Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
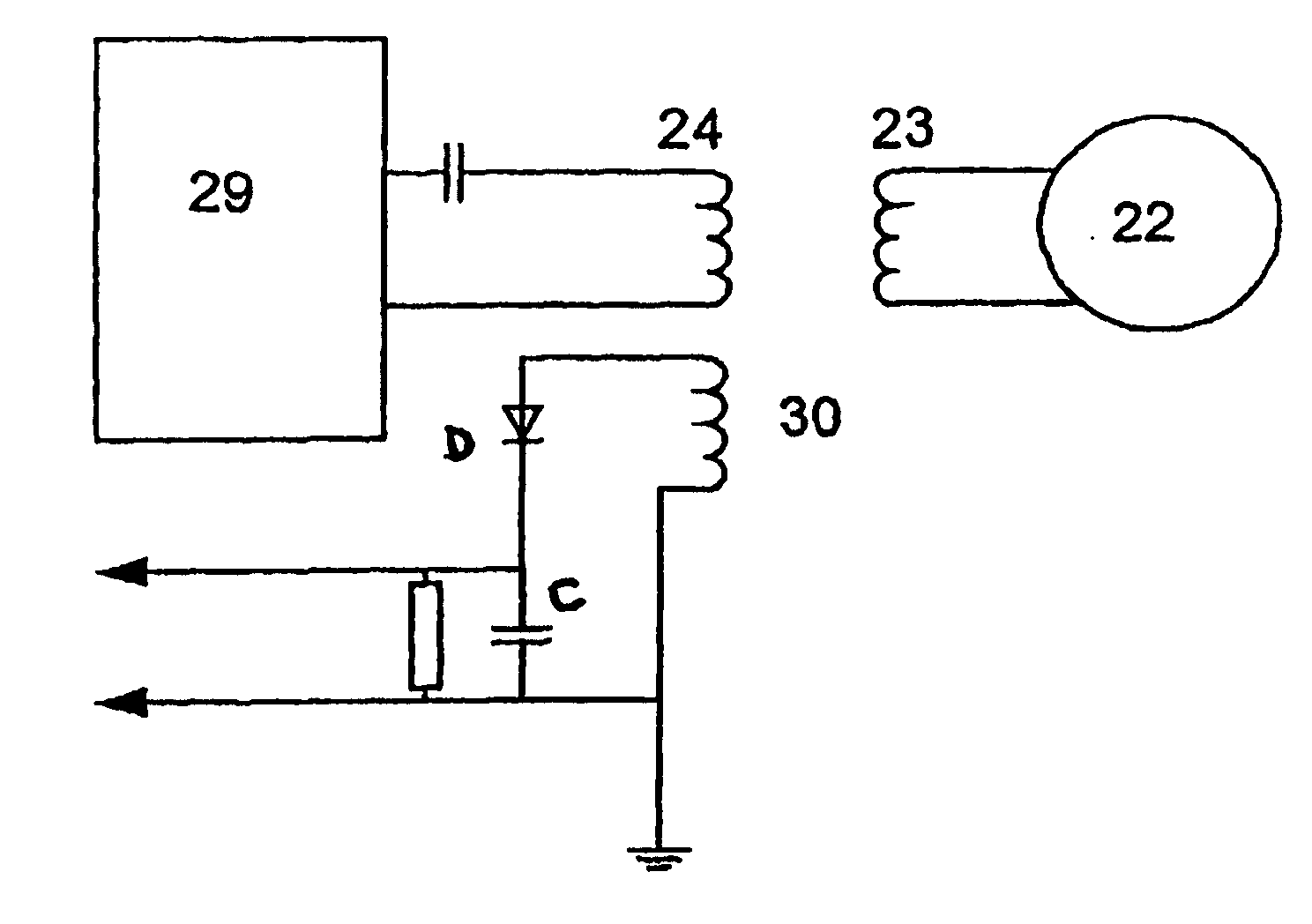
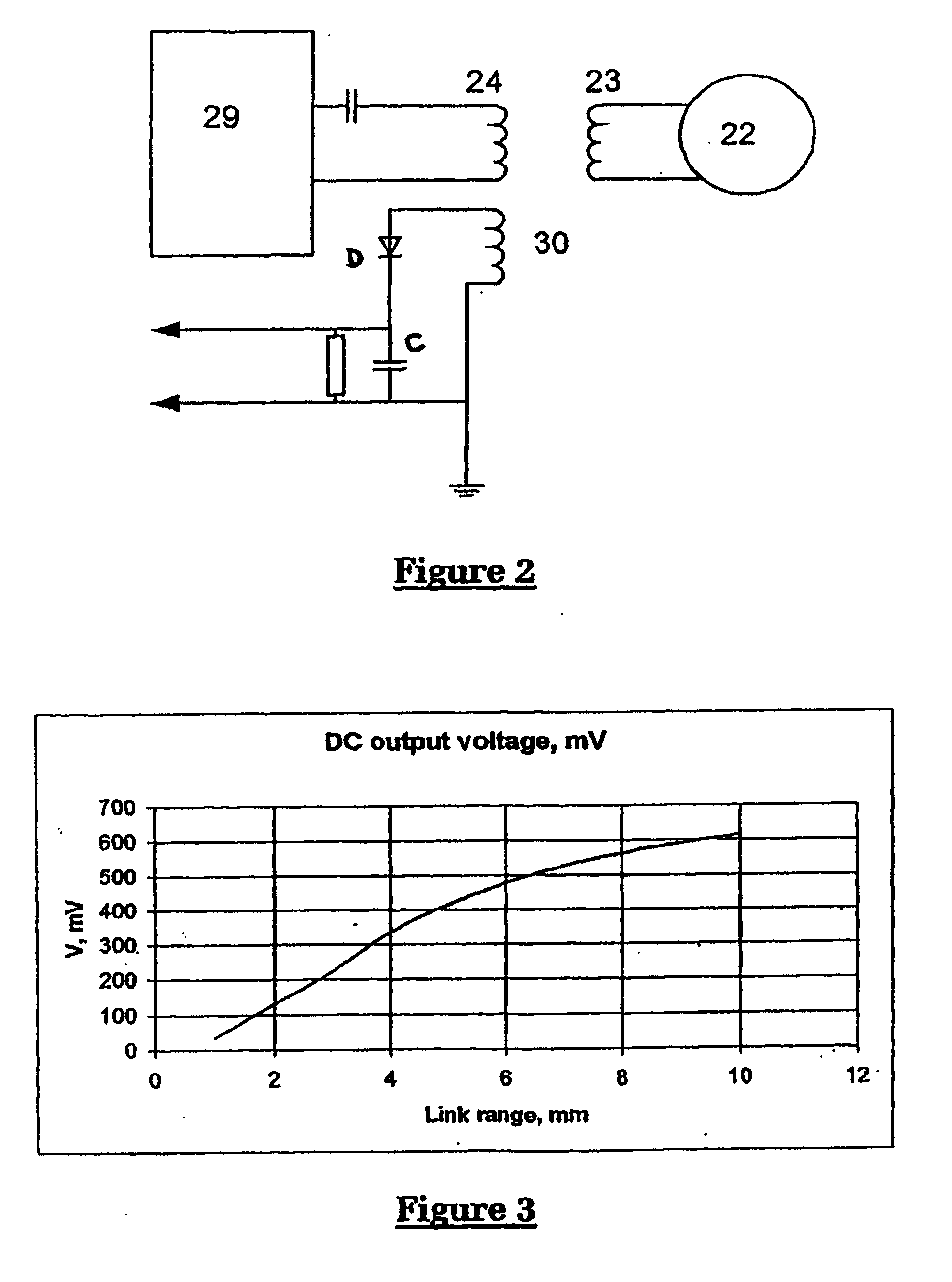
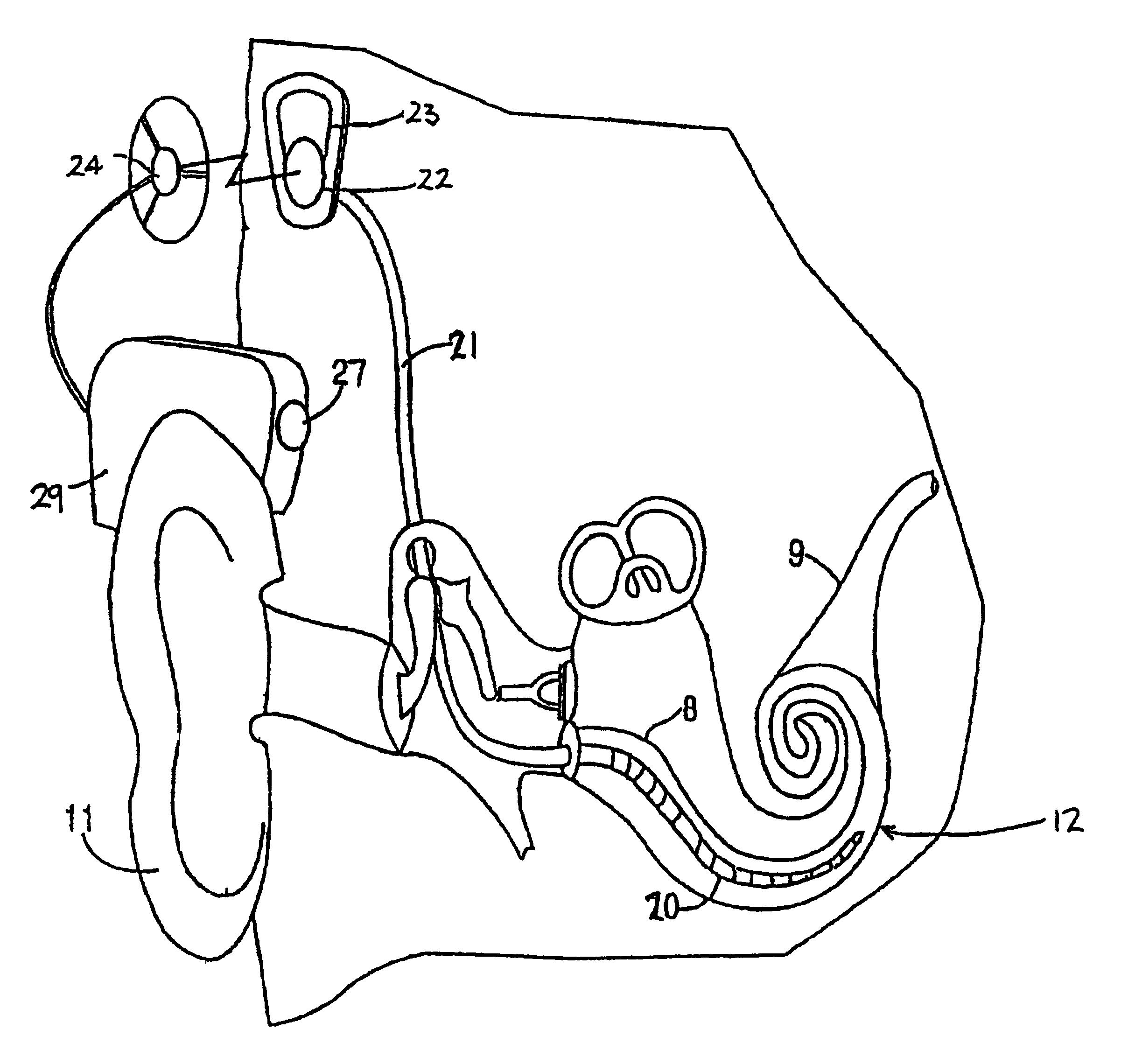
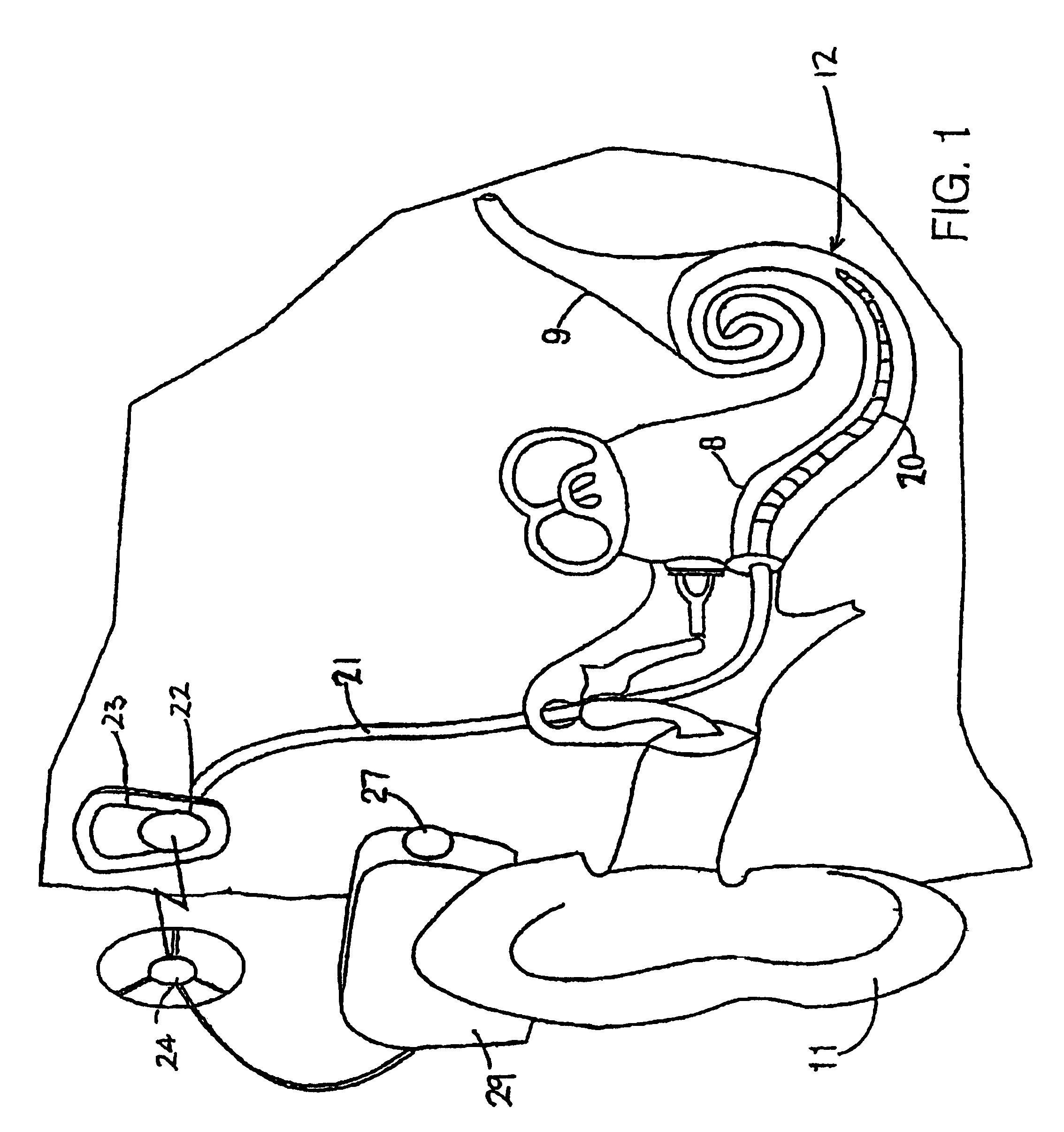
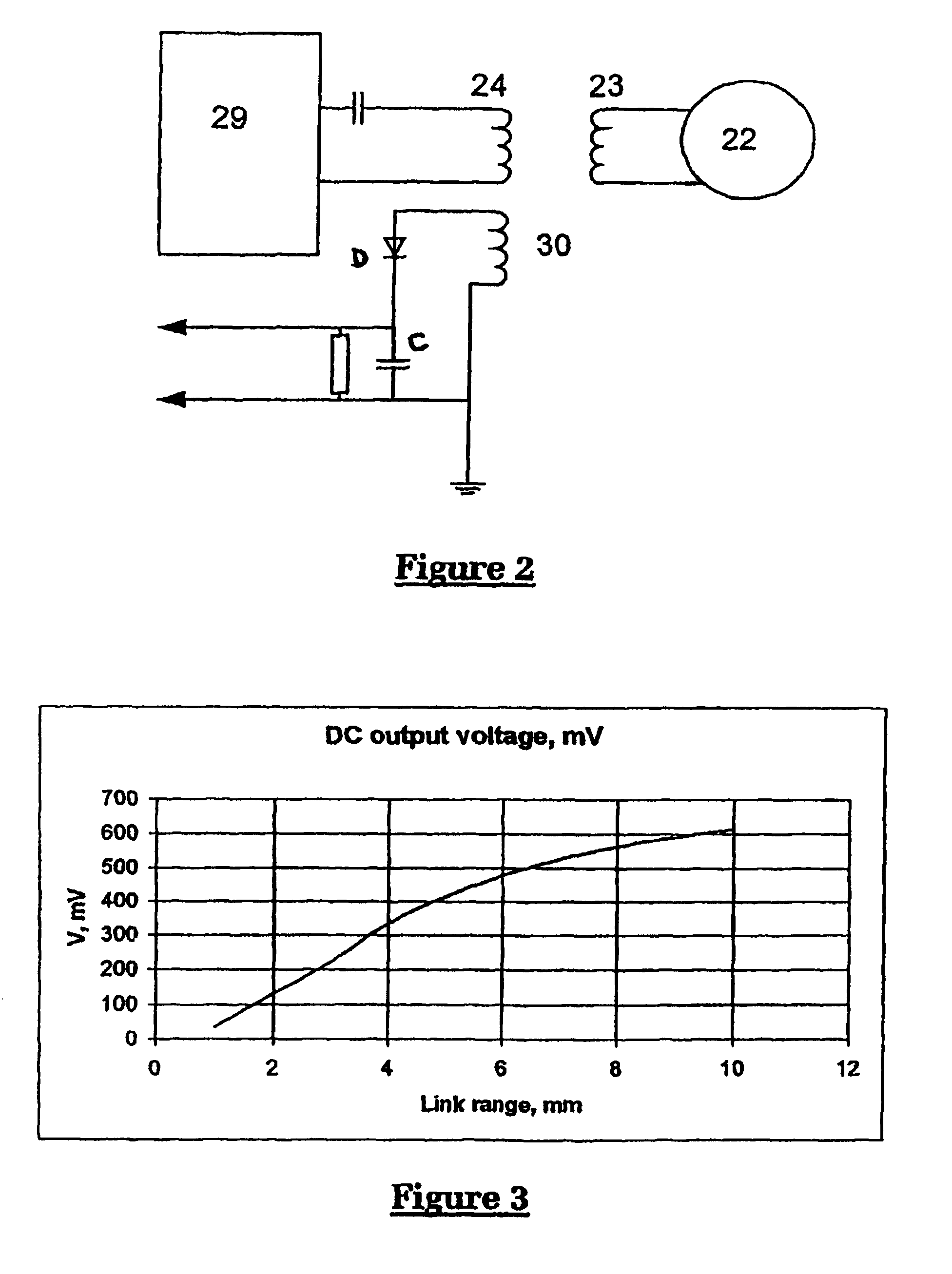
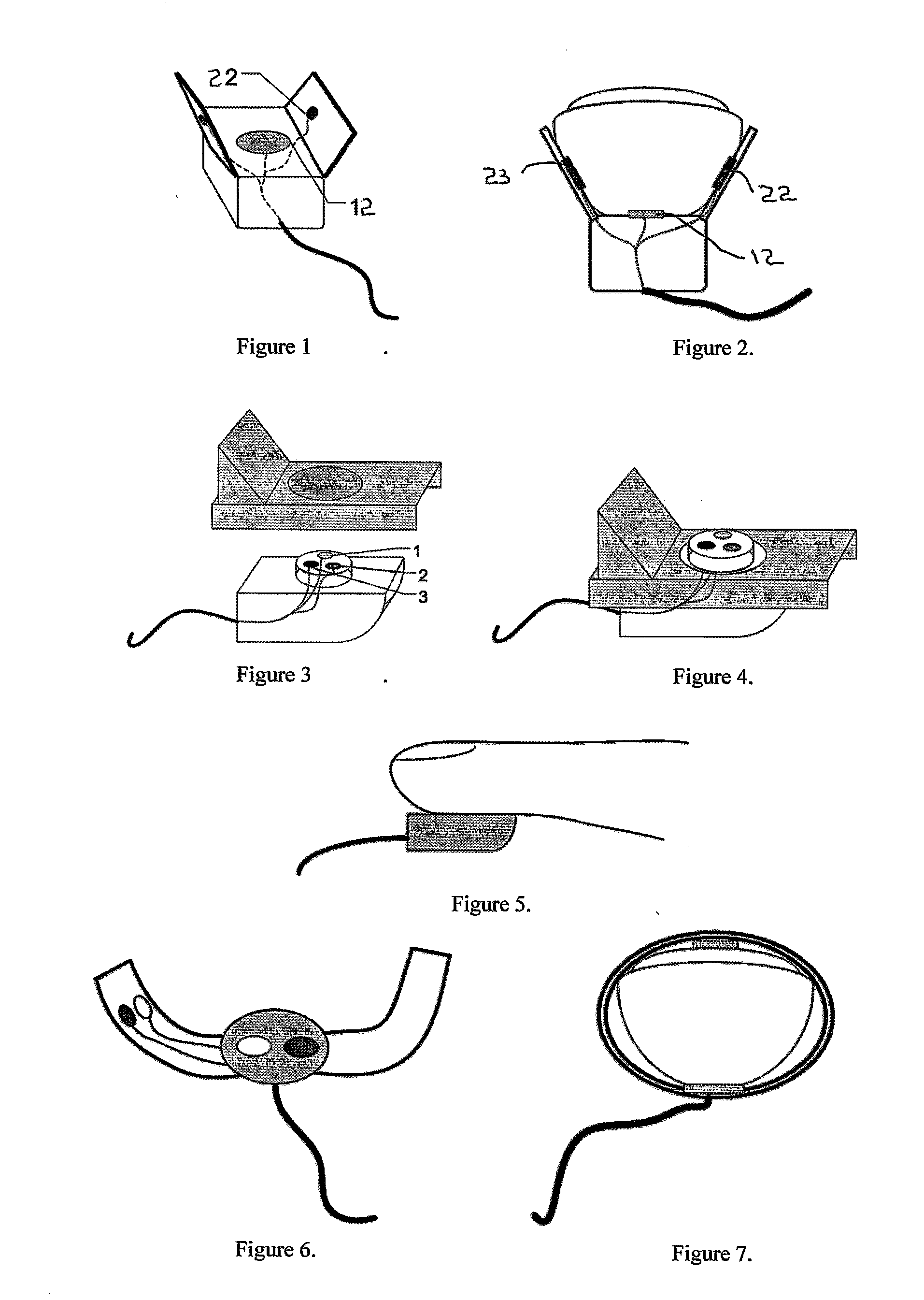
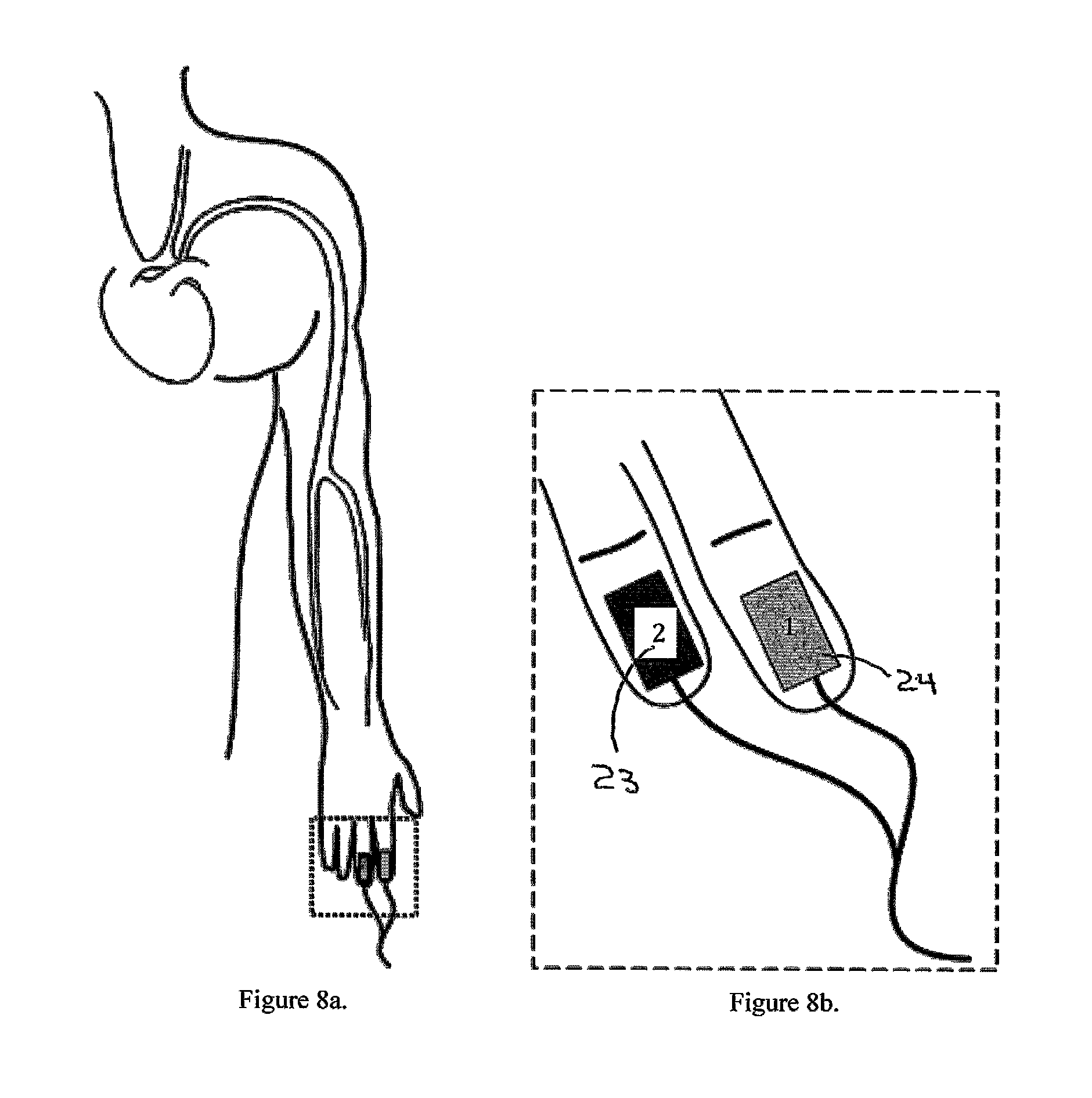
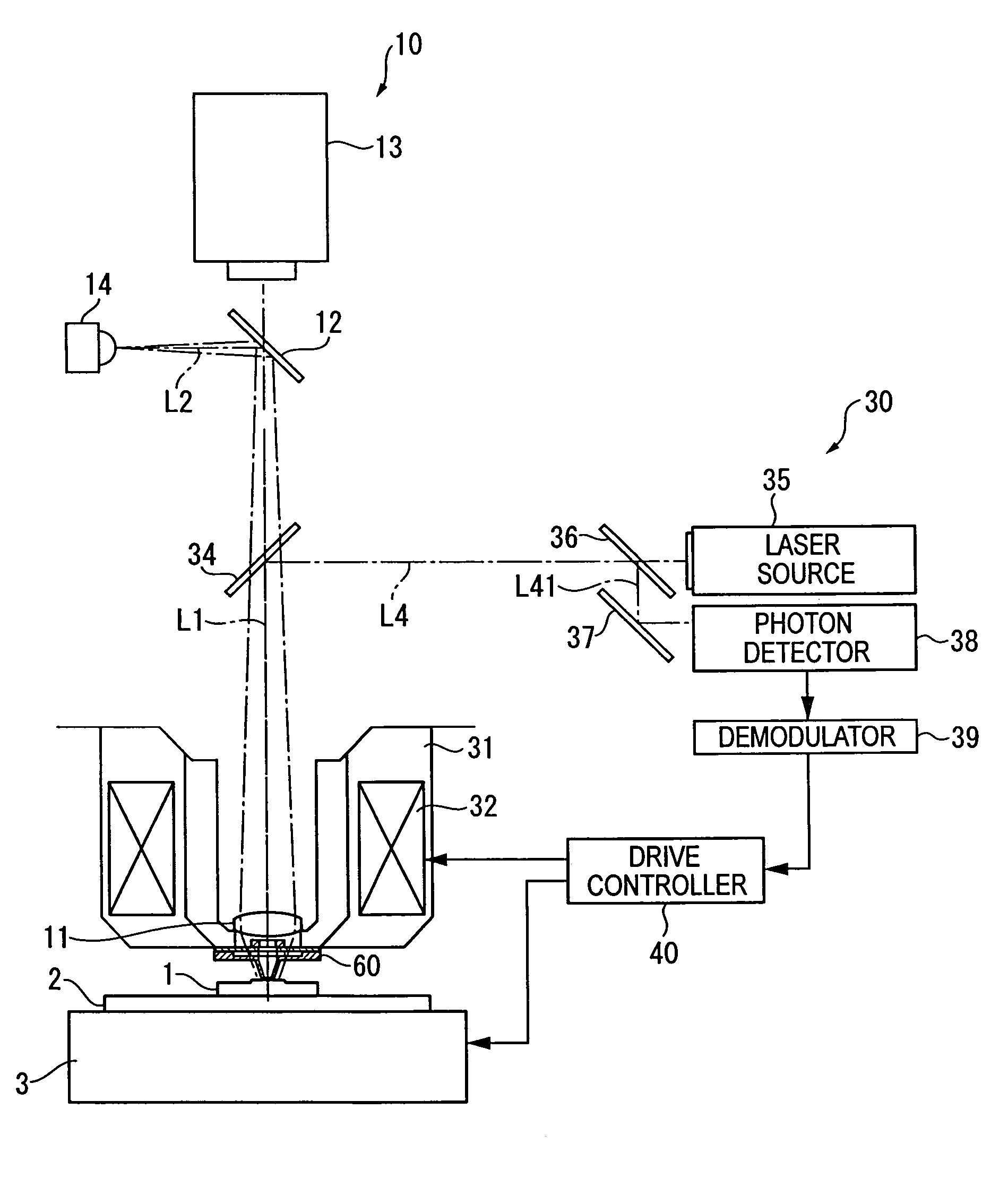
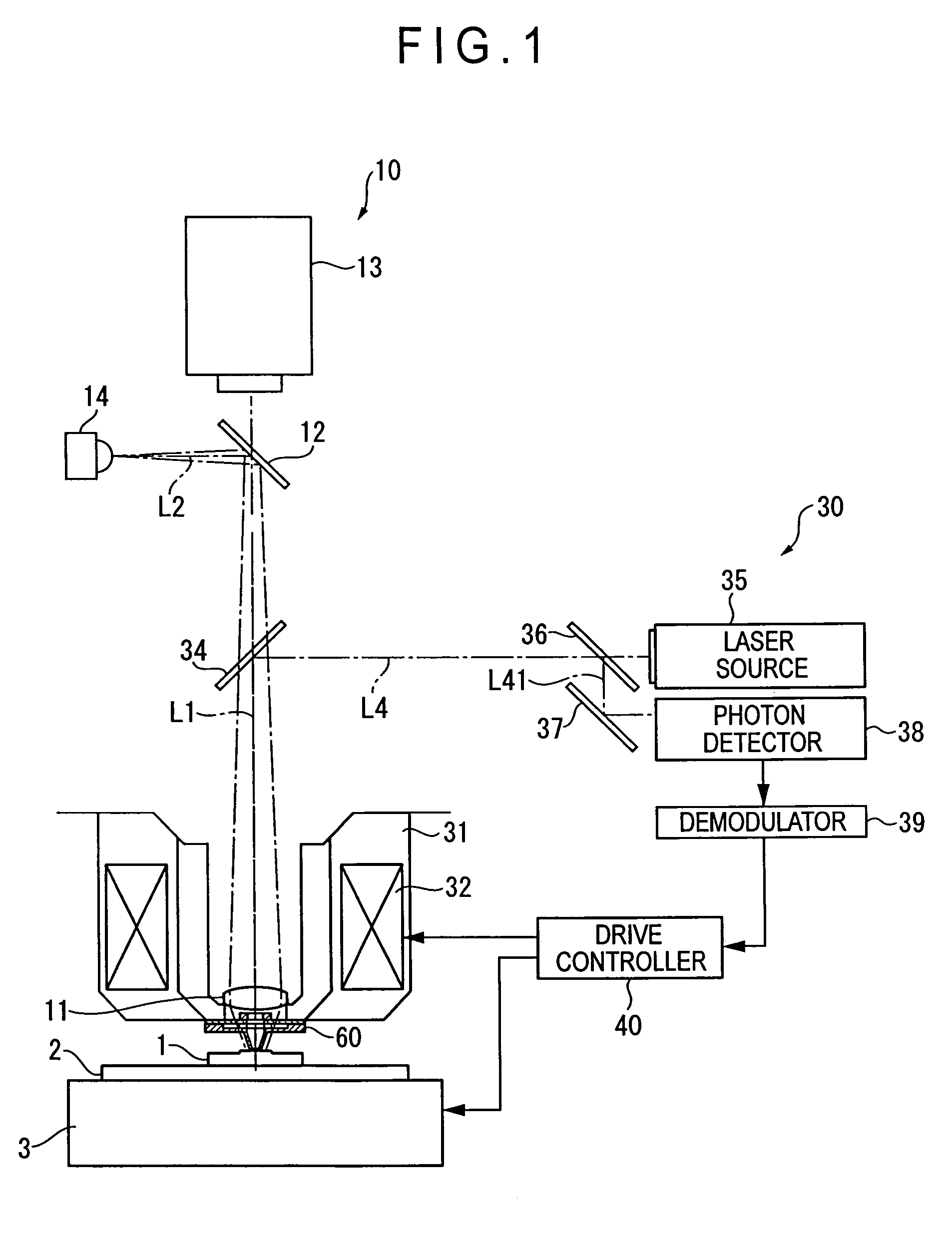
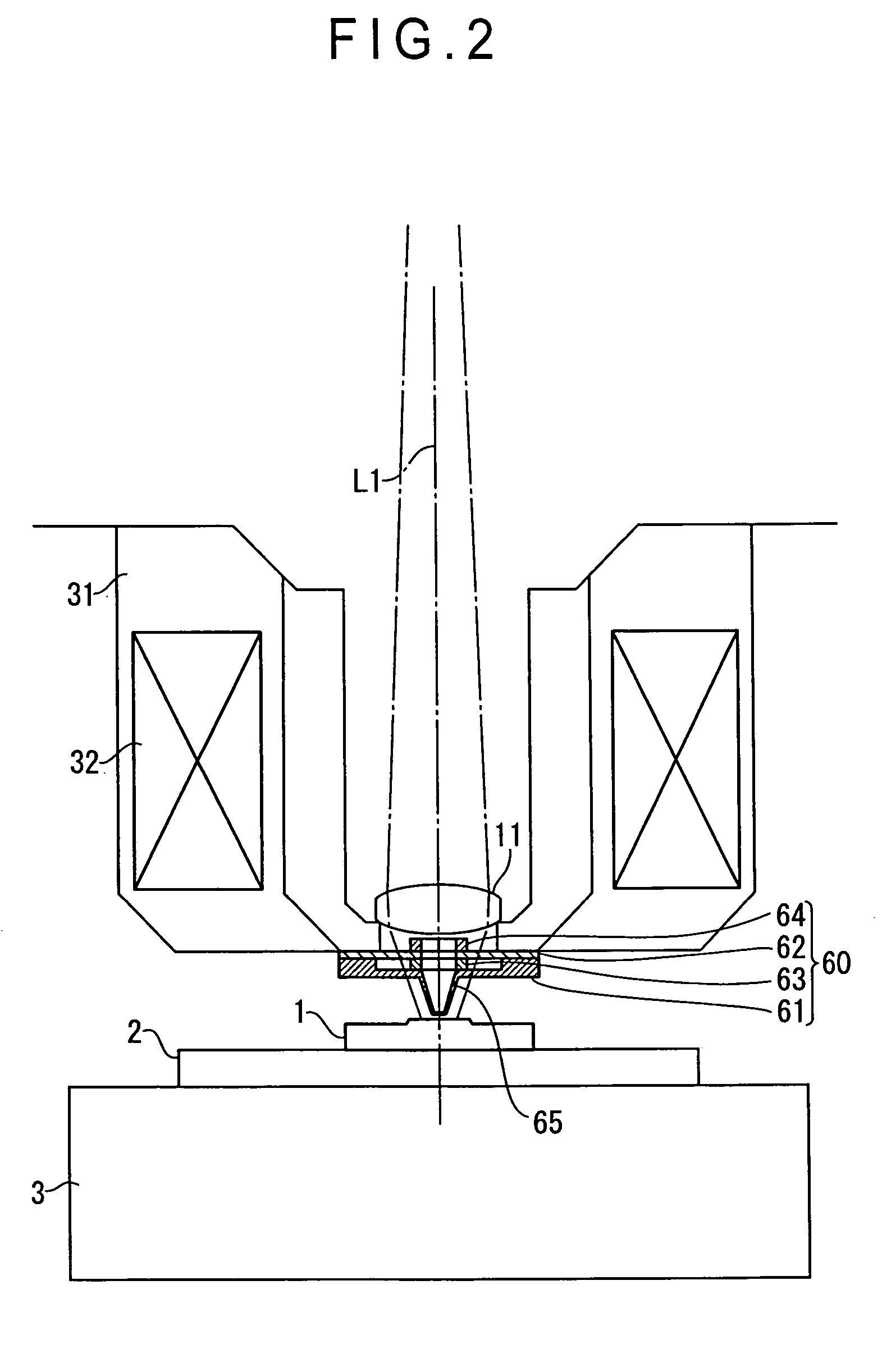
Method and apparatus for measurement of transmitter/receiver separation
InactiveUS20070100395A1Extend lifetime of battery packMeasurementElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringTransceiverProsthesis
A method and apparatus for determining a position of an external transceiver (24) relative to an implanted transceiver (23) comprising means (30) for measuring the strength of a magnetic field proximal to thc external transceiver (24) and means for determining a position of the external transceiver (24) relative to the implanted transceiver (23) from said measured magnetic field strength. Furthermore there is disclosed is a method and apparatus for determining a skin flap thickness of a recipient of a prosthesis including a transcutaneous link between the external transceiver (24) and the implanted transceiver (23). A skin-flap thickness meter is also provided.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
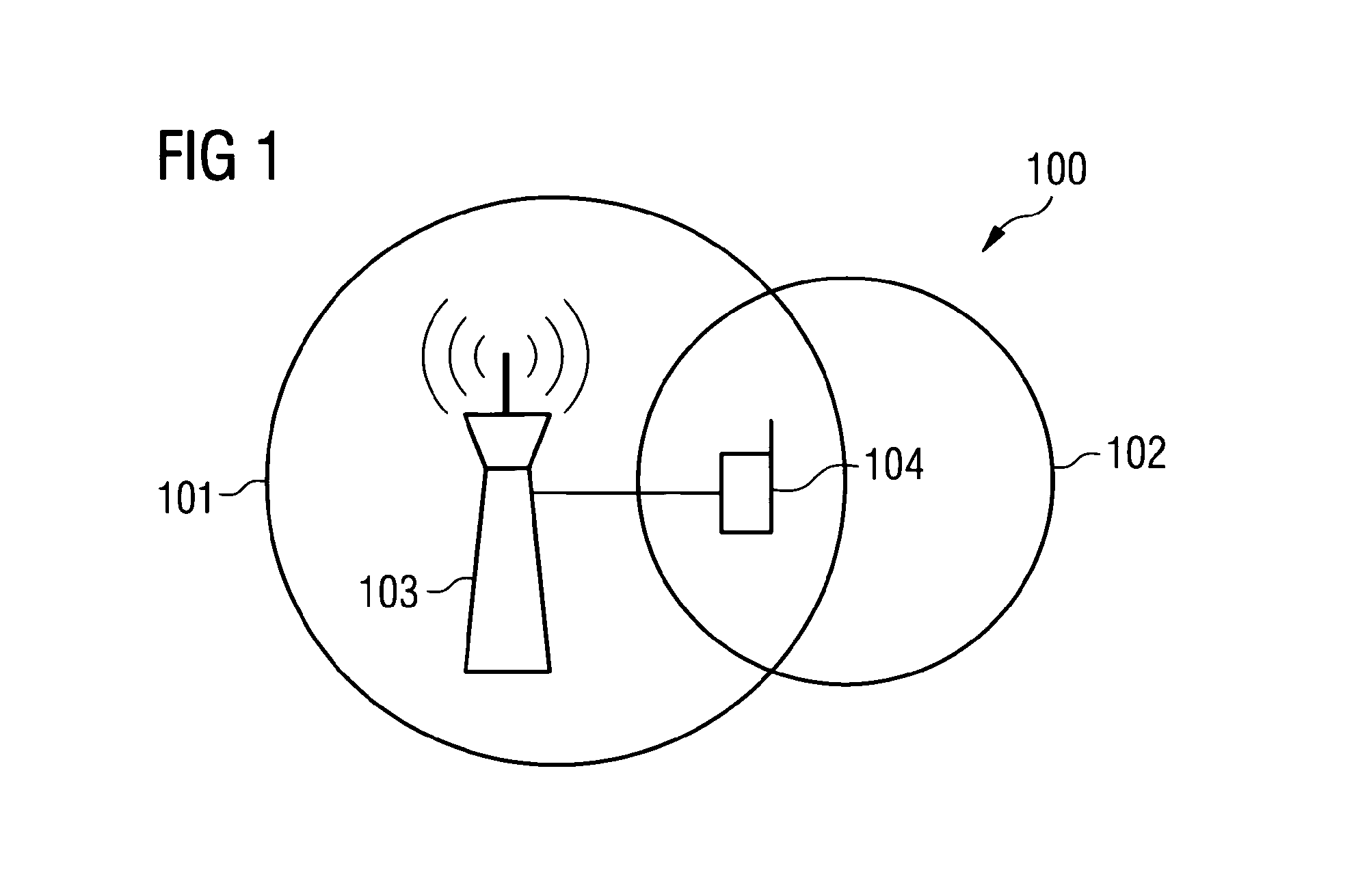
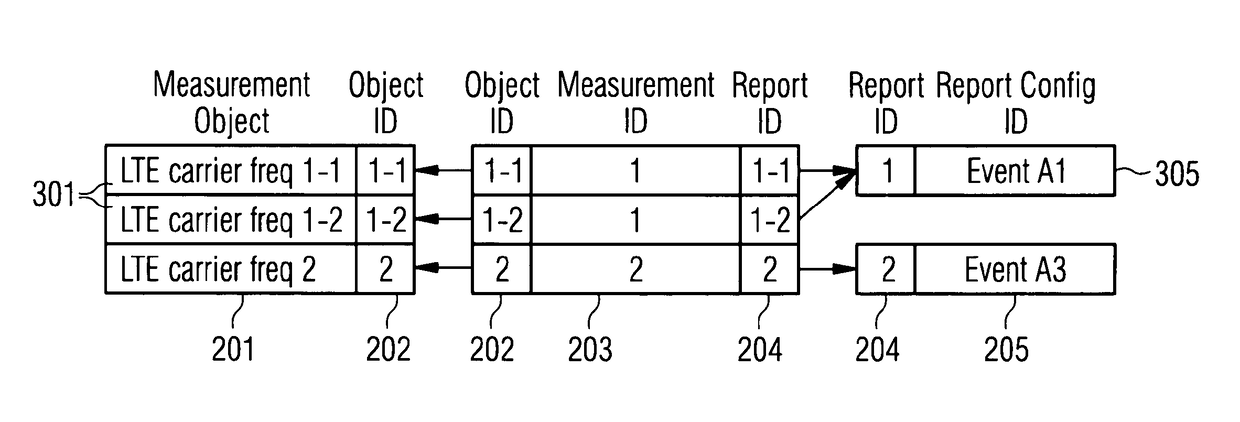
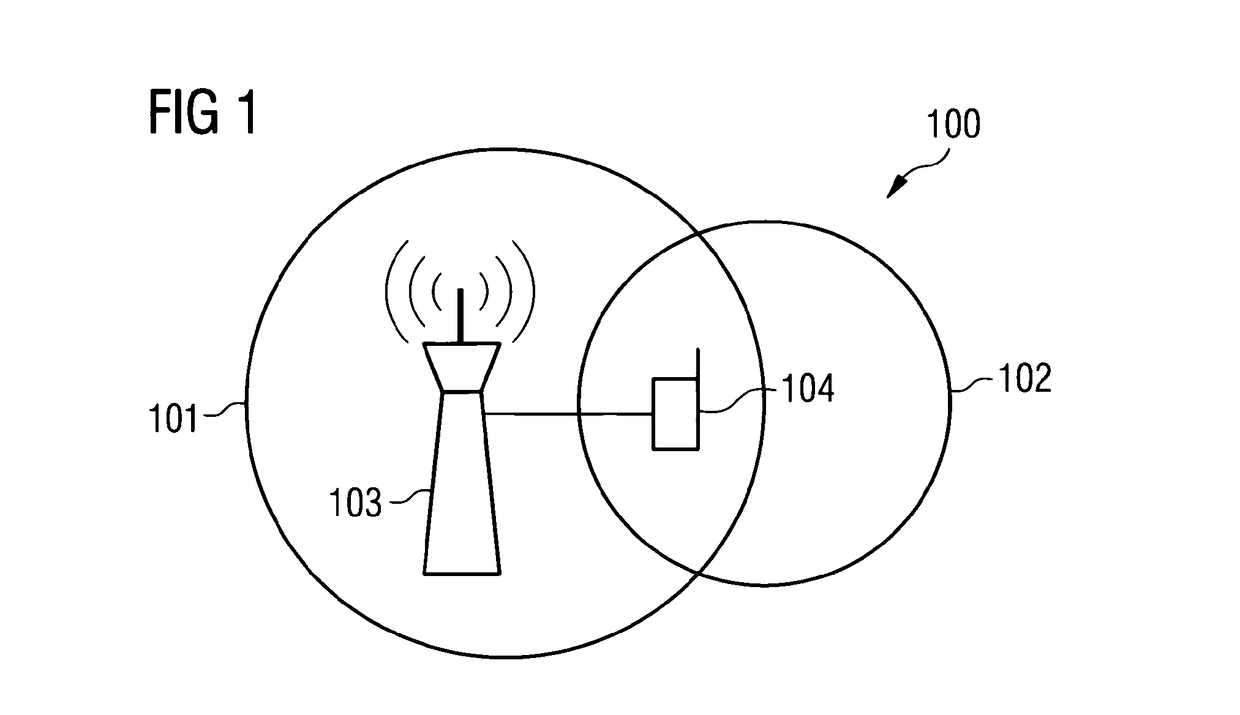
Controlling Radio Measurements of a User Equipment within a Cellular Network System
ActiveUS20150011219A1MeasurementImprove performanceNetwork topologiesTransmissionUser equipmentCellular network
It is described a method for controlling radio measurements of a user equipment within a cellular network system, wherein the user equipment is served by a cell of a first cell type characteristic, the cell being assigned to a base station, wherein the cellular network system includes the cell and at least one further cell of a second cell type characteristic. The method includes providing, by the base station, a radio measurement configuration to the user equipment, wherein the radio measurement configuration is indicative for parameters to be applied by the user equipment for radio measurements, the radio measurement configuration includes different parameters being assigned to different cell type characteristics, and controlling the radio measurements of the user equipment based on the provided radio measurement configuration.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
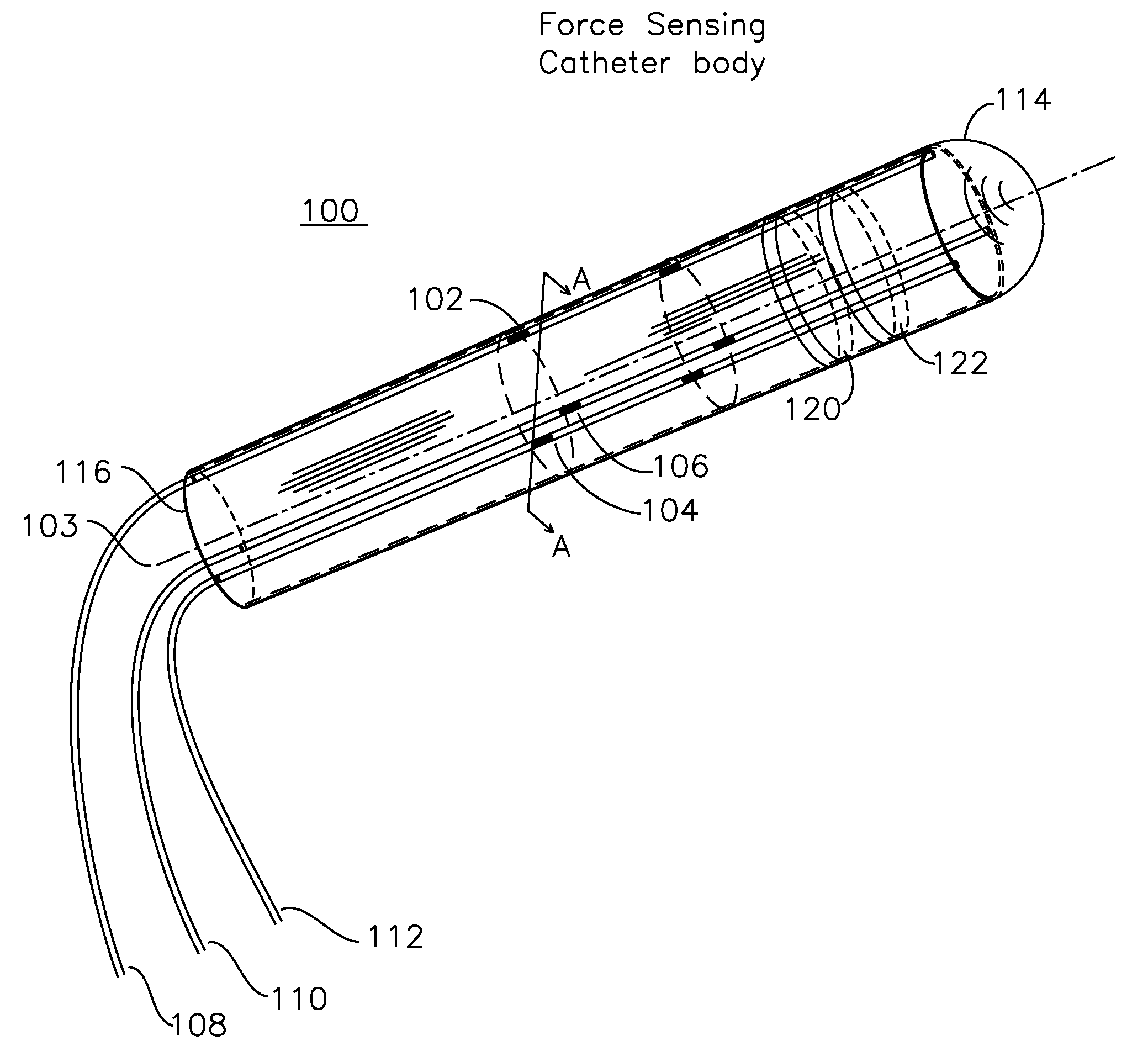
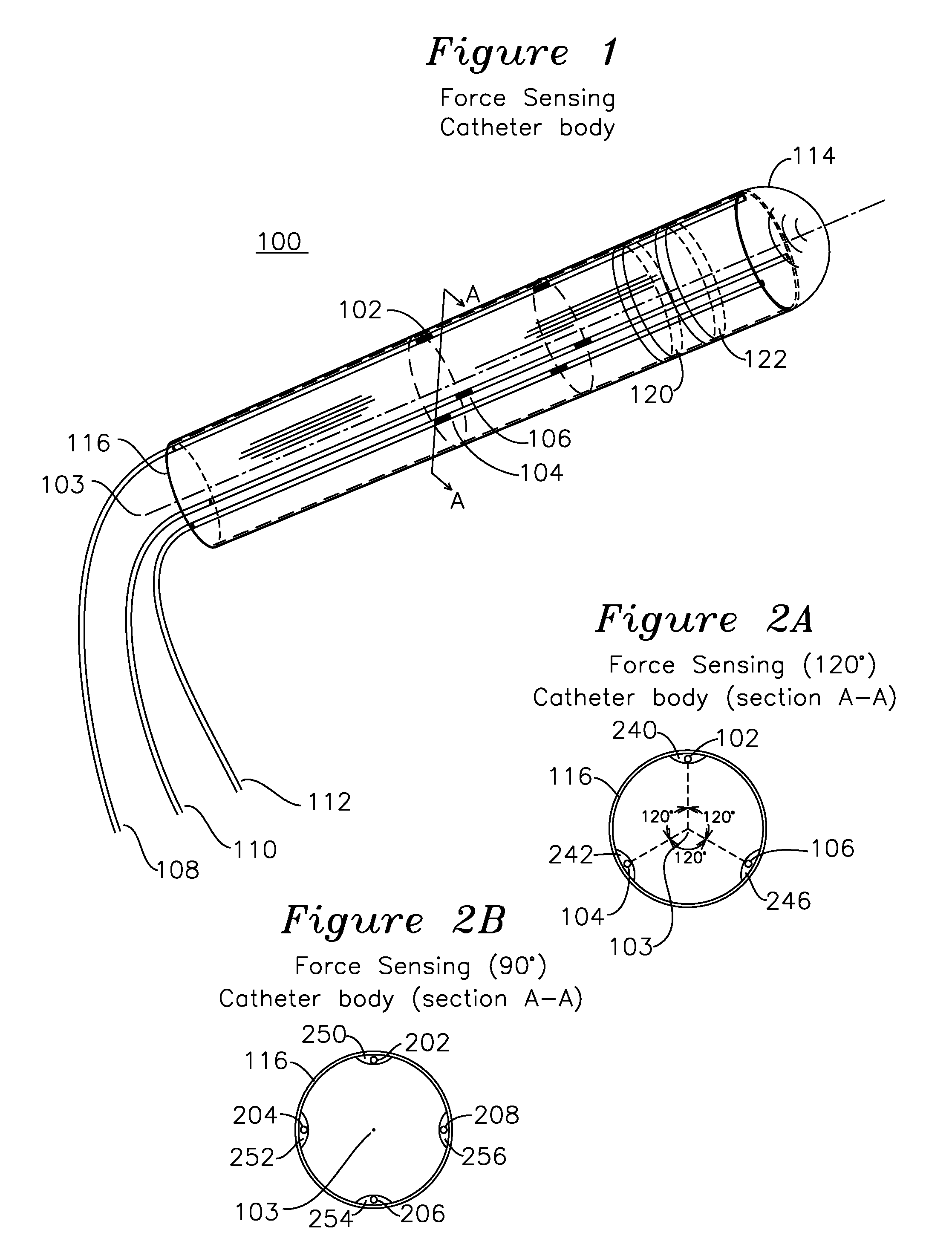
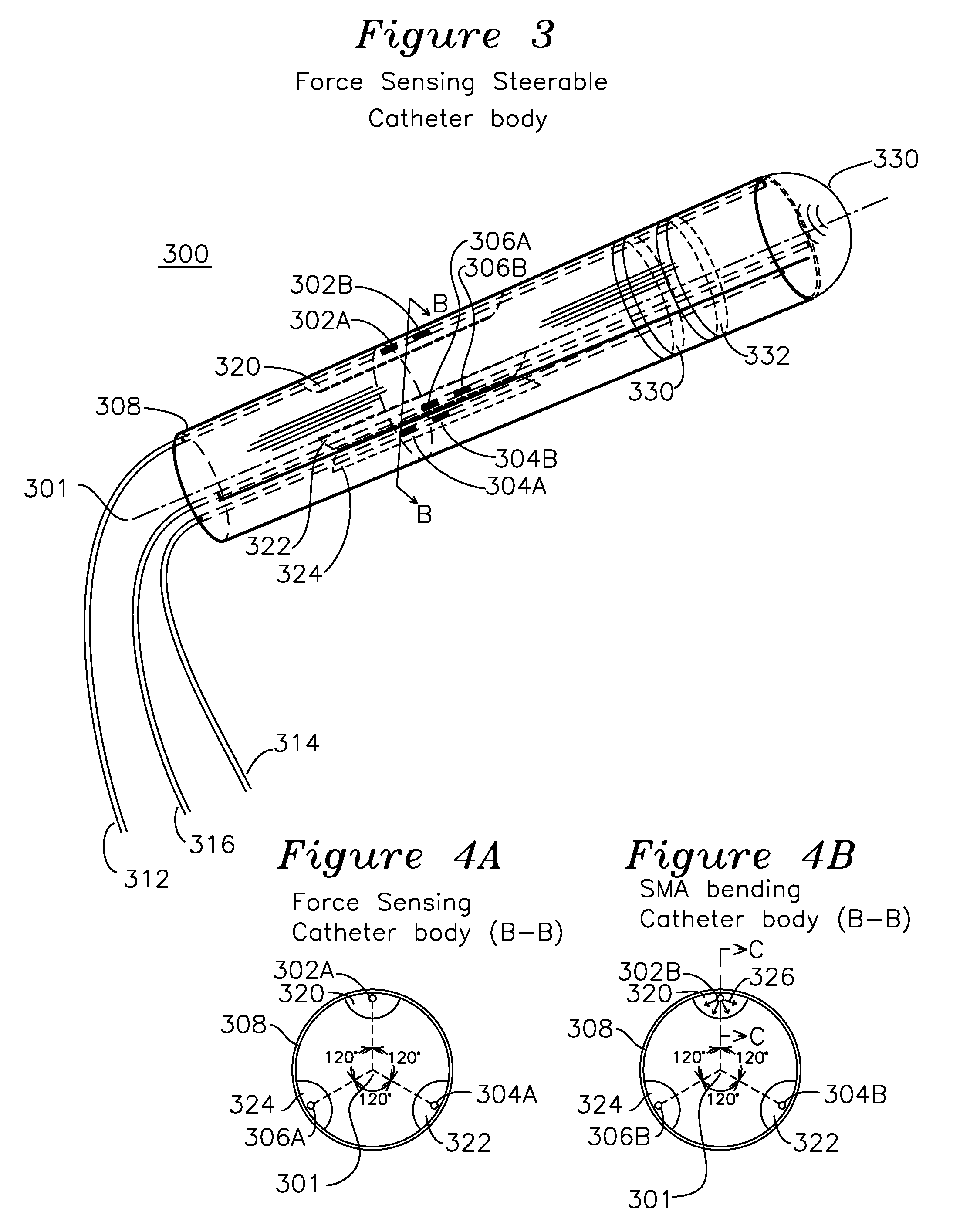
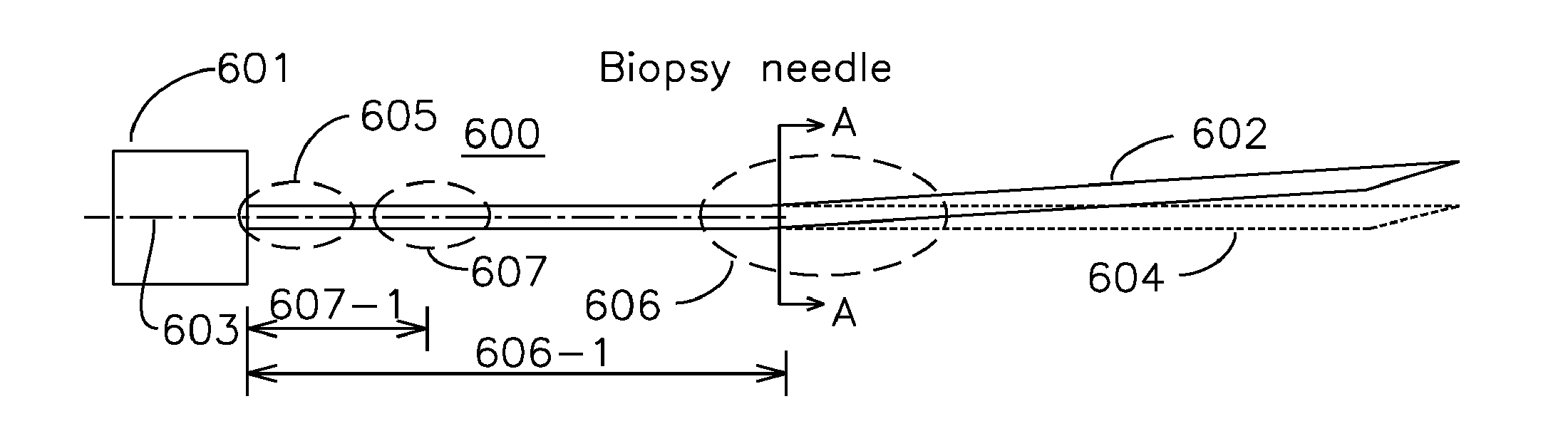
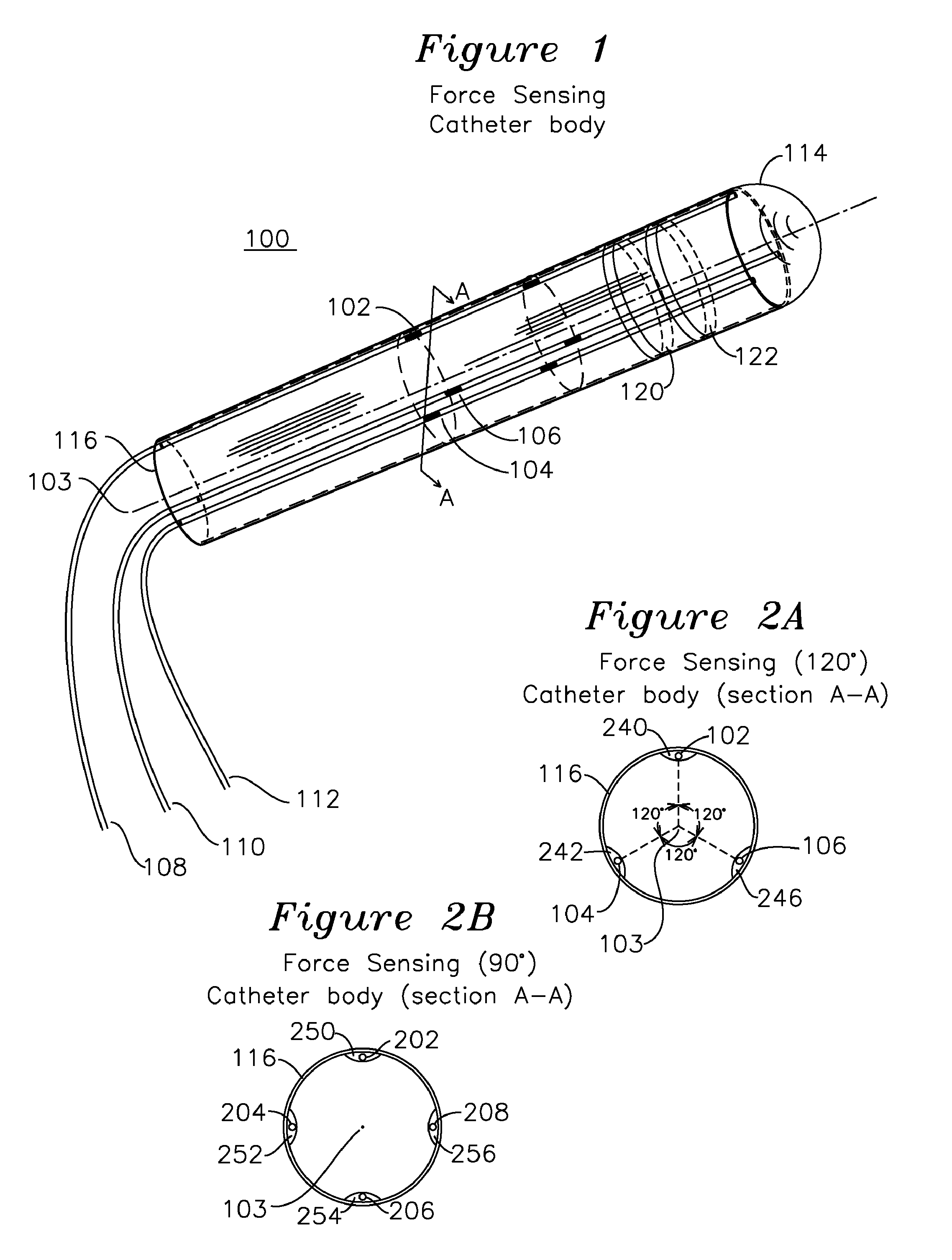
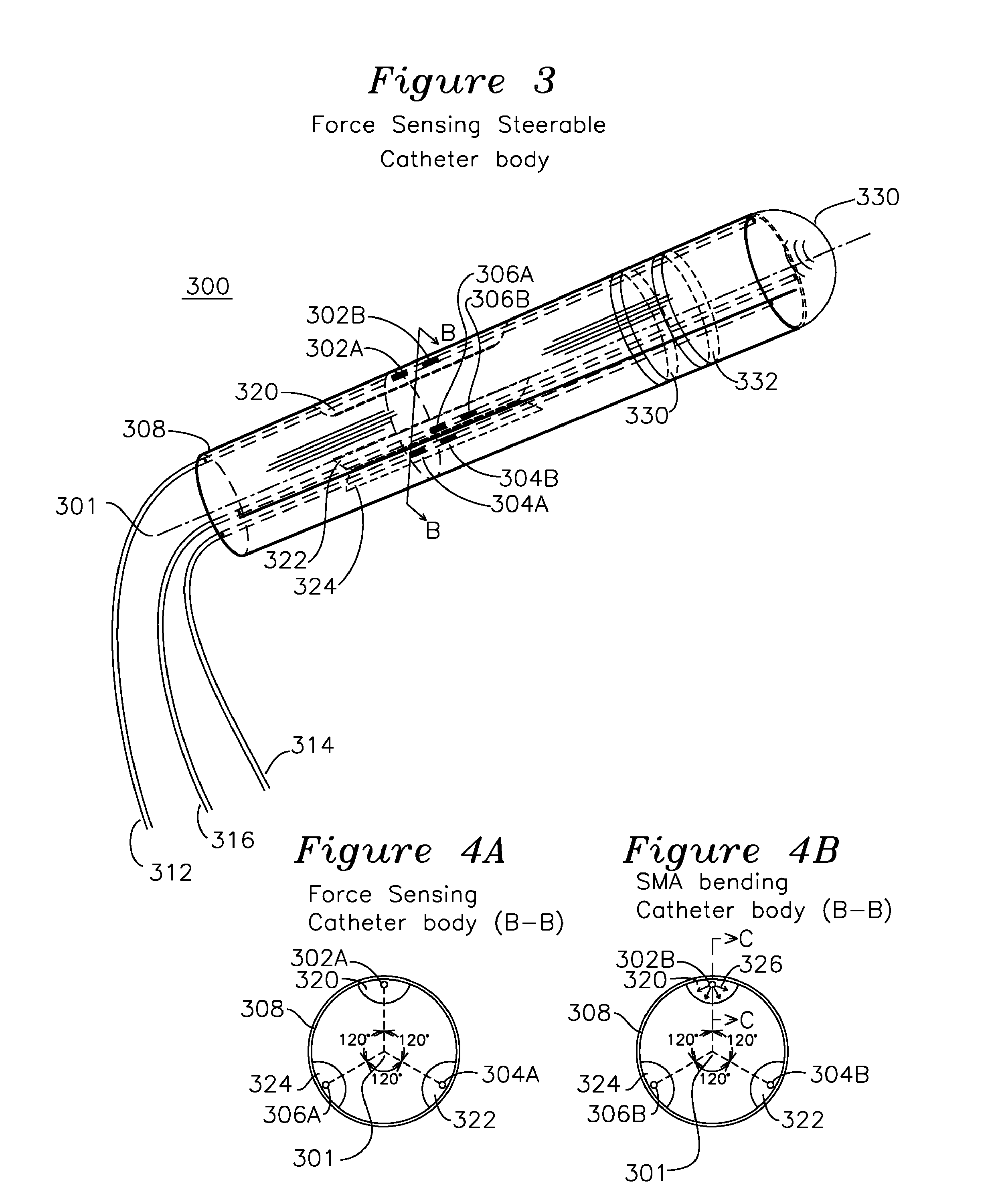
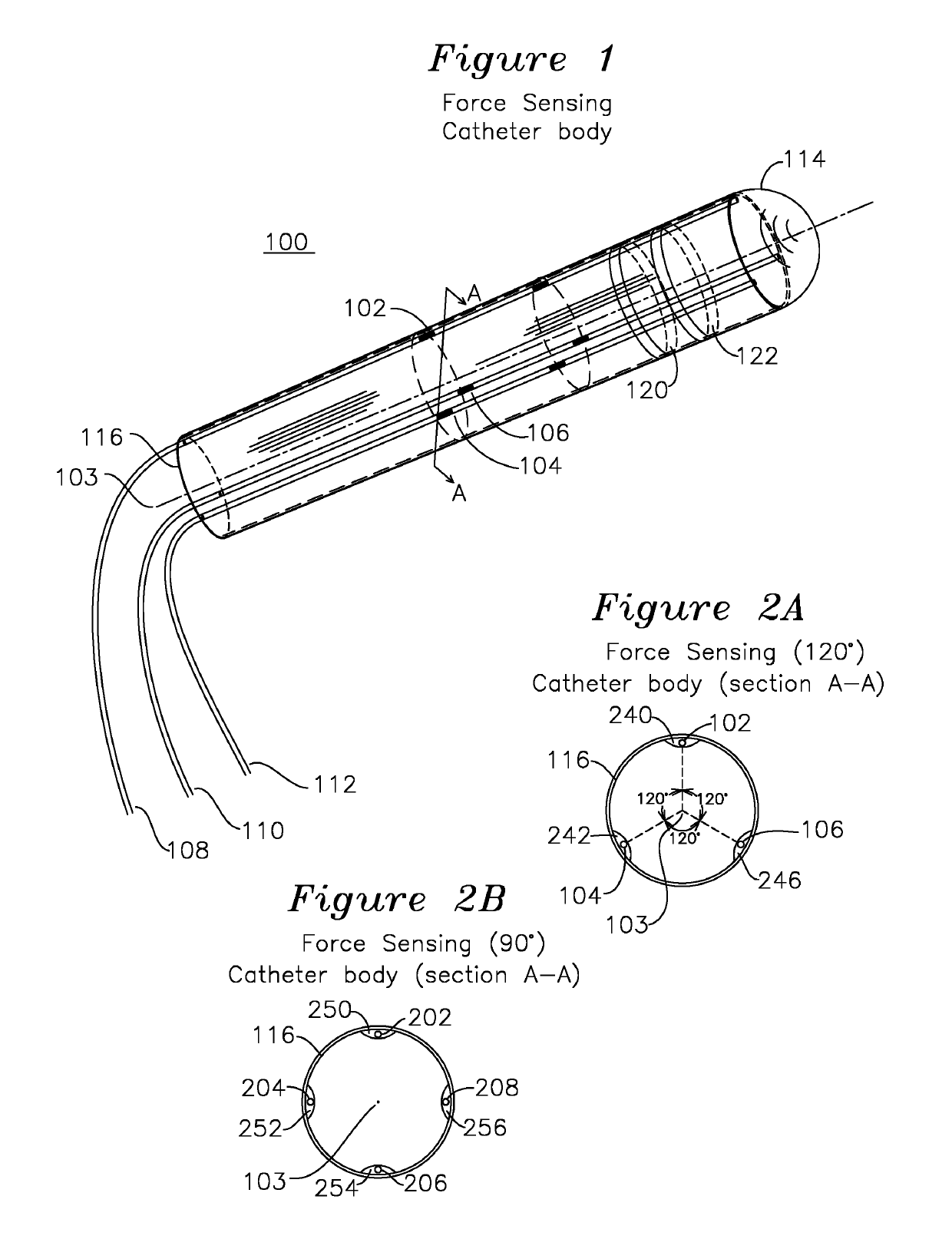
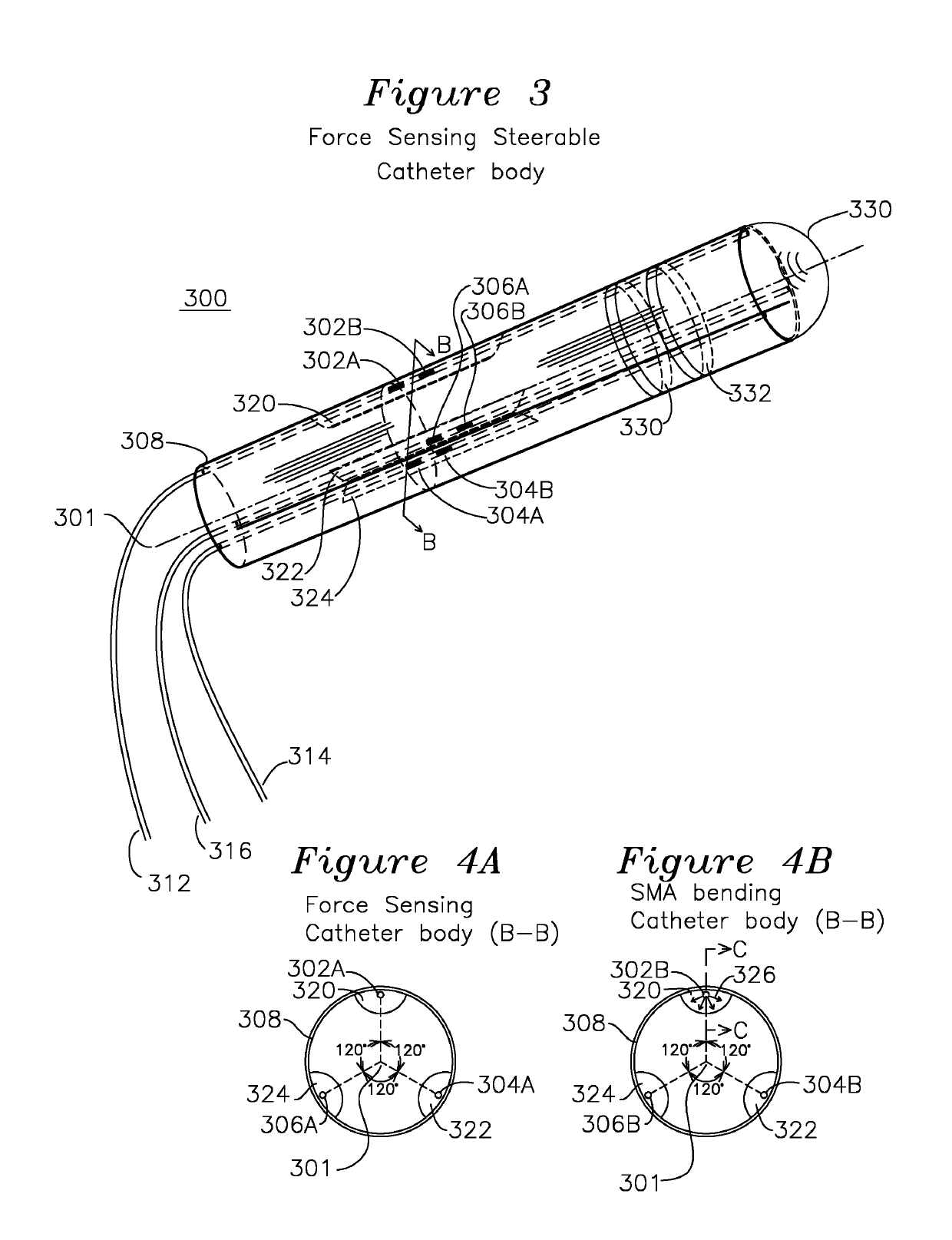
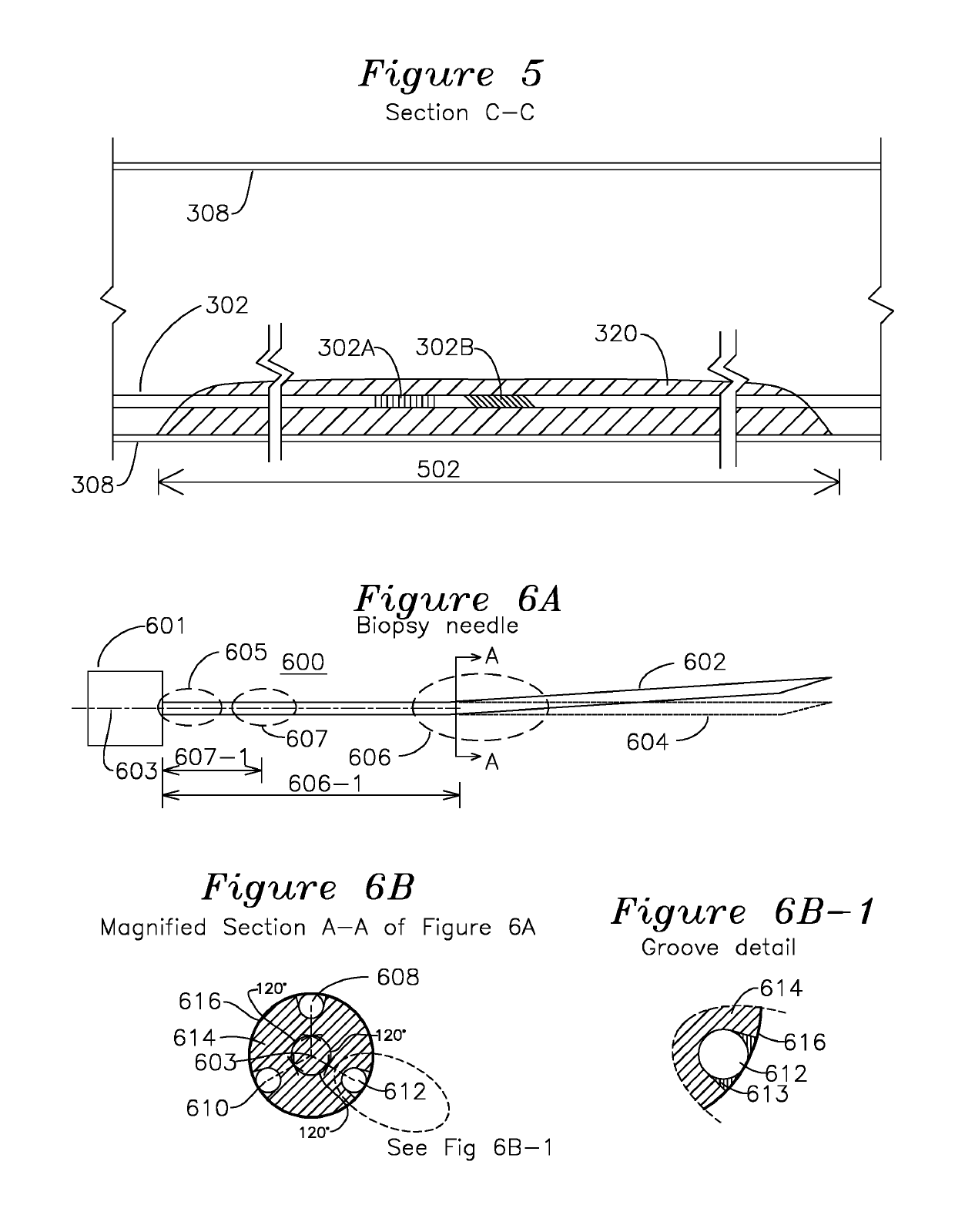
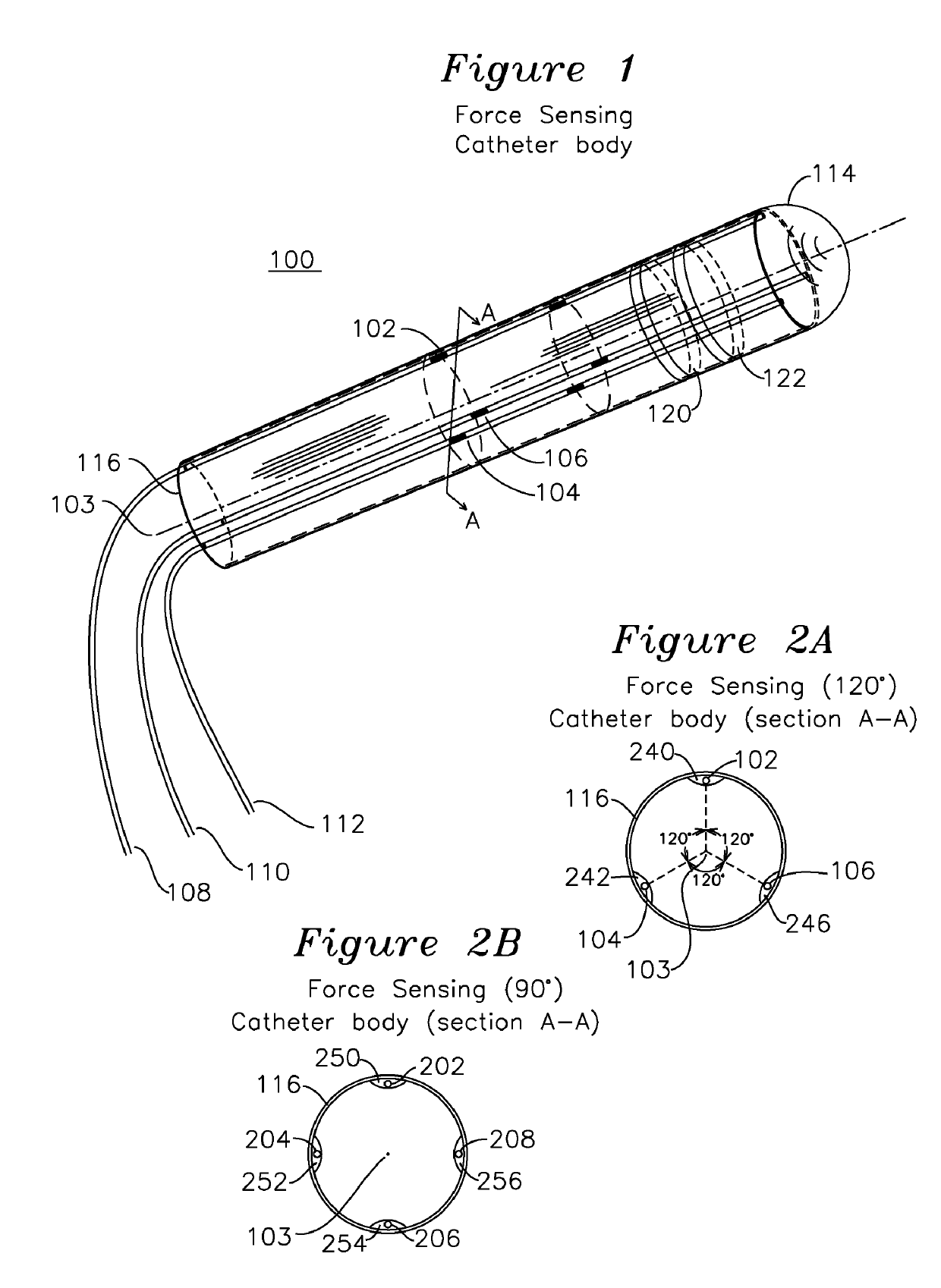
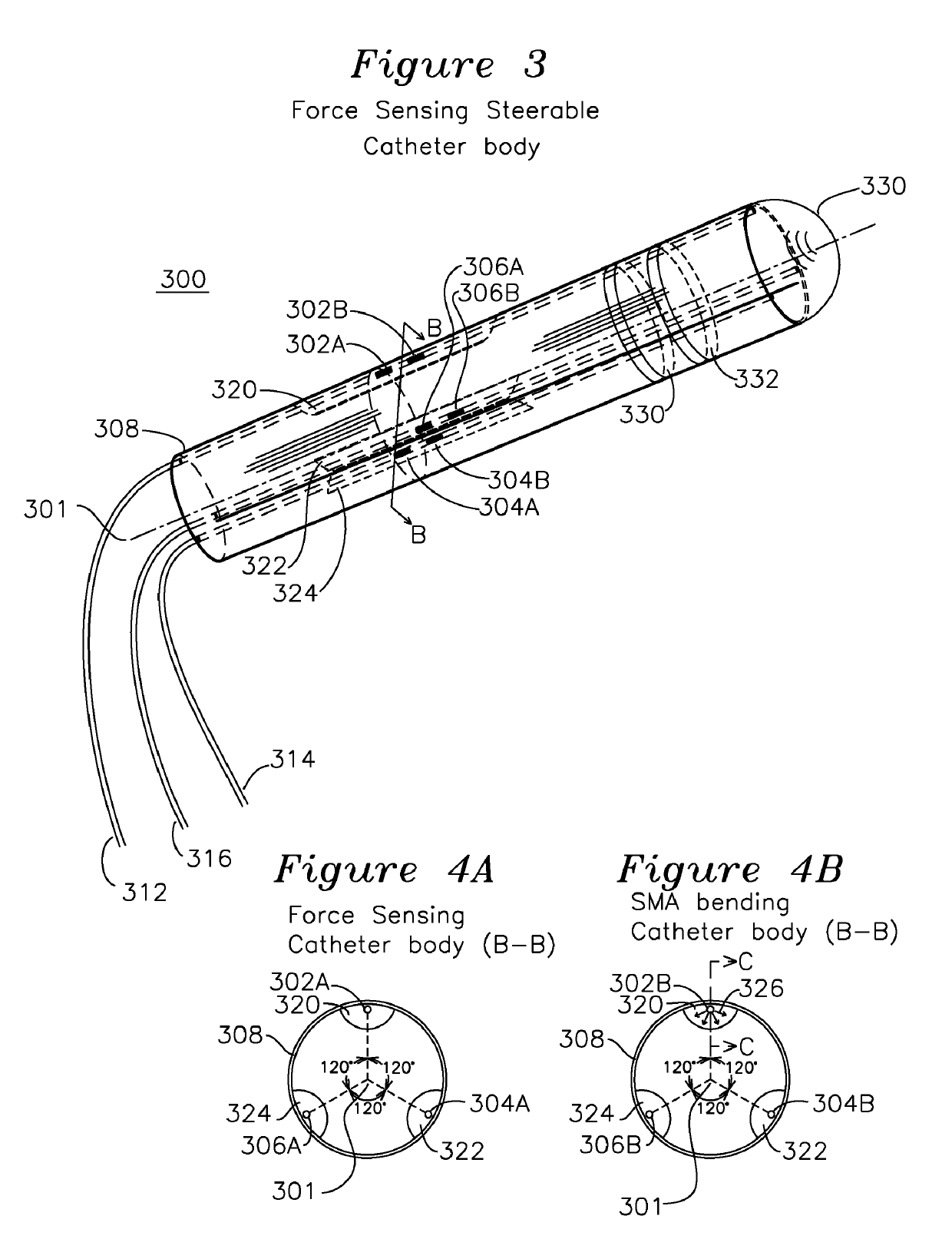
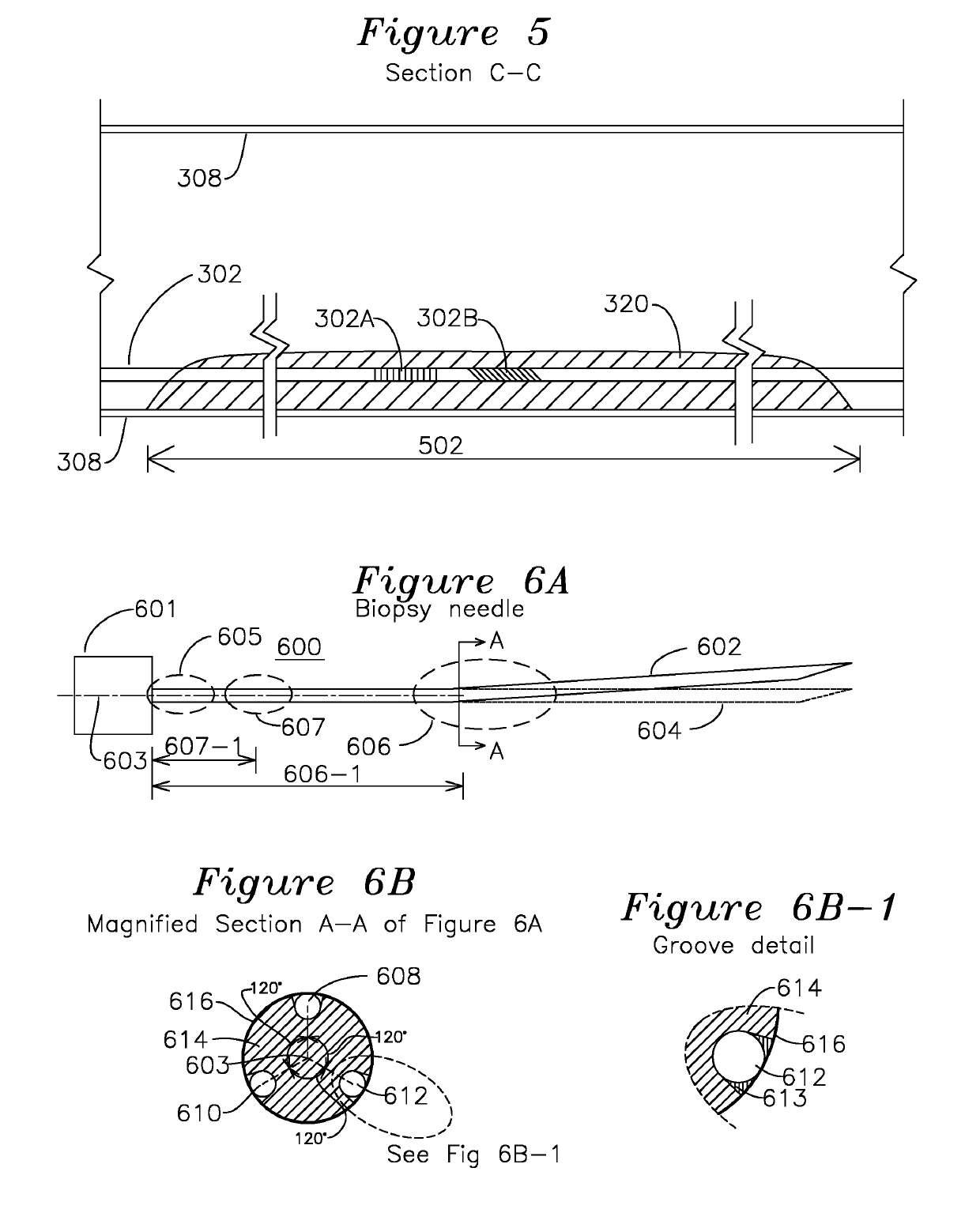
Steerable shape sensing biopsy needle and catheter
