Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
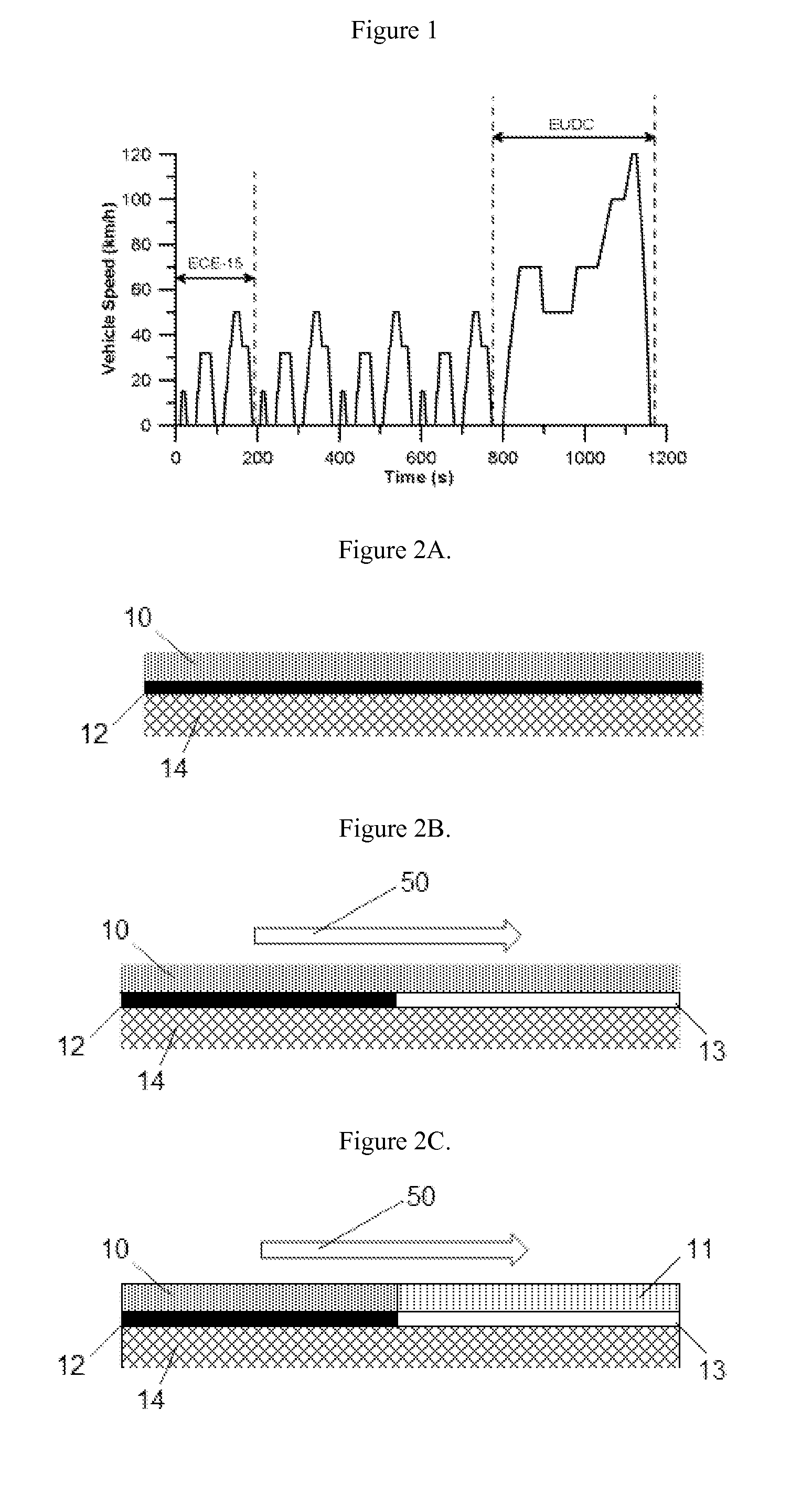
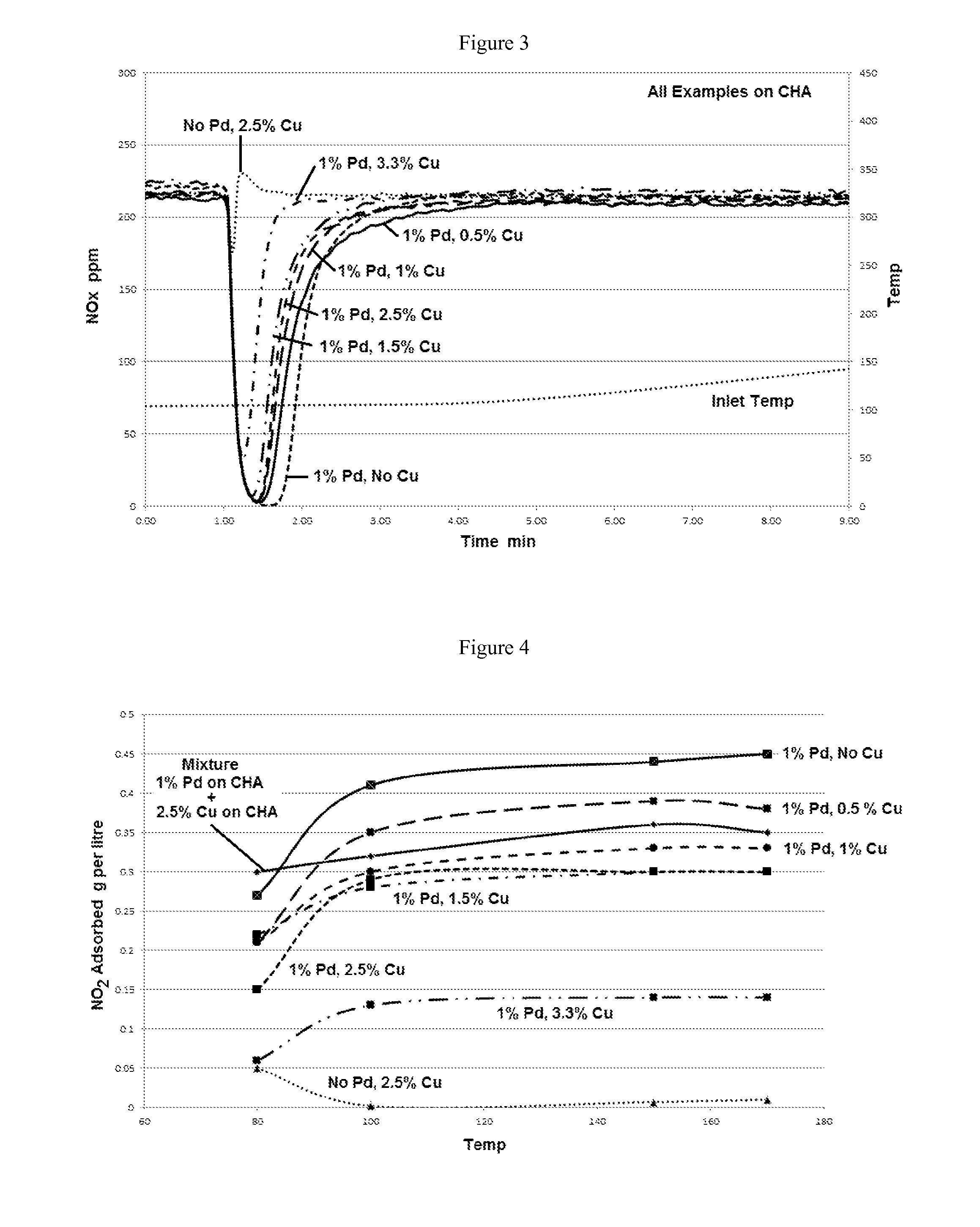
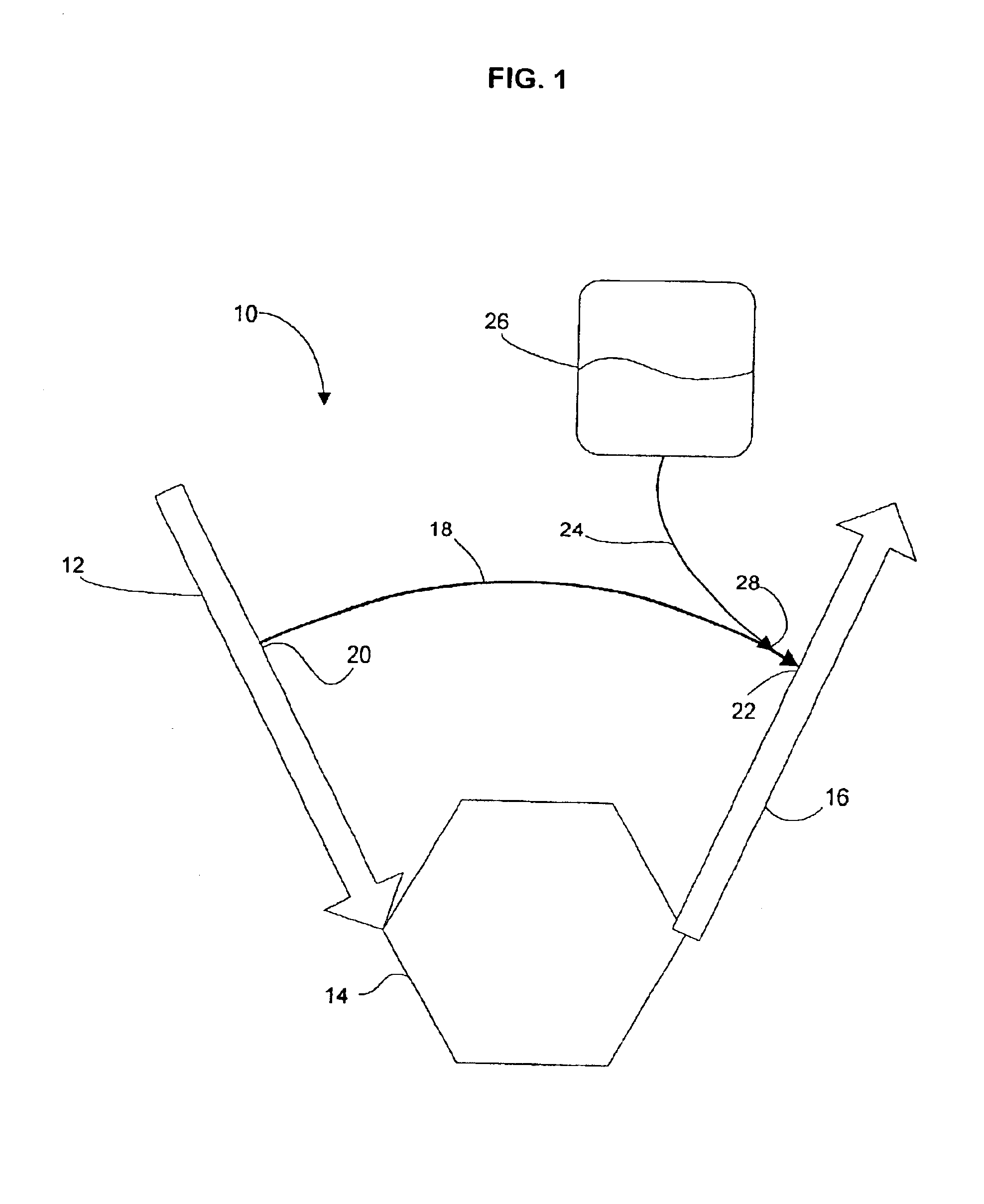
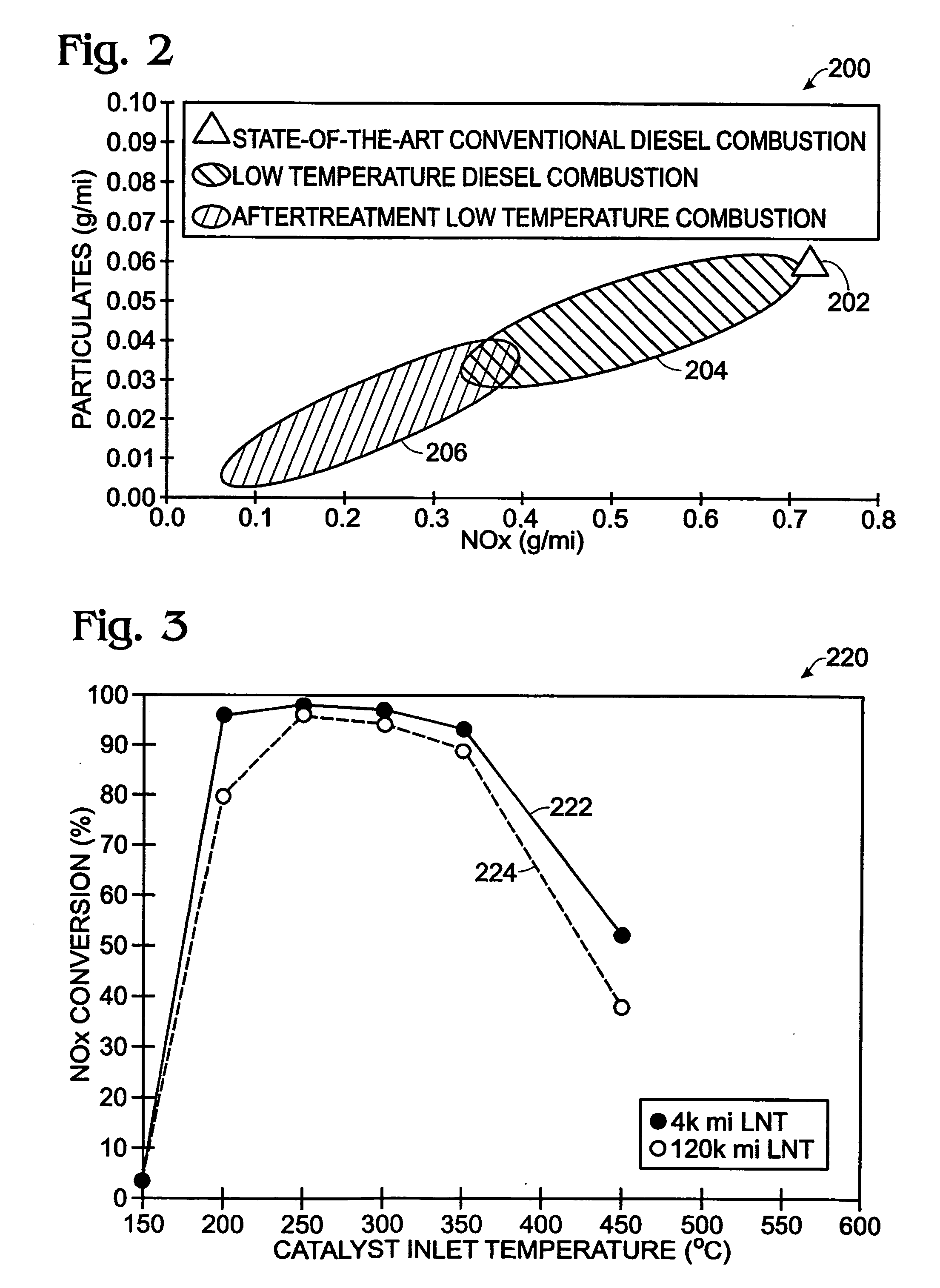
Combining SCR with PNA for Low Temperature Emission Control
ActiveUS20160136626A1Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesReducing stored NOxCombination devicesGas treatmentMolecular sievePtru catalyst
A catalyst article comprises an SCR catalyst and a NOx adsorber catalyst, where each of these catalysts comprise a metal molecular sieve, each with a different metal. The catalyst article can be close coupled with other components to give a NOX performance advantage from cold start to a combined DOC and SCRF system. Higher NOX conversion is also shown in under-floor location due to NOx storage before SCR light off and selective NH3 slip control, allowing higher NH3 fill levels. Systems comprising the catalyst article and methods of using the catalyst article to give improved hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide control, as well as ammonia slip control, are described. The systems can include flow-through or wall-flow monoliths.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
System and method for reducing nitrogen oxides in combustion exhaust streams
InactiveUS6865881B2Reduce concentrationReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesNitrogen oxidesCombustion
A system and method for reducing nitrogen oxide emissions (NOx) in the exhaust from a combustion device, such as a reciprocating engine, using a solution containing a NOx reducing agent which is mixed with and atomized by air flow drawn from the combustion intake and injected into the combustion exhaust.
Owner:COMBUSTION COMPONENTS ASSOCS +1
Catalyst and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20090263297A1Emission reductionReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesNitrous oxide captureCombination devicesCatalytic metalZeolite
Disclosed herein is a catalytic composition comprising a first catalyst composition portion that comprises a zeolite; and a second catalyst composition portion that comprises a catalytic metal disposed upon a porous inorganic substrate; the first catalyst composition portion and the second catalyst composition portion being in an intimate mixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and systems for operating combustion systems
ActiveUS7168947B2Reducing nitrogen oxideReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesStaged combustionFurnace typesCombustion systemCombustion
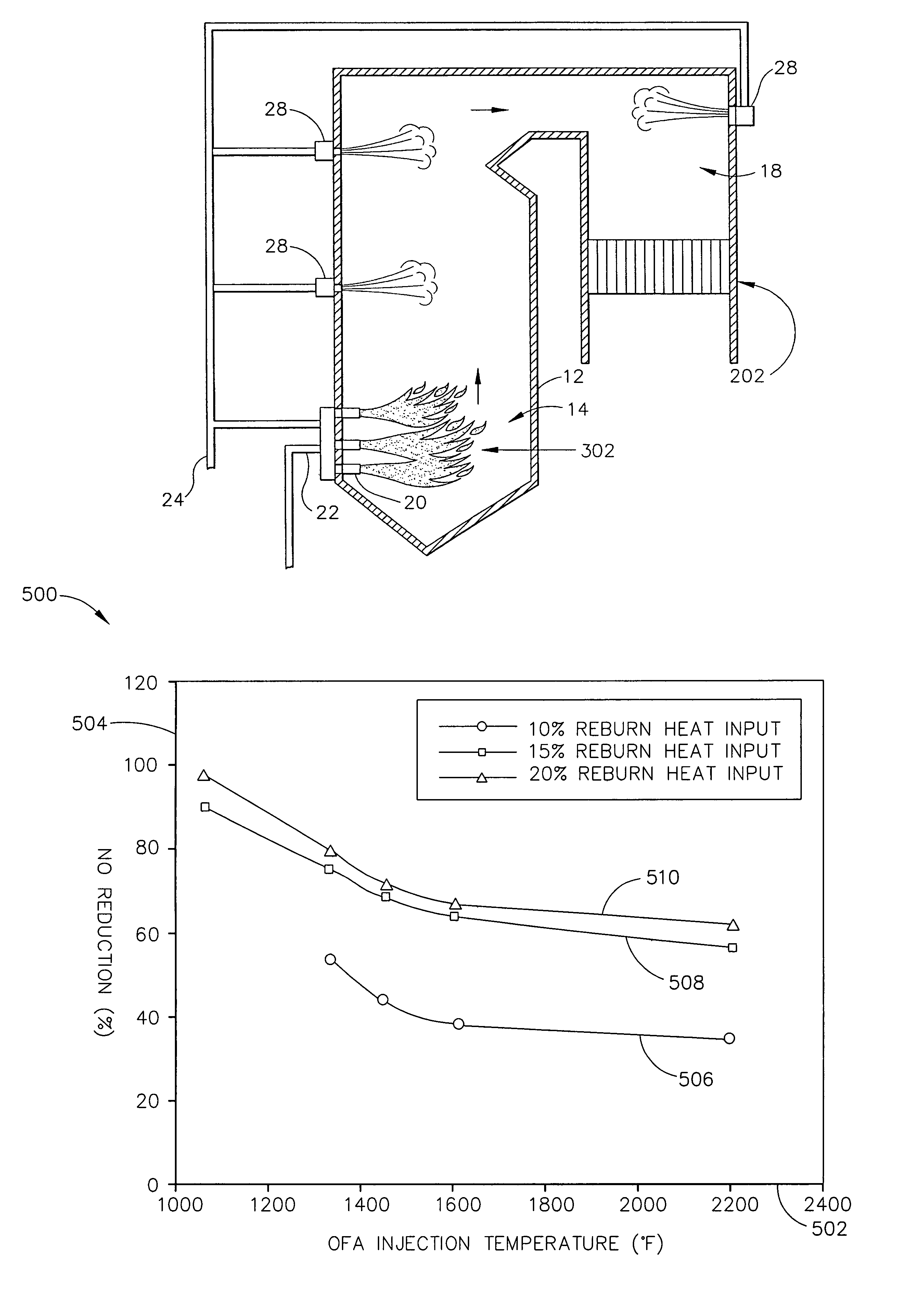
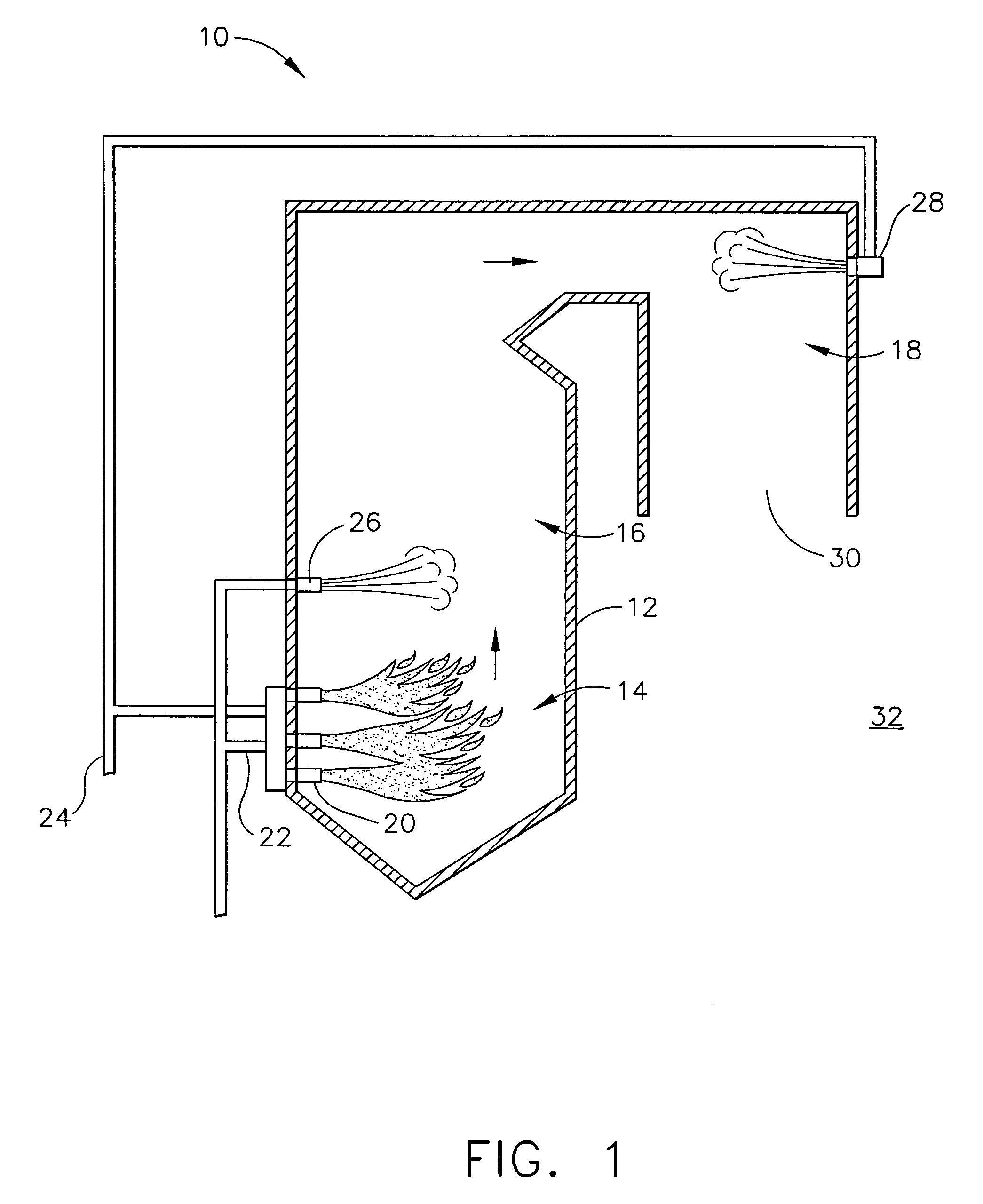
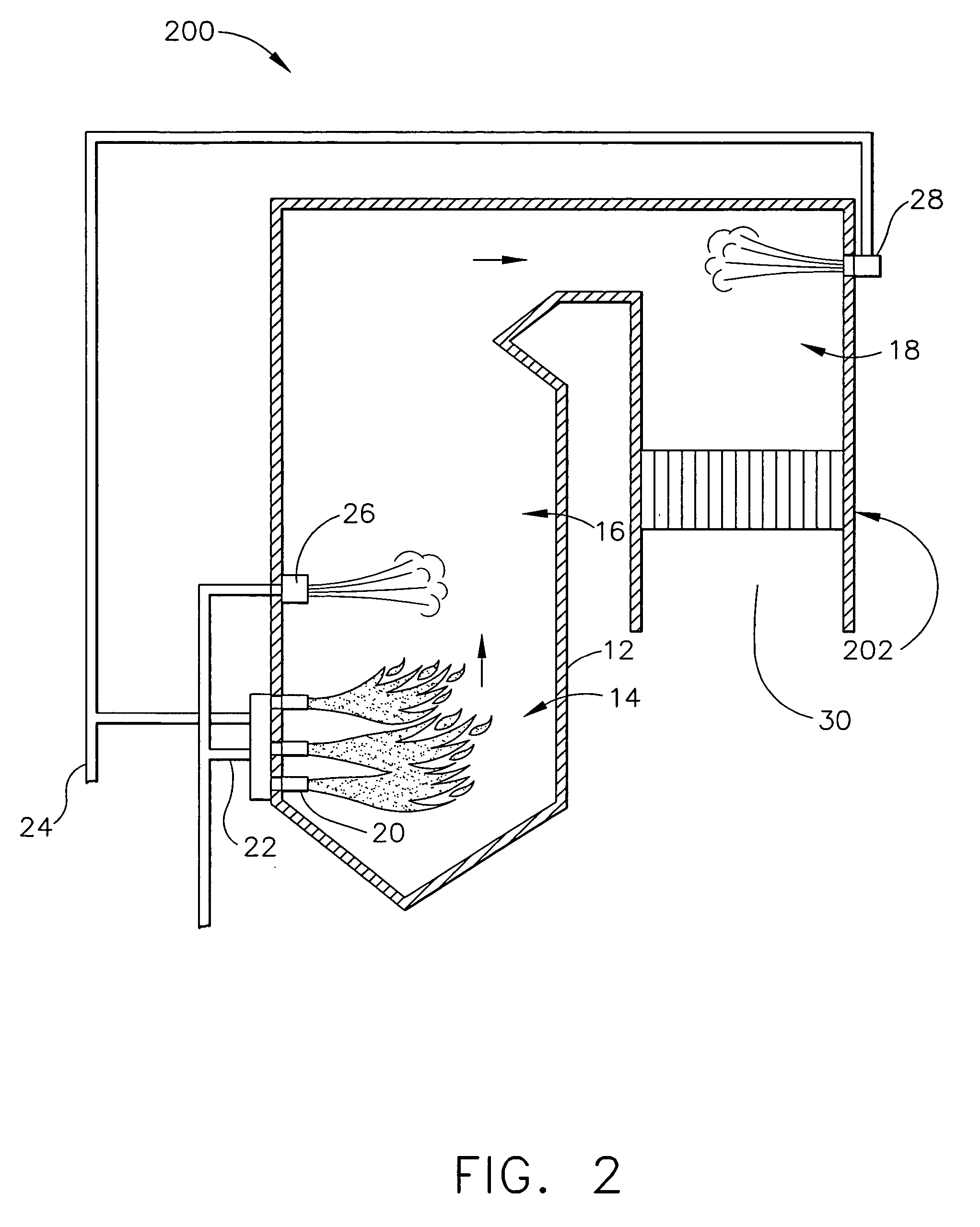
Methods and systems for reducing nitrogen oxides in combustion flue gas is provided. The method includes combusting a fuel in a main combustion zone such that a flow of combustion flue gas is generated wherein the combustion flue gas includes at least one nitrogen oxide species, establishing a fuel-rich zone, forming a plurality of reduced N-containing species in the fuel rich zone, injecting over-fire air into the combustion flue gas downstream of fuel rich zone, and controlling process parameters to provide conditions for the reduced N-containing species to react with the nitrogen oxides in the OFA zone to produce elemental nitrogen such that a concentration of nitrogen oxides is reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for reducing NOx emissions in an apparatus having a diesel engine
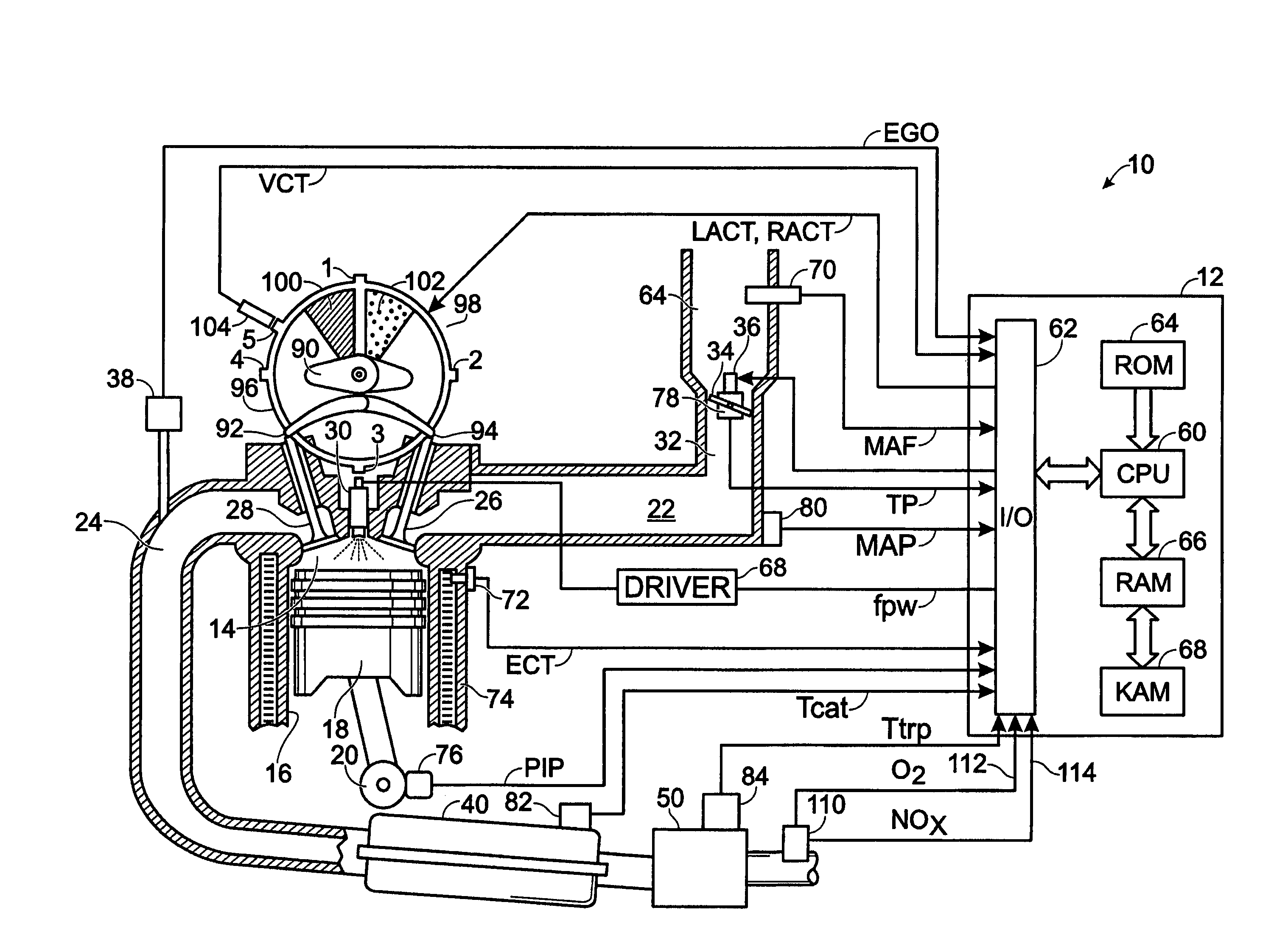
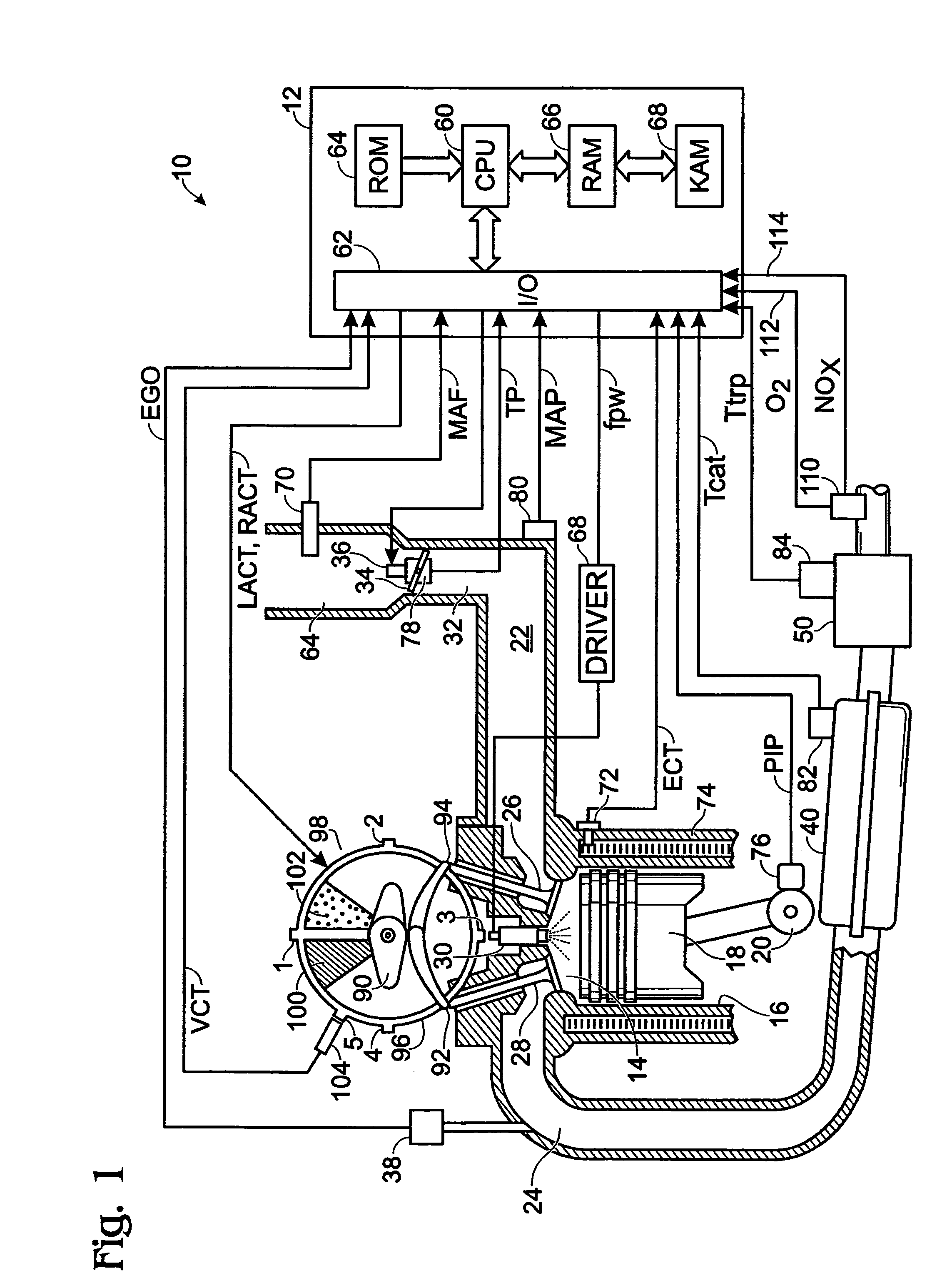
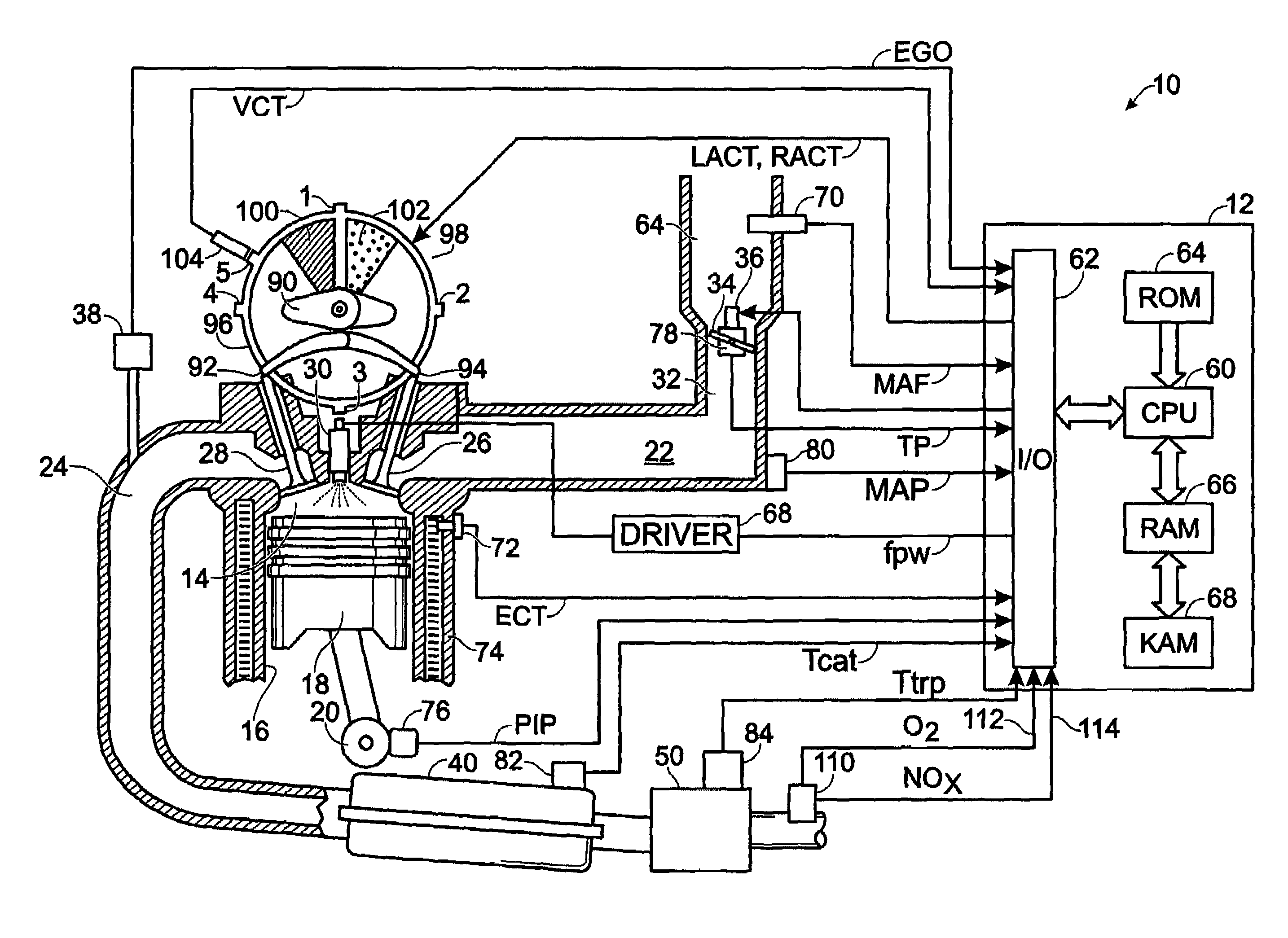
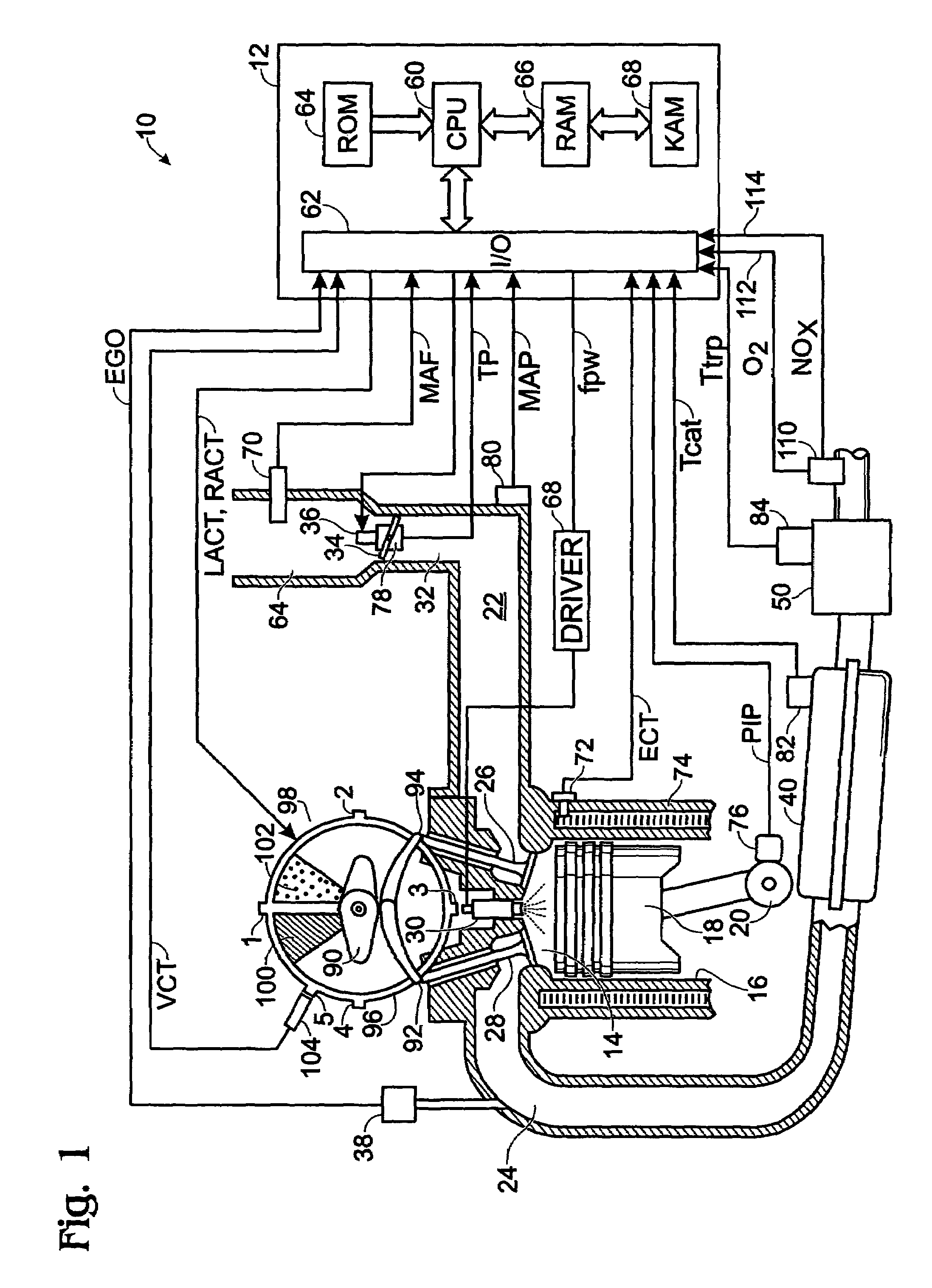
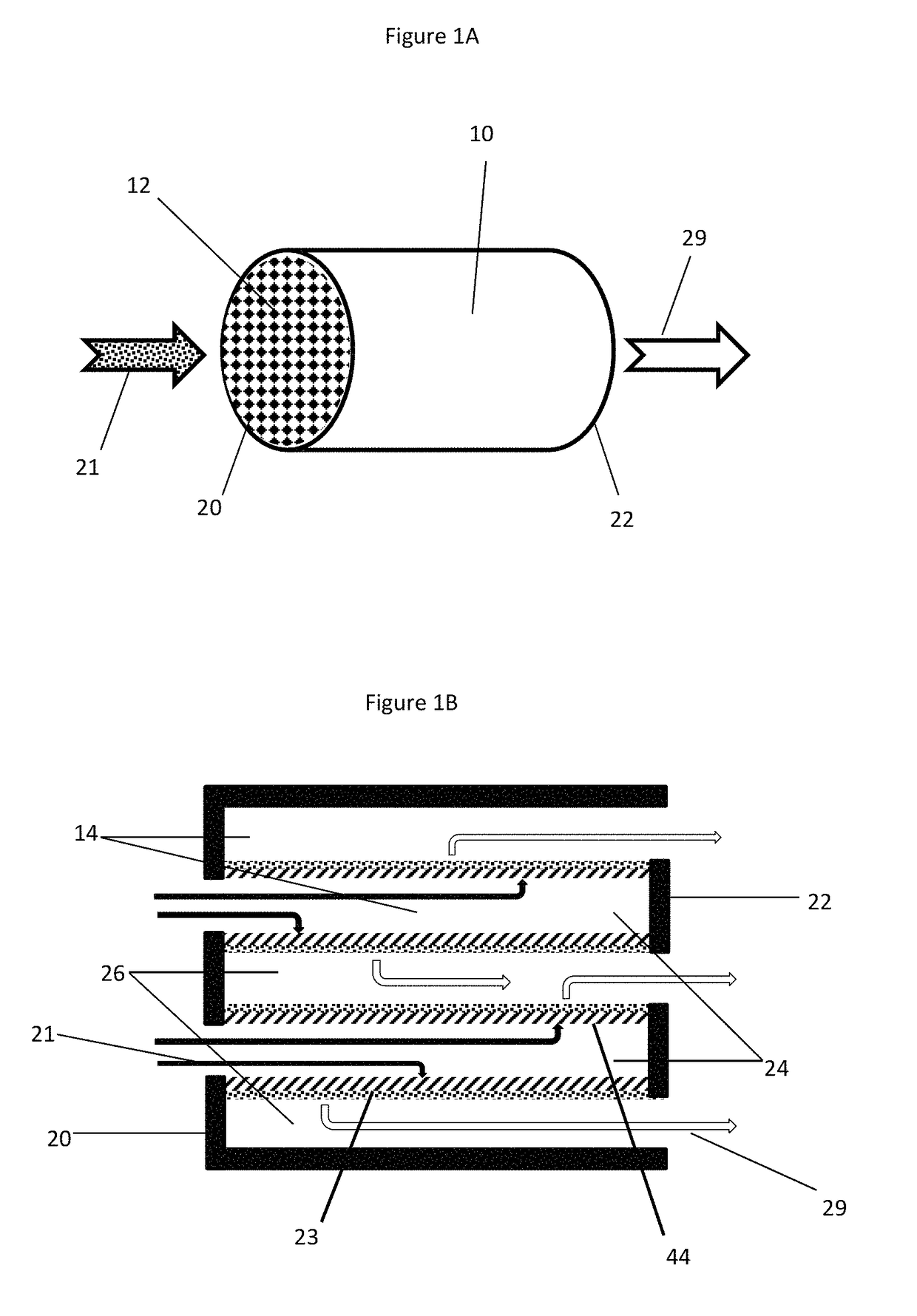
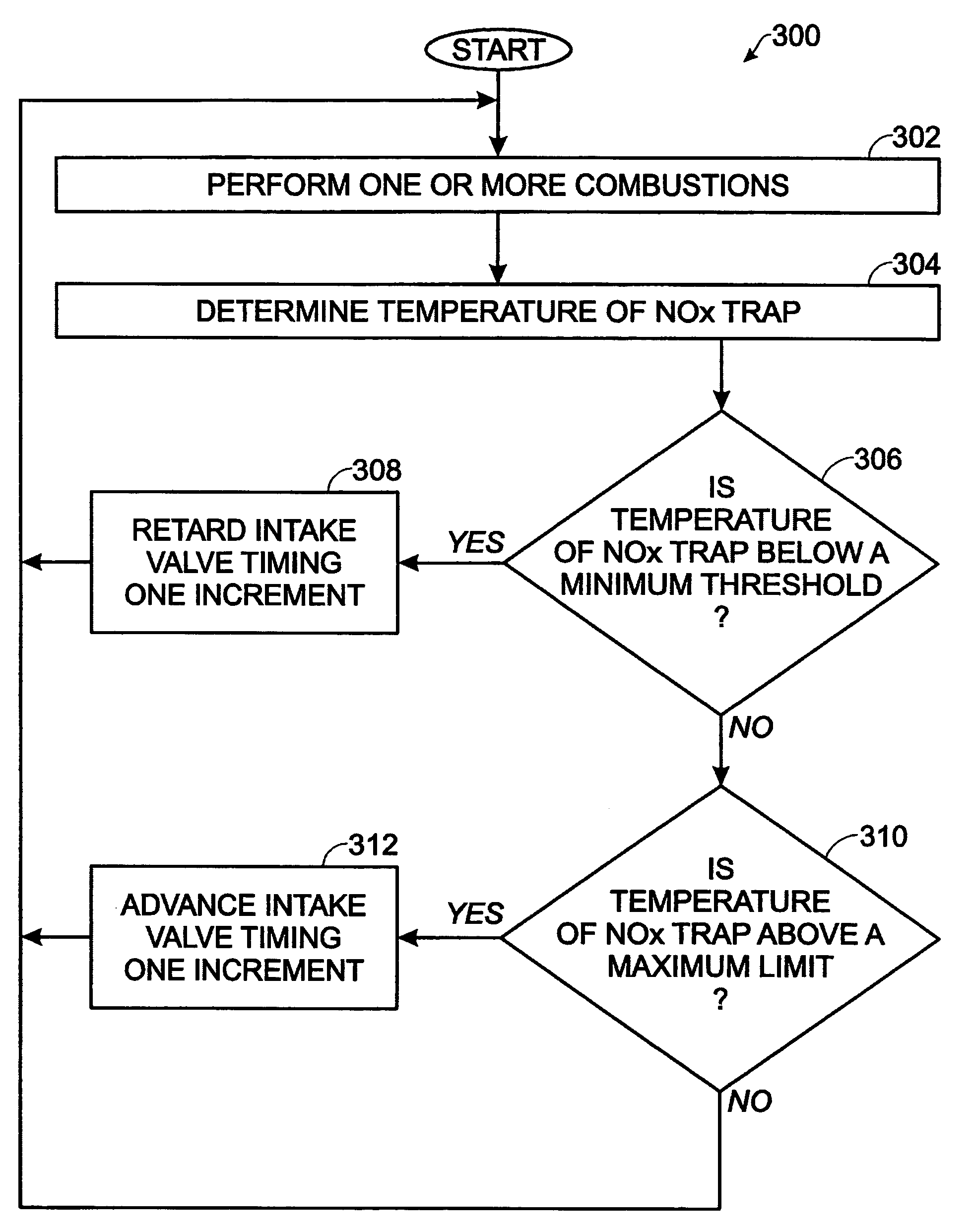
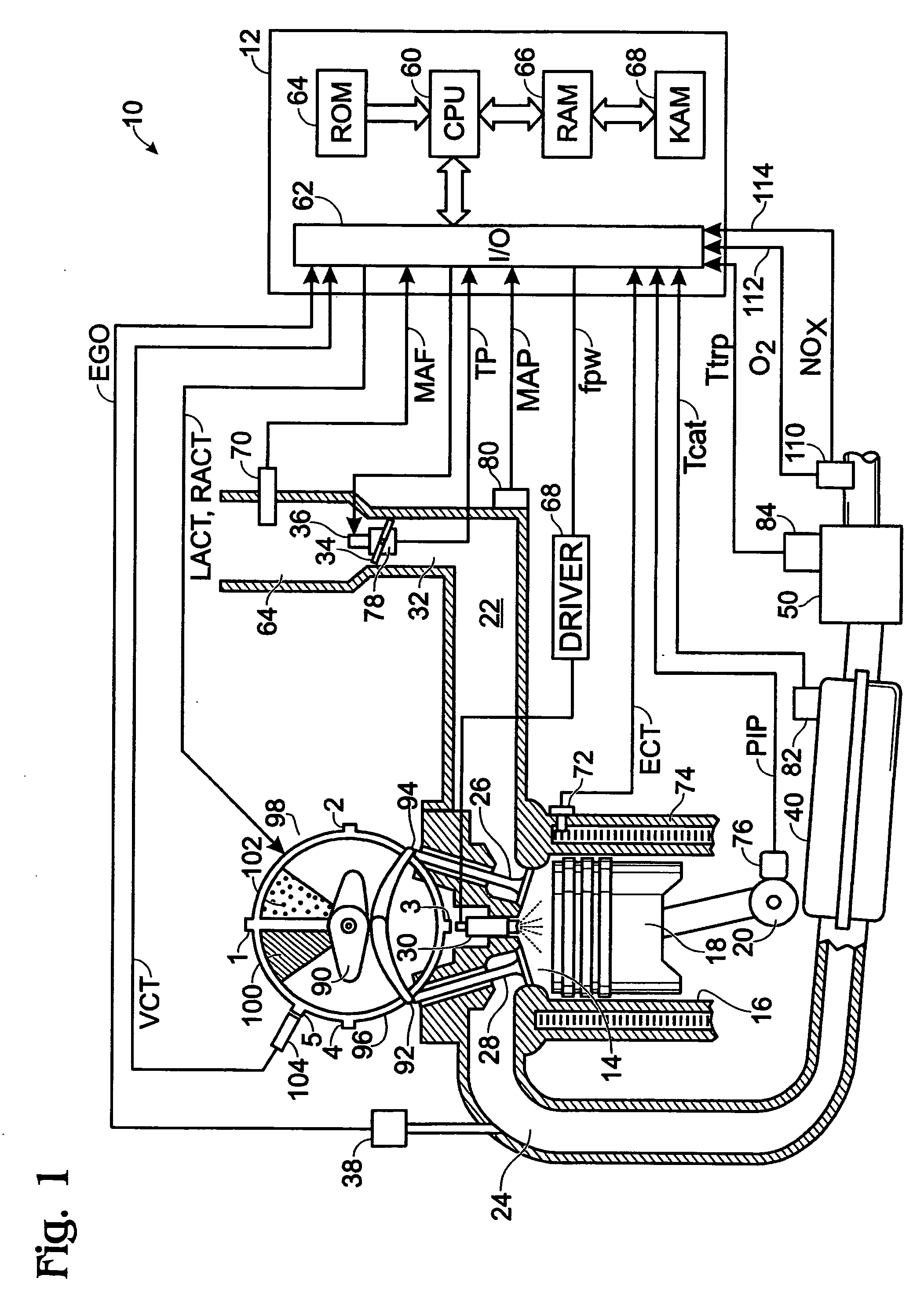
ActiveUS7398644B2Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesNegatively impact performanceValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberExhaust fumes
