Patents
Literature
43 results about "Arterial valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
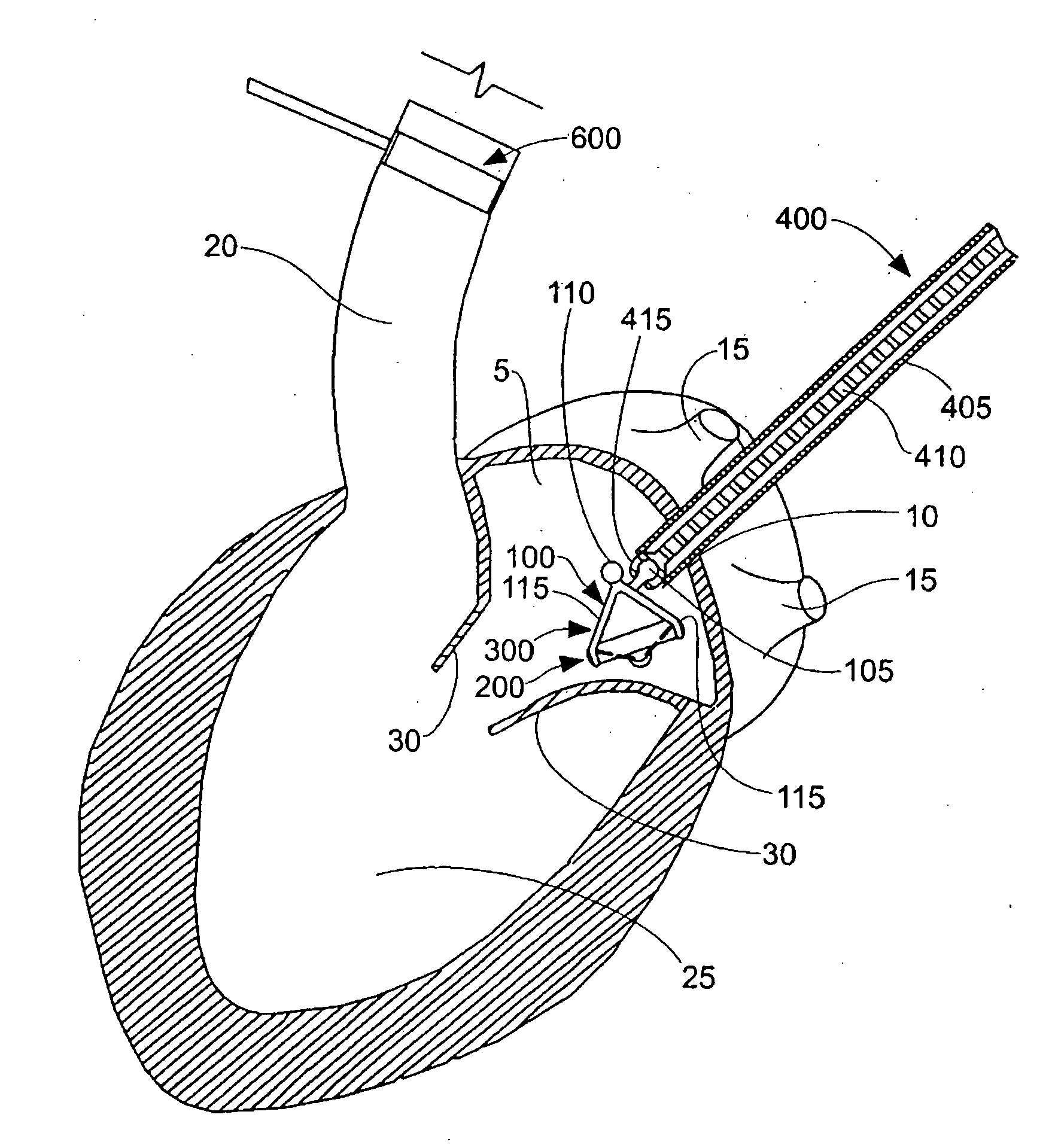
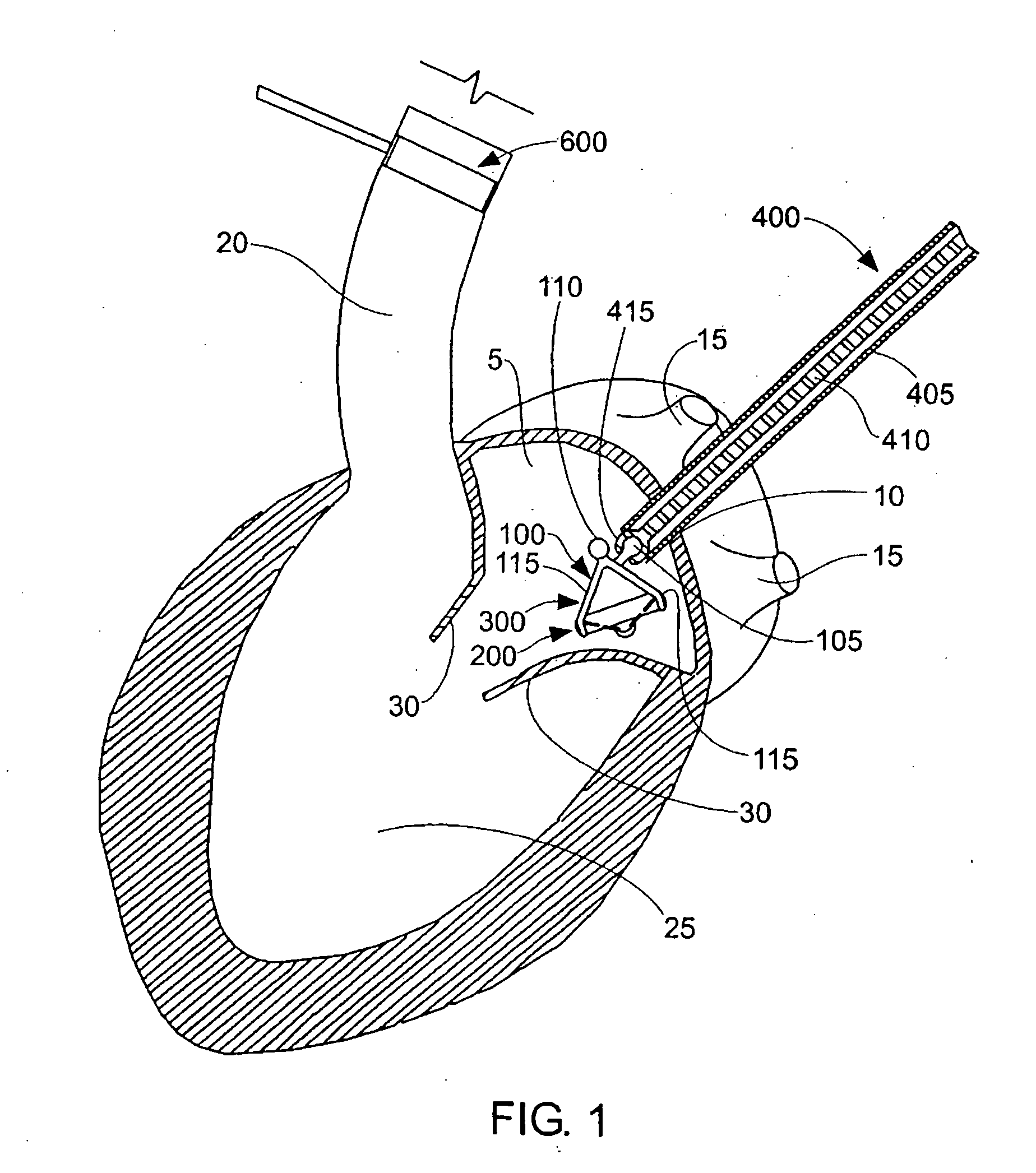
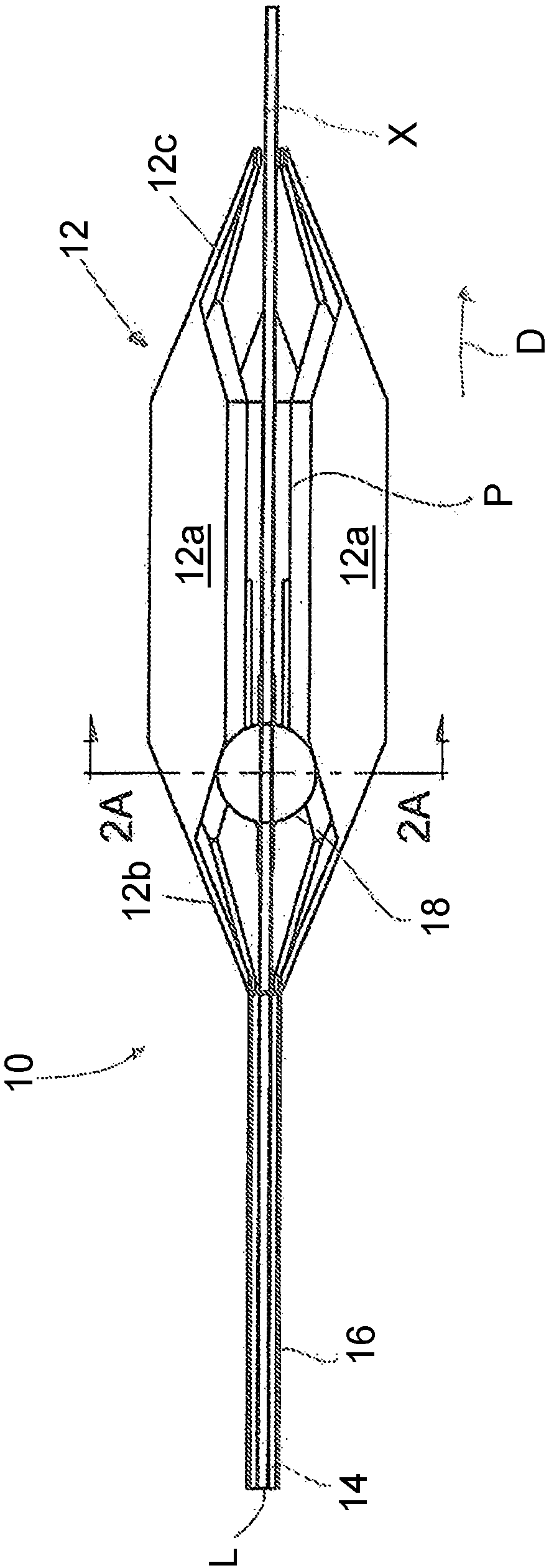
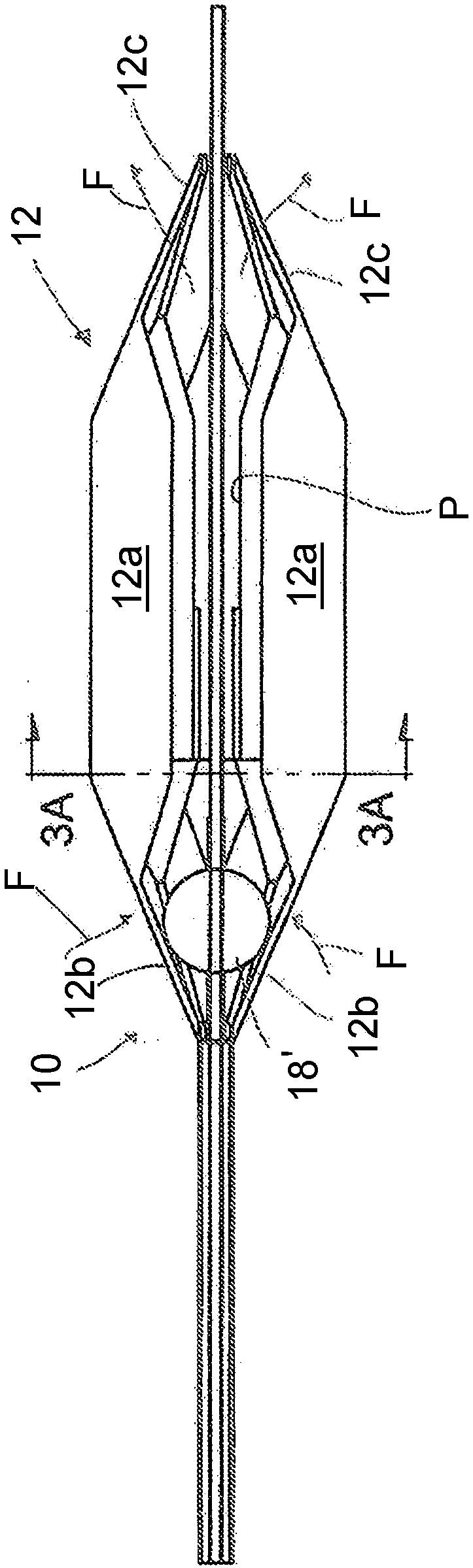
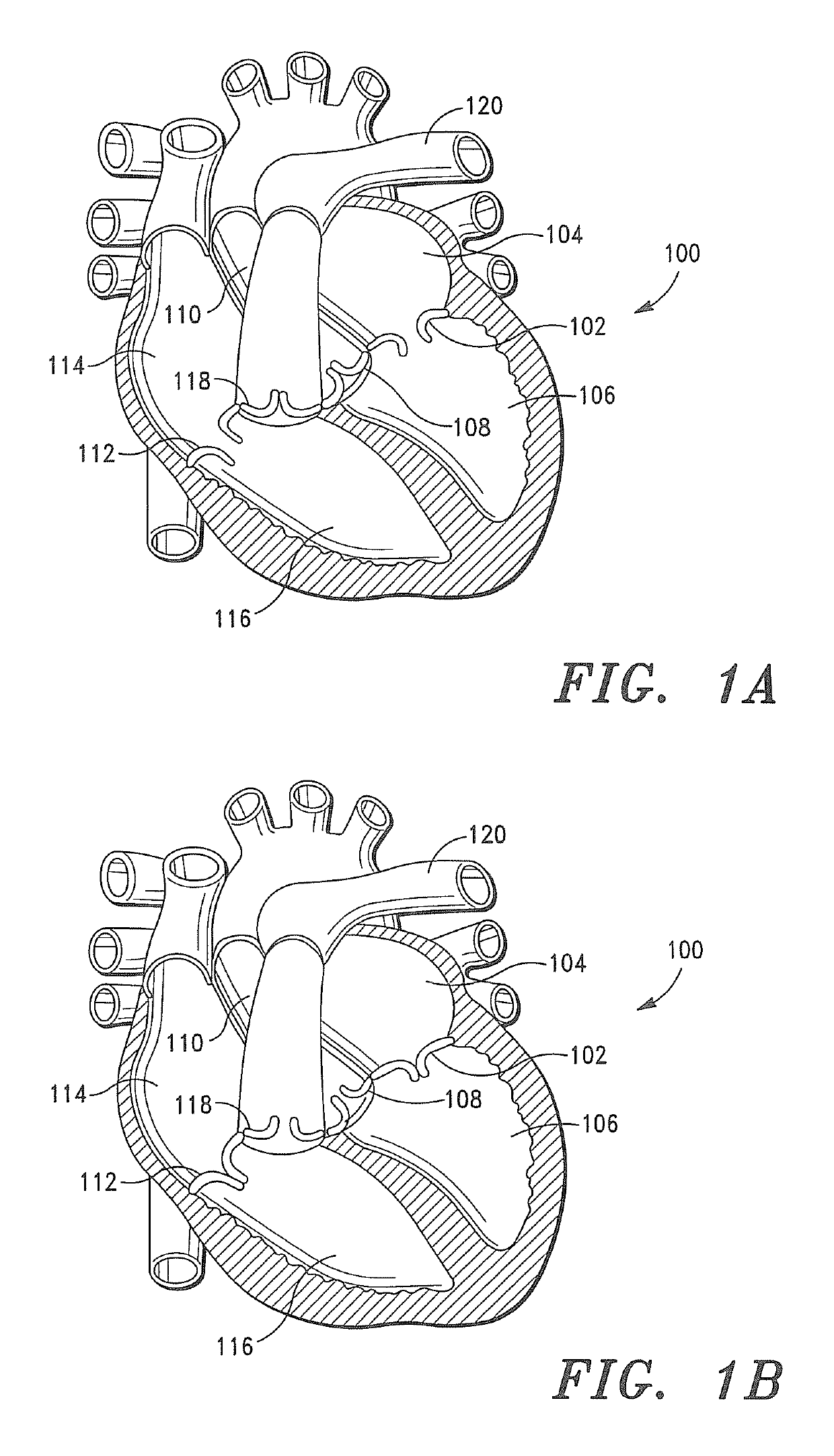
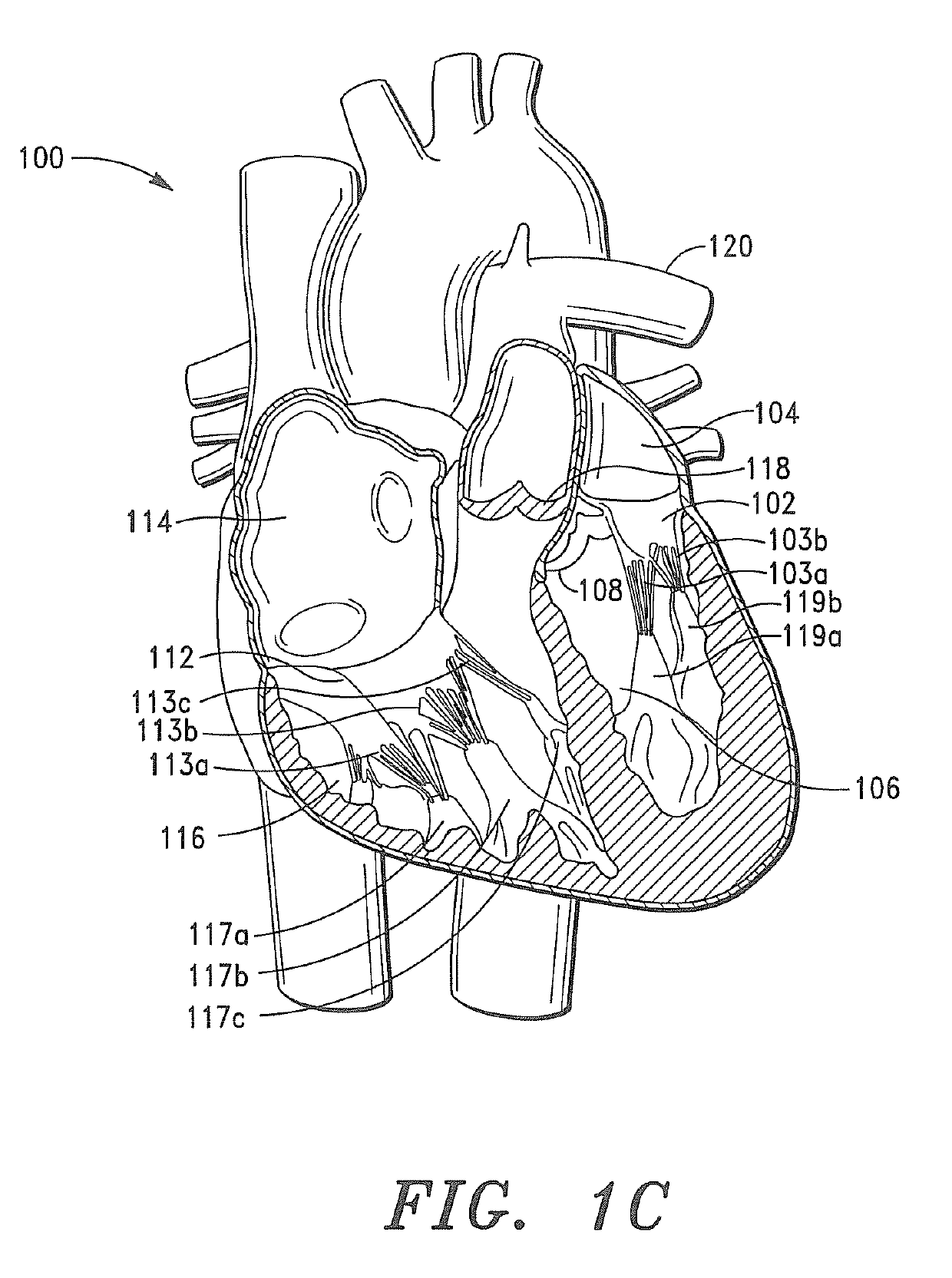
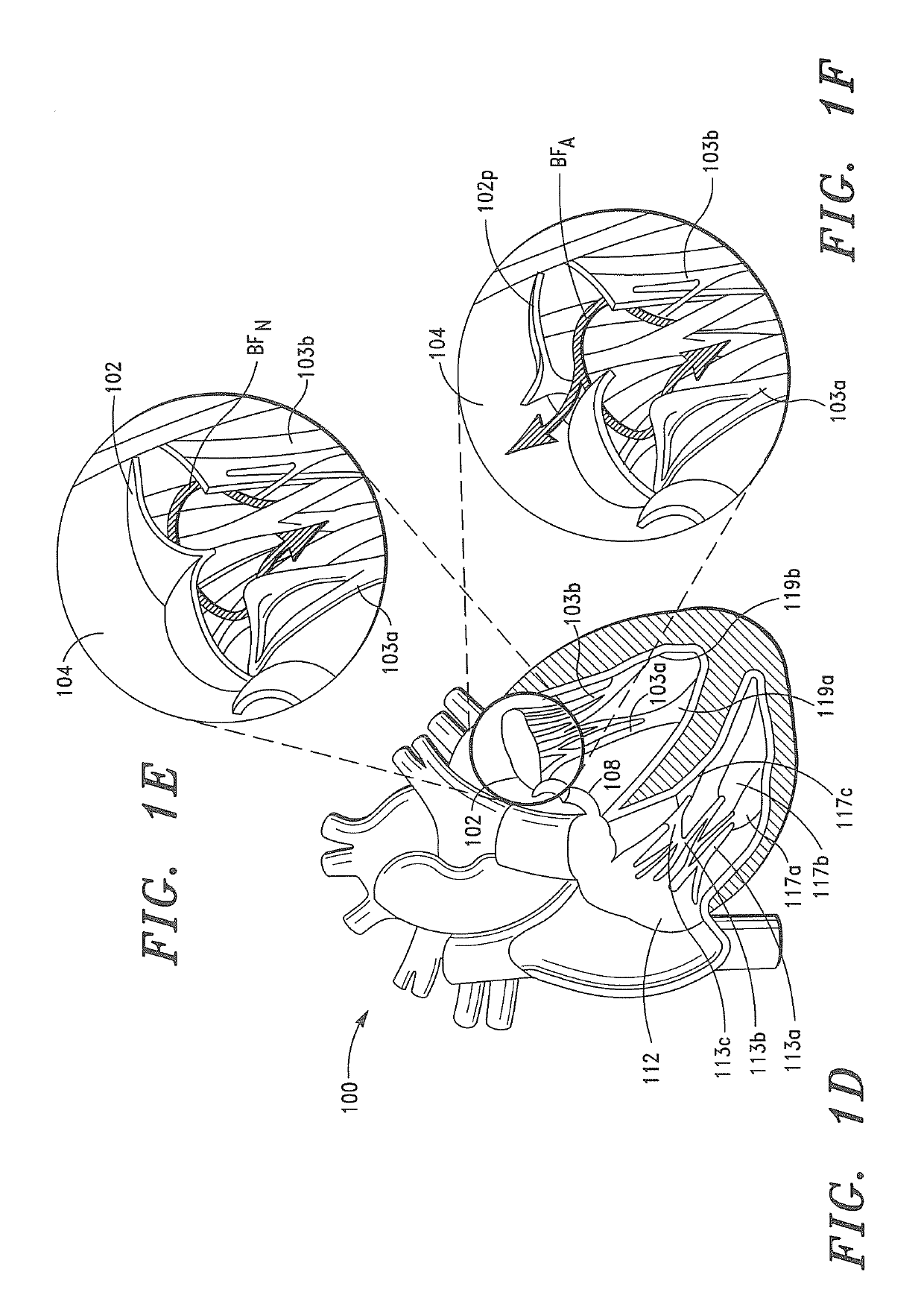
Methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve
The present invention relates to an apparatus for replacing a native aortic valve, the apparatus includes an expandable anchor adapted to be endovascularly delivered and secured at a site within the native aortic valve. The expandable anchor has a delivery length in a delivery configuration substantially greater than a deployed length in a deployed configuration. The apparatus may also include and a replacement valve configured to be secured within the anchor.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Prosthetic heart valves
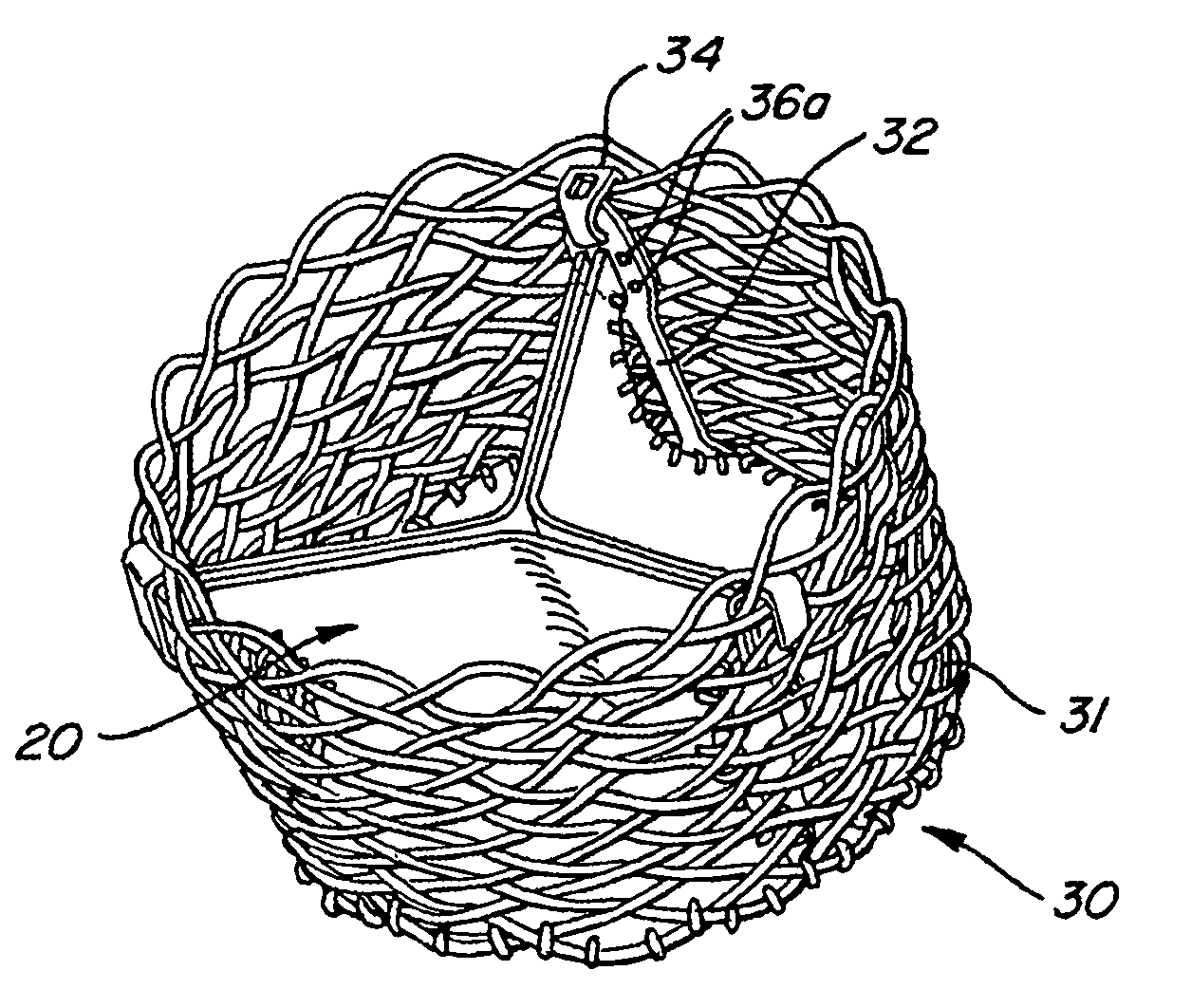
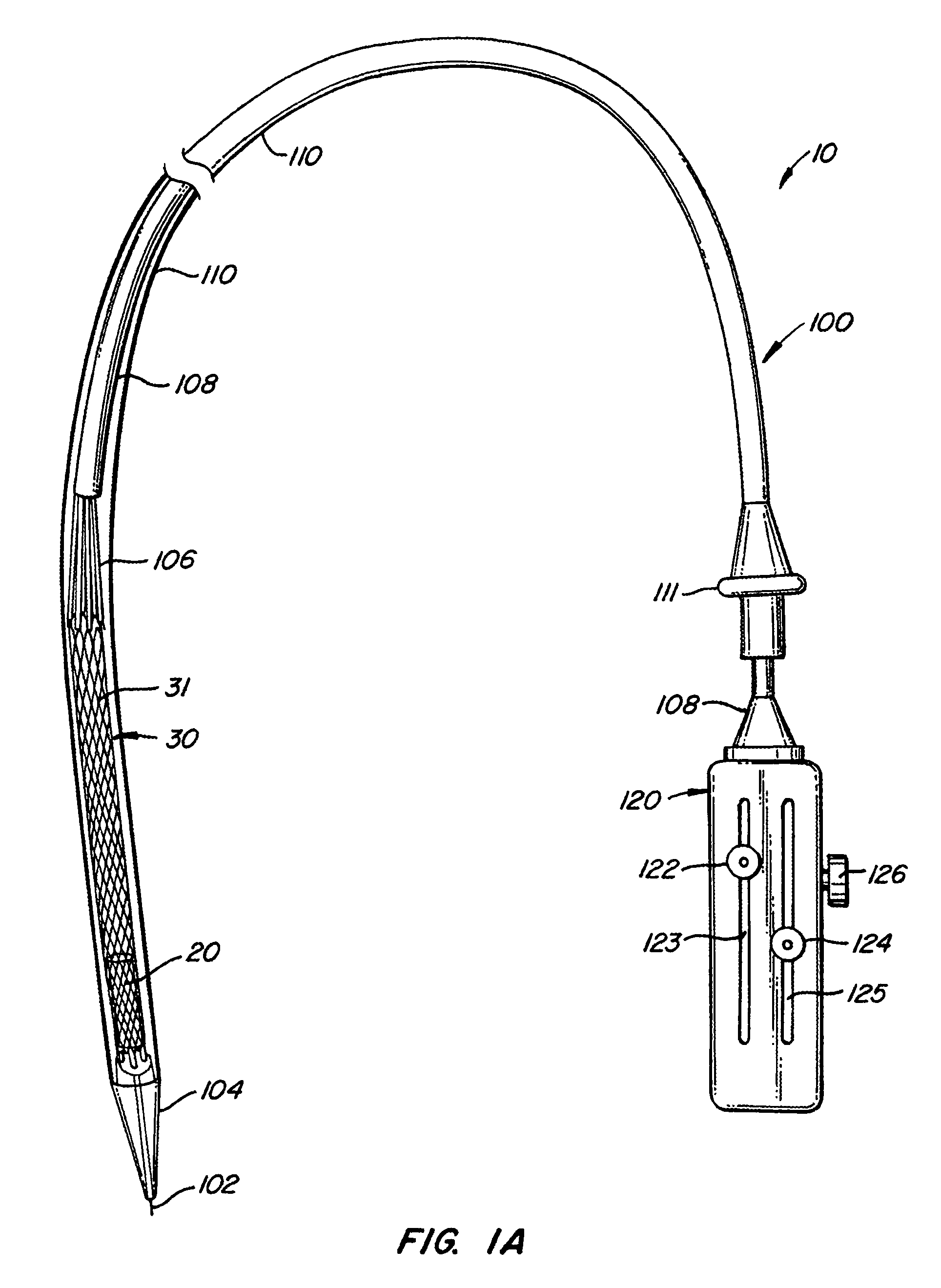
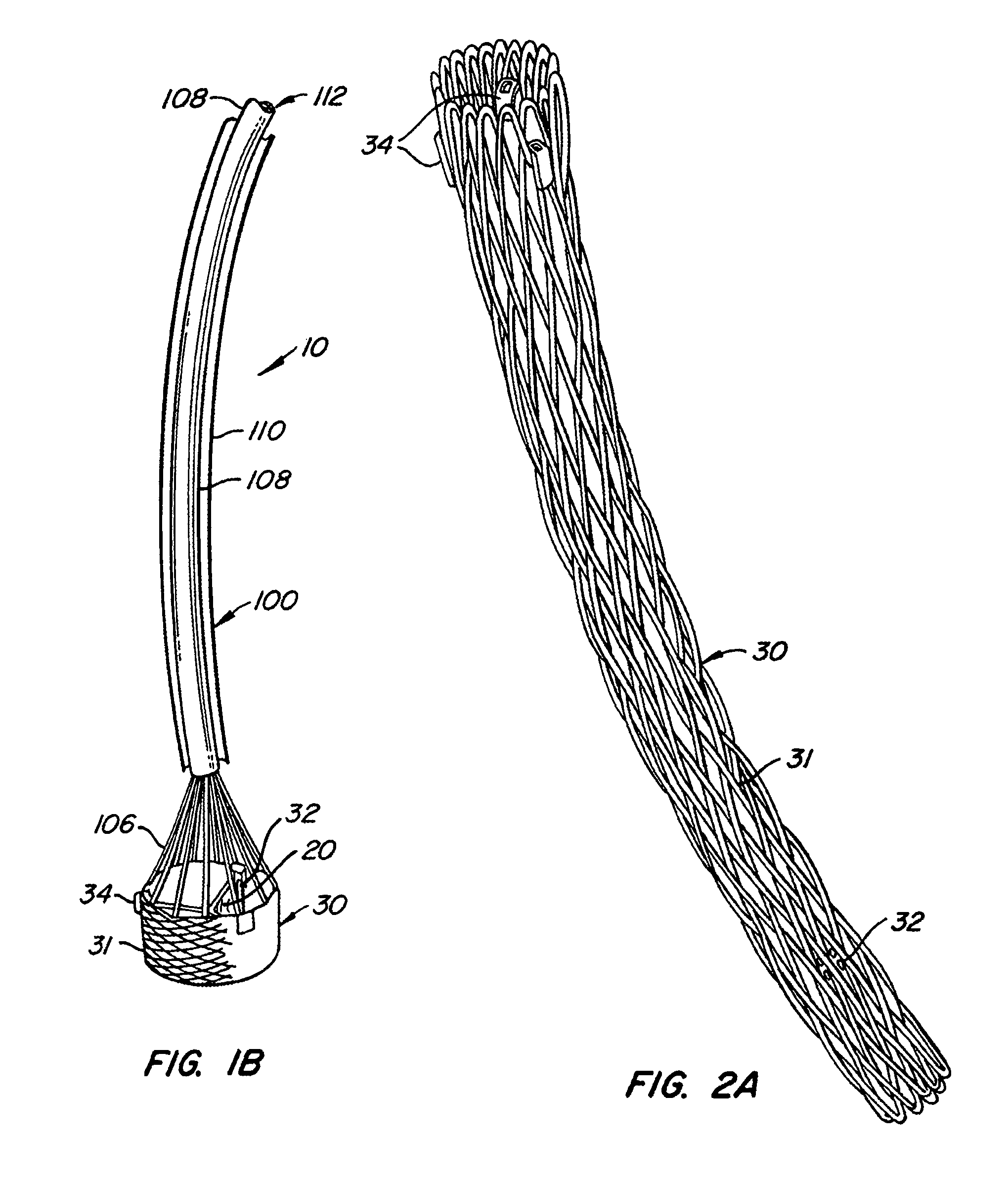
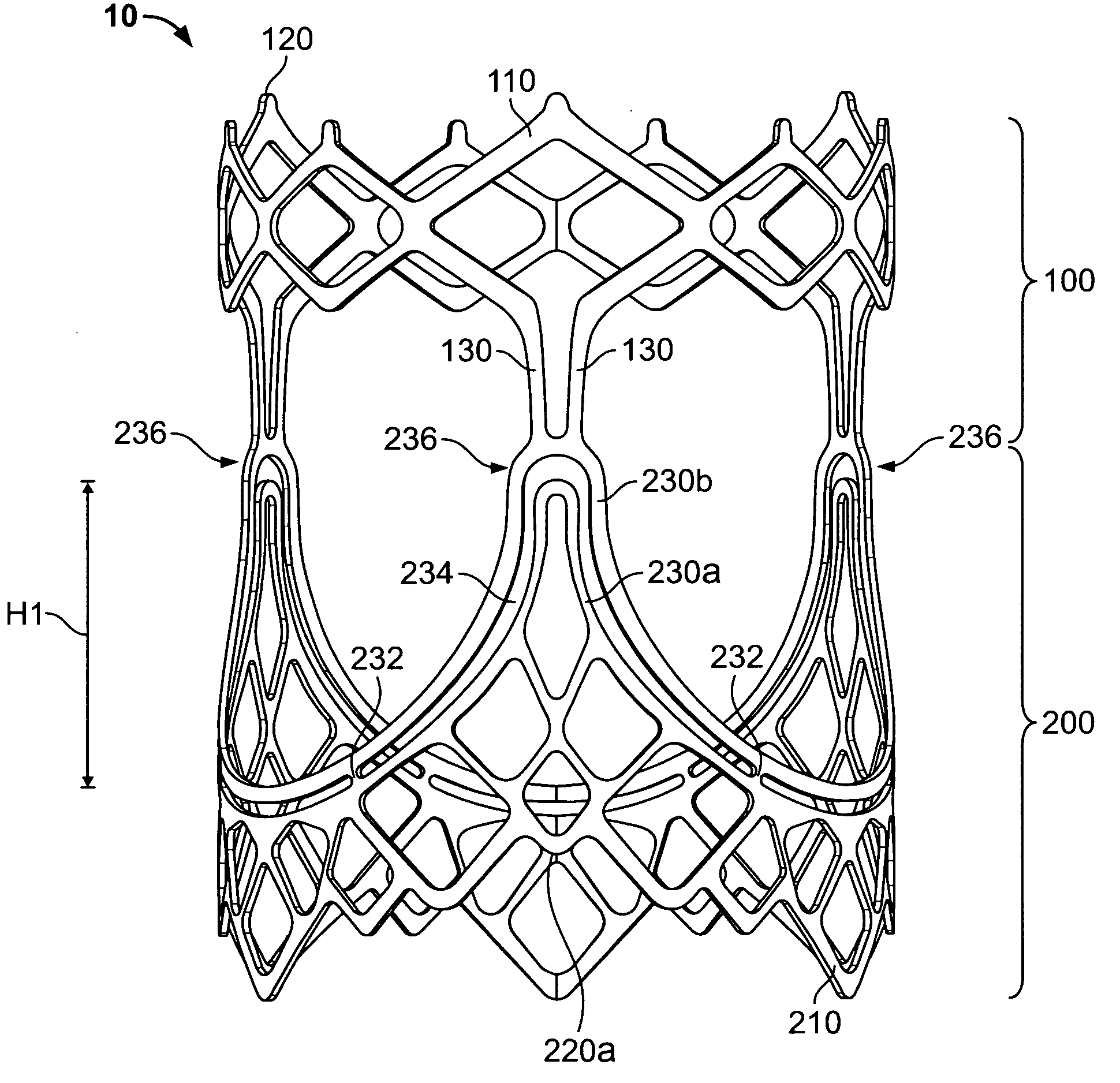
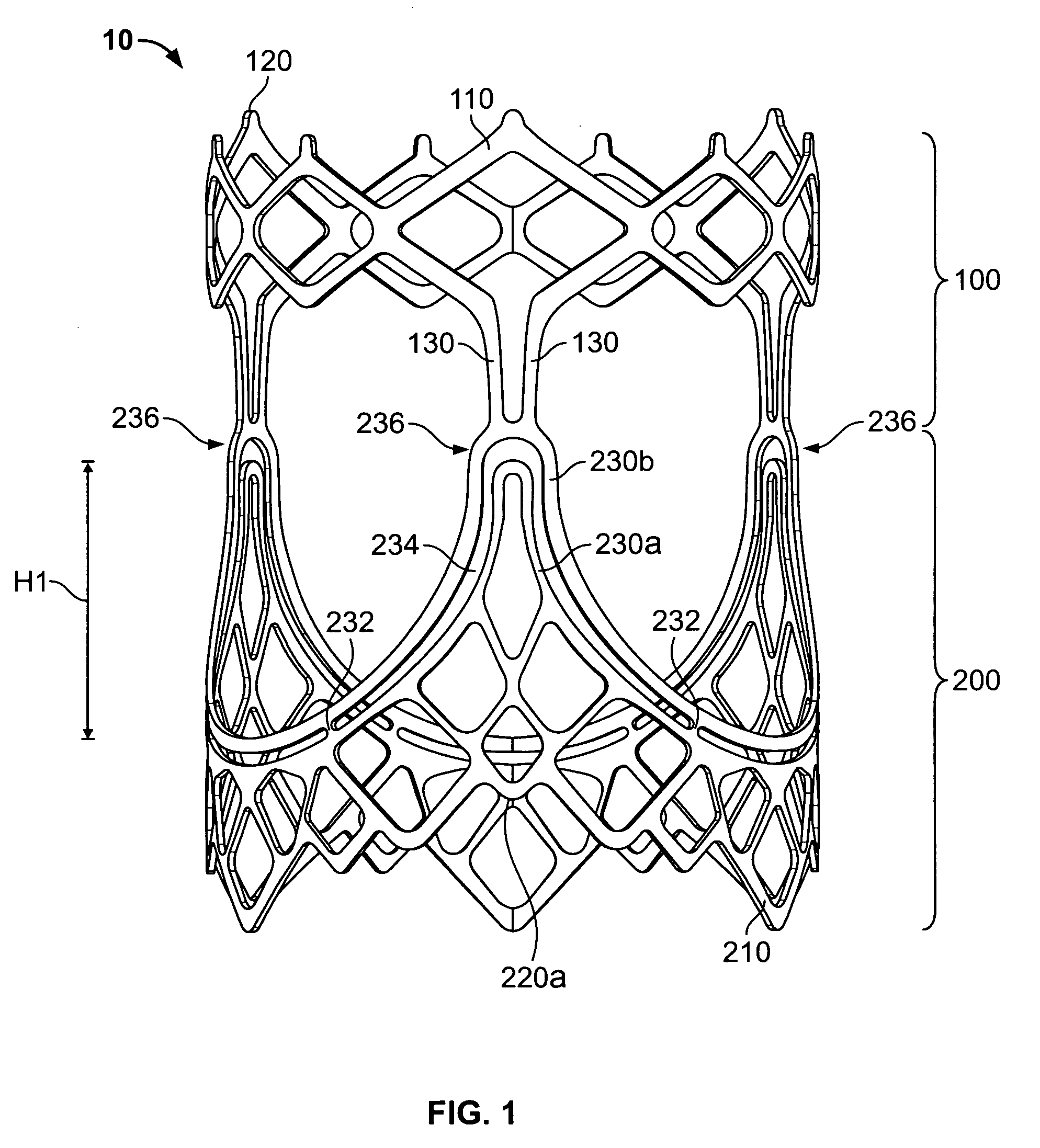
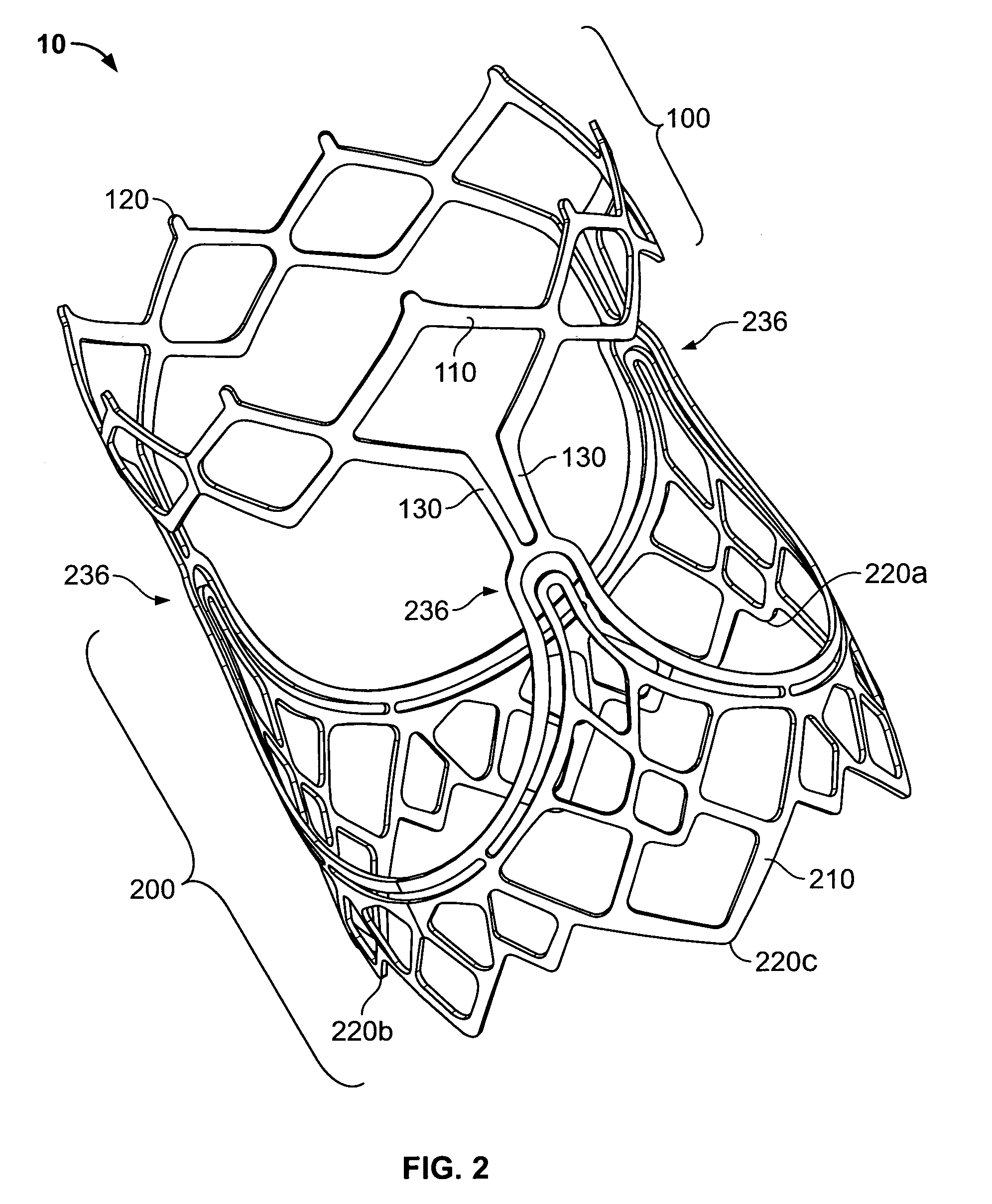
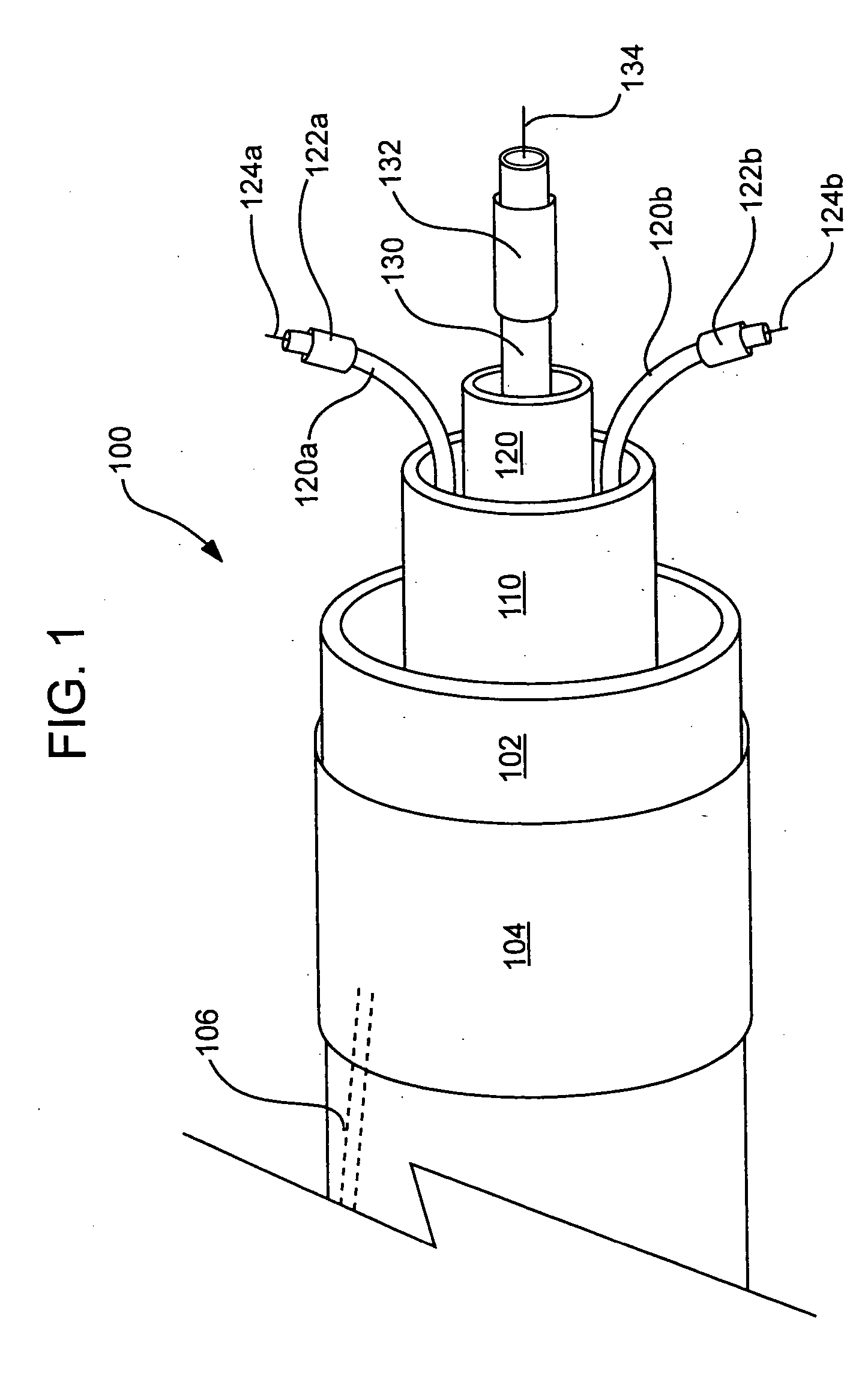
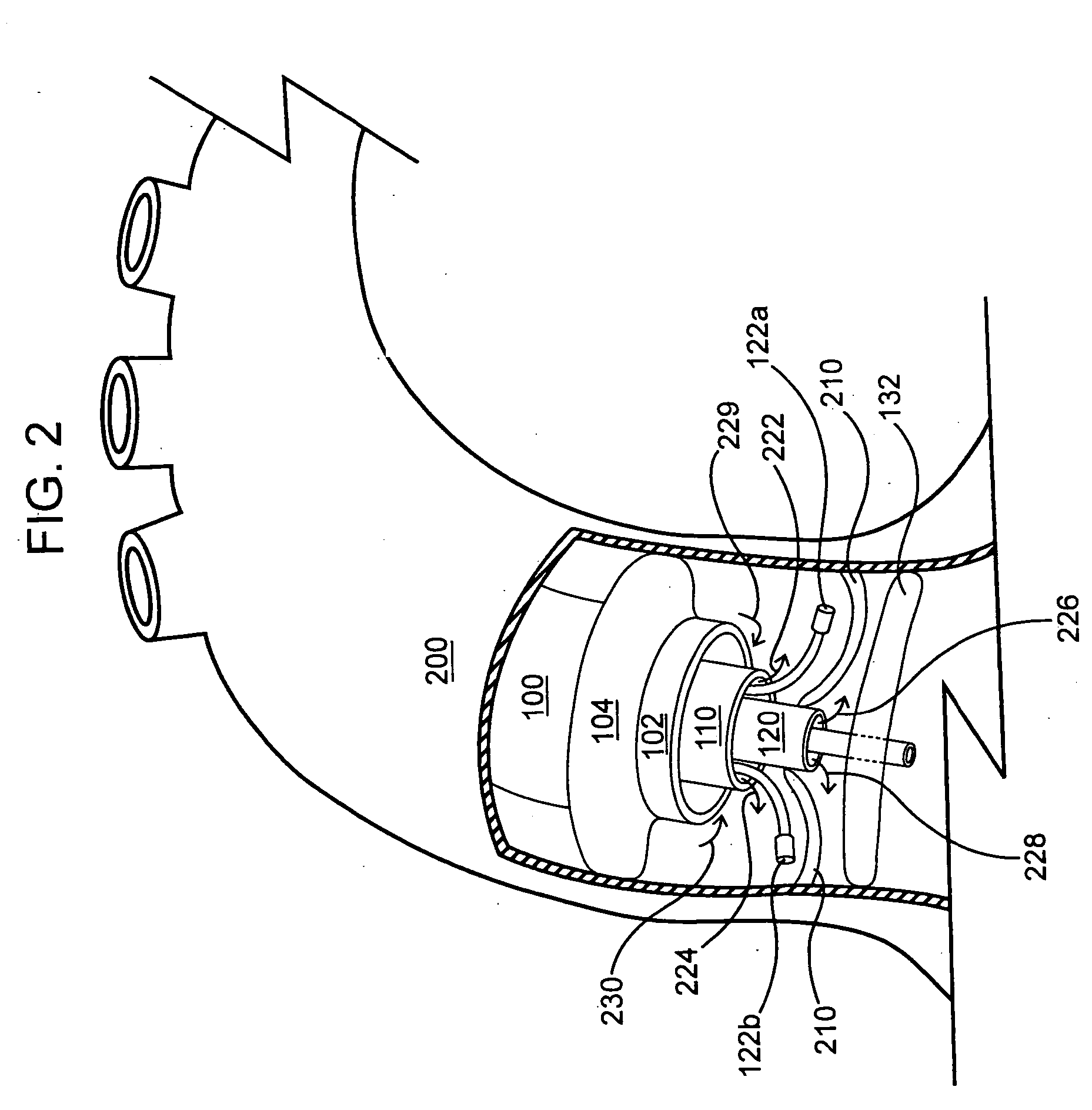