A biopsy needle has a central axis and includes one or more sensing regions, each sensing region formed by a plurality of sensing optical fibers located over a particular extent of said central axis and inside the outer shell of the needle. The sensing optical fibers are coupled to a wavelength interrogator. A steerable catheter has a central axis and outer shell, the outer shell coupled to a plurality of optical fibers in sensing regions and actuation regions, the sensing regions formed over particular extents of the central axis by bonding gratings to the inner surface of the outer shell, and the actuation regions formed by coupling optical energy into shape memory alloys bonded to the outer shell.
Owner:INTELLIGENT FIBER OPTIC SYST
Measurement of transmitter/receiver separation
InactiveUS8452412B2MeasurementSolve the large power consumptionElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringTransceiverProsthesis
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Measuring a hollow space by means of cylindrically symmetrical triangulation
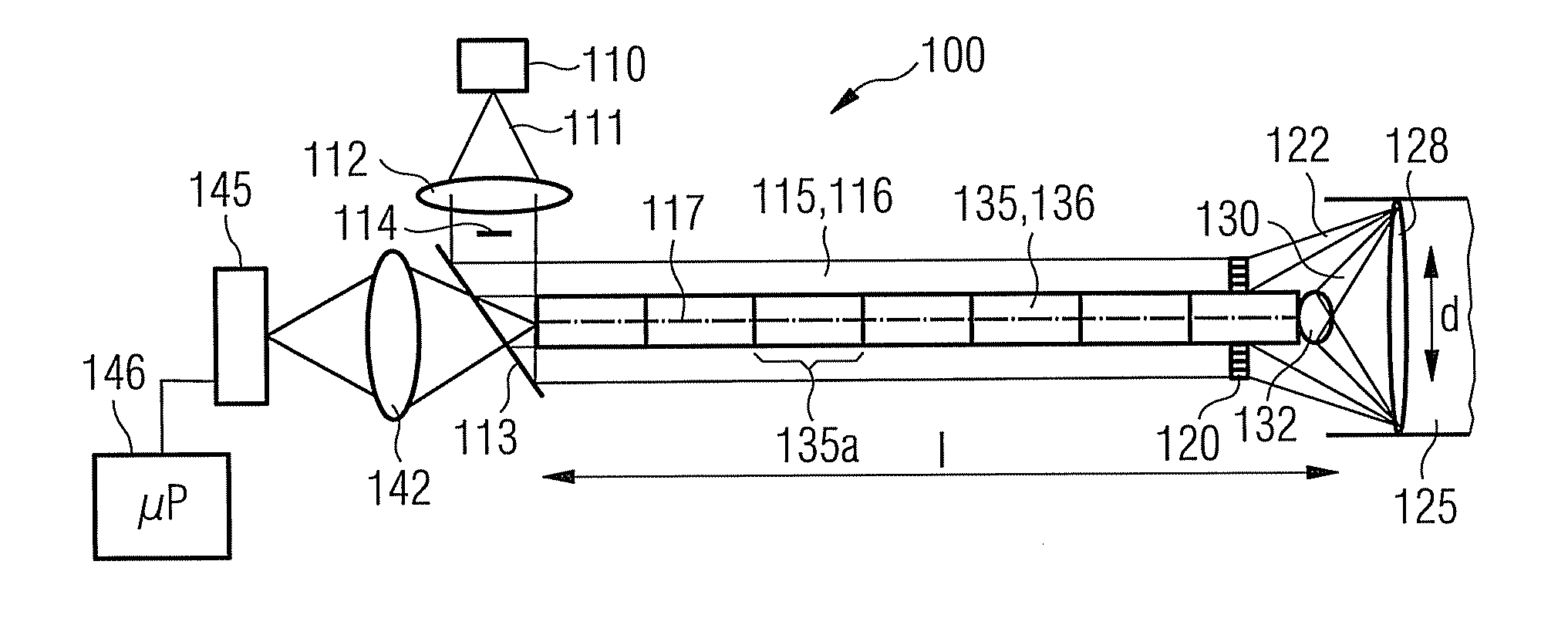
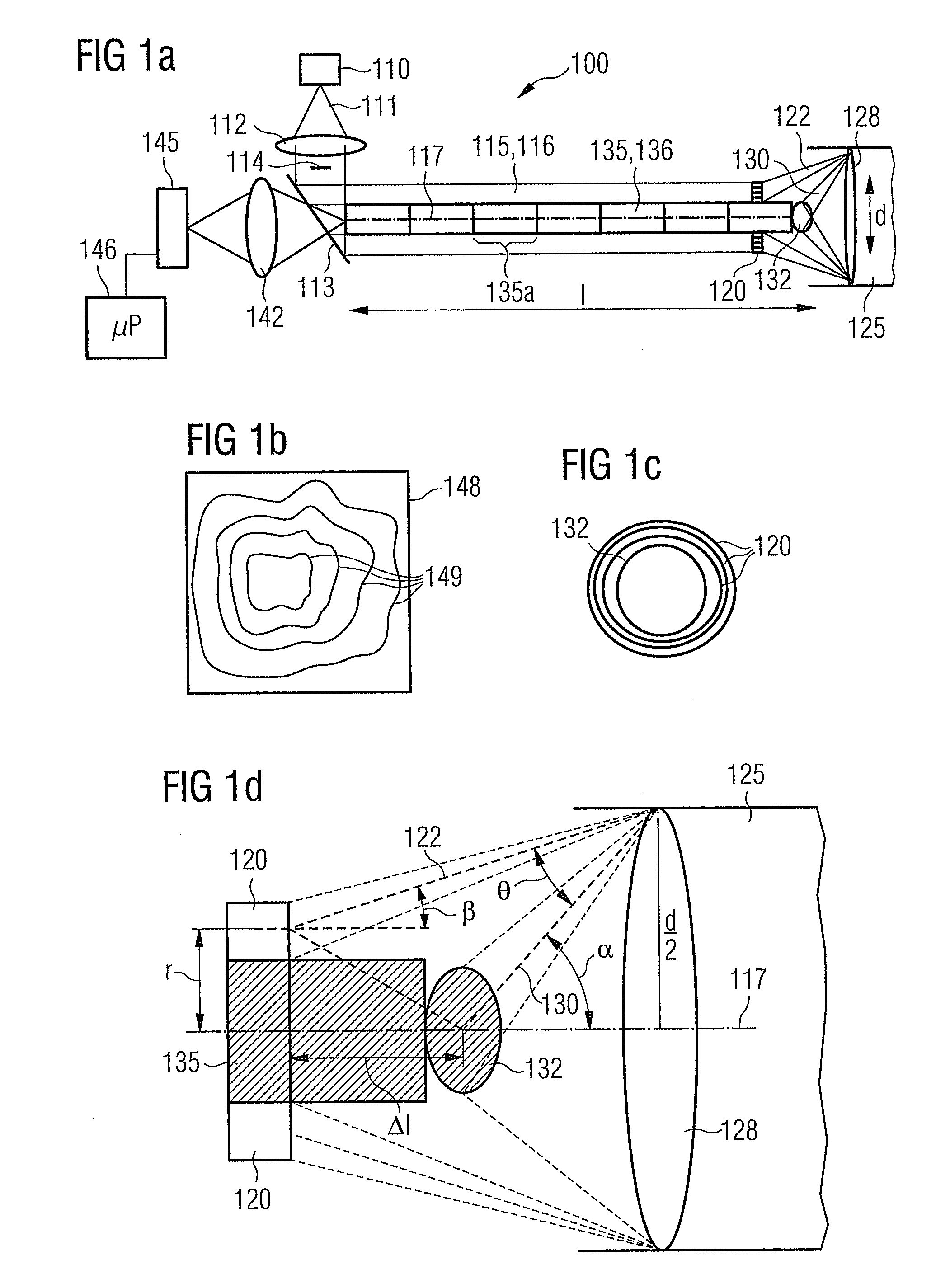
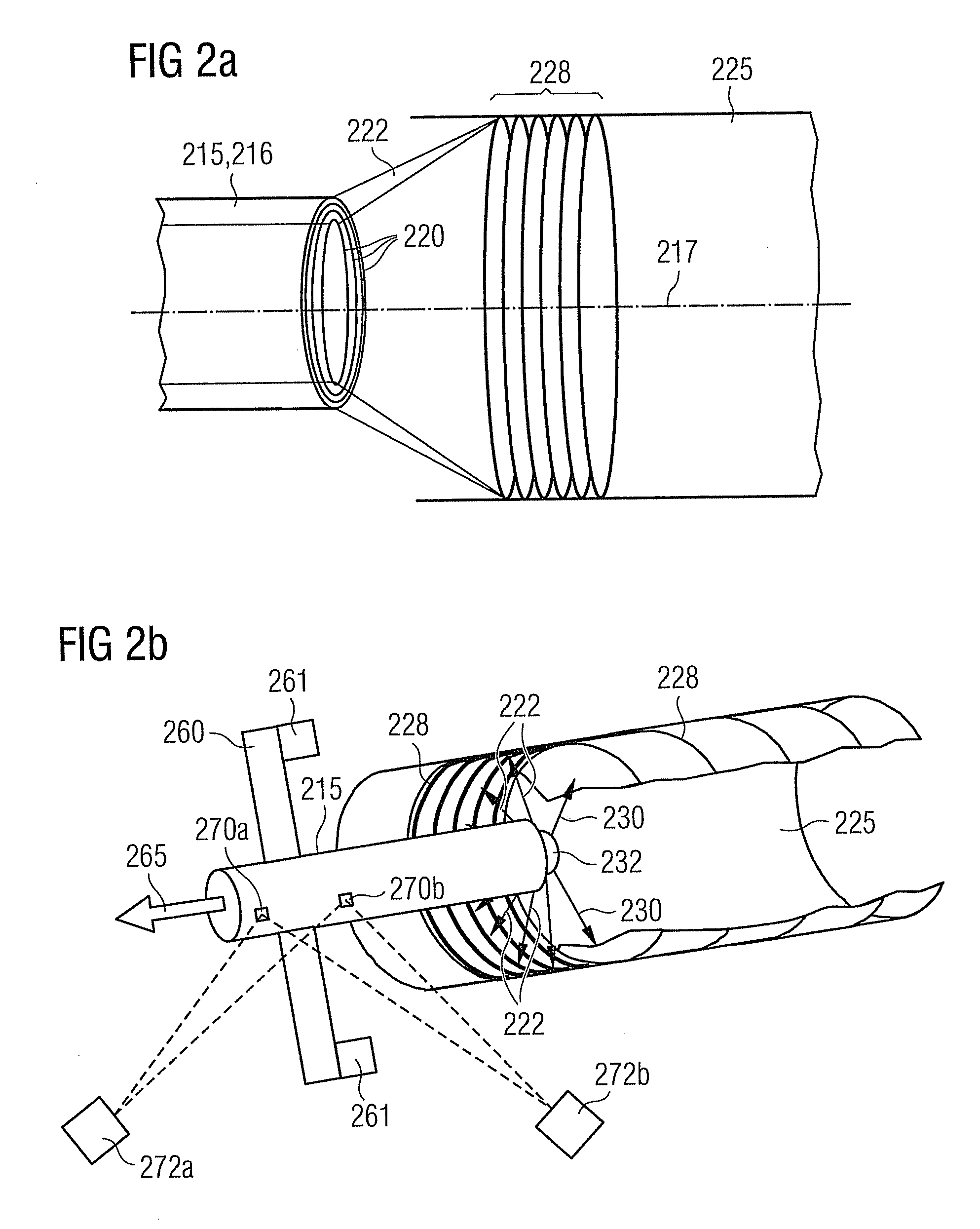
An optical measuring device for a three-dimensional measuring of a hollow space formed within an object is provided. The optical measurement device has a light source, which is provided for emitting illumination light along an illumination beam path, and an optical deflection element, which spatially structures the radiated illumination light such that on an inside wall an illumination line forms, which extends along the longitudinal axis. The shape of the line is dependant on the size and shape of the hollow space. Further, the optical measuring device has a camera, which detects the illumination line via an imaging beam path at a triangulation angle. Through an appropriate evaluation of the image of the detected shape and size of the illumination line by the camera, the three-dimensional shape of the hollow space is determined.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Steerable Shape Sensing Biopsy Needle
ActiveUS20150190123A1MeasurementSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsGratingShape-memory alloy
A biopsy needle has a central axis and includes one or more sensing regions, each sensing region formed by a plurality of sensing optical fibers located over a particular extent of said central axis and inside the outer shell of the needle. The sensing optical fibers are coupled to a wavelength interrogator. A steerable catheter has a central axis and outer shell, the outer shell coupled to a plurality of optical fibers in sensing regions and actuation regions, the sensing regions formed over particular extents of the central axis by bonding gratings to the inner surface of the outer shell, and the actuation regions formed by coupling optical energy into shape memory alloys bonded to the outer shell.
Owner:INTELLIGENT FIBER OPTIC SYST
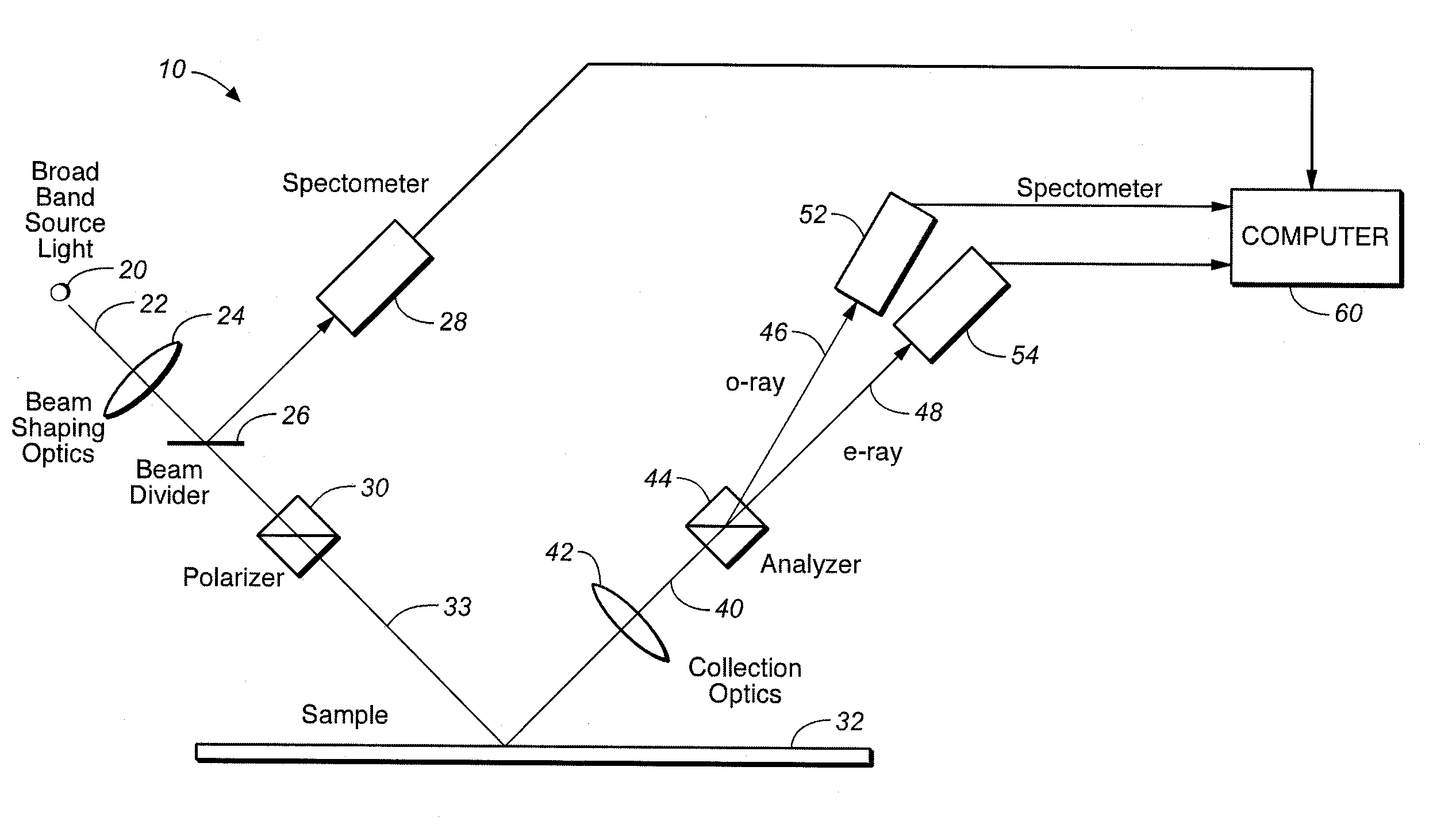
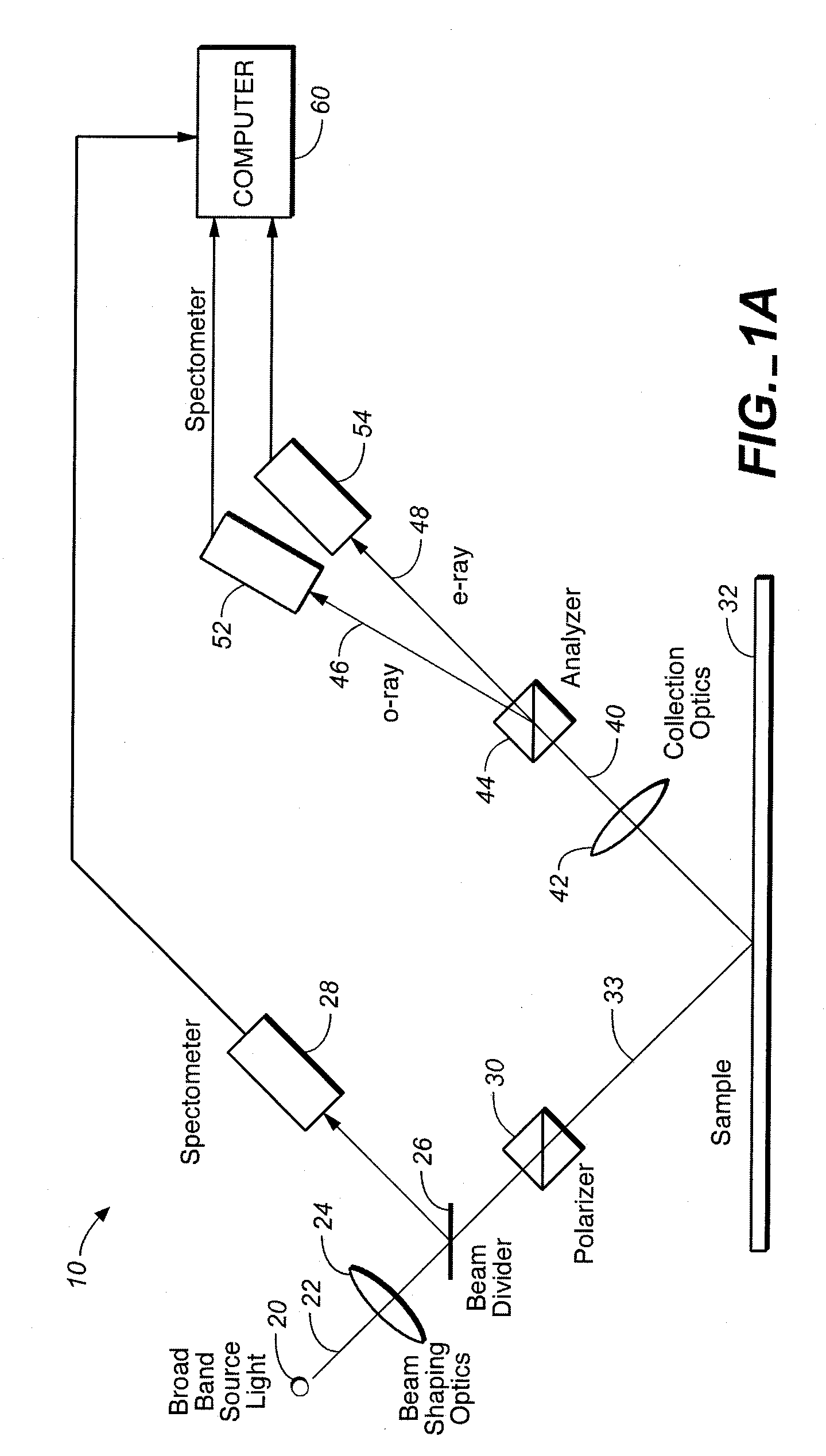
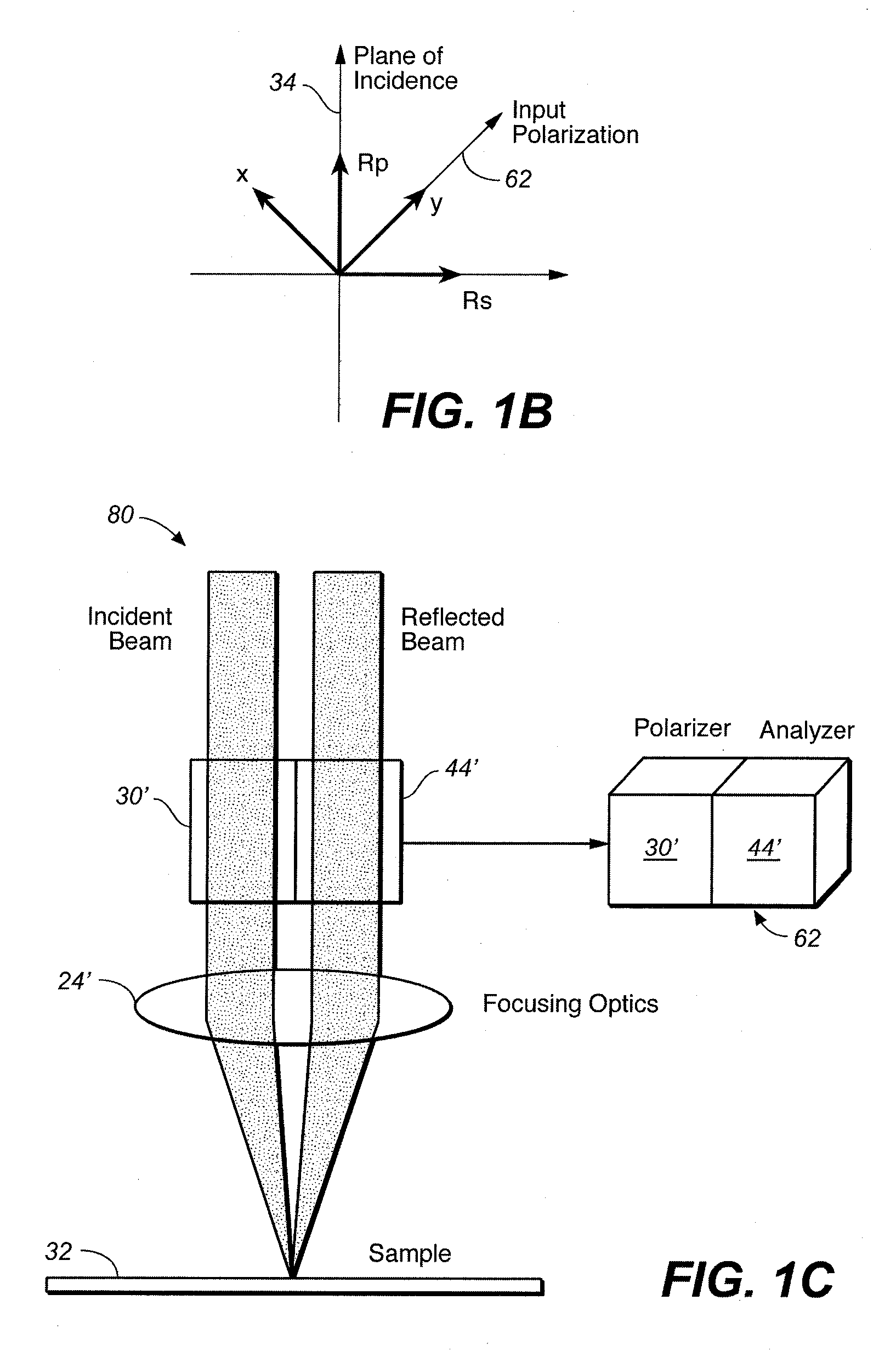
System for Measuring Periodic Structures
InactiveUS20060290931A1Easy constructionMeasurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesUsing optical meansMeasuring instrumentElectromagnetic radiation
