Patents
Literature
66results about How to "Will not collide with each other" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
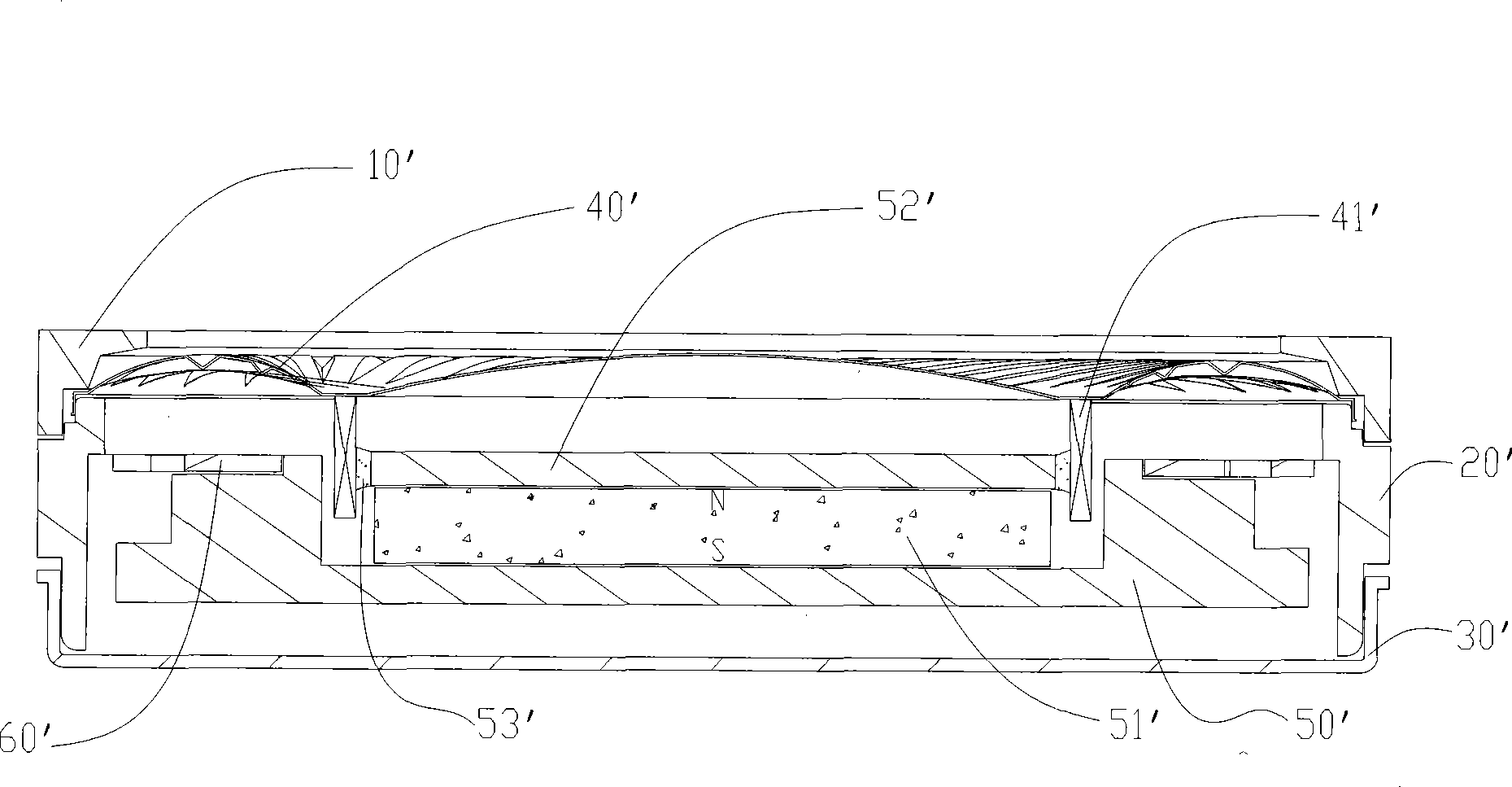
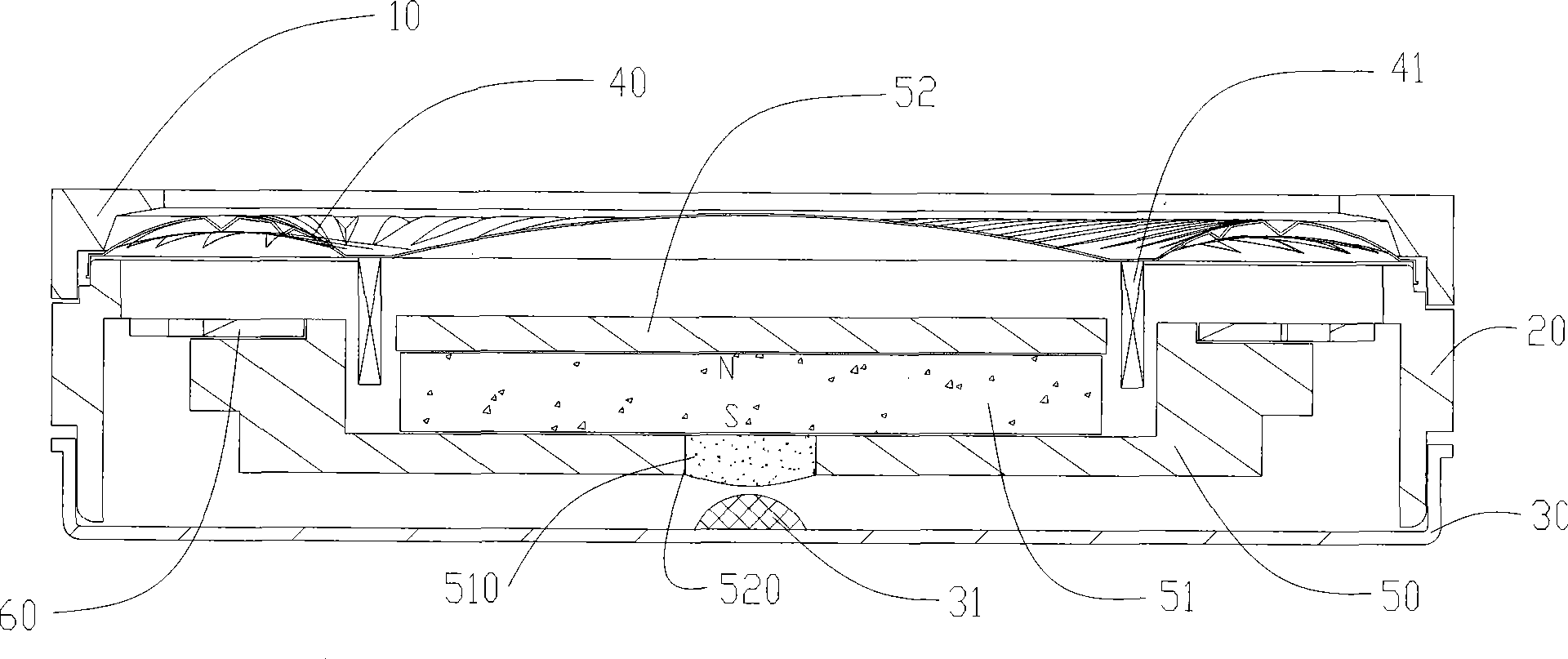
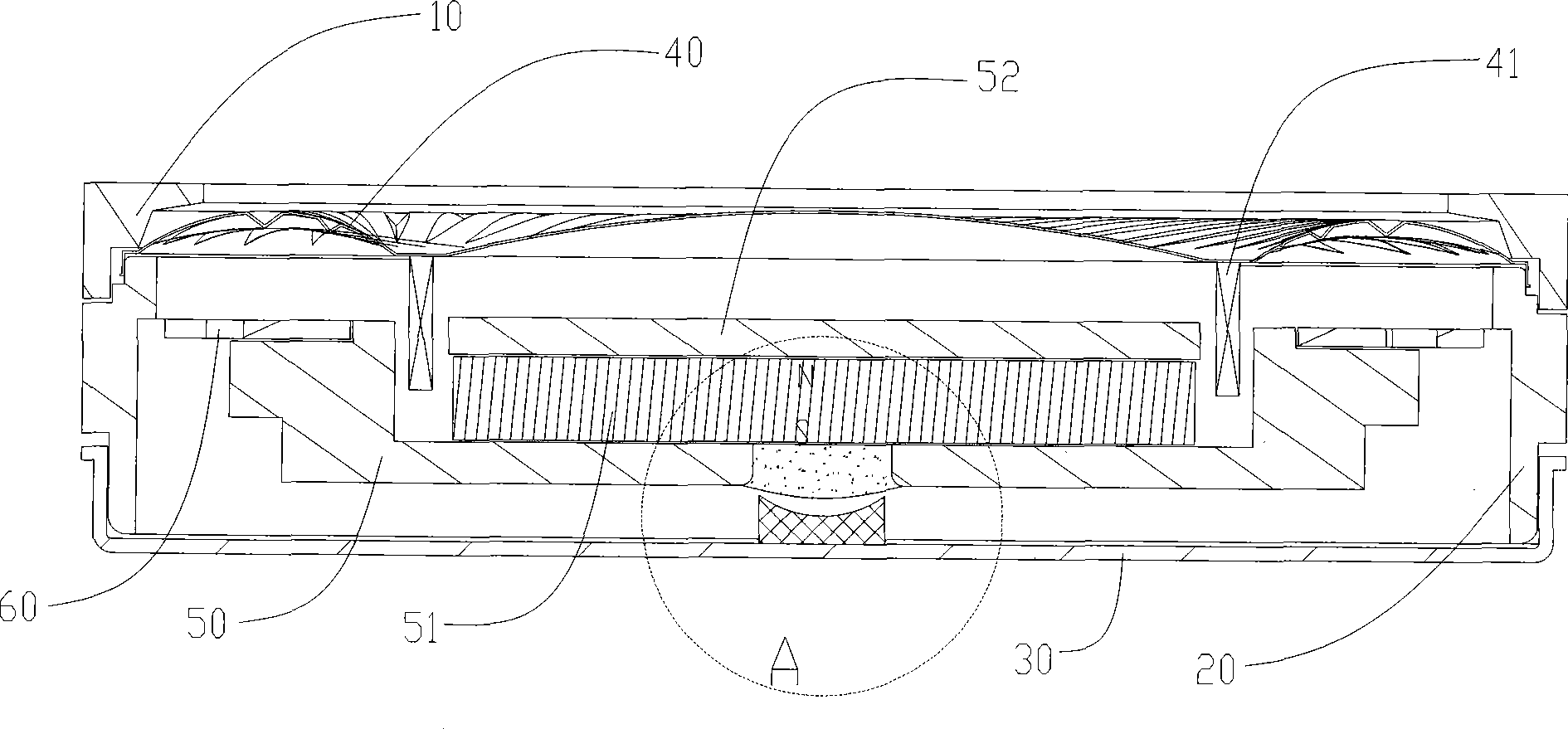
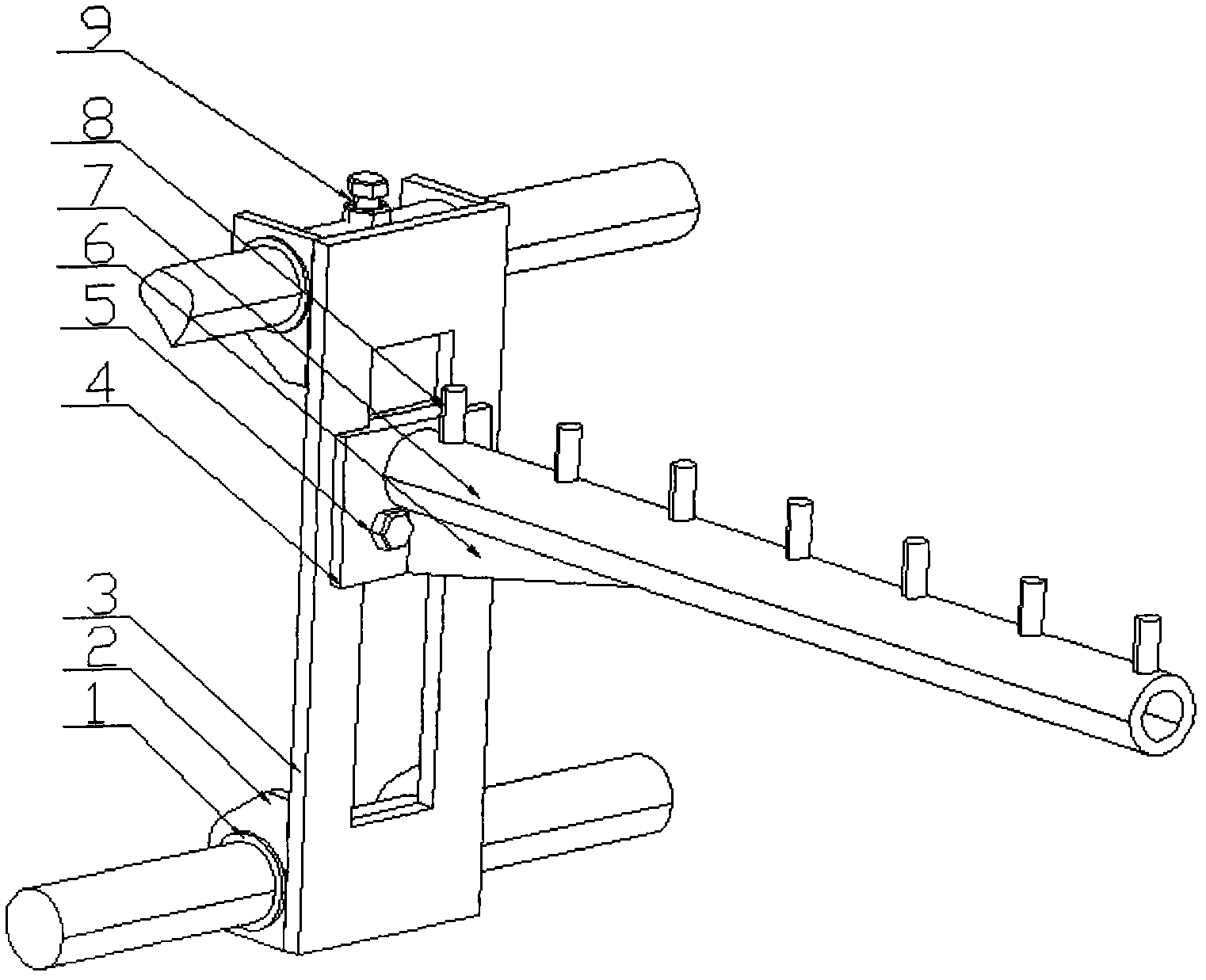
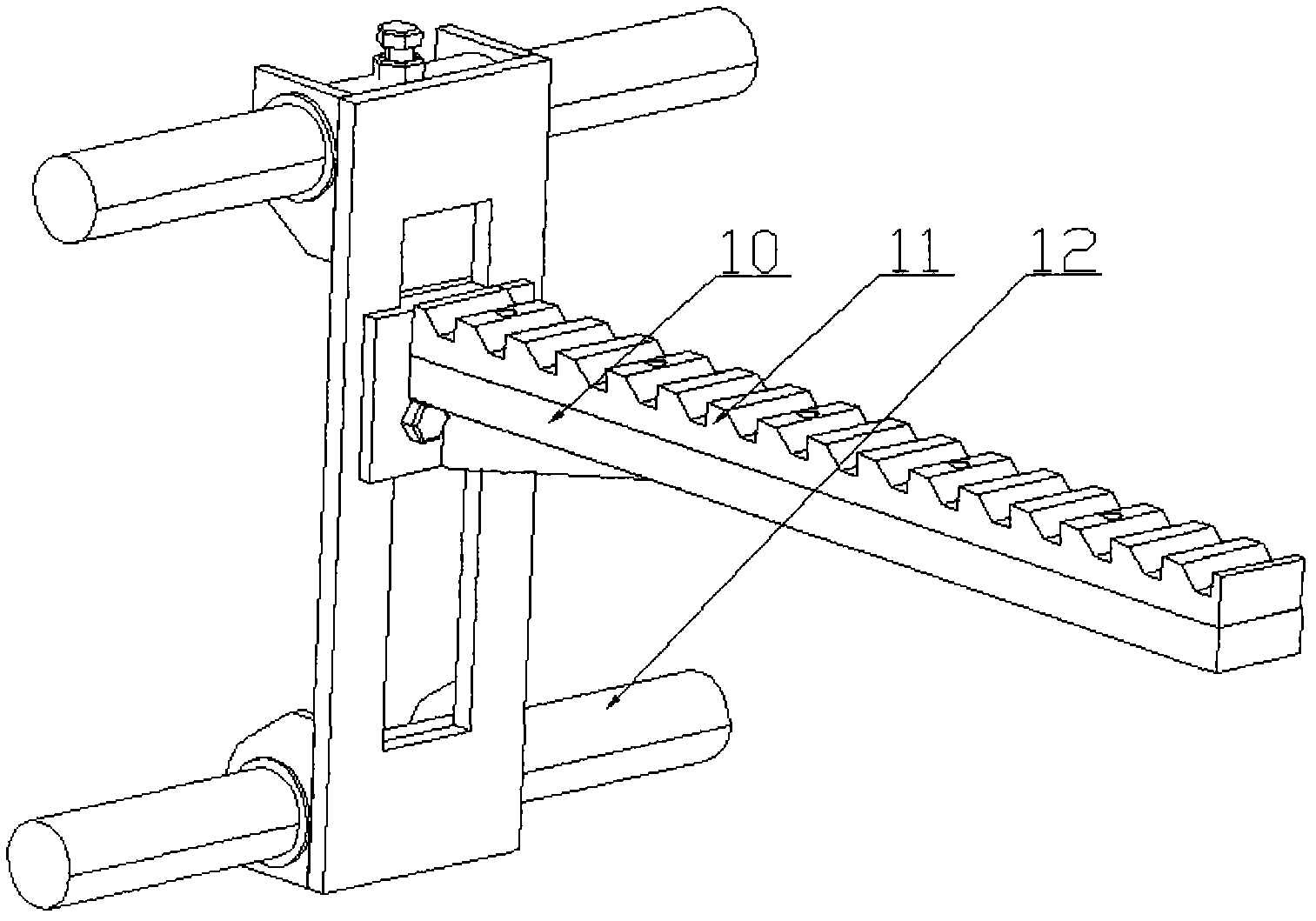
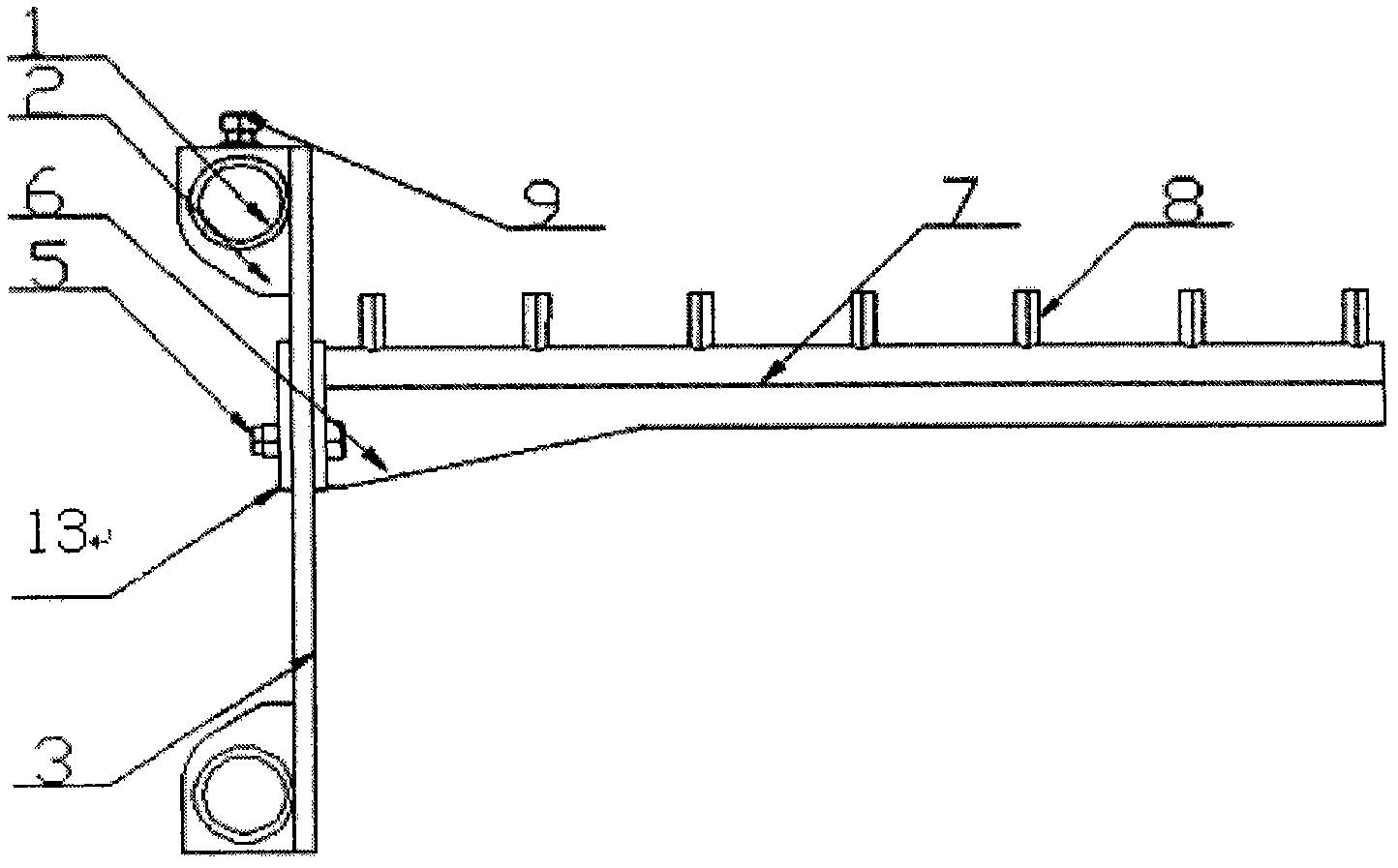
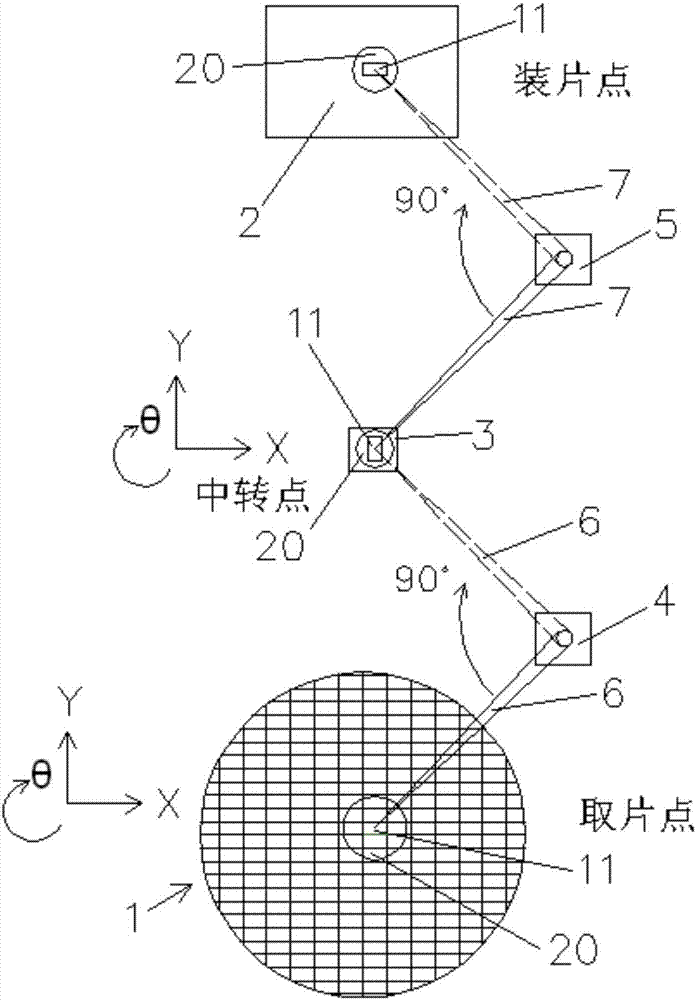
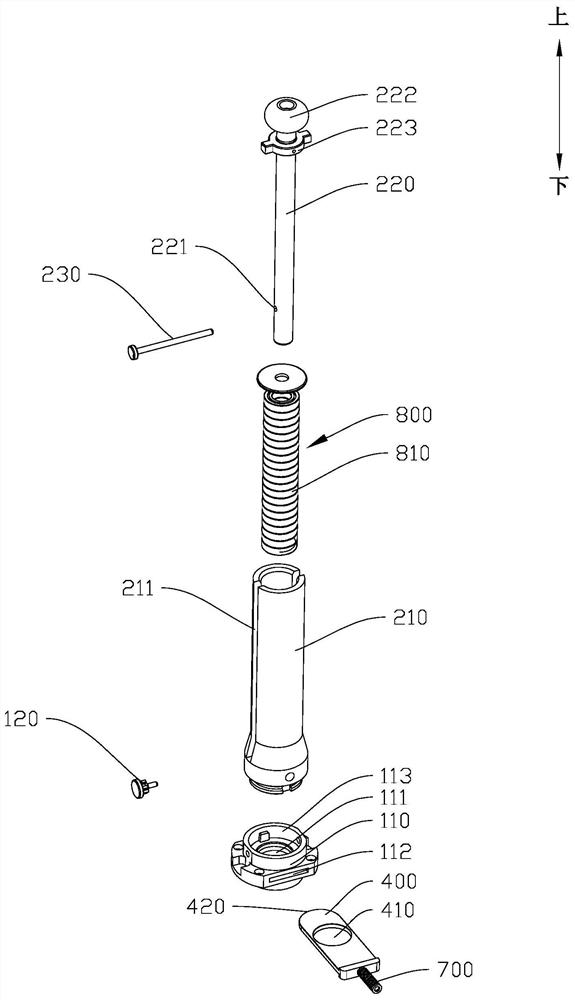
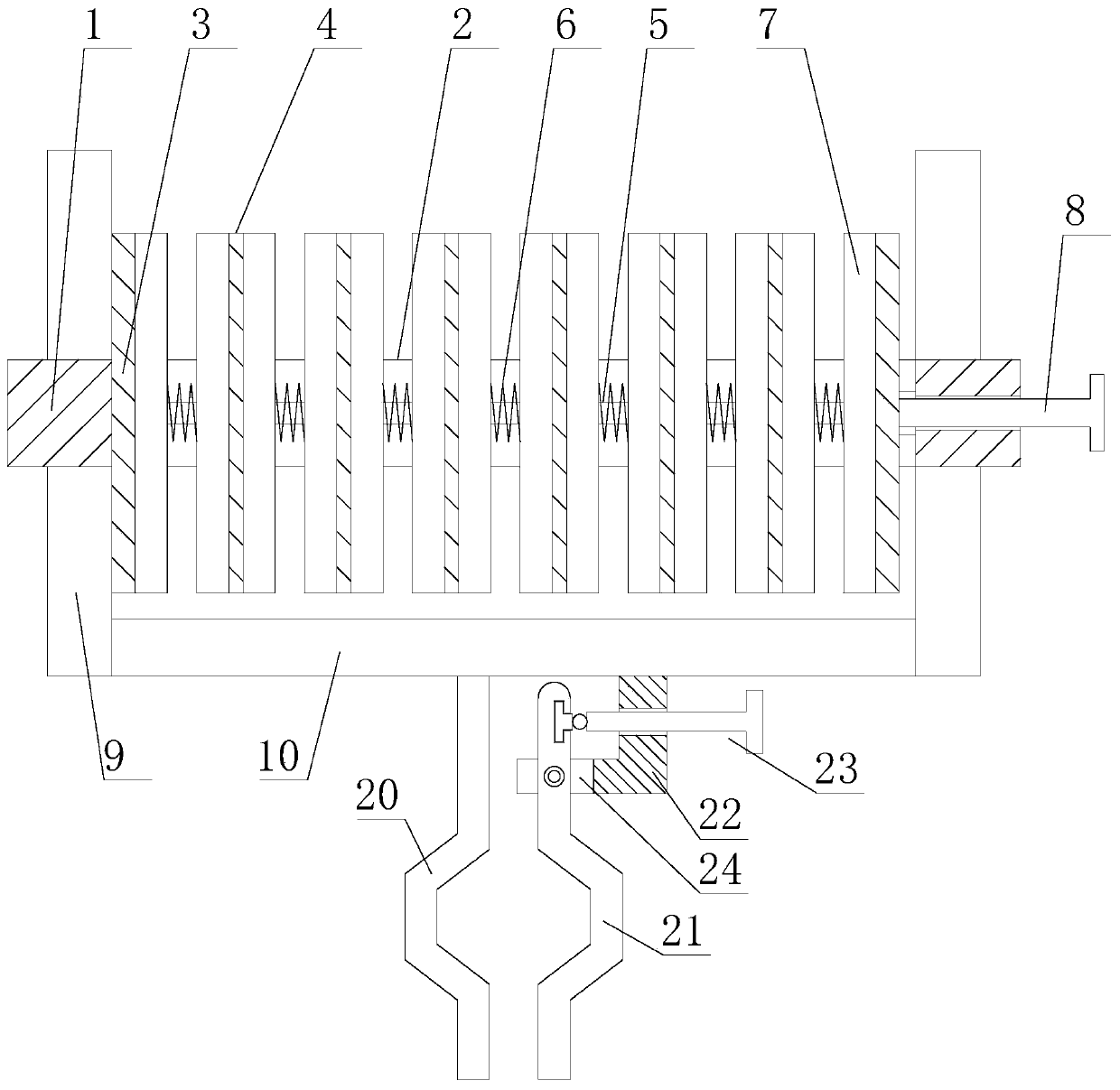
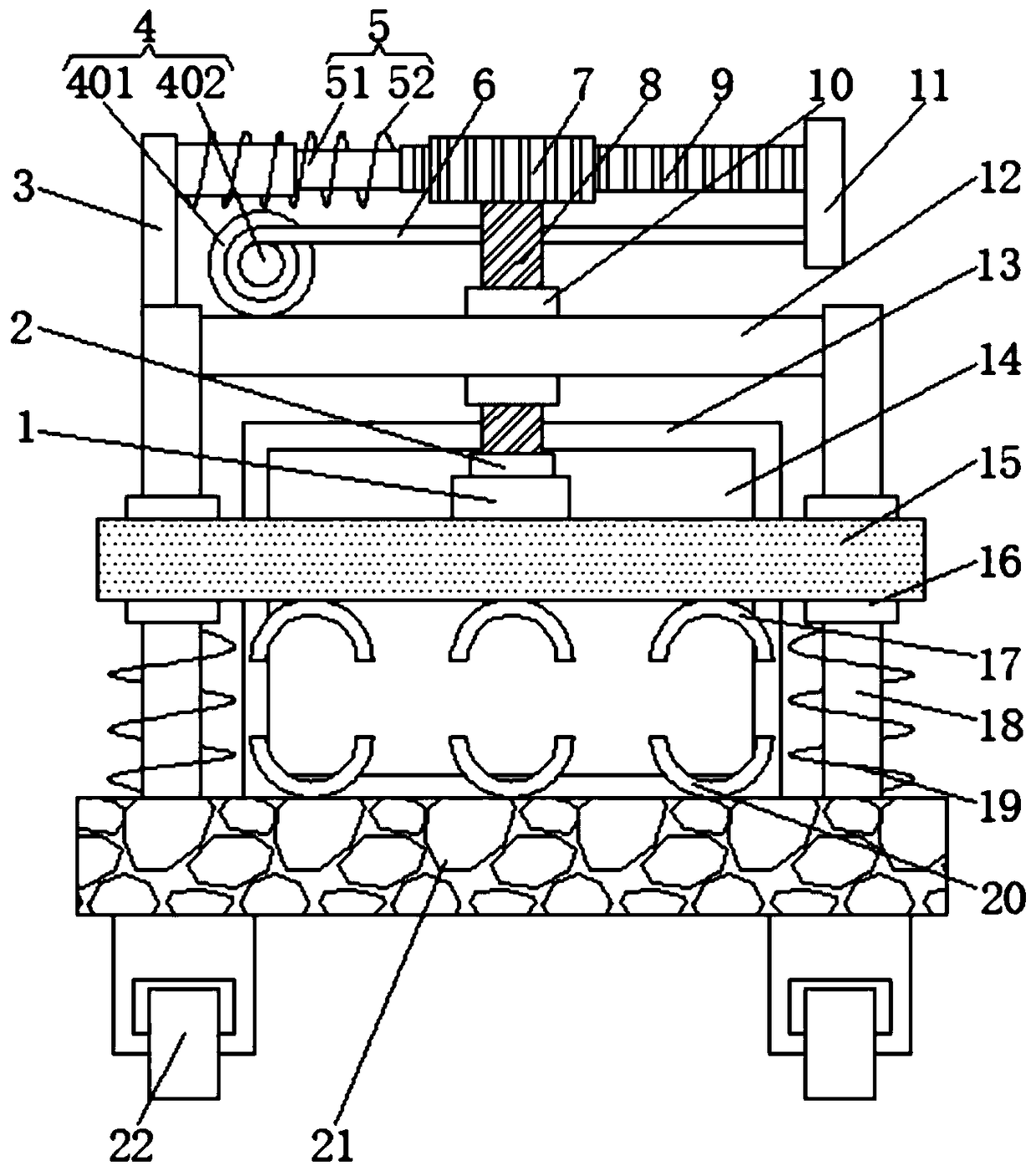
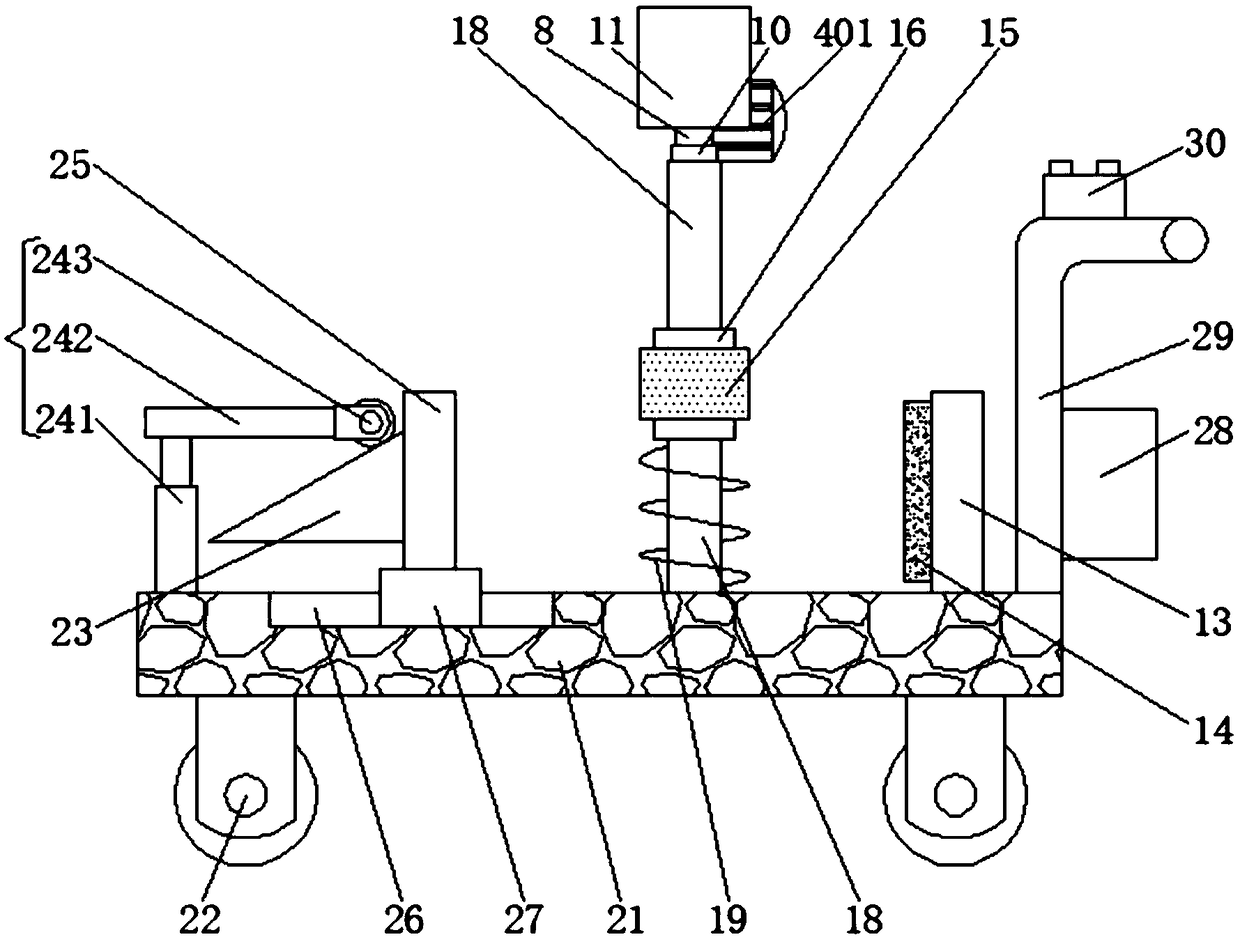
Linear vibrator device
InactiveCN101365256AResonance Amplitude SuppressionWithstand high voltageElectrical transducersResonance amplitudeEngineering
The invention relates to a vibrator, in particular to an electric-acoustic transformation acoustic generator with the function of vibration. A magnetic fluid is arranged at the bottom of a bowl-shaped magnetizer. A protruding elastic damping balance is arranged in the corresponding position of the magnetic fluid on a bottom cover. The elastic damping balance and a vibration unit with magnetic fluid are propped against each other in the vibration state, so as to overcome the disadvantage of small damp in a miniature electric-acoustic generator in the related technology, enable the resonance amplitude to be inhibited when the miniature electric-acoustic generator works, increase the voltage to be borne by the miniature electric-acoustic generator and widen the effective frequency band of the miniature electric-acoustic generator. Therefore, the resonance amplitude is inhibited, so that the collision of the inner parts of the acoustic generator can be avoided, and the power to be borne by the invention is increased. Besides, the counterforce is strengthened when the resonance happens, so that the effective frequency band of the electric-acoustic transformation acoustic generator gets wider.
