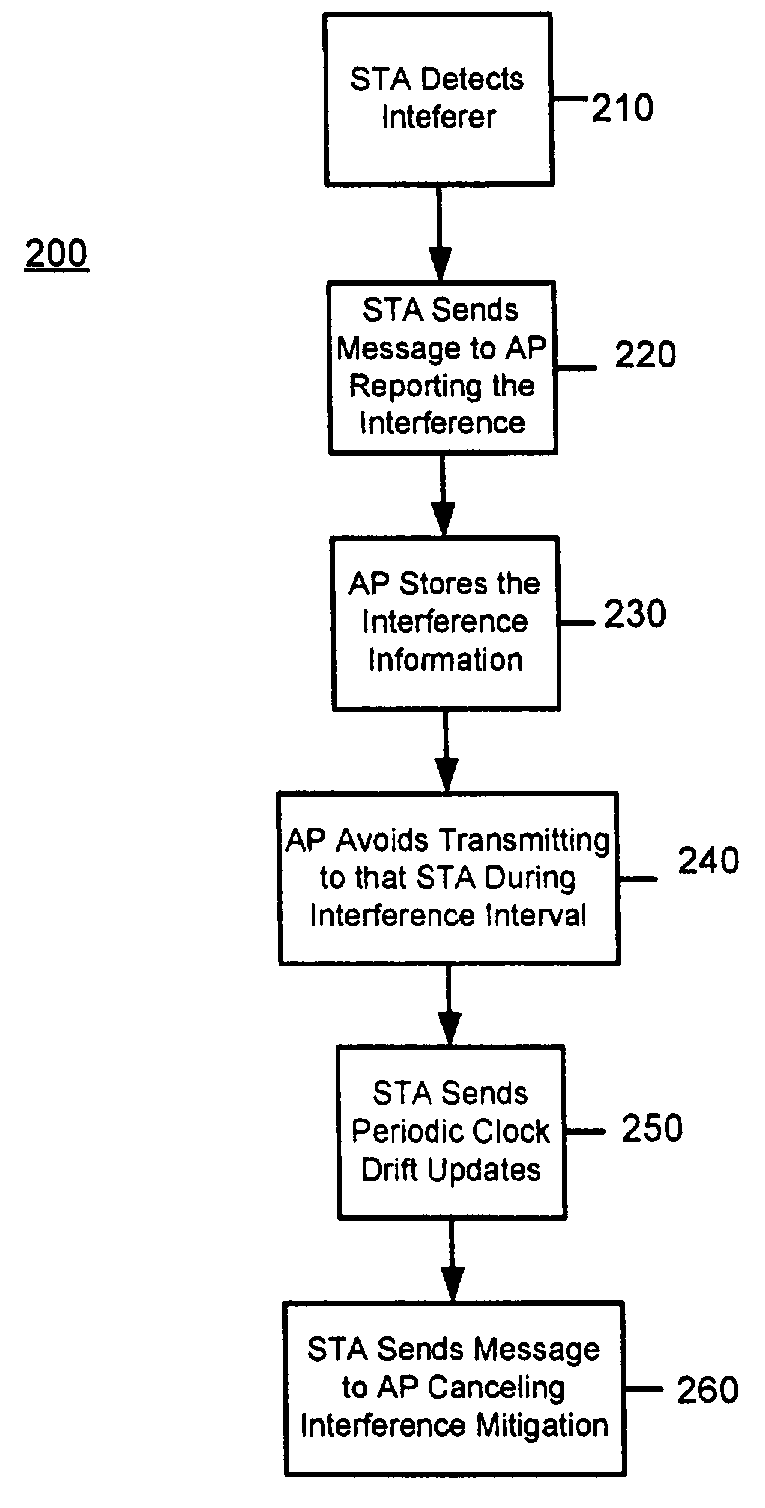
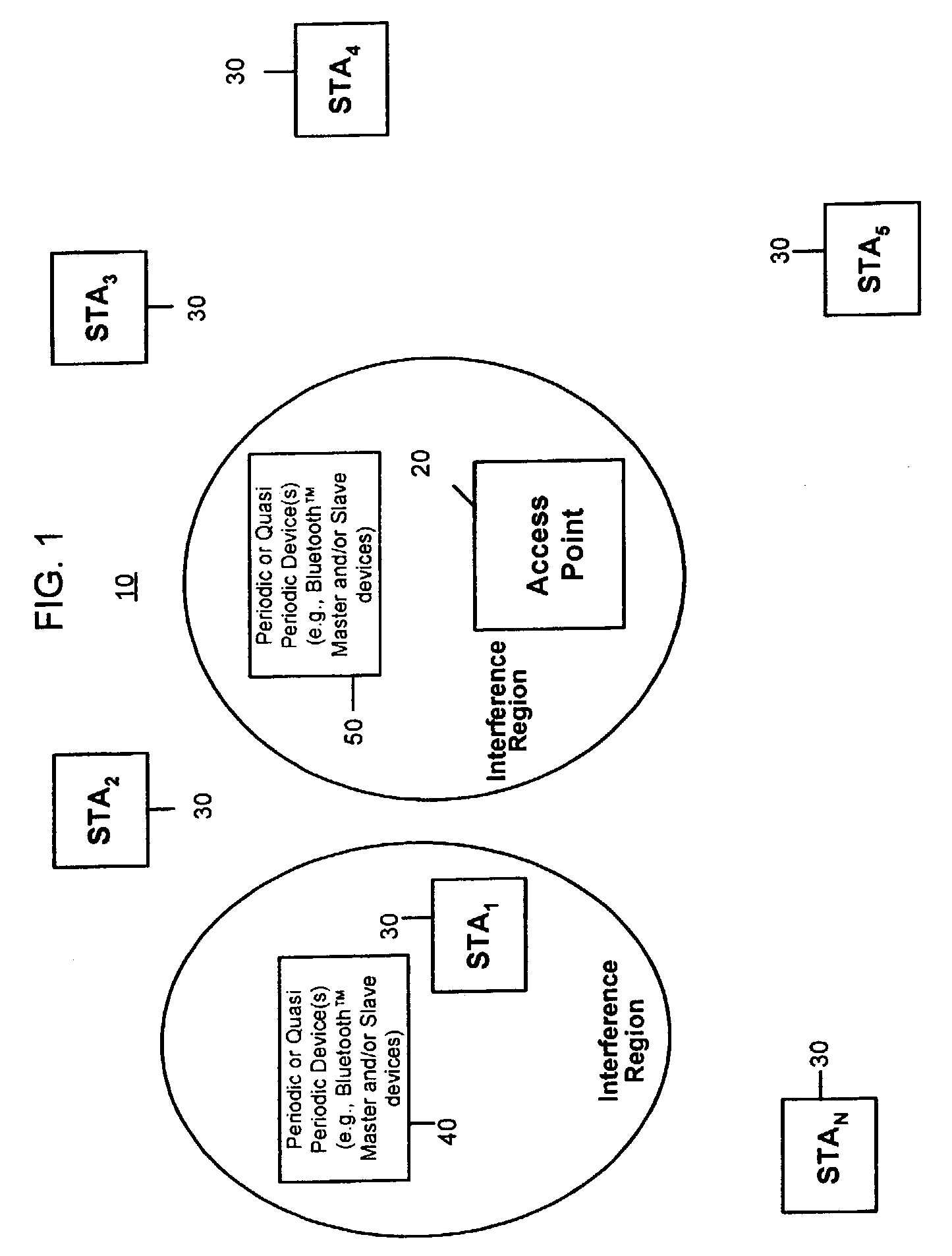
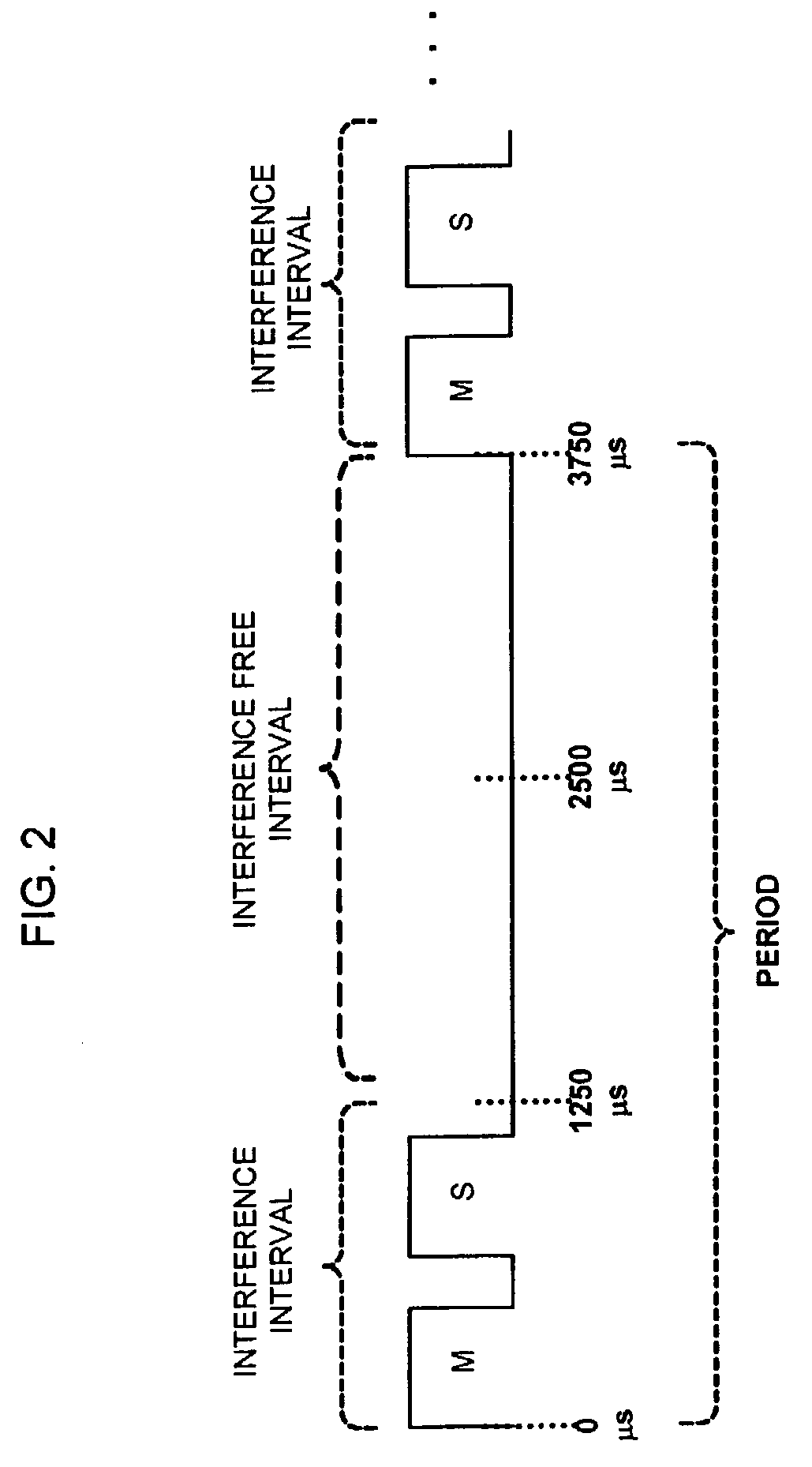
Systems and methods for interference mitigation with respect to periodic interferers in short-range wireless applications
InactiveUS7079812B2Improve service qualityAvoid interferenceData switching by path configurationTransmission monitoringQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
Several techniques are provided for use by wireless devices to avoid interference with signals that are of a periodic or quasi-periodic nature that may operate in the same frequency band and proximity. In some cases, the periodic signals are detected and their timing is determined so as to predict when a next interfering event will occur. Devices that are affected by the periodic signal (such as an affected device with information to be transmitted or devices that have information to be transmitted to the affected device) are controlled to prevent transmissions during the interfering intervals. In addition, a process is provided to dynamically fragment a transmit frame of information to transmit part of the information before the interfering interval and the remainder of the information after the interfering interval, rather than waiting to transmit the entire frame until after the interfering interval. Moreover, techniques are provided to correct for clock drift between the periodic signal and a device affected by the periodic signal, as well as for clock drift between a device affected by the periodic signal and other devices that communicate with that device. These techniques prevent interference with periodic signals and in so doing, improve the quality of service of the communication link for both the interfering devices and the other devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
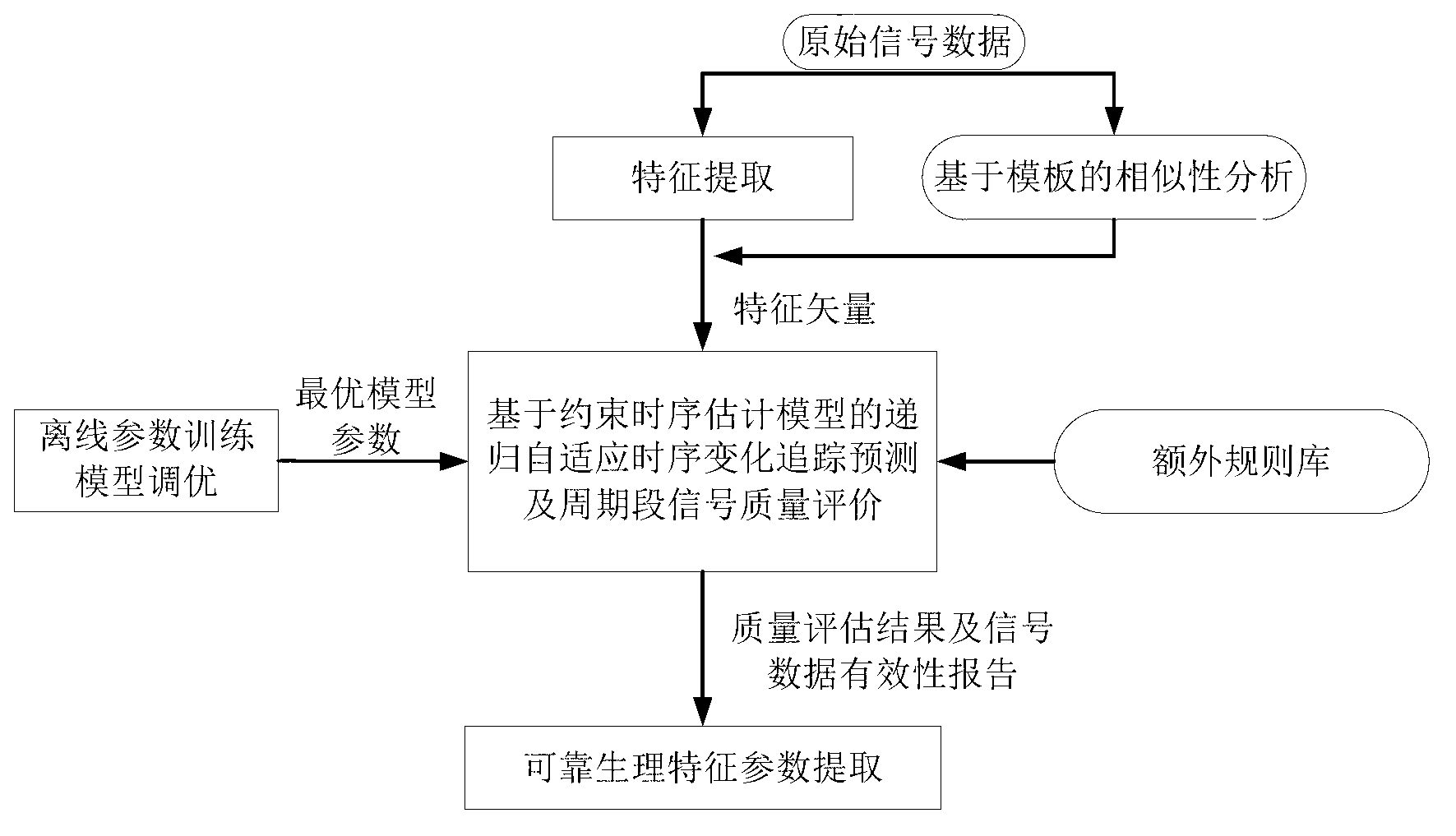
Physiological signal quality evaluation method and system based on constrained estimation
ActiveCN103020472AEffective assessmentComprehensive assessmentSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorWaveform analysis
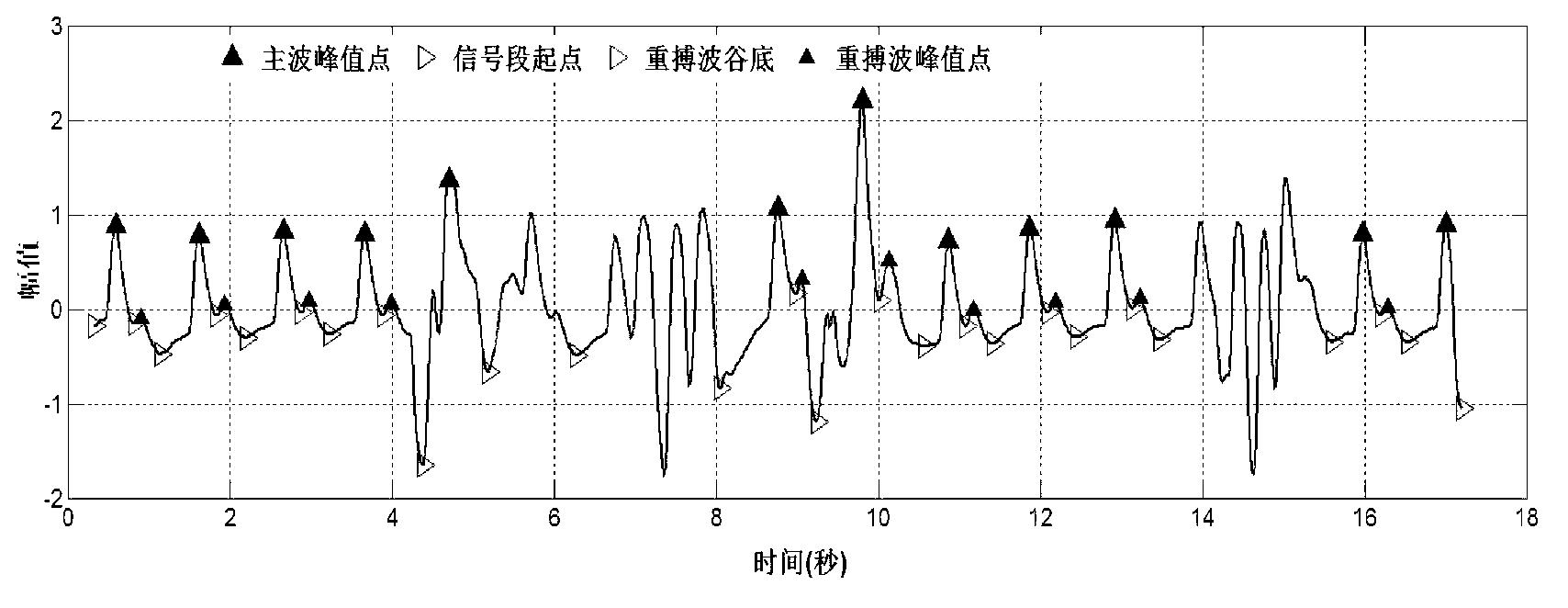
The invention relates to a physiological signal quality evaluation method and system based on constrained estimation. The method comprises the following steps: receiving to-be-evaluated signal sections of a quasi-periodic physiological signal, performing pretreatment, waveform analysis identification and signal period segmentation to the signal sections, carrying out feature point detection to each cycle of signal section, and extracting preset physiological feature parameters of the physiological signal; for each signal section, combining the extracted physiological feature parameters to form feature vectors, performing constraint-based modeling according to transcendental knowledge of the physiological signal, and further establishing an analyzable evaluation system with constraint timing; and using a constraint evaluation model to trace sequential change of physiological parameters, combing a preset rule base and sequential change information, rating the signal quality of the quasi-periodic physiological signal, evaluating the validity of signal data of the signal sections of the quasi-periodic physiological signal, updating a time sequence evaluation system, and rating according to iteration of the periodic signal sections until the signal quality rating of all the signal sections of the quasi-periodic physiological signal is finished.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for signal decomposition, analysis and reconstruction
ActiveUS20060200035A1Digital technique networkCharacter and pattern recognitionDecompositionComputer science
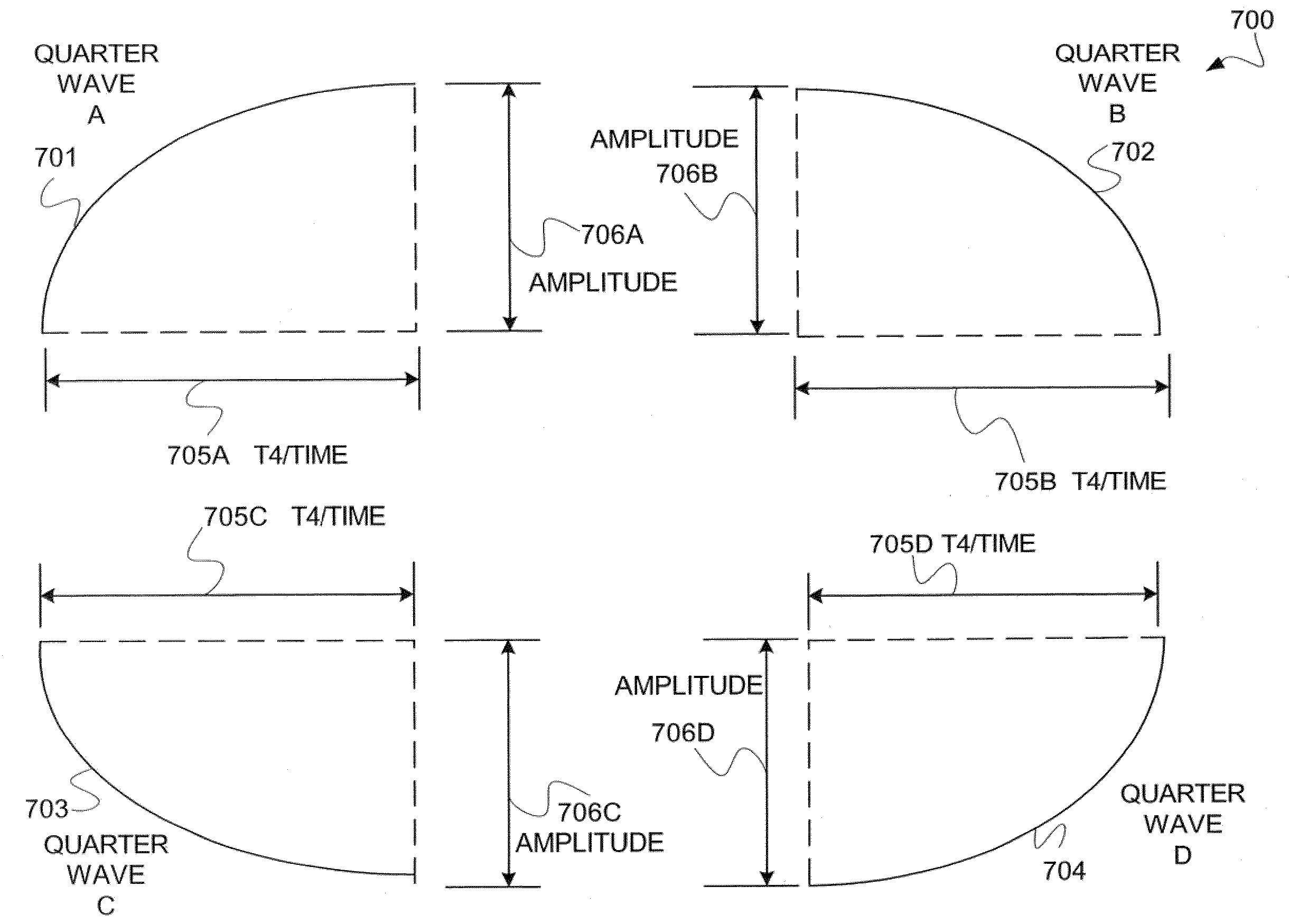
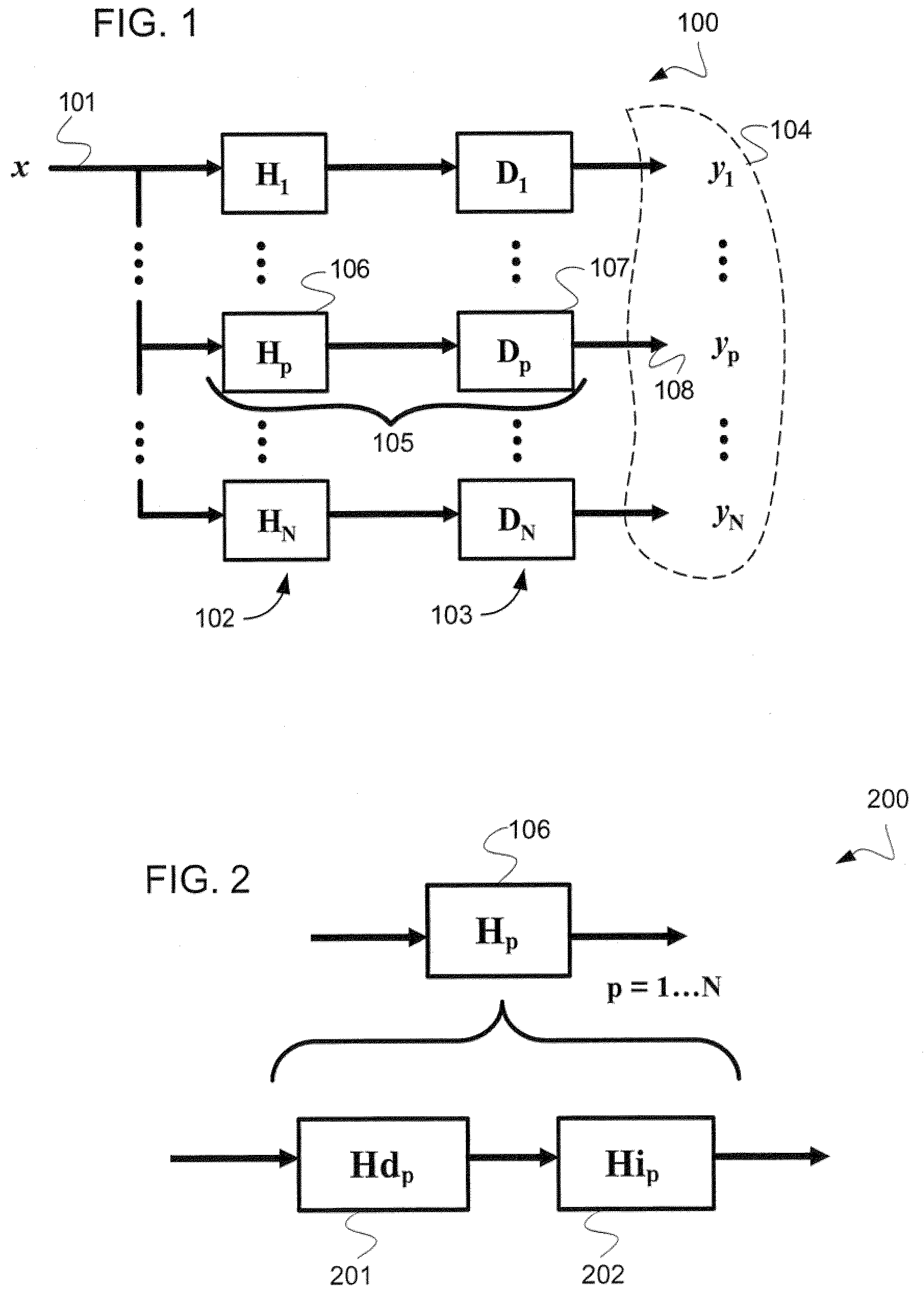
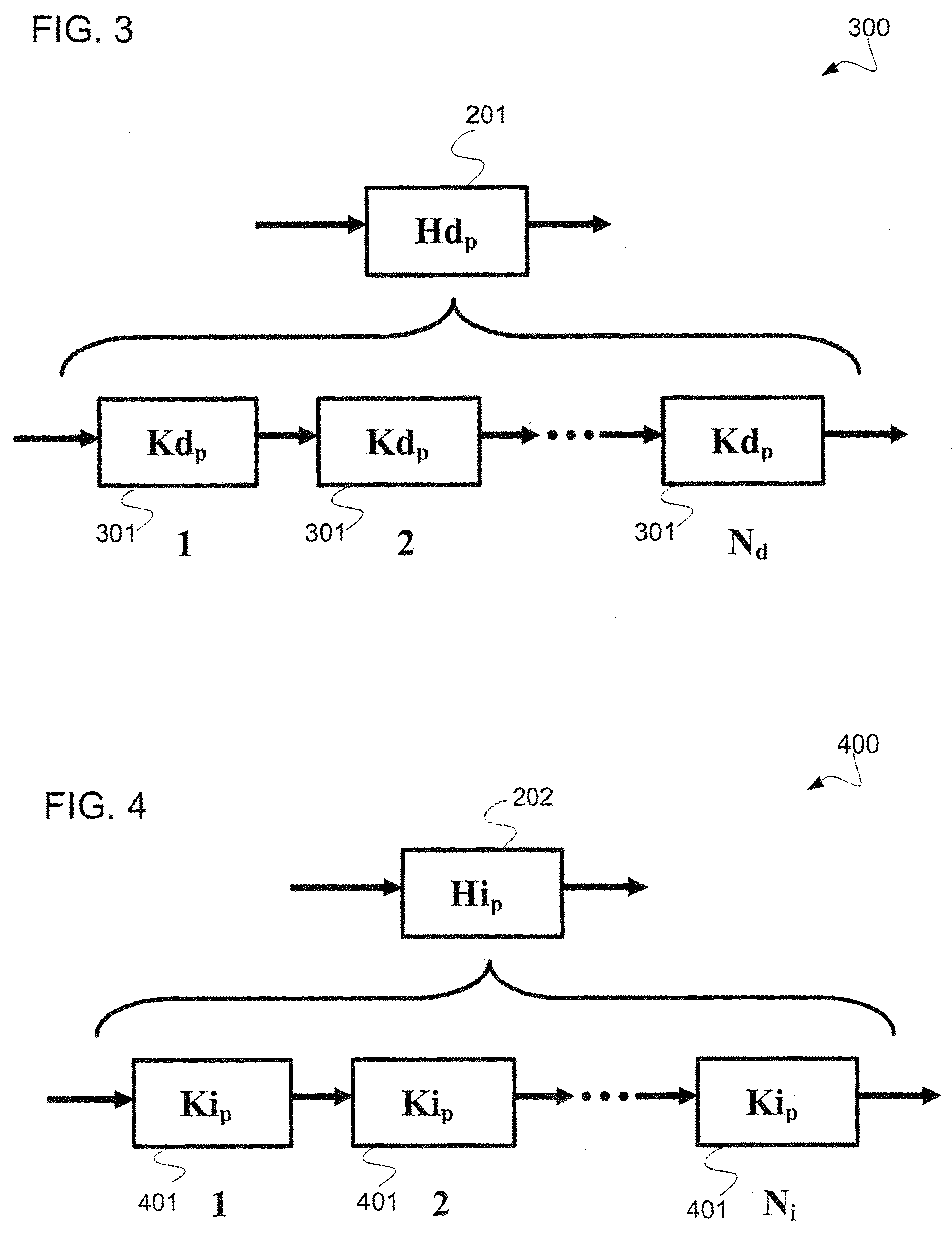
The present invention provides a system and method for representing quasi-periodic (“qp”) waveforms comprising, representing a plurality of limited decompositions of the qp waveform, wherein each decomposition includes a first and second amplitude value and at least one time value. In some embodiments, each of the decompositions is phase adjusted such that the arithmetic sum of the plurality of limited decompositions reconstructs the qp waveform. These decompositions are stored into a data structure having a plurality of attributes. Optionally, these attributes are used to reconstruct the qp waveform, or patterns or features of the qp wave can be determined by using various pattern-recognition techniques. Some embodiments provide a system that uses software, embedded hardware or firmware to carry out the above-described method. Some embodiments use a computer-readable medium to store the data structure and / or instructions to execute the method.