A periodic structure is illuminated by polychromatic electromagnetic radiation. Radiation from the structure is collected and divided into two rays having different polarization states. The two rays are detected from which one or more parameters of the periodic structure may be derived. In another embodiment, when the periodic structure is illuminated by a polychromatic electromagnetic radiation, the collected radiation from the structure is passed through a polarization element having a polarization plane. The element and the polychromatic beam are controlled so that the polarization plane of the element are at two or more different orientations with respect to the plane of incidence of the polychromatic beam. Radiation that has passed through the element is detected when the plane of polarization is at the two or more positions so that one or more parameters of the periodic structure may be derived from the detected signals. At least one of the orientations of the plane of polarization is substantially stationary when the detection takes place. To have as small a footprint as possible, one employs an optical device that includes a first element directing a polychromatic beam of electromagnetic radiation to the structure and a second optical element collecting radiation from the structure where the two elements form an integral unit or are attached together to form an integrated unit. To reduce the footprint, the measurement instrument and the wafer are both moved. In one embodiment, both the apparatus and the wafer undergo translational motion transverse to each other. In a different arrangement, one of the two motions is translational and the other is rotational. Any one of the above-described embodiments may be included in an integrated processing and detection apparatus which also includes a processing system processing the sample, where the processing system is responsive to the output of any one of the above embodiments for adjusting a processing parameter.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Methods And Apparatus For Assessing Vascular Health
ActiveUS20160166157A1Minimal discomfortGood reproducibilityElectrocardiographyCatheterThermal monitoringArterial occlusions
A method for digital thermal monitoring assessment of vascular function comprising a temporary arterial occlusion using a pneumatic cuff positioned on a subject's upper limb, monitoring skin temperature at the fingertip of the occluded limb for a period of time before, during, and after the occlusion, calculating a Zero Reactivity Curve based on variables including start temperature, room temperature, and the slope of temperature decline during the occlusion, and assessing vascular function based on comparing the Zero Reactivity Curve and the observed temperature rebound after the occlusion is removed. A vascular reactivity monitoring apparatus for measuring skin surface temperature comprising an inflatable cuff for placement around a subject's limb, a digital thermal measuring device and photoplethysmography measuring device for placement on a finger of the subject's limb wearing the cuff and a second digital monitoring device and photoplethysmography measuring device for placement on a finger of the subject's contralateral limb.