Owner:瑞声声学科技(常州)有限公司
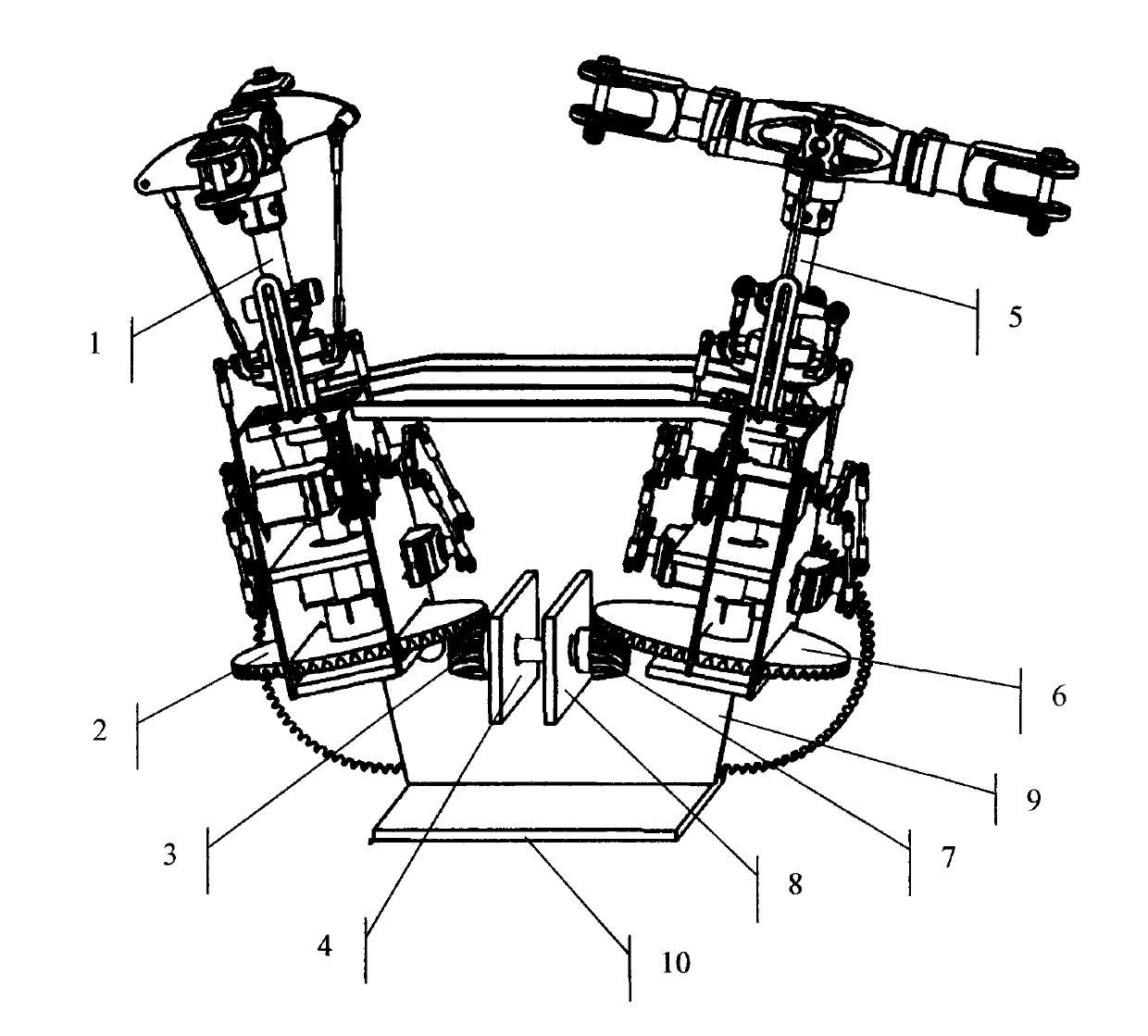
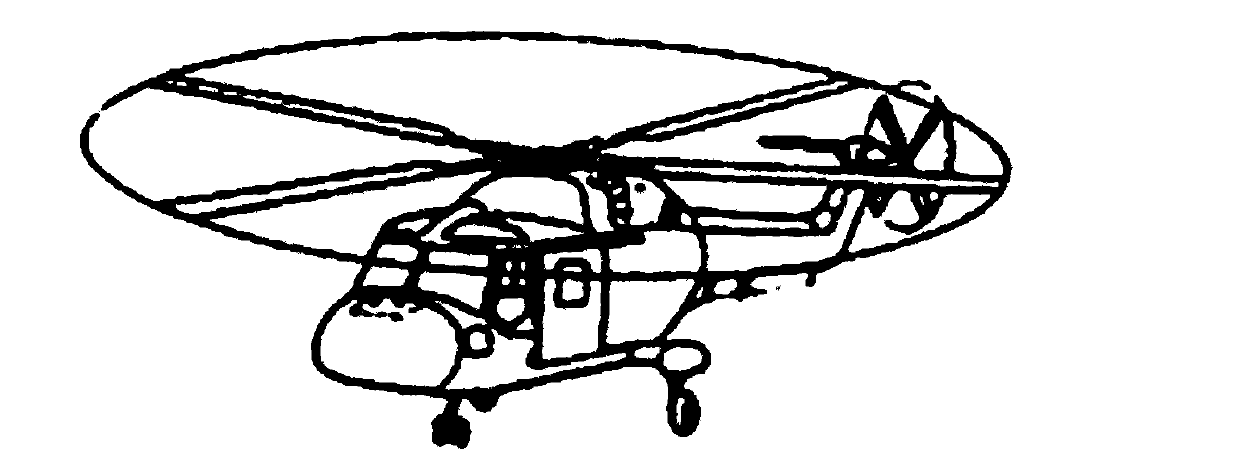
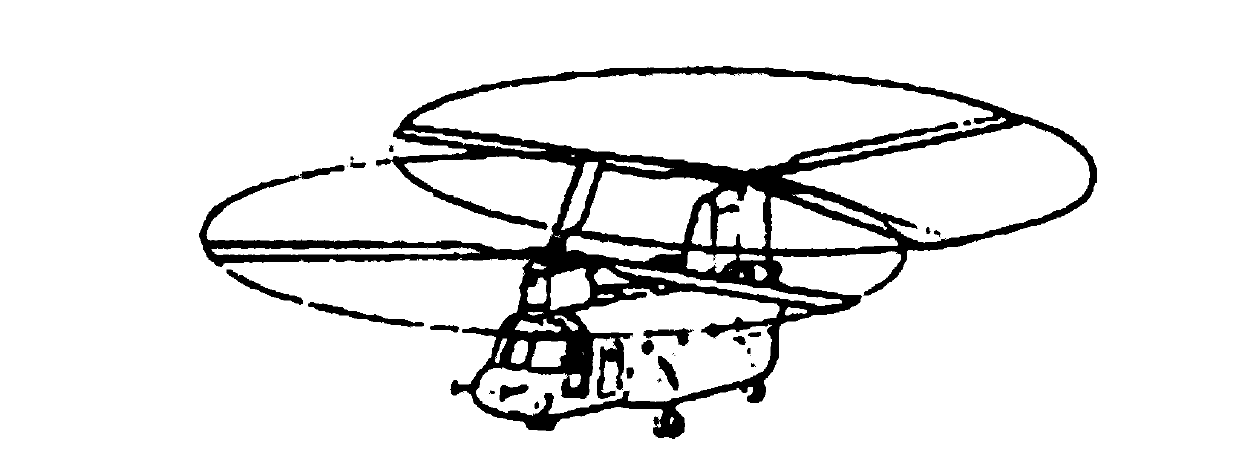
Two-rotor unmanned helicopter
The invention relates to a rotor type unmanned helicopter, and further relates to a two-rotor unmanned helicopter which aims to solve the simultaneous problem of a rotor spindle of the existing two-rotor unmanned helicopter in the process of flying. The technical scheme includes that the two-rotor unmanned helicopter comprises a machine body, two crossed rotors, the rotor spindle, spindle gears and a power source, wherein the spindle gears are respectively connected with the rotor spindle. The crossed state of the crossed rotors is that when a rotor is longitudinally vertical to the machine body and the other rotor is longitudinal parallel to the machine body, the two rotors are perpendicular to each other exactly. The two-rotor unmanned helicopter further comprises a simultaneous device. Compared with the prior art, the two-rotor unmanned helicopter has the advantages that due to the fact that simultaneous device is meshed in a mechanical mode, the coordination of the rotation of the two rotors are ensured, and the two rotors can not collide with each other when working.
Owner:TIANJIN AURORA UAV TECH +1
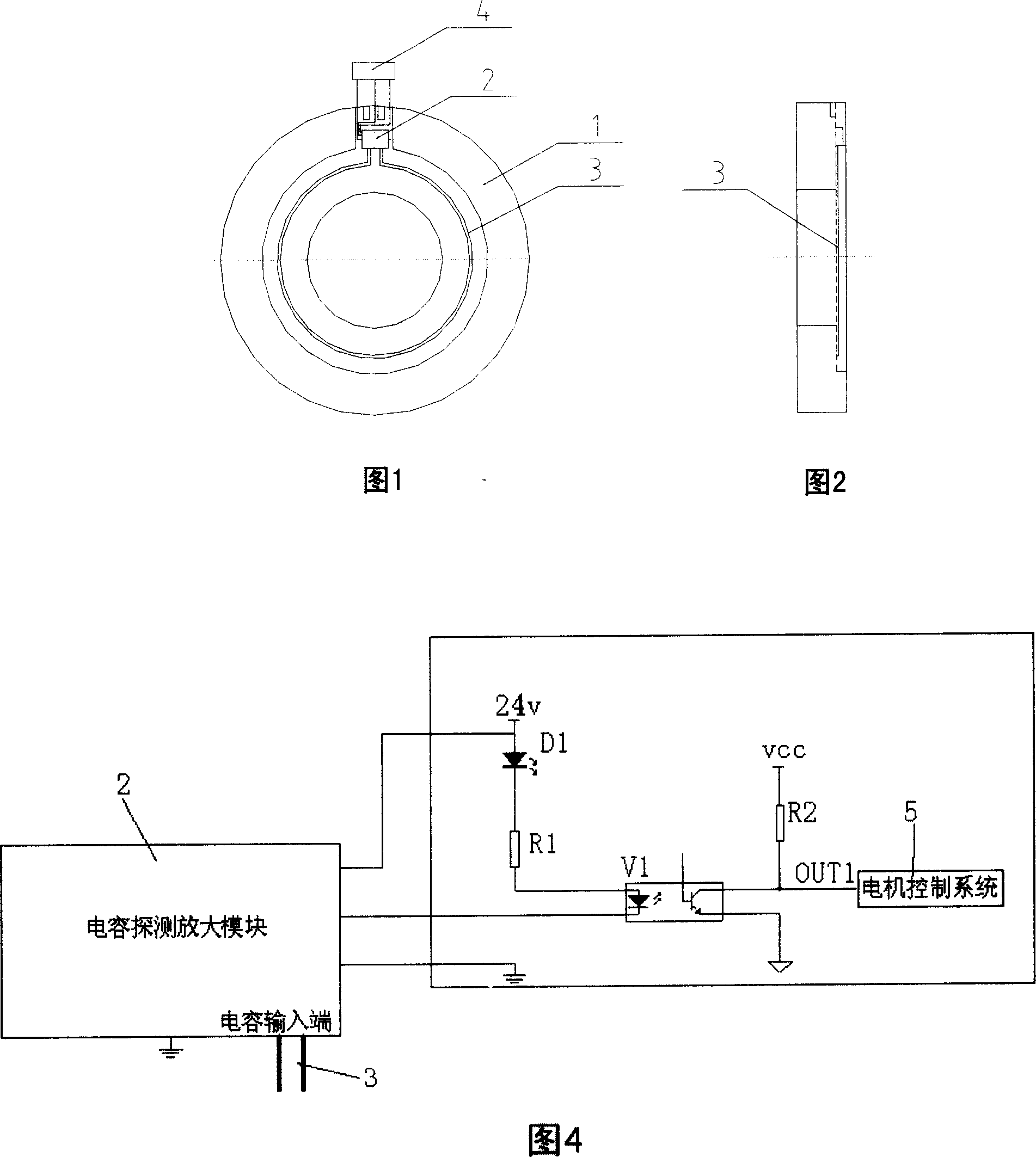
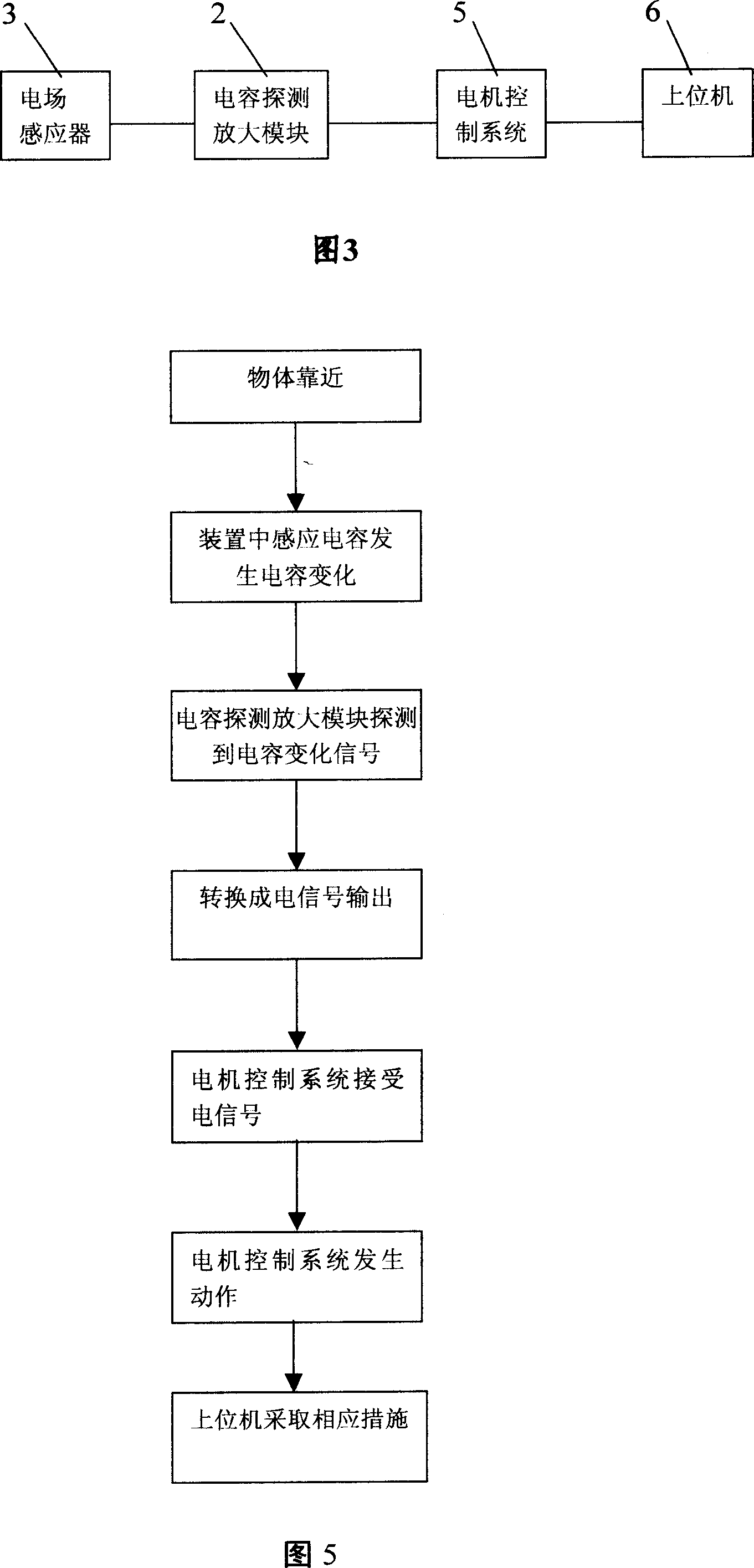
Non-contact anti-collision device used for medical X-ray equipment
InactiveCN1969752AWill not collide with each otherRealize non-contact collision avoidanceElectronic switchingRadiation safety meansVIT signalsCapacitance
The invention discloses a non-contact crashproof device for medical X-ray equipment, which comprises the following parts: case of crashproof area, upper-position set, capacitance detecting amplifying mode in the case and capacitance sensor on the mode, wherein the capacitance sensor senses capacitance signal of crashproof area; the capacitance detecting amplifying mode transmits the detected capacitance signal of crashproof area into electric signal to motor control system, which makes motor generate corresponding movement; the upper-position set displays the crash-proof condition.