A prosthetic heart valve (10) (e.g., a prosthetic aortic valve) is designed to be somewhat circumferentially collapsible and then re-expandable. The collapsed condition may be used for less invasive delivery of the valve into a patient. When the valve reaches the implant site in the patient, it re-expands to normal operating size, and also to engage surrounding tissue of the patient. The valve includes a stent portion (200) and a ring portion (100) that is substantially concentric with the stent portion but downstream from the stent portion in the direction of blood flow through the implanted valve. When the valve is implanted, the stent portion engages the patient's tissue at or near the native valve annulus, while the ring portion engages tissue downstream from the native valve site (e.g., the aorta).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for resecting and replacing an aortic valve
Apparatus for resecting a diseased heart valve, the apparatus comprising: a body portion; a first handle and a second handle; a cutting blade; a set of retaining arms; a pass-off tool having a first attachment device configured to selectively engage the first handle attached to the body portion so as to allow placement of the second handle of the body portion adjacent to the diseased heart valve, and a controller tool having a second attachment device at the distal end thereof, the second attachment device configured to selectively engage the second handle attached to the body portion so as to allow positioning of the body portion adjacent to the diseased heart valve, a cutting blade actuator configured to cause the cutting blade to selectively rotate, and a retaining arm actuator configured to selectively position the set of retaining arms from the contracted state to the expanded state.