Owner:AMERICAN HEART TECH LLC
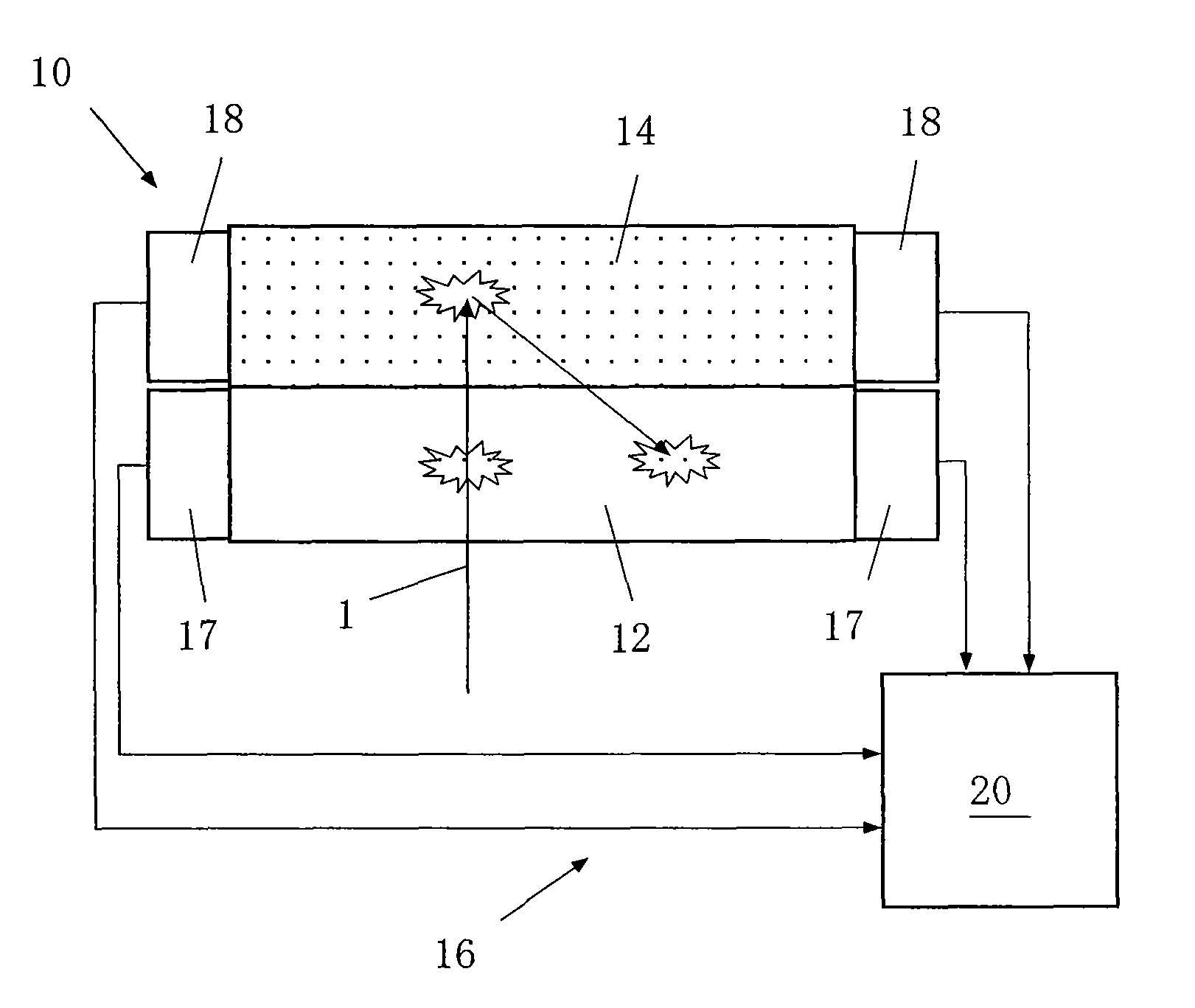
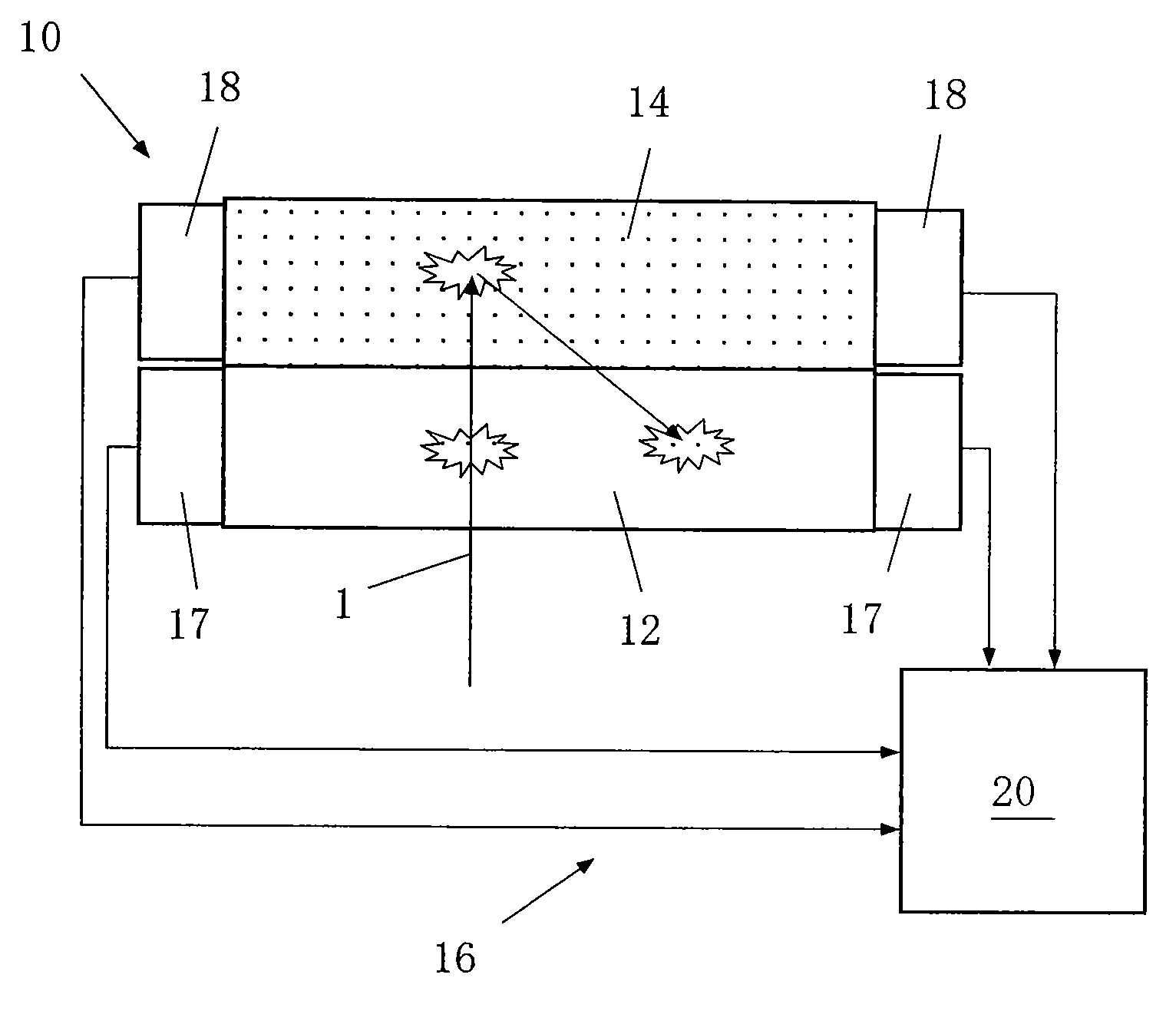
Beta ray detector and beta ray reconstruction method
InactiveUS8384034B2Wide energy regionImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementAbsorption ratioHigh rate
A beta ray detector and a beta ray reconstruction method are capable of achieving consistently high detection efficiency of beta rays in a wider energy region compared to that of a conventional beta ray detector while enhancing energy resolution. The beta ray detector comprises an absorber scintillator disposed to face a subject emitting beta rays and that is made from an absorptive substance exhibiting a high permeability and a high rate of absorption with respect to beta rays, a backscattering scintillator disposed on the backside of the absorber scintillator and that is made from a backscattering substance exhibiting a low permeability and a high rate of backscattering with respect to beta rays, and an energy detector that combines the amounts of beta ray energy absorption simultaneously measured by the two types of scintillators to reconstruct the energy and detection position of the beta rays emitted from the subject.
Owner:NAT INST OF RADIOLOGICAL SCI
Beta ray detector and beta ray reconstruction method
InactiveUS20100308225A1Weaken energyImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementAbsorption ratioHigh rate
Provided are a beta ray detector and a beta ray reconstruction method capable of achieving consistently high detection efficiency of beta rays in a wider energy region compared to that of a conventional beta ray detector while enhancing energy resolution. The beta ray detector comprises an absorber scintillator 12 which is disposed to face a subject emitting beta rays and is made from an absorptive substance exhibiting a high permeability and a high rate of absorption with respect to beta rays, a backscattering scintillator 14 which is disposed on the backside of the absorber scintillator and is made from a backscattering substance exhibiting a low permeability and a high rate of backscattering with respect to beta rays, and an energy detector 16 which combines the amounts of beta ray energy absorption simultaneously measured by the two types of scintillators to reconstruct the energy and the detection position of the beta rays emitted from the subject.
Owner:NAT INST OF RADIOLOGICAL SCI
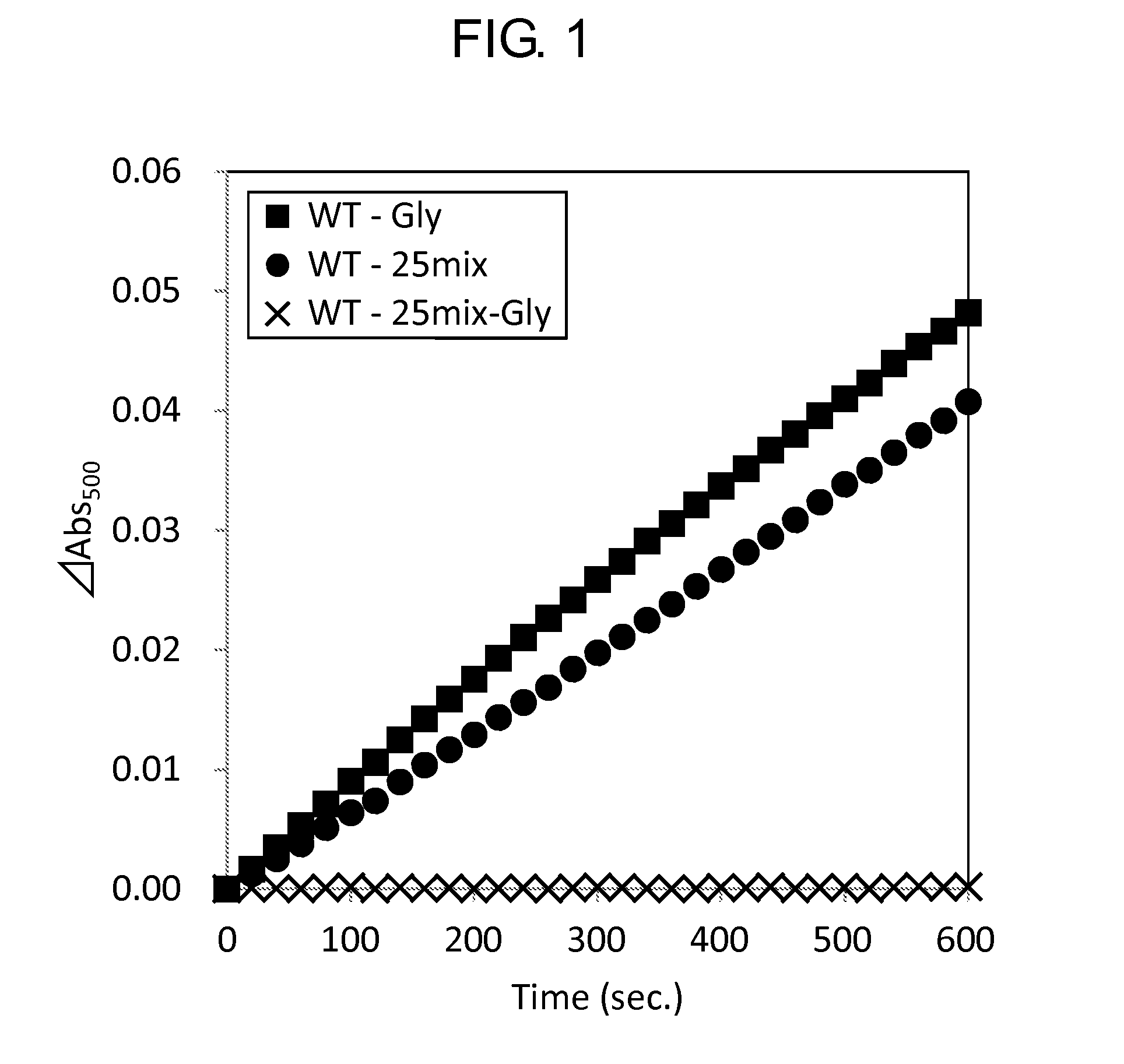
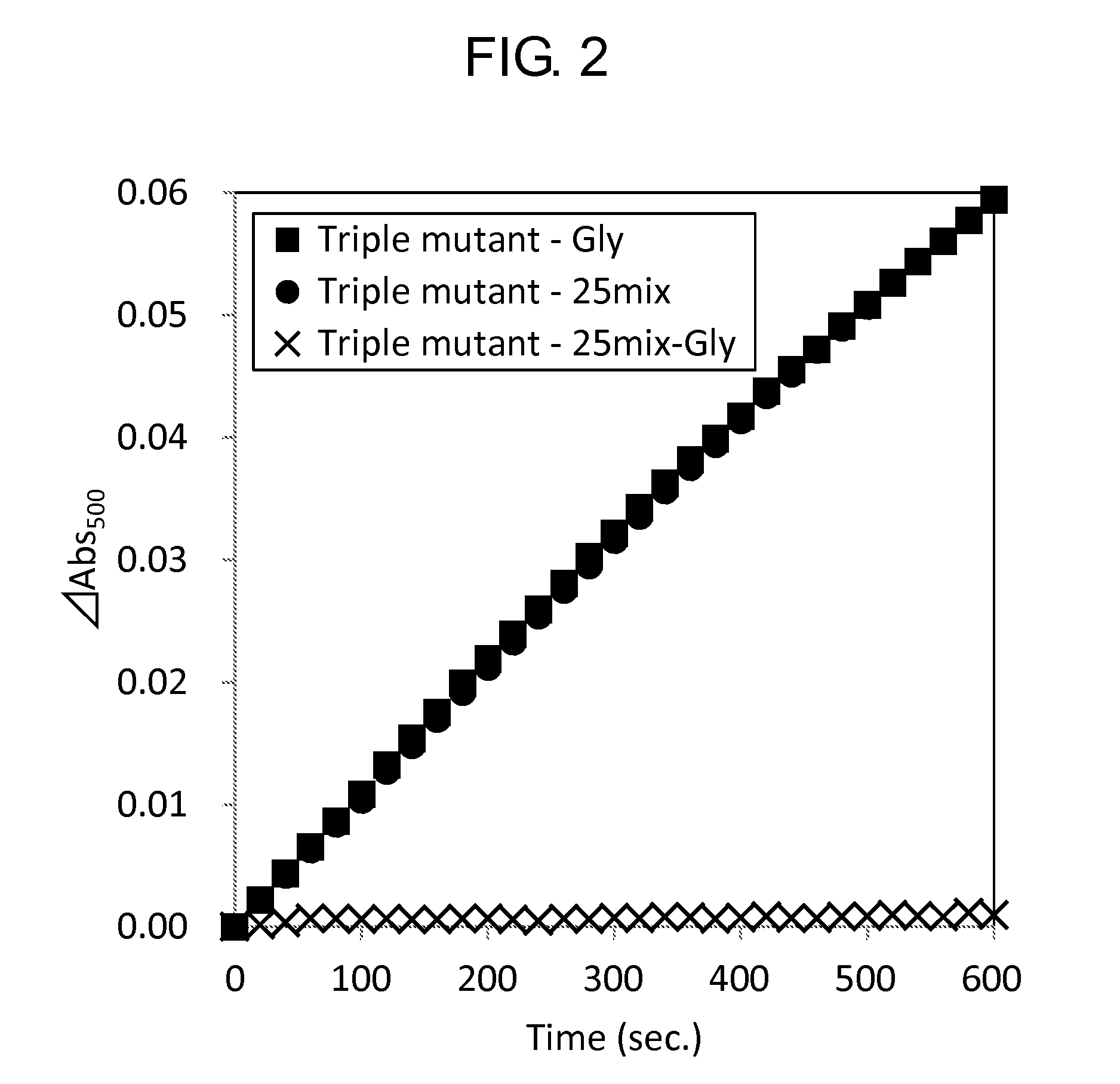
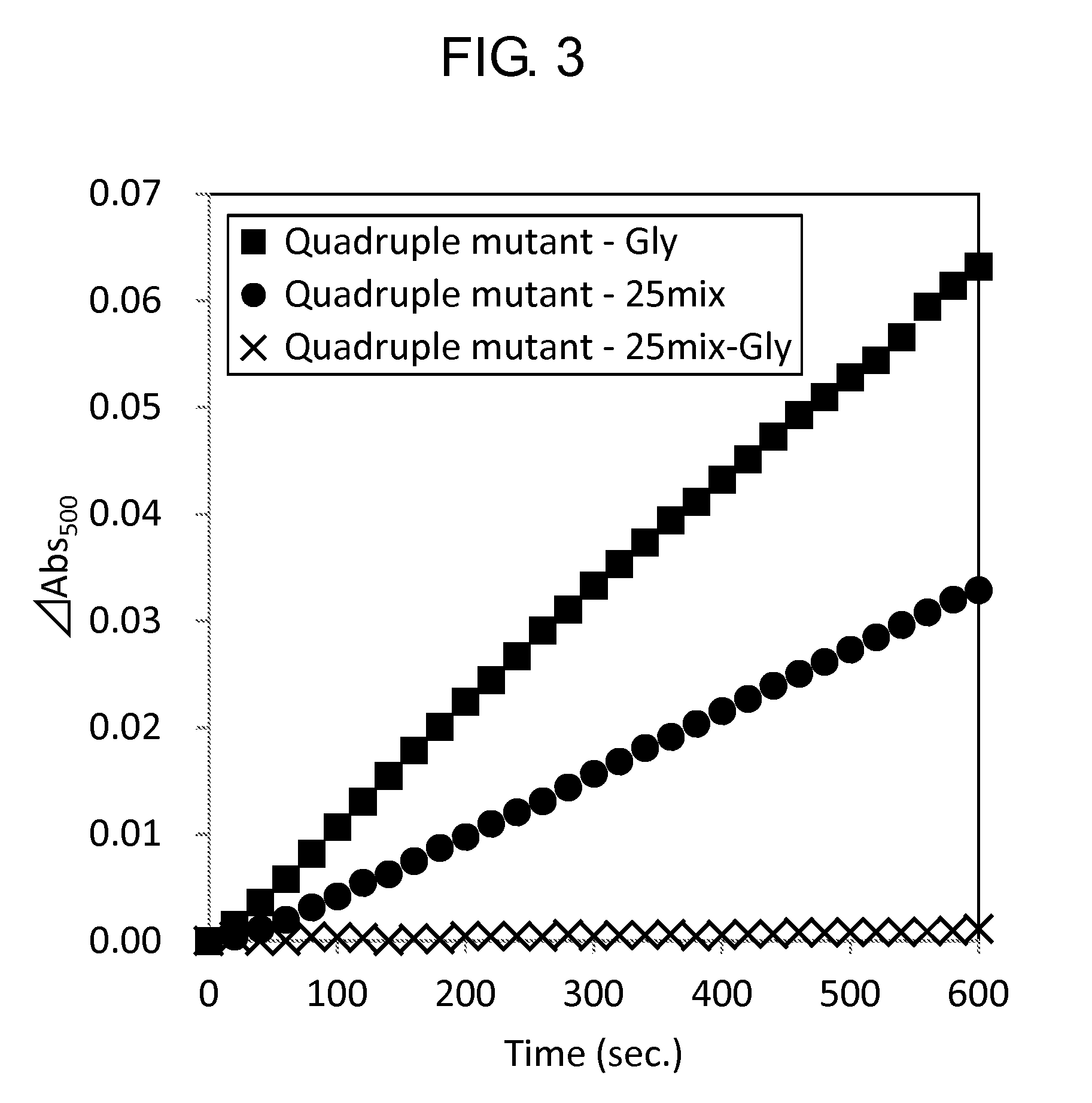
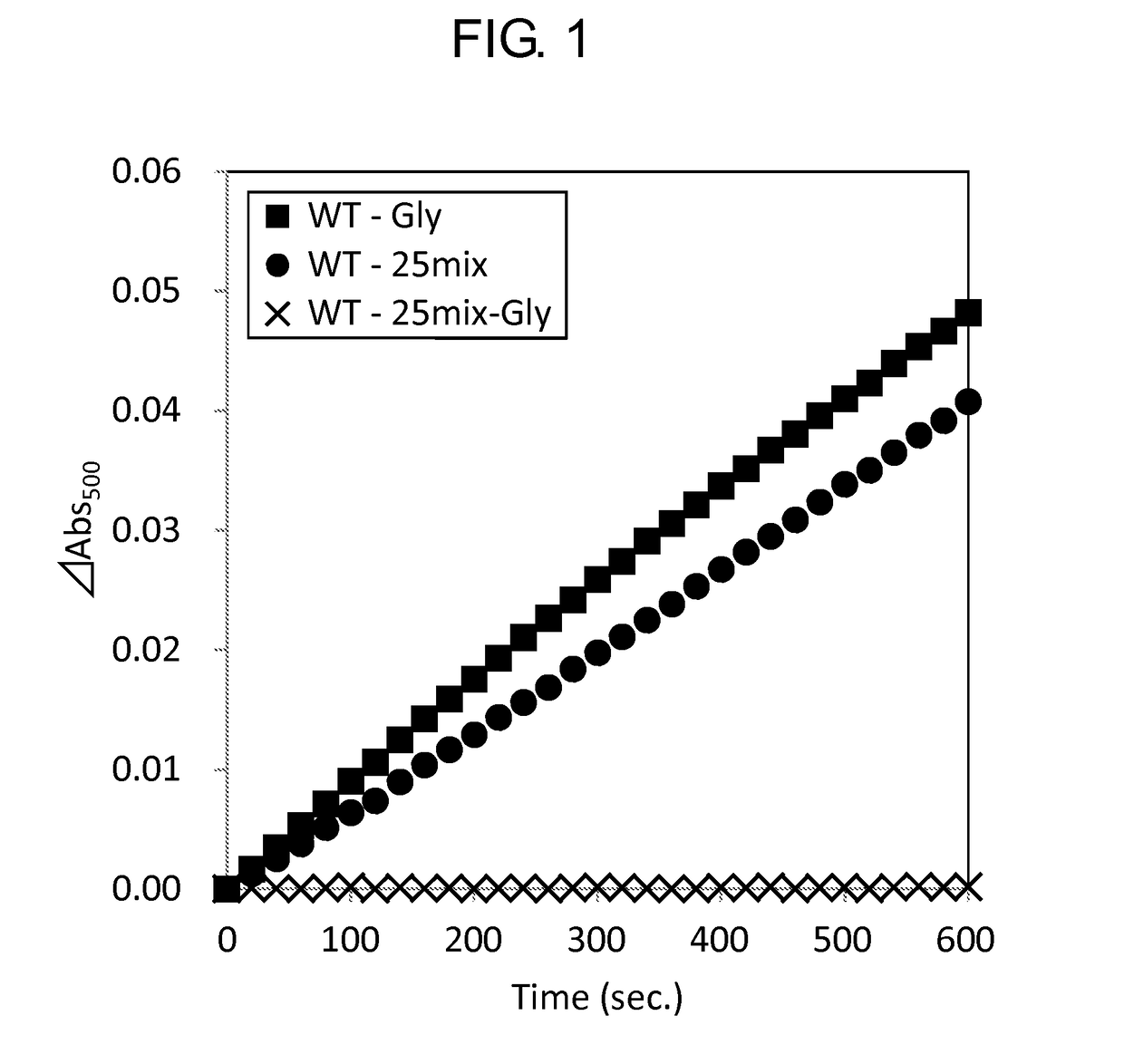
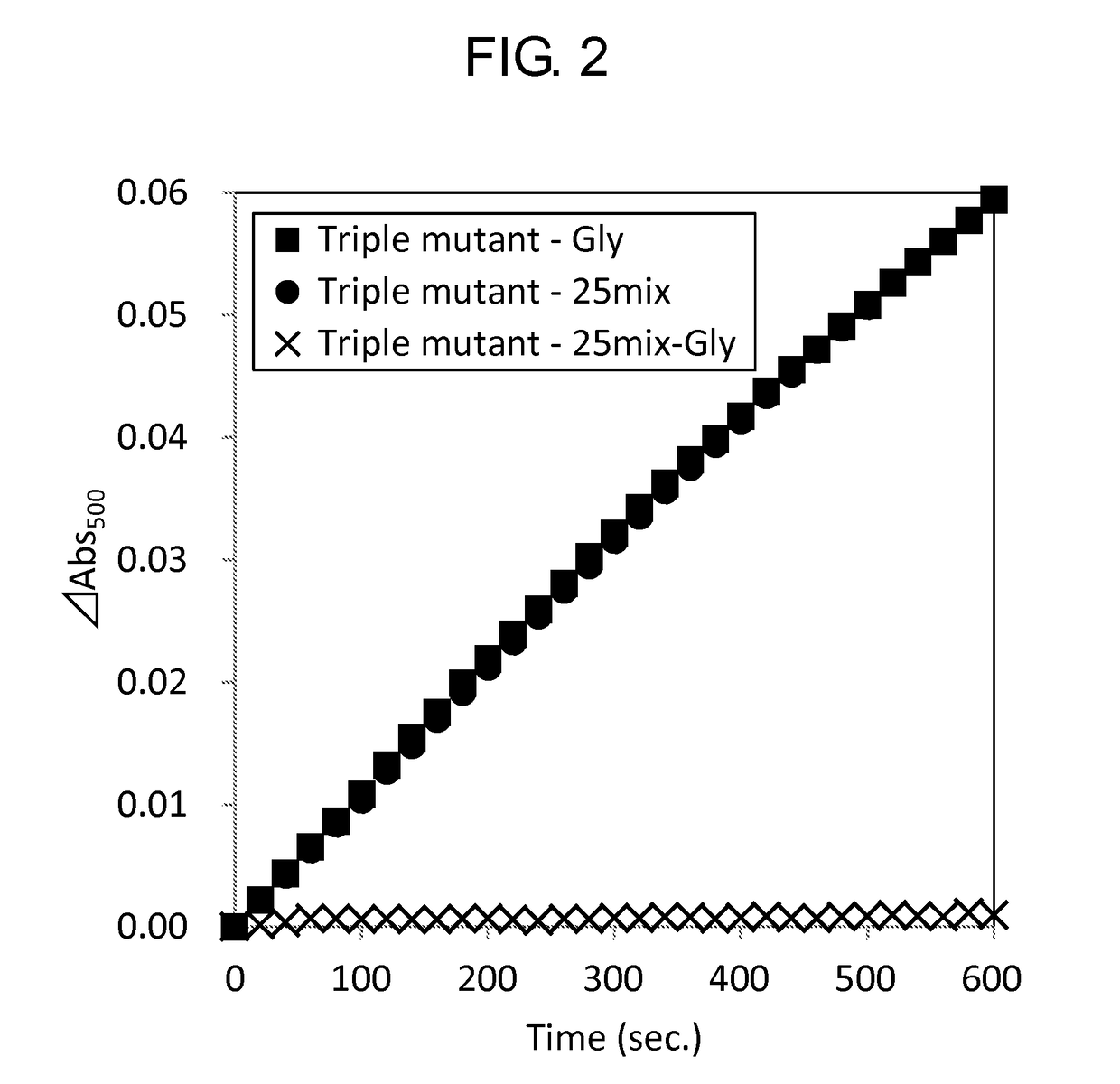
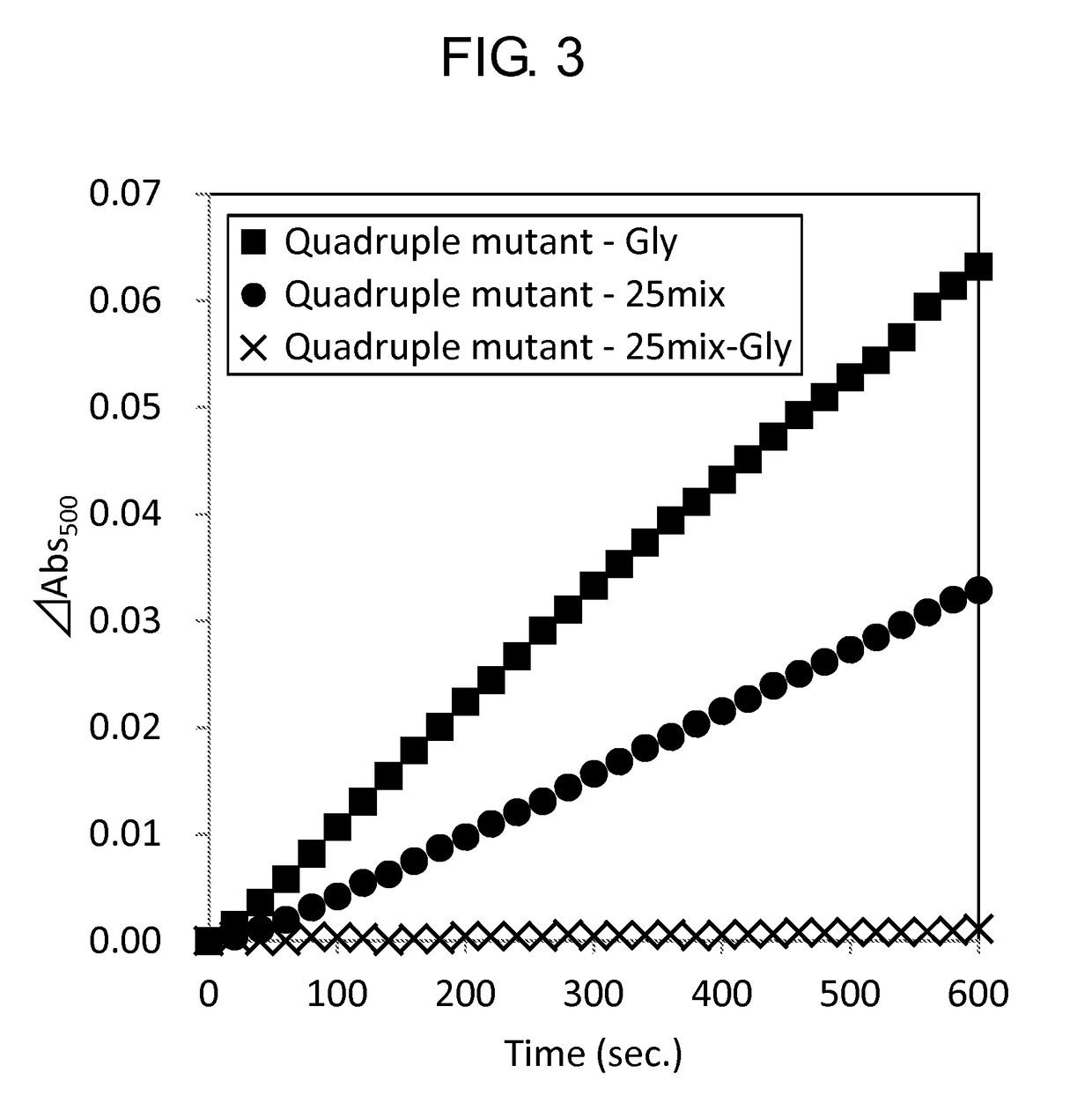
Modified Glycine Oxidase
ActiveUS20160002610A1MeasurementImprove propertiesImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTest sampleThermal stability
The present invention provides a novel enzyme and methods of using the enzyme for measuring glycine concentration. Specifically, the present invention provides an enzyme in which at least one amino acid residue is mutated so as to improve a property of a glycine oxidase which is associated with the measurement of glycine (e.g., activity of glycine oxidase for glycine, thermal stability of glycine oxidase, and substrate specificity of glycine oxidase for glycine,); and a method of analyzing glycine, that includes measuring glycine contained in a test sample using the modified enzyme; and the like.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
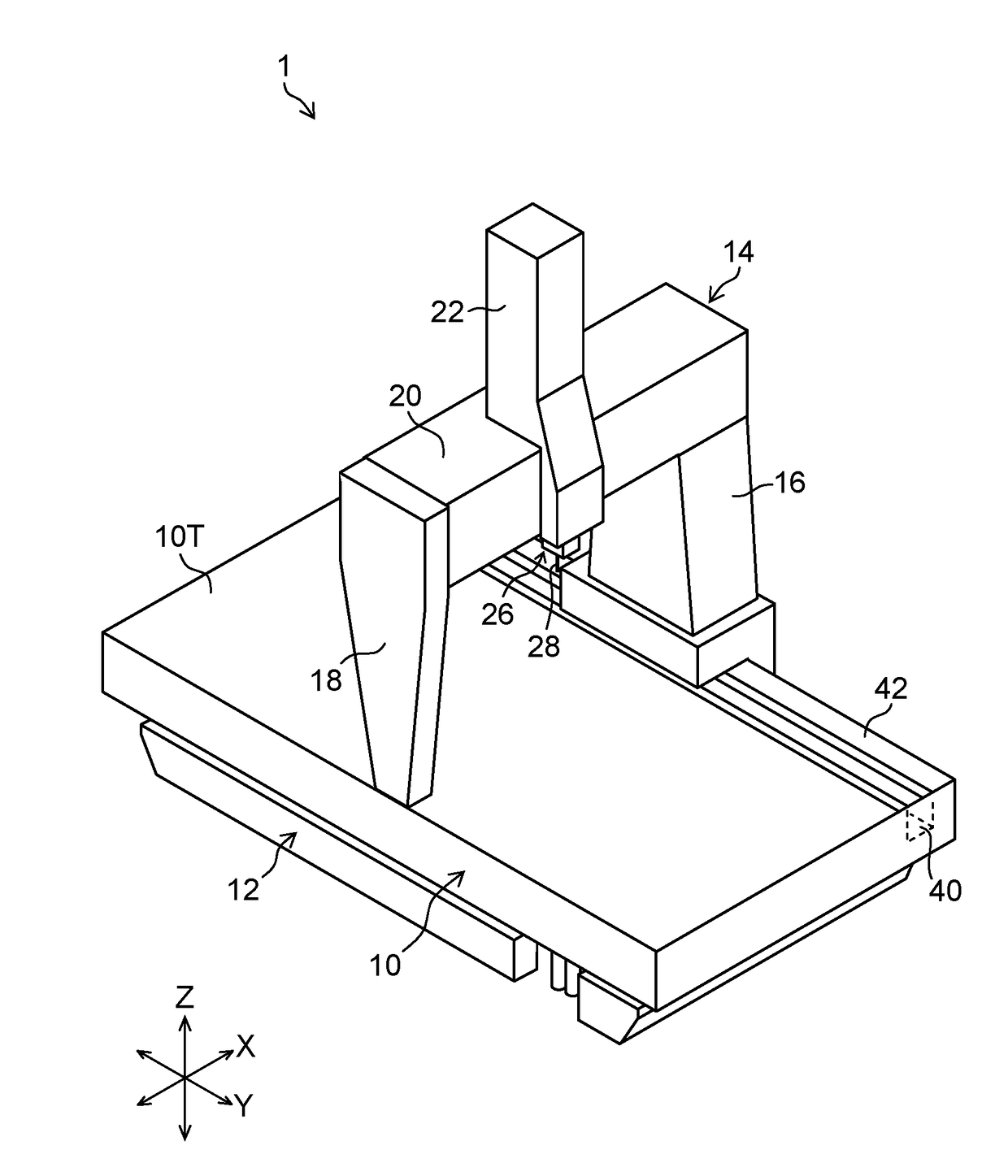
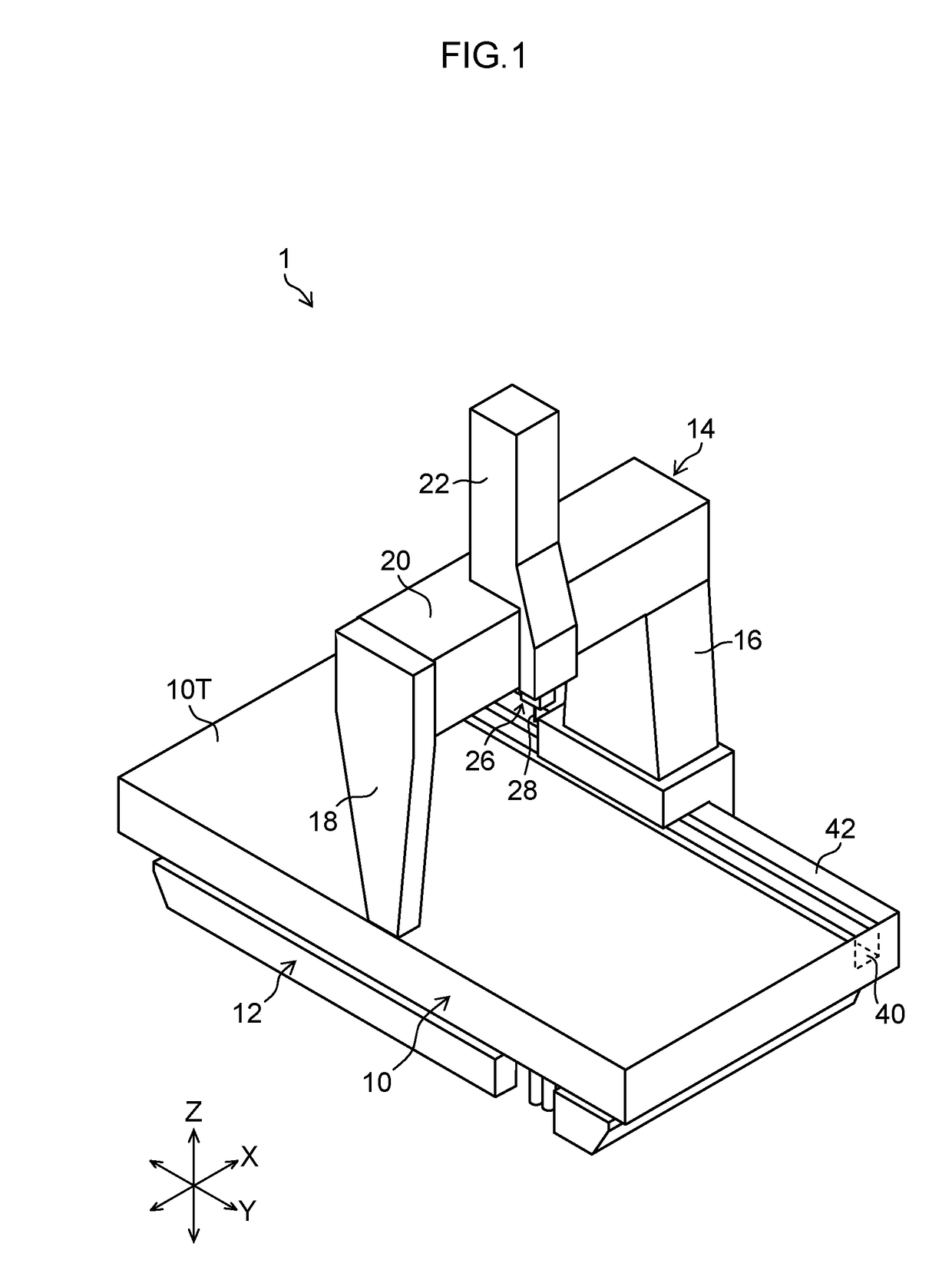
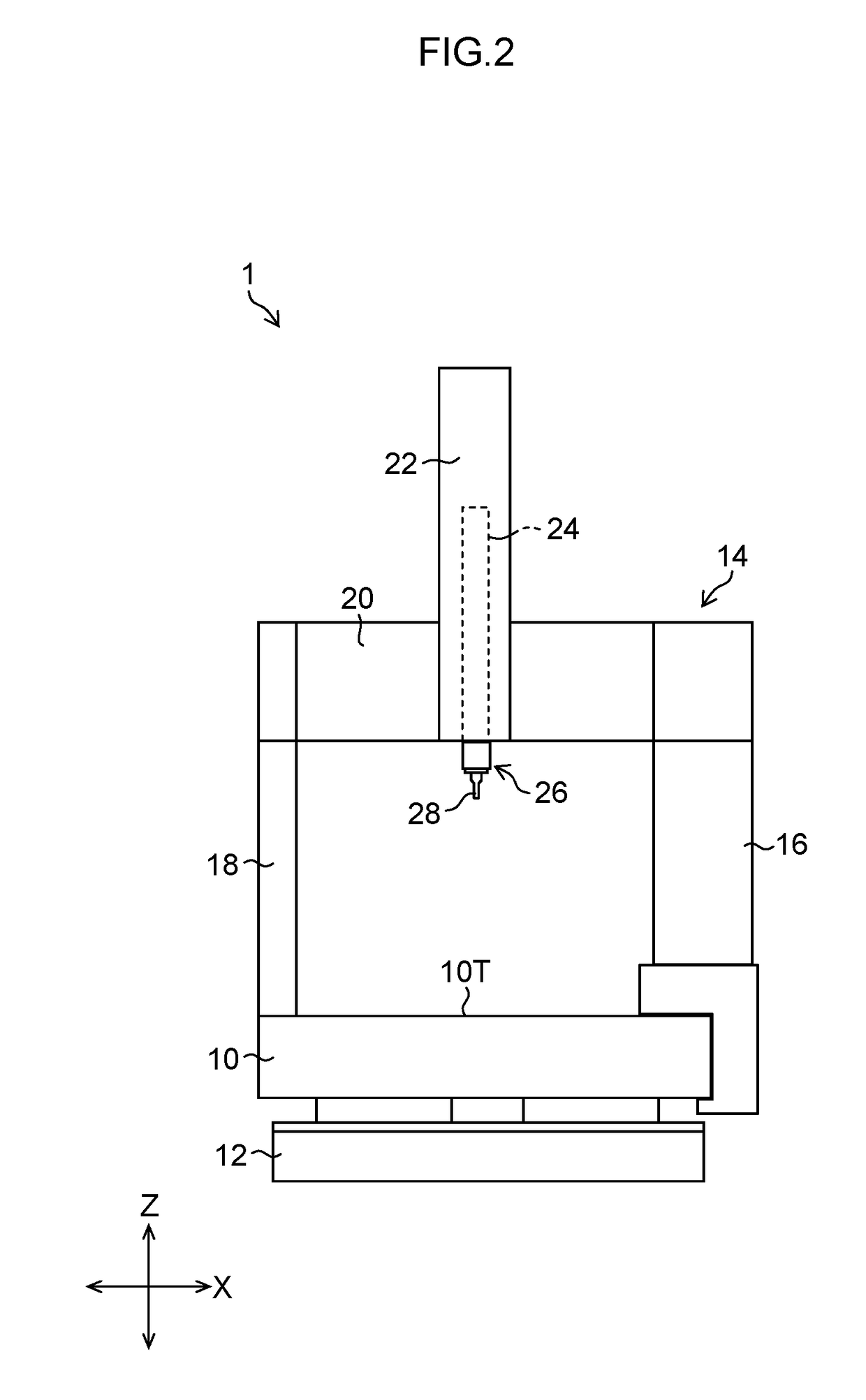
Three-dimensional coordinate measurement apparatus
