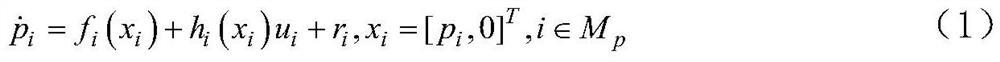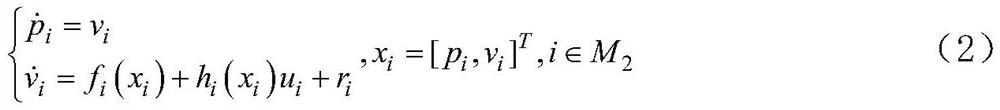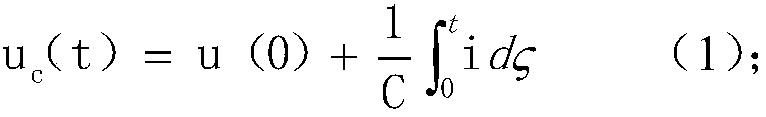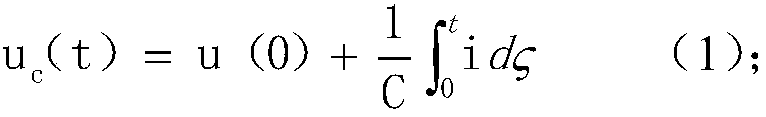Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Save control resources" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
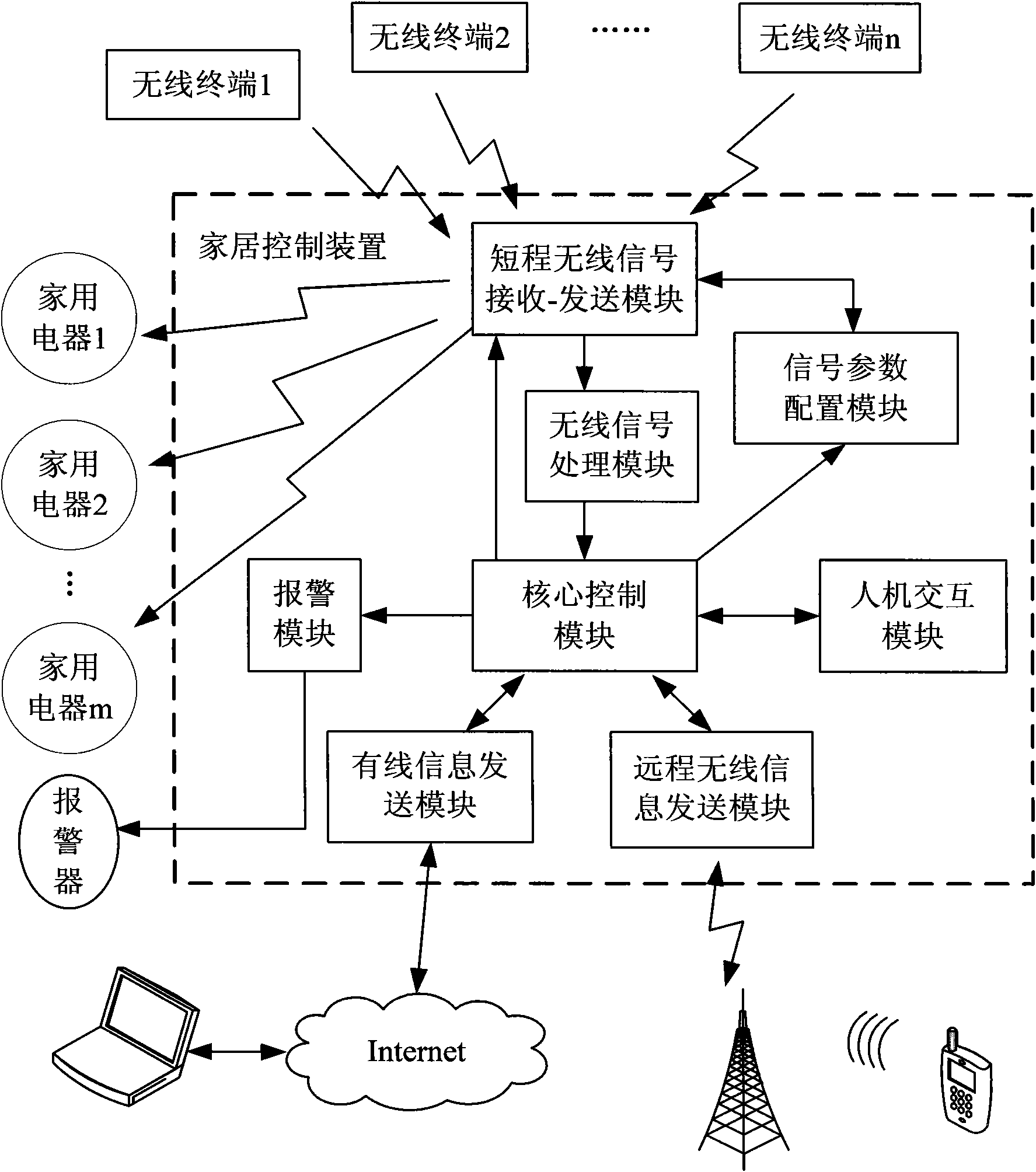
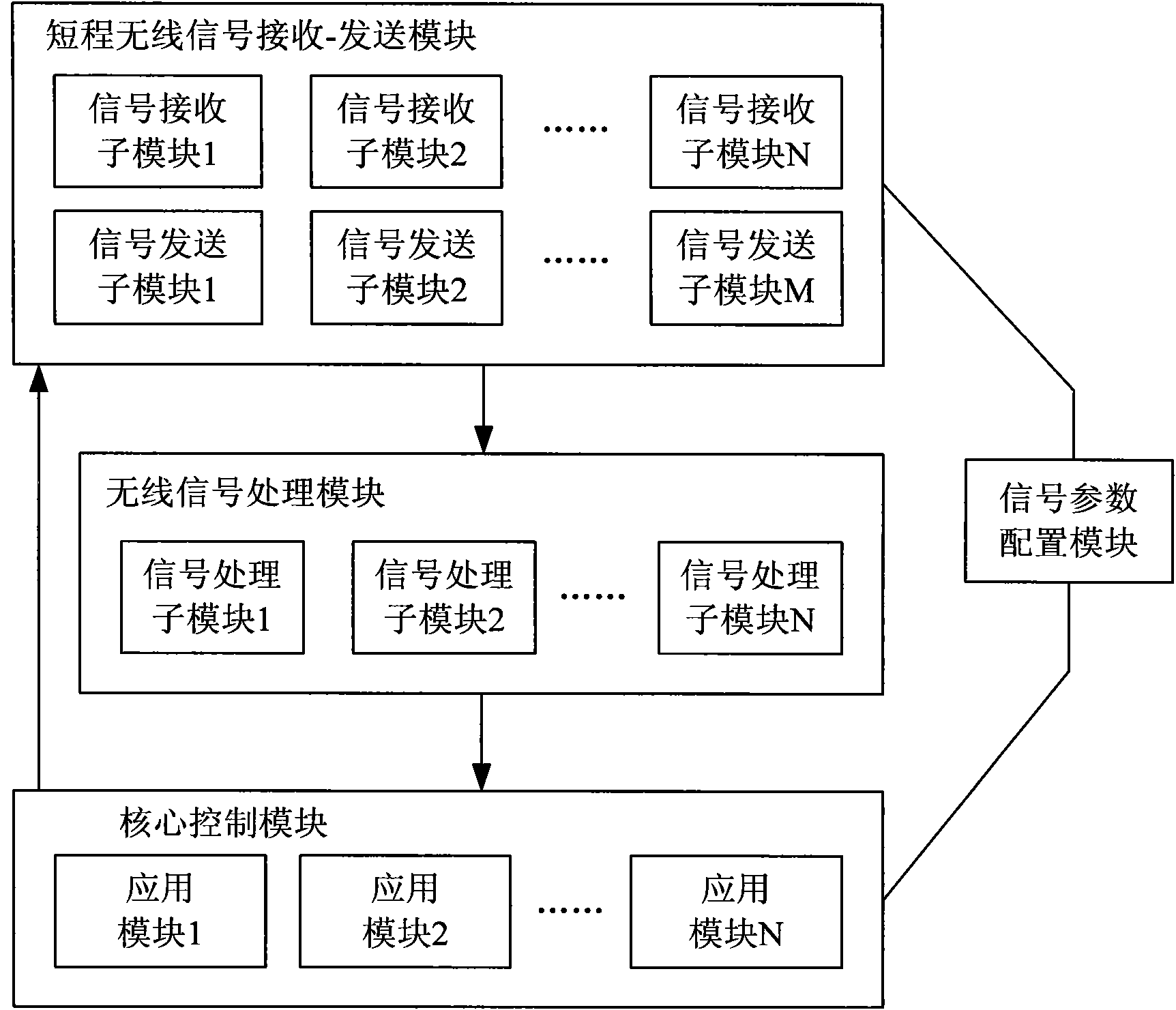
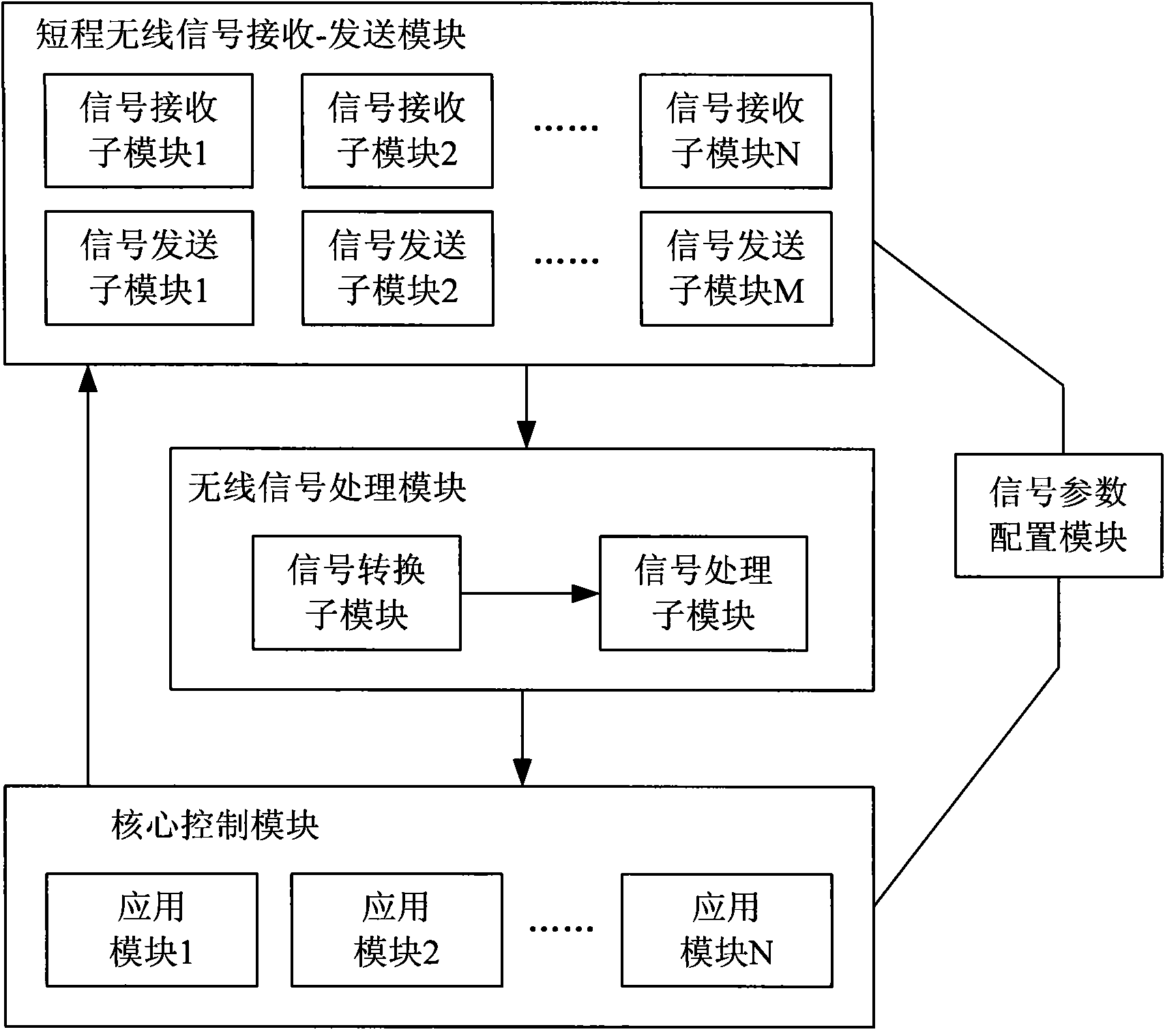
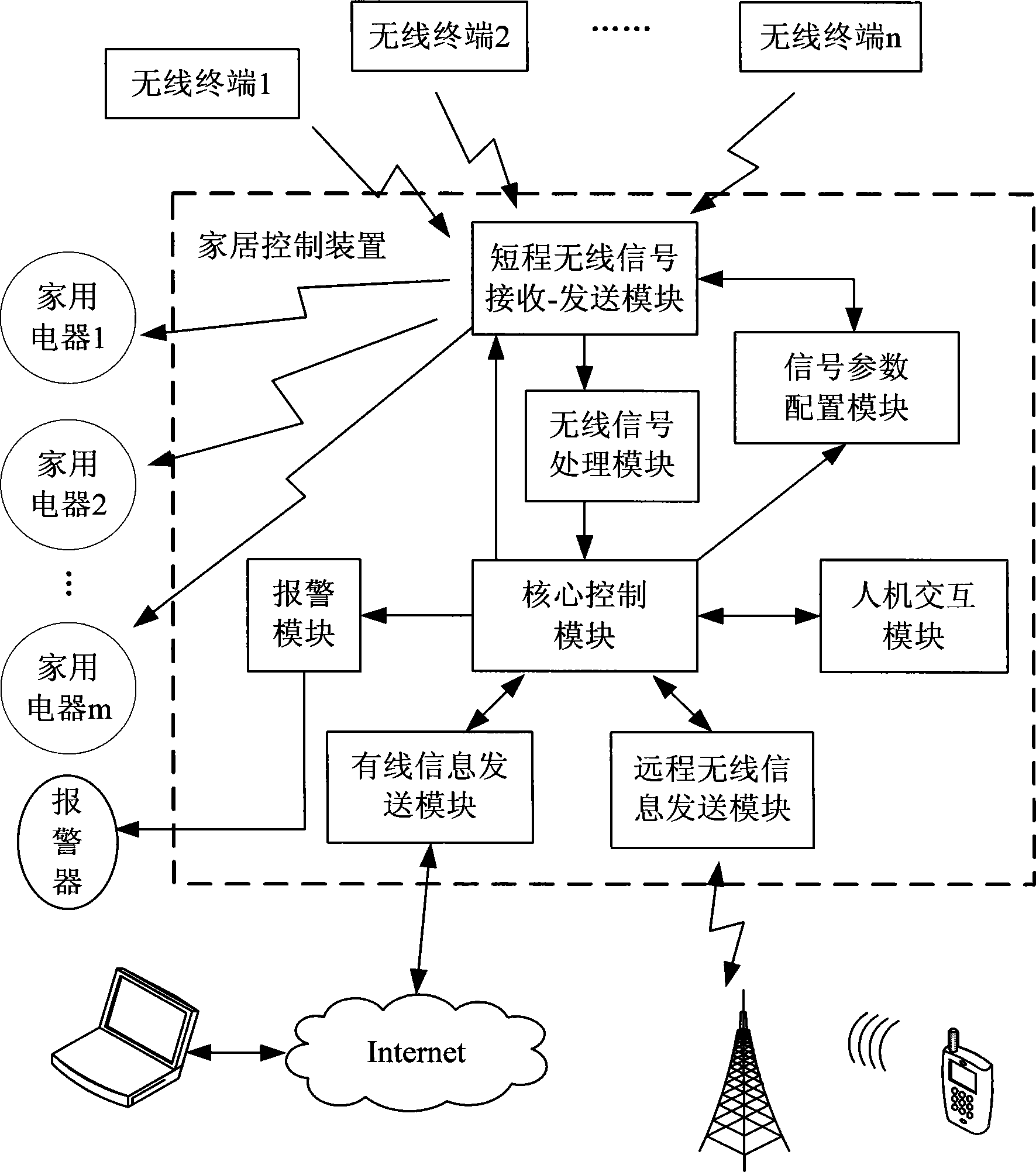
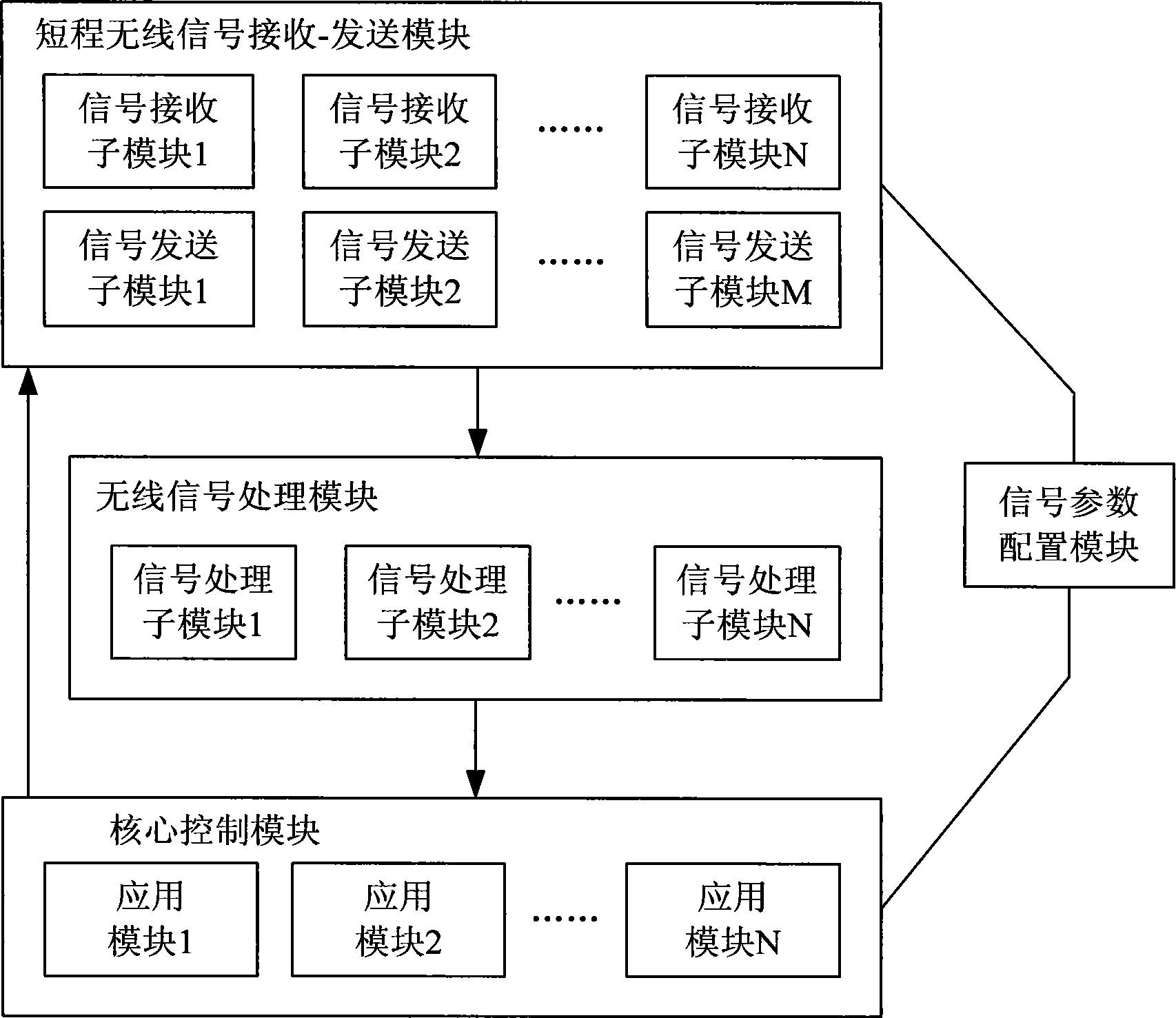
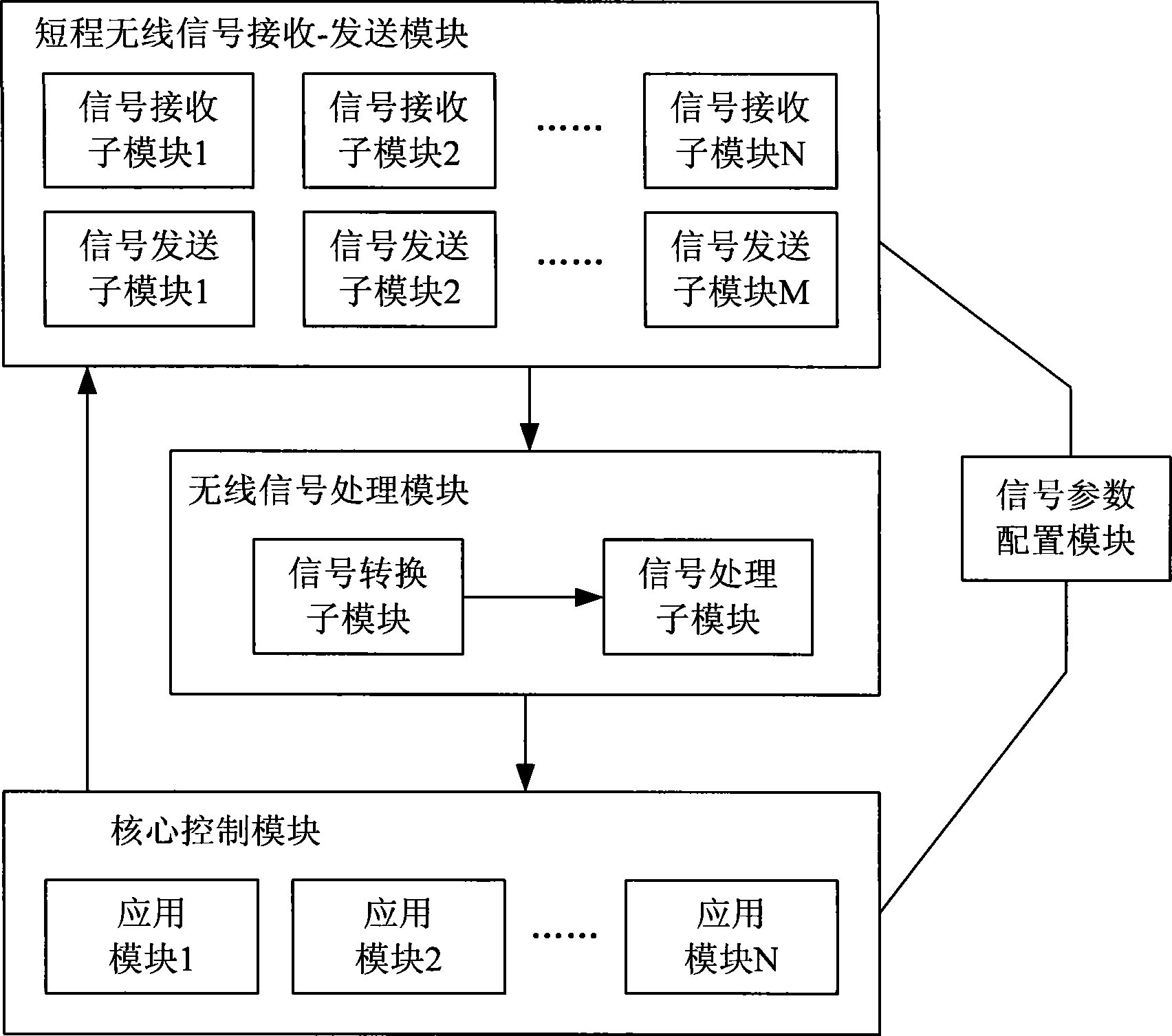
Intelligent home network system, control device and method
ActiveCN101945493AEasy remote accessRealize managementTransmission systemsNetwork topologiesIntelligent NetworkComputer terminal
The invention discloses an intelligent home network system, a control device and a control method. The system comprises a plurality of different wireless terminals and a home control device, wherein the wireless terminals transmit various wireless access request signals to the home control device respectively; and the home control device correspondingly sets matched access parameters for the different wireless terminals, receives the wireless access request signals according to the configured access parameters, resolves and processes the signals to obtain corresponding data, simultaneously analyzes and judges the data and converts the processed data into corresponding real-time monitoring information for storage. The intelligent home network system, the control device and the control method have the advantages of solving problems on the simultaneous access of the intelligent home network system by the wireless signals adopting different transport protocols and bringing great convenience to integrated management on the diversified wireless terminal products in the market so as to promote the development of wireless terminal product technology.