Owner:BEIJING ORIENTAL E T MEDICAL EQUIP
Adjustable storage transfer device
InactiveCN102491042AWill not collide with each otherReasonable placementManual conveyance devicesElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Relay type rapid chip taking and chip assembling device and chip assembling machine employing same
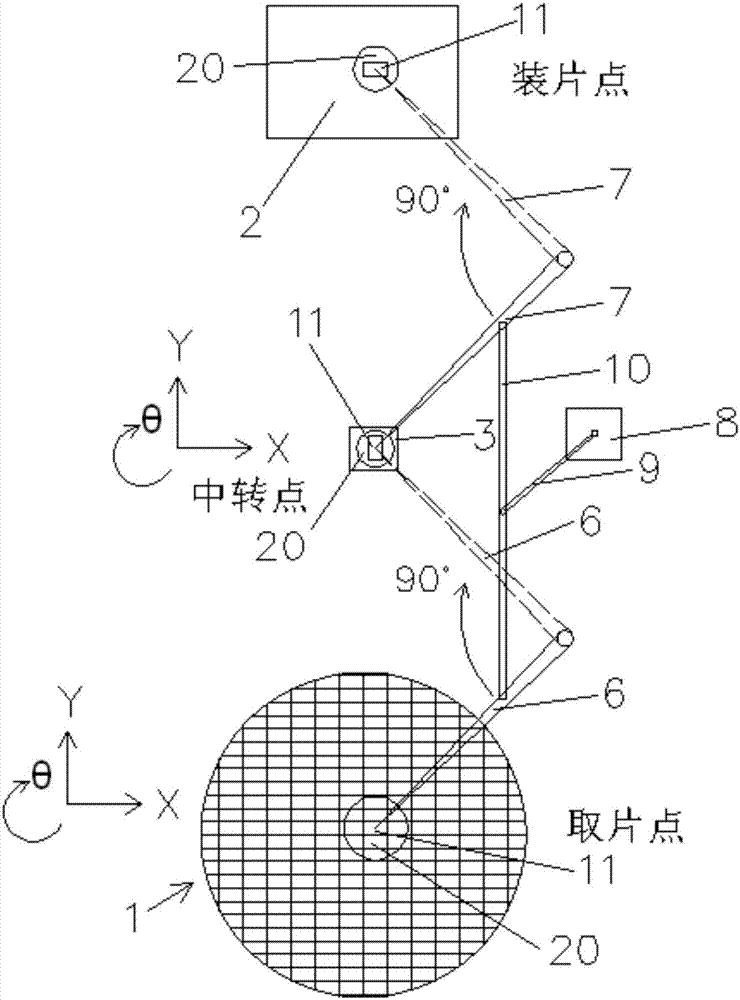
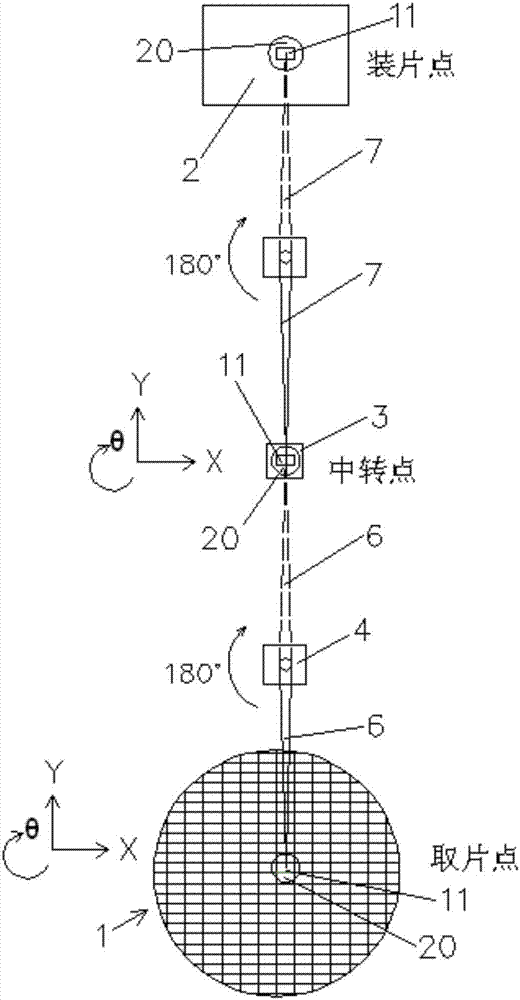
PendingCN107248501AShorten the lengthShort strokeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConveyor partsComputer hardwareWafer
The invention discloses a relay type rapid chip taking and chip assembling device and a chip assembling machine employing the same. A first rotation arm is used for taking out a chip on a wafer and placing the chip on a transit table after rotation, a second rotation arm is used for taking out the chip on the transit table and placing the chip on a substrate after rotation, a welding head is used for taking out the chip and placing the chip and is arranged at one end of the first rotation arm and one end of the second rotation arm, the welding head moves in a reciprocating way along a direction parallel to a rotation shaft of the first rotation arm or the second rotation arm, and a driving device is used for driving the first rotation arm and / or the second rotation arm to rotate. The relay type rapid chip taking and chip assembling device has the beneficial effects that with the arrangement of the chip transit table, chip taking and chip assembling of the rotation arms can be synchronously performed; and remote chip taking and chip assembly is required, compared with a traditional chip taking and chip assembling mode employing a single rotation arm, the relay type rapid chip taking and chip assembling device has the advantages that the efficiency is improved by 50-70%, and the chip assembling accuracy is higher.
Owner:SUZHOU ACCURACY ASSEMBLY AUTOMATION CO LTD
Bearing feeding device and automatic feeding method
ActiveCN111806980APrevent slippingWill not slipDe-stacking articlesMetal working apparatusEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention discloses a bearing feeding device and an automatic feeding method. The bearing feeding device comprises a rack, a storage assembly and a feeding disc, wherein a positioning seat is arranged on the rack, and a first through hole is formed in the positioning seat; the storage assembly comprises a storage barrel, a penetrating rod and a first bolt, the storage barrel is arranged on thepositioning seat, the side wall of the storage barrel is provided with an opening groove, and the first bolt is inserted into the lower end of the penetrating rod in the radial direction of the penetrating rod; and the feeding disc is rotationally connected with the rack, and the feeding disc is provided with a trough. By using the bearing feeding device, the penetrating rod penetrates through abearing string, the first bolt is inserted into the lower end of the penetrating rod, then the bearing string and the penetrating rod are put into the storage barrel together, the first bolt is pulleddown, the feeding disc is rotated clockwise so that the front end of the trough can be located below the first through hole, one bearing at the lowest end in the storage barrel can fall into the front end of the trough, and the feeding disc is rotated anticlockwise so that the bearing can be sent to a bearing press mounting position, so that automatic feeding is achieved, and working efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG HESHI AUTOMATION TECH CO LTD
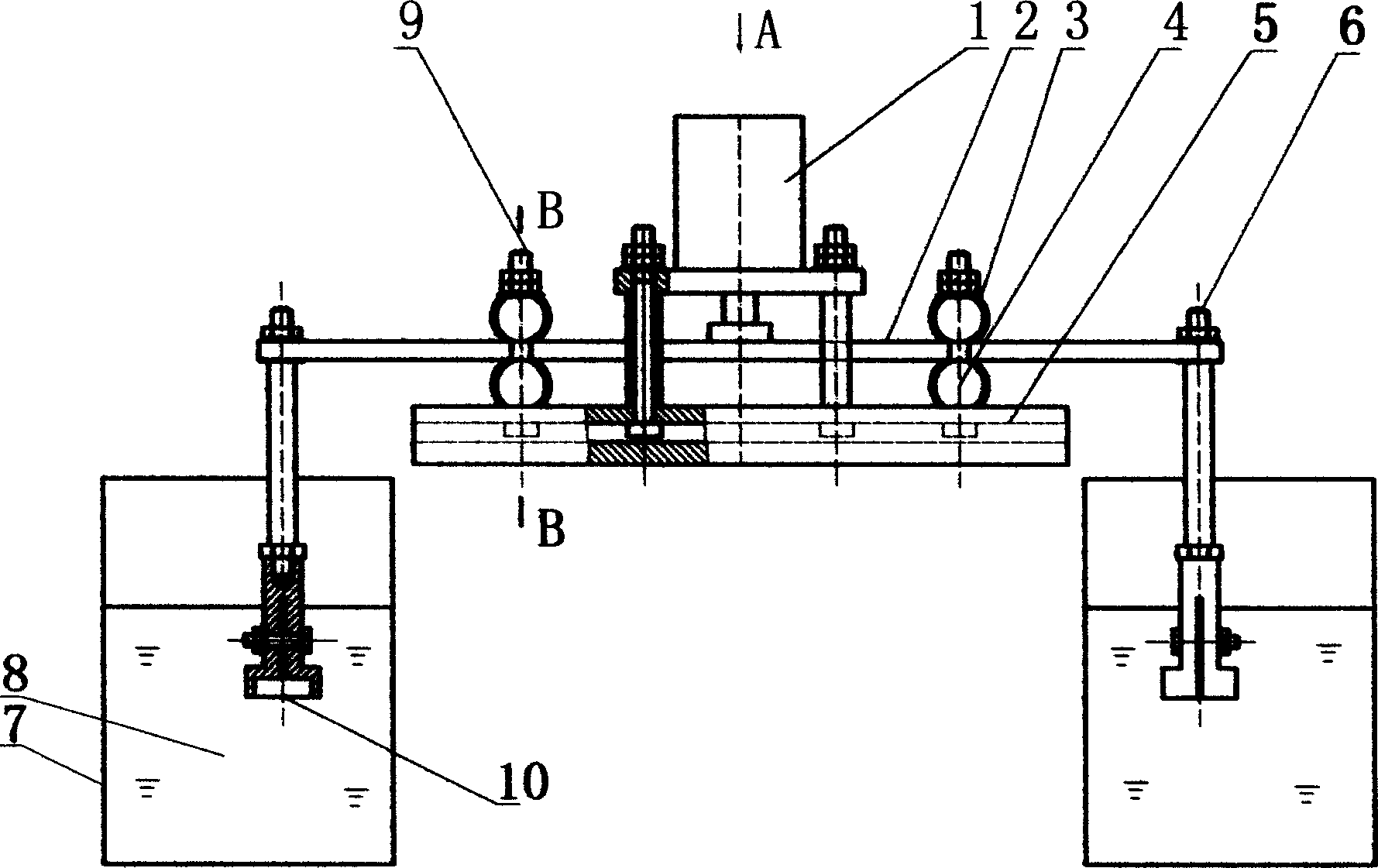
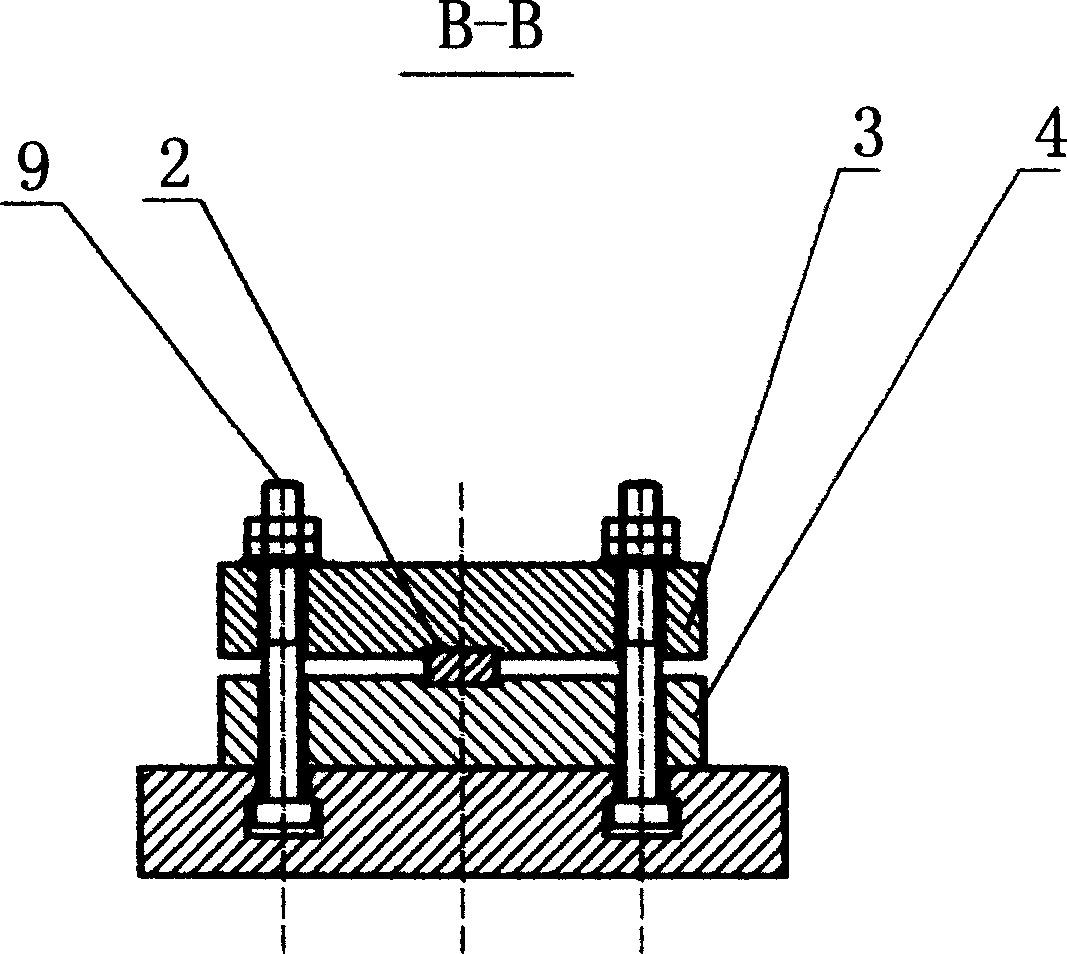
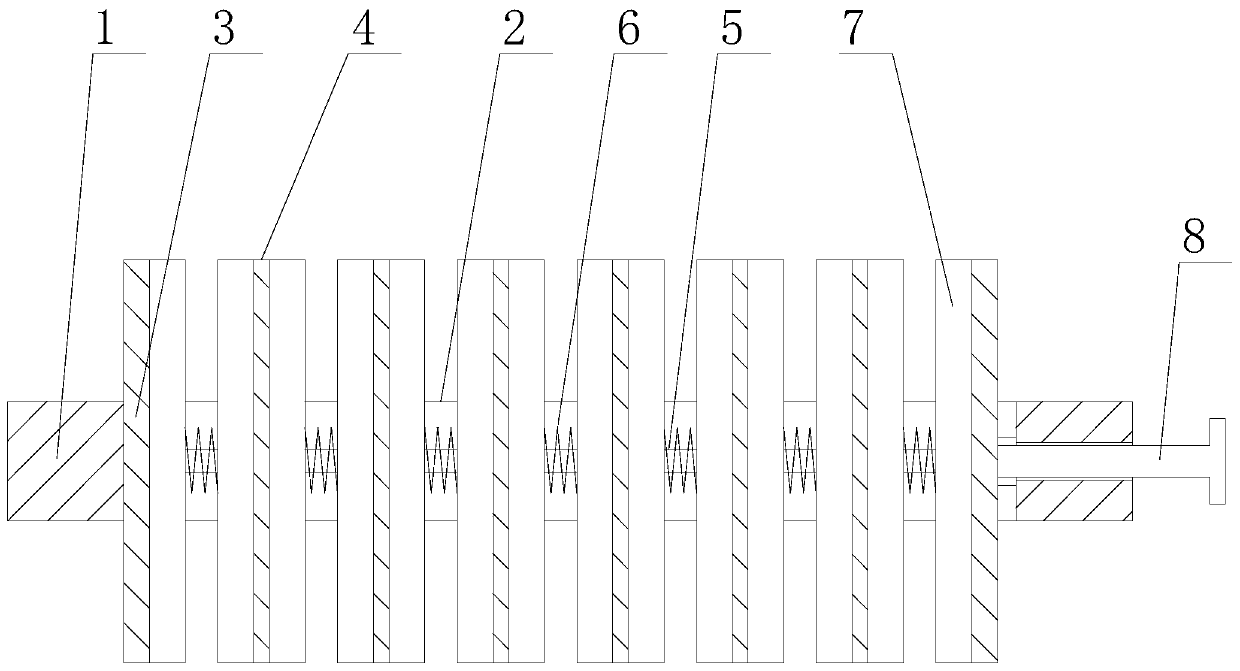
Mud covering machine for preserved duck egg production equipment
ActiveCN104286950AAvoid wastingWill not collide with each otherFood preparationEngineeringPower transmission
The invention discloses a mud covering machine for preserved duck egg production equipment. The mud covering machine comprises a rack (1), a mud basin (2), a pusher dog mechanism (3), a pusher dog mechanism bracket (4) and a power transmission shaft (5), wherein the mud basin (2) is fixed on the rack (1); the section shape of the mud basin (2) is semicircular; the pusher dog mechanism (3) is mounted on the power transmission shaft (5); the power transmission shaft (5) is fixed above the mud basin (2) by the pusher dog mechanism bracket (4); and one end of the power transmission shaft (5) is provided with a belt wheel (6). According to the mud covering machine for the preserved duck egg production equipment, manual mud covering can be replaced; mud covering work of duck eggs can be rapidly and efficiently finished; and the mud covering machine has the advantages of simple structure and low manufacturing cost.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for producing injection-molded and in-mold decorated article and mold for injection molding with in-mold decoration
In a manufacturing method for injection-molded and in-mold decorated articles including injection of molding resin (4) into a molding space (3) defined by a decorating film (5) and a mold (1), the molding space has a product molding space (31) and a resin-discharging-use molding space (33) which is formed around the product molding space and into which the molding resin is let to flow for discharge of the molding resin from the product molding space. The molding resin is injected into the product molding space, and while part of the injected molding resin is discharged from the product molding space into the resin-discharging-use molding space, the molding resin is filled into the product molding space.