ActiveUS20170322016A1High measurement accuracyHigh positioning accuracyUsing optical meansConverting sensor outputEngineeringSurface plate
There is provided a three-dimensional coordinate measurement apparatus capable of reducing shaking of a Y carriage and improving measurement accuracy. A groove is formed along a Y-axis direction in a right side part of a surface plate made of stone, and a Y guide is formed between the groove and a right side surface of the surface plate to support a Y carriage in a portal shape in a movable manner in the Y-axis direction. A support section is provided at a lower end of a right Y carriage on the right side of the Y carriage, and the support section is supported by the surface plate through air pads which are disposed by two air pads back and forth on the corresponding one of a top surface, a right side surface, and a bottom surface, of the surface plate, and a right side surface of the groove.
Owner:TOKYO SEIMITSU
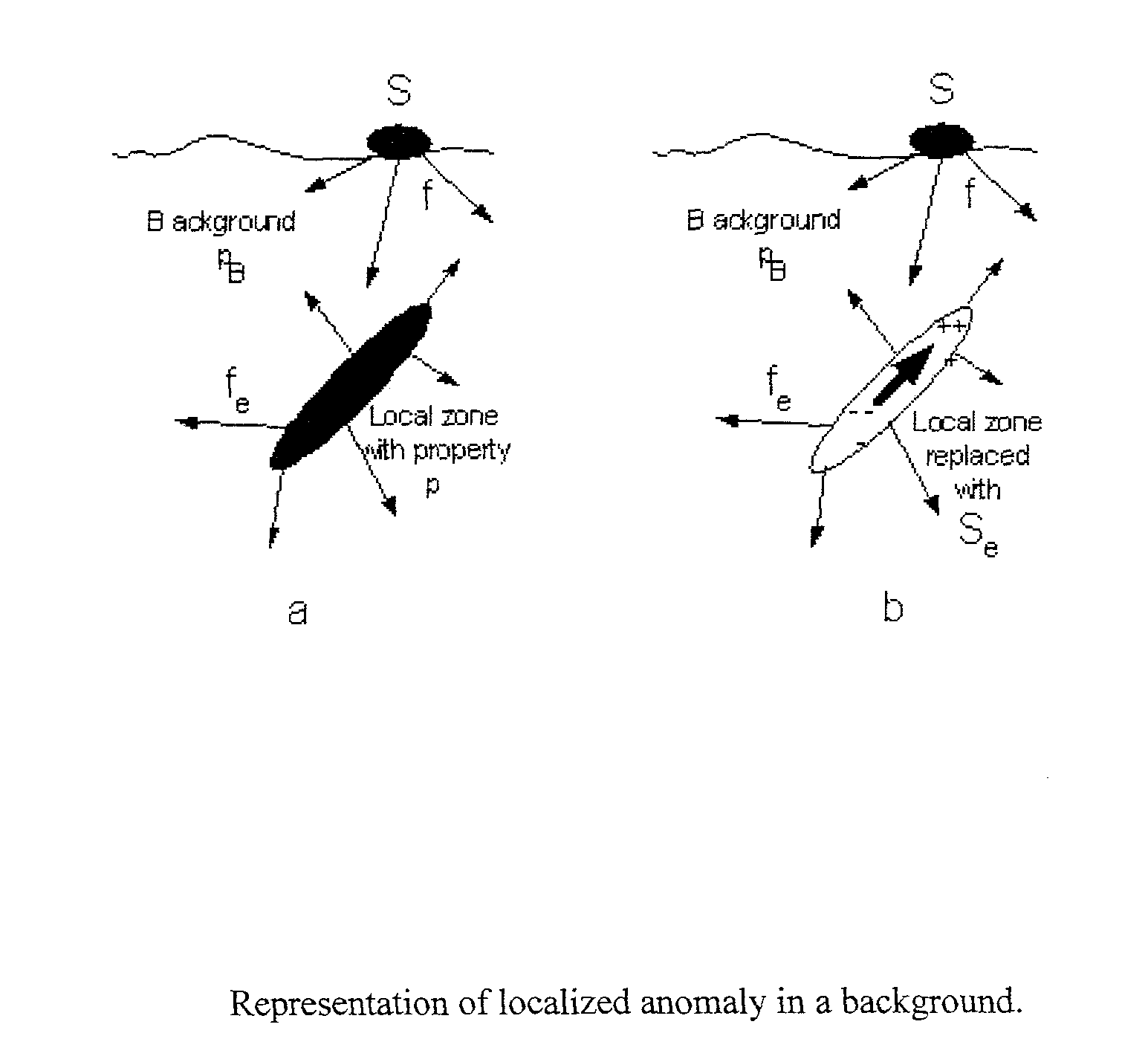
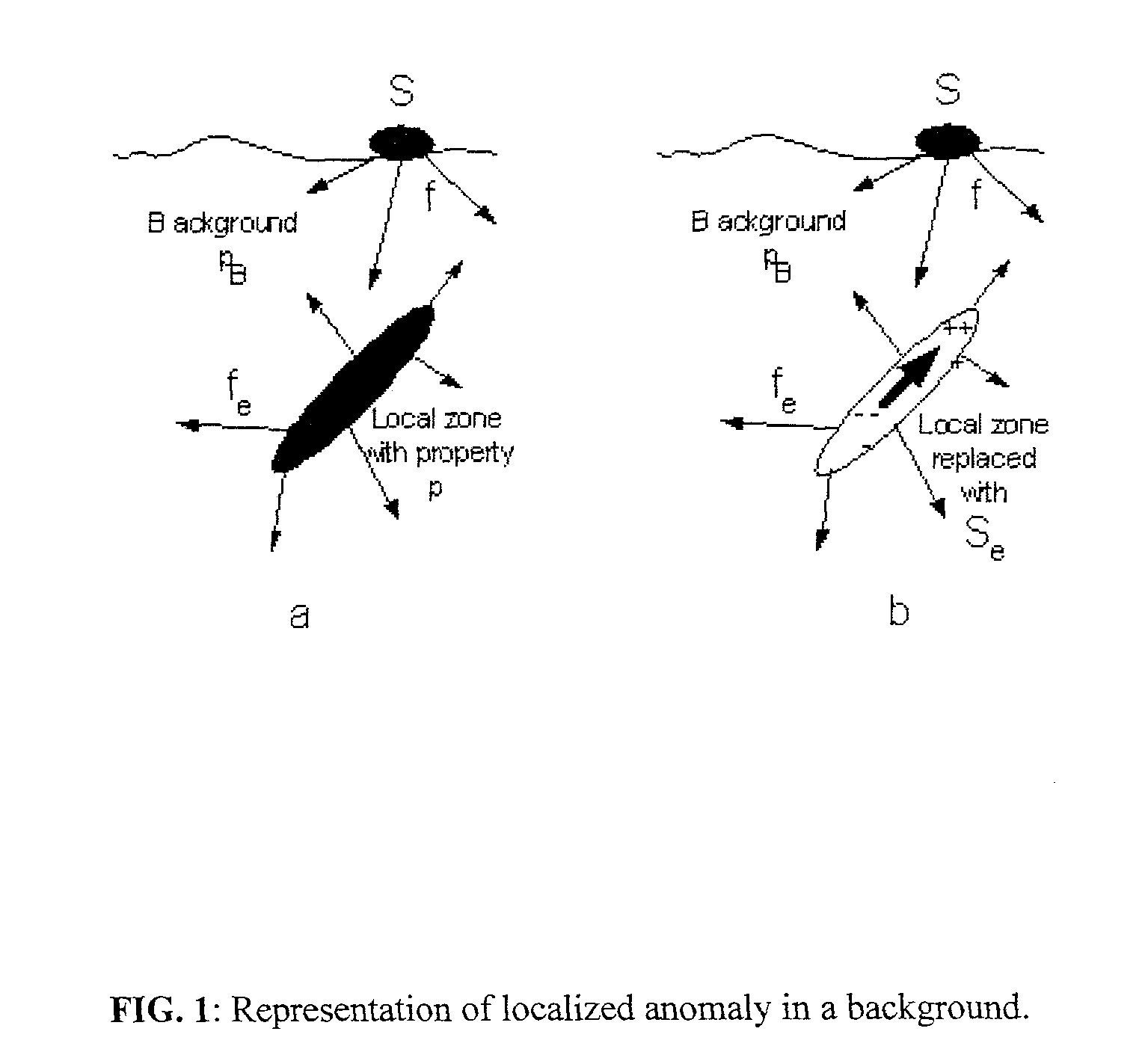
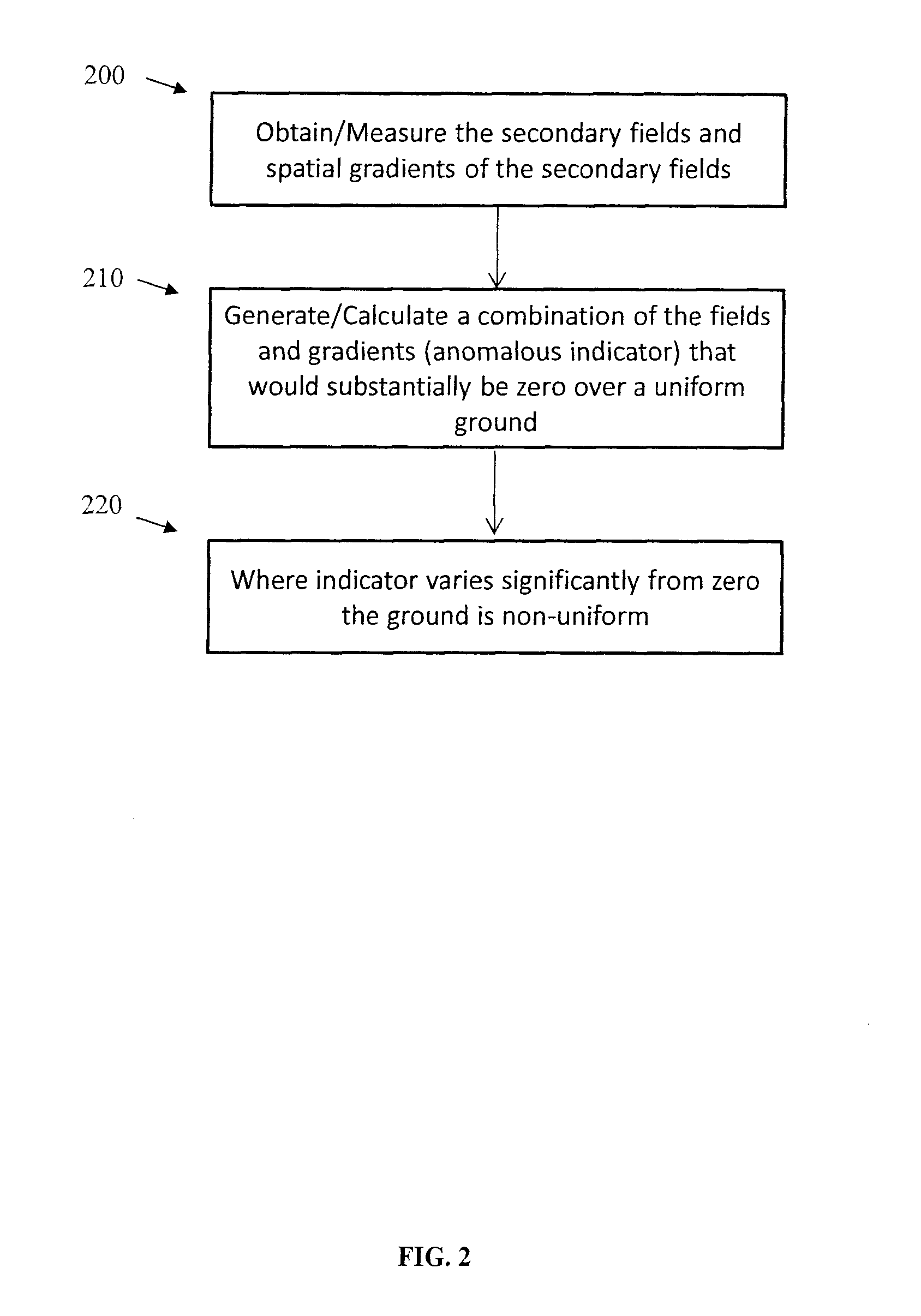
System and method for geophysical surveying using electromagnetic fields and gradients
InactiveUS20150153473A1Simple and effectiveMinimize system noiseElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingElectric fieldTime derivative
Electromagnetic exploration methods are used to identify a subsurface anomalous feature. This is sometimes difficult in the presence of large fields from the transmitter or other surrounding material that may be above and around the subsurface feature. By constructing linear combinations of the field and gradients of the field it is possible to remove the large fields associated with the transmitter and the surrounding material to make identification of the anomalous subsurface material easier. The fields and gradients can also be combined so as to provide estimates of other electromagnetic field quantities that would be otherwise difficult to measure, for example the electric field or the time derivative of the electric field.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
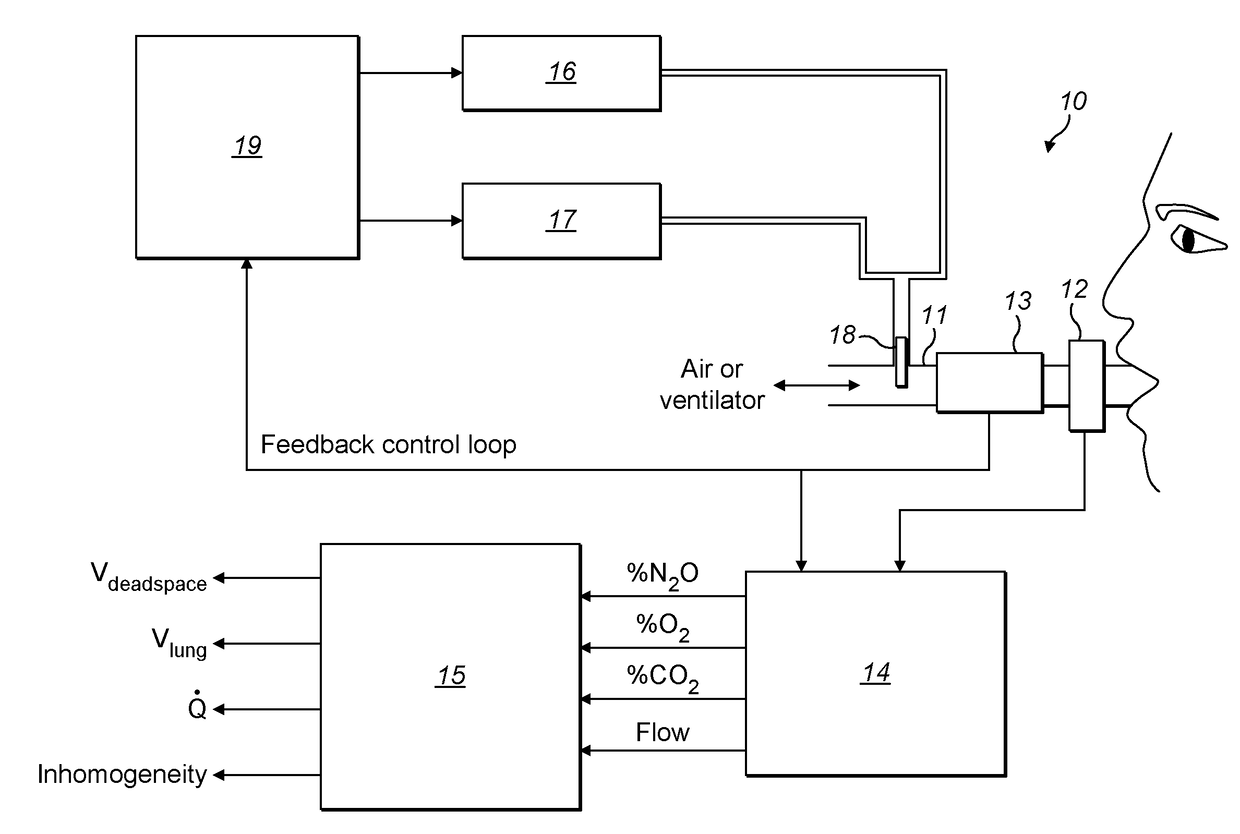
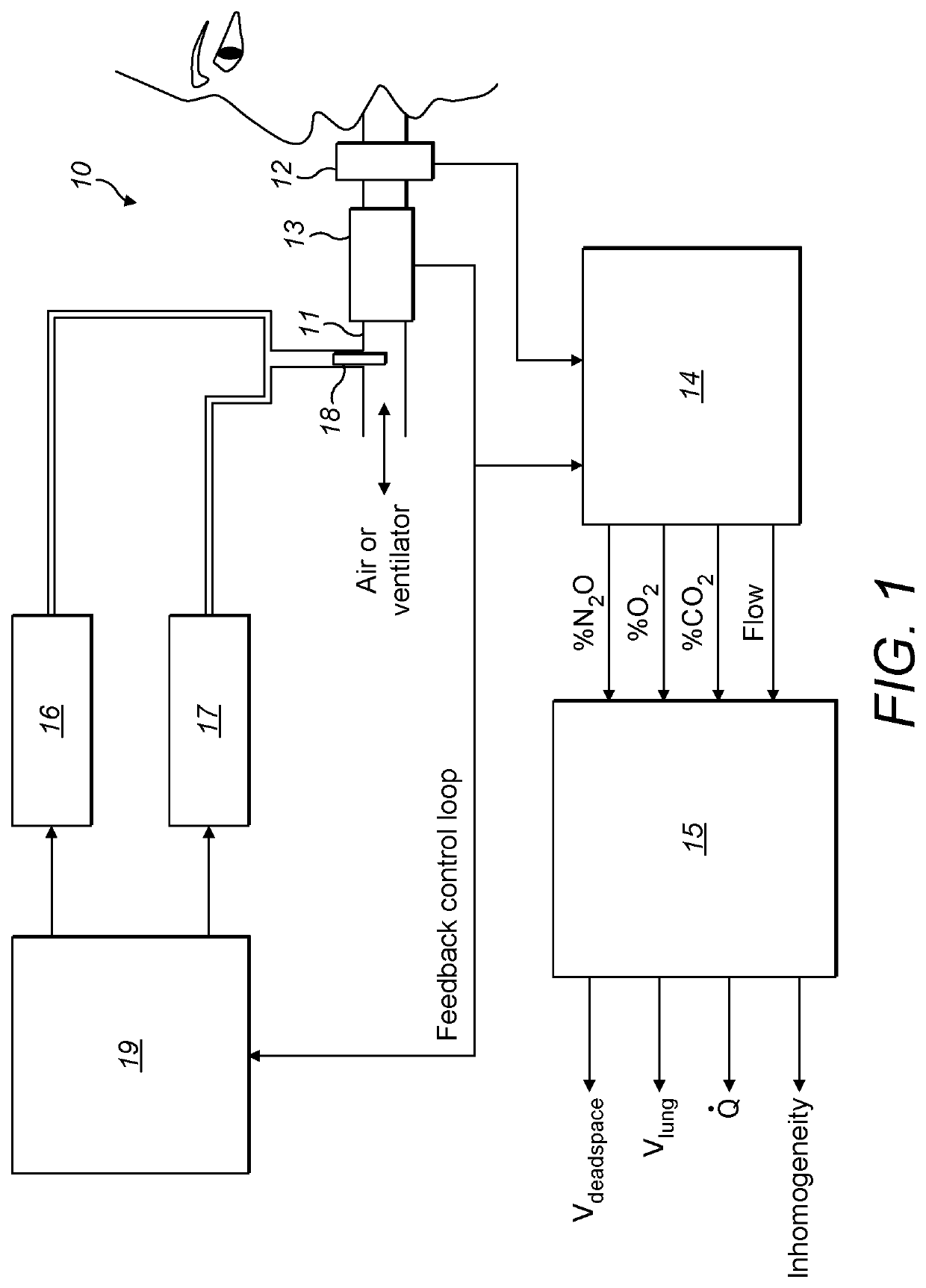
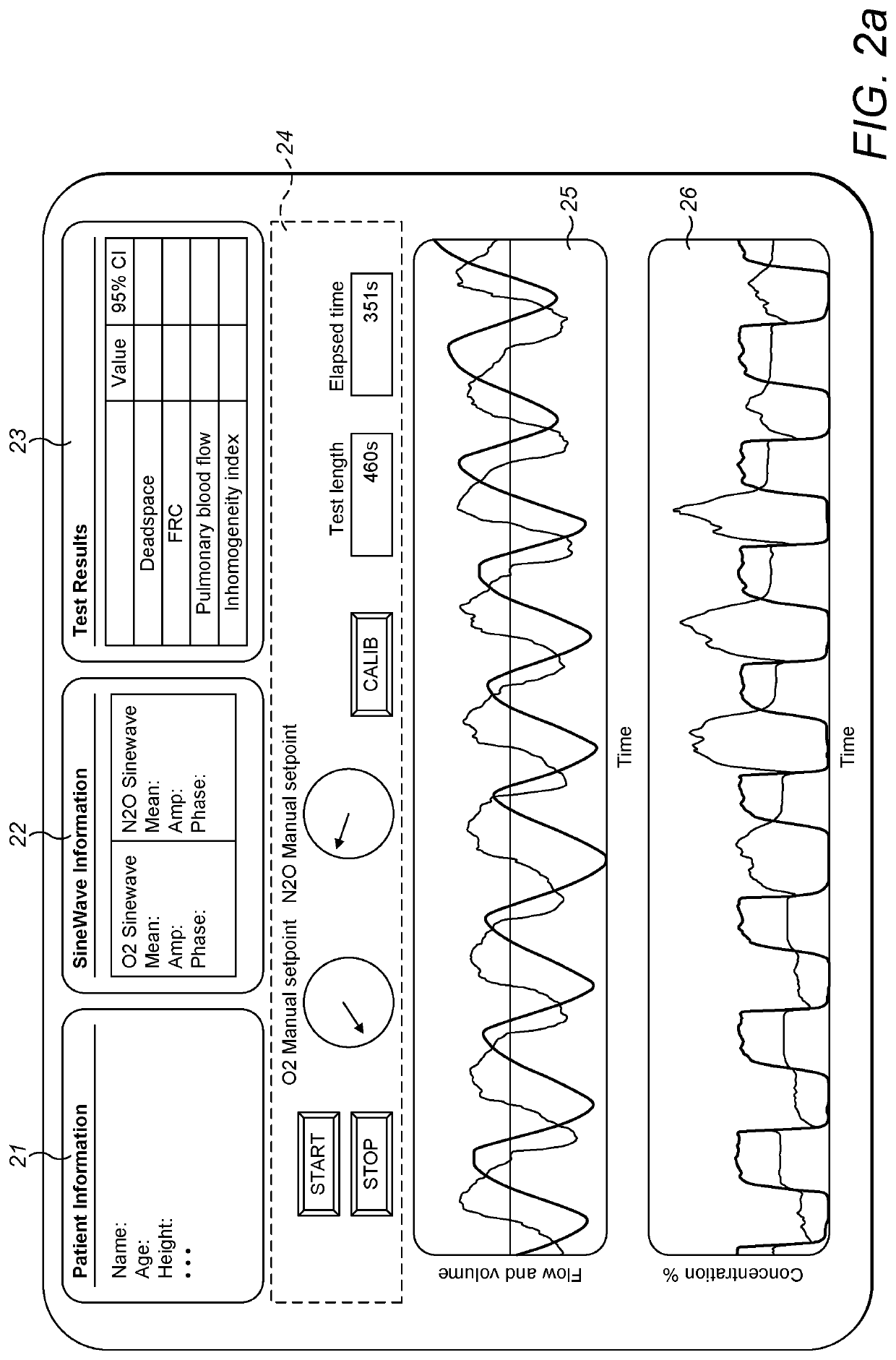
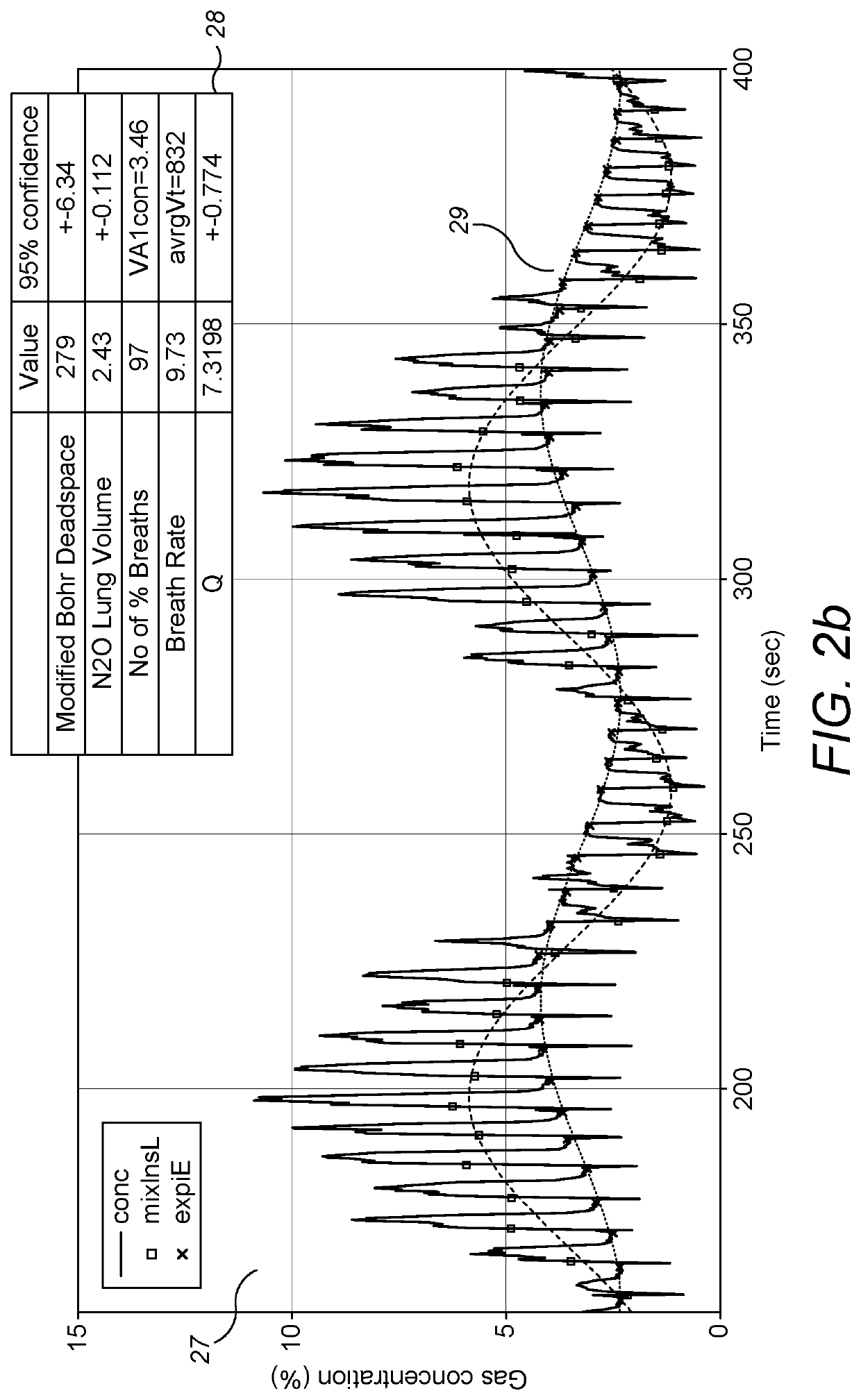
Method and apparatus for measurement of cardiopulmonary function
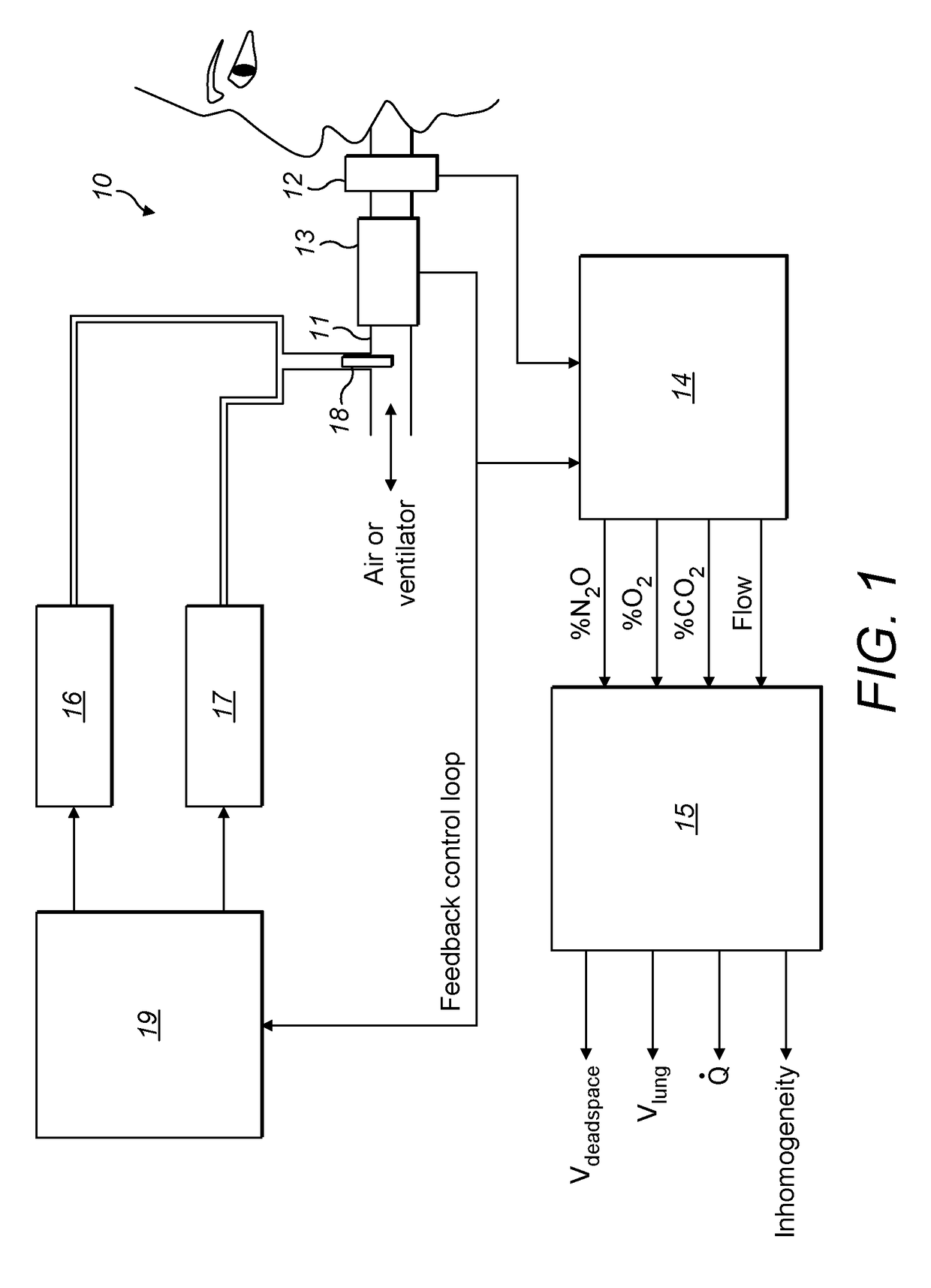
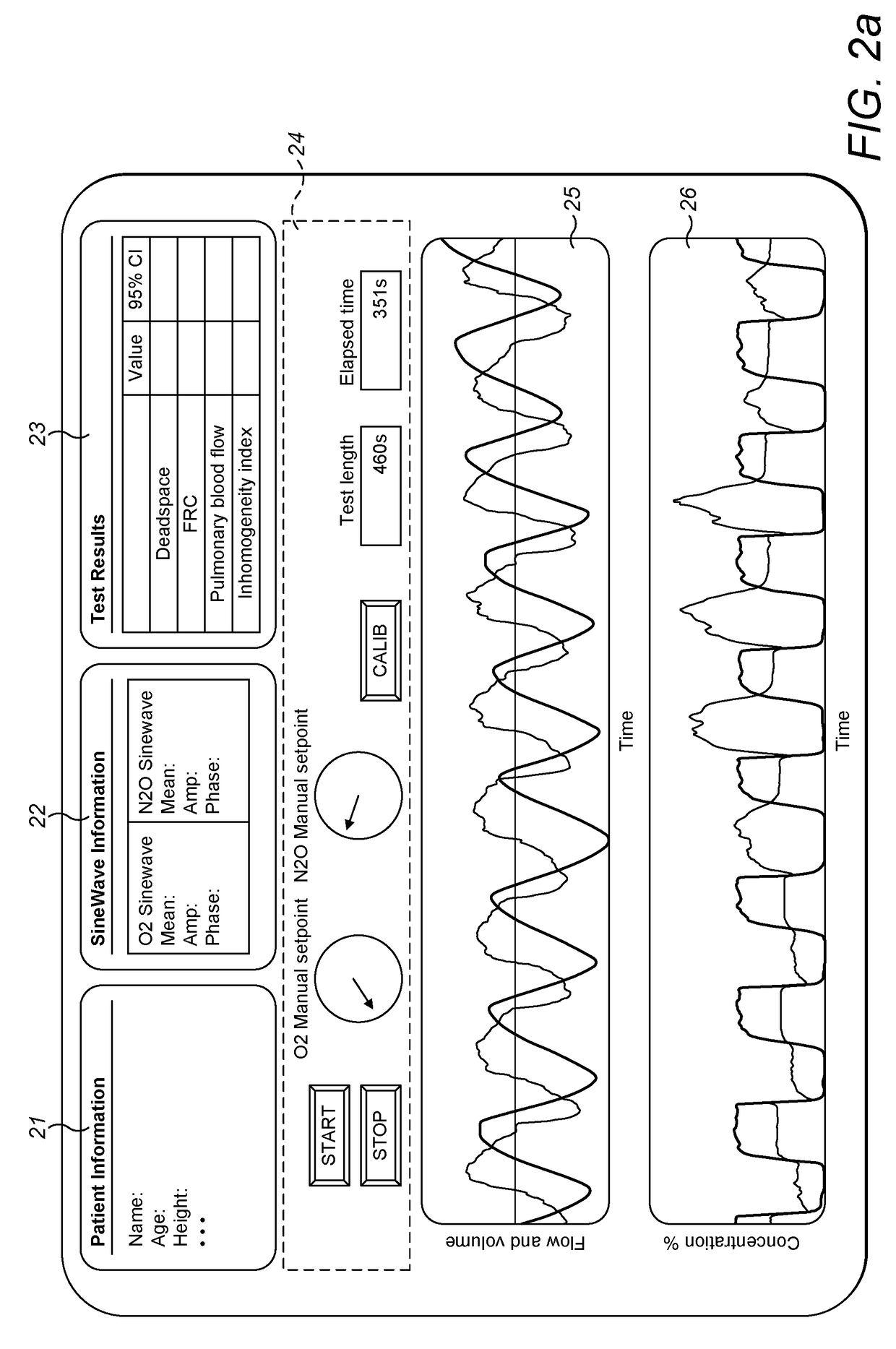
ActiveUS20170100043A1Robust methodAccurate measurementRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsAnatomical dead spaceMedicine
A method for measuring anatomical dead space in a lung, the method comprising: (a) providing, in a supply of inspired gas, at least one indicator gas for inhalation by a patient during a test, the concentration of the indicator gas being controlled such as to follow a sinewave pattern over successive breaths; (b) measuring, over successive breaths, the flow rate and concentration of the indicator gas during both inspiration and exhalation of the patient; (c) fitting sinewave envelopes to the measured concentration values of the indicator gas over the successive breaths and, from the fitted sinewave envelopes, determining the inspired concentration, the mixed expired concentration, and the end expired concentration in respect of the indicator gas for each breath; and (d) calculating the anatomical dead space for each of a plurality of inspirations based on a conservation-of-mass principle. Also provided is a test apparatus for carrying out such a method, and a computer program or set of instruction code which, when executed, causes a processor to implement such a method.