Owner:ZTE CORP
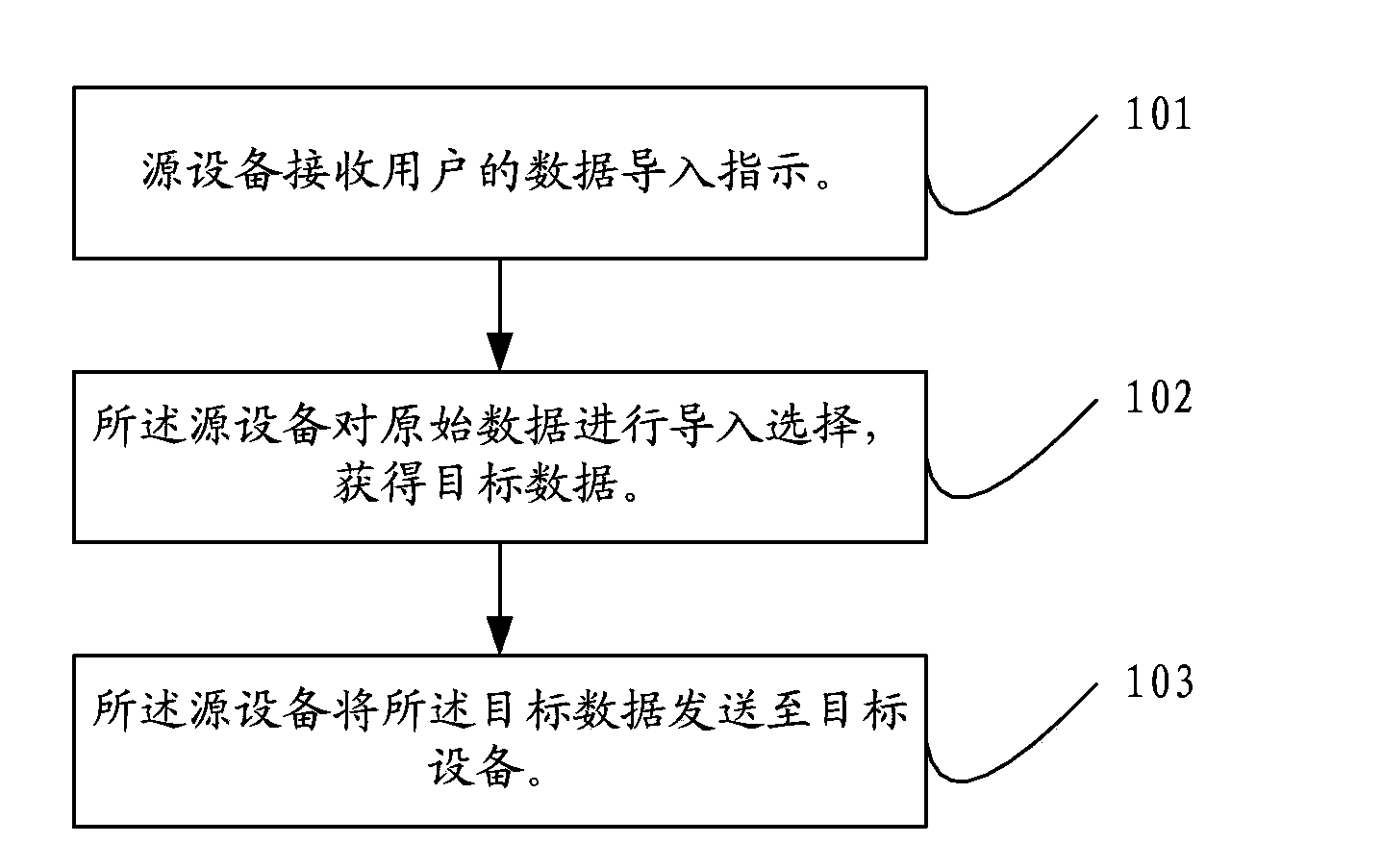
Method and device for data transmission
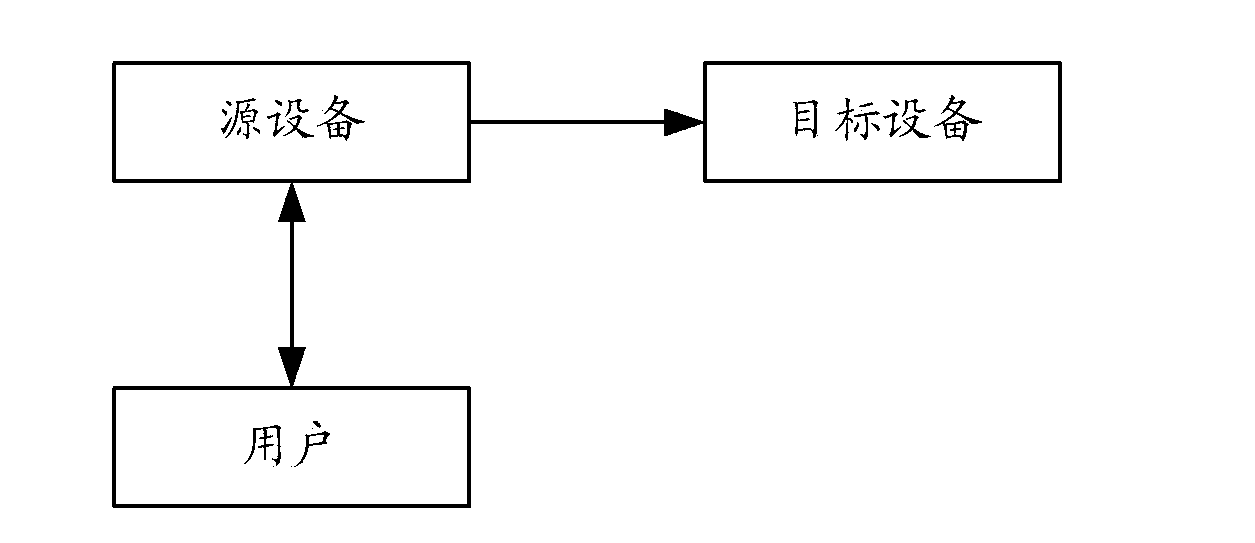
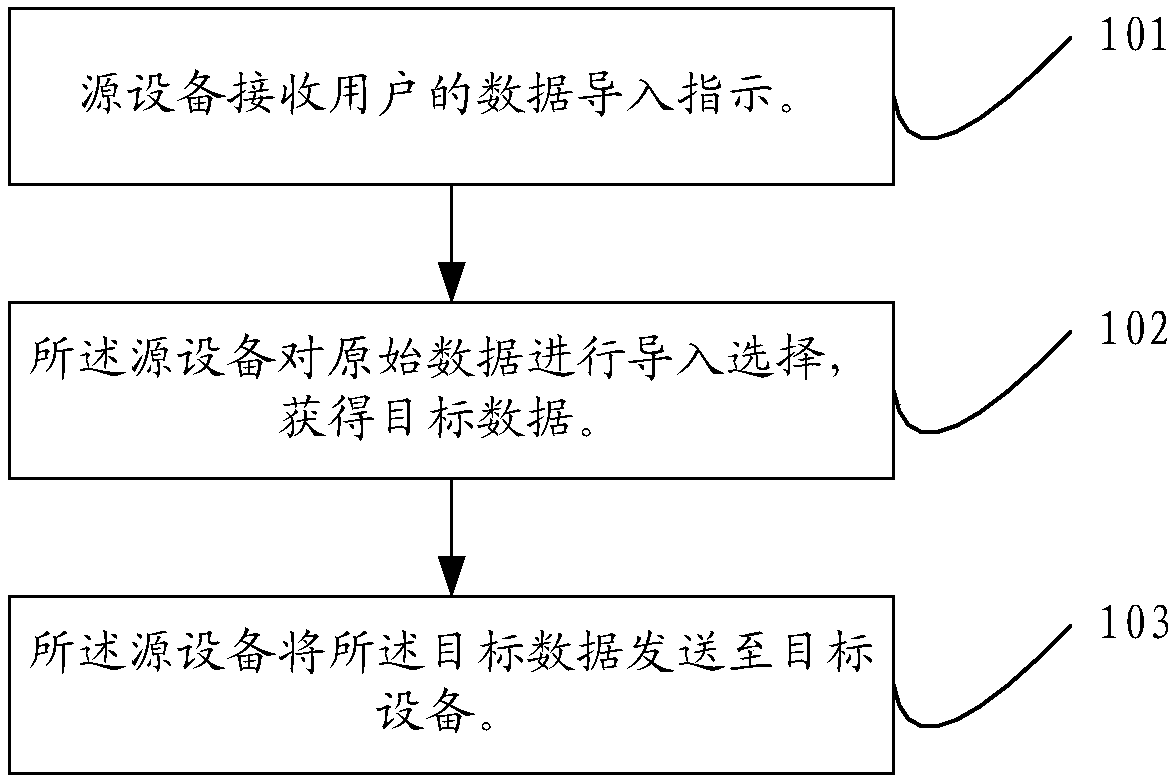
ActiveCN103838683AImprove transmission efficiencySave control resourcesElectric digital data processingOriginal dataData transmission
The invention discloses a method and device for data transmission, relates to the field of electronic equipment application and aims at saving system control resources and improving data transmission efficiency. The method for the data transmission comprises the steps that a source device receives data guide-in indication of a user; the source device conducts guide-in selection on original data so as to obtain target data; the source device sends target data to a target device, so that the target device can conduct classification processing on the target data according to the attribute of the target data. The method and device for the data transmission are mainly used in the data guide-in process between electronic equipment.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Downlink control channel sending method and receiving method and corresponding device
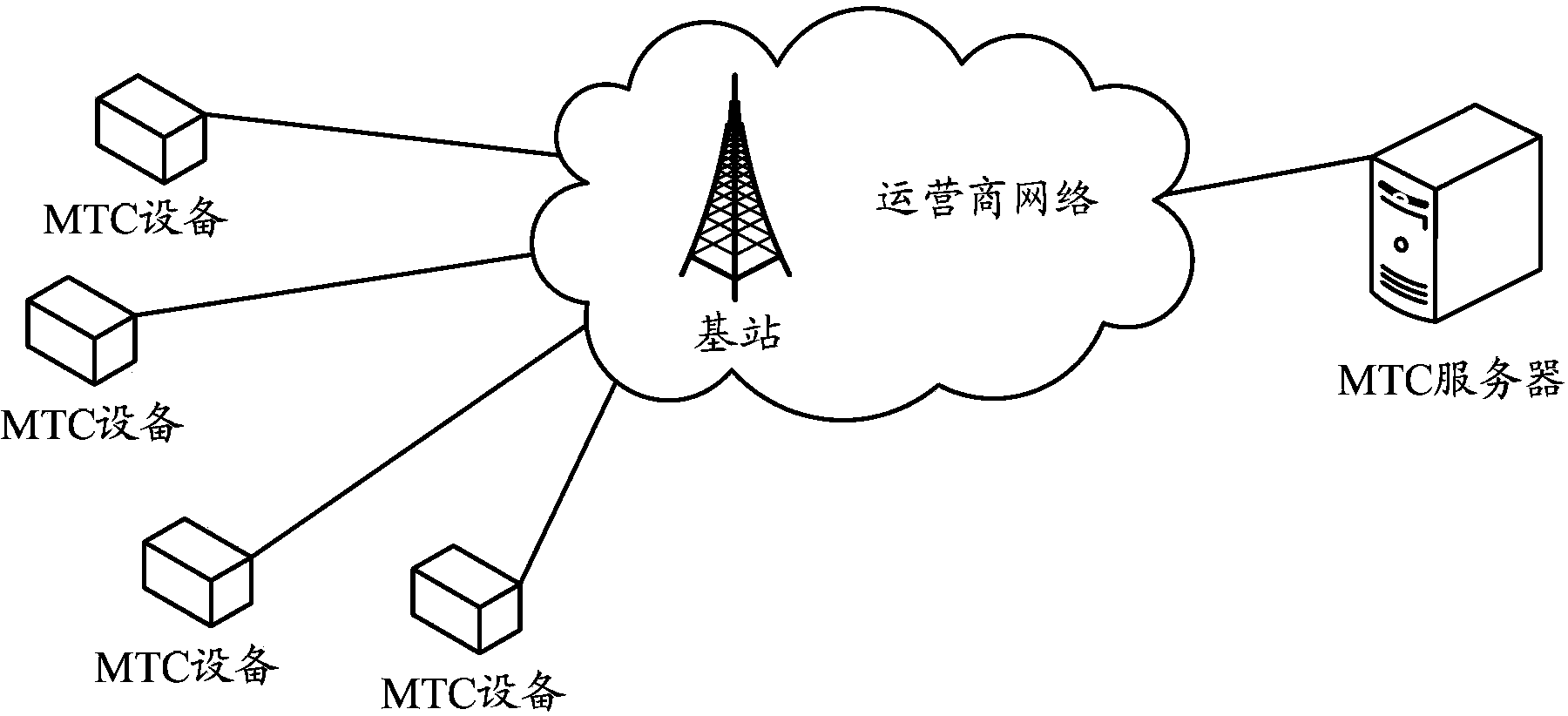
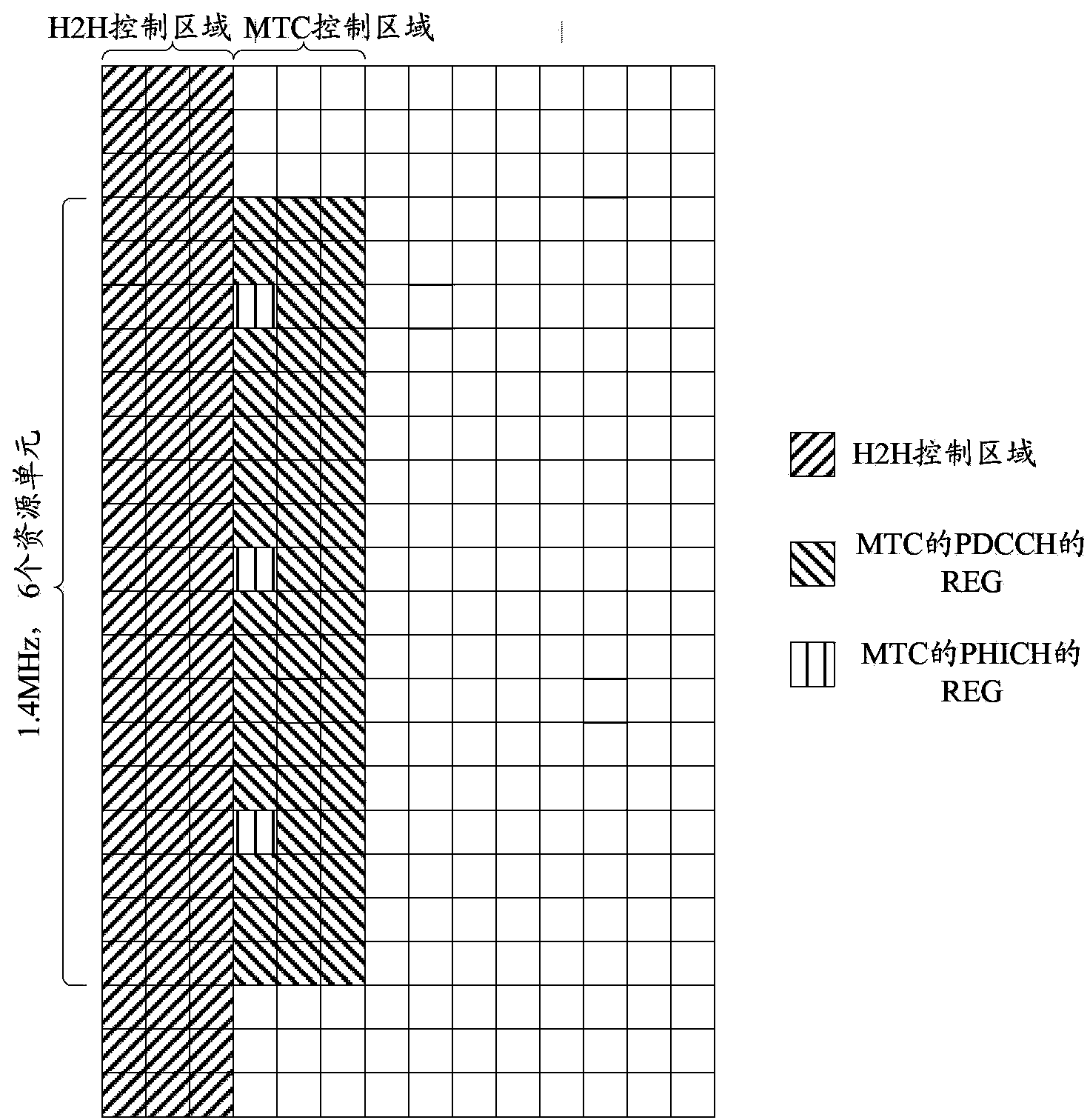
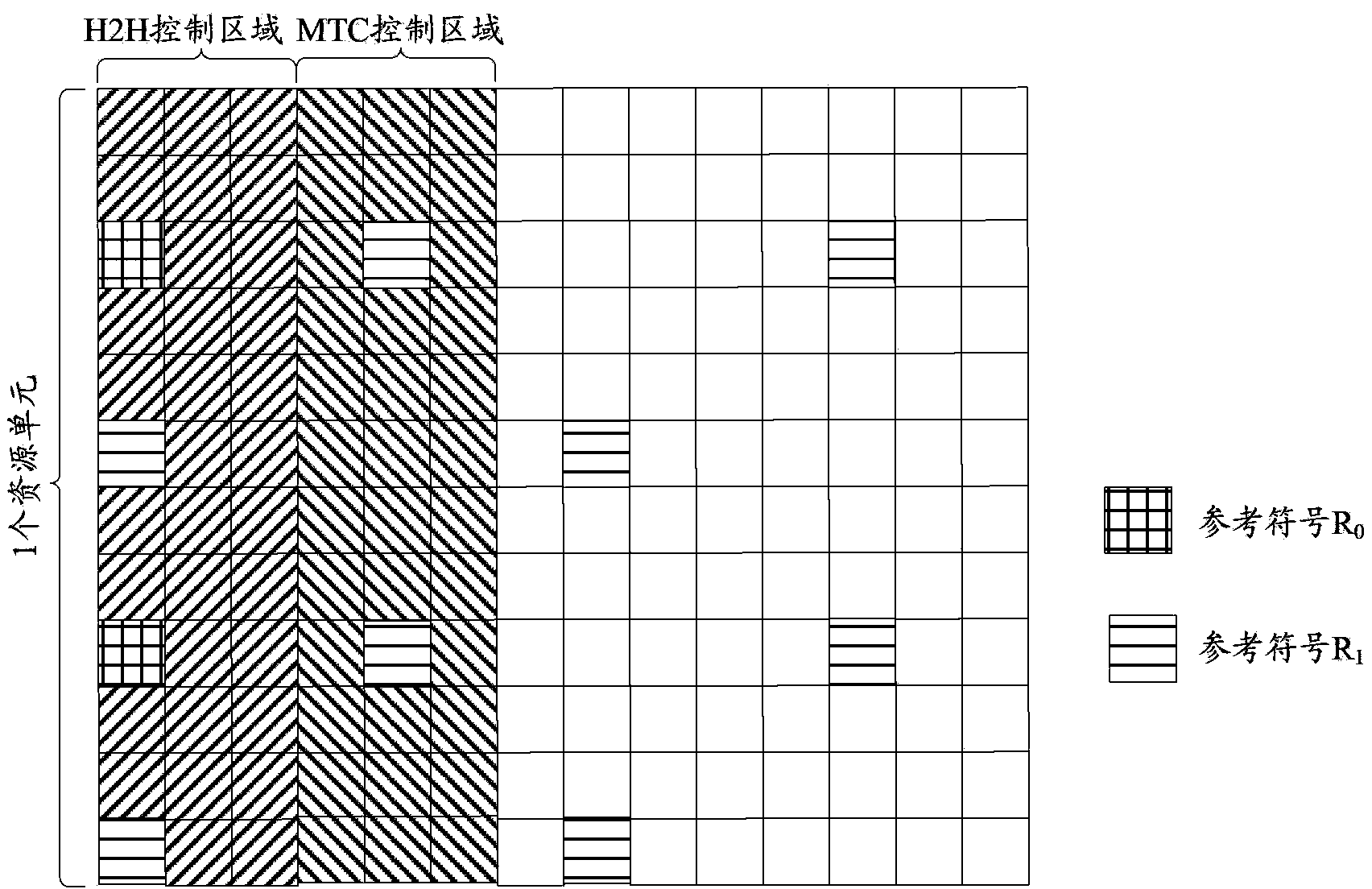
InactiveCN103582098AStrong periodicityLong change cyclePower managementAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsControl channel
Disclosed are a method for sending and receiving downlink control channel, and corresponding device thereof. The method for sending downlink control channel includes the following steps: network side device sends the downlink control channel to Machine Type Communication (MTC) device, wherein, the downlink control channels sent to MTC device do not contain Physical Control Format Indicator Channel (PCFICH), said network side device predetermines Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol occupied by Physical Downlink Control Channel (PDCCH) with the MTC device, or said network side device notifies OFDM symbol occupied by PDCCH to the MTC device by broadcasting a system message to the MTC device. The solution in the present invention provides the design scheme of downlink control channel applied in MTC technology.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
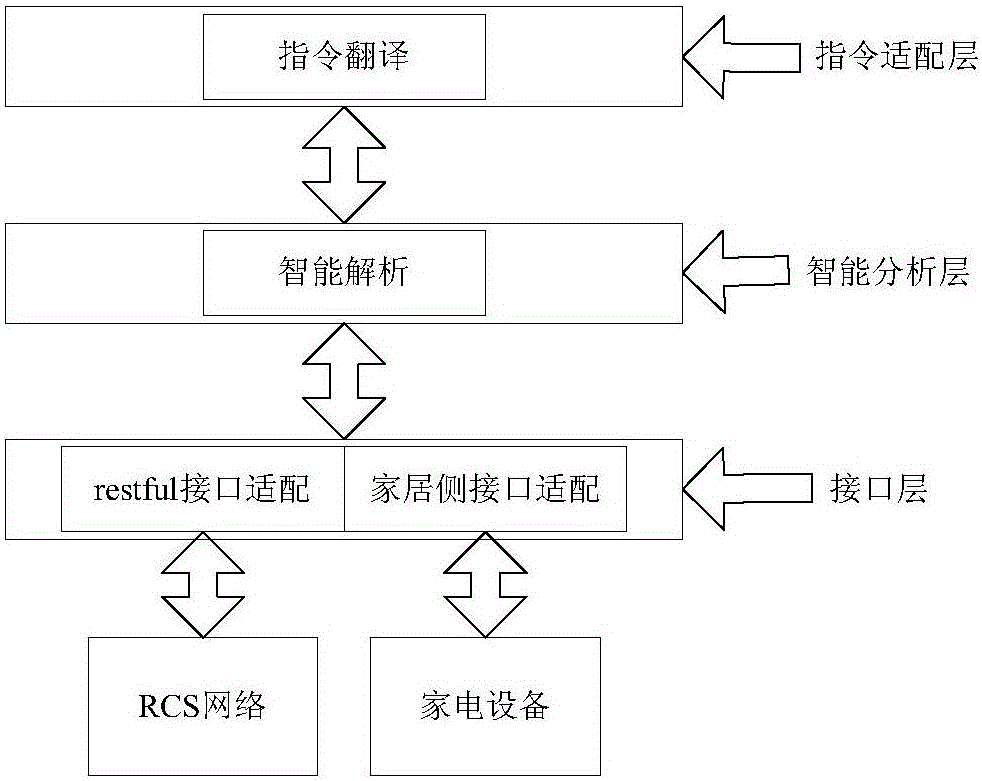
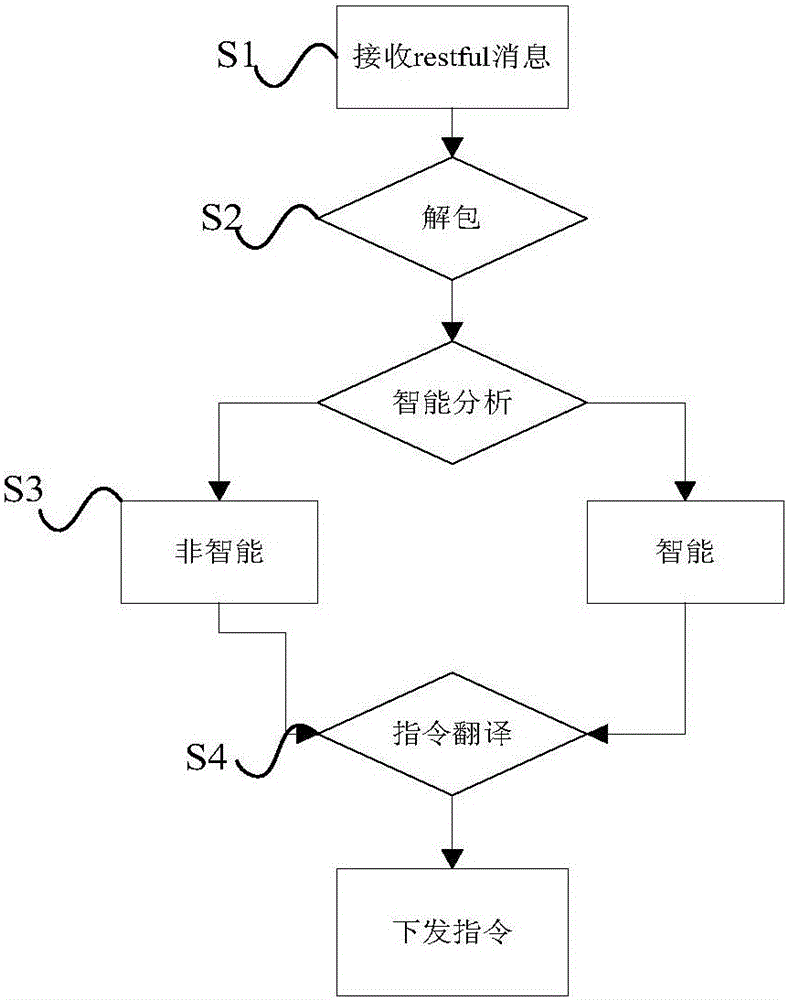
Intelligent home control method, device and system
ActiveCN106371322ASolve wasteSave control resourcesComputer controlProgramme total factory controlControl systemResource saving
The invention provides an intelligent home control method, device and system. The method comprises: a control message that is forwarded by a rich communication suite (RCS) and is from a mobile terminal is received, wherein the control message is used for indicating at least one household appliance to execute a corresponding operation; according to a pre-stored household appliance list, the control message is parsed to obtain a control instruction corresponding to the at least one household appliance; and the control instruction is sent to the at least one household appliance. Therefore, a problem that compatibility of intelligent household control systems can not be realized because of multiple APPs pushed for intelligent household controlling by multiple manufacturers and thus control resources are wasted can be solved; and thus effects of control resource saving and control efficiency improvement are realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
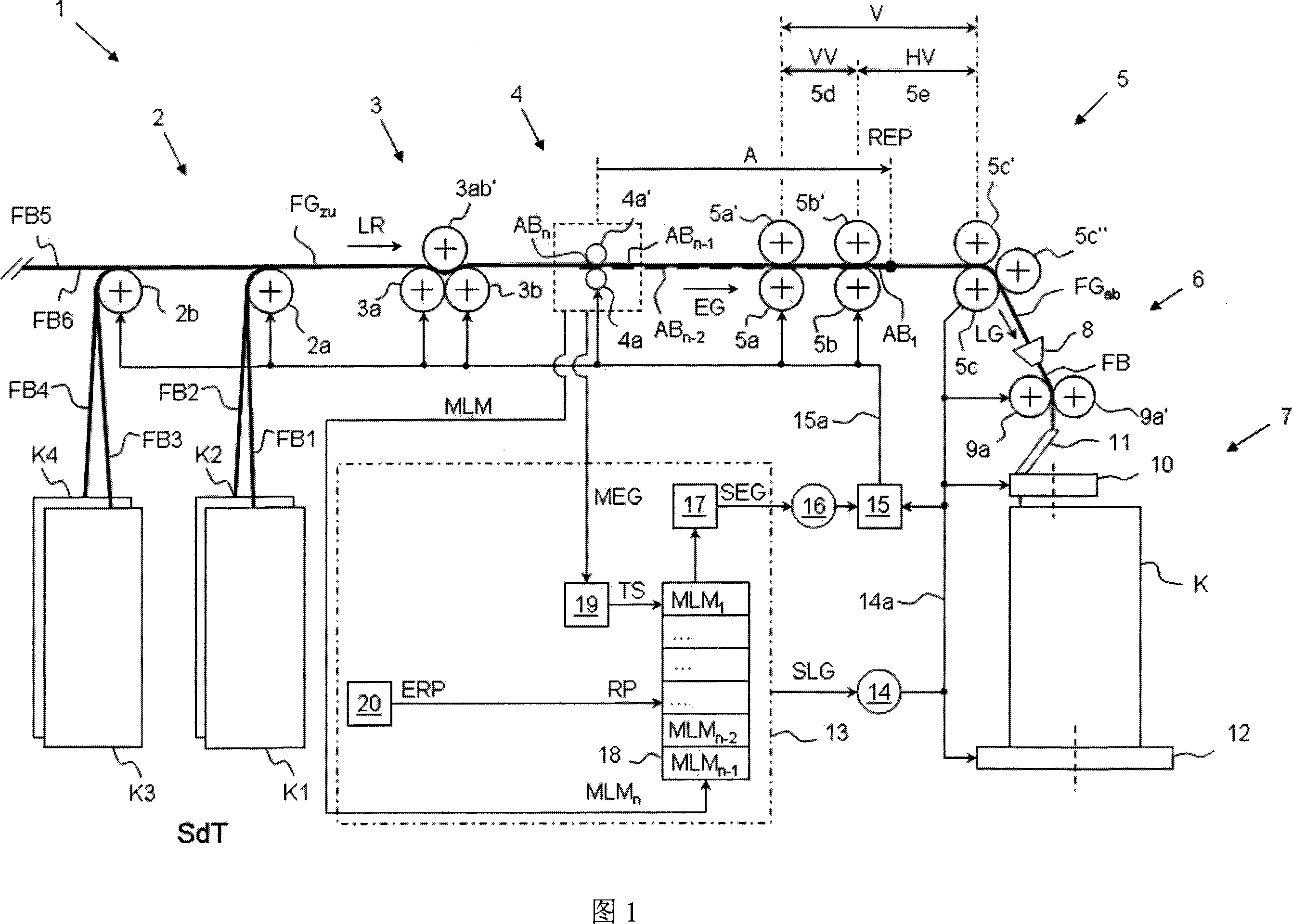
Stretching control method of the stretching unit of a spinning machine and a spinning machine
ActiveCN101096788ABest specified valueReduce computing workDrafting machinesCarding machinesFiberControl theory
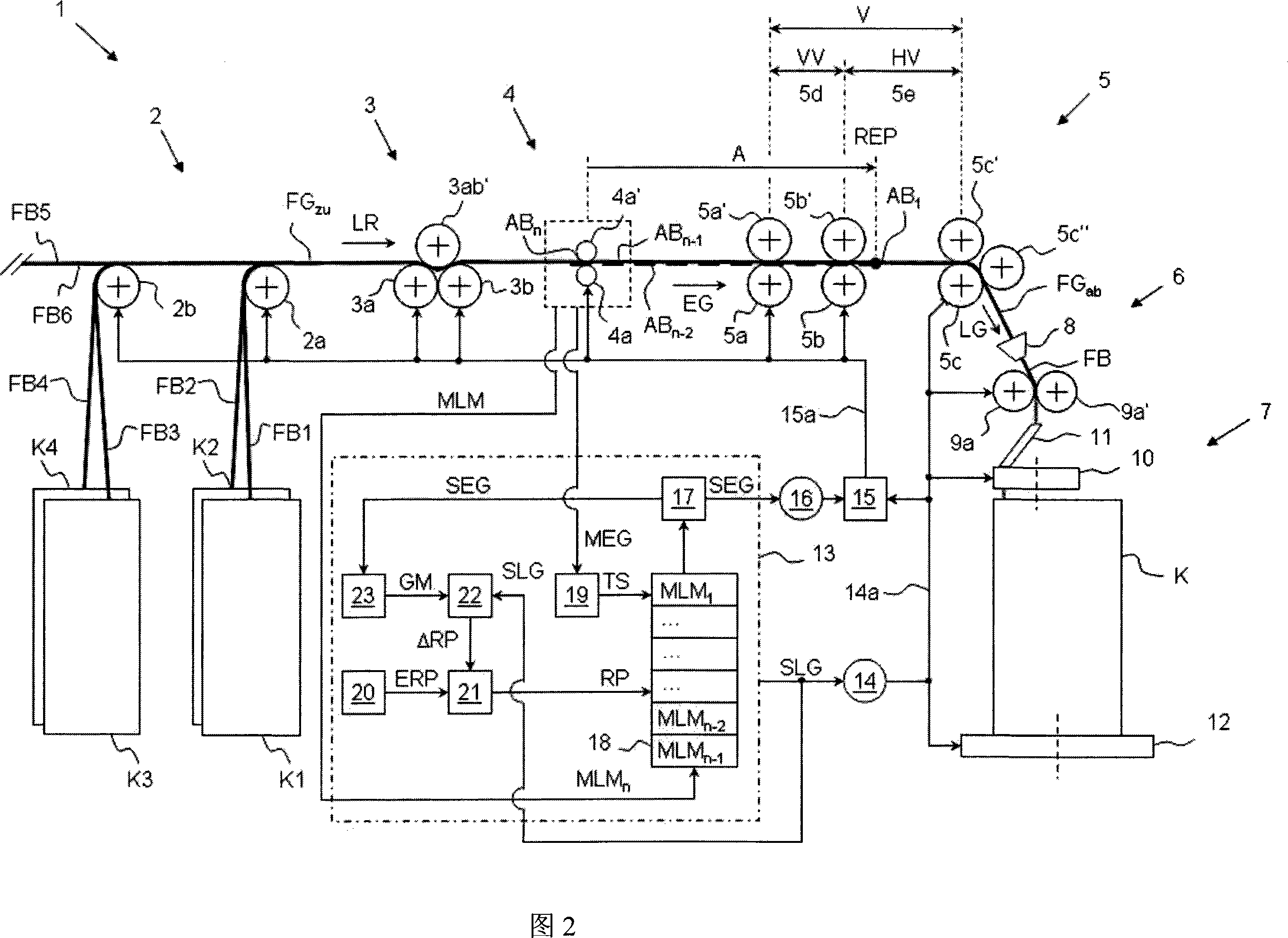
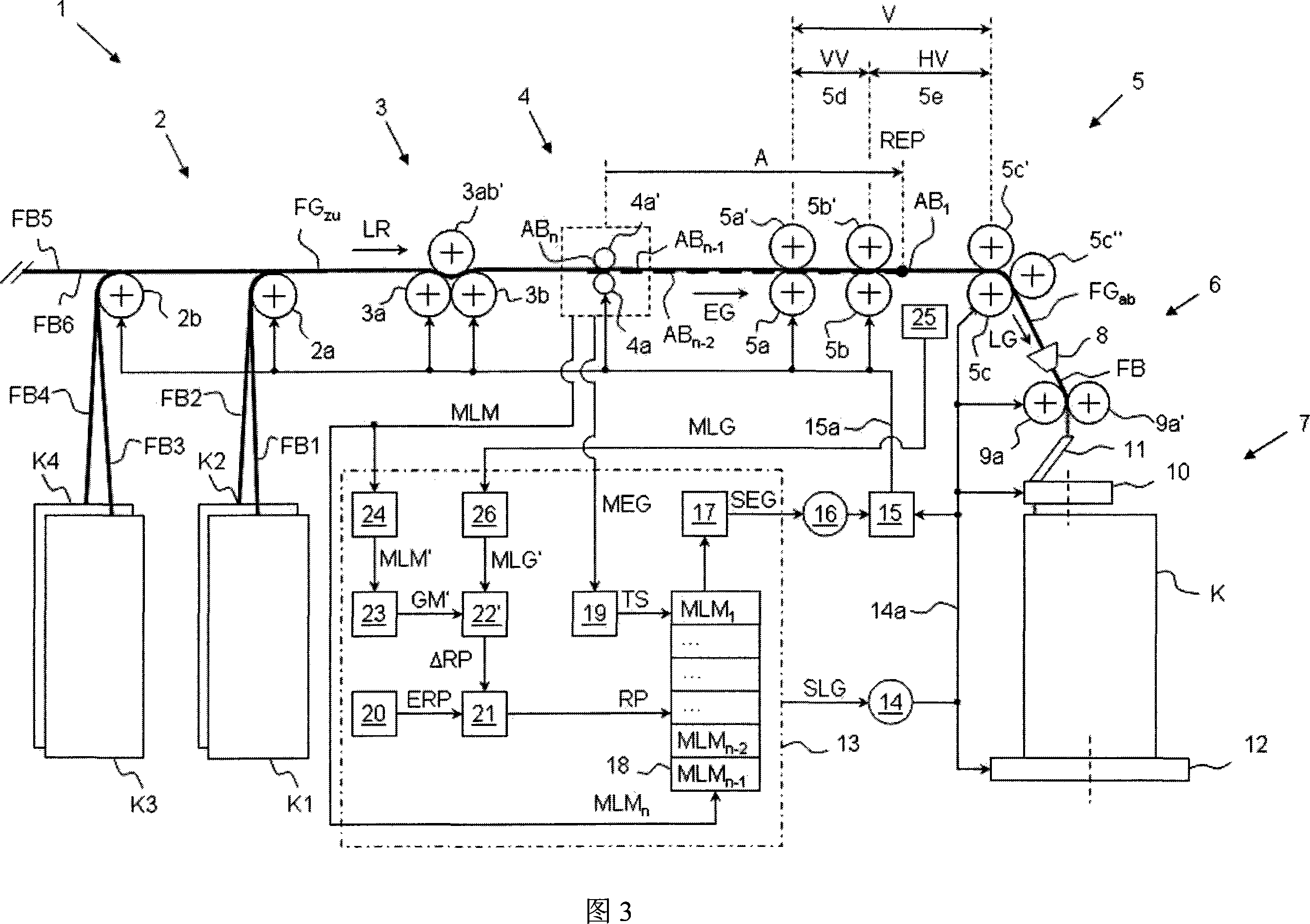