Owner:MURATA VIOS INC
Optical transmission apparatus with directionality and divergence control
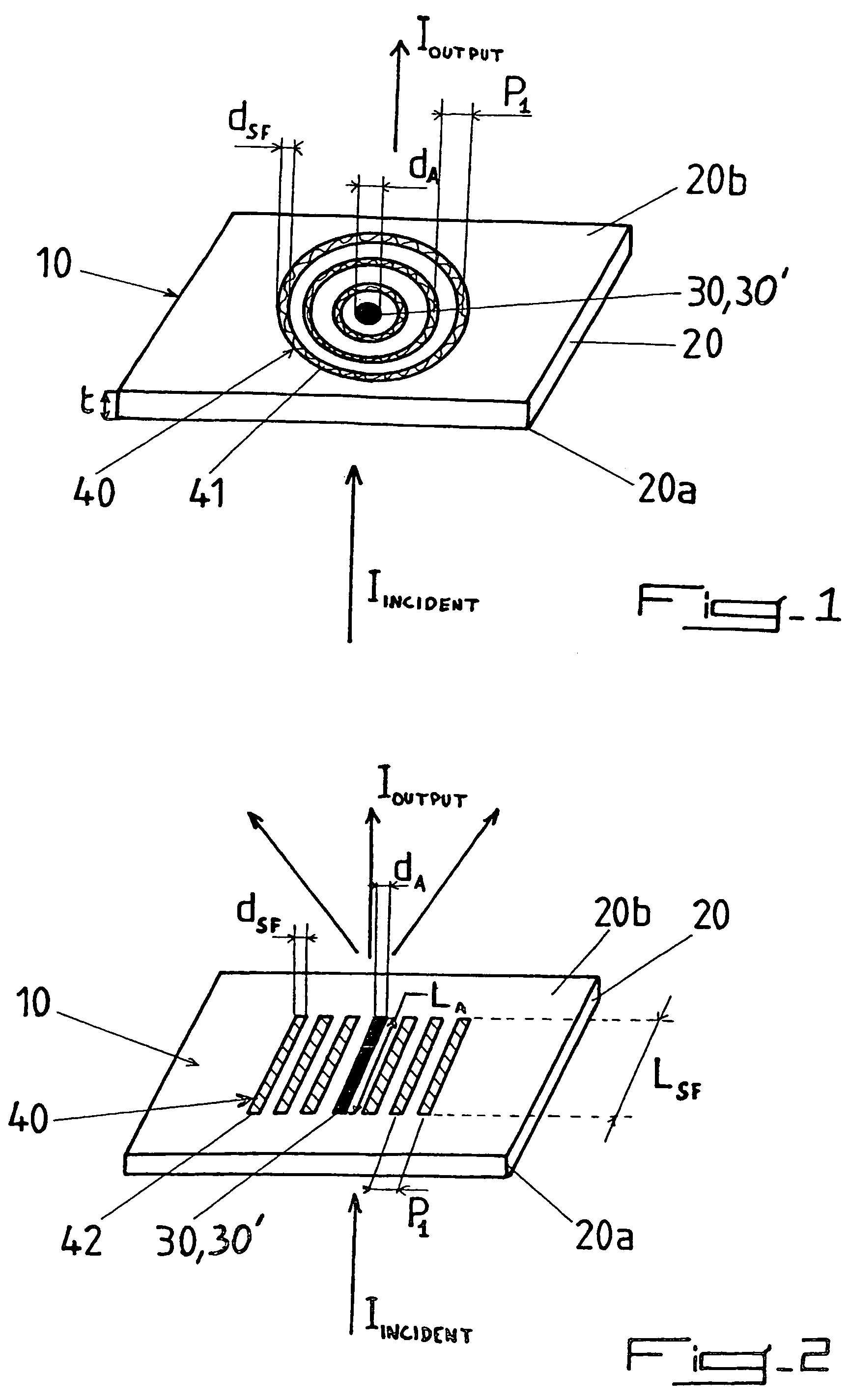
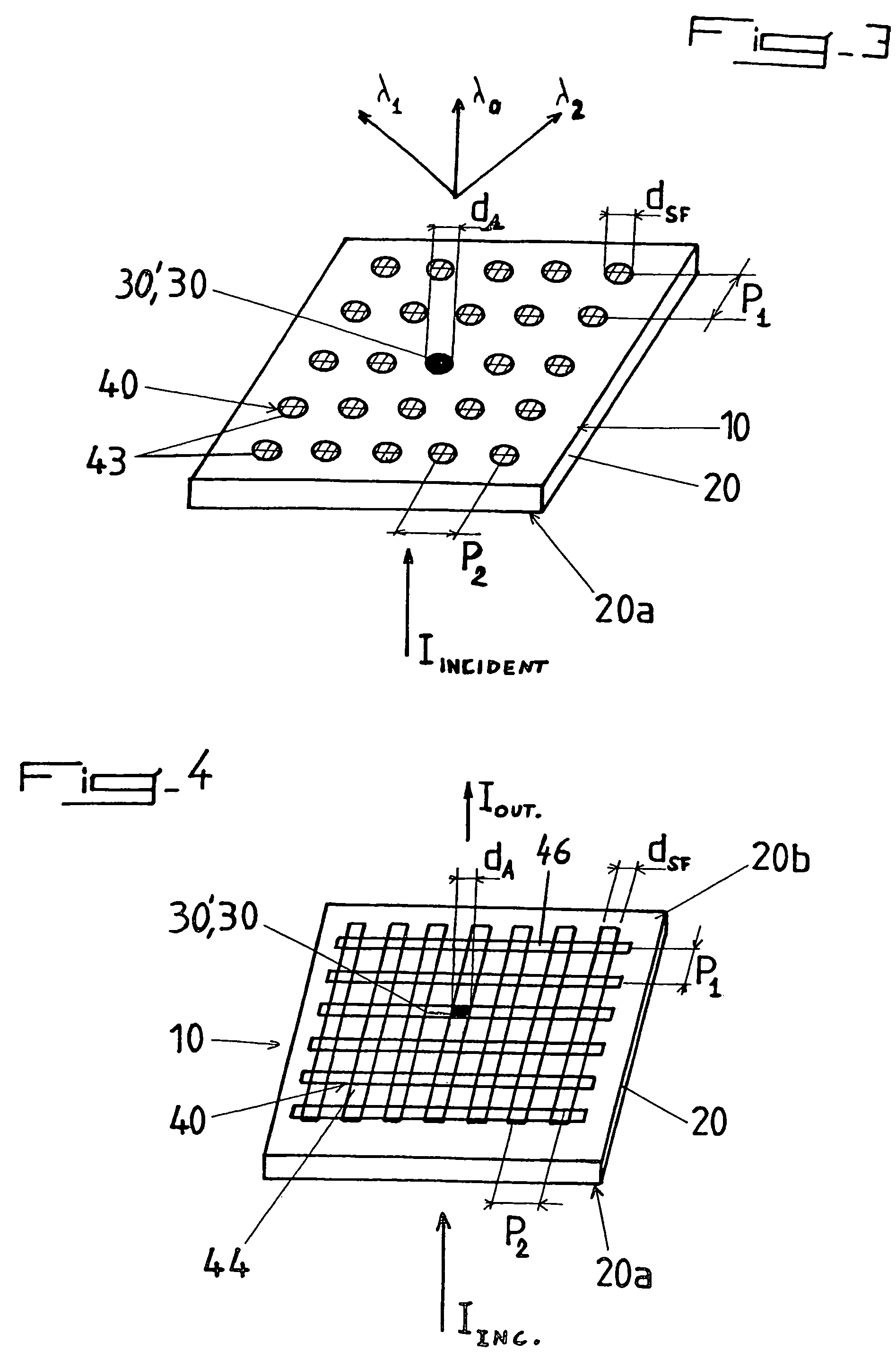
InactiveUS7057151B2Spread the wordLow optical divergence output lightBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsOptical filtersTopographySurface structure
An apparatus for emitting light with a controlled directionality and optical divergence from at least one opening includes a light impervious surface structure having the at least one opening, a periodic or quasi-periodic surface topography including one or several surface feature(s) and associated with the at least one opening on the surface structure, whereby light emerging from the opening(s) interacts with surface waves on the surface structure (20) thereby providing controlled directionality and optical divergence of the emitted light.
Owner:UNIV LOUIS PASTEUR ULP +1
Apparatus for signal decomposition, analysis and reconstruction
ActiveUS20060200034A1Digital technique networkCharacter and pattern recognitionDecompositionComputer science
The present invention provides a system and method for representing quasi-periodic (“qp”) waveforms comprising, representing a plurality of limited decompositions of the qp waveform, wherein each decomposition includes a first and second amplitude value and at least one time value. In some embodiments, each of the decompositions is phase adjusted such that the arithmetic sum of the plurality of limited decompositions reconstructs the qp waveform. These decompositions are stored into a data structure having a plurality of attributes. Optionally, these attributes are used to reconstruct the qp waveform, or patterns or features of the qp wave can be determined by using various pattern-recognition techniques. Some embodiments provide a system that uses software, embedded hardware or firmware to carry out the above-described method. Some embodiments use a computer-readable medium to store the data structure and / or instructions to execute the method.
Owner:MURATA VIOS INC
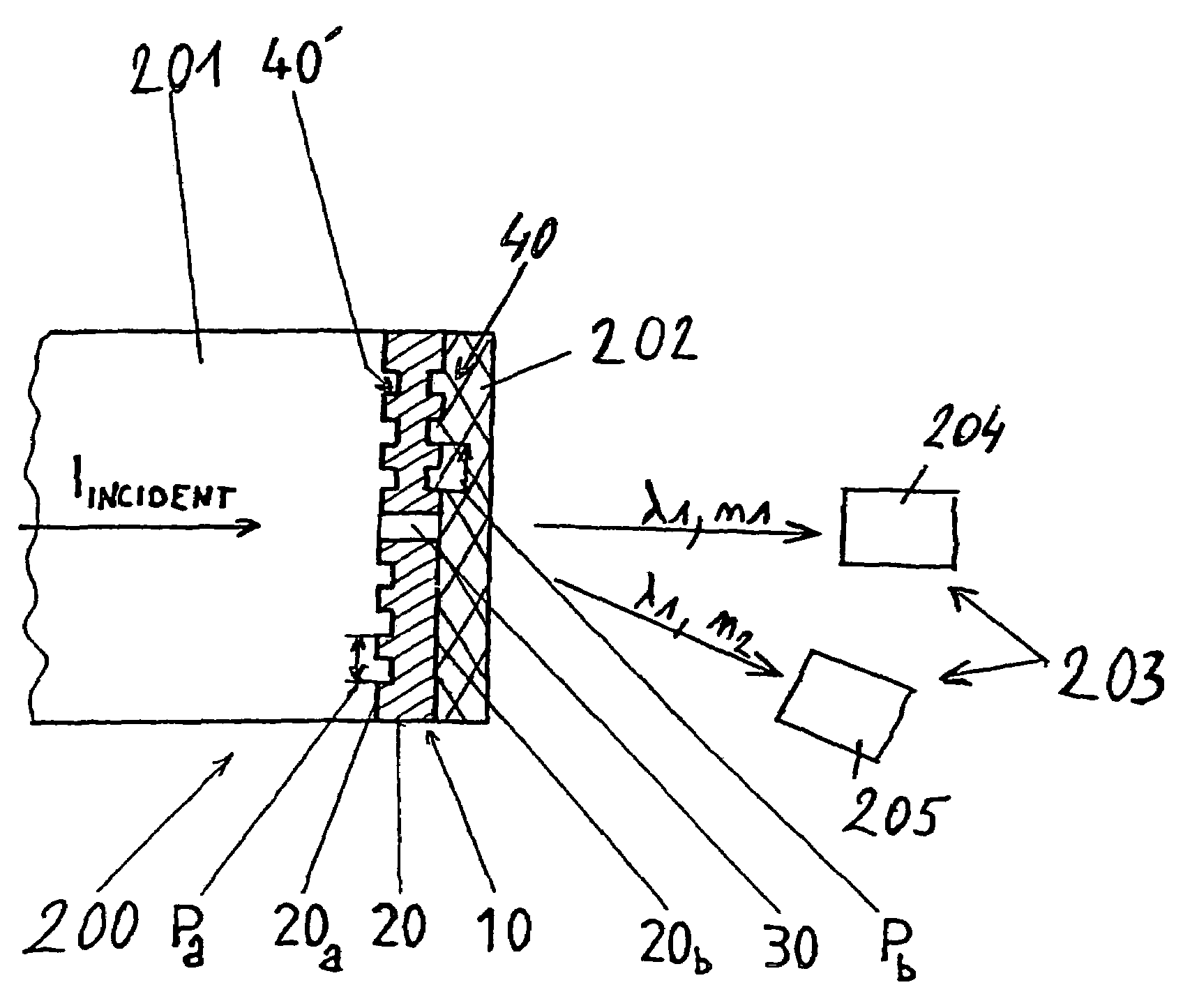
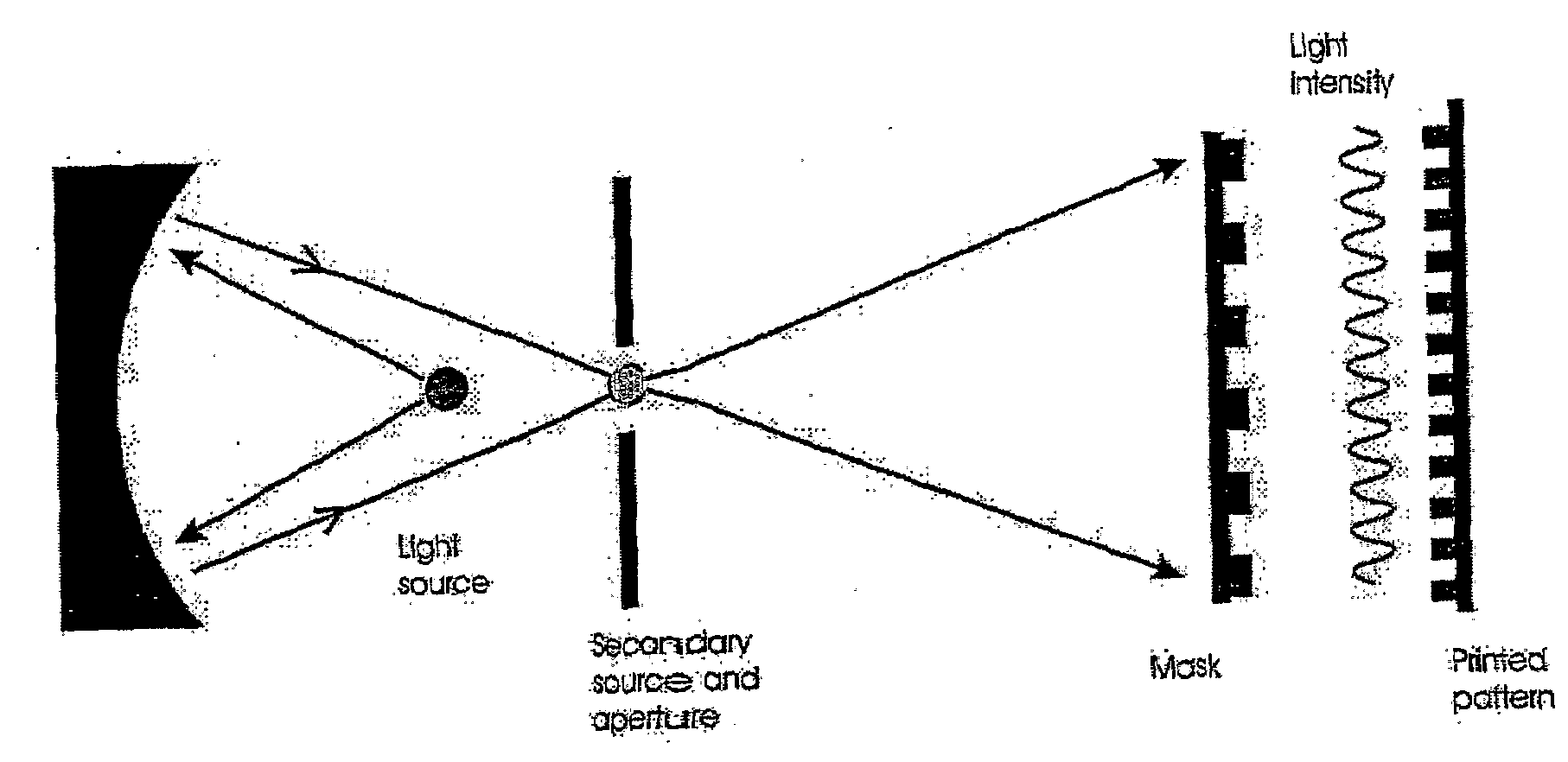
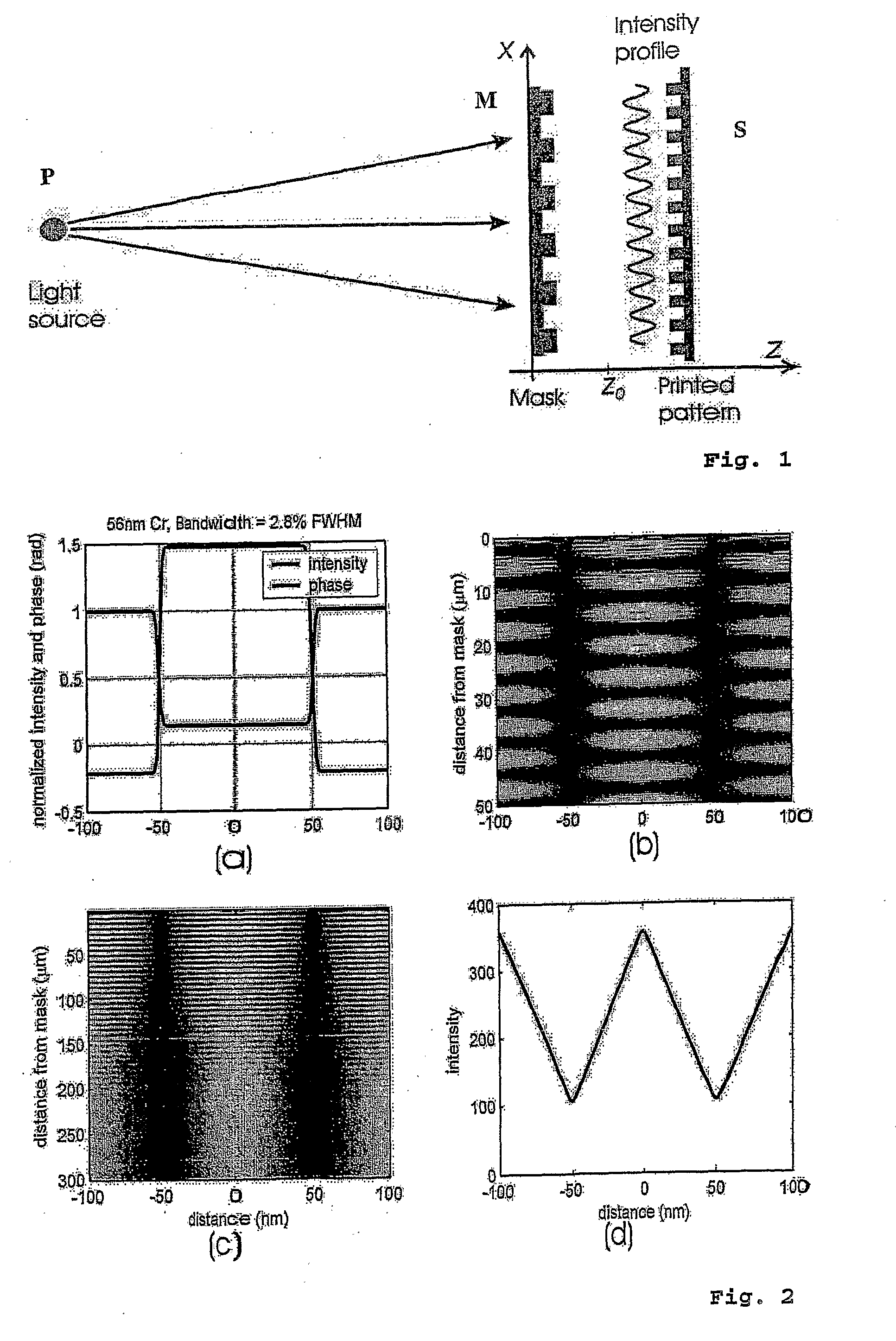
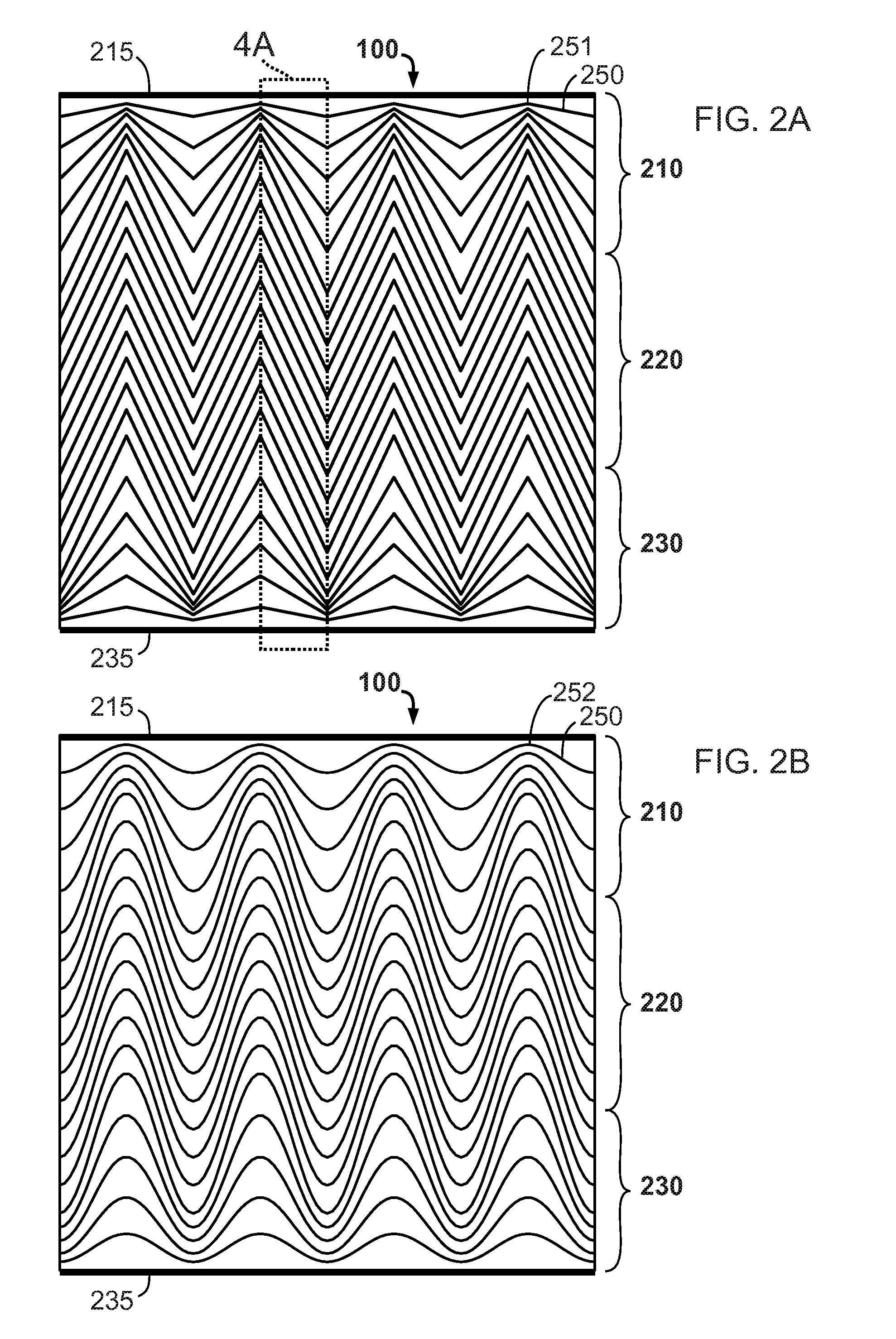
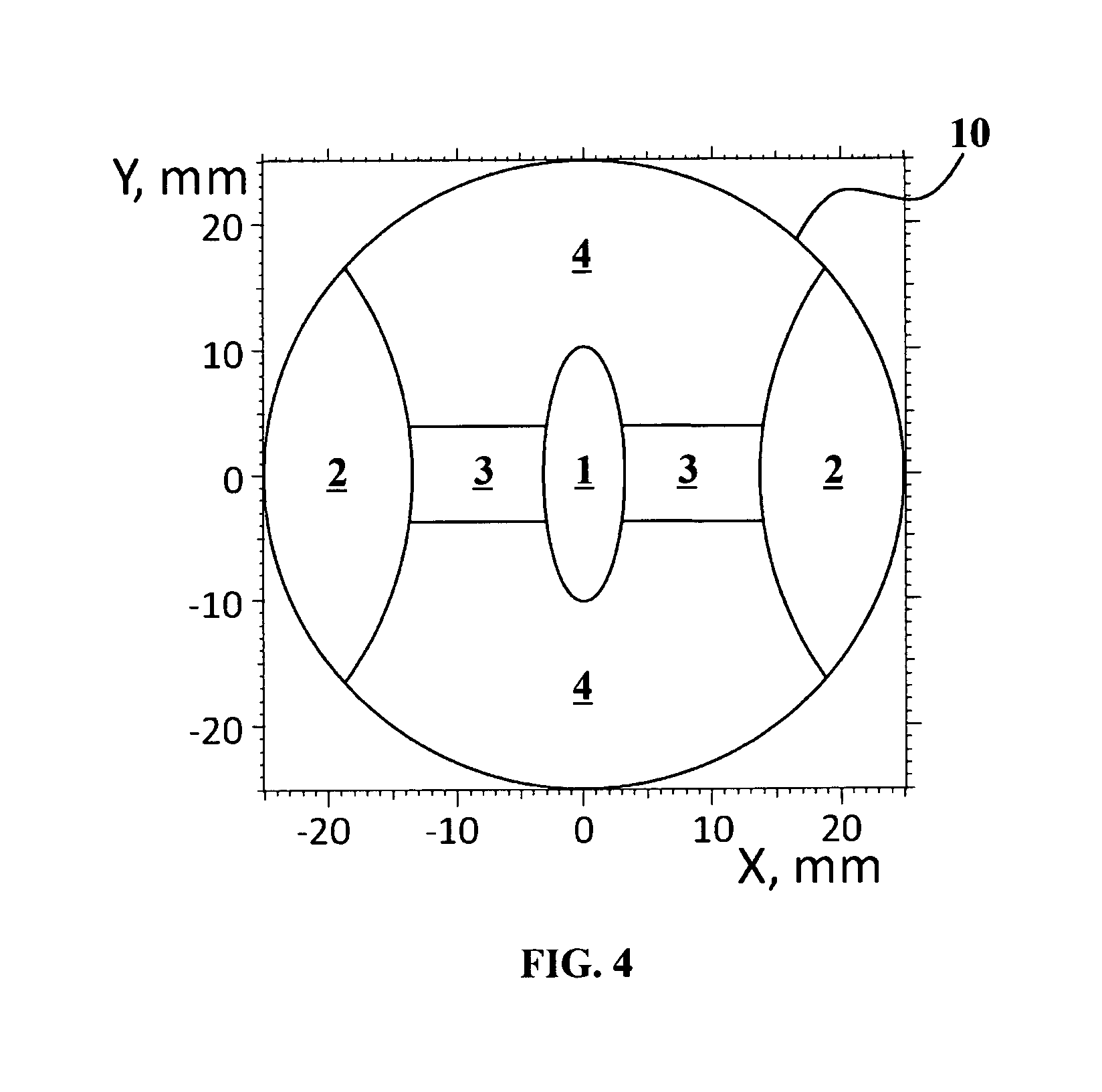
System and a Method for Generating Periodic and/or Quasi-Periodic Pattern on a Sample
ActiveUS20080186579A1Effective protectionPhotomechanical apparatusOptical elementsGratingInterference lithography
A system for generating periodic or quasi-periodic patterns on a sample by means of an interference lithography technique includes a photon source, a mask and a sample holder. The mask has a grating for generating a predetermined pattern, wherein the mask is positioned at a first distance from the photon source. The sample holder is disposed at a second distance from the mask on a side facing away from the photon source. The second distance is selected to be where an intensity distribution is substantially stationary and distance-invariant, or the second distance is varied to obtain a desired average intensity distribution on the sample surface.