Owner:PHAN PHI ANH +2
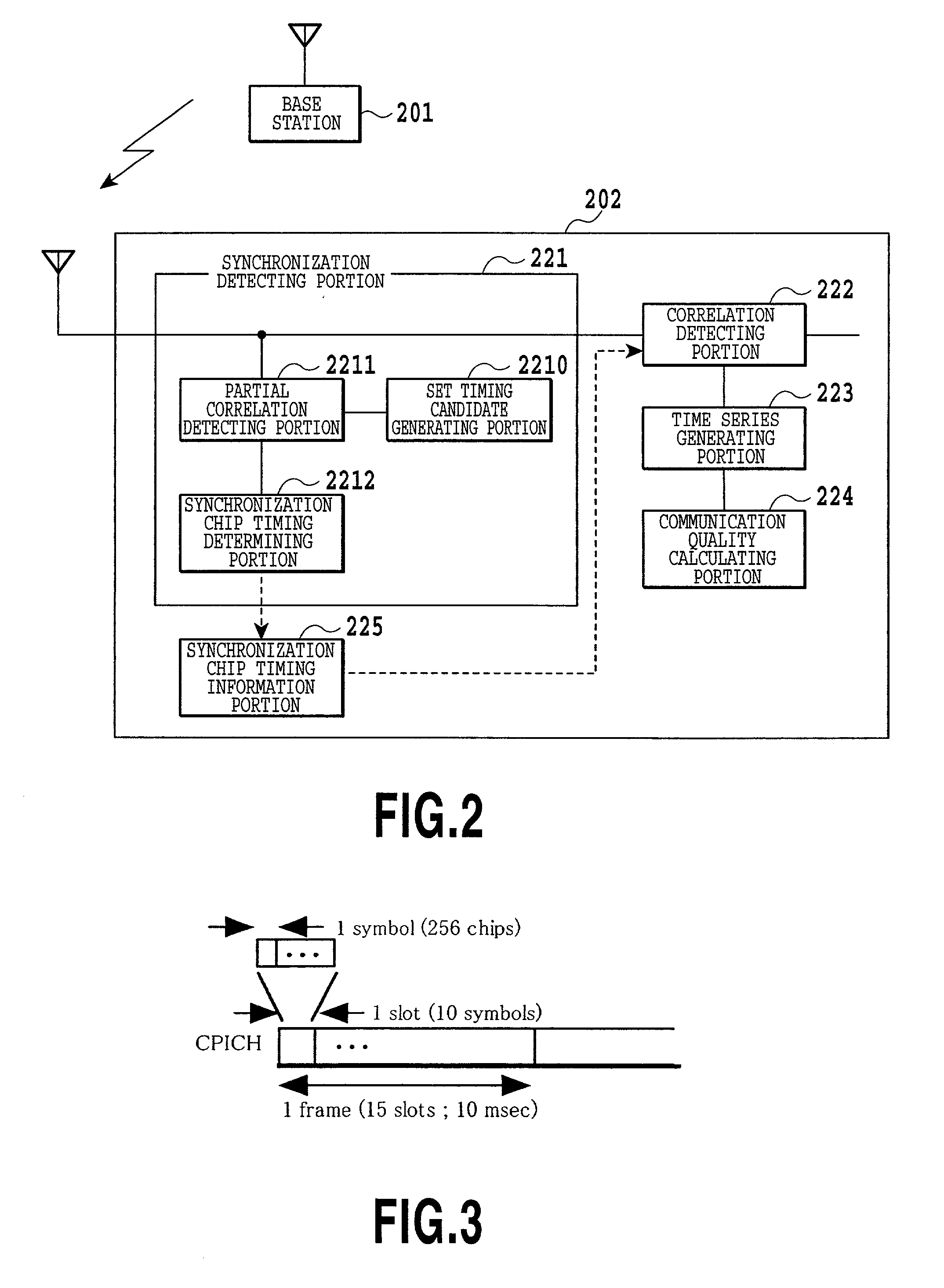
Apparatus and method for measurement of communication quality in CDMA system
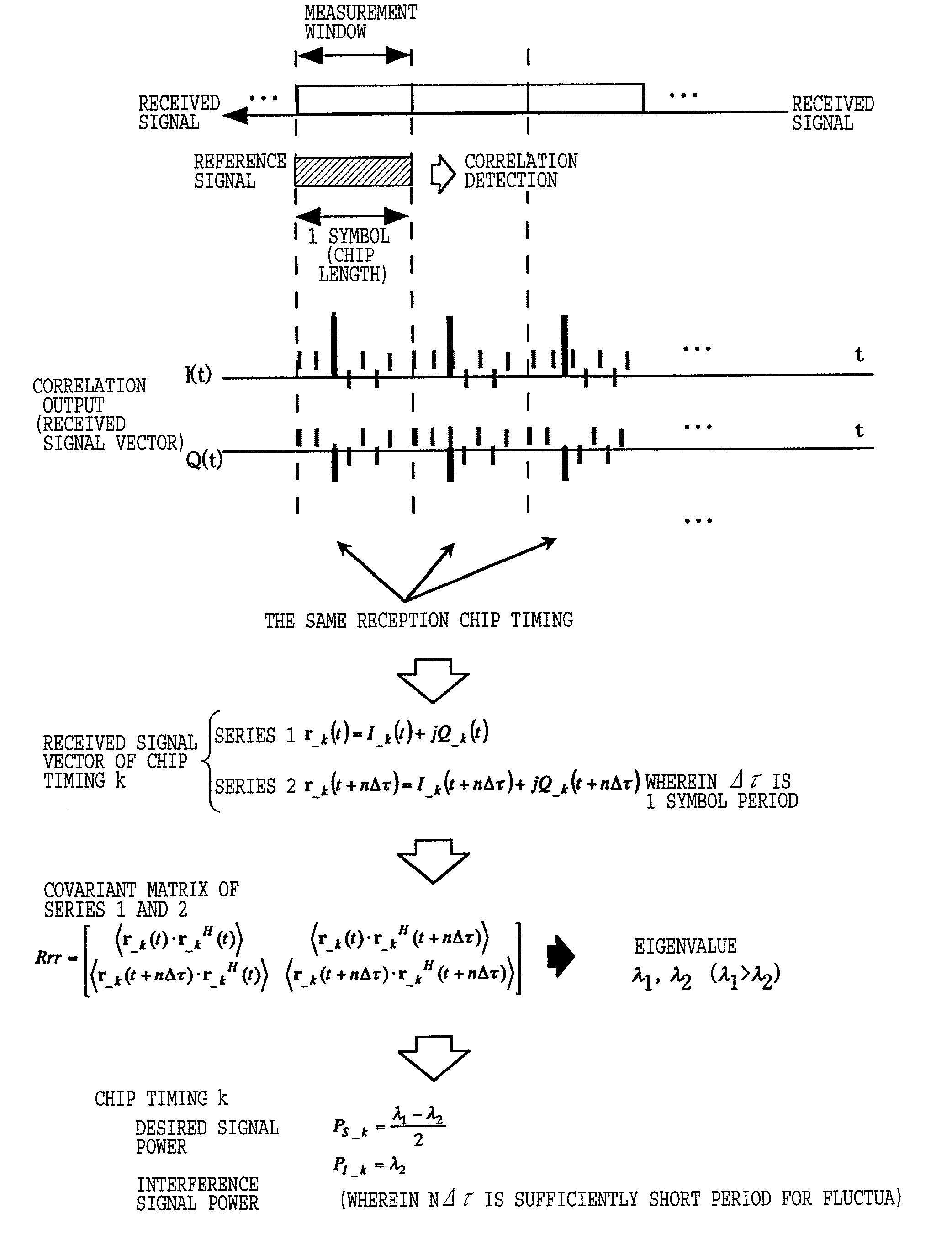
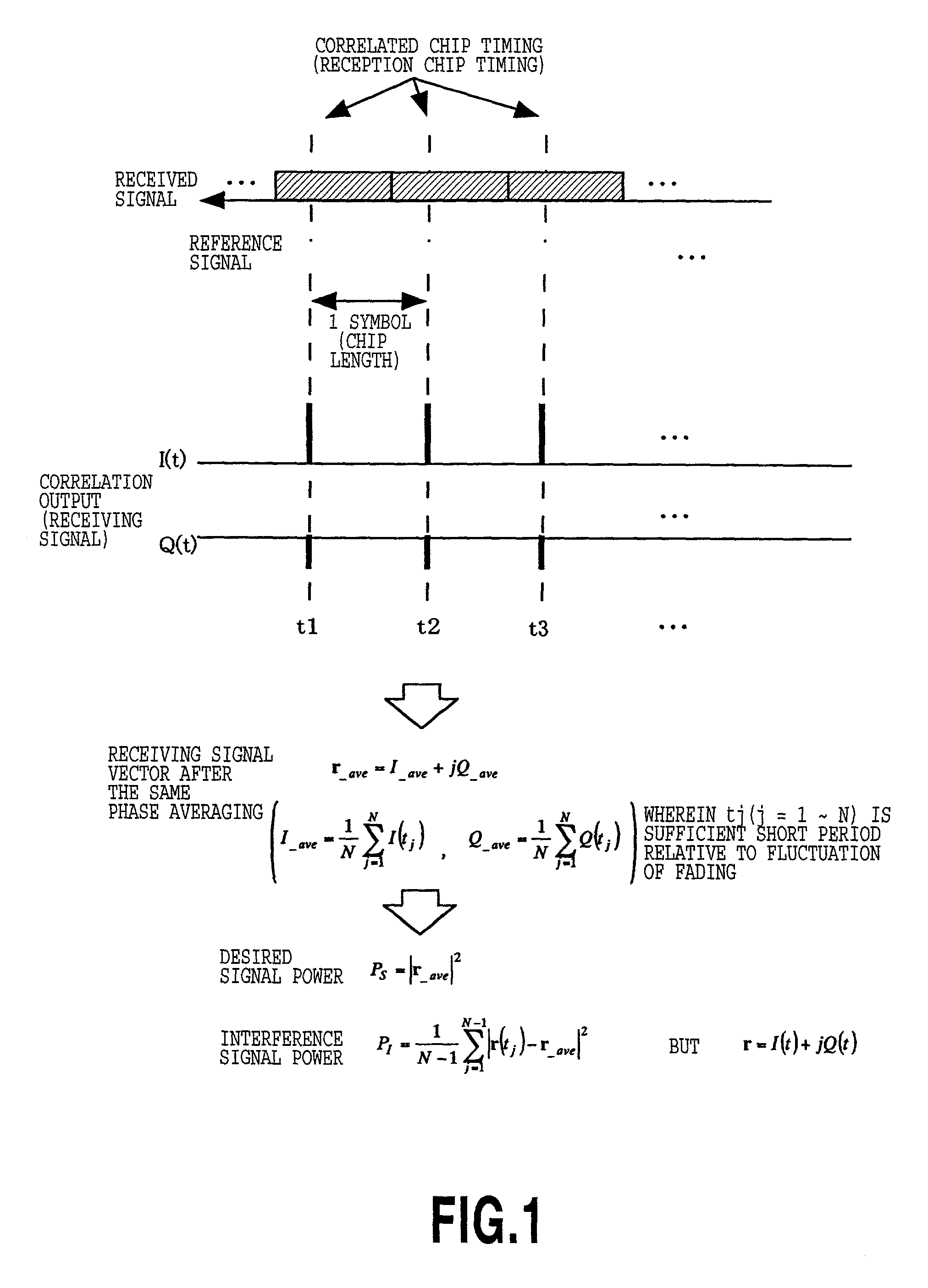
ActiveUS7050482B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencySynchronisation arrangementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTime informationCommunication quality
In order to perform synchronization detection with high speed, high precision and high reliability and to measure communication quality (propagation characteristics) at high precision and high efficiency, a mobile station includes synchronization detecting portion for detecting synchronization chip timing of channel to be measured, a synchronization chip timing information portion accumulating information of detected synchronization chip timing, a correlation detecting portion deriving a correlation value between spreading code of the channel to be measured and a received signal for performing communication with a base station and measurement of communication quality with taking the detected synchronization chip timing as a reception chip timing, a time series generating portion for generating a time series data of received signal vector after correlation detection, and a communication quality calculating portion for calculating communication quality from generated time series data.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Steerable Shape Sensing Biopsy Needle
A biopsy needle has a central axis and includes one or more sensing regions, each sensing region formed by a plurality of sensing optical fibers located over a particular extent of said central axis and inside the outer shell of the needle. The sensing optical fibers are coupled to a wavelength interrogator. A steerable catheter has a central axis and outer shell, the outer shell coupled to a plurality of optical fibers in sensing regions and actuation regions, the sensing regions formed over particular extents of the central axis by bonding gratings to the inner surface of the outer shell, and the actuation regions formed by coupling optical energy into shape memory alloys bonded to the outer shell.
Owner:INTELLIGENT FIBER OPTIC SYST
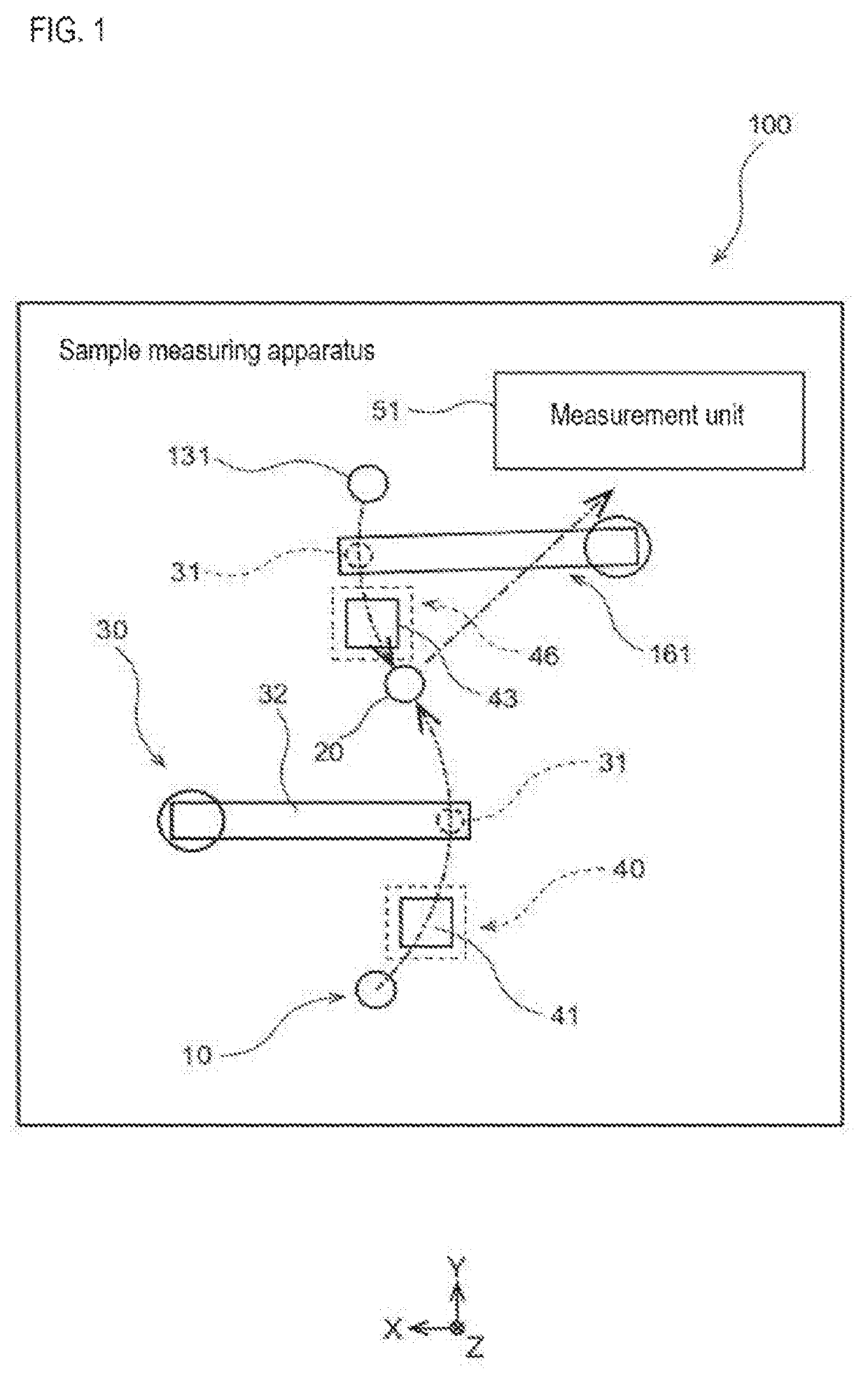
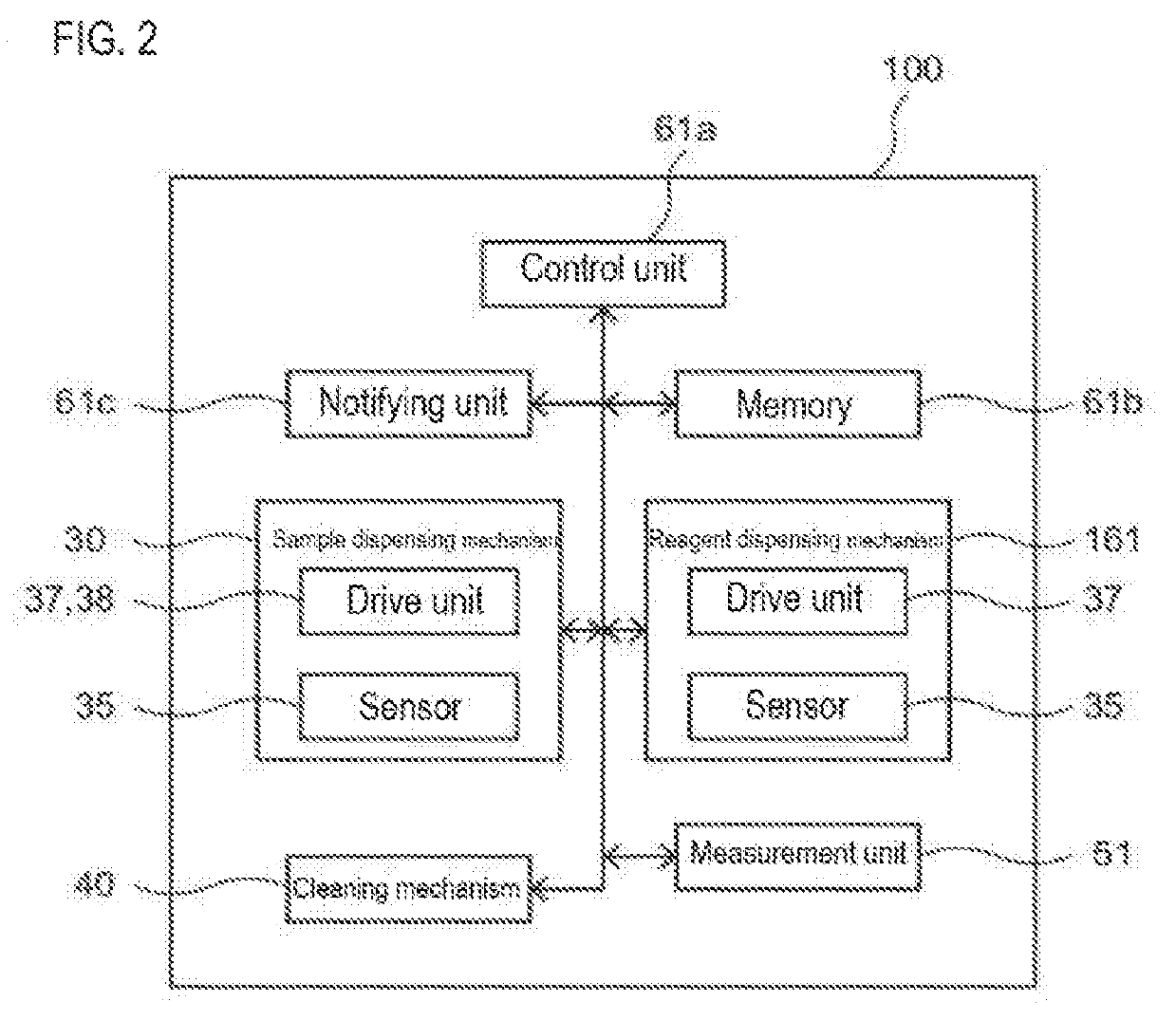
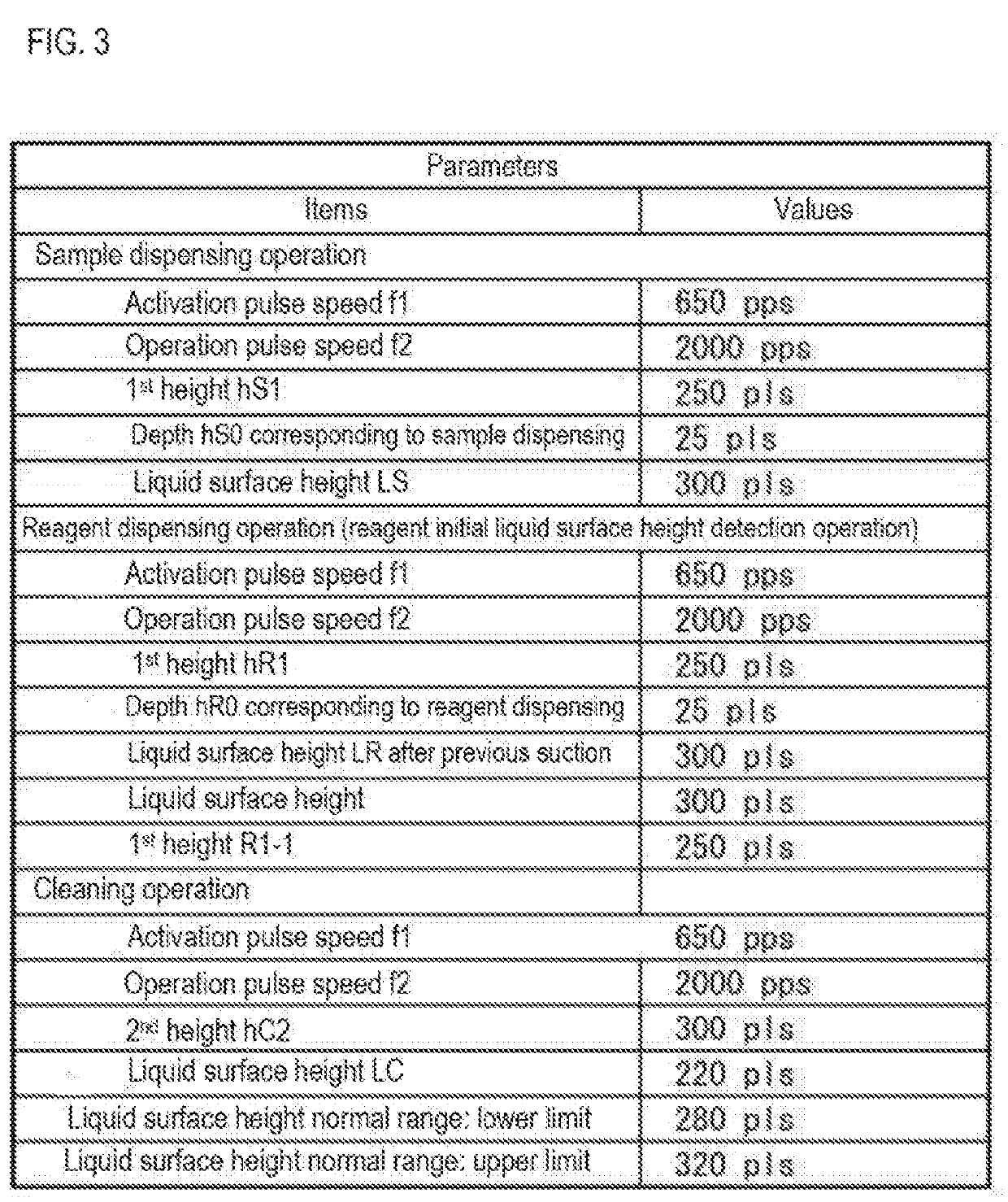
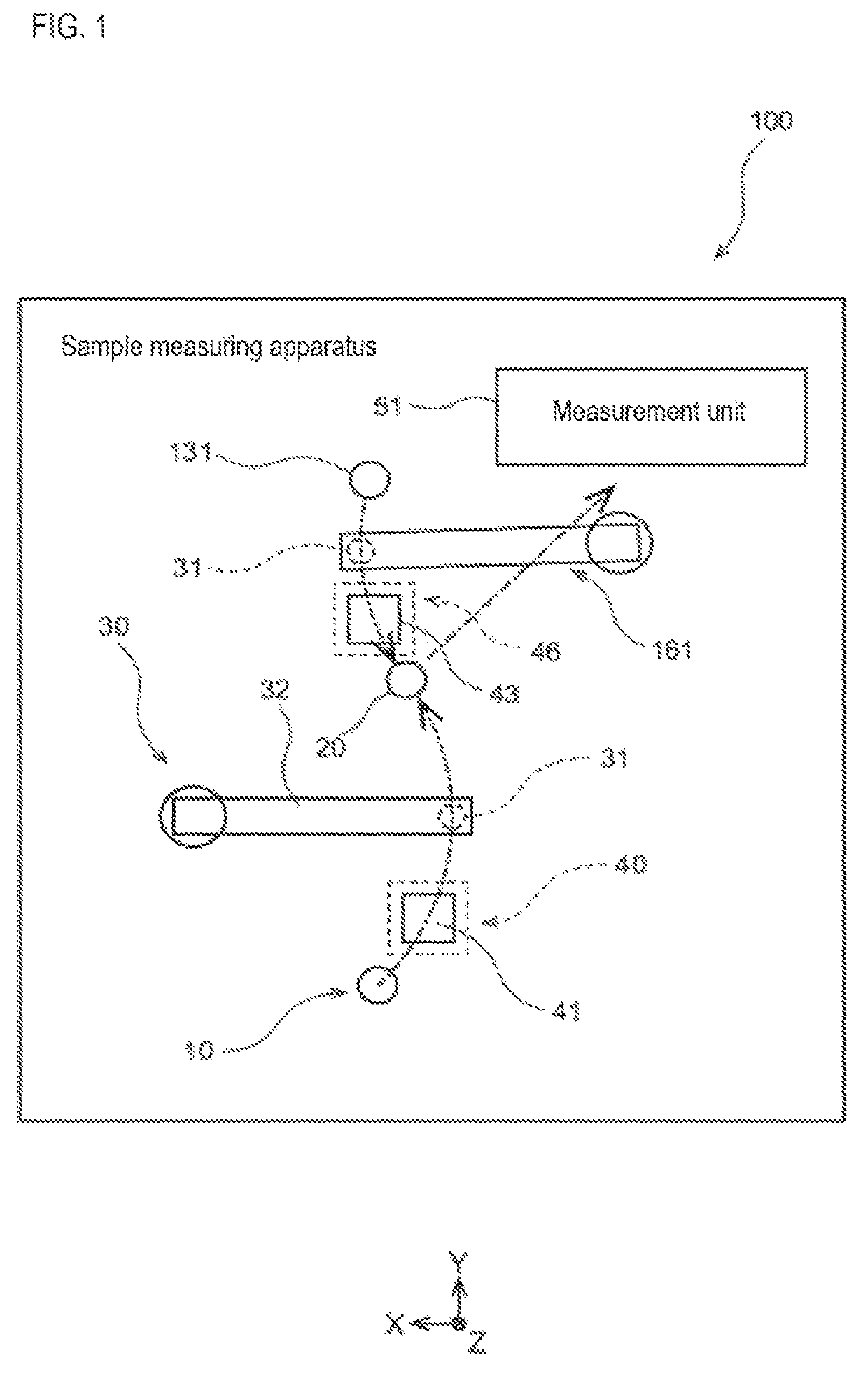
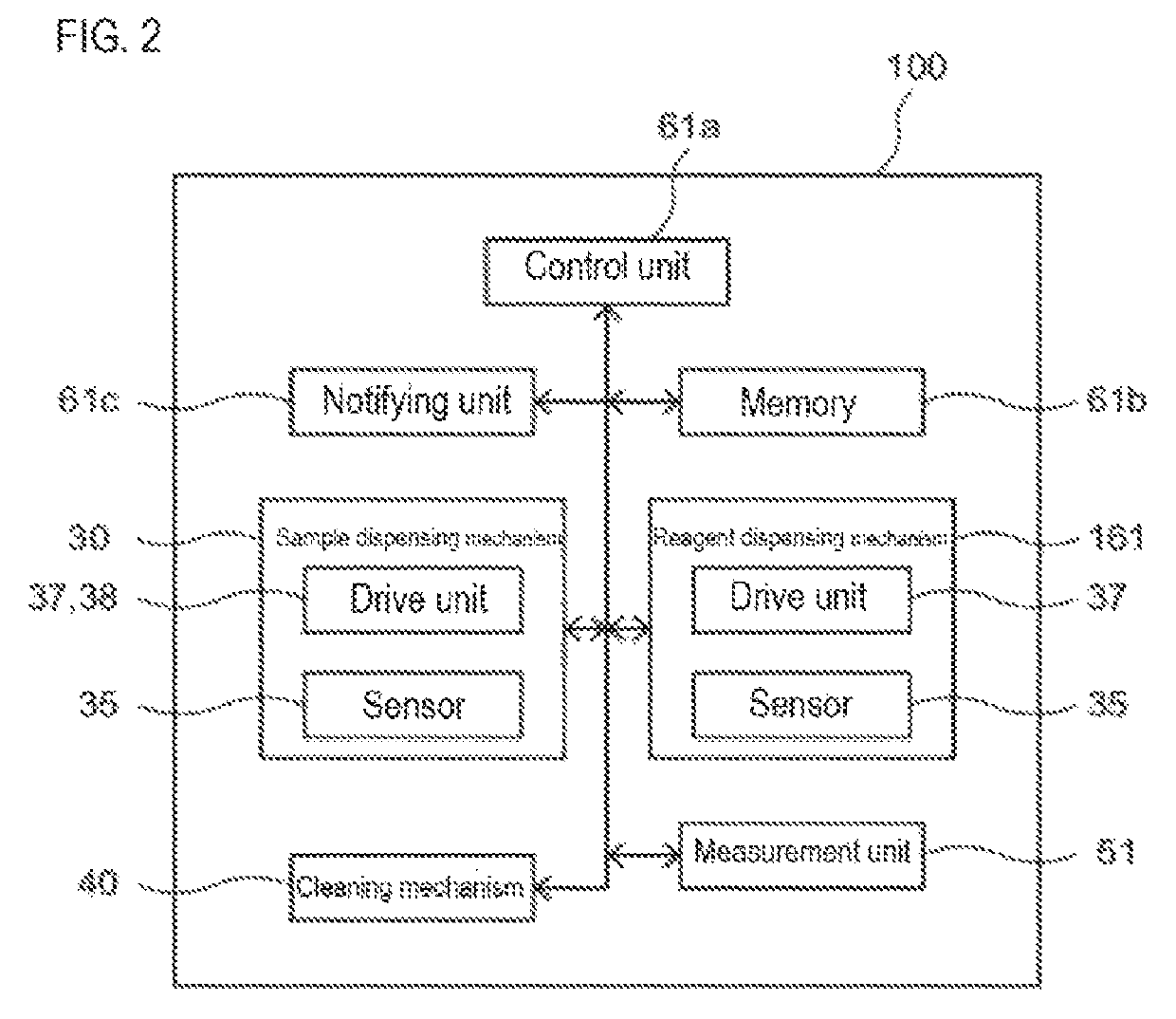
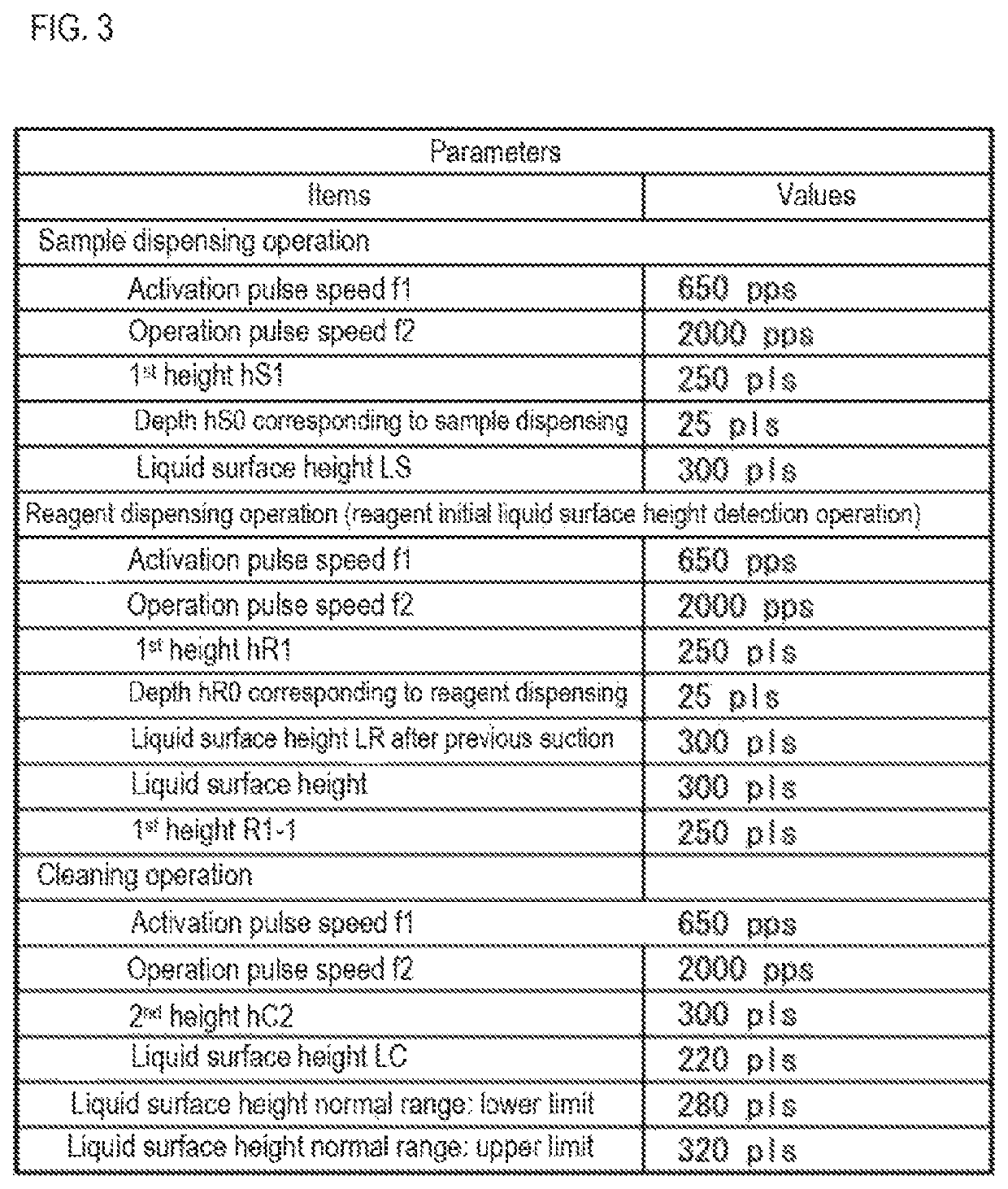
Sample measuring apparatus and sample measuring method
ActiveUS20190265264A1Measurement can be speededAccurate measurementMaterial analysisMeasurement deviceSample Measure
The sample measuring apparatus includes a suction unit that includes a nozzle and a drive unit that raises and lowers the nozzle, and suctions a first liquid and a second liquid that is different from the first liquid; a liquid surface detecting unit that detects liquid surfaces of the first liquid and the second liquid; a control unit that controls the suction unit, and a measuring unit that measures a measurement sample prepared from the suctioned first liquid; wherein the control unit controls the suction unit to suction the first liquid and the second liquid based on the respective liquid surface detection result of the first liquid and the second liquid detected while lowering the nozzle, and a second speed at which the nozzle descends when detecting the liquid surface of the second liquid is faster than a first speed at which the nozzle descends when detecting the liquid surface of the first liquid.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
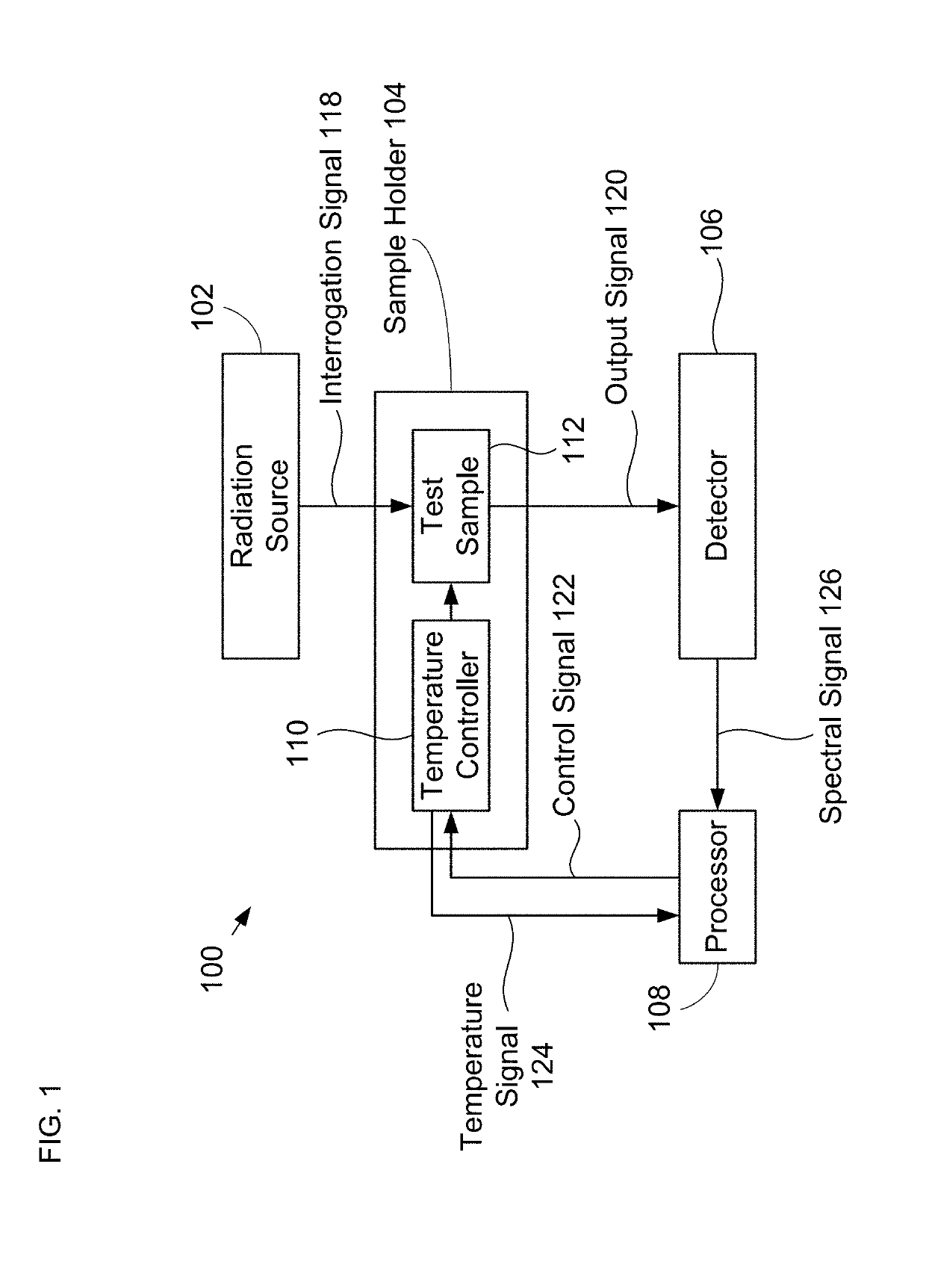
System for Analyzing a Test Sample and Method Therefor
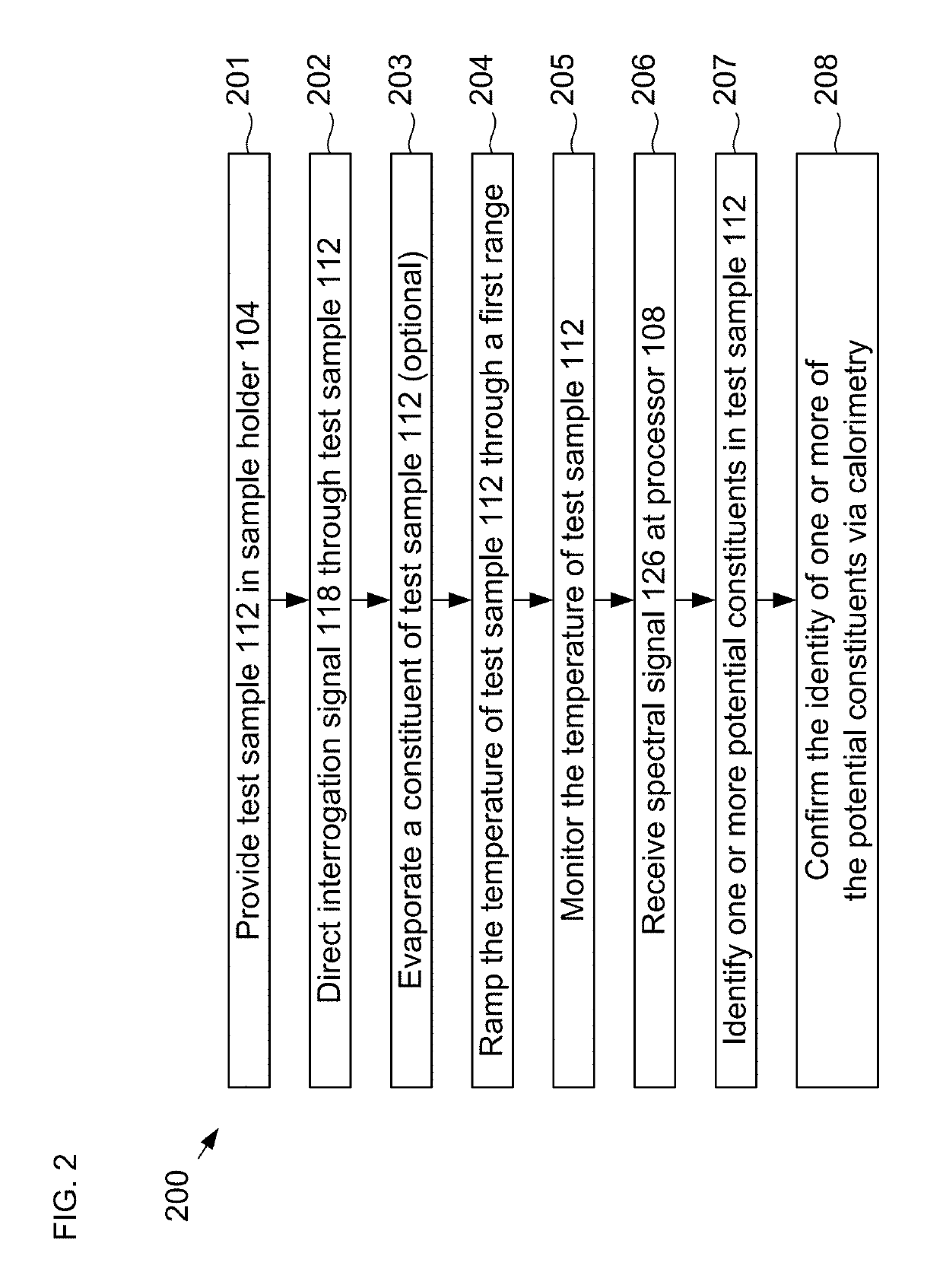
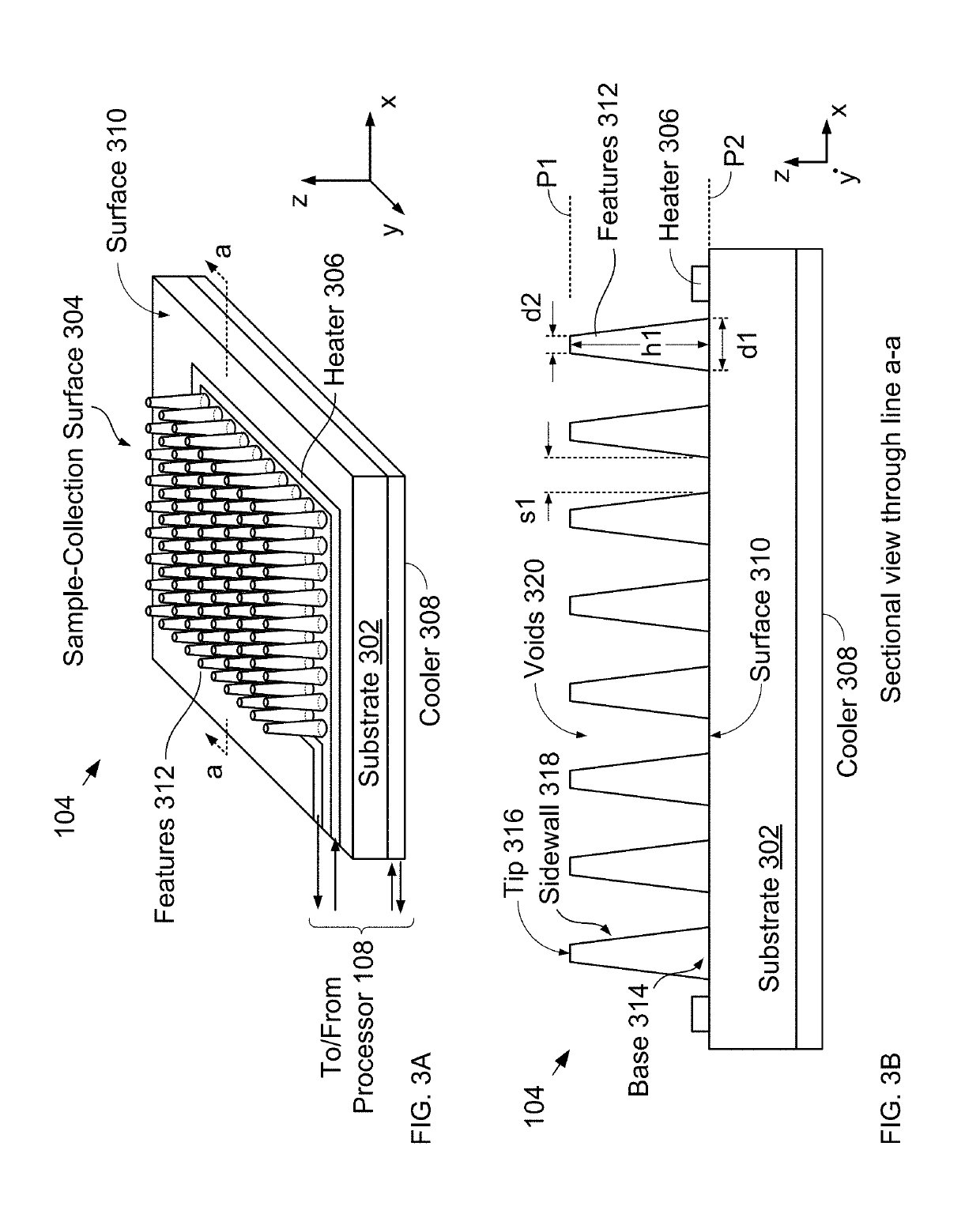
ActiveUS20190170637A1Increase surface areaMeasurementPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsTemperature controlFourier transform infrared spectroscopy
The present disclosure is directed toward a measurement system capable of rapid spectroscopic and calorimetric analysis of the chemical makeup of a test sample. Systems in accordance with the present disclosure include a low-thermal-mass sample holder having a substrate whose surface has been engineered to create a large-area sample-collection surface. The sample holder includes an integrated temperature controller that can rapidly heat or cool the test sample. As a result, the sample holder enables differential scanning calorimetry Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (DSC-FTIR) that can be performed in minutes rather than hours, as required in the prior art.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Steerable shape sensing biopsy needle
A biopsy needle has a central axis and includes one or more sensing regions, each sensing region formed by a plurality of sensing optical fibers located over a particular extent of said central axis and inside the outer shell of the needle. The sensing optical fibers are coupled to a wavelength interrogator. A steerable catheter has a central axis and outer shell, the outer shell coupled to a plurality of optical fibers in sensing regions and actuation regions, the sensing regions formed over particular extents of the central axis by bonding gratings to the inner surface of the outer shell, and the actuation regions formed by coupling optical energy into shape memory alloys bonded to the outer shell.