The present invention provides a drafting controlling method for the drafting system (5) of the textile machinery (1), wherein, for the continuous fragments (AB1, ellipsis, ABn-2, ABn-1, ABn) of the fiber strip (FGzu) of the inputting drafting system (5), the feeding sensor unit (4) at the upriver of the drafting system (5) gets the measured value (MLM1, ellipsis, MLMn-2, MLMn-1, MLMn) of weight at unit length of each fragment; to regulate the weight at unit length of the inputting fiber strip (FGzu) when the fragment (AB1) which is relative to a certain measured value (MLM1) reaches a control action point (REP) assigned by the appointed control value (MLM1), it will do controlling and regulation to the drafting (V) of the drafting system (5) on the basis of the measured value (MLM1); it modifies the appointed value (RP) used to control the action point (REP) in the making process of the textile machinery (1), wherein, the appointed value (RP) is from the predefined setting value (ERP) and corrected value (delta RP), at the same time the corrected value (delta RP) is confirmed by the values (MEG, GM, GM', SEG) relative to the feeding velocity (EG) of the fiber strip (FGzu) of the inputting drafting system (5) and the values (MLG, SLG) relative to the outputting velocity (LG) of the fiber strip (FGab) of the outputting drafting system (5). The invention also provides a textile machinery.
Owner:RIETER INGOLSTADT SPINNEREI
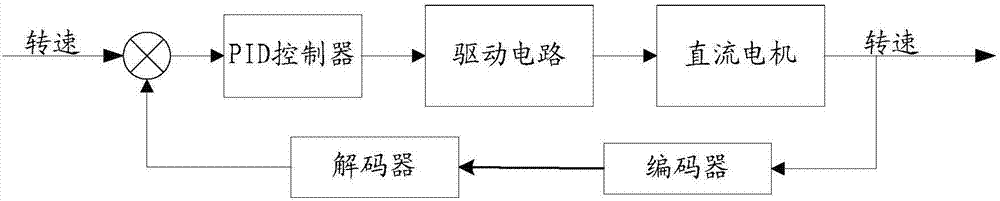
Control system and method of series DC motor
InactiveCN107017804ASave control resourcesSolve technical problems that take up a lot of resourcesElectric motor speed/torque regulationCommunication unitControl system
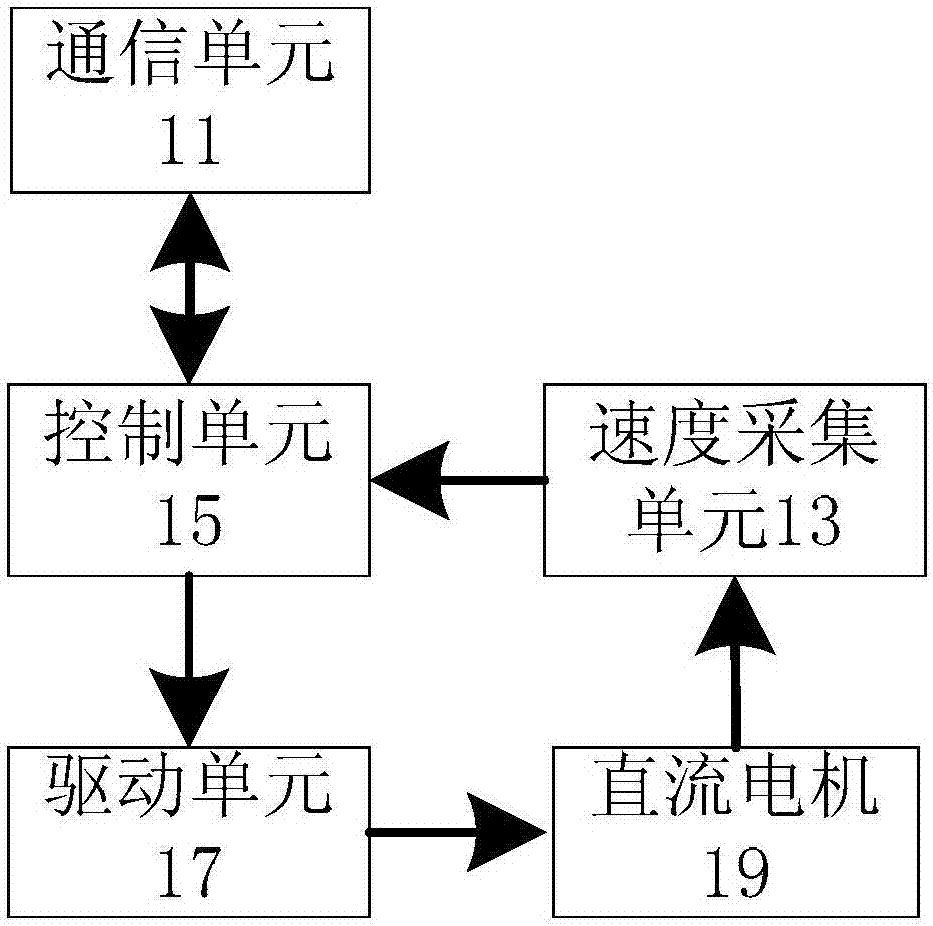
The invention discloses a control system and method of a series DC motor. The control system comprises a communication unit, a speed acquisition unit, a control unit and a driving unit, wherein the communication unit is used for sending received control information to the control unit of the control system and is also used for sending the control information and state information of a DC motor corresponding to the control system to at least one control system which is connected in series, the speed acquisition unit is connected with the DC motor and is used for acquiring rotational speed information of the DC motor, the rotational speed information comprises a pulse output parameter of the DC motor, the control unit is used for generating a rotational speed regulation parameter according to the control information and the rotational speed information, and the driving unit is connected with the control unit and the DC motor and is used for adjusting a driving voltage according to the rotational speed regulation parameter. By the control system, the technical problem of large resource occupancy when a plurality of motors are needed to be controlled by the motor control system is solved.
Owner:海航生态科技集团有限公司
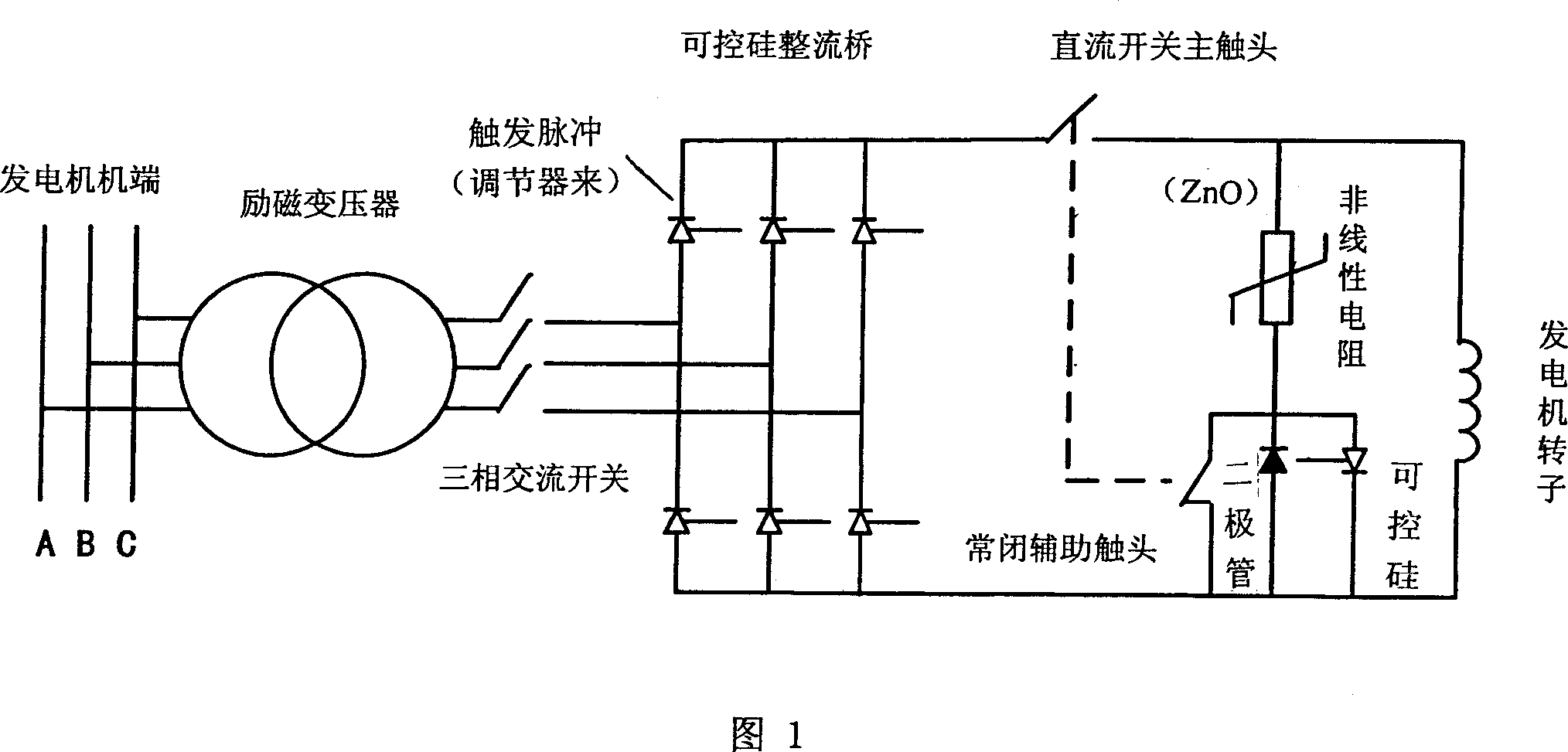
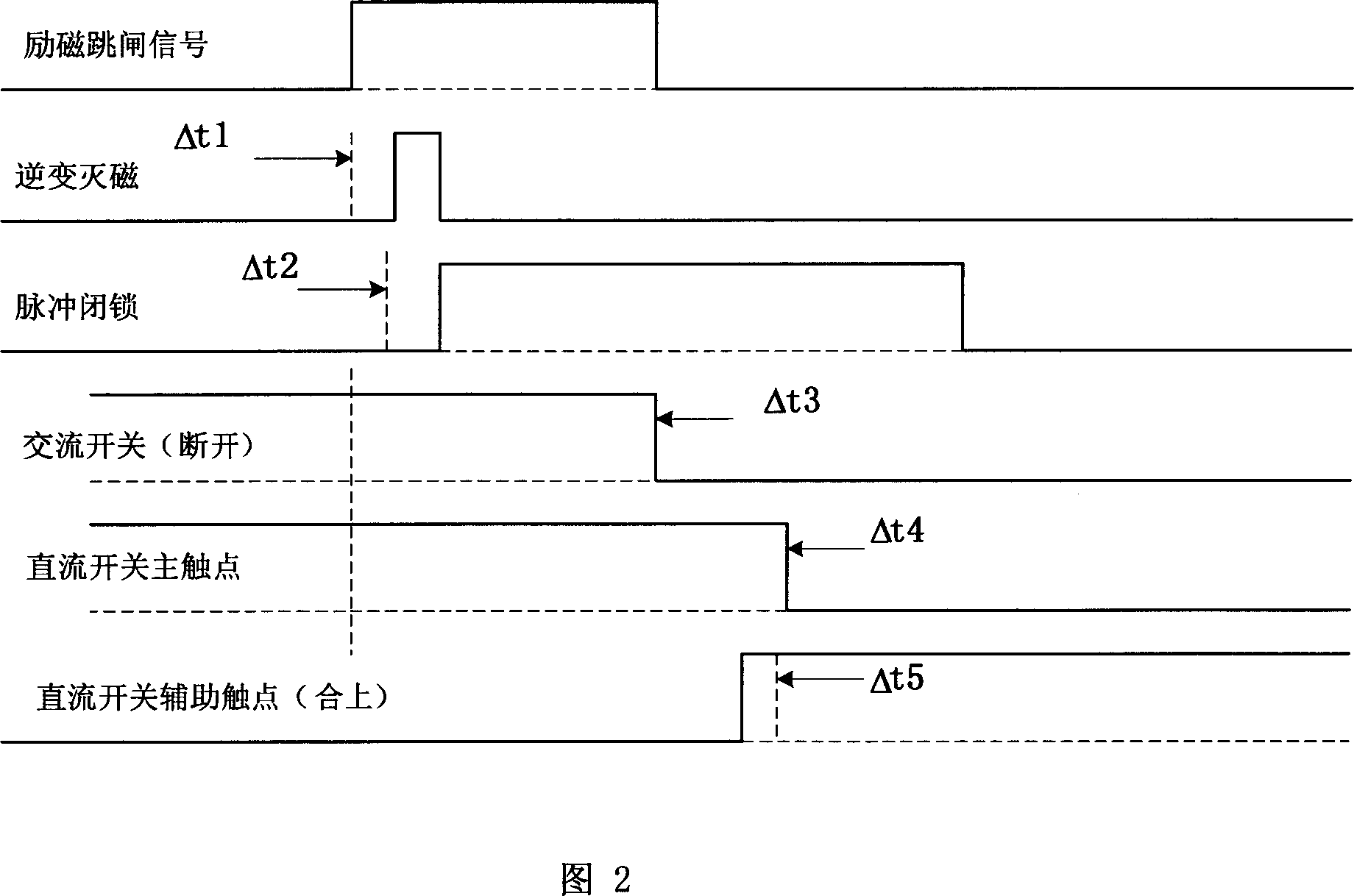
High reliable de-excitation method for generater
InactiveCN101090199AHigh demagnetizationImprove securityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPulse controlNonlinear resistor
This invention relates to a stable demagnetization method, which controls de-magnet according to the time sequence at the state when a generator is faulty: 1, at the time when an excitation regulator gets an excitation trip order from a set protection device, it starts up inversion de-magnet, 2, sending the trip order to an AC de-magnet switch and a DC de-magnet switch, 3, the excitation regulator executes the inversion to set a pulse control angle an inversion angle after delta-t1, 4, closing down the output pulse of the regulator with software or hardware after inverting for delta-t2, in which, delta-t1 is in the sphere greater than 0ms but smaller than or equal to 10ms, and delta-t2 is in the sphere greater than 4ms and smaller than or equal to 10ms, and the demagnetization methods of DC, AC, inverted and non-linear resistor energy-moving and closing pulse of thyristor are used inter-grate to realize stable demagnetization.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
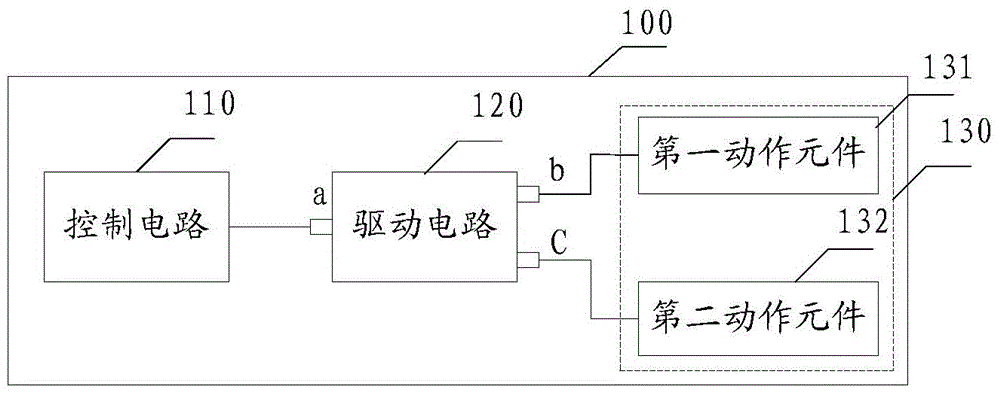
Mechanical control device and driving device thereof
ActiveCN104090525AImprove exercise efficiencyReduce in quantityWeft knittingNumerical controlEngineeringControl circuit
The invention discloses a mechanical control device and a driving device thereof. The mechanical control device comprises a control circuit, a driving circuit and action element which are connected in sequence. The action element comprises, at least, a first action element and a second action element, wherein at least one driving circuit is connected with the first action element and the second action element and respectively and independently drives the first action element and the second action element. By adopting the mode, the cost can be reduced, and the size can be decreased.