Owner:NISSHA PRINTING COMPANY
Guide bar structure in warp knitting machine, knitting machine and thread guide set
The invention relates to the technical field of a warp knitting machine, in particular to a guide bar structure in the warp knitting machine, the warp knitting machine and a thread guide set. The guide bar structure comprises at least one lateral-moving row. The lateral-moving row is provided with the thread guide set which is arranged in a common supporting device. Each thread guide row is capable of moving along a lateral-moving direction. The thread guide set is composed of at least one long belt which is arranged in the supporting device. A hole section is arranged on the lower portion of the long belt. At least one thread guide hole is formed in the hole section side by side along the lateral-moving direction. Extensions are arranged on the long belt extends along the lateral-moving direction, and extensions are arranged between the lower portion of a supporting section in the supporting device and the hole section of the thread guide hole. The guide bar structure, the warp knitting machine with the guide bar structure and the thread guide set on a guide bar all enable the existing monotonous warp knitting machine weaving to be provided with abundant pattern design, and are simple in structure.
Owner:KARL MAYER CHINA
Polishing, deburring and cleaning equipment
InactiveCN1593847AWill not collide with each otherSolve the problem of quickly realizing the adjustment of vibration characteristicsCleaning using liquidsEngineeringVibration exciter
The invention relates to a kind of adjustable vibrating polishing, deburring and cleaning device. The invention combines the steel cantilever beam and the vibration exciter. Vibration exciter and bearing column are both on the the seat's moving T slot. The steel cantilever beam is between the two series of bearing column. So adjust the bearing column position can change the vibration character to come true a best vibration efficiency. It is simple and effective to solve the problem of adjusting the vibration character of the deburring device. The efficiency of the invention is as 2~5 times as artificially working .The working intensity are low, and the work pieces won't collide each other, so it won't damage the surface that doesn't be processed. The device is simple and credible, and has few chances to go wrong. The cost is low. The device is easy to be produced and applied, so it can be used for the process of polishing, deburring and cleaning the workpieces of middle bulk or small bulk.
Owner:XIAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE
Guide bar structure in warp knitting machine, knitting machine and thread guide set
ActiveCN103132229BRigid enoughWill not hinder each otherWarp knittingEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of a warp knitting machine, in particular to a guide bar structure in the warp knitting machine, the warp knitting machine and a thread guide set. The guide bar structure comprises at least one lateral-moving row. The lateral-moving row is provided with the thread guide set which is arranged in a common supporting device. Each thread guide row is capable of moving along a lateral-moving direction. The thread guide set is composed of at least one long belt which is arranged in the supporting device. A hole section is arranged on the lower portion of the long belt. At least one thread guide hole is formed in the hole section side by side along the lateral-moving direction. Extensions are arranged on the long belt extends along the lateral-moving direction, and extensions are arranged between the lower portion of a supporting section in the supporting device and the hole section of the thread guide hole. The guide bar structure, the warp knitting machine with the guide bar structure and the thread guide set on a guide bar all enable the existing monotonous warp knitting machine weaving to be provided with abundant pattern design, and are simple in structure.
Owner:KARL MAYER CHINA
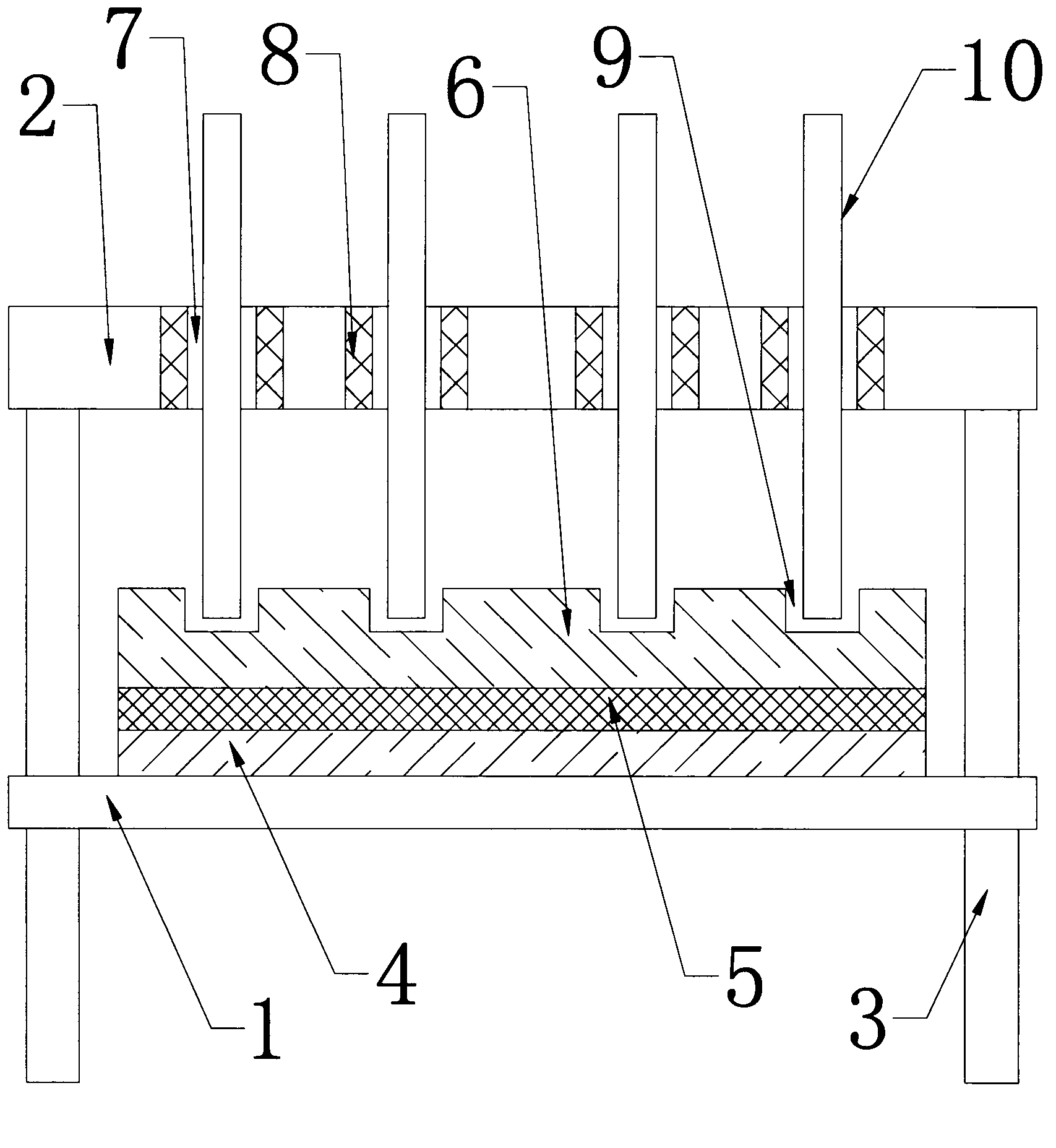
Blade storage plate
InactiveCN103224095AAvoid colliding with each otherWill not collide with each otherExternal framesWork tools storageRubber ringArchitectural engineering
The invention discloses a cutter storage plate, which comprises two base plates and two positioning plates which are horizontally arranged, wherein the base plates and the positioning plates are fixed via four vertical support rods; positioning plates are located above the base plates; the four support rods are distributed on the base plates in a shape of rectangle; first rubber layers are fixed on the top surfaces of the base plates; foam layers are fixed on the top surfaces of the first rubber layers; second rubber layers are fixed on the top surfaces of the foam layers; the positioning plates are provided with a plurality of vertical through holes, and rubber rings are fixed on the inner peripheries of the through holes; and the top surfaces of the second rubber layers are provided with concave pits corresponding to the through holes. Blades are inserted into the through holes and are stably placed on the top surfaces of the second rubber layers at intervals so as so avoid collision between every two blades.
Owner:常熟市三骏精密刃具制造厂
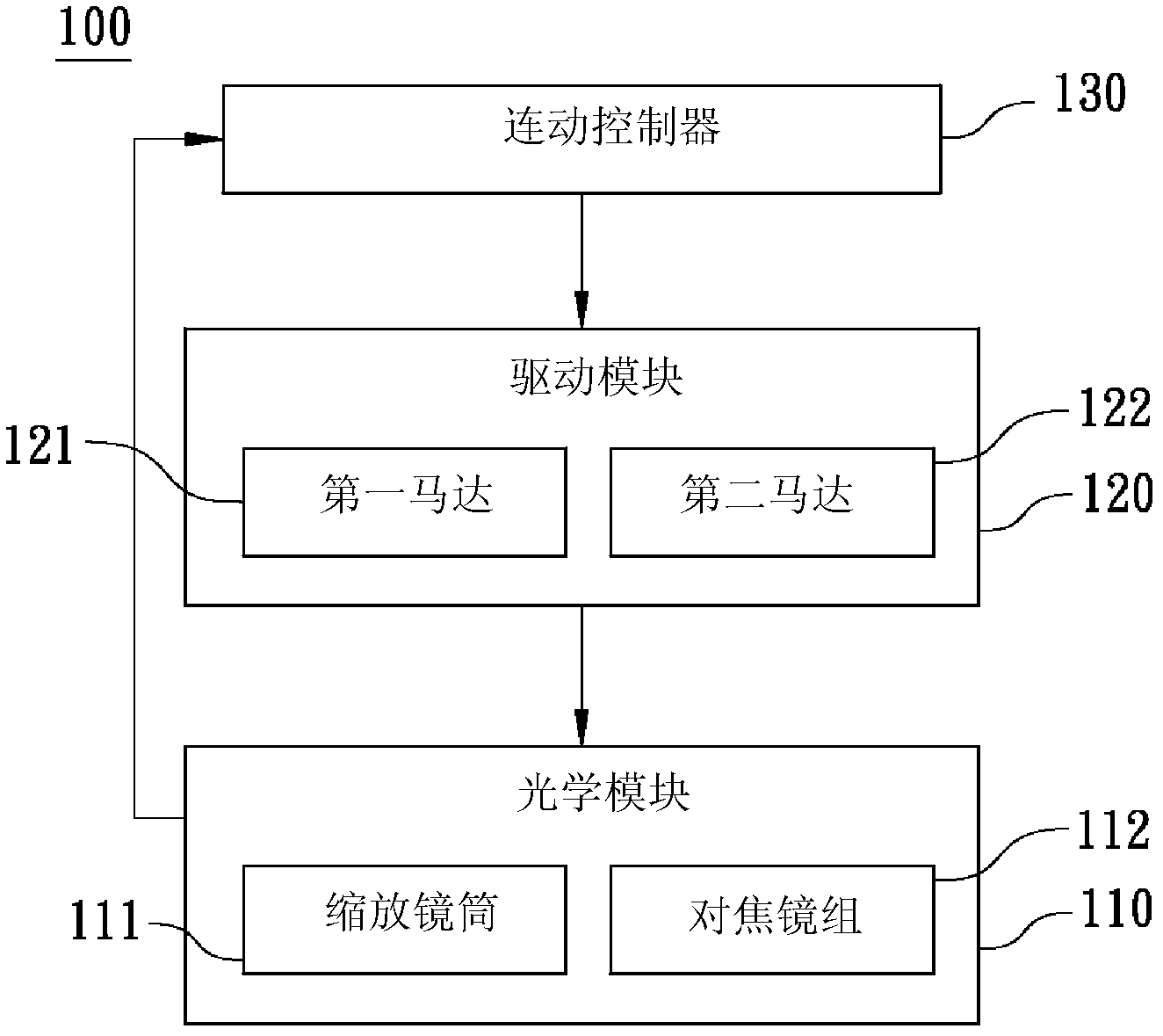
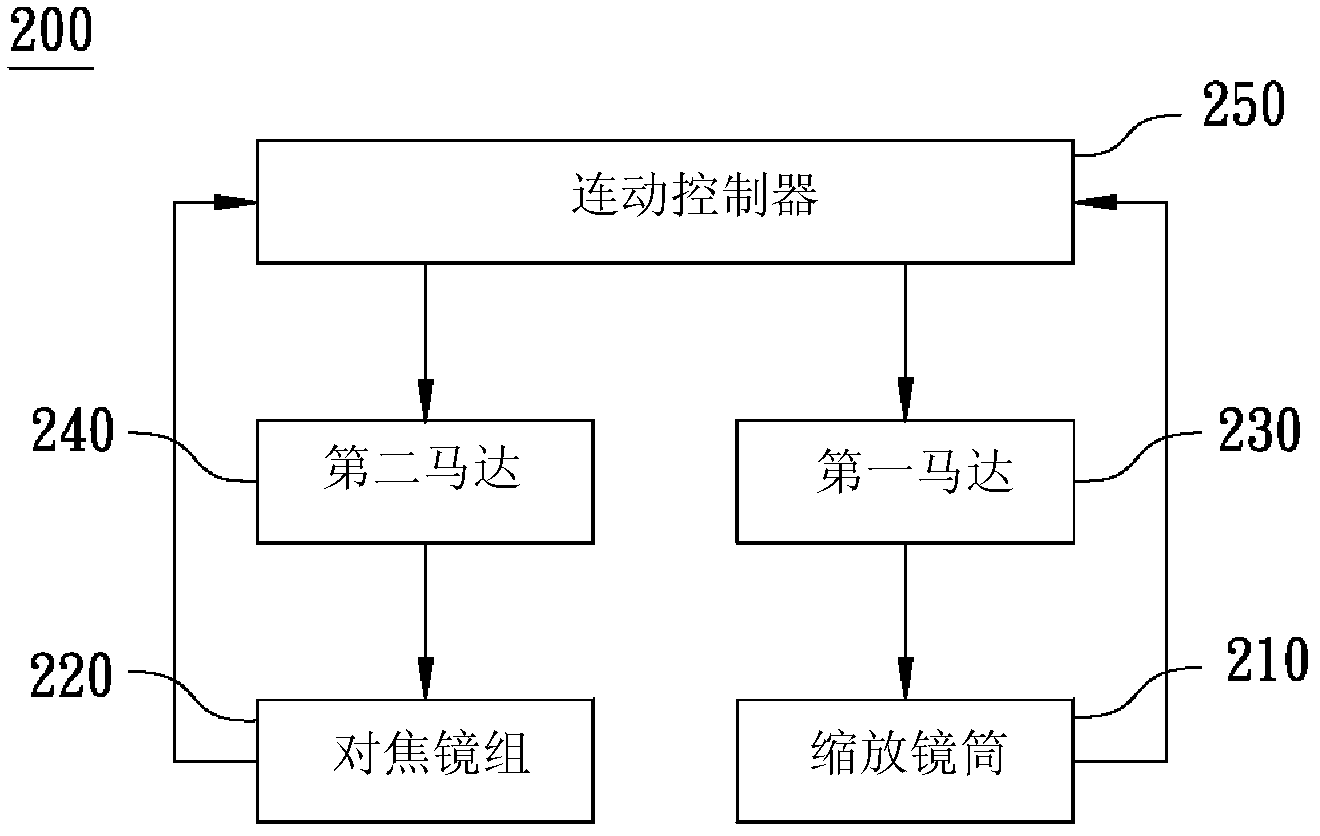
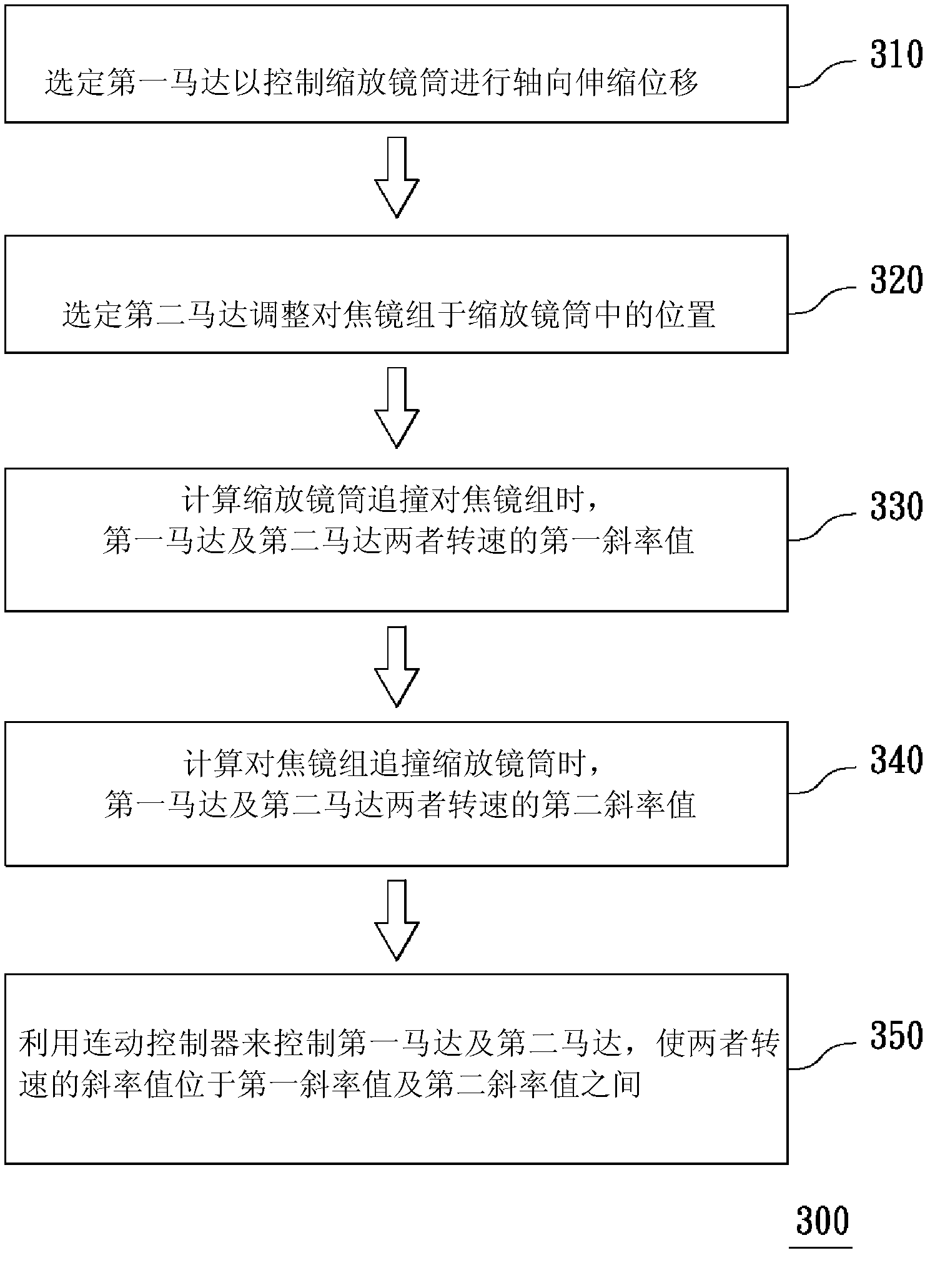
Lens continuous moving anti-collision device and method
InactiveCN102841487AOvercome the problem of collision with each otherWill not collide with each otherTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical ModuleEngineering