Owner:INTELLIGENT FIBER OPTIC SYST
Method and apparatus for measurement of cardiopulmonary function
ActiveUS10799125B2Accurate measurementEliminate inaccuraciesRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsAnatomical dead spaceEngineering
A method for measuring anatomical dead space in a lung, the method comprising: (a) providing, in a supply of inspired gas, at least one indicator gas for inhalation by a patient during a test, the concentration of the indicator gas being controlled such as to follow a sinewave pattern over successive breaths; (b) measuring, over successive breaths, the flow rate and concentration of the indicator gas during both inspiration and exhalation of the patient; (c) fitting sinewave envelopes to the measured concentration values of the indicator gas over the successive breaths and, from the fitted sinewave envelopes, determining the inspired concentration, the mixed expired concentration, and the end expired concentration in respect of the indicator gas for each breath; and (d) calculating the anatomical dead space for each of a plurality of inspirations based on a conservation-of-mass principle. Also provided is a test apparatus for carrying out such a method, and a computer program or set of instruction code which, when executed, causes a processor to implement such a method.
Owner:PHAN PHI ANH +2
Surface texture measuring probe and microscope utilizing the same
ActiveUS7581438B2MeasurementHigh measurement accuracyNanoopticsMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsMicroscope
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Sample measuring apparatus and sample measuring method
The sample measuring apparatus includes a suction unit that includes a nozzle and a drive unit that raises and lowers the nozzle, and suctions a first liquid and a second liquid that is different from the first liquid; a liquid surface detecting unit that detects liquid surfaces of the first liquid and the second liquid; a control unit that controls the suction unit, and a measuring unit that measures a measurement sample prepared from the suctioned first liquid; wherein the control unit controls the suction unit to suction the first liquid and the second liquid based on the respective liquid surface detection result of the first liquid and the second liquid detected while lowering the nozzle, and a second speed at which the nozzle descends when detecting the liquid surface of the second liquid is faster than a first speed at which the nozzle descends when detecting the liquid surface of the first liquid.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
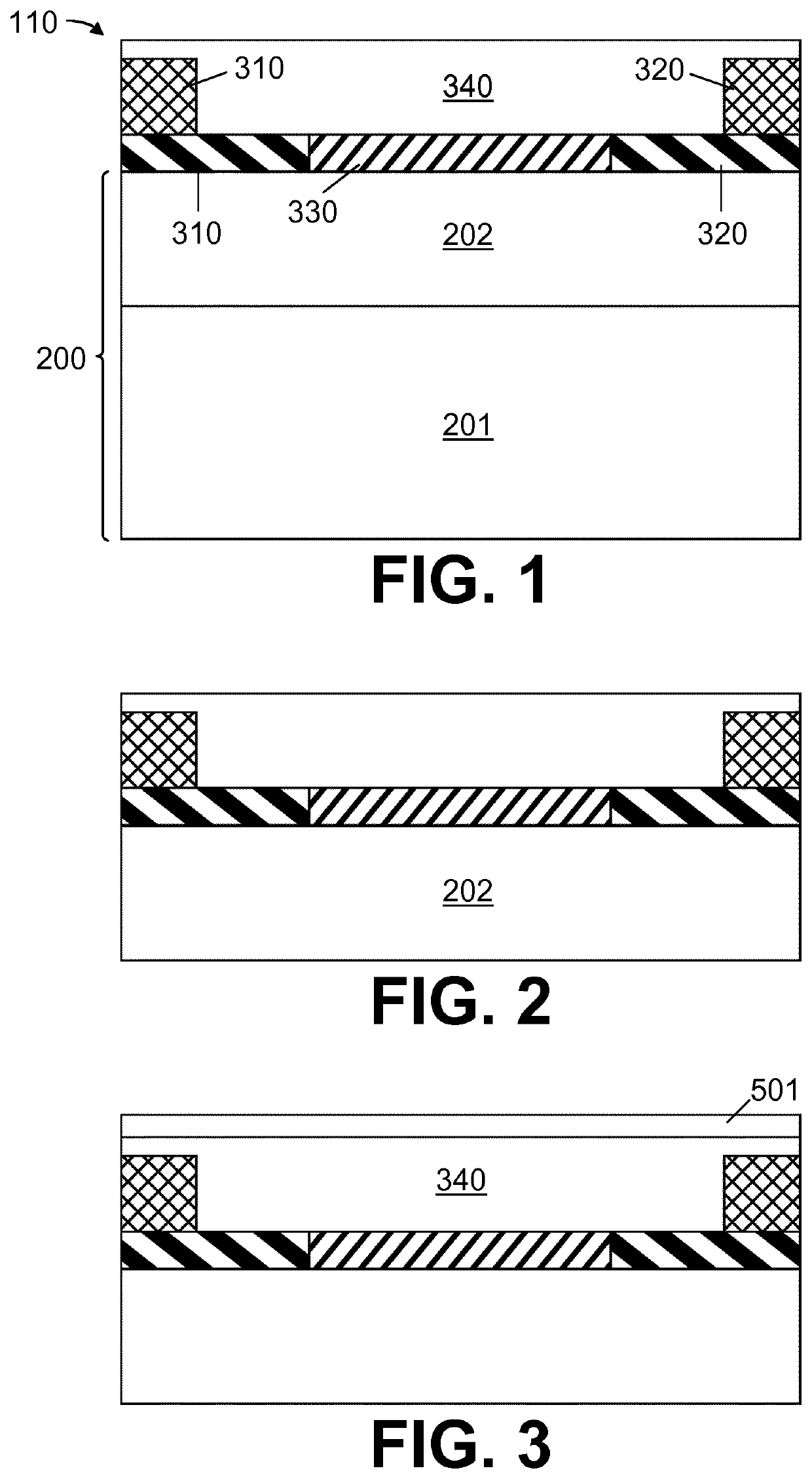
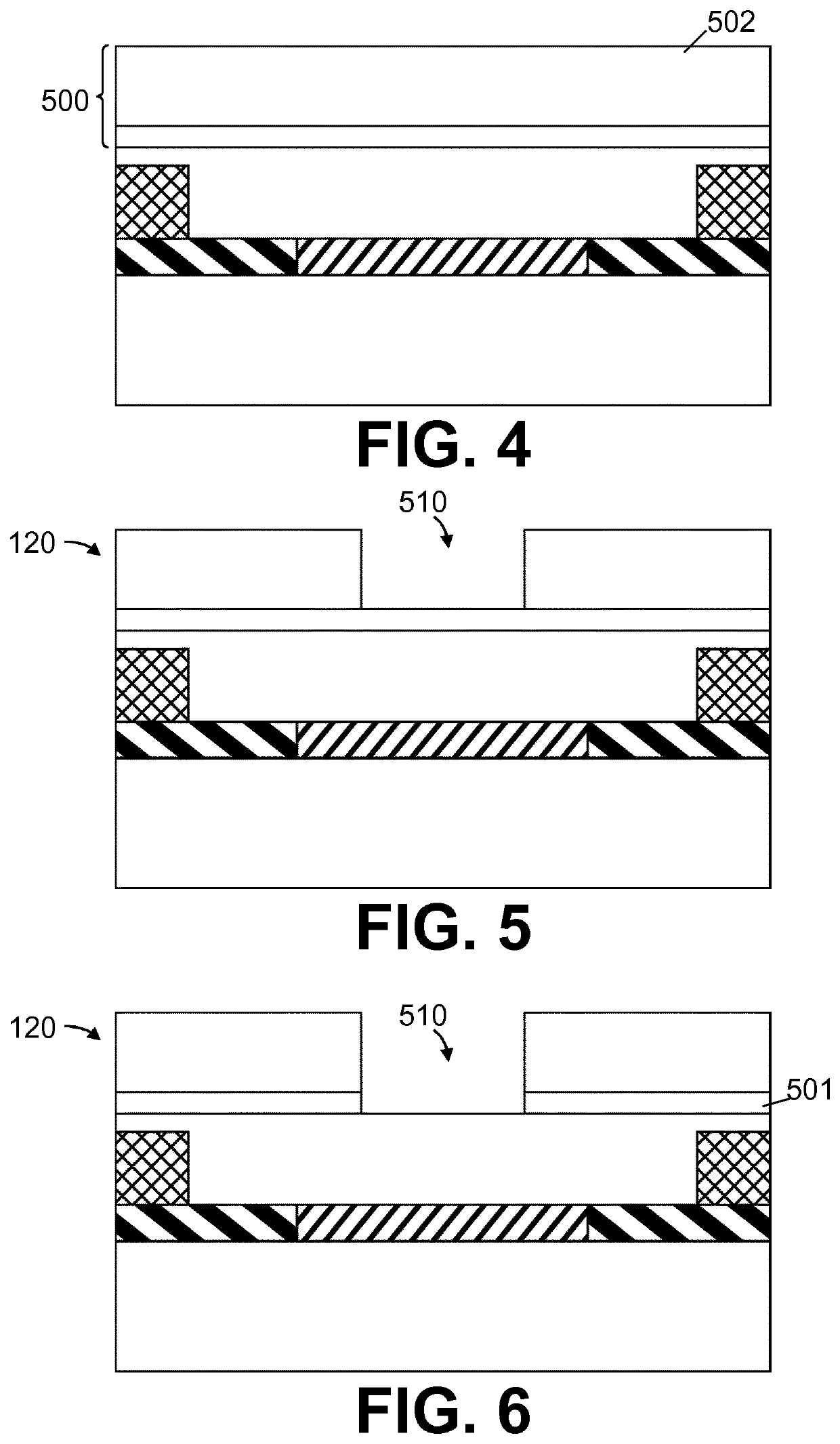
Nanopore FET Sensor with Non-Linear Potential Profile
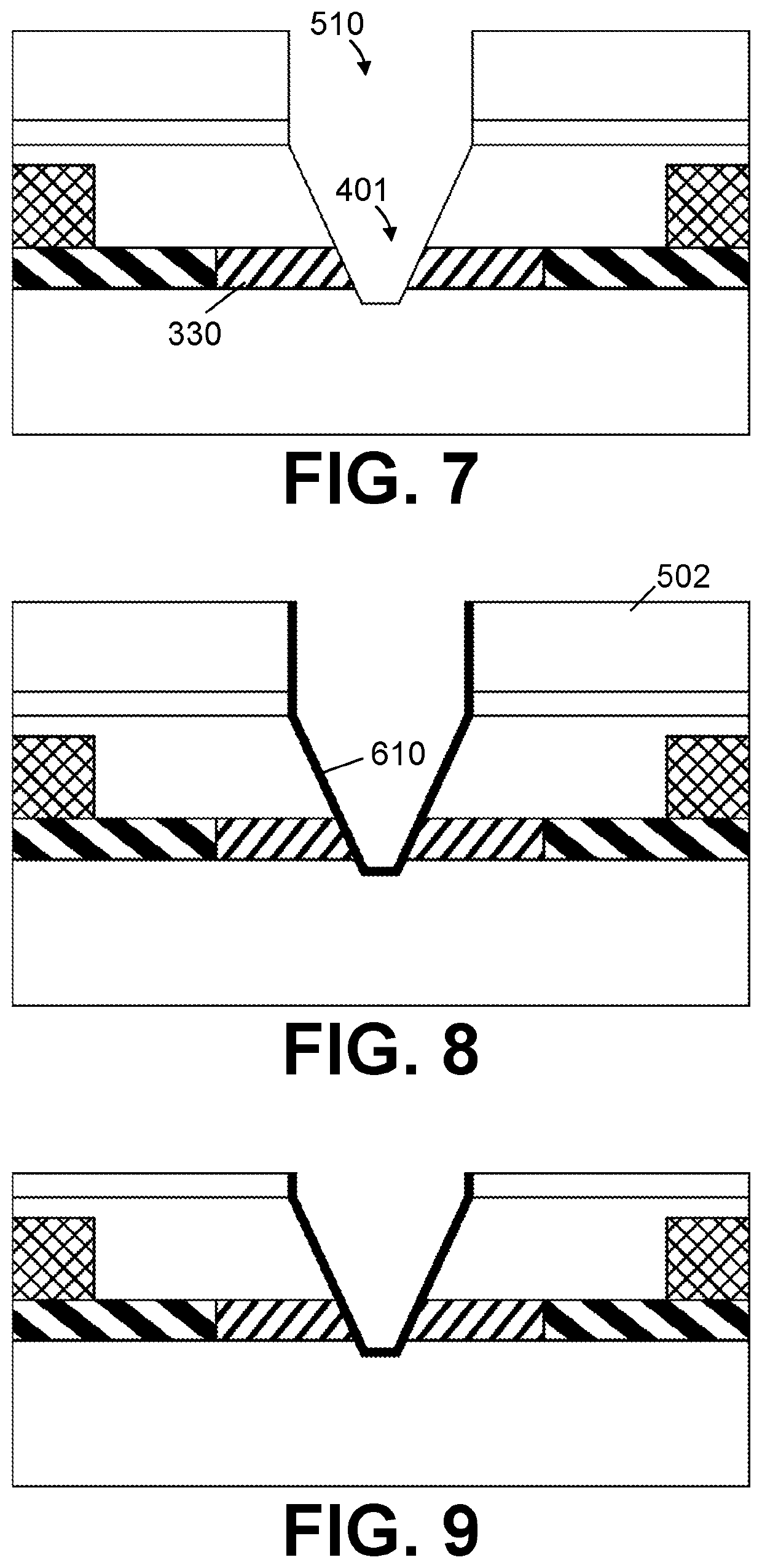
ActiveUS20210184053A1Uniform widthFacilitate detectionTransistorMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringLinear potential
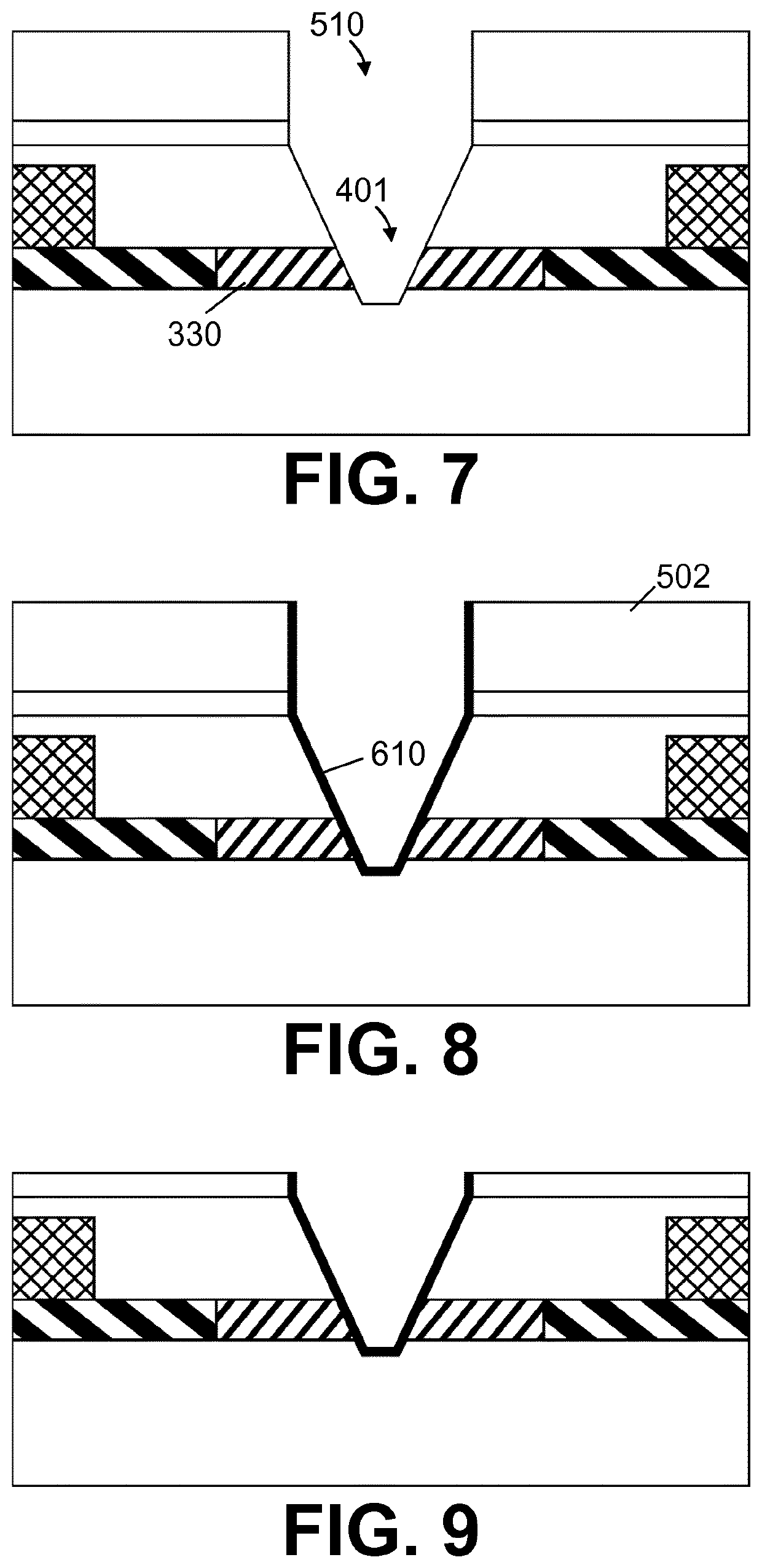
In a first aspect, the present invention relates to a nanopore field-effect transistor sensor (100), comprising: i) a source region (310) and a drain region (320), defining a source-drain axis; ii) a channel region (330) between the source region (310) and the drain region (320); iii) a nanopore (400), defined as an opening in the channel region (330) which completely crosses through the channel region (330), oriented at an angle to the source-drain axis, having a first orifice (410) and a second orifice (420), and being adapted for creating a non-linear potential profile between the first (410) and second (420) orifice.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Modified glycine oxidase
ActiveUS9976126B2MeasurementImprove propertiesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTest sampleThermal stability
The present invention provides a novel enzyme and methods of using the enzyme for measuring glycine concentration. Specifically, the present invention provides an enzyme in which at least one amino acid residue is mutated so as to improve a property of a glycine oxidase which is associated with the measurement of glycine (e.g., activity of glycine oxidase for glycine, thermal stability of glycine oxidase, and substrate specificity of glycine oxidase for glycine,); and a method of analyzing glycine, that includes measuring glycine contained in a test sample using the modified enzyme; and the like.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
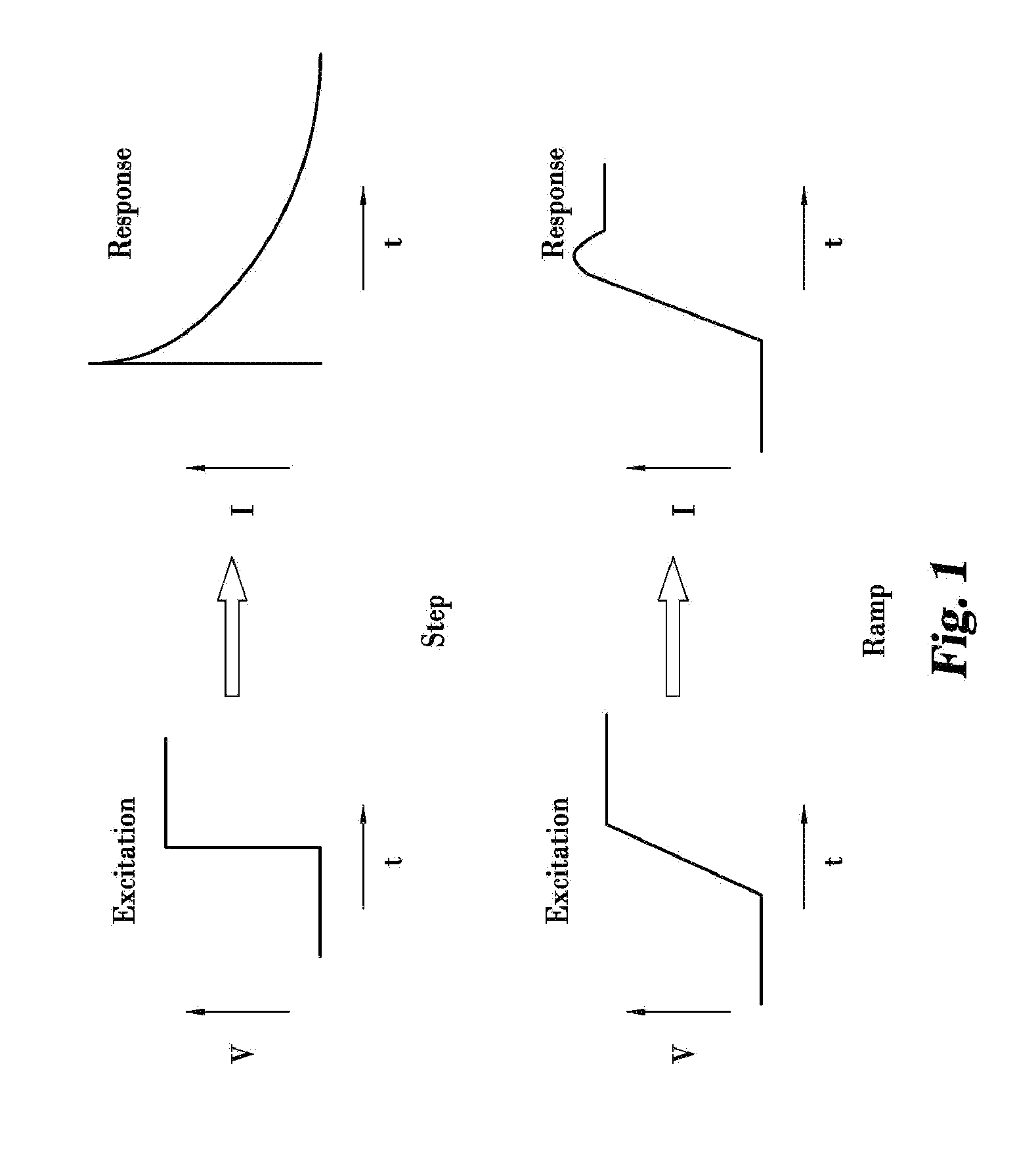
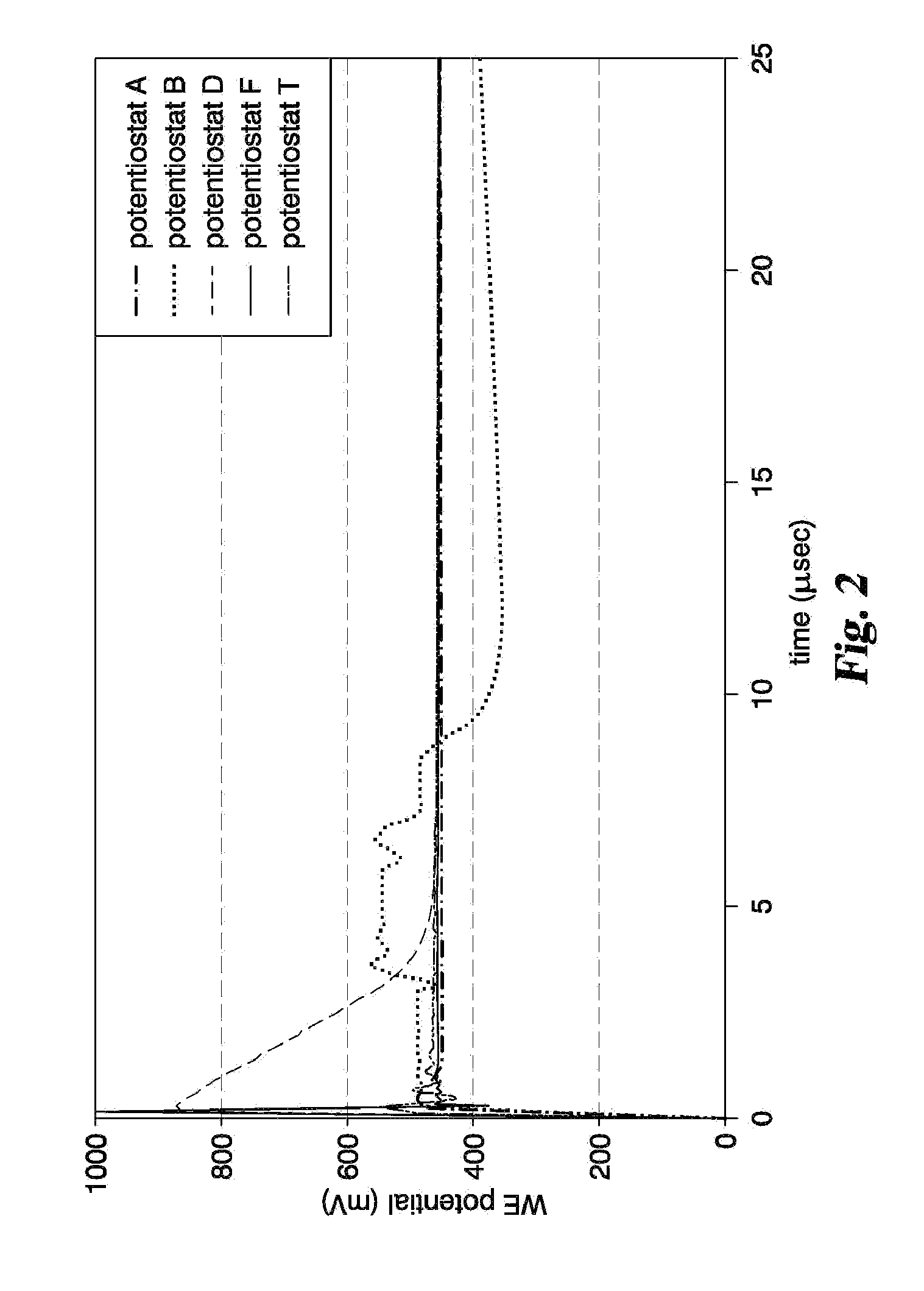
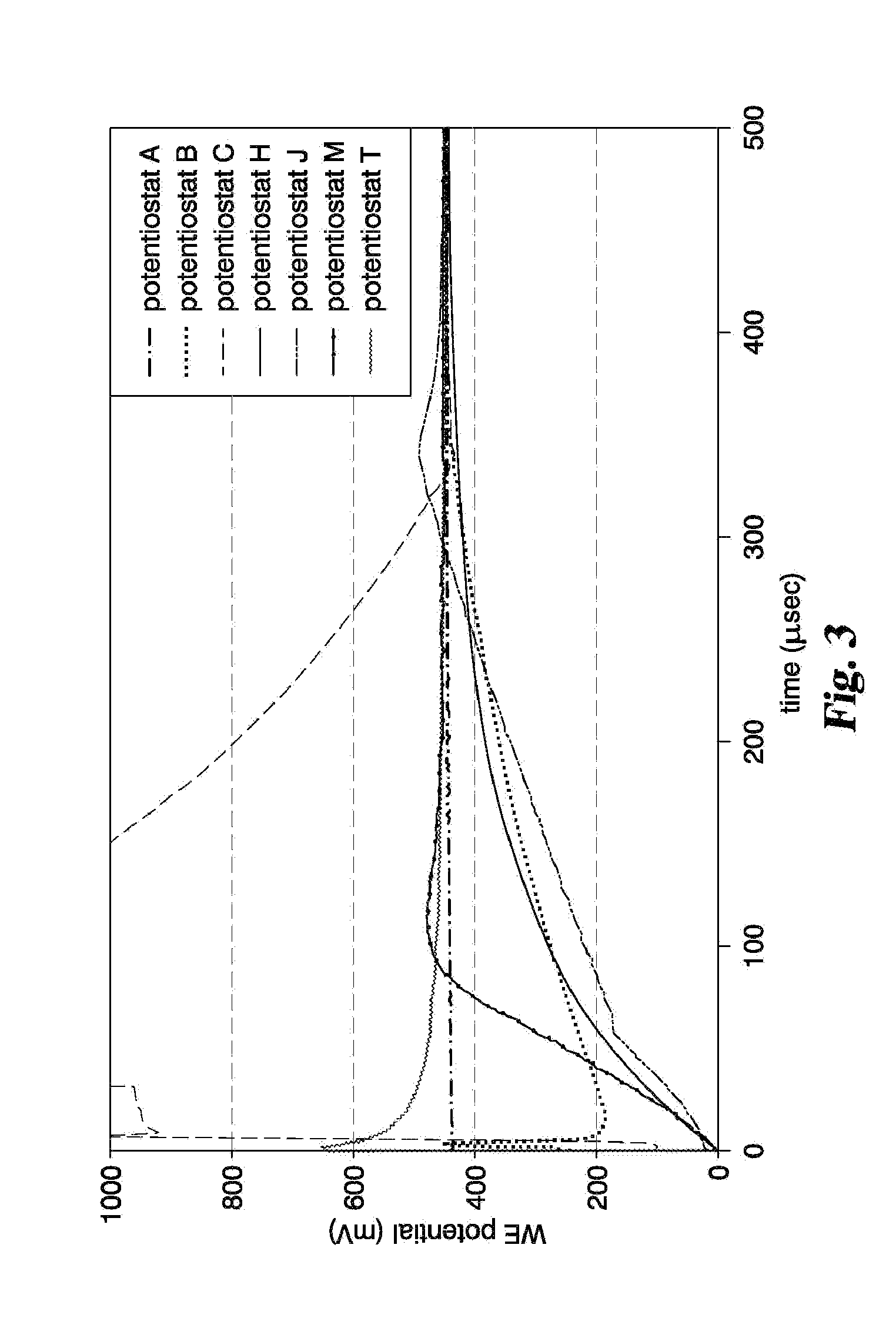
Controlled slew rate transition for electrochemical analysis
ActiveUS20130277235A1Limitation in slew rate capabilityMeasurementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAudio power amplifierTested time