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Replacement
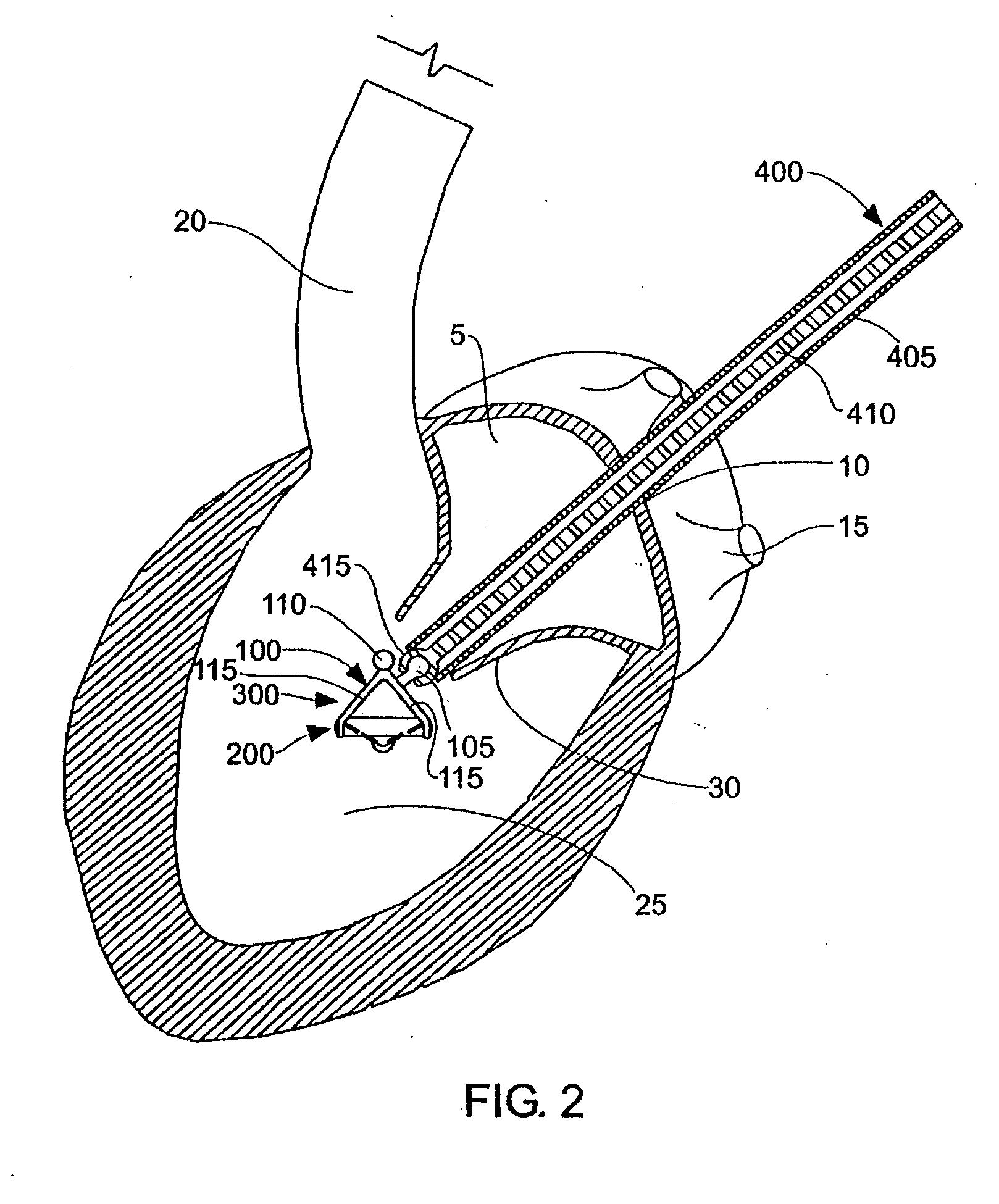
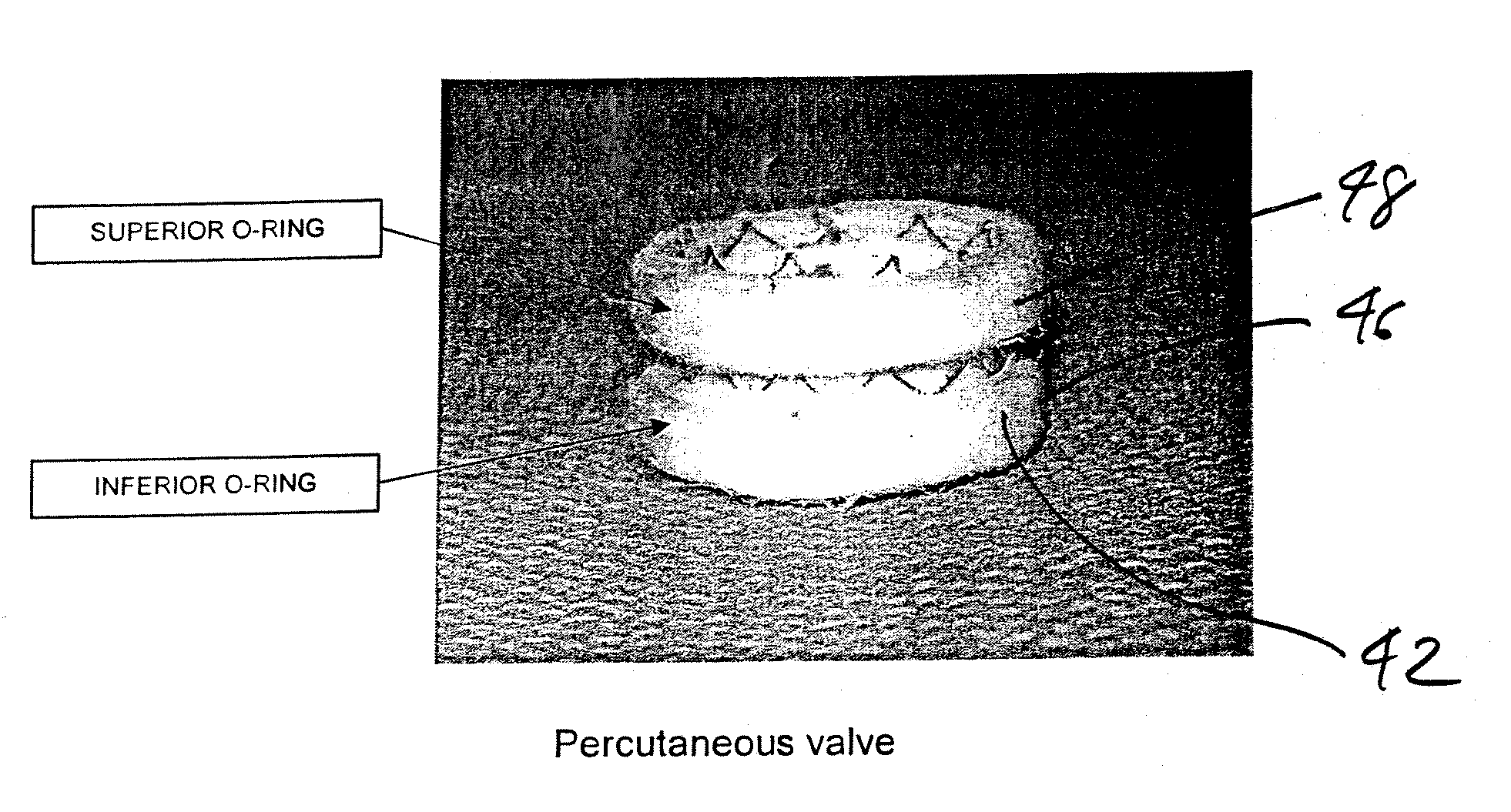
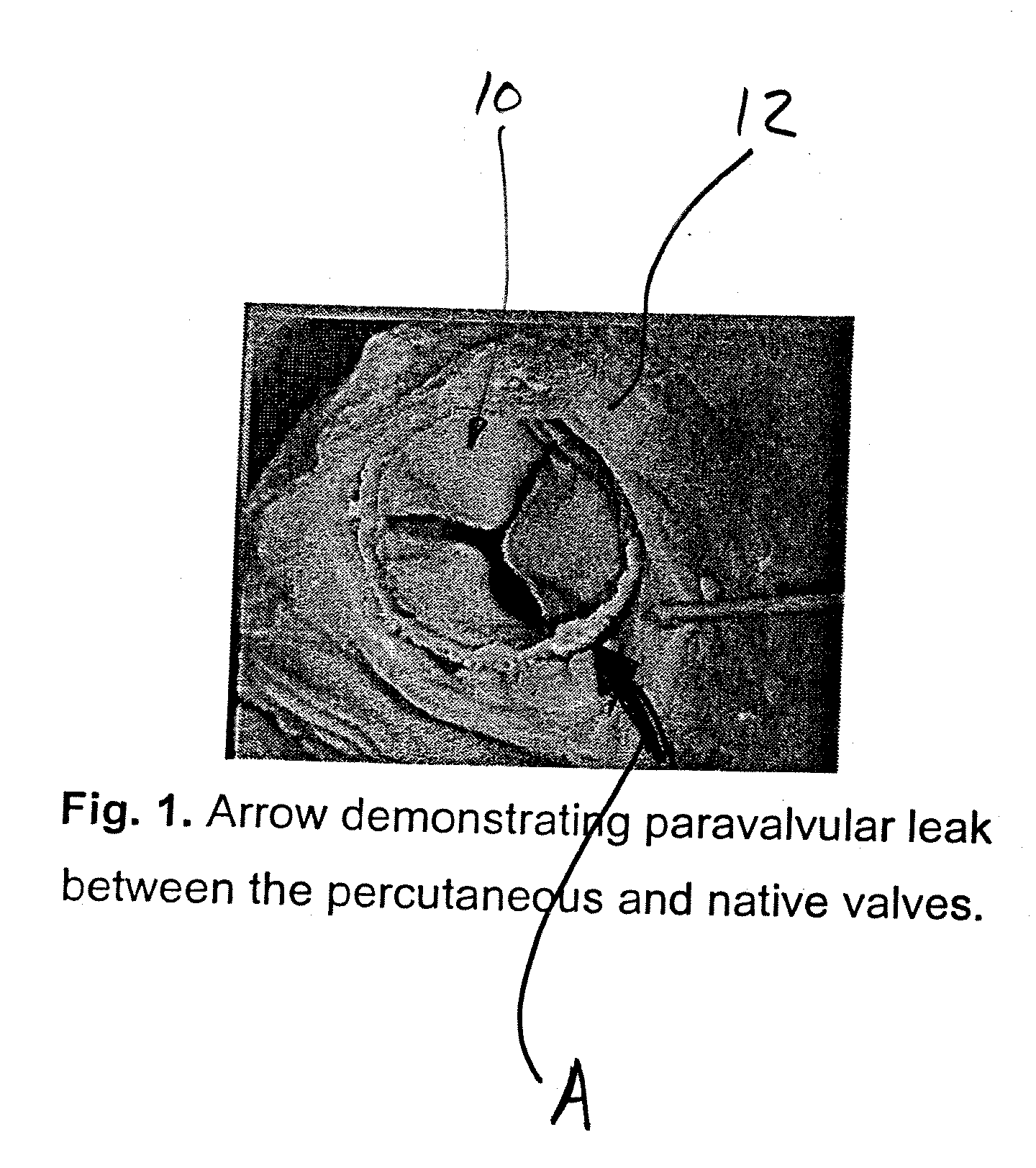
A replacement cardiac valve for placement adjacent the native annulus comprises a valve body having a multi-leaflet valve, a supporting stent surrounding and operatively coupled to the valve body, a superior O-ring and an inferior O-ring spaced from one another to span the native annulus, the O-rings surrounding the valve body and operatively coupled the valve body or the supporting stent, the valve body, the supporting stent, and the O-rings adapted for transcatheter placement using a deployment catheter.
Owner:TEHRANI HASSAN
Device for replacing aortic valve membrane or pulmonary valve membrane percutaneously
The invention relates to a novel percutaneous aortic valve and pulmonary valve exchanger, which is a self-expand support with biological valve, formed by the support in special shape and made from nickel titanium alloy skeleton and the three-blade one-way opening valve formed by pig heart, wherein, the support has fixing and supporting functions, and the pig heart forms three valves fixed in the support. The invention has little hurt, high safety and reduced complication.