The invention relates to a lens continuous moving anti-collision device and a method. The lens continuous moving anti-collision device comprises an optical module, a driving module and a linkage controller, wherein the optical module comprises a telescopic lens cone and a focusing lens set arranged in the telescopic lens cone; the driving module is used for driving the optical module to displace, wherein the driving module comprises a first motor and a second motor; the first motor is used for driving the telescopic lens cone to axially telescopically displace; the second motor is used for adjusting a position of the focusing lens set in the telescopic lens cone; and the linkage controller is used for controlling linkage between the first motor and the second motor, as well as controlling a rotating speed of the first motor to reach a state of being in direct proportion to the rotating speed of the second motor, so that the telescopic lens cone and the focusing lens set cannot be collided to each other during a linkage process.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
Refrigerating bottle base in refrigerator with overturn bottle-clip device
InactiveCN1971186APlace safeEasy to placeLighting and heating apparatusCooling fluid circulationCool storageWine bottle
The invention relates to a cool storage bottle seat of refrigerator with reversible bottle-clamped machine, comprising the bottom part of bottle seat, two vertical side walls upwards from four sides of the bottom, and groove structure formed by one front wall and one back wall. The bottle-clamped machine, which can reverse up and down, is connected with the upper edge of said back wall actively. Said bottle-clamped machine is flake structure, which can be parallel with the back wall of bottle seat when it reverses down and be with certain angle with the back wall and stops at the angle position when it reverses up. Bottled goods such as drink or wine bottles can be set on the bottle seat in safety and convenience. The height and thickness of bottle can not be considered and bottles can be fixed in the bottle seat. When the refrigerator door is opened or closed bottled goods are not be turned down from the bottle seat and bottles in bottle seat are not interfered with each other.
Owner:HAIER GRP CORP +1
Building system combined truss with steel shaped like Chinese character 'zhi'
PendingCN107761956AReduce dosageLow costBuilding constructionsChinese charactersArchitectural engineering
The invention provides a building system combined a truss with steel shaped like a Chinese character 'zhi'. The building system is used for constructing a warehouse or a plant and comprises rigid frame column beams, middle columns, purlines, cornice supporting units, wall frame columns, truss type secondary beams and truss type joists. The rigid frame column beams are connected with the cornice supporting units and provided with the middle columns; the purlines are arranged between rigid frame beams and comprise cornice purlines and roof purlines; the cornice supporting units are arranged between the cornice purlines and connected with one ends of the rigid frame beams; the wall frame columns are parallelly arranged between the rigid frame columns; the truss type secondary beams are parallelly arranged between the rigid frame beams and located below the purlines; and the two ends of the truss type secondary beams are connected with the truss type joists correspondingly. According to the building system combined the truss with the steel shaped like the Chinese character 'zhi', all kinds of components with the cost performance ratio are economically combined, characteristics of the components are fully exerted, so that a plant or warehouse building within a certain specification and load range has small deflection and the low comprehensive construction cost, the steel content isgreatly reduced, and construction is convenient and fast.
Owner:SHANGHAI OPEN STEEL JOIST
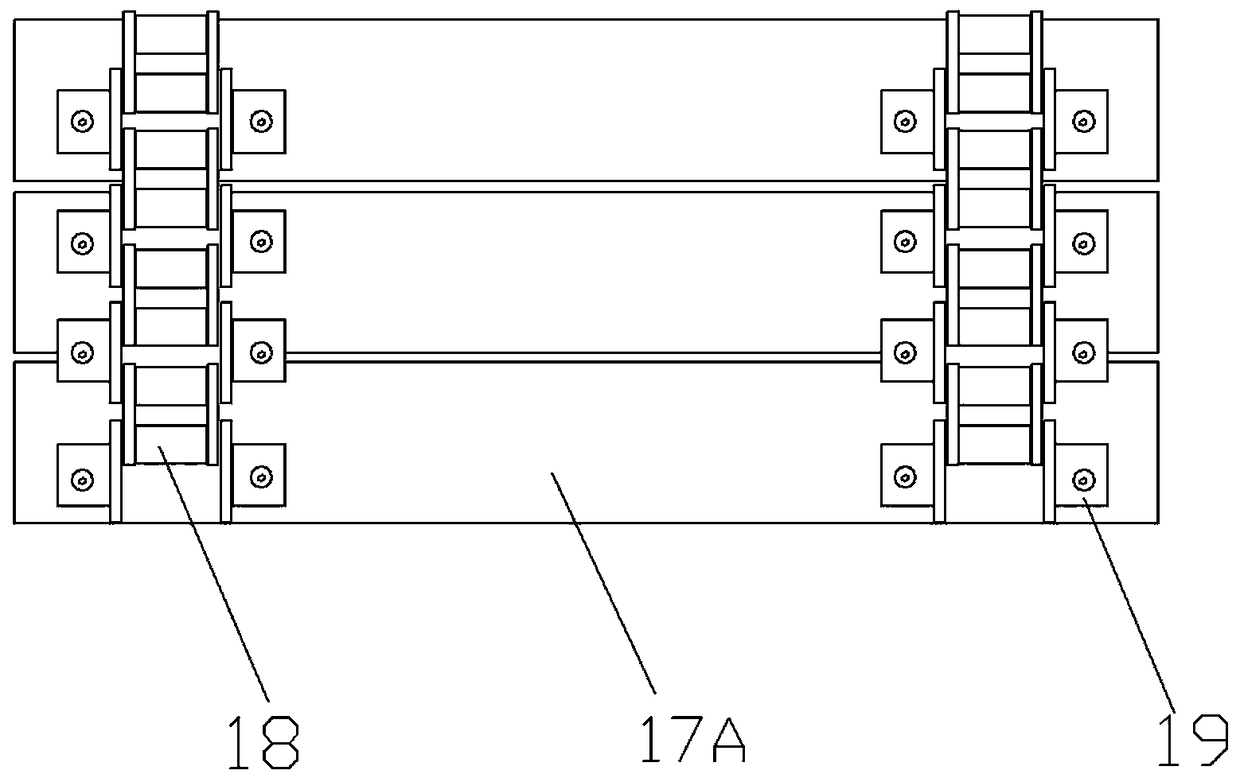
Rolling shaft conveying dolly
InactiveCN105564483AWill not collide with each otherPrevent fallingHand carts with multiple axesRear quarterEngineering
Owner:WUXI HONGYI LOGISTICS EQUIP CO LTD
Fruit and vegetable transportation fresh-keeping device
InactiveCN112938189AAvoid damageReasonable structurePackaging under vacuum/special atmosphereContainers preventing decayEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of fruit and vegetable transportation, particularly relates to a fruit and vegetable transportation fresh-keeping device. The device aims to solve the problems that in the conveying process of spherical fruits and vegetables conveyed by an existing fruit and vegetable transportation fresh-keeping device, the fruits and vegetables often extrude each other, many fruits and vegetables are damaged, and the fruits and vegetables cannot be circularly moisturized. The device comprises a transport box, air bags are fixed to the outer walls of the two sides of the transport box through bolts, a suction cup is arranged at one end of each air bag, and the outer wall of each suction cup is connected with a telescopic spring in a sleeving mode. According to the device, due to the fact that the temperature of the fruits and vegetables is lower than the temperature of fresh-keeping water during fresh keeping, part of water on the surfaces of the fruits and vegetables can be evaporated, the evaporated water can be gathered on the lower surface of a mounting plate, the part of water finally enters into a water collecting pipe through a gathering groove and a conical confluence block, and the water collecting pipe guides the part of water into a sterilization box again through a return pipe for sterilization and standby application, so that the fruits and vegetables can be humidified and kept fresh in a circulating manner.