Owner:FUJIAN RAYNEN TECH
Switched reluctance motor intelligent control system based on WIFI
ActiveCN110299874ARealize wireless controlSave control resourcesMultiple motor speed/torque controlSoftware algorithm controlProduction lineReinforcement learning algorithm
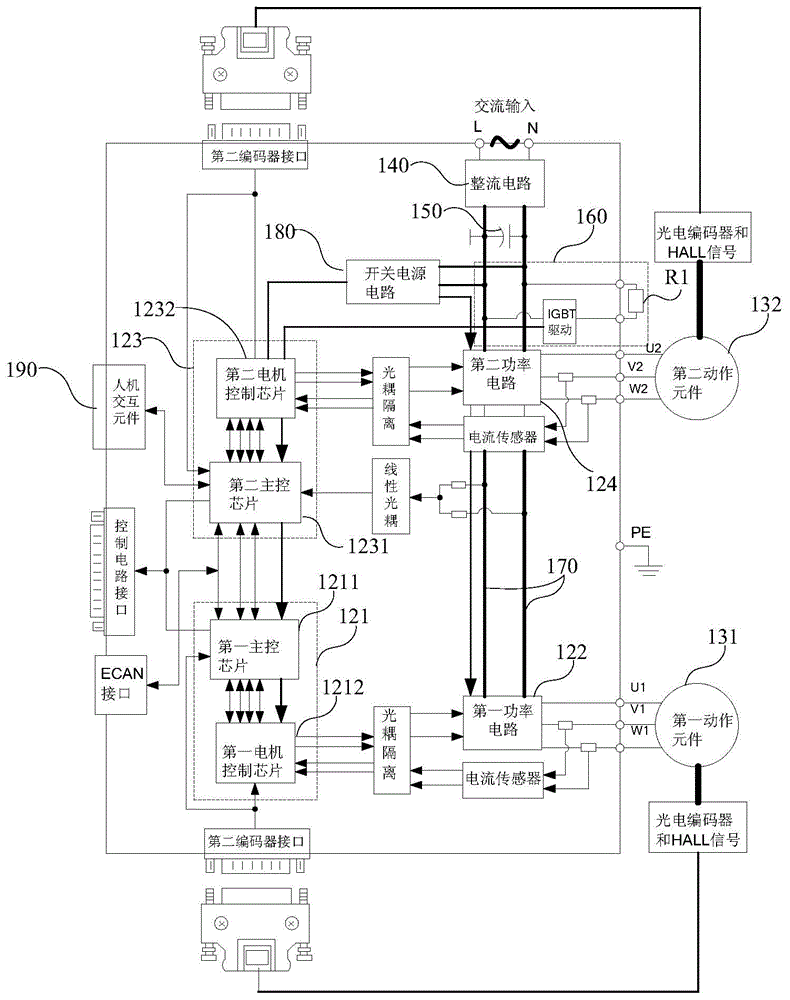
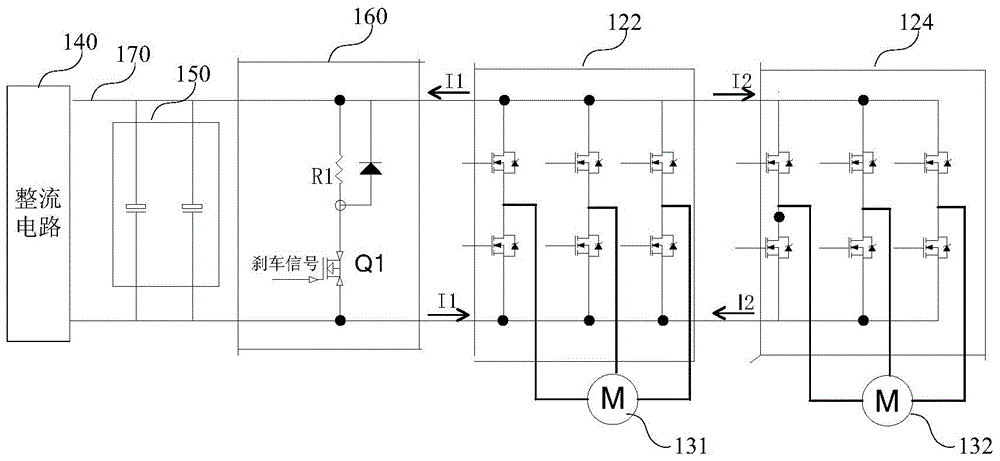
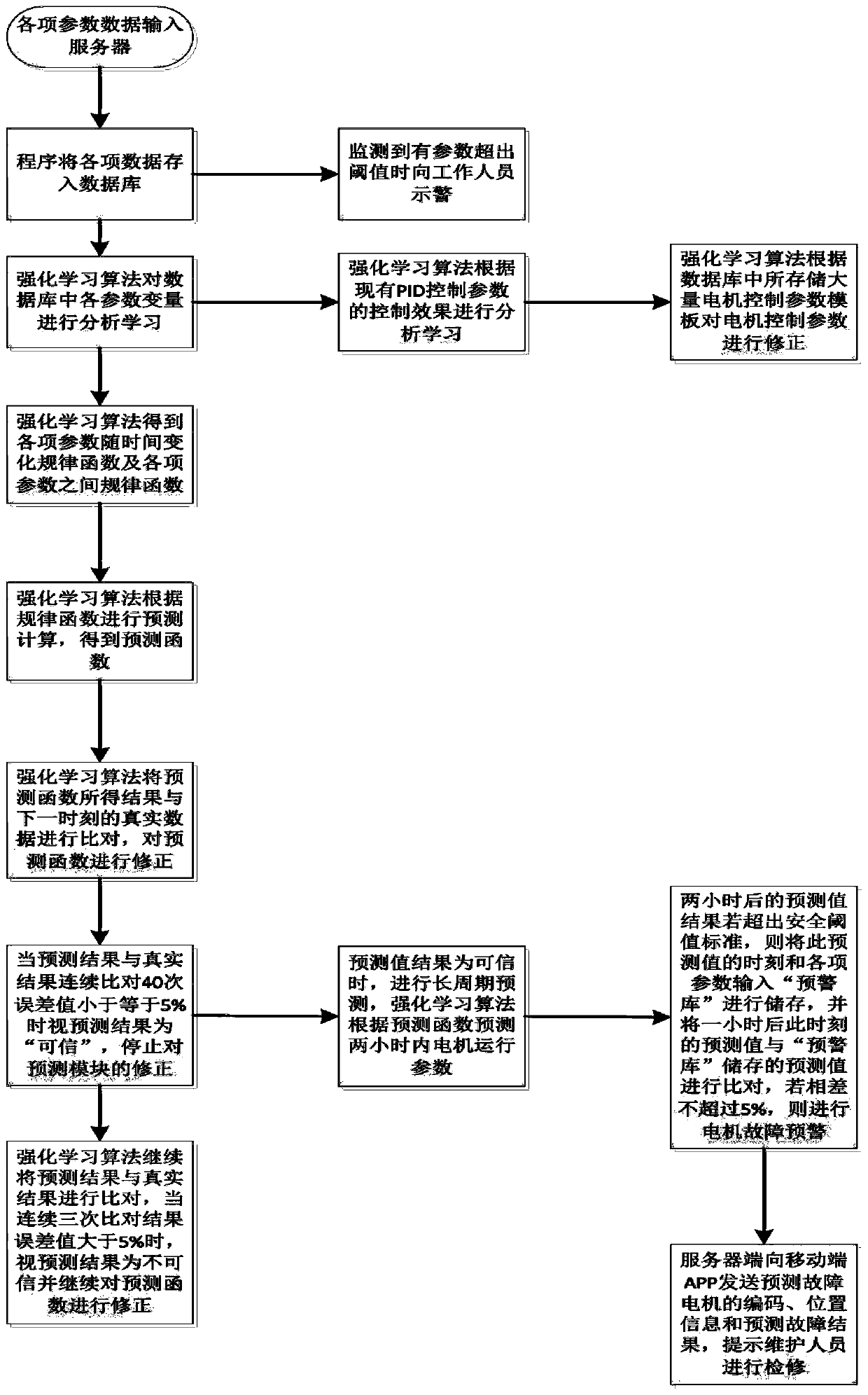
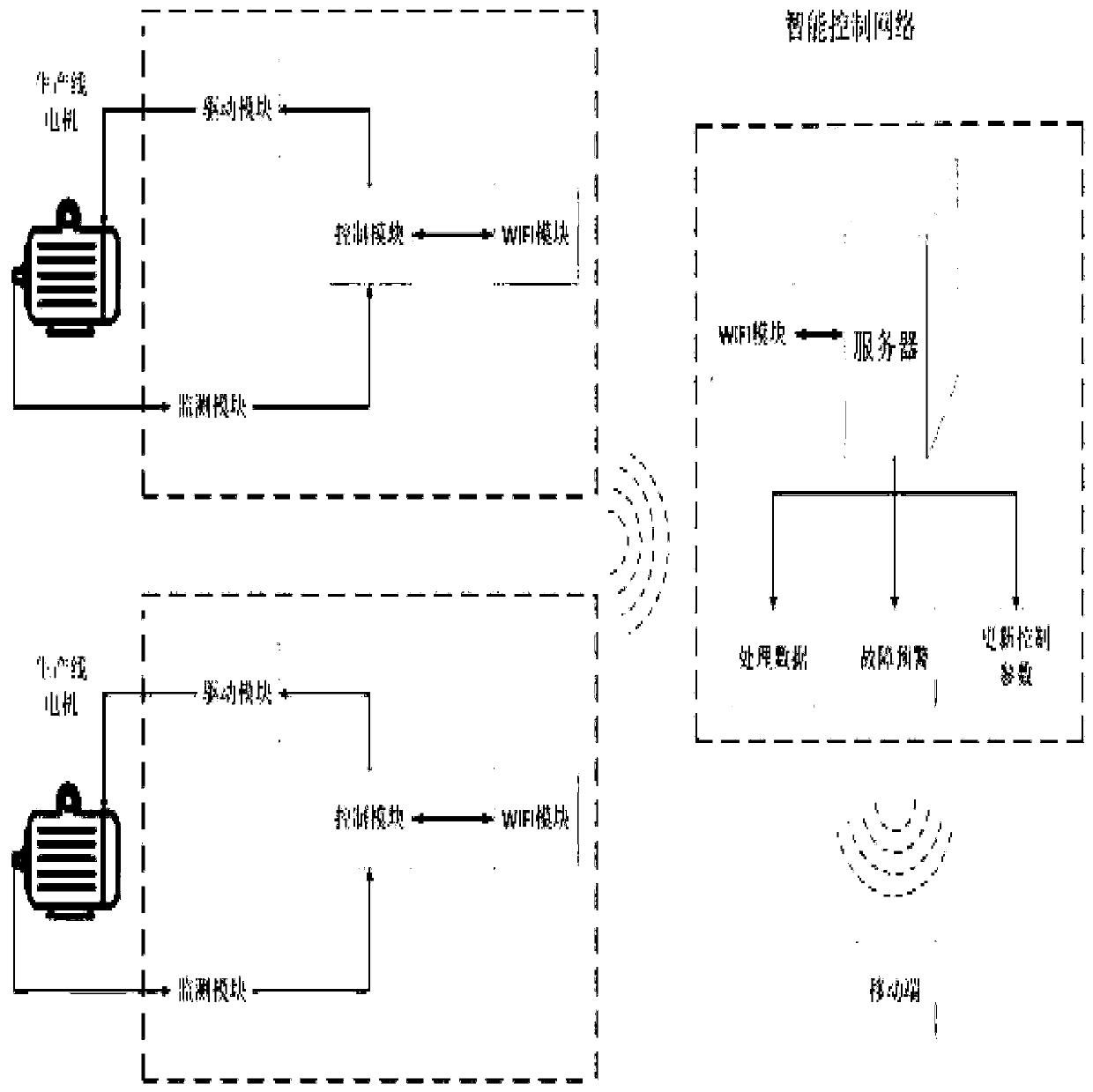
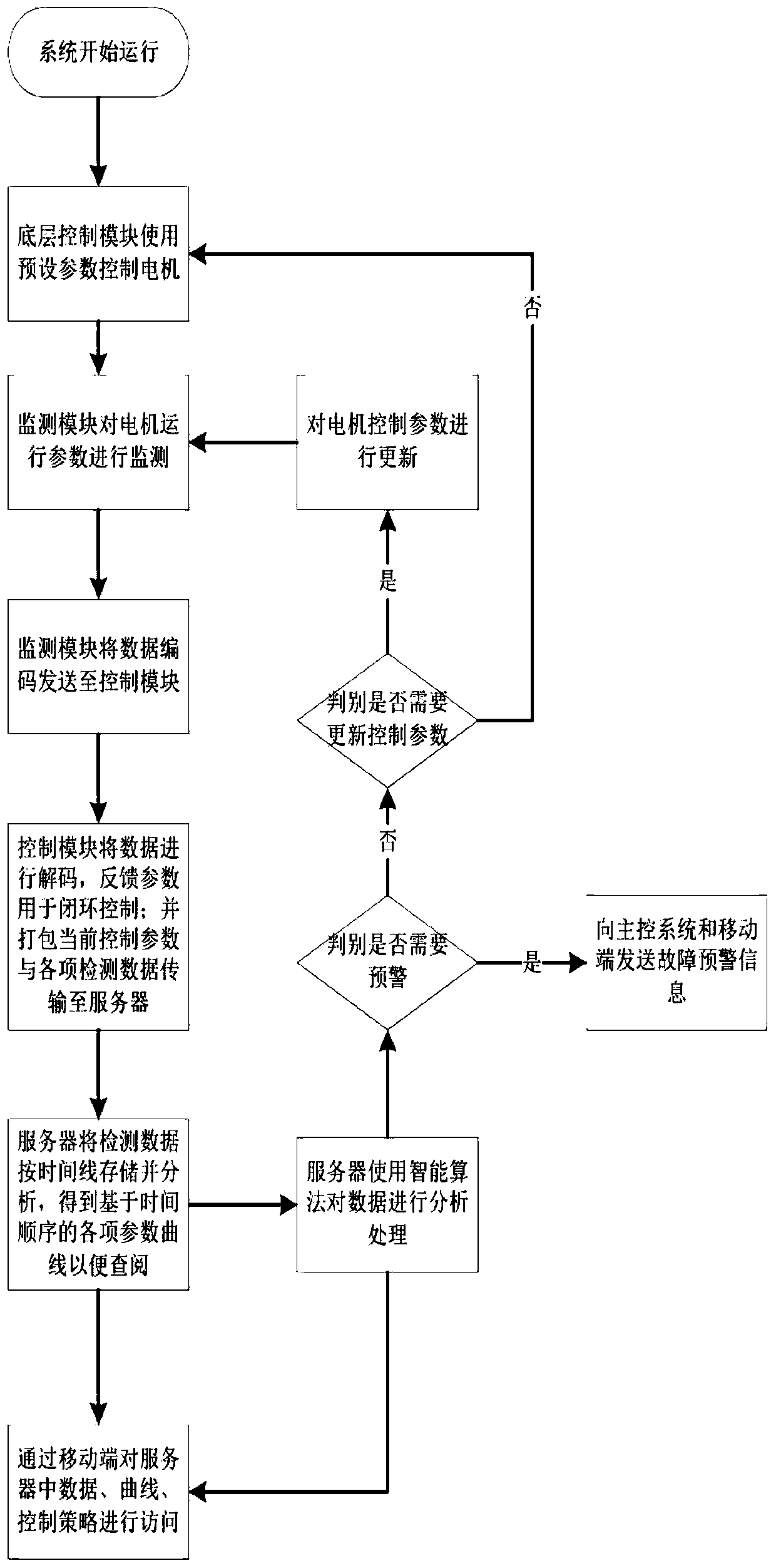
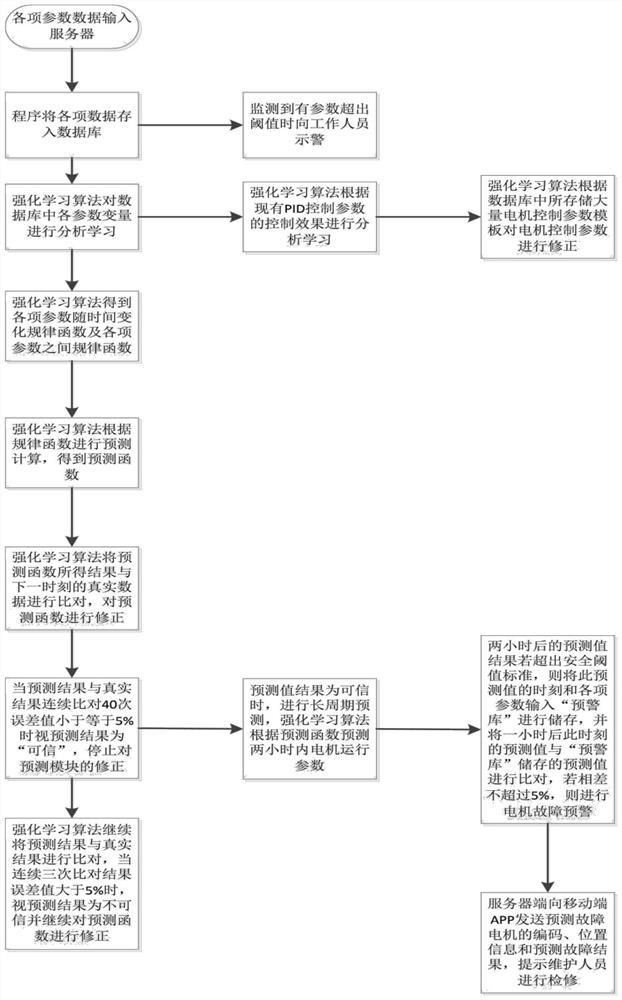
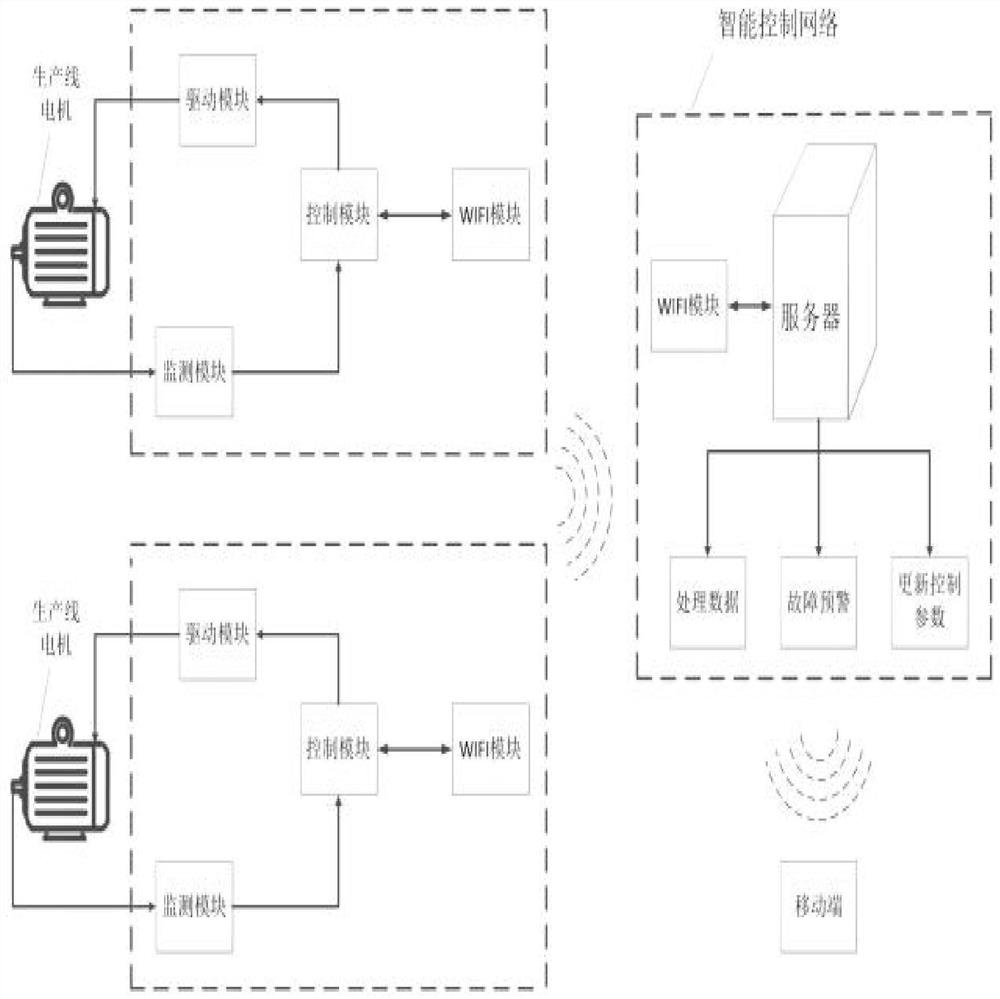
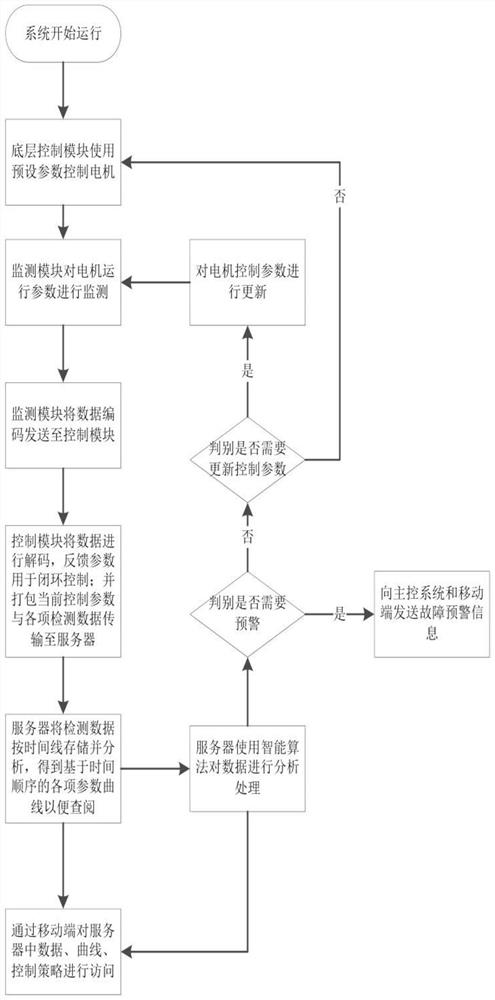
The invention is a switched reluctance motor intelligent control system based on WIFI, which includes a server, a WIFI communication module, a mobile terminal, multiple bottom intelligent switched reluctance motor controllers and multiple switched reluctance motors. Each bottom intelligent switched reluctance motor controller is connected with one switched reluctance motor on the production line,and includes a monitoring module, a drive module, a control module and a WIFI module. The mobile terminal accesses and modifies various functions in the server, and can receive fault warning information. The switched reluctance motors feed back the operation parameters of the switched reluctance motors in real time during normal operation and send the data to the server periodically. The server optimizes and records the operation parameters of the switched reluctance motors according to a lot of received data and a reinforcement learning algorithm, and optimizes and updates the control parameters of the control modules when the collected parameters of the switched reluctance motors deviate from a normal value and reach a safety threshold, so as to better control the operation of the switched reluctance motors.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Circuit structure for implementing alternative of messages
ActiveCN106656852AEasy to implementSave control resourcesData switching networksMultiplexingComputer module
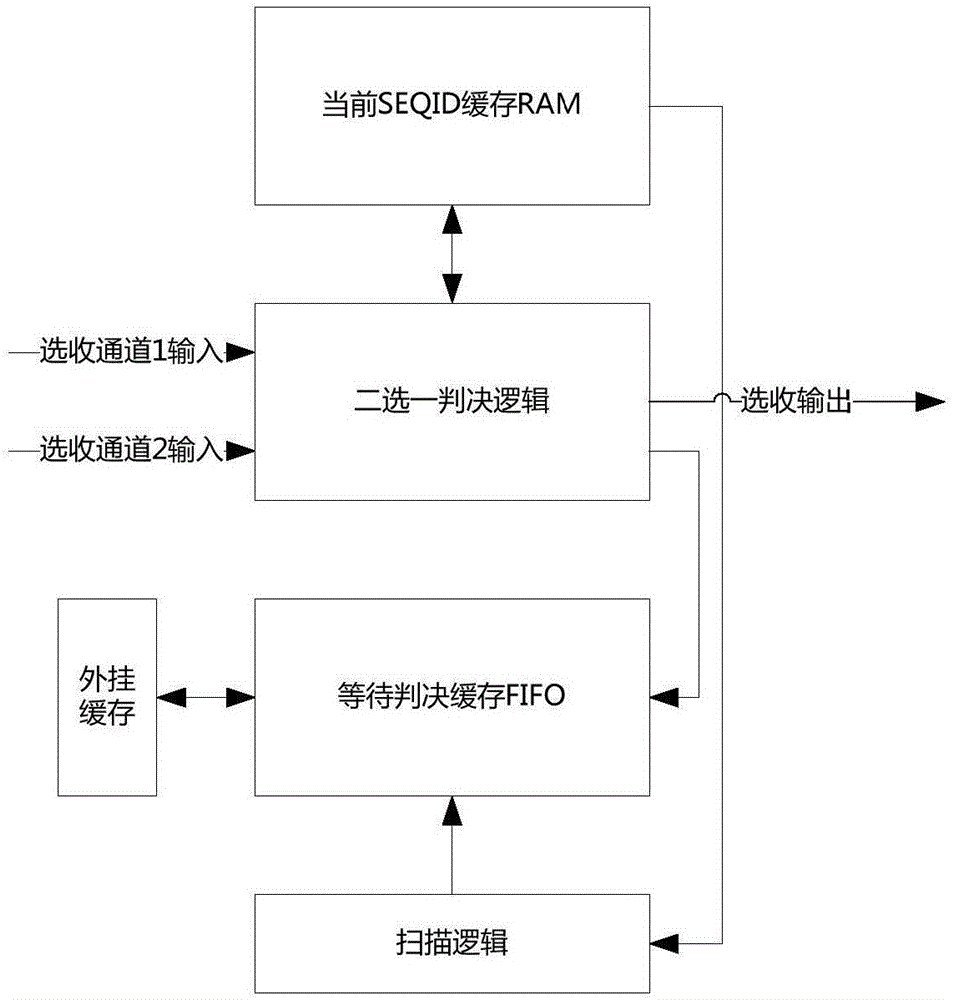
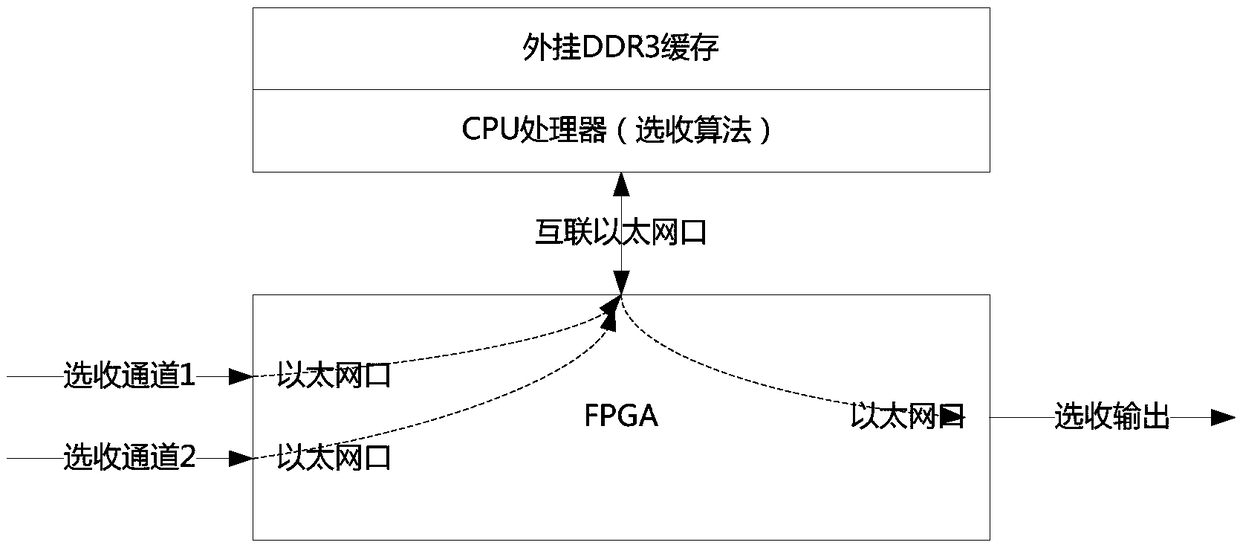
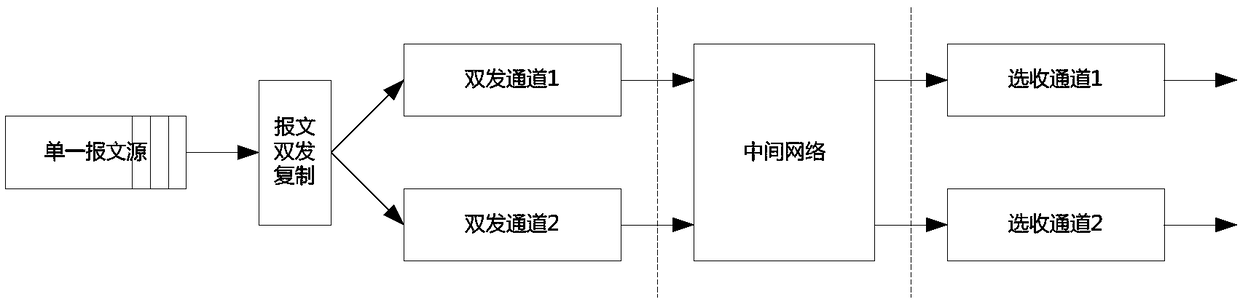
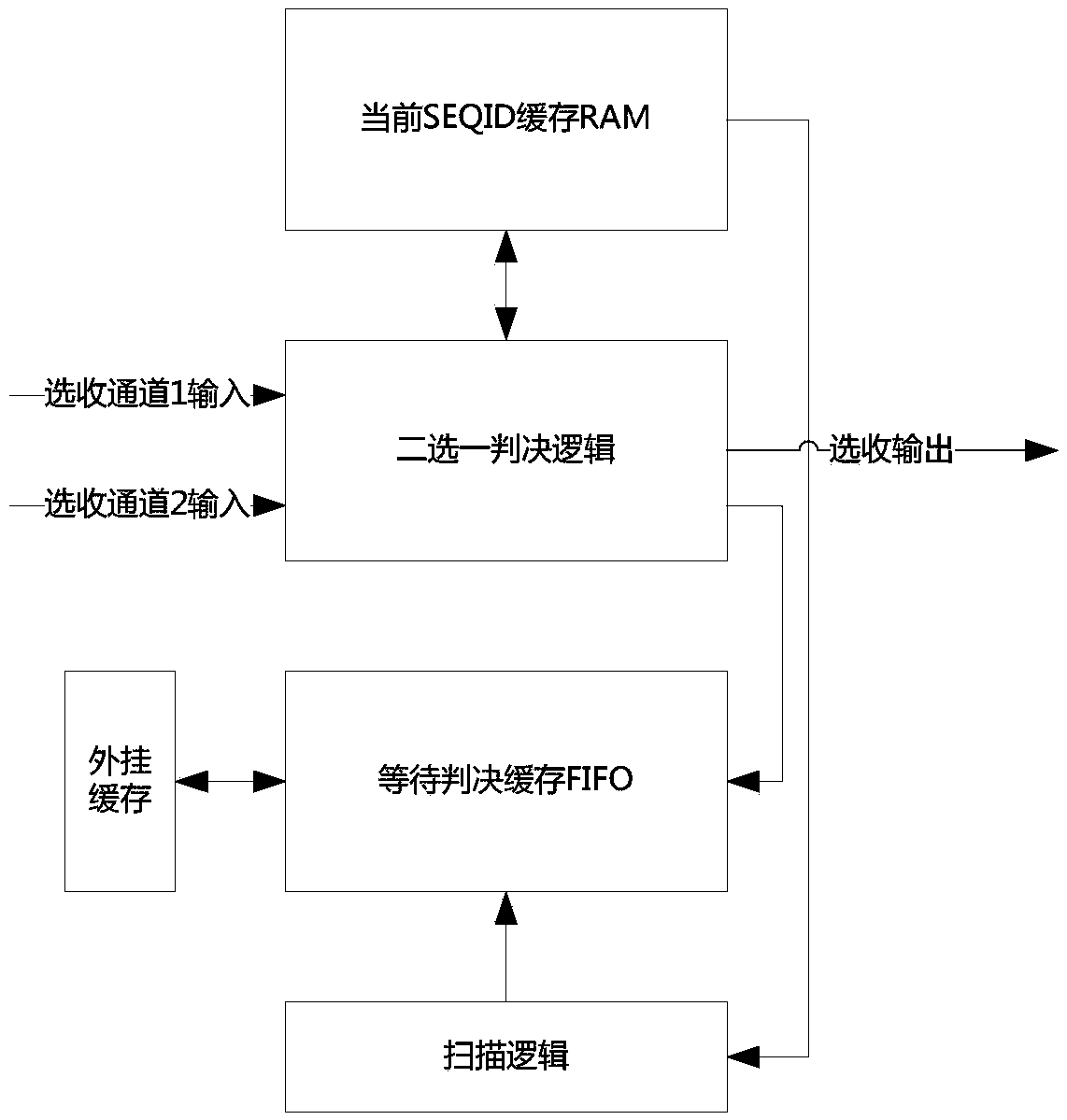
The invention discloses a circuit structure for implementing alternative of messages. The circuit structure comprises an alternative judgment logic module, a judgment waiting buffer module, a current SEQID (SEQuence IDentifier) buffer module, and a scanning logic module, wherein the judgment waiting buffer module and the current SEQID buffer module are connected with the alternative judgment logic module; the scanning logic module is connected with the judgment waiting buffer module; an inlet of the alternative judgment logic module is connected with two selecting and receiving channels; and messages of two selecting and receiving channels are from dual-transmitter messages of the same source equipment. The circuit structure for implementing alternative of the messages, which