In a mechanical apparatus having a diesel engine including a combustion chamber, the mechanical apparatus also having an aftertreatment device configured to treat emissions from the diesel engine and an intake valve for passing air into the combustion chamber, a method of operating the engine is disclosed, wherein the method includes performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a first intake valve closure timing, determining a temperature of the aftertreatment device, and if the temperature of the aftertreatment device is equal to or below a preselected temperature threshold, then performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a second intake valve closure timing to thereby increase the temperature of exhaust emitted by the diesel engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus to reduce flue gas NOx by injection of n-agent droplets and gas in overfire air
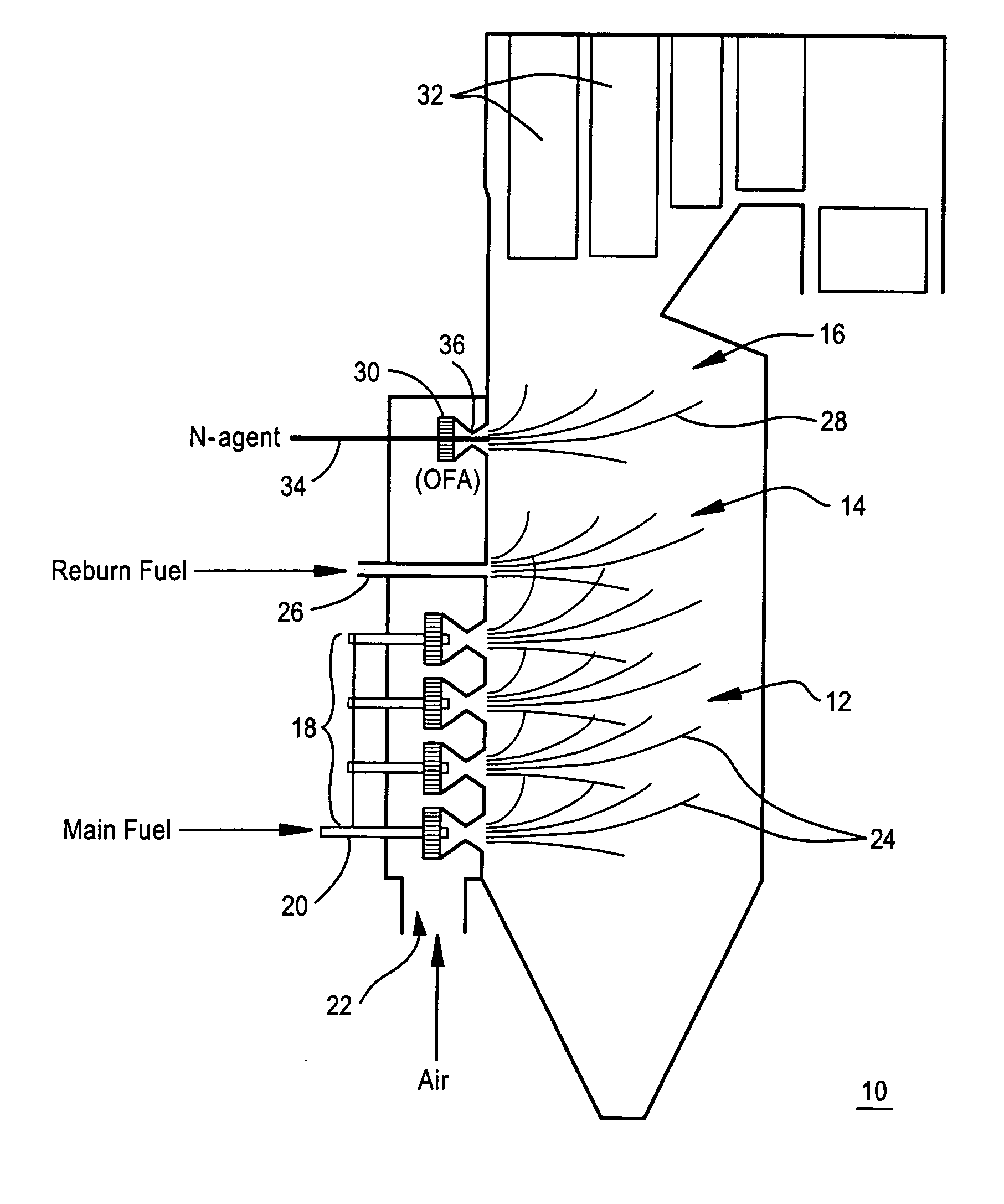
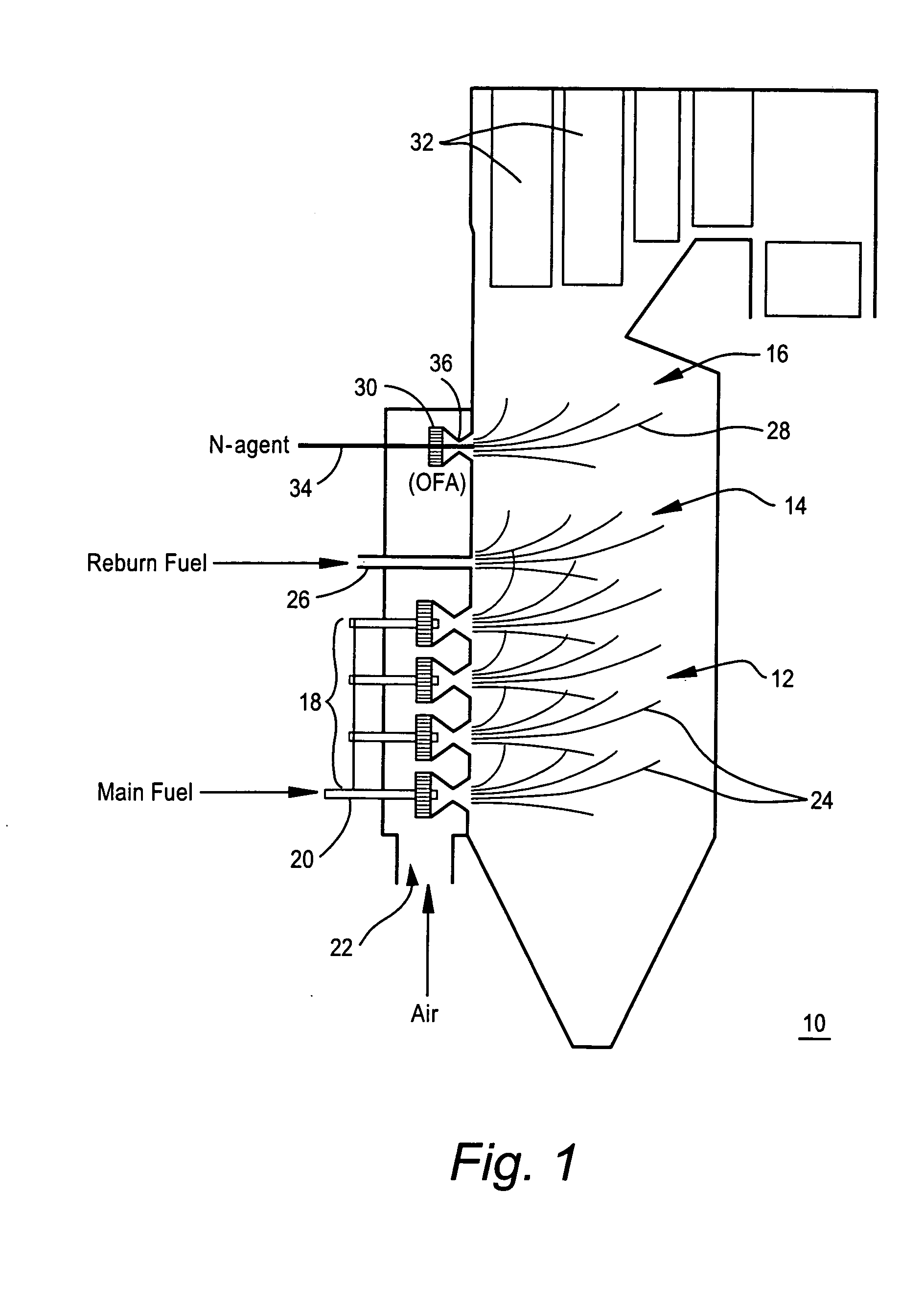
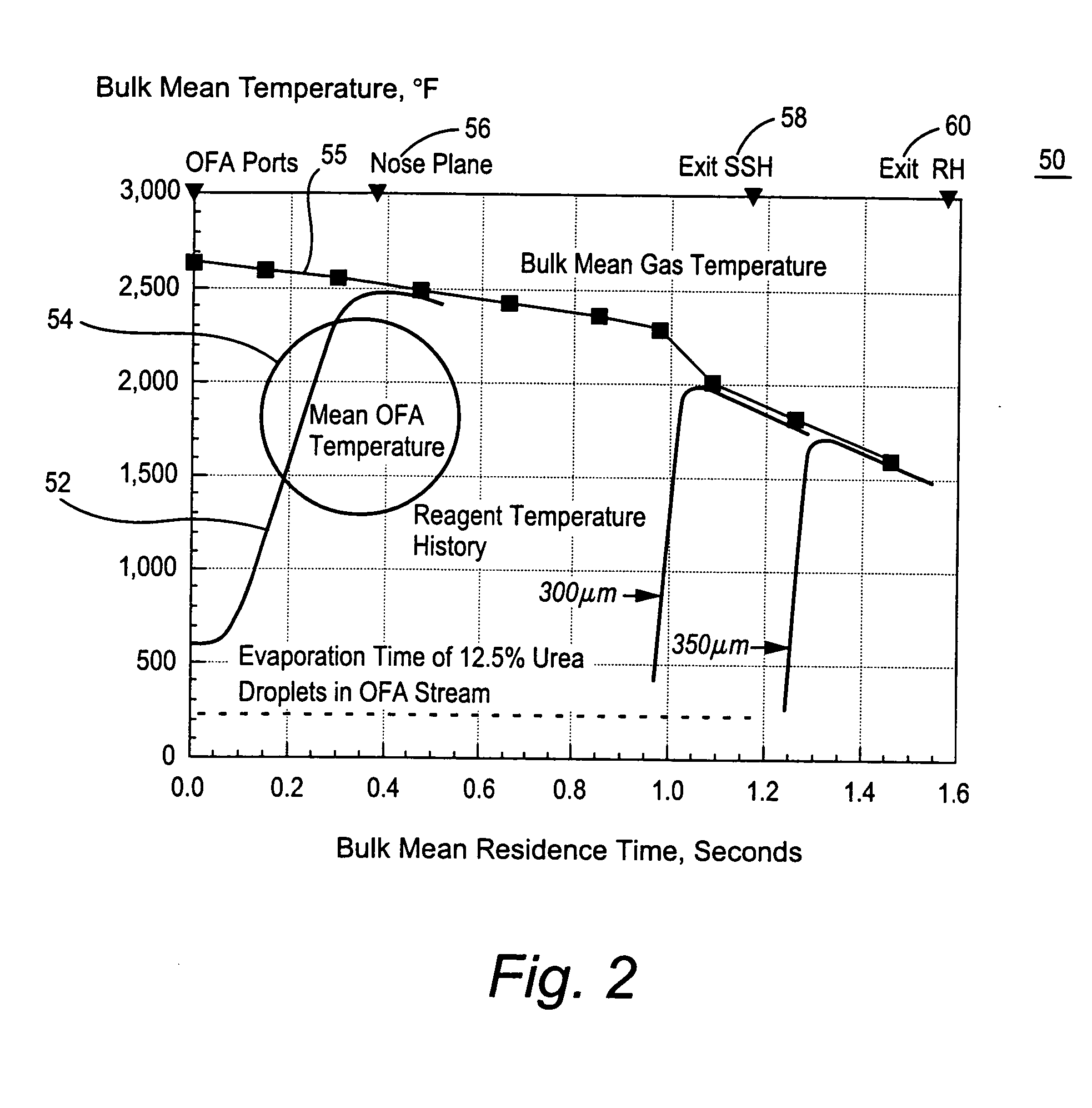
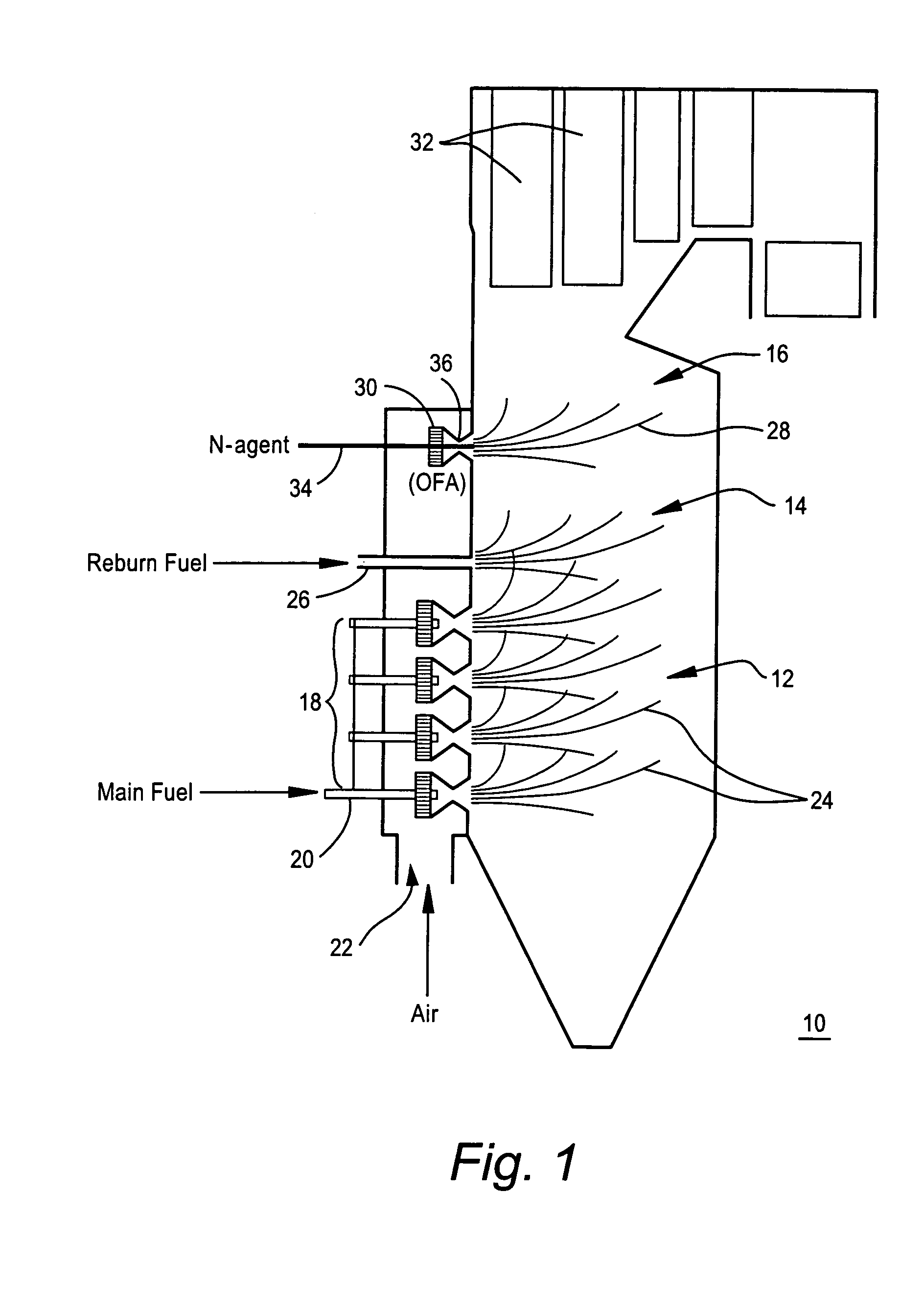
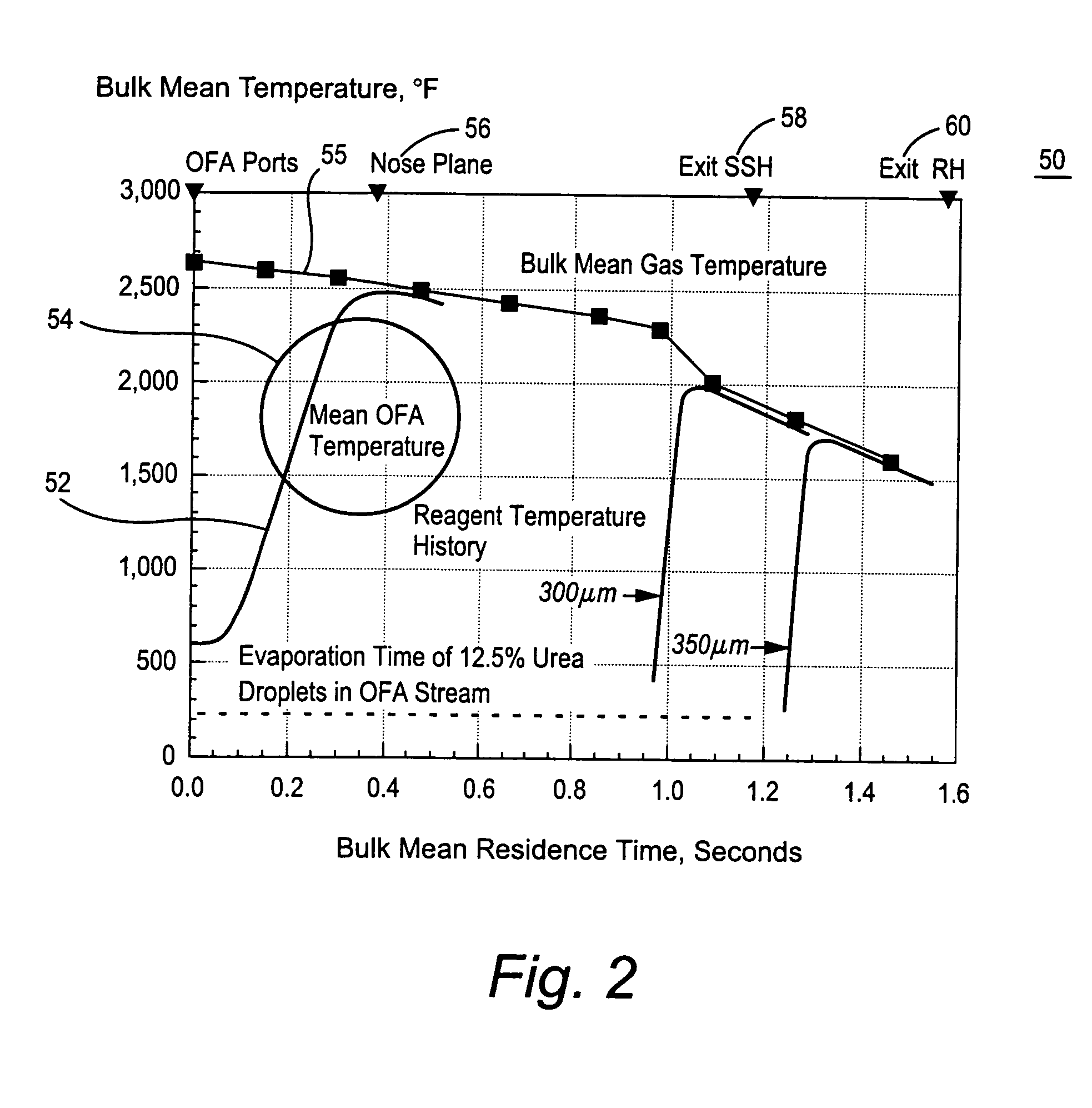
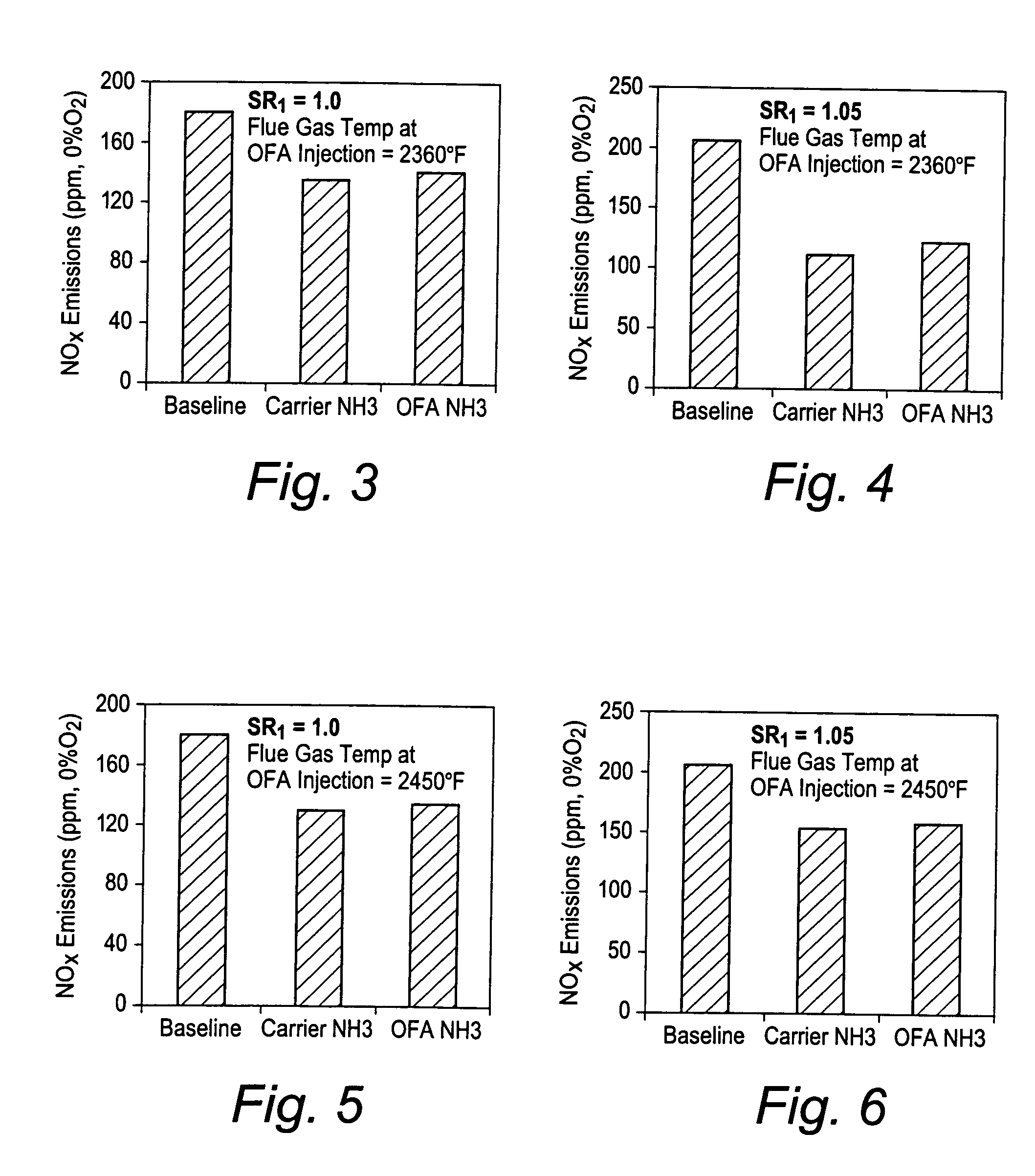
ActiveUS20050106516A1Minimizing ammonia slipReduce concentrationPulsating combustionNitrogen compoundsSmall dropletReducing agent
A method of decreasing the concentration of nitrogen oxides in a combustion flue gas is disclosed in which the nitrogen reducing agent, either in gaseous form, as small particles, or as small droplets of an aqueous solution, is introduced together with the overfire air in such a way that it mixes with the products of primary combustion along with the overfire air. The nitrogen agent reduced NOx as it passes through the temperature regime that is optimum for the NOx reduction as overfire air and flue gas mix. The transition from low to high temperature effectively eliminates ammonia slip. Additionally, the nitrogen agent may be mixed with the overfire air stream in such a manner that it is optimally shielded from early mixing with the products of primary combustion, where a portion of the overfire air reacts initially with any residual carbon monoxide (CO) that would otherwise interfere with the NOx reduction chemistry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
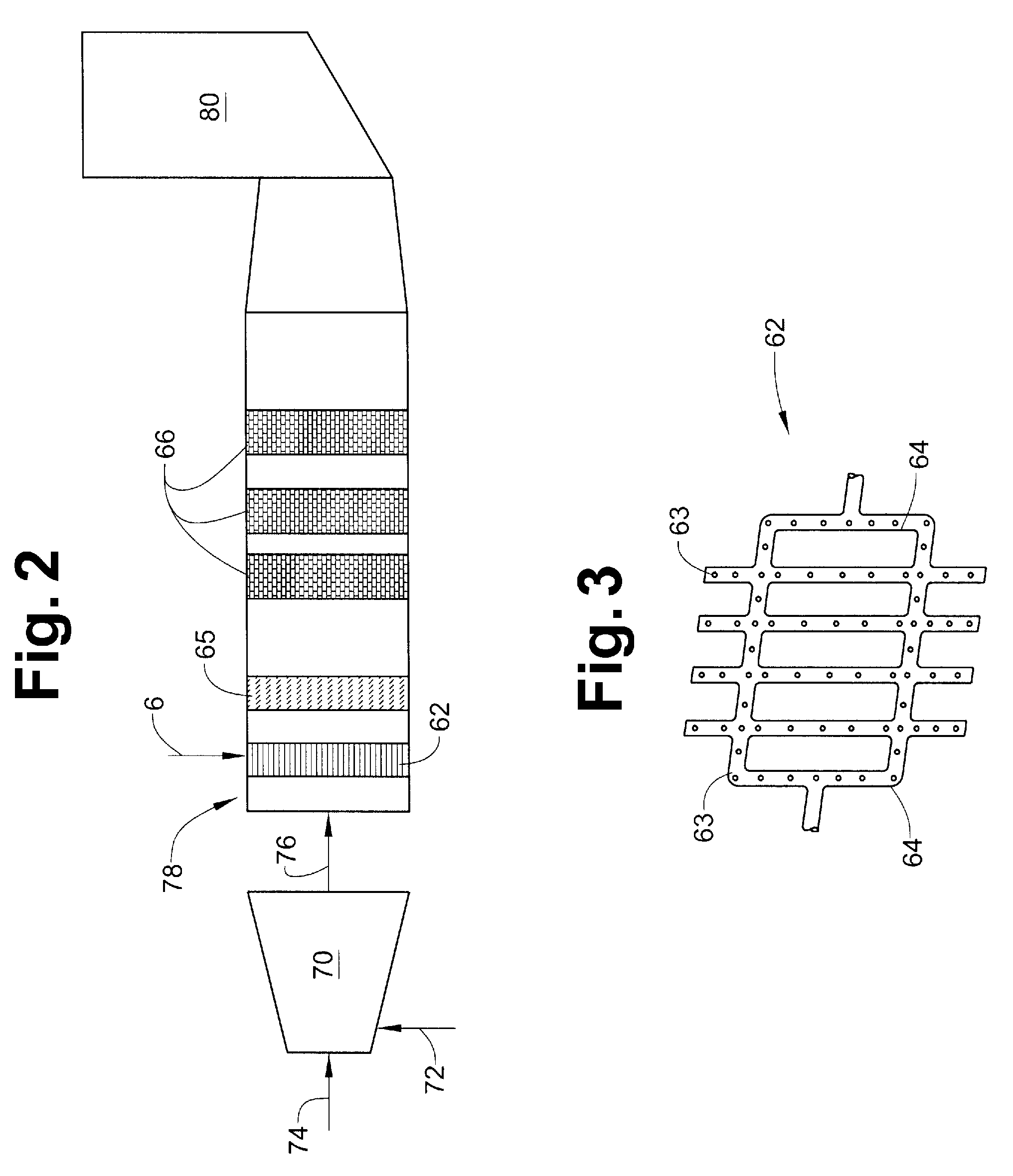
Catalyzed Filter for Treating Exhaust Gas
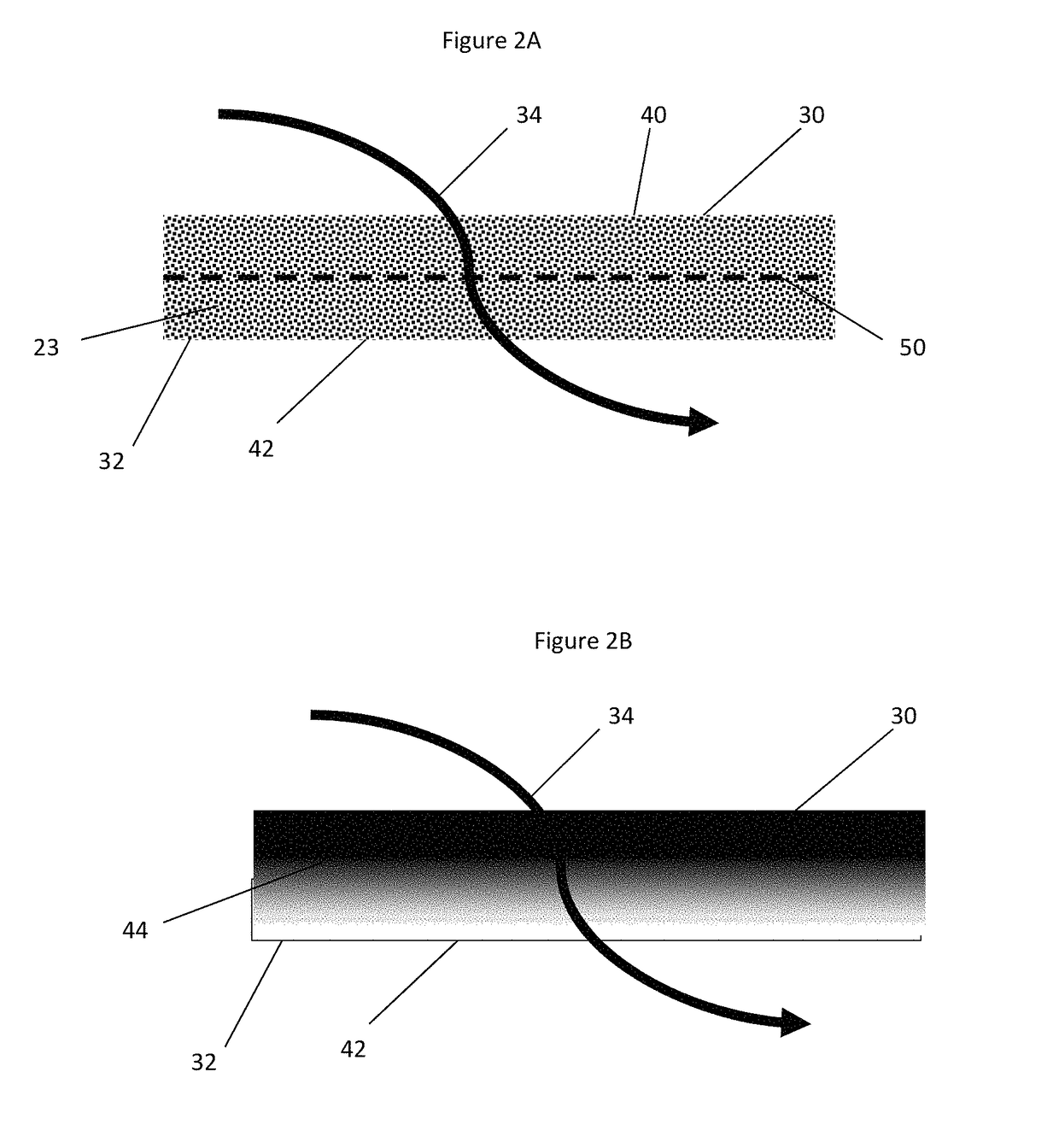
ActiveUS20140356266A1Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesBackpressure across a wall-flow filter can be reducedCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesPore diameterSoot
Provided is a diesel particulate filter capable of removing soot from an exhaust gas while operating at low backpressure, the filter comprising (a) a wall-flow filter substrate having a mean pore size, an inlet side, an outlet side, and a porous interior between the inlet and outlet sides; and (b) a catalyst composition coated from the inlet side of the substrate, wherein the catalyst composition has a d50 particle size distribution, wherein the d50 particle size distribution is less than the mean pore size divided by 4.9, and wherein the outlet side is substantially free of a catalyst coating.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Exhaust gas scrubber
ActiveUS20170165609A1Reducing concentration of sulfur oxideSpeed up the processGas treatmentDispersed particle separationSulfurEngineering
According to principles of the embodiments as disclosed herein, an exhaust gas scrubber system with a two-chamber exhaust gas scrubber is provided which allows for scrubbing of exhaust gases without the use of chemicals. In particular, the process fluid used in the system may be seawater. The exhaust gas scrubber includes a first scrubbing chamber having a fluid spraying system, such as an array of atomizing nozzles that spray atomized seawater into the chamber. The atomized seawater aids in reducing the concentration of sulfur oxides in an exhaust gas stream.