Owner:杭州玄策贸易有限公司
Low-noise food processor
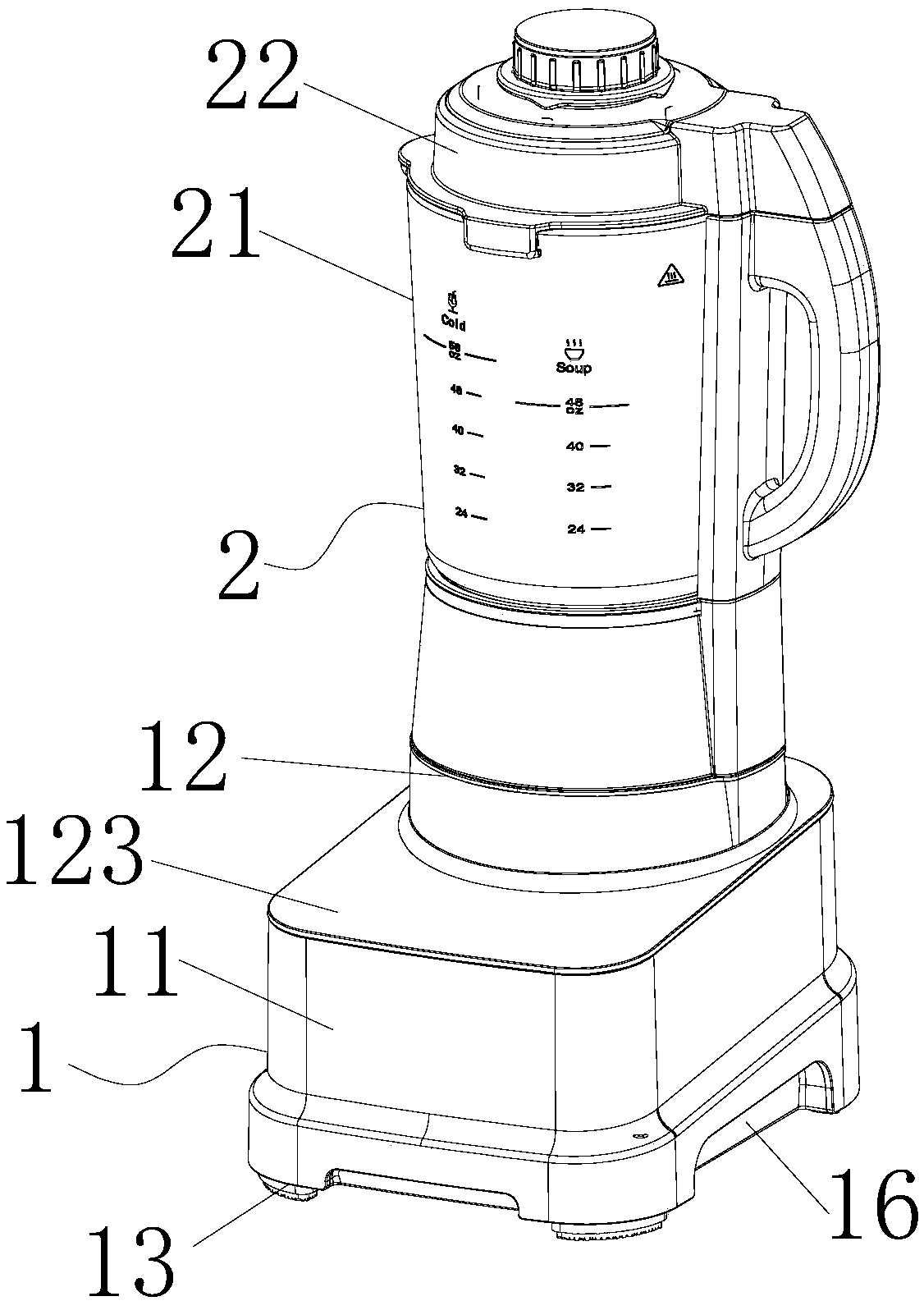
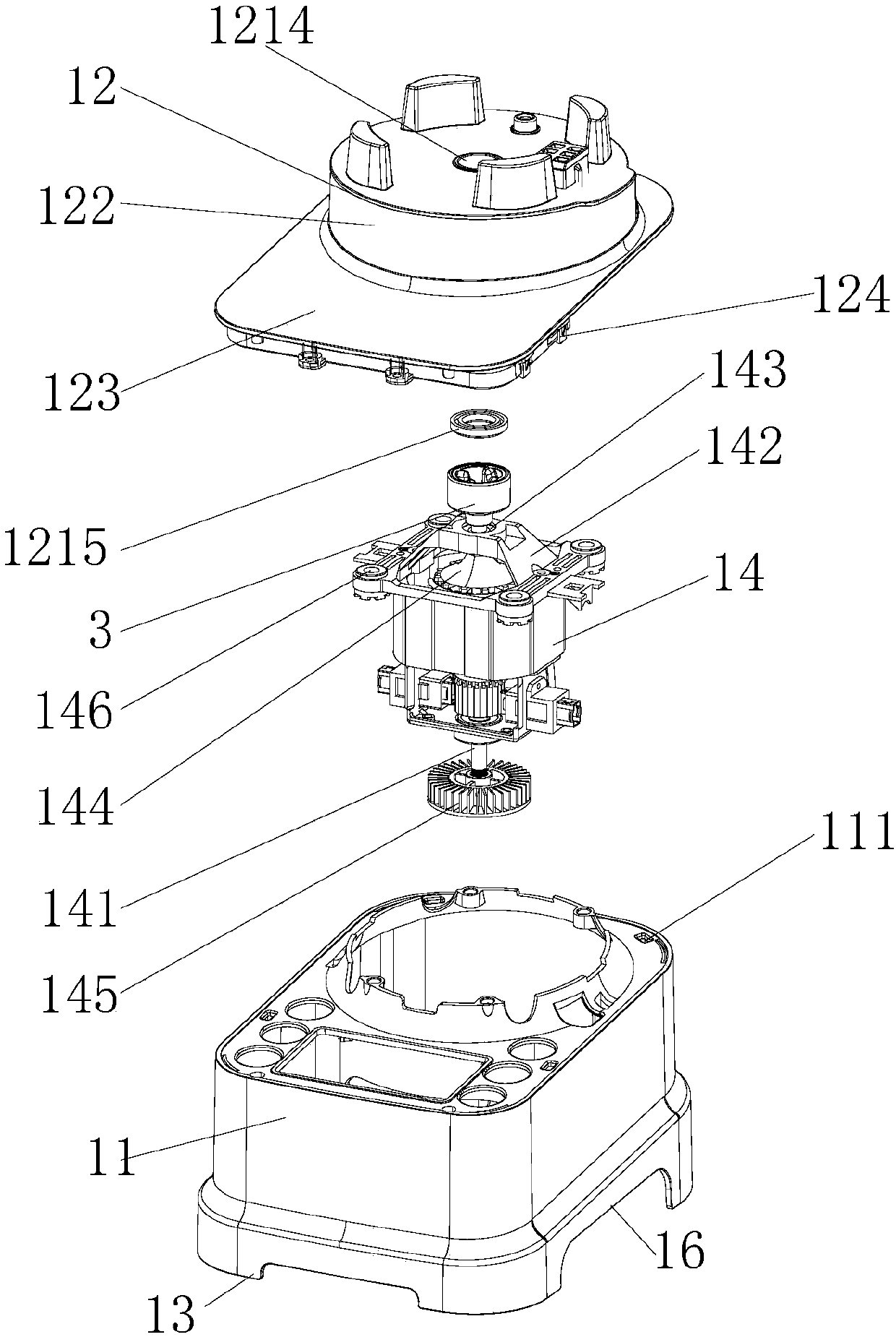
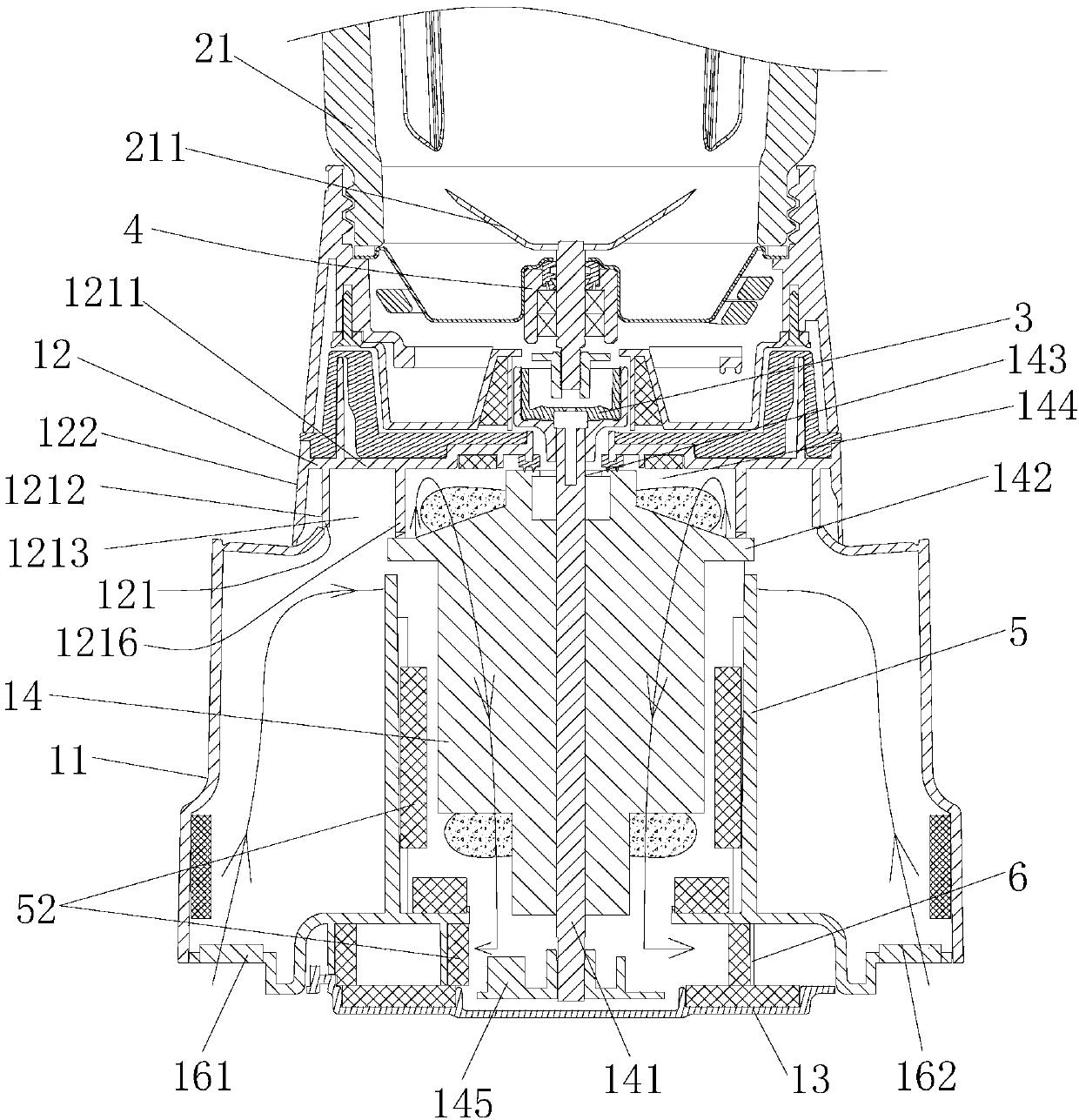
ActiveCN110876571AEffective coolingPlay a guiding roleKitchen equipmentElectric machineryControl theory
The invention discloses a low-noise food processor. The low-noise food processor comprises a machine base with a motor, a stirring cup connected with the machine base and a pulverizing cutter arrangedin the stirring cup. A fan is arranged at the lower end of a motor shaft of the motor; the machine base is provided with an air inlet and an air outlet. The air outlet is positioned on one side belowthe machine base; the machine base comprises a machine shell, a top cover and a bottom cover. A motor cylinder used for containing a motor is arranged in the machine shell. A motor support is arranged at the upper end of the motor, the motor support is mounted at the top of the motor barrel; a shaft hole through which the upper end of the motor shaft penetrates is formed in the center of the motor support; the motor support is provided with a communication port communicated with the interior of the machine shell. The top cover is provided with a wind scooper; the wind scooper stretches into the machine shell and covers the upper portion of the motor support. When the motor works, the fan is driven to rotate, so that external air enters the machine shell from the air inlet and flows into the motor barrel through the communicating opening after being guided by the a wind scooper, and the wind scooper can play a role in guiding airflow and can prevent noise generated in the working process of the motor from being exhausted outwards.
Owner:JOYOUNG CO LTD
Rotating disk type automobile stepped shaft storage device
The invention discloses a rotating disk type automobile stepped shaft storage device which is characterized in that automobile stepped shafts can be vertically and orderly placed, the size universality of the stored automobile stepped shafts is good, and the automobile stepped shafts are easily stored and taken out. The device comprises a base and a rotating disk rotatably arranged on the base, anannular chain and a plurality of movable chain wheels engaged with the annular chain are arranged on the rotating disk, the annular chain and the rotating disk are coaxially arranged, the movable chain wheels are positioned on the inner side of the annular chain, the movable chain wheels are uniformly distributed along a circumferential direction of the rotating disk, a fixed chain wheel is arranged on the base and positioned at the center of the rotating disk, the fixed chain wheel is connected with one movable chain wheel through a chain, a clamping plate is horizontally arranged on the movable chain wheels and comprises two opposite clamping portions, and the clamping portions are horizontally and slidably arranged on the movable chain wheels. The device can be used for vertically placing the automobile stepped shaft with different sizes, the automobile stepped shafts are conveniently stored and taken out, oil can be automatically fed through an oil tank, and storage is facilitated.
Owner:HUZHOU ANRUINENG HYDRAULICPNEUMATIC TECH CO LTD
Battery module
PendingCN114824620AIncrease battery capacityImprove securitySecondary cellsCell component detailsBusbarEngineering
The invention discloses a battery module. The battery module comprises a busbar, a battery cell, a shell, an end bracket and a busbar protection shell, the battery cell is provided with tabs extending towards the two ends, a containing cavity is formed in the shell, a plurality of heat conduction supporting pieces are arranged at the bottom of the shell, the bottoms of the heat conduction supporting pieces are connected with the bottom wall of the shell, the tops of the heat conduction supporting pieces abut against the battery cell, the end supports are connected to the two sides of the containing cavity, and the end supports and the heat conduction supporting pieces are arranged at intervals; a plurality of guide holes are formed in the end support, the busbars are connected to one side of the end support, the tabs extend out of the guide holes and are connected with the busbars, each busbar protection shell is connected to one side face of the end support, and the busbars are arranged between the end support and the busbar protection shells. One of the busbar protection shell and the end support is provided with a first clamping pin, the other one is provided with clamping holes, and the clamping holes are connected with the first clamping pin in a clamping mode and are in multiple pairs. The battery module provided by the embodiment of the invention is stable in structure, quick and convenient to assemble and disassemble and good in insulativity.
Owner:昆山聚创新能源科技有限公司
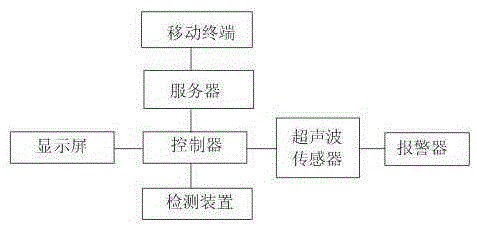
Parking lot management system and method thereof with mobile terminal navigating driving route
InactiveCN106530801AImprove parking efficiencyEnsure parking safetyIndication of parksing free spacesAnti-collision systemsElectricityParking space
The invention relates to a parking lot management system and a method thereof with a mobile terminal navigating a driving route. The system comprises a controller, and a detection device and a server electrically connected with the controller respectively, wherein the detection device is arranged in a carport. The system also comprises a vehicle pier fixed at the tail part of the carport, an ultrasonic sensor arranged on the vehicle pier and an alarm electrically connected with the ultrasonic sensor, wherein the ultrasonic sensor and the controller are in signal connection; and the server stores micro map information drawn according to building conditions inside the parking lot. The system also comprises a mobile terminal connected with the server through a network. Due to the setting of the controller, the mobile terminal, the detection device and the server, a vehicle owner can be guided to quickly find an empty carport, and the parking efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:付建军
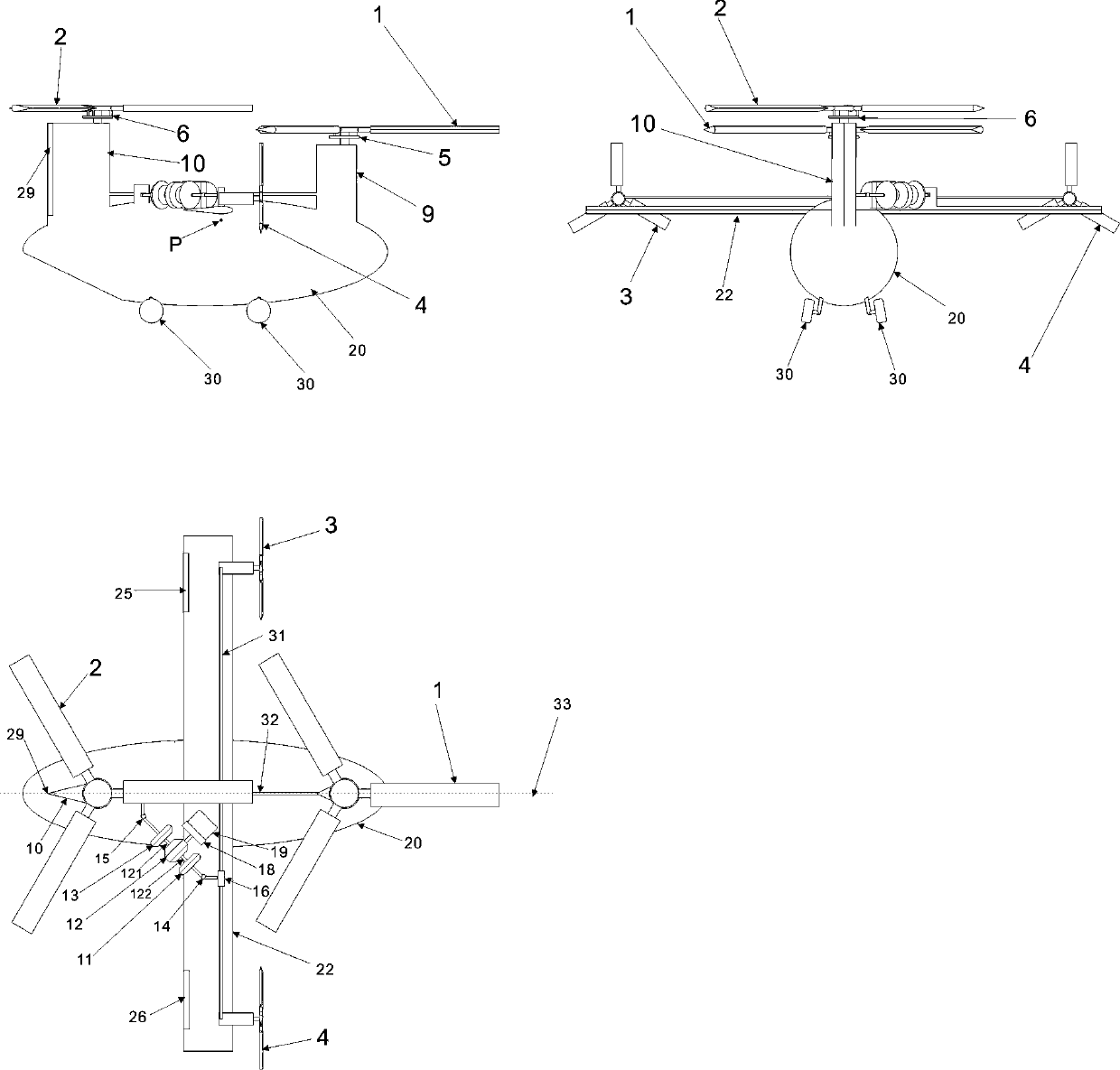
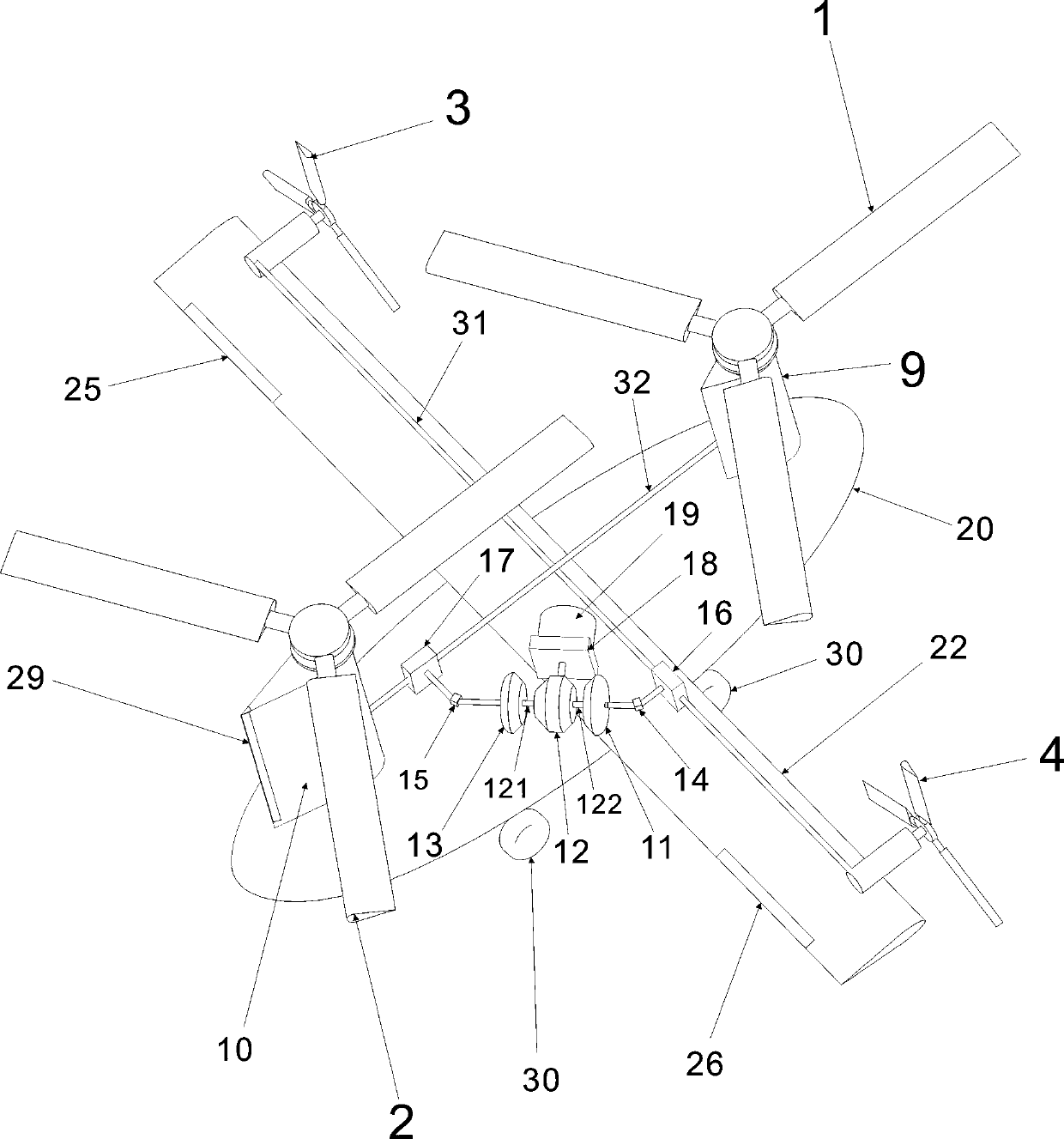
Braking differential type rotor wing propeller fixed wing helicopter
InactiveCN110979649AWill not collide with each otherReduce the required heightAircraft controlRotocraftPropellerControl theory
The invention discloses a braking differential type rotor wing propeller fixed wing helicopter. Two rotor wings are arranged on wing-shaped small towers at the head and the tail of a fuselage. The paddles of the rotor wings are connected with a rotor wing shaft through a paddle shell which is provided with a flapping hinge, a shimmy hinge and a variable-pitch hinge. A total pitch controller and aperiodic variable pitch controller are arranged to control the paddle pitch of the rotor wings. An upper single-wing fixed wing with high aspect ratio is arranged in the middle of the fuselage, and variable-pitch propellers are arranged on the left and right of the fixed wing. An engine is arranged to drive a differential mechanism through a gearbox and a clutch. A first output shaft of the differential mechanism drives the two rotors through an overrunning clutch, a universal shaft and a rotor synchronous reverser. A second output shaft of the differential mechanism drives the left and rightvariable-pitch propellers through an overrunning clutch, a universal shaft and a propeller synchronous reverser. A wheel type undercarriage is arranged, and different output shafts of the differentialmechanism are braked through a brake. The power of the engine is distributed to the rotor wings or variable-pitch propellers, and various flight modes of helicopters, fixed wings and autorotation rotor wings are freely switched. The helicopter has the advantages of being high in speed, low in energy consumption and suitable for taking-off and landing occasions requiring no airports.