is disclosed by the invention, adopts the independent alternative judgment logic module and judgment waiting buffer module, so that functions of the respective modules are relatively single, and the circuit structure is convenient to implement a logic circuit; and moreover, the judgment waiting buffer module is managed in an RAM (SDP BLOCK RAM) multiplexing mode, so that a great quantity of judgment waiting buffer module control resources are saved, and a message group number of an alternative circuit can support a range to 1K (1024) and even more.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD SHAOXING POWER SUPPLY CO +3
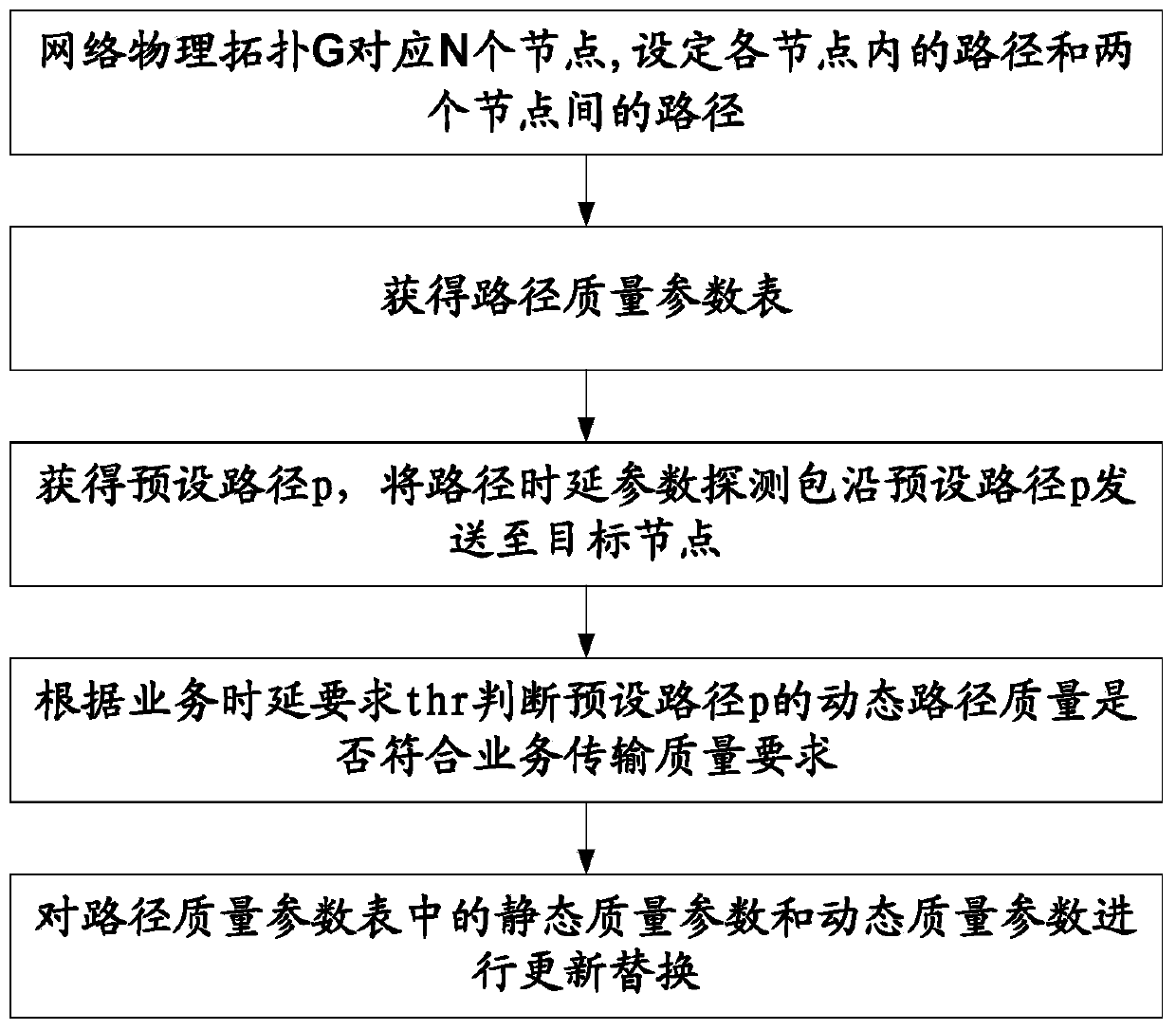
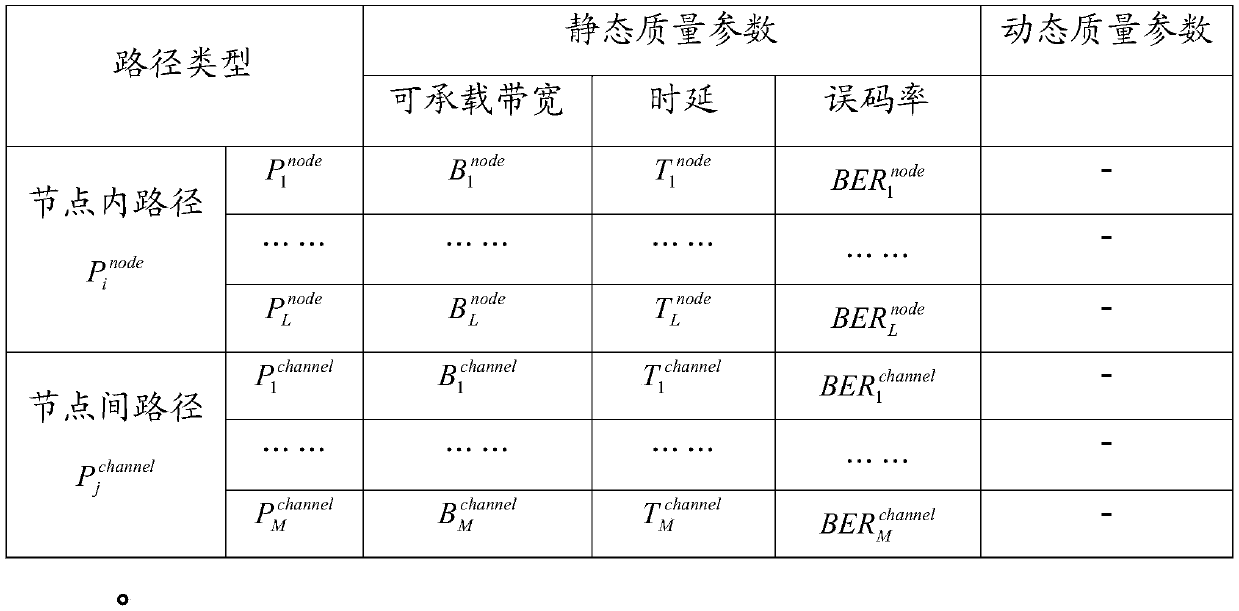
Dynamic and static evaluation method for path quality of wireless network
ActiveCN110113794AComprehensive basisAccurate basisData switching networksWireless communicationWireless mesh networkTransmission quality
The invention discloses a dynamic and static evaluation method for path quality of a wireless network, and relates to the field of data communication transmission. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, setting any path in nodes of N nodes corresponding to a network physical topology G as Pinode, wherein the path between the two nodes is P<j><channel>; step 2, obtaining a path quality parameter table; step 3, obtaining a preset path p, and sending the path delay parameter detection packet to a target node Vq along the preset path p; step 4, judging whether the dynamic path quality of the preset path p meets the service transmission quality requirement or not according to the service delay requirement thr; and step 5, updating and replacing the static quality parameter and the dynamic quality parameter in the path quality parameter table. According to the invention, the sending frequency of the detection packet is adjusted in real time, and optimization of the dynamic and static path quality parameter table is realized.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
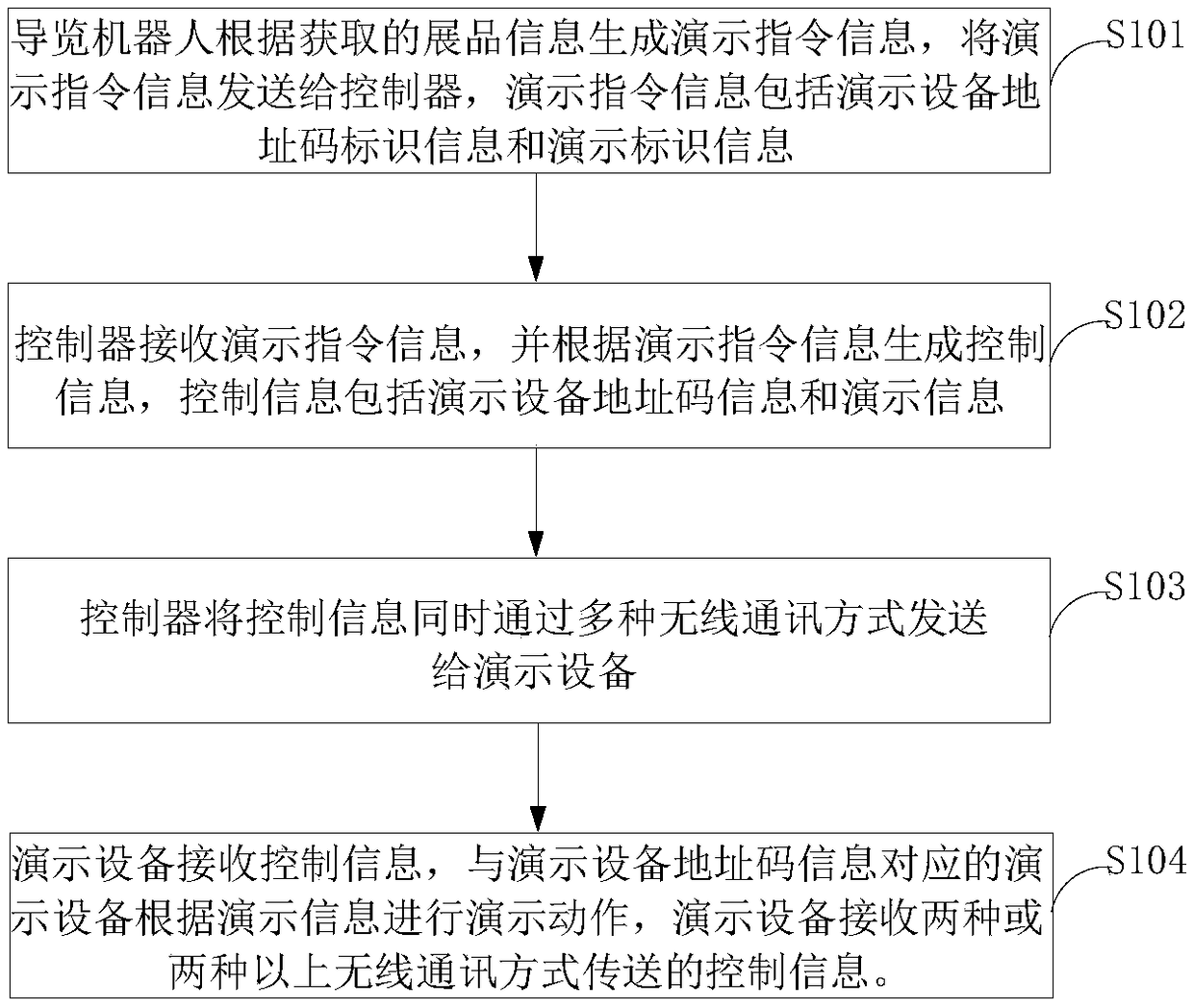
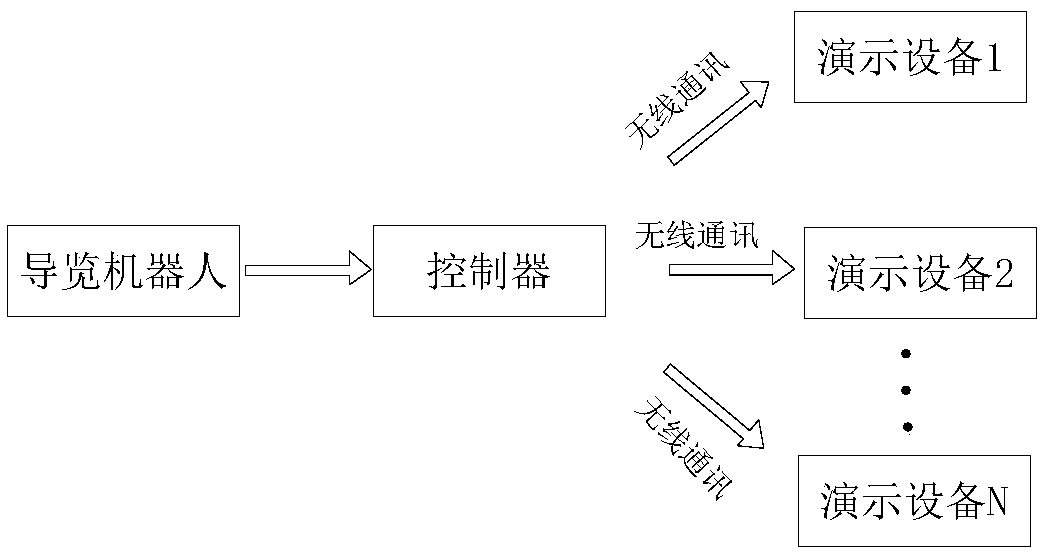
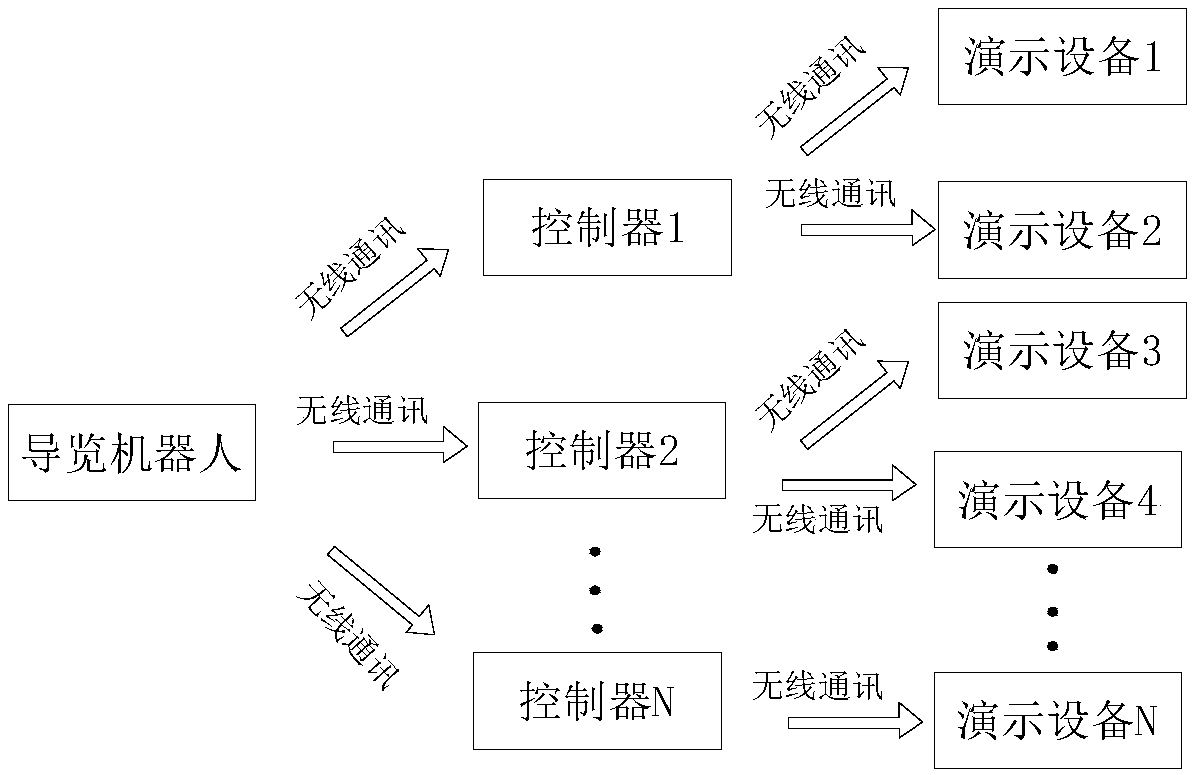
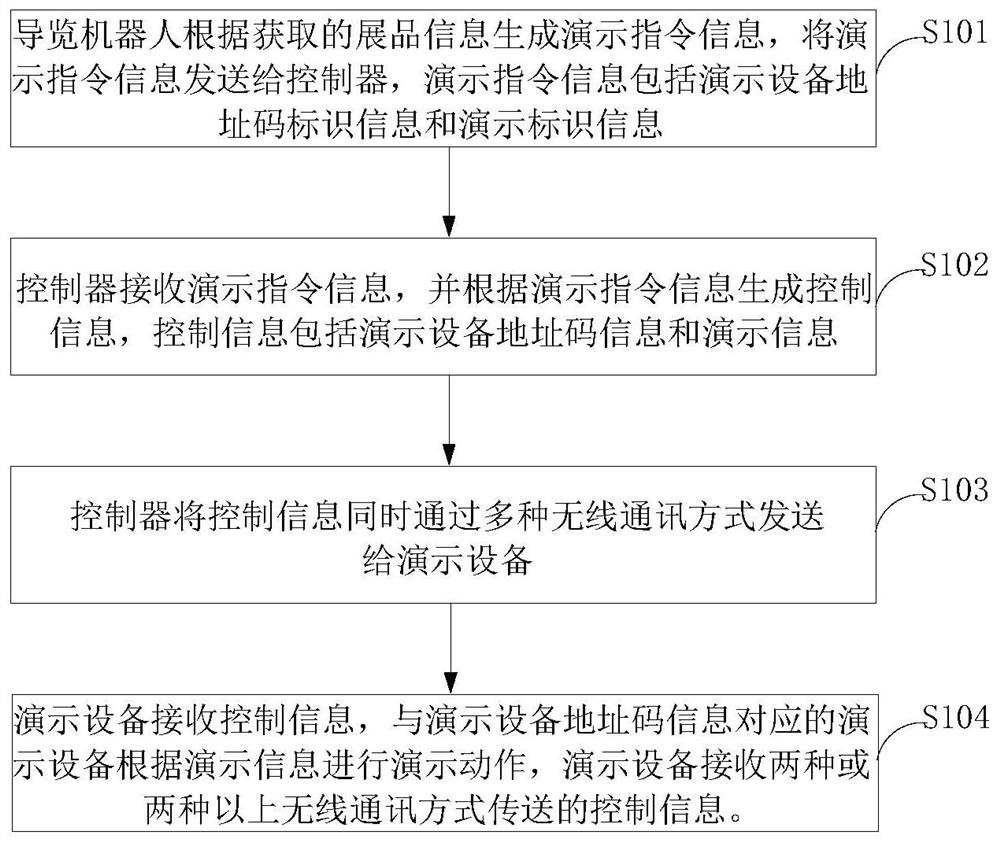
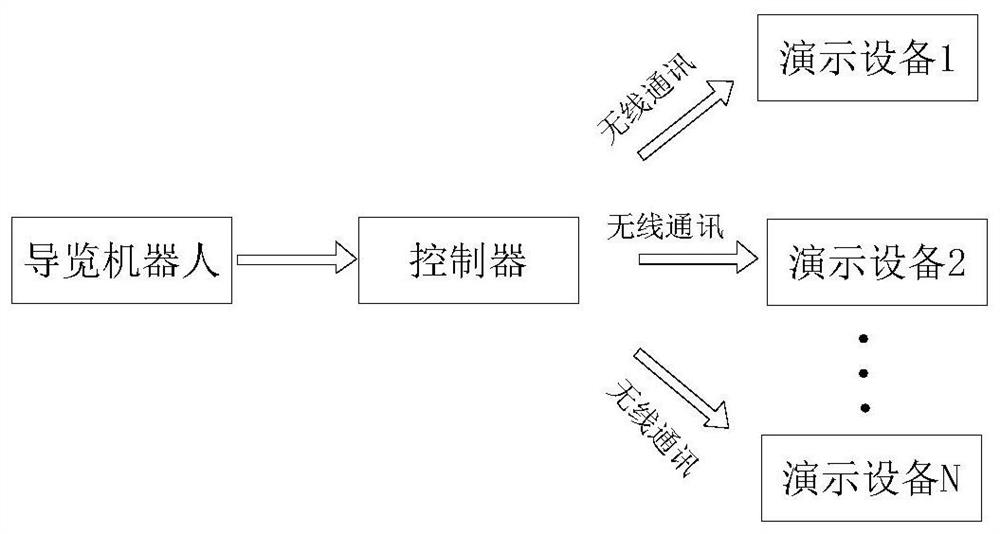
Method of controlling demonstration equipment used for guiding robot
ActiveCN108922148AEnsure normal wireless communicationMeet the needs of wireless controlNon-electrical signal transmission systemsShort range communication serviceComputer scienceEquipment use
The invention provides a method of controlling demonstration equipment used for a guiding robot. The method comprises steps that the guiding robot is used to generate demonstration instruction information according to acquired exhibit information, and demonstration instruction information is transmitted to a controller, and comprises demonstration equipment address code identification informationand demonstration identification information; a controller is used to