Owner:孔祥清
Methods and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS20090030510A1Optimize timingAccurate placementBalloon catheterHeart valvesVascular tissueCardiac cycle
A delivery system and method for percutaneous aortic valve (PAV) replacement and apparatus used therein. A temporary aortic valve comprised of a reversibly expandable occluding means, such as balloons, surrounds a central catheter mechanism. The temporary valve is positioned within the ascending aorta, just above and downstream from the coronary ostia. The occluding means is configured such that, when fully expanded against the aortic wall, gaps are left that promote continuous coronary perfusion during the cardiac cycle. The temporary valve with occluding means substitutes for the function of the native aortic valve during its replacement. The native aortic valve is next dilated, and then ablated through deployment of low profile, elongated, sequentially delivered stents. The ablation stent(s) displace the native valve tissues and remain within the aortic annulus to receive and provide a structure for retaining the PAV. The PAV is delivered, positioned and deployed within the ablation stent(s) at the aortic annulus with precision and relative ease. Ablation of the native aortic valve removes the structural obstacles to precise PAV placement. The temporary aortic valve mediates the hemodynamic forces upon the devices as encountered by the surgeon following native valve ablation. The temporary valve also promotes patient stability through continuous coronary perfusion and a moderated transvalvular pressure gradient and regurgitation. Sequential delivery of low profile PAV components minimize the risk of trauma and injury to vascular tissues. Mathematical considerations for determining the optimum cross-sectional area for the temporary valve blood perfusion gaps are also described.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Methods and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS8663319B2Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesCardiac cyclePerfusion
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Devices and methods for treating aortic valve stenosis
Fluid delivery devices having a porous applicator, as well as methods for using the same in the treatment of aortic valve stenosis, are provided. The subject devices further include a ventricular occlusion balloon and a compliant element that is configured to envelope the occlusion balloon. Also provided are systems and kits that include the subject fluid delivery devices.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Portable blood purifying system
InactiveCN102389594AEfficient removal capacityImprove purification efficiencyDialysis systemsExtracorporeal circulationLiquid waste
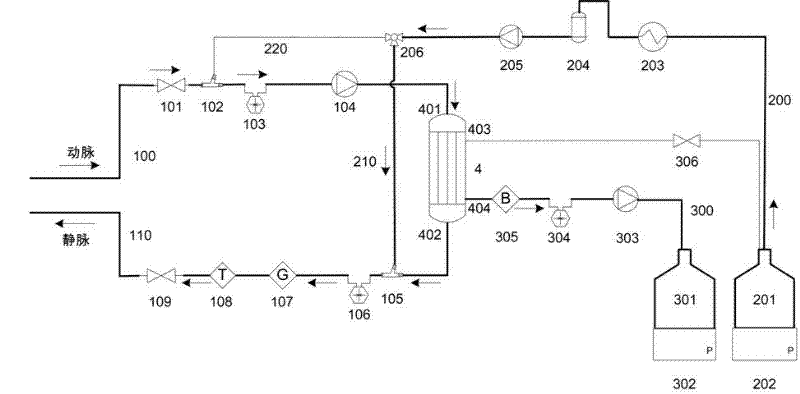
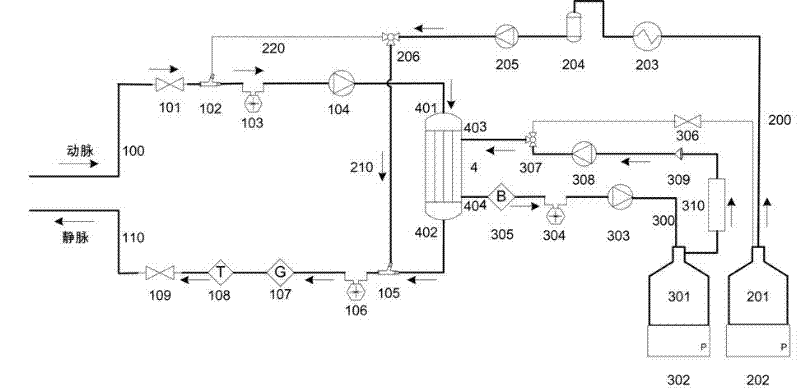
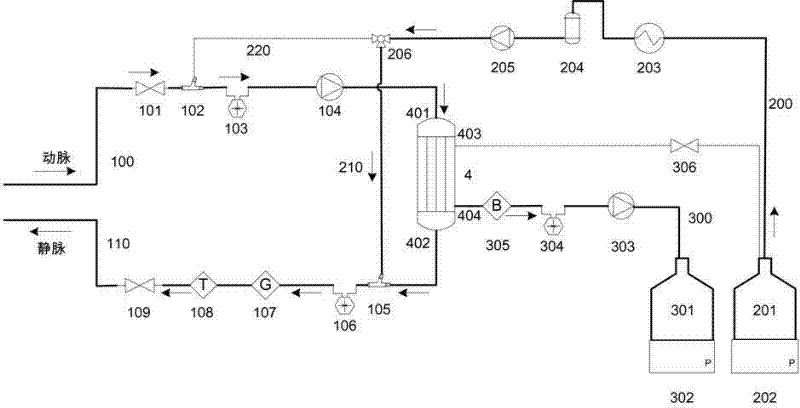
The invention relates to a portable blood purifying system, which comprises a high throughput dialyzer with an arterial duct, a venous duct, a washing liquid tube and a transfusion tube; the arterial duct is in turn connected in series with an arterial valve, an arterial pressure sensor and a blood pump; the venous duct is in turn connected in series with a venous valve, a venous temperature sensor, a venous bubble detector and a venous pressure sensor, so that an external circulation unit is formed; the washing liquid tube is connected in series with a pre-charging valve and is communicated with a washing liquid container; the transfusion tube is in turn connected in series with a temperature controller, a transfusion tube bubble collector and a transfusion pump, and is communicated with a waste liquid container, so that a waste liquid processing unit is formed; and the system also comprises a transfusion pump, a temperature control device, a transfusion tube, a gating valve and a first transfusion branch and a second transfusion tube branch, so that a transfusion unit is formed. The system is simplified in structure and convenient to carry; and the system is suitable for patients to do short-time dialysis for several times or night dialysis treatment at home as household treatment equipment, so that toxin tolerance of dialysis patients during dialysis period is relieved while medical cost is reduced.
Owner:黄昱
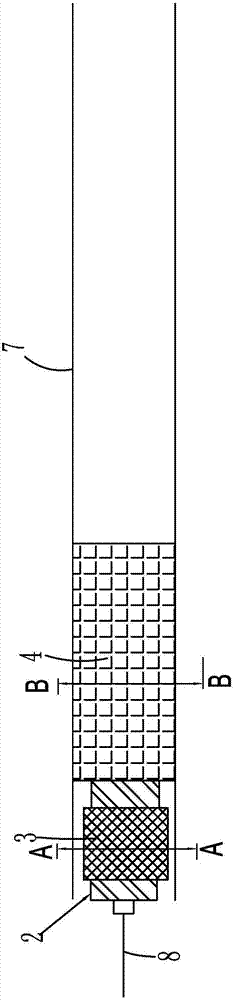
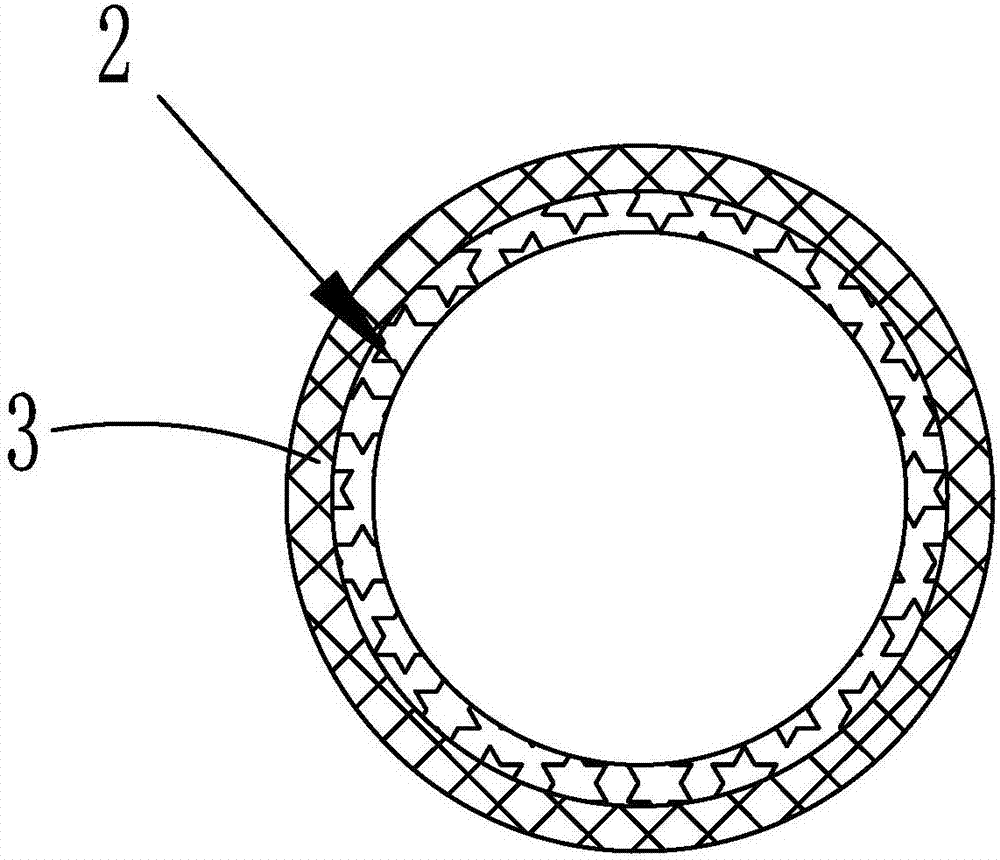
Conveying appliance with valve locating function for use during percutaneous aortic valve replacement operation
InactiveUS20140052239A1Adjustable positionIncrease success rateHeart valvesPostoperative complicationPercutaneous aortic valve replacement
A conveying appliance with valve locating function for use during percutaneous aortic valve replacement operation includes a conveying rod (1), a sheath pipe (5), a round ring (3), at least two locating rods (2) and at least two round ring operating ropes (4). The round ring (3) is sleeved on the lower end of the conveying rod (1) and located in the conveying sheath pipe (5). An end of the locating rod (2) is hinged on the conveying rod (1) and the hinge point is located on the upper portion of the round ring (3). A lower end of the round ring operating rope (4) is provided with a structure for supporting the round ring (3) or is directly connected with the round ring (3). An upper end of the round ring operating rope (4) extends out of a human body along the axial direction of the conveying rod (1). The appliance can locate the implanted valve in a better manner so as to increase the success rate of percutaneous aortic valve replacement operation and reduce the operation difficulty and the postoperative complications. The appliance reduces the pain and the risk of the operation, and lowers the medical cost.
Owner:CAI JING +1
Method For Replacing Native Valve Function Of A Diseased Aortic Valve
InactiveUS20100217384A1Risk minimizationAccurate placementHeart valvesGuide tubeArtificial heart valve
Methods for replacing native valve function of a diseased aortic valve are disclosed. In an embodiment, a method for replacing native valve function of a diseased aortic valve in a patient includes: (a) receiving an artificial heart valve assembly mounted about a first mounting position on a catheter system, (b) guiding the artificial heart valve assembly through the vasculature of the patient, (c) while the catheter system having the artificial heart valve assembly mounted thereto is in the patient's vasculature, mounting the artificial heart valve assembly about a second mounting position on the catheter system, (d) delivering the artificial heart valve assembly to the region of the diseased aortic valve, (e) expanding the artificial heart valve assembly in the region of the diseased aortic valve, and (f) withdrawing the catheter system from the patient's vasculature.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
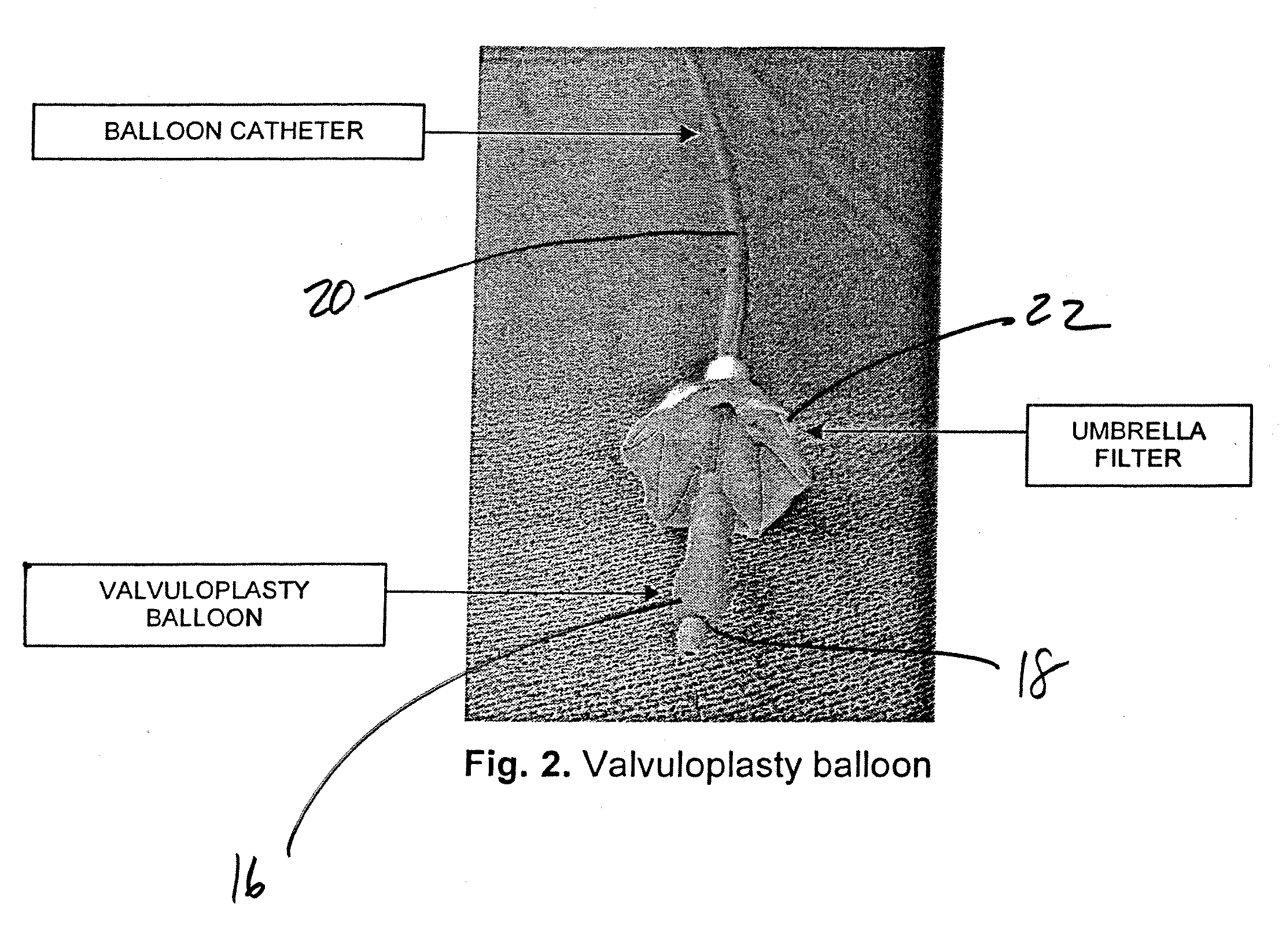
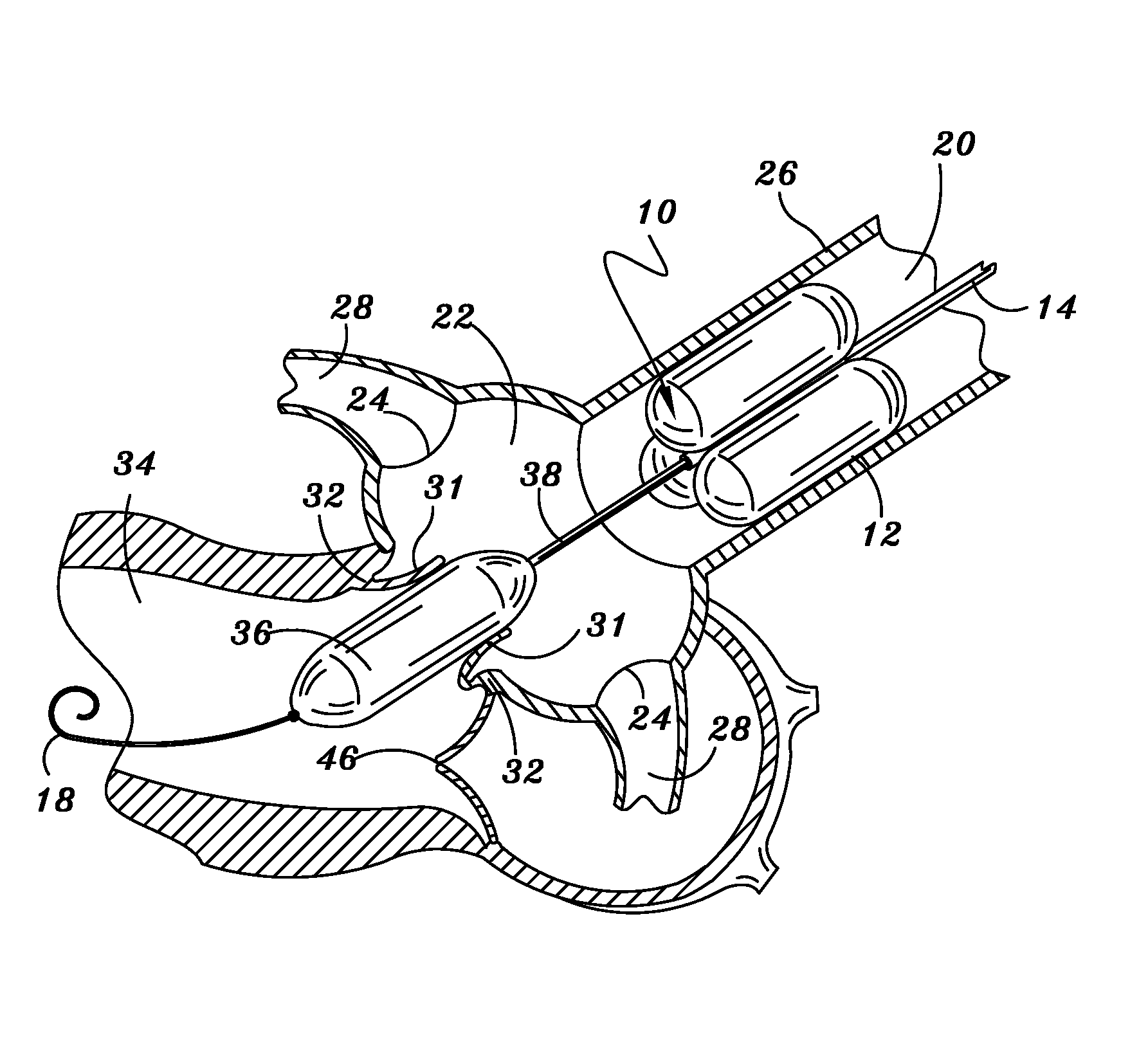
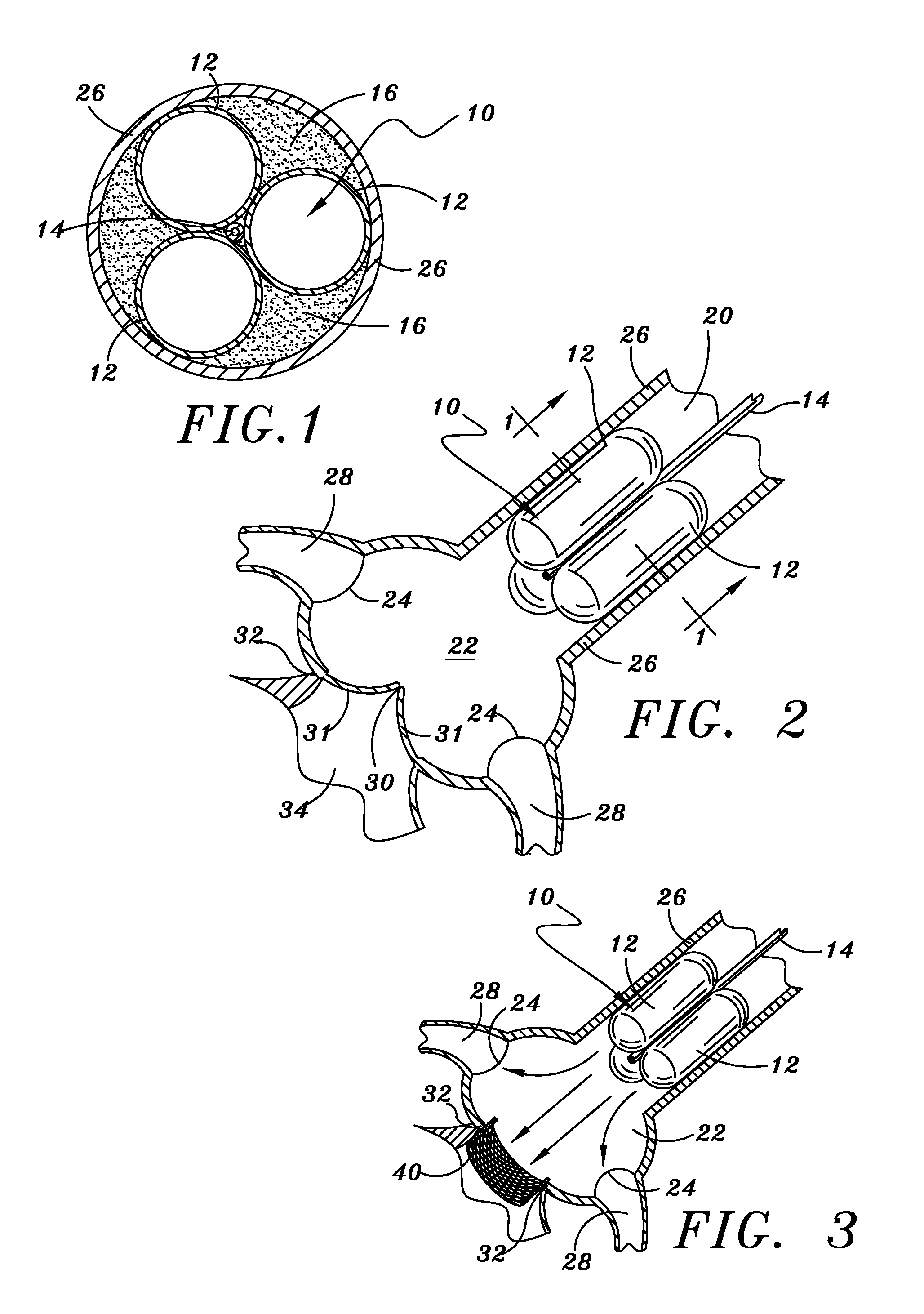
Perfusion balloon with selectively actuatable valve
An apparatus for performing a medical procedure and, in particular, an aortic valvuloplasty, in a vessel for transmitting a flow of fluid includes a first inflatable balloon, such a perfusion balloonwith a plurality of cells in a single cross-section of the balloon for permitting the fluid flow in the vessel. An inflatable valve, which may take the form of a second inflatable balloon, may be provided for controlling the fluid, flow through the first balloon when inflated. Through selective movement of the second balloon when inflated via the flow rhythms created by the beating heart, a one way valve results that can be used to mimic the natural flow created by the valve under treatment.