Owner:EULITHA
Non-invasive method and system for characterizing cardiovascular systems
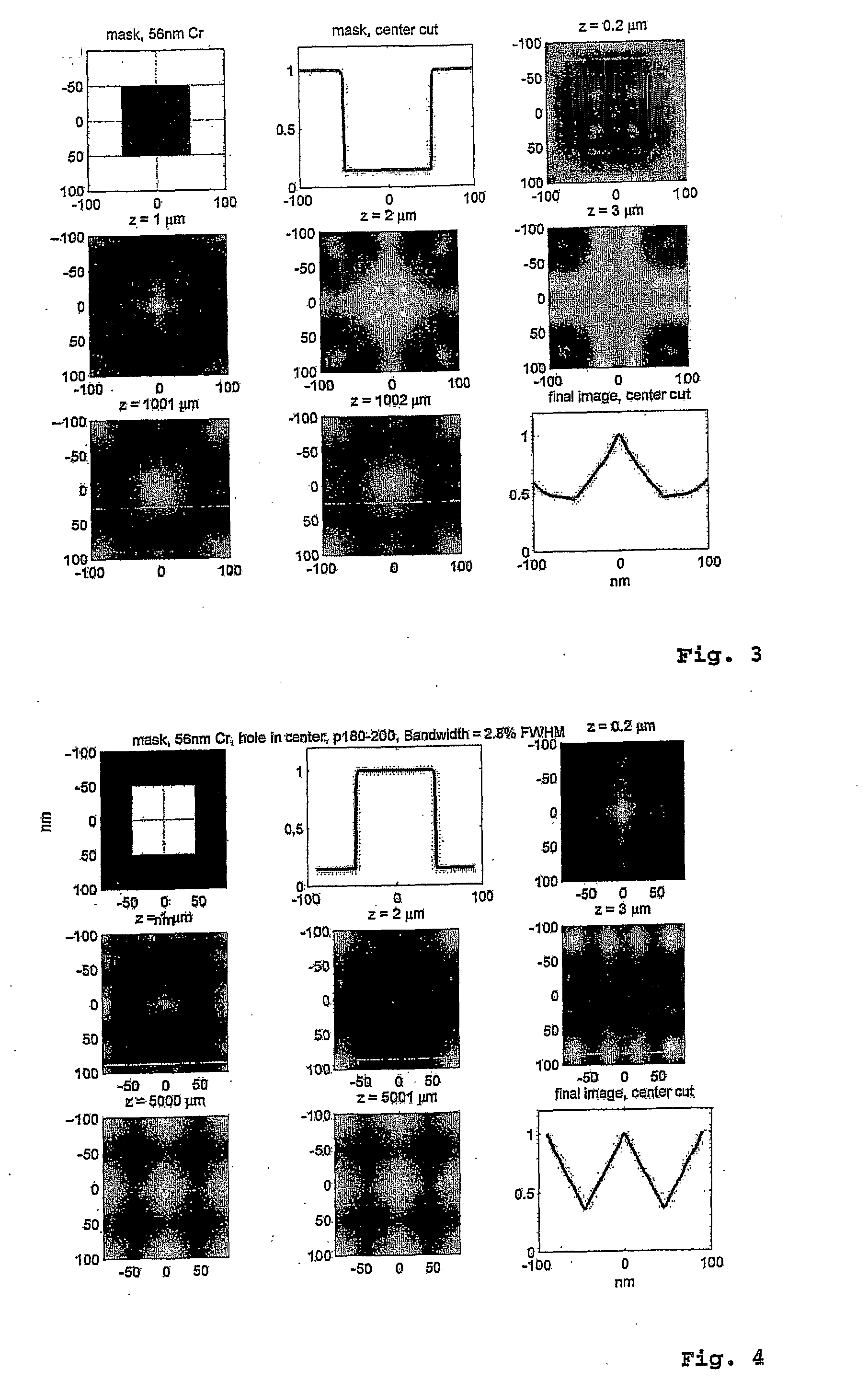
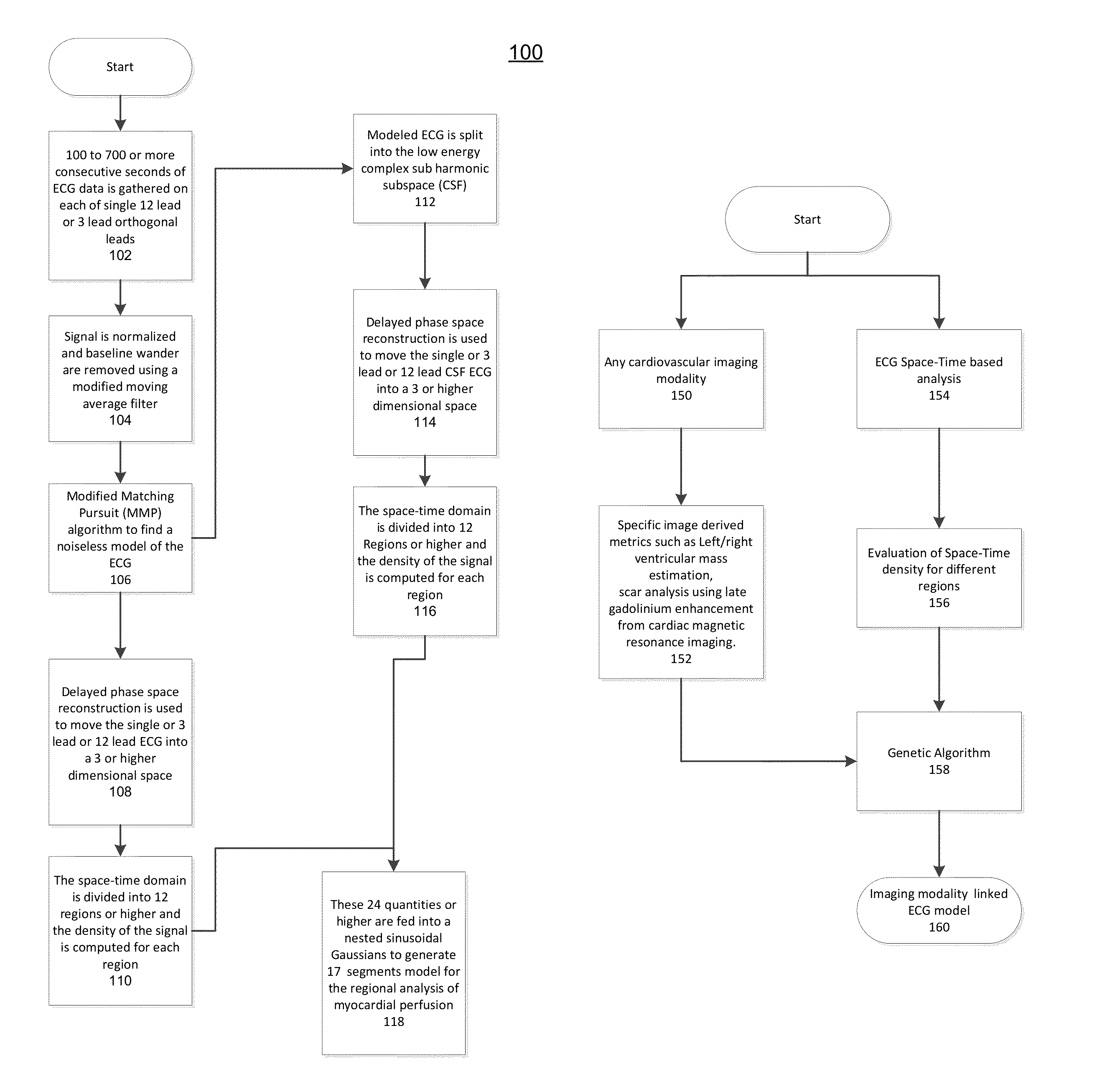
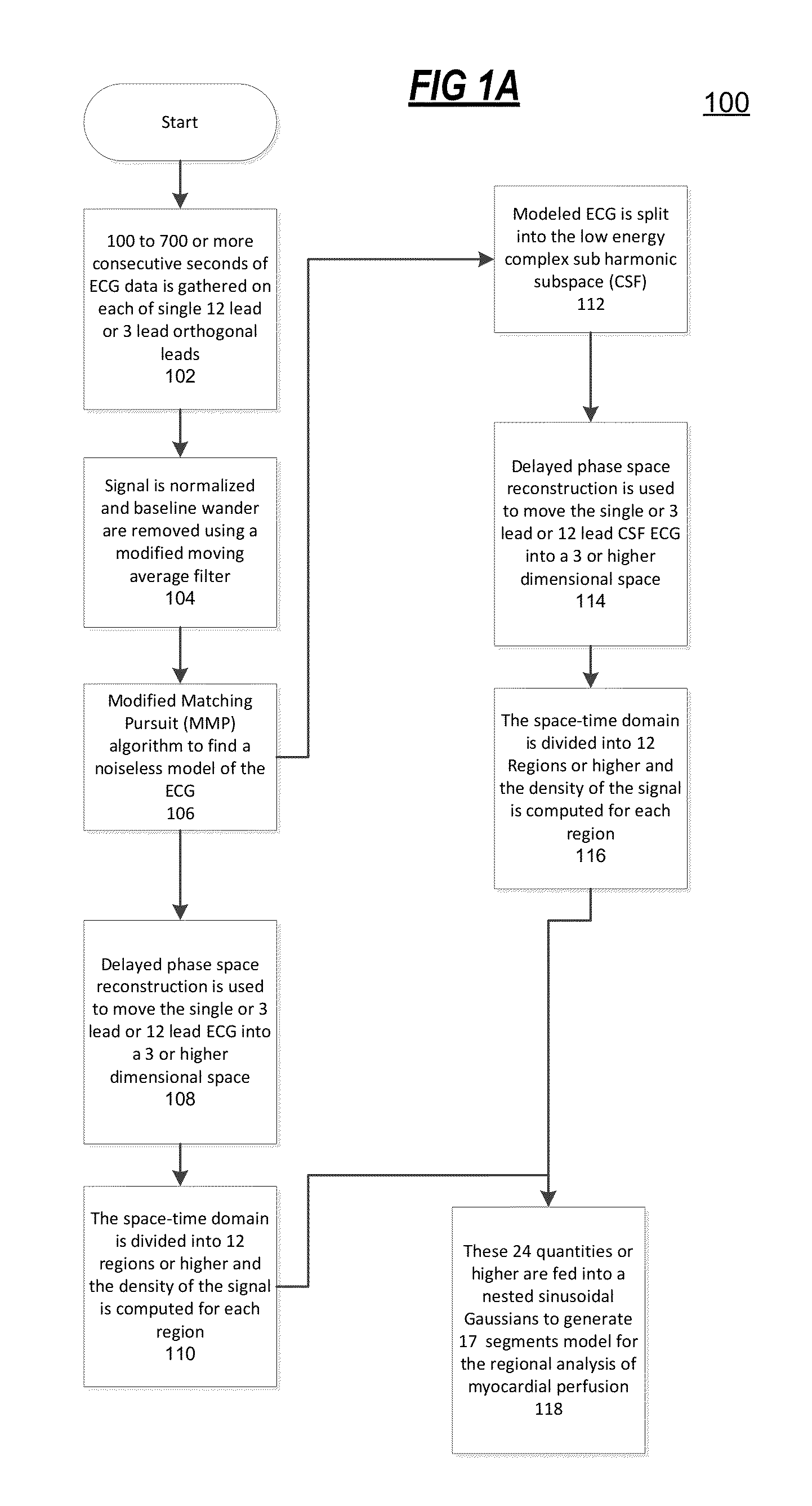
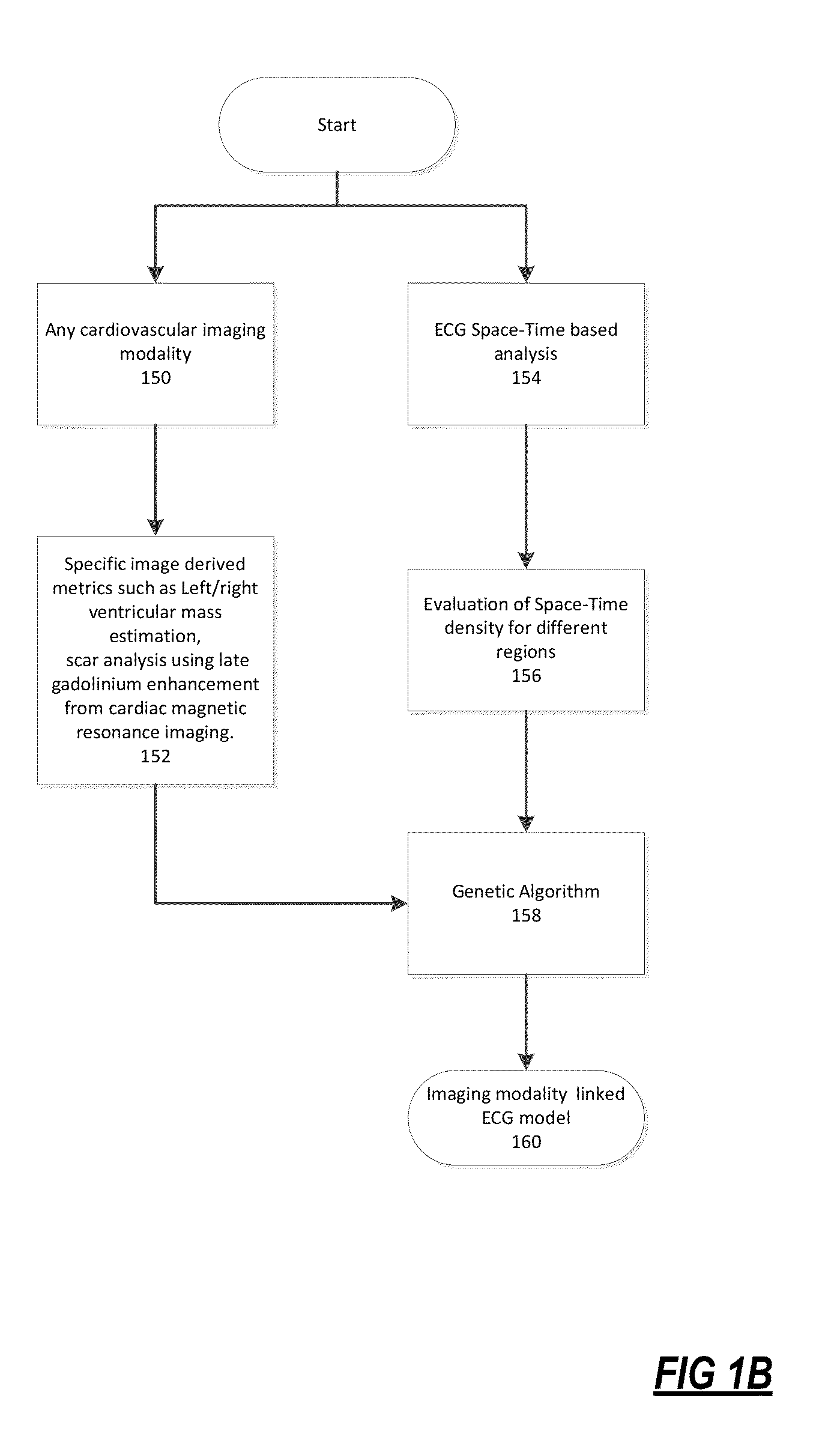
The present disclosure uses physiological data, ECG signals as an example, to evaluate cardiac structure and function in mammals. Two approaches are presented, e.g., a model-based analysis and a space-time analysis. The first method uses a modified Matching Pursuit (MMP) algorithm to find a noiseless model of the ECG data that is sparse and does not assume periodicity of the signal. After the model is derived, various metrics and subspaces are extracted to image and characterize cardiovascular tissues using complex-sub-harmonic-frequencies (CSF) quasi-periodic and other mathematical methods. In the second method, space-time domain is divided into a number of regions, the density of the ECG signal is computed in each region and inputted into a learning algorithm to image and characterize the tissues.