Owner:TRITON EMISSION SOLUTIONS
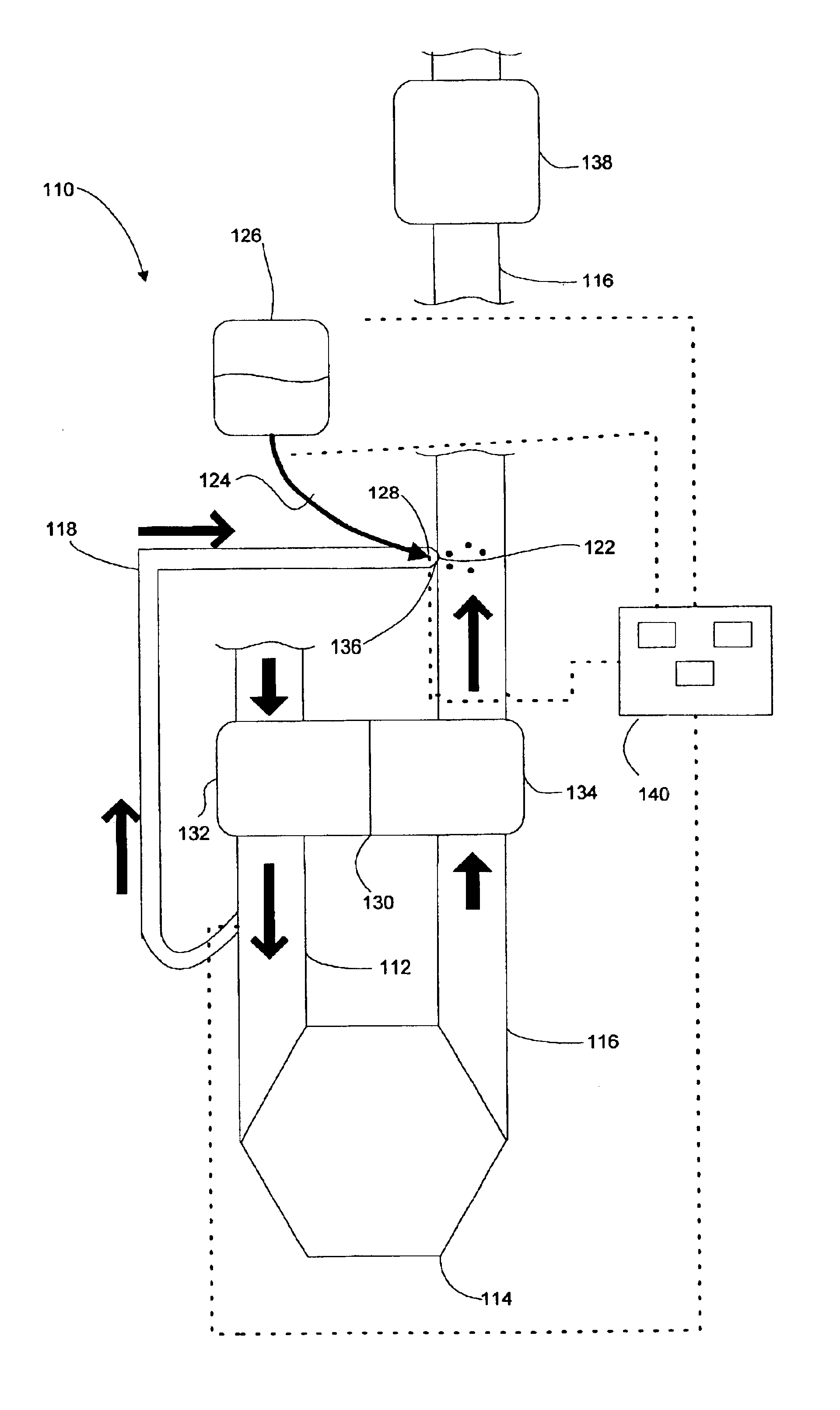
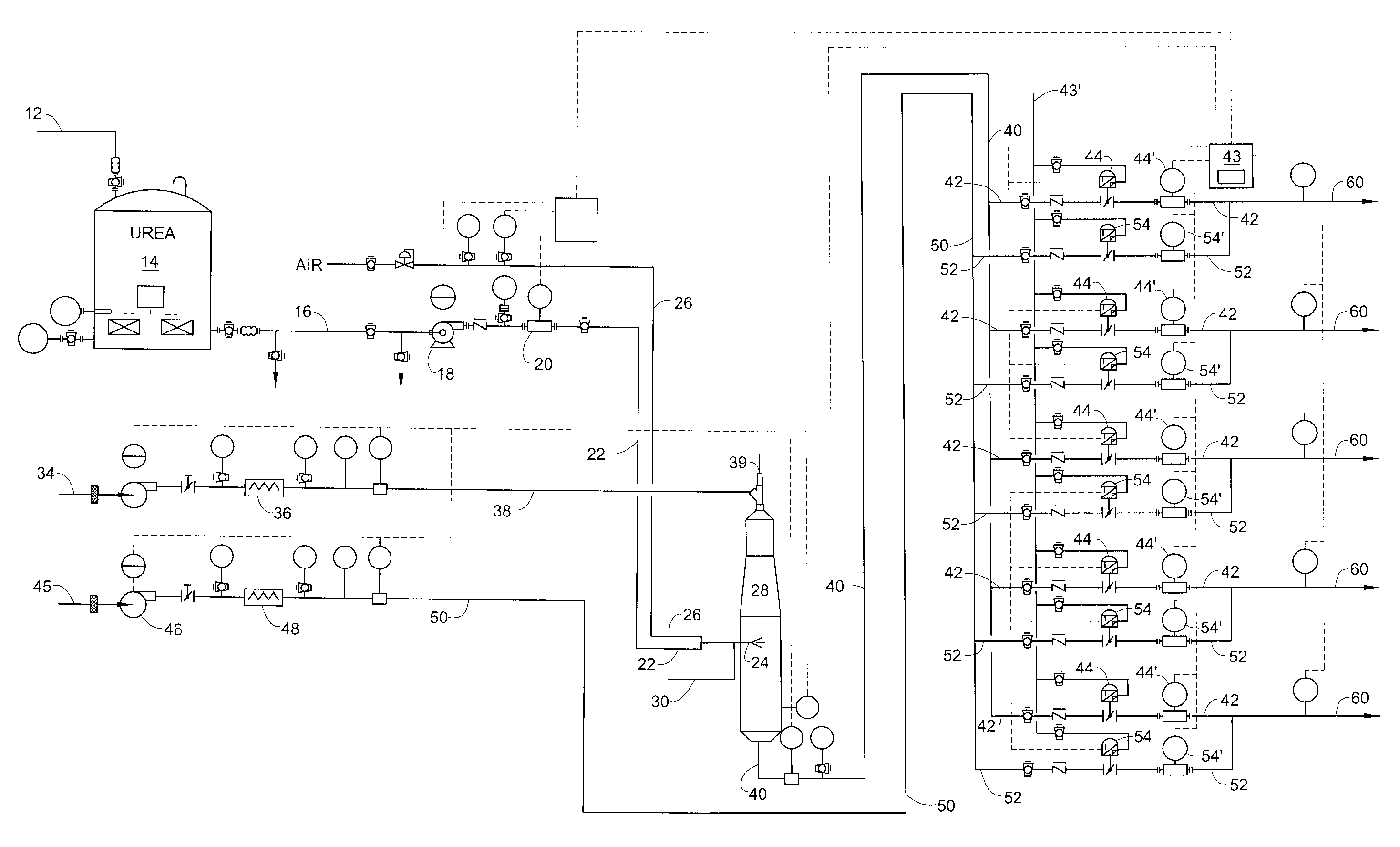
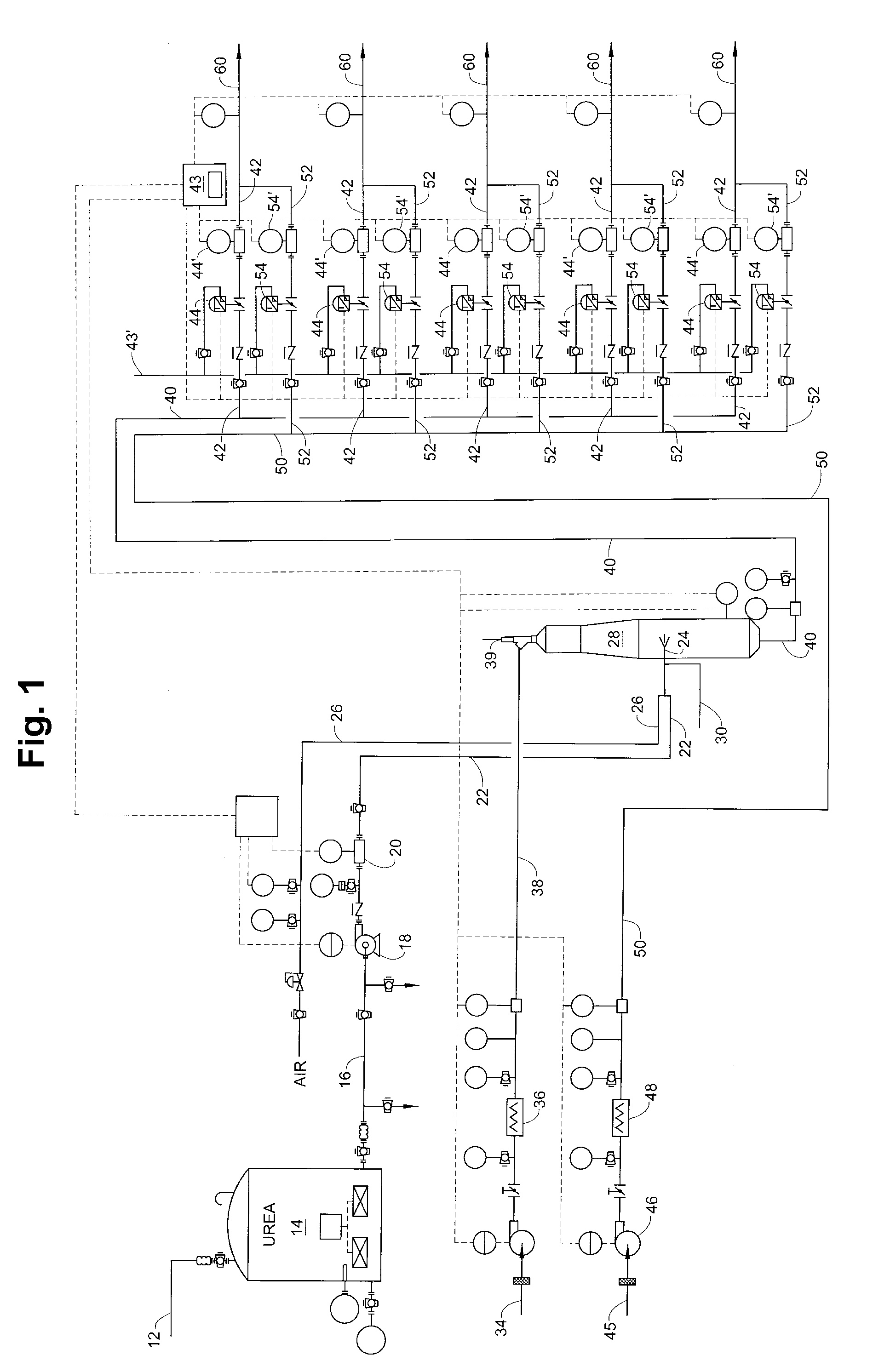
Selective Catalytic NOx Reduction Process and Control System
ActiveUS20100061907A1Reduce concentrationReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsControl systemProduct gas
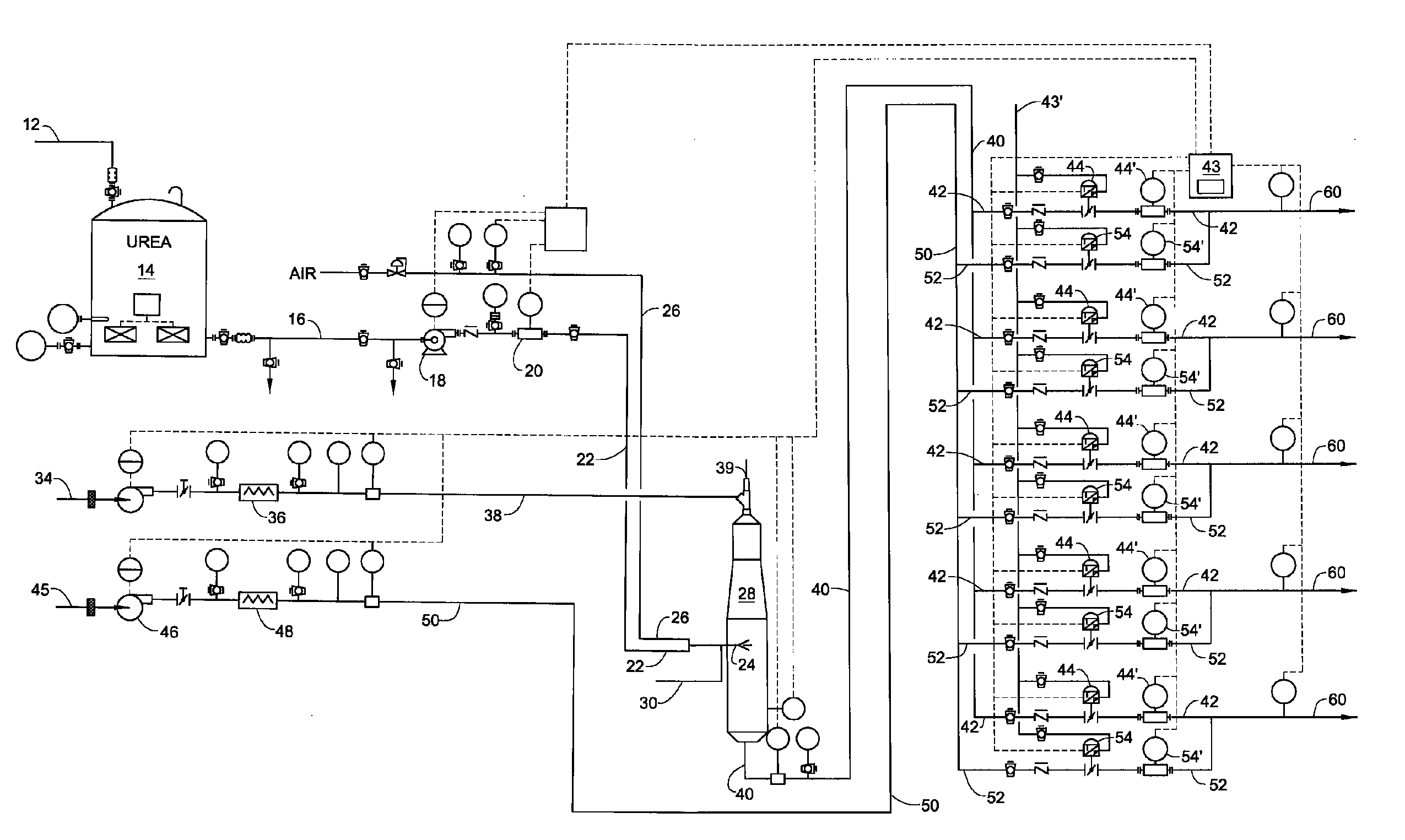
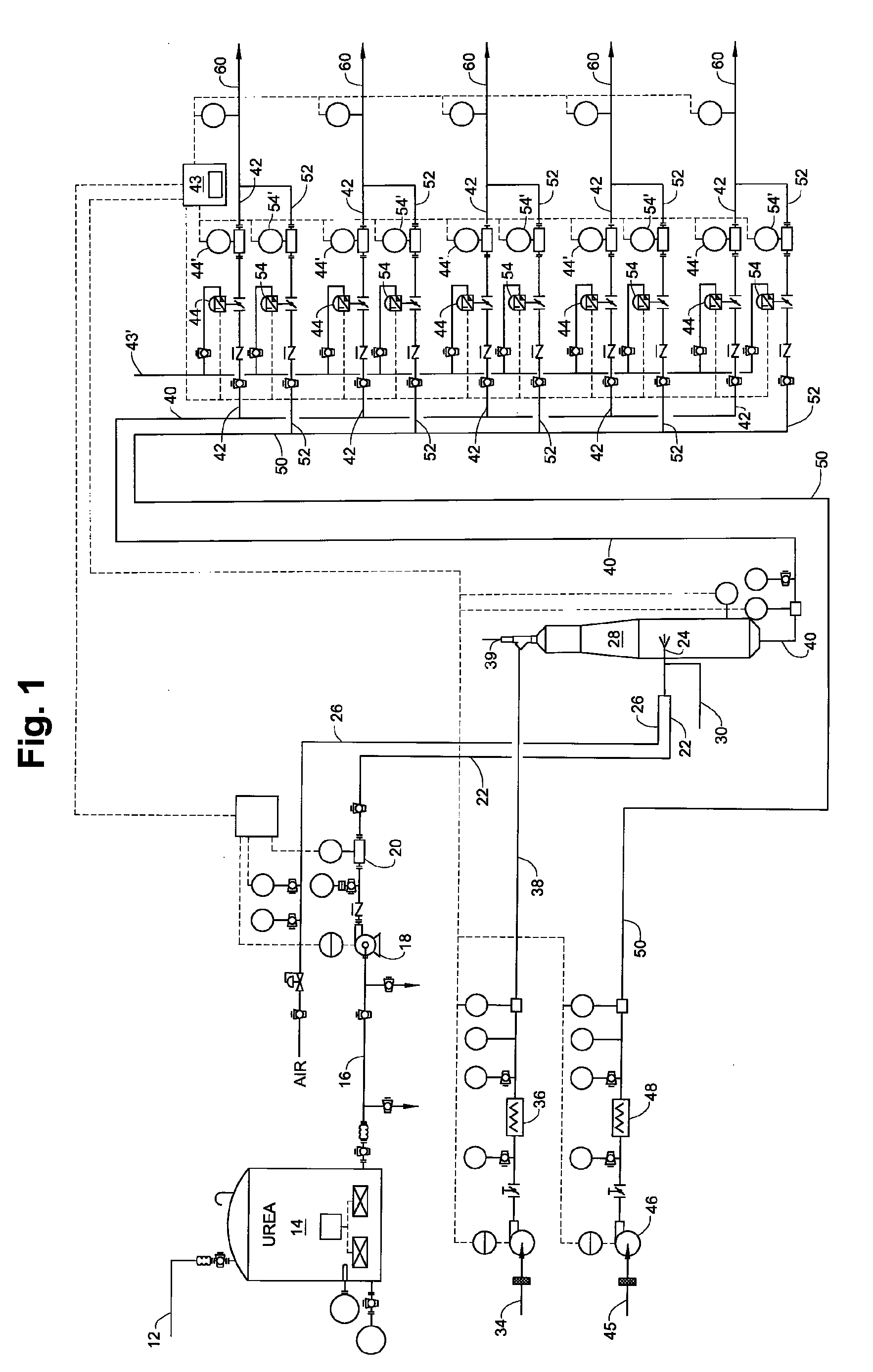
Disclosed is a system which enables the efficient utilization of urea for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx by gasifying it and feeding it to a plurality of selective catalytic reduction units associated with a plurality of gas turbines. The invention enables feeding a gasified product of the urea with the ability to fully control separate SCR units without excessive reagent usage or loss of pollution control effectiveness. Controllers determine the amount of reagent required for each turbine to control NOx emissions and then mixes the gasified urea with the correct amount of carrier gas for efficient operation of each separate SCR unit despite the demand variation between the turbines. In this manner the gasification unit can be properly controlled to provide urea on demand without the need for storing large inventories of ammonia-containing gasses to correct for fluctuations in demand.
Owner:FUEL TECH
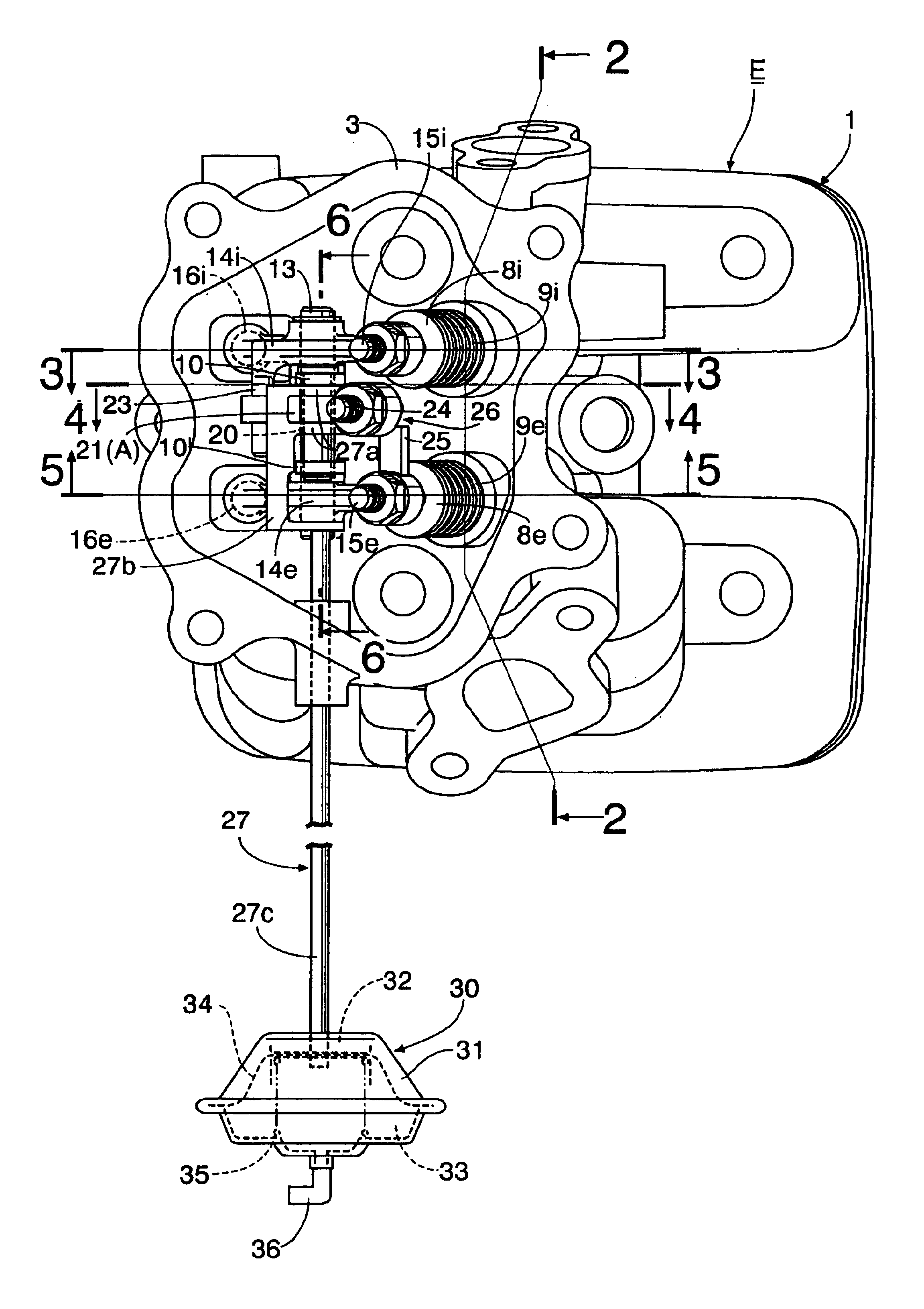
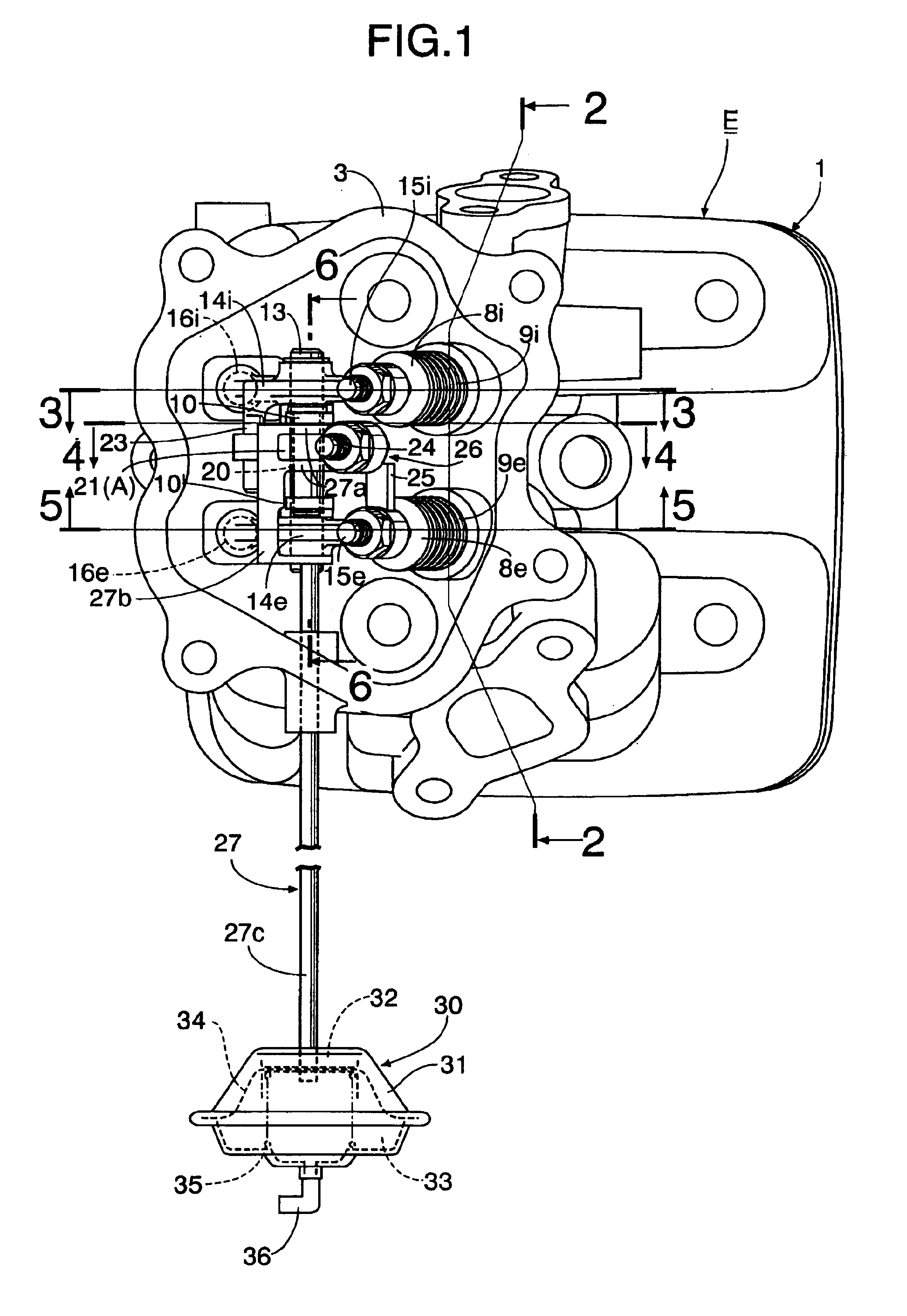
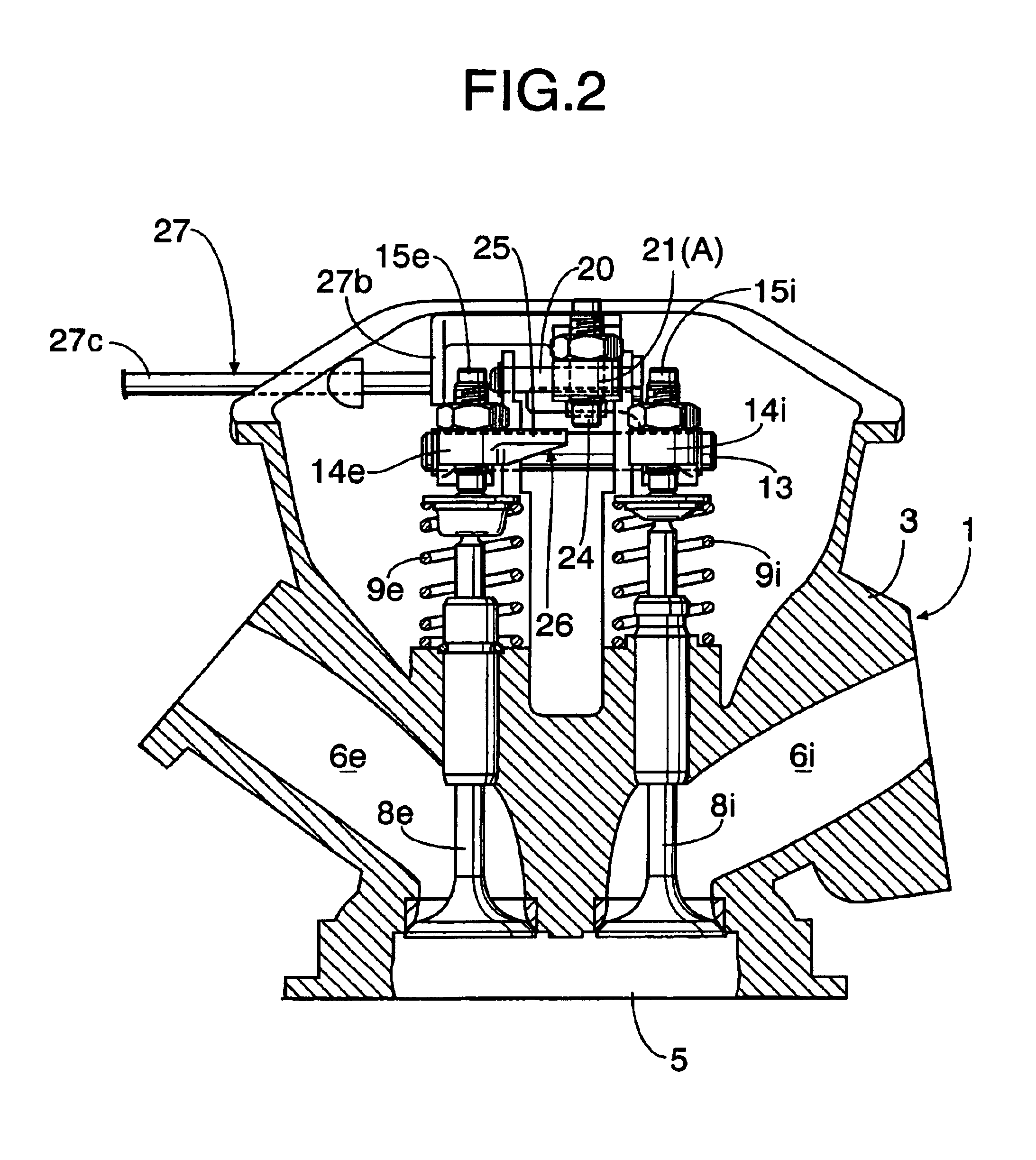
Exhaust gas reflux apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6892714B2Improve output performanceSimple configurationValve arrangementsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gasExhaust fumes
An exhaust gas reflux apparatus for an internal combustion engine includes one-way connection means provided between an intake rocker arm and an exhaust rocker arm. The one-way connection means moves between a non-operating position where the intake and exhaust rocker arms are released and an operating position where the intake and exhaust rocker arms are connected to open the exhaust valve only when the intake rocker arm rocks in a valve opening direction of the intake valve. An actuator for switching the one-way connection means between the non-operating position and the operating position is connected to the one-way connection means. Thus, an exhaust gas is sucked into a combustion chamber from an exhaust port using a general exhaust valve in an intake stroke, when exhaust gas reflux is required.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method to reduce flue gas NOx
ActiveUS7374736B2Reduce concentrationMinimizing ammonia slipPulsating combustionNitrogen compoundsFlue gasNitrogen
A method of decreasing the concentration of nitrogen oxides in a combustion flue gas in which a nitrogen reducing agent is introduced together with the overfire air to mixes with the products of primary combustion along with the overfire air. The nitrogen agent reduced NOx as it passes through the temperature regime that is optimum for the NOx reduction as overfire air and flue gas mix. The transition from low to high temperature effectively eliminates ammonia slip. Additionally, the nitrogen agent may be mixed with the overfire air stream in such a manner that it is optimally shielded from early mixing with the products of primary combustion, where a portion of the overfire air reacts initially with any residual carbon monoxide (CO) that would otherwise interfere with the NOx reduction chemistry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for reducing NOx emissions in an apparatus having a diesel engine
ActiveUS7204227B2Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesNegatively impact performanceValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveCombustion chamber