Owner:CR BARD INC
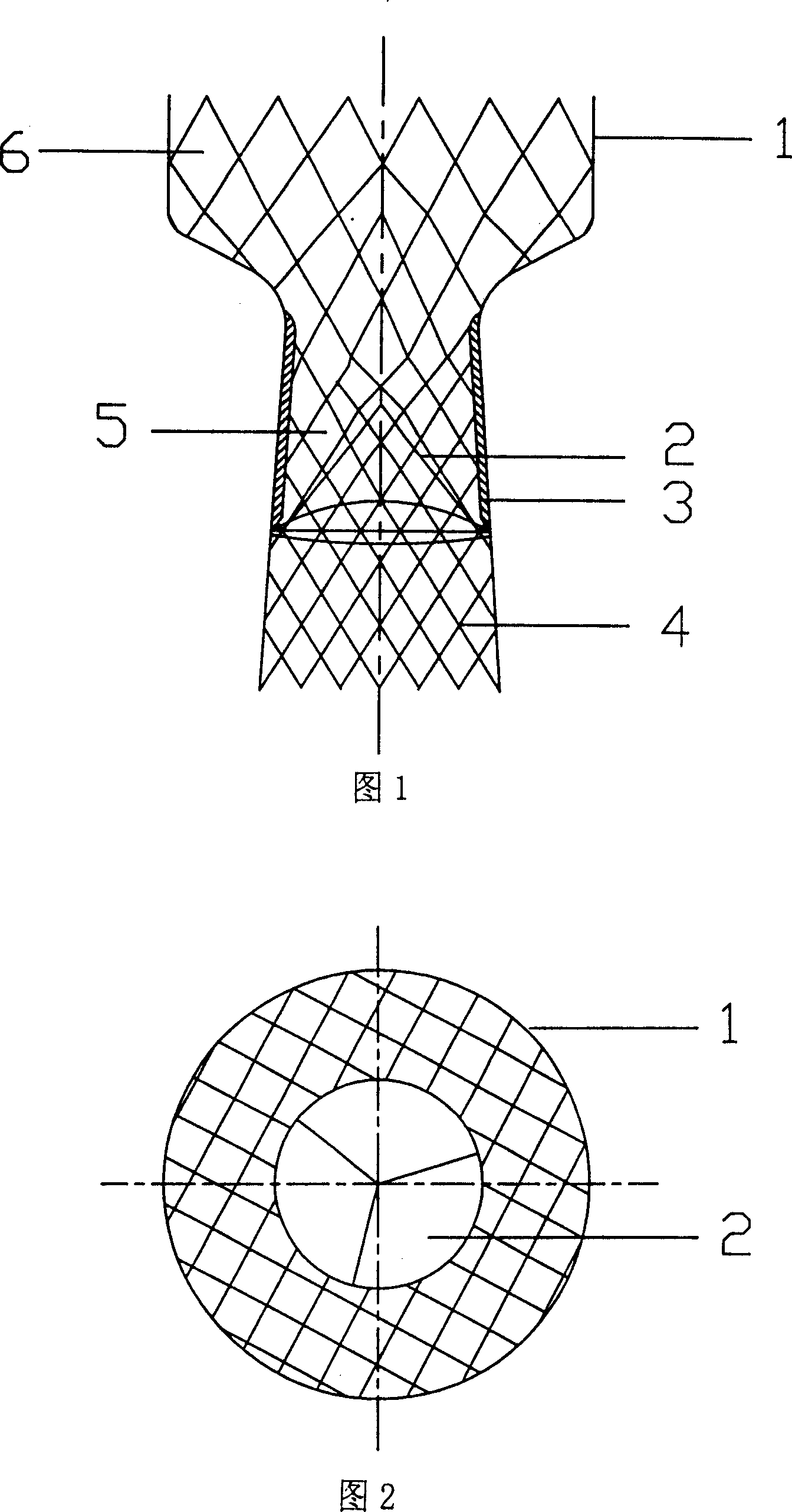
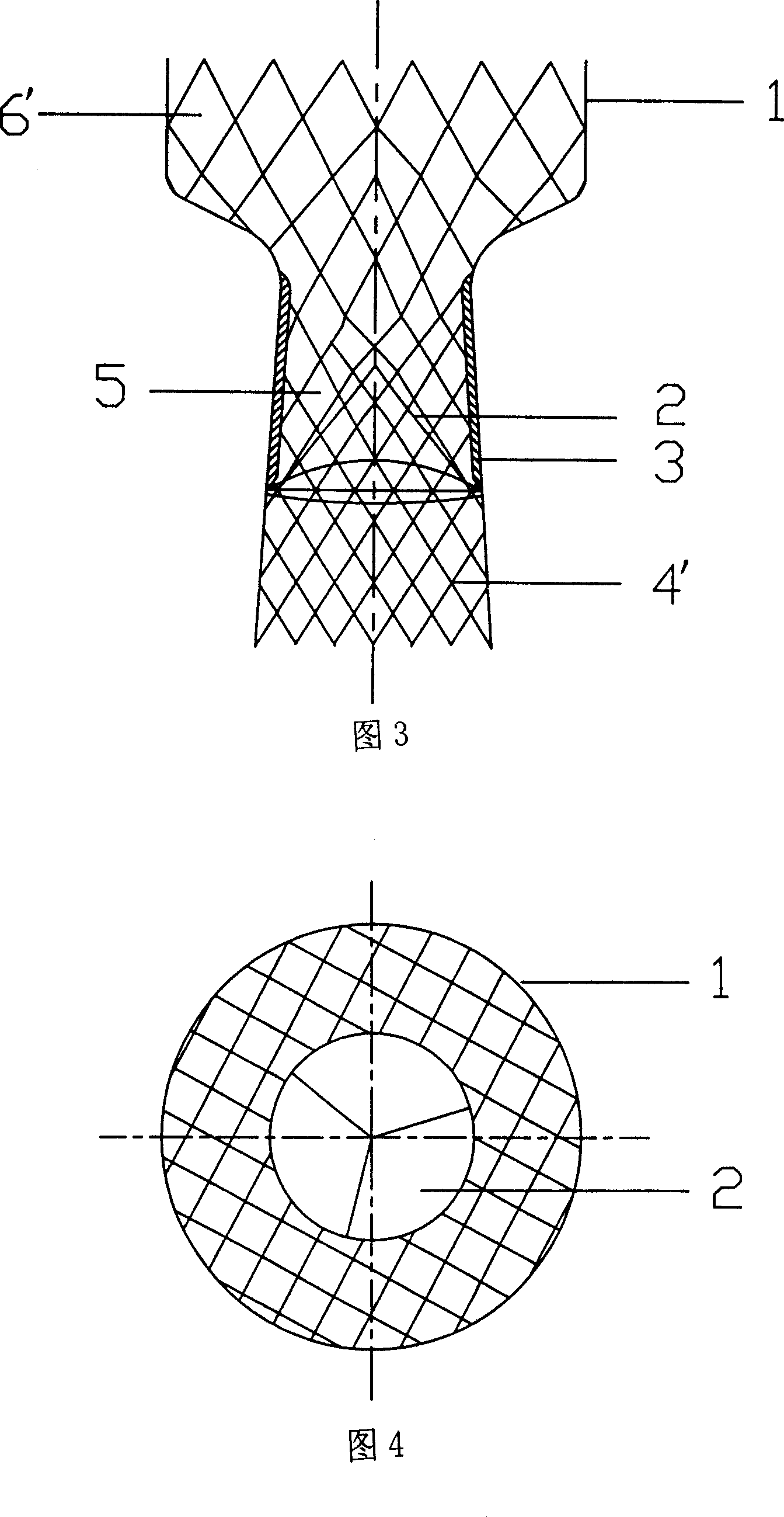
Aortic valve stent
The invention relates to an aortic valve stent. The aortic valve stent comprises a stent body and a prosthetic valve connected to the stent body, the stent body is of a double-layer stent body and specifically comprises a balloon expanding stent body and a self-expanding stent body, the prosthetic valve is connected to the self-expanding stent body, and after the stent body is conveyed, the self-expanding stent body is located on the inner periphery of the balloon expanding stent body and tightly abuts against the balloon expanding stent body to the outer periphery; the balloon expanding stent body tightly abuts against the aortic valve of the human body to the outer periphery, and an anchoring structure is formed between the balloon expanding stent body and the self-expanding stent body. According to the stent with the prosthetic valve, through the double-layer design, the full expansion and fixation of the aortic valve are ensued, the shape and area in the stent are ensured, and meanwhile, the compliance and support strength of the stent are ensured; the occurrence of perivalvular leakage and central regurgitation is reduced, the diameter of the sheath is not increased, and the risks of vascular complications are avoided.
Owner:姜正明 +1
Aorta valve stent conveying system and aorta valve system
PendingCN107468379AEasy to set upReduce or prevent weekly leakageBalloon catheterHeart valvesHuman aortaBalloon dilations
The invention relates to an aorta valve stent conveying system which comprises a push release device for conveying an aorta valve stent. Particularly, the aorta valve stent conveying system further comprises a special-shaped balloon catheter arranged at the front end of the push release device, the special-shaped balloon catheter comprises a balloon, the balloon is provided with a cylindrical connecting portion and a balloon expanding portion communicated with the cylindrical connecting portion, and the cylindrical connecting portion is connected with the front end of the push release device; according to the design of the balloon, after expansion, a positioning face is formed in the side, close to the cylindrical connecting portion, of the balloon expanding portion, when the aorta valve stent conveying system is in use, the balloon expanding portion of the balloon is located inside a left ventricle outflow tract and tightly fits the bottom of the human aorta valve through the positioning face, and the effects of positioning and reducing and / or resisting valve leakage are achieved.
Owner:姜正明 +1
Establishment method for mathematical model of geometrical shape of pulmonary valve
ActiveCN107315911AHelp to deal withHelp with refactoringSpecial data processing applicationsImage generationSINGLE LOBEData validation
The invention discloses an establishment method for a mathematical model of the geometrical shape of a pulmonary valve. The method comprises the steps that based on motion characteristics of the pulmonary valve in a cardiac cycle, it is assumed that the valve is in symmetry, and only a single lobe is researched; based on structural and physiological characteristics of the pulmonary valve, it is assumed that the pulmonary valve is a part of a cylindrical shell in an elastic shell body; according to medical images and relevant data, a fitting function is found, and the shape of the lobe and relevant parameters are determined; and the conclusion is verified through data, and the accuracy of the research result is determined. In the research process, based on the similarity between structures and sizes of three lobes, it is assumed that the lobes are in complete symmetry, only one lobe is researched, and therefore the problem is simplified; and the given mathematical model of the geometrical shape of the pulmonary valve has a certain theoretical basis and accuracy, will be beneficial for treating diseases about the pulmonary valve in clinical medicine and is more beneficial for reconstruction of heart valve prosthesis substitute goods in medicine.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for manufacturing aortic intervention valve
InactiveCN106726009AAvoid immune rejectionRealize physiological functionHeart valvesTissue regenerationYarnAutomatic control
The invention relates to an implantable intravascular arterial intervention valve and discloses a method for manufacturing an aortic intervention valve. The method includes the following steps that 1, iPSCs are directionally induced in vitro to be differentiated into valves VICs and precursor cells VECs; 2, porcine aortic valves are selected, and enzymes and a detergent are used for removing original valve cells; 3, a protein power processing method is applied to build a core-shell structure fiber-state drug control release system; 4, constructing a skin-core structure superfine composite yarn; 5, the cell-valve-free matrix micro-morphology is processed and modified by plasma etching; 6, positioning is conducted through 3D printing cells, and the controlled release of the drug concentration gradient is conducted. By adopting a nickel-titanium alloy wire material weaving and shaping method, a nickel-titanium alloy support is produced. The automatic control performance of the support is achieved, the optimal stress state of aortic valves of the human body is achieved. The enzymes and the detergent are used for removing valve cells attached to the original aortic valves, cell matrixes are completely preserved, and thus the durability and the anti-calcification property of a product are improved.
Owner:WUHAN VICKOR MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Methods and Apparatus for Percutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement
ActiveUS20140142692A1Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesCardiac cyclePerfusion