receive the demonstration instruction information, and is used to generate control information according to the demonstration instruction information, and then the control information comprises the demonstration equipment address code information and the demonstration information; the controller is used to transmit the control information to the demonstration equipment at the same time by a plurality of wireless communication ways; the demonstration equipment is used to receive control information, and the demonstration equipment corresponding to the demonstration equipment address code information is used for demonstration motion according to the demonstration information, and the demonstration equipment can be used toreceive the control information transmitted by two or more than two wireless communication ways. Various communication ways are integrated together, and different control requirements in a complicatedexhibition hall can be satisfied, and the method can be adapted to the environment of the complicated exhibition hall, and therefore control over all demonstration equipment is facilitated, and goodcontrol effect is provided.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
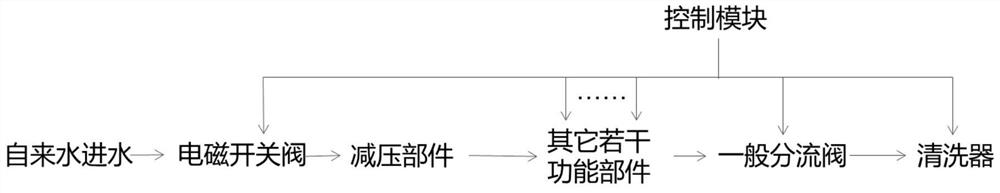
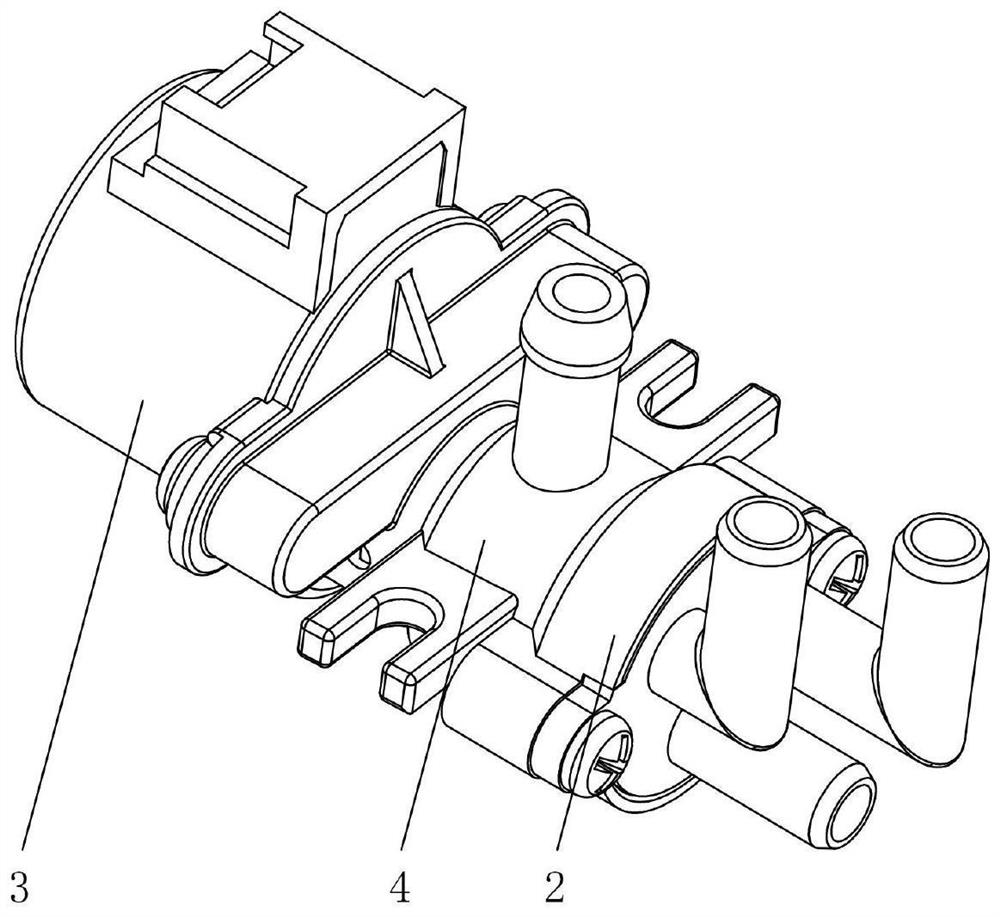
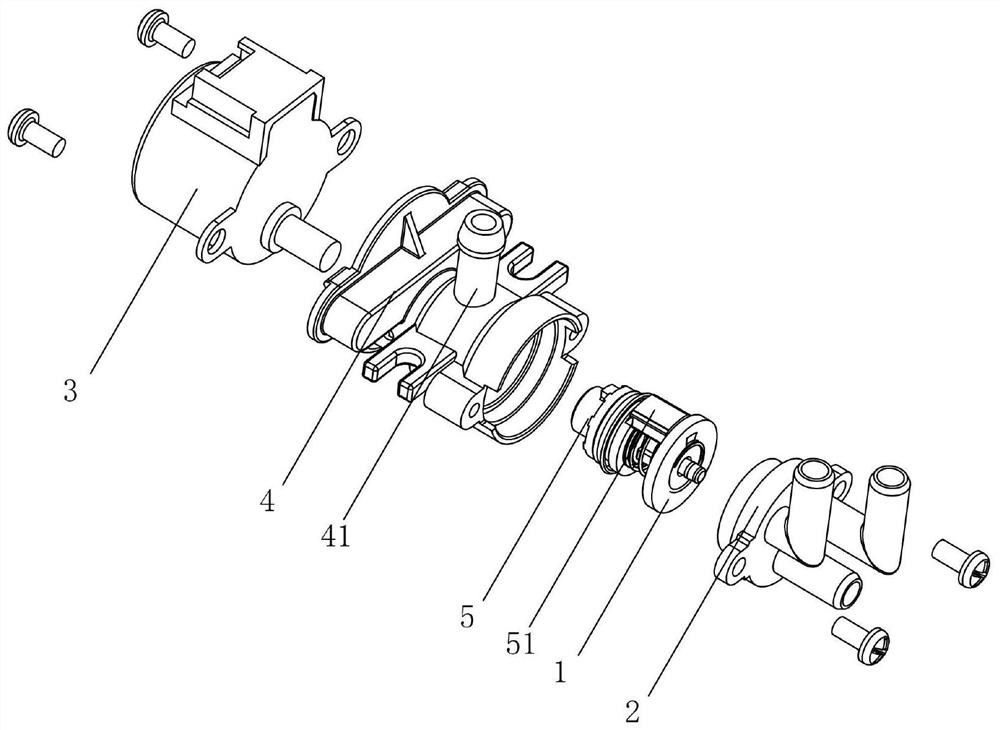
Diverter valve integrated with waterway switch, waterway control method and cleaning waterway
PendingCN113531159ALow costSimple controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesWater useEnvironmental geology
The invention discloses a diverter valve integrated with a waterway switch, a waterway control method and a cleaning waterway. The diverter valve comprises a valve element, a valve seat and a rotary driving part, a plurality of water outlets communicated with water use channels are formed in the end face, making contact with the valve element, of the valve seat, water passing holes communicated with a water inlet are formed in the end face, making contact with the valve seat, of the valve element, and the rotary driving part drives the valve element to rotate relative to the valve seat; and the water outlets and the water passing holes are distributed in a circular ring with the relative rotation center as the circle center, a blocking piece used for blocking the water inlet when the valve element rotates to the set position where the water passing holes and the water outlets are not communicated is further included, and the blocking piece and the valve element rotate synchronously. The diverter valve has the advantages of being simple in structure, flexible and convenient to adjust, integrated in function and the like; the waterway control method has the advantages of being high in adjusting sensitivity, eliminating the delay phenomenon, optimizing the use feeling of a user and the like; and the cleaning waterway has the advantages of being high in stability, obvious in cost optimization and the like.