In a mechanical apparatus having a diesel engine including a combustion chamber, an intake valve for passing air into the combustion chamber, and an exhaust valve for passing exhaust from the chamber, the mechanical apparatus also having an aftertreatment device configured to treat emissions from the diesel engine, a method of operating the engine is disclosed, wherein the method includes performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber with a first quantity of fuel, determining a temperature of the aftertreatment device, and if the temperature of the aftertreatment device is equal to or below a preselected temperature threshold, then performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber with a second, greater quantity of fuel and varying at least one of an intake valve timing and an exhaust valve timing relative to a default valve timing to cause at least one of a compression loss and a pumping loss.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
Exhaust gas reflux mechanism for multipurpose engine
InactiveUS20090320792A1Reduce concentration of NOxSimple constructionValve arrangementsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gasAutomotive engineering
An exhaust gas reflux mechanism for a multipurpose engine includes an exhaust reflux cam formed as an integral part of an single cam of the engine and having a cam lobe profiled to open an exhaust valve while an intake valve stays open during the intake stroke of the engine so that part of an exhaust gas remaining on the side of an exhaust port of the engine is drawn into a combustion chamber during the intake stroke.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
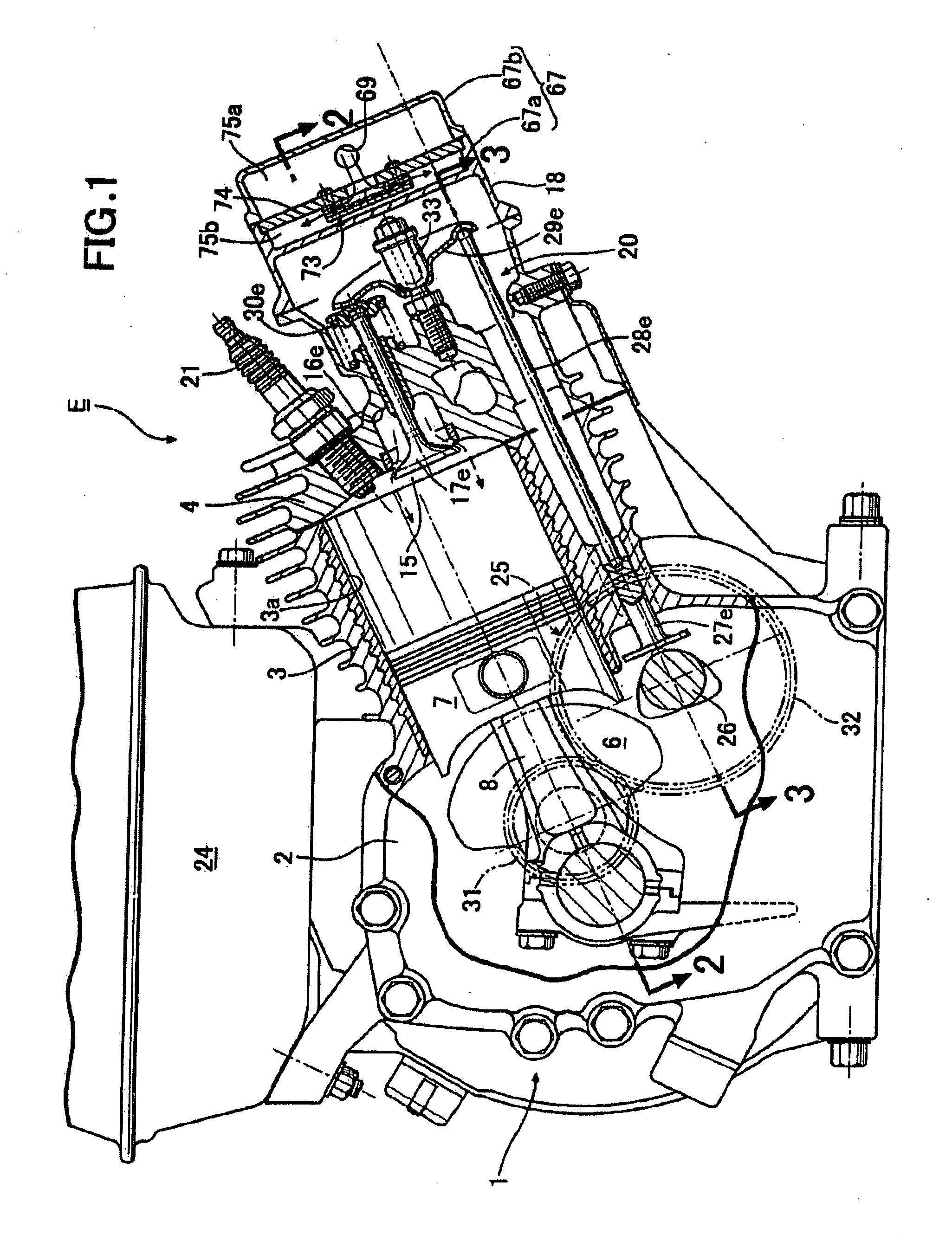
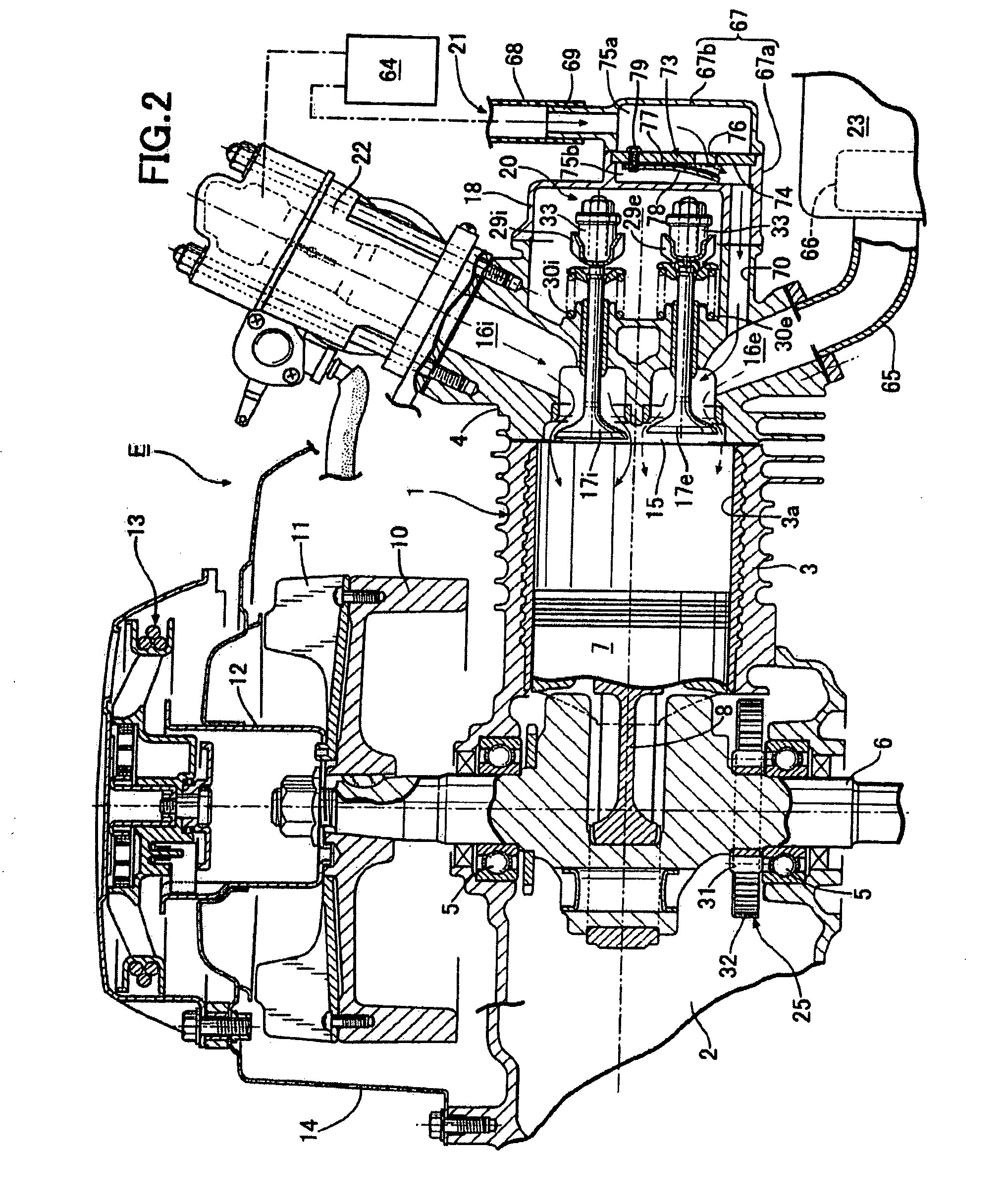
Exhaust emission control system for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20090282819A1Reduce CO2 concentrationReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesSystem structureInternal combustion engine cooling
In an exhaust emission control system for an internal combustion engine, an exhaust gas recirculation device that operates so as to partially open an exhaust valve to introduce exhaust gas into a cylinder in an intake stroke is provided; a secondary air passage capable of supplying secondary air to an exhaust passage is connected to the exhaust passage; and a one-way valve opened by negative pressure applied from the cylinder to the exhaust passage following an operation of the exhaust gas recirculation device in the intake stroke is provided in the secondary air passage. Accordingly, it is possible to provide an exhaust emission control system for an internal combustion engine that allows secondary air to be supplied into an exhaust passage to reduce HC and CO concentrations and also a NOx concentration in an exhaust gas without using an air pump regardless of an exhaust system structure of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Catalyzed filter for treating exhaust gas
ActiveUS9687785B2Backpressure across a wall-flow filter can be reducedReduce loadMolecular sieve catalystsInternal combustion piston enginesDiesel particulate filterSoot
Provided is a diesel particulate filter capable of removing soot from an exhaust gas while operating at low backpressure, the filter comprising (a) a wall-flow filter substrate having a mean pore size, an inlet side, an outlet side, and a porous interior between the inlet and outlet sides; and (b) a catalyst composition coated from the outlet side of the substrate, wherein the catalyst composition has a d50 particle size distribution, wherein the d50 particle size distribution is greater than or equal to the mean pore size divided by 4.9, and wherein the inlet side is substantially free of a catalyst coating.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Sintering flue gas SCR denitration and vapor removal system and technology