A delivery system and method for percutaneous aortic valve (PAV) replacement and apparatus used therein. A temporary aortic valve including a reversibly expandable occluding means surrounds a central catheter mechanism. The temporary valve is positioned within the ascending aorta, just above and downstream from the coronary ostia. The occluding means is configured such that, when fully expanded against the aortic wall, gaps are left that promote continuous coronary perfusion during the cardiac cycle. The temporary valve substitutes for the function of the native aortic valve during its replacement. The native aortic valve is next dilated, and then ablated through deployment of low profile, elongated, sequentially delivered stents. The stent(s) displace the native tissues and remain within the aortic annulus to receive and provide a structure for retaining the PAV. The PAV is delivered, positioned and deployed within the stent(s) at the aortic annulus with precision and relative ease.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECHNOLOGIES LLC
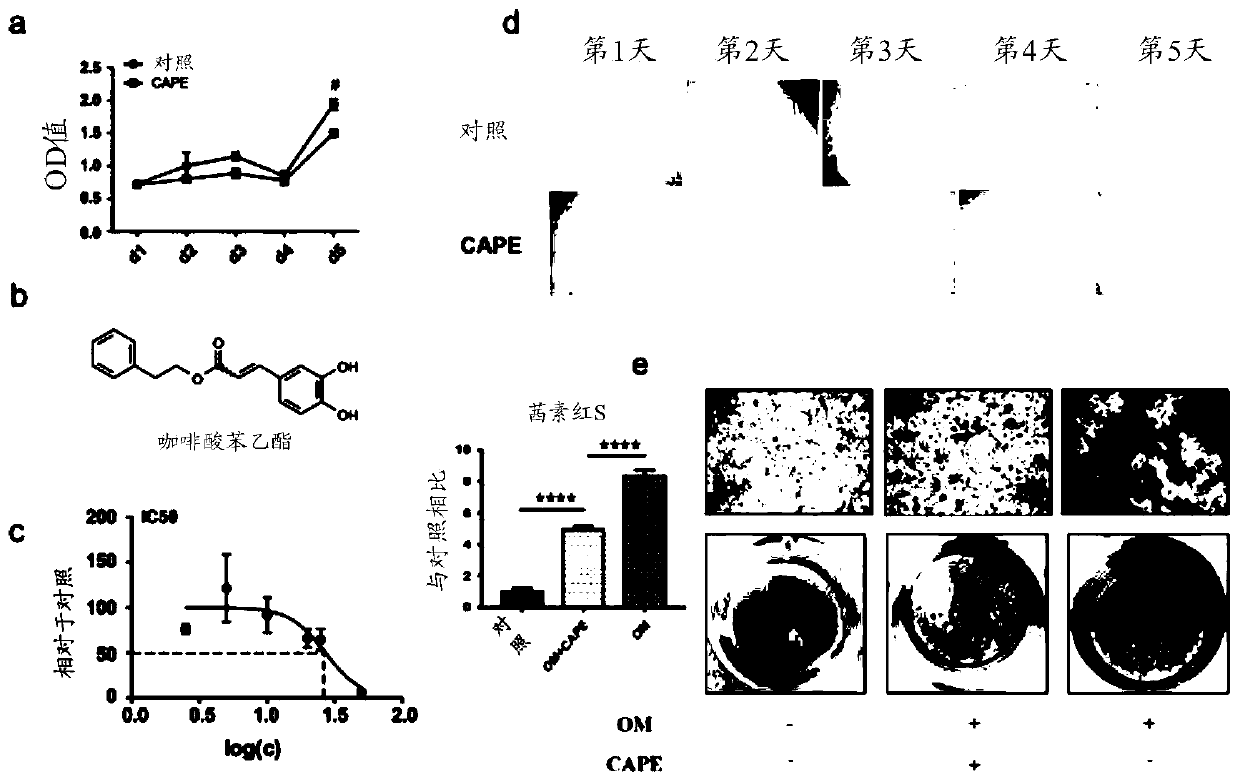
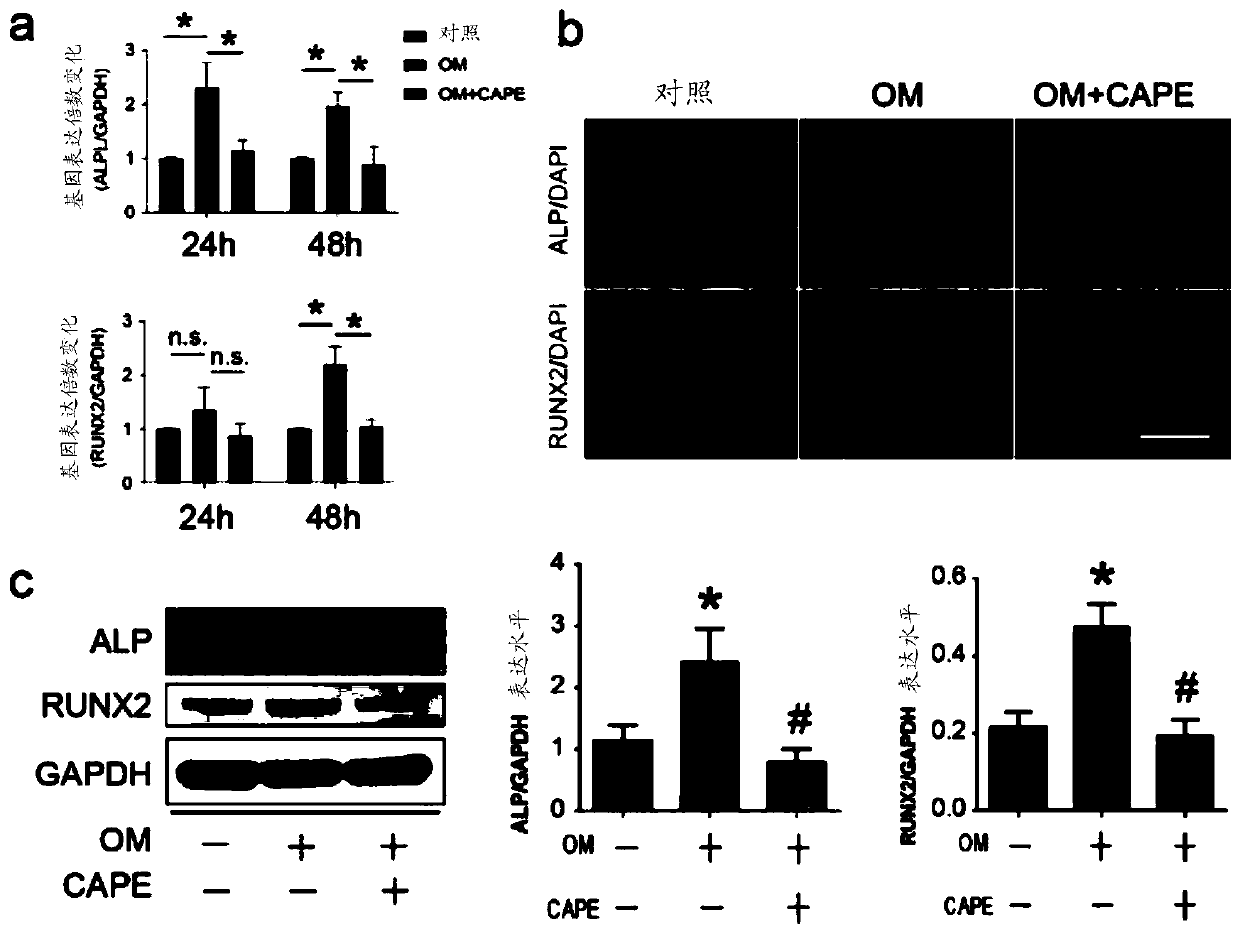
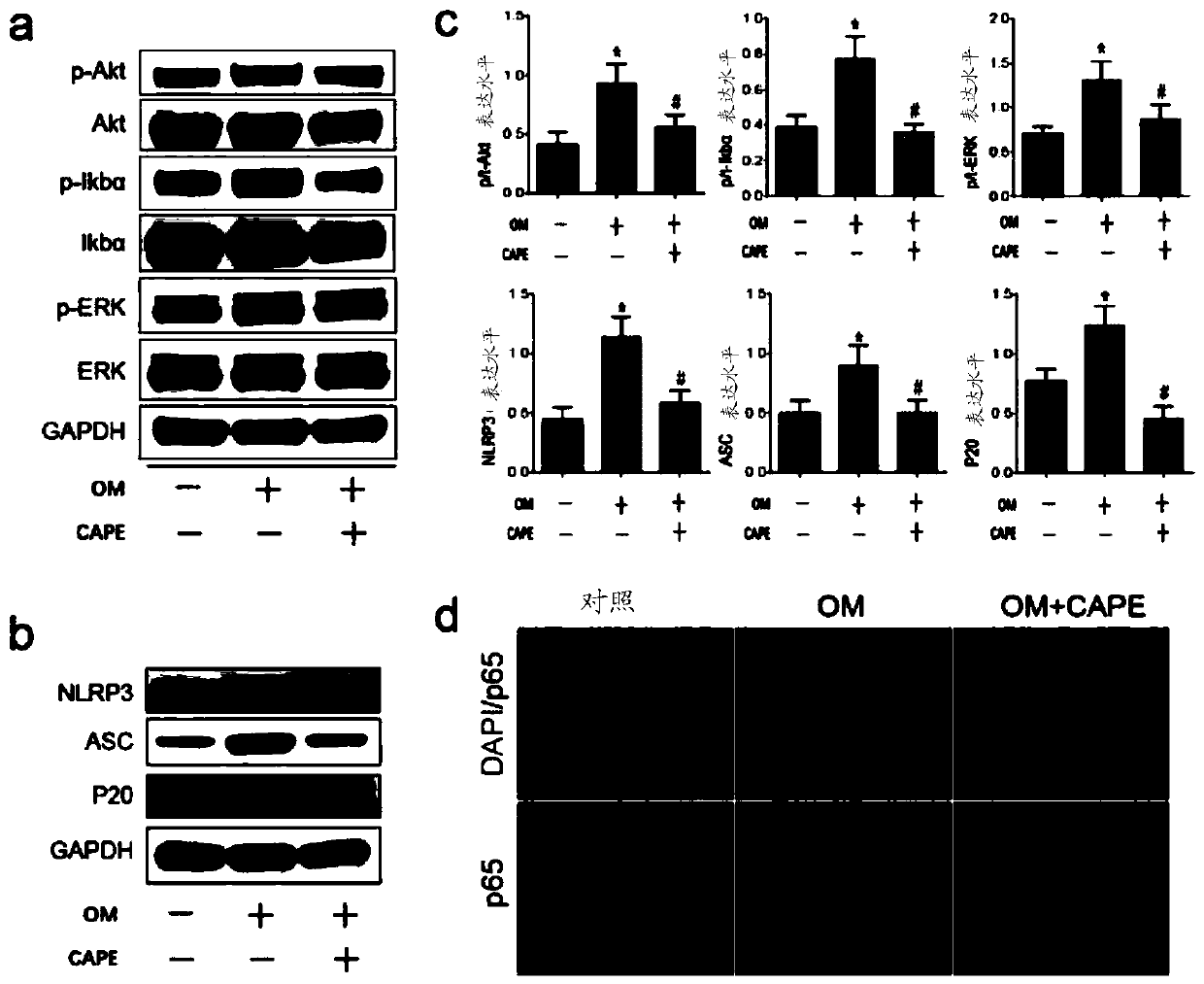
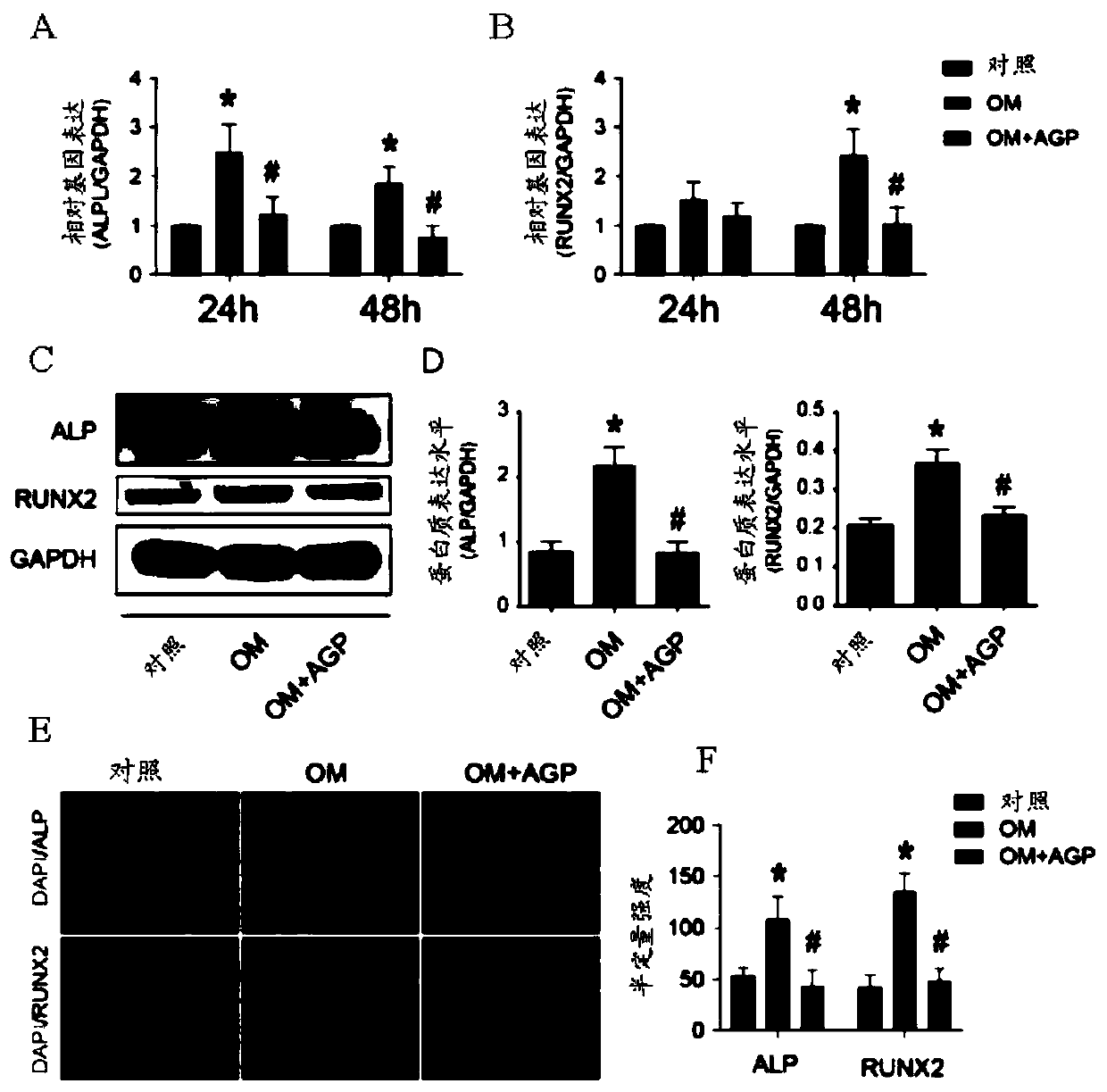
Application of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in treatment of CAVD
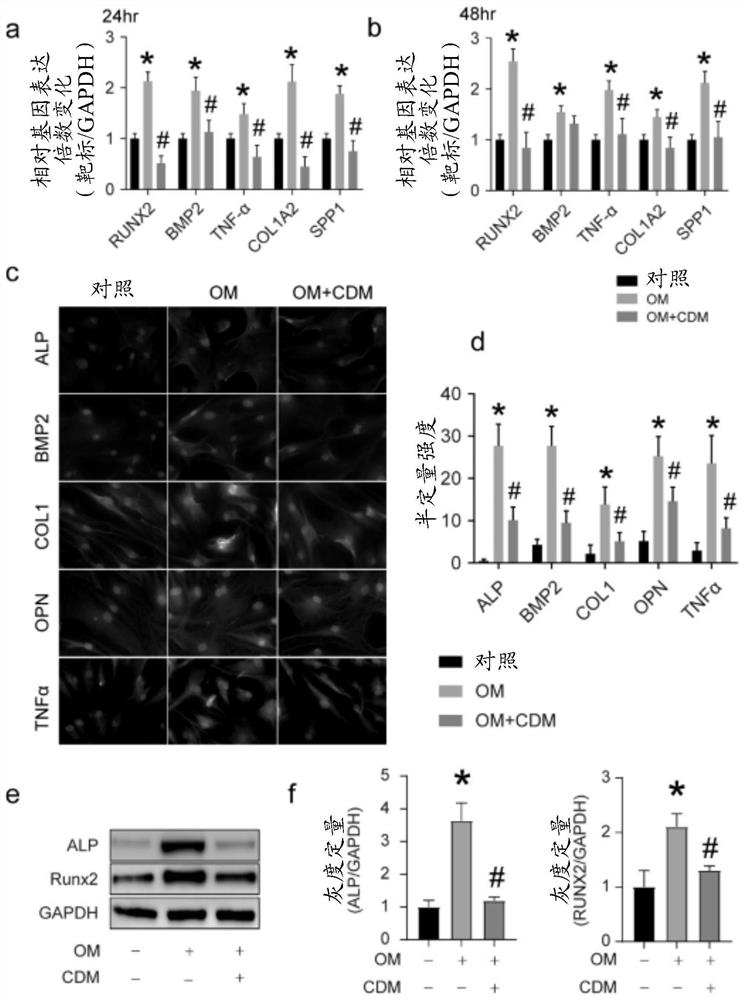
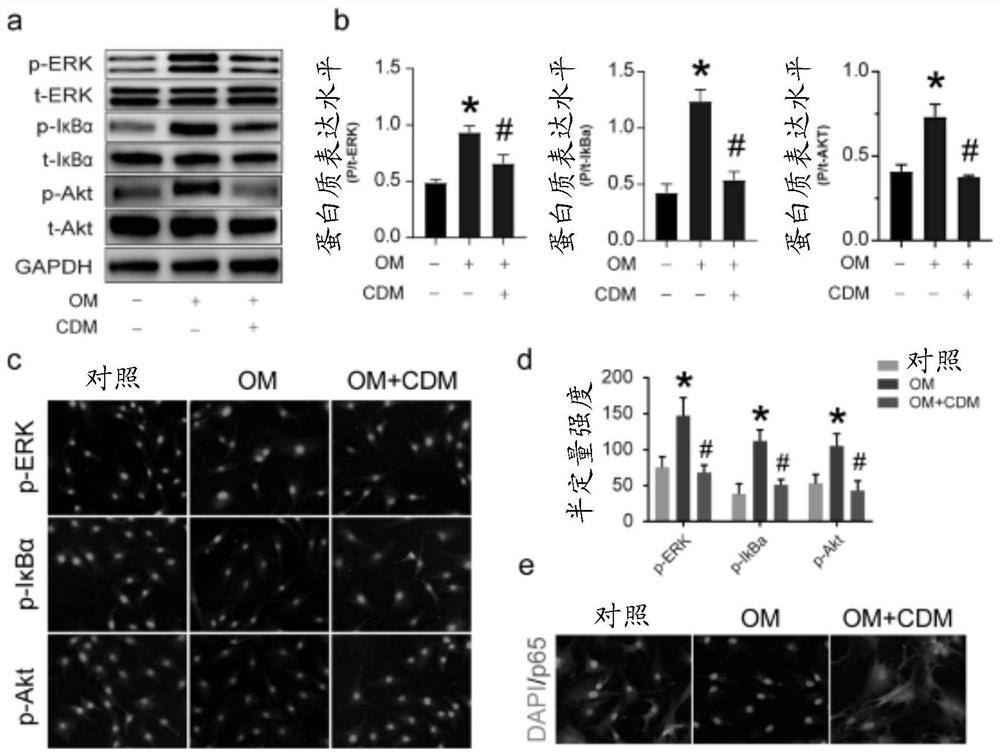
ActiveCN111012772AInhibit calcificationCalcification inhibition or delayOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderRUNX2Pharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to the field of prevention and / or treatment of CAVD. The inventor finds that caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) can effectively down-regulate the expression of osteogenic differentiation marker genes RUNX2 and ALP in valvular interstitial cells to inhibit the calcification of the valvular interstitial cells, thereby suppressing or delaying the valve calcification; and thus application of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in preparation of the medicine for preventing and / or treating the individual CAVD is provided. Therefore, novel selection is provided for treating the CAVD by using a non-surgical method.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Prosthetic Tissue Valves and Methods for Replacing Native Atrioventricular Valves with Same
A percutaneous transseptal surgical implantation method for replacing a defective atrioventricular (AV) valve with a conical shaped prosthetic valve formed from extracellular matrix (ECM) tissue. When the method is employed to replace a native mitral valve, the method positions the prosthetic tissue valve in the mitral valve region, whereby the valve does not obstruct the outflow tract of the aortic valve and prevents the leaflets of the aortic valve from coapting.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
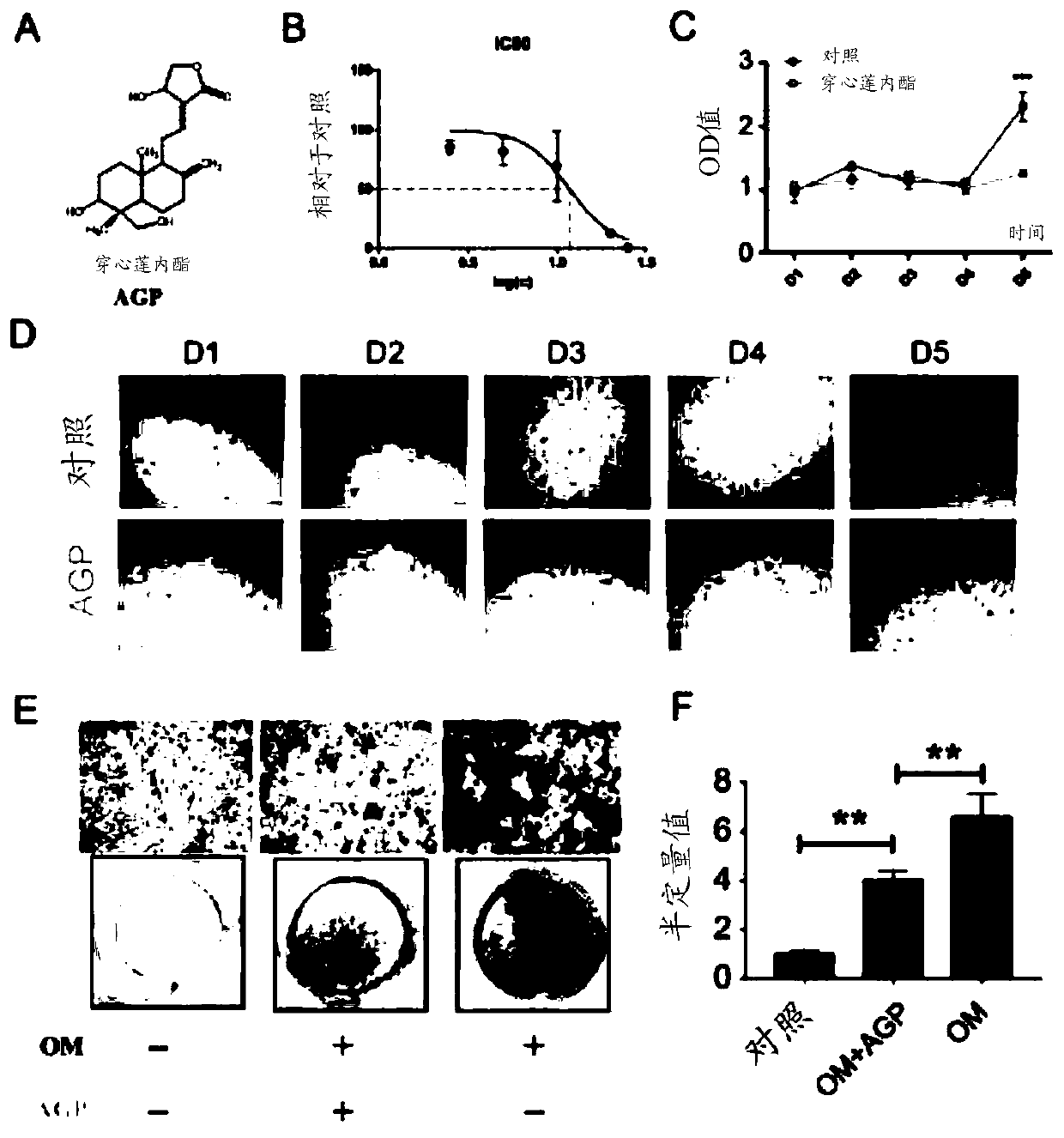
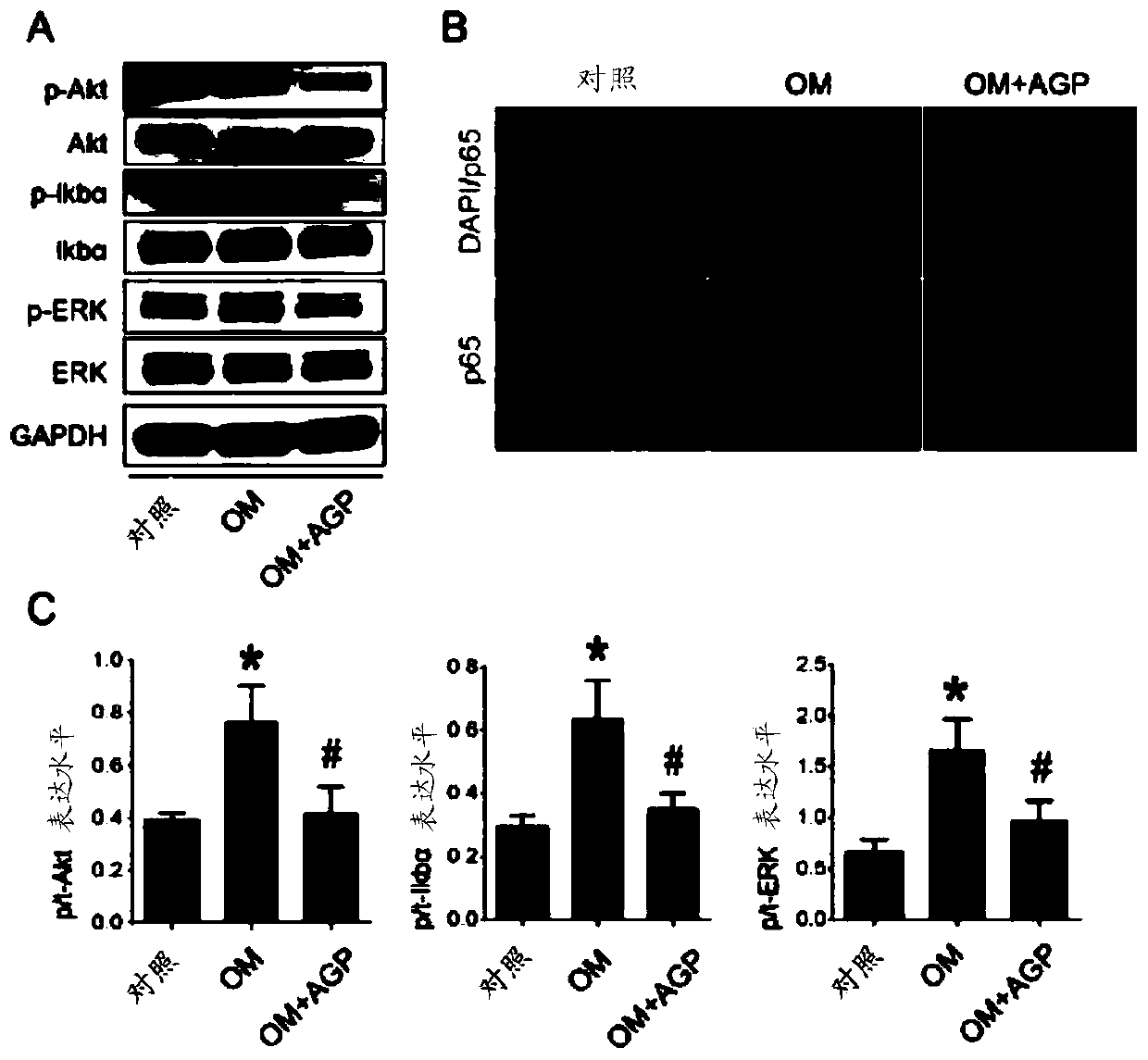
Use of andrographolide in treatment of calcific aortic valve disease
PendingCN111096966AInhibit calcificationCalcification inhibition or delayOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderRUNX2Pharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to the field of prevention and / or treatment of calcific aortic valve disease. Researches show that andrographolide can effectively down-regulate expressions of osteogenicdifferentiation marker genes RUNX2 and ALP in valvular interstitial cells, inhibit valvular interstitial cell calcification, and thus inhibit or delay valve calcification, thereby providing a use ofthe andrographolide in preparation of medicines for preventing and / or treating the individual calcific aortic valve disease. A new option for using a non-surgical method to treat the calcific aortic valve disease is provided.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
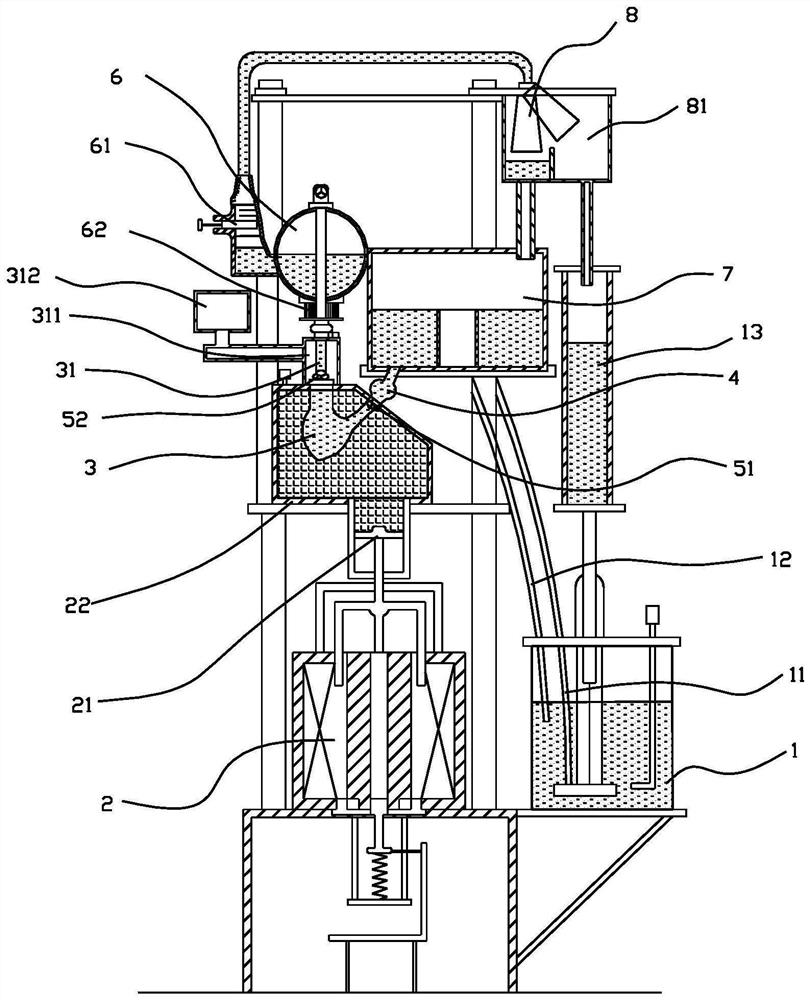
Artificial heart valve extracorporeal circulation pulsating flow experiment system and experiment method
PendingCN113925647ACompliance regulationClose to pressureHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationLeft atrium
The invention discloses an artificial heart valve extracorporeal circulation pulsating flow experiment system and an experiment method. The invention belongs to the technical field of medical experiment equipment, and particularly relates to improvement of an artificial heart valve extracorporeal circulation pulsating flow experiment system technology. The simulated circulation system comprises an experimental medium supply source, a simulated vein system, a simulated left atrium, a simulated left ventricle and a simulated artery system, the simulated left ventricle is further provided with a pulsation driving device, and the tested artificial heart valve comprises an artificial mitral valve and an artificial aortic valve. According to the system, preclinical safety and risk assessment can be carried out on the artificial heart valve, an important role is played in verification of a calculation model and fluid simulation, and an experimental basis is provided for performance optimization of the valve. The extracorporeal circulation pulsating flow experiment system not only can evaluate the performance of an artificial heart valve, but also plays an important role and significance in developing artificial heart, artificial lung and other cardiovascular artificial organs.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Interventional valve frame and aortic valve
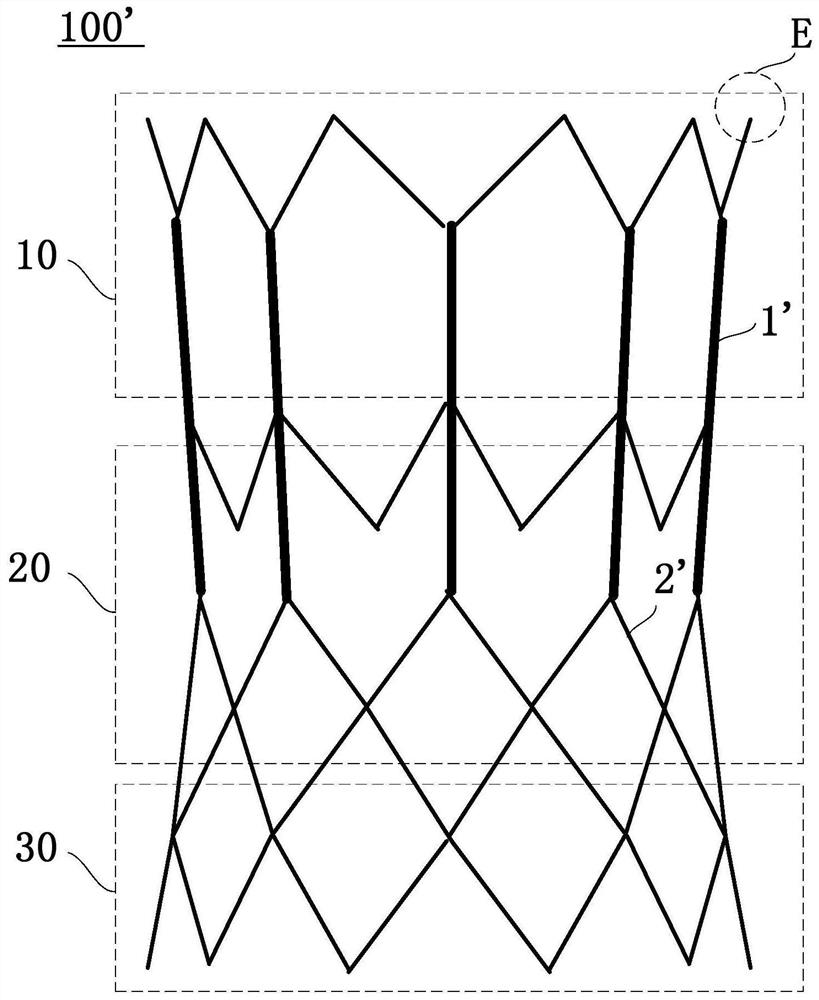
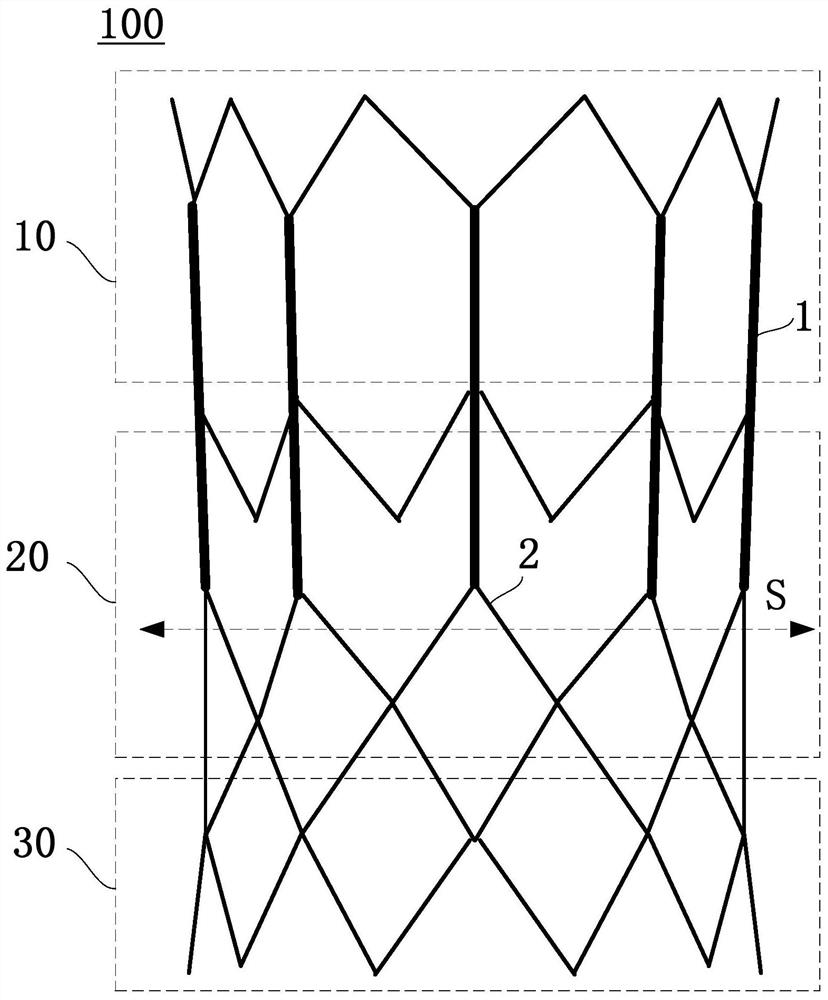
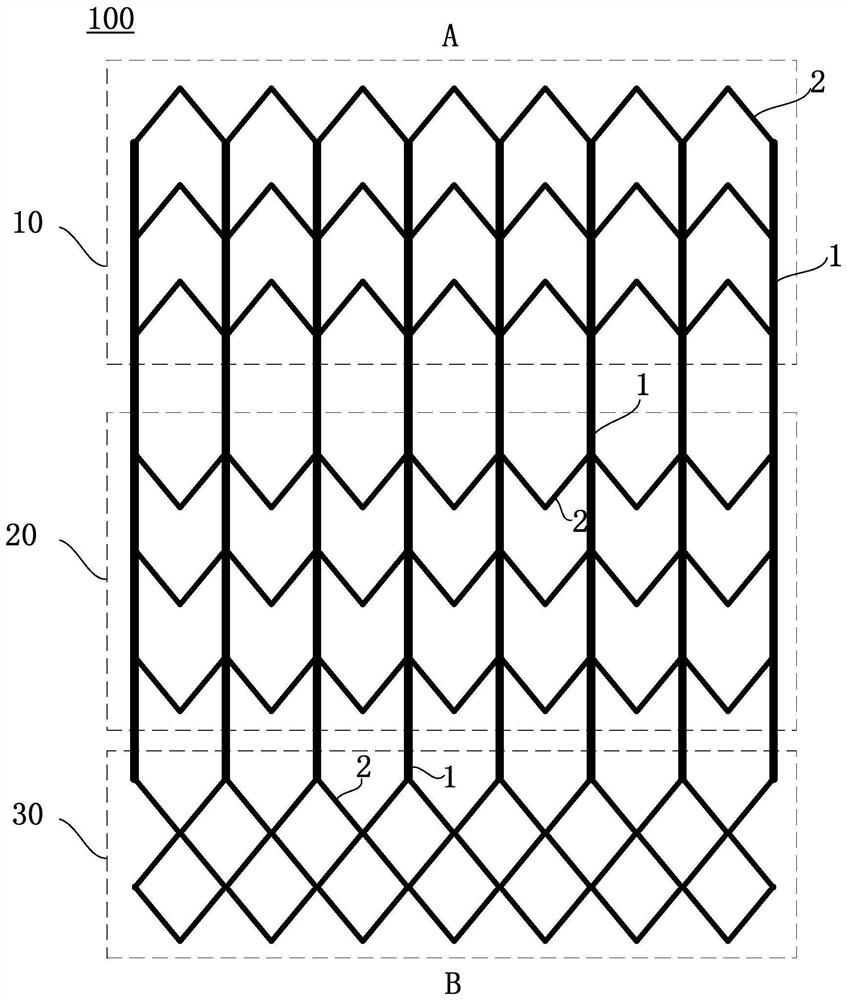
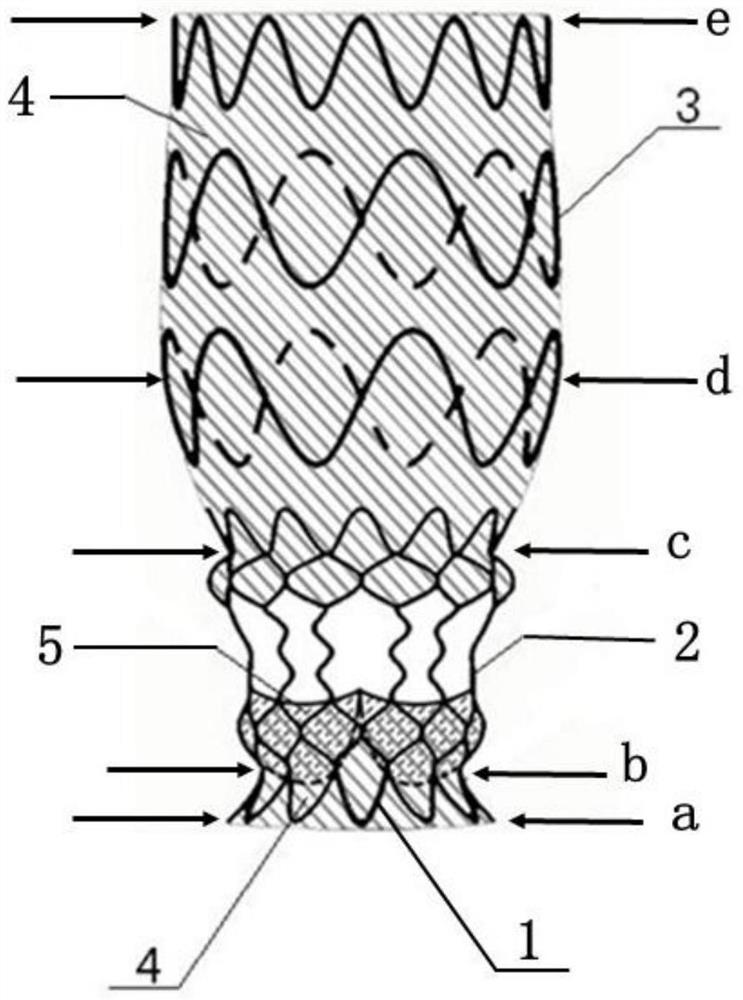
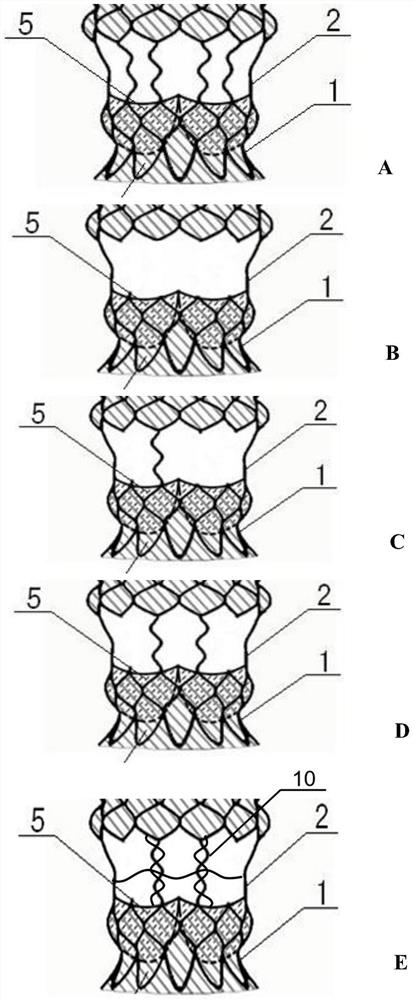
PendingCN111938872AEasy to expandEnhance internal stress transferStentsHeart valvesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides an interventional valve frame and an aortic valve. The interventional valve frame comprises a valve frame body for defining a frame lumen, the valve frame body comprises straight rods connecting an upstream port and a downstream port and inclined rods connected between the straight rods, an upstream section, a midstream section and a downstream section are sequentially formed in the direction from the upstream port to the downstream port, and when the valve frame body is expanded from a compression state to an expansion state, the expansion strain provided by the inclined rods located on the midstream section to the circumferential direction of the valve frame body is larger than the expansion strain provided by the inclined rods located on the upstream section and / or the downstream section to the circumferential direction of the valve frame body, so that the rate difference between the circumferential expansion rate of the midstream section and the circumferential expansion rate of the upstream section and / or the downstream section is compensated. According to the interventional valve frame and the aortic valve, by effectively receiving the stress transmitted by the inclined rods on the midstream section, the stress concentration of the inclined rods on the midstream section is reduced, so that the inclined rods on the midstream section is prone to be stressed and expand to achieve the expansion rate of the inclined rods at the two ends, and then the adverse effect that the two ends expand outwards to form a dog-bone-like structure when the valve frame expands is reduced or relieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEWMED MEDICAL CO LTD