Owner:湖南麦格米特电气技术有限公司
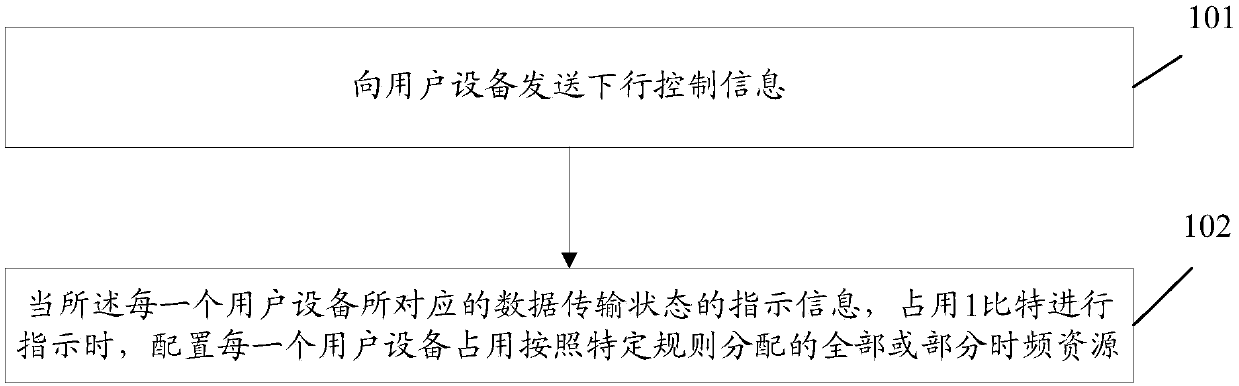
Method for sending downlink control information, network equipment and storage medium
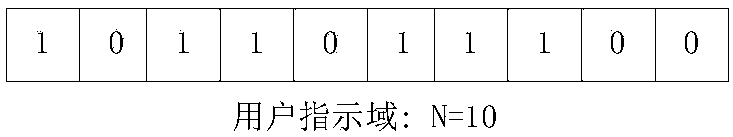
PendingCN110139385AImprove scheduling efficiencySave control resourcesWireless communicationModulation codingData transmission
The invention discloses a method for sending downlink control information, network equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: sending the downlink control information to userequipment, the format of the downlink control information at least comprising a user indication domain and / or other feature domains, the user indication domain being used for indicating a group of user equipment comprising N pieces of user equipment and indication information of a data transmission state corresponding to each piece of user equipment, N being a positive integer, the other feature domains comprising at least one of a modulation and coding scheme (MCS) domain and / or a resource allocation domain, the MCS domain being used for indicating the group of user equipment to adopt the same MCS mode, and the resource allocation domain being used for indicating the user equipment to occupy all allocated time-frequency resources or part of time-frequency resources.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM LTD RES INST +1
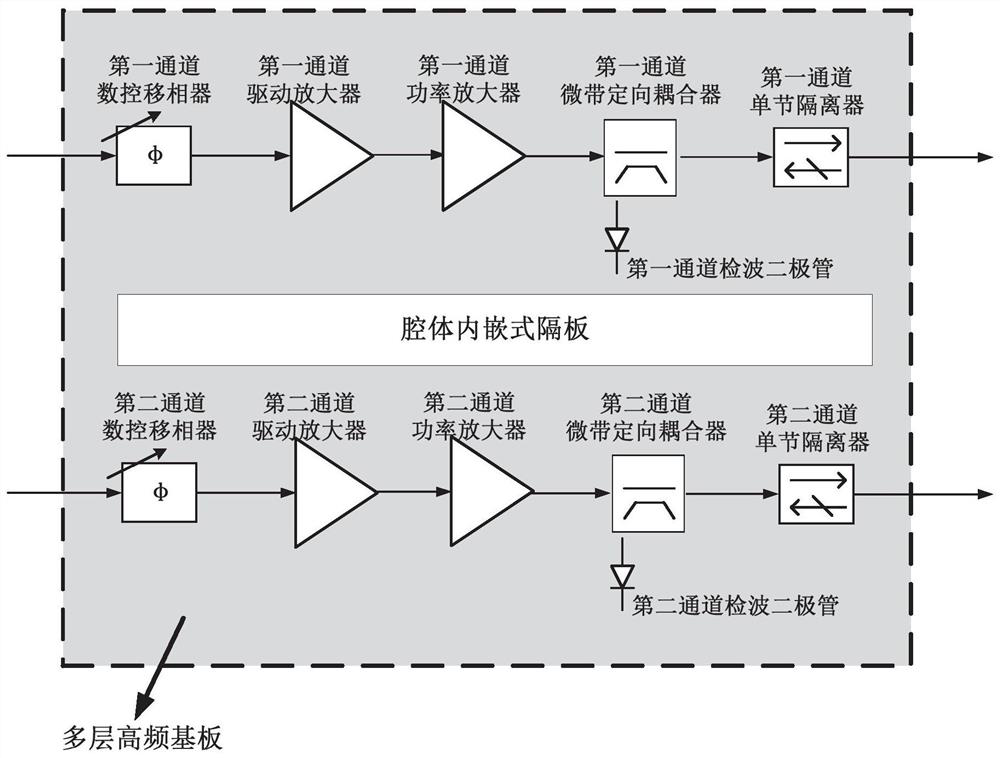
Dual-channel launch assembly for the phased array antenna of the relay user terminal of the launch vehicle
ActiveCN110808745BReduce front areaReduce the weight of the whole machineRadio transmissionChannel powerIsolator
The invention discloses a dual-channel transmitting assembly for a phased array antenna of a carrier rocket relay user terminal, which includes a first channel radio frequency circuit and a second channel radio frequency circuit; the first channel radio frequency circuit includes: a sequentially connected second channel radio frequency circuit A digitally controlled phase shifter for one channel, a driving amplifier for the first channel, a power amplifier for the first channel, a microstrip directional coupler for the first channel, a single-section isolator for the first channel, and a first channel connected to the microstrip directional coupler for the first channel channel detection diode; the second channel radio frequency circuit includes: a second channel digitally controlled phase shifter, a second channel drive amplifier, a second channel power amplifier, a second channel microstrip directional coupler, a second channel A single-section isolator, and a second-channel detection diode connected to the second-channel microstrip directional coupler. Compared with the single-channel phase-shifting transmitting assembly, the present invention has a compact structure, which is beneficial to reducing the front area of the phased array antenna and reducing the weight of the whole machine of the phased array antenna.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACEFLIGHT INST OF TT&C & TELECOMM
Hybrid MMC sub-module capacitor voltage bidirectional equalization topology
PendingCN112821793AOmit the balance control linkLow costAc-dc conversionCapacitanceCapacitor voltage
The invention provides a bi-directional balanced hybrid MMC topological structure based on a diode clamping circuit. The bi-directional balanced hybrid MMC topological structure is composed of n / 2 half-bridge sub-modules, n / 2 full-bridge sub-modules and n-1 additional series devices. The topology is explained by taking five-level hybrid MMC topology as an example. The topology is composed of two half-bridge-type modules, two full-bridge-type modules and three additional units. The additional unit connected between the HBSMs is the same as the additional unit connected between the HBSM and the FBSM. Each unit comprises two parallel branches. A branch circuit 1 only comprises a diode, a branch circuit 2 is formed by reversely connecting the diode and a switch in series (an IGBT and a reverse parallel diode), and the inductor is connected to a common branch circuit of the branch circuit 1 and the branch circuit 2. In the additional unit connected between the FBSMs, the branch circuit 1 and the branch circuit 2 have the same structures, and each of the branch circuit 1 and the branch circuit 2 consists of a series diode, an inductor and a switch (an IGBT and an anti-parallel diode). Compared with a traditional software voltage balance method, the topology mainly has the two advantages that firstly, a control framework is simplified, a voltage balance control link is omitted, and control resources are saved; and secondly, the number of voltage sensors is reduced, the complexity of the control system is reduced, and the communication pressure is reduced. In addition, compared with other hardware voltage balance circuits, the topology not only can realize bidirectional balance, but also reduces the number of inductors in the circuit, and effectively reduces the hardware cost.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Methods of data transmission and equipment
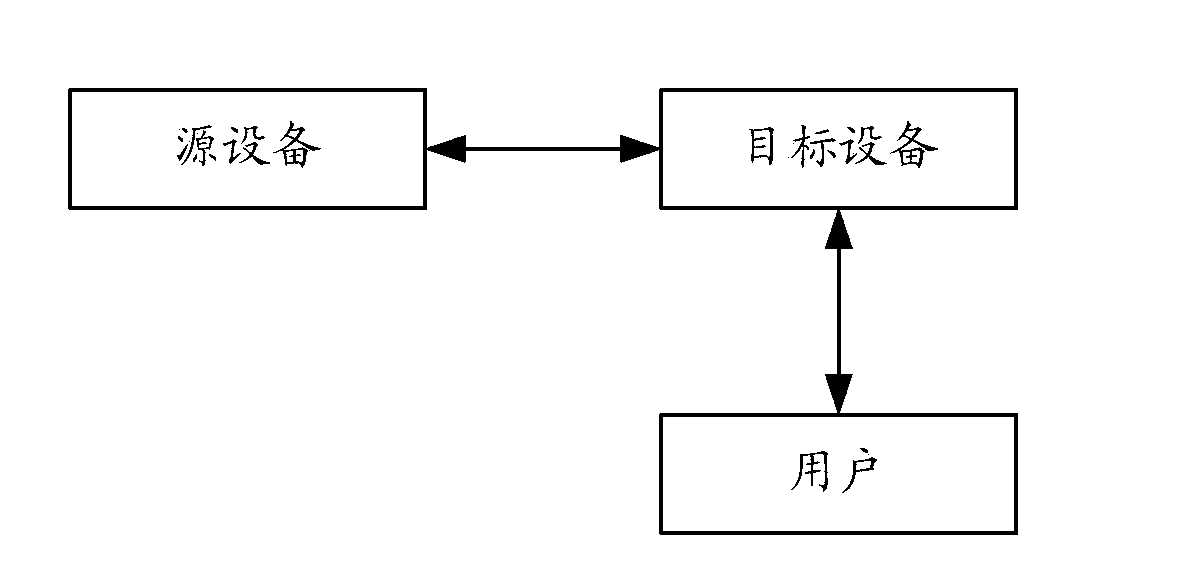
ActiveCN107622025AImprove transmission efficiencySave control resourcesElectric digital data processingOriginal dataApplication areas
The invention discloses methods of data transmission and equipment, relates to the field of electronic-equipment application, and aims to realize saving of system control resources and improvement ofdata transmission efficiency. One of the methods of data transmission includes: receiving a data importing instruction of a user by source equipment; carrying out importing selection on original databy the source equipment to obtain target data; and sending the target data to target equipment by the source equipment for classifying the target data by the target equipment according to attributes of the target data. The method is mainly applied to a data importing process between the electronic equipment.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
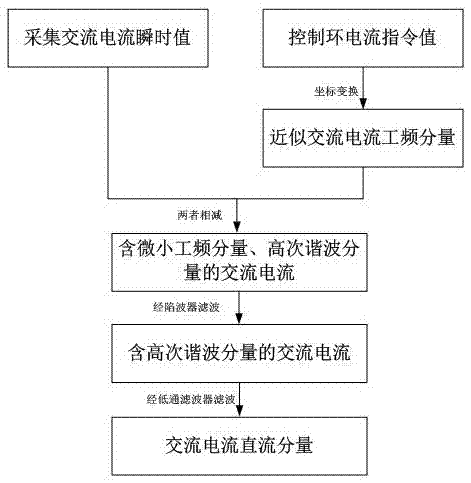
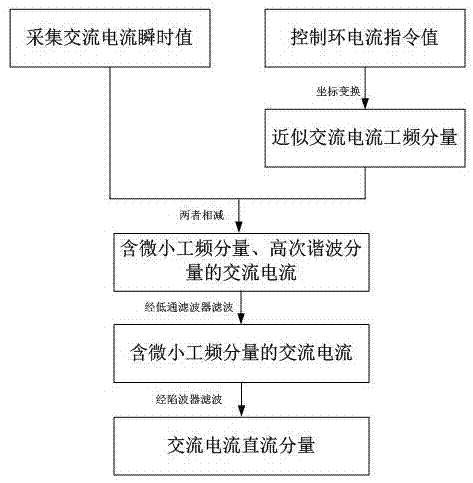
Method of extracting grid-connected electronic power equipment output direct current component
The invention discloses a method of extracting a grid-connected electronic power equipment output direct current component. Alternating-current instantaneous values are collected. An alternating-current power frequency component is calculated. The alternating-current power frequency component is subtracted from the alternating-current instantaneous values to acquire an error value of the two. Low pass filtering is performed on the error value to weaken a high frequency component. The error value after the low pass filtering is input into a power frequency wave trap so as to acquire a direct current component output by grid-connected electronic power equipment. By using the method in the invention, implementation is simple; chip resources are saved and controlled; high precision is possessed; through an existing direct current component control method, effective control of the direct current component can be realized.
Owner:江苏中天互联科技有限公司
A charging connection control system and a swap station
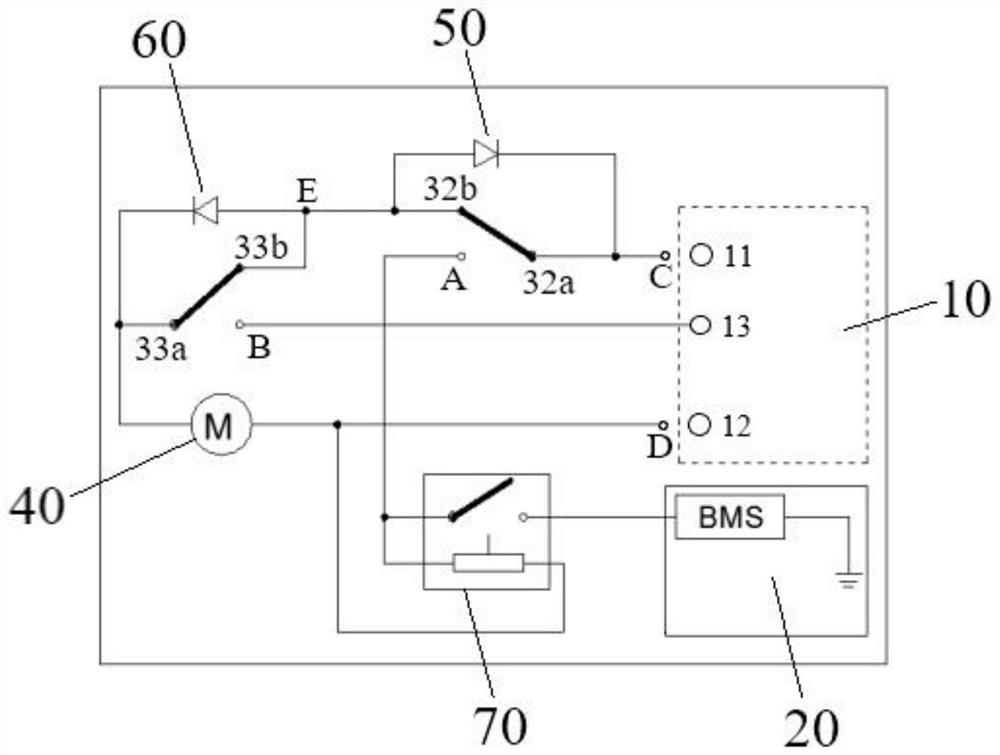
ActiveCN111953036BAchieve electrical connectionResolve lagCharging stationsElectric powerControl systemControl engineering
The invention provides a charging connection control system, including a controller, a battery pack management system and a charging circuit, the charging circuit is connected to the controller and the battery pack management system, the battery pack management system includes a battery pack and a battery pack controller; the charging circuit includes a charging The connecting device and the driving device, the driving device is electrically connected to the controller, the driving device drives the charging connecting device to switch between the first contact and the second contact, when the charging connecting device is connected to the first contact, The charging circuit is turned on; when the charging connection device is in contact with the second contact, the charging circuit is disconnected; the charging connection control system provided by the present invention can simultaneously communicate with the battery pack and the battery pack controller , or by disconnecting the charging connection with the battery pack and the electrical connection with the battery pack controller to simplify the control logic and save control resources while overcoming the hysteresis problem caused by connecting the battery pack first and then connecting the battery pack controller in the prior art.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIZHI NEW ENERGY AUTOMOBILE TECH CO LTD +1
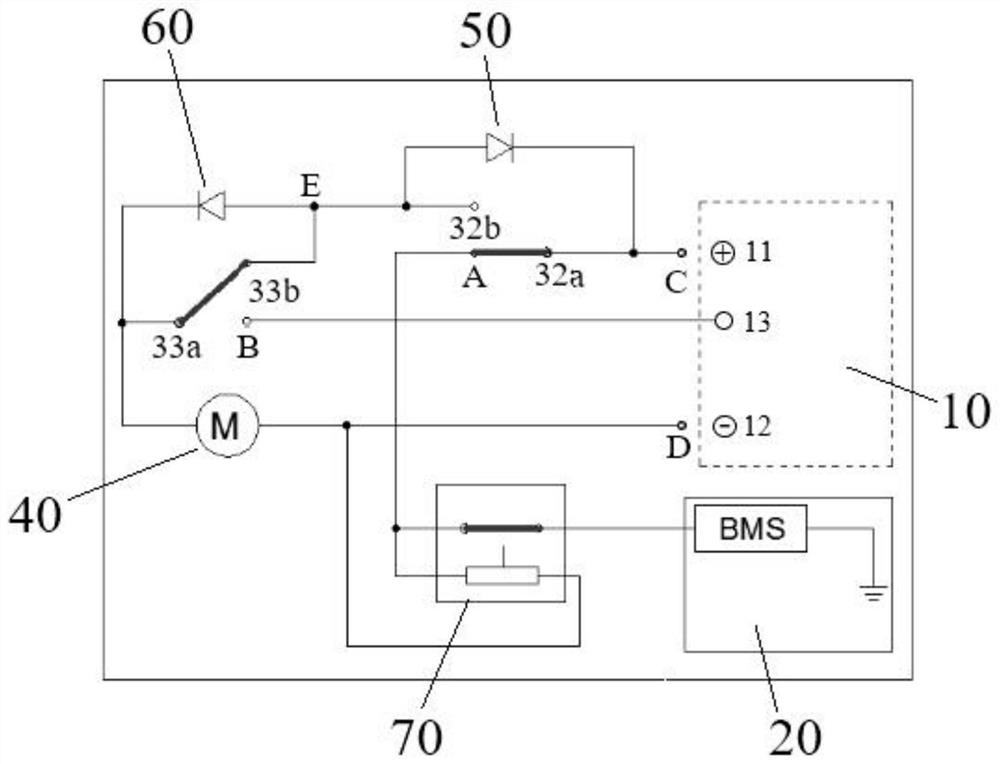
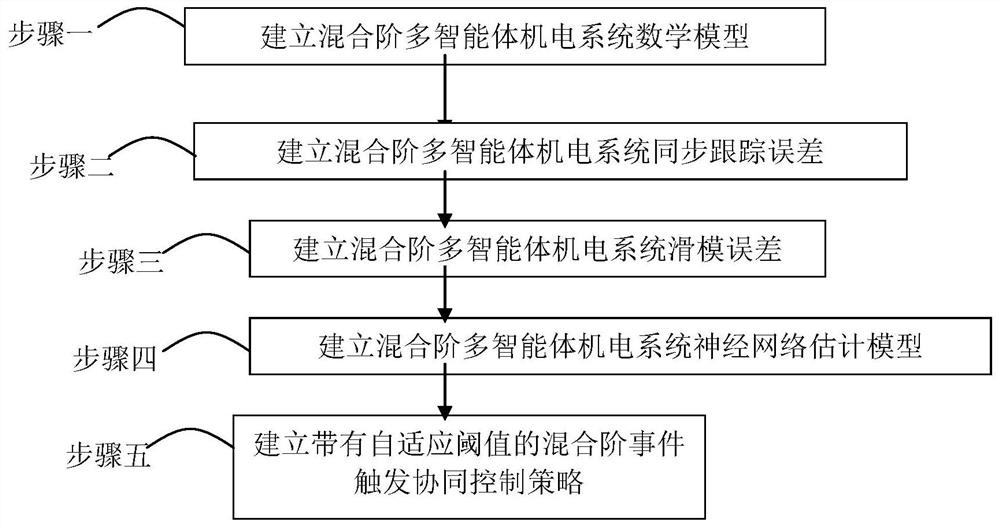
An Event-triggered Cooperative Control Method for Mixed-Order Nonlinear Systems with Adaptive Thresholds
ActiveCN113504727BIncrease the frequency of trigger controlsSave control resourcesAdaptive controlMathematical modelEvent trigger
An event-triggered cooperative control method for a mixed-order nonlinear system with an adaptive threshold, which belongs to the field of electromechanical system cooperative control, and is mainly solved by adaptively adjusting the trigger threshold in the event-triggered cooperative control of a mixed-order multi-agent electromechanical system Trigger control efficiency issues. The invention includes: 1. Establishing the mathematical model of the mixed-order multi-agent electromechanical system; 2. Establishing the synchronous tracking error of the mixed-order multi-agent electromechanical system; 3. Establishing the sliding mode error of the mixed-order multi-agent electromechanical system; 4. Establishing the mixed-order multi-agent electromechanical system A neural network estimation model for multi-agent electromechanical systems; 5. Establish a mixed-order event-triggered cooperative control strategy with an adaptive threshold. The invention is used for event-triggered control of mixed-order electromechanical systems.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A circuit structure for realizing message selection from two
ActiveCN106656852BEasy to implementSave control resourcesData switching networksMultiplexingStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses a circuit structure for realizing two-choice one of messages, including a two-choice one judgment logic module, a waiting judgment cache module connected with the two-choice one judgment logic module, a current SEQID cache module, and a waiting judgment cache module connected The scanning logic module, the entrance of the one-of-two decision logic module is connected to two selective receiving channels, and the messages of the two selective receiving channels come from double-sending messages of the same source device. The circuit structure for realizing message two-choice one according to the present invention adopts independent two-choose one judgment logic module and waiting judgment cache module, so that the functions of the respective modules are relatively single, which is convenient for logic circuit realization; in addition, the waiting judgment cache module adopts The form management of RAM multiplexing saves a lot of resources waiting for the control of the decision buffer module, so that the message group number of the two-choice circuit can support up to 1K (1024), or even more.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD SHAOXING POWER SUPPLY CO +3
Insulation resistance detection circuit, method and device for vehicle
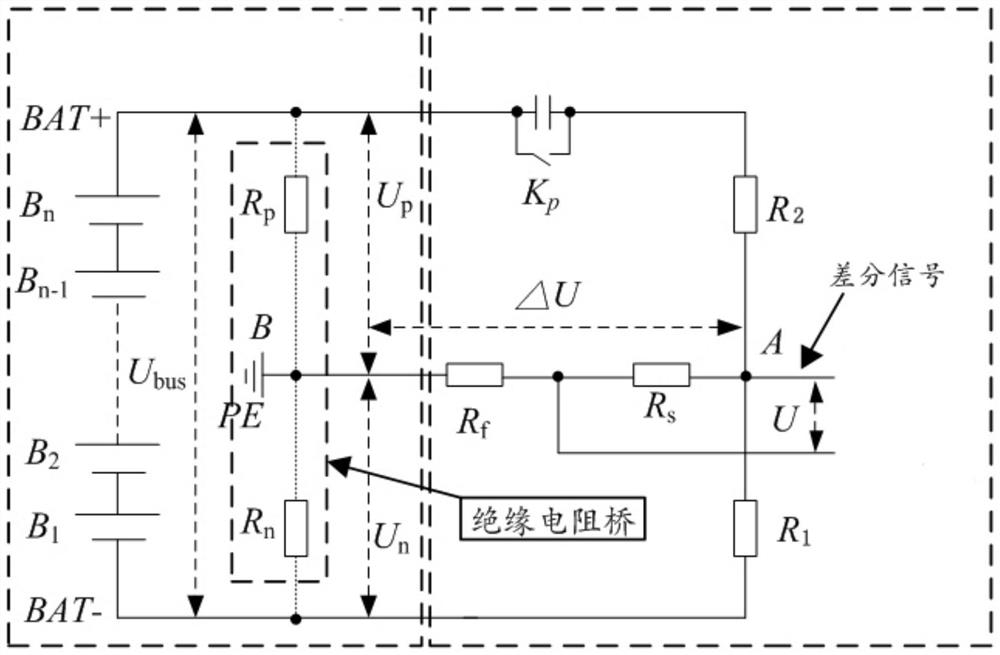
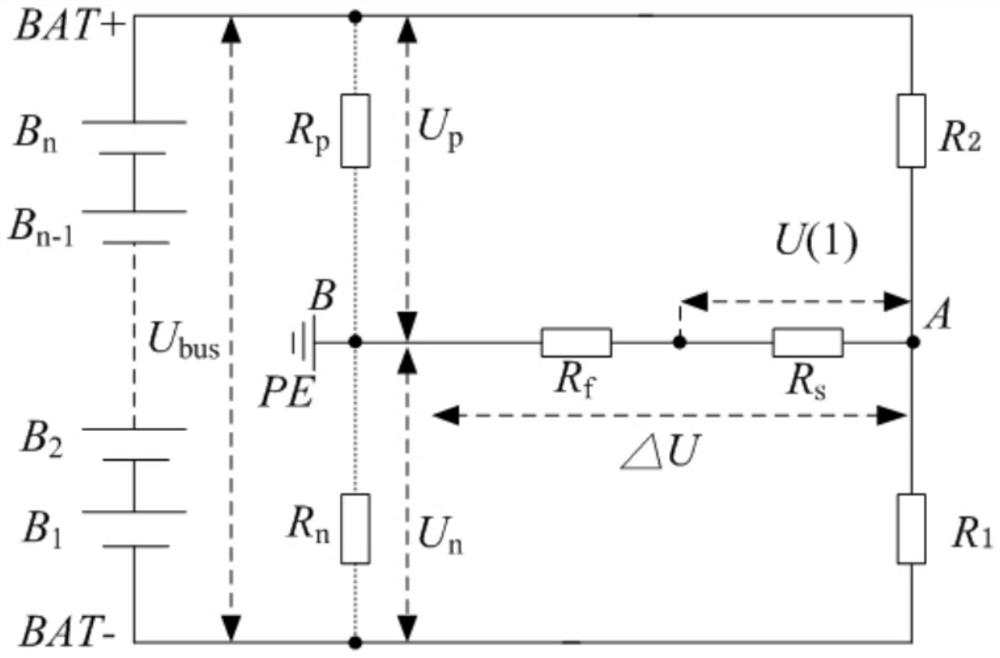
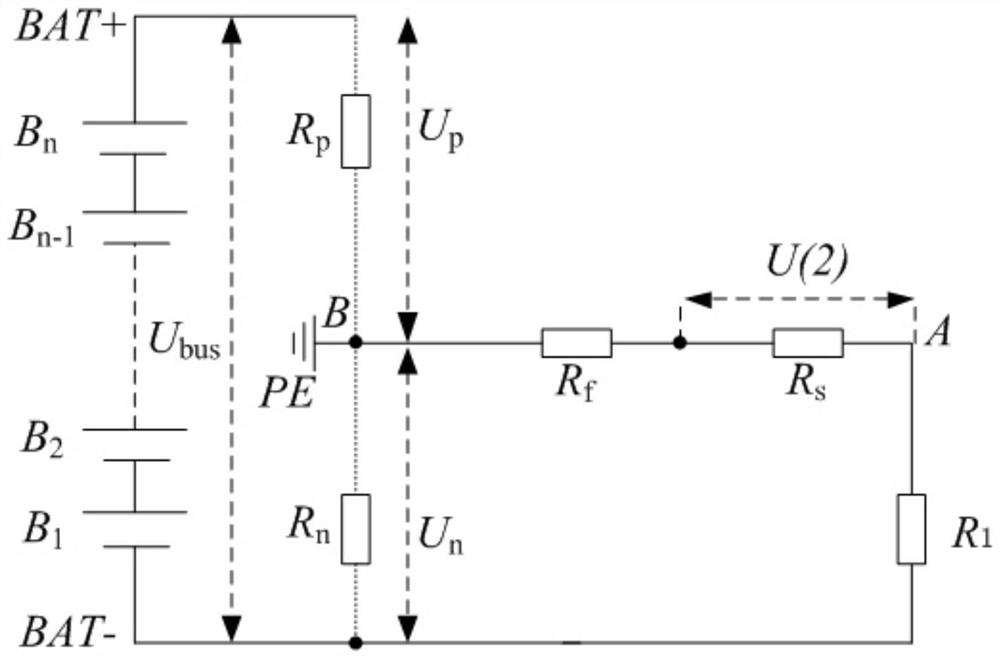
PendingCN114325101ASave control resourcesSave AD sampling resourcesResistance/reactance/impedencePower batteryAutomatic control
The invention discloses a vehicle insulation resistance detection circuit, method and device, and relates to the technical field of automatic control, and the vehicle insulation resistance detection circuit comprises a switch KP, a divider resistor R1, a divider resistor R2, a divider resistor Rf, a voltage sampling resistor Rs, an insulation resistor Rp, an insulation resistor Rn and a vehicle-mounted power battery pack. The divider resistor R1, the divider resistor R2, the insulation resistor Rp, the insulation resistor Rn and the vehicle-mounted power battery pack form a Wheatstone bridge; according to the invention, the control resource of the MCU chip and the AD sampling resource of the MCU chip can be saved, devices used by the system are few, the device cost is low, the economic applicability is high, the insulation fault occurring under the working condition that the insulation resistance is seriously unbalanced is directly judged by detecting and judging the balance of the insulation resistance bridge, and the reliability of the system is improved. In the process, detection of an insulation resistance value is not needed any more, shutdown and alarm operation are directly carried out, insulation fault alarm is timely and effective, and the insulation detection process is simple and reliable.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
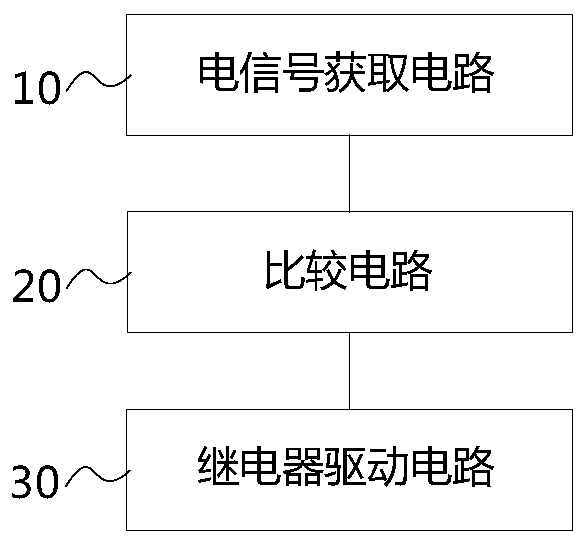
Compressor overcurrent protection device, method and electrical equipment
ActiveCN107565507BSave control resourcesQuick responseArrangements responsive to excess currentComputer moduleEngineering
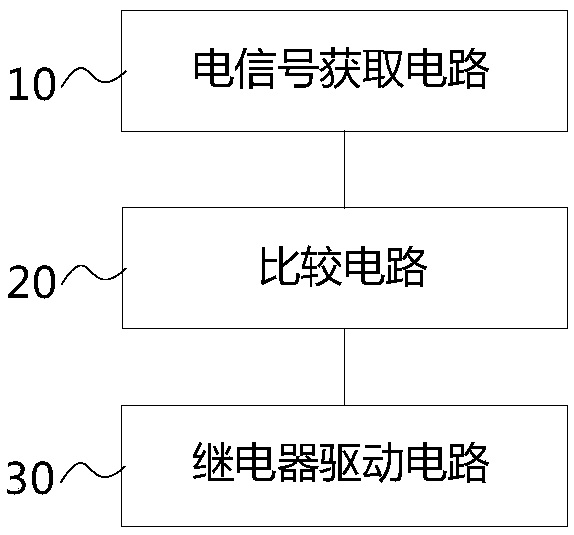
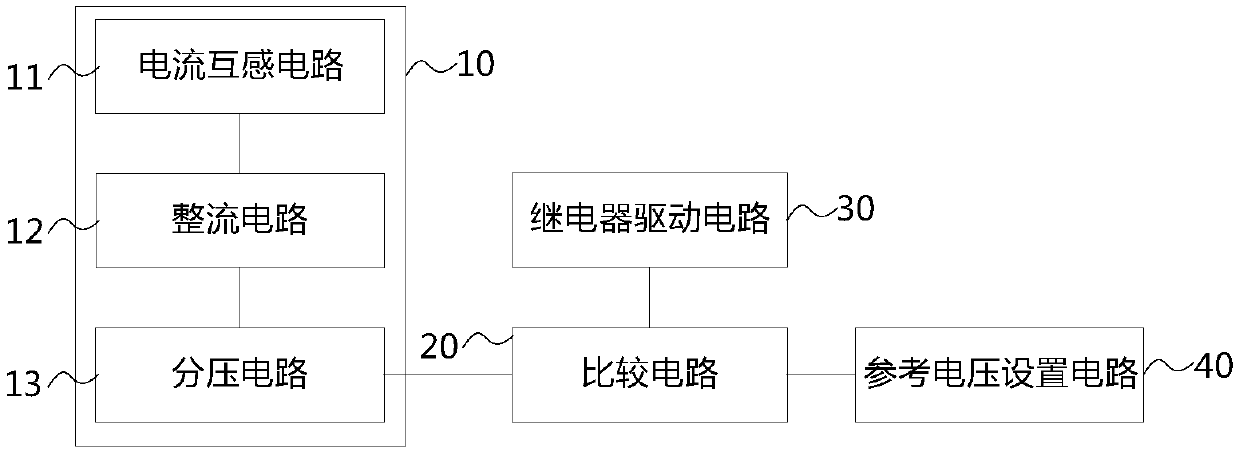
The present invention relates to a compressor over-current protection device and method, and an electric appliance device. The compressor over-current protection device comprises: an electric signal obtaining circuit (10) configured to obtain electric signals in a compressor loop; a comparison circuit (20) configured to compare the electric signals obtained by the electric signal obtaining circuit(10) with a reference value and output triggering signals in the condition that the electric signals obtained by the electric signal obtaining circuit (10) exceed the reference value; and a relay drive circuit (30) configured to control motion of a relay when triggering signals output by the comparison circuit (20) are received to disconnect a compressor loop. The over-current protection circuitcan be independent operated off from a main controller, can save control resources of the main controller, does not need logic determination of the main controller, is fast in reaction speed, and avoids mutual interference of the over-current protection circuit and the main controller. The protection circuit can be an independent module and used for various types of compressors, and the cost is low.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Buck-boost circuit and voltage stress control method
PendingCN113938010AImprove reliabilityReduce voltage stressDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceHemt circuits
The invention relates to a buck-boost circuit and a voltage stress control method, the buck-boost circuit comprises a logic control circuit, a first switch tube, a second switch tube, an inductor, a resistor, a first capacitor and a second capacitor, the input end of the logic control circuit couples the two ends of the resistor respectively, the output end of the logic control circuit is coupled with the first end of the first switch tube and the first end of the second switch tube, the first end of the resistor is coupled with the first end of the first capacitor and the first end of the second capacitor, and the second end of the resistor is coupled with the first end of the inductor. The second end of the inductor is coupled with the second end of the first switch tube and the second end of the second switch tube, the third end of the first switch tube is coupled with the second end of the first capacitor, and the third end of the second switch tube is coupled with the second end of the second capacitor; and the logic control circuit is used for reducing the switching frequency of the first switch tube and the second switch tube to a first frequency range or a second frequency range under the condition that the current value is greater than a first threshold value. According to the embodiment of the invention, the circuit voltage stress can be reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A home intelligent network system, control device and method
ActiveCN101945493BEasy remote accessRealize managementTransmission systemsNetwork topologiesTransmission protocolIntelligent Network
Disclosed are an intelligent home network system, a control device and a method. The system comprises a plurality of wireless terminals and a home control device. The wireless terminals respectively transmit various wireless access request signals to the home control device; the home control device correspondingly sets matching access parameters for the plurality of wireless terminals, receives the wireless access request signals according to the configured access parameters, parses and processes the parameters into corresponding data, performs analysis and determination for the data, and converts the data into corresponding real-time monitoring information for storage. The invention solves the problem of an intelligent home network system accessing wireless signals using different transmission protocols at the same time, and conveniently enables integrated management of diversified wireless terminal products available in the market, thereby promoting the development of wireless terminal product technologies.