The invention relates to a sintering flue gas SCR denitration and vapor removal system. The system comprises a flue gas condensation vapor-removal defogging dedusting tower, a heat exchange device, ahot-blast stove, an ammonium hydroxide evaporator, a dilution fan, an ammonia injection grid, an SCR denitration reaction device and a flue gas exhaust device. The heat exchange device is arranged between the flue gas condensation vapor-removal defogging dedusting tower and the SCR denitration reaction device. The heat exchange device is used for heat exchange on flue gas to be denitrated or denitrated flue gas to change the temperature, an original flue gas outlet of the heat exchange device is connected with a gas inlet of the SCR denitration reaction device through a second main flue, the hot-blast stove and the ammonia injection grid are arranged in sequence in the flowing direction of the flue gas in the second main flue, and the ammonium hydroxide evaporator and the dilution fan arearranged between the ammonia injection grid and a gas outlet of the SCR denitration reaction device. The sintering flue gas SCR denitration and vapor removal system can carry out SCR denitration on desulfurated sintering flue gas while carrying out vapor removal treatment, the effect of purifying sintering flue gas desulfurated with a wet method is improved, and environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:江苏朗润环保科技有限公司
Catalyzed Filter for Treating Exhaust Gas
ActiveUS20140356265A1Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesBackpressure across a wall-flow filter can be reducedCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesPore diameterDiesel particulate filter
Provided is a diesel particulate filter capable of removing soot from an exhaust gas while operating at low backpressure, the filter comprising (a) a wall-flow filter substrate having a mean pore size, an inlet side, an outlet side, and a porous interior between the inlet and outlet sides; and (b) a catalyst composition coated from the outlet side of the substrate, wherein the catalyst composition has a d50 particle size distribution, wherein the d50 particle size distribution is greater than or equal to the mean pore size divided by 4.9, and wherein the inlet side is substantially free of a catalyst coating.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Catalyzed filter for treating exhaust gas
ActiveUS9687786B2Backpressure across a wall-flow filter can be reducedReduce loadMolecular sieve catalystsInternal combustion piston enginesPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
Provided is a diesel particulate filter capable of removing soot from an exhaust gas while operating at low backpressure, the filter comprising (a) a wall-flow filter substrate having a mean pore size, an inlet side, an outlet side, and a porous interior between the inlet and outlet sides; and (b) a catalyst composition coated from the inlet side of the substrate, wherein the catalyst composition has a d50 particle size distribution, wherein the d50 particle size distribution is less than the mean pore size divided by 4.9, and wherein the outlet side is substantially free of a catalyst coating.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
System and method for reducing NOx emissions in an apparatus having a diesel engine
ActiveUS20060283172A1Improve engine efficiencyLow exhaust temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust fumesCombustion chamber
In a mechanical apparatus having a diesel engine including a combustion chamber, an intake valve for passing air into the combustion chamber, and an exhaust valve for passing exhaust from the chamber, the mechanical apparatus also having an aftertreatment device configured to treat emissions from the diesel engine, a method of operating the engine is disclosed, wherein the method includes performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber with a first quantity of fuel, determining a temperature of the aftertreatment device, and if the temperature of the aftertreatment device is equal to or below a preselected temperature threshold, then performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber with a second, greater quantity of fuel and varying at least one of an intake valve timing and an exhaust valve timing relative to a default valve timing to cause at least one of a compression loss and a pumping loss.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