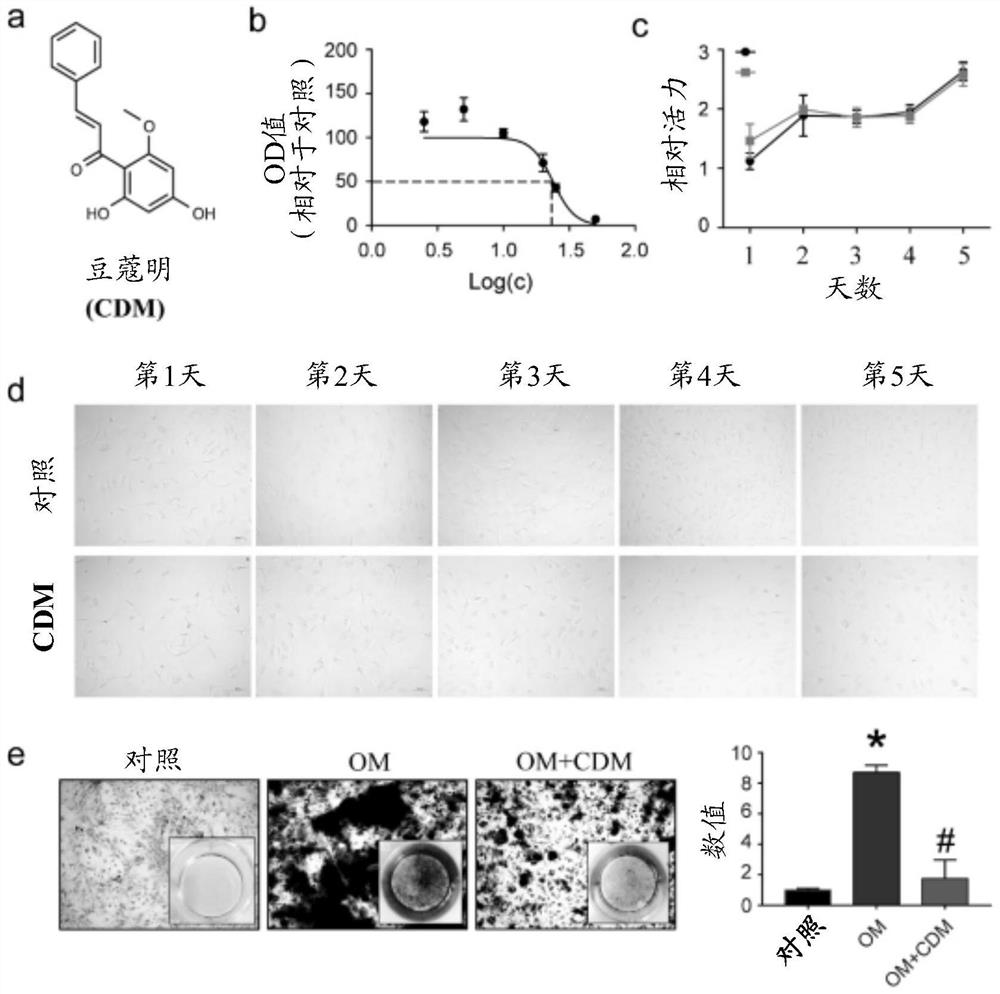
Use of cardamonin in the treatment of aortic valve calcification
ActiveCN112618521BInhibit calcificationCalcification inhibition or delayKetone active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseRUNX2
The present invention relates to the field of prevention and / or treatment of aortic valve calcification. The inventors found that cardamomine can effectively down-regulate the activity of ALP, RUNX2, BMP2, OPN, TNF-α, and type I collagen (COL1) in valve interstitial cells. The expression of the protein inhibits the calcification of interstitial cells of the valve, thereby inhibiting or delaying the calcification of the valve, and further provides the use of cardamonin in the preparation of a medicament for preventing and / or treating individual aortic valve calcification. It provides a new option for non-surgical treatment of aortic valve calcification.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
An ascending aortic aortic valve integrated intravascular stent
ActiveCN107019581BSufficient anchoring forceAvoid shadowsStentsBlood vesselsAscending aortaIntravascular stent
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
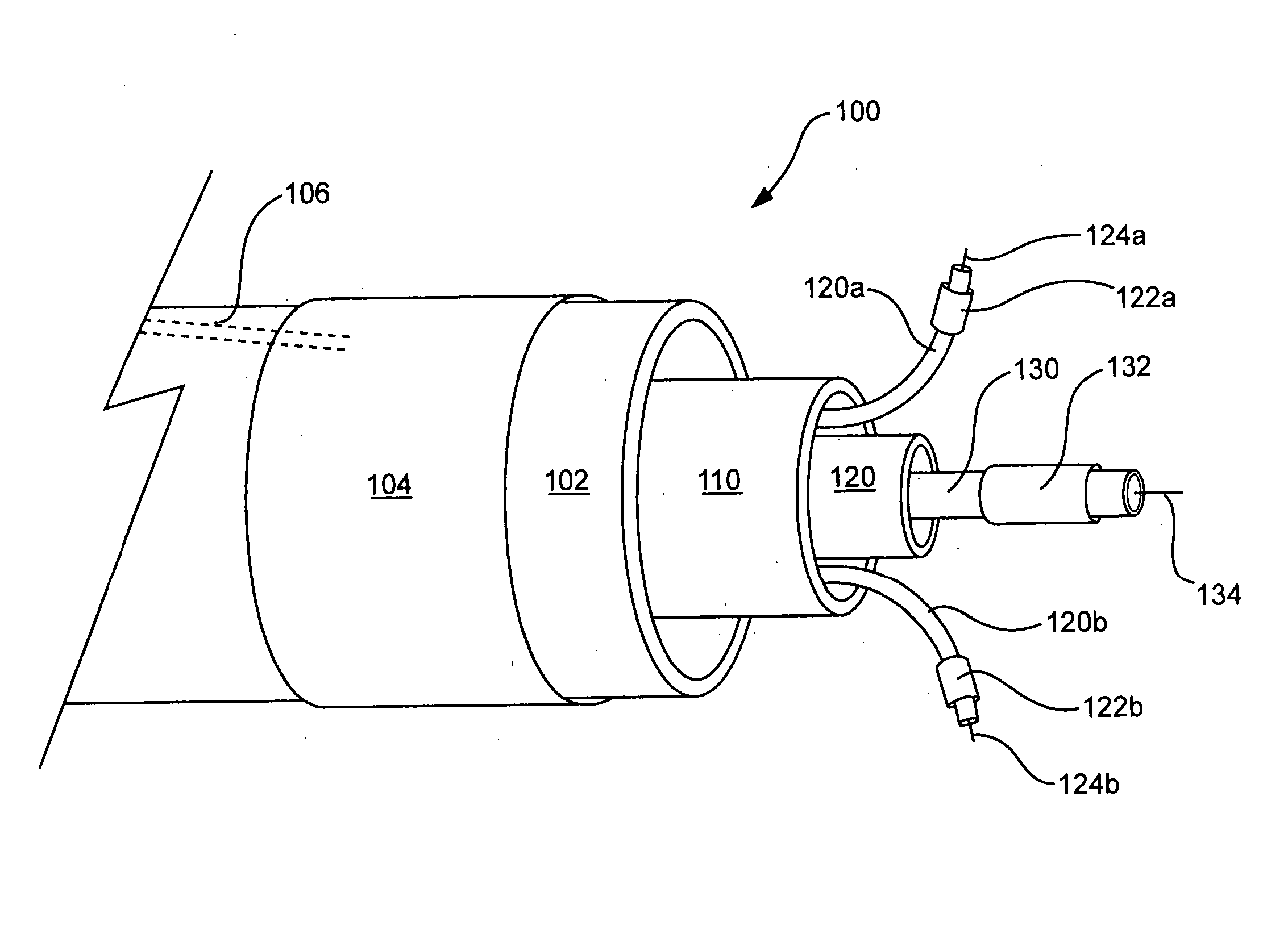
Method and apparatus for implanting an aortic valve prosthesis
Owner:REYNOLDS M DELGADO III
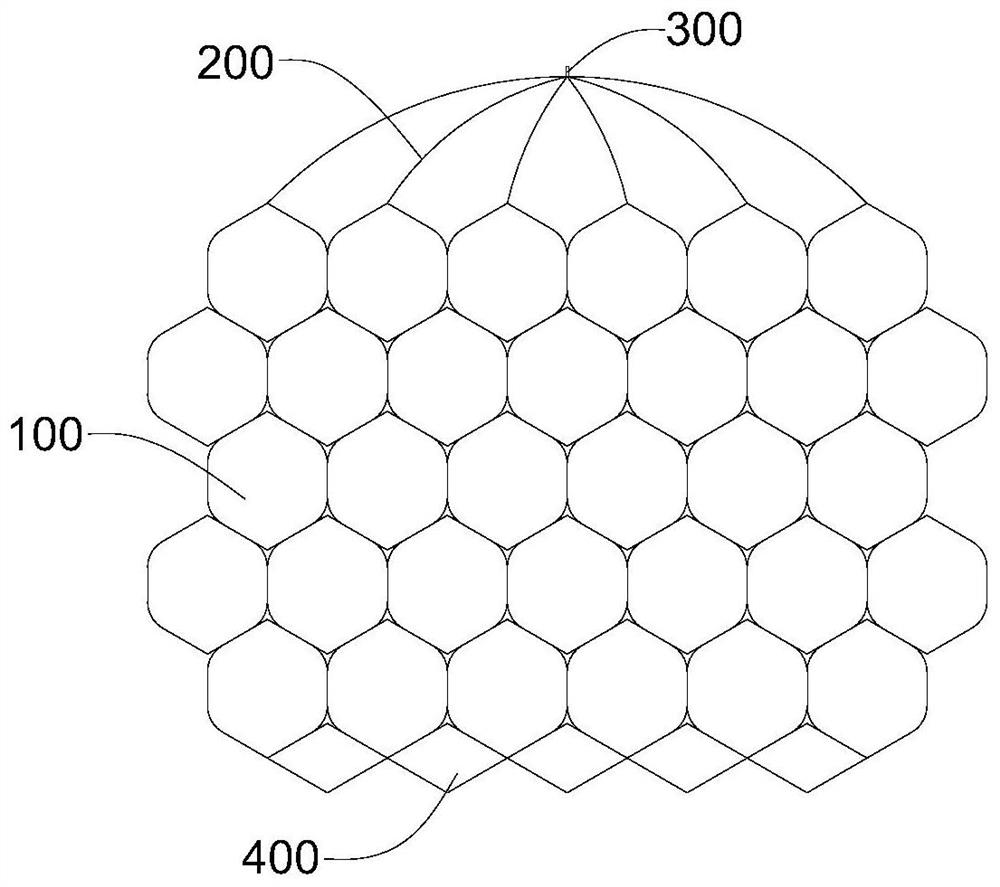
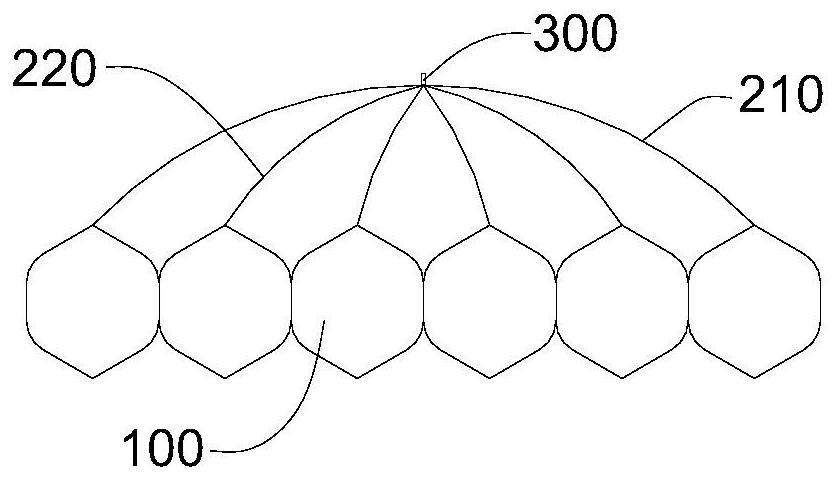
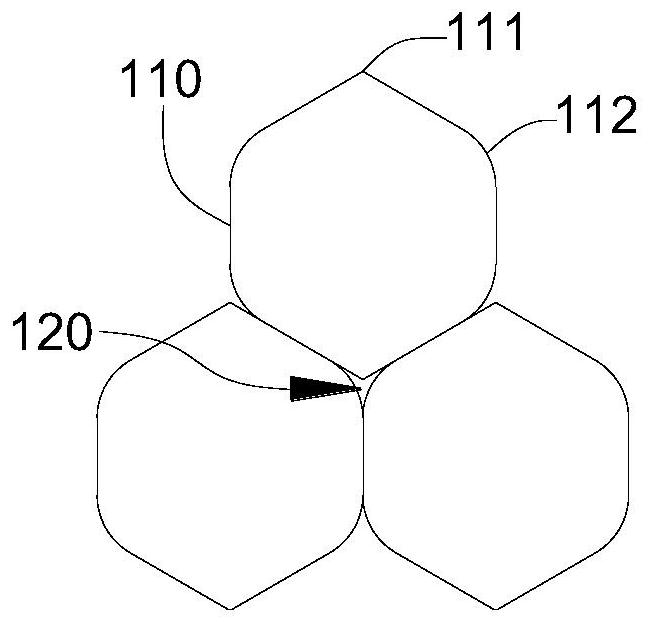
Pulmonary artery stent convenient to control, and pulmonary artery valve replacement device
ActiveCN111772882AEasy to adjustOpen quicklyAnnuloplasty ringsPulmonary arteryBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a pulmonary artery stent convenient to control. The pulmonary artery stent convenient to control comprises a tubular supporting net frame, fixing pieces, a flowing out stent and at least two groups of aorta stents, wherein the supporting net frame consists of continuous regular hexagon rotating units, and top points located at two ends of the supporting net frame, of the rotating units are connecting points; each aorta stent comprises a supporting strip and four auxiliary strips, two ends of each supporting strip are respectively connected with two connecting points which are the farthest from each other, the four auxiliary strips are connected with four connecting points in the middle in a one-to-one correspondence, one end departing from the connecting points, ofeach auxiliary strip and the corresponding supporting strip are connected to one point, and the corresponding fixing piece is located at the connecting position of each supporting strip and the corresponding auxiliary strip; and the flowing out stent is located at the other end of the supporting net frame. According to the pulmonary artery stent convenient to control disclosed by the invention, the connecting lines between rotating units in the pulmonary artery stent convenient to control are long, every two adjacent rotating units rotate along the corresponding connecting line, during rotation, the rotation direction is stable and reliable, and accidental situations appearing in a mounting process can be effectively avoided and reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Devices and methods for treating aortic valve stenosis
Devices and methods for their use in increasing the aortic valve flow of a stenotic aortic valve are provided. The subject devices include an aortic valve isolation element and an aortic valve flushing element. The aortic valve isolation element is made up of a ventricular side aortic valve occlusion element, coronary ostia occlusion elements and an ascending aorta occlusion element. The aortic valve flushing element is made up of a dissolution fluid introducing element and a fluid removal element. In practicing the subject methods, a stenotic aortic valve is first isolated. Next, the isolated valve is flushed with a dissolution fluid, e.g., an acidic dissolution fluid, for a period of time sufficient for the aortic valve flow of the treated valve to be increased. In certain embodiments, the valve is also contacted with a dissolution fluid attenuating fluid, e.g., a buffer, during the flushing step in order to limit the contact of non-valve tissue with the dissolution fluid. Also provided are systems and kits that include the subject devices and can be employed in practicing the subject methods. The subject devices, methods, systems and kits find use in treating conditions associated with the presence of stenotic aortic valves.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Auxiliary occlusion device used for aortic valve insufficiency
PendingCN111248952AReduce or avoid refluxPrevent backflowSurgeryAortic Valve InsufficiencyBlood flow
The invention provides an auxiliary occlusion device used for aortic valve insufficiency. The auxiliary occlusion device comprises a positioning mechanism and an auxiliary occlusion piece arranged atthe near end of the positioning mechanism; the positioning mechanism is fixed in an aorta in a released state, so that the auxiliary occlusion piece is located between aortic valves. The auxiliary occlusion device provided by the invention can assist the aortic valves in occluding pores between the aorta and a left ventricle in the case of the aortic valve insufficiency so as to reduce or avoid that blood flows back through the aortic valves, and when ventricles contract, the auxiliary occlusion device cannot block flowing of the blood in the aorta.