Owner:ANALYTICS FOR LIFE
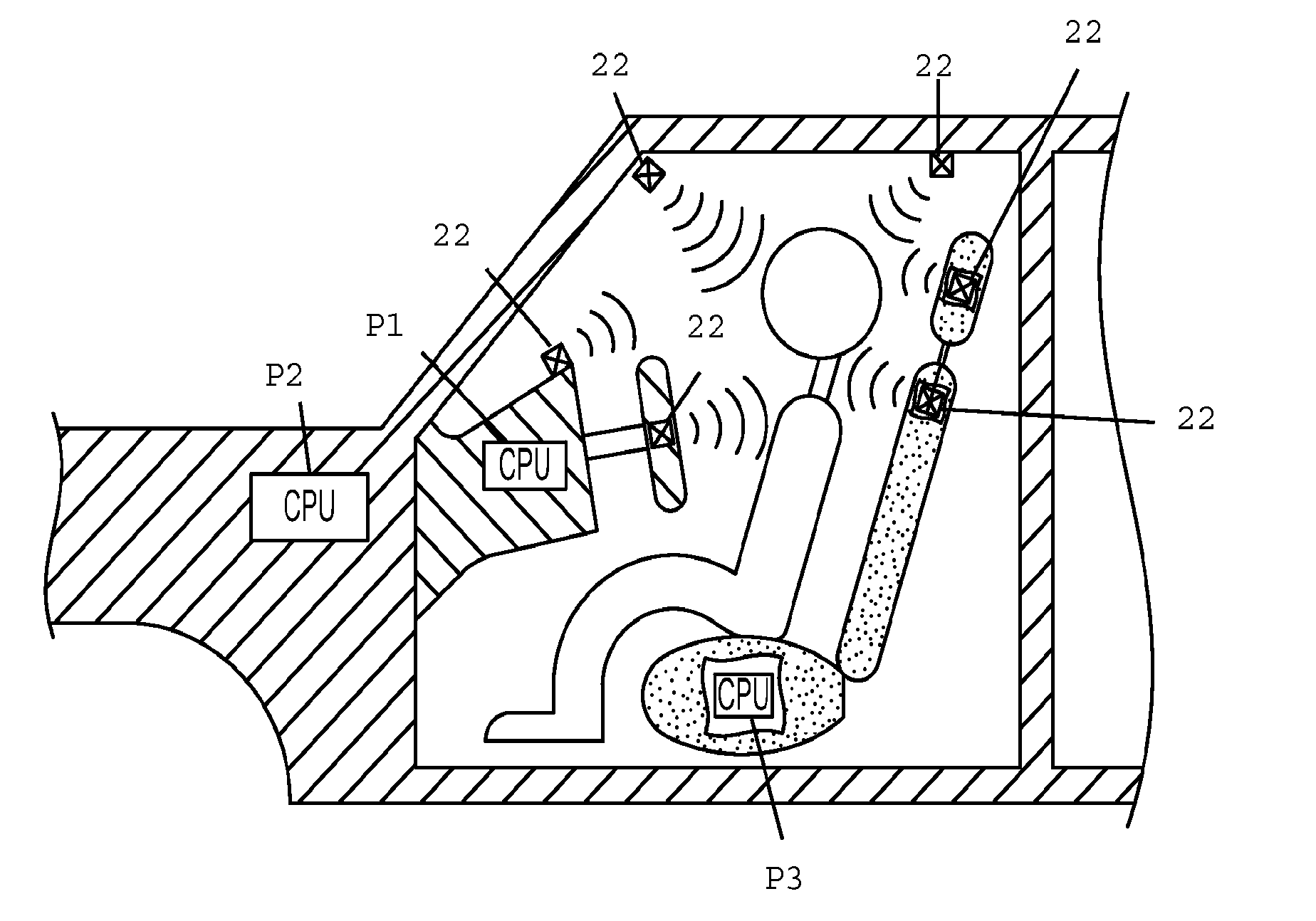
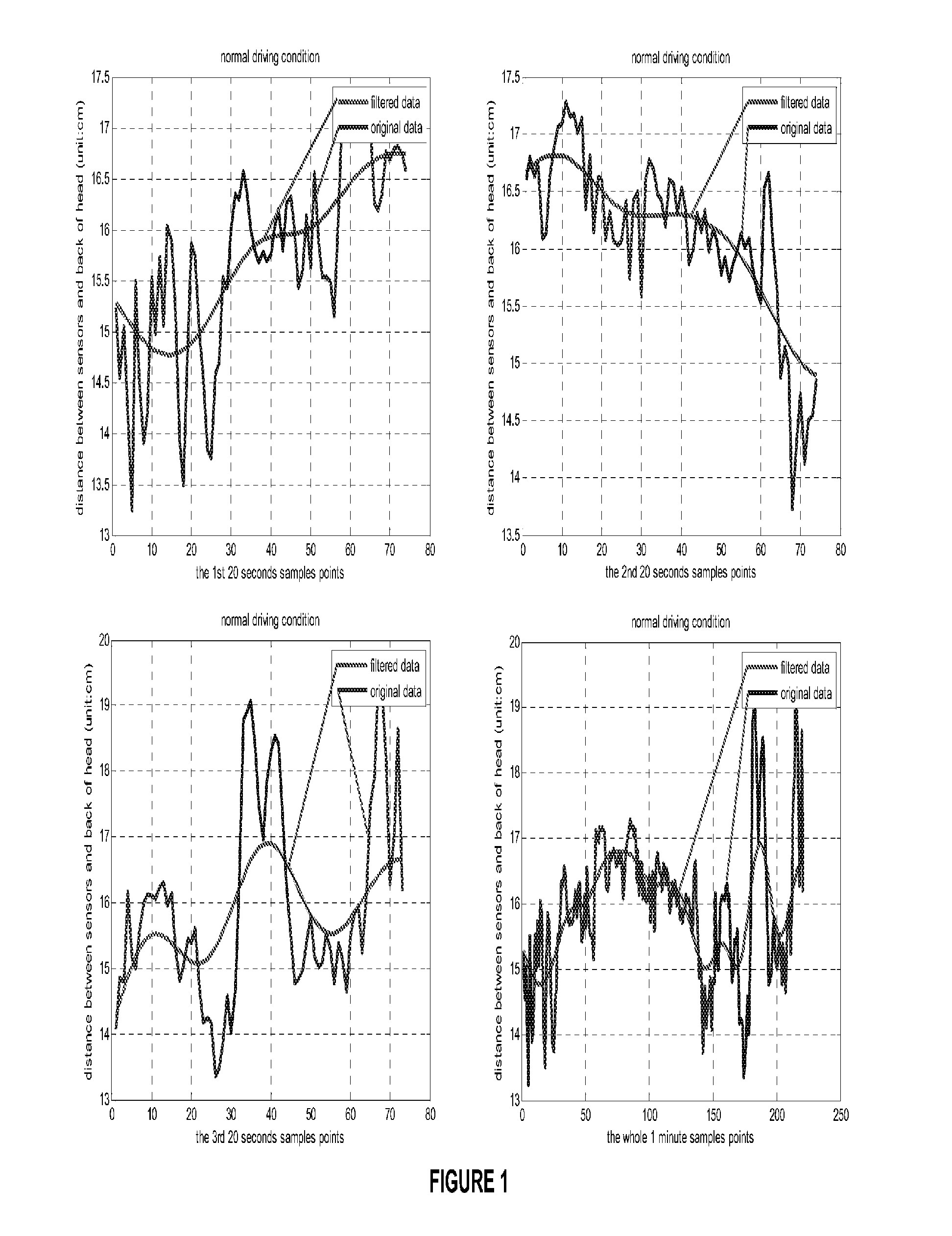
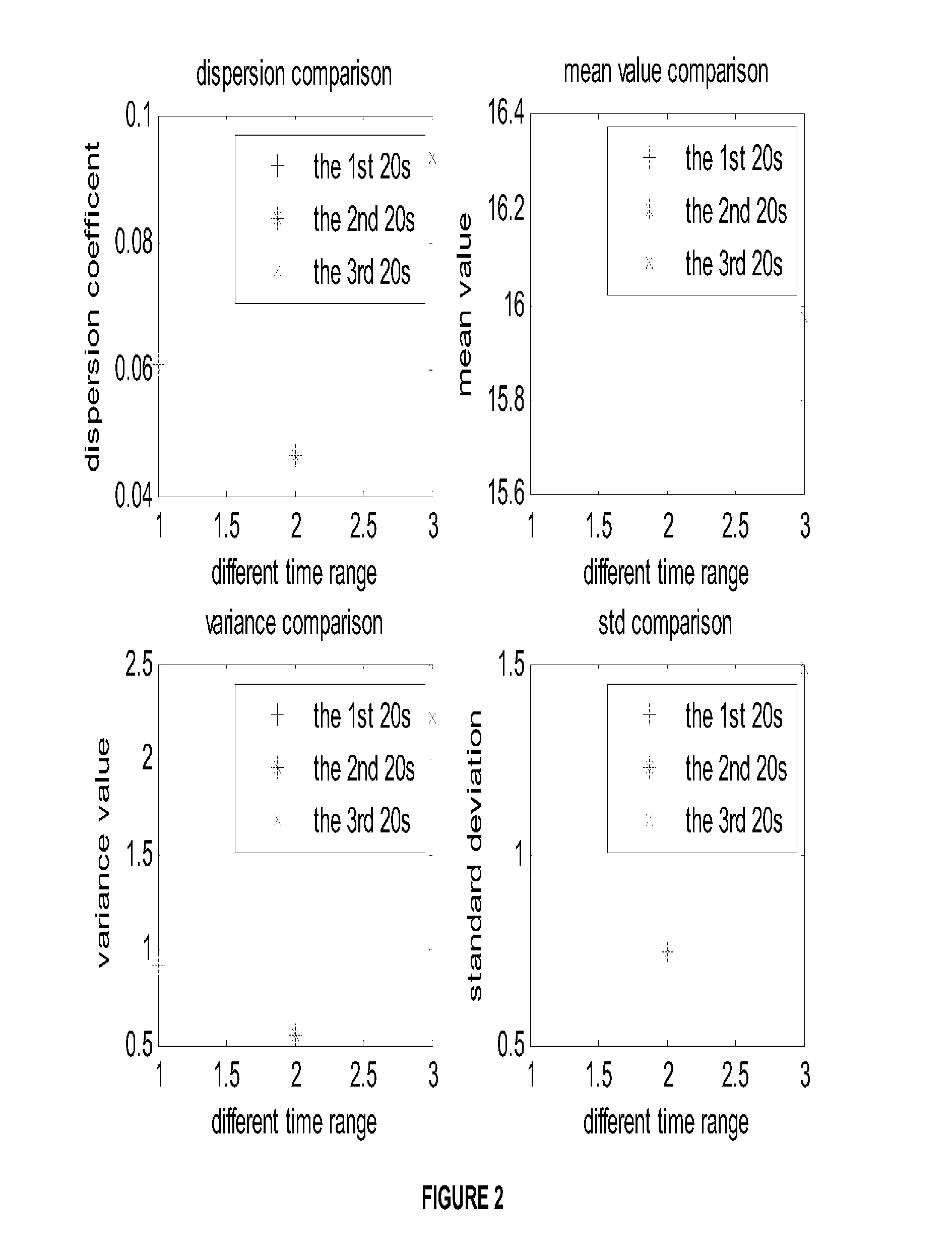
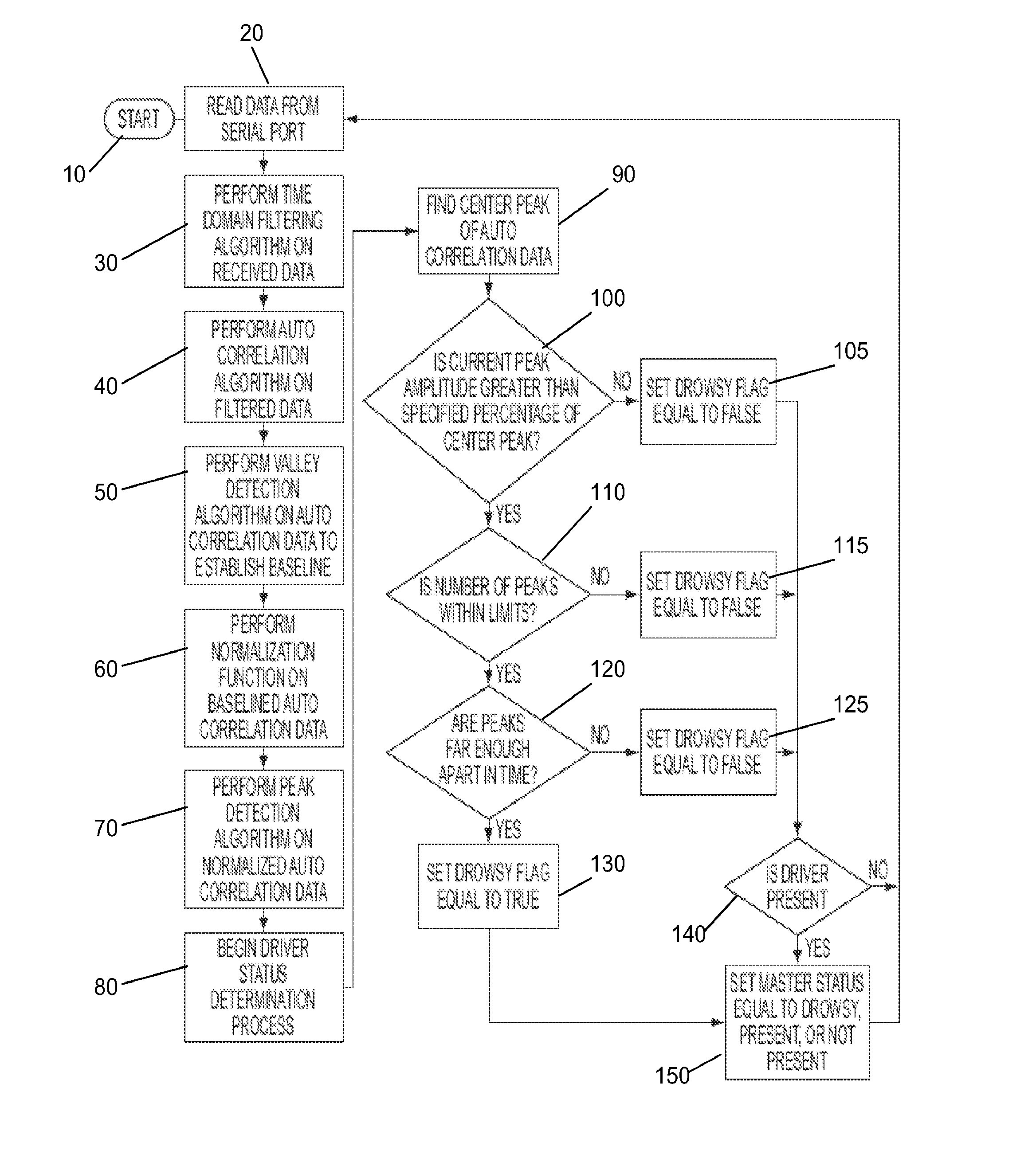
Drowsy driver detection system
A method of detecting impairment of a driver of a vehicle. The method includes sensing, using a sensor, a position of the driver's head at a plurality of time points; determining, using a microprocessor, changes in the position of the driver's head between the plurality of time points; evaluating, using a microprocessor, whether the changes in the position of the driver's head between the plurality of time points exhibit at least one of a periodic and a quasi-periodic pattern; determining whether the driver is impaired based on the pattern of the changes in the position of the driver' s head; and if the driver is impaired, alerting the driver using an alarm.
Owner:L & P PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO
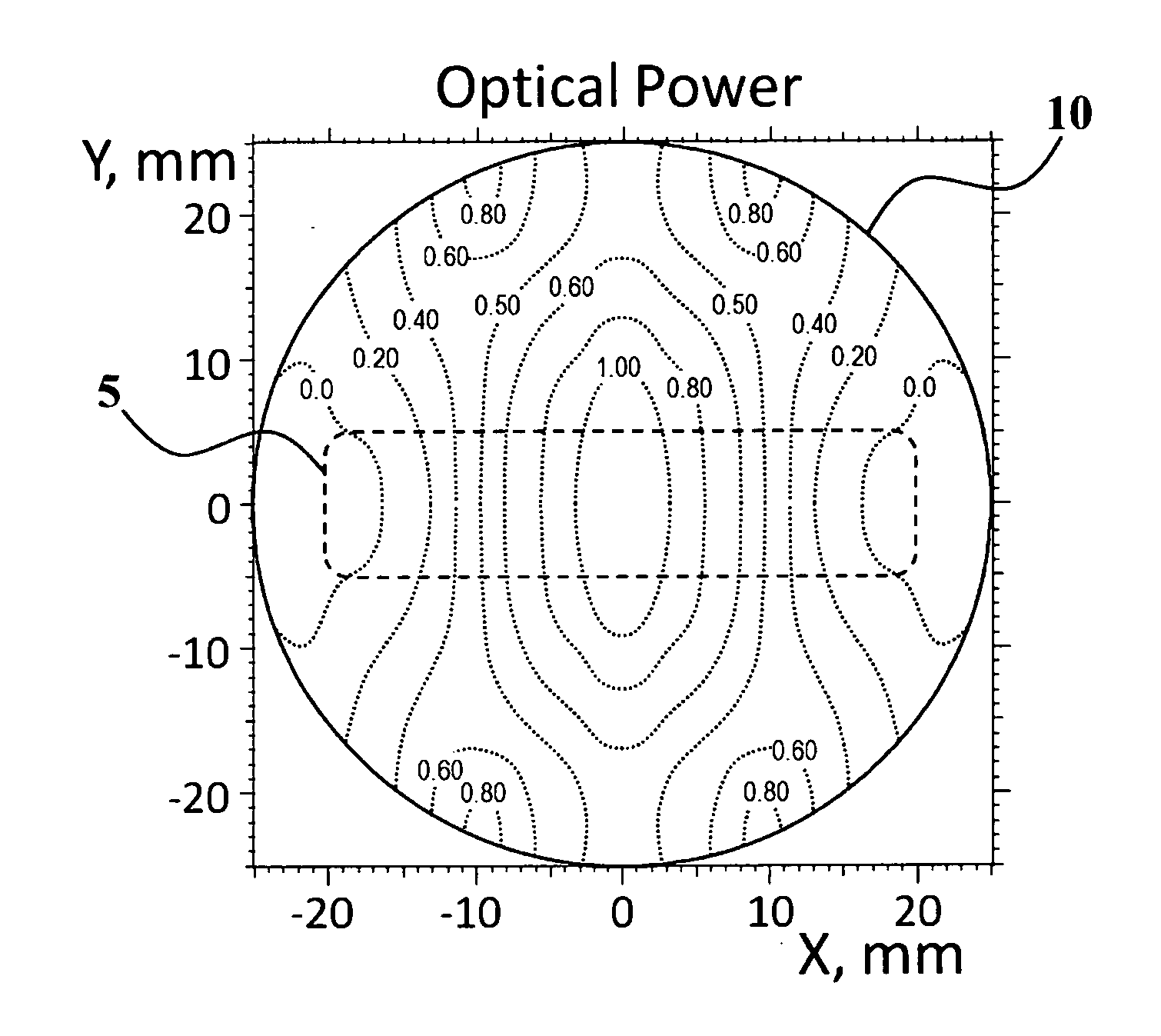
Training method for accommodative and vergence systems, and multifocal lenses therefor
ActiveUS20120019775A1Simple and inexpensiveSpectales/gogglesChiropractic devicesEye lensVisual perception
Accommodative and vergence systems training method and multifocal ophthalmic lenses of Horizontal periodic or quasi-periodic Optical Power Stepless Alternating (HOPSA-lenses) therefor are proposed. Reading the text with HOPSA-lenses worn, while the head is stationary, provides a continuous alternating of accommodation and vergence strain / relaxation and, therefore, provides dynamic training of both systems. The method is applicable for human visual system therapy, eye diseases treatment / prevention and ophthalmology researches. The method enables combining the effective visual trainings with documents reading / processing, visual target examining, watching TV / video, playing computer games, etc., as well as combining the training with conventional vision correction. Several embodiments of HOPSA-lenses are disclosed, such as multi- and mono-cyclic, multi-layer, splitting the basic correction and training functions between lens' sides or layers, having left and right lenses' surfaces individually configured to provide the congruence of optical power for fixation, and / or the convergence invariability for fixation during the training.
Owner:TYRIN ALBERT +1
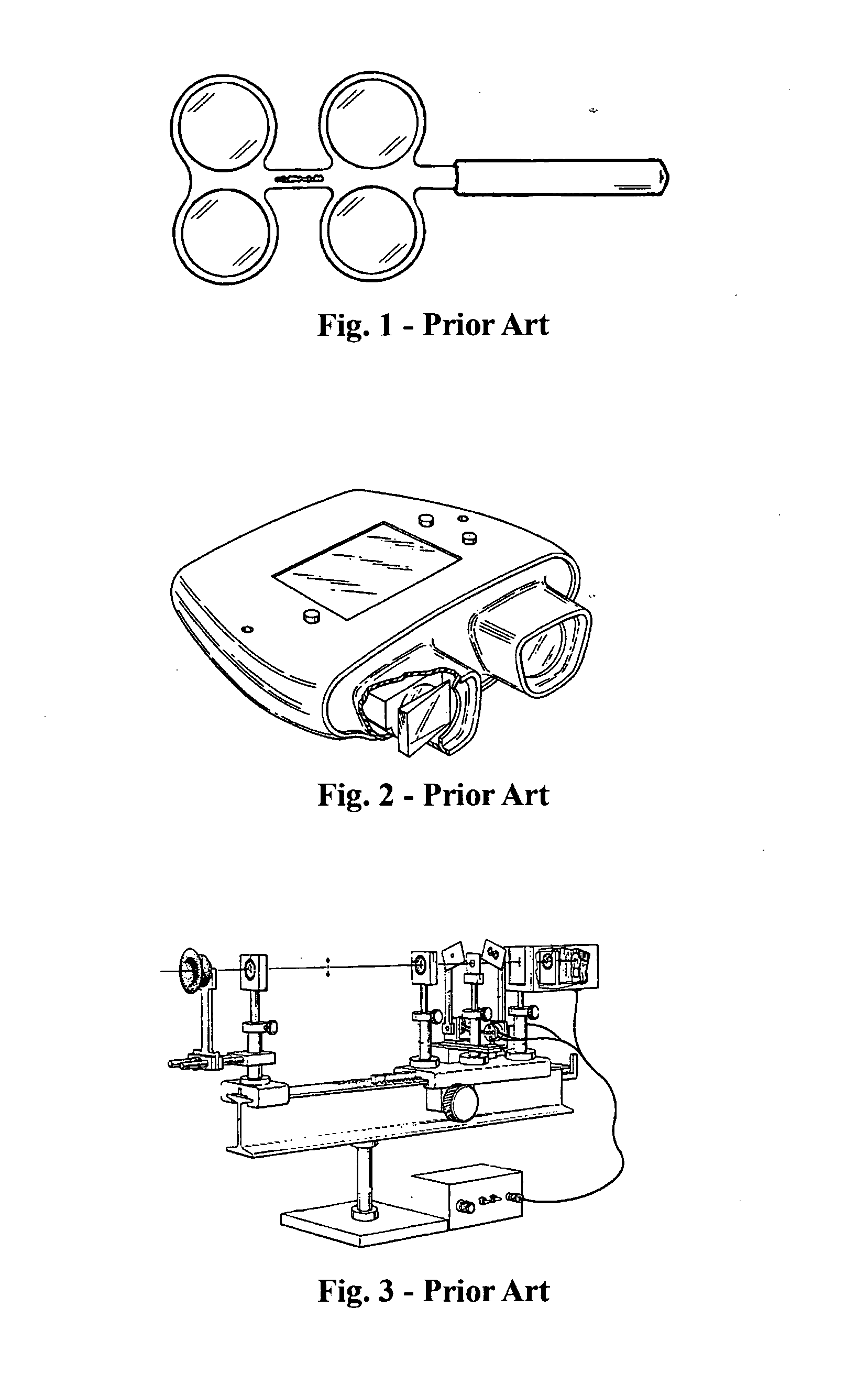
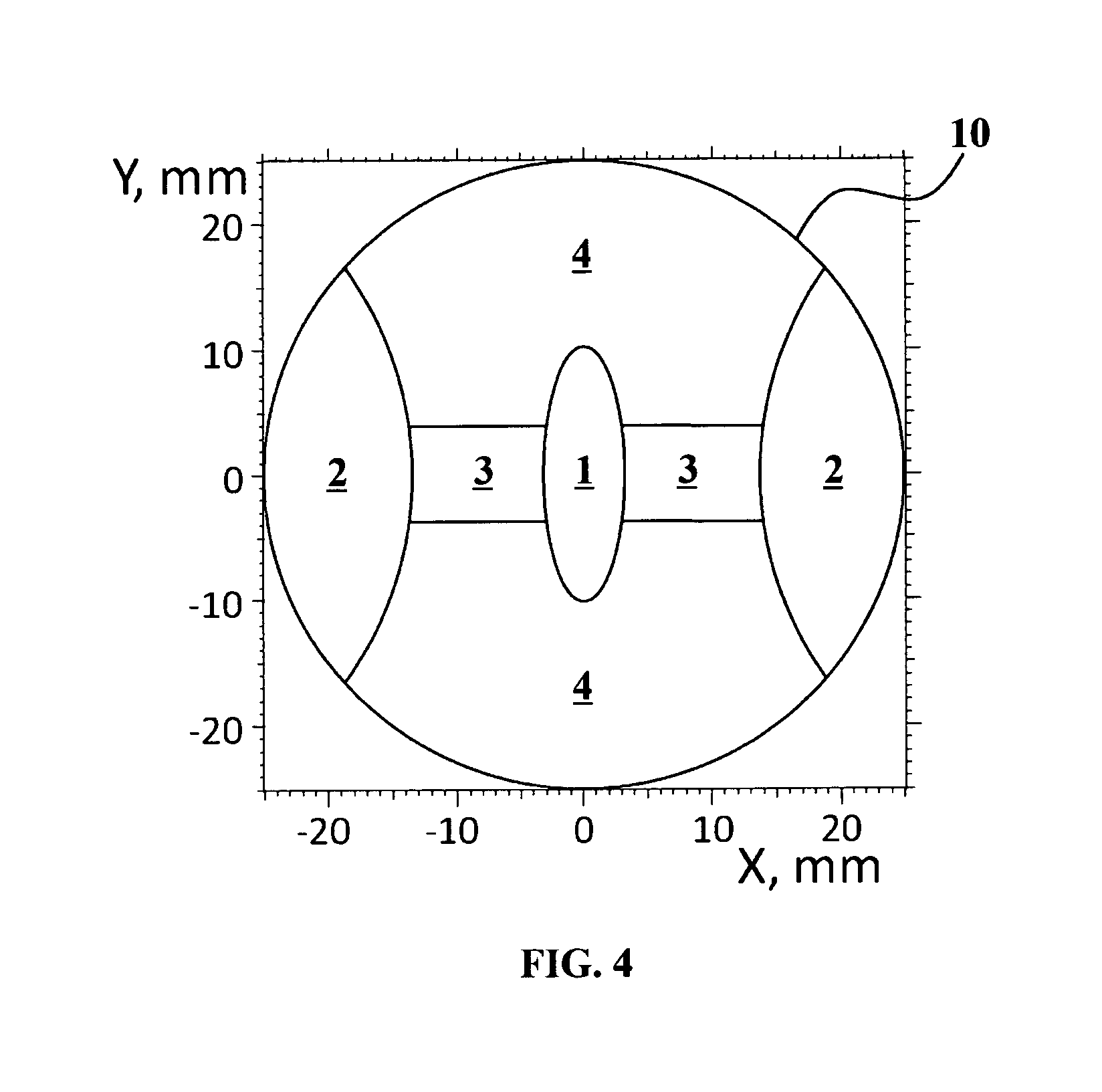
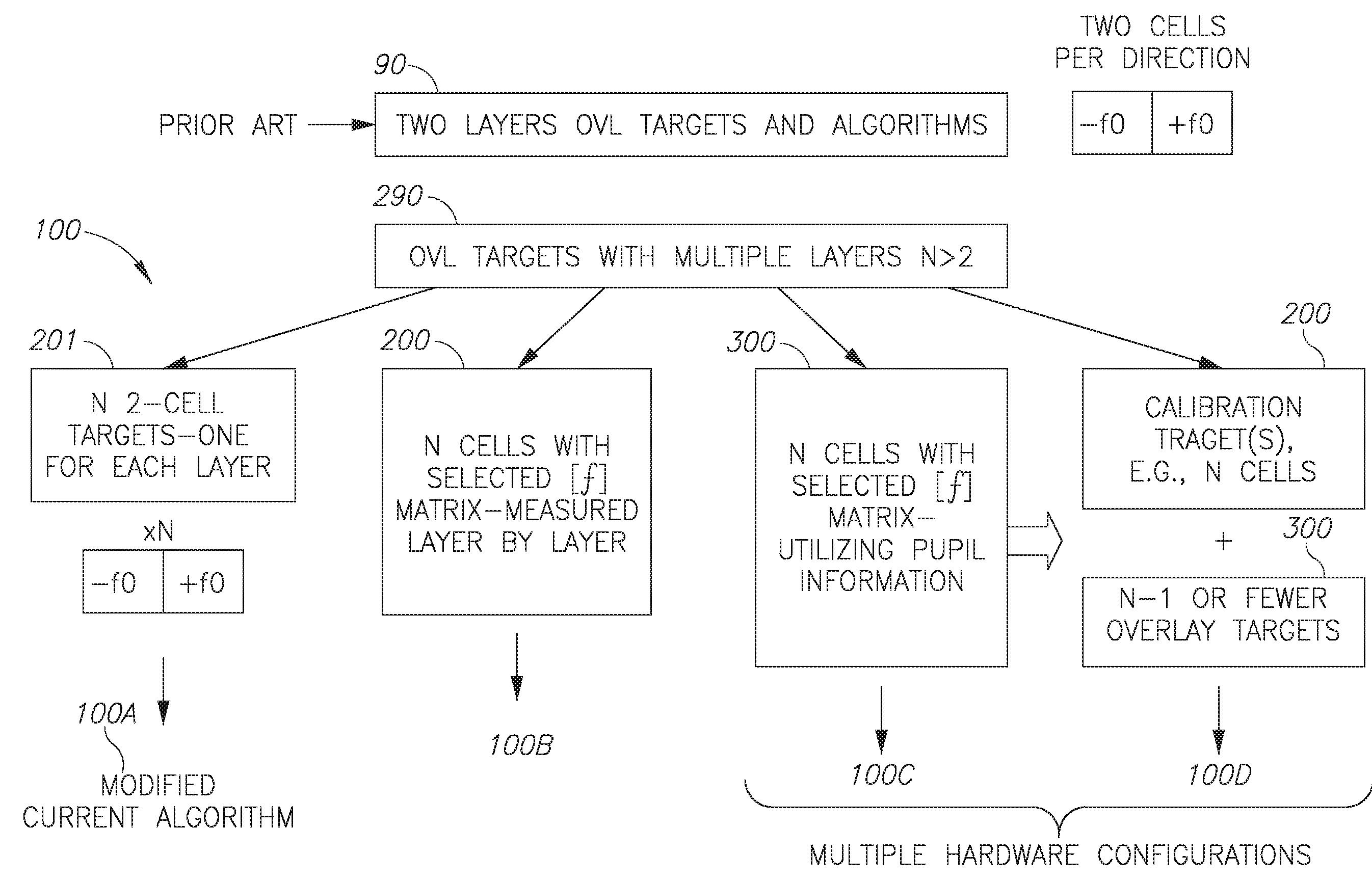
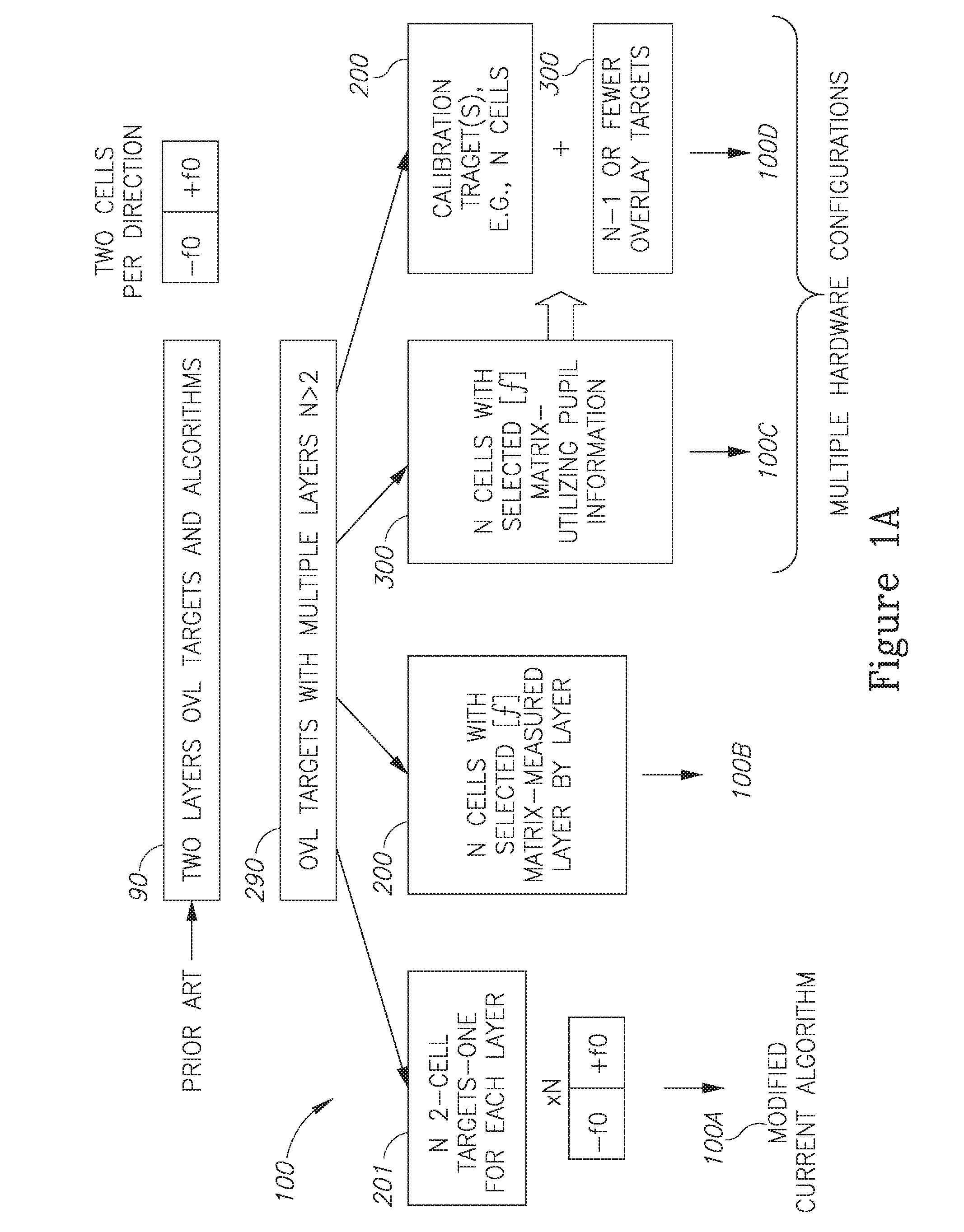
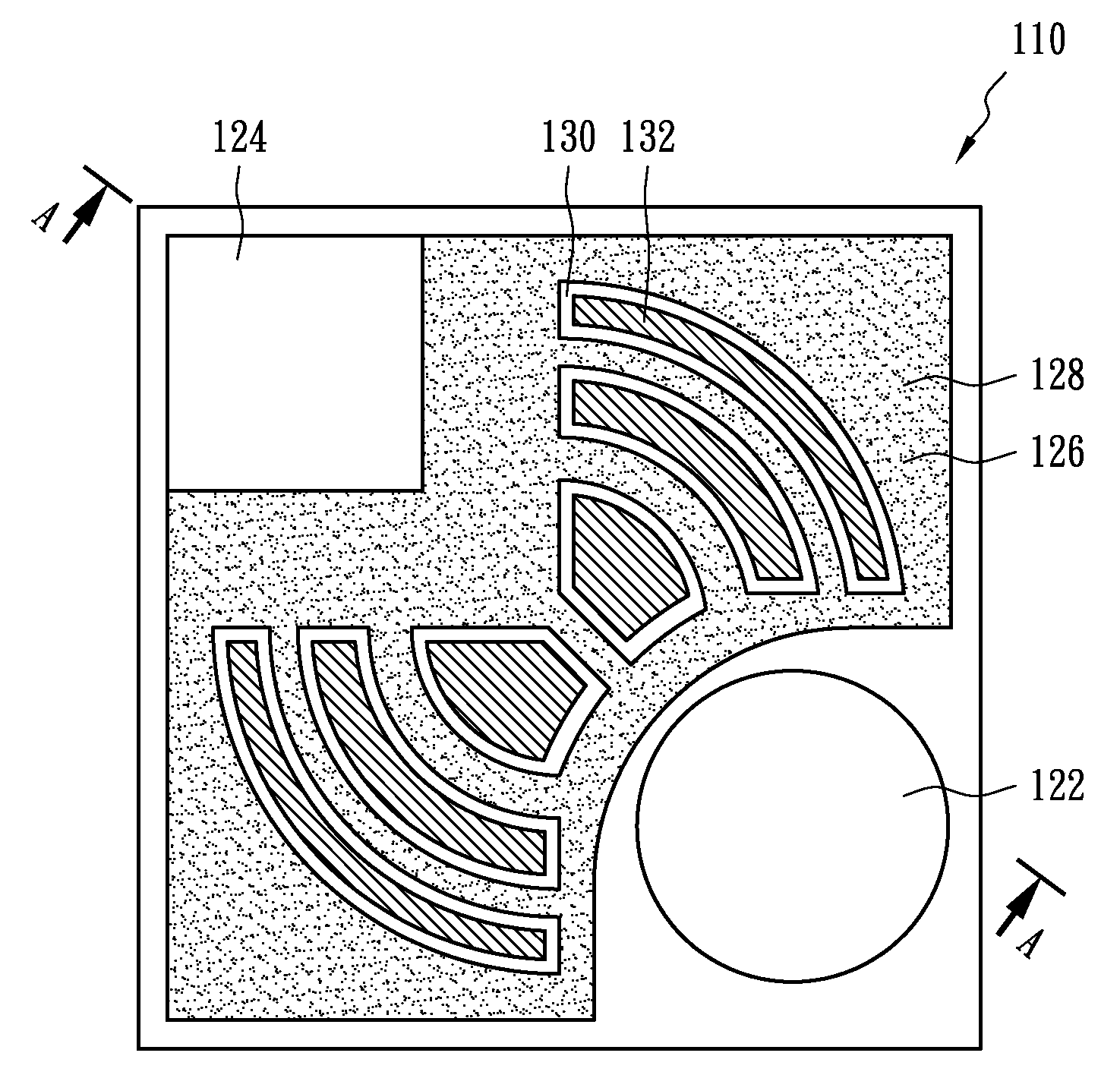
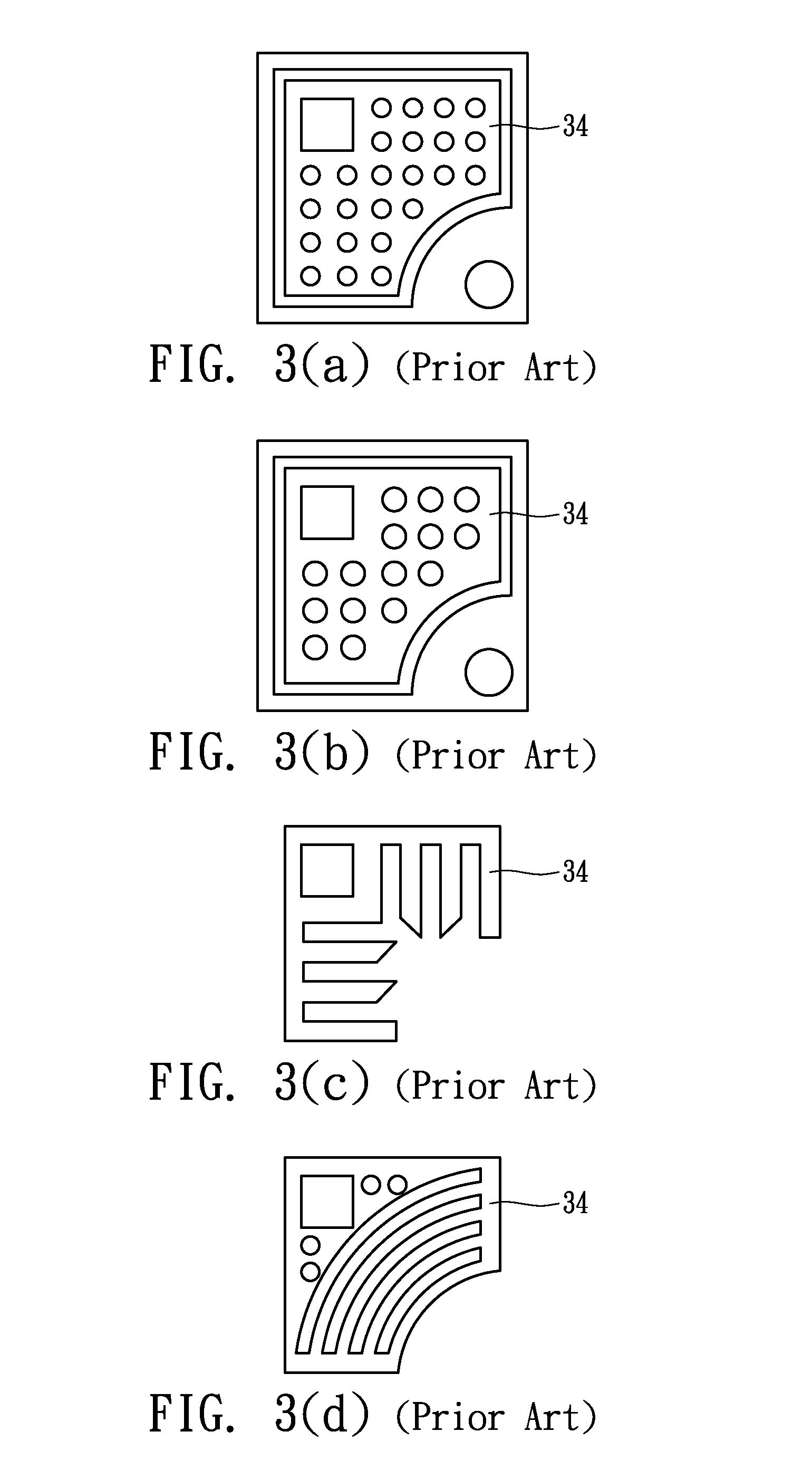
Device metrology targets and methods
ActiveUS20160266505A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAlgorithmOptical metrology