Measurement systems and methods are disclosed for minimizing the effects created by a meter's output amplifier during electrochemical measurements. In the systems and methods, transition of an excitation potential applied between electrodes of a test strip is controlled so that it is at a sufficiently slow rate below a slew rate capability of the system (but still fast enough to minimally impact overall test time) to reduce variability in the test results. The methods and systems therefore use a transition having a ramp-shaped waveform, a sinusoidal-shaped waveform or an exponential-shaped waveform. Additionally, the excitation potential can be purposefully controlled by a processor, memory driven digital-to-analog converter or external circuitry at a rate sufficiently slow to make variations in the analog electronics slew rate insignificant for all sample types and test conditions.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Controlling radio measurements of a user equipment within a cellular network system
ActiveUS9622125B2MeasurementImprove performanceNetwork topologiesTransmissionEngineeringUser equipment
It is described a method for controlling radio measurements of a user equipment within a cellular network system, wherein the user equipment is served by a cell of a first cell type characteristic, the cell being assigned to a base station, wherein the cellular network system includes the cell and at least one further cell of a second cell type characteristic. The method includes providing, by the base station, a radio measurement configuration to the user equipment, wherein the radio measurement configuration is indicative for parameters to be applied by the user equipment for radio measurements, the radio measurement configuration includes different parameters being assigned to different cell type characteristics, and controlling the radio measurements of the user equipment based on the provided radio measurement configuration.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Nanopore FET sensor with non-linear potential profile
ActiveUS11367797B2Maximum sensitivityImprove spatial resolutionTransistorMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLinear potentialNanohole
In a first aspect, the present invention relates to a nanopore field-effect transistor sensor (100), comprising: i) a source region (310) and a drain region (320), defining a source-drain axis; ii) a channel region (330) between the source region (310) and the drain region (320); iii) a nanopore (400), defined as an opening in the channel region (330) which completely crosses through the channel region (330), oriented at an angle to the source-drain axis, having a first orifice (410) and a second orifice (420), and being adapted for creating a non-linear potential profile between the first (410) and second (420) orifice.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Furnace atmosphere measurement
ActiveUS10345229B2MeasurementRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsLength waveElectromagnetic radiation
A method of determining the concentration of a species in a portion of a furnace atmosphere is described. The method comprises the steps of measuring first, second and third intensities of electromagnetic radiation in the furnace at first, second and third wavelengths respectively. The third wavelength is selected to be representative of absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the species. A fourth intensity of electromagnetic radiation is calculated, being an estimate of the intensity of electromagnetic radiation in the furnace at the third wavelength absent any absorbing species in the furnace atmosphere. The third intensity and the fourth intensities are used to determine a parameter that is proportional to the concentration of absorbing species in the portion of the furnace atmosphere. Apparatus for carrying out the method is also described.
Owner:PILKINGTON GROUP LTD
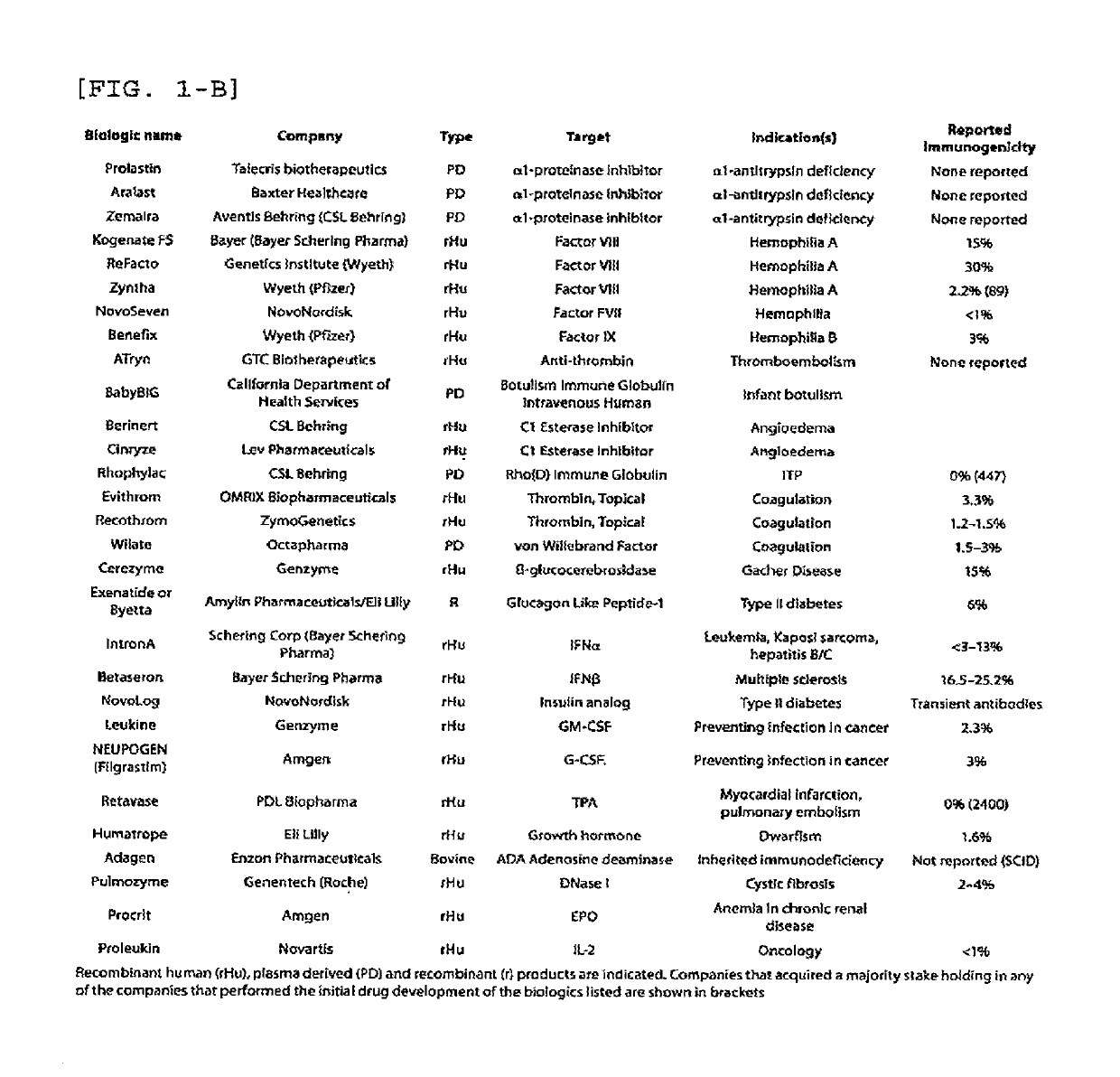
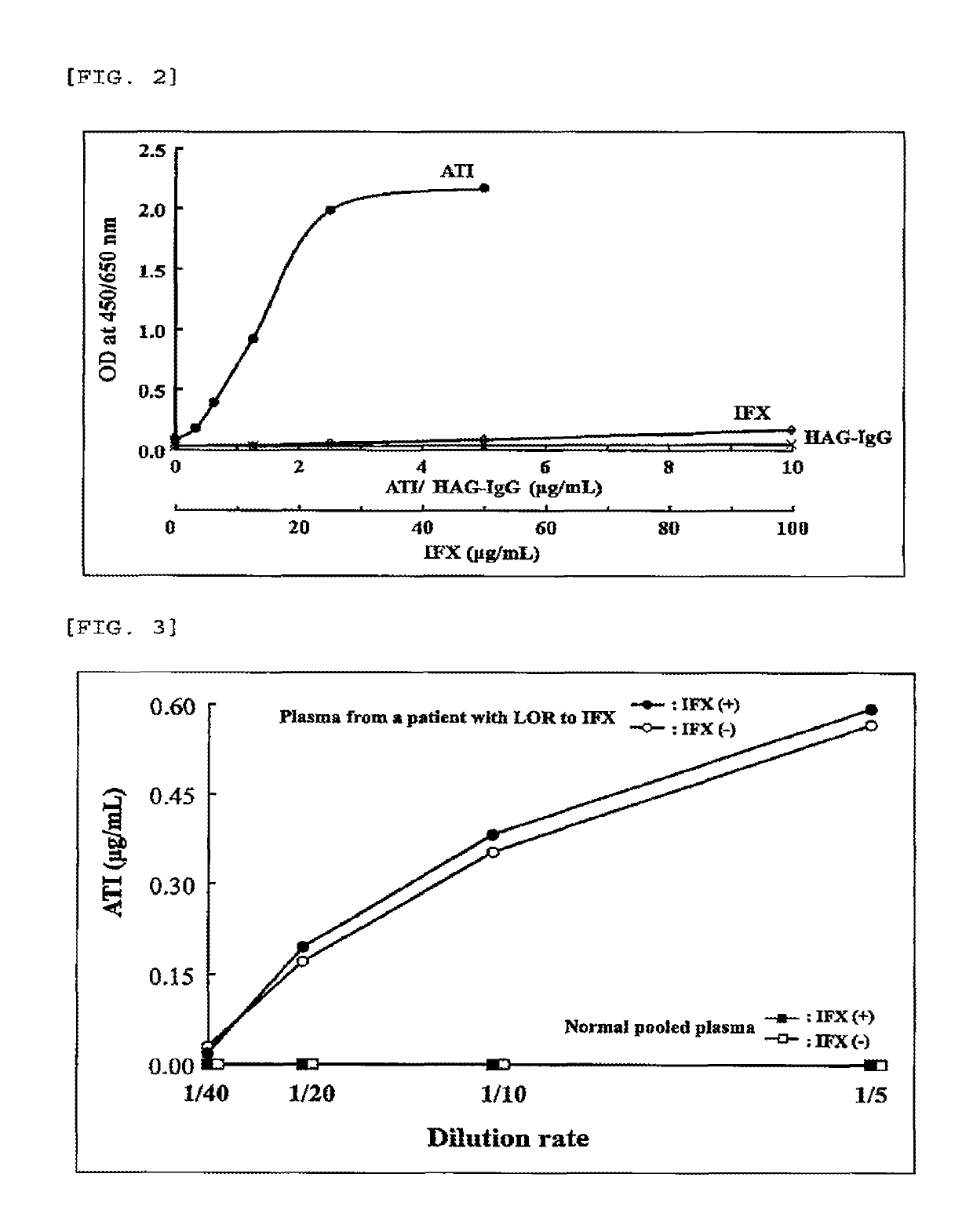
Method for measuring anti-drug antibody
ActiveUS10295534B2MeasurementSimple and accurate mannerAntipyreticAnalgesicsMolecular Targeted TherapiesTargeted therapy
Provided is a method for measuring anti-drug antibodies ADAs appearing in a patient receiving molecular-targeted therapy in a simpler and more accurate manner.
Owner:JIMRO
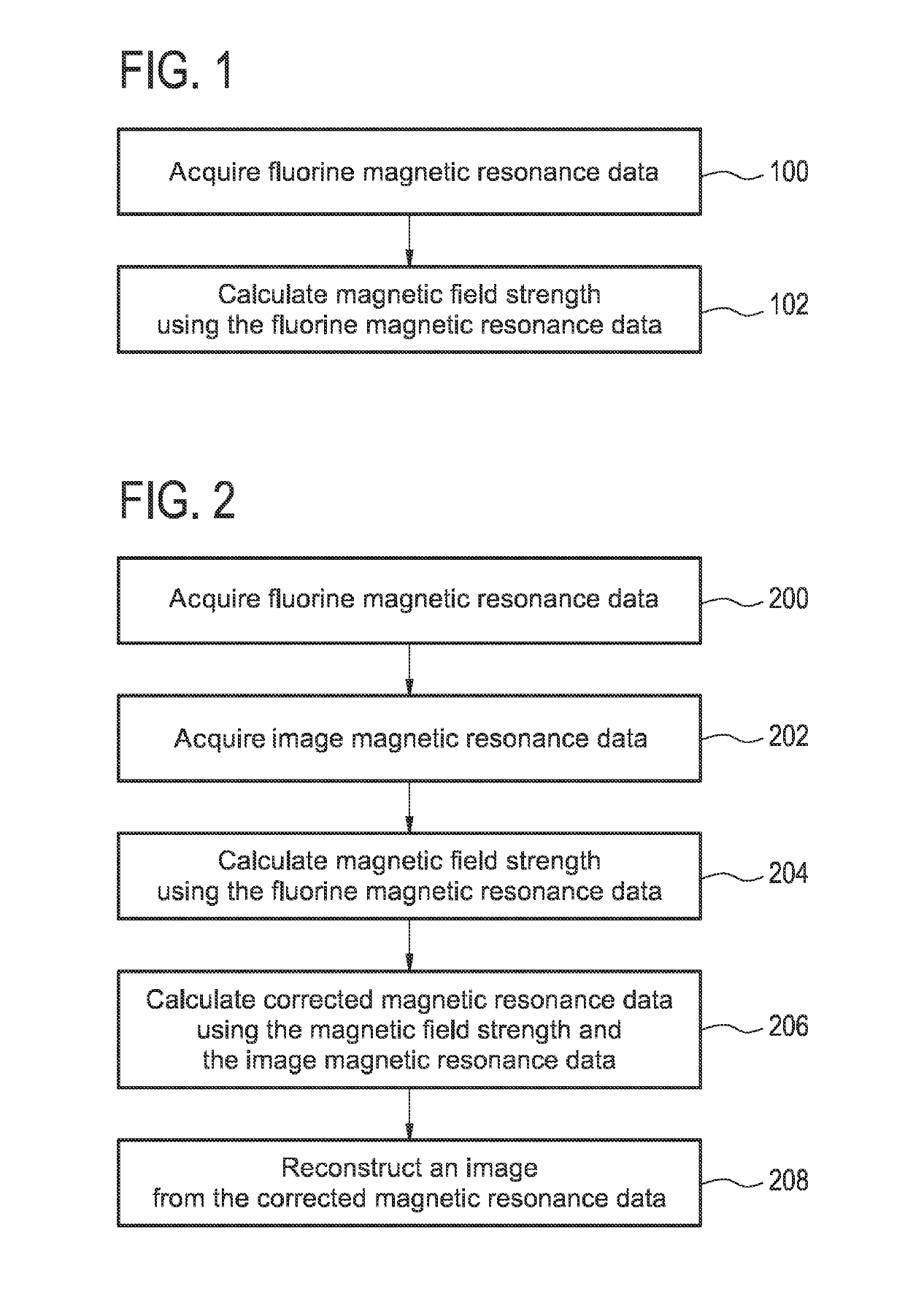
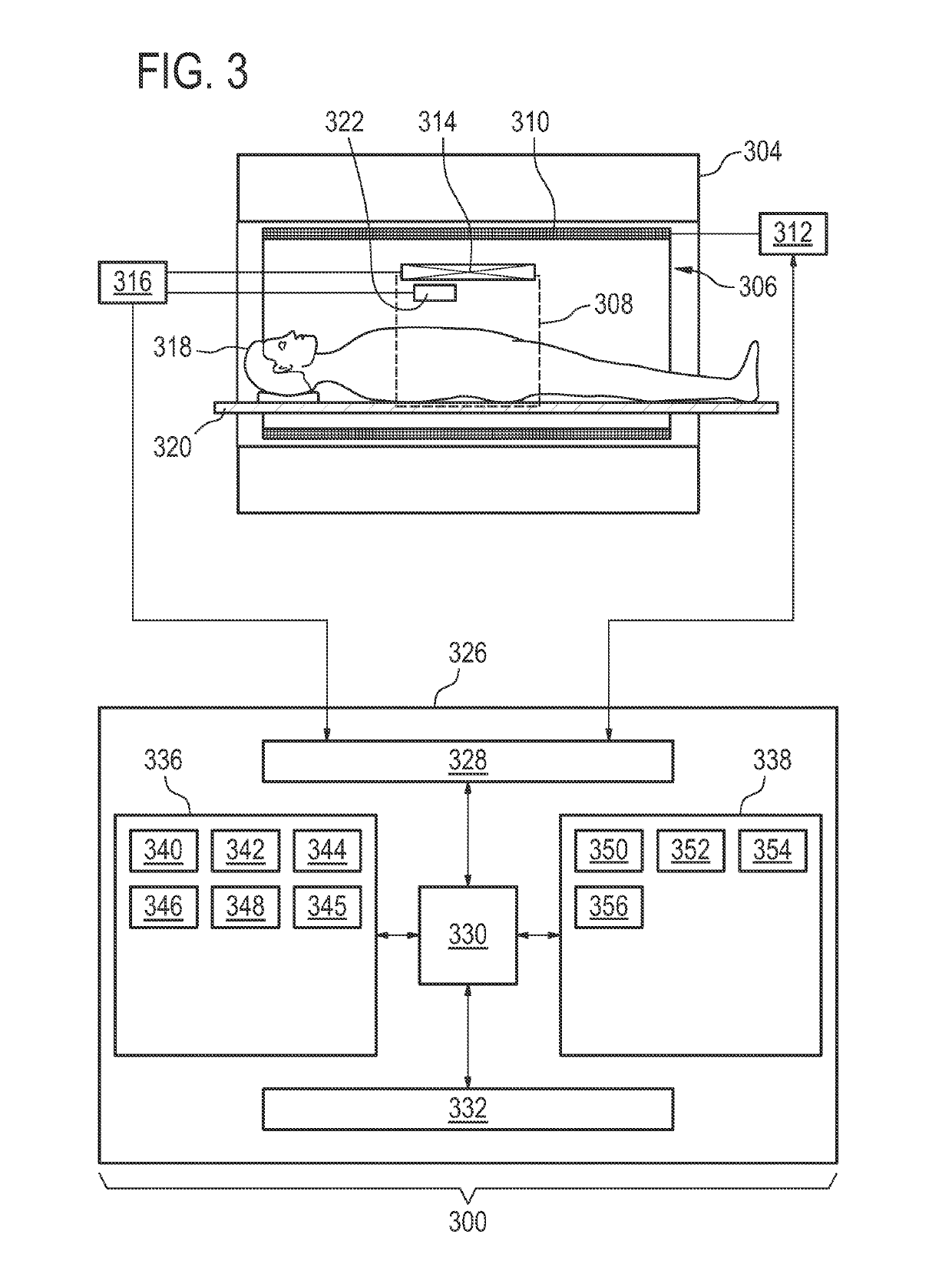
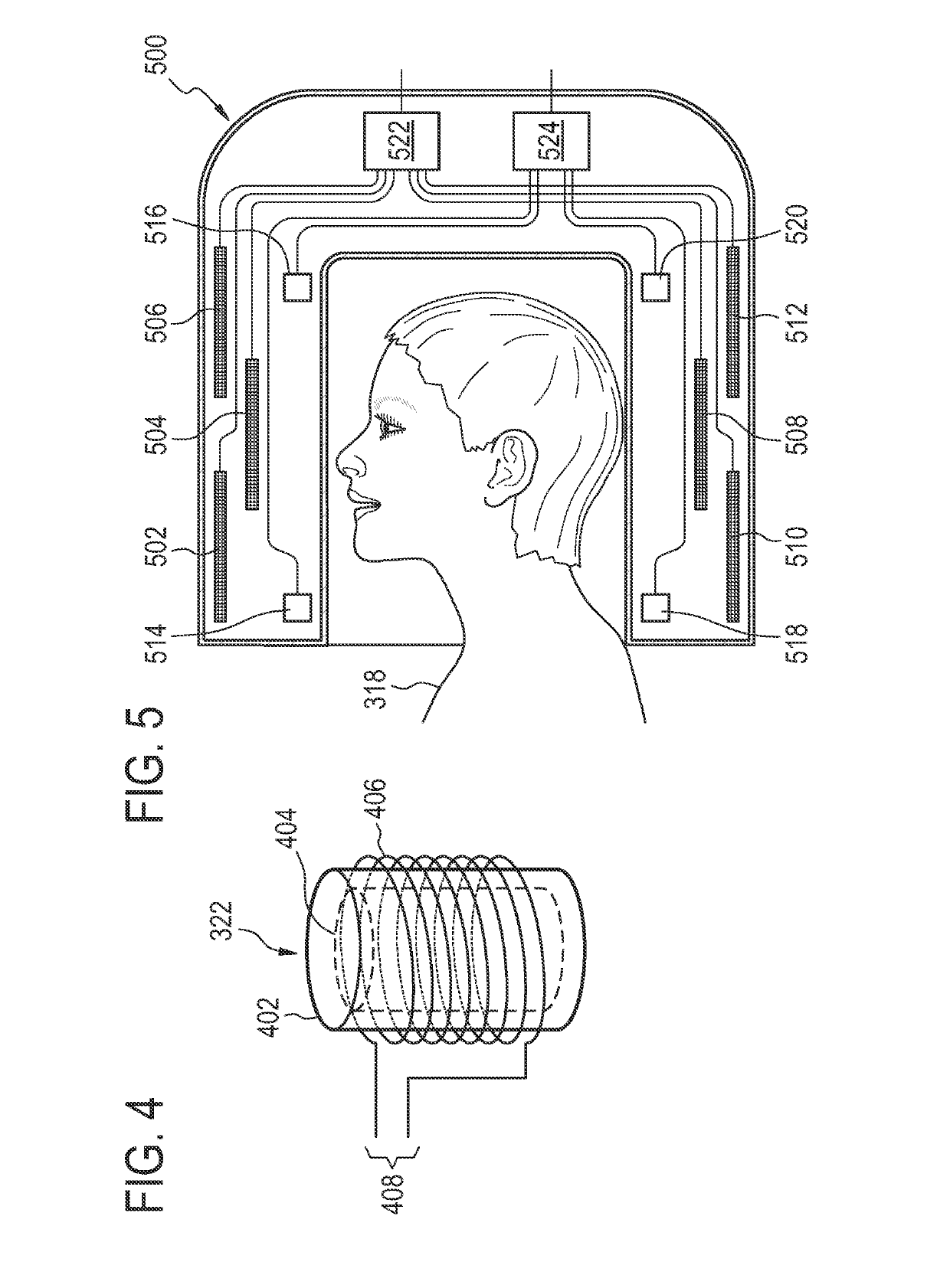
Magnetic field probe for MRI with a fluoroelastomer or a solution of a fluorine-containing compound
ActiveUS10416260B2Not easily encapsulatedDifficult to handleMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsTransceiverRadio frequency
A magnetic field within a magnetic resonance (MR) imaging system (300) is measured. The MR system includes a magnet (304) with an imaging zone (308), a radio-frequency transceiver (316), and a magnetic field probe (322) located within the imaging zone. The magnetic field probe includes a fluorine sample (404) including any one of the following: a fluoroelastomer (700), a fluorine containing ionic liquid (600), and a solution of a fluorine containing compound. The field probe further includes an antenna (406) for manipulating the magnetic spins of the fluorine sample and for receiving fluorine magnetic resonance data from the fluorine sample. The antenna is connected to the radio-frequency transceiver. The method includes acquiring (100, 200) the fluorine magnetic resonance data using the magnetic resonance imaging system and calculating (102, 206) a magnetic field strength (344) using the fluorine magnetic resonance data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com