Owner:HANGZHOU WEIQIANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
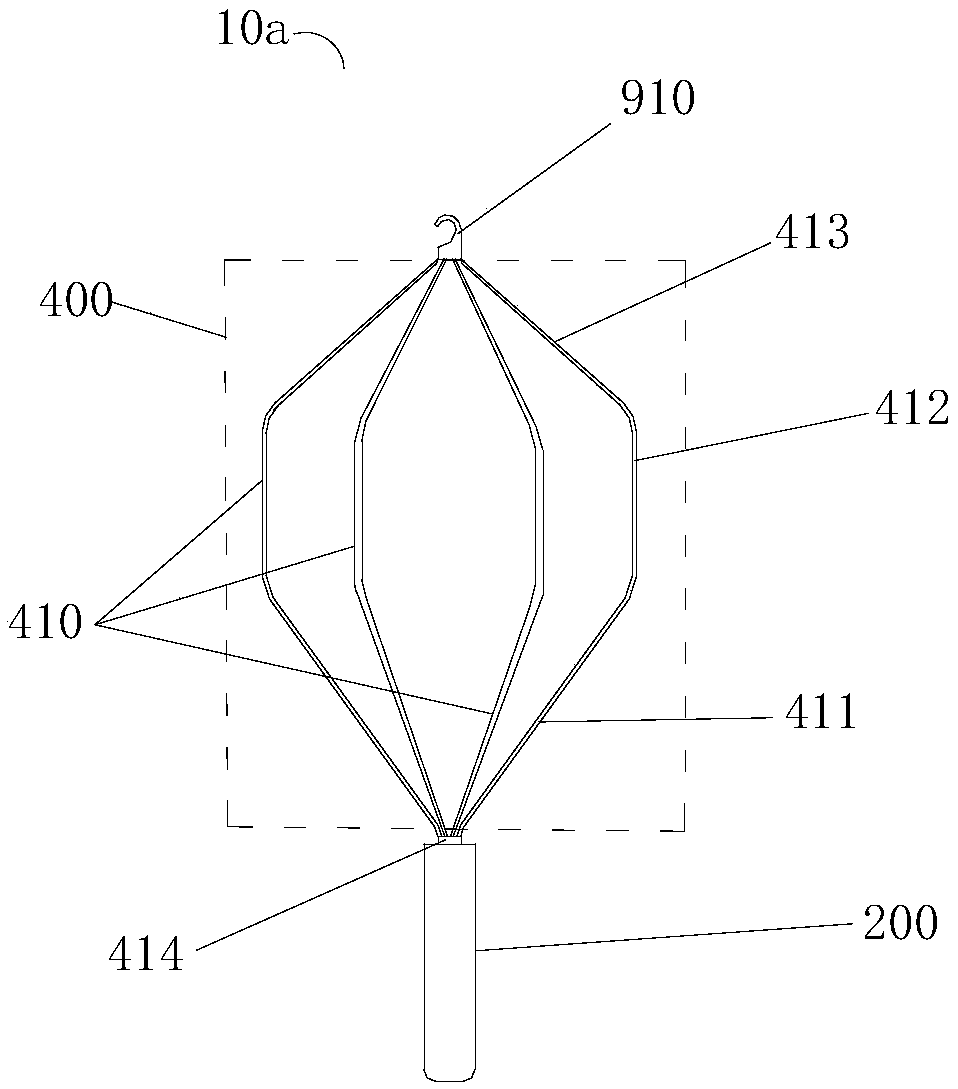
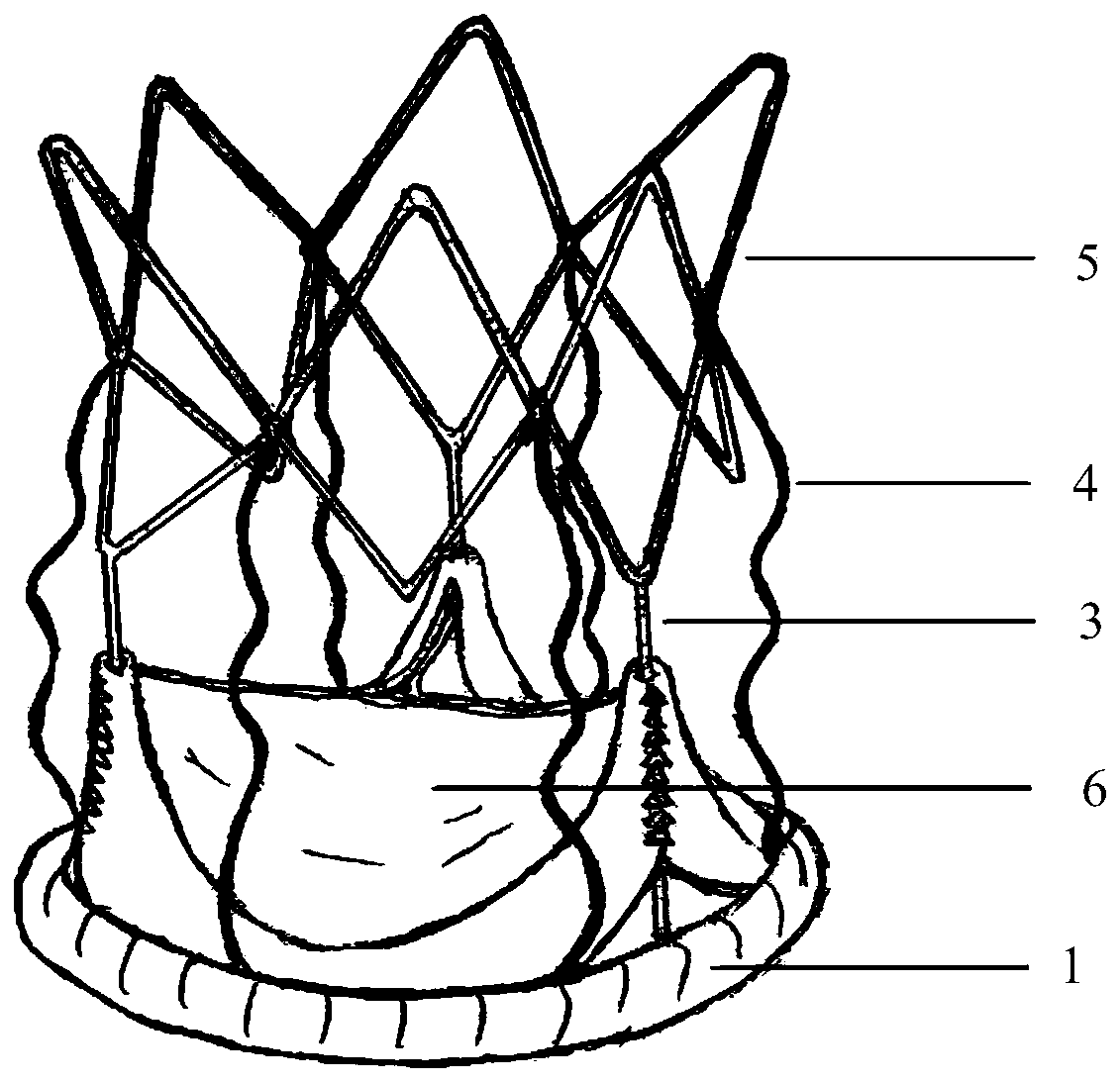
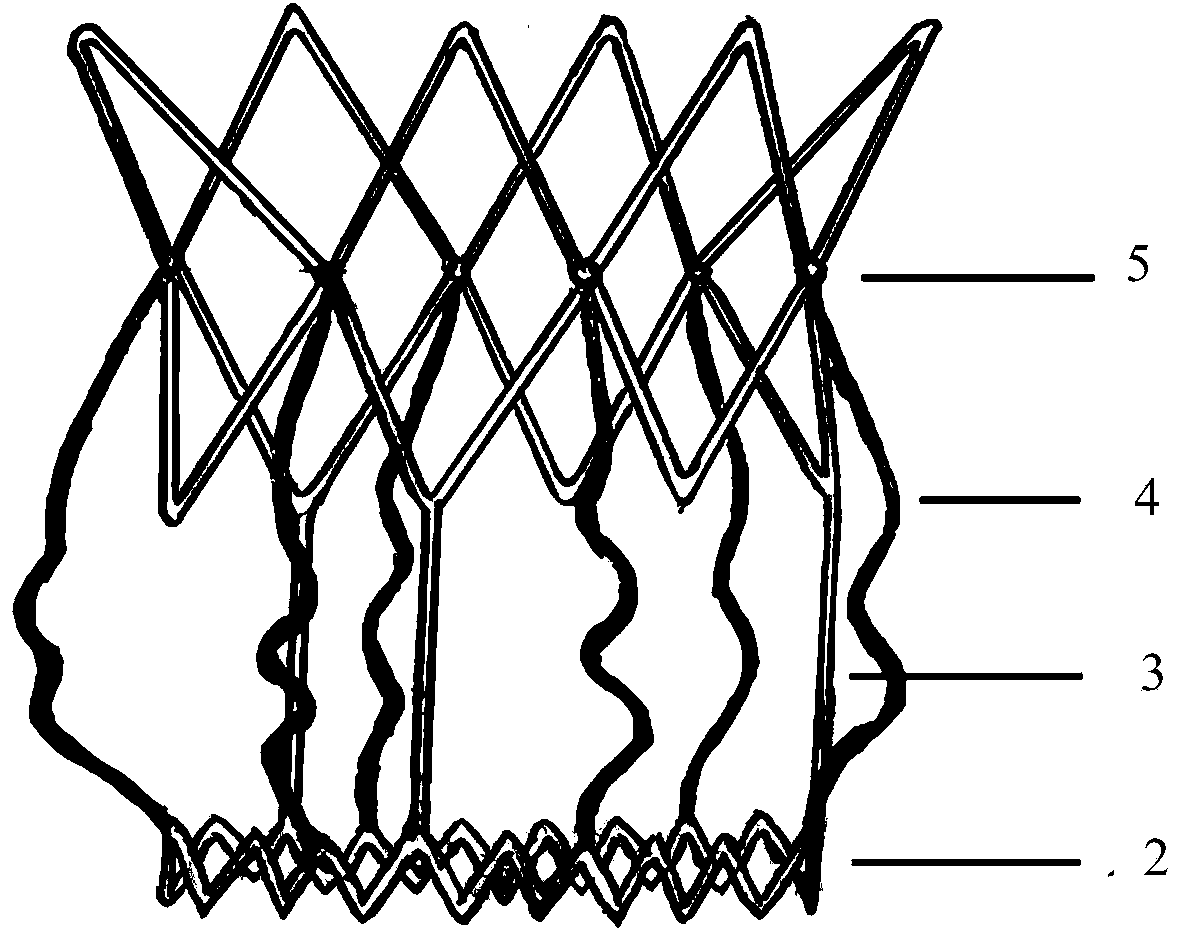
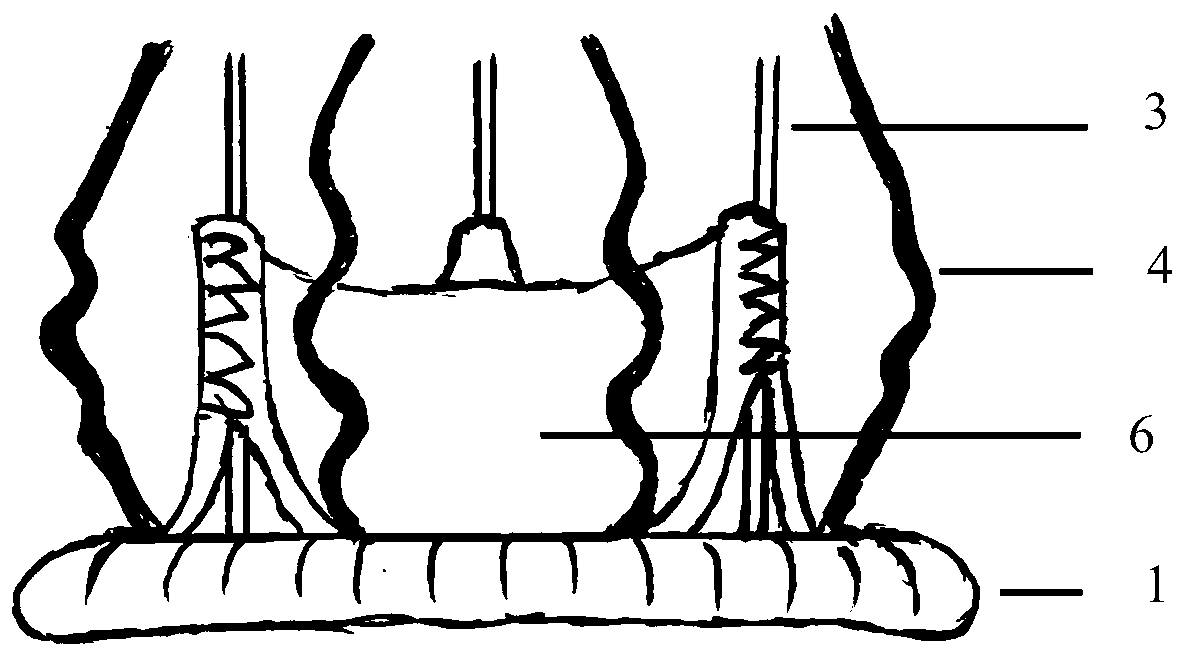
Aortic biovalve with compressible suture edge
PendingCN111000662AExpand the scope of activitiesIncrease stressAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringVascular surgery
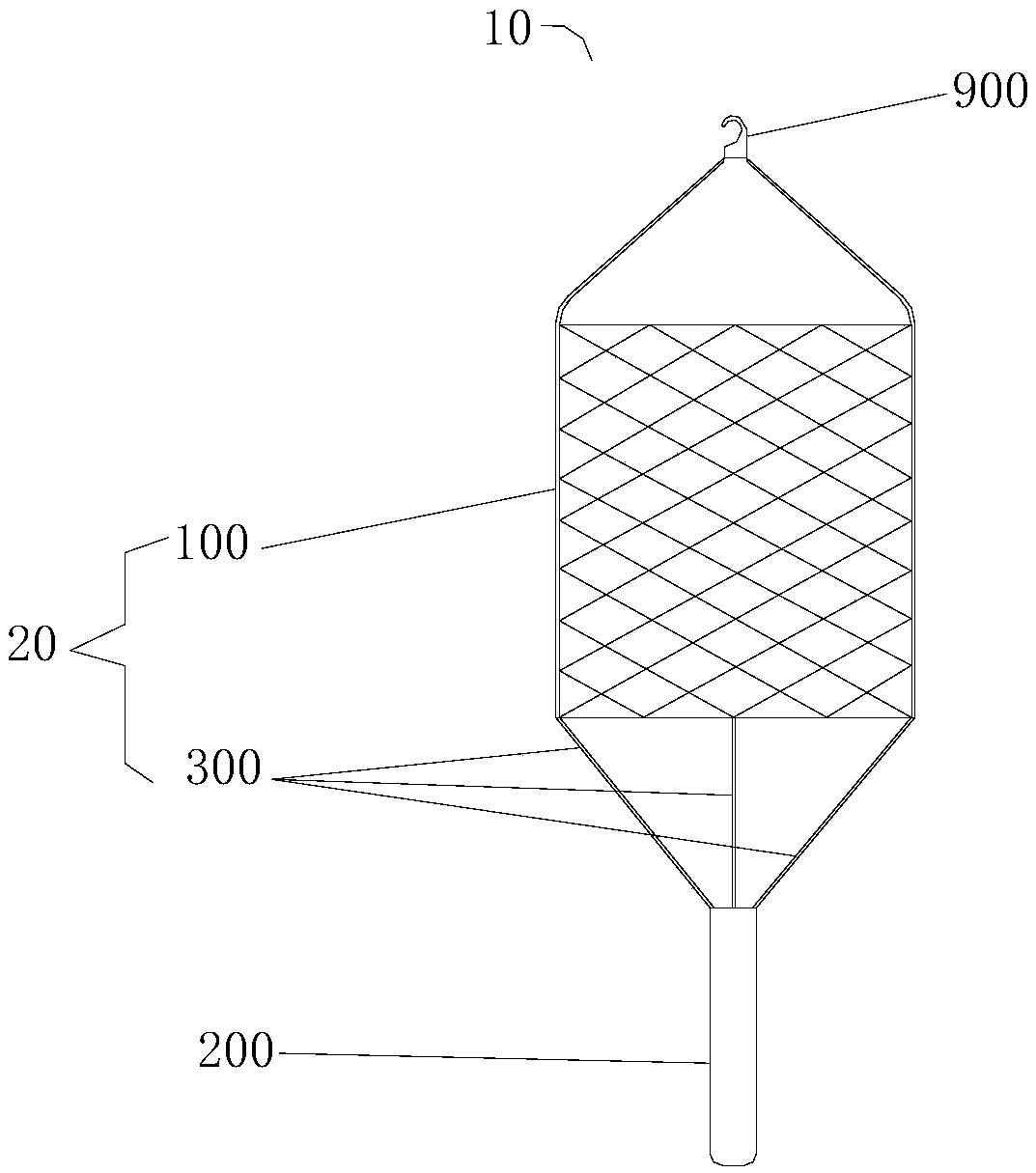
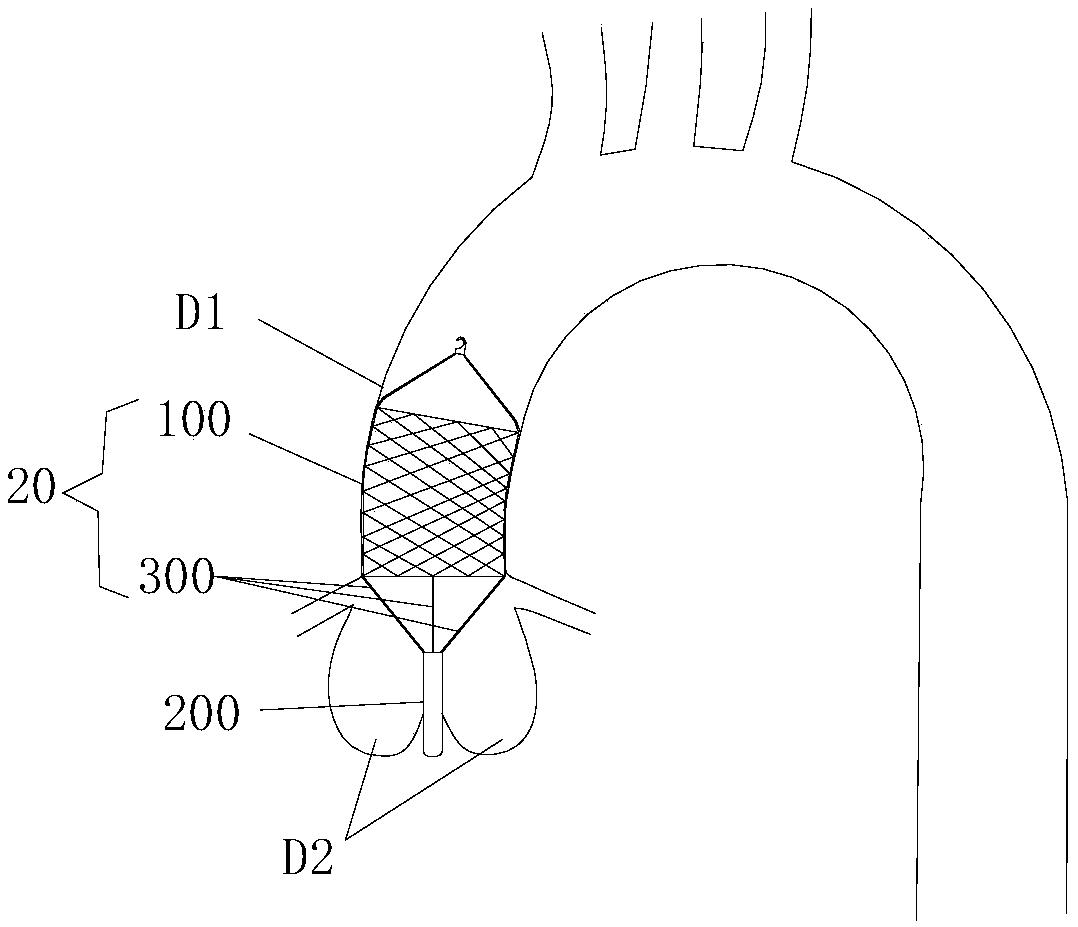
The invention relates to an aorta biovalve with a compressible suture edge, which belongs to the field of passive medical instruments in the cardiovascular surgery field. The valve comprises a valve stent and a valve leaflet, wherein the valve stent comprises an inflow end, a middle section and an outflow end; the inflow end is composed of a compressible base ring, a polymer layer wrapping the base ring and a polymer sewing edge wrapping the polymer layer, the middle section is composed of a straight supporting rod and an arc-shaped positioning rod protruding outwards, one end of the supporting rod and one end of the positioning rod are fixed to the compressible base ring, and the other end of the supporting rod and the other end of the positioning rod are connected with the outflow end. The outflow end is of a horn-mouth-shaped grid structure; the valve leaflets are located in the middle section of the valve stent and fixed to the supporting rod and the base ring, and three or more parts capable of being movably opened and closed are formed. The valve can be implanted into the position of an in-situ aortic valve with aortic membrane stenosis and aortic insufficiency lesion, and has the characteristics of wide application range, accurate positioning, tight fitting, small comprehensive damage and long valve durability.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com