Metrology methods and targets are provided, that expand metrological procedures beyond current technologies into multi-layered targets, quasi-periodic targets and device-like targets, without having to introduce offsets along the critical direction of the device design. Several models are disclosed for deriving metrology data such as overlays from multi-layered target and corresponding configurations of targets are provided to enable such measurements. Quasi-periodic targets which are based on device patterns are shown to improve the similarity between target and device designs, and the filling of the surroundings of targets and target elements with patterns which are based on device patterns improve process compatibility. Offsets are introduced only in non-critical direction and / or sensitivity is calibrated to enable, together with the solutions for multi-layer measurements and quasi-periodic target measurements, direct device optical metrology measurements.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
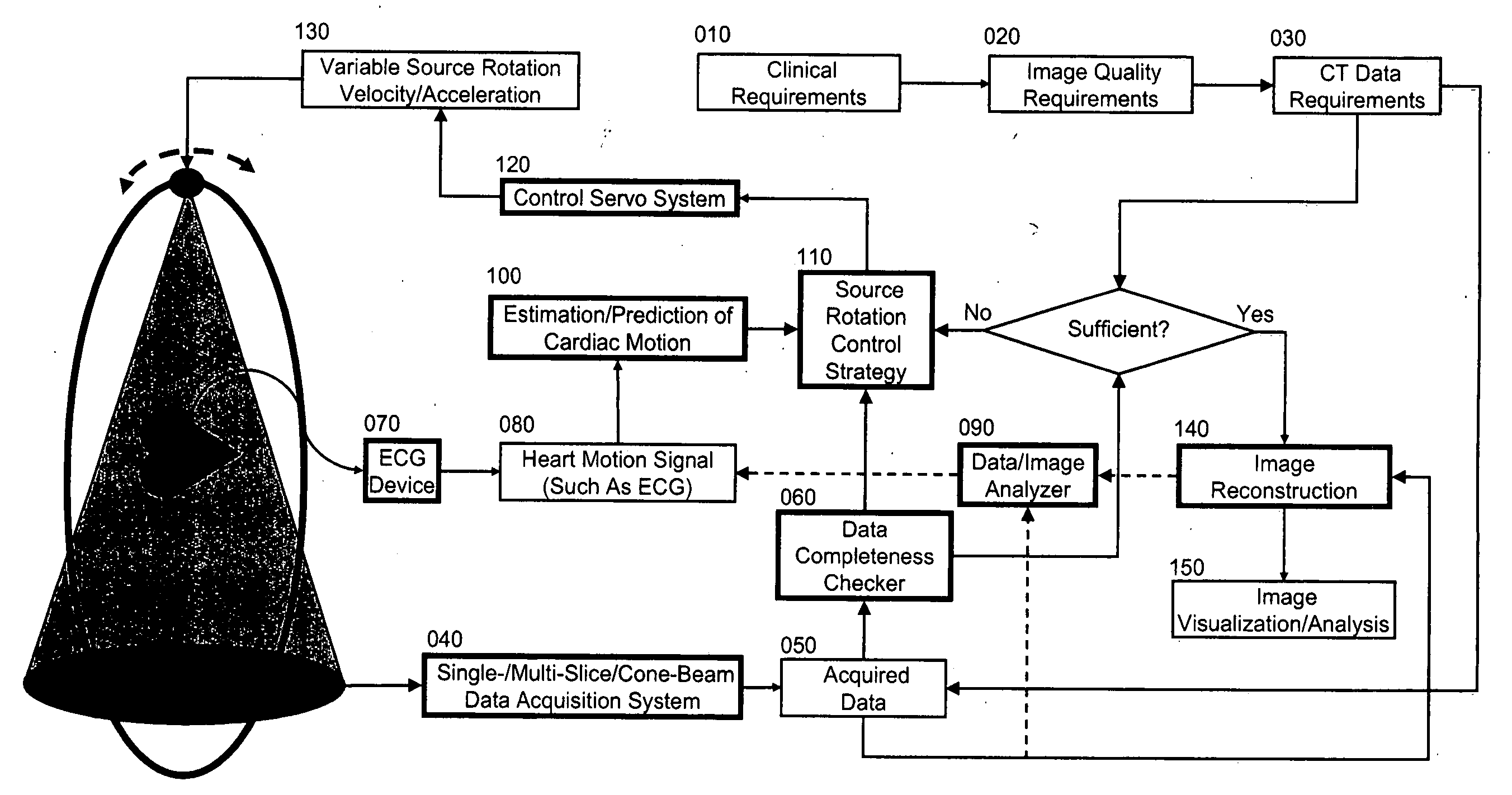
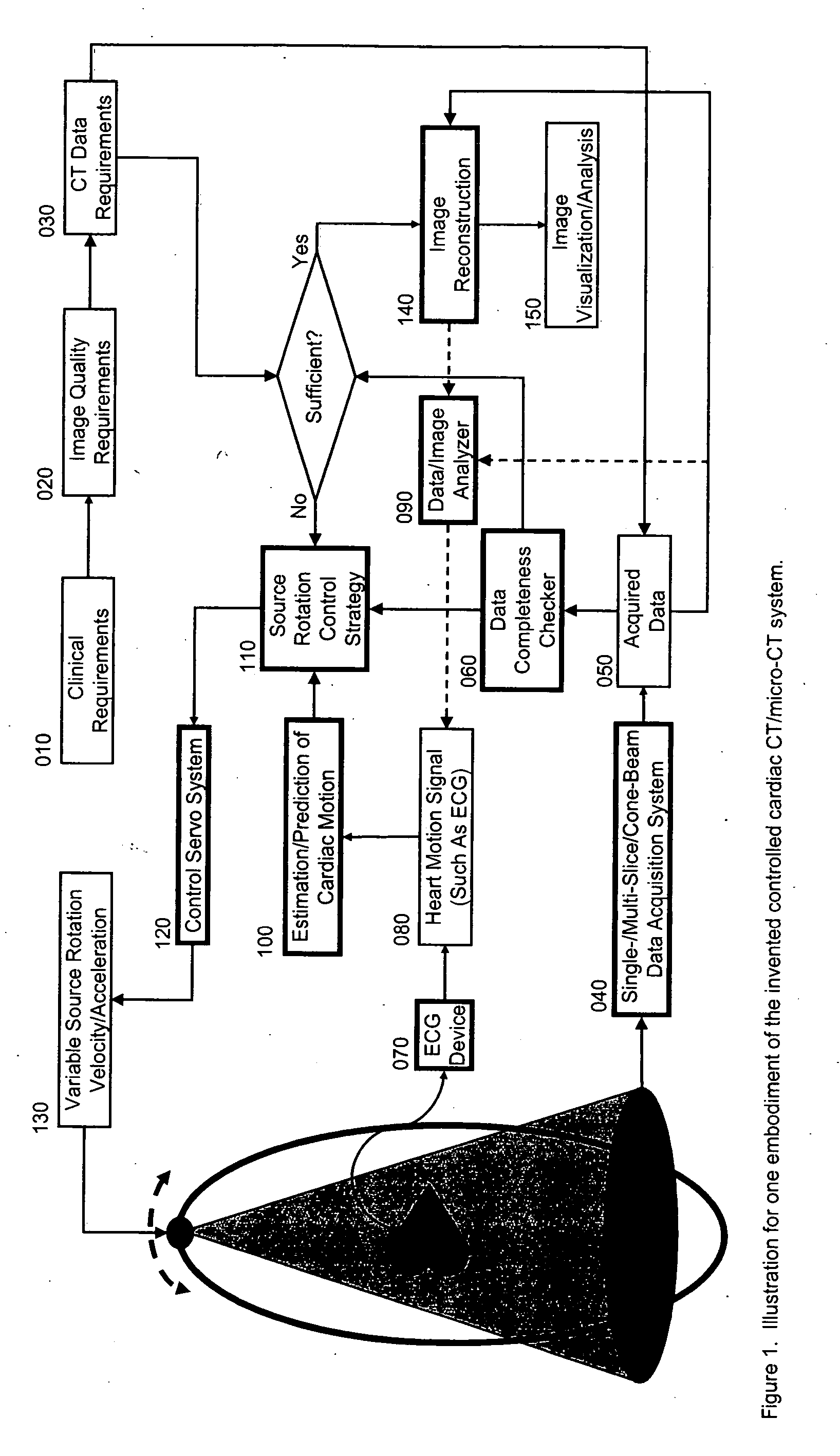
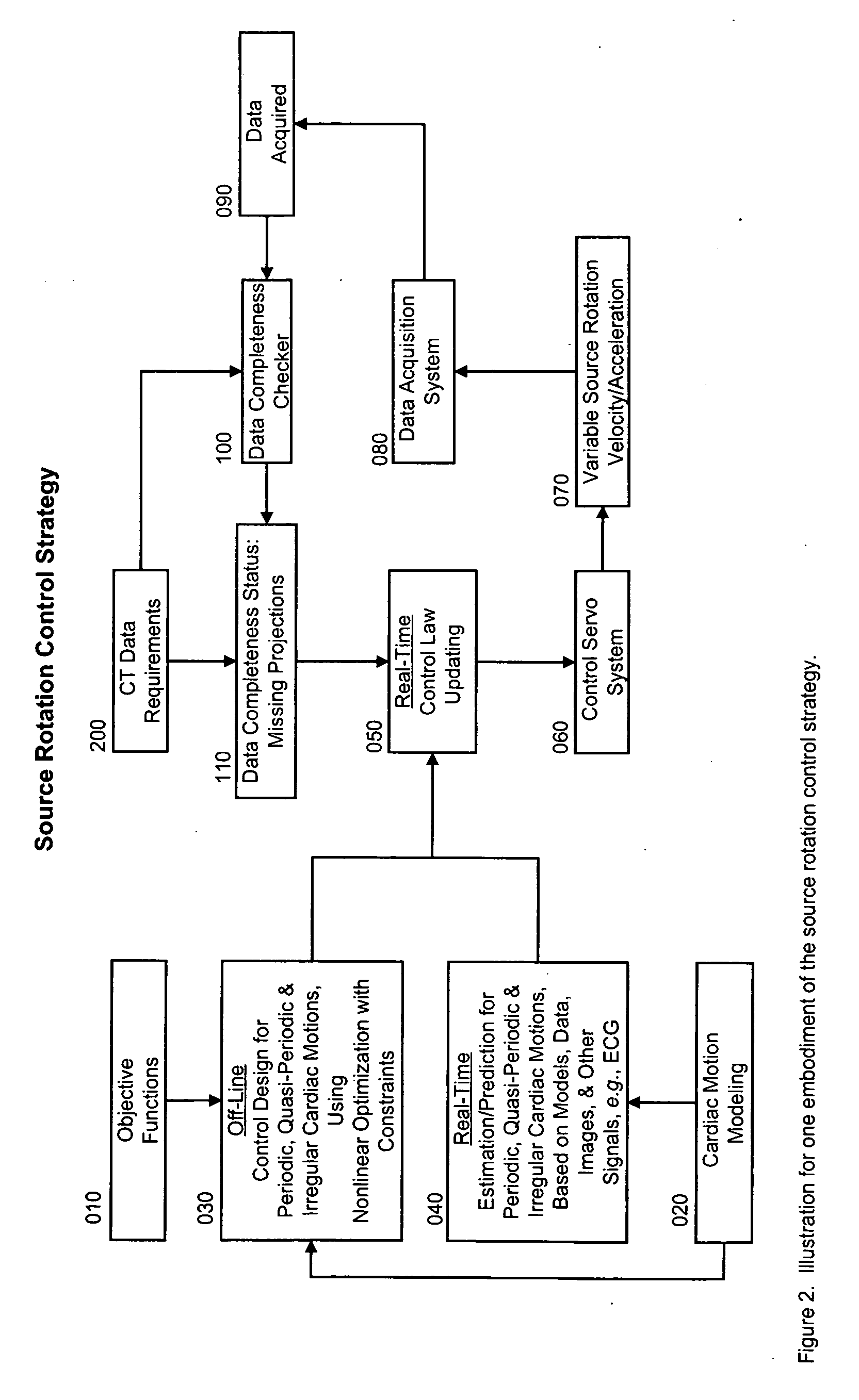
Controlled cardiac computed tomography
InactiveUS20070153971A1Minimize impactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCardiac computed tomographyData acquisition
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) has been a hot topic for years because of the clinical importance of cardiac diseases and the rapid evolution of CT systems. In this application, we disclose a novel strategy for controlled cardiac CT (CCCT) that may effectively reduce image artifacts due to cardiac and respiratory motions and reduce the scan time. Our approach is radically different from existing ones and is based on controlling the x-ray source rotation velocity and powering status in reference to the cardiac motion. By such a control-based intervention the data acquisition process can be optimized for cardiac CT in the cases of periodic and quasi-periodic cardiac motions. Specifically, we present the corresponding coordination / control schemes for either exact or approximate matches between the ideal and actual source positions.
Owner:WANG CHENGLIN +1
Apparatus for signal decomposition, analysis and reconstruction
The present invention provides a system and method for representing quasi-periodic (“qp”) waveforms comprising, representing a plurality of limited decompositions of the qp waveform, wherein each decomposition includes a first and second amplitude value and at least one time value. In some embodiments, each of the decompositions is phase adjusted such that the arithmetic sum of the plurality of limited decompositions reconstructs the qp waveform. These decompositions are stored into a data structure having a plurality of attributes. Optionally, these attributes are used to reconstruct the qp waveform, or patterns or features of the qp wave can be determined by using various pattern-recognition techniques. Some embodiments provide a system that uses software, embedded hardware or firmware to carry out the above-described method. Some embodiments use a computer-readable medium to store the data structure and / or instructions to execute the method.