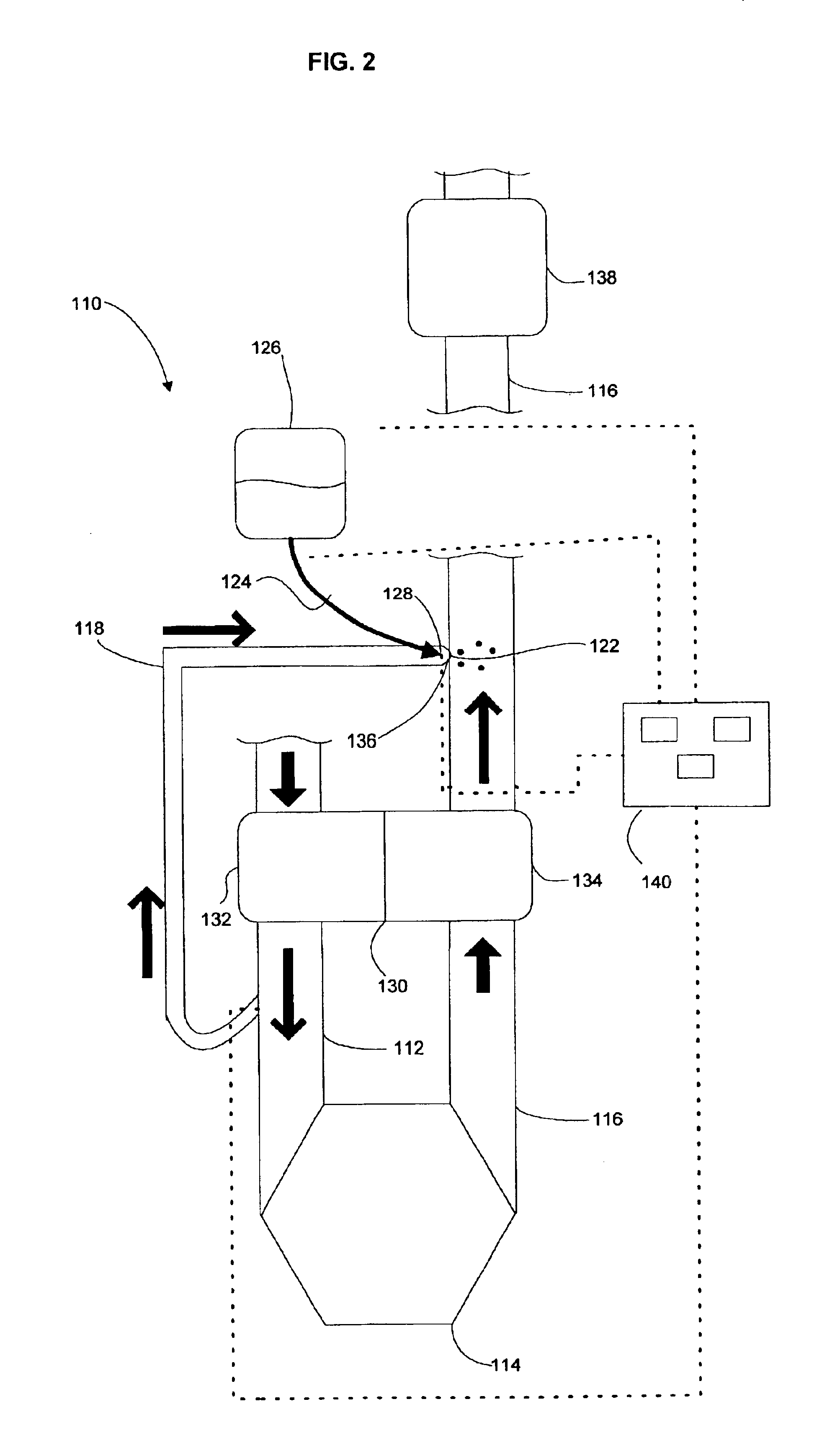
Combining SCR with PNA for low temperature emission control
ActiveUS10179329B2Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesReducing stored NOxGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesMolecular sievePtru catalyst
A catalyst article comprises an SCR catalyst and a NOx adsorber catalyst, where each of these catalysts comprise a metal molecular sieve, each with a different metal. The catalyst article can be close coupled with other components to give a NOX performance advantage from cold start to a combined DOC and SCRF system. Higher NOX conversion is also shown in under-floor location due to NOx storage before SCR light off and selective NH3 slip control, allowing higher NH3 fill levels. Systems comprising the catalyst article and methods of using the catalyst article to give improved hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide control, as well as ammonia slip control, are described. The systems can include flow-through or wall-flow monoliths.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Combustion system
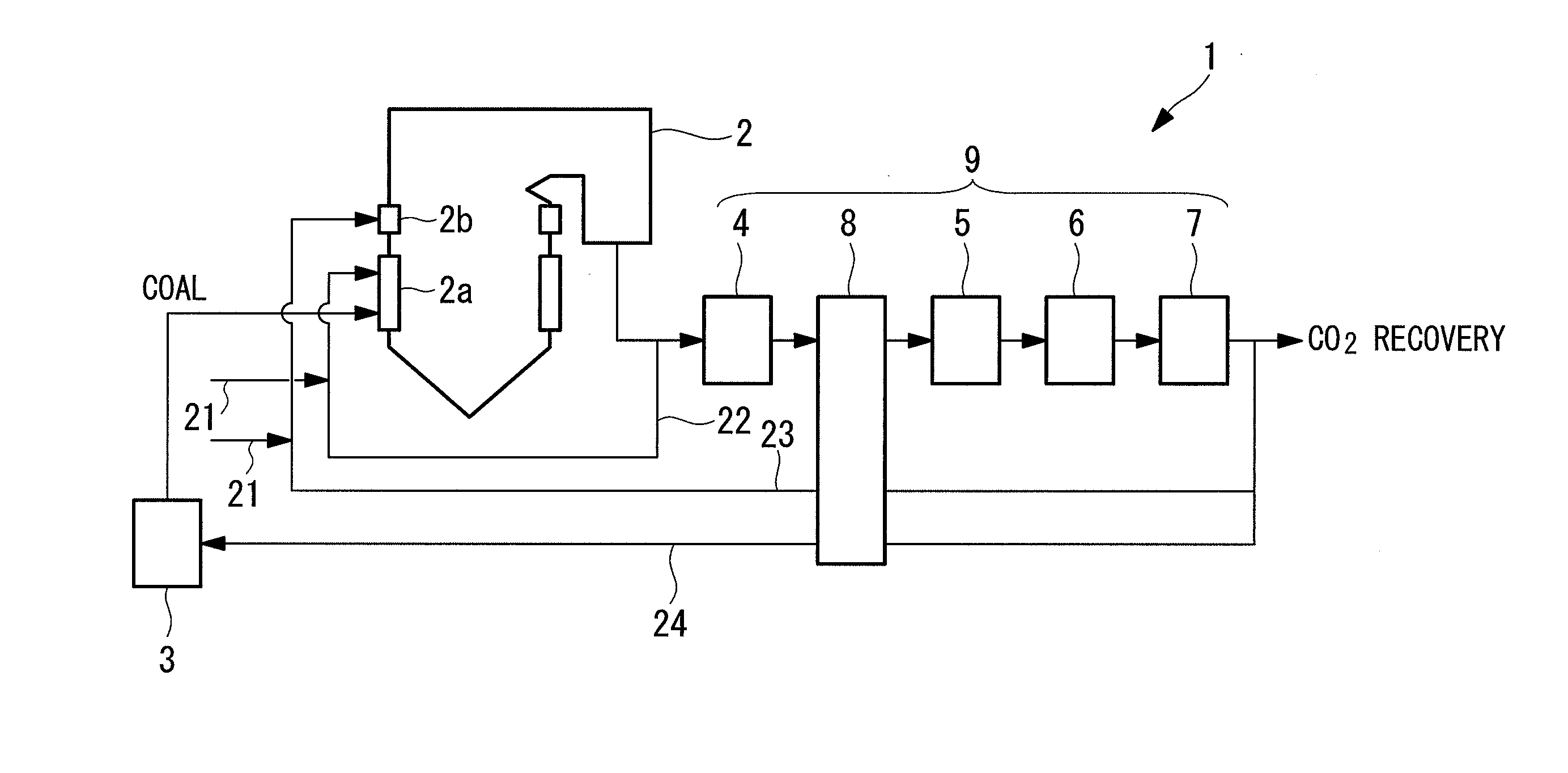
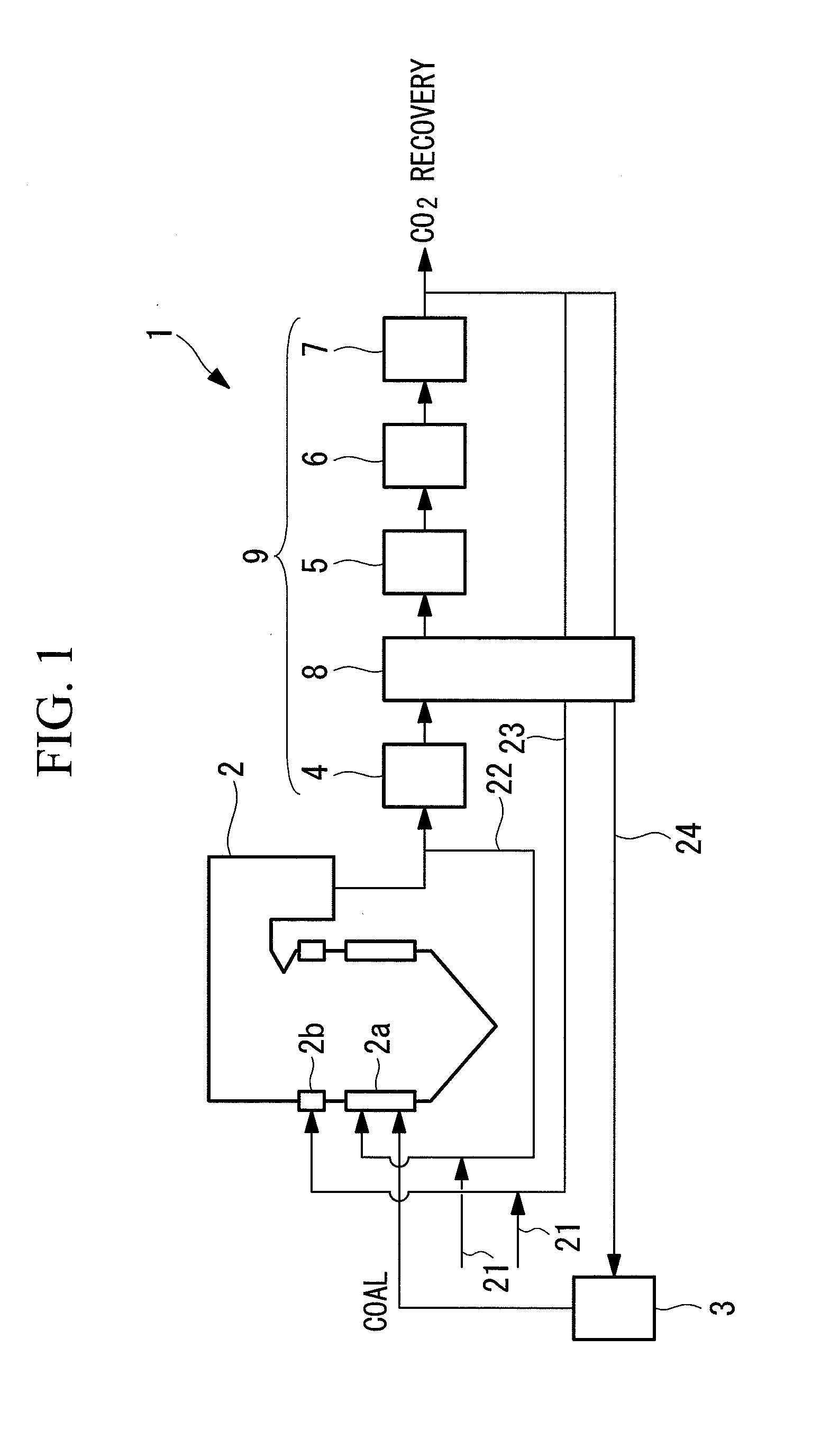
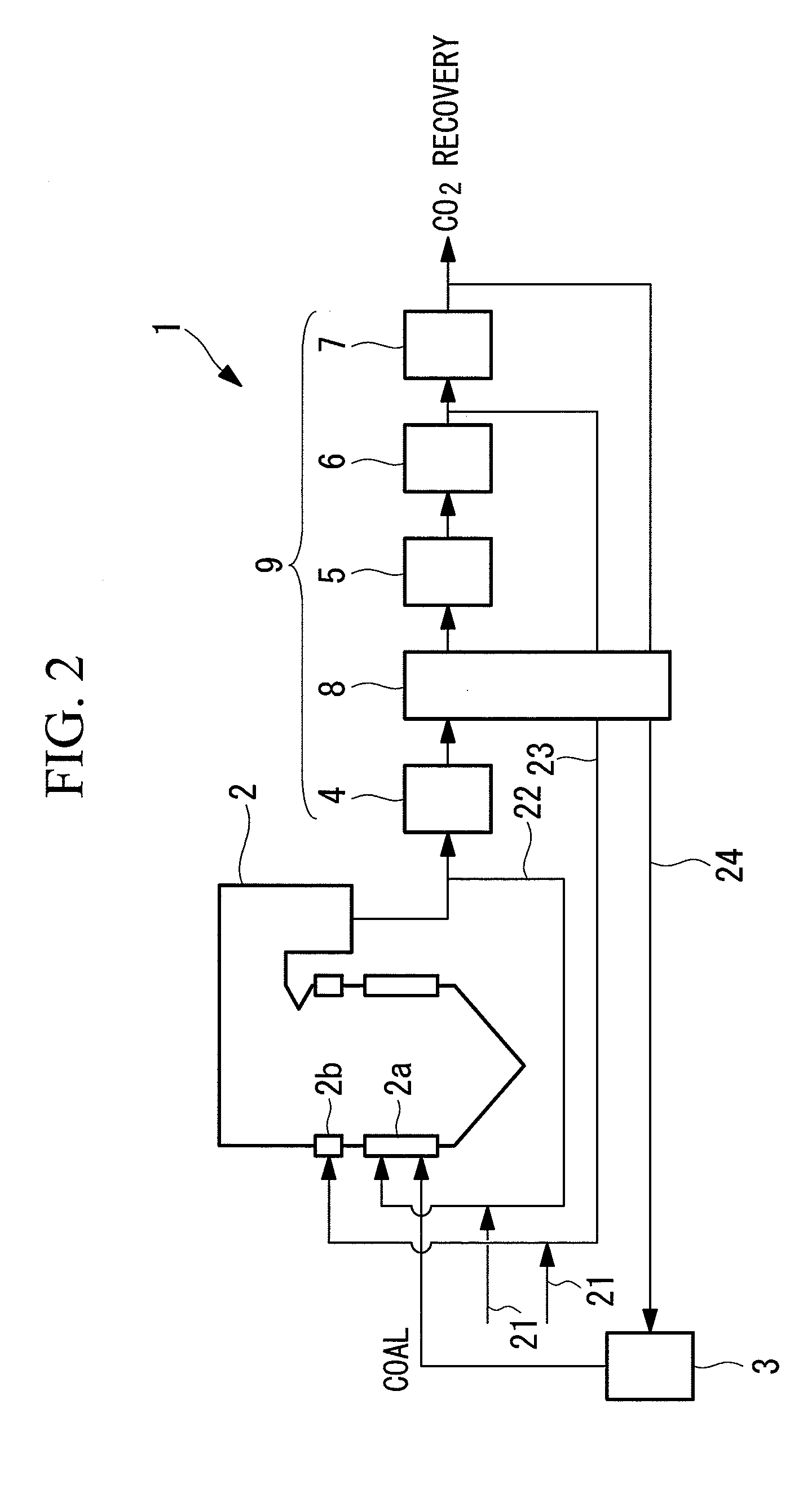
InactiveUS20130092062A1Reduce flow rateReduce capacityFluegas recirculationDirect carbon-dioxide mitigationCombustion systemNitrogen oxides
A combustion system capable of decreasing nitrogen oxide discharged from exhaust gas is provided. The combustion system includes: a combustion furnace (2) having a burner unit (2a) for supplying fuel and combustion oxygen to the inside of the furnace, a reduction zone formed on a downstream side of the burner unit (2a) for combusting the fuel, and a combustion oxygen supply port (2b) for supplying combustion oxygen (21) so that unburned fuel which has passed the reduction zone completely combusts; and a smoke removal device (9) for removing smoke in the exhaust gas discharged from the combustion furnace (2). Part of exhaust gas (22) diverging from between the combustion furnace (2) and the smoke removal device (9) is introduced to the burner unit (2a), while part of exhaust gas (23) diverging from a downstream side of the smoke removal device (9) is introduced to the combustion oxygen supply port (2b).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
Emission control system and method
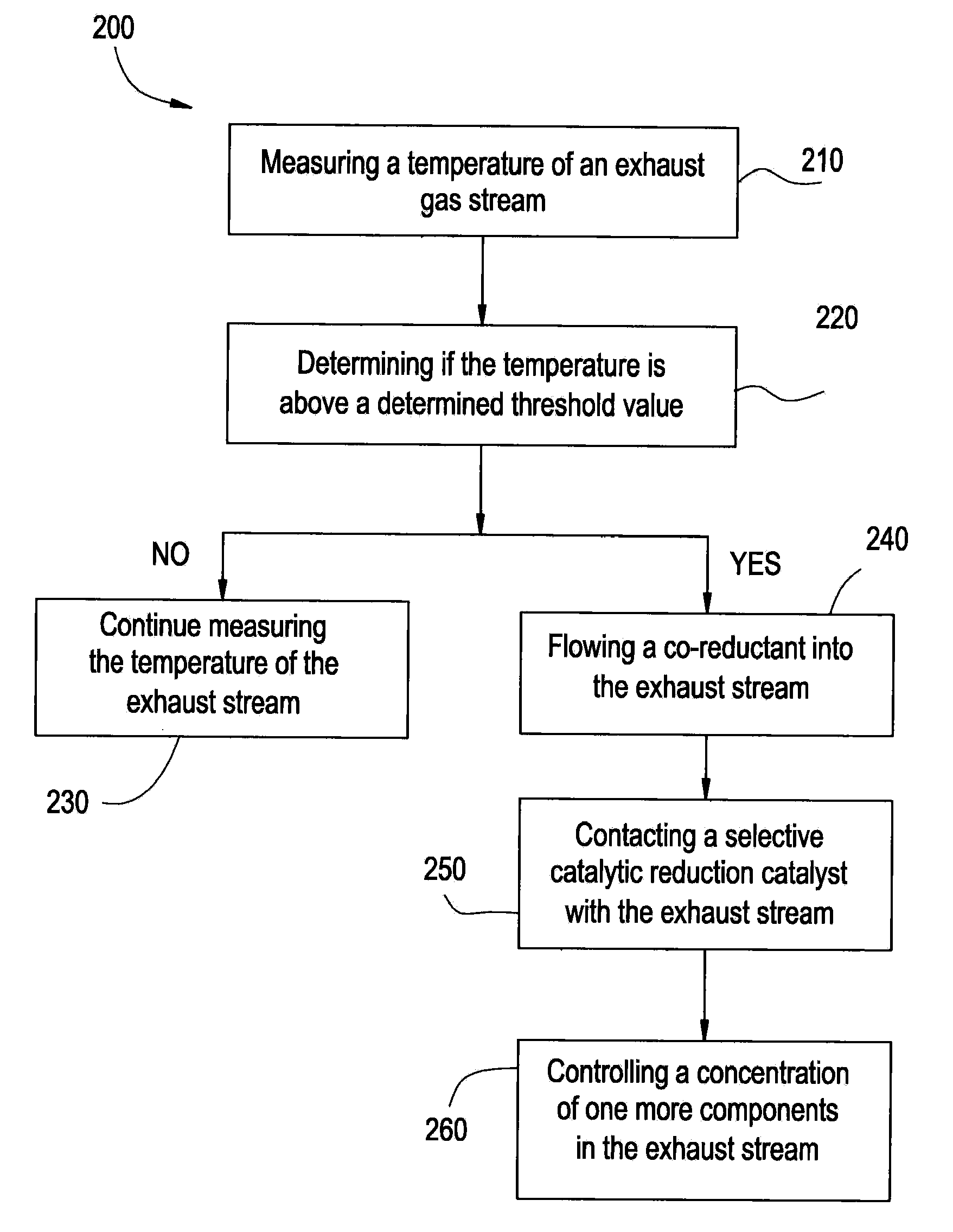
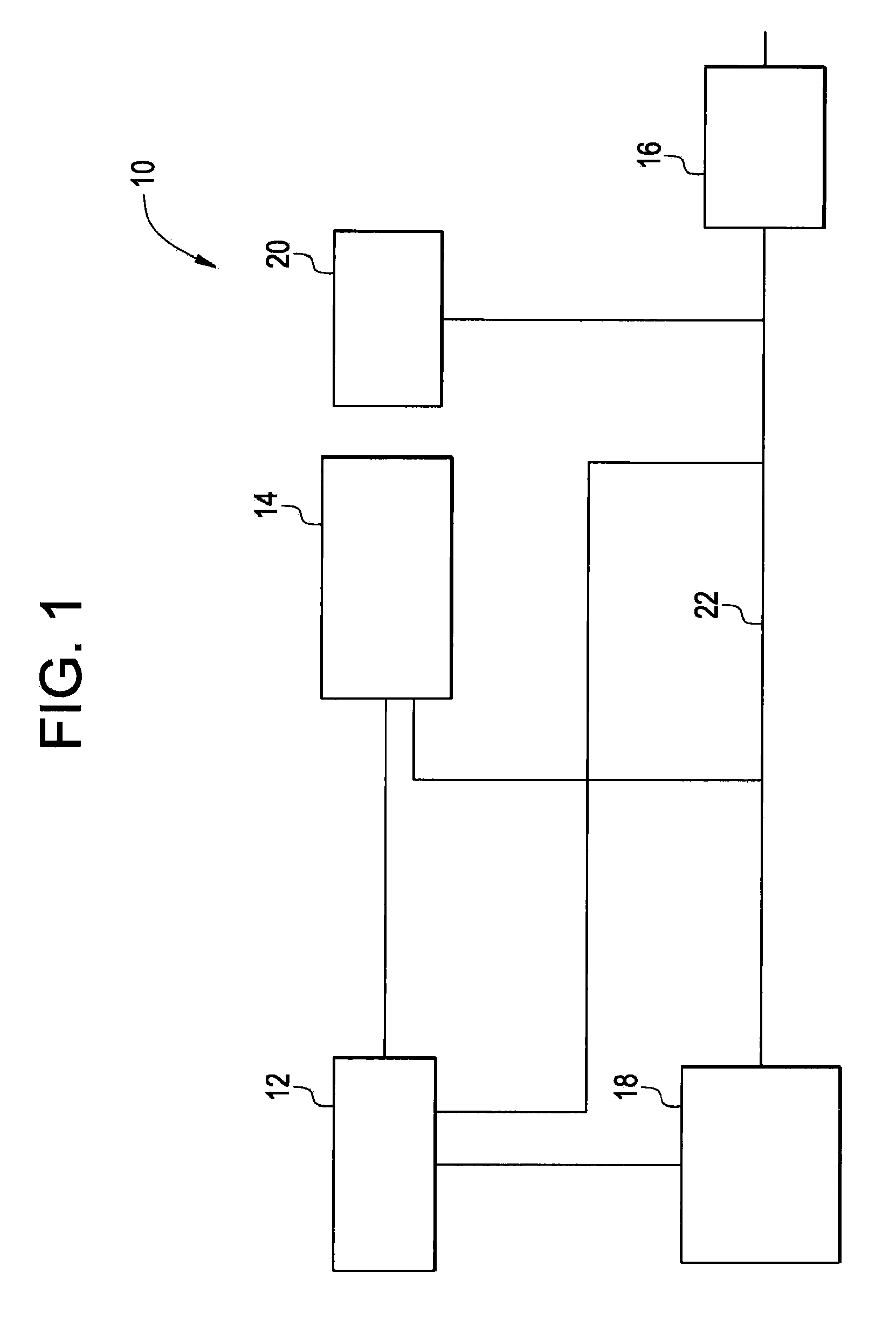
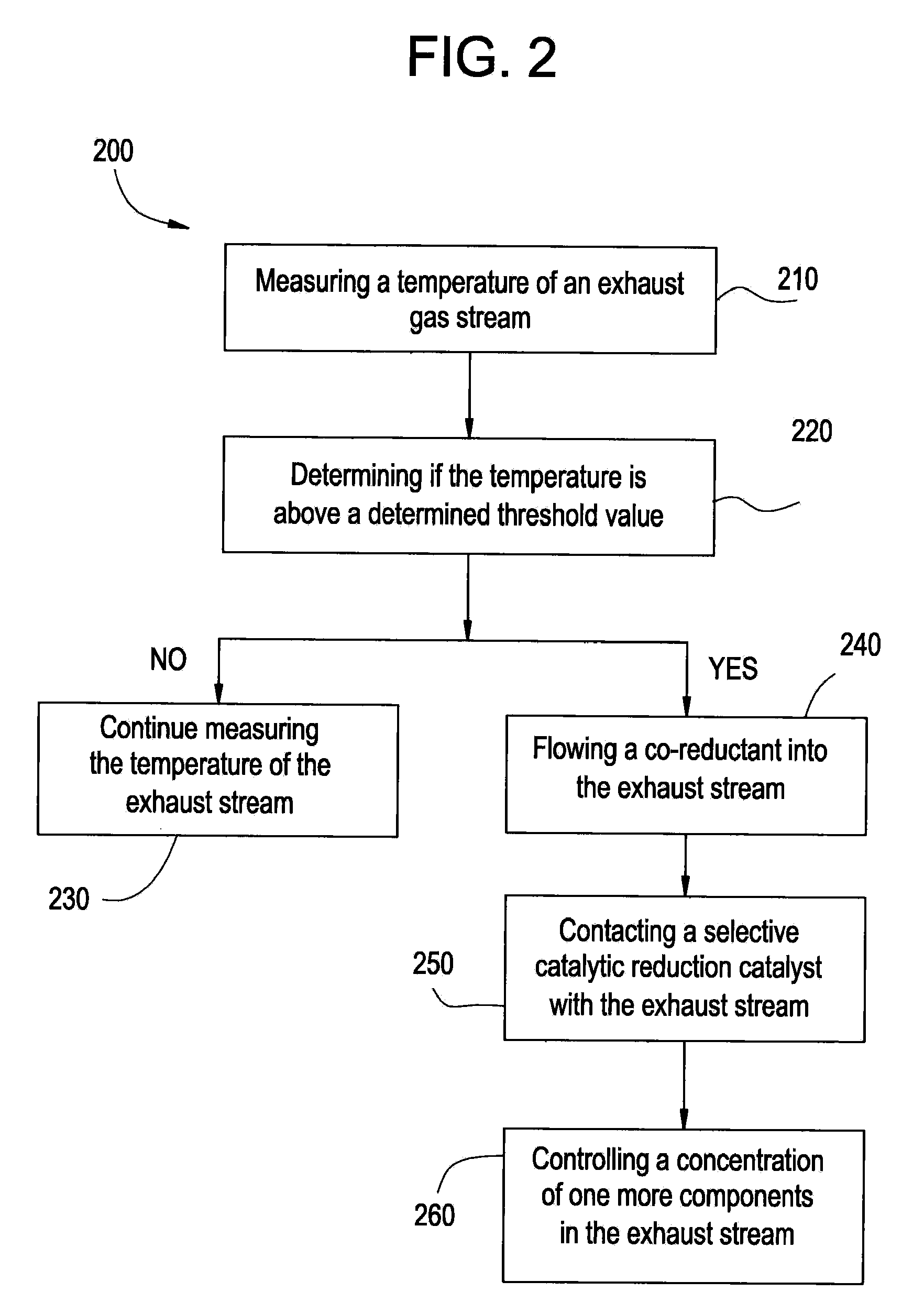
InactiveUS20100024400A1Promote lowerReduce NOx to nitrogenGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust gasSyngas
A system includes an exhaust conduit configured to conduct a stream of exhaust gas, wherein the exhaust conduit comprises a selective catalytic reduction catalyst reactor comprising a first catalyst composition; an fuel source configured to introduce a fuel into the exhaust gas stream within the exhaust conduit upstream of the selective catalytic reduction catalyst reactor; a catalytic partial oxidation reformer in fluid communication with the exhaust gas stream and upstream from the selective catalytic reduction catalyst reactor, wherein the catalytic partial oxidation reformer can introduce a hydrogen-rich syngas co-reductant into the exhaust gas stream, when a temperature of the exhaust fluid is less than a determined threshold temperature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combustion device
InactiveUS20130340659A1Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesControlled absorptionCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelCombustorEngineering
In a boiler having plurality of burners arranged on a furnace wall of a furnace, each burner includes a cylindrical fuel nozzle for injecting a mixture of fuel and carrier gas therefor into the furnace; one or more cylindrical air nozzles provided on the outer circumference of the nozzle for injecting combustion air into the furnace, and a wind box for supplying combustion air to the nozzles in common. The wind box is provided with openings through which combustion air flows in from one direction perpendicular to the axial direction of the burner, and is partitioned by a partition wall to form plurality of parallel flow paths for the air flowing in through the openings. Some of the plurality of flow paths are connected to an upper part of the combustion air nozzle, and the other flow paths are connected to a lower part of the nozzle.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
Hydrogen gas burner device
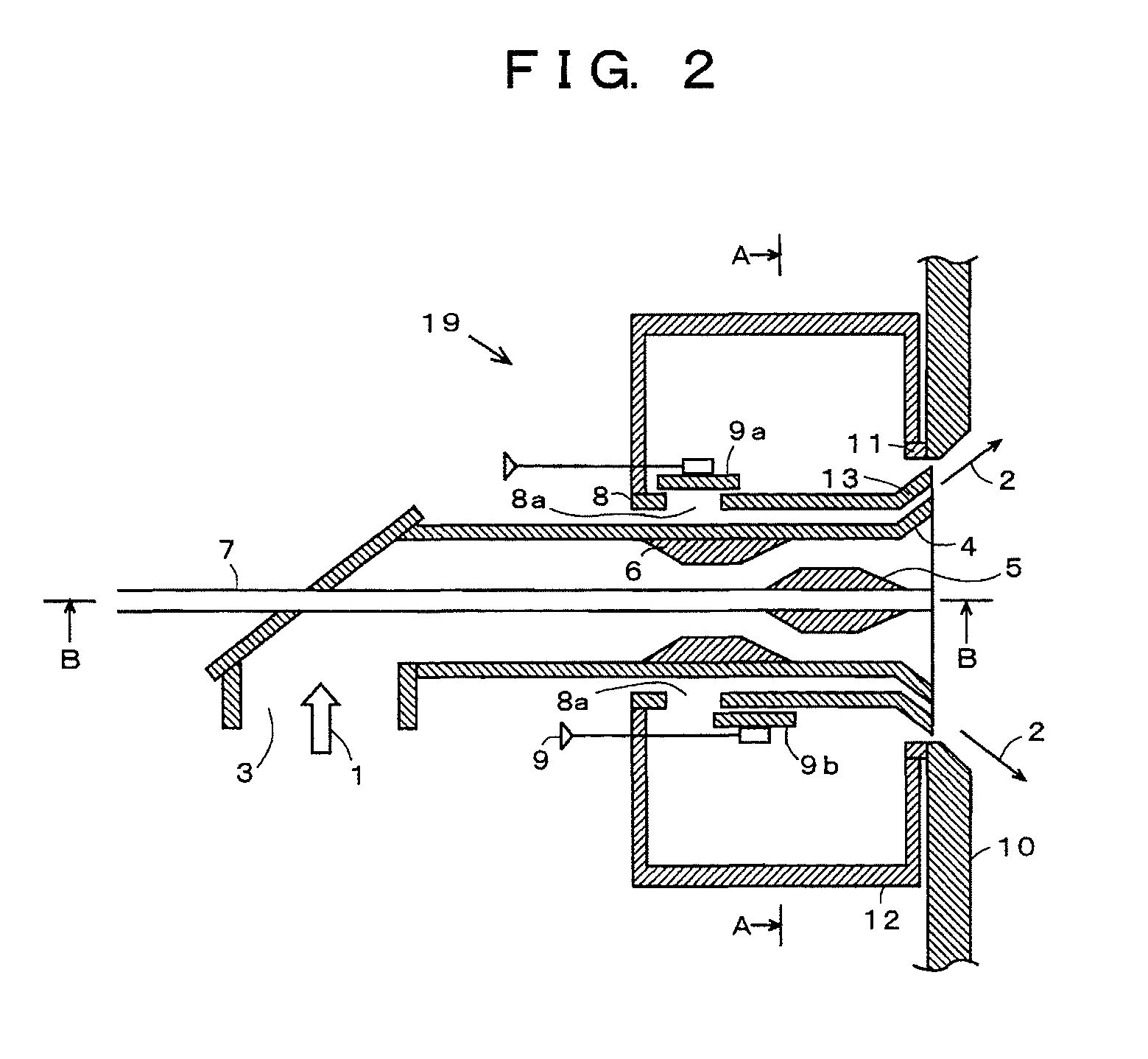
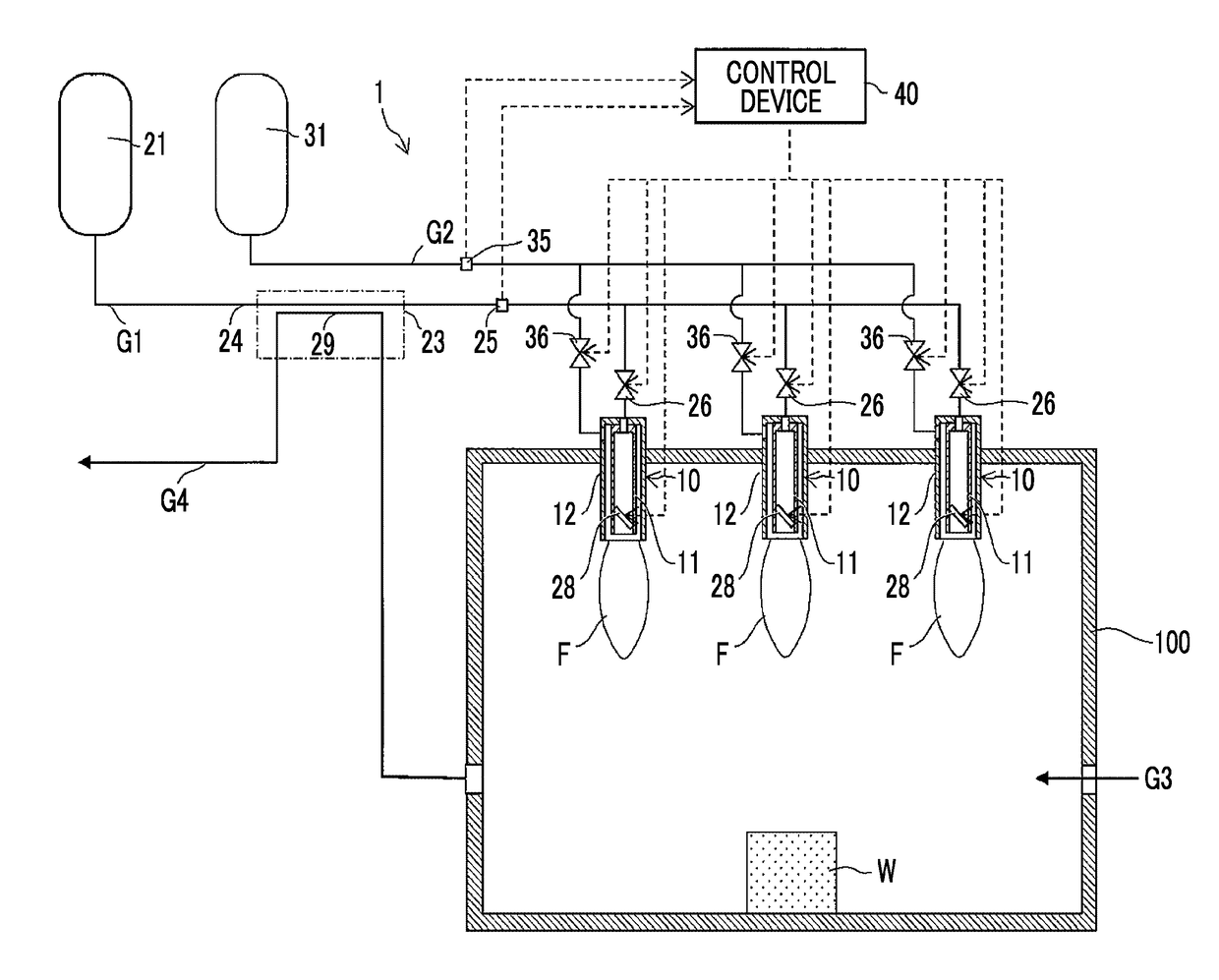
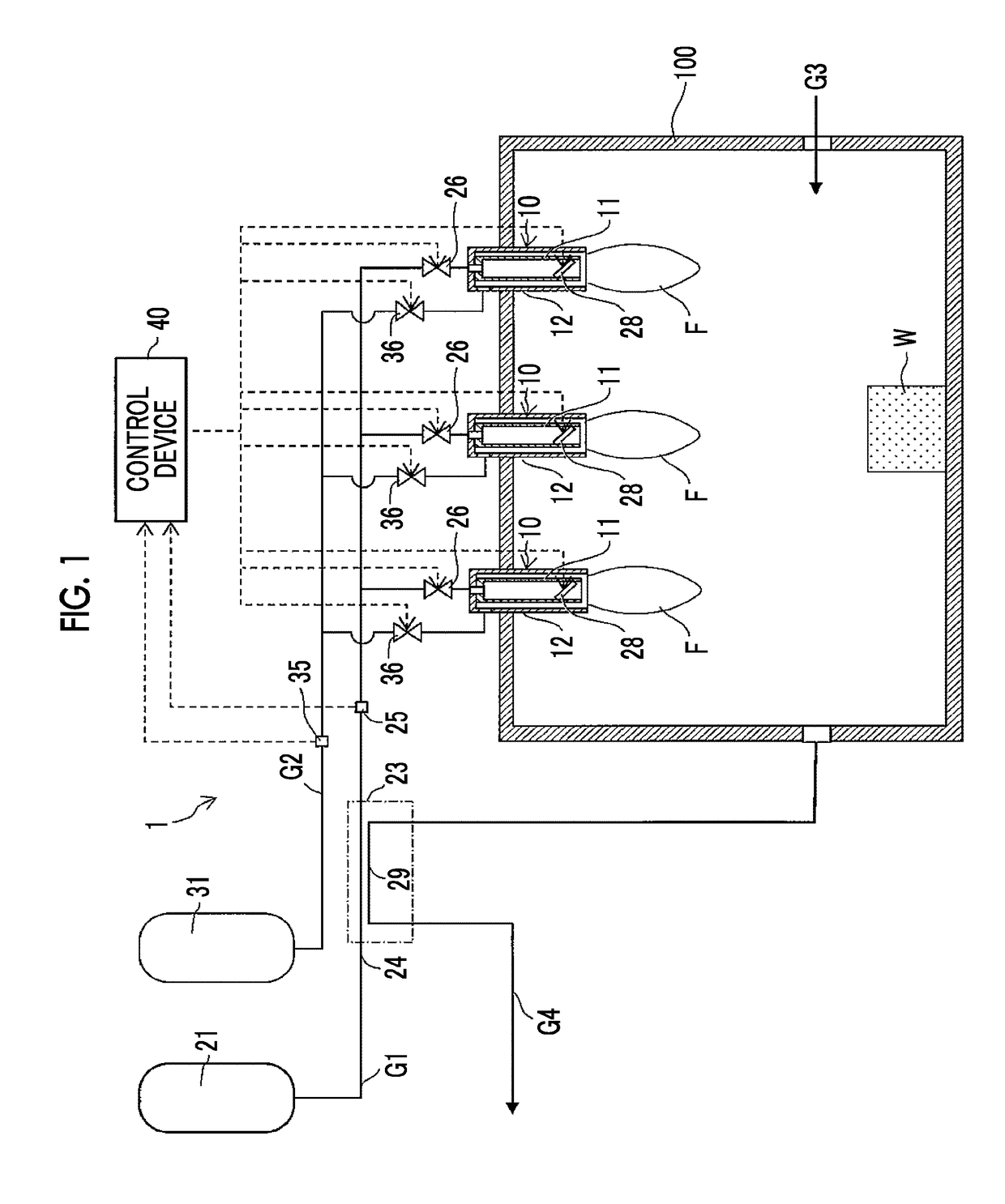
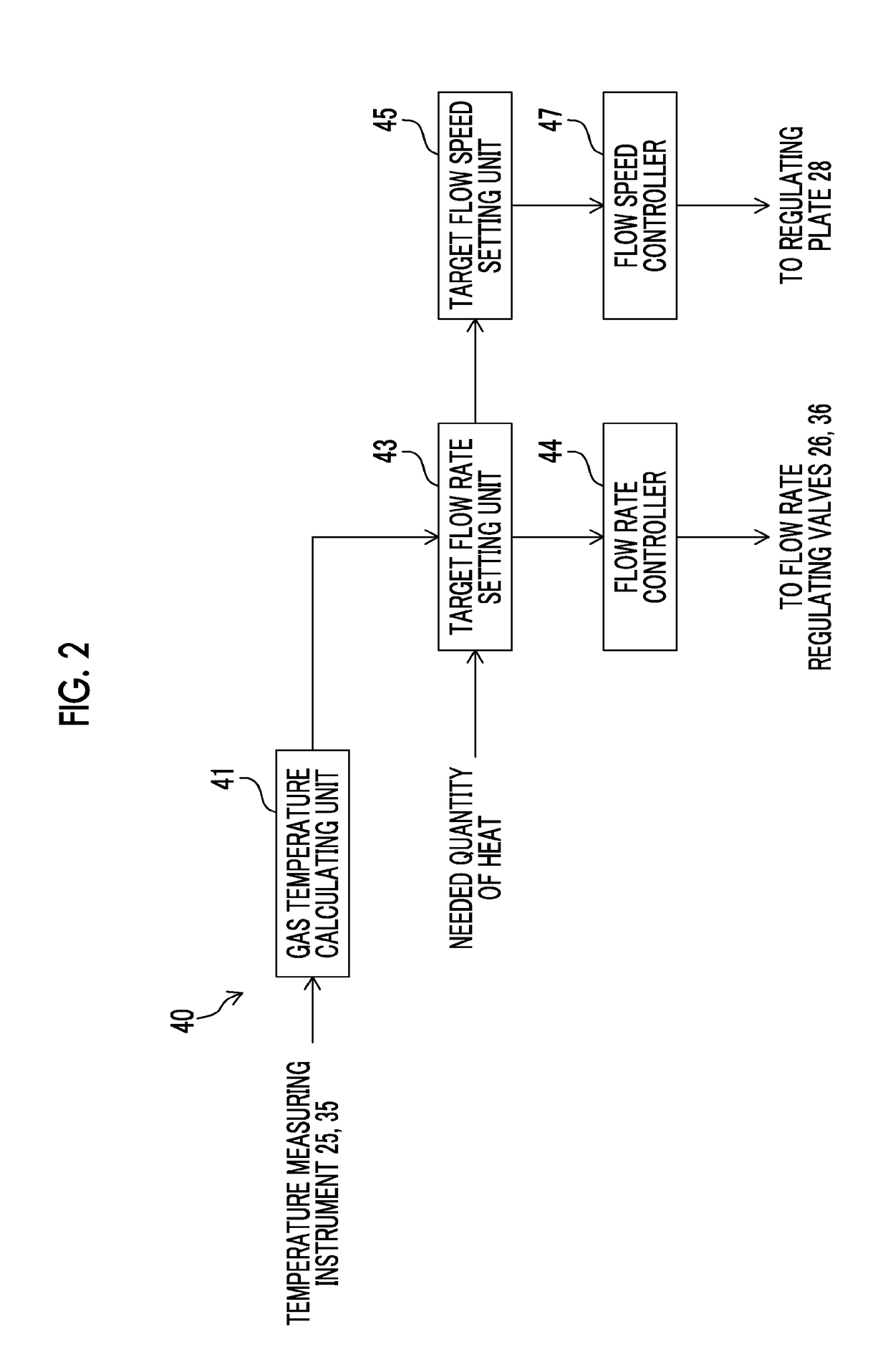
ActiveUS20180224122A1Burn fasterIncrease temperatureFuel supply regulationGaseous fuel feeder/distributionHydrogenEngineering
A control device of a hydrogen gas burner device sets a target flow rate of a hydrogen gas such that a flow rate of the hydrogen gas decreases as a temperature of the hydrogen gas becomes higher, based on the temperature of the hydrogen gas and a needed quantity of heat of the hydrogen gas during the combustion, sets a target flow speed such that the flow speed of the hydrogen gas released from a combustion nozzle via a flow speed regulator becomes a flow speed based on the target flow rate and the flow speed of the hydrogen gas increases as a value of the target flow rate decreases, controls the flow rate regulator such that the flow rate of the hydrogen gas reaches the target flow rate, and controls the flow speed regulator such that the flow speed of the hydrogen gas reaches the target flow speed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Catalyst and method of manufacture
InactiveUS9375710B2Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesNitrogen purification/separationGas treatmentCatalytic metalZeolite
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
NOX formation prediction for improved catalytic converter control
InactiveUS20200116093A1Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesReduce the overall heightGas treatmentElectrical controlCatalytic transformationThermodynamics
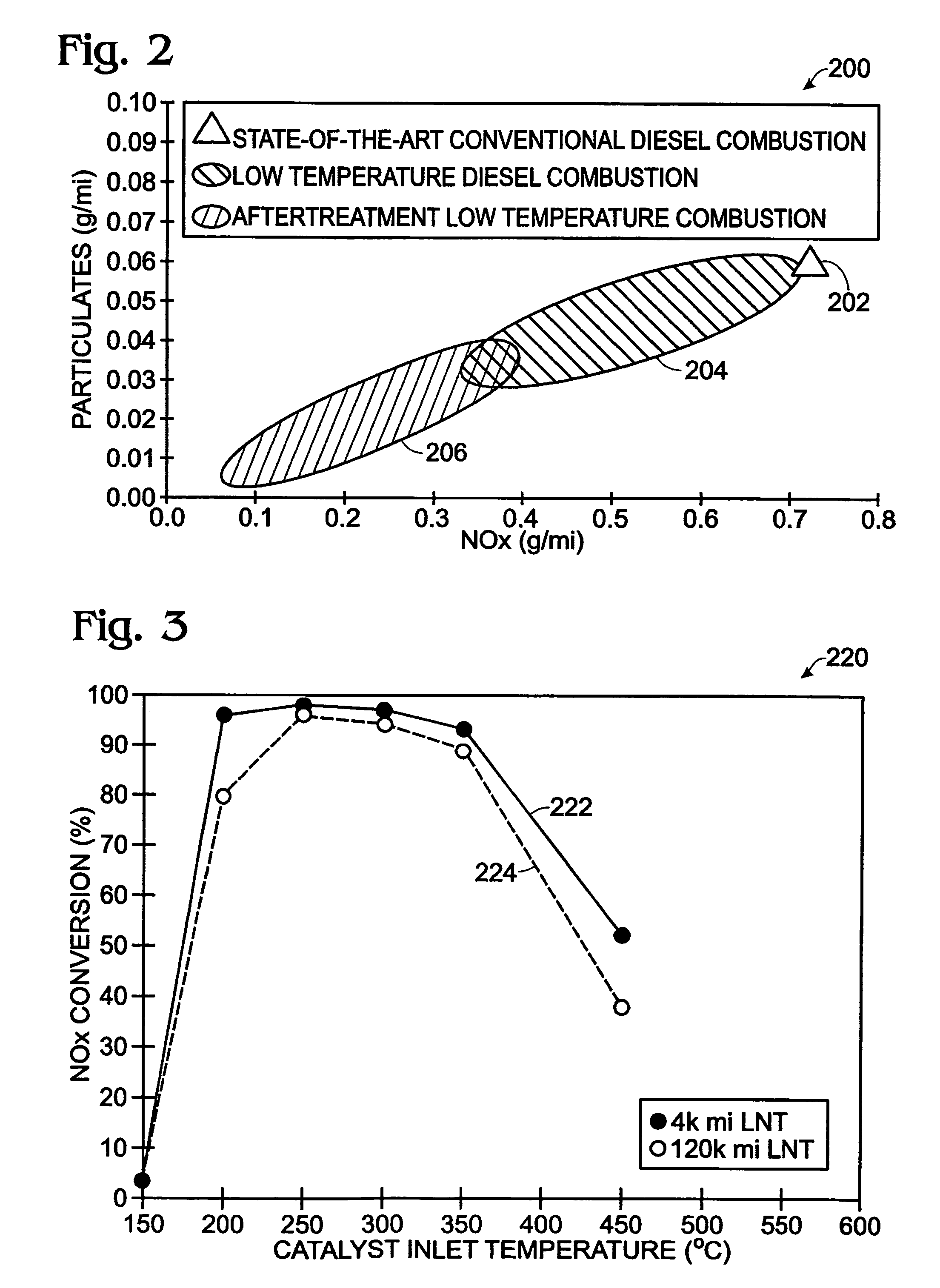
Methods of treating exhaust in a vehicle, and exhaust systems for a vehicle, are disclosed. Example methods may include providing a catalytic converter in an exhaust tailpipe and an oxygen sensor downstream of the catalytic converter. The catalytic converter may be configured to reduce a concentration of a nitrogen oxide (NOx) present in an exhaust flow through the catalytic converter. The method further includes predicting an increase in an oxygen concentration within the catalytic converter based upon at least one or more real-time vehicle operating parameters, wherein the increase is predicted before a corresponding increase in oxygen concentration is measured by the downstream oxygen sensor. The method may also include adjusting an air-fuel ratio of an engine of the vehicle based upon the predicted increase in oxygen concentration, thereby at least partially preventing the corresponding increase in the oxygen concentration.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Selective catalytic NOx reduction process and control system
ActiveUS8591848B2Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsControl systemAmmonia