Owner:江富余
Plastic foam disc hanger
InactiveCN103303570AAvoid lostEasy to compressContainers for annular articlesExternal framesEngineeringPlastic foam
The invention discloses a plastic foam hanger which comprises a hanger and wheels, wherein the wheels are mounted at the bottom of the hanger. On the basis of the structure, telescopic rods, clamp blocks and sun shading cloth are further added. Compared with a traditional plastic foam hanger, a plurality of the telescopic rods are arranged in the hanger, plastic foam discs are hung on the telescopic rods through middle through holes in the plastic foam discs during storage and transportation of the plastic foam discs, the lengths of the telescopic rods are adjusted according to the quantity of the plastic foam discs, and simultaneously, the clamp blocks are added to tightly press the plastic foam discs, so that the plastic foam discs can be prevented from mutual collision; one piece of sun shading cloth is arranged at the periphery of the upper end of the hanger respectively, so that the plastic foam discs can be prevented from being damaged due to overhigh temperatures when loaded outside, and unnecessary loss is avoided.
Owner:江苏恒旭玻璃制品有限公司
Vibration coating method for molybdenum disulfide
InactiveCN105149179ALow costIncrease productivityLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsMolybdenum disulfideMetal
The invention discloses a vibration coating method for molybdenum disulfide. The method comprises the following steps of pelletizing, encasing, vibrating and separating. The vibration coating method for the molybdenum disulfide is low in cost. Compared with the manual coating technology, the production efficiency is high, the labor cost is reduced, and the problem of environment protection is solved. Components to be coated are placed in a vibration box, the components cannot collide with one another during vibration, and the vibration coating method is suitable for coating of small metal components. After the components are coated, the surfaces of the components are smooth, the components are free of drifting, the molybdenum disulfide seeps into surface grain of the components, and the size is not changed.
Owner:WUXI LEHUA AUTOMATION TECH
Neck massager part conveying device
InactiveCN109229759AWill not collide with each otherEasy subsequent assemblyLinings/internal coatingsPlastic containersMechanical engineeringEngineering
The invention relates to a neck massager part conveying device. The device comprises a box body, and a conveying rail, the upper end of the box body is opened, a lining body is arranged in the box body, and a containing cavity is formed by the lining body; vertical sliding grooves are formed in the two opposite inner walls of the lining body respectively, a plurality of sliding grooves are formedin each inner wall at intervals, and the sliding grooves in the two inner walls are in one-to-one correspondence; partition plates are detachably inserted into the opposite sliding grooves in the twoinner walls, and guide inclined planes are arranged at the bottom ends of the partition plates; each partition plate comprises two outer layers and an elastic layer in the middle, through holes running through the centers of the partition plates are formed in the centers of the partition plate, and the conveying rail is used for conveying the box body. The lining body is divided into a plurality of placement cavities through the partition plates, parts of a neck massager can be placed at a time, subsequent assembly is facilitated, and the parts cannot collide with one another in the vehicle transportation process.
Owner:苏州康恩健电子科技有限公司
Paintbrush fixer
ActiveCN110053417AEasy accessEasy to replaceOther artistic work equipmentsBiochemical engineeringPaintbrush
The invention discloses a paintbrush fixer, and relates to the field of paintbrushes. The paintbrush fixer comprises a flat plate, a fixed part and a threaded rod, wherein the flat plate is provided with an inner groove, the fixed part is arranged in the inner groove, the fixed part comprises side clamping blocks positioned on the two sides of the inner groove and a plurality of middle clamping blocks positioned between the side clamping blocks, the middle clamping blocks and the side clamping blocks can move in the inner groove movably, one end of the threaded rod extends into the inner groove, when the paintbrush is placed between the middle clamping blocks and / or between the middle clamping blocks and the side clamping blocks, the middle clamping blocks and the side clamping blocks areclose to each other through the threaded rod, so that the paintbrush is fixed, during use, the fixed part is loosened through the threaded rod, during use, the paintbrush can be conveniently taken orreplaced on the flat plate, the corresponding paintbrush is found, the creation time is saved, after drawing is completed, the fixed part is fixed, a gap is reserved between the paintbrush fixed in the flat plate, so that the paintbrush cannot collide with each other under the action of an external force, the cross contamination of the paintbrush is avoided, and the color of the paintbrush is changed.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Transporting equipment for multiple lamp poles of solar streetlamp
The invention discloses transporting equipment for a plurality of lamp poles of a solar streetlamp. The transporting equipment comprises a bottom plate, the upper surface of the bottom plate is fixedly connected with three lower clamping plates, the upper surface of the bottom plate is fixedly connected with two sliding rods, the outer surfaces of the sliding rods are connected with second springsin a sleeved mode, and the top ends and the bottom ends of the second springs are fixedly connected with the lower surfaces of sliding sleeves and the upper surface of the bottom plate correspondingly. The transporting equipment for the multiple lamp poles of the solar streetlamp is provided with a motor, a rope, a rope disc, a toothed rod, a telescopic device, a bearing, a threaded column, a supporting plate, upper clamping plates and the sliding rods, the three lamp poles are placed on the three lower clamping plates correspondingly, then an electric push rod is controlled to retract to drive a fixed pulley to move downward through a connecting rod, thus each lamp pole can be well fixed when the multiple lamp poles are transported by workers, the lamp poles do not shake and do not collide mutually during transporting, the lamp poles are not scratched and damaged, and thus the loss of merchants is avoided.
Owner:孙益锋
Production line for LED lamp processing
InactiveCN107477531AWill not collide with each otherReduce frictionLight fasteningsSemiconductor devices for light sourcesProduction linePunching
The invention discloses a production line for LED lamp processing. The production line comprises a paste coating mechanism, a lamp chip assembly mechanism, a drying mechanism, and a conveying rail arranged between the paste coating mechanism and the lamp chip assembly mechanism; the lamp chip assembly mechanism comprises a mobile worktable, and a lamp chip punching column matched with the mobile worktable; the mobile worktable comprises a baseplate capable of acting in all directions, a mobile rail arranged on the baseplate in a up-down acting manner, a first driving piece for driving the baseplate to move front and back, a second driving piece for driving the baseplate to move left and right, and a third driving piece for driving the mobile rail to act up and down; a first stop device is arranged at the tail part of the conveying rail; and a second stop device is arranged at the tail part of the mobile rail. The production line realizes automatic assembly of lamp chips through the lamp chip punching column to greatly improve the working efficiency, and can realize synchronous implementation of feeding and discharging of the mobile rail without stop in middle to achieve higher efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEIKE ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE
Multi-piece continuous stone cutter
InactiveCN108247857AAdvanced technologyReasonable workmanshipWorking accessoriesStone-like material working toolsSTONE CUTTEREngineering
The invention discloses a multi-piece continuous stone cutter which comprises a bracket, a conveyor belt arranged on the bracket, a gear motor fixedly arranged at one side of the conveyor belt, a sawweb set located above the conveyor belt, a saw web set motor fixedly arranged above the saw web set, a lifting device for controlling the saw web set to lift and a distribution box fixedly arranged atthe right side of the saw web set, wherein the conveyor belt is in transmission connection with the gear motor, and the saw web set is in transmission connection with the saw web set motor. Accordingto the invention, stone can be cut into multiple pieces of stone plates at one time, the saw web set is fixed in the cutting process, continuous cutting is realized by the constant-speed horizontal movement of the stone, and the cutting efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:段双庆
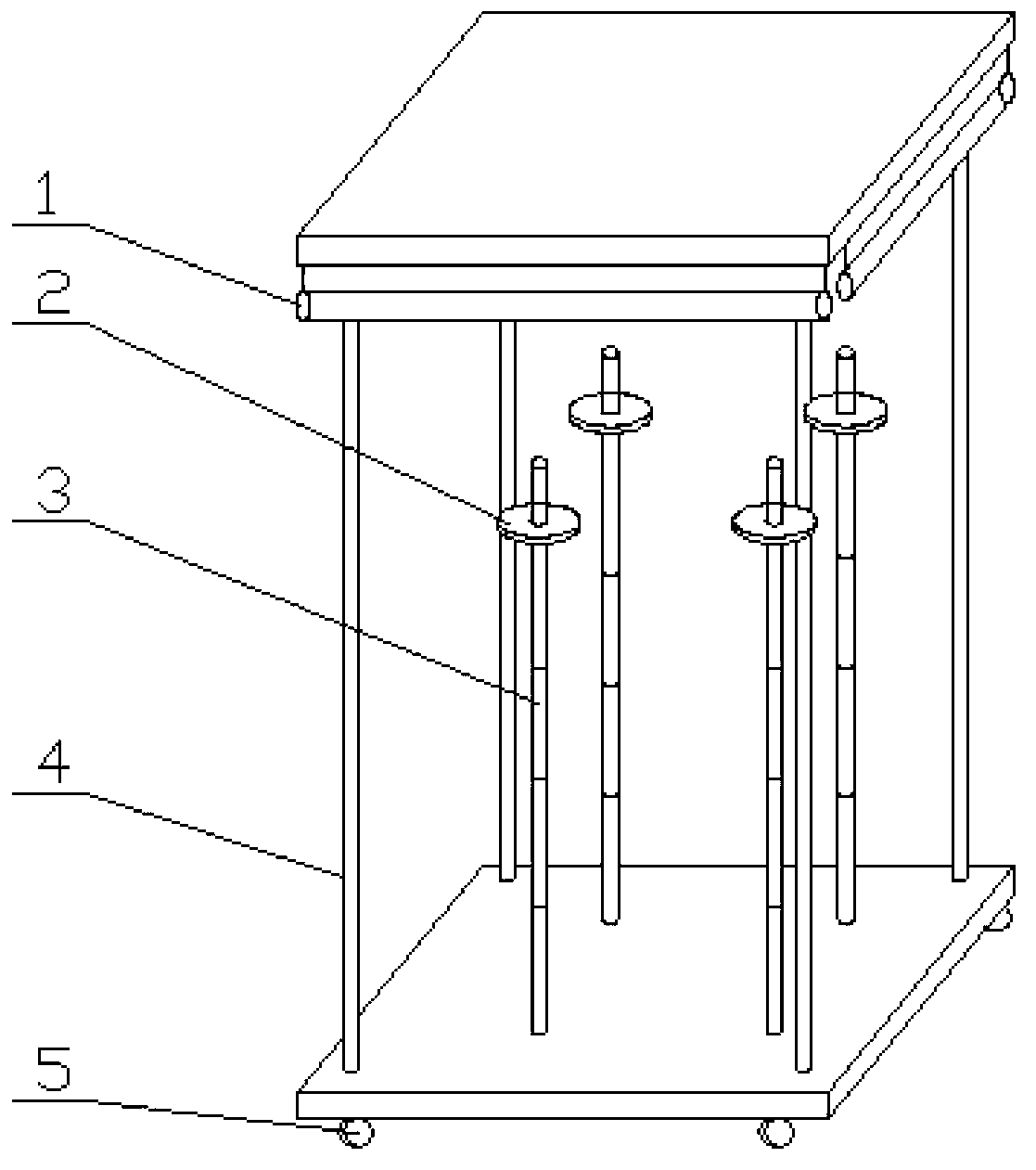
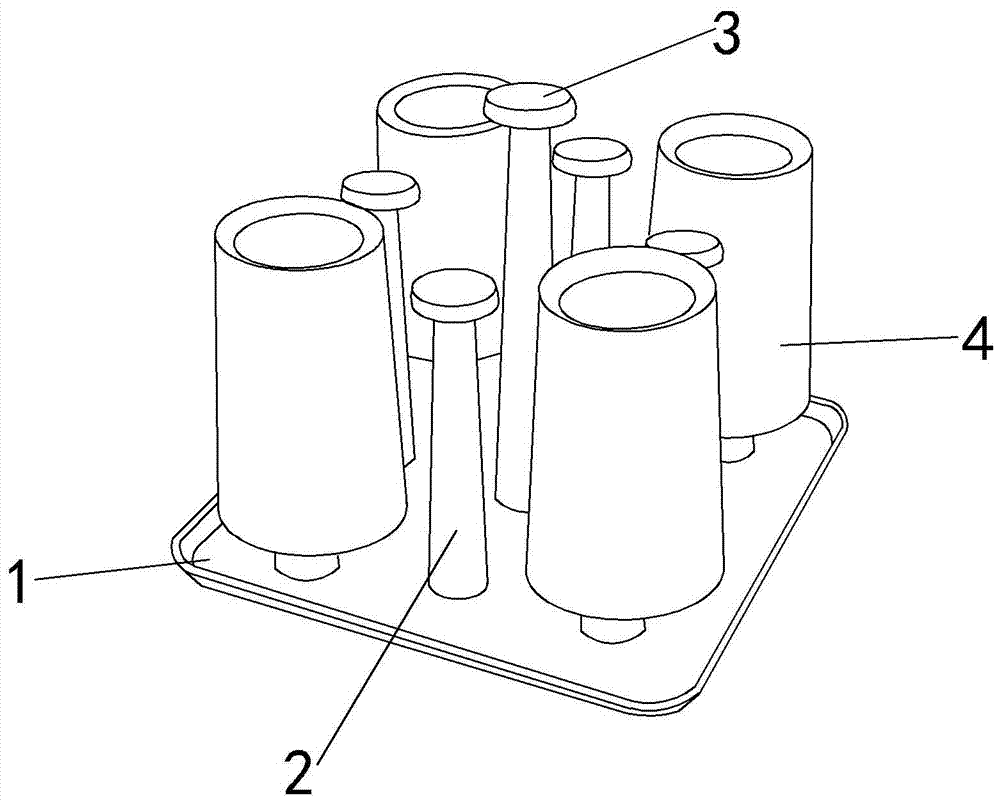
Cup storage rack
Owner:XIANGYANG NO 42 MIDDLE SCHOOL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com