Owner:MURATA VIOS INC
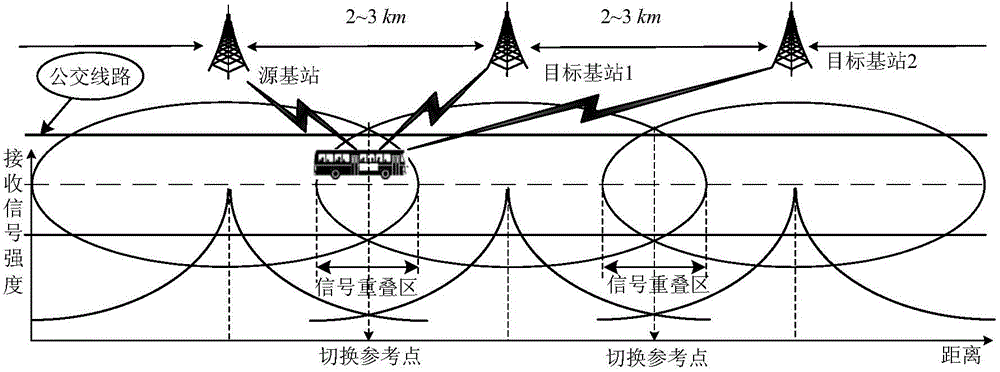
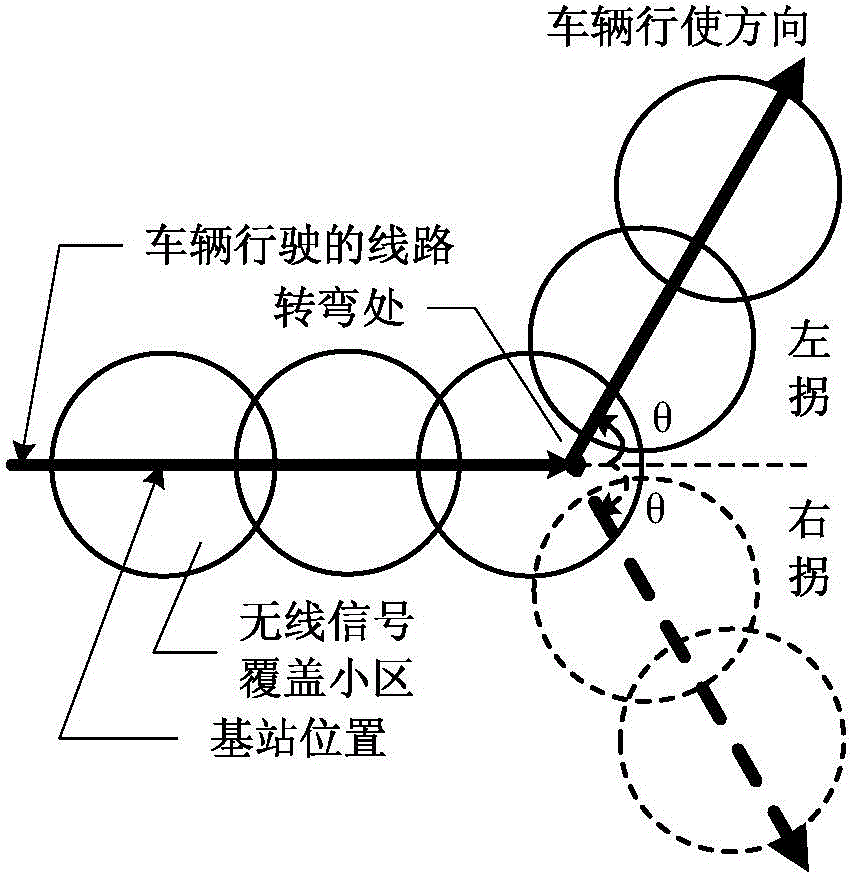
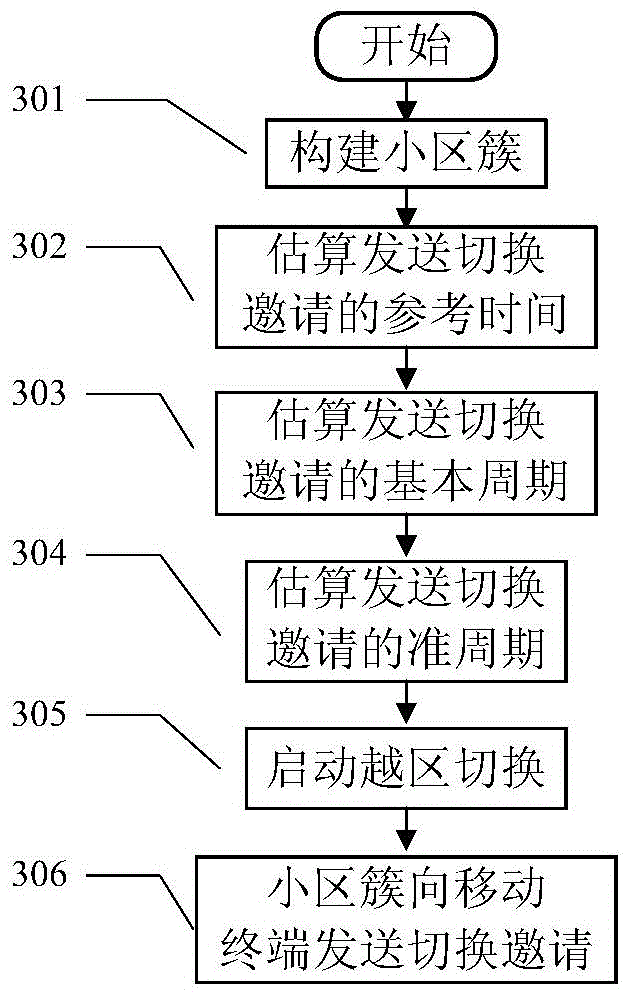
Quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending
The invention discloses a quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending. The quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending comprises, according to the mobile line diagram and the moving speed of a mobile terminal as well as the localization information of the base station of a serving cell and the base station of a neighboring cell to structure a cell cluster and to determine the reference time, the basic period and the quasi-period for transmitting handoff invitation; transmitting the handoff invitation to the mobile terminal periodically through every substation in the cell cluster and accordingly triggering handoff. The quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending overcomes the shortcomings of traditional handoff triggering mechanisms based on signal strength receiving and enables handoff triggering to be timely, accurate and reliable, and meanwhile, shortens the executing time for handoff, improves the handoff speed and efficiency and avoids ping-pong handoff, thereby having a broad application prospect in wireless communication environments with relatively fixed mobile lines and relatively high moving speed such as high-speed railways, highways, urban BRT (bus rapid transit) and the like.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Device for sorting and concentrating electromagnetic energy and apparatus comprising at least one such device
A device for sorting and concentrating electromagnetic energy impinging a surface of the device, the surface including at least one plasmonics-based surface structure or similar structure of periodic or quasi-periodic surface topography. The device is characterized in that the surface (V) is provided with at least two such surface structures (2), acting as individual concentrator structures, which are at least partially spatially overlapped or superposed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF STRASBOURG +2
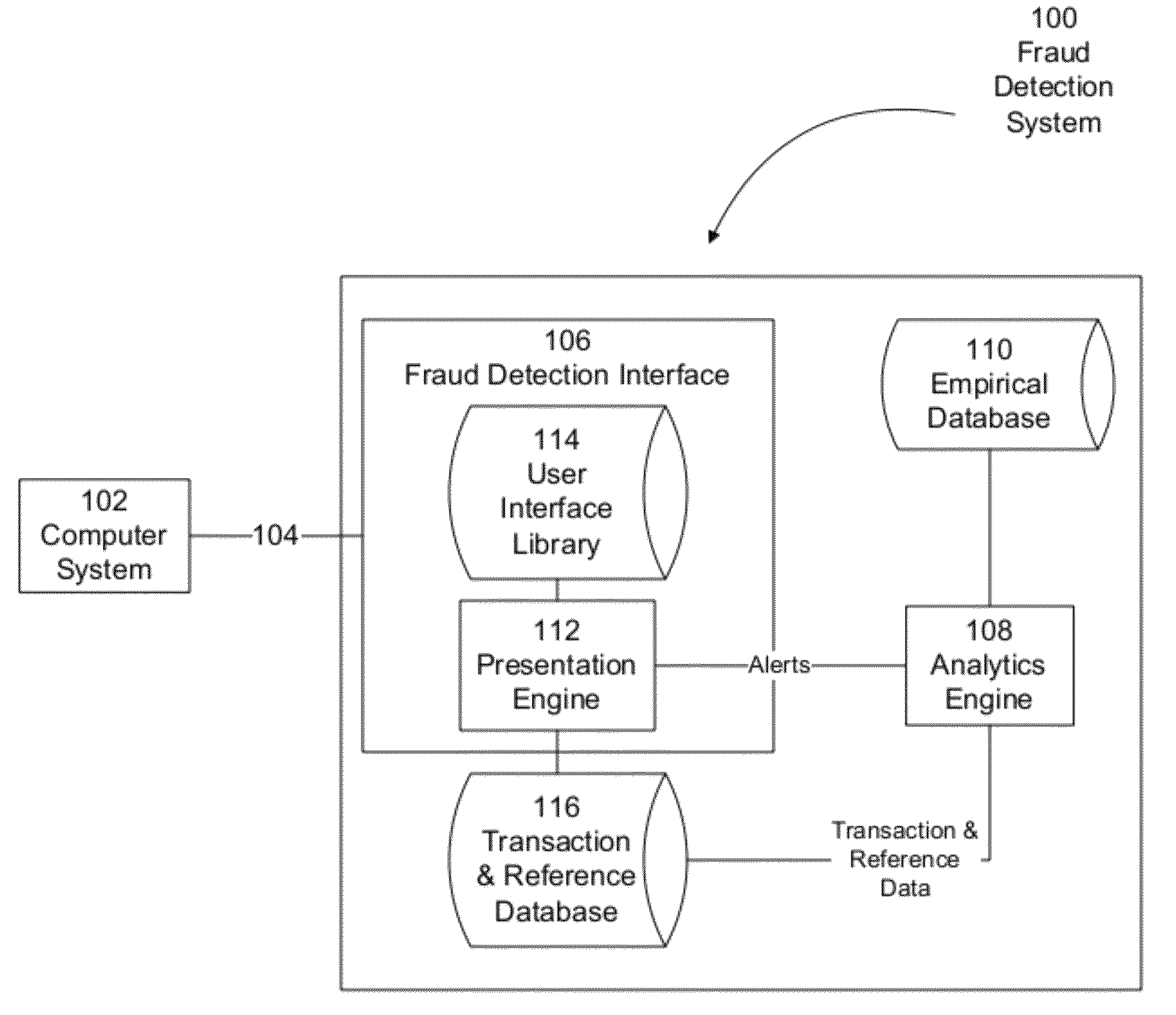
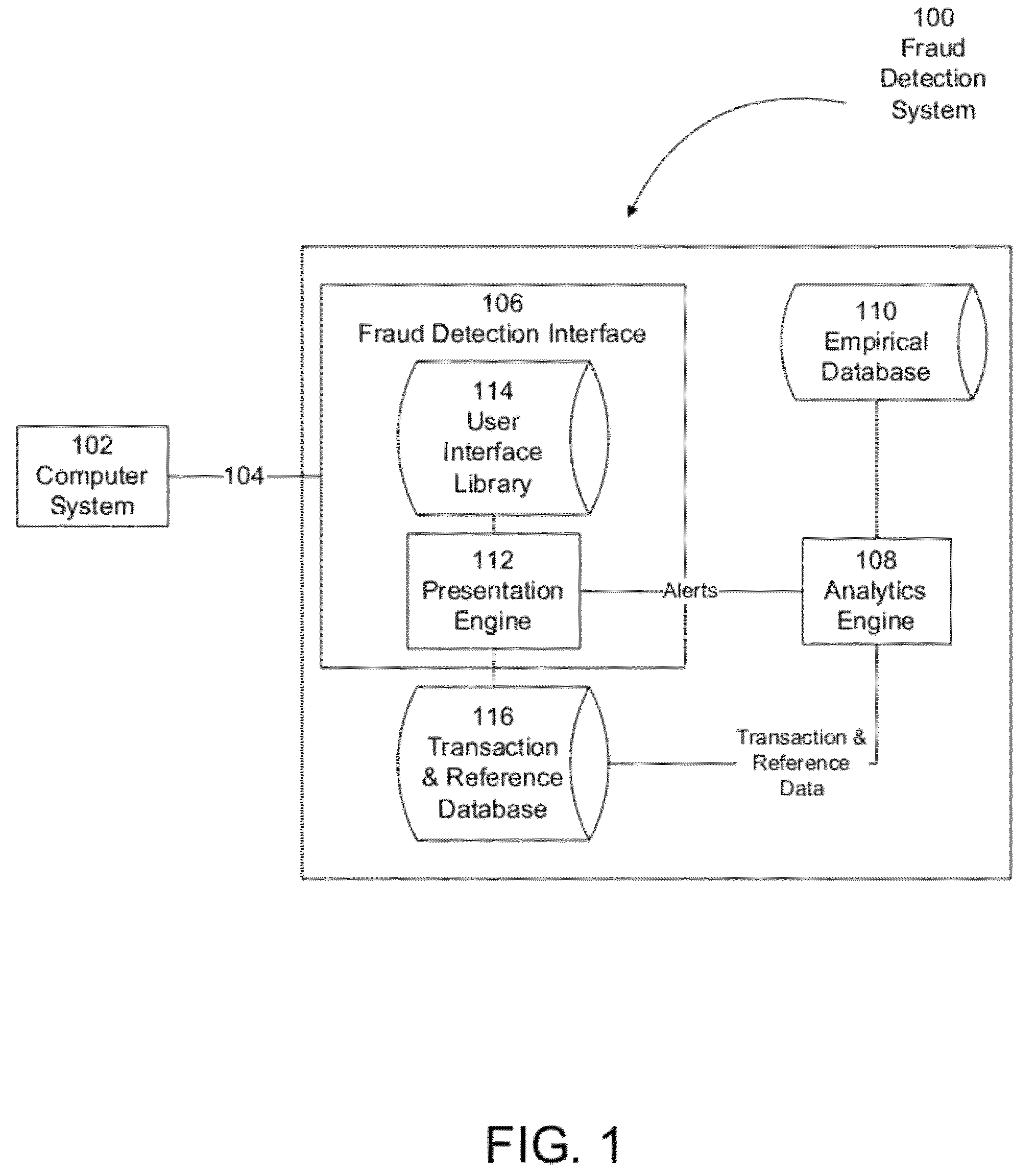
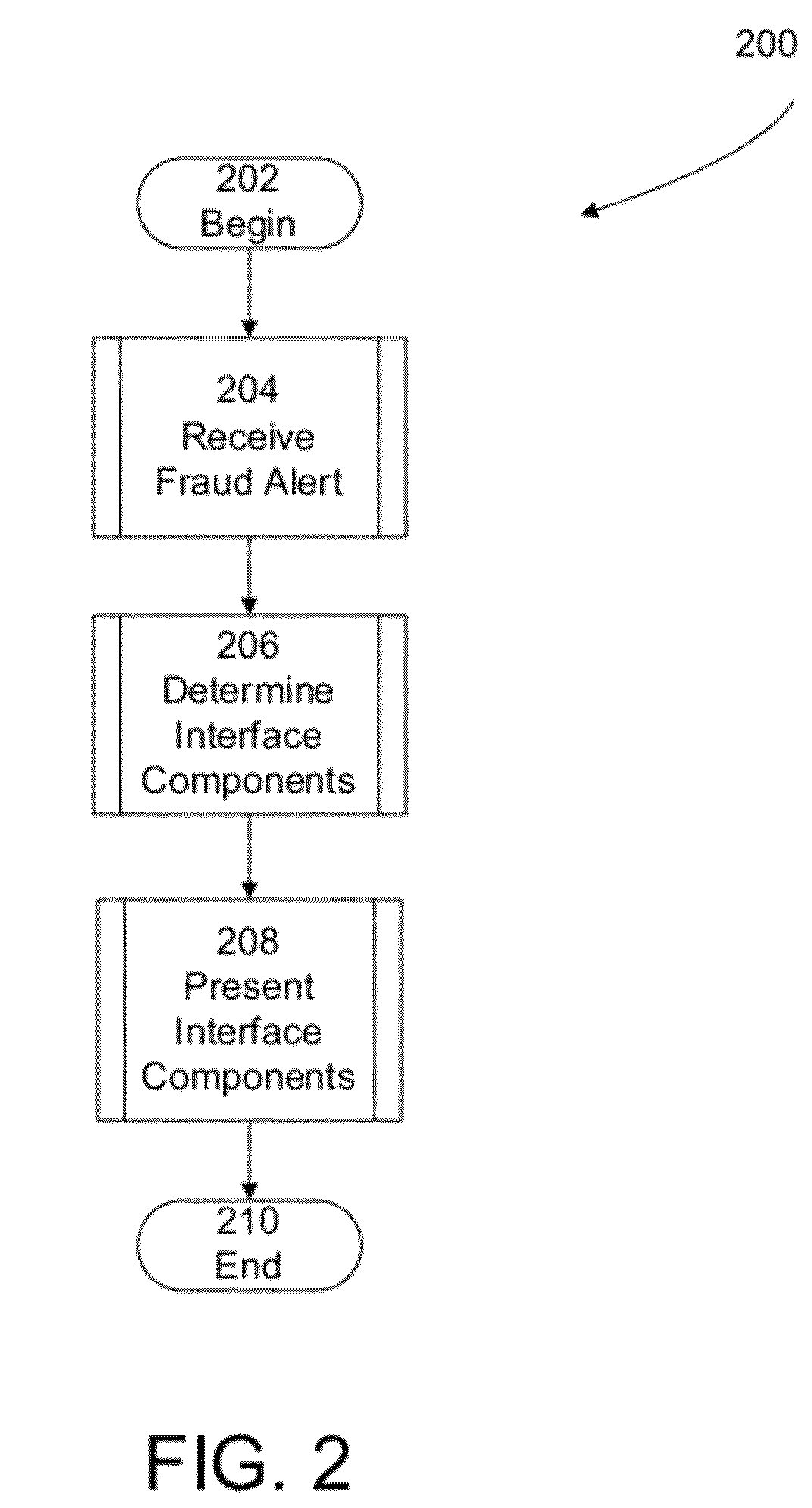
System and method for presenting quasi-periodic activity
Systems and methods for presenting fraud detection information are presented. In one example, a computer system analyzes empirical data to detect potentially fraudulent activity and alerts users of the potentially fraudulent activity via a fraud detection user interface. The fraud detection user interface determines a set of user interface components to suitable to present the potentially fraudulent activity and presents facts associated with the potentially fraudulent activity to a user for further analysis and investigation.
Owner:FIS FINANCIAL COMPLIANCE SOLUTIONS
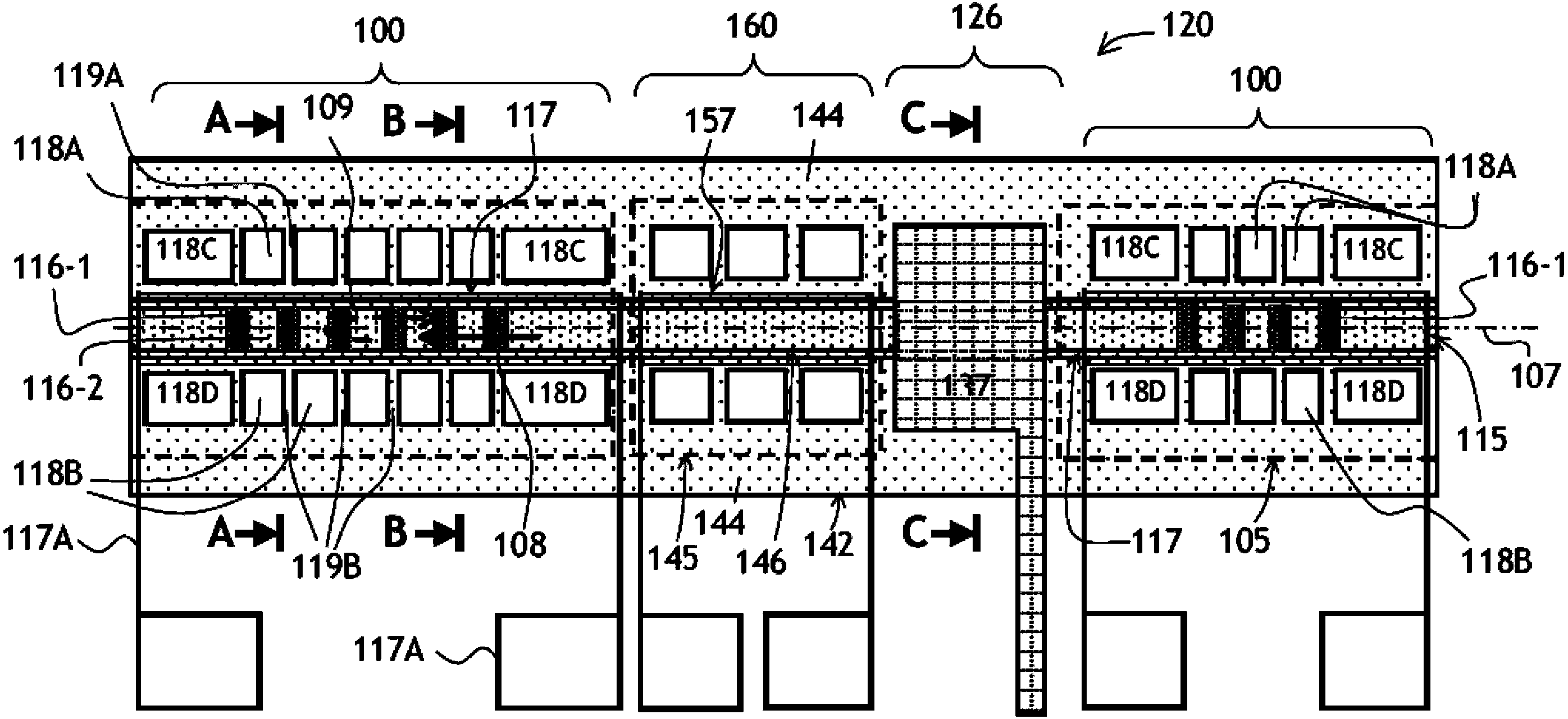
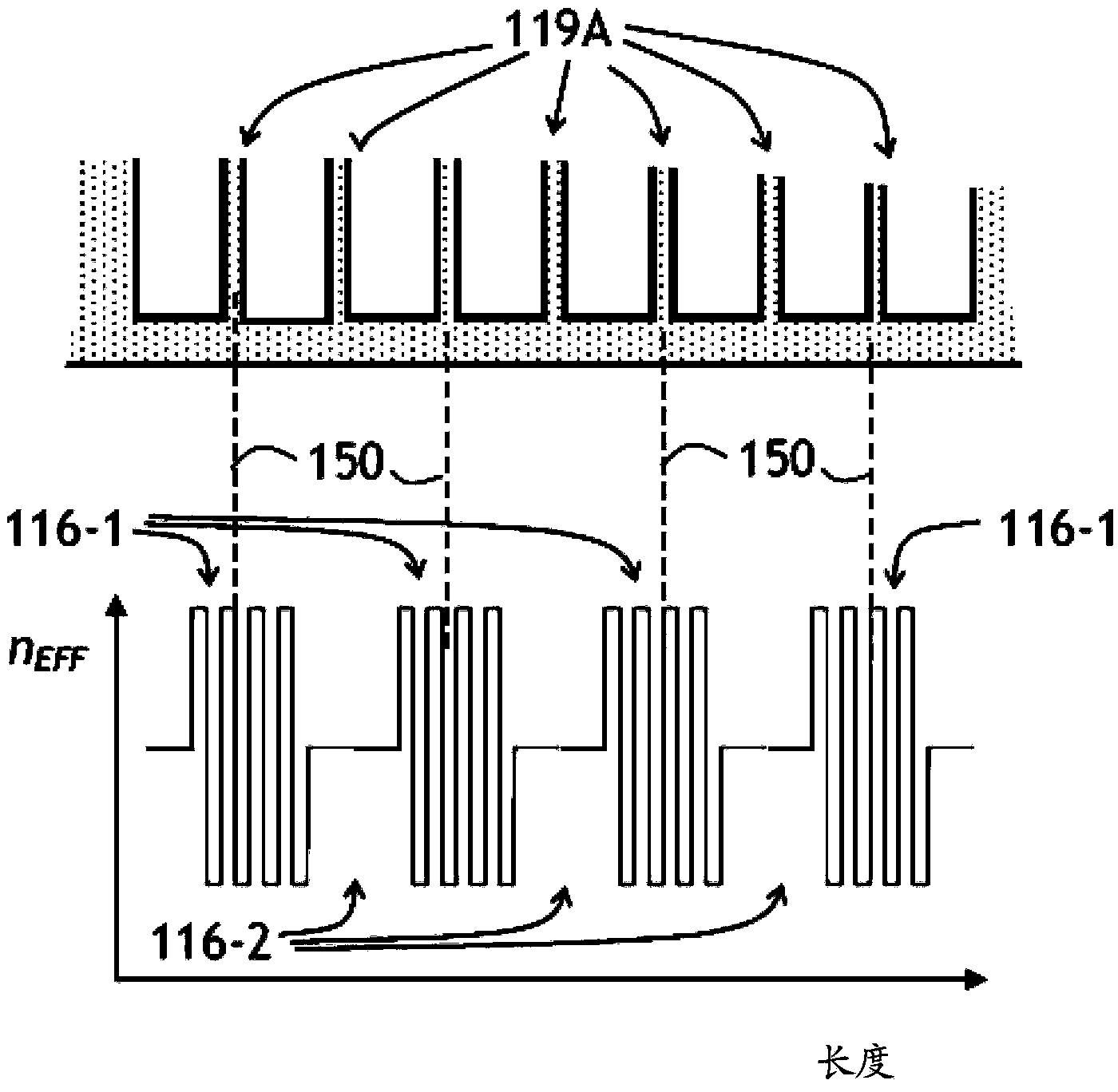
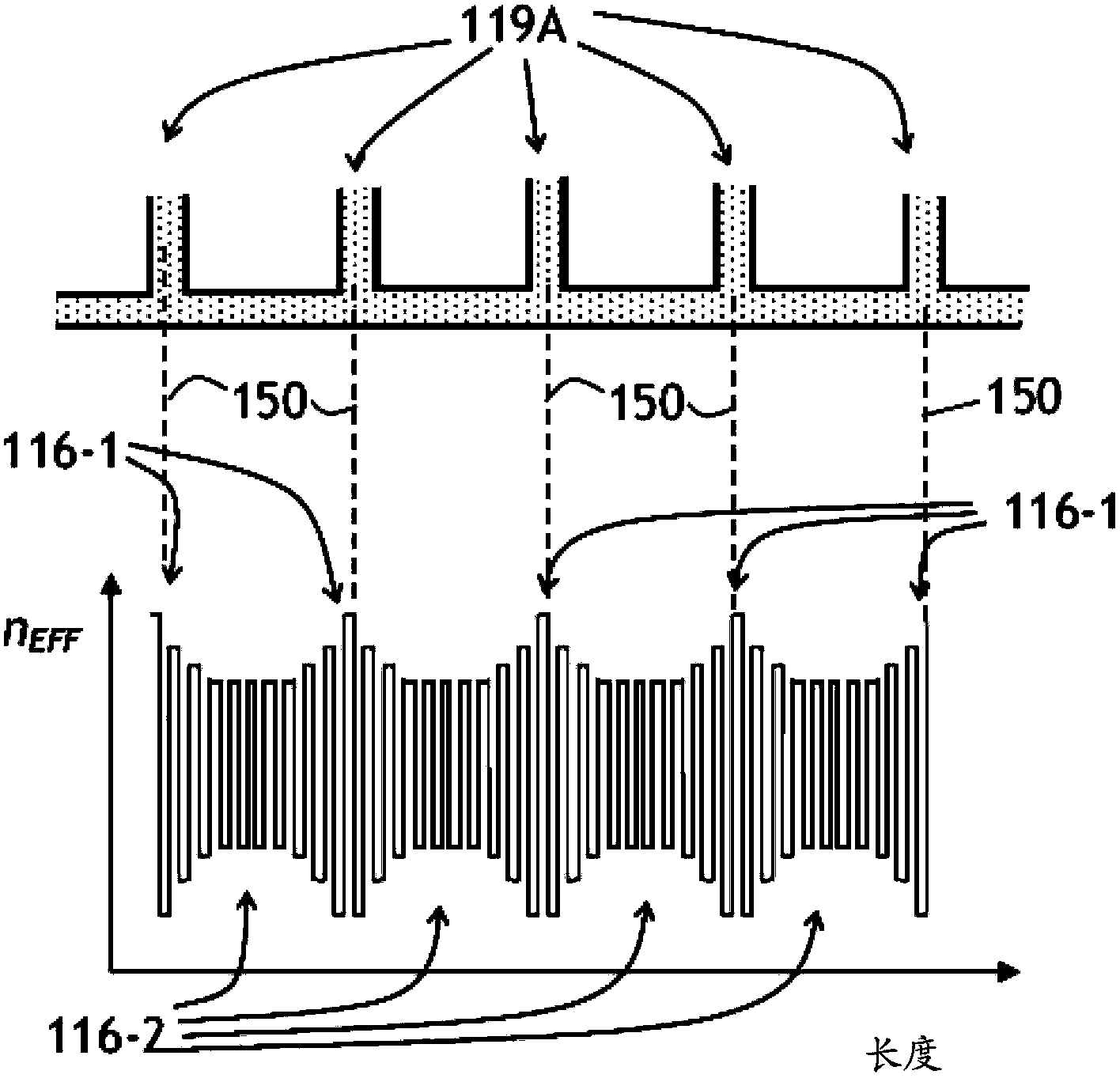
Tunable bragg grating and tunable laser diode using same
The invention provides a tunable bragg grating and a tunable laser diode using same. A spatially modulated waveguide Bragg grating mirror is suspended over a substrate by plurality of fingers extending laterally away from the waveguide centerline. The positions of the fingers are coordinated with the positions of crests and valleys of amplitude or phase modulation of the Bragg grating, to avoid disturbing the Bragg grating when it is tuned by heating. When the Bragg grating is heated, the heat flows through the fingers creating a quasi-periodic refractive index variation along the Bragg grating due to quasi-periodic temperature variation created by the heat flow from the grating through the supporting fingers. Due to coordination of the positions of supporting fingers with positions of the crests and valleys of modulation, the optical phase coherence is maintained along the Bragg grating, so that the spectral lineshape or filtering property of the Bragg grating is substantially preserved.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Method for preparing quasi-periodic micro-lens arrays through femtosecond laser wet etching
ActiveCN103018799AImprove etching efficiencyEfficient processing technologyLaser beam welding apparatusLensWater bathsEtching
Disclosed is a method for preparing quasi-periodic micro-lens arrays through femtosecond laser wet etching. The method comprises that the velocity of a target material moved by an accurate processing platform is controlled according to the individual average size of quasi-periodic micro lenses needed to be processed, femtosecond lasers act for one pulse on the target material surface at a fixed interval, and a light damage area is produced on the target material with the acting focus of each femtosecond laser pulse serving as a center; chemical corrosion is performed on the target material processed by the femtosecond lasers through a hydrofluoric acid solution with a volume concentration in a range of 1% to 10%, and ultrasonic water-bath heating is assisted; and the corroded target material is cleaned thoroughly in deionized water to obtain a template finished product of mass quasi-periodic micro-lens arrays. The method has the advantages of being high in efficiency, low in cost, controllable in micro-lens individual shape size and the like, and negative effects of air breakdown effects of laser focusing, periodic light field coupling stacking effects and the like generated in a dodging process can be prevented effectively.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Compact continuous wave tunable infrared lasers and method therefor
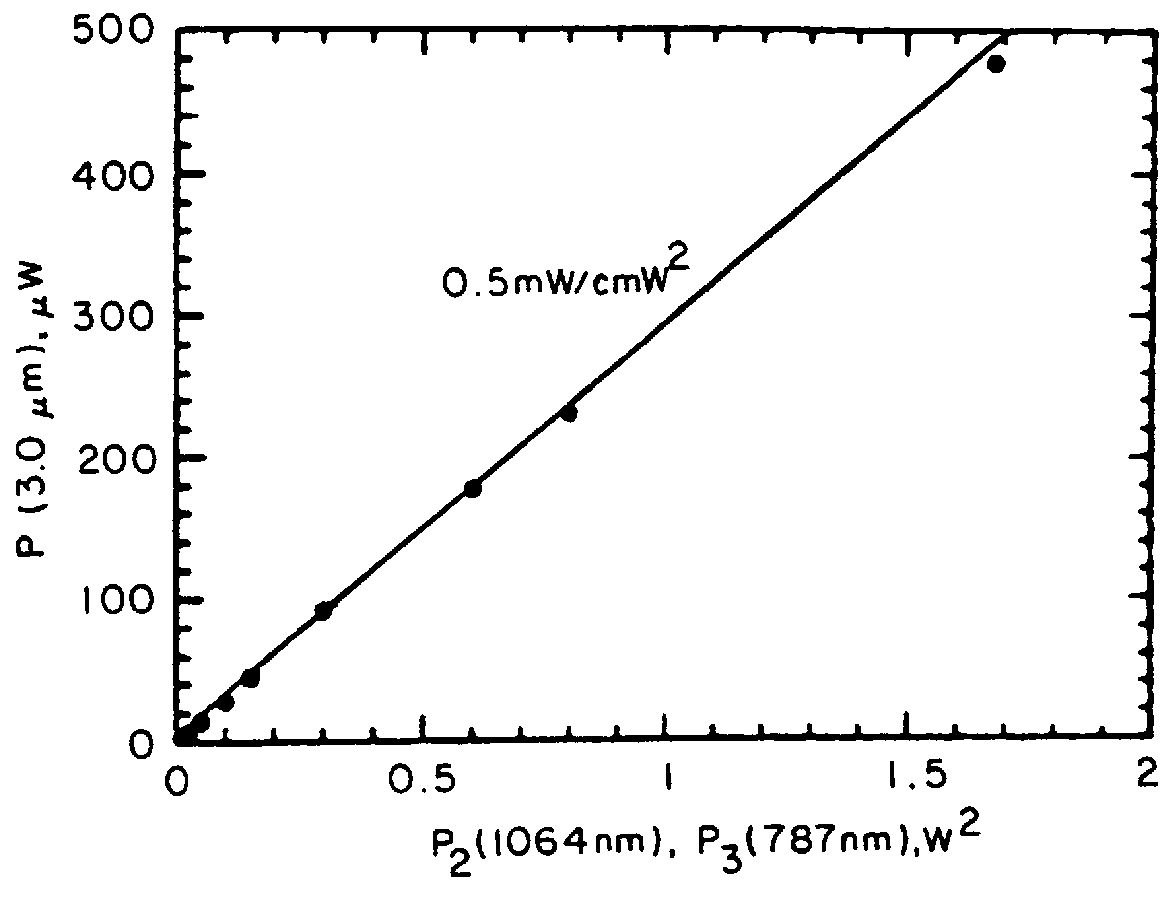
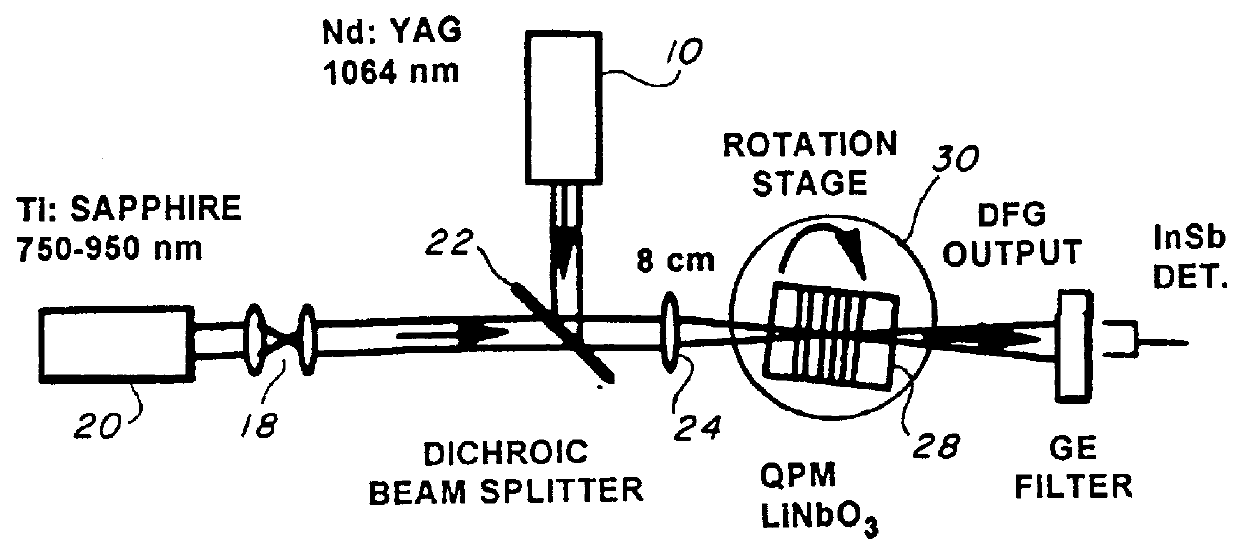
A bulk, quasi-periodic phase-matched difference-frequency (DFG) process in field-poled LiNbO.sub.3 bulk crystal permits continuous tunability of the output radiation in the 3.0-4.1 .mu.m wavelength range through grating rotation. DFG in QPM-LiNbO.sub.3 crystal, carried out using a Nd:YAG laser and a high power semiconductor laser at the quasi-phased matching (QPM) degeneracy point, results in an ultra wide 0.5 .mu.m acceptance bandwidth, permitting crystal rotation-free wavelength tuning of 4.0-4.5 .mu.m, with 0.2 mW output power at 4.5 .mu.m.