Owner:ZTE CORP
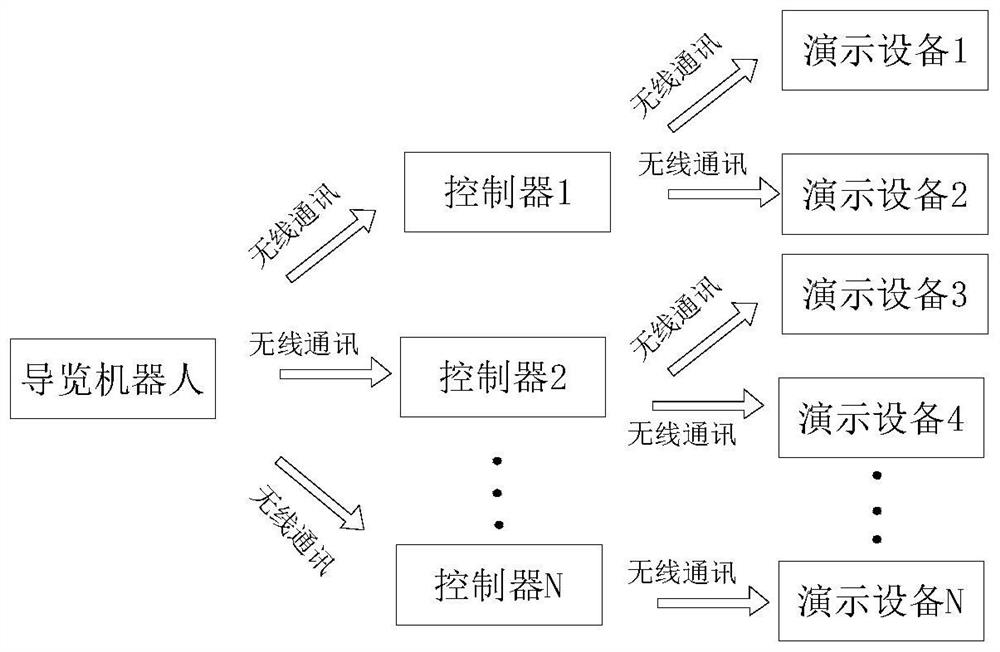
A control method for a demonstration device for a tour robot
ActiveCN108922148BEnsure normal wireless communicationMeet the needs of wireless controlNon-electrical signal transmission systemsShort range communication serviceInformation controlControl engineering
The present application provides a demonstration device control method for a tour robot, which includes the following steps: the tour guide generates demonstration instruction information according to the acquired exhibit information, and sends the demonstration instruction information to the controller, and the demonstration instruction information includes demonstration equipment address code identification information and demo identification information. The controller receives demonstration instruction information, and generates control information according to the demonstration instruction information, and the control information includes demonstration device address code information and demonstration information. The controller sends the control information to the demonstration equipment through multiple wireless communication methods at the same time. The demonstration device receives control information, and the demonstration device corresponding to the address code information of the demonstration device performs demonstration actions according to the demonstration information. The demonstration device can receive control information transmitted by two or more wireless communication methods. Integrate multiple communication methods into one, meet different control requirements in complex venues, adapt to the environment of complex exhibition venues, facilitate the control of all demonstration equipment, and have a good control effect.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
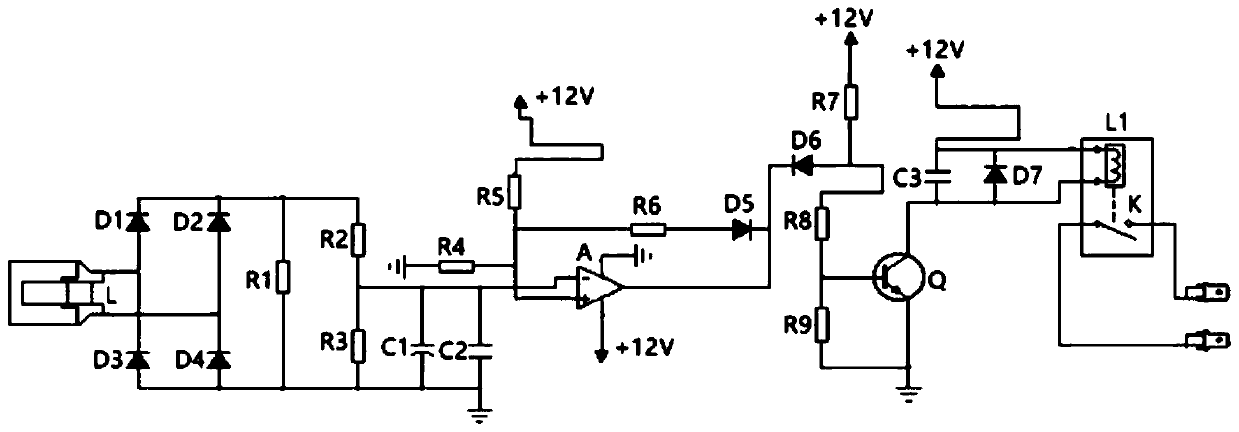
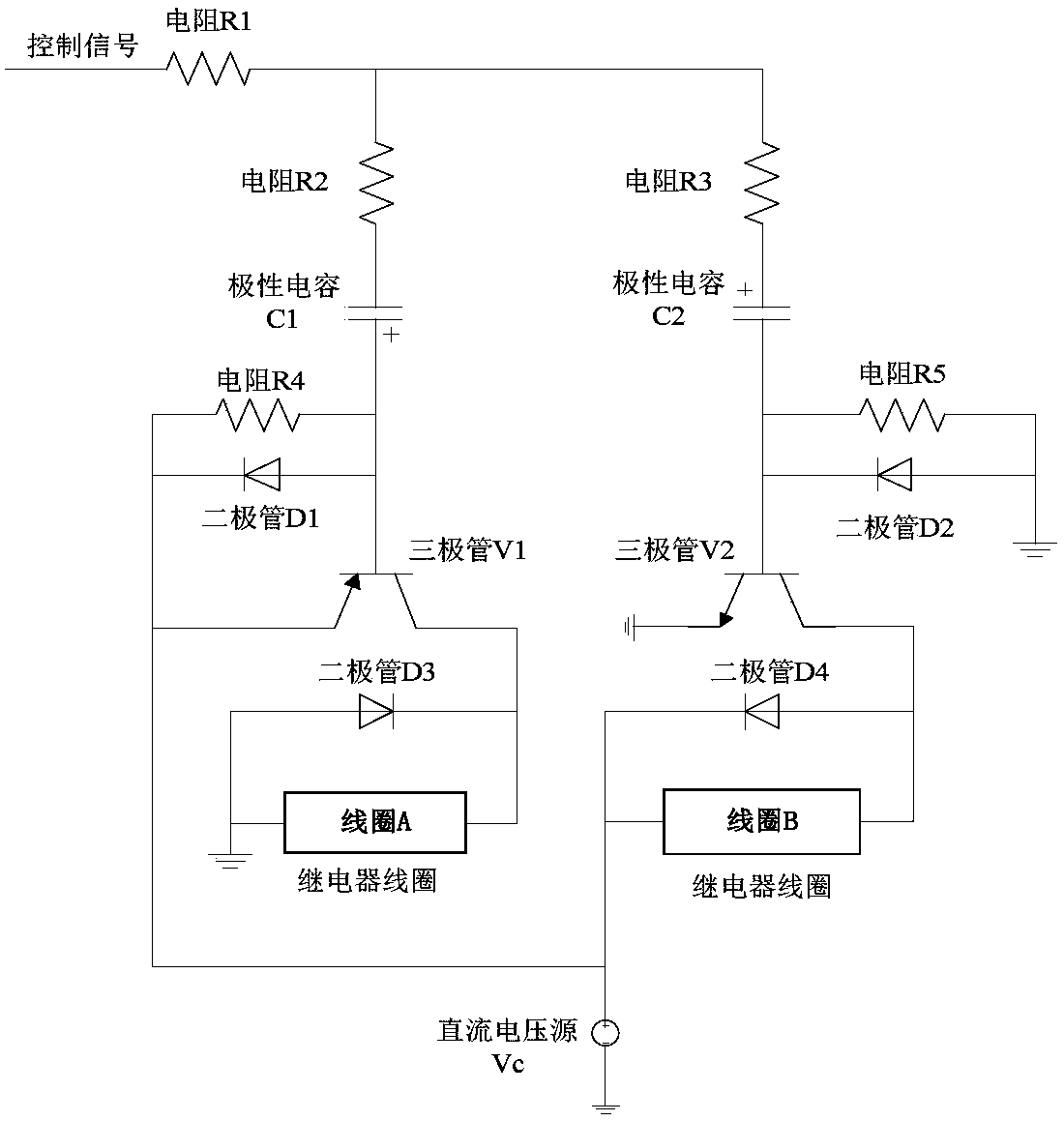
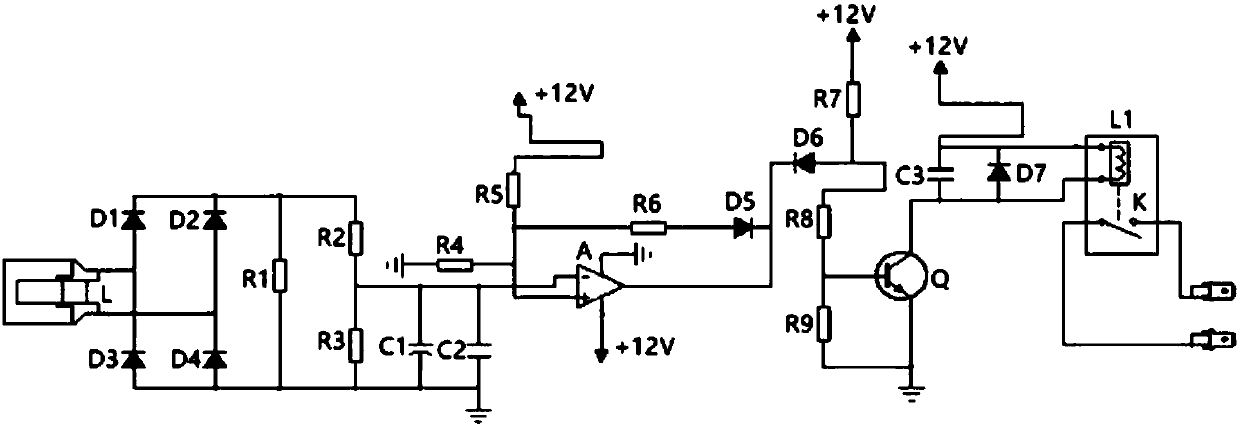
A Universal Magnetic Latch RF Relay Drive Circuit and Its Design Method
The invention discloses a general magnetic latch radio frequency relay drive circuit and a design method thereof, belonging to the field of microelectronics. The drive circuit design of the present invention is all constructed of discrete components, and the circuit structure is simple and clear. By adjusting the RC circuit parameters at the input end of the control signal, the duration of the drive current can be adjusted, which has versatility; when the control signal is switched, 1 The root control signal generates drive currents in two different paths through the reverse connection of two polar capacitors in the two paths and the switching characteristics of the triode, thereby completing the switching action of different states of the relay; in the circuit design of the triode and the power supply circuit of the relay A diode is introduced in the design to protect the circuit and enhance the stability of the circuit.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
An intelligent control system of switched reluctance motor based on wifi
ActiveCN110299874BRealize wireless controlSave control resourcesMultiple motor speed/torque controlSoftware algorithm controlMobile endSmart switch
The present invention is a WIFI-based switched reluctance motor intelligent control system. The system includes a server, a WIFI communication module, a mobile terminal, a plurality of underlying intelligent switched reluctance motor controllers, and a plurality of switched reluctance motors. Each underlying intelligent The switched reluctance motor controller is connected to a switched reluctance motor on the production line, including a monitoring module, a driving module, a control module, and a WIFI module; the mobile terminal can access and modify various functions in the server, and can receive fault warning information . Multiple switched reluctance motors feed back the operating parameters of switched reluctance motors in real time during normal operation, and periodically send the data to the server; the server optimizes the control parameters of switched reluctance motors using a large amount of received data combined with reinforcement learning algorithms. Record, and optimize and update the control parameters of the control module when the collected switched reluctance motor parameters deviate from the normal value and reach the safety threshold, so as to better control the operation of the switched reluctance motor.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Compressor over-current protection device and method, and electric appliance device
ActiveCN107565507ASave control resourcesQuick responseArrangements responsive to excess currentComputer moduleMaster controller
The present invention relates to a compressor over-current protection device and method, and an electric appliance device. The compressor over-current protection device comprises: an electric signal obtaining circuit (10) configured to obtain electric signals in a compressor loop; a comparison circuit (20) configured to compare the electric signals obtained by the electric signal obtaining circuit(10) with a reference value and output triggering signals in the condition that the electric signals obtained by the electric signal obtaining circuit (10) exceed the reference value; and a relay drive circuit (30) configured to control motion of a relay when triggering signals output by the comparison circuit (20) are received to disconnect a compressor loop. The over-current protection circuitcan be independent operated off from a main controller, can save control resources of the main controller, does not need logic determination of the main controller, is fast in reaction speed, and avoids mutual interference of the over-current protection circuit and the main controller. The protection circuit can be an independent module and used for various types of compressors, and the cost is low.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
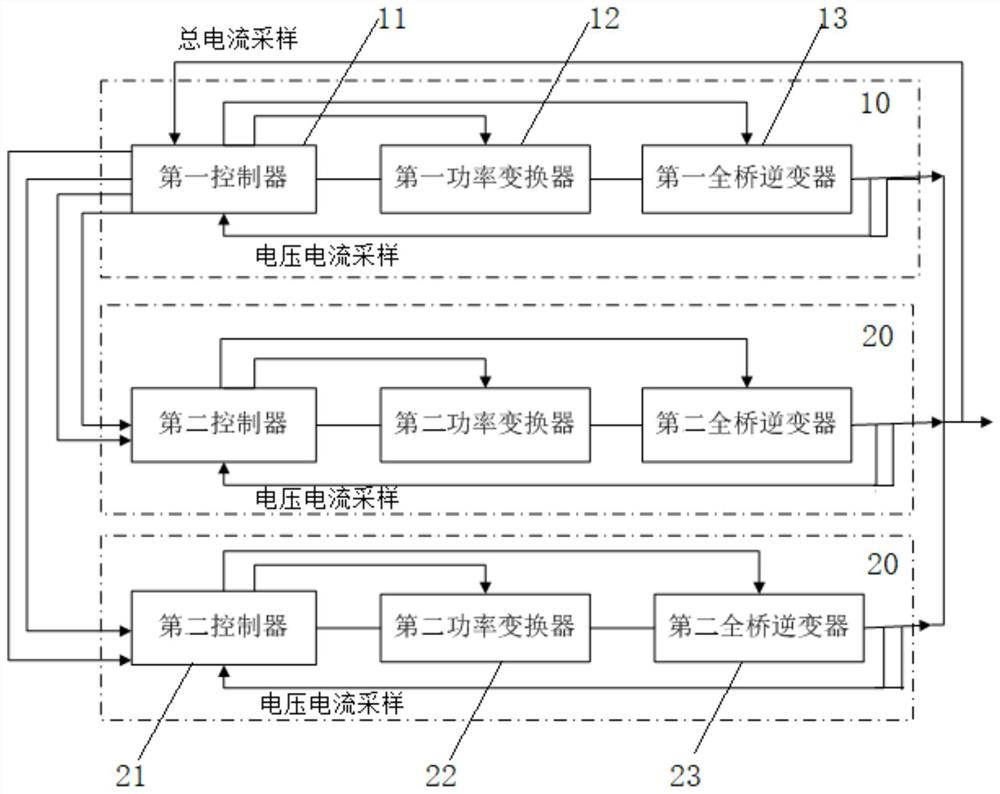
Wireless Power Transfer System Modular Inversion Source System
ActiveCN109861400BGuaranteed reliabilitySave control resourcesAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsFull bridgeControl engineering
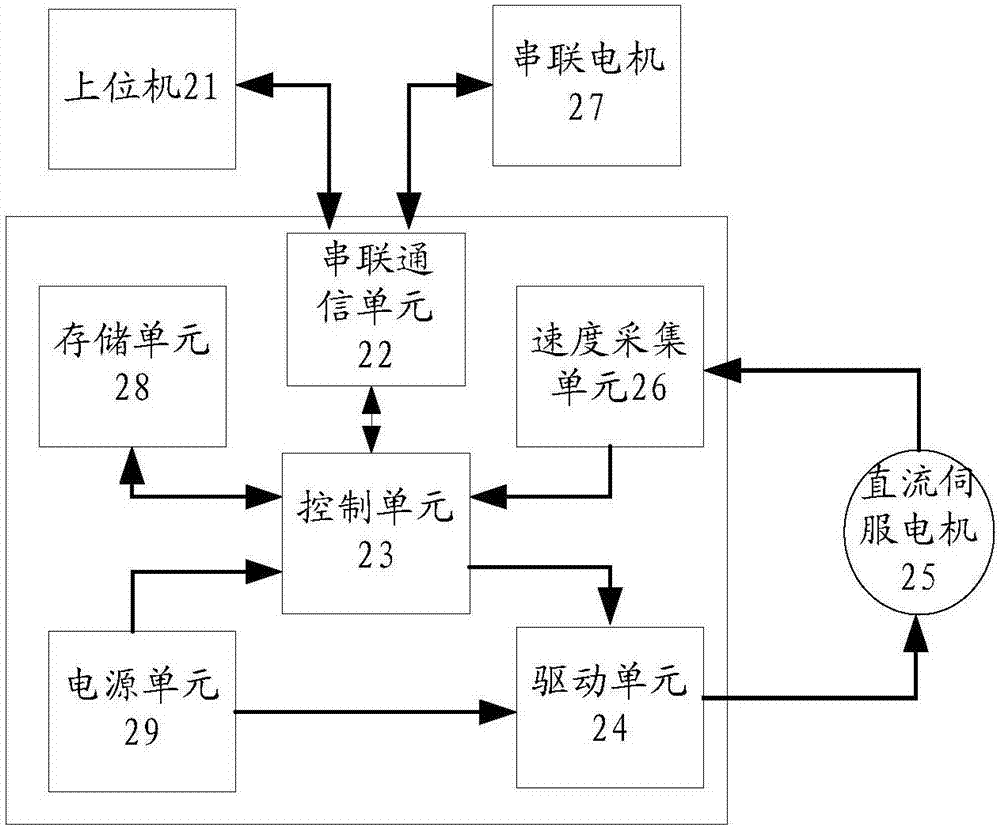
The invention relates to a modular inverter source system for a wireless power transmission system, comprising a first module and at least one second module, the first module includes a first controller, a first power converter and a first full-bridge inverter converter, and the first controller sends driving signals to the first power converter and the first full-bridge inverter respectively, and the second module includes a second controller, a second power converter and a second Two full-bridge inverters, and the second controller sends driving signals to the second power converter and the second full-bridge inverter respectively, and the first controller collects the total output current and calculates it in real time A current reference, the first controller sends a full-bridge inverter clock signal and a current reference to the second controller. The invention ensures the reliability of system control and saves control resources.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com