Disclosed is a system which enables the efficient utilization of urea for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx by gasifying it and feeding it to a plurality of selective catalytic reduction units associated with a plurality of gas turbines. The invention enables feeding a gasified product of the urea with the ability to fully control separate SCR units without excessive reagent usage or loss of pollution control effectiveness. Controllers determine the amount of reagent required for each turbine to control NOx emissions and then mixes the gasified urea with the correct amount of carrier gas for efficient operation of each separate SCR unit despite the demand variation between the turbines. In this manner the gasification unit can be properly controlled to provide urea on demand without the need for storing large inventories of ammonia-containing gasses to correct for fluctuations in demand.
Owner:FUEL TECH
Exhaust gas reflux mechanism for multipurpose engine
InactiveUS7886714B2Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesEasy constructionValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveCombustion chamber
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Biomass charcoal gas co-production coupled biomass power generation system and biomass power generation method
PendingCN112852458AReduce dust accumulationReduce corrosionGaseous fuel feeder/distributionBiofuelsFlue gasProcess engineering
The invention provides a biomass charcoal gas co-production coupled biomass power generation system and a biomass power generation method, and relates to the technical field of biomass power generation. The system comprises a feeding device, a carbon-gas co-production device, a fuel gas purification device, a heat exchanger, a biomass direct-fired boiler, a fuel gas purification device, a pulse soot blower and a boiler blower. The feeding equipment is communicated with the carbon-gas co-production equipment, a flue gas outlet of the carbon-gas co-production equipment is in fluid communication with the heat exchanger, and a fuel gas outlet of the carbon-gas co-production equipment is in fluid communication with the fuel gas purification equipment; a fuel gas outlet of the fuel gas purification equipment is in fluid communication with the fuel gas purification equipment, a purified fuel gas outlet of the fuel gas purification equipment is in fluid communication with the pulse soot blower, and a gas outlet of the pulse soot blower is in fluid communication with the biomass direct-fired boiler. According to the biomass charcoal-gas co-production coupled biomass power generation system, the problems of ash deposition and low-temperature corrosion of the air pre-heater of the biomass direct-fired boiler can be solved.
Owner:大成华钰(北京)环境科技有限公司
Equipment for reducing concentration of nitrogen oxides in flue gas emission of glass kiln
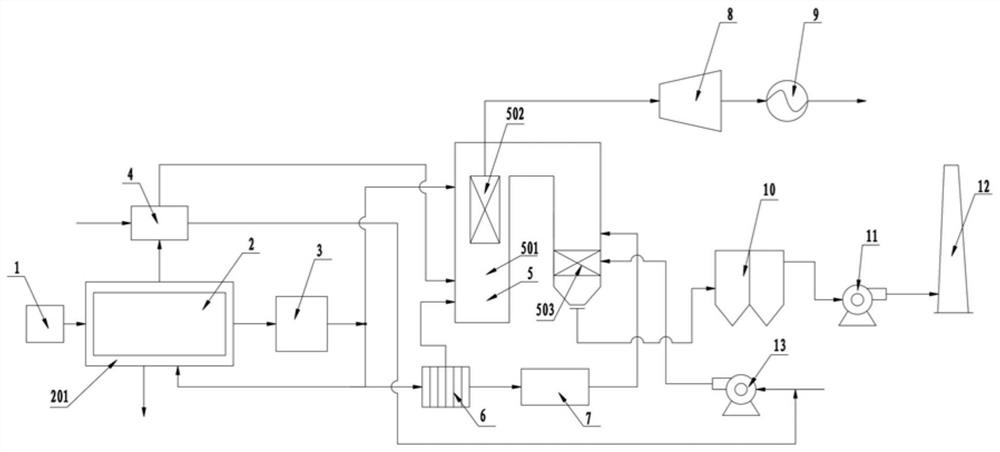
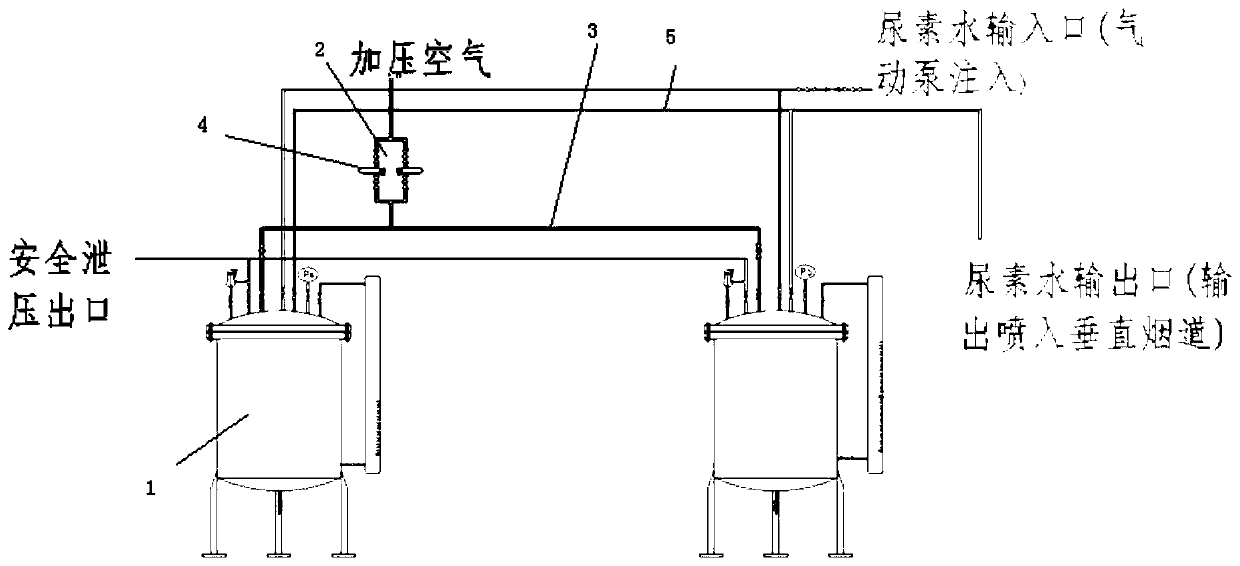
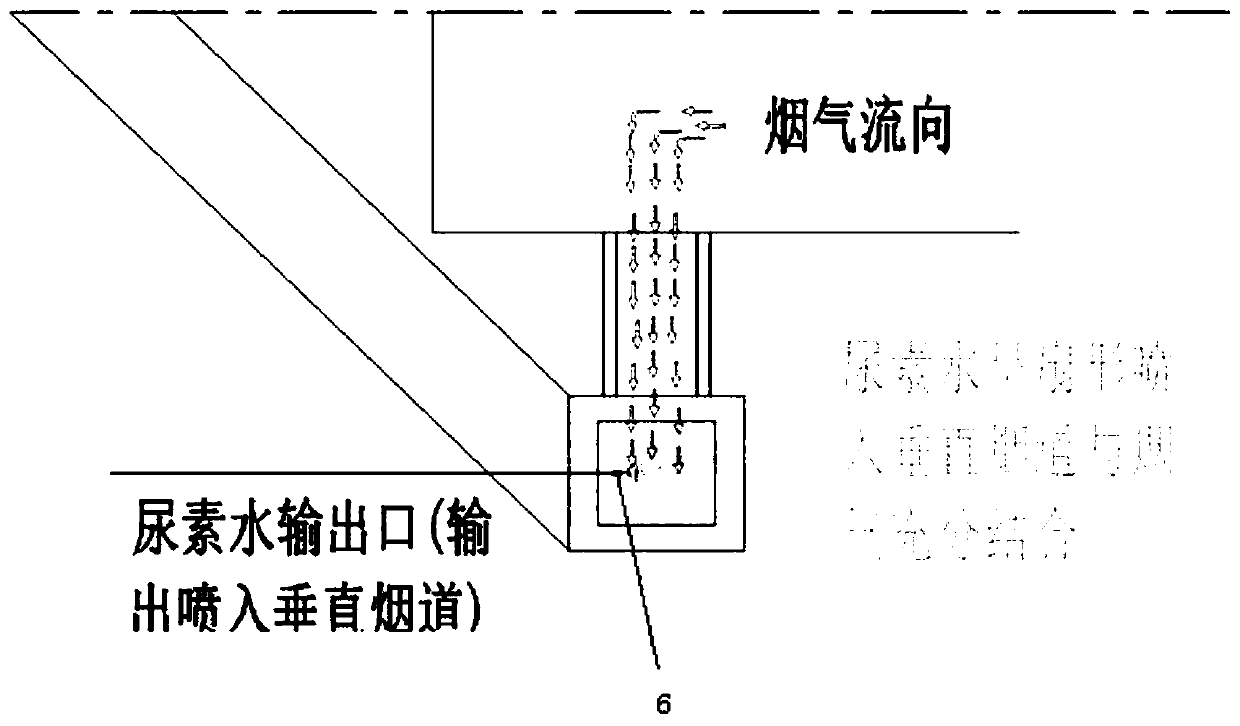
PendingCN110215823AReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesMeet environmental emission requirementsGas treatmentDispersed particle separationNitrogen oxidesFlue gas
The invention relates to equipment for reducing the concentration of nitrogen oxides in flue gas emission of a glass kiln. The equipment comprises at least one high-pressure tank; the input end of theat least one high-pressure tank is connected with a urea liquid output end, and the urea liquid output end is pumped by a pump; an air pressurizing device for air pressurization is installed at the top end of the at least one high-pressure tank, and the air pressurizing device is connected with the at least one high-pressure tank through a compressed air pipeline; and the output end of the at least one high-pressure tank is connected with spray guns through a urea water pipeline. The equipment provided by the invention has the characteristics of a simple structure, ingenious design, easy operation and convenient use.
Owner:CAIHONG GRP ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com