Owner:BURNS WILLIAM K +2
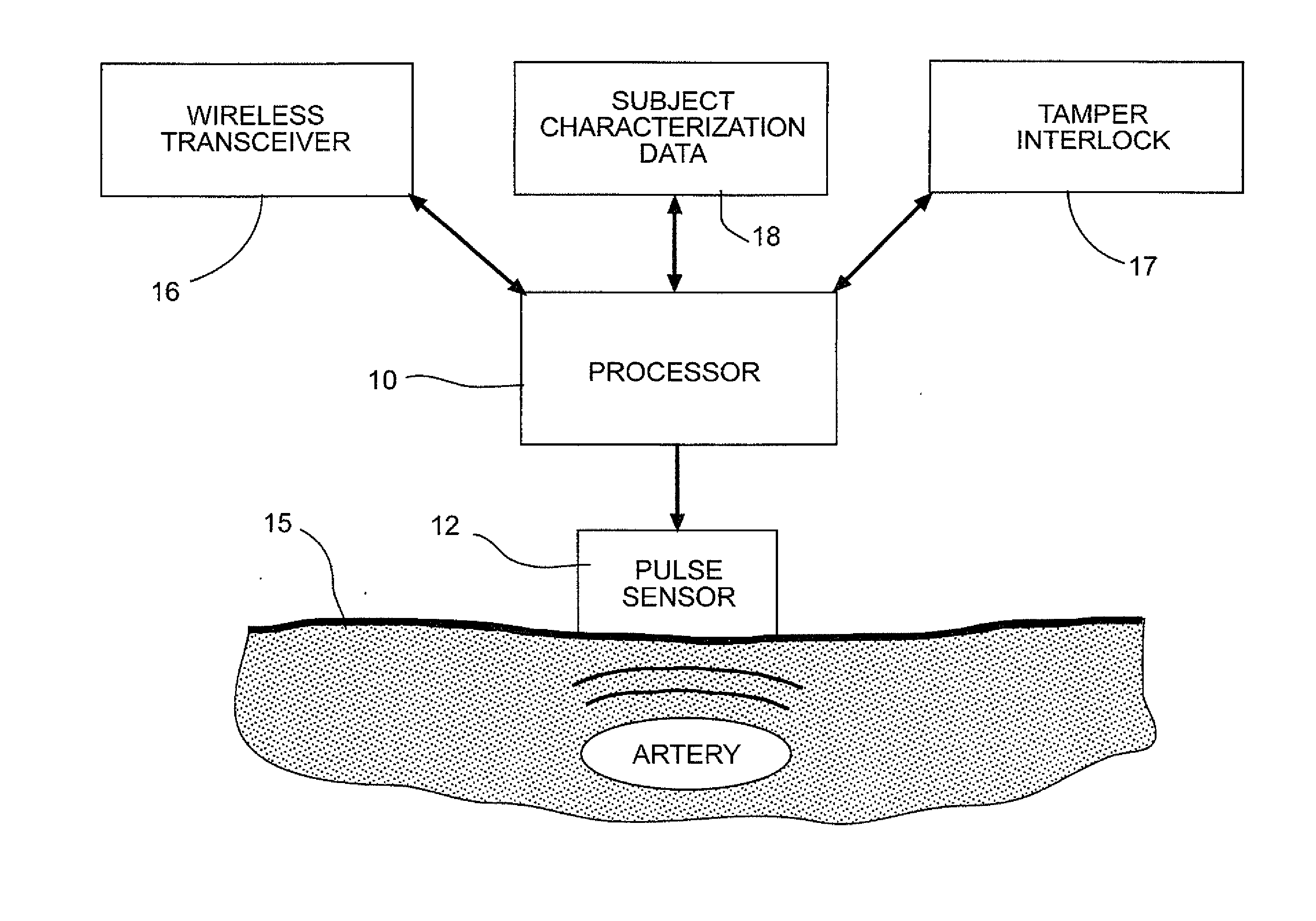
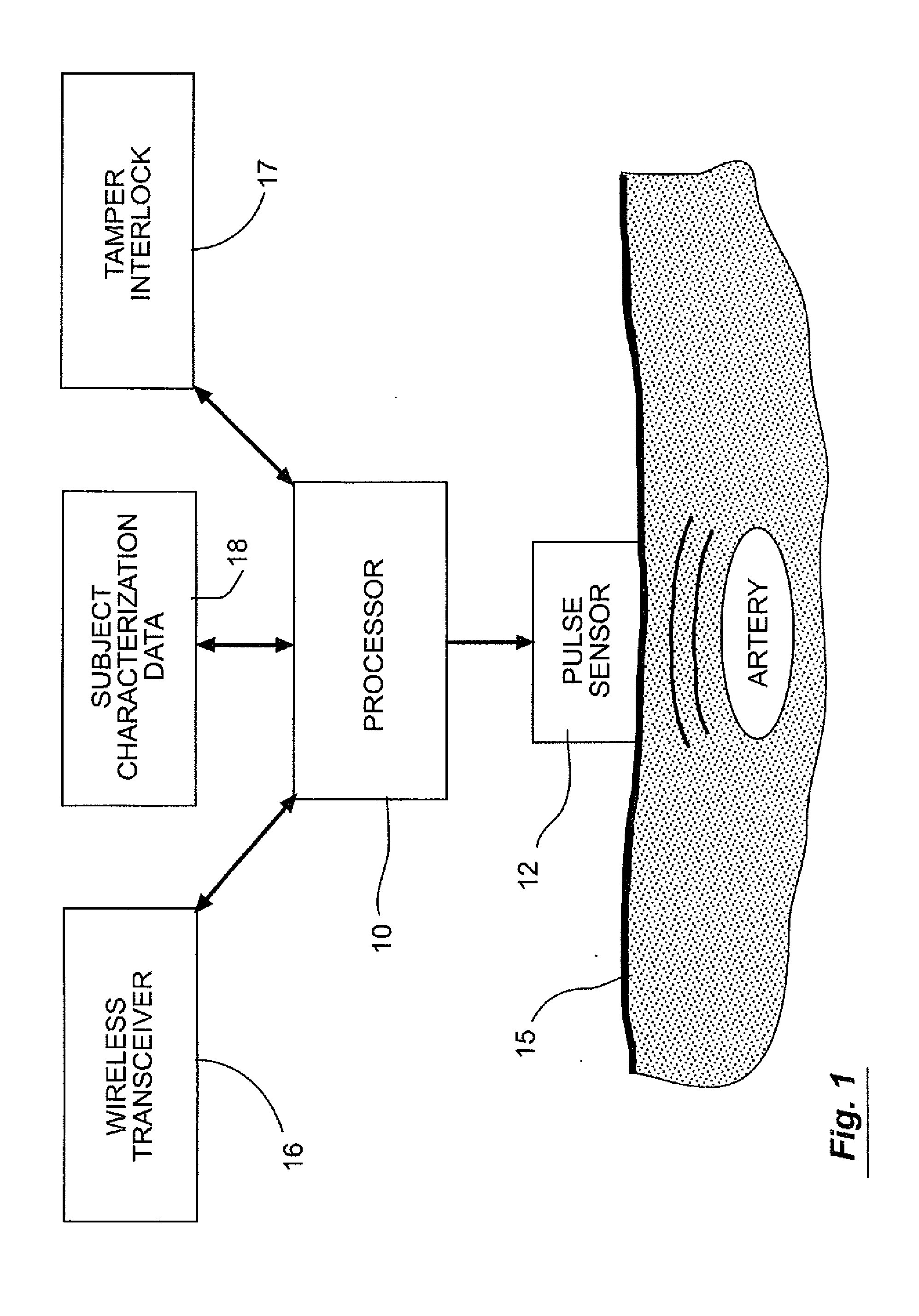
Biometric identification system using pulse waveform
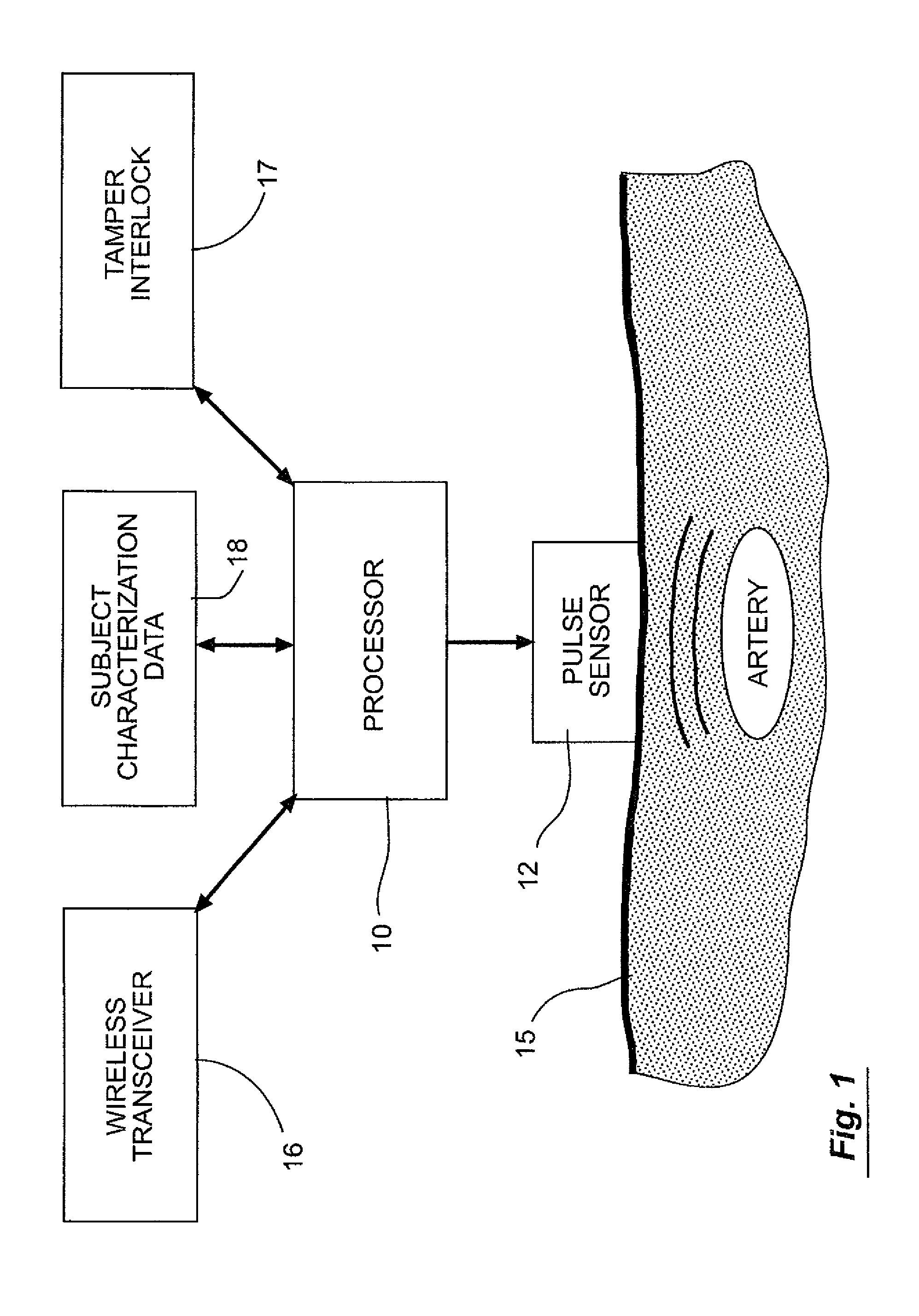
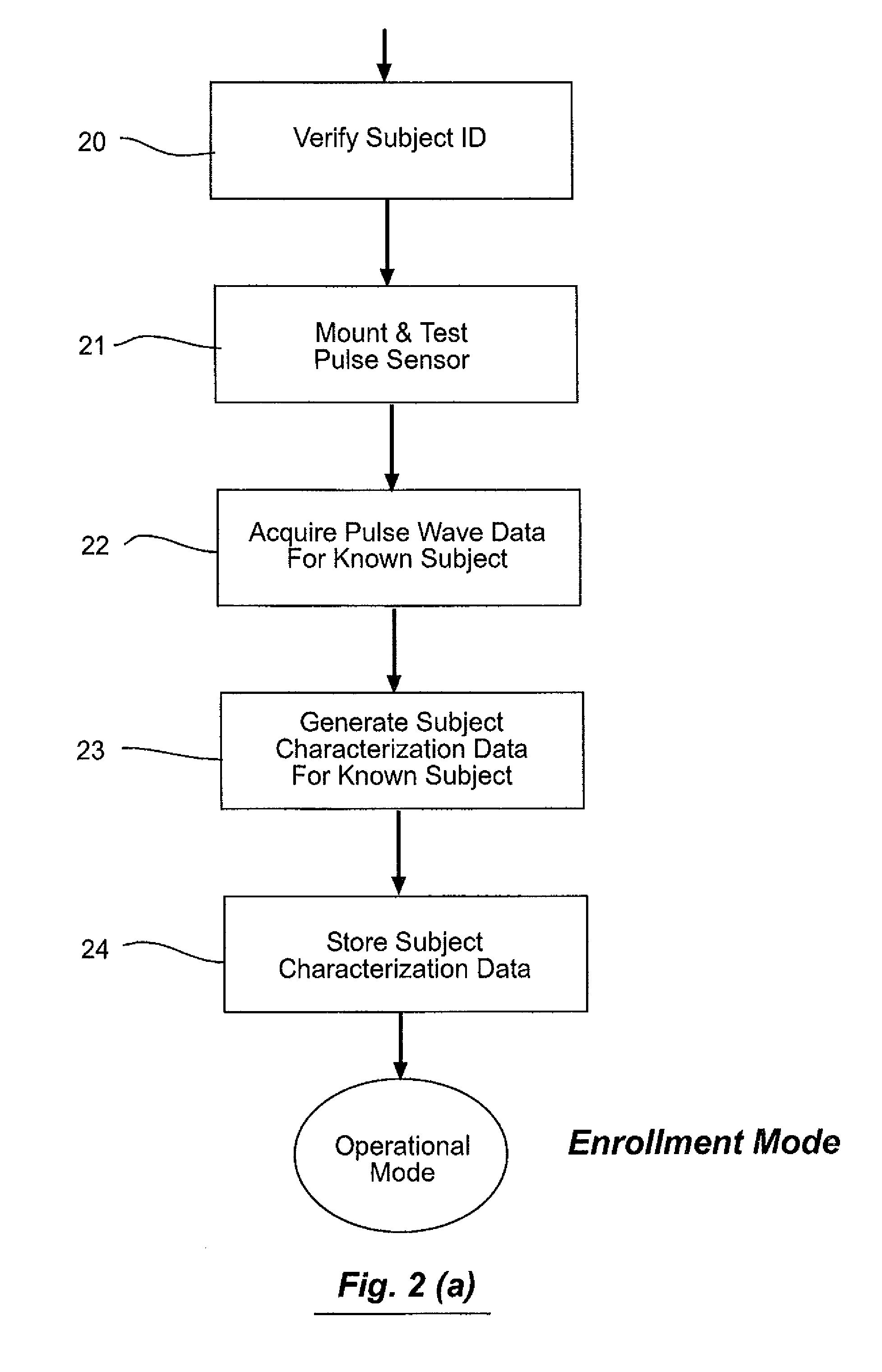
ActiveUS8773239B2Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsPhase spaceBlood pressure
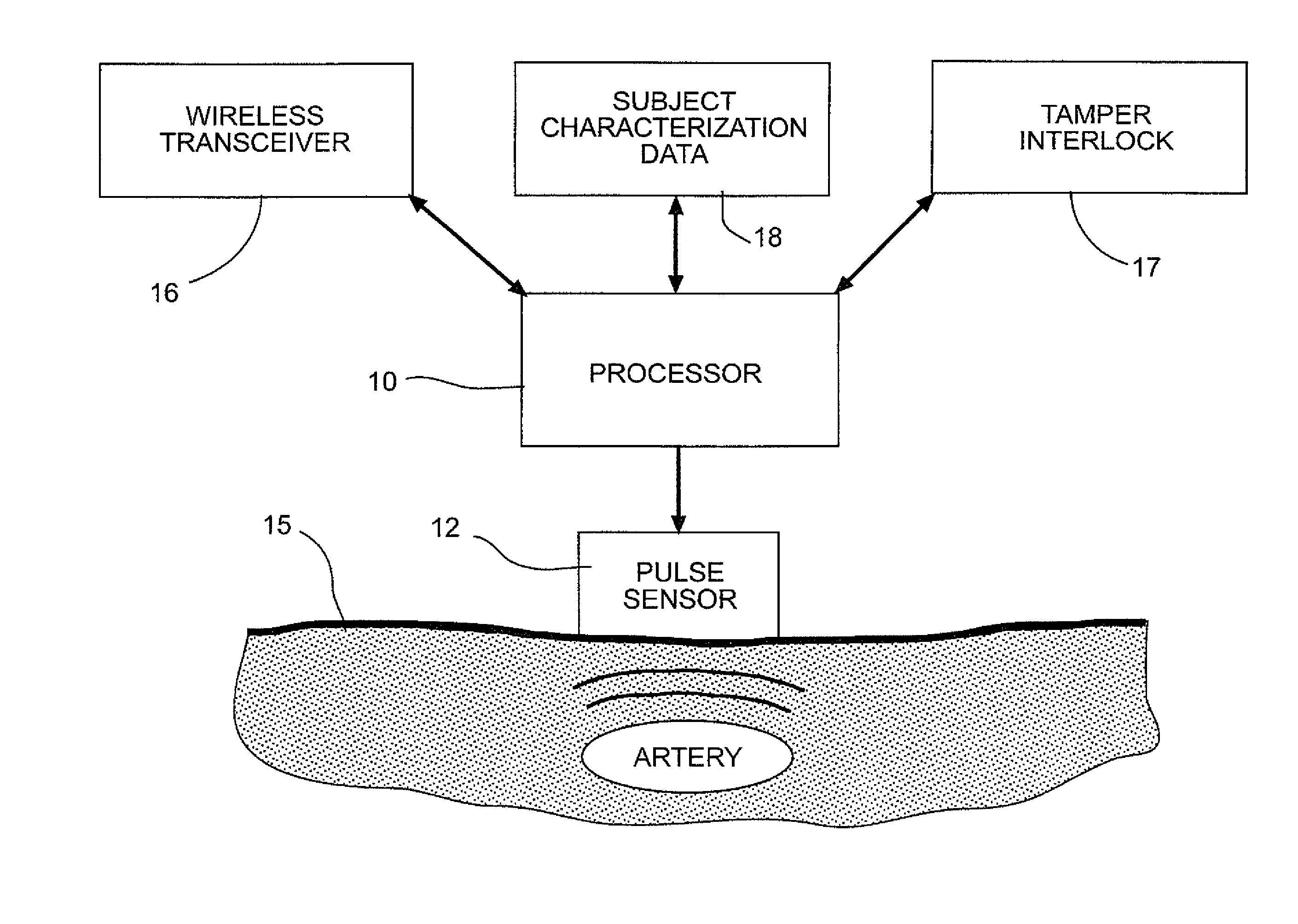
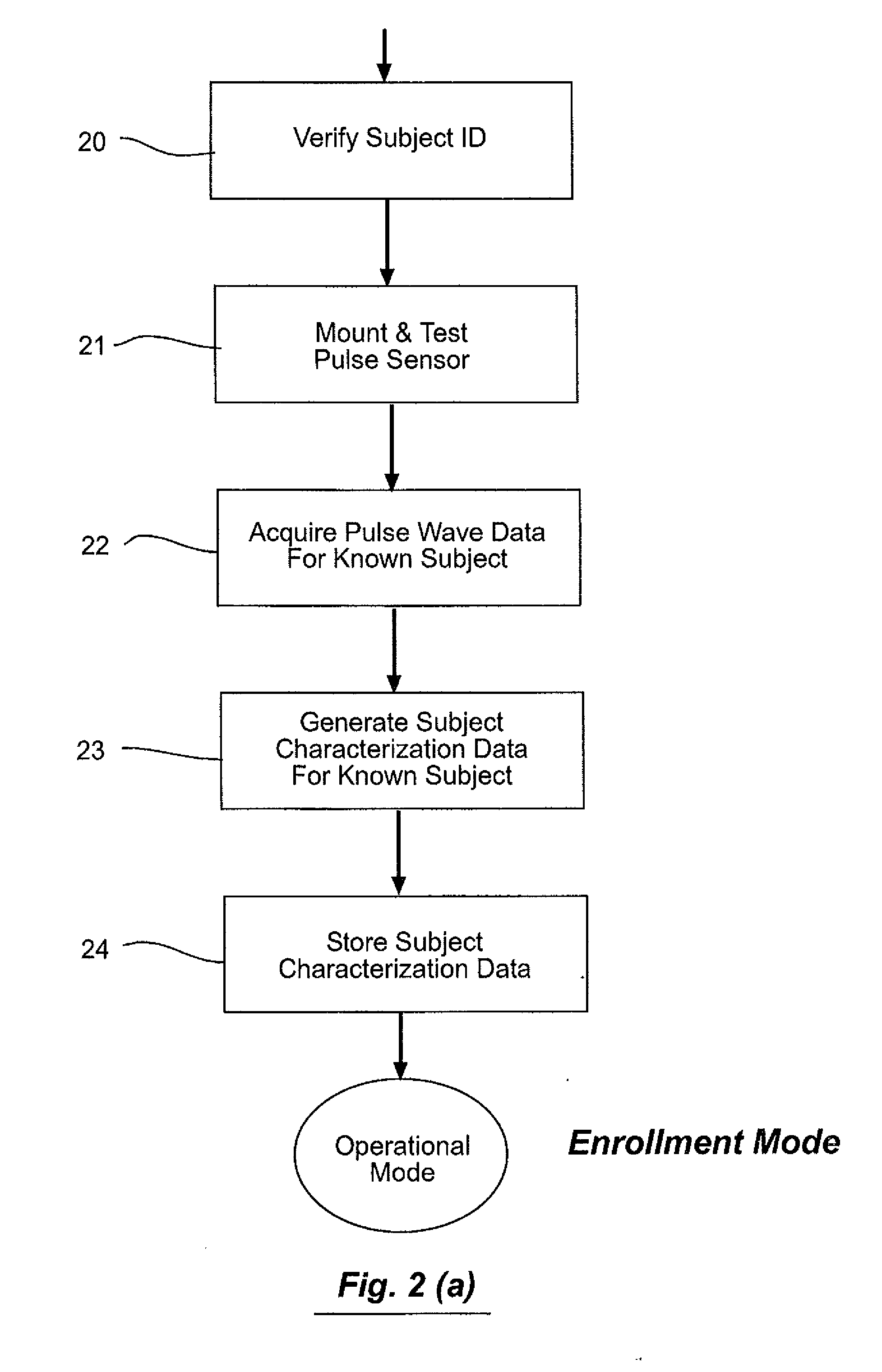
A method and system for biometric identity confirmation is based on the pulse wave of a subject. During an initial enrollment mode, pulse wave data for a known subject are used to generate subject characterization data for the known subject. During a subsequent operational mode, pulse wave data for a test subject are analyzed using the subject characterization data to confirm whether the identity of the test subject matches the known subject. The subject characterization data can be a probability density in a phase space in which at least two quasi-periodic variables based on the pulse wave (e.g., blood pressure and volume time-series data) are correlated.
Owner:LIFELOC TECH
Thin-film photovoltaic device with wavy monolithic interconnects
ActiveUS20150214409A1Reduce needImprove efficiencyPV power plantsComputer aided designComputer moduleEngineering
A thin-film optoelectronic module device (100) and design method comprising at least three monolithically-interconnected cells (104, 106, 108) where at least one monolithically-interconnecting line (250) depicts a spatial periodic or quasi-periodic wave and wherein the optoelectronic surface of said thin-film optoelectronic module device (100) presents at least one set of at least three zones (210, 220, 230) having curves of substantially parallel monolithic interconnect lines. Border zones (210, 230) have a lower front-contact sheet resistivity than th at of internal zone (220). Said curves of substantially parallel interconnecting lines may comprise peaks of triangular or rounded shape, additional spatial periods that are smaller than a baseline period, and mappings from one curve to the adjacent curve such as in the case of non-rectangular module devices (100). The device (100) and design method are advantageous to reduce costs and materials to manufacture thin-film optoelectronic module devices (100) while increasing production yield, reliability, aesthetic appearance, and range of applications.
Owner:FLISOM
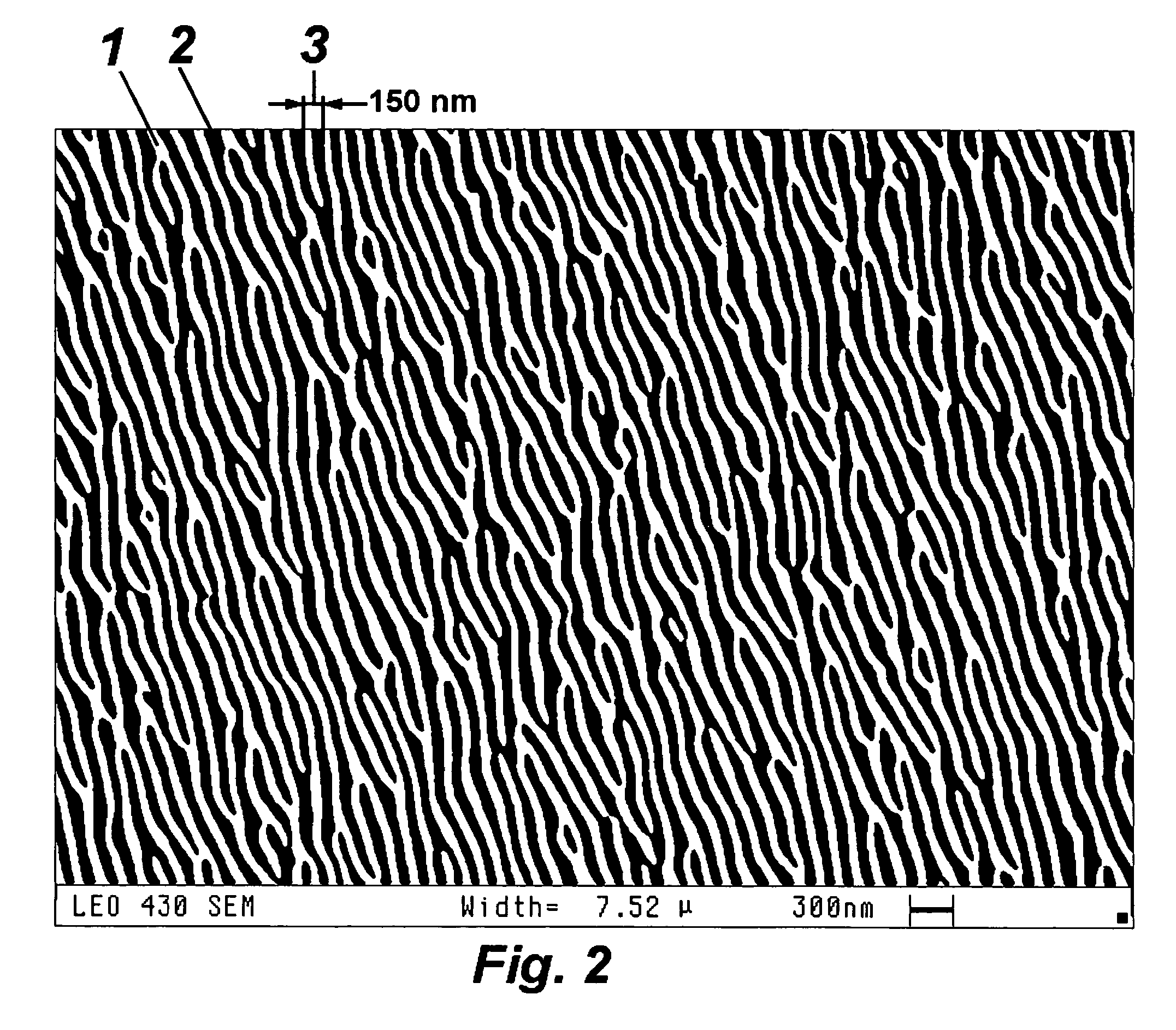
Composite material for ultra thin membranes
ActiveUS7604690B2Improve performanceStrong mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesLength waveNanometre
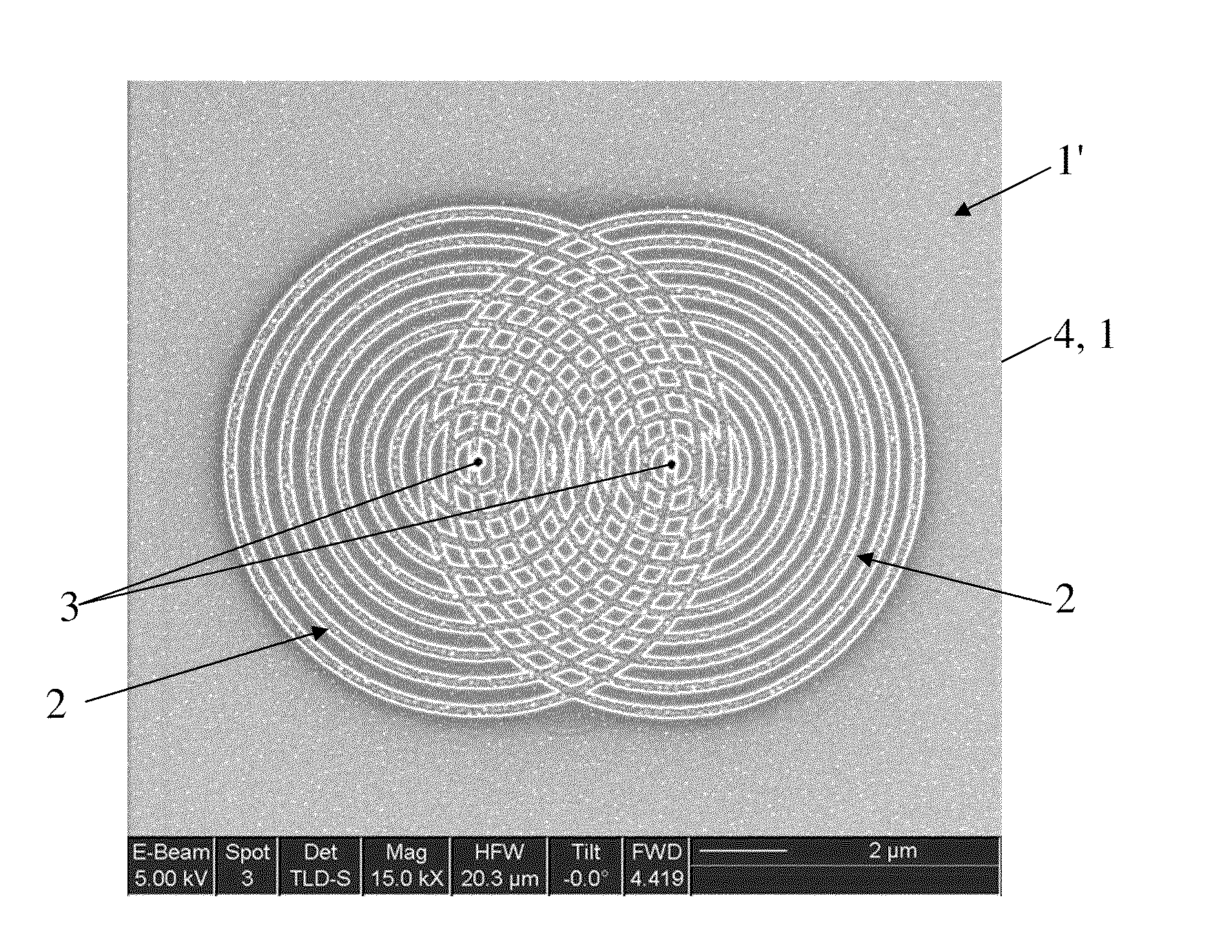
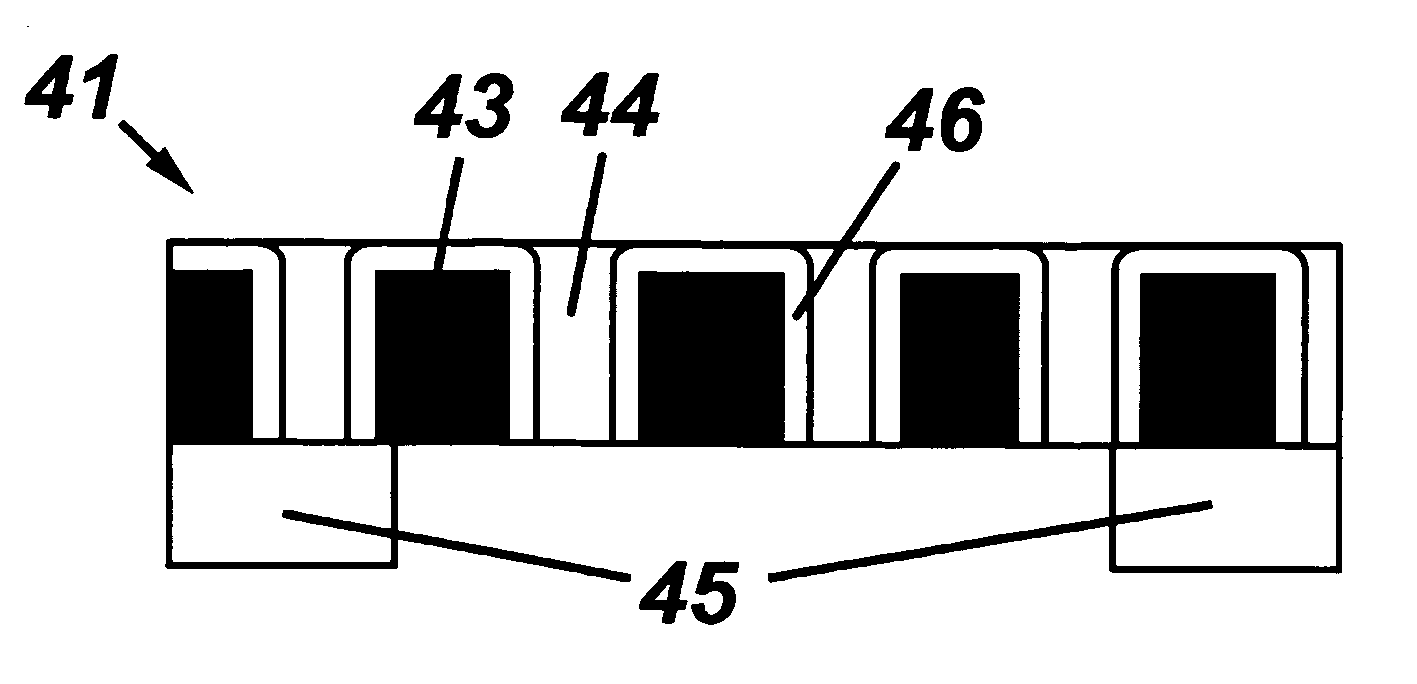
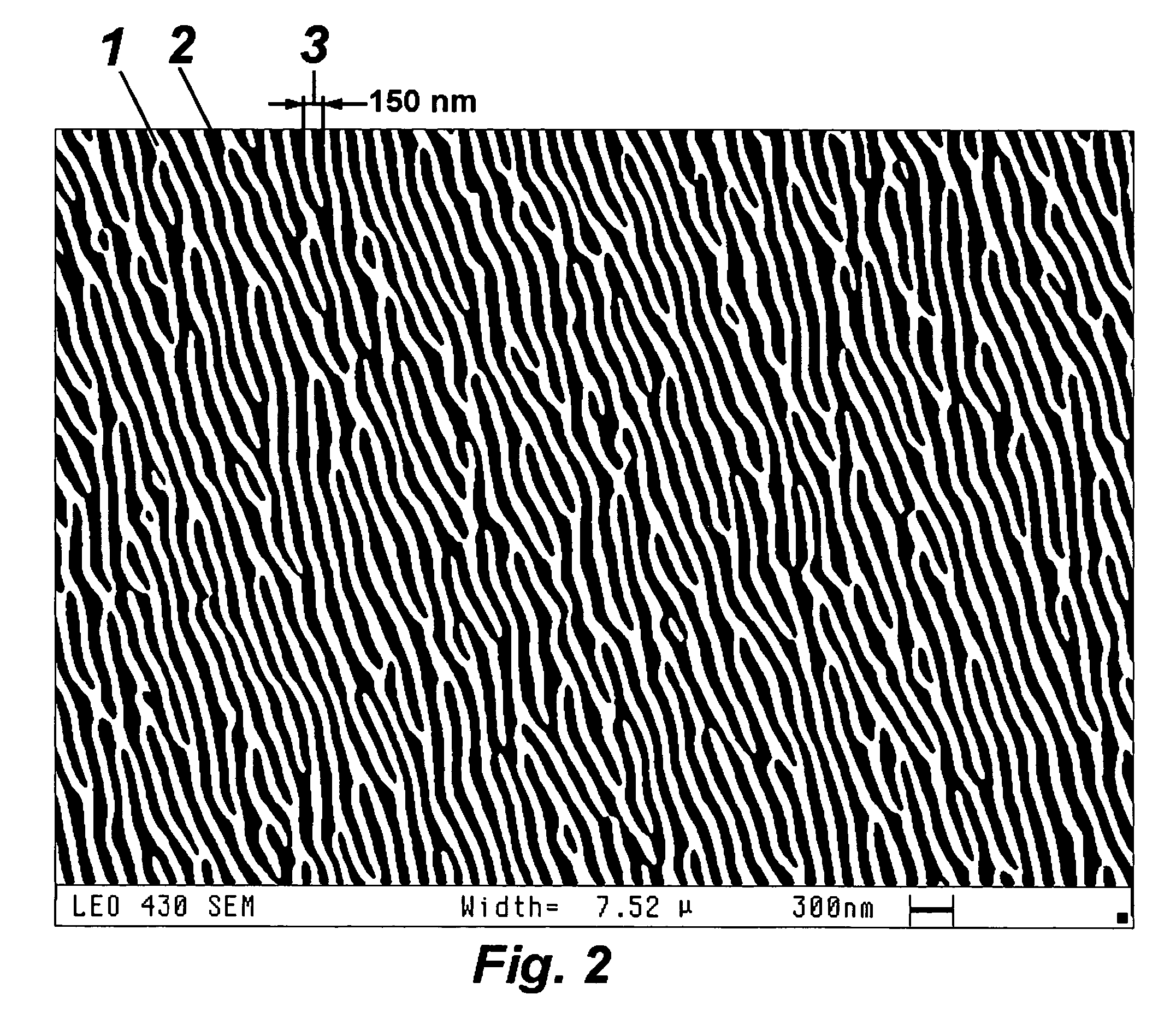
A composite material that may be used for a thin membrane is disclosed. This composite material includes first material that has a quasi-periodic system of vertical trenches (nanotrenches) with wavelength period that may be in the range between 20 and 500 nm. These nanotrenches are formed as openings between bordering elongated elements. The nanotrenches are at least partially filled with a second material that has physical-chemical characteristics substantially different from the first material.
Owner:WOSTEC
Lithographic fabrication of general periodic structures
ActiveUS20110199598A1Easy to controlLarge depth of fieldPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLight beamWavelength
A lithographic method related to Talbot imaging for printing a desired pattern of features that is periodic or quasi-periodic in at least one direction onto a substrate surface, which method includes providing a mask bearing a pattern of mask features, arranging the substrate parallel and in proximity to the mask, providing an illumination source having a central wavelength and a spectral bandwidth, forming from said source an illumination beam with an angular distribution of intensity, arranging the distance of the substrate from the mask and exposing the mask pattern to said beam so that each angular component of illumination exposes the substrate to substantially the entire range of lateral intensity distributions that occur between successive Talbot image planes for the illumination wavelengths, wherein the angular distribution of the beam is designed in conjunction with the pattern of features in the mask and the distance of the substrate from the mask.
Owner:EULITHA
Composite material for ultra thin membranes
ActiveUS20060230937A1Improve performanceStrong mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesThin membraneLength wave
A composite material that may be used for a thin membrane is disclosed. This composite material includes first material that has a quasi-periodic system of vertical trenches (nanotrenches) with wavelength period that may be in the range between 20 and 500 nm. These nanotrenches are formed as openings between bordering elongated elements. The nanotrenches are at least partially filled with a second material that has physical-chemical characteristics substantially different from the first material.
Owner:WOSTEC
Light-Emitting Device
InactiveUS20080043795A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedImprove light extraction efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPhotonic crystalMicrometer
A light-emitting device includes a substrate, a semiconductor stacked structure positioned on the substrate, a transparent electrode positioned on a first region of the semiconductor stacked structure, and at least one photonic crystal positioned in a second region of the semiconductor stacked structure. Preferably, the first region surrounds the second region, the area of the first region is larger than that of the second region, and the width of the second region is smaller than 40 micrometers. The structure of photonic crystals can be holes, pillars, continuous protrusions or depressions, discontinuous protrusions or depressions or the combination thereof, and the lattice of photonic crystals can be square, hexagonal, rectangular, periodic, multi-periodic, quasi-periodic or non-periodic.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
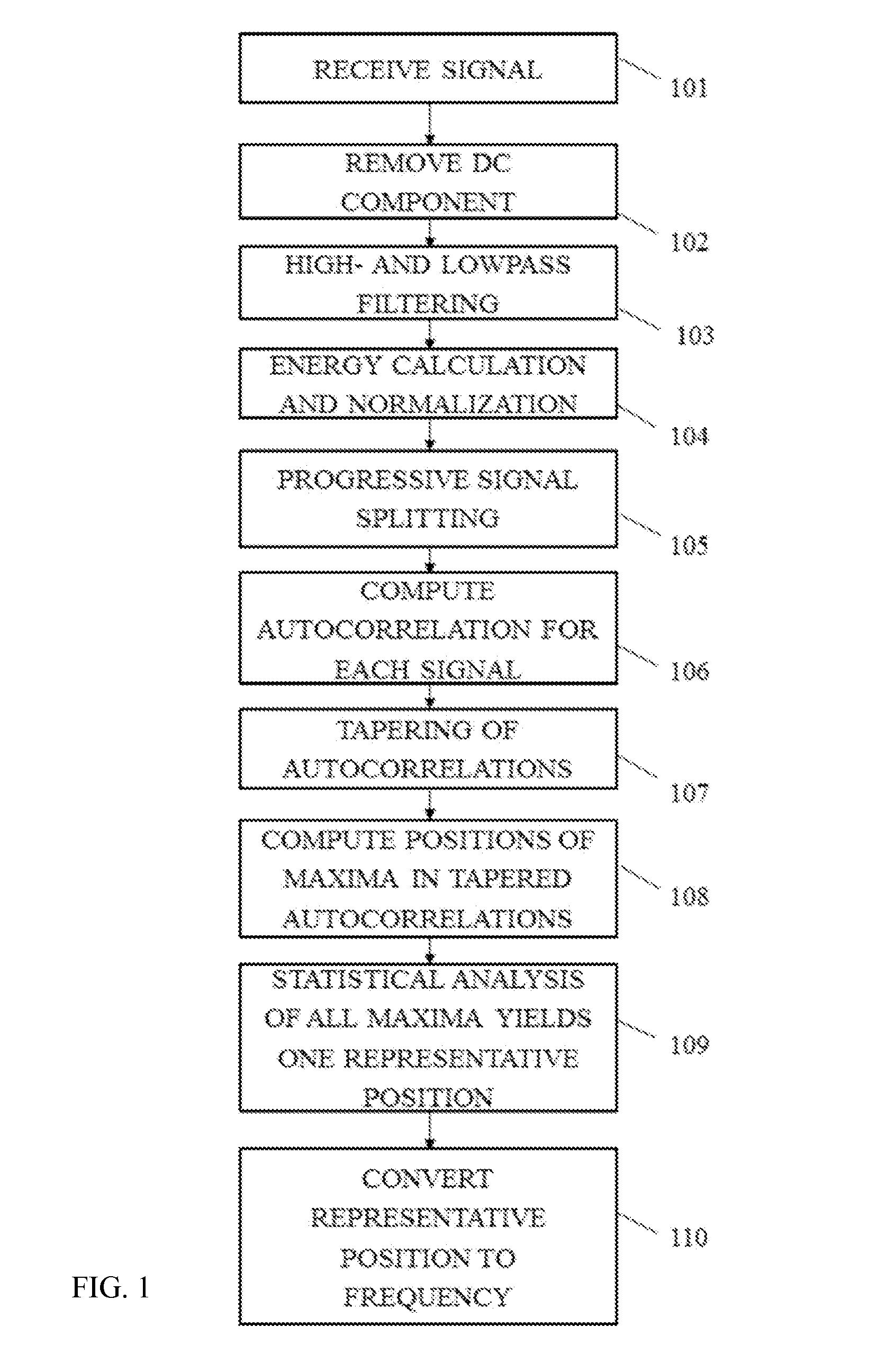
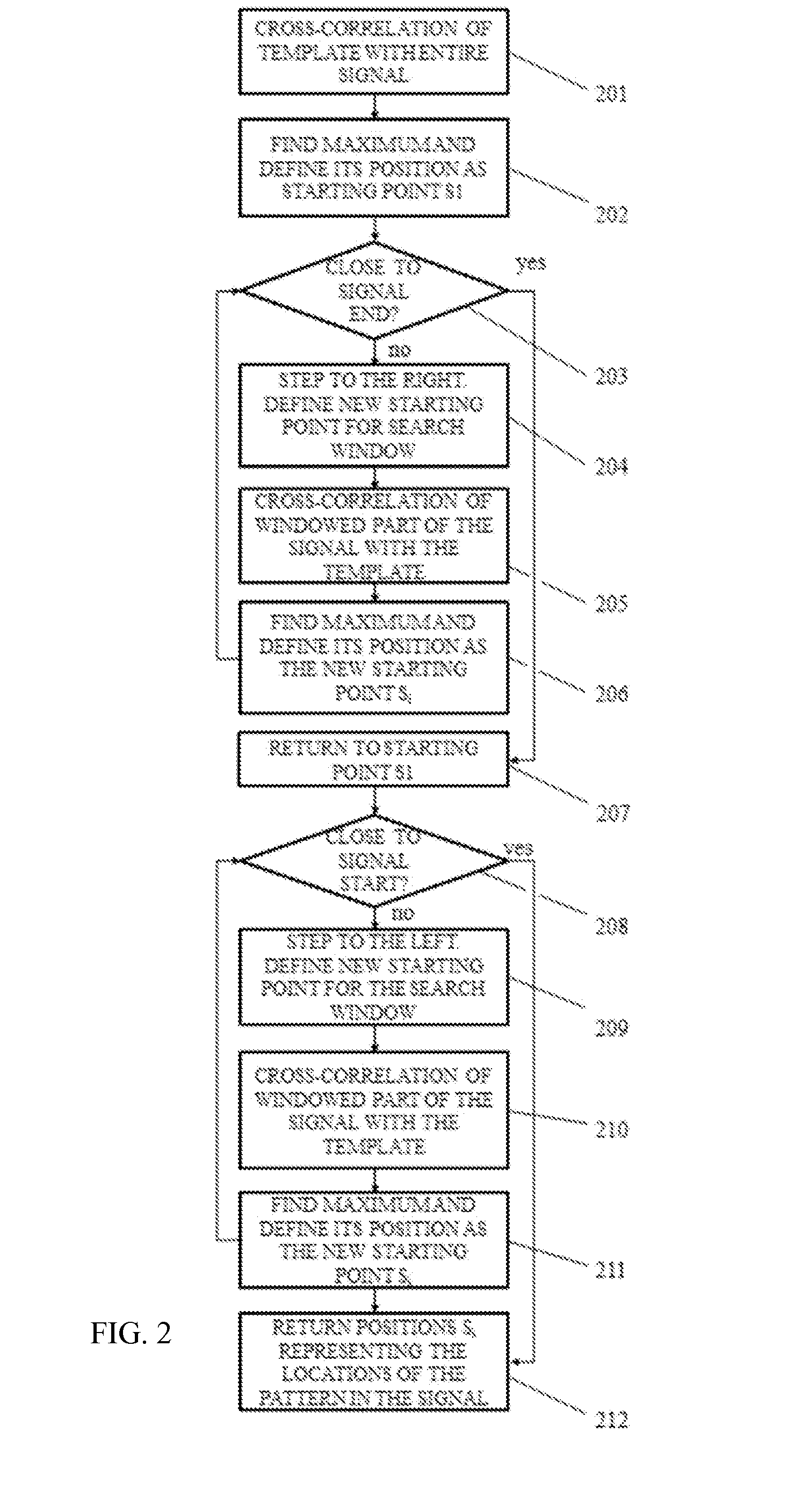
Automated Diagnosis-Assisting Medical Devices
InactiveUS20140276133A1Not hinder taskImprove accuracyDiagnostic signal processingStethoscopeElectronic stethoscopeComputer science
A system includes an electronic stethoscope producing a quasi-periodic signal, a processor, and a memory device with stored instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the system to receive a representation of the quasi-periodic signal, to remove a DC component from the received representation of the quasi-periodic signal to produce a purely time-varying signal, and to filter, the time-varying signal to produce a pre-processed signal. A portion of the pre-processed signal is auto-correlated with itself, and a corresponding auto-correlation output is stored. A biphasic tapering function is applied to the auto-correlation output and produces a first maximum, the function including a time constant parameter that is a function of the quasi-periodic signal. A representation is stored, based on the first maximum, as an indication of a rate or frequency of the quasi-periodic signal.
Owner:CSD LABS GMBH
Tunable bragg grating and a tunable laser diode using same
ActiveUS20140010248A1Simple and efficient structureAvoid disturbing the Bragg grating upon thermal tuningOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGratingHeat flow
A spatially modulated waveguide Bragg grating mirror is suspended over a substrate by plurality of fingers extending laterally away from the waveguide centerline. The positions of the fingers are coordinated with the positions of crests and valleys of amplitude or phase modulation of the Bragg grating, to avoid disturbing the Bragg grating when it is tuned by heating. When the Bragg grating is heated, the heat flows through the fingers creating a quasi-periodic refractive index variation along the Bragg grating due to quasi-periodic temperature variation created by the heat flow from the grating through the supporting fingers. Due to coordination of the positions of supporting fingers with positions of the crests and valleys of modulation, the optical phase coherence is maintained along the Bragg grating, so that the spectral lineshape or filtering property of the Bragg grating is substantially preserved.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Training method for accommodative and vergence systems, and multifocal lenses therefor
Accommodative and vergence systems training method and multifocal ophthalmic lenses of Horizontal periodic or quasi-periodic Optical Power Stepless Alternating (HOPSA-lenses) therefor are proposed. Reading the text with HOPSA-lenses worn, while the head is stationary, provides a continuous alternating of accommodation and vergence strain / relaxation and, therefore, provides dynamic training of both systems. The method is applicable for human visual system therapy, eye diseases treatment / prevention and ophthalmology researches. The method enables combining the effective visual trainings with documents reading / processing, visual target examining, watching TV / video, playing computer games, etc., as well as combining the training with conventional vision correction. Several embodiments of HOPSA-lenses are disclosed, such as multi- and mono-cyclic, multi-layer, splitting the basic correction and training functions between lens' sides or layers, having left and right lenses' surfaces individually configured to provide the congruence of optical power for fixation, and / or the convergence invariability for fixation during the training.
Owner:TYRIN ALBERT +1
Biometric identification system using pulse waveform
A method and system for biometric identity confirmation is based on the pulse wave of a subject. During an initial enrollment mode, pulse wave data for a known subject are used to generate subject characterization data for the known subject. During a subsequent operational mode, pulse wave data for a test subject are analyzed using the subject characterization data to confirm whether the identity of the test subject matches the known subject. The subject characterization data can be a probability density in a phase space in which at least two quasi-periodic variables based on the pulse wave (e.g., blood pressure and volume time-series data) are correlated.
Owner:LIFELOC TECH
Drowsy driver detection system
Owner:L & P PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com